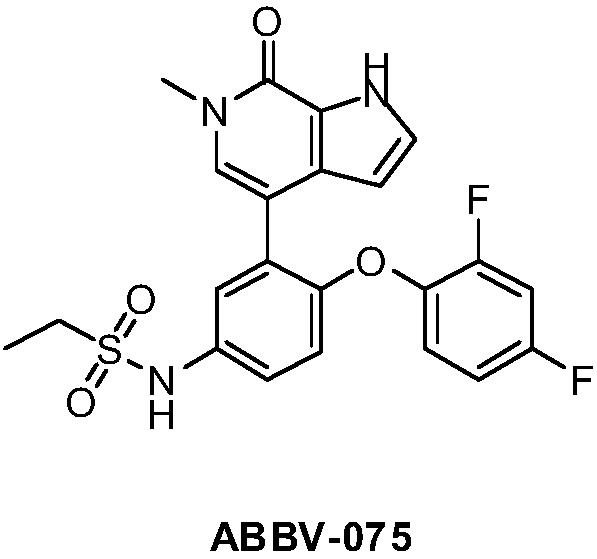
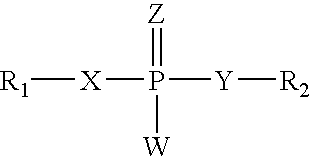Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
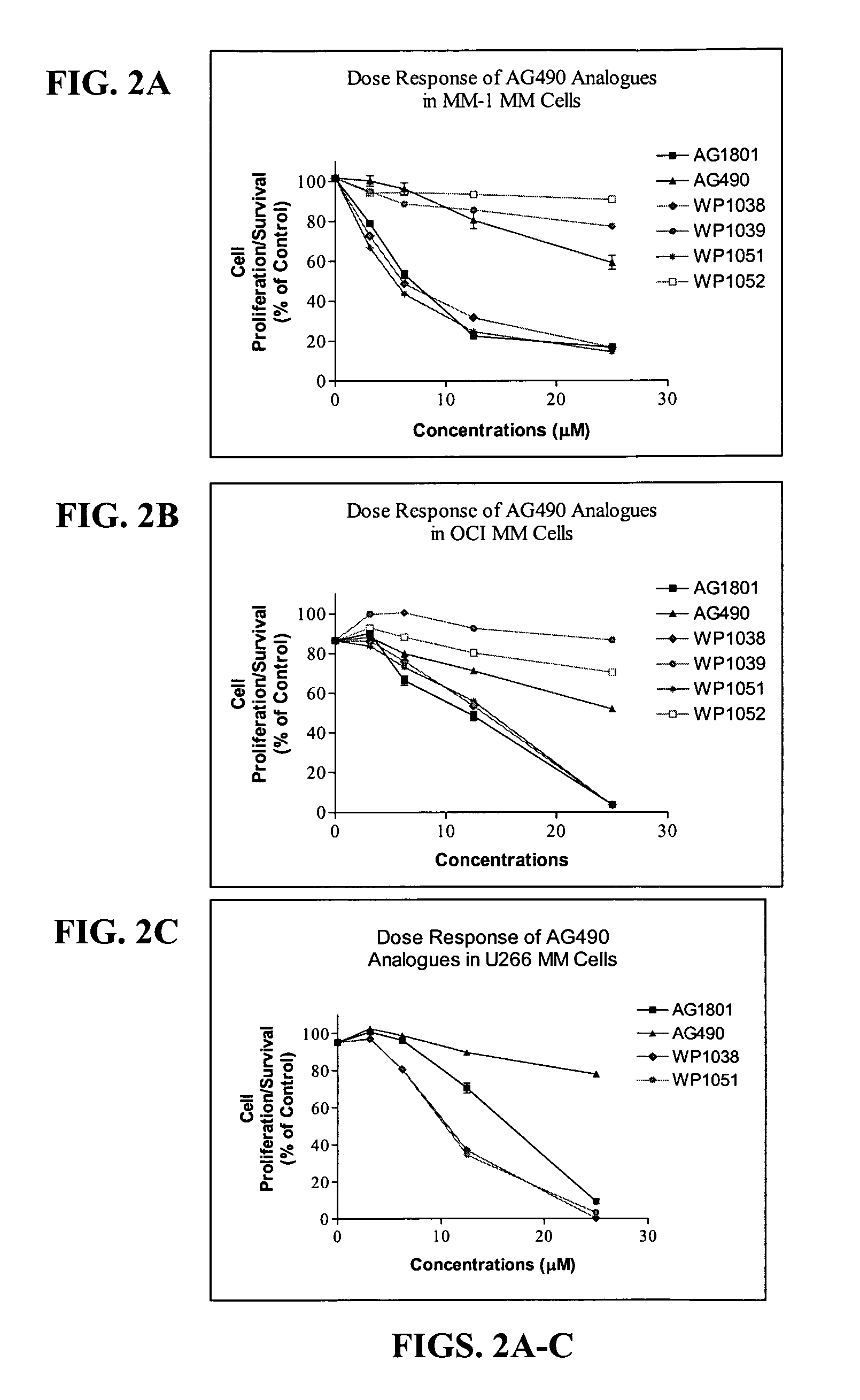
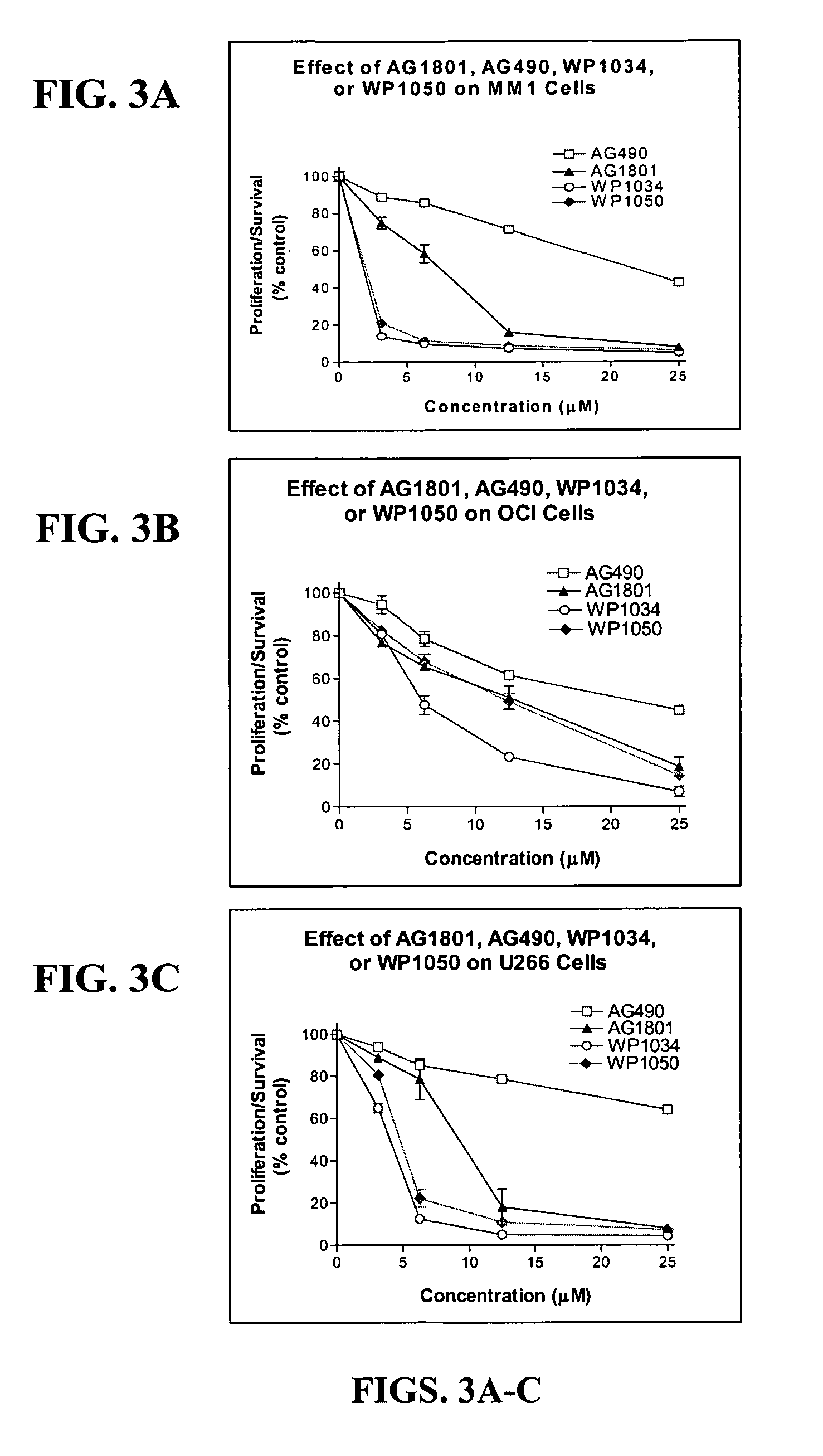
111 results about "MYC Translocation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A common human translocation involving c-myc is critical to the development of most cases of Burkitt lymphoma. Constitutive upregulation of Myc genes have also been observed in carcinoma of the cervix, colon, breast, lung and stomach. Myc is thus viewed as a promising target for anti-cancer drugs.
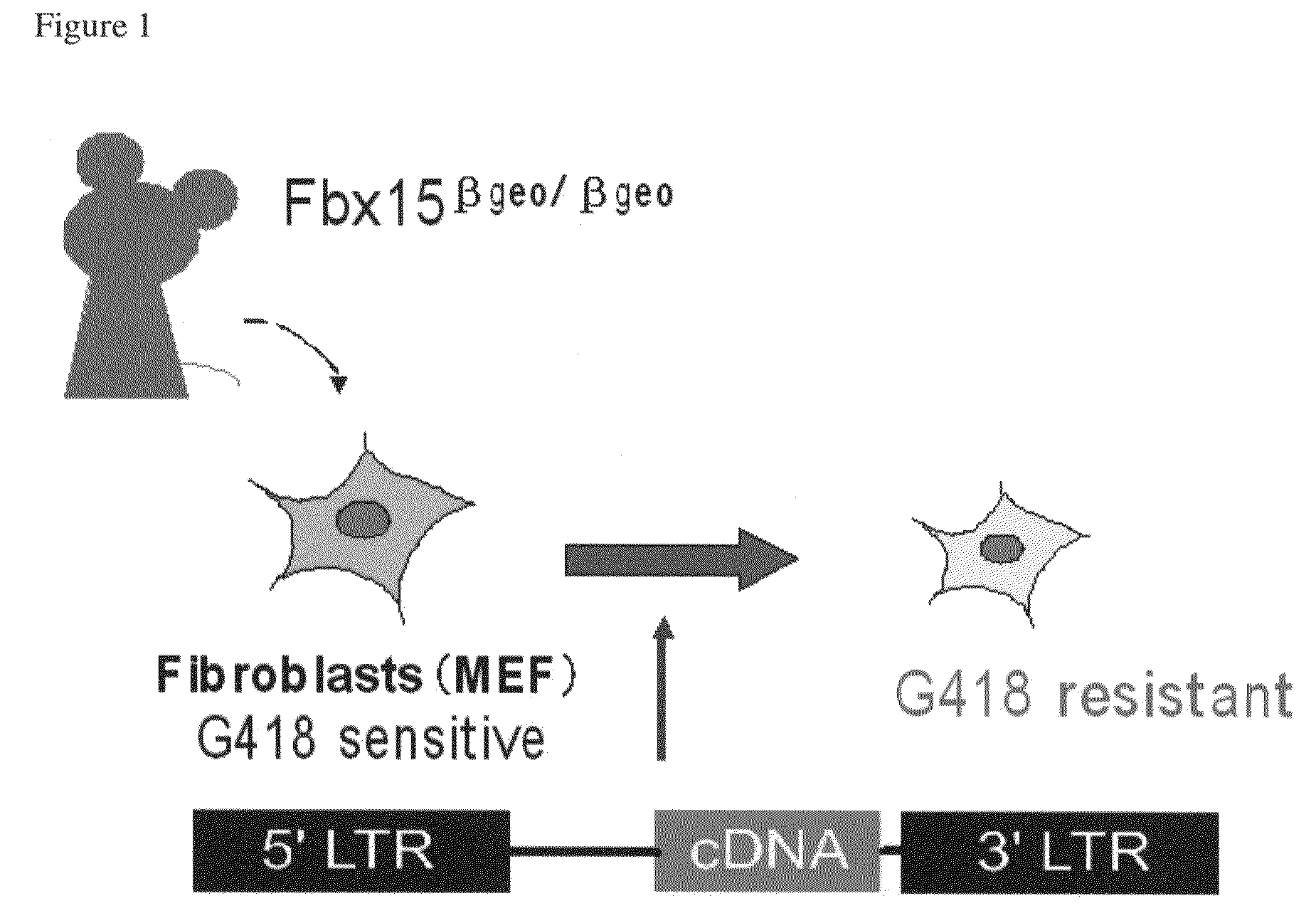
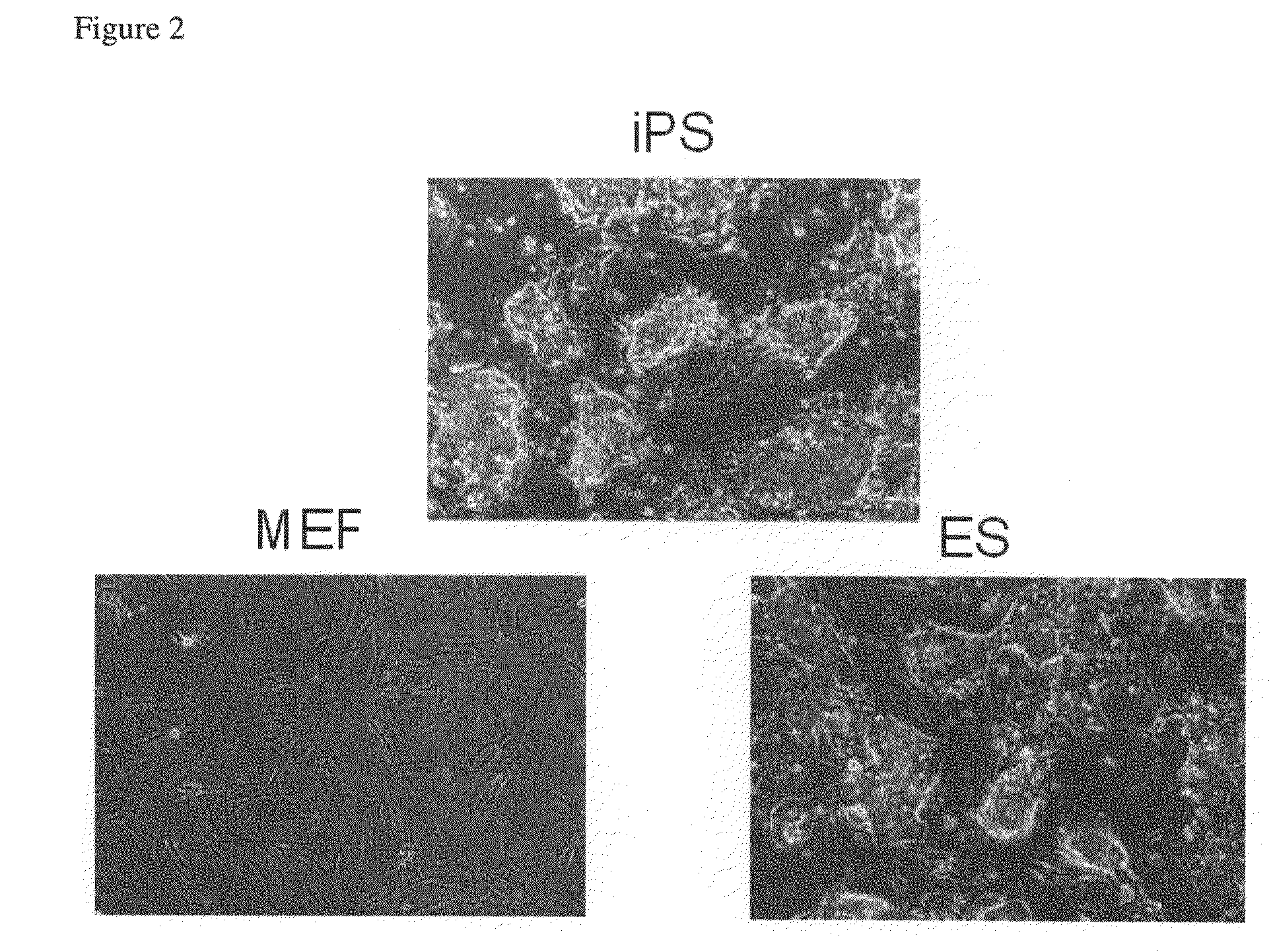
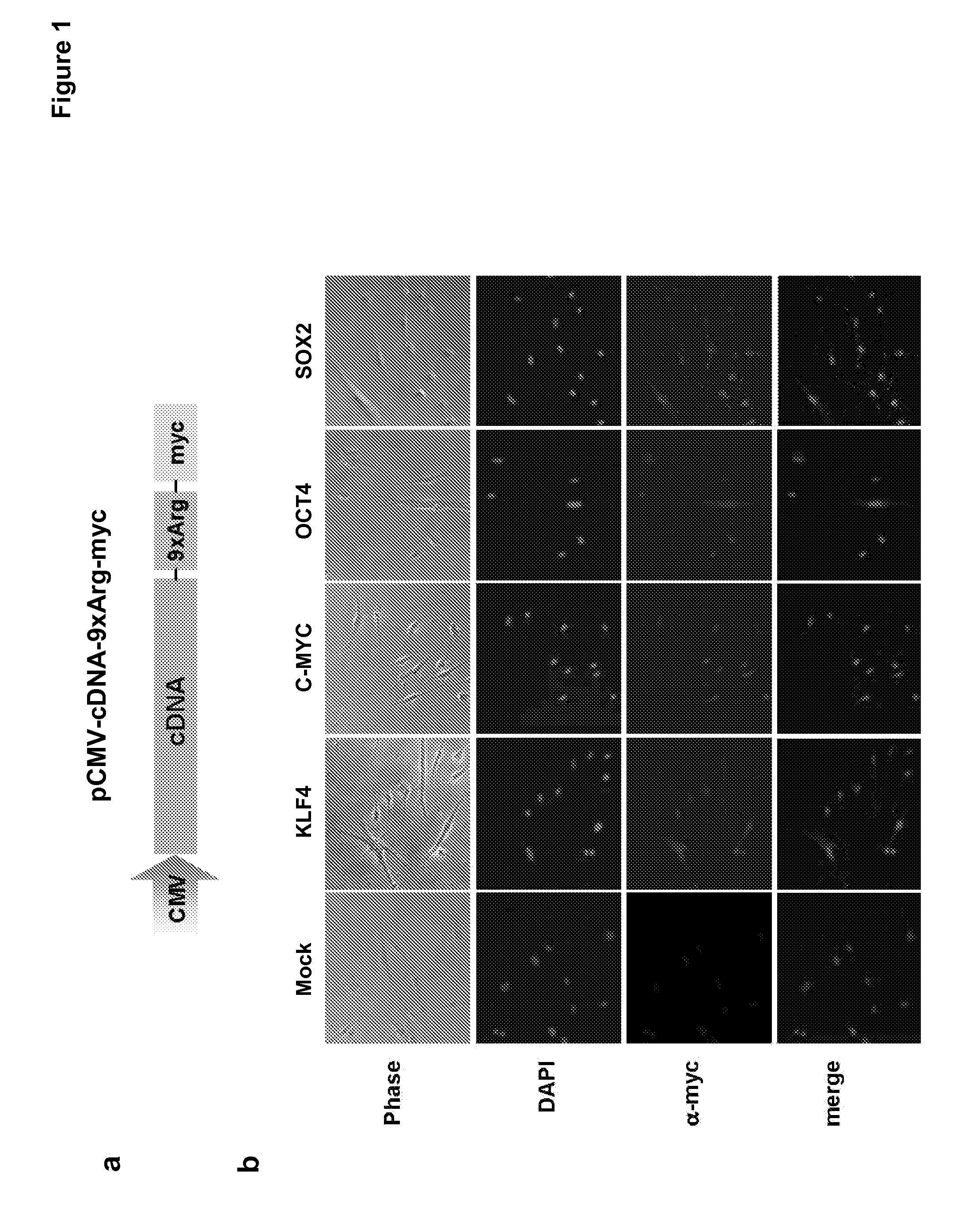
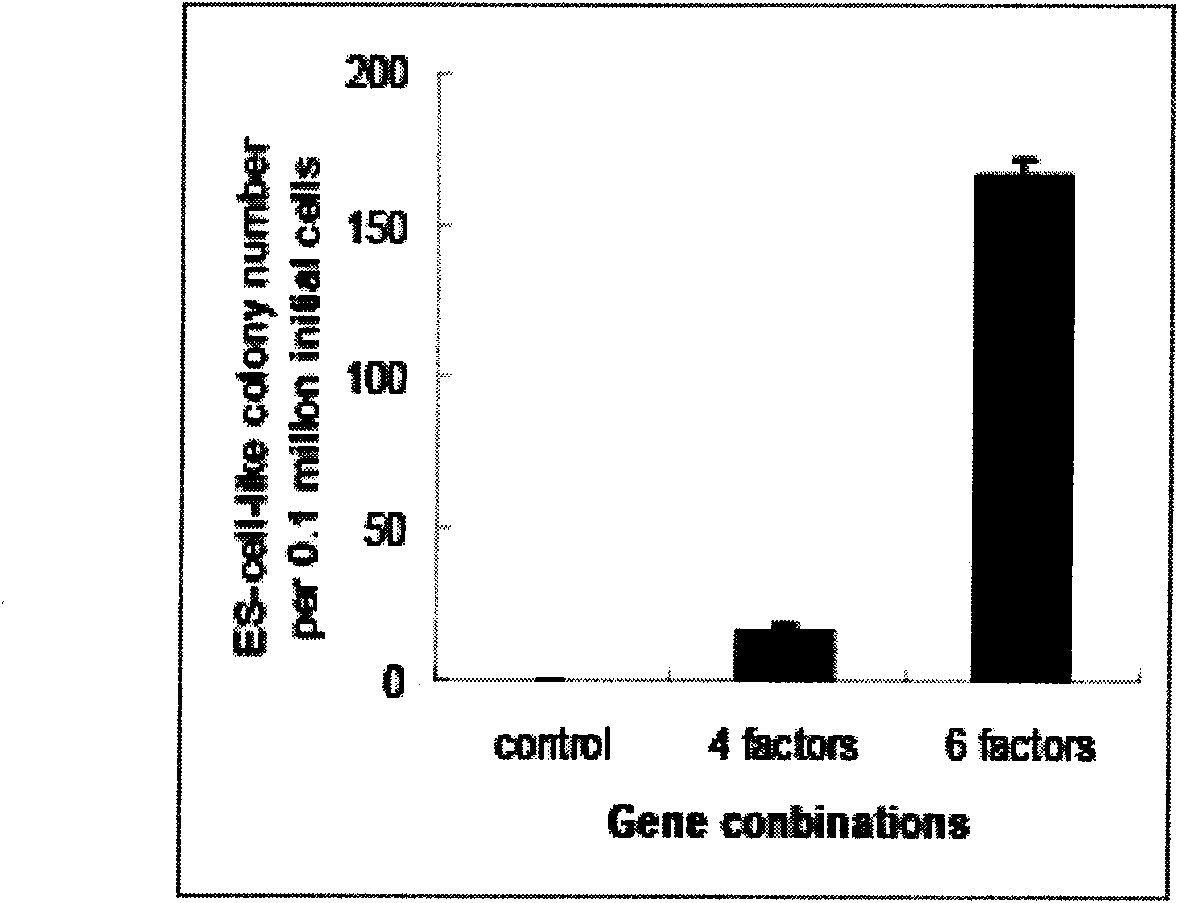
Somatic cell reprogramming by retroviral vectors encoding Oct3/4. Klf4, c-Myc and Sox2
ActiveUS8129187B2Easy to prepareEffective isolationGenetically modified cellsArtificial cell constructsNuclear reprogrammingCell therapy
The present invention relates to a nuclear reprogramming factor having an action of reprogramming a differentiated somatic cell to derive an induced pluripotent stem (iPS) cell. The present invention also relates to the aforementioned iPS cells, methods of generating and maintaining iPS cells, and methods of using iPS cells, including screening and testing methods as well as methods of stem cell therapy. The present invention also relates to somatic cells derived by inducing differentiation of the aforementioned iPS cells.
