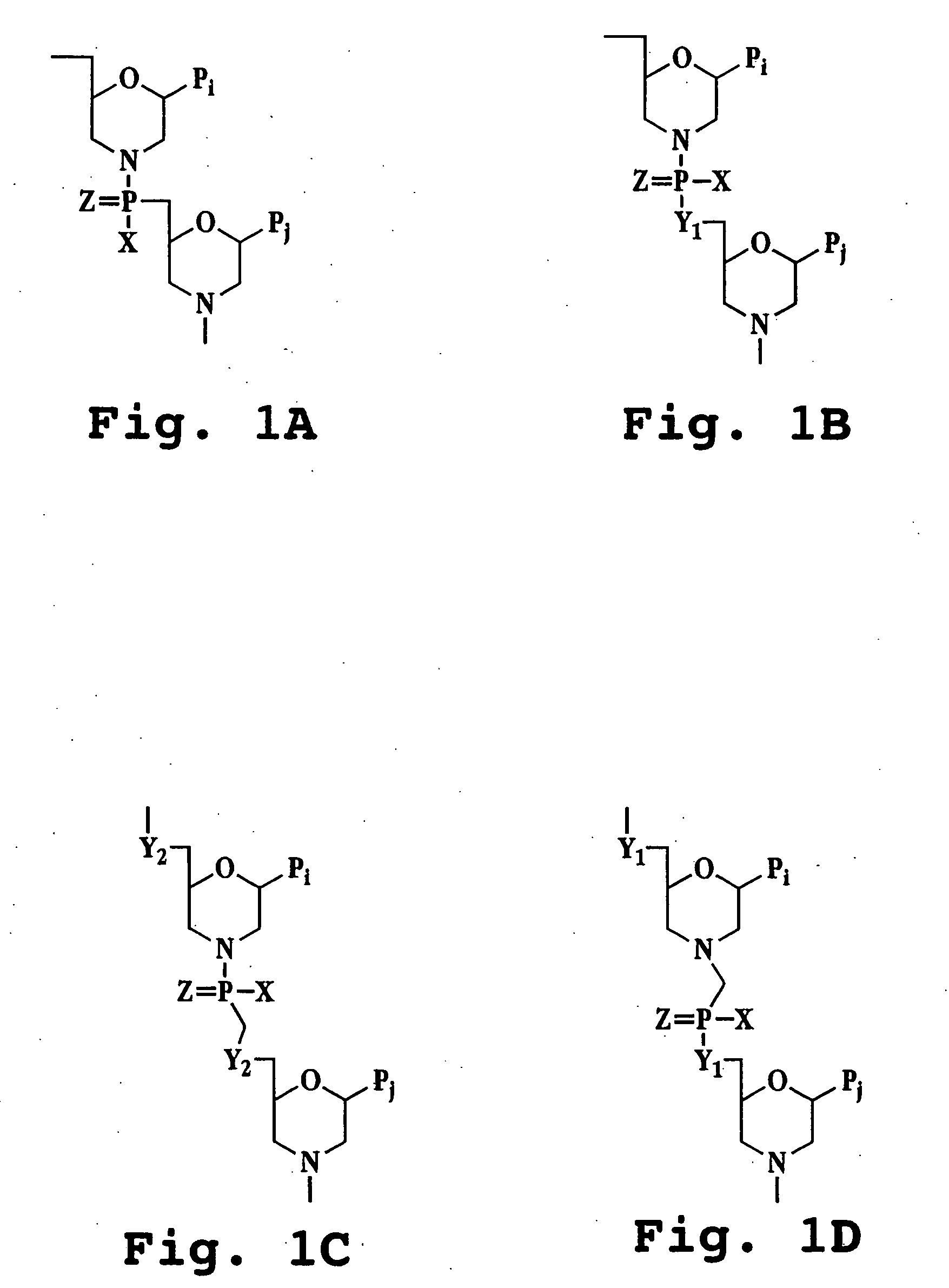
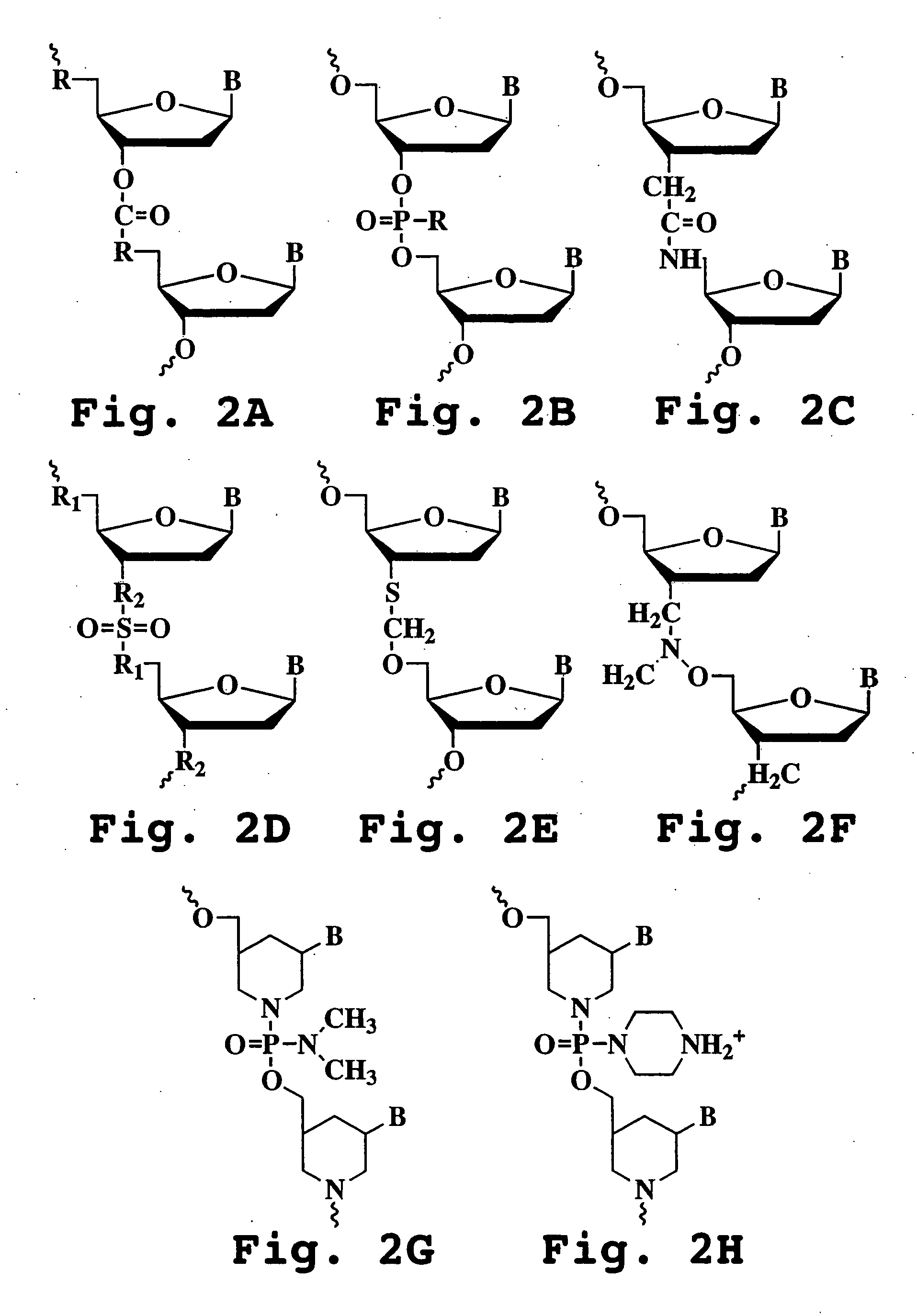
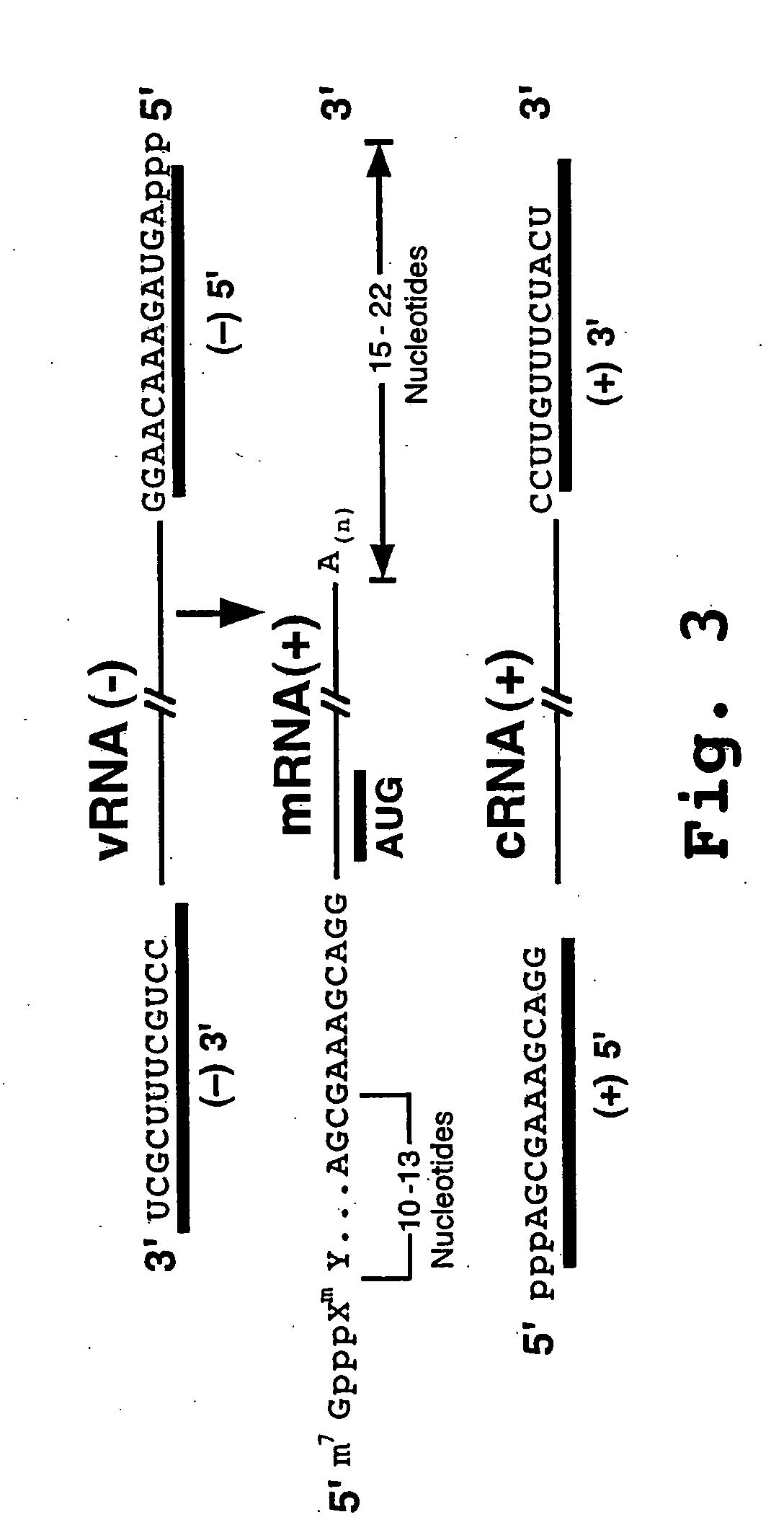
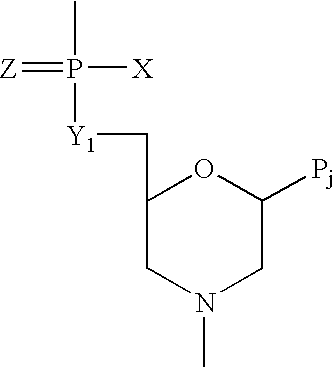
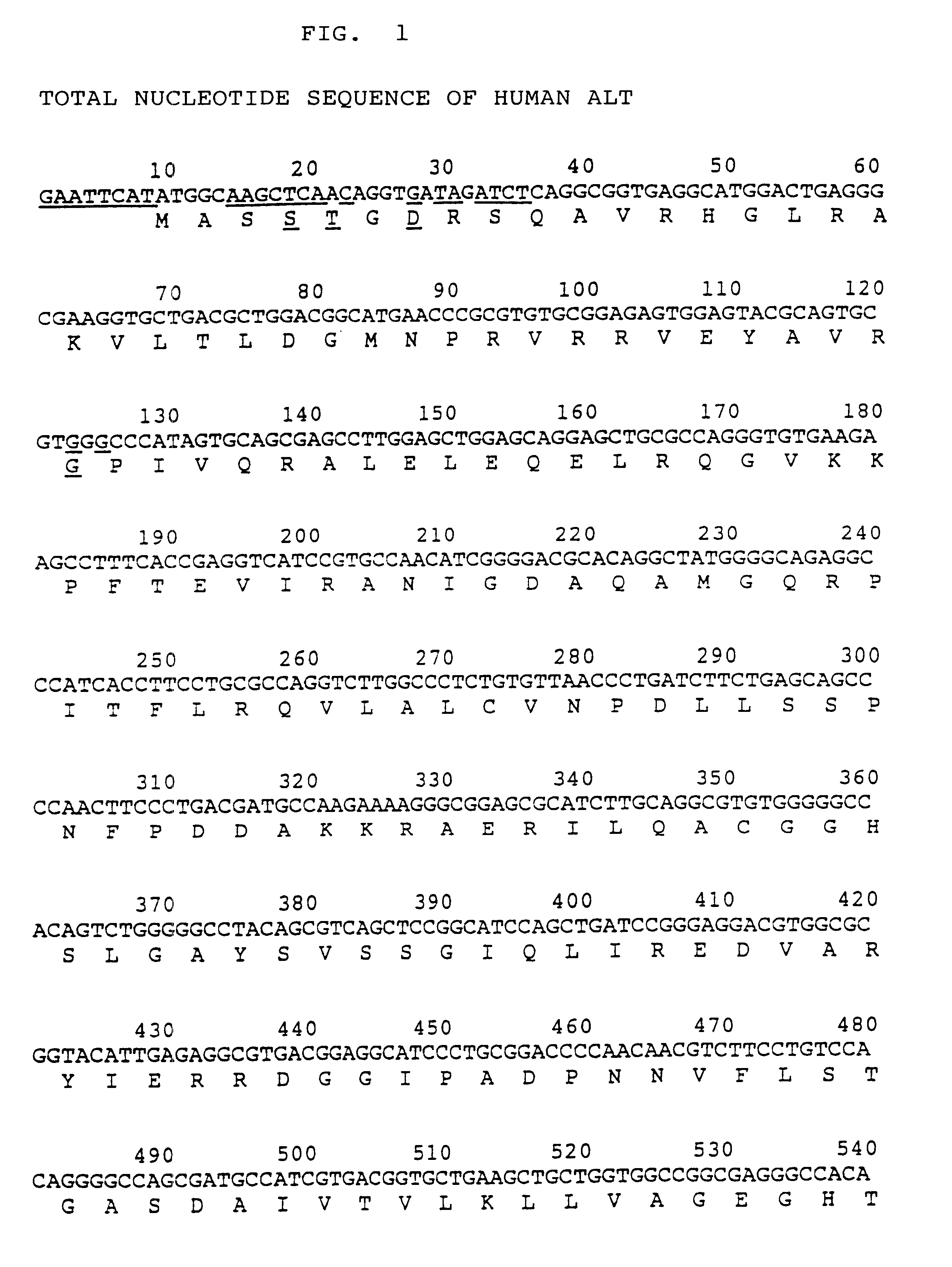Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
290 results about "Start codon" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The start codon is the first codon of a messenger RNA (mRNA) transcript translated by a ribosome. The start codon always codes for methionine in eukaryotes and Archaea and a modified Met (fMet) in bacteria, mitochondria and plastids. The most common start codon is AUG.
