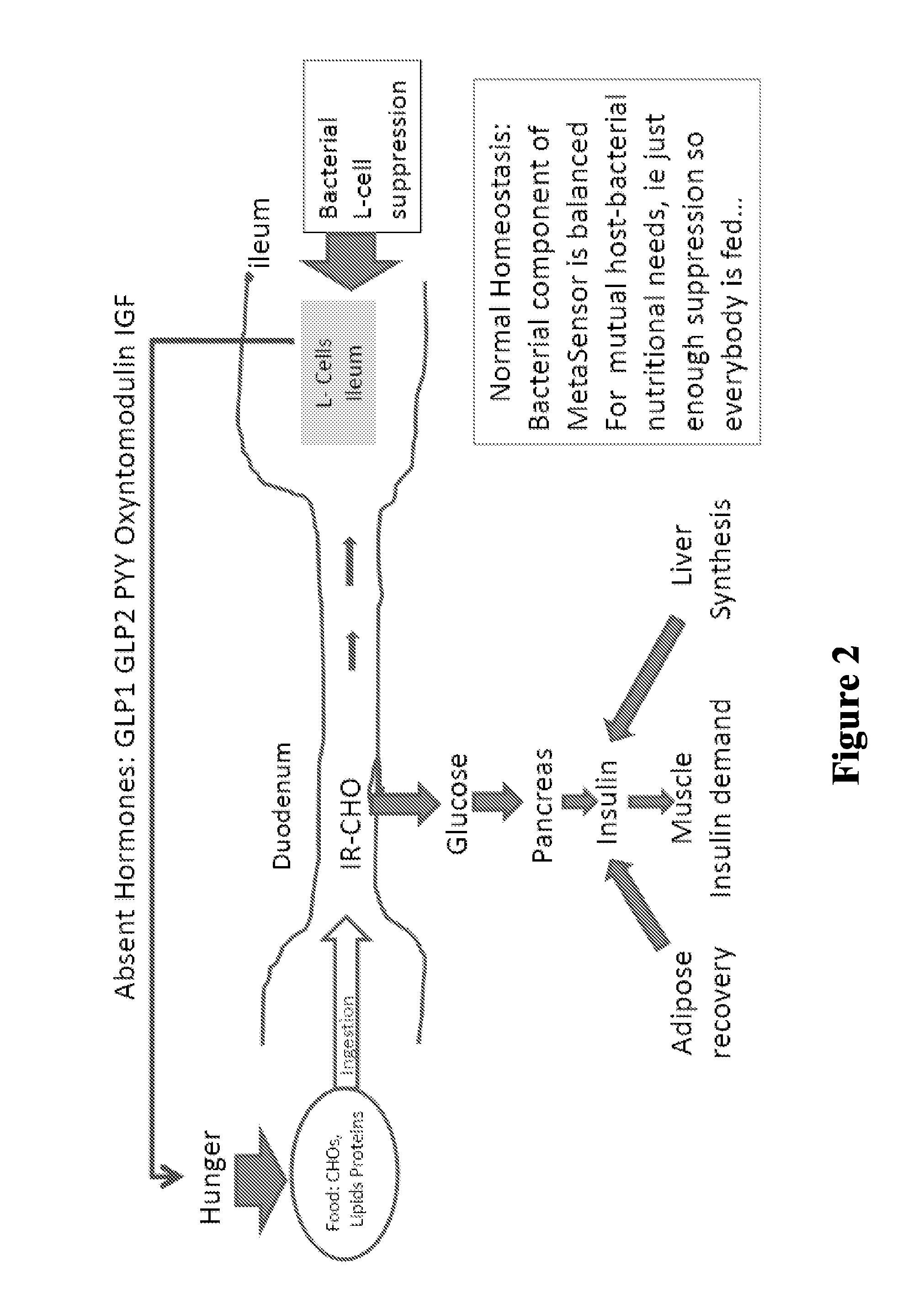
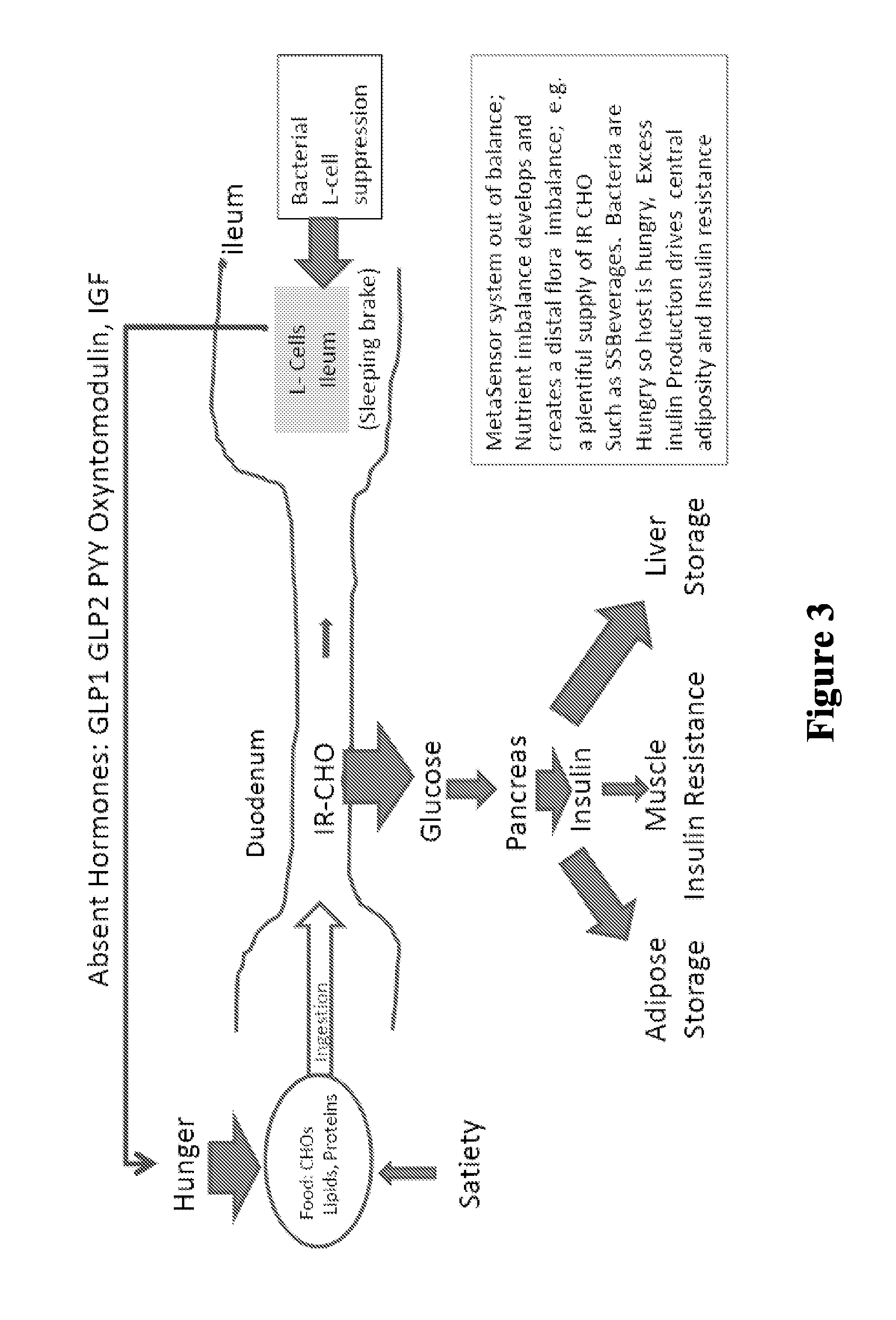
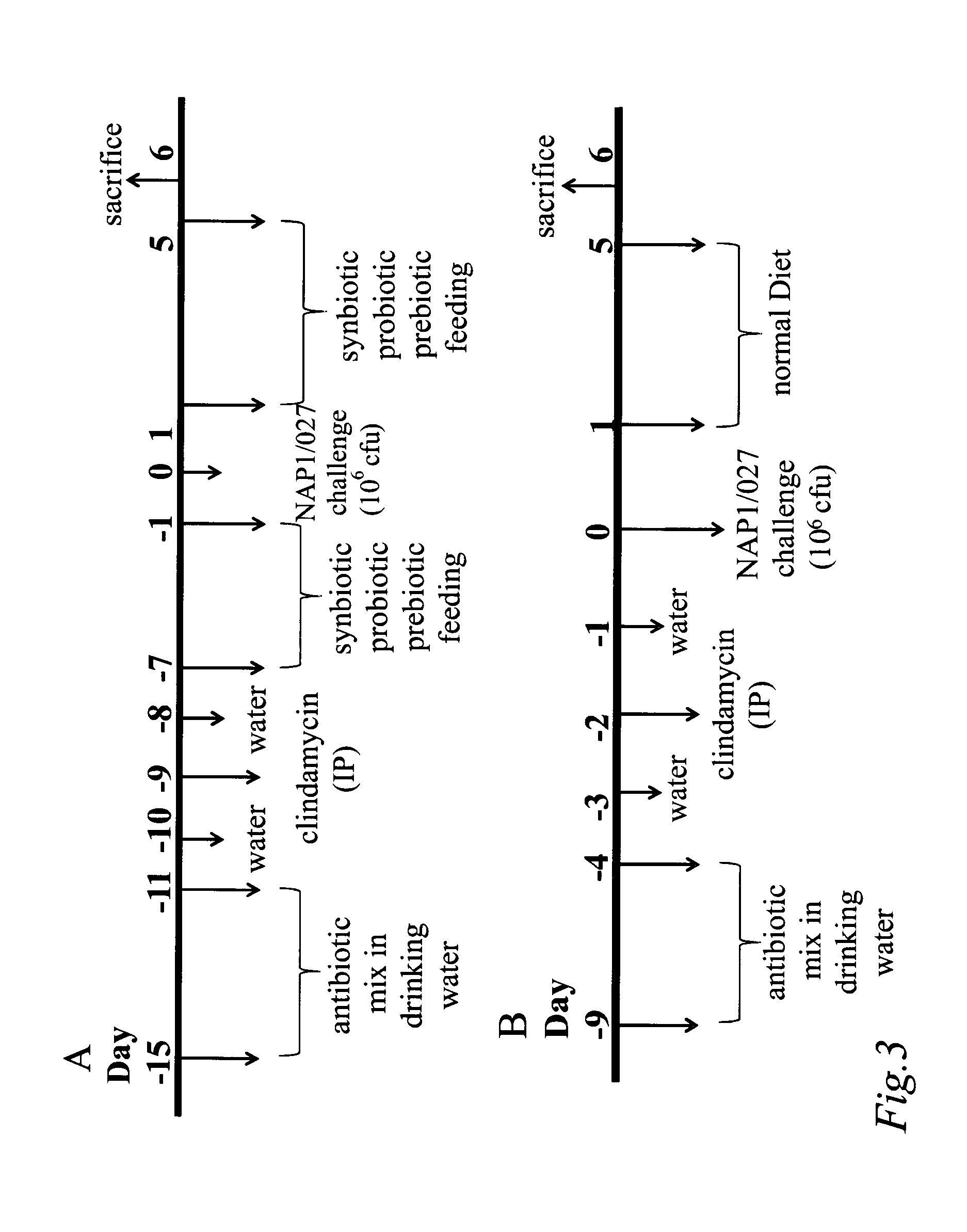
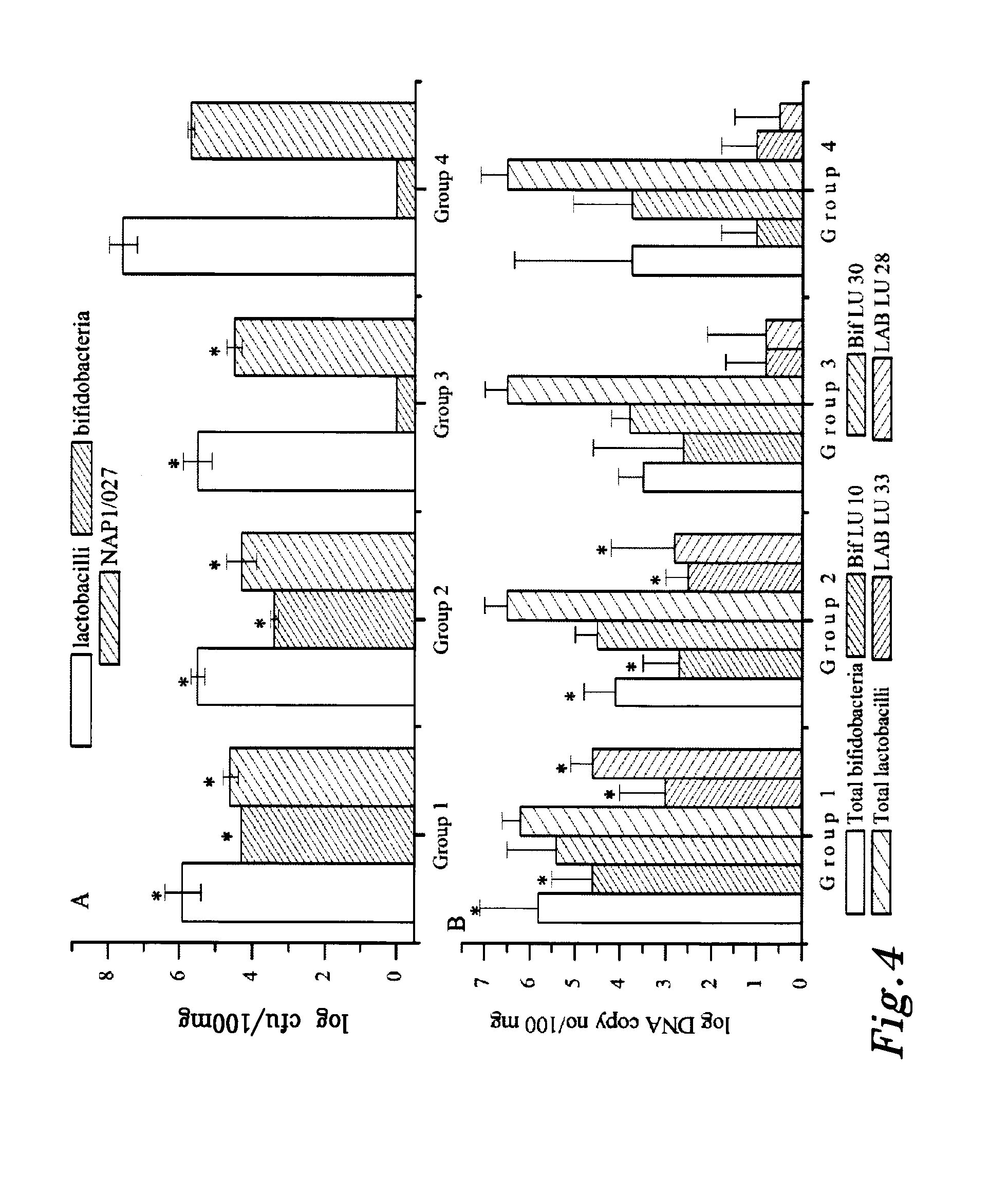
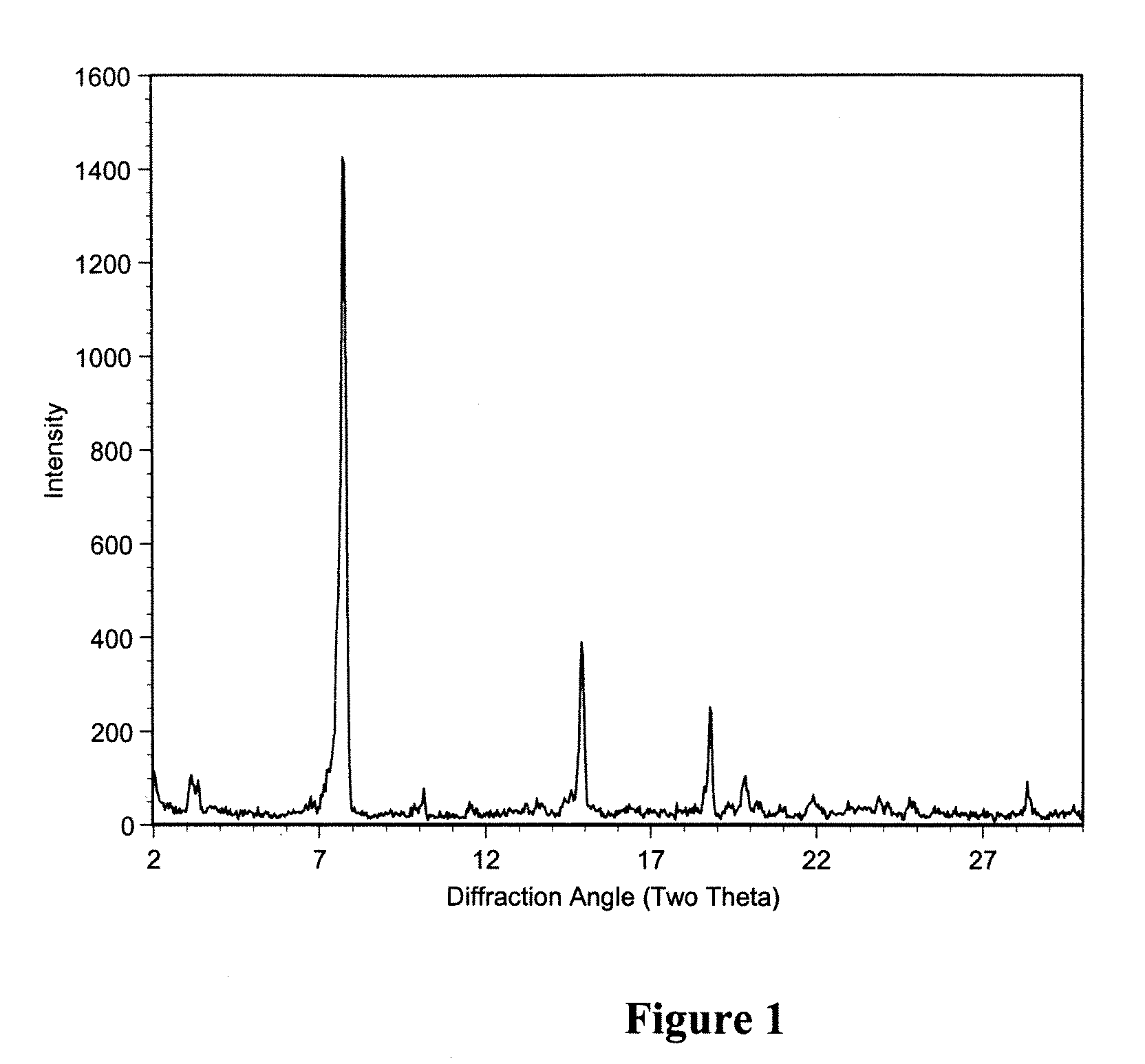
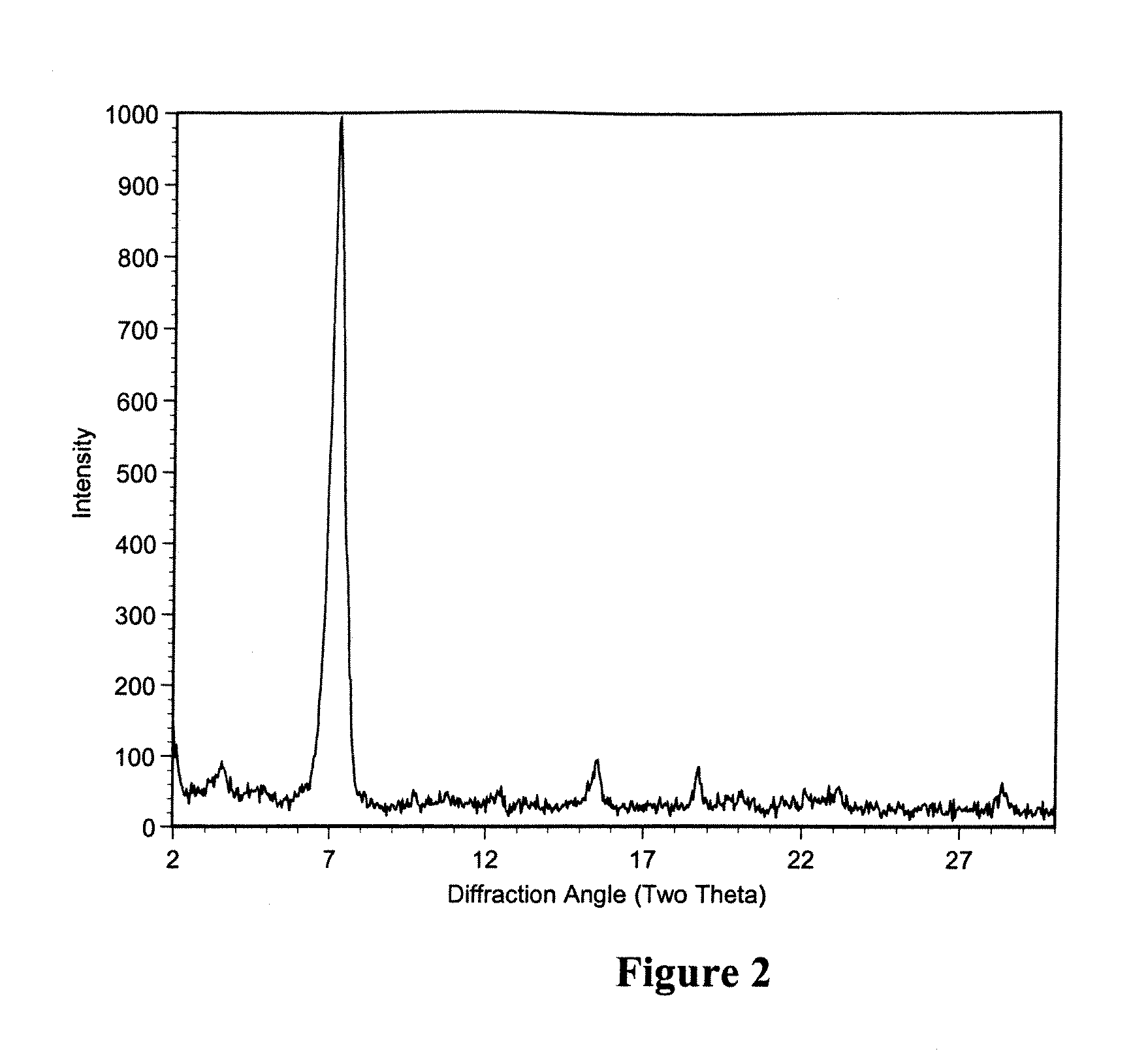
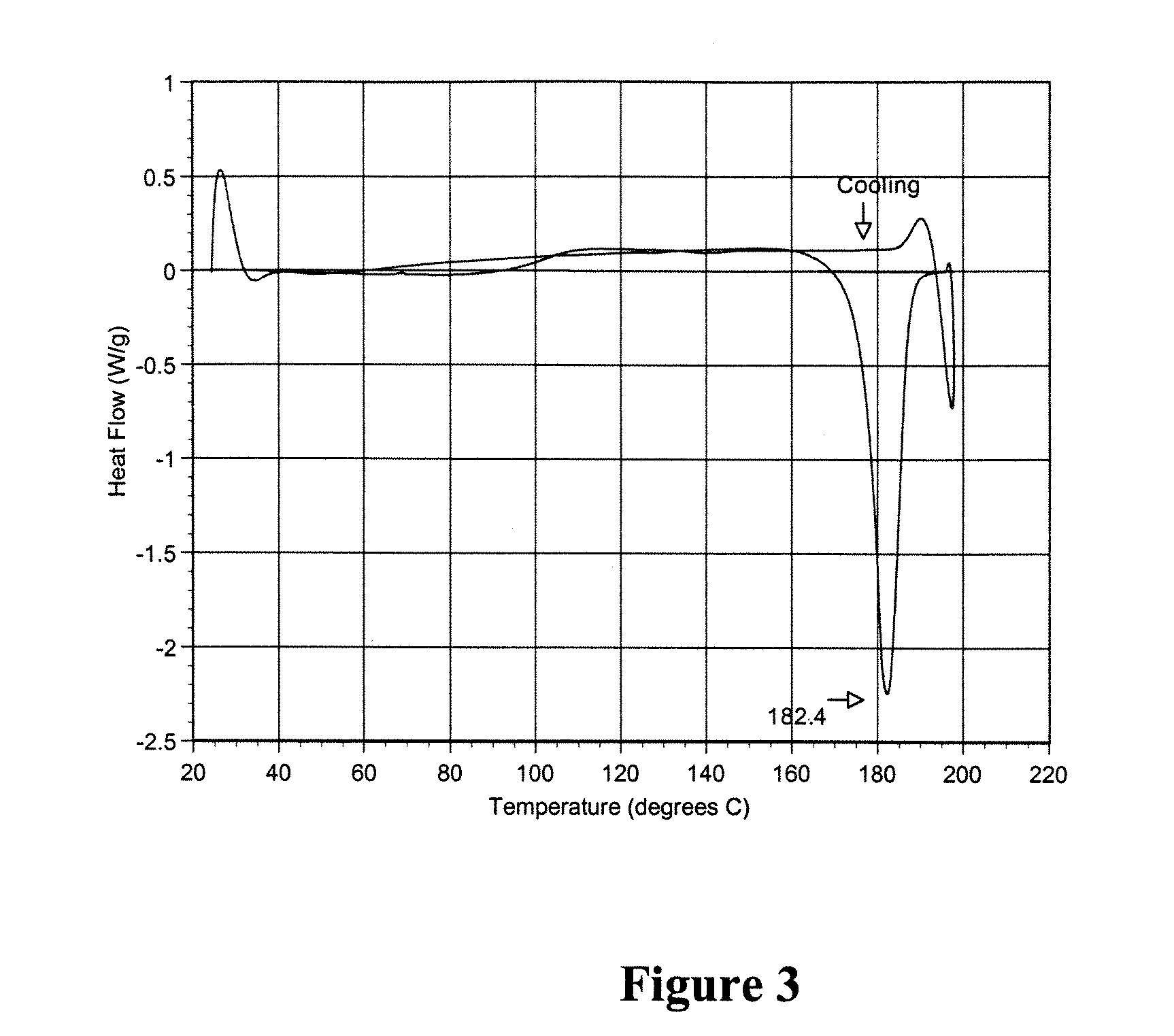
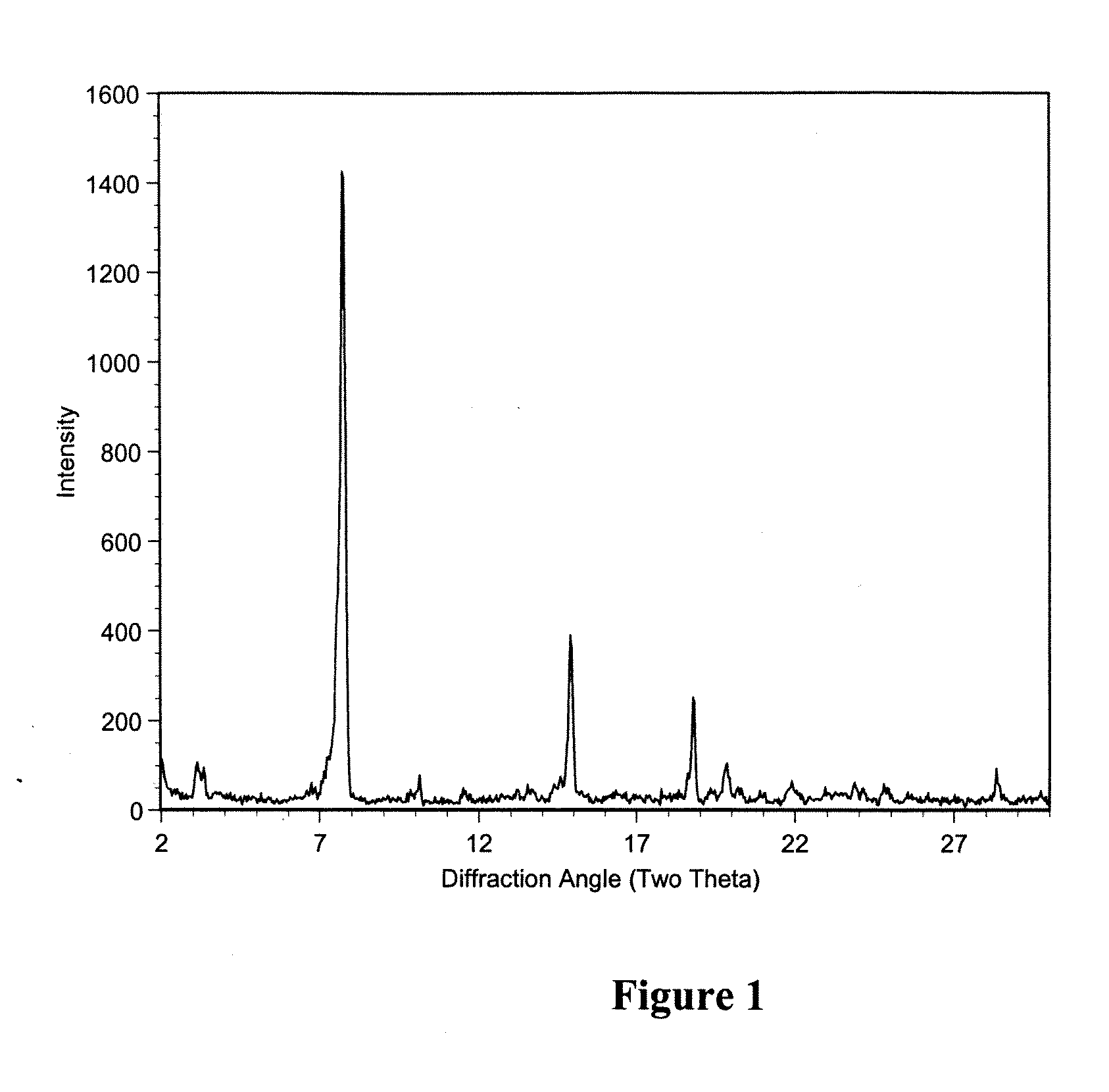
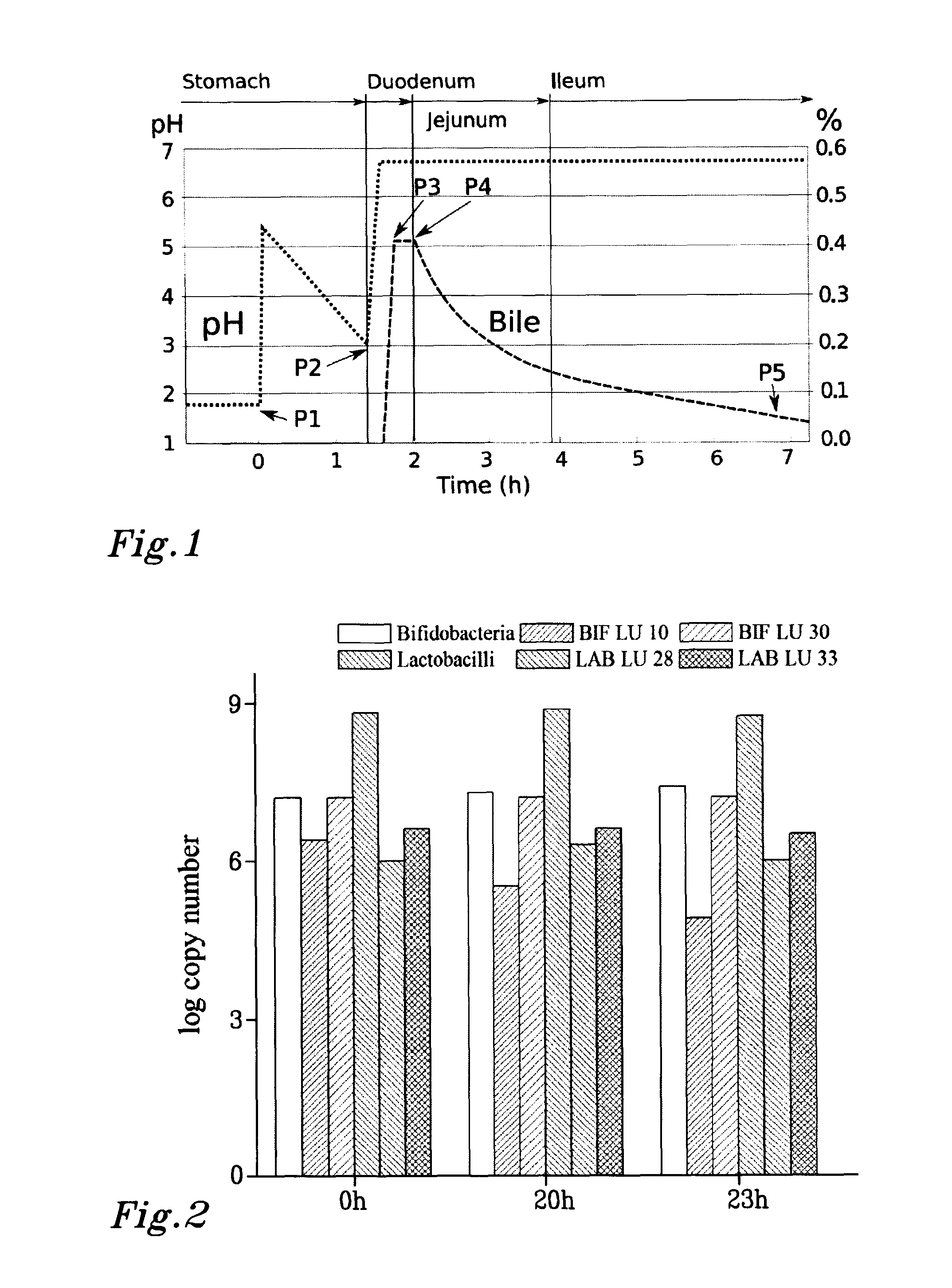
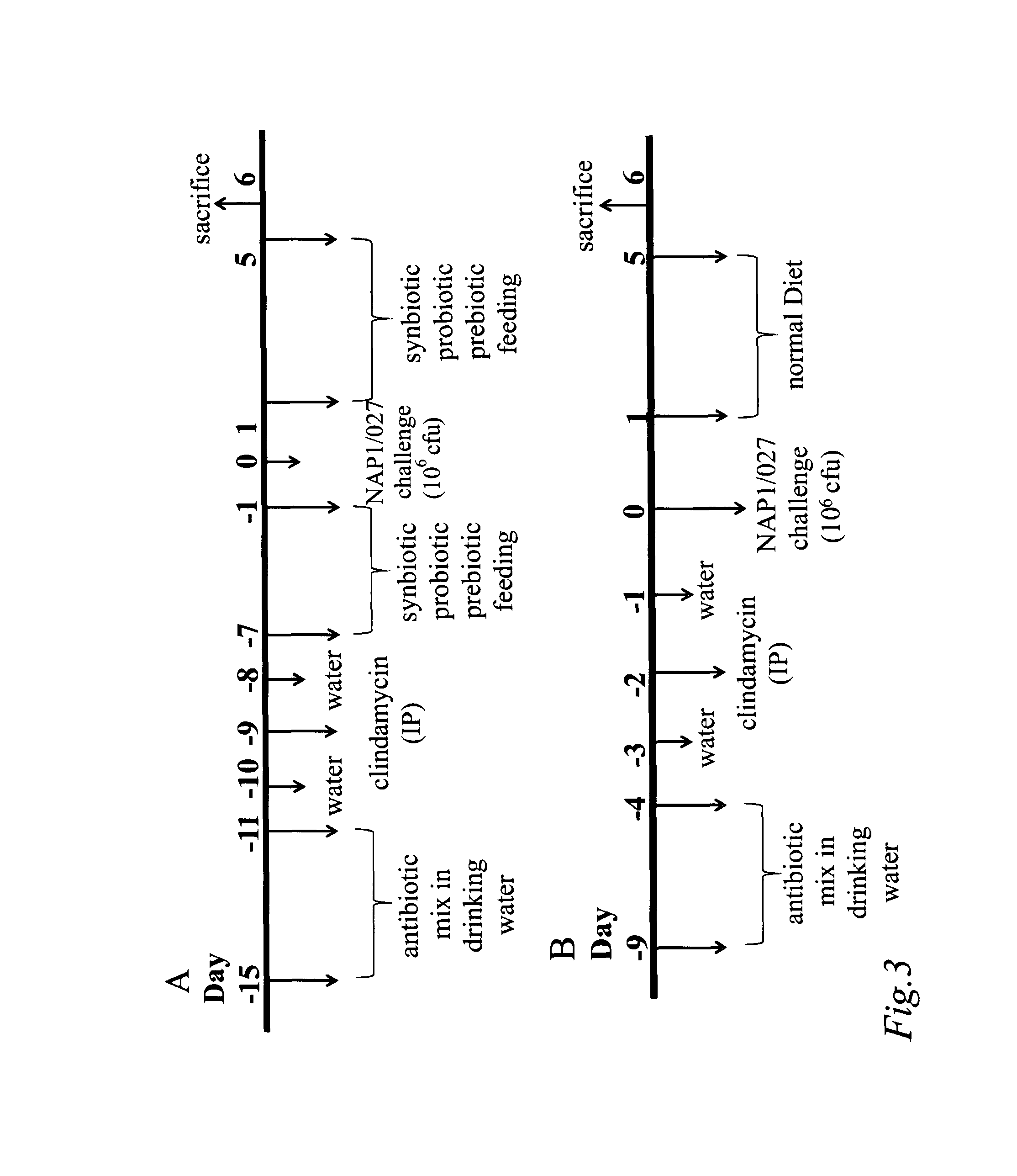
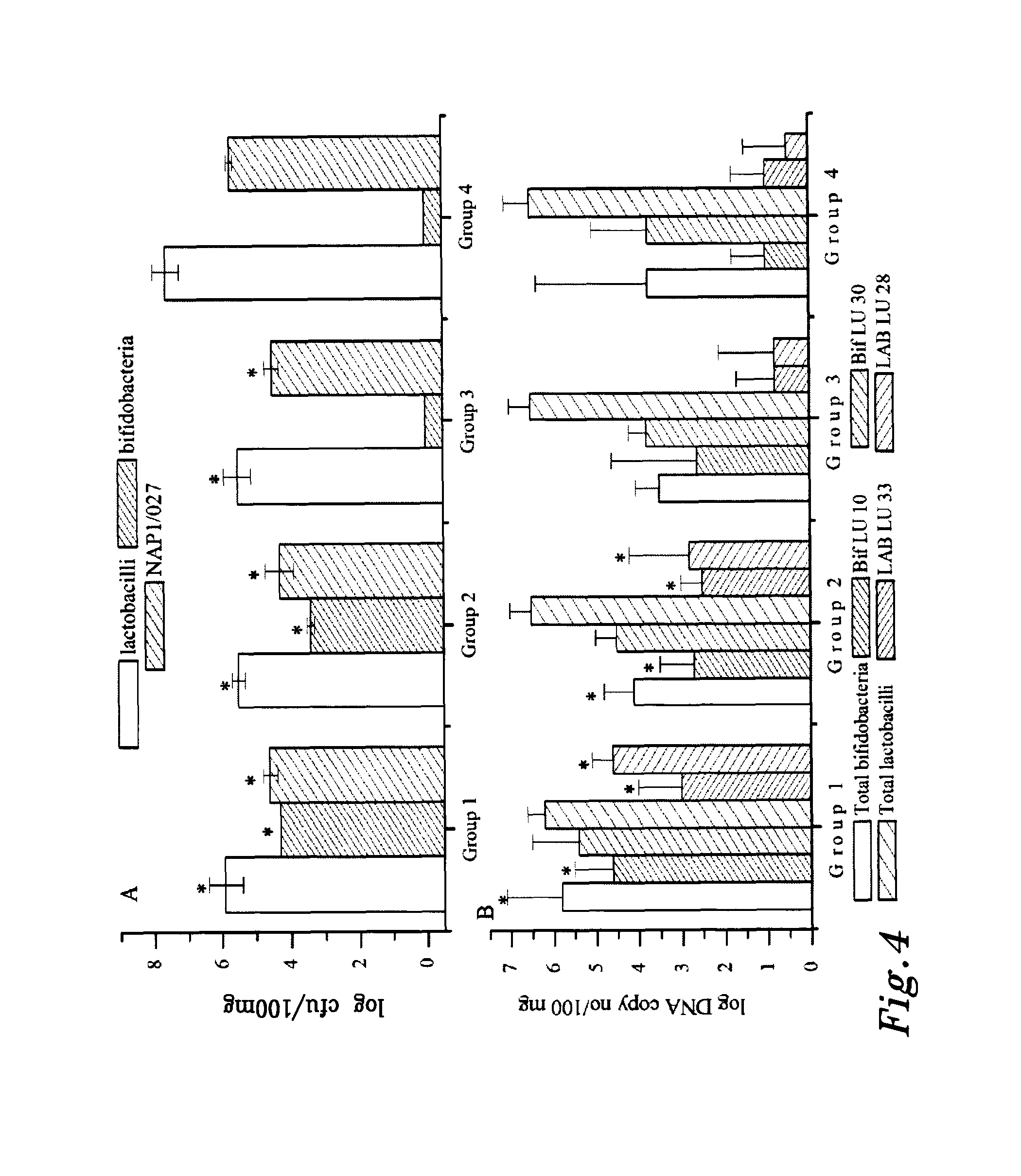
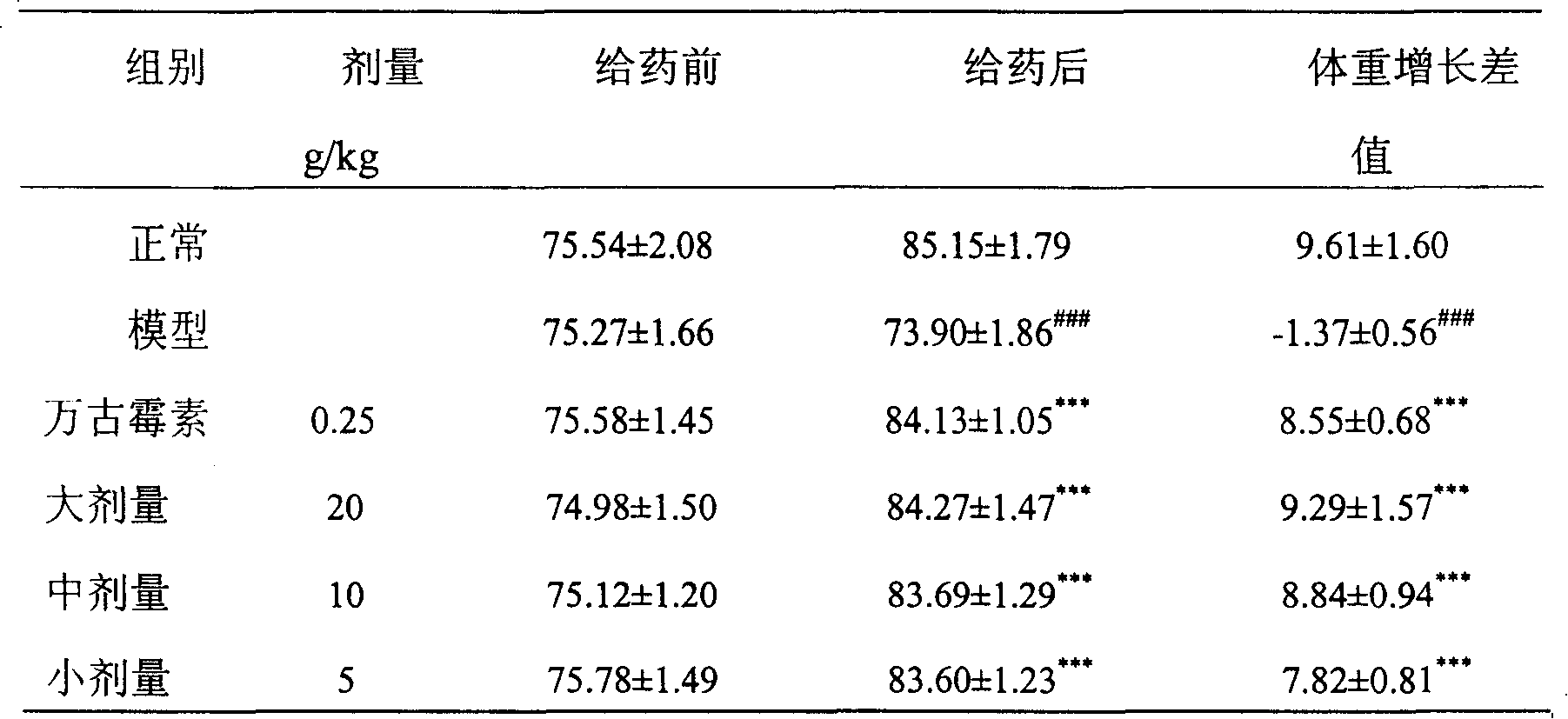
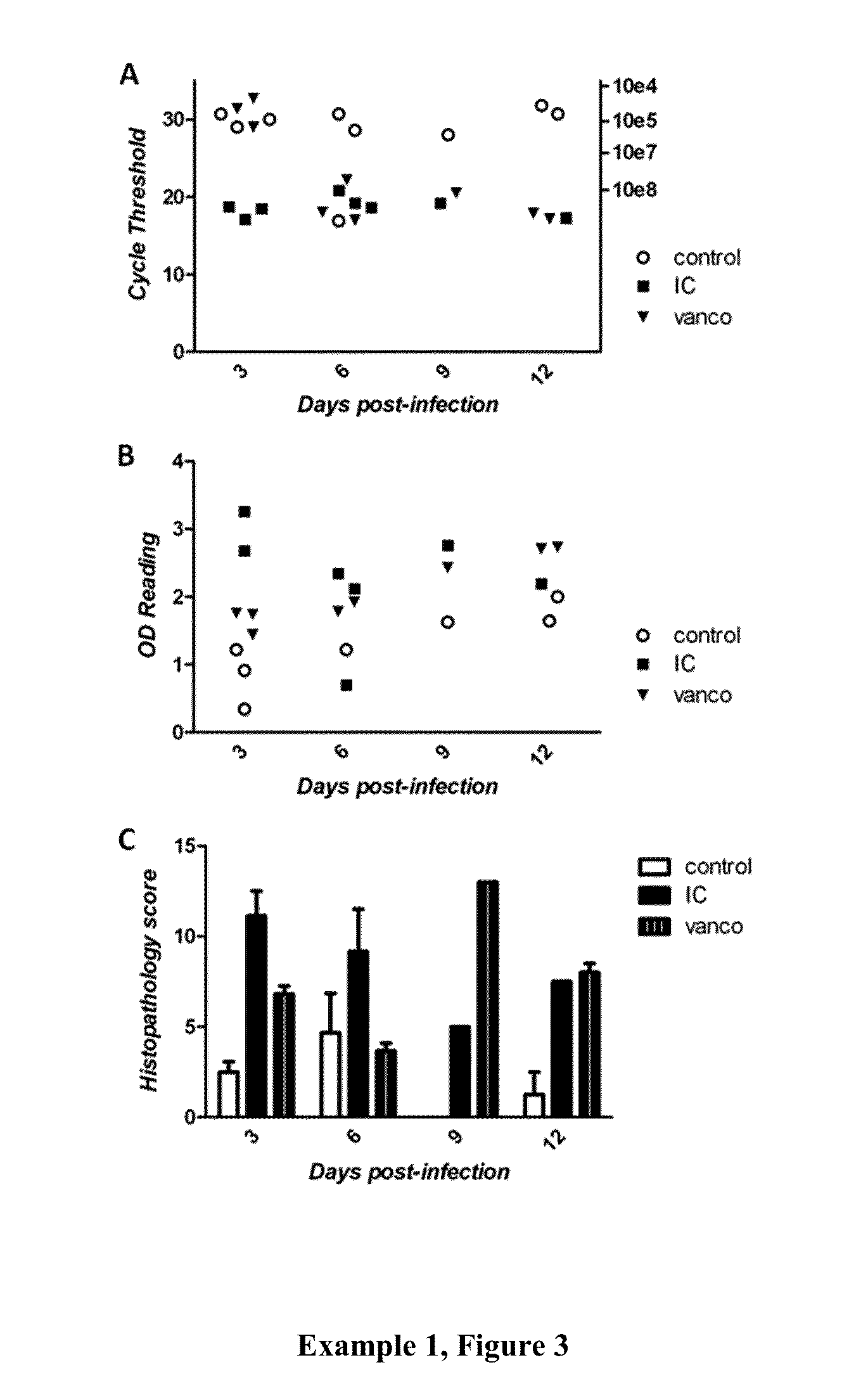
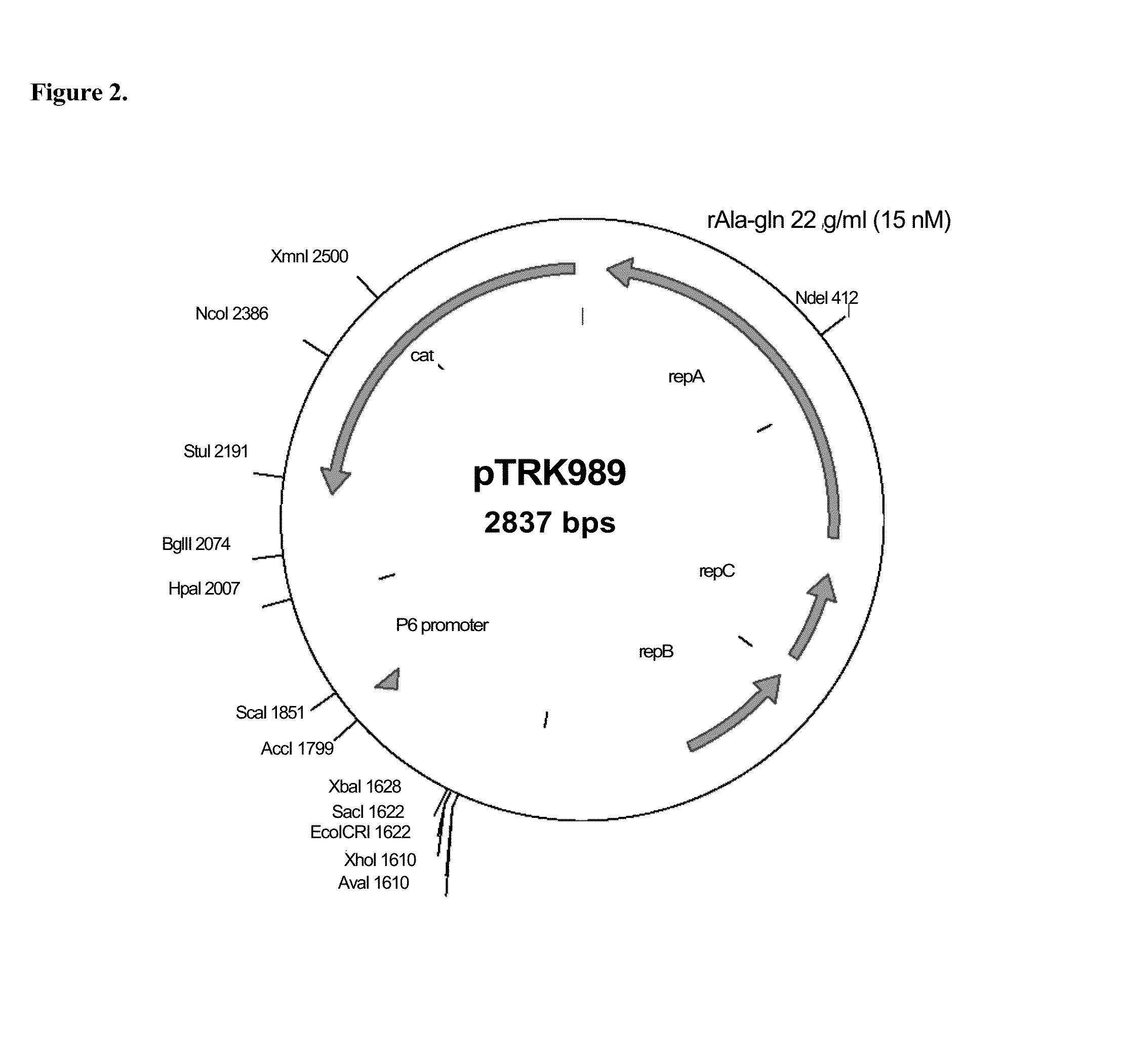
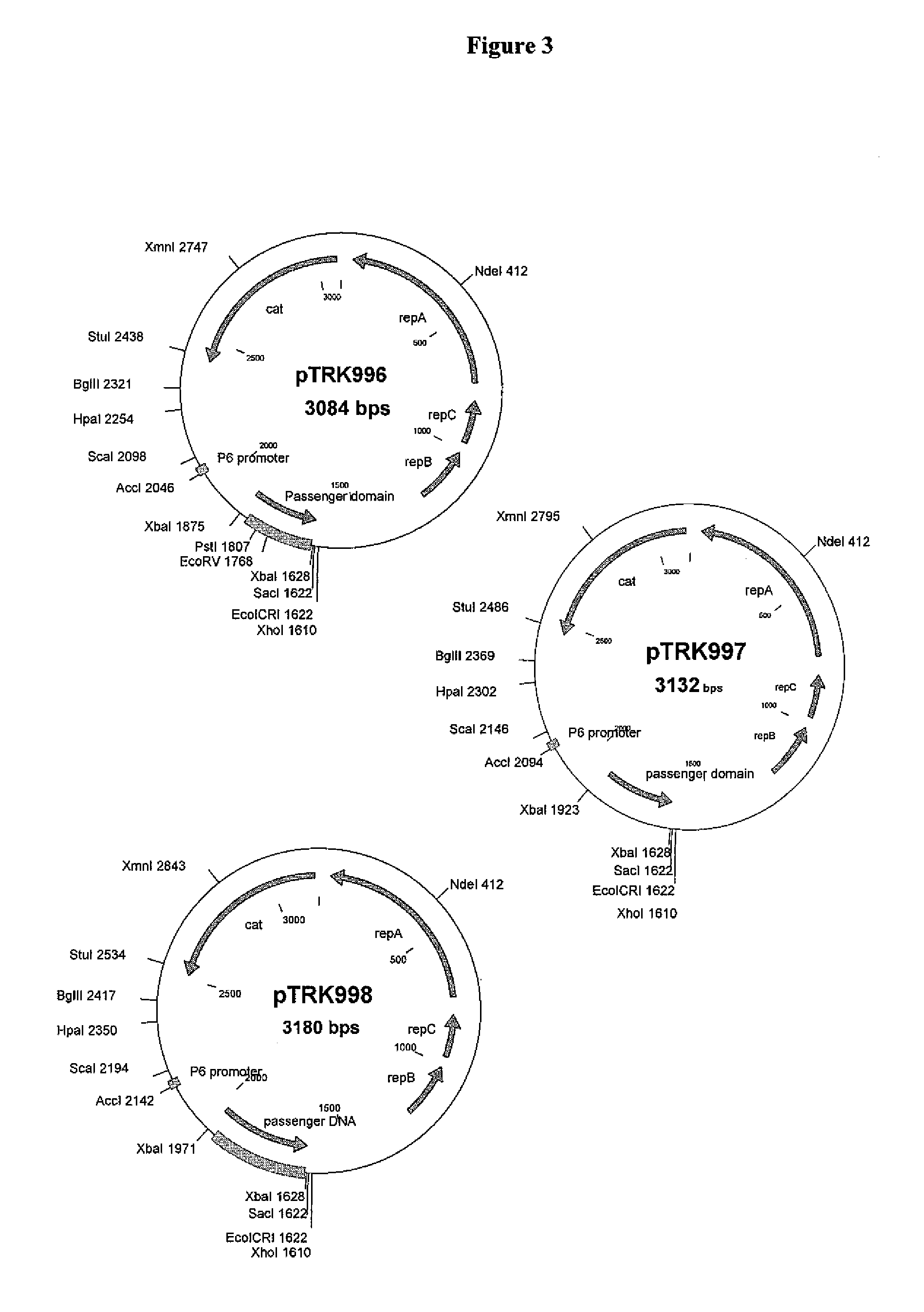
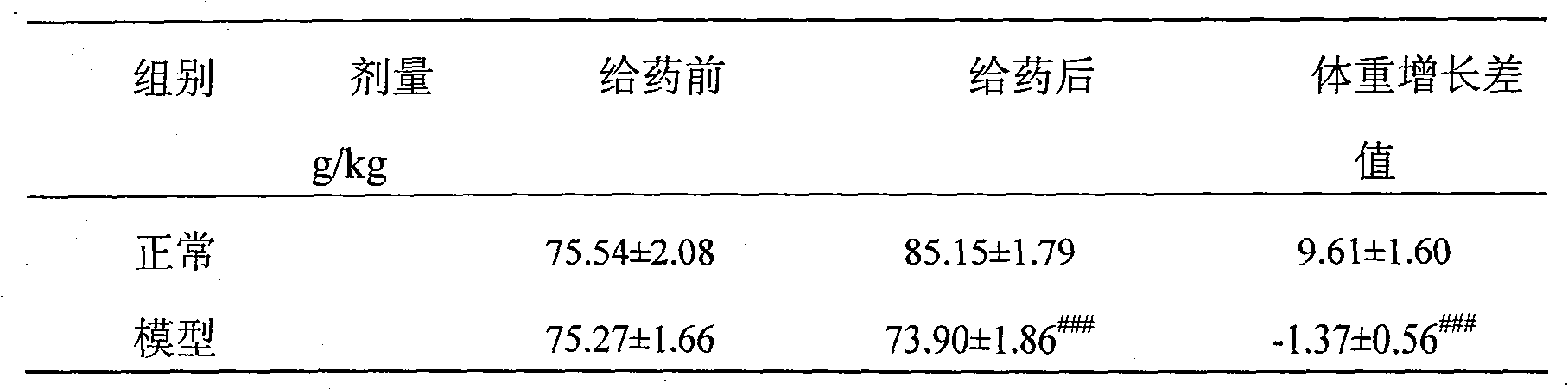
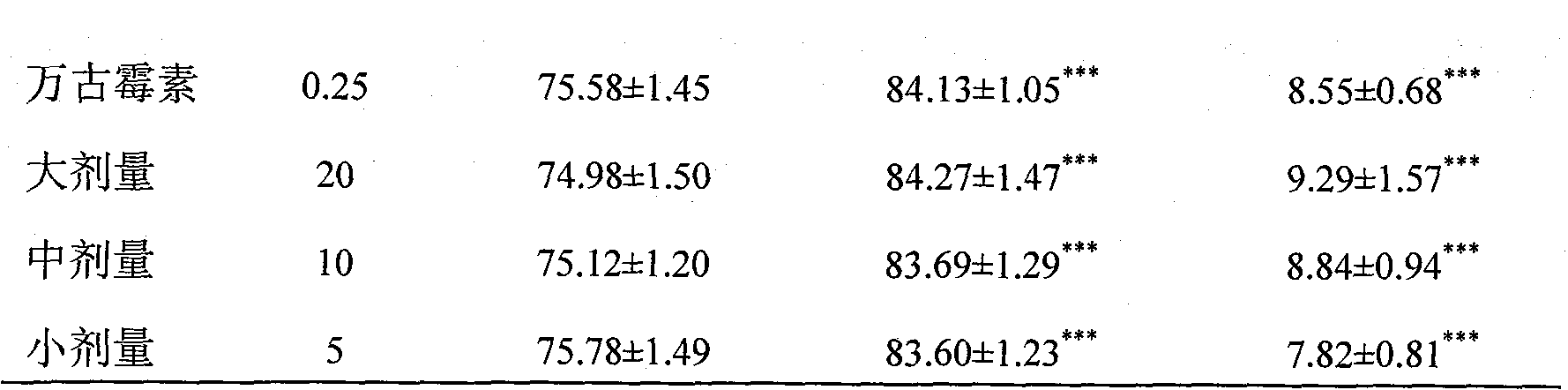
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
32 results about "Antibiotic-associated diarrhoea" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The antibiotics most likely to cause diarrhea. Nearly all antibiotics can cause antibiotic-associated diarrhea. Antibiotics most commonly involved include: Cephalosporins, such as cefixime (Suprax) and cefpodoxime. Penicillins, such as amoxicillin (Amoxil, Larotid, others) and ampicillin.
Bacteroides fragilis and applications thereof
ActiveCN106399141AEffective for diarrheaGood probiotic propertiesBacteriaBacteria material medical ingredientsAntibiotic-associated diarrhoeaFood additive
The invention relates to Bacteroides fragilis and applications thereof, particularly to Bacteroides fragilis ZY-312 having the preservation number of CGMCC No.10685, and applications of the Bacteroides fragilis ZY-312 in preparation of medicines, pharmaceutical compositions, foods, health products and food additives for prevention and / or treatment of antibiotic-associated diarrhea, wherein the Bacteroides fragilis ZY-312 is preserved in the China general microbiological culture collection center on April 2, 2015, has the preservation number of CGMCC No.10685, does not contain enterotoxin gene bft, has characteristics of significantly-improved cholate resistance and significantly-improved gastric acid resistance compared to the existing Bacteroides fragilis, and can effectively prevent and / or treat antibiotic-associated diarrhea.
Owner:GUANGZHOU ZHIYI PHARMA INC
Targeted gastrointestinal tract delivery of probiotic organisms and/or therapeutic agents
ActiveUS20160022592A1Improve imbalanceAntibacterial agentsBiocideAntibiotic-associated diarrhoeaClostridium difficile infections
