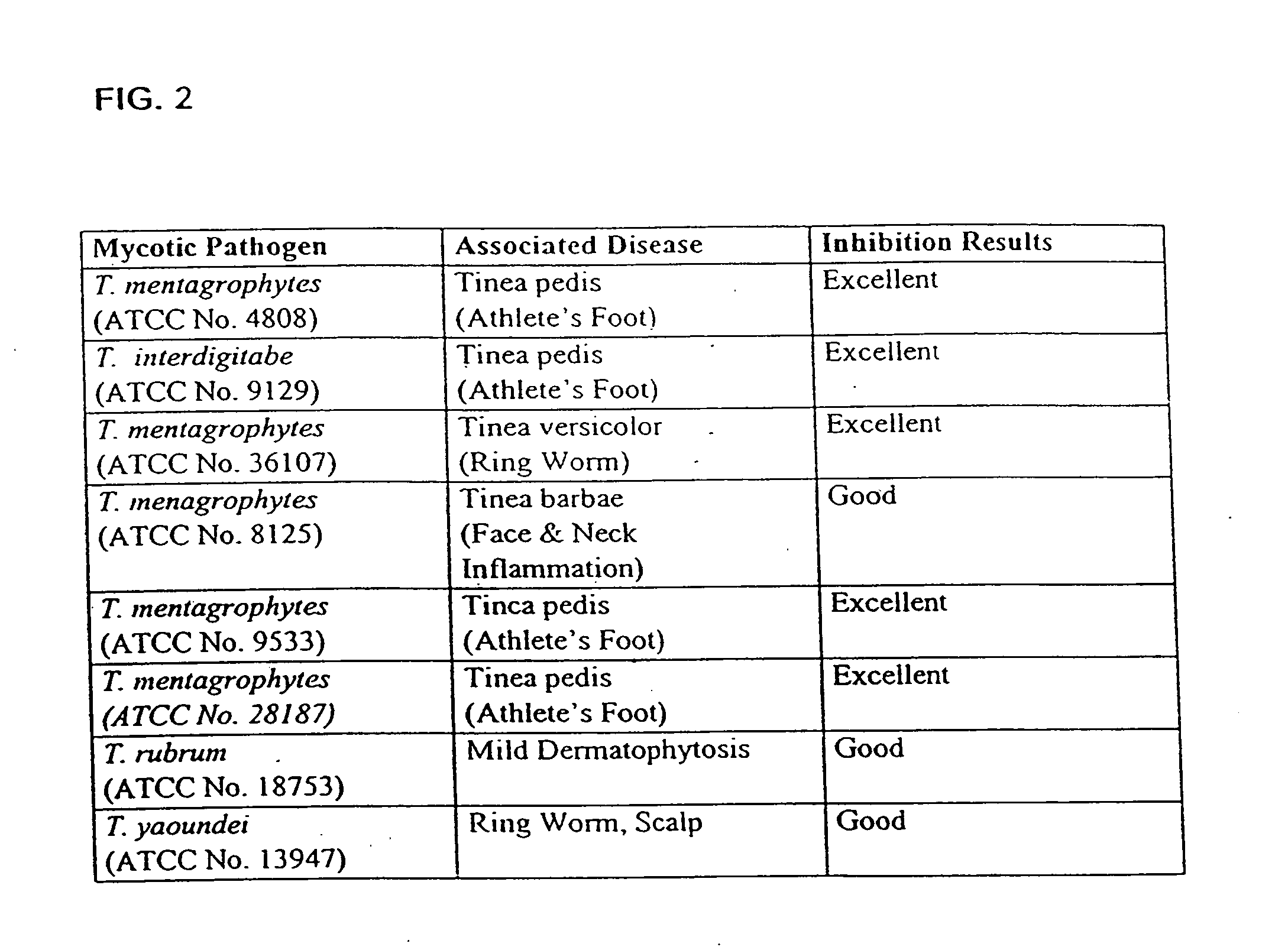
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
175 results about "Bacteroides dorei" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
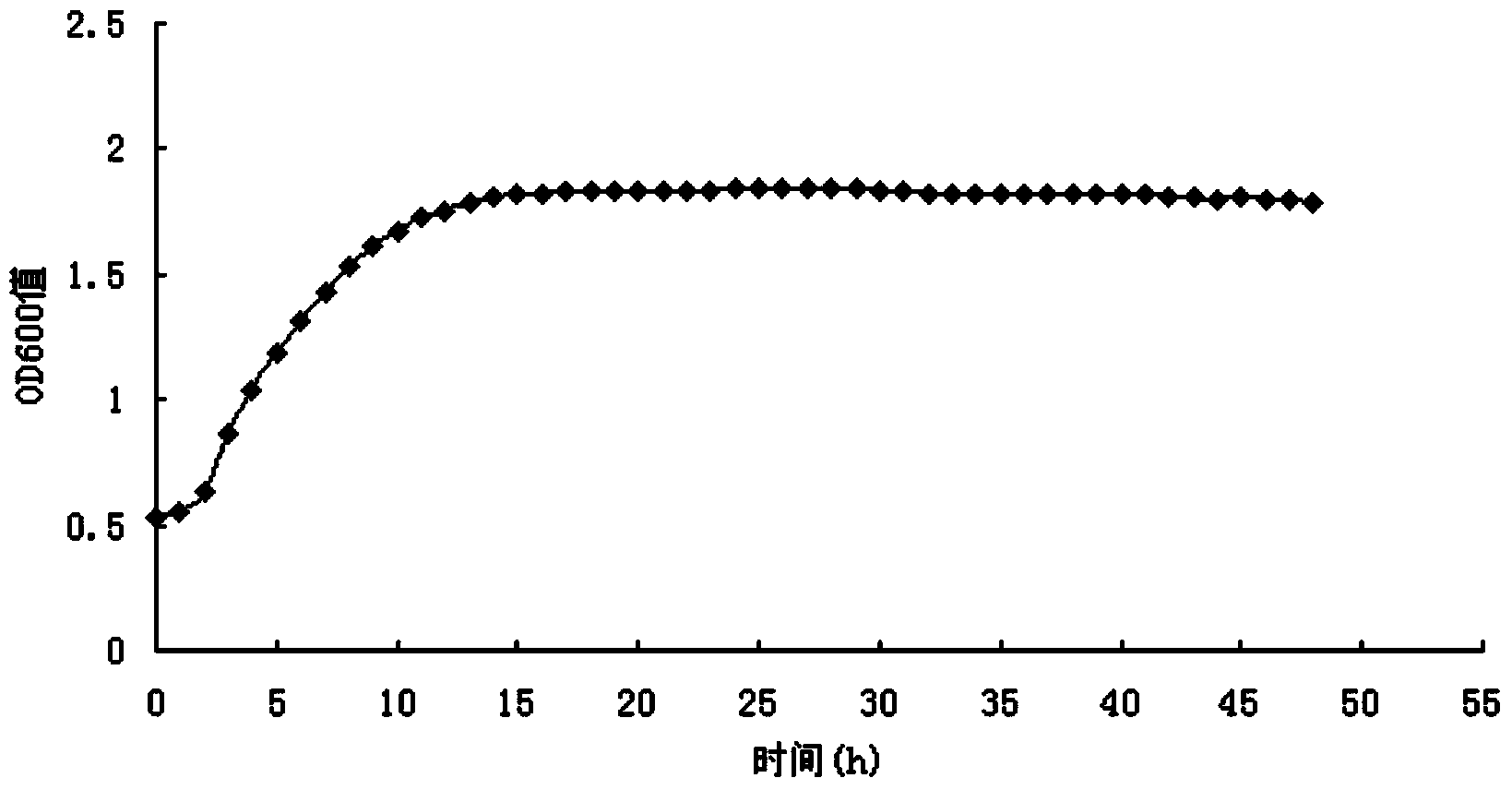
Bacteroides dorei is a species of bacteria within the genus Bacteroides, first isolated in 2006. It is found in the intestinal systems of humans and animals. Research is being conducted to better understand the relationship Bacteroides dorei has on the human intestinal system and the autoimmune disease, Type 1 Diabetes (T1D).
