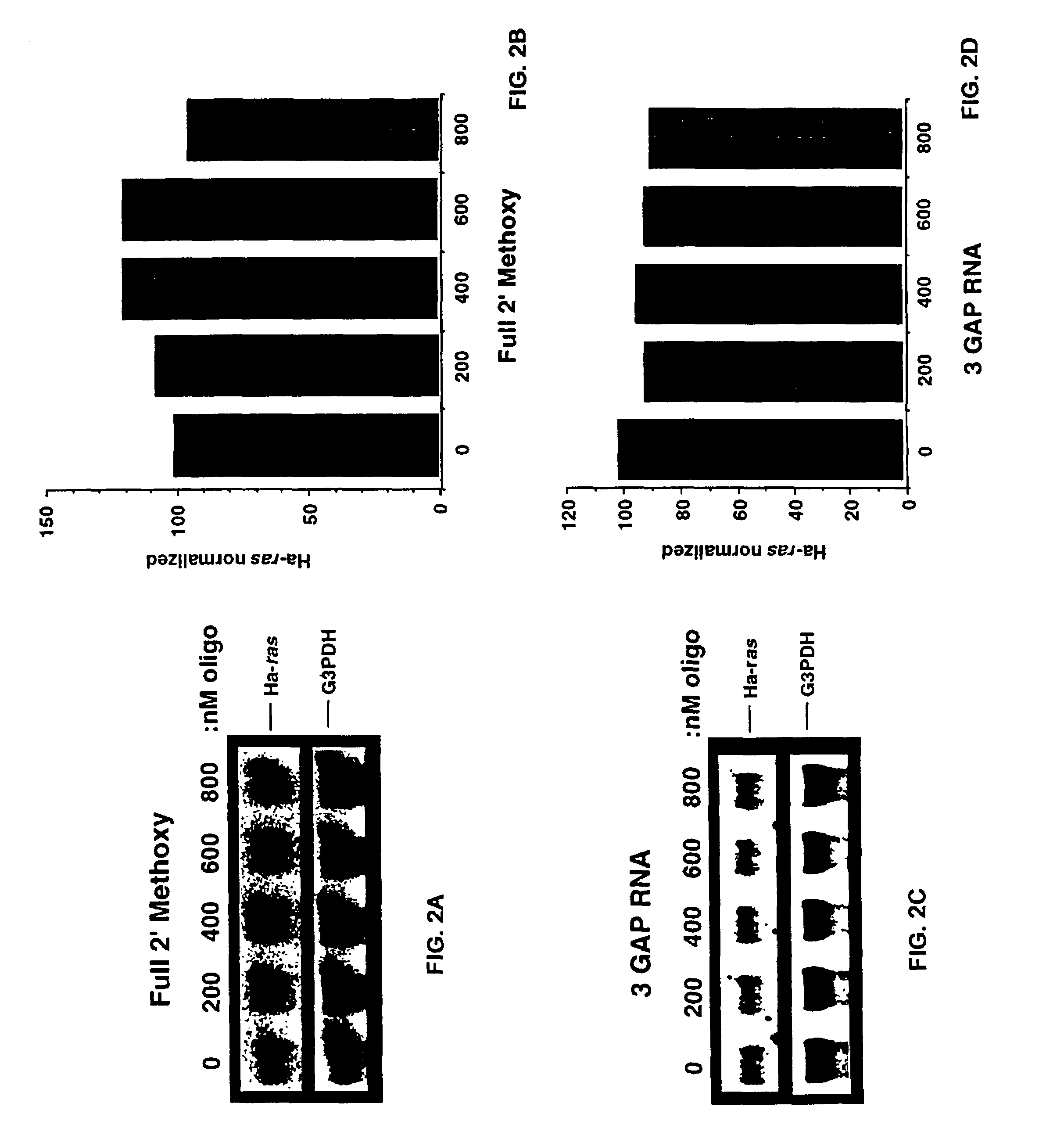
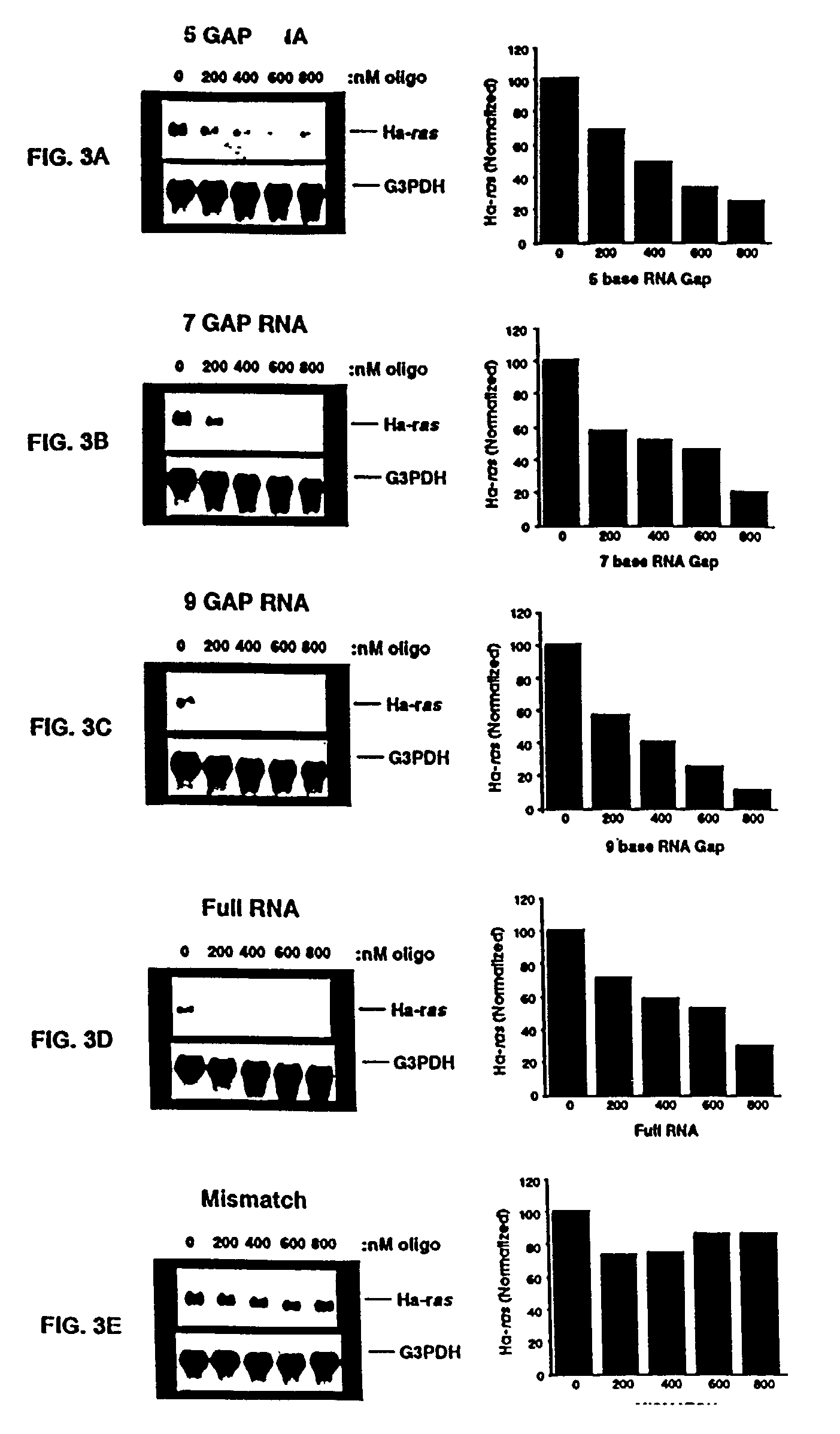
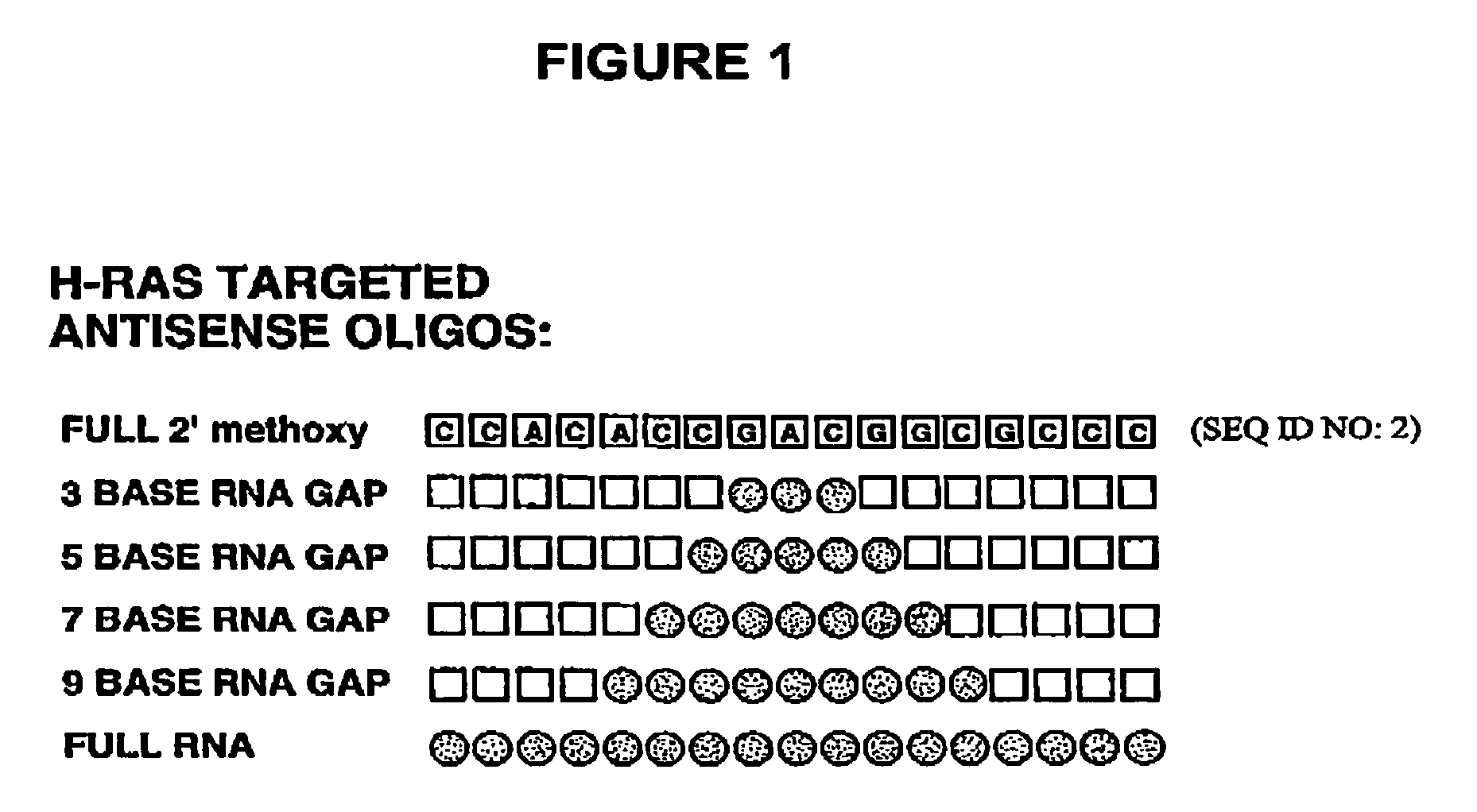
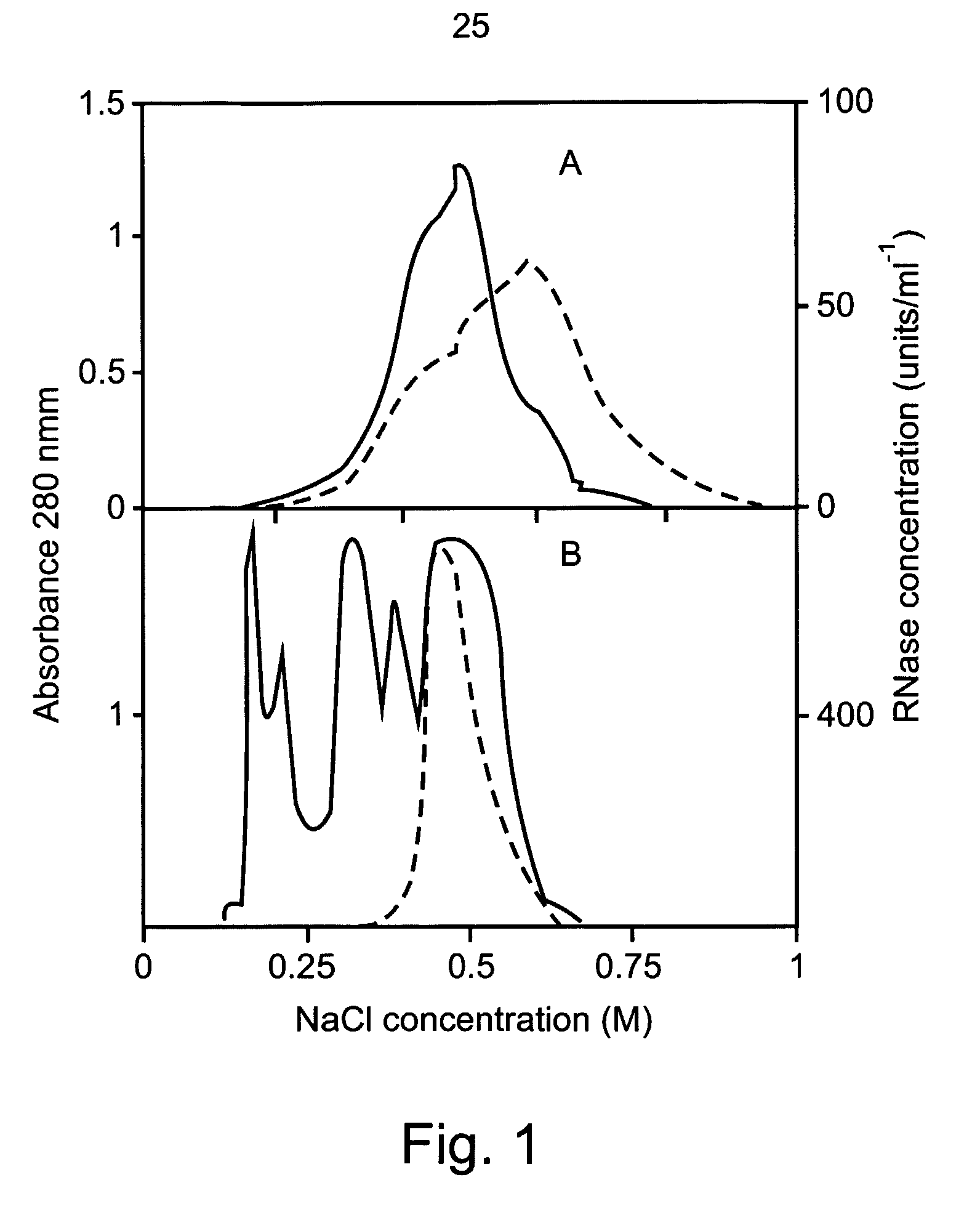
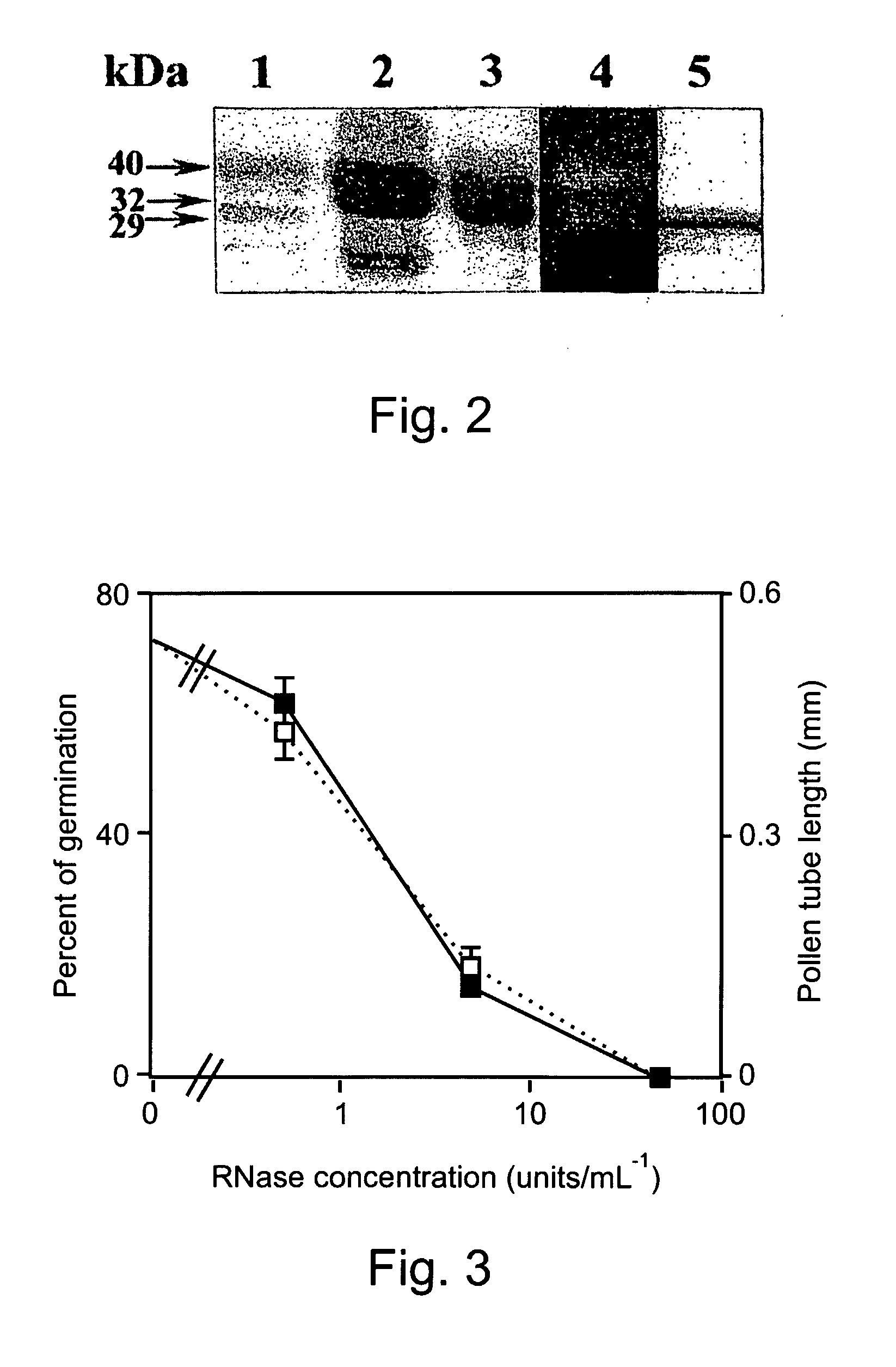
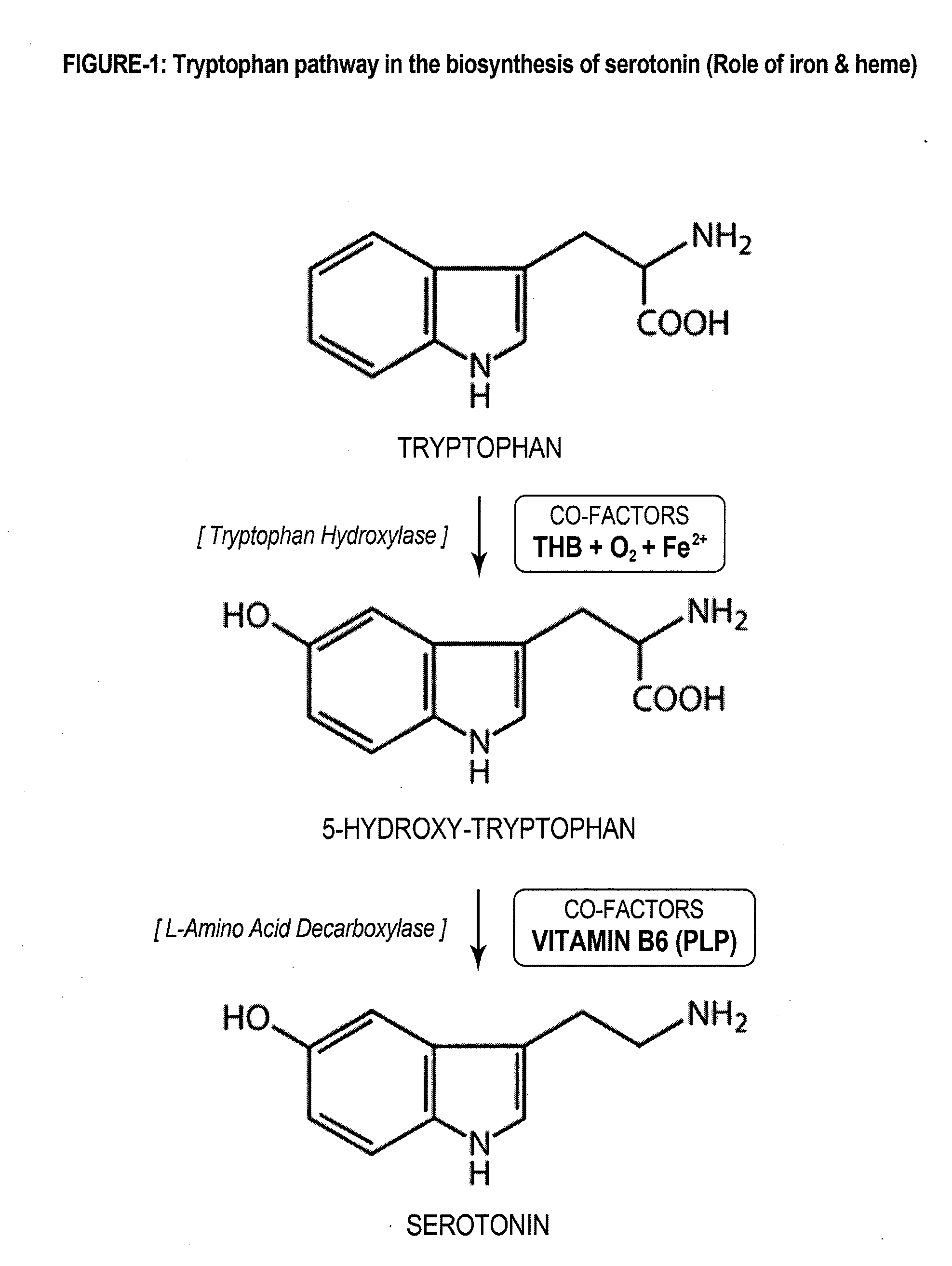
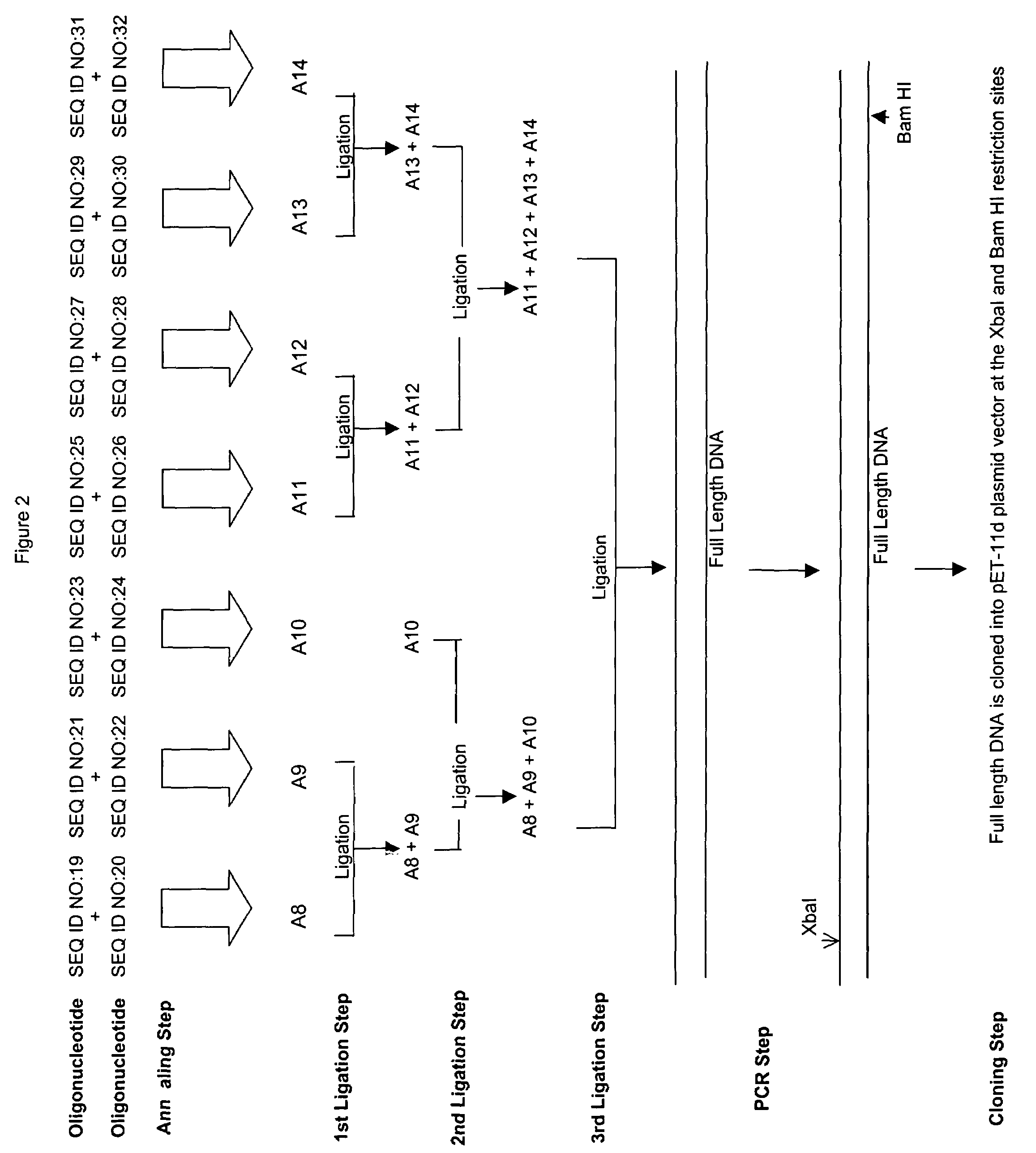
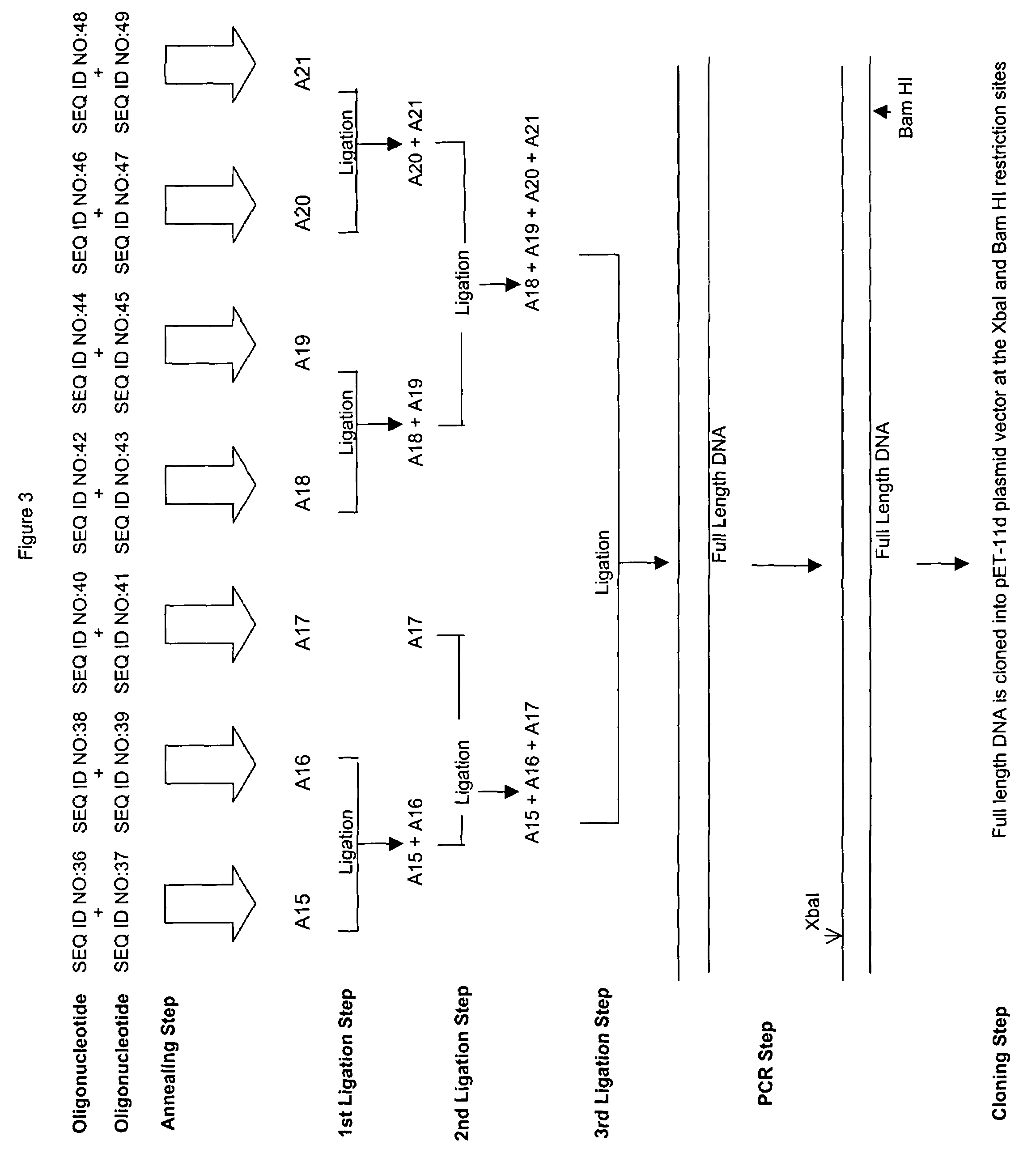
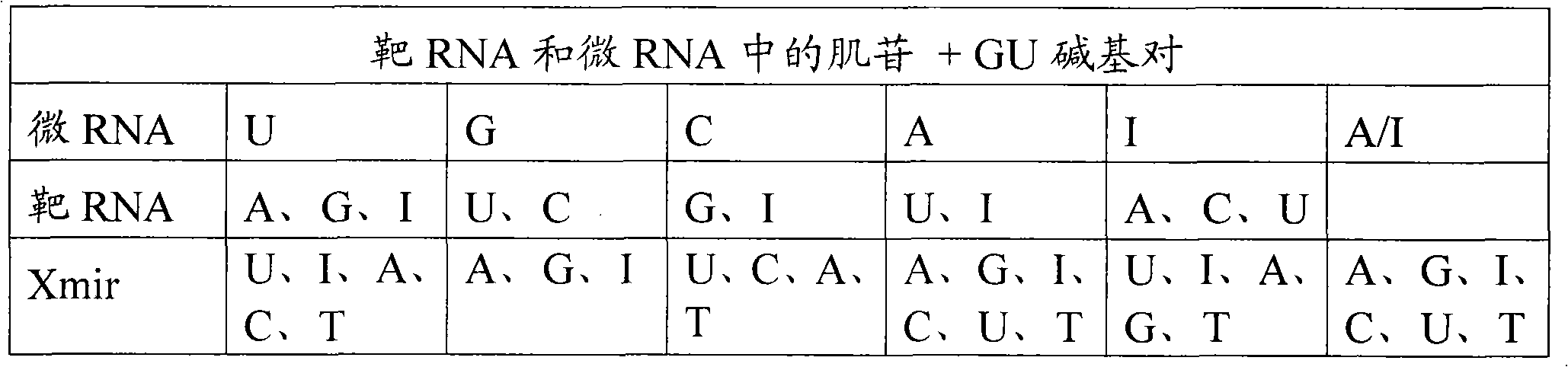
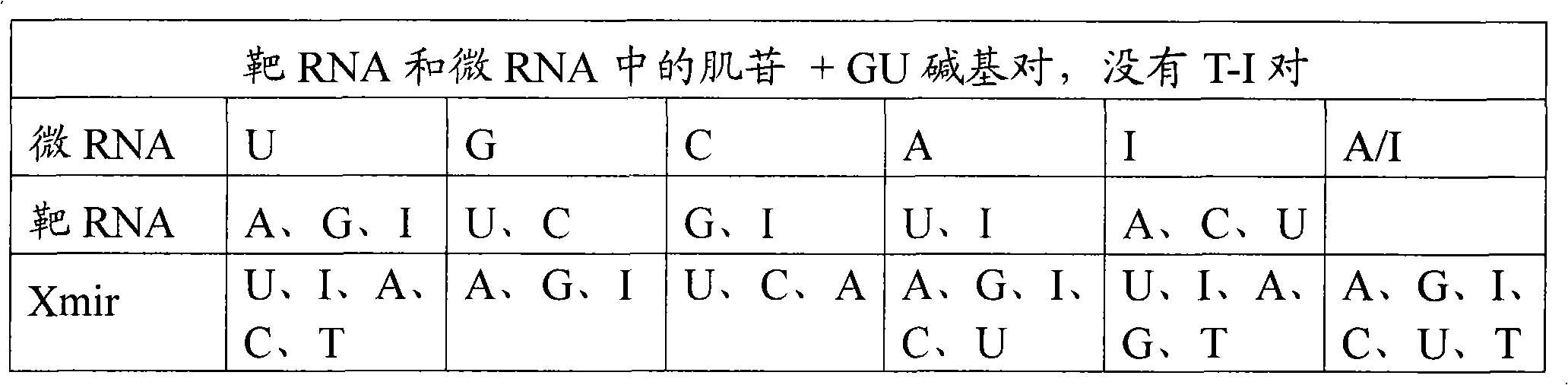
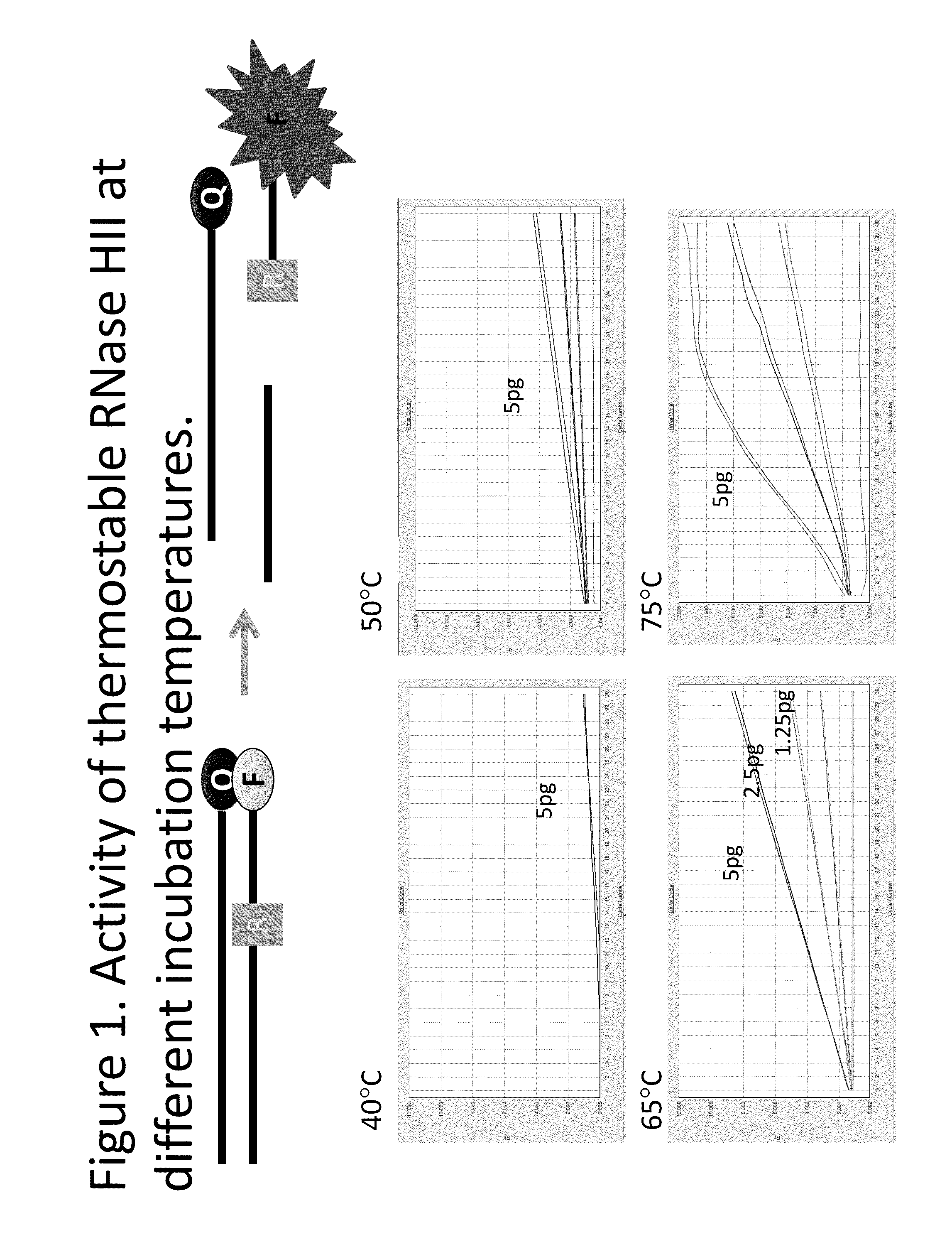
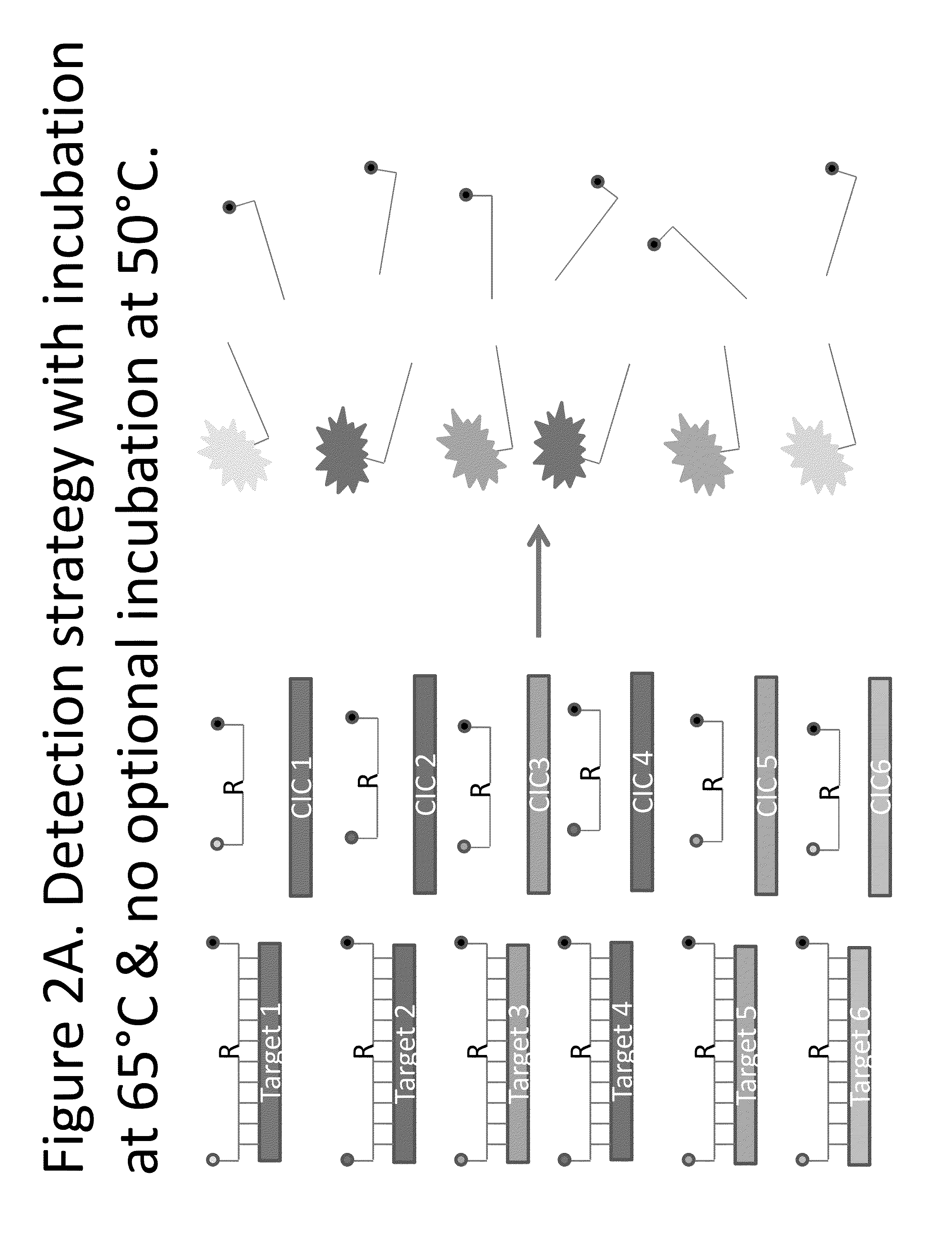