The present invention relates to the development of a targeted delivery system for the oral delivery of probiotics or therapeutic agent for various indications, including and not limited to active and prophylaxis treatment of Clostridium difficile infection, antibiotic associated diarrhea, irritable bowel syndrome, Crohn's disease, intestinal flora replacement, supplemental flora treatments for patients taking antibiotics, and for restoration of balance and signaling between the intestinal microbiome and the intestinal cells in patients under treatment of metabolic syndrome manifestations, specifically diabetes, insulin resistance, obesity, hyperlipidemia and hypertension.
Owner:THERABIOME
Synbiotic compositions for restoration and reconstitution of gut microbiota
ActiveUS20130336931A1Promote growthAntibacterial agentsBiocideAntibiotic-associated diarrhoeaIntestinal microorganisms
The present invention relates to synbiotic compositions comprising probiotic bacterial strains and prebiotic substances that, when combined exhibit synergistic behavior. The synergetic compositions will stimulate the indigenous microflora to restore and reconstitute in vivo gut like conditions after antibiotic associated diarrhea (AAD), and / or other gut infections caused by gastrointestinal pathogens, and relapses thereof, as well as the prevention of said disorders.
Owner:SYNBIOTICS CORP
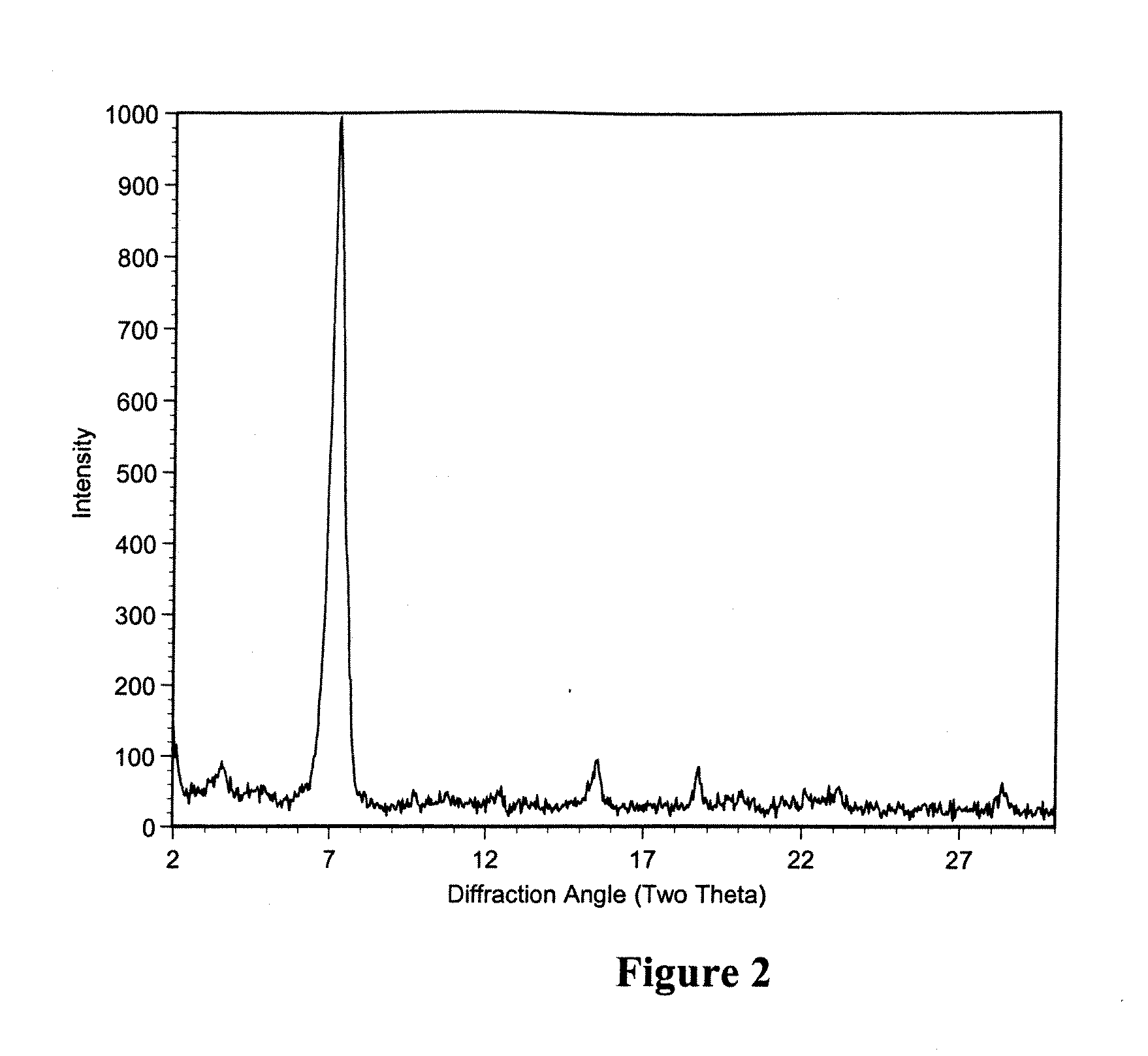
Polymorphic crystalline forms of tiacumicin B
ActiveUS7378508B2Antibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsAntibiotic-associated diarrhoeaDisease
The invention relates to novel forms of compounds displaying broad spectrum antibiotic activity, especially crystalline polymorphic forms and amorphous forms of such compounds, compositions comprising such crystalline polymorphic forms and amorphous forms of such compounds, processes for manufacture and use thereof. The compounds and compositions of the invention are useful in the pharmaceutical industry, for example, in the treatment or prevention of diseases or disorders associated with the use of antibiotics, chemotherapies, or antiviral therapies, including, but not limited to, colitis, for example, pseudo-membranous colitis; antibiotic associated diarrhea; and infections due to Clostridium difficile (“C. difficile”), Clostridium perfringens (“C. perfringens”), Staphylococcus species, for example, methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus, or Enterococcus including Vancomycin-resistant enterococci.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME LLC
Use of bacillus amyloliquefaciens PB6 for the prophylaxis or treatment of gastrointestinal and immuno-related diseases
InactiveUS20080057047A1BiocideBacteriaAntibiotic-associated diarrhoeaClostridium difficile (bacteria)
