Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
125 results about "Stenotrophomonas sp." patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Jump to navigation Jump to search. Stenotrophomonas is a genus of Gram-negative bacteria. With species ranging from common soil organisms (S. nitritireducens) to opportunistic human pathogens (S. maltophilia), the molecular taxonomy of the genus is still somewhat unclear.
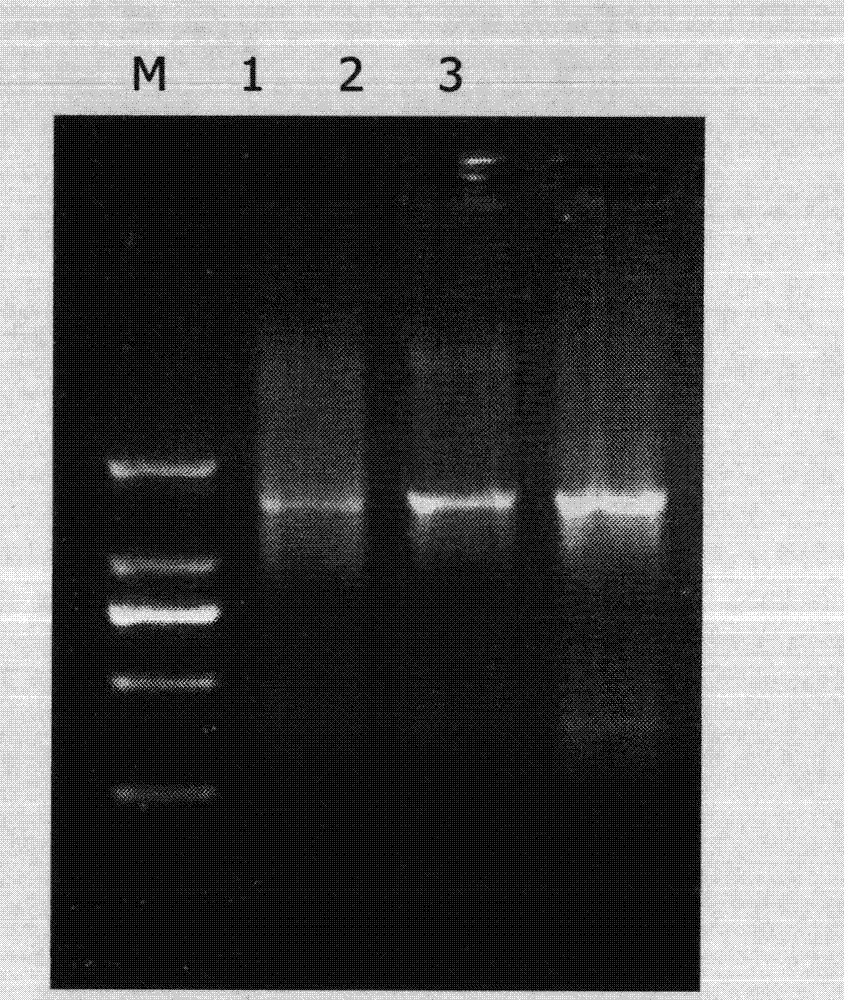
Heterotrophic nitrification microbial preparation, cultivation method and use thereof
ActiveCN101302485AWide range of substratesEasy to trainImmobilised enzymesBacteriaHigh concentrationMicroorganism
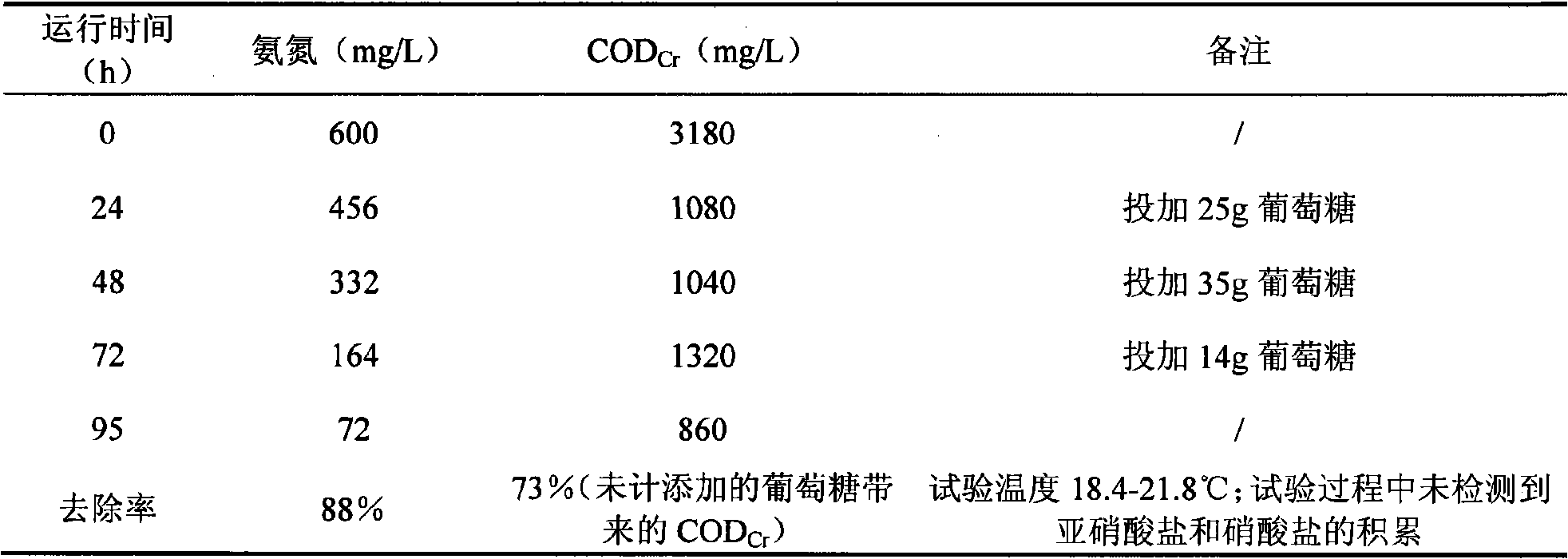
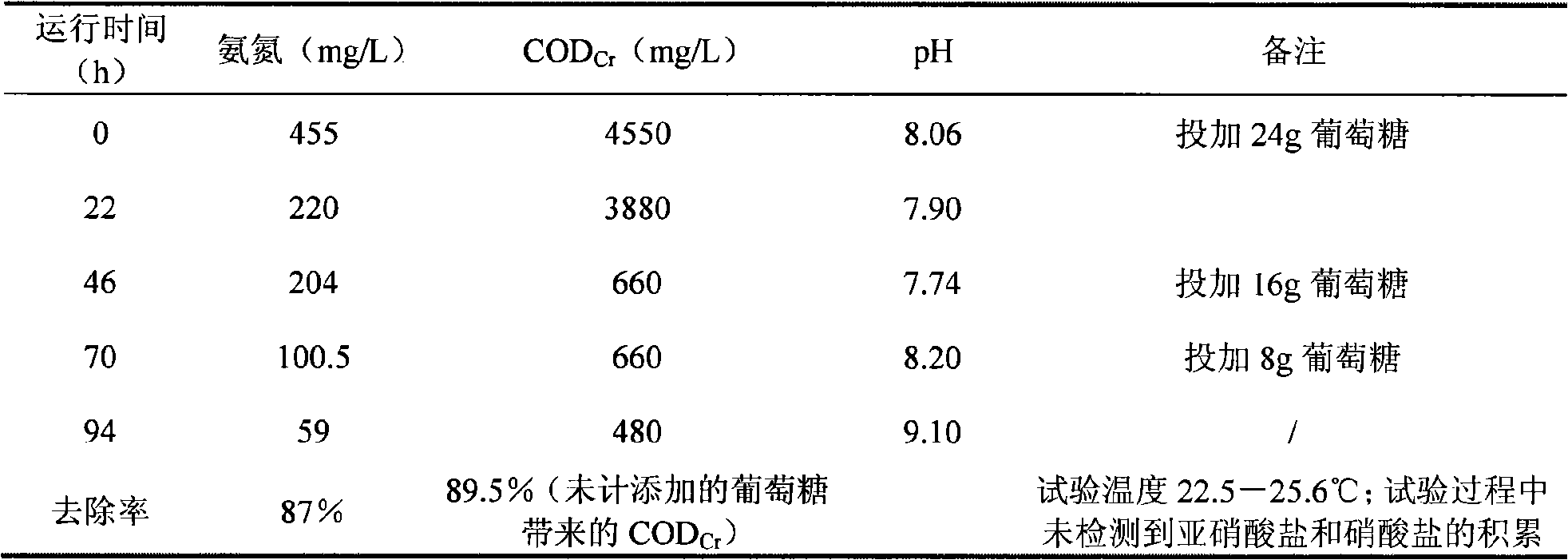
The invention belongs to the environmental microorganism field, and in particular relates to a heterotrophic nitrification microorganism agent, a method for cultivating the same, and a use of the same in culture wastewater treatment. The microorganism agent contains Stenotrophomonas maltophilias strain DN1.1 and Pseudomonas putida strain DN1.2 which have the preservation registration numbers respectively as CCTCC M 207074 and CCTCC M 207075. The microorganism agent can effectively remove ammonia nitrogen and total nitrogen in a water body, accumulates no nitrite or nitrate during denitrification, and can simultaneously remove CODCr in organic wastewater, which is applicable to the treatment of high-concentration culture wastewater. The use of the microorganism agent in treating culture wastewater is simple in process and stable in effect.