Owner:KYOTO UNIV
Antisense restenosis composition and method
Owner:SAREPTA THERAPEUTICS INC
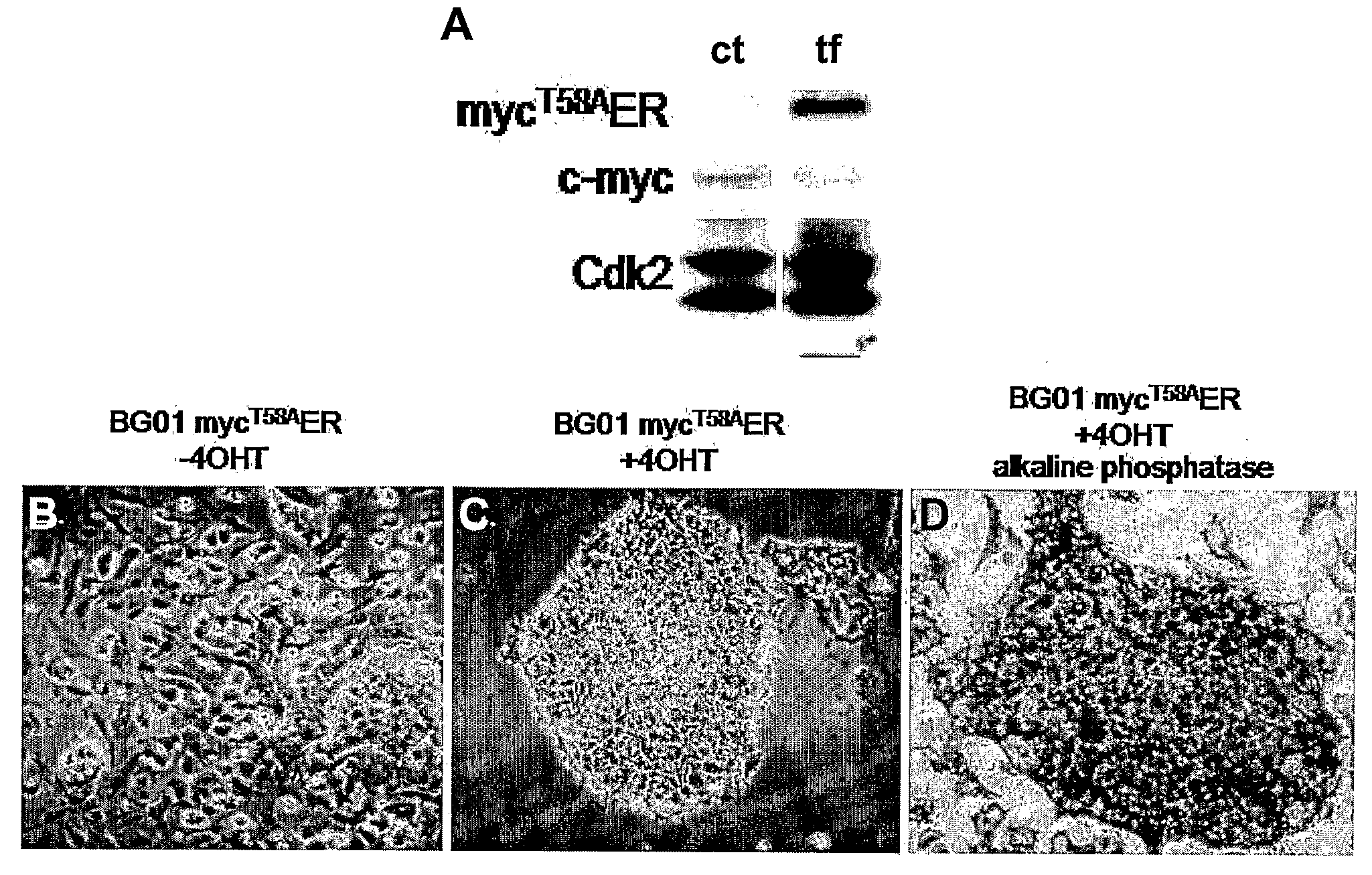
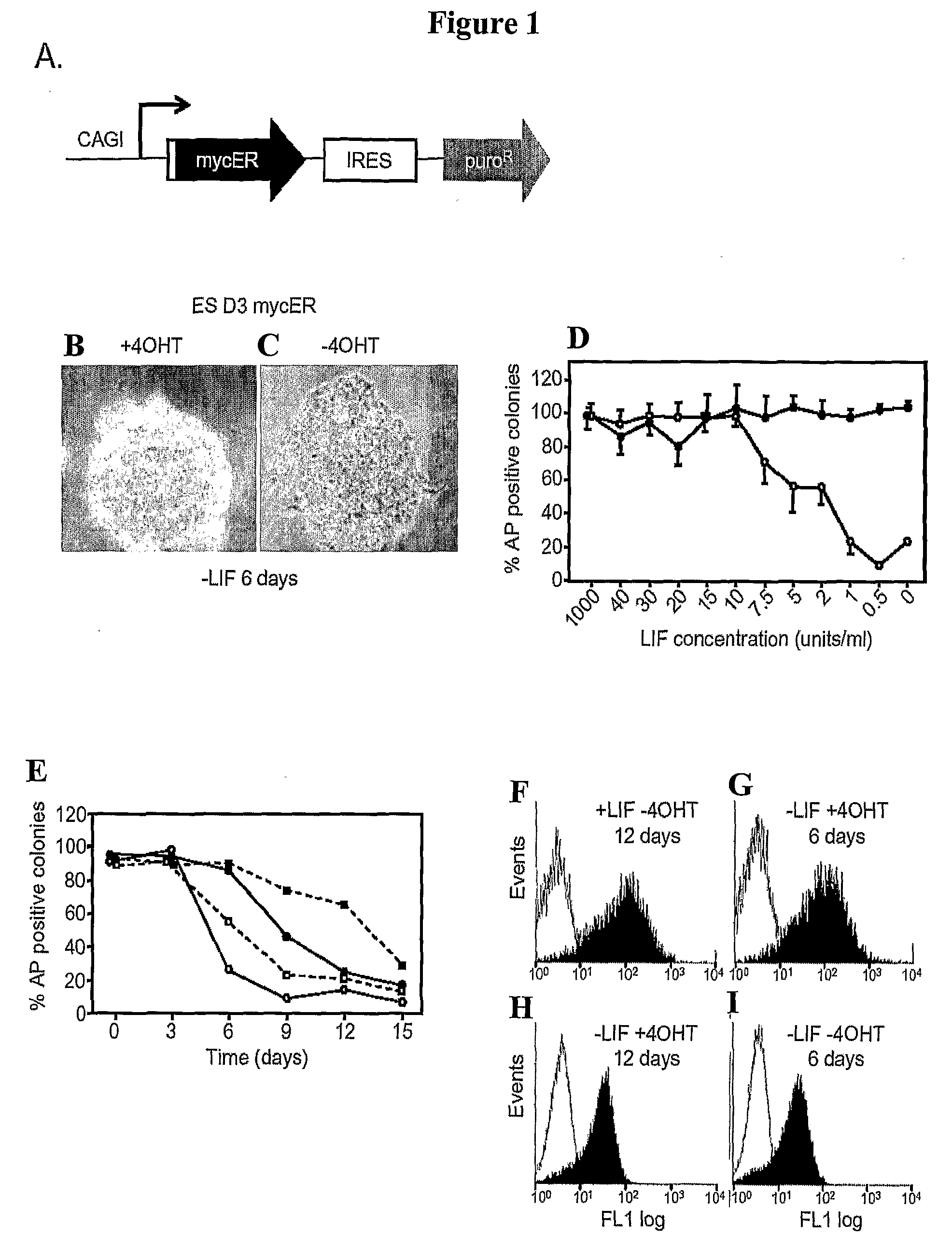
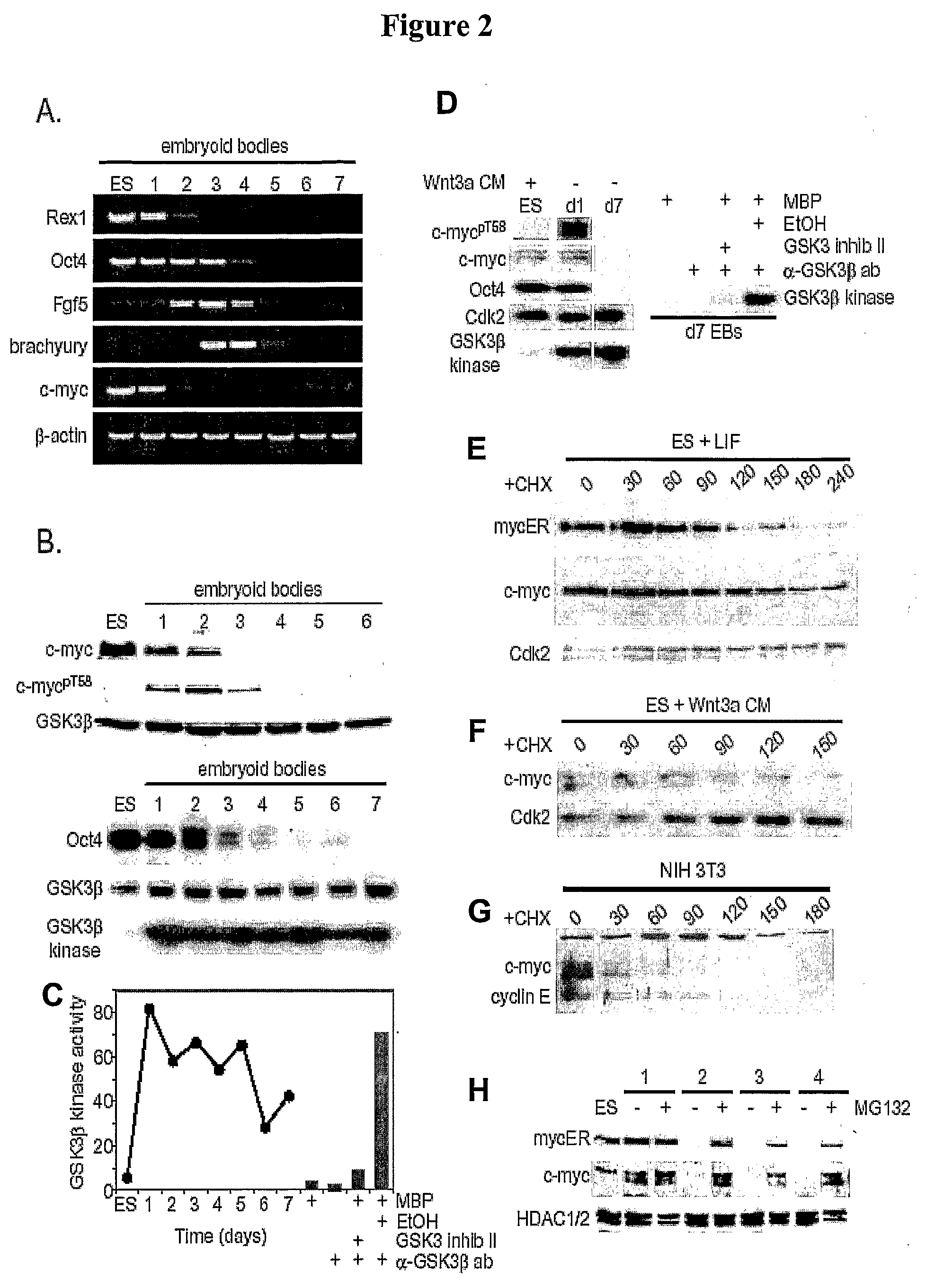
Methods and Compositions Utilizing Myc and Gsk3Beta to Manipulate the Pluripotency of Embryonic Stem Cells
InactiveUS20080268533A1Process stabilityReduce phosphorylationArtificial cell constructsCell culture active agentsMyc proteinsBiological activation
The present invention provides methods for stabilizing pluripotent cells through the transcriptional activation of c-myc. Alternatively, the cells are stabilized through the transcriptional activation of c-myc, and the stabilization of c-myc protein levels. c-myc protein can be stabilized through the inhibition of GSK3β or through other components of the cellular machinery that impact on c-myc stability. The invention contemplates the stabilized pluripotent cells produced using the methods described herein. Methods for the identification of compounds that modulate the stabilization of pluripotent cells through modulating transcriptional activation of c-myc, stabilization of c-myc protein levels, and / or inhibition of GSK3β activity are also contemplated.
