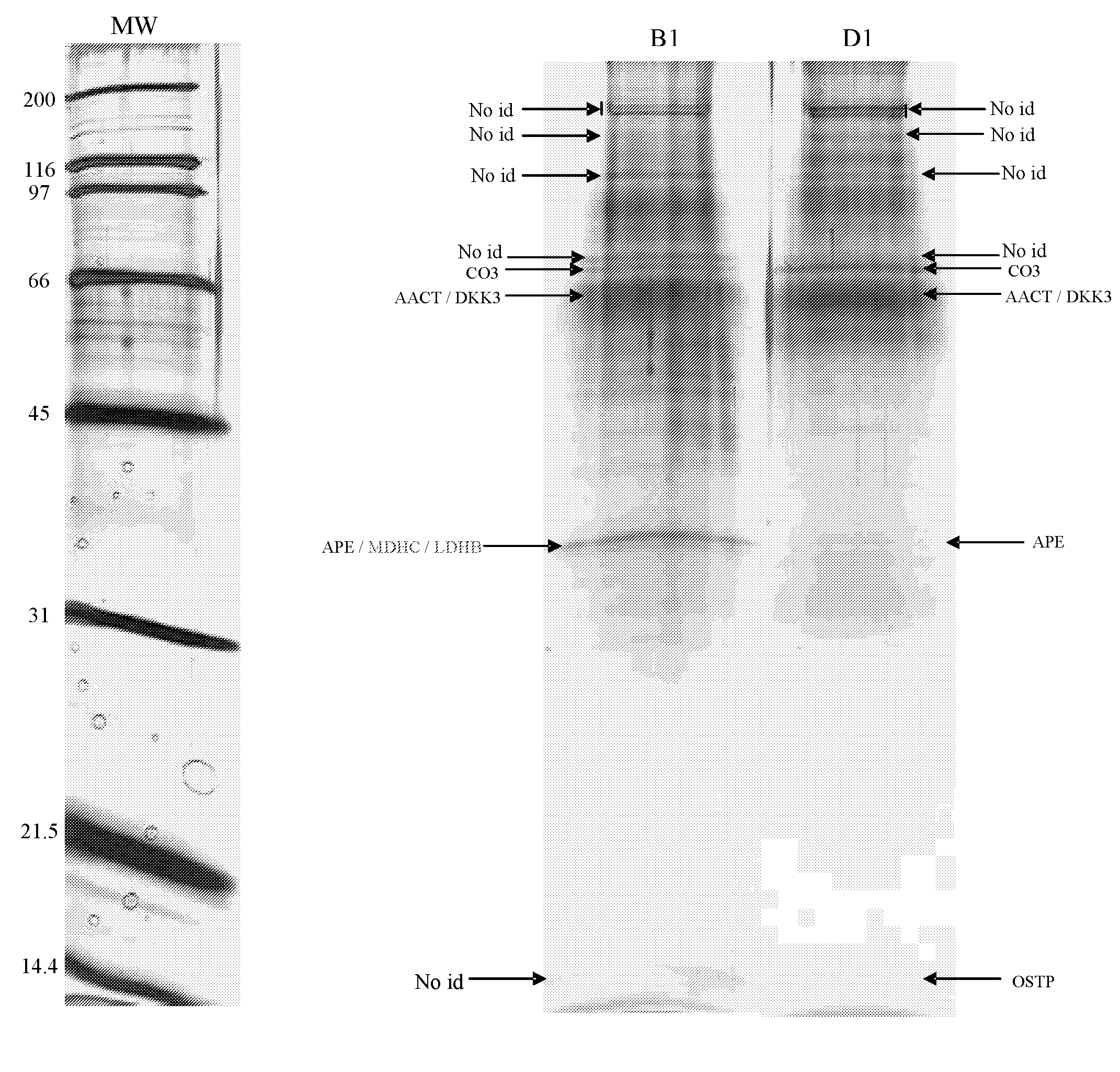
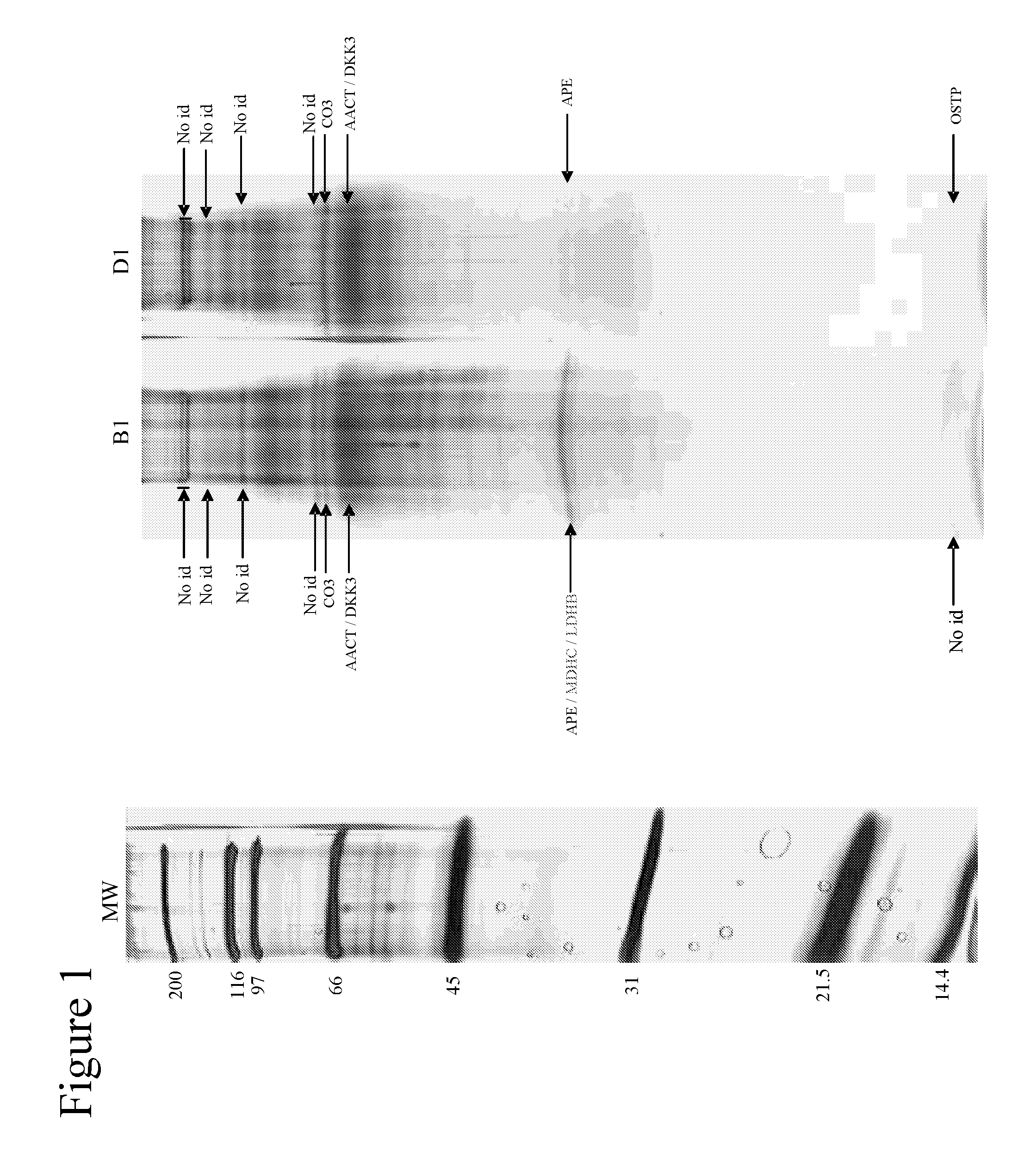
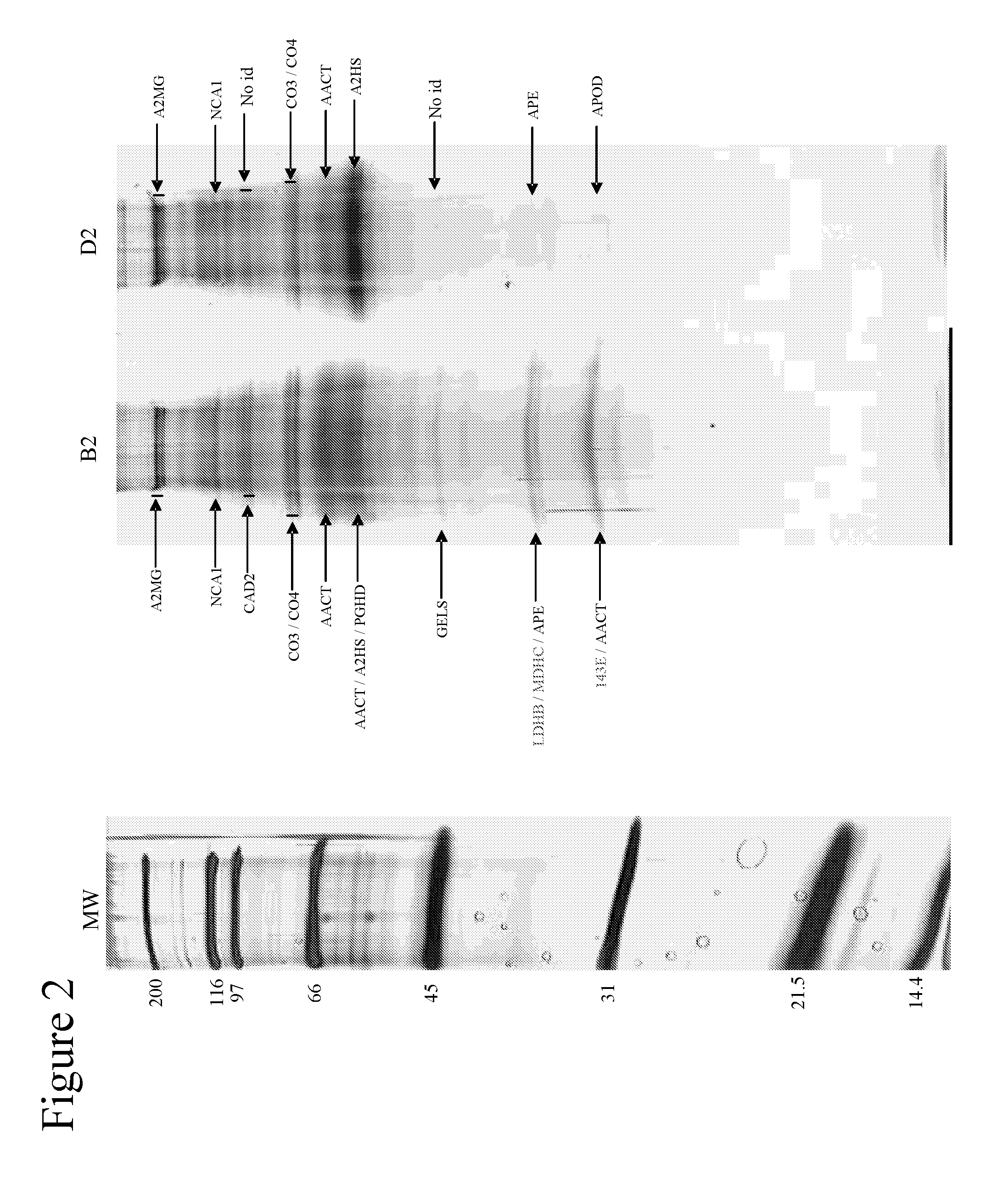
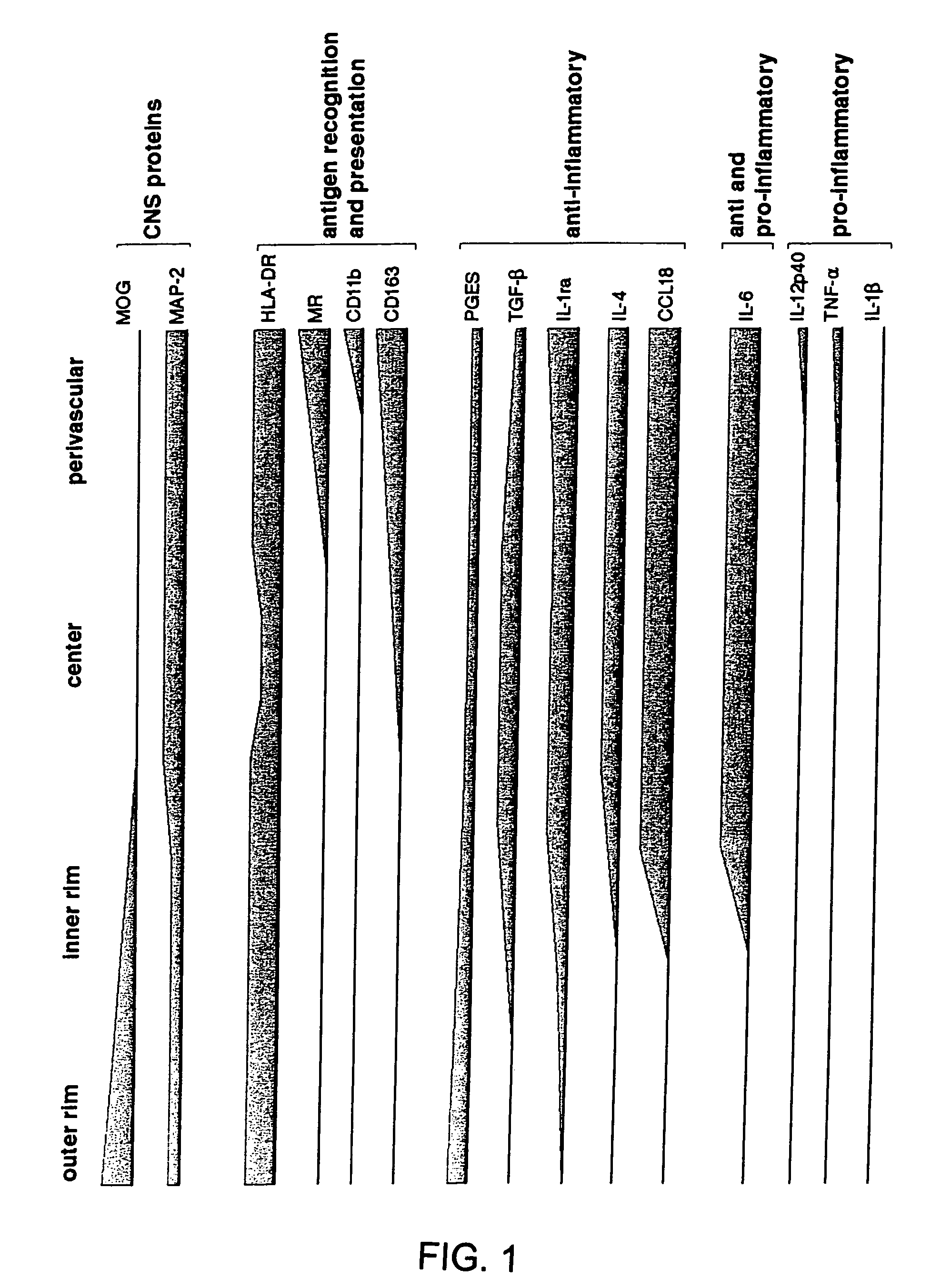
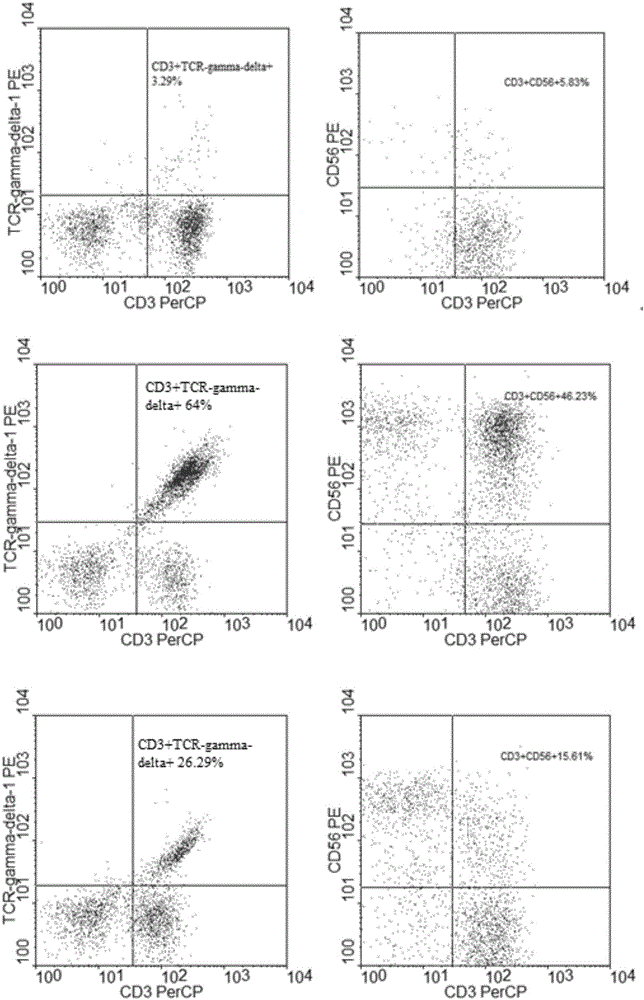
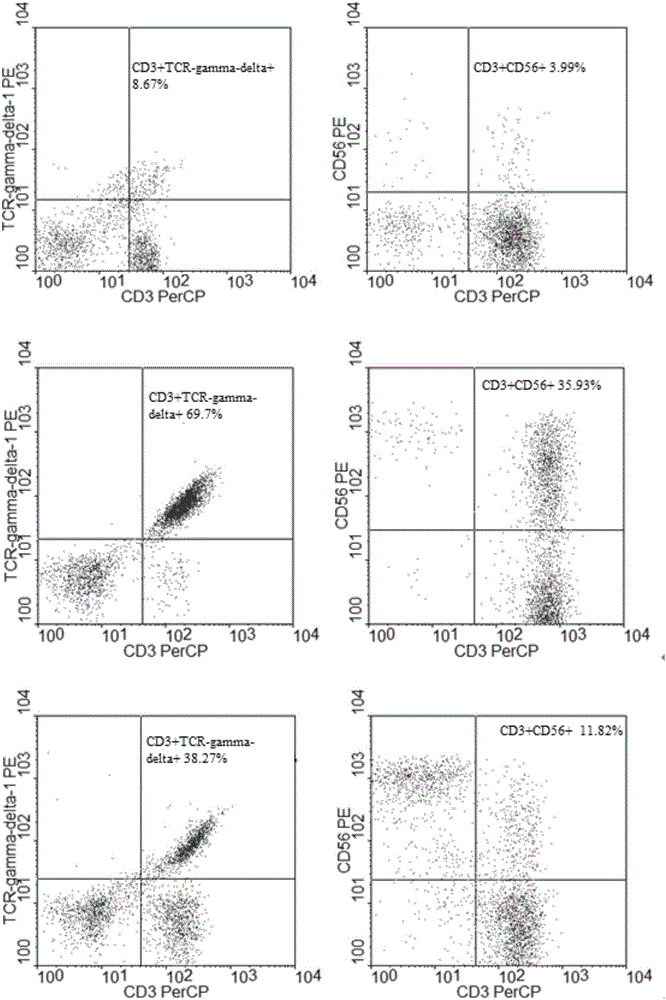
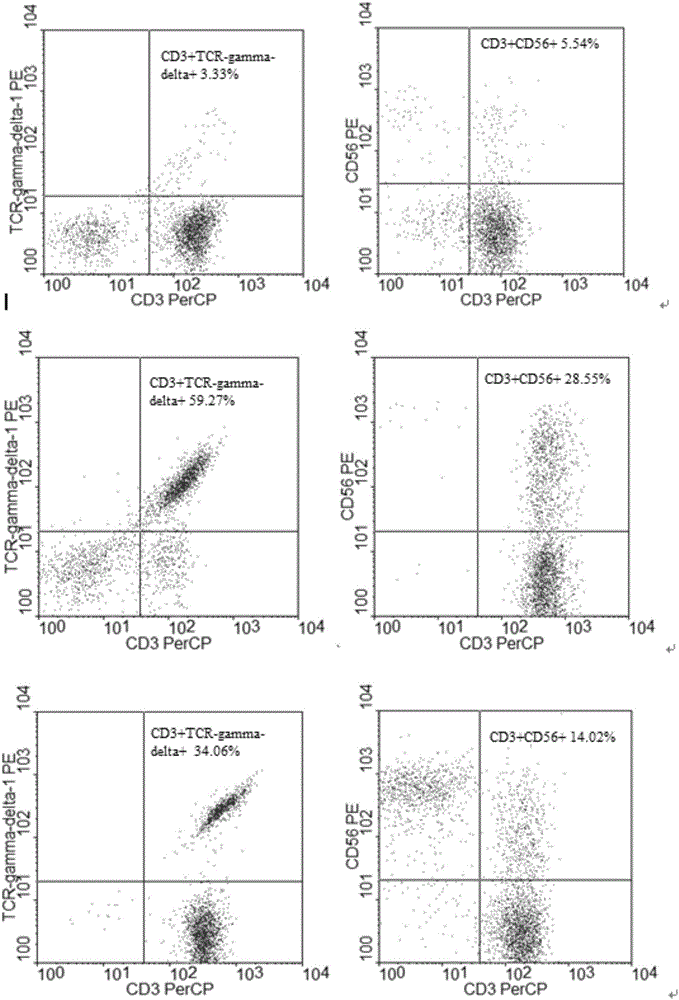
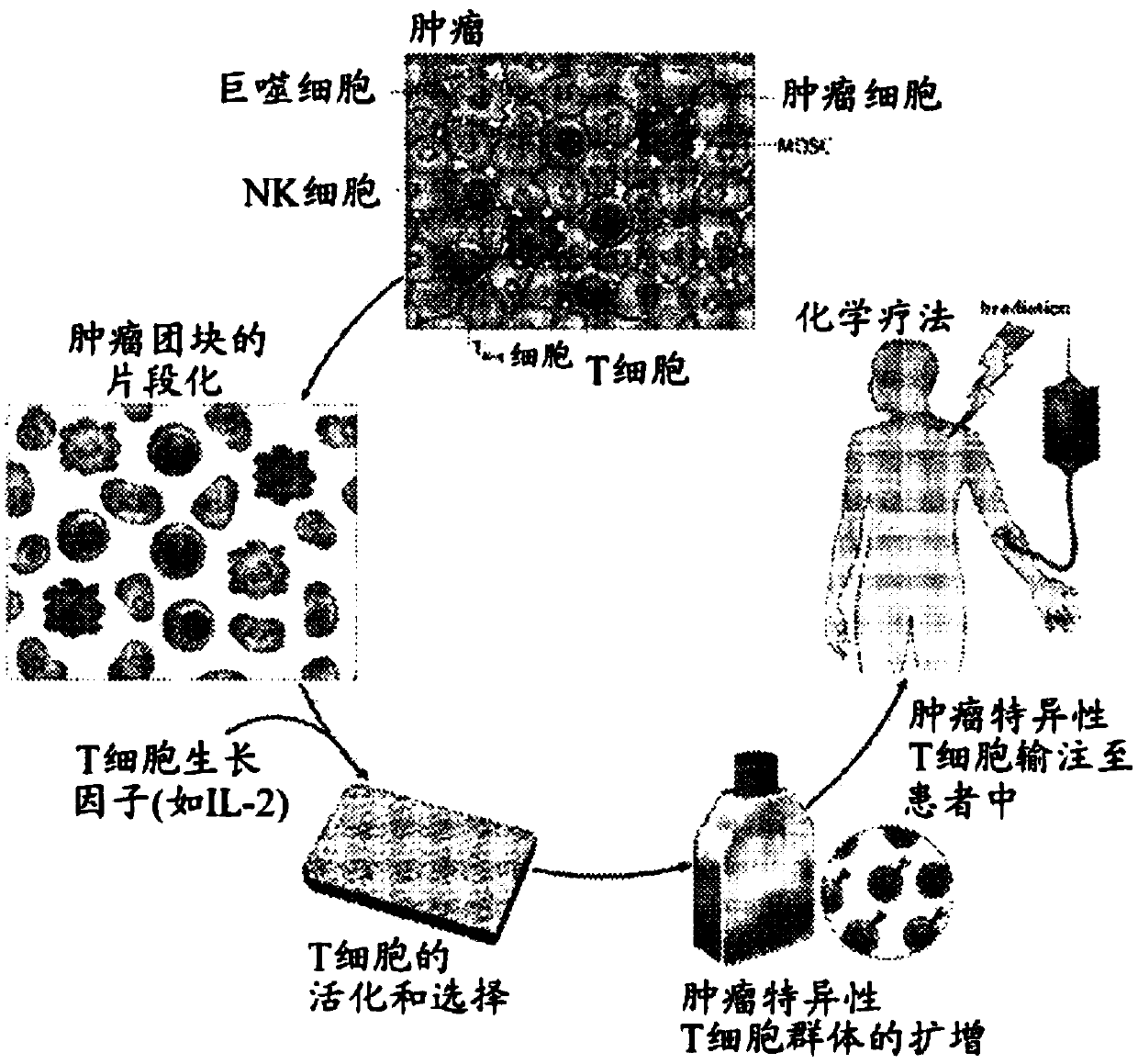
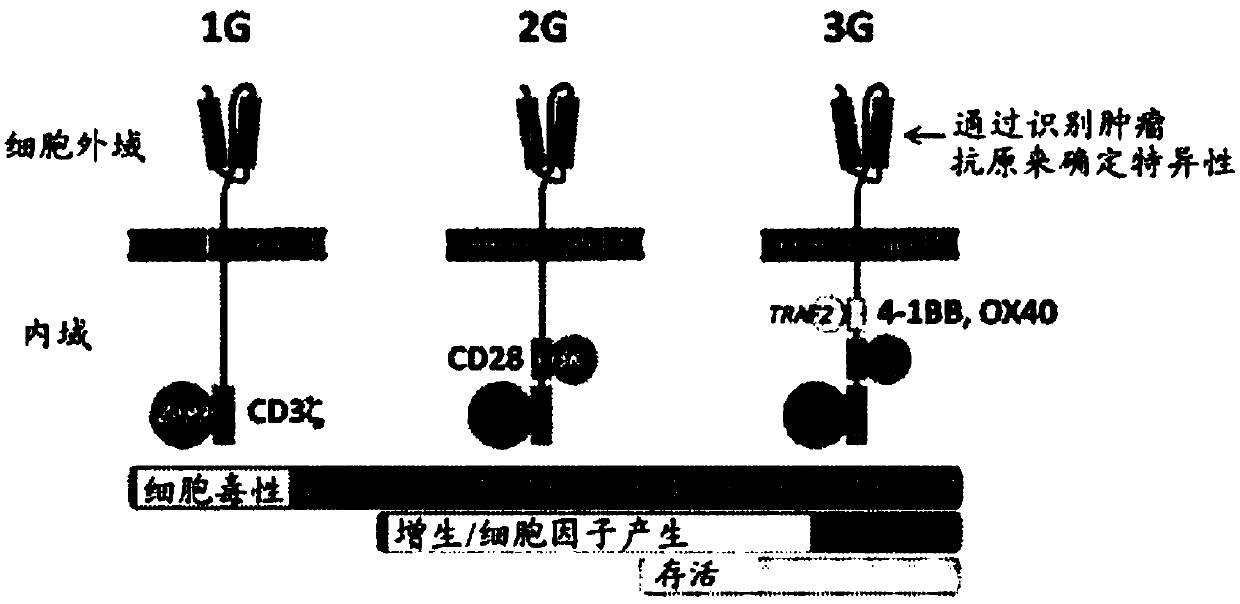
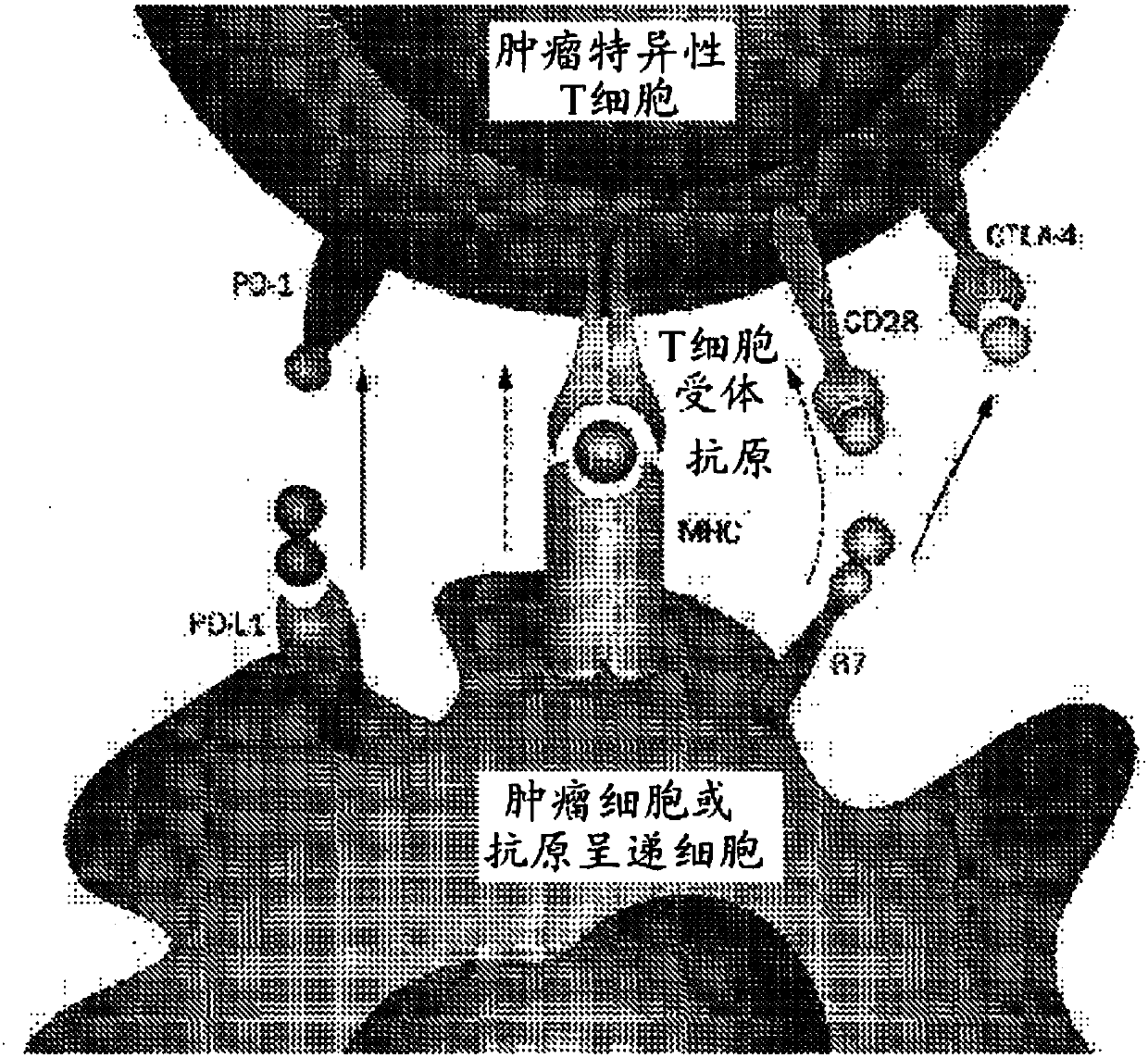
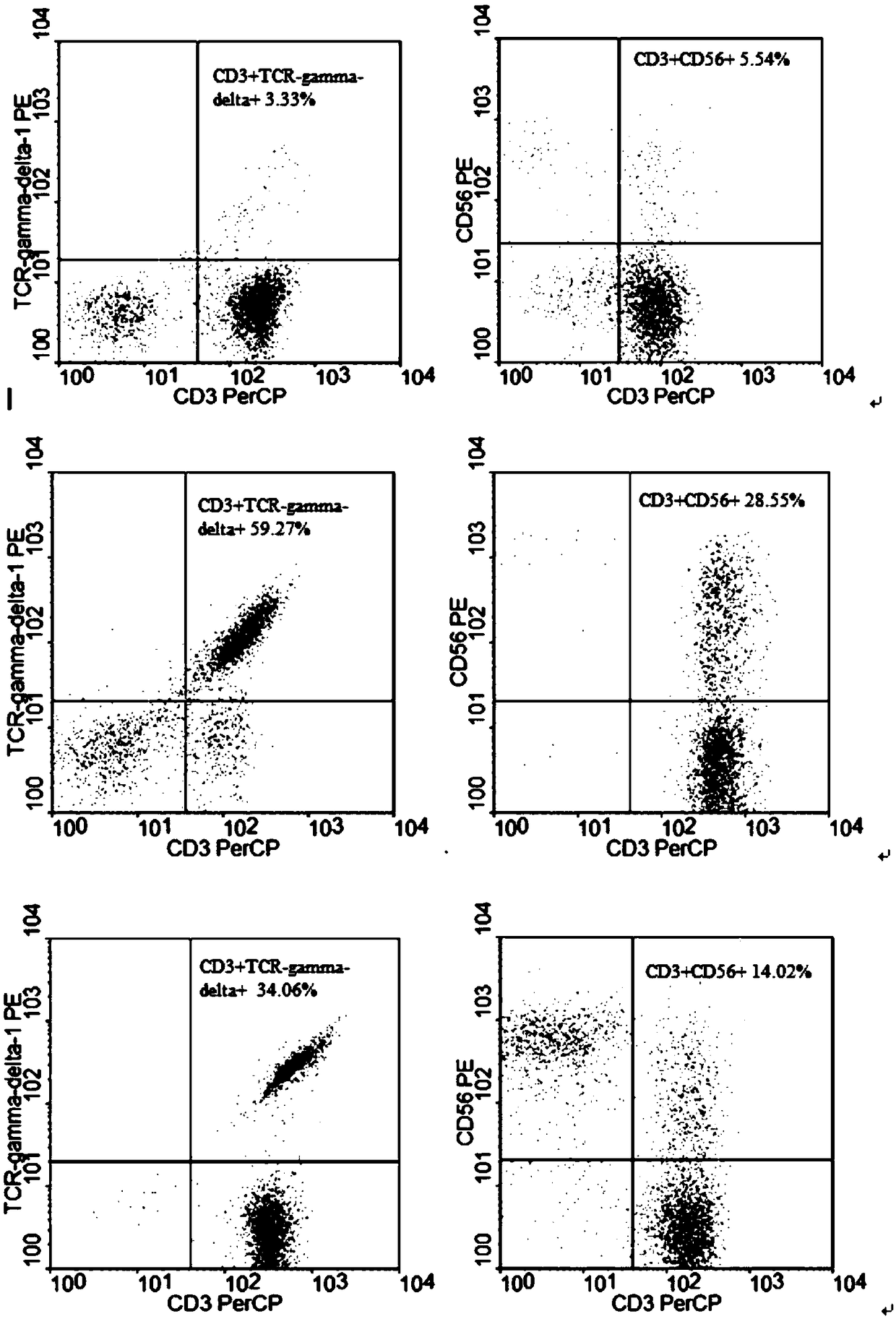
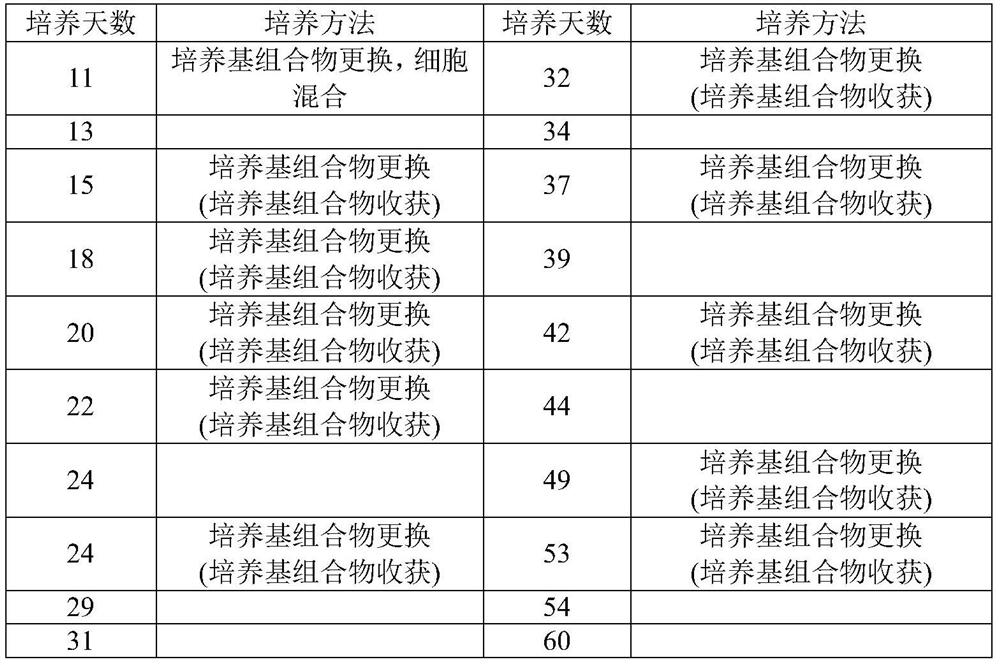
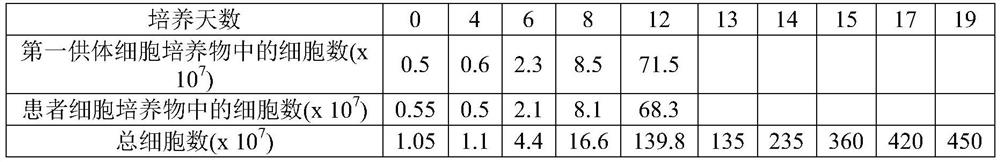
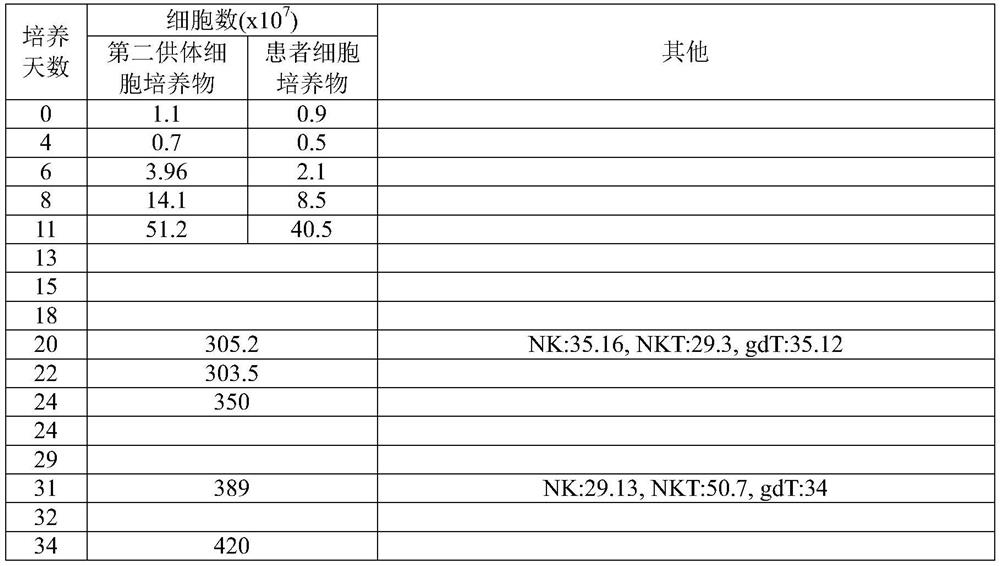
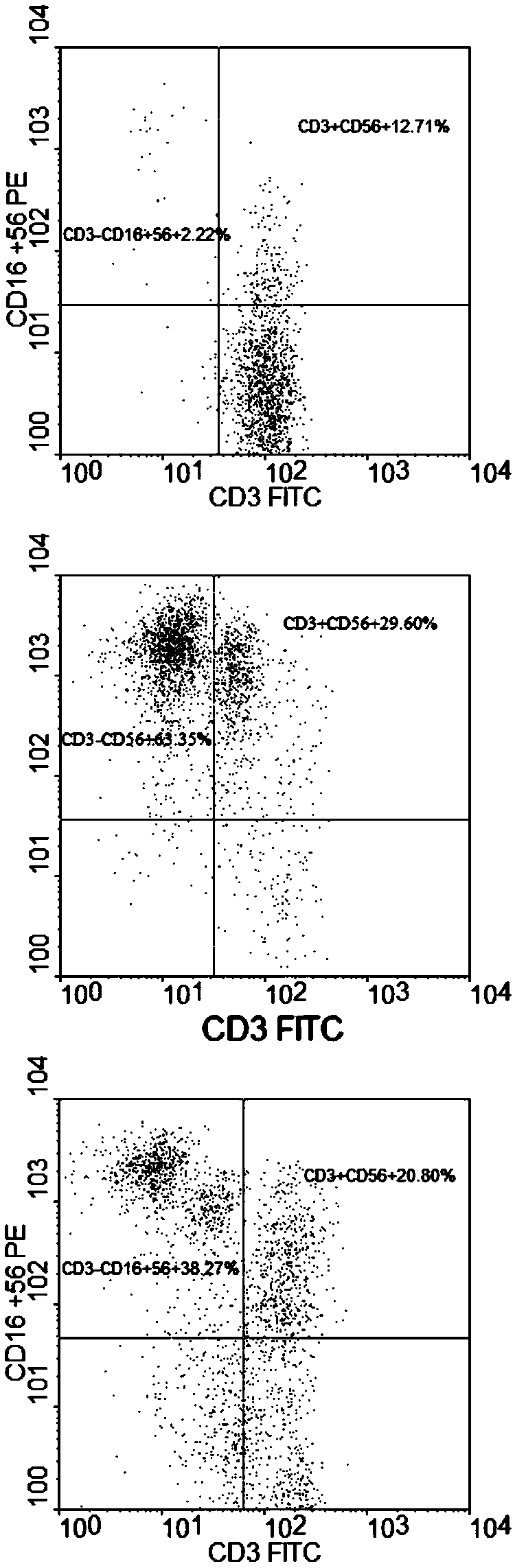
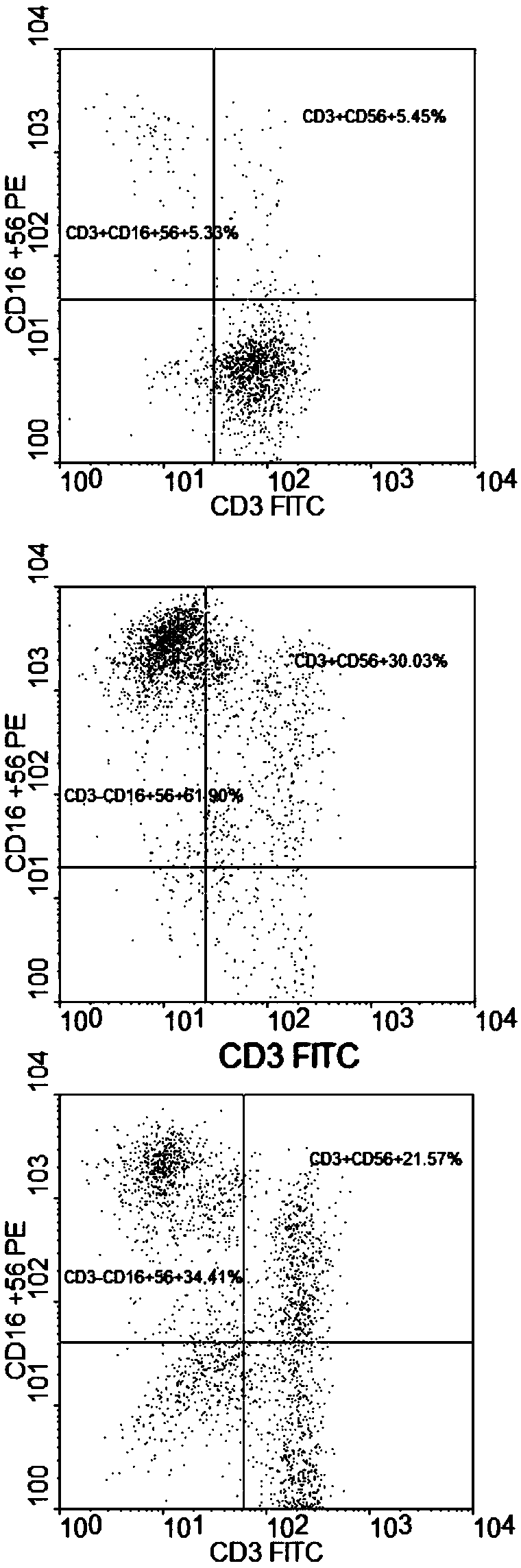
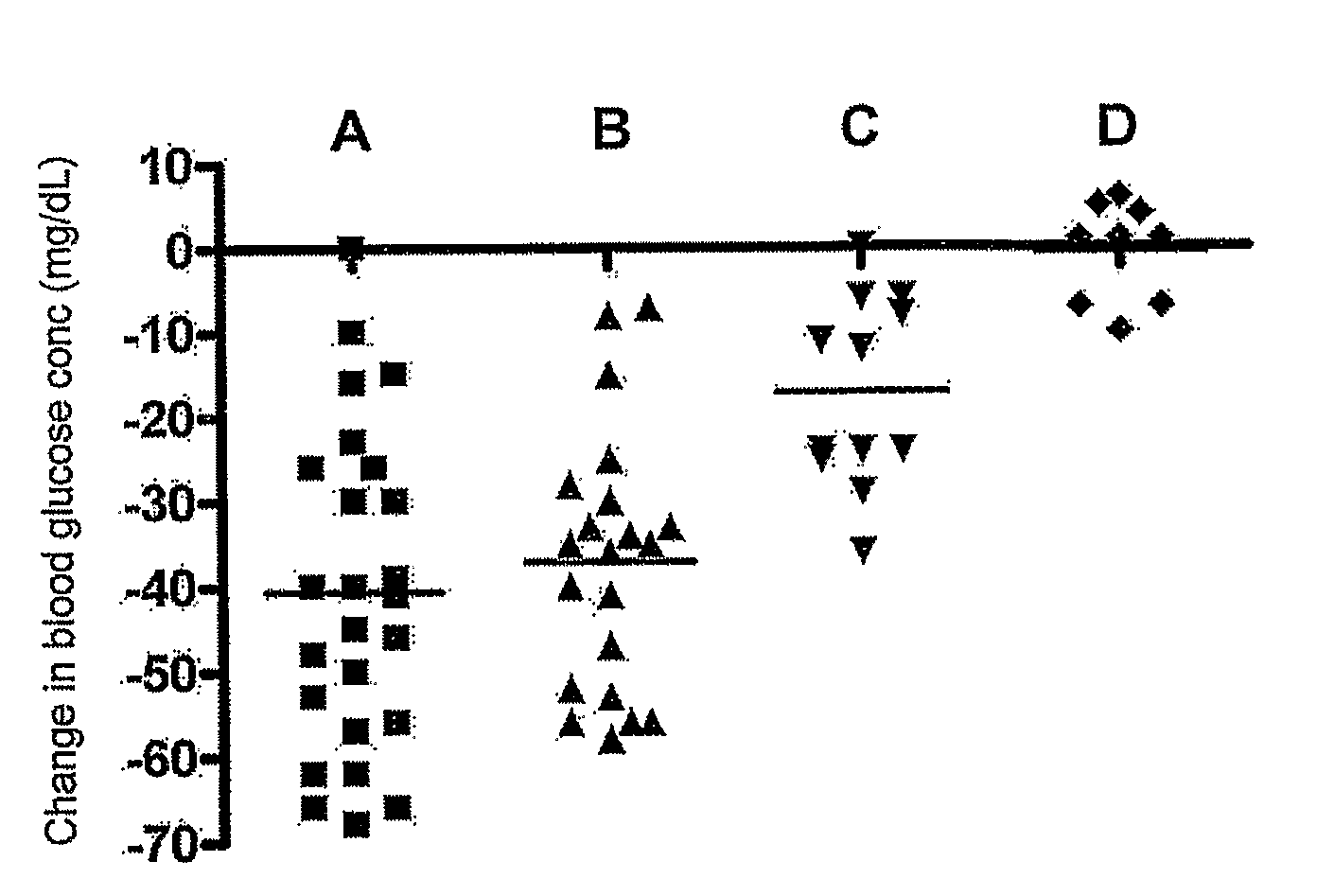
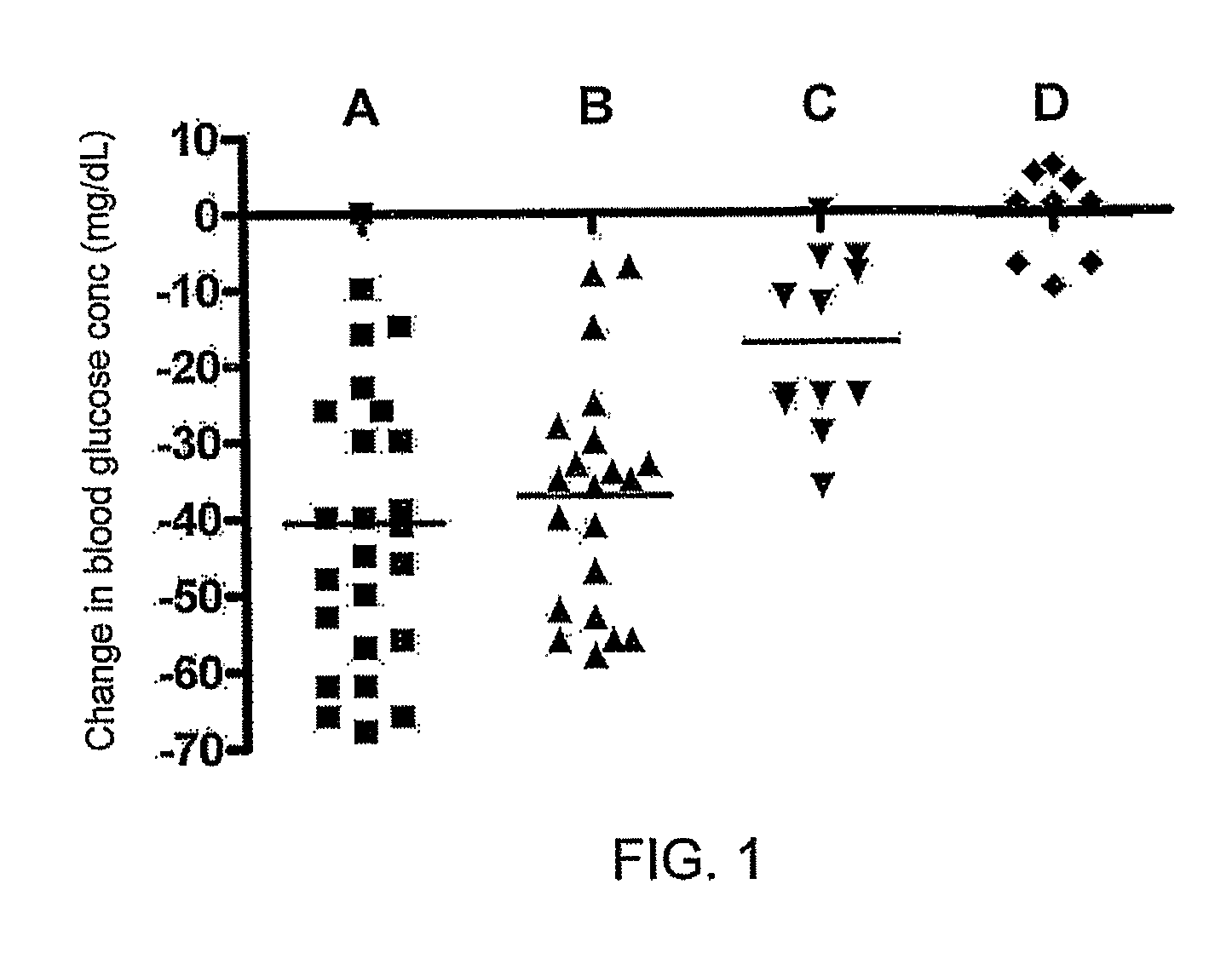
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
58 results about "Healthy donor" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Method for treatment of disorders of the gastrointestinal system
There are provided novel synthetic stool preparations comprising bacteria isolated from a fecal sample from a healthy donor. The synthetic stool preparations are used for treating disorders of the gastrointestinal tract, including dysbiosis, Clostridium difficile infection and recurrent Clostridium difficile infection, prevention of recurrence of Clostridium difficile infection, treatment of Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis, irritable bowel syndrome, inflammatory bowel disease, and diverticular disease, and treatment of food poisoning such as salmonella. Methods of preparation and methods of use of the synthetic stool preparations are also provided.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF GUELPH +2
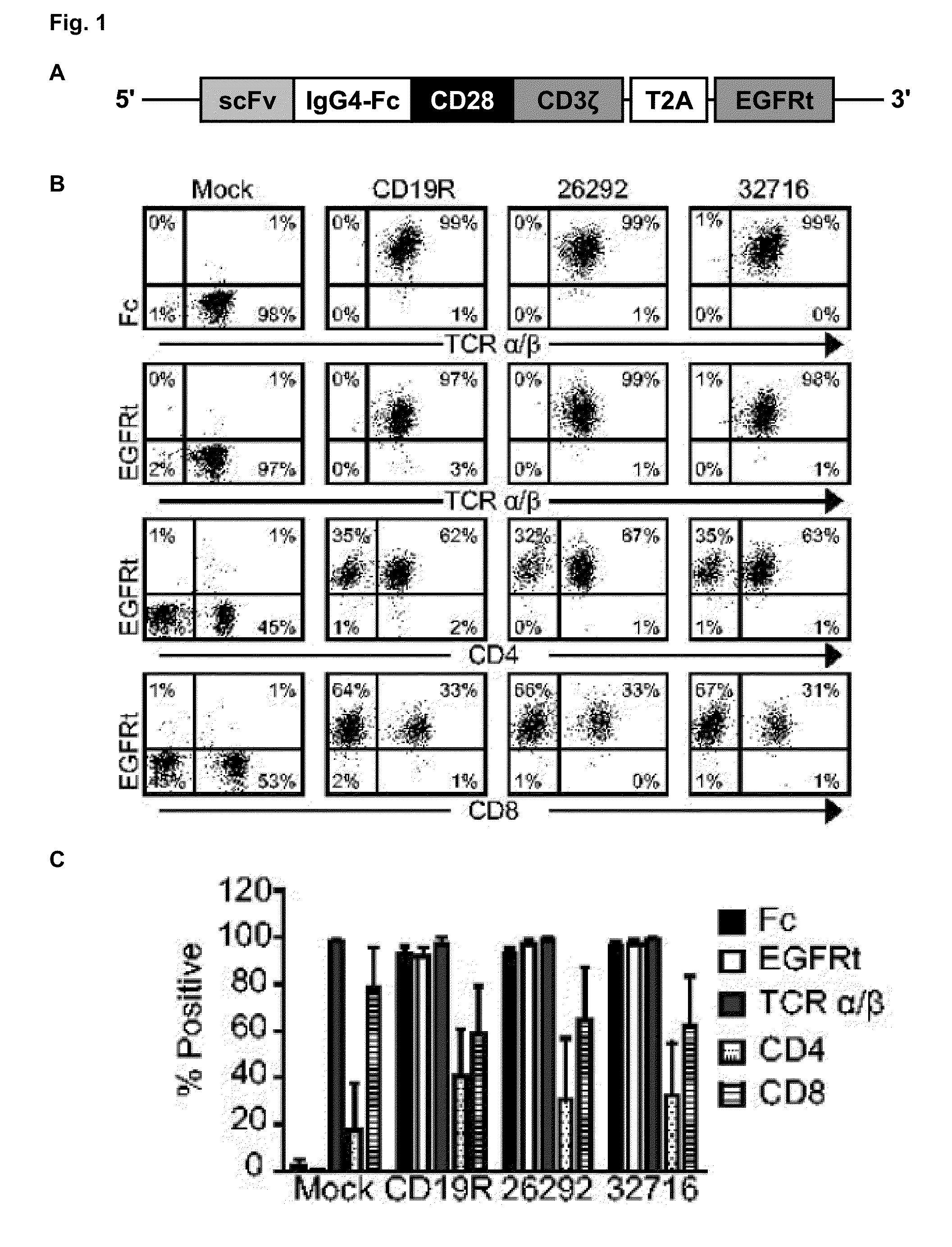
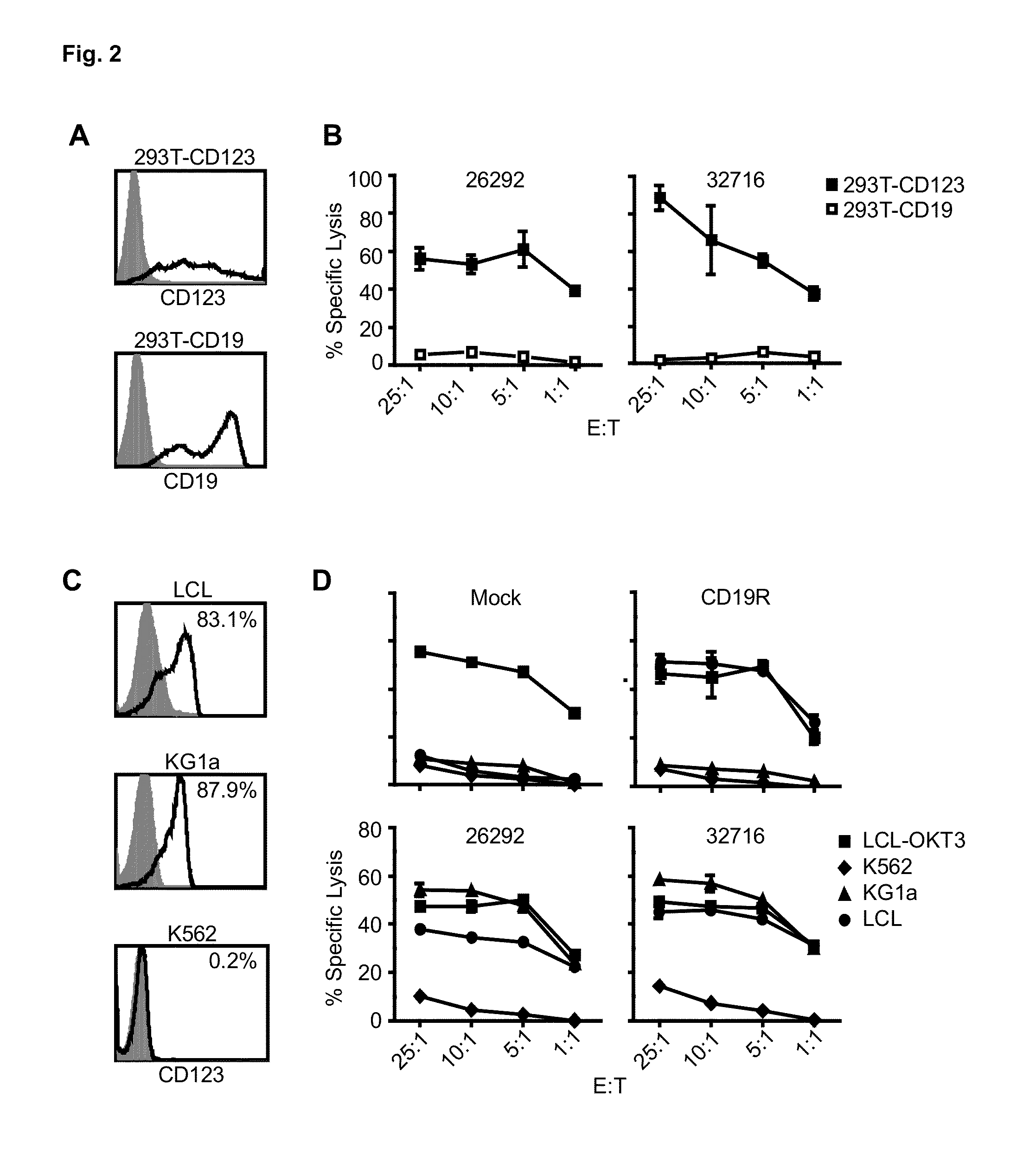
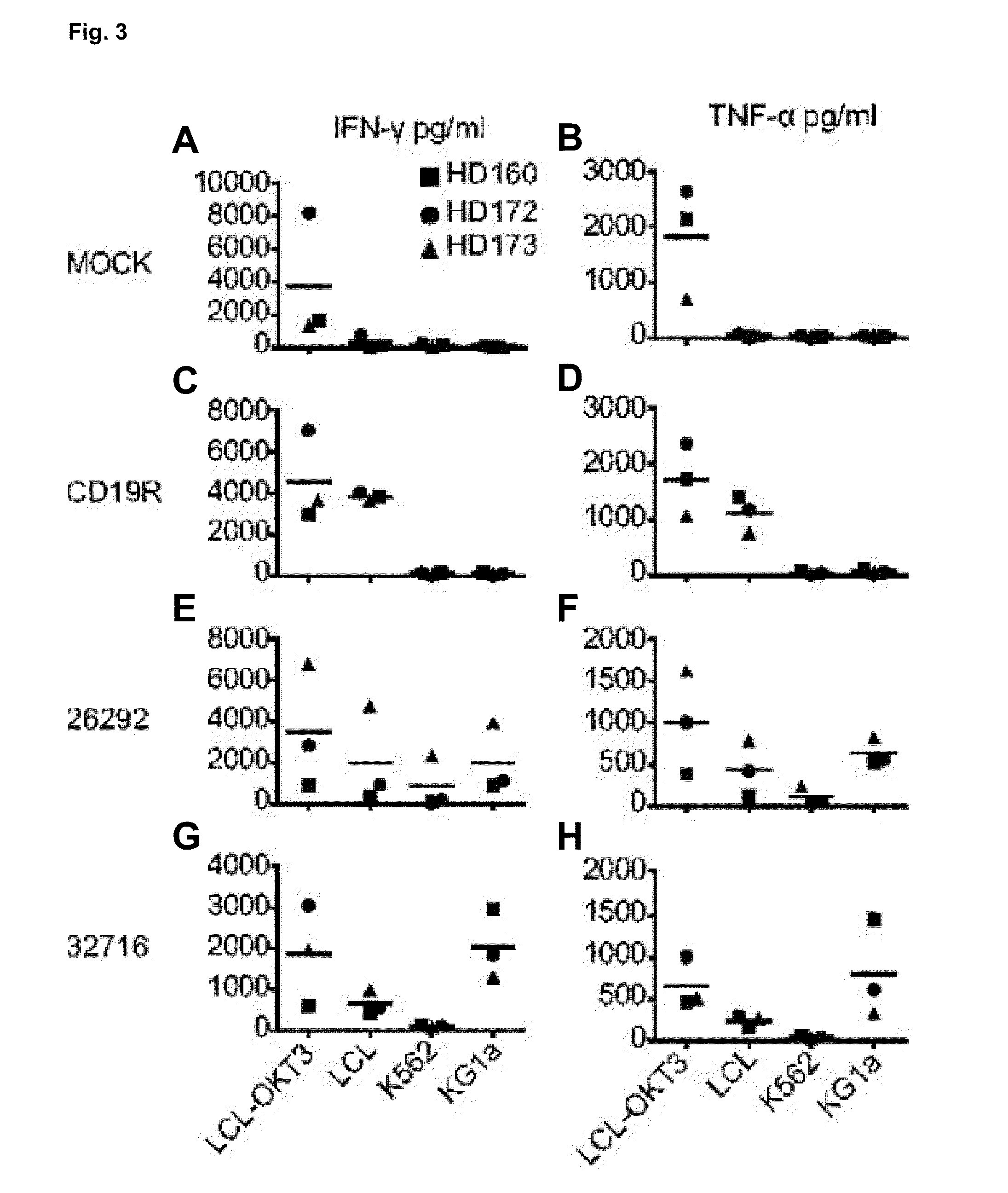
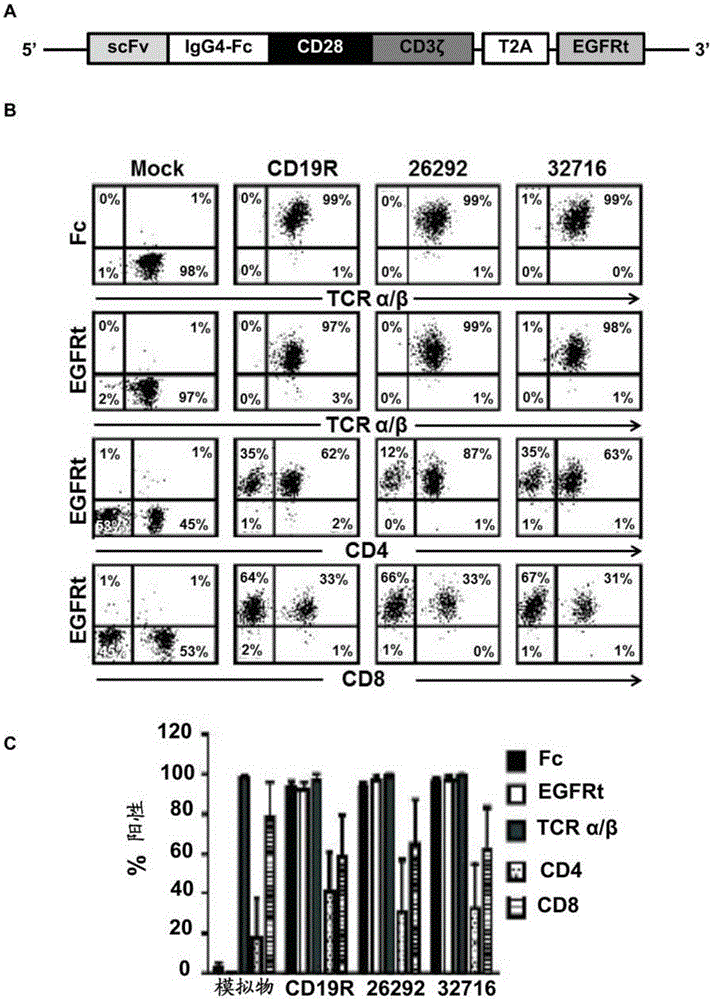
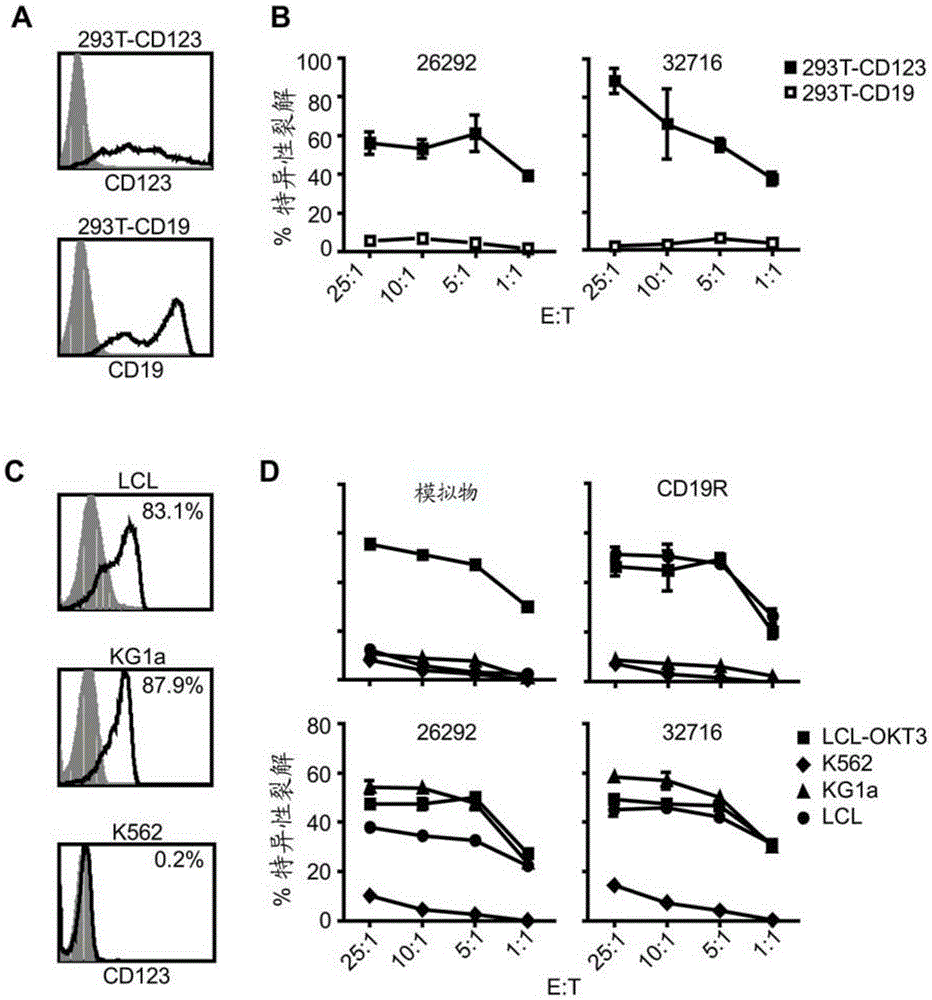
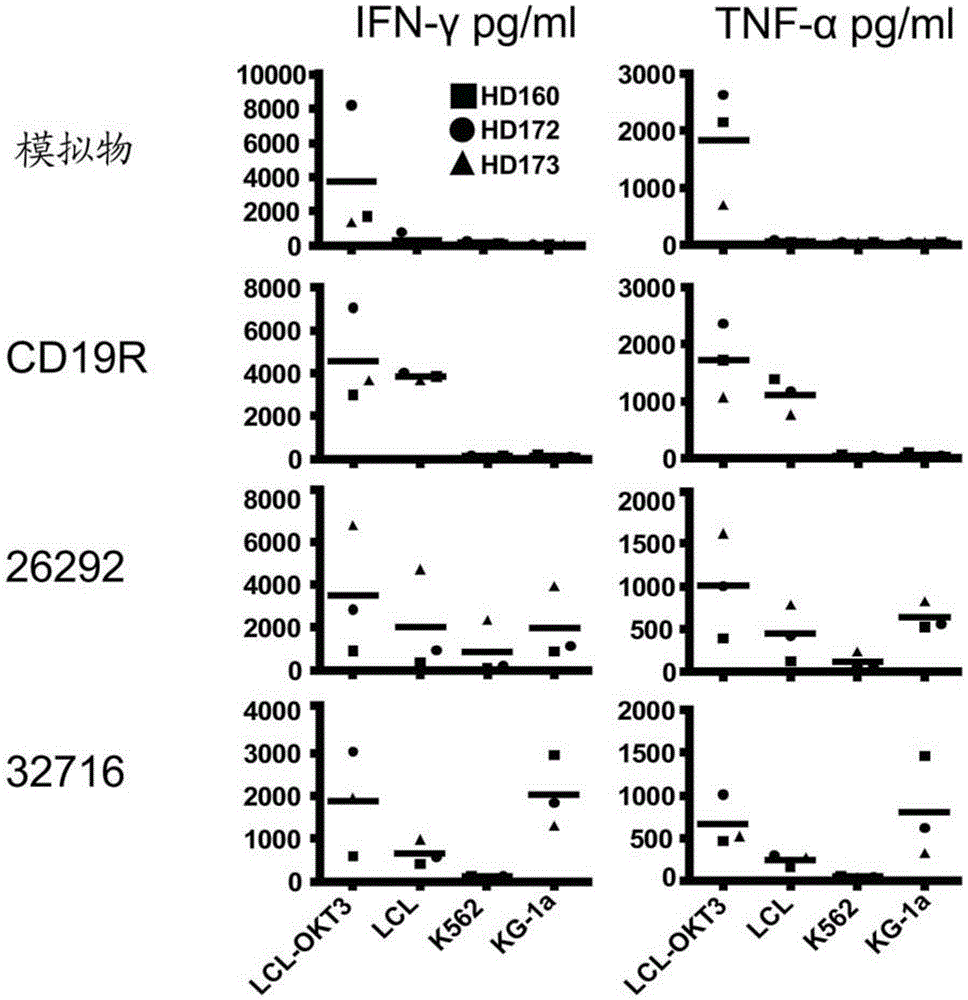
Cd123-specific chimeric antigen receptor redirected t cells and methods of their use
ActiveUS20140271582A1BiocideAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsCD19-specific chimeric antigen receptorT-Cell Specificity