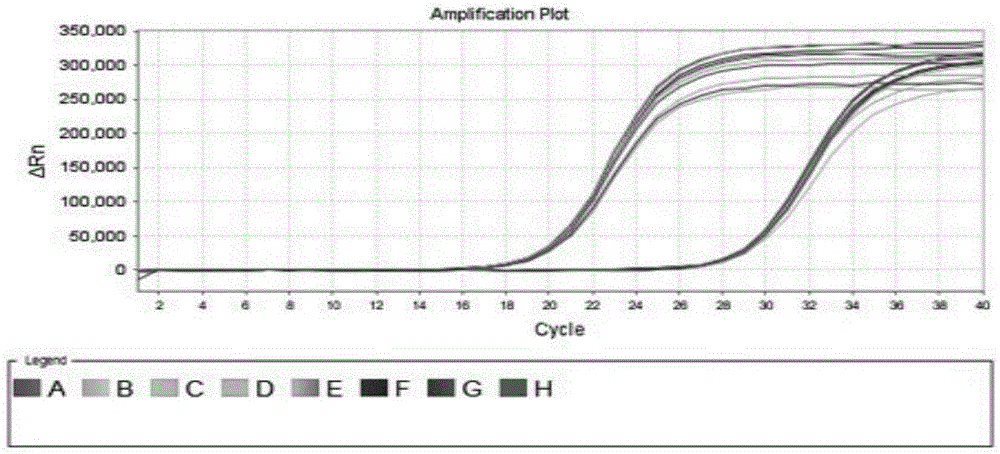
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
243 results about "Ribonuclease" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Ribonuclease (commonly abbreviated RNase) is a type of nuclease that catalyzes the degradation of RNA into smaller components. Ribonucleases can be divided into endoribonucleases and exoribonucleases, and comprise several sub-classes within the EC 2.7 (for the phosphorolytic enzymes) and 3.1 (for the hydrolytic enzymes) classes of enzymes.