Owner:UNIV OF GEORGIA RES FOUND INC
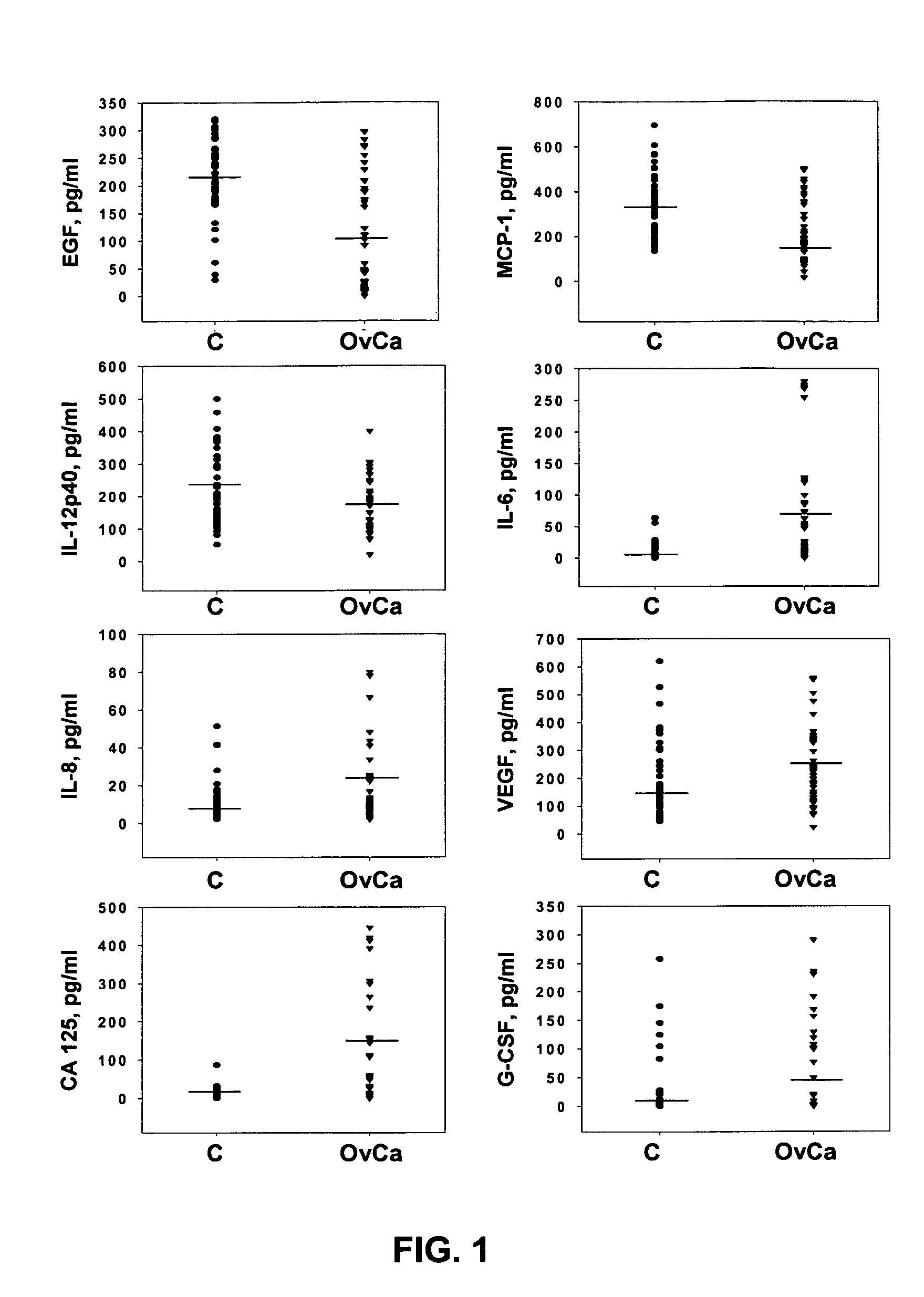
Multifactorial assay for cancer detection
InactiveUS20050069963A1Rapid and early detectionPeptide/protein ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementAnti her2Anti-MUC-1
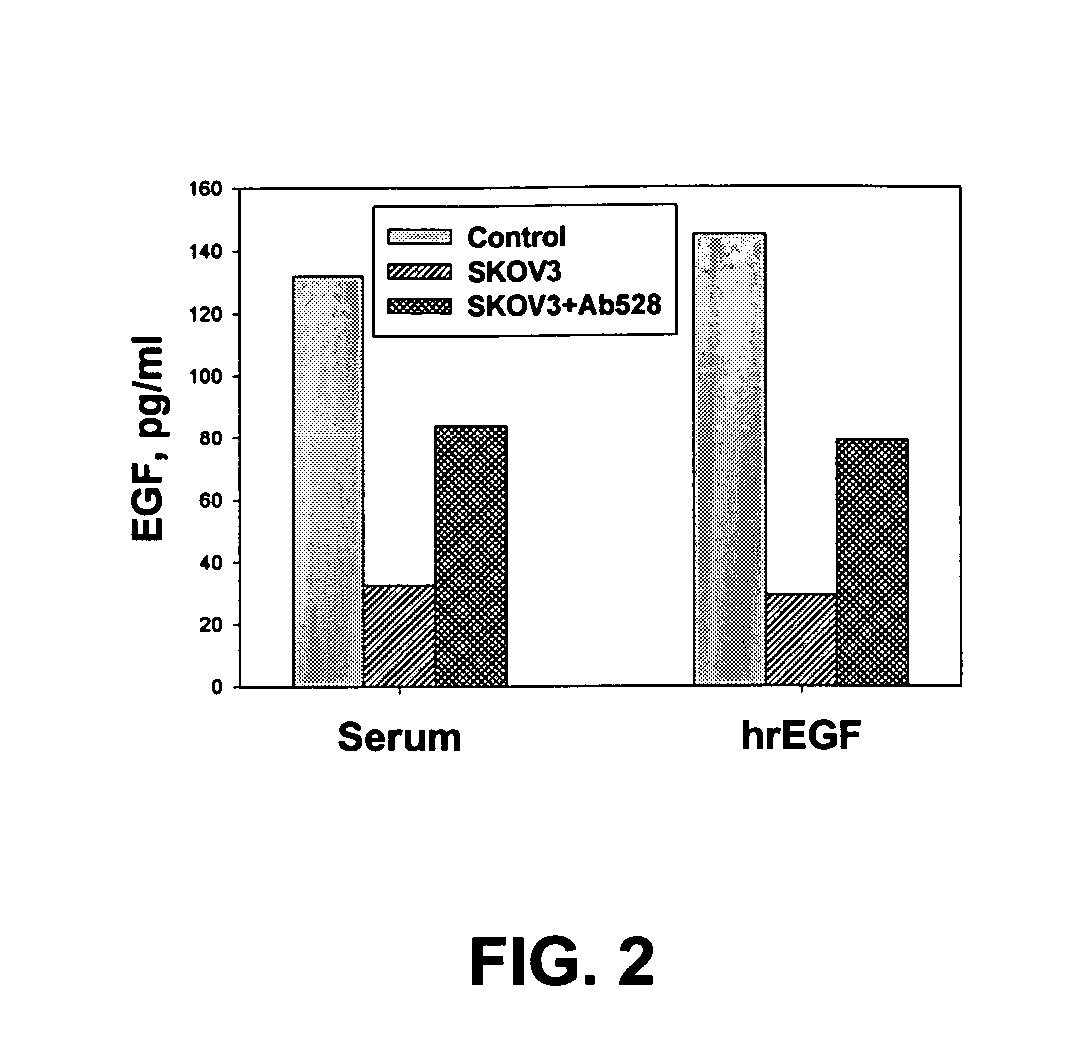
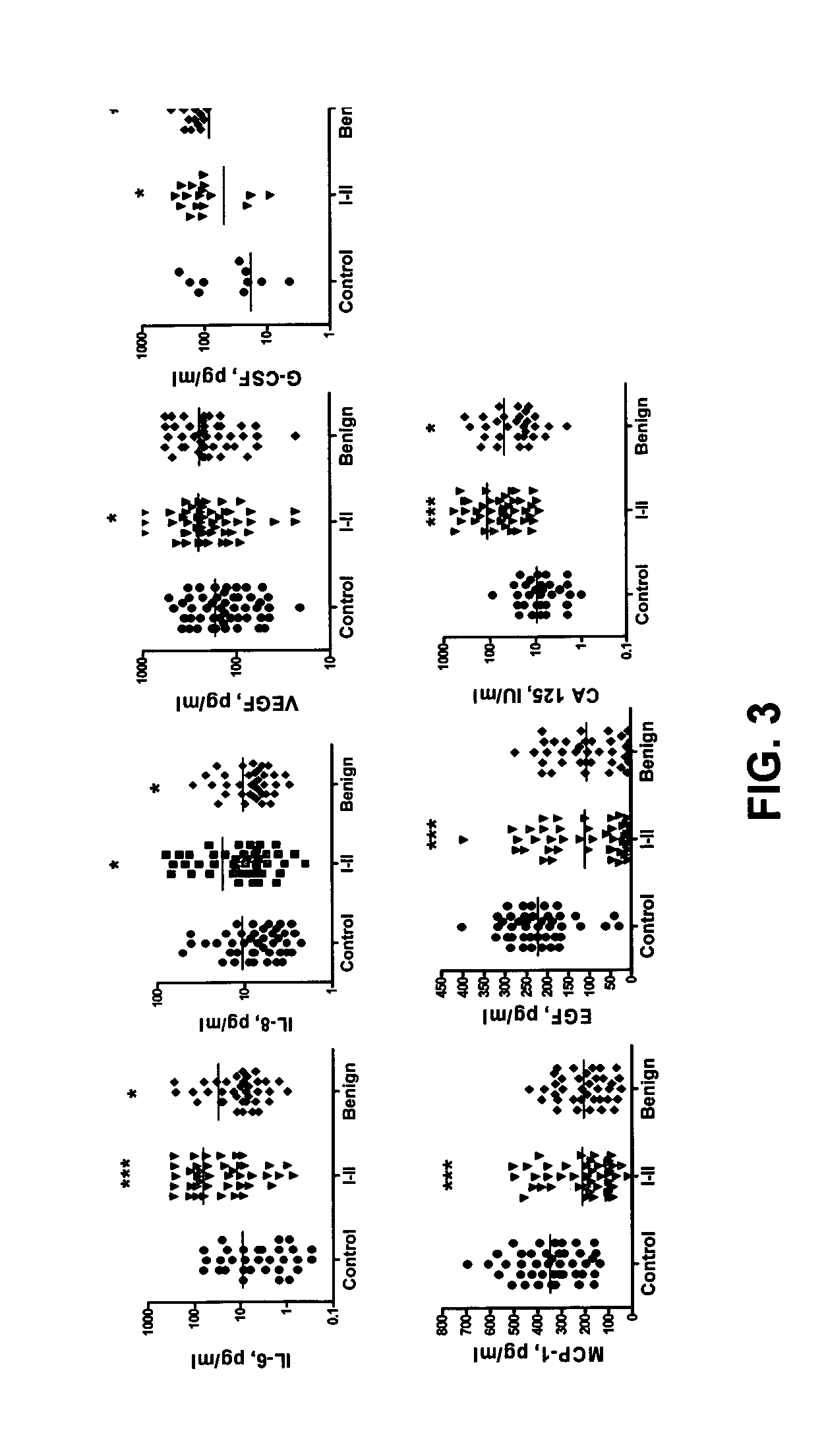
Provided are methods for the rapid detection of ovarian cancer. The methods employ a multiplex immunoassay to detect levels of two or more of the markers EGF, G-CSF, IL-6, IL-8, CA-125, VEGF, MCP-1, anti-IL6, anti-IL8, anti CA-125, anti-c-myc, anti-p53, anti-CEA, anti-CA 15-3, anti-MUC-1, anti-survivin, anti-bHCG, anti-osteopontin, anti-PDGF, anti-Her2 / neu, anti-Akt1, anti-cytokeratin 19, cytokeratin 19, EGFR, CEA, kallikrein-8, M-CSF, FasL, ErbB2 and Her2 / neu in a sample of the patient's blood, where the presence of abnormal levels of two or more of the markers indicates the presence of ovarian cancer in the patient. An array also is provided to quantitate levels of these markers in a patient's blood. Also provided is a method of predicting onset of clinical ovarian cancer comprising determining the change in concentration over time of two or more of anti-Her2 / neu, anti-MUC-1, anti-c-myc, anti-p53, anti-CA-125, anti-CEA, anti-CA 72-4, anti-PDGFRα, IFNγ, IL-6, IL-10, TNFα, MIP-1α, MIP-1β, EGFR and Her2 / neu in a patient's blood.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF PITTSBURGH
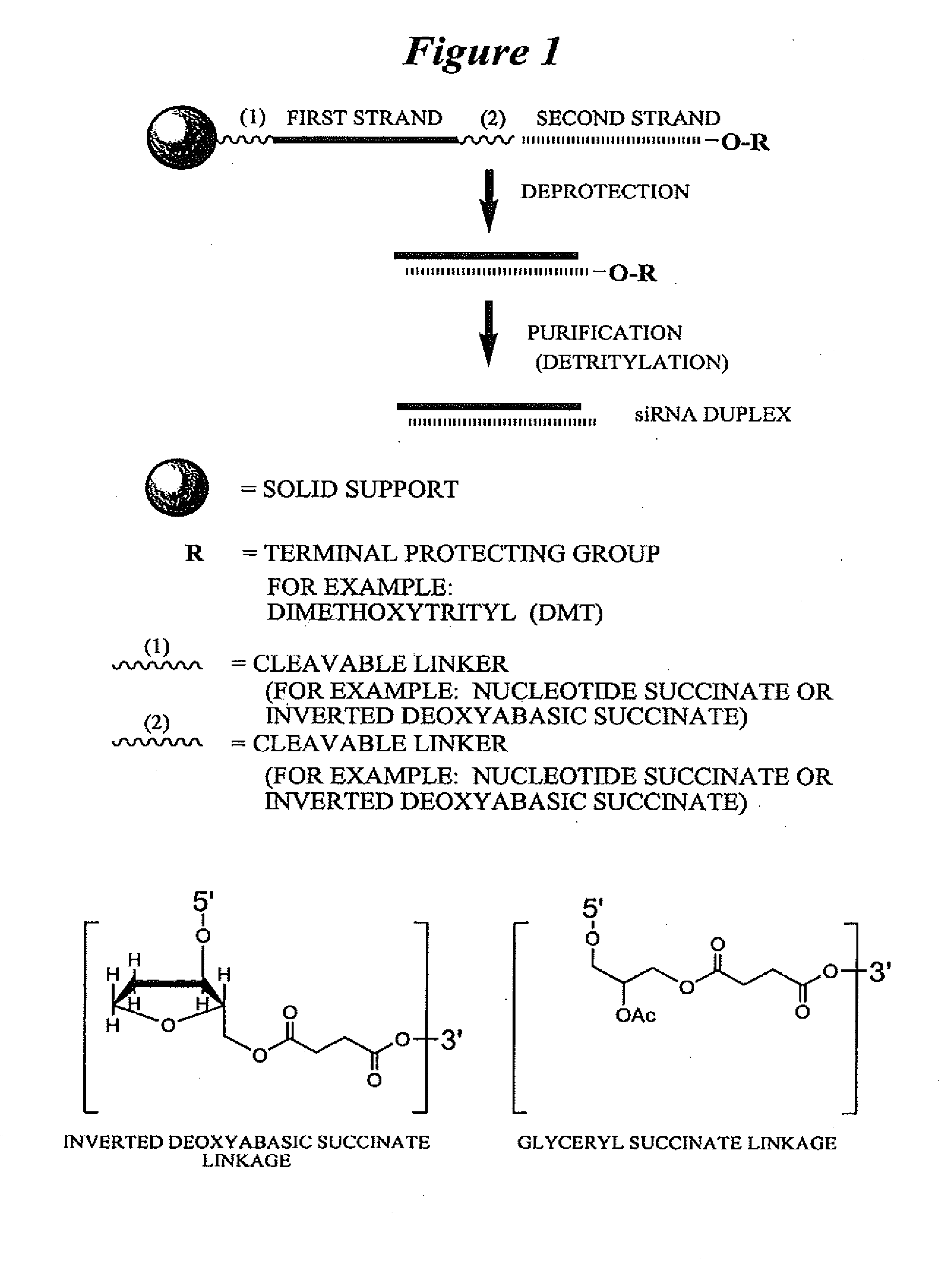
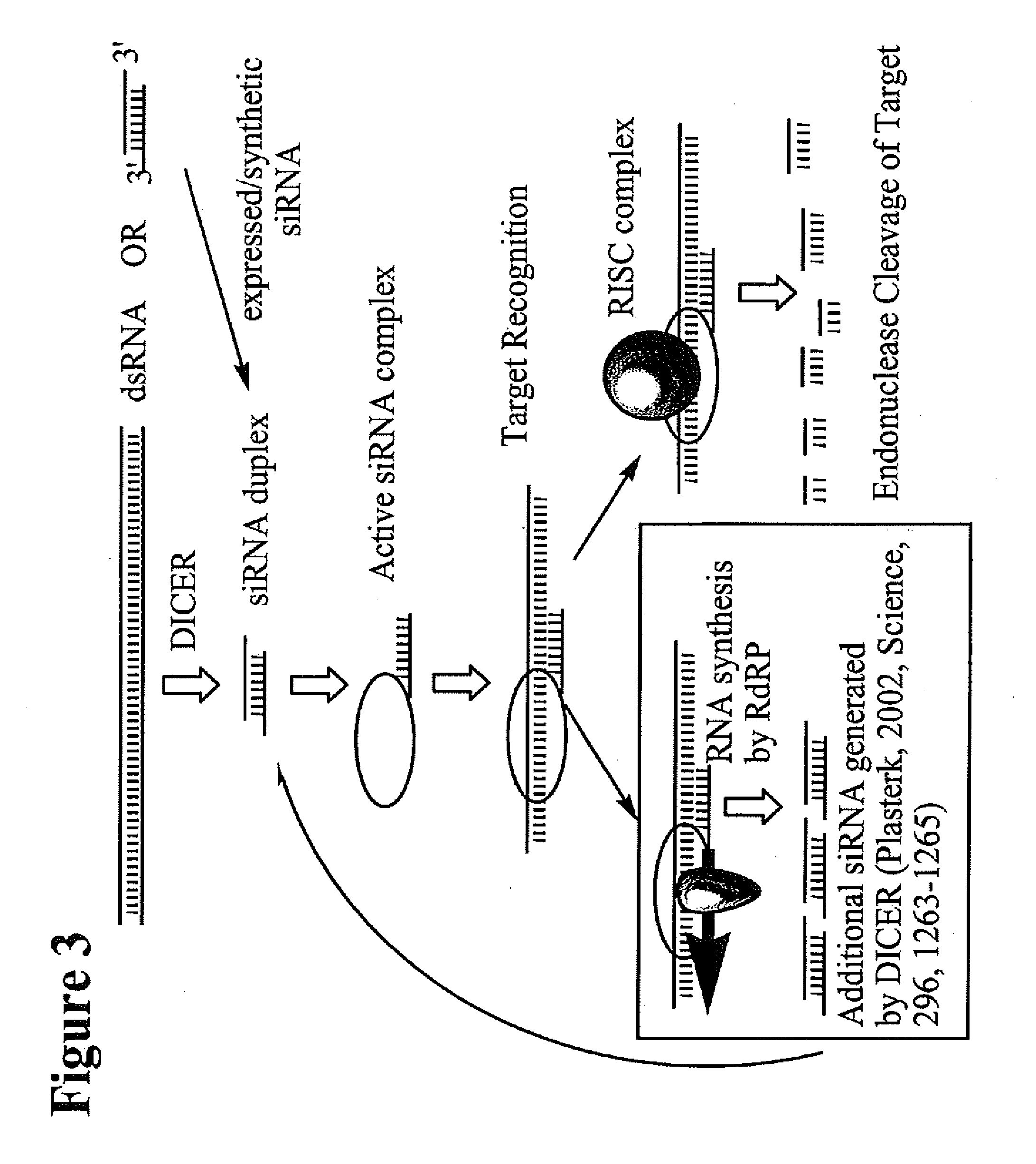
RNA interference mediated inhibition of Myc and/or Myb gene expression using short interfering nucleic acid (siNA)
InactiveUS20050159378A1Improve bioavailabilityMinimize the possibilityCompounds screening/testingSpecial deliveryDiseaseN-Myc
This invention relates to compounds, compositions, and methods useful for modulating Myc and / or Myb gene expression using short interfering nucleic acid (siNA) molecules. This invention also relates to compounds, compositions, and methods useful for modulating the expression and activity of other genes involved in pathways of Myc and / or Myb gene expression and / or activity by RNA interference (RNAi) using small nucleic acid molecules. In particular, the instant invention features small nucleic acid molecules, such as short interfering nucleic acid (siNA), short interfering RNA (siRNA), double-stranded RNA (dsRNA), micro-RNA (miRNA), and short hairpin RNA (shRNA) molecules and methods used to modulate the expression of Myc and / or Myb (e.g., c-Myc, N-Myc, L-Myc, c-Myb, a-Myb, b-Myb, and v-Myb) genes. The small nucleic acid molecules are useful in the treatment of cancer and other diseases and disorders.
Owner:SIRNA THERAPEUTICS INC
RNA INTERFERENCE MEDIATED INHIBITION OF MYC AND/OR MYB GENE EXPRESSION USING SHORT INTERFERING NUCLEIC ACID (siNA)
InactiveUS20090099115A1Improves various propertyImprove the immunityCompounds screening/testingOrganic active ingredientsDiseaseN-Myc
This invention relates to compounds, compositions, and methods useful for modulating Myc and / or Myb gene expression using short interfering nucleic acid (siNA) molecules. This invention also relates to compounds, compositions, and methods useful for modulating the expression and activity of other genes involved in pathways of Myc and / or Myb gene expression and / or activity by RNA interference (RNAi) using small nucleic acid molecules. In particular, the instant invention features small nucleic acid molecules, such as short interfering nucleic acid (siNA), short interfering RNA (siRNA), double-stranded RNA (dsRNA), micro-RNA (miRNA), and short hairpin RNA (shRNA) molecules and methods used to modulate the expression of Myc and / or Myb (e.g., c-Myc, N-Myc, L-Myc, c-Myb, a-Myb, b-Myb, and v-Myb) genes. The small nucleic acid molecules are useful in the treatment of cancer and other diseases and disorders.
Owner:SIRNA THERAPEUTICS INC
RNA INTERFERENCE MEDIATED INHIBITION OF MYC AND/OR MYB GENE EXPRESSION USING SHORT INTERFERING NUCLEIC ACID (siNA)
InactiveUS20100093835A1Improves various propertyImprove the immunityOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesDiseaseN-Myc
This invention relates to compounds, compositions, and methods useful for modulating Myc and / or Myb gene expression using short interfering nucleic acid (siNA) molecules. This invention also relates to compounds, compositions, and methods useful for modulating the expression and activity of other genes involved in pathways of Myc and / or Myb gene expression and / or activity by RNA interference (RNAi) using small nucleic acid molecules. In particular, the instant invention features small nucleic acid molecules, such as short interfering nucleic acid (siNA), short interfering RNA (siRNA), double-stranded RNA (dsRNA), micro-RNA (miRNA), and short hairpin RNA (shRNA) molecules and methods used to modulate the expression of Myc and / or Myb (e.g., c-Myc, N-Myc, L-Myc, c-Myb, a-Myb, b-Myb, and v-Myb) genes. The small nucleic acid molecules are useful in the treatment of cancer and other diseases and disorders.