A family of chimeric antigen receptors (CARs) containing a CD123 specific scFv was developed to target different epitopes on CD123. In some embodiments, such a CD123 chimeric antigen receptor (CD123CAR) gene includes an anti-CD123 scFv region fused in frame to a modified IgG4 hinge region comprising an S228P substitution, an L235E substitution, and optionally an N297Q substitution; a costimulatory signaling domain; and a T cell receptor (TCR) zeta chain signaling domain. When expressed in healthy donor T cells (CD4 / CD8), the CD123CARs redirect T cell specificity and mediated potent effector activity against CD123+ cell lines as well as primary AML patient samples. Further, T cells obtained from patients with active AML can be modified to express CD123CAR genes and are able to lyse autologous AML blasts in vitro. Finally, a single dose of 5.0×106 CAR123 T cells results in significantly delayed leukemic progression in mice. These results suggest that CD123CAR-transduced T cells may be used as an immunotherapy for the treatment of high risk AML.
Owner:CITY OF HOPE
Diagnostic Method for Brain Damage-Related Disorders
A brain damage-related disorder is diagnosed in a subject by detecting at least one polypeptide, or a variant or mutant thereof, in a sample of body fluid taken from the subject, wherein the polypeptide is one for which the level is either increased or decreased in cerebrospinal fluid from deceased patients compared to cerebrospinal fluid from healthy donors.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF GENEVA
Compounds of therapeutic value in the treatment of multiple sclerosis and other diseases wherein foamy cells are involved in the disease etiology
InactiveUS7524820B1Requirement reductionLow costAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsDisease etiologyMedicine
The invention provides a method for assessing or determining activity of a test compound on modulation of gene product levels comprising culturing cells, contacting at least one of the cultured cells with a lipid-rich fraction, contacting at least one of the cultured cells with said test compound, determining the presence of a gene product of at least one cell of the cultured cells, and optionally determining the presence of the gene product of at least one cultured cell not contacted with said test compound. To assess human conditions most fully, it is preferred that the cell is of human origin, for example a peripheral blood monocyte taken from a healthy donor.
Owner:BIOTEMPT
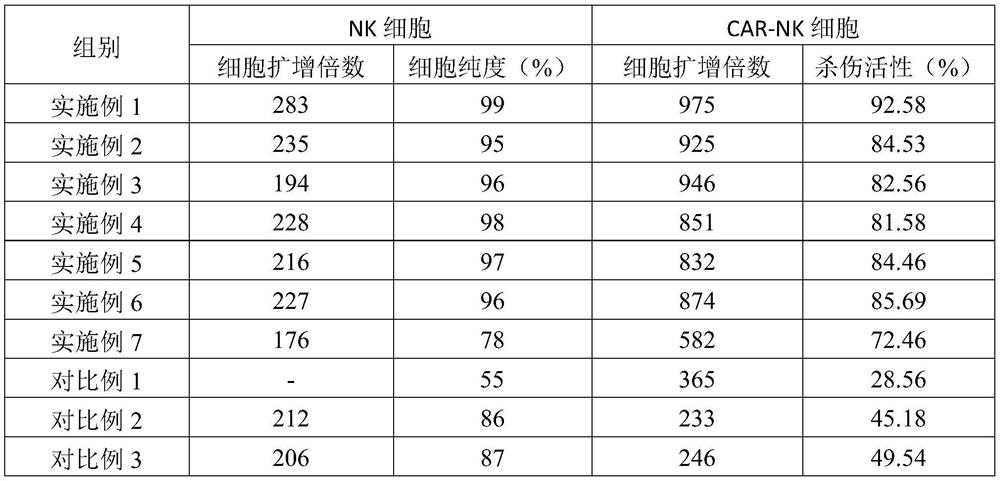
Method for jointly preparing CAR-NK (chimeric antigen receptor-natural killer) cells and CAR-NKT (natural killer T) cells
