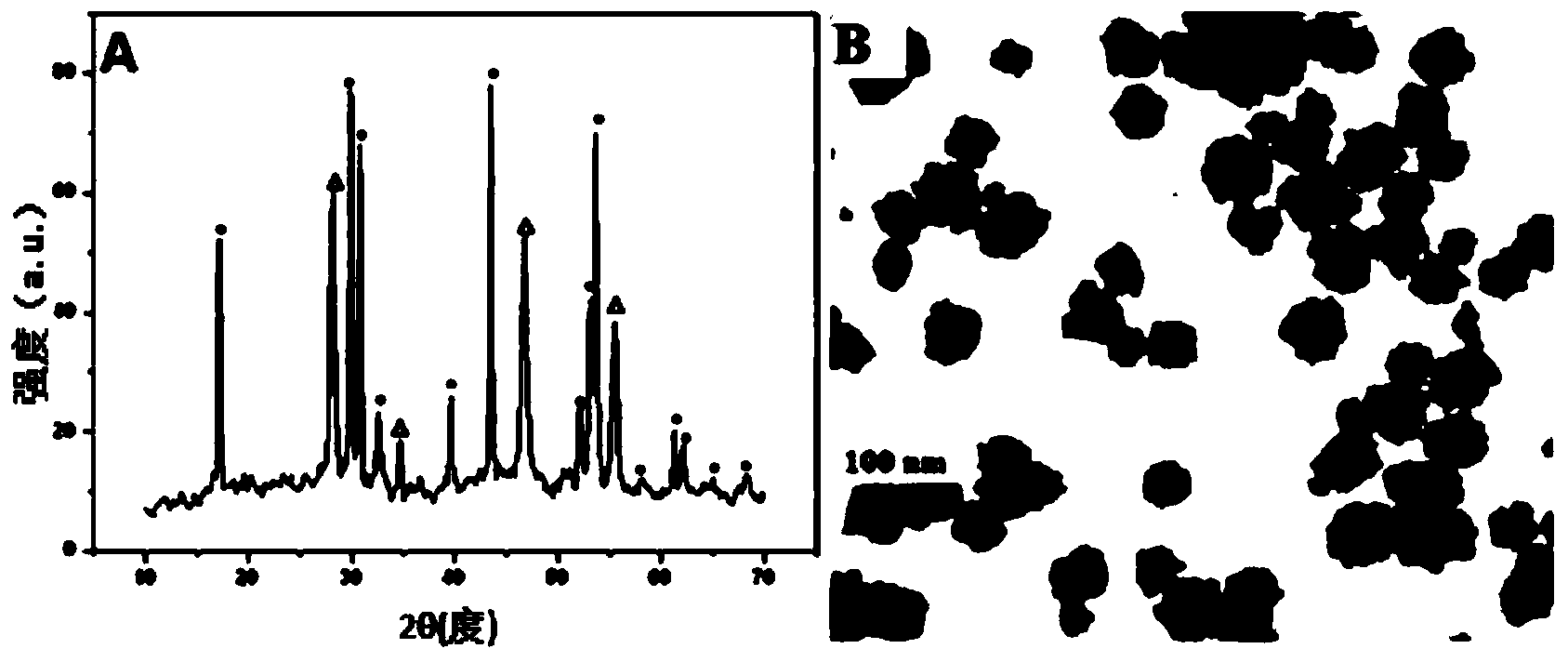
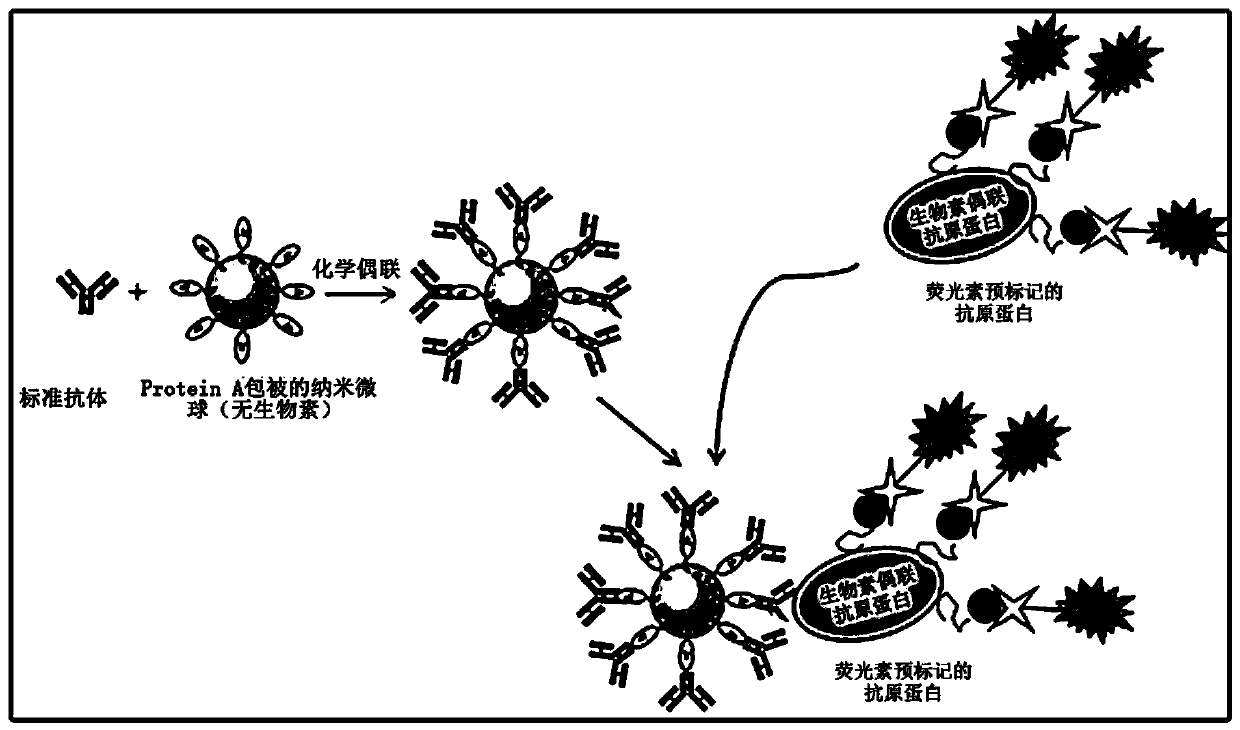
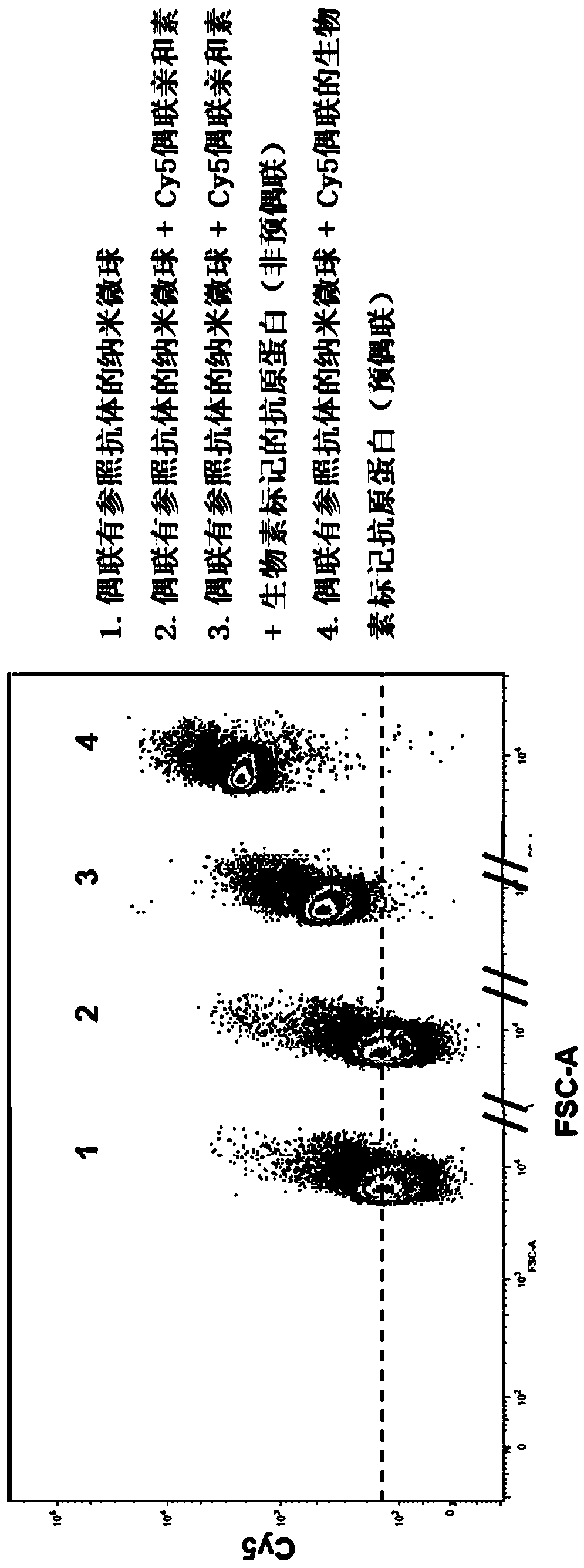
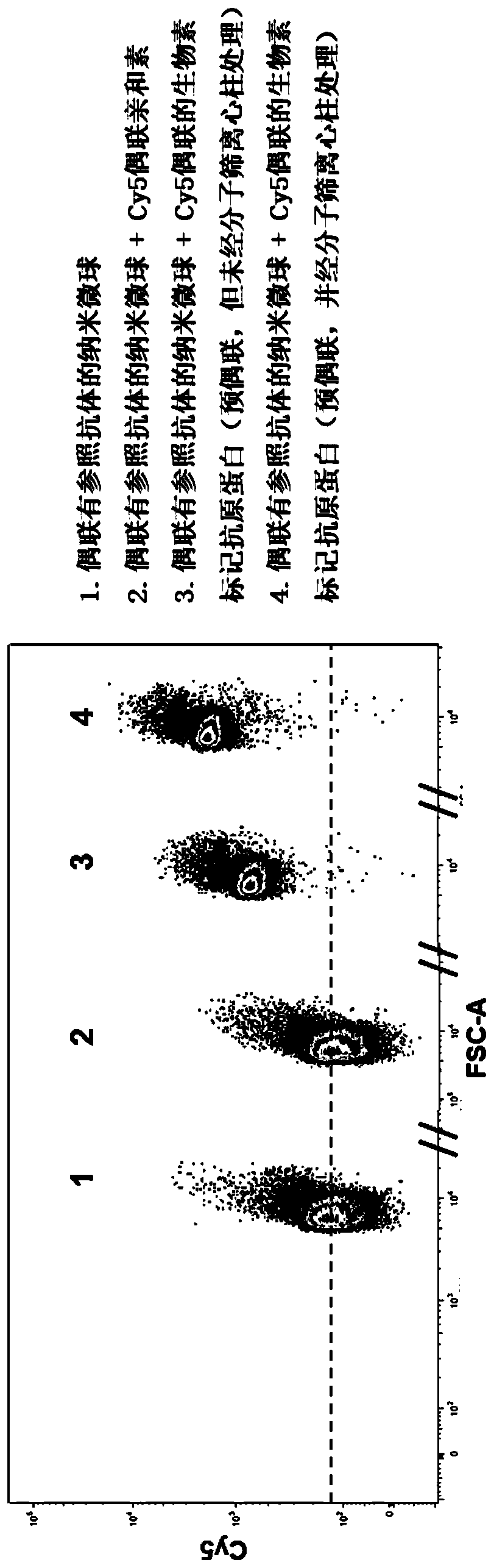
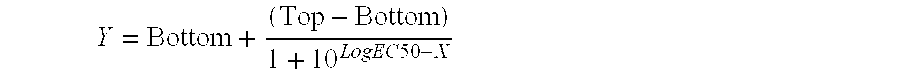Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
542 results about "Surface marker" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
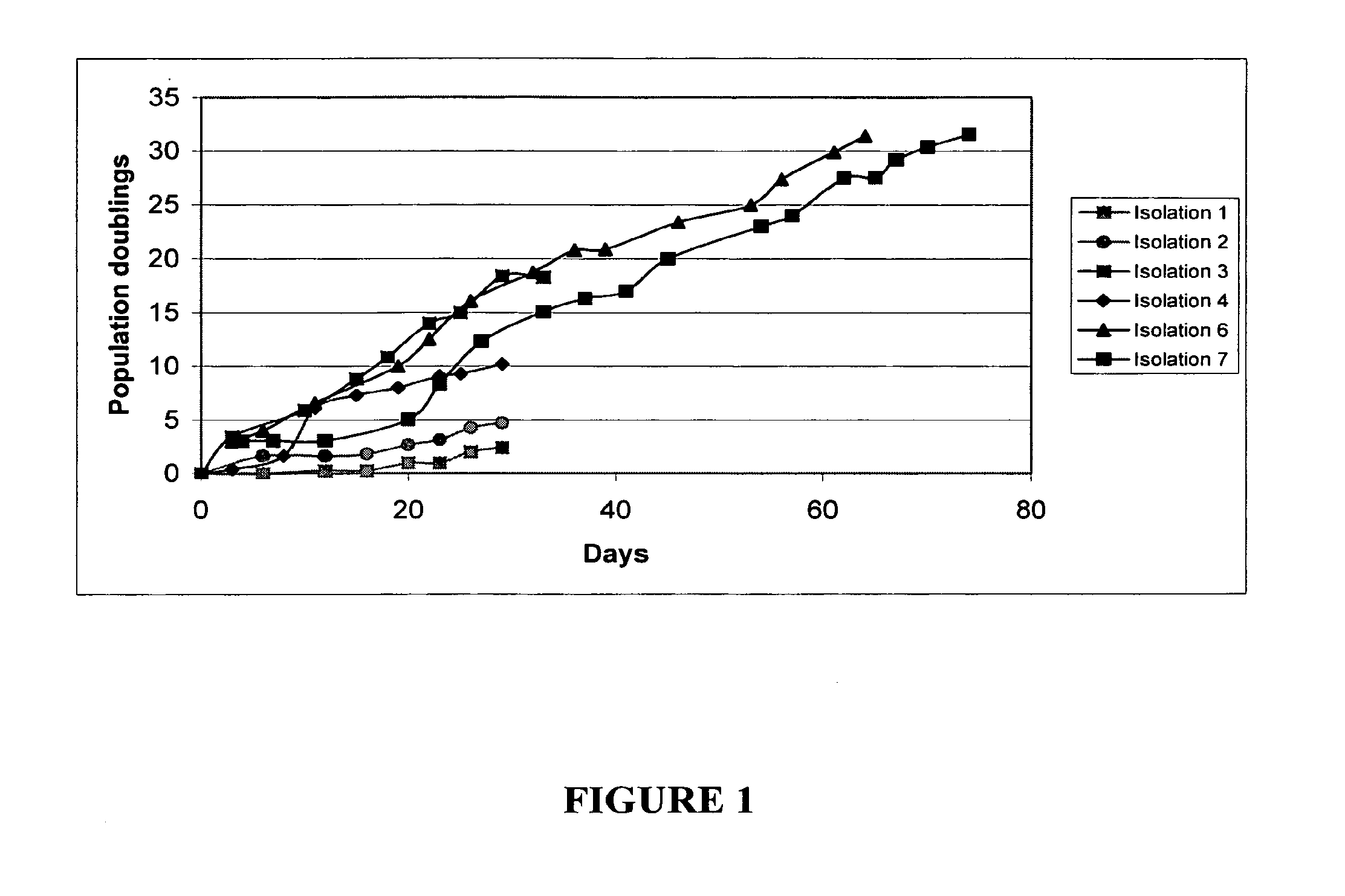
Multipotent amniotic fetal stem cells
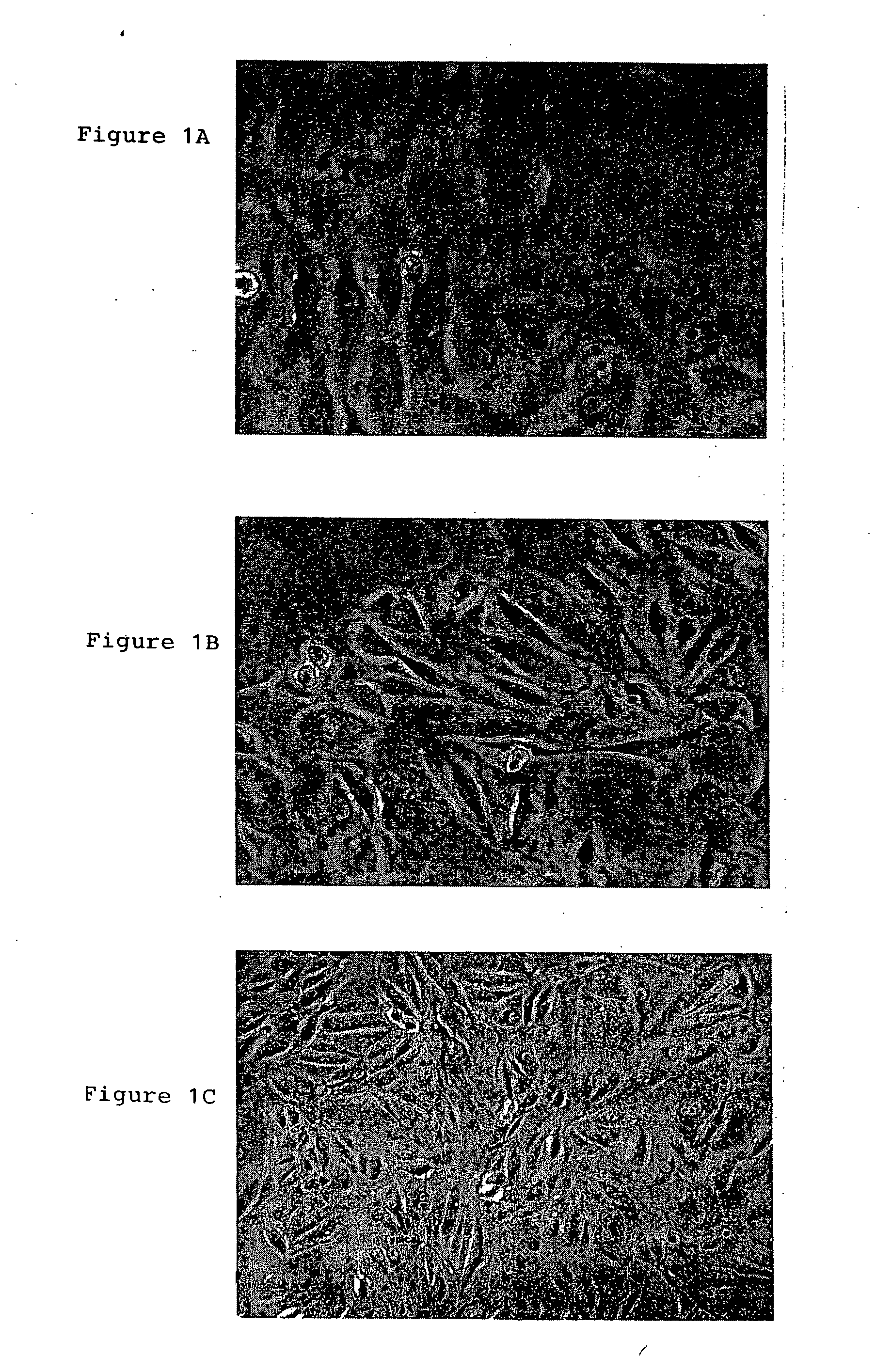
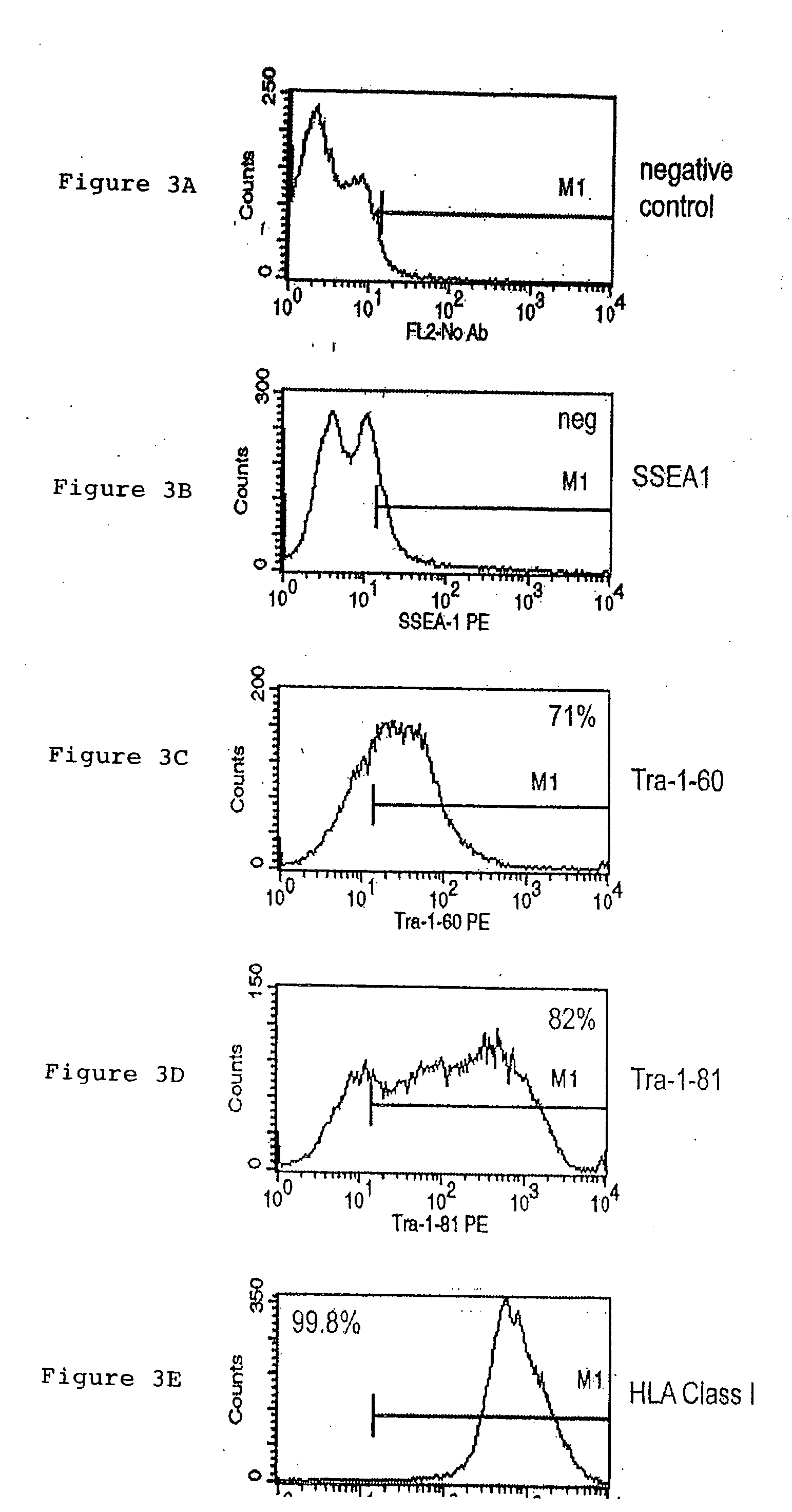
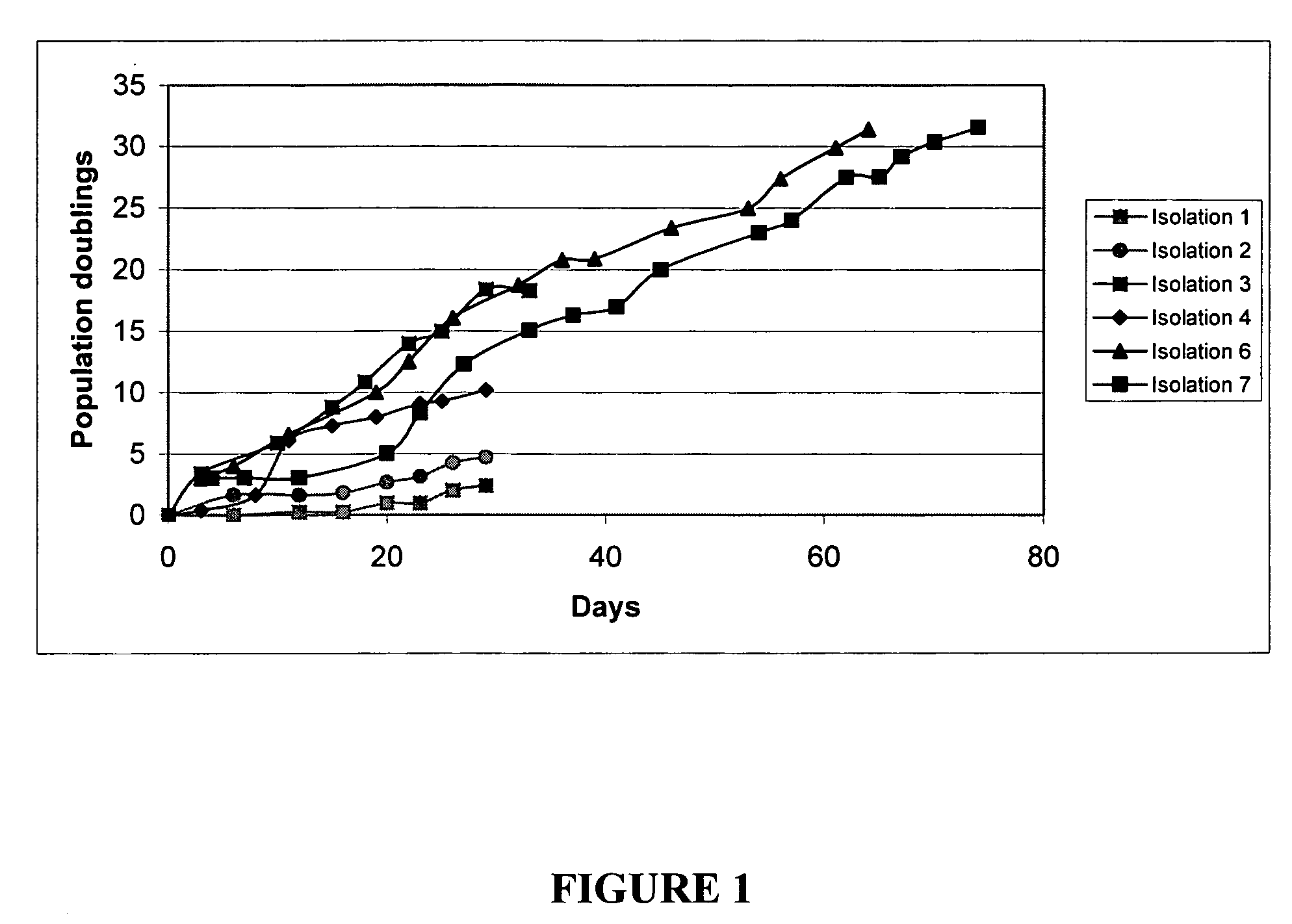
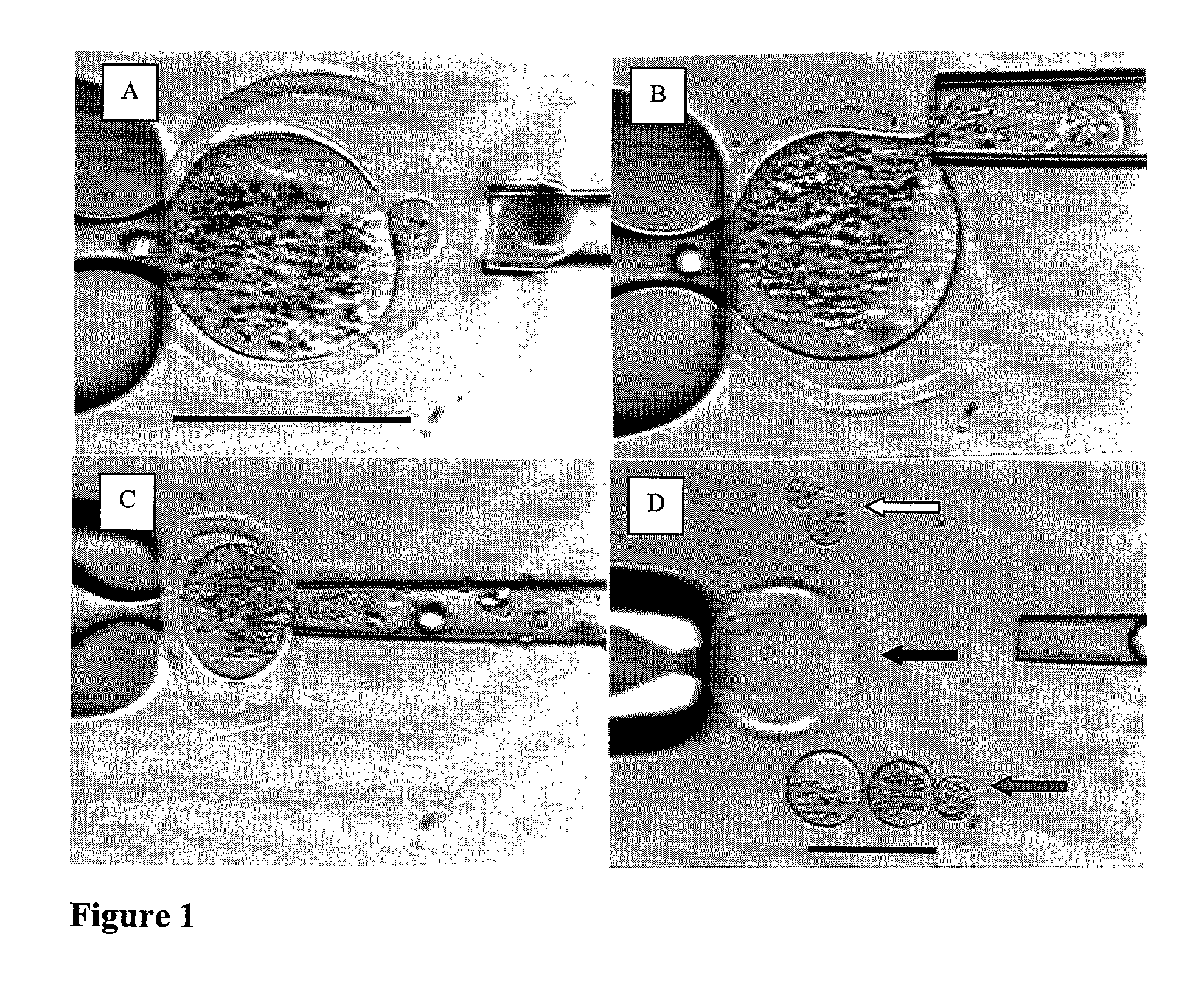
A source of multipotent amniotic fluid / fetal stem cells (MAFSCs) is disclosed. MAFSC are of fetal origin and have a normal diploid karyotype. These cells are characterized by the following cell surface markers: SSEA3, SSEA4, Tra-1-60, Tra-1-81, Tra-2-54, HLA class I, CD13, CD44, CD49b, CD105 and are distinguished by the absence of the antigen markers CD34, CD45, and HLA Class II, but are distinguished from mouse embryonic stem cells in that these cells do not express the cell surface marker SSEA1. MAFSC express the stem cell transcription factor Oct-4. MAFSC cells can be propagated for an indefinite period of time in continuous culture in an undifferentiated state. The MAFSCs have the ability to differentiate in culture in a regulated manner, into three or more subphenotypes. Cells can then be differentiated into endodermal, mesodermal and ectodermal derived tissues in vitro and in vivo. A method for isolating, identifying, expanding and differentiating MAFSCs is disclosed.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Postpartum cells derived from umbilical cord tissue, and methods of making and using the same
Cells derived from human umbilical cords are disclosed along with methods for their therapeutic use. Isolation techniques, culture methods and detailed characterization of the cells with respect to their cell surface markers, gene expression, and their secretion of trophic factors are described.
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC
Pluripotent stem cells derived without the use of embryos or fetal tissue
InactiveUS20030113910A1New breed animal cellsArtificial cell constructsPluripotential stem cellGerm layer
Owner:STEMA
Postpartum cells derived from umbilical cord tissue, and methods of making, culturing, and using the same
Cells derived from human umbilical cords are disclosed along with methods for their therapeutic use. Isolation techniques, culture methods and detailed characterization of the cells with respect to their cell surface markers, gene expression, and their secretion of trophic factors are described.
Owner:ADVANCED TECH & REGENERATIVE MEDICINE
Detecting Cell Surface Markers
InactiveUS20110111435A1Quantitative precisionBiological material analysisBiological testingSurface markerCell surface staining
In one aspect, the present invention provides a method for detecting an expression level of a cell surface marker in a sample, comprising staining the sample with a reagent that labels the cell surface marker; obtaining an image of the stained sample; and determining a value for continuity of cell surface staining in the image, wherein the value is indicative of the expression level.
