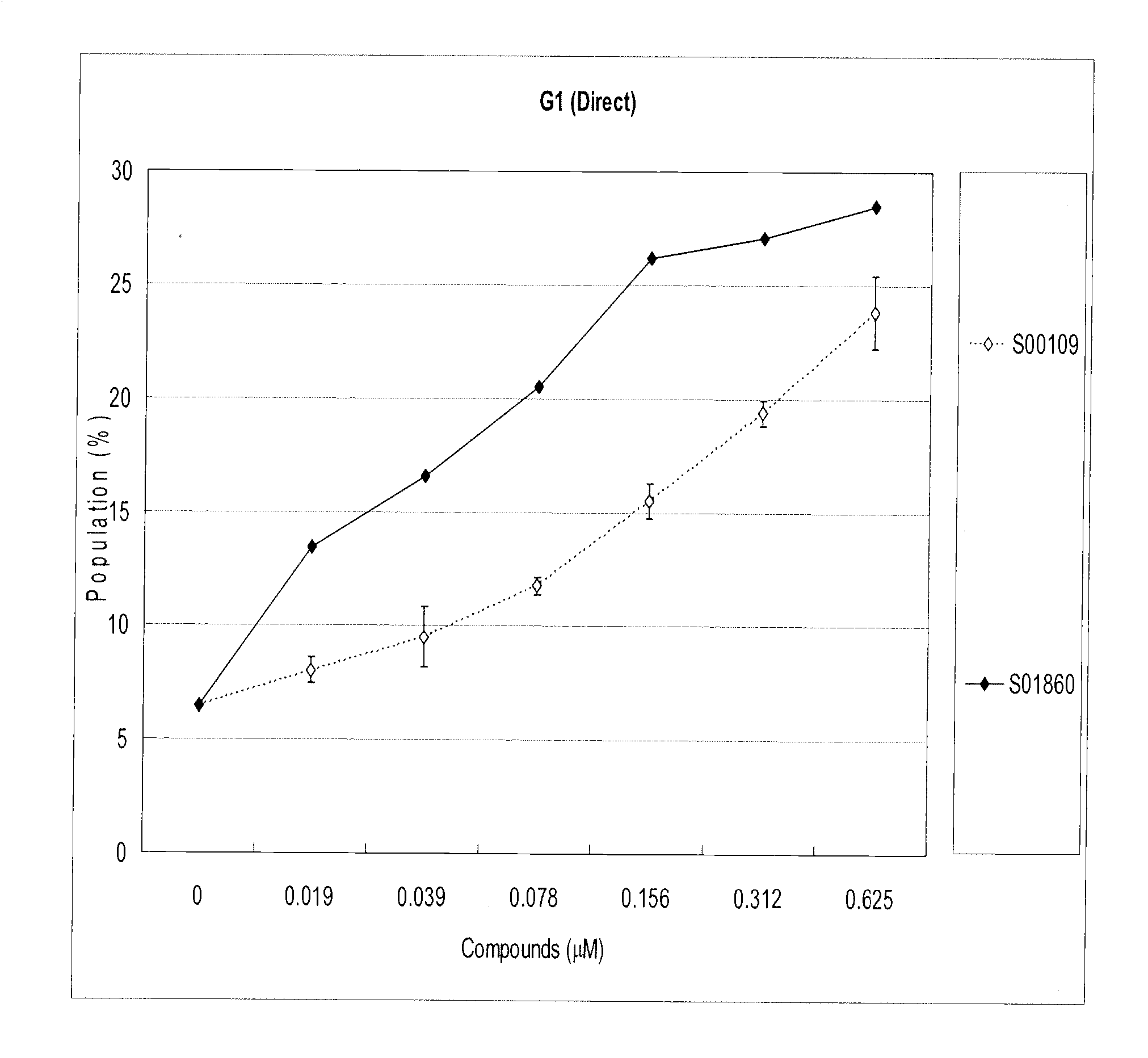
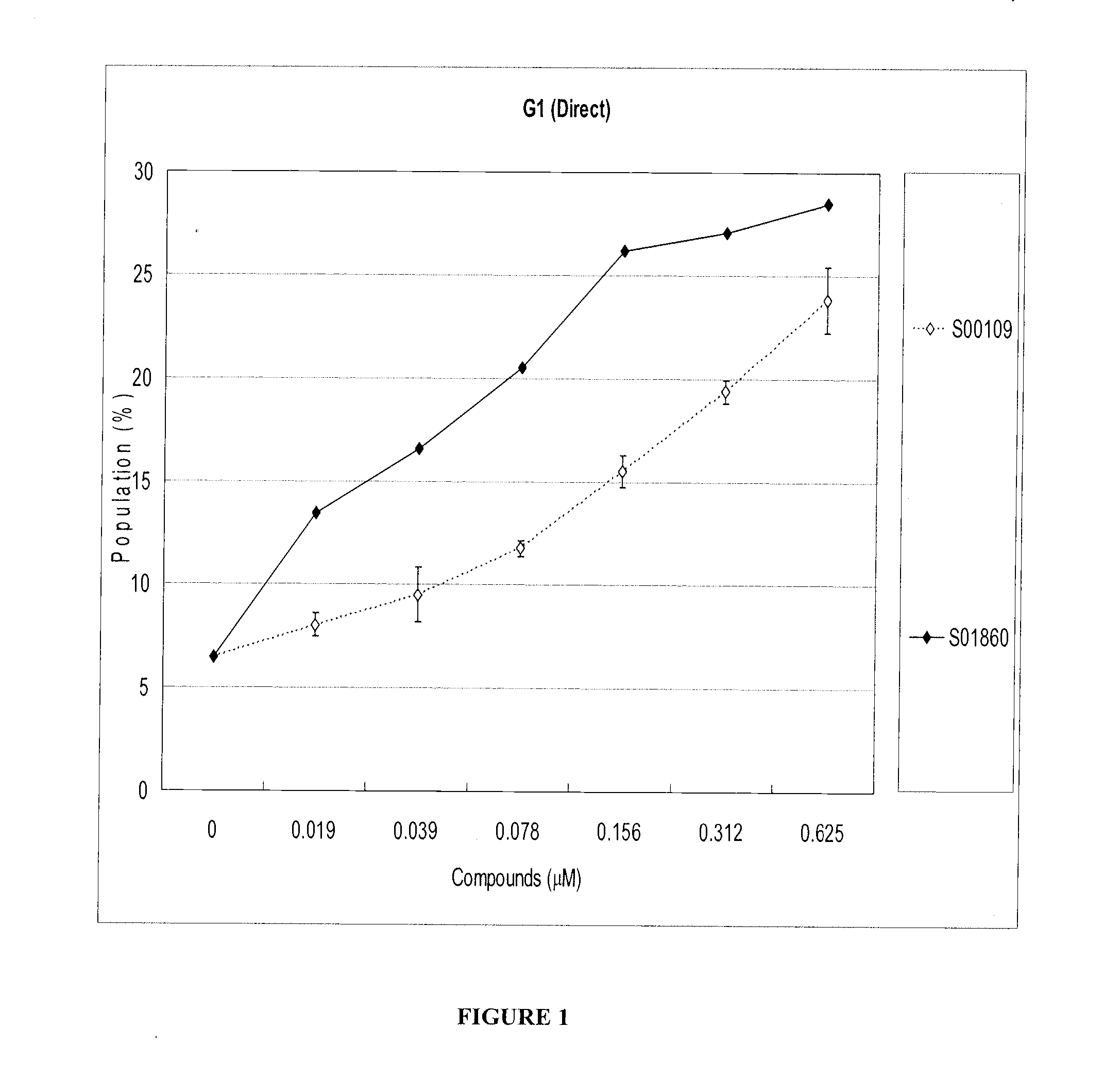
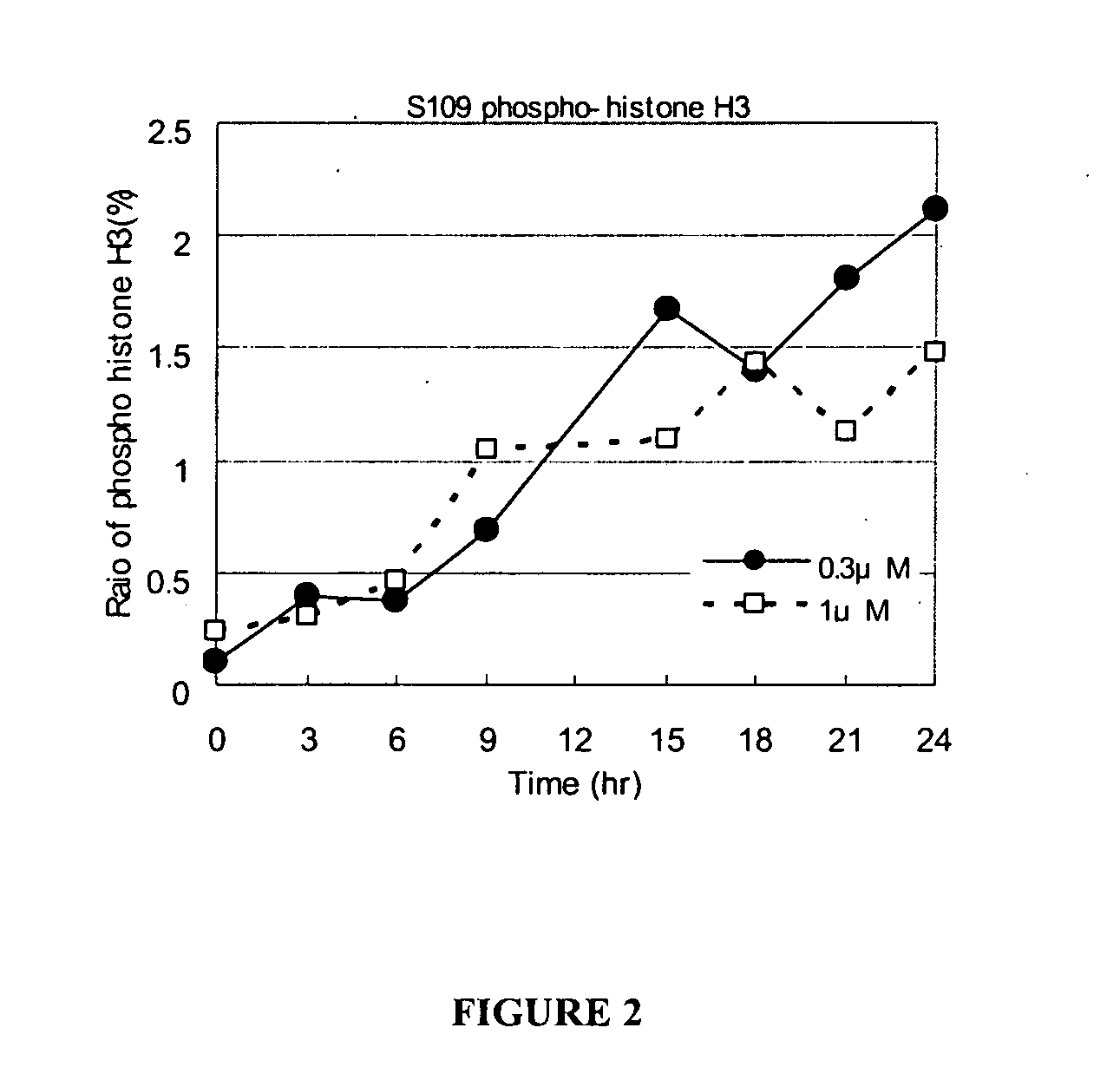
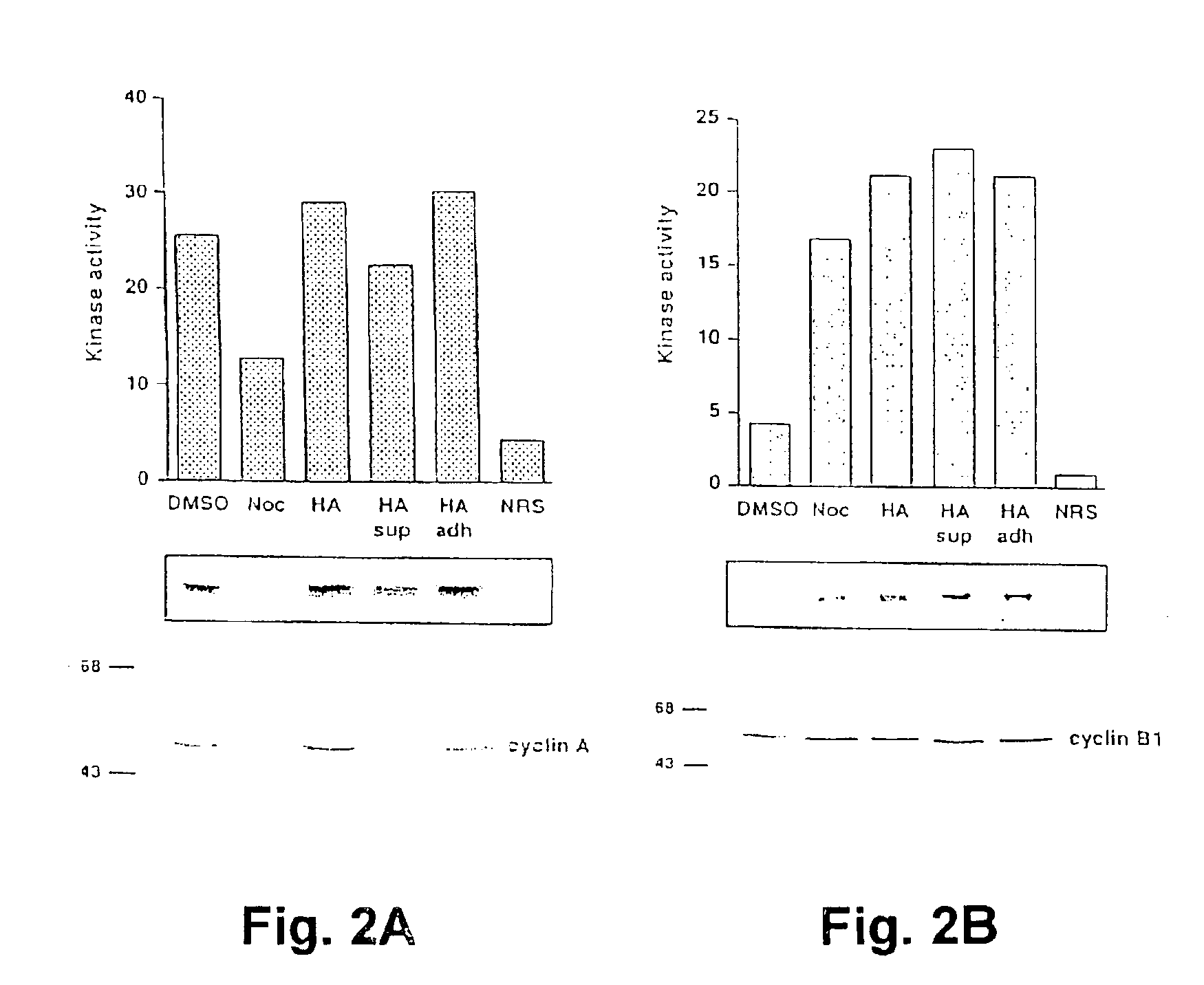
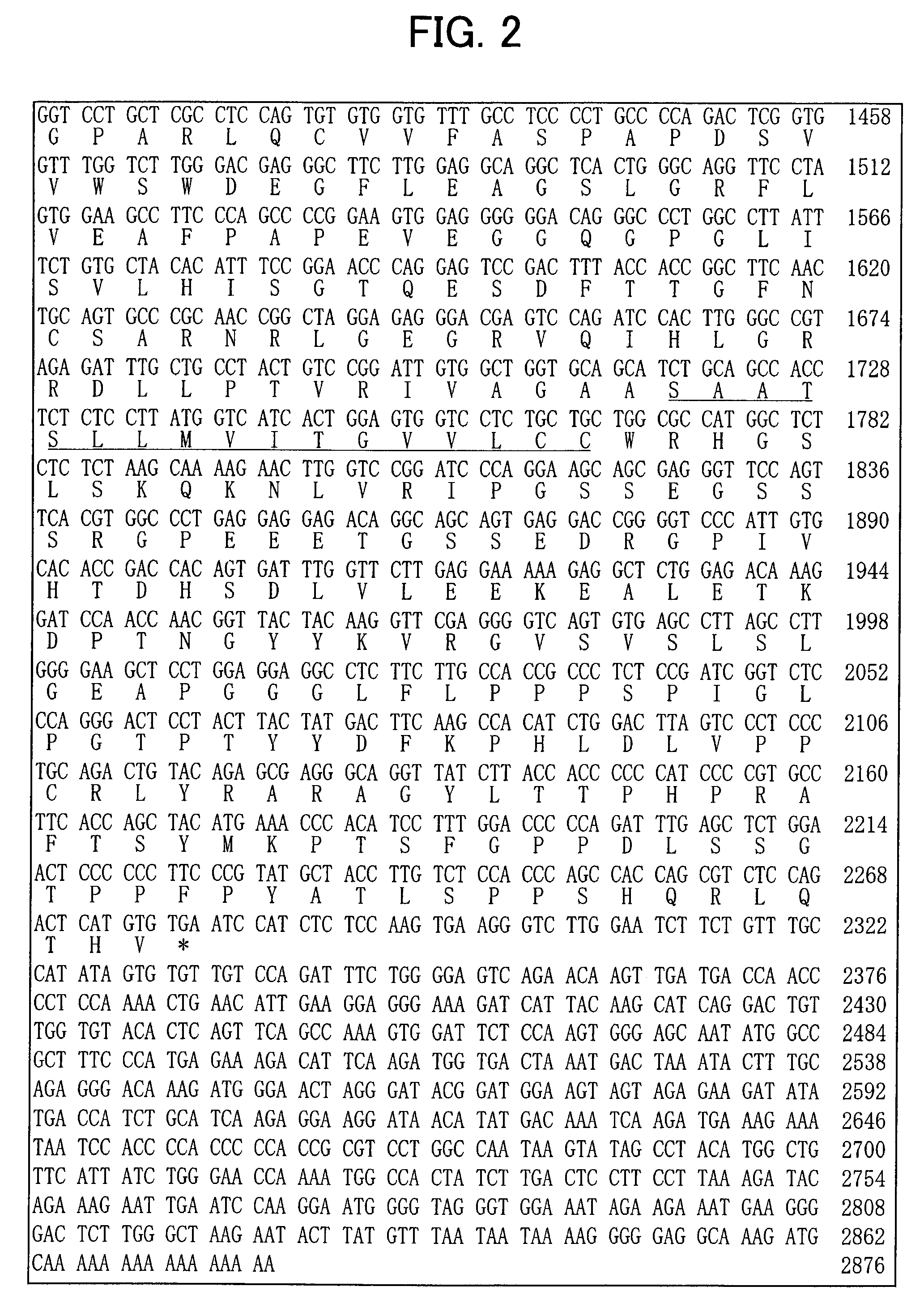
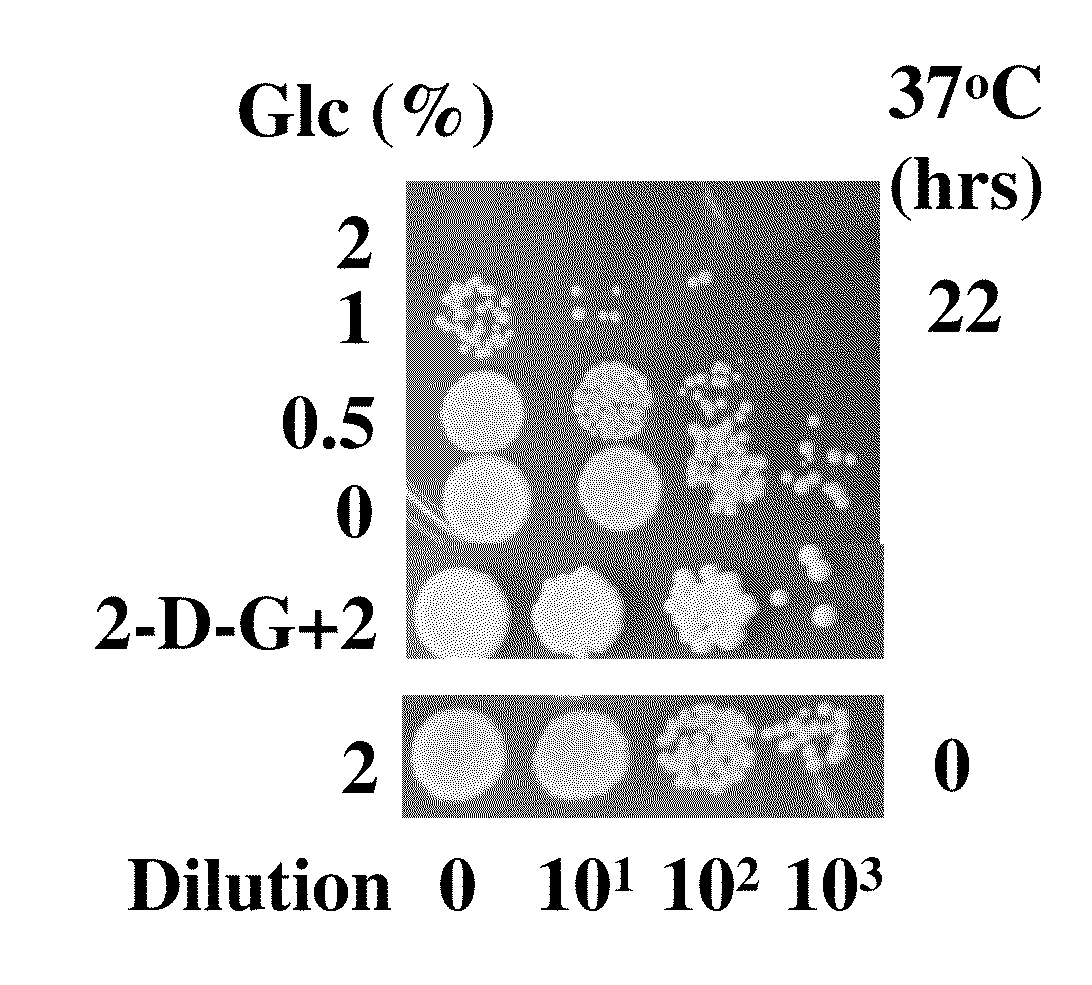
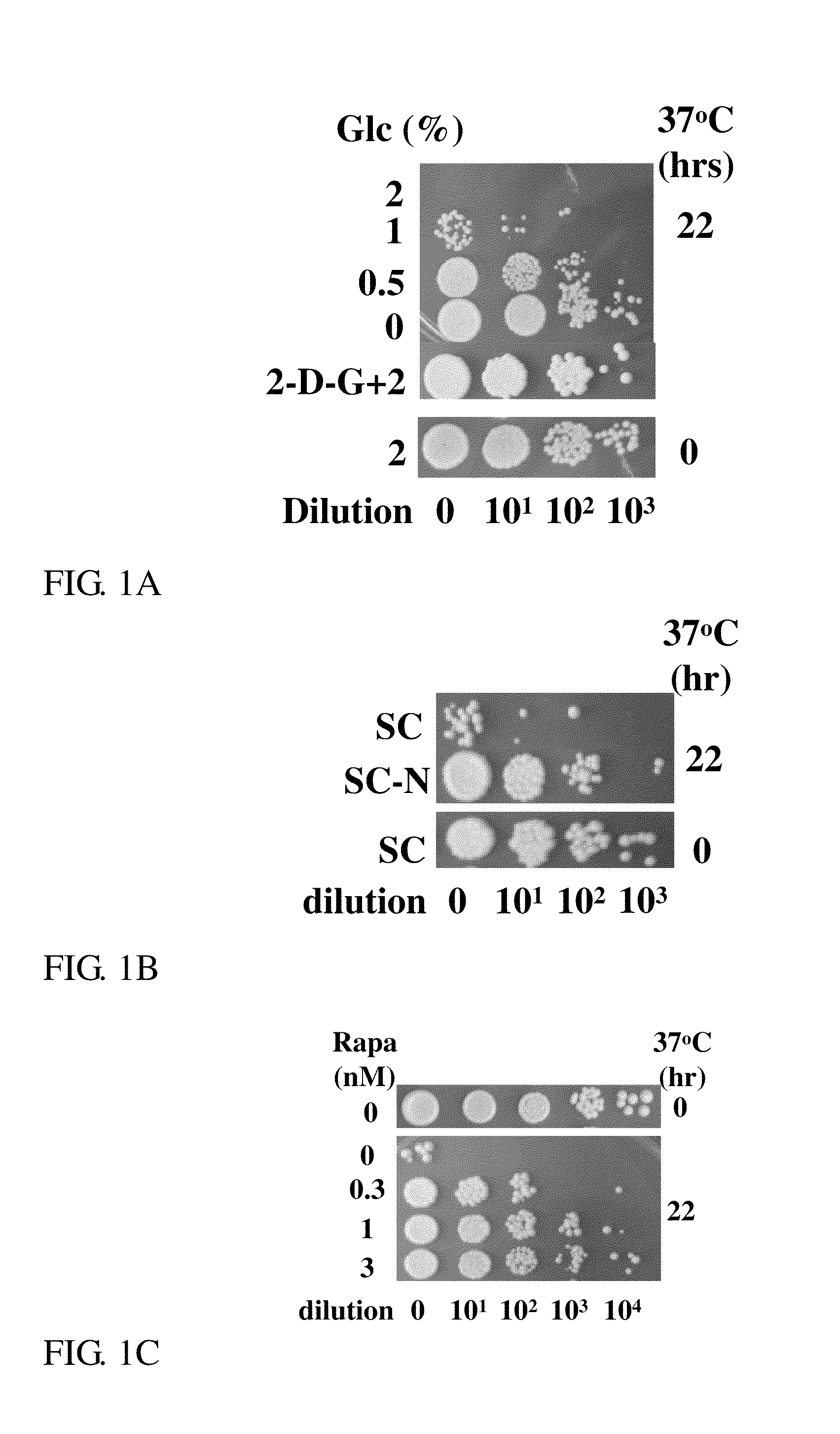
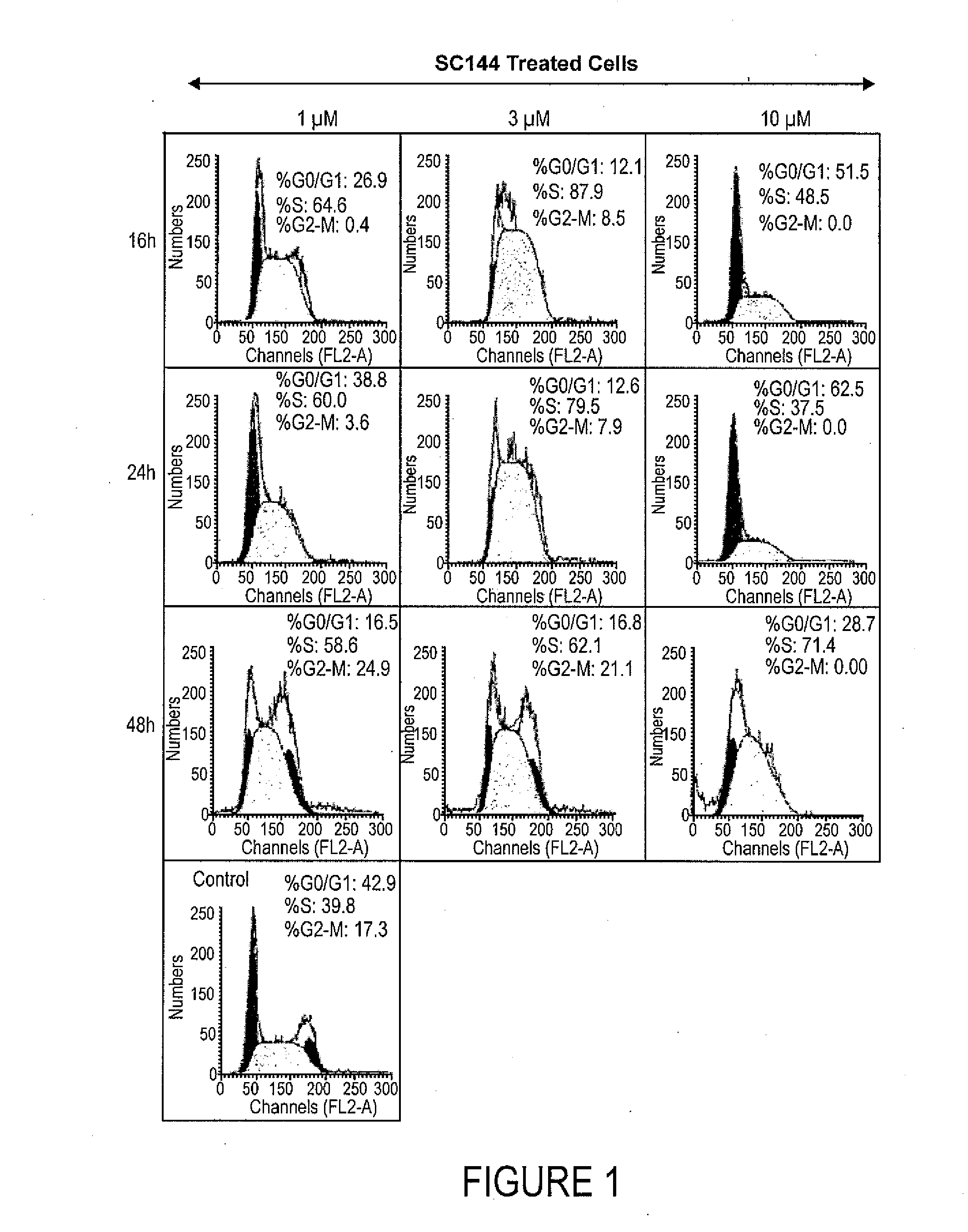
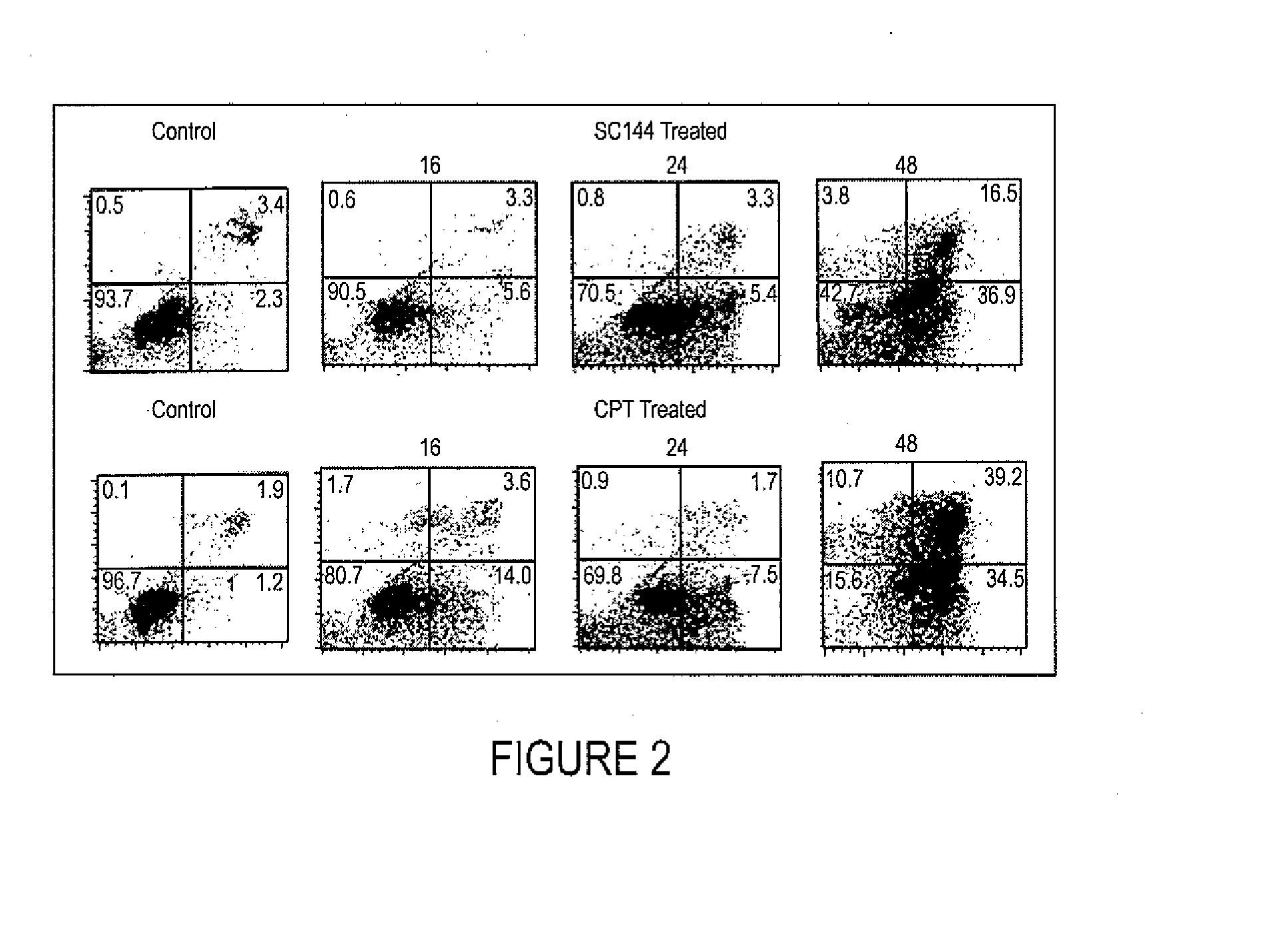
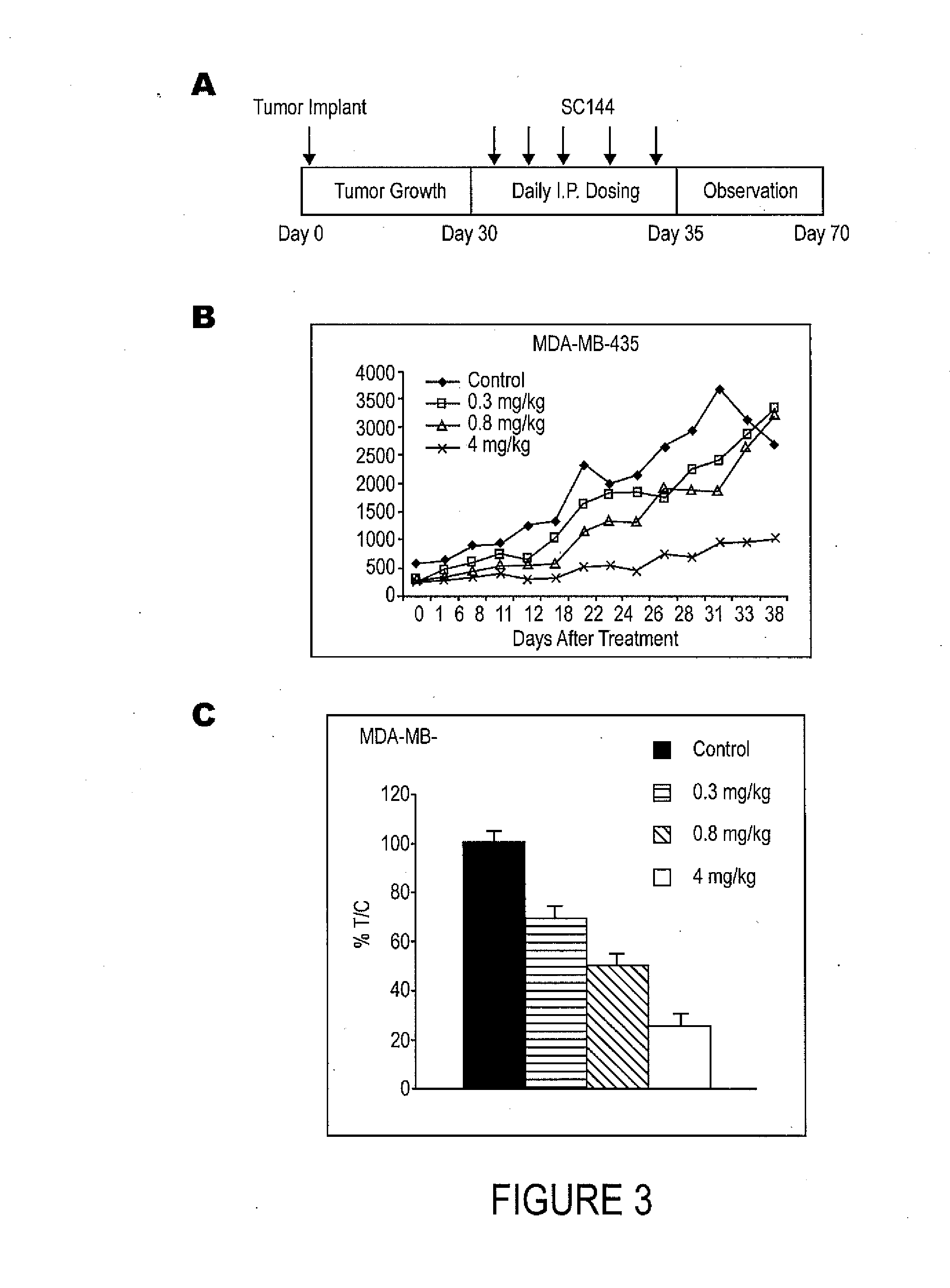
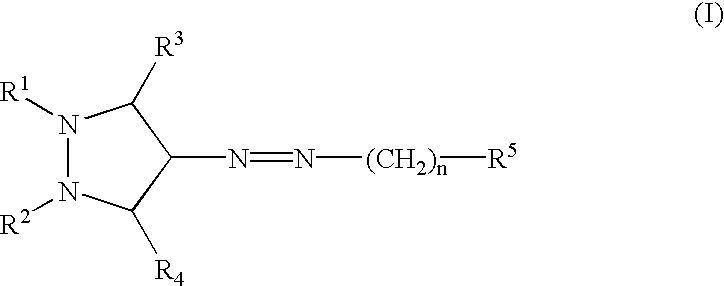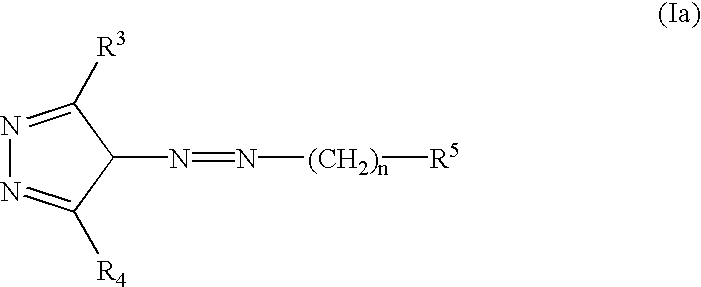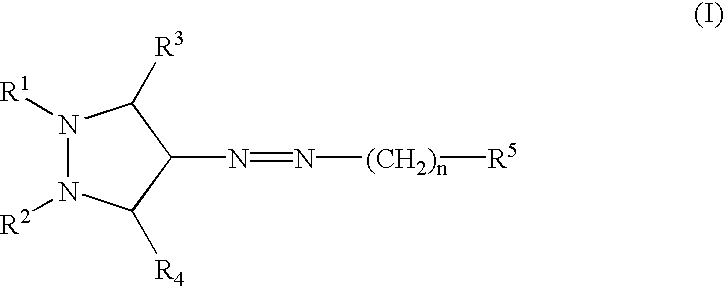Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
965 results about "Cell cycle" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The cell cycle, or cell-division cycle, is the series of events that take place in a cell leading to duplication of its DNA (DNA replication) and division of cytoplasm and organelles to produce two daughter cells. In bacteria, which lack a cell nucleus, the cell cycle is divided into the B, C, and D periods. The B period extends from the end of cell division to the beginning of DNA replication. DNA replication occurs during the C period. The D period refers to the stage between the end of DNA replication and the splitting of the bacterial cell into two daughter cells. In cells with a nucleus, as in eukaryotes, the cell cycle is also divided into two main stages: interphase and the mitotic (M) phase (including mitosis and cytokinesis). During interphase, the cell grows, accumulating nutrients needed for mitosis, and undergoes DNA replication preparing it for cell division. During the mitotic phase, the replicated chromosomes and cytoplasm separate into two new daughter cells. To ensure the proper division of the cell, there are control mechanisms known as cell cycle checkpoints.
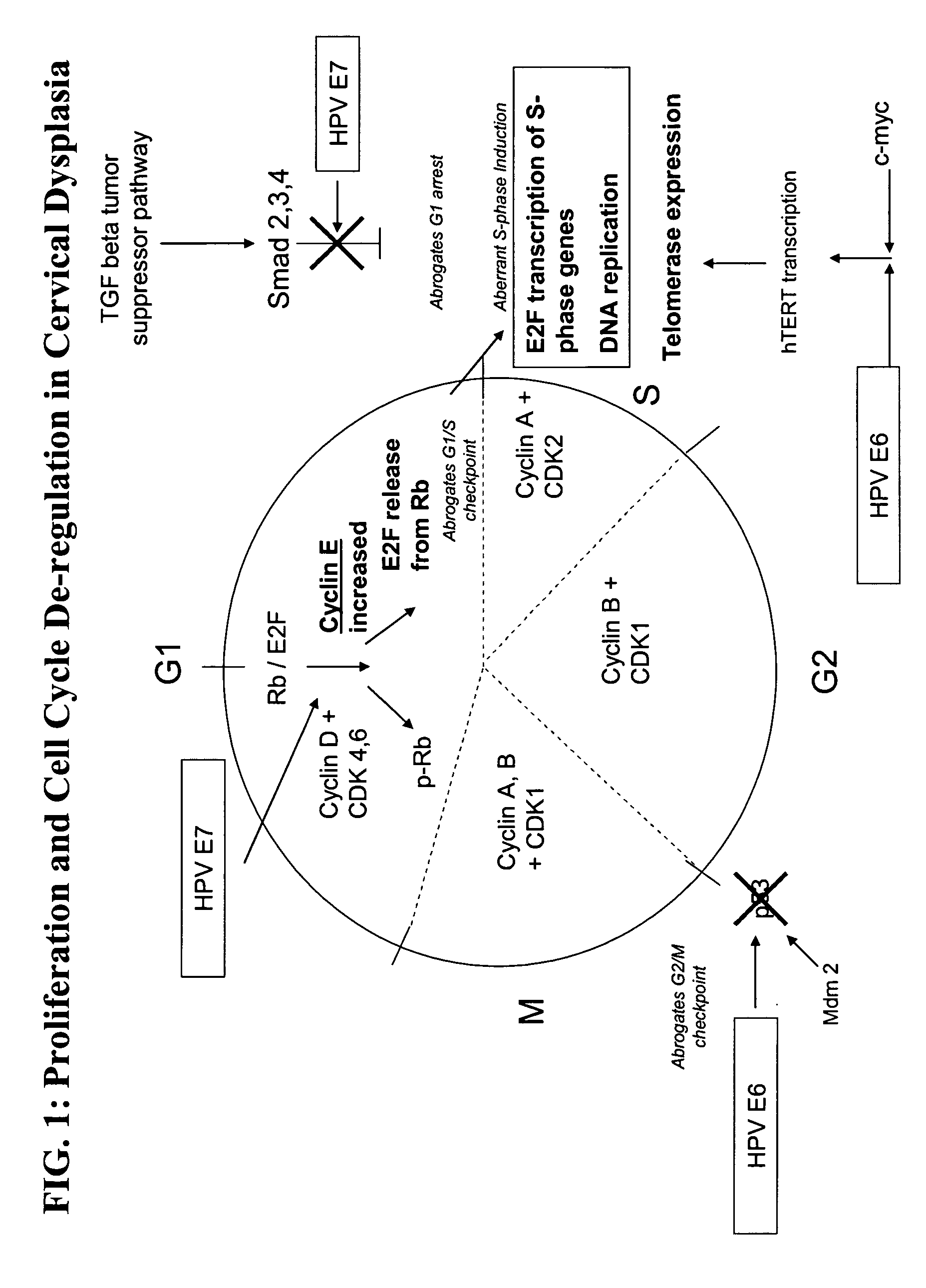
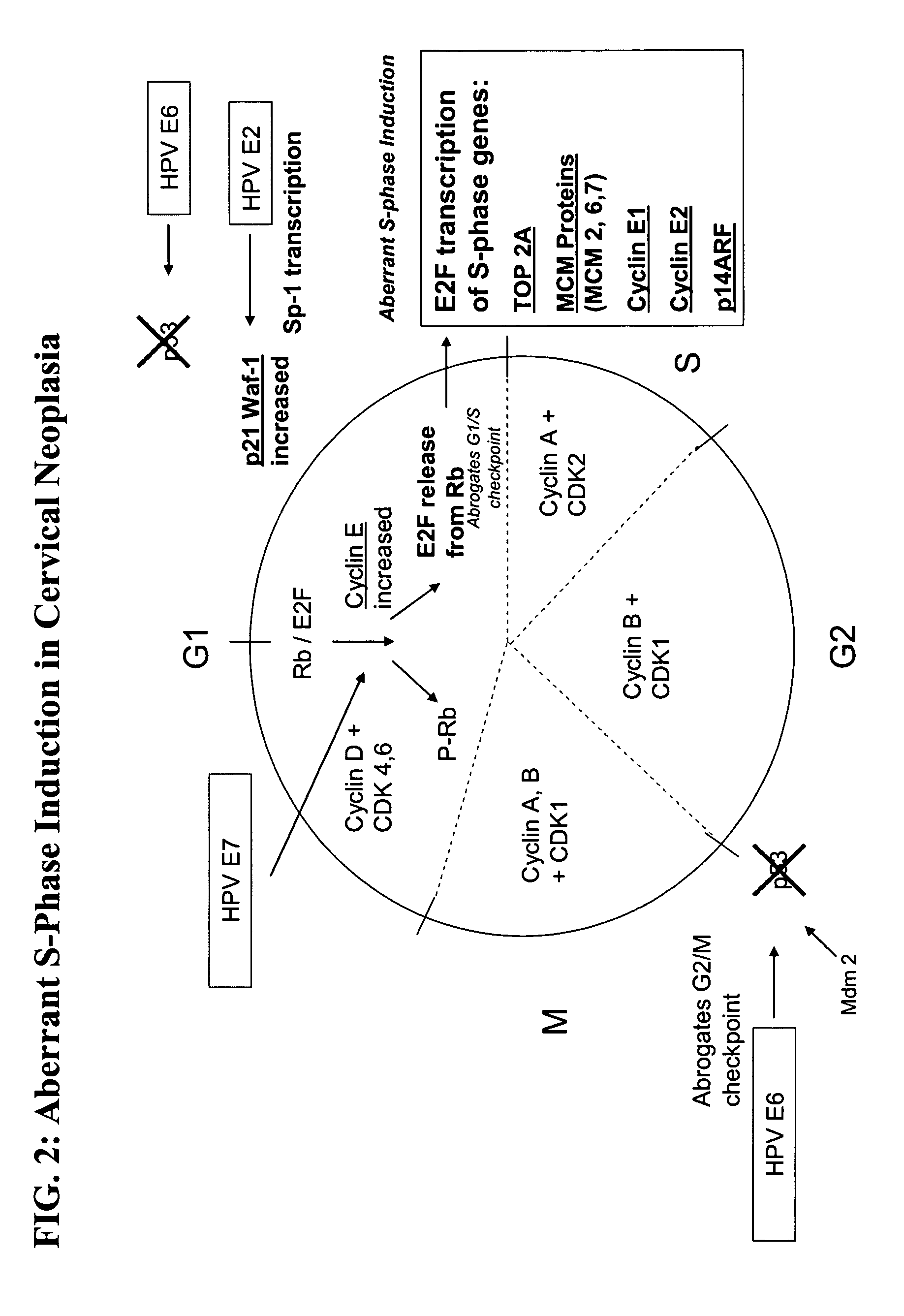
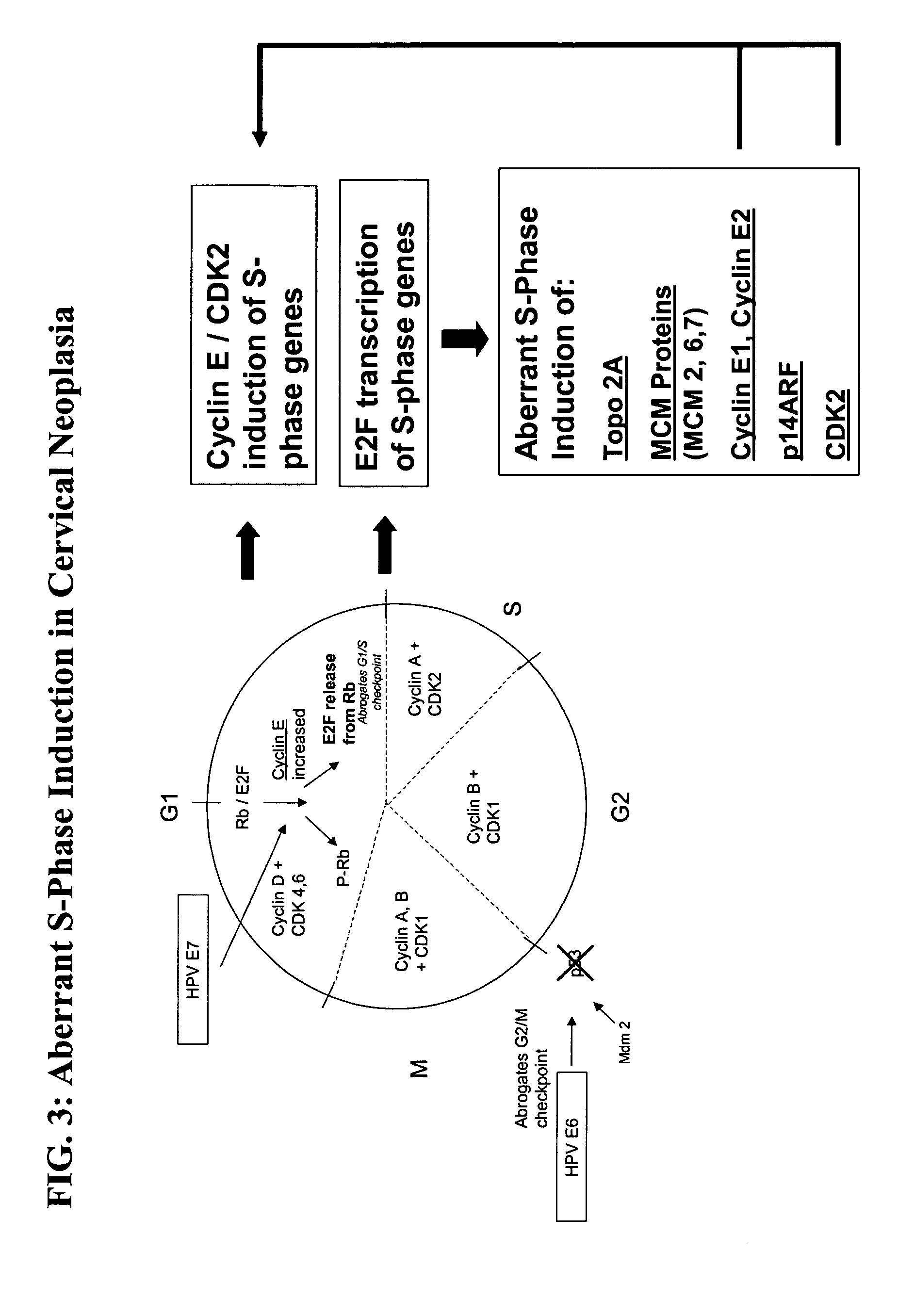
Methods and compositions for the detection of cervical disease
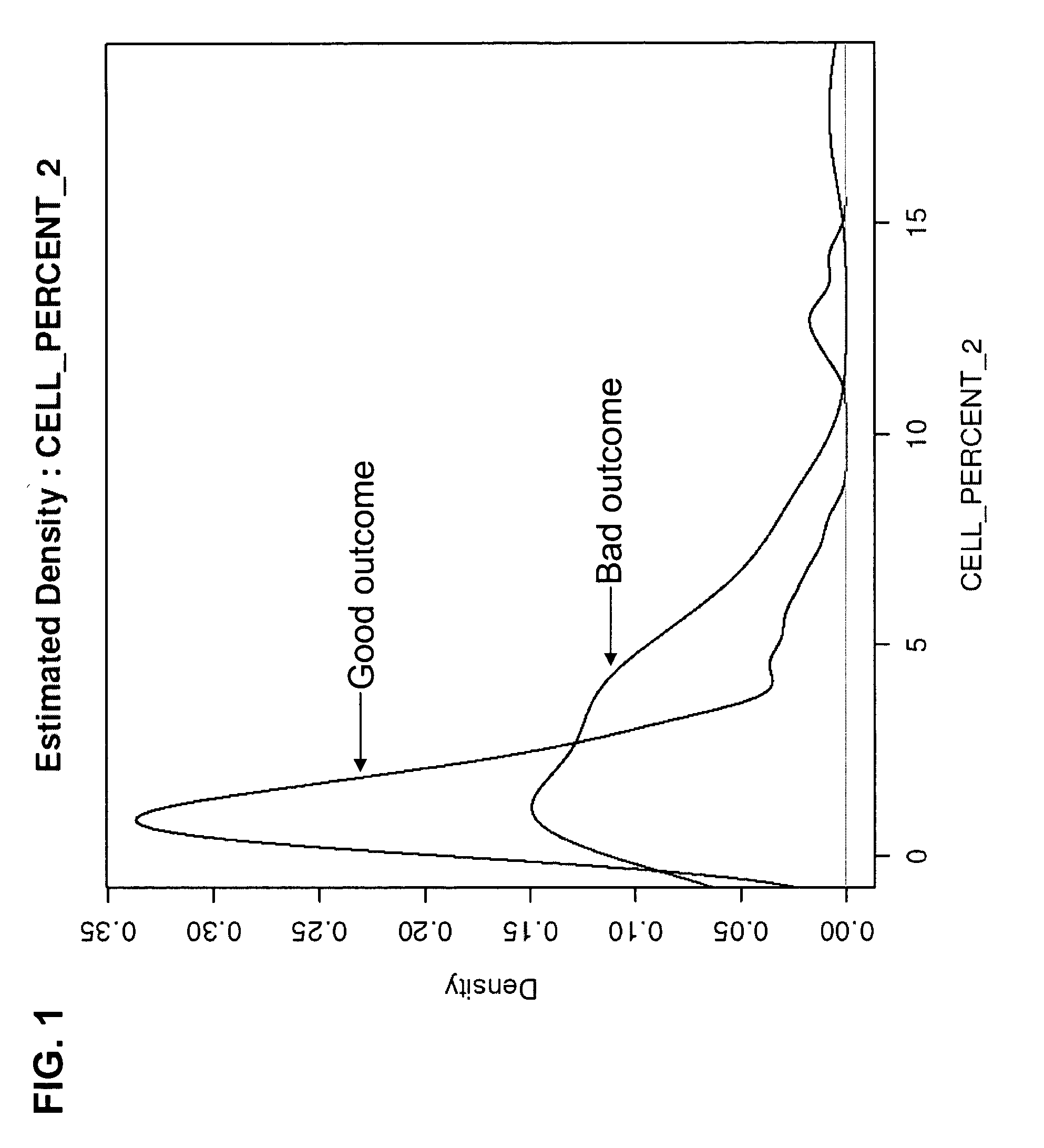