ActiveCN106350487AReduce purification costsEfficient killingBlood/immune system cellsCell culture active agentsPeripheral blood mononuclear cellNatural Killer Cell Inhibitory Receptors
The invention discloses a method for jointly preparing CAR-NK (chimeric antigen receptor-natural killer) cells and CAR-NKT (natural killer T) cells. The method includes steps of 1), adding peripheral blood mononuclear cells into cell culture media, pre-activating NK cells and NKT cells in the peripheral blood mononuclear cells and selectively activating and amplifying the NK cells and the NKT cells in an in-vitro manner; 2), transducing mixed cells obtained at the step 1) by the aid of lentiviral vectors with gene sequences of chimeric antigen receptors. The method has the advantages that the CAR-NK cells and the CAR-NKT cells can be prepared from NKs and NKTs of healthy donors in a standardized and batched manner; the purity of the NK cells and the NKT cells can respectively reach 60% and 30% at least without purification, and accordingly preliminary purification can be omitted; the in-vivo activation and amplification degrees and the in-vivo existence time of the CAR-NK cells and the CAR-NKT cells which are jointly prepared by the aid of the method can be controlled by means of clinical medication.
Owner:BEIJING DOINGTIMES INST OF TRANSLATIONAL MEDICINE
Cd123-specific chimeric antigen receptor redirected t cells and methods of their use
A family of chimeric antigen receptors (CARs) containing a CD123 specific scFv was developed to target different epitopes on CD123. In some embodiments, such a CD123 chimeric antigen receptor (CD123CAR) gene includes an anti-CD123 scFv region fused in frame to a modified IgG4 hinge region comprising an S228P substitution, an L235E substitution, and optionally an N297Q substitution; a costimulatory signaling domain; and a T cell receptor (TCR) zeta chain signaling domain. When expressed in healthy donor T cells (CD4 / CD8), the CD123CARs redirect T cell specificity and mediated potent effector activity against CD123+ cell lines as well as primary AML patient samples. Further, T cells obtained from patients with active AML can be modified to express CD123CAR genes and are able to lyse autologous AML blasts in vitro. Finally, a single dose of 5.0 x 106 CAR123 T cells results in significantly delayed leukemic progression in mice. These results suggest that CD123CAR-transduced T cells may be used as an immunotherapy for the treatment of high risk AML.