Bacteria of the sp. Bacillus that produce a lipopeptide are found to be effective in the treatment and prophylaxis of gastro-intestinal disease when administered as a probiotic. In particular, a strain of Bacillus bacteria identified as PB6 is useful for the treatment of Antibiotic Associated Diarrhea (AAD) or the more serious condition Clostridium difficile associated diarrhea (CDAD) when administered as a probiotic. Additionally, these bacteria have been found efficient for the treatment of immunorelated diseases such as Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD).
Owner:KEMIN IND INC
Macrolide polymorphs, compositions comprising such polymorphs, and methods of use and manufacture thereof
The invention relates to novel forms of compounds displaying broad spectrum antibiotic activity, especially crystalline polymorphic forms and amorphous forms of such compounds, compositions comprising such crystalline polymorphic forms and amorphous forms of such compounds, processes for manufacture and use thereof. The compounds and compositions of the invention are useful in the pharmaceutical industry, for example, in the treatment or prevention of diseases or disorders associated with the use of antibiotics, chemotherapies, or antiviral therapies, including, but not limited to, colitis, for example, pseudo-membranous colitis; antibiotic associated diarrhea; and infections due to Clostridium difficile (“C. difficile”), Clostridium perfringens (“C. perfringens”), Staphylococcus species, for example, methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus, or Enterococcus including Vancomycin-resistant enterococci.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME LLC
Antibiotic Formulations Providing Reduced Gastrointestinal Side Effects and Clostridium difficile Infection Relapse, and Related Methods
InactiveUS20110240512A1Antibacterial agentsSmall article dispensingClostridial infectionAntibiotic-associated diarrhoea
The invention includes a formulation comprising: (i) a therapeutically effective amount of at least one antibiotic; and (ii) a therapeutically effective amount of at least one probiotic material. The formulation is prepared in a dosage form for delivery to the gastrointestinal tract. The invention further includes a method of preventing or minimizing the proliferation of Clostridium difficile in the gastrointestinal tract of a mammal undergoing an antibiotic therapy comprising by administration of the formulation of the invention for the duration of the antibiotic therapy; methods of preventing or minimizing the occurrence of antibiotic-associated diarrhea in a mammal undergoing an antibiotic therapy that includes administering the formulation; and methods of preventing or minimizing the occurrence of antibiotic-associated colitis or pseudomembranous