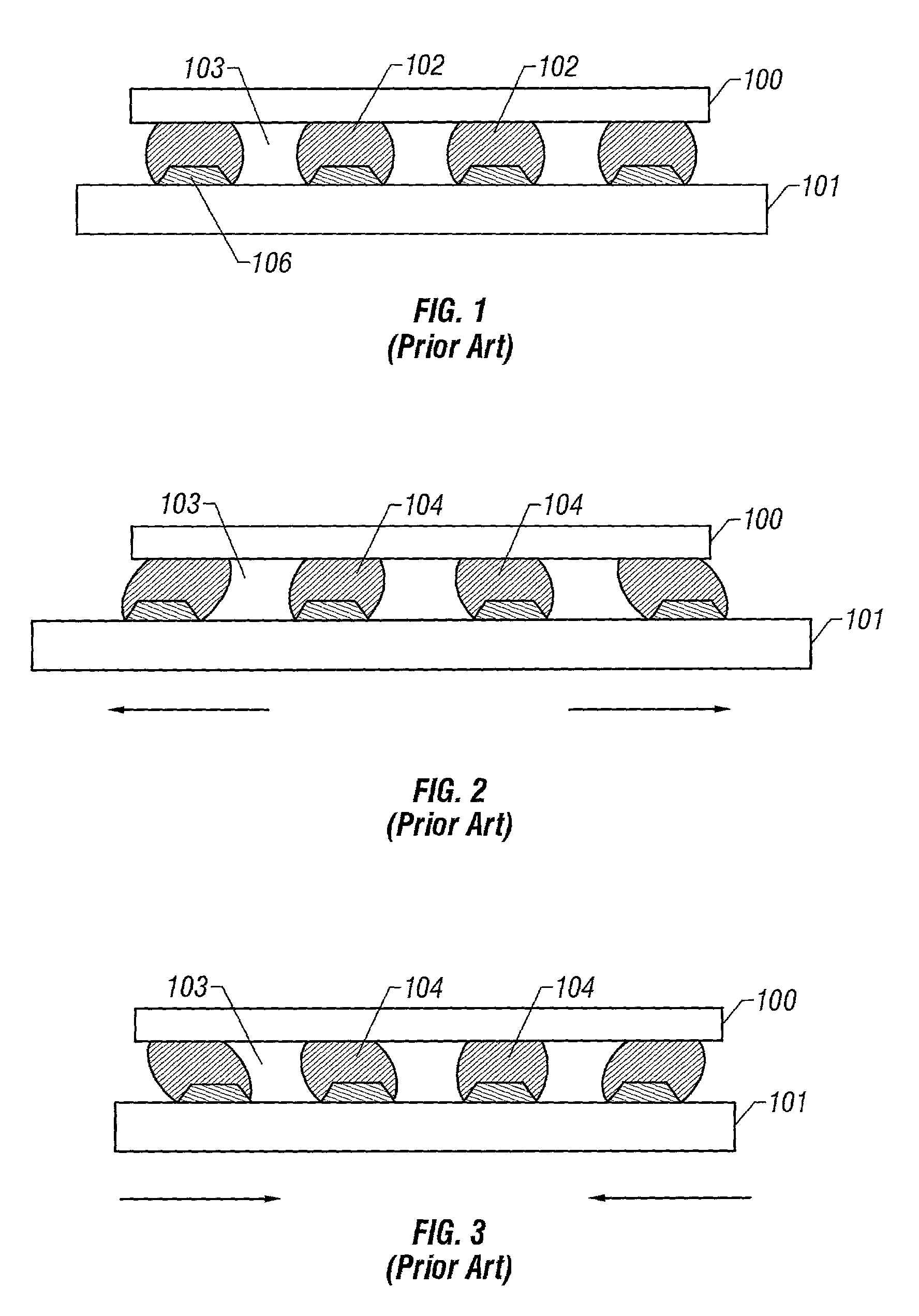
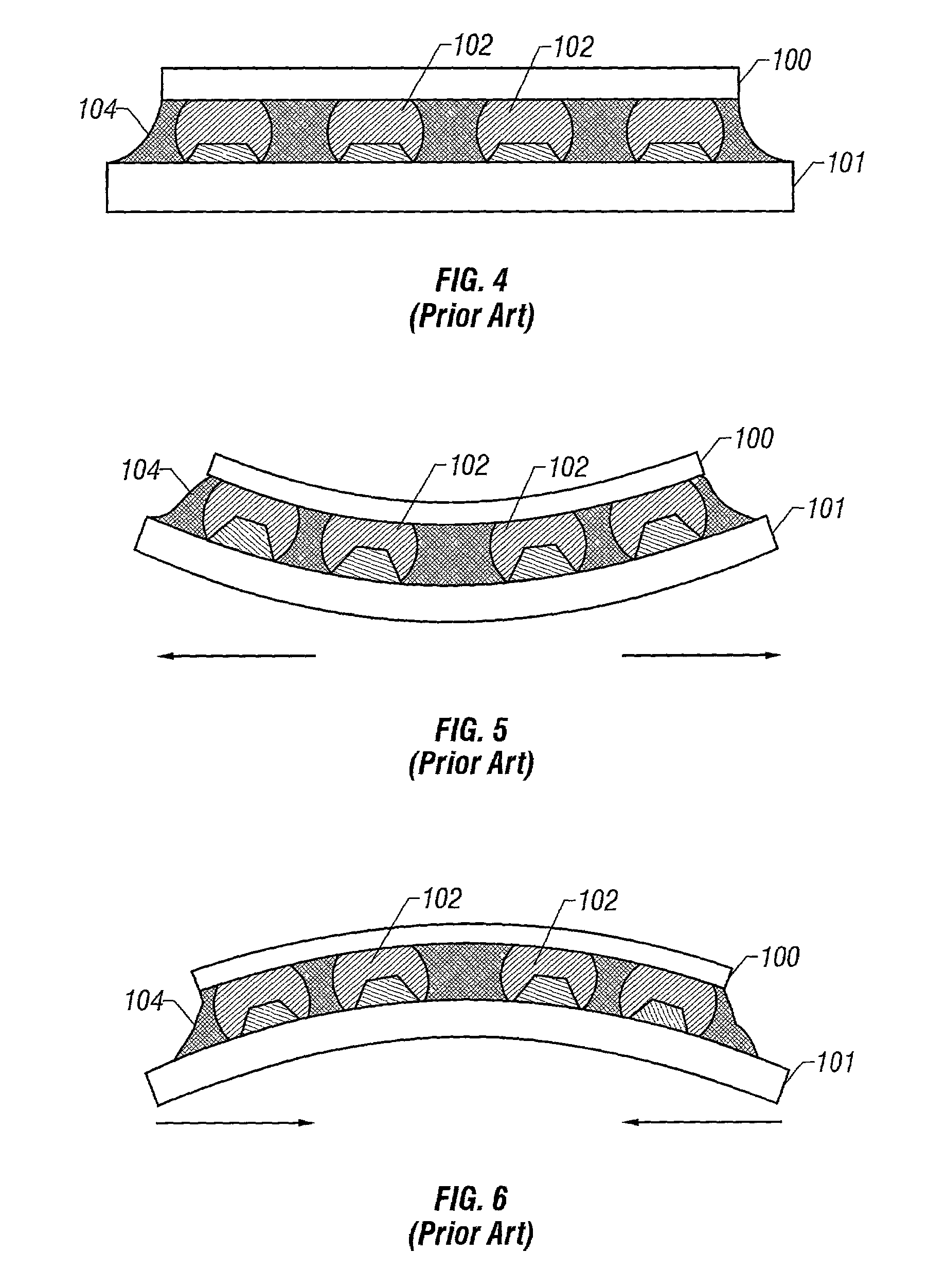
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1253results about How to "Improves Structural Integrity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
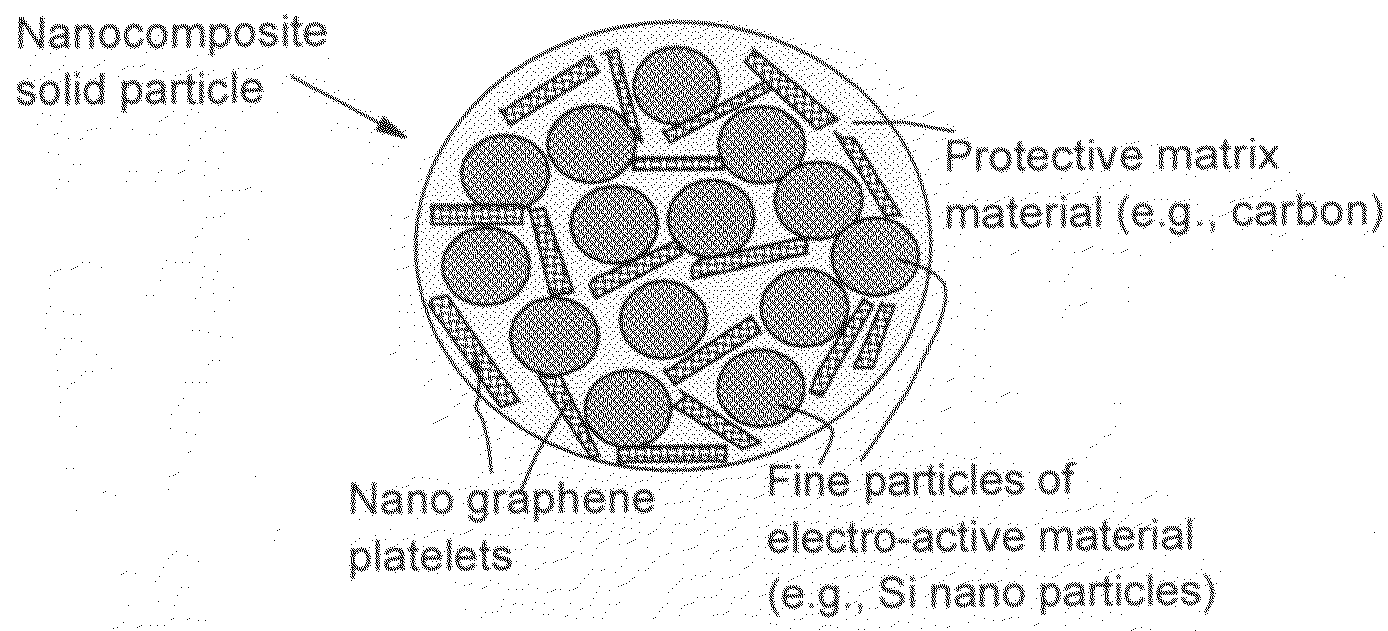
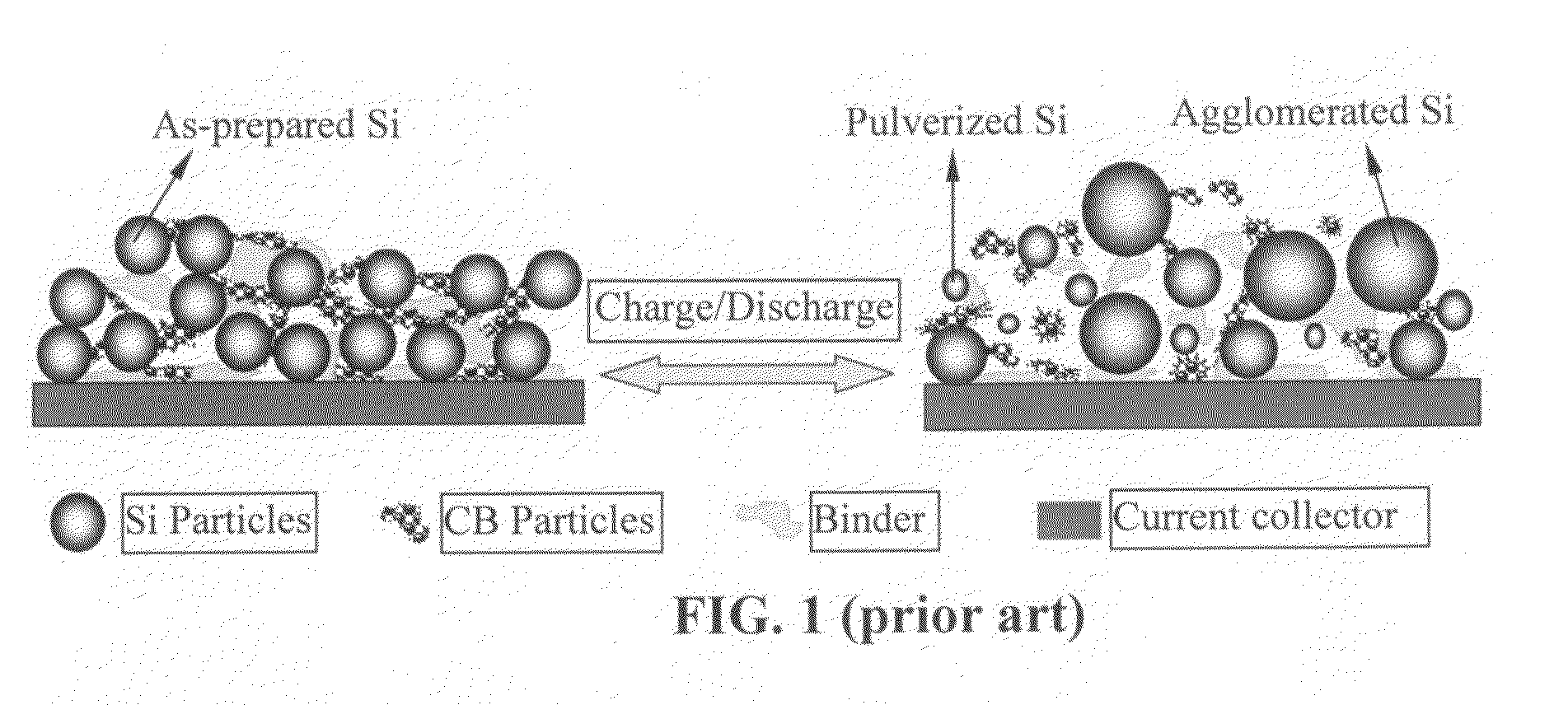
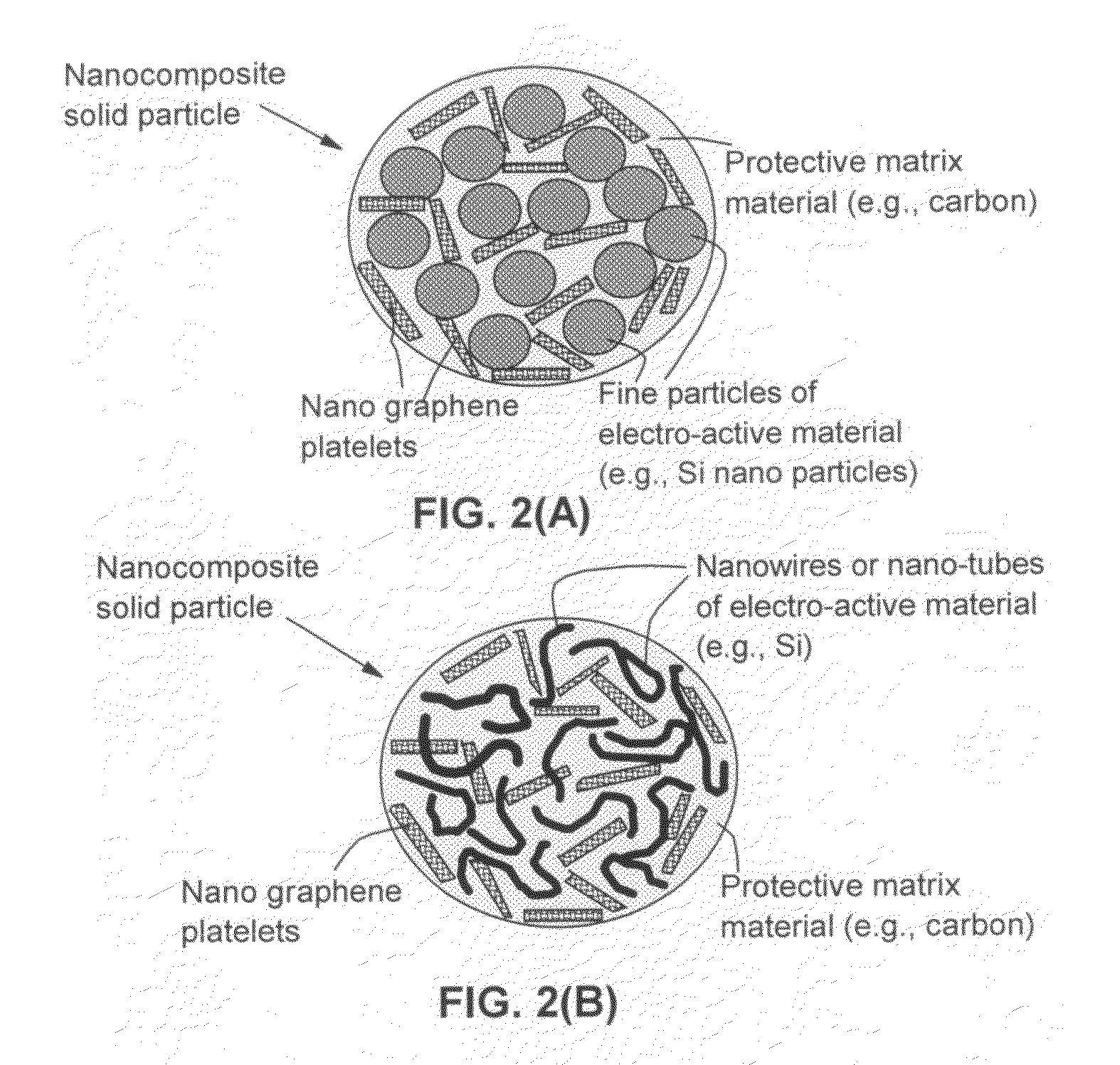
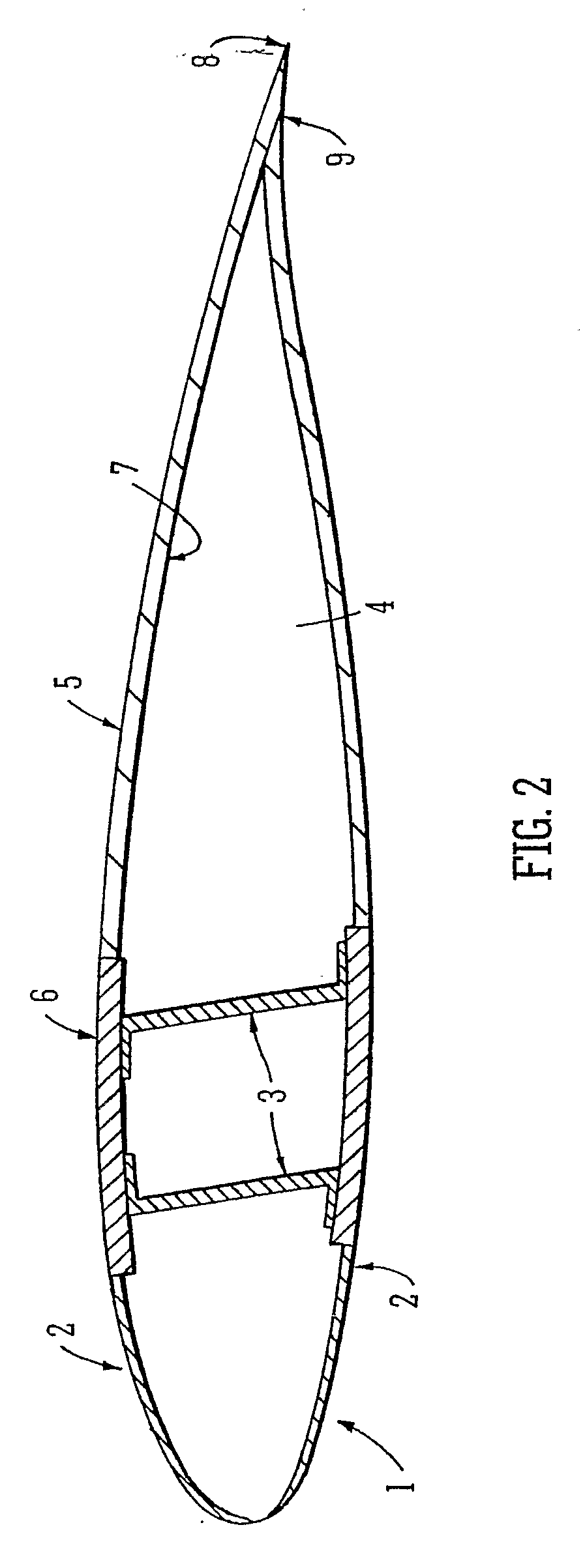
Process for producing nano graphene reinforced composite particles for lithium battery electrodes
ActiveUS20100176337A1Increase stiffnessHigh strengthCell electrodesLi-accumulatorsFiberLithium metal
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
