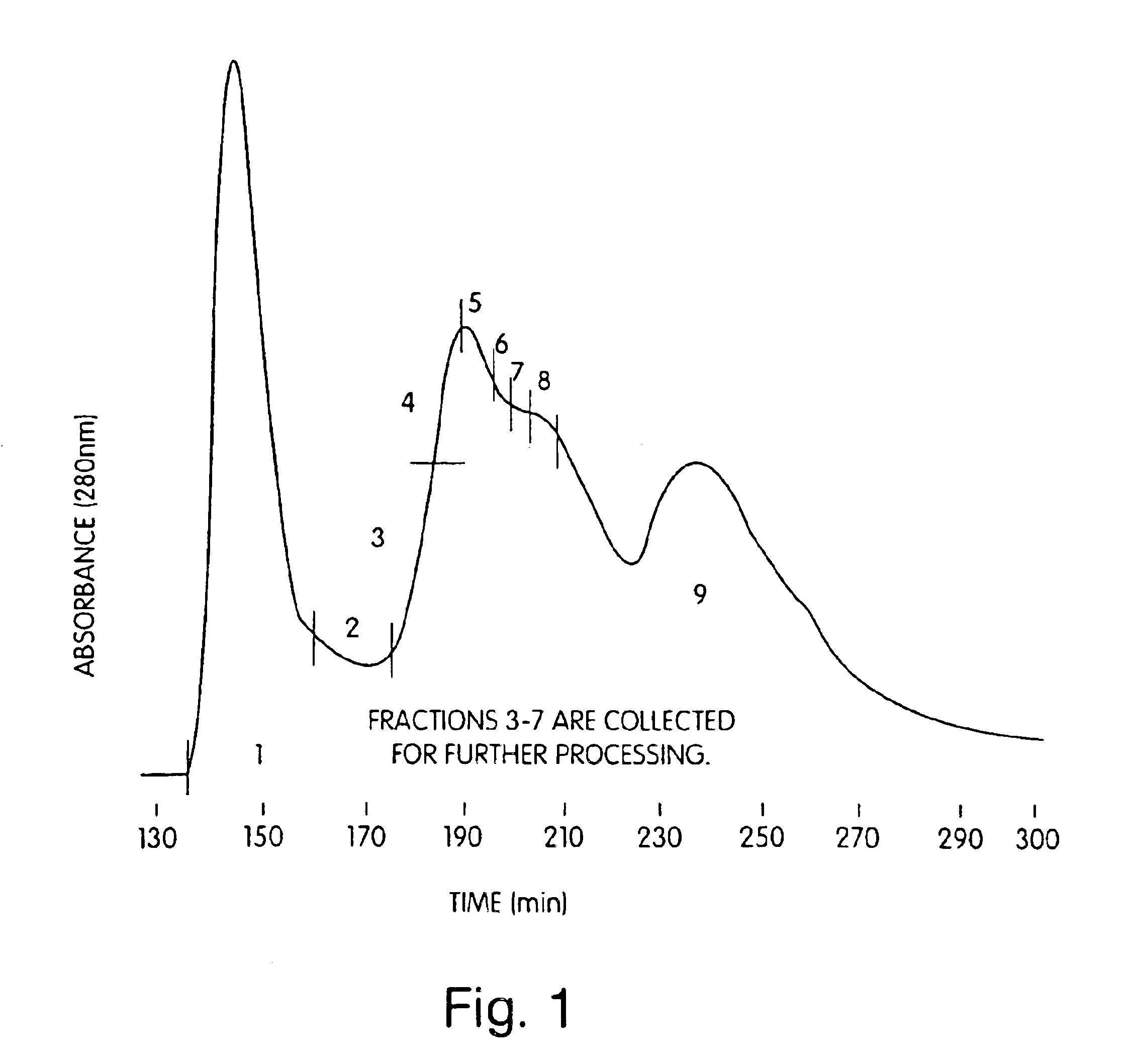
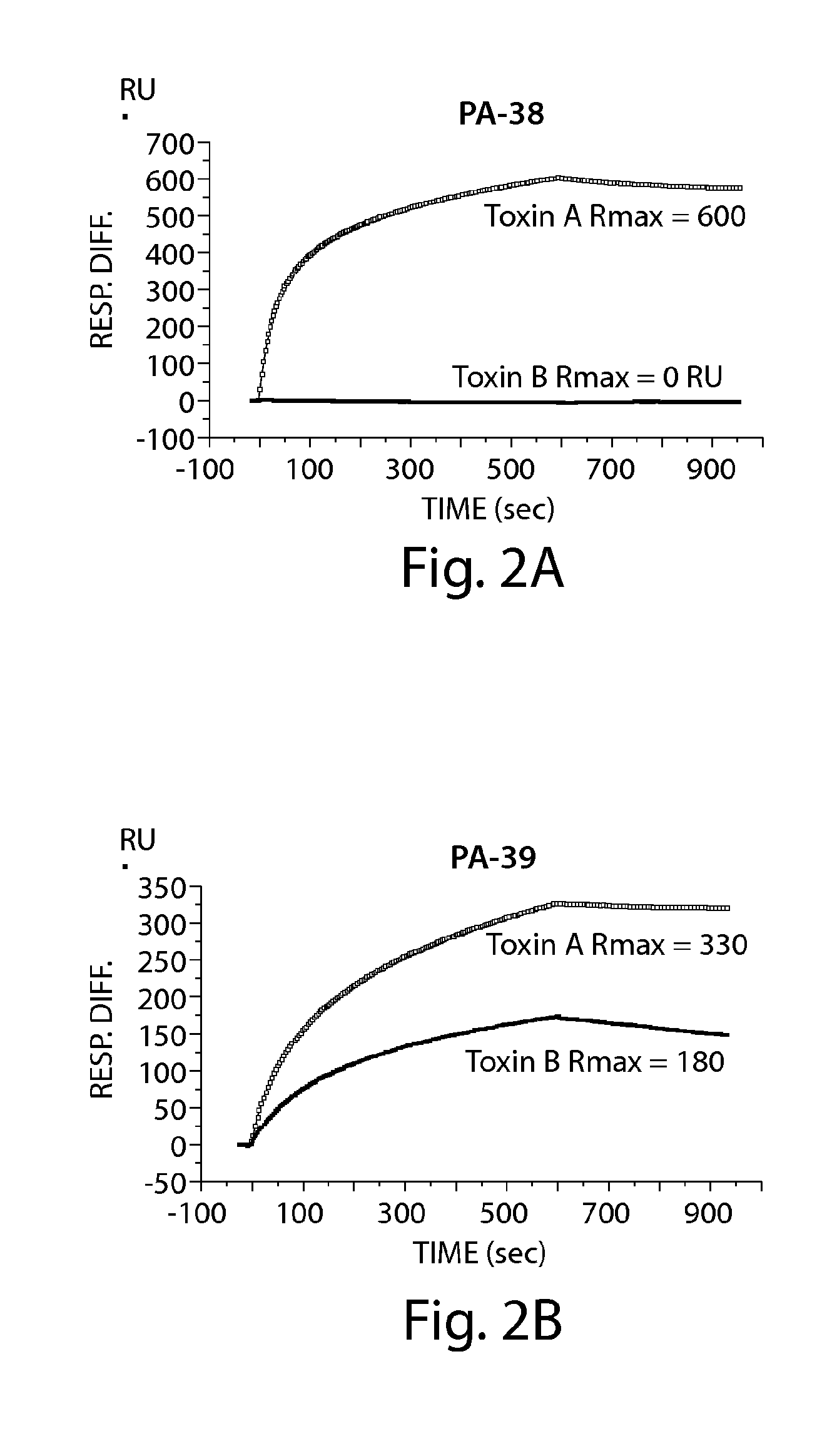
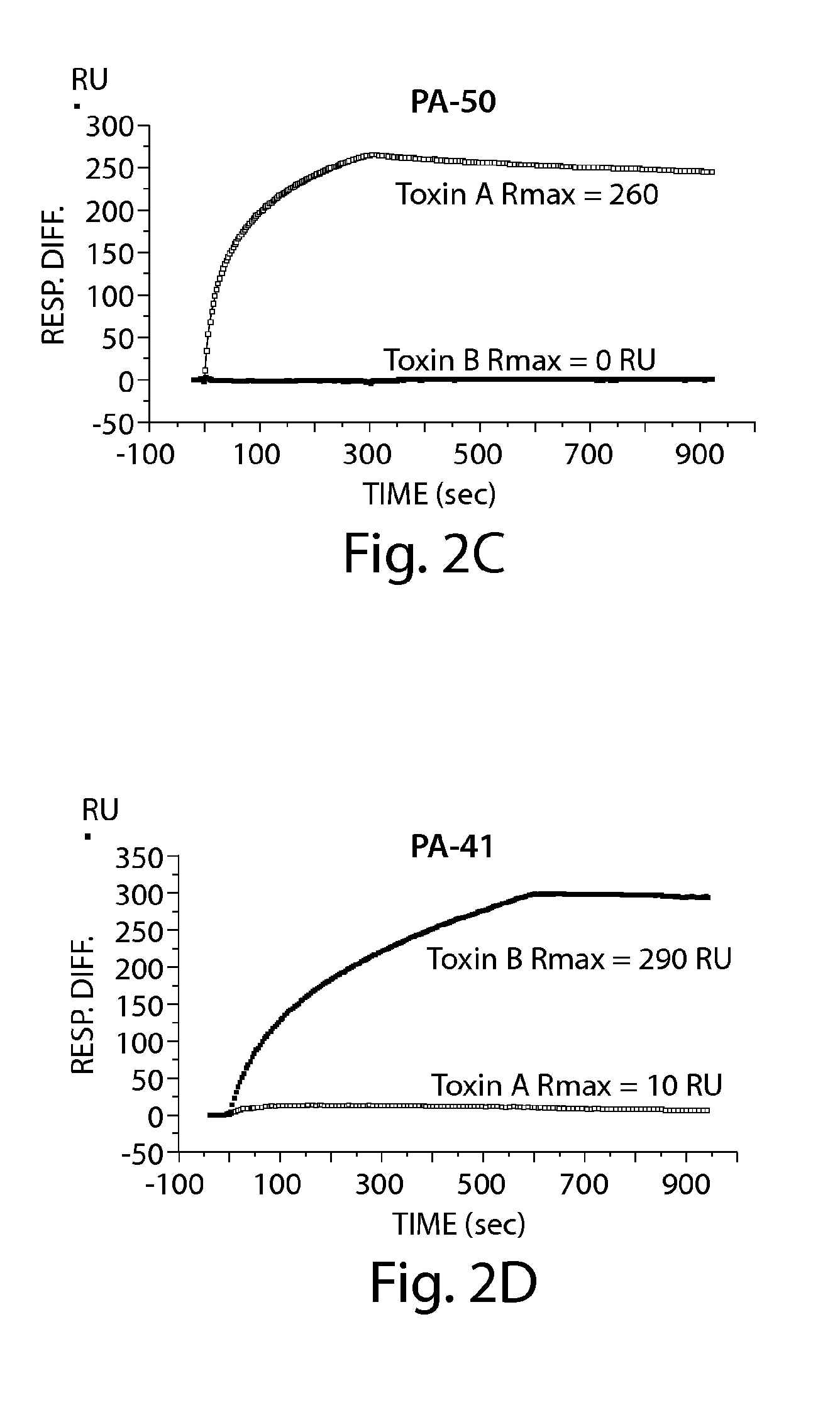
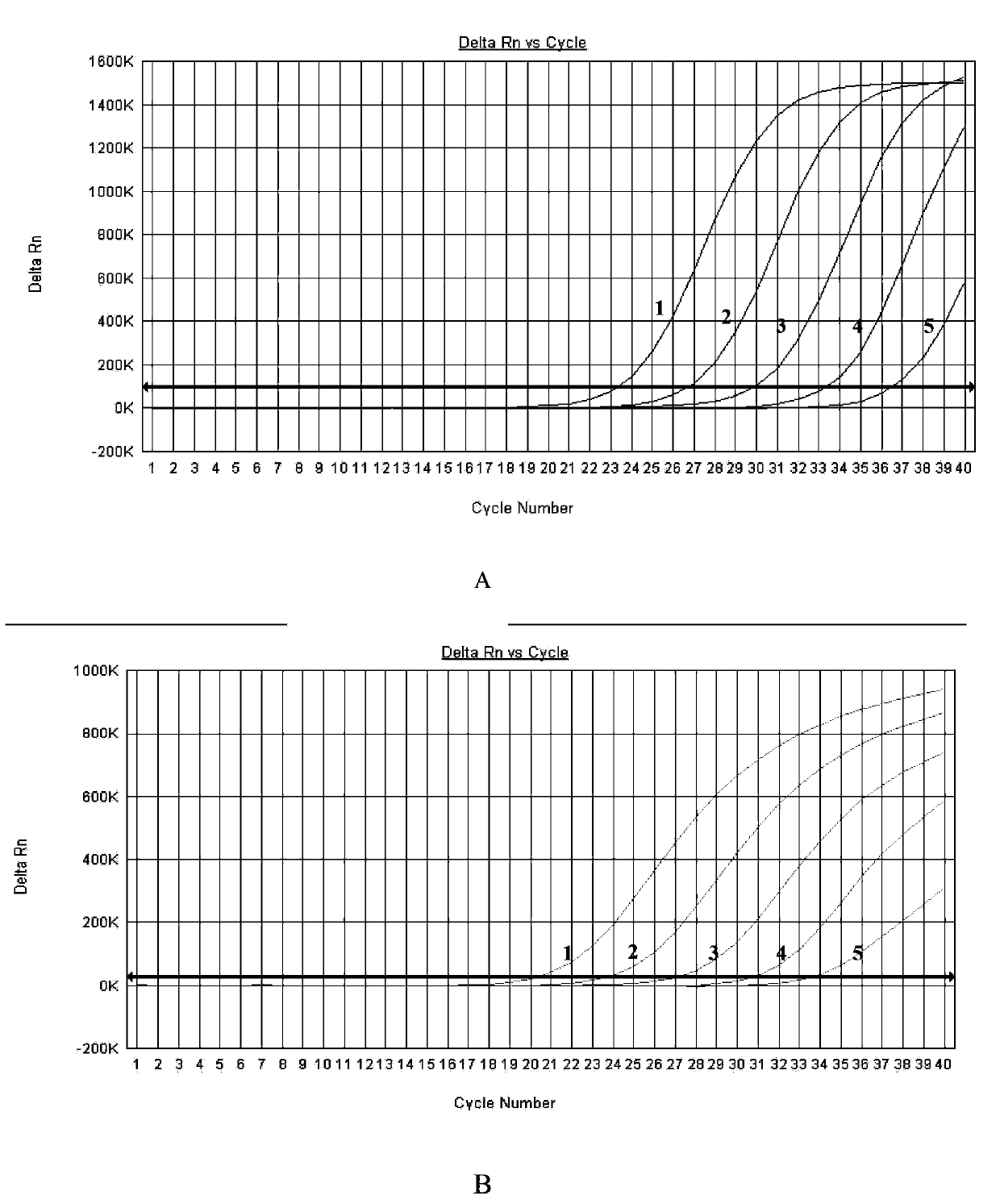
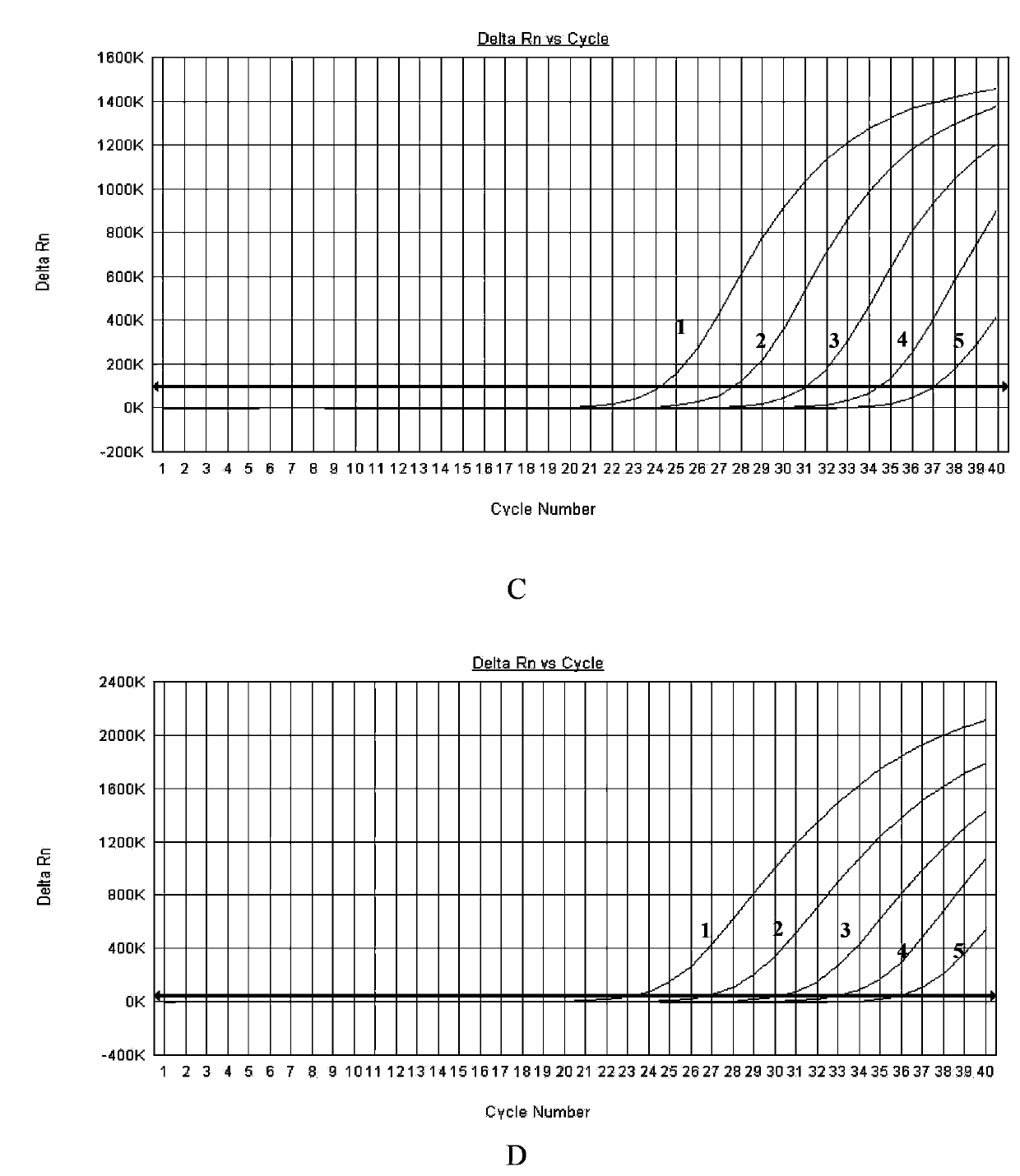
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
243 results about "Clostridium difficile (bacteria)" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
