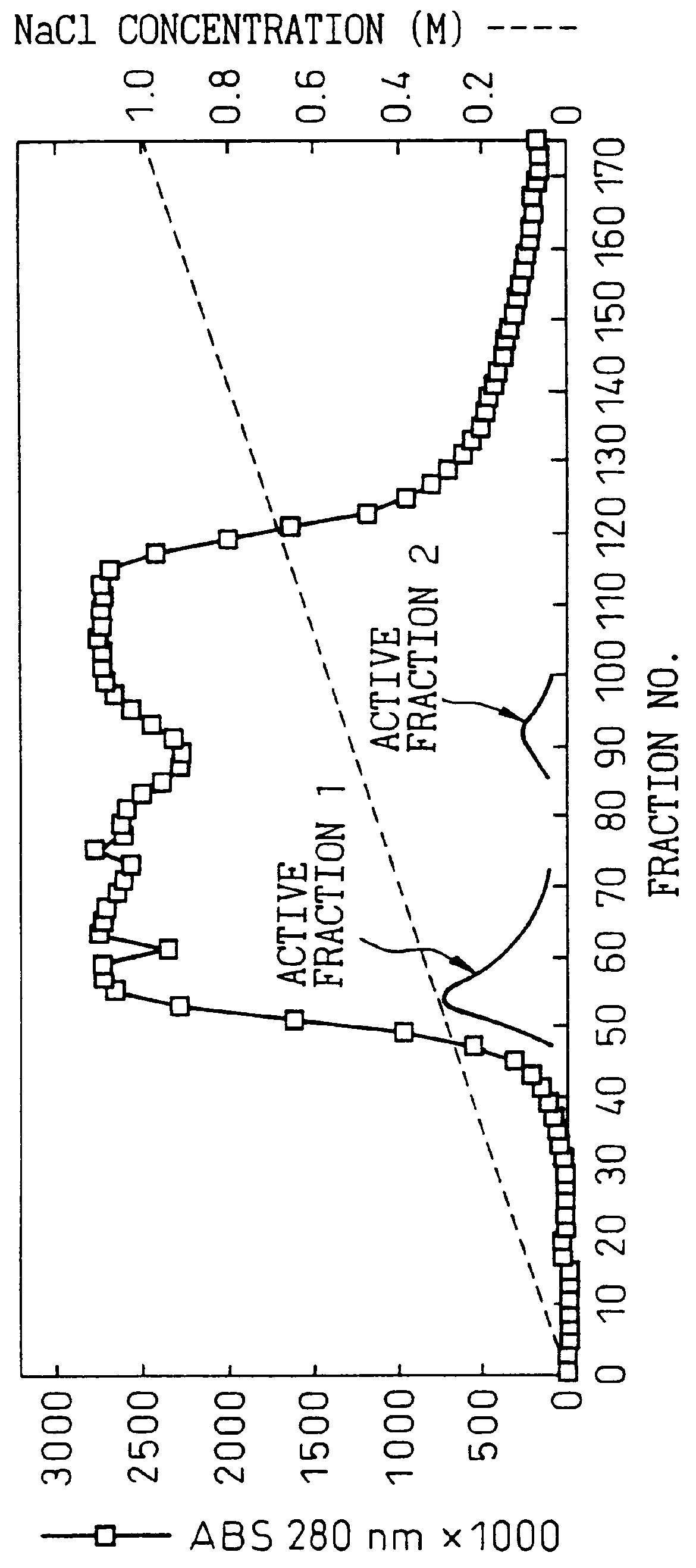
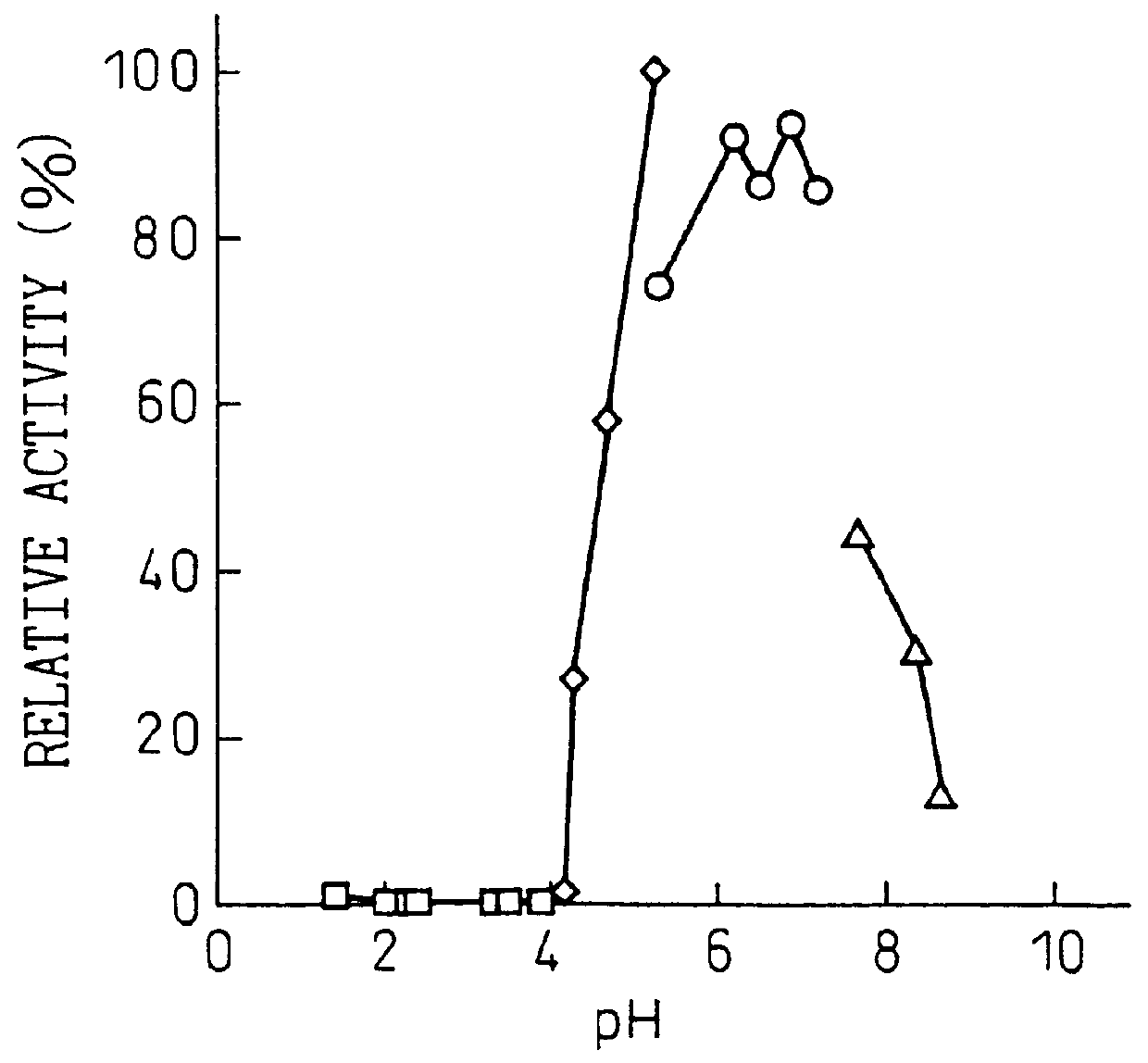
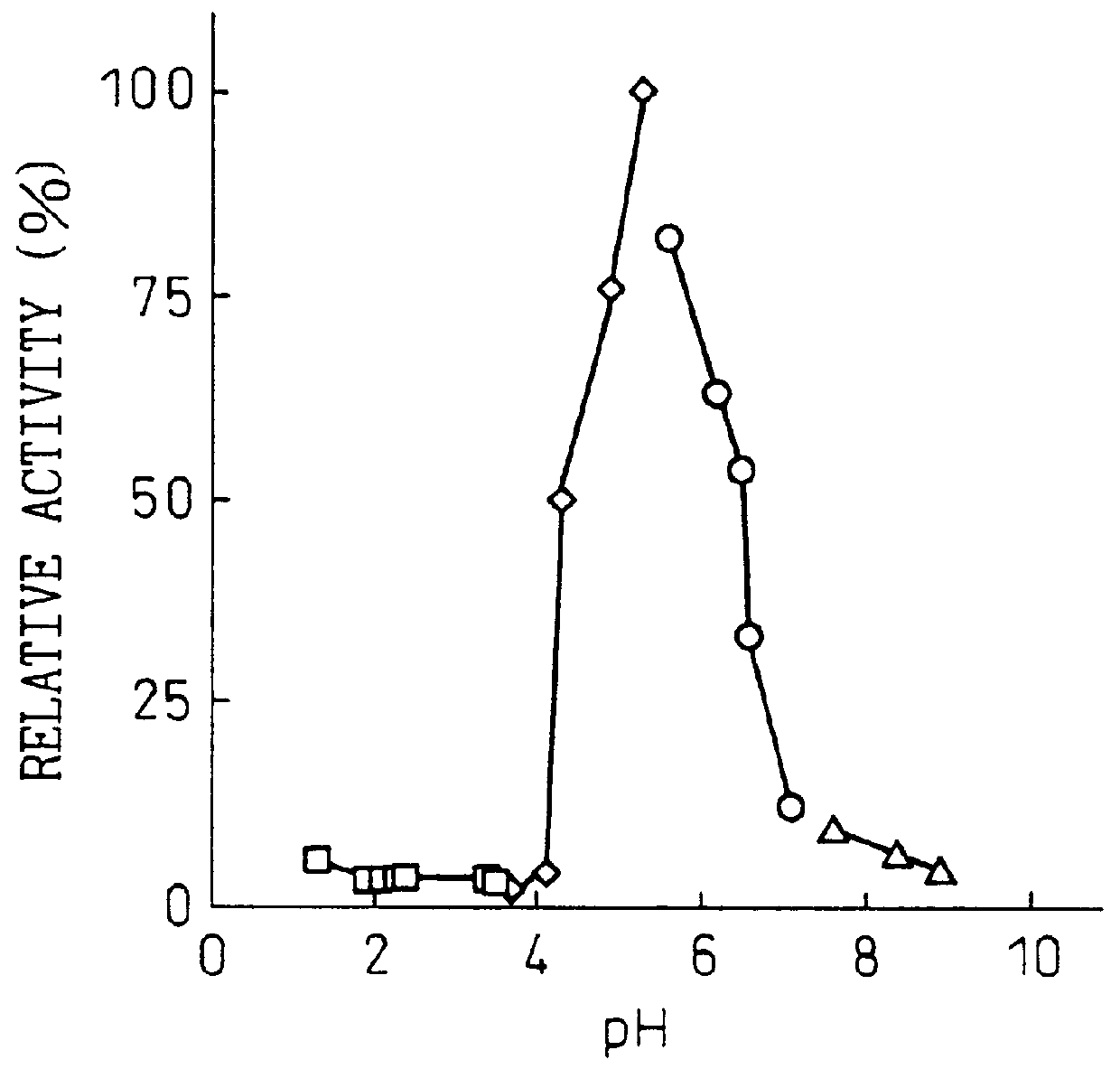
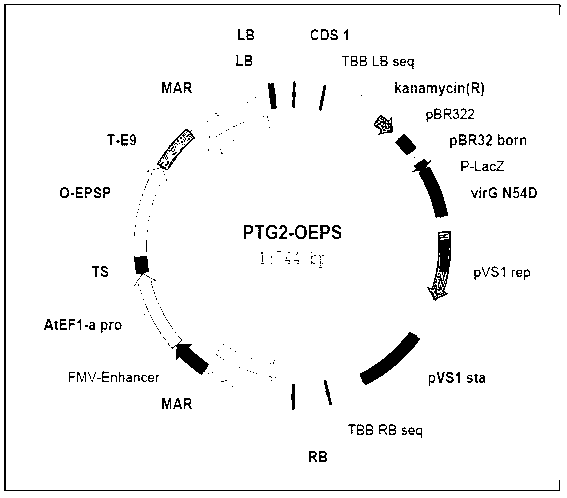
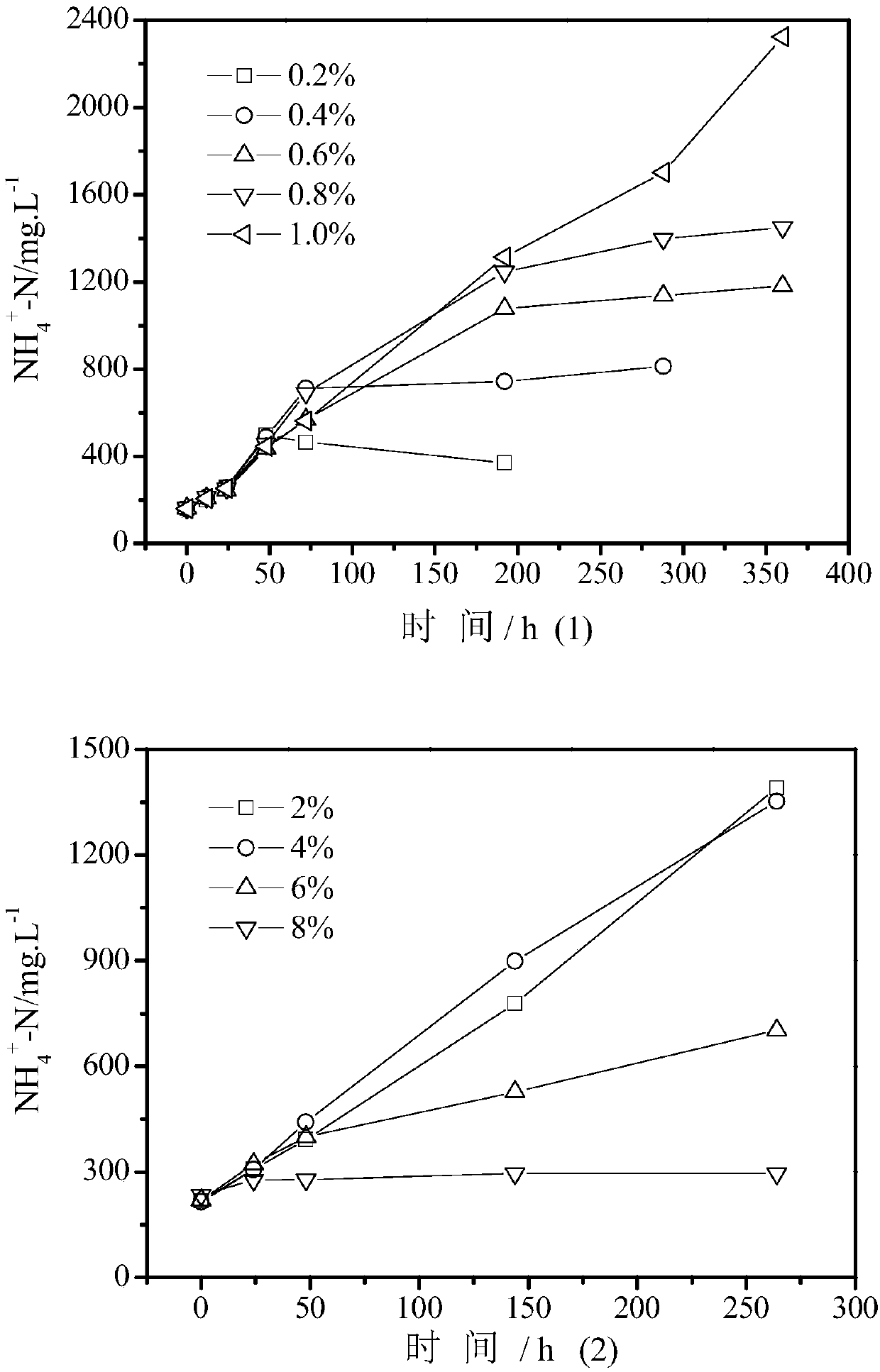
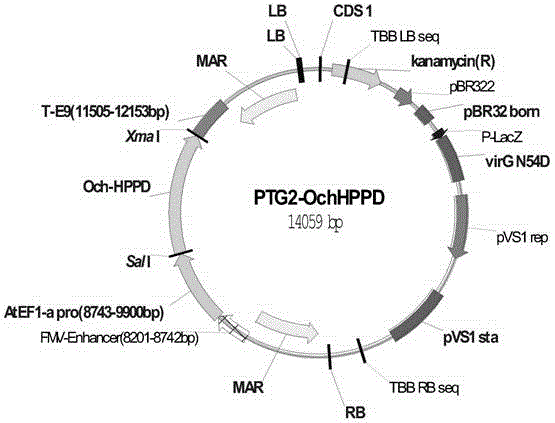
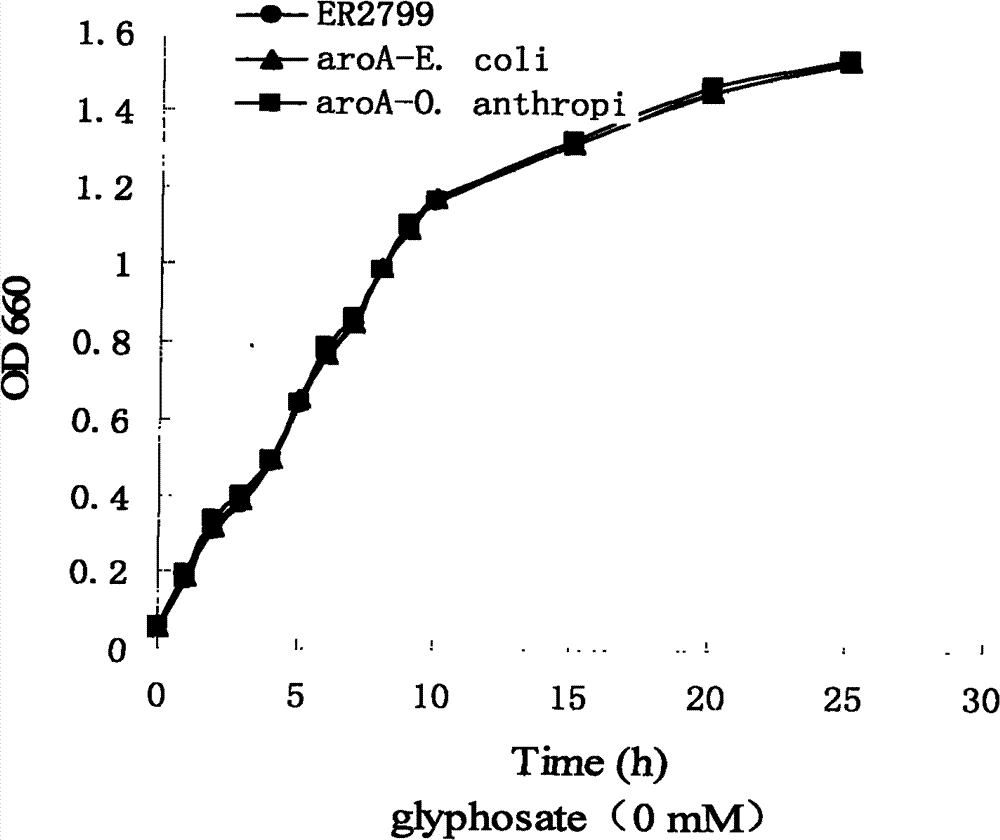
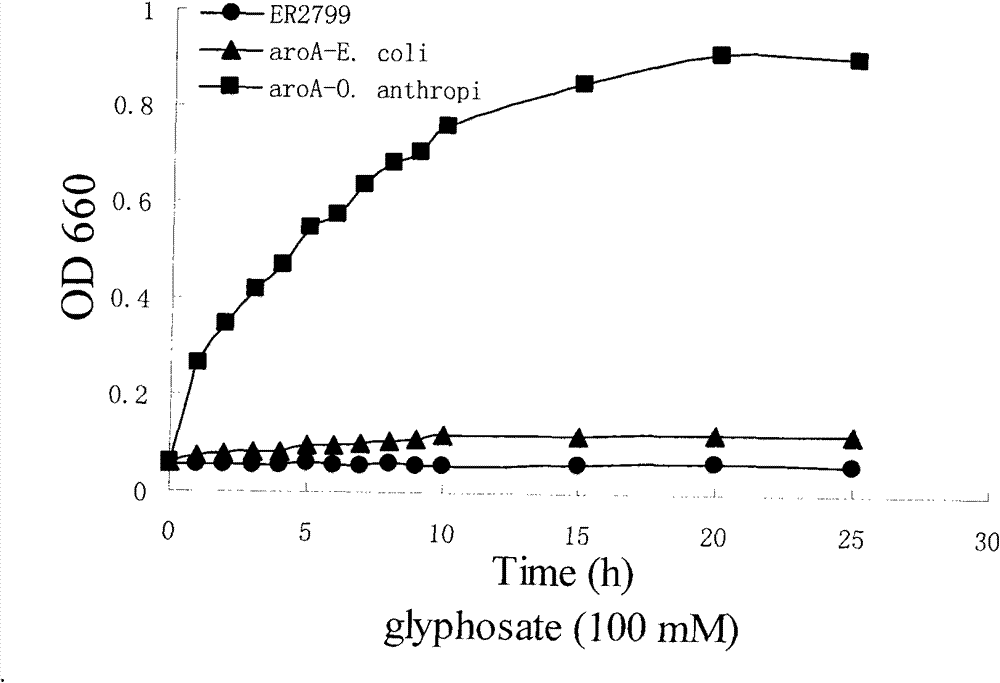
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
33 results about "Ochrobactrum anthropi" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Ochrobactrum anthropi is a bacterium. The type strain is strain CIP 82.115 (= CIP 14970 = NCTC 12168 = LMG 3331). O. anthropi strains are rod-shaped, aerobic, gram-negative, non-pigmented and motile by means of peritrichous flagella.
Aminopherase for producing L-2-aminobutyric acid
ActiveCN105441403AOvercoming conversion rateOvercome concentrationBacteriaTransferasesAminopheraseL-2-Aminobutyric Acid
The invention establishes aminopherase through genetic engineering. Compared with ochrobactrum anthropi based wild w-aminopherase coming from ochrobactrum anthropi, the enzyme activity of aminopherase is remarkably improved, and aminopherase can be used for industrially producing L-2-aminobutyric acid.