Owner:CITY OF HOPE
Detecting method for lung cancer characteristic metabolite fingerprint spectrum in urine
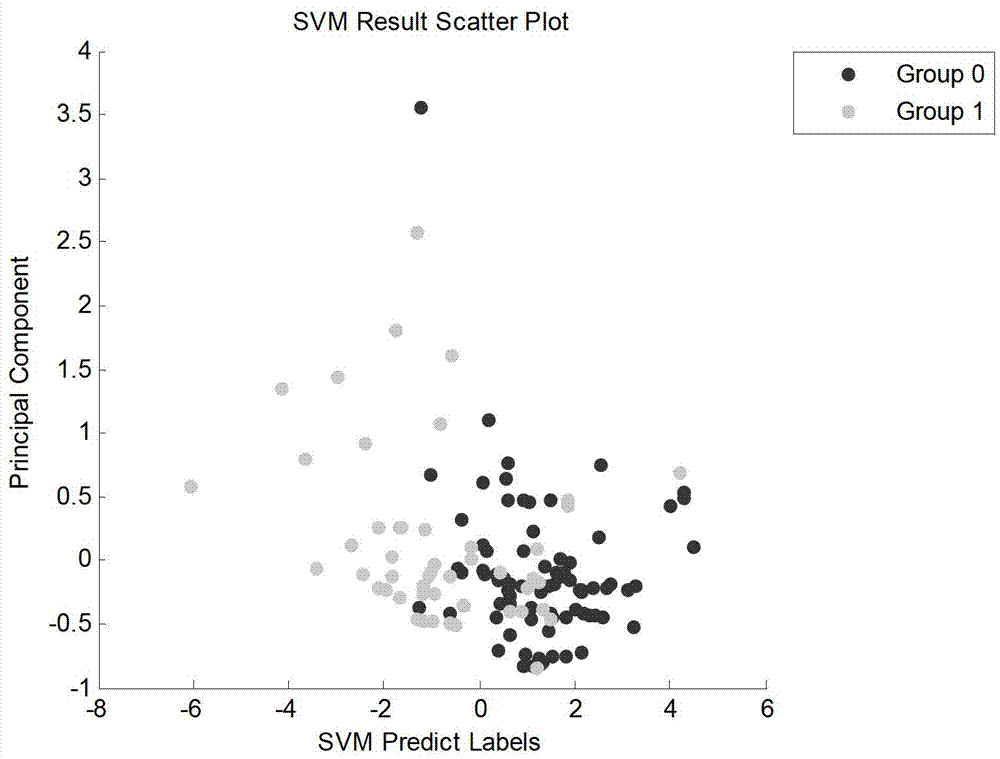
The invention discloses an establishing method for a lung cancer characteristic metabolite fingerprint spectrum in urine. The gas chromatography and mass spectrum combined technology is adopted to detect metabolic profiles of urine samples of lung cancer patients and healthy donors, and is combined with the biological method of a support vector machine to build a smoker lung cancer metabolite fingerprint spectrum and a non-smoker lung cancer metabolite fingerprint spectrum, wherein the smoker lung cancer metabolite fingerprint spectrum comprises oxalic acid, phosphoric acid, uracil, threonine, 5-pidolic acid, citric acid and galactose or comprises phosphoric acid, uric acid, citric acid and oxalic acid; and the non-smoker lung cancer metabolite fingerprint spectrum comprises alanine, oxalic acid, phosphoric acid, uracil, serine, threonine, 5-pidolic acid, ribose, aconitate, citric acid, galactose, tyrosine, palmitic acid and stearic acid. The method can detect only needing the urine samples, satisfies the requirements of effectiveness, simplicity and feasibility in the operation aspect, and is suitable for large-scale application.
Owner:CHINA TOBACCO ZHEJIANG IND
Blood Co-Processing For Contingent Autologous Leukocyte Transplantation
InactiveUS20070212674A1Strict controlHigh retention rateData processing applicationsOther blood circulation devicesWhite blood cellBlood plasma
A process for producing a leukocyte bank suitable for CAT therapy comprising the steps of providing a blood sample from a healthy donor individual; selectively separating and collecting leukocytes from the sample; selectively separating and collecting red blood cells and / or platelets and / or plasma from the sample; and cryogenically preserving the leukocytes (and optionally the red blood cells and / or platelets and / or plasma); wherein steps are conducted with an automated leukapheresis device comprising a separation device (e.g. a centrifuge rotor or filter), a leukapheresis tubing set and one or more pumps for conveying the sample through the tubing set and the separated leukocytes into a collection vessel.
