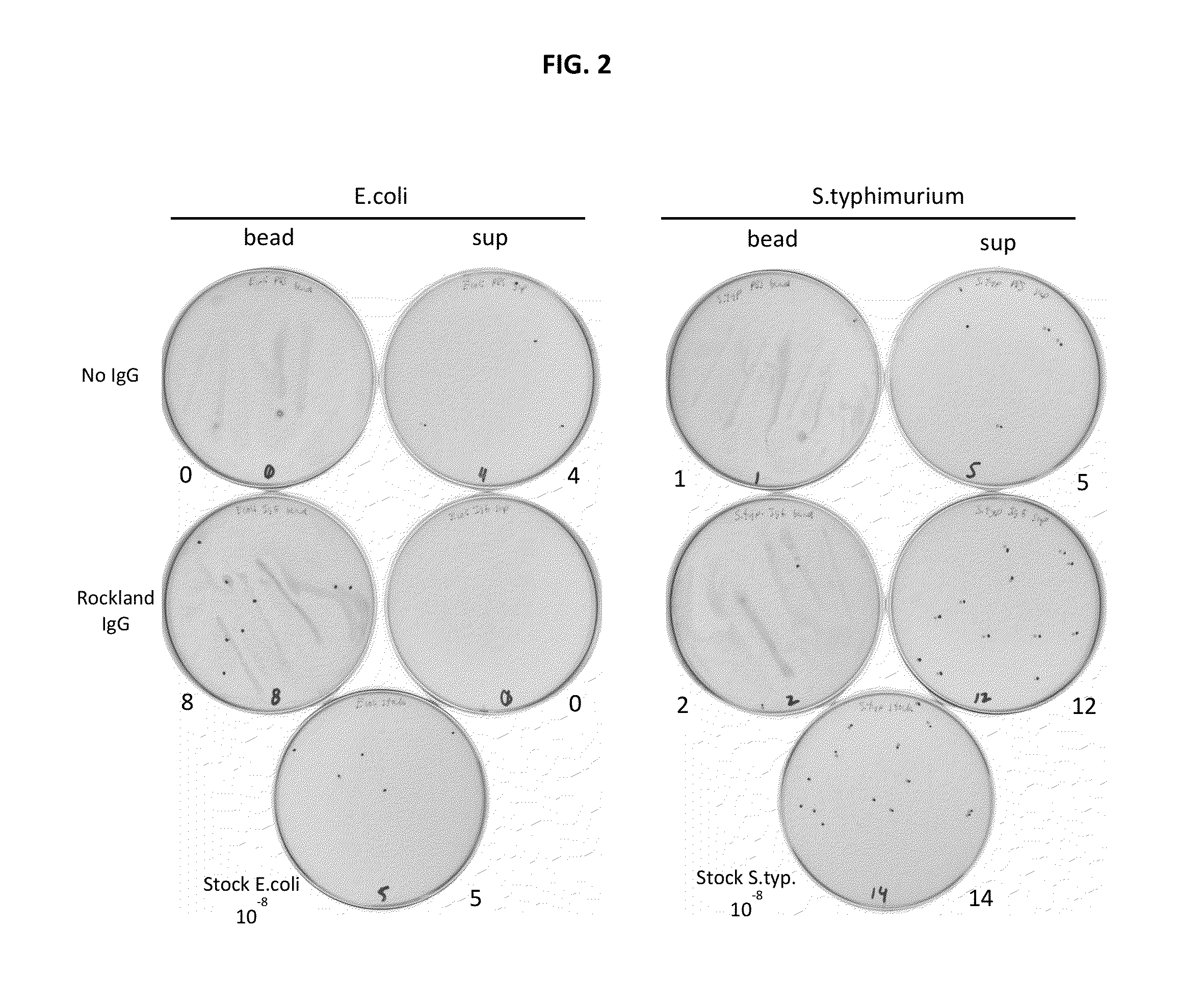
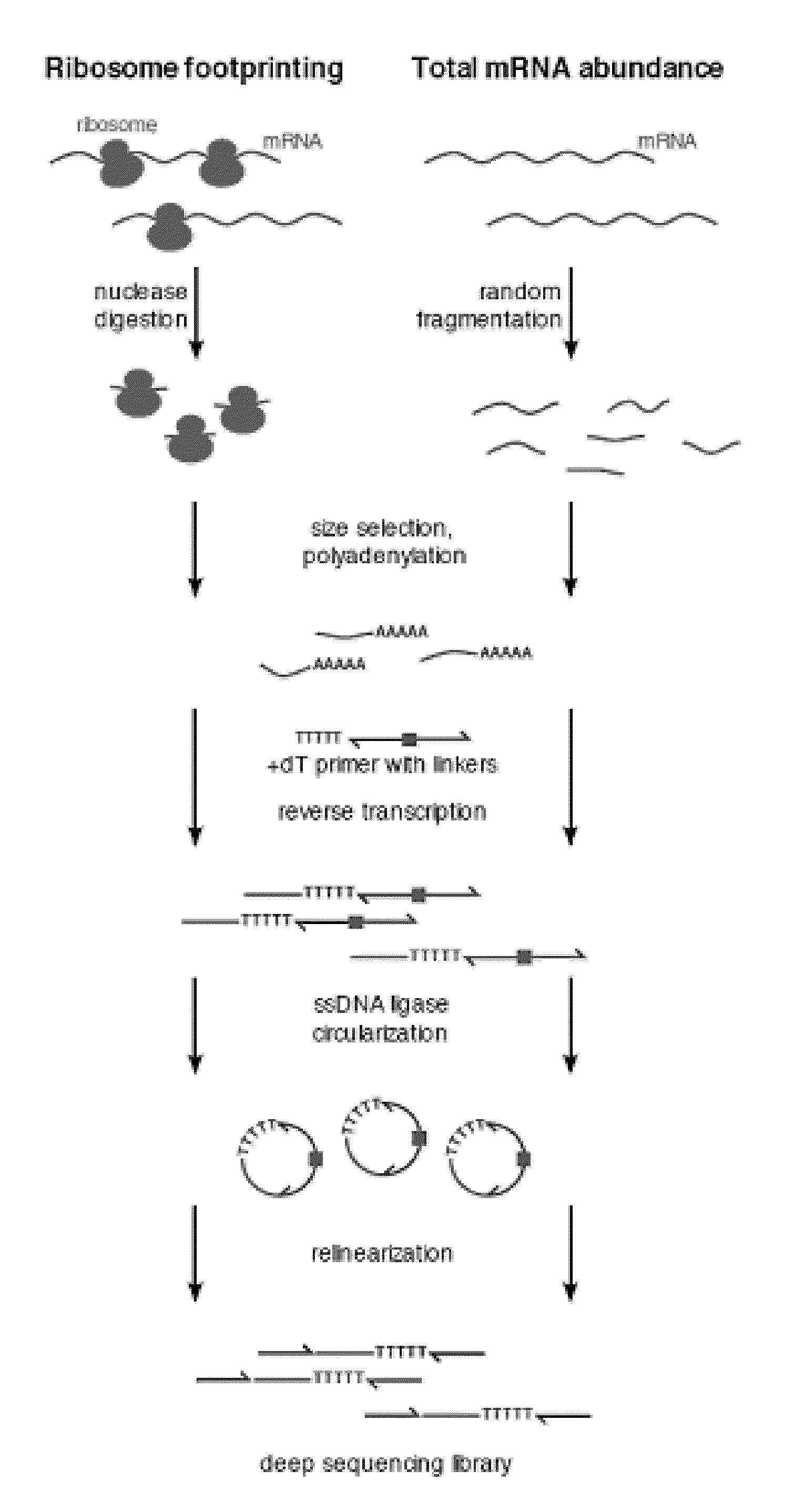
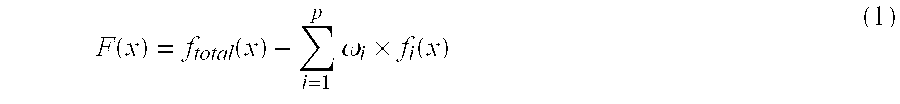Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
615 results about "Ribosome" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Ribosomes (/ˈraɪbəˌsoʊm, -boʊ-/) comprise a complex macromolecular machine, found within all living cells, that serves as the site of biological protein synthesis (translation). Ribosomes link amino acids together in the order specified by messenger RNA (mRNA) molecules. Ribosomes consist of two major components: the small ribosomal subunits, which read the mRNA, and the large subunits, which join amino acids to form a polypeptide chain. Each subunit consists of one or more ribosomal RNA (rRNA) molecules and a variety of ribosomal proteins (r-protein or rProtein). The ribosomes and associated molecules are also known as the translational apparatus.
Novel strain of bacillus amyloliquefaciens and its use
InactiveUS20100143316A1Inhibits pathogenic growthPromote biodegradationAntibacterial agentsBiocideBiotechnologyAmylase
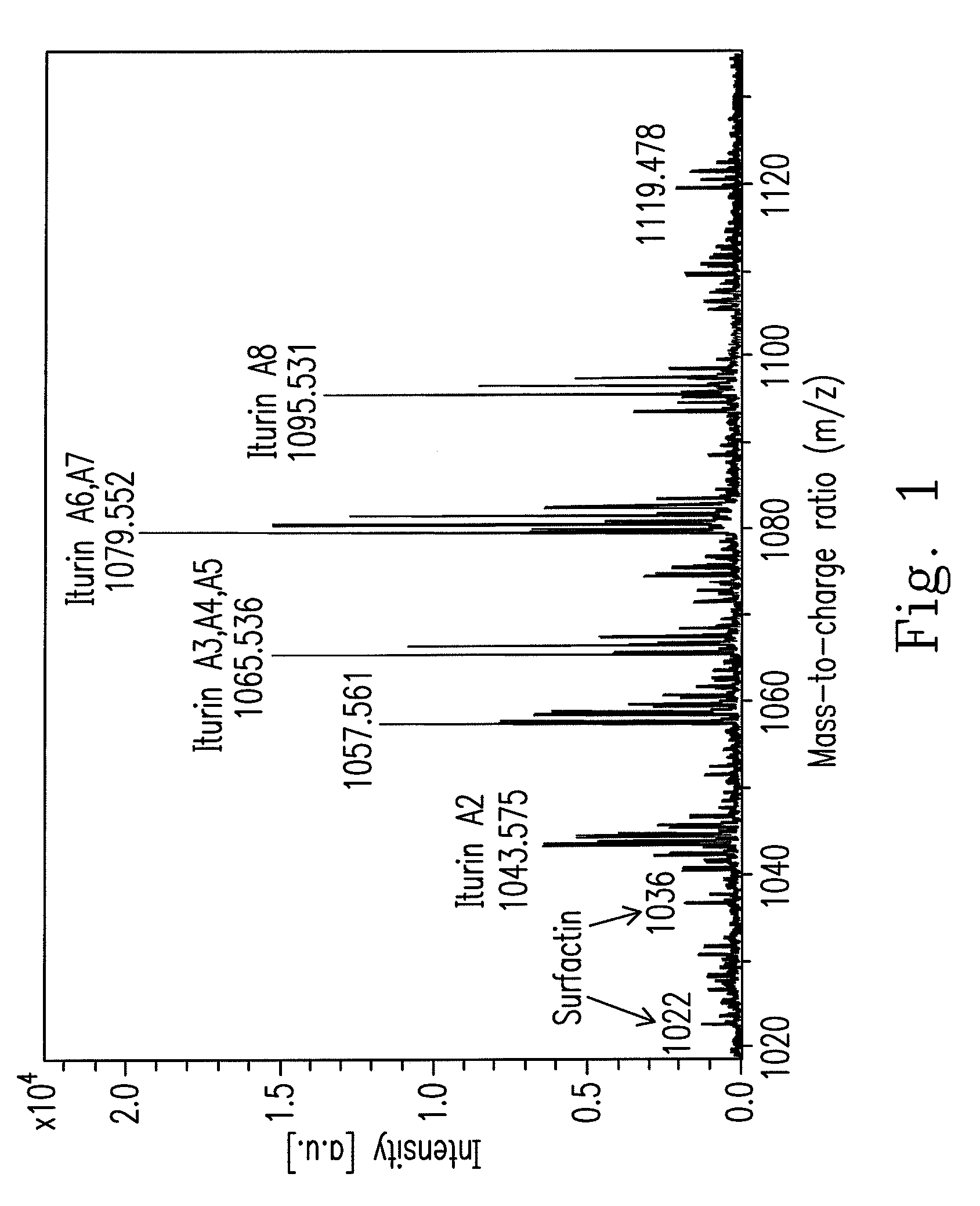
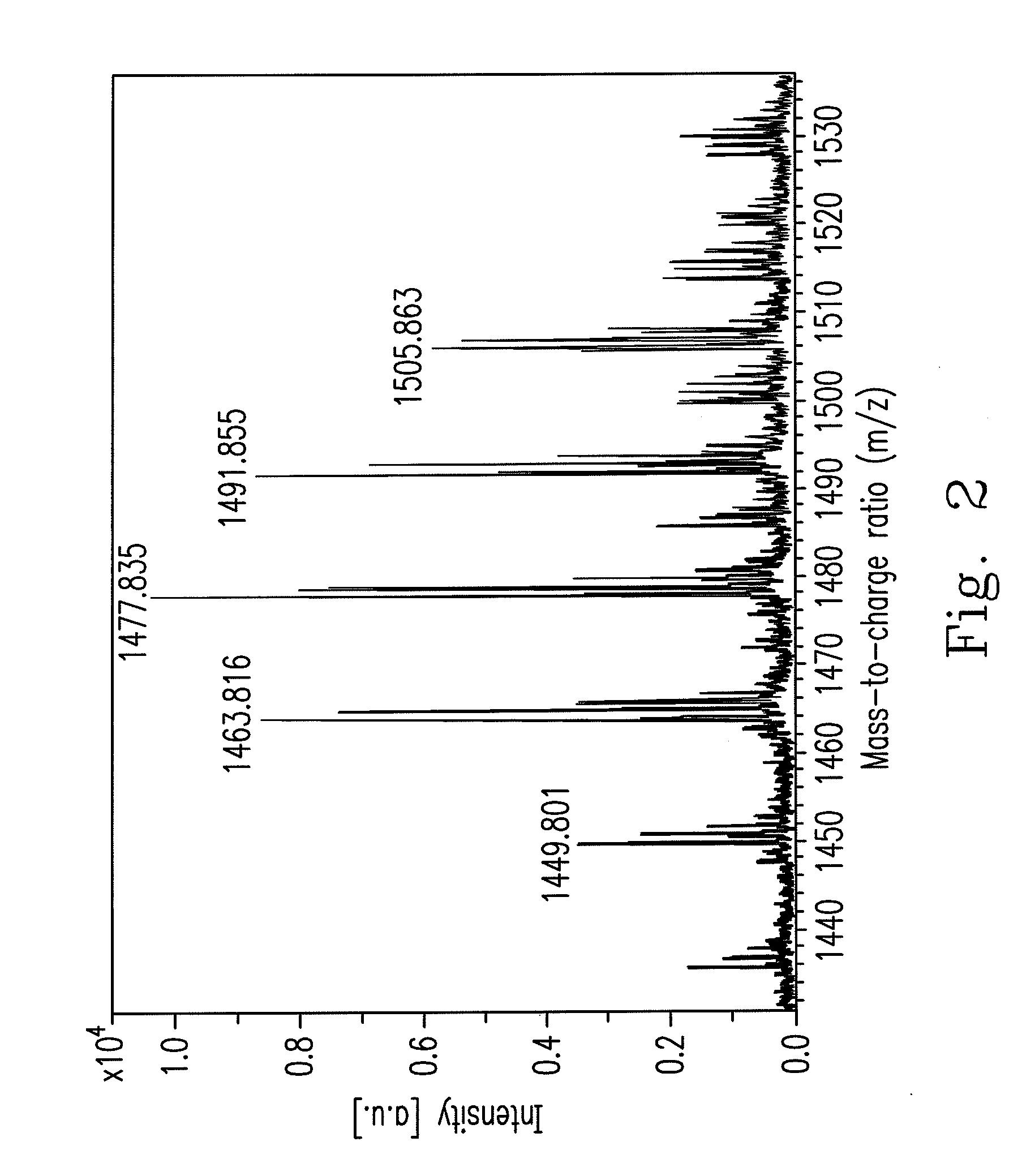
An isolated Bacillus amyloliquefaciens Ba-BPD1 having an Accession No. of DSM 21836 is provided. This novel strain has unique 16S ribosomal RNA sequenced as SEQ ID NO:1 and produces amylase, protease, cellulase and lipase, fibrinolytic enzyme to show their biodegradation capacities. Further, B. amyloliquefaciens Ba-BPD1 produces the antibiotic substances, such as iturin, fengycin and surfactin, and has antimicrobial capacity for inhibiting the fungal or bacterial growth. In conclusion, the novel strain of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens Ba-BPD1 and its products can be applied in agriculture, wastewater treatment, food industry and chemical industry.