Owner:湖州颐盛生物科技有限公司
Human ochrobactrum anthropi and its application in degrading plant stalks and preparing important enzyme
The present invention discloses one kind of human Ochrobactrum anthropi IBL01 (Ochrobactrum anthropi CCTCC M 206046) and its application in degrading plant stalks. Ochrobactrum anthropi IBL01 has high plant stalk degrading effect and can produce high activity cellulase, hadromse and hemicellulase. The present invention also discloses the preparation process of cellulose, xylanase, lignin peroxidase, laccase and manganese peroxidase with the human Ochrobactrum anthropi. The human Ochrobactrum anthropi of the present invention is bacterium with short growth period of about one week, and can produce fiber degrading enzyme as well as hemicellulose degrading enzyme and lignin degrading enzyme.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Compound microbial active filling material for removing sulphur-containing repugnant substances, as well as preparation and application thereof
ActiveCN103272477AShort adaptation periodHigh efficiency of hydrogen sulfide degradationDispersed particle separationAir quality improvementPorosityEcological environment
The invention discloses a compound microbial active filling material for removing sulphur-containing repugnant substances, as well as preparation and application of the compound microbial active filling material. Ochrobactrum anthropi SL1 and aquamicrobium defluvii SU1 related in the invention are isolated bacteria obtained in a reactor for processing repugnant substances, such as H2S, in a water pollution control laboratory of the ecological environment research centre of the Chinese academy of sciences. The bacterial strains are preserved in the general microbial centre of the Chinese general microbial strain preservation and management committee. The preservation numbers are CGMCC No.7400 and CGMCC No.7399 respectively. The compound microbial active filling material disclosed by the invention has the advantages of being large in specific area, high in porosity, good in air permeability, low in resistance, high in bacterial cell loading capacity and less prone to run away; and because of being loaded with ochrobactrum anthropi SL1 and aquamicrobium defluvii SU1, the compound microbial active filling material is difficult to decay and deform in a bioreactor for purifying waste gas, and therefore, the compound microbial active filling material can be used for a long time and is applied to complex processing conditions.
Owner:RES CENT FOR ECO ENVIRONMENTAL SCI THE CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Ochrobactrum anthropi FX02 strain and application thereof to wastewater denitrification
The invention belongs to the technical field of microbial denitrogenation, and particularly discloses an ochrobactrum anthropi FX02 strain and application thereof to wastewater denitrification. The strain is preserved in Guangdong Microbiological Culture Collection Center (GDMCC) on August 17, 2016 with the preservation number of GDMCC No:60062. The strain is a heterotrophic nitrification-aerobic denitrification bacteria, nitrification and denitrification can be conducted simultaneously, and the strain has high application value in sewage treatment.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
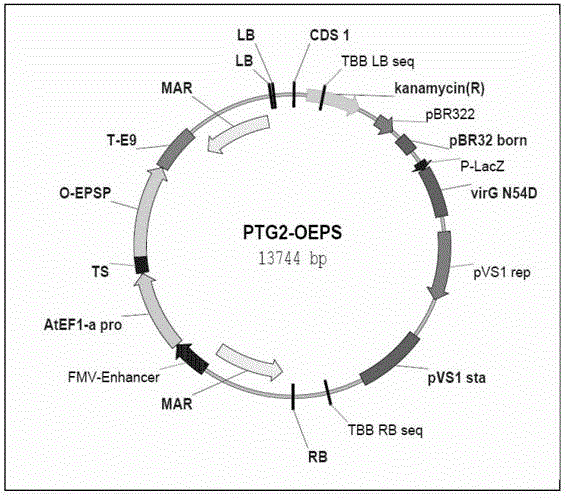
Gene for encoding 5-enolpyrul-shikimate-3-phosphate synthase and application thereof
The invention discloses a gene for encoding 5-enolpyrul-shikimate-3-phosphate synthase (EPSPS). The EPSPS has an amino acid sequence shown as SEQ ID No.2, the gene has the amino acid sequence shown as SEQ ID No.1, and the gene is obtained by cloning from the strain of an ochrobactrum anthropi obtained by separating a soil sample collected at the periphery of a Nalati grassland in Xinjiang by a homologous cloning method. Through an experiment of glyphosate resistance, the gene is found to have good glyphosate resistance and is an excellent gene in the genes of the same kind. The invention also provides a cloning vector and an expression vector thereof which are used for biotransformation and used for transforming crops, thereby the purpose of resisting a herbicide by plants is achieved.
Owner:THE INST OF BIOTECHNOLOGY OF THE CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
EPSP synthase gene derived from ochrobactrum anthropi and application thereof
InactiveCN102108363AImprove toleranceTransferasesMicroorganism based processesNucleotideGenetically modified crops
The invention discloses an EPSP synthase gene derived from ochrobactrum anthropi and application thereof. The EPSP synthase gene contains 1353 basic groups and 451 coded amino acids, the nucleotide sequence of the EPSP synthase gene is as shown in SEQ ID NO1, and the amino acid sequence of the coded proteins is as shown in SEQ ID NO2. The EPSP synthase gene derived from ochrobactrum anthropi disclosed by the invention is synthesized by a manual method, has high homology with the reported EPSP synthase gene derived from agrobacterium tumfaciens, has higher glyphosate tolerance, and can be used for culturing genetically modified crops.
Owner:SHANGHAI ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Composite microbial preparation of linear alkyl benzene sulphonic acid as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN102899278AGrowth inhibitionInhibition of reproductionBacteriaWater contaminantsBenzeneWastewater
The invention relates to a composite microbial preparation of linear alkyl benzene sulphonic acid as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The composite microbial preparation of the linear alkyl benzene sulphonic acid contains Bacillus subtilis, Ochrobactrum anthropi and pseudomonas aeruginosa; the microbial content of the Bacillus subtilis accounts for 15-35% that of the total microbial content; the microbial content of the Ochrobactrum anthropi accounts for 40-60% that of the total microbial content; and the microbial content of the pseudomonas aeruginosa accounts for 10-30% that of the total microbial content. The composite microbial preparation has the advantages that the linear alkyl benzene sulphonic acid can be rapidly decomposed and thoroughly oxidized into CO2 and H2O, so that the growth of harmful microbe is effectively suppressed, the biological treatment efficiency of LAS (Sodium Dodecyl Benzene Sulfonate) wastewater is greatly increased, and the odor of sewage is eliminated.
Owner:ANHUI AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY +1
Purine nucleosidase
InactiveUS6066484AReduce the amount requiredIncrease volumeSugar derivativesBacteriaMicroorganismHaemophilus
Novel purine nucleosidase derived from Ochrobactrum anthropi microorganisms, a gene system coding therefor, uses therefor and particularly its use in the production of beer.
Owner:SUNTORY HLDG LTD
Ochrobactrum anthropi SL1 and application thereof to removal of repugnant substances containing sulfur
ActiveCN103266075AHigh efficiency of hydrogen sulfide degradationShort adaptation periodBacteriaDispersed particle separationSludgeEnvironmental studies
The invention discloses ochrobactrum anthropi SL1 and application thereof to removal of repugnant substances containing sulfur. Ochrobactrum anthropi SL1 is an isolate obtained from a reactor for treating repugnant substances containing H2S and the like in a water pollution control laboratory in Research Center for Eco-Environmental Sciences, Chinese Academy of Sciences. The strain is collected in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (CGMCC), with collection number of CGMCC No.7400. The strain can be used for preparing microbial active fillers, is used for purifying the repugnant substances containing sulfur and solving the problem of odor pollution produced in the processes of sewage, sludge and refuse treatment and composting, and has more than 90% of efficiency of degrading repugnant substances containing sulfur such as hydrogen sulfide, methanethiol, dimethyl sulfide and the like.