Owner:LEICA BIOSYST IMAGING
Treatment of bone disorders
InactiveUS20060263355A1Enhance osteoblast formationImprove bone formationBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseCD20
Methods of treatment of various bone indications, such as osteoporosis, in a mammal are provided wherein an effective amount of an antagonist that binds to a B-cell surface marker, such as a CD20 antibody, is administered, optionally also with another medicament such as an agent that treats such disorders in an effective amount. Articles of manufacture are also provided. Further, a method of inhibiting osteolysis in a mammal is provided comprising introducing into said mammal an isolated odontoprogenitor or osteoprogenitor cell comprising a nucleic acid encoding an antibody that binds to a B-cell surface marker.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
Method for treating lupus
InactiveUS20060024295A1Reduce and minimize needAvoid much side effectAntipyreticAnalgesicsSurface markerRegimen
A method of treating lupus in a subject eligible for treatment is provided involving administering an effective amount of an antibody that binds to a B-cell surface marker to the subject to provide an initial exposure and a subsequent exposure to the antibody within certain dosing regimens and an article of manufacture therefor.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
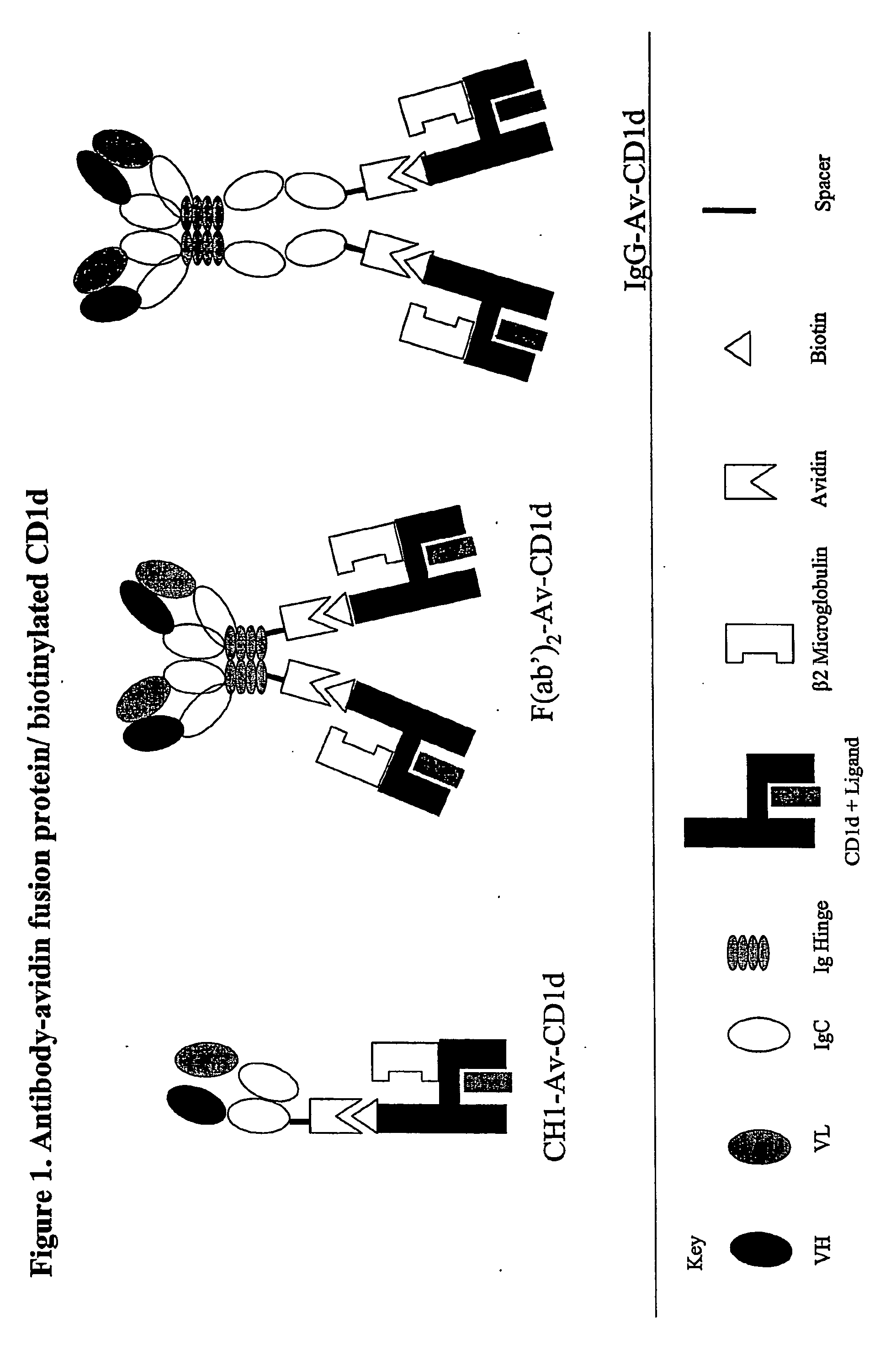
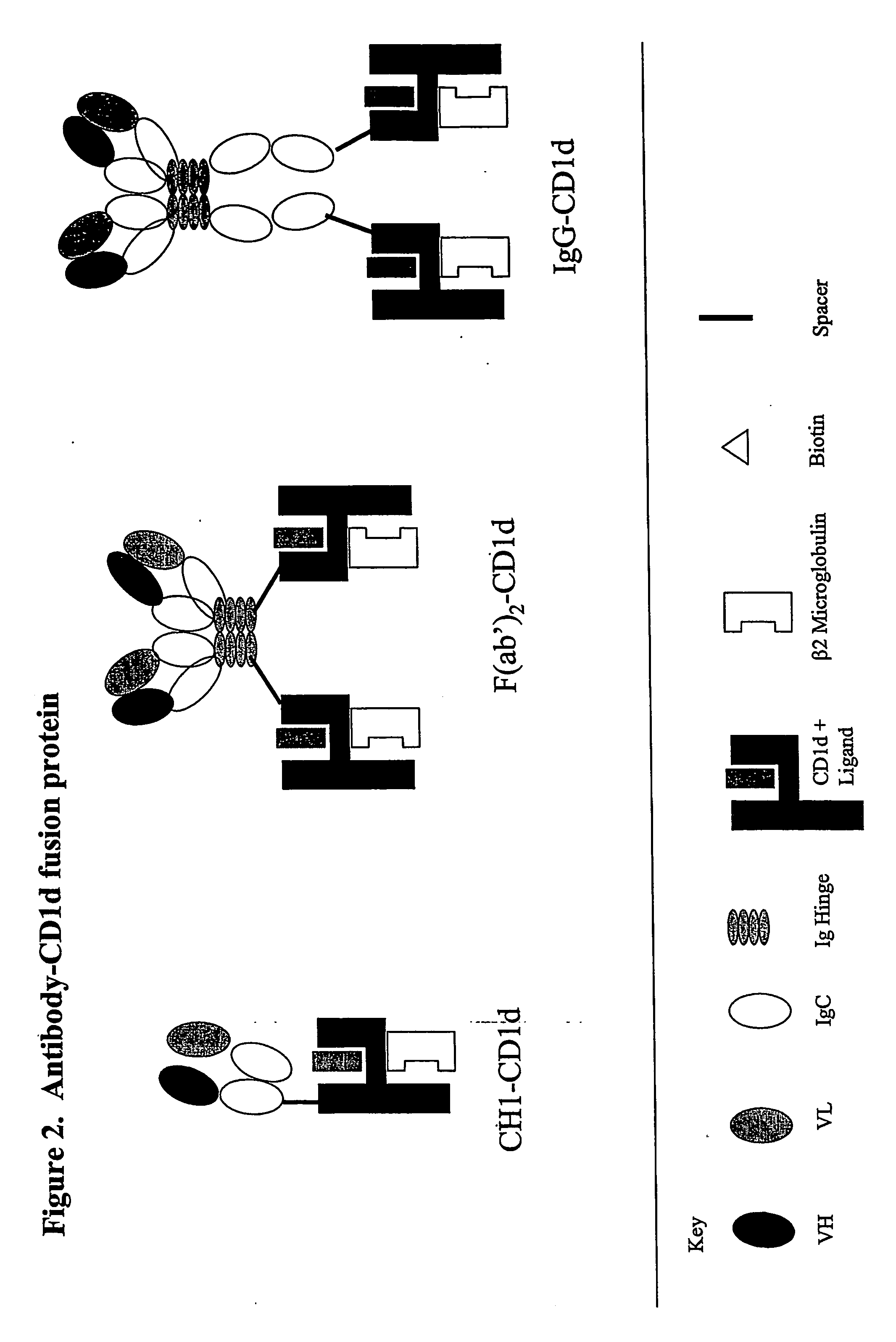
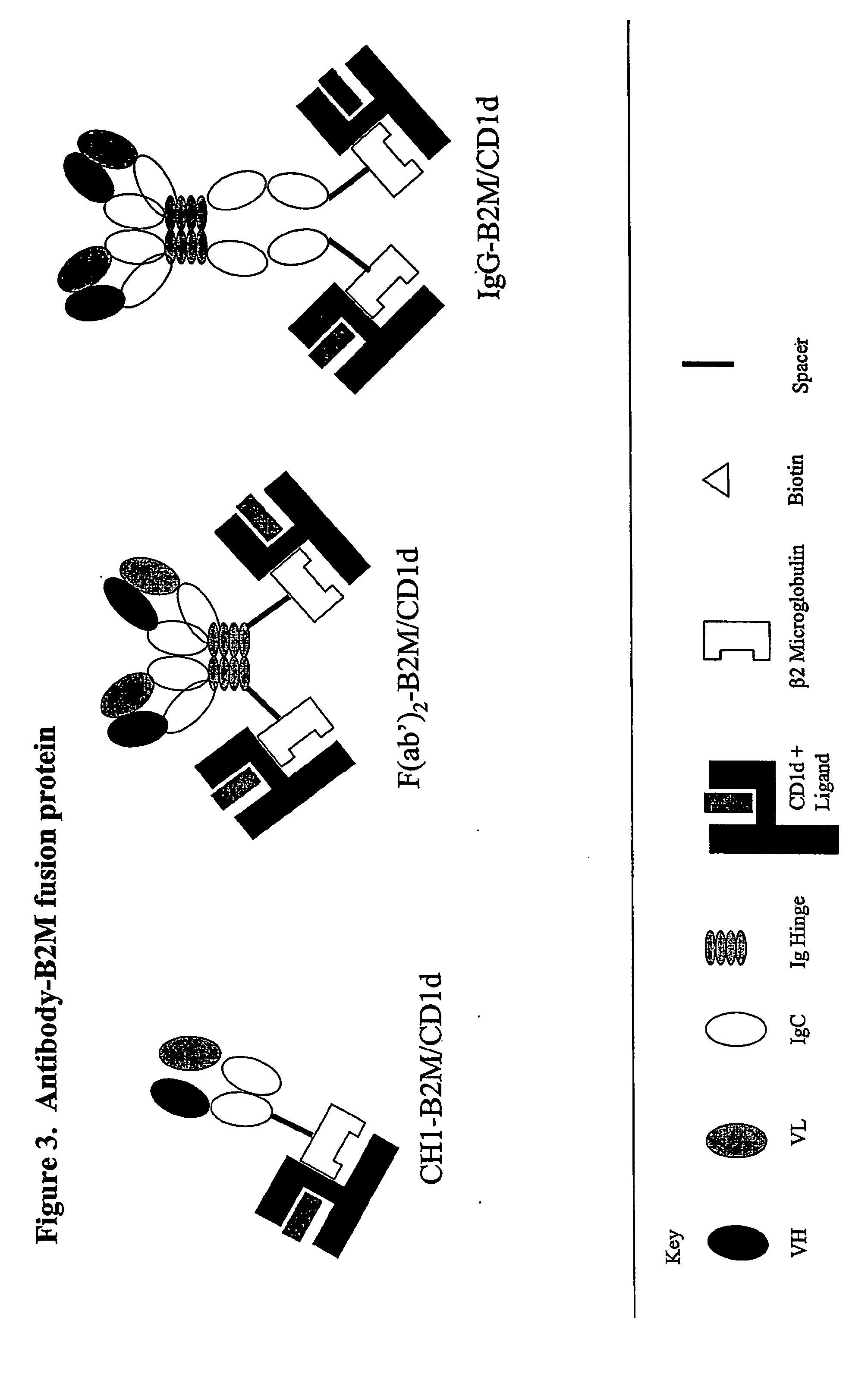
Targeted cd1d molecules
The invention is directed to a compound comprising one or more CD1d complexes in association with an antibody specific for a cell surface marker. The CD1d complexes comprise a CD1d, a β2-microglobulin molecule, and may further comprise an antigen bound to the CD1d binding groove. The invention is further directed to methods of inhibiting or stimulating an immune response with the CD1d-antibody compounds, in particular anti-tumor and autoimmunity responses.
Owner:VACCINEX
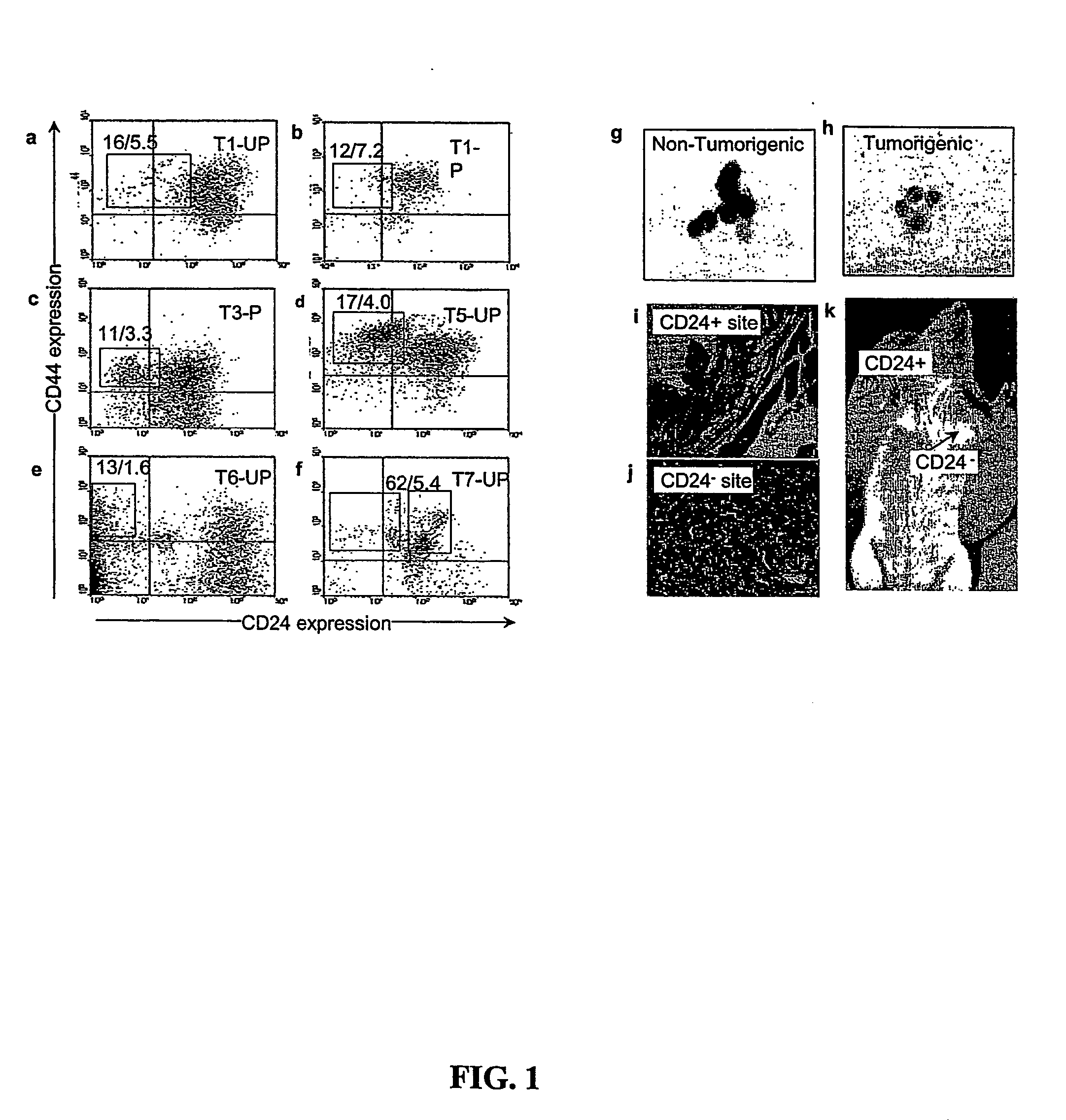
Prospective identification and characterization of breast cancer stem cells
InactiveUS20050089518A1Capacity loseOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsAbnormal tissue growthSurface marker
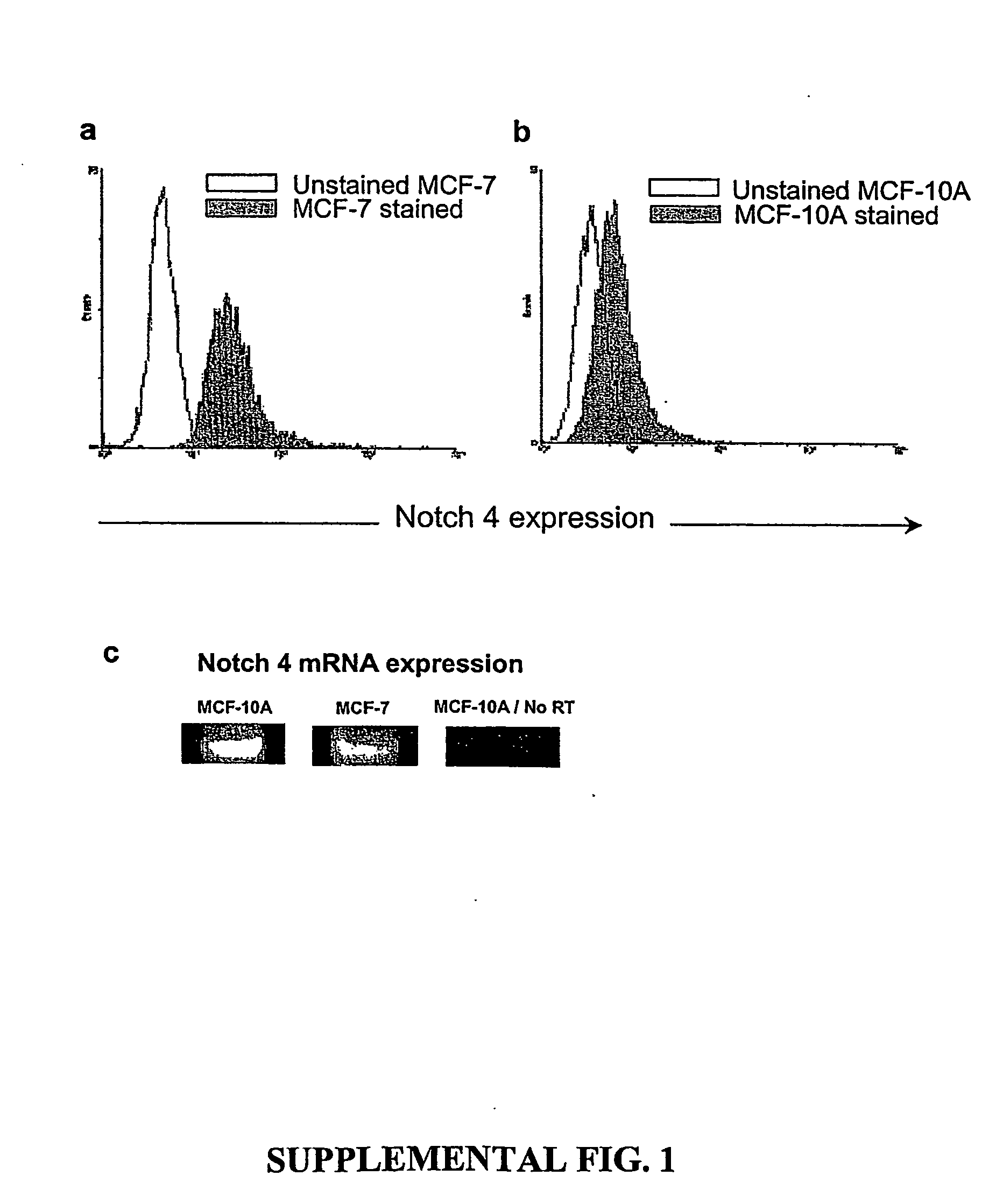
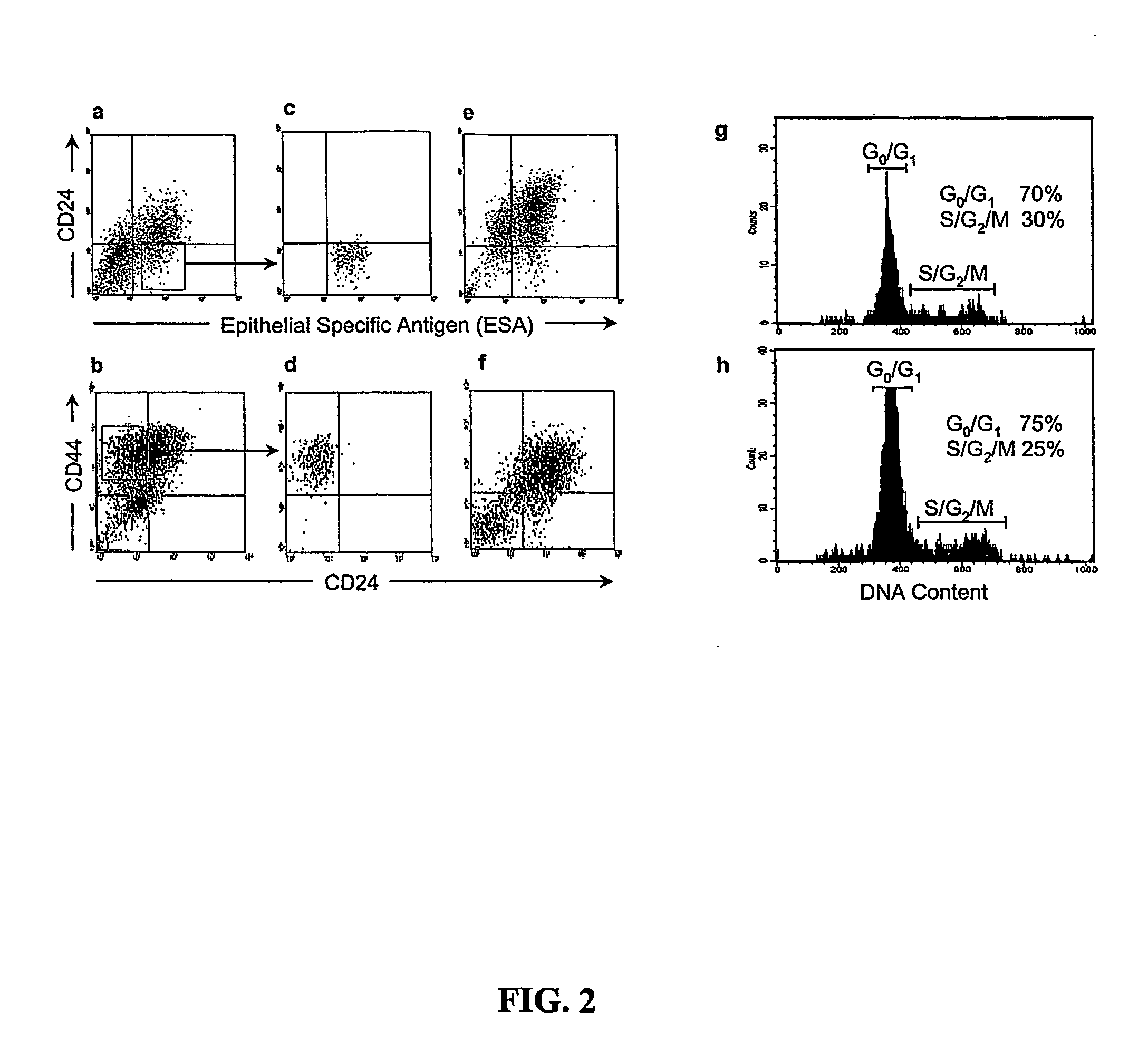
Human breast tumors contain hetrogeneous cancer cells. using an animal xenograft model in which human breast cancer cells were grown in immunocompromised mice we found that only a small minority of breast cancer cells had capacity to form new tumors. The ability to form new tumors was not a slochastic property, rather certain populations of cancer cells were depleted for the ability to form new tumors, while other populations were enriched for the ability to form new tumors. Tumorigenic cells could be distinguished from non-tumorigenic cancer cells based on surface marker expression. We prospectively identified and isolated the tumorigenic cells as CD4430CD24− / lowLINEAGE A few as 100 cells from this population were able to form tumors the animal xenograft model, while tens of thousands of cells from non-tumorigenic populations failed to form