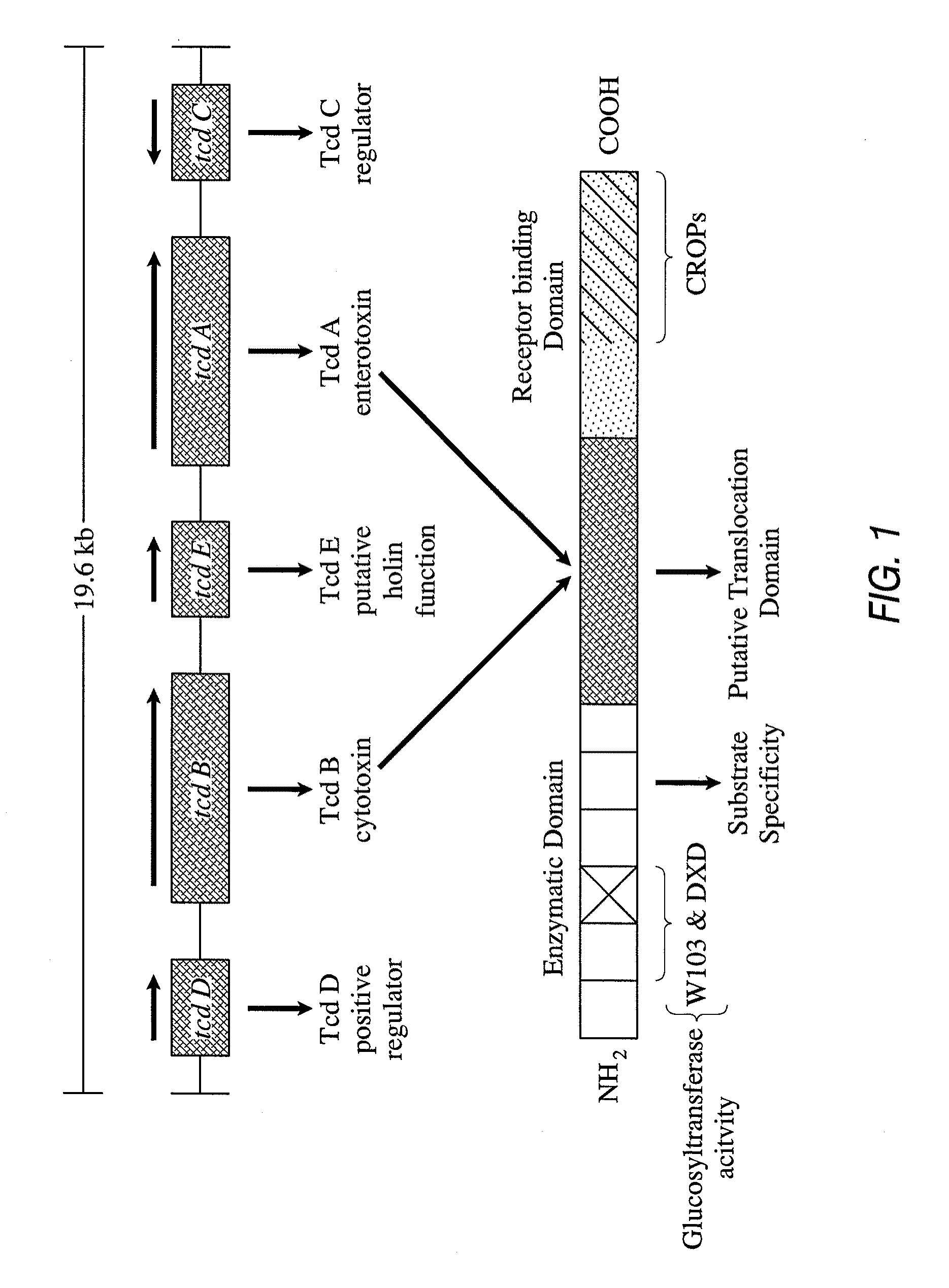
Clostridium difficile is a species of bacteria. It is often called C. diff (pronounced "see diff"). It is a gram-positive bacteria which belongs to the genus Clostridium. C. diff can live in the human colon (the large intestine) without causing any problems.