colitis in a patient undergoing an antibiotic therapy that includes administering the formulation.Also included are methods of reducing or preventing a failure of treatment for an antibiotic-treatable infection in a patient comprising orally administering the formulation.Described by the invention are formulations for the treatment of a C. difficile infection comprising: (i) a therapeutically effective amount of at least one antibiotic; and (ii) a therapeutically effective amount of at least one probiotic material. The antibiotic includes a non-systemic gram negative antibiotic (such as, for example, fodaximicin) and formulation is prepared in a dosage form for delivery to the gastrointestinal tract.Also included are methods of treatment of a C. difficile infection in mammal that include administering to the digestive tract of the mammal the above described formulation. Such methods provide that the likelihood that the mammal shall experience a reoccurrence of the C. difficile infection is 70% or less.
Owner:TECOPPA BIOPHARMA
Targeted gastrointestinal tract delivery of probiotic organisms and/or therapeutic agents
ActiveUS9907755B2Antibacterial agentsMetabolism disorderAntibiotic-associated diarrhoeaClostridium difficile infections
The present invention relates to the development of a targeted delivery system for the oral delivery of probiotics or therapeutic agent for various indications, including and not limited to active and prophylaxis treatment of Clostridium difficile infection, antibiotic associated diarrhea, irritable bowel syndrome, Crohn's disease, intestinal flora replacement, supplemental flora treatments for patients taking antibiotics, and for restoration of balance and signaling between the intestinal microbiome and the intestinal cells in patients under treatment of metabolic syndrome manifestations, specifically diabetes, insulin resistance, obesity, hyperlipidemia and hypertension.
Owner:THERABIOME
Toxin binding compositions
InactiveUS20060078534A1Powder deliveryOrganic active ingredientsAntibiotic-associated diarrhoeaClostridium difficile (bacteria)
Methods and compositions for the treatment of toxin-mediated diseases are provided herein. One aspect of the invention is oligosaccharide-based therapeutics that interact with toxins and methods of uses thereof. In one embodiment the oligosaccharide-based therapeutics of the invention comprise polymeric particles with attached oligosaccharide binding moieties. The compositions of the invention can be used in the treatment of toxin-mediated diseases such as antibiotic-associated diarrhea and pseudomembranous colitis, including Clostridium difficile associated diarrhea.
