Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
447results about How to "Maintain structural integrity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
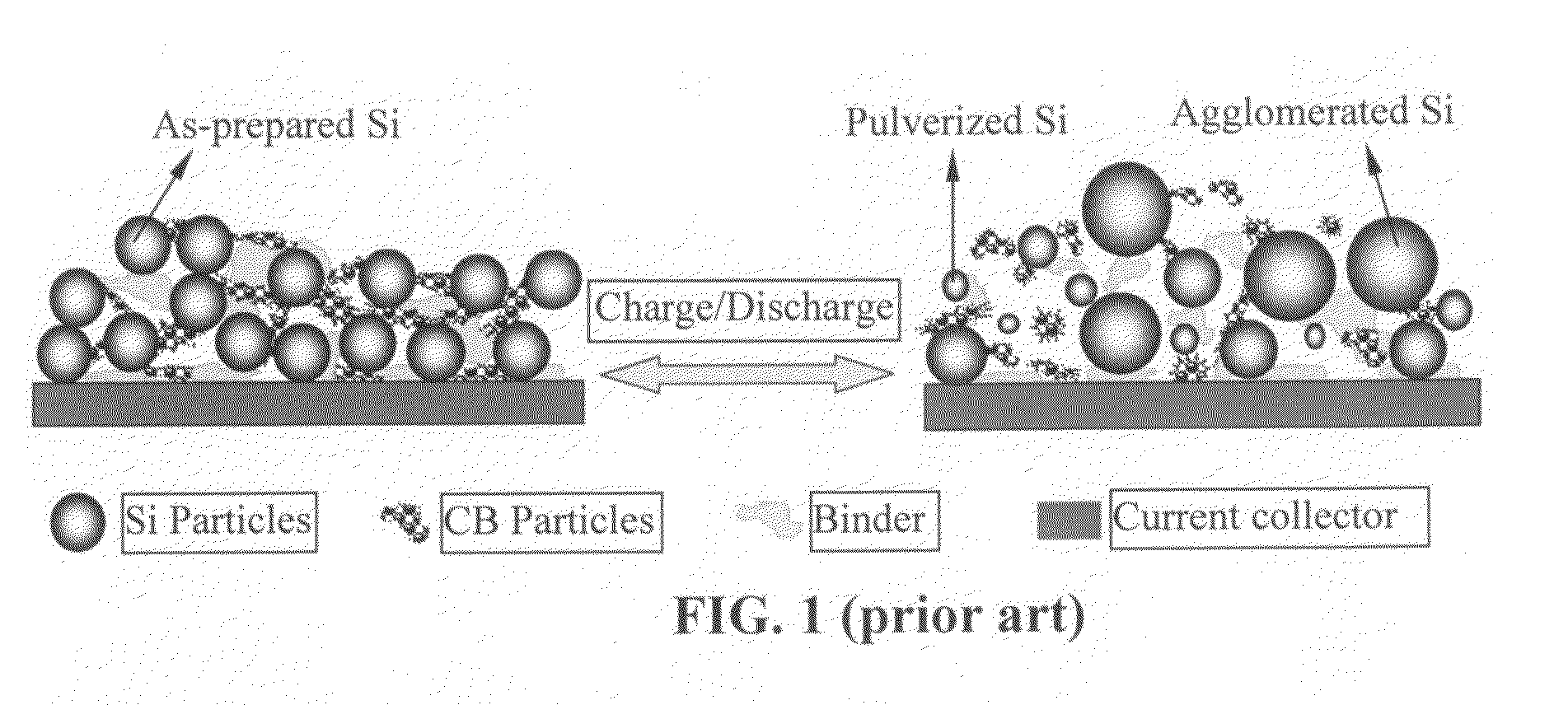
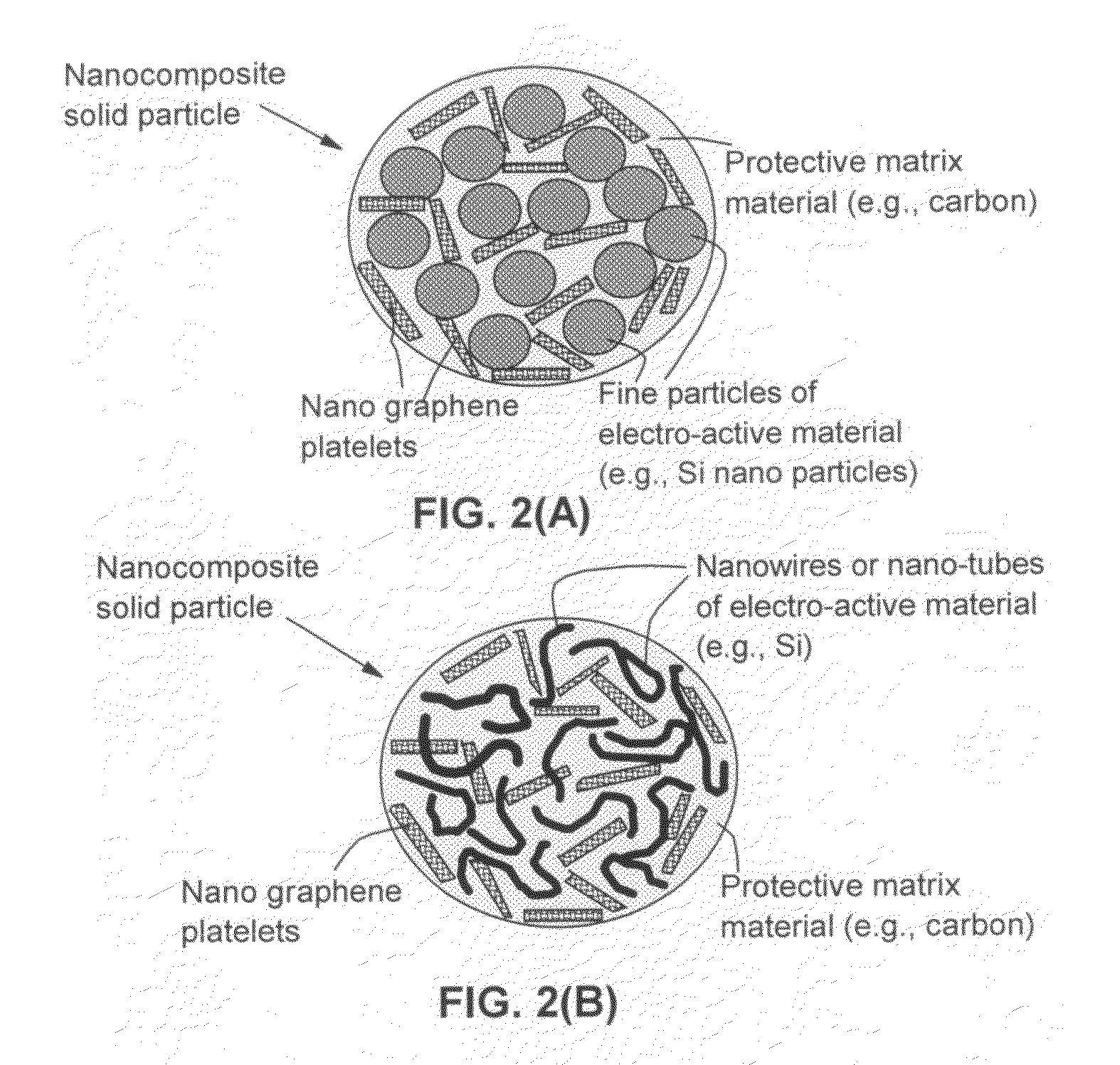
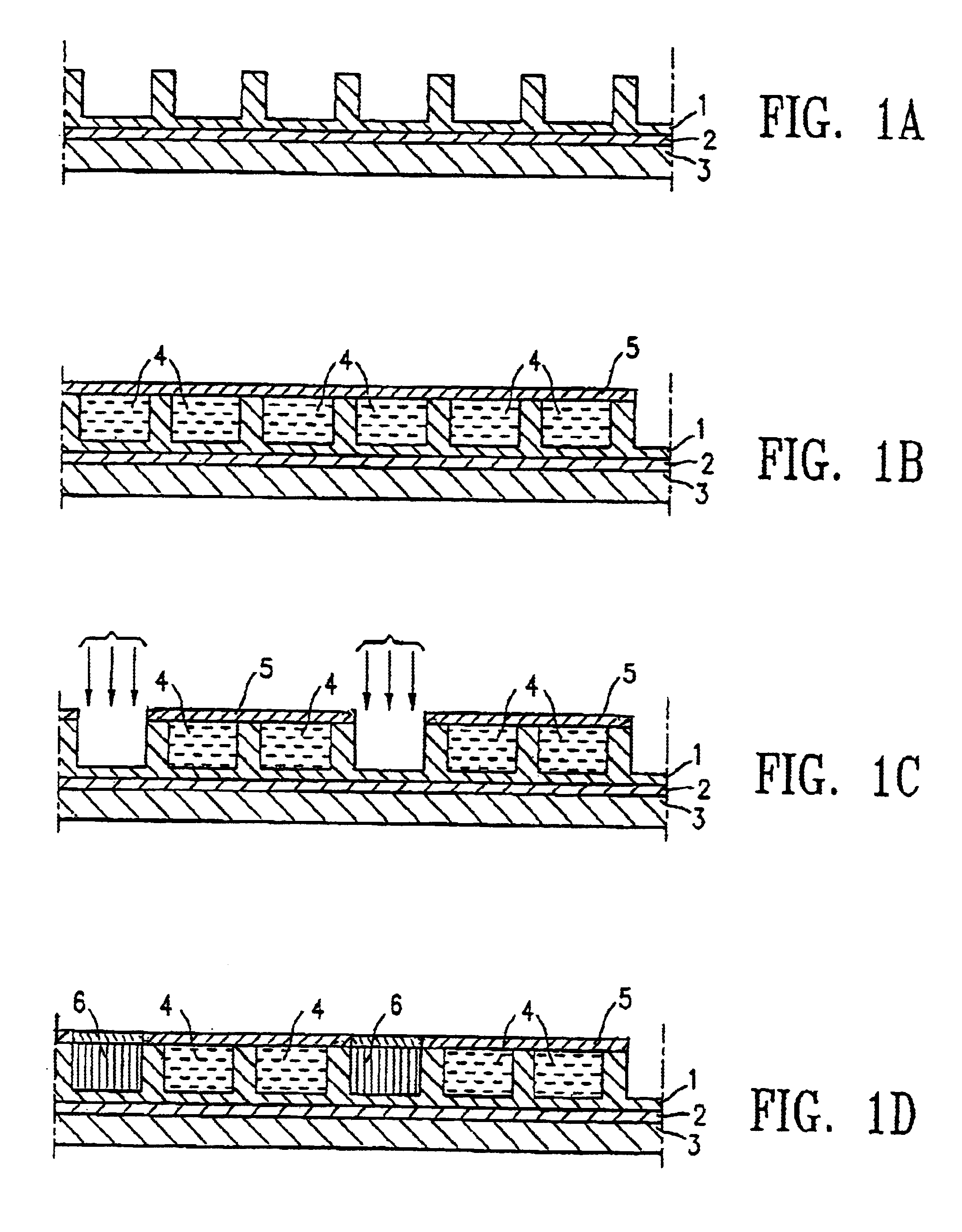
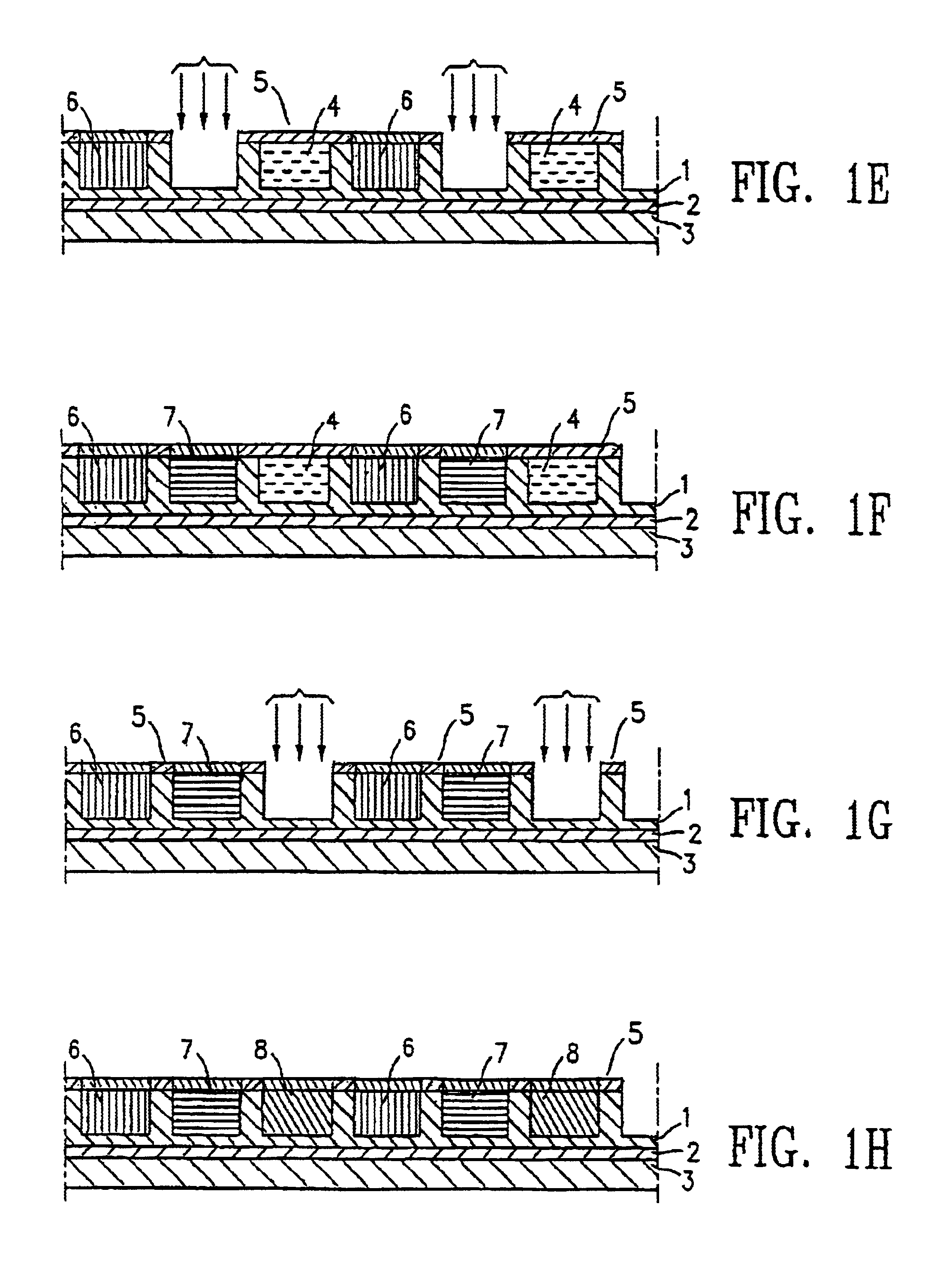
Nano graphene reinforced nanocomposite particles for lithium battery electrodes
ActiveUS20100143798A1Increase stiffnessHigh strengthActive material electrodesSecondary cellsLithium metalNanocomposite
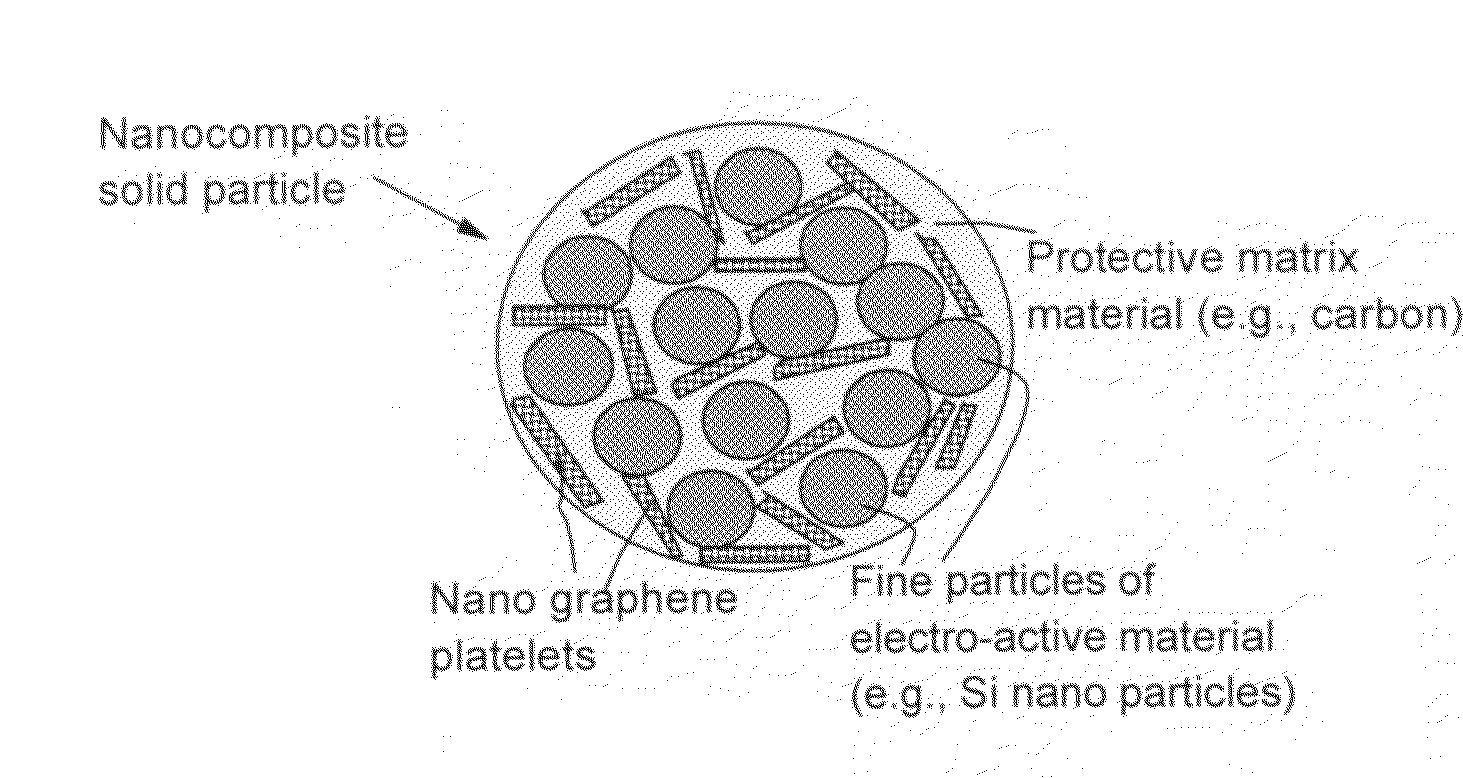
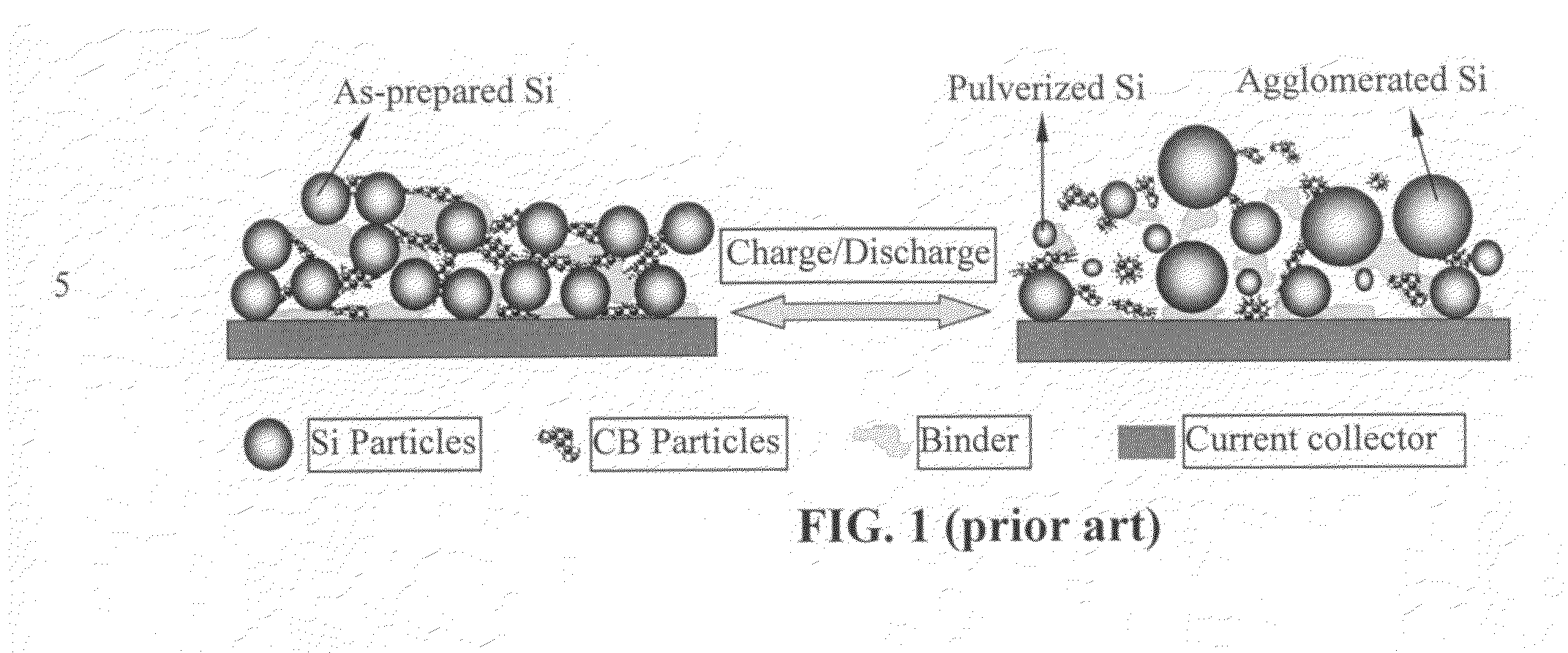
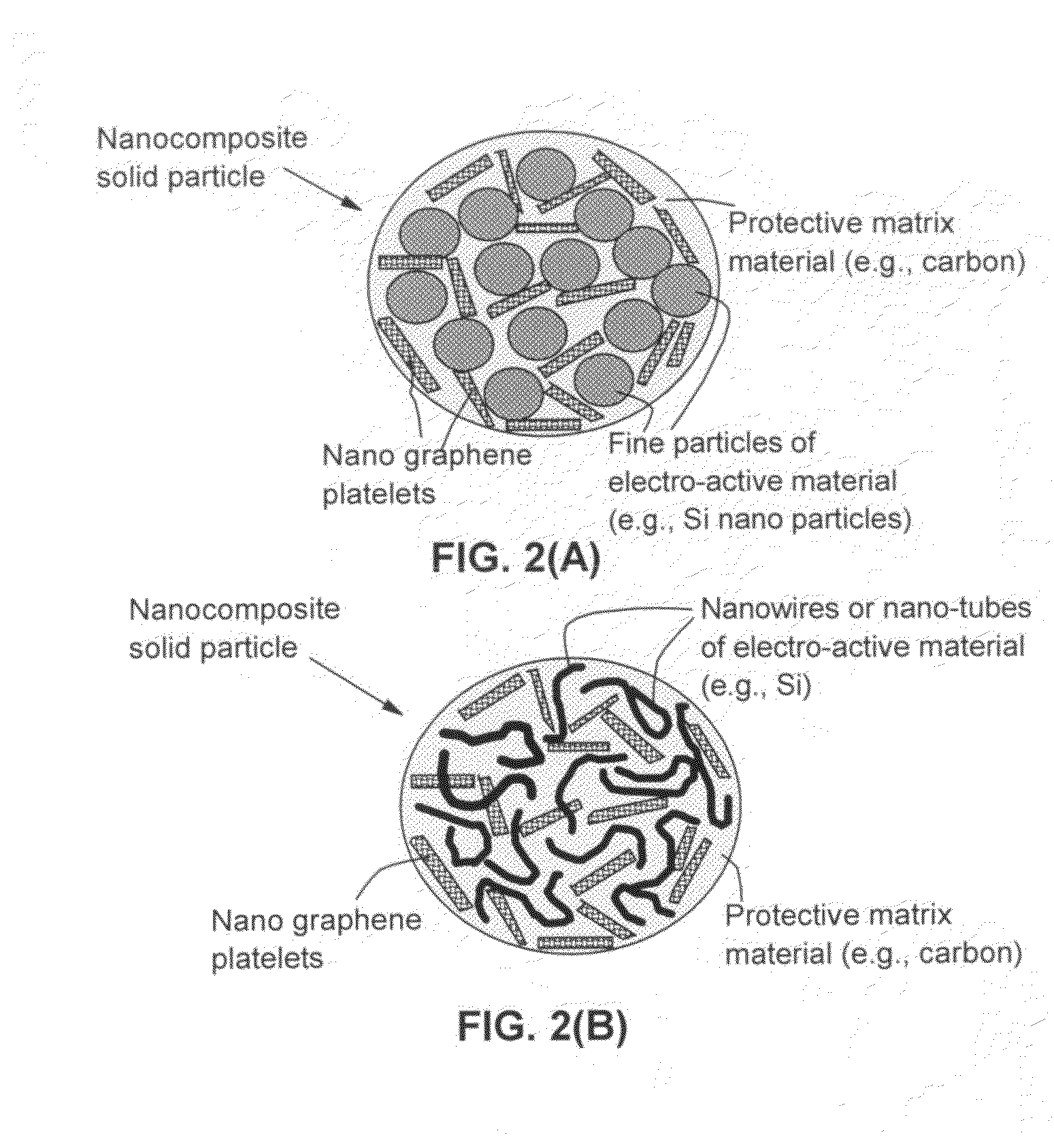
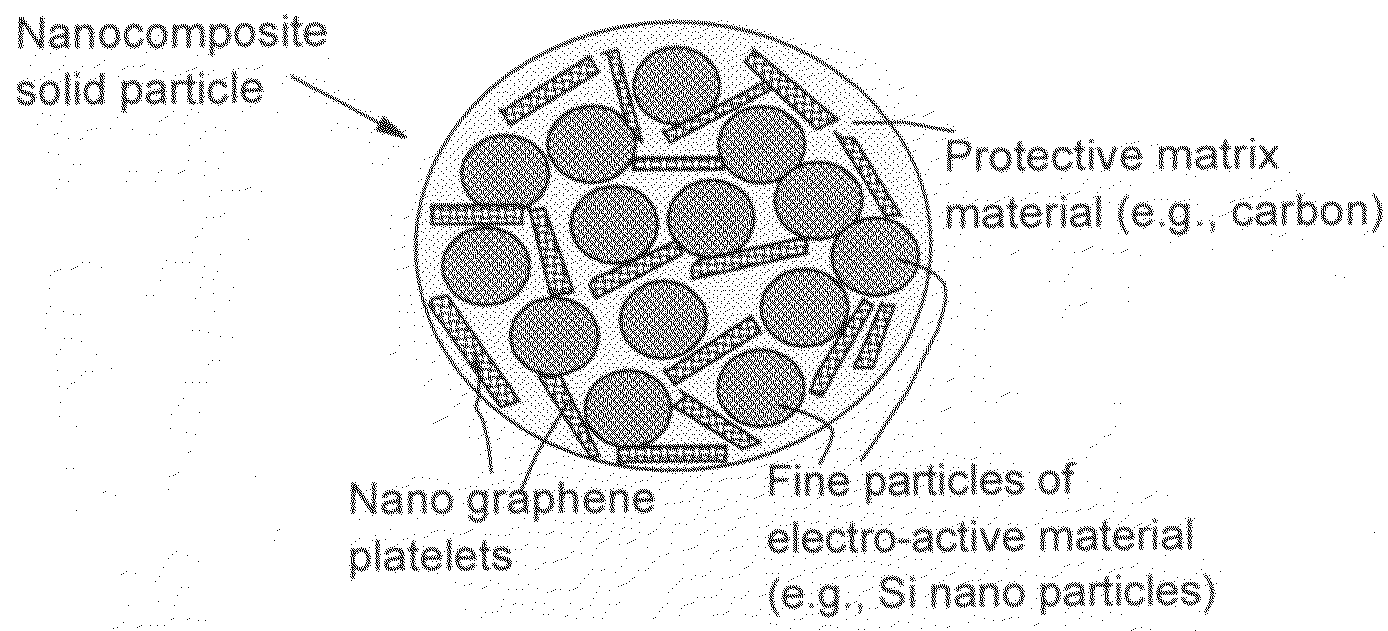
A solid nanocomposite particle composition for lithium metal or lithium ion battery electrode applications. The composition comprises: (A) an electrode active material in a form of fine particles, rods, wires, fibers, or tubes with a dimension smaller than 1 μm; (B) nano graphene platelets (NGPs); and (C) a protective matrix material reinforced by the NGPs; wherein the graphene platelets and the electrode active material are dispersed in the matrix material and the NGPs occupy a weight fraction wg of 1% to 90% of the total nanocomposite weight, the electrode active material occupies a weight fraction wa of 1% to 90% of the total nanocomposite weight, and the matrix material occupies a weight fraction wm of at least 2% of the total nanocomposite weight with wg+wa+wm=1. For a lithium ion battery anode application, the matrix material is preferably amorphous carbon, polymeric carbon, or meso-phase carbon. Such a solid nanocomposite composition provides a high anode capacity and good cycling stability. For a cathode application, the resulting lithium metal or lithium ion battery exhibits an exceptionally high cycle life.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Process for producing nano graphene reinforced composite particles for lithium battery electrodes
ActiveUS20100176337A1Increase stiffnessHigh strengthCell electrodesLi-accumulatorsFiberLithium metal
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
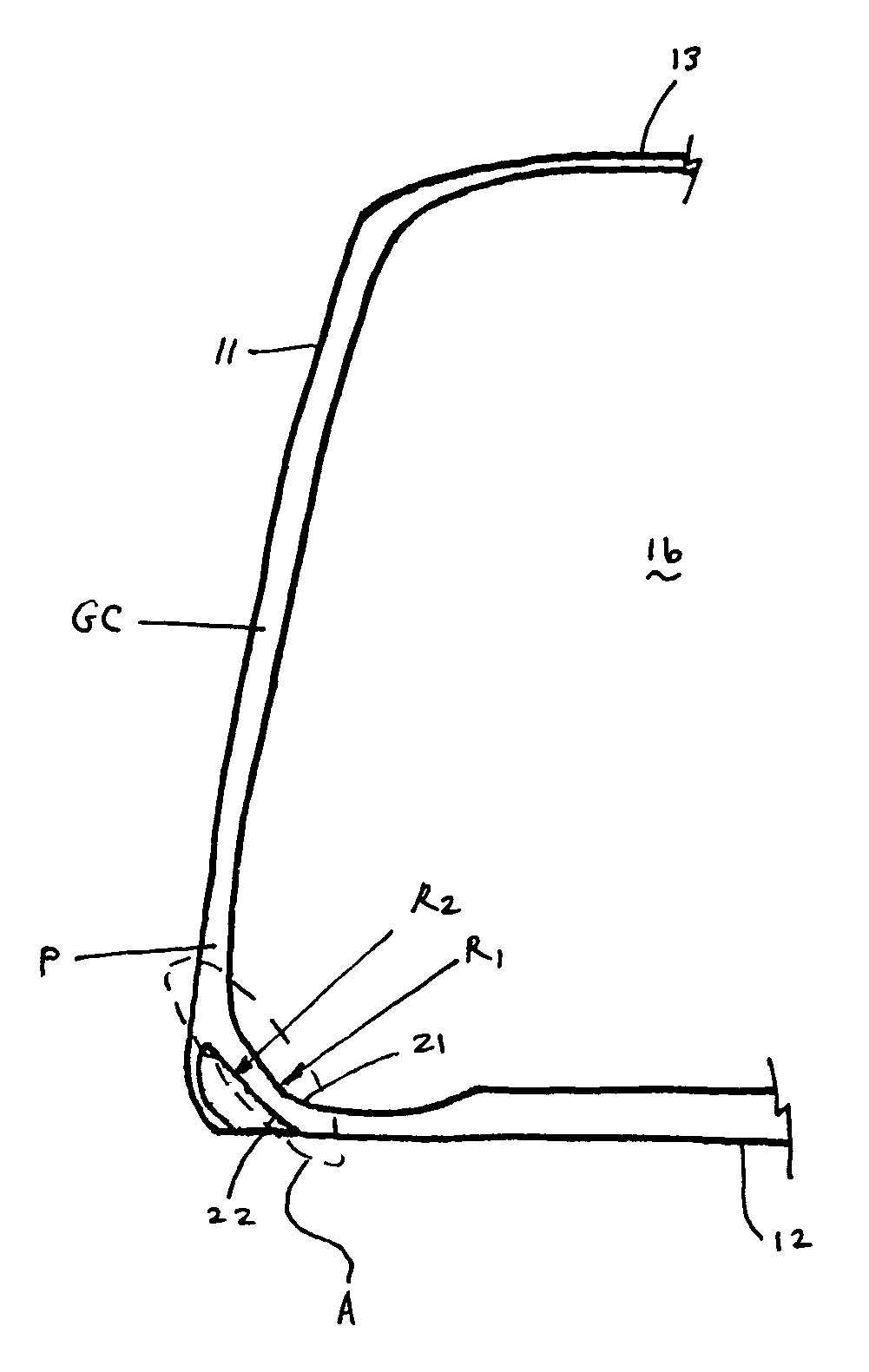
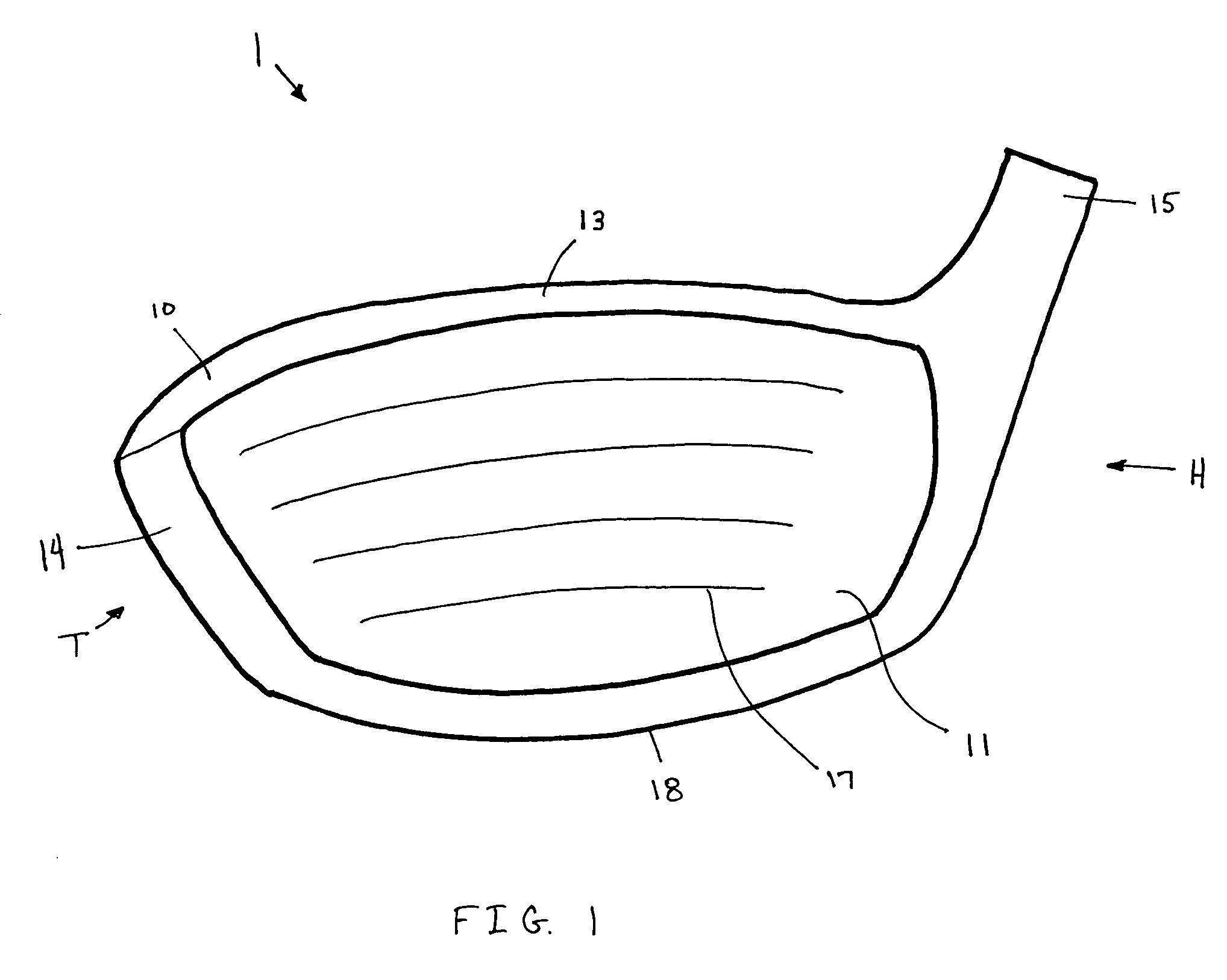
Hollow golf club
InactiveUS7396293B2Improve performanceMaintain structural integrityGolf clubsRacket sportsCoefficient of restitutionGolf Ball
A golf club with improved performance over a larger percentage of the strike face, including the lower extremities of the face, is disclosed and claimed. The club head has a coefficient of restitution that approaches substantial uniformity across the face. The golf club head includes a body having a face, a sole, a transition zone between the face and the sole. The transition zone has an internal surface and an external surface. Both the internal and external surfaces have radii of curvature greater than 0.2 inch. The transition zone transitions smoothly from the face, through the transition zone, to the sole. An extension may be provided adjacent the transition zone, cooperating with the transition zone to form a chamber. Dampening and / or weight inserts may be positioned within the chamber.