Method for treatment of disorders of the gastrointestinal system
There are provided novel synthetic stool preparations comprising bacteria isolated from a fecal sample from a healthy donor. The synthetic stool preparations are used for treating disorders of the gastrointestinal tract, including dysbiosis, Clostridium difficile infection and recurrent Clostridium difficile infection, prevention of recurrence of Clostridium difficile infection, treatment of Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis, irritable bowel syndrome, inflammatory bowel disease, and diverticular disease, and treatment of food poisoning such as salmonella. Methods of preparation and methods of use of the synthetic stool preparations are also provided.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF GUELPH +2
Compositions and methods for characterizing and restoring gastrointestinal, skin, and nasal microbiota
ActiveUS20100074872A1Growth inhibitionFacilitate calorie uptakeBiocideMetabolism disorderBacteroidesDisease
The present invention relates to characterizing changes in mammalian bacterial gastrointestinal, cutaneous and nasal microbiota associated with antibiotic treatment and various disease conditions (such as asthma, allergy, obesity, metabolic syndrome, gastrointestinal reflux disease (GERD), eosinophilic esophagitis, gastro-esophageal junction adenocarcinomas (GEJAC), infections due to bacteria that are resistant to antibiotics, including Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), Clostridium difficile, vancomycin-resistant enterococci, etc.) and related diagnostic and therapeutic methods. Therapeutic methods of the invention involve the use of live bacterial inoculants that are capable of restoring healthy mammalian bacterial gastrointestinal, skin, and nasal microbiota.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
Active immunization against clostridium difficile disease
InactiveUS6969520B2Prevent relapseImmune responseAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsDiseasePassive Immunizations
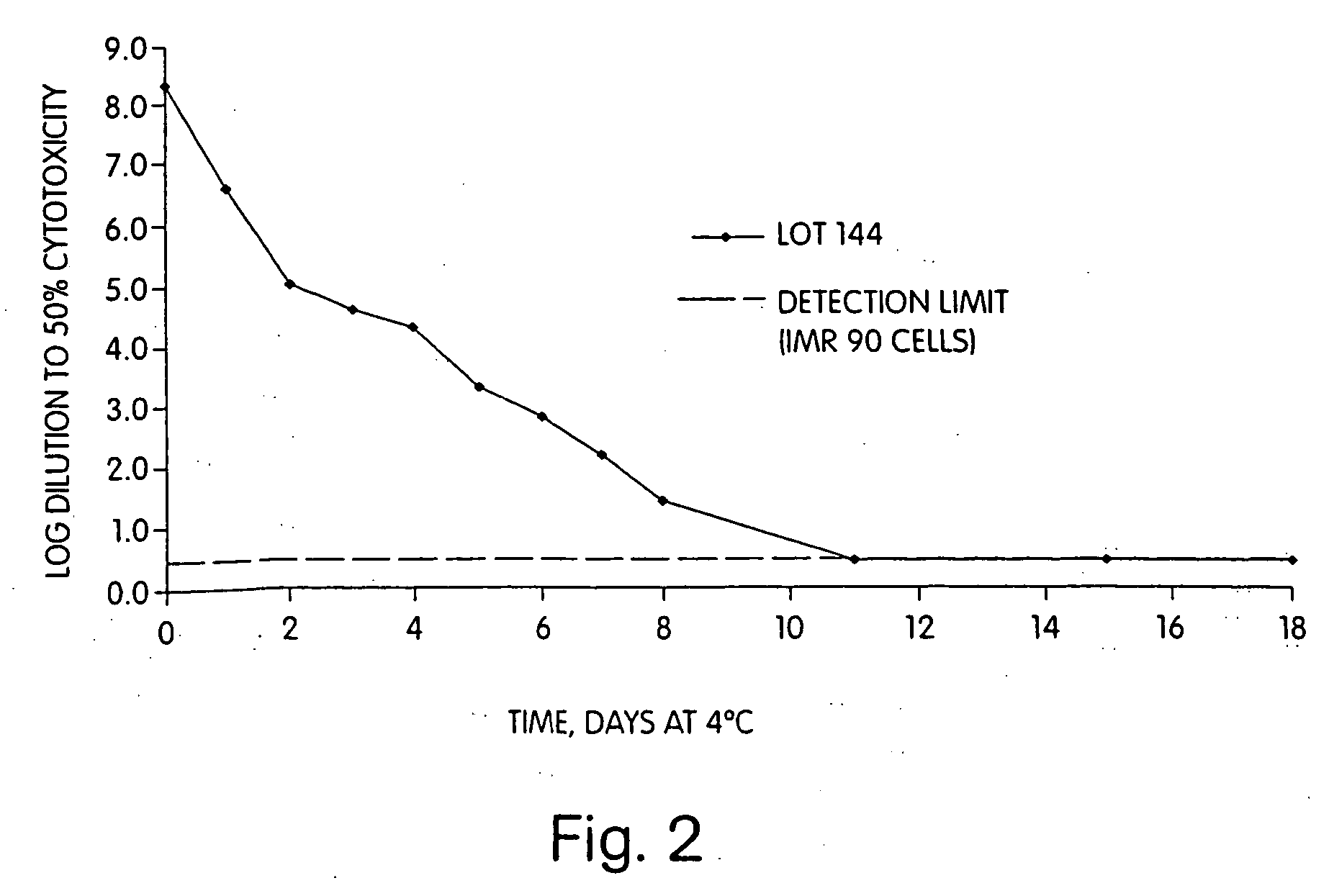
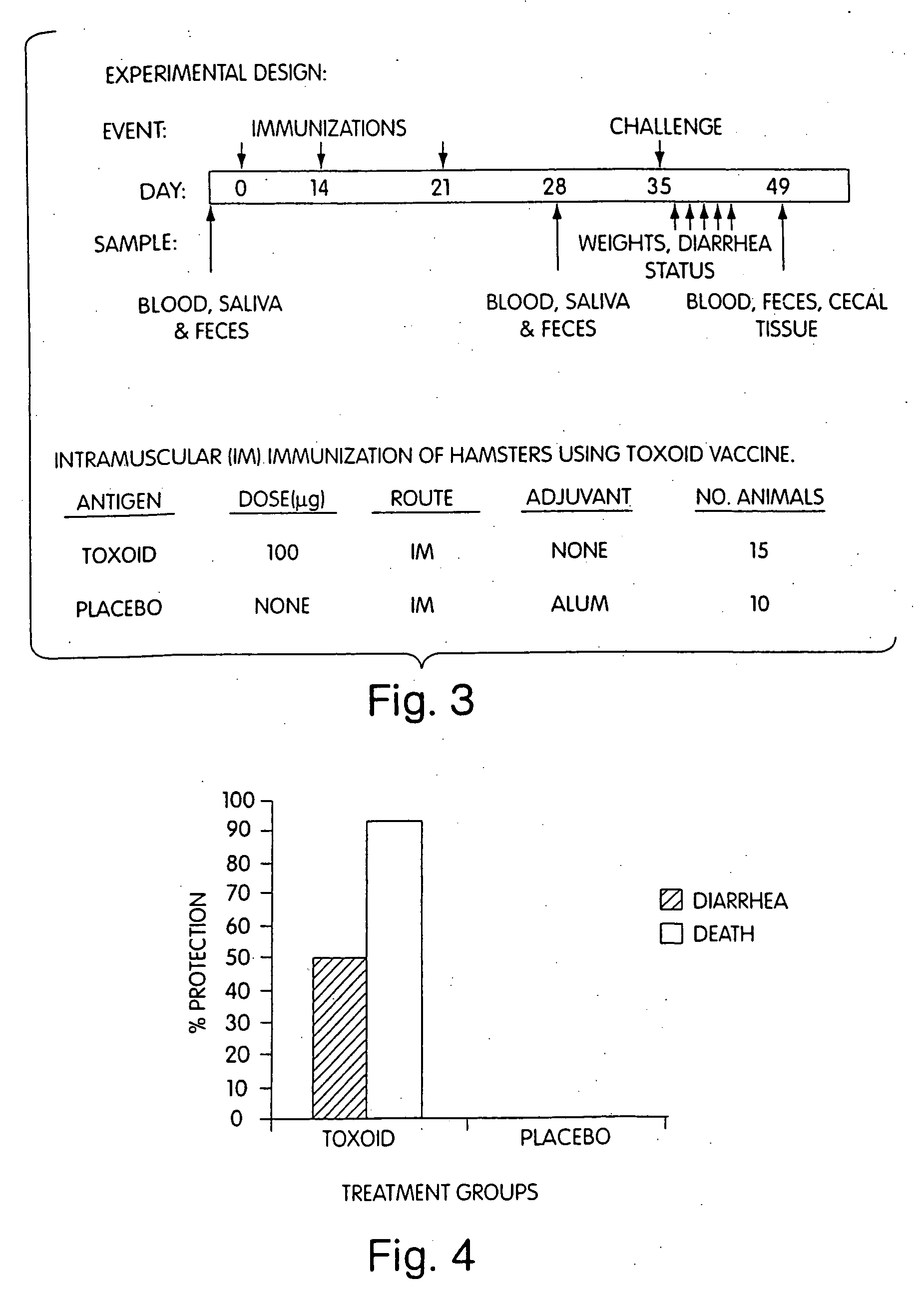
The invention provides active and passive immunization methods for preventing and treating Clostridium difficile infection, which involve percutaneous administration of C. difficile toxin-neutralizing polyclonal immune globulin, C. difficile toxoids, or combinations thereof. Also provided by the invention are C. difficile toxoids, C. difficile toxin-neutralizing polyclonal immune globulin, and methods of identifying subjects that produce C. difficile toxin-neutralizing polyclonal immune globulin.
Owner:SANOFI PASTEUR BIOLOGICS CO
Antimicrobial compounds from Bacillus subtilis for use against animal and human pathogens
ActiveUS7247299B2Enhanced inhibitory effectRetain viabilityAntibacterial agentsBiocideBacillus perfringensClostridium difficile (bacteria)
Antimicrobial compounds from Bacillus subtilis for use against animal and human pathogens. A novel strain of Bacillus subtilis was isolated from the gastrointestinal tract of poultry and was found to produce a factor or factors that have excellent inhibitory effects on Clostridium perfringens, Clostridium difficile, Campylobacter jejuni, Campylobacter coli, and Streptococcus pneumoniae. The factor(s) retain full viability and antimicrobial activity after heat treatment. The invention provides a method of treatment of pathogenic microorganisms including C. perfringens.
Owner:KEMIN IND INC
Antibodies against Clostridium difficile toxins and uses thereof
ActiveUS7625559B2High affinityLess immunogenicAntibacterial agentsGenetic material ingredientsClostridium difficile toxin AClostridium difficile (bacteria)
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS UNIV OF +2
Antibodies against Clostridium difficile toxins and uses thereof
ActiveUS20050287150A1High affinityLess immunogenicAntibacterial agentsBacteriaClostridium difficileClostridium difficile (bacteria)
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS UNIV OF +2
Antibacterial composition and method of production
An electrolysis method is described for generating an aqueous solution of copper citrate that has bacteriocidal activity against methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) bacteria. Gram positive bacteria are known to be relatively more sensitive to the bacteriocidal activities of copper ions than are Gram negative bacteria. Situations exist in which a disinfectant that is relatively more toxic for Gram positive bacteria will be advantageous over a more broadly active disinfectant, such as that provided by most other disinfectants. In particular, a disinfectant that is relatively selective for Gram positive bacteria could help preserve various non-pathogenic Gram negative microbial populations. The residual Gram negative bacteria can potentially compete with, and thereby lessen the chances of the reintroduction of pathogenic Gram positive bacteria, such as MRSA, Streptococcus, Clostridium difficile and Listeria monocytogenes.
Owner:MI HOPE
Immunization against clostridium difficile disease
InactiveUS20060029608A1Prevent relapseQuick treatmentAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsPassive ImmunizationsClostridium difficile infections
The invention provides active and passive immunization methods for preventing and treating Clostridium difficile infection, which involve percutaneous administration of C. difficile toxin-neutralizing polyclonal immune globulin, C. difficile toxoids, or combinations thereof. Also provided by the invention are C. difficile toxoids, C. difficile toxin-neutralizing polyclonal immune globulin, and methods of identifying subjects that produce C. difficile toxin-neutralizing polyclonal immune globulin.