Owner:AGRI CHEM & TOXIC SUBSTANCES RES INST COUNCIL AGRI EXECUTIVE YUAN
Method of Sequence Optimization for Improved Recombinant Protein Expression using a Particle Swarm Optimization Algorithm
An improved gene sequence optimization method, the systematic optimization method, is described for boosting the recombinant expression of genes in bacteria, yeast, insect and mammalian cells. This general method takes into account of multiple, preferably most or all, of the parameters and factors affecting protein expression including codon usage, tRNA usage, GC-content, ribosome binding sequences, promoter, 5′-UTR, ORF and 3′-UTR sequences of the genes to improve and optimize the gene sequences to boost the protein expression of the genes in bacteria, yeast, insect and mammalian cells. In particular, the invention relates to a system and a method for sequence optimization for improved recombinant protein expression using a particle swarm optimization algorithm. The improved systematic optimization method can be incorporated into a software for more efficient optimization.
Owner:NANJING GENSCRIPT BIOTECH CO LTD
Microbial identification based on the overall composition of characteristic oligonucleotides
InactiveUS20050142584A1Create accuracyCreate speedMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganismBiological body
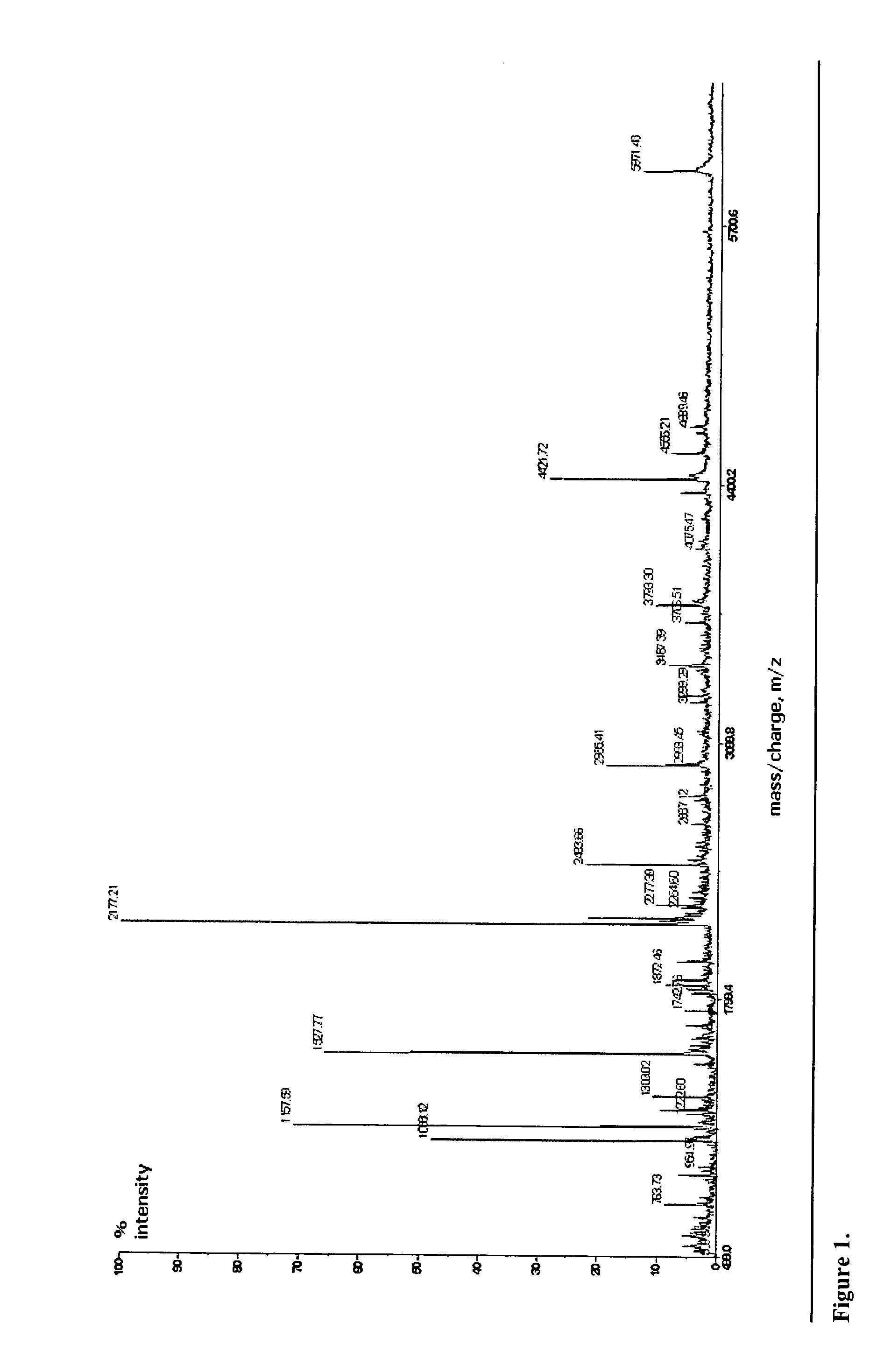
Identification of microorganisms based on the sequences of their 5S, 23S and particularly 16S ribosomal RNAs is growing in utility as the database of known ribosomal RNA sequences expands. Experimental identification is usually based on matching the experimentally-determined sequence of an organisms rRNA to a previously-determined sequence in the databank, or hybridization of the organisms rRNA or encoding rDNA to an oligonucleotide probe specific for an organism anticipated to be present in the sample. Here we propose the identification of microorganisms based on the overall composition (not sequence or hybridization propensity) of characteristic molecules derived from their rRNA or rDNA sequences by enzymatic cleavage or localized amplification. Ribonuclease T1 fragments of rRNA composition determination by mass spectrometry are especially favored. The characteristic molecules used can be chosen to be “compositional signatures” whose presence / absence is known to be associated with particular groups of organisms.
Owner:JACKSON GEORGE W
Vectors, mutant viruses and methods for generating mutant viruses
InactiveUS20070110720A1Easy to identifyEnhanced cytotoxic potentialBiocideGenetic material ingredientsHeterologousBinding site
A nucleic acid vector comprising first and second nucleotide sequences corresponding to nucleotide sequences flanking an insertion site in the genome of a selected herpes simplex virus strain; and a cassette located between said first and second nucleotide sequences comprising nucleic acid encoding: (a) one or a plurality of insertion sites and / or a nucleotide sequence of interest; and (b) a ribosome binding site or a regulatory nucleotide sequence; and (c) a marker is disclosed. Herpes simplex viruses generated using said vector, methods for their generation and herpes simplex viruses having a genome comprising heterologous nucleic acid are also disclosed.
Owner:CRUSADE LAB
Protein synthesis monitoring (psm)
ActiveUS20060228708A1Unprecedented sensitivityHighly accurate quantitationPeptide/protein ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorophoreIn vivo
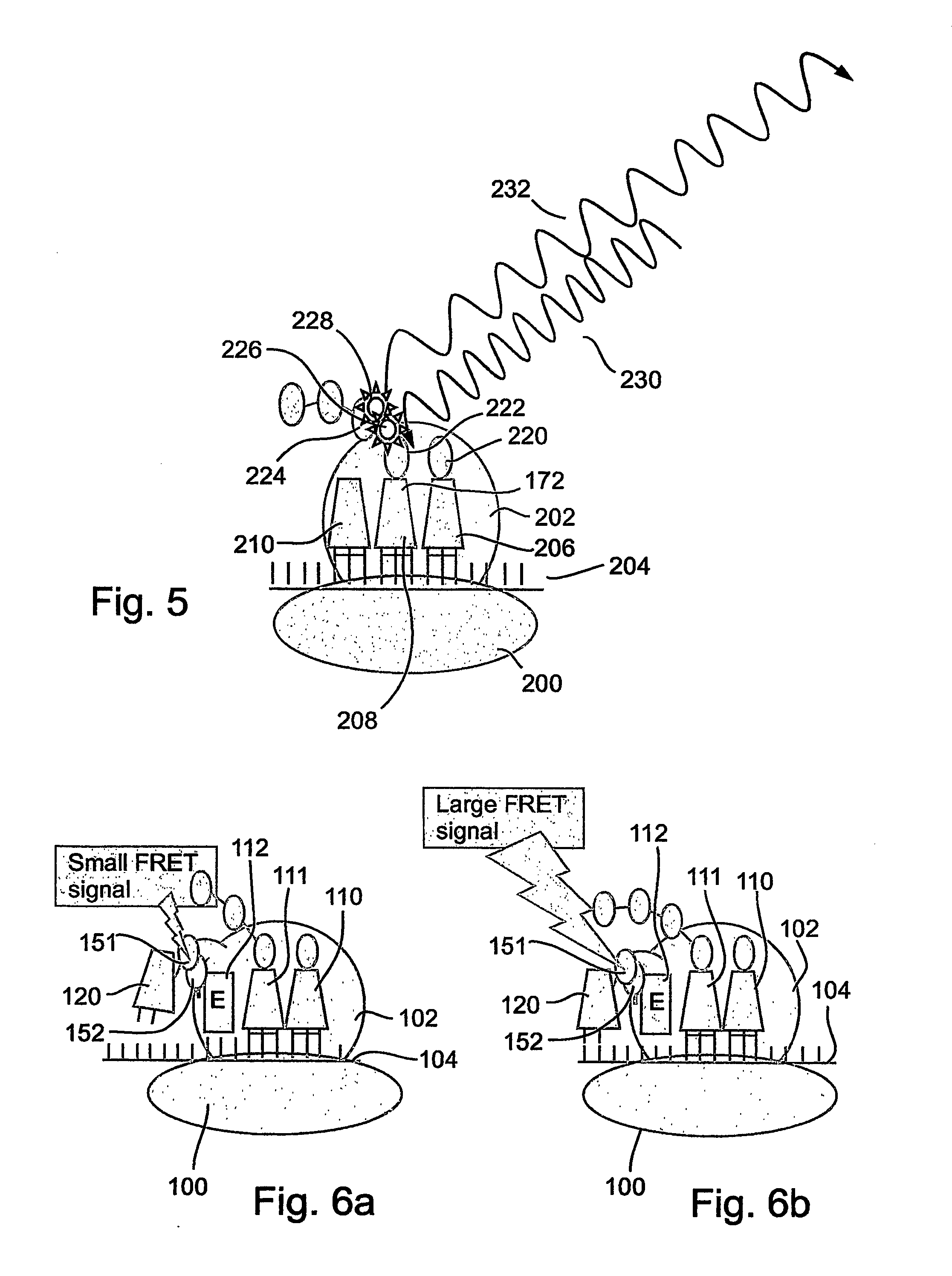
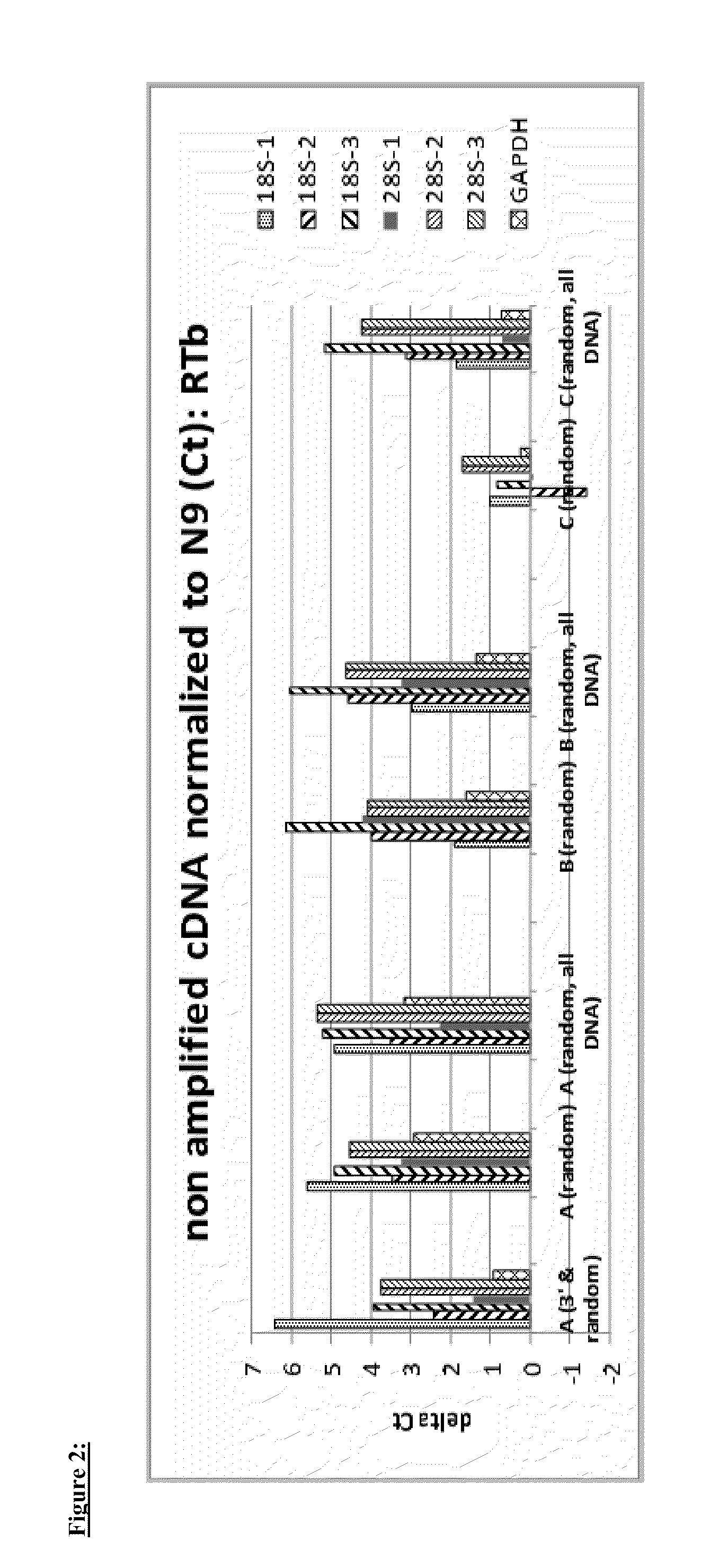
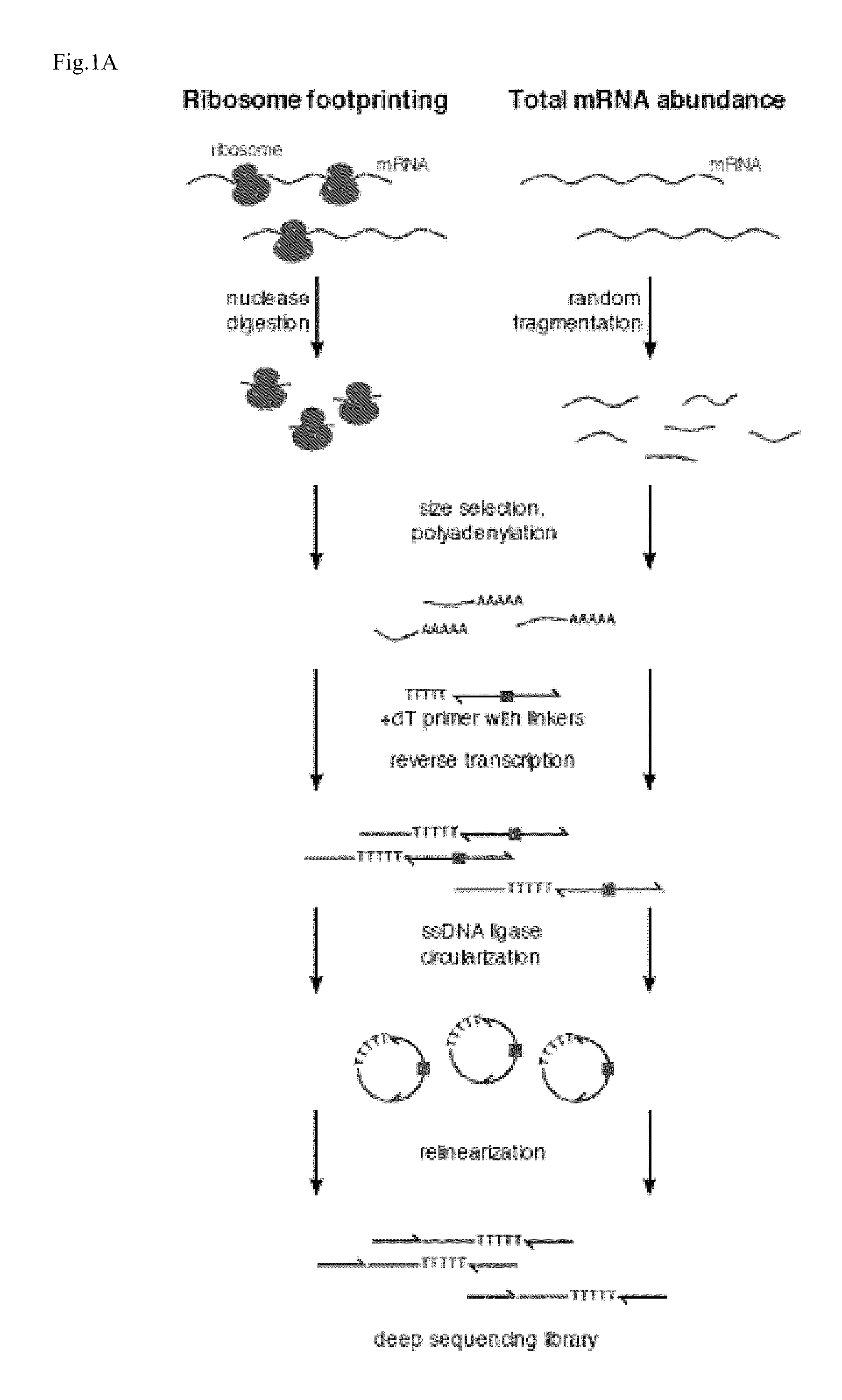
A method and a device are disclosed for monitoring the synthesis of proteins by the ribosome in real time, in vivo as well as in in-vitro. The ribosome is engineered to carry a donor fluorophore, and tRNA and / or amino acids and / or some other part of the ribosome are either engineered to carry acceptor fluorophores or else their natural fluorescent properties are utilized as acceptors. As the ribosomes mechanism processed the mRNA and tRNA molecules and synthesizes a polypeptide chain, a light source illuminates the ribosome, exciting the donor fluorophores and thereby the acceptor fluorophores whenever these are in sufficient proximity to a donor. The resulting signals are detected and used as a key for real-time database searching and identification of the protein being synthesized. The resulting data can be tabulated and interpreted in different ways. FIG. (1) describes the properties of a FRET pair and the dependence of FRET on pair distance.
Owner:ANIMA CELL METROLOGY
Method of sequence optimization for improved recombinant protein expression using a particle swarm optimization algorithm
An improved gene sequence optimization method, the systematic optimization method, is described for boosting the recombinant expression of genes in bacteria, yeast, insect and mammalian cells. This general method takes into account of multiple, preferably most or all, of the parameters and factors affecting protein expression including codon usage, tRNA usage, GC-content, ribosome binding sequences, promoter, 5′-UTR, ORF and 3′-UTR sequences of the genes to improve and optimize the gene sequences to boost the protein expression of the genes in bacteria, yeast, insect and mammalian cells. In particular, the invention relates to a system and a method for sequence optimization for improved recombinant protein expression using a particle swarm optimization algorithm. The improved systematic optimization method can be incorporated into a software for more efficient optimization.
Owner:NANJING GENSCRIPT BIOTECH CO LTD
Methods for evaluating ribonucleotide sequences
ActiveUS20090081643A1Easy accessMicrobiological testing/measurementNanoinformaticsRibonucleotide synthesisRibosome