Owner:SIRNA THERAPEUTICS INC
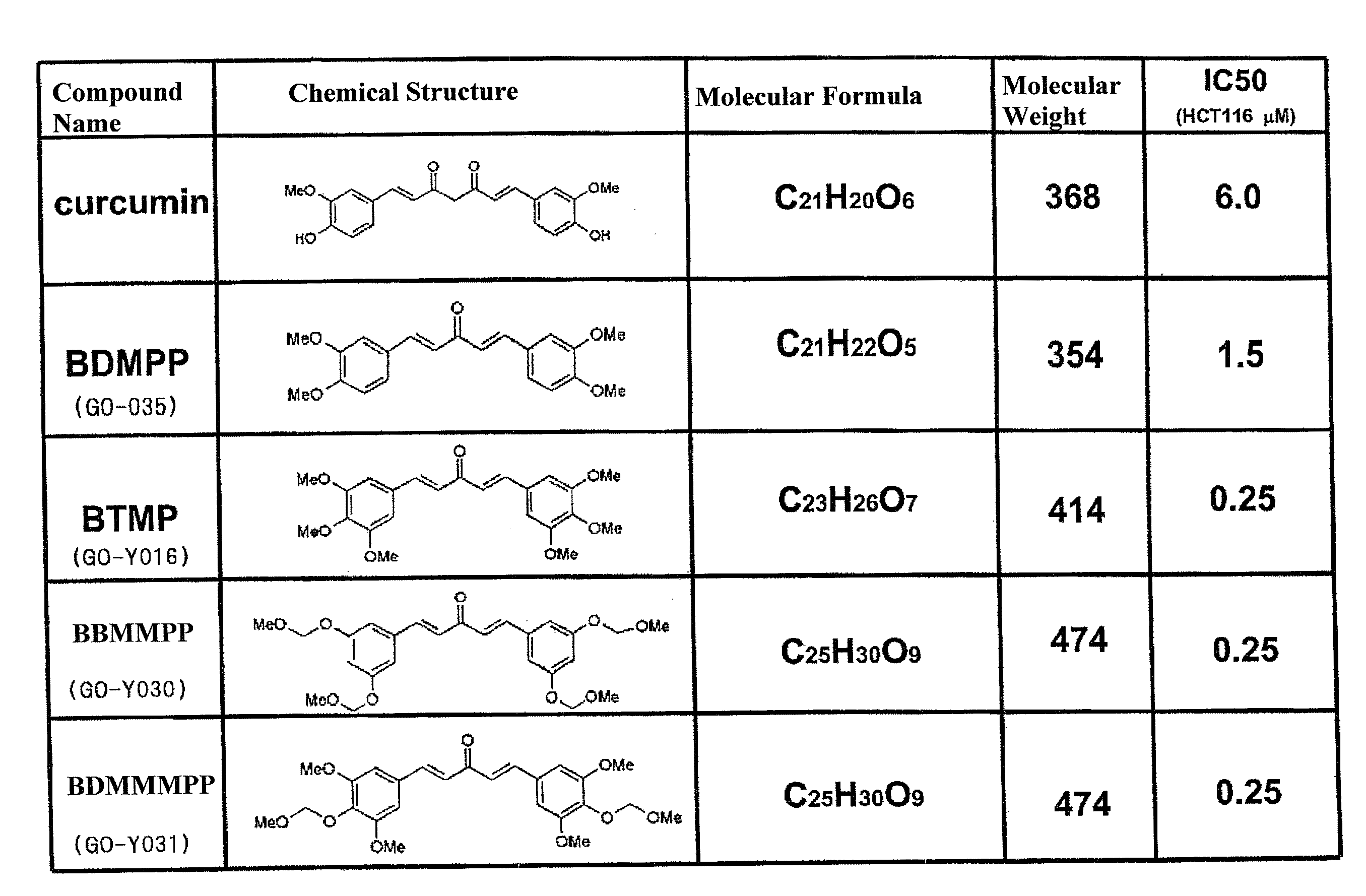
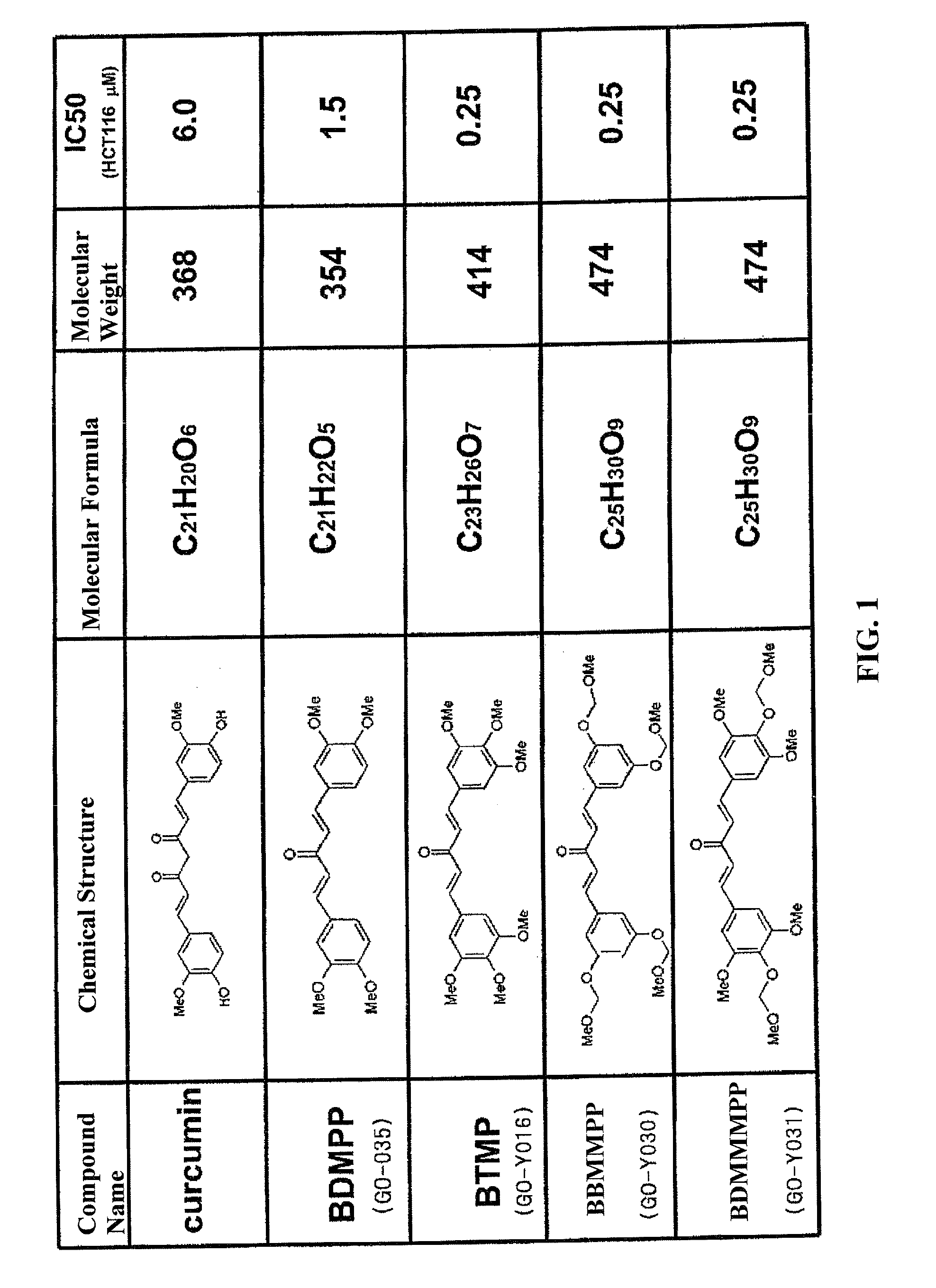
BIS(ARYLMETHYLIDENE)ACETONE COMPOUND, ANTI-CANCER AGENT, CARCINOGENESIS-PREVENTIVE AGENT, INHIBITOR OF EXPRESSION OF Ki-Ras, ErbB2, c-Myc AND CYCLINE D1, BETA-CATENIN-DEGRADING AGENT, AND p53 EXPRESSION ENHANCER
ActiveUS20100152493A1Growth inhibitionPrevent cancerOrganic chemistryAntineoplastic agentsSolubilityCancer cell
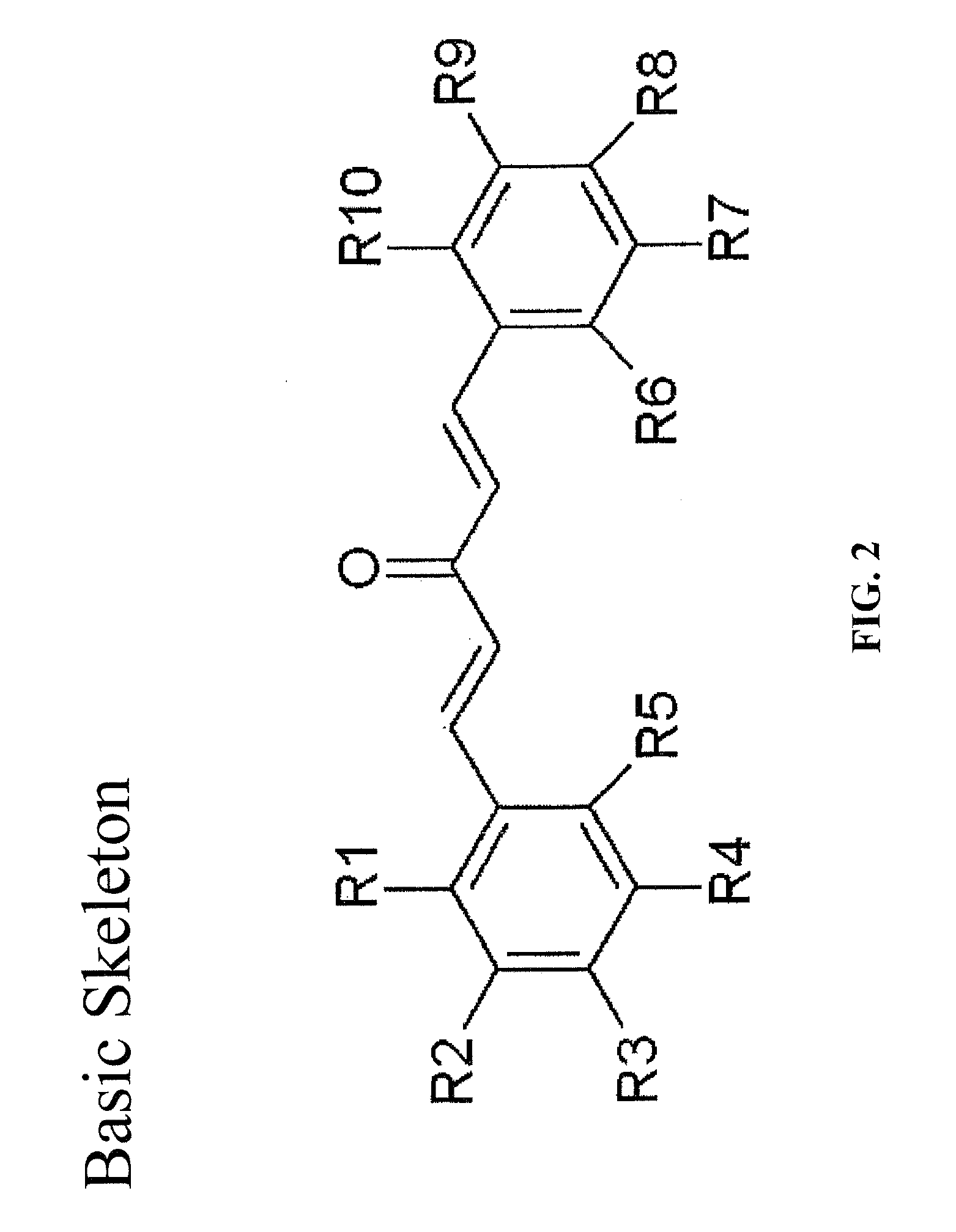
It has been demanded to improve the poor solubility of curcumin to develop an anti-tumor compound capable of inhibiting the growth of various cancer cells at a low concentration. Thus, disclosed is a novel synthetic compound, a bis(arylmethylidene)acetone, which has both of an excellent anti-tumor activity and a chemo-preventive activity. A bis(arylmethylidene)acetone (i.e., a derivative having a curcumin skeleton) which is an anti-tumor compound and has a chemo-preventive activity is synthesized and screened. A derivative having enhanced anti-tumor activity and chemo-preventive activity can be synthesized.
Owner:SHIBATA HIROYUKI
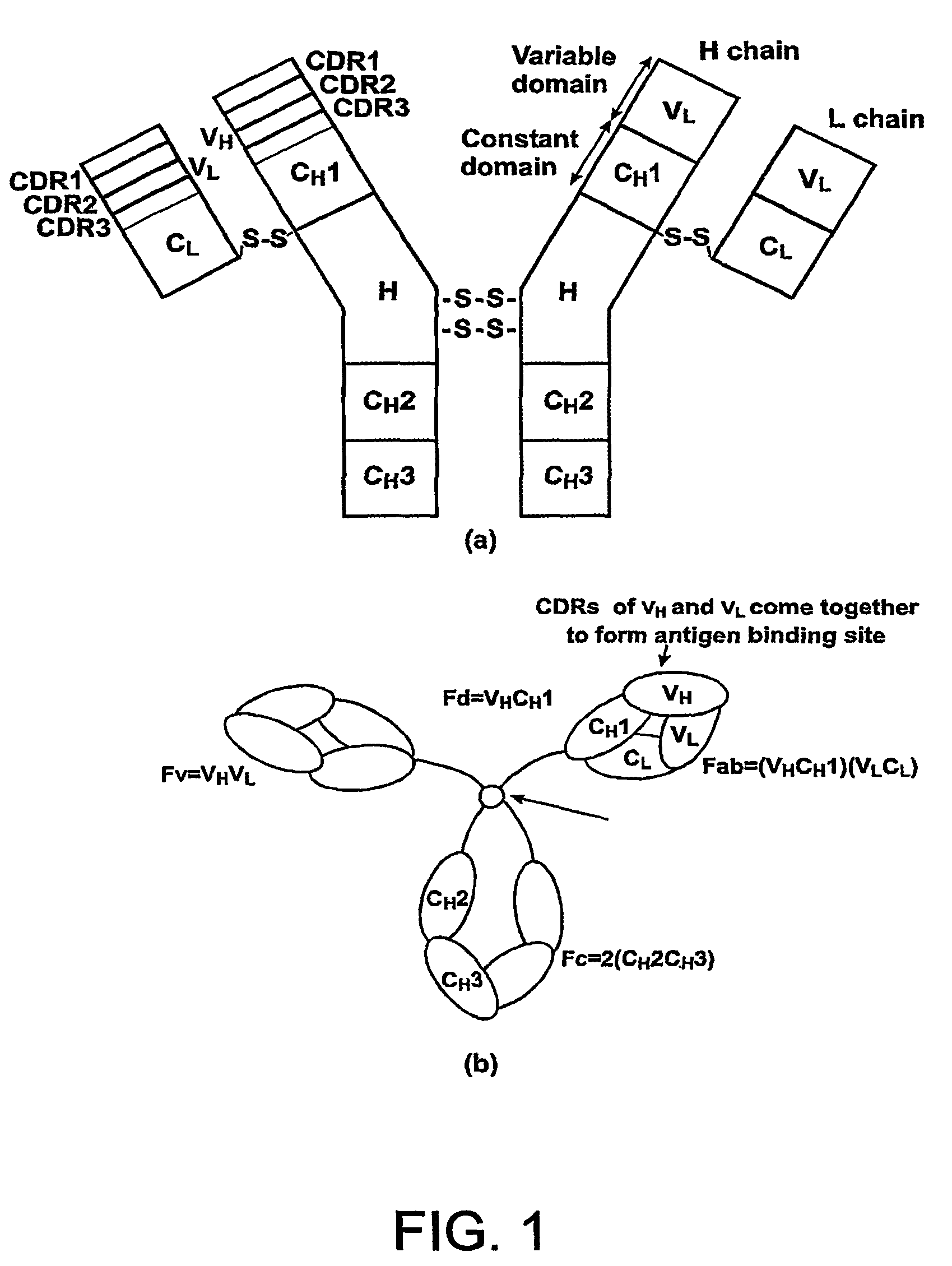
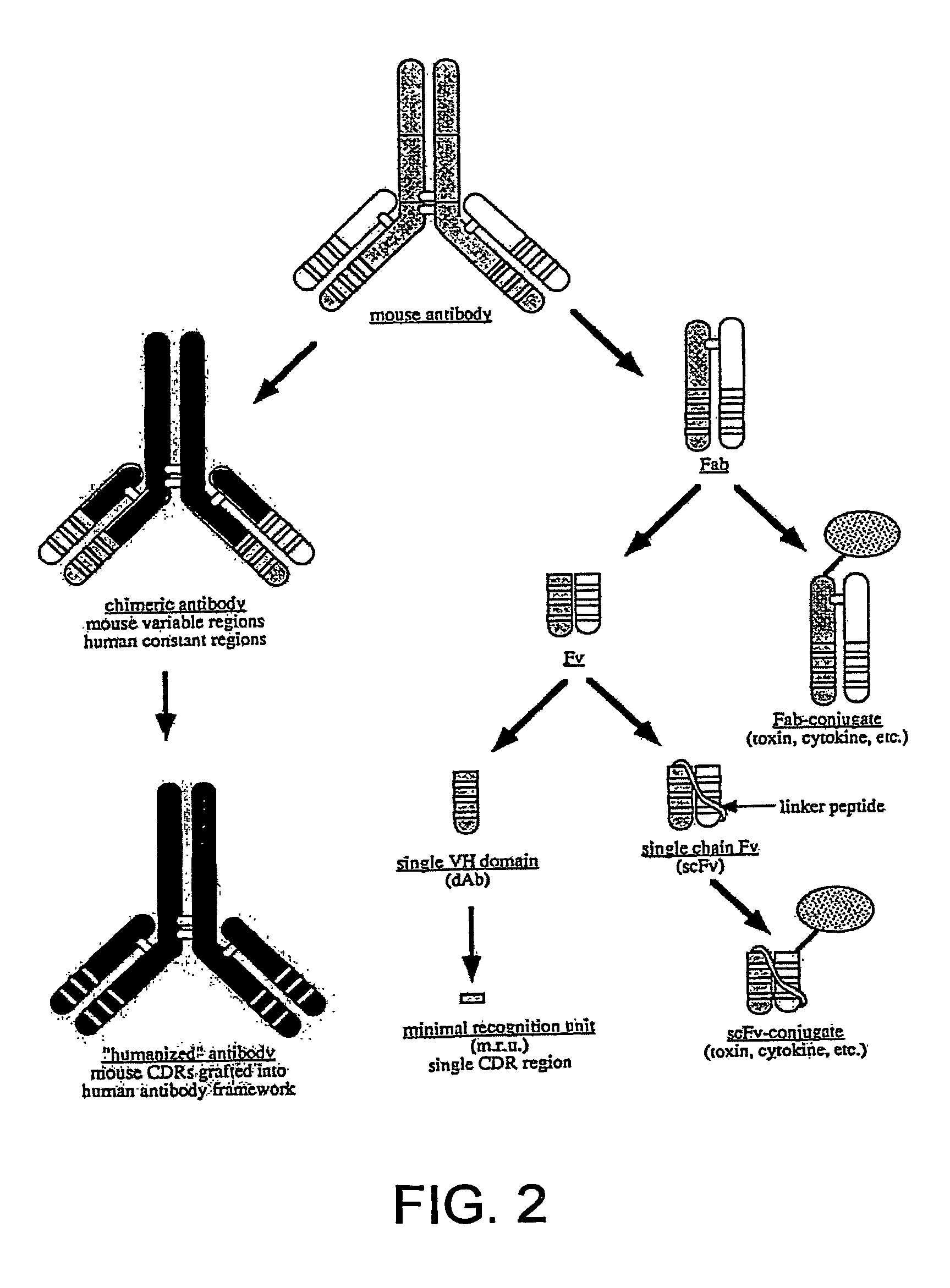
Gene Engineering Recombinant Anti-CEA, Anti-CD3, And Anti-CD28 Single-Chain Tri-Specific Antibody
InactiveUS20090117108A1Increase production costHigh expressionBacteriaSugar derivativesAntibody fragmentsSingle-domain antibody
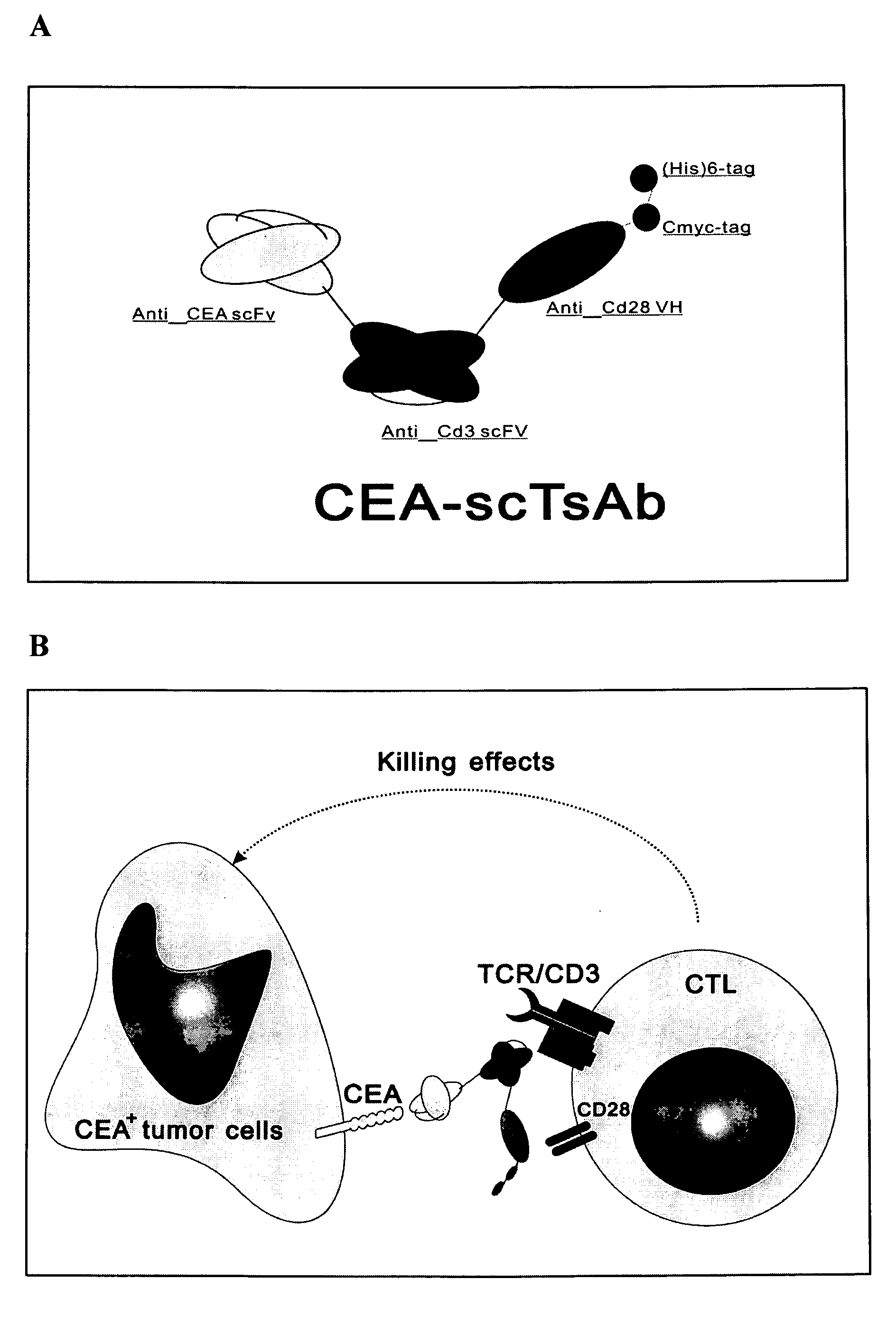
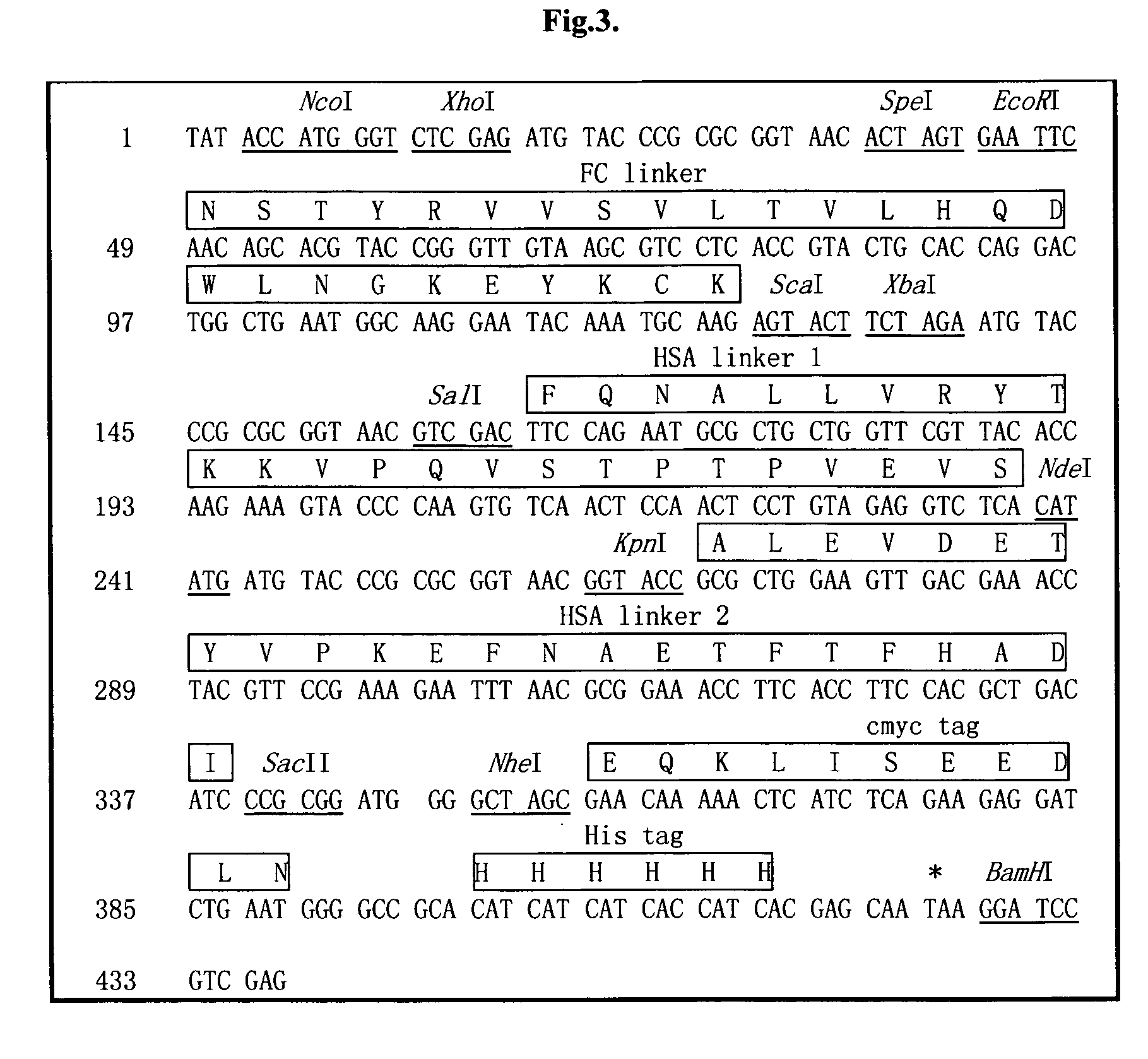
The invention is related to a recombinant single-chain tri-specific antibody made from anti-Tumor Associated Antigen (TAA) antibody, FC interlinker, anti-CD3 antibody, HSA interlinker and anti-CD28 antibody in turn. Particularly, the invention relates to an anti-CEA, anti-CD3, anti-CD28 recombinant single-chain tri-specific antibody, CEA-scTsAb, which was constructed with three tandem antibody fragments (anti-CEA scFv, anti-CD3 scFv and anti-CD28 single-domain antibody) linked by two interlinkers (FC interlinker, HSA interlinker), and could be appended by C myc tag or histidine tag ((His)6-tag) at the C terminal. It also concerns a method for construction, expression and purification of the antibody. It also offers the encoded DNA sequence of the antibody, expression vectors and host cells for the vectors.