Owner:RES CENT FOR ECO ENVIRONMENTAL SCI THE CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for culturing bacteria and application thereof
InactiveCN102191188AMeet growthPromote growthBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBacteroidesEscherichia coli
The invention provides a method for culturing bacteria and application thereof and relates to a method for culturing microorganisms with low price and application thereof to high-efficiency reduction and fixation of heavy metal. In the method for culturing the bacteria by using a low-price culture medium, bean curd water comprises rich carbon sources and nitrogen sources and low-price sugar dreg lixivium is added, human ochrobactrum lupini grows well when the pH value is 7.5, and escherichia coli, bacillus subtilis and bacillus cereus can grow under the conditions, so culture cost is greatly reduced. The human ochrobactrum lupini are further used for treating chromium-containing and nickel-containing industrial waste water in an optimized culture medium, and the result shows that the nickel and chromium reducing efficiency of the human ochrobactrum lupini is high.
Owner:FUJIAN INST OF RES ON THE STRUCTURE OF MATTER CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
5-enolpyruvyl-shikimate-3-phosphate (EPSP) synthase gene from ochrobactrum anthropi and application thereof
The invention discloses a 5-enolpyruvyl-shikimate-3-phosphate (EPSP) synthase gene from ochrobactrum anthropi and application thereof. The invention also provides genetic engineering intermediates (such as an expression cassette, a carrier and a cell) of the gene, a method for obtaining a plant with glyphosate resistance, and application of the method, and provides an identification method for judging whether the plant has the glyphosate resistance. The EPSP synthase gene plays an important role in research and development of the glyphosate-resistant plant.
Owner:BEIJING WEIMING KAITUO CROP DESIGN CENT COMPANYLIMITED
Human pallid bacillus ZJB-061 and uses thereof
InactiveCN101063090AImprove conversion rateProcess greenBacteriaGenetic engineeringChemical synthesisMicroorganism
The invention discloses a microbe strain human pallid bacillus ZJB-061(Ochrobactrum anthropi ZJB-061) and appliance in beta-alanien preparation, which is characterized by the following: keeping human pale bacillus ZJB-061 in Chinese typical culture preserve center with the preserve number at CCTCC No: M 206039 and preserve date at 20060414; seeding human pale bacillus ZJB-061 bacterial in ferment cultural medium; adding light beta-amido ethyl cyanide into ferment culture medium; proceeding ferment culture; centrifuging the ferment liquid; getting thallus; adding bacterial cell or treated bacterial cell into beta-amido ethyl cyanide solution; proceeding hydrolytic reaction; separating inverting liquid; getting beta-alanien. This invention can replace chemosynthesis method, which possesses high conversion rate, good environment and green course.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Azoxystrobin degrading bacterium and microbial inoculum produced by using degrading bacterium and applications of degrading bacterium
