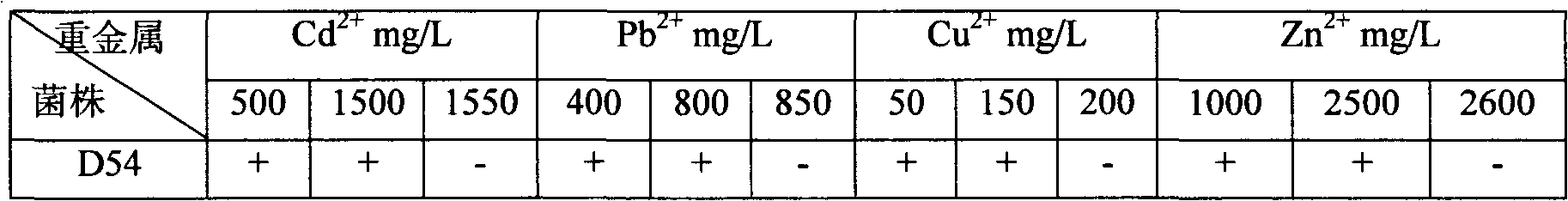Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1559 results about "Bioremediation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Bioremediation is a process used to treat contaminated media, including water, soil and subsurface material, by altering environmental conditions to stimulate growth of microorganisms and degrade the target pollutants. In many cases, bioremediation is less expensive and more sustainable than other remediation alternatives. Biological treatment is a similar approach used to treat wastes including wastewater, industrial waste and solid waste.
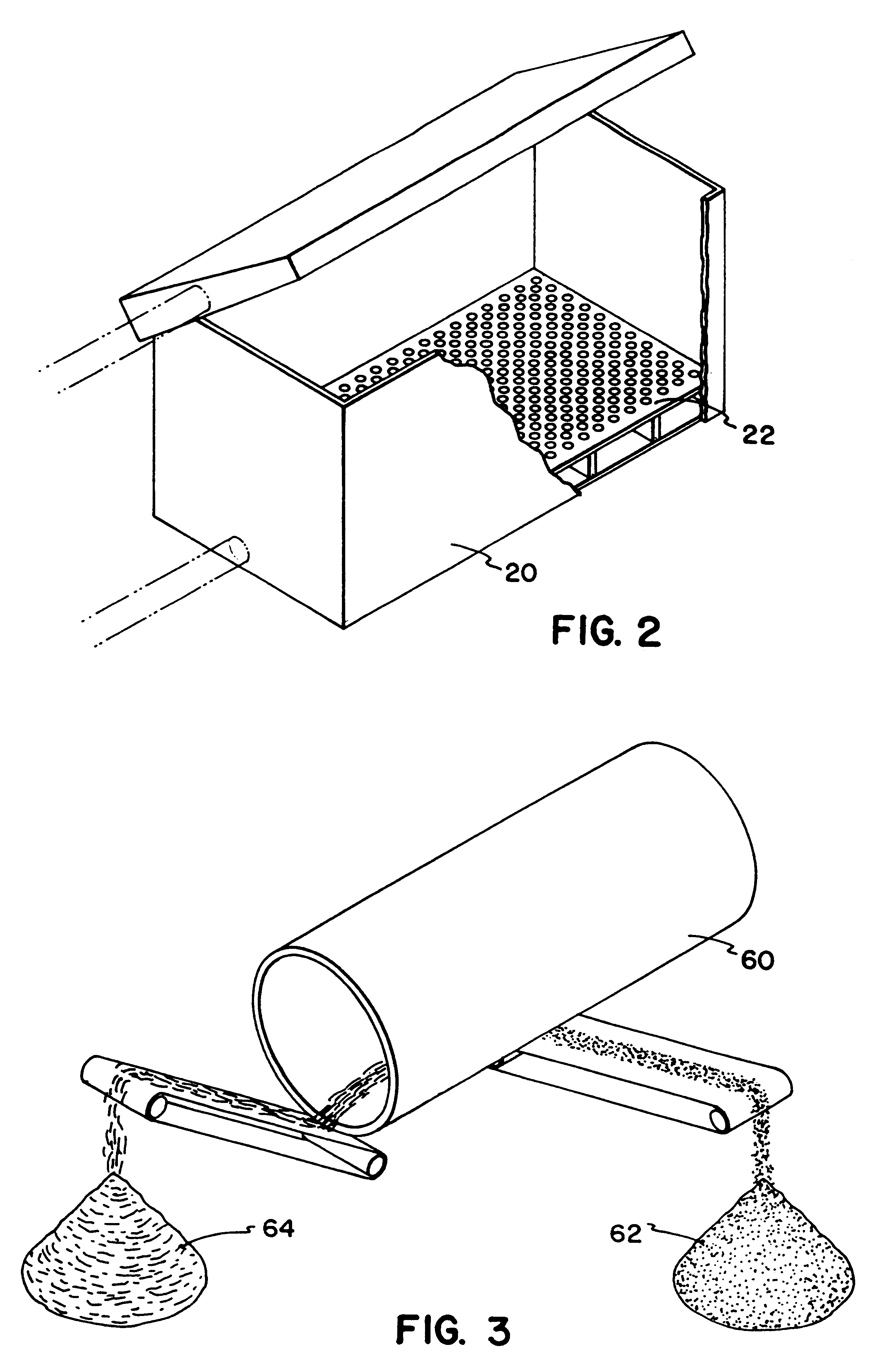
Soil remediation method for treating heavy metal pollutants
ActiveCN101947539AReduce the amount requiredNo secondary pollutionContaminated soil reclamationSoil scienceSoil remediation
Owner:浙江博世华环保科技有限公司
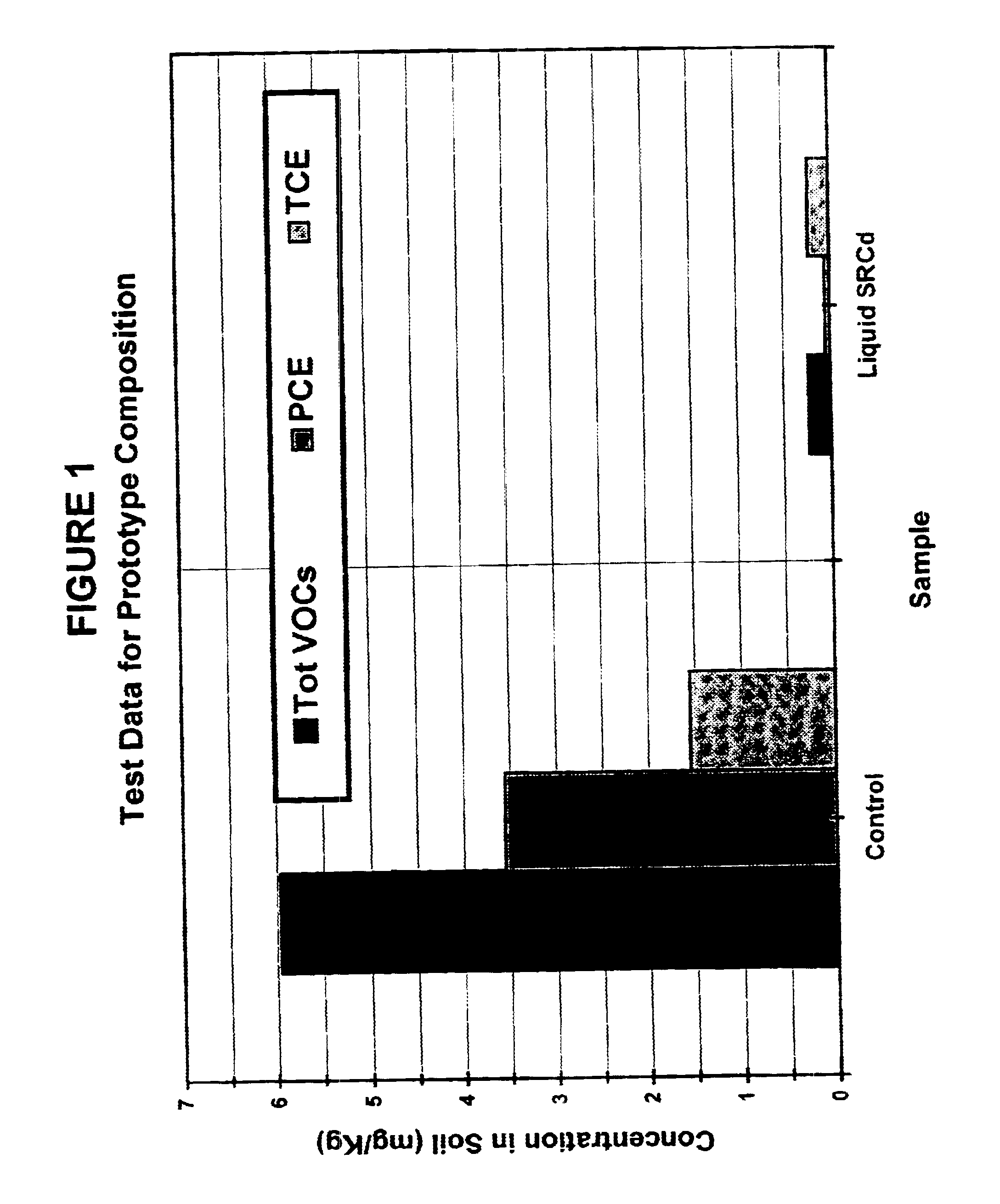
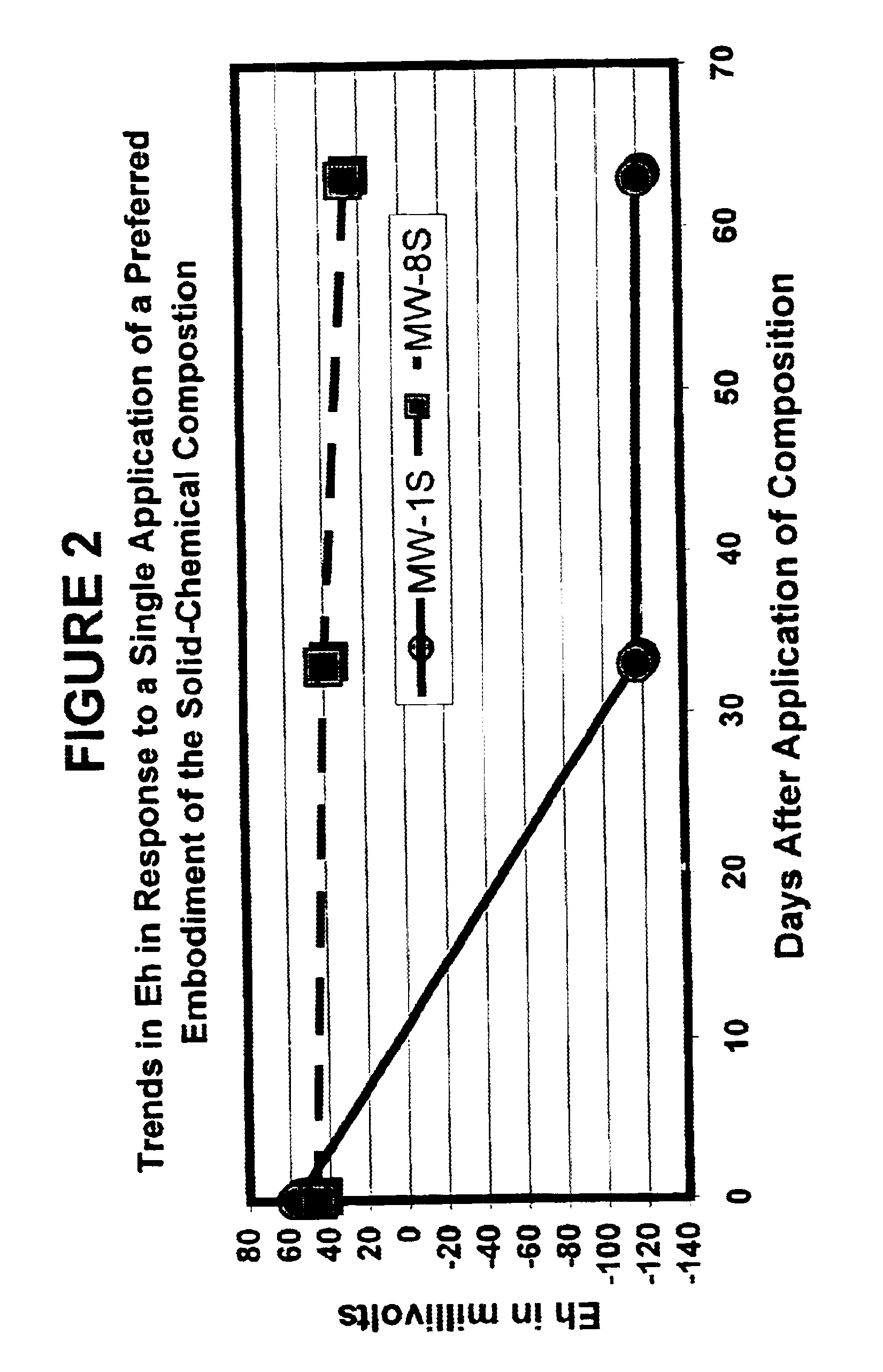
Solid-chemical compositions, geochemical binder system, and improved high-shear granulation process for both conventional and slow-release fertilizer and bioremediation nutrient compositions
InactiveUS20020178772A1Less-expensive to produceWiden meansSolid/semi-solid fertilisersMatrix fertilisersSolubilityAdditive ingredient
This invention discloses advanced means for the formulation and preparation of solid-chemical compositions which provide sources of water-soluble nutrients, electron acceptors and other agents for agriculture and waste-treatment, in particular, the bioremediation of contaminated environmental media. The disclosed formulations and means of production of the slow-release solid-chemical compositions of the present invention utilize a novel and economical "biphasic" chemical-system technology which involves a combination of a first "nutrient" component (1) which comprises water-soluble nutrients and other biologically utilizable substances with a second component (2) which comprises an inorganic geochemical-binder system. The simplest embodiment of the geochemical-binder system comprises one or more salts of phosphoric acid. In the preferred embodiments of the present invention intended for the slow-release of the ingredients contained in the "nutrient" component (1), the geochemical-binder system of component (2) comprises a combination of one or more salts of phosphoric acid with a inorganic binder matrix preferably containing a mixture of low-solubility carbonates, carbonate minerals, phosphates and phosphate minerals. The different embodiments of the geochemical-binder system of this invention allows a wide variation of formulations of the nutrient component (1) to be prepared in both conventional and slow-release forms using an improved high-shear granulation process whereby the dangerous chemicals typically used in the granulation process are largely or completely replaced with water. The present invention discloses means by which such compositions can be economically prepared in large quantities so as to meet the specific needs of different sectors of the agricultural / agribusiness and phytoremediation / bioremediation markets. The disclosed solid-chemical compositions of the present invention provide improved, cost-effective means for slowing and controlling the release-rate profiles of water-soluble nutrients, such as nitrogen- and phosphorus-rich compounds, and improved means for enhanced and / or time-targeted nutrient uptake by plants and microorganisms. The present invention also provides improved means for the reduction of nutrient run-off from agricultural areas into surface waters and means of preventing or minimizing nutrient-contamination of ground-water aquifers.