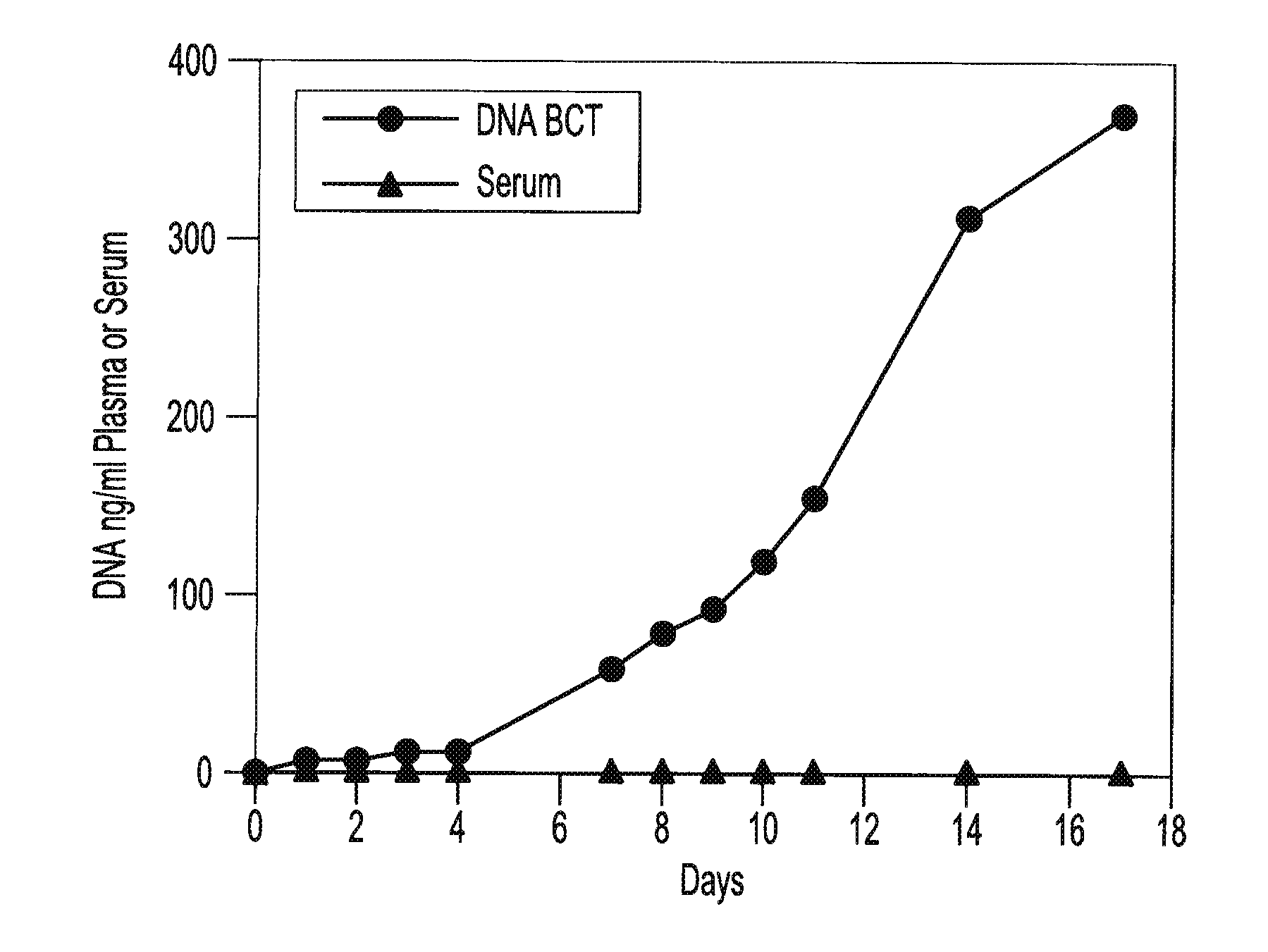
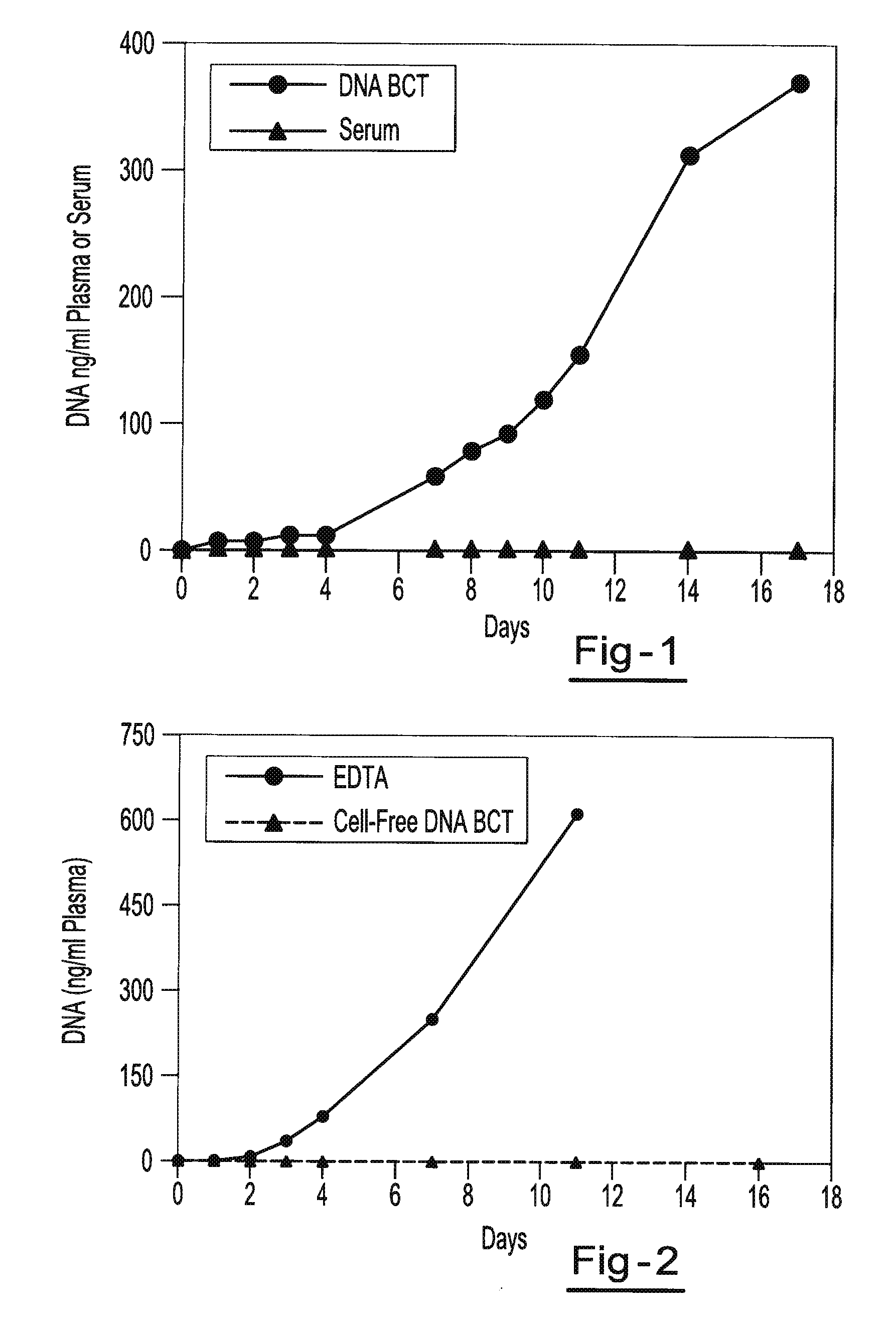
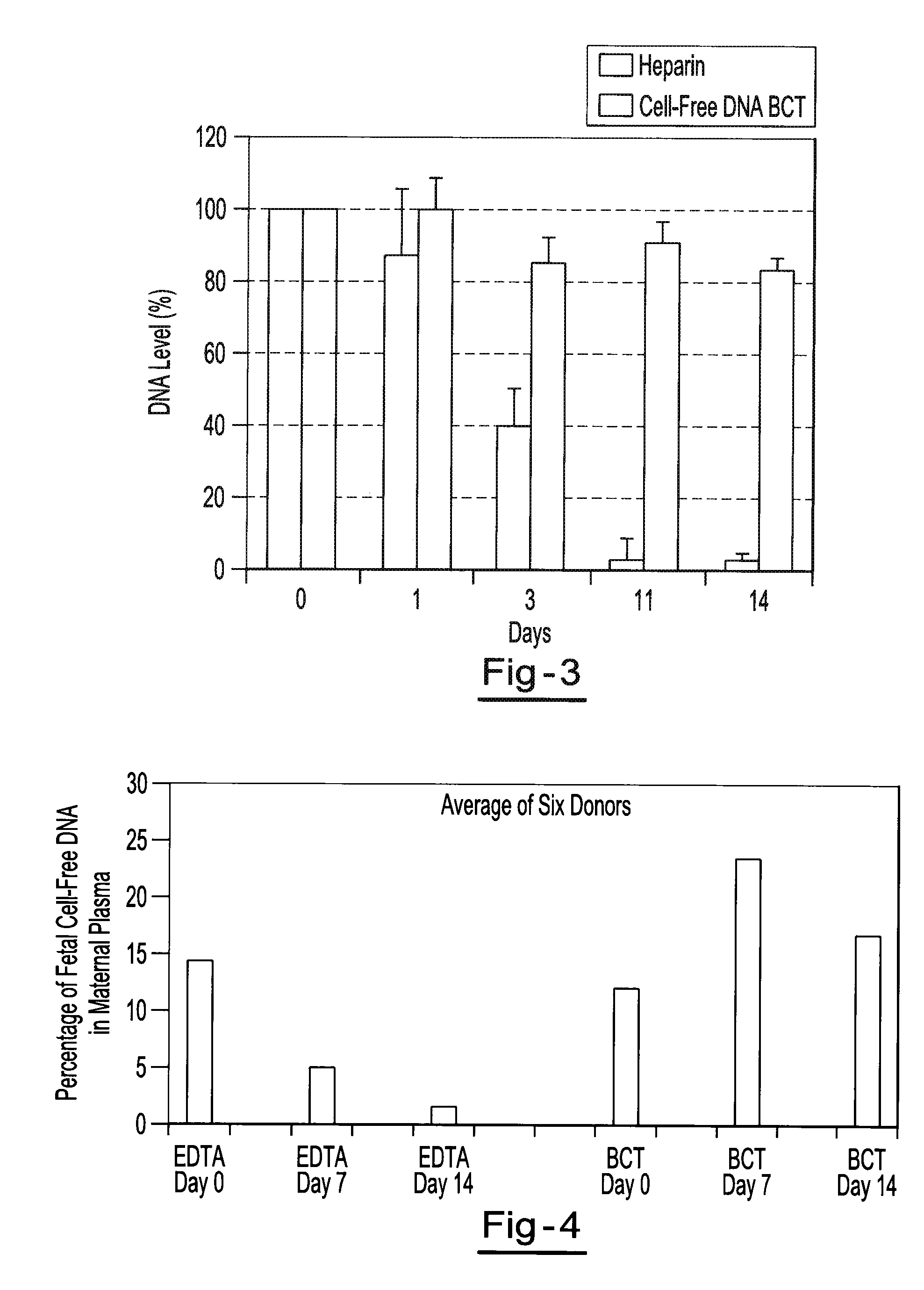
Preservation of fetal nucleic acids in maternal plasma
ActiveUS20100184069A1Maintain structural integrityInhibition releaseMicrobiological testing/measurementRibonucleaseLysis
A method for preserving and processing fetal nucleic acids located within maternal plasma is disclosed, wherein a sample of maternal blood containing fetal nucleic acids is treated to reduce both cell lysis of the maternal blood cells and deoxyribonuclease (DNase) and ribonuclease (RNase) activity within the fetal nucleic acids. The treatment of the sample aids in increasing the amount of fetal nucleic acids that can be identified and tested while maintaining the structure and integrity of the fetal nucleic acids.
Owner:STRECK LLC
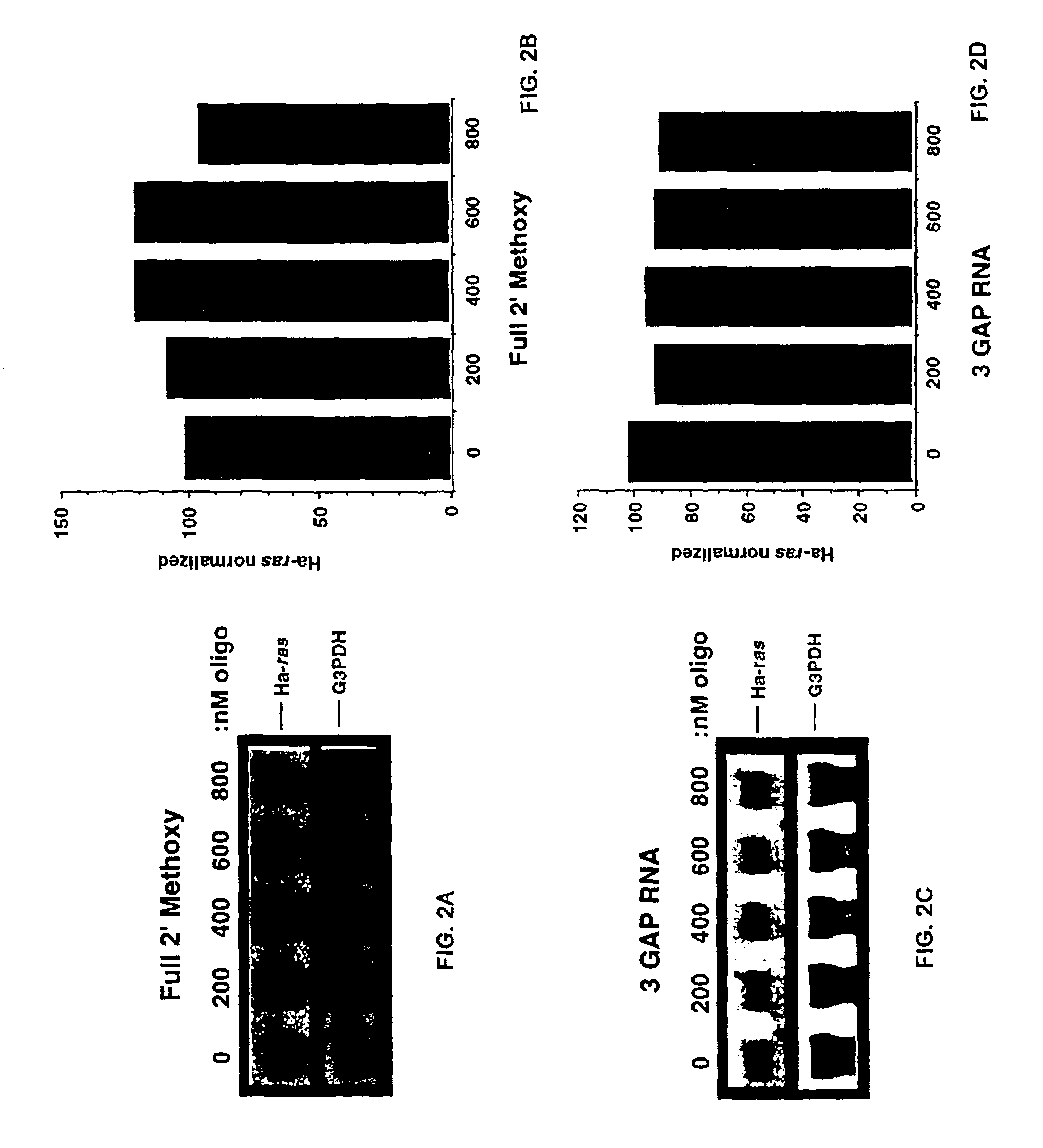
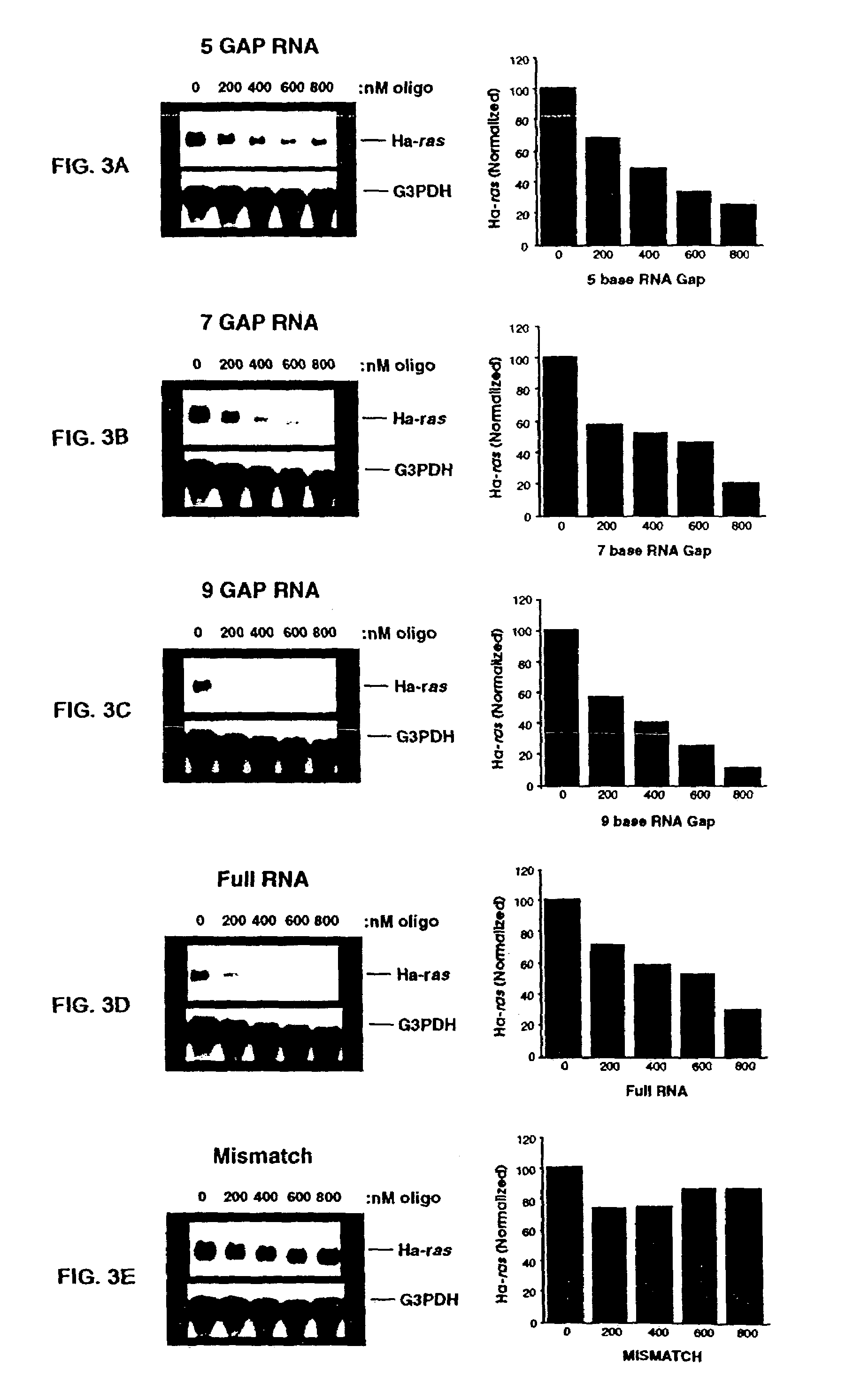
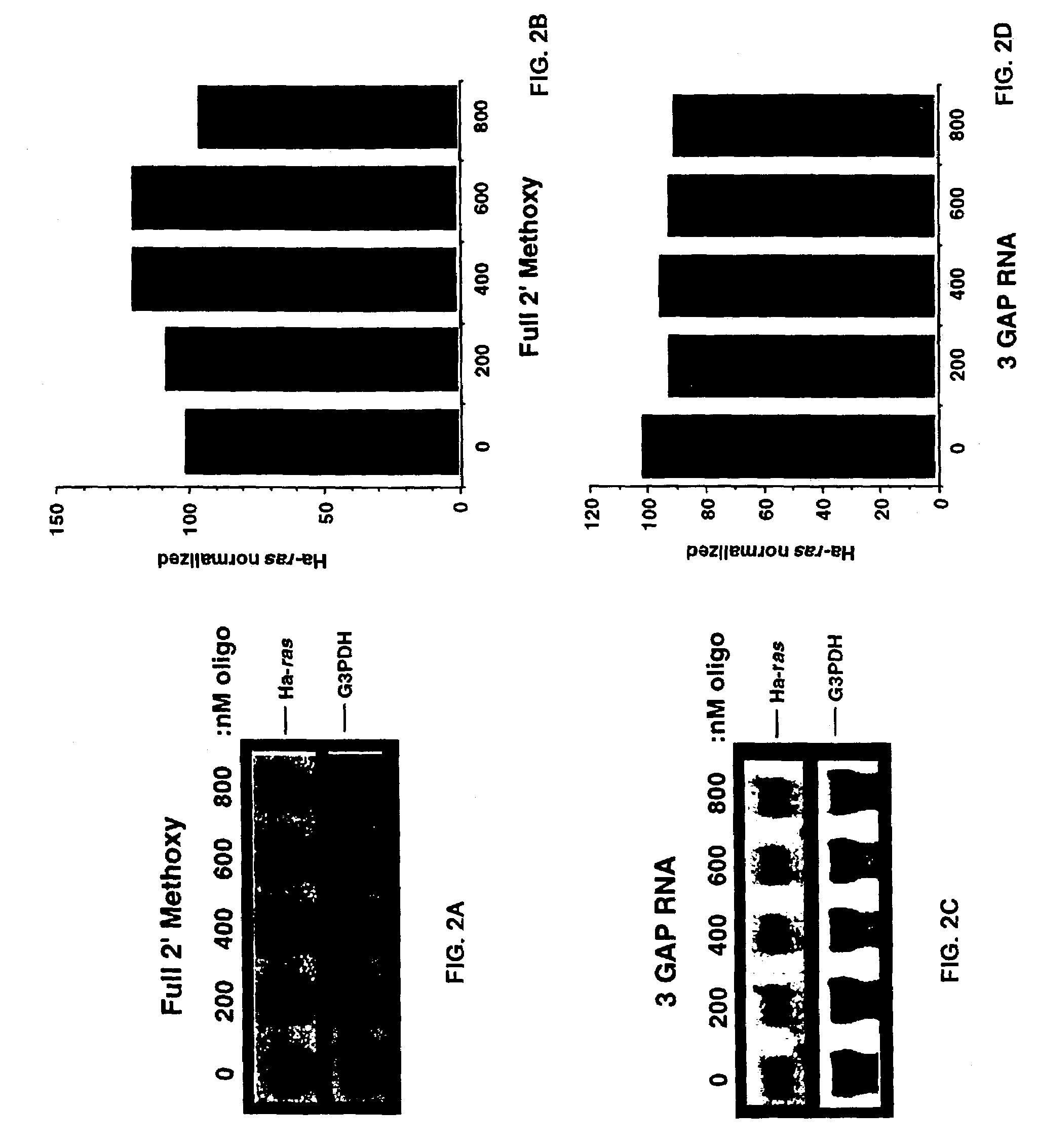
Oligoribonucleotides and ribonucleases for cleaving RNA
InactiveUS7432250B2High affinityStrong specificityHydrolasesPeptide/protein ingredientsOrganismResearch purpose
Oligomeric compounds including oligoribonucleotides and oligoribonucleosides are provided that have subsequences of 2′-pentoribofuranosyl nucleosides that activate dsRNase. The oligoribonucleotides and oligoribonucleosides can include substituent groups for increasing binding affinity to complementary nucleic acid strand as well as substituent groups for increasing nuclease resistance. The oligomeric compounds are useful for diagnostics and other research purposes, for modulating the expression of a protein in organisms, and for the diagnosis, detection and treatment of other conditions susceptible to oligonucleotide therapeutics. Also included in the invention are mammalian ribonucleases, i.e., enzymes that degrade RNA, and substrates for such ribonucleases. Such a ribonuclease is referred to herein as a dsRNase, wherein “ds” indicates the RNase's specificity for certain double-stranded RNA substrates. The artificial substrates for the dsRNases described herein are useful in preparing affinity matrices for purifying mammalian ribonuclease as well as non-degradative RNA-binding proteins.