ActiveUS20050260566A1Improve the level ofIncreased proliferationAnimal cellsMicrobiological testing/measurementDiseaseCervical cells
Methods and compositions for identifying high-grade cervical disease in a patient sample are provided. The methods of the invention comprise detecting overexpression of at least one biomarker in a body sample, wherein the biomarker is selectively overexpressed in high-grade cervical disease. In particular claims, the body sample is a cervical smear or monolayer of cervical cells. The biomarkers of the invention include genes and proteins that are involved in cell cycle regulation, signal transduction, and DNA replication and transcription. In particular claims, the biomarker is an S-phase gene. In some aspects of the invention, overexpression of a biomarker of interest is detected at the protein level using biomarker-specific antibodies or at the nucleic acid level using nucleic acid hybridization techniques. Kits for practicing the methods of the invention are further provided.
Owner:TRIPATH IMAGING INC
Antisense antibacterial cell division composition and method
Antisense oligomers directed to bacterial cell division and cell cycle-encoding nucleic acids are capable of selectively modulating the biological activity thereof, and are useful in treatment and prevention of bacterial infection. The antisense oligomers are substantially uncharged, and contain from 8 to 40 nucleotide subunits, including a targeting nucleic acid sequence at least 10 nucleotides in length which is effective to hybridize to (i) a bacterial tRNA or (ii) a target sequence, containing a translational start codon, within a bacterial nucleic acid which encodes a protein associated with cell division or the cell cycle. Such proteins include zipA, sulA, secA, dicA, dicB, dicC, dicF, ftsA, ftsI, ftsN, ftsK, ftsL, ftsQ, ftsW, ftsZ, murC, murD, murE, murF, murG, minC, minD, minE, mraY, mraW, mraZ, seqA, ddlB, carbamate kinase, D-ala D-ala ligase, topoisomerase, alkyl hydroperoxide reductase, thioredoxin reductase, dihydrofolate reductase, and cell wall enzyme.
