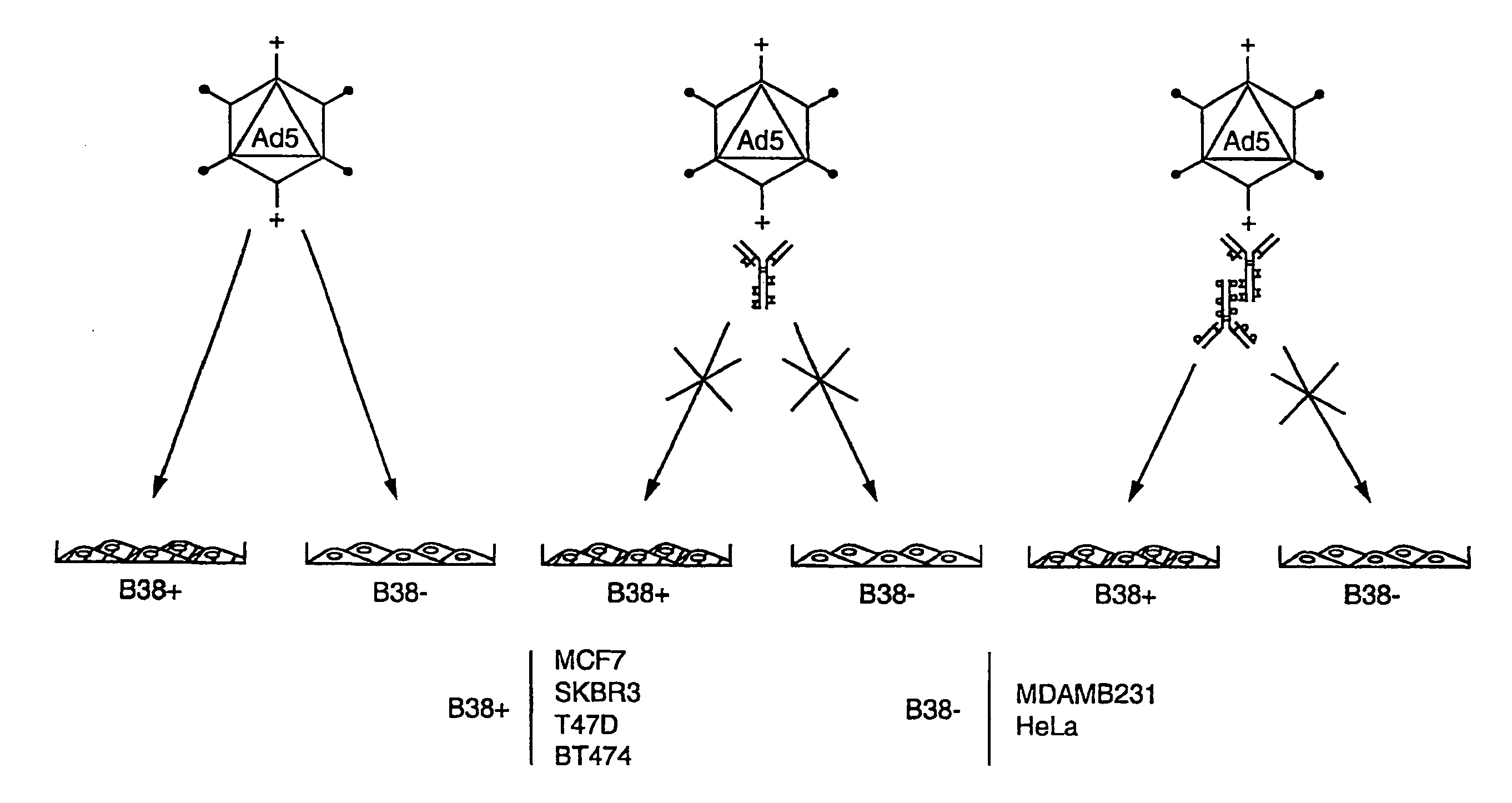
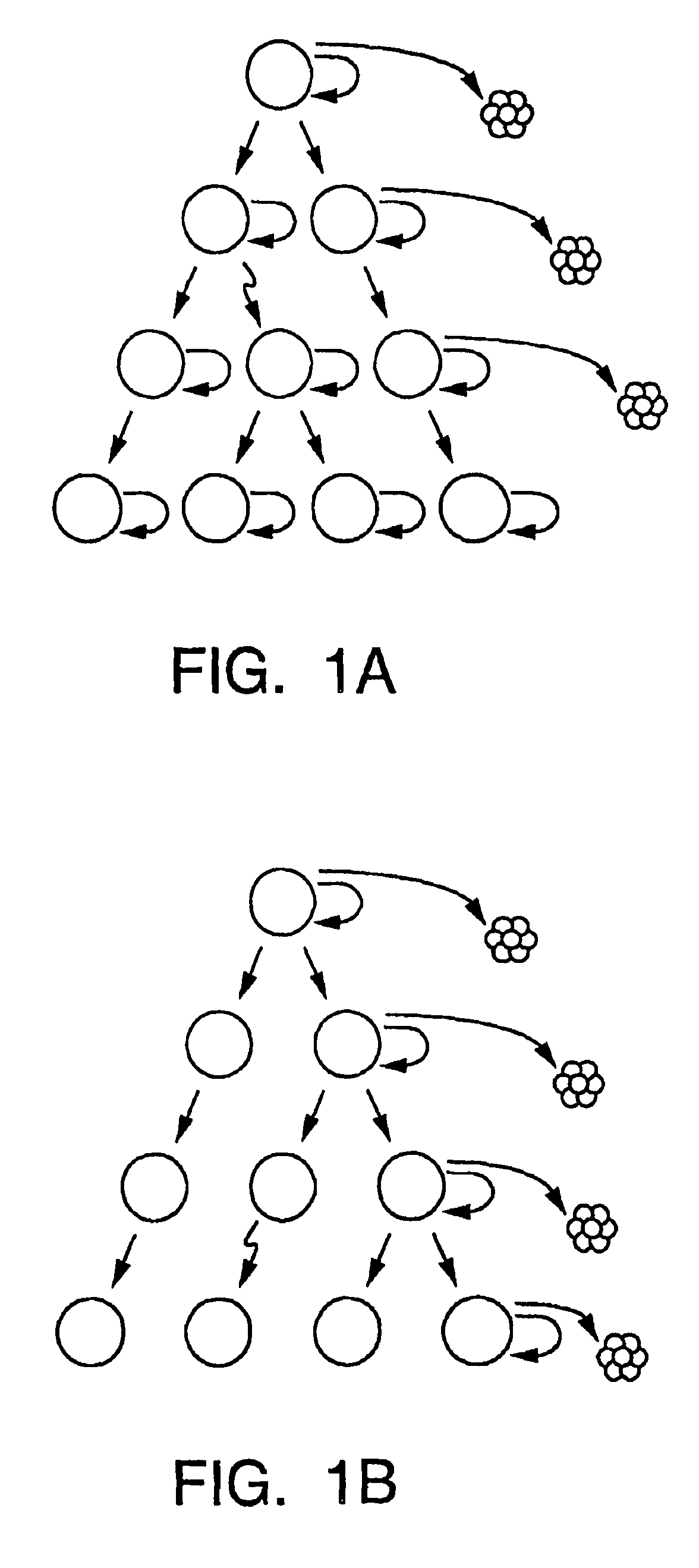
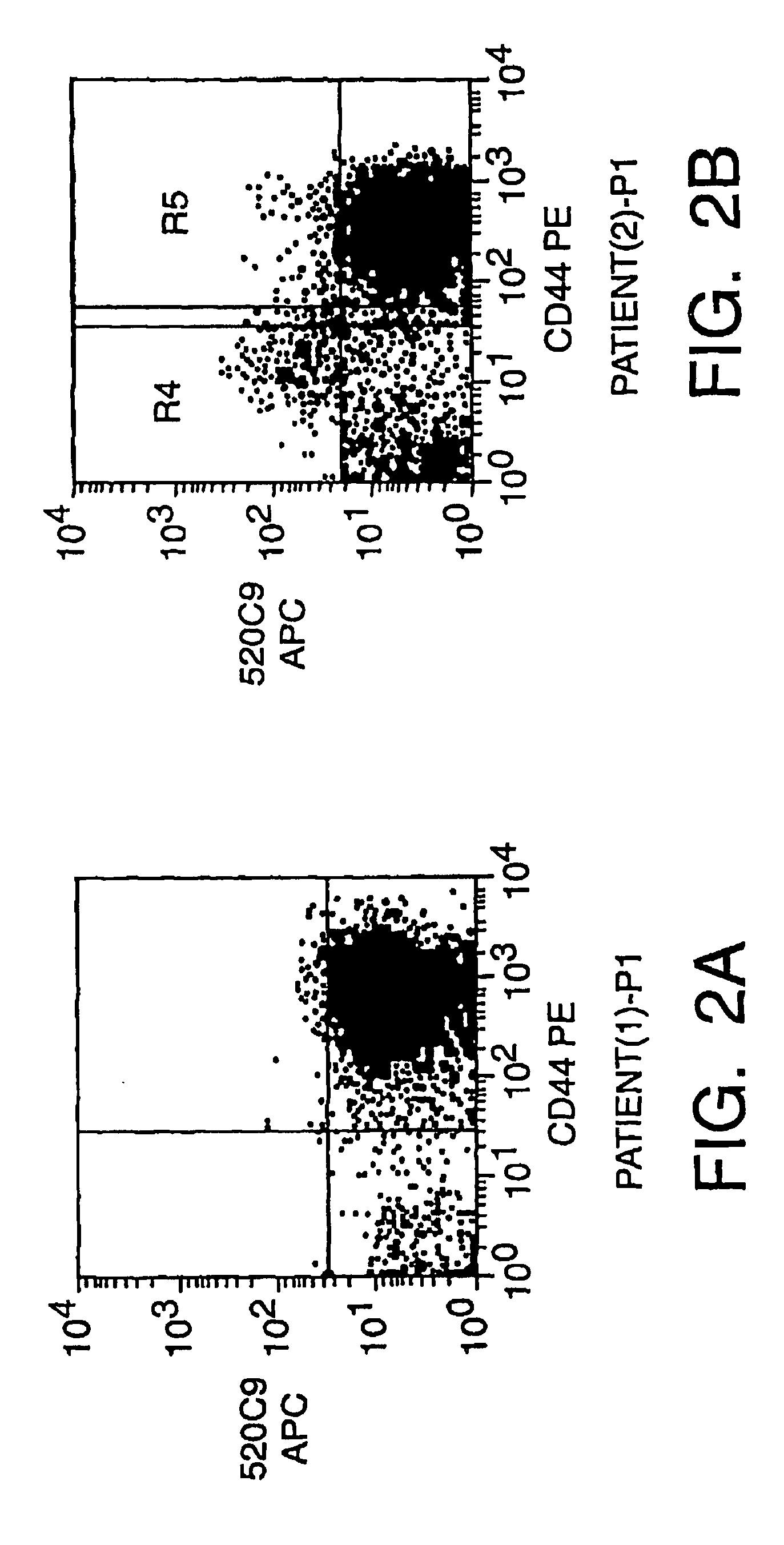
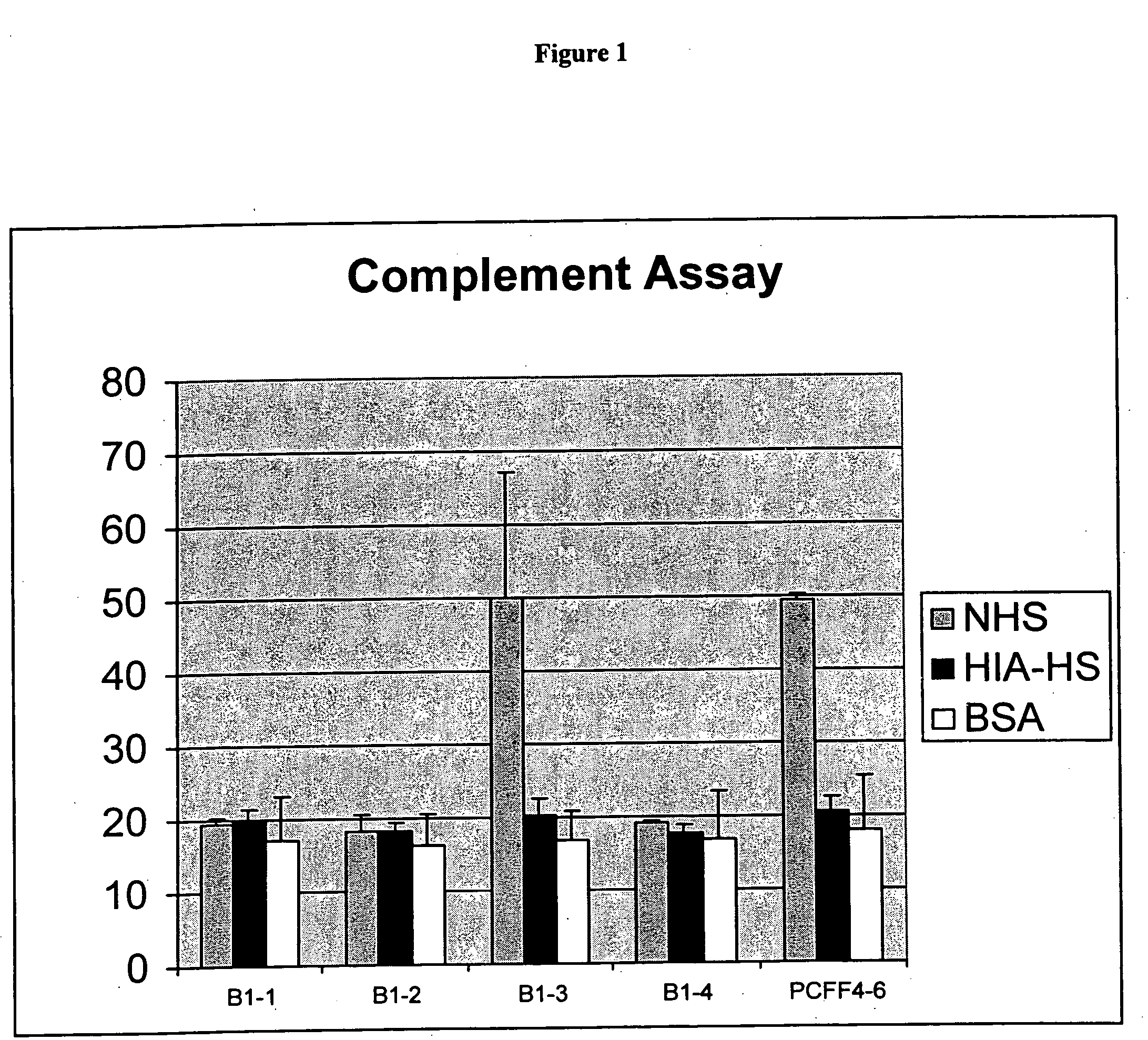
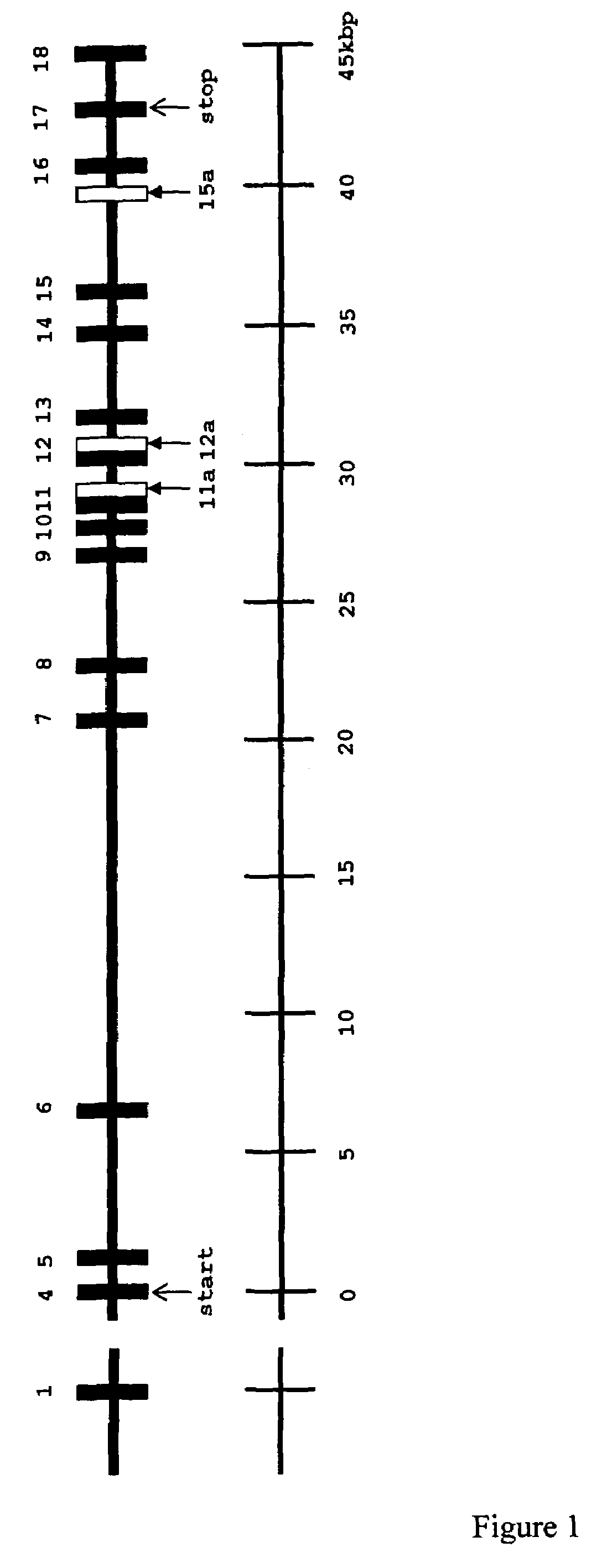
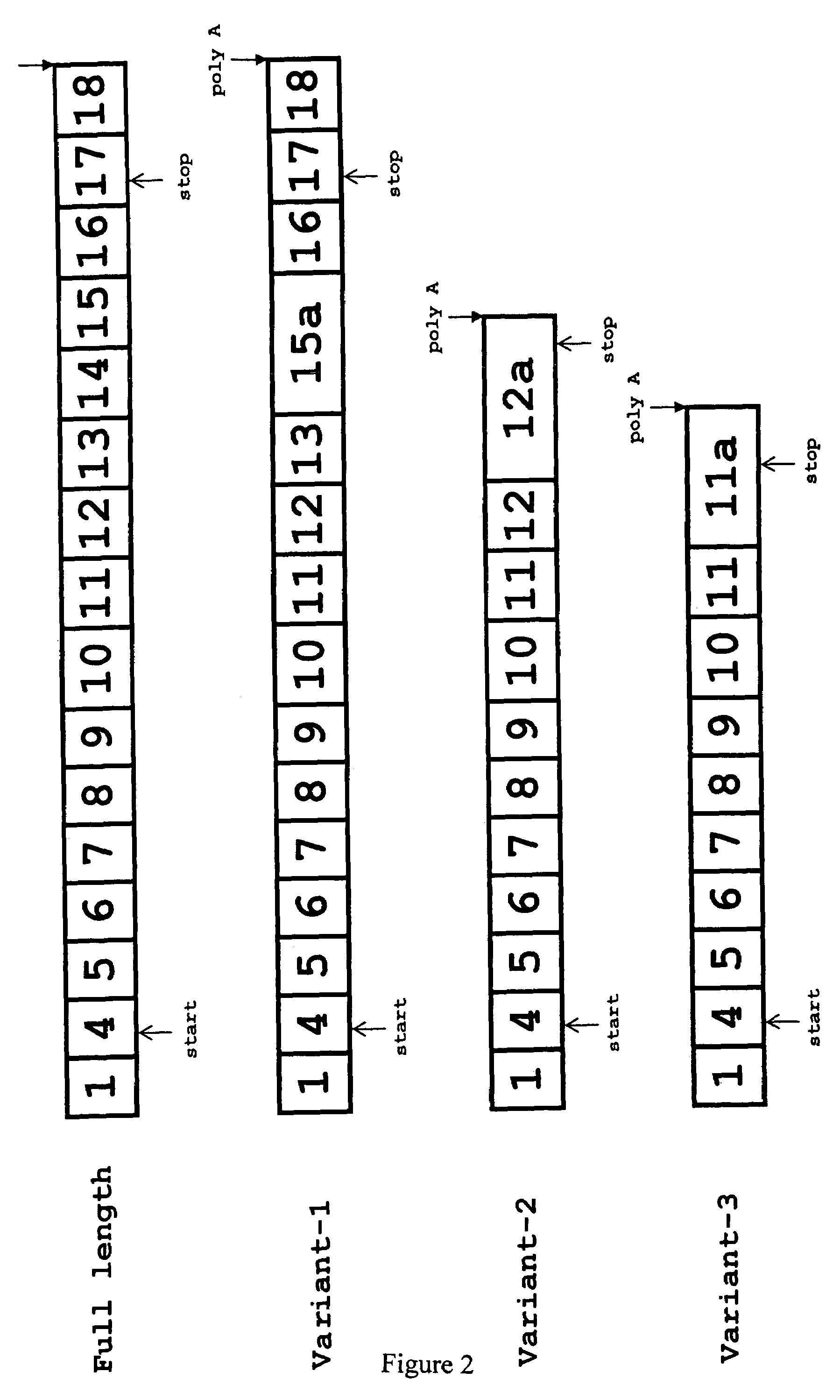
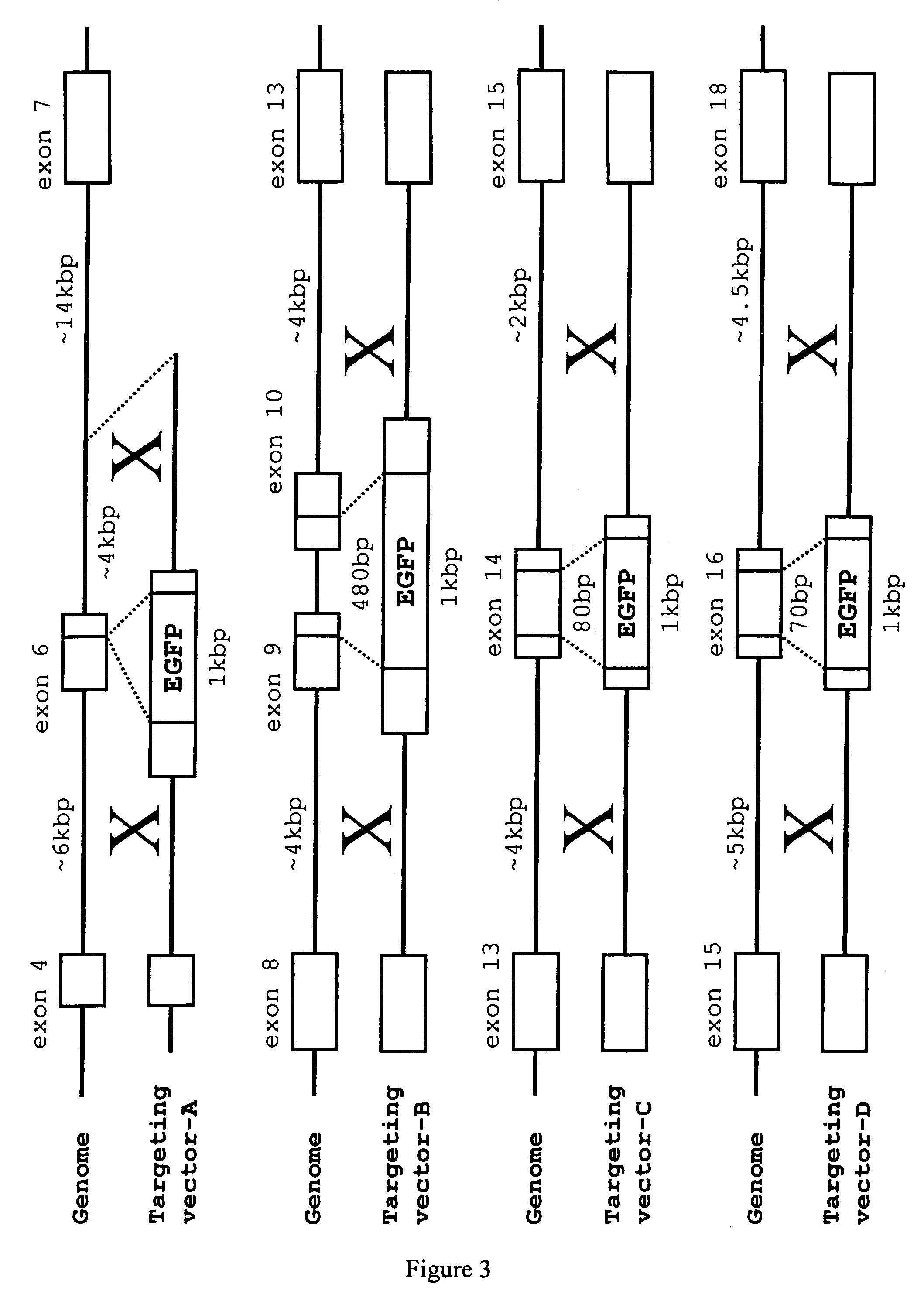
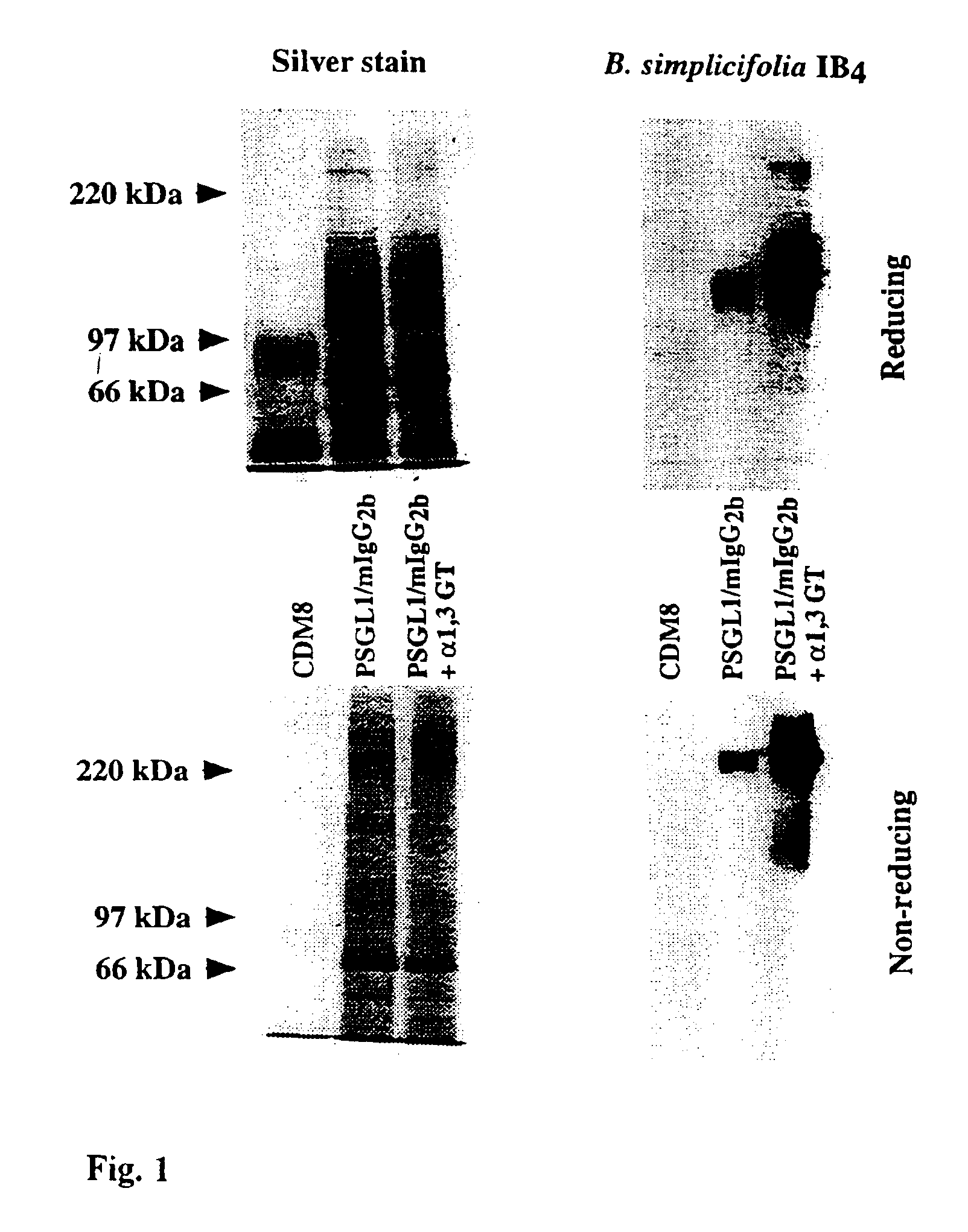
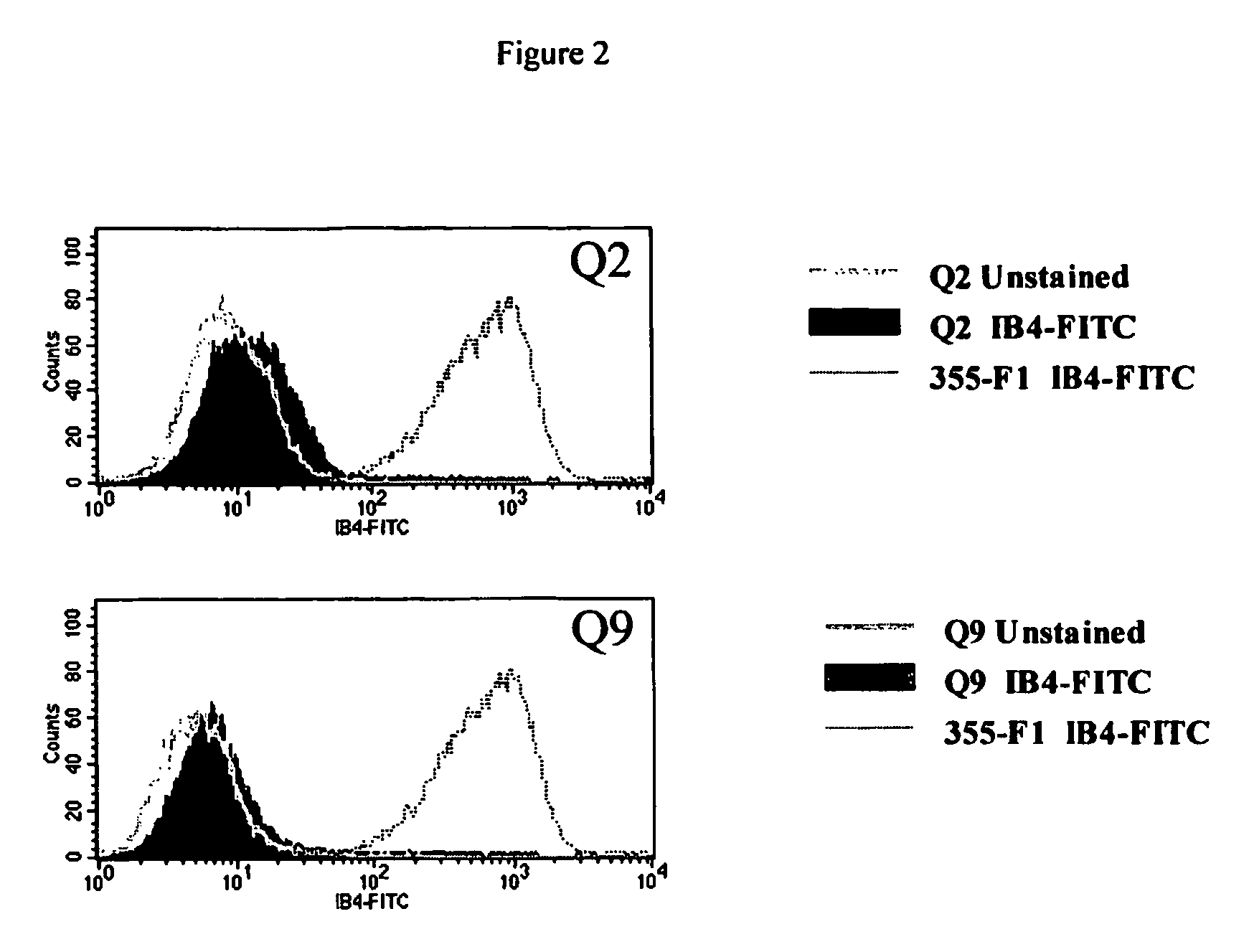
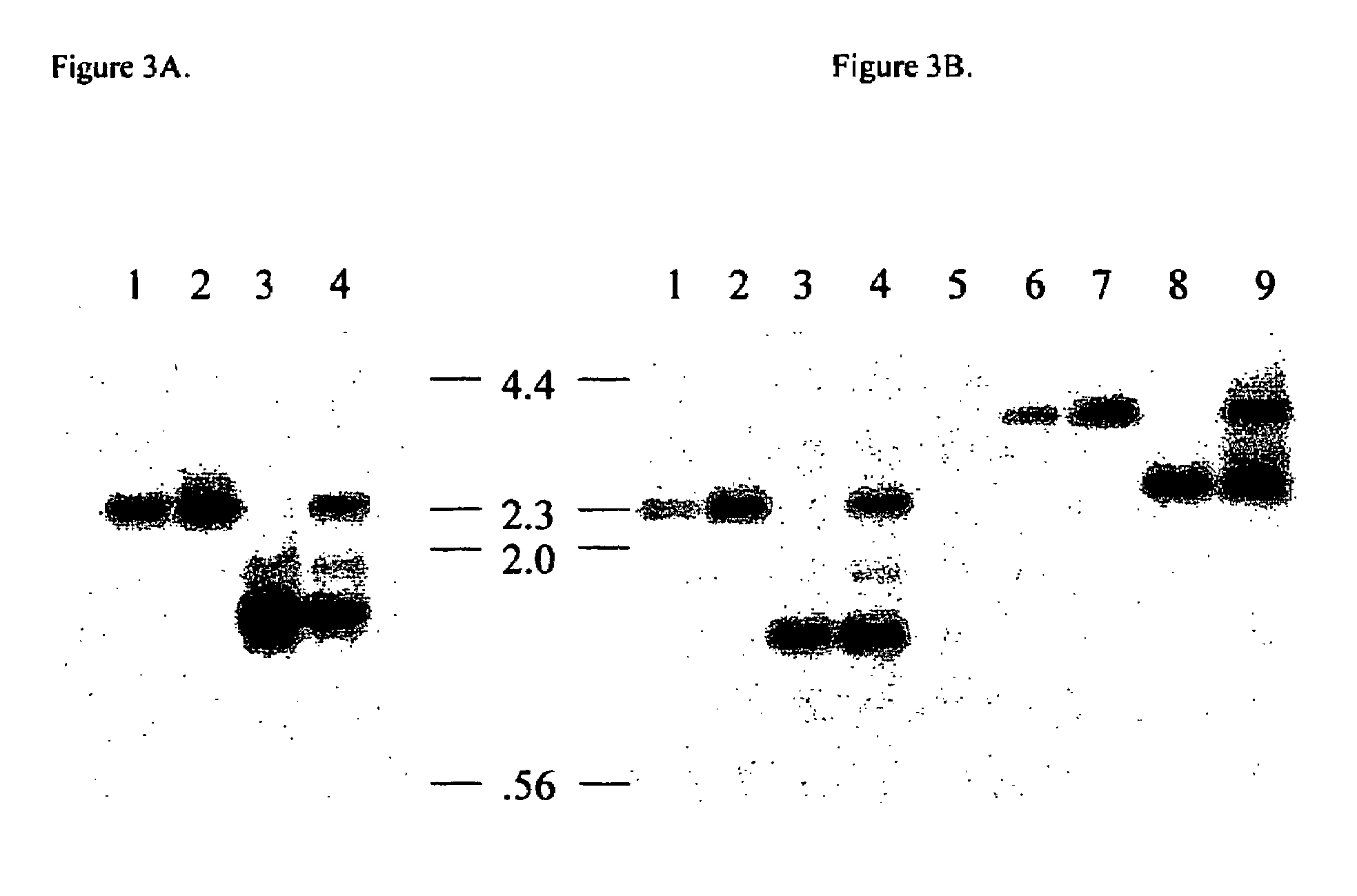
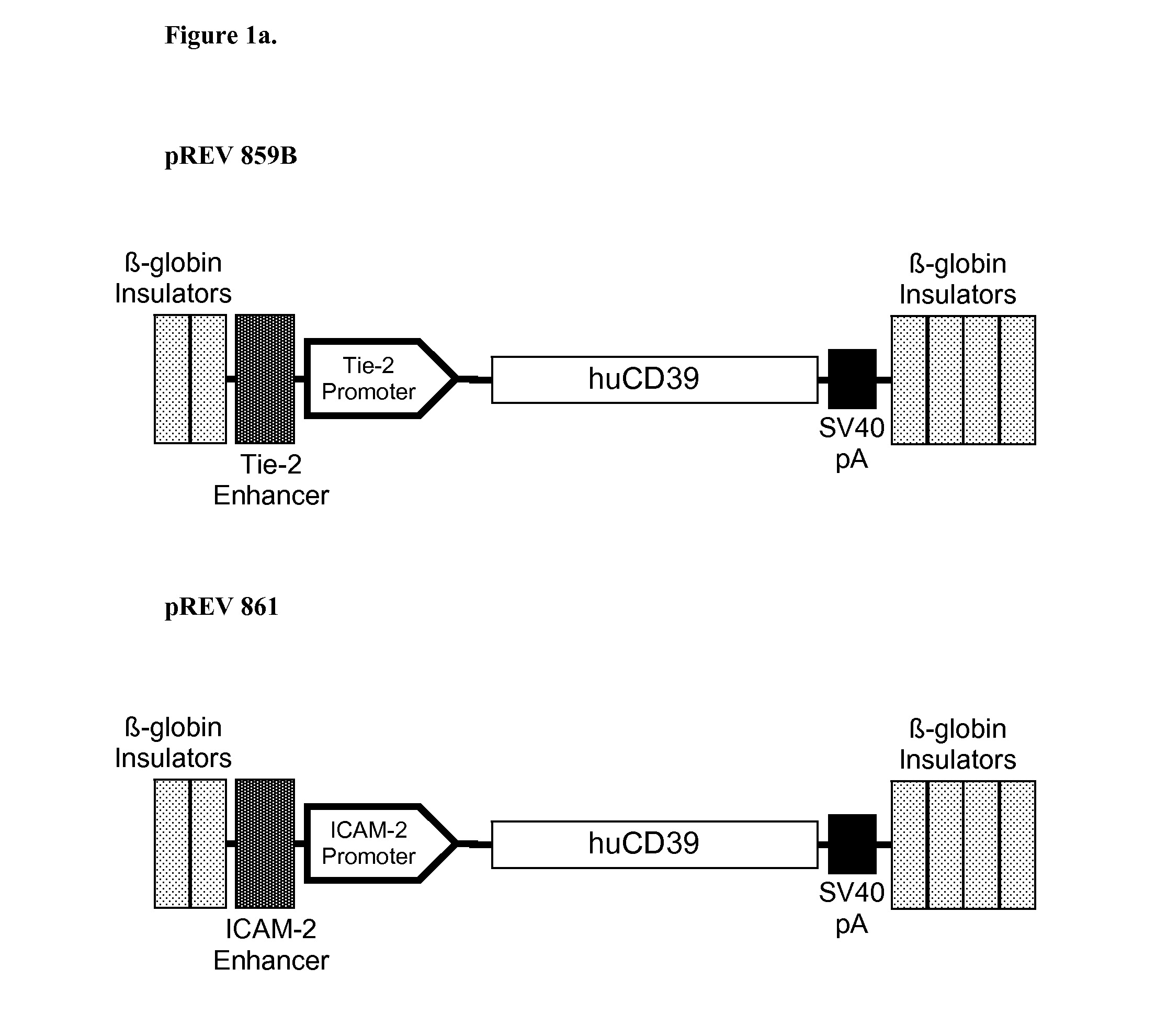
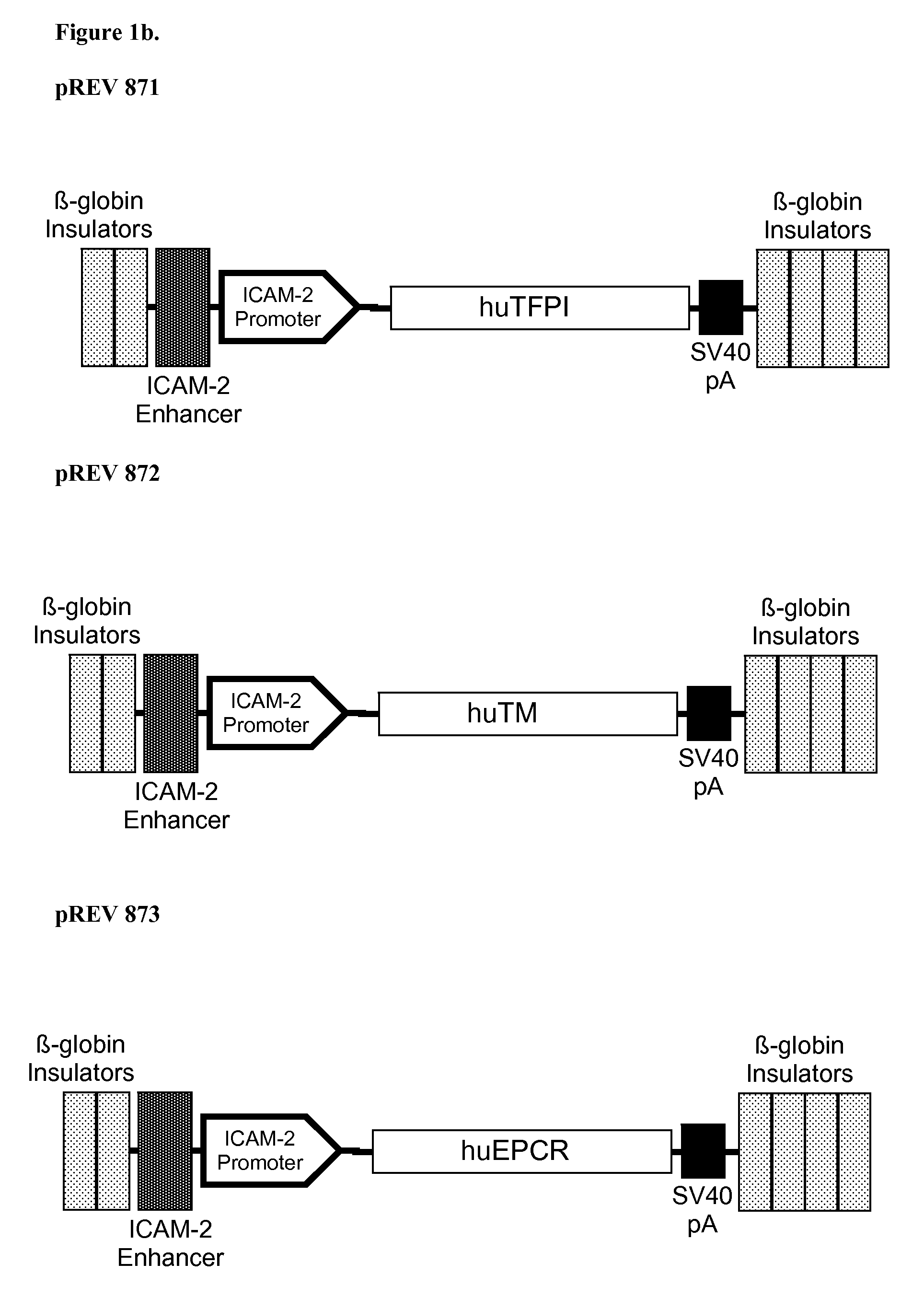
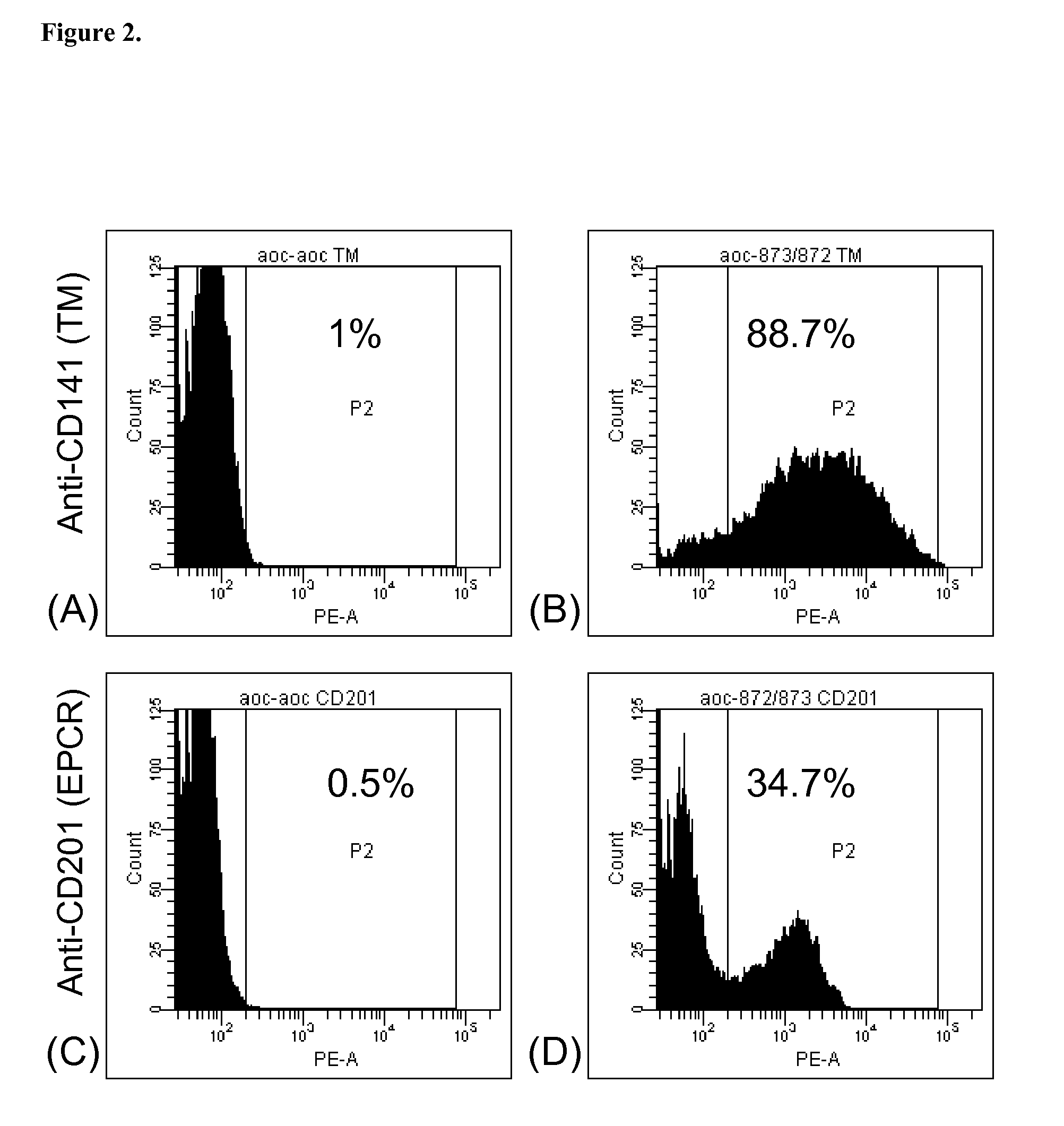
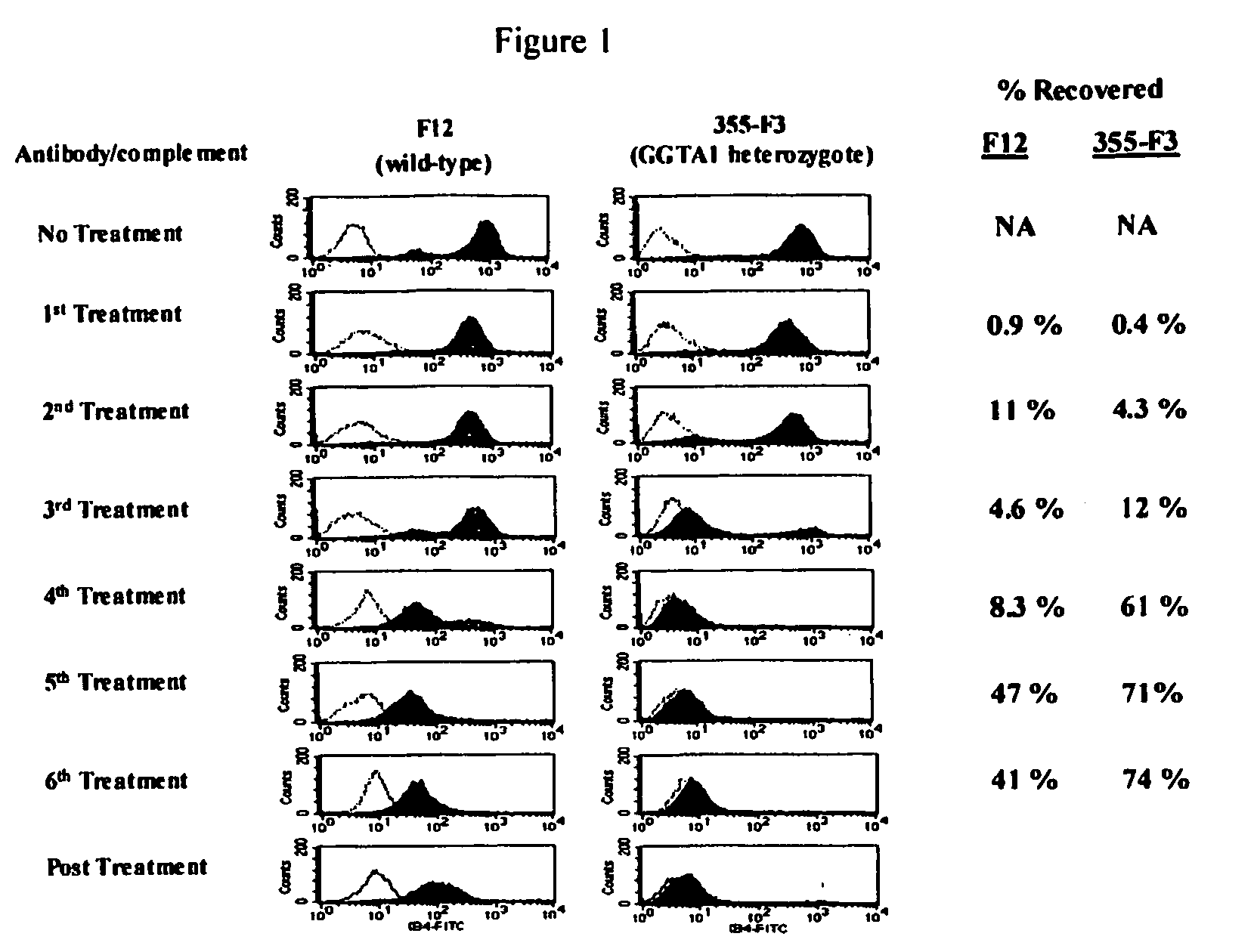
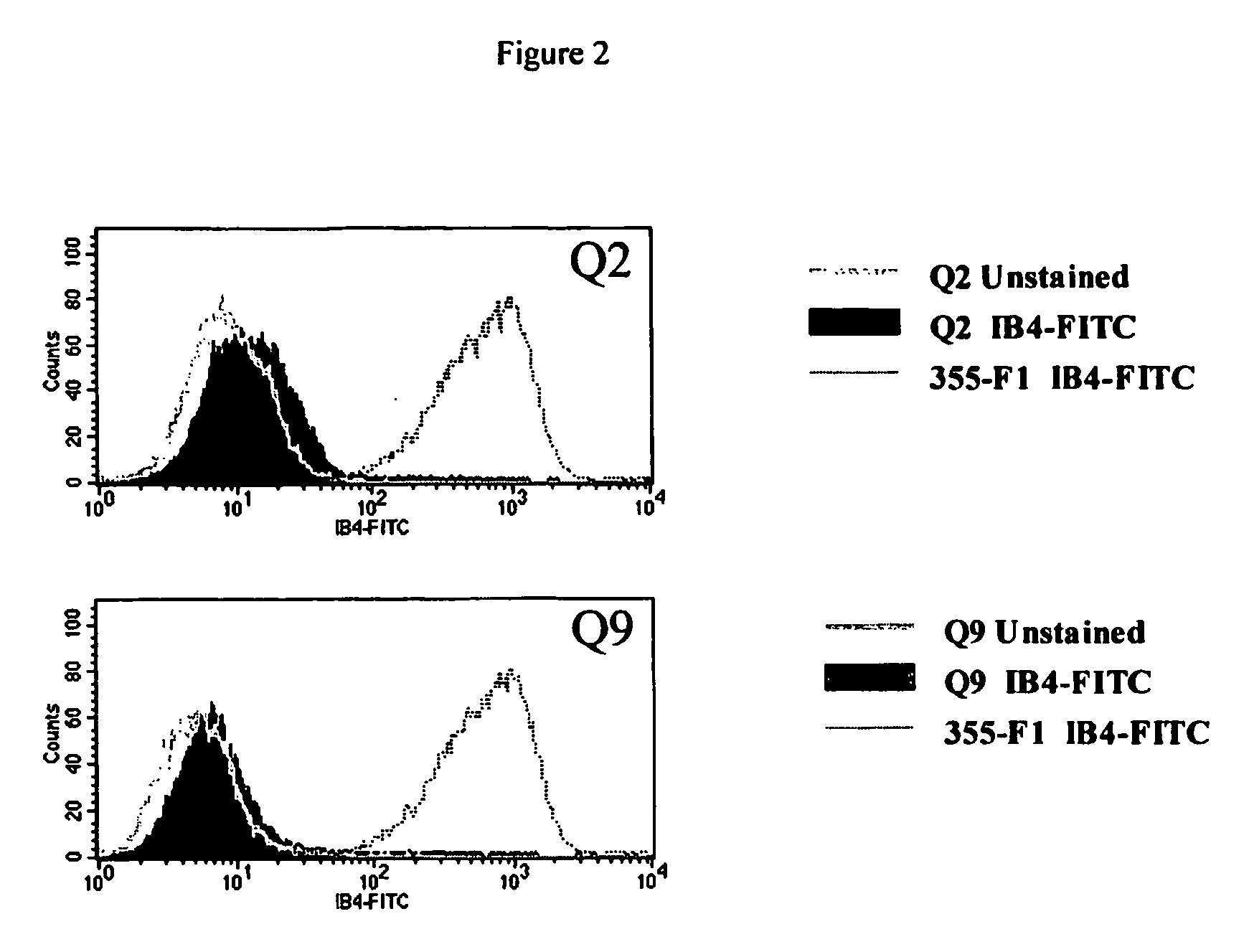
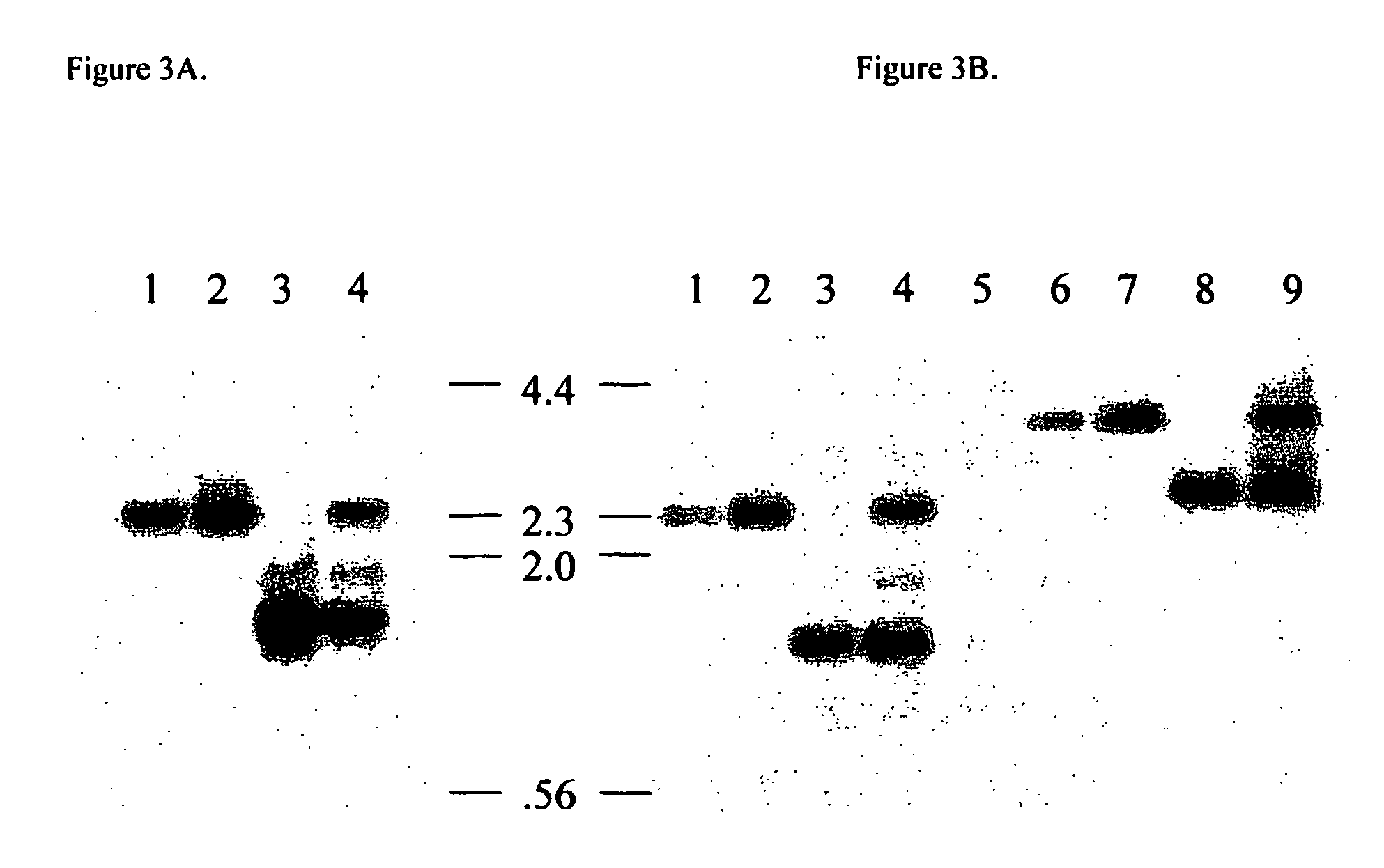
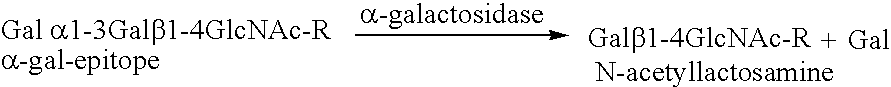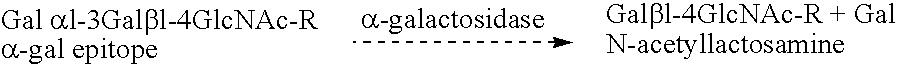Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
241 results about "Xenotransplantation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Xenotransplantation (xenos- from the Greek meaning "foreign" or strange), or heterologous transplant is the transplantation of living cells, tissues or organs from one species to another. Such cells, tissues or organs are called xenografts or xenotransplants. It is contrasted with allotransplantation (from other individual of same species), syngeneic transplantation or isotransplantation (grafts transplanted between two genetically identical individuals of the same species) and autotransplantation (from one part of the body to another in the same person).