Owner:ILYPSA
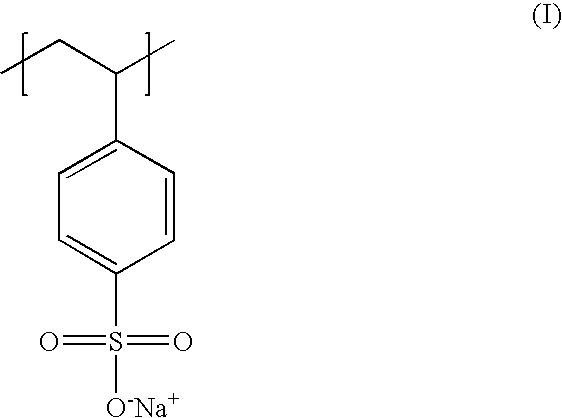
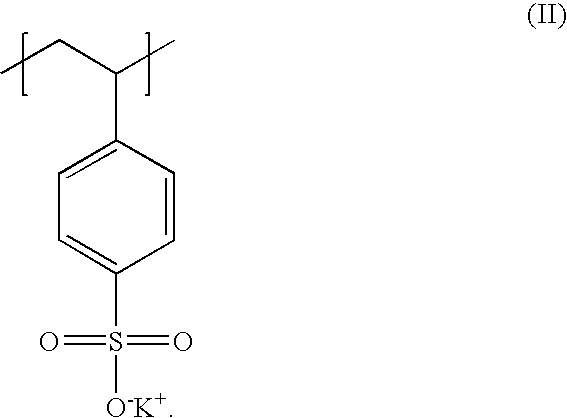
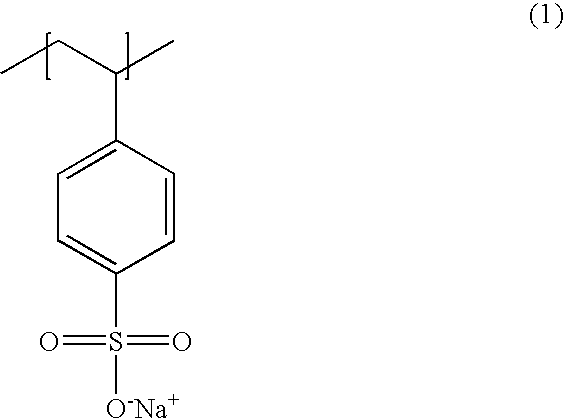
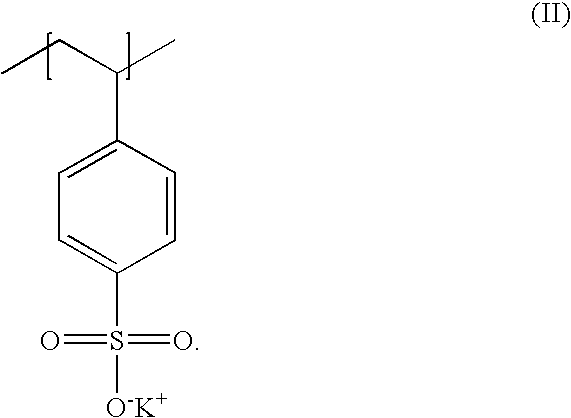
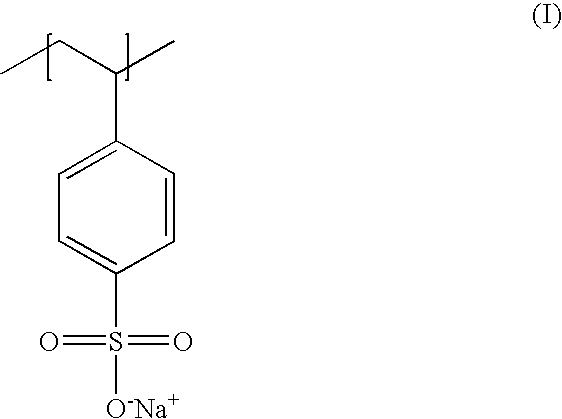
Poly(potassium and sodium styrene sulfonate), its manufacture and its uses
InactiveUS20050214246A1Easy to prepareInhibit and prevent relapseAntibacterial agentsDigestive systemAntibiotic-associated diarrhoeaSulfonate
Antibiotic-associated diarrhea, such as that caused by Clostridium difficile, represents a serious medical complication that can result from administering a broad-spectrum antibiotic to a subject. Such diarrhea leads to significant potassium loss from the subject. The present invention discloses a polymeric therapeutic agent that treats antibiotic-associated diarrhea and is physiologically potassium neutral. This polymer contains polystyrene sodium sulfonate and polystyrene potassium sulfonate repeat units.
Owner:GENZYME CORP
Preparation method and application of dendrobium officinale yoghurt
InactiveCN106070609AShort fermentation cycleEasy to operateMilk preparationFood ingredient functionsAntibiotic-associated diarrhoeaSaccharum
The invention discloses a preparation method and application of dendrobium officinale yoghurt. The preparation method comprises uniformly mixing whole milk powder, water and cane sugar, or fresh milk and cane sugar, and performing homogenization processing; then adding dendrobium officinale fine powder, performing sterilization processing, then adding mixed bacteria composed of lactobacillus bulgaricus and streptococcus thermophiles, stirring uniformly, adding into a container, performing sealing, fermenting, cooling and post-ripening, so as to obtain the dendrobium officinale yoghurt which possesses high probiotics living bacterium quantity and contains dendrobium officinale active composition. The preparation method possesses advantages of short fermentation period, simple operation and low cost. The prepared dendrobium officinale yoghurt is applicable to prepare food possessing functions of treating spleen deficiency and constipation and treating antibiotic-related diarrhea.
Owner:谭恺
Macrocyclic polymorphs, compositions comprising such polymorphs and methods of use and manufacture thereof
The invention relates to novel forms of compounds displaying broad spectrum antibiotic activity, especially crystalline polymorphic forms and amorphous forms of such compounds, compositions comprising such crystalline polymorphic forms and amorphous forms of such compounds, processes for manufacture and use thereof. The compounds and compositions of the invention are useful in the pharmaceutical industry, for example, in the treatment or prevention of diseases or disorders associated with the use of antibiotics, chemotherapies, or antiviral therapies, including, but not limited to, colitis, for example, pseudo-membranous colitis; antibiotic associated diarrhea; and infections due to Clostridium difficile (“C. difficile”), Clostridium perfringens (“C. perfringens”), Staphylococcus species, for example, methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus, or Enterococcus including Vancomycin-resistant enterococci.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME LLC
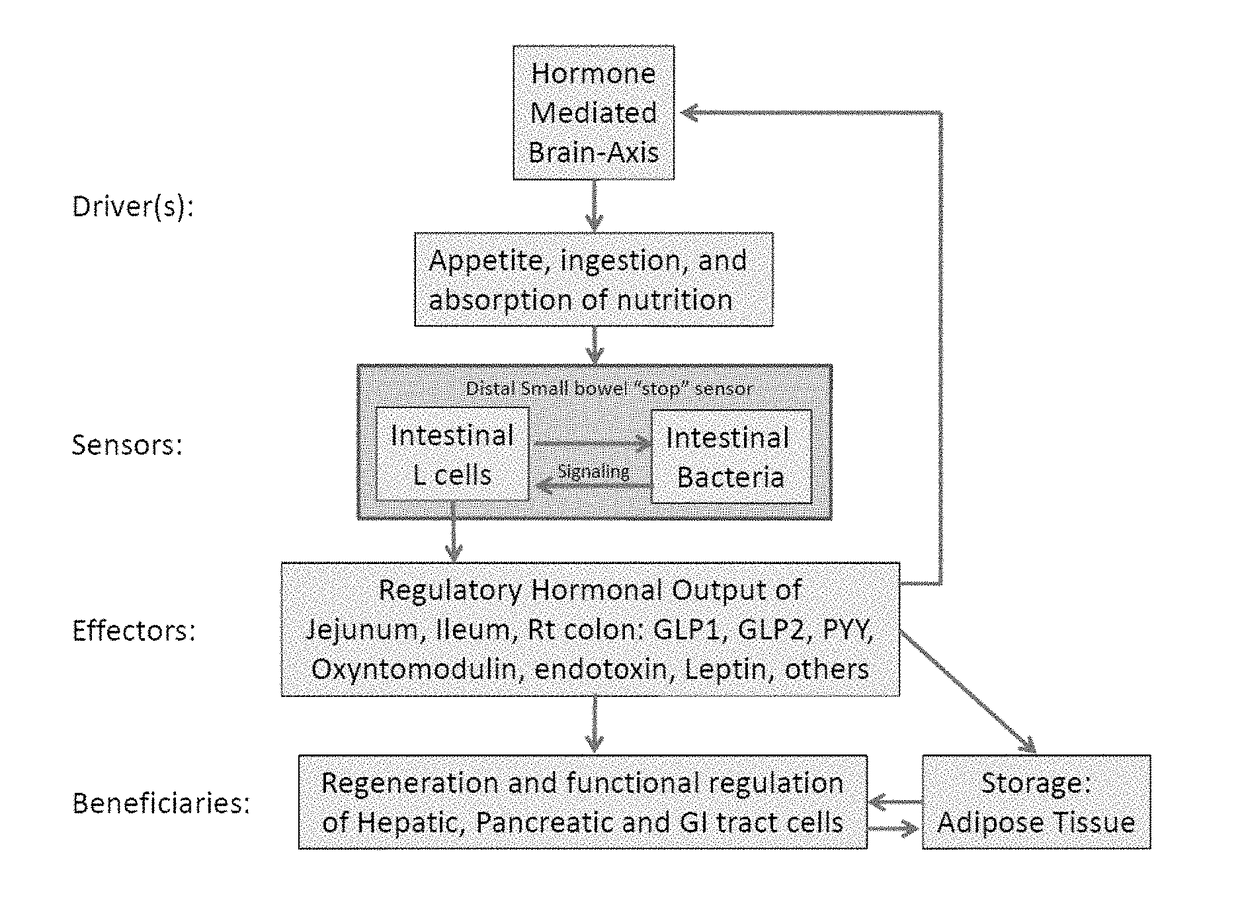
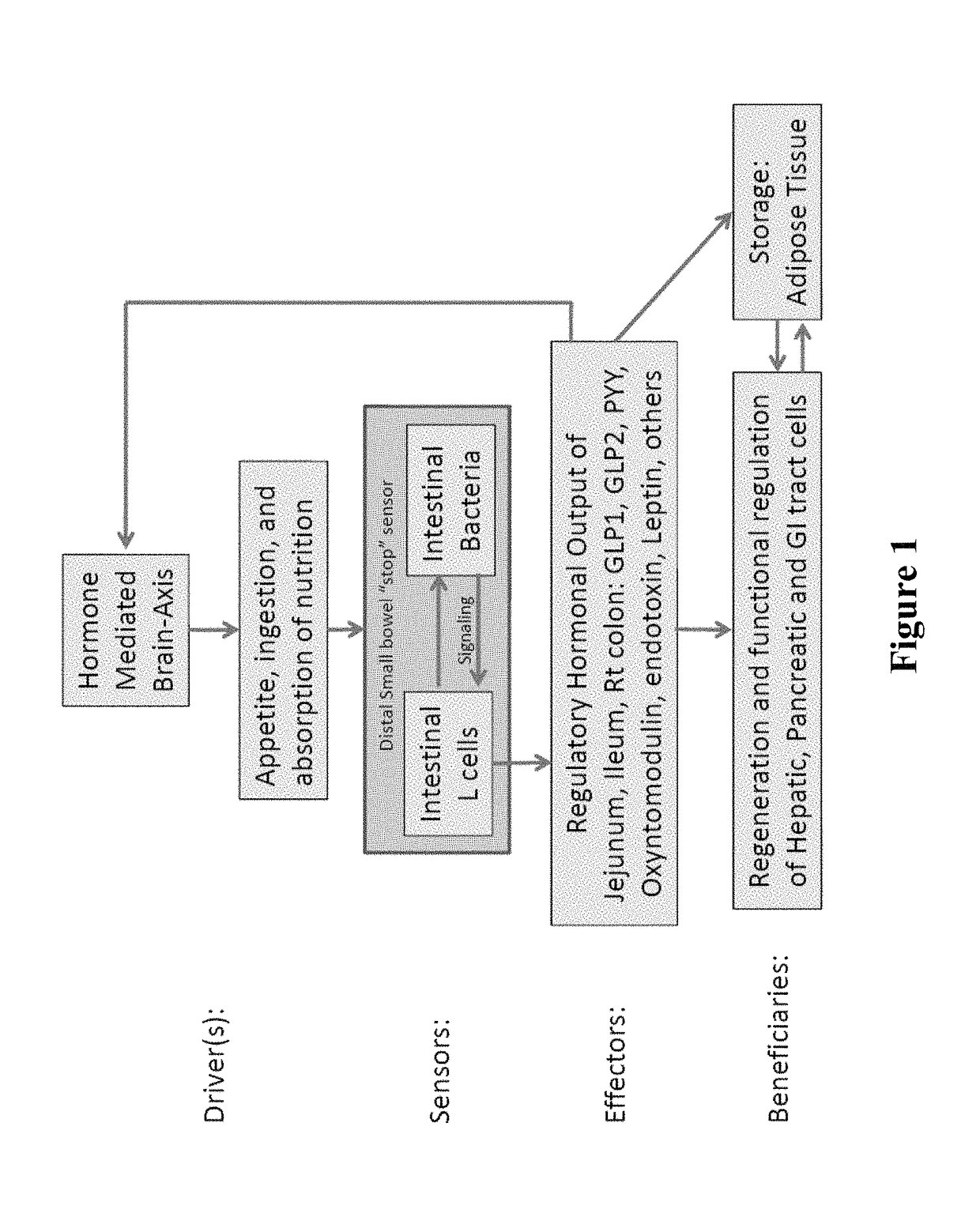
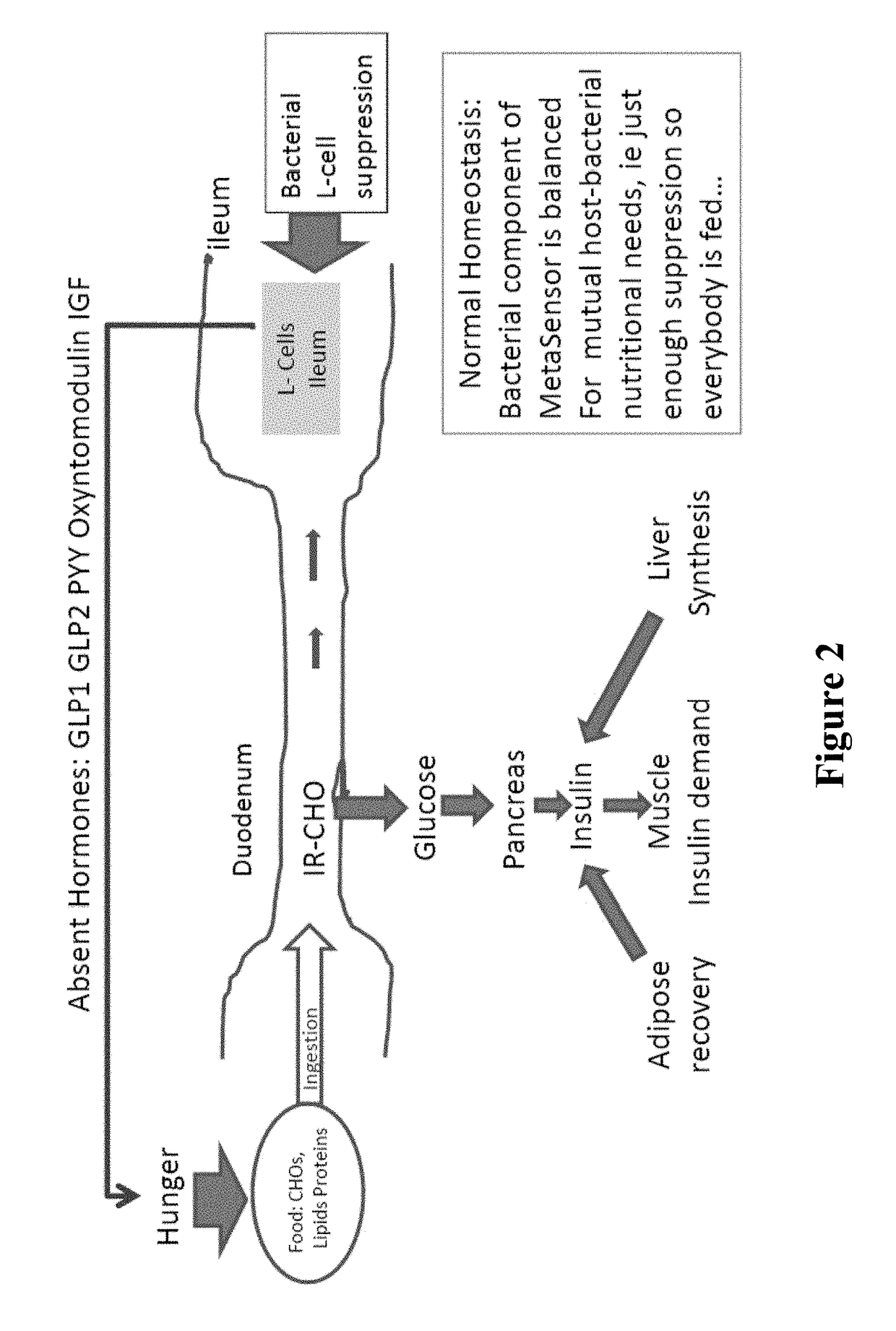
Targeted synbiotic therapy for dysbiosis-related intestinal and extra-intestinal disorders
InactiveUS20180110800A1Increase productionOrganic active ingredientsDigestive systemAntibiotic-associated diarrhoeaSynbiotics
Various types of synbiotic therapies are provided for the treatment of a variety of gastrointestinal and other disorders. The combination of prebiotics to probiotics is defined as a synbiotic therapy. The principal GI disorders associated with dysbiosis that can be treated from such a therapeutic intervention include but are not limited to: inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) (Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis), irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), antibiotic-associated diarrheas such as recurrent Clostridium difficile infection, and possibly variants of Celiac disease. Other disorders that may also be ameliorated by the proposed synbiotic therapy include metabolic syndromes and central nervous system disorders. The disclosed methods and compositions were developed to improve upon currently available probiotics through consideration of the human intestinal microbiota, and its relationship to various intestinal metabolic and neuropsychiatric disorders. In one embodiment, the disclosed synbiotic compositions include prebiotics and a targeted delivery system, which altogether promote the survival, growth, and attachment of probiotic microbiota.