Owner:HINCE ERIC CHRISTIAN MR
Production and use of biosolid granules
This invention relates to the production and use of encapsulated and / or concentrically-constructed fertilizer or bioremediation granules such as, for example, granules of 0.5 mm to 10 mm in diameter constructed so that there are at least two components to the granule including a core with a surrounding capsule or a core with one or more concentric layers that are distinguishable from the core with respect to nutrient content, density, hardness, solubility, composition, microbial content and permeability, as in permeability to odors or the permeability of nutrients that might volatize to the atmosphere or leach into the soil. The basic idea was to create a method for manufacturing and using fertilizer granules, which incorporate multiple concentric layers or a core plus an encapsulating outer layer.
Owner:UNIFIED ENVIRONMENTAL SERVICES GROUP
Method for biologically remediating water body and soil comprehensively utilizing resources
ActiveCN103736721ALow costSimple technologyContaminated soil reclamationSustainable biological treatmentAlgal growthBioremediation
The invention discloses a method for biologically remediating a water body and soil comprehensively utilizing resources. The method comprises the steps: (1), determining main pollutants in a selected land area or water body area; (2), selecting to plant and / or cultivate fast-growing herbaceous plants, fast-growing alga, trees, bushes, fungi or microorganisms with high remediation efficiency in the selected land area or water body area; (3), harvesting or collecting the fast-growing herbaceous plants and the fast-growing alga after growing to reach a suitable height or size; (4), concentratedly processing the harvested or collected fast-growing herbaceous plants and the fast-growing alga, and comprehensively utilizing to prevent the pollutants from dispersing; (5), remediating an eutrophic water body by adopting an artificial floating island; (6), remediating a heavy metal polluted water body by confining floating plants; (7), repairing cadmium and zinc polluted soil by mixed-cropping festuca arundinacea and bluegrass; (8), remediating polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) polluted soil by mixed-cropping alfalfa and italian ryegrass; and (9), extracting and recovering silver from silver-containing wastewater remediation plants.
Owner:湖南绿心科技有限公司
Process for controlled composting of organic material and for bioremediating soils
InactiveUS6281001B1Prevent escapeSlow and hinder microbial degradationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBio-organic fraction processingBioremediationOrganic chemistry
Owner:MCNELLY JAMES J
Production and use of biosolid granules
This invention relates to the production and use of encapsulated and / or concentrically-constructed fertilizer or bioremediation granules such as, for example, granules of 0.5 mm to 10 mm in diameter constructed so that there are at least two components to the granule including a core with a surrounding capsule or a core with one or more concentric layers that are distinguishable from the core with respect to nutrient content, density, hardness, solubility, composition, microbial content and permeability, as in permeability to odors or the permeability of nutrients that might volatize to the atmosphere or leach into the soil. The basic idea was to create a method for manufacturing and using fertilizer granules, which incorporate multiple concentric layers or a core plus an encapsulating outer layer.
Owner:UNIFIED ENVIRONMENTAL SERVICES GROUP
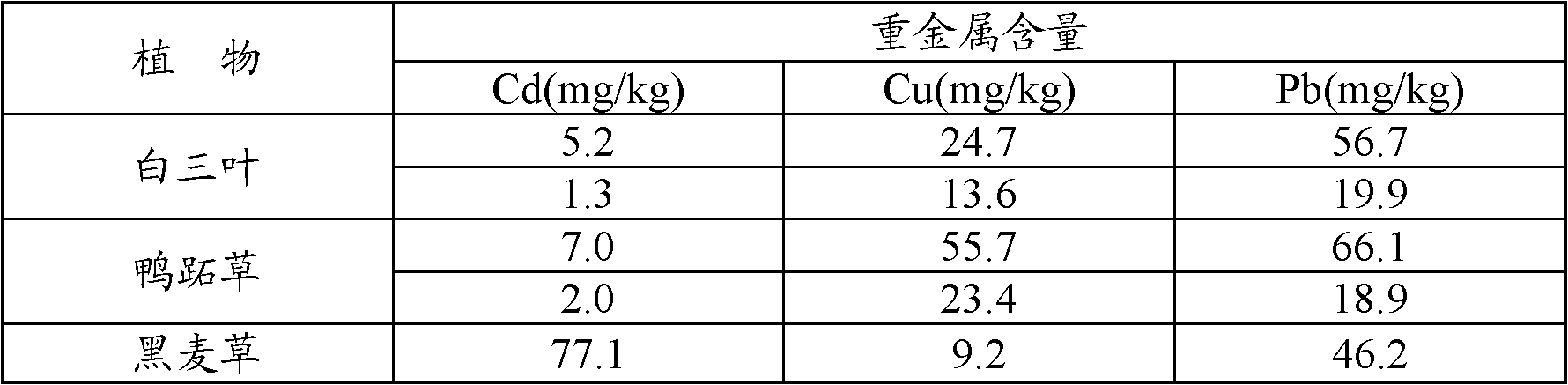
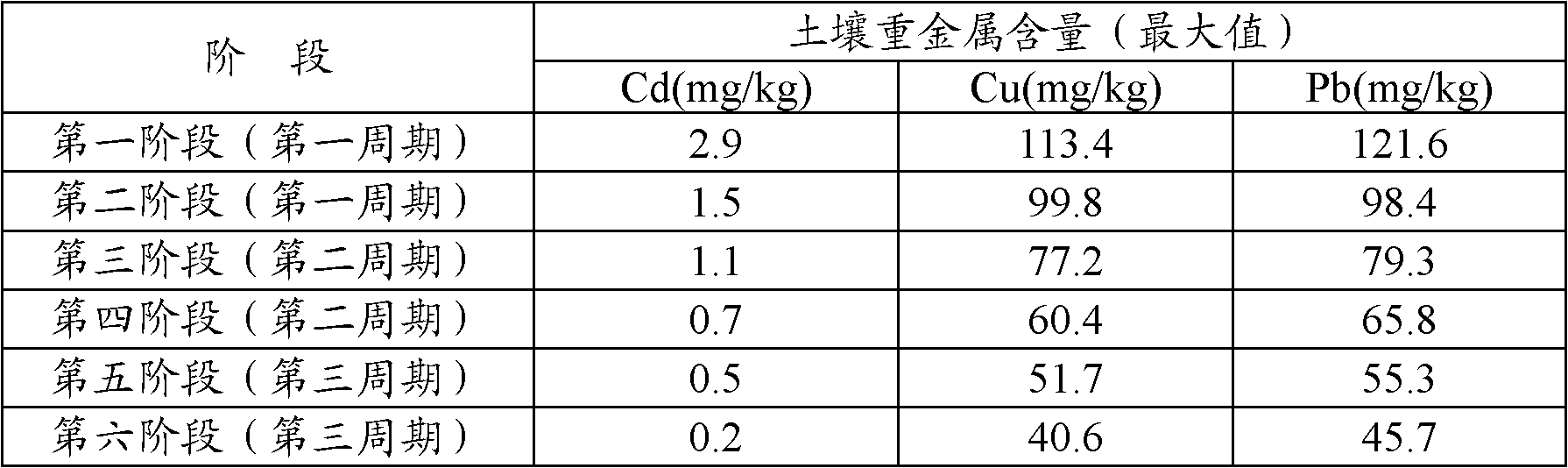
Bioremediation method for soil polluted by heavy metals
ActiveCN102553904AComposite treatment effect is goodConsiderable enrichmentContaminated soil reclamationMicroorganismPollution soil
The invention discloses a bioremediation method for soil polluted by heavy metals. The bioremediation method comprises the following steps of: adding earthworm feeds into the soil polluted by the heavy metals, turning the soil, uniformly mixing, and putting earthworms into the soil and cultivating the earthworms; after the earthworms are cultivated for 28 to 35 days, collecting earthworm excrements in the upper layer soil, collecting adult earthworms by adopting a natural lighting method, and retaining young earthworms and earthworm eggs in the soil; planting plants by adopting a hedge planting method, cradling the parts of the plants growing for 78 to 90 days, which are positioned above the ground, and removing the whole plants after the plants grow for another 50 to 70 days; collecting the adult earthworms and the earthworm excrements for 1 to 3 days by adopting an outdoor collection method every 28 to 35 days during planting of the plants; and after the whole plants are removed, collecting all the adult earthworms and the young earthworms by adopting the natural lighting method, and collecting the earthworm excrements and the earthworm eggs. The soil is subjected to remediationby combining animals, plants and microorganisms according to a proper remediation sequence and a remediation period, so that the bioremediation method is economic, environment-friendly, easy to operate, high in remediation efficiency and easy to popularize, and is particularly suitable for mild or moderate copper, cadmium and lead combined polluted soils.