Owner:WANG XIANGBIN +5
Antisense restenosis composition and method
InactiveUS20070265215A1Reduce riskOrganic active ingredientsBiocideStart codonPercent Diameter Stenosis
The present invention provides an improved method for reducing the risk or severity of restenosis following cardiac angioplasty. The method includes administering to a target vessel region, a morpholino antisense compound having a phosphorus-containing backbone linkages, and spanning the start codon of a human c-myc mRNA. Also disclosed are novel antisense compounds and compositions, and a method for assaying the effectiveness of antisense delivery and uptake to a target vessel region.
Owner:AVI BIOPHARMA
Single-domain brain-targeting antibody fragments derived from llama antibodies
InactiveUS7943129B2Microbiological testing/measurementSnake antigen ingredientsAntibody fragmentsBacteriophage
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
New use of tripterine in pharmacy
InactiveCN101352444ASignificant cytotoxicityEffective anti-tumor proliferation effectOrganic active ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsOncologyWilms' tumor
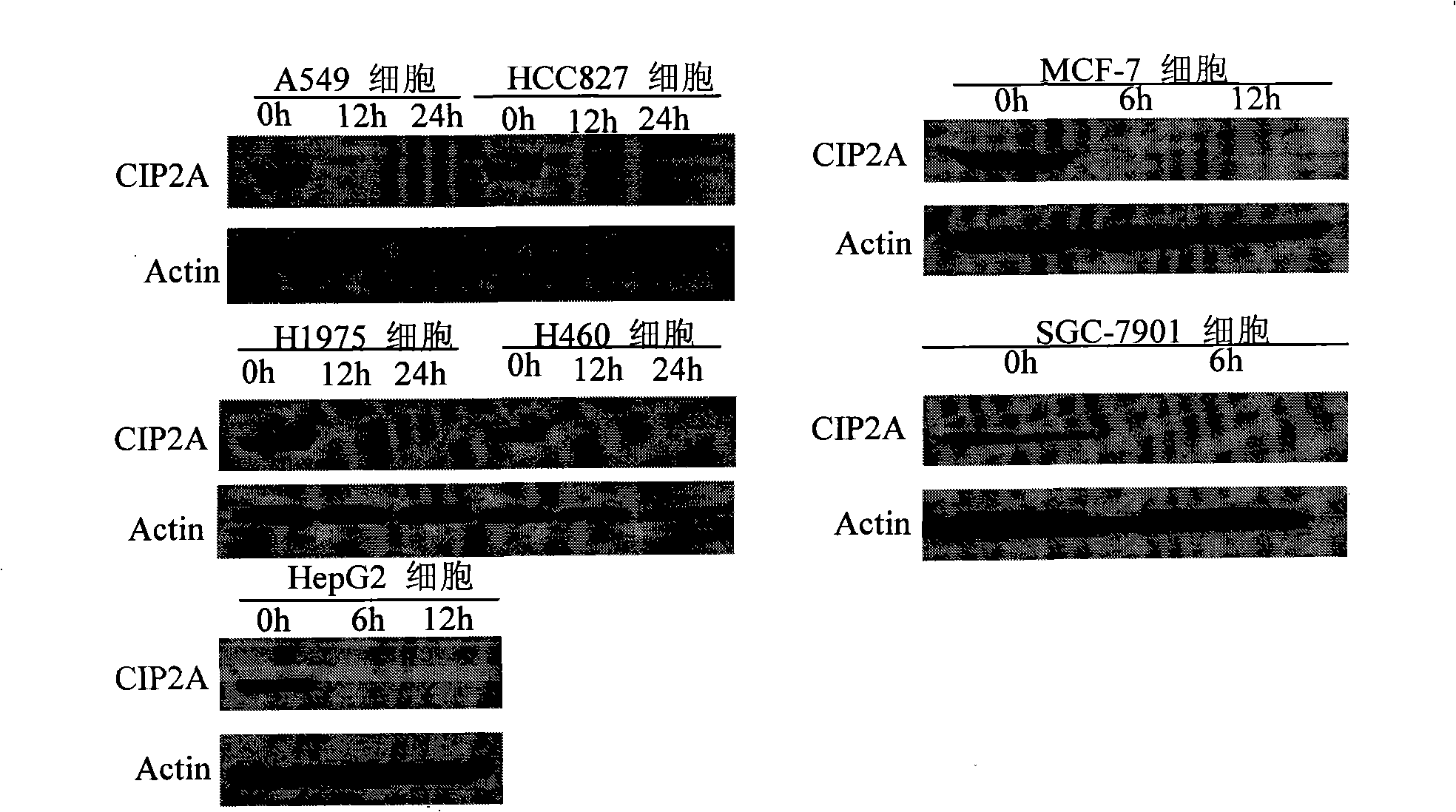
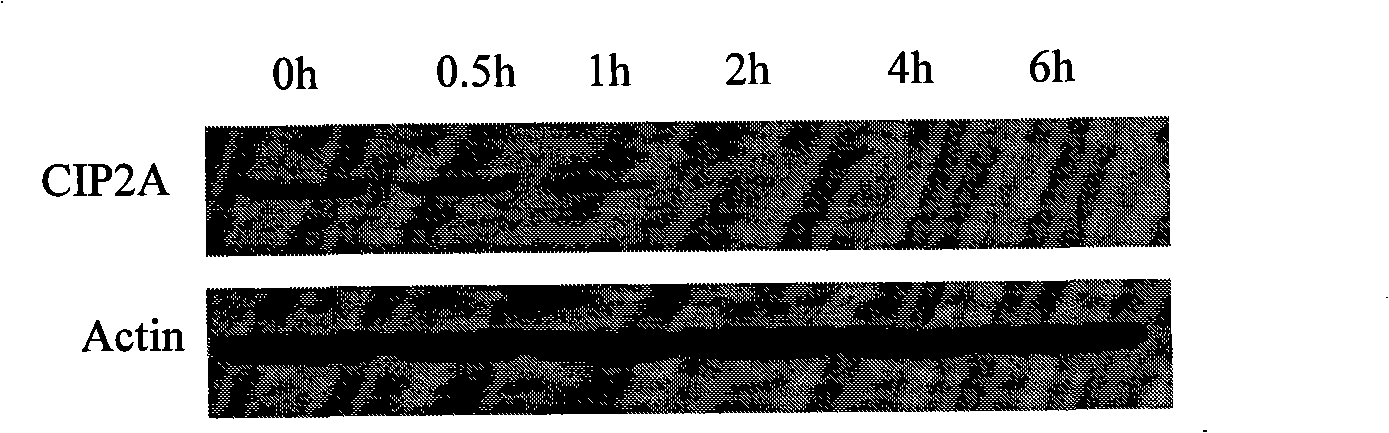
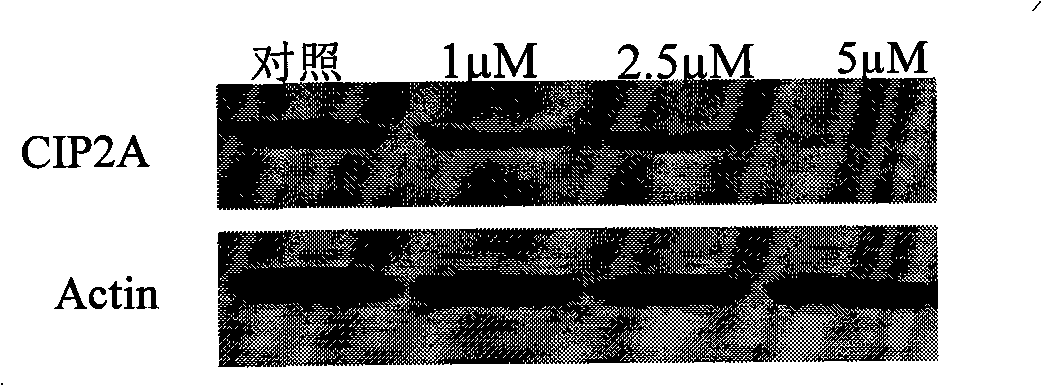
The invention discloses the application of celastrol in the preparation of the medicine for treating cancer expressing CIP2A protein. The celastrol of the invention has the characteristics of having no obvious down regulation CIP2A protein with the cell line particularity, reducing the expressing of oncoprotein in lung cancer, liver cancer, breast cancer and gastric cancer with time and dose pendence, causing oncoprotein C-Myc steadied by CIP2A to generate corresponding retrogradation, displaying remarkable cytotoxic activity in the cell of lung cancer and liver cancer, and having effective function of anti-tumor proliferation in the transplant model of tumor of nude mice lung cancer. The celastrol has a wide application prospect in treating lung cancer, head and neck squamous cell carcinoma, carcinoma of colon, gastric cancer, liver cancer, breast cancer and other cancer expressing CIP2A oncoprotein.
Owner:GUANGZHOU INST OF BIOMEDICINE & HEALTH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
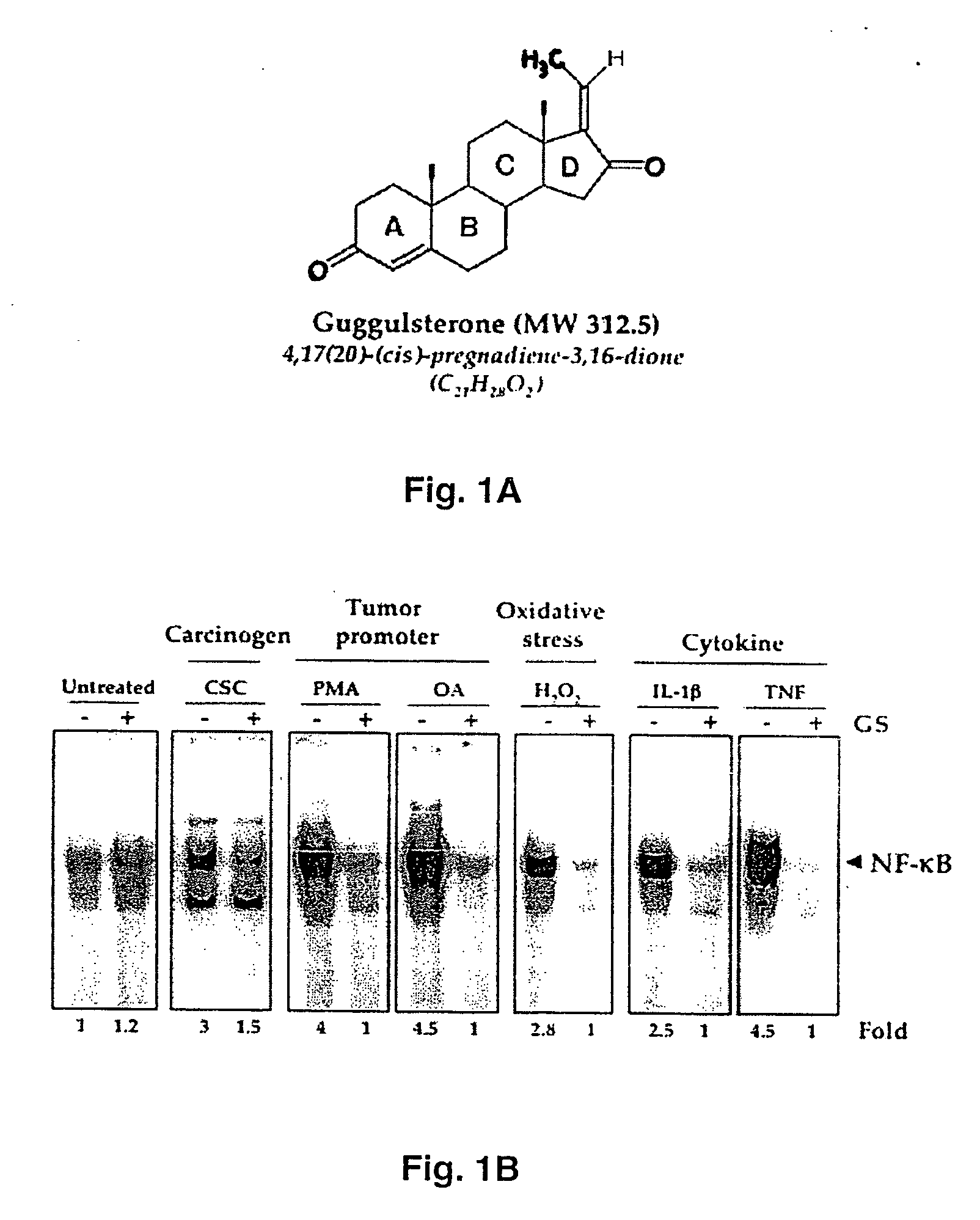
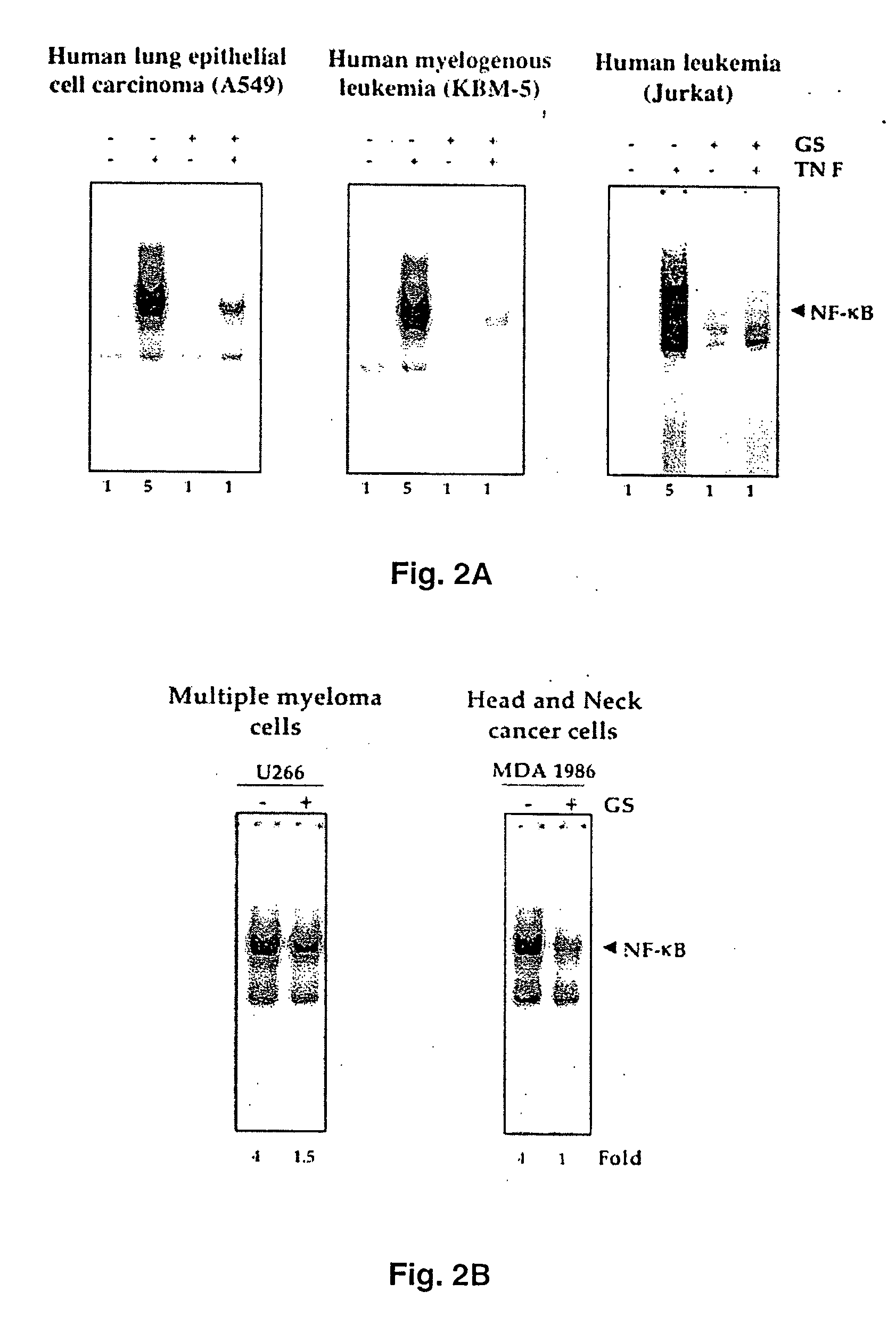
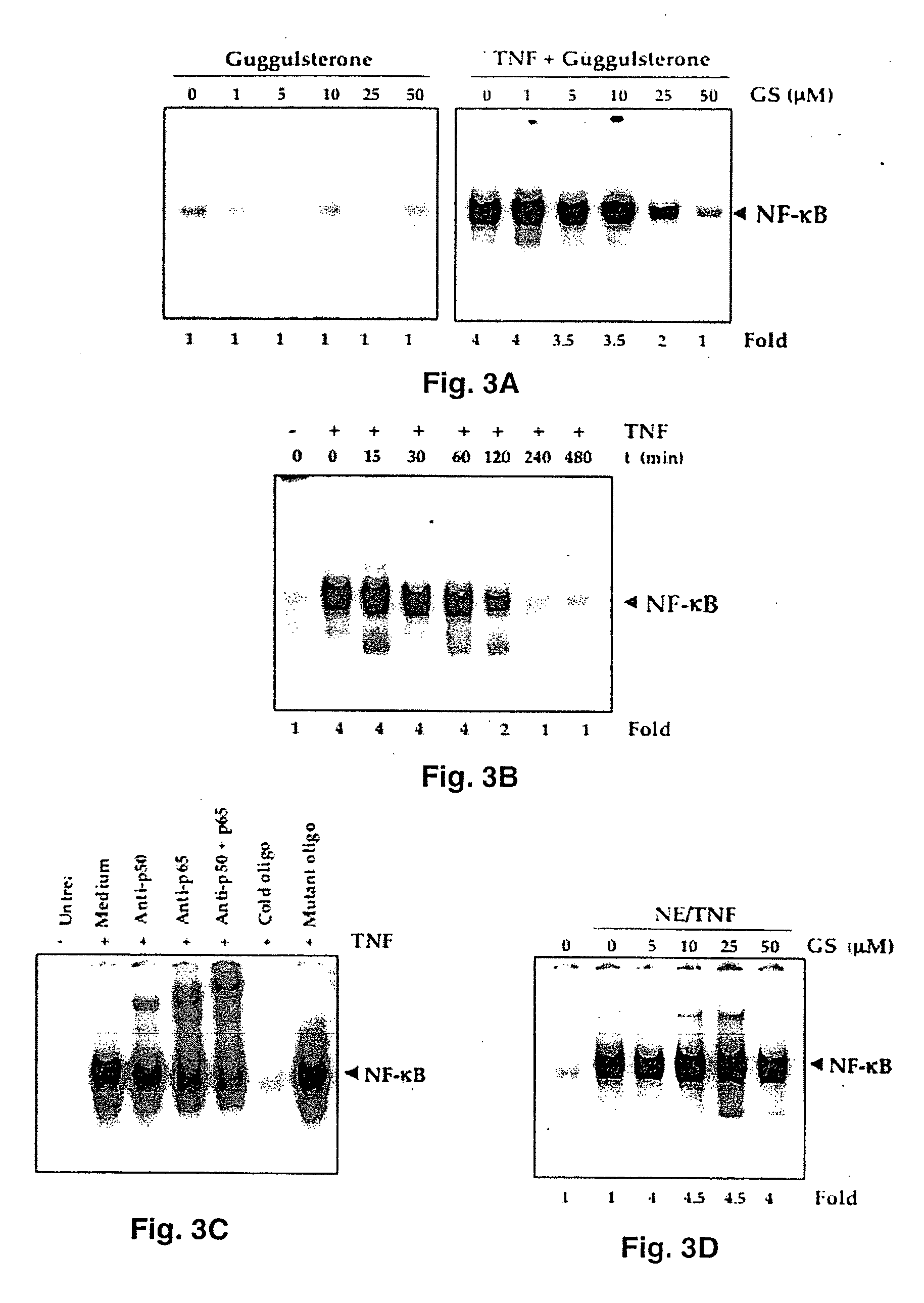
Guggulsterone: an inhibitor of nuclear factor - kappaB and IkappaBalpha kinase activation and uses thereof
InactiveUS20060019907A1Good effectHigh activityBiocideOrganic active ingredientsLymphatic SpreadCyclin D1
The present invention provides an inhibitor of NF-κB, guggulsterone and its analogs. Guggulsterone suppresses NF-κB activation induced by TNF, phorbol ester, okadaic acid, cigarette smoke, H2O2 and IL-1β, as well as constitutive NF-κB activation expressed in most tumor cells. One mechanism by which guggulsterone inhibits activation of NF-κB is through suppression of IκBα phosphorylation and IκBα degradation. NF-κB-dependent gene transcription is modulated by guggulsterone and its analogs. In particular, induction by TNF, TNFR1, TRADD, TRAF2, NIK and IKK, is modulated by guggulsterone and its analogs. In addition, guggulsterone decreased the expression of genes involved in anti-apoptosis (IAP1, XIAP, Bfl-1 / A1, bcl-2, cFLIP, survivin), proliferation (cyclin D1, c-myc) and metastasis (MMP-9, COX2 and VEGF).