Owner:COBRA GOLF
Process for imagewise opening and filling color display components and color displays manufactured thereof
InactiveUS6972893B2Maintain structural integrityWider materialStatic indicating devicesElectrographic processes using photoelectrophoresisDisplay deviceEngineering
Owner:E INK CALIFORNIA
Electrical connector having improved terminal configuration
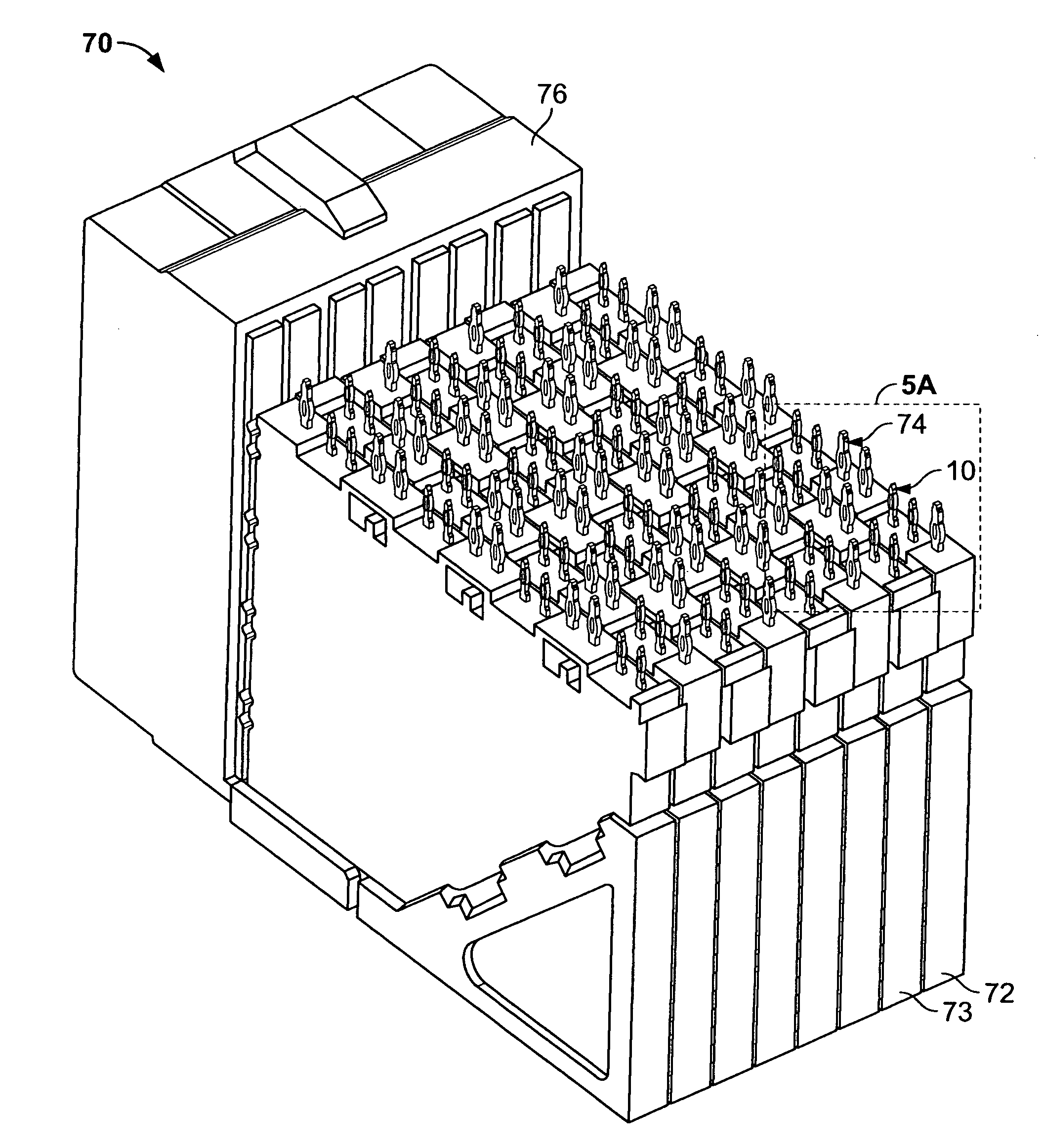
ActiveUS7549897B2Small sizeImproving impedanceElectric discharge tubesSecuring/insulating coupling contact membersElectrical performanceEngineering
An electrical terminal of the type to be inserted into an aperture of an electrical panel member is provided. The electrical terminal may include a base, an insertion portion extending from the base to a first end, a slit formed through the insertion portion and defining a compliant portion having a first leg and a second leg. Midpoints of each or both legs may be offset from the midpoint of the slit to achieve improved mechanical and electrical performance within a connector. Also provided is an electrical terminal having a tip that facilitates alignment with a panel member aperture and provides tactile feedback to a user, as well as an electrical terminal having a mounting end that is substantially smaller than its mating end, and connectors containing such terminals. Methods of routing electrical traces between adjacent electrical terminals are also provided.
Owner:TYCO ELECTRONICS LOGISTICS AG (CH)
Vapor chamber structure and method for manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20090040726A1Improve structural strengthImprove sealingSpacing meansReinforcing meansWorking fluidEngineering
A vapor chamber structure includes a casing, a working fluid, a wick layer, a plurality of structure strengthening bodies, and a plurality of backflow accelerating bodies. The casing has an airtight vacuum chamber. The working fluid is filled into the airtight vacuum chamber. The wick layer is formed on a surface of the airtight vacuum chamber. The structure strengthening bodies are respectively arranged in the airtight vacuum chamber for supporting the casing. The backflow accelerating bodies are respectively arranged in the airtight vacuum chamber for increasing the backflow velocity of the working fluid. Therefore, the present invention can maintain the completeness of the vapor chamber structure and increase the backflow velocity of the working fluid due to the match of the structure strengthening bodies and backflow accelerating bodies. Because the backflow velocity of the working fluid is increased, the heat-transmitting efficiency is increased.