Owner:SAREPTA THERAPEUTICS INC
Few seconds beam on time, breathing synchronized image guided all fields simultaneous radiation therapy combined with hyperthermia
This invention relates to single session image guided all field simultaneous radiation therapy combined with hyperthermia. Hyperthermia renders the radiation resistant cells as more radiation sensitive cells. The high and super-high dose rate radiation greatly improves the RBE of the photon radiation. It also minimizes photon radiation therapy's OER and cell cycle dependent tumor cell kill by minimizing the repair capacity of cell after photon radiation. Single session hyperthermia and radiation therapy overcomes the thermotolerance-associated inefficiency of hyperthermia treatment as it is when hyperthermia is combined with fractionated, lower dose rate radiation. The synergetic effects of sublethal damage repair inhibiting single session hyperthermia-combined with high dose and dose rate single session radiation therapy, and combined chemotherapy brings the photon radiation therapy's tumor cure and control capabilities closer to high LET radiation therapy.
Owner:SAHADEVAN VELAYUDHAN
Small molecule inhibitors of MDM2 and the uses thereof
InactiveUS7759383B2Extended half-lifeIncrease the function(s) of p53BiocideOrganic chemistrySensitized cellMdm2 Protein
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Compounds with anti-cancer activity
ActiveUS20080275057A1Strong cytotoxicityLittle and cytotoxic activityBiocideOrganic chemistryCancer cellG2 Cell Cycle Arrest