Methods for identifying ribonucleotide sequences, in vitro, using the ribosome-mediated translation, are provided.
Owner:ANIMA CELL METROLOGY
Construction method of recombinant bacillus subtilis capable of generating hyaluronic acid with specific molecular weight
ActiveCN105087456AIncrease productionReduce viscosityBacteriaTransferasesStreptococcus zooepidemicusHigh-Throughput Screening Methods
The invention discloses a construction method of recombinant bacillus subtilis capable of generating hyaluronic acid with specific molecular weight, belonging to the field of the bioengineering technology. According to the method, the production of hyaluronic acid is realized through integration of hyaluronic synthase (hasA) with streptococcus zooepidemicus source to bacillus subtilis; meanwhile, overexpression is realized on key genes of the synthetic route of HA, so that the high yield of bacillus subtilis is realized; on the basis, the hyaluronidase with the leech source is integrated to the genome of the bacillus subtilis, then mutant library construction is realized on ribosome bind sites (RBS) from the genetic expression translational level, and thus a series of mutants with different expression levels of hyaluronidases are obtained through high throughput screening; the yield of the hyaluronic acid achieves 19.38g / L, the molecular weight ranges from 103-106 Dalton, certain basis is laid for efficiently preparing micromolecule hyaluronic acids, and the construction method is suitable for industrial production and application.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Kit for detecting guinea pig aeromonas by utilizing Loop-mediated isothermal amplification technique
InactiveCN101235411AAccurate identificationRapid identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementAeromonas caviaeLoop-mediated isothermal amplification
The invention relates to a reagent kit and a detecting method for using loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) technique to detect aeromonas caviae, which belongs to the pathogen diagnosis field. The main technical scheme of the invention comprises: utilizing the LAMP technique, designing four pairs of high specificity primers aiming at six zones of 16s and 23s ribosome RNA gene transcription spacer region, and achieving the purpose for detecting the aeromonas caviae with specificity. Compared with a traditional method, equipment and operational steps which are needed in the method are simple, the method has the advantages of rapidness and high specificity, and the detecting cost is lower, which is suitable for common clinics and field detections.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Compositions and methods for whole transcriptome analysis
InactiveUS20110189679A1Reduction and substantial eliminationMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationRibosomal RNABioinformatics
The present invention provides methods and compositions, including kits, for the generation of cDNA from mRNA with reduced ribosomal RNA representation.
Owner:NUGEN TECH
Detection of fermentation-related microorganisms
InactiveUS6248519B1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganismOligonucleotide primers
DNA sequences are provided which are useful in identifying different fermentation-related microorganisms, such as those involved in fermentations. These DNA sequences can be used to provide oligonucleotide primers in PCR based analysis for the identification of fermentation-related microorganisms. The DNA sequences of the present invention include the internal transcribed spacer (ITS) of the ribosomal RNA gene regions of particular fermentation-related microorganisms, as well as oligonucleotide primers which are derived from these regions which are capable of identifying the particular microorganism.
Owner:E & J GALLO WINERY
Cyanobacterial Isolates Having Auto-Flocculation and Settling Properties
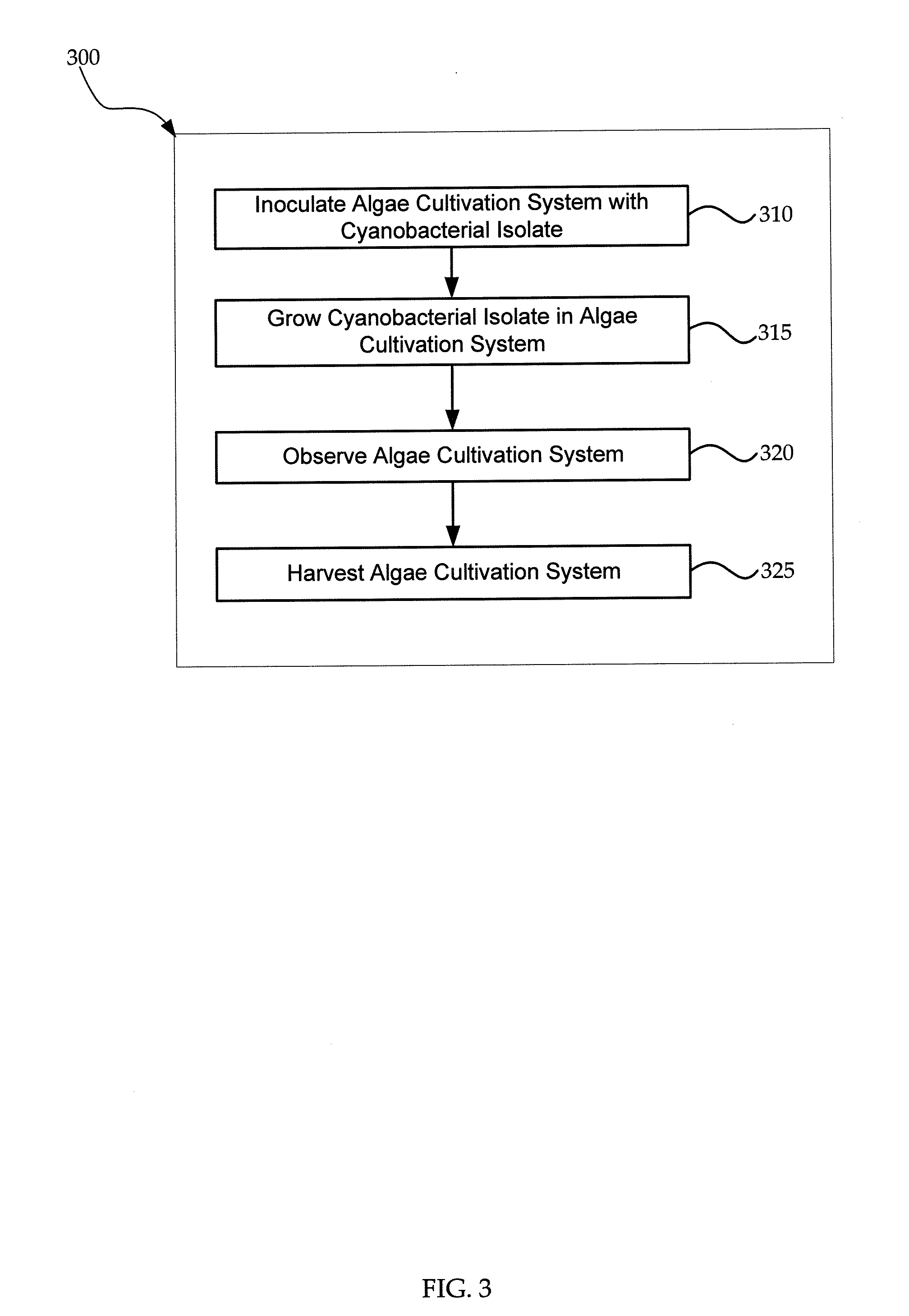
Provided herein are exemplary methods for production of biomass with a cyanobacterial isolate having auto-flocculation properties. One exemplary method includes isolating a cyanobacterial strain having a 16S ribosomal RNA sequence corresponding to SEQ. ID. NO. 1 herein, inoculating an algae cultivation system with the cyanobacterial strain, growing the cyanobacterial strain, and harvesting the biomass produced by the cyanobacterial strain. According to a further method, the harvesting of the biomass comprises ceasing agitation of the algae cultivation system, and pooling a slurry of the biomass produced by the cyanobacterial strain. In a further method, the harvesting of the biomass may comprise ceasing agitation within the algae cultivation system and / or allowing the biomass produced by the cyanobacterial strain to settle to near or at a bottom of the algae cultivation system. Also provided herein are exemplary cyanobacterial strains having flocculation properties for production of a biomass.
Owner:AURORA ALGAE
Screening methods for identifying specific staphylococcus aureus inhibitors
ActiveUS20140163037A1Provide stabilitySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementStaphylococcus cohniiArginine
Methods of inhibiting S. aureus propagation, and screening for compounds that inhibit S. aureus propagation, are described. A method of inhibiting S. aureus propagation comprises either inhibiting or stabilizing ribosomal binding of a specific S. aureus tRNA in the S. aureus by an amount sufficient to inhibit S. aureus protein expression. A method of screening for compounds useful for inhibiting S. aureus propagation comprises contacting a specific S. aureus tRNA to a ribosome that binds that tRNA in the presence of the test compound and an mRNA that codes for methionine and arginine (i.e., includes the sequence AUGAGA), and then determining whether the compound inhibits the binding of that tRNA.