ActiveCN104593287ASolve pollutionSolve the problem of excessive pesticide residuesBacteriaWater contaminantsEcological environmentPesticide residue
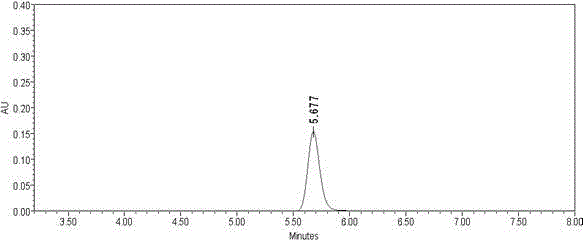
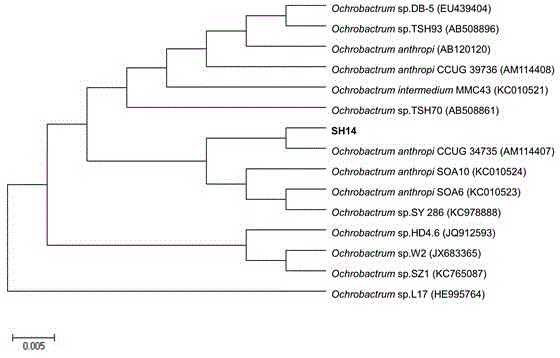
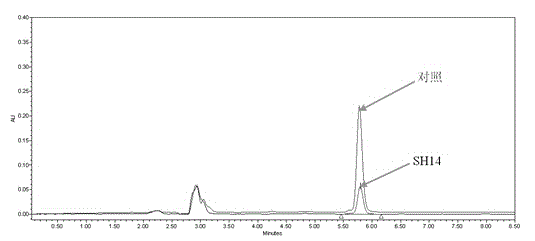
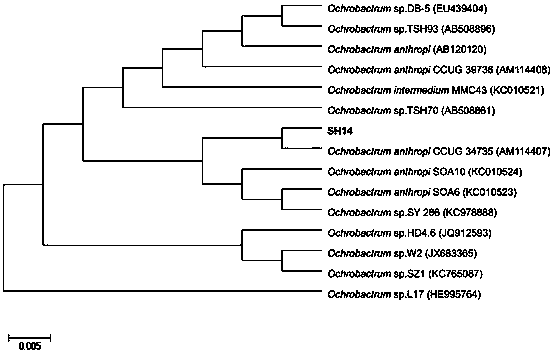
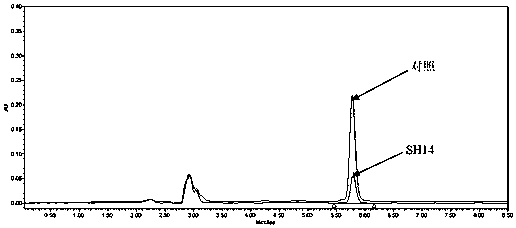
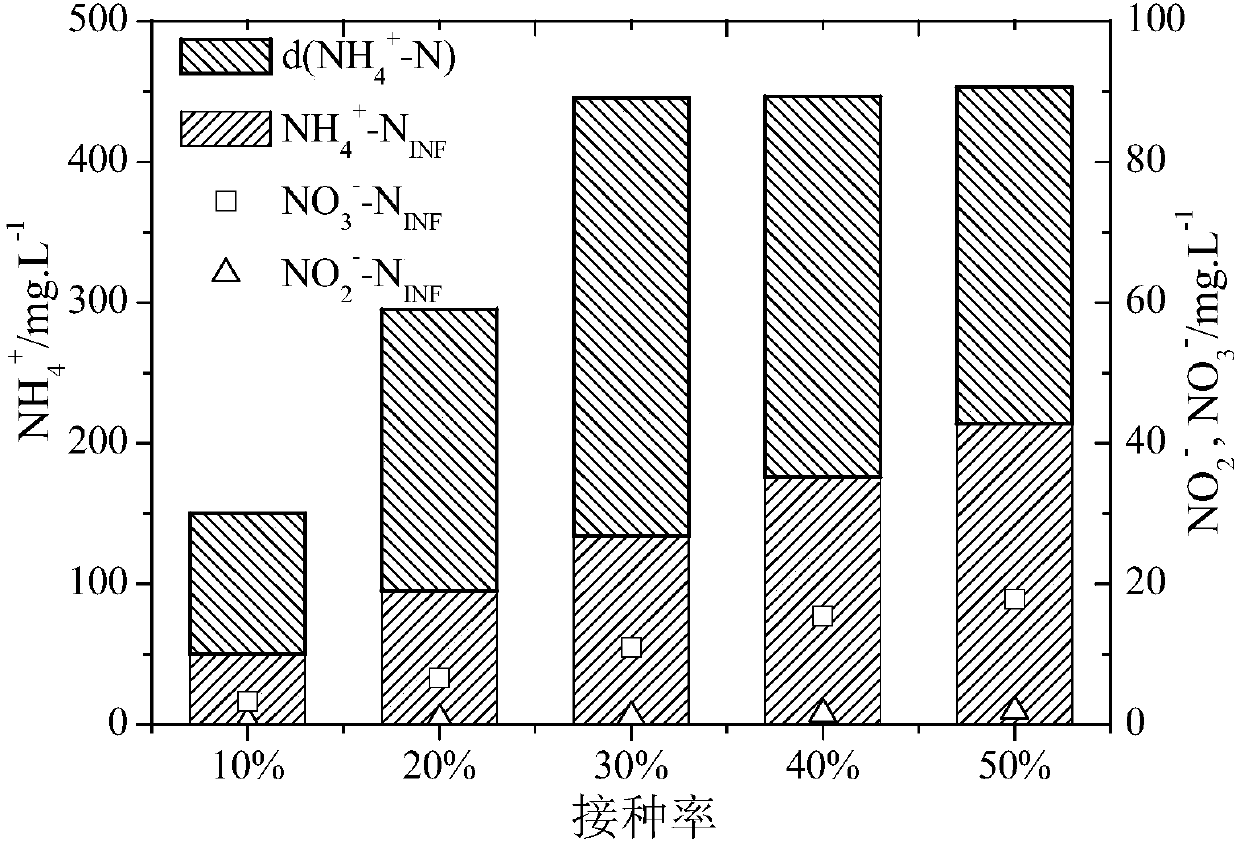
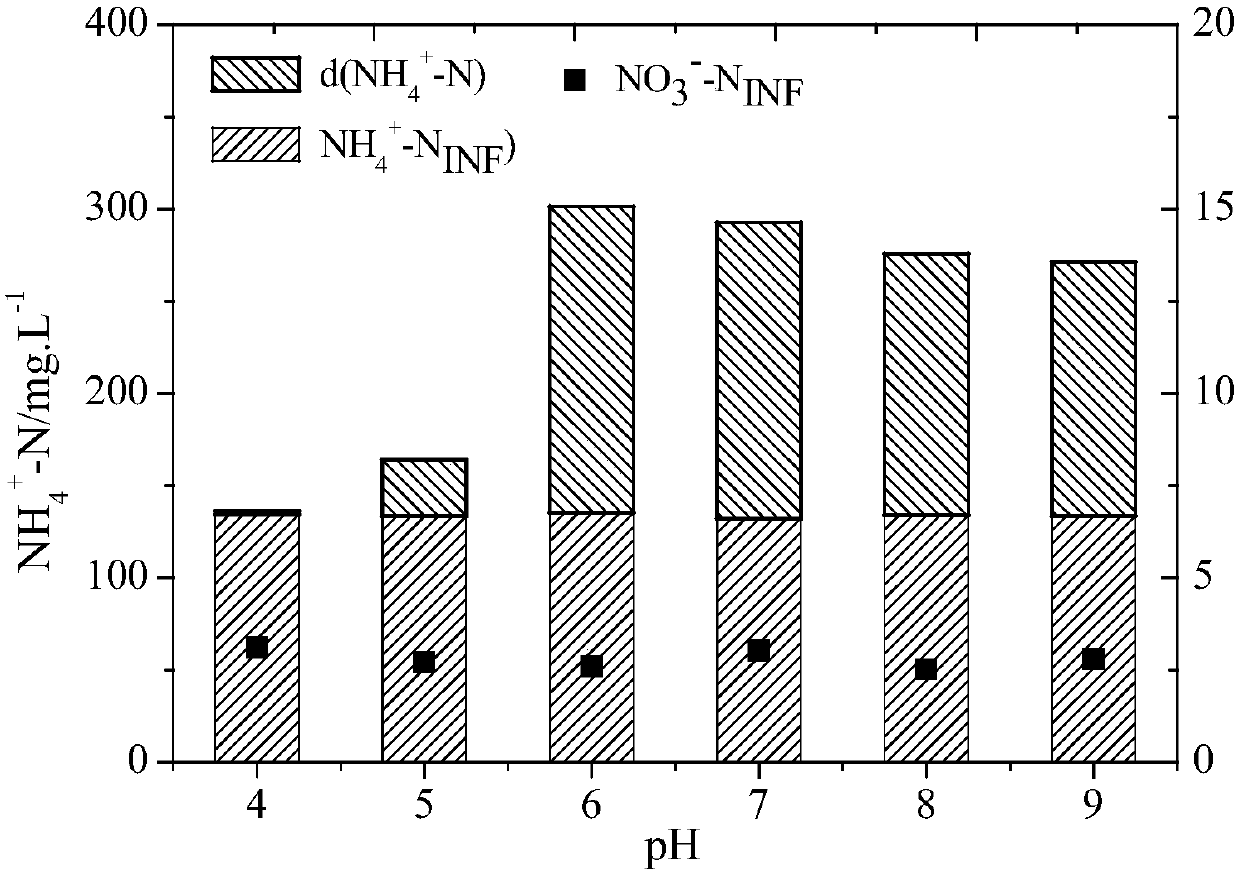
The invention discloses an azoxystrobin degrading bacterium and a microbial inoculum produced by using the degrading bacterium and applications of the degrading bacterium. The strain is ochrobactrum anthropi (Ochrobactrum (anthropi) SH14, the strain is preserved in China Center For Type Culture Collection on December 20, 2013, and the Preservation Number is CCTCC NO: M 2013681. The strain can effectively degrade azoxystrobin pesticide residues in a short time, so that the strain can be used for restoring natural environments such as water and soil and the like polluted by azoxystrobin. A preparation prepared by using the strain has the advantages of low production cost, easiness for use, good removal effect, and the like. By using the microbial inoculum, the residual quantity of azoxystrobin in water and soil can be reduced by over 85% in a short period of time, so that natural environments polluted by azoxystrobin are effectively restored, and the excessive pesticide residue problem and the environmental pollution problem in agricultural production are solved, thereby protecting the ecological environment and the human health.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Microbial inoculum for degrading straw at low temperature and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN113652365AReduce pollutionPromote degradationBio-organic fraction processingBacteriaBiotechnologyCellulose
The invention discloses a microbial inoculum for degrading straws at low temperature and a preparation method thereof. The microbial inoculum disclosed by the invention is prepared from ochrobactrum anthropi, lindernia procumbens, variovorax and nitrogen-producing pseudomonas. The bacterial strains comprise the following components in parts by weight: 30 to 50 parts of ochrobactrum anthropi, 10 to 25 parts of lindernia procumbens, 20 to 30 parts of variovorax and 25 to 40 parts of nitrogenous pseudomonas. The microorganisms are all screened from a low-temperature environment, various microorganisms have strong degradation ability to cellulose, and the microbial agent obtained by compounding the microorganisms can improve the degradation rate of straw at low temperature and effectively promote straw decomposition. The application of the fertilizer can promote straw returning to the field, improve soil fertility and reduce environmental pollution caused by random stacking and rotting of the straw.