Owner:LIFEBRIDGE HEALTH INC
Use of Bifidobacterium animalis A6 in the preparation of medicaments
InactiveCN109200064ACompounds screening/testingOrganic active ingredientsAntibiotic-associated diarrhoeaMedicine
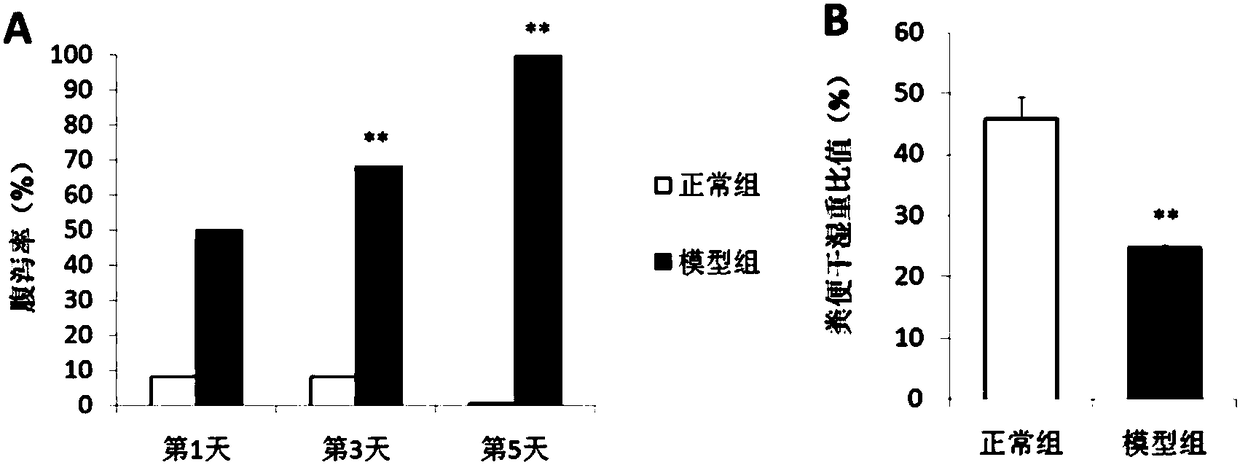
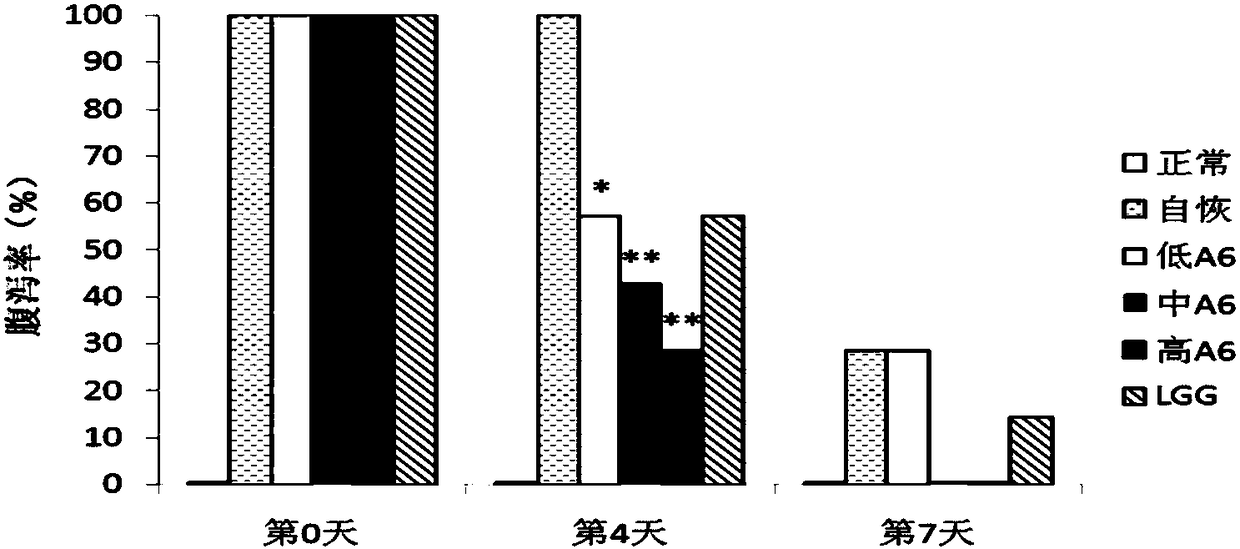
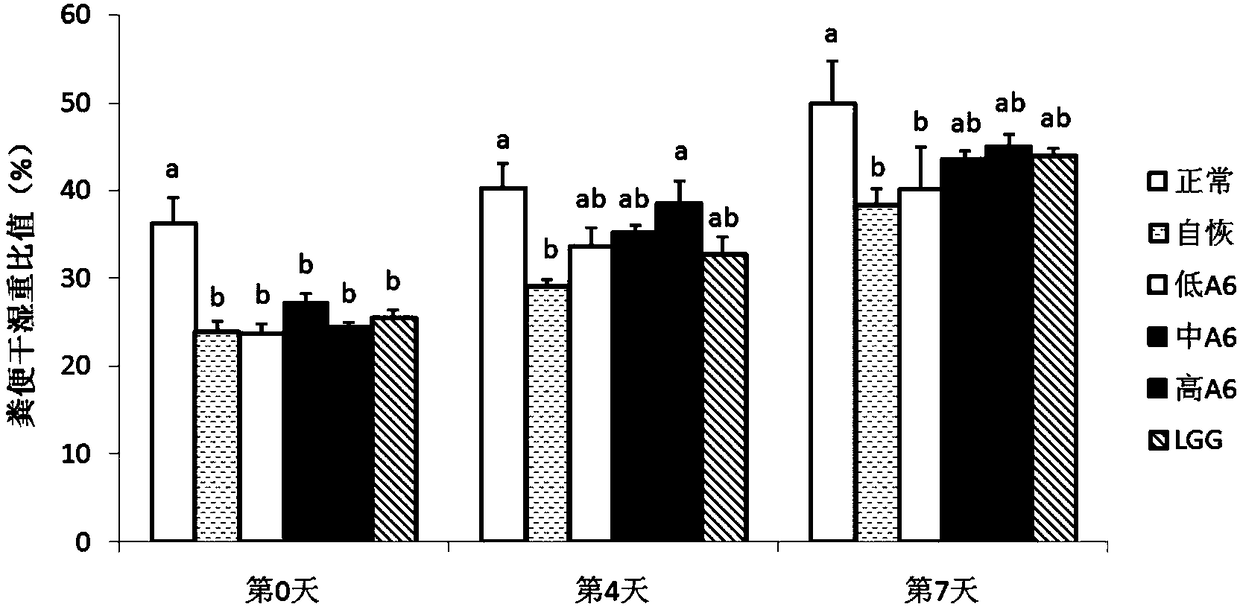
The present invention proposes the use of Bifidobacterium animalis A6 in the preparation of medicaments for the treatment or prevention of antibiotic-associated diarrhea. The inventors found through experiments that Bifidobacterium animalis A6 can effectively alleviate antibiotic-associated diarrhea by improving intestinal function of mice.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Preparation method of mice intestinal flora alteration ERIC-PCR (Enterobacterial Repetitive Intergenic Consensus sequence-based Polymerase Chain Reaction) fingerprint spectrum
InactiveCN103773887AAccurate detectionEfficient detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementAgainst vector-borne diseasesLaboratory mouseAntibiotic-associated diarrhoea
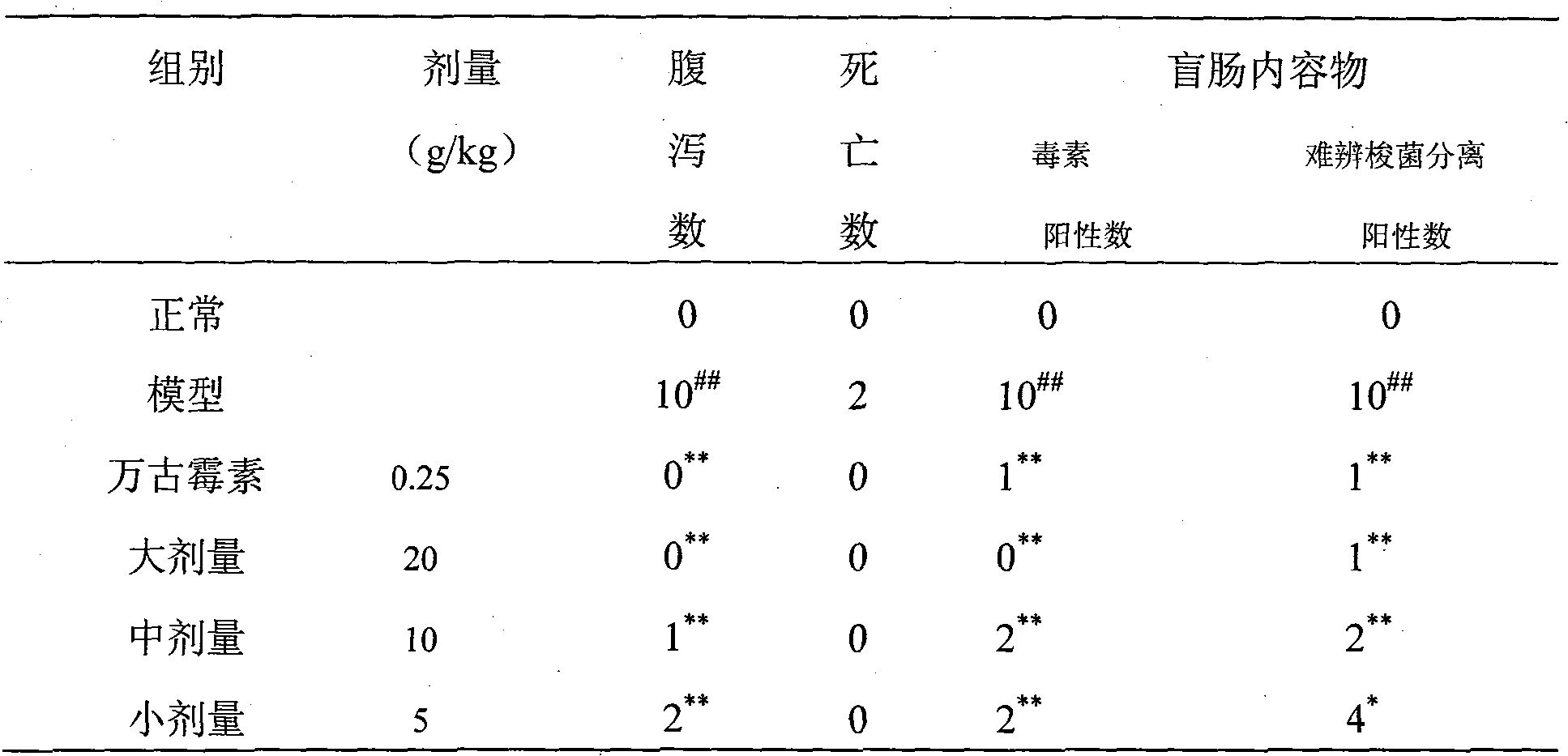
The invention provides a preparation method of a mice intestinal flora alteration ERIC-PCR (Enterobacterial Repetitive Intergenic Consensus sequence-based Polymerase Chain Reaction) fingerprint spectrum. The preparation method comprises the steps: moulding mice intestinal flora alteration caused by antibacterial-associated diarrhea, extracting a cecum content DNA, eliminating humic acid in the cecum content DNA, eliminating a PCR inhibitor in the cecum content DNA, performing ERIC-PCR amplification and native polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (Native-PAGE), and comparing with a conventional flora analysis result so as to establish the ERIC-PCR fingerprint spectrum of the mice intestinal flora alteration. According to the preparation method, with a pure-series mice as a research object, the defect caused when a conventional bacterium culturing method is applied to the microflora analysis is solved. The preparation method can be used for rapid detection of the laboratory mice intestinal flora alteration, prevents the defects of complicated operation, long time consumption, large workload and the like of conventional bacterium separation and culturing, and is capable of accurately, rapidly and effectively detecting the mice intestinal flora distribution condition.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV
Lactic Bacteria and Their Use in the Prevention of Diarrhea
InactiveUS20070248582A1Non invasiveAvoid it happening againAntibacterial agentsBiocideLactobacillusAntibiotic-associated diarrhoea
The present invention concerns a lactic composition useful for the prevention or treatment of diarrhea such as antibiotic associated diarrhea or “tourista”. The composition according to the invention contains at least a bacterial strain selected from the group consisting of Lactobacillus acidophilus, Lactobacillus acidophilus I-1492 Lactobacillus casei and a mixture of thereof.
Owner:BIO K PLUS INT
Application of stachyose in preparing medicine for preventing and curing diarrhea
InactiveCN101810631AOrganic active ingredientsDigestive systemAntibiotic-associated diarrhoeaStachyose
The invention discloses application of stachyose in preparing a medicine for preventing and curing diarrhea. Experiments prove that the stachyose has certain alleviating and curing effects for intestinal infection diarrhea, antibiotic-associated diarrhea, bacillary dysentery diarrhea, rotavirus infection diarrhea, non-specific diarrhea and the like.
Owner:CHINA NAT RES INST OF FOOD & FERMENTATION IND CO LTD
Synbiotic compositions for restoration and reconstitution of gut microbiota
ActiveUS8927252B2Promote growthAntibacterial agentsBiocideAntibiotic-associated diarrhoeaIntestinal microorganisms
The present invention relates to synbiotic compositions comprising probiotic bacterial strains and prebiotic substances that, when combined exhibit synergistic behavior. The synergetic compositions will stimulate the indigenous microflora to restore and reconstitute in vivo gut like conditions after antibiotic associated diarrhea (AAD), and / or other gut infections caused by gastrointestinal pathogens, and relapses thereof, as well as the prevention of said disorders.
Owner:SYNBIOTICS CORP
Medicine for treating antibacterial drugs associated enteritis and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN101190299AClearing damp heatFunctionalDigestive systemPill deliveryAntibiotic-associated diarrhoeaGut flora
The invention discloses a medicine for treating antibiotic-associated diarrhea. The effective components contained in the invention are prepared by rhizoma coptidis, radix scutellariae, radix codonopsitis, rhizoma atractylodis alba, Indian buead, liquoric root, rhizoma alismatis and costus root according to a certain proportion by weight. The effective components can be prepared into any common oral formulation. The invention has the functions of clearing heat and dampness, reinforcing the spleen, replenishing qi, alleviating the symptoms of diarrhea and bellyache and facilitating the recovery of alteration of intestinal flora, and can treat the antibiotic-associated diarrhea or intestinal flora alterative enteritis. The invention further discloses the preparation method of the medicine.
Owner:BEIJING ZHONGYAN TONGRENTANG CHINESE MEDICINE R & D
Compositions and methods for treating clostridium infection and preventing recurrence of infection
ActiveUS20150133366A1High IgG levelReduce productionBiocideSaccharide peptide ingredientsAntibiotic-associated diarrhoeaRegimen
C. difficile infection (CDI) is the most common cause of antibiotic-associated diarrhea. Unfortunately, antibiotic therapy remains as the standard treatment for this antibiotic-induced disease and relapses are common. Antibiotic treatment typically is given for 10 to 14 days for initial or second episode of CDI. For recurrent episodes, more prolonged courses are recommended. It is disclosed herein that lower dose or shorter course of the antimicrobial treatment is sufficient to treat the disease and prevent recurrent disease by enabling a good immunologic response to infection, and perhaps also by better preserving normal flora, thus protecting against relapses or reinfection.
Owner:UNIV OF VIRGINIA ALUMNI PATENTS FOUND
Poly(potassium and sodium styrene sulfonate) its manufacture and its uses
InactiveUS20070053865A1Easy to prepareInhibit and prevent relapseAntibacterial agentsIon-exchanger regenerationAntibiotic-associated diarrhoeaPotassium
Antibiotic-associated diarrhea, such as that caused by Clostridium difficile, represents a serious medical complication that can result from administering a broad-spectrum antibiotic to a subject. Such diarrhea leads to significant potassium loss from the subject. The present invention discloses a polymeric therapeutic agent that treats antibiotic-associated diarrhea and is physiologically potassium neutral. This polymer contains polystyrene sodium sulfonate and polystyrene potassium sulfonate repeat units.
Owner:GENZYME CORP
Poly(potassium and sodiumstyrene sulfonate) its manufacture and its uses
InactiveUS20070053864A1Easy to prepareInhibit and prevent relapseAntibacterial agentsBiocideAntibiotic-associated diarrhoeaSulfonate
Antibiotic-associated diarrhea, such as that caused by Clostridium difficile, represents a serious medical complication that can result from administering a broad-spectrum antibiotic to a subject. Such diarrhea leads to significant potassium loss from the subject. The present invention discloses a polymeric therapeutic agent that treats antibiotic-associated diarrhea and is physiologically potassium neutral. This polymer contains polystyrene sodium sulfonate and polystyrene potassium sulfonate repeat units.
Owner:GENZYME CORP
Synthetic composition for treating antibiotic associated complications
ActiveUS10864224B2Increase abundanceReduce abundanceAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsAntibiotic-associated diarrhoeaMicroorganism
The invention relates to a synthetic composition comprising human milk oligosaccharides for use in at least partially restoring the commensal gastrointestinal microbiota and preventing or mitigating antibiotic associated diarrhoea.