Owner:TRANA DISCOVERY
Method of reducing non-specific amplification in PCR
InactiveUS20030104395A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementAmplification dnaRibosomal DNA
The invention provides methods for reducing non-specific amplification DNA in a polymerase chain reaction comprising providing a sample comprising a target DNA sequence of interest; contacting the sample with at least one enzyme having nucleic acid polymerase activity; and incubating the sample with said enzyme for a time and under conditions sufficient to amplify the target DNA sequence, forming amplified target sequence; wherein the incubation is performed in the presence of an amount of sorbitol, or sorbitol and DMSO effective to reduce the non-specific amplification relative to the amount of non-specific amplification observed in the absence of sorbitol, or sorbitol and DMSO. The methods are suitable for amplification of ribosomal DNA, particularly from clinical samples. Compositions and kits containing sorbitol, or sorbitol and DMSO for reducing non-specific amplification are also provided.
Owner:APPL BIOSYSTEMS INC
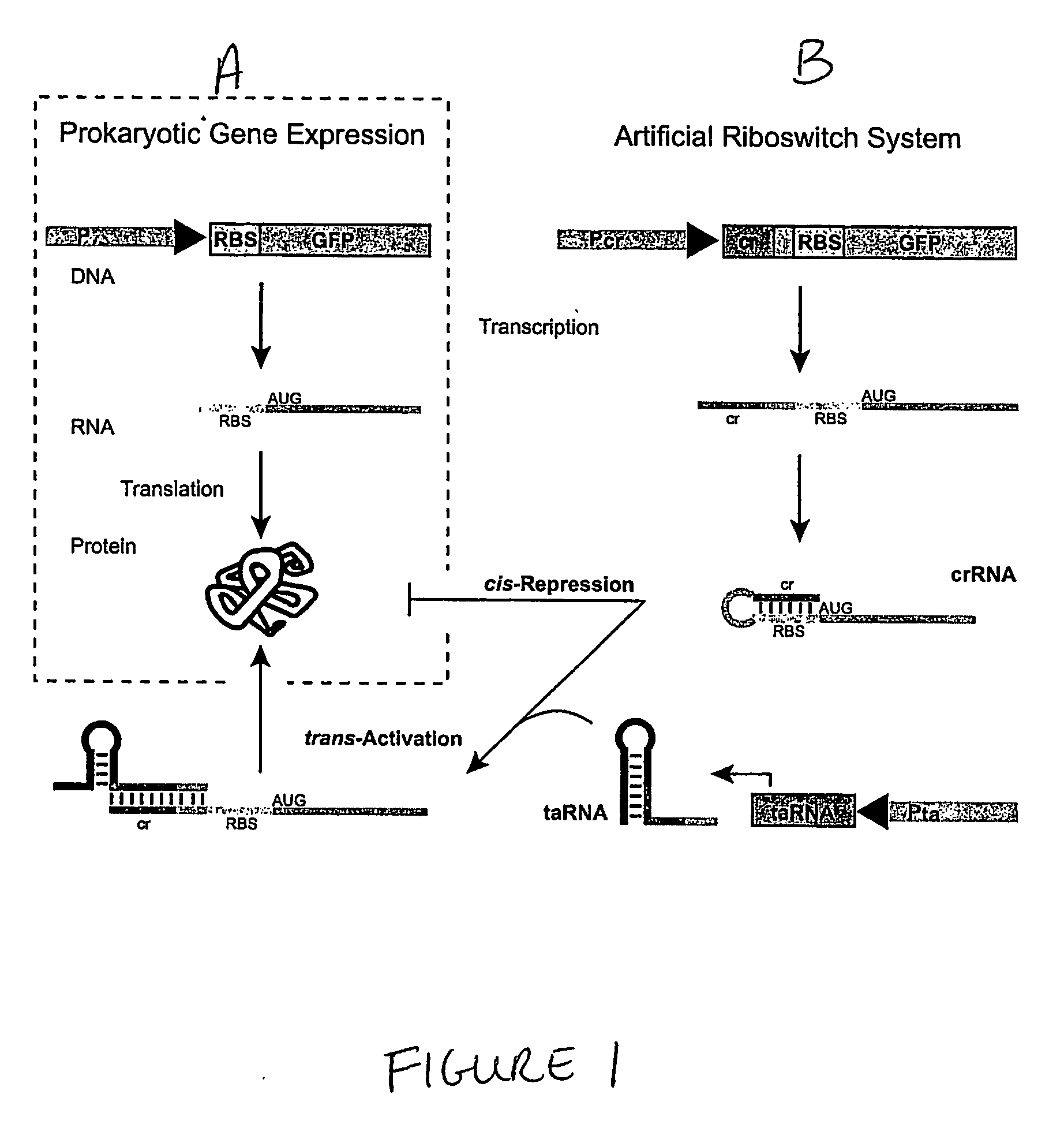
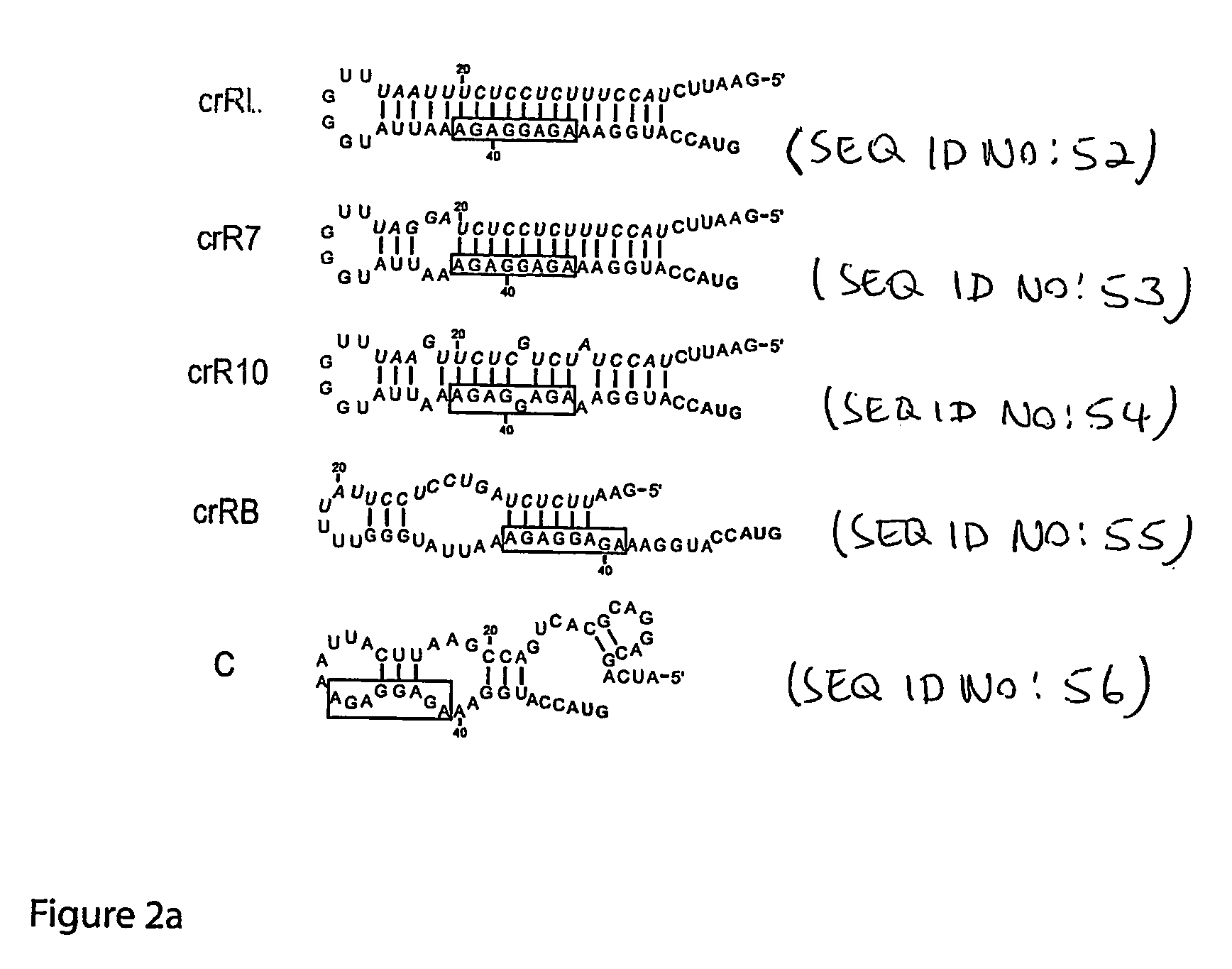
Cis/trans riboregulators
ActiveUS20070136827A1Easy to controlInhibition of translationSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementOpen reading frameBinding site
The present invention provides nucleic acid molecules, DNA constructs, plasmids, and methods for post-transcriptional regulation of gene expression using RNA molecules to both repress and activate translation of an open reading frame. Repression of gene expression is achieved through the presence of a regulatory nucleic acid element (the cis-repressive RNA or crRNA) within the 5′ untranslated region (5′ UTR) of an mRNA molecule. The nucleic acid element forms a hairpin (stem / loop) structure through complementary base pairing. The hairpin blocks access to the mRNA transcript by the ribosome, thereby preventing translation. In particular, in embodiments of the invention designed to operate in prokaryotic cells, the stem of the hairpin secondary structure sequesters the ribosome binding site (RBS). In embodiments of the invention designed to operate in eukaryotic cells, the stem of the hairpin is positioned upstream of the start codon, anywhere within the 5′ UTR of an mRNA. A small RNA (trans-activating RNA, or taRNA), expressed in trans, interacts with the crRNA and alters the hairpin structure. This alteration allows the ribosome to gain access to the region of the transcript upstream of the start codon, thereby activating transcription from its previously repressed state.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF BOSTON UNIV
Novel vectors for animal cells and use thereof
InactiveUS20060078992A1Decrease productivityFold preciselyMicroorganismsMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyForeign protein
Protein synthesis inhibitor resistance genes (typified by a cycloheximide resistance gene) are capable of imparting resistance to a protein synthesis inhibitor (typified by cycloheximide) to animal cells sensitive to the inhibitor. The genes have a sequence mutated by substitution in a gene encoding a ribosome-constituting protein derived from an animal. The genes may be placed in recombinant vectors, including expression vectors containing the gene together with a foreign protein structural gene.
Owner:KIRIN HOLDINGS KK
Methods and Systems for Detection of Microorganisms
ActiveUS20130216997A1Easy to detectMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingMicroorganismInfected cell
Disclosed are methods and systems for the isolation and detection of microbes from a sample. The use of binding agents for isolation of a microbe of interest from a sample are described. In certain embodiments, the methods use ribosome-based and / or bacteriophage-based amplification of the signal in detection of bacteria and other microorganisms. For example, embodiments of the present invention can achieve total amplification of at least 10,000 from a single infected cell.
Owner:LAB OF AMERICA HLDG
Pediococcus pentosaceus and application thereof
ActiveCN103540545AImprove acid resistanceGood resistance to bile saltsAntibacterial agentsBacteriaBiotechnologyStaining
The invention discloses pediococcus pentosaceus and application thereof. The Latin name of the pediococcus pentosaceus is Pediococcus pentosaceus LI05, and the pediococcus pentosaceus is preserved in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center and has a preservation number of CGMCC No.7049. The pediococcus pentosaceus disclosed by the invention has the morphological characteristics that the thallus is rod-shaped, dose not generate spores, does not have motility, and has masculine Gram staining. The whole-cell fatty acid of the pediococcus pentosaceus disclosed by the invention comprises the following main components in percentage by weight: about 1.45% of 14:0, about 3.26% of 16:1w7c / 16:1w6c, about 31.25% of 16:0, about 6.31% of 18:1w9c, about 38.59% of 18:1w7c, about 1.37% of 18:0 and about 14.59% of un18.846 / 19:1w6c. The invention also discloses a complete sequence of 16S ribosome DNA (16SrDNA) of the pediococcus pentosaceus. The pediococcus pentosaceus and a preparation thereof disclosed by the invention can be used for adjusting the micro-ecological balance of intestinal tracts of human or animals, promoting digestive absorption and slowing down the happening and development of liver failure of experimental animals.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Process for producing the enzyme D-amino acid oxidase of Rhodotorula gracilis in host cells
Process for producing the enzyme D-amino acid oxydase of Rhodotorula gracilis in host cells. The process for the expression of the enzyme comprises isolating the complementary DNA corresponding to the messager RNA of the gene which codes for the D-amino acid oxydase of any strain of Rhodotorula gracillis producing said enzyme; fusing the fragment of DNA which codes for D-amino acid oxydase of Rhodotorula gracillis with a DNA sequence which contains a site of union to the ribosome and a high efficiency promoter sequence for the express of genes in host cells; inserting the DNA fragment into a plasmid appropriate for the host cell; cultivating the host cells transformed with said plasmid; and collecting the enzyme.
Owner:ANTIBIOTICOS SA
Separation of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi as well as preparation and application of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi fungicide
The invention discloses separation of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi as well as preparation and application of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi fungicide, and belongs to the technical field of biology. The arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi is arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi rhizophagus irregularis which is called arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi rhizophagus irregularis CD-1 and is separated from soils; a specific sequence of verifying ribosome 28S rDNA is shown in SEQ ID NO.1; by utilizing the fungicide prepared by the fungi, the height of strains, the number of petioles, the overground fresh weight, the overground dry weight, the root fresh weight and the root dry weight of tomatoes can be increased, and the mycorrhizal infection rate delta gt can be obviously prompted; 80 percent of corns are high in selfing line strains and heavy in overground fresh weight and overground dry weight; the resistance to banded sclerotial blight by the corns is improved, and the arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi has an extremely-high genetic use value.
Owner:SHANDONG AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Method for identifying honeysuckle and lonicera confuse and application of same
ActiveCN103173532AEfficient extractionQuick extractionMicrobiological testing/measurementGermplasmRibosomal DNA
The invention relates to a method for identifying honeysuckle and lonicera confuse and an application of the method. The method disclosed by the invention comprises the step of performing PCR (polymerase chain reaction) amplification on ITS2 nucleotide sequence, and particularly comprises the steps of 1) extracting the DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) of a sample; 2) performing PCR amplification on the segments of the ITS2 sequence containing ribosome DNA; 3) splicing the amplification products to obtain a complete ITS2 intergenic region; and 4) establishing the NJ (neighbour-joining) tree of the ITS2 sequence of the sample. The method disclosed by the invention can be used for effectively solving the problems of variety identification, variety improvement and breeding of honeysuckle medicinal materials, development and utilization of germplasm resources, and the like; and the method disclosed by the invention is wide in applicability, simple to operate, easy to grasp, high in accuracy, and capable of successfully realizing rapid and accurate identification on honeysuckle medicinal materials or powder and lonicera confuse medicinal materials or powder.