Owner:LIFEFORCE GROUP
Method for in vitro preconditioning of myoblasts before transplantation
InactiveUS20020012657A1Increase secretionIncrease the number ofBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsFiberCell-Extracellular Matrix
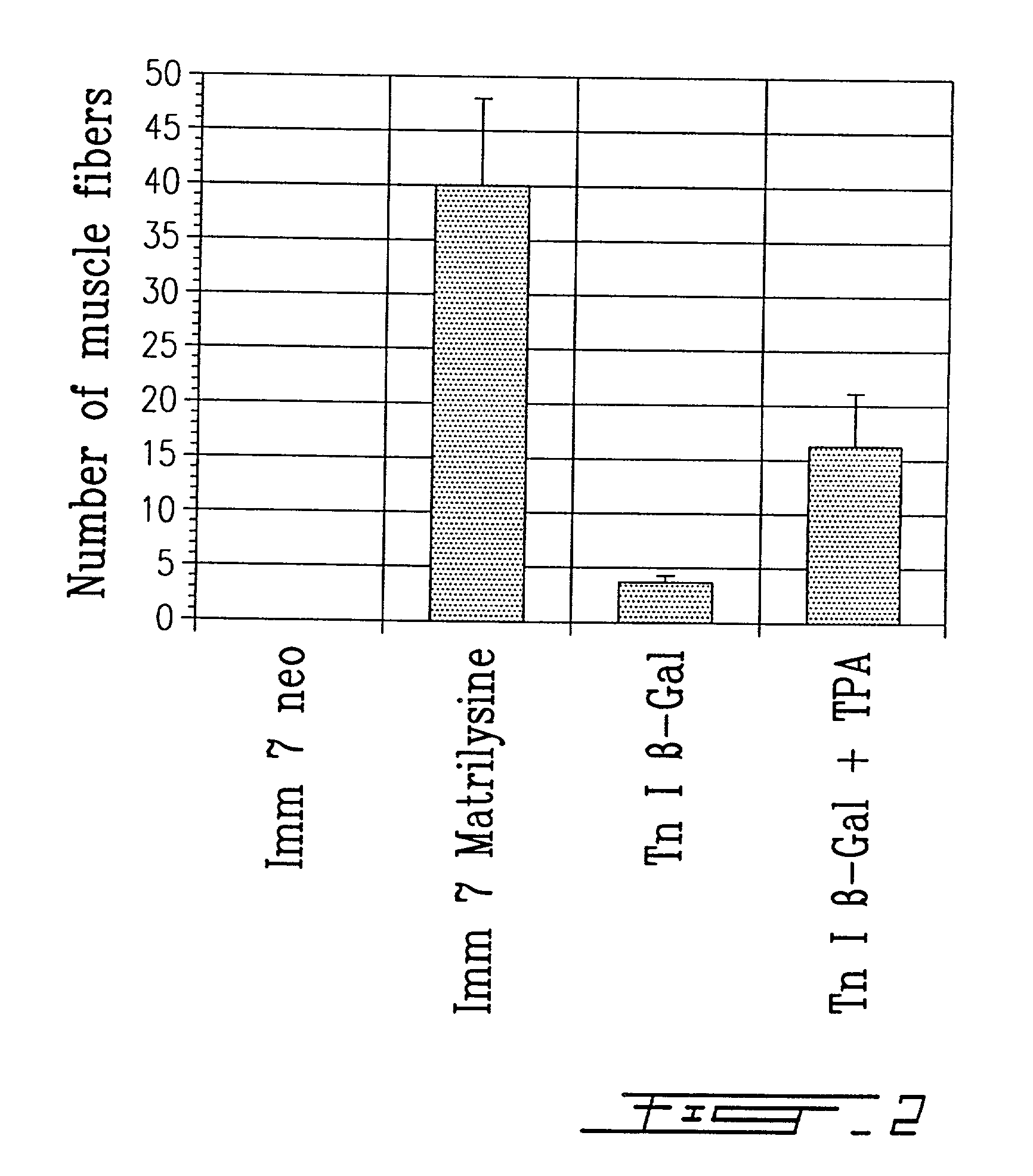
A method of pretreating healthy donor's myoblast cultures with growth or trophic factors like basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF) and with concanavalin A on transplantation to subjects suffering of myopathy like muscular dystrophy is disclosed and claimed. Recipient muscles show a higher percentage of functional cells, a four-fold increase, demonstrated by the higher incidence of dystrophin-positive fibers, and does not require previous preconditioning of recipient muscles by irradiation or toxin administration. The recipient subjects were immunosuppressed with FK 506. When growing myoblasts with 20 mug / ml concanavalin A or 100 ng / ml TPA for two to four days, migration of donor cells in recipient tissue was increased by 3-4 fold. This suggests that, when using primary cultures, metalloproteases are secreted by fibroblasts, resulting in a greater degradation of the extracellular matrix. Both metalloproteases and bFGF appear beneficial for the success of the transplantation. The use of recombinant myoblast expressing metalloproteases is also contemplated.
Owner:UNIV LAVAL
Method for jointly preparing CAR-VGamma9VDelta2T cells and CAR-NKT cells
ActiveCN106399242ANo immune rejectionEfficient killingCulture processBlood/immune system cellsPeripheral blood mononuclear cellCell culture media
The invention discloses a method for jointly preparing CAR-VGamma9VDelta2T cells and CAR-NKT cells, comprising the steps of 1) adding peripheral blood mononuclear cells to a cell medium, pre-activating VGamma9VDelta2T cells and NKT cells therein, and amplifying the VGamma9VDelta2T cells and NKT cells by selective in-vitro activation; 2) transducing the mixed cells of step 1) by using a lentiviral vector carrying chimeric antigen receptor's gene sequence. It is possible to carry out standard and batch preparation herein by using GammaDeltaT of a healthy donor; the purities of the VGamma9VDelta2T cells and NKT cells in the application can reach 60% and 30% and above respectively without purification, and therefore pre-purification can be omitted; in-vivo activation proliferation level and existence time of CAR-VGamma9VDelta2T cells and CAR-NKT cells jointly prepared by using the method can be controlled through clinical medication.
Owner:BEIJING DOINGTIMES INST OF TRANSLATIONAL MEDICINE
Modified t cells and methods of making and using the same
PendingCN107847524AEasy to understandAntibacterial agentsImmunoglobulin superfamilyHost immunityMedicine
Disclosed herein are modified primary human T cells and populations thereof comprising a genome in which the CTLA4, PD1, TCRA, TCRB, and / or B2M genes have been edited to generate an off-the-shelf universal CAR T cell from allogeneic healthy donors that can be administered to any patient while reducing or eliminating the risk of immune rejection or graft versus host disease, and which are not proneto T cell inhibition, and methods for allogeneic administration of such cells to reduce the likelihood that the cells will trigger a host immune response when the cells are administered to a subjectin need of such cells.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE 17 Q
Screening method of an intestinal flora transplantation donor
PendingCN111681733AAvoid wastingAdd filter itemsMedical data miningTherapiesMicrobiologyHealthy donor
The invention discloses a screening method of an intestinal flora transplantation donor. The method comprises the steps of firstly communicating with a donor, informing the donor of a flora transplantation concept and filling out notes of a questionnaire, and screening out qualified healthy donors through the processes of donor basic information registration, clinical evaluation, gastrointestinaltract pathogen detection and blood detection, wherein the expiration date of the donors is three months. And the healthy donor needs to be screened again in the gastrointestinal tract pathogenic bacteria detection and blood detection processes after three months, and only the donor meeting the requirements needs to be screened again and is the qualified donor. The invention aims to establish a scientific and reasonable screening method for the flora transplantation donors, which can improve the quality of healthy donors to ensure the safety and the effectiveness of transplantation to the maximum extent and provide basis and reference for the national establishment of relevant standards.
Owner:厦门承葛生物科技有限公司
CAR-NK cell culture method
PendingCN112266900APromote proliferationEnhance killing activityGenetically modified cellsCulture processPeripheral blood mononuclear cellWhite blood cell
The invention provides a CAR-NK cell culture method. The culture method comprises the following steps of S1, collecting peripheral blood of a healthy donor, and separating to obtain peripheral blood mononuclear cells; S2, sorting out NK cells from peripheral blood mononuclear cells; S3, infecting the NK cells in the step S2 with a lentiviral vector with a chimeric antigen receptor gene; and S4, carrying out multiplication culture on the CAR-NK cells by using a culture medium containing interleukin-2, inositol, quercetin glucoside, formononetin, sheep placenta and galactose to obtain a large number of CAR-NK cells. The CAR-NK cell culture method disclosed by the invention is simple to operate, and the cultured NK cells are high in purity, large in quantity, large in quantity of CAR-NK cellsand high in killing activity.
Owner:广东康盾创新产业集团股份公司
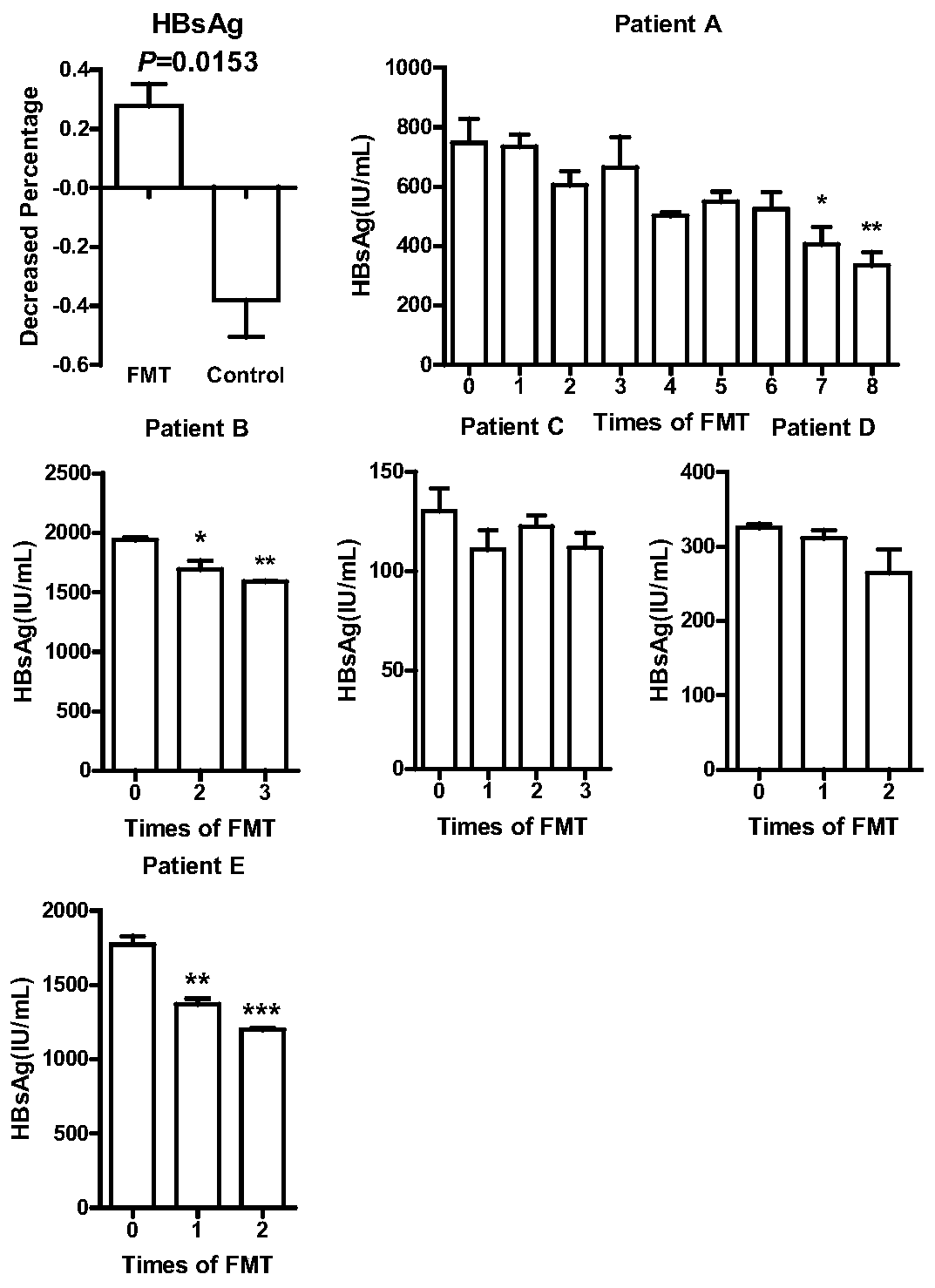
Application of fecal flora in preparing micro-ecological preparation for treating chronic hepatitis B
InactiveCN110664847ADecreased HBsAg titerAchieve clinical improvementDigestive systemAntiviralsEnteral Nutrition PreparationDietary supplement
The invention discloses application of a fecal flora in preparing a micro-ecological preparation for treating chronic hepatitis B and relates to the technical field of intestinal micro-ecology. A transplanting method of the fecal flora comprises the following steps of 1) separating and purifying the fecal flora in healthy donor feces; and 2) transplanting the fecal flora into an intestinal tract of a patient, and remodeling the unbalanced intestinal flora of the patient to a balanced state. The fecal flora can be applied to preparing a drug for treating HBeAg negative chronic hepatitis B, canbe used by combining with other antiviral drugs, such as entecavir, as long as no other adverse effect, such as anaphylaxis, is generated and can be applied to preparing a drug for relieving disease response of a patient with the chronic hepatitis B, a drug for lowering the HBsAg content of the patient with the chronic hepatitis B, a drug for regulating the immune function of the patient with thechronic hepatitis B and a health care product, a beverage, a enteral nutrition preparation or a dietary supplement for relieving or adjunctively treating the chronic hepatitis B.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
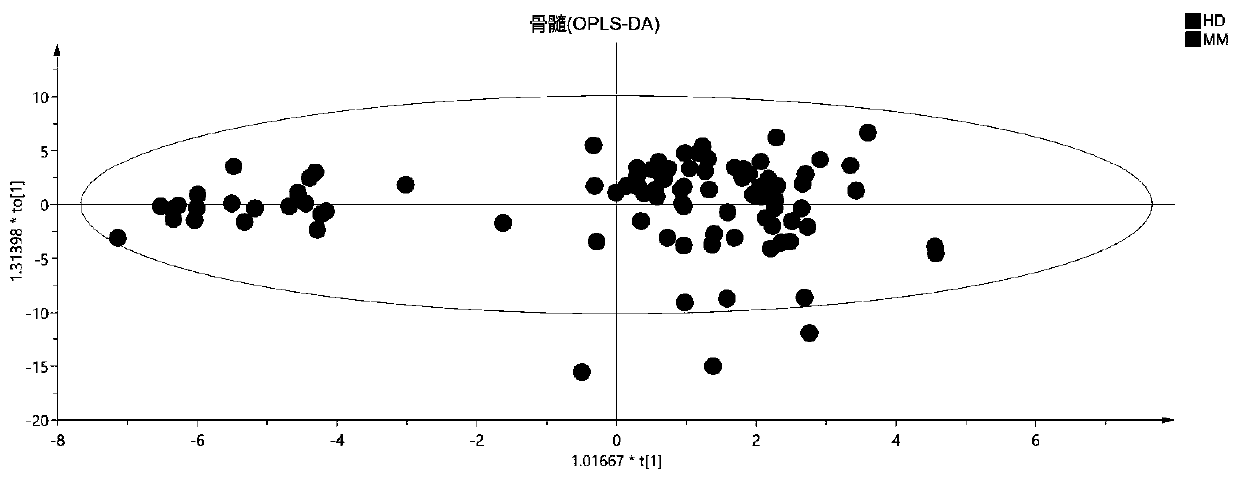
Blood metabolite marker for diagnosing multiple myeloma, and application
ActiveCN110749732AImprove accuracyReliable resultsComponent separationBiological testingStearic acidMetabolome
The invention relates to a blood metabolite marker for diagnosing multiple myeloma, and application. Untargeted metabolomics detection are firstly performed on a healthy donor (HD), and the marrow andperipheral blood sample of a primary-care patient of multiple myeloma (mm) to screen out 5 metabolites that have significant differences in marrows and peripheral blood samples, wherein the 5 metabolites are respectively L_Proline, L_Aspartic acid, L_Cystine, Stearic acid, and Palmitic acid. The analysis result of the ROC curve shows that the 5 different metabolites as a whole can more accuratelydiagnose MM. Targeted metabolomics detection further confirmed that the metabolome composed of these 5 metabolites is an ideal MM diagnostic method. The invention can accurately diagnose MM and is ofgreat significance for promoting the diagnosis of MM in basic research and clinical treatment.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
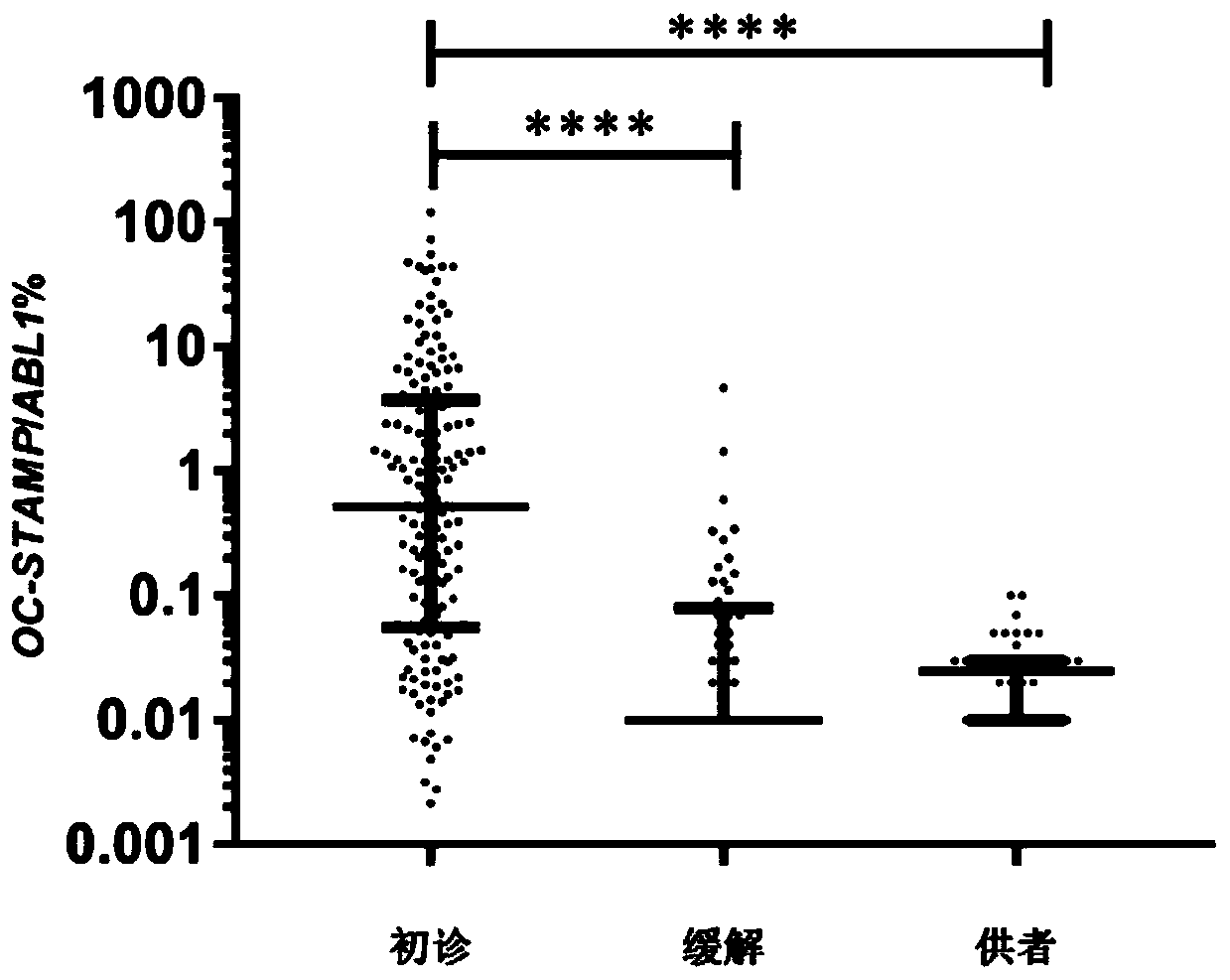
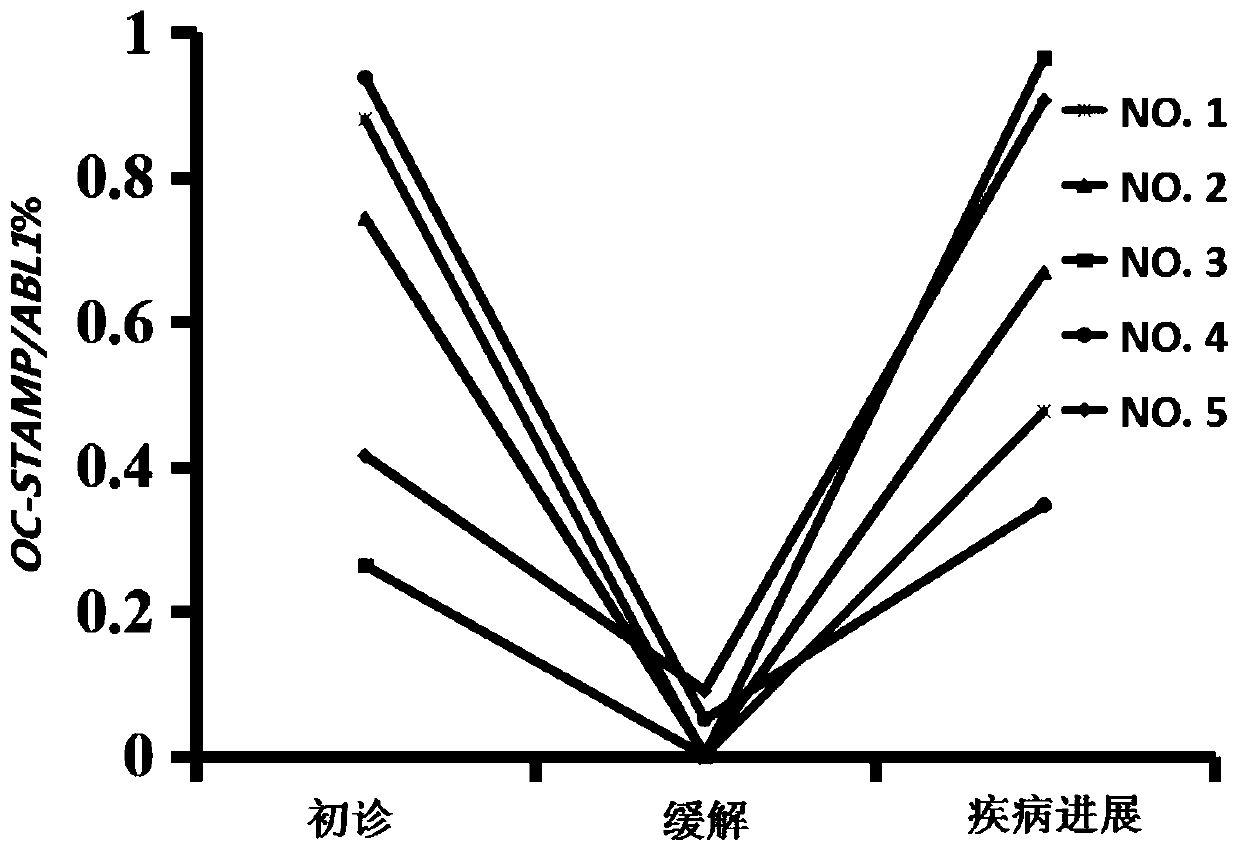
Application of OC-STAMP (osteoclast stimulatory transmembrane protein) as prognostic risk marker in evaluating multiple myeloma patients
ActiveCN110734979AMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisBone marrow cellHealthy donor
The invention discloses application of application of OC-STAMP (osteoclast stimulatory transmembrane protein) as a prognostic risk marker in evaluating multiple myeloma patients. According to the application, expression levels of OC-STAMP in bone marrow cells of newly diagnosed and released MM (multiple myeloma) patients and healthy donors are analyzed by using an RT-qPCR (real-time-quantitative real time polymerase chain reaction) method, and results show that the expression level of the gene in an MM patient is remarkably higher than that of a normal reference level and is possibly related to clinical courses. Subsequently, the clinical significance of the gene is investigated and results show that high expression of the gene is an independent risk factor of low progression-free survival(PFS) of the MM patient. OC-STAMP has important value in evaluating the prognostic risk of the multiple myeloma patients.
