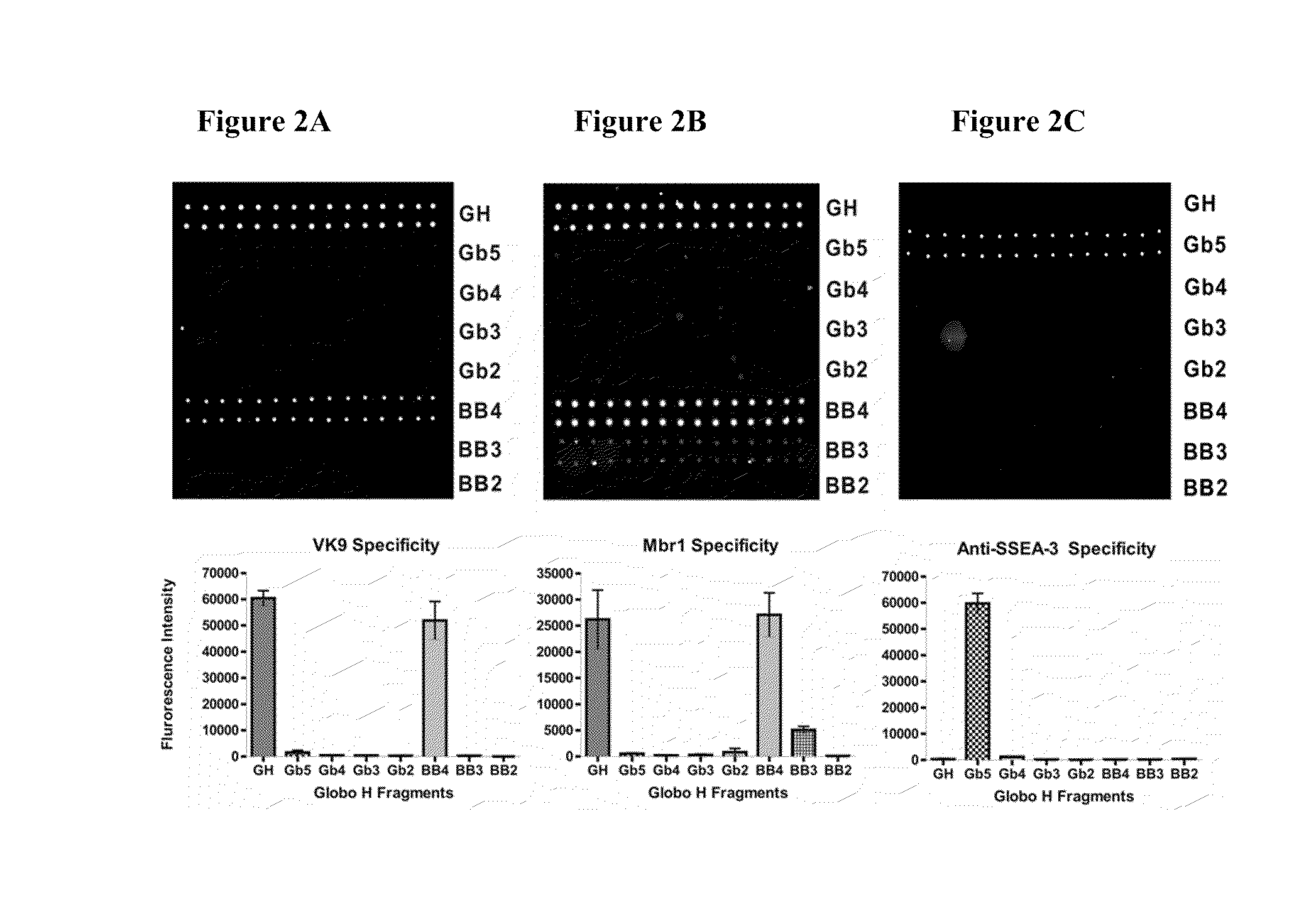
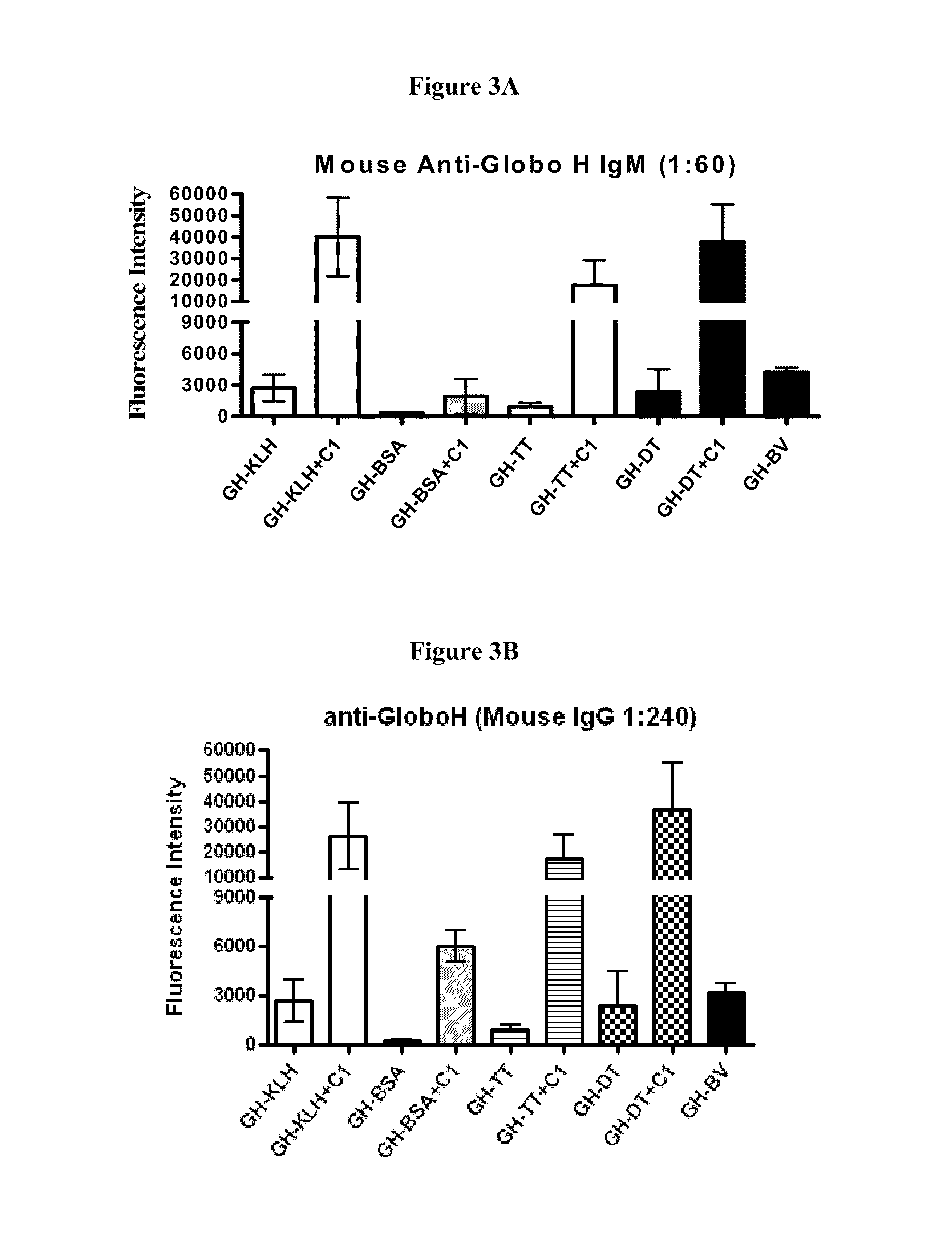
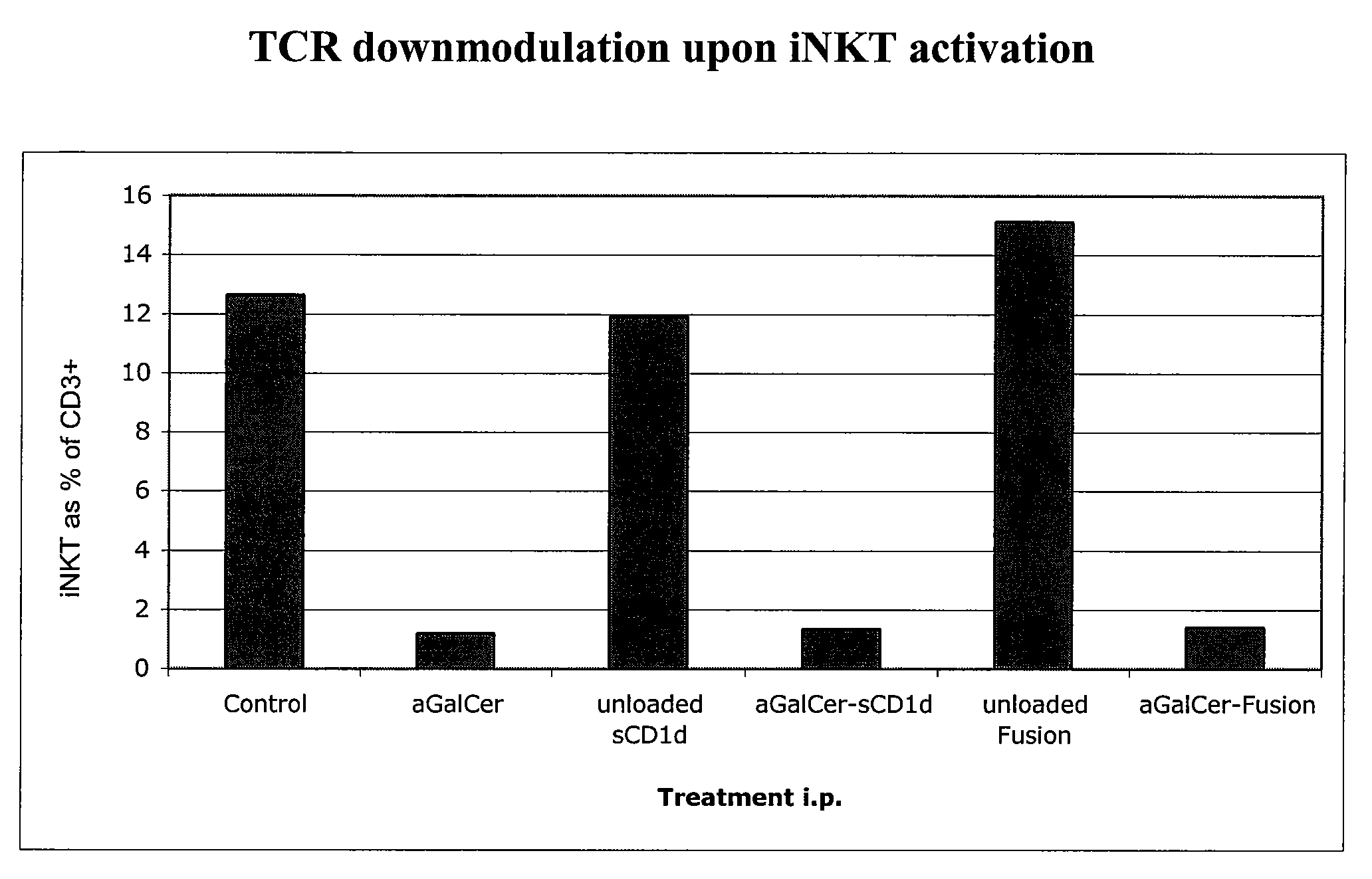
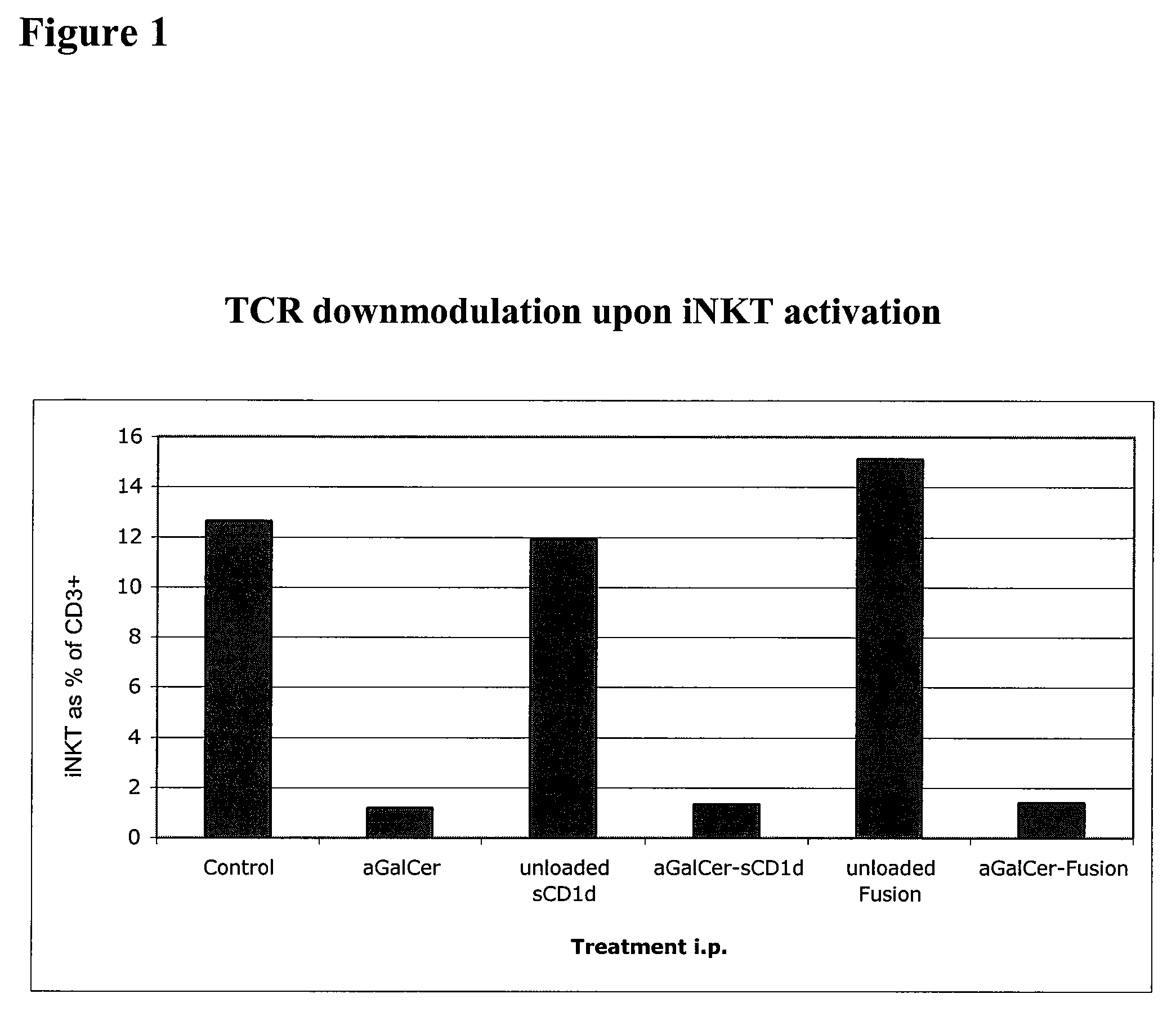
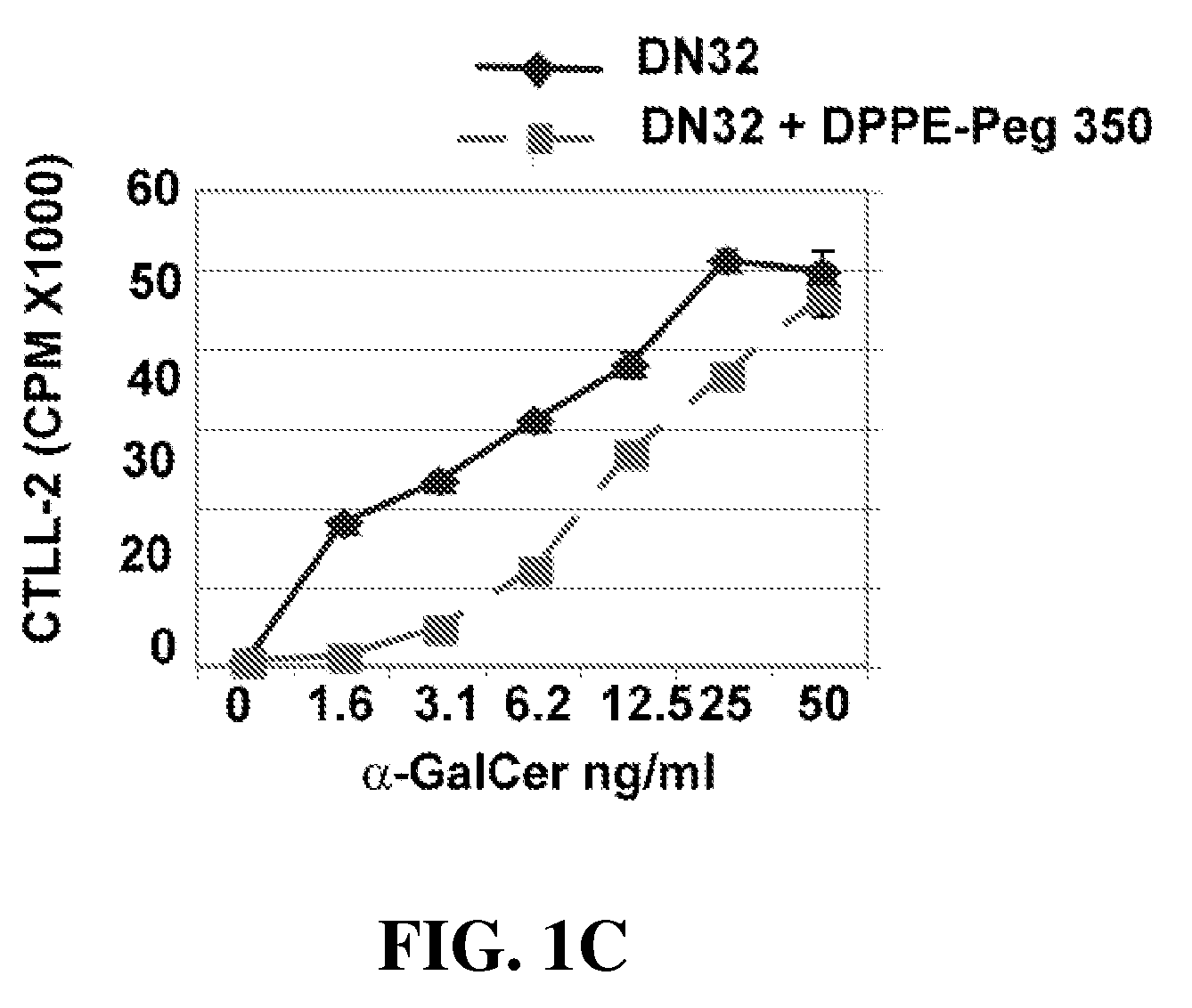
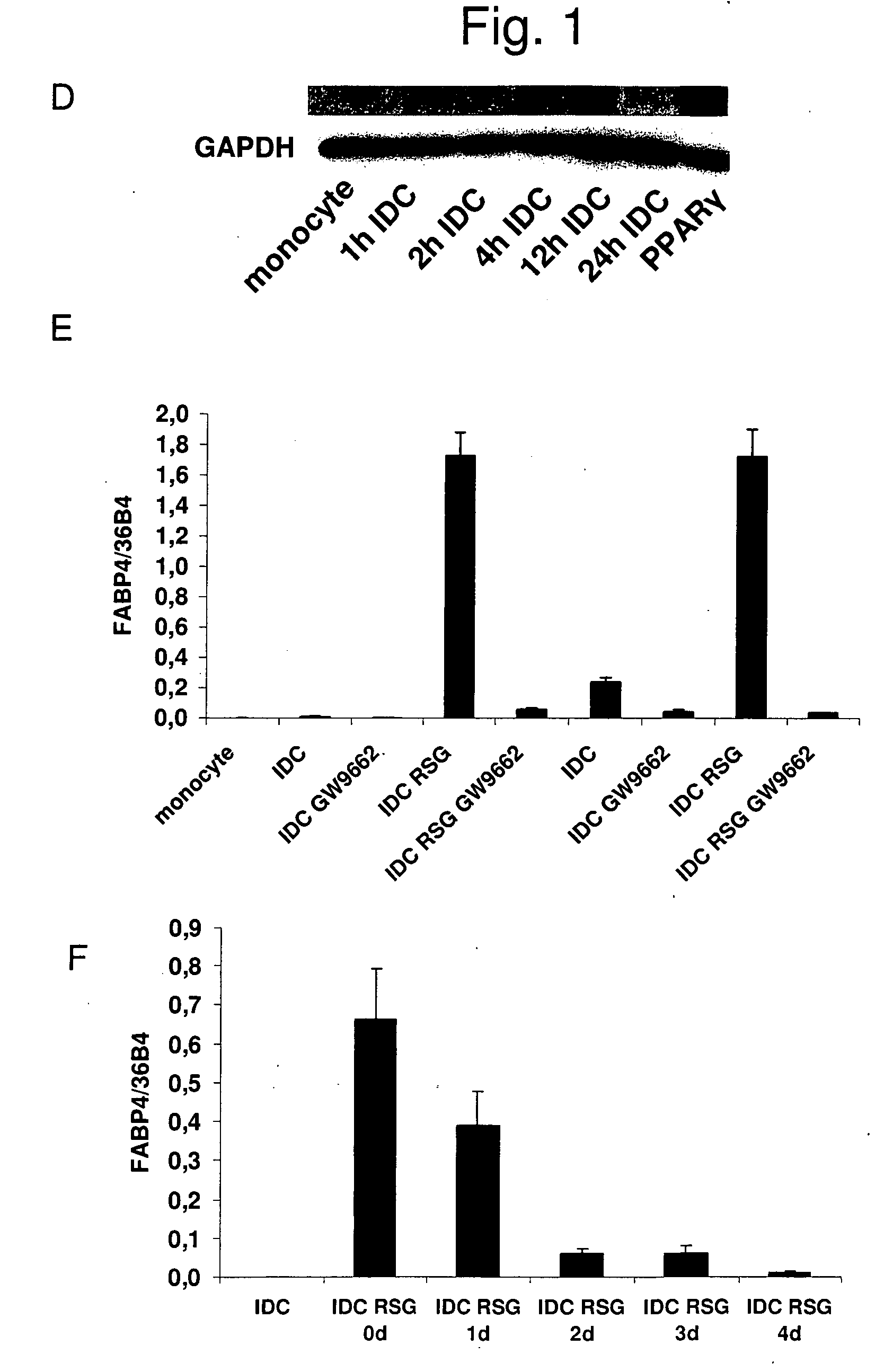
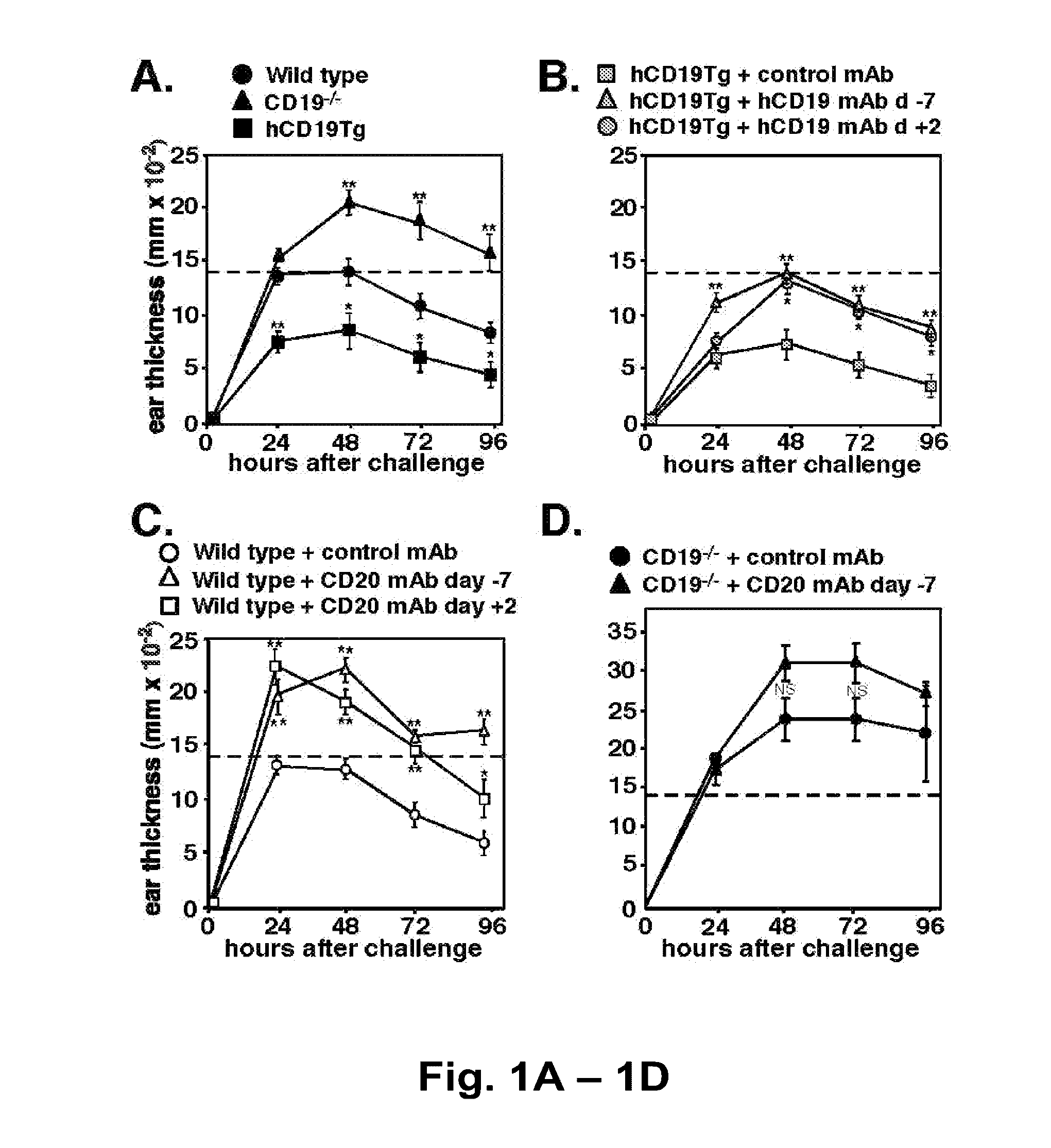
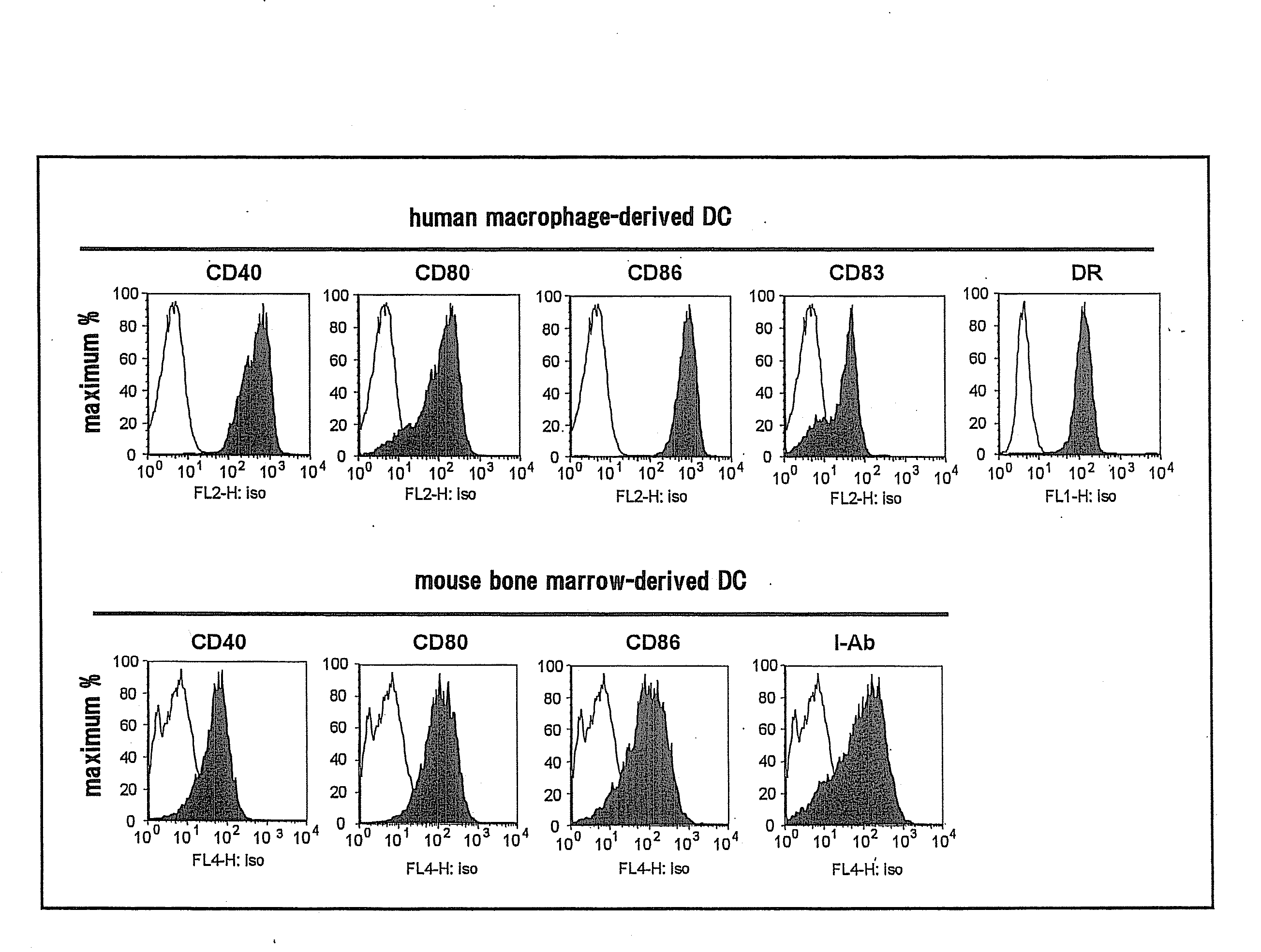
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
43 results about "CD1D" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
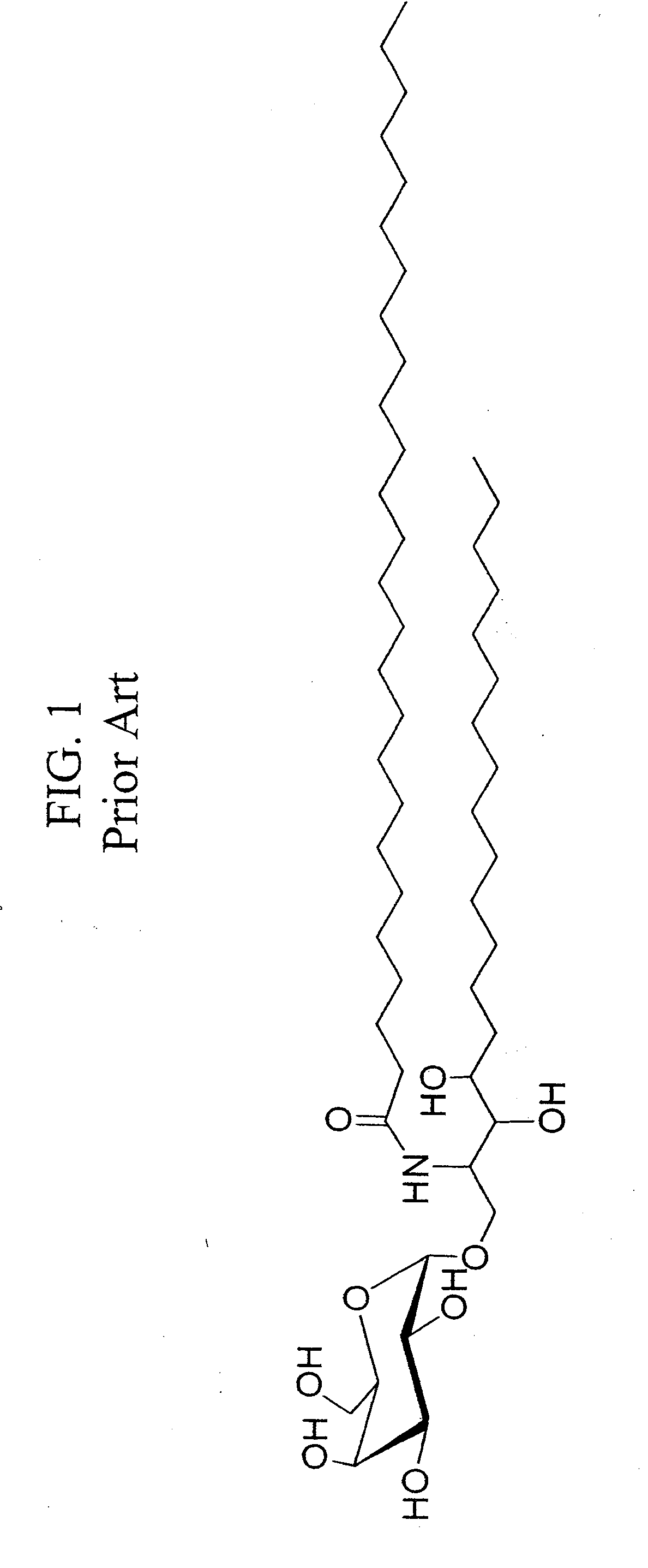
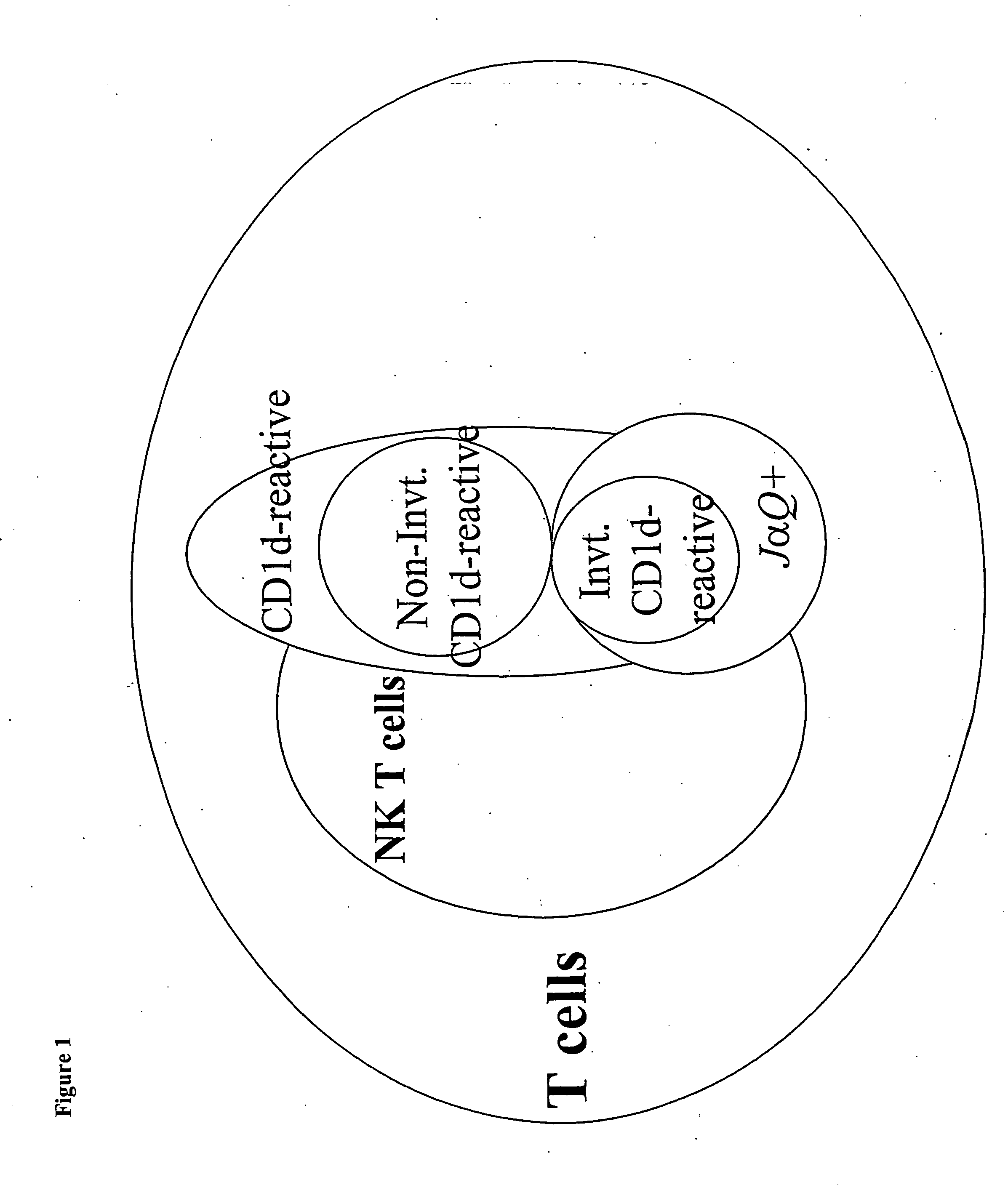
CD1D is the human gene that encodes the protein CD1d, a member of the CD1 (cluster of differentiation 1) family of glycoproteins expressed on the surface of various human antigen-presenting cells. They are non-classical MHC proteins, related to the class I MHC proteins, and are involved in the presentation of lipid antigens to T cells. CD1d is the only member of the group 2 CD1 molecules.