Owner:INST OF MEDICINAL PLANT DEV CHINESE ACADEMY OF MEDICAL SCI +1
Methods for detecting modification resistant nucleic acids
Methods are provided for, inter alia, detecting nucleic acid molecules resistant to degradation, such as a plurality of RNA molecules bound to a ribosome, using various technologies including deep sequencing.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
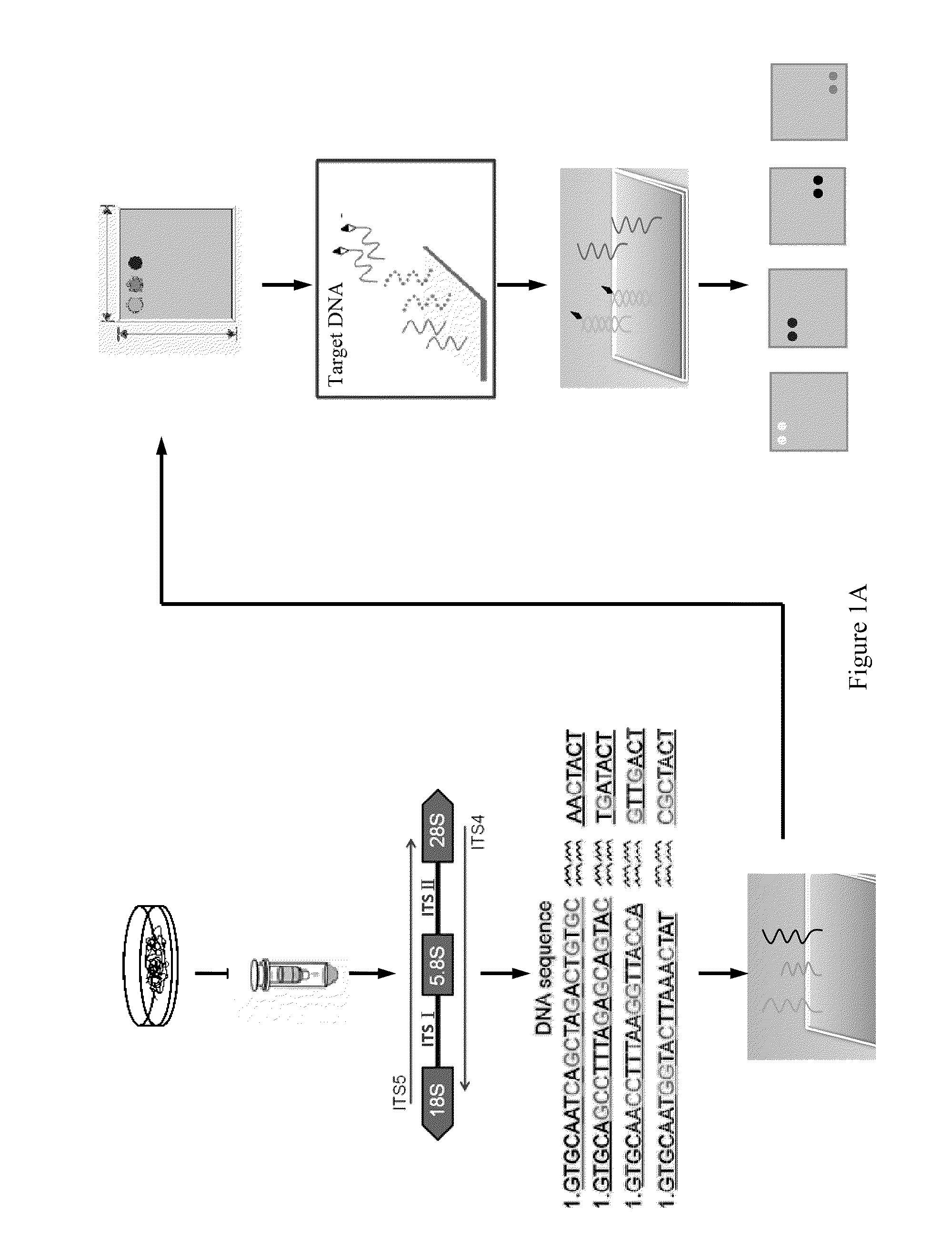
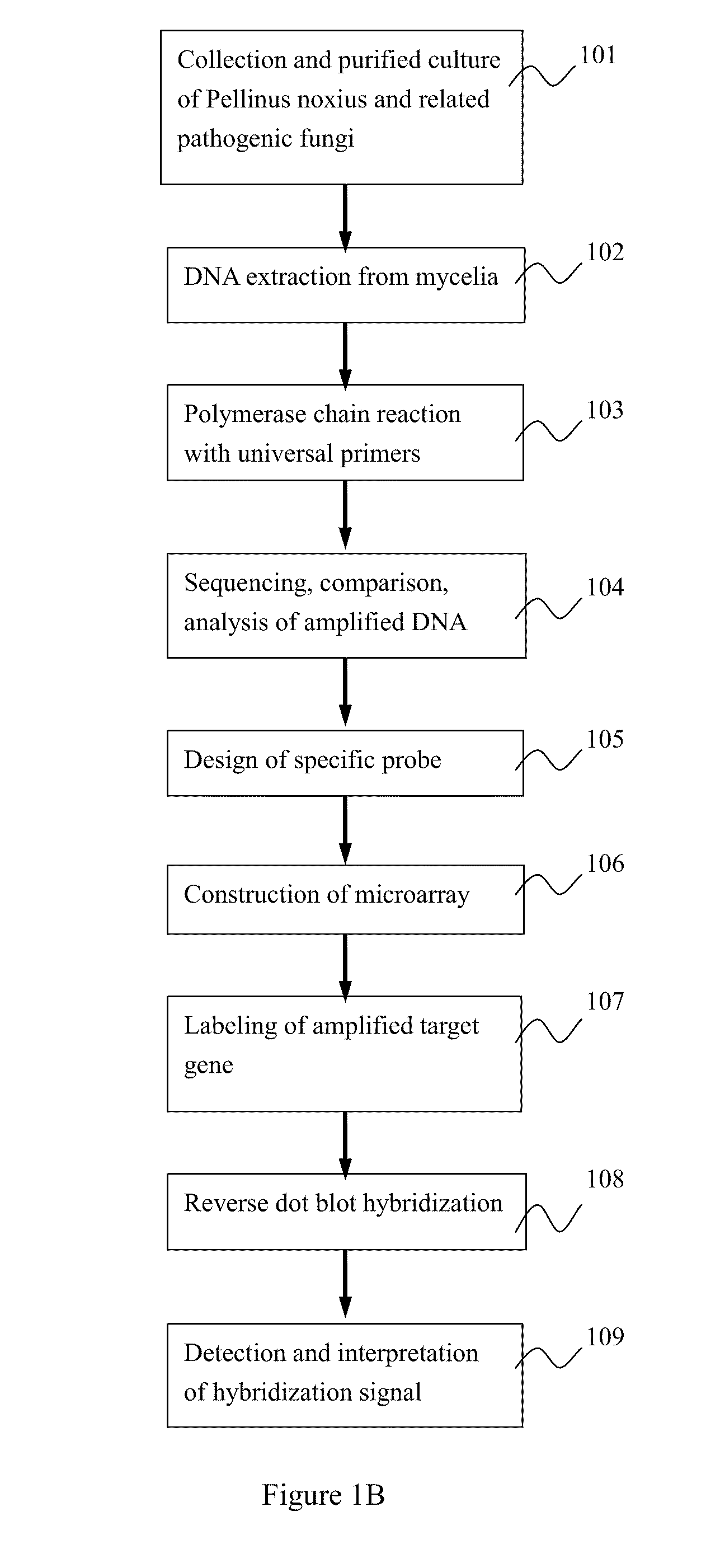
Microchip for identifying phellinus species and the method thereof
InactiveUS20110111970A1Improve accuracyLess time-consumingBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsRapid identificationRibosomal DNA
The developed oligonucleotide microchip for simultaneous, rapid identification of multiple crucial forest Phellinus pathogens was based on the DIG or biotin-labeled specific probes derived form ribosomal DNA genes (ITS1-5.8S-ITS2), by using reverse-dot hybridization. The chip can precisely and accurately identify and diagnose seventeen Phellinus species, including notorious hardwood and conifer tree killer, P. noxius and P. weirii, with a sensitivity of 1 pg DNA / μl on Nylon membrane, and 100 fg DNA / μl on plastic chip, respectively. Verification and identification of forest Phellinus pathogens infested authentic samples or voucher specimens can be accomplished within 7 hr.
Owner:NAT TAIWAN UNIV
Translation driver system and methods for use thereof
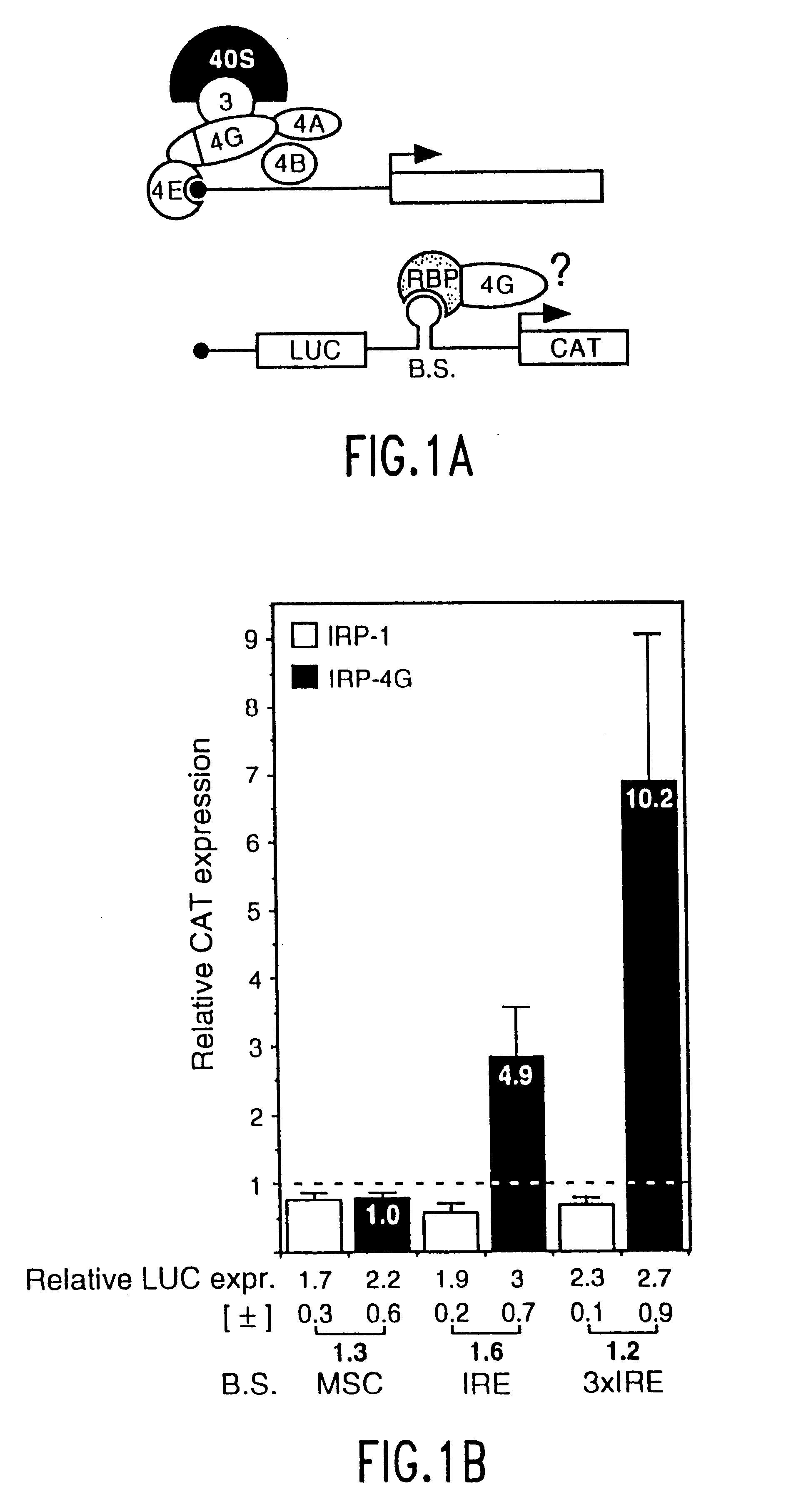
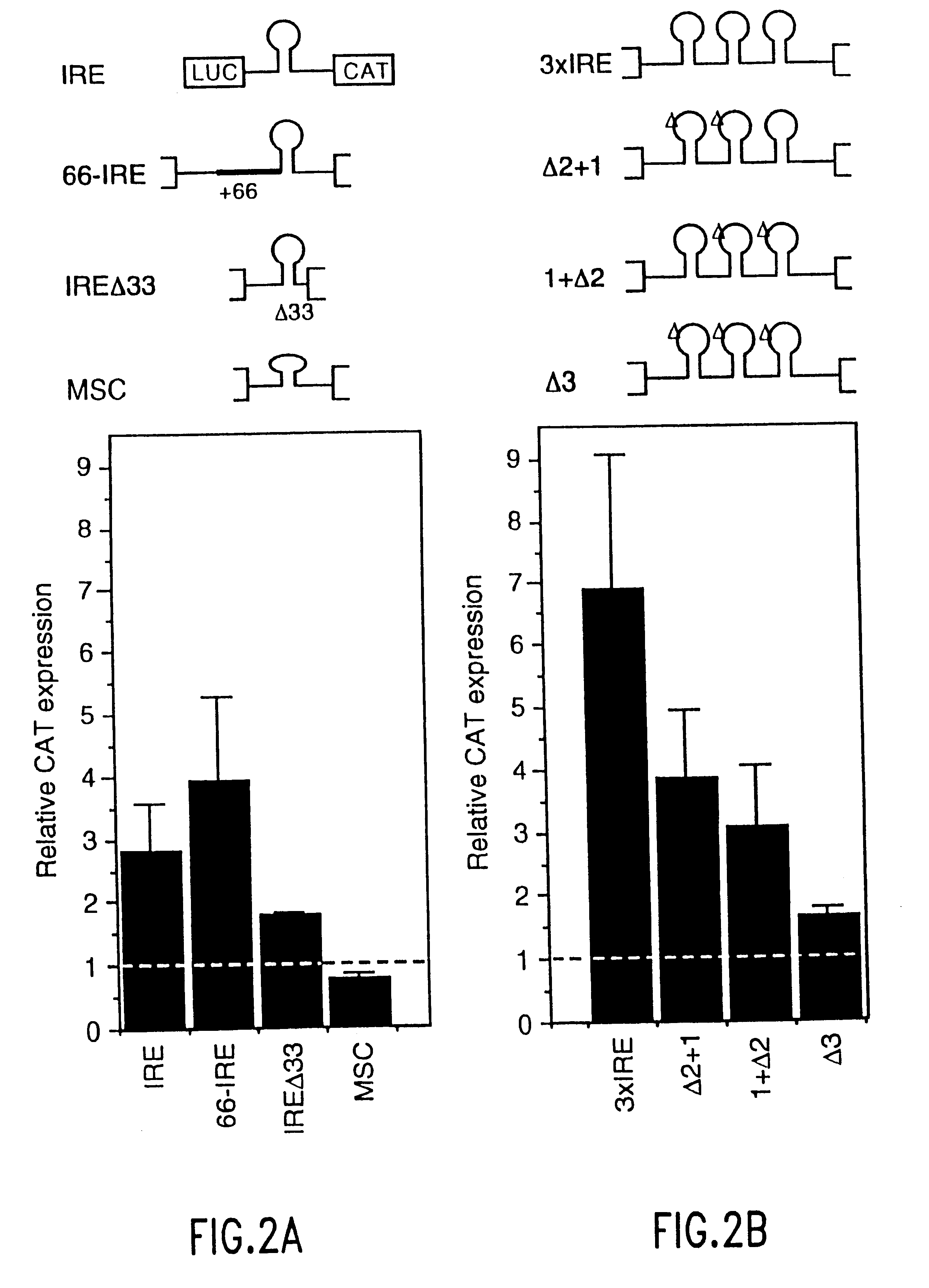
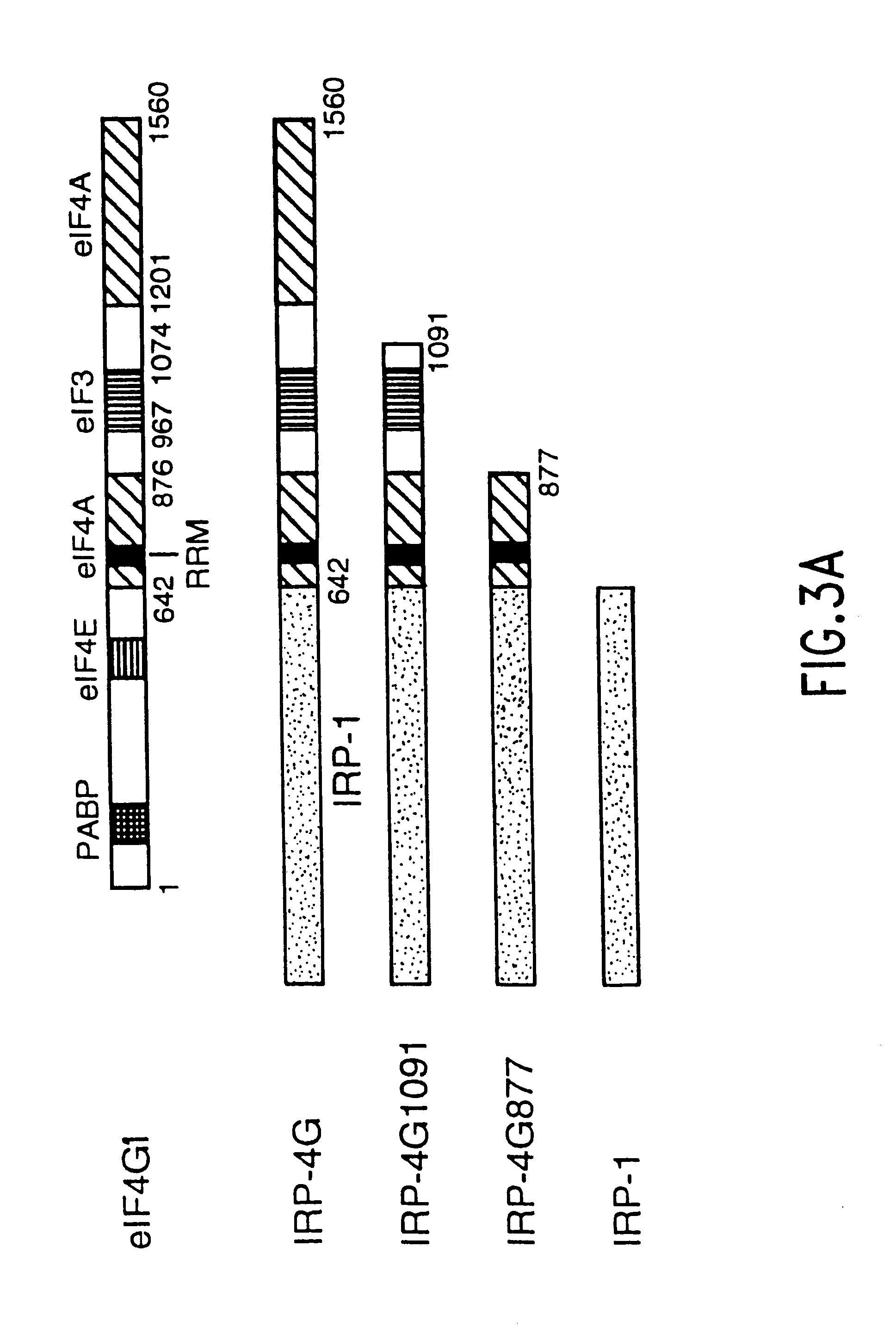
InactiveUS6610508B1Preserving functionBacteriaSugar derivativesTranslational ActivationPresent method
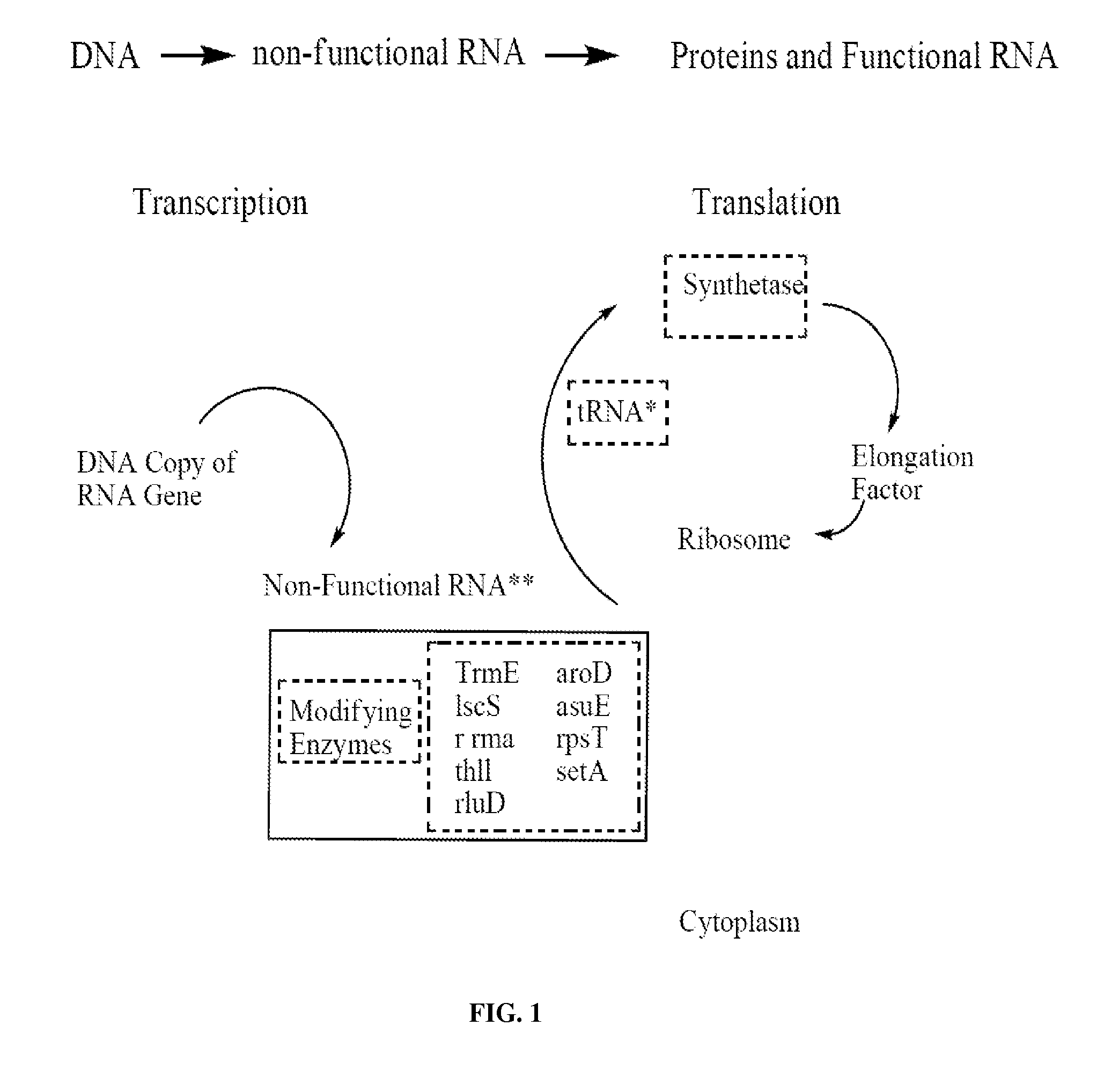
The present method relates to the translational activation of genes using the ribosome recruitment protein, eIF4G or an eIF4G-like protein. The invention relates to the translation of RNA molecules containing heterologous protein-binding sites, which RNA molecules encode one, two, three or more proteins. The invention provides products and methods for the identification of RNA-binding proteins. The invention further provides a system by which protein-protein interactions and inhibitors or enhancers of these interactions may be identified. Further, the invention provides products and methods to provide a cell with one or more therapeutic proteins. The invention provides products and methods for controlling the levels of translation of such proteins. The invention provides products and methods to control the translation and stoichiometry of multiple subunit proteins. The invention provides products for and methods of screening for proteins which interact with an RNA binding site, and methods for identifying RNA binding sites.