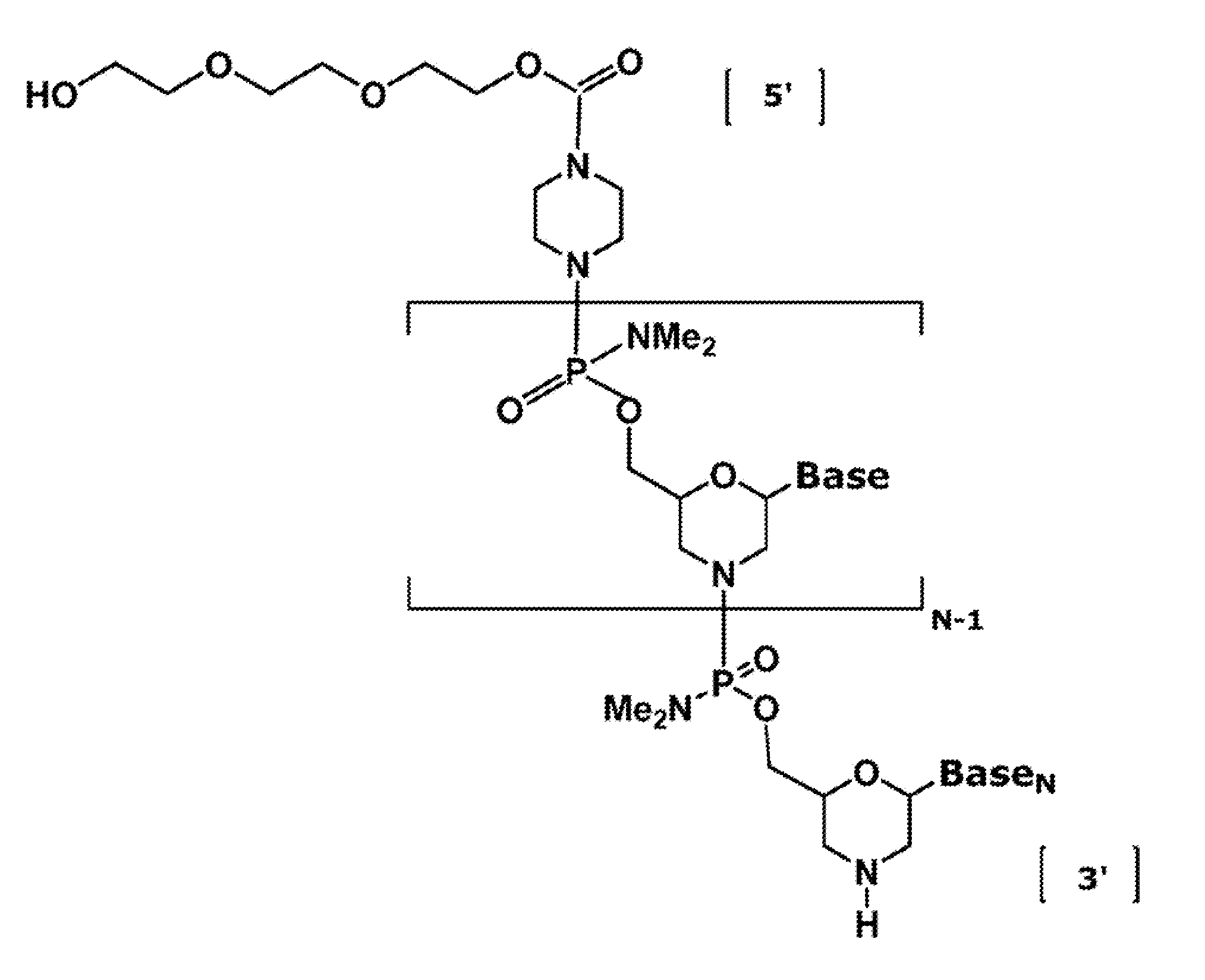
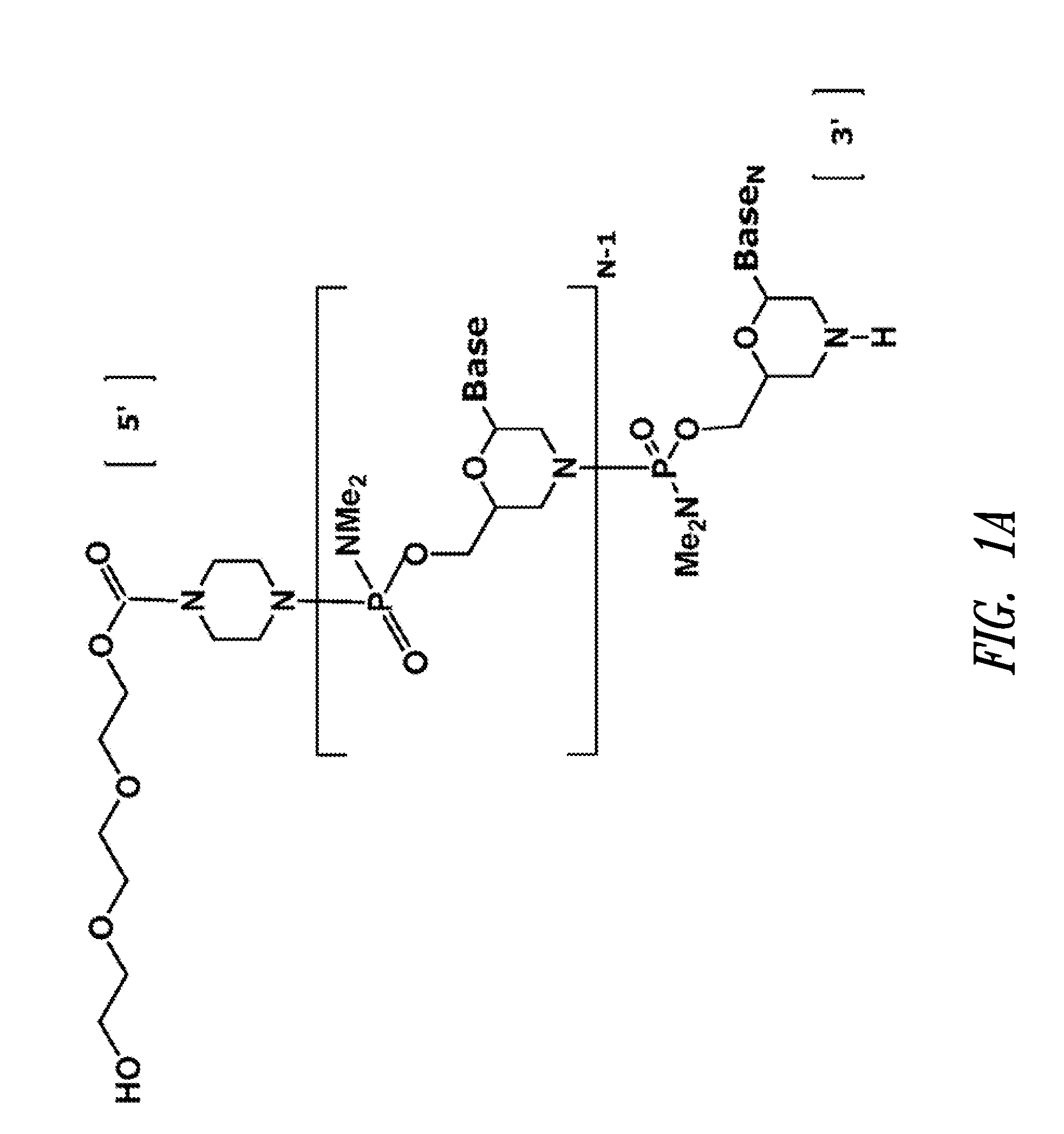
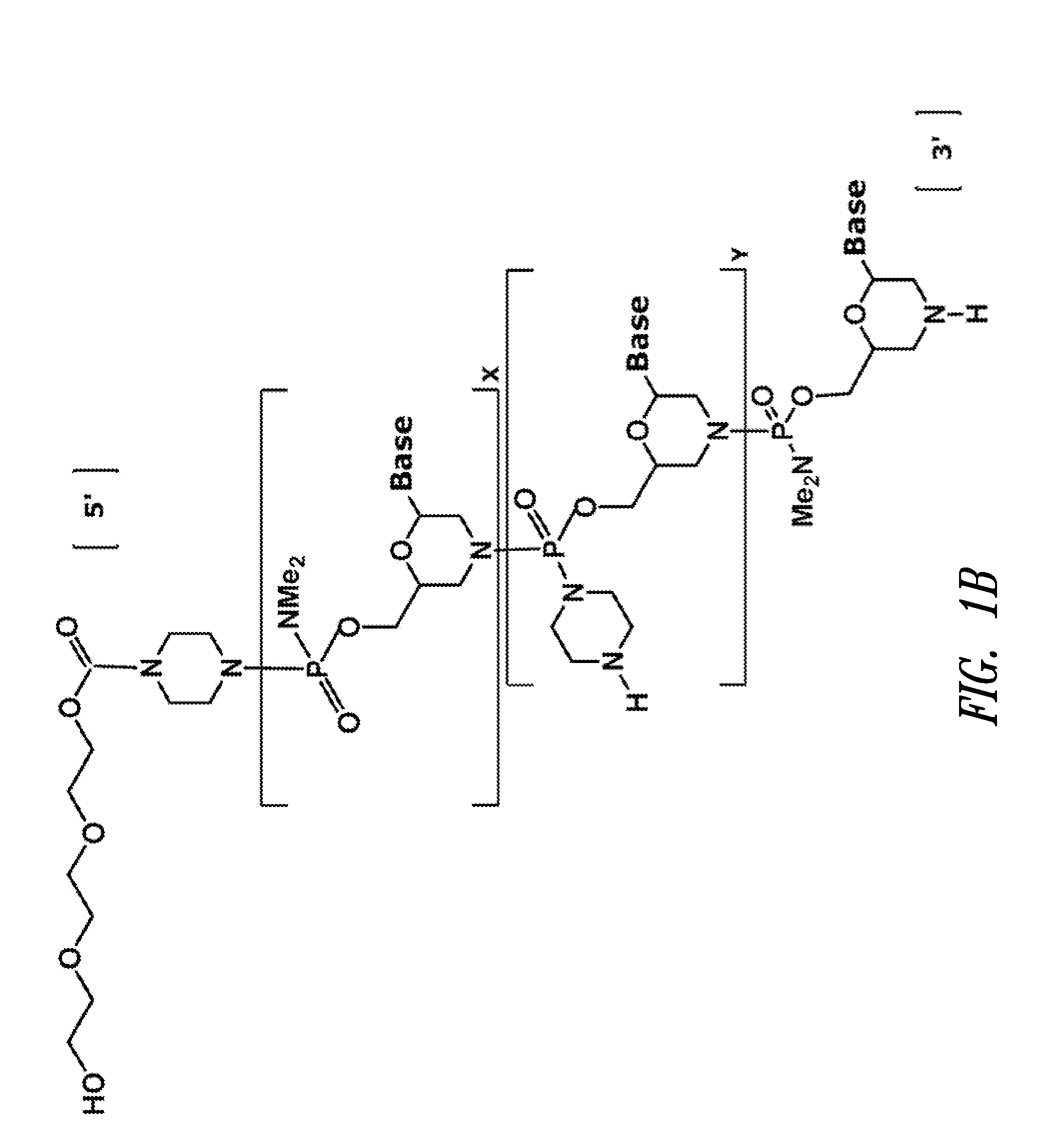
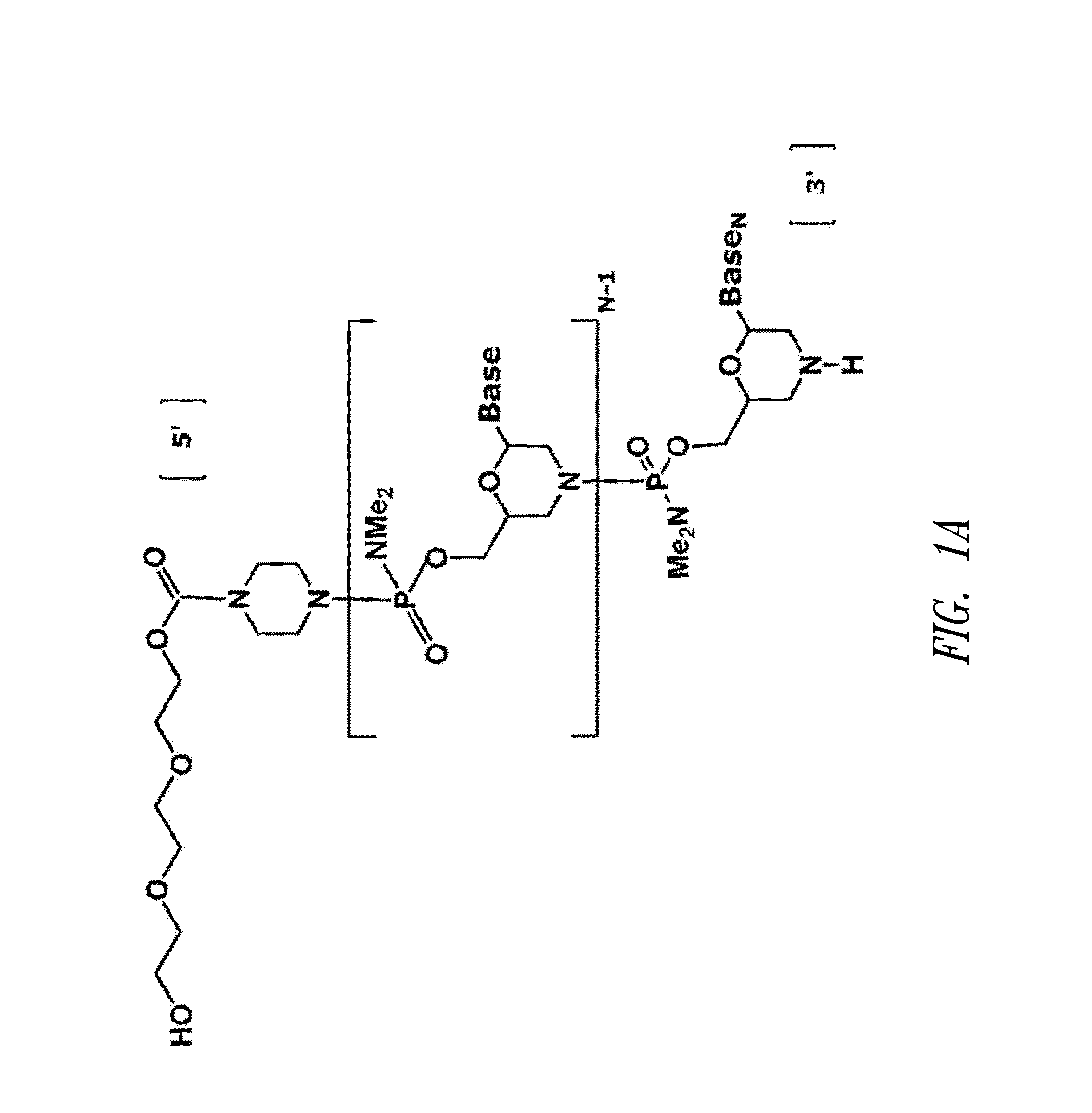
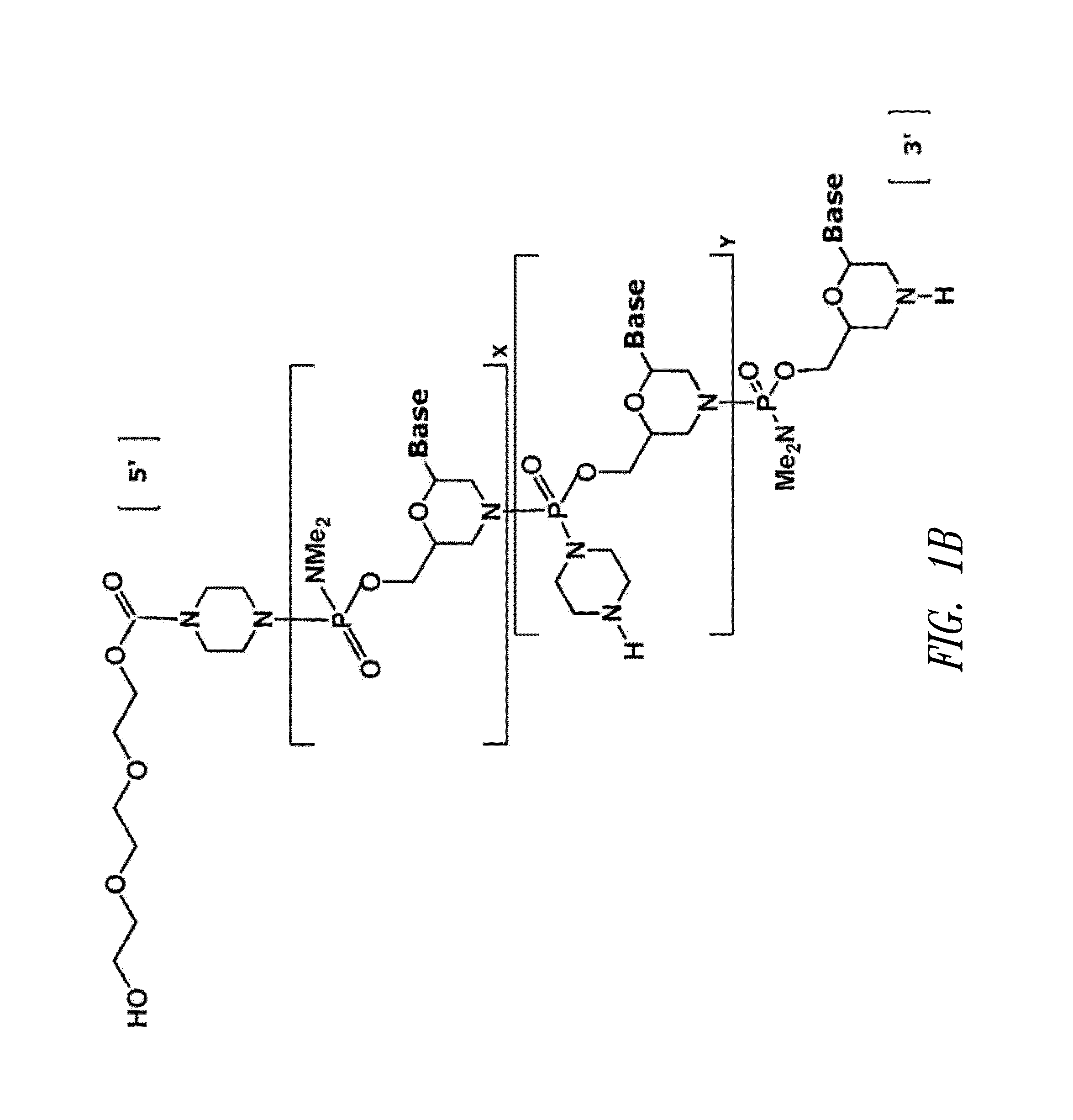
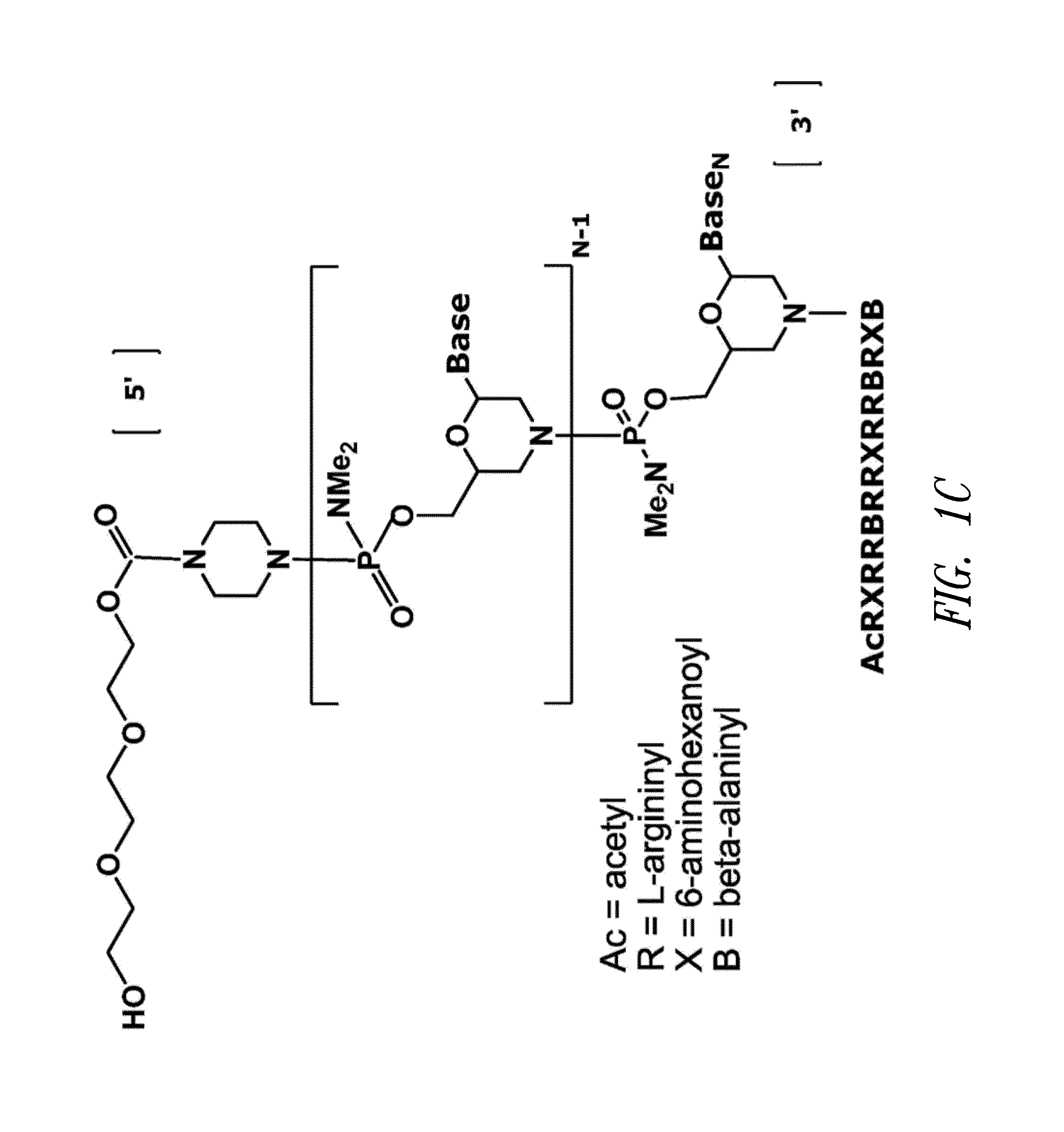
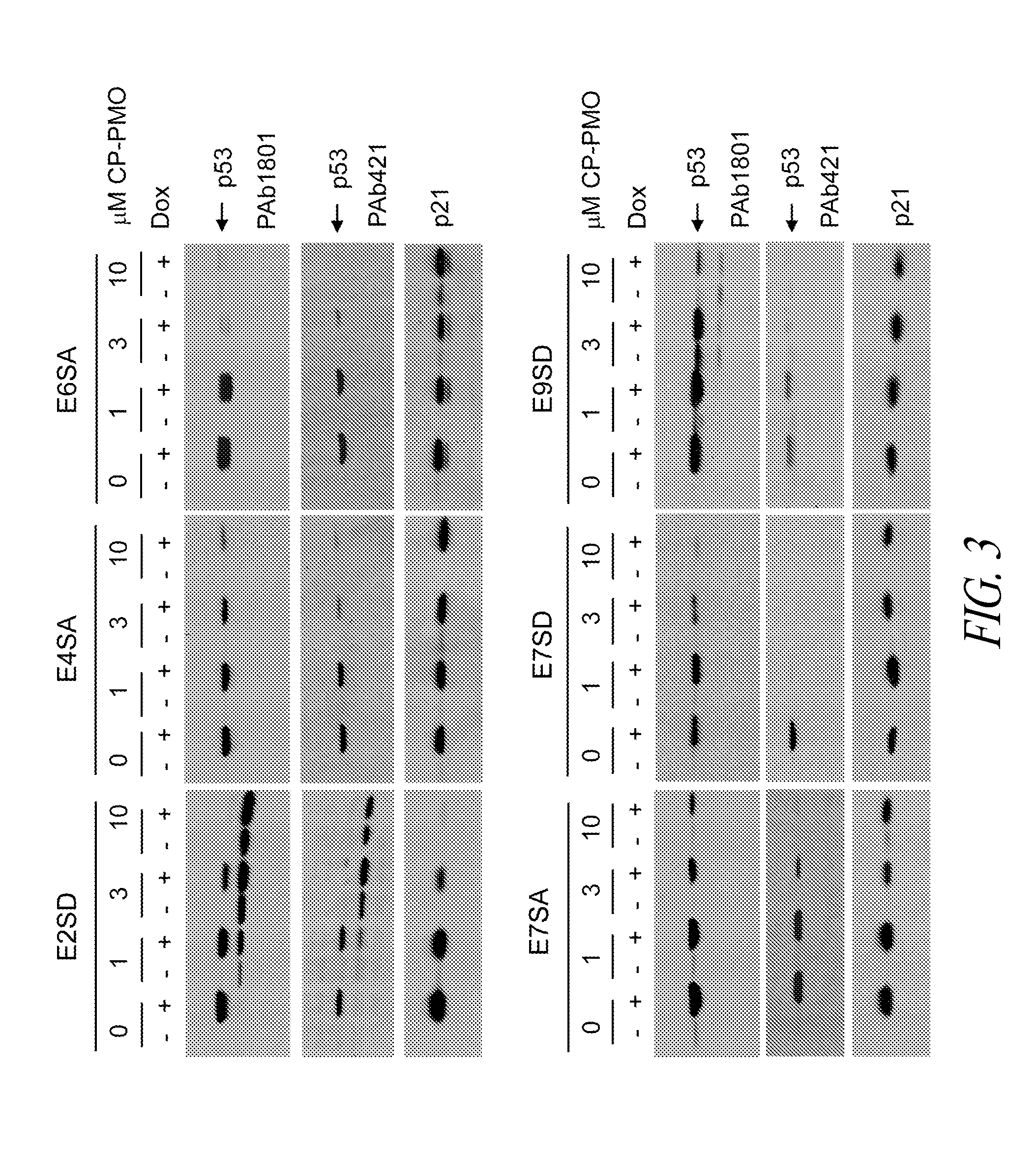
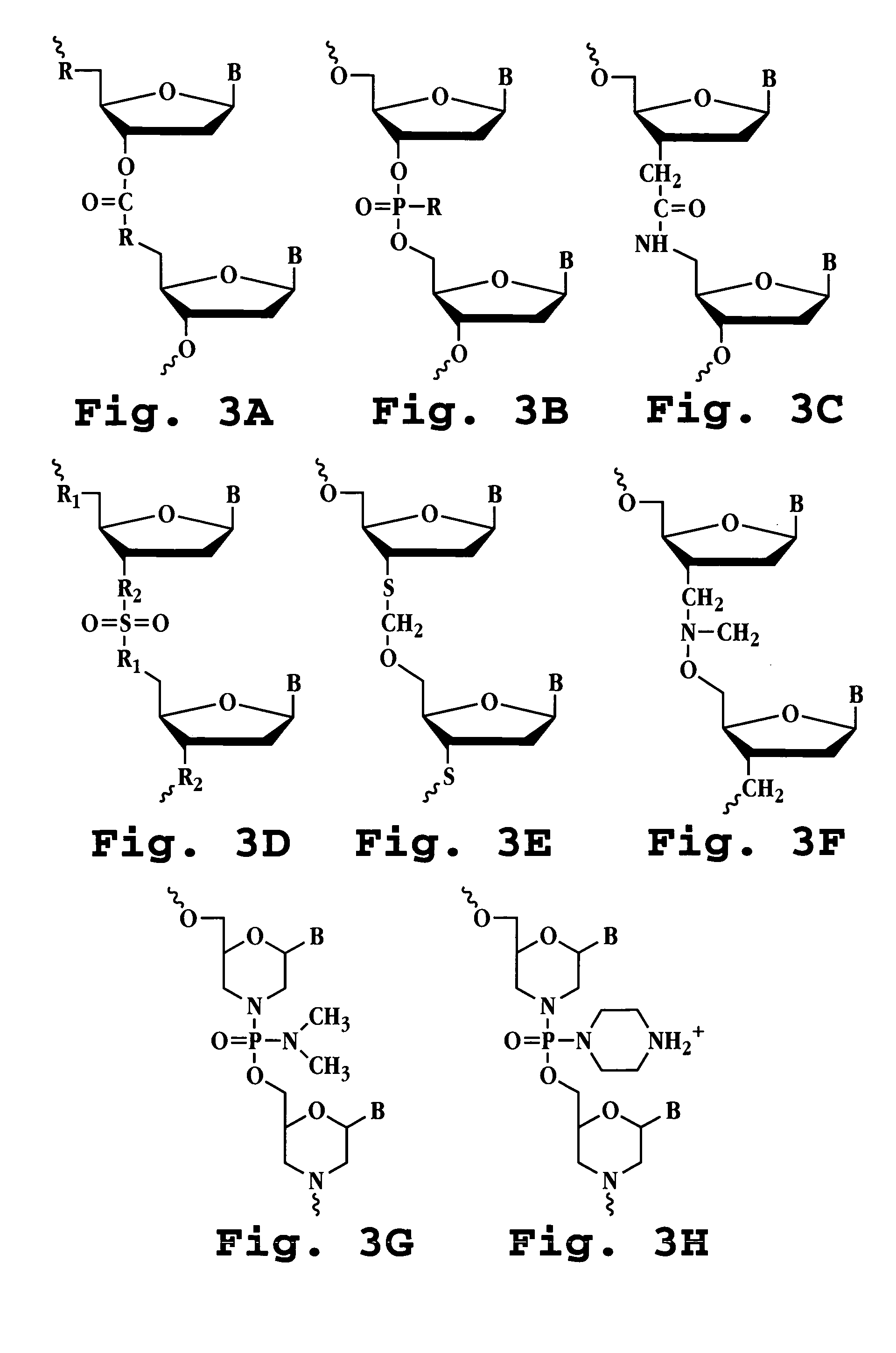
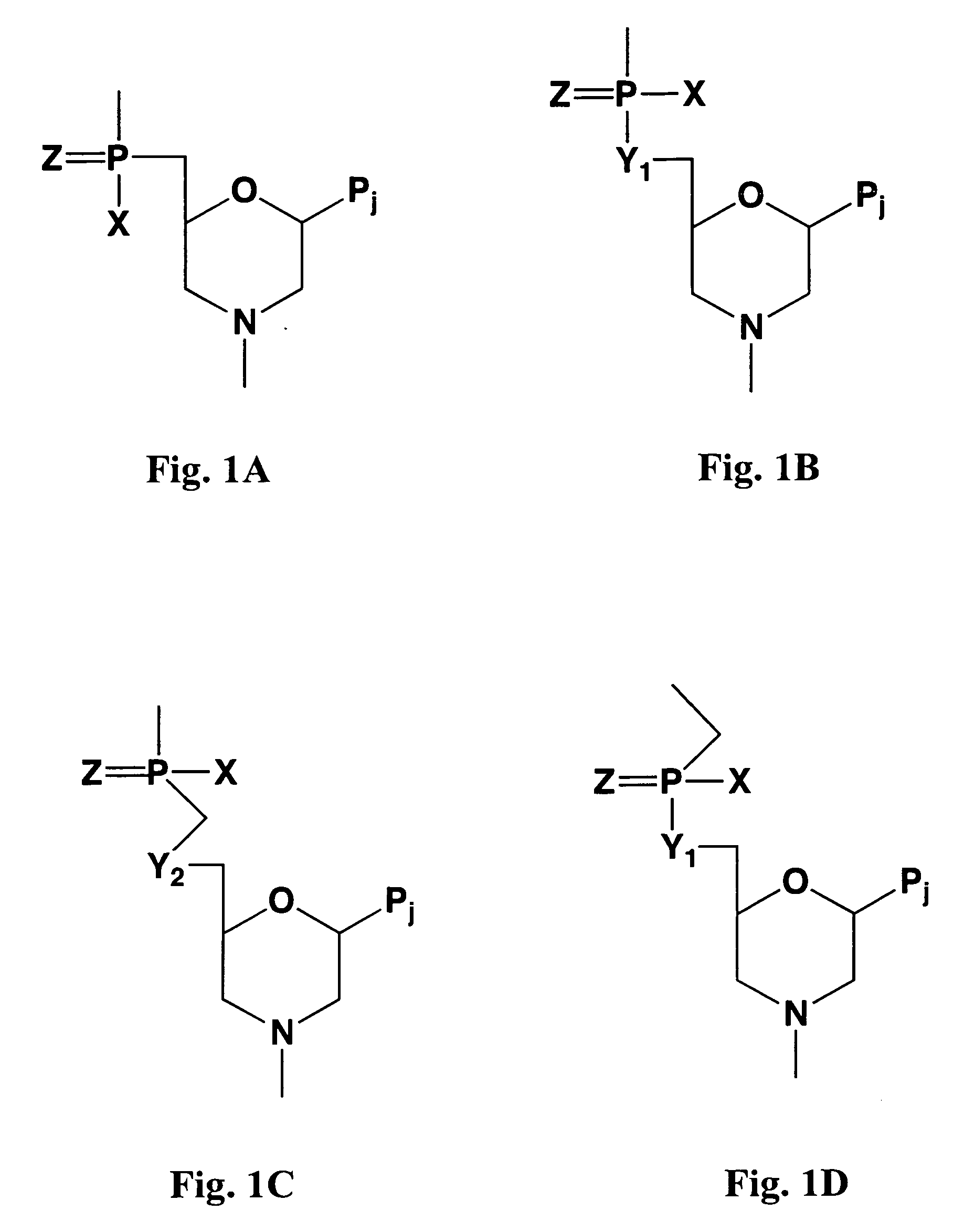
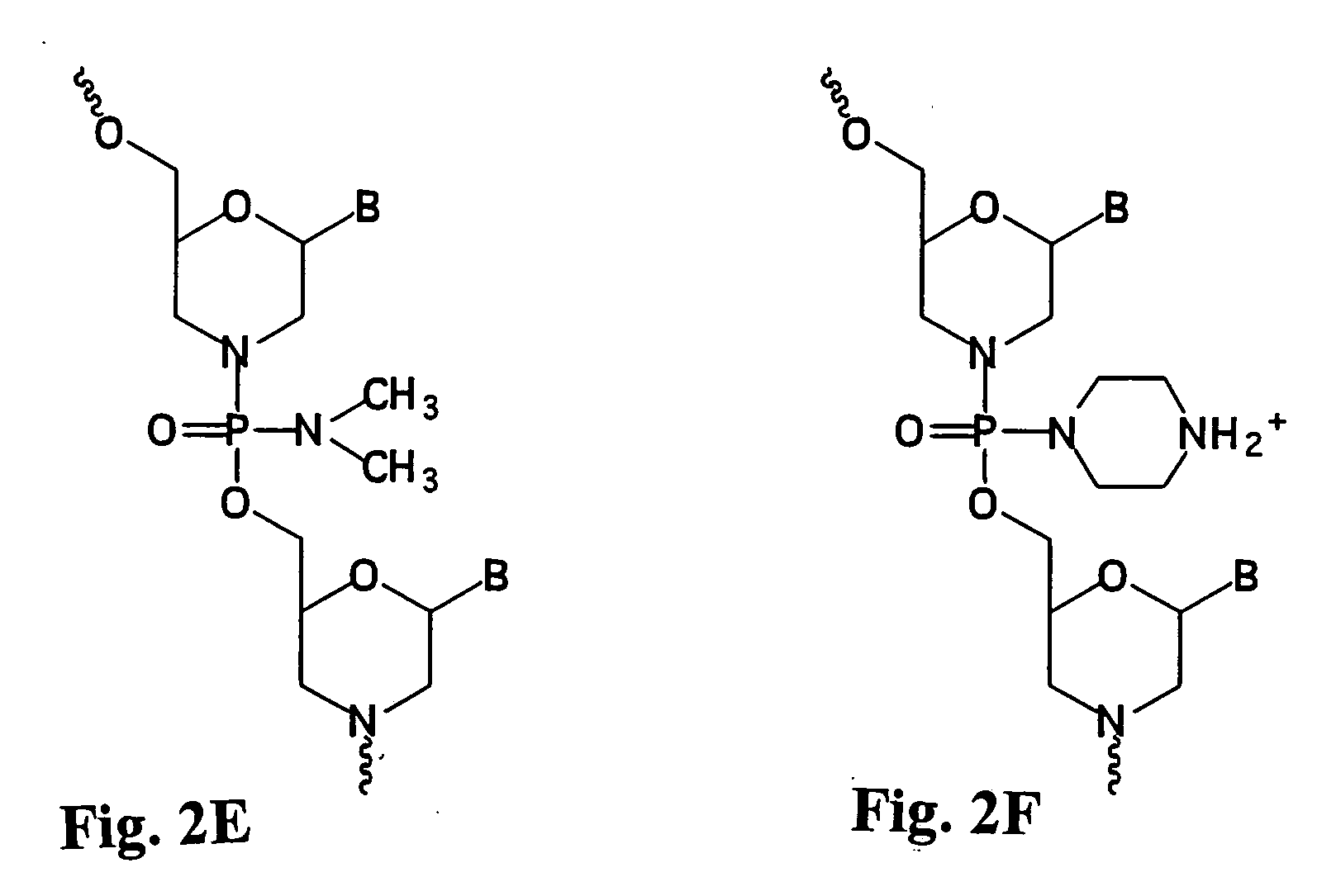
Antisense restenosis composition and method
Owner:SAREPTA THERAPEUTICS INC
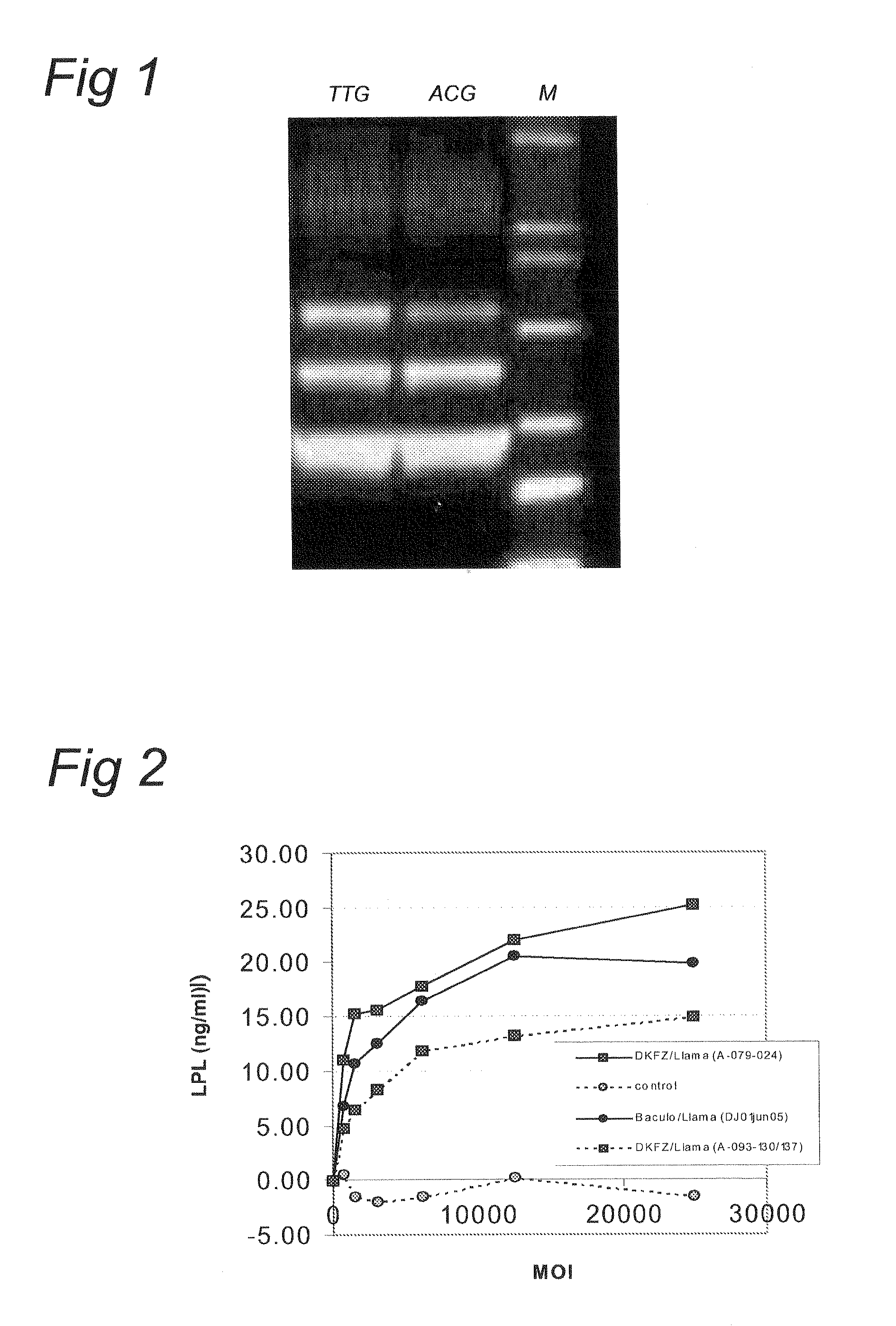
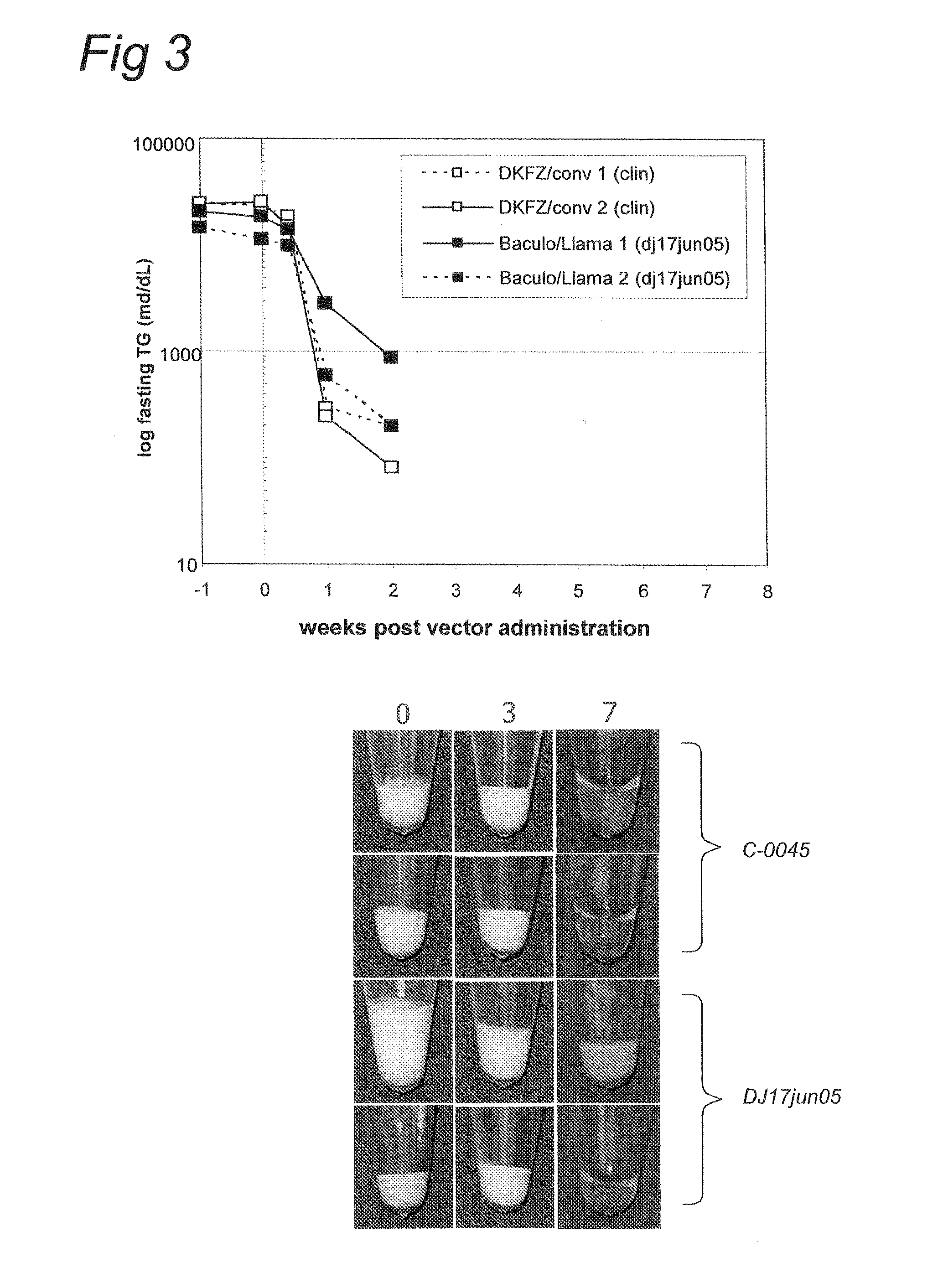
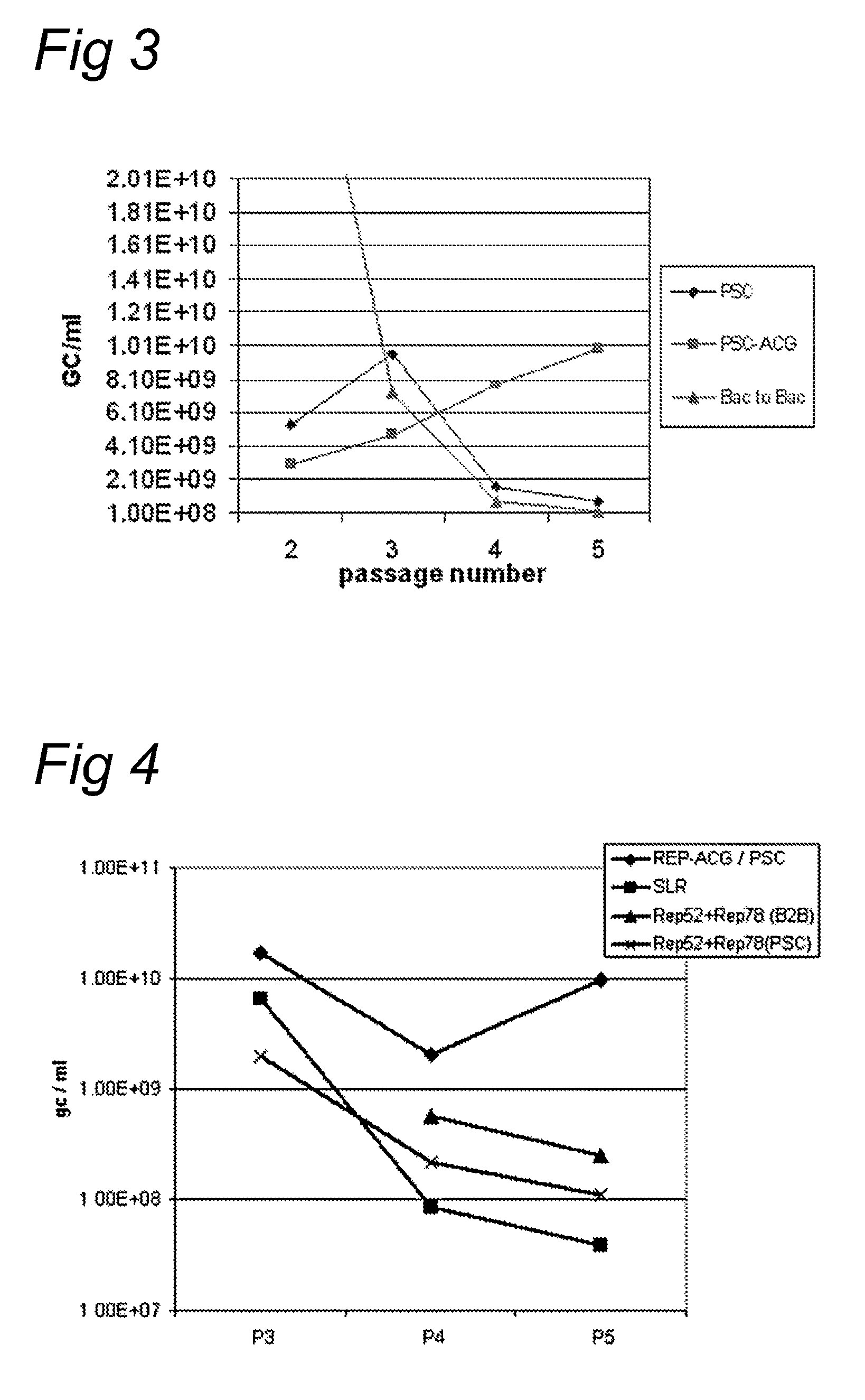