Owner:北京金域医学检验实验室有限公司
Compositions for the treatment of skin conditions
InactiveUS20190321416A1Reduce decreaseEnsure adequate treatmentBacteriaBacteria material medical ingredientsAtopic dermatitisGram
Described herein are methods and compositions for the treatment of skin conditions associated with dysbiosis. Skin conditions associated with dysbiosis for treatment using compositions and methods described herein include atopic dermatitis, eczema, dermatitis, psoriasis, rosacea, and acne. Compositions include single or more than one strain of healthy donor derived bacteria for administration to provide therapy for skin conditions associated with dysregulated microbiota. Such compositions include gram negative and / or gram positive bacteria.
Owner:FORTE SUBSIDIARY INC
Method for jointly preparing car-vγ9vδ2t cells and car-nkt cells
ActiveCN106399242BEfficient killingMeet needsCulture processBlood/immune system cellsPeripheral blood mononuclear cellCell culture media
The invention discloses a method for jointly preparing CAR-VGamma9VDelta2T cells and CAR-NKT cells, comprising the steps of 1) adding peripheral blood mononuclear cells to a cell medium, pre-activating VGamma9VDelta2T cells and NKT cells therein, and amplifying the VGamma9VDelta2T cells and NKT cells by selective in-vitro activation; 2) transducing the mixed cells of step 1) by using a lentiviral vector carrying chimeric antigen receptor's gene sequence. It is possible to carry out standard and batch preparation herein by using GammaDeltaT of a healthy donor; the purities of the VGamma9VDelta2T cells and NKT cells in the application can reach 60% and 30% and above respectively without purification, and therefore pre-purification can be omitted; in-vivo activation proliferation level and existence time of CAR-VGamma9VDelta2T cells and CAR-NKT cells jointly prepared by using the method can be controlled through clinical medication.
Owner:BEIJING DOINGTIMES INST OF TRANSLATIONAL MEDICINE
Method for culturing allogeneic immune cell, immune cell culture obtained thereby, and immune cell therapeutic agent comprising same
PendingCN113795573APromote proliferationExtend your lifeCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsNatural Killer Cell Inhibitory ReceptorsLymphocyte
The present invention relates to a method for culturing natural killer cells (NK cells) applicable to immunotherapy and, more particularly, to: a method for culturing allogeneic immune cells wherein lymphocytes derived from blood from a healthy donor, but not from a patient to be administered an immune cell therapeutic, are cultured to effectively amplify and activate NK cells excellently effective for the therapy of malignant tumor; an immune cell culture obtained thereby; and an immune cell therapeutic comprising the same.
Owner:申志燮 +1
Detecting method for lung cancer characteristic metabolite fingerprint spectrum in urine
The invention discloses an establishing method for a lung cancer characteristic metabolite fingerprint spectrum in urine. The gas chromatography and mass spectrum combined technology is adopted to detect metabolic profiles of urine samples of lung cancer patients and healthy donors, and is combined with the biological method of a support vector machine to build a smoker lung cancer metabolite fingerprint spectrum and a non-smoker lung cancer metabolite fingerprint spectrum, wherein the smoker lung cancer metabolite fingerprint spectrum comprises oxalic acid, phosphoric acid, uracil, threonine, 5-pidolic acid, citric acid and galactose or comprises phosphoric acid, uric acid, citric acid and oxalic acid; and the non-smoker lung cancer metabolite fingerprint spectrum comprises alanine, oxalic acid, phosphoric acid, uracil, serine, threonine, 5-pidolic acid, ribose, aconitate, citric acid, galactose, tyrosine, palmitic acid and stearic acid. The method can detect only needing the urine samples, satisfies the requirements of effectiveness, simplicity and feasibility in the operation aspect, and is suitable for large-scale application.
Owner:CHINA TOBACCO ZHEJIANG IND
Method for jointly preparing car-nk cells and car-nkt cells
ActiveCN106350487BReduce purification costsEfficient killingBlood/immune system cellsCell culture active agentsPeripheral blood mononuclear cellAntigen receptors
The invention discloses a method for jointly preparing CAR-NK (chimeric antigen receptor-natural killer) cells and CAR-NKT (natural killer T) cells. The method includes steps of 1), adding peripheral blood mononuclear cells into cell culture media, pre-activating NK cells and NKT cells in the peripheral blood mononuclear cells and selectively activating and amplifying the NK cells and the NKT cells in an in-vitro manner; 2), transducing mixed cells obtained at the step 1) by the aid of lentiviral vectors with gene sequences of chimeric antigen receptors. The method has the advantages that the CAR-NK cells and the CAR-NKT cells can be prepared from NKs and NKTs of healthy donors in a standardized and batched manner; the purity of the NK cells and the NKT cells can respectively reach 60% and 30% at least without purification, and accordingly preliminary purification can be omitted; the in-vivo activation and amplification degrees and the in-vivo existence time of the CAR-NK cells and the CAR-NKT cells which are jointly prepared by the aid of the method can be controlled by means of clinical medication.
Owner:BEIJING DOINGTIMES INST OF TRANSLATIONAL MEDICINE
Methods and Agents to Treat Autoimmune Diseases
A therapeutic method for preventing, suppressing, or treating an autoimmune disease is described. This method involves administering to a patient suffering from an autoimmune disease an effective amount of a composition containing an allogeneic or autologous leucocyte cell population derived from a healthy donor. The composition is administered by subcutaneous injection and induces an immunological response in recipient patients sufficient to reduce incidence, prevalence, frequency, or severity of the autoimmune disease.
Owner:ADVANCED IMMUNE BIOTECH
Method for in vitro testing of compounds for assessing therapeutic value in the treatment of multiple sclerosis and other diseases wherein foamy cells are involved in the disease etiology
InactiveUS20110033843A1Increase productionReduced degradation-catabolismMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysisBiologyDisease cause
The invention provides a method for assessing or determining activity of a test Compound on modulation of gene product levels comprising culturing cells, contacting at least one of the cultured cells with a lipid-rich fraction, contacting at least one of the cultured cells with the test Compound, determining the presence of a gene product of at least one cell of the cultured cells and, optionally, determining the presence of the gene product of at least one cultured cell not contacted with the test Compound. To assess human conditions most fully, it is preferred that the cell is of human origin, for example, a peripheral blood monocyte taken from a healthy donor.
Owner:ERASMUS UNIV MEDICAL CENT ROTTERDAM ERASMUS MC
Prostate-specific tumor antigens and uses thereof
ActiveUS20150202273A1Peptide/protein ingredientsAntibody ingredientsProstate cancer cellPeripheral blood mononuclear cell
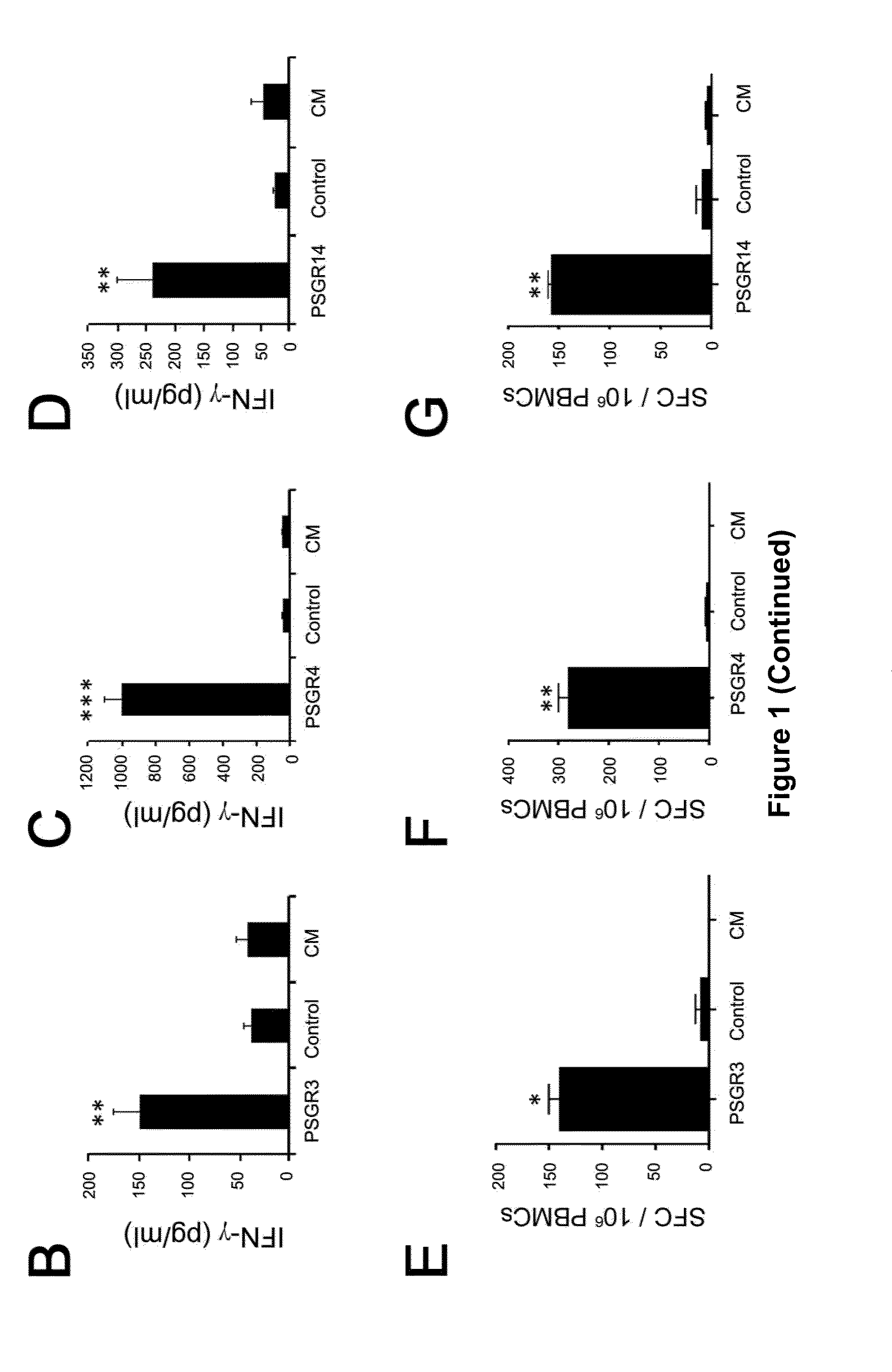
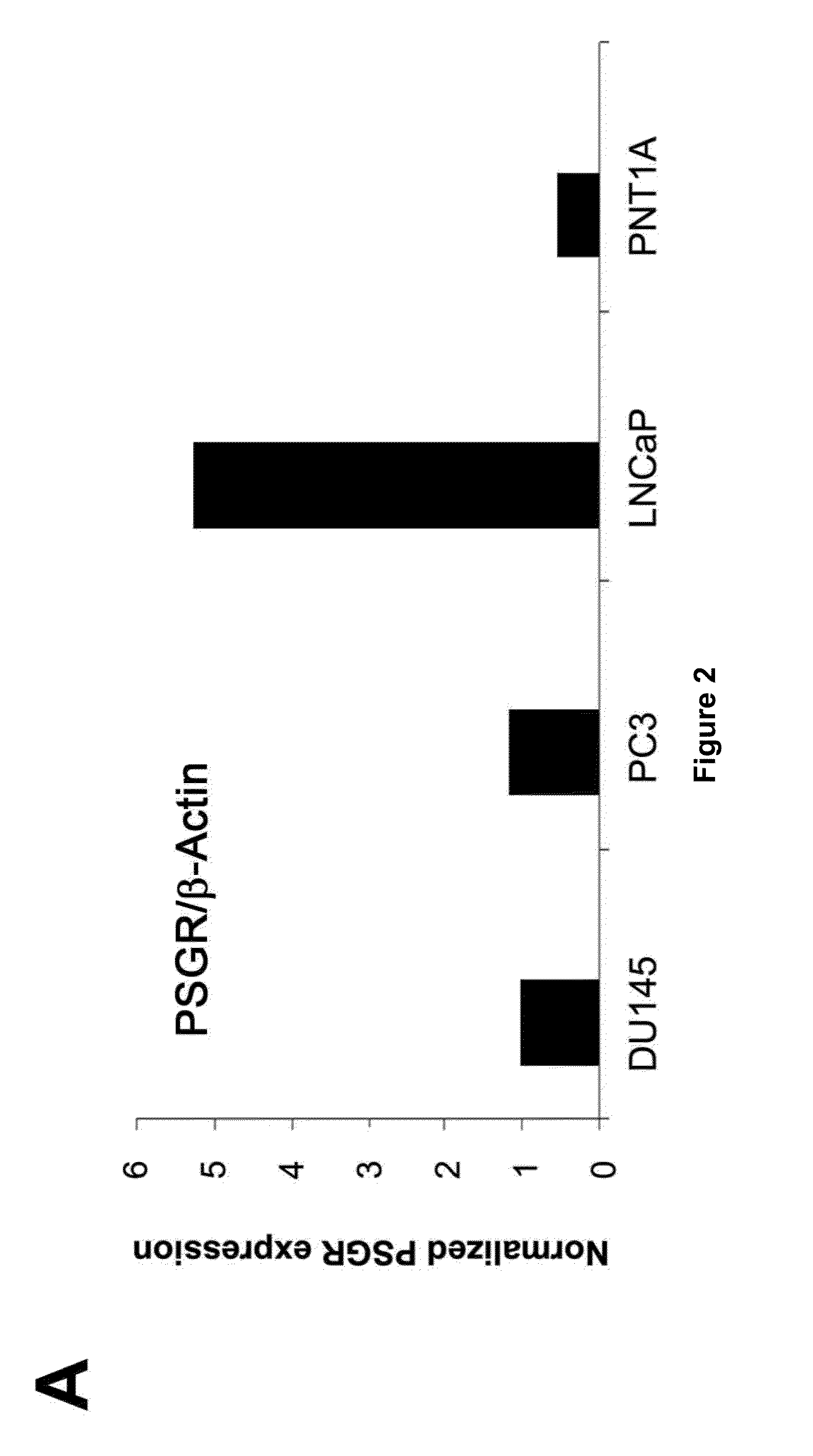
Twenty-one PSGR-derived peptides predicted by an immuno-informatics approach based on the HLA-A2 binding motif were examined for their ability to induce peptide-specific T cell responses in peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) obtained from either HLA-A2+ healthy donors or HLA-A2+ prostate cancer patients. The recognition of HLA-A2 positive and PSGR expressing LNCaP cells was also tested. Three peptides, PSGR3, PSGR4 and PSGR14 frequently induced peptide-specific T cell responses in PBMCs from both healthy donors and prostate cancer patients, and are recognized by CD8+ T cells in an HLA-A2 dependent manner. These peptide-specific T cells recognize HLA-A2+ and PSGR+ tumor cells, and killed LNCaP prostate cancer cells in an HLA class I-restricted manner. These PSGR-derived peptides identified are useful as diagnostic markers as well as immune targets for anticancer vaccines.