Owner:ANDADYS PHARMA INC
Vectors for animal cells and utilization thereof
InactiveUS7064194B2Decrease productivityFold preciselyOrganic active ingredientsMicroorganismsBiotechnologyForeign protein
Owner:KIRIN HOLDINGS KK
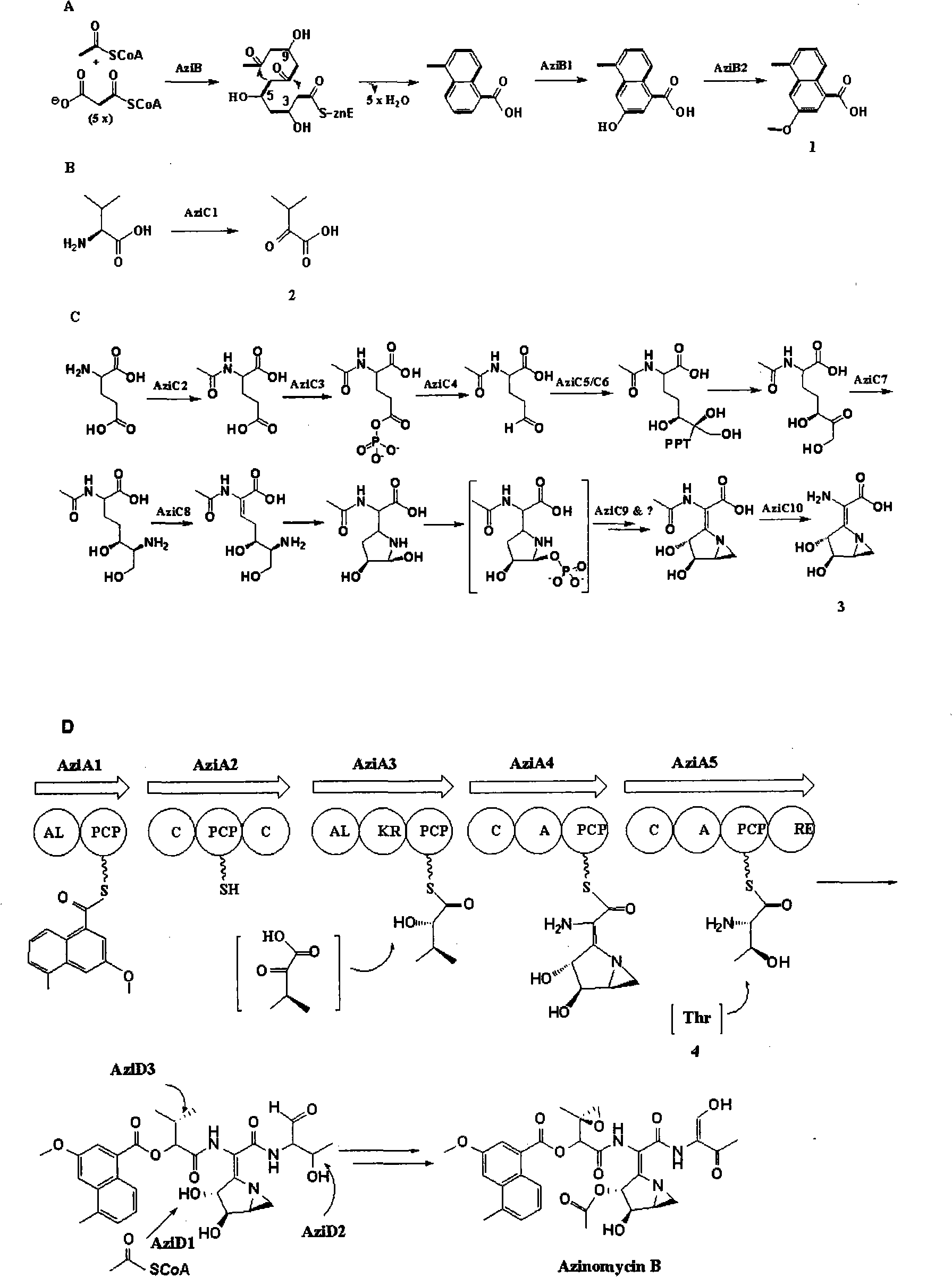
Biological synthesis gene cluster for Azintamide
InactiveCN101275141AUnderstanding Biosynthetic MechanismsFermentationPlant genotype modificationHeterologousEnzyme Gene
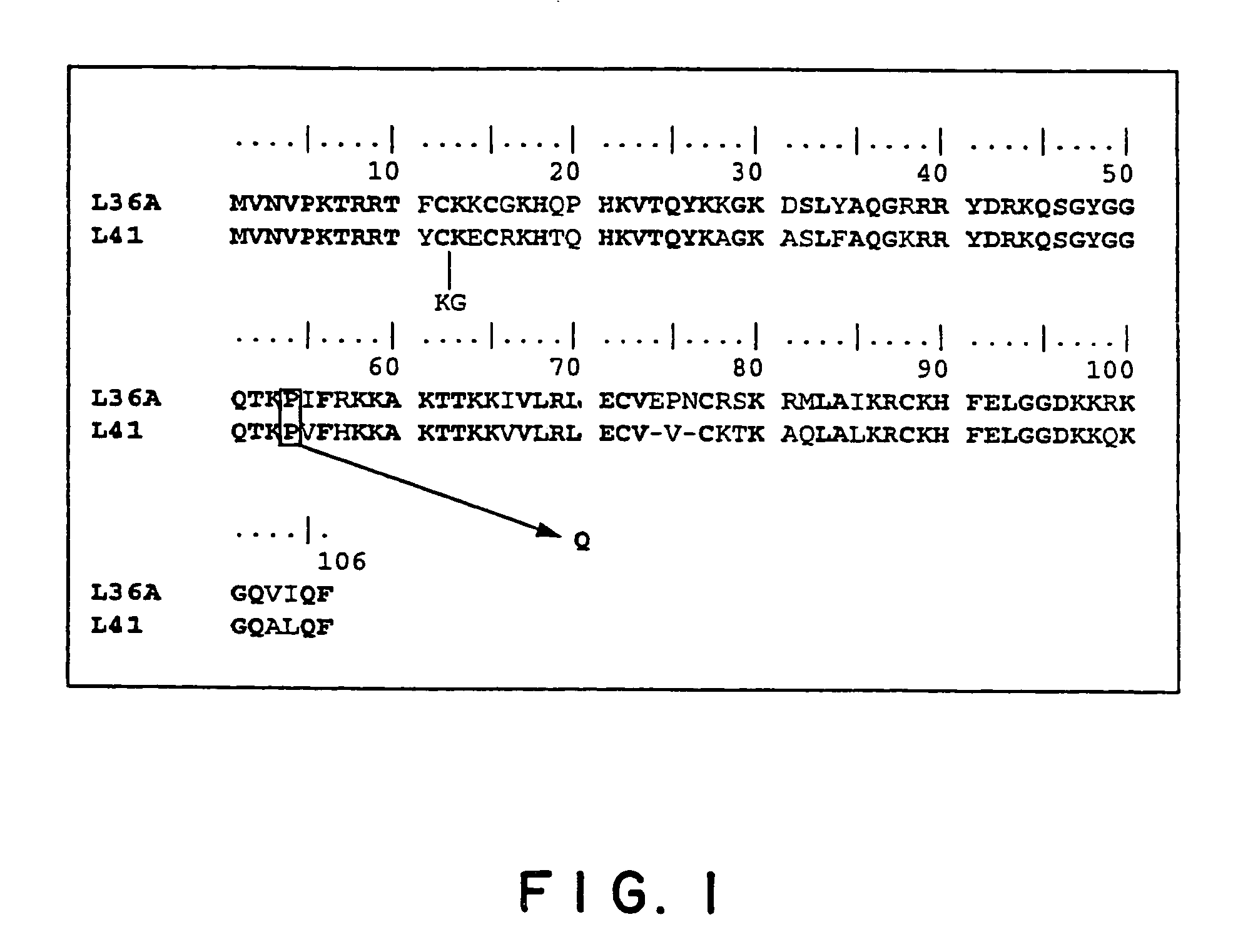
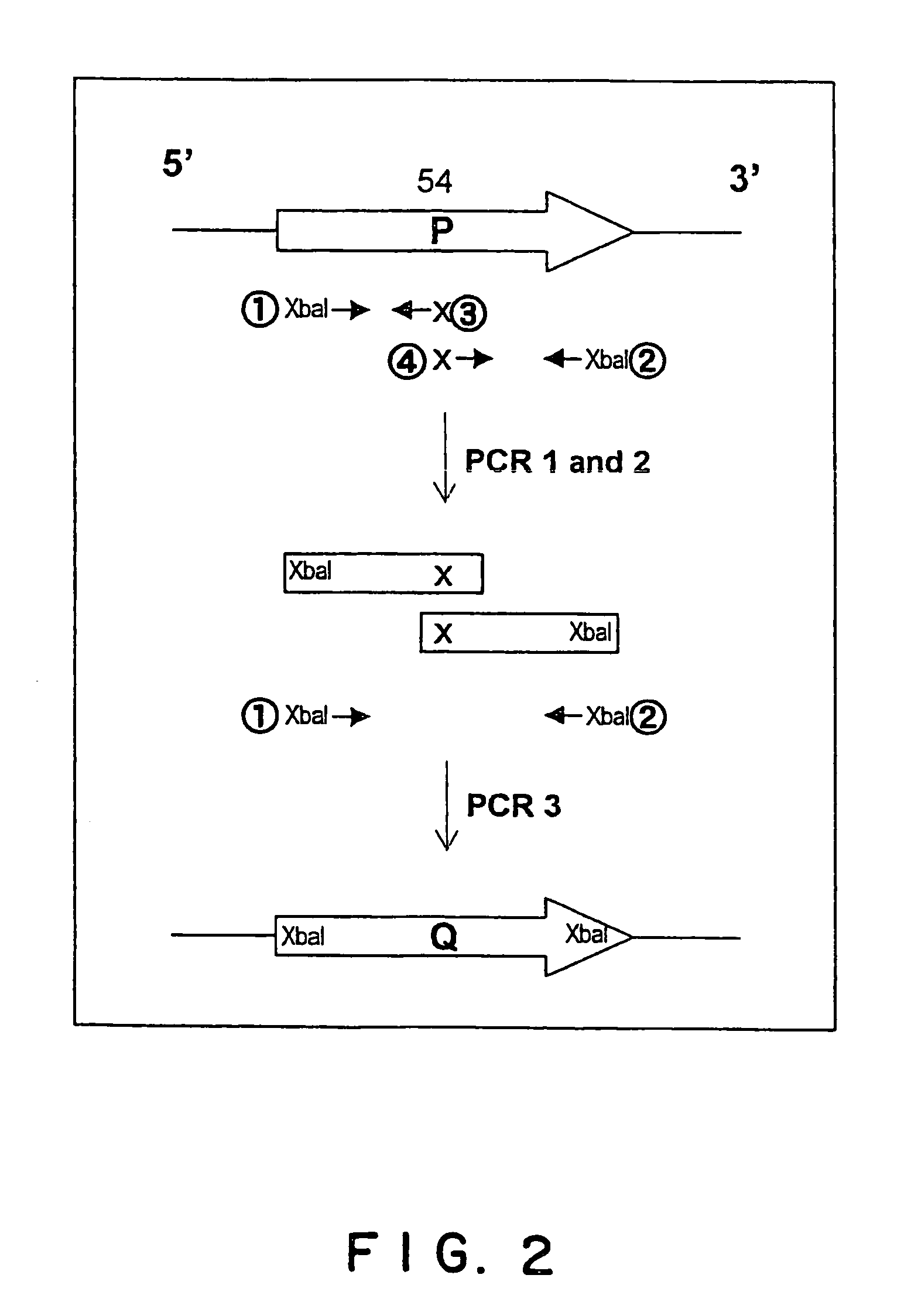
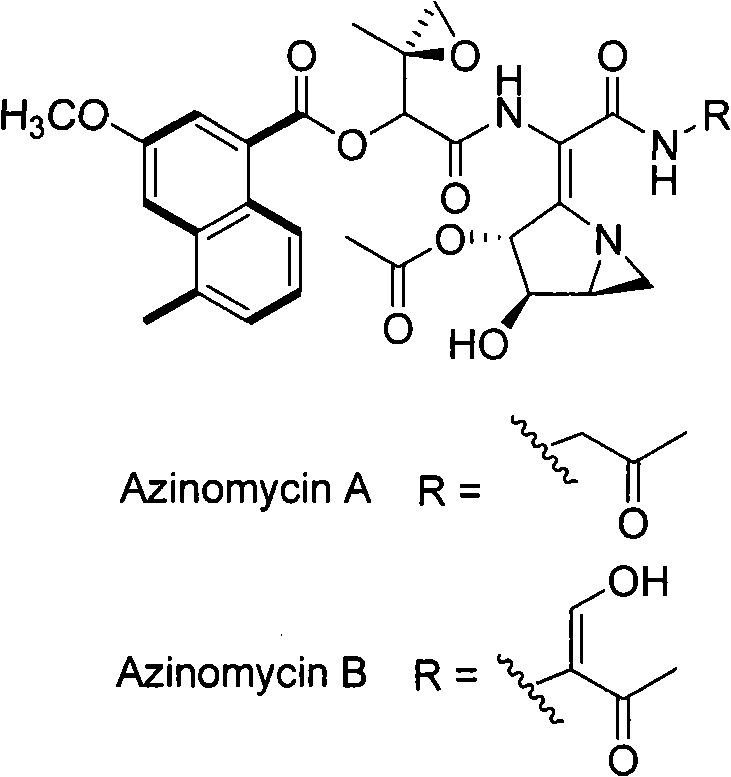
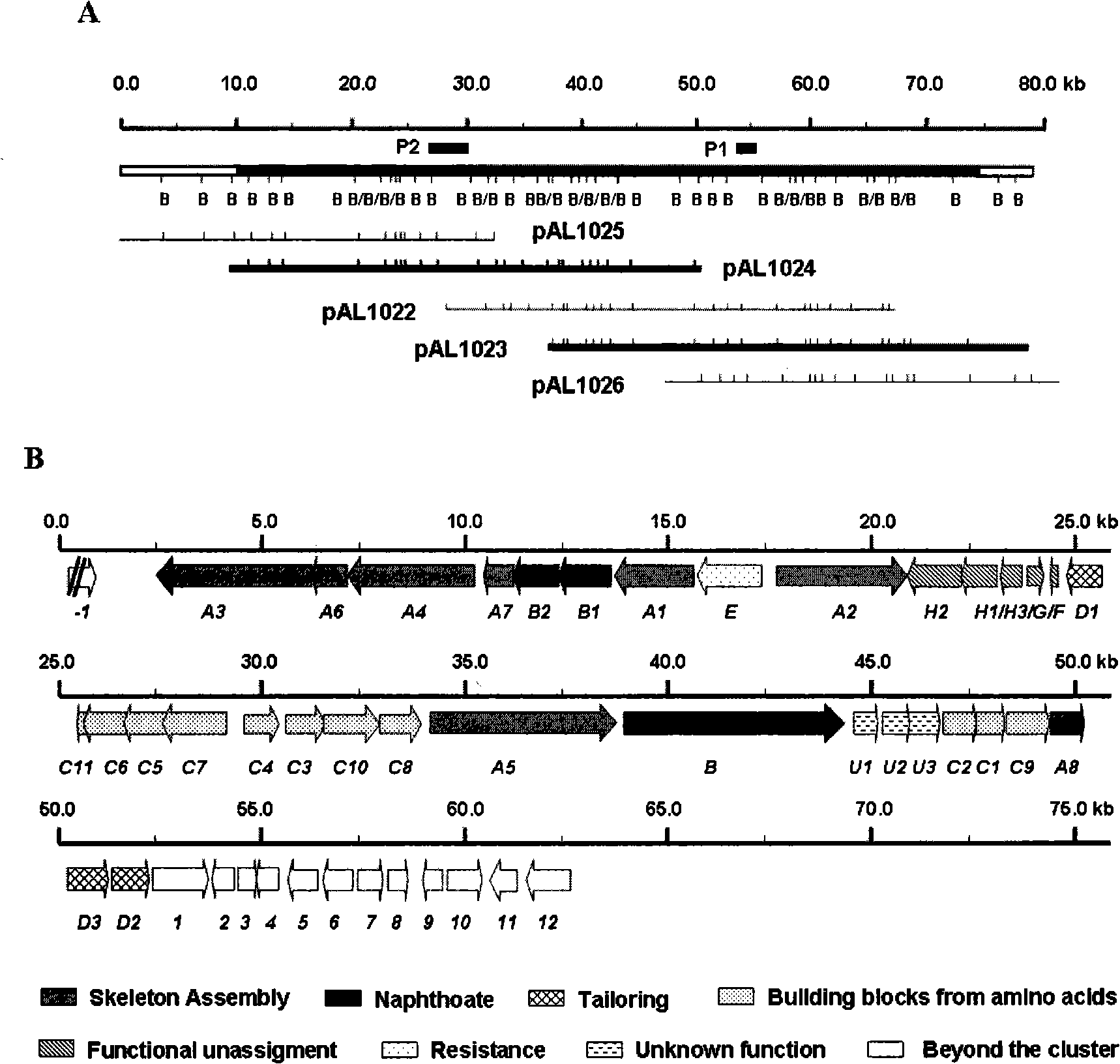
The present invention provides cloning sequencing, analyzing, function research of a biosynthesis gene cluster of an antibiotic-Azinomycin B having antitumor activity produced by streptomyces, and its application. The whole gene cluster includes 34 genes: one repeatedly using I type polyketide synthase gene; two naphthalene ring modification enzyme genes; 8 non-ribosomal polypeptide skeleton synthesis and modification enzyme genes; 11 non-natural amino acid structure unit synthase genes; 1 resistance gene; 3 post modification enzyme genes and 8 genes which functions are not determined. The genetic operation of the biosynthesis gene breaks the synthesis of Azinomycin B; the precursor compound is produced by the heterologous expression of synthesis gene and modification gene of naphthalene ring. The gene of the invention and the protein can be used for searching and finding compound or gene, protein applied in medical, industry or agriculture.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF ORGANIC CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
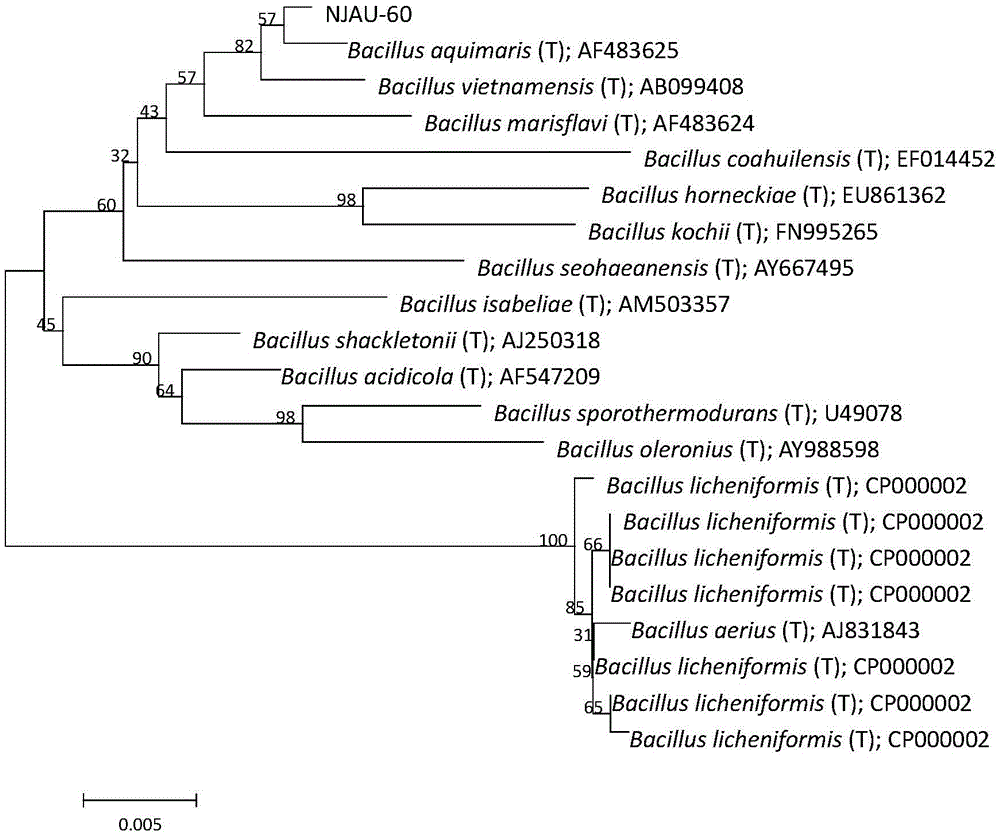
Bacillus aquimaris L-60 capable of effectively prompting growth of crops and application thereof
InactiveCN105462898AFast growthPromote growthPlant growth regulatorsBiocideGrowth promotingDeoxyribose
The invention provides bacillus aquimaris L-60 capable of effectively prompting the growth of crops and application thereof. The strain is separated from potato rhizosphere, and is classified into bacillus aquimaris based on physiological-biochemical characteristics and 16S rDNA (ribosome Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid) analysis. As proved by a high performance liquid chromatography analysis result, the strain L-60 has a high indole Acetic acid (IAA) producing capability. As proved by a pot experiment result, a growth-promoting bio-fertilizer researched on the basis of the strain can remarkably promote the growth of corn, cucumber and tomato plants.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY +1