Owner:IONIS PHARMA INC
RNase L activators and antisense oligonucleotides effective to treat RSV infections
The present invention relates to methods of inhibiting infection by RNA viruses with complexes of an activator of RNase L and an oligonucleotide that is capable of binding to the genome, antigenome or mRNAs of a negative strand RNA virus to specifically cleave the genomic or antigenomic RNA strand of the virus. In accordance with the present invention, the methods and complexes of the invention may be applied to target any negative strand RNA virus. The invention in one embodiment relates to a covalently linked complex of an oligonucleotide that is capable of binding to the genomic or antigenomic template RNA strand of a negative strand RNA virus and / or binding to an mRNA of a viral protein (an "antisense oligonucleotide") coupled to an activator of RNase L. In a preferred embodiment of the present invention, the oligonucleotide component of the complex is complementary to a region of the viral genomic RNA strand characterized by repeated or consensus sequences.
Owner:THE CLEVELAND CLINIC FOUND +1
Oligoribonucleotides and ribonucleases for cleaving RNA
InactiveUS7432249B2High affinityStrong specificityPeptide/protein ingredientsHydrolasesADAMTS ProteinsOrganism
Oligomeric compounds including oligoribonucleotides and oligoribonucleosides are provided that have subsequences of 2′-pentoribofuranosyl nucleosides that activate dsRNase. The oligoribonucleotides and oligoribonucleosides can include substituent groups for increasing binding affinity to complementary nucleic acid strand as well as substituent groups for increasing nuclease resistance. The oligomeric compounds are useful for diagnostics and other research purposes, for modulating the expression of a protein in organisms, and for the diagnosis, detection and treatment of other conditions susceptible to oligonucleotide therapeutics. Also included in the invention are mammalian ribonucleases, i.e., enzymes that degrade RNA, and substrates for such ribonucleases. Such a ribonuclease is referred to herein as a dsRNase, wherein “ds” indicates the RNase's specificity for certain double-stranded RNA substrates. The artificial substrates for the dsRNases described herein are useful in preparing affinity matrices for purifying mammalian ribonuclease as well as non-degradative RNA-binding proteins.
Owner:IONIS PHARMA INC
Oligoribonucleotides and ribonucleases for cleaving RNA
InactiveUS7629321B2High affinityStrong specificityHydrolasesPeptide/protein ingredientsOrganismResearch purpose
Oligomeric compounds including oligoribonucleotides and oligoribonucleosides are provided that have subsequences of 2′-pentoribofuranosyl nucleosides that activate dsRNase. The oligoribonucleotides and oligoribonucleosides can include substituent groups for increasing binding affinity to complementary nucleic acid strand as well as substituent groups for increasing nuclease resistance. The oligomeric compounds are useful for diagnostics and other research purposes, for modulating the expression of a protein in organisms, and for the diagnosis, detection and treatment of other conditions susceptible to oligonucleotide therapeutics. Also included in the invention are mammalian ribonucleases, i.e., enzymes that degrade RNA, and substrates for such ribonucleases. Such a ribonuclease is referred to herein as a dsRNase, wherein “ds” indicates the RNase's specificity for certain double-stranded RNA substrates. The artificial substrates for the dsRNases described herein are useful in preparing affinity matrices for purifying mammalian ribonuclease as well as non-degradative RNA-binding proteins.
Owner:IONIS PHARMA INC
Methods and compositions for the production of guide RNA
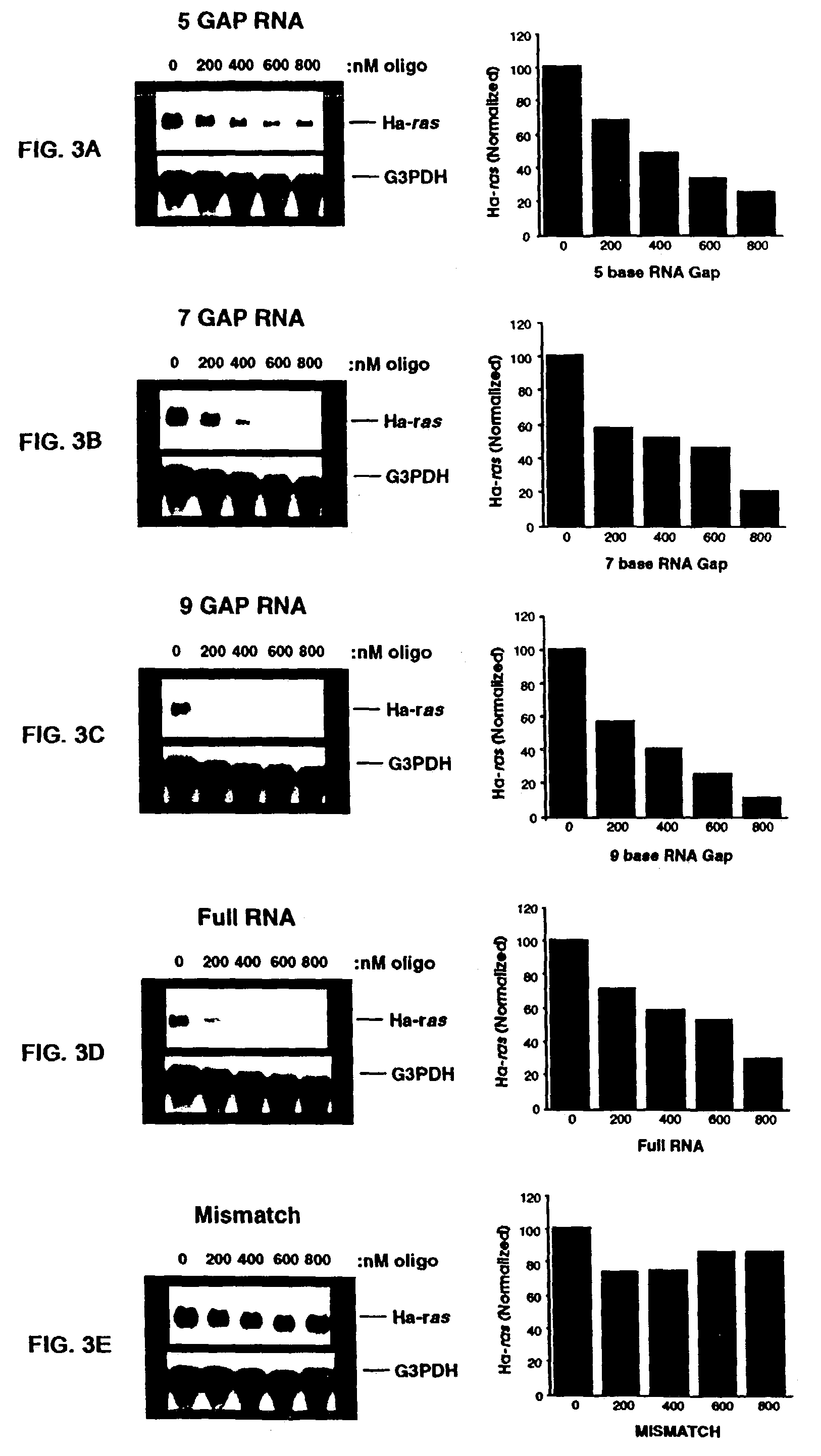
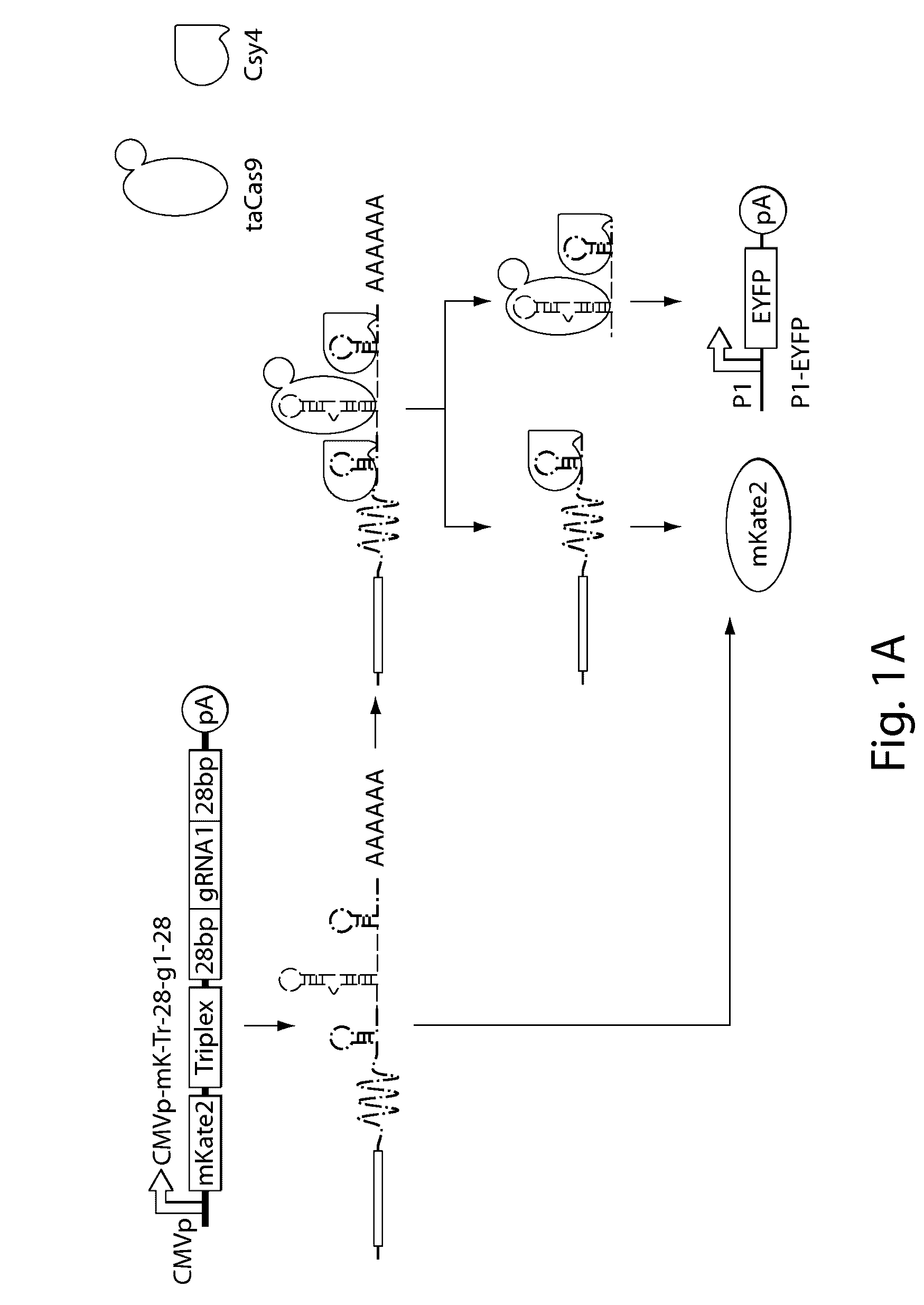
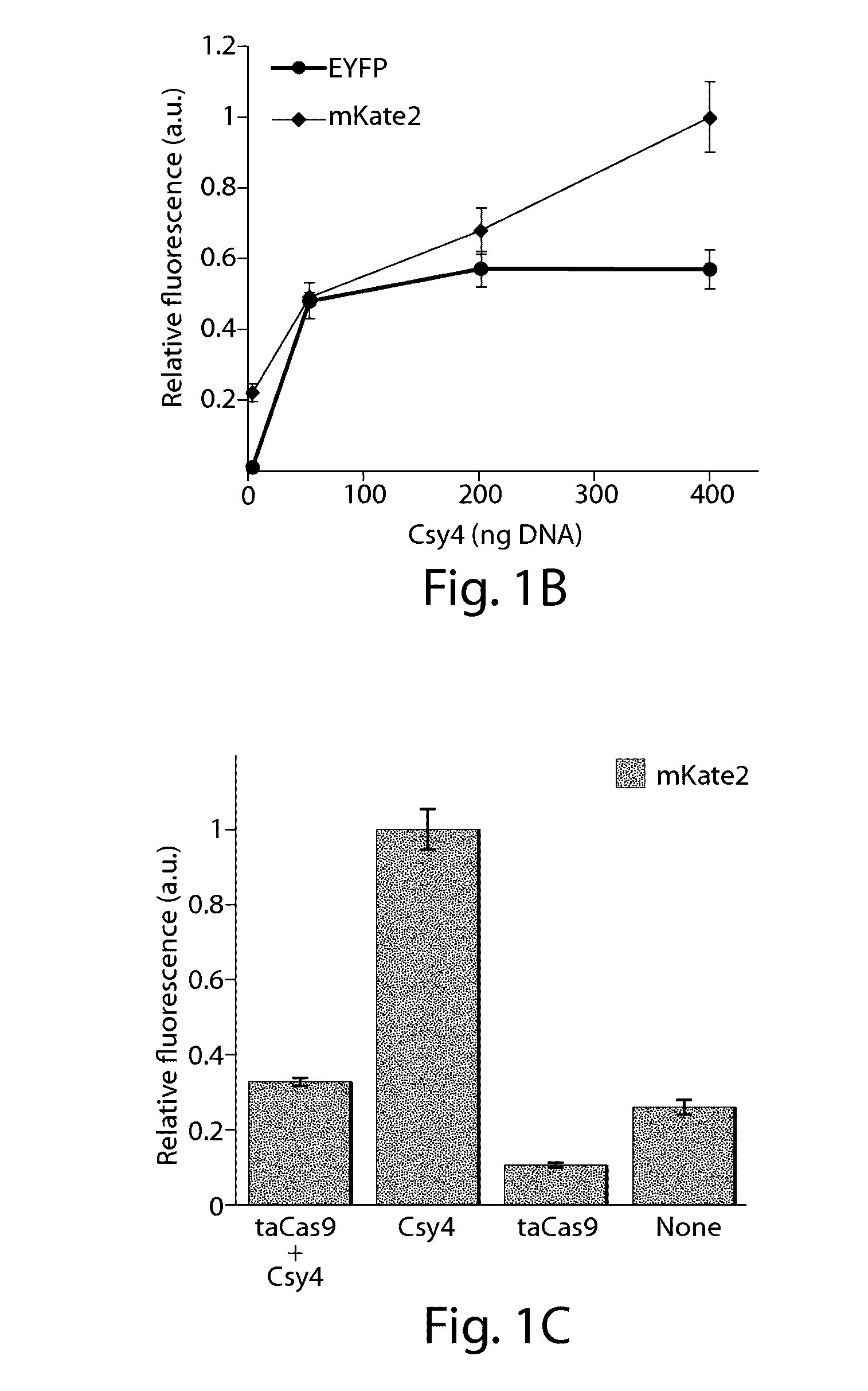
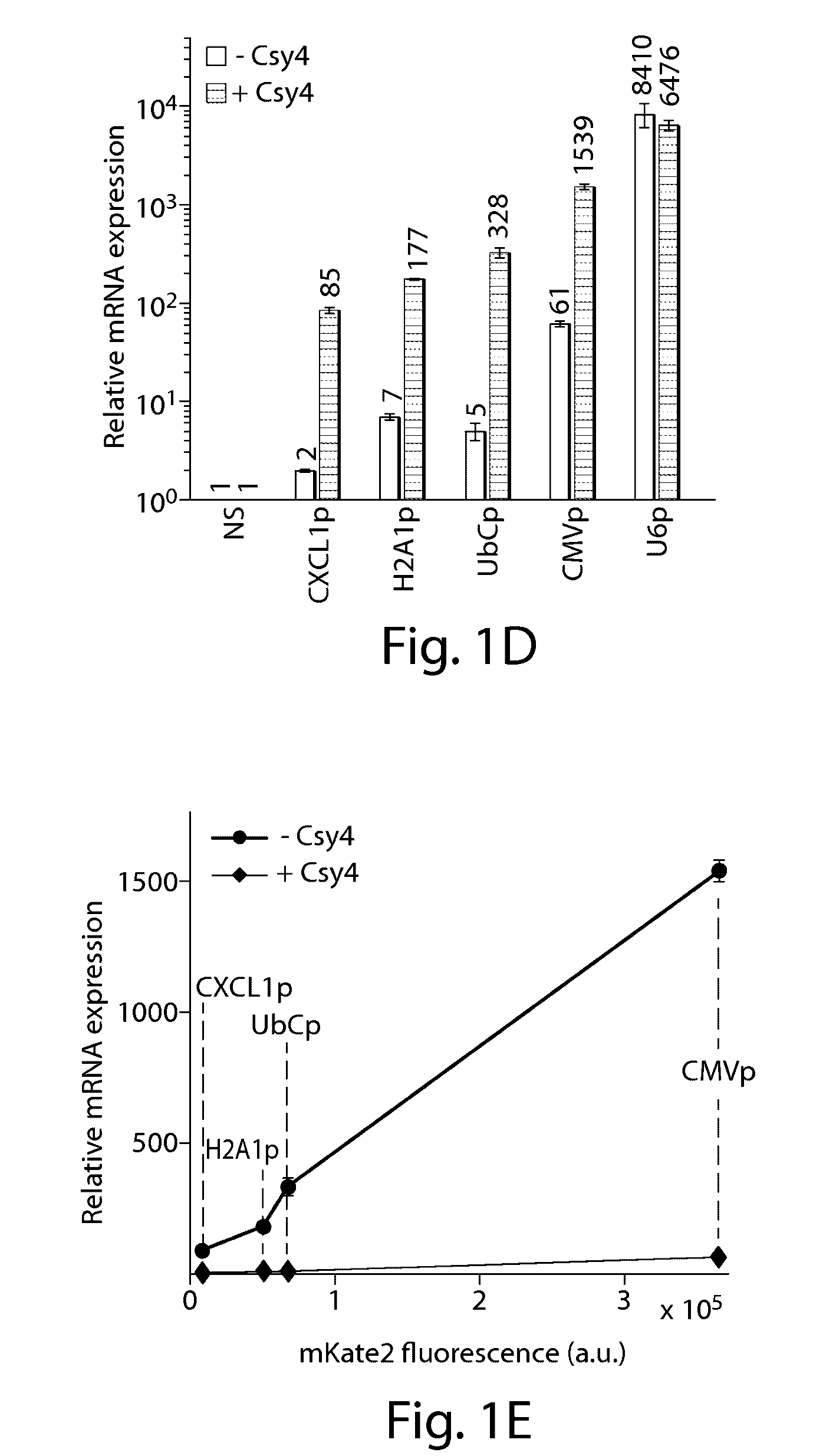
Various aspects and embodiments of the present disclosure relate to methods and compositions that combine multiple mammalian RNA regulatory strategies, including RNA triple helix structures, introns, microRNAs, and ribozymes with Cas-based CRISPR transcription factors and ribonuclease-based RNA processing in human cells. The methods and compositions of the present disclosure, in some embodiments, enable multiplexed production of proteins and multiple guide RNAs from a single compact RNA-polymerase-II-expressed transcript for efficient modulation of synthetic constructs and endogenous human promoters.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Microbial identification based on the overall composition of characteristic oligonucleotides
InactiveUS20050142584A1Create accuracyCreate speedMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganismBiological body
Identification of microorganisms based on the sequences of their 5S, 23S and particularly 16S ribosomal RNAs is growing in utility as the database of known ribosomal RNA sequences expands. Experimental identification is usually based on matching the experimentally-determined sequence of an organisms rRNA to a previously-determined sequence in the databank, or hybridization of the organisms rRNA or encoding rDNA to an oligonucleotide probe specific for an organism anticipated to be present in the sample. Here we propose the identification of microorganisms based on the overall composition (not sequence or hybridization propensity) of characteristic molecules derived from their rRNA or rDNA sequences by enzymatic cleavage or localized amplification. Ribonuclease T1 fragments of rRNA composition determination by mass spectrometry are especially favored. The characteristic molecules used can be chosen to be “compositional signatures” whose presence / absence is known to be associated with particular groups of organisms.
Owner:JACKSON GEORGE W
Method for treating oncological diseases
ActiveUS7612032B2Promote growthImprove efficiencyPeptide/protein ingredientsHydrolasesDiseaseWhole body
A method to treat solid tumors and other oncological diseases consists of parenterally injecting an agent which destroy's blood's extracellular DNA into the systemic blood circulation of a cancer patient to slow down malignant. The agent is embodied in the form of a DNAse enzyme and, more particularly, as a bovine pancreatic DNAse. Doses from 50,000-250,000,000 Kunz units / day are injected for 5-360 days. A binding agent or an agent that modifies the chemical composition of the blood extracellular DNA is additionally injected into the blood. This modifying agent is preferably an enzyme-ribonuclease.