Novel substituted azole diones are provided that kill cells, suppress cell proliferation, suppress cell growth, abrogate the cell cycle G2 checkpoint and / or cause adaptation to G2 cell cycle arrest. Methods of making and using the invention compounds are provided. The invention provides substituted azole diones to treat cell proliferation disorders. The invention includes the use of substituted azole diones to selectively kill or suppress cancer cells without additional anti-cancer treatment. The invention includes the use of cell cycle G2-checkpoint-abrogating substituted azole diones to selectively sensitize cancer cells to DNA damaging reagents, treatments and / or other types of anti-cancer reagents.
Owner:CANBAS CO LTD (JP)
Indole inhibitors of MDM2 and the uses thereof
InactiveUS7737174B2Growth inhibitionExtended half-lifeBiocideOrganic chemistrySensitized cellMdm2 Protein
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Methods and compositions for evaluating breast cancer prognosis
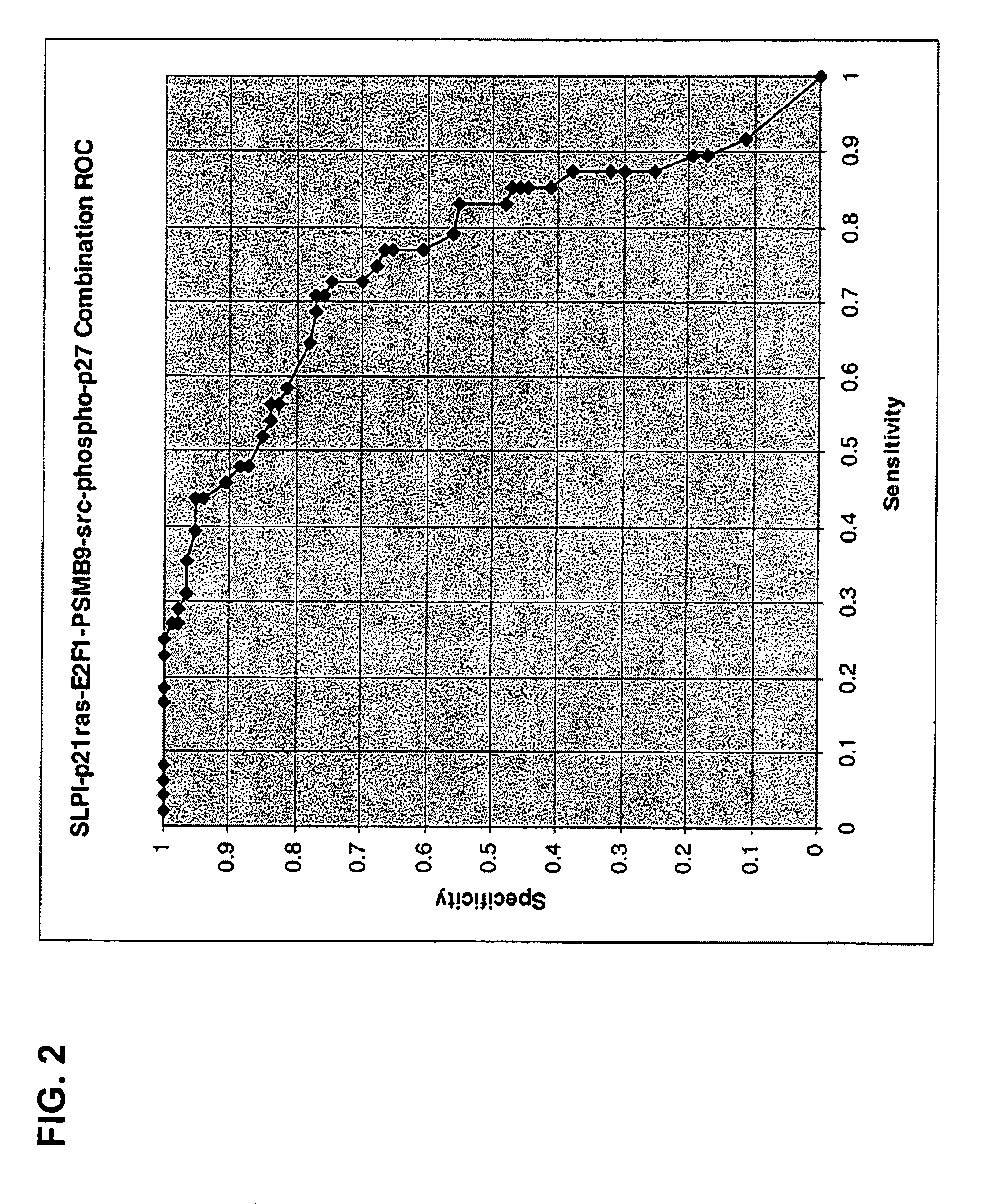
InactiveUS20060063190A1Accurate assessmentImproved prognosisMicrobiological testing/measurementProteomicsLymphatic SpreadNucleic acid hybridisation
Methods and compositions for evaluating the prognosis of a breast cancer patient, particularly an early-stage breast cancer patient, are provided. The methods of the invention comprise detecting expression of at least one, more particularly at least two, biomarker(s) in a body sample, wherein overexpression of the biomarker or a combination of biomarkers is indicative of breast cancer prognosis. In some embodiments, the body sample is a breast tissue sample, particularly a primary breast tumor sample. The biomarkers of the invention are proteins and / or genes whose overexpression is indicative of either a good or bad cancer prognosis. Biomarkers of interest include proteins and genes involved in cell cycle regulation, DNA replication, transcription, signal transduction, cell proliferation, invasion, proteolysis, or metastasis. In some aspects of the invention, overexpression of a biomarker of interest is detected at the protein level using biomarker-specific antibodies or at the nucleic acid level using nucleic acid hybridization techniques.