Method for identifying structure of yeast colony of Daqu starter or fermented grain of distilled spirit by using denaturing gradient electrophoresis
InactiveCN101570786AMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansBiotechnologyMolecular Technique
The invention relates a method for identifying a structure of a yeast colony of a Daqu starter or a fermented grain of distilled spirit by using denaturing gradient electrophoresis, which belongs to the field of microbial ecological techniques. The method comprises the following steps: extracting a genome DNA of the Daqu starter or fermented grain sample of the distilled spirit by using a bead milling method; by designing a general DGGE primer of yeasts in a common wine-making microbe, performing PCR amplification on a specific specificity DNA segment in a yeast ribosome; separating corresponding DNA segments of different varieties by DGGE electrophoresis; gel-cutting and recovering straps corresponding to preponderant microbes; performing the PRC application again, connecting a T carrierand selecting a positive clone; and after re-comparison by the DGGE electrophoresis, checking orders and identifying microbe information corresponding to gel-cutting straps. The method adopts a molecular technique without depending on cultivation, and has the characteristics of simplicity, convenience, quick speed, sensitivity and the like; besides, the method provides a detection method for identifying the structure of the yeast colony of the Daqu stater or the fermented grain of the distilled spirit, and further provides a reference frame for developing wine-brewing microbes oriented to distilled spirit flavors with different odor types.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
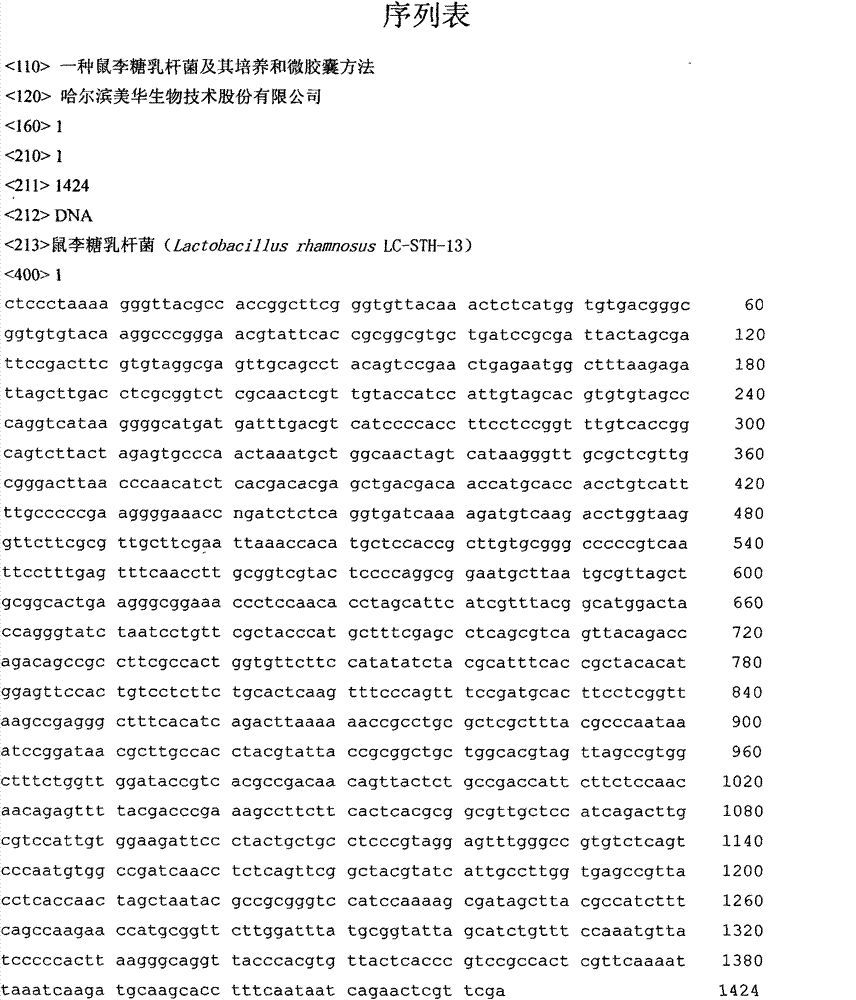
Lactobacillus rhamnosus, cultivation of lactobacillus rhamnosus and microcapsule method
InactiveCN103031263AShorten the growth cycleReproduce fastBacteriaMicroorganism based processesLactobacillus rhamnosusBacteroides dorei