Owner:ACAMBIS INC
Compositions relating to a mutant clostridium difficile toxin and methods thereof
ActiveUS20120269841A1Antibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsClostridium difficile toxin BNucleotide
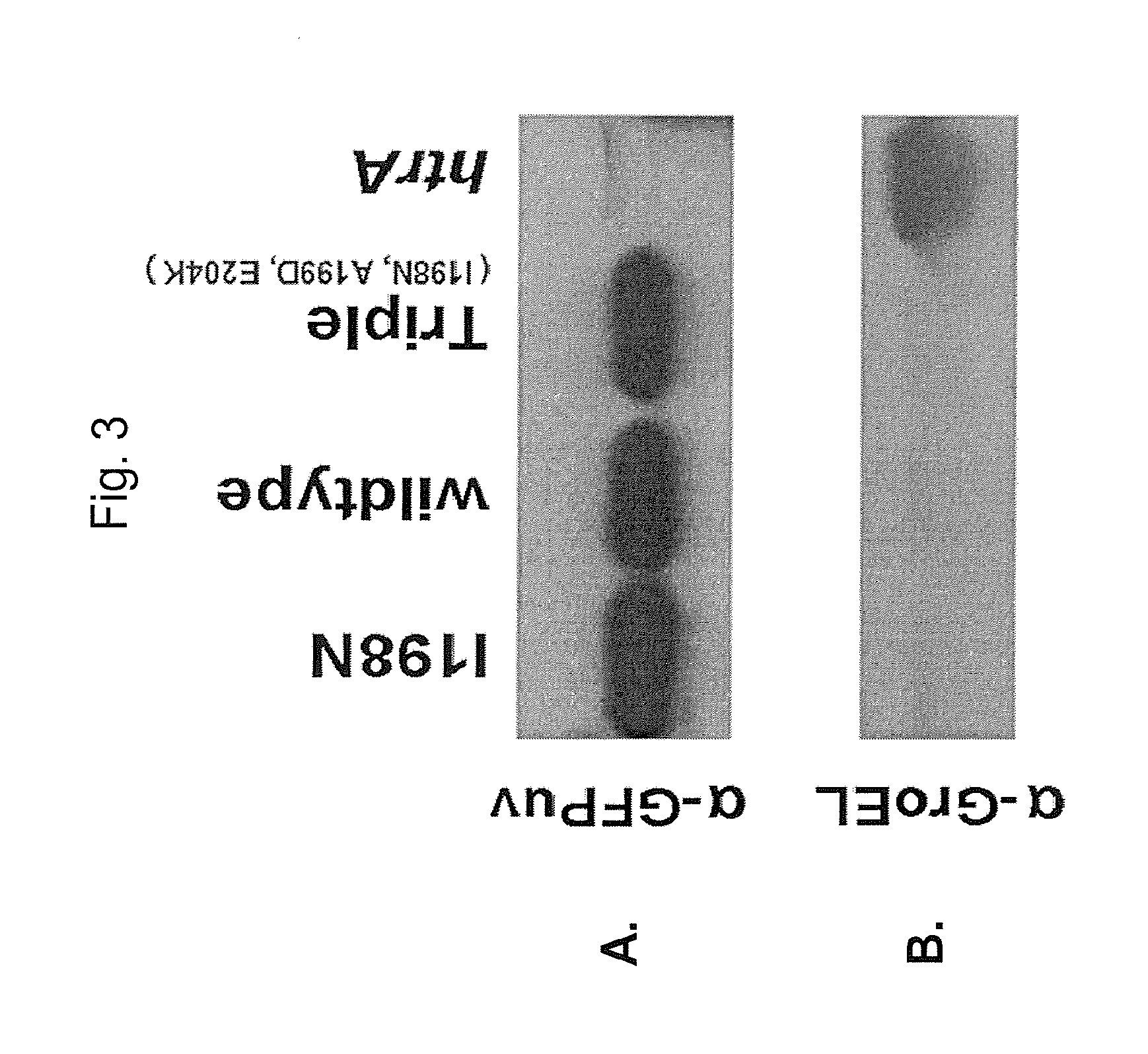
In one aspect, the invention relates to an immunogenic composition that includes a mutant Clostridium difficile toxin A and / or a mutant Clostridium difficile toxin B. Each mutant toxin includes a glucosyltransferase domain having at least one mutation and a cysteine protease domain having at least one mutation, relative to the corresponding wild-type C. difficile toxin. The mutant toxins may further include at least one amino acid that is chemically crosslinked. In another aspect, the invention relates to antibodies or binding fragments thereof that binds to said immunogenic compositions. In further aspects, the invention relates to isolated nucleotide sequences that encode any of the foregoing, and methods of use of any of the foregoing compositions.
Owner:WYETH LLC
Polymorphic crystalline forms of tiacumicin B
ActiveUS7378508B2Antibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsAntibiotic-associated diarrhoeaDisease
The invention relates to novel forms of compounds displaying broad spectrum antibiotic activity, especially crystalline polymorphic forms and amorphous forms of such compounds, compositions comprising such crystalline polymorphic forms and amorphous forms of such compounds, processes for manufacture and use thereof. The compounds and compositions of the invention are useful in the pharmaceutical industry, for example, in the treatment or prevention of diseases or disorders associated with the use of antibiotics, chemotherapies, or antiviral therapies, including, but not limited to, colitis, for example, pseudo-membranous colitis; antibiotic associated diarrhea; and infections due to Clostridium difficile (“C. difficile”), Clostridium perfringens (“C. perfringens”), Staphylococcus species, for example, methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus, or Enterococcus including Vancomycin-resistant enterococci.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME LLC
Multivalent Live Vector Vaccine against Clostridium difficile-Associated Disease
ActiveUS20120282293A1Easy to exportLow hemolytic activityAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsClostridium difficile (bacteria)Live vector vaccine
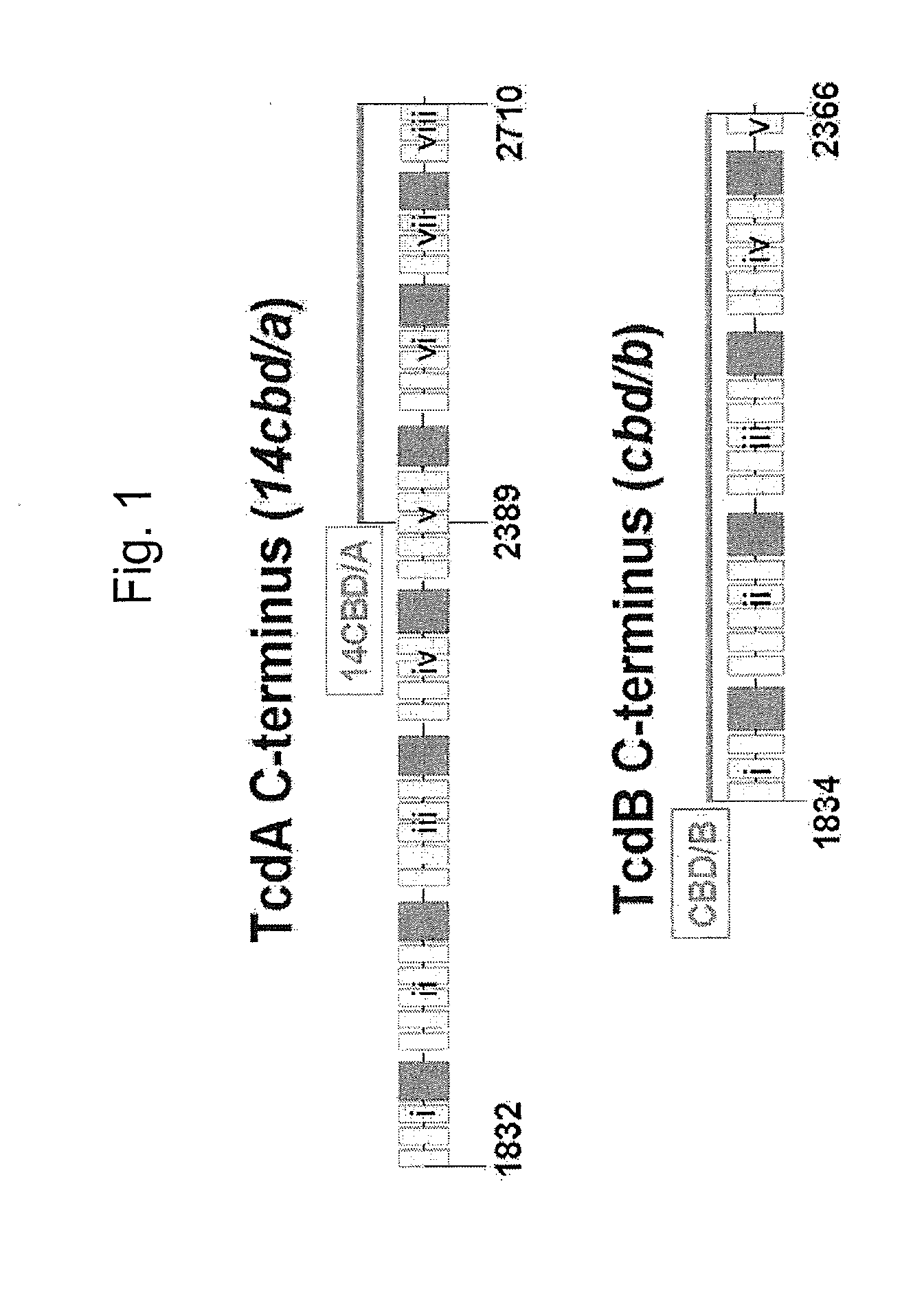
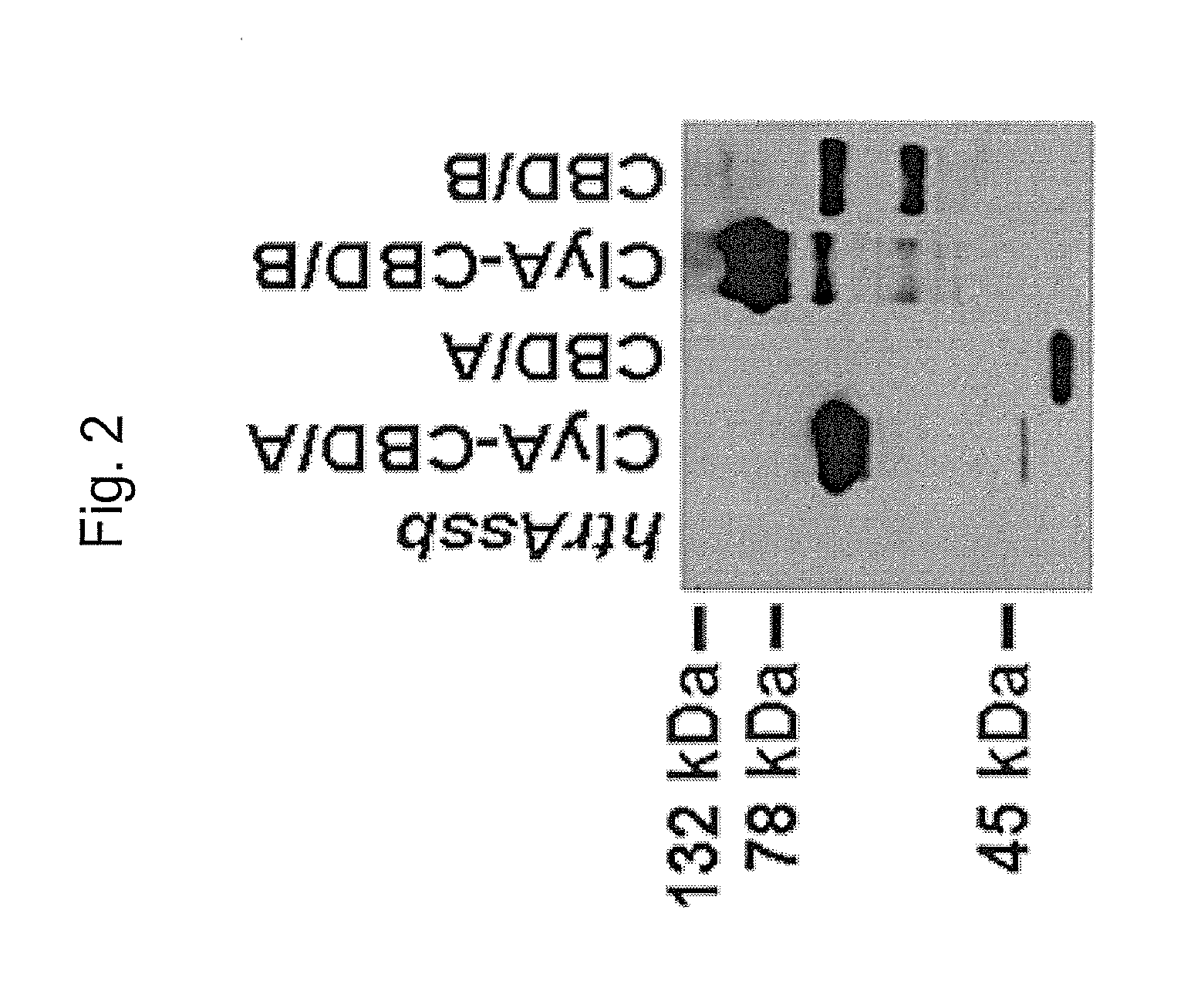
The invention relates to a multivalent Clostridium difficile vaccine comprising a Salmonella Typhi live vector comprising the cell binding domain of TcdA toxin (CBD / A) of Clostridium difficile or an antigenic fragment thereof and the cell binding domain of TcdB toxin (CBD / B) of Clostridium difficile or an antigenic fragment thereof and optionally the cell-binding subunit component (CdtB) of binary toxin of Clostridium difficile or an antigenic fragment thereof. The invention further provides methods of inducing an immune response and methods of preventing recurrence of C. difficile infections in subjects.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND BALTIMORE
Antibacterial compounds
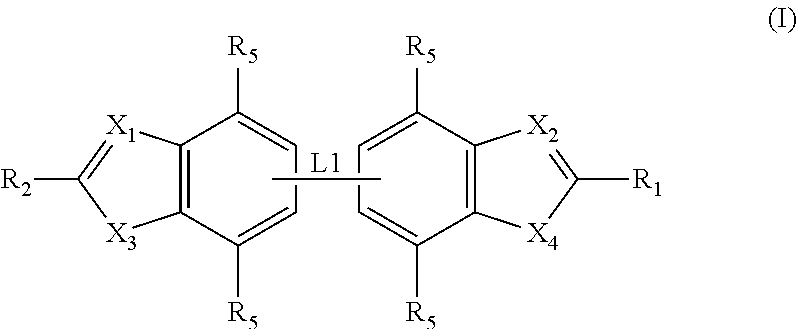
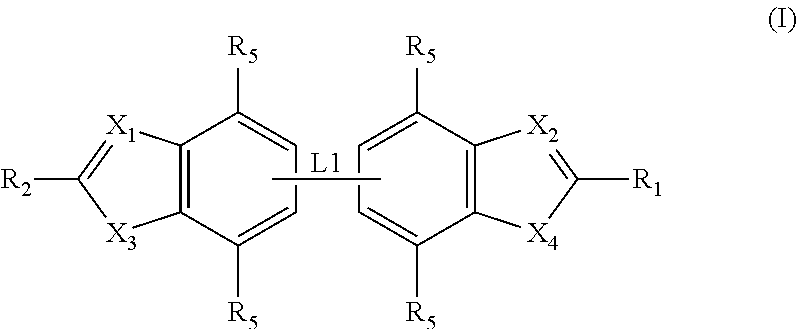
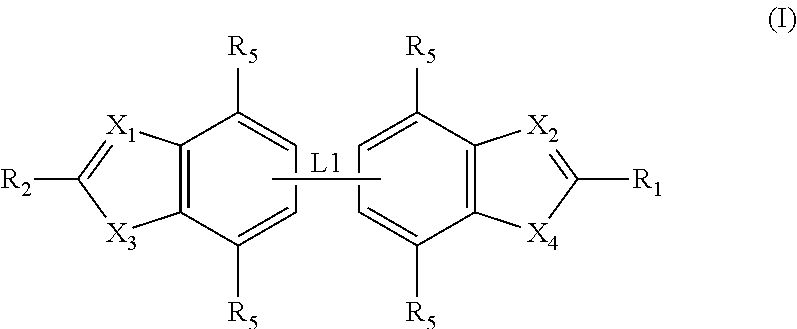
ActiveUS20120020950A1Augment other biological activityHigh activityAntibacterial agentsBiocideClostridium difficileBacterial Disorder