AAV vectors produced in insect cells
ActiveUS8163543B2Improve stabilityReduced expression levelAnimal cellsGenetic material ingredientsNucleotideViral vector
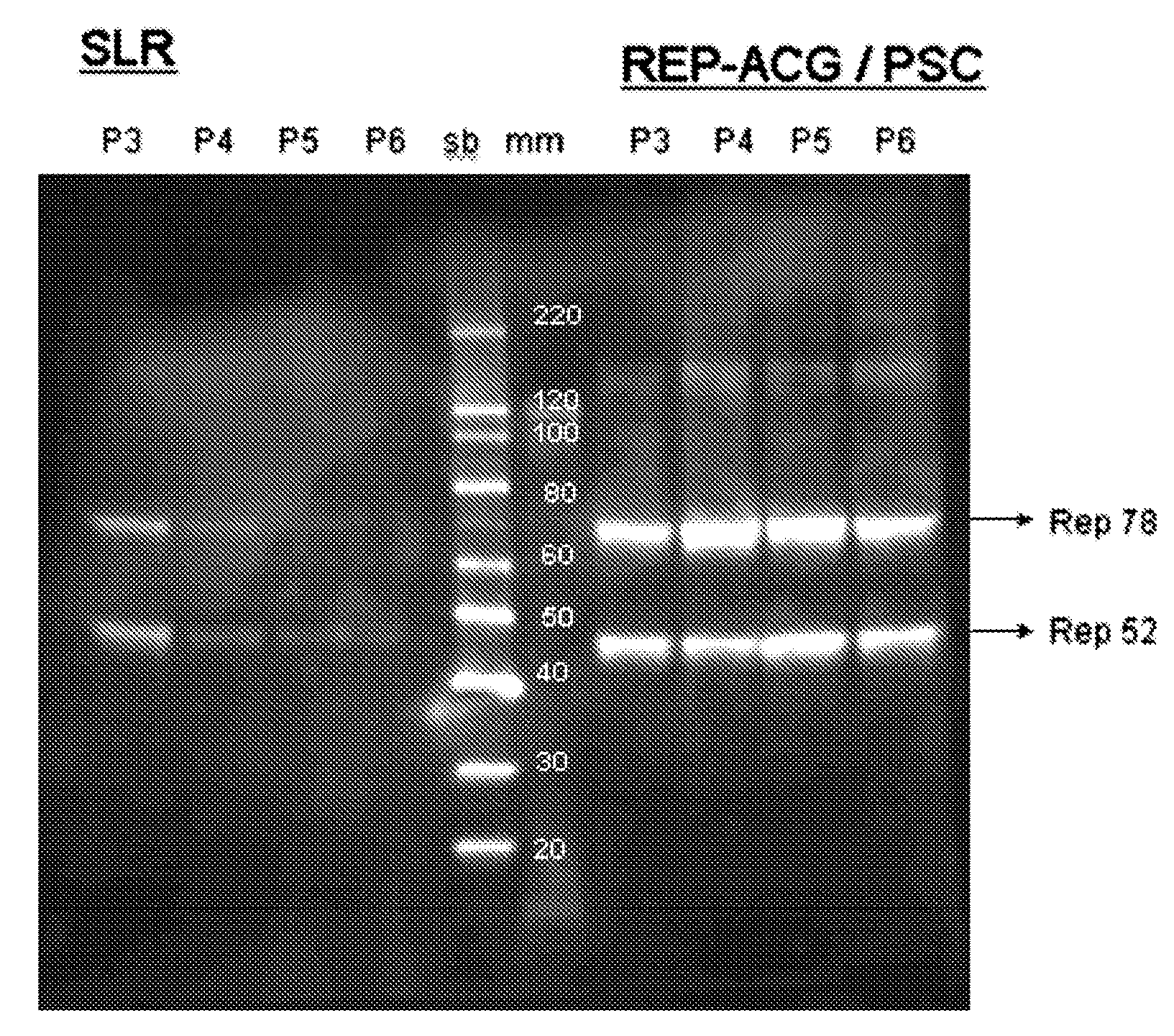
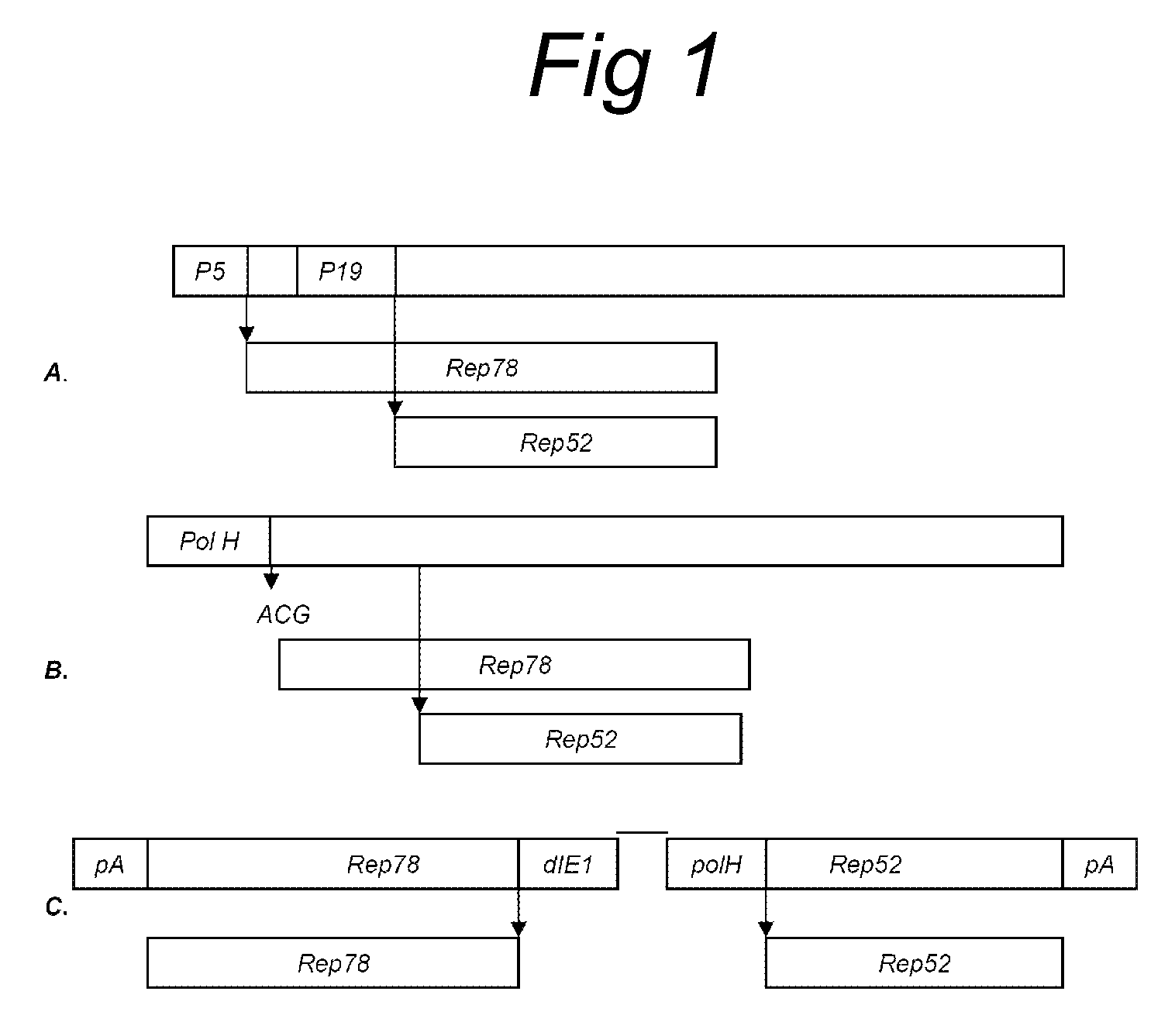
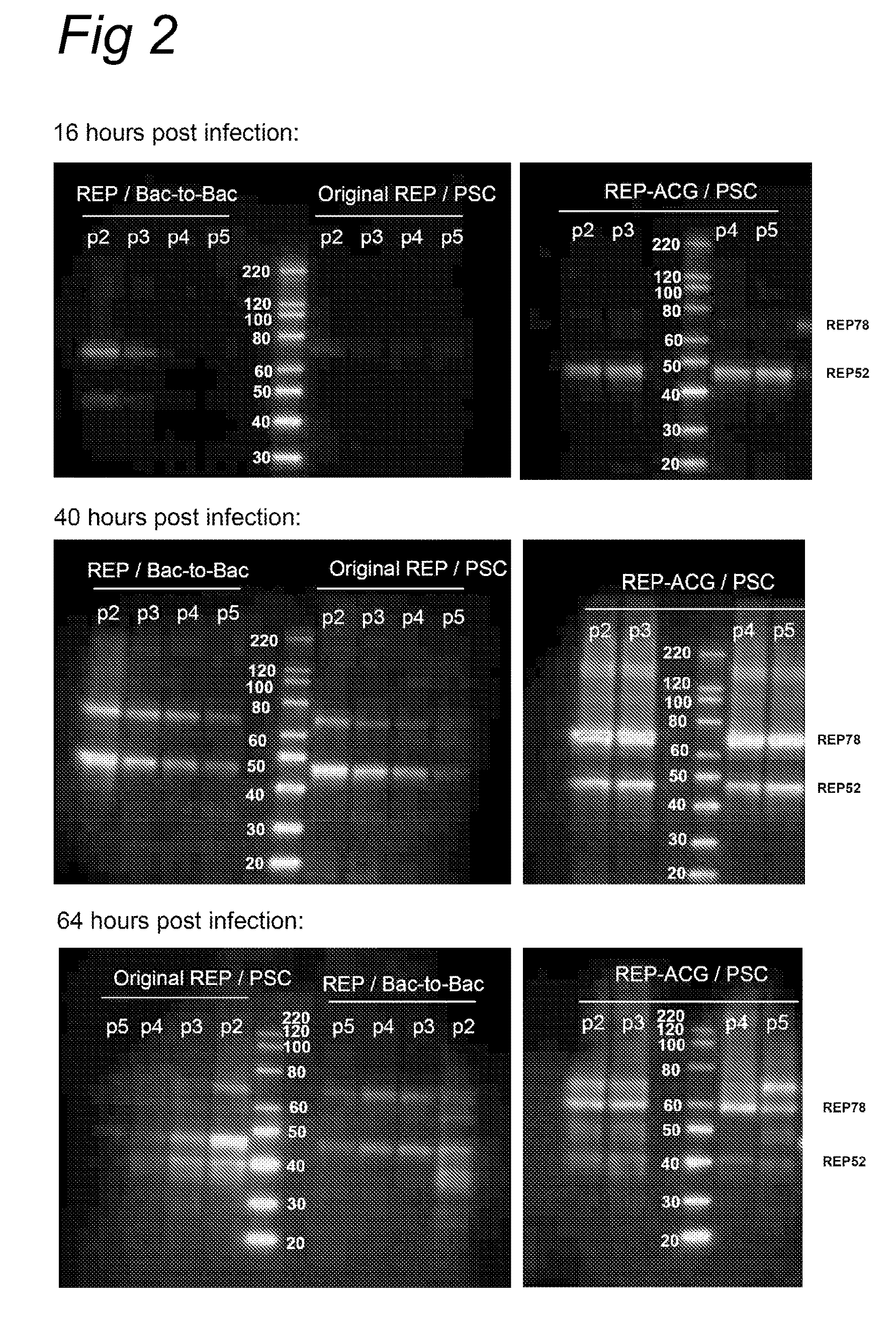
The present invention relates to the production of adeno-associated viral vectors in insect cells. The insect cells therefore comprise a first nucleotide sequence encoding the adeno-associated virus (AAV) capsid proteins, whereby the initiation codon for translation of the AAV VP1 capsid protein is a non-ATG, suboptimal initiation codon. The insect cell further comprises a second nucleotide sequence comprising at least one AAV inverted terminal repeat (ITR) nucleotide sequence; a third nucleotide sequence comprising a Rep52 or a Rep40 coding sequence operably linked to expression control sequences for expression in an insect cell; and, a fourth nucleotide sequence comprising a Rep78 or a Rep68 coding sequence operably linked to expression control sequences for expression in an insect cell. The invention further relates to adeno-associated viral vectors with an altered ratio of the viral capsid proteins that provides improved infectivity of the viral particles.