Owner:CHENGDU INST OF BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF S
Bioreactor for remediation of pollutants with butane utilizing bacteria
InactiveUS6051130AReduce and eliminate hydrocarbon pollutantEasy to transportGas treatmentBacteriaBacteroidesComamonas
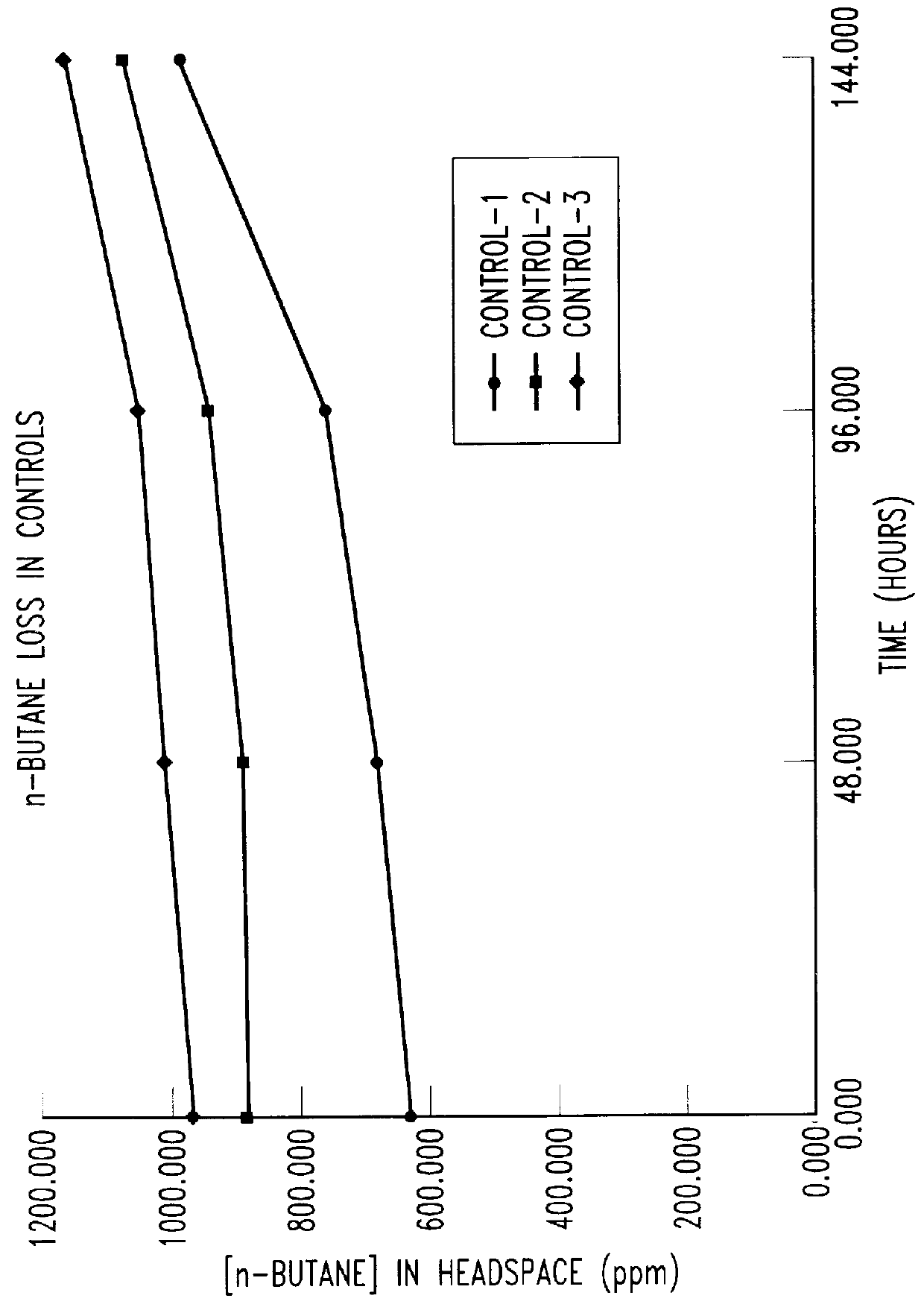
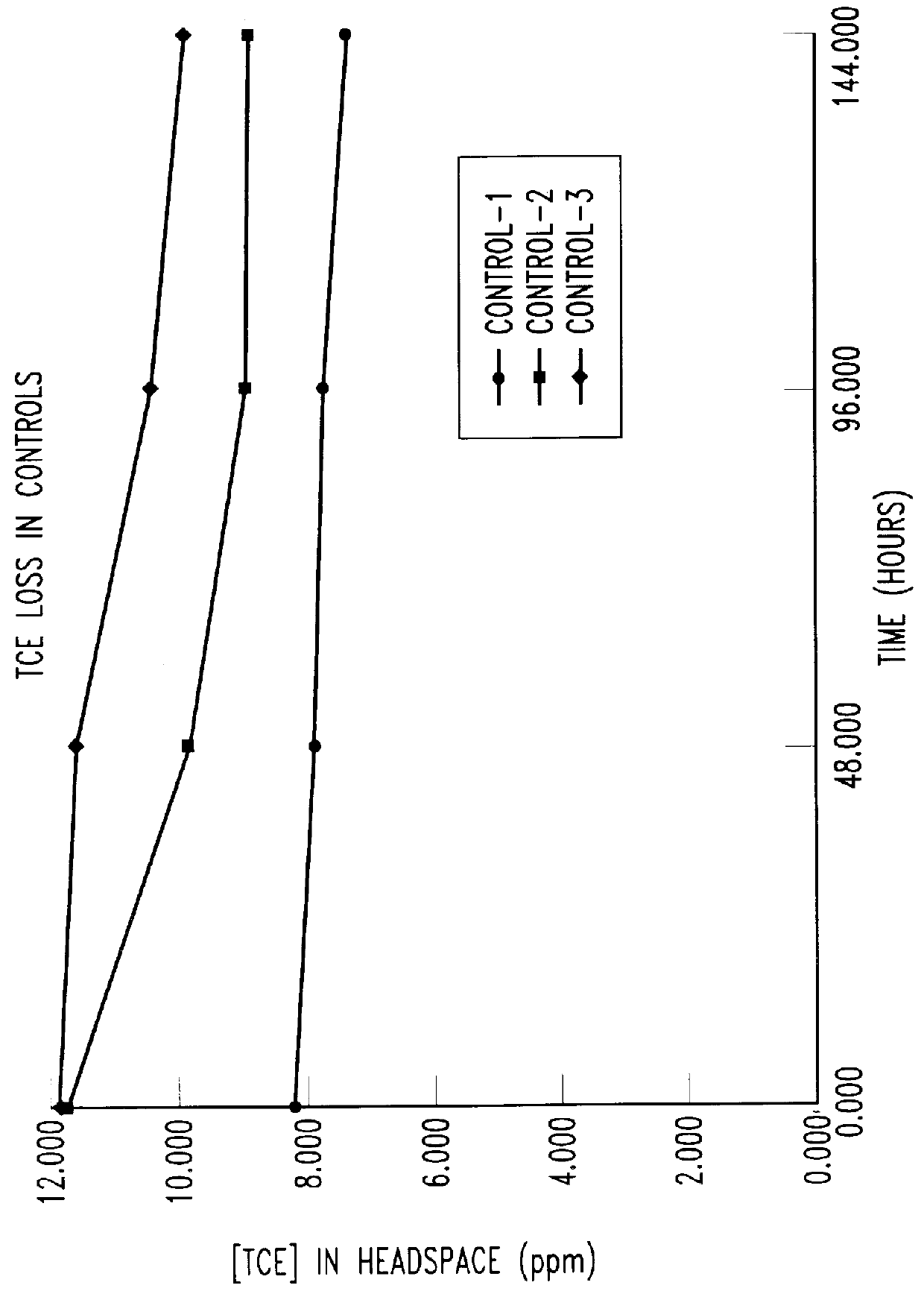
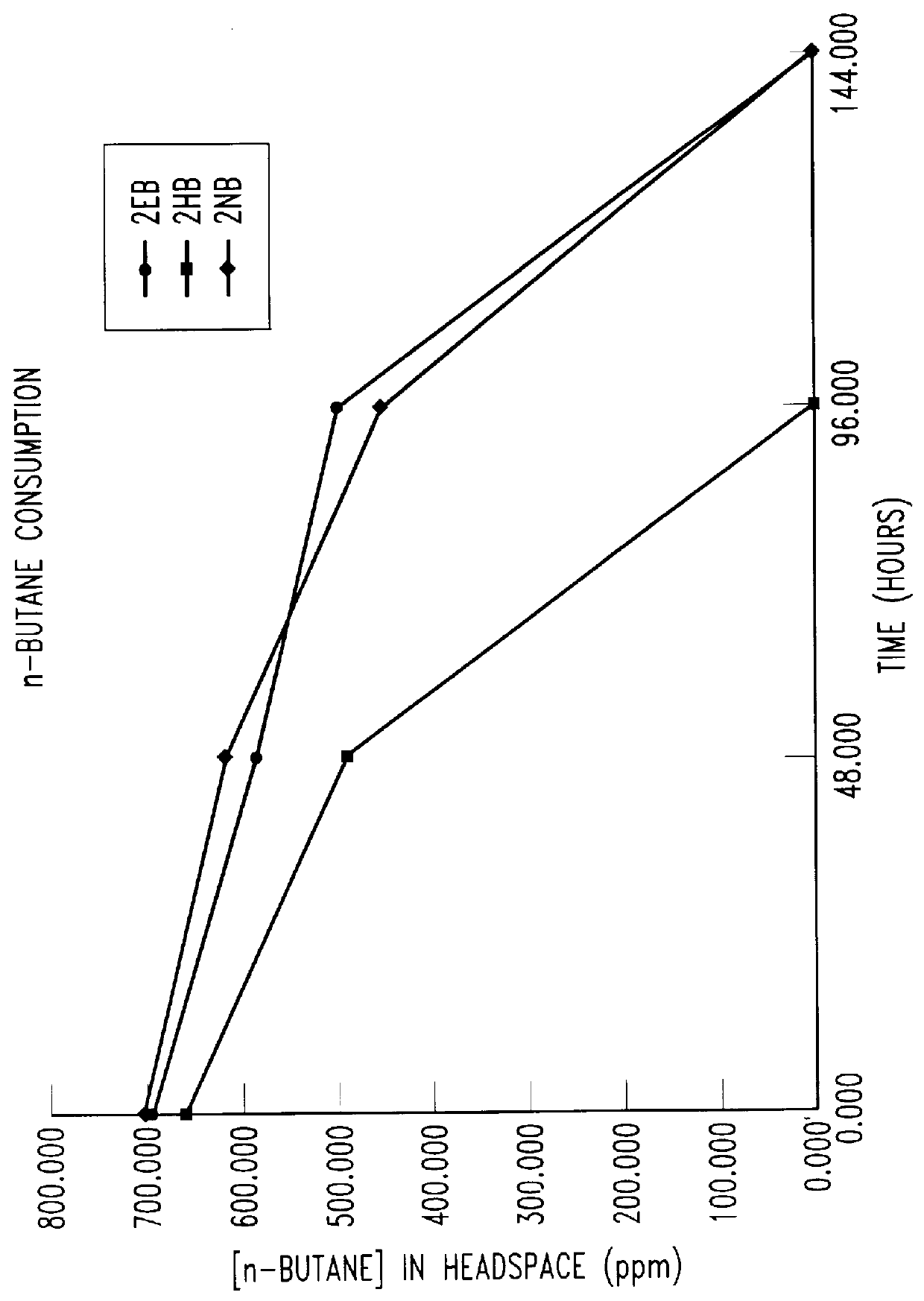
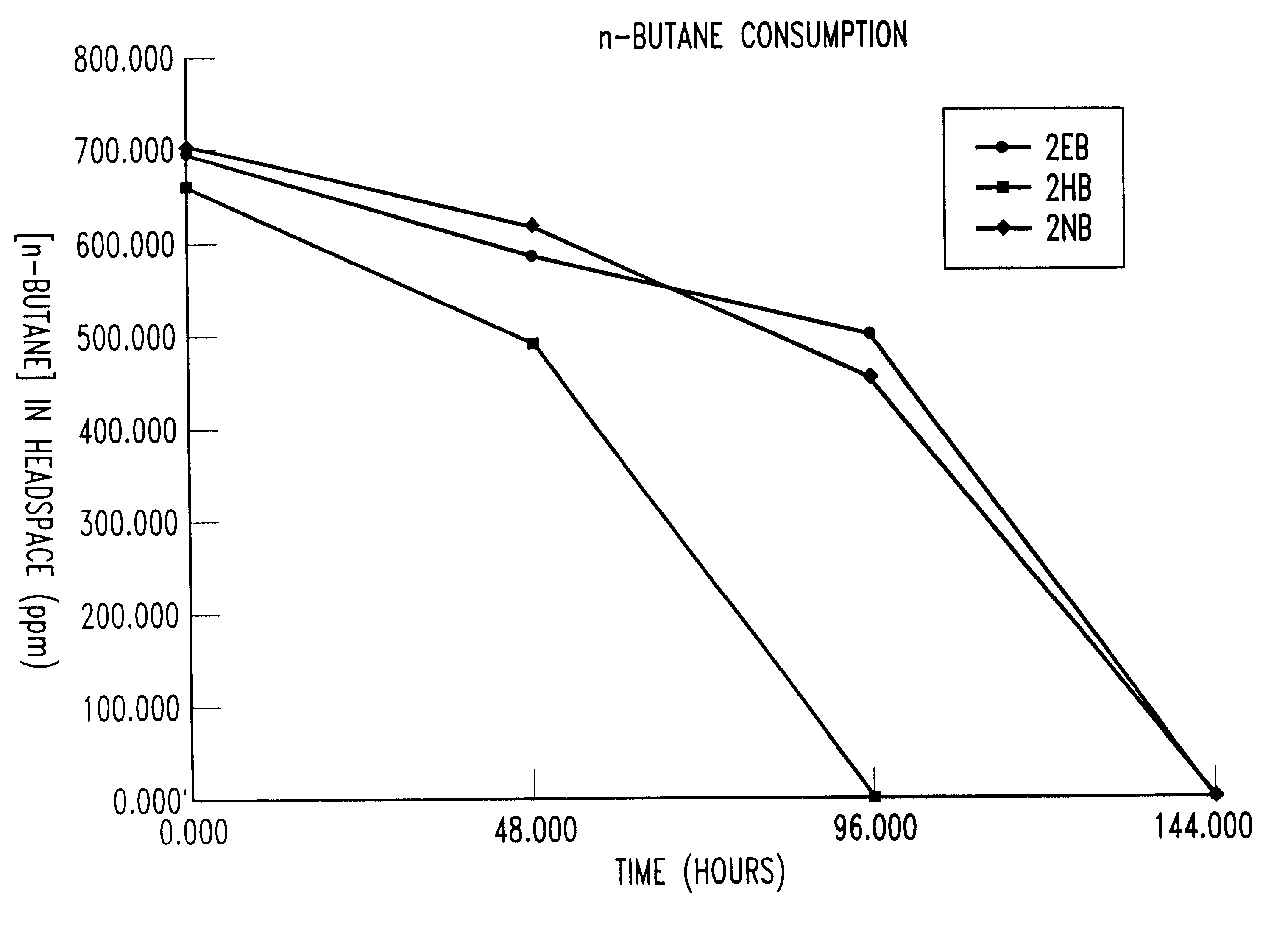
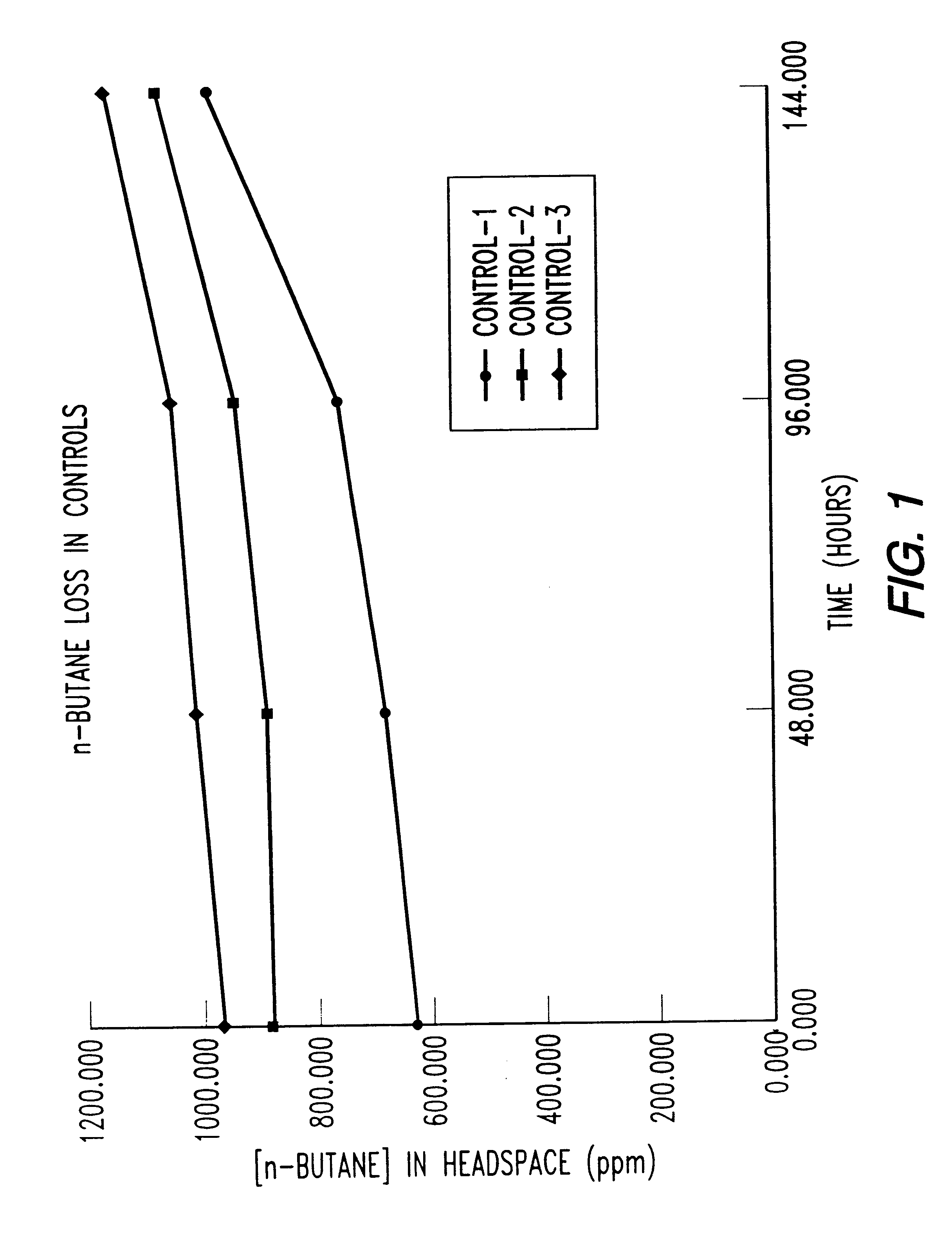
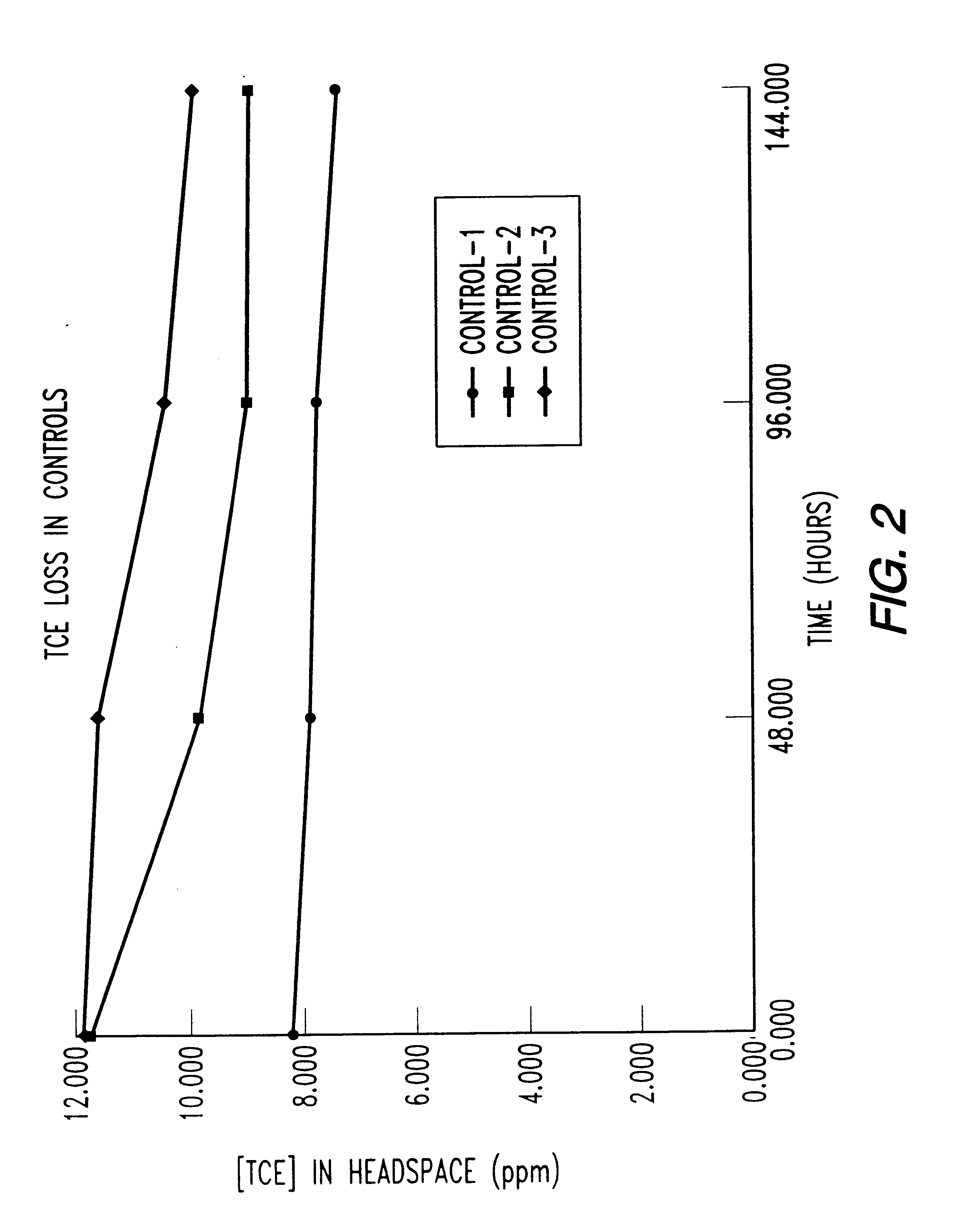
Butane-utilizing bacteria are used to degrade hydrocarbon pollutants such as trichloroethene (TCE). In-situ or ex-situ techniques may be used to reduce or eliminate hydrocarbon pollutants from liquid, gas and solid sources. In a preferred embodiment, TCE concentrations in various aqueous environments are reduced by contacting a contaminated water source with butane-utilizing bacteria in the presence of oxygen to degrade the TCE by cometabolism or direct metabolism. Suitable butane-utilizing bacteria include Pseudomonas, Variovorax, Nocardia, Chryseobacterium, Comamonas, Acidovorax, Rhodococcus, Aureobacterium, Micrococcus, Aeromonas, Stenotrophomonas, Sphingobacterium, Shewanella, Phyllobacterium, Clavibacter, Alcaligenes, Gordona, Corynebacterium and Cytophaga. The butane-utilizing bacteria have relatively low TCE toxicity in comparison with conventional methane-utilizing bacteria, and demonstrate an improved ability to degrade TCE.
Owner:GLOBAL BIOSCI
Bioremediation of pollutants with butane-utilizing bacteria
InactiveUS6210579B1Reduce and eliminate hydrocarbon pollutantEasy to transportGas treatmentTreatment using aerobic processesBacteroidesComamonas