The invention discloses lactobacillus rhamnosus, cultivation of the lactobacillus rhamnosus and a microcapsule method. The bacterial strain is preserved in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (CGMCC); a registering number is CGMCC NO.3994; a Latin name of the bacterial strain is Lactobacillus rhamnosus LC-STH-13; morphological characteristics are gram-positive bacteria, short-rod bacterial thallus, no motion, no gemma, circular bacterial colony, milk white, tidy edges, smooth surfaces and protuberant cores. The invention further discloses a 16S ribosome DNA (Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid) (16S rDNA) complete sequence of the lactobacillus rhamnosus. The lactobacillus rhamnosus has the advantages that a culture is short in growth cycle, high in breeding speed and- produced lactic acid concentration. The lactobacillus rhamnosus can -colonize and survive in an intestinal tract, improves a mucosal barrier function of a gastrointestinal tract, has a function of improving the gastrointestinal tract, and restrains the colonization of harmful bacteria; and after being embedded by a microcapsule, the lactobacillus rhamnosus has stronger ability to resist the poor environment.
Owner:哈尔滨美华生物技术股份有限公司
Model mouse preparation method and recombinant vector for conditional cell removal
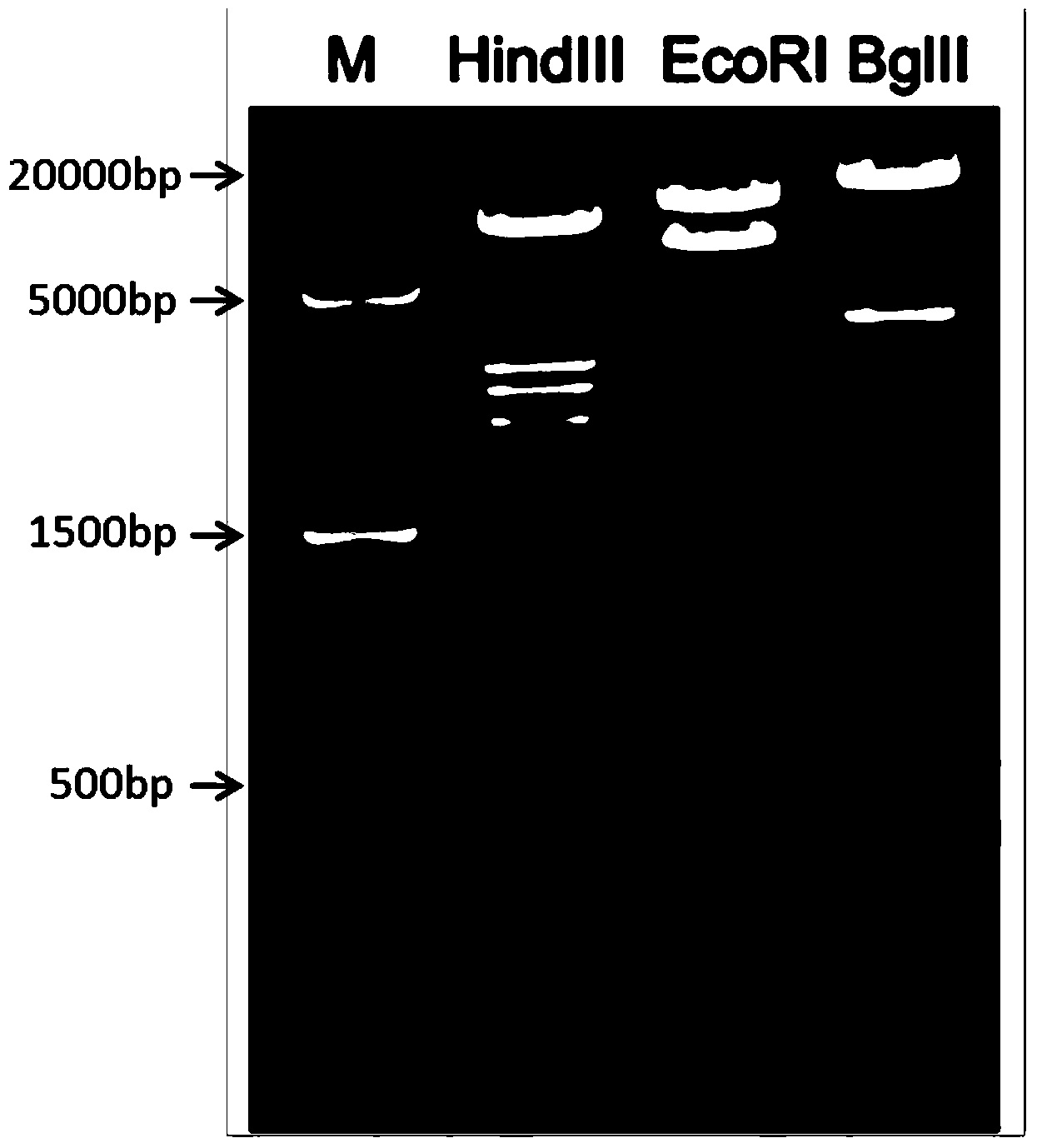
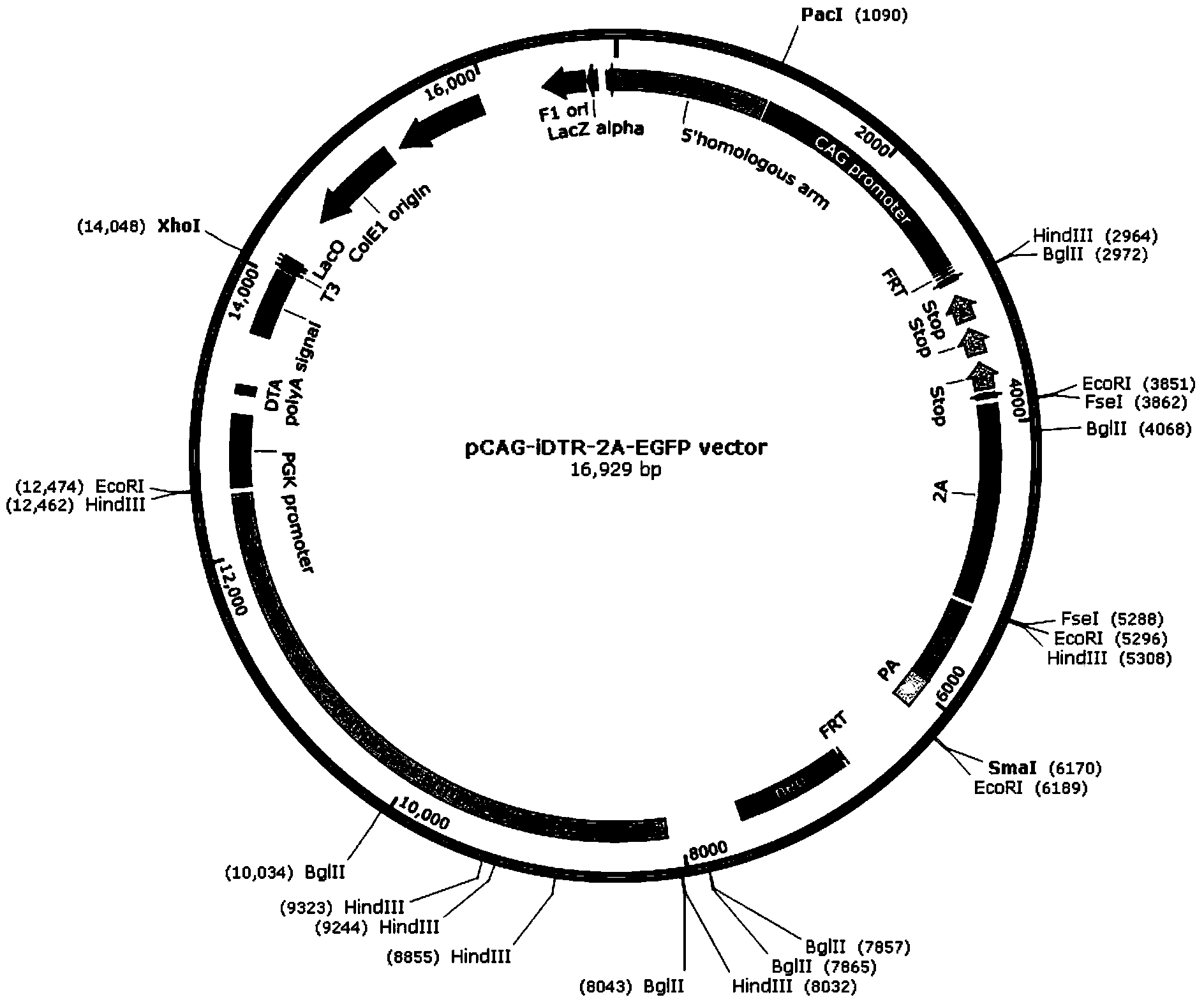
ActiveCN103409448AShorten the timeAccurate and intuitive experimental resultsVector-based foreign material introductionForeign genetic material cellsA-DNAIn vivo
The invention discloses a recombinant vector for conditional cell removal and a preparation method thereof. The recombinant vector comprises a DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) fragment structure iDTR-2A-FP, wherein iDTR is a coding gene of a diphtheria toxin receptor, 2A can realize a coded nucleic acid sequence of a sheared polypeptide fragment through ribosome jumping, and FP is a coding gene of fluorescent protein. The invention further provides a method for preparing a model mouse for conditional cell removal. A descendant mouse, obtained after the model mouse for cell removal, prepared by the method provided by the invention, is mated with a Cre mouse, has the following characteristics: through expression conditions of the fluorescent protein, direct detection on cell removal efficiency can be carried out, and whether cells are completely removed from in vivo or not can be determined, so that more accurate and intuitive results can be obtained; and the expression or deletion of target genes can be controlled from time through controlling the inducer giving time.
Owner:BIOCYTOGEN PHARMACEUTICALS (BEIJING) CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com