Owner:GLYCOM AS
Application of American ginseng in forest mountain to preparation of medicine for treating antibiotic-associated diarrhea
PendingCN113384609ARestorativeDigestive systemPlant ingredientsBiotechnologyAntibiotic-associated diarrhoea
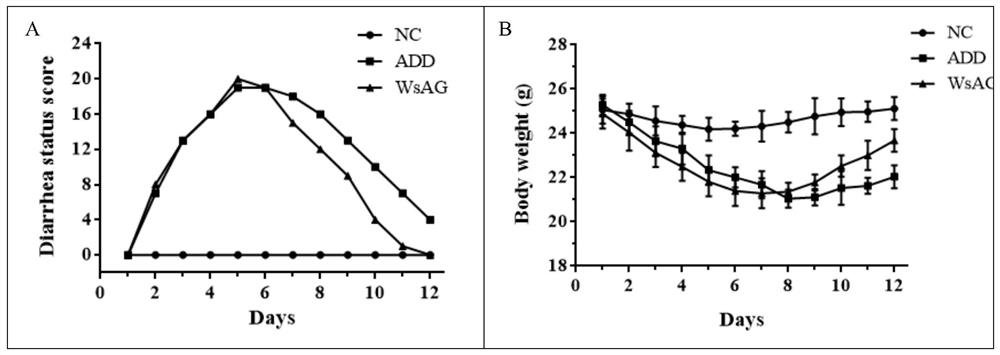
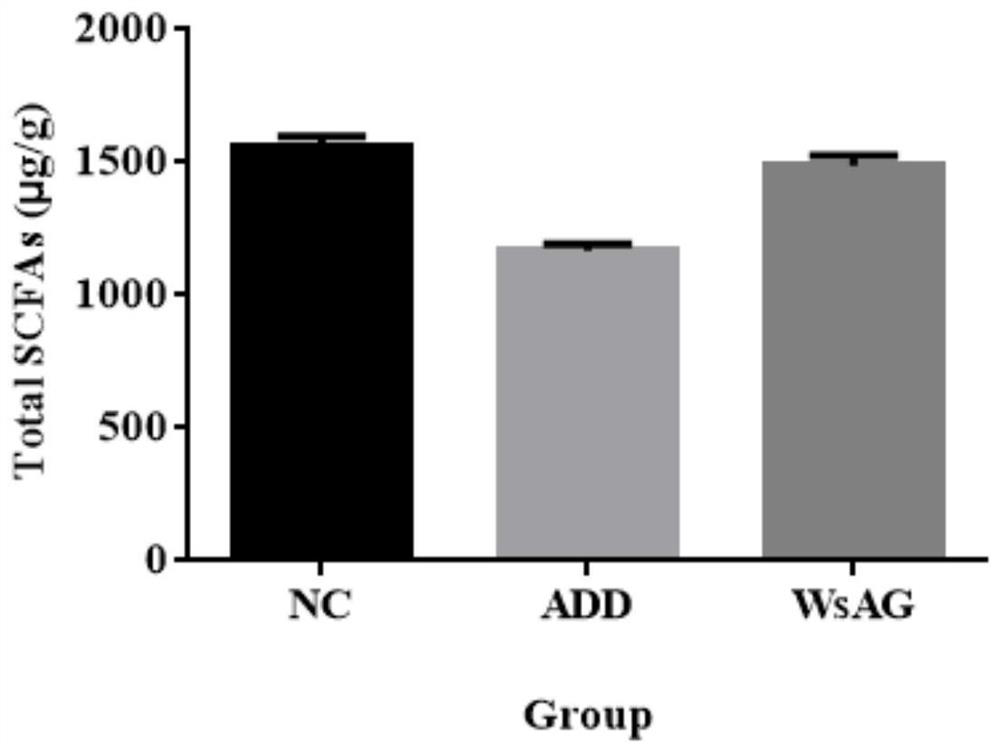
The invention relates to application of American ginseng in forest mountain in preparation of a medicine for treating antibiotic-associated diarrhea, and belongs to the field of biomedicine. Animal model experiments are carried out by adopting an ethanol extract of the American ginseng in the forest mountain. Experimental results prove that the ethanol extract of the American ginseng under the forest mountain has a relatively good protection effect on an antibiotic-related diarrhea experimental model caused by antibiotic drug combination, and has a reversal effect on pathological changes of colon and ileum of mice; expression of proinflammatory factors TNF-alpha, IL-1beta and IL-6 in serum of mice is inhibited, so that intestinal inflammation is relieved; the level of short-chain fatty acid in the intestinal tract of the mice can be recovered; the intestinal flora structure and diversity are improved; and pains of patients can be relieved, and life quality can be improved.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Compositions and methods for treating clostridium difficile infection
ActiveUS20190290732A1Reduce mortalityReduce severityAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsClostridial infectionAntibiotic-associated diarrhoea
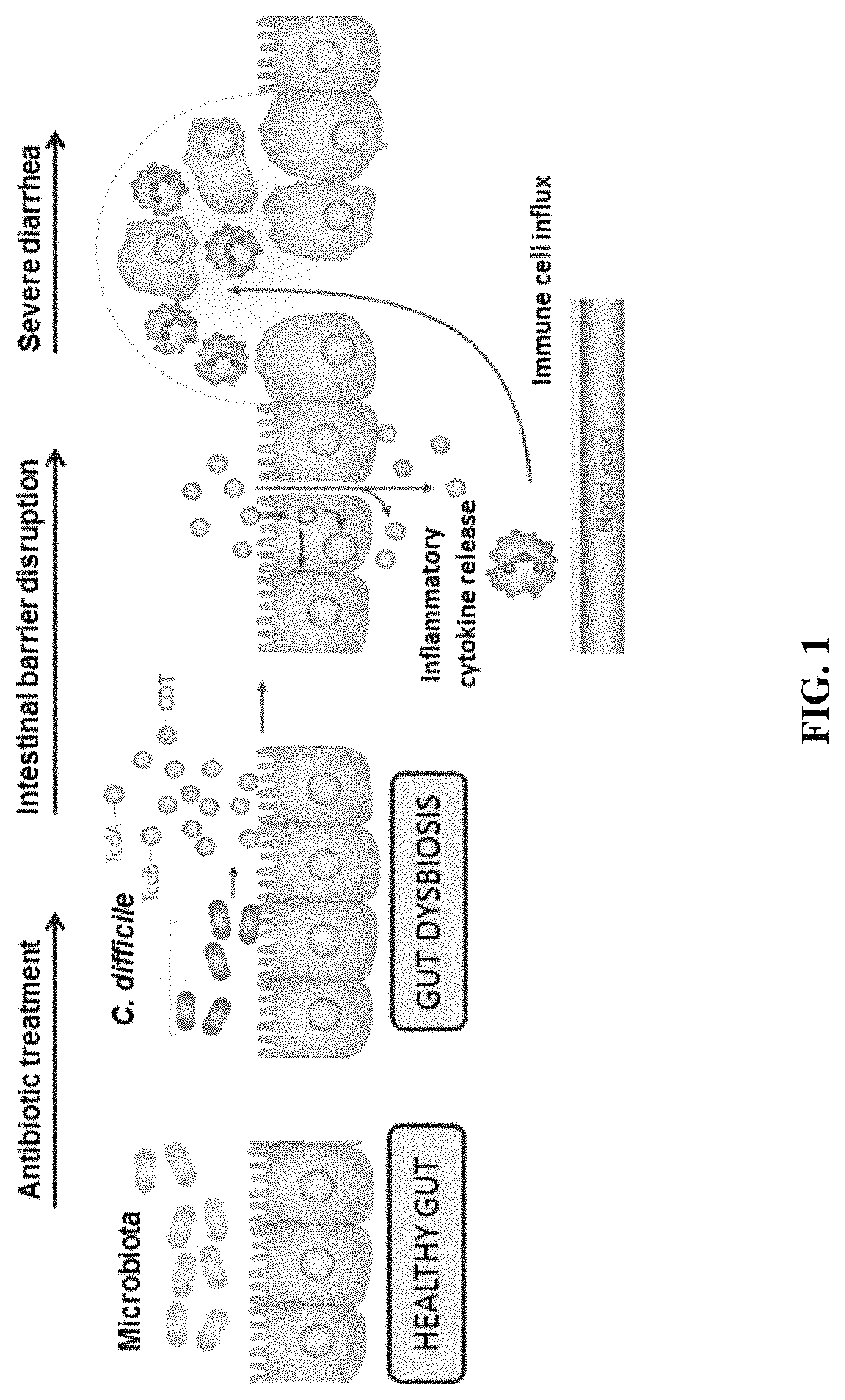
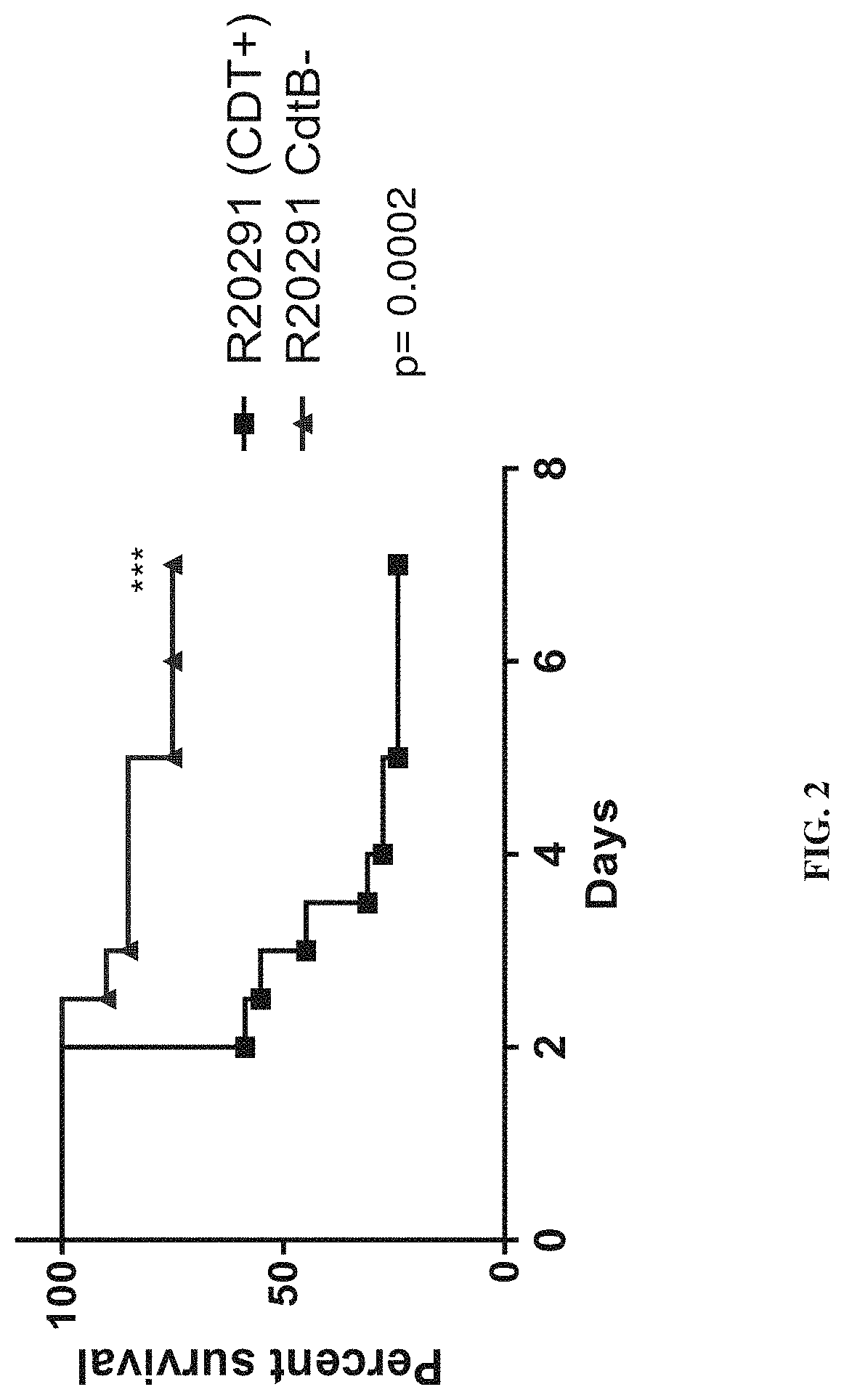
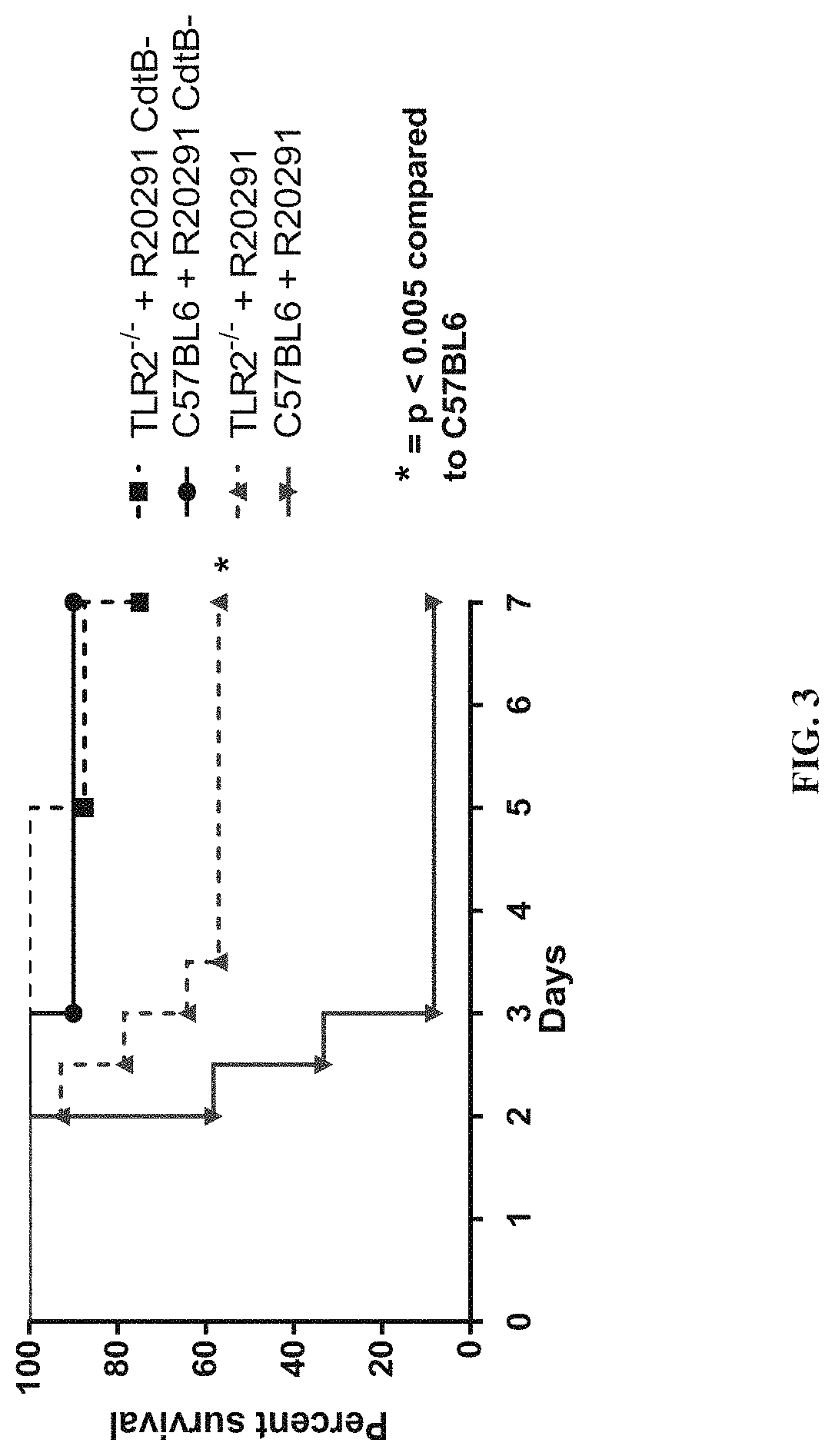
Clostridium difficile infection is the leading cause of hospital acquired antibiotic-associated diarrhea in the US (Bartlett, in 2006). The increased prevalence of circulating C. difficile strains poses a significant health threat to US health care facilities. Strains expressing the toxin C. difficile Transferase (CDT), in addition to Toxins A and B (TcdA and TcdB), are more virulent and are associated with higher mortality rates (Bacci et al., 2011). We recently identified a protective role for eosinophils against C. difficile pathogenesis (Buonomo et al., 2016). We have also defined CDT's ability to increase host inflammation and suppress protective eosinophils through a TLR2 dependent mechanism (Cowardin et al., 2016). How CDT promotes virulence and eosinophil suppression via TLR2 is still under investigation. We employed a genome-wide microarray approach to reveal divergent transcriptional profiles between protected (TLR2− / −) and unprotected (WT) mice infected with either CDT expressing or CDT mutant strains of C. difficile. This work revealed novel host mediated TLR2-dependent inflammatory pathways to CDT. We provide an unbiased framework for understanding the host immune response to the binary toxin CDT produced by C. difficile and how TLR2 signaling enhances virulence.
Owner:UNIV OF VIRGINIA ALUMNI PATENTS FOUND
Compositions and methods for treating clostridium difficile infection
ActiveUS10758591B2Reduce mortalityReduce severityAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsAntibiotic-associated diarrhoeaClostridium difficile infections
Clostridium difficile infection is the leading cause of hospital acquired antibiotic-associated diarrhea in the US (Bartlett, in 2006). The increased prevalence of circulating C. difficile strains poses a significant health threat to US health care facilities. Strains expressing the toxin C. difficile Transferase (CDT), in addition to Toxins A and B (TcdA and TcdB), are more virulent and are associated with higher mortality rates (Bacci et al., 2011). We recently identified a protective role for eosinophils against C. difficile pathogenesis (Buonomo et al., 2016). We have also defined CDT's ability to increase host inflammation and suppress protective eosinophils through a TLR2 dependent mechanism (Cowardin et al., 2016). How CDT promotes virulence and eosinophil suppression via TLR2 is still under investigation. We employed a genome-wide microarray approach to reveal divergent transcriptional profiles between protected (TLR2− / −) and unprotected (WT) mice infected with either CDT expressing or CDT mutant strains of C. difficile. This work revealed novel host mediated TLR2-dependent inflammatory pathways to CDT. We provide an unbiased framework for understanding the host immune response to the binary toxin CDT produced by C. difficile and how TLR2 signaling enhances virulence.