Butane-utilizing bacteria are used to degrade hydrocarbon pollutants such as trichloroethene (TCE). In-situ or ex-situ techniques may be used to reduce or eliminate hydrocarbon pollutants from liquid, gas and solid sources. In a preferred embodiment, TCE concentrations in various aqueous environments are reduced by contacting a contaminated water source with butane-utilizing bacteria in the presence of oxygen to degrade the TCE by cometabolism or direct metabolism. Suitable butane-utilizing bacteria include Pseudomonas, Variovorax, Nocardia, Chryseobacterium, Comamonas, Acidovorax, Rhodococcus, Aureobacterium, Micrococcus, Aeromonas, Stenotrophomonas, Sphingobacterium, Shewanella, Phyllobacterium, Clavibacter, Alcaligenes, Gordona, Corynebacterium and Cytophaga. The butane-utilizing bacteria have relatively low TCE toxicity in comparison with conventional methane-utilizing bacteria, and demonstrate an improved ability to degrade TCE.
Owner:GLOBAL BIOSCI
Composite microbial inoculant for degrading aflatoxin B1 and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN105925513AEfficient degradationLow costBacteriaMicroorganism based processesFlavobacteriumFermentation
The invention discloses a preparation method of a composite microbial inoculant for degrading aflatoxin B1 and a composite microbial inoculant prepared by the method. The method comprises the following steps: respectively culturing pseudomonad, Flavobacterium, Rhodococcus, Stenotrophomonas and Bacillus to obtain a pseudomonad solution, a Flavobacterium solution, a Rhodococcus solution, a Stenotrophomonas solution and a Bacillus solution; mixing the pseudomonad solution, Flavobacterium solution, Rhodococcus solution, Stenotrophomonas solution and Bacillus solution to obtain a composite bacterium solution; and putting the composite bacterium solution into a composite bacterium culture medium, and carrying out mixed culture fermentation to obtain the composite microbial inoculant for degrading aflatoxin B1. The composite microbial inoculant can efficiently degrade aflatoxin B1, and has the advantages of low cost and no secondary pollution.