Targeted cd1d molecules
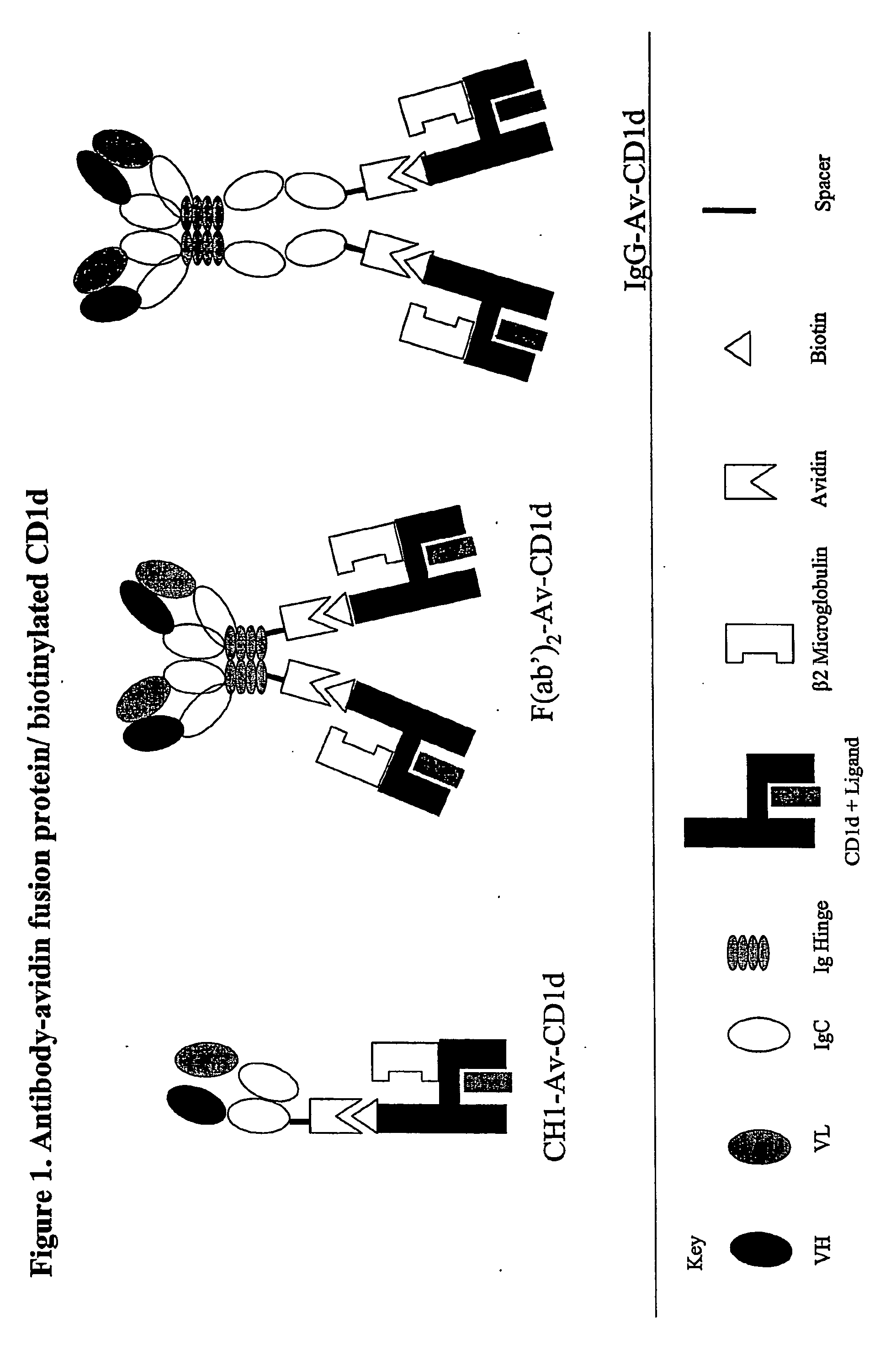
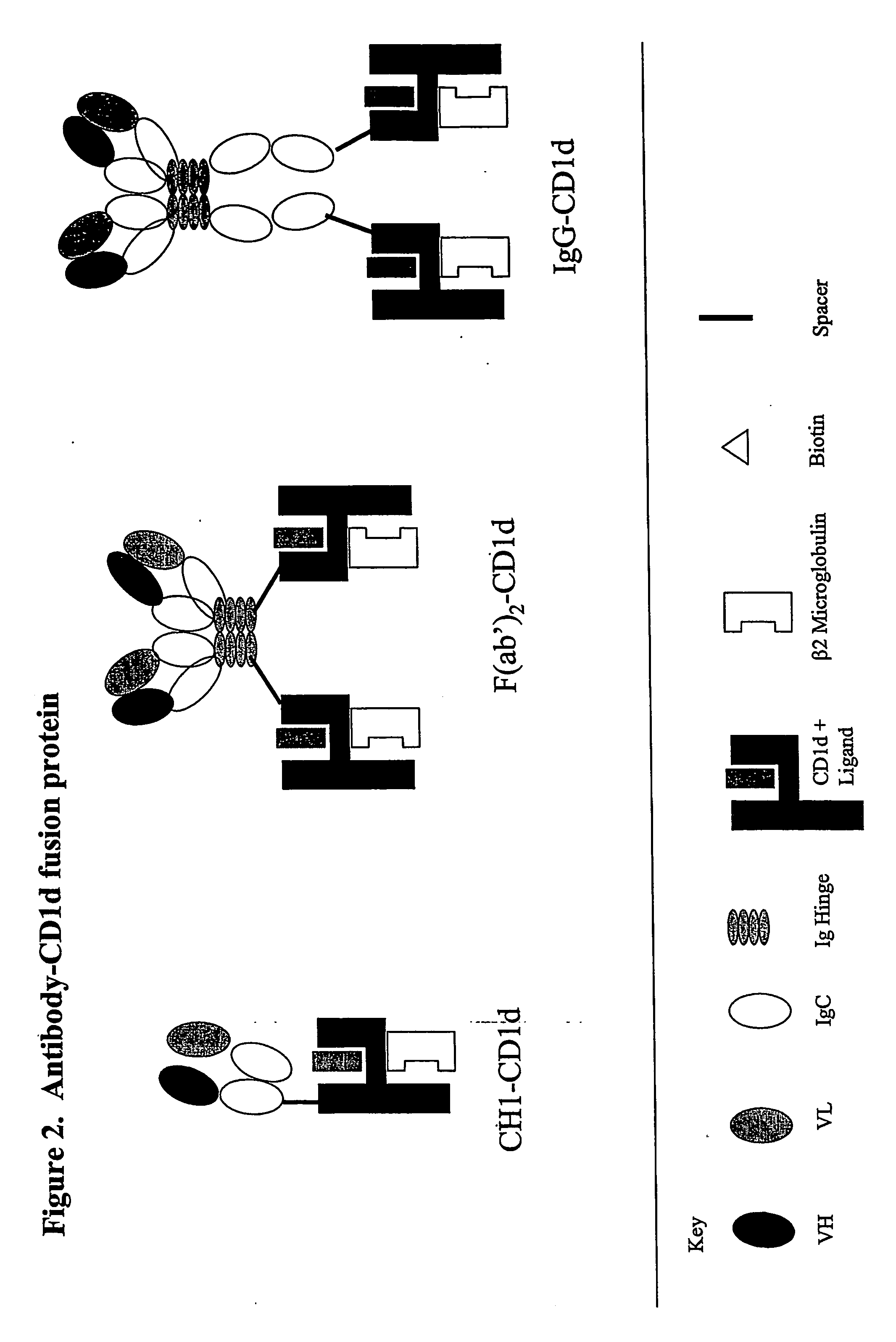
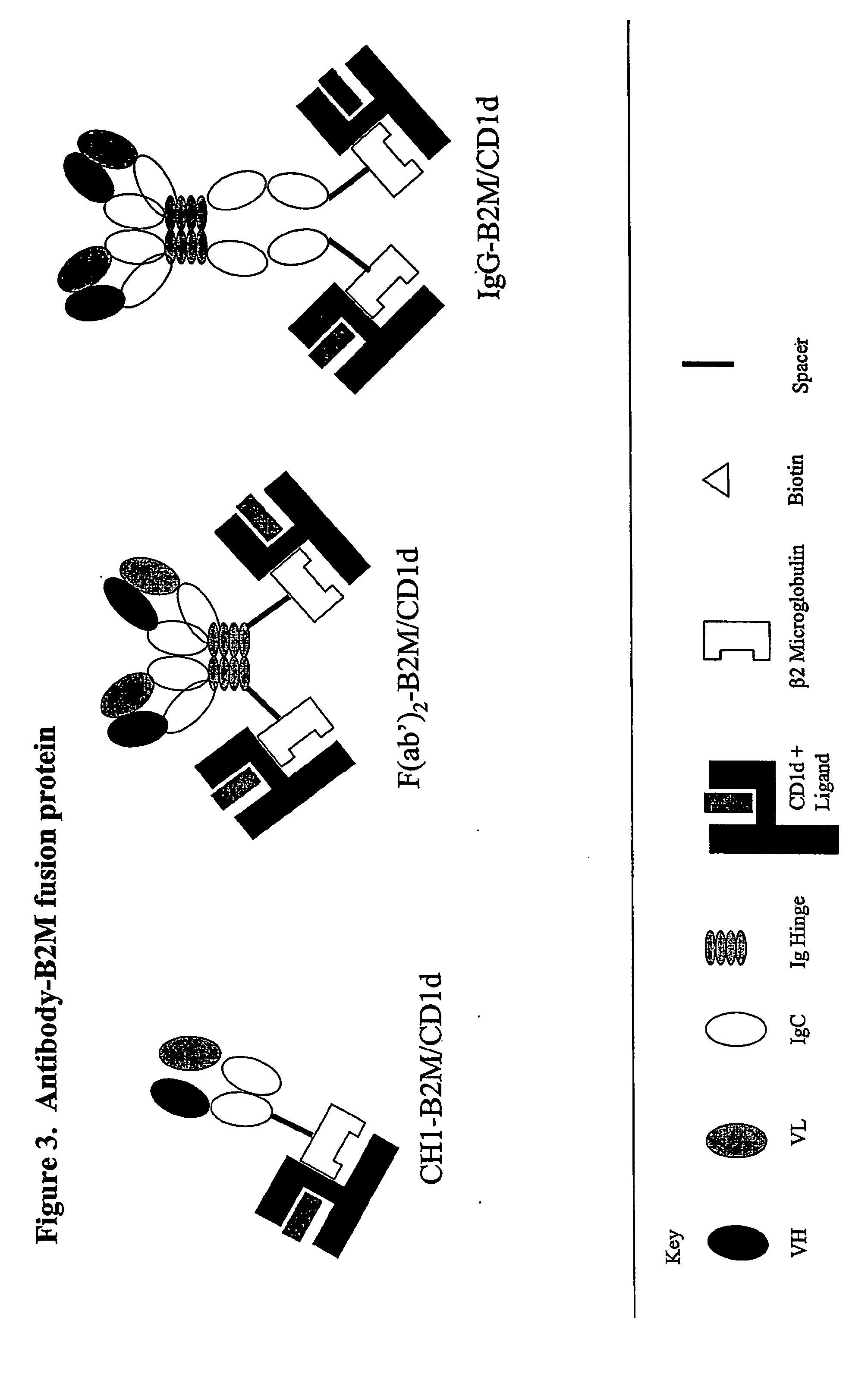
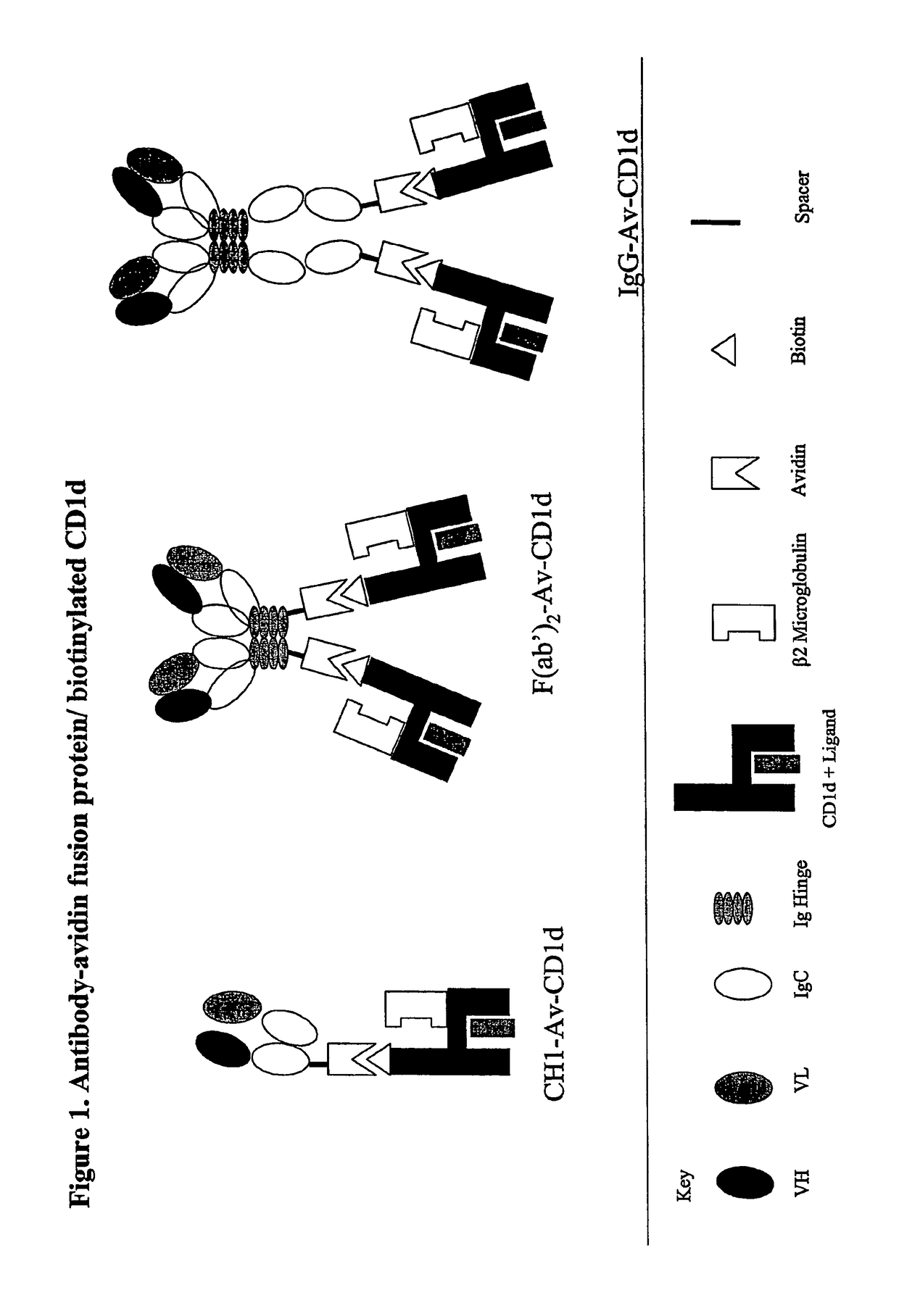
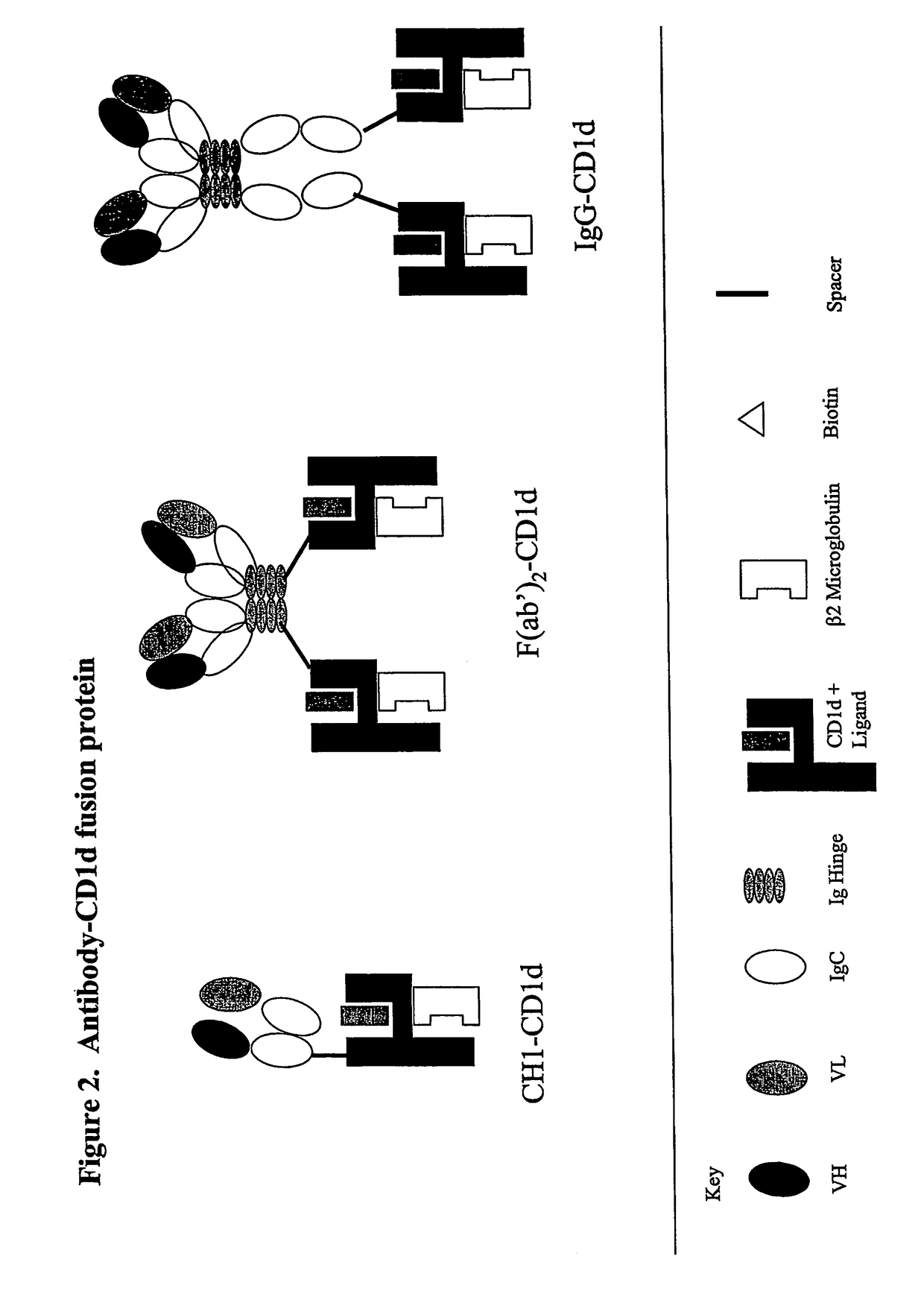
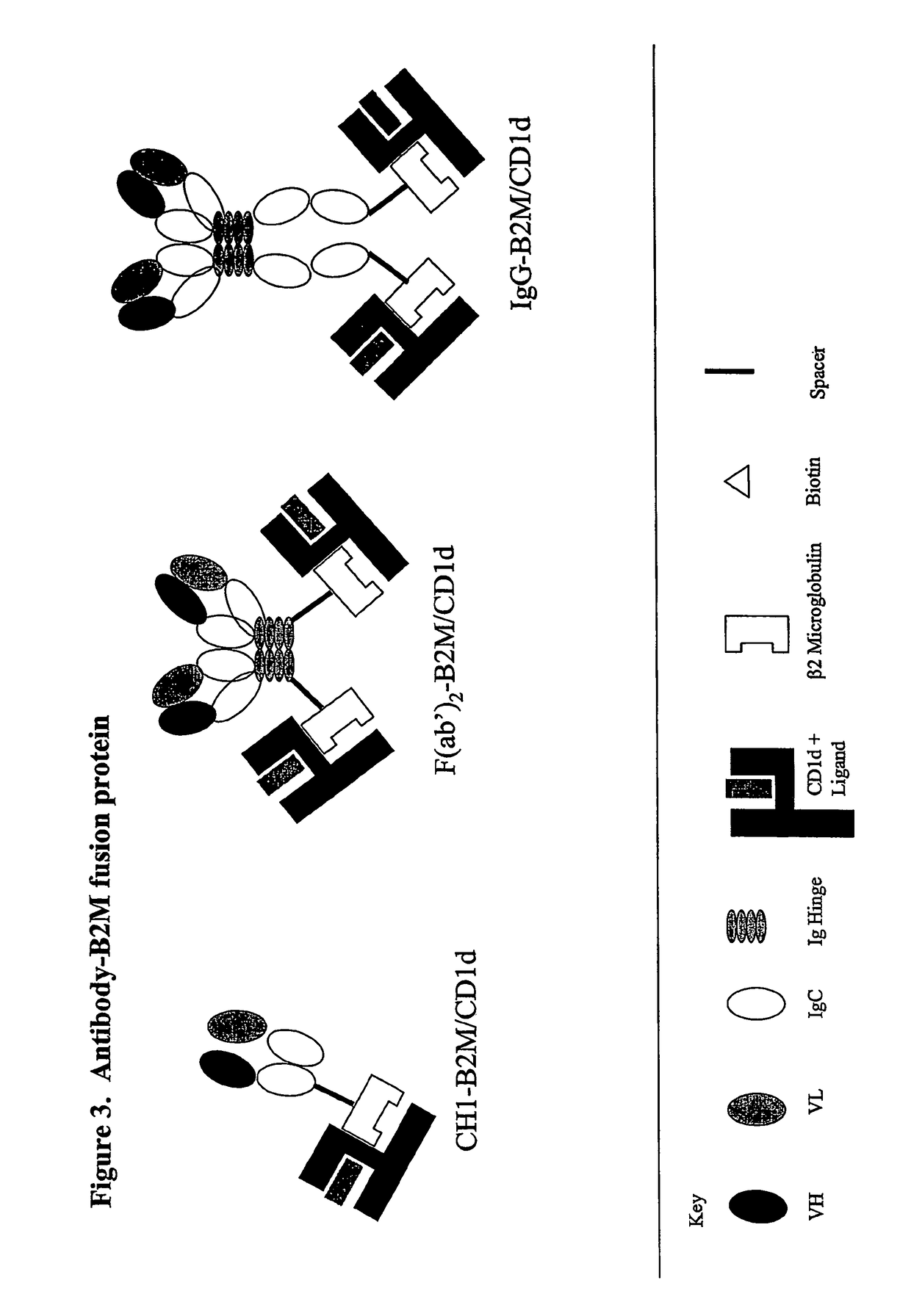
The invention is directed to a compound comprising one or more CD1d complexes in association with an antibody specific for a cell surface marker. The CD1d complexes comprise a CD1d, a β2-microglobulin molecule, and may further comprise an antigen bound to the CD1d binding groove. The invention is further directed to methods of inhibiting or stimulating an immune response with the CD1d-antibody compounds, in particular anti-tumor and autoimmunity responses.