Disclosed are compounds of formula (I), which are of use in the treatment of bacterial diseases and infections, to compositions containing those compounds and to methods of treating bacterial diseases and infections using the compounds. In particular, the compounds are useful for the treatment of infection with, and diseases caused by, Clostridium difficile.
Owner:SUMMIT OXFORD
Amino acid sequences for therapeutic and prophylactic use against diseases due to clostridium difficile toxins
InactiveUS7151159B2Antibacterial agentsFungiClostridium difficile toxin AClostridium difficile (bacteria)
The invention relates to monoclonal antibodies capable of recognizing and neutralizing epitopes from the ligand domain, the translocation domain or the catalytic domain of the enterotoxin (toxin A) and cytotoxin (toxin B) from Clostridium difficile, as well as their production and therapeutic and prophylactic applications to diseases caused by said toxins.
Owner:VON EICHEL STREIBER CHRISTOPH
Use of bacillus amyloliquefaciens PB6 for the prophylaxis or treatment of gastrointestinal and immuno-related diseases
InactiveUS20080057047A1BiocideBacteriaAntibiotic-associated diarrhoeaClostridium difficile (bacteria)
Bacteria of the sp. Bacillus that produce a lipopeptide are found to be effective in the treatment and prophylaxis of gastro-intestinal disease when administered as a probiotic. In particular, a strain of Bacillus bacteria identified as PB6 is useful for the treatment of Antibiotic Associated Diarrhea (AAD) or the more serious condition Clostridium difficile associated diarrhea (CDAD) when administered as a probiotic. Additionally, these bacteria have been found efficient for the treatment of immunorelated diseases such as Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD).
Owner:KEMIN IND INC
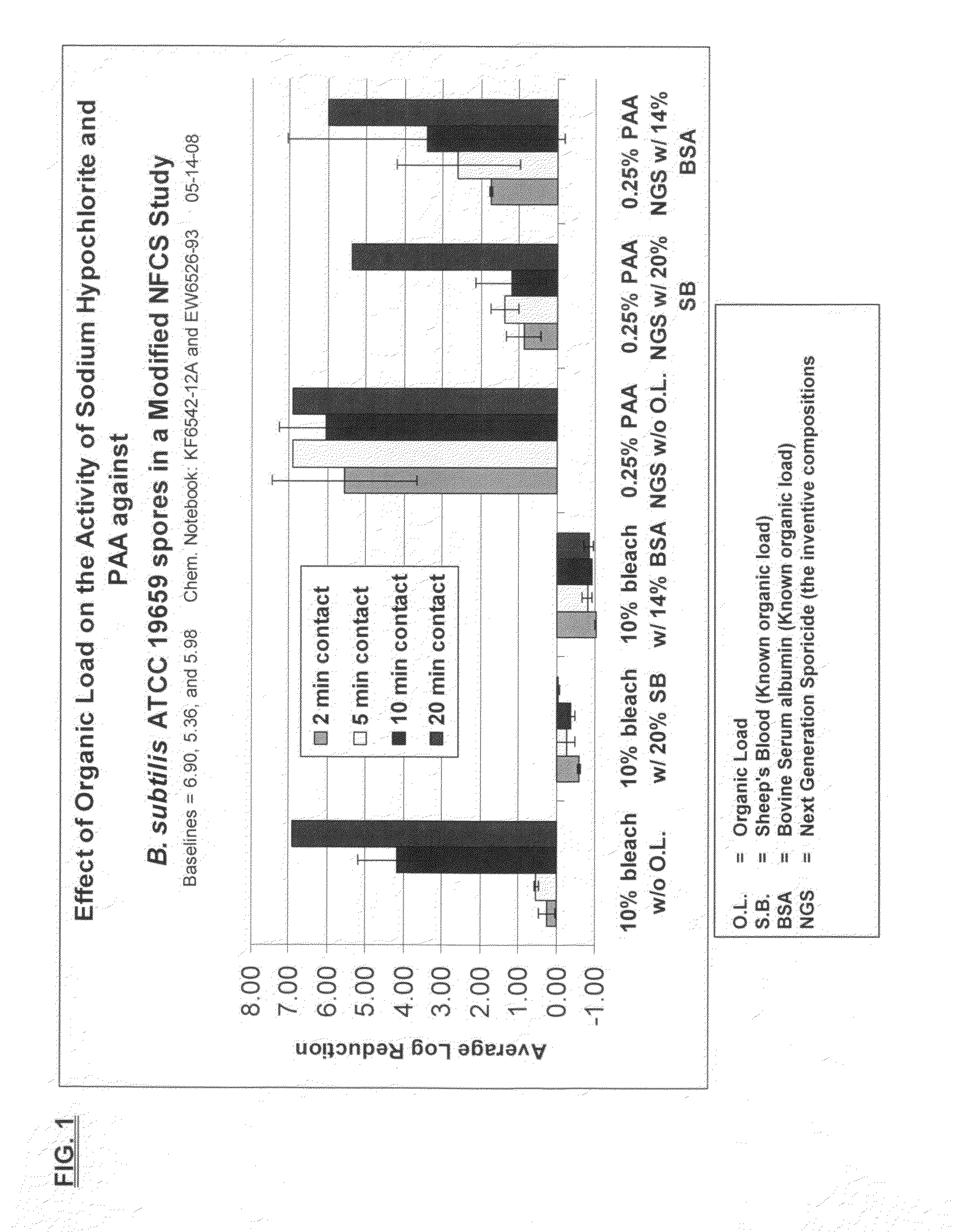
Sporicidal composition for clostridium difficile spores
A cleaning medium or formulation that contains a sporicidal composition is described. The composition includes about 0.1-20% weight / weight of a germinant agent, about 0.01-75% w / w of an antimicrobial agent, in terms of dry or wet total weight, and which is admixed with water to generate a solution with a pH of 3.5-9.5. The composition can help trigger the germination of spores, in particular C. difficile, and subsequently deactivate or kill the spores. A means of applying the cleaning formulation in a medium and process for cleaning are also described.
Owner:KIMBERLY-CLARK WORLDWIDE INC
Low odor, hard surface sporicides and chemical decontaminants
ActiveUS20100196505A1Safer and easy to handleSafer and easy to and transportInorganic/elemental detergent compounding agentsBiocideClostridium difficile (bacteria)Clostridium sporogenes
A low odor, liquid disinfectant composition comprising multiple components, which, upon mixing, provide an aqueous solution comprising low levels of peracetic acid for use in decontaminating articles and surfaces contaminated with bacteria, viruses, fungi and other chemical and biological contaminants including, but not limited to, spores, such as Clostridium difficile (C. diff), Clostridium sporogenes, and anthrax, mouse parvo virus, and mustard, nerve and other chemical and biological warfare agents. The disinfectant composition is prepared just prior to use by combining two or more separately packaged components, one component which is an acetyl donor comprising TAED or DAMA, and the other component which is a hydrogen peroxide solution.