Owner:THERMAL TECH
Process for imagewise opening and filling color display components and color displays manufactured thereof
InactiveUS7385751B2Wider materialWider processElectrographic processes using photoelectrophoresisElectrographic process apparatusDisplay deviceEngineering
Owner:E INK CALIFORNIA
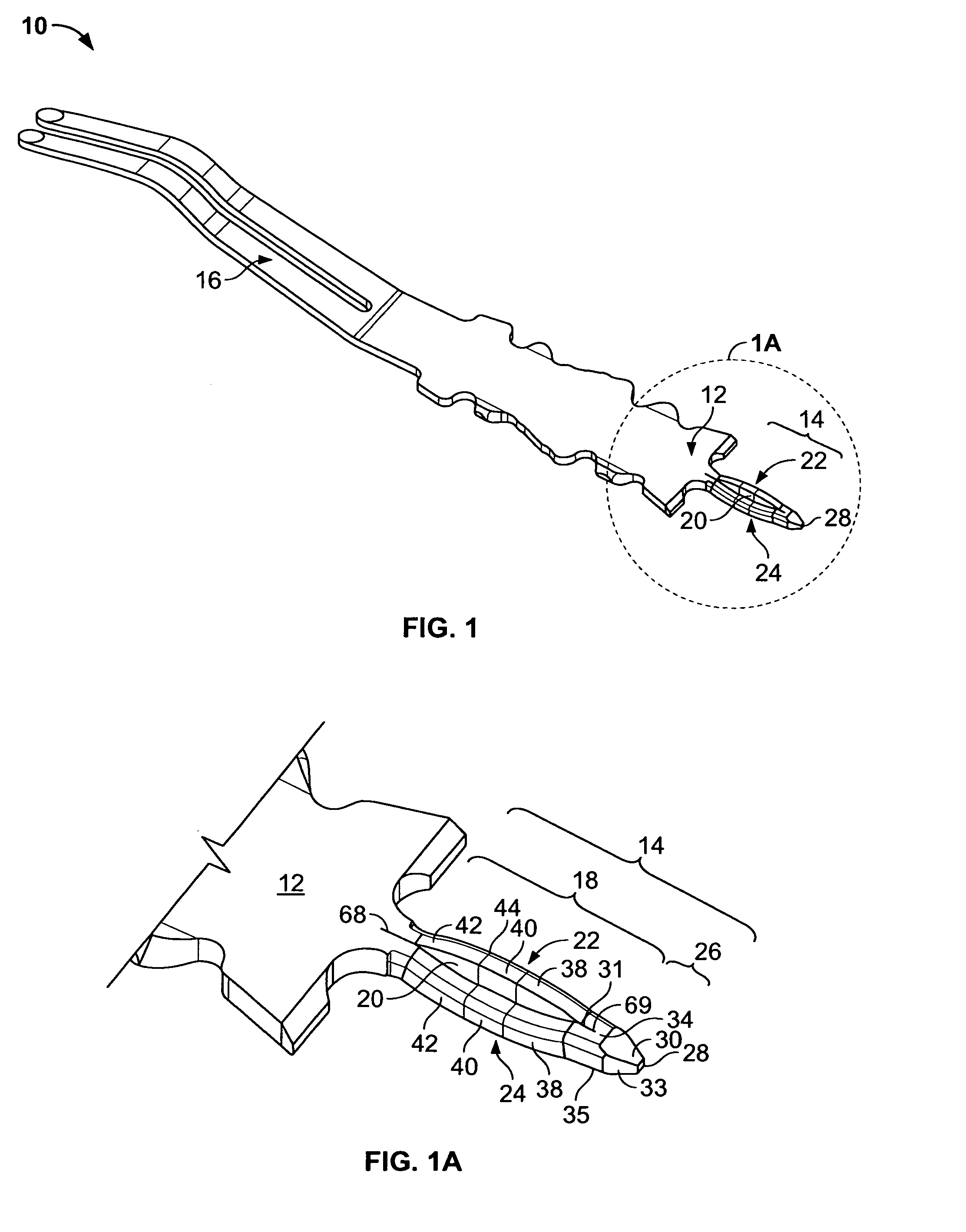
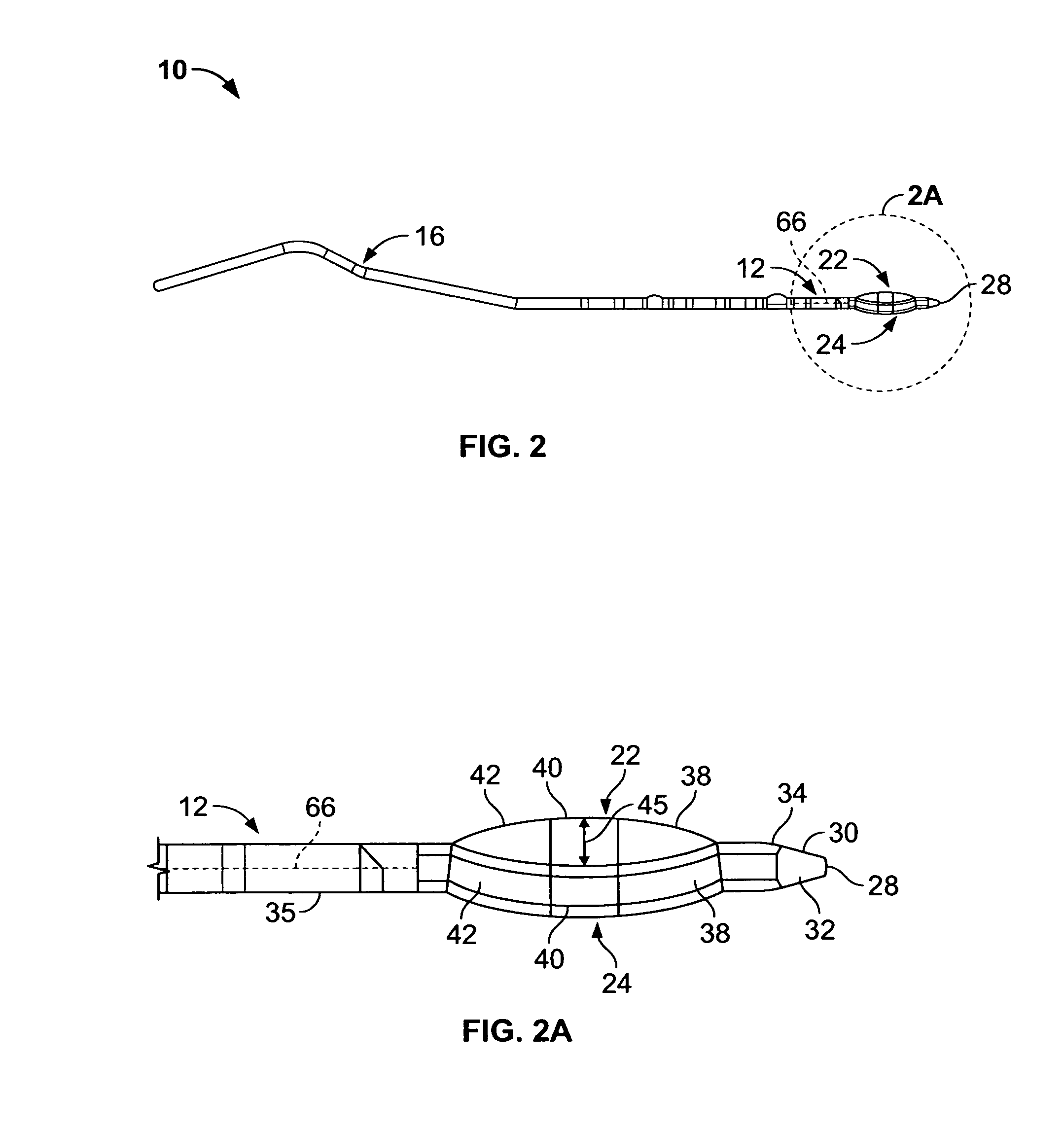
Smart bio-nanoparticle elements
ActiveUS20070141163A1Easy to handleLow profileUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsMaterial nanotechnologyNanoparticleProtein molecules
The invention in suitable embodiments is directed to smart bio-nanoparticle elements and intelligent bio-nanoparticle platforms employing such smart bio-nanoparticle elements. In one aspect, the smart bio-nanoparticle elements are formed with self-assembling protein molecules.
Owner:METAQOR
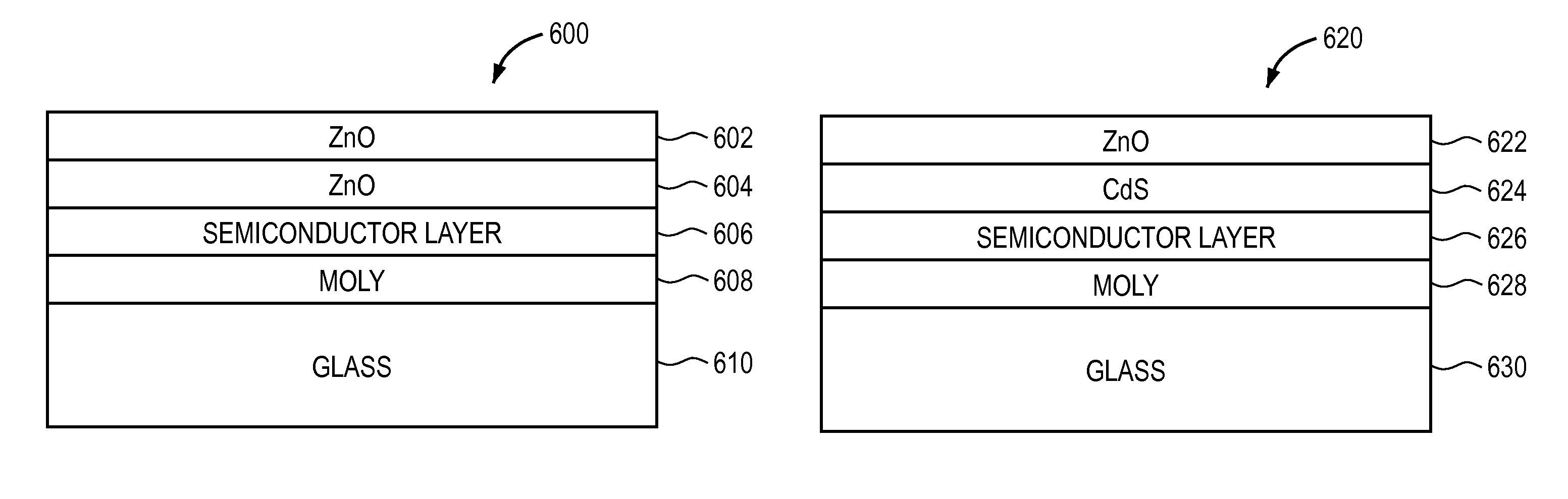
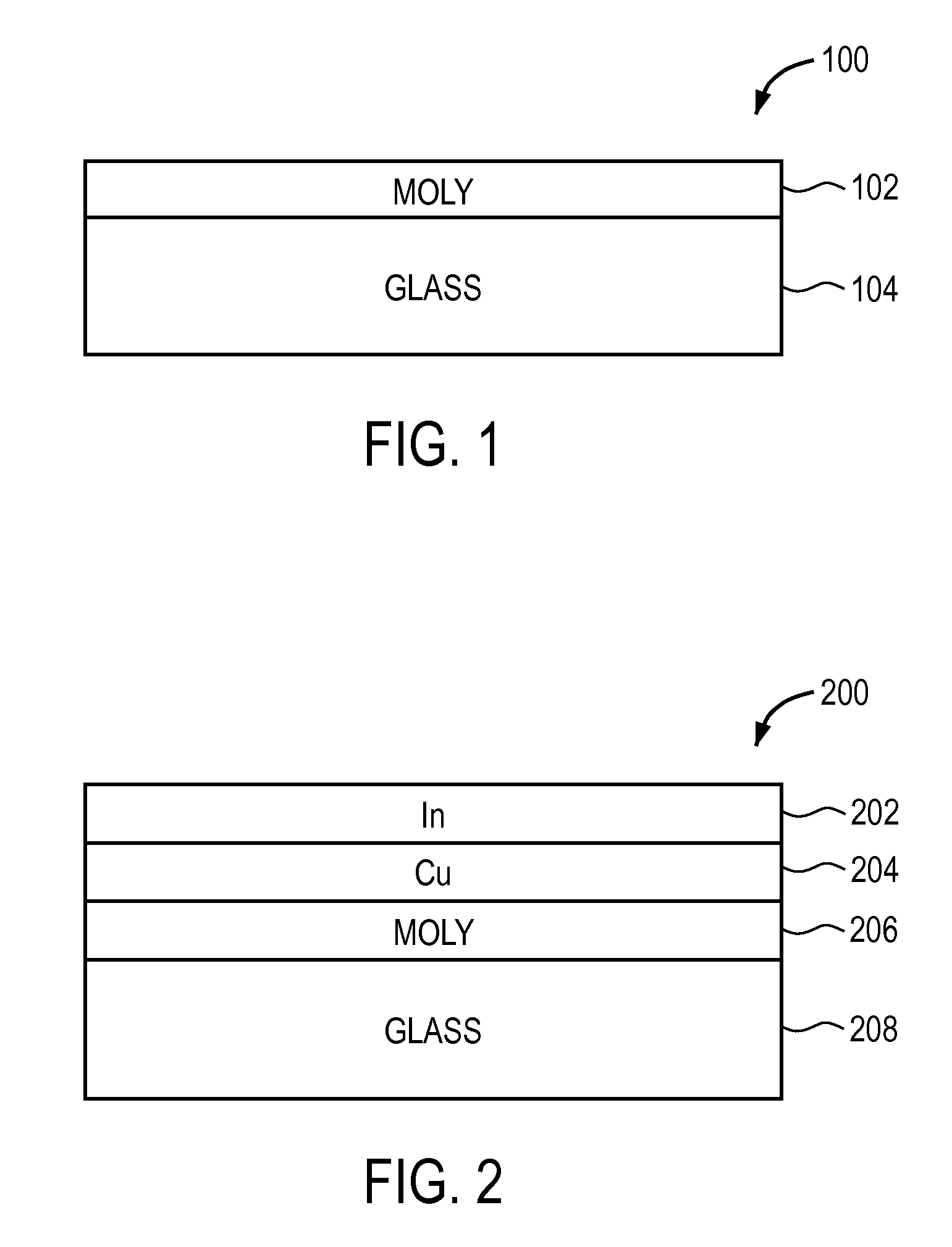
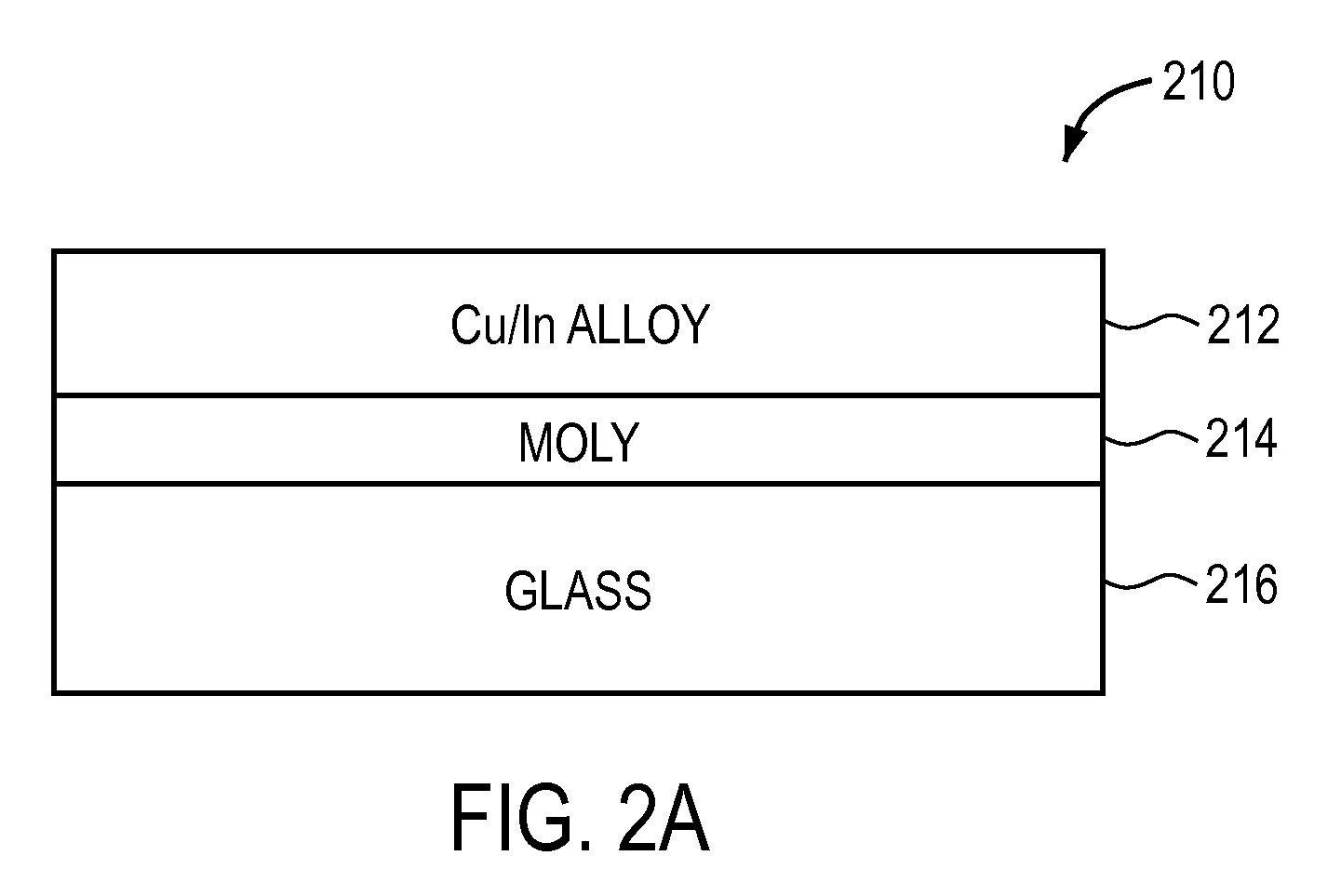
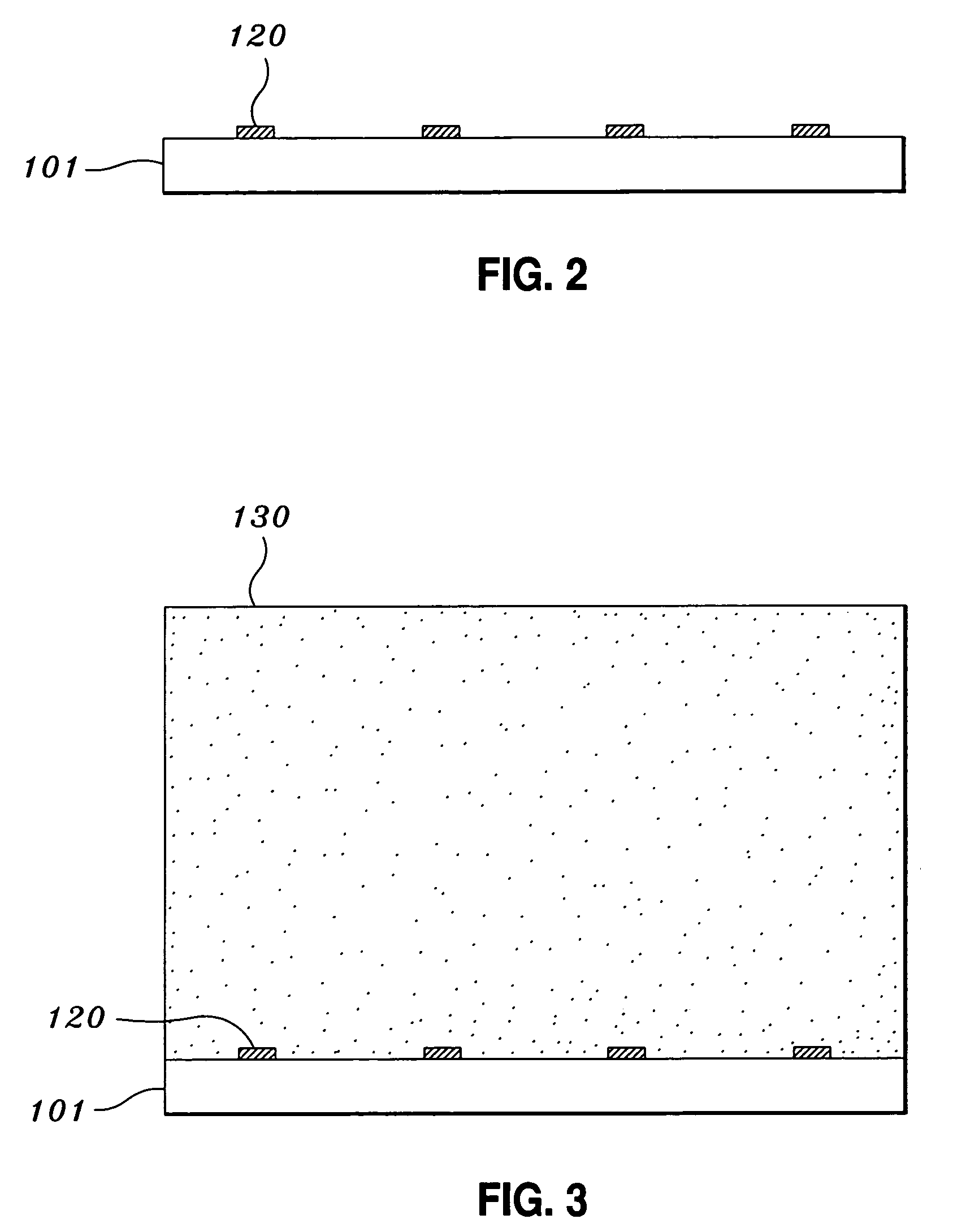
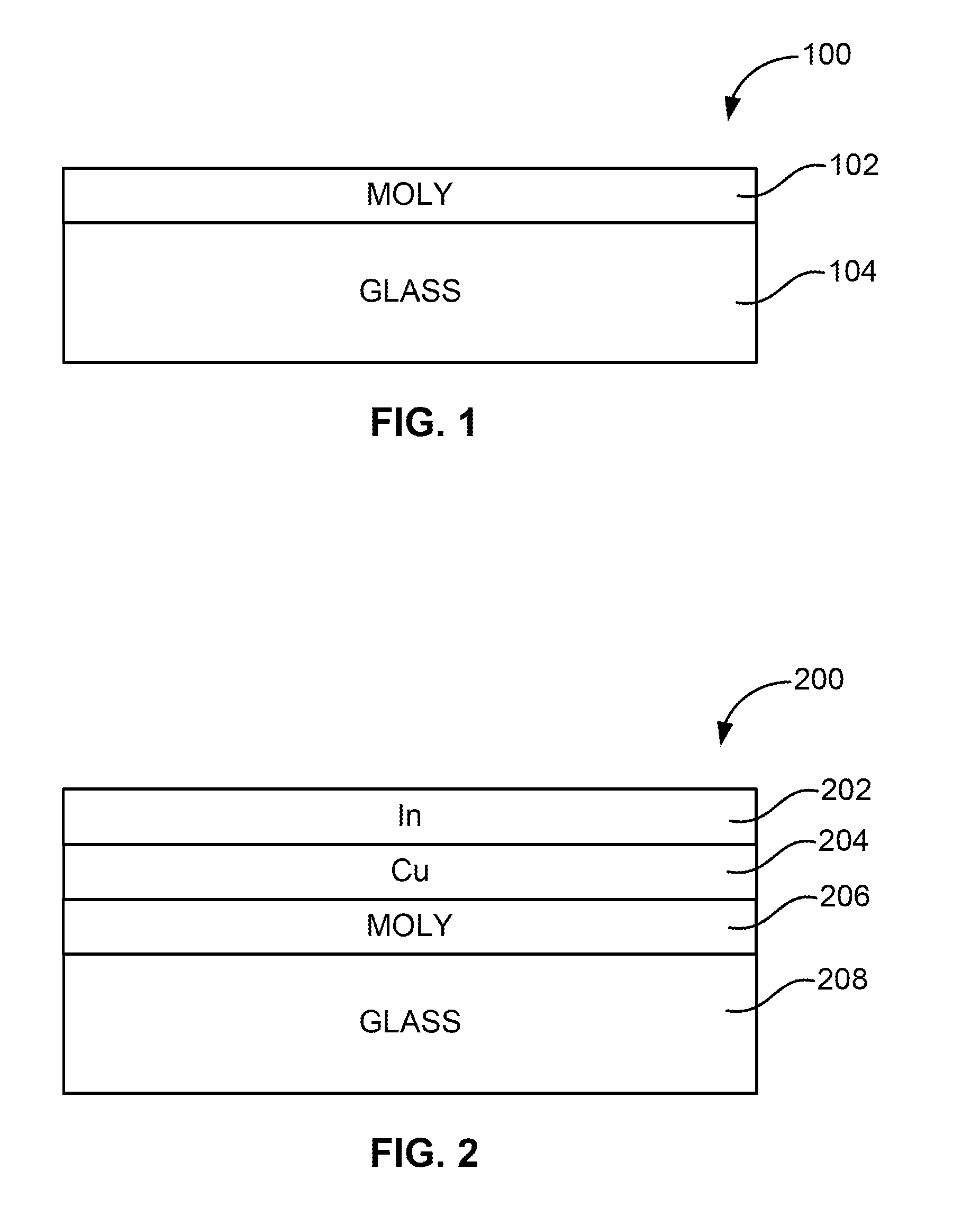
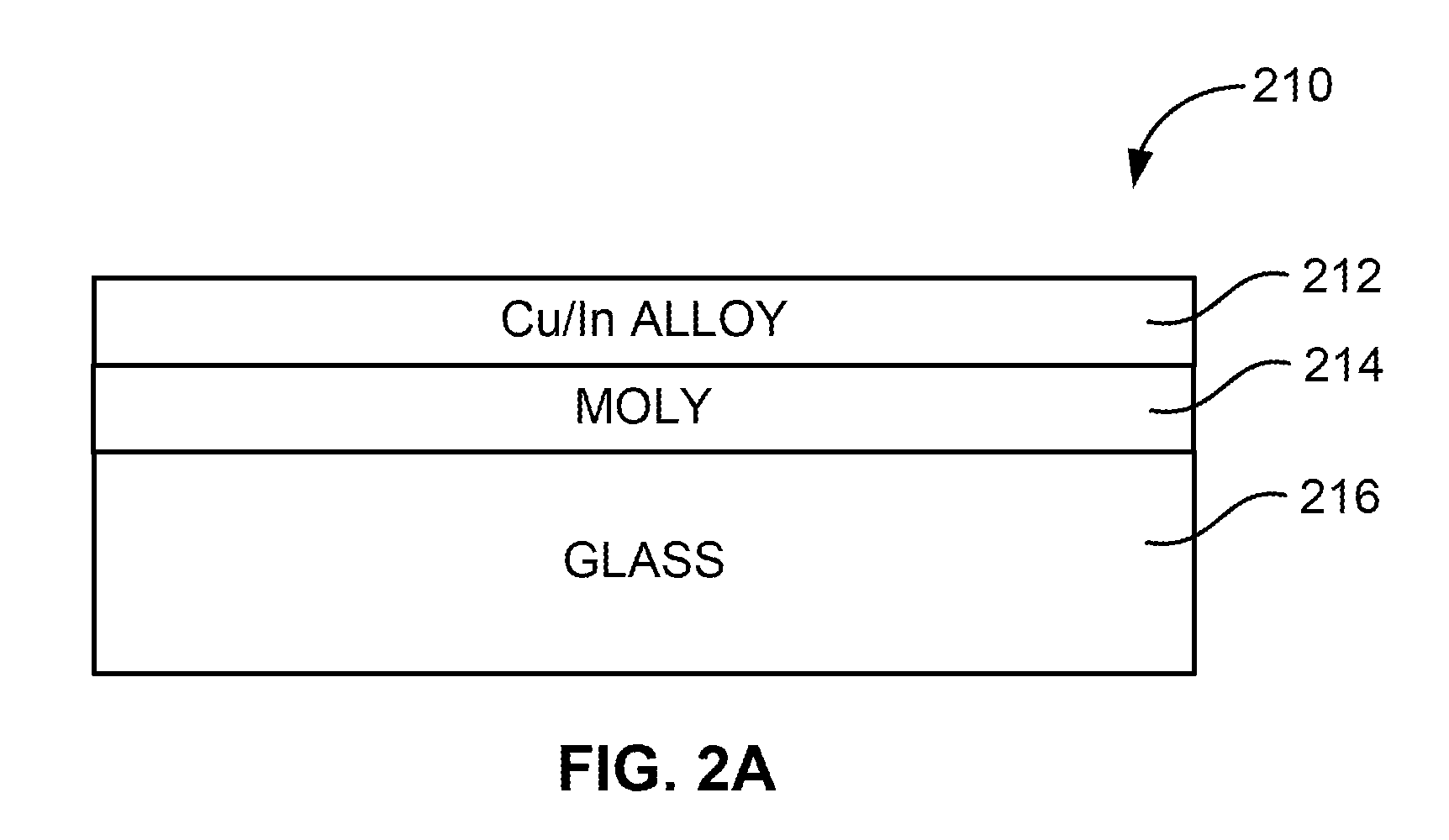
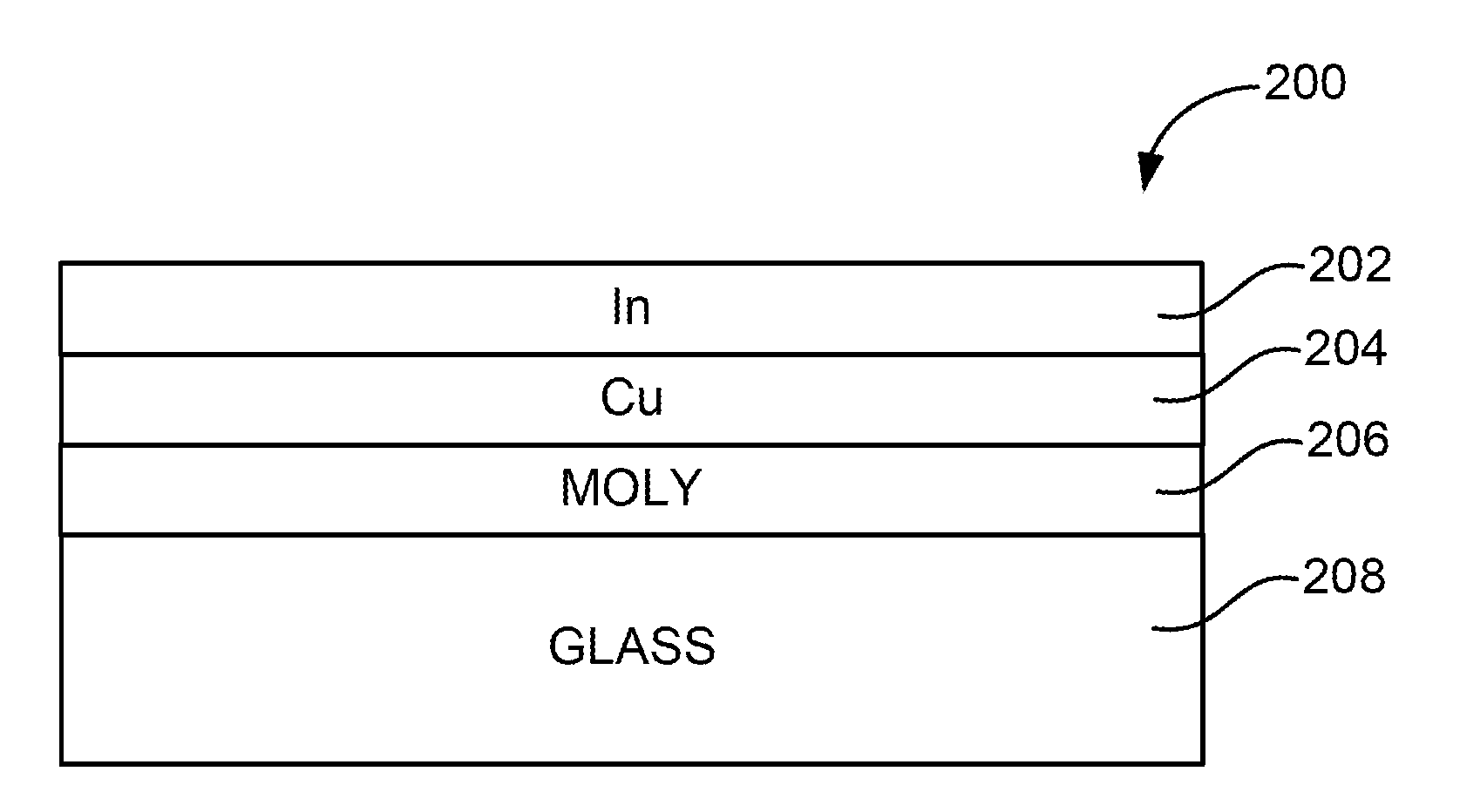
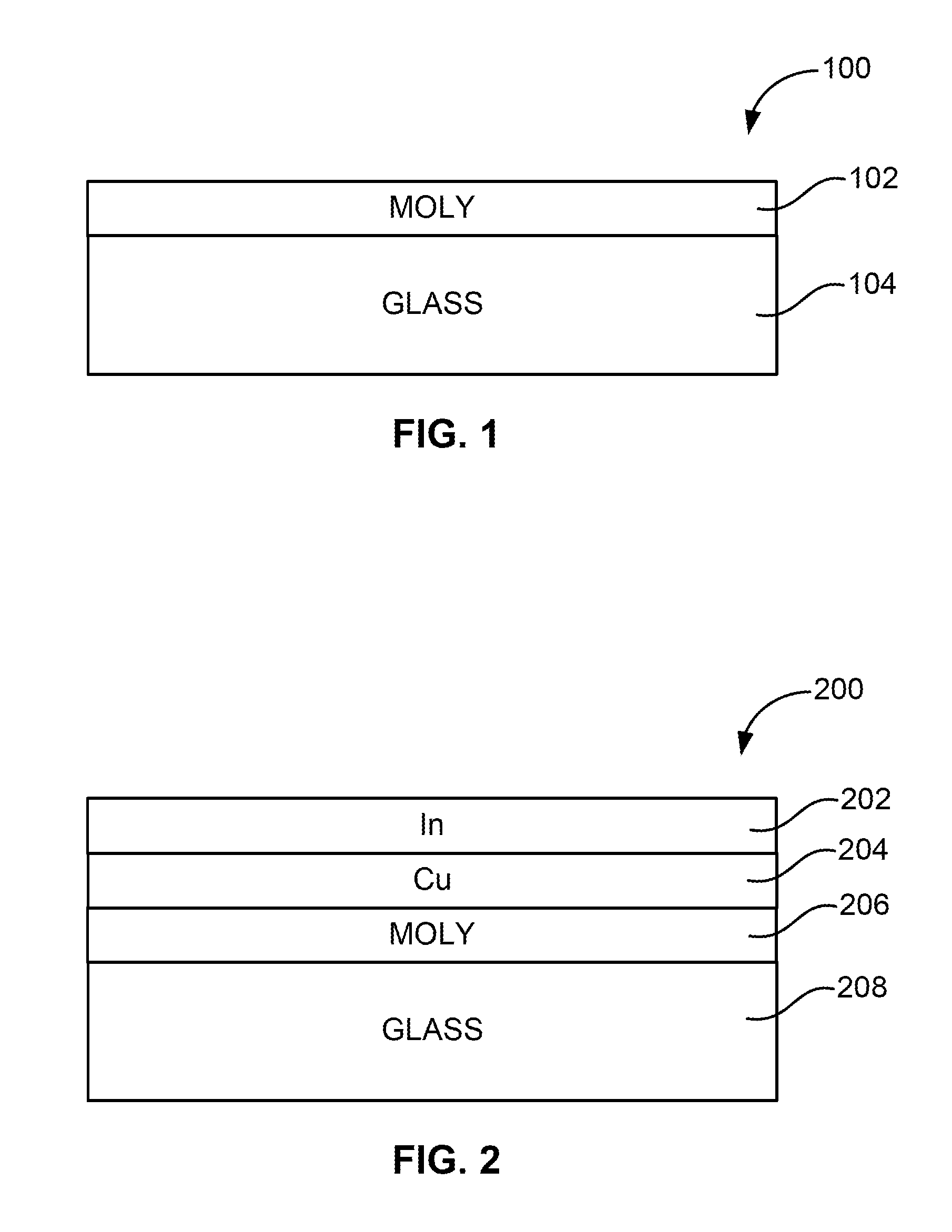
Thermal management and method for large scale processing of CIS and/or CIGS based thin films overlying glass substrates
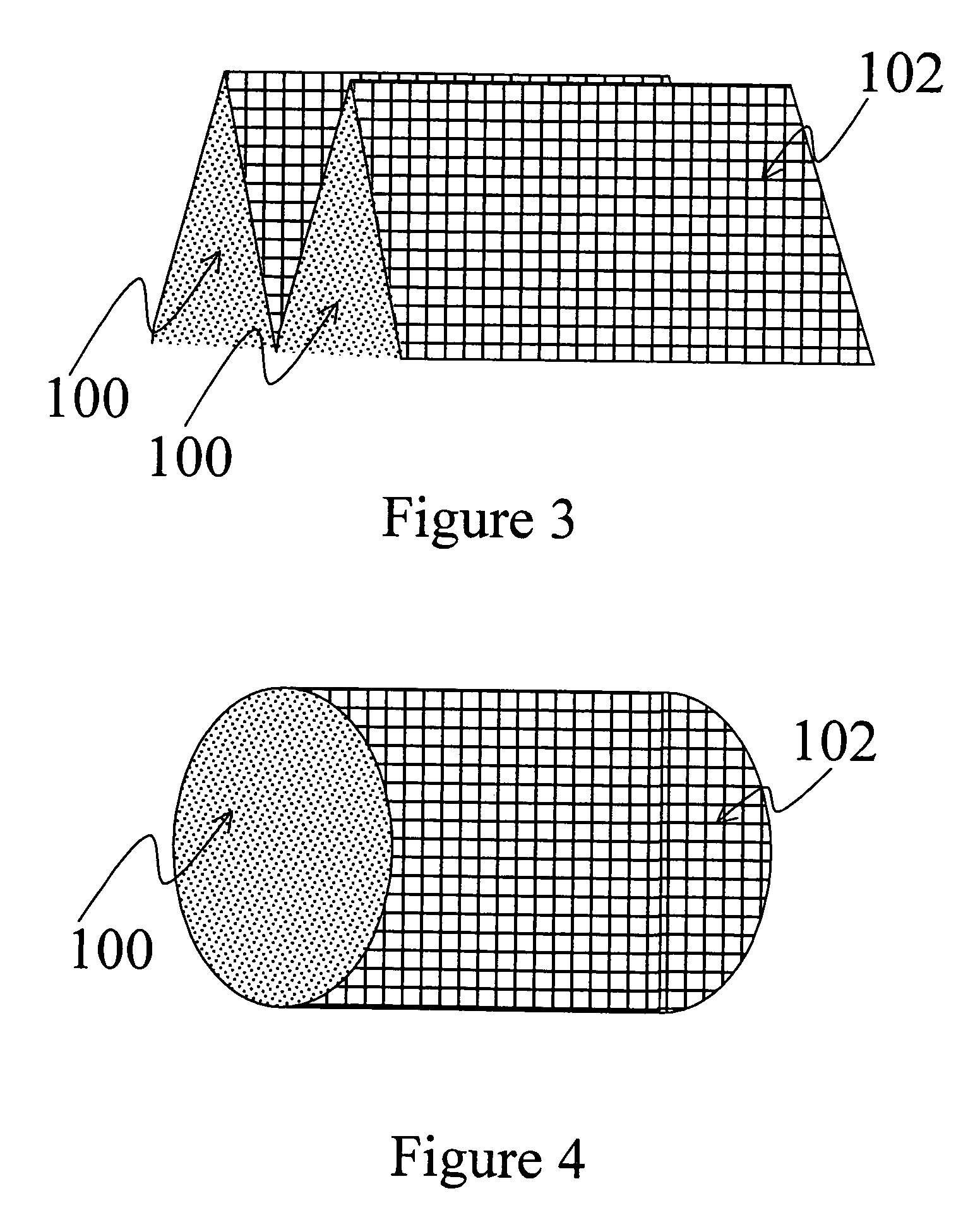
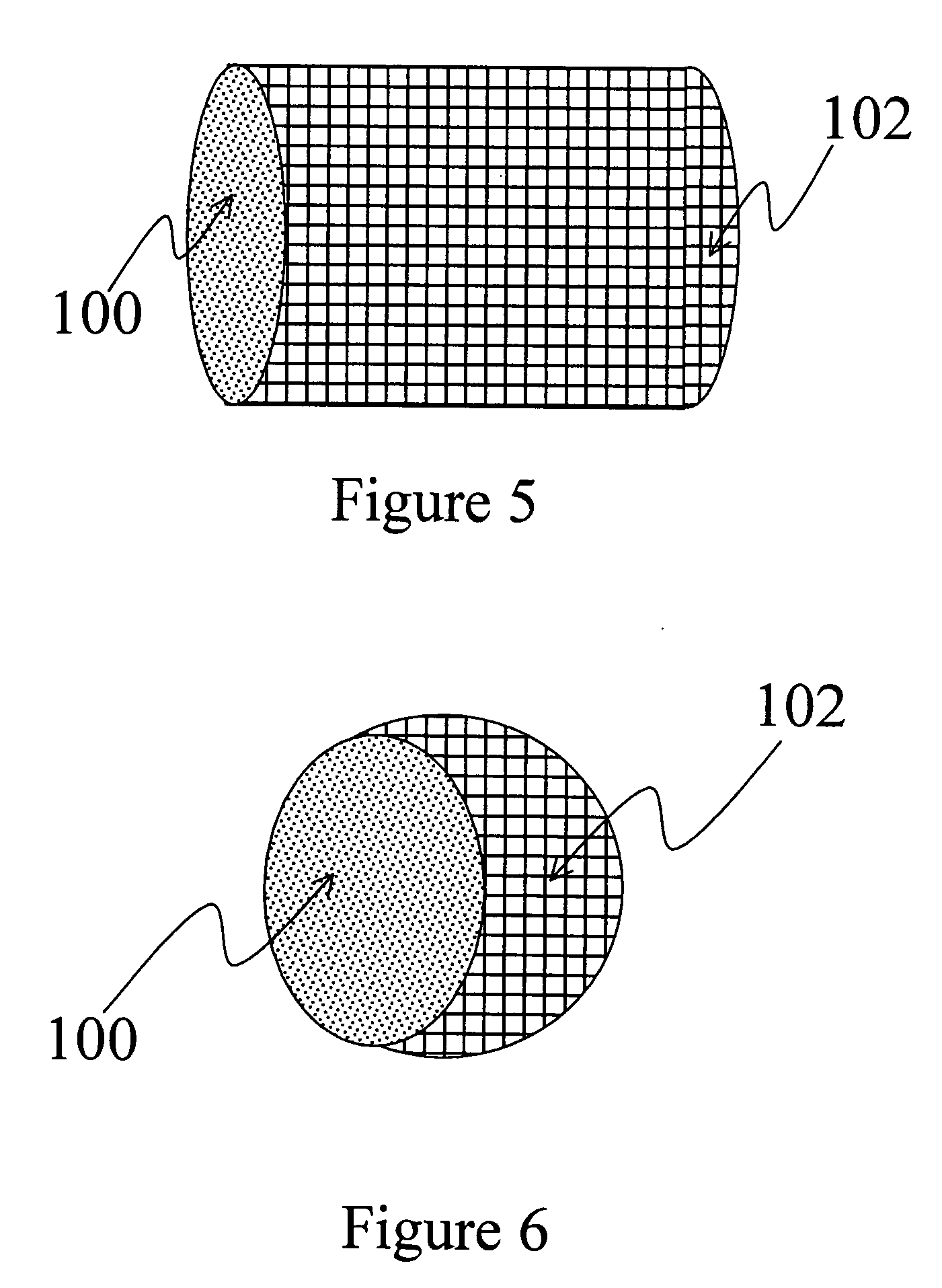
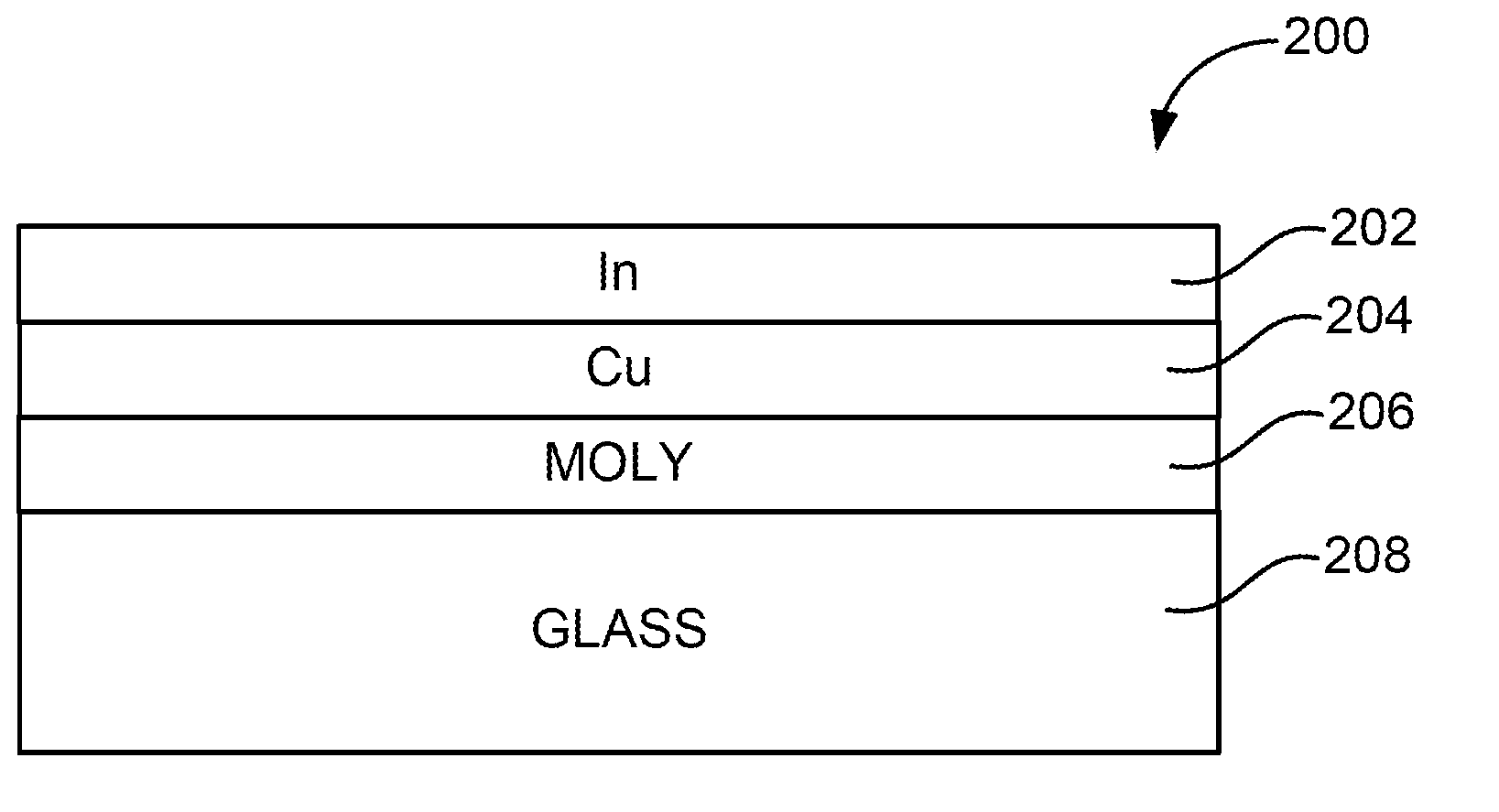
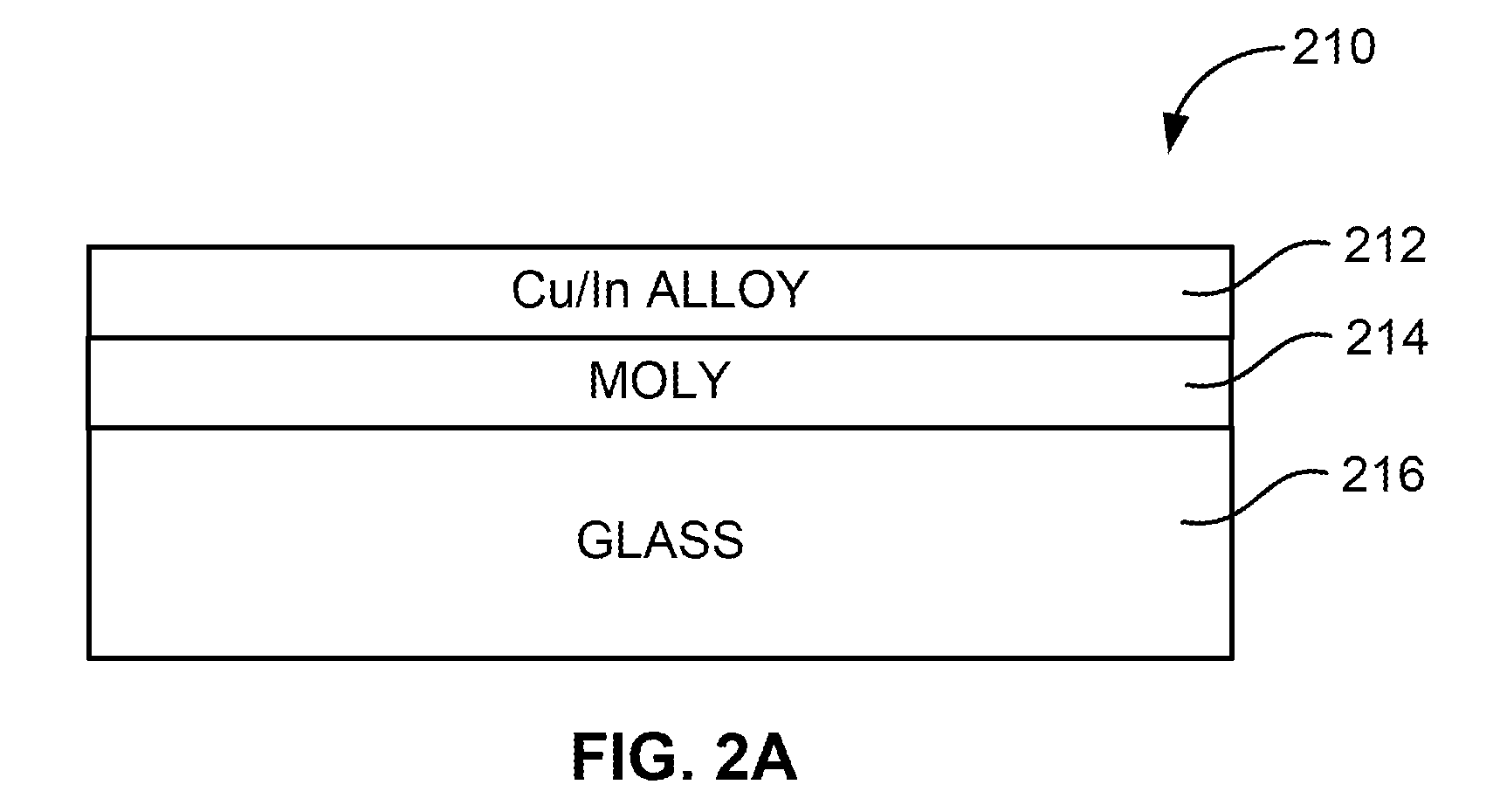
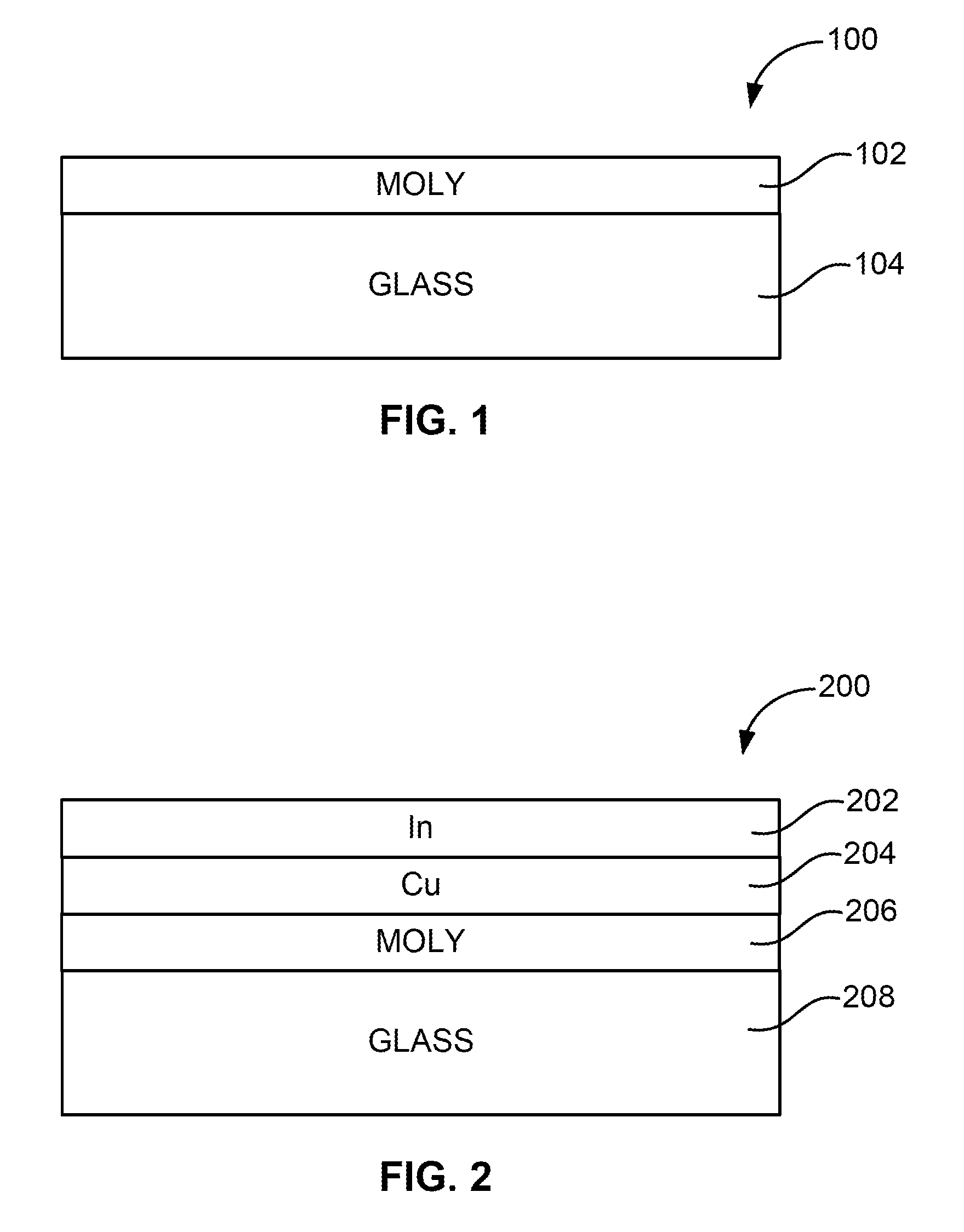
InactiveUS7910399B1Implemented cost-effectivelyMaintain structural integrityFinal product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingThermal energyIndium
The thermal management and method for large scale processing of CIS and / or CIGS based thin film overlaying glass substrates. According to an embodiment, the present invention provides a method for fabricating a copper indium diselenide semiconductor film. The method includes providing a plurality of substrates, each of the substrates having a copper and indium composite structure. The method also includes transferring the plurality of substrates into a furnace, each of the plurality of substrates provided in a vertical orientation with respect to a direction of gravity, the plurality of substrates being defined by a number N, where N is greater than 5. The method further includes introducing a gaseous species including a selenide species and a carrier gas into the furnace and transferring thermal energy into the furnace to increase a temperature from a first temperature to a second temperature, the second temperature ranging from about 350° C. to about 450° C. to at least initiate formation of a copper indium diselenide film from the copper and indium composite structure on each of the substrates.
Owner:CM MFG
Process for imagewise opening and filling color display components and color displays manufactured thereof
InactiveUS6914714B2Easy and efficient to prepareReduce processing costsStatic indicating devicesElectrographic processes using photoelectrophoresisEngineeringDisplay device
Owner:E INK CALIFORNIA
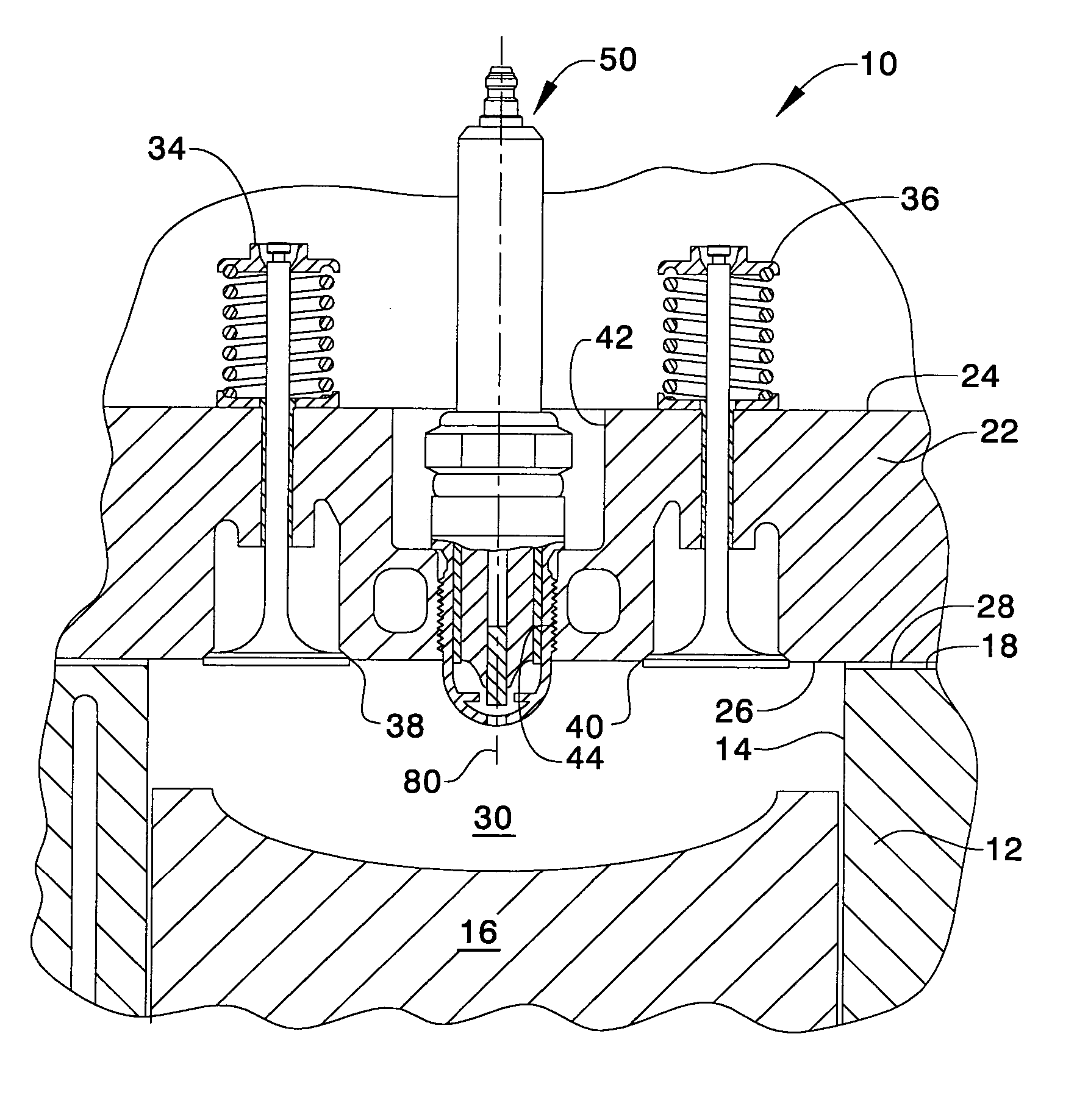