Owner:浙江博世华环保科技有限公司
Method for repairing soil polluted by heavy metal by combining chemical leaching and bioremediation
ActiveCN102909215AGood restorativeAvoid secondary pollutionContaminated soil reclamationHigh concentrationBioremediation
The invention belongs to the technical field of environment protection, and discloses a method for repairing soil polluted by heavy metal by combining chemical leaching and bioremediation. To repair soil with a high heavy metal content and high toxicity, the invention provides the method adopting a strategy of carrying out chemical leaching and bioremediation in sequence. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, classifying different types of polluted soil into seriously polluted soil and mildly polluted soil; then leaching seriously polluted soil by adding acidic chelating agent and extracting high-concentration heavy metal in soil; and conducting bioremediation on part of residual low-concentration polluted soil which is not leached completely. The method is used for in-situ repairing of heavy metal, has an obvious effect in repairing soil polluted by heavy metal, and successfully avoids secondary pollution to soil.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV (BAODING)
Salination soil modifying agent composition and use thereof
The invention discloses a new-typed salted soil modifier composition and making method, which comprises the following parts: superphosphate, calcium sulfate, poromeric material, decomposed rough organics, phosphogypsum, rough stream and macromolecular (water retention) agent for alkali soil of littoral area.
Owner:魏凤巢 +4
Microporous diffusion apparatus
InactiveUS6872318B2Efficient removalTreatment using aerobic processesTransportation and packagingDecompositionBioremediation
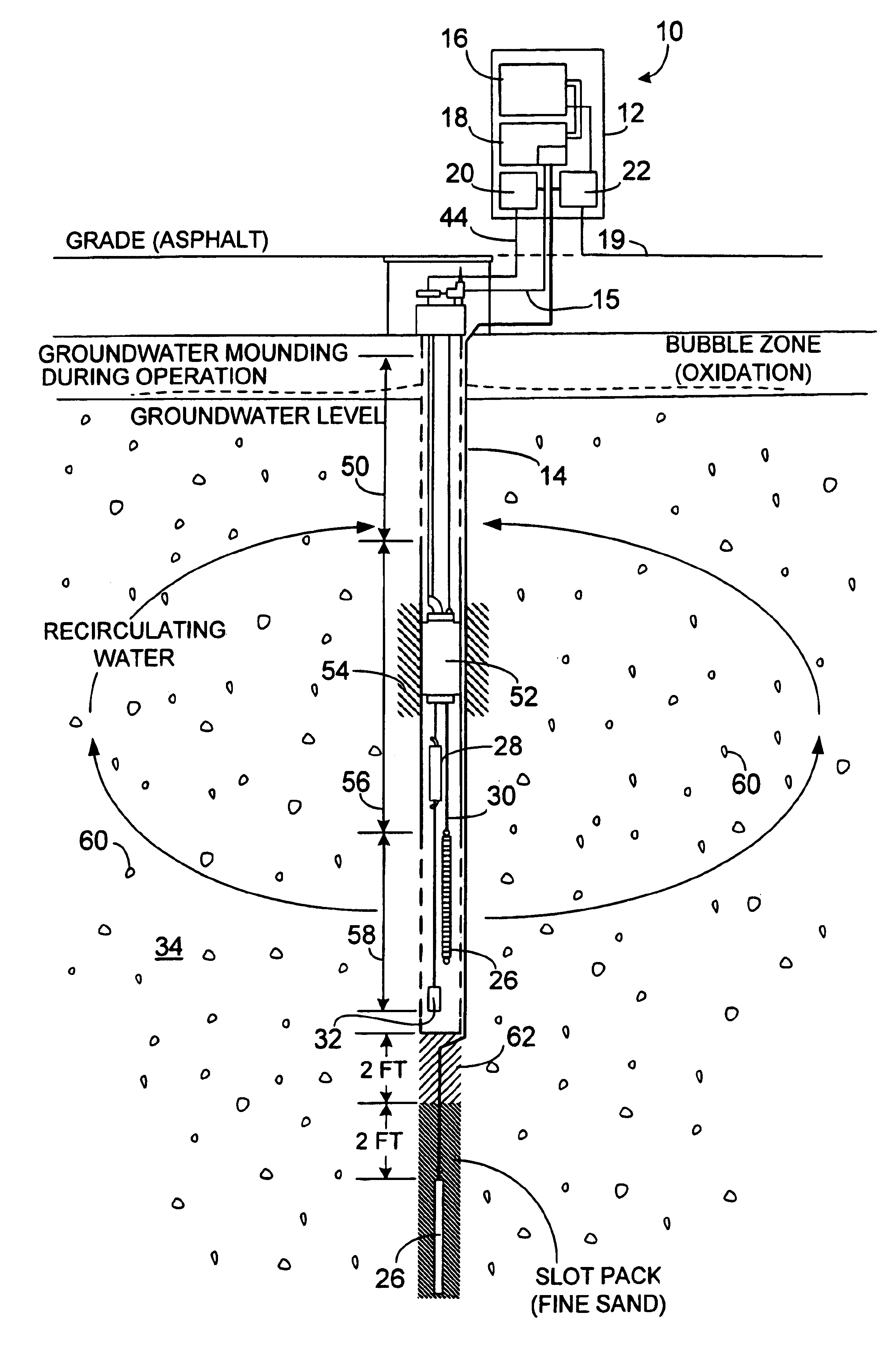
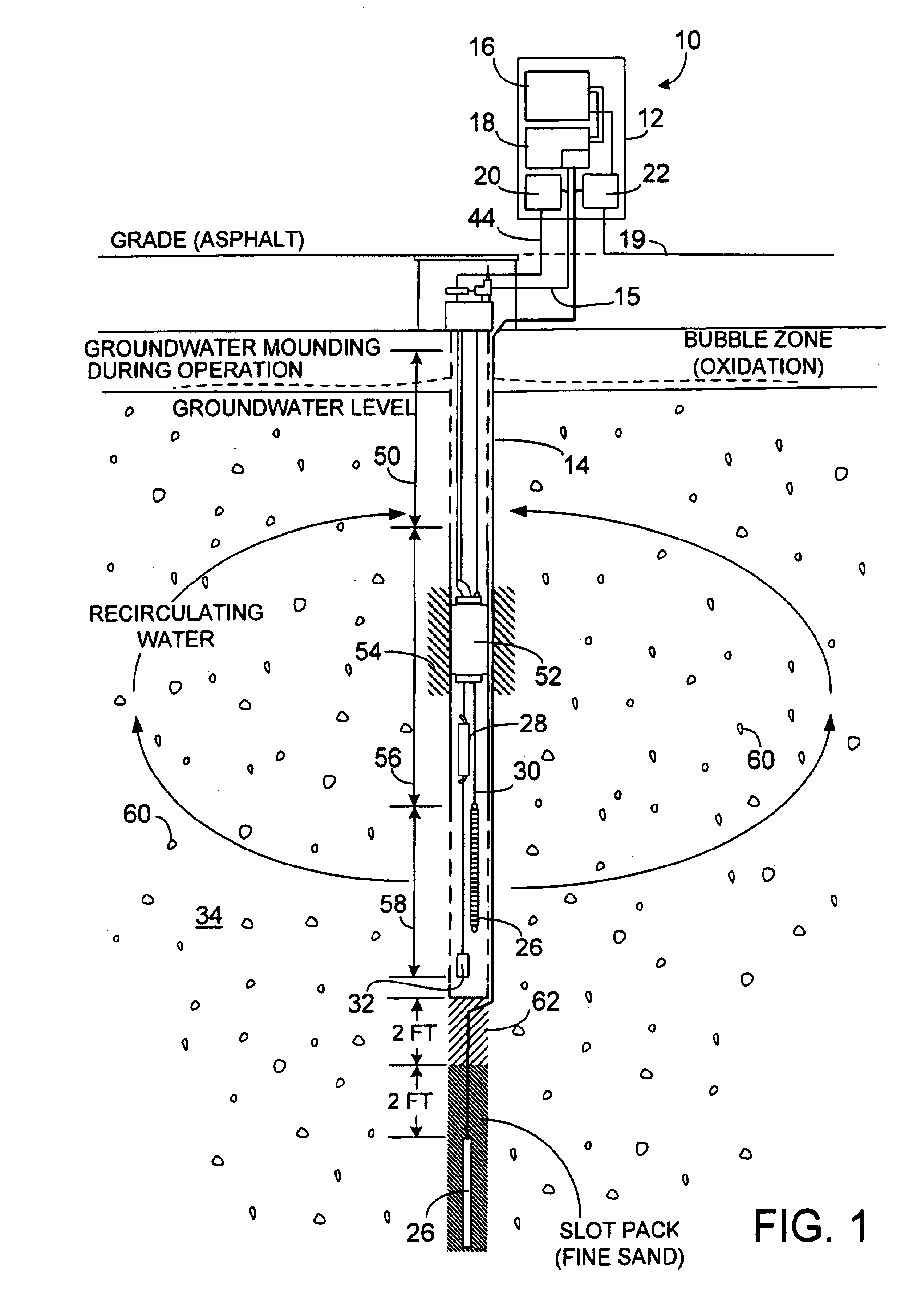
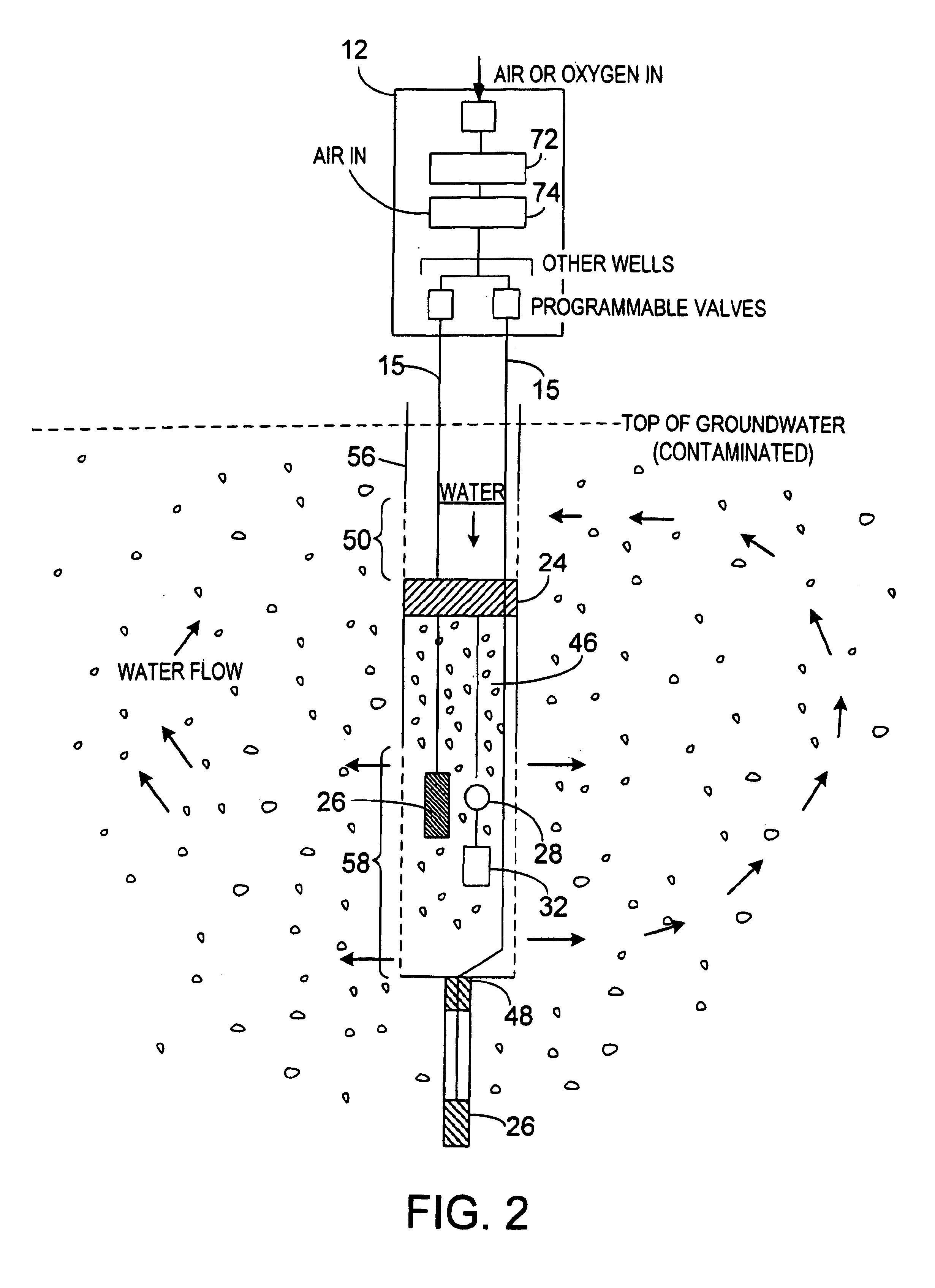
Apparatus for active in situ multi-element gas sparging for bioremediation or physico-chemical degration for removal of contaminants in a soil formation containing a subsurface groundwater aquifer or a substantially wet unsaturated zone, the multi-gas contained in bubbles, wherein the apparatus includes a plurality of injection wells extending to a depth of a selected aquifer; introducing an oxidizing agent comprising ozone mixed with ambient air to provide a multi-element gas by means of microporous diffusers, without applying a vacuum for extraction of stripped products or biodegration by-products, wherein said diffusers form micro-fine bubbles containing said multi-element gas that oxidizes, by stripping and decomposition, chlorinated hydrocarbons from the aquifer and surrounding saturated soil formation into harmless by-products; also including a pump for agitating water in the well selecting microbubbles, injecting them into the aquifer and effective to alter the path of micro-fine bubbles through a porous solid formation whereby enhanced contact between the oxidizing agent contained in each said bubble by stripping pollutant from solution in ambient water into the mini-atmosphere of each bubble effective to increase the efficiency and speed of remediation of a site.
Owner:KERFOOT TECH
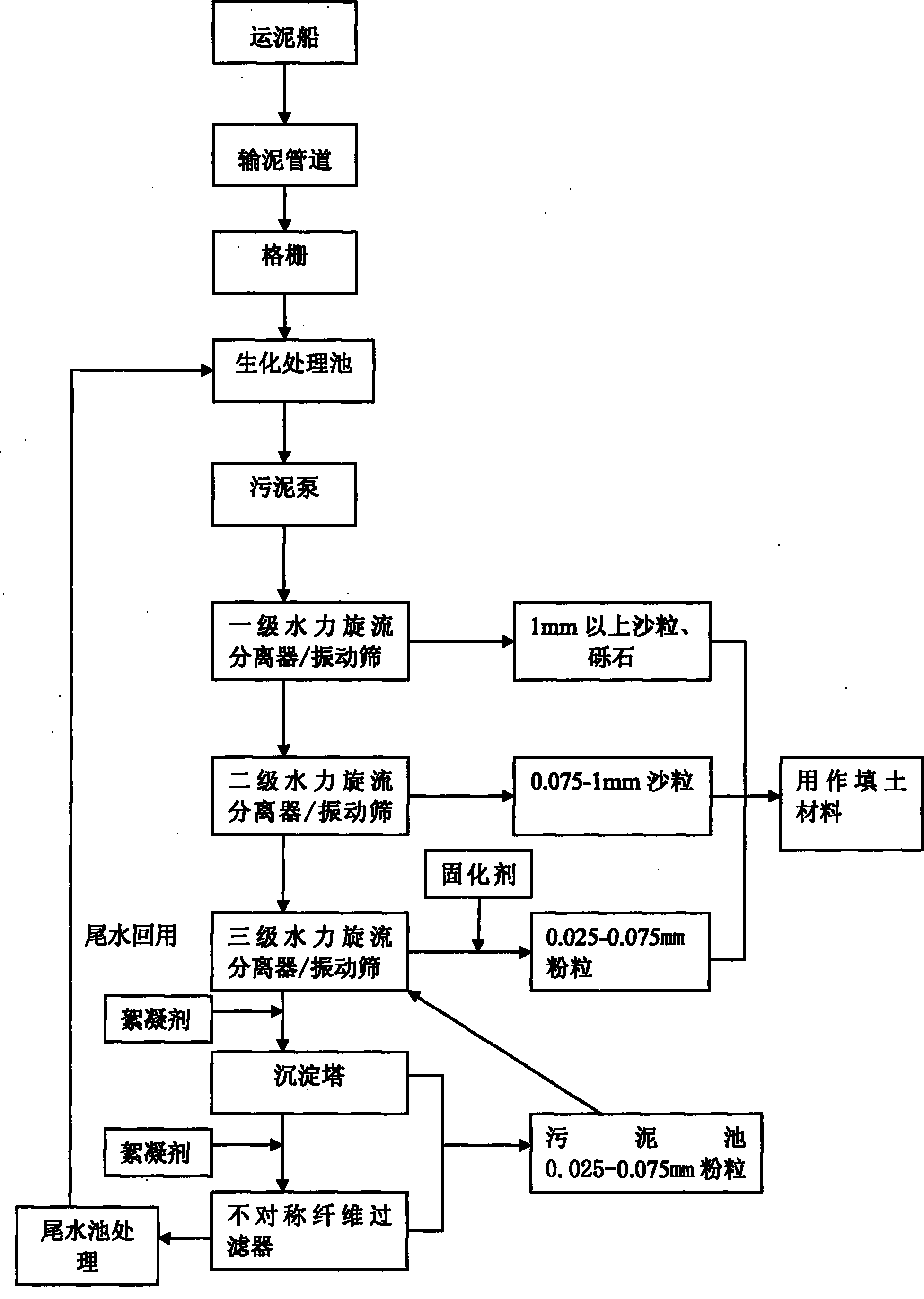
River surge silt harmless and recycling treatment method
InactiveCN101870546ALower redox potentialSmooth processSludge treatment by de-watering/drying/thickeningSolid waste managementFiberResource utilization
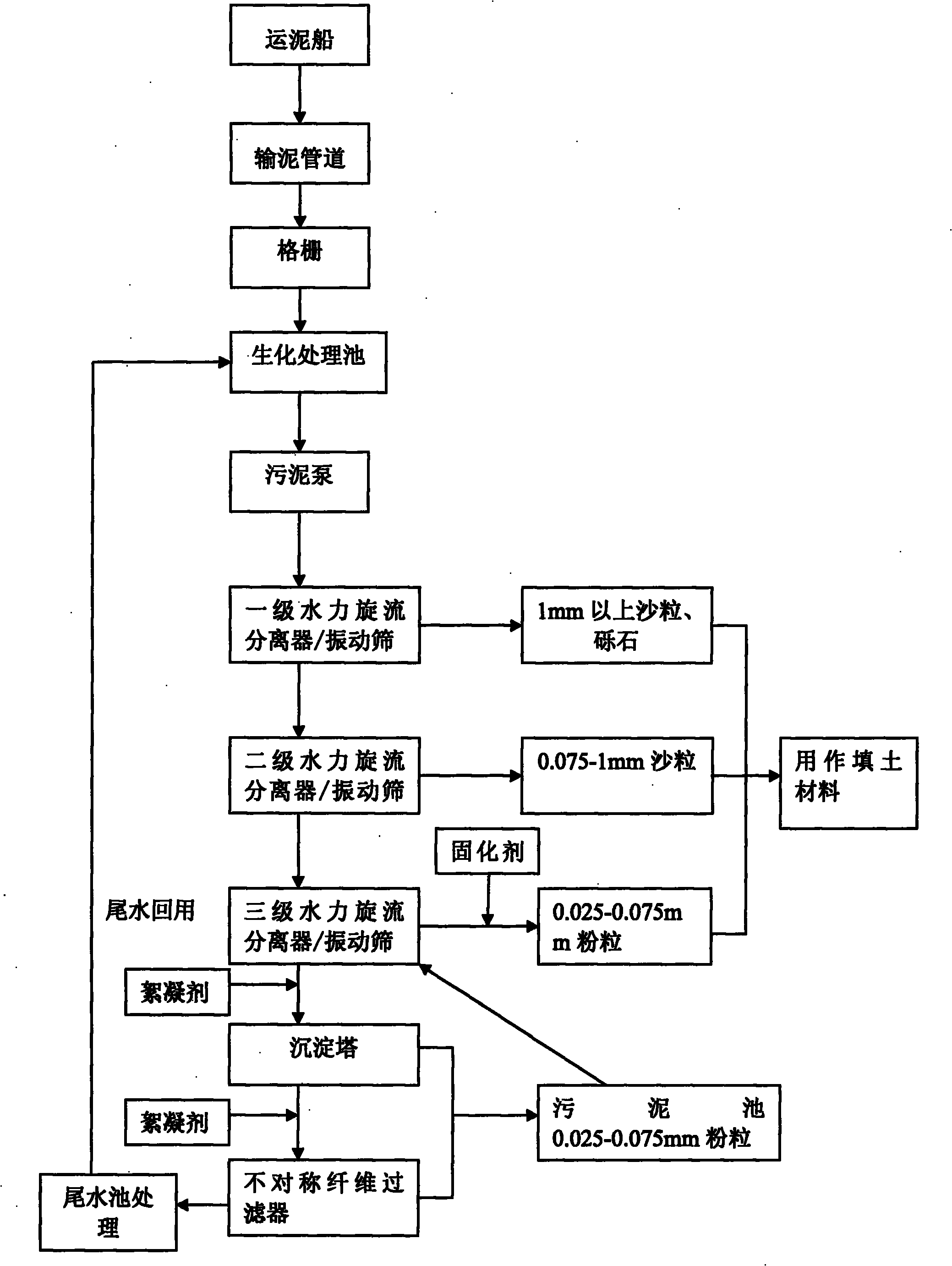
The invention provides a river surge silt d harmless and recycling treatment method. In the method, a dredger is utilized to suck silt, the silt is sent into a biochemical treatment pond from the ship through a silt transmission pipeline, compound enzyme is utilized to carry out bioremediation, gravels and sands with the particle size bigger than 1mm are filtered out by a primary hydrocyclone and a vibration screen, sands with the particle size of 0.075-1mm are filtered out by a secondary hydrocyclone and the vibration screen, powdery particles with the particle size of 0.025-0.075mm are filtered out by a third-level hydrocyclone and the vibration screen, powder particles are further separated out from outlet silt tail water through a sediment tower, sewage from the sediment tower is filtered by utilizing a fiber filter after flocculant is added into the sewage, and powdery particles are deposited from backflushing silt after being filtered by utilizing the sediment tower again, and the powdery particles are dehydrated by the third-level hydrocyclone and the vibration screen after entering a sludge pool and are cured by a curing agent after dehydration. The method has high resource utilization ratio, meets the requirements for the environmental protection, particularly carries out stage treatment on the silt, lowers the cost and enhances the efficiency.