Owner:VACCINEX
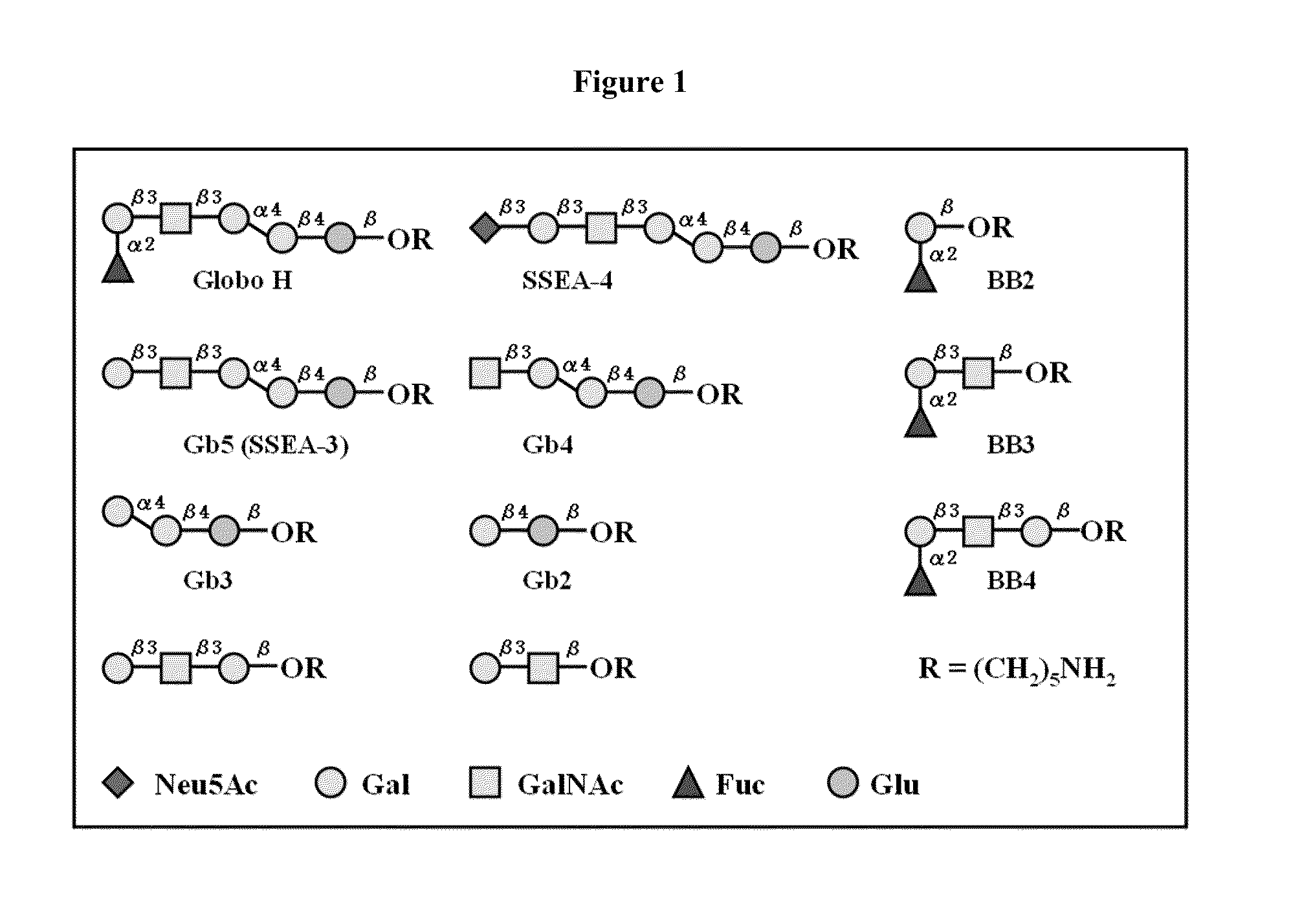
Globo h and related Anti-cancer vaccines with novel glycolipid adjuvants
ActiveUS20100136042A1Shrink tumorInhibit tumor growthOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesDendritic cellAdjuvant
Owner:ACAD SINIC
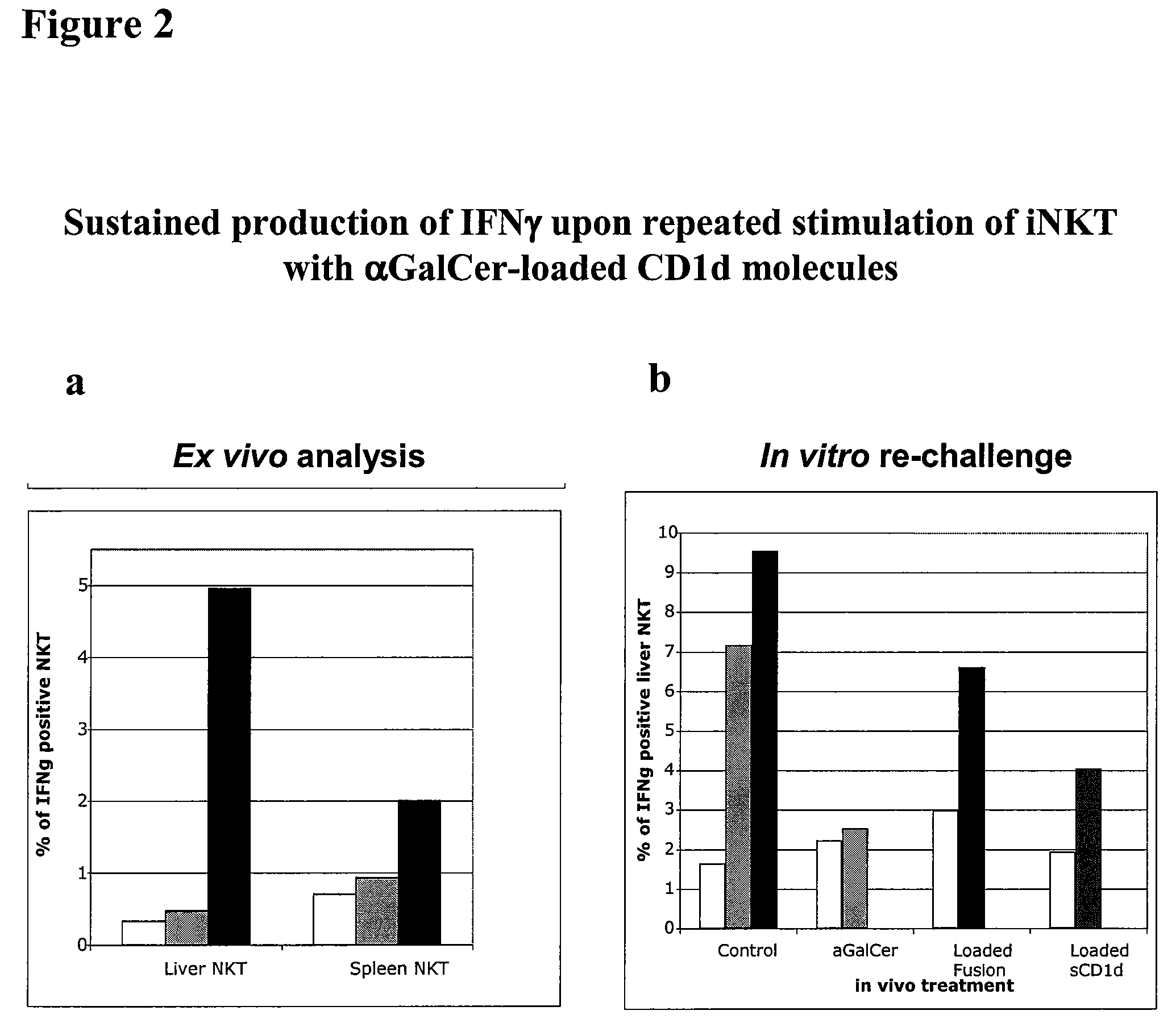
Modulation of NKT Cell Activity with Antigen-Loaded CD1d Molecules
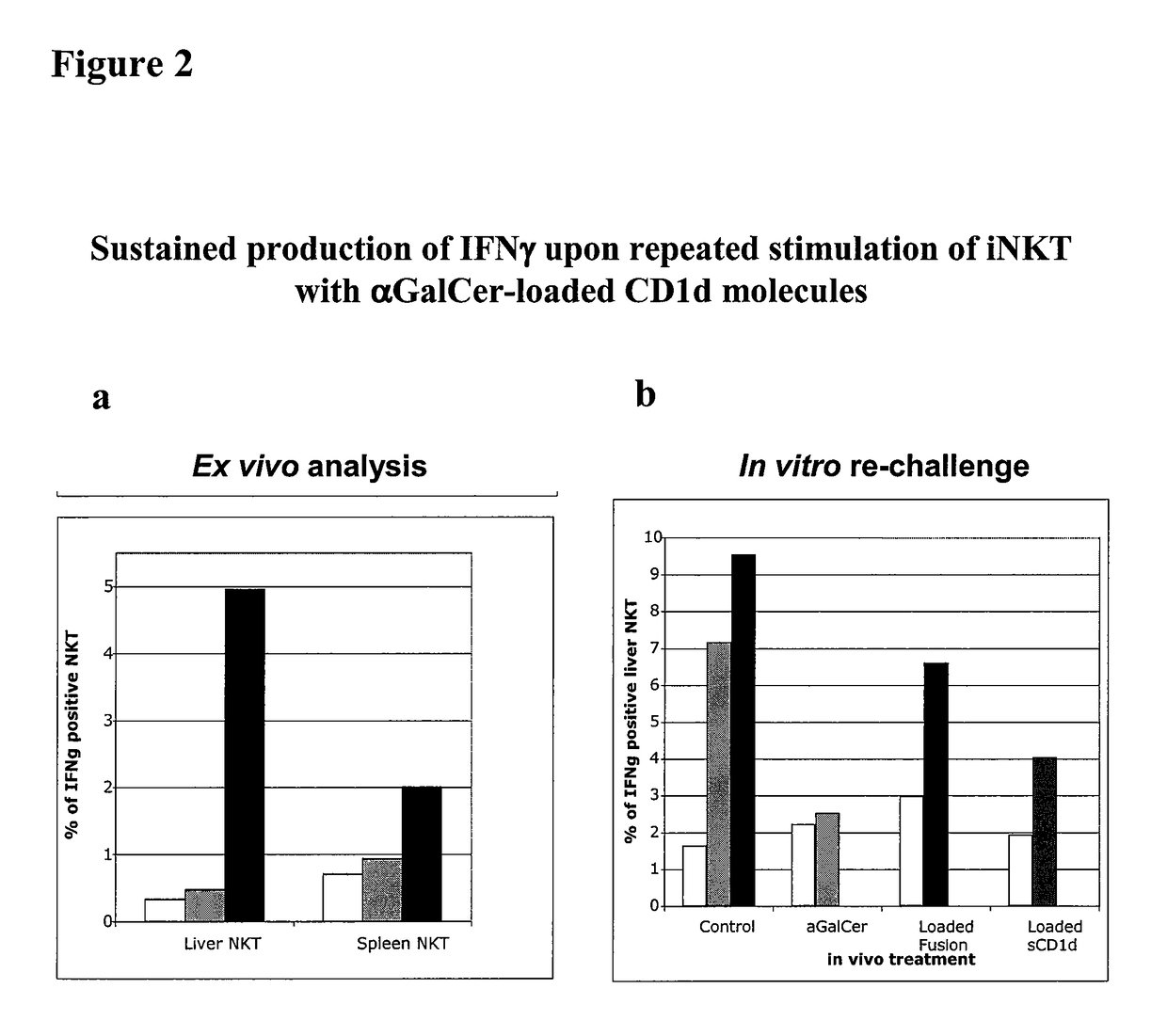
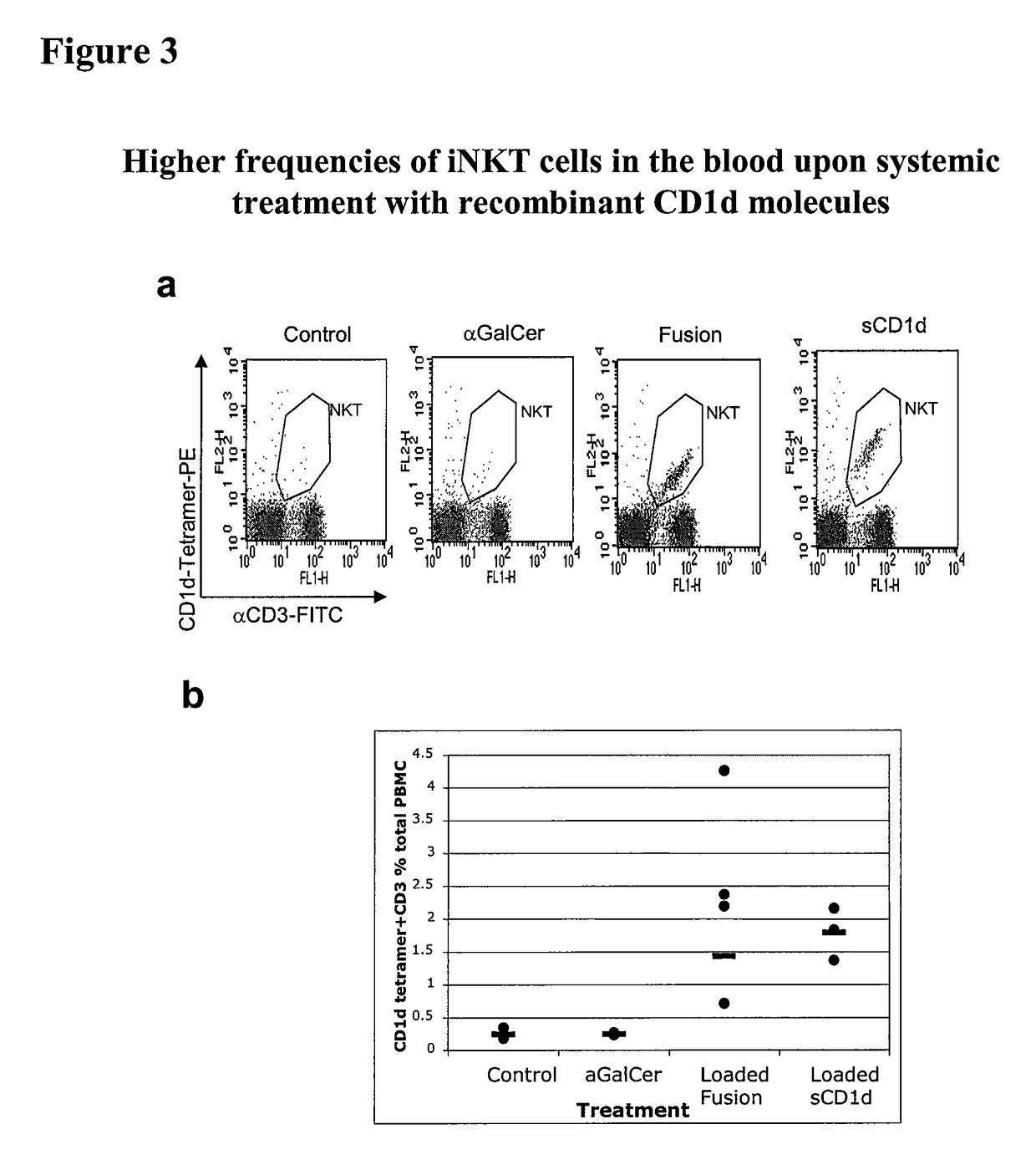
The invention is directed to methods of modulating an immune response in an animal, comprising administering a composition comprising one or more soluble CD1d complexes, in particular non-specific soluble CD1d complexes. Soluble CD1d complexes comprise a soluble CD1d polypeptide, a β2-microglobulin polypeptide, and a ceramide-like glycolipid antigen bound to the CD1d antigen binding groove, and in certain embodiments, an immunogen. The administration of compositions of the present invention affects the activity of CD1d-restricted NKT cells, and in particular, allows for multiple administrations without causing CD1d-restricted NKT cell anergy.