Pre-chambered type spark plug with pre-chamber entirely below a bottom surface of a cylinder head
InactiveUS20050211217A1Maintain structural integritySparking plugsInternal combustion piston enginesCombustion chamberEngineering
The present spark plug is of the encapsulated design and facilitates the life of the spark plug, enhances the combustion process and reduces emissions. The position of an ignition chamber of the spark plug is substantially within a combustion chamber of an engine. The configuration of a parabolic end forms the ignition chamber, reduces the heat transferred to the spark plug and increases the life of the spark plug. The configuration or design of the spark plug makes the manufacturing process less costly and facilitates the combustion process by using one of a single orifice or a plurality of orifices positioned at and in a preestablished manner. The configuration will reduce or eliminate pre-ignition and other detonation problems enabling the timing to be advanced further reducing emissions.
Owner:CATERPILLAR INC
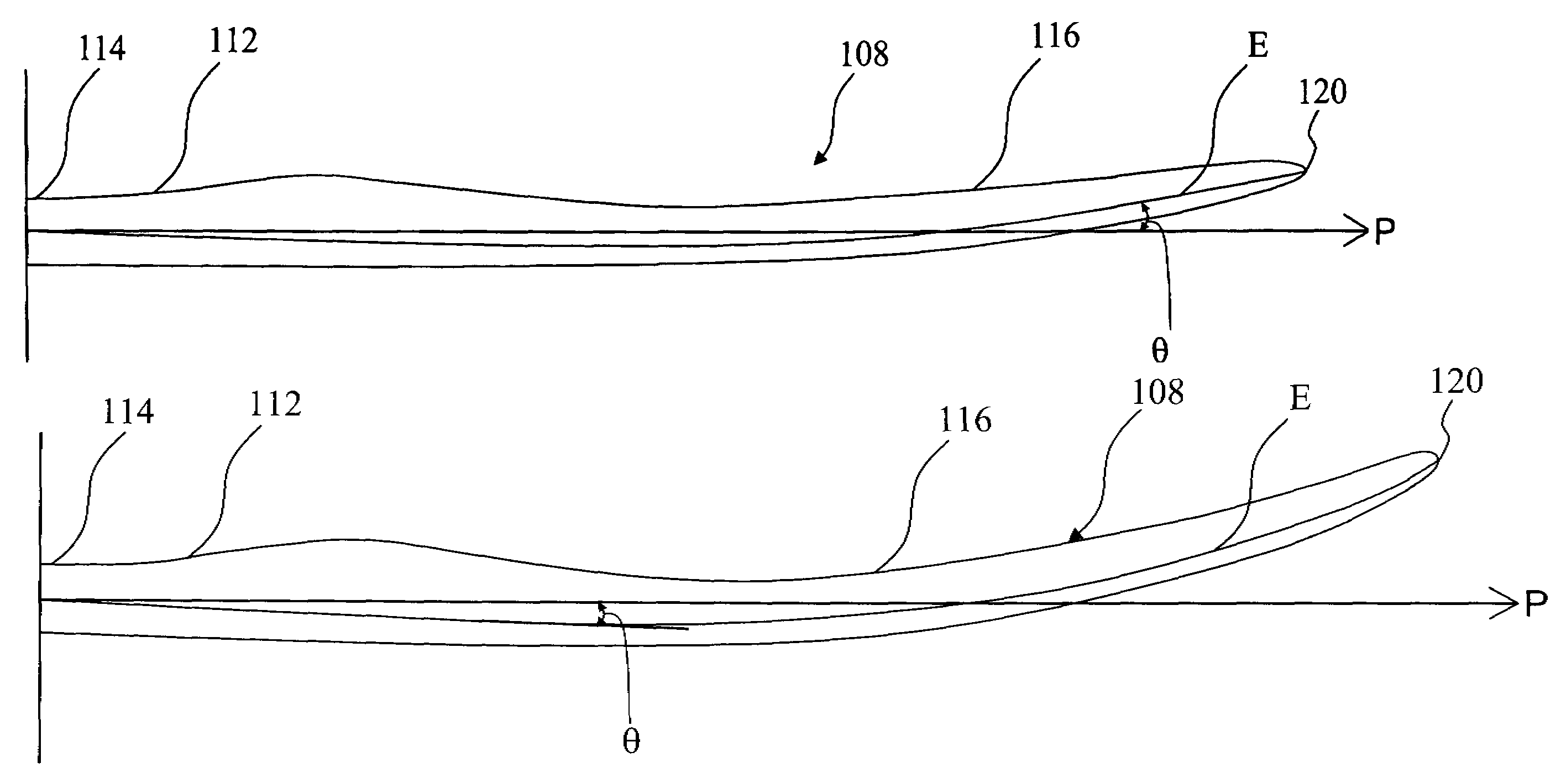
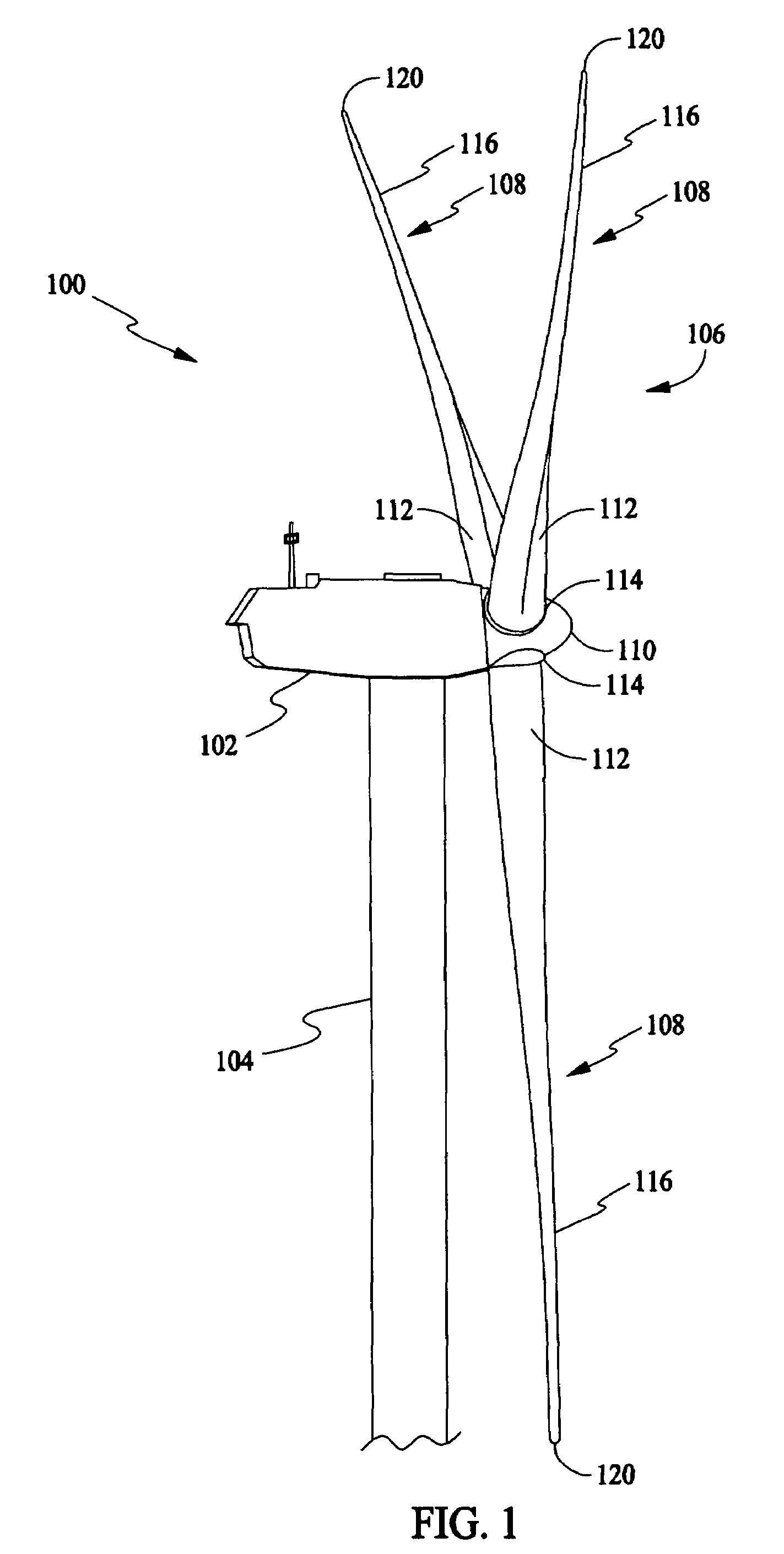
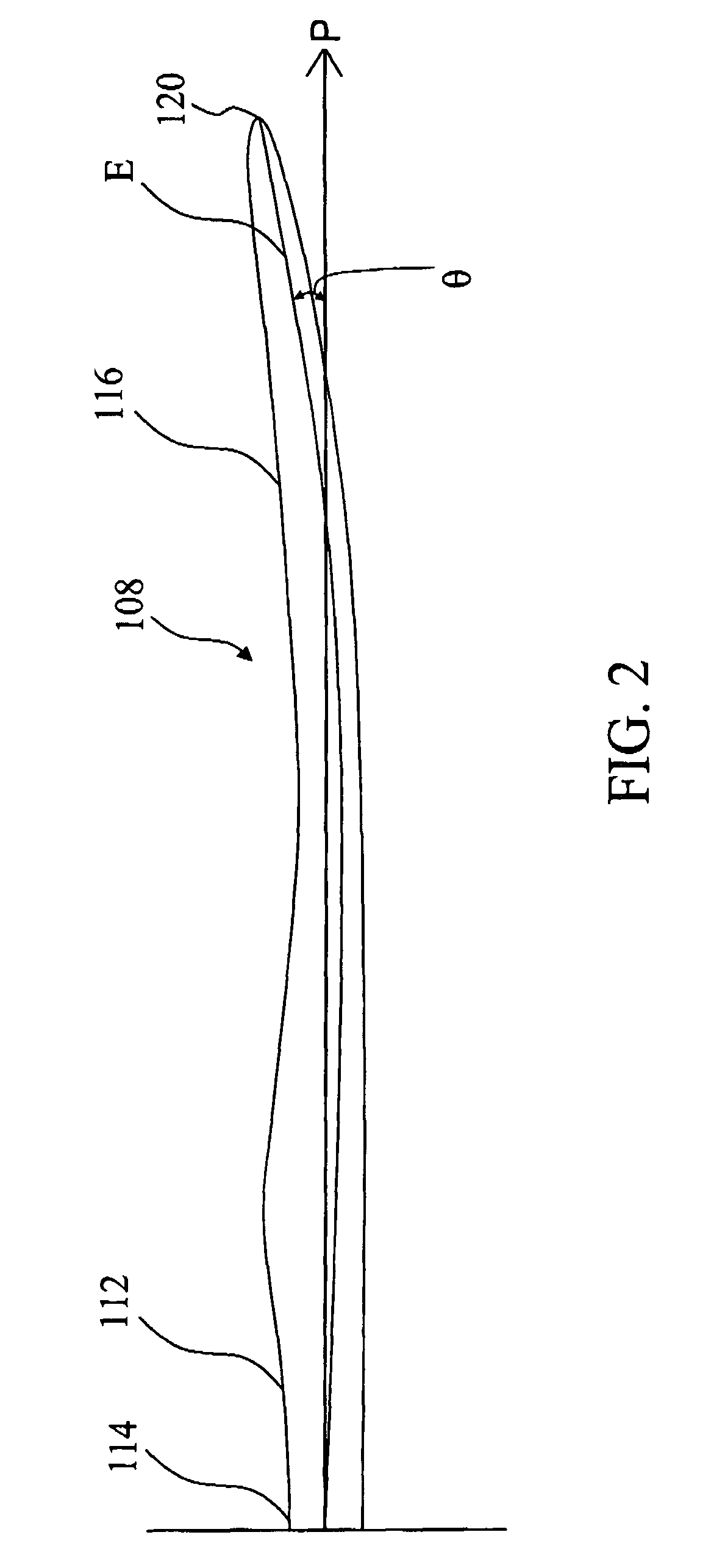
Wind turbine rotor blade with in-plane sweep and devices using same, and methods for making same
ActiveUS7344360B2Quantity maximizationReduce loadPropellersPump componentsClassical mechanicsEngineering
A wind turbine includes a rotor having a hub and at least one blade having a torsionally rigid root, an inboard section, and an outboard section. The inboard section has a forward sweep relative to an elastic axis of the blade and the outboard section has an aft sweep.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
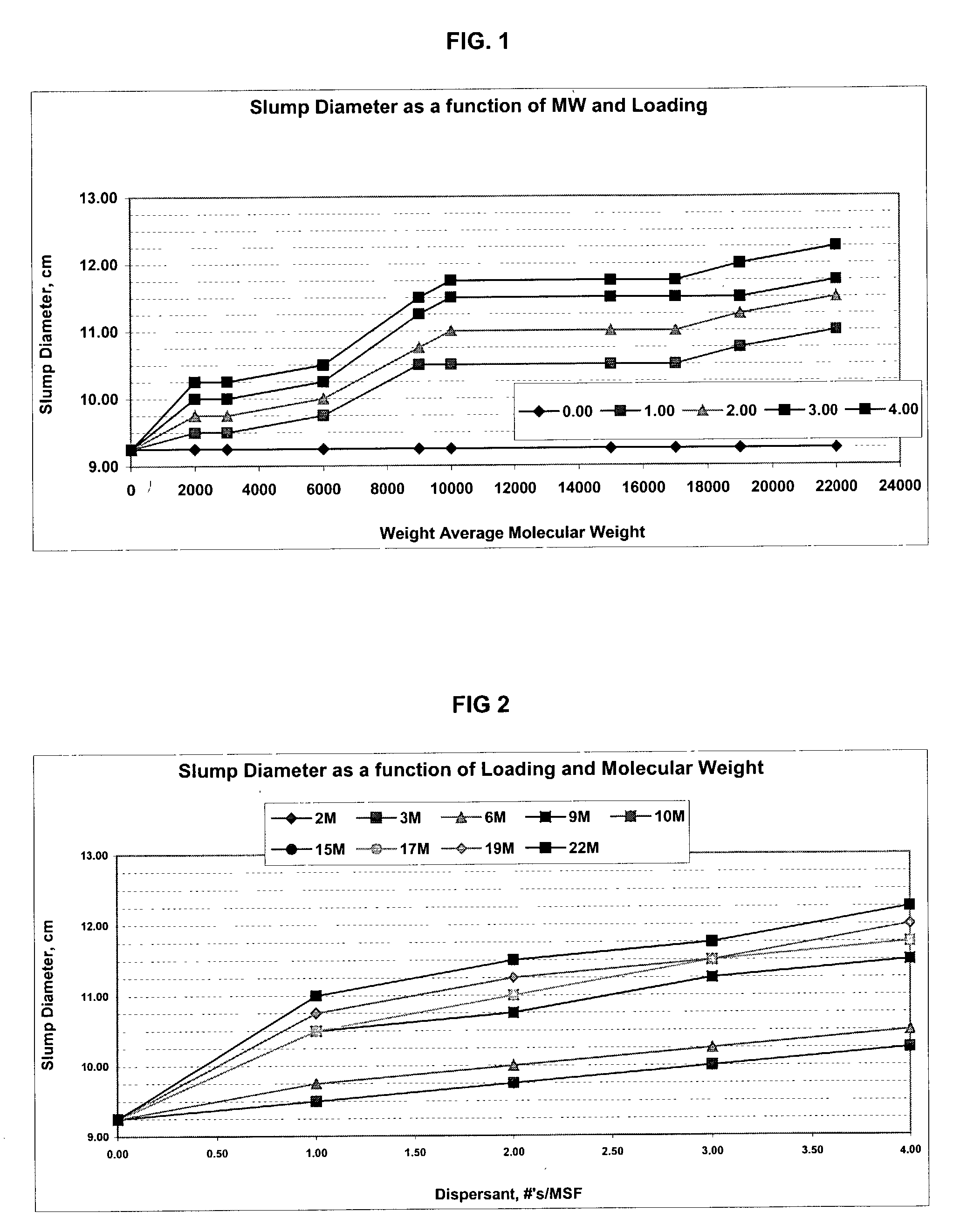
Dispersant and foaming agent combination
InactiveUS20040028956A1Low densityReduce weightConstruction materialOther chemical processesAlkaline earth metalAir entrainment
The present invention provides a dispersant and foaming agent combination that is useful in the production of gypsum wallboard and other aqueous cementitious products, a method of forming a gypsum wallboard and a gypsum wallboard. The dispersant in the combination according to the invention is a naphthalene sulfonate-aldehyde condensate alkali salt polymer having a weight average molecular weight of from about 17,000 to about 47,000. The alkali is preferably an alkali metal and / or an alkaline earth metal. The aldehyde is preferably formaldehyde. The foaming agent used in the combination according to the invention is a soap, preferably an alkali salt of an alkyl ether sulfate and / or an alkyl sulfate. The combination of a high molecular weight dispersant and a foaming agent produces a gypsum wallboard core effect that more efficiently entrains air (i.e., creates void space), thereby lowering overall board weight without detrimentally affecting strength. A gypsum wallboard formed using the dispersant and foaming agent combination according to the invention exhibits a higher nail pull value than gypsum wallboard formed using a conventional dispersant and a foaming agent at the same solids loading ratio.
Owner:GEO SPECIALTY CHEM
Phonon-blocking, electron-transmitting low-dimensional structures
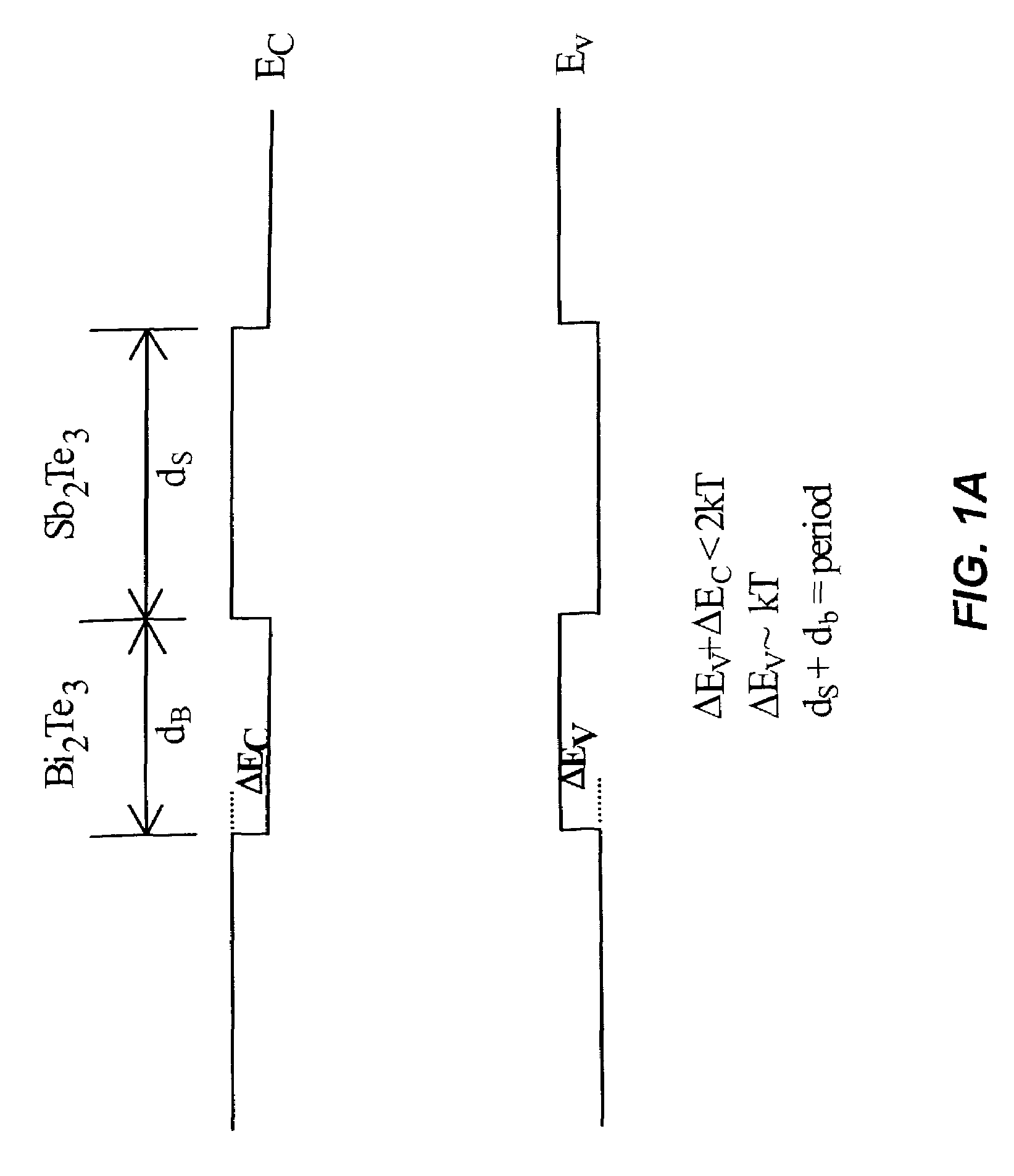