Owner:FARM PROD PROCESSING & NUCLEAR AGRI TECH INST HUBEI ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Stenotrophomonas acidaminiphila and application in control of apple tree canker thereof
The invention discloses a stenotrophomonas acidaminiphila and an application in control of apple tree canker thereof, and belongs to the technical field of plant disease biological control. A strain of stenotrophomonas acidaminiphila BJ1 used for apple fungal disease biological control is screened from rhizosphere soil of a commercial apple grove in Xixia, Shandong, is preserved in China center for type culture collection with a preservation number of CCTCC NO: M 2011475. The microbial agent of the invention is prepared by the following steps of: 1) preparation of a medium, 2) activation of the BJ1 strain, 3) liquid culture of the BJ1 strain, 4) preparation of a BJ1 biological control preparation, and 5) dilution. The stenotrophomonas acidaminiphila BJ1 strain of the invention has obvious control effect on apple tree canker, has stable control effect, is environment-friendly, is simple in fermentation process for large-scale production, and low in production cost.
Owner:QINGDAO AGRI UNIV
Bacteria for efficiently degrading residual pesticide carbendazim and use thereof
The invention discloses a bacterium for efficiently degrading residual pesticides carbendazim and application thereof. The bacterium for degrading the residual pesticides carbendazim is stenotrophomonas (Stenotrophomonas sp.) DJL1614 and has the preservation number of CGMCC No.5151 in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (CGMCC). The degradation rate of 10d of the stenotrophomonas (Stenotrophomonas sp.) DJL1614 CGMCC No.5151 provided by the invention on 500ml / L of carbendazim in an inorganic salt culture medium reaches 73.41 percent. Therefore, the strain can efficiently degrade the carbendazim. The stenotrophomonas has wide application prospect on the aspect of repairing the carbendazim pollution of soil.