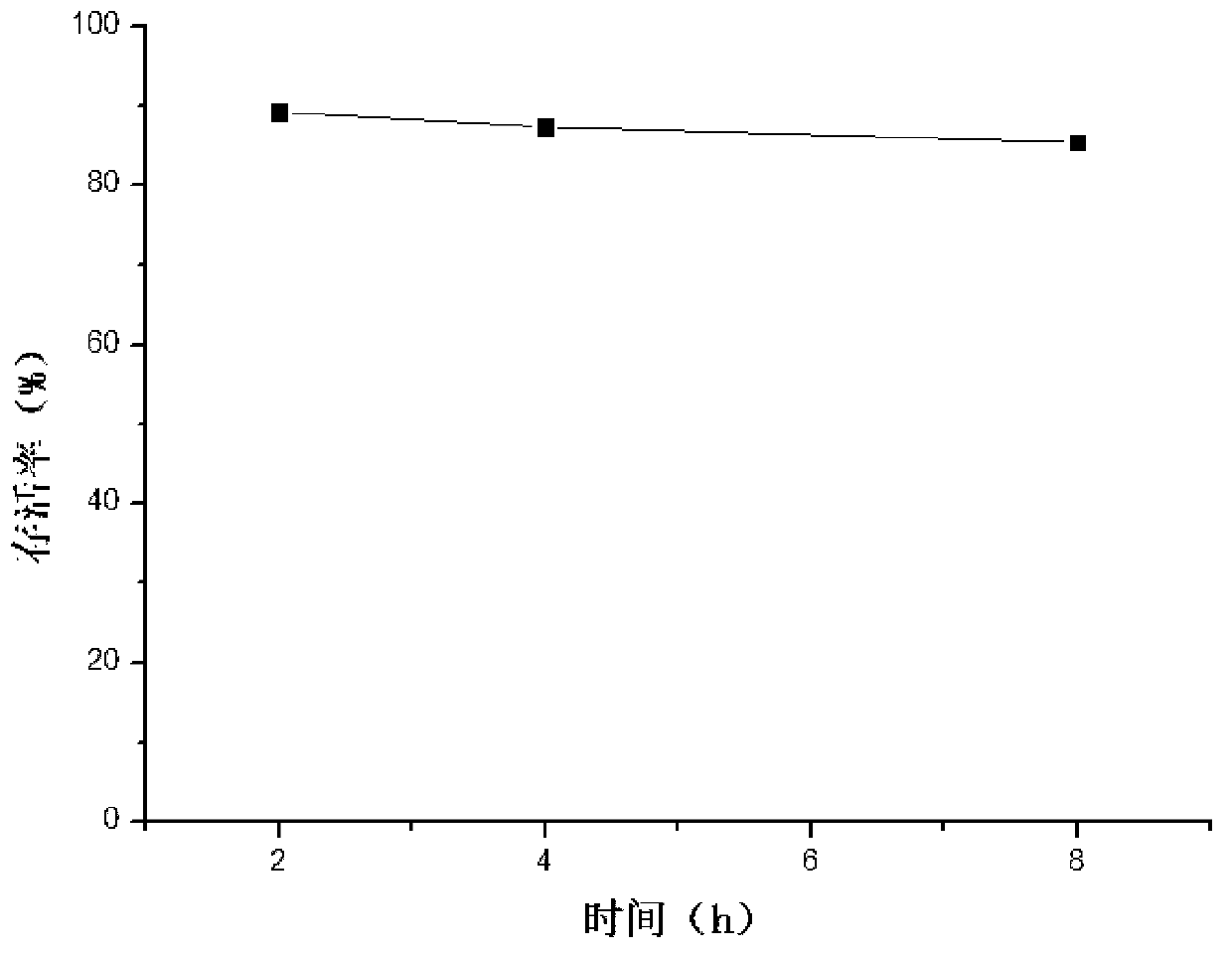
Application of bacteroides dorei in treating or preventing rheumatoid arthritis or related diseases thereof
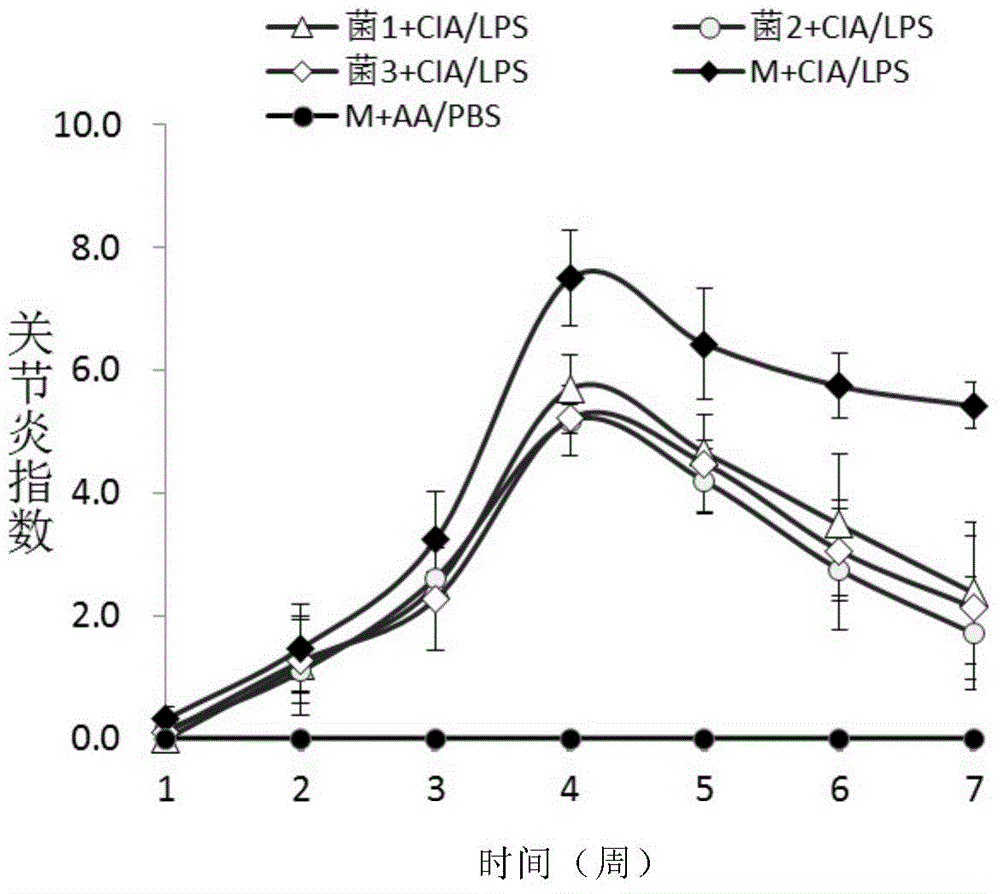
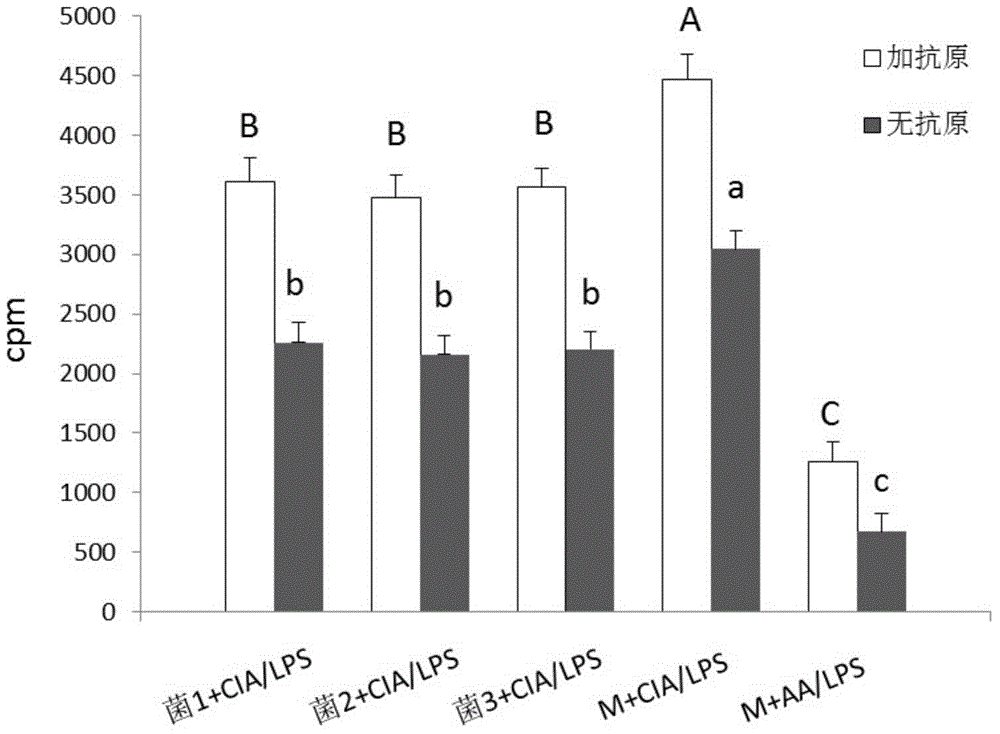
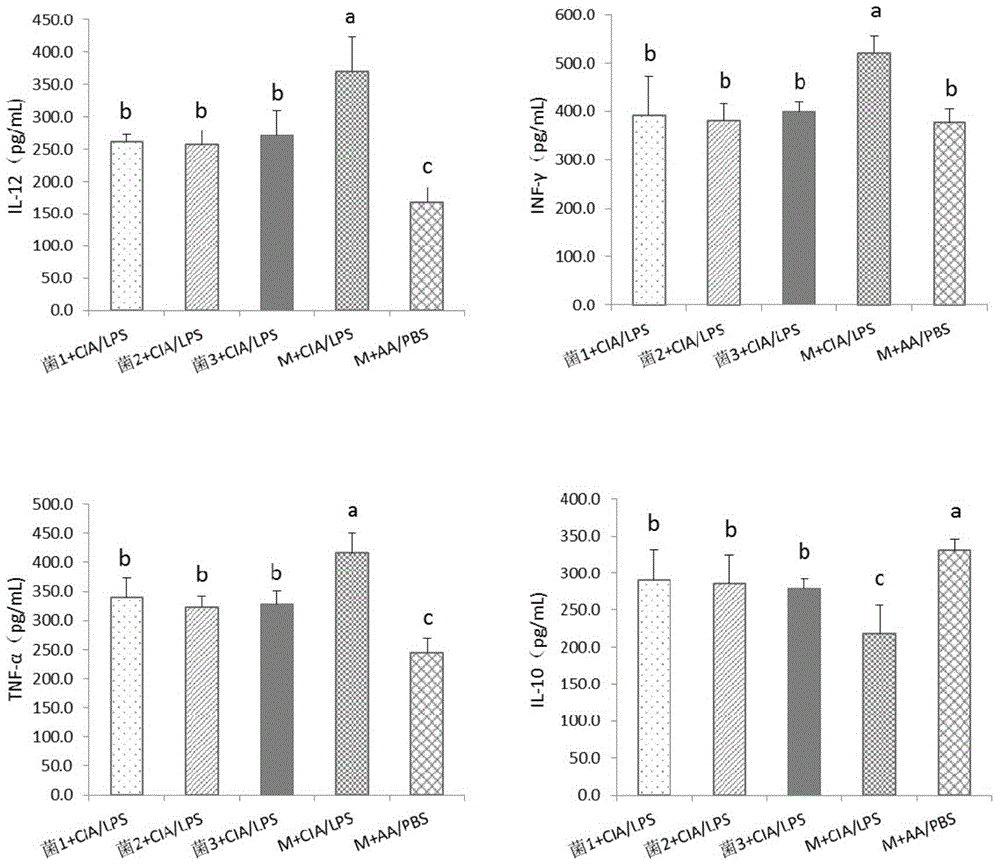
The invention provides application of bacteroides dorei in treating or preventing rheumatoid arthritis or related diseases thereof, and further provides a pharmaceutical composition, a medicine, a food and feed containing the bacteroides dorei. Applied to animals, the bacteroides dorei can be used for effectively developing an anti-inflammatory efficacy, so that the symptom of redness and swelling of joint is effectively improved and the symptom of arthritis is remarkably relieved; and the bacteroides dorei can be effectively used for treating or preventing rheumatoid arthritis or related diseases thereof.
Owner:BGI SHENZHEN CO LTD +1
Bacteroides fragilis and applications thereof
ActiveCN106399141AEffective for diarrheaGood probiotic propertiesBacteriaBacteria material medical ingredientsAntibiotic-associated diarrhoeaFood additive
The invention relates to Bacteroides fragilis and applications thereof, particularly to Bacteroides fragilis ZY-312 having the preservation number of CGMCC No.10685, and applications of the Bacteroides fragilis ZY-312 in preparation of medicines, pharmaceutical compositions, foods, health products and food additives for prevention and / or treatment of antibiotic-associated diarrhea, wherein the Bacteroides fragilis ZY-312 is preserved in the China general microbiological culture collection center on April 2, 2015, has the preservation number of CGMCC No.10685, does not contain enterotoxin gene bft, has characteristics of significantly-improved cholate resistance and significantly-improved gastric acid resistance compared to the existing Bacteroides fragilis, and can effectively prevent and / or treat antibiotic-associated diarrhea.
Owner:GUANGZHOU ZHIYI PHARMA INC
Probiotic, lactic acid-producing bacteria and uses thereof
InactiveUS20080233104A1Good curative effectMitigating deleterious side-effectsAntibacterial agentsAntimycoticsDiseaseMicrobial agent
The present invention discloses compositions and methodologies for the utilization of probiotic organisms in therapeutic compositions. More specifically, the present invention relates to the utilization of one or more species or strains of lactic acid-producing bacteria, preferably strains of Bacillus coagulans, for the control of gastrointestinal tract pathogens, including antibiotic-resistant gastrointestinal tract pathogens, and their associated diseases by both a reduction in the rate of colonization and