Owner:TRIPATH IMAGING INC
Recording and mapping lineage information and molecular events in individual cells
InactiveUS20150225801A1Nucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementCellular pathwaysFluorescent imaging
Methods and systems for recording and mapping lineage information and molecular events in individual cells are provided. Molecular changes, which may result from random or specific molecular events, are introduced to defined regions in cells over multiple cell cycle generations. Techniques such as fluorescent imaging are applied to track and identify the molecular changes before such information is used for lineage analysis or for identifying key processes and key players in cellular pathways.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Methods for treating cell proliferative disorders and viral infections
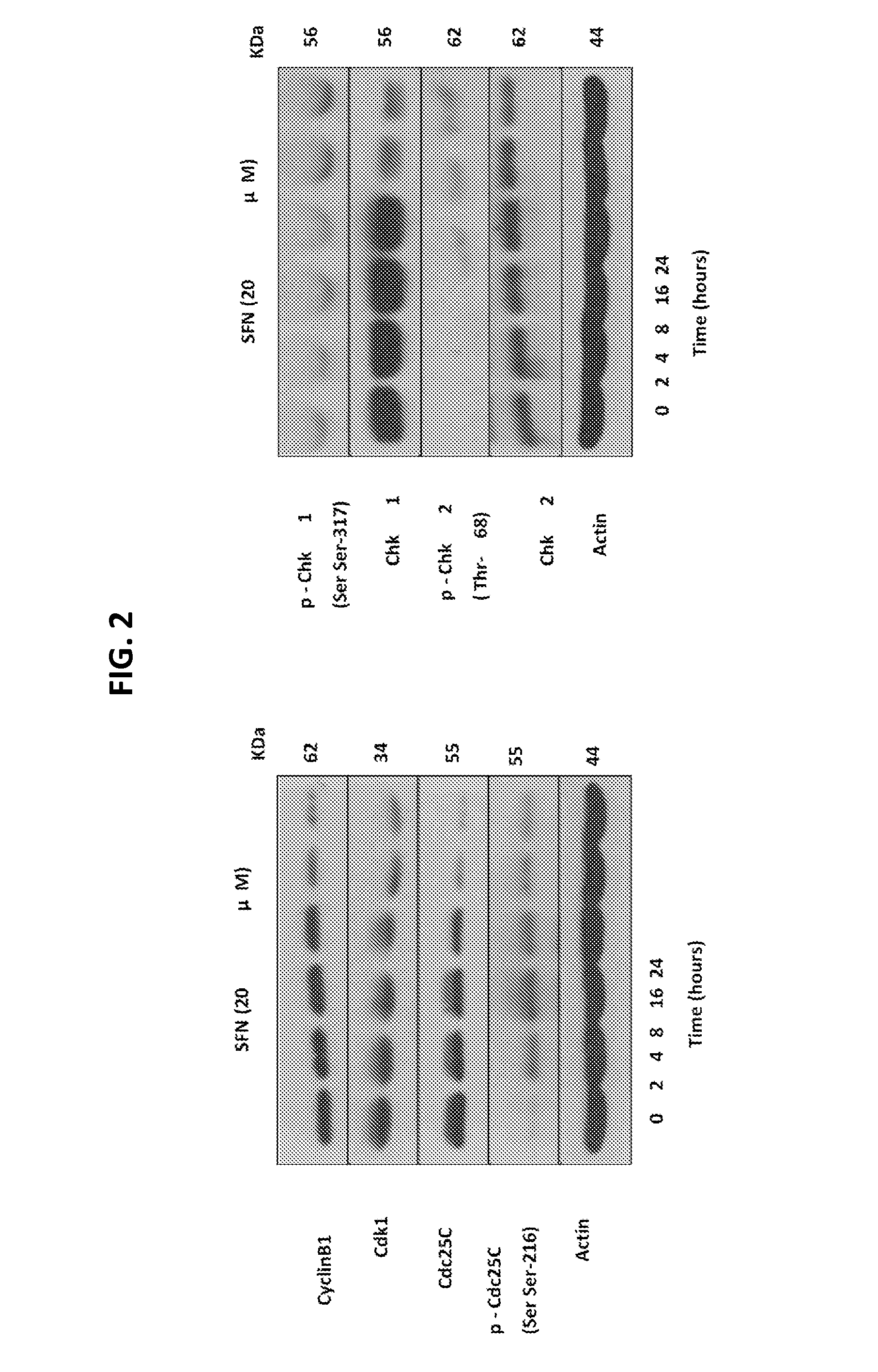
The present invention concerns methods for treating cell proliferative diseases, tumors associated with viral infections, and certain viral infections. The disclosed methods use compounds which inhibit heat shock protein 90 proteins. Such methods block Rb negative or deficient cells in the G2 / M phase of the cell cycle and rapidly causes their destruction.
Owner:SLOAN KETTERING INST FOR CANCER RES
Gene specifically expressed in postmitotic dopaminergic neuron precursor cells
InactiveUS20070122882A1Efficient separationEasy to prepareFungiBacteriaNeuro-degenerative diseaseNovel gene
A novel gene 65B13 expressed specifically and transiently in dopaminergic neuron precursor cells immediately after cell cycle exit was obtained by the present invention. The cellular expression of 65B13 can be used as an index to select cells that are suitable in terms of their safety, survival rate, and network formation ability, for transplant therapy of neurodegenerative diseases such as Parkinson's disease.
Owner:EISIA R&D MANAGEMENT CO LTD
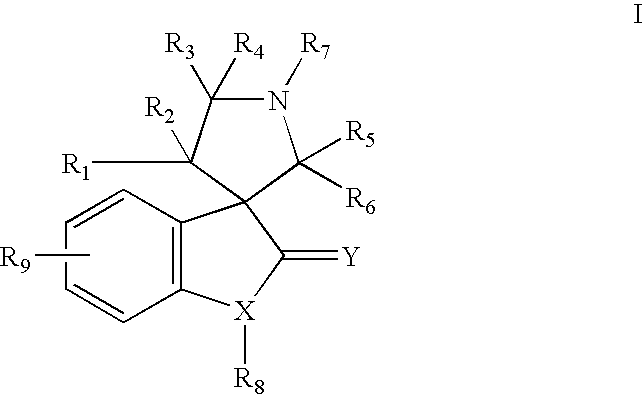
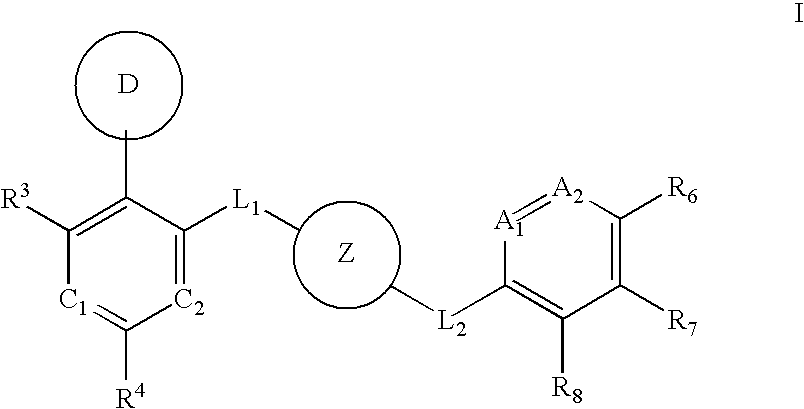
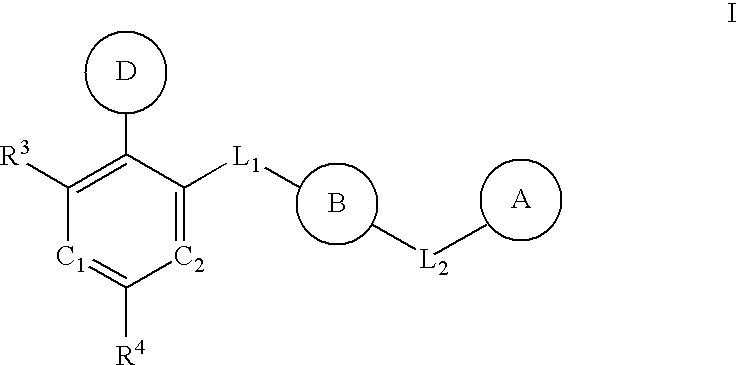
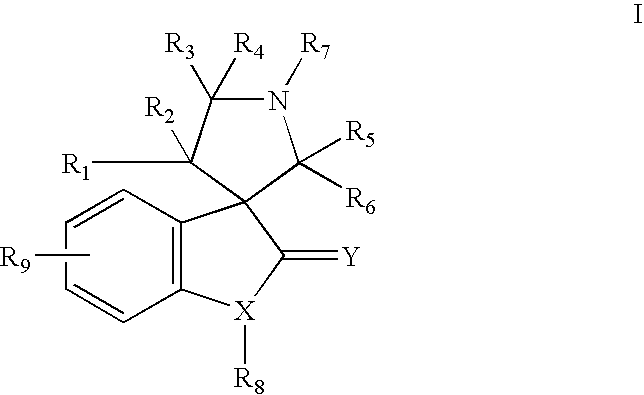
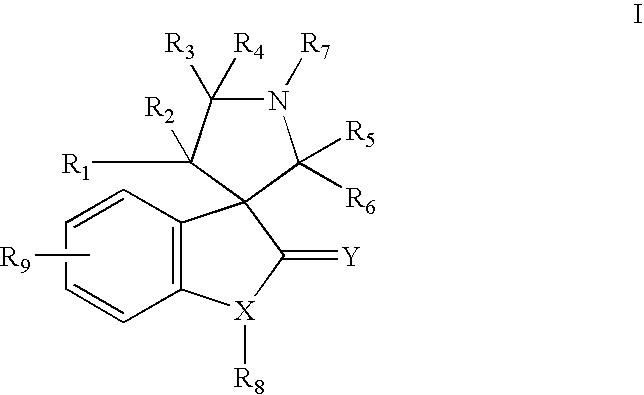
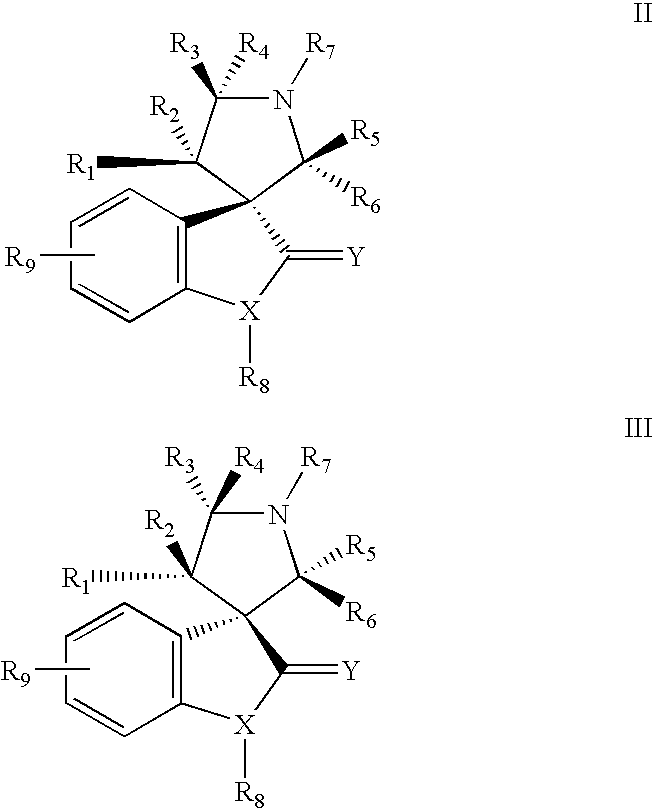
Aurora kinase modulators and method of use
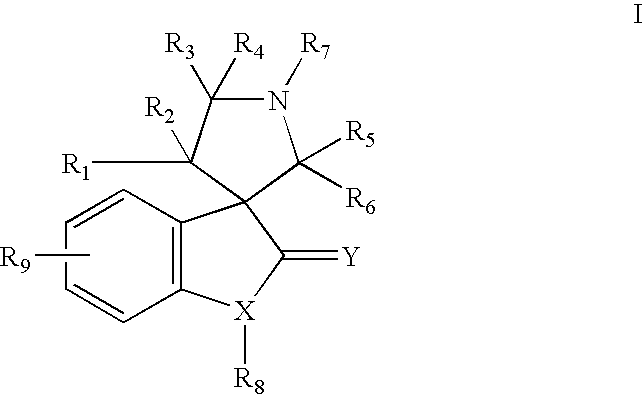
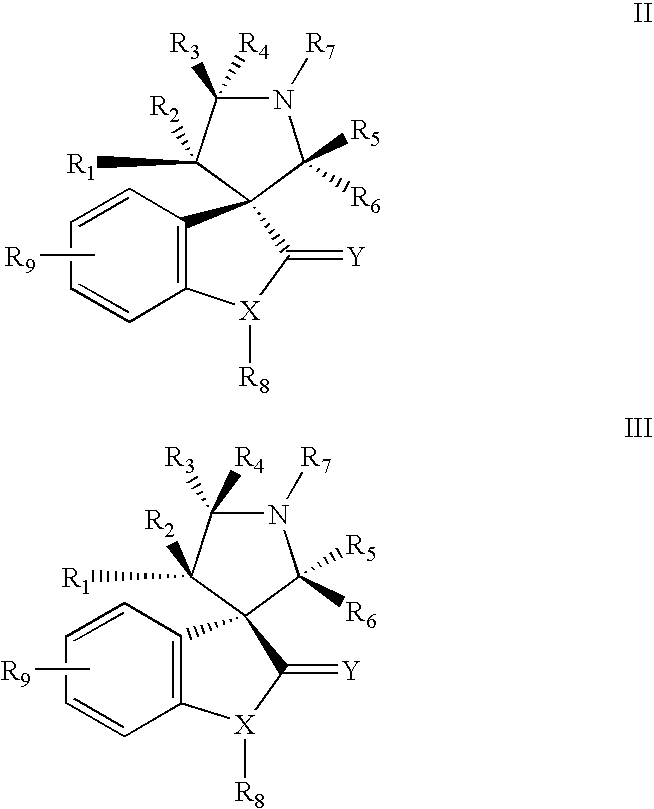
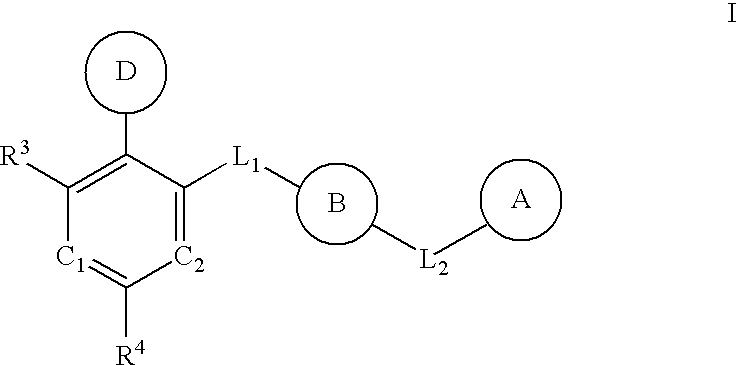
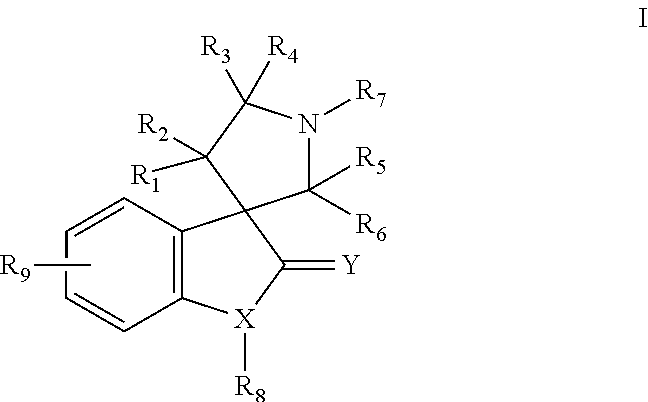
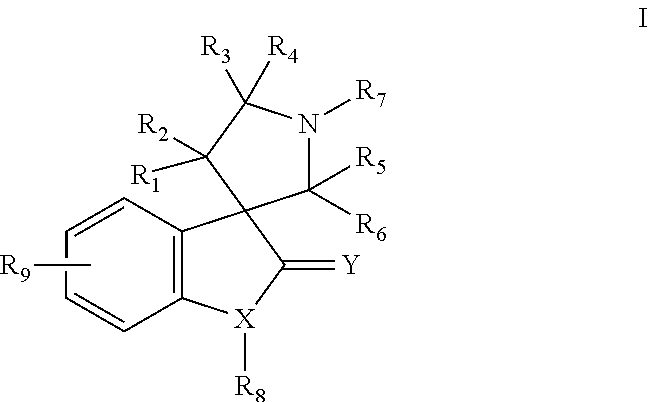
The present invention relates to chemical compounds having a general formula Iwherein A1, A2, C1, C2, D, L1, L2, Z and R1-8 are defined herein, and synthetic intermediates, which are capable of modulating various protein kinase receptor enzymes and, thereby, influencing various disease states and conditions related to the activities of such kinases. For example, the compounds are capable of modulating Aurora kinase thereby influencing the process of cell cycle and cell proliferation to treat cancer and cancer-related diseases. The invention also includes pharmaceutical compositions, including the compounds, and methods of treating disease states related to the activity of Aurora kinase.