Owner:AMERICAN STERILIZER CO
Detection of toxigenic strains of clostridium difficile
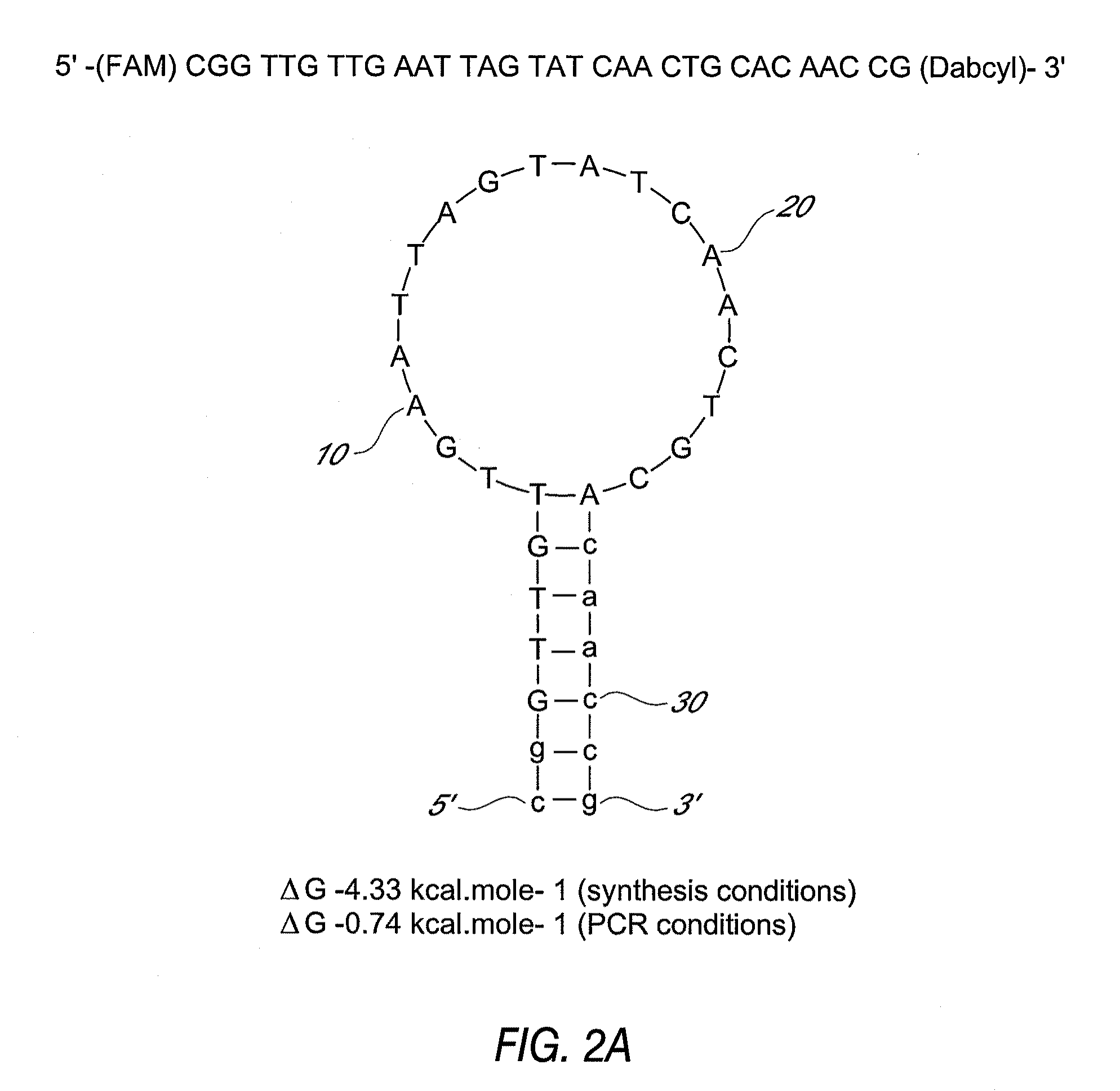
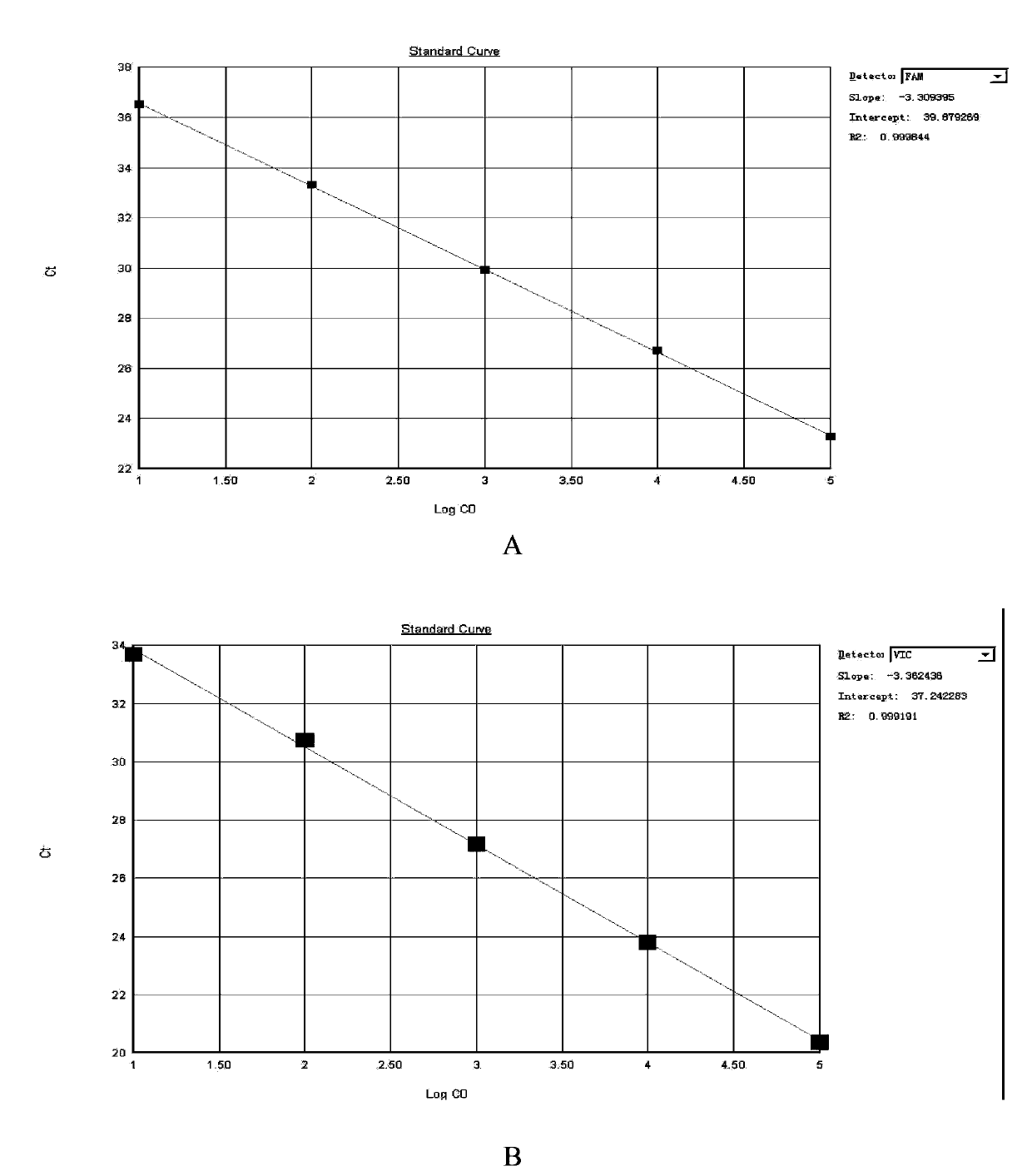
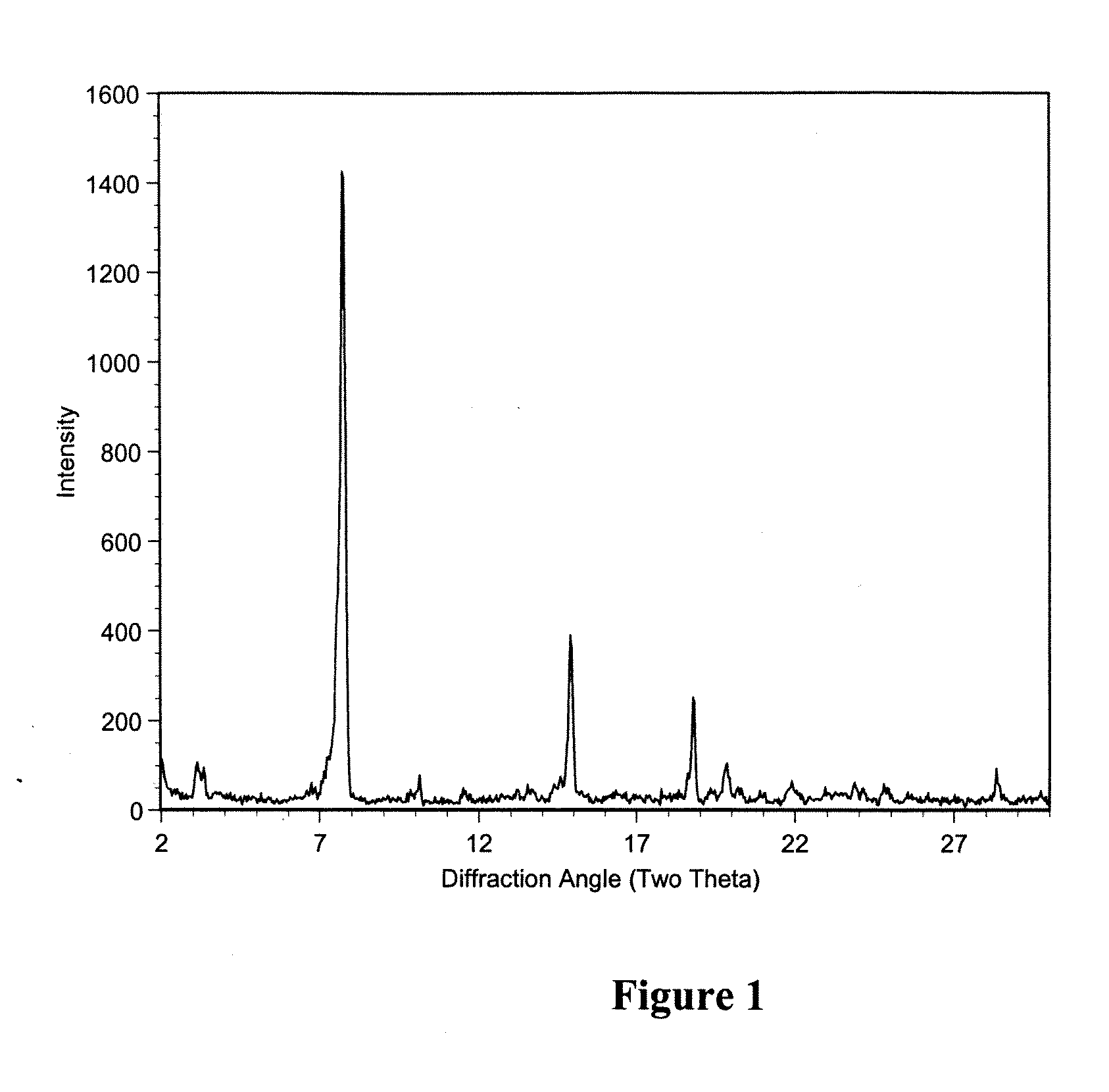
ActiveUS20090208948A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementClostridium difficileClostridium difficile (bacteria)
Primers and probes for detection of toxin-producing (toxigenic) strains of Clostridium difficile, and to methods of detecting toxigenic strains using these primers and probes. Toxigenic strains of C. difficile are detected by nucleic acid-based amplification methods using particular primers and probes that bind to the toxin B (TcdB) gene. These primers and probes are used to amplify C. difficile nucleic acids in clinical samples to determine the presence of these toxigenic strains.
Owner:GENEOHM SCI CANADA
Compositions relating to a mutant Clostridium difficile toxin and methods thereof
In one aspect, the invention relates to an immunogenic composition that includes a mutant Clostridium difficile toxin A and / or a mutant Clostridium difficile toxin B. Each mutant toxin includes a glucosyltransferase domain having at least one mutation and a cysteine protease domain having at least one mutation, relative to the corresponding wild-type C. difficile toxin. The mutant toxins may further include at least one amino acid that is chemically crosslinked. In another aspect, the invention relates to antibodies or binding fragments thereof that binds to said immunogenic compositions. In further aspects, the invention relates to isolated nucleotide sequences that encode any of the foregoing, and methods of use of any of the foregoing compositions.
Owner:WYETH LLC
Antibodies for the treatment of Clostridium difficile-associated infection and disease
ActiveUS8986697B2Improve the quality of lifeImprove survivabilityAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsAntigenDisease
Provided herein are reagents, compositions, and therapies with which to treat Clostridium difficile infection and related disease conditions and pathologies, such as Clostridium difficile-associated diarrhea, resulting from infection by Clostridium difficile bacteria and the enterotoxins produced by these bacteria. In particular, antibodies or antigen-binding fragments thereof that bind specifically to toxin A and / or toxin B of C difficile and neutralize the activities of these toxins; compositions comprising such antibodies; and methods of using the antibodies and the compositions are provided.