Owner:UNIQURE IP BV
Antisense antibacterial cell division composition and method
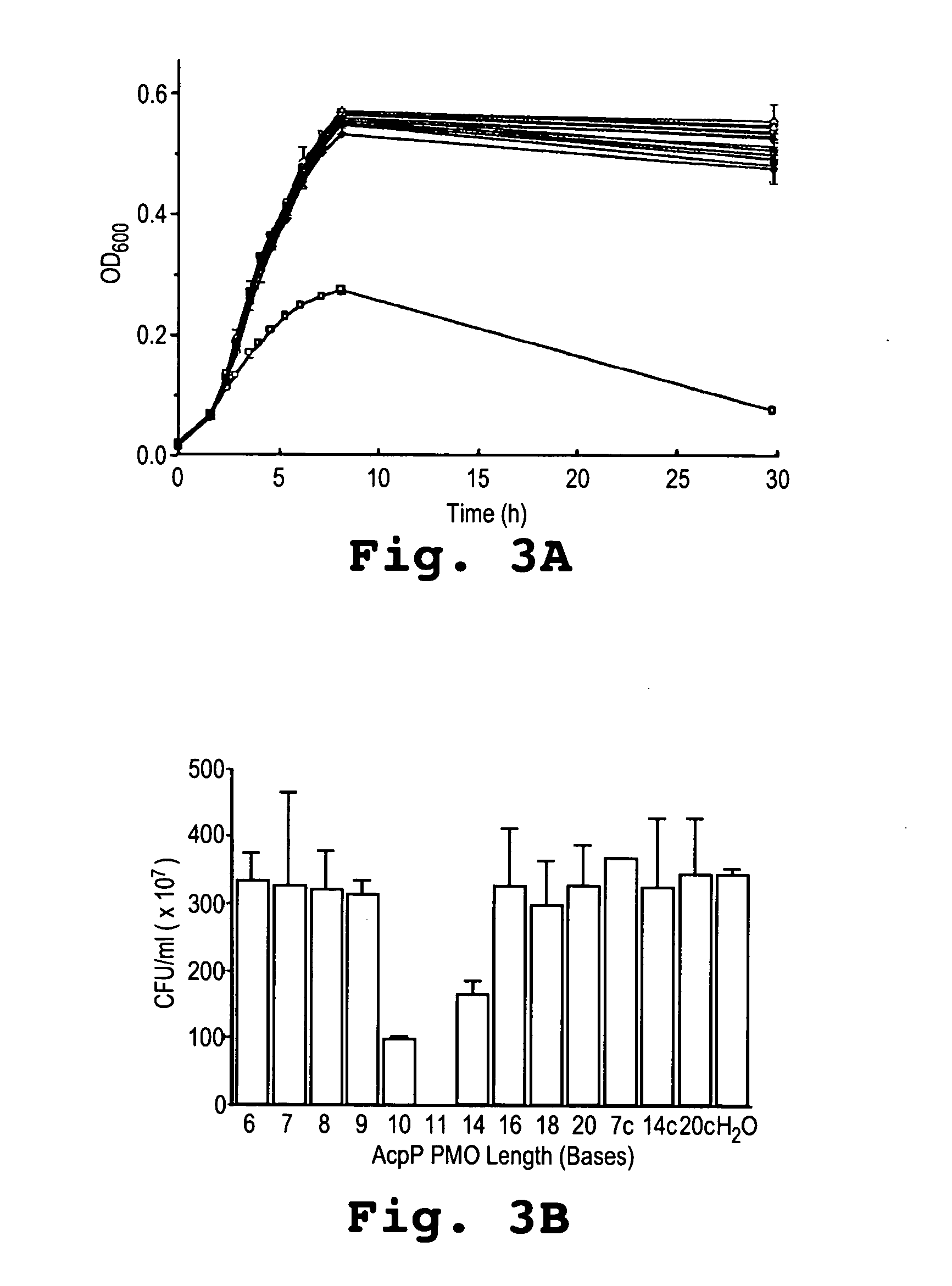
Antisense oligomers directed to bacterial cell division and cell cycle-encoding nucleic acids are capable of selectively modulating the biological activity thereof, and are useful in treatment and prevention of bacterial infection. The antisense oligomers are substantially uncharged, and contain from 8 to 40 nucleotide subunits, including a targeting nucleic acid sequence at least 10 nucleotides in length which is effective to hybridize to (i) a bacterial tRNA or (ii) a target sequence, containing a translational start codon, within a bacterial nucleic acid which encodes a protein associated with cell division or the cell cycle. Such proteins include zipA, sulA, secA, dicA, dicB, dicC, dicF, ftsA, ftsI, ftsN, ftsK, ftsL, ftsQ, ftsW, ftsZ, murC, murD, murE, murF, murG, minC, minD, minE, mraY, mraW, mraZ, seqA, ddlB, carbamate kinase, D-ala D-ala ligase, topoisomerase, alkyl hydroperoxide reductase, thioredoxin reductase, dihydrofolate reductase, and cell wall enzyme.
Owner:SAREPTA THERAPEUTICS INC
Antisense antiviral compound and method for treating influenza viral infection
The invention provides antisense antiviral compounds and methods of their use and production in inhibition of growth of viruses of the Orthomyxoviridae family and in the treatment of a viral infection. The compounds are particularly useful in the treatment of influenza virus infection in a mammal. The antisense antiviral compounds are substantially uncharged, including partially positively charged, morpholino oligonucleotides having 1) a nuclease resistant backbone, 2) 12-40 nucleotide bases, and 3) a targeting sequence of at least 12 bases in length that hybridizes to a target region selected from the following: a) the 5′ or 3′ terminal 25 bases of the negative sense viral RNA segment of Influenzavirus A, Influenzavirus B and Influenzavirus C; b) the terminal 25 bases of the 3′ terminus of the positive sense cRNA and; and c) the 50 bases surrounding the AUG start codon of an influenza viral mRNA.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH +1
Antisense antiviral compound and method for treating influenza viral infection
InactiveUS20060148747A1Inhibition of replicationPromote absorptionOrganic active ingredientsBiocideInfluenzavirus CInfluenzavirus B
The invention provides antisense antiviral compounds and methods of their use and production in inhibition of growth of viruses of the Orthomyxoviridae family and in the treatment of a viral infection. The compounds are particularly useful in the treatment of influenza virus infection in a mammal. The antisense antiviral compounds are substantially uncharged morpholino oligonucleotides having 1) a nuclease resistant backbone, 2) 12-40 nucleotide bases, and 3) a targeting sequence of at least 12 bases in length that hybridizes to a target region selected from the following: a) the 5′ or 3′ terminal 25 bases of the negative sense viral RNA segment of Influenzavirus A, Influenzavirus B and Influenzavirus C; b) the terminal 25 bases of the 3′ terminus of the positive sense cRNA and; and c) the 50 bases surrounding the AUG start codon of an influenza viral mRNA.
Owner:SAREPTA THERAPEUTICS INC +1
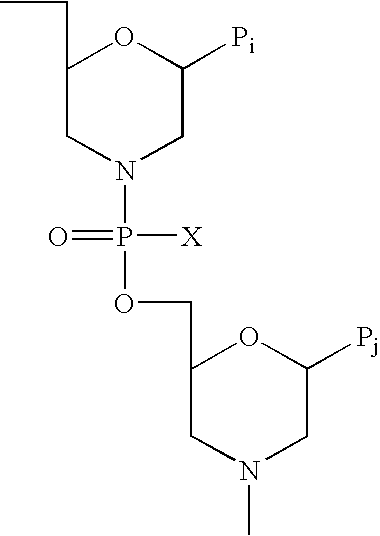
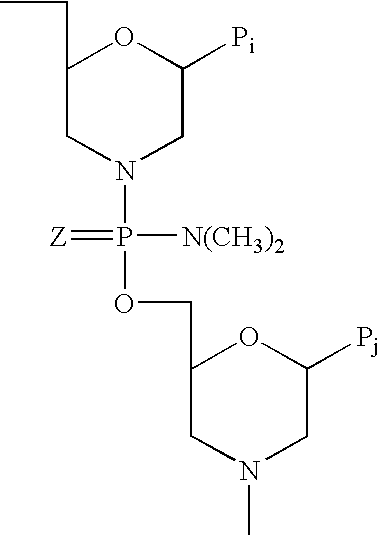
Vectors with modified initiation codon for the translation of AAV-Rep78 useful for production of AAV
ActiveUS8512981B2Improve stabilityReduced expression levelVirus peptidesNucleic acid vectorStart codonNucleotide
The present invention relates nucleic acid constructs for the production of recombinant parvoviral (e.g. adeno-associated viral) vectors in insect cells, to insect cells comprising such constructs and to methods wherein the cells are used to produce recombinant parvoviral virions. The insect cells preferably comprise a first nucleotide sequence encoding the parvoviral rep proteins whereby the initiation codon for translation of the parvoviral Rep78 protein is a suboptimal initiation codon that effects partial exon skipping upon expression in insect cells. The insect cell further comprises a second nucleotide sequence comprising at least one parvoviral (AAV) inverted terminal repeat (ITR) nucleotide sequence and a third nucleotide sequence comprising a sequences coding for the parvoviral capsid proteins.
Owner:AMSTERDAM MOLECULAR THERAPEUTICS +1
Antisense antiviral compound and method for treating influenza viral infection
ActiveUS20110118334A1Improve throughputLimit deliveryAntibacterial agentsSugar derivativesInfluenzavirus CStart codon
The present invention relates to antisense antiviral compounds and methods of their use and production in inhibition of growth of viruses of the Orthomyxoviridae family and in the treatment of a viral infection. The compounds are particularly useful in the treatment of influenza virus infection in a mammal. Exemplary antisense antiviral compounds are substantially uncharged, or partially positively charged, morpholino oligonucleotides having 1) a nuclease resistant backbone, 2) 12-40 nucleotide bases, and 3) a targeting sequence of at least 12 bases in length that hybridizes to a target region selected from the following: a) the 5′ or 3′ terminal 25 bases of the negative sense viral RNA segment of Influenzavirus A, Influenzavirus B and Influenzavirus C; b) the terminal 30 bases of the 5′ or 3′ terminus of the positive sense vcRNA; c) the 45 bases surrounding the AUG start codon of an influenza viral mRNA and; d) 50 bases surrounding the splice donor or acceptor sites of influenza mRNAs subject to alternative splicing.
Owner:SAREPTA THERAPEUTICS INC
Antisense antibacterial method and compound
ActiveUS20070135333A1Inhibition of replicationSimple designAntibacterial agentsBiocideArginineNucleotide
An antibacterial antisense conjugate and method of using the same for treating a bacterial infection in a mammalian host are disclosed. The conjugate includes an antisense oligonucleotide conjugated to a carrier peptide that significantly enhances the antibacterial activity of the oligonucleotide. The antisense oligonucleotide contains 10-20 nucleotide bases and has a targeting nucleic acid sequence complementary to a target sequence containing or within 10 bases, in a downstream direction, of the translational start codon of a bacterial mRNA that encodes a bacterial protein essential for bacterial replication, where the compound binds to a target mRNA with a Tm of between 50° to 60° C. The carrier peptide is an arginine-rich peptide containing between 6 and 12 amino acids.
Owner:SAREPTA THERAPEUTICS INC
Selection of host cells expressing protein at high levels
InactiveUS20060141577A1Decreases translation initiation efficiencyVectorsCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsStart codonA-DNA
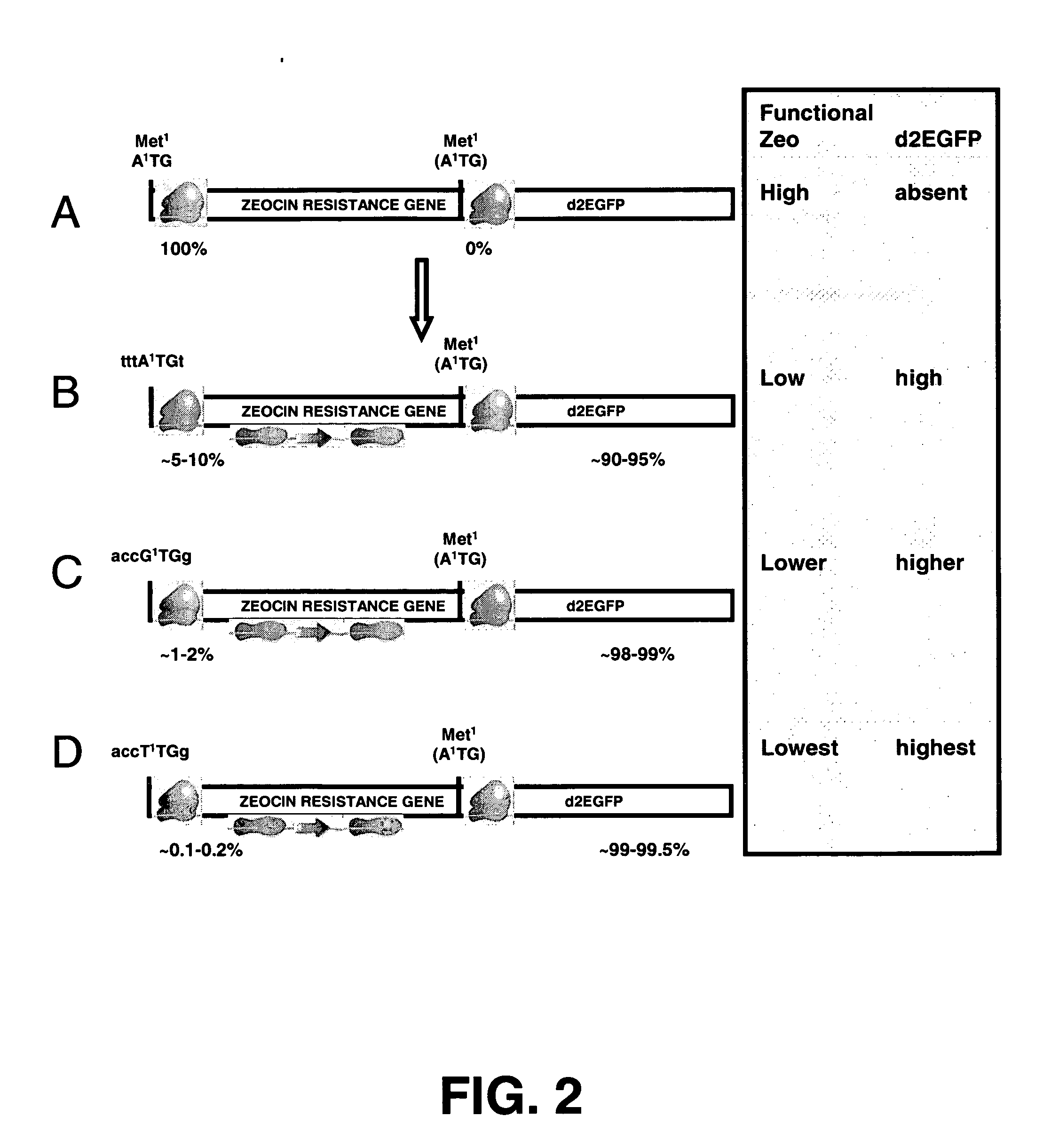
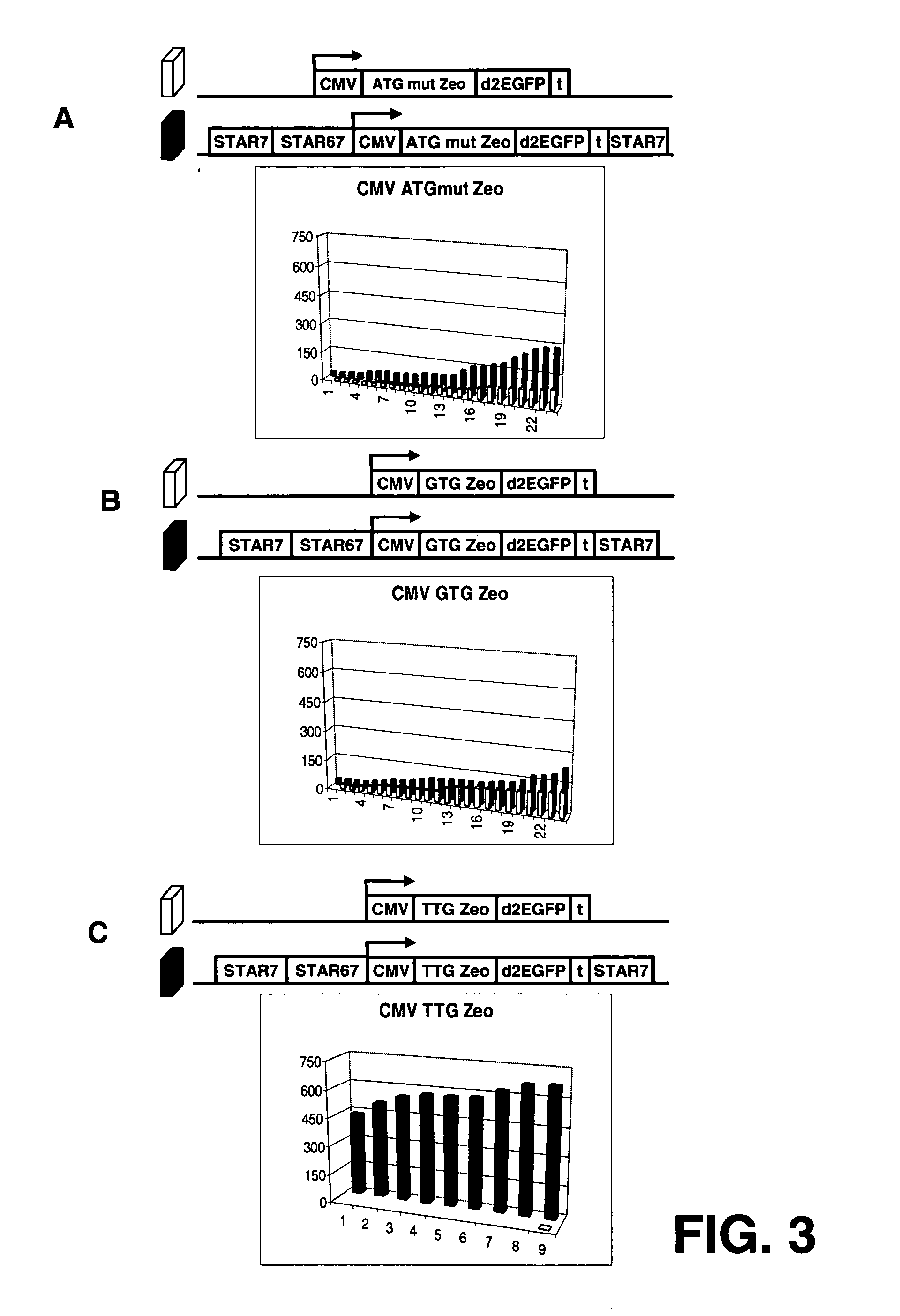
The invention provides a DNA molecule comprising a multicistronic transcription unit coding for i) a polypeptide of interest, and for ii) a selectable marker polypeptide functional in a eukaryotic host cell, wherein the polypeptide of interest has a translation initiation sequence separate from that of the selectable marker polypeptide, and wherein the coding sequence for the polypeptide of interest is upstream from the coding sequence for the selectable marker polypeptide in said multicistronic transcription unit, and wherein an internal ribosome entry site (IRES) is present downstream from the coding sequence for the polypeptide of interest and upstream from the coding sequence for the selectable marker polypeptide, and wherein the nucleic acid sequence coding for the selectable marker polypeptide in the coding strand comprises a GTG or a TTG startcodon. The invention also provides methods for obtaining host cells expressing a polypeptide of interest, said host cells comprising the DNA molecules of the invention. The invention further provides the production of polypeptides of interest, comprising culturing host cells comprising the DNA molecules according to the invention.