tumors. The tumorigenic cells could be serially passaged, each time generating new tumors containing and expanded numbers of CD44+CD24 Lineage tumorigenic cells as well as phenotypically mixed populations of non-tumorigenic cancer cells. This is reminiscent of the ability of normal stem cells to self-renew and differentiate. The expression of potential therapeutic targets also differed between the tumorigenic and non-tumorigenic populations. Notch activation promoted the survival of the tumorigenic cells, and a blocking antibody against Notch 4 induced tumorigenic breast cancer cells to undergo apoptosis.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
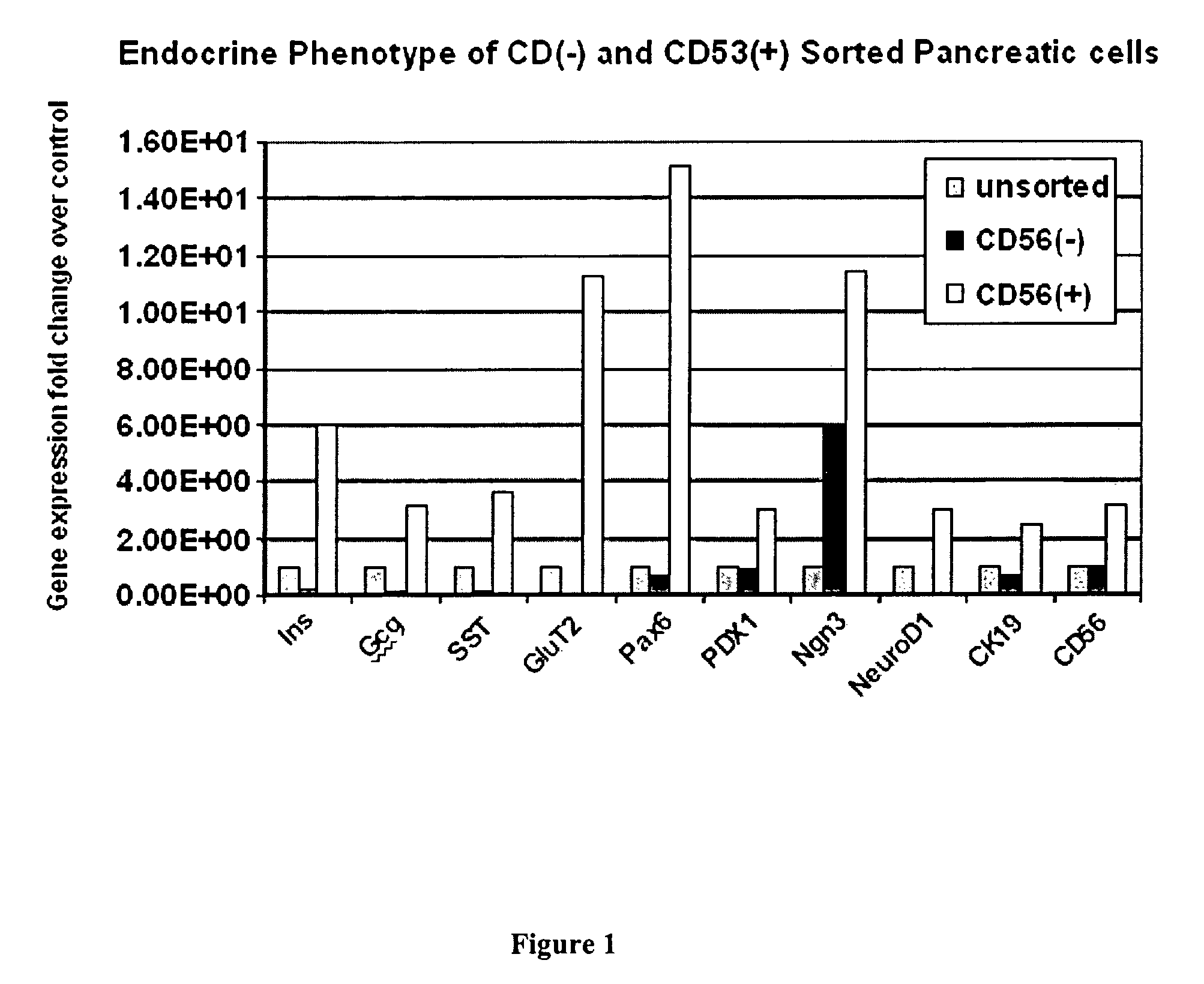
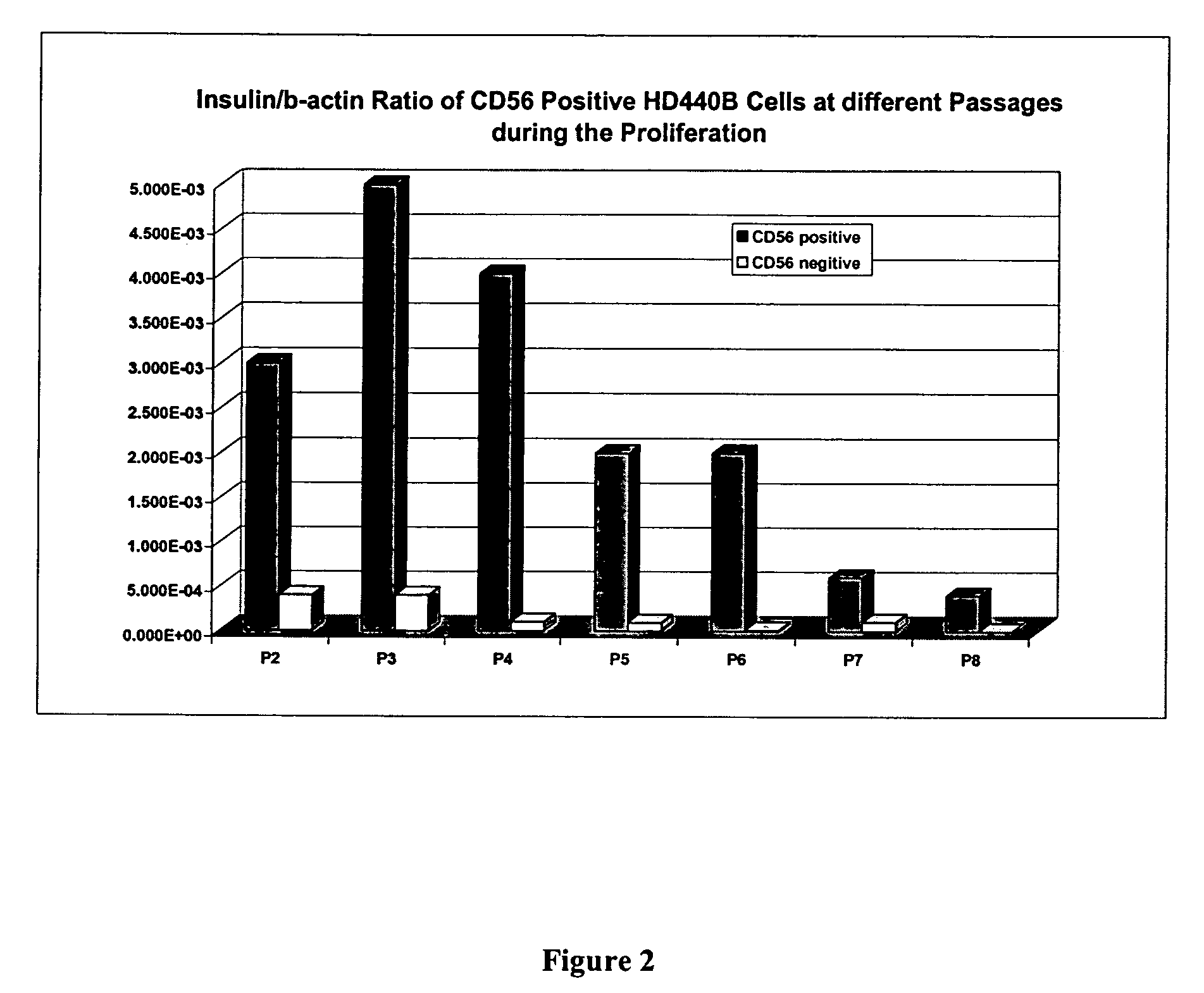
CD56 positive human adult pancreatic endocrine progenitor cells
The invention relates to the discovery of a selective cell surface marker that permits the selection of a unique subset of pancreatic stems cells having a high propensity to differentiate into insulin producing cells or into insulin producing cell aggregates.
Owner:RENEURON INC
Method for treating vasculitis
A method of treating anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies-associated vasculitis (ANCA-associated vasculitis) in a patient eligible for treatment is provided involving administering an antagonist that binds to a B-cell surface marker, such as CD20 antibody, to the patient in a dose of about 400 mg to 1.3 grams at a frequency of one to three doses within a period of about one month. Another method of treating ANCA-associated vasculitis in a subject eligible for treatment is provided involving administering an effective amount of an antibody that binds to a B-cell surface marker to the subject to provide an initial exposure and a subsequent exposure to the antibody within certain dosing regimens. Further provided are articles of manufacture useful for such methods.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
Method, apparatus and system for electroporation
InactiveUS20130108667A1High dielectric constantImprove conductivityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsOrganic active ingredientsSurface markerNanoparticle
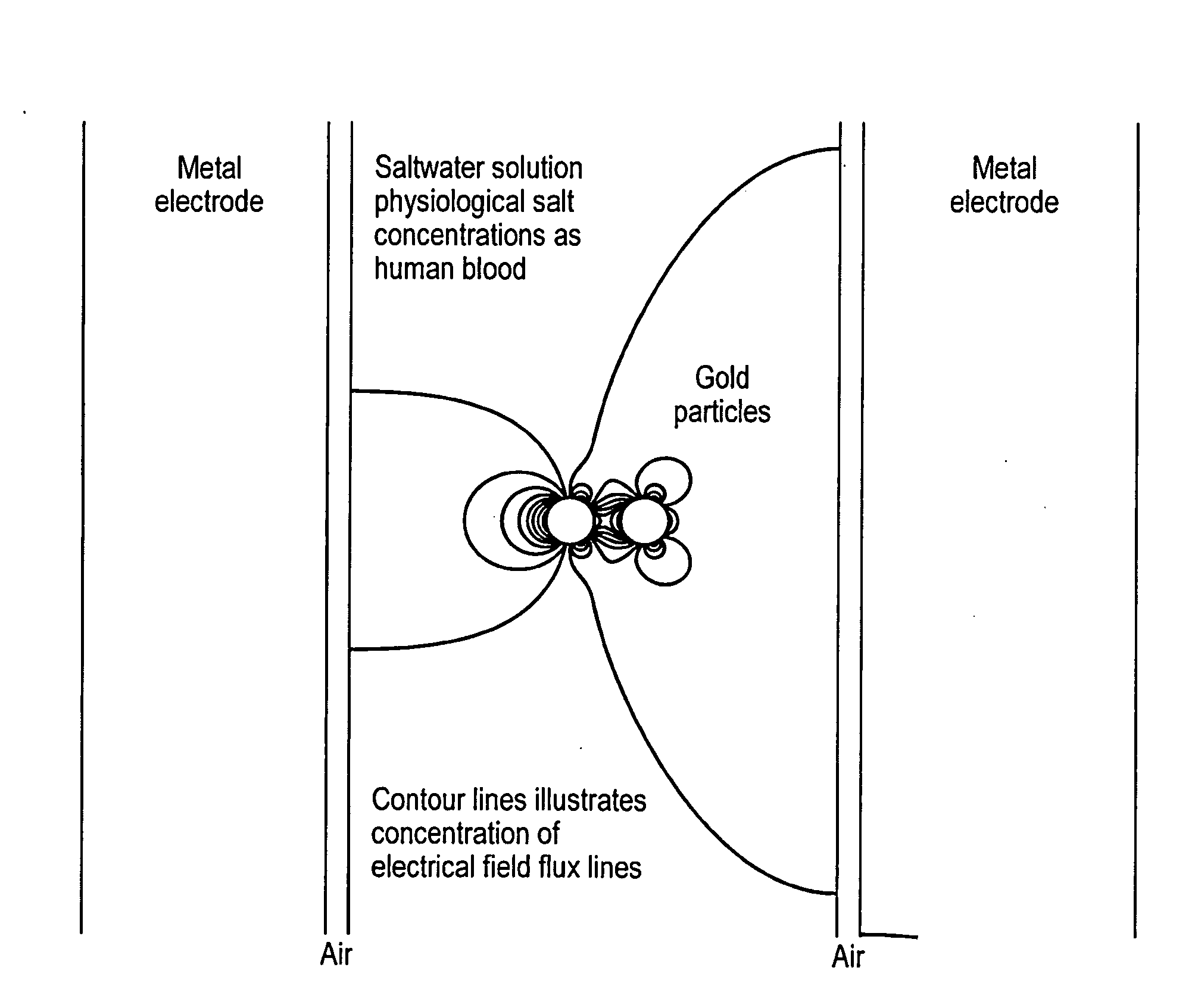
A method, apparatus and system that employs particles, e.g., nanoparticles, and an electric or electro-magnetic field, to cause electroporation in target cells at reduced fields. Electroporation may be irreversible, leading to targeted cell death, or reversible, allowing species to be introduced into the target cell. The method introduces a particle to a position adjacent to the cell membrane of a target cell and exposes the target cell to a transient electromagnetic field for a time interval to cause targeted electroporation. A smaller electric field is applied, thereby surmounting similar methods. The particle enhances the effect of the electric field in its immediate vicinity, so reducing the field strength needed to achieve electroporation and thereby reducing the risk of damage to cells through high field exposure. Electroporation can be targeted to a subset of target cells by targeting the particles to surface markers on the target cell membrane.