Owner:SHENYANG AGRI UNIV
A kind of azoxystrobin degrading bacterium and its production bacterium agent and application
ActiveCN104593287BSolve pollutionProtect healthBacteriaWater contaminantsPesticide residueAzoxystrobin
The invention discloses an azoxystrobin-degrading bacterium as well as the bacterium agent produced therefrom and application thereof. The strain is Ochrobactrum anthropi SH14, which was deposited in China Center for Type Culture Collection (CCTCC) on December 20, 2013, and the preservation number is CCTCC NO: M 2013681. The strain can effectively degrade azoxystrobin pesticide residues in a short period of time, and can be used to restore natural environments such as water bodies and soils polluted by azoxystrobin. The preparation prepared by the bacterial strain has the advantages of low production cost, convenient use, good removal effect and the like. The use of this bacterial agent can reduce the residual amount of azoxystrobin in water and soil by more than 85% in a short period of time, effectively repair the natural environment polluted by azoxystrobin, solve the problem of excessive pesticide residues and environmental pollution in agricultural production, and protect the ecology environment and human health.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Microbial flora for decomposing dimethylformamide and culture method thereof
InactiveCN108410755AEfficient removalLow running costBacteriaWater contaminantsOchrobactrum anthropiFlavobacterium
The present invention relates to a method for decomposing dimethylformamide, and more particularly to a microbial flora for decomposing the dimethylformamide and a culture method thereof. The microbial flora for decomposing the dimethylformamide includes: Brevundimonas vesicularis, Brevibacillus parabrevis, achromobacter, Flavobacterium, Stenotrophomonas, Ochrobactrum anthropi, Aquamicrobium defluvii, Sphingobacteria and Nocardioides. The microbial flora utilizes the dimethylformamide as a carbon source and a nitrogen source to oxidatively decompose the dimethylformamide while satisfying the own growth of the microbial flora; the microbial flora can efficiently remove the refractory organic matter dimethylformamide in industrial wastewater, and reduces the operating costs of wastewater treatment.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF TECH
A strain of * degrading bacteria and its application
InactiveCN104673725BPromote degradationBacteriaContaminated soil reclamationMicrobiologyOchrobactrum anthropi
The invention discloses a bacterial strain with degradative function belonging to the technical field of biodegradation treatment. The degrading bacterium was identified as Ochrobactrum anthropi DW1, and the strain preservation number was CGMCC No.8621. The bacterial strain was made into a bacterial suspension with a bacterial content of 1.25×108CFU / ml, and the degradation removal rate of the initial concentration of 0.14mg / L after 7 days was 56.2%.
Owner:BEIJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Microbial agent used for degrading quinclorac herbicides
The invention discloses a microbial agent used for degrading quinclorac herbicides. The microbial agent takes several strains of bordetella, arthrobacterium, bacillus megatherium, burkholderia cepacia, ochrobactrum anthropi, pseudomonas, alcaligenes faecalis, aspergillus niger and neurospora and cellulase, amylase, protease, lipase and a biological accelerating agent as raw materials, and fermented solutions obtained after the several strains of the bordetella, the arthrobacterium, the bacillus megatherium, the burkholderia cepacia, the ochrobactrum anthropi, the pseudomonas, the alcaligenes faecalis, the aspergillus niger and the neurospora undergo fermentation culture are mixed to form a mixed fermented solution, after thalli are collected by centrifugation from the mixed fermented solution, skimmed milk and sucrose are added, freeze drying is performed, and then, the thalli are compounded with the cellulase, the amylase, the protease, the lipase and the biological accelerating agentto obtain the microbial agent.
Owner:SHANDONG SUNWAY LANDSCAPE TECH
HPPD inhibitor-resistant gene derived from ochrobactrum anthropi and application thereof
InactiveCN105567705AMicrobiological testing/measurementBacteria peptidesHigh resistanceResistant genes
The invention discloses an HPPD inhibitor resistant gene having high resistance to an HPPD inhibitor and derived from ochrobactrum anthropi and an application thereof in transgenic plants. A method for transforming plants by the gene and high HPPD inhibitor-resisting activity expressed in the transgenic plants play an important role in research and development of plants resisting the HPPD inhibitor.
Owner:BEIJING WEIMING KAITUO CROP DESIGN CENT COMPANYLIMITED
EPSP synthase gene derived from ochrobactrum anthropi and application thereof
InactiveCN102108363BImprove toleranceTransferasesMicroorganism based processesNucleotideHigh homology
The invention discloses an EPSP synthase gene derived from ochrobactrum anthropi and application thereof. The EPSP synthase gene contains 1353 basic groups and 451 coded amino acids, the nucleotide sequence of the EPSP synthase gene is as shown in SEQ ID NO1, and the amino acid sequence of the coded proteins is as shown in SEQ ID NO2. The EPSP synthase gene derived from ochrobactrum anthropi disclosed by the invention is synthesized by a manual method, has high homology with the reported EPSP synthase gene derived from agrobacterium tumfaciens, has higher glyphosate tolerance, and can be usedfor culturing genetically modified crops.
Owner:SHANGHAI ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Composite microbial preparation of linear alkyl benzene sulphonic acid as well as preparation method and application thereof
The invention relates to a composite microbial preparation of linear alkyl benzene sulphonic acid as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The composite microbial preparation of the linear alkyl benzene sulphonic acid contains Bacillus subtilis, Ochrobactrum anthropi and pseudomonas aeruginosa; the microbial content of the Bacillus subtilis accounts for 15-35% that of the total microbial content; the microbial content of the Ochrobactrum anthropi accounts for 40-60% that of the total microbial content; and the microbial content of the pseudomonas aeruginosa accounts for 10-30% that of the total microbial content. The composite microbial preparation has the advantages that the linear alkyl benzene sulphonic acid can be rapidly decomposed and thoroughly oxidized into CO2 and H2O, so that the growth of harmful microbe is effectively suppressed, the biological treatment efficiency of LAS (Sodium Dodecyl Benzene Sulfonate) wastewater is greatly increased, and the odor of sewage is eliminated.
Owner:ANHUI AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY +1
Ochrobactrum anthropi DW3 with function of degrading benzo[ghi] perylene
The invention discloses a bacterial strain with a function of degrading benzo[ghi] perylene, and belongs to the technical field of biodegradation processing. The benzo[ghi] perylene degrading bacterium is identified as ochrobactrum anthropi DW3 with a culture preservation number of CGMCC No.8623. The bacterial strain is prepared into a bacterial suspension with bacteria content of 1.25*10<8>CFU / ml, so that a degradation removal rate for the benzo[ghi] perylene with initial concentration of 0.11mg / L after 7 days is 48.7%.
Owner:BEIJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Ochrobactrum anthropic with hexavalent chromium reduction and active black 5 degradation functions and application of ochrobactrum anthropic
The invention belongs to the technical field of microbial agents, and particularly relates to ochrobactrum anthropic with hexavalent chromium reduction and active black 5 degradation functions and anapplication of the ochrobactrum anthropic. The ochrobactrum anthropic is ochrobactrum anthropic S1 and is preserved in China Center for Type Culture Collection, and the preservation number is CCTCC NO: M 2020461. The ochrobactrum anthropic disclosed by the invention can perform hexavalent chromium reduction and active black 5 degradation at the same time, and has good treatment prospects on Cr pollution and active black 5 pollution.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
5-enolpyruvyl-shikimate-3-phosphate (EPSP) synthase gene from ochrobactrum anthropi and application thereof
The invention discloses a 5-enolpyruvyl-shikimate-3-phosphate (EPSP) synthase gene from ochrobactrum anthropi and application thereof. The invention also provides genetic engineering intermediates (such as an expression cassette, a carrier and a cell) of the gene, a method for obtaining a plant with glyphosate resistance, and application of the method, and provides an identification method for judging whether the plant has the glyphosate resistance. The EPSP synthase gene plays an important role in research and development of the glyphosate-resistant plant.