Owner:AMGEN INC
Novel anti aging agents and methods to identify them
ActiveUS20100260733A1Stimulate mitochondrial functionPrevent and treat deteriorationOrganic active ingredientsSenses disorderAge related diseaseHigh-Throughput Screening Methods
The present invention discloses novel mechanisms in the aging process and describes novel methods for high-throughput screening to identify, detect, and purify agents to be used for improving mitochondrial function, maintaining the cell cycle-arrested state in senescent and post mitotic cells, and thus preventing or treating age-related diseases or disorders associated with accelerated mitochondrial function loss, telomere dysfunction, and / or deterioration of the growth-arrested state. The present invention also discloses a number of compounds or compositions identified from this method. The present invention further provides the use of low doses of rapamycin or its analogs as a mimic of caloric restriction in preventing age-related diseases or disorders.
Owner:QI HAIYAN
Melanoma chemoprevention
ActiveUS9393225B2Inhibits melanoma cell growthLowered STAT expressionPharmaceutical delivery mechanismDisease diagnosisEnteral administrationMedicine
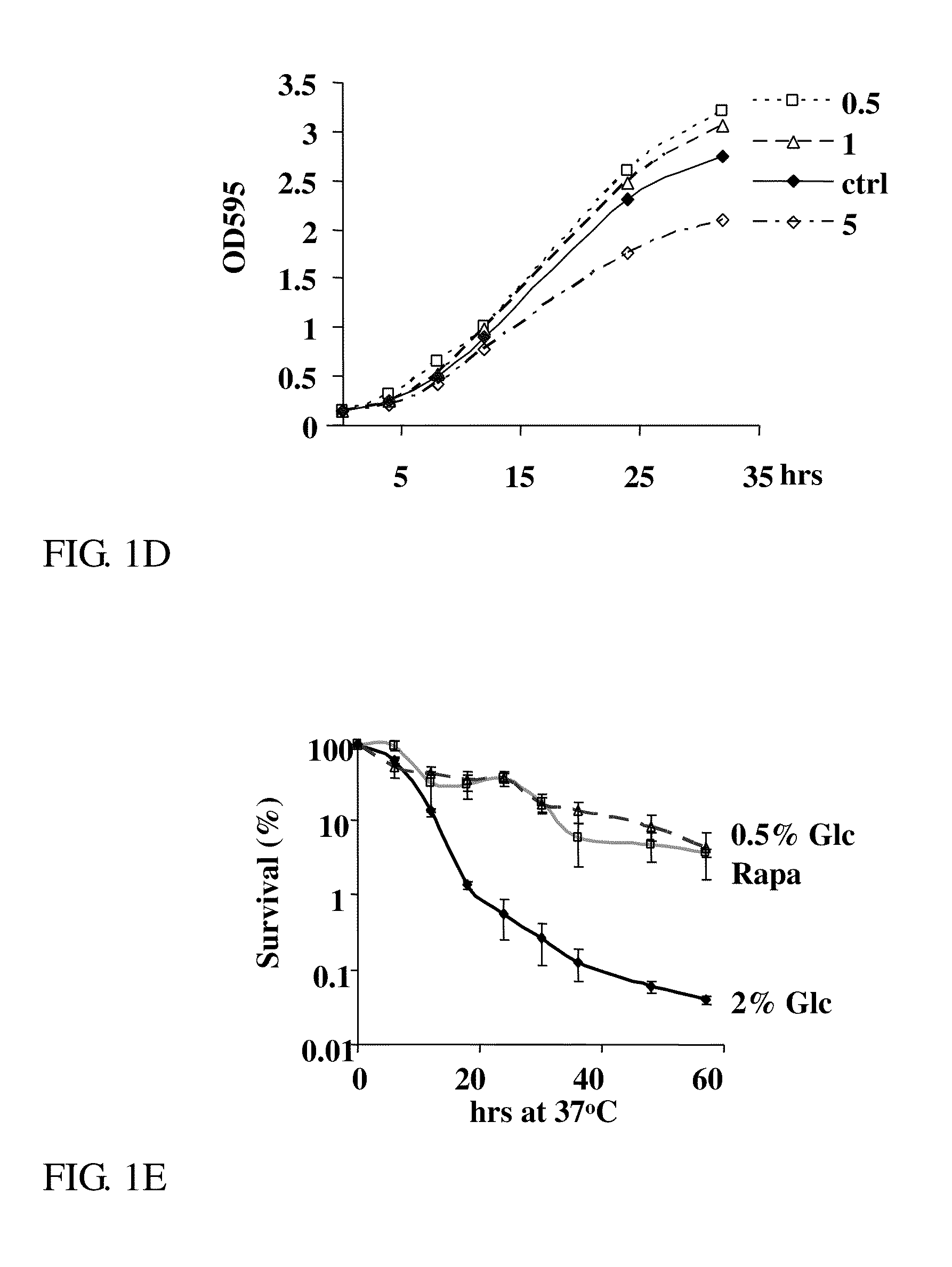
Disclosed herein are methods and uses for preventing melanoma, reducing progression of atypical nevi, and inducing cell cycle arrest and / or apoptosis in a melanoma cell through oral and enteral administration of sulforaphane to subjects indicated to be at risk due to factor(s) such as medical history of atypical nevi, melanoma, or UV exposure. Sulforaphane can be administered orally as a safe and well-tolerated natural agent as a chemopreventive strategy in individuals with atypical melanocytic nevi.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF PITTSBURGH
Small molecule inhibitors of MDM2 and the uses thereof
InactiveUS20060211757A1Growth inhibitionExtended half-lifeBiocideOrganic chemistrySensitized cellMdm2 Protein
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Micro-fluidic chip detection system based on single-cell multi-parameter representation
ActiveCN103439241AAchieve rotation-free stretchingImprove accuracyLaboratory glasswaresIndividual particle analysisElectrical resistance and conductanceHigh flux
The invention discloses a micro-fluidic chip detection system based on single-cell multi-parameter representation. The micro-fluidic chip detection system mainly comprises a micro-fluidic chip, an optical detection module, an impedance detection module and a processor, wherein the micro-fluidic chip is formed by sequentially aligning and bonding three layers of substrates, two symmetrical transport focusing runners and two symmetric outlet runners are arranged on the runner layer, a cross-shaped structure is formed by a junction of the two transport focusing runners and the outlet runners, electrodes of the upper layer of substrate and the lower layer of substrate are oppositely arranged to form a counter electrode structure, and each of the two outlet runners is provided with the counter electrode structure. According to the micro-fluidic chip detection system disclosed by the invention, a plurality of parameter of a single cell can be simultaneously represented, the accuracy and the sensitivity of cell detection are improved, a sheath liquid is not needed, and complex immunolabelling pretreatment is not needed. The micro-fluidic chip detection system has the advantages of low cost, simplicity in operation, high flux, high integration and automation degree and the like. The micro-fluidic chip detection system disclosed by the invention can be widely applied to the fields of cell cycle, cell differentiation, drug screening, early diagnosis and treatment of illnesses, and the like.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
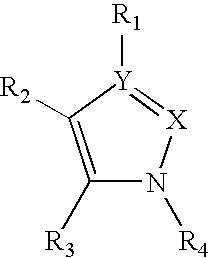
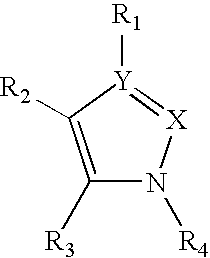
Pyrazole compounds
InactiveUS20030060453A1Useful in treatmentBiocideMonoazo dyesLymphoproliferative diseaseAngiogenesis growth factor
Pharmaceutical compositions and compounds are provided. The compounds of the invention demonstrate anti-proliferative activity, and may promote apoptosis in cells lacking normal regulation of cell cycle and death. In one embodiment of the invention, pharmaceutical compositions of the compounds in combination with a physiologically acceptable carrier are provided. The pharmaceutical compositions are useful in the treatment of hyperproliferative disorders, which disorders include tumor growth, lymphoproliferative diseases, angiogenesis. The compounds of the invention are substituted pyrazoles and pyrazolines.
Owner:DERMIRA CANADA
Aurora kinase modulators and method of use
The present invention relates to chemical compounds having a general formula I wherein A1, A2, C1, C2, D, L1, L2, Z and R1- are defined herein, and synthetic intermediates, which are capable of modulating various protein kinase receptor enzymes and, thereby, influencing various disease states and conditions related to the activities of such kinases. For example, the compounds are capable of modulating Aurora kinase thereby influencing the process of cell cycle and cell proliferation to treat cancer and cancer-related diseases. The invention also includes pharmaceutical compositions, including the compounds, and methods of treating disease states related to the activity of Aurora kinase.
Owner:AMGEN INC
Plant cell cycle genes and methods of use
InactiveUS20050044591A1Promote regenerationImprove transformation efficiencySugar derivativesHydrolasesGrowth plantPlant cell
This application discloses plant polynucleotide sequences encoding polypeptide regulators of plant growth and reproduction, and their methods of use.
Owner:ARBORGEN
Novel Compounds for Treatment of Cancer and Disorders Associated with Angiogenesis Function
Novel compounds for treatment of cancer and disorders associated with angiogenesis function. Also disclosed are a method of preparing the compounds, pharmaceutical compositions and packaged products containing the compounds, a method of using these molecules to treat cancer (e.g., leukemia, non-small cell lung cancer, colon cancer, CNS cancer, melanoma, ovarian cancer, breast cancer, renal cancer, and prostate cancer) and disorders associated with angiogenesis function (e.g., age-related macular degeneration, macular dystrophy, and diabetes), a method of monitoring the treatment, a method of profiling gene expression, and a method of modulating cell growth, cell cycle, apoptosis, or gene expression.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA
Multi-cyclic compounds and method of use
The present invention relates to chemical compounds having a general formula Iwherein A, B, C1, C2, D, L1, L2 and R3-4 are defined herein, and synthetic intermediates, which are capable of modulating various protein kinase receptor enzymes and, thereby, influencing various disease states and conditions related to the activities of such kinases. For example, the compounds are capable of modulating Tie-2 and Aurora kinase enzymes thereby influencing angiogenesis and the process of cell cycle and cell proliferation, respectively, to treat cancer and cancer-related diseases. The invention also includes pharmaceutical compositions, including the compounds, and methods of treating disease states related to the activity of various protein kinases.
Owner:AMGEN INC
Compositions, methods and kits relating to reprogramming adult differentiated cells and production of embryonic stem cell-like cells
InactiveUS20060222636A1Improve the level ofBiocideGenetic material ingredientsNuclear transferSignalling pathways
The present invention includes compositions, methods and kits for non-nuclear transfer reprogramming an adult differentiated cell obtained from an adult tissue into an ES-like cell. The reprogrammed cell can be converted into an ES-like cell which can be re- or trans-differentiated into various differentiated cell types. The present invention further relates to identification of a novel signaling pathway, and components thereof, which effect reprogramming of a cell. The present invention further comprises compositions, methods and kits for regulating the mammalian cell cycle and cellular proliferation, as well as for treating diseases and for identifying components that affect the cell cycle, and reprogram cells, among other things.