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Culture medium for establishing pig iPS cell line and culture method thereof
InactiveCN103333920AEfficiently obtainedNeat edgesEmbryonic cellsGenetic engineeringBiotechnologyGerm layer
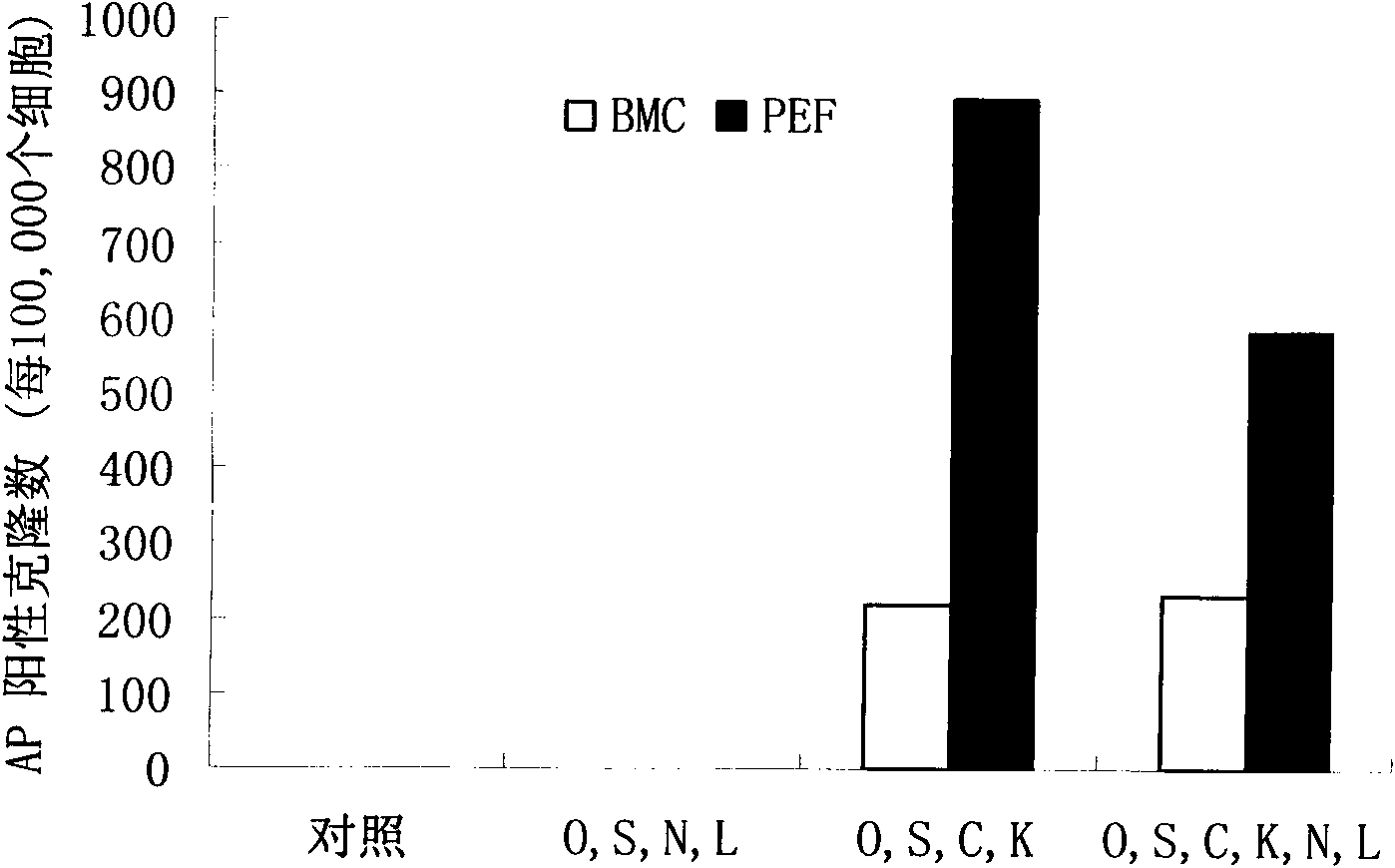
The invention discloses a culture medium for establishing a pig iPS cell line and a culture method thereof. A typical pig iPS cell is obtained in the ninth day through transfection by four transcription factors of OCT4, SOX2, KLF4 and c-MYC and induction culture of the culture medium, and the pig iPS cell can be obtained efficiently. The obtained pig iPS cell clone is flat clone, has a regular edge and is similar to the ES cellular morphology of the human body. According to the pig iPS cell line, the pig iPS cell through subculture keeps the undifferentiated state, shows positive in the AP dyeing displaying result and has a pluripotency mark, and the differentiated cell in vitro expresses NCSTN (entoderm), NESTIN (ectoderm) and DESMIN (mesoblast).
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
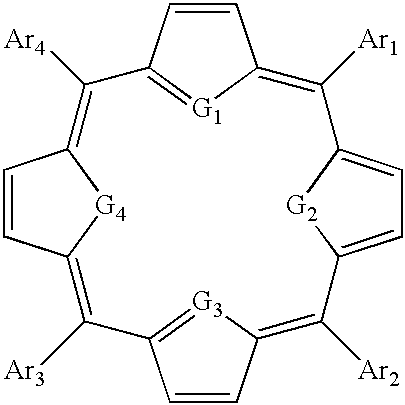
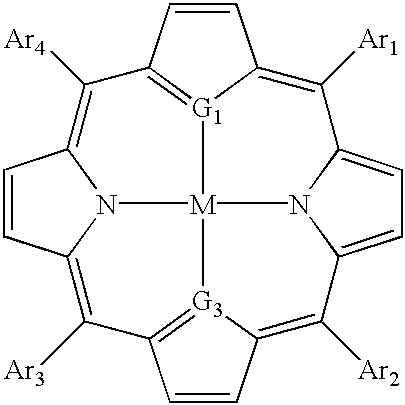
Thiaporphyrin, selenaporphyrin, and carotenoid porphyrin compounds as c-myc and telomerase inhibitors
The present invention has identified thiaprophyrin, selenaporphyrin, and carotenoid porphyrin compounds that bind the G-quadruplex formed by the folding of single-stranded human telomeric DNA. These compounds have been shown to be effective telomerase and c-myc inhibitors and are contemplated to be useful in developing cancer treatments.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Compounds for treatment of cell proliferative diseases
ActiveUS7745468B2Reduce activationReduce expressionBiocideOrganic chemistryCancer cellKinase inhibition
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Methods and compositions for regenerating hair cells and/or supporting cells
InactiveUS20150209406A1Promotes cycle reentryPromotes proliferationSenses disorderNervous disorderVestibular dysfunctionCell cycle
Provided are methods and compositions for inducing cells of the inner ear (for example, cochlear and utricular hair cells) to reenter to cell cycle and to proliferate. More particularly, the invention relates to the use of agents that increase c-myc activity and / or Notch activity for inducing cell cycle reentry and proliferation of cochlear or utricular hair cells and / or cochlear or utricular supporting cells. The methods and compositions can be used to promote the proliferation of hair cells and / or supporting cells to treat a subject at risk of or affected with, hearing loss or a subject at risk of or affected with vestibular dysfunction.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS EYE & EAR INFARY
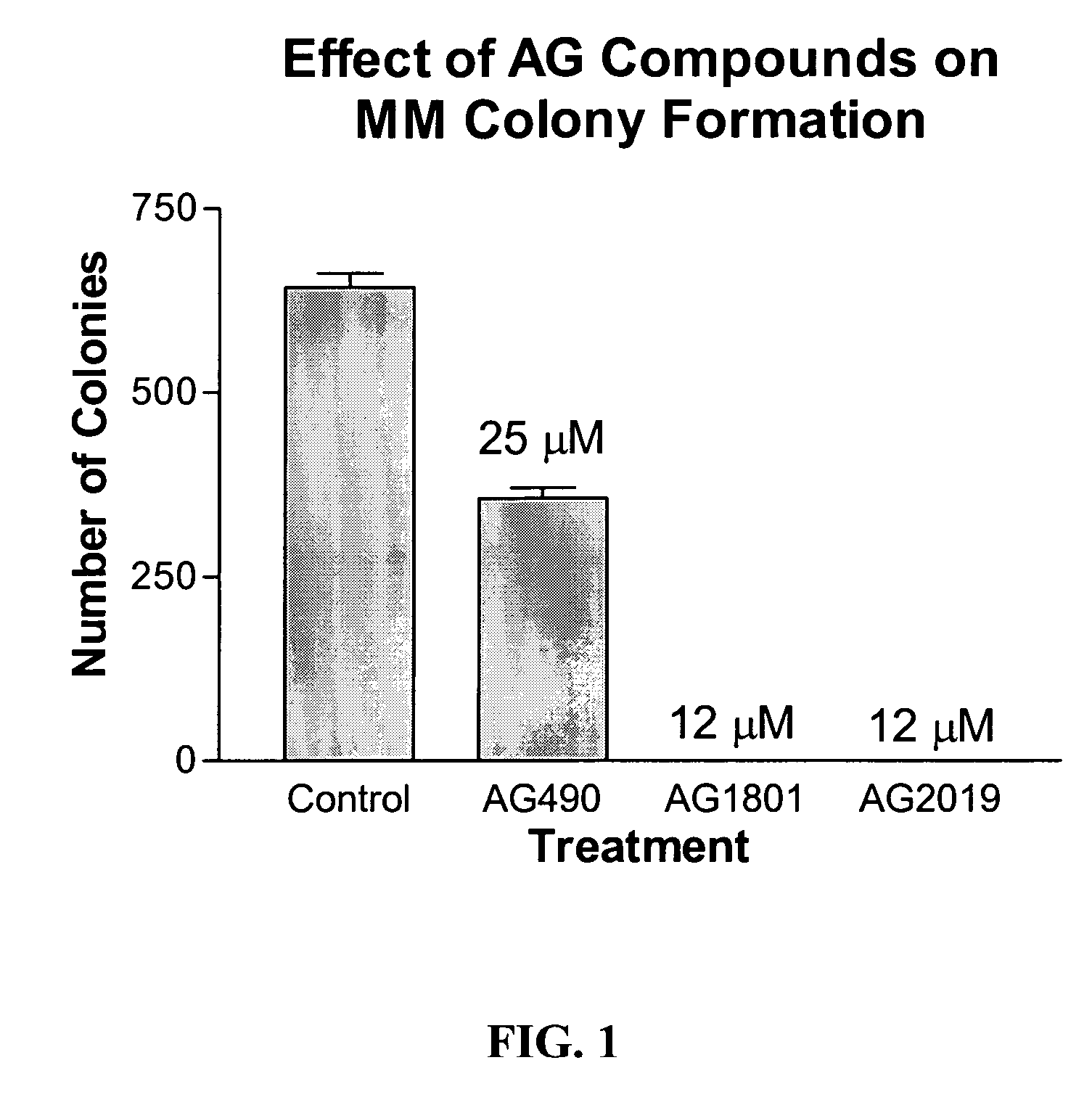
Pharmacologic inhibition of Myc function
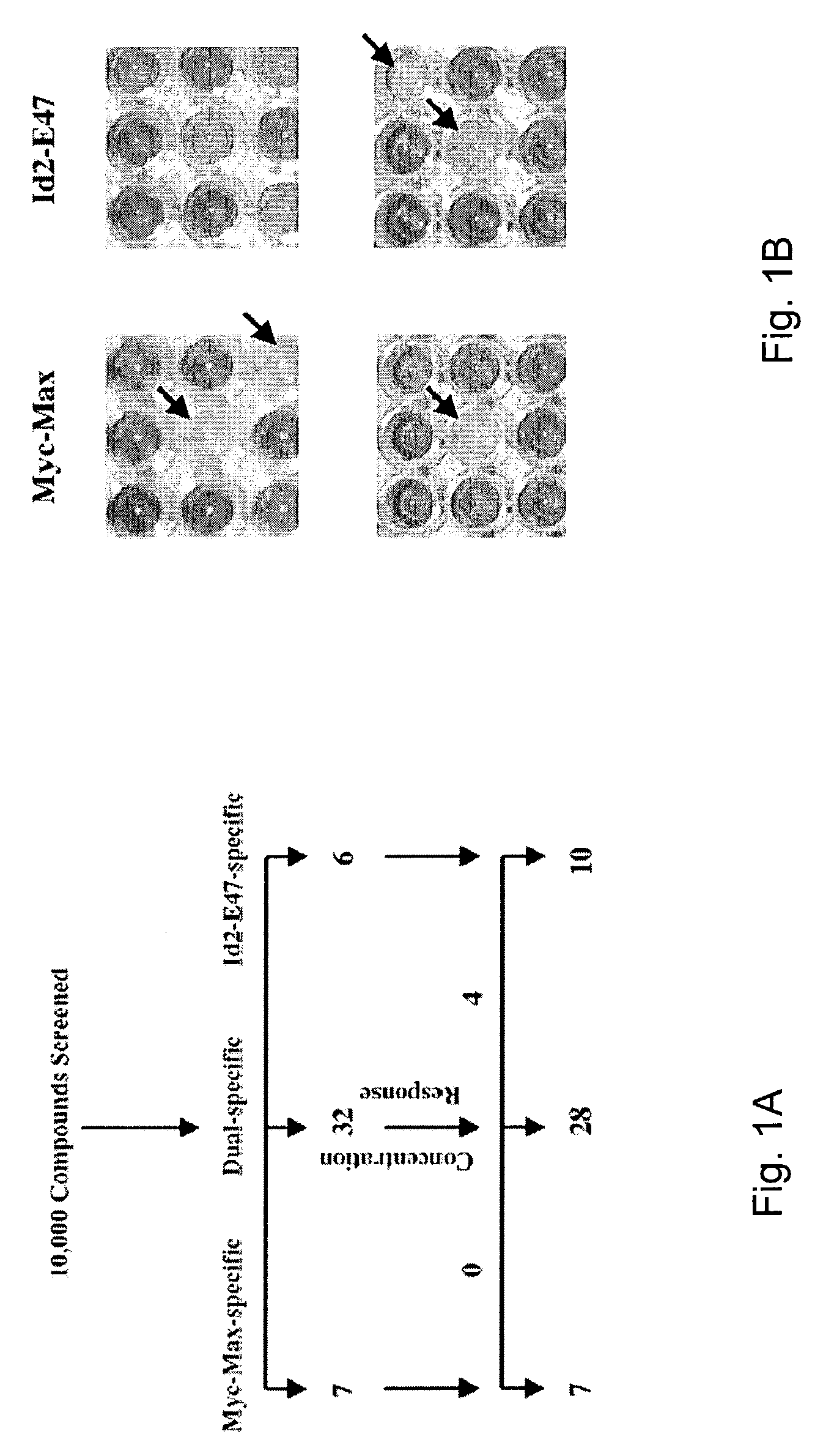
The c-Myc oncoprotein, a helix-loop-helix-leucine zipper (HLH-ZIP) transcription factor, is frequently deregulated in human cancers. All known functions of c-Myc, including those pertaining to transformation, require that it heterodimerize with another HLH-ZIP protein, Max. Using a high throughput yeast-based assay, we identified seven low molecular weight substances that inhibit c-Myc-Max association. Each compound also prevented this interaction in vitro and inhibited the growth of c-Myc-expressing fibroblasts, although not of fibroblasts lacking c-Myc. Finally, short-term exposure of c-Myc over expressing fibroblasts to several of the compounds markedly reduced their in vivo tumorigenicity. These studies suggest that yeast-based assays can be used to identify inhibitors of protein-protein interactions and that these frequently function in mammalian cells. The signature specificities of each of the c-Myc-Max compounds identified here further suggest synergistic in vivo function.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF PITTSBURGH
Induced pluripotent stem cells
InactiveUS20120128655A1Use injuryCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsPresent methodReprogramming
The present invention concerns the delivery of certain reprogramming factor proteins into cells, such as differenti-atedsomatic cells, in order to induce the epi-genetic reprogramming of the cell so it becomes a pluripotent stem cell. The reprogramming factor protein(s) may be Sox2, Klf4, Oct3 / 4, c-Myc, Lin28, Nanog, or any protein with reprogramming (-enhancing) activity. These proteins may be linked recombinantly or chemically to a cell penetrating peptide that helps facilitate the introduction of these proteins into the target cell and may be preferably expressed in mammalian cells to maintain them in active forms. Accordingly, the present method of inducing pluripotent stem cell (iPS) formation avoids the use of viral or DNA-based expression vectors or the expression of reprogramming factor genes within target cells, which are known to be harmful to the host target cell and cause cancer.