Owner:BEIJING WEIMING KAITUO CROP DESIGN CENT COMPANYLIMITED
Polymerase chain reaction primers for quantitatively detecting Ochrobactrum anthropi, kit and method for quantitatively detecting Ochrobactrum anthropi
PendingCN111254208AQuantitatively accurateRapid determinationMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesFloraOchrobactrum anthropi
The invention provides a pair of primers for detecting Ochrobactrum anthropi. The primers can rapidly determine any flora samples containing the Ochrobactrum anthropi so as to realize the specific recognition on the Ochrobactrum anthropi. A provided method includes extracting the metagenome of a to-be-detected sample, and performing dilution and split charging; respectively taking a small amount of the diluted metagenome sample to equally mix, and using a pair of primers to perform amplification; taking an amplified product as a QPCR quantitative standard stock solution through concentration determination; and performing the quantitative determination of the Ochrobactrum anthropi on all samples. The interference from other strains with highly similar ribosomal RNA gene fragments can be avoided by adopting the provided primers to detect the Ochrobactrum anthropi; and therefore, accurate determination on the Ochrobactrum anthropi can be realized.
Owner:威海以琳生物科技有限责任公司 +1
Ochrobactrum anthropi M11 for degrading unsymmetrical dimethylhydrazine and method for degrading unsymmetrical dimethylhydrazine by using ochrobactrum anthropi M11
InactiveCN102367425BImprove degradation rateBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMicrobiologyOchrobactrum anthropi
The invention discloses an ochrobactrum anthropi M11 for degrading unsymmetrical dimethylhydrazine and a method for degrading the unsymmetrical dimethylhydrazine by using the ochrobactrum anthropi M11. The method comprises the steps of: inoculating a strain of the ochrobactrum anthropi M11 to a slant culture medium, and culturing to obtain a slant culture product; inoculating the slant culture product into a container in which a seed culture medium is arranged, and culturing to obtain a seed liquid; immobilizing the seed liquid to obtain immobilized mycelial pellets; and inoculating the immobilized mycelial pellets into a container in which a substrate solution is filled according to an inoculation amount of 10-30%, mixing, and degrading for 72 hours at a temperature of 30-37 DEG C and the oscillation rate of 120-200r / min, wherein the inoculation amount is calculated based on the volume proportion of the seed liquid to the substrate solution. According to the invention, the degrading rate for the unsymmetrical dimethylhydrazine is high up to 97.7%.
Owner:LOGISTICS DEPT ANTIEPIDEMIC ARMY OF THE GENERAL ARMAMENT DEPT PLA
Composite microbial active filler for removing sulfur-containing malodorous substances and its preparation and application
ActiveCN103272477BShort adaptation periodHigh efficiency of hydrogen sulfide degradationDispersed particle separationAir quality improvementPorosityEcological environment
The invention discloses a compound microbial active filling material for removing sulphur-containing repugnant substances, as well as preparation and application of the compound microbial active filling material. Ochrobactrum anthropi SL1 and aquamicrobium defluvii SU1 related in the invention are isolated bacteria obtained in a reactor for processing repugnant substances, such as H2S, in a water pollution control laboratory of the ecological environment research centre of the Chinese academy of sciences. The bacterial strains are preserved in the general microbial centre of the Chinese general microbial strain preservation and management committee. The preservation numbers are CGMCC No.7400 and CGMCC No.7399 respectively. The compound microbial active filling material disclosed by the invention has the advantages of being large in specific area, high in porosity, good in air permeability, low in resistance, high in bacterial cell loading capacity and less prone to run away; and because of being loaded with ochrobactrum anthropi SL1 and aquamicrobium defluvii SU1, the compound microbial active filling material is difficult to decay and deform in a bioreactor for purifying waste gas, and therefore, the compound microbial active filling material can be used for a long time and is applied to complex processing conditions.
Owner:RES CENT FOR ECO ENVIRONMENTAL SCI THE CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Paleobacterium hominis and its application in removing sulfur-containing malodorous substances
ActiveCN103266075BHigh efficiency of hydrogen sulfide degradationShort adaptation periodBacteriaDispersed particle separationOchrobactrum anthropiRefuse Disposals
The invention discloses ochrobactrum anthropi SL1 and application thereof to removal of repugnant substances containing sulfur. Ochrobactrum anthropi SL1 is an isolate obtained from a reactor for treating repugnant substances containing H2S and the like in a water pollution control laboratory in Research Center for Eco-Environmental Sciences, Chinese Academy of Sciences. The strain is collected in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (CGMCC), with collection number of CGMCC No.7400. The strain can be used for preparing microbial active fillers, is used for purifying the repugnant substances containing sulfur and solving the problem of odor pollution produced in the processes of sewage, sludge and refuse treatment and composting, and has more than 90% of efficiency of degrading repugnant substances containing sulfur such as hydrogen sulfide, methanethiol, dimethyl sulfide and the like.
Owner:RES CENT FOR ECO ENVIRONMENTAL SCI THE CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Human ochrobactrum capable of efficiently degrading glyphosate and application of human ochrobactrum
ActiveCN114717159AEfficient degradationResidue reductionBacteriaContaminated soil reclamationMicroorganismPesticide residue
The invention discloses Ochrobactrum anthropi (Ochrobactrum anthropi) capable of efficiently degrading glyphosate and an application of the Ochrobactrum anthropi. The human ochrobactrum anthropi A-1 capable of efficiently degrading glyphosate is obtained through screening, separation and research, the strain is preserved in Guangdong Microbial Culture Collection Center on July 21, 2021, and the preservation number of the strain is GDMCC NO: 61823. After the strain is directly applied for 24 hours, the residual amount of glyphosate in a water-sediment system can be reduced by 93% or above, glyphosate can be completely degraded within 36 hours, and the strain can be used for repairing natural environments such as water bodies and soil polluted by glyphosate. The strain A-1 provided by the invention enriches a germplasm resource library of pesticide degrading bacteria, has an important application value in the bioremediation of water bodies and soil polluted by glyphosate residues, and provides a new development way for breaking through the bottleneck of existing pesticide residue pollution treatment; and a theoretical basis and a practical basis are provided for developing a green and safe glyphosate pesticide residue removal technology.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Water awakening type self-healing microbial capsule and waterproof material prepared from same
The invention belongs to the technical field of waterproof materials, particularly relates to a water-awakening type self-healing microbial capsule, and further relates to a waterproof material prepared from the microbial capsule. The microbial capsule is prepared from the following raw materials: ochrobactrum, a culture medium, nutrient substances, a calcium source, urea, a mixture of aluminate and gypsum, and swelling resin. The waterproof material provided by the invention can realize secondary repair, and can be directly awakened when meeting water, when a concrete member cracks, water flows into a crack, and the aluminate and the gypsum finish the first repair. And when the expanded crystal repaired for the first time cracks, water is in contact with the ochrobactrum anthropi along with the cracks, the ochrobactrum anthropi has a mineralization deposition effect, and the cracks are filled with mineralization deposition products again, so that the second time of repairing is completed. The microbial capsule and the waterproof material provided by the invention have the advantages of low cost of adopted materials, easily available raw materials, simple product production process and remarkable social and economic effects.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU UNIV
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com