ActiveUS7342169B2Lower lattice thermal conductivityImprove ZTThermoelectric device with peltier/seeback effectThermoelectric device manufacture/treatmentLattice mismatchCharge carrier
A thermoelectric structure and device including at least first and second material systems having different lattice constants and interposed in contact with each other, and a physical interface at which the at least first and second material systems are joined with a lattice mismatch and at which structural integrity of the first and second material systems is substantially maintained. The at least first and second material systems have a charge carrier transport direction normal to the physical interface and preferably periodically arranged in a superlattice structure.
Owner:LAIRD THERMAL SYST INC
Method for preparing and processing a sample for intensive analysis
ActiveUS20050012244A1Accurate measurementReduce concentrationRadiation pyrometryLaser detailsEpoxyComposition analysis
A method for pelletizing and taking intensive measurements of a raw sample is disclosed. The method includes homogenizing and pelletizing the sample that is to be subjected to compositional or intensive analysis. The raw sample is mixed with several solutions containing epoxies and activators based in carrier solutions or solvents, and ground to a fine powder or gel. The gel is partially dried and conformed to a pellet shape. The pellet is then cured such that the epoxy and activator solutions react and form a binding agent capable of maintaining the structural integrity of the sample pellet during intensive analysis. An intensive analysis instrument, such as LIBS, may then be used to ablate the surface of the pellet. The pellet provides consistent ablation of the sample material for accurate intensive measurements.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
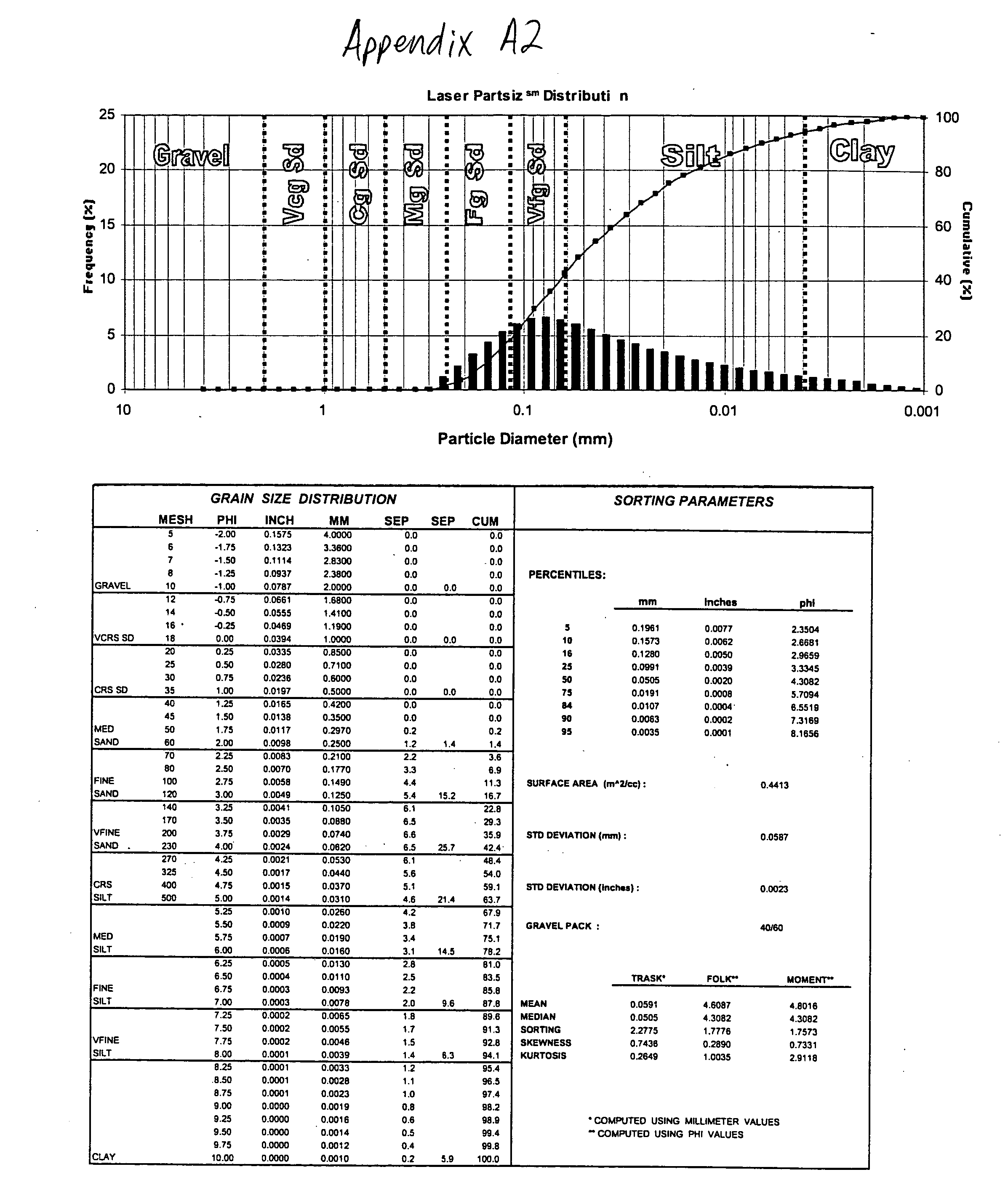
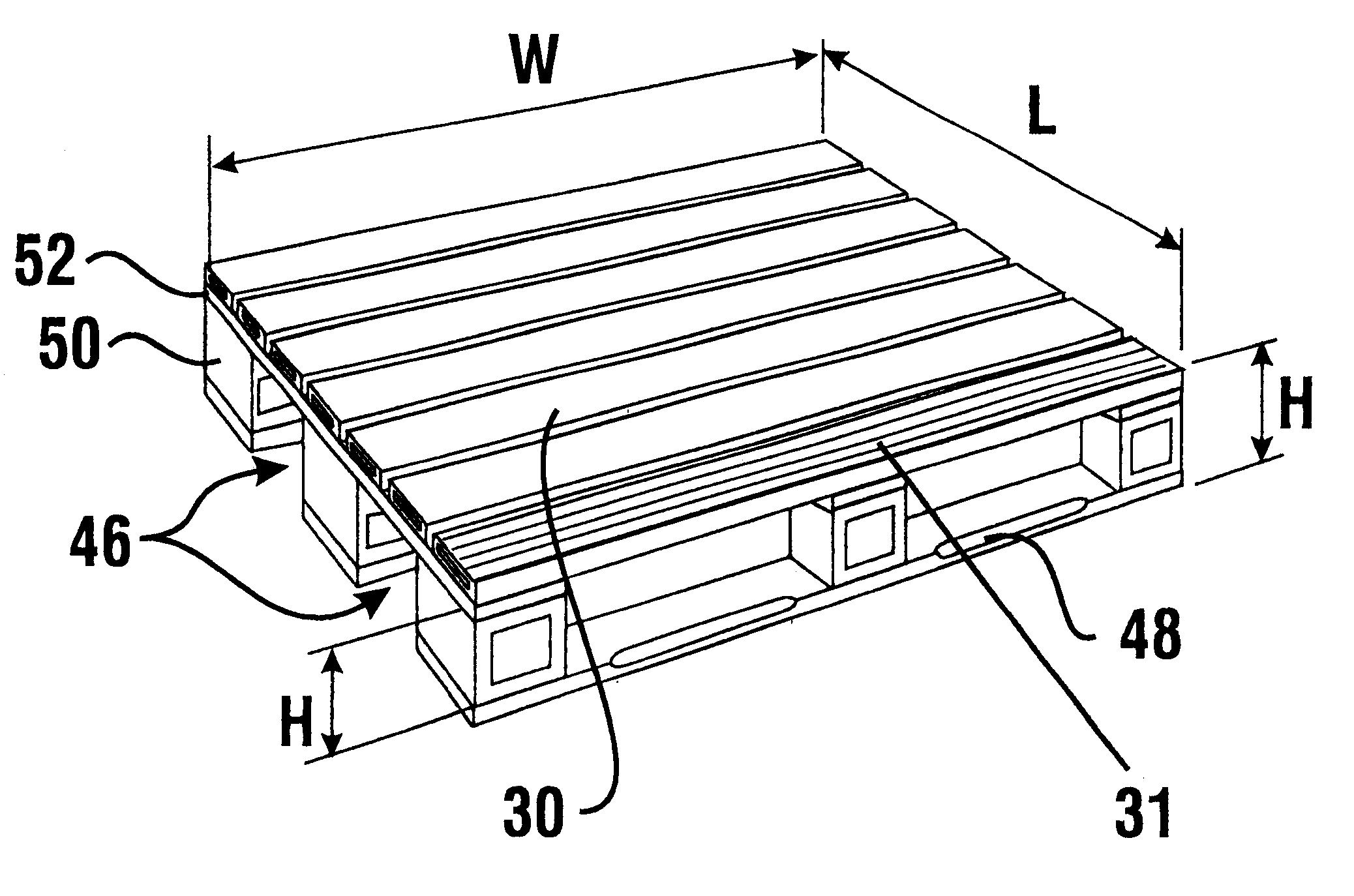
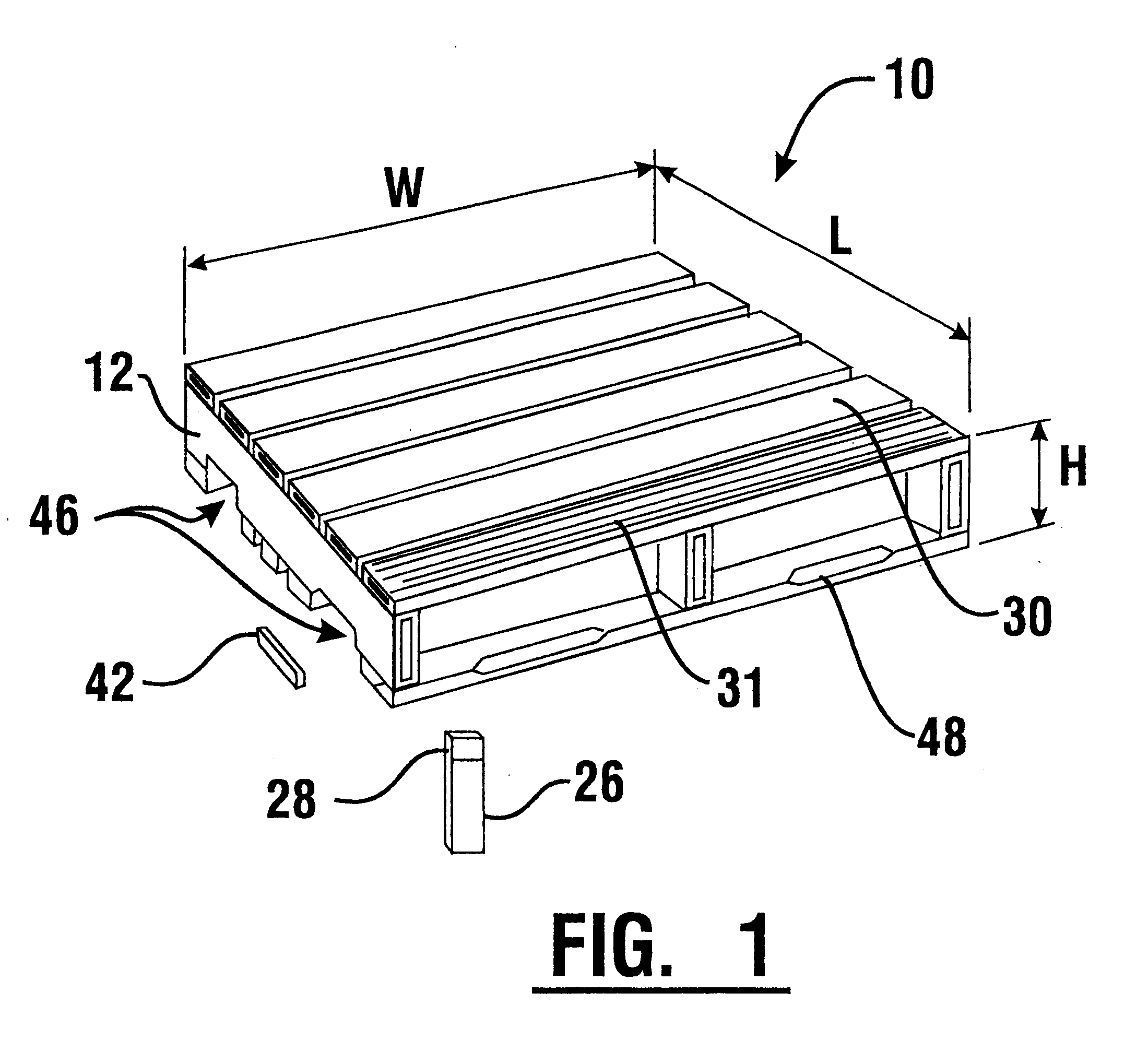
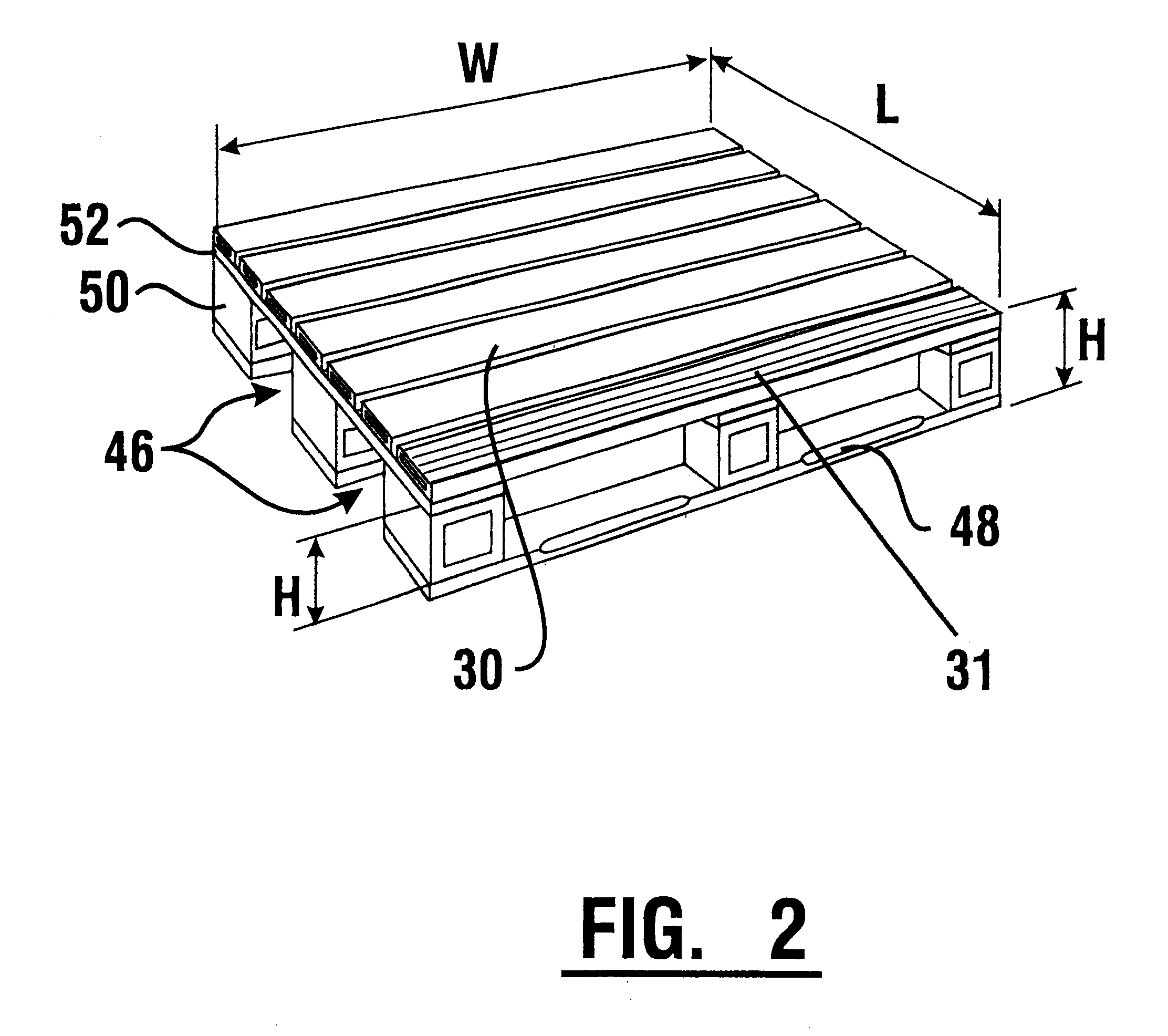
Plastic pallet
A plastic pallet (10) having good load bearing construction and held together without mechanical fasteners, includes deck boards (30). The deck boards include ridges (24) on an upper side (32) and a lower side (34) thereof. Deck boards are positioned transversely on stringers (12) and joined thereto by either an adhesive or thermoplastic welding processes. The stringers and deck boards may be provided with end caps (26, 42) which seal interior areas of the stringers and deck boards and prevent tearing thereof. The stringers and deck boards have interior reinforcement ribs (22,40). The cross sectional profiles of the stringers, deck boards, and end caps provide a cost effective and light weight pallet. Openings which extend between the stringers allow for either two way fork entry and / or four way fork entry. The stringers and deck boards provide flexibility in constructing pallets of various designs. The plastic pallet preferably is highly durable and fully recyclable.
Owner:THE GEON CO
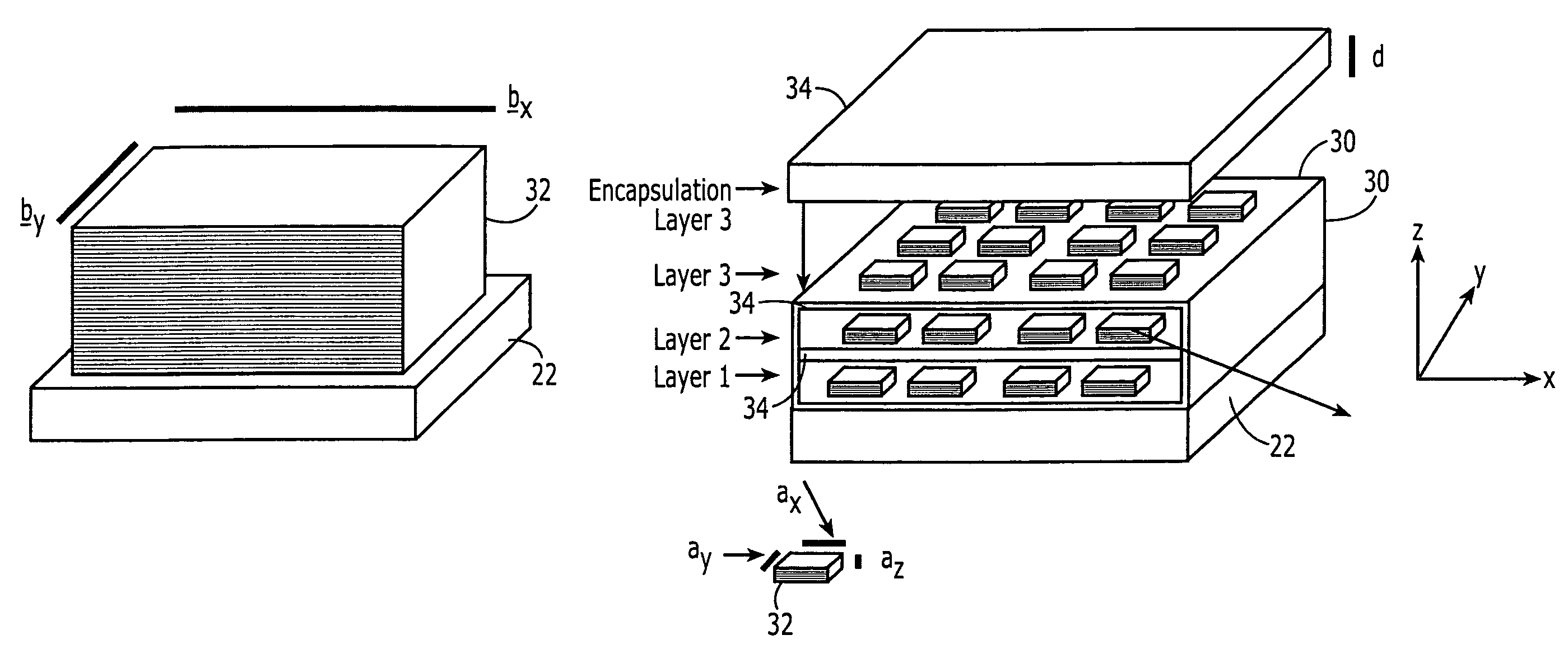
Fabrication of nanoscale thermoelectric devices