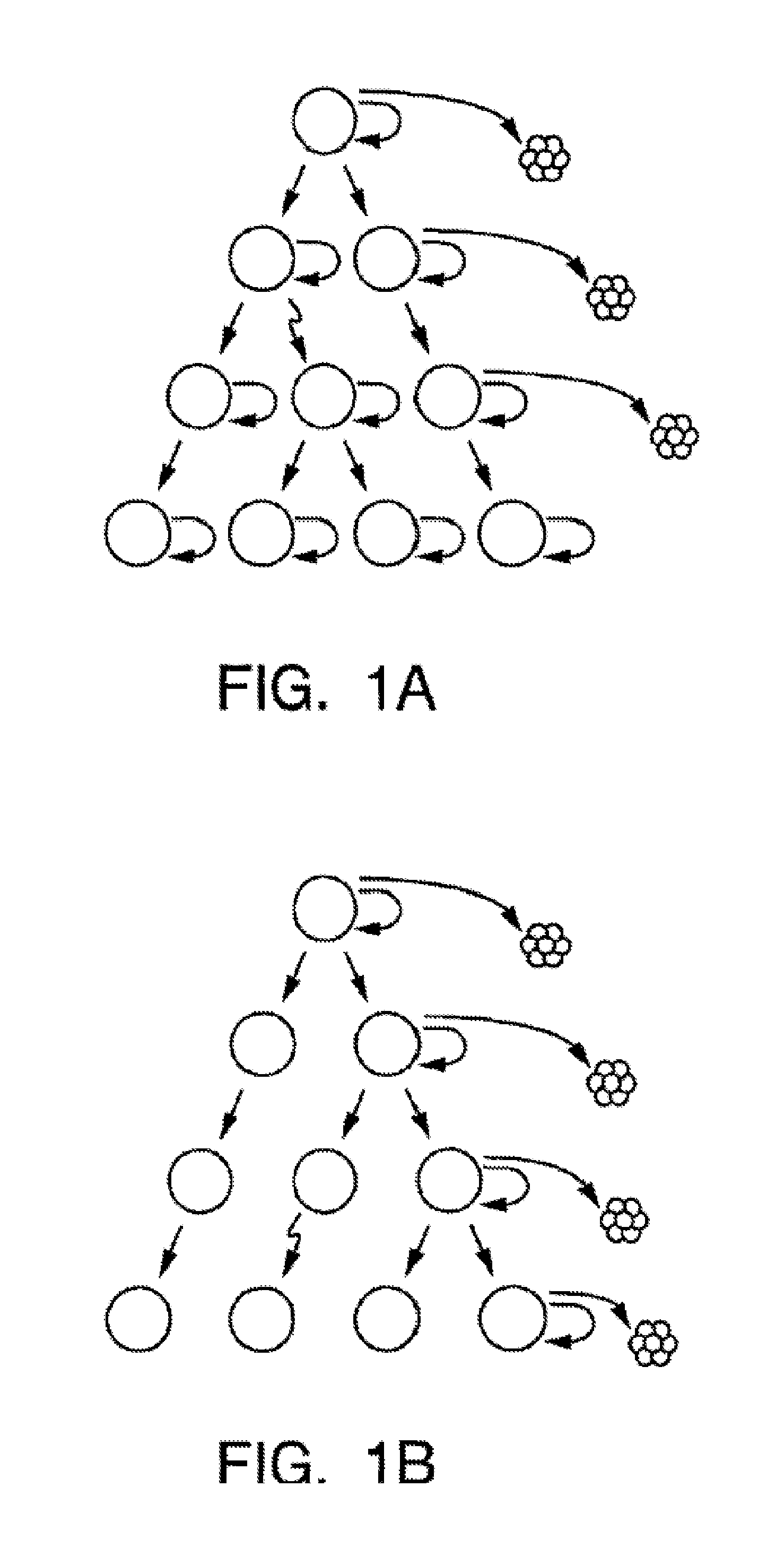
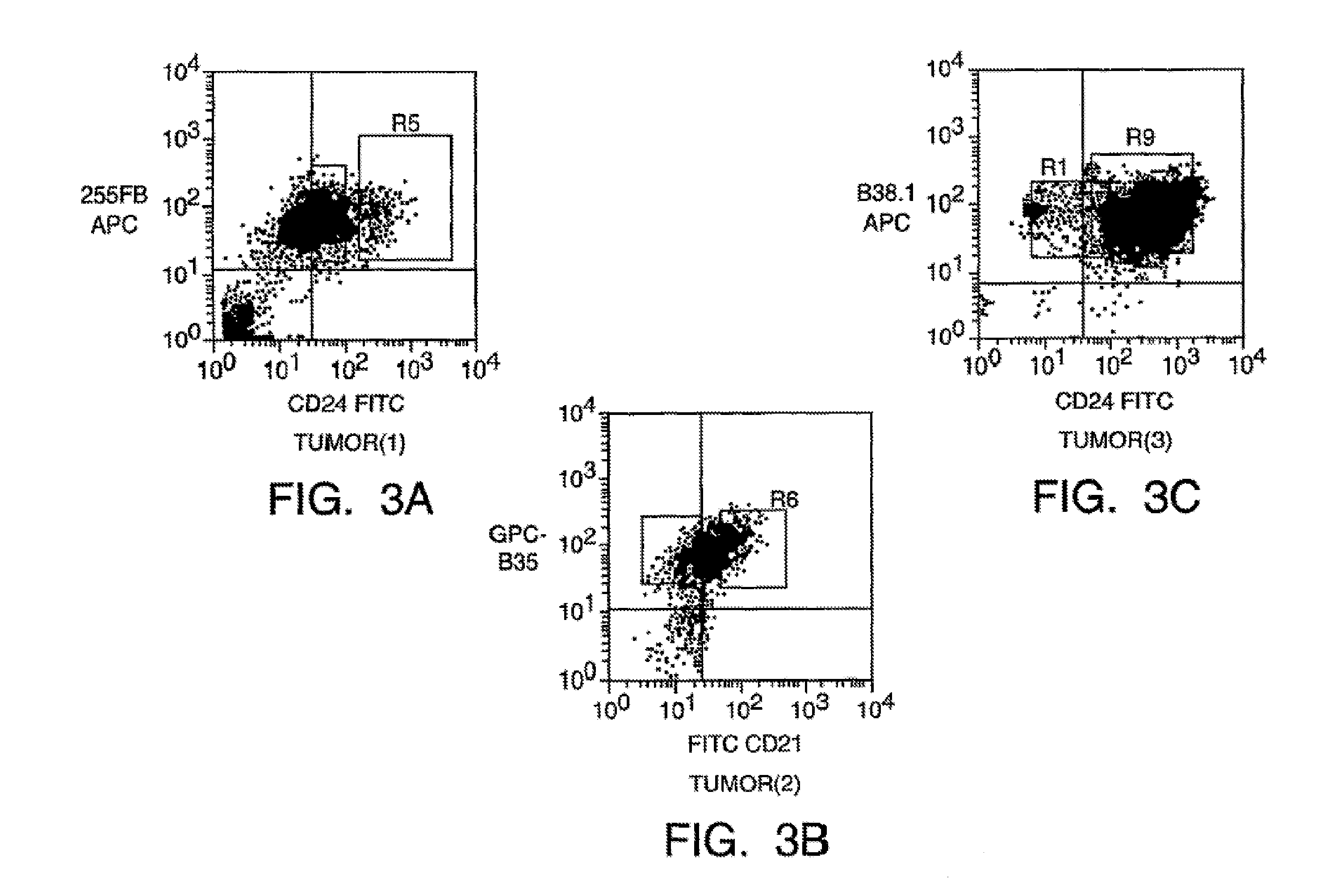
Isolation And Use Of Solid Tumor Stem Cells
InactiveUS20080178305A1Reduce spreadIncreased proliferationMaterial nanotechnologyMicrobiological testing/measurementAbnormal tissue growthMammary gland structure
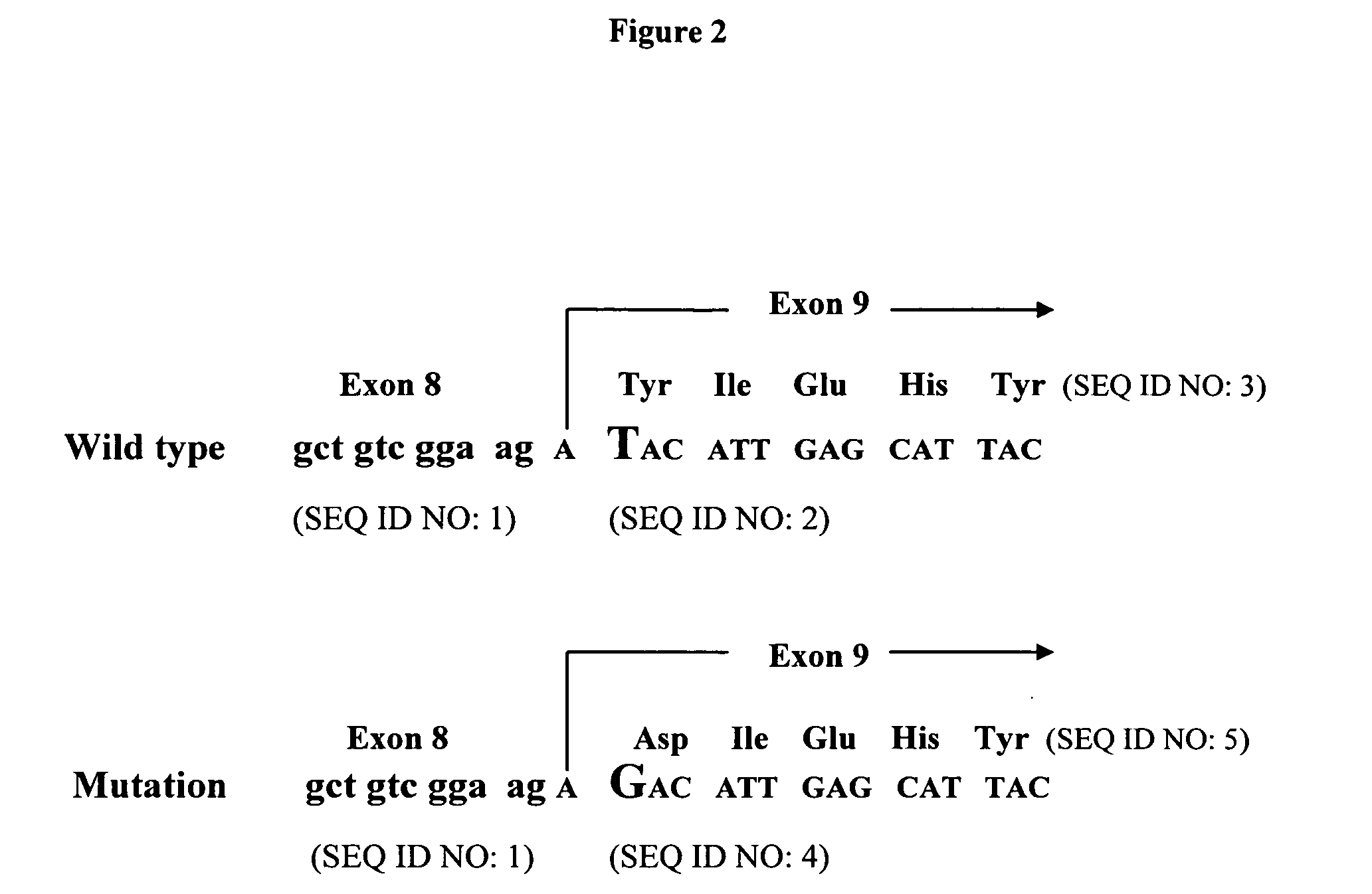
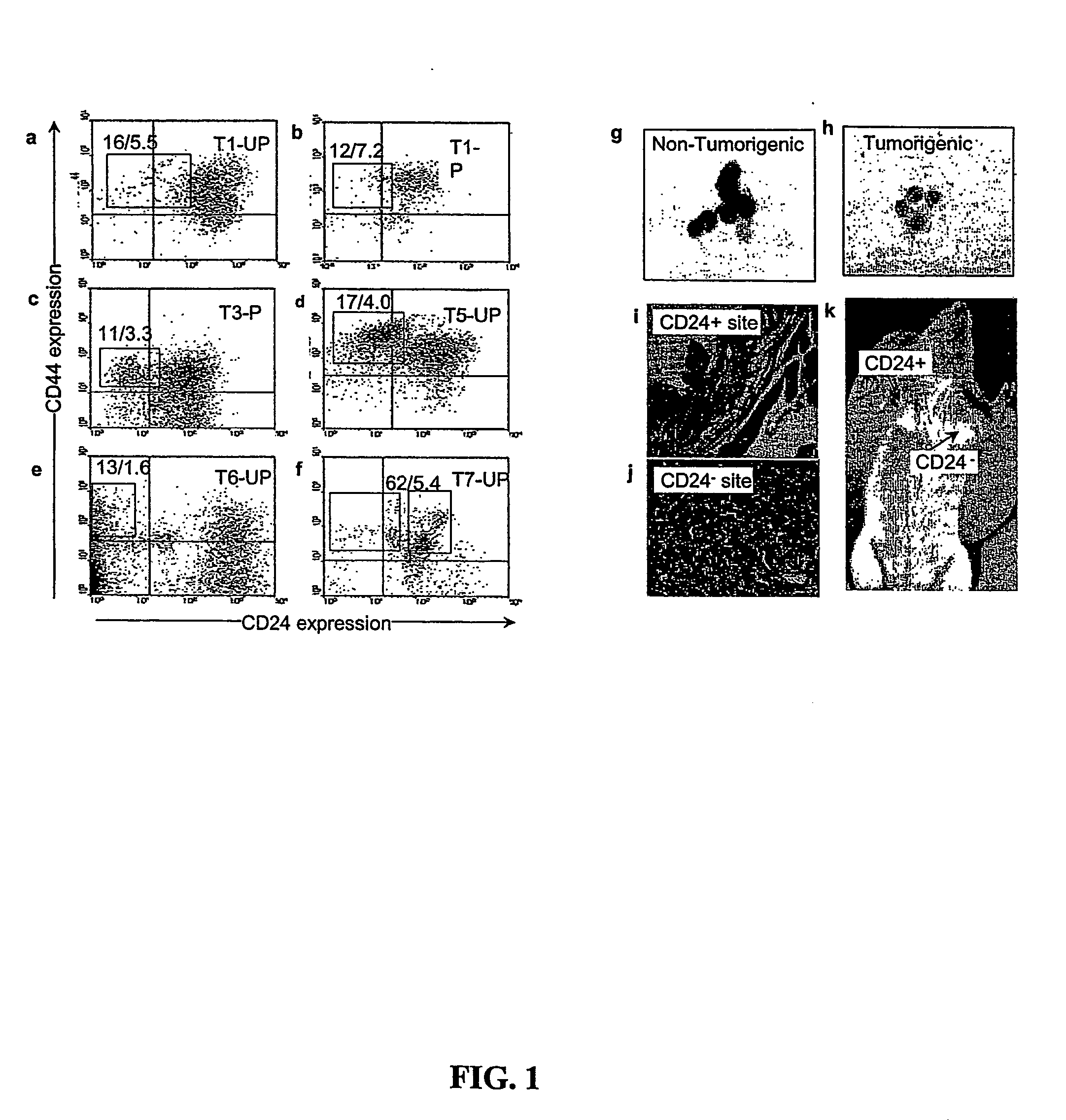
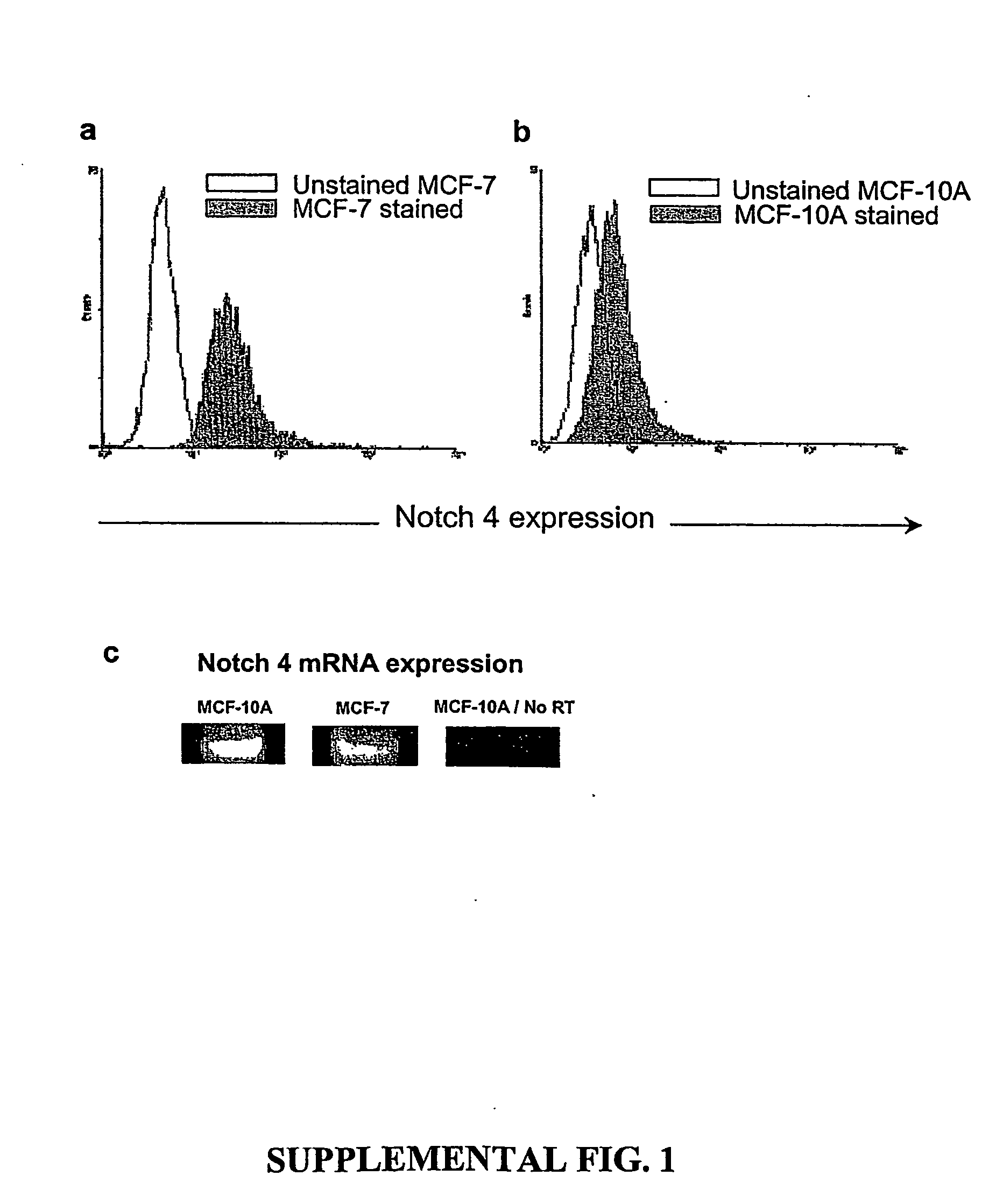
A small percentage of cells within an established solid tumor have the properties of stem cells. These solid tumor stem cells give rise both to more tumor stem cells and to the majority of cells in the tumor that have lost the capacity for extensive proliferation and the ability to give rise to new tumors. Thus, solid tumor heterogeneity reflects the presence of tumor cell progeny arising from a solid tumor stem cell. We have developed a xenograft model in which we have been able to establish tumors from primary tumors via injection of tumor cells in the mammary gland of severely immunodeficient mice. These xenograft assay have allowed us to do biological and molecular assays to characterize clonogenic solid tumor stem cells. We have also developed evidence that strongly implicates the Notch pathway, especially Notch 4, as playing a central pathway in carcinogenesis.
Owner:ONCOMED PHARMA +1
Tissue products derived from animals lacking any expression of functional alpha 1,3 galactosyltransferase
InactiveUS20050260176A1Prevent rejectionPromote wound healingBiocideGenetic material ingredientsTissue repairSkin repair
The present invention provides tissues derived from animals, which lack any expression of functional alpha 1,3 galactosyltransferase (alpha-1,3-GT). Such tissues can be used in the field of xenotransplantation, such as orthopedic reconstruction and repair, skin repair and internal tissue repair or as medical devices.