Owner:VACCINEX
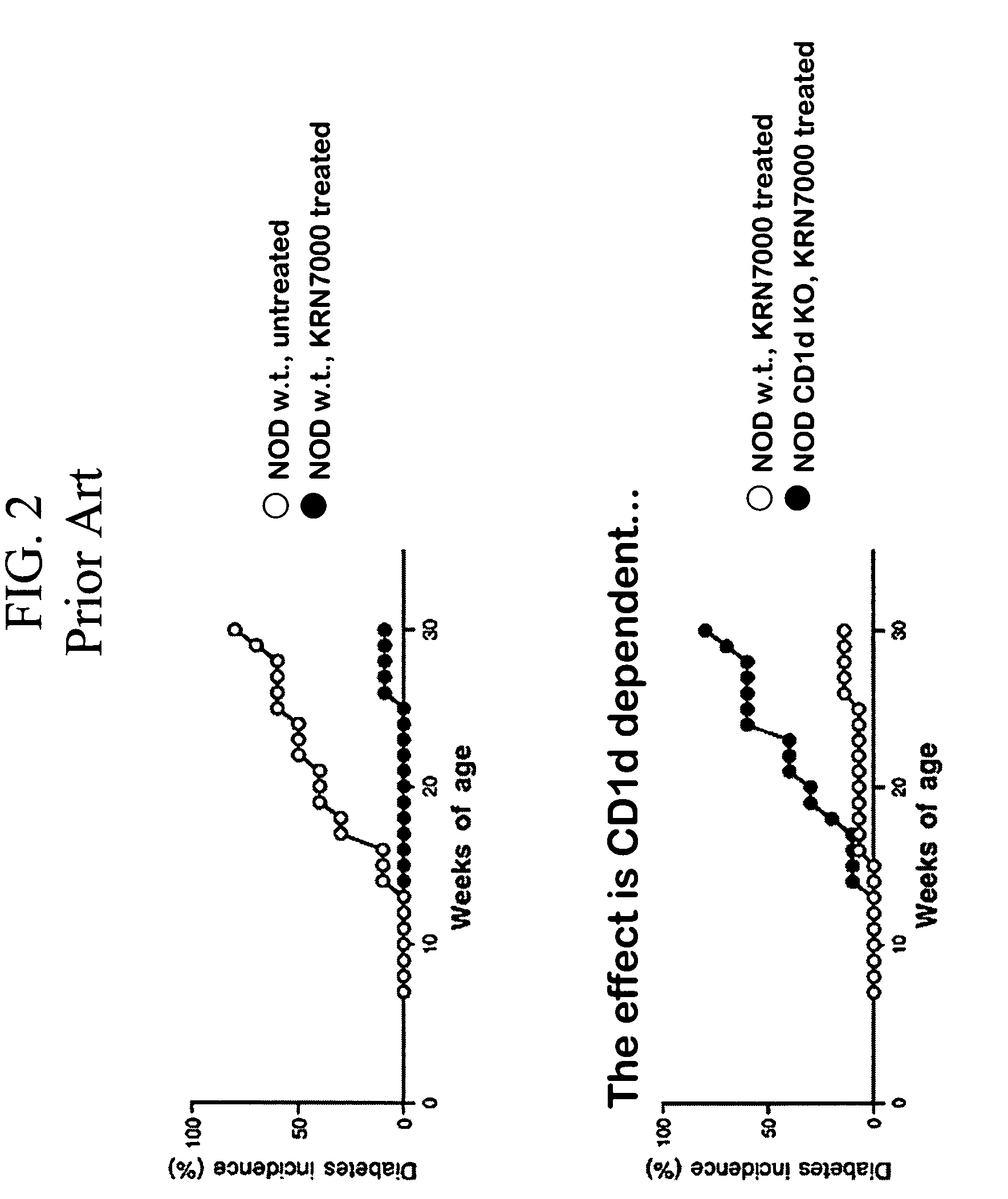
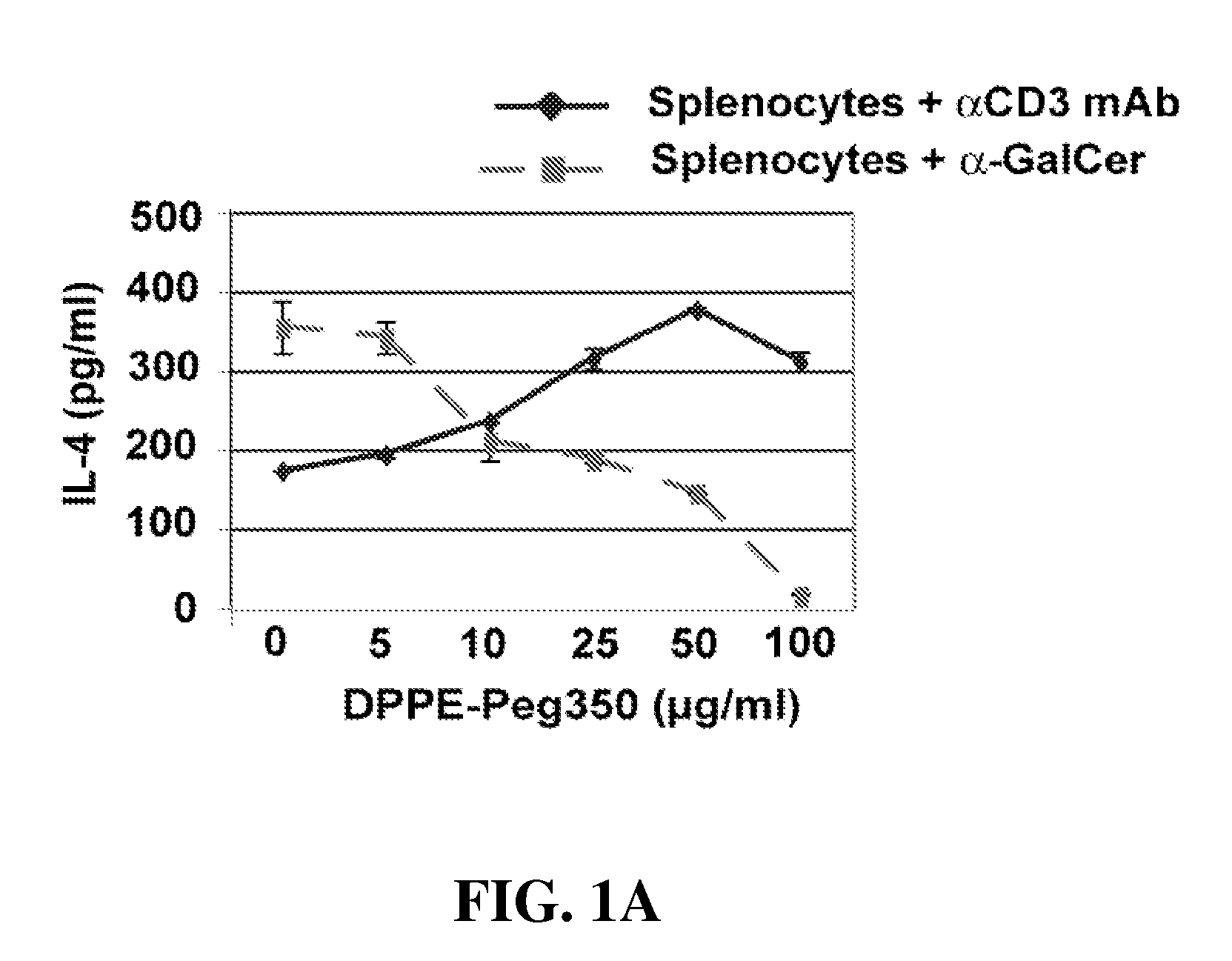
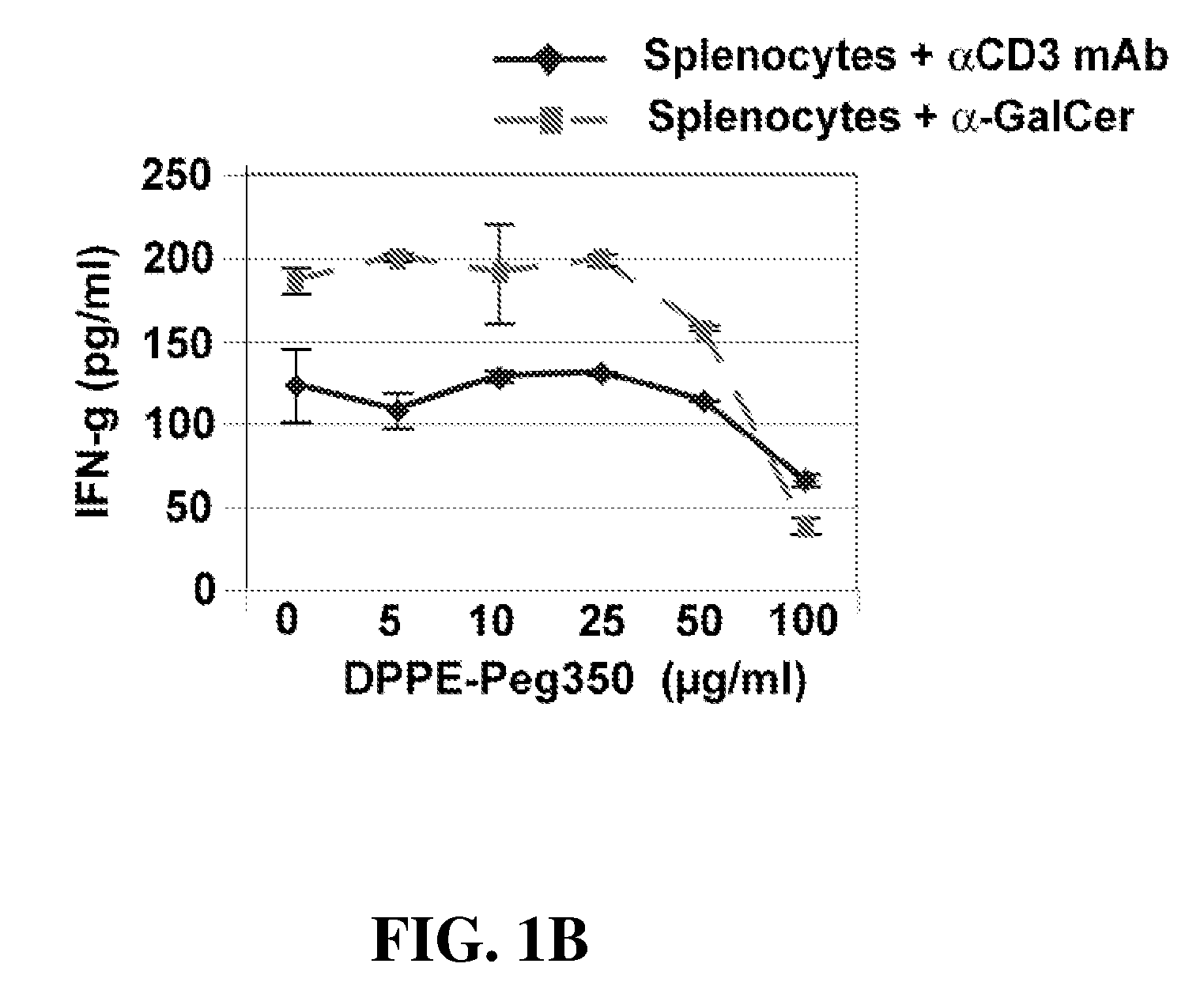
Ceramide derivatives as modulators of immunity and autoimmunity
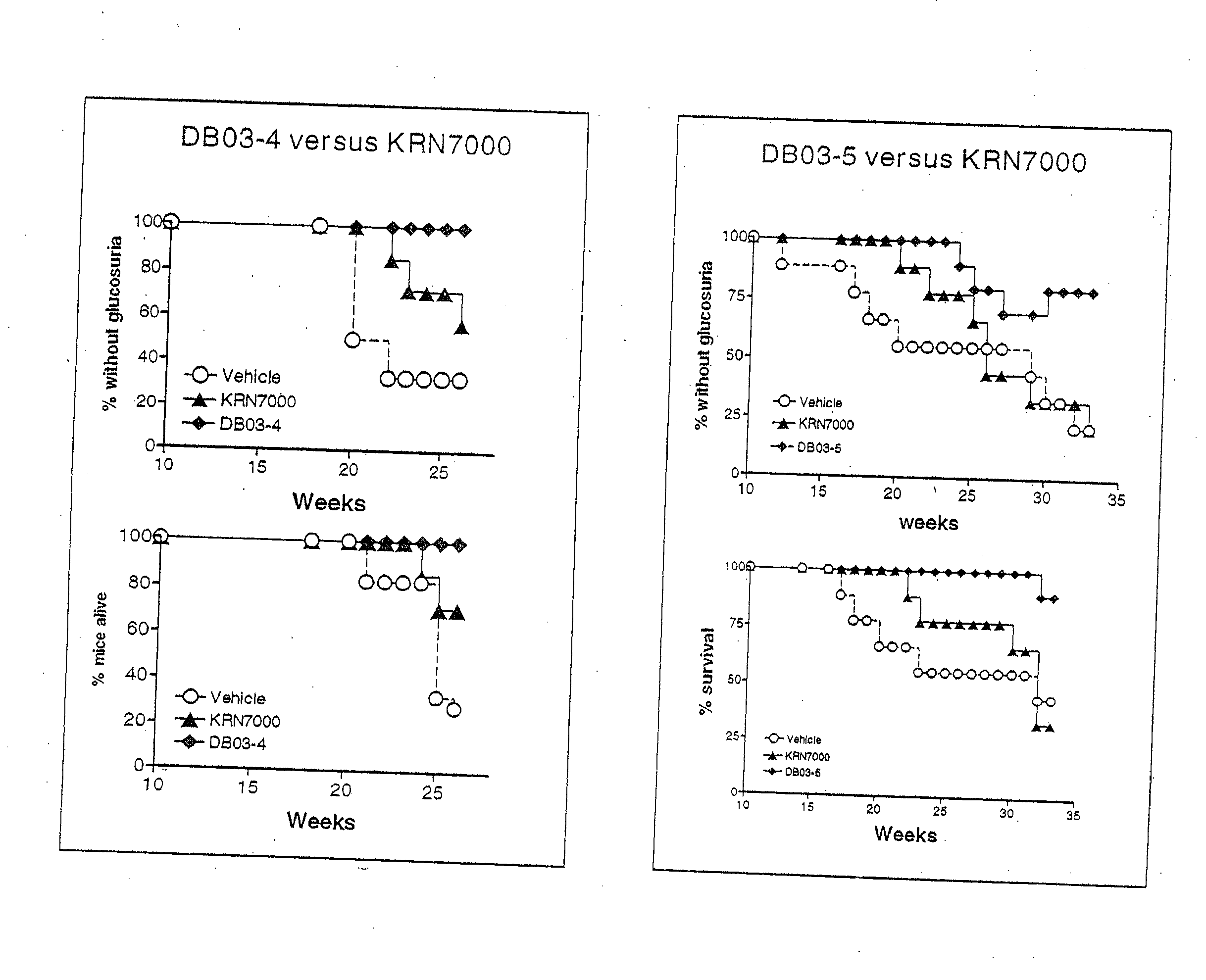
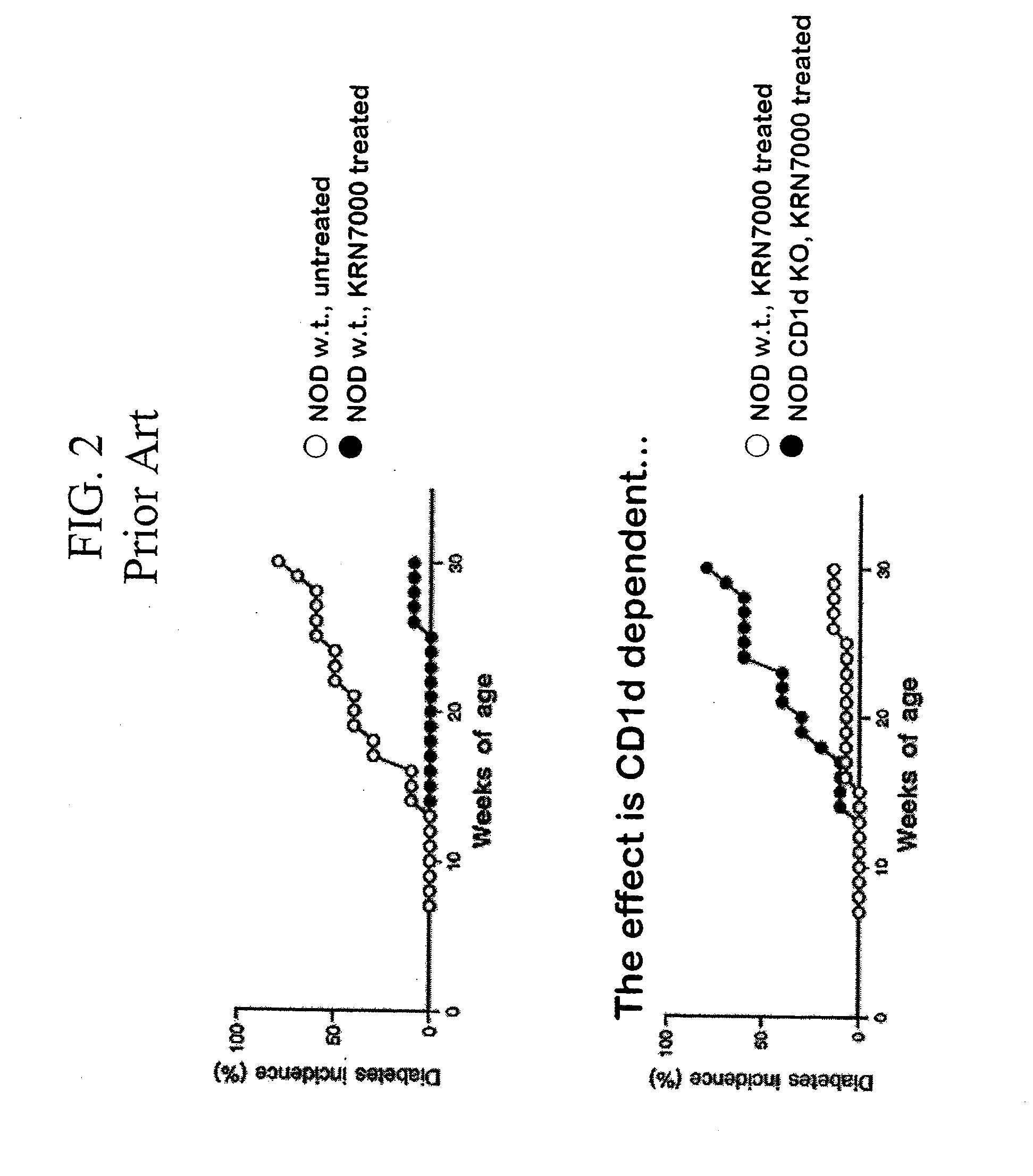
α-Galactosylceramides and glycosylceramides (“ceramide-like glycolipids”) that modulate NK T cells. The ceramide-like glycolipids vary in the cytokines induced in NK T cells and vary in the antigen-presenting cells that are capable of efficiently presenting the compounds to NK T cells. Pharmaceutical compositions of the ceramide-like glycolipids are provided, as are pharmaceutical compositions of the ceramide-like glycolipids combined with dendritic cells. Methods utilizing the ceramide-like glycolipids in vaccines, to activate NK T cells, to stimulate the immune system, and to treat mammals are also provided. The invention also provides methods of evaluating a compound for its ability to activate an NK T cell in the presence of a cell expressing a CD1d protein.
Owner:ALBERT EINSTEIN COLLEGE OF MEDICINE OF YESHIVA UNIV
Ceramide derivatives as modulators of immunity and autoimmunity
α-Galactosylceramides and glycosylceramides (“ceramide-like glycolipids”) that modulate NK T cells. The ceramide-like glycolipids vary in the cytokines induced in NK T cells and vary in the antigen-presenting cells that are capable of efficiently presenting the compounds to NK T cells. Pharmaceutical compositions of the ceramide-like glycolipids are provided, as are pharmaceutical compositions of the ceramide-like glycolipids combined with dendritic cells. Methods utilizing the ceramide-like glycolipids in vaccines, to activate NK T cells, to stimulate the immune system, and to treat mammals are also provided. The invention also provides methods of evaluating a compound for its ability to activate an NK T cell in the presence of a cell expressing a CD1d protein.
Owner:ALBERT EINSTEIN COLLEGE OF MEDICINE OF YESHIVA UNIV
Preventative or therapeutic agent and method for immune disease
InactiveUS20120121688A1Augmenting immunosuppressive functionEfficient inductionOrganic active ingredientsAllergen ingredientsDiseaseAutoimmune responses
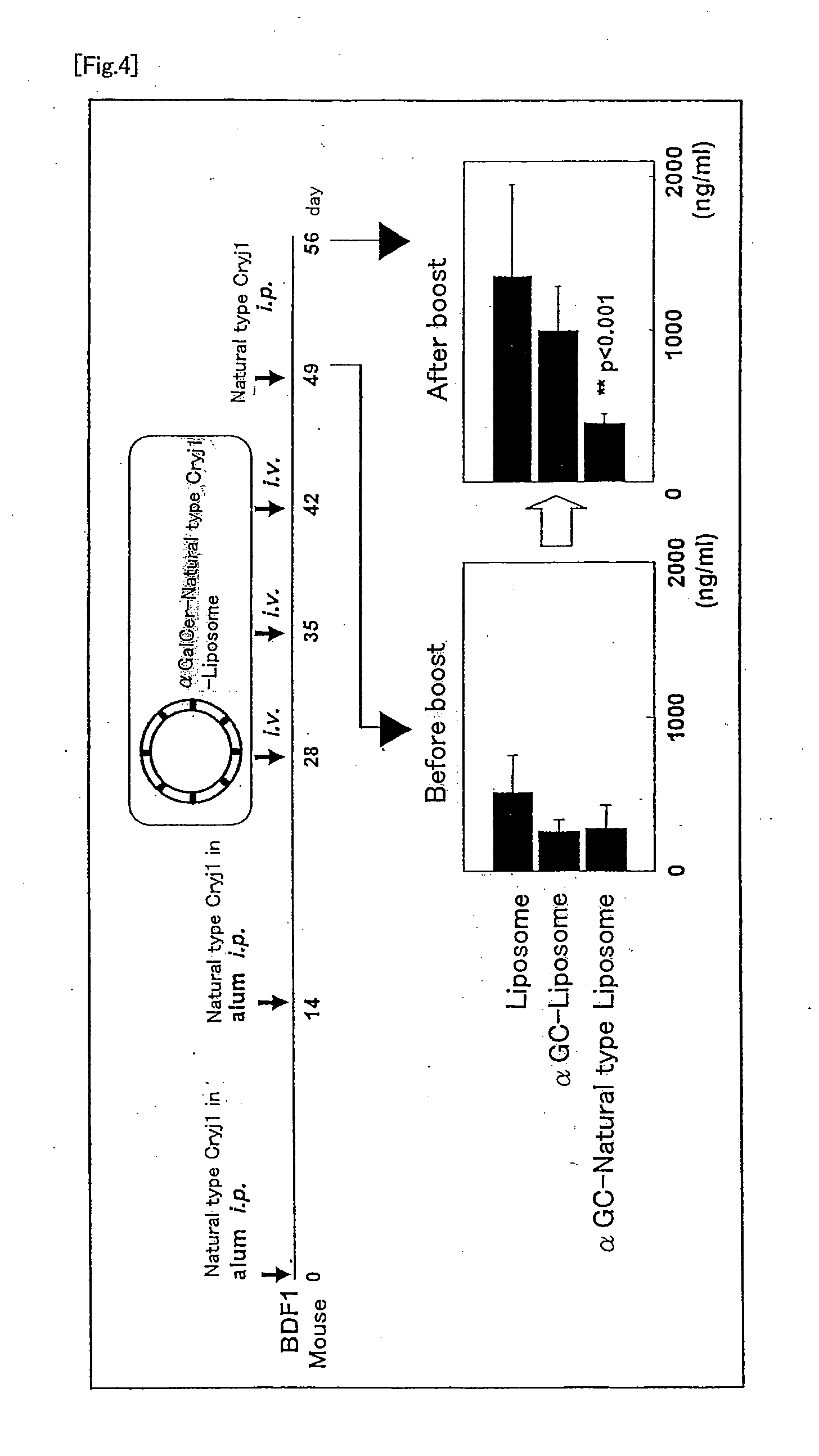
The present invention provides a method of selectively augmenting an immunosuppressive function in various functions of NKT cells, and a method of efficiently inducing an antigen specific immunosuppression in vivo, as well as a pharmaceutical obtained by applying the same.More particularly, the present invention provides a pharmaceutical (e.g., a preventive or therapeutic agent for immune diseases such as allergic disease and autoimmune disease) containing a CD1d ligand and a target antigen (e.g., allergen, autoantigen). Preferably, the pharmaceutical contains a drug delivery vehicle including the CD1d ligand and the target antigen and having a lumen.
Owner:RINKEN
Ceramide derivatives as modulators of immunity and autoimmunity
α-Galactosylceramides and glycosylceramides (“ceramide-like glycolipids”) that modulate NK T cells. The ceramide-like glycolipids vary in the cytokines induced in NK T cells and vary in the antigen-presenting cells that are capable of efficiently presenting the compounds to NK T cells. Pharmaceutical compositions of the ceramide-like glycolipids are provided, as are pharmaceutical compositions of the ceramide-like glycolipids combined with dendritic cells. Methods utilizing the ceramide-like glycolipids in vaccines, to activate NK T cells, to stimulate the immune system, and to treat mammals are also provided. The invention also provides methods of evaluating a compound for its ability to activate an NK T cell in the presence of a cell expressing a CD1d protein.