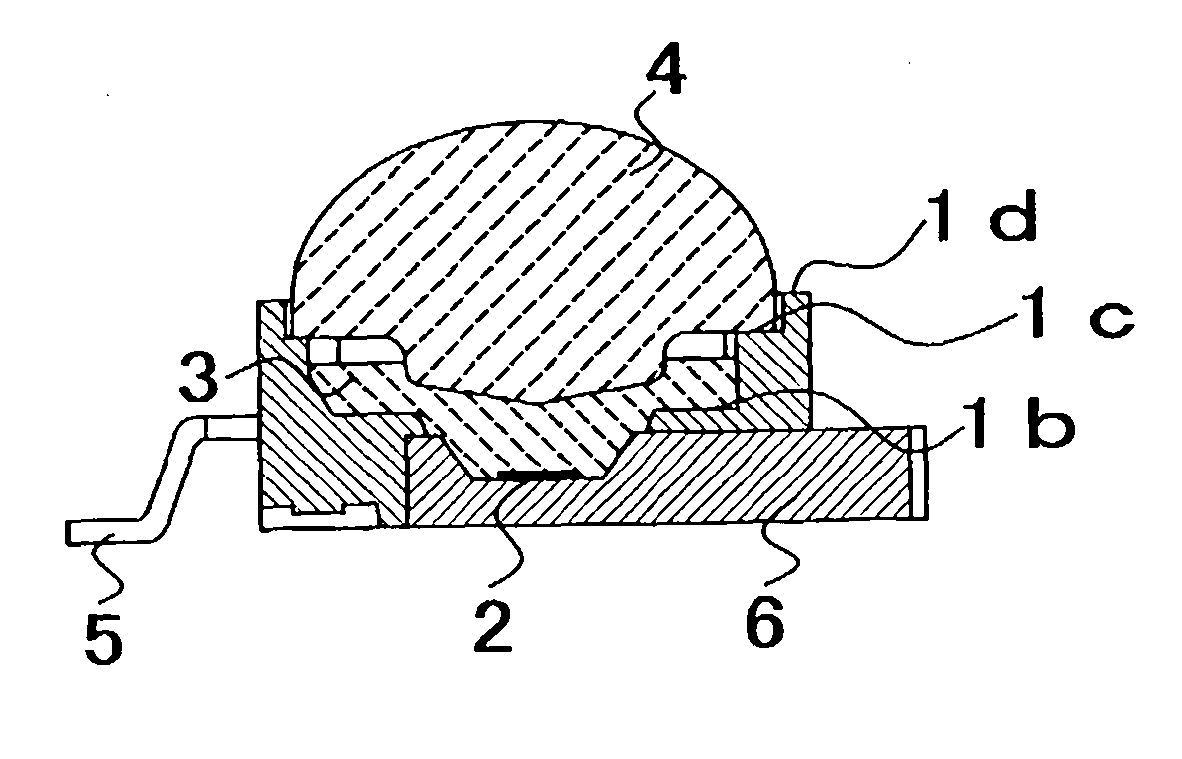
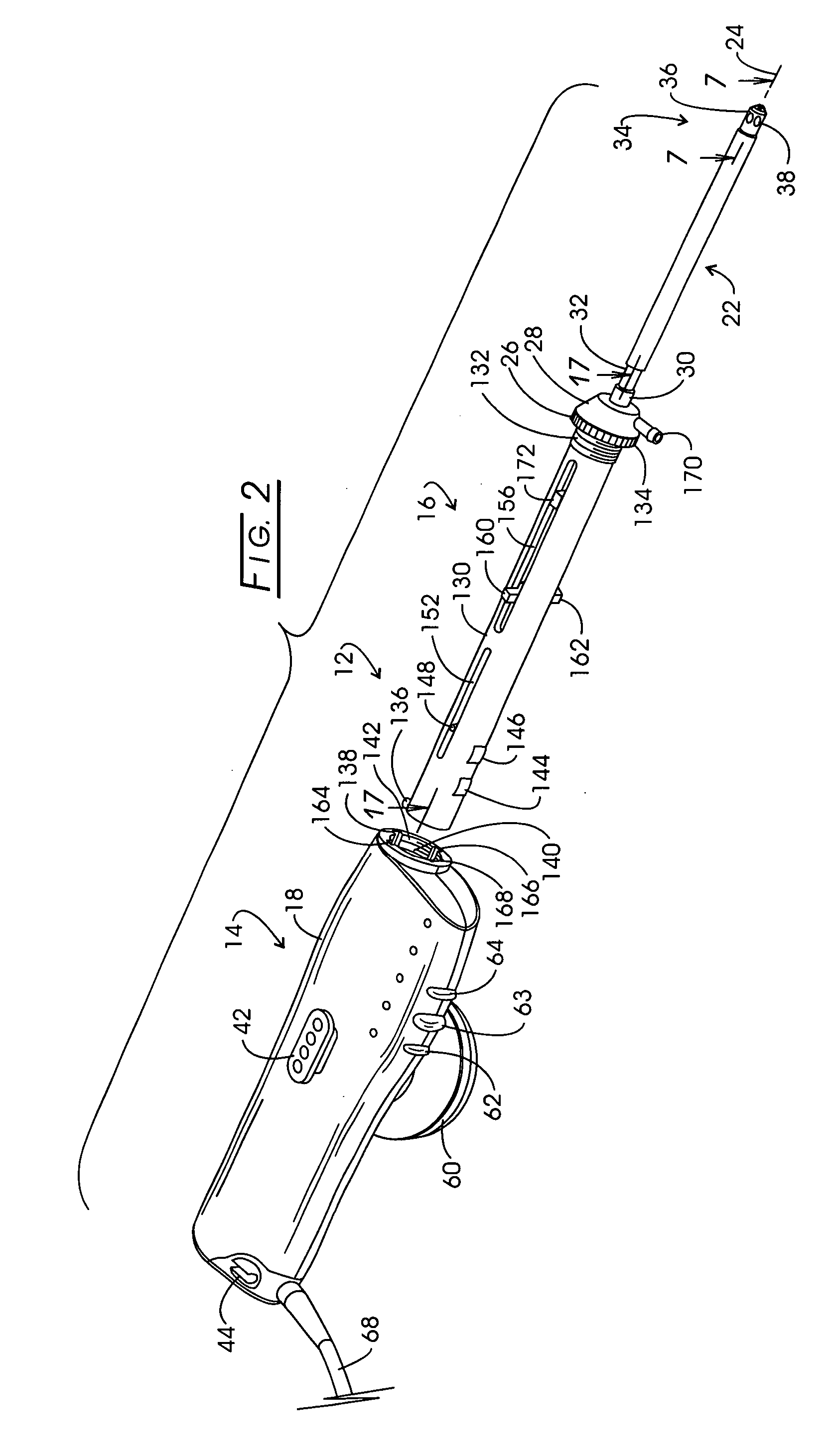
Light-emitting device and process for producing thereof
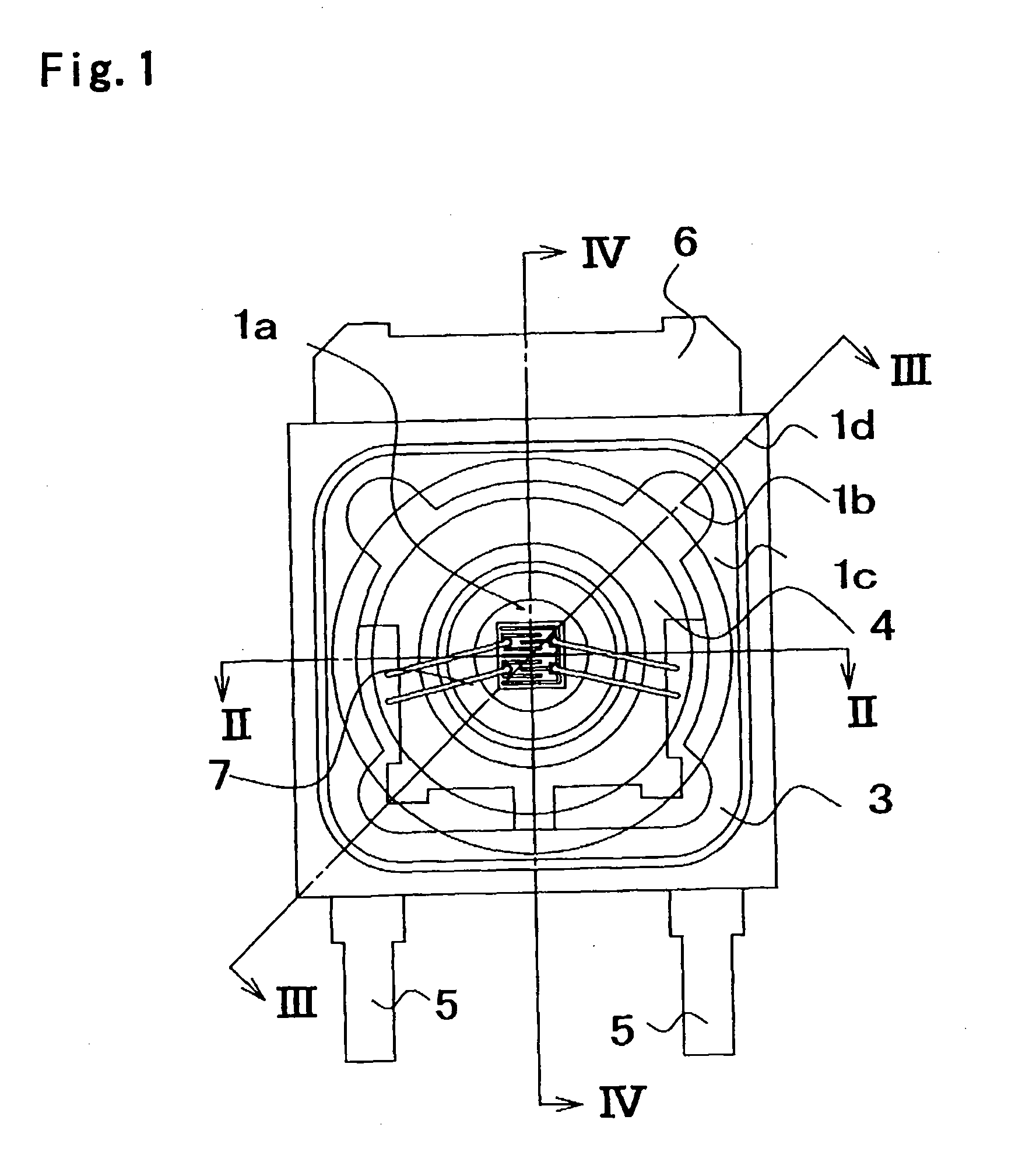
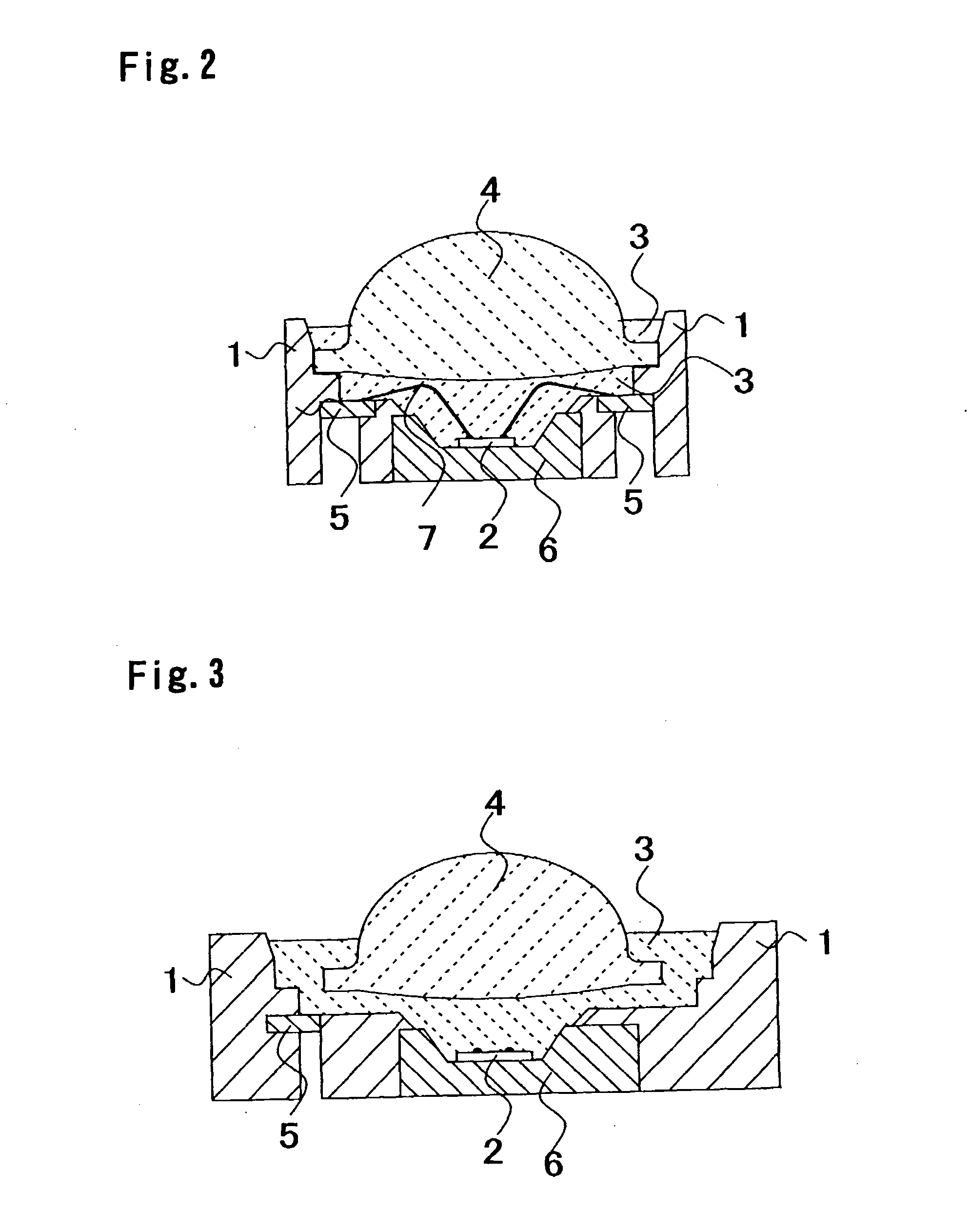
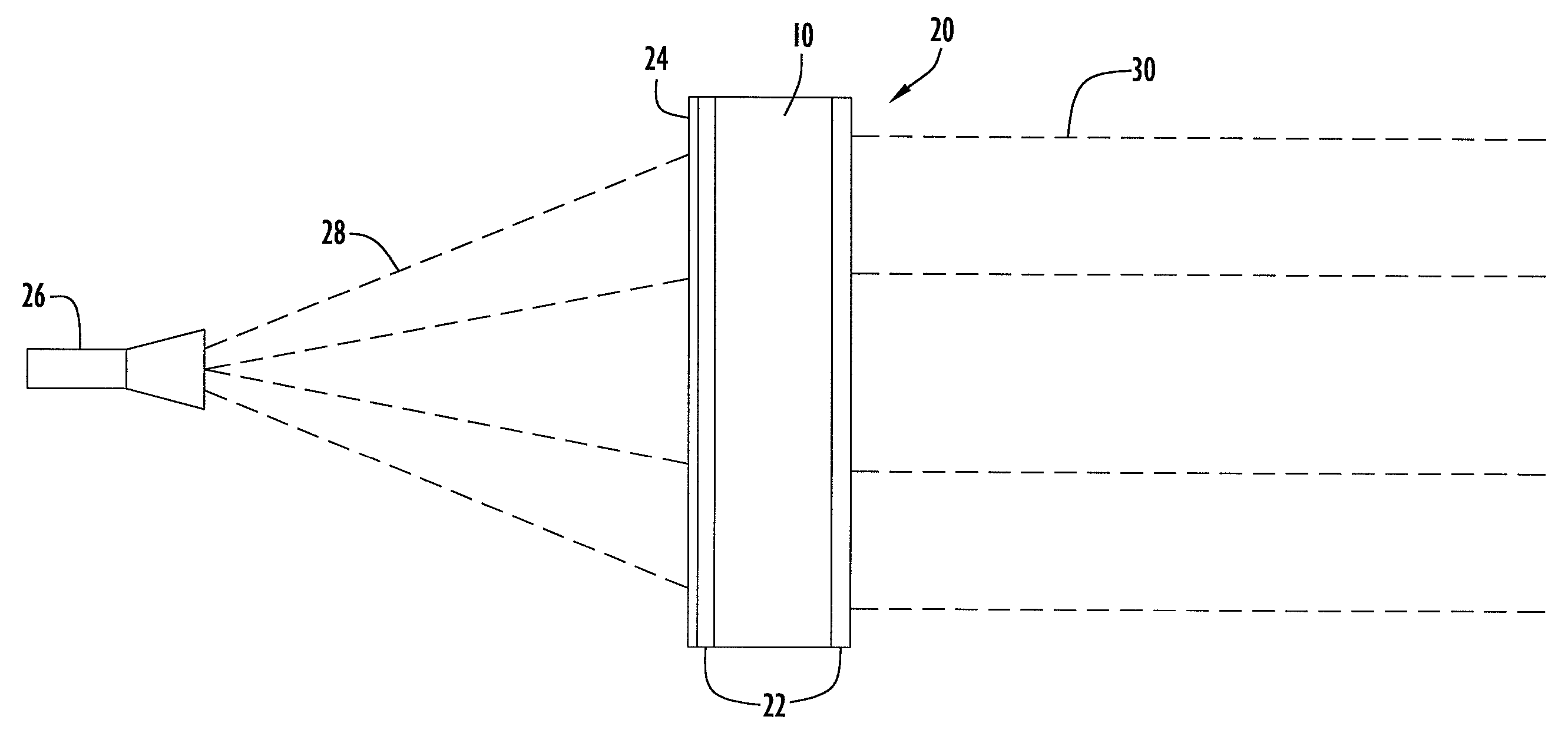
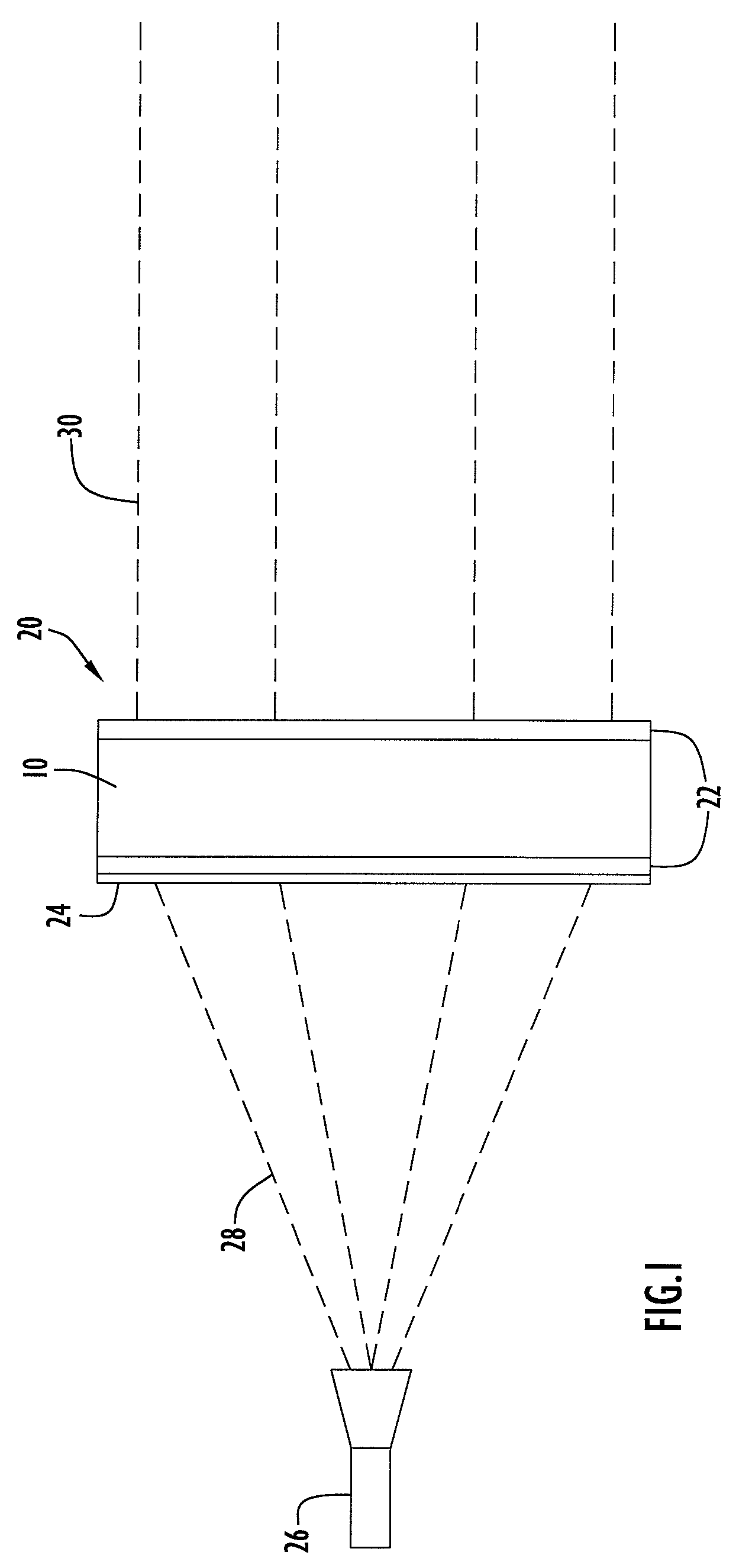
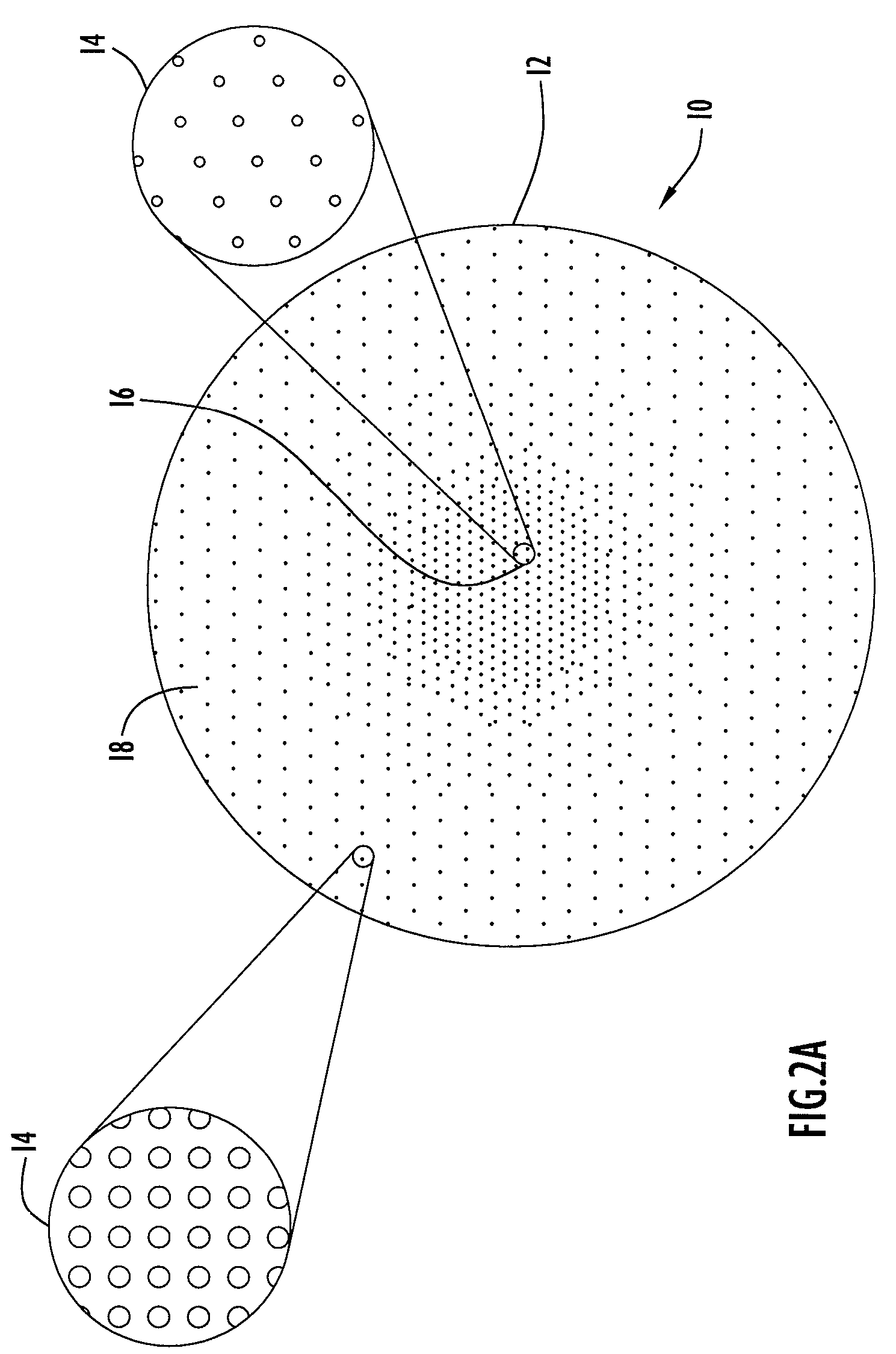
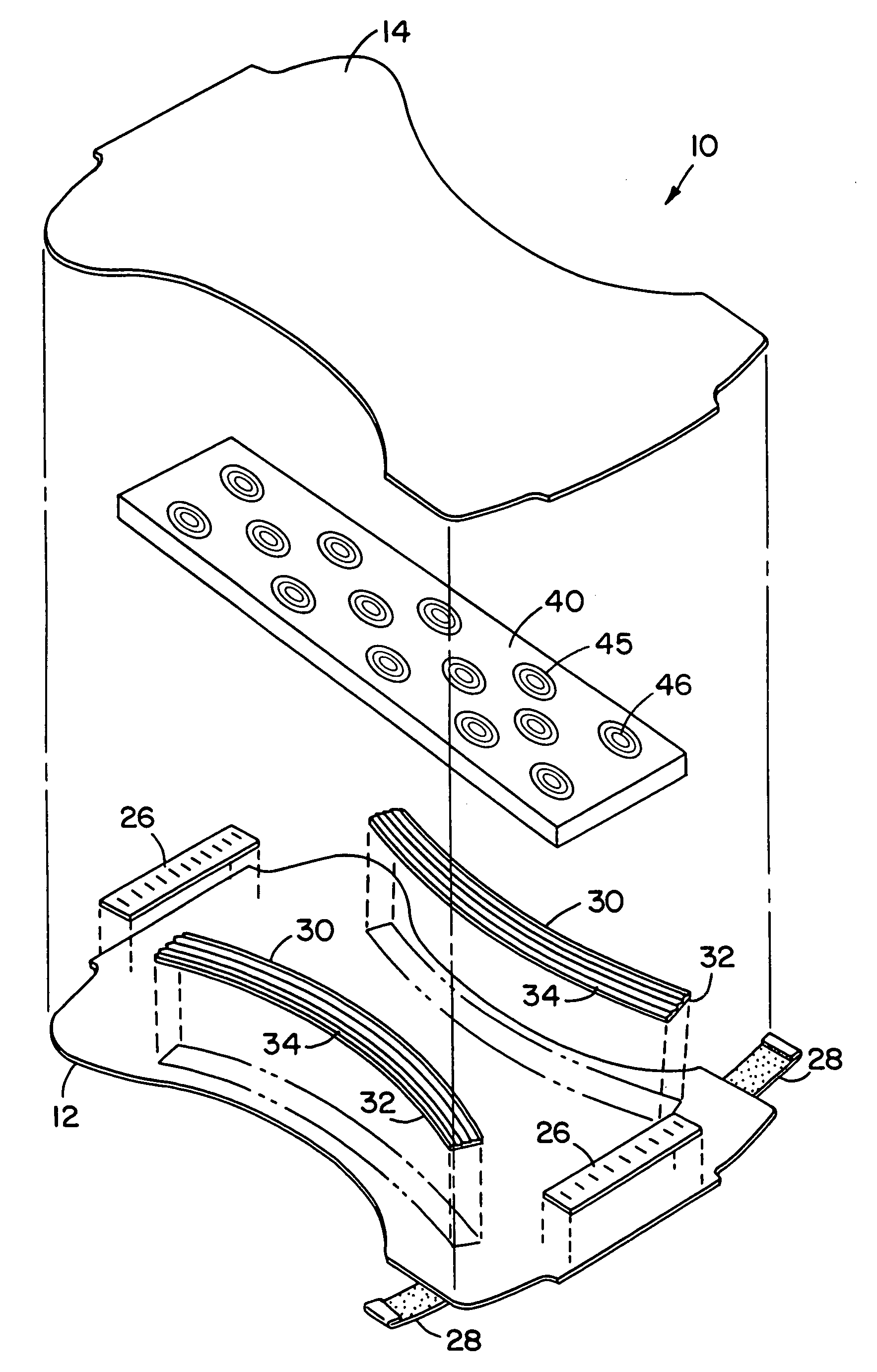
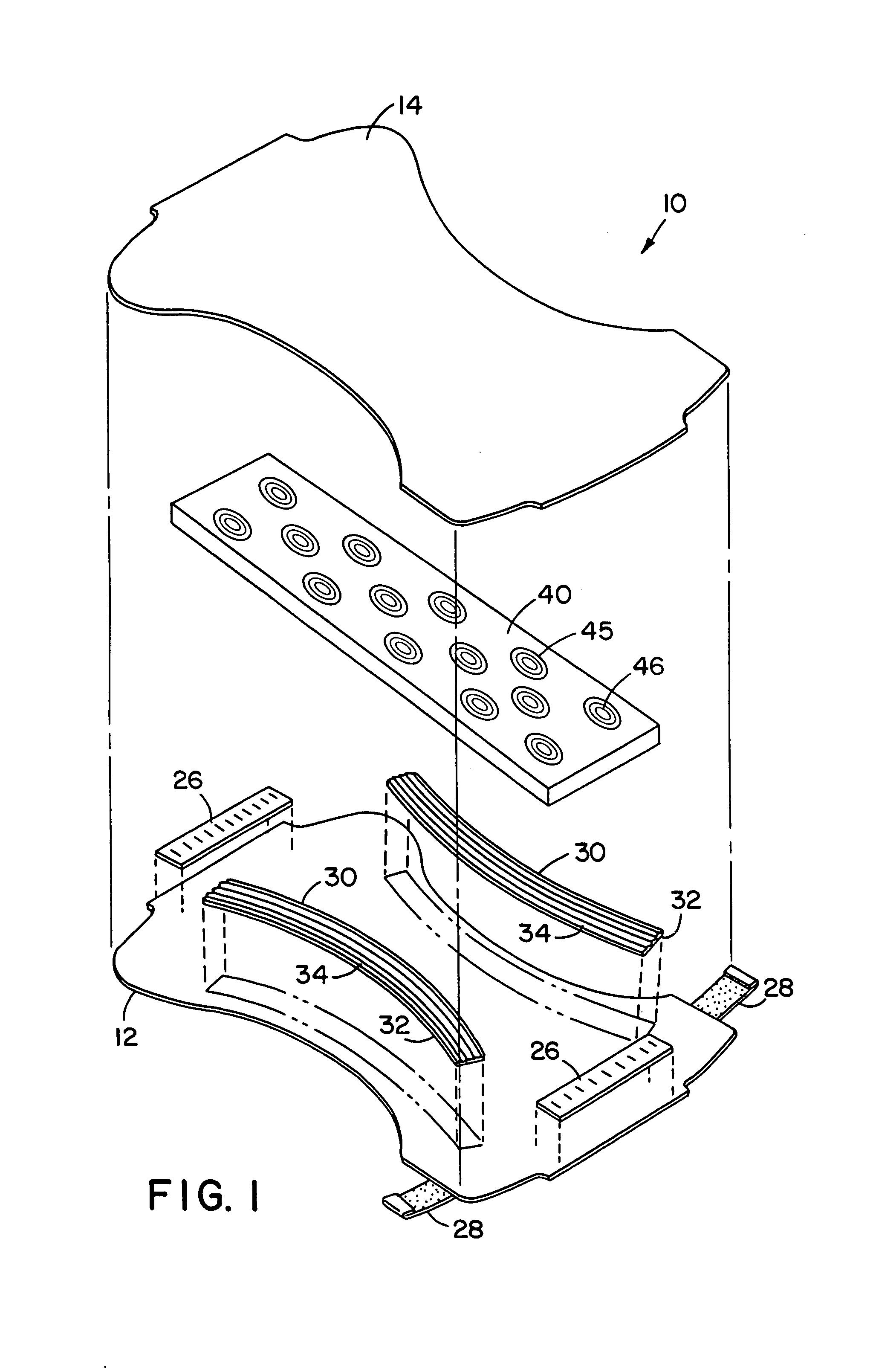
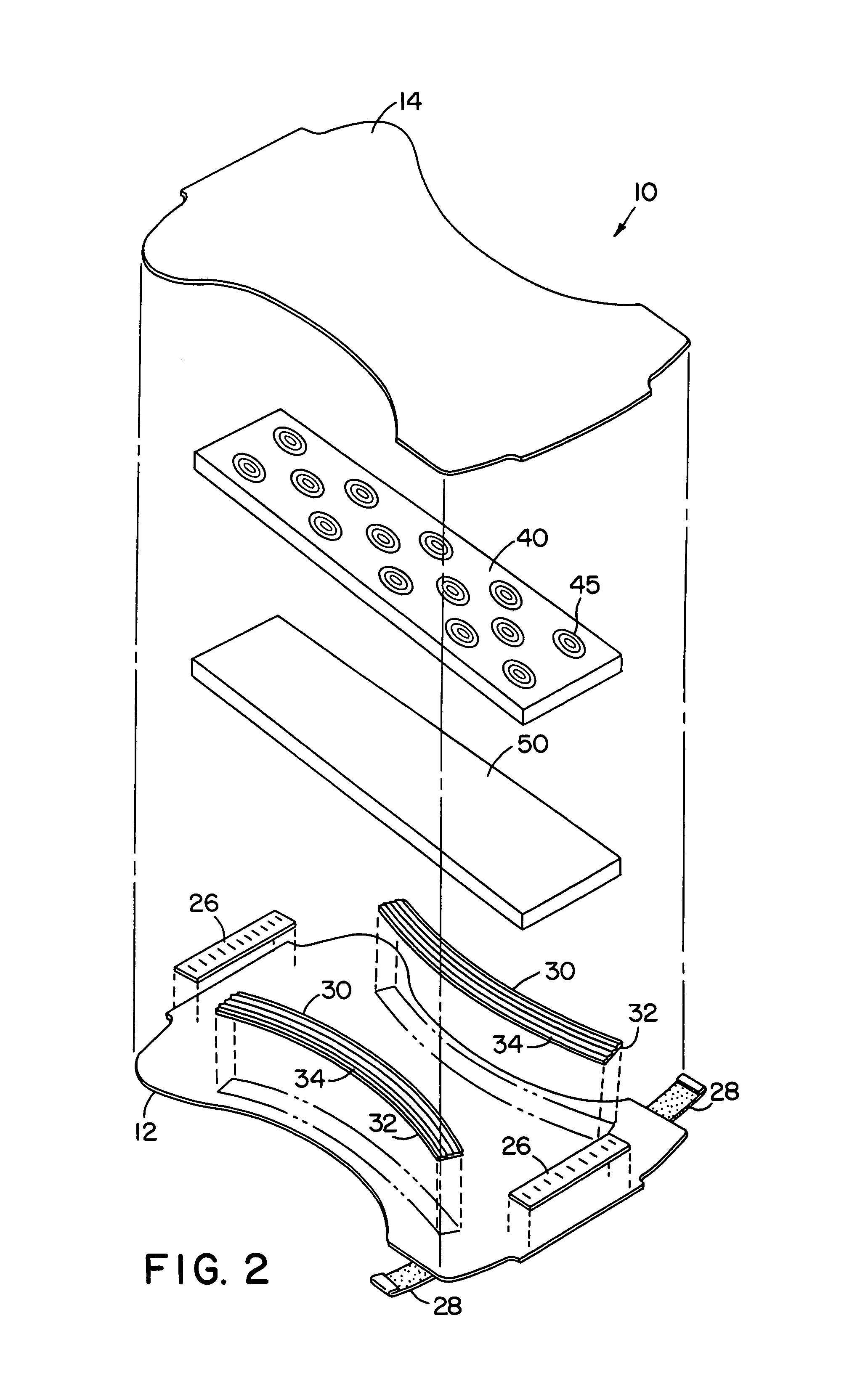
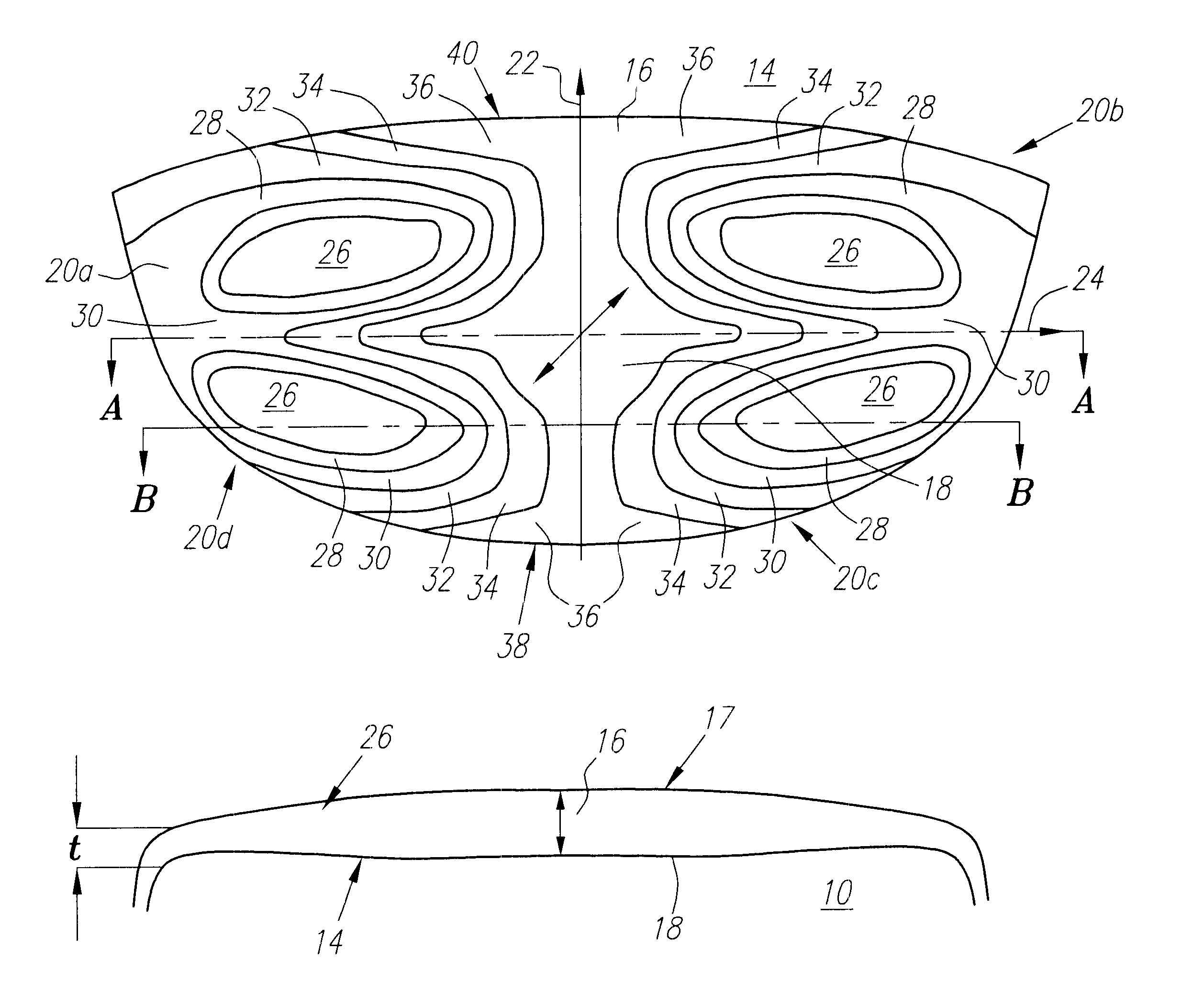
InactiveUS20050072981A1Improves Structural IntegrityImprove lighting efficiencySolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesLight emitting deviceMechanical engineering