Owner:THE MCLEAN HOSPITAL CORP
Hoofed mammal inducible multipotential stem cell and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101864451AImprove disease resistanceMeet the needs of lifeVector-based foreign material introductionForeign genetic material cellsDiseaseMammal
The invention relates to a hoofed mammal inducible multipotential stem cell and a preparation method thereof. The method comprises the following steps of: A) constructing an expression vector carrying a transcription factor, wherein the transcription factor is Oct4, Sox2, c-Myc, Klf4, Lin28 and Nanog; and B) introducing the transcription factor in the step A) into the cells of the hoofed mammal in a combining form; picking clones of which the form is similar to that of the embryonic stem cell for subculturing; and screening the cell clones meeting the characteristic of the embryonic stem cell to obtain the hoofed mammal iPS cell. The method contributes to determining the most proper culturing condition and the most proper culturing method for establishing an ES cell line of pig, sheep, cattle and other hoofed mammals; and experimental models for various genetic diseases of human beings can be established with the hoofed mammal iPS cell line.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF BIOLOGICAL SCI CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
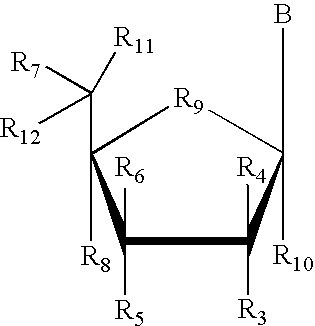
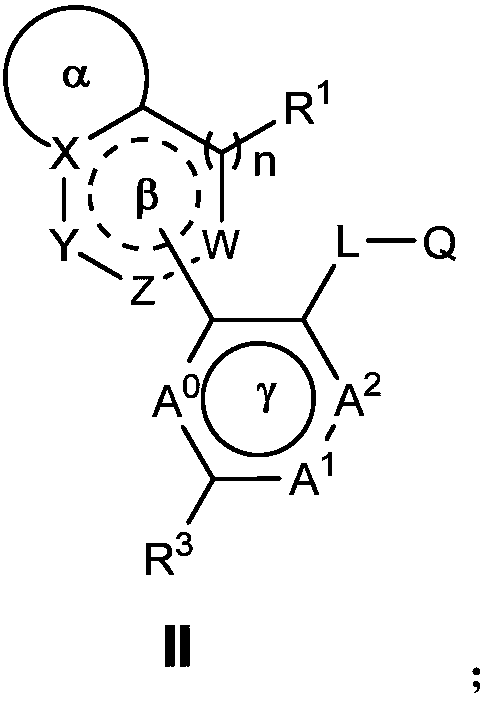
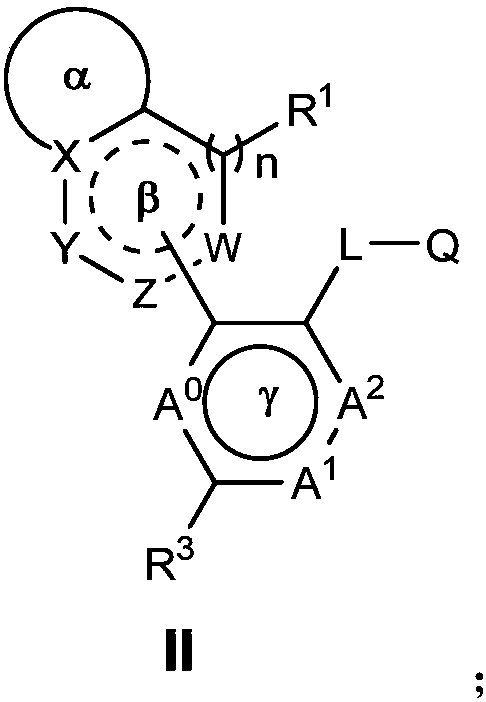
Nitrogen-containing heterocyclic ring compounds, and preparation method, pharmaceutical compositions and application thereof
InactiveCN108069959AHigh activityGood activity and stabilityOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryDiseaseHigh activity
The invention discloses nitrogen-containing heterocyclic ring compounds, and a preparation method, pharmaceutical compositions and application thereof. The nitrogen-containing heterocyclic ring compounds as shown in a formula II which is described in the specification can effectively bind to the bromodomains of BRD4, BRD3, BRD2 and BRDT in the BET family so as to regulate the transcription of thedownstream gene c-myc and related target genes thereof, thereby regulating downstream signal pathways and playing specific roles, including treatment of diseases such as inflammatory diseases, cancersand AIDS; and a part of the compounds have high activity, and good cell activity and metabolic stability, and thus can be used as effective drugs for treating tumors.
Owner:KAIHUI SCI & TECH DEV SHANGHAI +1
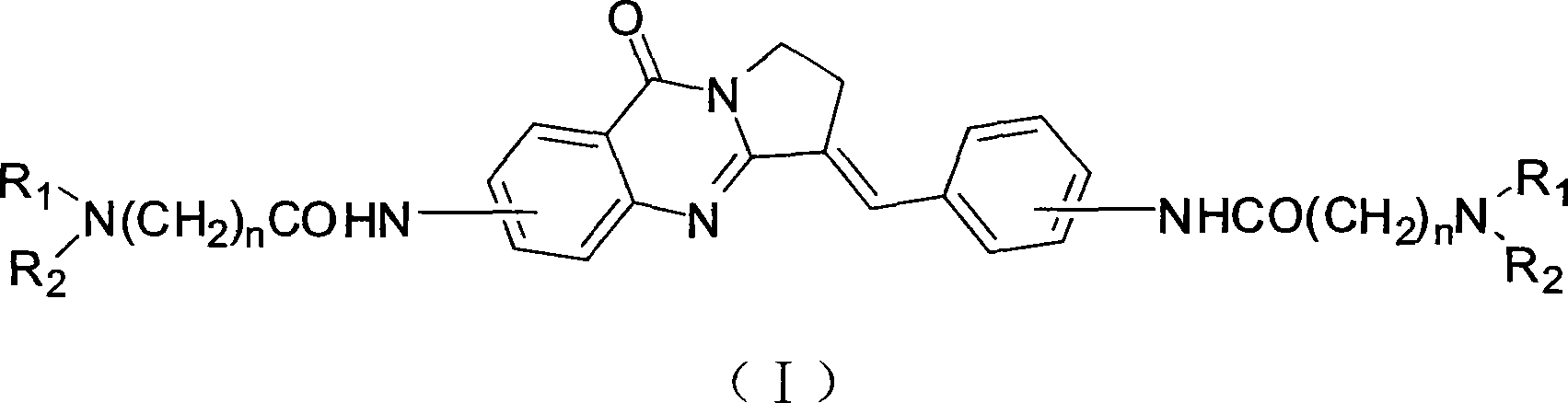
Bisfatty amido substituted quinazolone derivatives as well as preparation method and use thereof as anti-cancer drugs
InactiveCN101250189AGood antitumor activitySmall toxicityOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryQuinoxalineTelomerase
The invention discloses a dual fatty ammonia substituted quinazolinone derivative, represented as formula (I), wherein n is 1, 2, 3, 4 or 5, R1 and R2 are same or different, selected from the alkyl of H and C1-6, and naphthenic group, piperidyl, morpholinyl, piperazinyl or quinoxaline of C3-6. The derivative has strong interaction on the telomere DNA rich with guanine and c-myc DNA of proto-oncogene, strong inhibition on telomere / telomerase of cancer cell and strong inhibition on the c-myc expression of proto-oncogene. The derivative has low toxicity and side effect, which can be developed to a new anti-tumor drug. The derivative has simple preparation method, cheap materials and strong inhibition on various cancer cell lines, which can be prepared into anti-tumor drug, with wide application.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Use of cytoplasmic c-myc for regulating immune responses
InactiveUS20120107317A1Convenient treatmentReduced activityAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsAutoimmune responsesAutoimmune disease
The subject invention provides novel uses of cytoplasmic c-Myc for modulation of innate immune responses. The invention is based, at least in part, on the surprising discovery that cytoplasmic c-Myc, instead of nuclear c-Myc, modulates pro-inflammatory immune responses via its role as a positive feedback regulator. Specifically, the subject invention provides methods for treatment or amelioration of inflammatory diseases and / or immune disorders via inhibition c-Myc expression or its activity. Also provided are methods for the development of therapeutic agents for treating infection, inflammation, immune diseases and autoimmune diseases.
Owner:THE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG
Method for producing induced multipotential stem cell
InactiveCN101550428APotential for differentiationImprove efficiencyMicroorganism based processesUnknown materialsLIN28Histiocyte
The invention provides a method for producing induced multipotential stem cell, comprising steps of: A) constructing viral vectors carrying transcription factors, wherein the transcription factors are selected from: Oct4, Sox2, c-Myc, Klf4, Lin28 and Nanog; B) respectively transfecting viral vectors obtained in step A), and obtaining virus liquid containing the transcription factors; and C) infecting cells in combination manner by the virus liquid containing the transcription factors obtained from step B)selecting clones with human embryo like stem cell for subculturing, and obtaining induced multipotential stem cell by screening cell clone according to human embryo stem cell characteristic. The method of the invention for preparing human embryo stem cell has high efficiency, can avoid rejection reaction, differentiates to be different histiocytes in specific condition, and has an extensive application future.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF BIOLOGICAL SCI CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
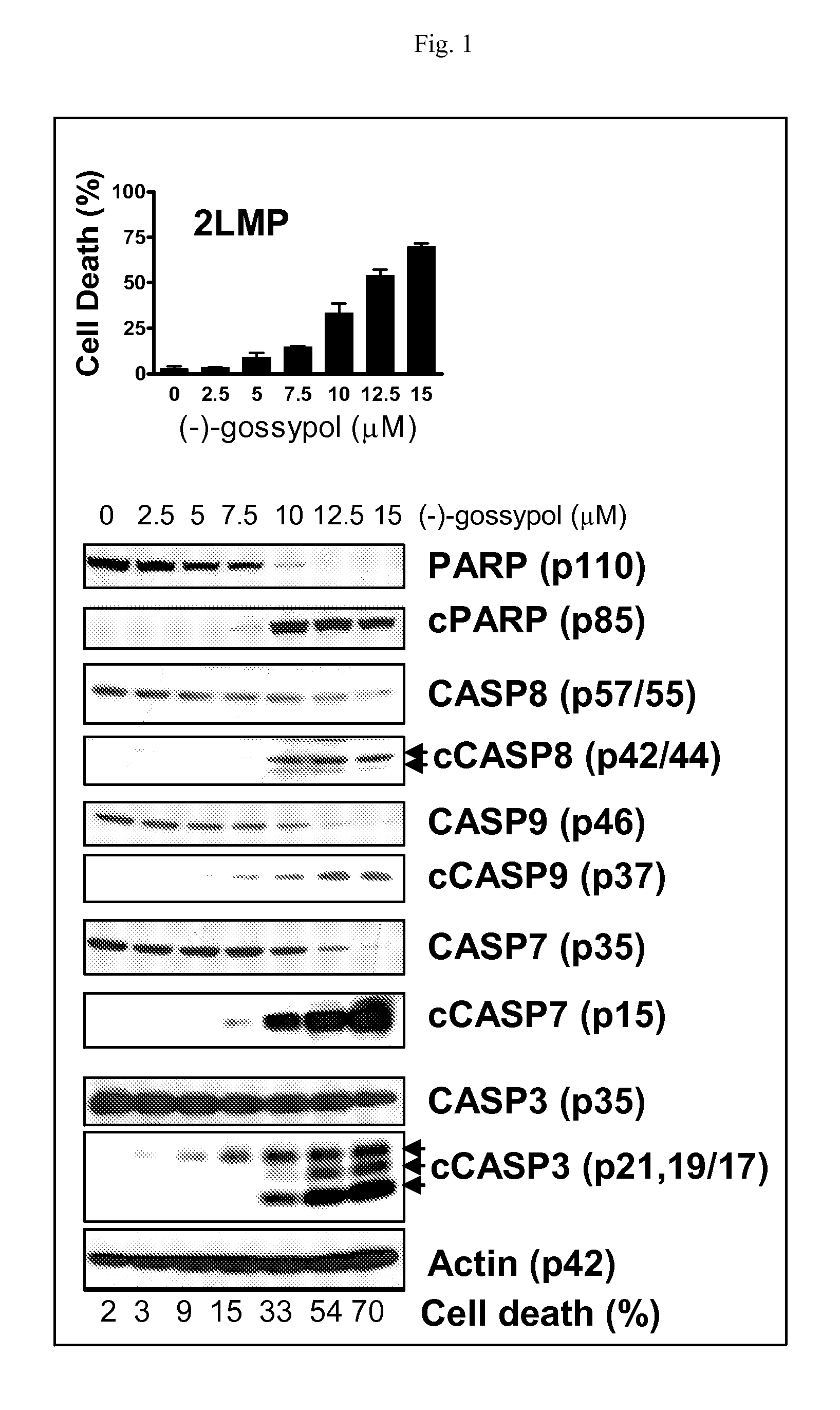
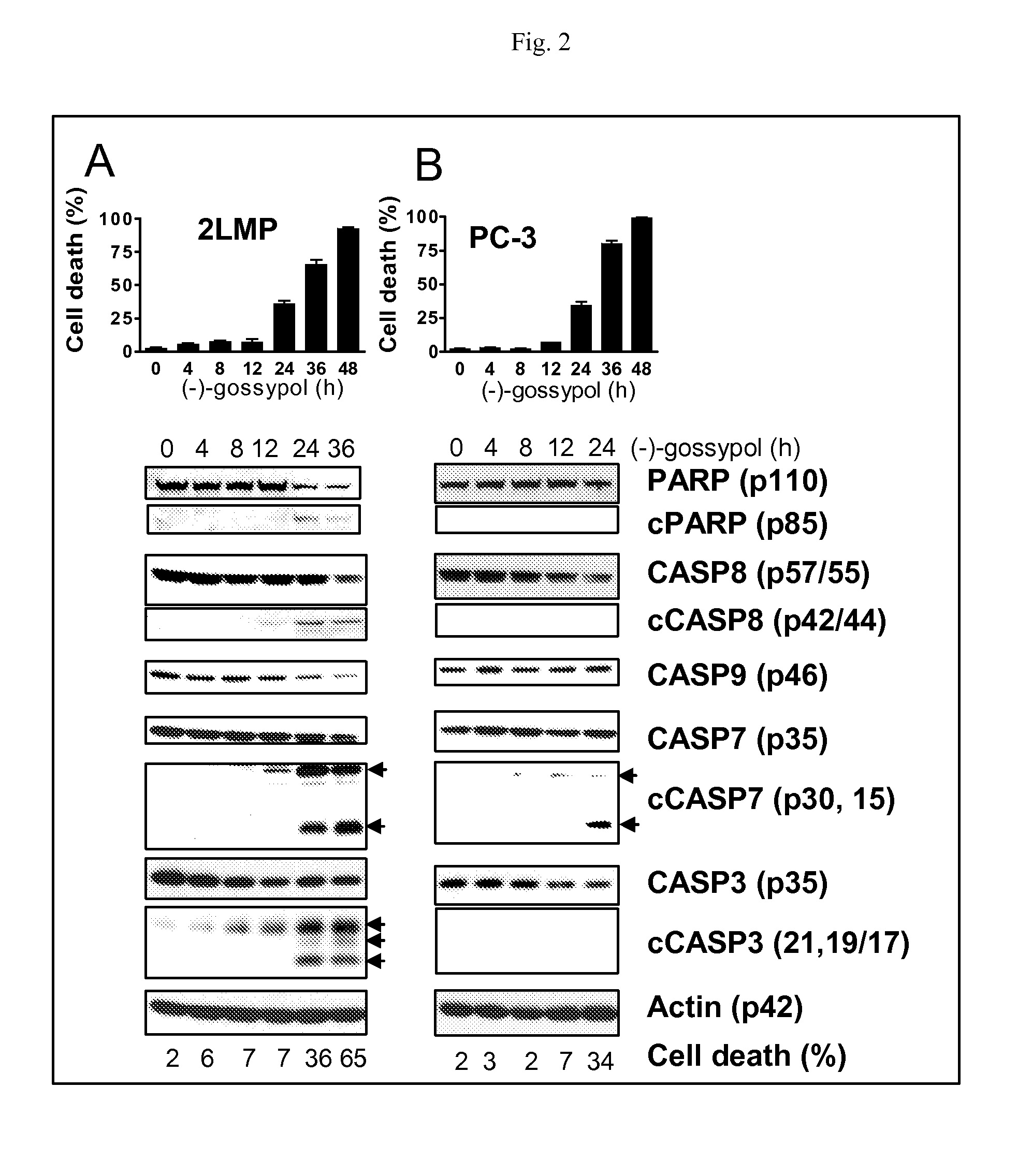
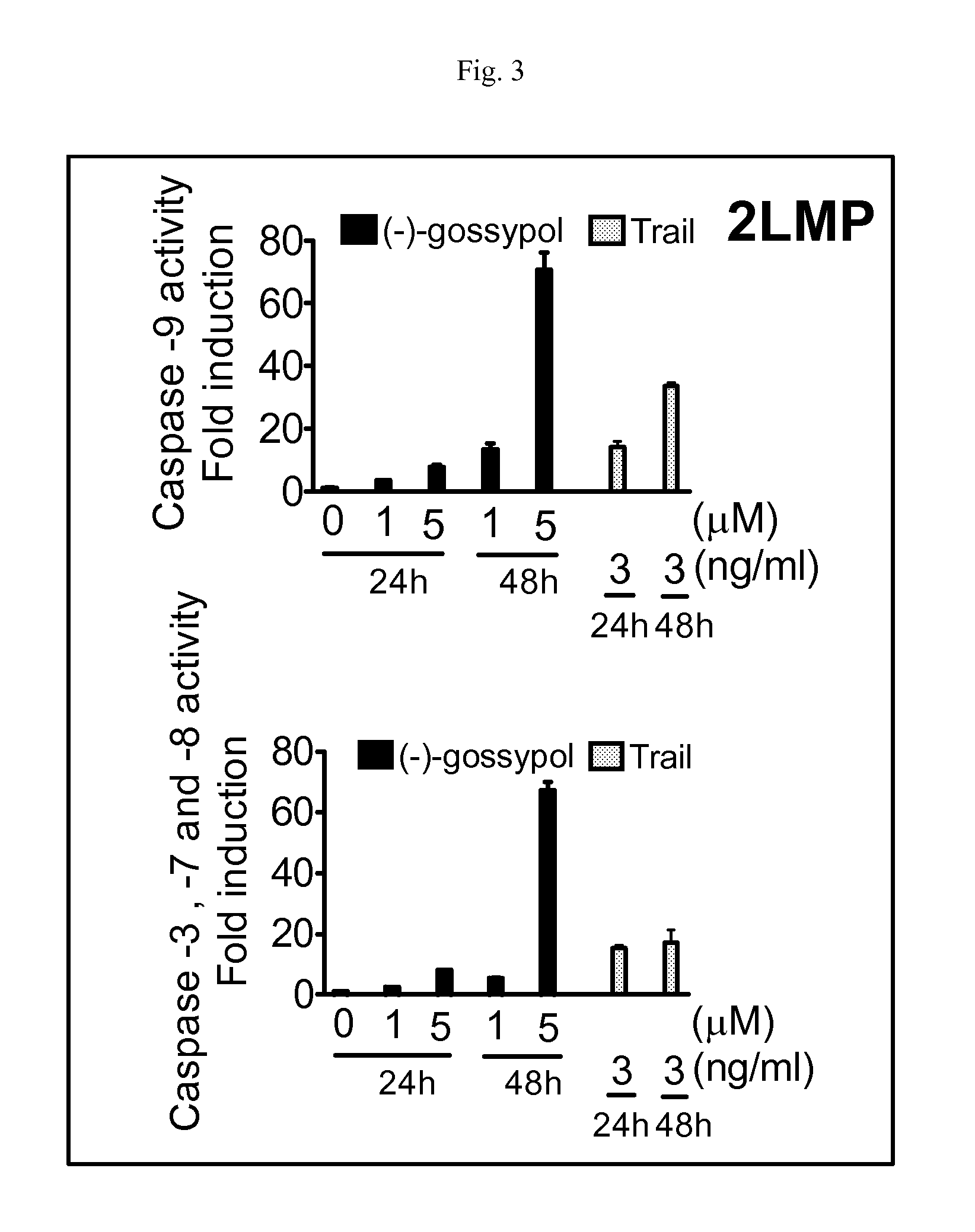
Biomarkers for gossypol chemotherapy and methods of treating disease