Owner:REVIVICOR INC
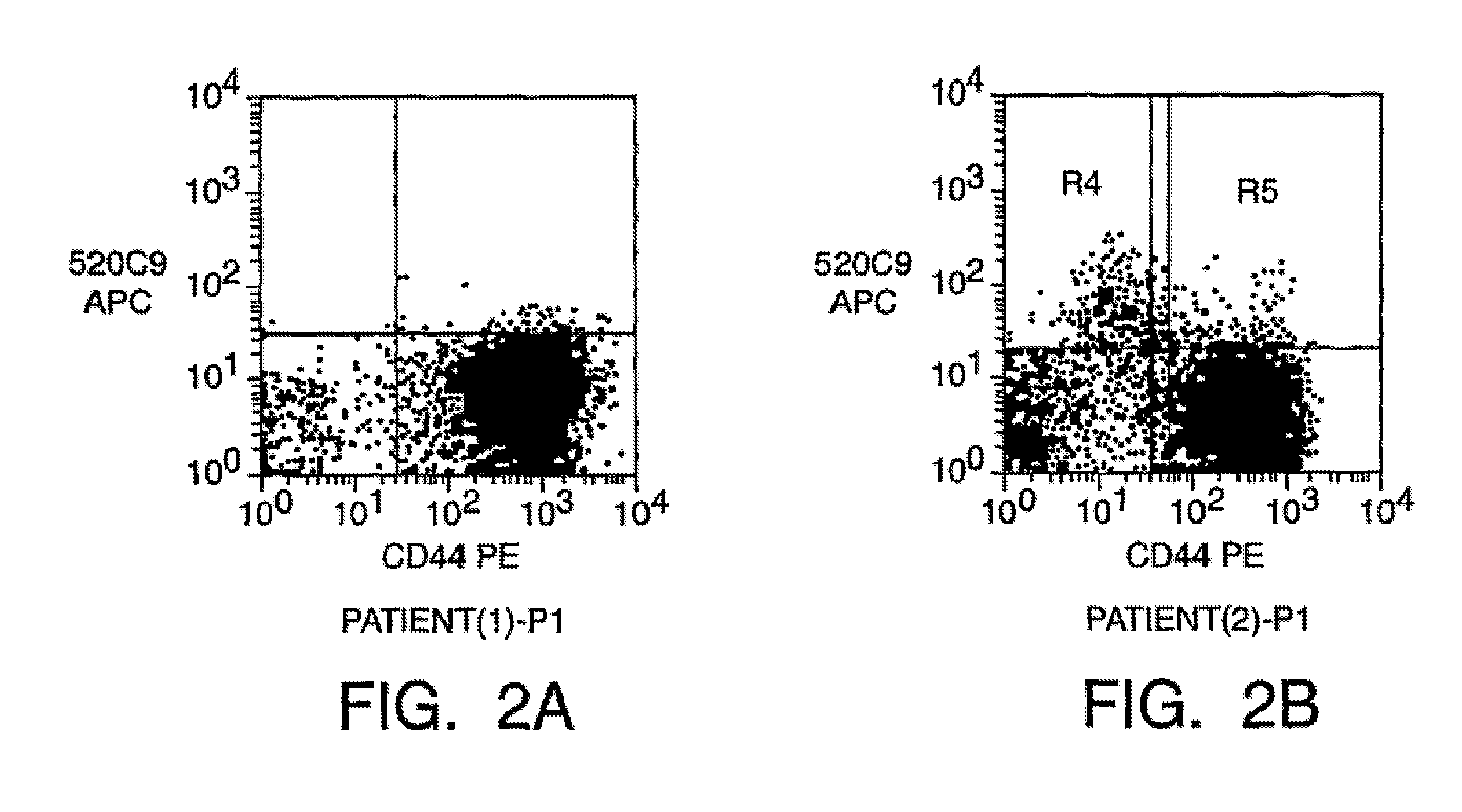
Prospective identification and characterization of breast cancer stem cells
InactiveUS20050089518A1Capacity loseOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsAbnormal tissue growthSurface marker
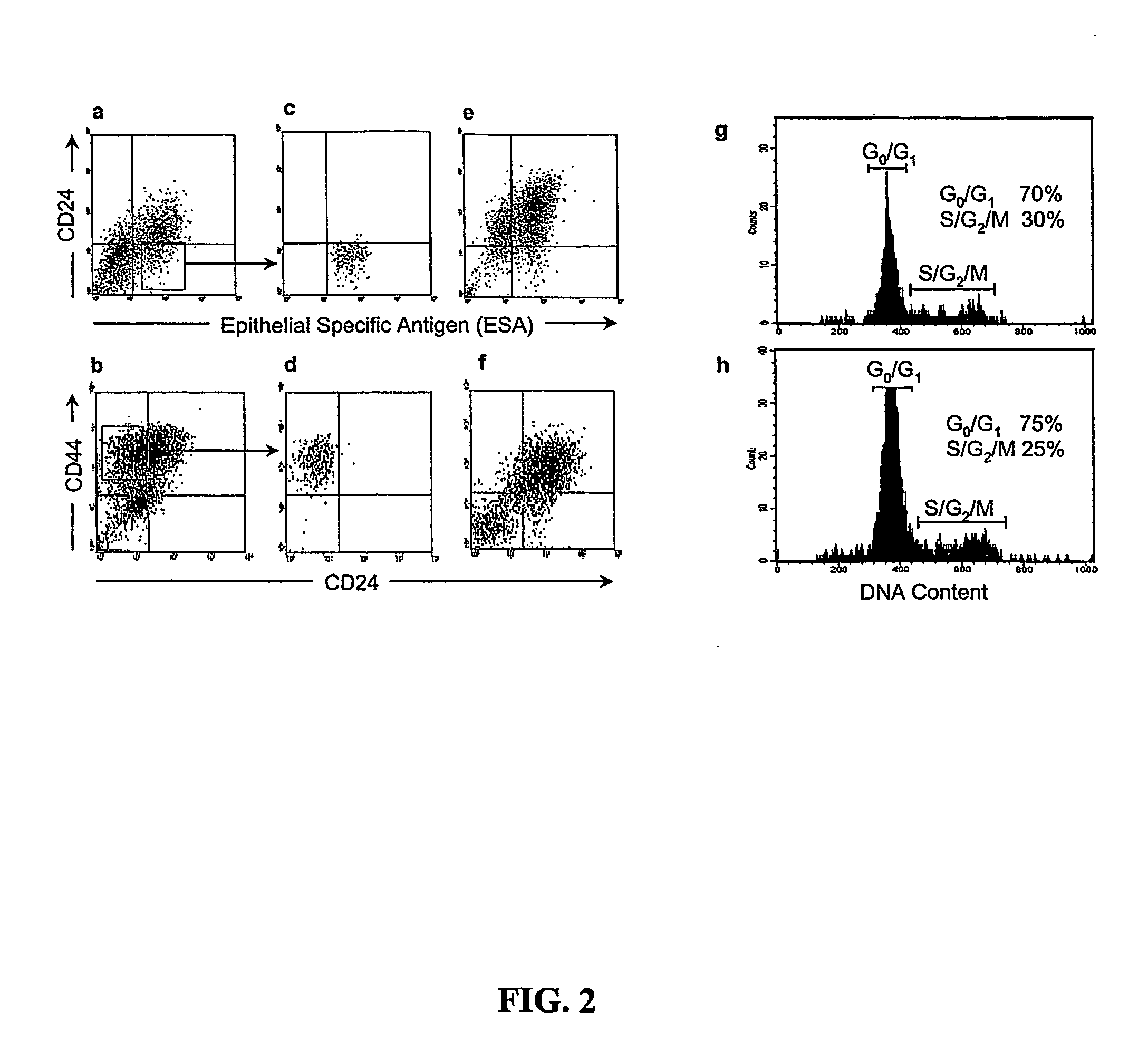
Human breast tumors contain hetrogeneous cancer cells. using an animal xenograft model in which human breast cancer cells were grown in immunocompromised mice we found that only a small minority of breast cancer cells had capacity to form new tumors. The ability to form new tumors was not a slochastic property, rather certain populations of cancer cells were depleted for the ability to form new tumors, while other populations were enriched for the ability to form new tumors. Tumorigenic cells could be distinguished from non-tumorigenic cancer cells based on surface marker expression. We prospectively identified and isolated the tumorigenic cells as CD4430CD24− / lowLINEAGE A few as 100 cells from this population were able to form tumors the animal xenograft model, while tens of thousands of cells from non-tumorigenic populations failed to form tumors. The tumorigenic cells could be serially passaged, each time generating new tumors containing and expanded numbers of CD44+CD24 Lineage tumorigenic cells as well as phenotypically mixed populations of non-tumorigenic cancer cells. This is reminiscent of the ability of normal stem cells to self-renew and differentiate. The expression of potential therapeutic targets also differed between the tumorigenic and non-tumorigenic populations. Notch activation promoted the survival of the tumorigenic cells, and a blocking antibody against Notch 4 induced tumorigenic breast cancer cells to undergo apoptosis.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
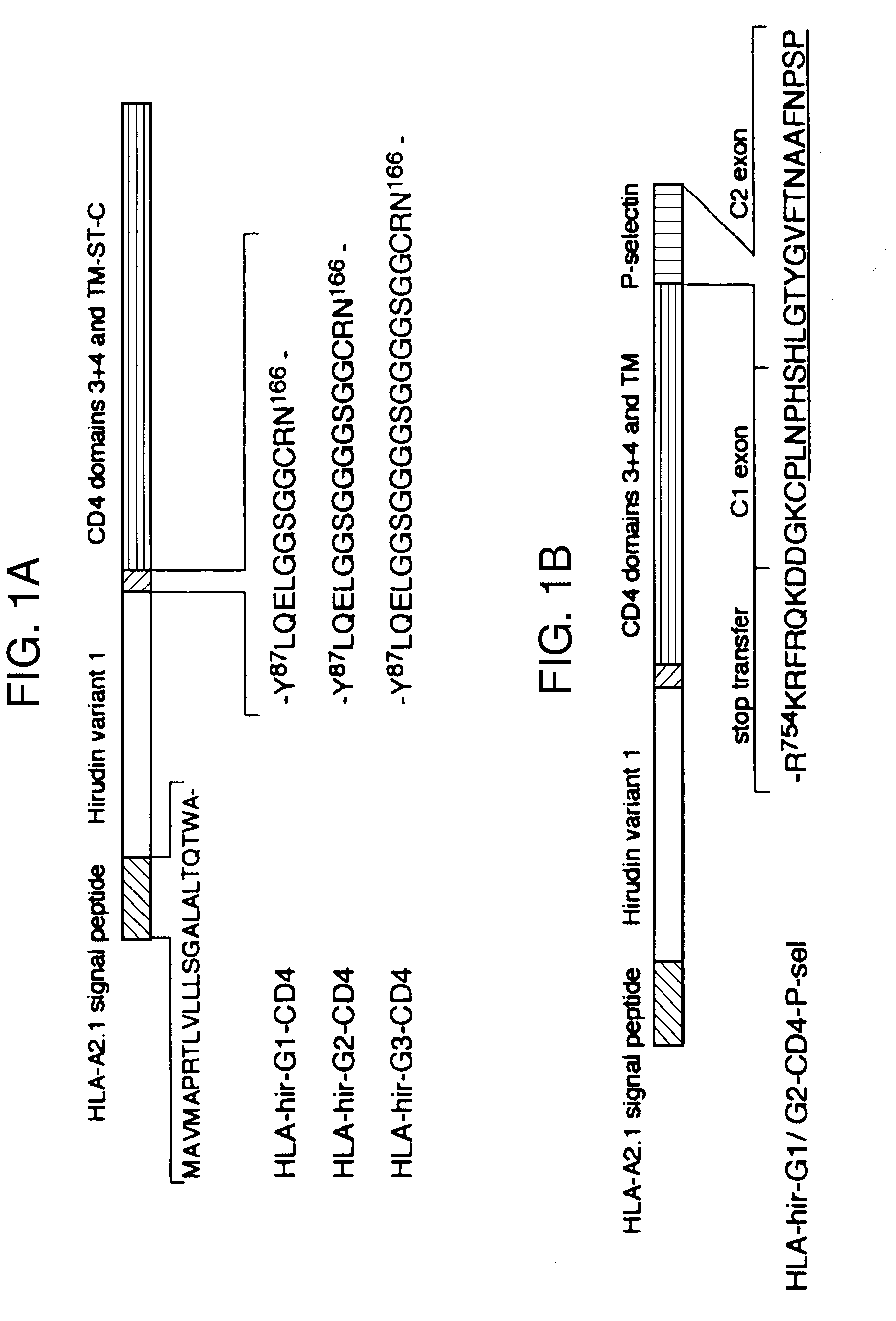
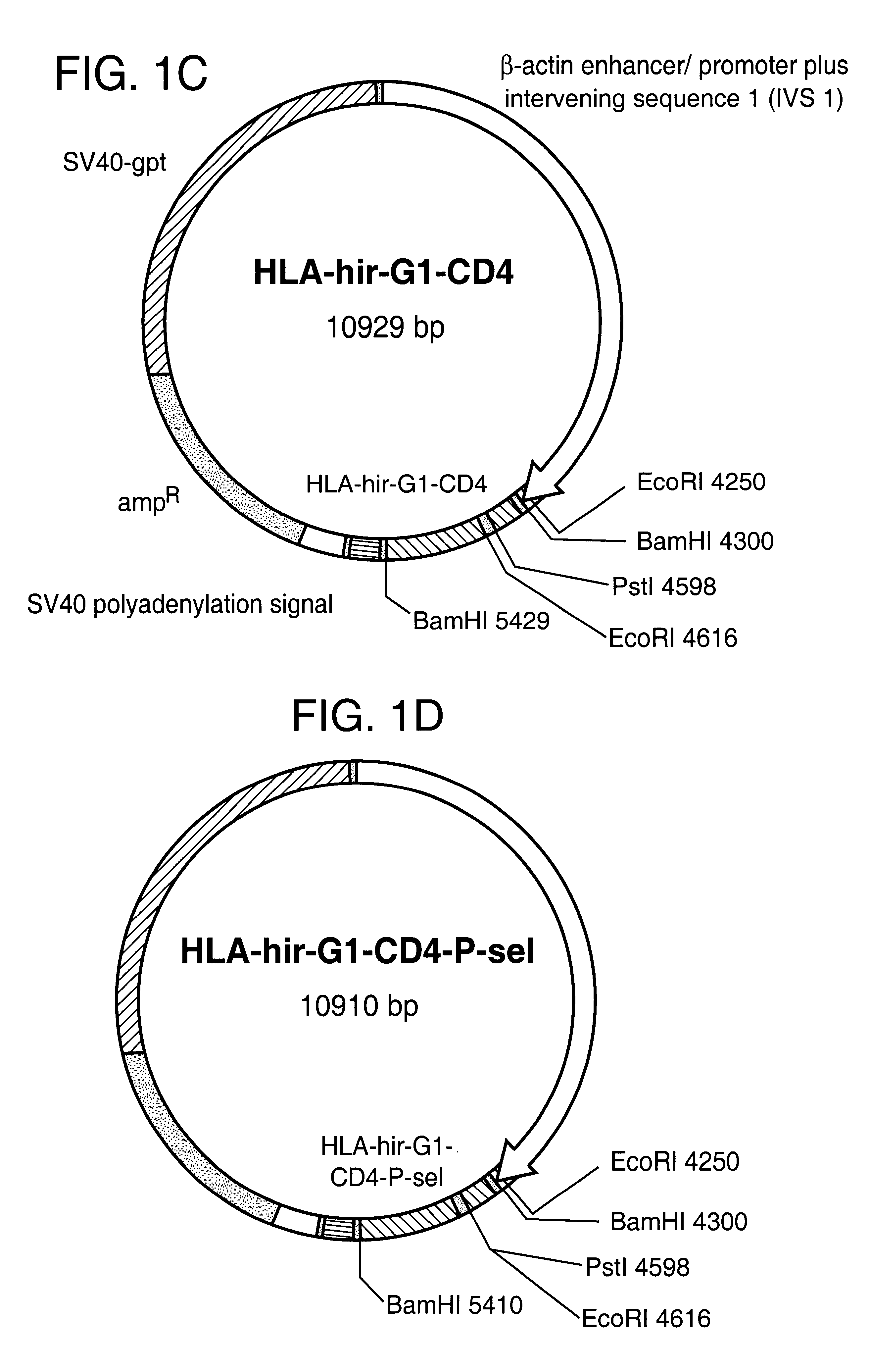
Anticoagulant fusion protein anchored to cell membrane
InactiveUS6423316B1Prolong clotting timeGood curative effectFungiVirusesCell membraneBlood coagulations
The invention relates to the inhibition of blood coagulation, especially during organ rejection, and in particular the inhibition of delayed vascular rejection. The invention provides anticoagulant proteins which are anchored to cell membranes. The anticoagulant function preferably provided by heparin, antithrombin, hirudin, TFPI, tick anticoagulant peptide, or a snake venom factor. These anticoagulant proteins are preferably prevented from being constitutively expressed at the cell surface. In particular, expression at the cell surface is regulated according to cell activation, for instance by targeting the protein to a suitable secretory granule. Expression of these proteins renders cells, tissues and organs less vulnerable to rejection after transplantation (e.g. after xenotransplantation).
Owner:IMPERIAL INNOVATIONS LTD
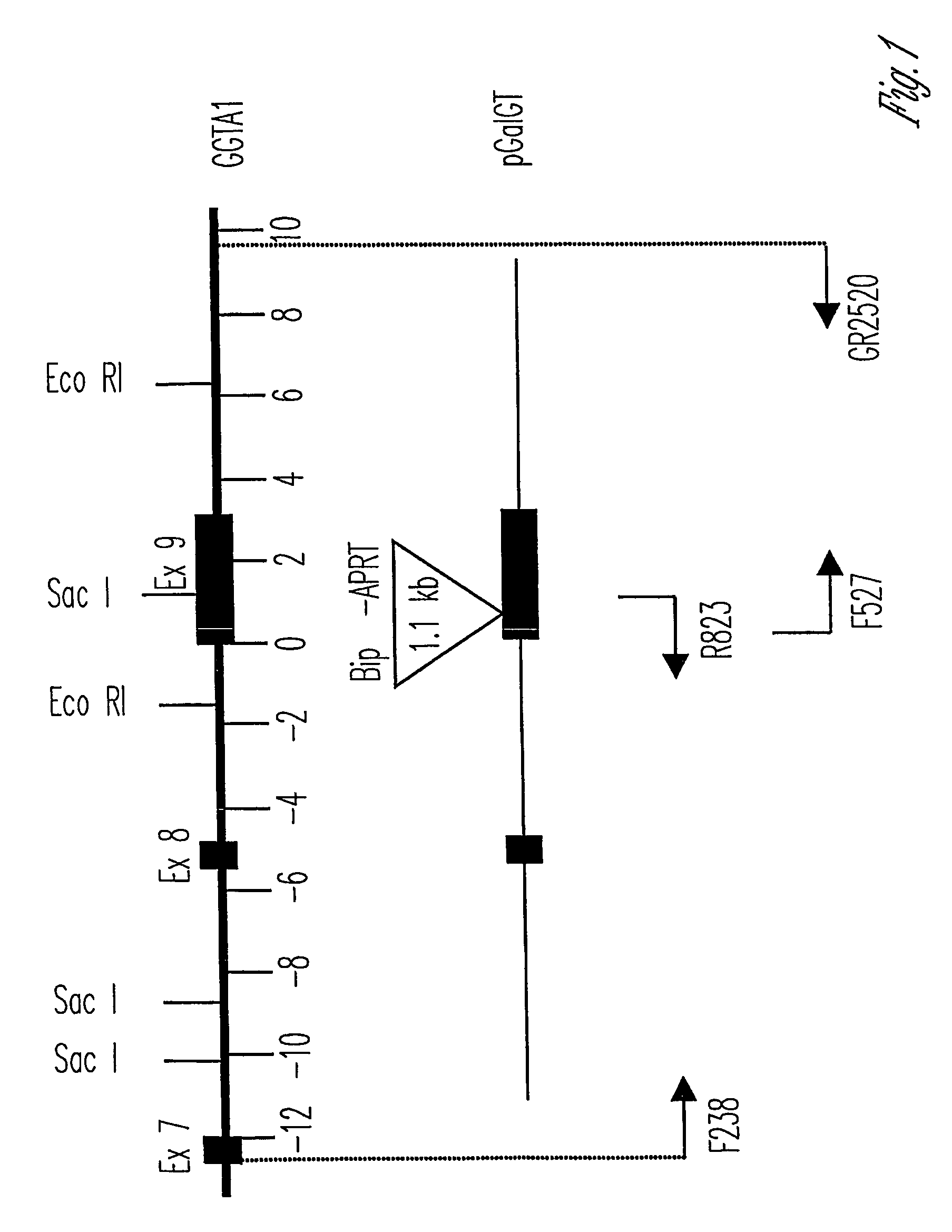
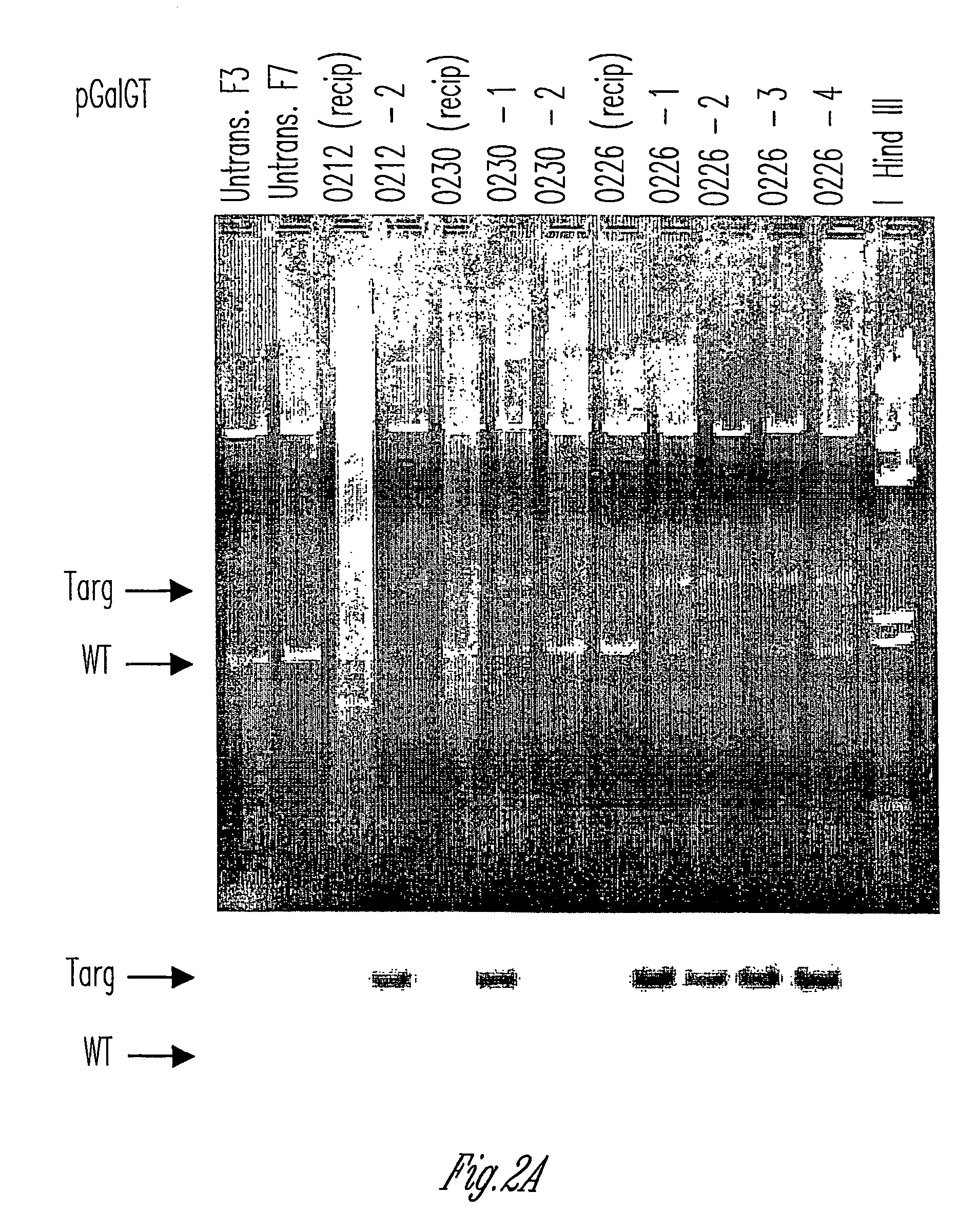
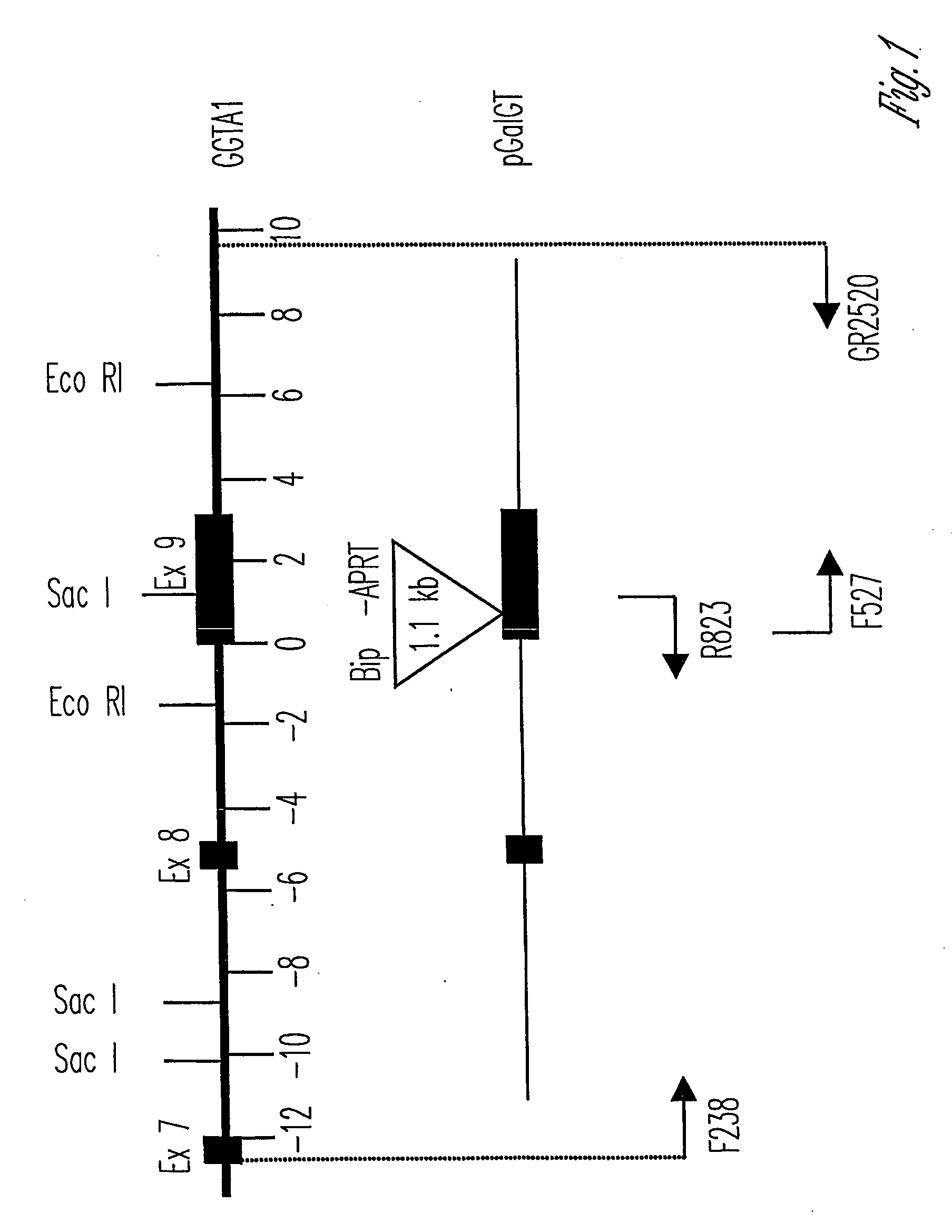
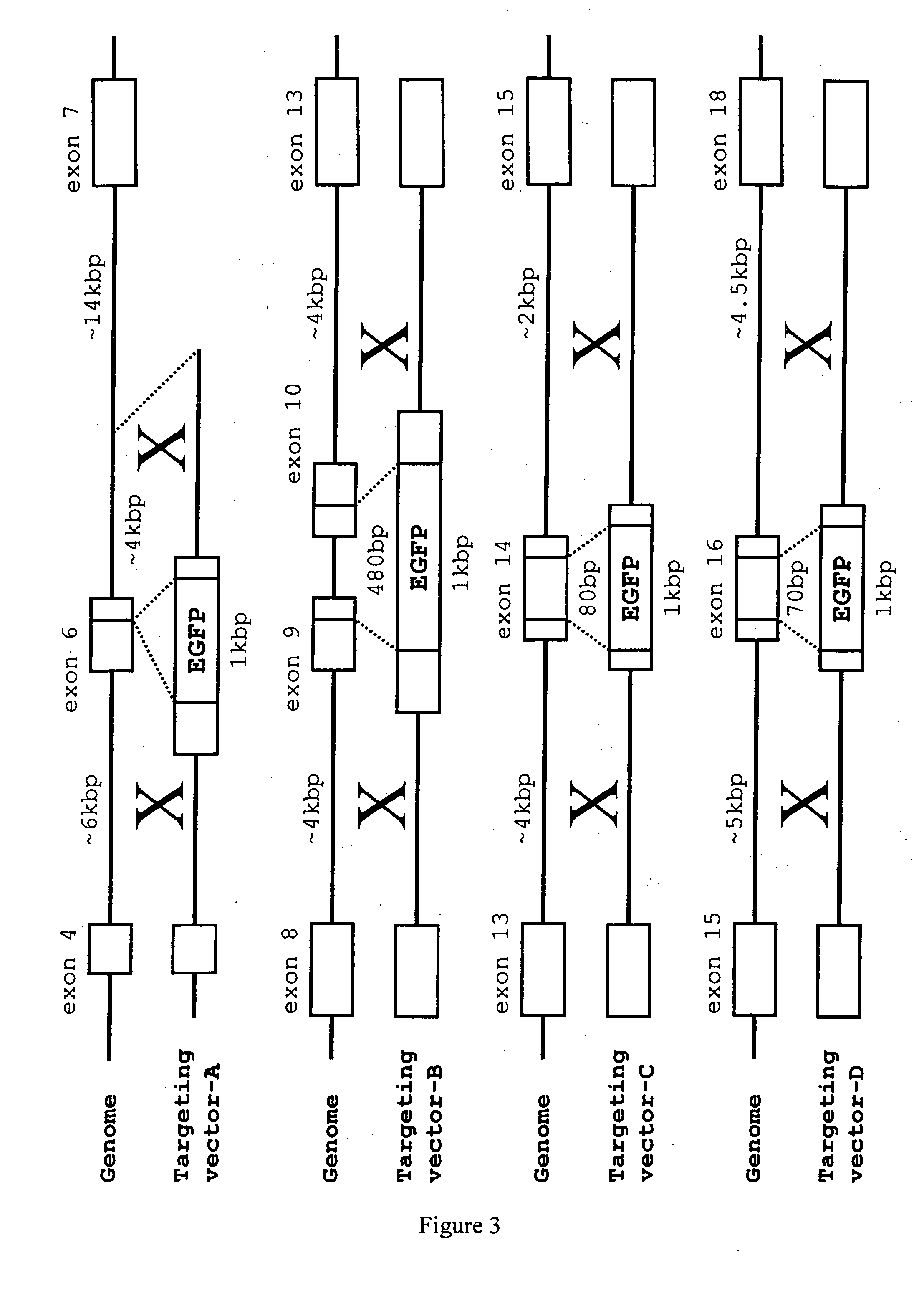
Alpha(1,3)-galactosyltransferase knockout swine, tissues and organs
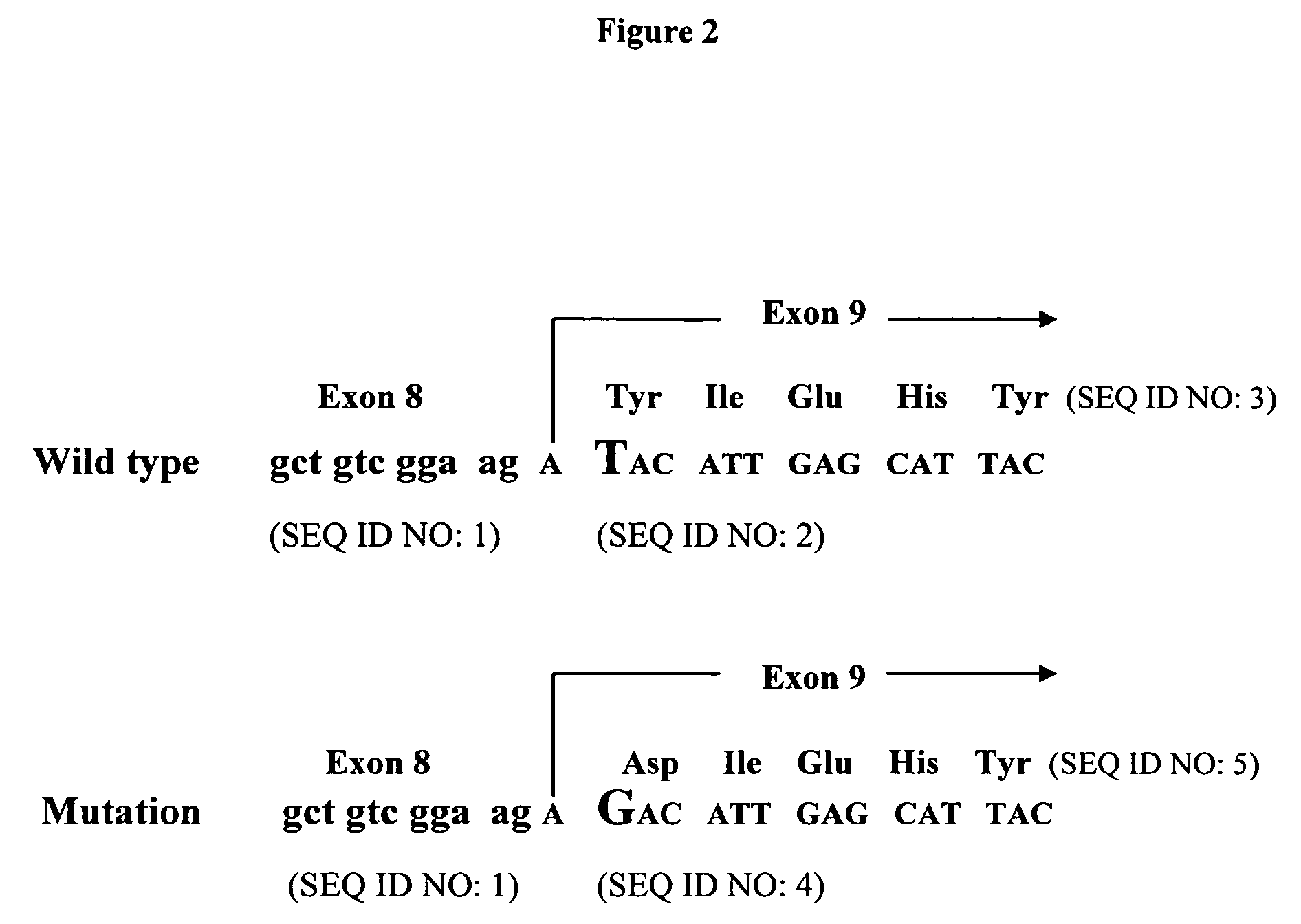
The invention relates to the genetic manipulation of non-human animals. More particularly, the invention relates to genetic manipulation of non-human animals to be used for xenotransplantation. The invention provides viable gene knockout swine including swine in which the α(1,3)-galactosyltransferase gene has been disrupted, methods for making such swine, and methods of using the tissues and organs of such swine for xenotransplantation.