InactiveUS20050112872A1Well formedPrevent removalNanotechThermoelectric device with peltier/seeback effectThermocoupleMaterials science
In a method for fabricating a nanowire thermoelectric device, a first electrode pattern is formed on a substrate, wherein the first electrode pattern includes bottom electrodes and a first set of connections which connects the bottom electrodes to form first and second groups of electrically connected bottom electrodes. P-type nanowires and n-type nanowires are selectively formed on the substrate by selectively activating either the first group of electrically connected bottom electrodes and the second group. The p-type and n-type nanowires are then connected by top electrodes. A first set of holes in the substrate is formed to remove the first set of connections. A second set of holes to allow for electrical access to the bottom electrodes, and a second set of connections are formed, so as to result in an array of thermocouples connected to each other in parallel banks of series-connected thermocouples.
Owner:CANON KK
Thermal management and method for large scale processing of cis and/or cigs based thin films overlying glass substrates
ActiveUS20110070690A1Cost effectiveMaintain structural integrityFinal product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingThermal energyIndium
The thermal management and method for large scale processing of CIS and / or CIGS based thin film overlaying glass substrates. According to an embodiment, the present invention provides a method for fabricating a copper indium diselenide semiconductor film. The method includes providing a plurality of substrates, each of the substrates having a copper and indium composite structure. The method also includes transferring the plurality of substrates into a furnace, each of the plurality of substrates provided in a vertical orientation with respect to a direction of gravity, the plurality of substrates being defined by a number N, where N is greater than 5. The method further includes introducing a gaseous species including a selenide species and a carrier gas into the furnace and transferring thermal energy into the furnace to increase a temperature from a first temperature to a second temperature, the second temperature ranging from about 350° C. to about 450° C. to at least initiate formation of a copper indium diselenide film from the copper and indium composite structure on each of the substrates.
Owner:CM MFG
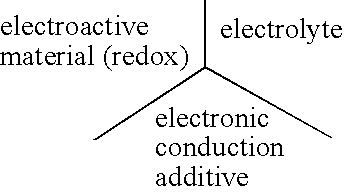
Electrode materials with high surface conductivity
InactiveUS20040140458A1Simple structureHigh crystallinityElectrode manufacturing processesDouble layer capacitorsSurface conductivityIon exchange
The present invention concerns electrode materials capable of redox reactions by electrons and alkaline ions exchange with an electrolyte. The applications are in the field of primary (batteries) or secondary electrochemical generators, super capacitors and light modulating system of the super capacitor type.
Owner:CENT NAT DE LA RECHERCHE SCI +2
Thermal management and method for large scale processing of cis and/or cigs based thin films overlying glass substrates
InactiveUS20110070683A1Cost effectiveMaintain structural integrityFinal product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingThermal energyIndium