Owner:CLS THERAPEUTICS
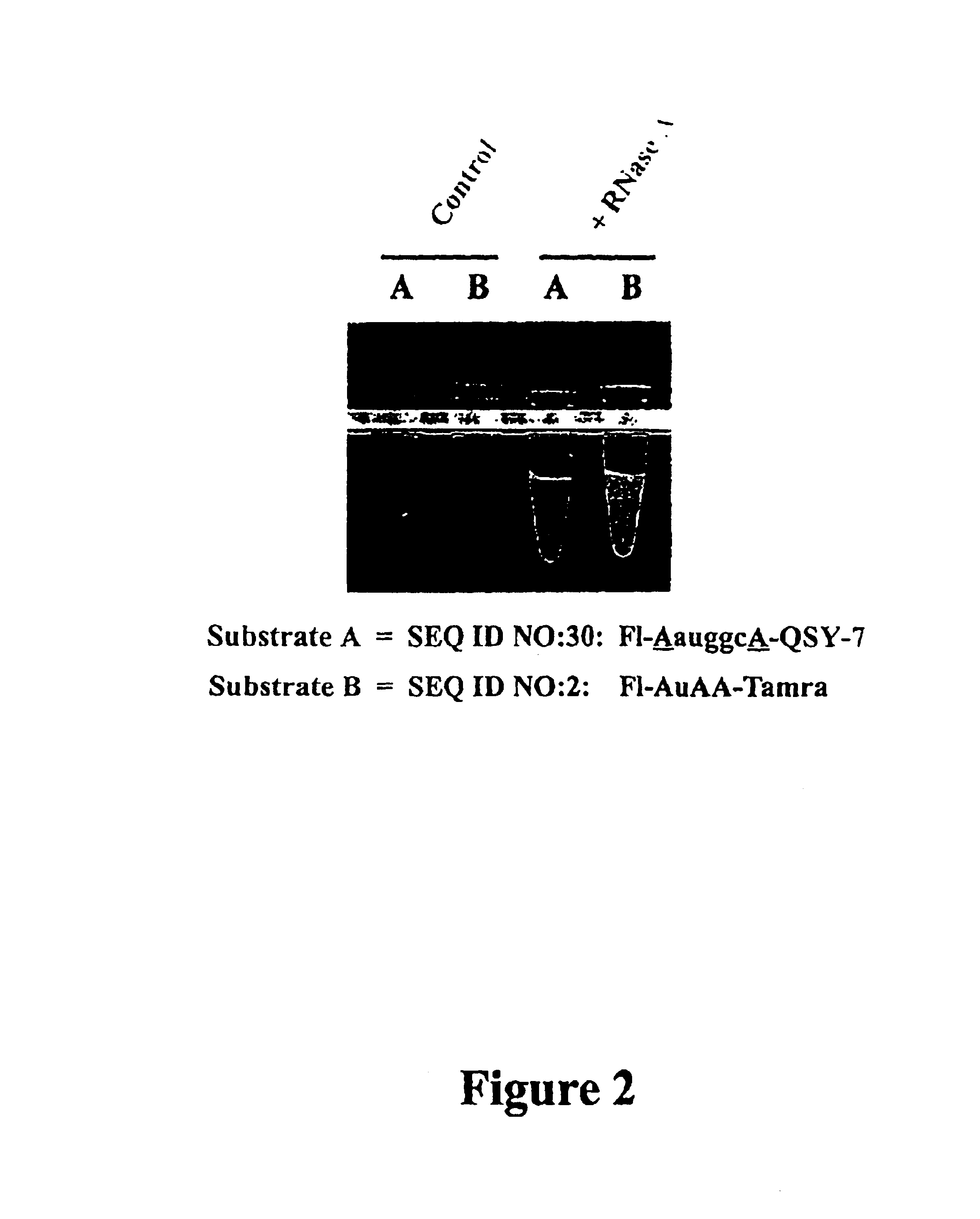
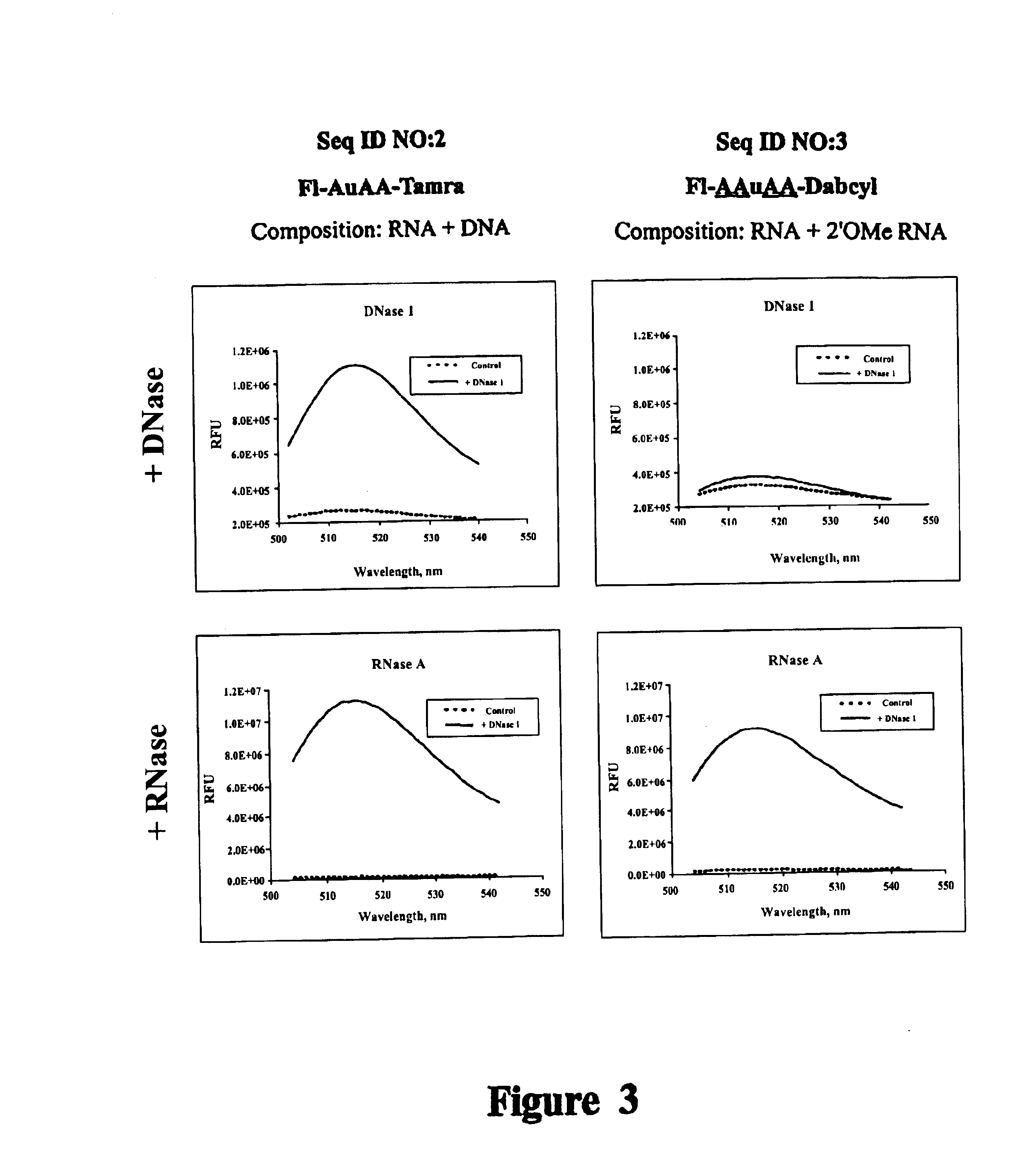
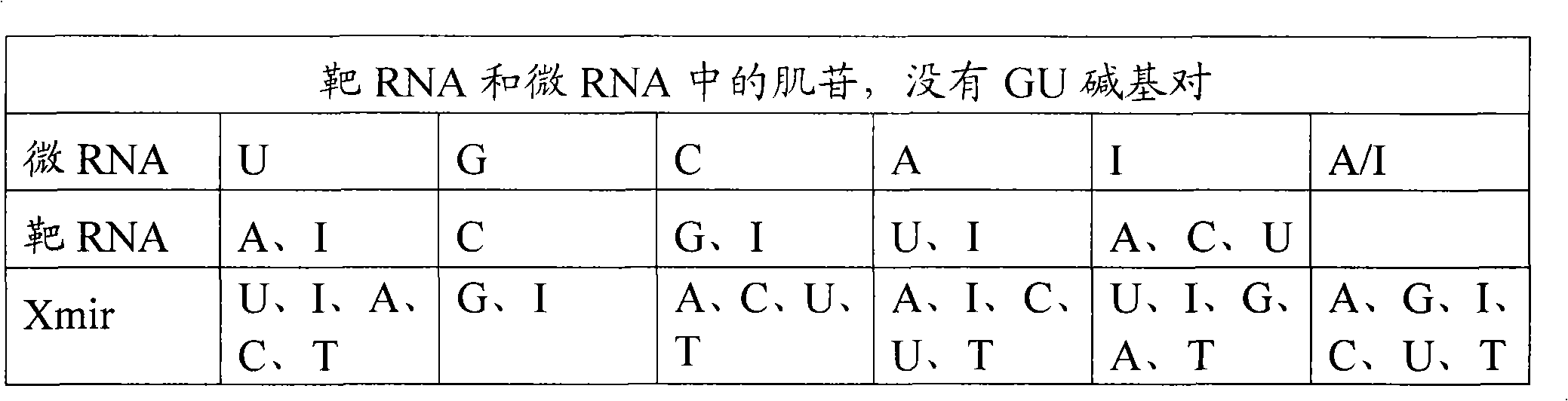
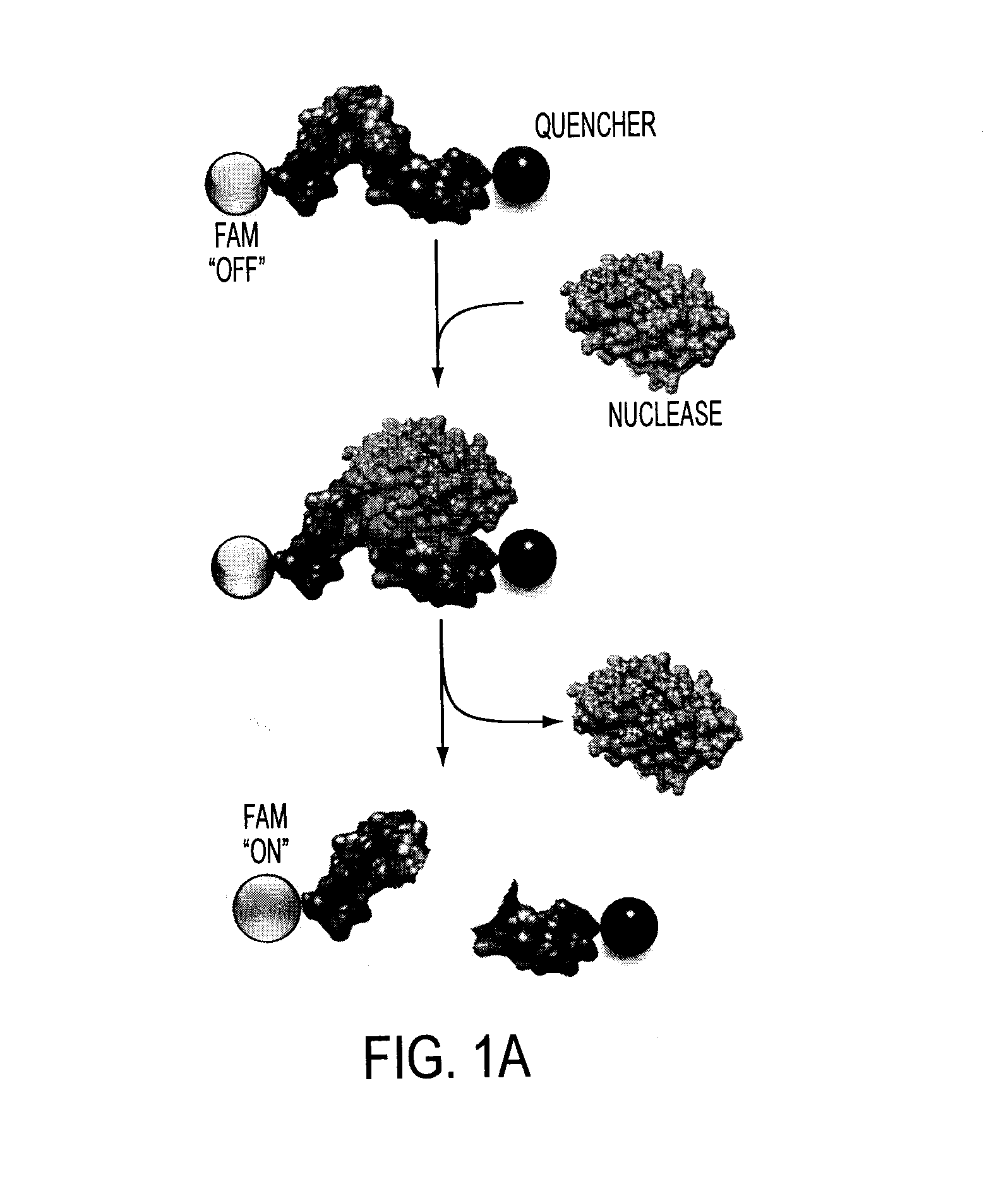
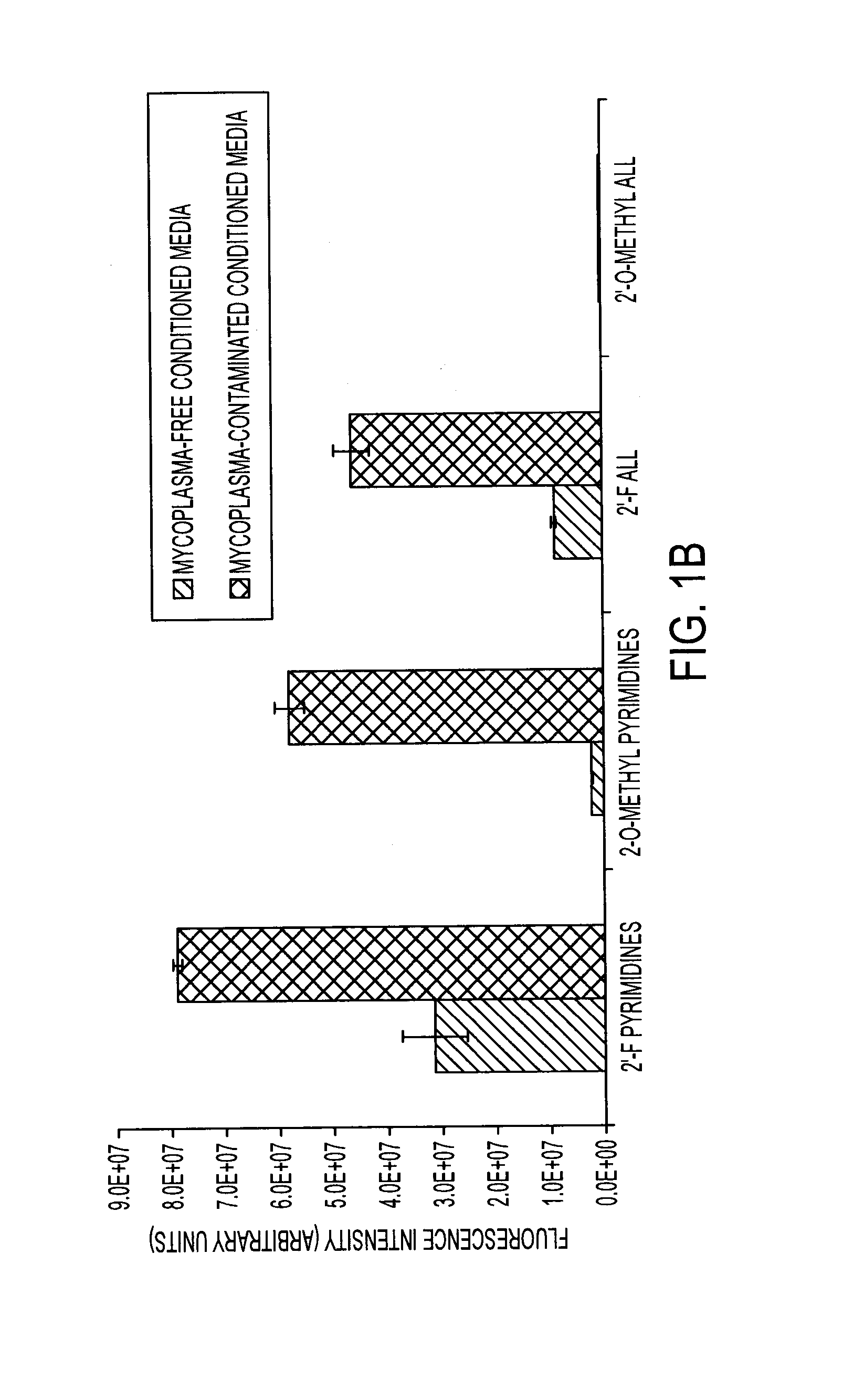
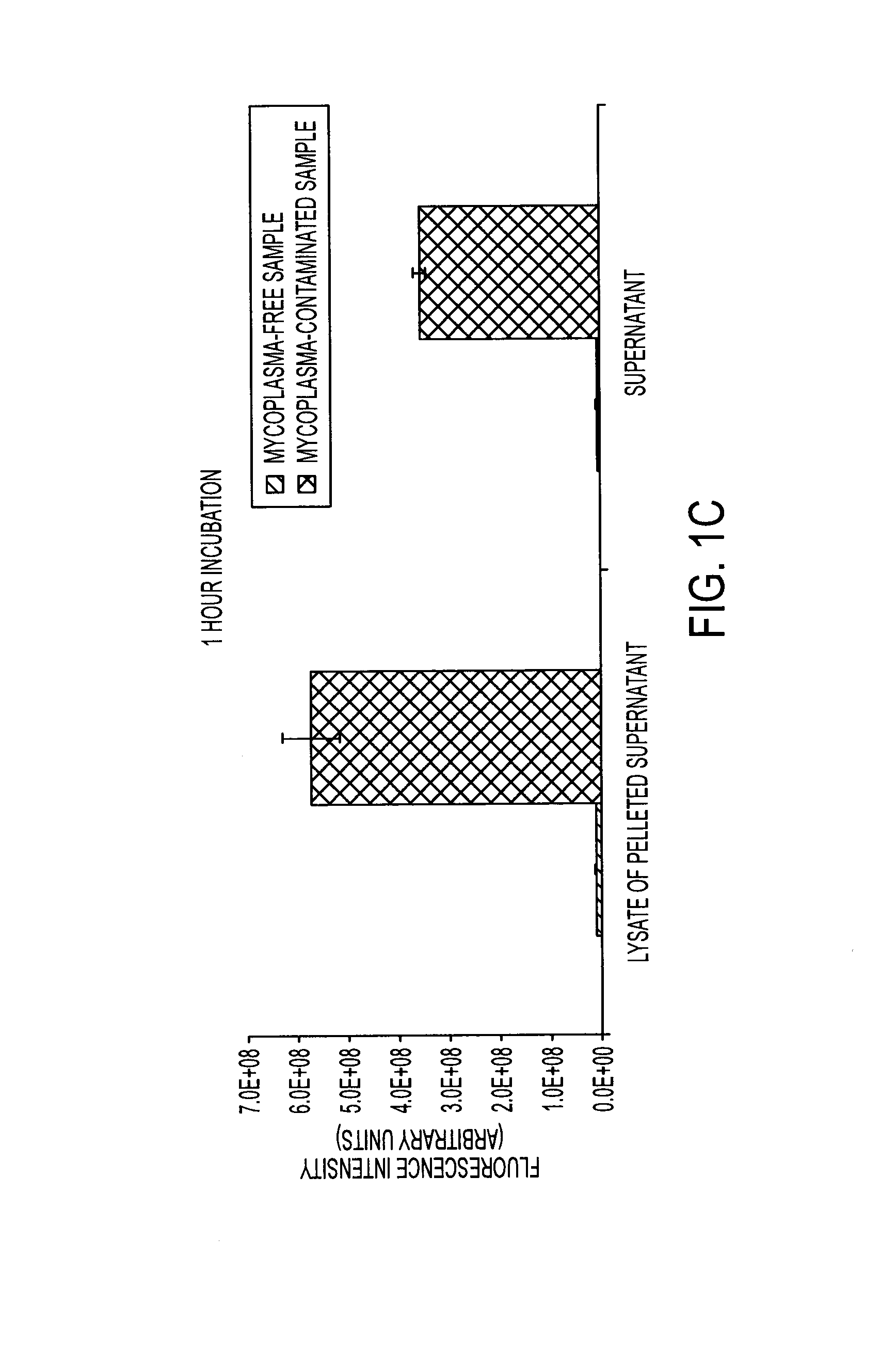
Compositions and methods for visual ribonuclease detection assays
InactiveUS6773885B1Performed rapidly and easilyOvercome deficienciesSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementRibonucleaseTest sample
The present invention relates to methods for detecting the presence of ribonuclease enzymes, more specifically to methods that provide for a visual detection assay. The methods entail contacting a test sample suspected of containing ribonuclease activity with a substrate containing a ribonuclease-sensitive internucleotide linkage flanked directly or indirectly by a fluorescence reporter group and a dark quencher, such that if a ribonuclease activity is present in the sample, the ribonuclease-sensitive internucleotide linkage is cleaved and the fluorescence reporter group emits a visually detectable signal. The present invention further provides novel nucleic acid compositions used as substrates for such assays and encompasses kits for performing the methods of the invention.