Owner:INST OF AGRI RESOURCES & REGIONAL PLANNING CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Microbe method for preparing enamine and amine from valinemia
A microorganism preparation method relates to the microorganism of stenotrophomonas maltrophilia of stenotrophomonas utilized by CCTCC NoM 204024 of its fermentation and decomposition or its cells or zymes decomposite substrates validamycin or validamycin imide to produce validamy enamine and validemy amine. Composition of the culture media is(weight / volume): validamycin 0.5-20.0%,(NH4)2 SO4 0.5%-10.0, KCL 0.5%-5.0%, Na2HPO4, 12H2 00.1%-10.0%, Na2H2PO4 2H2O 0.1-5.0%, MgSO4 0.01%-1.0% matched by running water, fermenting temperature: 20deg.C-40-deg.C initial PH:6.0-8.0 for 1-180h by ionic exchanges, chromatography and purify, the two products are finished.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH +2
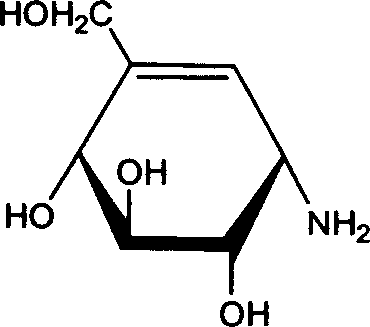
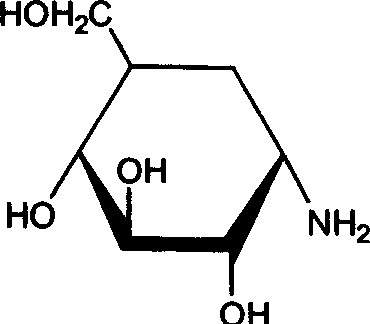
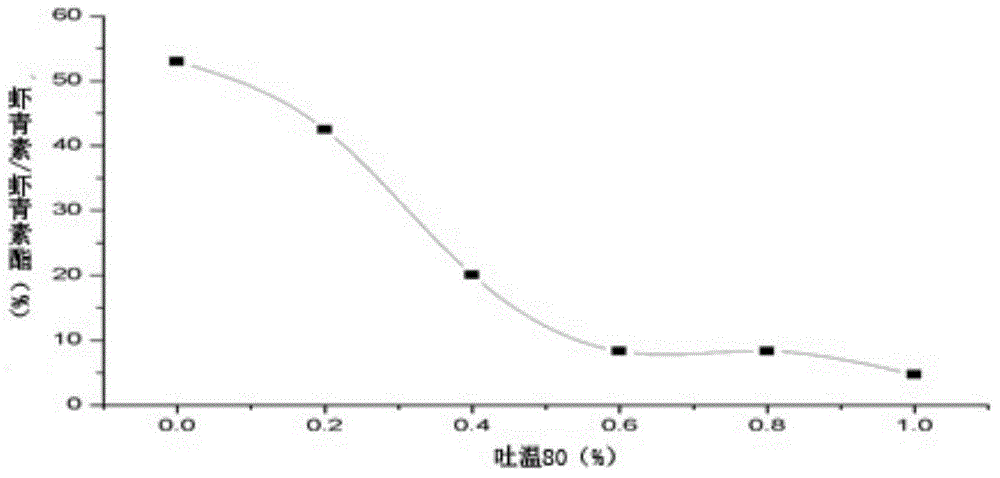
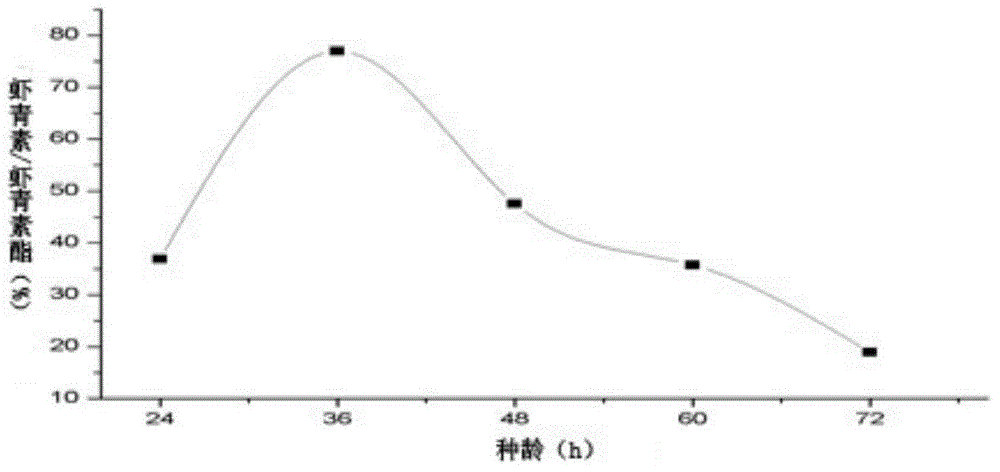
Astaxanthin esterase production strain and application of strain in preparation of free astaxanthin
The invention aims at providing an astaxanthin esterase production strain and application of the astaxanthin esterase production strain in preparation of free astaxanthin. The strain for producing lipase and esterase is stenotrophomonas and stored with the number of CGMCC NO.10672. The stenotrophomonas strain can be used for producing free astaxanthin by efficiently utilizing an organic solvent extract of haematococcus pluvialis oil and / or aquatic animal (such as shrimp and crab); the strain can effectively degrade astaxanthin ester to prepare free astaxanthin; in addition, the experiment shows that the quantity of added tween 80 in fermenting liquid, inoculation amount, initial pH of fermenting liquid and fementing time condition can be determined; a method for efficiently preparing the free astaxanthin is provided.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
Composition of bacterial strains, bioremediation mixture and use of this composition for the removal of contaminants from the soil and the method for purifying the soil contaminants
InactiveUS20140141494A1Low costFacilitates quick acquisition of appropriate amountBacteriaBiochemical fibre treatmentBacteroidesFood contaminant
The object of the present invention is a composition of bacterial strains which may comprise Stenotrophomonas sp. strain 2L, Stenotrophomonas sp. strain 5L, Stenotrophomonas sp. strain 6L, Stenotrophomonas sp. strain 3N, Achromobacter sp. strain 4P, Arthrobacter sp. strain 1N, Brevundimonas sp. strain 2N, Brevundimonas sp. strain 5N, Brevundimonas sp. strain 6N, Pseudomonas sp. strain 3G, and Pseudomonas sp. strain 4, deposited under the number KKP 2041p (IAFB Collection of Industrial Microorganisms—Institute of Agricultural and Food Biotechnology in Warsaw), a bioremediation vaccine (bioremediation mixture) which may comprise the composition of these strains, the use of the vaccine in the removal of contaminants from the soil, and the method for the treatment of contaminated soil.
Owner:UNIWERSYTET WARSZAWSKI
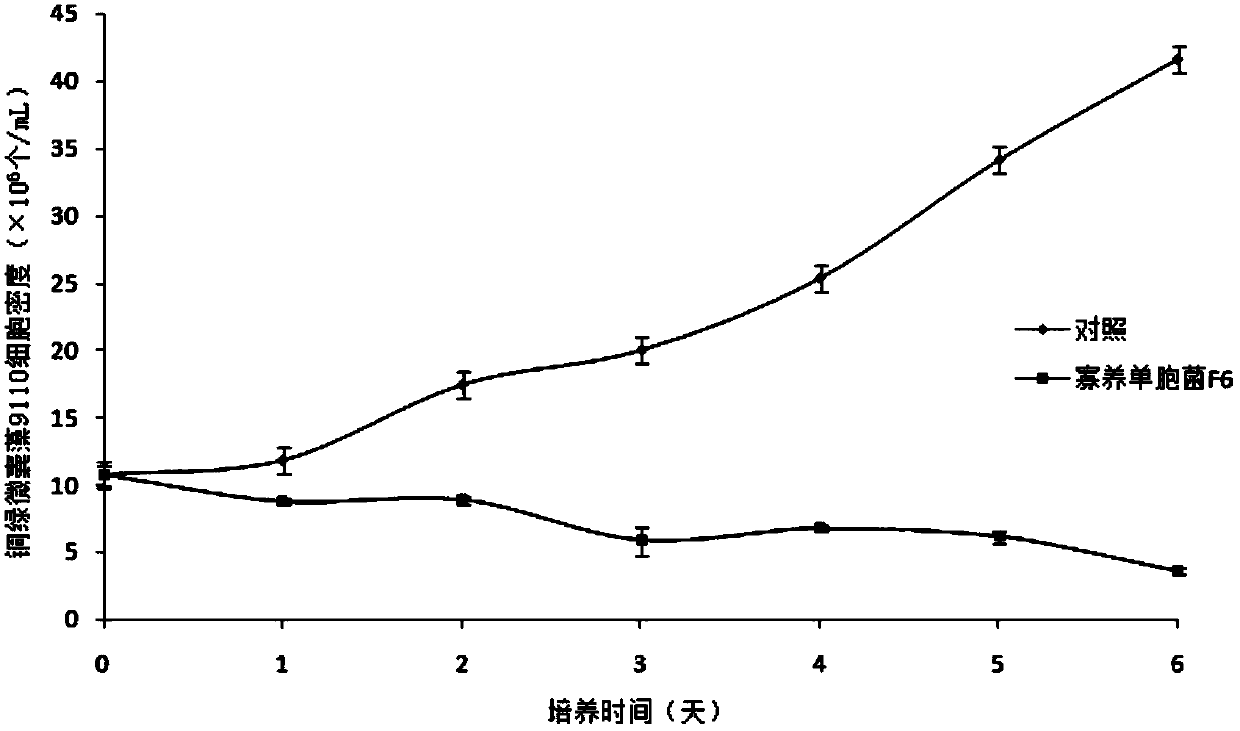
Stenotrophomonas and applications thereof
InactiveCN103667135ASimple screening methodBroad-spectrumBacteriaMicroorganism based processesSynechococcusMetabolite
The invention provides a strain of stenotrophomonas sp., which is named as stenotrophomonas F6, and has a preservation number of CGMCC No.6547. Two active algicidal substances, namely cyclo(glycine-proline) and hydroquinone, are separated from the metabolism products of the stenotrophomonas F6, and then the substances are purified and identified. The half effective concentration of the cyclo(glycine-proline) on inhibiting microcystis aeruginosa 9110 is 9.5 mg / L, and the cyclo(glycine-proline) has no inhibiting effect on synechococcus BN60. The half effective concentrations of hydroquinone on inhibiting microcystis aeruginosa 9110 and synechococcus BN60 are 0.96 mg / L and 5.6 mg / L. The stenotrophomonas F6 and the active algicidal substances (cyclo(glycine-proline) and hydroquinone) can be applied to the development and production of novel algicide, and finally are applied to the control of cyanobacterial bloom in fresh water.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Stenotrophomonas (sp.) and application thereof
The invention discloses stenotrophomonas (sp.) and application thereof. The stenotrophomonas (sp.) provided by the invention is stenotrophomonas (sp.) FJSB3 with the collection number of CGMCC No.4344. As an experiment proves, the stenotrophomonas (sp.) FJSB3 with the collection number of CGMCC No.4344 can degrade pure Bt proteins and the Bt proteins in trans-Bt rice straw. The stenotrophomonas (sp.) strain has good application prospect in the fields of degradation of Bt proteins in soil and improvement on the soil environment.