The thermal management and method for large scale processing of CIS and / or CIGS based thin film overlaying glass substrates. According to an embodiment, the present invention provides a method for fabricating a copper indium diselenide semiconductor film. The method includes providing a plurality of substrates, each of the substrates having a copper and indium composite structure. The method also includes transferring the plurality of substrates into a furnace, each of the plurality of substrates provided in a vertical orientation with respect to a direction of gravity, the plurality of substrates being defined by a number N, where N is greater than 5. The method further includes introducing a gaseous species including a selenide species and a carrier gas into the furnace and transferring thermal energy into the furnace to increase a temperature from a first temperature to a second temperature, the second temperature ranging from about 350° C. to about 450° C. to at least initiate formation of a copper indium diselenide film from the copper and indium composite structure on each of the substrates.
Owner:CM MFG
Processes for making crush recoverable polymer scaffolds
ActiveUS20120073733A1Improves deployment uniformityReduce fracturesStentsDomestic articlesBalloon catheterPolymer scaffold
Methods for making scaffolds for delivery via a balloon catheter are described. The scaffold, after being deployed by the balloon, provides a crush recovery of about 90% after the diameter of the scaffold has been pinched or crushed by 50%. The scaffold structure has patterns that include an asymmetric or symmetric closed cell, and links connecting such closed cells.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
Method of joining ceramics: reaction diffusion-bonding
InactiveUS20060162849A1Suitable characteristicMaintain structural integrityAfter-treatment detailsLamination ancillary operationsBond interfaceSolid solution
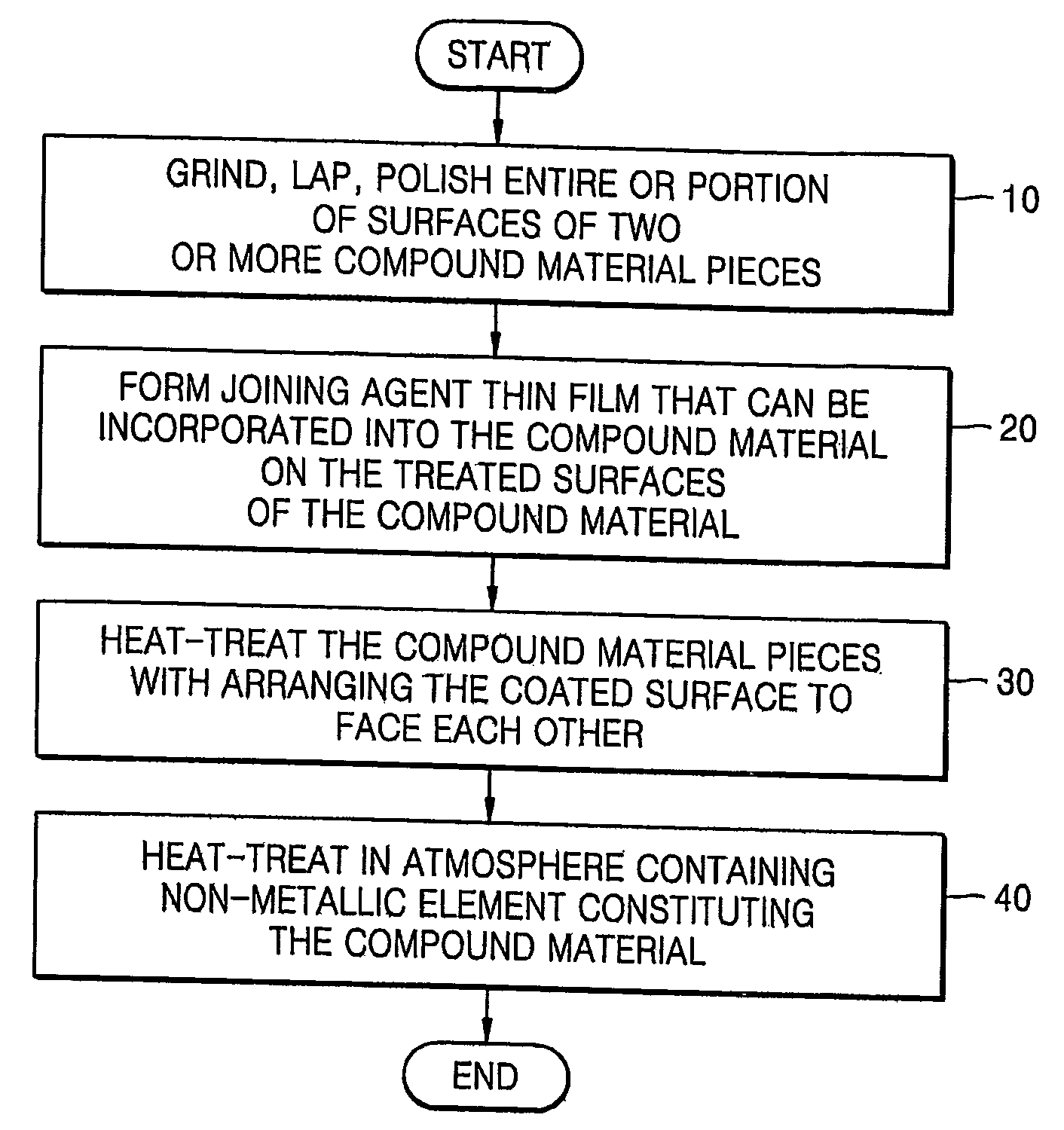
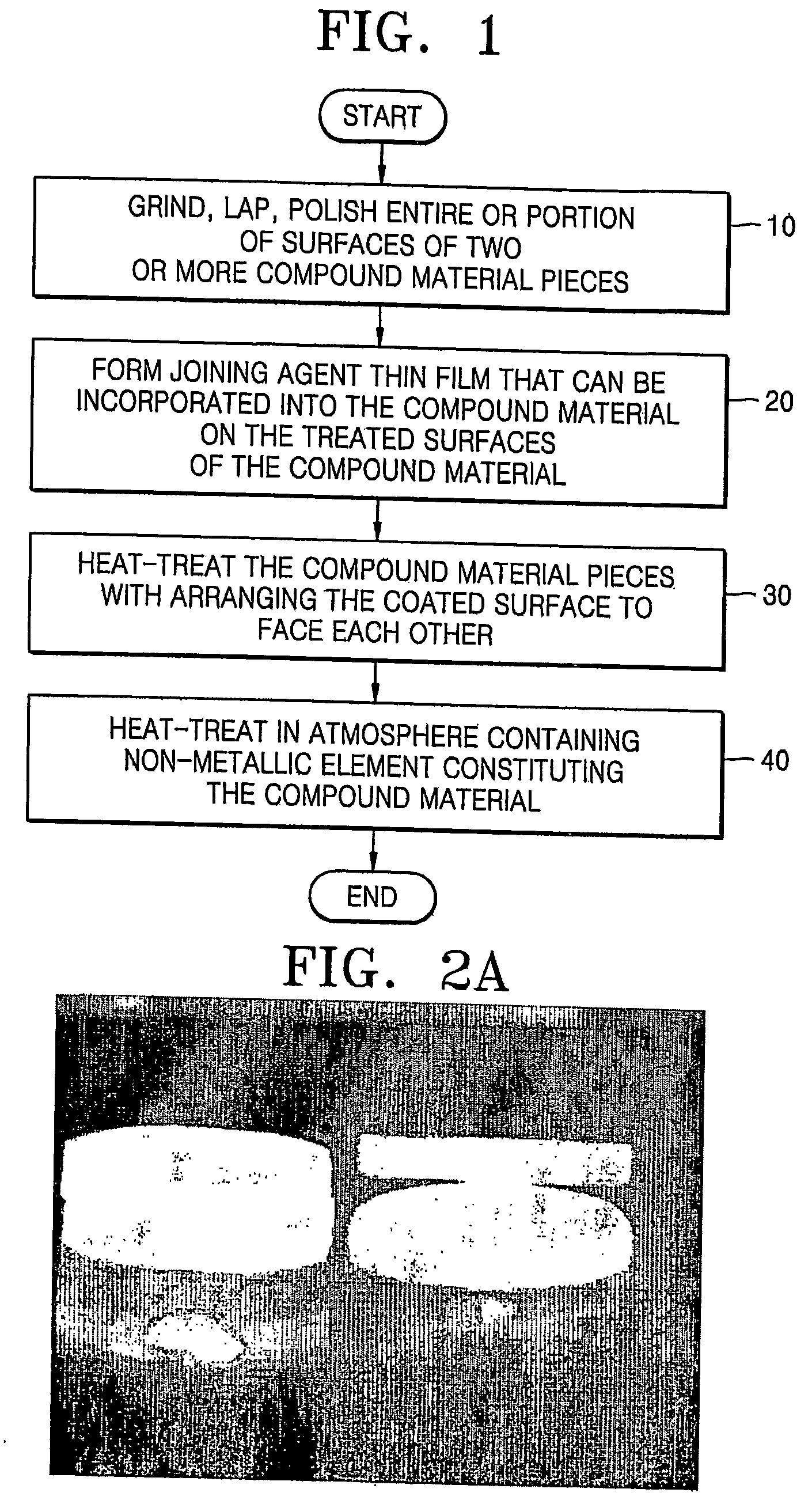
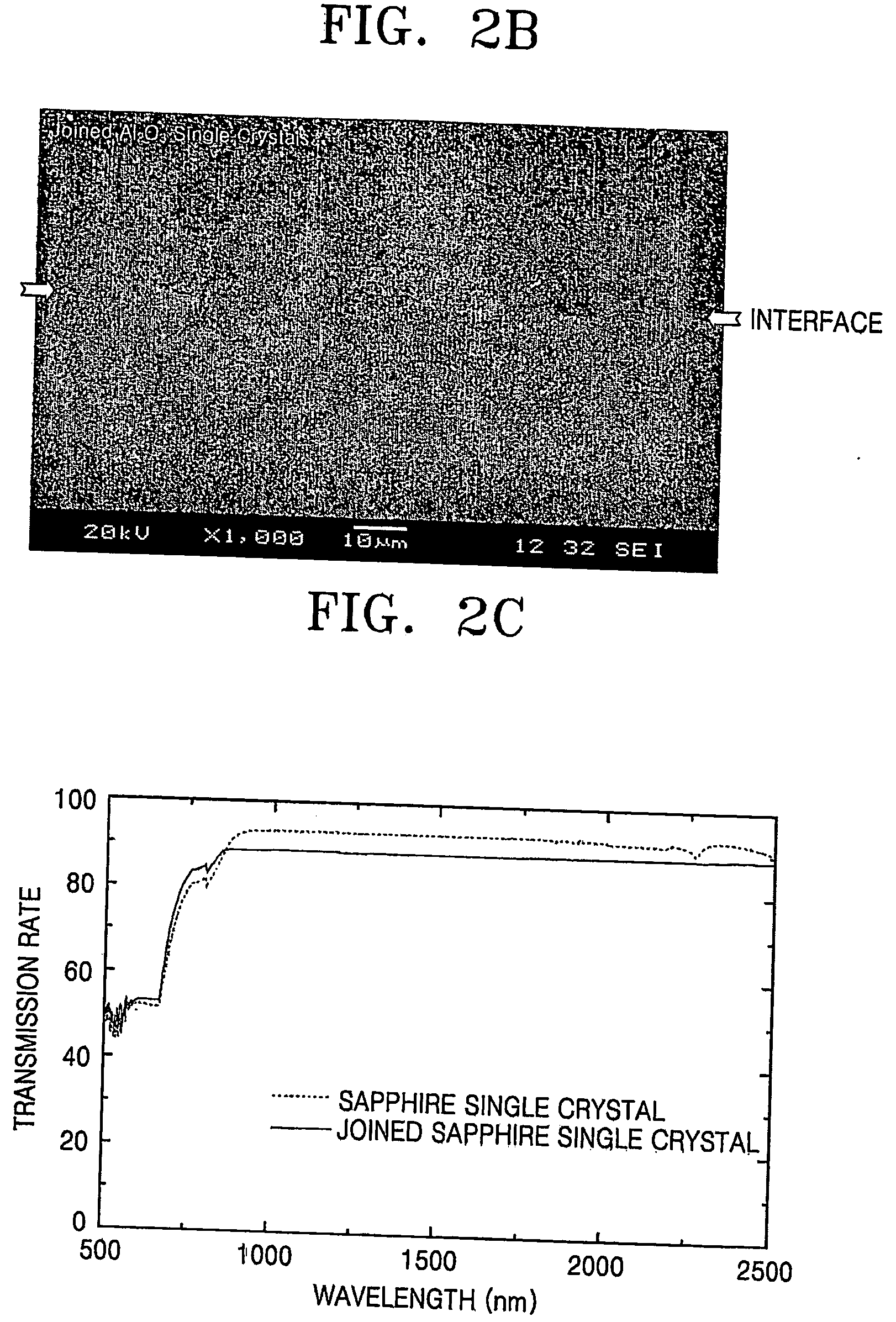
Provided is a method of joining compound materials such as ceramics. The method is a combination of diffusion bonding and reaction bonding, which is called reaction diffusion bonding (RDB). The method includes: grinding, lapping, or polishing entire or portions of surfaces to be joined of two or more pieces of a compound material; forming a thin film of a joining agent on one or more of the ground, lapped, or polished surfaces by one of inserting, spreading, depositing, plating, and coating, the joining agent being able to transform into the compound material by being incorporated into the compound material or by forming a solid solution with the compound material upon heat treating; and forming a directly bonded interface without a second phase by heat treating the pieces of the compound material with the to-be-joined surfaces on which the joining agent film is formed arranged to face each other, wherein the joining agent thin film is composed of a material selected from the group consisting of metals, metal organics, and metal compounds.