Owner:IMMERGE BIOTHERAPEUTICS +1
Surrogate tolerogenesis for the development of tolerance to xenografts
InactiveUS6060049AIncrease differentiationIncreased proliferationBiocideGenetic material ingredientsHematopoietic cellTolerability
PCT No. PCT / US94 / 05844 Sec. 371 Date Jun. 6, 1995 Sec. 102(e) Date Jun. 6, 1995 PCT Filed May 24, 1994 PCT Pub. No. WO94 / 27622 PCT Pub. Date Dec. 8, 1993This invention provides a method for developing immune tolerance in xenogeneic organ graft recipients, in which lympho-hematopoietic cells from an intended organ graft recipient are differentiated within a xenogeneic surrogate, such as a fetal animal. After birth of the surrogate, the matured lympho-hematopoietic cells containing antigen specific regulatory cells, including suppressor cells, veto cells, select B cells, anti-idiotype antibodies, and other related factors responsible for antigen specific tolerance in a surrogate animal are reintroduced into the intended organ graft recipient, in conjunction with an organ transplant or a tissue transplant from the xenograft surrogate. The invention also provides an organ graft repopulated with cells from the intended organ graft recipient produced in a surrogate animal.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Knockout swine and methods for making the same
The invention relates to the genetic manipulation of non-human animals. More particularly, the invention relates to genetic manipulation of non-human animals to be used for xenotransplantation. The invention provides viable gene knockout swine including swine in which the α(1,3)-galactosyltransferase gene has been disrupted, methods for making such swine, and methods of using the tissues and organs of such swine for xenotransplantation.
Owner:IMMERGE BIOTHERAPEUTICS +1
Multi-Transgenic Pigs for Diabetes Treatment
ActiveUS20110038841A1Reduce needInhibit the inflammatory responseBiocideVectorsTransgenePancreatic islets
The present invention provides certain animals, and in particular porcine animals, tissue and cells derived from these, which lack any expression of functional alpha 1,3 galactosyltransferase (αGT) and express one or more additional transgenes which make them suitable donors for pancreatic islet xenotransplantation. Methods of treatment and prevention of diabetes using cells derived from such animals are also provided.
Owner:REVIVICOR INC
Tissue products derived from porcine animals lacking any expression of functional alpha 1,3 galactosyltransferase
InactiveUS8106251B2Prevent rejectionPromote wound healingHeart valvesGenetic material ingredientsTissue repairSkin repair
The present invention provides tissues derived from animals, which lack any expression of functional alpha 1,3 galactosyltransferase (alpha-1,3-GT). Such tissues can be used in the field of xenotransplantation, such as orthopedic reconstruction and repair, skin repair and internal tissue repair or as medical devices.
Owner:REVIVICOR INC
Porcine CMP-N-Acetylneuraminic acid hydroxylase gene
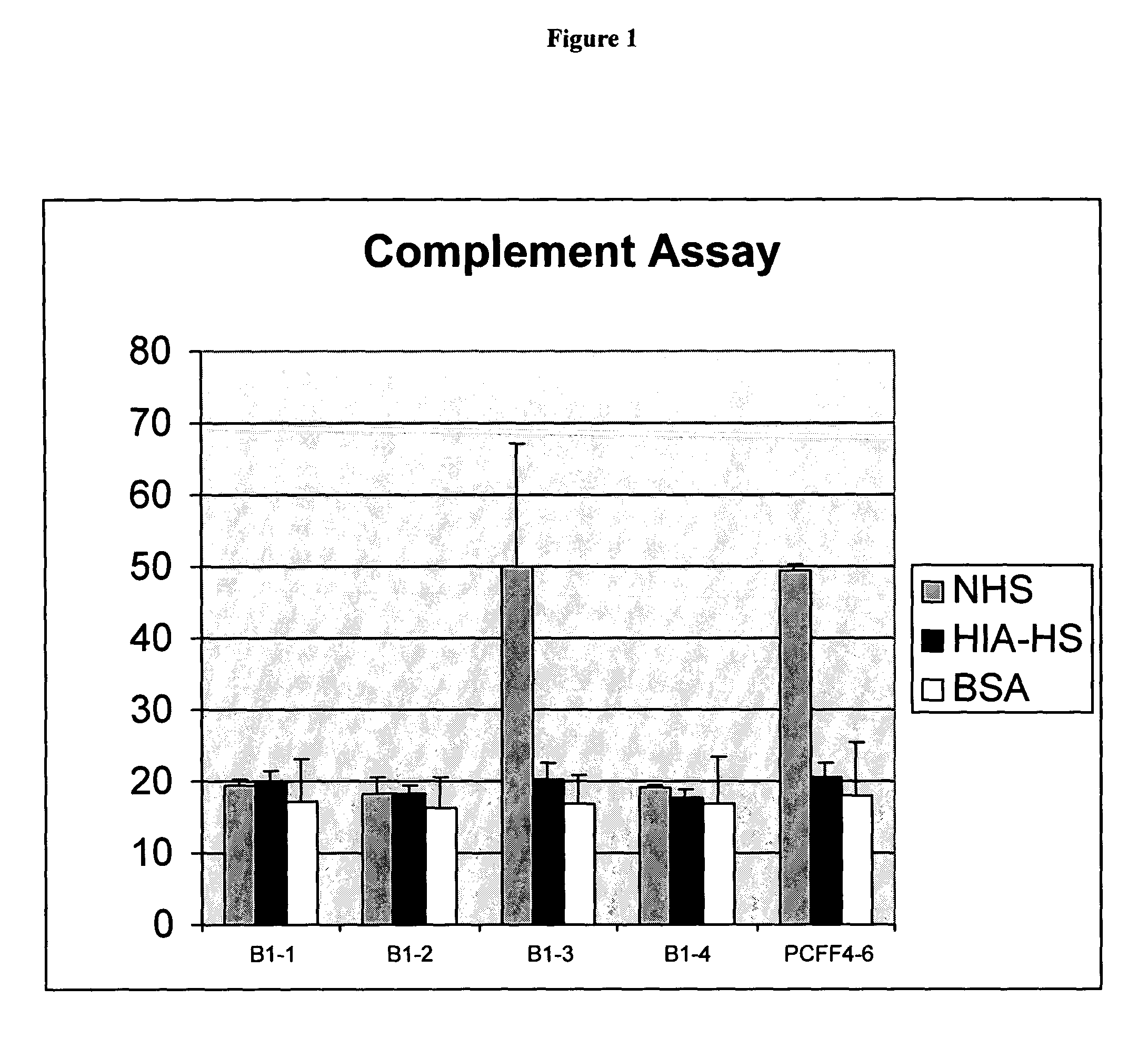
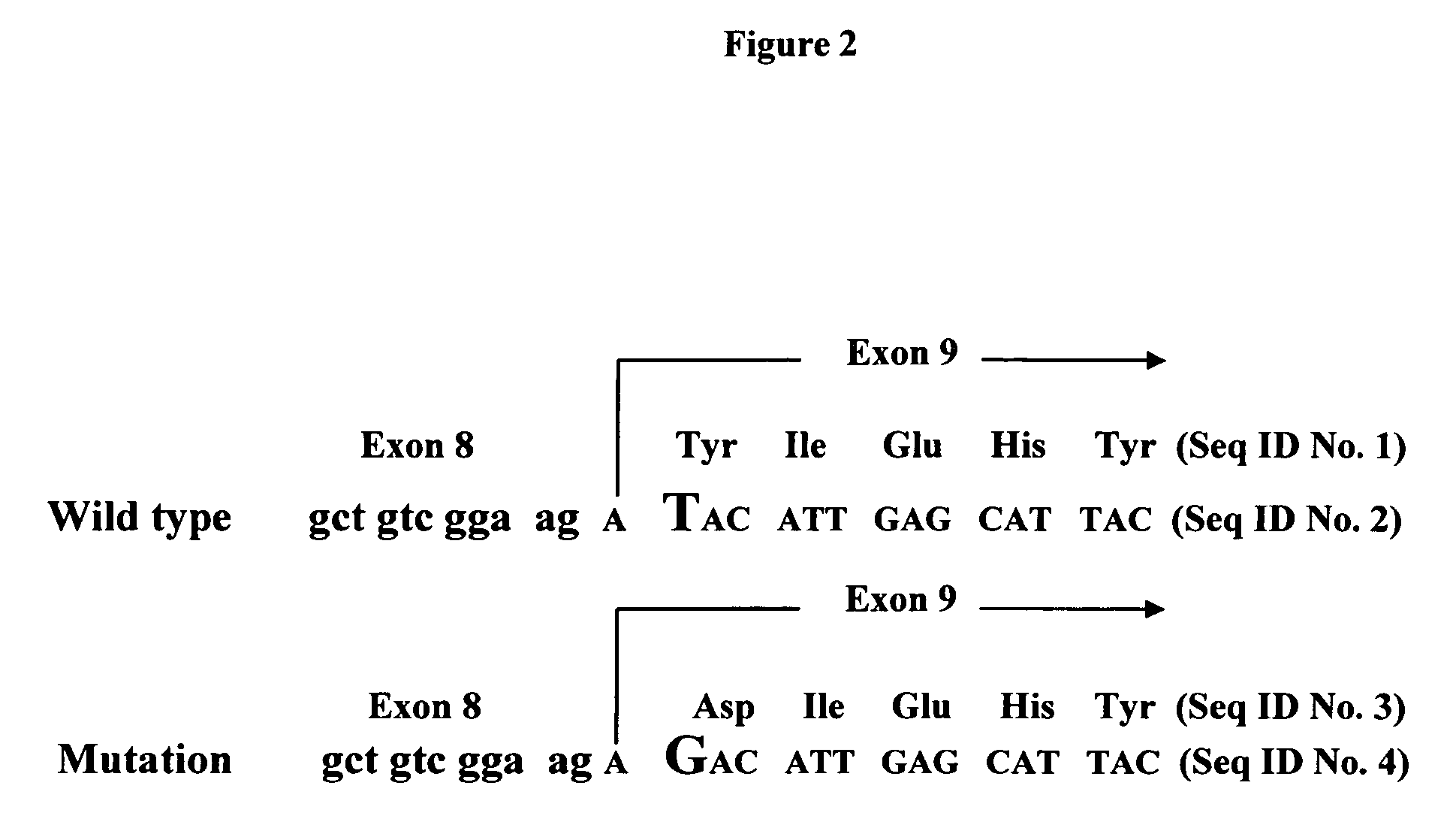
InactiveUS7368284B2Reduce immune rejectionNervous disorderSugar derivativesGenomic DNACMP-N-acetylneuraminic acid hydroxylase
The present invention provides porcine CMP-N-Acetylneuraminic-Acid Hydroxylase (CMP-Neu5Ac hydroxylase) protein, cDNA, and genomic DNA regulatory sequences. Furthermore, the present invention includes porcine animals, tissues, and organs, as well as cells and cell lines derived from such animals, tissues, and organs, which lack expression of functional CMP-Neu5Ac hydroxylase. Such animals, tissues, organs, and cells can be used in research and in medical therapy, including in xenotransplantation, and in industrial livestock farming operations.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF PITTSBURGH
Antigenic fusionprotein carrying Galalpha1,3Gal epitopes
InactiveUS6943239B2Effective absorptionEasy and cheap to produceOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsEpitopeImmunoglobulin IgE
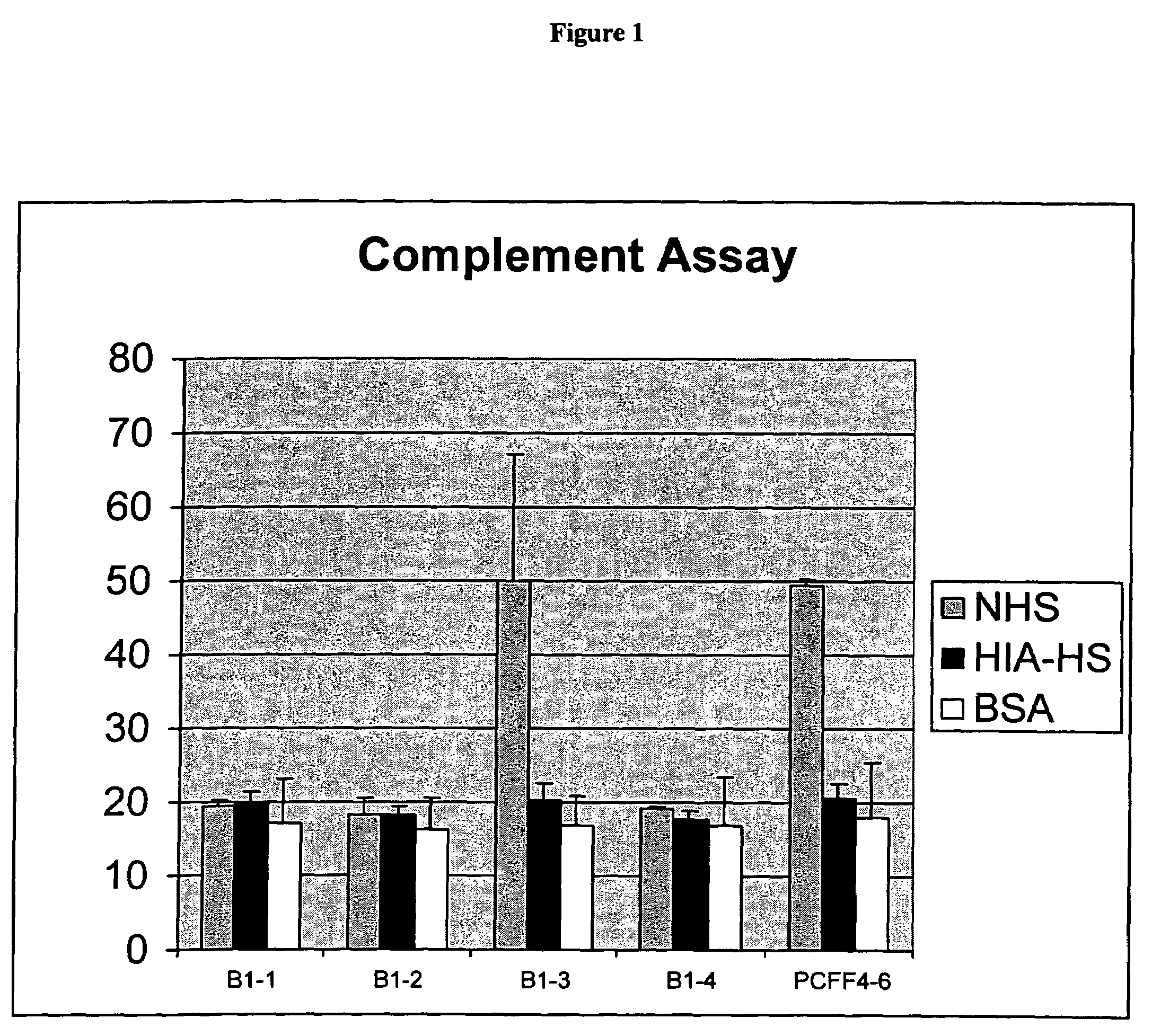
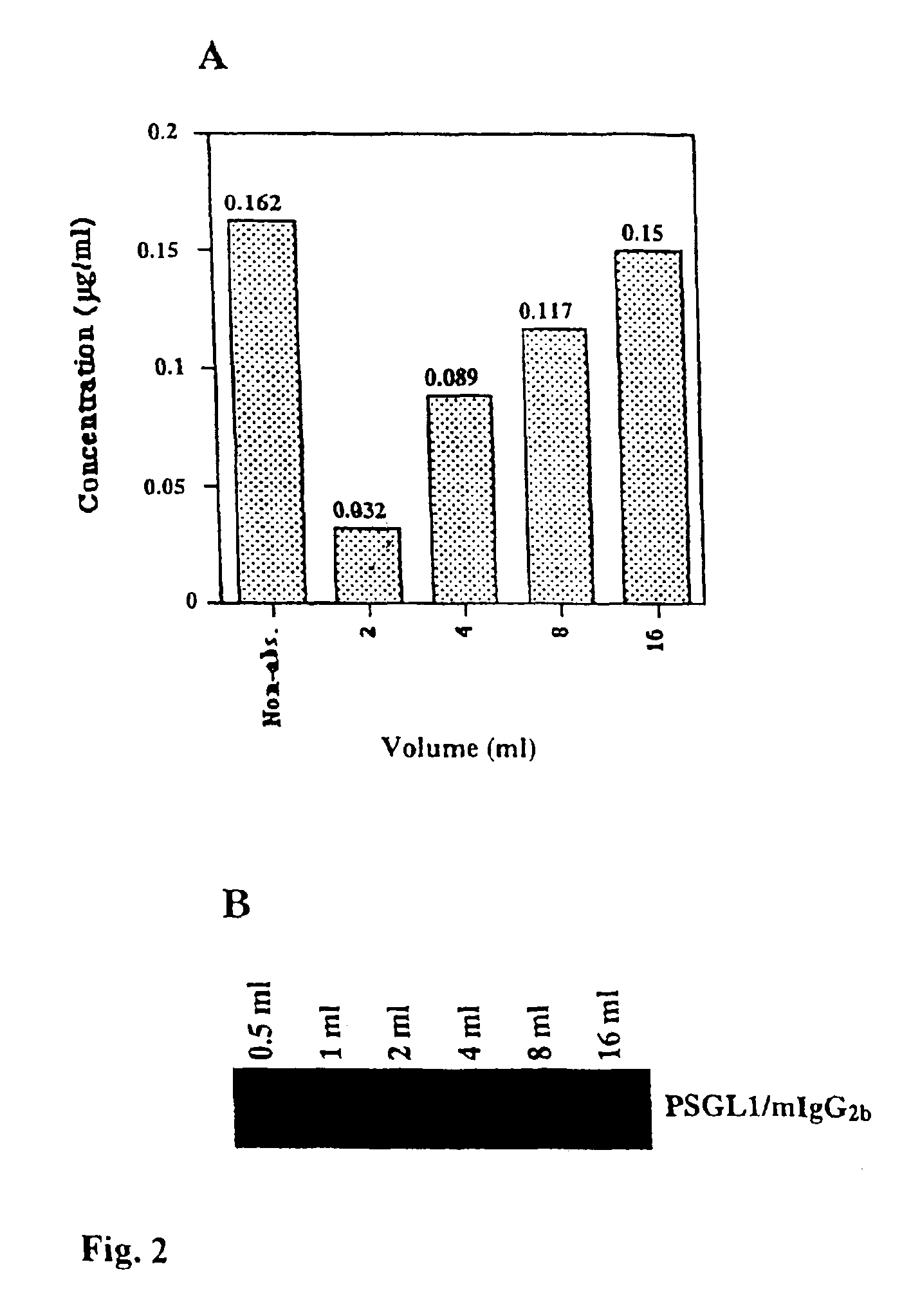
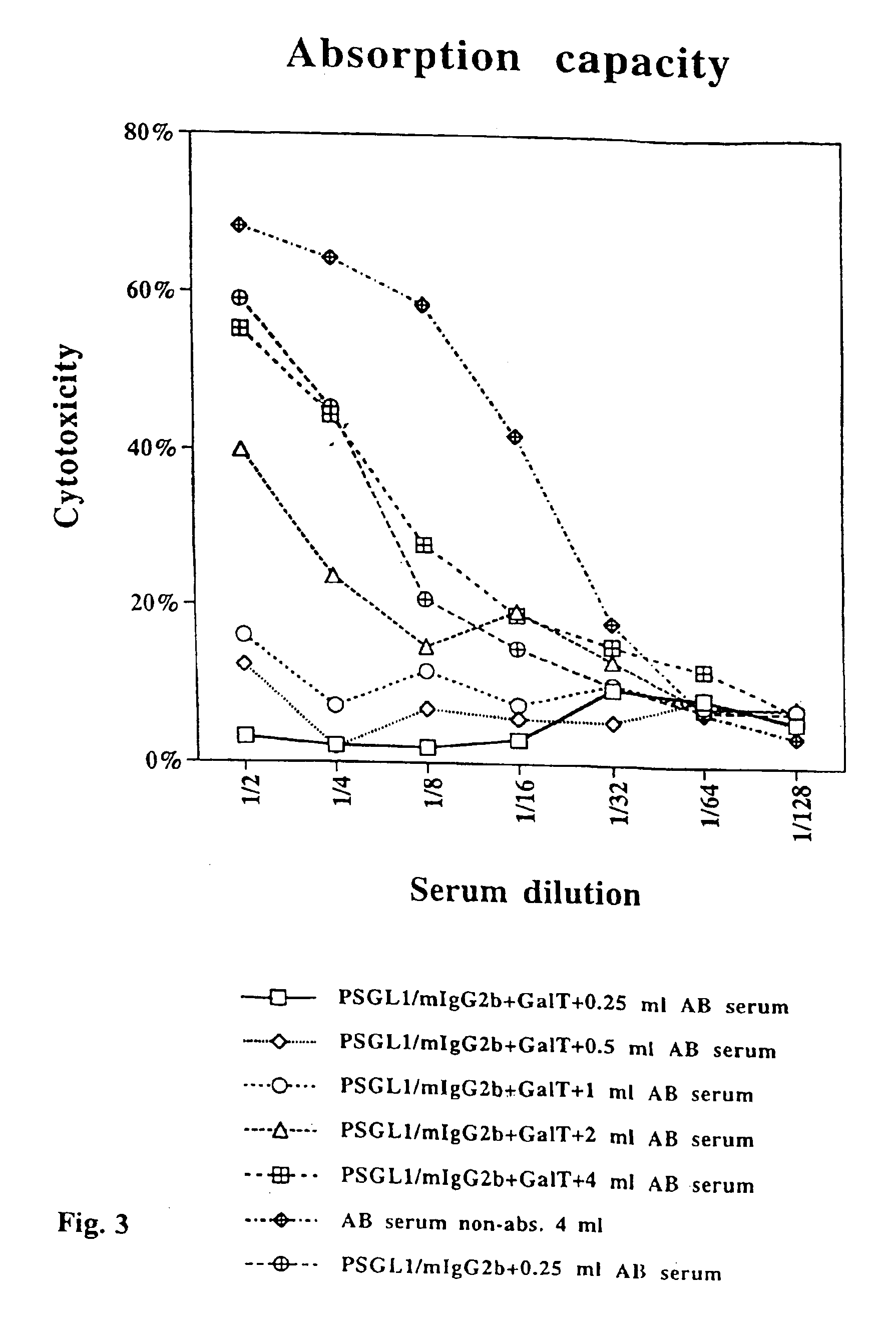
The present invention relates to an antigenic fusionprotein, which carries multiple Galα1,3Gal epitopes. The fusion protein according to the invention may also be comprised of a heavily glycosylated mucin part, which mediates binding to selectins, such as PSGL-1, and a part, which exhibits immunoglobulin properties, such as the Fc part of IgG. The fusionprotein according to the invention is preferably used as an absorber to prevent a hyperacute rejection of a xenotransplant, such as a pig tissue or organ transplanted into a human patient. In addition, the invention relates to a method for the prevention of hyperacute rejection reaction in a patient who is to receive a xenotransplant.