Owner:中农科合肥食品营养与健康创新研究院有限公司
Method of removing recalcitrant organic pollutants
InactiveUS20130334135A1Efficient biodegradationReducing the recalcitrant chemical oxygen demand (COD)Treatment using aerobic processesBacteriaChemical oxygen demandComamonas
Recalcitrant chemical oxygen demand (COD) of a liquid is reduced in a water treatment system. The method includes pretreating the liquid in a pretreatment unit to remove indigenous bacteria or microbes to a population level below which the indigenous organisms can interfere with the screened and externally introduced microorganisms. The liquid is then provided to a reactor that has a filter bed formed with a carrier material. Special microbes are screened and used to colonize the carrier material to remove recalcitrant COD. A biofilm is cultured on the surface of the carrier material to immobilize the screened microbes in the reactor. The method further includes percolating the liquid from the pretreatment unit through the filter bed colonized with the screened microbes to degrade at least part of the recalcitrant COD under aerobic conditions. In one embodiment, the filter is formed with biological granular activated carbon (GAC) as the carrier material and the screened microbes comprise at least one microbial species selected from the group consisting of Bacillus, Comamonas, Arthrobacter, Micrococcus, Pseudomonas, Pediococcus, Achromobacter, Flavobacterium, Mycobacterium, Rhodanobacter, Stenotrophomonas and Yeast.
Owner:BL TECH INC
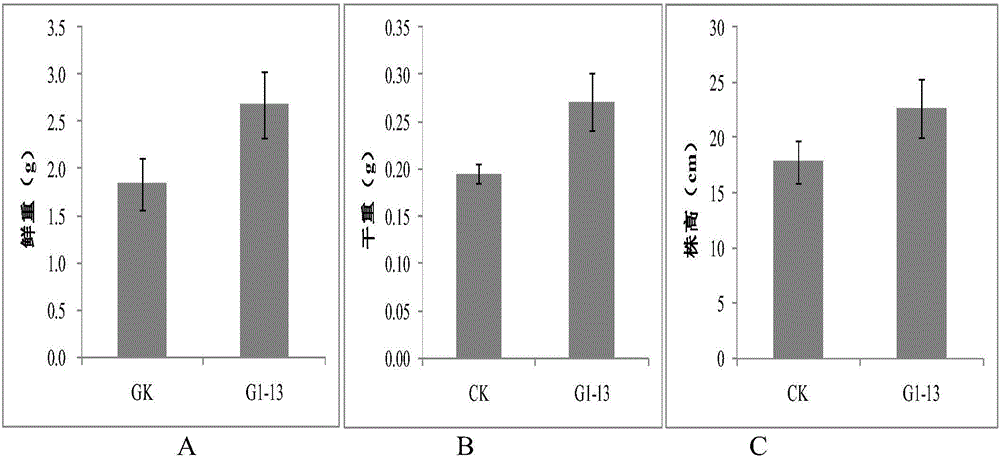
Stenotrophomonas sp and application thereof
InactiveCN106434472APromote growthIncreased fresh weightPlant growth regulatorsBiocideDry weightStenotrophomonas sp.
The invention provides a stenotrophomonas sp C1-13 strain, which is preserved with a preservation number of CGMCC NO.12835. The stenotrophomonas sp C1-13 strain can significantly promote the growth of cucumber seedlings. Pot experiments show that the stenotrophomonas sp C1-13, in comparison with blank control, can improve the fresh weight of the cucumber seedlings by 42.85%, dry weight by 34.97% and plant height by 27.00%.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Microbial agent for degrading fomesafen and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN110358717AReduce growth impactPromote degradationBacteriaContaminated soil reclamationMicroorganismMicrobial agent
The invention discloses a microbial agent for degrading fomesafen and a preparation method and application thereof, and belongs to the field of microorganisms. The microbial agent aims at solving theproblem that currently, there is no microbial agent for effectively degrading fomesafen; bacteria adopted in the microcapsule microbial agent are mixed bacteria of bacillus velezensis FB11 and stenotrophomonas sp. FB14, the preservation numbers of the bacteria are CGMCC No.17732 and CGMCC No.17731 respectively, the preservation dates are both May 8th, 2019, and the preservation address is BuildingNo.3, NO.1 West Beichen Road, Chaoyang District, Beijing. After the two strains are mixed, auxiliary materials are added to prepare the microbial agent. The microbial agent is used for degrading theherbicide fomesafen. The mixed strains adopted for the microbial agent have a remarkable degradation effect on the herbicide fomesafen in soil.
Owner:HEILONGJIANG UNIV
Screening and application of polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) degrading bacterium
ActiveCN106282070APromote degradationNo secondary pollutionBacteriaWater contaminantsStenotrophomonas pavaniiDecabromobiphenyl ether
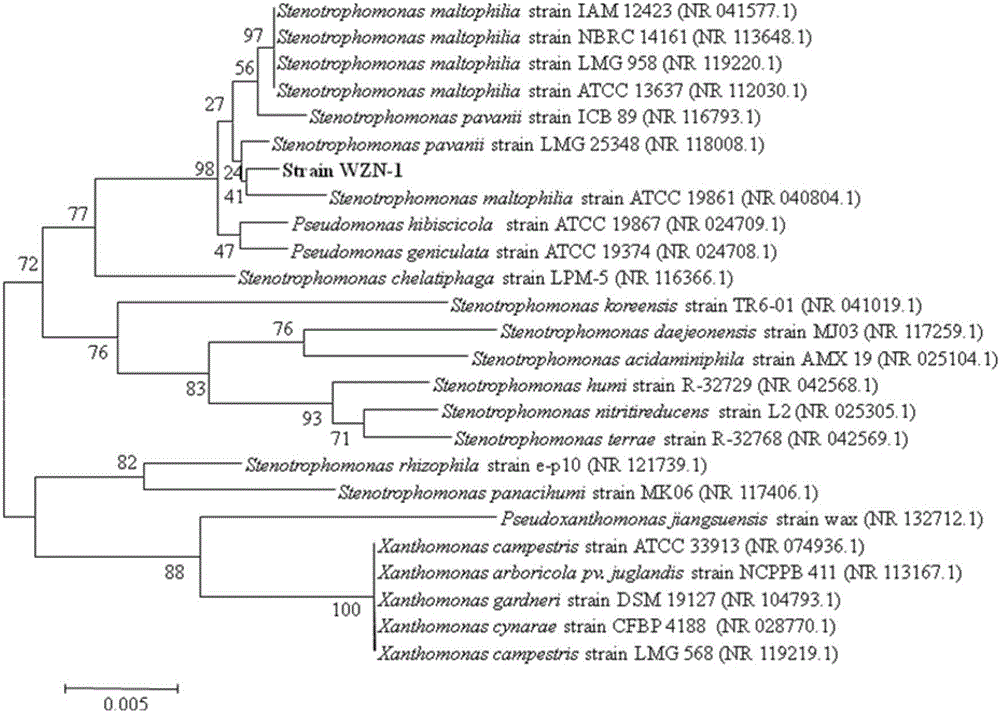
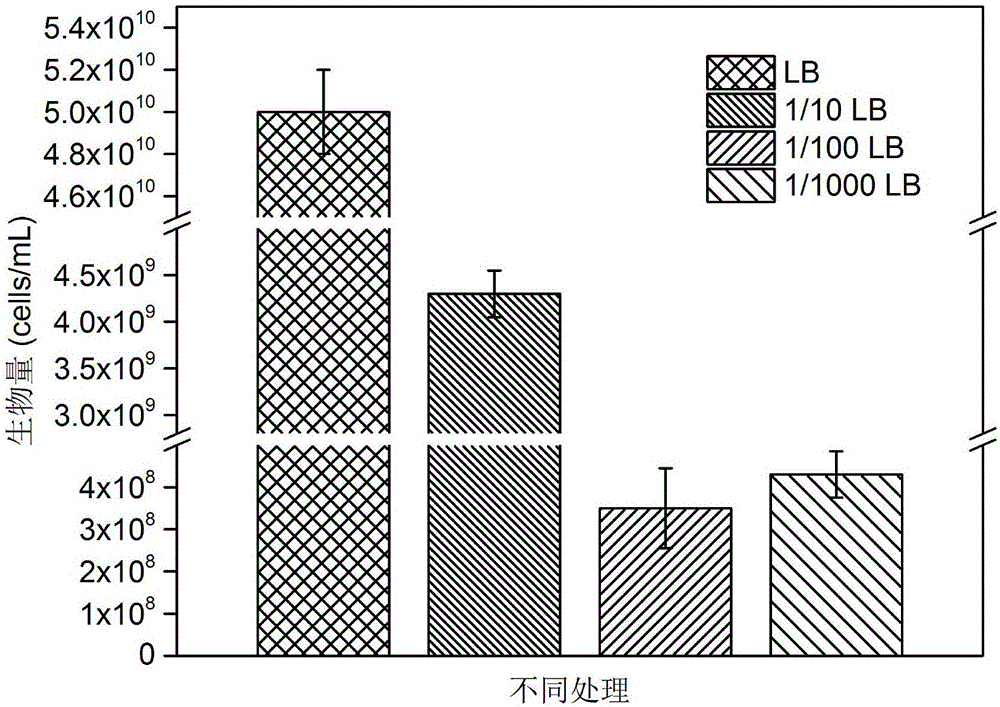
The invention discloses screening and application of a polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) degrading bacterium, and belongs to the technical field of biological treatment of environmental pollutants. The PBDEs degrading bacterium comes from soil contaminated by PBDEs and is obtained through artificial enrichment, separation and purification. The strain is a stenotrophomonas pavanii strain WZN-1 and is preserved in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center, the preservation date is August 30, 2016, and the preservation serial number is CGMCC No.12918. The WZN-1 strain is a Gram-negative bacterium, is faint yellow and presents a milk white and non-transparent circular bacterial colony with the surface raised; in a scanning electron microscope, the bacterium is in a rod shape, and the diameter is (0.5-0.7) micrometer*(1-2) micrometer. In a liquid culture medium, the strain has the good degrading capability on both decabromodiphenyl ether (BDE 209) and tetrabromodiphenyl ether (BDE 47).