Owner:GUANGZHOU BAOMINGLAI ENVIRONMENT SCI & TECH
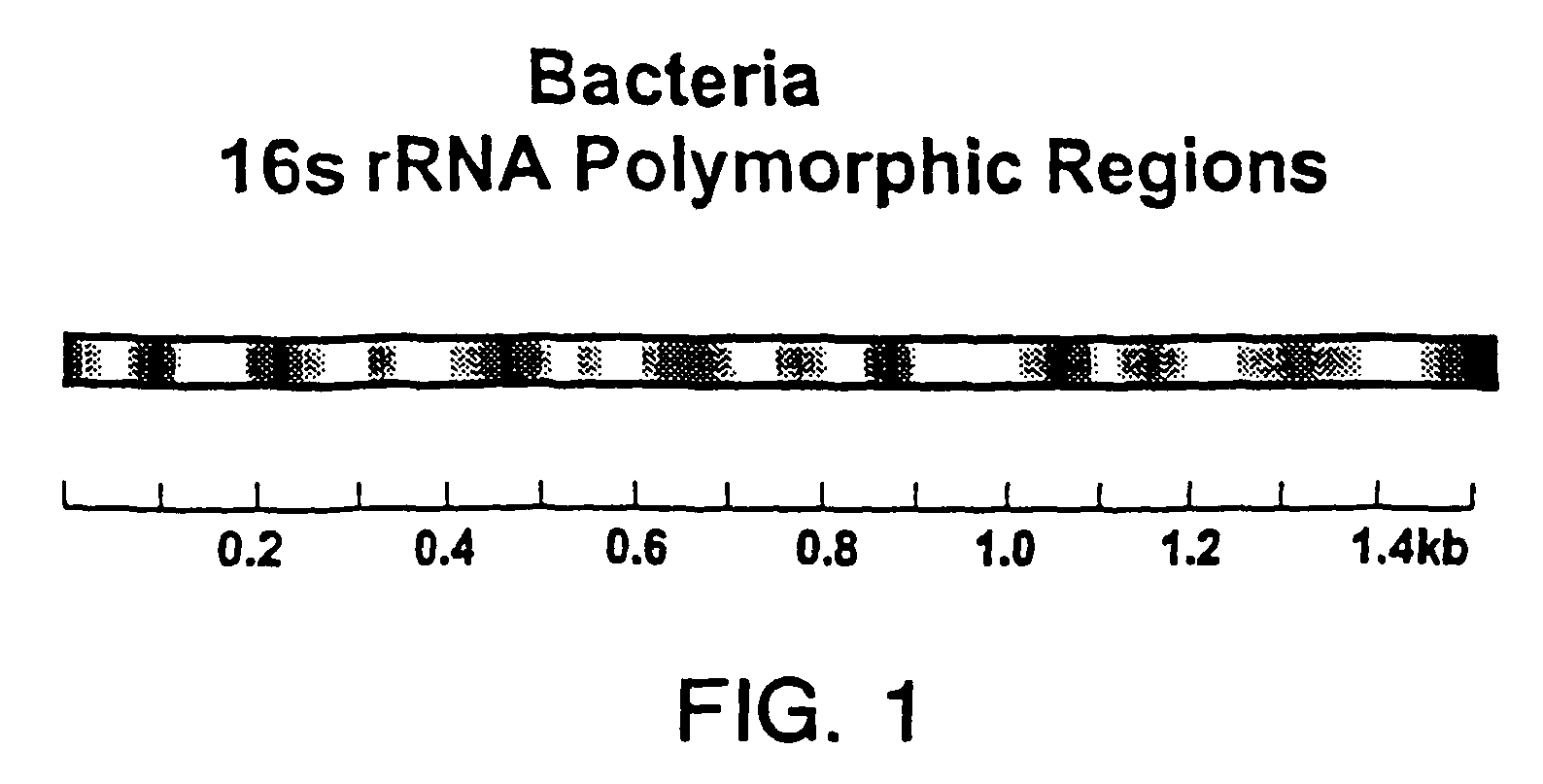
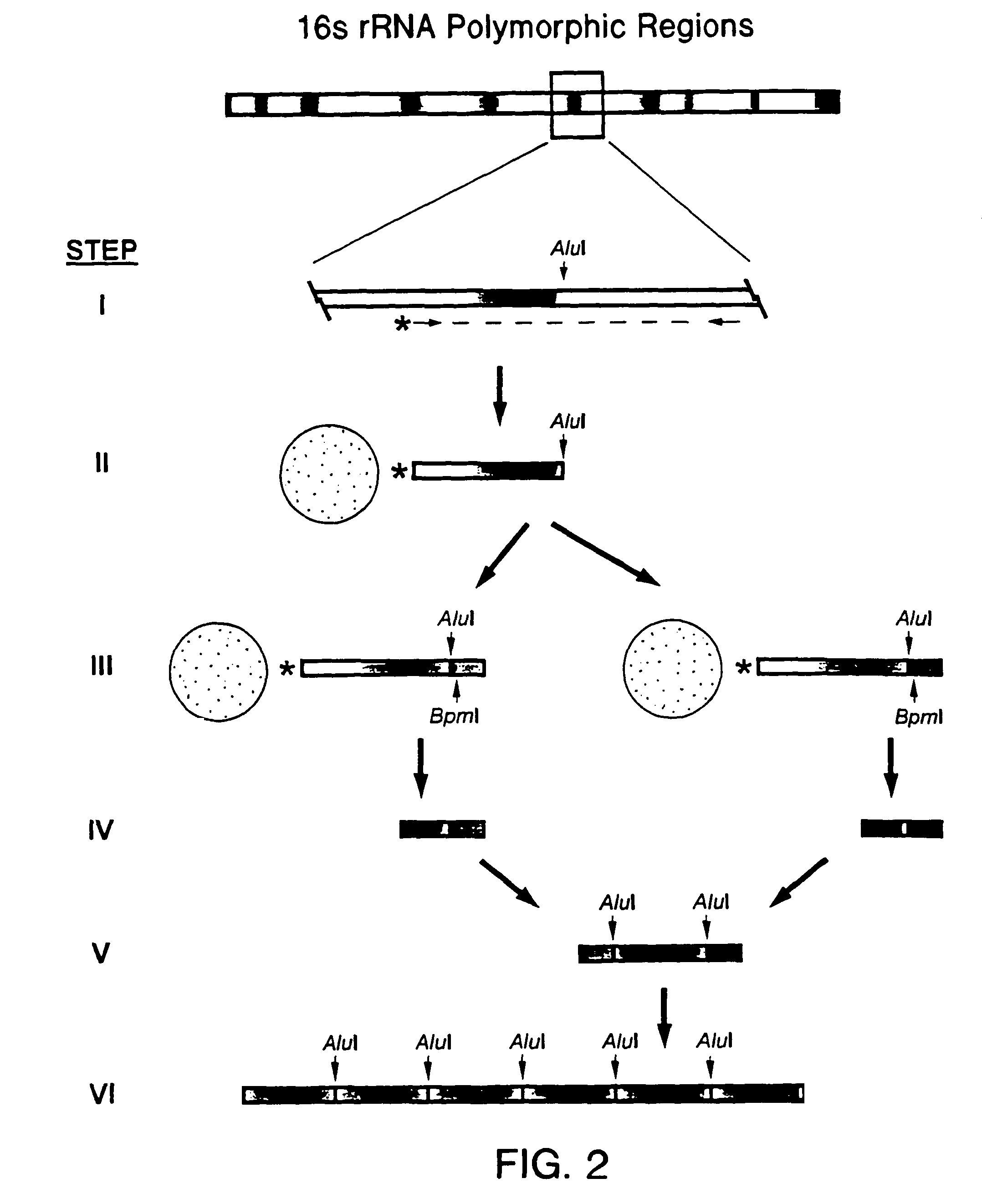
DNA-based methods of geochemical prospecting
InactiveUS8071295B2Quick fixQuick snapSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementGenetic diversityForensic science
The present invention relates to methods for performing surveys of the genetic diversity of a population. The invention also relates to methods for performing genetic analyses of a population. The invention further relates to methods for the creation of databases comprising the survey information and the databases created by these methods. The invention also relates to methods for analyzing the information to correlate the presence of nucleic acid markers with desired parameters in a sample. These methods have application in the fields of geochemical exploration, agriculture, bioremediation, environmental analysis, clinical microbiology, forensic science and medicine.
Owner:TAXON BIOSCI
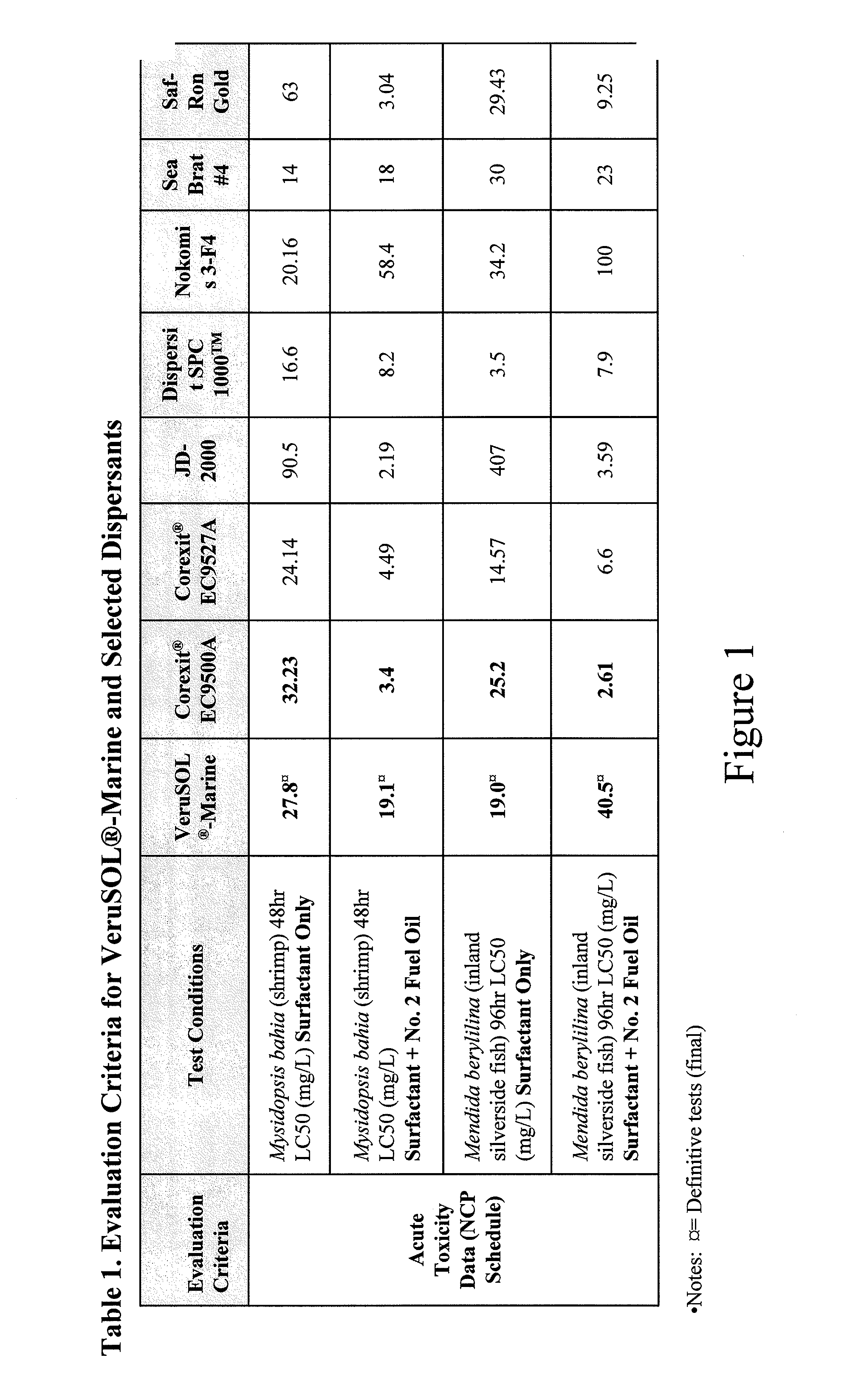
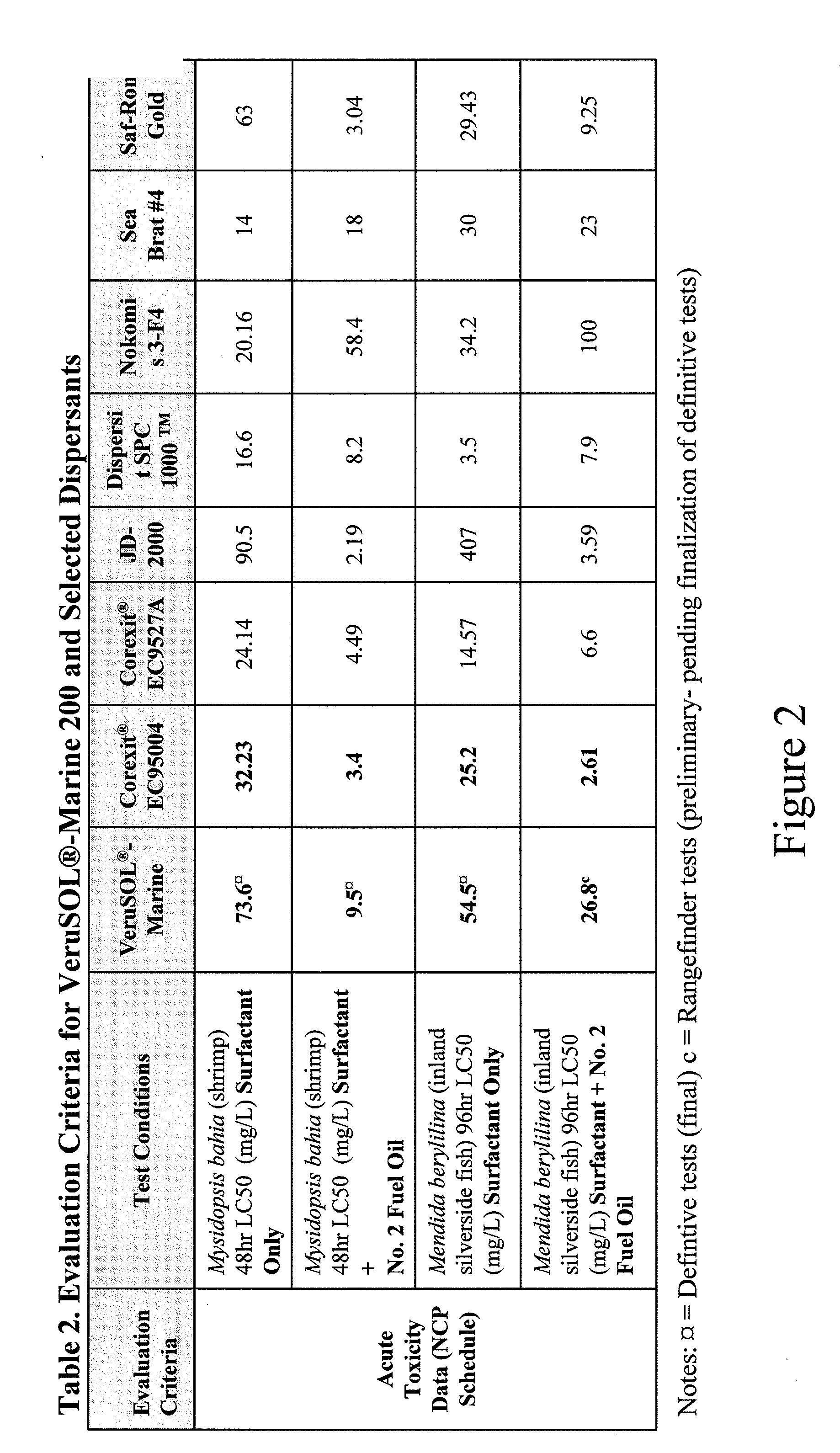
Compositions and methods for oil spill remediation
InactiveUS20140110344A1Promote degradationQuick responseOrganic detergent compounding agentsNon-ionic surface-active compoundsOil spillBioremediation
Compositions and methods for remediation of oil spills in a oil spill impacted water environment are described. The methods may further include degrading spilled oil by oxidation or bioremediation.