Owner:SHENZHEN INNOVATION IMMUNOTECH CO LTD
In vitro artificial lymph node for sensitization and expansion of t cells for therapy and epitope mapping
InactiveCN108289910AMammal material medical ingredientsBlood/immune system cellsCulture expansionInvasive breast carcinoma
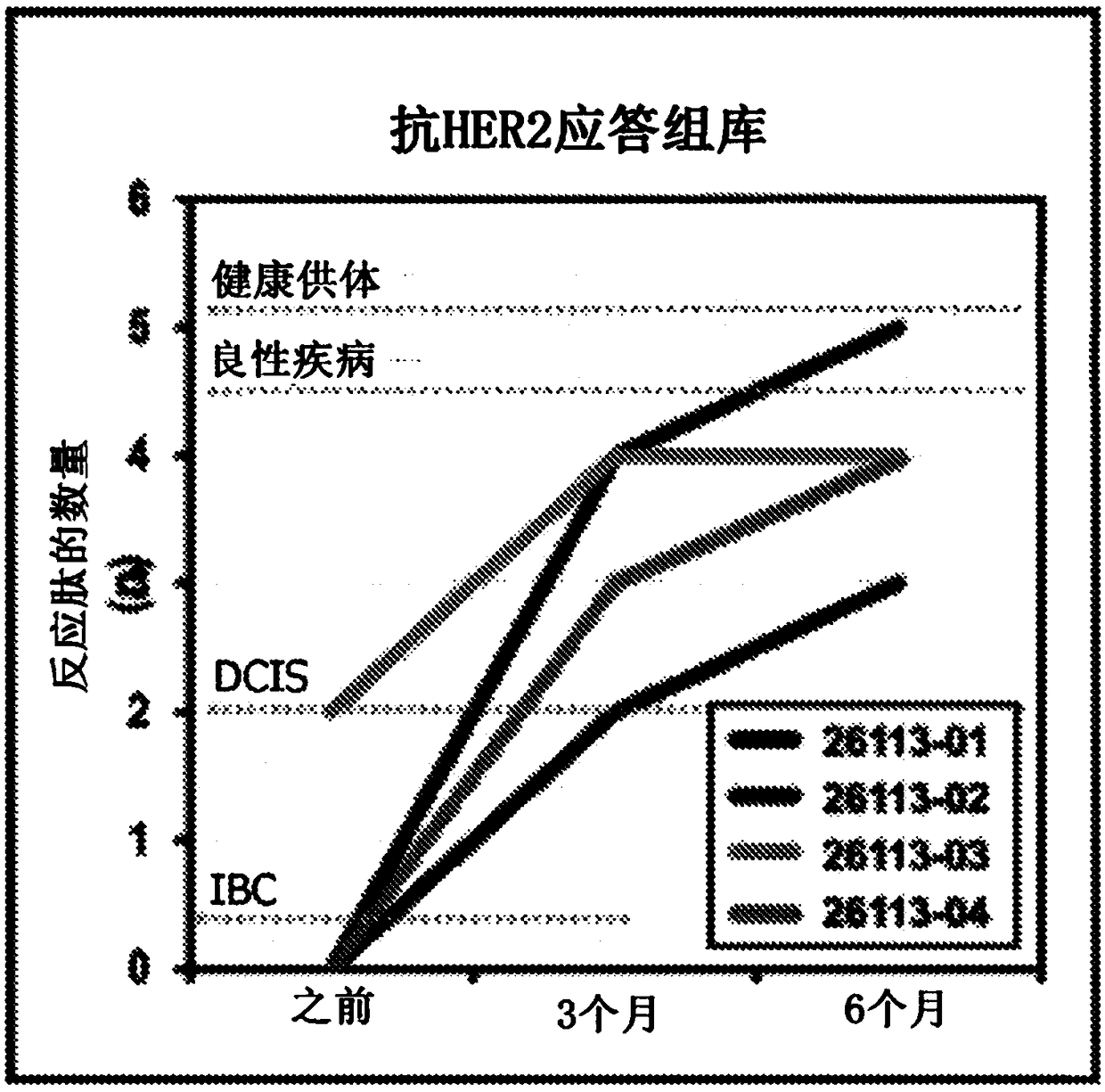
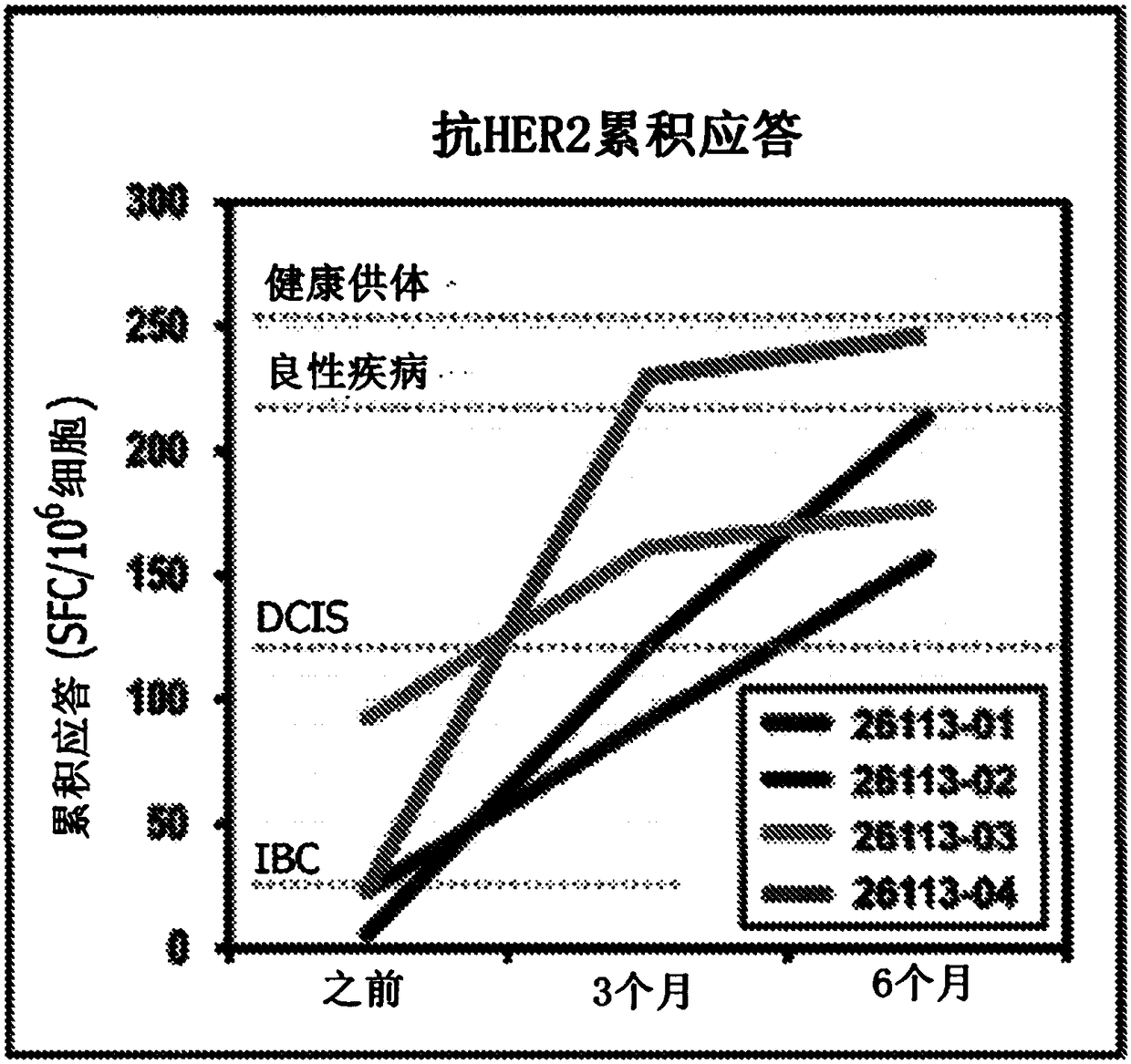
HER2+ invasive breast cancer (IBC) patients with residual disease following neoadjuvant chemotherapy have an anti-HER2 Type 1 T helper (Th1) cell immune deficit and a significant risk of recurrent disease. It has been shown that anti-HER2 CD4+ T-cell responses incrementally decrease along the breast cancer continuum - a robust response in healthy donors and patients with benign disease, a depressed response in patients with HER2+ ductal carcinoma in situ, and a nearly absent response in patients with HER2+ IBC. This invention relates to a method of creating a microenvironment for culture expansion of T cells. The expanded T cells can be used for a variety of therapeutic and research purposes.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
Personalized, allogeneic cell therapy of cancer
The present invention describes methods of preparing a cell composition for treating cancer in a human being by obtaining lymphocytes from a partially or fully HLA-matched healthy donor, activating and expanding T cells reactive to neo-antigens (i.e. new epitopes resulting from somatic mutations in the cancer cell), and enriching for tumor-specific T cells that are not reactive against non-tumor tissue of the cancer patient. Provide herein are lymphocyte compositions comprising partially or fully HLA-matched healthy donor T cells reactive to neo-antigens. Also provided herein are methods of treating human cancer with such neo-antigen-specific, non-alloreactive T cells.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Application of CKAP4 reagent in detection specimen and bladder cancer detection kit
PendingCN114563571AAvoid Missing ConditionsAvoid influenceBiological material analysisBiological testingOncologyNon invasive
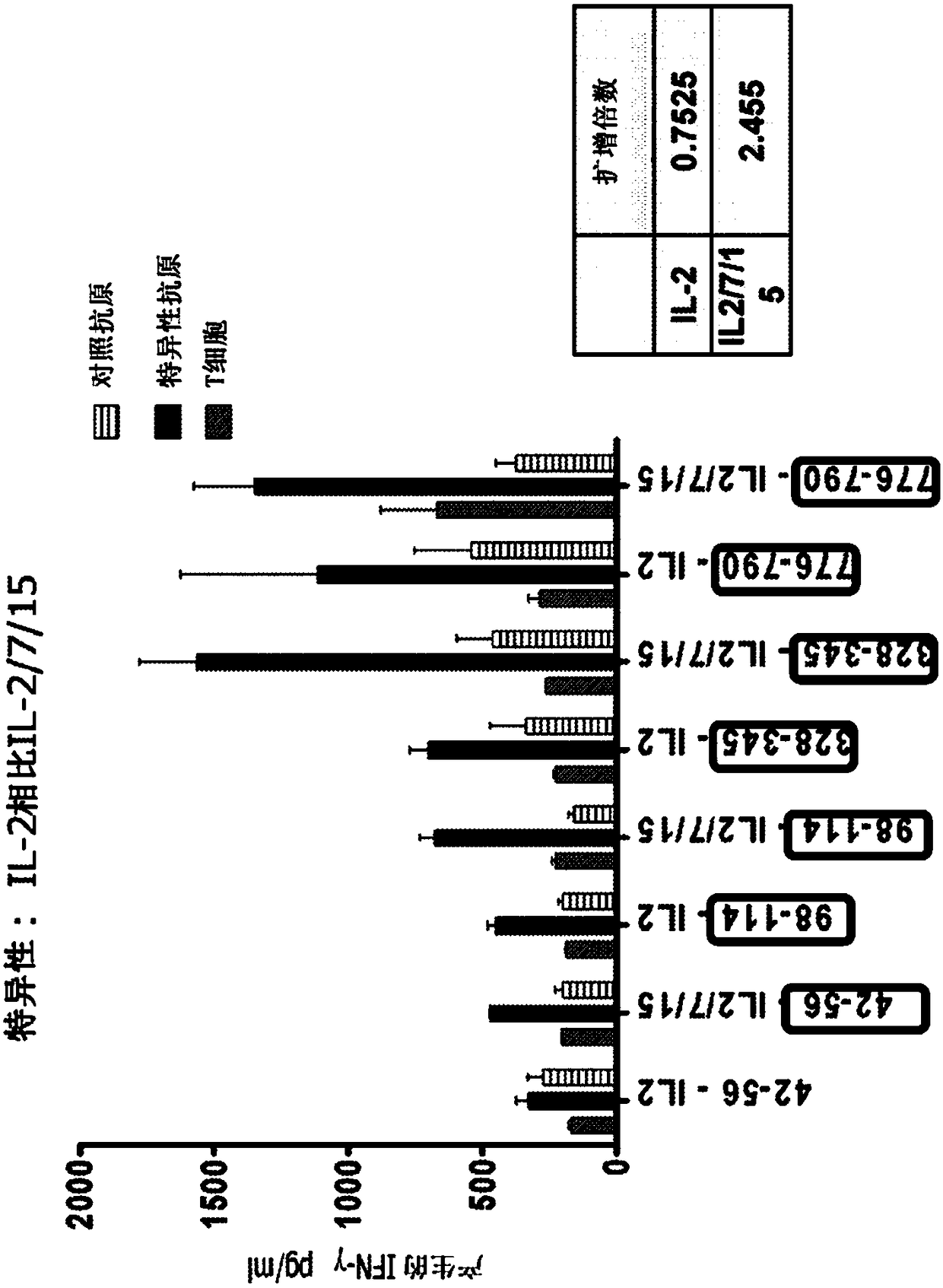
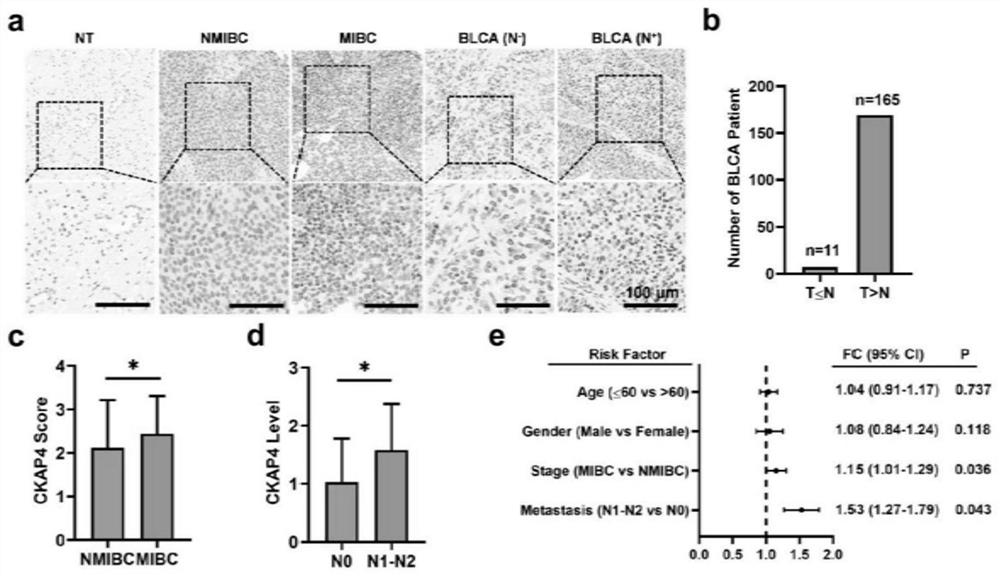
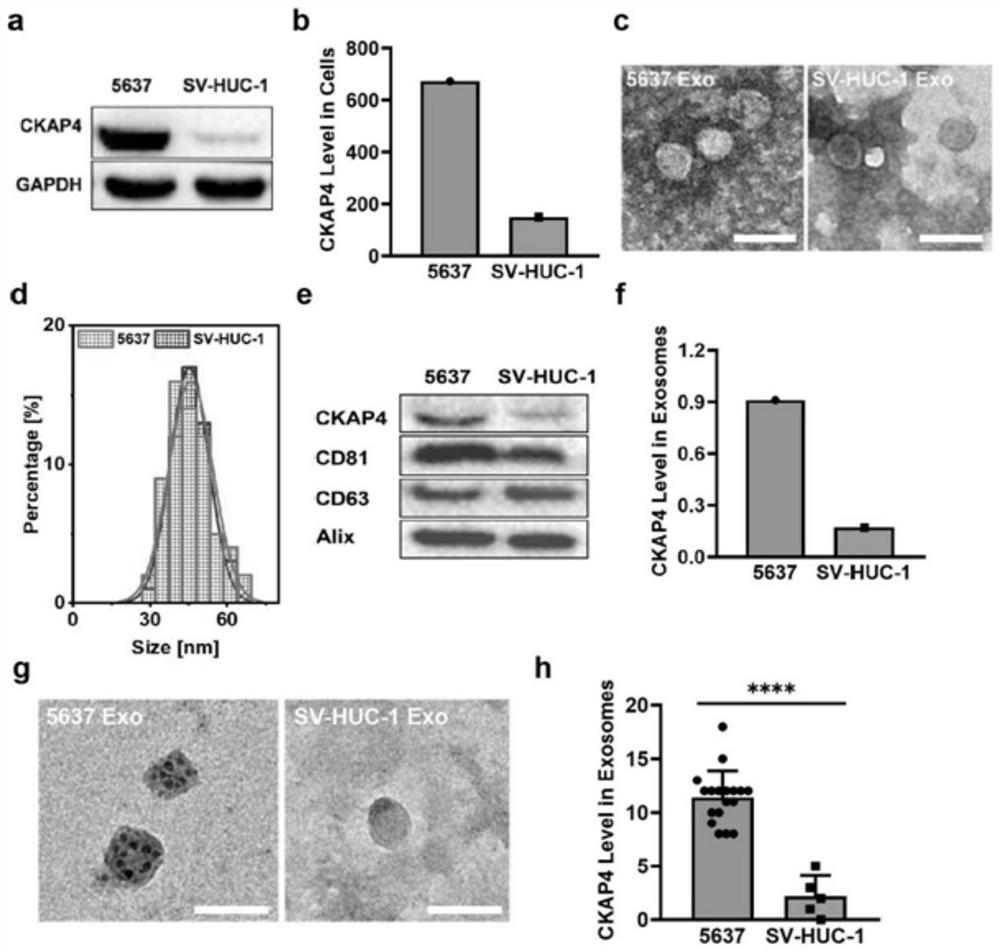
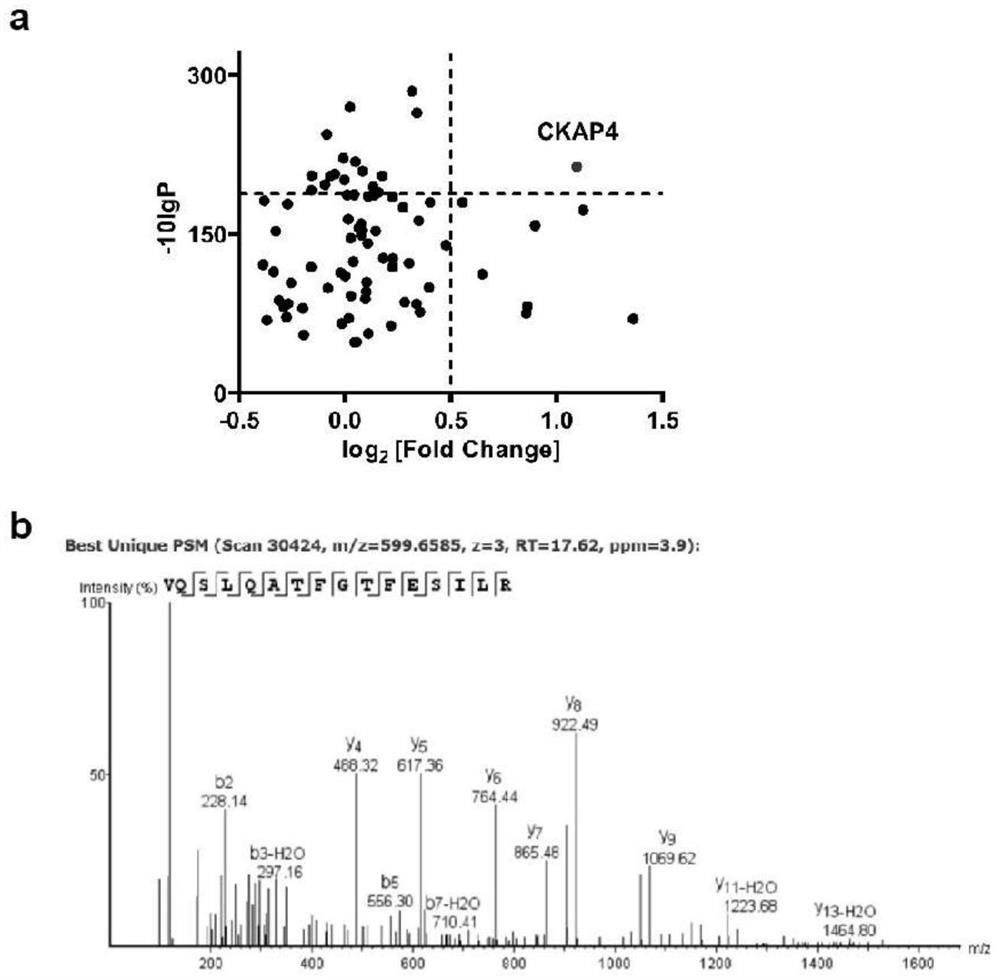
The invention discloses application of a reagent for detecting CKAP4 in a sample and a bladder cancer detection kit. The CKAP4 is not only highly expressed in bladder cancer cell lines and exosomes secreted by the bladder cancer cell lines, but more importantly, the CKAP4 is remarkably and highly expressed in urine exosomes of bladder cancer patients clinically, but the expression quantity in urinary system cancers such as prostatic cancer and renal cell carcinoma, urinary system inflammation and urine exosomes of healthy donors is very low, and the CKAP4 has remarkable specificity. Therefore, the detection means based on the urine exosome CKAP4 is a non-invasive liquid biopsy method which is low in cost, simple and convenient, can meet the requirement for multiple times of detection, and is particularly suitable for diagnosis and relapse monitoring of bladder cancer patients.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
New vaccinal strategy
PendingUS20210154282A1Suitable for processingEfficient processingCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsSkin cancer vaccineIn vitro stimulationDisease
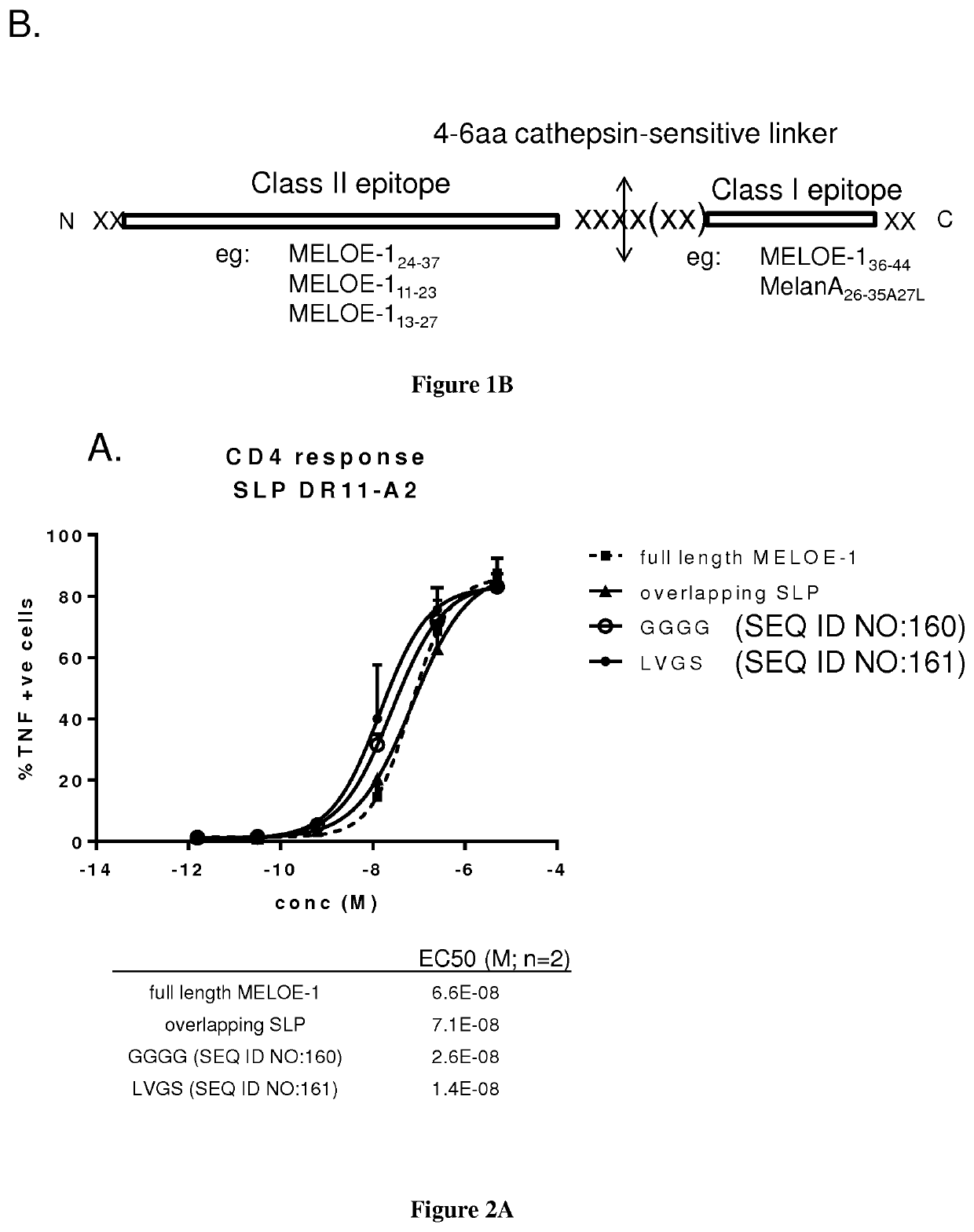
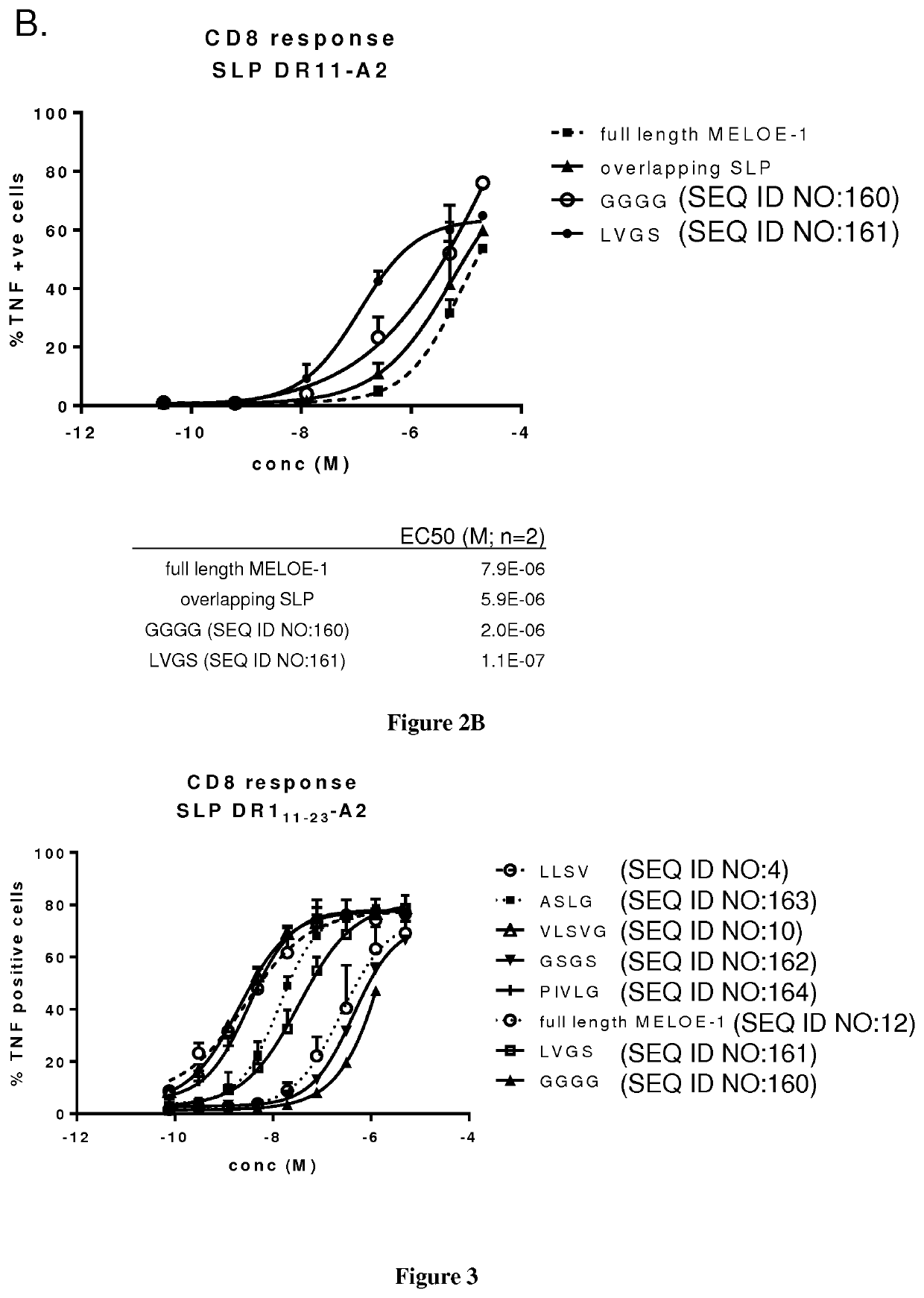
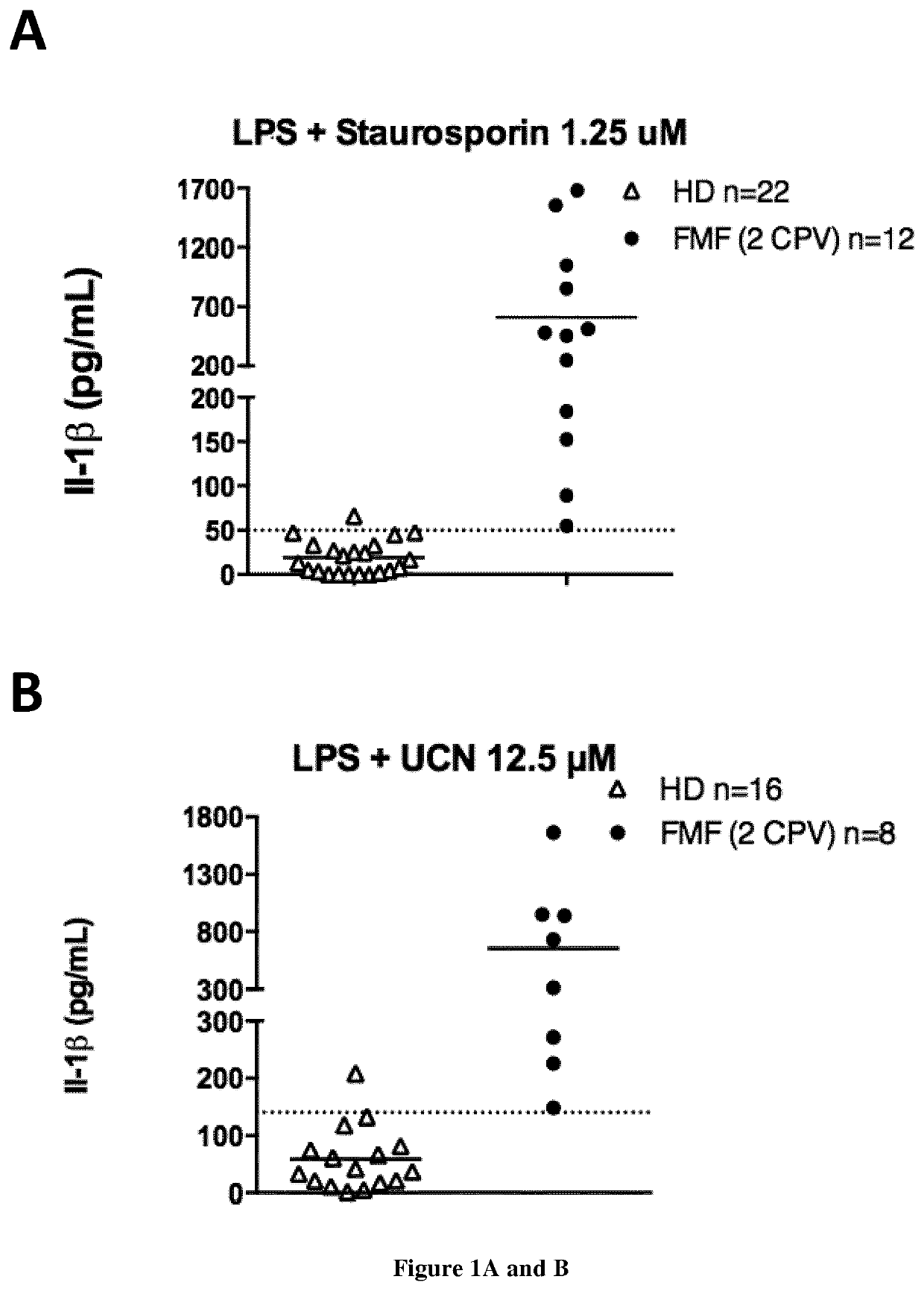