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Pyrethroid pesticide degrading bacteria and bactericide thereof
InactiveCN101974453ASolve usabilityEfficient solutionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesWrinkle skinGram
The invention discloses pyrethroid pesticide degrading bacteria and a bactericide thereof, belonging to the field of biological high-tech. The adopted strain ZS-S-01 is identified as Stenotrophomonas sp. with the preservation number of CCTCC M 2010095, wherein, the Genbank registry number of the 16S rDNA of the strain is HM016874. The main biological characteristics are as follows: the strain is Gram-negative and has multiple polar flagellum and cells in a short rod shape; and the bacterial colony is milky white and slight yellowish, thicker and non-transparent, the diameter is 0.5mm-1mm, the edge is regular and orderly, the middle part is slightly protruding, and the surface is smooth and bright without wrinkles. The bactericide of the invention has the advantages of low production cost, convenient use and good degradation effect, thus being applicable to the national fruit and vegetable production and export bases or places with green food brand marks at a large area. The bactericide is of great significance to promoting production of nuisance-free vegetables and green food.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Stenotrophomonas and application thereof as well as microorganism bacterium agent
ActiveCN109401997AReduce pollutionPromote degradationBacteriaWater contaminantsMicroorganismNitrate nitrogen
The invention relates to stenotrophomonas. The strain is stenotrophomonas (Stenotrophomonas sp.) DB-2 and is preserved in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (CGMCC); the preservation number is CGMCC No.16355. The DB-2 strain can be used for rapidly degrading nitrate nitrogen under the condition that the bacterium concentration is relatively low after the strain passes througha short adaptive phase; the preparation cost of a microorganism bacterium agent is reduced when the strain is industrially applied and the sewage treatment effect is not influenced; a good denitrification effect can be realized under the condition that the C / N ratio is 4; a few of carbon sources are used and the additional carbon source cost of sewage denitrification treatment is saved; a denitrification process of the DB-2 strain is complete and no intermediate harmful gas including NO and, N2O and the like is not generated, so that the environment pollution is small.
Owner:中原环保股份有限公司
Stenotrophomonassp. H-4 and preparation method of degrading enzyme preparation thereof as well as application
The invention provides stenotrophomonassp. H-4 and a preparation method of degrading enzyme preparation thereof as well as application. The stenotrophomonassp. H-4 has been conserved in the conservation unit specified by the State Intellectual Property Office; the conservation date is February 1, 2013; the name of the conservation unit is China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center; and the conservation number is CGMCC No.7274. The stenotrophomonassp. H-4 can be grown on a culture medium with chlorothalonil as the unique carbon source and energy, and after being cultivated for 7 days, the degradation rate of the stenotrophomonassp. H-4 reaches 83.6%; the enzyme activity is 3.28 U and the degradation rate of the degrading enzyme to the chlorothalonil is 86% when the extraction conditions for crude enzyme in the stenotrophomonassp. H-4 are as follows: ultrasonic powder: 30 W; and ultrasonic time: 5 minutes. Obviously, the degrading enzyme preparation provided by the invention has bright application prospect in clearing away residual pesticides on vegetables and fruits.
Owner:上海阿斯沃特企业发展有限公司 +1
Efficient degrading strain for chlorothalonil, and application of efficient degrading strain in greenhouse soil environment
ActiveCN107916238AReduced genotoxicityLow costBacteriaContaminated soil reclamationEcological environmentGreenhouse soil
The invention relates to a degrading strain BJ1 capable of efficiently degrading a bactericide-chlorothalonil, and application of the degrading strain in greenhouse soil environment, belonging to thetechnical field of biodegradation. The degrading strain is identified as stenotrophomonas acidaminiphila and has a strain preservation number of CCTCC No. M2011475. The strain can use the chlorothalonil as an only carbon source; after the degrading strain is cultured in an inorganic salt culture solution for seven days, the degradation rate of the 50mg / L chlorothalonil can reach 93.2%. In the high-temperature and high-humidity greenhouse environment, the application of strain BJ1 can promote the degradation of the chlorothalonil in the soil, and the degradation rate can be increased by 45.6%;furthermore, the strain BJ1 can significantly reduce chlorothalonil-induced soil genotoxicity. The degrading stain is mainly used for the biological purification of chlorothalonil residues in the soil, especially in the soil in the greenhouse environment, thus reducing the harm, caused by the chlorothalonil, to the environment, and realizing functions of repairing the chlorothalonil-contaminated soil and protecting the ecological environment.
Owner:QINGDAO AGRI UNIV
Stenotrophomonas FQ1 strain and its screening method and use
ActiveCN103695333AEfficient degradationReduce manufacturing costBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementScreening methodBiological activation
The invention belongs to the technical field of microorganism and especially relates to a stenotrophomonas FQ1 strain and its screening method and use. The stenotrophomonas FQ1 strain has the accession number of CGMCC No.8272. A use method of the stenotrophomonas FQ1 strain for enteromorpha prolifera enzymolysis comprises the following steps of carrying out activation culture on the frozen stenotrophomonas FQ1 strain by a LB slant culture medium, picking a full ring of the culture, putting it into a LB liquid culture medium, carrying out shaking culture for 24-28h, taking 1-2mL of the bacterial solution, putting the bacterial solution into a sterilized cellulose liquid fermentation medium, carrying out shaking culture for 5-7 days, and carrying out low-temperature centrifugation on the fermentation broth and collecting a supernatant as a crude enzyme liquid, or filtering the fermentation broth and collecting the filtrate as a crude enzyme liquid; and carrying out a process of reaction of the crude enzyme liquid and clean enteromorpha prolifera powder at a temperature of 45-55 DEG C. The stenotrophomonas FQ1 strain has a cellulase production capability and can effectively degrade cellulose materials in enteromorpha prolifera into reducing sugar. A production cost is low, production equipment is simple, reaction conditions are mild, and the stenotrophomonas FQ1 strain is suitable for large-scale industrial production.
Owner:SHANGHAI OCEAN UNIV
Stenotrophomonas sp. HY-2 and application thereof in degradation of organic compounds
The invention discloses a new bacterial strain namely stenotrophomonas sp. (Stenotrophomonas sp.) HY-2 which is preserved in China Center for Type Culture Collection, the address of the China Center for Type Culture Collection is Wuhan University, Wuhan 430072, China, the preservation data is 26th, October, 2018, and the preservation number is CCTCC No: M 2018714. The bacterial strain disclosed bythe invention can grow and propagate by using organic compounds of ethyl acetate, butyl acetate and the like as a sole carbon source and energy, and substrates are mineralized into CO2 and H2O; underthe pure cultivation condition, the bacterium has better degradation capacity on the ethyl acetate and the butyl acetate when the pH is 6.0-8.0 and the temperature is in the range of 25-35 DEG C; andthe bacterial strain has high adaptive capacity to environment, and provides powerful guarantee for the engineering application of purification of ethyl acetate / butyl acetate exhaust gas and ethyl acetate / butyl acetate waste water by a biological method.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Efficient mixed flora for treating sludge
InactiveCN105624063AEfficient decompositionBacteriaSpecific water treatment objectivesSludgeStenotrophomonas sp.
The invention discloses efficient mixed flora for treating sludge which comprises comamonas testosteroni, pseudomonas alcaligenes, stenotrophomonas rhizophila, pseudomonas pseudoalcaligenes and azospirillum. The mixed flora can effectively decompose the sludge.