Owner:VERUTEK TECH
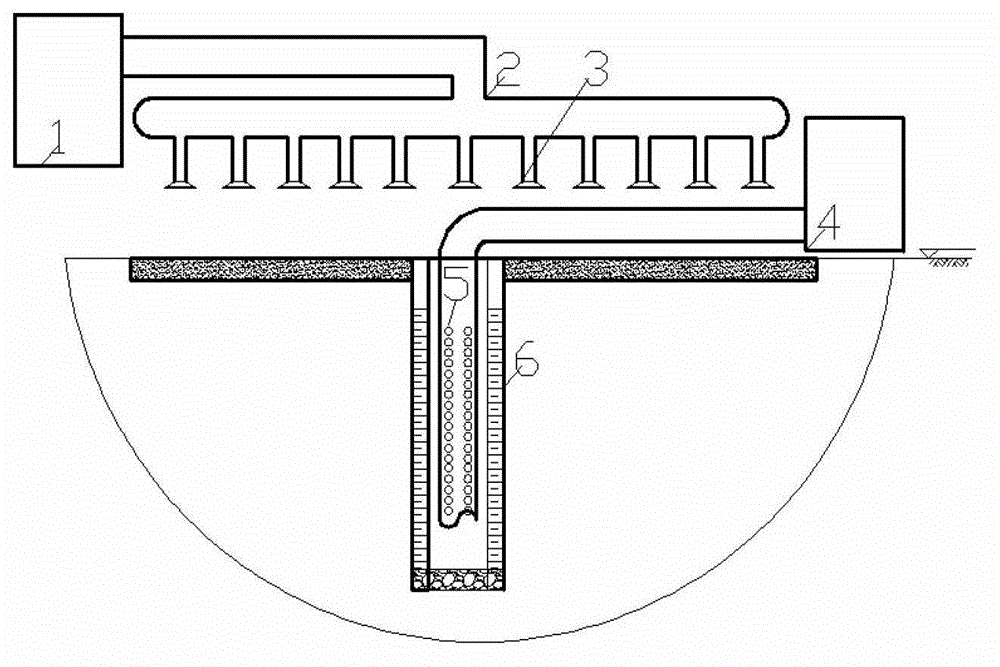
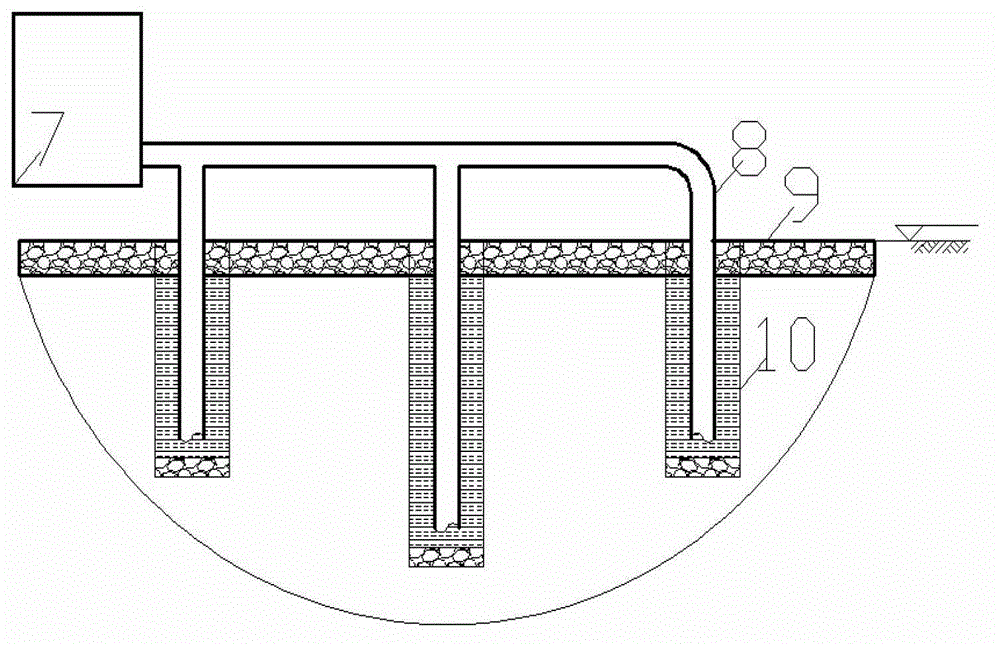
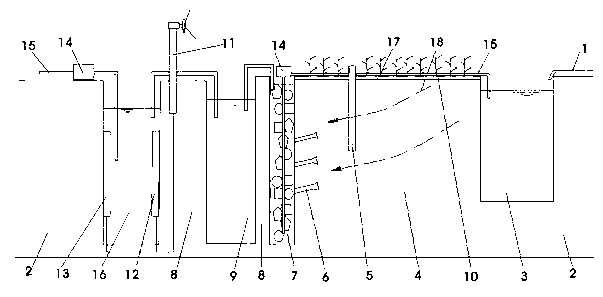
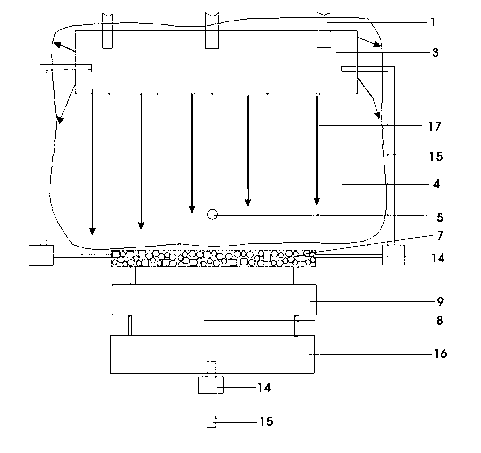
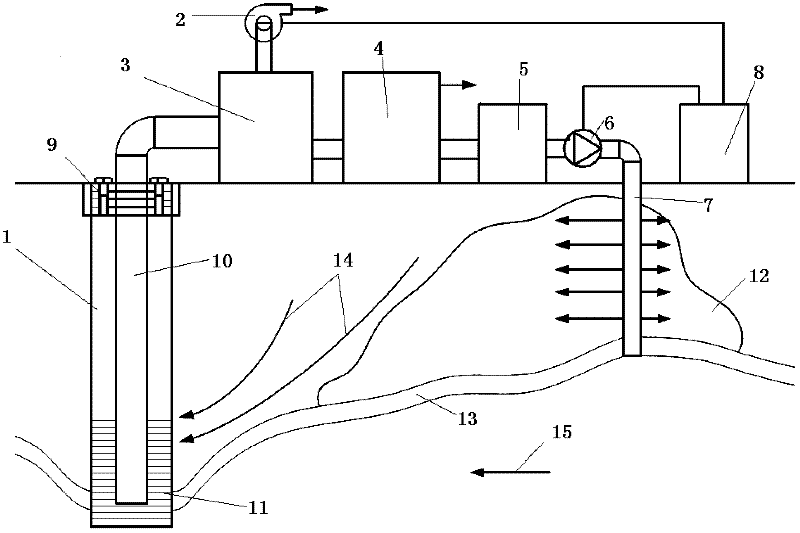
In-situ rainwater leaching repair system for contaminated soil
The invention relates to an in-situ rain leaching repair system for contaminated soil. The in-situ rain leaching repair system at least comprises three parts, namely a rain collection part, a leaching repair part and a waste water treatment part, wherein the rain collection part is provided with water guiding pipes, a water collecting tank and canals, the leaching repair part is provided with an observation well, water collecting pipes and plants planted for the soil phytoremediation, the observation well is built in a middle-upper layer of contaminated soil, and the water collecting pipes are in the middle-lower layer; and the waste water treatment part is provided with a filter tank, a microorganism putting tank, an electric separation tank, a wind power generating set and the like, leaching waste water is firstly filtered by the filter tank, and is then repaired by the microorganism putting tank, and finally, the leaching waste water passes through the electric separation tank to process heavy metal so as to obtain the purified liquid. The in-situ rain leaching repair system establishes a complete contaminated soil simulated repairing system for the soil in an aeration zone, and combines repair technologies of leaching, plants, microorganisms, electric separation and the like. The in-situ rain leaching repair system has the characteristics of energy conservation, emission reduction and no secondary pollution, and is suitable for repairing the soil in a large-area aeration zone with little pollution.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF GEOSCIENCES (WUHAN)
Solid microbe agent for degrading petroleum pollution, and petroleum products, and preparation method
ActiveCN101050435AEasy to makeLow costBacteriaContaminated soil reclamationMicroorganismMicrobial agent
This invention discloses a solid microbial agent for degrading petroleum pollutants and petroleum products. The solid microbial agent is prepared by: mixing primary seed solutions of Bacillus subtilis and Sphingobacterium multivorum at a volume ratio of (0.5-20):1, fermenting to obtain mixed bacterial fermentation solution, and mixing the mixed bacterial fermentation solution and turfy soil at a weight ratio of (0.1-1):1. The active living bacteria number of Bacillus subtilis is 106-1010 / mL, and that of Sphingobacterium multivorum is 107-1012 / mL. The solid microbial agent has such advantages as high activity in soil, rapid growth and no secondary pollution to environment, and can be used for biological bioremediation of petroleum polluted soil and petroleum product leakage fields.
Owner:山东百科利生态科技有限公司
Heavy metal resistance plant growth-promoting bacteria preparation and applying method thereof
InactiveCN101671636APromote absorptionPromote growthBiocidePlant growth regulatorsHigh resistanceDisease
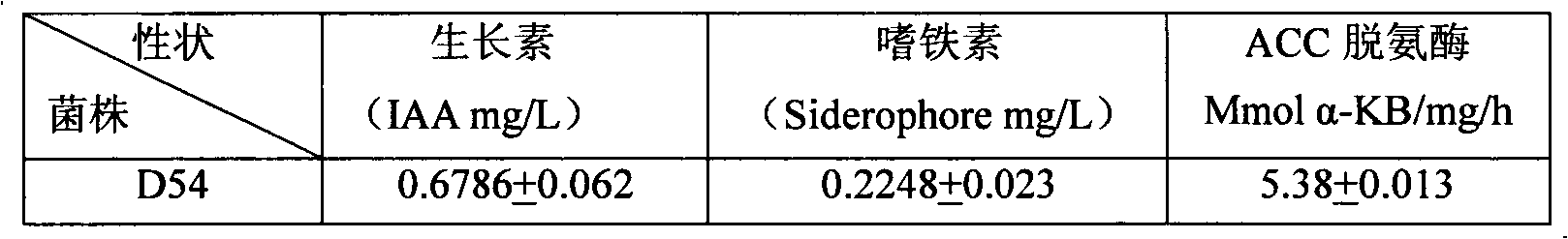
The invention relates to heavy metal resistance plant growth-promoting bacteria and a preparation applying method thereof, which belongs to the bioremediation field of heavy metal polluted environment. A bacteria strain D54 with a preservation number of CGMCC No. 3223 belongs to the Burkholderia sp. and has higher resistance to a plurality of heavy metals, wherein the resistances to Pb <2+>, Cd <2+>, Cu <2+>, Zn <2+> respectively reach 800 mg / L, 1500 mg / L, 150 mg / L and 2500 mg / L. In addition, the bacteria strain D54 has the plant growth-promoting functions of producing plant growth hormone (IAA), producing 1-amino-1-carboxyl cyclopropane (ACC) deaminase, secreting siderophore, dissolving inorganic phosphate, fixing nitrogen and the like, has the biological prevention functions of antagonizing plant pathogenic bacteria inbreak and the like, and can obviously improve the biomass of the plants applied the invention and improve the resistance to diseases and stresses. The number of the effective viable bacteria in liquid preparation reaches 1-2 billion / ml and the number of the effective viable bacteria in solid preparation reaches 1 billion / g. Soaking seeds for 1-2 hours in the liquidpreparation which is diluted 100 times and irrigating the diluted liquid preparation 1-2 times (10ml / kg) after 2-3 weeks of the sprouting of the seeds can effectively improve plant viable bacteria infection probability.
Owner:AGRO ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION INST OF MIN OF AGRI
Method for governing pollution of river surge
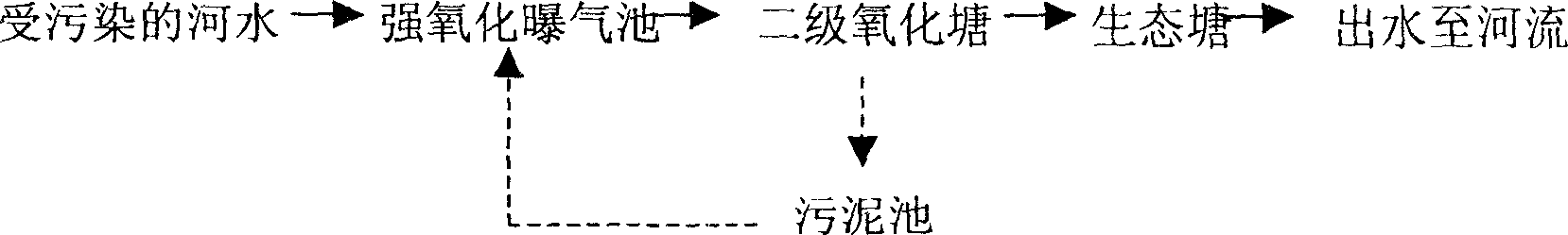
InactiveCN101050041APurify waterEliminate black odorTreatment using aerobic processesSludge processingCombined methodWater quality
This invention provides a combined method for treating urban river surge with bioremediation as the major technique. The method comprises: pre-treating polluted water body of upstream urban river surge in an oxidation pool, performing biological oxidative remediation on bottom deposits in river, aerating river channel, performing bioremediation on middle reach water body, and performing ecological remediation on downstream water body. The method utilizes abandoned fishpond, vacant land or modified oxidation pool to perform pre-treatment on heavily polluted water body of urban river surge that cannot be treated by sewage interception. Then the method adopts biological oxidative remediation on bottom deposits to control internal pollution source of urban river surge, and artificial aeration, and biological-ecological remediation to effectively eliminate pollutants and odor of water body, improve water quality of urban river surge, and improve self-cleaning ability of urban river surge water body. The method is a feasible method in treating urban river surge.