the severity of the deleterious physiological effects of the colonization of the antibiotic-resistant pathogen. In addition, the present invention relates to the utilization of therapeutic compounds comprised of lactic acid-producing bacteria and anti-microbial agents such as antibiotics, anti-fungal compounds, anti-yeast compounds, or anti-viral compounds. The present invention also discloses methodologies for: (i) the selective breeding and isolation of probiotic, lactic acid-producing bacterial strains which possess resistance or markedly decreased sensitivity to anti-microbial agents (e.g., antibiotics, anti-fungal agents, anti-yeast agents, and anti-viral agents); and (ii) treating or preventing bacteria-mediated infections of the gastrointestinal tract by use of the aforementioned probiotic bacterial strains with or without the concomitant administration of antibiotics. While the primary focus is on the treatment of gastrointestinal tract infections, the therapeutic compositions of the present invention may also be administered to buccal, vaginal, optic, and like physiological locations.
Owner:GANEDEN BIOTECH
Bacillus subtilis for effectively degrading grease and application thereof
ActiveCN106929449AEfficient degradationMeet the needs of aerobic compostingNon-ionic surface-active compoundsOrganic detergent compounding agentsAdditive ingredientBacteroides dorei
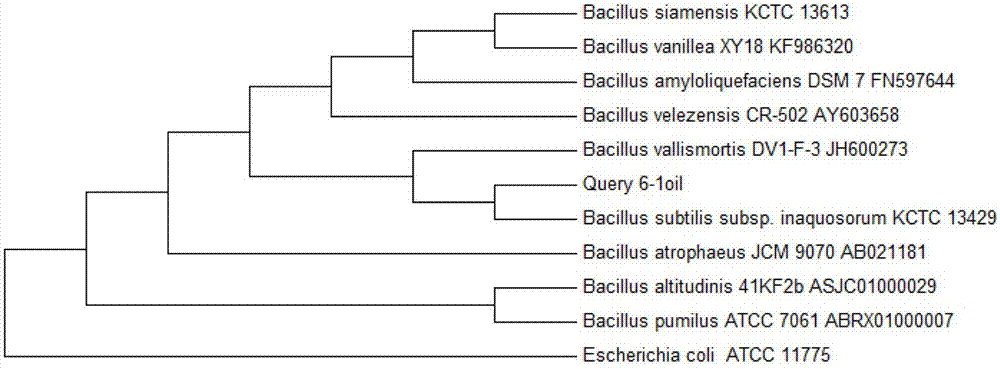
The invention provides a bacillus subtilis for effectively degrading grease. The bacillus subtilis 6-loil is preserved at Guangdong Province Microbiological Culture Collection Center on December 22, 2016. The preservation number is GDMCC No. 60134. The bacillus subtilis 6-loil provided by the invention can utilize the grease as a growth carbon source, can normally grow under an environment of higher grease content and has a capacity of efficiently degrading grease. The bacillus subtilis 6-loil provided by the invention can be compounded with bacillus coagulans, brewer yeast and carrier ingredients so as to be prepared into a kitchen garbage disposal fungicide. The prepared kitchen garbage disposal fungicide can adapt to the condition of high grease content of the domestic kitchen garbage, so that the condition of failure in aerobic composting caused by the reduction of microbial activity resulted from the microorganism wrapped by the grease in aerobic composting can be effectively avoided and the bacillus subtilis can meet the requirement of the domestic kitchen garbage aerobic composting. The bacillus subtilis 6-loil also can be applied to the fields of soil oil stain treatment, biosurfactant production, biological detergent preparation, and the like.