Owner:THE ROCKEFELLER UNIV
Method for promoting human bone mesenchymal stem cell proliferation based on exosome
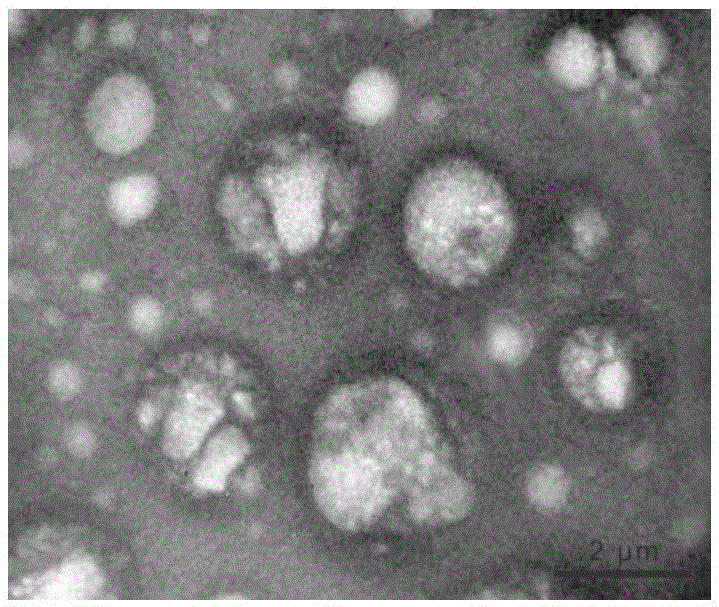
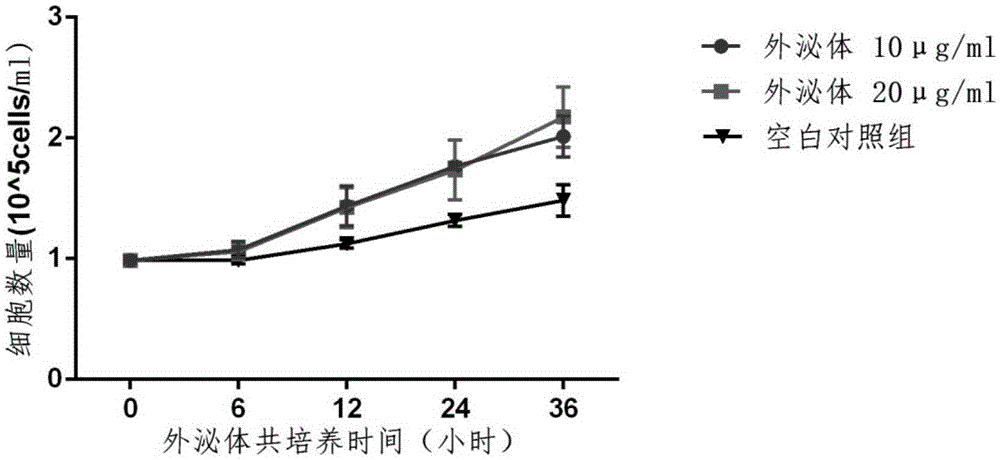
ActiveCN105349487AStable in natureComposition determinedUnknown materialsSkeletal/connective tissue cellsEarly generationMesenchymal stem cell proliferation
The invention relates to the field of biotechnology and mainly relates to a use of an early-generation human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell exosome in promotion of human bone mesenchymal stem cell growth. The use method is a method for promoting bone mesenchymal stem cell growth. The invention also relates to an extraction method of a human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell exosome. The early-generation human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell exosome and human bone mesenchymal stem cells are co-cultured so that human bone mesenchymal stem cell growth is obviously promoted, cell doubling time is shortened and a ratio of an S period in a cell period is increased.
Owner:SECOND MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV OF THE PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY
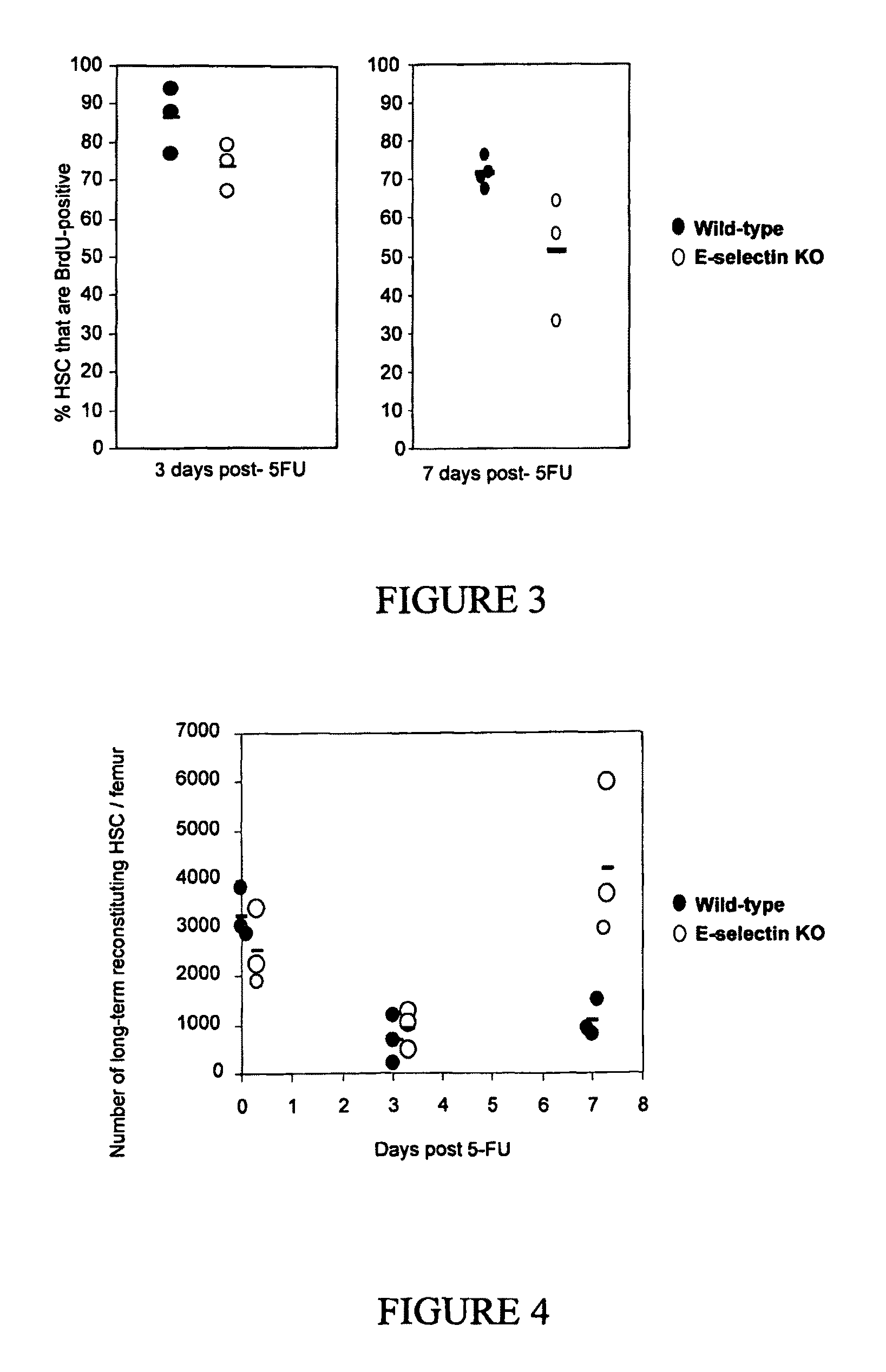
Compositions comprising E-selectin antagonists and uses therefor
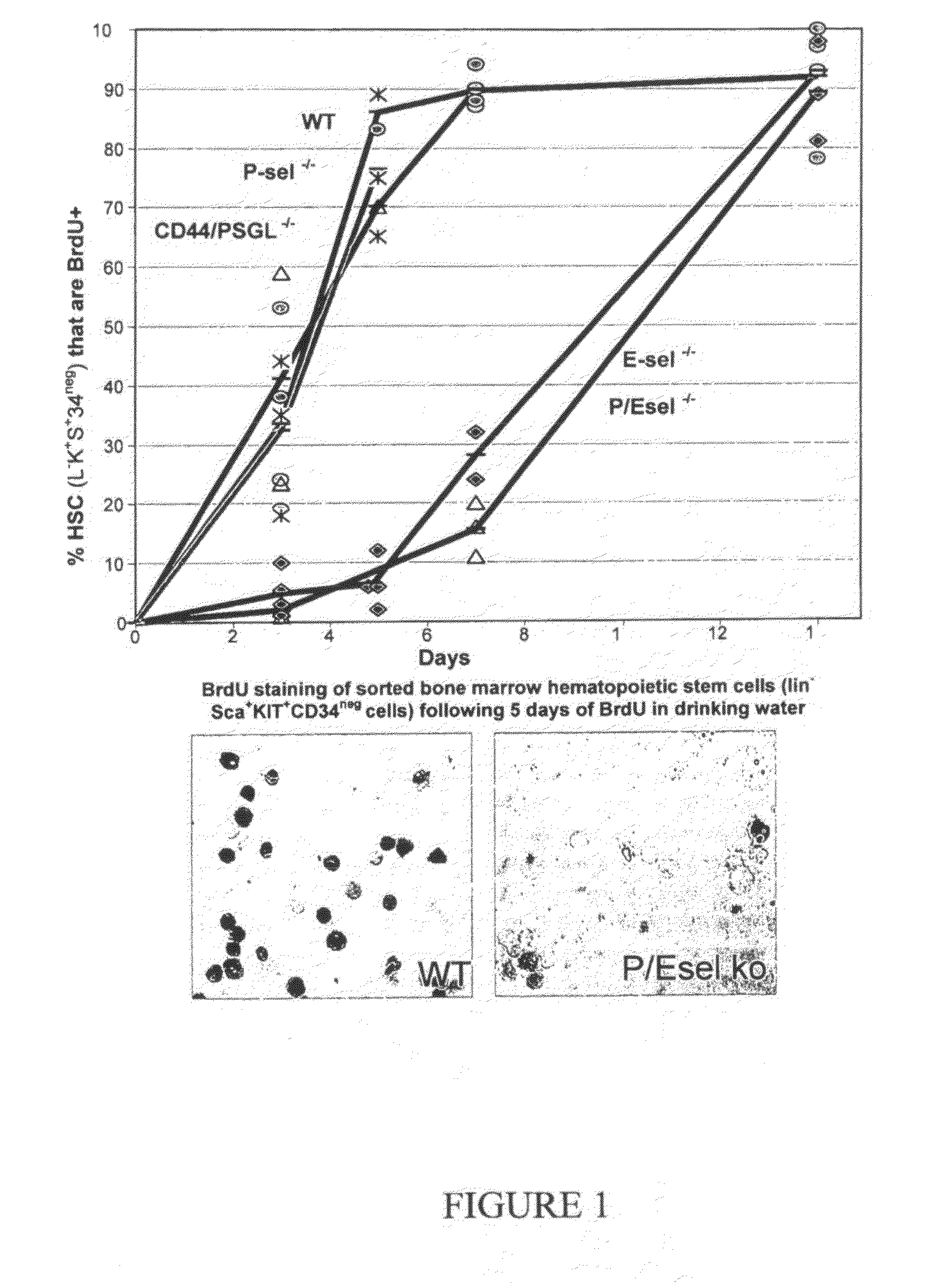
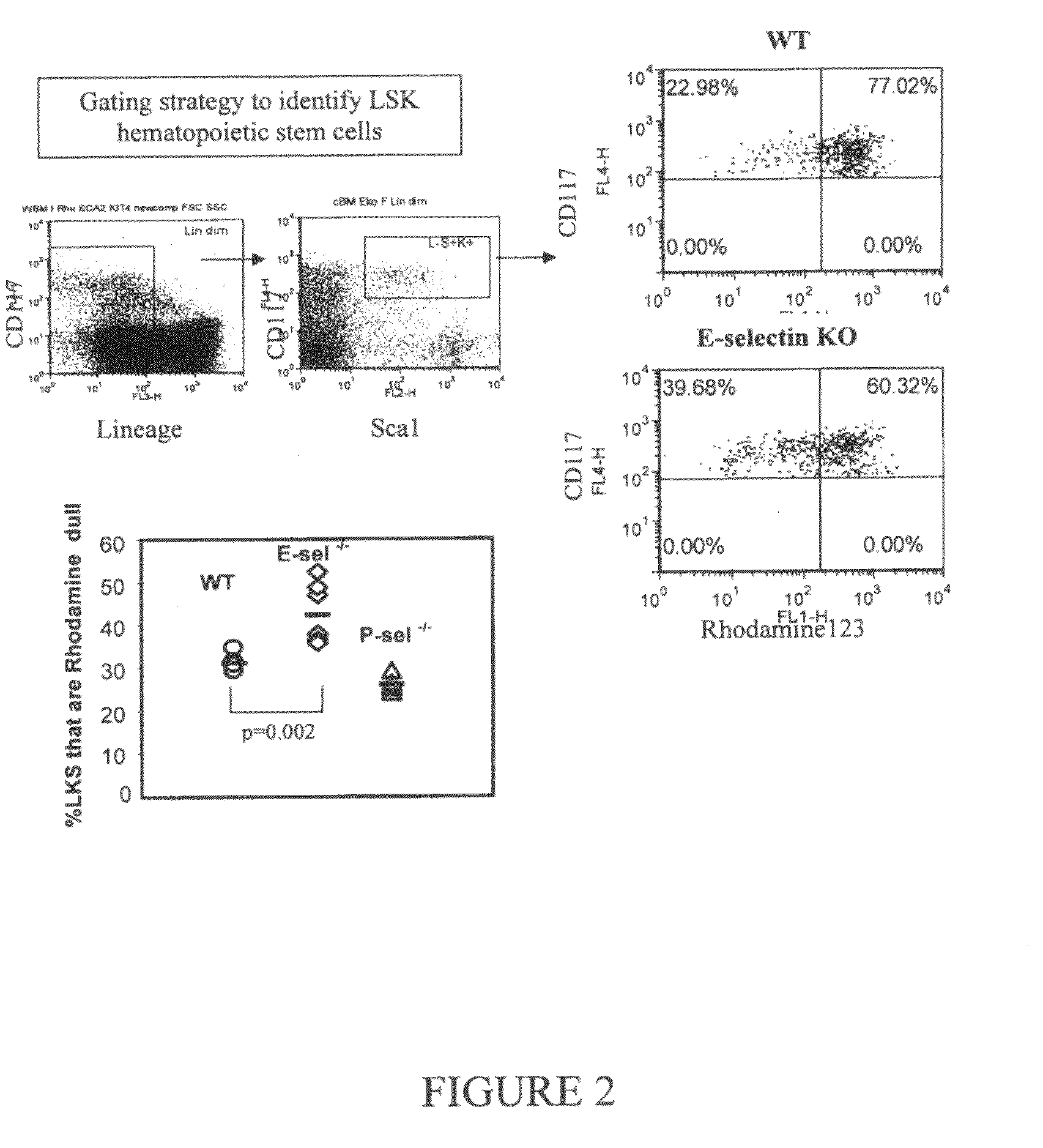
ActiveUS9254322B2Stimulating and enhancing hematopoiesisAvoid adjustmentPeptide/protein ingredientsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsProgenitorSurgery
This invention discloses the use of an E-selectin antagonist and a mobilizer of hematopoietic stem cells or progenitor cells in methods and compositions for treating or preventing immunocompromised conditions resulting from medical treatment. The present invention is particular relevant for prophylaxis and / or treatment of hematopoeitic disorders including neutropenia, agranulocytosis, anemia and thrombocytopenia in individuals receiving or proposed to receive treatments that target rapidly dividing cells or that disrupt the cell cycle or cell division.