Owner:国家环境保护总局华南环境科学研究所
Erythro micrococcus Em and usage for generating biologic emulsifier as well as degrading polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon
InactiveCN1519312AStrong solubilizationPromotes the degradation of petroleum hydrocarbonsBacteriaFermentationSolubilityAlkane
A Rhodococcus ruber Em (CGMCC No.0868) features that its cells, cell suspension, or immobilized cells can degradate the paraffin and polycyclic arylhydrocarbon because the paraffin and polycyclic arylhydrocarbon are used as its only carbon source and energy source for growing to generate the bioemulsifier of ester. Said emulsifier can obviously decrease the surface tension of aqueous solution, has strong emulsifying power to ester substance, and can increase the solubility of paraffin and polycyclic arylhydrocarbon in water, so it can be used for treating the oil-contained sewage and repairing the petroleum polluted soil.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Preparation method of algae amino acid microbial fertilizer
InactiveCN102173907AGrowth inhibitionPromote growthFertilizer mixturesMicrobial agentMonopotassium phosphate
The invention discloses a preparation method of an algae amino acid microbial fertilizer, which comprises the following steps: (1) crushing algae, adding water and a fermentation promoter, sterilizing for 20-40 minutes at the temperature of 120-125 DEG C, reducing the temperature to room temperature, adding a composite strain to ferment the mixed solution for 3-5 days at 25-35 DEG C, and adjusting the pH value to 7.2-8.0; and (2) sequentially adding urea and / or monopotassium phosphate and chelating-state trace elements into the solution obtained in the step (1) in a stirring state, and stirring for 20-50 minutes to obtain the liquid algae amino acid microbial fertilizer. According to the invention, algae is subjected to deep fermentation by use of a high-activity microbial agent, the natural active ingredients in algae are perfectly maintained; and due to compatibility with the chelating-state trace elements, the nutrient elements and utilization rate of the fertilizer are improved, and the algae amino acid microbial fertilizer is a novel algae microbial fertilizer for bioremediation and soil adjustment and conforming to ecological balance of animals, plants and microorganisms.
Owner:山东金利丰生物科技股份有限公司
In situ integrated restoring system and method of petroleum polluted soil
InactiveCN102228900AImprove repair efficiencyShort processContaminated soil reclamationAutomatic controlGas phase
The invention discloses an in situ integrated restoring system and a method of petroleum polluted soil, and belongs to the technical field of petroleum polluted soil restoration. The system provided by the invention is composed of a suction well, a vacuum pump, a steam-water separation system, an oil-water separation system, a dosage pot, an injector pump, an injection well and an automatic control system. With the combination of the merits of vacuum suction and biological restoration, free-phase and high-density gas-phase pollutants in soil can be sucked and pumped in the invention; and simultaneously a surfactant reinforced biological restoration method can be adopted to accelerate the degradation or transformation and distribution of petroleum pollutants adsorbed on soil, so as to raise the in situ soil restoration efficiency, shorten the technological process, reduce the restoration cost and widen the application range of the in situ restoration technology.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV (BAODING)
Rhodococcus ruber and application thereof in degradation of hydrocarbon compounds
InactiveCN101580808ABacteriaContaminated soil reclamationPolycyclic aromatic hydrocarbonPhenanthrene
The invention relates to a bacterial strain of Rhodococcus ruber P14 CGMCC NO.2343. The bacterial strain has the characteristic of floating up from oil matters; the bacterial strain can grow by taking the oil matters as unique carbon source and energy source and degrade the oil matters; and the bacterial strain can grow by taking polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon as unique carbon source and energy source and degrade hydrocarbon compounds, such as phenanthrene, pyrene, benzopyrene, and the like. The bacterial strain can degrade the oil matters and hydrocarbon compounds, especially the polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon can be applied in the biological treatment of oily waste water and the biological repair (biological remediation) of oil-contaminated soil.
Owner:SHANTOU UNIV
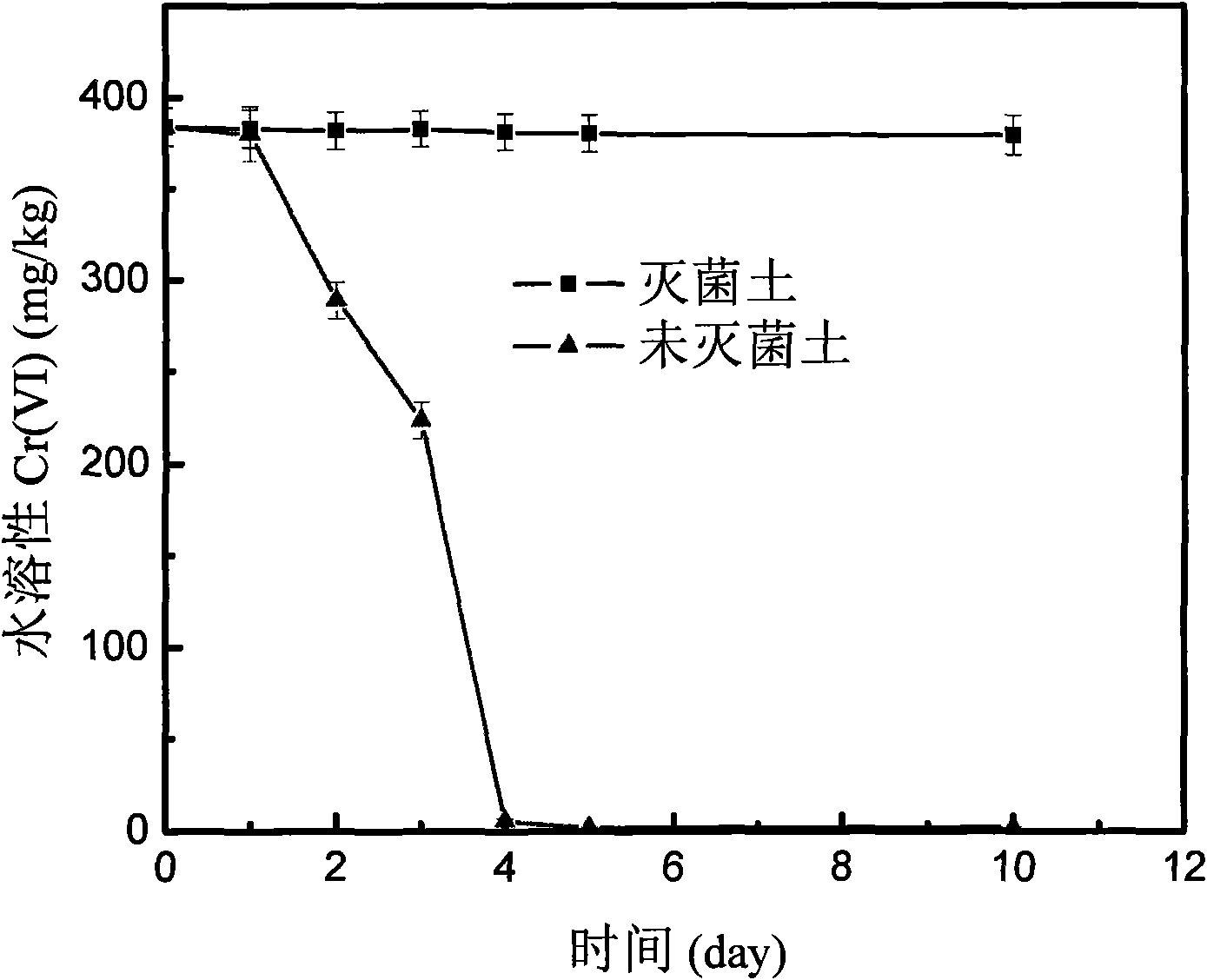
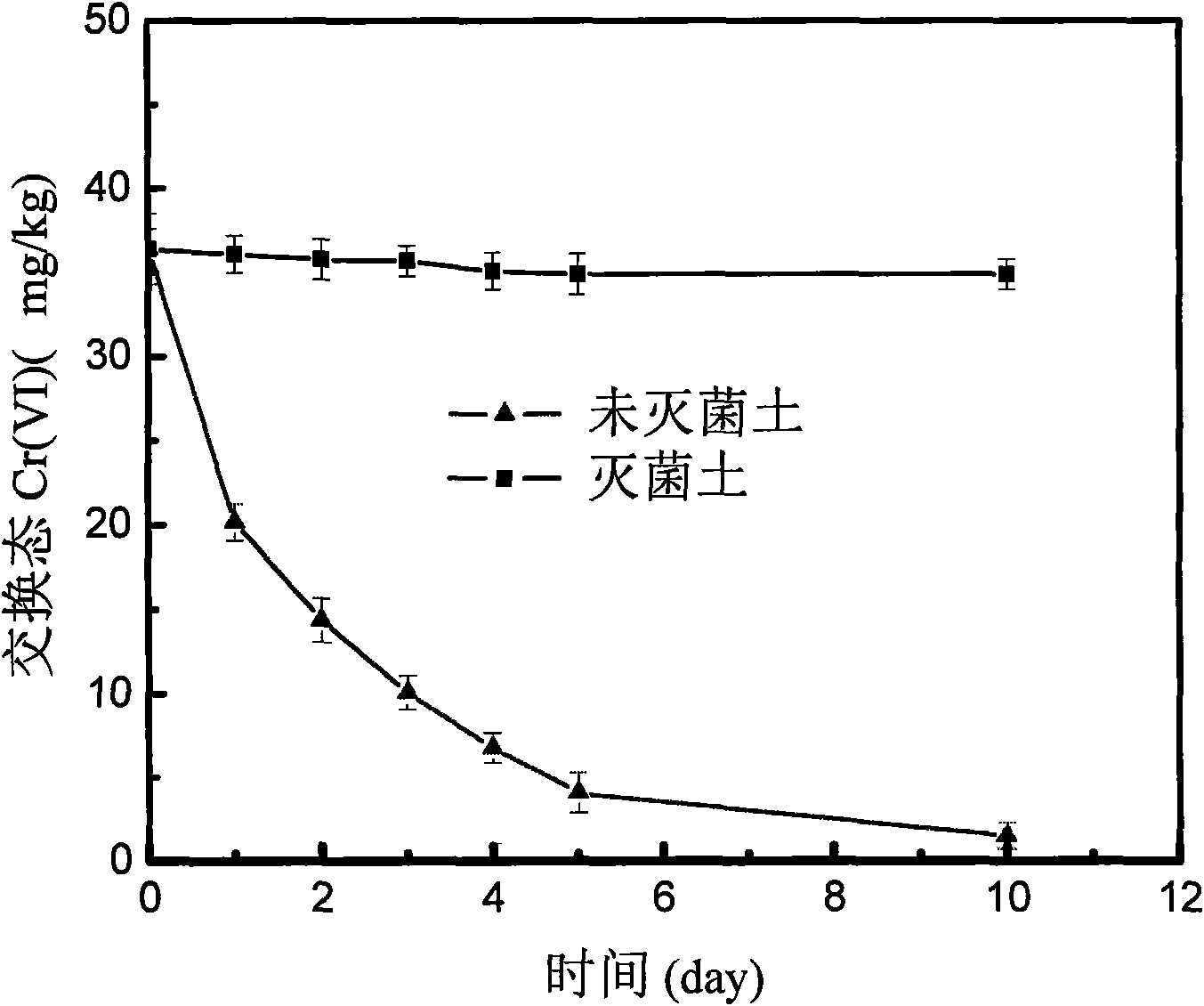
Repairing method of microorganism in contaminated soil of chromium slag storage yard
InactiveCN101602060ADoes not destroy physical and chemical propertiesLow costContaminated soil reclamationSlagCulture fluid
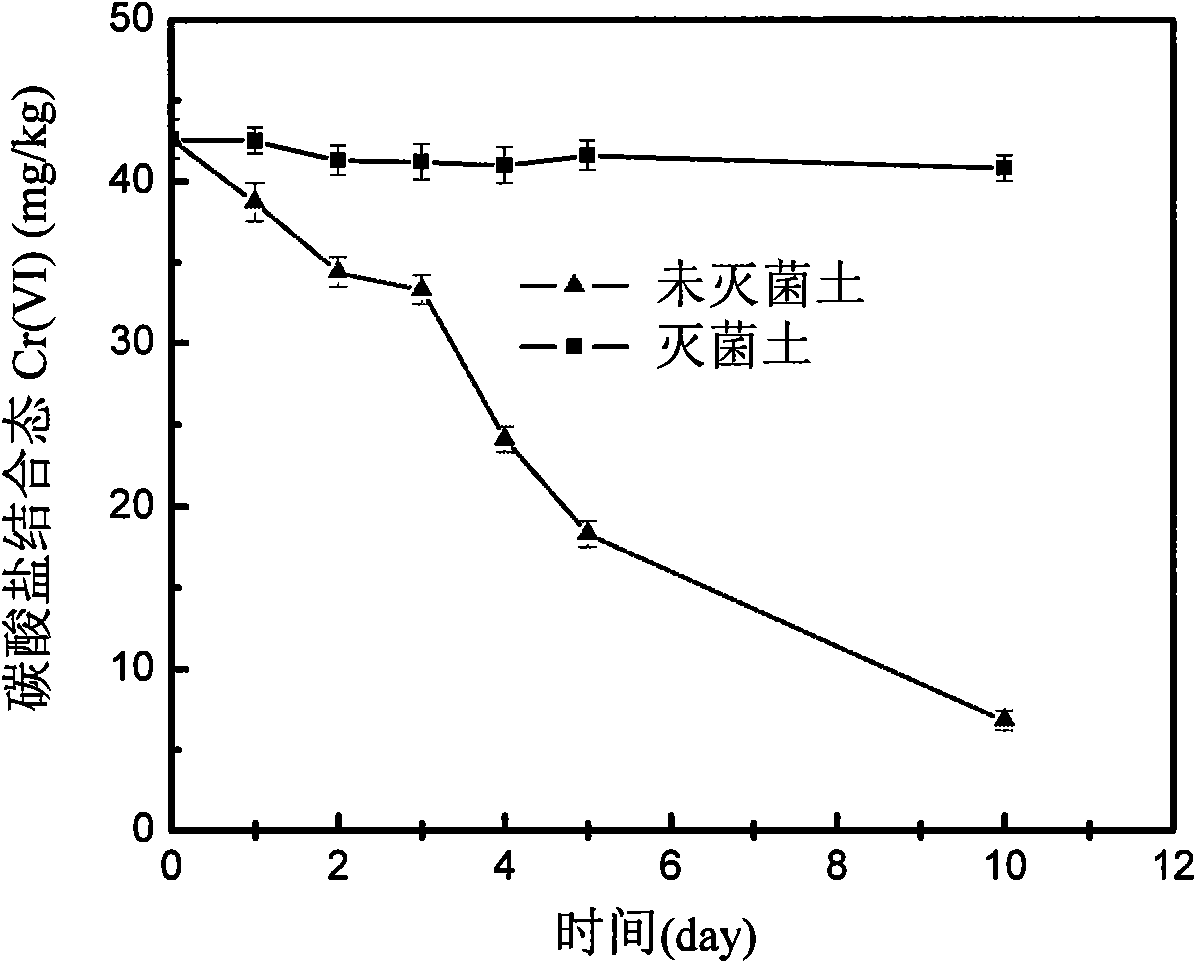