Owner:HANYU GRP CO LTD
Anthropogenic lactobacilus fermentum grx07 and application thereof
ActiveCN103937716AProtectiveImprove protectionMilk preparationBacteriaLactobacillus fermentumApoptosis
The invention relates to anthropogenic lactobacilus fermentum grx07 with a protection role on chronic alcoholic liver damage and application thereof. The lactobacilus fermentum grx07 strain disclosed by the invention is a probiotic strain separated from intestinal tracts of people in a Rugao longevity village of Jiangsu, the strain is preserved in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center, and the preservation number is CGMCC No.8874. The lactobacilus fermentum grx07 strain has significant in vitro antioxidant ability and pathogenic bacteria inhibition ability, the rat blood fat of chronic alcoholic liver damage and the toxin level in serum can be significantly reduced, expression of liver inflammatory cytokines is reduced, the inflammatory reaction of the liver is relieved, the expression quality of antioxidant specific protein Nrf2 of the liver is increased, and the liver cell apoptosis percentage is reduced. Therefore, the anthropogenic lactobacilus fermentum grx07 has a significant protective effect on the chronic alcoholic liver damage.
Owner:YANGZHOU YANGDA KANGYUAN DAIRY
Lactobacillus rhamnosus CCFM0528 having diabetes preventing effect
ActiveCN103275905ALower fasting blood sugar levelsImprove toleranceMilk preparationBacteriaLactobacillus rhamnosusAlpha-glucosidase activity
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Glutamine transaminase high productive bacteria and its screening method and fermentation method producing glutamine transaminase using said bacterial strain
A streptomyce shygeroscopicus (CCTCC No.M203062) able to generate glutamine transaminase wigh high output is extracted from the soil of milk cow farm through plate screening, primary fermenting, flask culture, comparing test with standard color tape, and enzyme activity test. Said glutamine transaminase is prepared by deep fermentation.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
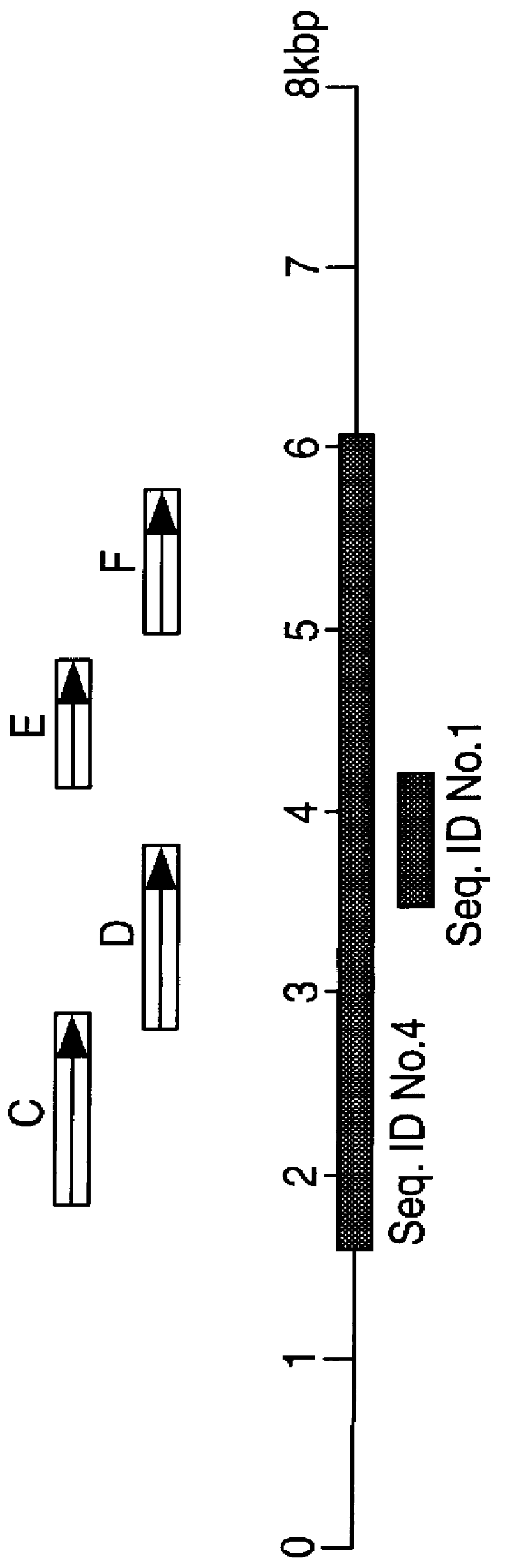
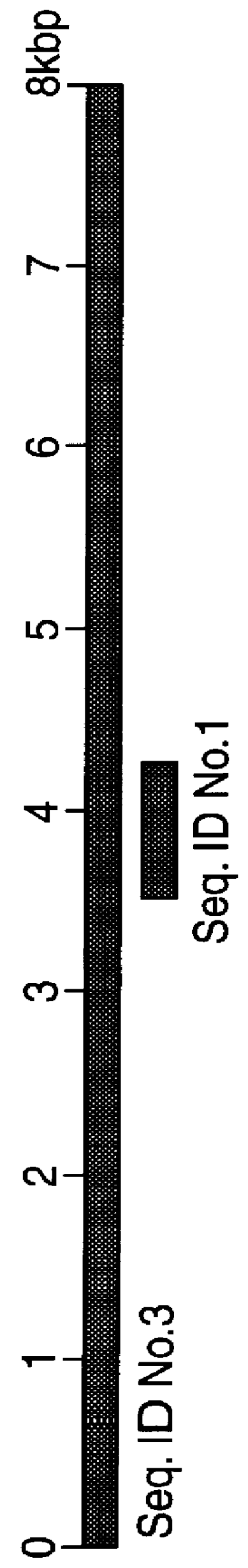
Polynucleotides and polypeptides in pathogenic mycobacteria and their use as diagnostics, vaccines and targets for chemotherapy
PCT No. PCT / GB96 / 03221 Sec. 371 Date Sep. 16, 1998 Sec. 102(e) Date Sep. 16, 1998 PCT Filed Dec. 23, 1996 PCT Pub. No. WO97 / 23624 PCT Pub. Date Jul. 3, 1997The invention provides a nucleotide sequence representing a pathogenicity island found in species of pathogenic mycobacteria. The islands are shown as SEQ ID NOs: 3 and 4 and comprises several open reading frames encoding polypeptides. These polypeptides and their use in diagnosis and therapy form a further aspect of the invention.
Owner:HAV VACCINES
Lactobacillus pentosus strain, ferment produced thereby and the use of ferment in meat ware
The invention discloses a lactobacillus pentosus strain and ferment produced thereby, wherein the docket number of the R1(Lactobacillus pentosus R1) strain in the Chinese Microbiological Culture Preservation Administration Commission Common Microbiological Center is CGMCC No.0917. The pentose lactobacillus R1 strain of the invention can endure 4.0% salt solution and nitrite solution whose concentration is 80-100mg / L. The leaven prepared from the bacterial can be applied into the fermentation production of meat food.