Owner:ALBERT EINSTEIN COLLEGE OF MEDICINE OF YESHIVA UNIV
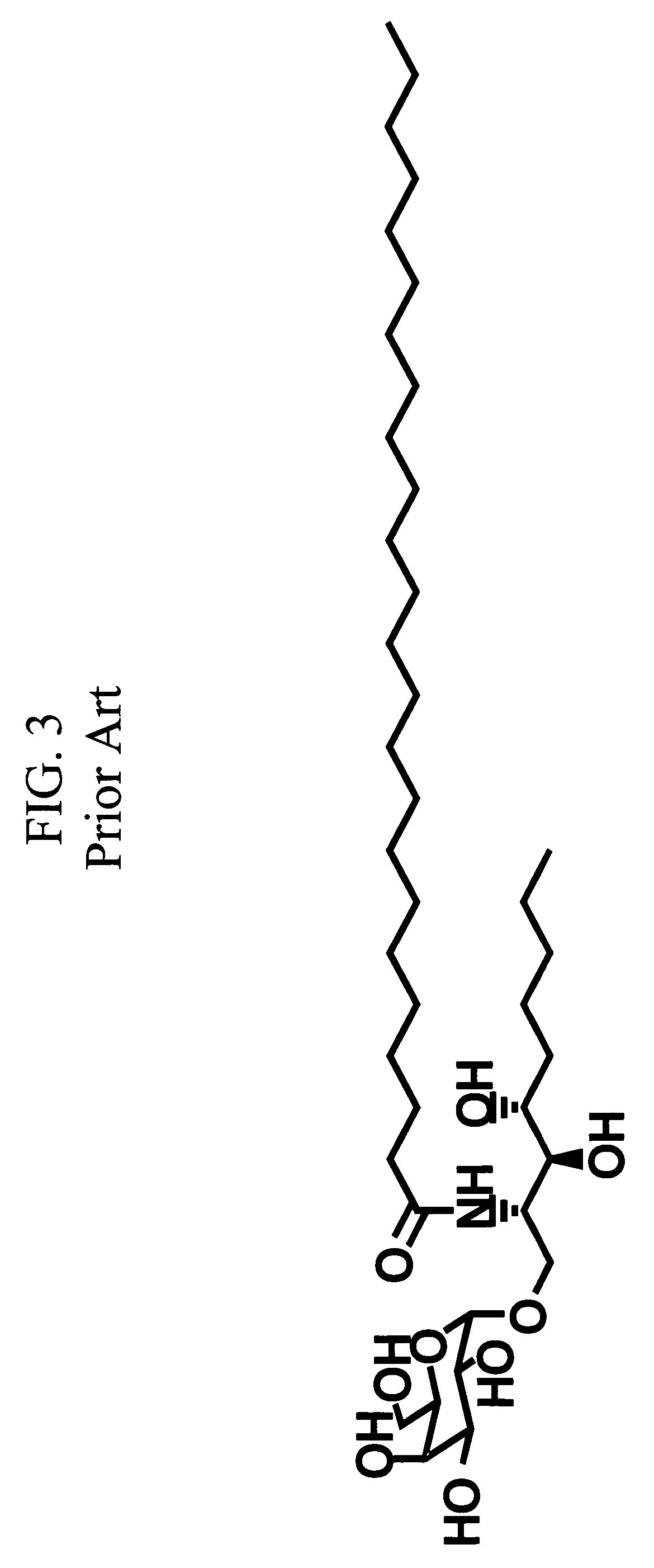
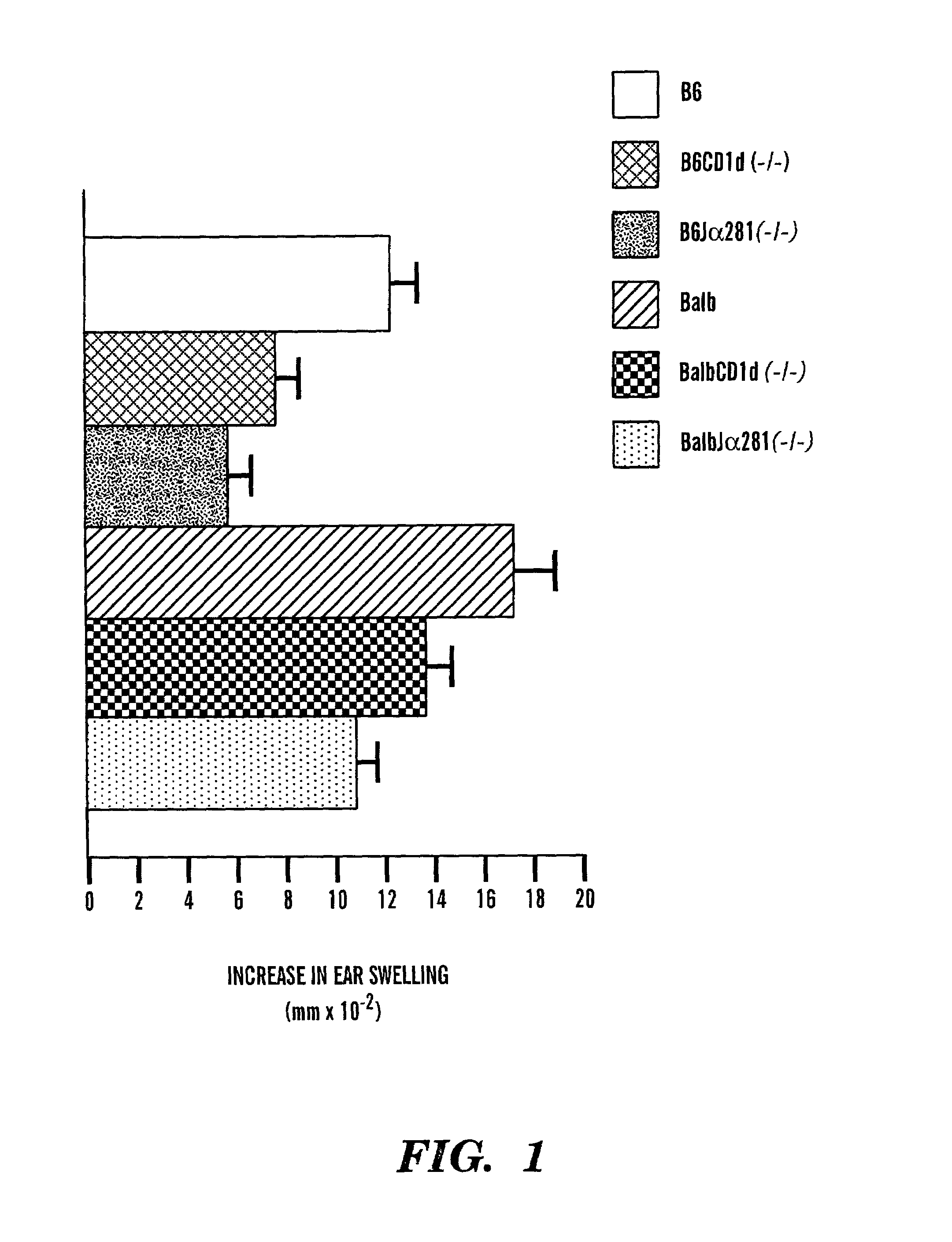
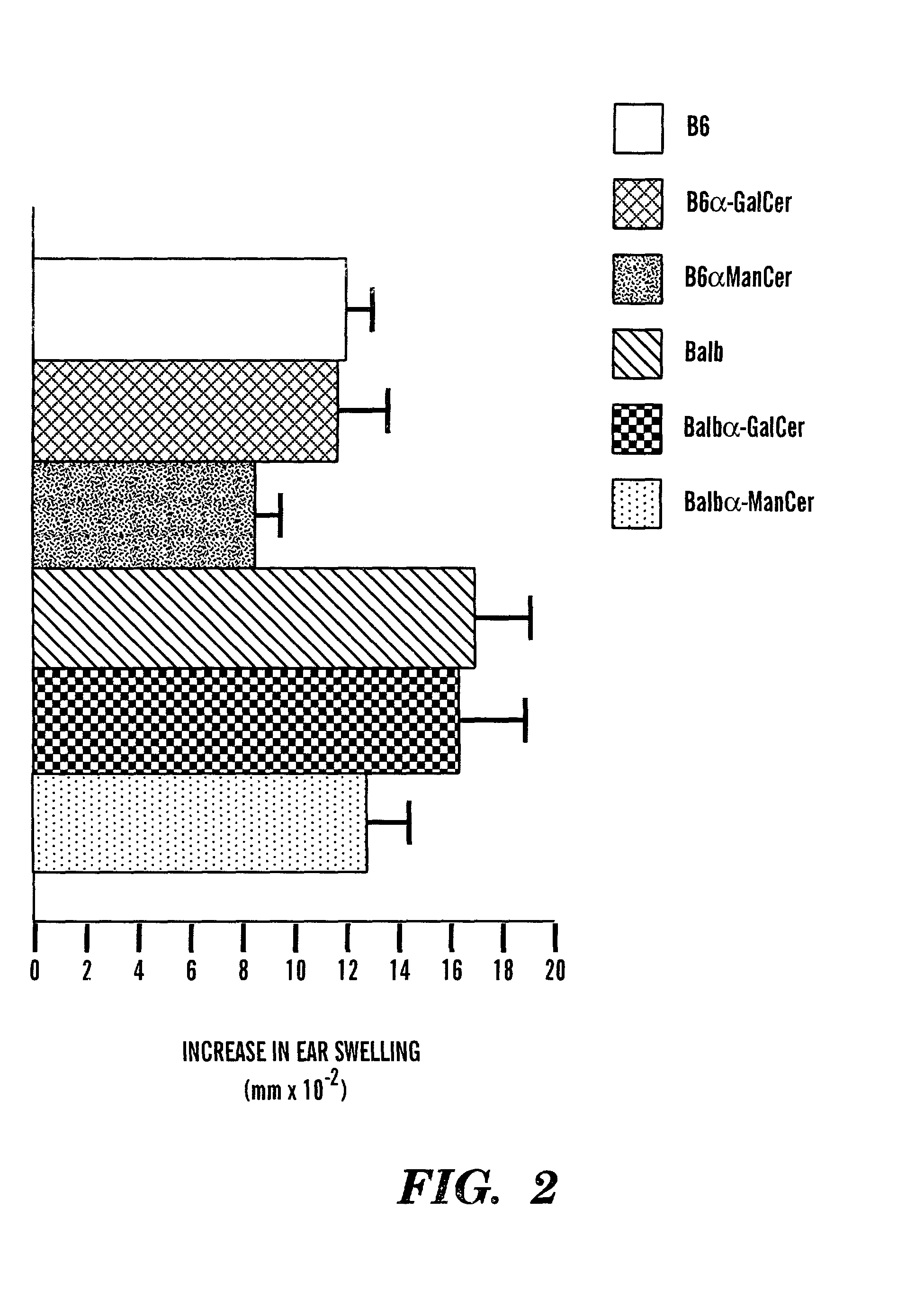
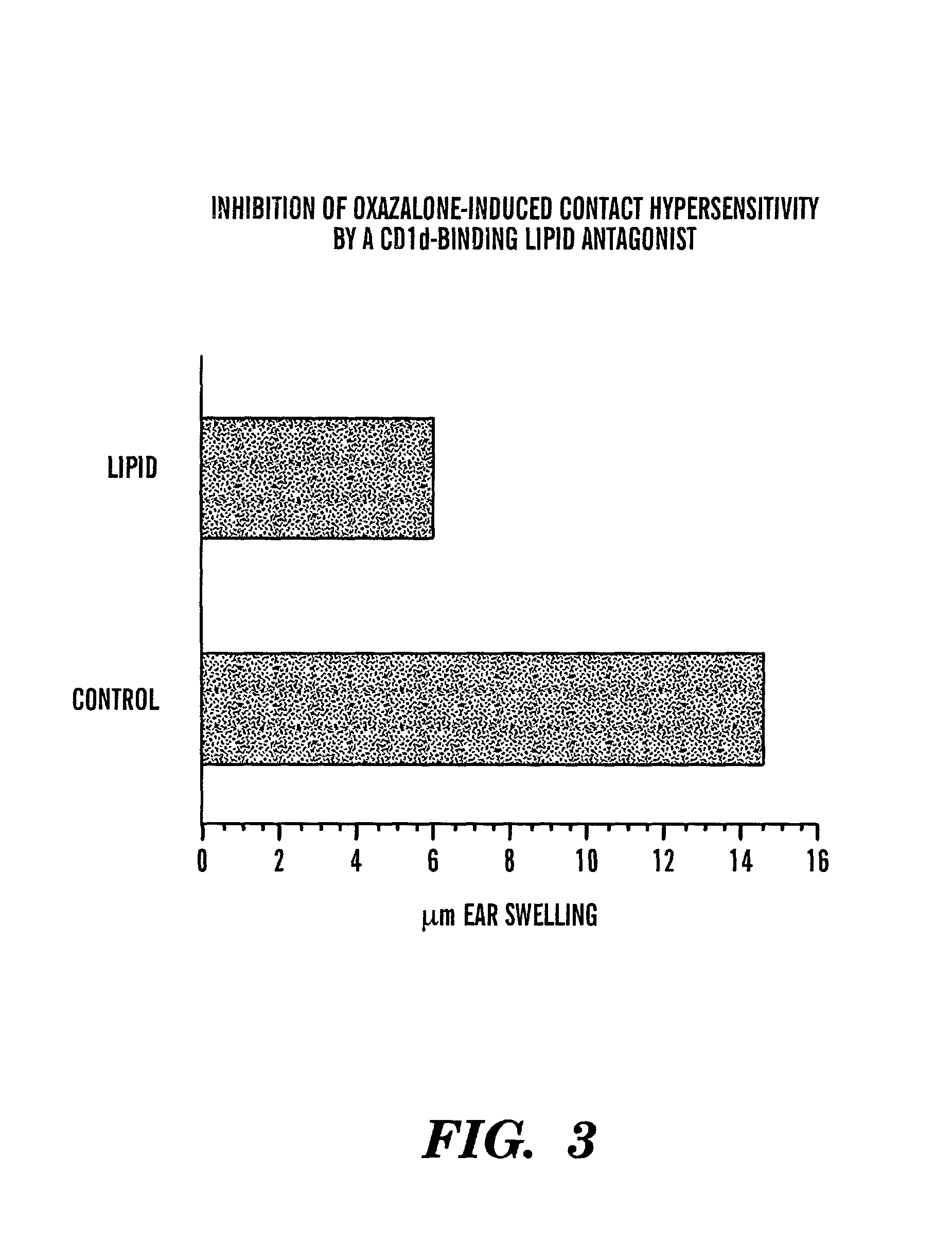
Method of attenuating reactions to skin irritants
InactiveUS7419958B2Preventing and treating skin sensitizationCosmetic preparationsBiocideCD1DUltrasound attenuation
The present invention is directed to a method of inhibiting CD1d activation by administering a composition containing a moiety that blocks CD1d activation. Compositions of the invention are useful for the attenuation of CD1d-restricted immune responses, including treatment of skin disorders due to hyperactive immune responses (e.g., contact hypersensitivity), for systemic administration to attenuate ongoing immune responses, and to provide hypoallergenic cosmetic products including pharmaceutical, cosmetic, and skin care compositions. Preferably, these compositions are in a form intended for topical administration.
Owner:DANA FARBER CANCER INST INC
Targeted CD1d molecules
ActiveUS9809654B2Antibody mimetics/scaffoldsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsSurface markerAntigen
The invention is directed to a compound comprising one or more CD1d complexes in association with an antibody specific for a cell surface marker. The CD1d complexes comprise a CD1d, a β2-microglobulin molecule, and may further comprise an antigen bound to the CD1d binding groove. The invention is further directed to methods of inhibiting or stimulating an immune response with the CD1d-antibody compounds, in particular anti-tumor and autoimmunity responses.
Owner:VACCINEX
Compositions and methods of monoclonal and polyclonal antibodies specific for T cell subpopulations
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP +1
Methods for induction of antigen-specific regulatory t cells
The present invention relates to methods of obtaining antigen-specific regulatory cells in vitro or in vivo. The regulatory cells are obtainable by inducing apoptosis of antigen-presenting cells by NKT cells. In particular, NKT cells are elicited, in vitro or in vivo, by exposure to CD1d-restricted NKT cell peptide epitopes either in natural configuration or modified as to contain a thioreductase motif within flanking residues. The present invention discloses methods to elicit immature antigen-presenting cells loaded with apoptotic cells or with apoptotic bodies for suppressing or preventing diseases such as autoimmune diseases, graft rejection and allergic diseases, and medicaments related thereto. Further disclosed are the use of antigen-specific regulatory cells for suppressing or preventing diseases such as autoimmune diseases, graft rejection and allergic diseases, and medicaments related thereto. Further disclosed are populations of antigen-specific regulatory cells obtained by this method.
Owner:IMCYSE
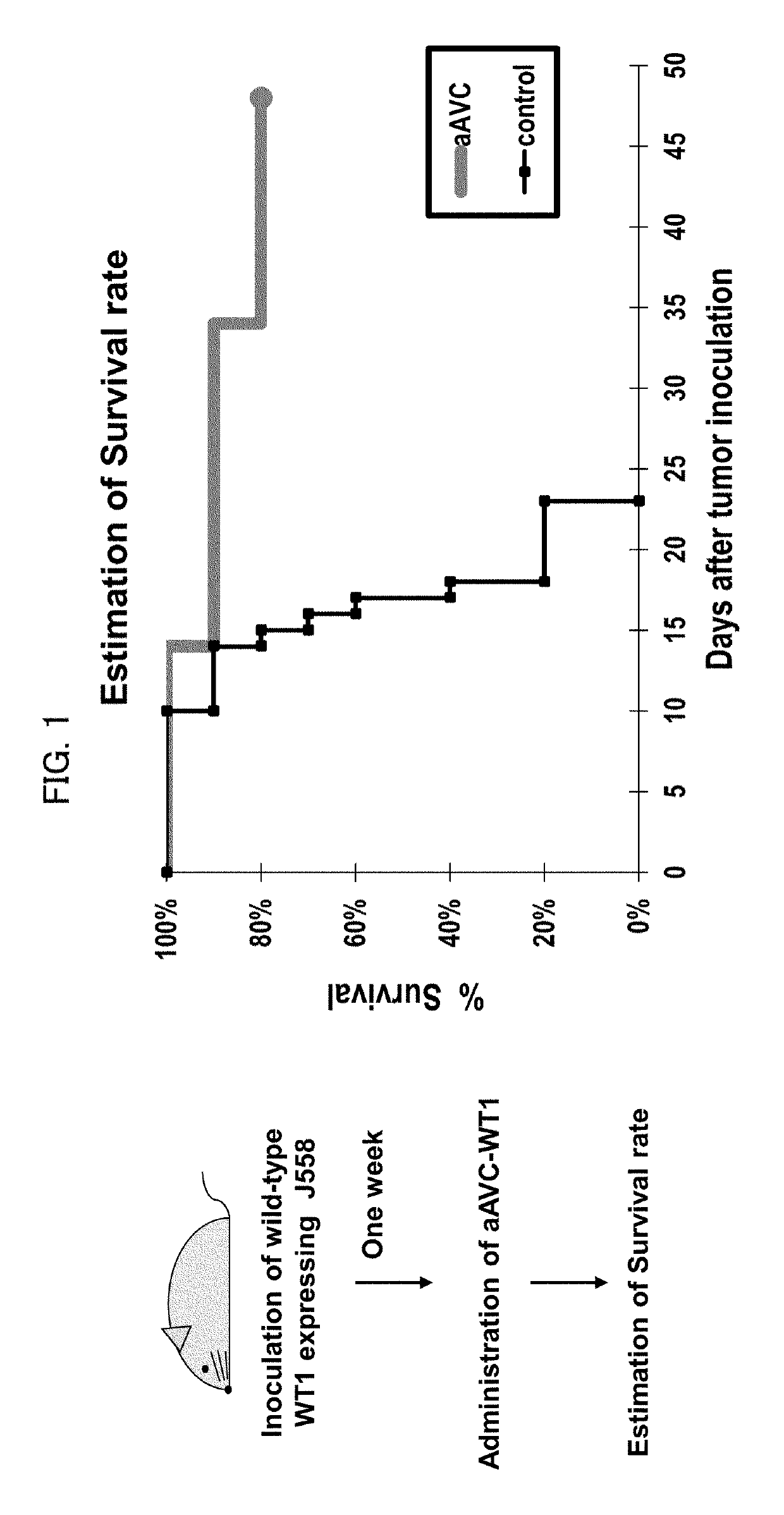
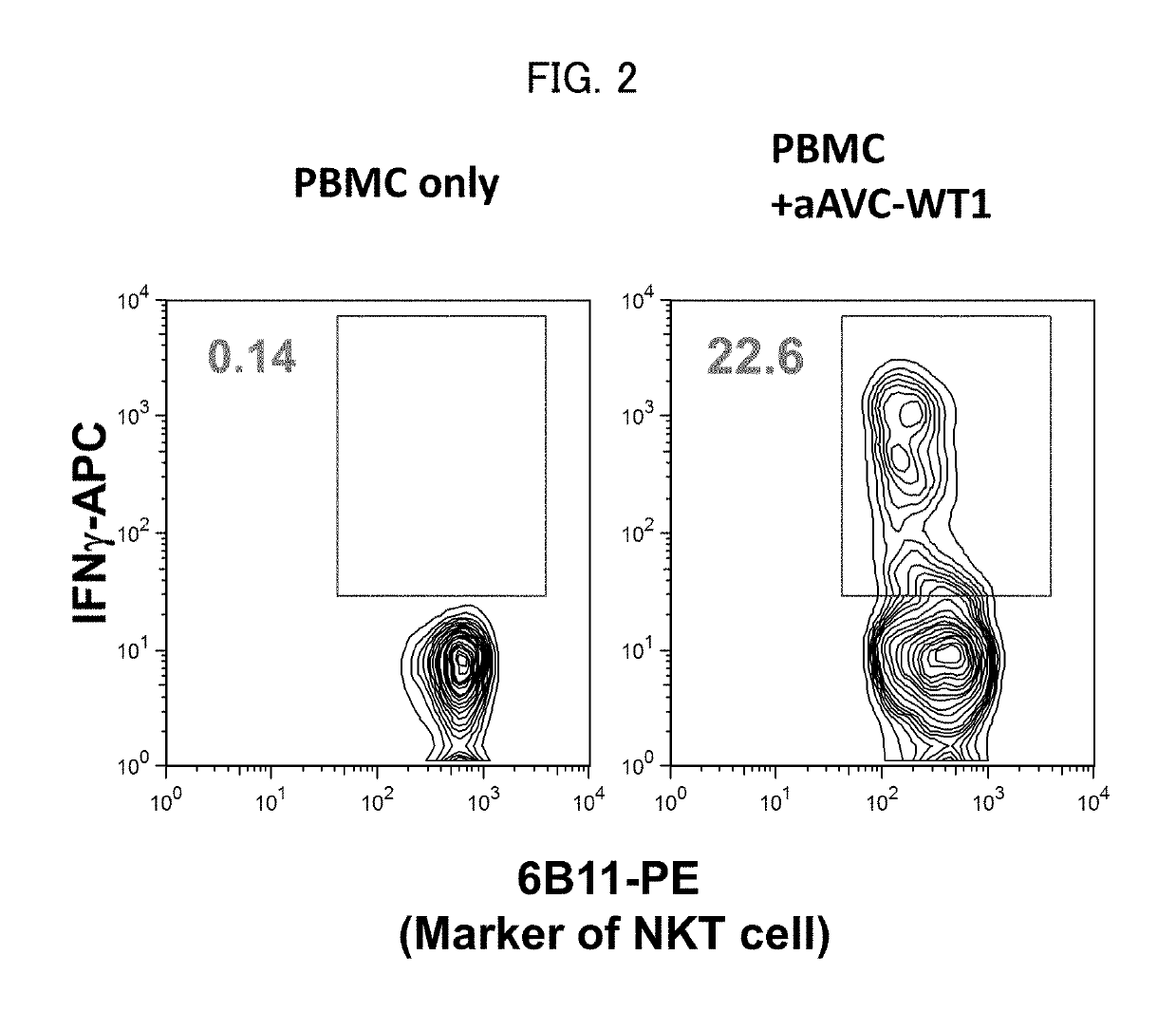
Immunotherapeutic method using artificial adjuvant vector cells that co-express cd1d and target antigen
Provided is immunotherapy of cancer or infection utilizing activation of dendritic cell (DC) by innate immunity, namely, a method of preparing an artificial adjuvant vector cell co-expressing a target antigen and CD1d and having an ability to activate immunity against the target antigen, comprising treating the target antigen and CD1d co-expressing cell with a CD1d ligand in a culture medium.
Owner:RIKEN
Modulation of NKT cell activity with antigen-loaded CD1d molecules
The invention is directed to methods of modulating an immune response in an animal, comprising administering a composition comprising one or more soluble CD1d complexes, in particular non-specific soluble CD1d complexes. Soluble CD1d complexes comprise a soluble CD1d polypeptide, a β2-microglobulin polypeptide, and a ceramide-like glycolipid antigen bound to the CD1d antigen binding groove, and in certain embodiments, an immunogen. The administration of compositions of the present invention affects the activity of CD1d-restricted NKT cells, and in particular, allows for multiple administrations without causing CD1d-restricted NKT cell anergy.
Owner:VACCINEX
Compositions and methods of monoclonal and polyclonal antibodies specific for T cell subpopulations
InactiveUS8138314B2Increase in sizeIncrease the number ofAntibacterial agentsAntipyreticCD1DPolyclonal antibodies
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP +1
ANTIBODIES TO CD1d
InactiveCN104144700ADigestive systemImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsCD1DAntigen binding
Owner:TEVA PHARMA AUSTRALIA PTY LTD
Cell for immunotherapy, including modified nucleic acid construct encoding Wilms tumor gene product
ActiveUS10316332B2Induce immune responseImprove expression levelTumor rejection antigen precursorsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsAntigen receptorsWilms' tumor
A cell for immunotherapy of the present invention includes a nucleic acid encoding a Wilms tumor 1 gene product or a fragment of the Wilms tumor 1 gene product, wherein the nucleic acid including (i) a region encoding a fragment of the Wilms tumor 1 gene product, the fragment being indicated by positions 194 to 493 of amino acid sequence of SEQ ID NO:1 or by positions corresponding to the positions 194 to 493 of amino acid sequence corresponding to SEQ ID NO:1 and (ii) only one AUG as a functional start codon, connected to a 5′ terminal side of the region via 3m (m is 124-192) bases intervening between the AUG as the functional start codon and the 5′ terminal side of the region, and a nucleic acid encoding CD1d, wherein the cell has been loaded with a glycolipid recognized by antigen receptor of NKT cell.
Owner:RIKEN
Methods for attenuating allergen-induced airway hyperreactivity using cd1d dependent antagonists
InactiveUS20100035843A1Inhibiting cytokine productionBiocidePhosphorous compound active ingredientsNasal passageNasal passages
The present invention is directed to a method of inhibiting allergen-induced airway CD1d activation by administering a composition containing a moiety that blocks CD1d activation. Methods of the invention are useful for treatment and prevention of air-way hyperactivity caused by an allergen, and results in the attenuation of CD1d-restricted immune responses, including treatment of hay fever and asthma are due to air-way hyperactivity, and for systemic administration to attenuate ongoing immune responses. Preferably, these compositions are in a form intended for administration via nasal passages or directly inhaled to the air-ways.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP +1
IMMUNOTHERAPEUTIC METHOD USING ALLO-CELLS WHICH CO-EXPRESS CD1d AND TARGET ANTIGEN
InactiveUS20110280895A1Sufficient treatment effectEfficient expressionAntibacterial agentsSnake antigen ingredientsCD1DDendritic cell
The present invention provides a means to be used for a new immunotherapy of cancer or infection utilizing activation of dendritic cell (DC) by innate immunity, namely, a method of preparing a cell co-expressing a target antigen and CD1d and having an ability to activate immunity against the target antigen, comprising the following steps (a) and (b):(a) a step of transfecting an mRNA encoding the target antigen into a CD1d-expressing cell to give a cell co-expressing the target antigen and CD1d; and (b) a step of treating the cell obtained in step (a) with a CD1d ligand in a culture medium.