Owner:YUNNAN SHENGQING ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION TECH CO LTD
Siderophore high-yielding strain preparation and application of same in remediation of heavy metal contaminated soil
ActiveCN106434497AEfficient degradationPromote degradationBacteriaContaminated soil reclamationSoil heavy metalsStenotrophomonas sp.
The invention belongs to the field of environment pollution bio-remediation, and particularly relates to a siderophore high-yielding strain preparation and an application of the same in remediation of heavy metal contaminated soil. The siderophore high-yielding strain preparation contains a combination of Bacillus sp. bacteria S86, Pseudomonas sp. bacteria S17 and Stenotrophomonas rhizophila LD-6. The siderophore high-yielding strain preparation can be used for remediation of heavy metal contaminated soil of the farmland. The application is mainly used for reinforcing remediation of typical heavy metal contaminated soil of sweet sorghum.
Owner:ZHEJIANG FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
Degradable seedling growing pot with function of promoting plant growth, method for preparing degradable seedling growing pot and application thereof
ActiveCN107242045AComprehensive and balanced nutritionPromote germinationFungiBacteriaSludgePoultry manure
The invention provides a degradable seedling growing pot with a function of promoting plant growth, a method for preparing the degradable seedling growing pot and application thereof. A seedling growing pot composition comprises mixed biological substrates and compound bacterial sludge. The mixed biological substrates comprise 50-80 parts of crop straw, 5-8 parts of sawdust, 5-10 parts of livestock and poultry manure, 2-5 parts of grass carbon, 2-5 parts of weathered coal and 3-6 parts of soil; the compound bacterial sludge comprises Azospirillum spp., Azobacter spp., Bacillus spp., Paenibacillus spp., Massilia spp., Stenotrophomonas spp. and Lysobacterspp. The degradable seedling growing pot, the method and the application have the advantages that the germination rates of plants can be increased by the degradable seedling growing pot prepared from the seedling growing pot composition, balanced nutrition required during growth can be supplied to seedlings, pathogenic microorganisms can be resisted, and accordingly the degradable seedling growing pot is favorable for strong seedlings.
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Composite microbial agent, and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN110551652ALow toxicityReduced ability to migrateBacteriaContaminated soil reclamationMicroorganismPseudomonas tolaasii
Owner:RES CENT FOR ECO ENVIRONMENTAL SCI THE CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Microbial agent for preventing and controlling brown spot of tobaccos and preparation method of microbial agent
The invention discloses a mixed microbial agent for preventing and controlling brown spot of tobaccos and a preparation method of the mixed microbial agent, and belongs to the technical field of biological pesticide. The mixed microbial agent comprises 15-25% of Achromobacter, 5-15% of Enterobacter sp., 5-15% of Ochrobactrum sp., 40-60% of Stenotrophomonas sp. and 5-15% of Bacillus subtilis. The preparation method of the mixed microbial agent comprises the step of preparing the composite microbial agent from the Achromobacter, Enterobacter sp., Ochrobactrum sp., Stenotrophomonas sp. and Bacillus subtilis at a volume ratio, and the application mode of the microbial agent comprises the steps: adopting spray application, and spraying the microbial agent to both sides of leaves. It is proved through experiments that the prepared microbial agent has a high inhibitory effect on pathogenic bacteria of tobacco brown spot, and a good disease prevention effect on tobacco brown spot is achieved;and the microbial agent has low cost, a good effect and environmental protection, and therefore good prospects for biopesticide development are achieved.
Owner:CHINA TOBACCO CENTRAL SOUTH AGRICULTURAL EXPERIMENTAL STATION +1
Stenotrophomonas M12 for degrading unsymmetrical dimethylhydrazine (UDMH) and method for degrading UDMH
InactiveCN102367427AImprove degradation rateBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMicrobiologyStenotrophomonas sp.
Owner:LOGISTICS DEPT ANTIEPIDEMIC ARMY OF THE GENERAL ARMAMENT DEPT PLA
Microbial agent for hexavalent chromium pollution treatment and hexavalent pollution treatment method
The invention relates to the technical field of microbial remediation of heavy metal chromium in environment, particularly to a microbial agent for hexavalent chromium pollution treatment. The effective component of the microbial agent is (stenotrophomonas acidaziphi) 4-1 or fermentation liquor of (stenotrophomonas acidaziphi) 4-1.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Stenotrophomonas capable of improving herbicide resistance in soybeans, method for preparing same and application thereof
The invention relates to stenotrophomonas maltophilia sneb 42, which is capable of inducing soybeans to generate atrazine resistance when used for treating soybean seeds, a method for preparing the same and application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of microbial pesticides. The bacterial strain of sneb 42 was preserved in the General Microbiological Culture Collection Center of China Committee for Culture Collection of Microorganisms on February 1st, 2010. The preservation number is CGMCC No. 3620. The stenotrophomonas is prepared by liquid fermentation culture, and when metabolites of the stenotrophomonas are used for treating soybean seeds, the soybean seeds can generate the atrazine resistance while germinating. After the soybeans are treated by the metabolites of the stenotrophomonas, the soybeans can be co-planted with gramineae plants such as corns, and all plants can be weeded by using the uniform atrazine herbicide, so that the problem that the weeding problem in the intercropping between corns and soybeans is solved. The stenotrophomonas and the method have promising application and development prospects.
Owner:SHENYANG AGRI UNIV
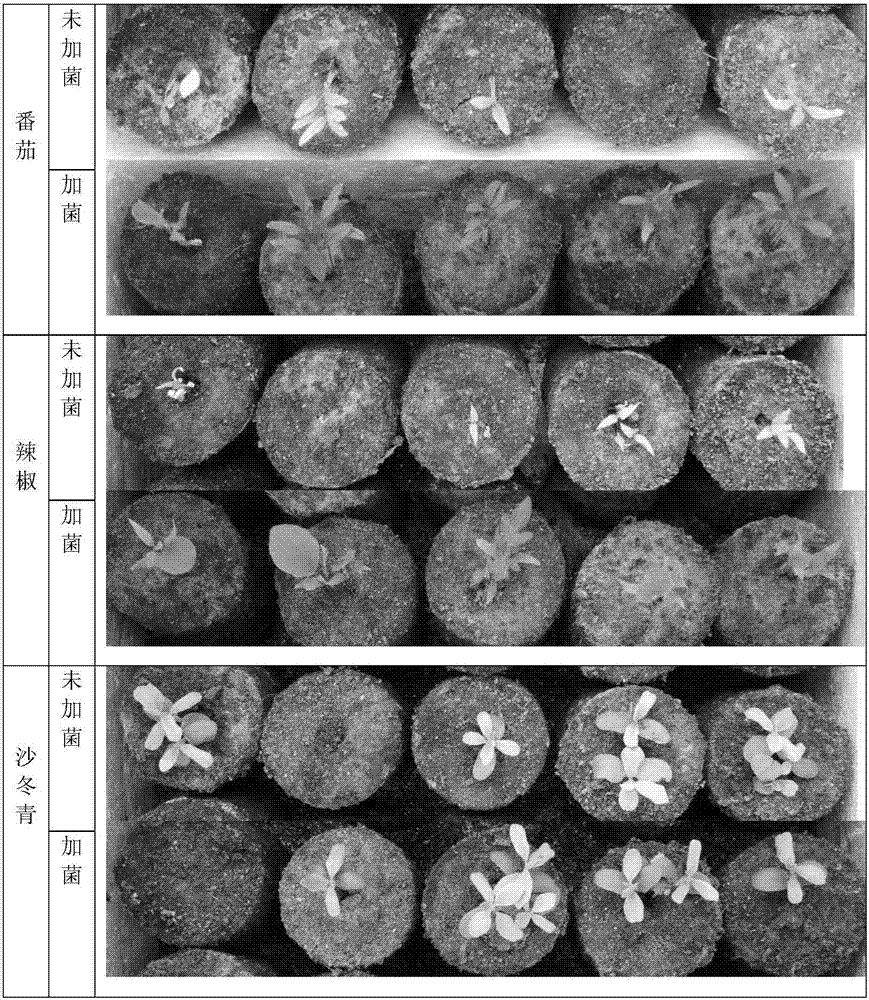
Stenotrophomonas for promoting growth and development of Lilium spp and/or antagonizing pathogenic bacteria of Lilium spp and application of stenotrophomonas
ActiveCN112592850AInhibitoryAntagonisticBiocidePlant growth regulatorsBiotechnologyStenotrophomonas rhizophila
The invention discloses stenotrophomonas for promoting growth and development of Lilium spp and / or antagonizing pathogenic bacteria of the Lilium spp and application of the stenotrophomonas. The stenotrophomonas is stenotrophomonas rhizophila, a strain number of the stenotrophomonas rhizophila is G44, and a registration number of the stenotrophomonas rhizophila in the China General MicrobiologicalCulture Collection Center is CGMCC No.20185. The stenotrophomonas has the characteristics of producing siderophore, producing indoleacetic acid, producing ACC deaminase and the like for promoting plant growth, and the growth and development of Lilium spp plants can be obviously optimized by inoculating the stenotrophomonas to the Lilium spp plants, namely, the growth of overground parts and underground parts of the Lilium spp is promoted, the flowering time of the Lilium spp is advanced, the reproductive growth period of the Lilium spp is prolonged, and the fresh weight of bulbs of the Liliumspp is increased. Meanwhile, the strain has an obvious inhibition or antagonism effect on the pathogenic bacteria of the Lilium spp, such as botrytis cinerea of the Lilium spp.
Owner:BEIJING AGRO BIOTECH RES CENT
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com