Owner:河南双汇投资发展股份有限公司
Antagonistic bacterium for controlling radix rehmannia root rot and application of antagonistic bacterium
InactiveCN104877943AStrong antagonistic effectEnhance colonization abilityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesContinuous croppingAspergillus flavus
The invention provides an antagonistic bacterium for controlling radix rehmannia root rot. The antagonistic bacterium is named as pseudomonas aeruginosa LK-12 (the Preservation No.: CGMCC 10966) after authentication. The pseudomonas aeruginosa LK-12 disclosed by the invention is obtained by screening from continuous cropping rhizosphere soil of radix rehmannia root through an agar disk diffusion method. Fusarium oxysporum and aspergillus flavus pathogenic bacteria separated from lesion parts of the radix rehmannia root have a high antagonistic effect; in the meanwhile, fusarium oxysporum, fusarium moniliforme, talaromyces sp. and other pathogenic bacteria separated from lesion parts of radix pseudostellariae also have a remarkable restriction effect and can be used for effectively controlling root rot diseases of medicinal plants comprising the radix rehmannia root to provide a strain for overcoming or relieving replant diseases of the medicinal plants. Therefore, the antagonistic bacterium is a potential biological control strain which is good in biological control effect, free of pollution as well as safe and ecological, and is wide in development and application prospects.
Owner:FUJIAN AGRI & FORESTRY UNIV
Lactobacillus crispatus and application
InactiveCN103074270AStrong acid resistanceHigh Yield Hydrogen PeroxideAntibacterial agentsBacteriaBacteroides doreiMicrobiological culture
The invention discloses a Lactobacillus crispatus and an application. The Lactobacillus crispatusis is preserved in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (CGMCC) with accession number of CGMCC NO.6406. The Lactobacillus crispatus has high acid resistance, high-yield hydrogen peroxide characteristic and vagina pathogenic bacteria growth inhibition effect, and the invention also relates to an application of the Lactobacillus crispatus LCR15 for adjusting vaginal flora, preventing and treating colpitis.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAODA ONLLY CO LTD +1
Process for producing, methods and compositions of glucuronoxylomannan as nutriceutical agent from higher basidiomycetes mushroom
InactiveUS6383799B1Decreased blood levelReduce riskOrganic active ingredientsFungiBiotechnologyTremella
The present invention describes new and distinct strains of higher Basidiomycetes mushrooms grown in submerged cultures. Specifically, the new strain of species of the genus Tremella offer superior yields of one-cell biomass and exocellular heteropolysaccharide glucuronoxylomannan, niacin and essential amino acids.
Owner:MEDMYCO
Pediococcus pentosaceus strain, ferment produced thereby and the use of ferment in meat ware
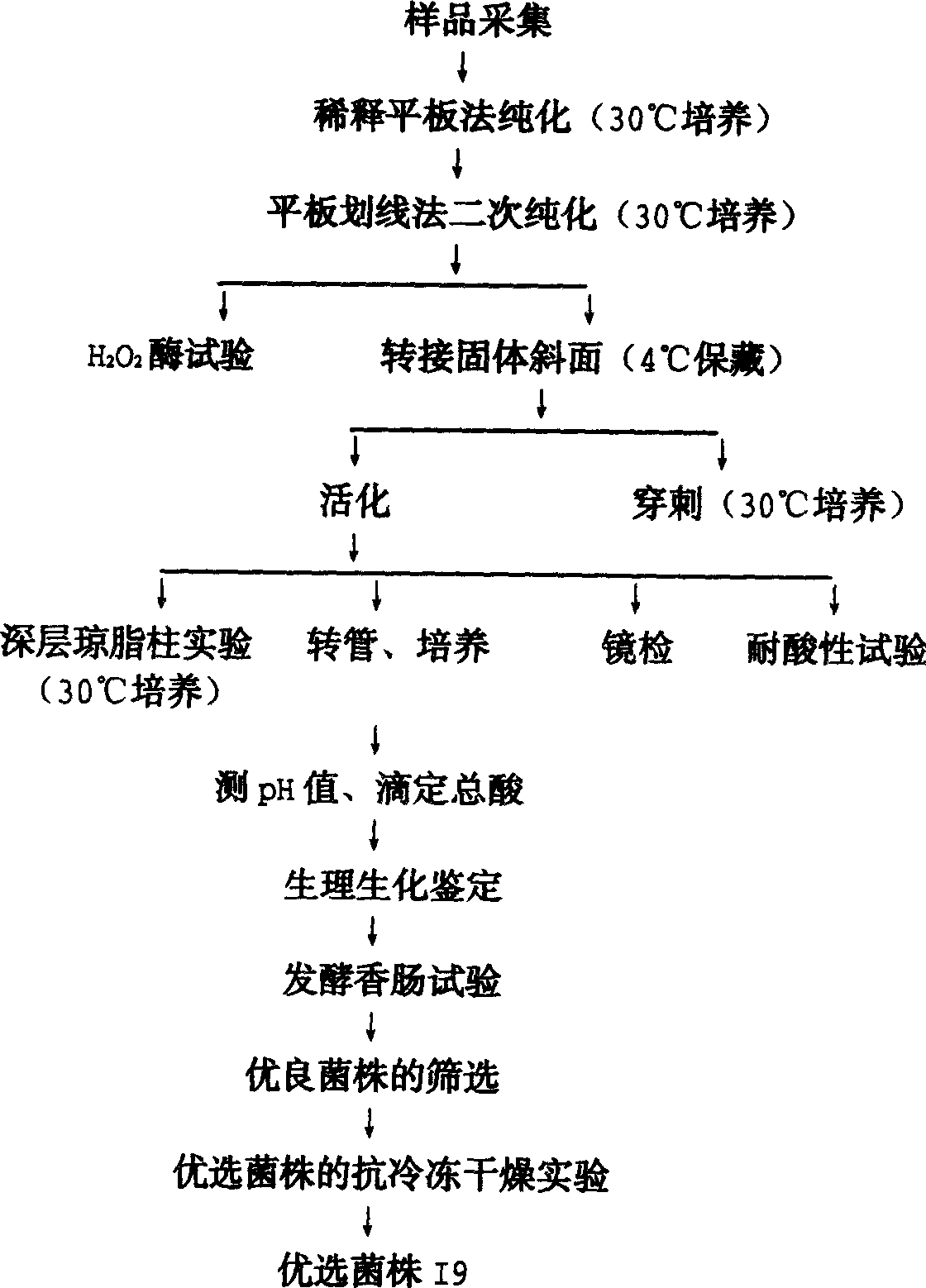
The invention discloses a pediococcus pentosaceus strain, ferment produced thereby and the use of ferment in meat product, wherein the docket number of the R9(Pediiococcus Pentosaceus I9) strain in the Chinese Microbiological Culture Preservation Administration Commission Common Microbiological Center is CGMCC No.0918. The leaven prepared from the bacterial can be applied into the fermentation production of meat food.
Owner:河南双汇投资发展股份有限公司
Method for breeding high-nucleic acid yeast and method for preparing ribonucleic acid by using high-nucleic acid yeast
InactiveCN101928674AHigh purityHigh yieldFungiSugar derivativesBiotechnologyVirulent characteristics
The invention relates to a method for breeding a high-nucleic acid yeast from Saccharomyces cerevisiae, which comprises the following steps: culturing a large amount of preserved Saccharomyces cerevisiae strains in an appropriate yeast growth medium, breeding initial strains, carrying out secondary screening on the initial strains and selecting growth media to obtain high-nucleic acid yeast strains for industrial production. Virulence tests show that thalli and metabolites can not cause intoxicating reactions. The Saccharomyces cerevisiae used in the method is one firstly recommended by Ministry of Health P.R.China for health food among fungi strains. The high-nucleic acid yeast bred from the Saccharomyces cerevisiae is used for the industrial production of nucleic acid, the bred high-nucleic acid yeast proves to be Saccharomyces cerevisiae by another microbiological assay and belongs to the traditional strains for producing beer, and the nucleic acid content of the thalli can be up to 12-14%(W / W) in the optimal culture condition. The method can be widely used for large-scale industrial production, and the prepared nucleic acid can be trustingly used in fields of health food, medicaments, infant food and the like.