Owner:PROGENICS PHARMA INC
Multiple fluorescence PCR detection kit and detection method for clostridium difficile toxin genes
ActiveCN103361434AMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesClostridium difficile infectionsClostridium difficile toxin B
A provided multiple fluorescence PCR detection kit for clostridium difficile toxin genes mainly comprises specific primers, probes and a PCR reaction reagent, and the specific primers and the probes respectively consist of specific primers and probes of clostridium difficile toxin A (tcdA), toxin B (tcdB), binary toxin A (cdtA) and binary toxinB (cdtB). The beneficial effects of the invention comprise: the fast, sensitive and specific multiple fluorescence PCR detection kit and a detection method are provided for the clostridium difficile toxin genes, and a foundation is provided for distinguishing between toxigenic strains and avirulent strains of clostridium difficile, and early diagnosis on infection of clostridium difficile.
Owner:杭州海基生物技术有限公司
Macrolide polymorphs, compositions comprising such polymorphs, and methods of use and manufacture thereof
The invention relates to novel forms of compounds displaying broad spectrum antibiotic activity, especially crystalline polymorphic forms and amorphous forms of such compounds, compositions comprising such crystalline polymorphic forms and amorphous forms of such compounds, processes for manufacture and use thereof. The compounds and compositions of the invention are useful in the pharmaceutical industry, for example, in the treatment or prevention of diseases or disorders associated with the use of antibiotics, chemotherapies, or antiviral therapies, including, but not limited to, colitis, for example, pseudo-membranous colitis; antibiotic associated diarrhea; and infections due to Clostridium difficile (“C. difficile”), Clostridium perfringens (“C. perfringens”), Staphylococcus species, for example, methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus, or Enterococcus including Vancomycin-resistant enterococci.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME LLC
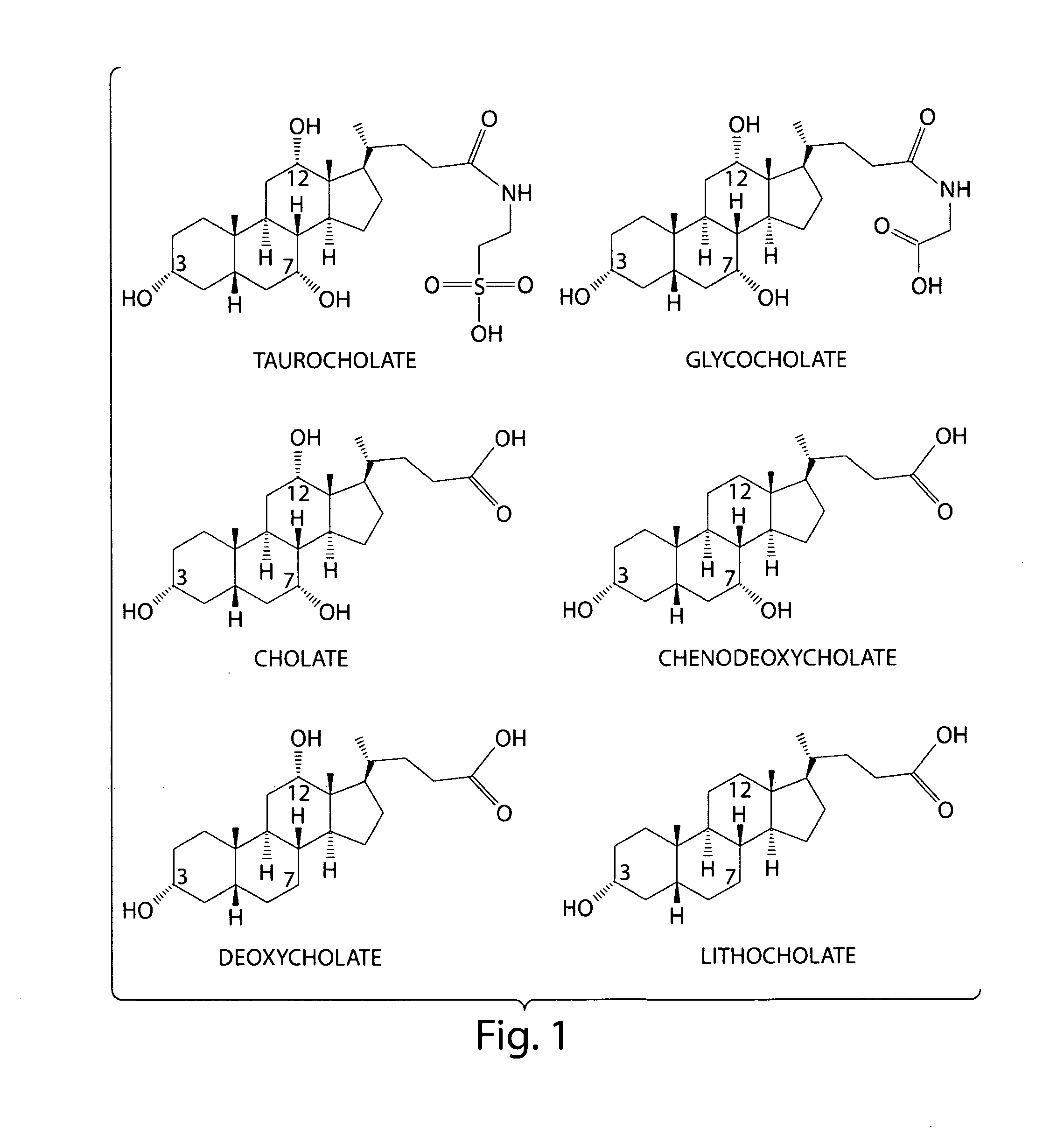
Methods and compositions for inhibiting clostridium difficile spore germination and outgrowth
ActiveUS20110280847A1Preventing Clostridium difficile-associated diseaseGrowth inhibitionAntibacterial agentsBiocideDiseaseSpore germination
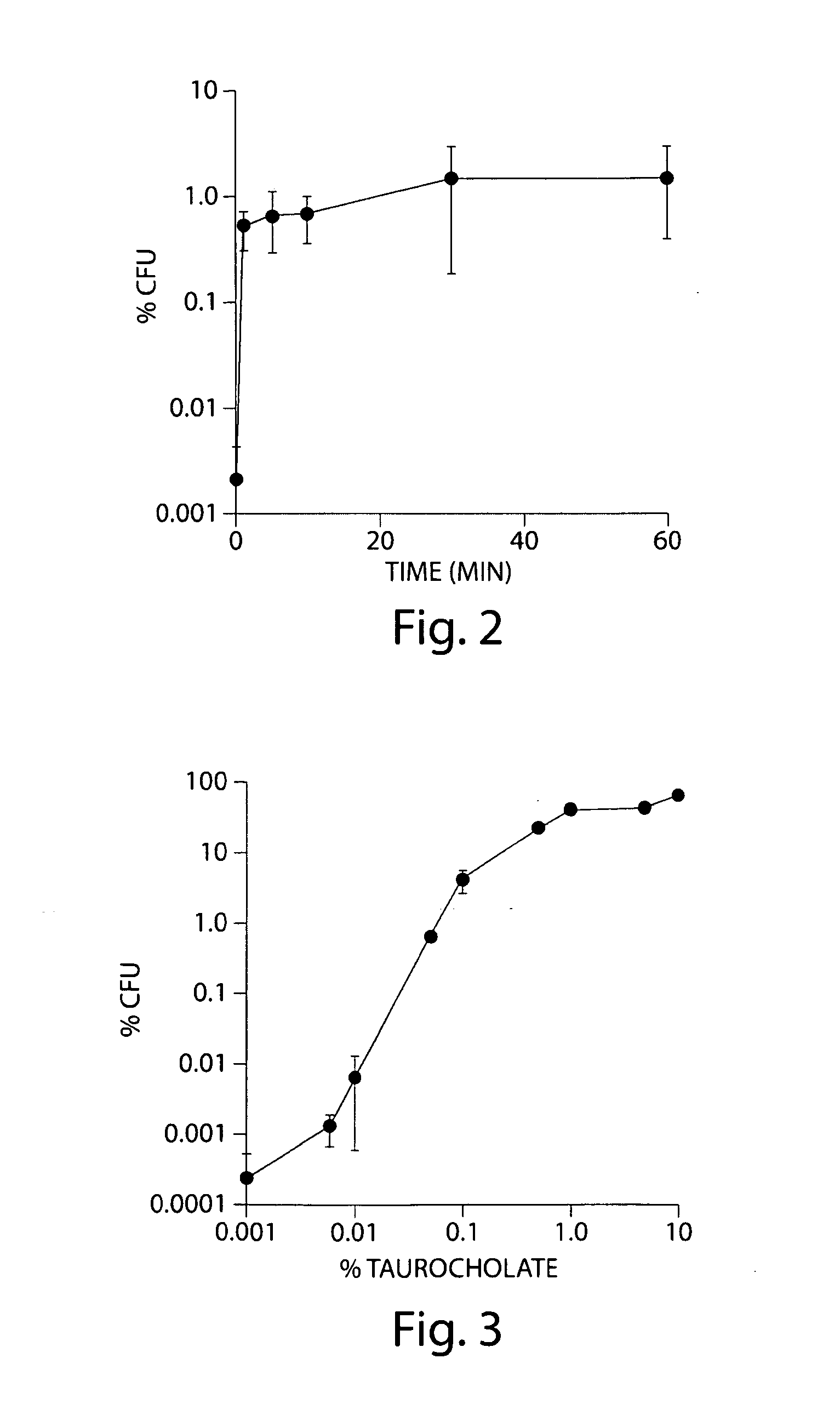
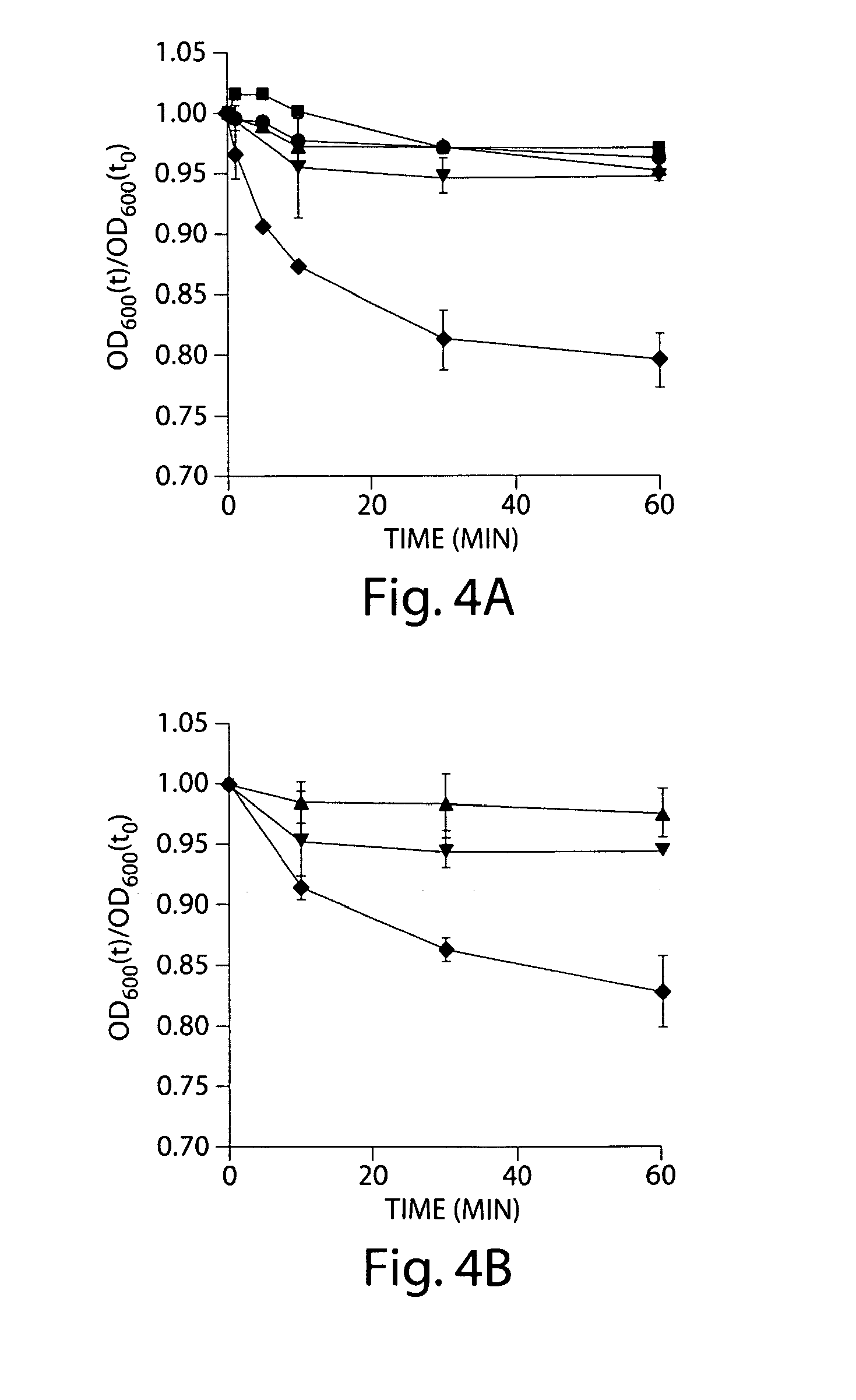
Certain bile acids, including novel bile acids, and derivatives thereof can be used to inhibit the germination of C. difficile spores and / or the growth of C. difficile cells. The methods and compositions of the invention are useful for preventing and treating C. difficile-associated diseases, including but not limited to C. difficile colitis.