Owner:INTEGRATED DNA TECHNOLOGIES
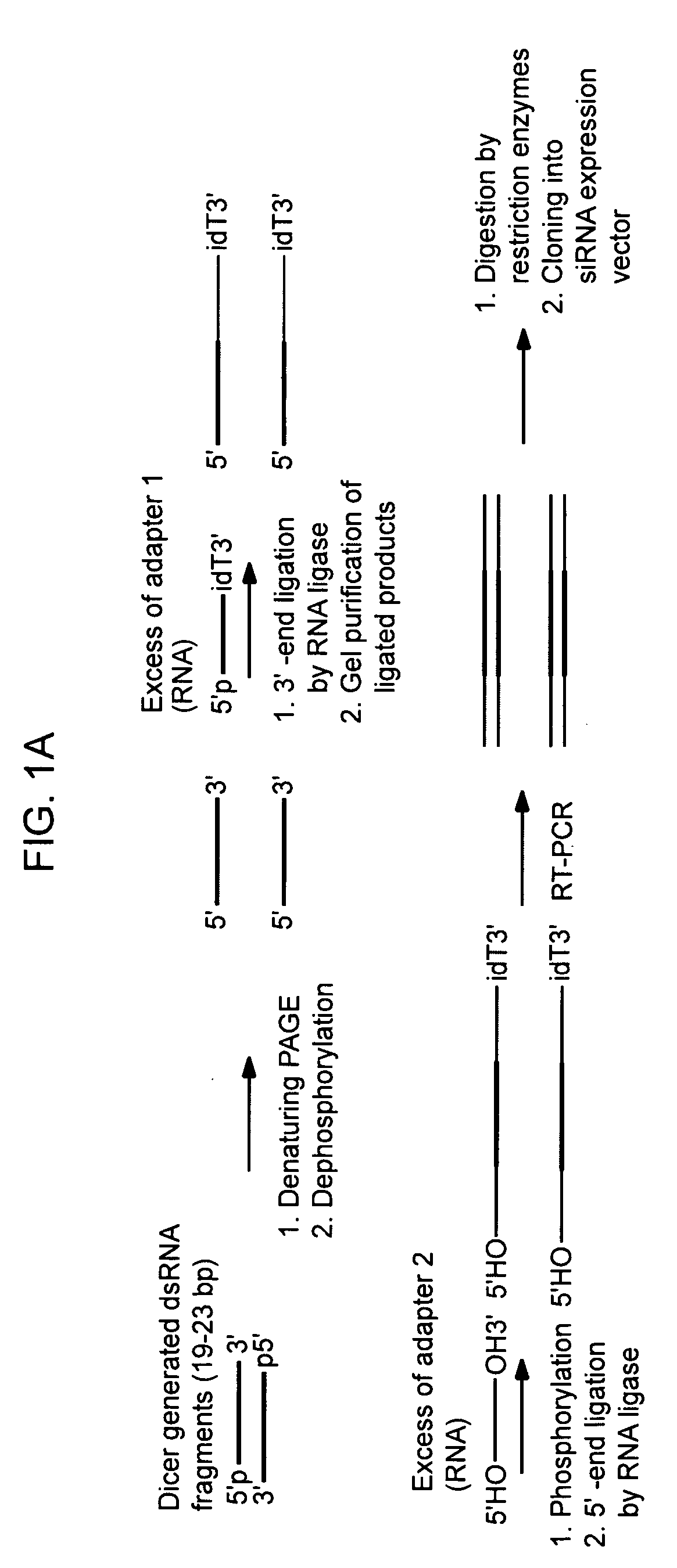
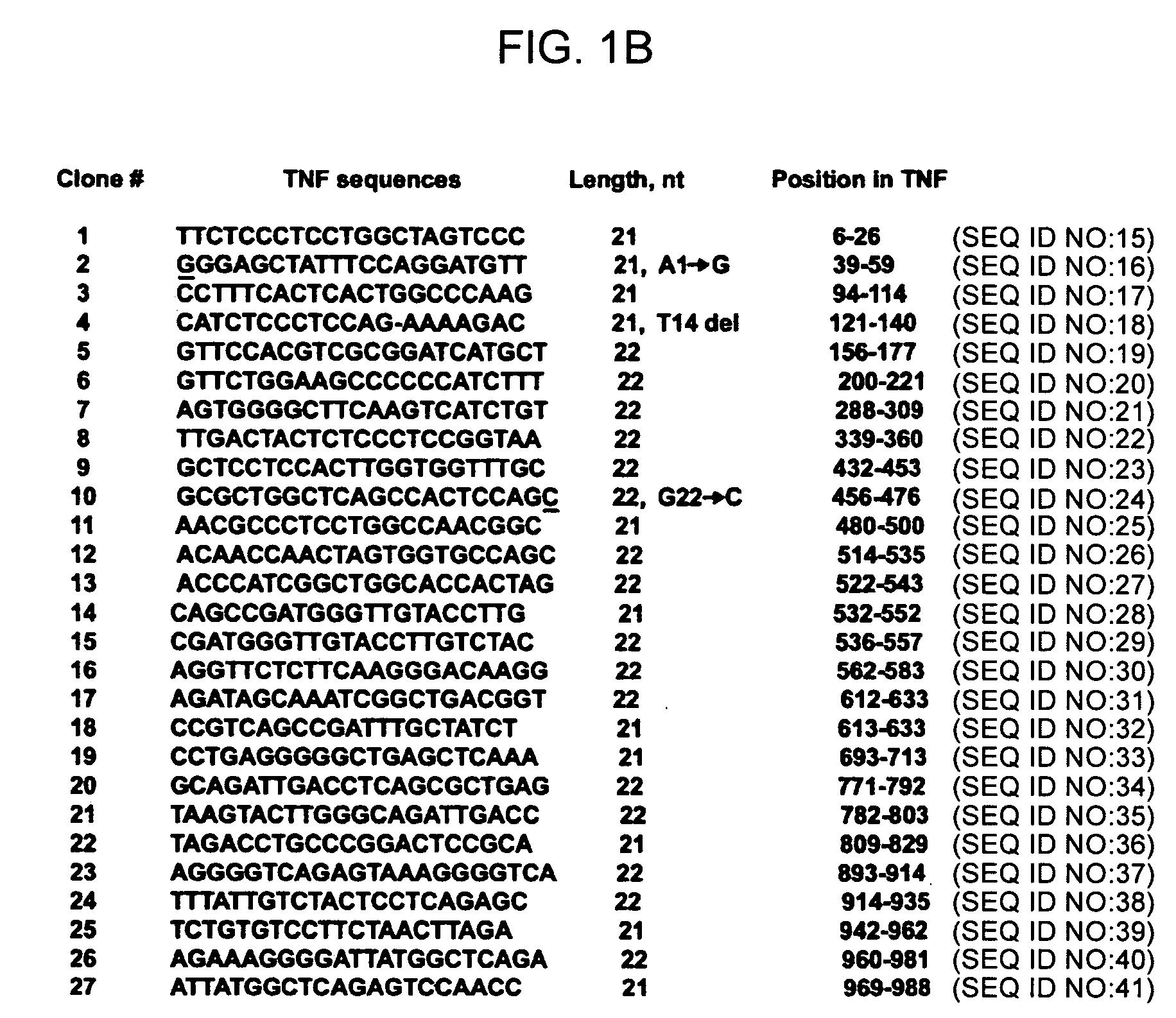
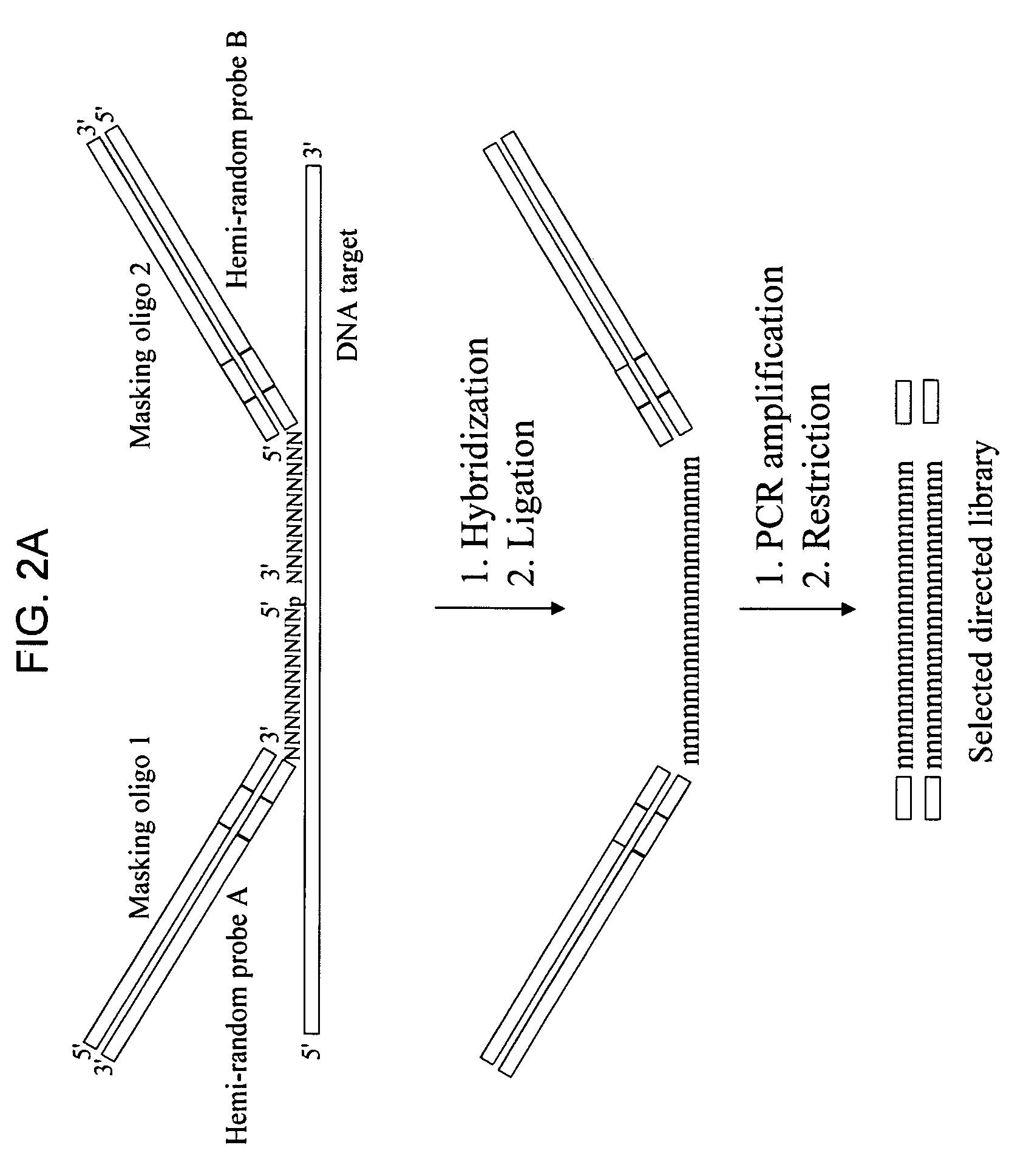
Methods of preparation of gene-specific oligonucleotide libraries and uses thereof
InactiveUS20060051789A1Microbiological testing/measurementFermentationOligoribonucleotidesRibonuclease
Methods of preparing gene-specific oligonucleotide libraries are disclosed. In one embodiment a double-stranded RNA corresponding to both sense and antisense strands of mRNA is digested by ribonuclease to produce short RNA fragments. In subsequent ligation steps, flanking oligoribonucleotides of defined sequences may be attached to the 3- and 5-ends of each fragment by RNA ligase (such as T4 RNA ligase). The products of ligation can be reverse transcribed and PCR amplified (RT-PCR) using the oligonucleotides attached to the gene-derived sequences as primer-binding sites. Various methods for incorporating libraries into expression vectors allowing expression of either siRNAs or shRNAs are also disclosed.
Owner:SOMAGENICS INC
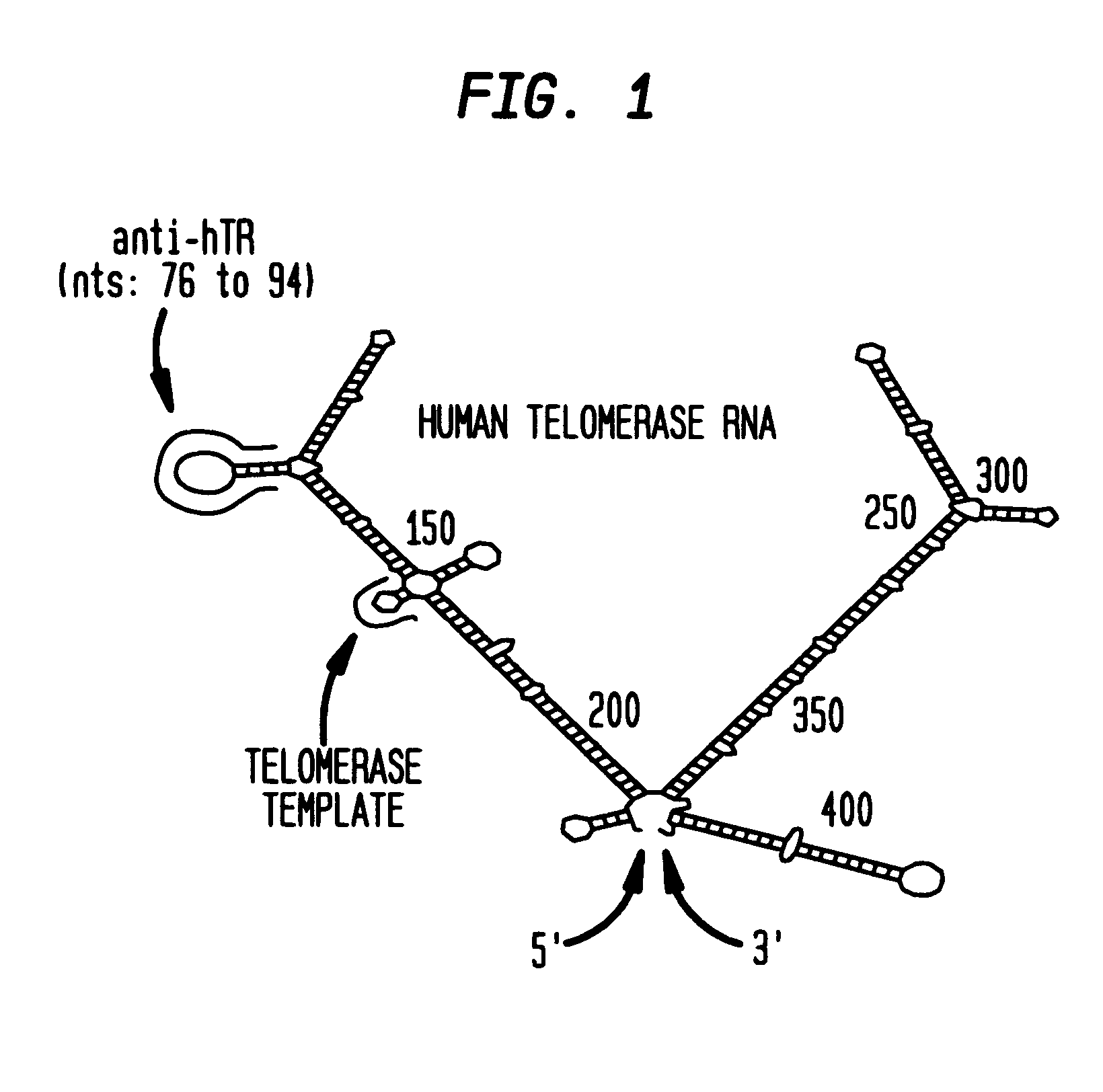
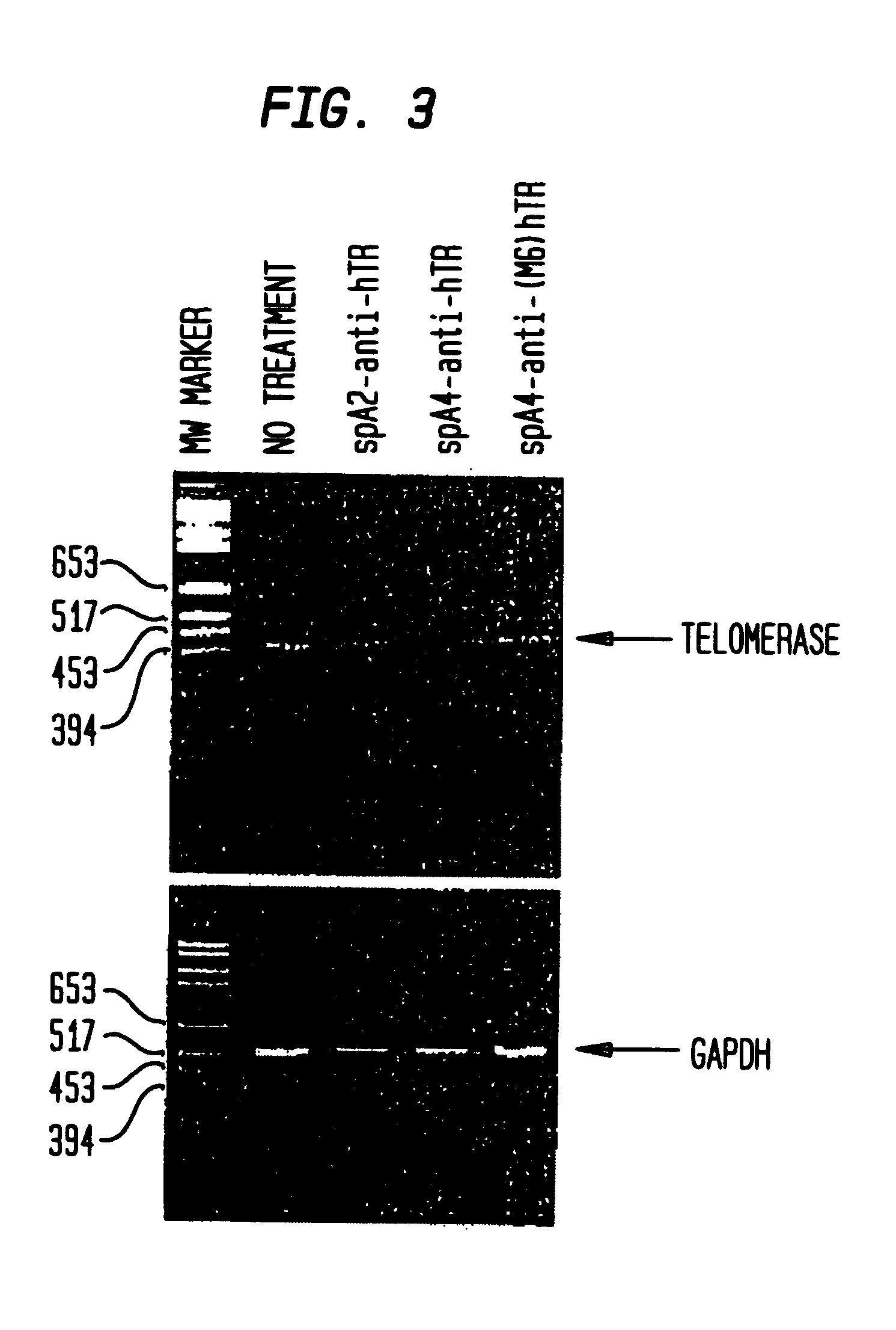
RNase L activators and antisense oligonucleotides effective to treat telomerase-expressing malignancies
InactiveUS6468983B2Facilitate cellular uptakeSuppressed growthOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesTelomeraseDisease
The present invention relates to chimeric molecules comprising an oligonucleotide complementary to a region of the ribonucleotide component of telomerase attached to an activator of RNase L ("activator-antisense complex") which specifically cleaves the ribonucleotide portion of a telomerase enzyme. The present invention relates to methods of inhibiting telomerase enzymatic activity with activator-antisense complexes targeted to the RNA component of telomerase. The present invention further relates to methods of treating malignant neoplastic disease, wherein the malignant cells contain a telomerase activity that is necessary for the growth of the malignant cells.
Owner:THE CLEVELAND CLINIC FOUND +1
Endoribonuclease compositions and methods of use thereof
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Methods of and compositions for inhibiting the proliferation of mammalian cells
A method of preventing, inhibiting and / or reversing cell motility, actin filament assembly or disassembly, proliferation, colonization, differentiation, accumulation and / or development of abnormal cells in a subject is disclosed. The method is effected by administering to the subject a therapeutically effective amount of a ribonuclease of the T2 family having actin binding activity.
Owner:YISSUM RES DEV CO OF THE HEBREWUNIVERSITY OF JERUSALEM LTD
Nuclease inhibitor cocktail
InactiveUS7163793B2Microbiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisMicroorganismRibonuclease
Methods and compositions for inhibiting and / or inactivating nucleases by employing nuclease inhibitors are provided. The nuclease inhibitors comprise anti-nuclease antibodies and non-antibody nuclease inhibitors. The anti-nuclease antibodies of the present invention may be a polyclonal or monoclonal antibodies, and may be anti-ribonuclease antibodies, anti-deoxyribonuclease antibodies, or antibodies to non-specific nucleases. A preferred embodiment comprises at least two nuclease inhibitors, and is referred to as a nuclease inhibitor cocktail. In some specific embodiments, the invention concerns methods of performing in vitro translation comprising obtaining a first nuclease inhibitor, which inhibitor is further defined as an anti-nuclease antibody, and placing the anti-nuclease antibody in an in vitro translation reaction. In many cases, the in vitro translation reaction comprises at least one nuclease, which may be a ribonuclease, a deoxyribonuclease, or a nonspecific nuclease. The invention also relates to kits for the performance of various microbiological procedures, which kits comprise the nuclease inhibitors described herein.