The present invention relates to the prevention and treatment of disease like cancer. The inventors have previously characterized MELOE-1 antigen as an IRES dependent, melanoma specific translation product from a lncRNA mainly transcribed in the melanocytic lineage. MELOE-1 contains numerous class II epitopes and one HLA-A*0201-restricted CD8 epitope eliciting a frequent repertoire of high avidity T cells. They designed various synthetic long peptide (SLPs) comprising a CD4 epitope coupled to the CD8 epitope by a serie of linkers of 4 to 6 aa and studied the efficacy of T cell clone activation by SLP-loaded DC in vitro. Particularly, they evaluated the ability of a few selected SLPs to stimulate specific T cells proliferation of PBL from healthy donors in vitro and finally, they explored the vaccination potential of their best SLP candidate in vivo in an HLA*A0201 / HLA-DRB0101 transgenic mouse. Thus, the present invention relates a SLP comprising a CD4 class II peptide linked to a CD8 class I peptide by a specific linker and its use in the treatment of disease like cancers.
Owner:INST NAT DE LA SANTE & DE LA RECHERCHE MEDICALE (INSERM) +1
Antigenic peptides deriving from urocortin 3 and uses thereof for the diagnosis and treatment of type 1 diabetes
PendingUS20210024603A1Peptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsUrocortinCellular antigens
Despite the notion that human CD8+ T cells are the final mediators of autoimmune β-cell destruction in type 1 diabetes (T1D), none of their target epitopes has been demonstrated to be naturally processed and presented by β cells. The inventors therefore performed an epitope discovery study combining HLA Class I peptidomics and transcriptomics strategies. Inflammatory cytokines increased β-cell peptide presentation in vitro, paralleling upregulation of HLA Class I expression. Peptide sources included known β-cell antigens and several insulin granule proteins. Urocortin 3 was identified as a novel β-cell antigen, which was processed into HLA-A2- and HLA-A3-restricted epitopes recognized by circulating naive CD8+ T cells in type 1 diabetic and healthy donors. Accordingly, the present invention relates to antigenic peptides derived from urocortin-3 and uses thereof for the diagnosis and treatment of T1D.
Owner:UNIVERSITÉ PARIS CITÉ +3
Methods and kits for diagnosis of familial mediterranean fever
InactiveUS20200264191A1Not sufficientHigh riskDisease diagnosisBiological testingDiagnostic testInflammasome
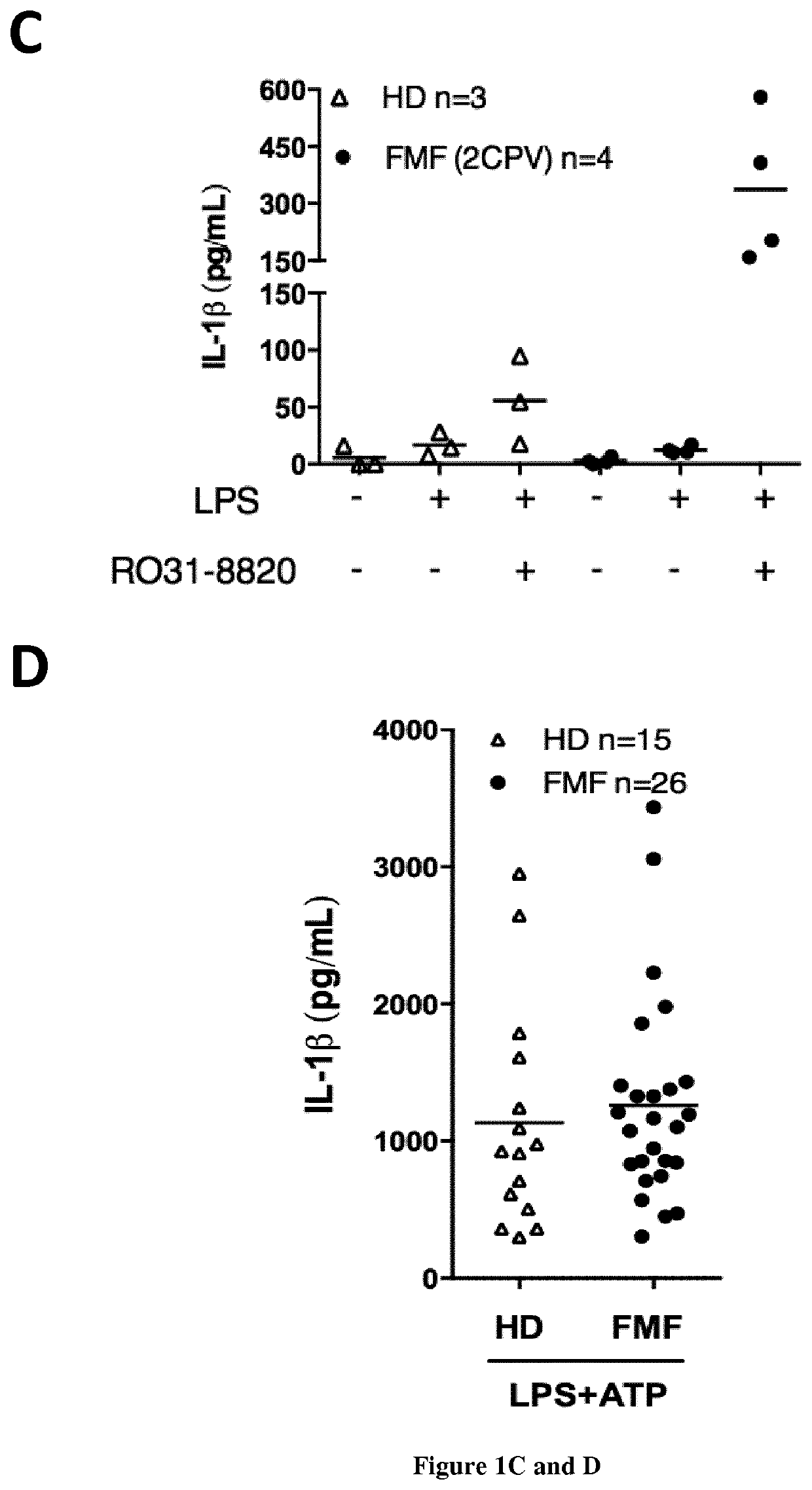
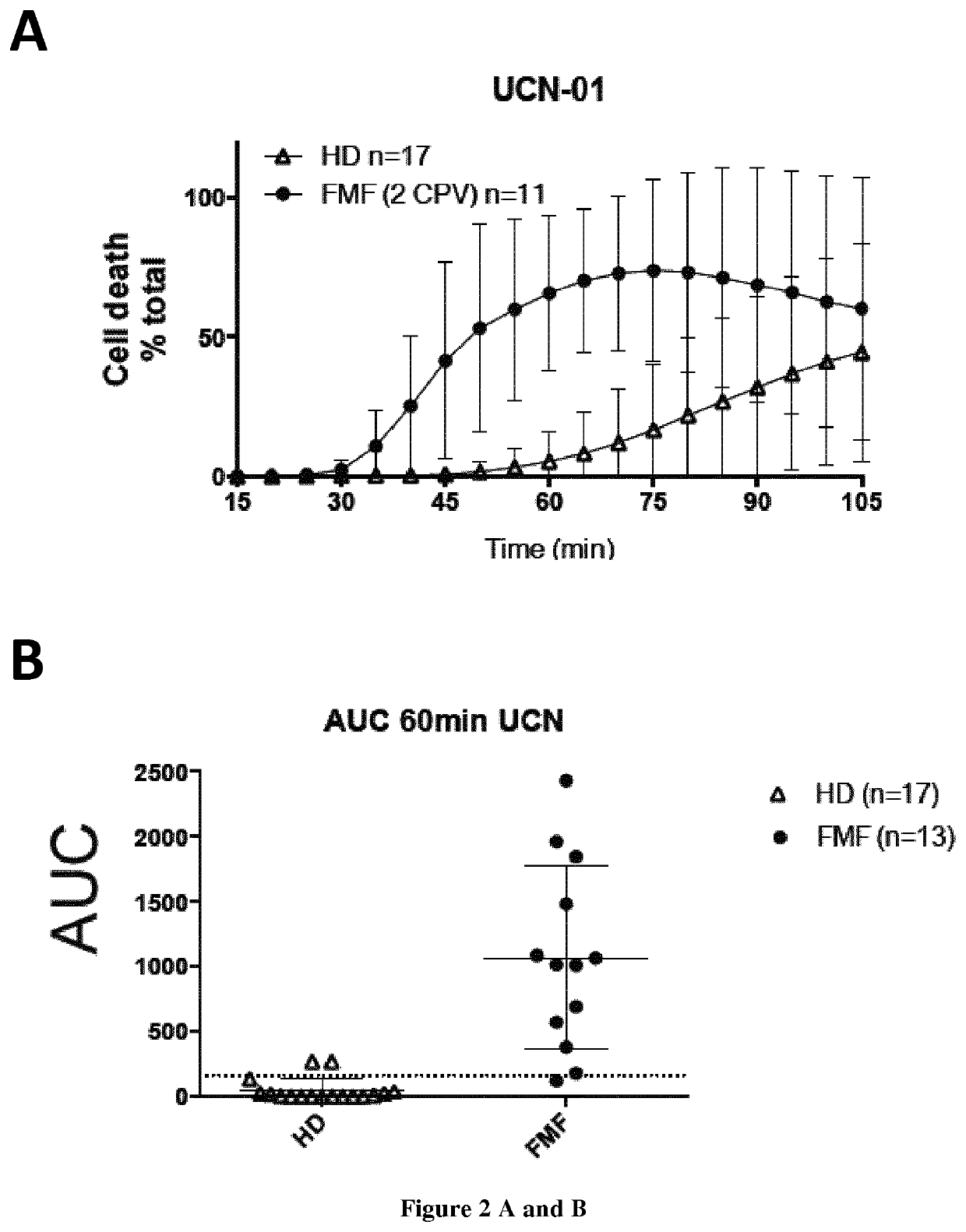
The present invention relates to a non-invasive, specific and rapid diagnostic method of Familial Mediterranean fever (FMF) in a subject said method comprising the step of measuring the level of cytokine (IL-18 or IL-1 beta) secreted by immune primary cells (or cell death level of these cells) obtained from said subject, which have been beforehand treated with a Protein Kinase C (PKC) inhibitor, and optionally beforehand treated with a NF-kB activator such as LPS. Inventors show based on the extensive study of the inflammasome process of the monocytes, that PKC superfamily inhibitors trigger inflammasome activation in monocytes from FMF patients while they are not sufficient to do so in monocytes from healthy donors (HD) or from patient having hyperimmunoglobulinemia D syndrome (HID S). Using cytokine release quantification or determination of real time cell death kinetics, inventors demonstrate that PKC superfamily inhibitors can discriminate FMF patients from HD or from patients with systemic inflammation from other aetiologies. These results thus set-up the basis for the development of a rapid functional specific diagnostic test for FMF. Methods of treatment are disclosed.
Owner:INST NAT DE LA SANTE & DE LA RECHERCHE MEDICALE (INSERM) +4
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com