Owner:CERAWEL
Thermal management and method for large scale processing of cis and/or cigs based thin films overlying glass substrates
InactiveUS20110070684A1Cost effectiveMaintain structural integrityFinal product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingThermal energyIndium
The thermal management and method for large scale processing of CIS and / or CIGS based thin film overlaying glass substrates. According to an embodiment, the present invention provides a method for fabricating a copper indium diselenide semiconductor film. The method includes providing a plurality of substrates, each of the substrates having a copper and indium composite structure. The method also includes transferring the plurality of substrates into a furnace, each of the plurality of substrates provided in a vertical orientation with respect to a direction of gravity, the plurality of substrates being defined by a number N, where N is greater than 5. The method further includes introducing a gaseous species including a selenide species and a carrier gas into the furnace and transferring thermal energy into the furnace to increase a temperature from a first temperature to a second temperature, the second temperature ranging from about 350° C. to about 450° C. to at least initiate formation of a copper indium diselenide film from the copper and indium composite structure on each of the substrates.
Owner:CM MFG
Method of making cell growth surface
InactiveUS20060292690A1Cell density be limitedReduced viabilityCell culture supports/coatingTissue/virus culture apparatusCell adhesionCell growth
The present invention discloses a three-dimensional porous growth surface made from polysaccharide material, especially the alginic acid, to enhance cell growth surface, promote cell adherence, immobilization and propagation, maintain surface structure integrity, enable programmable degradation, and thus increase cellular production. The present invention teaches several methods: a method to enhance the integrity of the growth surface by protecting the growth surface in a rigid solid support; a method of use for enhancing the performance of the surface; and a method of modifying a growth surface for eukaryotic and / or prokaryotic cells comprising the steps of increasing surface area by creating porous and 3-D structure, treating a surface to encourage cell attachment, promoting cell growth and proliferation, and disposing the growth surface in any conventional cell cultivating device. The growth surface is able to program degradation and release the cell / tissue mass after the culture is completed.
Owner:CESCO BIOENGINEERING CO LTD
Thermal management and method for large scale processing of cis and/or cigs based thin films overlying glass substrates
InactiveUS20110070685A1Cost effectiveMaintain structural integrityFinal product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingThermal energyIndium
The thermal management and method for large scale processing of CIS and / or CIGS based thin film overlaying glass substrates. According to an embodiment, the present invention provides a method for fabricating a copper indium diselenide semiconductor film. The method includes providing a plurality of substrates, each of the substrates having a copper and indium composite structure. The method also includes transferring the plurality of substrates into a furnace, each of the plurality of substrates provided in a vertical orientation with respect to a direction of gravity, the plurality of substrates being defined by a number N, where N is greater than 5. The method further includes introducing a gaseous species including a selenide species and a carrier gas into the furnace and transferring thermal energy into the furnace to increase a temperature from a first temperature to a second temperature, the second temperature ranging from about 350° C. to about 450° C. to at least initiate formation of a copper indium diselenide film from the copper and indium composite structure on each of the substrates.
Owner:CM MFG
Thermal management and method for large scale processing of cis and/or cigs based thin films overlying glass substrates
InactiveUS20110070682A1Cost effectiveMaintain structural integrityFinal product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingThermal energyIndium
Owner:CM MFG
Double hinge display package and method of use
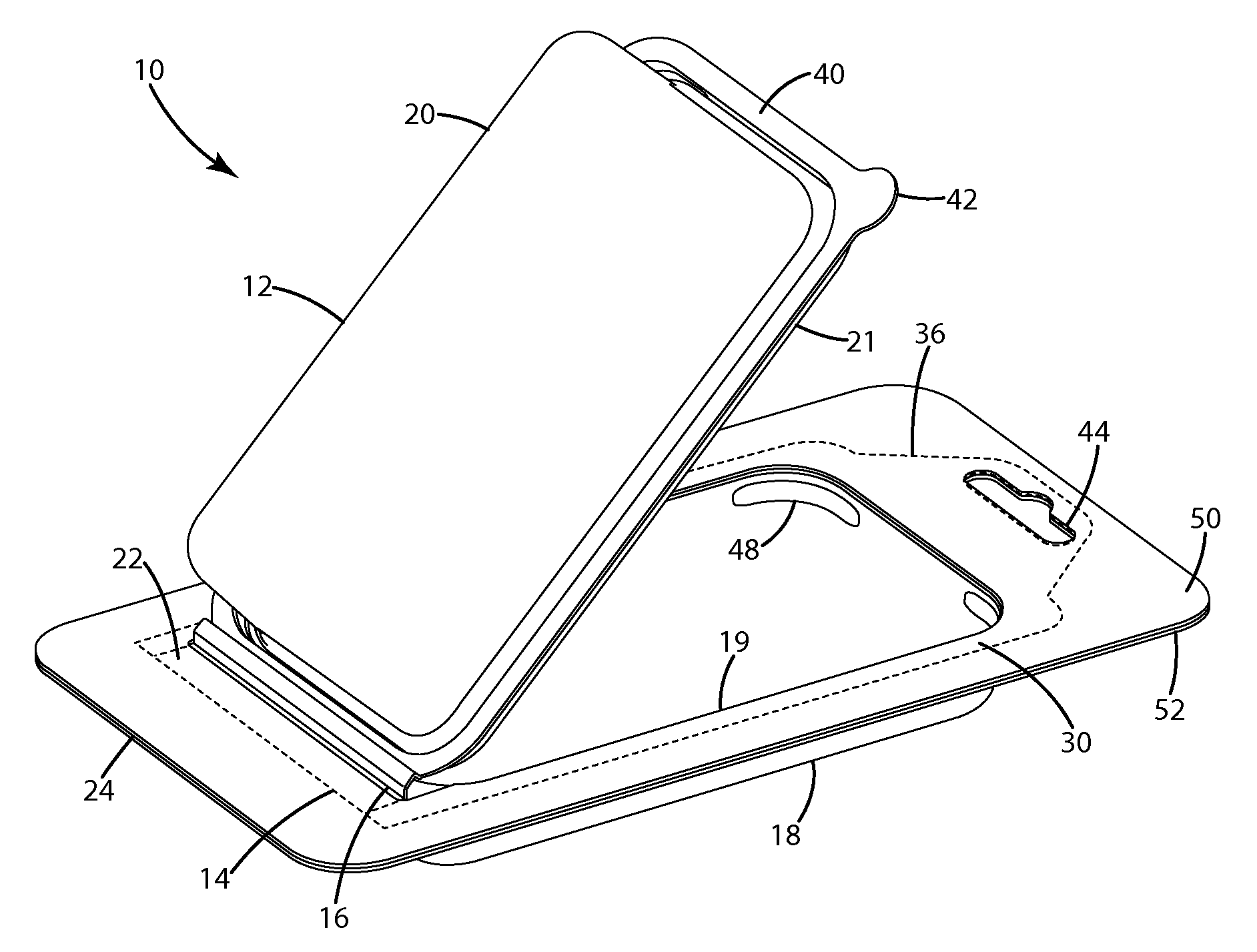
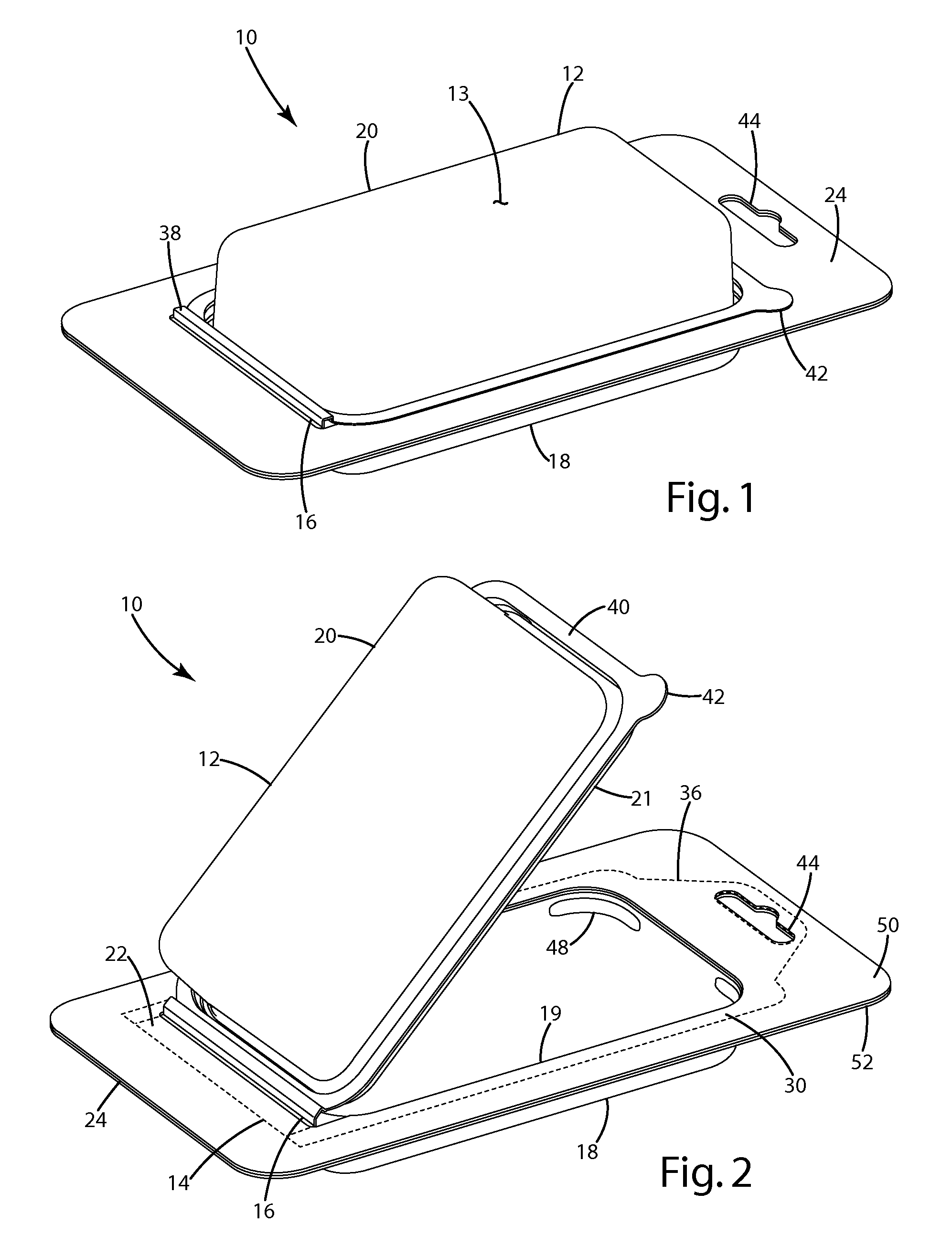
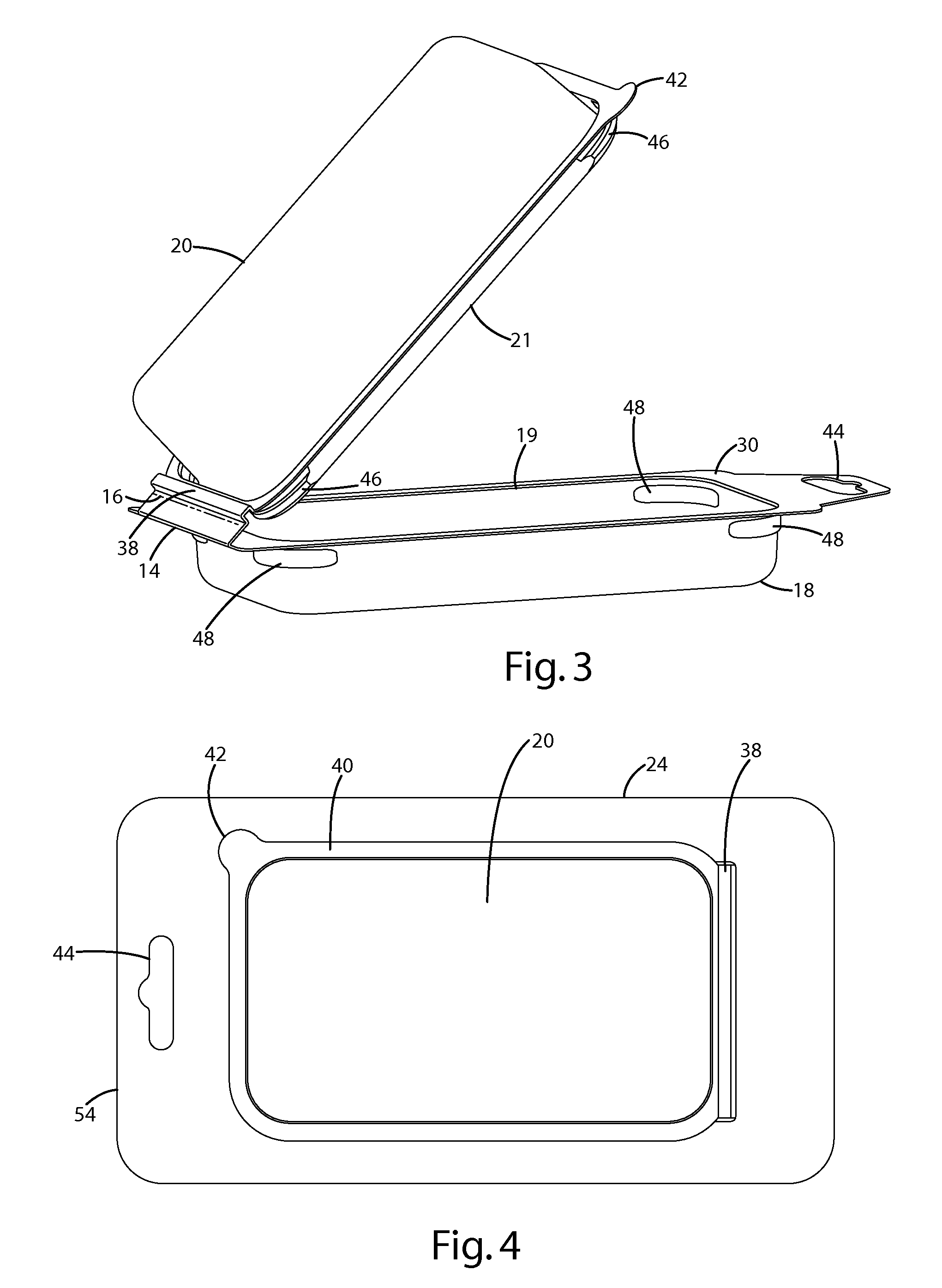
InactiveUS7931148B2Secure retentionEasy to manufactureOther accessoriesLidsDisplay deviceEngineering
A clamshell package for supporting an article is provided including a covered manufacturing hinge adapted to divide the clamshell into first and second parts adapted to form a cavity. The first and second parts partially overlap to form a flange adjacent the manufacturing hinge. The second part includes an uncovered operating hinge, about which the second part is adapted to pivot away from the first part to an open position. The clamshell package includes a panel adapted to engage the manufacturing hinge and flange to retain the manufacturing hinge in a folded position, with the panel being spaced from the operating hinge.
Owner:DISPLAY PACK
Thermal management and method for large scale processing of cis and/or cigs based thin films overlying glass substrates
ActiveUS20110070688A1Cost effectiveMaintain structural integrityFinal product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingThermal energyIndium
Owner:CM MFG
Thermal management and method for large scale processing of cis and/or cigs based thin films overlying glass substrates
InactiveUS20110070687A1Cost effectiveMaintain structural integrityFinal product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingThermal energyIndium
The thermal management and method for large scale processing of CIS and / or CIGS based thin film overlaying glass substrates. According to an embodiment, the present invention provides a method for fabricating a copper indium diselenide semiconductor film. The method includes providing a plurality of substrates, each of the substrates having a copper and indium composite structure. The method also includes transferring the plurality of substrates into a furnace, each of the plurality of substrates provided in a vertical orientation with respect to a direction of gravity, the plurality of substrates being defined by a number N, where N is greater than 5. The method further includes introducing a gaseous species including a selenide species and a carrier gas into the furnace and transferring thermal energy into the furnace to increase a temperature from a first temperature to a second temperature, the second temperature ranging from about 350° C. to about 450° C. to at least initiate formation of a copper indium diselenide film from the copper and indium composite structure on each of the substrates.
Owner:CM MFG
Method for preparing and processing a sample for intensive analysis
InactiveUS7195731B2Maintain structural integritySimple structureLaser detailsRadiation pyrometryEpoxySolvent
This application relates to a method for pellerizing and taking intensive measurements of a raw sample. The method includes homogenizing and pelletizing the sample that is to be subjected to compositional or intensive analysis. The raw sample is mixed with several solutions containing epoxies and activators based in carrier solutions or solvents, and ground to a fine powder or gel. The gel is partially dried and conformed to a pellet shape. The pellet is then cured such that the epoxy and activator solutions react and form a binding agent capable of maintaining the structural integrity of the sample pellet during intensive analysis. An intensive analysis instrument, such as LIBS, may then be used to ablate the surface of the pellet. The pellet provides consistent ablation of the sample material for accurate intensive measurements.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com