The present invention provides a biomarker for selecting a patient for treatment with gossypol, wherein the biomarker comprises an elevated expression level of c-Myc, Mcl-1, or combination thereof, relative to the normal expression level of c-Myc, Mcl-1, or combination thereof. The present invention also provides methods for targeting patients for treatment with gossypol, wherein the patient has a disease, condition, or disorder that overexpresses c-Myc, Mcl-1, or combination thereof. The present invention also provides methods for treating or ameliorating a disease, condition, or disorder in a patient comprising determining the expression level of c-Myc, Mcl-1, or combination thereof in the patient and administering gossypol to the patient. In certain embodiments of the invention, the disease is cancer, and the cancer cells show elevated expression levels of c-Myc compared to non-cancerous cells. The invention also provides methods for overcoming Mcl-1-mediated chemoresistance comprising administering gossypol to a patient in need thereof.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
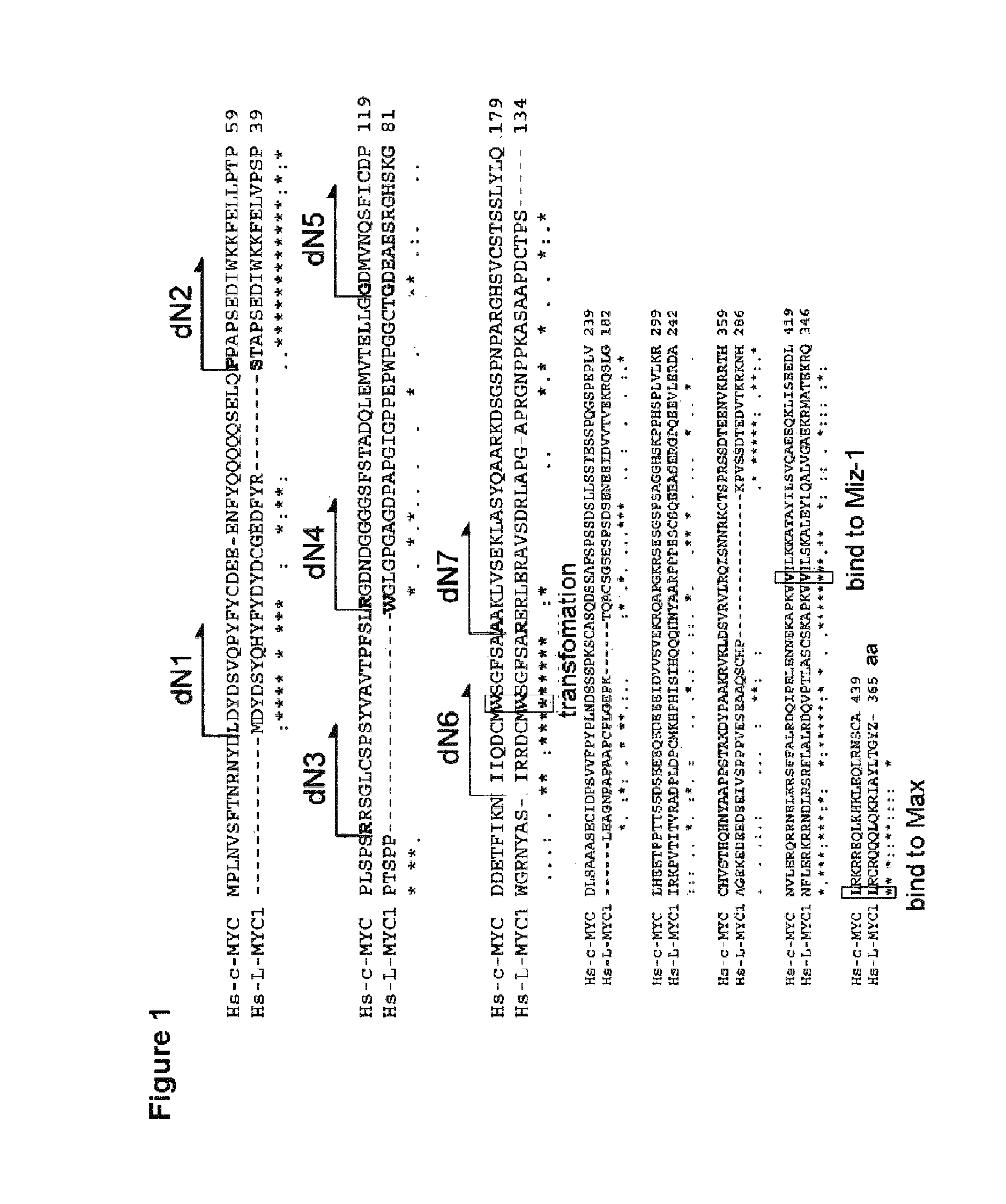
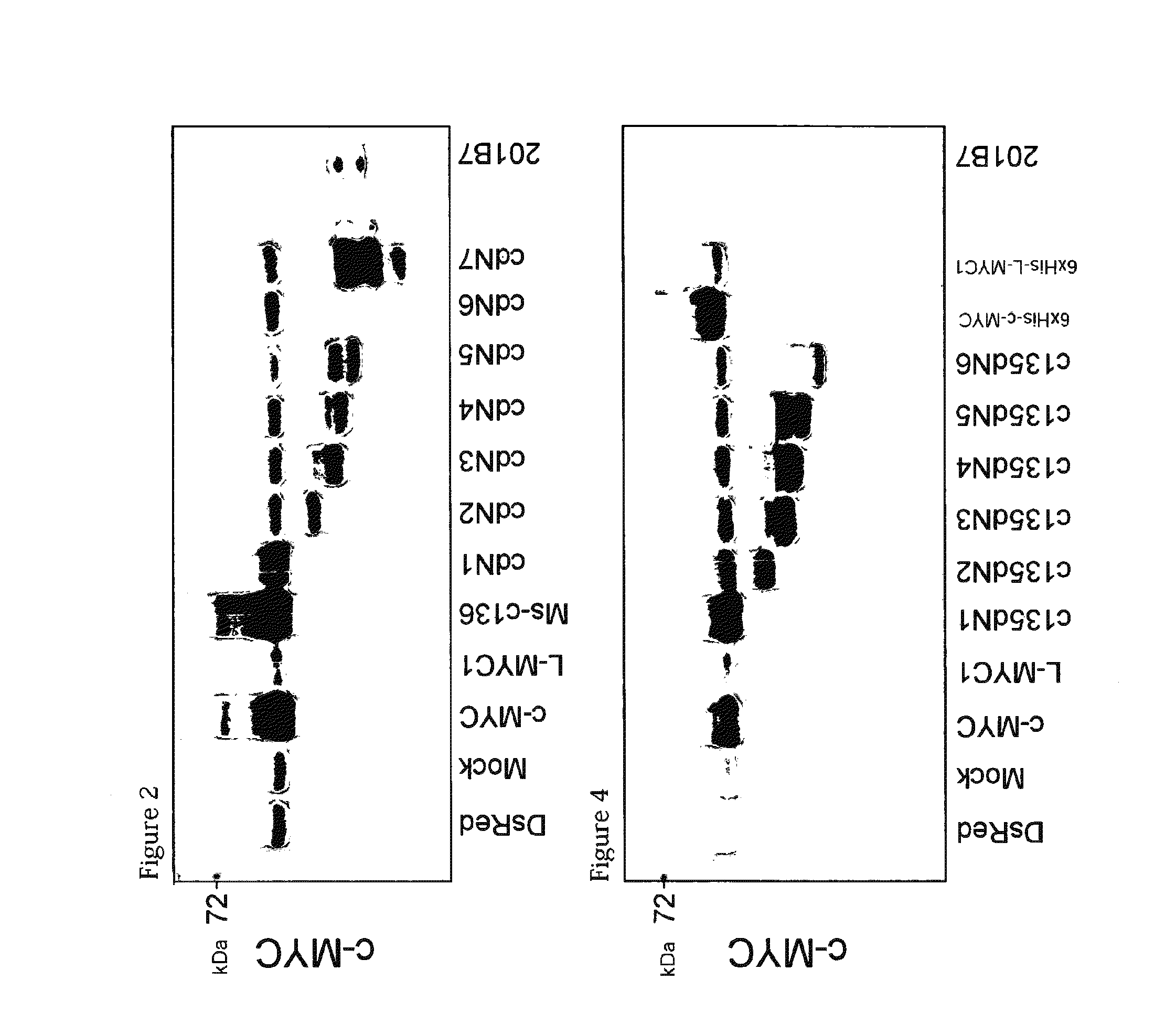
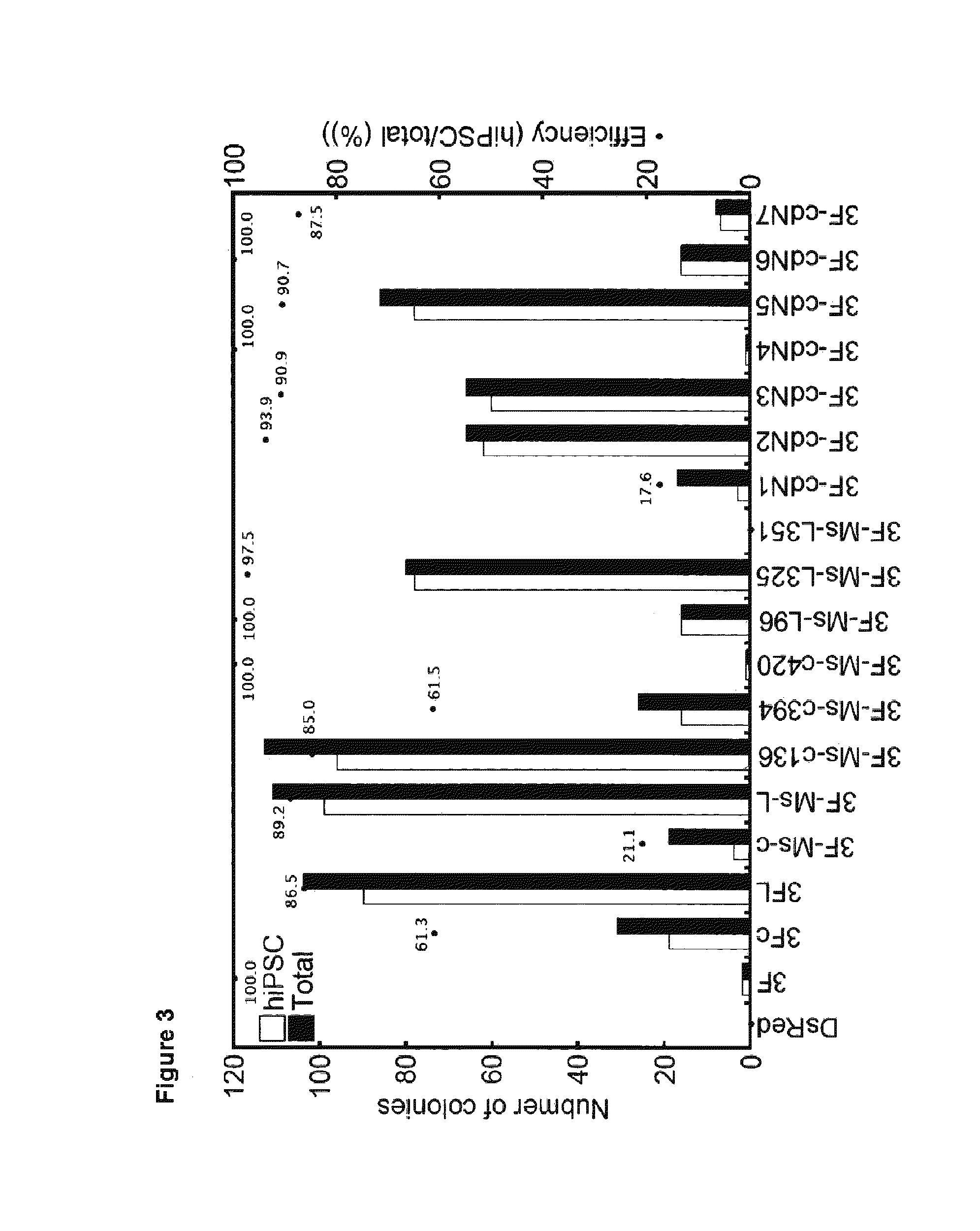
Myc variants improve induced pluripotent stem cell generation efficiency
ActiveUS9005967B2Improve power generation efficiencyHigh activityArtificial cell constructsArtificially induced pluripotent cellsNuclear reprogrammingMultipotential stem cell
The present invention provides a method for improving iPS cell generation efficiency, which comprises a step of introducing a Myc variant having the following features: (1) having an activity to improve iPS cell generation efficiency which is comparative to, or greater than that of c-Myc; and (2) having a transformation activity which is lower than that of c-Myc; or a nucleic acid encoding the variant, in a nuclear reprogramming step. Also, the present invention provides a method for preparing iPS cells, which comprises a step of introducing the above Myc variant or a nucleic acid encoding the variant and a combination of nuclear reprogramming factors into somatic cells. Moreover, the present invention provides iPS cells comprising the nucleic acid encoding the Myc variant which can be obtained by the above method, and a method for preparing somatic cells which comprises inducing differentiation of the iPS cells.
Owner:KYOTO UNIV
Nitrogen-containing heterocyclic ring compounds, and preparation method, pharmaceutical compositions and application thereof
InactiveCN108069958AHigh activityGood activity and stabilityOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryDiseaseHigh activity
The invention discloses nitrogen-containing heterocyclic ring compounds, and a preparation method, pharmaceutical compositions and application thereof. The nitrogen-containing heterocyclic ring compounds as shown in a formula II which is described in the specification can effectively bind to the bromodomains of BRD4, BRD3, BRD2 and BRDT in the BET family so as to regulate the transcription of thedownstream gene c-myc and related target genes thereof, thereby regulating downstream signal pathways and playing specific roles, including treatment of diseases such as inflammatory diseases, cancersand AIDS; and a part of the compounds have high activity, and good cell activity and metabolic stability, and thus can be used as effective drugs for treating tumors.
Owner:KAIHUI SCI & TECH DEV SHANGHAI +1
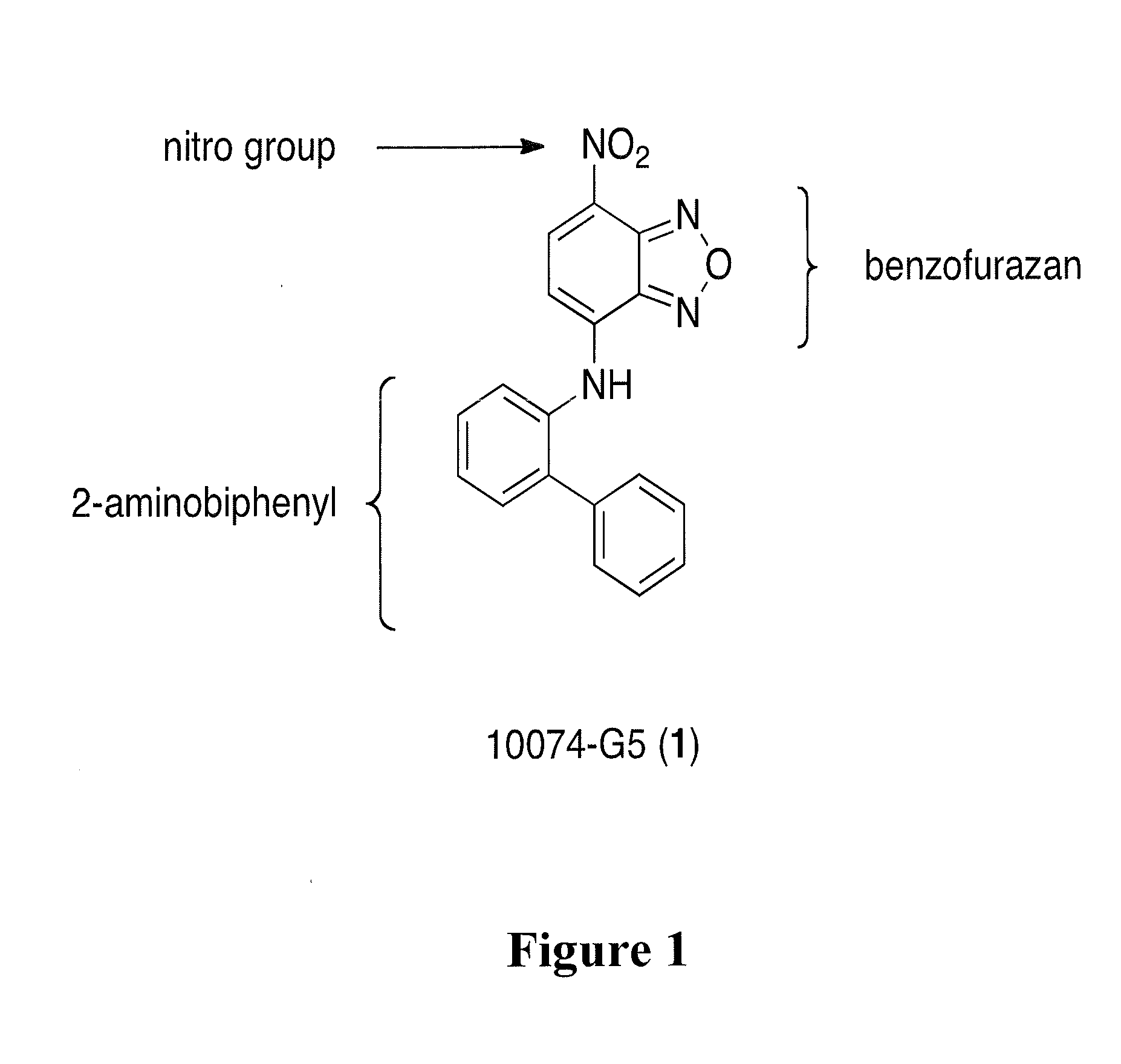
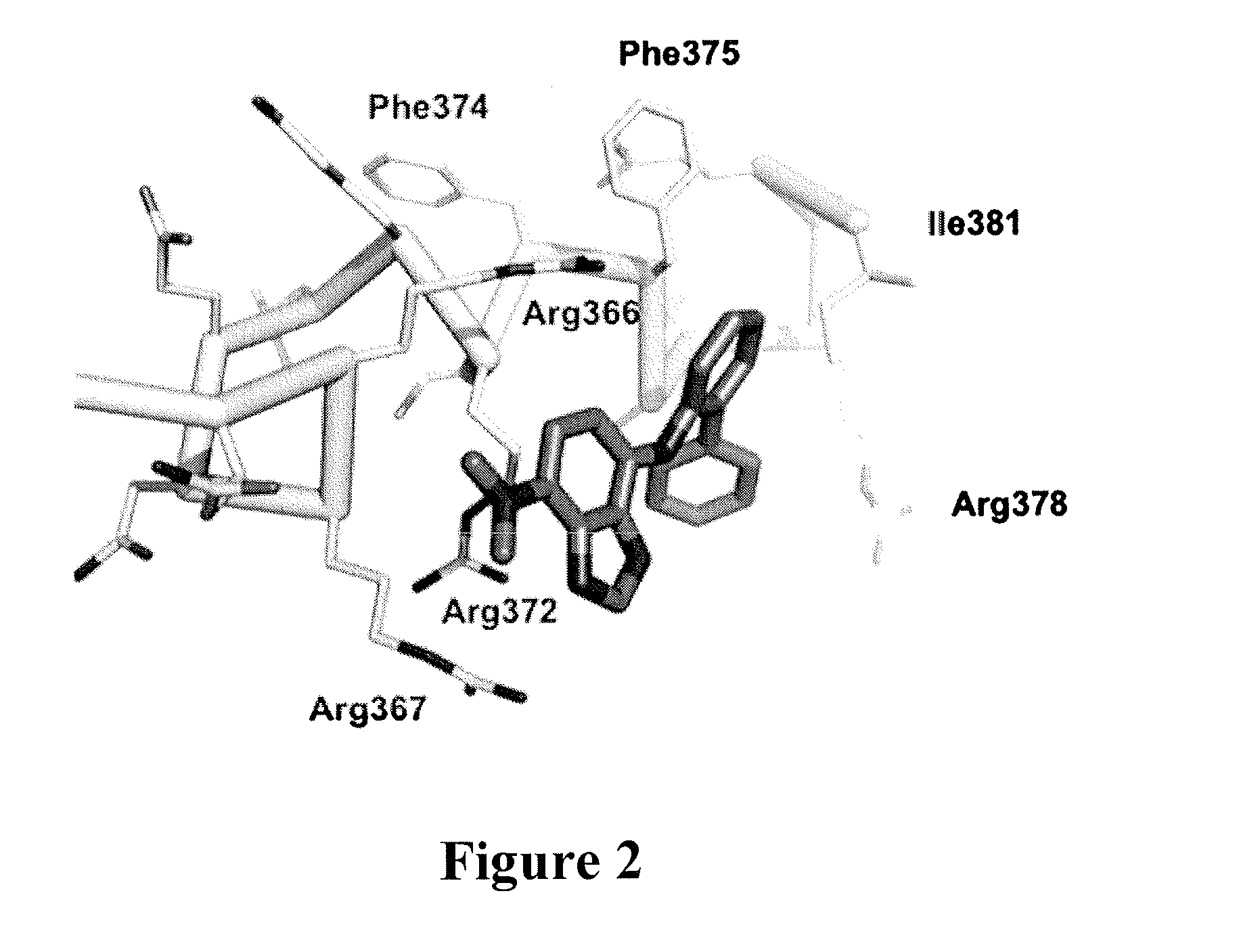
Potent analogues of the c-myc inhibitor 10074-g5 with improved cell permeability
The present invention relates compounds and compositions for interfering with the association of Myc and Max. These compounds and compositions are useful in methods for inhibiting growth or proliferation of a cell. Methods of inhibiting growth or proliferation of a cell comprise contacting the cell with an amount of a compound that interferes with Myc and Max association effective to inhibit growth or proliferation of the cell. The compounds exhibit increased inhibitory activity against c-Myc relative to the known c-Myc inhibitor small-molecule benzofurazan N-([1,1′-biphenyl]-2-yl)-7-nitrobenzo[c][1,2,5]oxadiazol-4-amine (10074-G5).
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND BALTIMORE
Preparation method of inducible pluripotent stem cell of goat
ActiveCN102653774AFacilitate revealing functionHelps reveal complexityVertebrate cellsArtificial cell constructsGene targetsLIN28
The invention relates to a preparation method of an inducible pluripotent stem cell of a goat. The preparation method comprises the following steps: A) constructing a lentiviral vector carrying a transcription factor which is selected from Oct4, Sox2, c-Myc, Klf4, Lin28 and Nanog; and B) infecting a goat adult cell by combining the transcription factor with the lentiviral vector prepared in the step A, selecting clone with a shape similar to an embryonic stem cell for subculturing, and preparing the inducible pluripotent stem cell of the goat by screening cell clone in accordance with the characteristics of the embryonic stem cell. According to the preparation method, an optimal culture condition and method of a goat ES (embryonic stem) cell line construction can be established; the inducible pluripotent stem cell of the goat is an excellent vector for goat gene targeting, and the inducible pluripotent stem cell of the goat facilitates the revelation of each gene function and the complex development of the goat.
Owner:苏州中科细胞转化研究院
Sheep induced pluripotent stem cell and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102586171AFacilitate revealing functionHelps reveal complexityArtificial cell constructsVertebrate cellsLentivirusLIN28
The invention relates to a sheep induced pluripotent stem cell and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the steps of: A) constructing lentivirus vectors with transcription factors, wherein the transcription factors are selected from Oct4, Sox2, c-Myc, K1f4, Lin28, Nanog, SV40 and hTERT; and B) infecting sheep adult cells to the transcription factors in a combining form by adopting the lentivirus vectors obtained in the step A), selecting cloned passages with forms similar to those of embryonic stem cells for culturing, and sieving the cells satisfied with characteristics of embryonic stem cells for cloning so as to obtain the sheep induced pluripotent stem cells. The sheep induced pluripotent stem cell and the preparation method thereof, disclosed by the invention, are good for determining most suitable culture condition and method of sheep ES cell establishment system; the sheep induced pluripotent stem cell is a good carrier for sheep gene targeting; and the sheep induced pluripotent stem cell is beneficial to revealing gene functions and complex development events of sheep and can be used for improving species and promoting economic growth.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF BIOLOGICAL SCI CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com