Microbial flora for decomposing dimethylformamide and culture method thereof
A technology of dimethylformamide and cultivation method, which is applied in the field of decomposing dimethylformamide, can solve problems such as the difficulty of degrading dimethylformamide wastewater, and achieve the effect of reducing operating costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0042] (1) In the ultra-clean bench, configure 100mL medium (10% inoculum rate) in the Erlenmeyer flask: 10mL+2mL10% dimethylformamide+1mL CaCl2+20μL FeSO4+87mL nutrient solution, adjust the pH to 7.0 , after the configuration is completed, use Para sealing film for sealing;
[0043] (2) The Erlenmeyer flask was cultured in a shaker at 30°C, and the rotation speed of the shaker was 150r / min. As the reaction progressed, the pH of the culture system gradually increased, so the pH was adjusted to 7.0 every 24 hours. Measure the OD600 of the reaction system every 48h (measure the concentration of bacteria or fungi according to OD600), and Concentration, based on system OD changes and nitrogen concentration changes to determine the reaction process, adjust the length of the reaction cycle. pH adjustment and sampling are completed in the ultra-clean bench;
[0044] (3) Determine the culture end point of each cycle: A large number of studies have shown that the decomposition of...
Embodiment 2
[0047] Embodiment 2 mixed flora batch test:
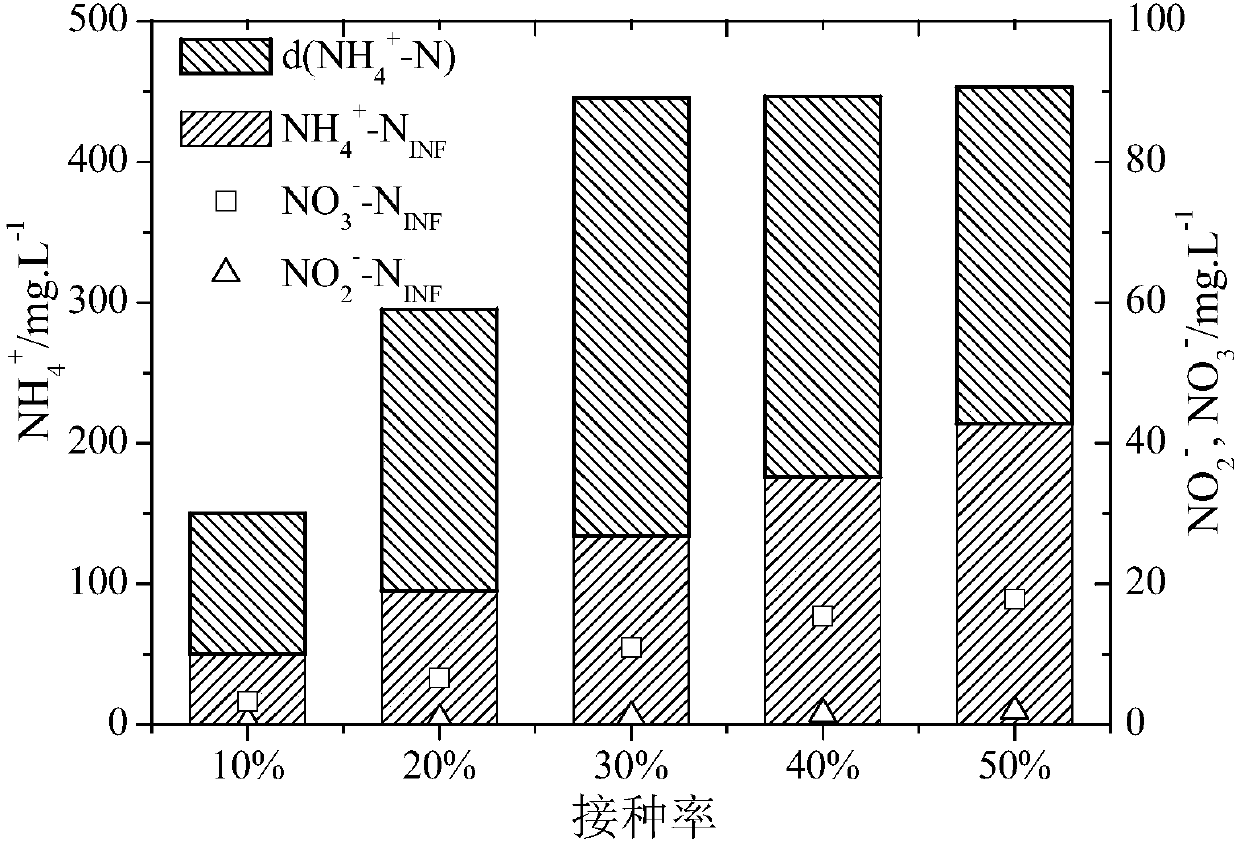
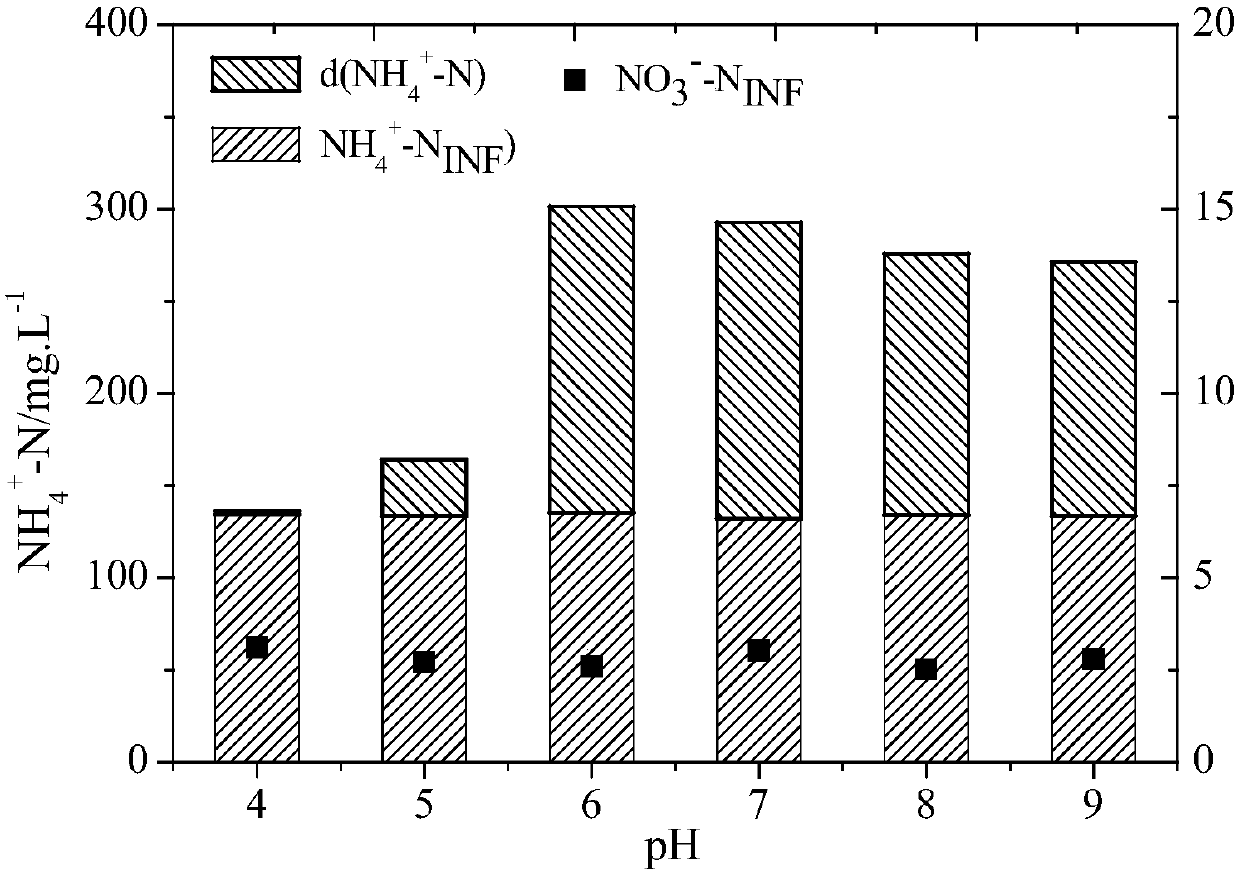
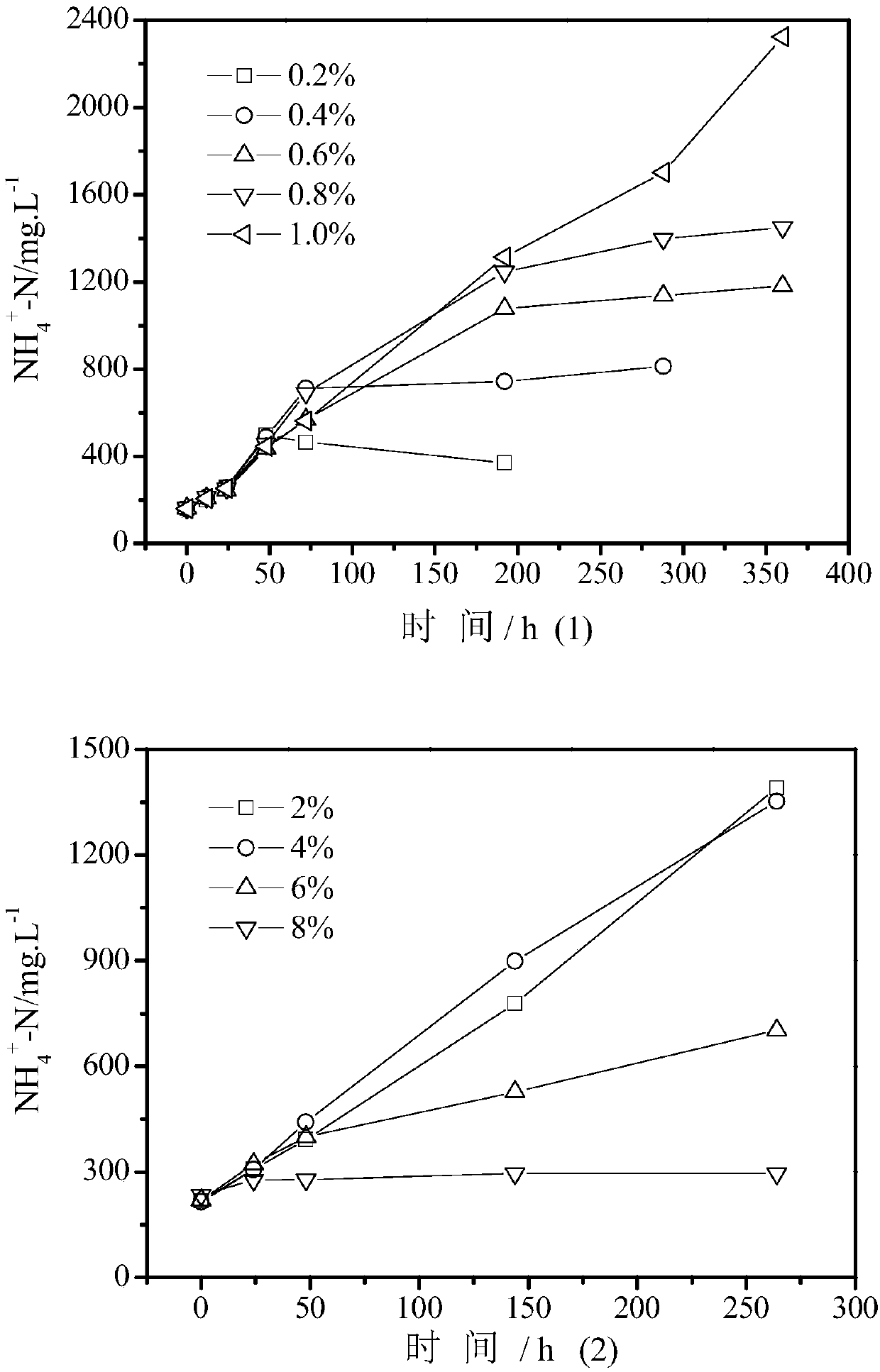
[0048] After completing 11 cycles of cultivation and acclimatization, a total of 4 groups of batch experiments were set up for the characteristics of the mixed flora. Figure 1-4 The vertical axis of is the concentration of ammonia nitrogen obtained by the decomposition of dimethylformamide.
[0049] (1) Effect of inoculation rate on the activity of flora
[0050] like figure 1 As shown, five inoculation rates were set in the test: 10%, 20%, 30%, 40% and 50%. The reaction volume was maintained at 100mL during configuration, and the volume of the bacterial solution was increased step by step from 10mL to 50mL. At the same time, the nutrient solution was Decrease from 87mL to 47mL step by step, the cycle time is controlled to 48h, and the remaining components and control conditions are consistent with the cultivation and acclimation stage. like figure 1 As shown, the optimal inoculation rate of the mixed flora is 30%, and the dim...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com