The light-emitting device includes a light-emitting element chip; a package having a first recessed portion thereon, in which the light-emitting chip is disposed; a transparent flexible member covering at least the recessed portion; and a transparent rigid member disposed on or above the transparent flexible member. The package has at least a first front surface extending at least outwardly above the first recessed portion; a second front surface extending outwardly above the first front surface; and a third surface as the outside of the package extending outwardly above the second front surface. The rigid member is disposed in the outline of the second front surface with at least three points of contact. The flexible member is continuously provided along the first front surface, the second front surface and the back surface of the rigid member. This light-emitting device is capable of improved reliability without deteriorating its optical characteristics.
Owner:NICHIA CORP
Methods for embolizing blood vessels
InactiveUS6335384B1Reduce molecular weightEasy to adjustHeavy metal active ingredientsOrganic active ingredientsParticulatesMedicine
Disclosed are methods useful for treating vascular lesions wherein a non-particulate agent such as a metal coil is introduced into a vascular site (e.g., an aneurysm cavity) in conjunction with an embolizing composition comprising a biocompatible polymer and a biocompatible solvent.The biocompatible solvent is miscible or soluble in blood and also solubilizes the polymer during delivery. The biocompatible polymer is selected to be soluble in the biocompatible solvent but insoluble in blood. Upon contact with the blood, the biocompatible solvent dissipates from the embolic composition whereupon the biocompatible polymer precipitates. Precipitation of the polymer in the presence of the non-particular agent permits