Owner:RECOPHARMA AB
Porcine animals lacking any expression of functional alpha 1, 3 galactosyltransferase
ActiveUS7795493B2Eliminating hyperacute rejectionTransferasesHybrid cell preparationHeterograftsXenotransplantation
The present invention is a porcine animal, tissue, organ, cells and cell lines, which lack any expression of functional alpha 1,3 galactosyltransferase (alpha1,3GT). These animals, tissues, organs and cells can be used in xenotransplantation and for other medical purposes.
Owner:REVIVICOR INC
Encapsulation system
InactiveUS20090214660A1Improve protectionReduce the degradation rateBiocideNervous disorderMedicineFunctional integrity
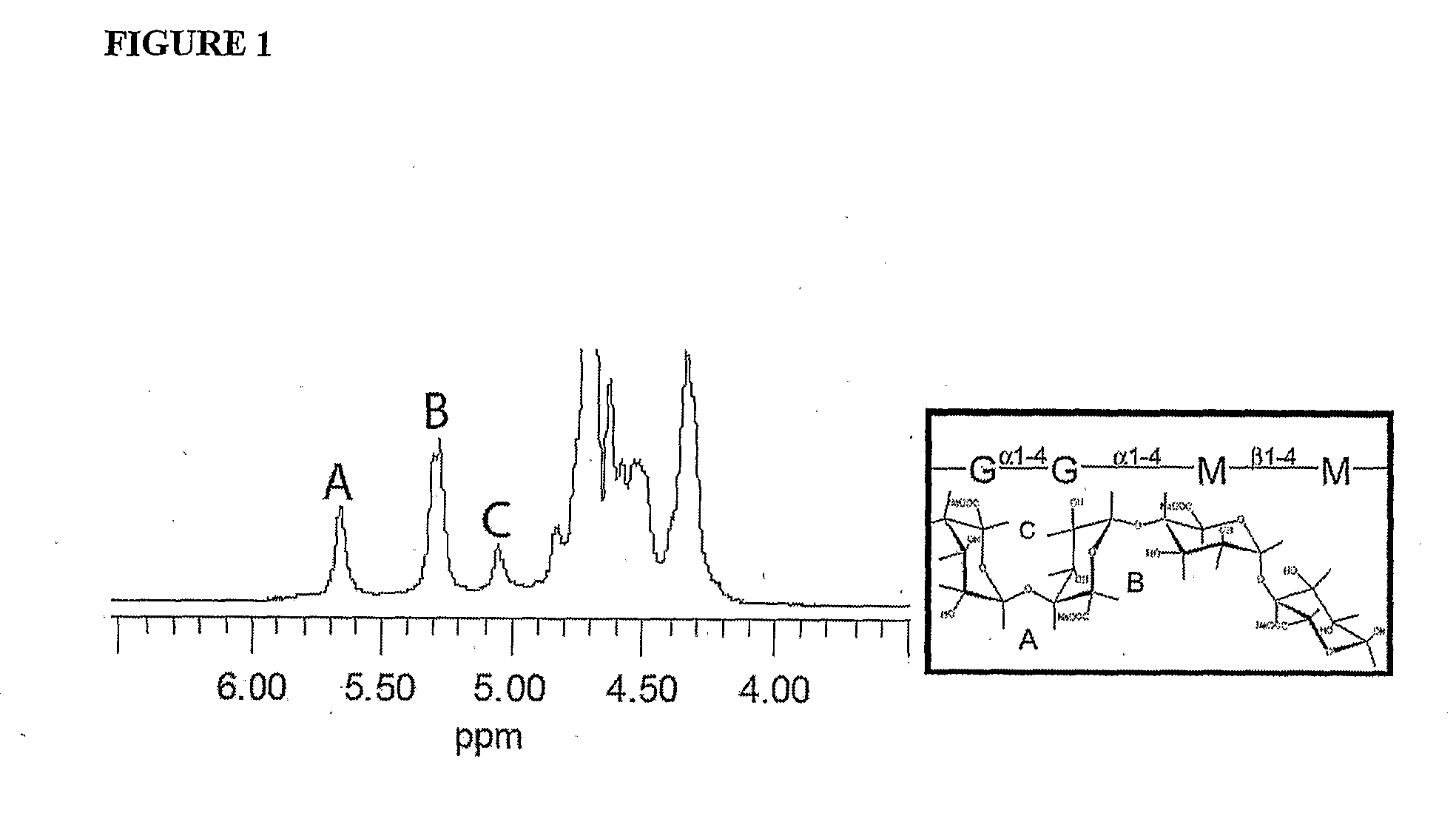
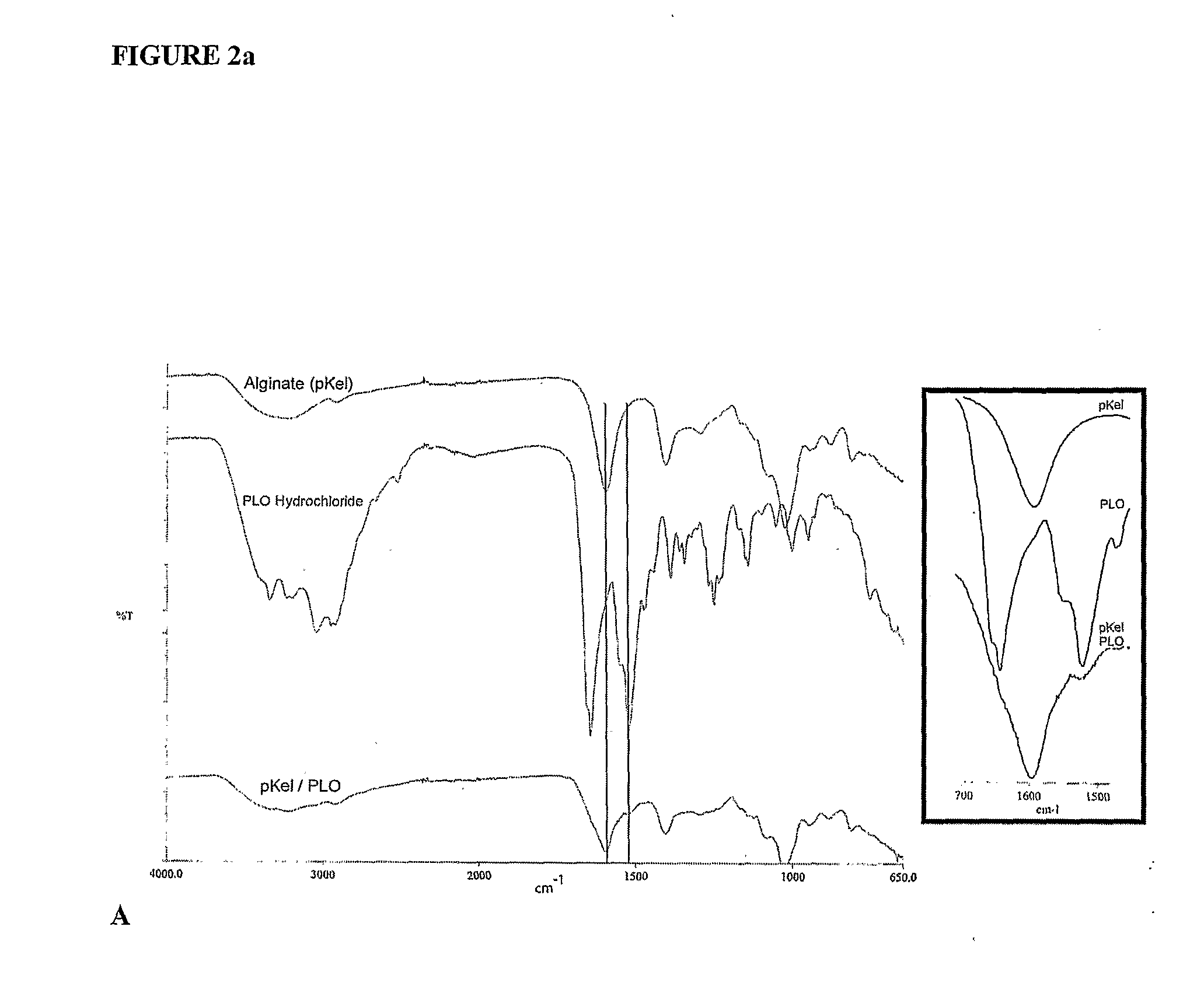
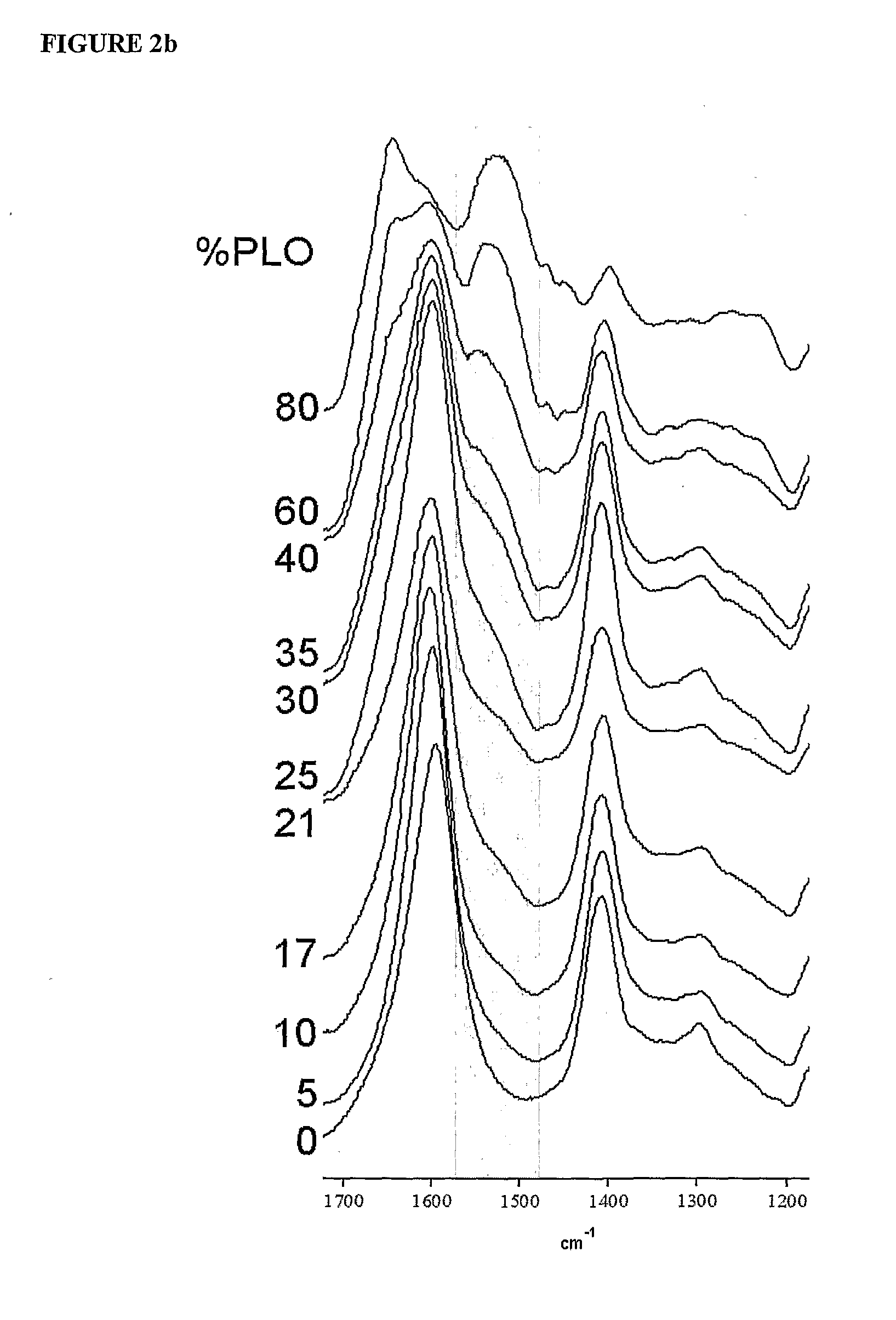
The present invention is directed to a composition comprising high mannuronic acid-containing alginate and a polycation having a polydispersity index of less than 1.5. The composition is particularly useful for making biocompatible microcapsules containing living cells for allo- or xeno-transplantation. Such microcapsules have enhanced durability and can maintain their structural and functional integrity over long periods of time compared to prior art alginate microcapsules.
Owner:LIVING CELL PRODS
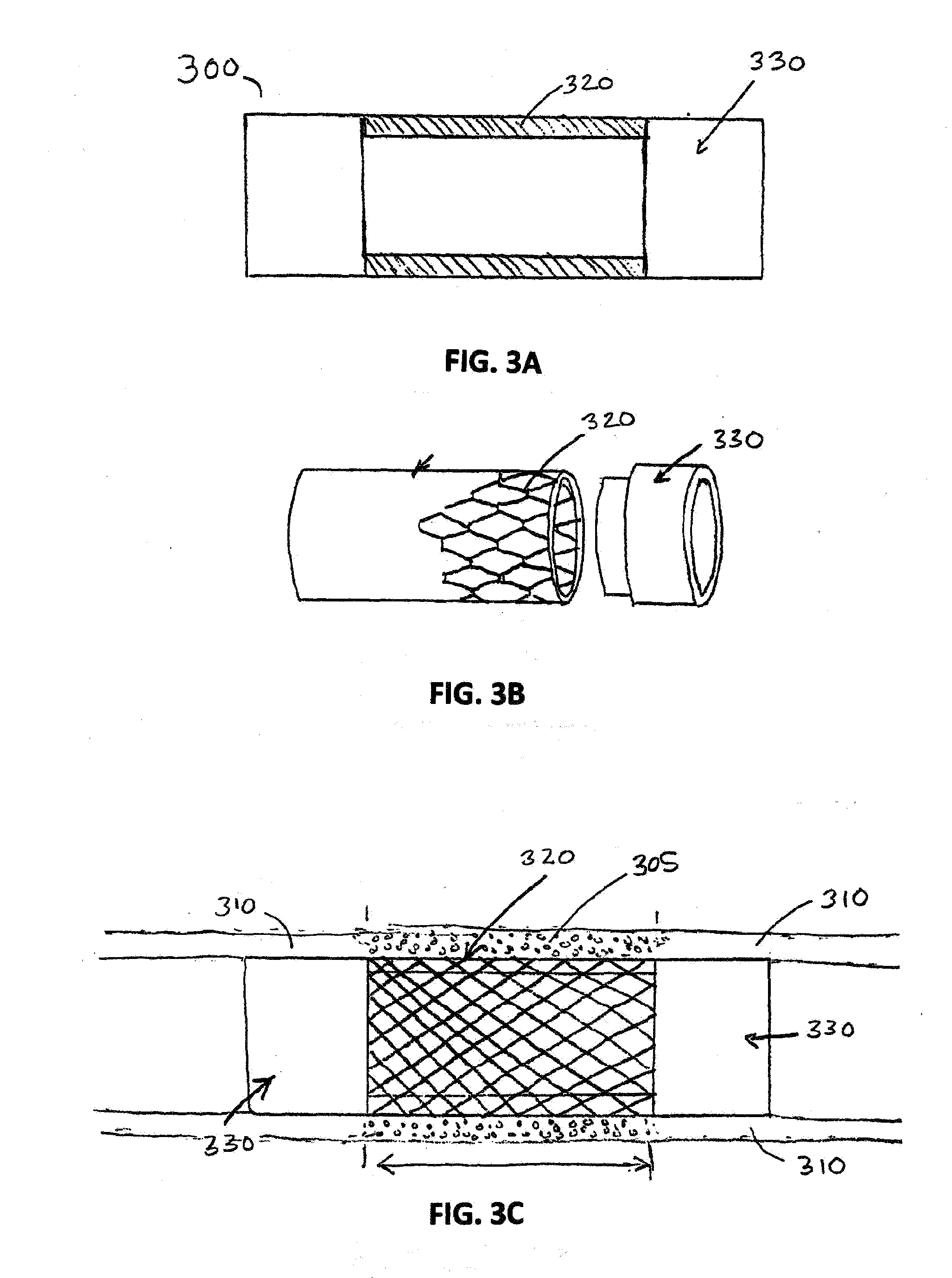
Biologically engineered stent
InactiveUS20100161032A1Promote formationPromote endothelial cell chemotaxisStentsOrganic active ingredientsMedicineIsograft
Biologically engineered stents are provided, some having novel double-walled and hybrid composition constructions that are suitable for multi-drug delivery. Some embodiments of biologically engineered stents (BES) in accordance with the invention can deliver drugs in the form of gene therapy vectors to cells in the walls of stented vessels, thereby promoting local production of therapeutic factors that attract and enhance the formation of endothelium in the stented vessel. Other embodiments of BES include xenografts, allografts or isografts comprising sleeve-like natural matrices derived from vessels of animal and human subjects including postmortem human donors.
Owner:AVELLANET FRANCISCO
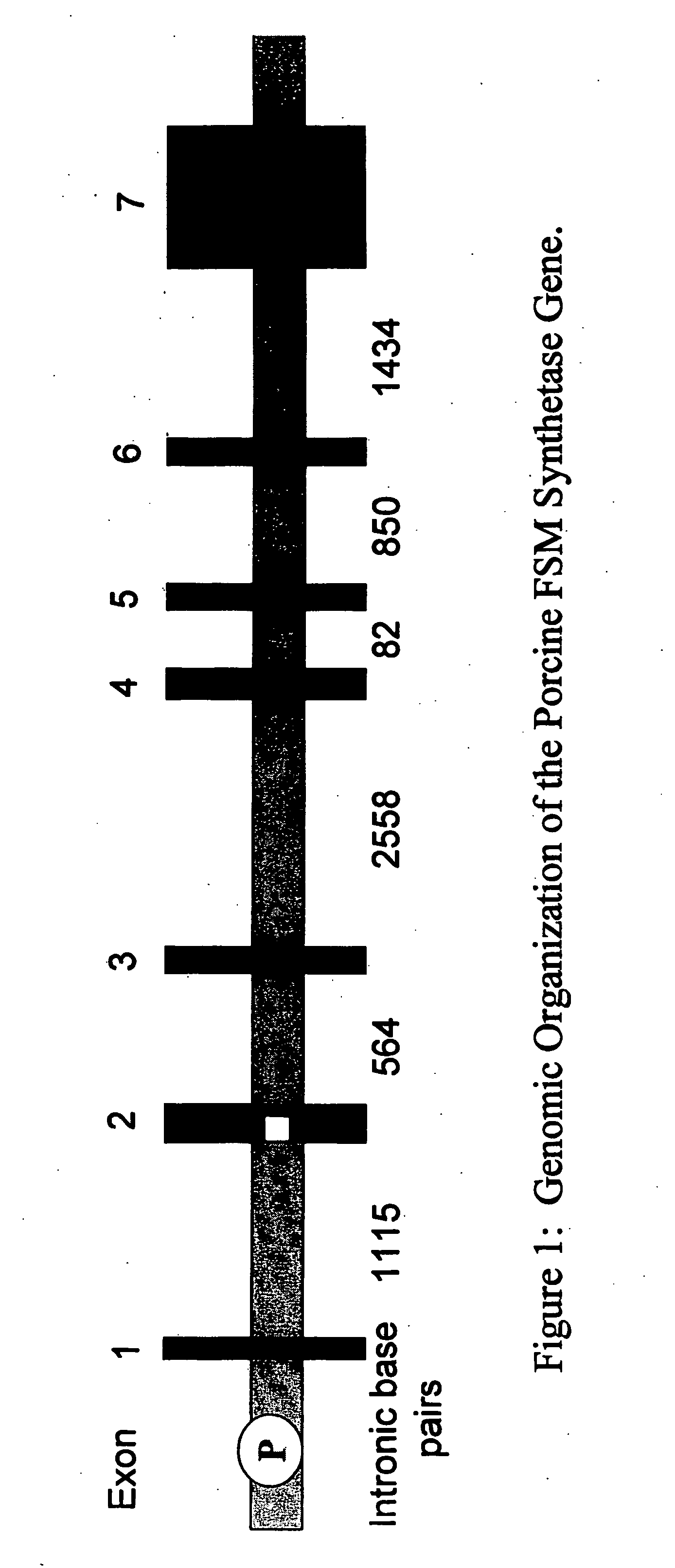
Porcine forssman synthetase protein, cDNA, genomic organization, and regulatory region
InactiveUS20060068479A1Low immunogenicityReduce expressionSugar derivativesTissue cultureN-AcetylgalactosaminyltransferasesGenomic DNA
The present invention provides porcine Forssman synthetase (FSM synthase) (Globoside α-N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase) protein, cDNA, and genomic DNA sequence. Furthermore, the present invention includes porcine animals, tissue and organs as well as cells and cell lines derived from such animals, tissue and organs, which lack expression of functional FSM synthetase. Such animals, tissues, organs and cells can be used in research and in medical therapy, including in xenotransplantation. In addition, methods are provided to prepare organs, tissues, and cells lacking the porcine FSM synthetase gene for use in xenotransplantation.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF PITTSBURGH
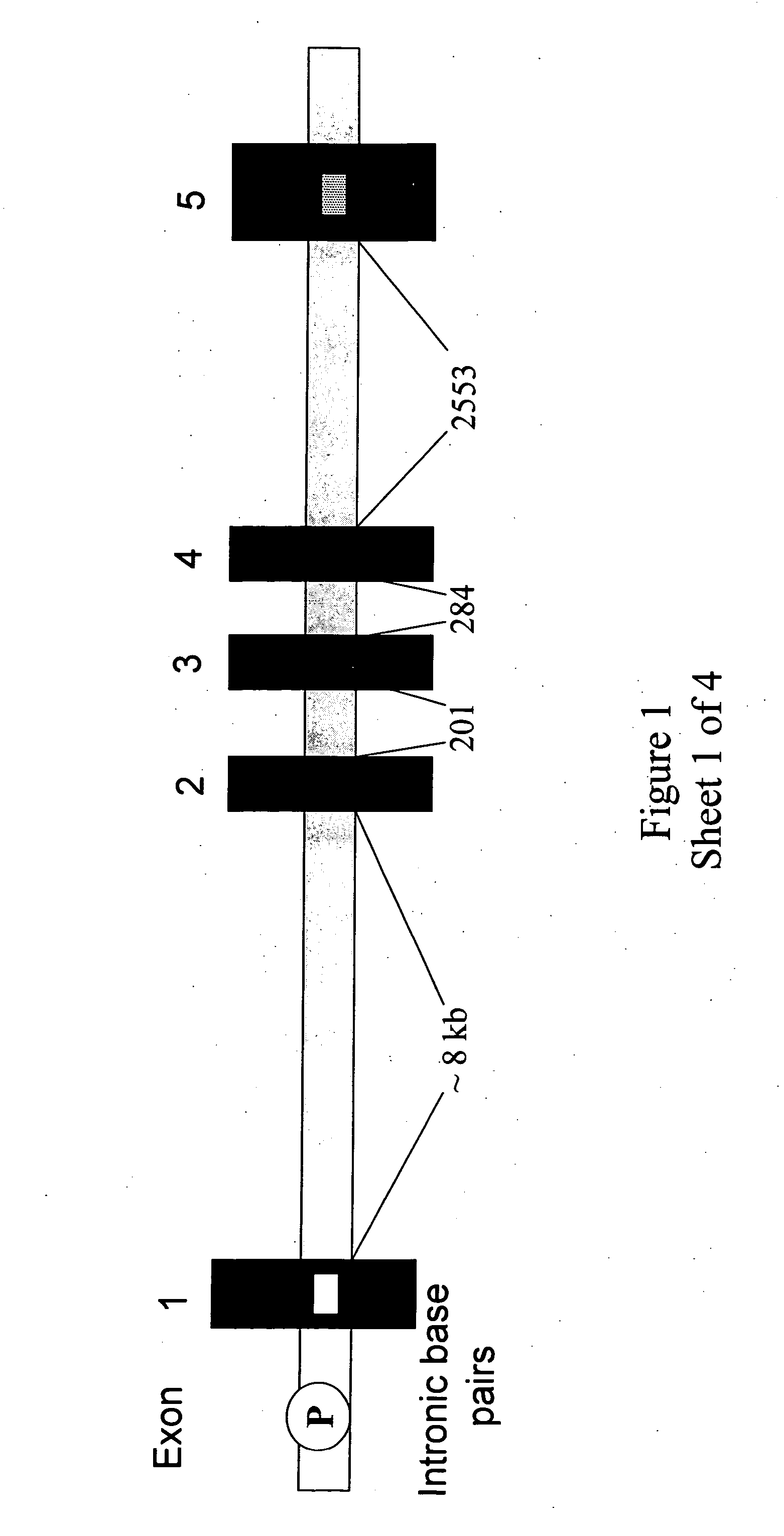
Porcine Isogloboside 3 synthase protein, cDNA, genomic organization, and regulatory region
InactiveUS20050155095A1Reduce immune rejectionReduce the amount requiredSugar derivativesHydrolasesGenomic DNARegulatory sequence
The present invention provides porcine isogloboside 3 (iGb3) synthase protein, cDNA, and genomic DNA regulatory sequence. The present also invention includes porcine animals, tissue and organs as well as cells and cell lines derived from such animals, tissue and organs, which lack expression of functional iGb3 synthase. Such animals, tissues, organs and cells can be used in research and in medical therapy, including xenotransplantation. In addition, methods are provided to prepare organs, tissues, and cells lacking the porcine iGb3 synthase gene for use in xenotransplantation.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF PITTSBURGH
Isolation and use of solid tumor stem cells
InactiveUS20110092378A1Promote resultsPromotes significant proliferationDiagnosticsMicrobiological testing/measurementPrimary tumorImmunodeficient Mouse
A small percentage of cells within an established solid tumor have the properties of stem cells. These solid tumor stem cells give rise to both more tumor stem cells and to the majority of cells in the tumor that have lost the capacity for extensive proliferation and the ability to give rise to new tumors. Thus, solid tumor heterogeneity reflects the presence of tumor cell progeny arising from a solid tumor stem cell.We have developed a xenograft model in which we have been able to establish tumors from primary tumors via injection of tumors in the mammary gland of severely immunodeficient mice. These xenograft assay have allowed us to do biological and molecular assays to characterize clonogenic solid tumor stem cells.We have also developed evidence that strongly implicates the Notch pathway, especially Notch 4, as playing a central pathway in carcinogenesis.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
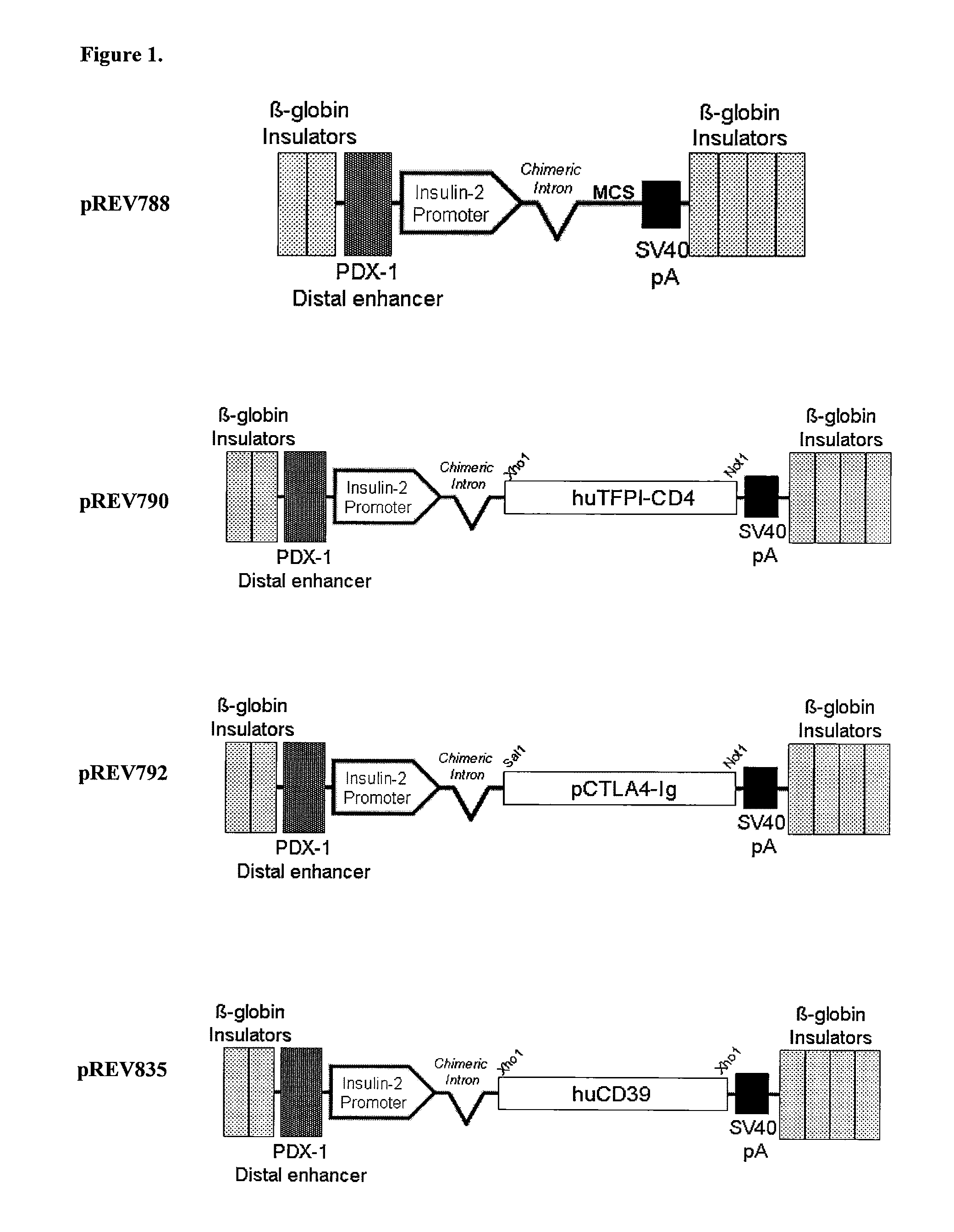
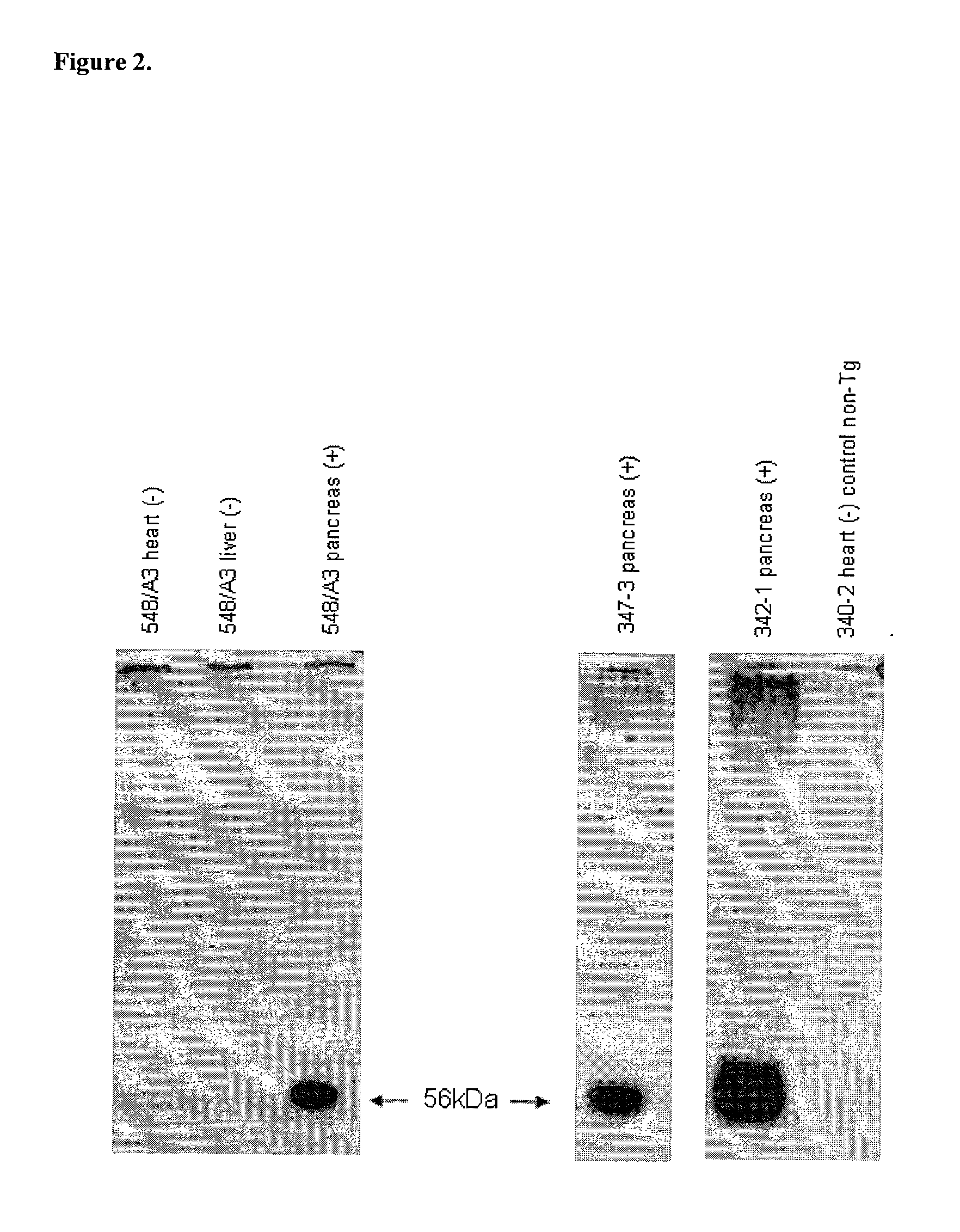
Transgenic Ungulates Expressing CTLA4-IG and Uses Thereof
The present invention provides ungulates, including pigs, expressing CTLA4-Ig, as well as tissue, organs, cells and cell lines derived from such animals. Such animals, tissues, organs and cells can be used in research and medical therapy, including xenotransplanation. In addition, methods are provided to prepare organs, tissues and cells expressing the CTLA4-Ig for use in xenotransplantation, and nucleic acid constructs and vectors useful therein.