Owner:大连珍奥生物技术股份有限公司
Multi-bacterium microbial compound preparations for aquaculture and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN101974434APromotes nutrient absorptionEnhance immune functionFungiBacteriaEcological environmentCulture fluid
The invention relates to multi-bacterium microbial compound preparations for aquaculture and a preparation method thereof. The multi-bacterium microbial compound preparations are characterized by comprising the following steps of: preparing seed culture solution by performing single strain culture on rhodoplanes elegans, pichia fermentans lodder, bacillus natto swamura, bacillus subtills, lactococcus lactis and bifidobacterium sp respectively; inoculating the seed culture solution onto the same culture medium; and then culturing the seed culture solution by a fermentation tank, and naturally reducing a pH value of the seed culture solution to 3.0 to 3.5 to obtain the multi-bacterium microbial compound preparations, wherein the bacterial content of the pichia fermentans lodder in the preparations is more than or equal to 0.1*10<9>cfu / ml; the bacterial content of the other strains is more than or equal to 5.0*10<9>cfu / ml. The multi-bacterium microbial compound preparations for aquaculture can improve the ecological environment of aquatic animals, prevents and treats diseases, reduces the emergency condition of the animals, improves the quality of the aquatic animals, and shortens a listed period.
Owner:山西博亚方舟生物科技有限公司
Preparation process and application of genetic engineering subunit vaccine of infectious bursal disease
ActiveCN1754959AAntigenic activityReduce manufacturing costBacteriaViral antigen ingredientsEscherichia coliVaccine Production
The invention relates to a bacterium for the production of genetically-engineered subunit oil-adjuvant vaccines against infectious bursal disease, i.e. Escherichia coli BL21 / pET-28a-VP2, CCTCC No: M204038. The process for constructing the bacterium consists of inserting VP2 protein gene of the infectious bursal disease virus onto expression plasmid pET-28a to construct prokaryotic expression plasmid, then using the prokaryotic expression plasmid to transform the escherichia coli BL21, using lactose as inducer to induce Escherichia coli BL21 / pET-28a-VP2 expression VP2 protein, purifying and charging oil-adjuvant to obtain the vaccines.
Owner:YEBIO BIOENG OF QINGDAO
Fish-sourced aeromonas hydrophila disease antagonistic strain and application thereof
The invention relates to a fish-sourced aeromonas hydrophila disease antagonistic strain and an application of the antagonistic strain and belongs to the field of aquaculture technology. A fish-sourced aeromonas hydrophila disease antagonistic strain is screened out, cultivated and added into a feed or a medicine as probiotics. The antagonistic strain is a novel antagonistic strain which is high in biological activity stability and high in specificity, is safe for cultured fish and environment, can be used as the probiotics strain for preventing and treating aeromonas hydrophila caused explosive hemorrhagic disease in large freshwater fish farming, and can be used as the main strain to prepare a microbial preparation.
Owner:FRESHWATER FISHERIES RES CENT OF CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERY SCI
Human ochrobactrum anthropi and its application in degrading plant stalks and preparing important enzyme
The present invention discloses one kind of human Ochrobactrum anthropi IBL01 (Ochrobactrum anthropi CCTCC M 206046) and its application in degrading plant stalks. Ochrobactrum anthropi IBL01 has high plant stalk degrading effect and can produce high activity cellulase, hadromse and hemicellulase. The present invention also discloses the preparation process of cellulose, xylanase, lignin peroxidase, laccase and manganese peroxidase with the human Ochrobactrum anthropi. The human Ochrobactrum anthropi of the present invention is bacterium with short growth period of about one week, and can produce fiber degrading enzyme as well as hemicellulose degrading enzyme and lignin degrading enzyme.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Detection method for drug resistant genes of Klebsiella pneumoniae against belta-lactamase
InactiveCN101519688AReduce infection rateReduce mortalityMicrobiological testing/measurementSequence analysisBacteria identification
The invention discloses a detection method for drug resistant genes of Klebsiella pneumoniae against belta-lactamase, pertaining to the technical field of gene detection methods. The detection method comprises the following steps: 1. Klebsiella pneumoniae strains of inpatients are selected and sampling for backup is carried out after strain identification is carried out to all strains using bacteria identifying apparatus; 2. the sensitivity of antibacterials is determined by adopting the micro dilution method so as to judge the sensitivity of antibiotic; and 3. drug resistant genes are detected by adopting a PCR method and belta-lactamase drug resistant genes are checked and DNA positive strains are selected for carrying out sequencing analysis. The detection method finds the drug resistant genes resulting in the resistance of Klebsiella pneumoniae to belta lactam drugs by carrying out a systematical and complete research on the drug resistant mechanism of the Klebsiella pneumoniae, thus having important value for instructing the clinical and reasonable use of antibacterials, being capable of reducing the infection rate in a hospital, reducing mortality rate and saving social medical resources, and having good social and economic benefits.
Owner:钟建平
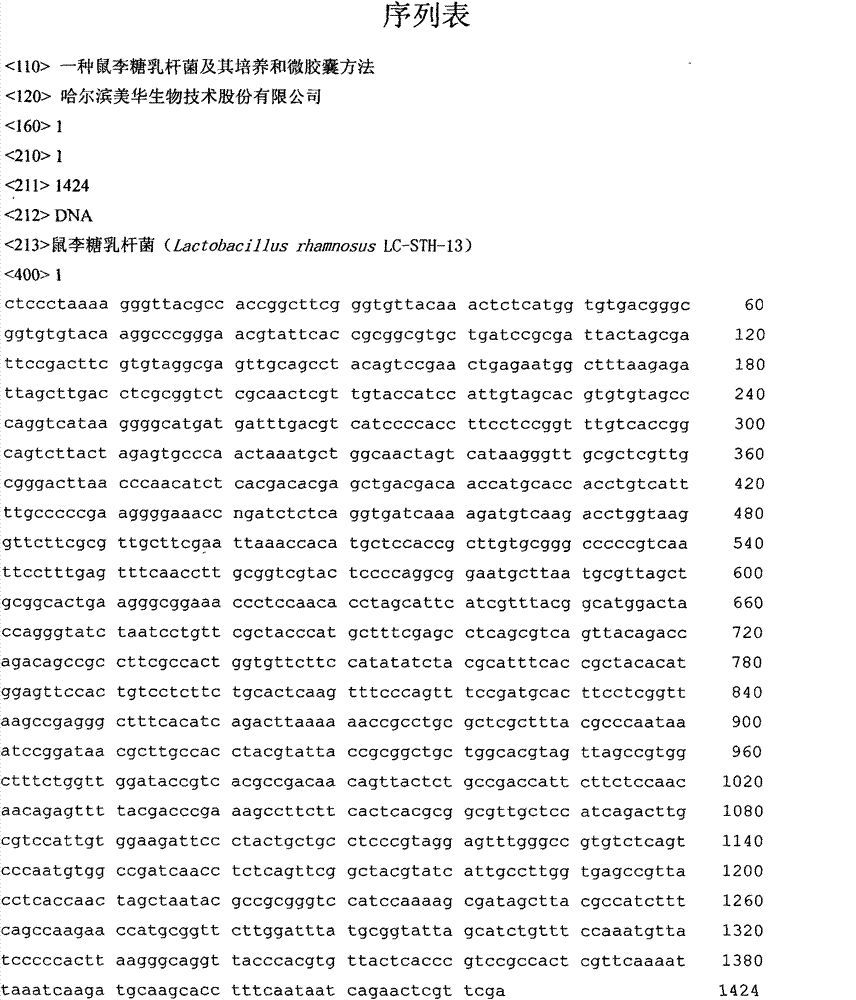
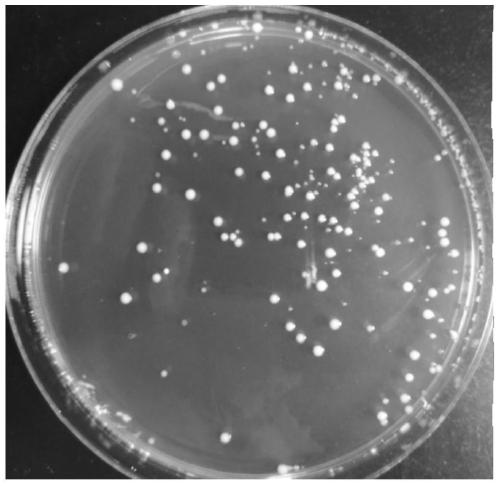
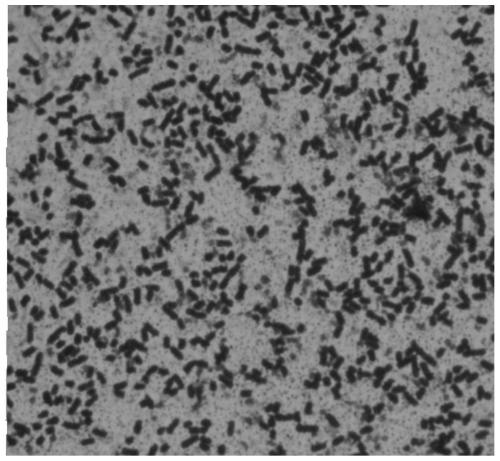
Lactobacillus rhamnosus, cultivation of lactobacillus rhamnosus and microcapsule method
InactiveCN103031263AShorten the growth cycleReproduce fastBacteriaMicroorganism based processesLactobacillus rhamnosusBacteroides dorei
The invention discloses lactobacillus rhamnosus, cultivation of the lactobacillus rhamnosus and a microcapsule method. The bacterial strain is preserved in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (CGMCC); a registering number is CGMCC NO.3994; a Latin name of the bacterial strain is Lactobacillus rhamnosus LC-STH-13; morphological characteristics are gram-positive bacteria, short-rod bacterial thallus, no motion, no gemma, circular bacterial colony, milk white, tidy edges, smooth surfaces and protuberant cores. The invention further discloses a 16S ribosome DNA (Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid) (16S rDNA) complete sequence of the lactobacillus rhamnosus. The lactobacillus rhamnosus has the advantages that a culture is short in growth cycle, high in breeding speed and- produced lactic acid concentration. The lactobacillus rhamnosus can -colonize and survive in an intestinal tract, improves a mucosal barrier function of a gastrointestinal tract, has a function of improving the gastrointestinal tract, and restrains the colonization of harmful bacteria; and after being embedded by a microcapsule, the lactobacillus rhamnosus has stronger ability to resist the poor environment.