Owner:SOIKUM SOIWISA +2
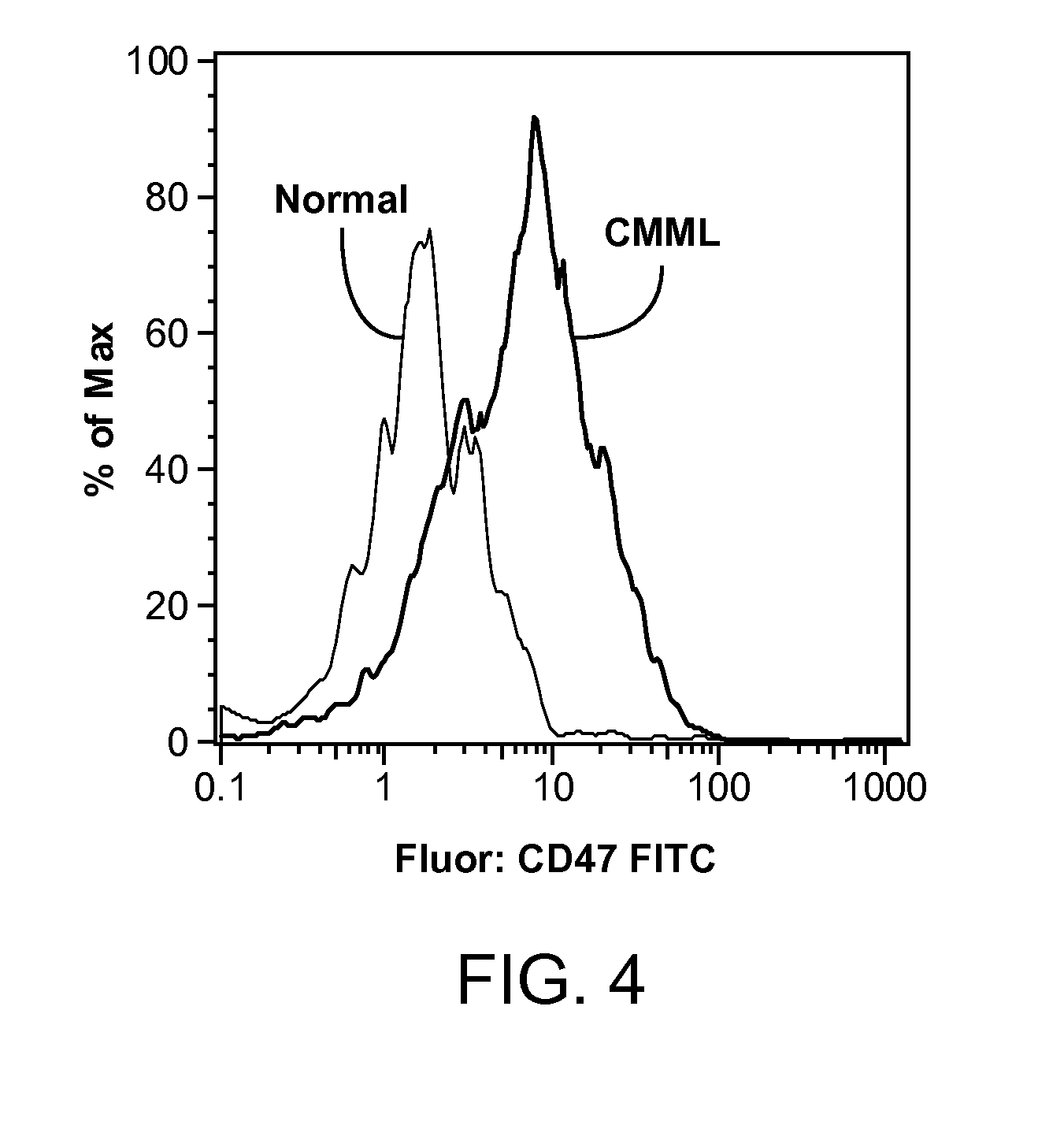
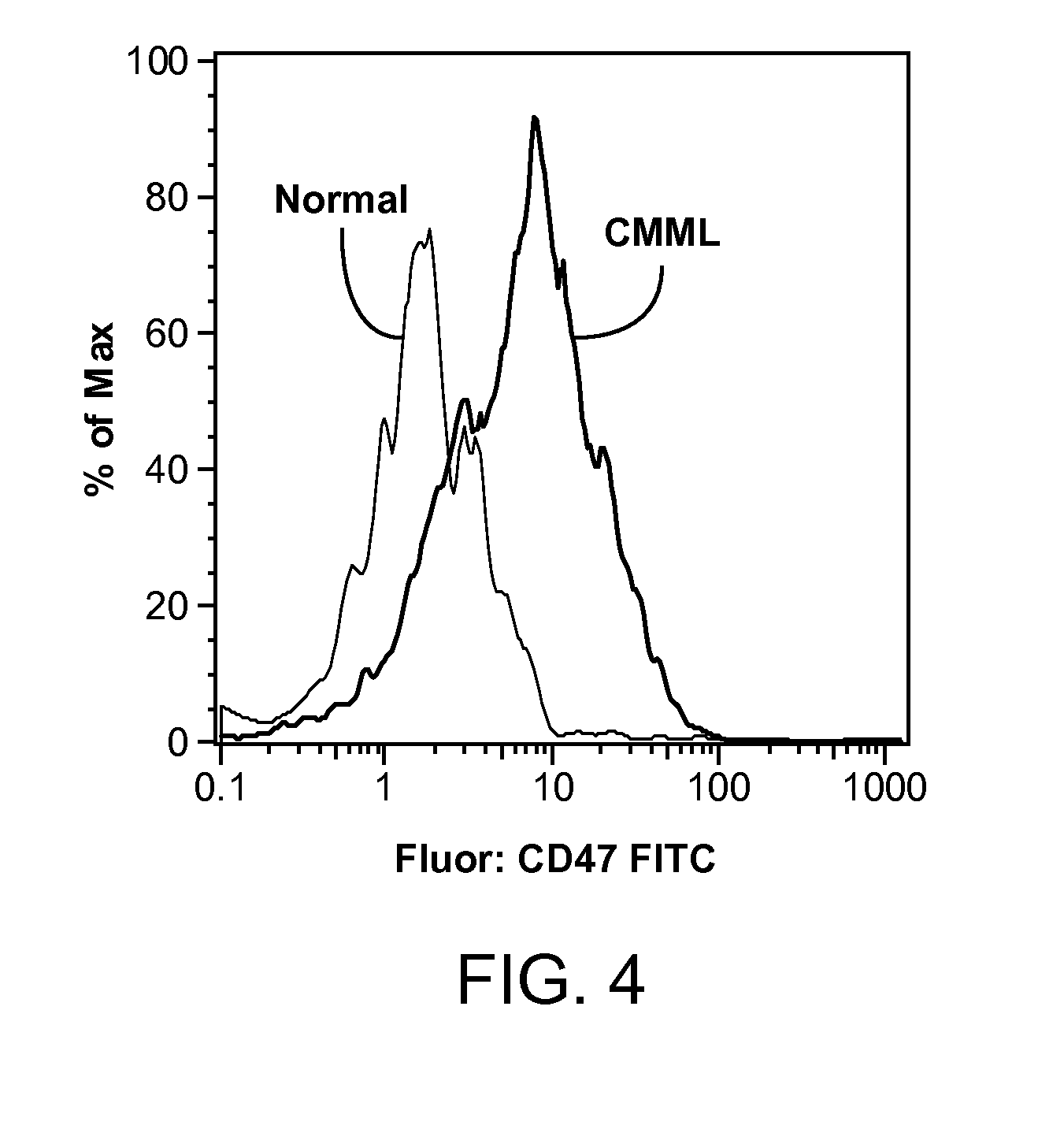
Synergistic Anti-CD47 Therapy for Hematologic Cancers
ActiveUS20120282174A1Immunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsRadioactive preparation carriersSurface markerCD20
Methods are provided for treatment of hematologic cancers, particularly lymphomas and leukemias, including without limitation myelogenous and lymphocytic leukemias. A combination of antibodies specific for CD47; and specific for a cancer associated cell surface marker are administered to the patient, and provide for a synergistic decrease in cancer cell burden. The combination of antibodies may comprise a plurality of monospecific antibodies, or a bispecific or multispecific antibody. Markers of interest include without limitation, CD20, CD22, CD52, CD33; CD96; CD44; CD123; CD97; CD99; PTHR2; and HAVCR2.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Bispecific binding agents for modulating biological activity
InactiveUS20090246206A1Decreasing activity of tyrosine kinaseModulating biological activityAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsAntibody ingredientsLow affinitySurface marker
Methods for improving the specific binding ability of bispecific binding compositions are described. The bispecific binding compositions are able to target cells by a high affinity targeting domain to a target cell surface marker and a low affinity binding domain that binds specifically to a second cell surface marker, wherein the binding of each domain to its respective cell surface marker increases or decreases, as desired, the biological activity of the respective cell surface markers. The invention further provides bispecific binding agents for use in the methods, as well as uses for the agents.
Owner:MERRIMACK PHARMACEUTICALS INC
Modulation of immune responses in blood-borne mesenchymal cells
The present invention relates to a population of blood borne mammalian cells that express a unique profile of surface markers that includes certain markers typical of connective tissue fibroblasts, and are referred to herein as "blood-borne mesenchymal cells." In particular, it relates to the isolation, characterization and uses of such blood-borne mesenchymal cells. The cells of the present invention can be distinguished from peripheral blood leukocytes by their distinct size, morphology, cell surface phenotype and biologic activities, and are likewise distinguishable from connective tissue fibroblasts by other surface phenotypic markers. These cells proliferate in culture, and in vivo, as demonstrated in animal models, are capable of migrating into wound sites from the blood. Therefore, such blood-borne mesenchymal cells may have a wide range of applications, including, but not limited to, the promotion of wound healing, tissue remodeling, and for gene therapy.
Owner:FERRING BV
Synergistic anti-CD47 therapy for hematologic cancers
Methods are provided for treatment of hematologic cancers, particularly lymphomas and leukemias, including without limitation myelogenous and lymphocytic leukemias. A combination of antibodies specific for CD47; and specific for a cancer associated cell surface marker are administered to the patient, and provide for a synergistic decrease in cancer cell burden. The combination of antibodies may comprise a plurality of monospecific antibodies, or a bispecific or multispecific antibody. Markers of interest include without limitation, CD20, CD22, CD52, CD33; CD96; CD44; CD123; CD97; CD99; PTHR2; and HAVCR2.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Blood-borne mesenchymal cells
InactiveUS6174526B1Promote wound healingBiocideMammal material medical ingredientsTissue remodelingSurface marker
The present invention relates to a population of blood borne mammalian cells that express a unique profile of surface markers that includes certain markers typical of connective tissue fibroblasts, and are referred to herein as "blood-borne mesenchymal cells." In particular, it relates to the isolation, characterization and uses of such blood-borne mesenchymal cells. The cells of the present invention can be distinguished from peripheral blood leukocytes by their distinct size, morphology, cell surface phenotype and biologic activities, and are likewise distinguishable from connective tissue fibroblasts by other surface phenotypic markers. These cells proliferate in culture, and in vivo, as demonstrated in animal models, are capable of migrating into wound sites from the blood. Therefore, such blood-borne mesenchymal cells may have a wide range of applications, including, but not limited to, the promotion of wound healing, tissue remodeling, and for gene therapy.
Owner:FERRING BV
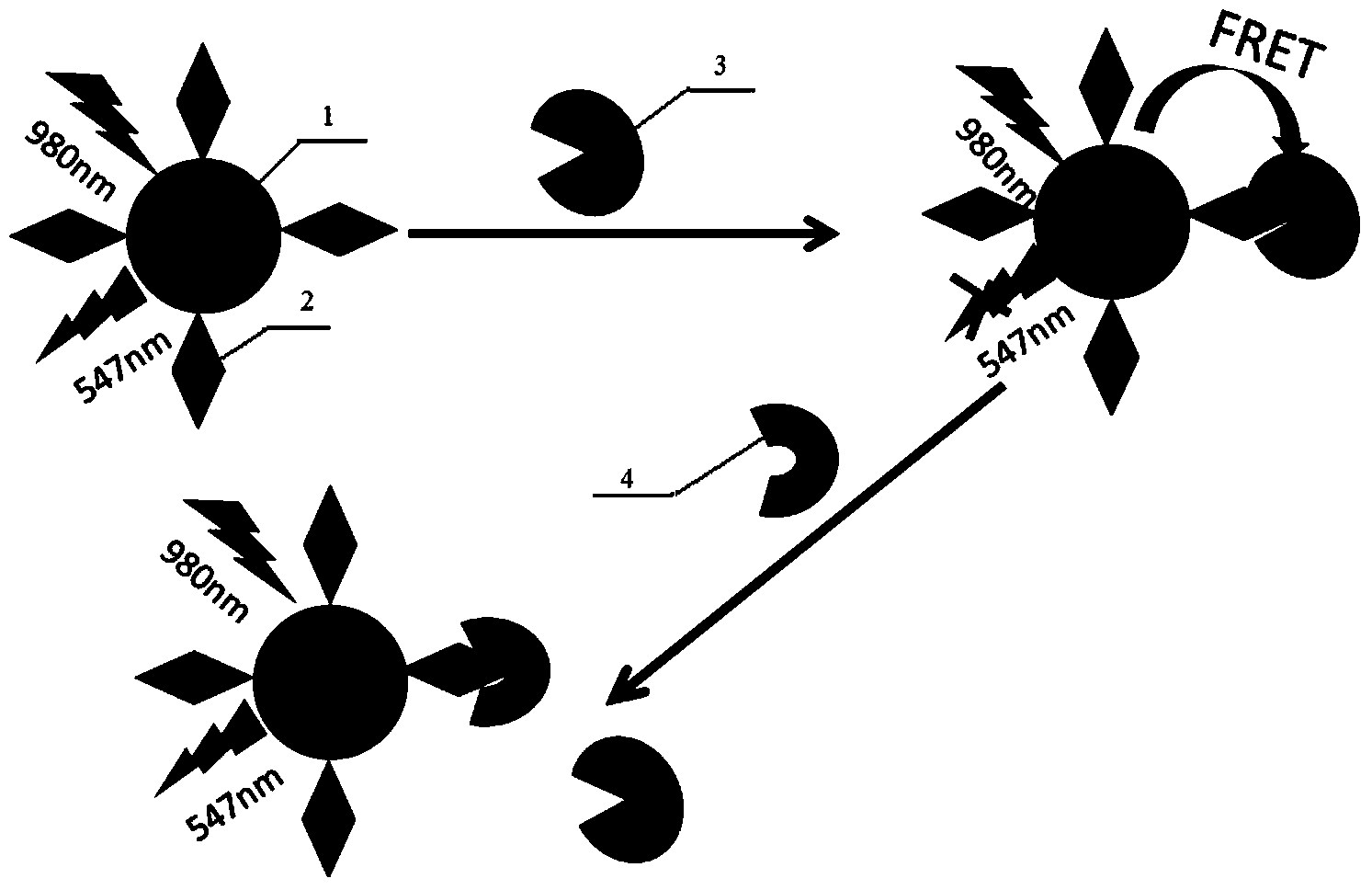
Method for detecting upconversion fluorescence resonance energy transfer by using carbon nanomaterial as receptor
InactiveCN103487418ACarbon source is easy to getEasy to prepareFluorescence/phosphorescenceLuminescent compositionsSurface markerQuenching
The invention discloses a method for detecting fluorescence resonance energy transfer by using a water-soluble upconversion fluorescence nanomaterial as a fluorescence donor and using a carbon nanomaterial as a fluorescence receptor. The method comprises the following specific steps: (1) preparing the water-soluble upconversion fluorescence nanomaterial and performing surface marker to obtain a fluorescence donor solution; (2) preparing the carbon nanomaterial to obtain a fluorescence receptor solution; (3) mixing the fluorescence donor solution and the fluorescence receptor solution for incubation and measuring the fluorescence intensity to obtain a fluorescence quenching curve; (4) mixing certain-concentration fluorescence donor solution and certain-concentration fluorescence receptor solution for incubation, adding a target object with different concentrations for continuous incubation, measuring the fluorescence intensity and drawing a standard curve; (5) calculating the concentration of the target object in an actual sample according to the standard curve. According to the method, interference of the background fluorescence of a biological sample can be avoided, detection to serum or the target object in a whole blood sample can be directly realized, the washing and separation processes are not needed, the detection speed is high, and the cost is low.