Owner:CHROMAGENICS BV
Human sodium channel isoforms
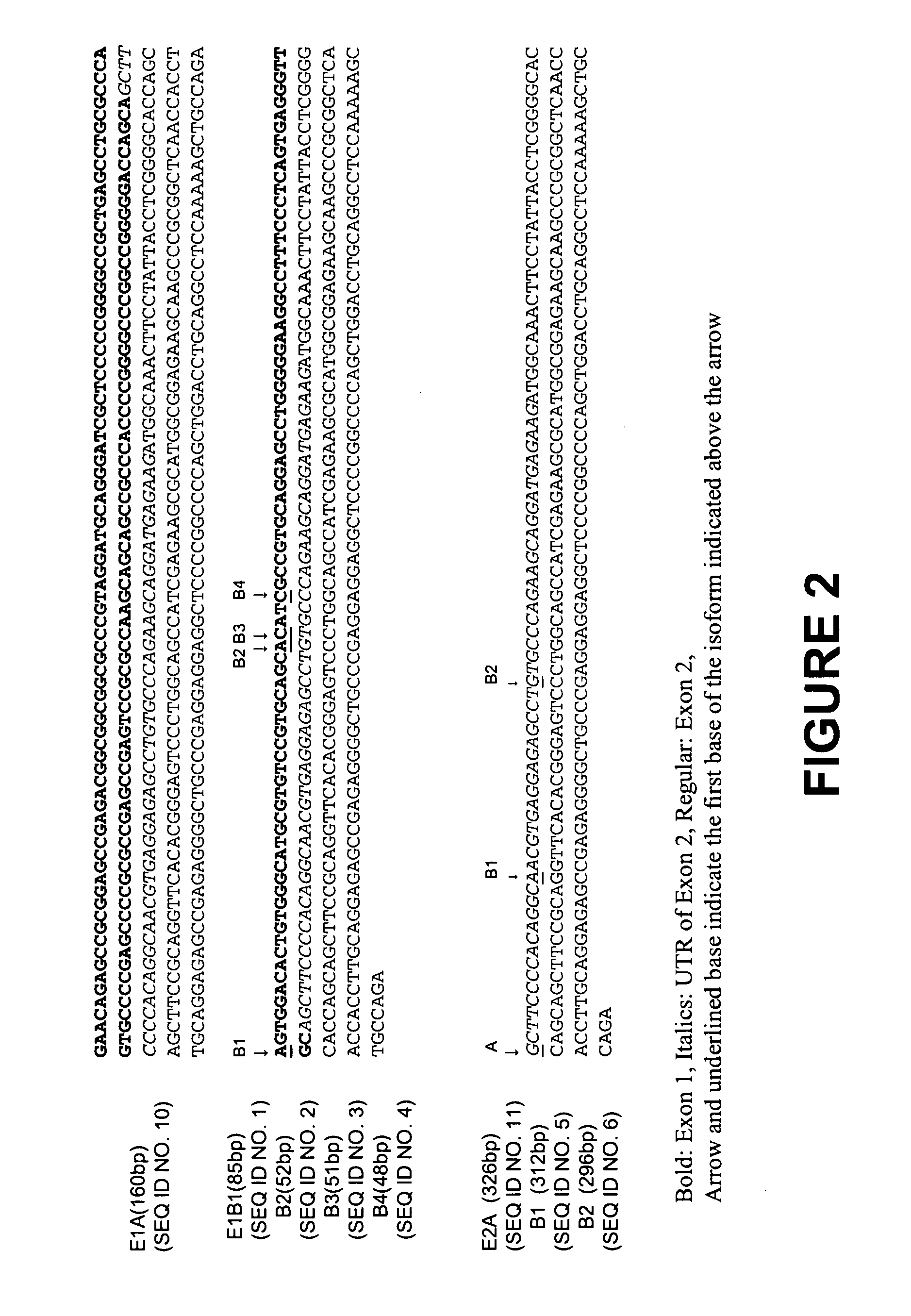
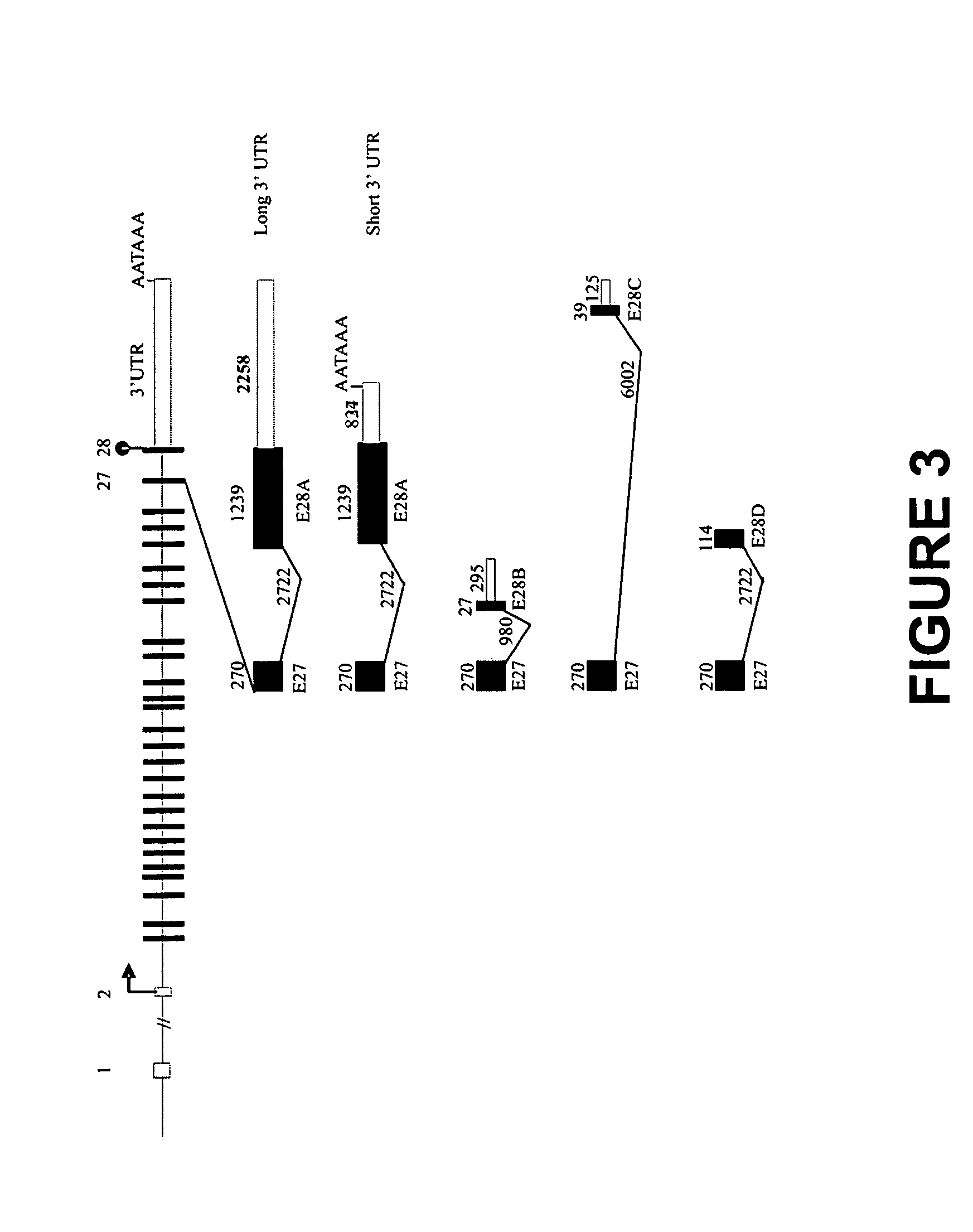
The present invention relates to novel isoforms in or near the 5′ untranslated region (upstream of the start codon) and the 3′ untranslated region (down stream of the start codon) which correlates with an increased risk of heart disease. These isoforms are various spliced variants of the wild-type sodium channel mRNA. Preferably, the isoforms that correlate with heart disease are E1B1 (SEQ ID NO. 1), E1B2 (SEQ ID NO. 2), E1B3 (SEQ ID NO. 3), E1B4 (SEQ ID NO. 4), E2B1 (SEQ ID NO. 5), E2B2 (SEQ ID NO. 6), E28B (SEQ ID NO. 7), E28C (SEQ ID NO. 8), and E28D (SEQ ID NO. 9).
Owner:U S GOVERNMENT REPRESENTED BY THE DEPT OF VETERANS AFFAIRS +2
Reengineering mRNA primary structure for enhanced protein production
ActiveUS8853179B2Improve efficiencyImprove protein stabilitySugar derivativesActivity regulationStart codonTranslational efficiency
Described herein are rules to modify natural mRNAs or to engineer synthetic mRNAs to increase their translation efficiencies. These rules describe modifications to mRNA coding and 3′ UTR sequences intended to enhance protein synthesis by: 1) decreasing ribosomal diversion via AUG or non-canonical initiation codons in coding sequences, and / or 2) by evading miRNA-mediated down-regulation by eliminating one or more miRNA binding sites in coding sequences.
Owner:THE SCRIPPS RES INST
Antisense antiviral compound and method for treating influenza viral infection
ActiveUS8697858B2Improve throughputLimit deliveryAntibacterial agentsSugar derivativesInfluenzavirus CBase J
The present invention relates to antisense antiviral compounds and methods of their use and production in inhibition of growth of viruses of the Orthomyxoviridae family and in the treatment of a viral infection. The compounds are particularly useful in the treatment of influenza virus infection in a mammal. Exemplary antisense antiviral compounds are substantially uncharged, or partially positively charged, morpholino oligonucleotides having 1) a nuclease resistant backbone, 2) 12-40 nucleotide bases, and 3) a targeting sequence of at least 12 bases in length that hybridizes to a target region selected from the following: a) the 5′ or 3′ terminal 25 bases of the negative sense viral RNA segment of Influenzavirus A, Influenzavirus B and Influenzavirus C; b) the terminal 30 bases of the 5′ or 3′ terminus of the positive sense vcRNA; c) the 45 bases surrounding the AUG start codon of an influenza viral mRNA and; d) 50 bases surrounding the splice donor or acceptor sites of influenza mRNAs subject to alternative splicing.
Owner:SAREPTA THERAPEUTICS INC
Antisense antibacterial method and compound
Owner:SAREPTA THERAPEUTICS INC
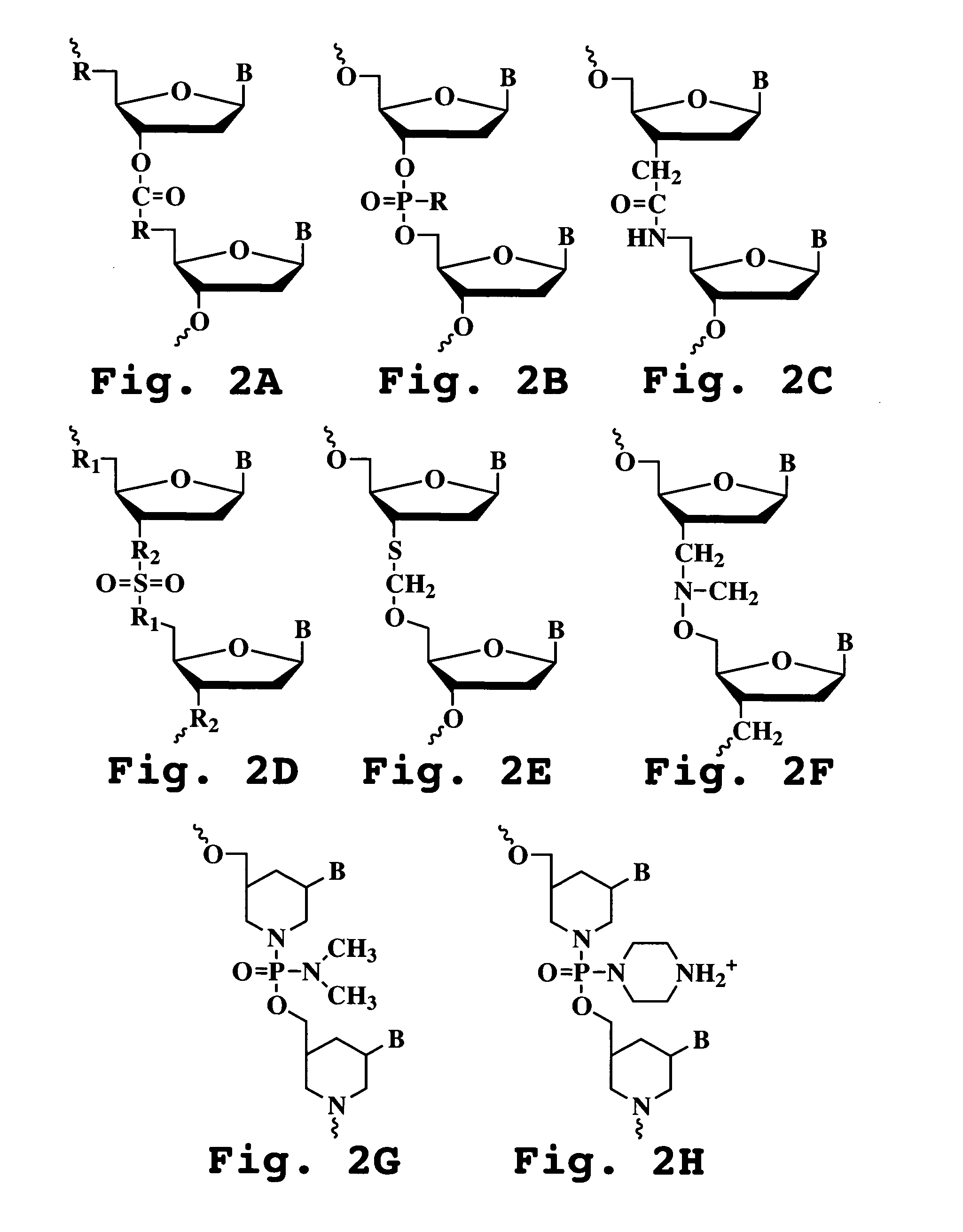
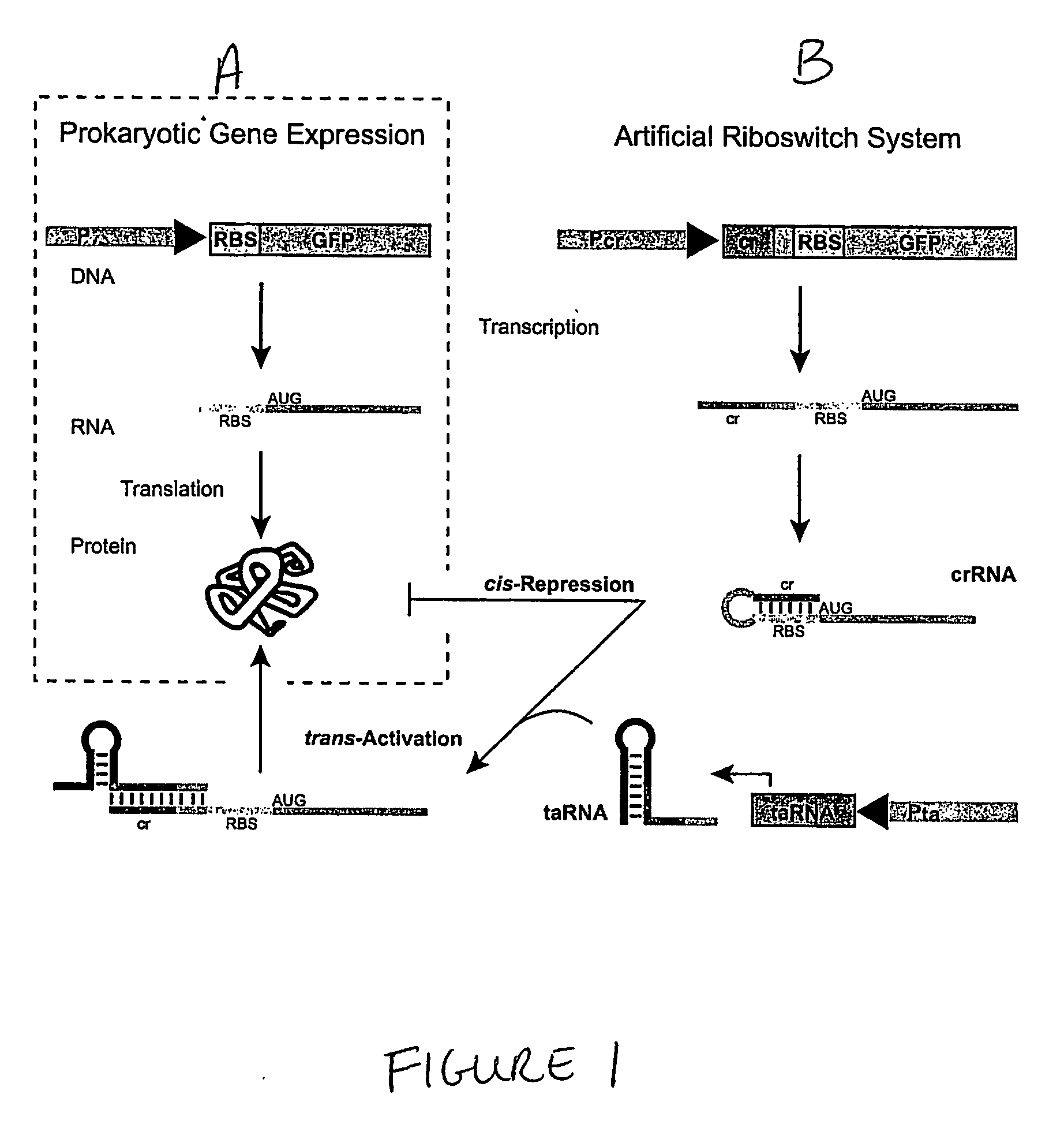
Small rna-dependent translational regulatory system in cell or artificial cell model
An object of the present invention is to construct an mRNA which specifically responds to a short RNA sequence and can activate, repress, and regulate the translation of the desired gene, and to construct an artificial cell model system using a liposome comprising the mRNA and a cell-free translational system encapsulated therein. The present invention provides: an mRNA comprising a target RNA-binding site located immediately 5′ to the ribosome-binding site, and a nucleotide sequence located 5′ to the target RNA-binding site, the nucleotide sequence being complementary to the ribosome-binding site; an mRNA comprising a small RNA-binding site located 3′ to the start codon, and a nucleotide sequence located 3′ to the small RNA-binding site, the nucleotide sequence encoding a protein; and a liposome comprising any of these mRNAs encapsulated therein.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP
Methods and compositions for manipulating translation of protein isoforms from alternative initiation of start sites
InactiveUS20140296321A1High sensitivityImprove translationSugar derivativesPolymorphism usesStart codonStart site
Provided herein are antisense oligonucleotides, compositions comprising antisense oligonucleotides, and methods for the use of antisense oligonucleotides in manipulating translation. Expression of isoforms of proteins expressed from different start codons of the same transcript are inhibited by antisense oligonucleotides, which may also enhance expression of non-target isoforms.