The invention discloses a repairing method of microorganism in contaminated soil of chromium slag storage yard, comprising the steps of selecting Pannonibacter phragmitetus BB single bacterium, dropping the single bacterium in a liquid culture medium containing Cr (VI) of 50-250mg / L for culturing until Cr (VI) is not detected in the culture solution, selecting strains in a bottle for transferring, gradually improving the Cr (VI) concentration for gradient domestication, adding the domesticated Pannonibacter phragmitetus BB lysate in the contaminated soil, and culturing for 4-5 days at a temperature below 30 DEG C, so as to repair the soil, wherein the amount of the added lysate is that the mass-volume ratio (g: mL) of the soil to the lysate is 1: 2. The invention treats and repairs hexavalent chromium-contaminated soil through the strains with hexavalent chromium reducing capacity, the operation is simple and feasible, the cost is low, and the method is an environment-friendly treatment method.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
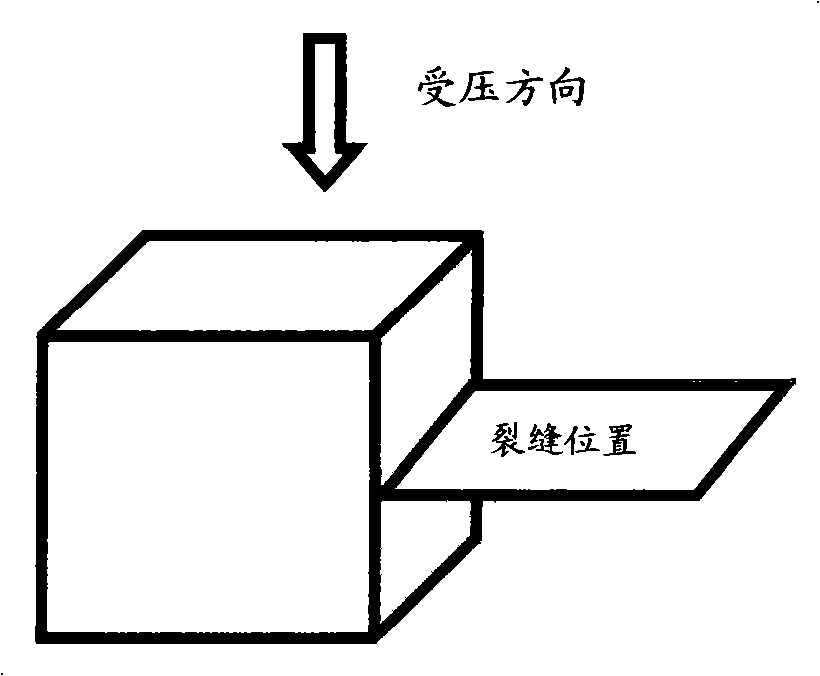
Method for recovering cement-based material crack by means of microorganism, culture fluid and repair nutrient fluid
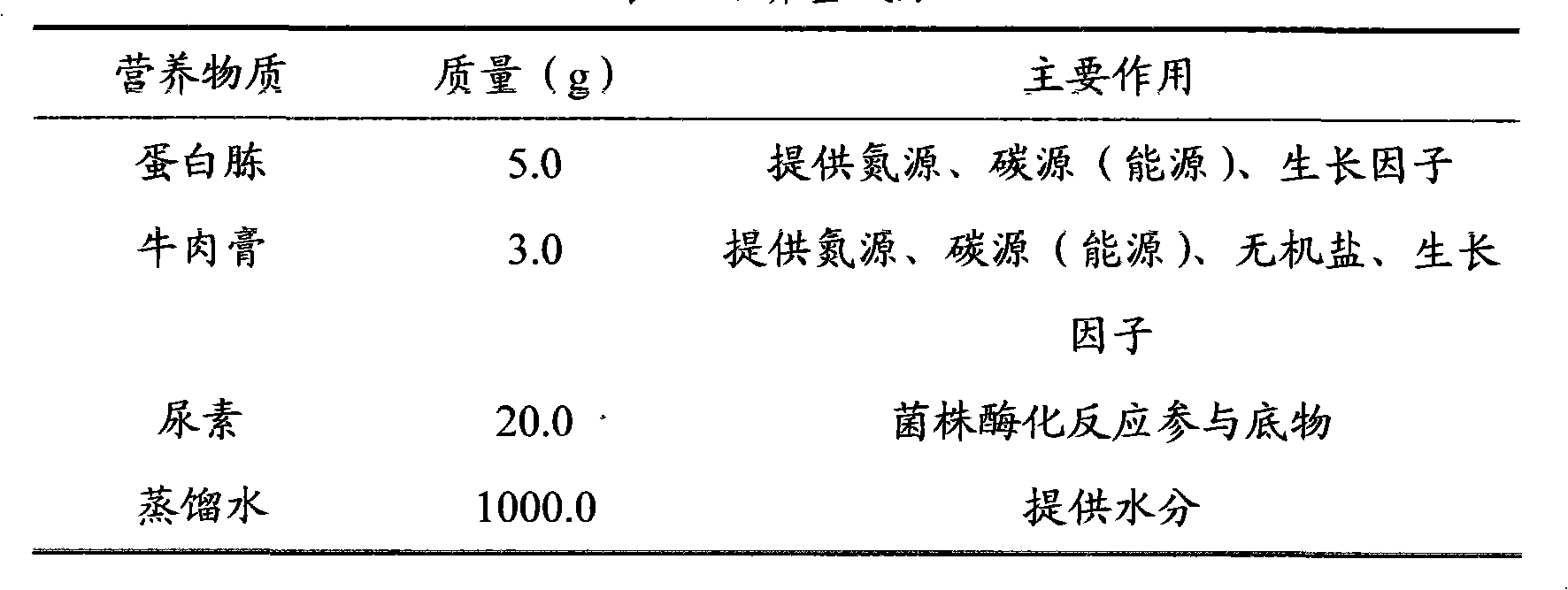
ActiveCN101302484AImprove volume stabilityIncreased durabilityBacteriaBuilding repairsCulture fluidNutrient solution
The invention discloses a method for repairing cement-based material cracks, as well as a culture solution and a repair nutrient solution. The method for repairing cement-based material cracks by through microorganisms comprises the following steps that: a Bacillus pasteurii strain is inoculate onto a culture medium provided with a urea-containing substrate; shake cultivation is carried out at a temperature of between 25 and 37 DEG C, and then a culture bacteria solution is taken out and centrifuged and has supernatant fluid removed; strain cells are collected through the culture solution; the concentration of the strain cells is controlled in a range of between 2x10<9> and 1x10<11> cell / ml; standard sand, urea and Ca(NO3)2.4H2O mixture are added to each milliliter of strain cell solution obtained through collection, mixed, stirred into slurry and injected into cement stone cracks; the frequency of the repair nutrient solution injection is not less than two times; finally, maintenance is carried out. In the culture solution, each liter of culture solution contains 4 to 6 g of peptone, 2 to 4 g of beef extract and 20 to 60 g of urea. The method fully utilizes microbial resources in nature; CO3<2-> decomposed out through microbial enzyme can chelate Ca<2+> in a substrate so as to be mineralized and deposit calcium carbonate, and is close in the combination with the substrate and good in stability.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
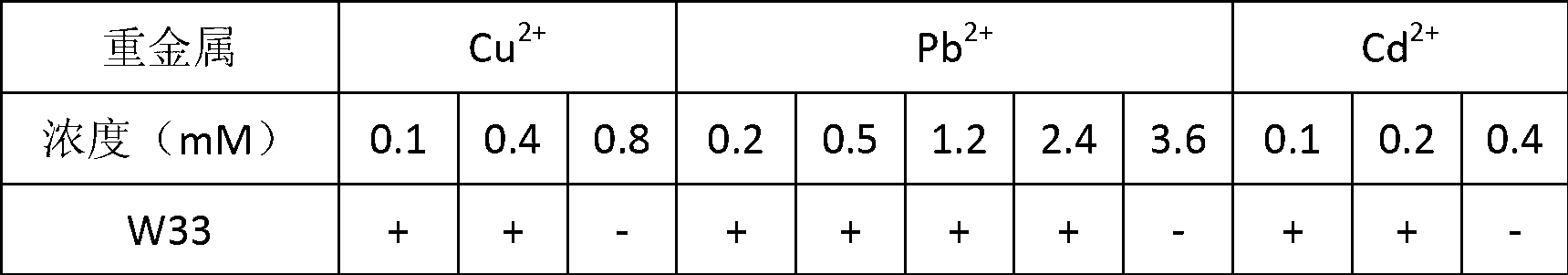
Heavy metal resistant nodule bacterium and method of promoting tailings area plant restoration by using same
ActiveCN102936574APromote growthImprove stress resistanceBacteriaContaminated soil reclamationPlant hormoneBacterial strain
The invention belongs to the technical field of agriculture and environmental pollution improvement and relates to a heavy metal resistant plant endogenous nodule bacterium and application thereof. The heavy metal resistant nodule bacterium is preserved at the China center for type culture collection (CCTCC) with the preservation date to be 2012 / 9 / 18 and culture preservation number to be CCTCC NO:M2012357. The bacterial strain liquid preparation contains more than a billion of effective living bacteria per milliliter, and the bacterial strain solid preparation contains 0.2 billion of effective living bacteria per gram. The heavy metal resistant nodule bacterium strain can secrete plant hormones indole acetic acid (IAA) and siderophores, and resists heavy metal copper and cadmium. When plants are planted in moist soil or tailings containing heavy metal and bioremediation preparation is inoculated, the heavy metal resistant nodule bacterium can promote plant growth and absorbs heavy metal copper, can improve plant restoration efficiency, can fix sandy soil and reduces water and soil loss.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
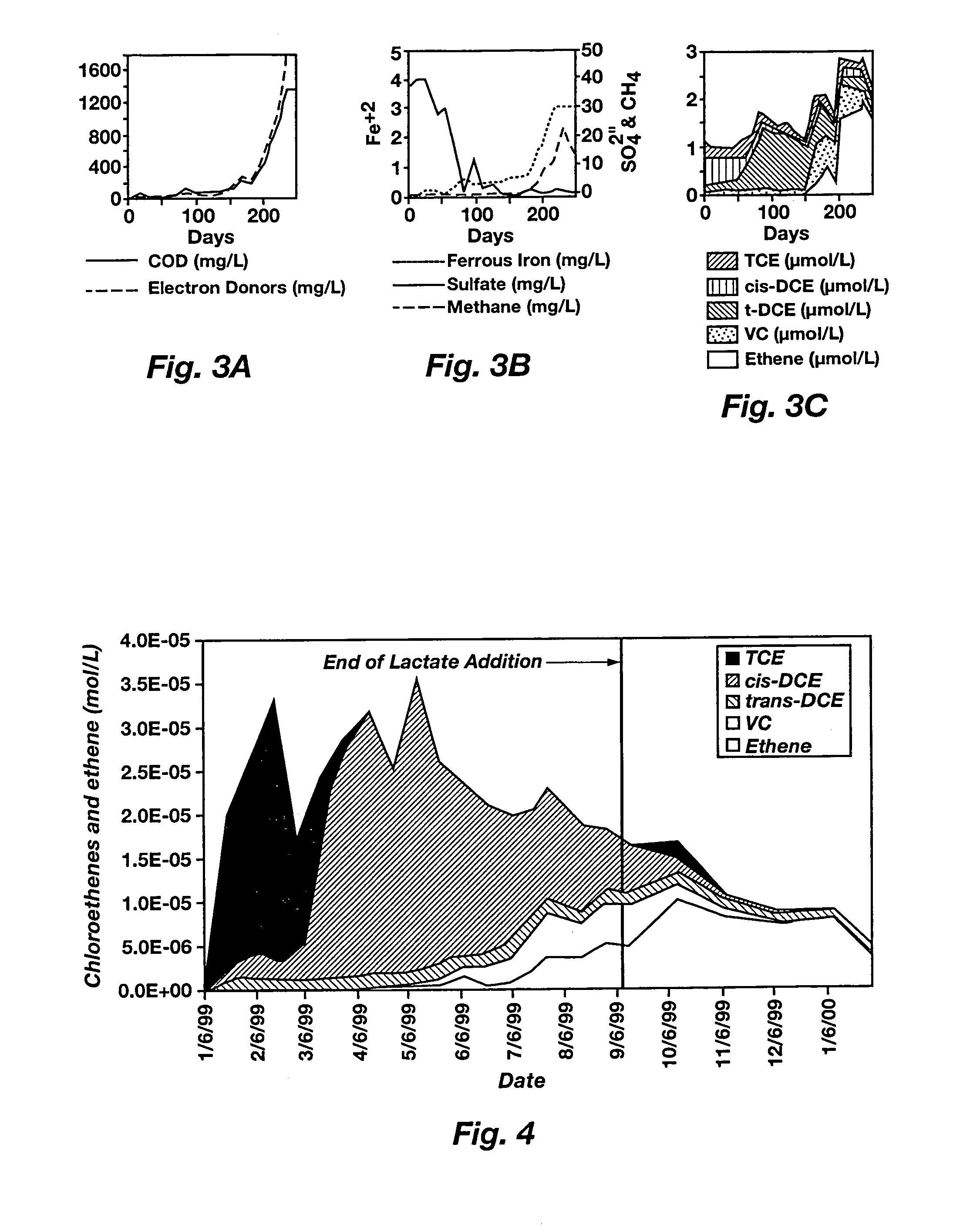
Electron donors for chlorinated solvent source area bioremediation
InactiveUS7045339B2Lower cost of capitalQuality improvementTreatment using aerobic processesSolid waste disposalSodium lactateElectron donor
Methods for enhancing bioremediation of ground water contaminated with nonaqueous halogenated solvents are disclosed. An illustrative method includes adding a composition to the ground water wherein the composition is an electron donor for microbe-mediated reductive dehalogenation of the halogenated solvents and enhances mass transfer of the halogenated solvents from residual source areas into the aqueous phase of the ground water. Illustrative compositions effective in these methods include surfactants such as C2–C4 carboxylic acids and hydroxy acids, salts thereof, esters of C2–C4 carboxylic acids and hydroxy acids, and mixtures thereof. Other illustrative compositions according to the present invention include oleyl lactylic acid and, optionally, oleic acid and lactic acid or salts thereof. Especially illustrative compositions for use in these methods include lactic acid, salts of lactic acid, such as sodium lactate, lactate esters, and mixtures thereof. The microbes are either indigenous to the ground water, or such microbes can be added to the ground water in addition to the composition.