Owner:哈尔滨美华生物技术股份有限公司
Lactobacillus fermentum capable of reducing blood uric acid
ActiveCN110079476AReduce contentControl levelBacteriaSkeletal disorderMicroorganismLactobacillus fermentum
The invention relates to the field of microorganisms, and discloses lactobacillus fermentum capable of reducing blood uric acid. The strain is named 2644 strain, and is preserved at the China GeneralMicrobiological Culture Collection Center on 19th, November, 2018, and a microbial preservation number is CGMCC NO.16754; and the preservation authority address is NO.3 1# Courtyard, Beichen West Road, Chaoyang District, Beijing, and the microorganism is classified and named Lactobacillus fermentum. The strain can effectively reduce the content of the blood uric acid; and not only can intake of exogenous purines be reduced, but also discharge of internal uric acid from an intestinal tract can be promoted so that the blood uric acid level of a body can be more effectively controlled.
Owner:HANGZHOU WAHAHA TECH +1
Porcine epidemic diarrhea virus strain MY01 and application thereof
InactiveCN105462936AEpidemic preventionAvoid spreadingSsRNA viruses positive-senseViral antigen ingredientsDiseaseMicroorganism
The invention relates to a porcine epidemic diarrhea virus strain MY01 and application thereof and belongs to the field of porcine epidemic diarrhea virus vaccine reagents. The porcine epidemic diarrhea virus strain MY01 is collected in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center under CGMCC No. 11495. The porcine epidemic diarrhea virus strain MY01 is higher in pathogenicity for pigs and good in immunogenicity, a deactivated oil emulsion vaccine prepared using the strain is safe and reliable, homologous attacking protection can be provided, protection is also provided for PEDV (porcine epidemic diarrhea virus) epidemic strains, higher immunity can be generated after immunization, inoculated pigs are significantly lower in morbidity and mortality, the immunization effect is superior than that of existing commercial vaccines in the market, and the strain has the advantage of competing with like products home and abroad, can effectively prevent the prevalence and spread of porcine epidemic diarrhea virus and reduce economic cost caused by the disease and has a promising application prospect.
Owner:INST OF ANIMAL SCI & VETERINARY MEDICINE SHANDONG ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Application of lactobacillus casei grx12 in preparation of product for treating chronic alcoholic liver injury
InactiveCN103893215AReduce inflammationReduce blood lipids in ratsMilk preparationBacteria material medical ingredientsInflammatory factorsBacteroides dorei
The invention relates to an application of anthropogenic lactobacillus casei grx12 in the aspect of chronic alcoholic liver injury. The lactobacillus casei grx12 is a probiotic strain with an obvious in-vitro antioxidant capacity, which is obtained in a separation mode from the intestinal tracts of people in the long life village of Rugao city, Jiangsu province. The lactobacillus casei grx12 is preserved in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (CGMCC) of China Committee for Culture Collection of Microorganisms (CCCCM) and has the preservation number of CGMCC No.7696. The lactobacillus casei grx12 can be used for obviously decreasing the level of toxins in blood fat and blood serum of a rat with the alcoholic liver injury, decreasing the expression of liver inflammatory factors in the liver and relieving the inflammatory reaction of the liver, thereby having obvious protection functions to the chronic alcoholic liver injury.
Owner:YANGZHOU UNIV
Composite gene chip for food-borne pathogenic bacteria detection
InactiveCN101397586AExplicitly excludeClear and distinctMicrobiological testing/measurementAgainst vector-borne diseasesEscherichia coliFood borne
The invention relates to a composite gene chip for detecting food pathogenic microbes, which comprises eight parallel sub-arrays constructed by detection probe groups for detecting each microbe in the eight food pathogenic microbes, blank lines are respectively arranged among the eight sub-arrays to be as intervals, thus constructing a big array; the eight food pathogenic microbes are listeria monocytogenes, comma bacillus, vibrio parahaemolyticus, salmonella, shigella, staphylococcus aureus, campylobacter jejuni and escherichia coli. The gene chip can clearly and accurately detect the species of eight target food pathogenic microbes, and also can definitely exclude other off-target microbe samples out of the eight target food pathogenic microbes. Each food pathogenic microbe detection sub-array on the chip can clearly and definitely distinguish off-target microbe samples from target microbe samples.
Owner:广东省疾病预防控制中心
Pathogenic aeromonas hydrophila assay kit
InactiveCN101942505AStable identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementPathogenic microorganismBacteroides dorei
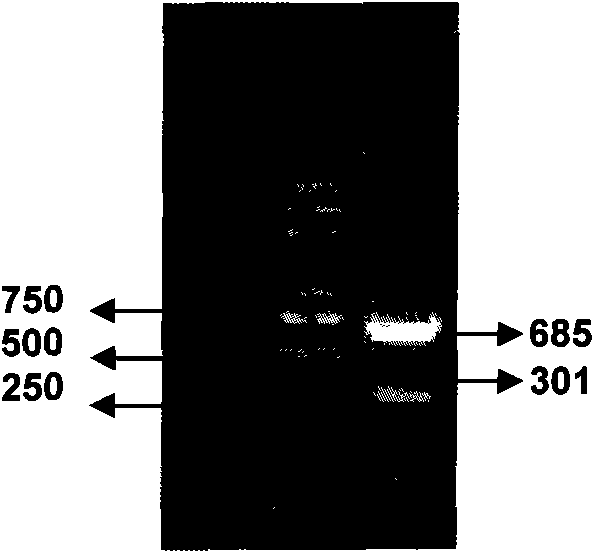
The invention relates to a pathogenic aeromonas hydrophila assay kit and belongs to the field of the detection of pathogenic microorganisms. A primer which is designed on the basis of a highly conserved interval of a standard strain J-1 strain 16S rDNA genome of the pathogenic aeromonas hydrophila is used for distinguishing and identifying strain characteristics of the pathogenic aeromonas hydrophila, and the amplified fragment is 685bp; and a second pair of primers which is designed according to specific proteinase aerolysin secreted by the strain is used for judging the pathogenicity of the aeromonas, and the fragment size is 301bp. The assay kit can rapidly and accurately judge the strain characteristics and pathogenicity of the strains to be tested. Comparison tests of the conventional biochemical identification method and pathogenicity identification method for experiment strains and clinical stains show that the coincidence rate of the kit is 100 percent. Evaluation tests for specificity, repeatability, sensitivity and retention period of the kit acquire ideal results.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Lactobacillus as well as composition and application thereof in treating autoimmune disease and complications
ActiveCN104017746AInhibitory activityBacteriaBacteria material medical ingredientsAutoimmune diseaseGenetics
The invention relates to a lactobacillus as well as a composition and an application thereof in treating an autoimmune disease and complications of the autoimmune disease. The composition contains separation strains of at least one strain of the following strains in effective quantity: lactobacillus paracasei GMNL-32, lactobacillus reuteri GMNL-89 or lactobacillus reuteri GMNL-263 and a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier agent. The lactobacillus and / or the composition thereof can be used for treating the autoimmune disease and the complications of the autoimmune disease.