Owner:SAREPTA THERAPEUTICS INC
Antisense restenosis composition and method
InactiveUS20070265215A1Reduce riskOrganic active ingredientsBiocideStart codonPercent Diameter Stenosis
The present invention provides an improved method for reducing the risk or severity of restenosis following cardiac angioplasty. The method includes administering to a target vessel region, a morpholino antisense compound having a phosphorus-containing backbone linkages, and spanning the start codon of a human c-myc mRNA. Also disclosed are novel antisense compounds and compositions, and a method for assaying the effectiveness of antisense delivery and uptake to a target vessel region.
Owner:AVI BIOPHARMA
Protein expression system
ActiveUS20100287670A1Improve expression levelBoost protein levelsVirus peptidesVaccinesStart codonForeign protein
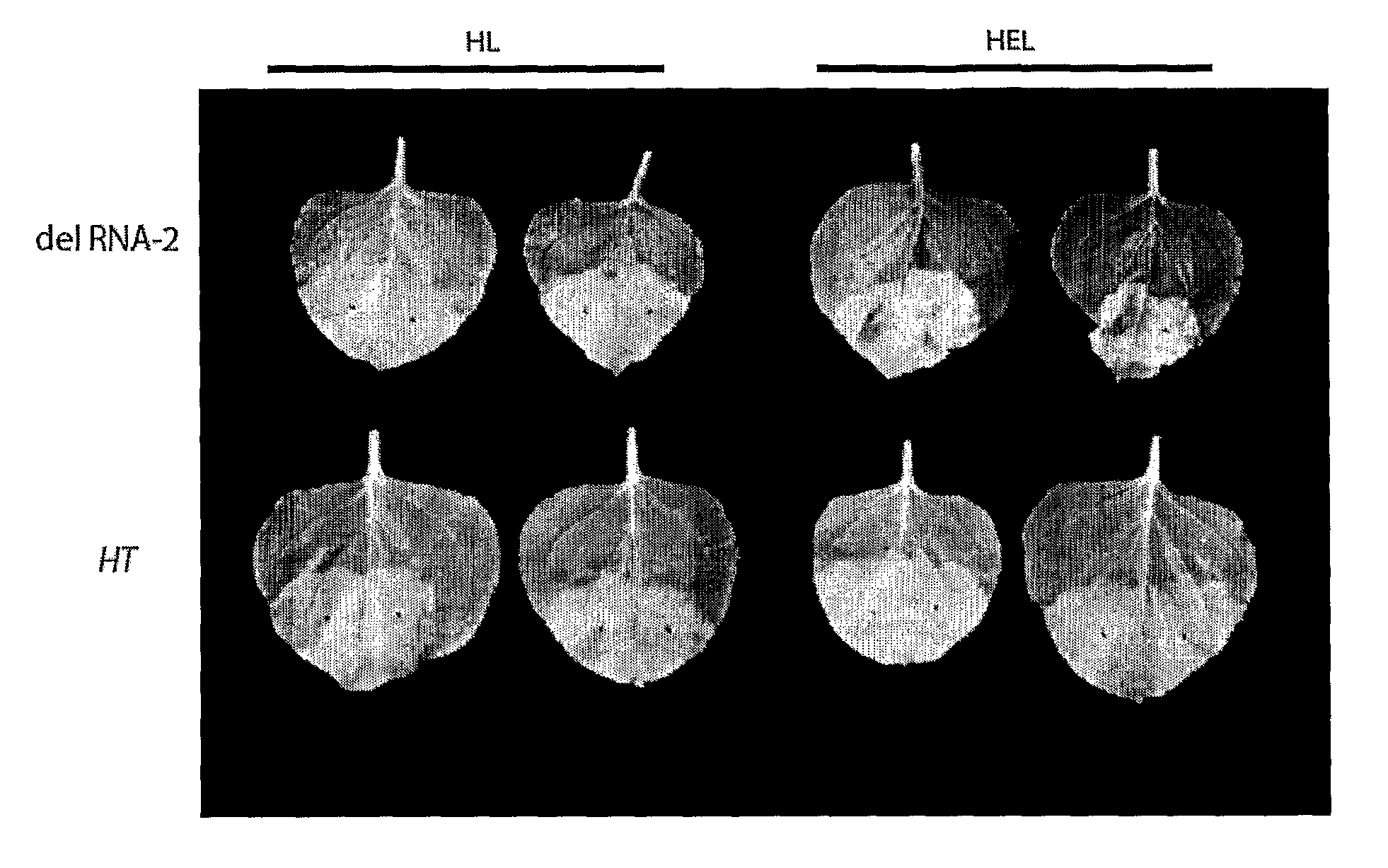
The inventions is based on an expression enhancer sequence derived from the RNA-2 genome segment of a bipartite RNA virus, in which a target initiation site in the RNA-2 genome segment has been mutated. Deletion of appropriate start codons upstream of the main RNA2 translation initiation can greatly increase in foreign protein accumulation without the need for viral replication. Also provided are methods, vectors and systems, including the ‘hyper-translatable’ Cowpea Mosaic Virus (‘CPMV-HT’) based protein expression system.
Owner:PLANT BIOSCI LTD
Antisense antibacterial method and compound
ActiveUS20070021362A1Growth inhibitionSimple designAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsCompound aStart codon
A method and antisense compound for inhibiting the growth of pathogenic bacterial cells are disclosed. The compound contains no more than 12 nucleotide bases and has a targeting nucleic acid sequence of no fewer than 10 bases in length that is complementary to a target sequence containing or within 10 bases, in a downstream direction, of the translational start codon of a bacterial mRNA that encodes a bacterial protein essential for bacterial replication. The compound binds to a target mRNA with a Tm of between 50° to 60° C. The relatively short antisense compounds are substantially more active than conventional antisense compounds having a targeting base sequence of 15 or more bases.
Owner:SAREPTA THERAPEUTICS INC
Antisense antibacterial method and compound
A method and antisense compound for inhibiting the growth of pathogenic bacterial cells are disclosed. The compound contains no more than 12 nucleotide bases and has a targeting nucleic acid sequence of no fewer than 10 bases in length that is complementary to a target sequence containing or within 10 bases, in a downstream direction, of the translational start codon of a bacterial mRNA that encodes a bacterial protein essential for bacterial replication. The compound binds to a target mRNA with a Tm of between 50° to 60° C. The relatively short antisense compounds are substantially more active than conventional antisense compounds having a targeting base sequence of 15 or more bases.
Owner:SAREPTA THERAPEUTICS INC
Cis/trans riboregulators
ActiveUS20070136827A1Easy to controlInhibition of translationSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementOpen reading frameBinding site
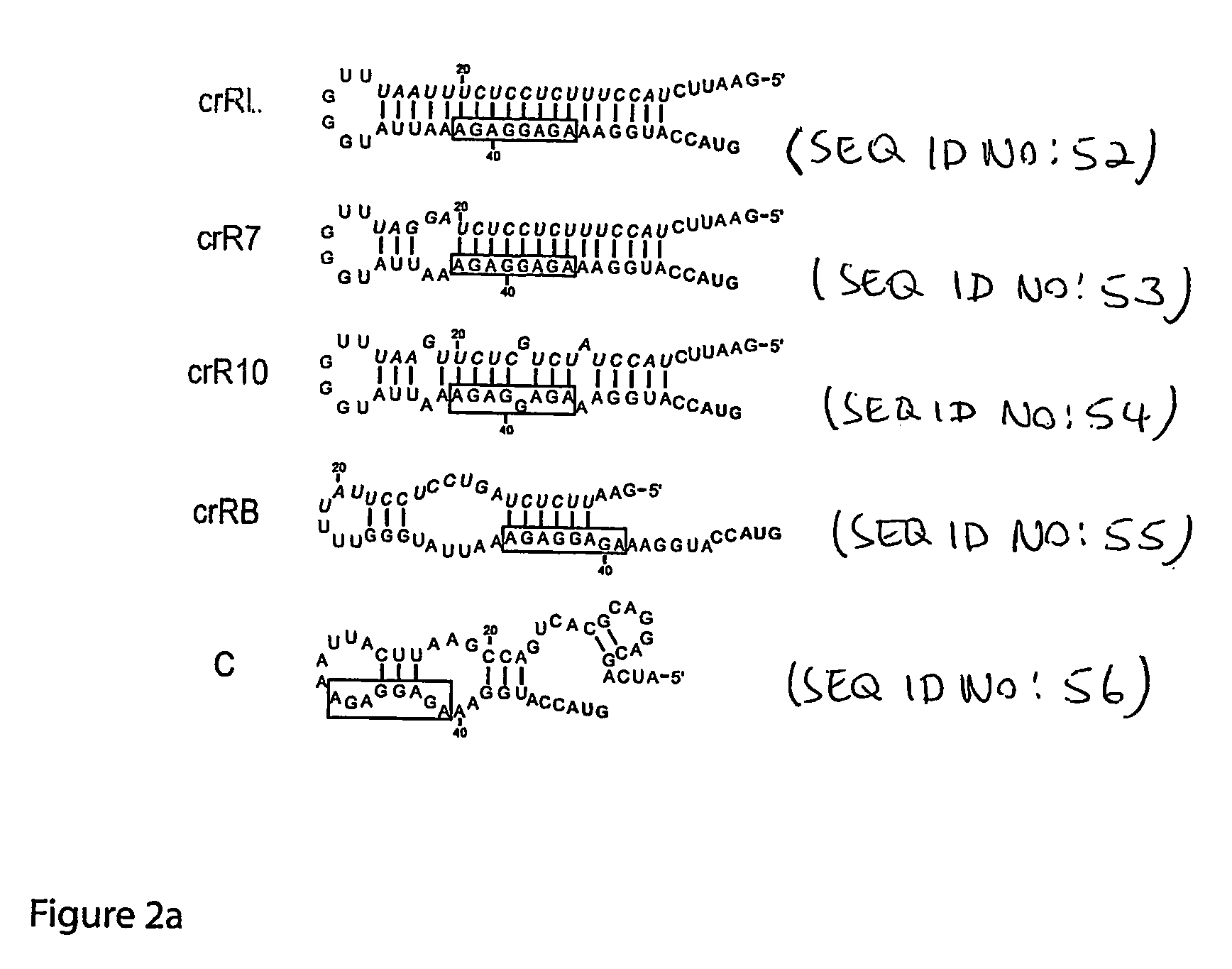
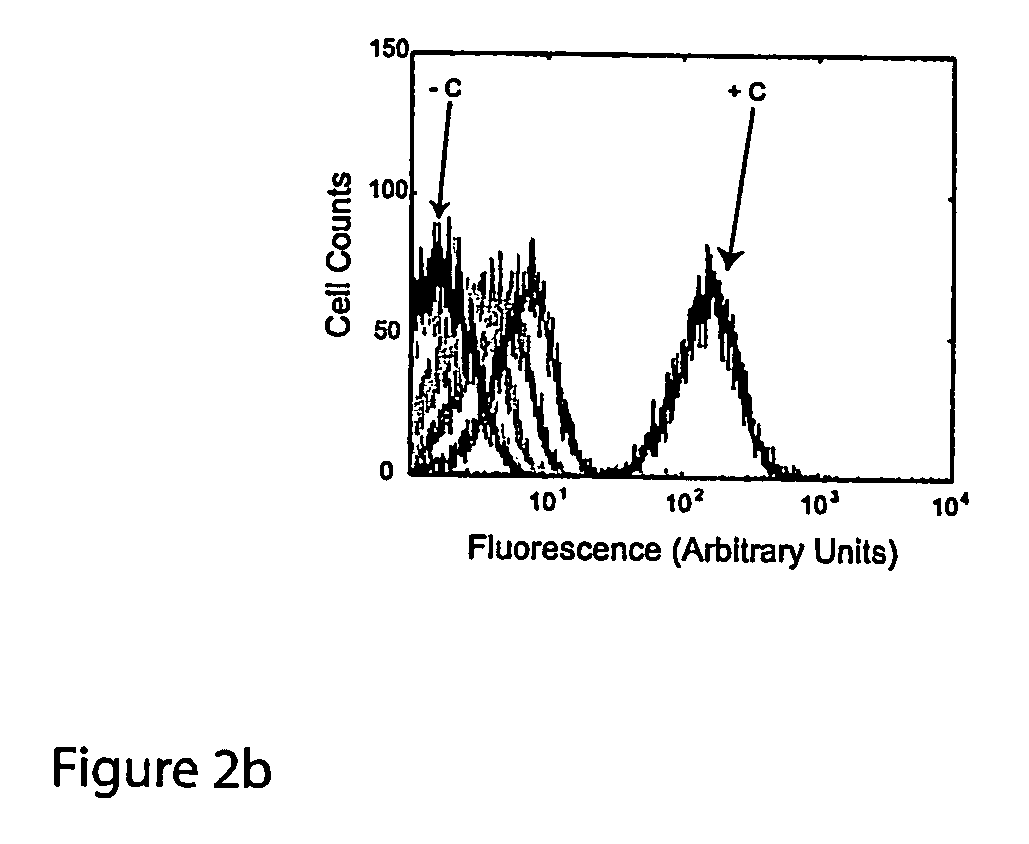
The present invention provides nucleic acid molecules, DNA constructs, plasmids, and methods for post-transcriptional regulation of gene expression using RNA molecules to both repress and activate translation of an open reading frame. Repression of gene expression is achieved through the presence of a regulatory nucleic acid element (the cis-repressive RNA or crRNA) within the 5′ untranslated region (5′ UTR) of an mRNA molecule. The nucleic acid element forms a hairpin (stem / loop) structure through complementary base pairing. The hairpin blocks access to the mRNA transcript by the ribosome, thereby preventing translation. In particular, in embodiments of the invention designed to operate in prokaryotic cells, the stem of the hairpin secondary structure sequesters the ribosome binding site (RBS). In embodiments of the invention designed to operate in eukaryotic cells, the stem of the hairpin is positioned upstream of the start codon, anywhere within the 5′ UTR of an mRNA. A small RNA (trans-activating RNA, or taRNA), expressed in trans, interacts with the crRNA and alters the hairpin structure. This alteration allows the ribosome to gain access to the region of the transcript upstream of the start codon, thereby activating transcription from its previously repressed state.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF BOSTON UNIV
Antisense restenosis composition and method
InactiveUS20060269587A1Reduce riskReduce severityBiocideHydroxy compound active ingredientsMorpholineBackbone chain
The present invention provides an improved method for reducing the risk or severity of restenosis following cardiac angioplasty. The method includes administering to a target vessel region, a morpholino antisense compound having uncharged phosphorus-containing backbone linkages, and spanning the start codon of a human c-myc mRNA. Also disclosed are novel antisense compounds and compositions, and a method for assaying the effectiveness of antisense delivery and uptake to a target vessel region.
Owner:AVI BIOPHARMA
Molecular marker related to color property of tomato fruit and application thereof
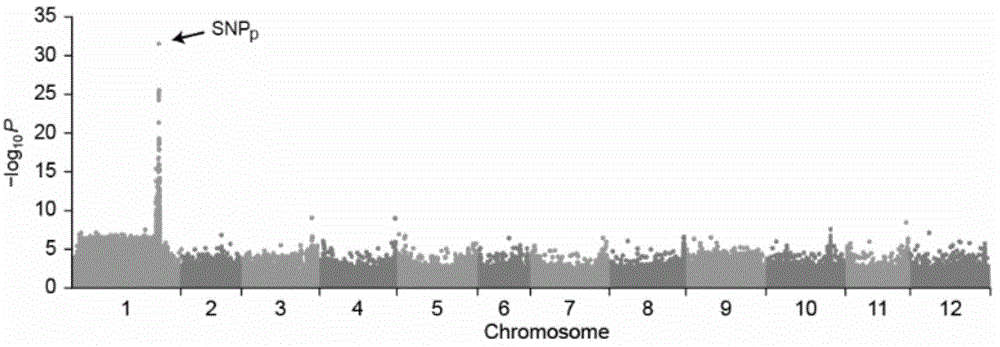
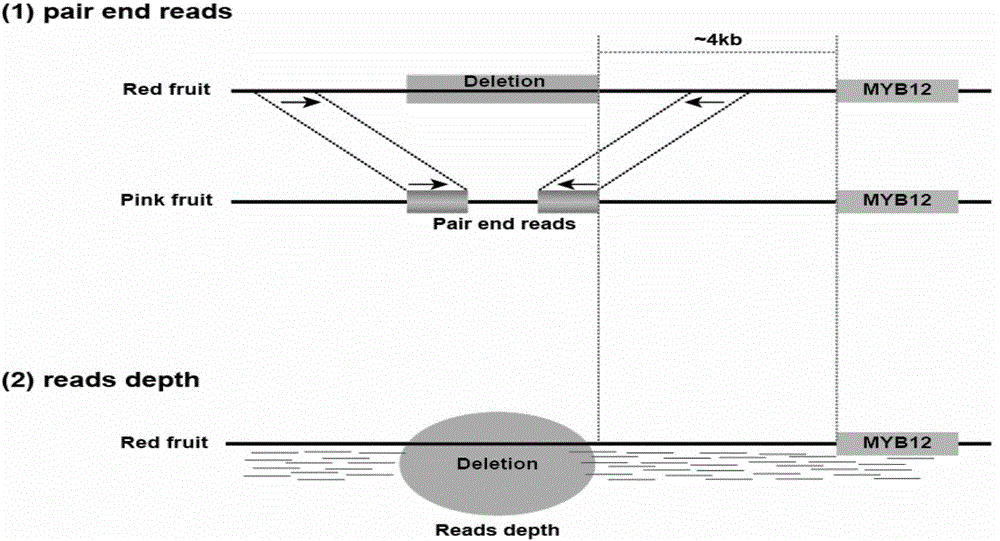
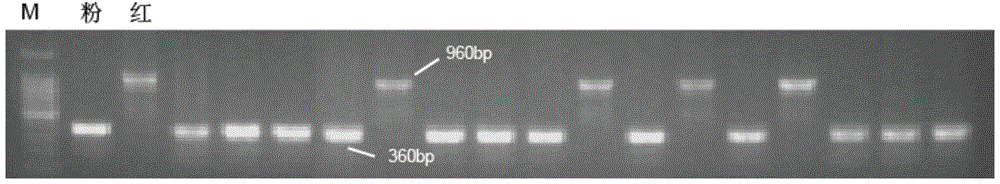
ActiveCN104087576ASpeed up the breeding processReliable resultsMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationStart codonAgricultural science
The invention provides a molecular marker related to the color property of tomato fruit and application thereof. The molecular marker includes 2 SNP markers and 2 InDel markers. SNP-p is located at site 8616bp of the upstream of initiator codon of a tomato SlMYB 12 gene, wherein bases which are C represent red tomatoes and bases which are A represent pink tomatoes. SNP-s is located at site 307bp of the downstream of the initiator codon of the tomato SlMYB 12 gene, wherein bases which are T represent pink tomatoes and bases which are C represent red tomatoes. InDel-p is a sequence located at about site 4kp of the upstream of the initiator codon of the tomato SlMYB 12 gene and having a size of 603 bp, wherein pink tomatoes are deleted in the sequence. InDel-i is located at site 248bp of the downstream of the initiator codon of the tomato SlMYB 12 gene, wherein A is located behind the site and is a pink tomato. The molecular marker can be applied to molecular marker-assisted breeding of tomatoes and can substantially accelerate the breeding process of tomatoes.