Owner:GUANGZHOU IMPROVE MEDICAL TECH CO LTD
Therapy of autoimmune disease in a patient with an inadequate response to a tnf-alpha inhibitor
The present application describes therapy with antagonists which bind to B cell surface markers, such as CD20. In particular, the application describes the use of such antagonists to treat autoimmune disease in a mammal who experiences an inadequate response to a TNFα-inhibitor.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
Method for efficiently separating single antigen-specific B lymphocyte from spleen cells
ActiveCN110016462AIncrease positive rateKeep activeCell dissociation methodsBlood/immune system cellsSurface markerSpleen cell
The invention discloses a method for efficiently separating single antigen-specific B lymphocyte from spleen cells. High-throughput rapid screening of single antigen-specific B lymphocyte is realizedby negative screening adopting multiple lymphocyte surface marker antibodies, establishment of a rapid fluorescence marked antigen substance method and high-specificity screening by use of a fluorescence marked antigen substance, and the positive rate of the finally obtained antibody-specific B lymphocyte is increased from less than 5% in a traditional hybridoma method to 30%. Therefore, the scheme can shorten monoclonal antibody development time to a great extent and greatly increase the number and diversity of obtained monoclonal antibodies.
Owner:优睿赛思(武汉)生物科技有限公司
Bispecific binding agents for modulating biological activity
InactiveUS20090181022A1Reduced activityModulating biological activityPeptide/protein ingredientsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsSurface markerLow affinity
Methods for improving the biological and pharmaceutical properties of bispecific binding agents are described herein where the bispecific binding agent are able to target cells by a high affinity binding domain to a first cell surface marker that does not induce a significant biological effect and a low affinity binding domain that binds specifically to a second cell surface marker, causing a significant and desired biological effect. Compositions of such bispecific binding agents, uses for them, and kits containing them are also provided.
Owner:MERRIMACK PHARMACEUTICALS INC
Immunotoxins directed against malignant cells
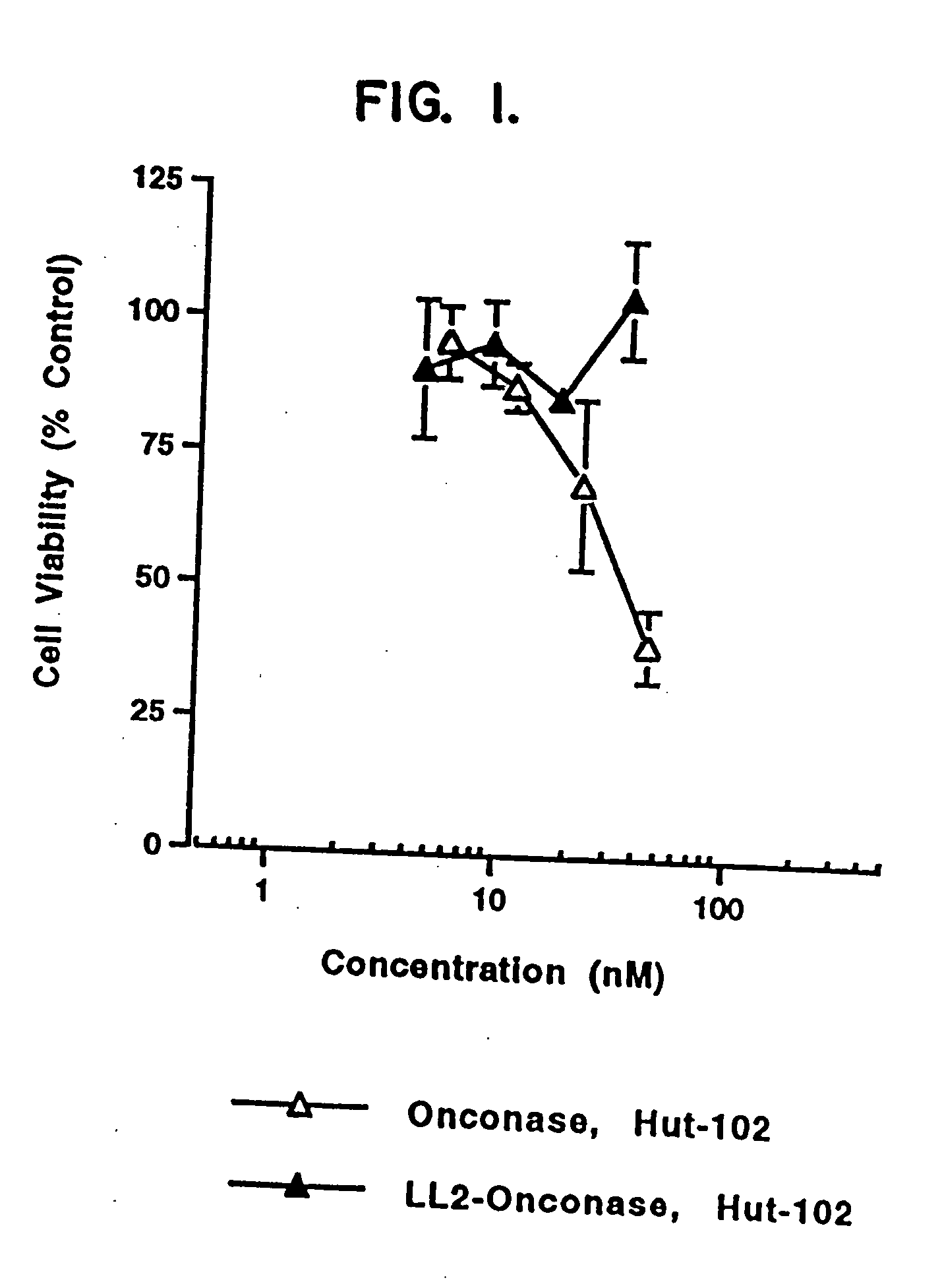
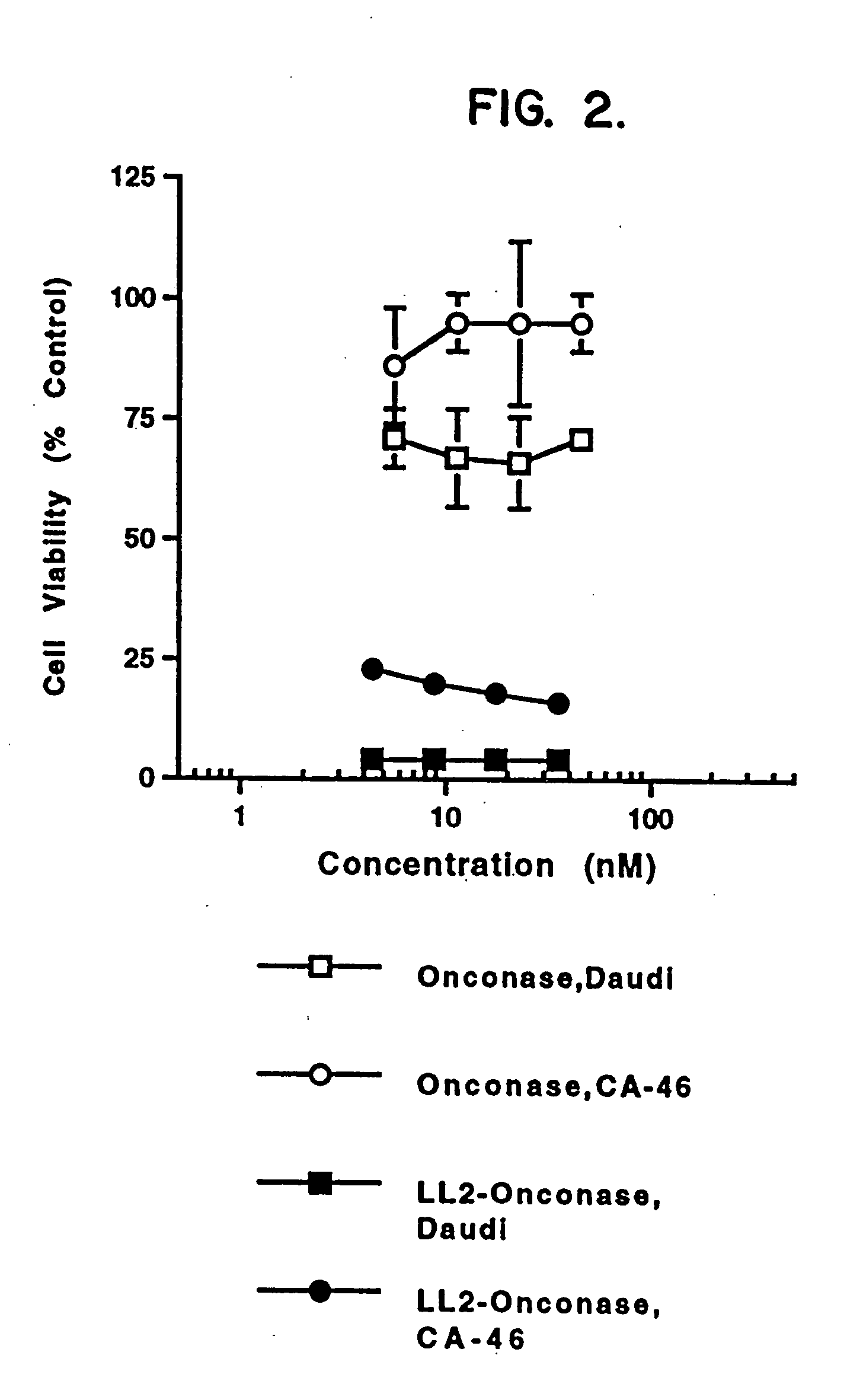
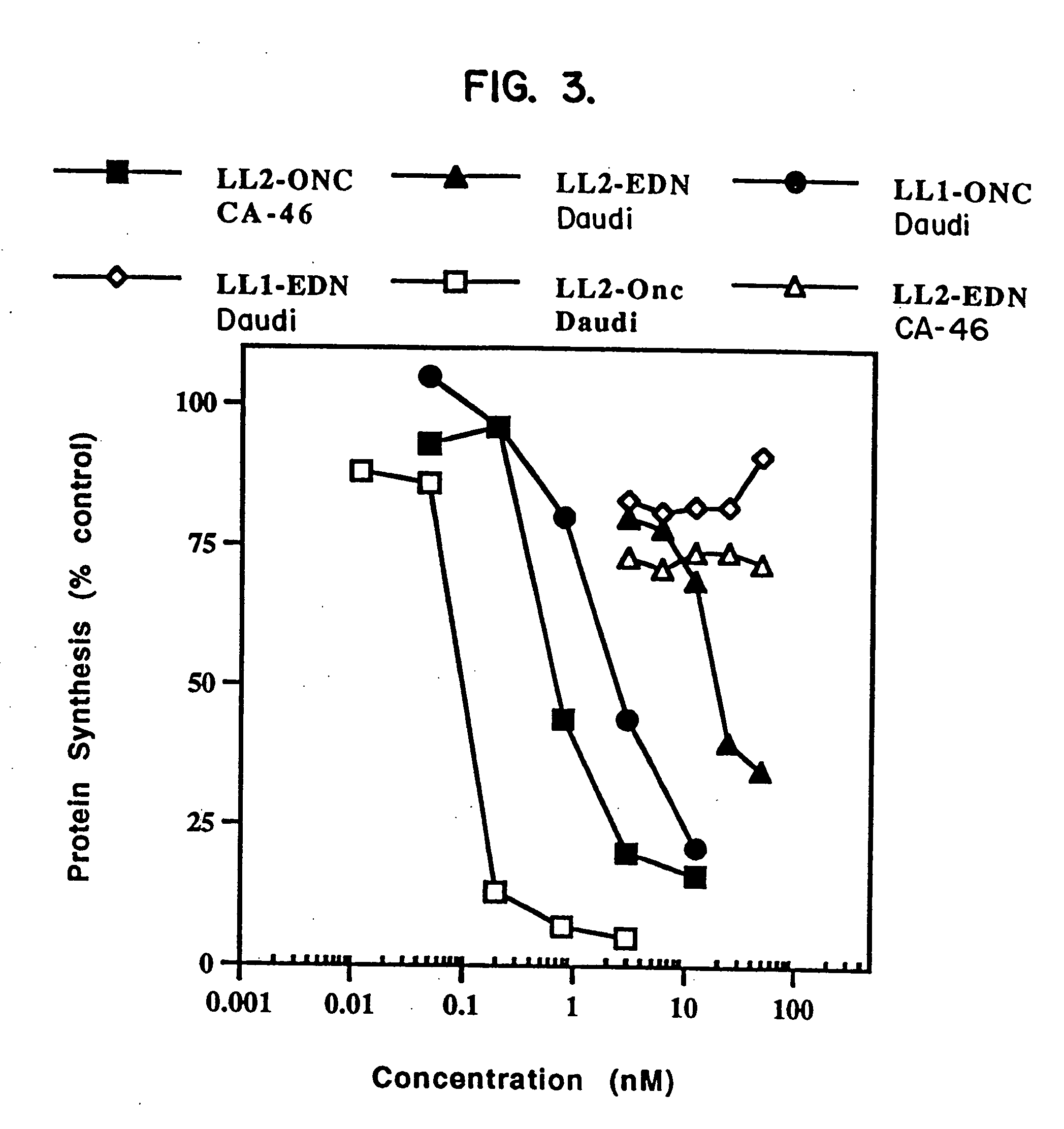
InactiveUS20050249738A1Eliminate side effectsHigh propertyPeptide/protein ingredientsHydrolasesSurface markerToxin
The present invention relates to immunotoxins, that effectively kill malignant cells having a given surface marker and nucleic acid constructs encoding them. These reagents comprise a toxic moiety that is derived from a Rana pipiens protein having ribonucleolytic activity linked to an antibody capable of specific binding with a chosen tumor cell.