Owner:AYARES DAVID LEE
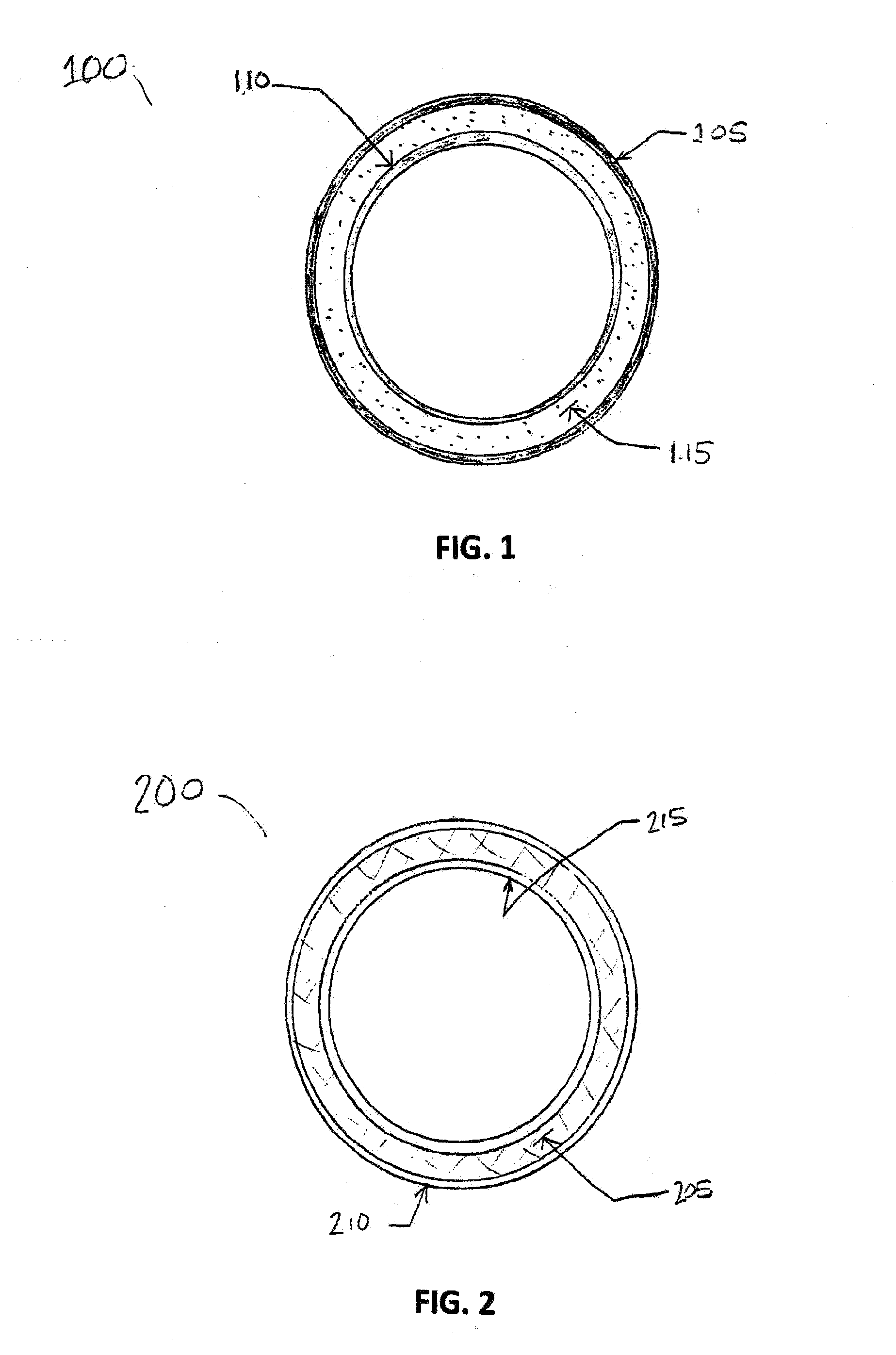
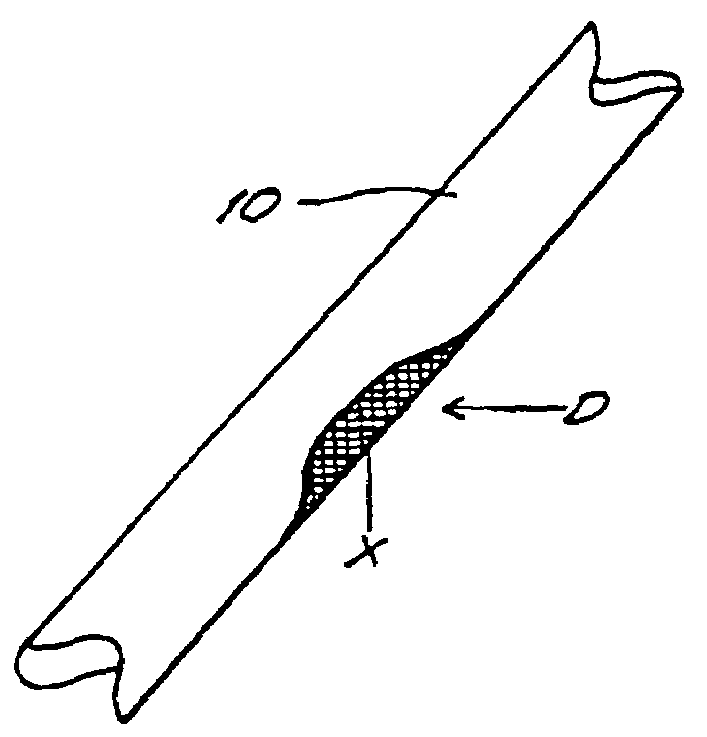
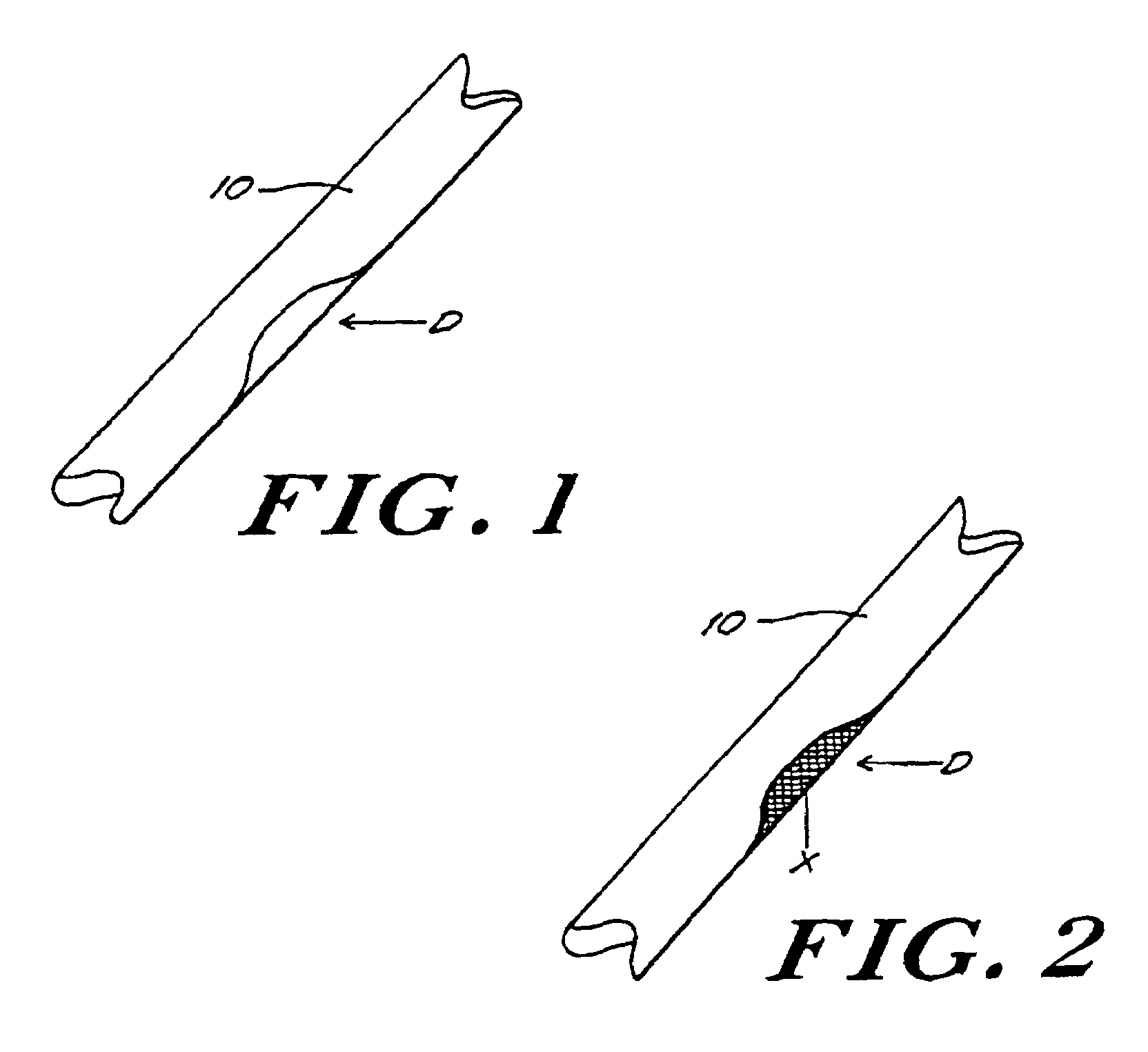
Bone xenografts
The invention provides an article of manufacture comprising a substantially non-immunogenic bone xenograft for implantation into humans. The invention further provides a method for preparing a bone xenograft by removing at least a portion of a bone from a non-human animal to provide a xenograft (X); washing the xenograft in saline and alcohol; subjecting the xenograft to a cellular disruption treatment; and treating the xenograft with a glycosidase to remove surface carbohydrate moieties. The invention also provides an article of manufacture produced by the above identified method of invention. The invention further provides a bone xenograft for implantation into a human including a portion (10) of a bone from a nonhuman animal, wherein the portion has substantially no surface carbohydrate moieties which are susceptible to glycosidase digestion. Each xenograft of the invention has substantially the same mechanical properties as a corresponding native bone.
Owner:APERION BIOLOGICS
Porcine CMP-N-Acetylneuraminic acid hydroxylase gene
InactiveUS20050223418A1Reduce immune rejectionNervous disorderBacteriaBiotechnologyCMP-N-acetylneuraminic acid hydroxylase
The present invention provides porcine CMP-N-Acetylneuraminic-Acid Hydroxylase (CMP-Neu5Ac hydroxylase) protein, cDNA, and genomic DNA regulatory sequences. Furthermore, the present invention includes porcine animals, tissues, and organs, as well as cells and cell lines derived from such animals, tissues, and organs, which lack expression of functional CMP-Neu5Ac hydroxylase. Such animals, tissues, organs, and cells can be used in research and in medical therapy, including in xenotransplantation, and in industrial livestock farming operations.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF PITTSBURGH
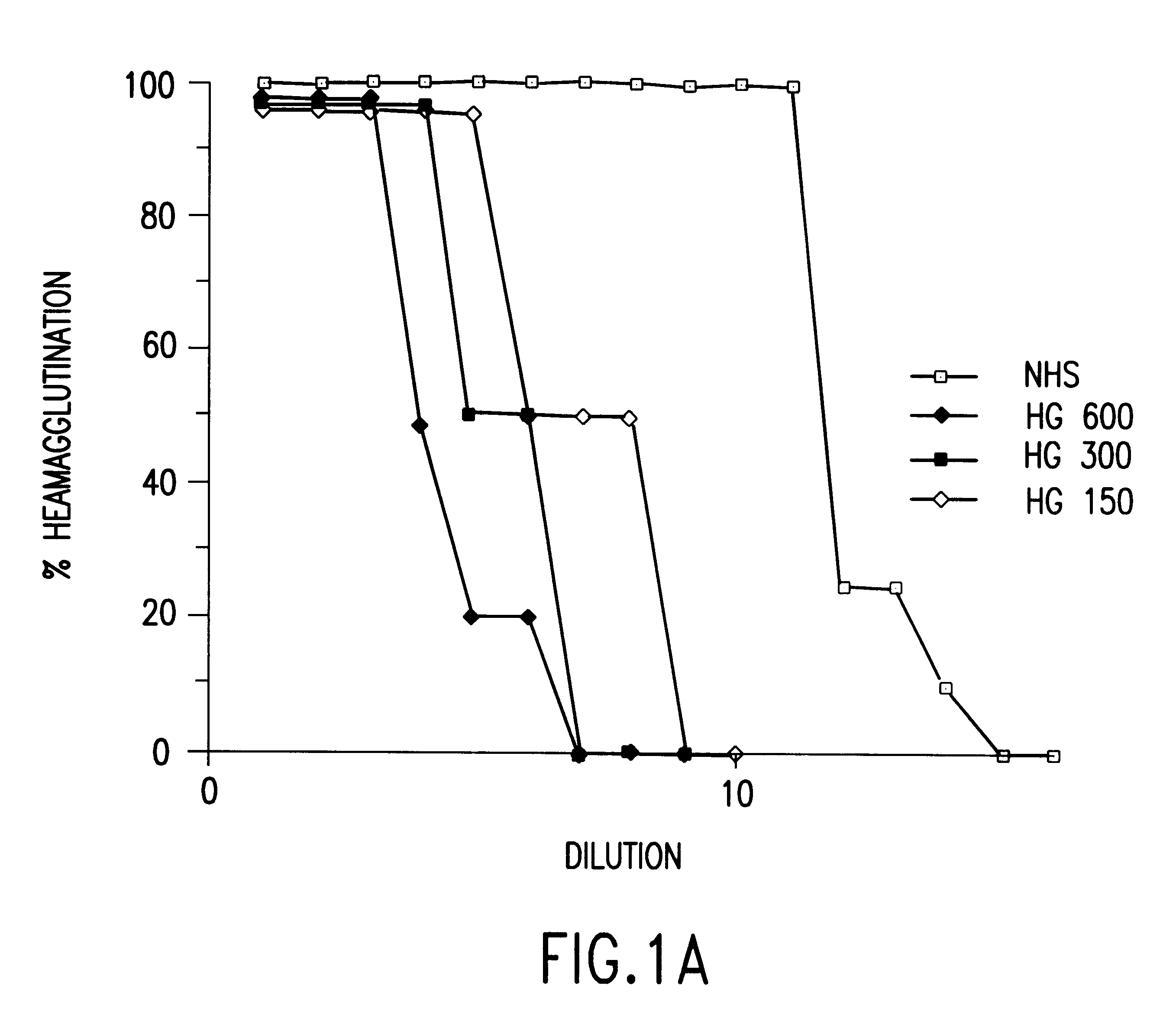
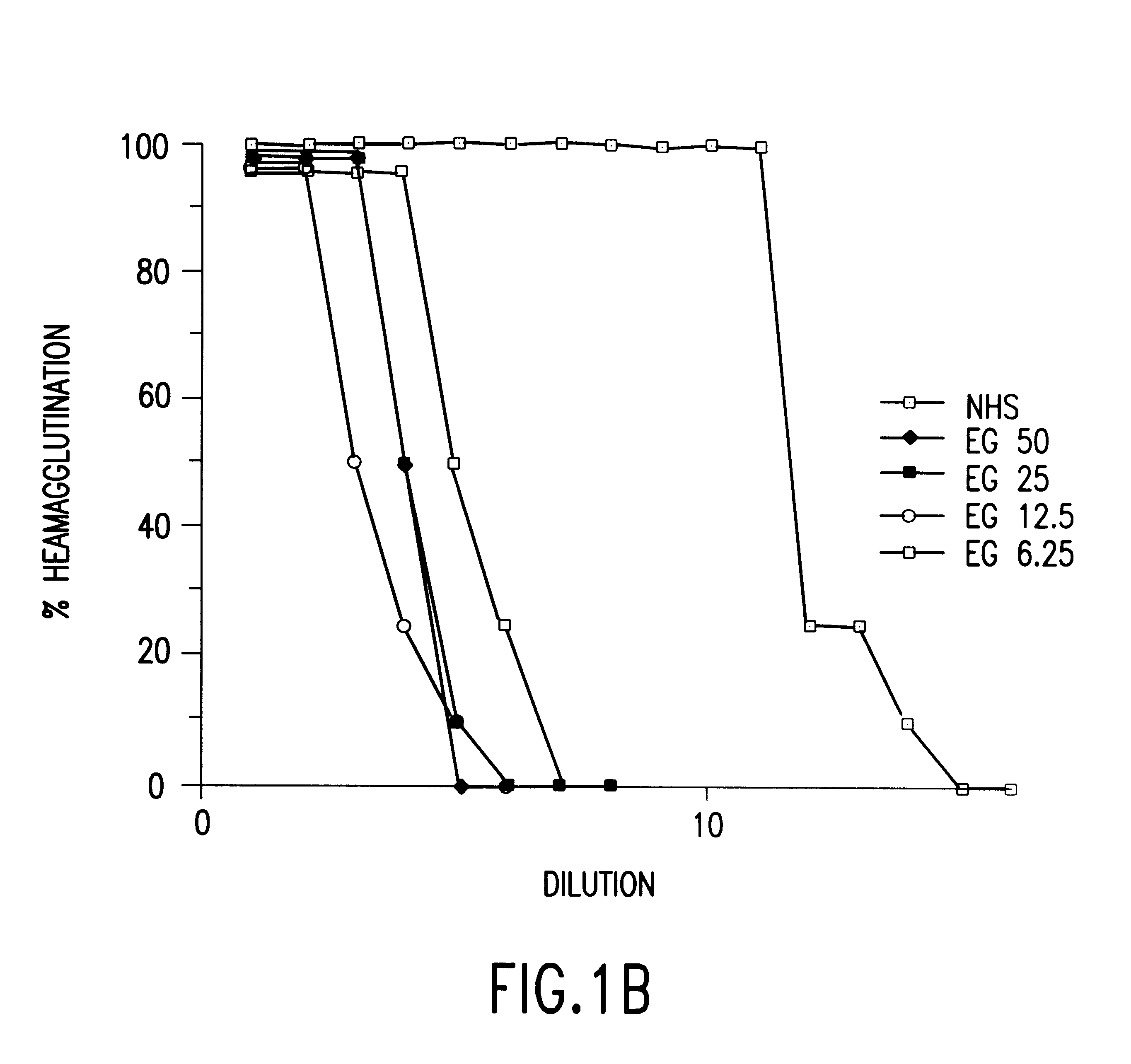
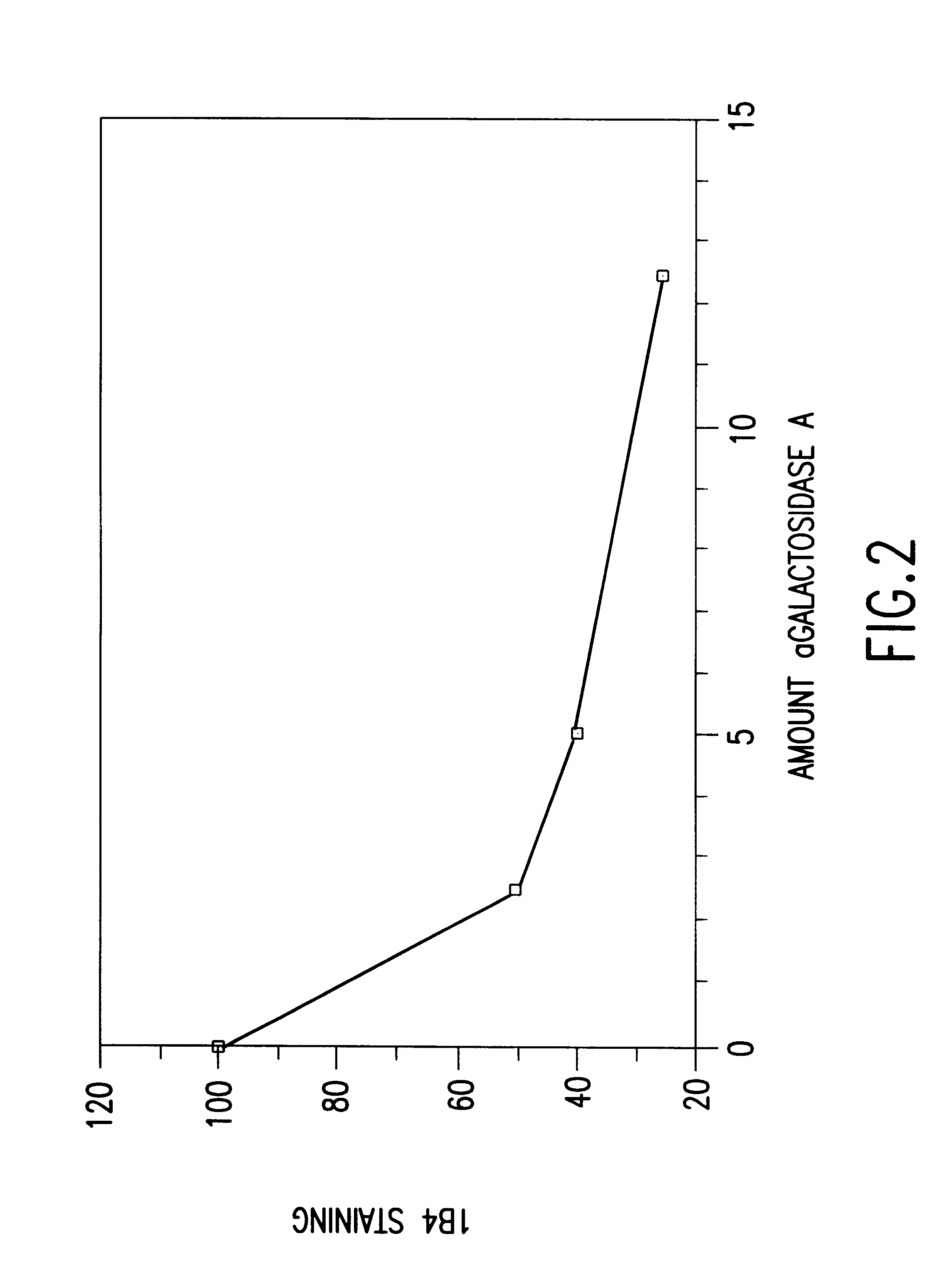
Cells expressing an alphagala nucleic acid and methods of xenotransplantation
The present invention relates to methods and compositions for the reduction of xenotransplantation rejection. Specifically, the present invention relates, first, to transgenic cells, tissues, organs and animals containing transgenic nucleic acid molecules that direct the expression of gene products, including, but not limited to enzymes, capable of modifying, either directly or indirectly, cell surface carbohydrate epitopes such that the carbohydrate epitopes are no longer recognized by natural human antibodies or by the human cell-mediated immune response, thereby reducing the human immune system response elicited by the presence of such carbohydrate epitopes. In a preferred embodiment, the transgenic cells, tissues, organs and animals express nucleic acid molecules encoding functional recombinant alpha-Galactosidase A (alphaGalA) enzyme which modifies the carbohydrate epitope Galalpha(1,3)Gal. In a more preferred embodiment, the transgenic cells, tissues, organs and animals expressing the functional recombinant alphaGalA are transgenic pig cells, organs, tissues and / or animals. Second, the present invention relates to methods for xenotransplantation comprising introducing the transgenic cells, tissues and / or organs into human recipients so that a lower level of hyperacute rejection (HAR) is observed in the human recipients relative to the level of HAR observed in human recipients having received non-transgenic cells, tissues and / or organs.