Owner:INST OF VEGETABLE & FLOWERS CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Vectors with modified initiation codon for the translation of aav-rep78 useful for production of aav
ActiveUS20090191588A1Improve stabilityReduced expression levelAnimal cellsSugar derivativesStart codonNucleotide
The present invention relates nucleic acid constructs for the production of recombinant parvoviral (e.g. adeno-associated viral) vectors in insect cells, to insect cells comprising such constructs and to methods wherein the cells are used to produce recombinant parvoviral virions. The insect cells preferably comprise a first nucleotide sequence encoding the parvoviral rep proteins whereby the initiation codon for translation of the parvoviral Rep78 protein is a suboptimal initiation codon that effects partial exon skipping upon expression in insect cells. The insect cell further comprises a second nucleotide sequence comprising at least one parvoviral (AAV) inverted terminal repeat (ITR) nucleotide sequence and a third nucleotide sequence comprising a sequences coding for the parvoviral capsid proteins.
Owner:AMSTERDAM MOLECULAR THERAPEUTICS +1
SNP markers related to grass carp growth speed and application thereof
ActiveCN106381331AEasy to identifyMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationStart codonNucleotide
Through amplification of a part of fragments of an NPY gene, and through an SNaPshot SNP typing method, provided is SNP markers related to the grass carp growth speed, wherein S1 is located at a 639th locus from an initiation codon (ATG, with an ATG first nucleotide as the first) in an intron 1 sequence of the NPY gene, and a base at the position is T or A; S2 is located at an 892nd locus from the initiation codon in the intron 1 sequence of the NPY gene, and a base at the position is C or A. The two SNP loci can be used for identification or breeding of grass carp with faster growth speed, and lay the foundation for screening and establishment of grass carp fast-growth new varieties.
Owner:PEARL RIVER FISHERY RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERY SCI
Antisense antibacterial compounds and methods
Antibacterial antisense compounds and methods of their use in treating a Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection in a mammalian host are disclosed. The compounds include an antisense oligonucleotide conjugated to a carrier peptide that significantly enhances the antibacterial activity of the oligonucleotide. The antisense oligonucleotides contain 10-20 nucleotide bases and have a targeting nucleic acid sequence complementary to a target sequence containing or within 20 bases, in a downstream direction, of the translational start codon of a bacterial mRNA that encodes a bacterial protein essential for bacterial replication, where the compound binds to a target mRNA with a Tm of between 45° to 60° C. The carrier peptide is an arginine-rich peptide containing between 6 and 14 amino acids. Antisense compounds that target host factor genes that facilitate Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection are also provided, as are methods of using these compounds to treat Mycobacterium tuberculosis infections, alone or in combination with other therapies.
Owner:AVI BIOPHARMA
Process for producing activated human ALT
The present invention relates to an altered-type human ALT gene in which the codons for the five amino acids in the human ALT (alanine aminotransferase) gene are replaced, i. e. the fourth amino acid codon from the initiation codon for methionine (Met) is replaced by a codon for serine (Ser), the fifth by a codon for threonine (Thr), the seventh by a codon for aspartic acid (Asp), the 39th by a codon for glycine (Gly) and the 222nd by a codon for alanine (Ala), and concurrently, restriction sites are added at the upstream and downstream of said gene.The active human ALT having properties similar to those of the native enzyme can be effectively produced by culturing E. coli transformed with a recombinant plasmid in which the altered-type human ALT gene of the present invention is ligated to a vector.
Owner:ORIENTAL YEAST
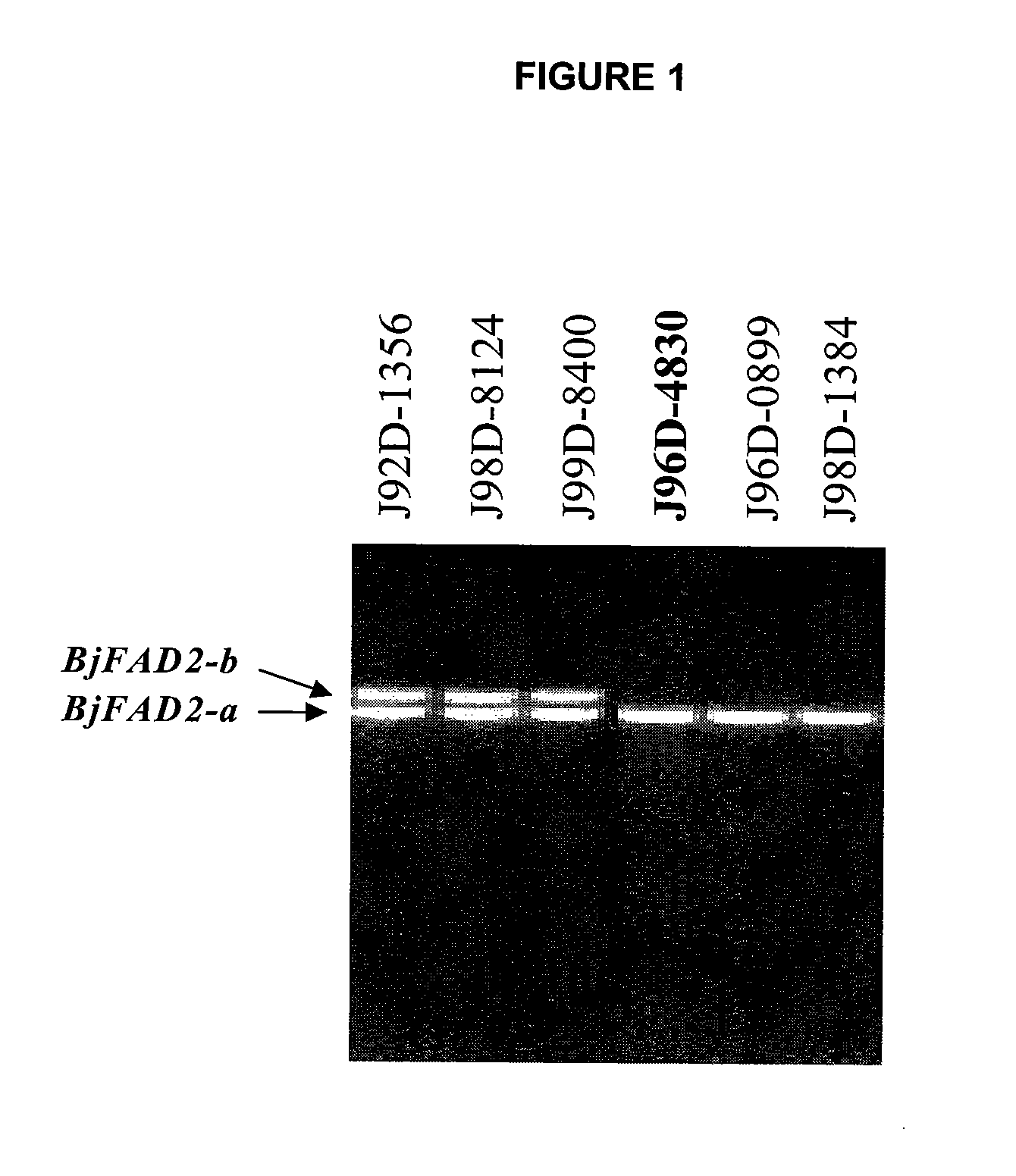
Brassica Juncea Lines With High Oleic Acid Profile In Seed Oil
In various aspects, the invention provides Brassica juncea plants, seeds, cells, nucleic acid sequences and oils. Edible oil derived from plants of the invention may have significantly higher oleic acid content than other B. juncea plants. In one embodiment, the B. juncea line MJ02-357-3 contains a mutant allele MJ02-313-1 / BjFAD2-a at the BjFAD2-a gene locus, having a single base-pair change (a G to A substitution in the ORF at position 281 in reference to the first ATG start codon) relative to the wild type sequence. The change is predicted to encode a Glycine-94 Aspartic acid mutation in the sequence of the predicted BjFAD2-a protein. In another embodiment, the B. juncea line MJ02-357-3 contains a mutant allele MJ02-357-3 / BjFAD2-a at the BjFAD2-a gene locus, having a single base-pair change (a C to T substitution in the ORF at position 647 in reference to the first ATG start codon) relative to the wild type sequence. The change is predicted to encode a Proline-216 Leucine mutation in the sequence of the predicted BjFAD2-a protein. As a result of these mutations, it can be predicted that the function of the BjFAD2-a proteins are negatively affected in Brassica juncea lines MJ02-313-1 and MJ357-3 as reflected in the increased levels of oleic acid in seed oil in comparison with the wild-type line J96D-4830. Seeds from MJ02-313-1 and MJ02-357-3 plants may for example yield an oil having oleic acid content of greater than 70% by weight.
Owner:NUTRIEN AG SOLUTIONS (CANADA) INC
Method for regulating gene expression intensity on microbial chromosome by using artificial regulatory element and its library
The invention discloses a method for regulating the expression intensity of genes on microorganism chromosomes by using artificial regulatory elements and libraries thereof. The method for regulating the gene expression intensity on the microbial chromosome by using the artificial regulatory element and its library provided by the present invention includes the following steps: amplify a DNA fragment by PCR, which includes the upstream sequence of the original regulatory region of the gene to be regulated on the microbial chromosome A homologous fragment containing 40-3000 bases, resistance marker gene, artificial regulatory element library or an artificial regulatory element with specific expression strength, homologous to the sequence downstream of the start codon of the gene to be regulated on the microbial chromosome A fragment containing 40-3000 bases; the DNA fragment is electrotransformed into the microorganism, and the original regulatory region of the gene to be regulated on the microbial chromosome is replaced by an artificial regulatory element library or an artificial regulatory element with a specific expression intensity .
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Real-time fluorescence quantitative PCR(Polymerase Chain Reaction) detection primers and kit for thalassemia
InactiveCN102409100AAvoid pollutionMeet the needs of rapid detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationStart codonCD43
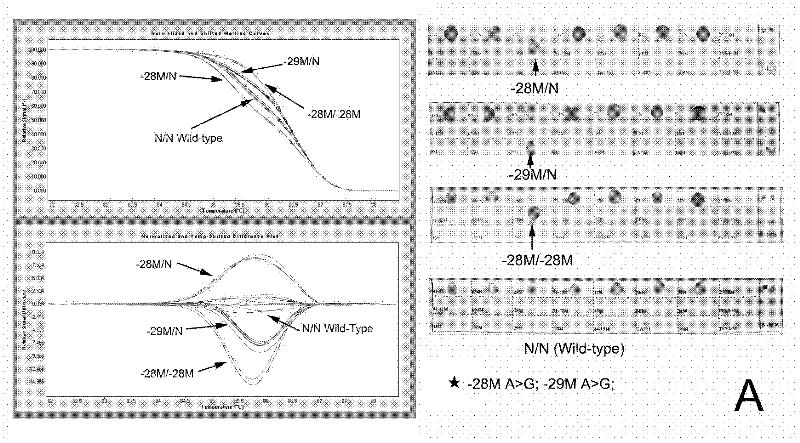
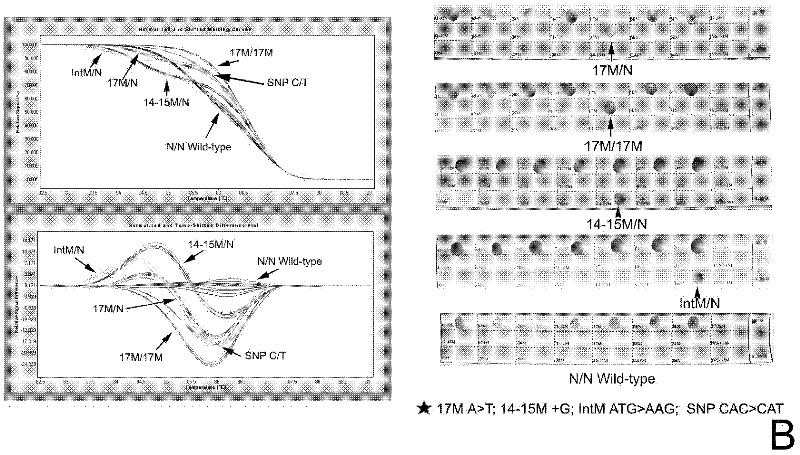
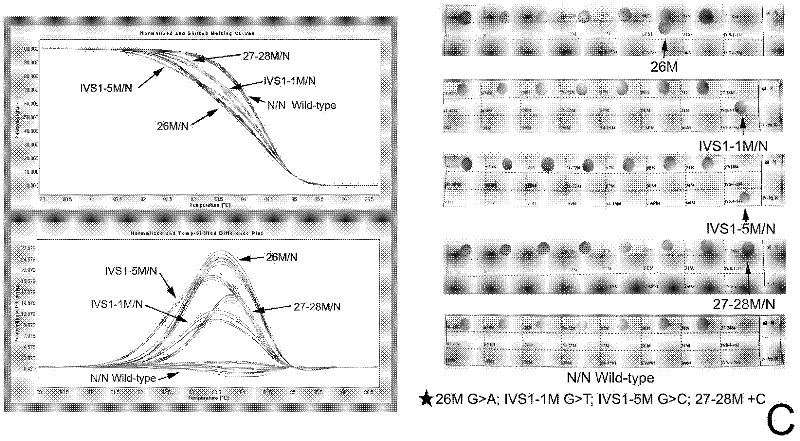
The invention discloses a real-time fluorescence quantitative PCR(Polymerase Chain Reaction) detection kit and related primers for thalassemia genes. The kit comprises more than one pair of the following primers: SEQ ID NO.1 and SEQ ID NO.2 aiming at TATA kits nt-28 (A->G) (-28M), -29 (A->G) (-29M) and CAP-40-43 (AACC) (CAPM) genotypes; SEQ ID NO.3 and SEQ ID NO.4 aiming at CD14-15 (+G) (14-15M), CD17 (A->T) (17M) and the initiation codon mutant ATG->AGG(IntM) genotypes; SEQ ID NO.5 and SEQ ID NO.6 aiming at CD26 (G->A)(betaEM) CDs27-28+C(27-28M), IVS1-1(G->T)(IVS1-1M), IVS1-5(G->C)(IVS1-5M) genotypes; SEQ ID NO.7 and SEQ ID NO.8 aiming at CDs41-42-TCTT (41-42M), CD43G->T(43M), 41-42M / 41-42M genotypes; SEQ ID NO.9 and SEQ ID NO.10 aiming at CD71-72(+A) (71-72M) genotypes; SEQ ID NO.11 and SEQ ID NO.12 aiming at IVS2-654C->T(654M) and 654M / 654M genotypes; and SEQ ID NO.13 and SEQ ID NO.14 aiming at constant spring (CS), Quong Sze (QS) and Westmead (WS) genotypes. The kit has the advantages of good detection specificity and high detection sensitivity.
Owner:潮州市中心医院
Aroma gene in rice and functional marker thereof
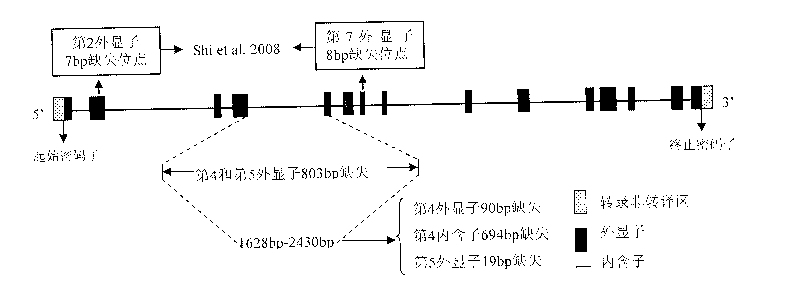
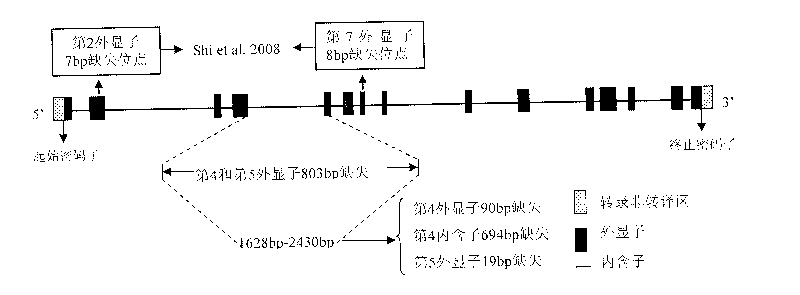
An aroma gene in rice and a functional marker thereof belong to the biotechnology field. The aroma gene is characterized in that the aroma gene is allelic to a coded betaine-aldehyde dehydrogenase gene Badh2 on chromosome 8; compared with the normal Badh2, in the aroma gene, 803bp is deleted between the fourth exon and the fifth exon; the deleted base is positioned between downstream 1628bp and 2430bp of a transcription initiator codon of the gene; and the 803bp deleted base corresponds to the fourth exon 90bp, the fourth intron 694bp and the fifth exon 19bp. The functional marker FMbadh2-E4-5 of the aroma gene is designed according to the aroma gene in rice. By the method, the aroma gene can be transplanted to the non-aroma rice varieties with target, thus greatly promoting cultivation of new high-quality aromatic rice varieties.
Owner:CHINA NAT RICE RES INST
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com