Owner:RIKEN
Novel uses of PPAR modulators and professional APCs manipulated by the same
InactiveUS20060159669A1Ameliorate any conditionAltered phenotypeBiocideGenetic material ingredientsAntigenAutoimmune condition
The invention relates to a manipulated professional antigen presenting cell (APC) having increased expression of a CD1 type II molecule, preferably at least a CD1d molecule, relative to a control non manipulated cell. The invention further relates to the use of PPARg modulators in the preparation of a pharmaceutical composition or kit for the treatment of a disease treatable by activation of CD1d restricted T-cells, e.g. in autoimmune diseases, allergies, post-transplant conditions or infectious diseases, or in the treatment of a neoplastic disease, e.g. skin cancer, hematological tumors, colorectal carcinoma, and therapeutic compositions and kits therefor. Furthermore, the invention relates to methods of manipulating professional APCs and kits therefor.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF DEBRECEN
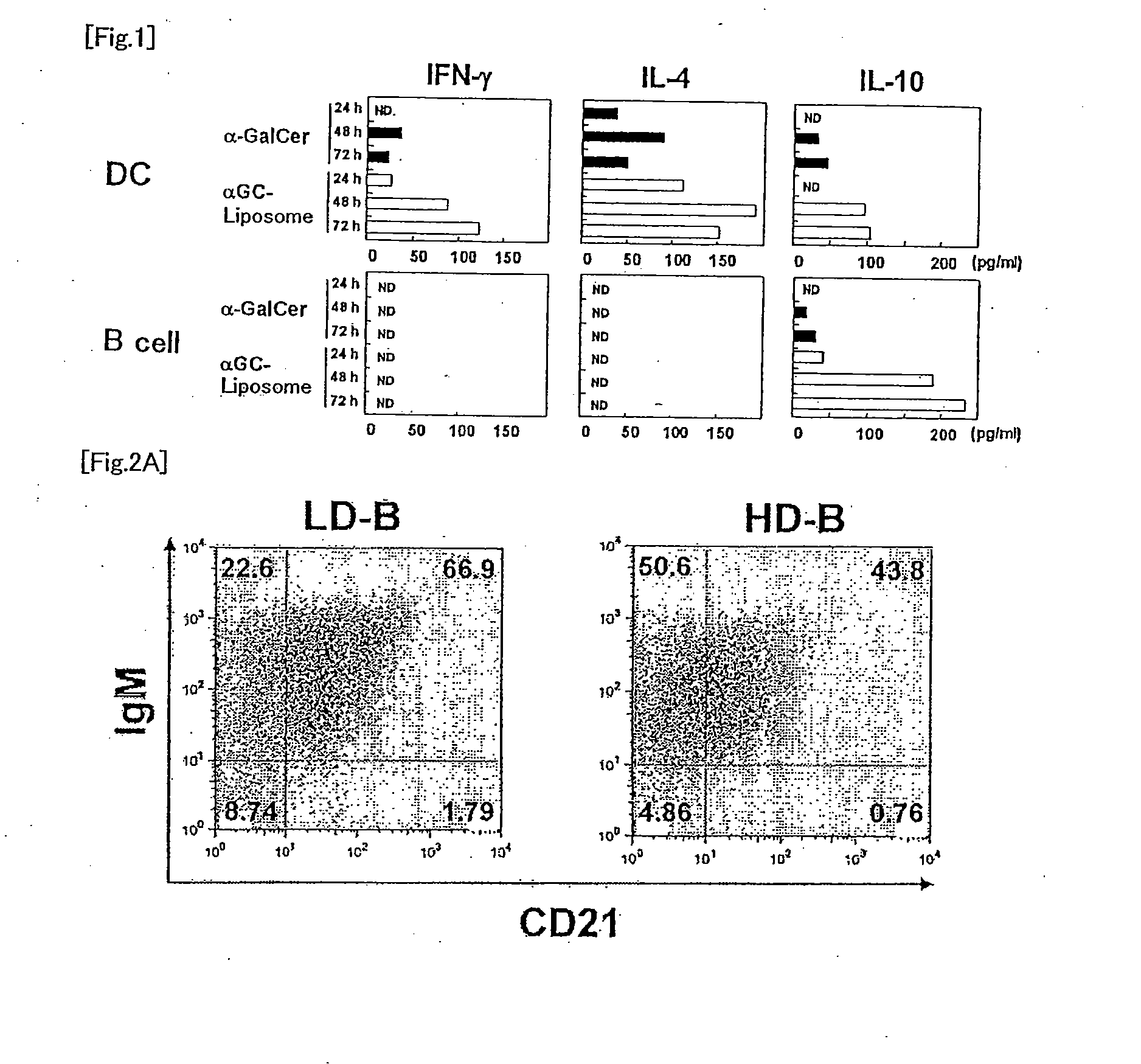
Regulatory b cells and their uses
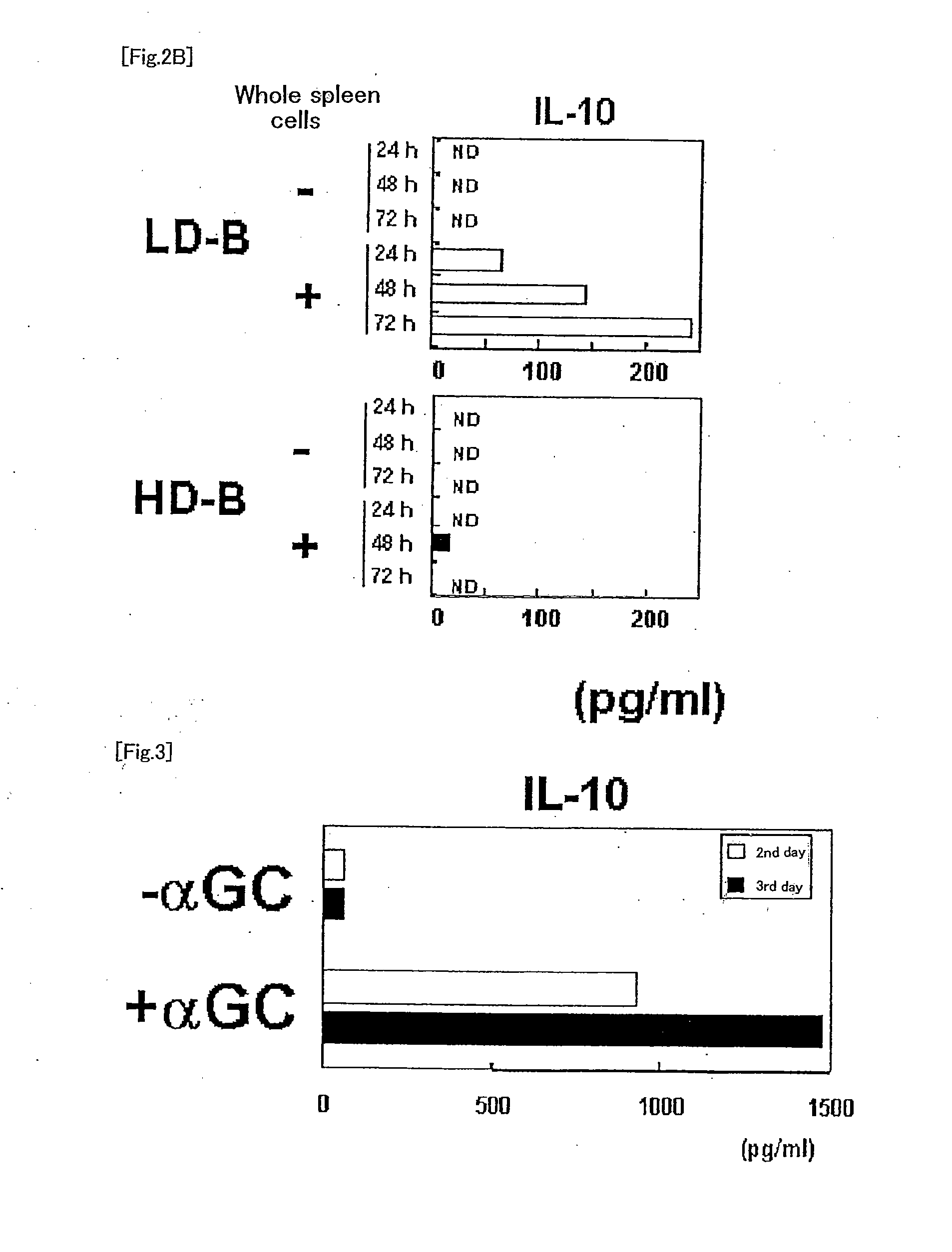
The present invention relates to a phenotypically distinct CD1dhighCD5+ B cell subset that regulates T cell mediated inflammatory responses through the secretion of interleukin-10 (IL-10). The invention also relates to the use of these IL-10 producing regulatory B cells in the manipulation of immune and inflammatory responses, and in the treatment of disease. Therapeutic approaches involving adoptive transfer of these regulatory B cells, or expansion of their endogenous levels for controlling autoimmune or inflammatory diseases and conditions are described. Ablation of this subset of regulatory B cells, or inhibition of their IL-10 production can be used to upregulate immunodeficient conditions, and / or to treat tumors / cancer. Diagnostic applications also are encompassed.
Owner:DUKE UNIV
Method for analysis of nkt cell function
InactiveUS20090233323A1Avoid influenceGood accuracy and reproducibilityGenetically modified cellsMicrobiological testing/measurementHeterologousAntigen
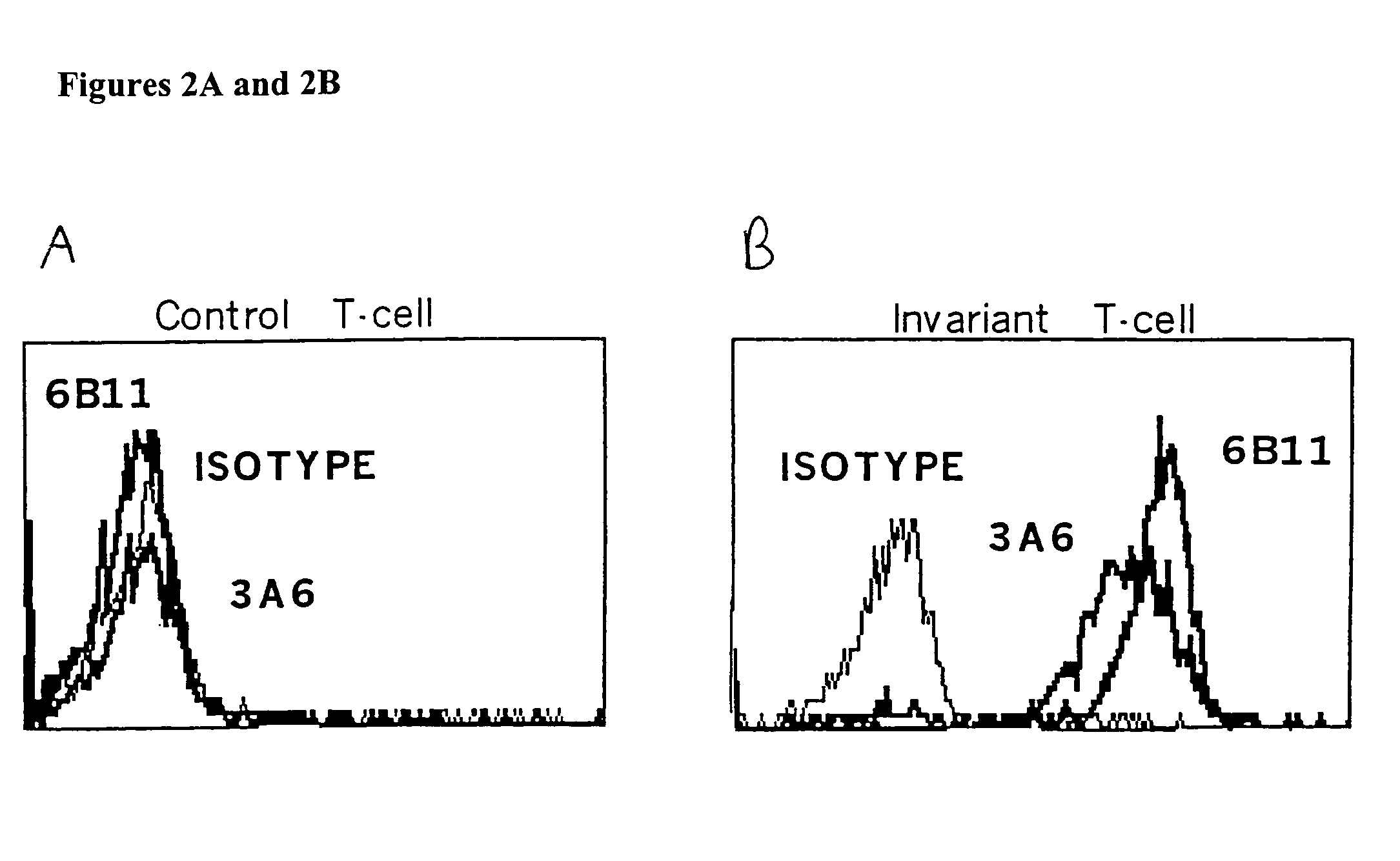
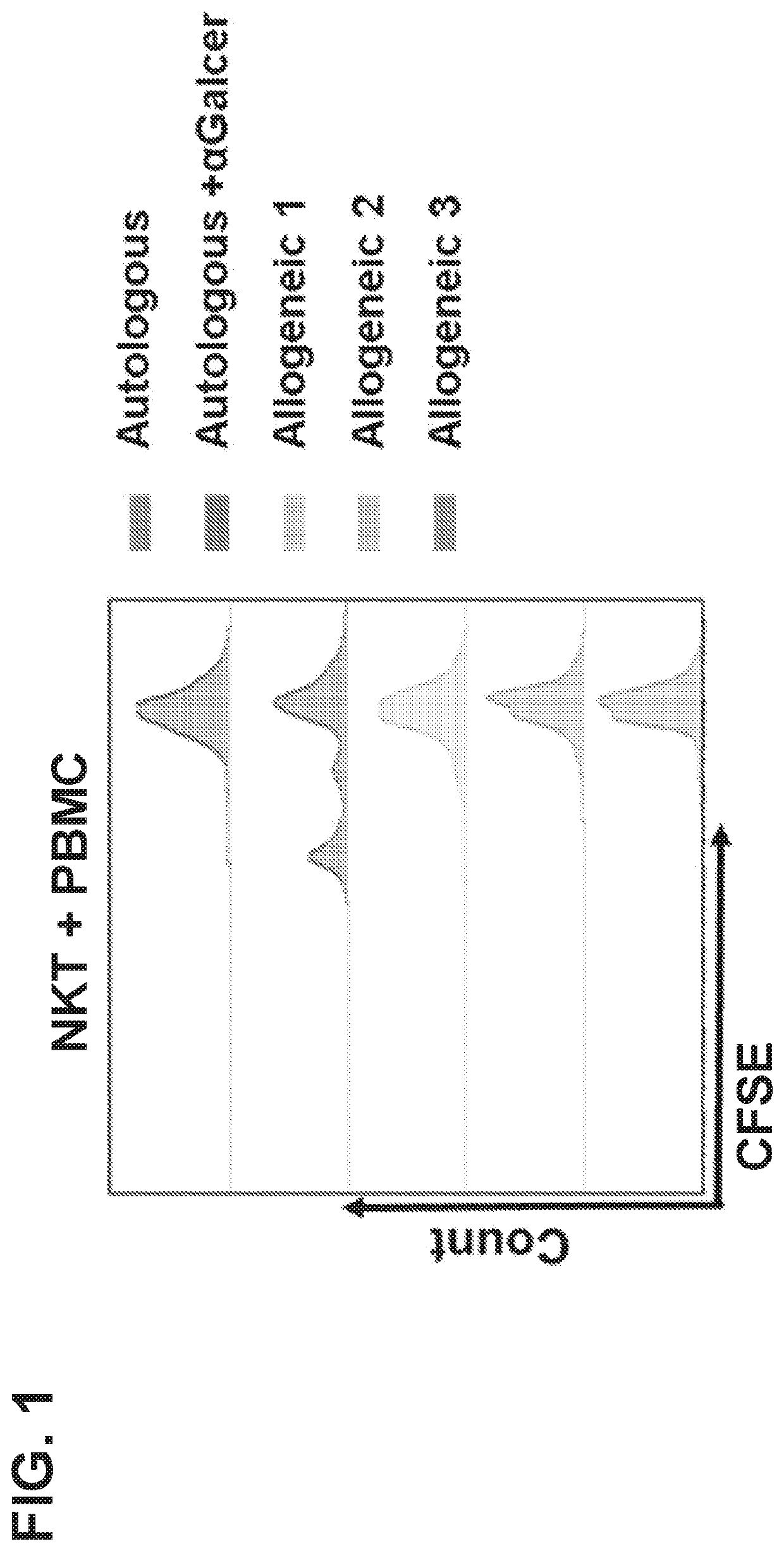
The present invention provides a superior method of functional analysis of NKT cells, which enables function analysis of low frequency NKT cells, is independent of the function of autologous APCs, and can avoid an influence of secondary factors and the like. More specifically, the present invention provides a method of functional analysis of human NKT cells including (a) cocultivating a mononuclear cell derived from human peripheral blood with a CD1d-expressing antigen presenting cell derived from a heterologous animal, and (b) evaluating the functionality of NKT cells with the number of NKT cells and / or a substance specific to functional NKT cells as an index; a reagent for analysis of human NKT cells containing a CD1d-expressing antigen presenting cell derived from a heterologous animal; a kit containing (a) a CD1d-expressing antigen presenting cell derived from a heterologous animal, and (b) at least one reagent selected from the group consisting of a reagent for selection of human mononuclear cell, a reagent for measurement of the number of human NKT cells and a reagent for measurement of a substance specific to human functional NKT cells; and the like.
Owner:RIKEN
CD1D-restricted NKT cells as a platform for off-the-shelf cancer immunotherapy
PendingCN111094555APolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifImmunoglobulin superfamilyAllogeneic cellCD1D
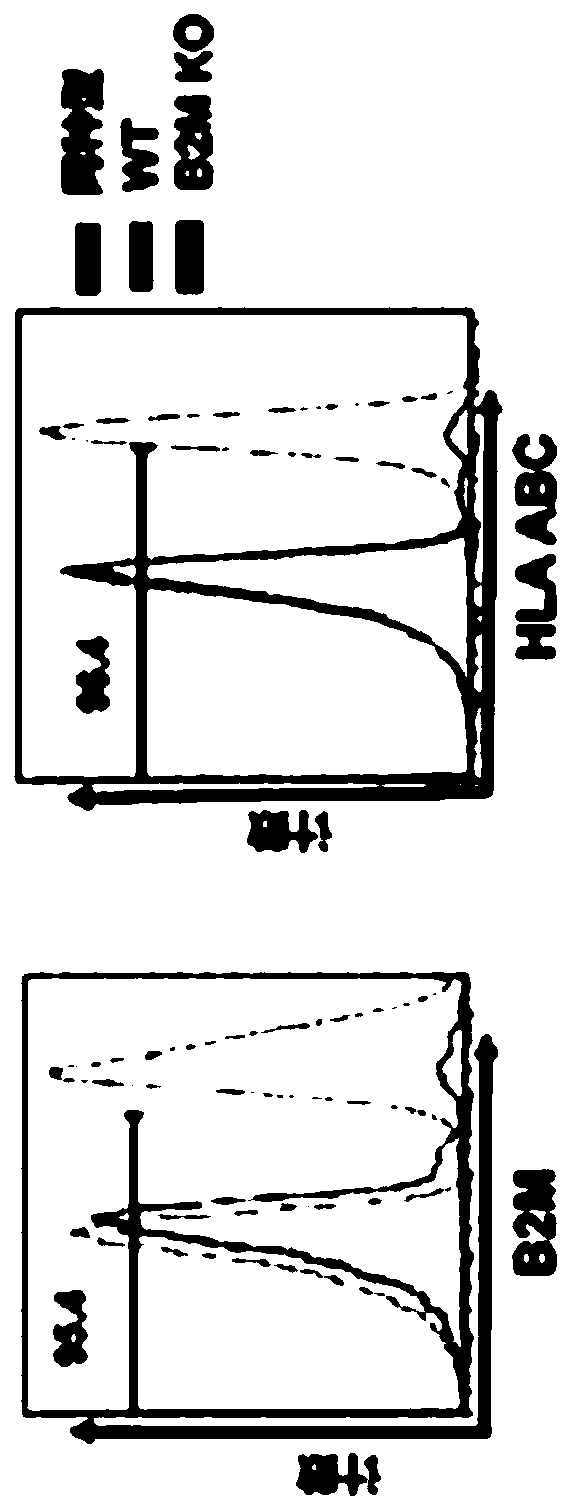
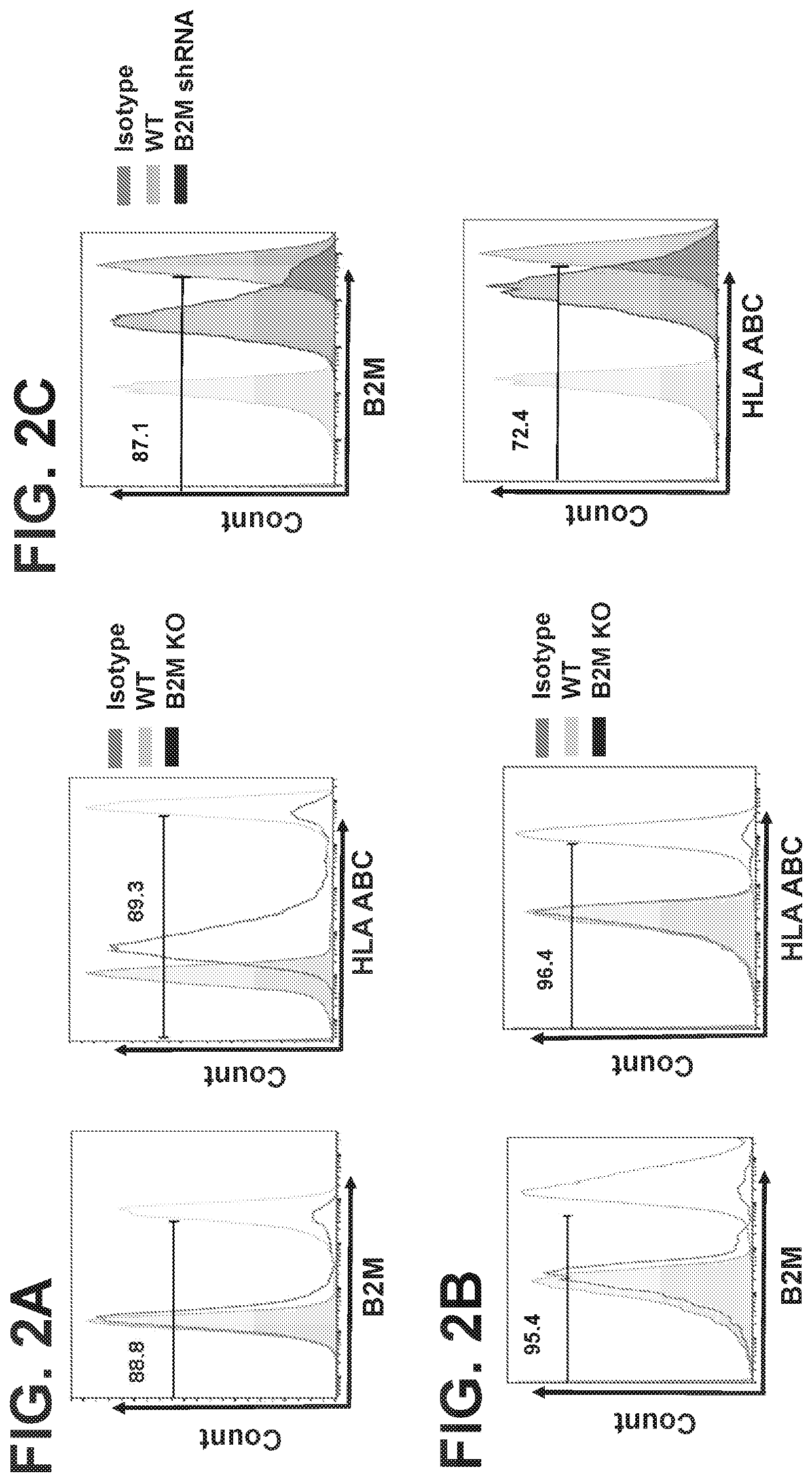
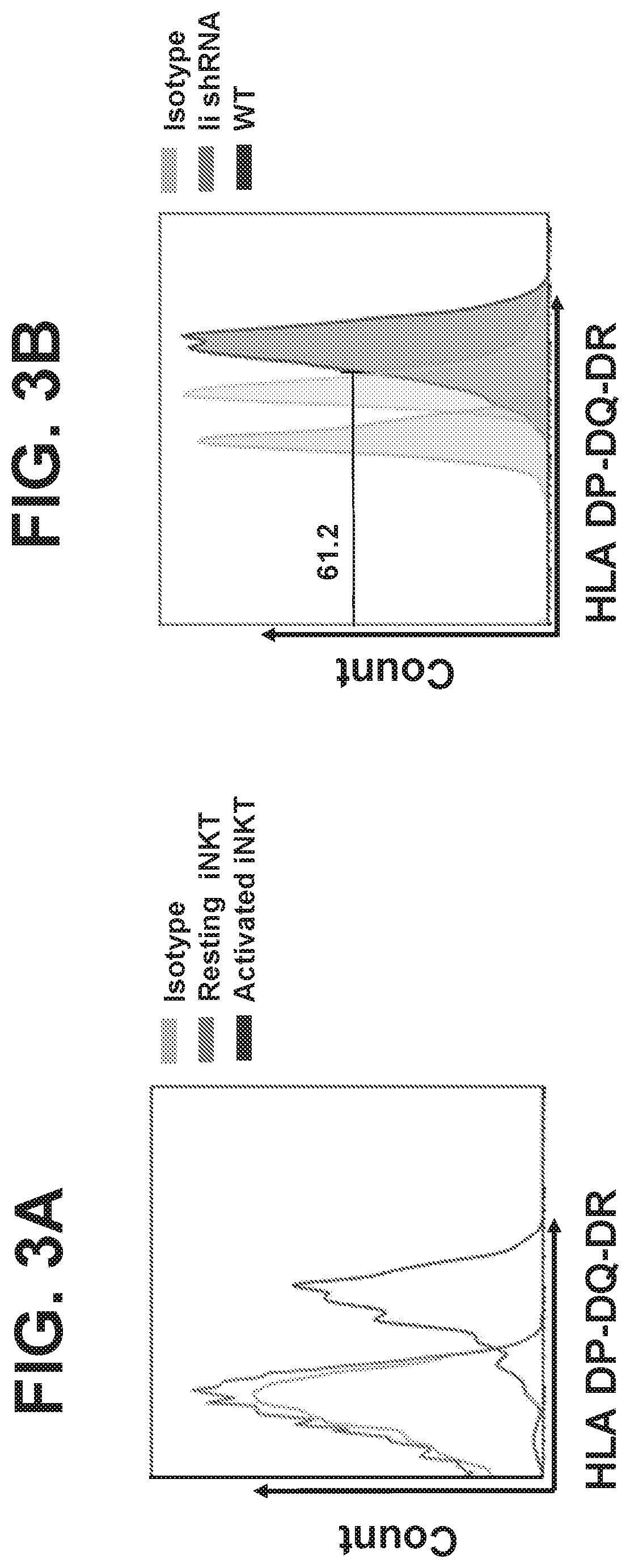
Embodiments of the disclosure include methods and compositions for immunotherapy that comprise allogeneic cells that are able to be universally tolerated in host individuals. In specific embodiments the cells have reduced expression of endogenous beta2-microglobulin (B2M) and / or MHC class II-associated invariant chain (Ii), and in particular cases the cells are NKT cells that lack the ability to damage host tissues, have much reduced recognition by host immune cells, and surprisingly avoid destruction by host NK cells. In some embodiments, B2M- and / or Ii-targeting molecules are engineered to be expressed in combination (including within a single construct) with recombinantly engineered receptors, for example, for a one-hit generation of universally tolerated off-the-shelf immunotherapy.