Owner:GENMONT BIOTECH
Saccharomyces cerevisiae and culture thereof and application thereof to feed
InactiveCN108085261AGrow fastImprove growth performanceFungiAnimal feeding stuffDiseaseEscherichia coli
The invention discloses saccharomyces cerevisiae 5-1 which is collected in the Guangdong Microbial Culture Collection Center, with the collection number of GDMCC No: 60243. The invention further discloses a fermentation solution, a culture and a culture dilution prepared from the saccharomyces cerevisiae 5-1. A metabolite of the saccharomyces cerevisiae 5-1 has a very strong inhibitory effect on pathogenic bacteria (escherichia coli, staphylococcus aureus and salmonella enteritidis); when the saccharomyces cerevisiae 5-1 is used as a feed additive and is added into feed for feeding animals, the disease incidence of the animals can be effectively reduced, the growth performance of the animals can be improved, and the intestinal microflora of the animals can be significantly improved, so that the saccharomyces cerevisiae 5-1 is of a great significance in development of the breeding industry.
Owner:潘韵
Inonotus obliquus extracellular and intracellular mixing crude polysaccharide with function of strengthening immunity
ActiveCN101805763AShorten the growth cycleOrganic active ingredientsMicroorganism based processesAscites tumorsHepatocellular carcinoma
The invention relates to the technical field of medicament, in particular to inonotus obliquus extracellular and intracellular mixing crude polysaccharide with a function of strengthening immunity, which is extracted from a submerged fermentation product of medical fungus inonotus obliquus liquid. The method comprises the following steps: taking slant strain under an asepsis condition, and inoculating the slant strain into a plate filled with fresh comprehensive solid culture medium; pumping and filtering a secondary fermentation product through primary fermentation and secondary fermentation to obtain inonotus obliquus mycelium and fermentation supernatant; and preparing the inonotus obliquus extracellular and intracellular mixing crude polysaccharide through concentration and water extraction and alcohol precipitation. In vivo experiments prove that the inonotus obliquus extracellular and intracellular mixing crude polysaccharide can prolong the surviving time of mice hepatocellular carcinoma H22 and S180 ascites tumor mice, and can obviously improve the thymus gland index and spleen index of the mice. Furthermore, the inonotus obliquus extracellular and intracellular mixing crude polysaccharide can obviously improve secretion of IL-2, TNF-alpha cell factors in the blood serum of the tumor-bearing mice, and can be used for preparing new immunity intensifying preparation. The invention opens up a new way for development and utilization of medical fungus resources.
Owner:王琦
Bacterial strain XY21 preventing and curing glasshouse vegetable bacterial wilt
InactiveCN101139565AConducive to pollution-free productionEasy to exportBiocideBacteriaGreenhouseBacteroides dorei
The invention provides a biologic bacterial strain XY21 for preventing and treating bacterial wilt in greenhouse vegetables, and pertains to the technical field for preventing and treating diseases in crops. The XY21 is verified to be Serratia sp., the culture preservation no. is CGMCC NO.2059. The XY21 bacterial strain expresses good colonization surrounding the roots of tomatoes. After soaking the culture for 14 days, the colonized volume of the bacterial strain surrounding a root of tomato tree is 5.05 is multiplied by 10<7>cfu / g soil. If the wet bacterial strain is mixed with a lab thallus-preservation solution in a proportion of 1:40 (g / ml), the bacterial strain can be stored 2-3 years under room temperature. Tests show that, by application XY21 bacterial strain in fields, the prevention effect is 64.84% and 79.80% respectively, the outputs of the diseased fields increased respectively 31.8% and 45.8%. The invention is of high prospective to be developed into commercial live-vaccine biologic preventing preparations.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Porcine epidemic diarrhea virus variant strain, and isolated culturing method and applications thereof
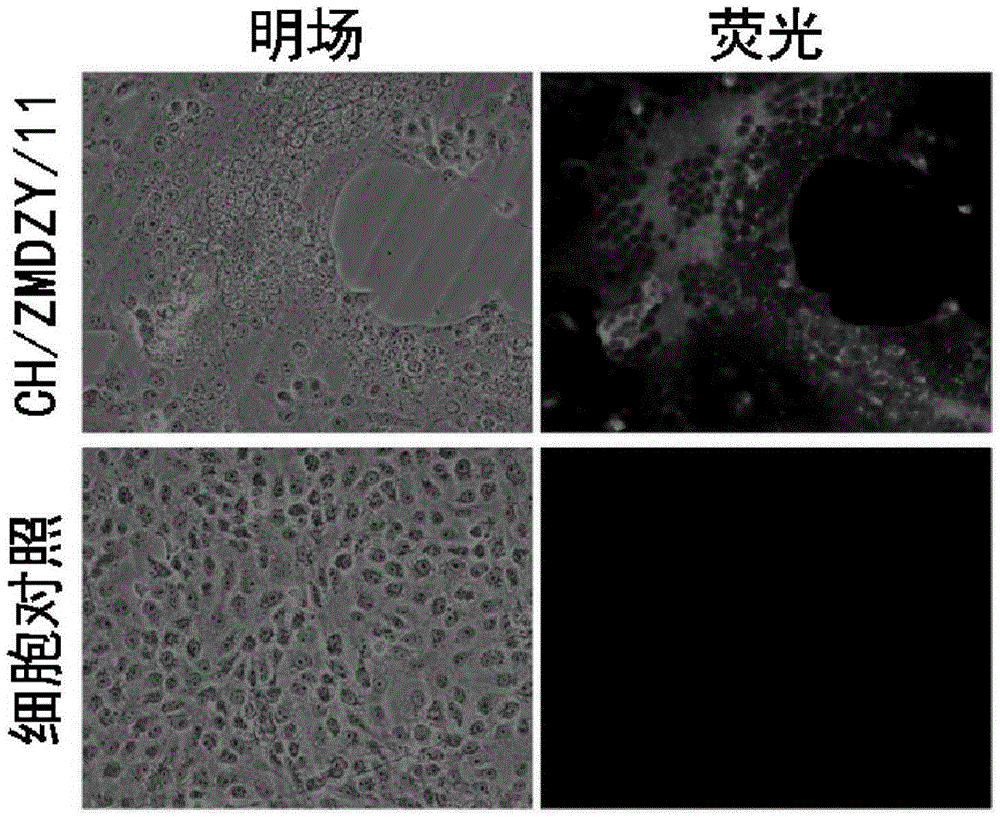
InactiveCN105400744AEffective means of preventionSsRNA viruses positive-senseViral antigen ingredientsMicroorganismDisease
The invention discloses a porcine epidemic diarrhea virus variant strain, and an isolated culturing method and applications thereof. The porcine epidemic diarrhea virus variant strain is named as CH / ZMDZY / 11, and is preserved in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center; and preservation number is CGMCC NO.10893. The porcine epidemic diarrhea virus variant strain can be used for preparing an inactivated vaccine which can be used for preventing porcine epizootic diarrhea effectively, so that an effective control method is provided for controlling porcine epizootic diarrhea caused by porcine epidemic diarrhea virus variant strains.
Owner:HENAN AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com