Owner:THE GOVT OF THE U S A AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECT OF THE DEPT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES +1
Pluripotent stem cells, method for preparation thereof and uses thereof
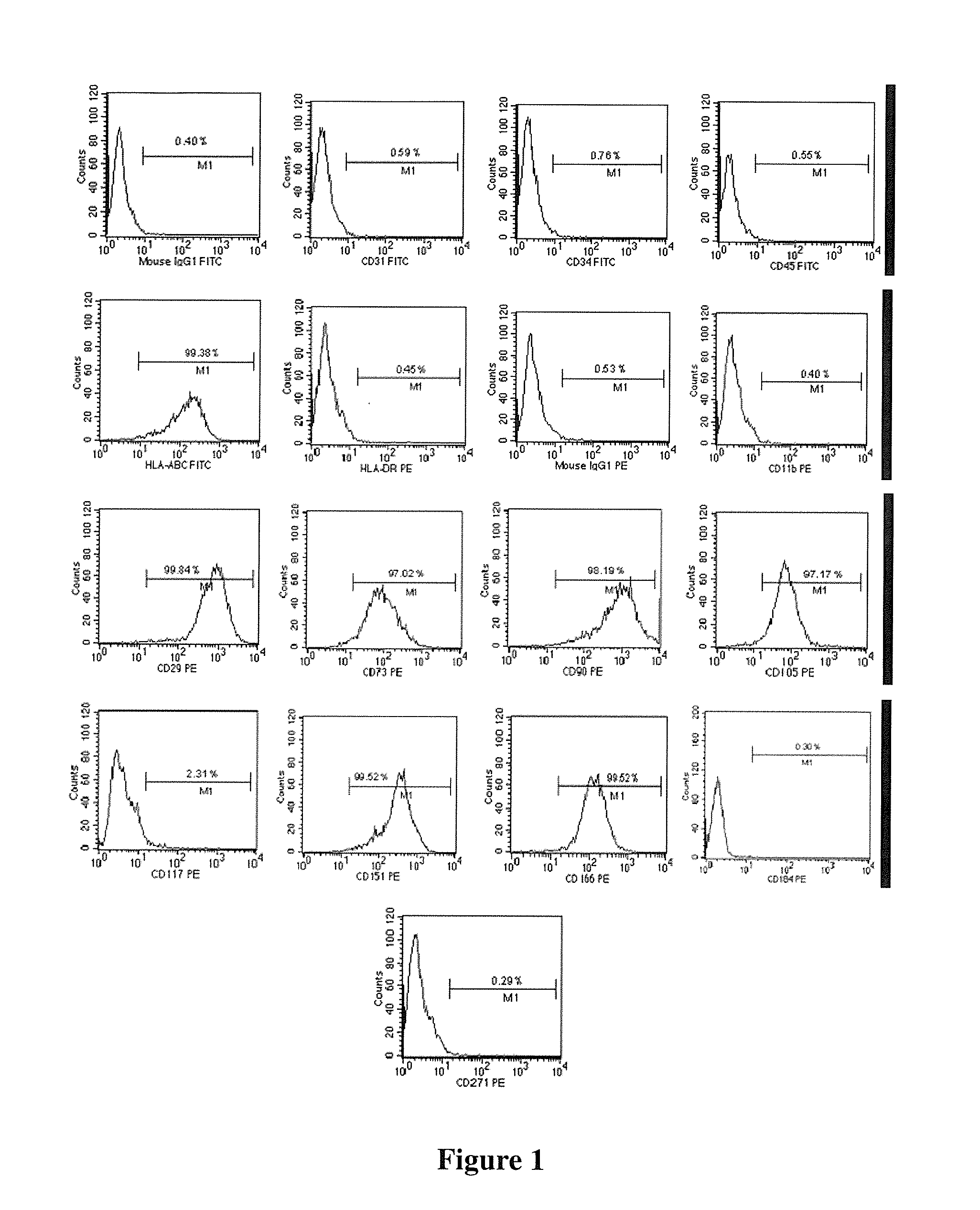
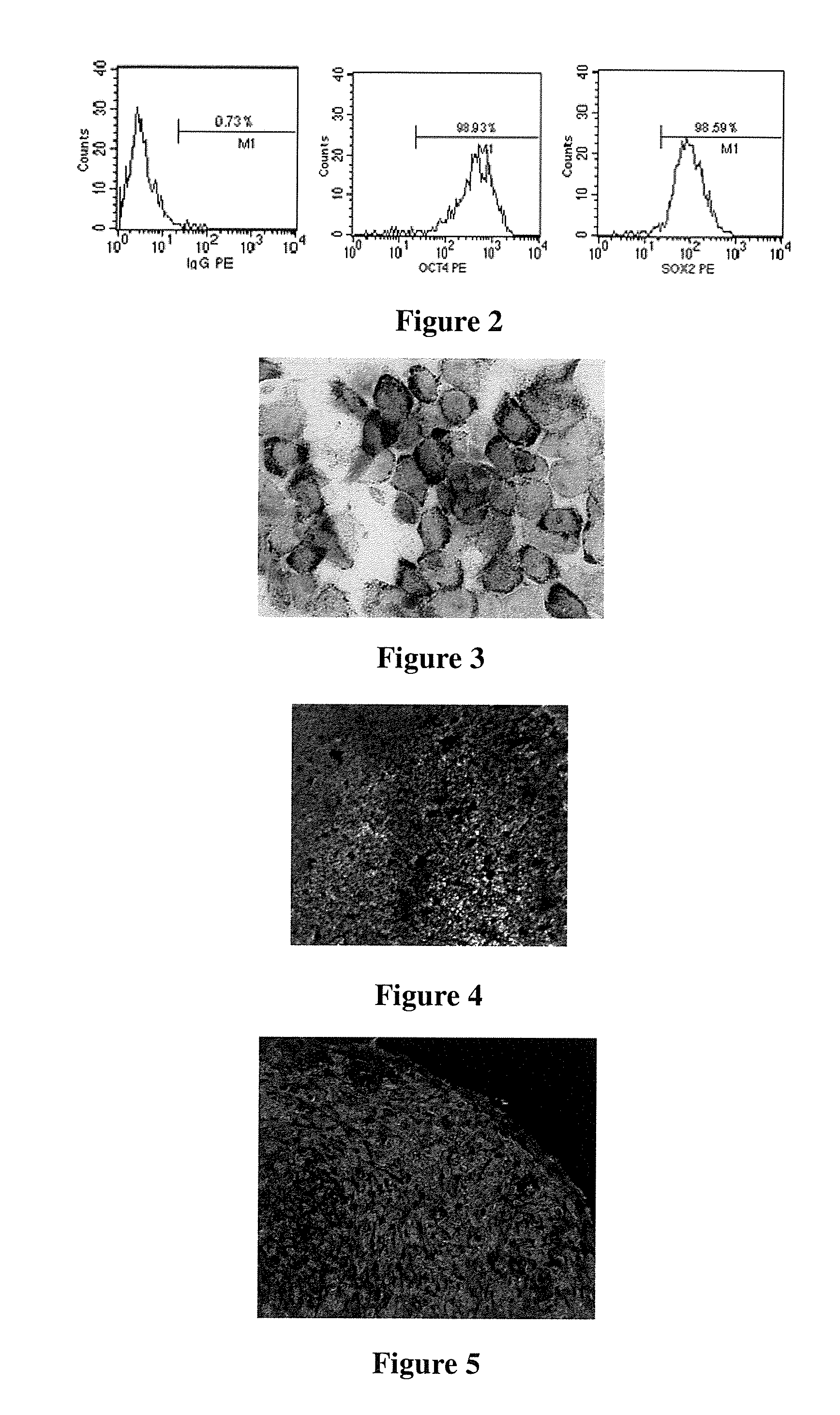
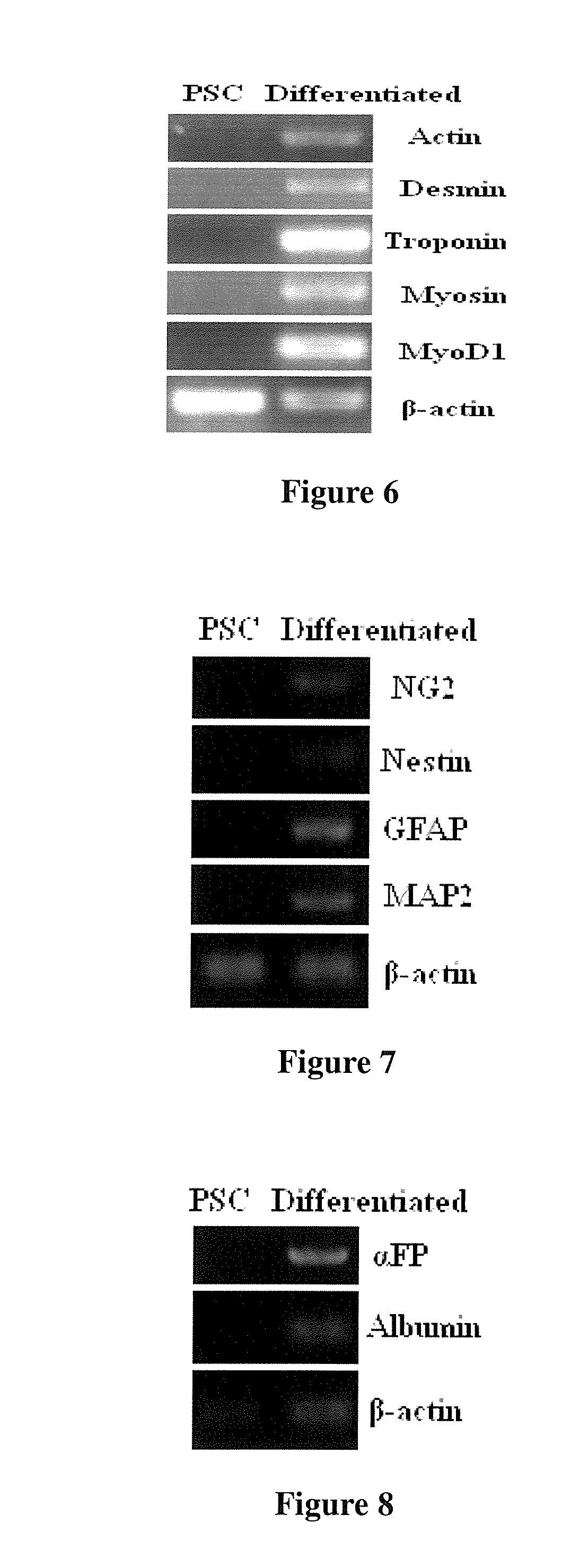
Human pluripotent stem cells which are isolated from cut human umbilical cord or placenta and characteristic of cell surface marker CD151+, OCT4+ and CD184−, can adhere to tissue culture plastic and have the potential to differentiate into three germ layers: endoderm, mesoderm and ectoderm. Methods of isolating, purifying and culturally expanding of a population of human pluripotent stem cells and uses for treating diseases caused by cell damage or cell aging, and as a kind of carrier cells in gene therapy are provided.
Owner:BEIJING HEALTH & BIOTECH (H&B) CO LTD
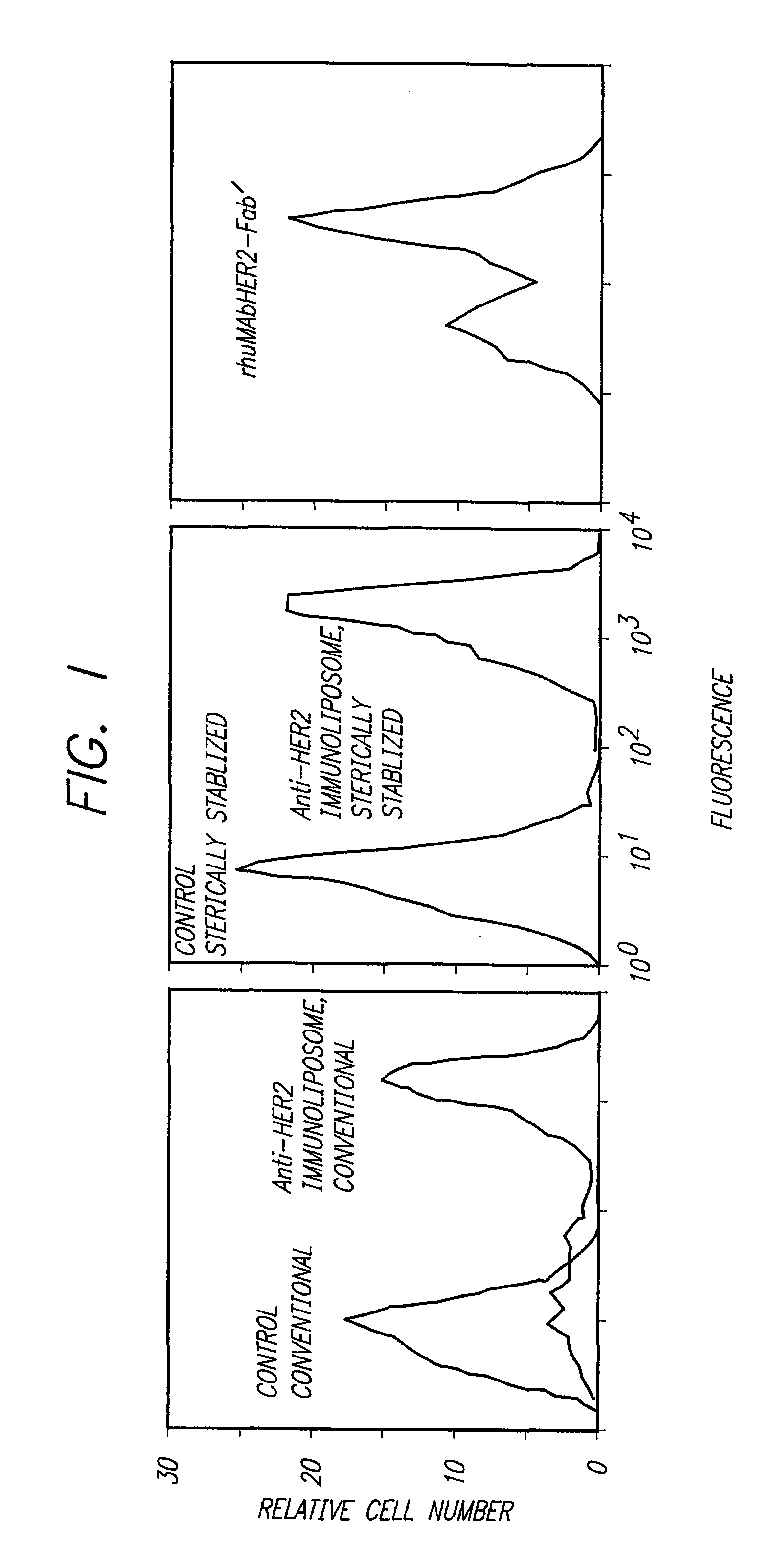
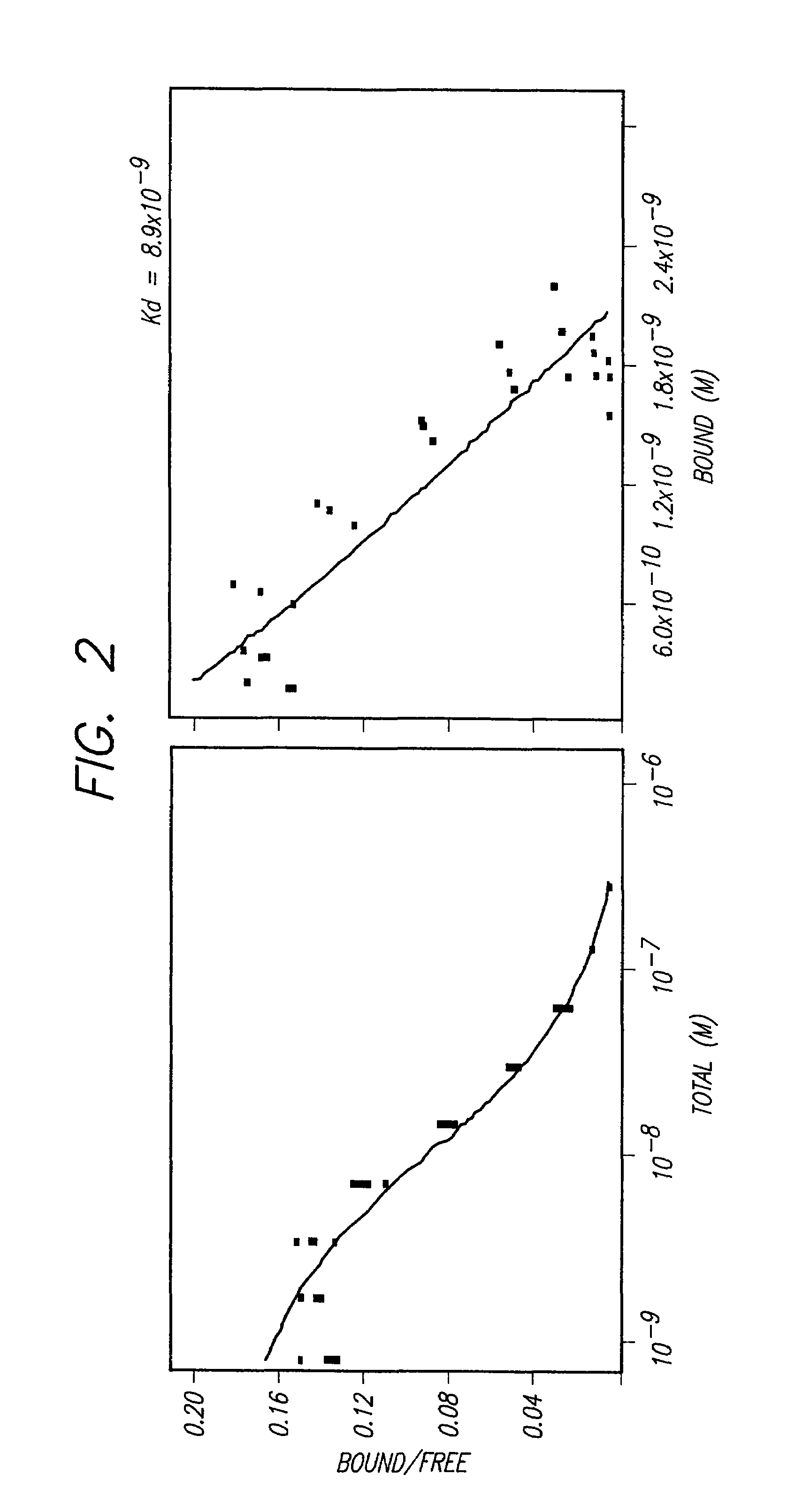
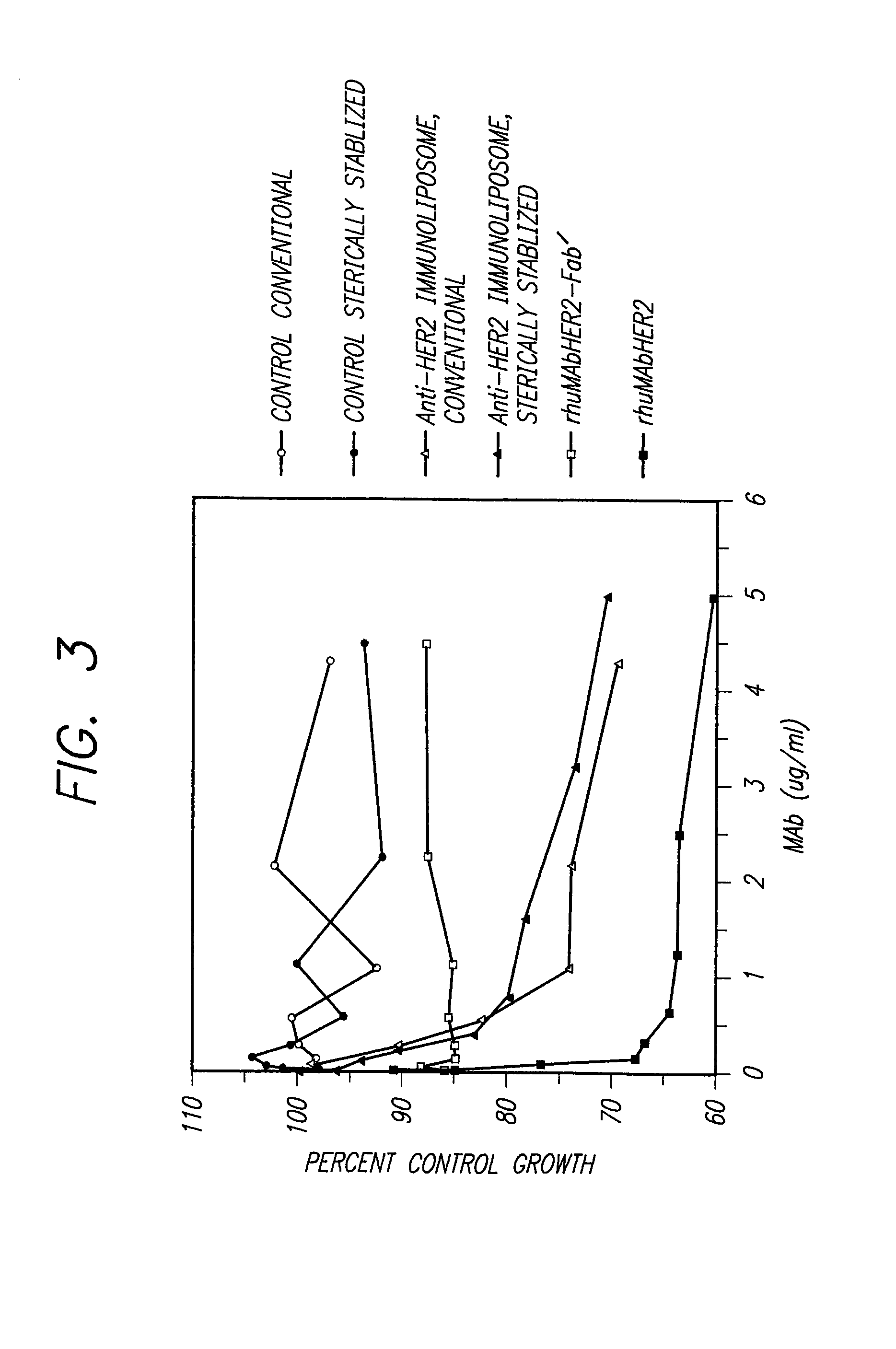
Immunoliposomes that optimize internalization into target cells
InactiveUS7135177B2Extended half-lifeAvoid lostBiocideHeavy metal active ingredientsSurface markerLipid formation
The present invention provides for immunoliposomes that optimizes internalization of a drug into target cells bearing a characteristic cell surface marker. The immunoliposomes comprise an Fab' domain of an antibody that specifically binds the characteristic marker, an amphipathic vesicle-forming lipid, and a polyethylene glycol derivatized lipid. The invention also provides for growth-inhibiting immunoliposomes that lack growth-inhibiting therapeutic agents and yet are capable of inhibiting the growth and proliferation of target cells.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
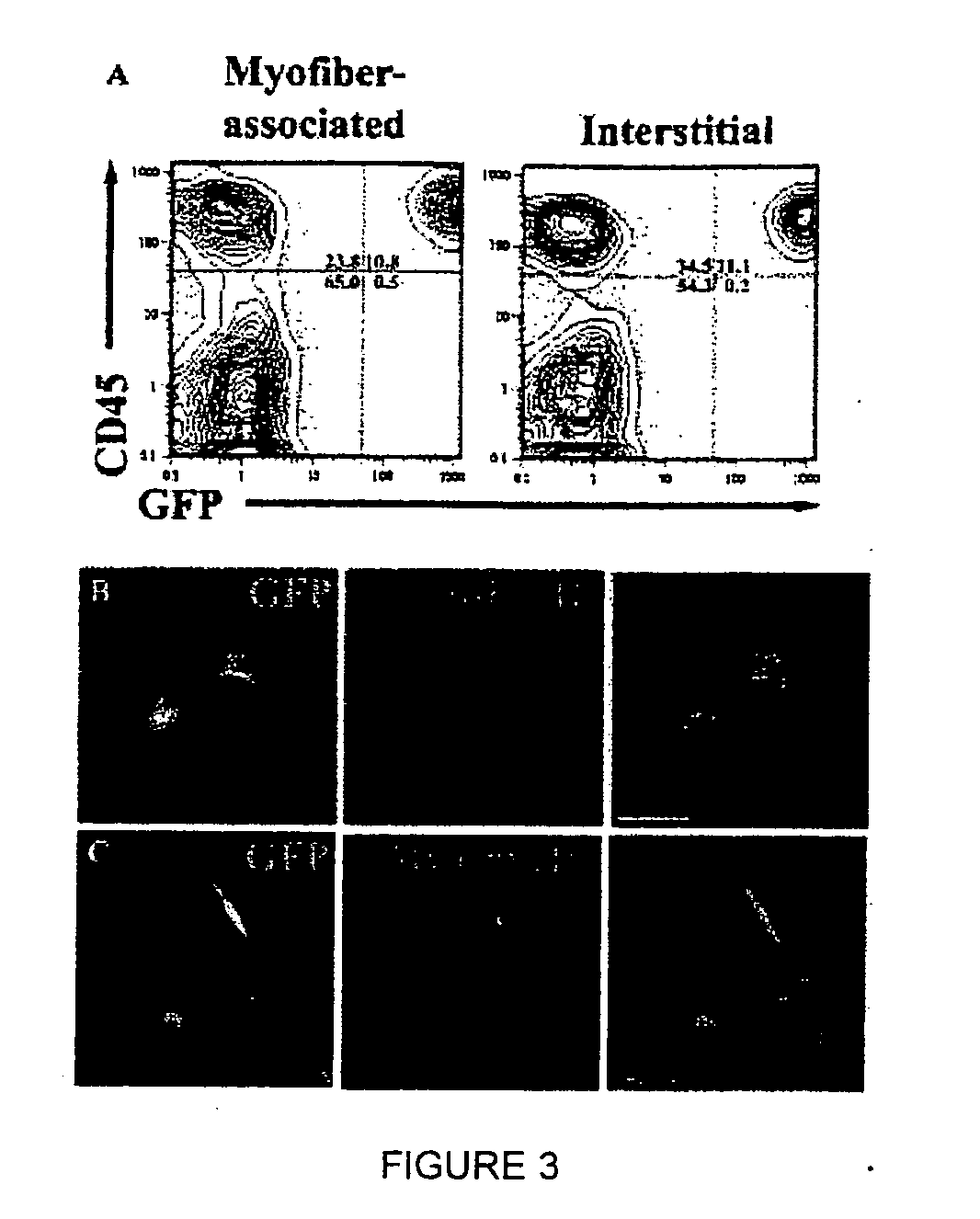
Isolation and characterization of muscle regenerating cells
InactiveUS20060014287A1Useful for transplantationBiocideArtificial cell constructsSurface markerProgenitor
Populations enriched for myogenic progenitors are obtained by selection on the basis of expression of specific cell surface markers. The muscle progenitor cells are characterized as being CD45− and CD34+, and may further be characterized as lacking expression of Mac-1 (CD11b) and positive for expression of CXCR4 (CD184) and β1-integrin (CD29).