Owner:APPL BIOSYSTEMS INC
Method for Treating Oncological Diseases
ActiveUS20100150903A1Promote growthImprove efficiencyPeptide/protein ingredientsHydrolasesDiseaseChemical composition
A method to treat solid tumors and other oncological diseases consists of parenterally injecting an agent which destroy's blood's extracellular DNA into the systemic blood circulation of a cancer patient to slow down malignant. The agent is embodied in the form of a DNAse enzyme and, more particularly, as a bovine pancreatic DNAse. Doses from 50,000-250,000,000 Kunz units / day are injected for 5-360 days. A binding agent or an agent that modifies the chemical composition of the blood extracellular DNA is additionally injected into the blood. This modifying agent is preferably an enzyme-ribonuclease.
Owner:CLS THERAPEUTICS
Therapeutic ribonucleases
InactiveUS8029782B2Good physical propertiesReduce the amount requiredPeptide/protein ingredientsHydrolasesDiseaseRibonuclease
The present invention relates to the use of ribonucleases (RNases) in the treatment or prevention of disease.
Owner:QUINTESSENCE BIOSCI
Recombinant Human T2 Rnase and Uses Thereof
The cloning and heterologous expression of human T2 RNase6PL are disclosed. Further disclosed are methods for preventing, inhibiting and / or reversing cell motility, actin filament assembly or disassembly, proliferation, colonization, differentiation, accumulation and / or development of abnormal cells in a subject is disclosed. The methods are effected by administering to the subject a therapeutically effective amount of a RNase6PL ribonuclease or close homologues thereof.
Owner:YISSUM RES DEV CO OF THE HEBREWUNIVERSITY OF JERUSALEM LTD
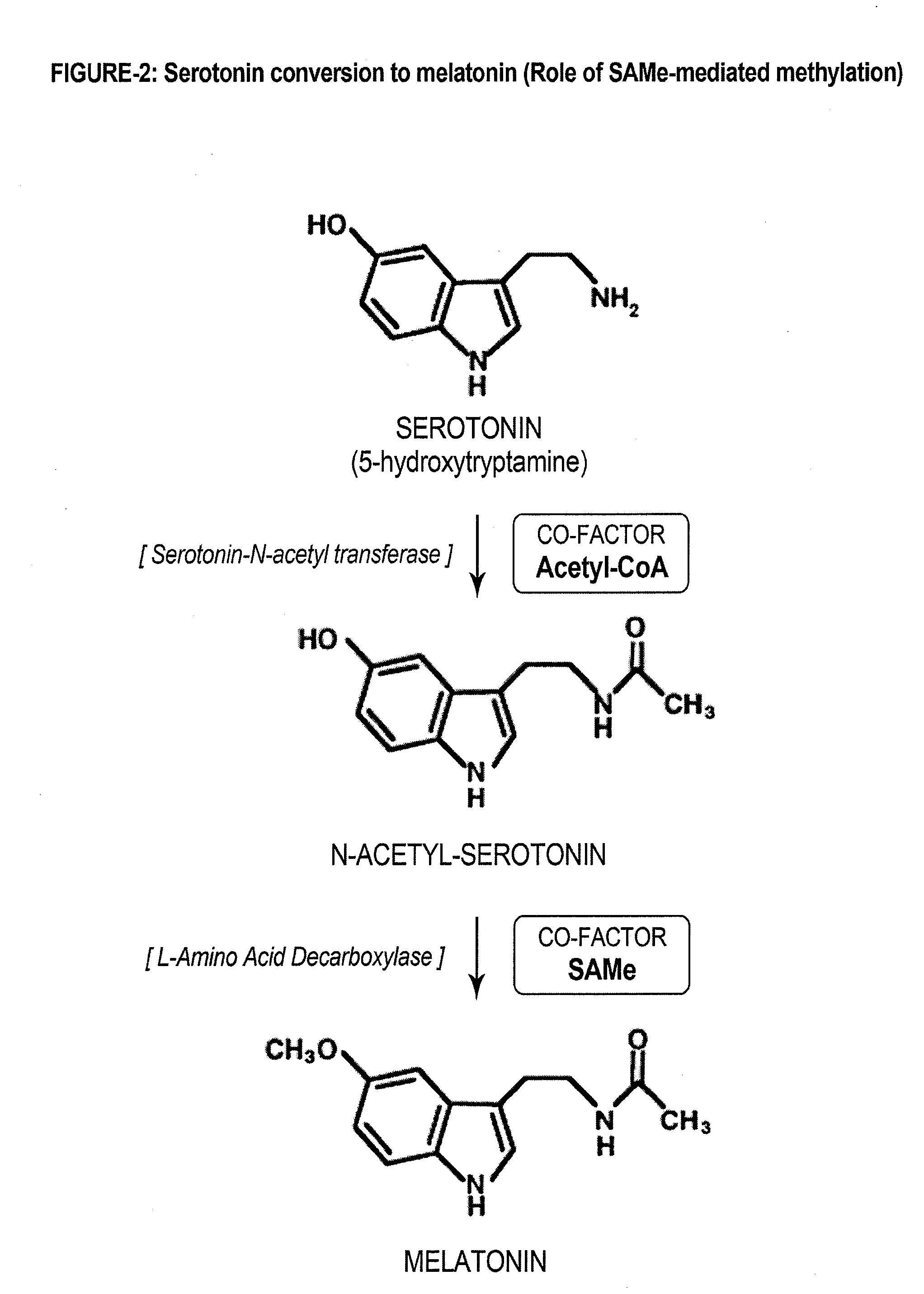
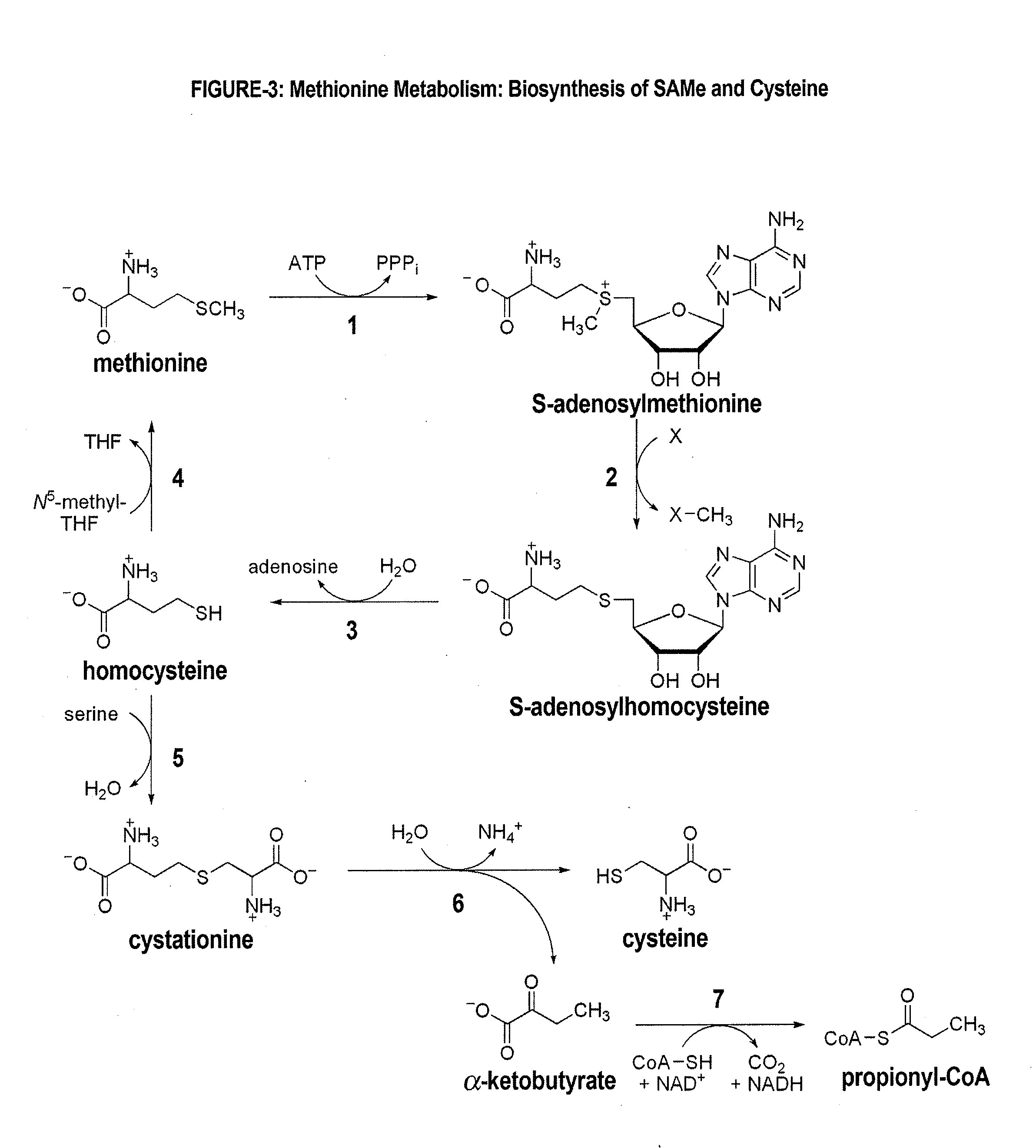
BIO-REPLENISHMENT (BioRep) FOR IMPROVING SLEEP ARCHITECTURE
InactiveUS20130064804A1Easy to pumpGood curative effectOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderSleep architectureS-Adenosyl methionine
Methods to prepare a bio-replenishment (BioRep) with specific combinations of S-adenosylmethionine (SAMe), lactoferrin (LF) and ribonuclease (RNAse) to restore regular sleep pattern are described. Additionally, compositions of functional delivery systems that recreate both alternate phases of non-rapid eye movement (NREM) and rapid eye movement (REM) sleep cycles are disclosed. These methods and compositions have implications in the clinical management of various sleep disorders including insomnia, circadian rhythm disorders and obstructive sleep apnea.
Owner:NAIDU LP
Immune modulatory activity of human ribonucleases
InactiveUS20040009503A1Microbiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisPhases of clinical researchWhite blood cell
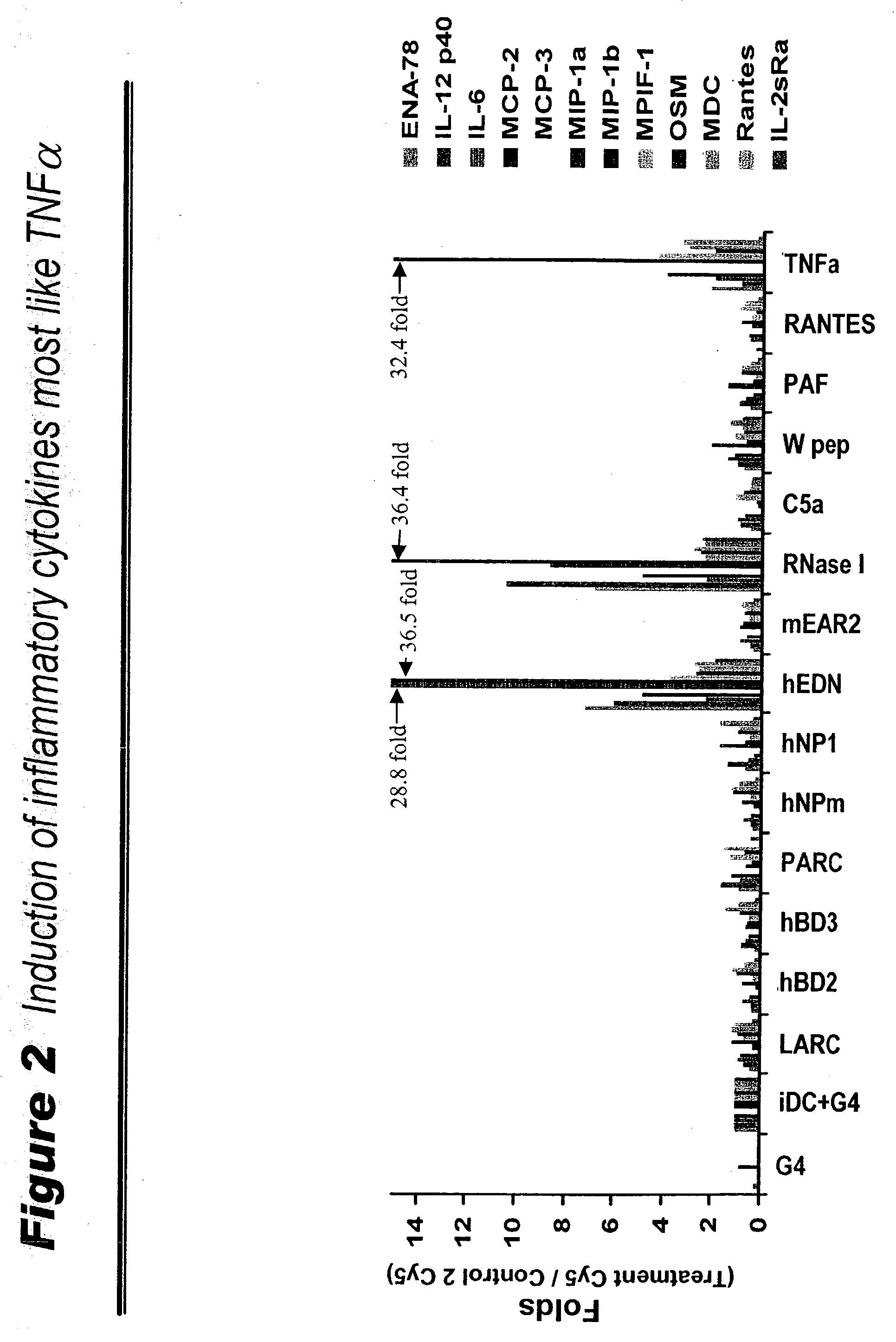
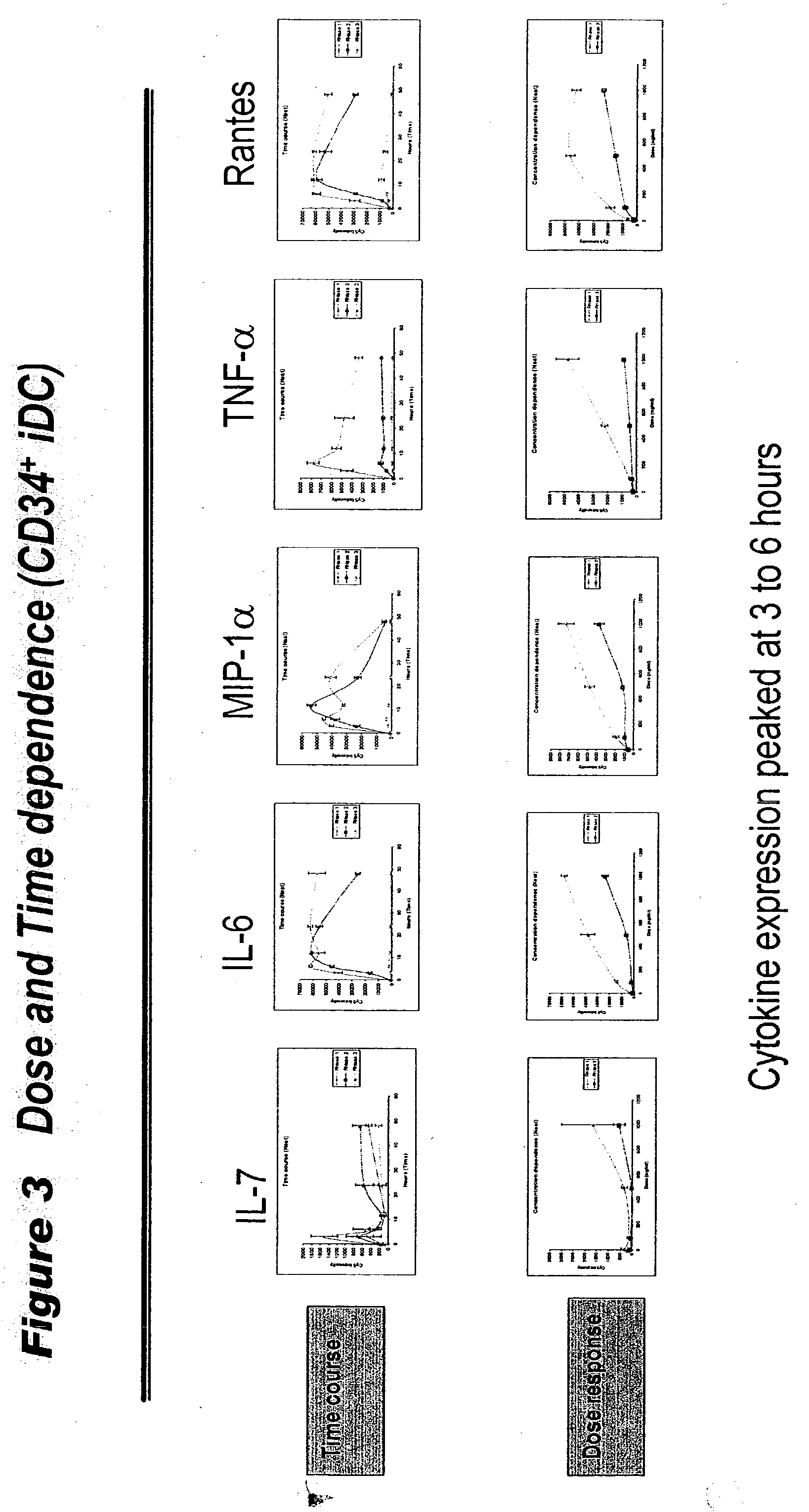
Human extracellular ribonucleases (RNases) are widely distributed in various organs and body fluids and together with other members of the mammalian RNase A superfamily. In addition to their RNase activity, several RNases have been shown to have special biological actions, i.e., antitumor, antiviral and angiogenic properties. However, the molecular mechanisms of such activities are unclear. Using protein microarrays amplified rolling circle amplification (RCA), we investigated the effects of EDN (Rnase 2), ECP (Rnase 3) and RNase 1 on leukocytes cytokine production. We measured the levels of 78 different cytokines and growth factors in culture supernatants to determine the cytokine profiles of cells treated with different combinations of RNases and RNase inhibitors. Members of human ribonuclease family (such as Rnase 1, hEDN (Rnase 2) and Rnase 3) induced expression of certain sets of cytokines in human leukocytes, including ENA-78, EOT2, BLC, GDNF, 1309, IFN-alpha, IFN-gamma, IL-10, IL-12P40, IL-12p70, IL-13, IL-16, IL-18, IL-1beta, IL-1ra, IL-2Sra, IL-3, IL-6, IL-6sR, IL-7, IL-8, IP-10, MCP-1, MCP-2, MCP-3, MCSF, MIG, MDC, MIP-1alpha, MIP-1beta, MPIF-1, NAP-2, RANTES, sCD23, OSM, TARC, TNF-alpha, TNF-R1 and uPAR. Thus members of the Rnase superfamily are therapeutic targets for treatment of inflammatory diseases and clinical conditions. Inhibition or augmentation of Rnase expression is used to modulate the immune system and is beneficial for host defense against various diseases and is exploited as an adjuvant. The expression of Rnases is a diagnostic marker for inflammation related conditions and is used to determine various disease stages. In addition, expression of cytokines, chemokines, growth factors is used to monitor efficacy of Rnase-base therapies.