Owner:UNIV OF VIRGINIA ALUMNI PATENTS FOUND
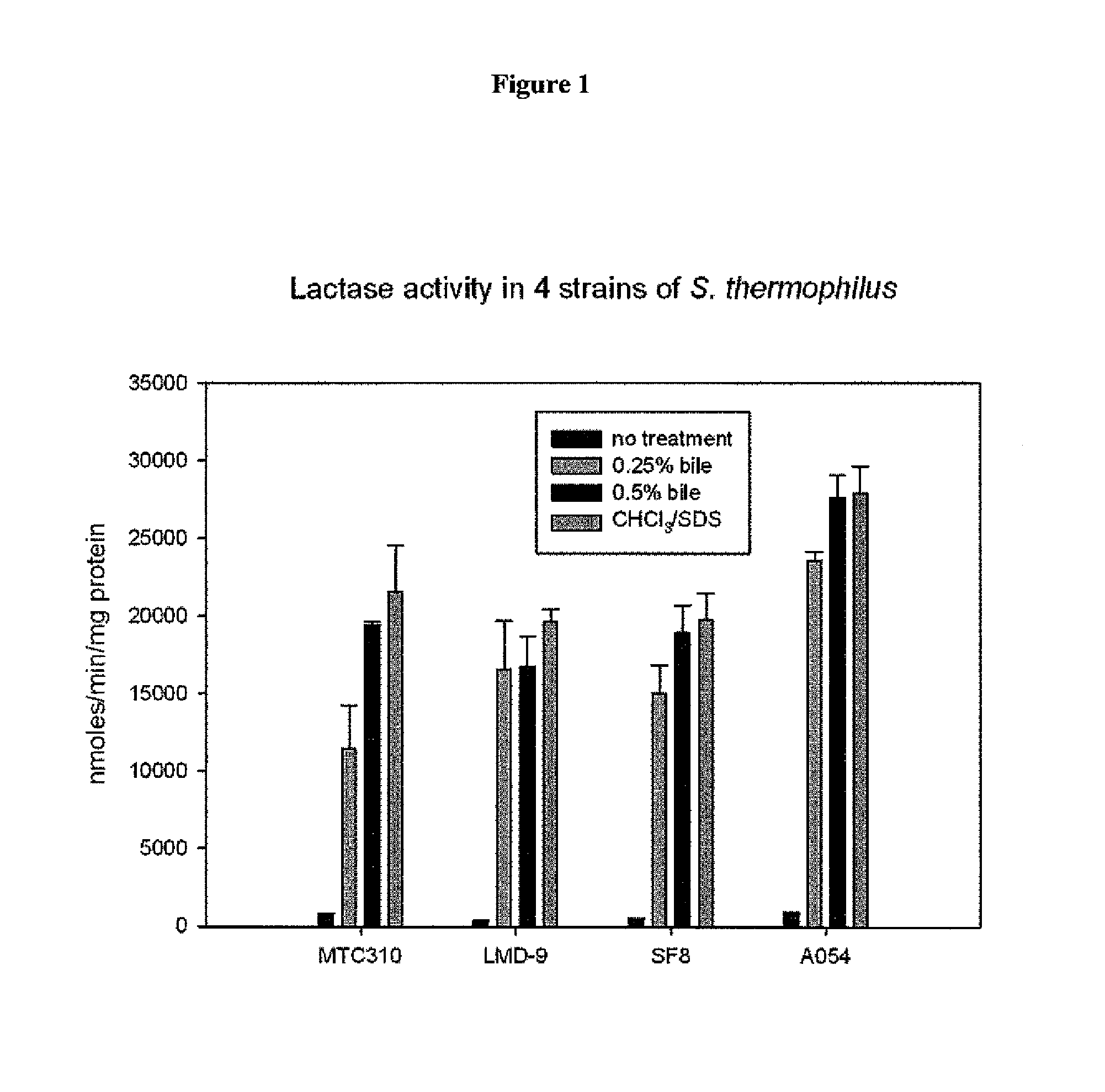
Genetically modified Streptococcus thermophilus bacterium
Owner:NORTH CAROLINA STATE UNIV +1
Synthetic Composition for Treating Antibiotic Associated Complications
ActiveUS20180325929A1Reduce the amount requiredReduce toxinsAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsAntibiotic-associated diarrhoeaPhysiology
The invention relates to a synthetic composition comprising human milk oligosaccharides for use in at least partially restoring the commensal gastrointestinal microbiota and preventing or mitigating antibiotic associated diarrhoea.
Owner:GLYCOM AS
Medicine for treating antibacterial drugs associated enteritis and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN101190299BEffective treatmentDigestive systemPill deliveryAntibiotic-associated diarrhoeaGut flora
The invention discloses a medicine for treating antibiotic-associated diarrhea. The effective components contained in the invention are prepared by rhizoma coptidis, radix scutellariae, radix codonopsitis, rhizoma atractylodis alba, Indian buead, liquoric root, rhizoma alismatis and costus root according to a certain proportion by weight. The effective components can be prepared into any common oral formulation. The invention has the functions of clearing heat and dampness, reinforcing the spleen, replenishing qi, alleviating the symptoms of diarrhea and bellyache and facilitating the recovery of alteration of intestinal flora, and can treat the antibiotic-associated diarrhea or intestinal flora alterative enteritis. The invention further discloses the preparation method of the medicine.
Owner:BEIJING ZHONGYAN TONGRENTANG CHINESE MEDICINE R & D
Method and pharmacological composition for the prevention of recurrent infections caused by clostridium difficile
PendingUS20220096510A1Inhibits internalizationReduce riskAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsAntibiotic-associated diarrhoeaRecurrent infections
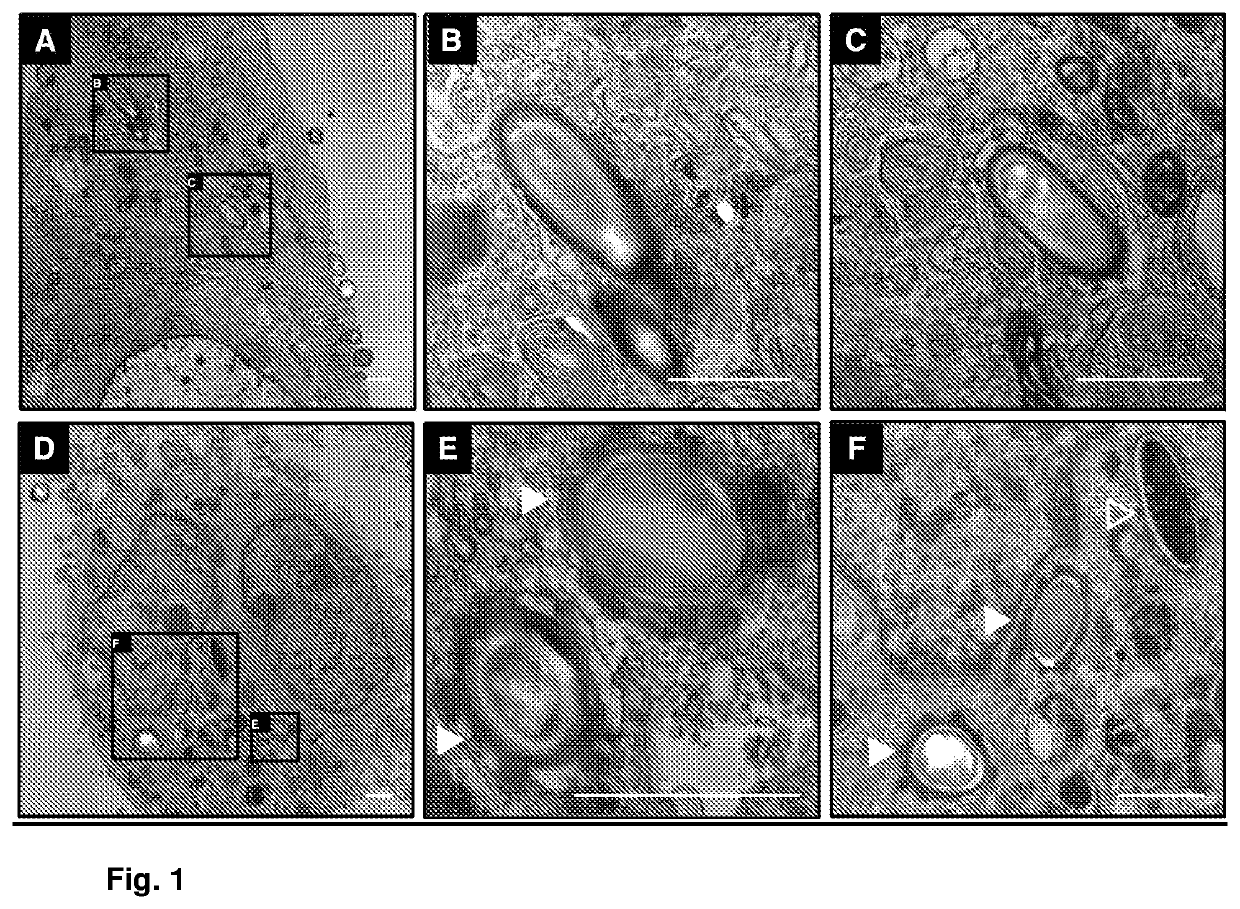
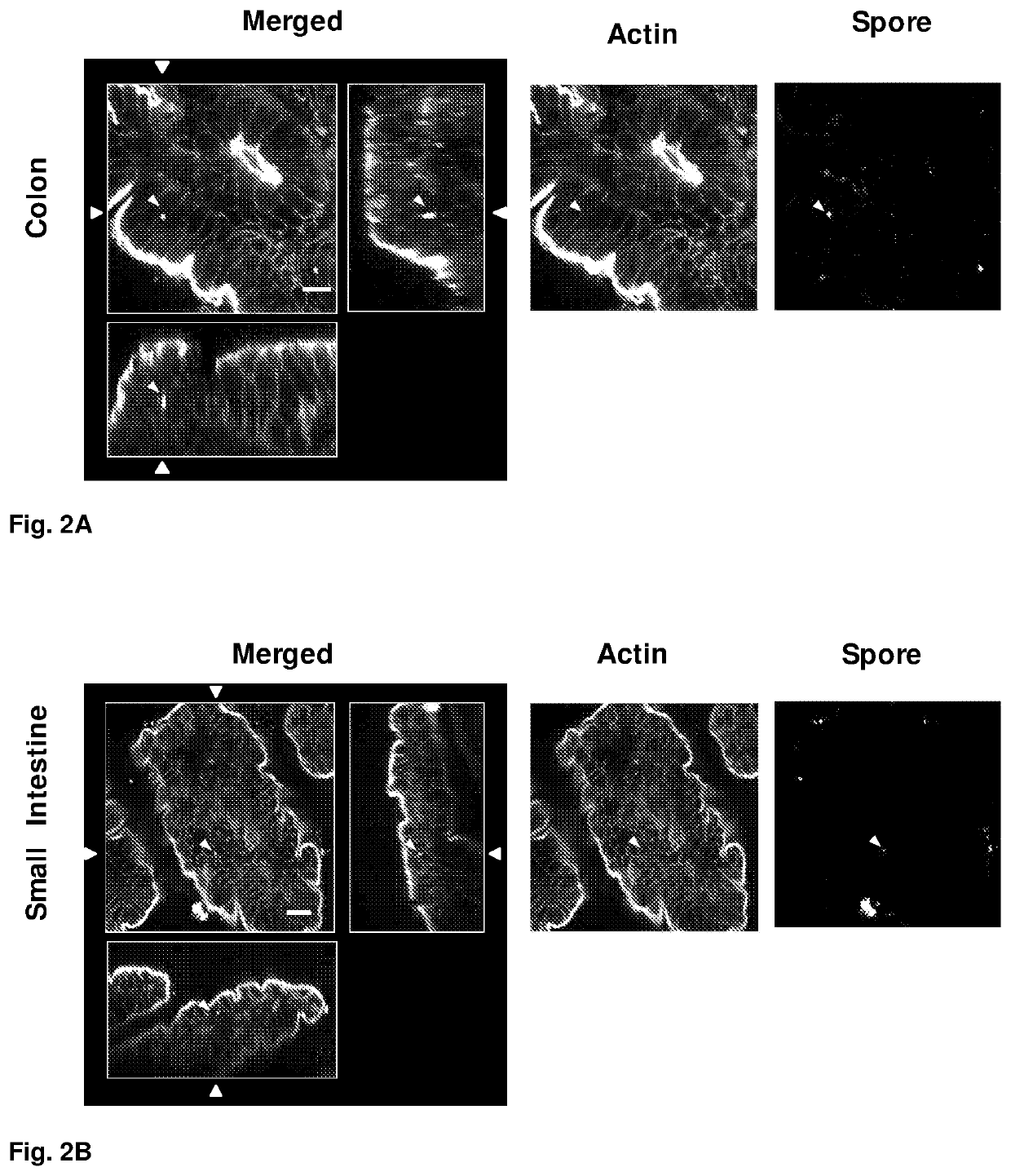
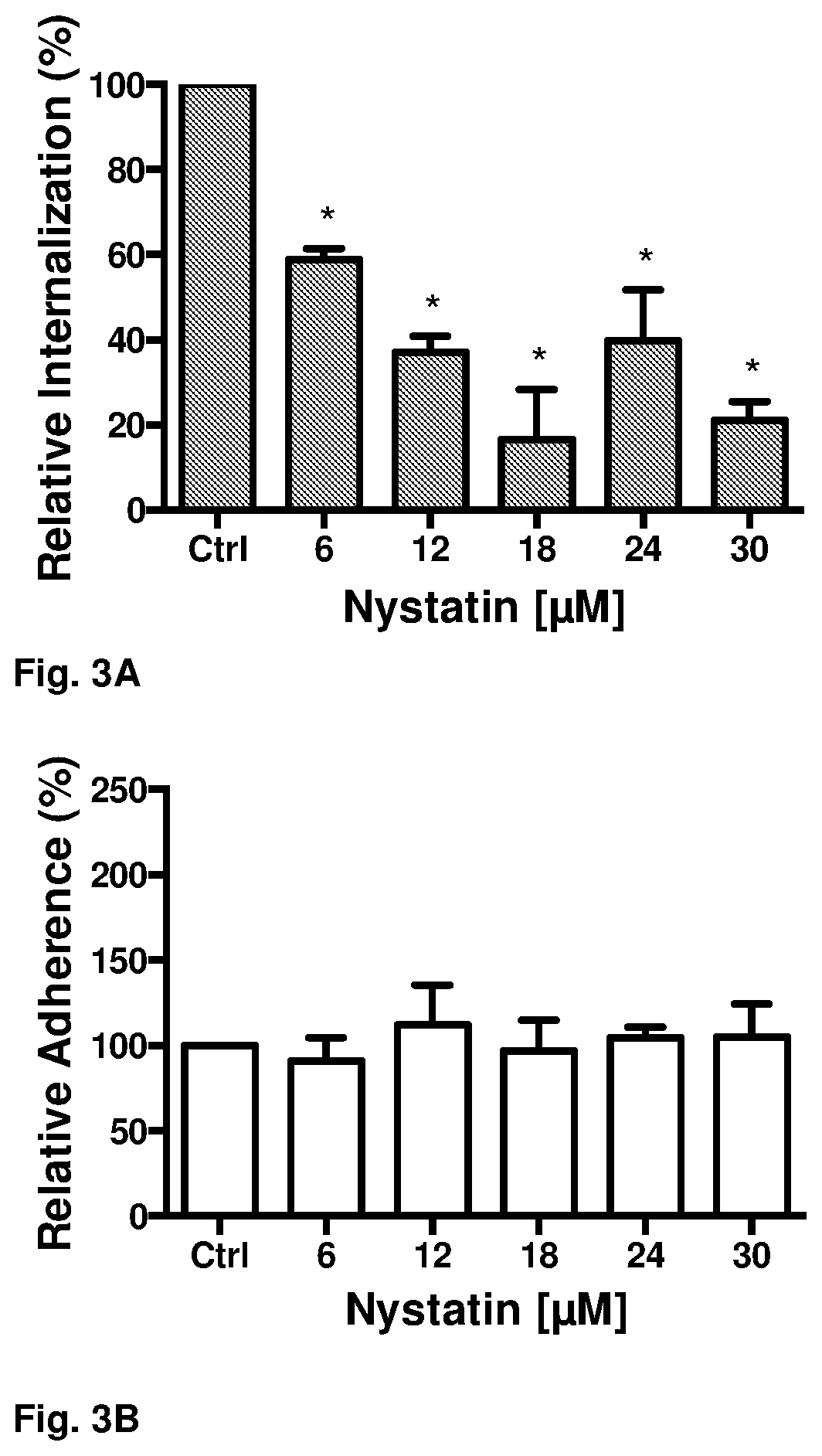
Recurrent C. difficile infections are the major cause of death due to C. difficile, which is the causative agent of approximately 20% of antibiotic-associated diarrheas. Conventional treatments for C. difficile infections are not capable of eliminating the rates of recurrence, which occurs in 20-30% of the cases and may be repetitive, the probability of death being greater in each cycle. Until now, the persistence mechanisms of C. difficile for producing recurrence conditions were unknown. In the present invention, we describe the mechanism by which C. difficile spores persist, and a method of treatment with a pharmacological composition based on an antibiotic and nystatin for preventing recurrent C. difficile infections. The route of administration of nystatin is also protected (i.e., oral, intraperitoneal).
Owner:UNIV ANDRES BELLO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com