Owner:THE UNIV OF QUEENSLAND
New small molecule inhibitors of mdm2 and the uses thereof
InactiveUS20080125430A1Growth inhibitionExtended half-lifeBiocideOrganic chemistrySensitized cellMdm2 Protein
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Electrodynamic profiling of genomic response in the cell
InactiveUS20060127879A1Highly preventive effectMicrobiological testing/measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCell EvaluationHydrogen
A method of cellular evaluation based on the electronic nature of cells is reveled though cellular reproductions use of a magnetic force. The dynamic process of nuclear response is shown to be electronic in nature relative to DNA mediating electrons hydrogen bonding in bases pairing of DNA though out the a cell cycle and finally during metaphase one see the magnetic component of interaction. The electrostatic understanding of magnetic force is not well defined in physics in the process of electrodynamic. Cells use electrodynamic interaction within the cell are being studied as the basis and using the cell to measure and define electrodynamic interaction with the system that is biological a call. Specifically DNA thought the electronic interaction interactions. It appears infrared spectrum holds promises to help in revel these mechanisms. The promise of understanding or merely evaluation of electrodynamic interaction holds great promise to science with the greatest medical implication to understand genomic responses in cells. Understanding how the DNA interacts within a cell dynamic transition are known to take place and these are regulated thought electrodynamic interaction.
Owner:FUCCIONE ANTHONY STEPHEN
Embryonic or stem-like cell lines produced by cross species nuclear transplantation and methods for enhancing embryonic development by genetic alteration of donor cells or by tissue culture conditions
InactiveUS20030229908A1Good curative effectIncrease productionNew breed animal cellsPeptide/protein ingredientsHeterologousEmbryo
An improved method of nuclear transfer involving the transplantation of differentiated donor cell nuclei into enucleated oocytes of a species different from the donor cell is provided. The resultant nuclear transfer units are useful for the production of isogenic embryonic stem cells, in particular human isogenic embryonic or stem cells. These embryonic or stem-like cells are useful for producing desired differentiated cells and for introduction, removal or modification, of desired genes, e.g., at specific sites of the genome of such cells by homologous recombination. These cells, which may contain a heterologous gene, are especially useful in cell transplantation therapies and for in vitro study of cell differentiation. Also, methods for improving nuclear transfer efficiency by genetically altering donor cells to inhibit apoptosis, select for a specific cell cycle and / or enhance embryonic growth and development are provided.
Owner:ADVANCED CELL TECH INC
Compounds, compositions and methods
The present invention provides methods and pharmaceutical compositions for inhibiting expressions of HIF and HIF regulated genes, inhibiting angiogenesis, inducing cell cycle arrest in tumor cells, and treating cell proliferating diseases or conditions.
Owner:HIF BIO +1
Pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide (PACAP) is an anti-mitogenic signal for selected neuronal precursors in vivo
InactiveUS20070149439A1Facilitated DiffusionNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseIn vivo
Pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide (PACAP) and its receptor system can be manipulated positively or negatively to regulate mitosis in neuronal precursor cells. The ligand / receptor system involves PACAP, PACAP receptor, PAC1, and related antagonists. The methods of regulation of the present invention may model be used to define cell cycle regulation in the developing neurons. The present invention may also be used to control or cure diseases related to or caused by damage to or destruction of neuronal cells.
Owner:DICICCO BLOOM EMANUEL +3
N2S2 chelate-targeting ligand conjugates
ActiveUS20050129619A1Sufficient amountHybrid immunoglobulinsRadioactive preparation carriersAngiostatinAbnormal tissue growth
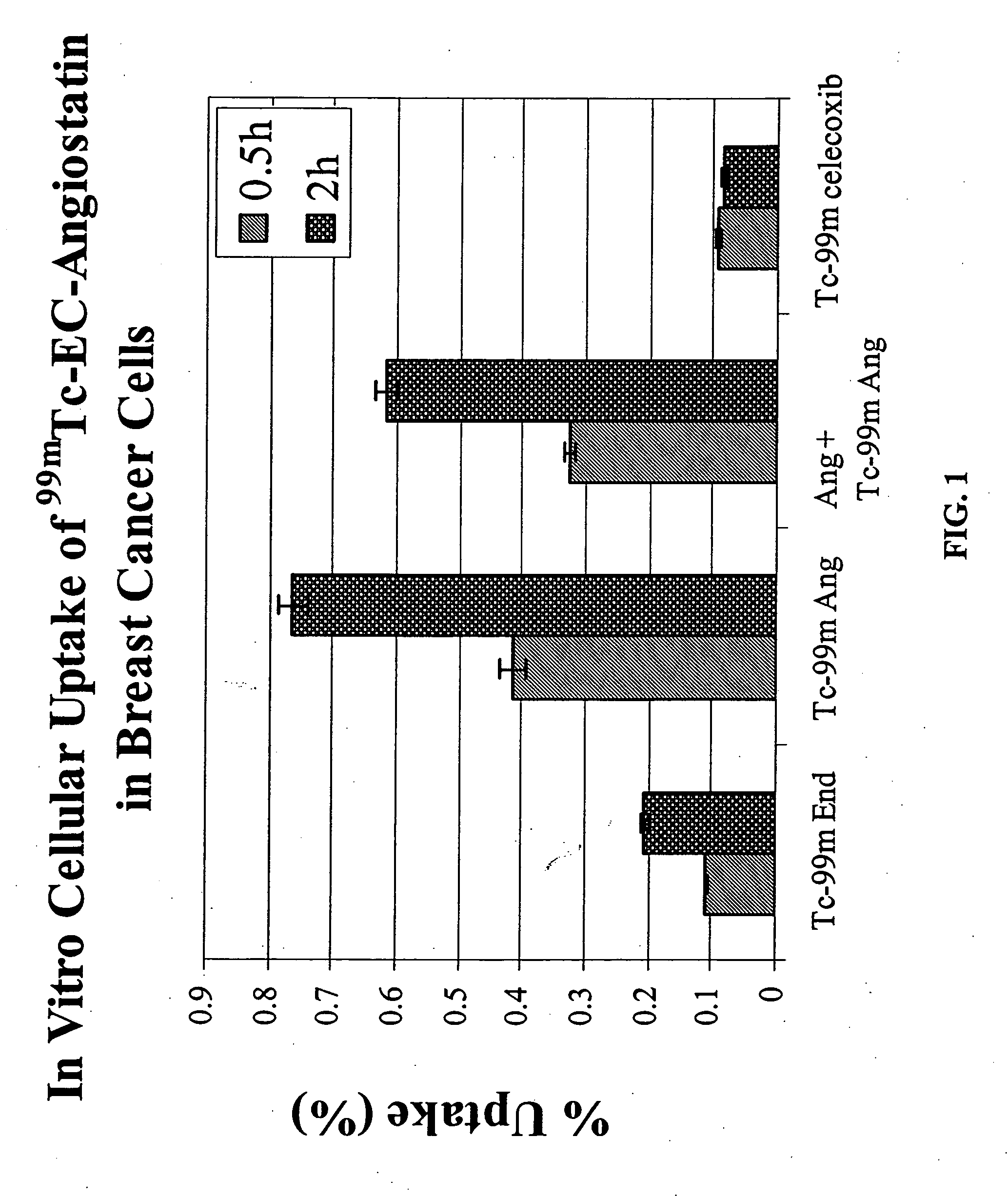
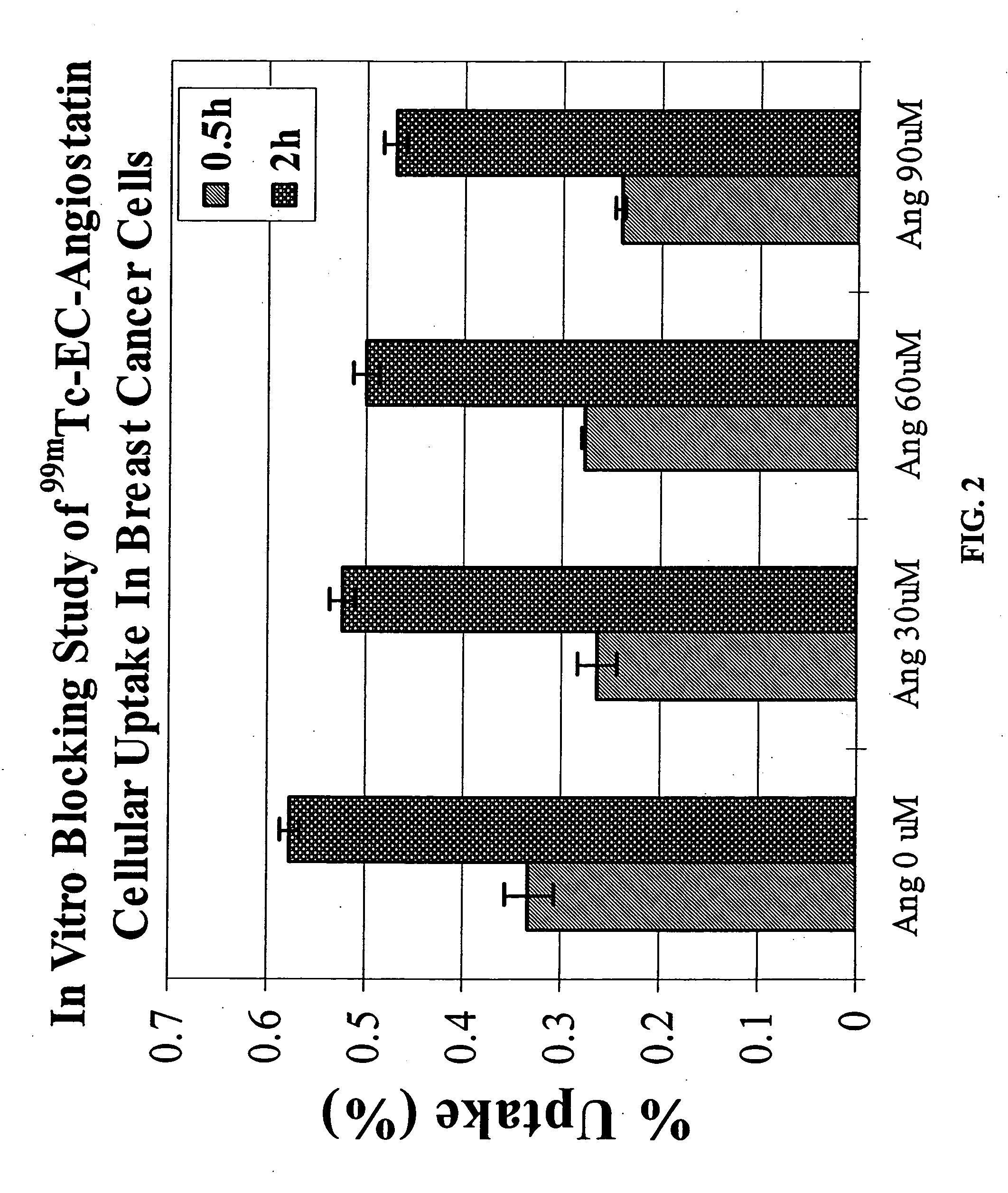
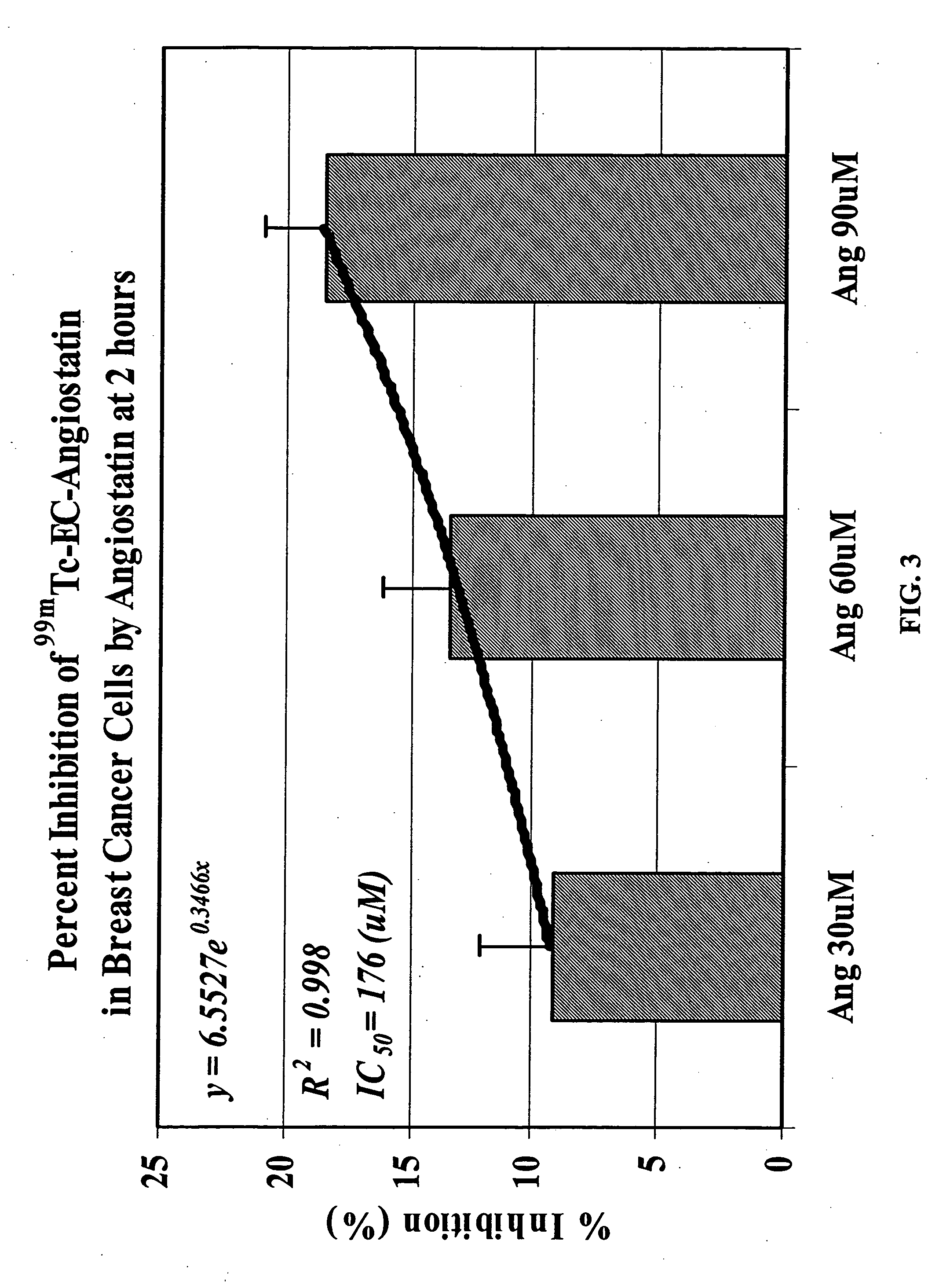
The invention provides, in a general sense, a new labeling strategy employing compounds that are are N2S2 chelates conjugated to a targeting ligand, wherein the targeting ligand is a disease cell cycle targeting compound, a tumor angiogenesis targeting ligand, a tumor apoptosis targeting ligand, a disease receptor targeting ligand, amifostine, angiostatin, monoclonal antibody C225, monoclonal antibody CD31, monoclonal antibody CD40, capecitabine, a COX-2 inhibitor, deoxycytidine, fullerene, herceptin, human serum albumin, lactose, leuteinizing hormone, pyridoxal, quinazoline, thalidomide, transferrin, or trimethyl lysine. The present invention also pertains to kits employing the compounds of interest, and methods of assessing the pharmacology of an agent of interest using the present compounds.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Small molecule inhibitors of MDM2 and the uses thereof
InactiveUS8222288B2Growth inhibitionExtended half-lifeBiocideOrganic chemistrySensitized cellCell growth
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com