Owner:BAYLOR COLLEGE OF MEDICINE
Method of using cd1d over-expression in human dendritic cells to enhance cd8+ t cell-based and invariant natural killer t cell-based antitumor immunity
InactiveUS20130344095A1Genetically modified cellsSnake antigen ingredientsAntitumor immunityDendritic cell
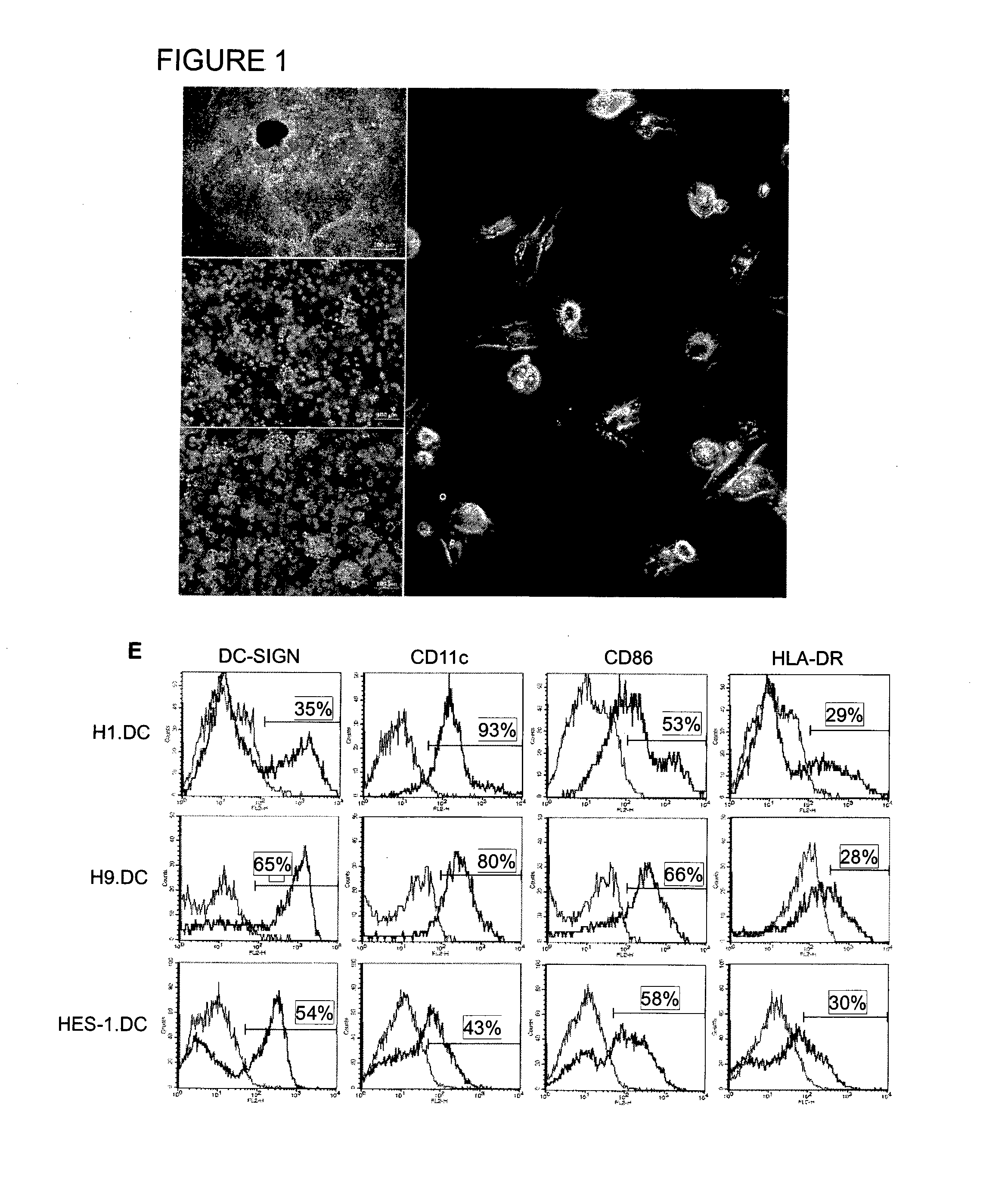
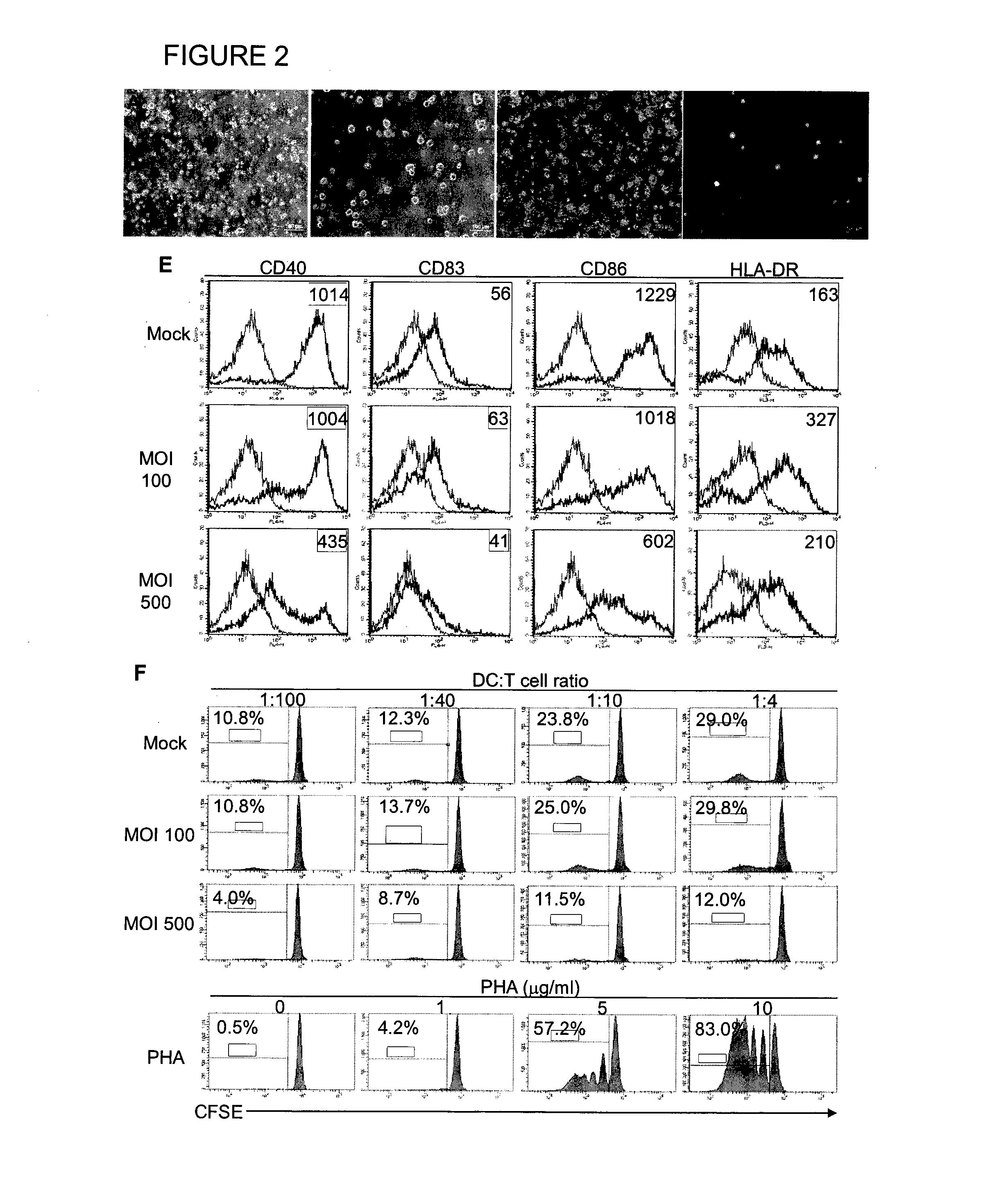
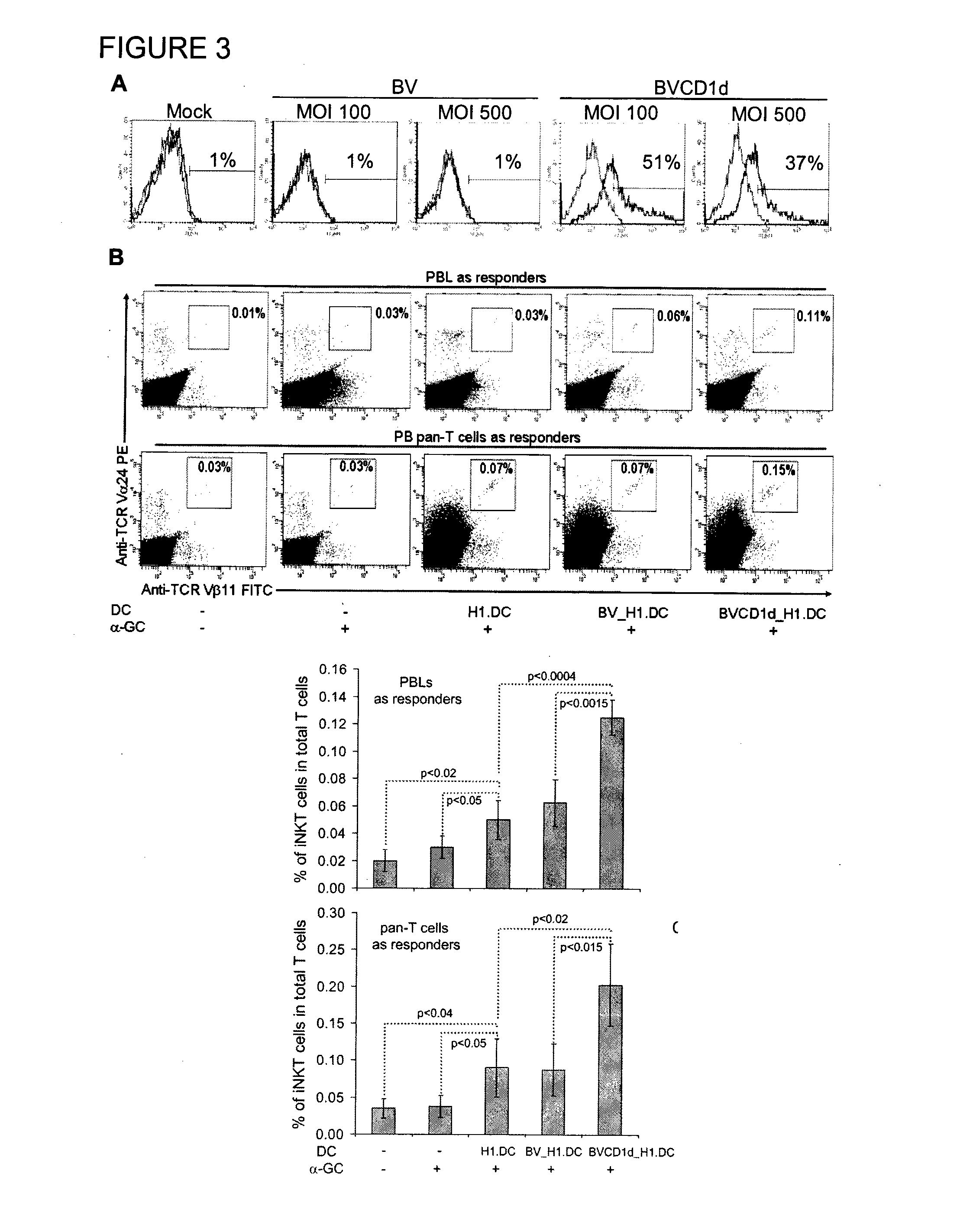
The manipulation of human dendritic cells (DCs) to induce potent anti-tumor immunity remains an essential subject of study. Here we report that the overexpression of CD1d in human DCs can enhance the priming of naïve CD8+ T cells against tumor antigen. We showed that CD1d can be overexpressed in the human DCs using baculoviral vector carrying the CD1d gene. This CD1d-overexpression is functional as demonstrated by the increased expansion of invariant natural killer T (iNKT) cells while using these modified DCs to present α-galactosylceramide (α-GC). Pulsed with tumor antigenic peptide, these CD1d-overexpressing human DCs showed enhanced capability to prime naïve CD8+ T cells. CD1d-overexpressing human DCs also induced a pro-inflammatory cytokine profile that may favor the priming. Moreover, this CD1d-overexpression strategy can be extrapolated to monocyte-derived human DCs. Therefore, our study suggest that overexpression of CD1d in human DCs may provide a novel strategy to enhance DC immunogenicity and the possible translation into human cancer immunotherapy.
Owner:AGENCY FOR SCI TECH & RES
Method for constructing HSAT H-T-S mouse-human chimeric model and application
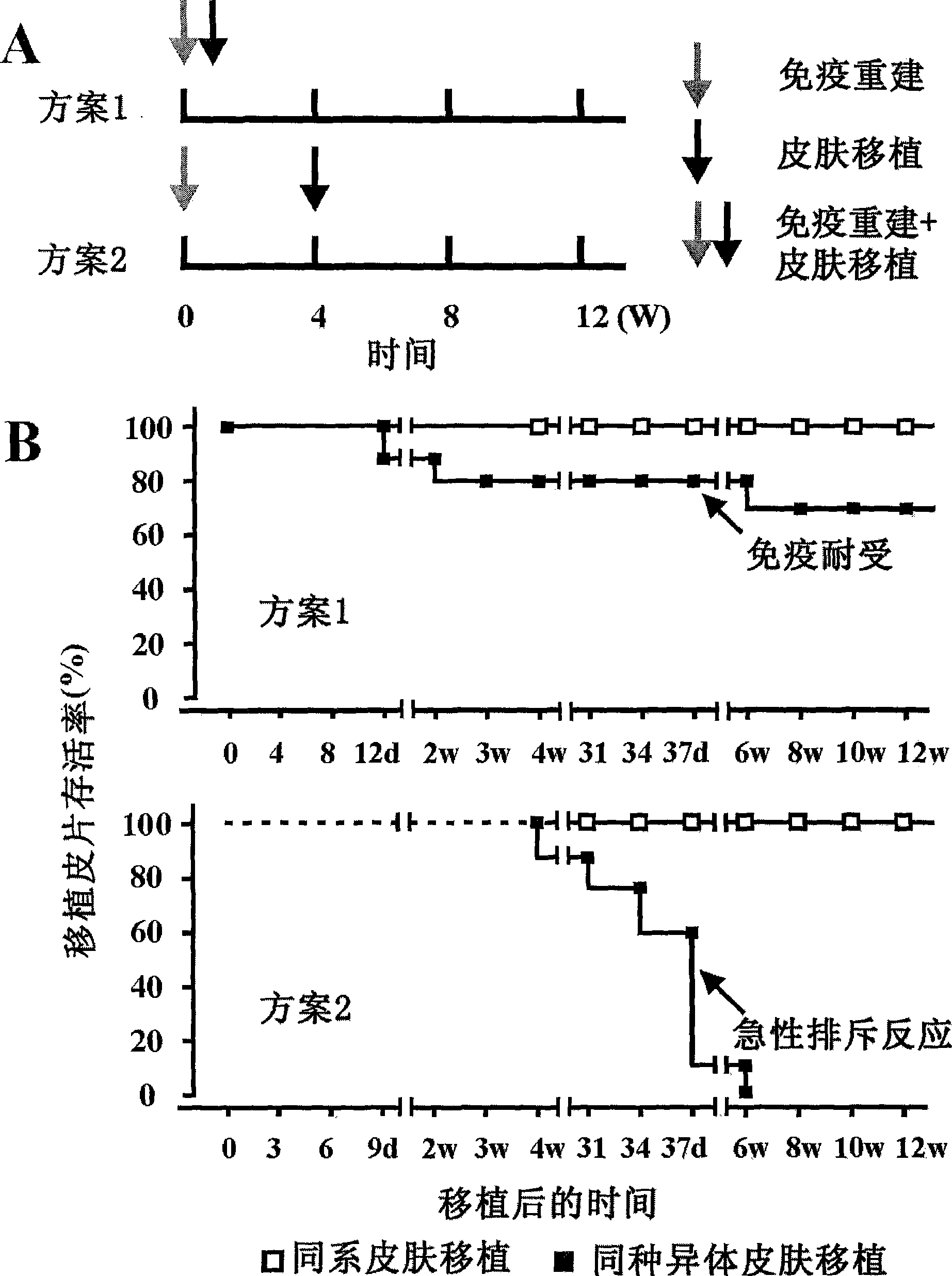
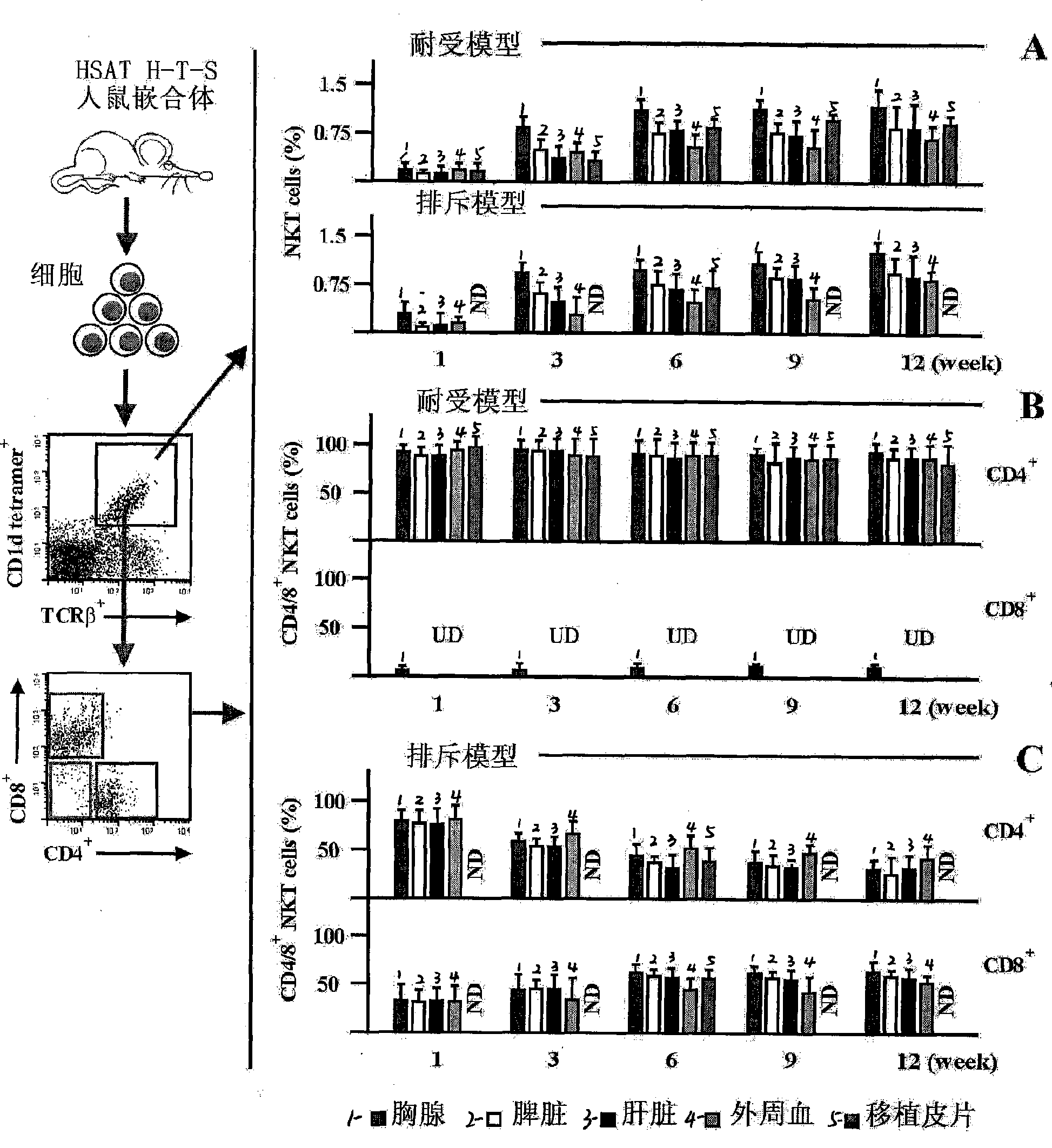
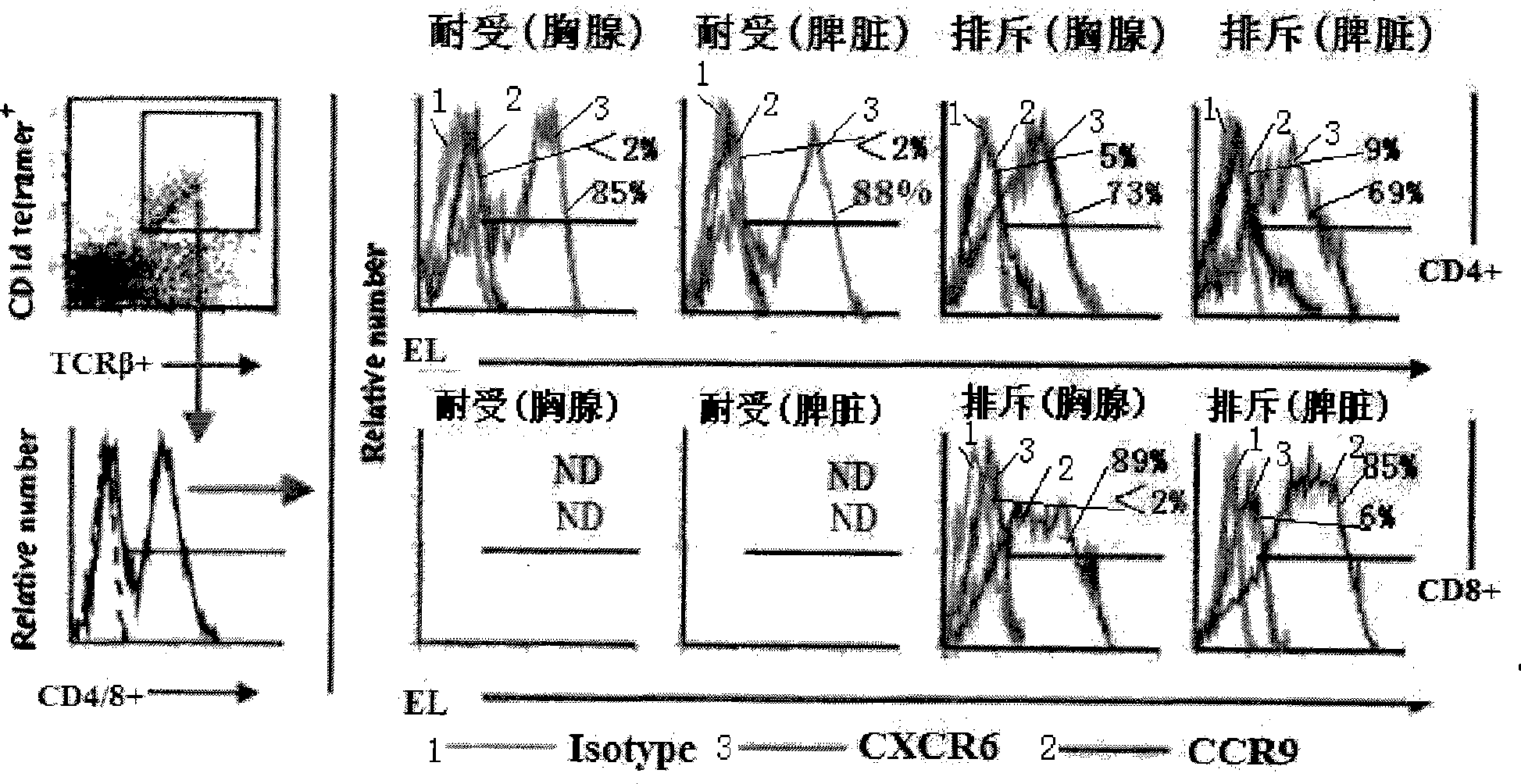
The invention discloses a method for constructing an HSAT H-T-S human-mouse chimera model and the application thereof. Firstly, a female Nod-SCID mouse in 6-8 weeks is selected; whole body exposure is carried out on the SCID mouse by radiation; secondly, human embryo thymic cells are taken; the cells come from the thymus of the embryo of a person who is voluntary to terminate the pregnancy, and the pregnant week is less than 24 weeks; the quantity of the cells is 1*10<7>, wherein, the quantity proportion of the thymic cells, as well as thymic epithelia and other stroma cells is 1:1, and the specificity of alpha-GalCer-CD1d tetramer is used for eliminating young and mature NKT cells; thirdly, the obtained embryo thymic cells are injected to the thymus of the SCID mouse subcutaneously to carry out dermatoplasty and obtain an HSAT H-T-S human-mouse chimera model. In the method, the human embryo thymic cells are implanted to the thymus of the mouse with severe combined immunodeficiency, and the full skin of human embryo trunk is grafted to the chest cavity of the SCID mouse, thereby reproducing the immune tolerance and rejection reaction of the dermatoplasty reaction in human body. The invention has good repeatability, obvious effect, simple method and good application prospect.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
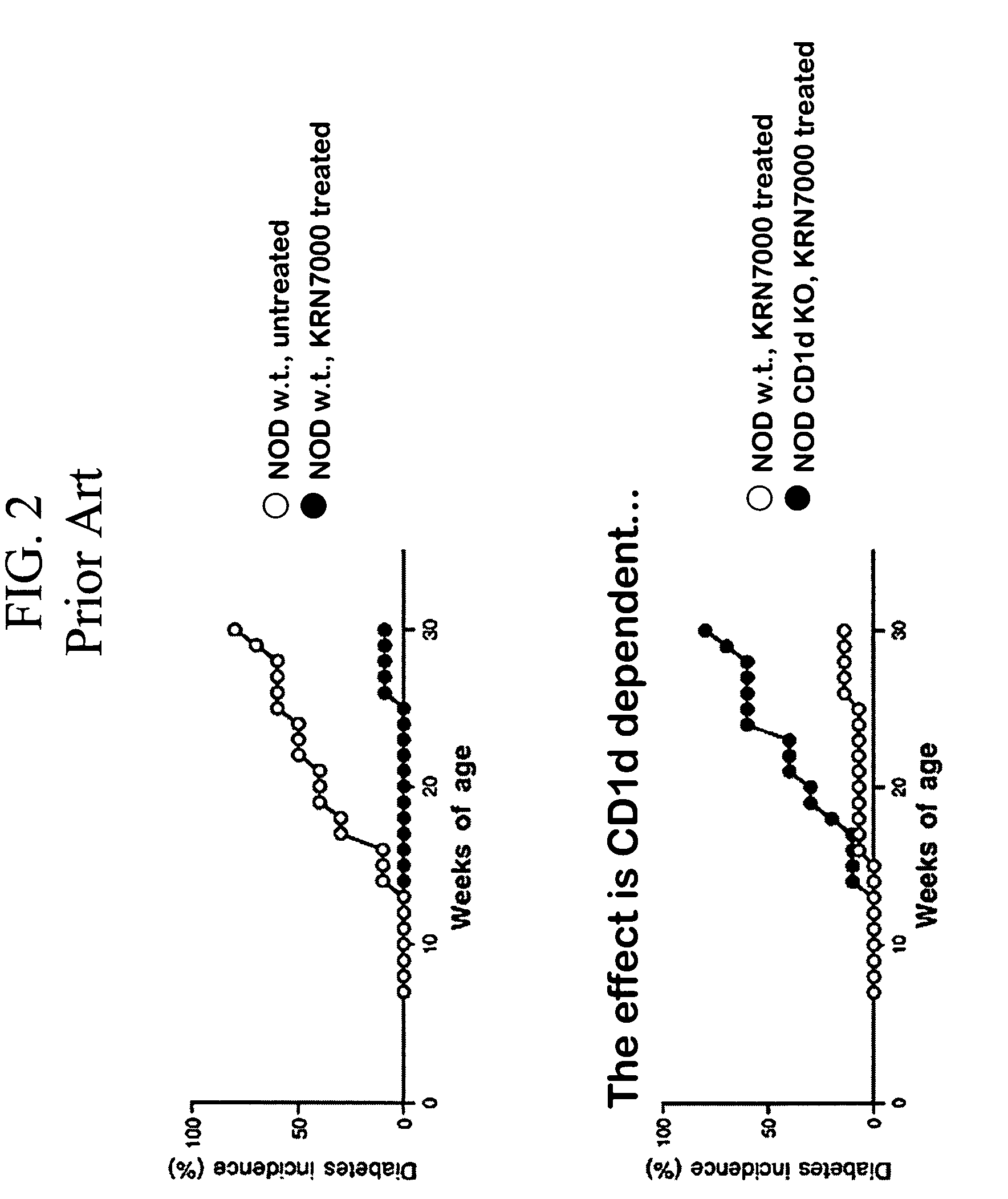
Bacterial glycolipid activation of CD1d-restricted NKT cells
Owner:THE SCRIPPS RES INST +2
Cd1d-restricted nkt cells as a platform for off-the-shelf cancer immunotherapy
PendingUS20200216810A1Avoid problemsSuitable as therapeuticPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifImmunoglobulin superfamilyCD1DMedicine
An isolated human NKT cell or a plurality of cells thereof, having reduced or no detectable expression of endogenous beta-2-microglobulin (B2M); endogenous MHC class II-associated invariant chain (Ii); or both. Methods to generate the cell or cells, and methods of treatment using the cell or cells are also provided.