Owner:TUFTS UNIV
Compositions and methods for restoring gastrointestinal microbiota following antibiotic treatment
ActiveUS9603876B2Increase the number ofGrowth inhibitionBiocideMetabolism disorderDiseaseIntestinal microorganisms
The present invention relates to characterizing changes in mammalian bacterial gastrointestinal, cutaneous and nasal microbiota associated with antibiotic treatment and various disease conditions (such as asthma, allergy, obesity, metabolic syndrome, gastrointestinal reflux disease (GERD), eosinophilic esophagitis, gastro-esophageal junction adenocarcinomas (GEJAC), infections due to bacteria that are resistant to antibiotics, including Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), Clostridium difficile, vancomycin-resistant enterococci, etc.) and related diagnostic and therapeutic methods. Therapeutic methods of the invention involve the use of live bacterial inoculants that are capable of restoring healthy mammalian bacterial gastrointestinal, skin, and nasal microbiota.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
Mutants of clostridium difficile toxin B and methods of use
InactiveUS20080107673A1Antibacterial agentsAnimal cellsHospitalized patientsClostridium difficile infections
An active, or passive vaccine utilizing purified non-toxic mutant TcdB toxins from Clostridium difficile for humans and animals against infections caused by C. difficile and / or C. sordellii. Persons most potentially affected by C. difficile infections include hospitalized patients, infants, and elderly persons. The TcdB toxin mutant of the vaccine preferably lacks the toxicity of a native C. difficile TcdB toxin. A serum comprising antibodies raised to the TcdB toxin mutant is also available for treating humans or animals against C. difficile infections. The serum may be used in a method for conferring passive immunity against C. difficile. Antibodies to the TcdB toxin mutant may be used in diagnostic tests or in treatments to clear TcdB toxin from bodily fluids. The mutant TcdB toxin may be produced by recombinant methods using cDNA encoding the toxin, the cDNA contained for example in a plasmid or host cell.
Owner:BALLARD JIMMY D +1
Antibodies against clostridium difficile toxins and uses thereof
ActiveUS20100233181A1High affinityLess immunogenicAntibacterial agentsGenetic material ingredientsClostridium difficile toxin AClostridium difficile (bacteria)
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS UNIV OF +1
Colonic delivery of antimicrobial agents
InactiveUS20100239682A1Provides for selectionMinimizes problemAntibacterial agentsPowder deliveryBacteroidesActive agent
Antimicrobial compositions for oral delivery, and administration to the colon, distal ileum, or other portion of the gastrointestinal tract other than the stomach, of bacteriophage, phage proteins, antimicrobial peptides, or antimicrobial aptamers, are disclosed. In one embodiment, the active agent is capable of lysing the bacterial cell wall. In another embodiment, the active agent is capable of interacting with a receptor or enzyme in the bacteria. In some embodiments, the active agents selectively act on one or more harmful bacteria, such as Clostridium difficile, and either do not act, or act to a lesser extent, on helpful bacteria, such as bifidobacteria. When the agents are not delivered directly to the colon, they active agents ultimately enter the colon and affect the bacteria that are present in the colon. The compositions can include beads of pectin in the form of a cationic salt enclosing the active agent, or other types of drug delivery systems designed for targeted delivery to the desired portion of the gastrointestinal tract.
Owner:ASSISTANCE PUBLIQUE HOPITAUX DE PARIS +2
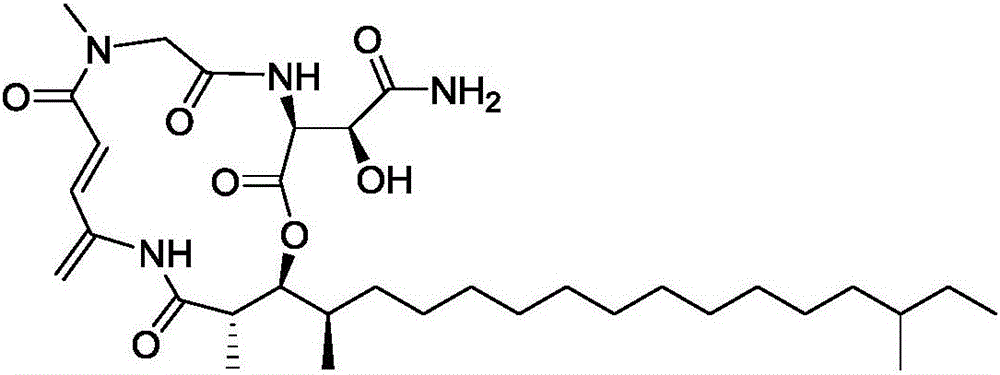
Application of Rakicidins compounds in resistance to clinical pathogenic anaerobic bacteria
ActiveCN105709205AQuite activeStrong inhibitory activityAntibacterial agentsBacteriaDiseaseUpper urinary tract infection
The invention relates to the field of biological medicine, in particular to an application of Rakicidins compounds in resistance to clinical pathogenic anaerobic bacteria. Pharmacodynamic experiments indicate that the Rakicidins compounds have good resistant effect on the clinical pathogenic anaerobic bacteria and have the resistant effect on vancomycin enterococcus infection diseases. The Rakicidins compounds can be used for treating diarrhea, enteritis, alimentary infection, oral infection or skin acne caused by clostridium difficile as well as diseases such as urinary tract infection, or skin soft-tissue infection and the like.
Owner:FUJIAN INST OF MICROBIOLOGY
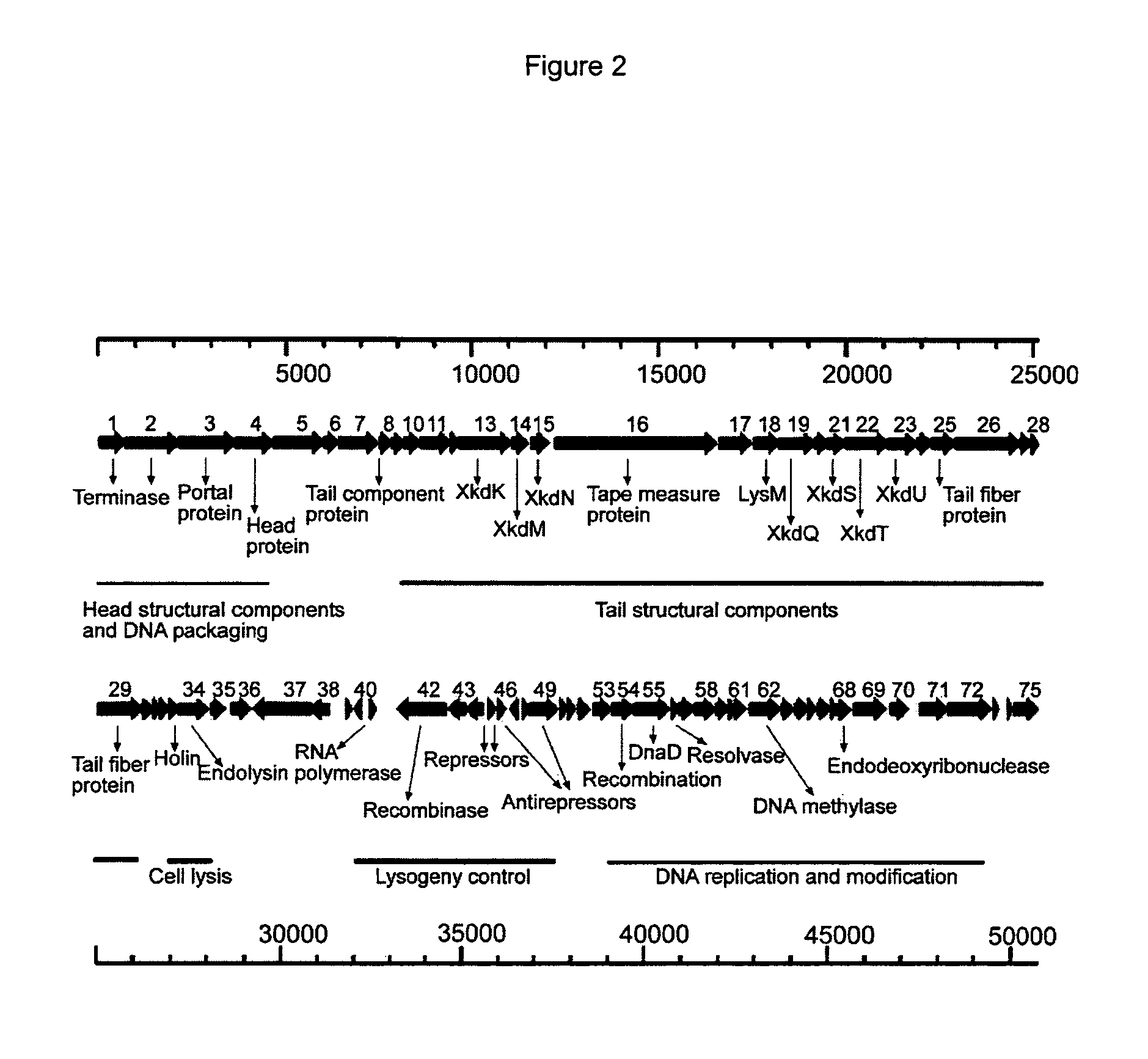
Novel Polypeptides Having Endolysin Activity and Uses Thereof
InactiveUS20100310522A1Reduce sensitivityExtended half-lifeAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsDiseaseLysin
The present invention provides isolated polypeptides comprising the amino acid sequence of SEQ ID NO:1, or a fragment, variant, derivative or fusion thereof which is capable of binding specifically to and / or lysing cells of Clostridium difficile, and means for producing the same, with the proviso that the fragment, variant, derivative or fusion is not a naturally occurring lysin of a bacteriophage of Clostridium difficile. The invention further provides methods for killing bacterial cells, such as cells of Clostridium difficile, and for diagnosing, treating and preventing diseases and conditions associated with infection of the same. The invention also provides diagnostic kits for use in such methods.
Owner:PLANT BIOSCI LTD
Composition And Method For Stabilizing And Maintaining The Viability Of Hardy Microorganisms
PendingUS20170226469A1Stabilizing and maintaining viabilityBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganismBacteroides
The present application is to provide a composition and method for stabilizing and maintaining the viability of hardy microorganisms from sample collection to downstream analysis. In particular, there is a method for preserving viable hardy bacteria, such as Mycobacteria, Bacillus anthracis, or Clostridium difficile, in a biological sample, comprising contacting the biological sample with a stabilization composition, wherein the stabilization composition comprises a chelating agent, a denaturing, a salt and has a pH between about 6 and about 11.
Owner:DNA GENOTEK
Selective antibacterials for clostridium difficile infections
ActiveUS8796292B2Reduce the possibilityHigh activityAntibacterial agentsBiocideDiseaseClostridium difficile infections
The invention features compounds of formula (I): The compounds are useful as antibacterial agents, especially again Clostridium difficile-associated diseases.
Owner:ACURX PHARMA LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com