Owner:PATHWAY DIAGNOSTICS CORP INC
Method for detecting one or more target nucleic acid sequences to be tested by single tube and kit thereof
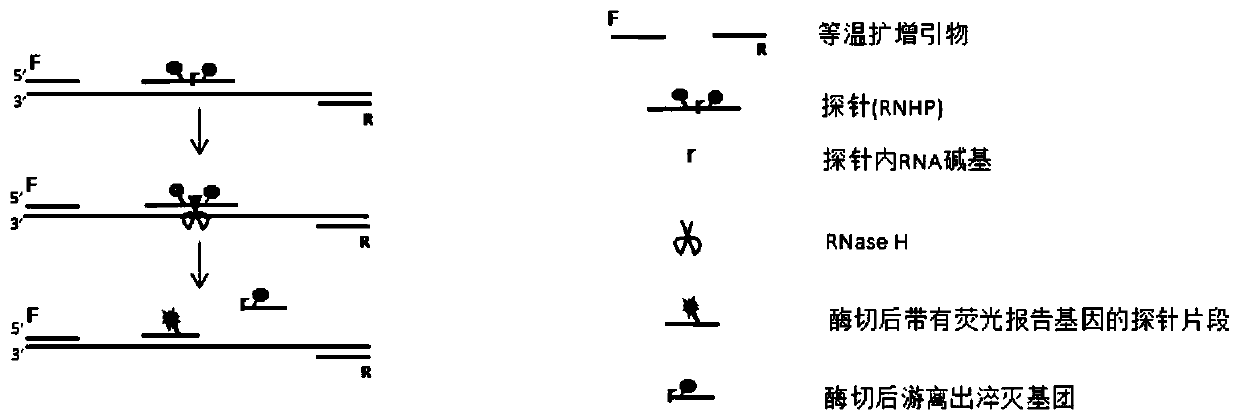
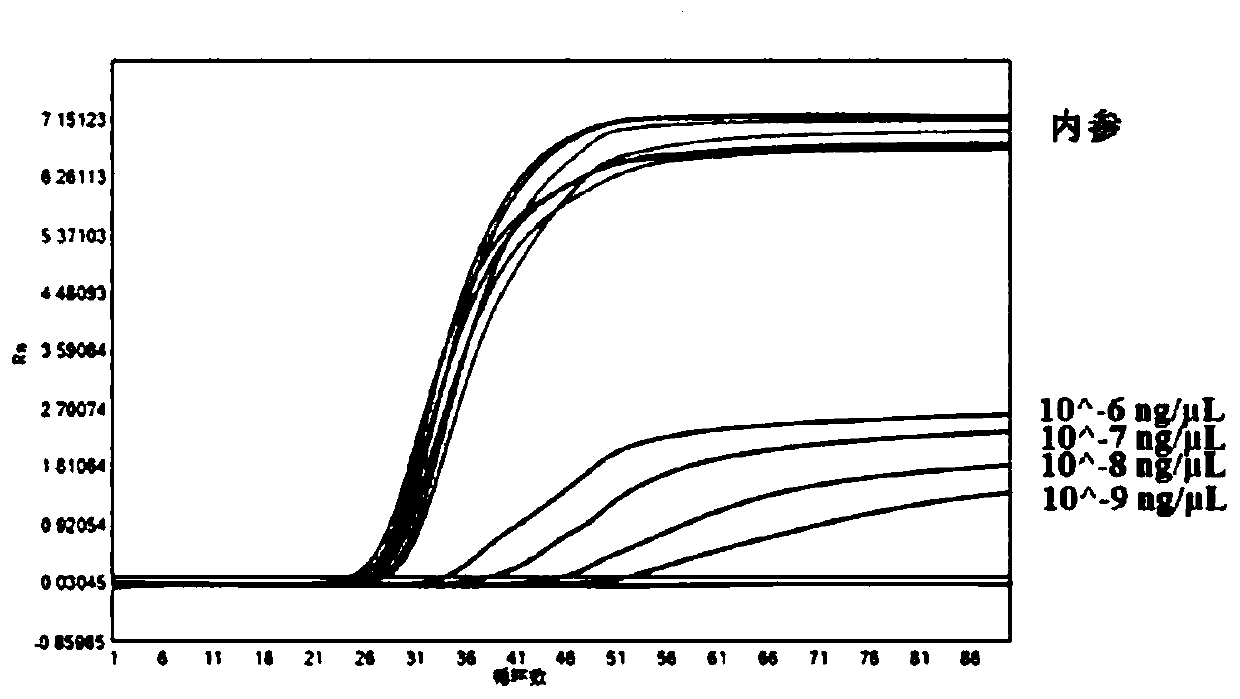
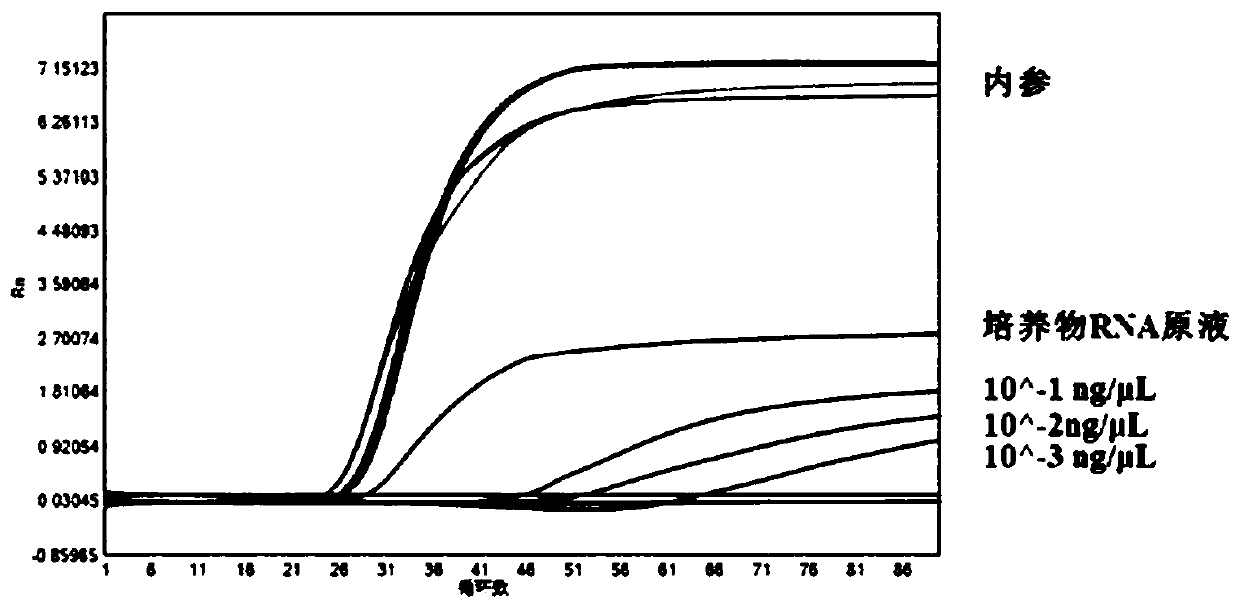
ActiveCN109750091AImprove bindingHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementRibonucleaseFluorescence
The invention provides a method for detecting one or more target nucleic acid sequences to be tested by a single tube and a kit thereof. The method comprises the steps of designing a specific isothermal amplification primer and a fluorescent probe RNHP for each target nucleic acid sequence to be tested, and labeling each of target nucleic acid sequence fluorescent probes RNHP to be tested with different fluorescence; in the presence of ribonuclease RNaseH, isothermally amplifying each target nucleic acid sequence to be tested by the action of polymerase; forming hybridization chain products labeled with the different fluorescence by the different target nucleic acid sequences to be detected, thereby achieving multiplex detection of the plurality of target nucleic acid sequences to be tested. Based on an isothermal amplification technique, the method can achieve real-time multiplex isothermal detection by introducing a special modified primer RNHP and being combined with RNaseH2.
Owner:JIANGSU MACRO&MICRO TEST MED TECH CO LTD
Ribonucleases and methods of making them recombinantly
Methods for recombinantly producing new RNases, as well as previously-known RNases, are disclosed. The new RNases are active against human carcinoma cells.
Owner:ALFACELL +1
Oligonucleotides for modulating target rna activity
The present invention describes oligonucleotides that bind to microRNA target sites in target RNAs, such as mRNAs. The oligonucleotides of the invention may mediate RNase H degradation of the target RNA, mediate RNAi of the target RNA or prevent microRNA regulation of the target RNA. The oligonucleotides of the invention are useful e.g. as research tools for studying microRNA:mRNA interactions andfor therapeutic development. The present invention also describes methods of identifying microRNA target sites, methods of validating microRNA target sites, methods of identifying oligonucleotides ofthe invention and methods of modulating the activity of a target RNA using the oligonucleotides of the invention.
Owner:米尔克斯治疗有限责任公司
Oligonucleotide-based probes for detection of bacterial nucleases
The present invention relates to a rapid detection of microbial-associated nuclease activity with chemically modified nuclease (e.g., ribonuclease) substrates, and probes and compositions useful in detection assays. Accordingly, in certain embodiments, the present invention provides a probe for detecting a microbial endonuclease comprising a substrate oligonucleotide of 2-30 nucleotides in length, a fluorescence-reporter group operably linked to the oligonucleotide, and a fluorescence-quencher group operably linked to the oligonucleotide. The fluorescence-reporter group and the fluorescence-quencher group are separated by at least one RNAse-cleavable residue, e.g., RNA base.
Owner:UNIV OF IOWA RES FOUND +1
Method for extracting high-molecular-weight genome from animal feces
InactiveCN102586234AHigh molecular weightSimple methodDNA preparationSodium acetateMolecular identification
The invention relates to a method for extracting high-molecular-weight genome from animal feces. The method comprises the steps of sample treatment, bacterial cell lysis and extraction of DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid). Specifically, the method comprises the steps of: dissolving an animal feces sample with aseptic PBS (Phosphate Buffered Saline) buffer, carrying out low-speed centrifuging and filtering to remove food residues in the feces, collecting bacterial cells, performing wall breaking on the bacteria by adopting lysozyme, decolorizing peptidase, protease and SDS (Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate), extracting with a mixture of phenol, chloroform and isoamyl alcohol as well as a mixture of chloroform and isoamyl alcohol, precipitating with isopropanol and sodium acetate, washing and drying, dissolving, and digesting RNA (Ribonucleic Acid) with RNAse (Ribonuclease). According to the invention, the method is simple in operation; and the DNA molecular weight of the extracted genome achieves more than 40kb, so that the researches on microorganism molecule ecological diversity, molecular identification, target gene amplification, macro genome library construction and the like are met.
Owner:YUNNAN NORMAL UNIV
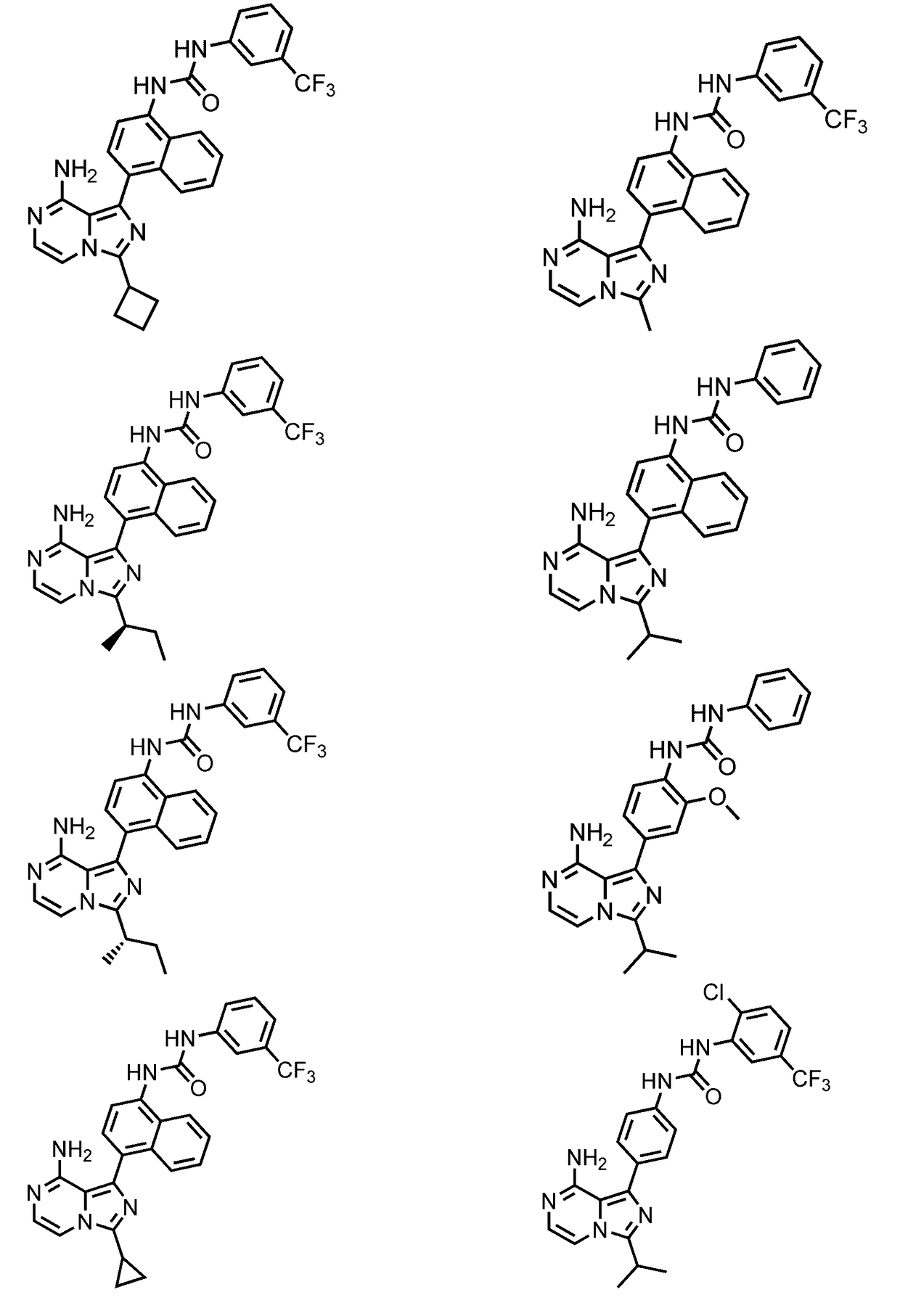
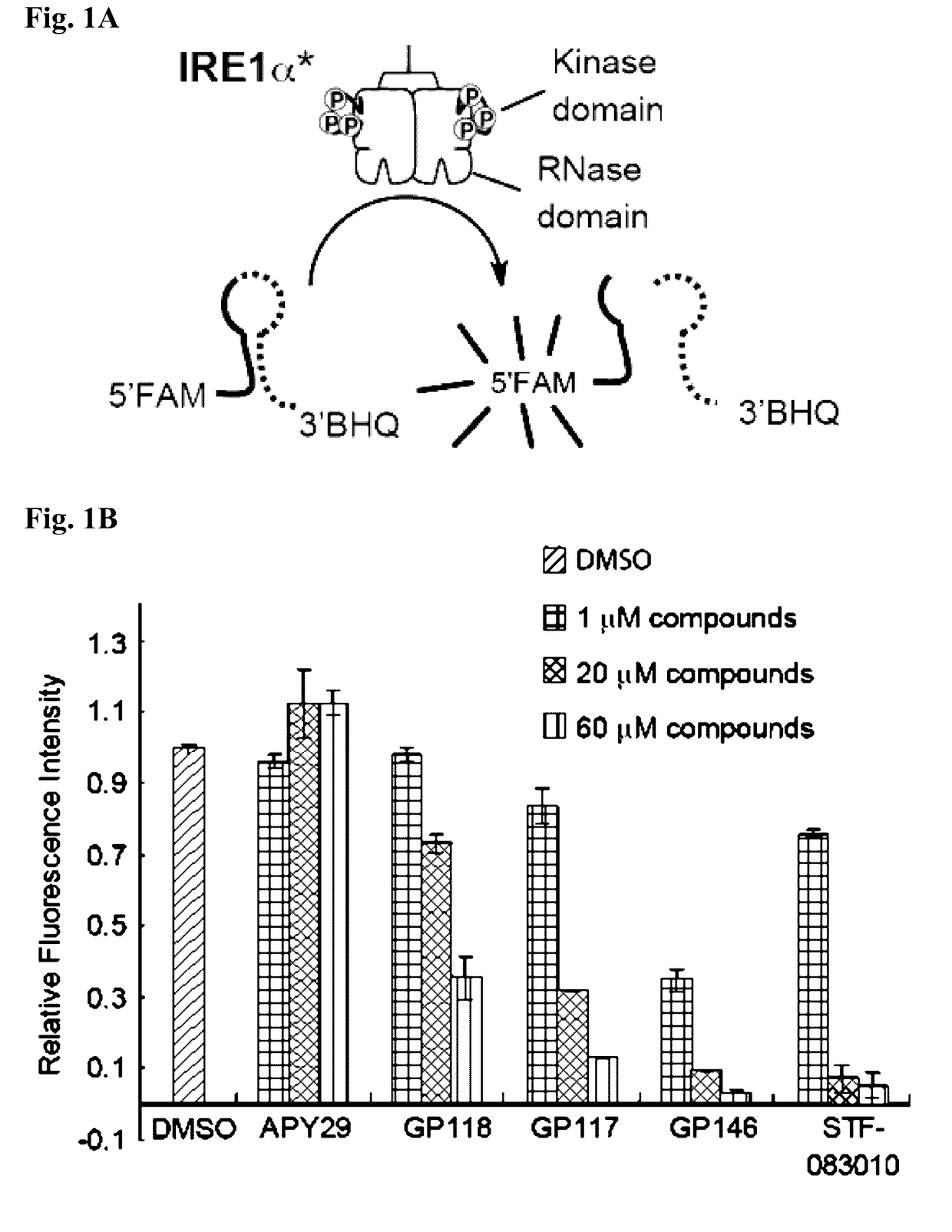
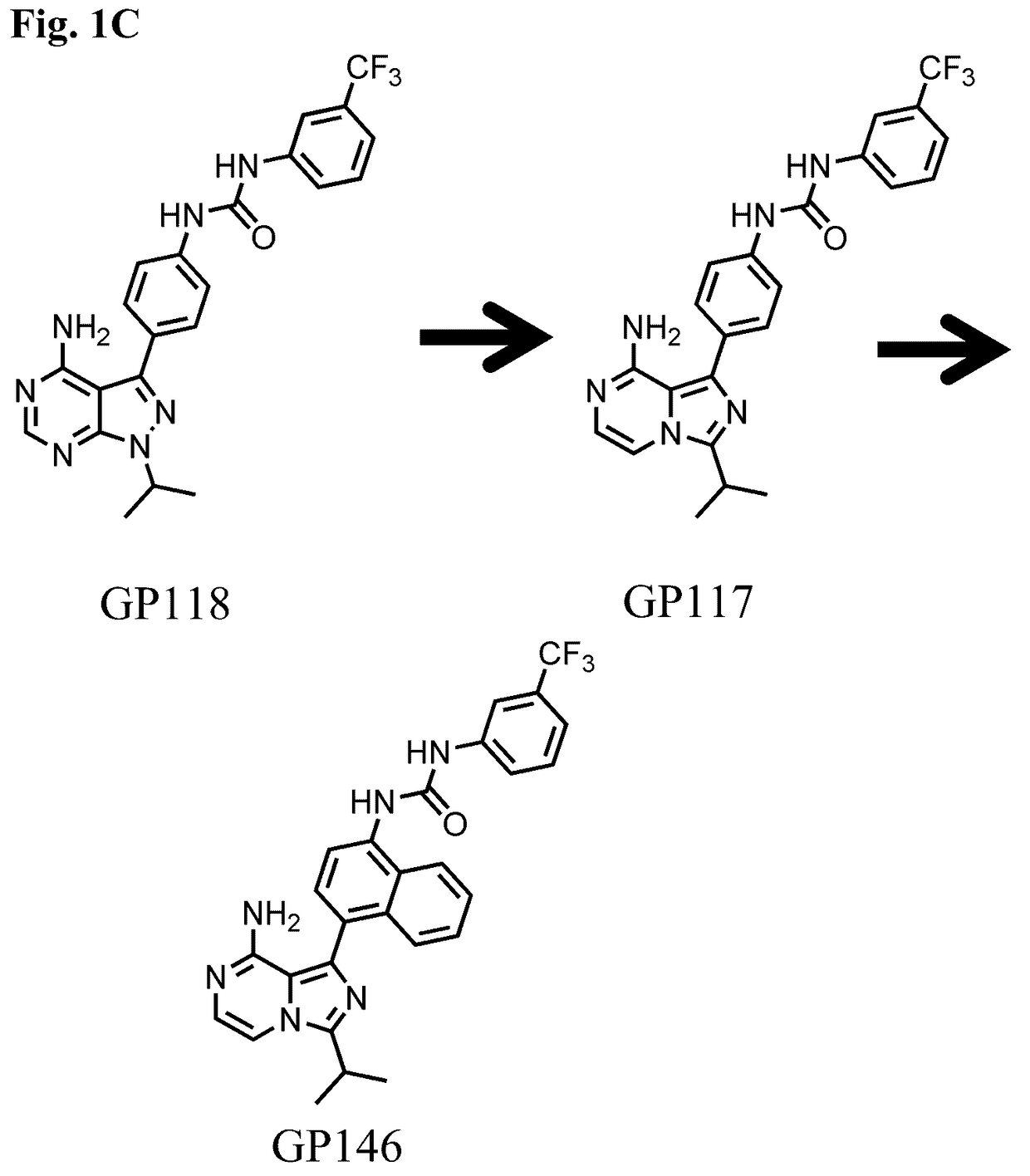
Combined modulation of ire1
InactiveUS20170165259A1Salicyclic acid active ingredientsHeterocyclic compound active ingredientsRibonucleaseKinase
Described herein, inter alia, are combined compositions of an Ire1 kinase modulating compound and an Ire1 ribonuclease modulating compound and methods of using the same.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA +1
Step-wise detection of multiple target sequences in isothermal nucleic acid amplification reactions
Compositions and methods useful in nucleic acid assays are provided. The invention permits detection of multiple target sequences and control nucleic acids using isothermal nucleic acid amplification methods and subsequent detection of amplification products at different temperature steps by at least two probes with different annealing temperatures. This method can be used in isothermal nucleic acid amplification reactions to detect multiple targets of interest. In a particular example, cycling hybridization probes with different spectral and hybridization temperatures are used to detect different target sequences. Probes become fluorescent when they are cleaved by a thermostable ribonuclease, which only acts when the probes are hybridized to their respective templates.
Owner:BIOHELIX CORP
Nuclease inhibitor cocktail
Methods and compositions for inhibiting and / or inactivating nucleases by employing nuclease inhibitors are provided. The nuclease inhibitors comprise anti-nuclease antibodies and non-antibody nuclease inhibitors. The anti-nuclease antibodies of the present invention may be a polyclonal or monoclonal antibodies, and may be anti-ribonuclease antibodies, anti-deoxyribonuclease antibodies, or antibodies to non-specific nucleases. A preferred embodiment comprises at least two nuclease inhibitors, and is referred to as a nuclease inhibitor cocktail. In some specific embodiments, the invention concerns methods of performing in vitro translation comprising obtaining a first nuclease inhibitor, which inhibitor is further defined as an anti-nuclease antibody, and placing the anti-nuclease antibody in an in vitro translation reaction. In many cases, the in vitro translation reaction comprises at least one nuclease, which may be a ribonuclease, a deoxyribonuclease, or a nonspecific nuclease. The invention also relates to kits for the performance of various microbiological procedures, which kits comprise the nuclease inhibitors described herein.
Owner:APPL BIOSYSTEMS INC
Pseudovirions and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN105200018ANon-infectiousImprove stabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementInactivation/attenuationNucleic acid detectionRibonuclease
The invention discloses pseudovirions; a capsid protein of MS2 bacteriophage is wrapped with a DNA-protein complex of a detection sequence formed by series connection of three base fragments of influenza A virus, influenza B virus and beta-actin successively. The invention also provides a preparation method of the pseudovirions and an application of the pseudovirions as quality control products for detecting the influenza A virus and the hepatitis B virus. The preparation method of the pseudovirions is simple and is easy to operate; the obtained pseudovirus is high in purity, can be used as the quality control products in an influenza A virus and influenza B virus nucleic acid detection kit, and has the characteristics of no infectivity, good stability, ribonuclease resistance and the like.
Owner:GUANGDONG HECIN SCI INC
Method of treating a fabric
InactiveUS20160319225A1Inorganic/elemental detergent compounding agentsSurface-active detergent compositionsBenzeneRibonuclease
A method of treating a textile in which a textile is contacted with an aqueous solution comprising a nuclease enzyme, preferably a deoxyribonuclease or ribonuclease enzyme and low levels of alkyl benzene sulphonate surfactant, and optionally rinsing and drying the textile.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com