Owner:BAYLOR COLLEGE OF MEDICINE
Single domain antibodies targeting cd1d
The invention relates to compounds, in particular polypeptides that specifically bind to the non-classical MHC protein CD1d and modulate CD1d-mediated biological functions. The invention in particularrelates to such compounds and polypeptides comprising or consisting of at least one single domain antibody, and wherein at least one single domain antibody specifically binds to CD1d. Also provided is for methods and use employing such compounds, polypeptides and / or single-domain antibodies.
Owner:LAVA THERAPEUTICS BV
Clostridium difficile immunogenic compositions and methods of use
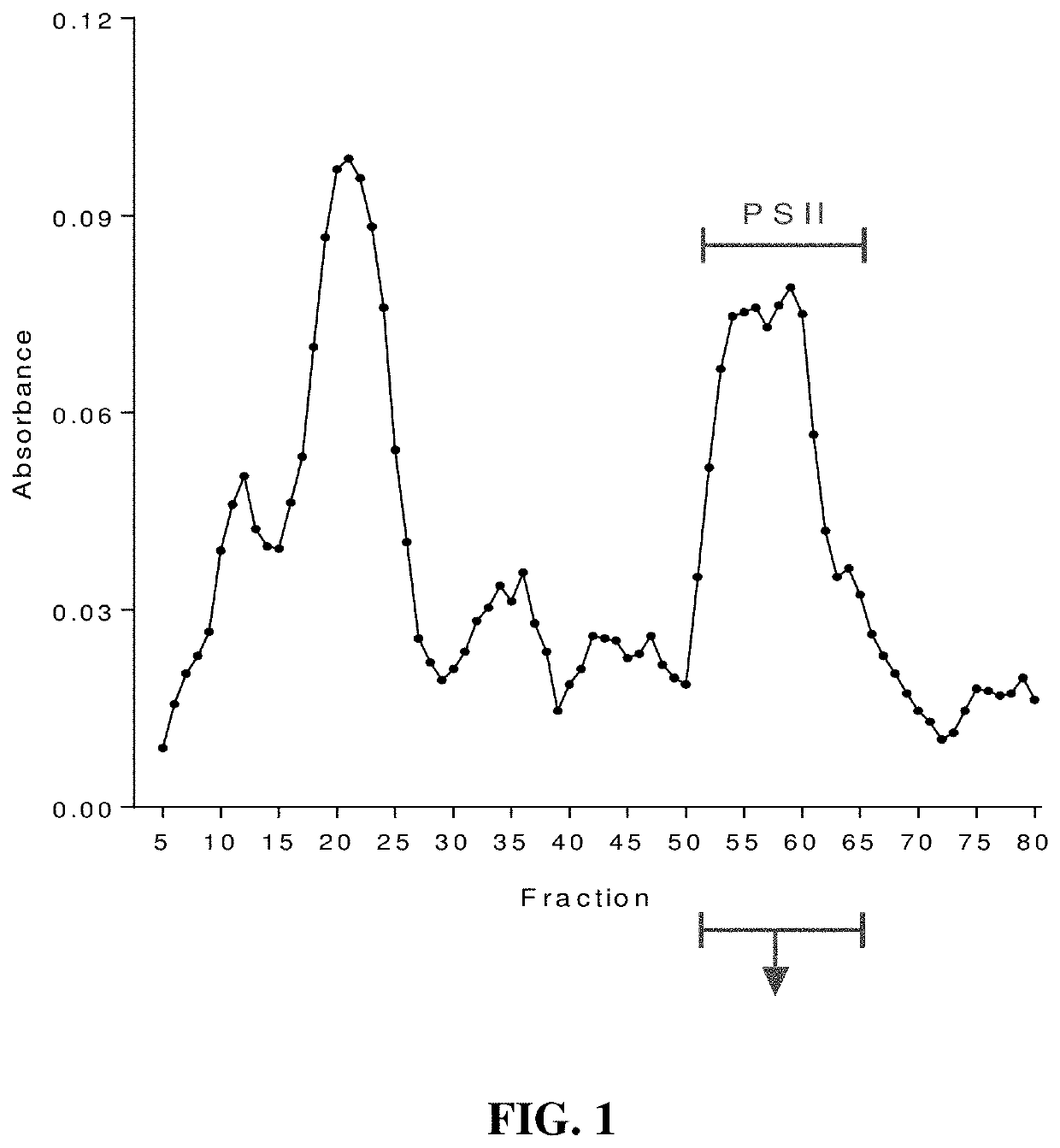
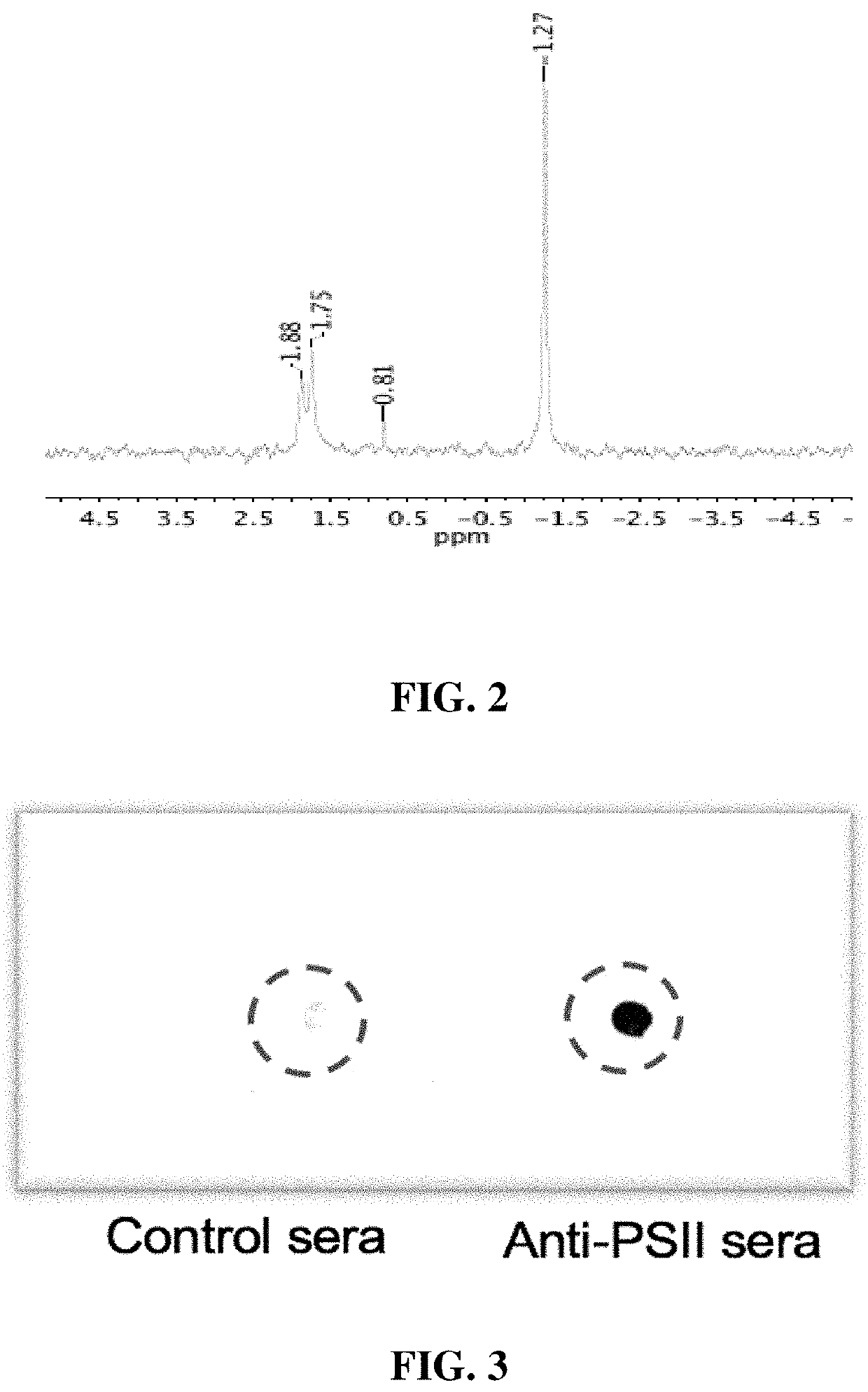
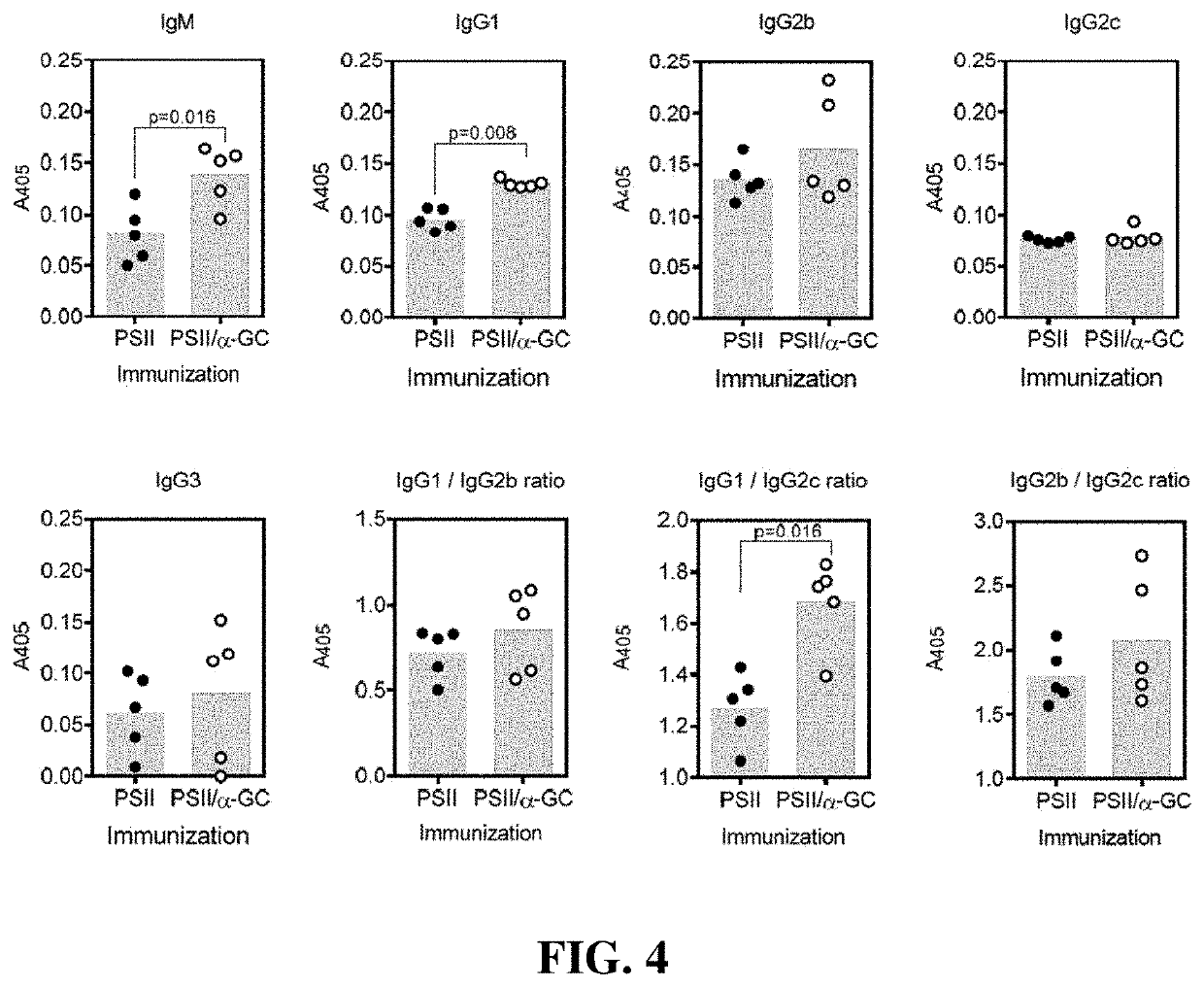
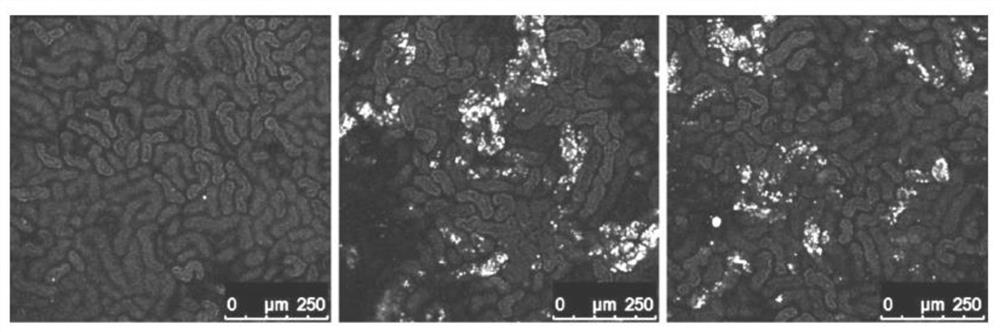
An immunogenic composition containing a Clostridium difficile (C. difficile) surface polysaccharide II (PSII) or an immunogenic portion thereof; and an α-galactosylceramide (α-GC) or analog or derivative thereof, which is able to bind to a CD1d glycoprotein, optionally containing a C. difficile TcdB C-terminal domain (CTD), or an immunogenic portion thereof, and / or an adjuvant. A method of treating, ameliorating, or inhibiting a C. difficile infection or a C. difficile-associated diarrhea in a subject by administering the immunogenic composition, particularly in subjects at risk for a C. difficile infection. A method of protecting a subject's gut microflora by administering the immunogenic composition or a composition containing α-GC and an alum adjuvant.
Owner:THE BOARD OF RGT UNIV OF OKLAHOMA
Spleen regulating type B lymphocyte as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN114686427AGood adoptive transferReduce fibrosisCell dissociation methodsMammal material medical ingredientsSpleen cellCD1D
The invention provides a spleen regulating type B lymphocyte as well as a preparation method and application thereof. On one hand, the invention provides a spleen regulating type B lymphocyte, wherein the proportion of CD1d, CD5 and CD21 / 35 antibody positive regulating type B lymphocytes in the cell is more than 94.6%. The invention further provides a method for preparing the spleen regulating type B lymphocyte. The method for preparing the spleen regulating type B lymphocyte comprises the following steps: taking a spleen cell suspension, and marking with surface antibodies CD1d, CD5 and CD21 / 35; the labeled cells are sorted by fluorescence activated cell sorting. The third aspect of the invention provides application of the spleen regulating type B lymphocyte in preparation of a preparation for targeted colonization in bilateral kidneys. The fourth aspect of the invention provides application of the spleen regulating type B lymphocyte in preparation of a product for kidney protection.
Owner:THE FIRST MEDICAL CENT CHINESE PLA GENERAL HOSPITAL
Antibody-mediated rejection inhibitor
InactiveUS20120046452A1Inhibition productionSignal can be impairedImmunoglobulins against blood group antigensImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsDiseaseCD1D
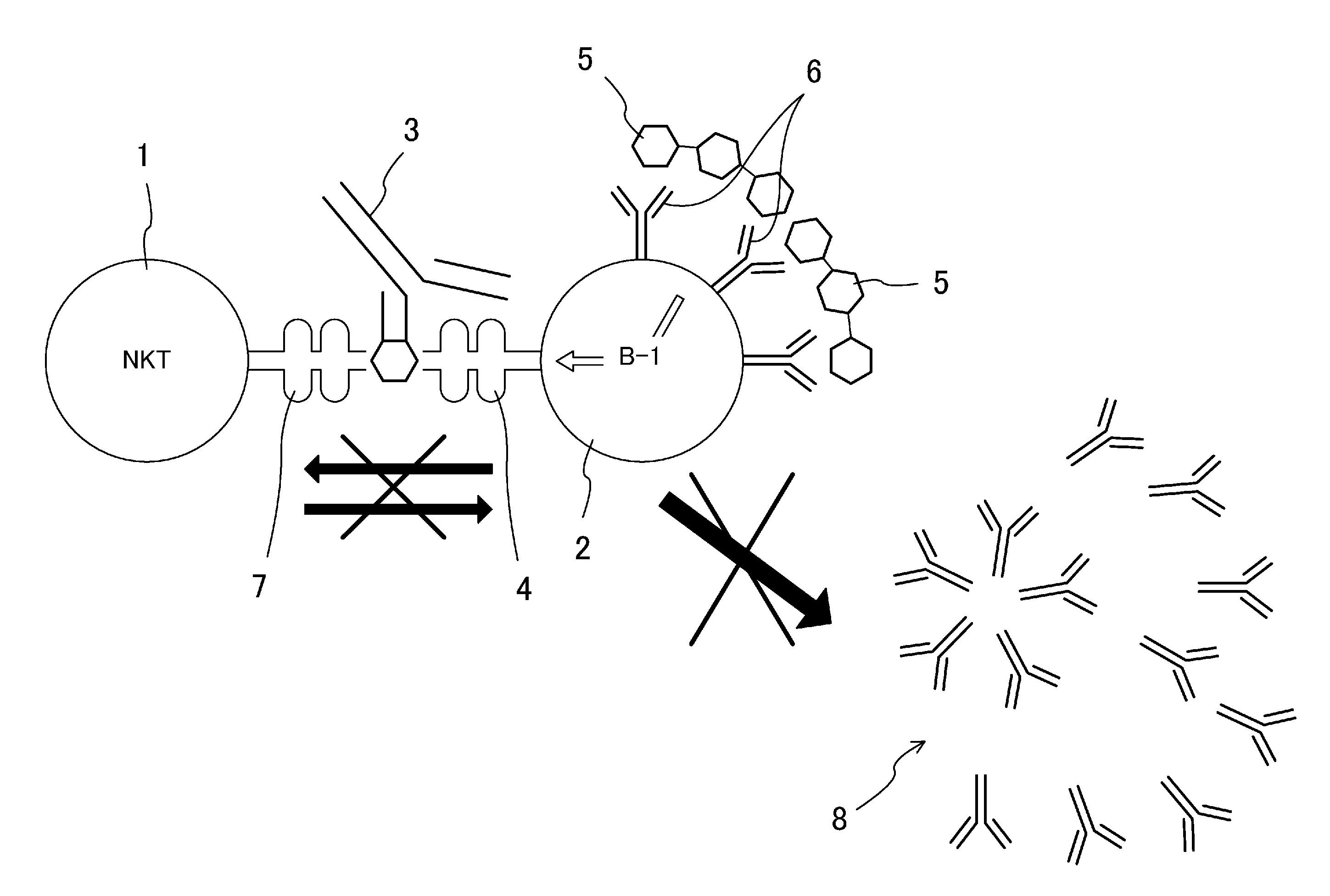
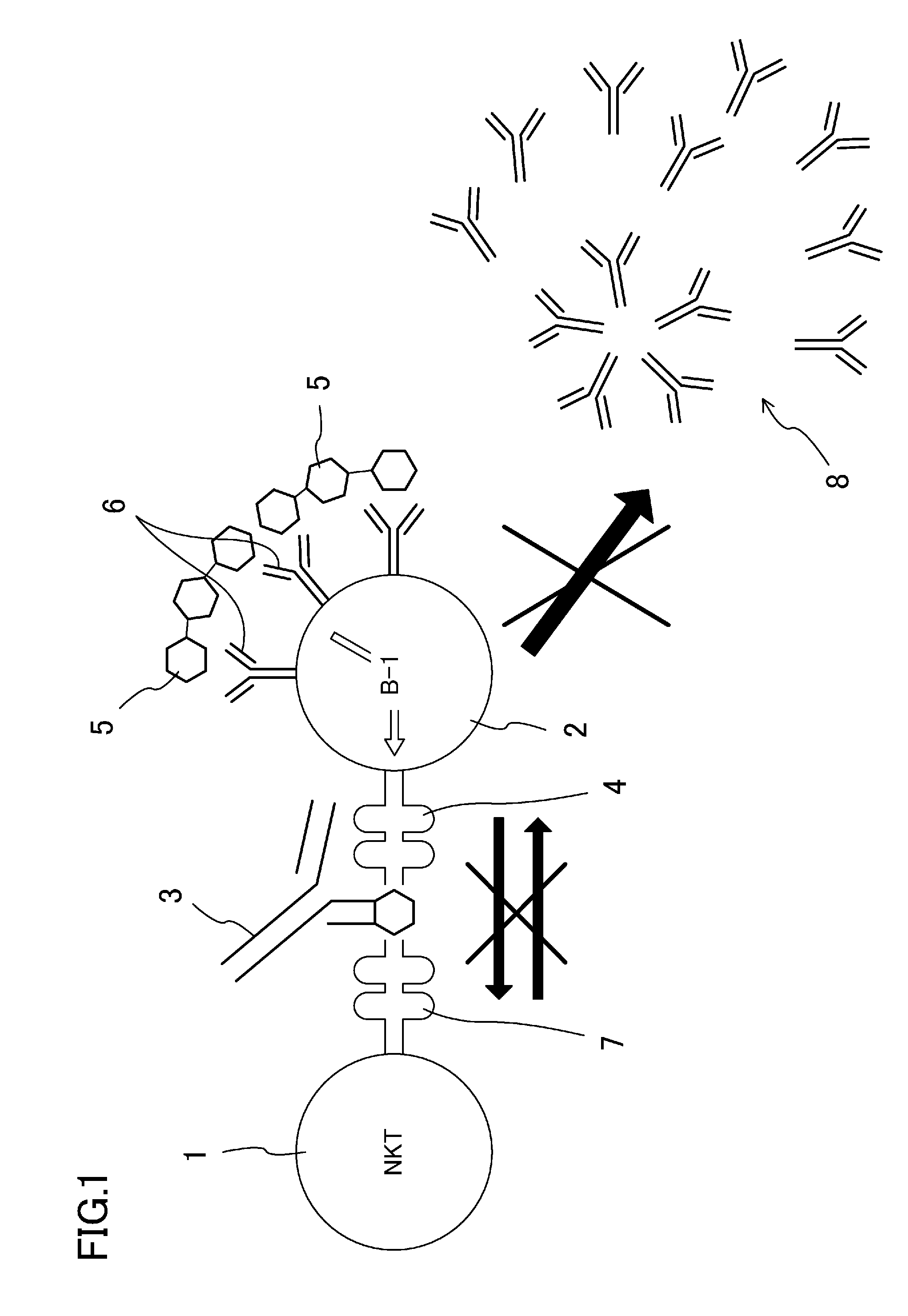
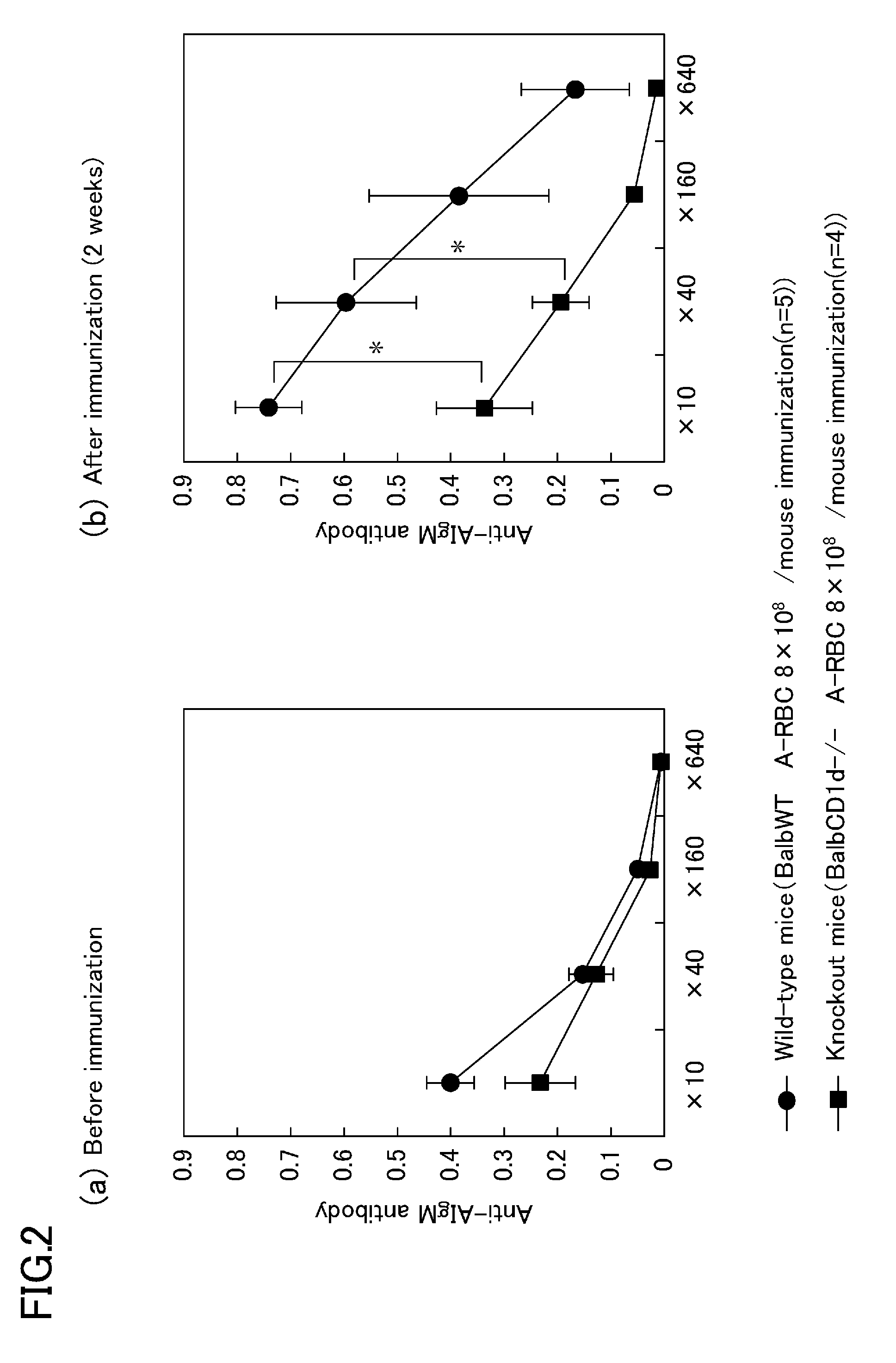
A purpose of the present disclosure to achieve transplantation from ABO-incompatible donors and inhibition of autoimmune disease, for example, without significantly impairing defense mechanisms.An antibody-mediated rejection inhibitor for impairing signal transduction between NKT-cells and B-cells to inhibit production of antibodies indicates anti-CD1d antibodies.
Owner:HIROSHIMA UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com