Owner:THE AUSTIN RES INST +1
Xenograft heart valves
The invention provides an article of manufacture comprising a substantially non-immunogenic heart valve xenograft for implantation into humans. The invention further provides methods for preparing a heart valve xenograft by removing at least a portion of a soft tissue from a non-human animal to provide a xenograft; washing the xenograft in saline and alcohol; subjecting the xenograft to cellular disruption treatment; treating the xenograft with crosslinking agents, and digesting the xenograft with a proteoglycan-depleting factor and / or glycosidase. The invention also provides an article of manufacture produced by the above-identified method of the invention. The invention further provides a heart valve xenograft for implantation into a human including a portion of a heart valve from a non-human animal, wherein the portion has extracellular components and substantially only dead cells. The extracellular components have reduced proteoglycan molecules. Each of the xenografts of the invention are substantially non-immunogenic and have substantially the same mechanical properties as a corresponding native heart valve.
Owner:APERION BIOLOGICS
Transgenic tilapia comprising a humanized insulin gene
InactiveUS6476290B1Stable integrationDevelopmental stability and uniformityNew breed animal cellsMammal material medical ingredientsTilapiaIslet cells
In accordance with the present invention, there are provided humanized fish insulin genes. Humanized insulin the present invention encode human insulin alpha and / or beta chains while using fish-preferred codons and regulatory sequences. These humanized genes are thus expressible in fish islet cells. Also provided are transgenic fish having islet cells containing and capable of expressing humanized insulin genes. These islet cells (Brockmann Bodies) can be xenotransplanted into subjects having diabetes. In this manner normoglycemia can be achieved in the recipient of the islets.
Owner:DALHOUSIE UNIV
Isolation and use of solid tumor stem cells
InactiveUS20080194022A1Promote resultsPromotes significant proliferationDiagnosticsBiological testingPrimary tumorImmunodeficient Mouse
A small percentage of cells within an established solid tumor have the properties of stem cells. These solid tumor stem cells give rise both to more tumor stem cells and to the majority of cells in the tumor that have lost the capacity for extensive proliferation and the ability to give rise to new tumors. Thus, solid tumor heterogeneity reflects the presence of tumor cell progeny arising from a solid tumor stem cell.We have developed a xenograft model in which we have been able to establish tumors from primary tumors via injection of tumors in the mammary gland of severely immunodeficient mice. These xenograft assay have allowed us to do biological and molecular assays to characterize clonogenic solid tumor stem cells.We have also developed evidence that strongly implicates the Notch pathway, especially Notch 4, as playing a central pathway in carcinogenesis.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
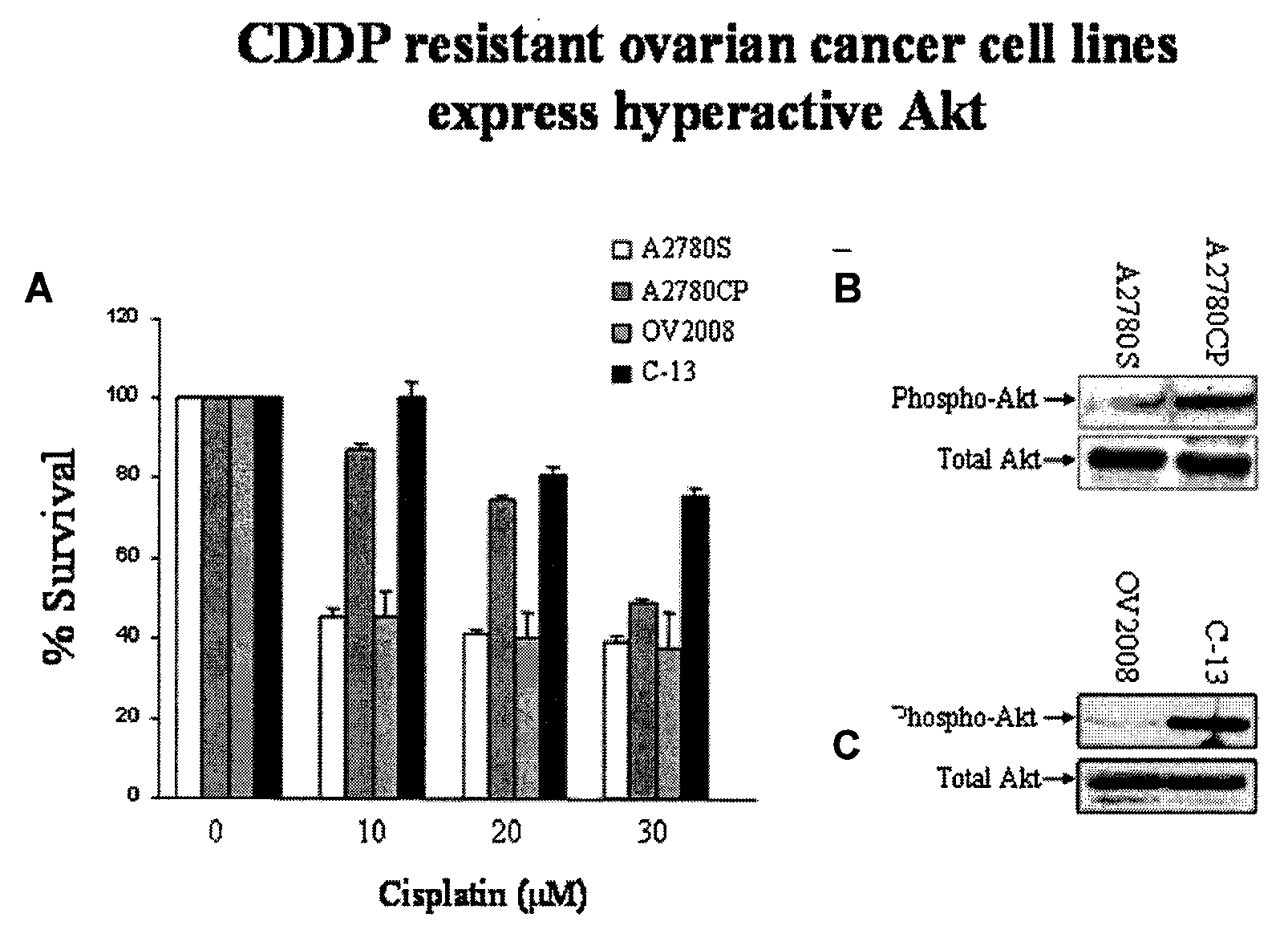
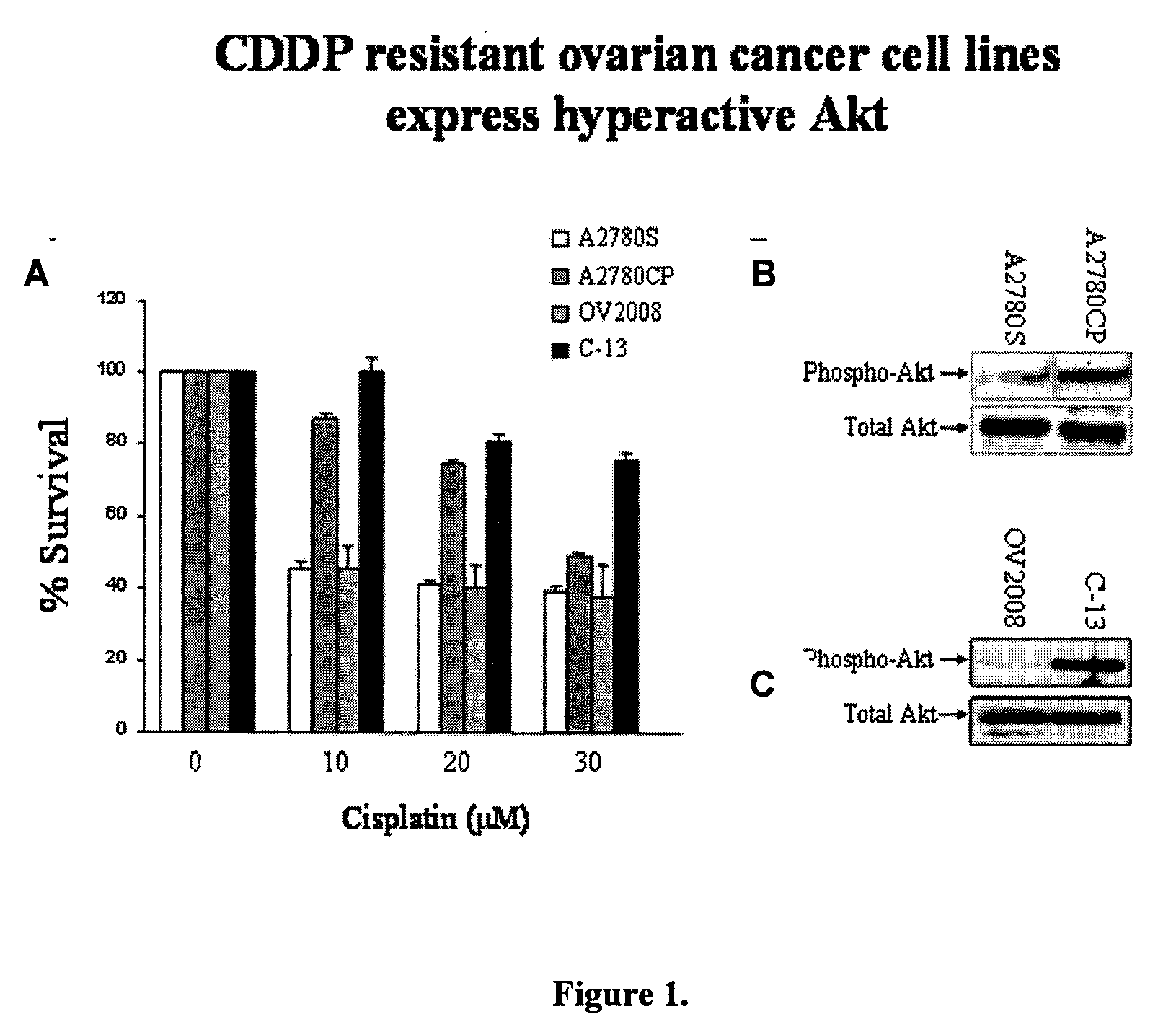
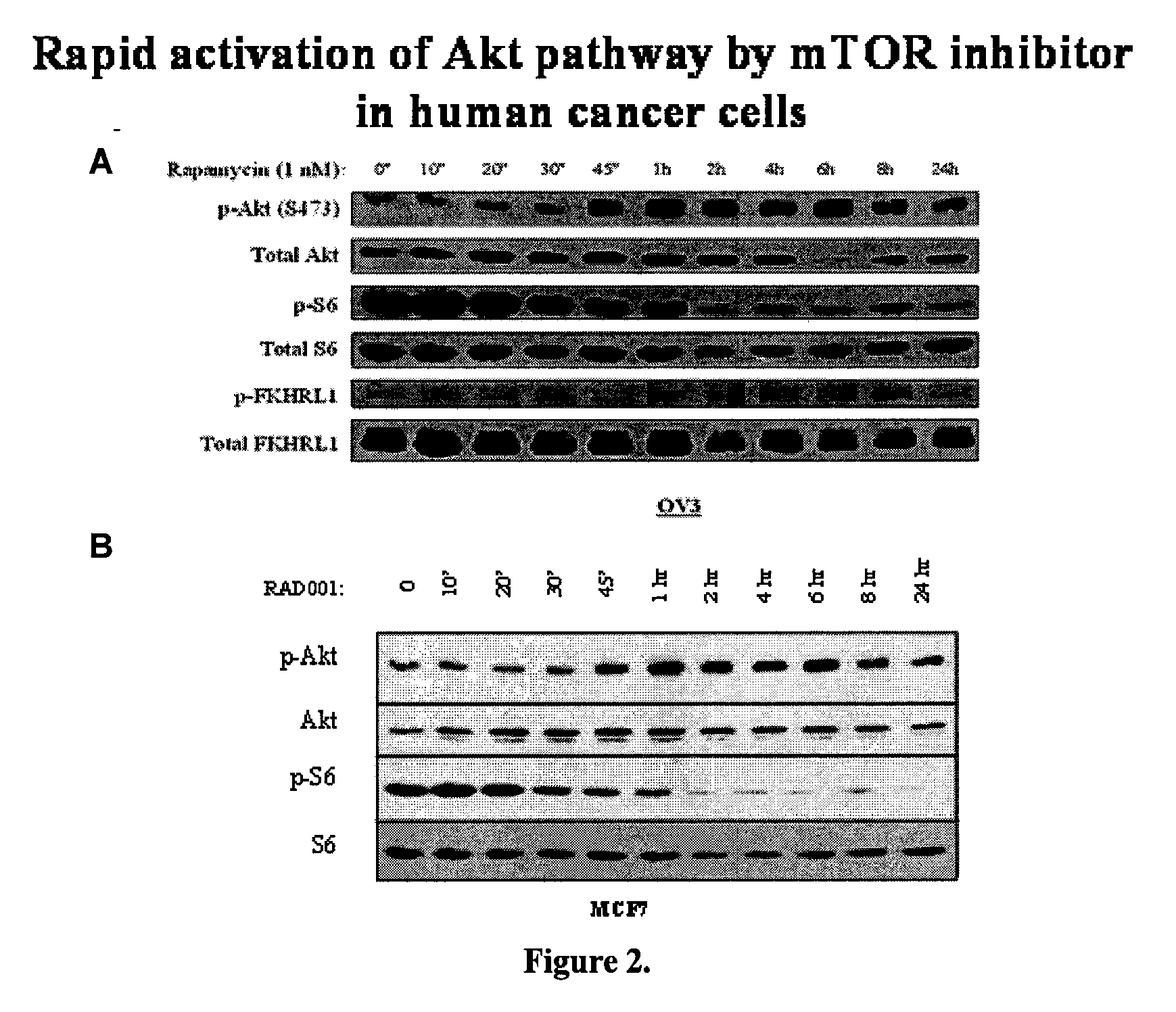
Akt sensitization of cancer cells
ActiveUS20080131526A1Broaden spectrumEffective treatmentHeavy metal active ingredientsAntibody ingredientsLung cancerTriciribine
Most human tumors find ways to resist anticancer drug monotherapy. Akt is considered a likely peptide providing such monotherapy drug resistance. Data indicates that Akt chemoresistance is induced in a p53-dependent manner and that inhibition of Akt may be an effective means of overcoming chemoresistance in cancer cells expressing wild-type p53. Breast, ovarian, lung cancer and leukemia cells lines were treated with combinations of Akt activation inhibitor Triciribine (TCN) or Triciribine phosphate (TCNP) and chemotherapeutic drugs to determine the efficiency of combination therapy. Additionally, cells were introduced into xenograft models to determine in vivo effects of combination treatment. Combining TCN or TCNP with other anticancer drugs overcame cytotoxic or treatment resistance. Thus, TCN and TCNP are shown to broaden the spectrum of human tumors that can be effectively treated.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTH FLORIDA
Method to enrich for alpha(1,3)-galactosyltransferase null pig cells
The invention relates to the genetic manipulation of non-human animals. More particularly, the invention relates to genetic manipulation of non-human animals to be used for xenotransplantation. The invention provides a method of selecting GGTA 1 null cells, a viable GGTA 1 null swine, methods for making such swine, and methods of using cells, tissues and organs of such swine for xenotransplantation.
Owner:IMMERGE BIOTHERAPEUTICS
Genetically Modified Pigs for Xenotransplantation of Vascularized Xenografts and Derivatives Thereof
ActiveUS20140017215A1Avoid damageReduce rejectionBiocideGenetic material ingredientsTransgeneBiology
The present invention provides certain donor animals, tissues and cells that are particularly useful for xenotransplantation therapies. In particular, the invention includes porcine animals, as well as tissue and cells derived from these, which lack any expression of functional alpha 1,3 galactosyltransferase (aGT) and express one or more additional transgenes which make these animals suitable donors for xenotransplantation of vascularized xenografts and derivatives thereof. Methods of treatment and using organs, tissues and cells derived from such animals are also provided.
Owner:REVIVICOR INC
Liver cancer patient source heterotransplantation tumour mouse model and construction method thereof
ActiveCN103828763ASimplify the build processEasy to manufactureAnimal husbandryLiver tissueLiver cancer
The invention provides a liver cancer patient source heterotransplantation tumour mouse model and a construction method of the mouse model. The liver cancer patient source heterotransplantation tumour mouse model comprises a mouse, wherein treated liver tissue blocks are vaccinated under the skin of the fore limb, the shoulders and the back of the mouse. The construction method comprises the steps of taking fresh liver cancer tissue, processing the tissue, vaccinating the treated liver cancer tissue blocks under the skin below the fore limb, the shoulders and the back of the mouse without the tumor, conducting conventional breeding, and obtaining the liver cancer patient source heterotransplantation tumour mouse model. The construction process is simple and easy, the tumor forming occurrence rate reaches 40 percent to 50 percent, and the method can be used for liver cancer medicine screening and liver cancer mechanism research. The built liver cancer patient source heterotransplantation tumour mouse model has the advantages of being simple and easy to manufacture, low in death rate caused by operation, high in success rate, easy to popularize, capable of being manufactured in mass, and good in synchronism, and is suitable for medicine screening and experiment research.
Owner:南京普恩瑞生物科技有限公司
Alpha(1,3)-galactosyltransferase null cells, methods of selecting and alpha(1,3)-galactosyl transferase null swine produced therefrom
ActiveUS20060242722A1New breed animal cellsMicrobiological testing/measurementHuman animalCell selection
The invention relates to the genetic manipulation of non-human animals. More particularly, the invention relates to genetic manipulation of non-human animals to be used for xenotransplantation. The invention provides a method of selecting GGTA 1 null cells, a viable GGTA 1 null swine, methods for making such swine, and methods of using cells, tissues and organs of such swine for xenotransplantation.
Owner:IMMERGE BIOTHERAPEUTICS
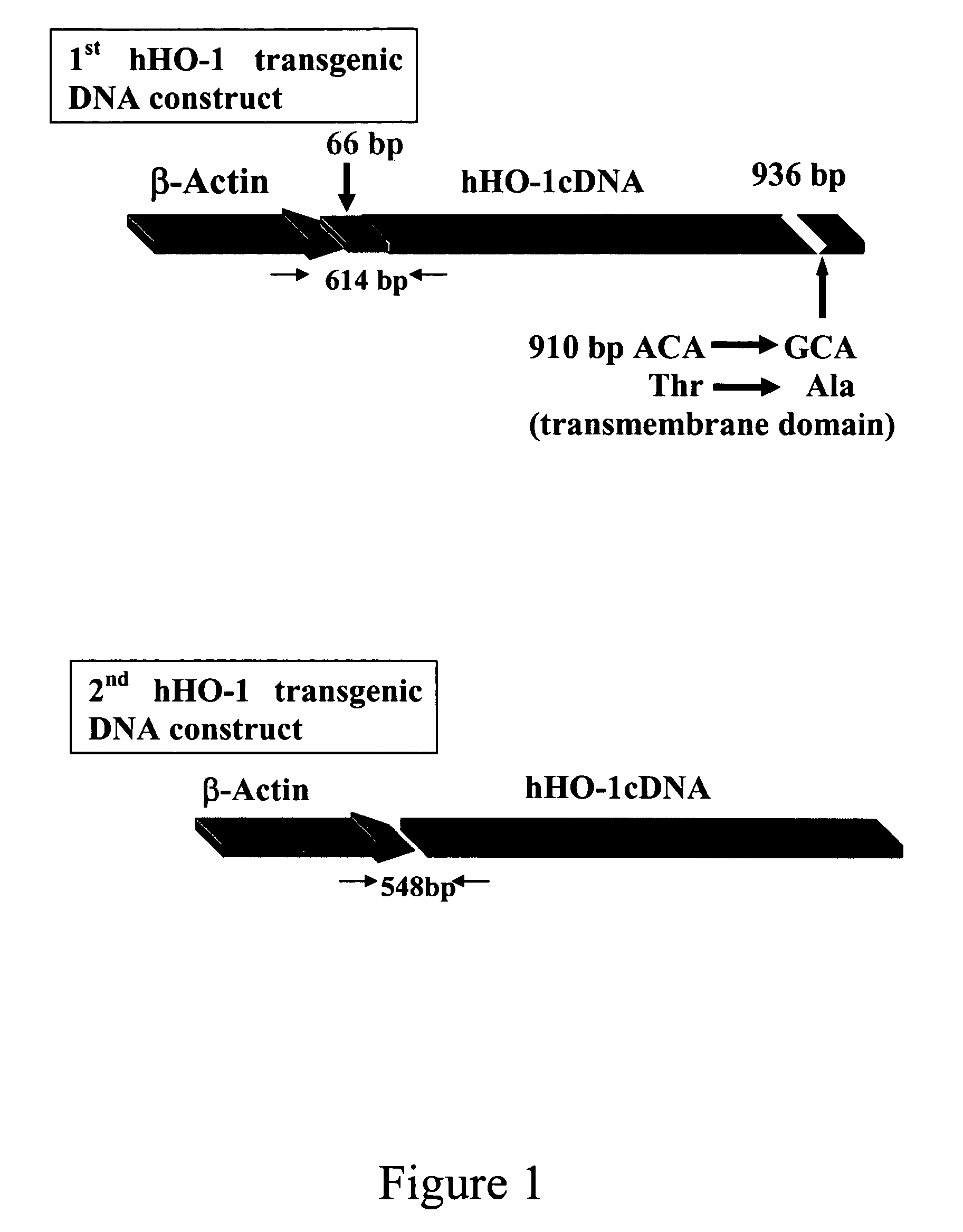
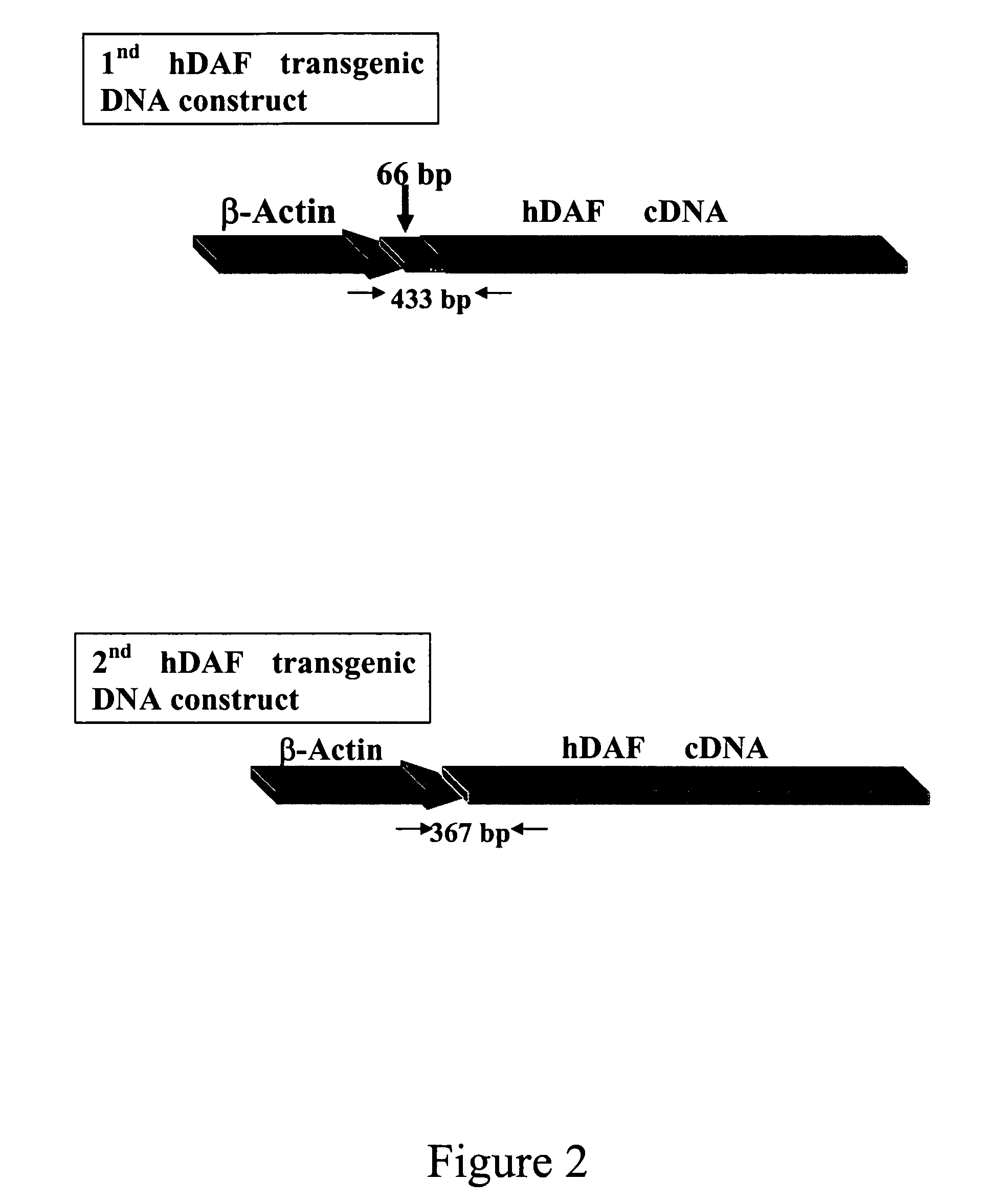
Transgenic pigs carrying both hHO-1 and hDAF transgenes for xenotransplantation
The invention provides a transgenic animal carrying two transgenes, one encoding a human decay accelerating factor (hDAF) and the other encoding a human heme oxygenase-1 (hHO)-1, which are useful for providing cells, tissues or organs therefrom for xenotransplantation.
Owner:AGRI TECH RES INST
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com