Owner:JRW BIOREMEDIATION +1
Solid-chemical composition for sustained release of organic substrates and complex inorganic phosphates for bioremediation
InactiveUS6620611B2Improve solubilityIncreasing speed and effectivenessBacteriaWater treatment compoundsPseudomonasTrichoderma spp
A slow-release solid chemical composition for environmental bioremediation is provided. The composition comprises a source of soluble organic substrates which include sugars, soluble organic polymers and mixtures of them in an amount of 7% to 90%, insoluble organic substrates an amount of 10% to 70%, complex inorganic phosphates in an amount of 0.5% to 7% and soluble organic salts in an amount of 2% to 70%. The insoluble organic substrates include fibrous plant materials, starches, cellulosic materials and mixtures of these substrates. The complex inorganic phosphates include ringed metaphosphates, linear polyphosphates and mixtures. The organic salts include lactates, formates, acetates, citrates, etc. Also the composition further comprises microorganisms which include Bacillus spp., Rhizobium spp., Bradyrhibzobium spp., Fibrobacter spp., Clostridium spp., Pseudomonas. spp., Geobacter spp., Arthrobacter spp., Nocardia, spp., aspergillus spp., Trichoderma spp., Candida spp., Yarrowia spp. and combinations of these microorganisms. The composition can be prepared in various forms, including granules, briquettes, pellets, tablets or capsules.
Owner:HINCE ERIC CHRISTIAN MR
Bioremediation method for petroleum-polluted soil
ActiveCN105170644AImprove repair effectShort repair timeContaminated soil reclamationWater contentBioremediation
The invention discloses a bioremediation method for petroleum-polluted soil. The method comprises the steps that 1, biomass containing biomass degrading bacteria is added in the petroleum-polluted soil with the petroleum content higher than 18 wt%, and ploughing is performed to mix the soil with the biomass, the water content of the petroleum-polluted soil is simultaneously kept at 10-30 wt%, and first degrading bacteria are added in the soil in 10-15 days after ploughing is performed to reduce the petroleum content of the soil to 8-18 wt%; 2, second degrading bacteria are added in the soil to reduce the petroleum content of the soil to 5-8 wt%; 3, third degrading bacteria are added in the soil to reduce the petroleum content of the soil to 1-5 wt%; 4, forth degrading bacteria are added in the soil to reduce the petroleum content of the soil below 1 wt%. The method can be applied to both in-situ remediation and ex-situ remediation, the remediation effect is good, the remediation time is short, the method is simple, and the cost is low.
Owner:李磊
Biological remediation type water system oil stain cleaning agent and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102586033AQuick washEfficient Pollution ReductionNon-ionic surface-active compoundsOrganic detergent compounding agentsMicroorganismEnvironmental engineering
The invention discloses a biological remediation type water system oil stain cleaning agent capable of quickly and effectively cleaning oil stain and decomposing oil stain in water by using a microorganism, a preparation method thereof and aims to solve the problems of more consumption, more pollution and bad cleaning effect when a traditional cleaning agent product is used for cleaning the oil stain, in particular to the problem that after the oil stain enters washing wastewater, as the pollution only can be transferred and can not be degraded, the serious environment friendliness can be caused. Aiming at the defects, the invention researches a novel bioremediation type water system oil stain cleaning agent which simultaneously contains a plurality of surfactants and microorganism bacterium agents for degrading the oil stain. Compared with the existing traditional cleaning agent, the novel bioremediation type water system oil stain cleaning agent has the remarkable advantages of quickness and high efficiency in washing, energy conservation and consumption reduction, direct oil stain degradation, environment friendliness and emission reduction, and the like. The bioremediation type water system oil stain cleaning agent for quickly degrading the oil stain has the advantages of good stability, high safety, strong oil degradation activity, quick growth and no secondary pollution tn the environment.
Owner:郑涵
A kind of pseudomonas and its use and method for removing cadmium pollution in environment
ActiveCN102286405ASolve pollutionAdaptableBacteriaWater contaminantsBiotechnologyEnvironmental engineering
The invention relates pseudomonas, use thereof and a method for removing cadmium pollution to the environment. The pseudomonas class is named pseudomonas putidaHN103 and the collection number in a collection center is CCTCCNo.M2011184; and the shape and characteristics of the pseudomonas putidaHN103 comprise: 1) on a culture medium, a bacterial colony which used to be colorless and transparent turns white, smooth and convex-like with irregular edges; and 2) according to the result of bacterial microscopic examination, pseudomonas belongs to brevibacterium and is gram negative. The use of the bacteria is the use of the bacteria as a biological repair material for removing cadmium pollution. The method for removing cadmium pollution to the environment comprises the following steps: 1) regulating the cadmium ion concentration in sewage to a range in which pseudomonas can grow normally; 2) placing pseudomonas; 3) keeping the pseudomonas in the sewage for a certain time period; and 4) removing bacterial absorbing cadmium ions. The pseudomonas requires small investment, is low in cost, high in adaptability and capable of effectively removing cadmium, can quickly and obviously lower the concentration of cadmium ions in the environment and is suitable for biological remediation environments polluted by cadmium.
Owner:武汉华中农大资产经营有限公司
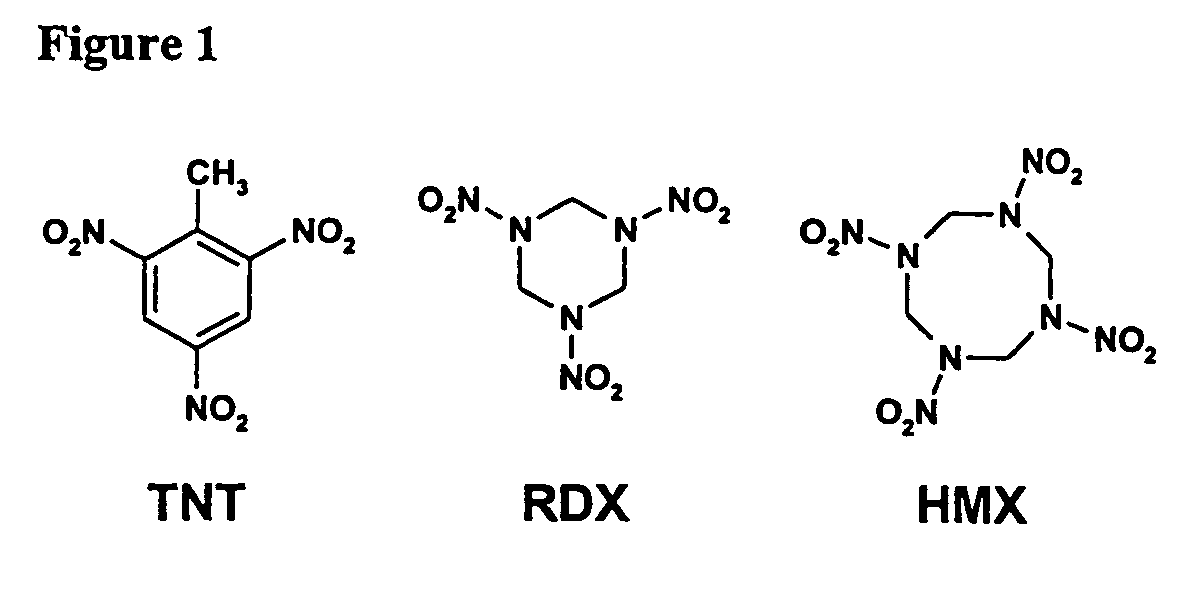
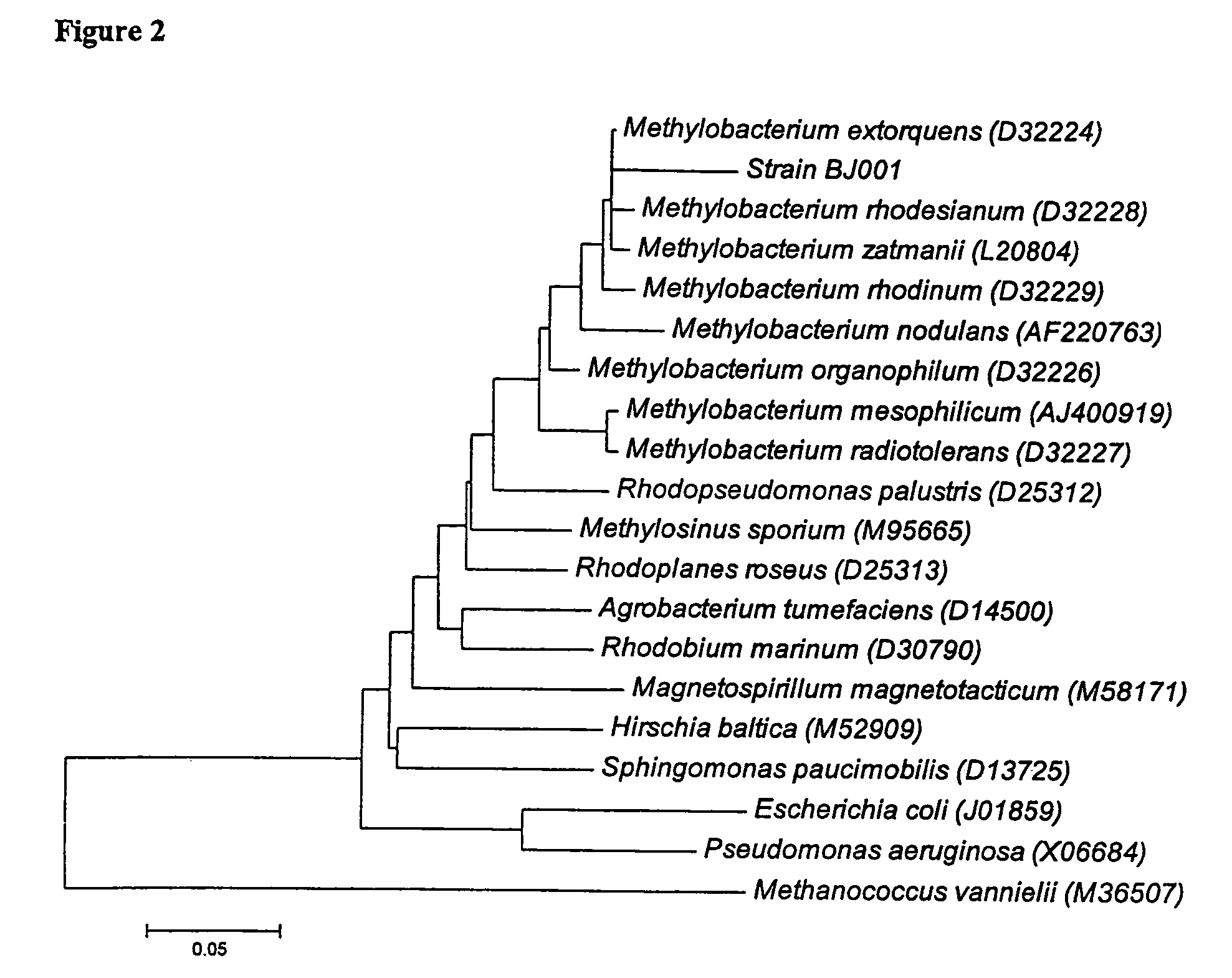
Methods and compositions for degradation of nitroaromatic and nitramine pollutants
InactiveUS7214509B2Low toxicityImprove abilitiesBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementNitroamineBioremediation
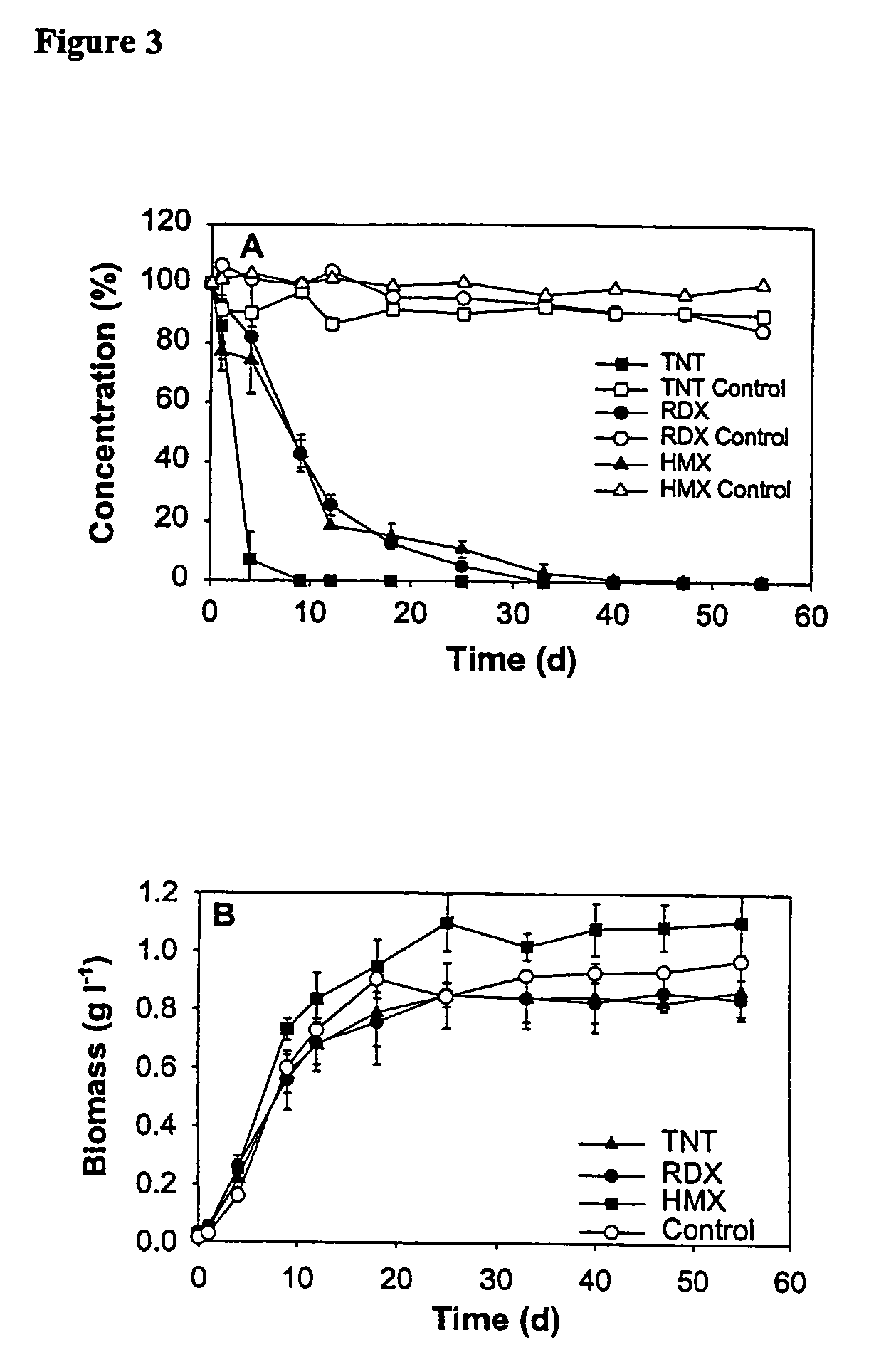
The invention relates to novel Methylobacterium species that are capable of degrading nitroaromatic and nitramine compounds. Compositions, kits and methods of using the Methylobacterium species for the degradation of nitroaromatic and nitramine pollutants are provided. More specifically, compositions and methods for the degradation or bioremediation of nitroaromatic and nitramine explosives and explosive residues are provided.
Owner:UNIV OF IOWA RES FOUND
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com