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
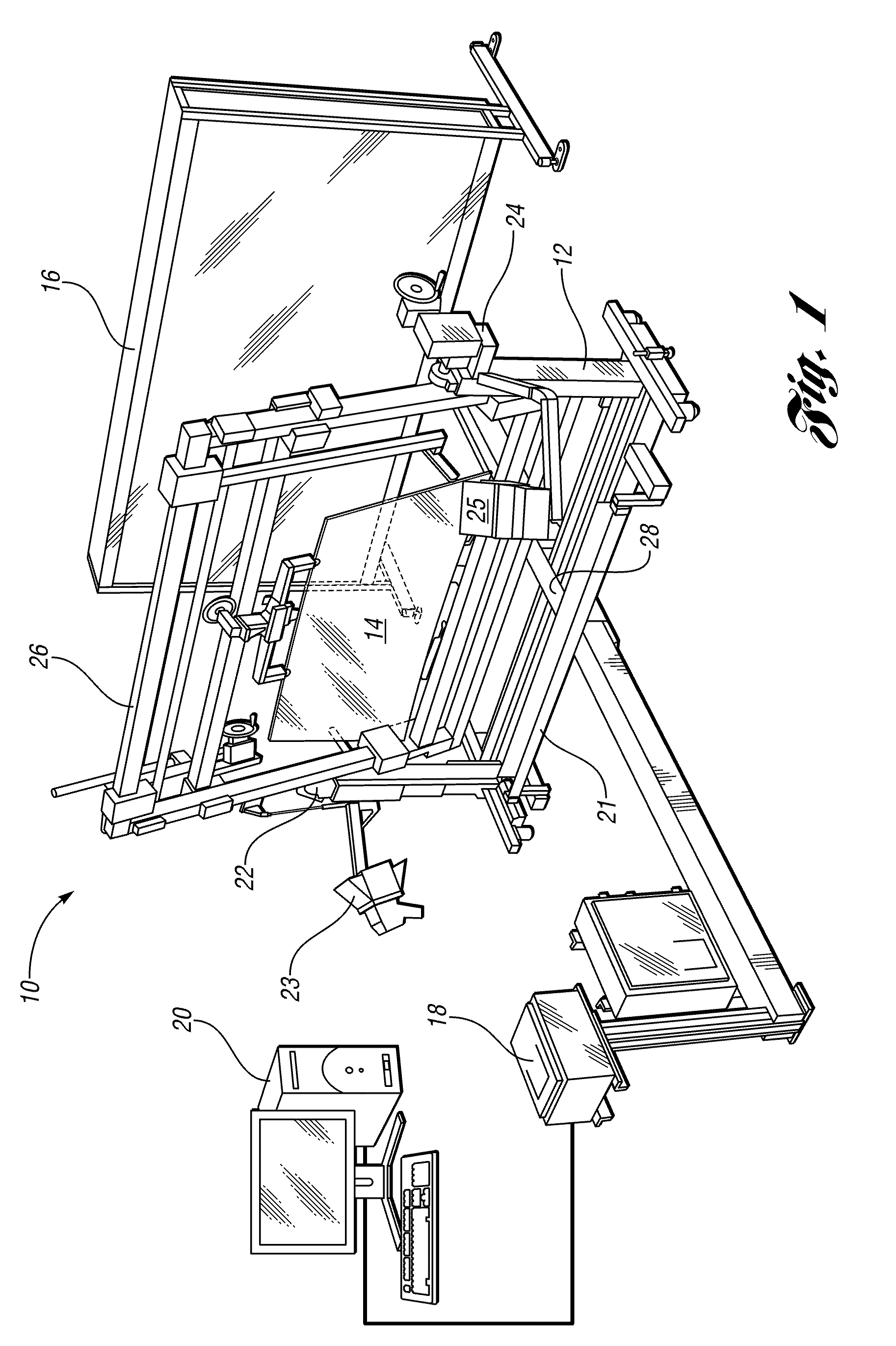
Method and apparatus for measuring transmitted optical distortion in glass sheets
ActiveUS20090282871A1Blowing machine gearingsMaterial analysis by optical meansSurface markerDot matrix
An apparatus and associated method for measuring transmitted optical distortion in a glass sheet includes a glass stand which receives a glass sheet for mounting between a background screen which includes a matrix of spaced apart dots, and a digital camera which captures (1) an image of the glass sheet surface, and (2) an image of the dot matrix transmitted through the glass sheet. The captured images are downloaded to a computer that is suitably programmed to analyze the image data to (1) determine the presence of any markings or elements on the surface of the glass sheet that should be isolated from the dot matrix image, (2) modify the background image to eliminate the image data corresponding to any such surface markings or elements from the image, and (3) determine characteristics indicative of optical distortion in the modified image of the dot matrix background transmitted through the glass sheet.
Owner:GLASSTECH
Postpartum cells derived from umbilical tissue and methods of making and using the same
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC
Tissue system with undifferentiated stem cells derived from corneal limbus
InactiveUS20050186672A1Senses disorderCulture processSurface markerStage-Specific Embryonic Antigens
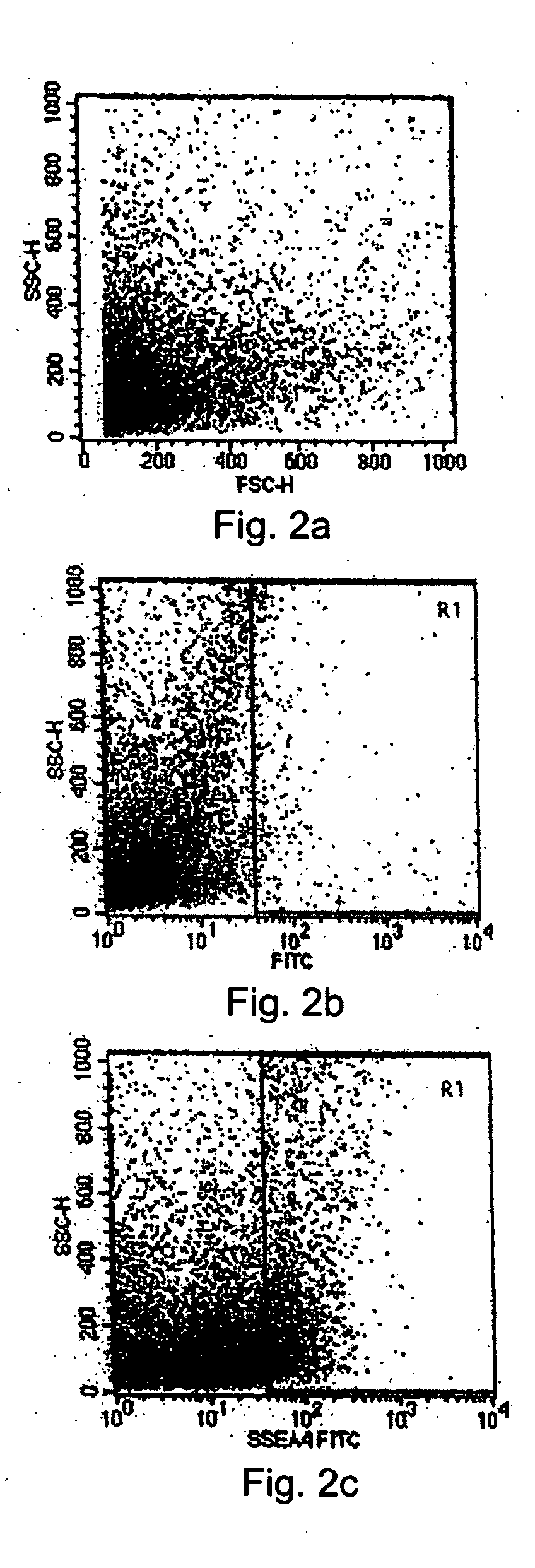
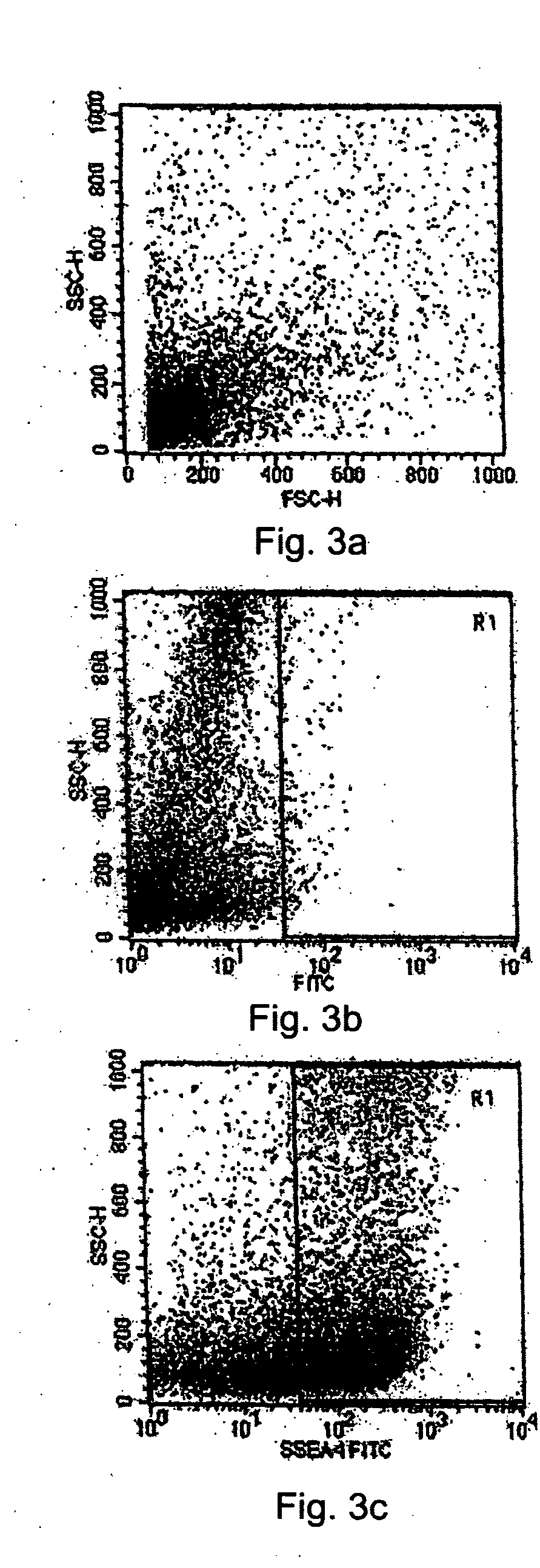
The present disclosure describes a tissue system with self-regenerating limbal stem cells, wherein the limbal stem cells are primarily undifferentiated stem cells (USCs). The tissue system is derived from isolated corneal limbal tissue, and is suitable for restoring ocular surface impairments, particularly those that result from limbal stem cell deficiencies. The tissue system is generated by selectively augmenting the tissue system for USCs, for example by selecting and sorting cells that express stem cell-specific surface markers, such as stage specific embryonic antigen marker 4 (SSEA-4). After isolation, the USCs are cultured on a tissue base in the presence of enriched medium to generate the tissue system, which is suitable for transplantation, implantation, or grafting.
Owner:RELIANCE LIFE SCI PVT
Bispecific binding agents for modulating biological activity
InactiveUS8124085B2Peptide/protein ingredientsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsSurface markerLow affinity
Methods for improving the biological and pharmaceutical properties of bispecific binding agents are described herein where the bispecific binding agent are able to target cells by a high affinity binding domain to a first cell surface marker that does not induce a significant biological effect and a low affinity binding domain that binds specifically to a second cell surface marker, causing a significant and desired biological effect. Compositions of such bispecific binding agents, uses for them, and kits containing them are also provided.
Owner:MERRIMACK PHARMACEUTICALS INC
Method for detecting non-humoral rare karyotes, and kit thereof
ActiveCN104007257AHigh detection sensitivityImprove featuresBiological material analysisBiological testingBiological bodySurface marker
The invention discloses a new method for detecting non-humoral rare karyotes. Non-humoral rare karyotes in a biological body fluid are obtained through many means, and the combined use of the antibody of a humoral cell surface marker and the specific probe of the non-humoral rare karyotes is carried out to discriminate the enriched rare karyotes. Compared with commercial discriminating methods existing in the present market, the method disclosed in the invention well combines a fluorescent in situ hybridization (FISH) method for processing the non-humoral rare karyotes with the immunofluorescence dyeing for processing humoral rare karyotes, realizes the systemic associative processing of a same specimen sheet, and can realize the intelligible observation of two processing results.
Owner:CYTTEL BIOSCI BEIJING
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com