the agent to act as a structural lattice for the growing polymer precipitate.In another embodiment, the biocompatible polymer composition can be replaced with a biocompatible prepolymer composition containing a biocompatible prepolymer.
Owner:MICRO THEREPEUTICS INC
Apparatus and methods for removing vertebral bone and disc tissue
ActiveUS20050203527A1Improves Structural IntegrityPrevents and minimizes buildExcision instrumentsEndoscopic cutting instrumentsDrive shaftVertebral bone
Tissue removal probes comprise an elongated member, a drive shaft rotatably disposed within the member, and a rotatably tissue removal element mounted to the distal end of the drive shaft. One tissue removal element comprises a plurality of tissue-cutting filaments affixed at proximal and distal ends of the tissue removal element. The cutting filaments may have optional hinge points that allow the distal end of the tissue removal element to be inverted, thereby transforming the tissue removal element from a tissue-cutting device to a tissue-grasping device. Another tissue removal element may have a blunted tip to prevent distal tissue trauma and an irrigation port to provide irrigation fluid to the removed tissue and / or tissue removal element. Another tissue removal element has a proximal and distal spiral grooves that are oppositely pitched, so that removed tissue can be collected in the middle of the tissue removal element. Another tissue removal element has independent counter-rotating tissue removal elements to maintain stability during a bone cutting procedure. Still another tissue removal element takes the form of a drill bit with fluted cutting grooves. Yet another tissue removal element has cascading tissue-cutting notches that can be reciprocatably moved to remove tissue within a hole.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Method and apparatus for strengthening the biomechanical properties of implants
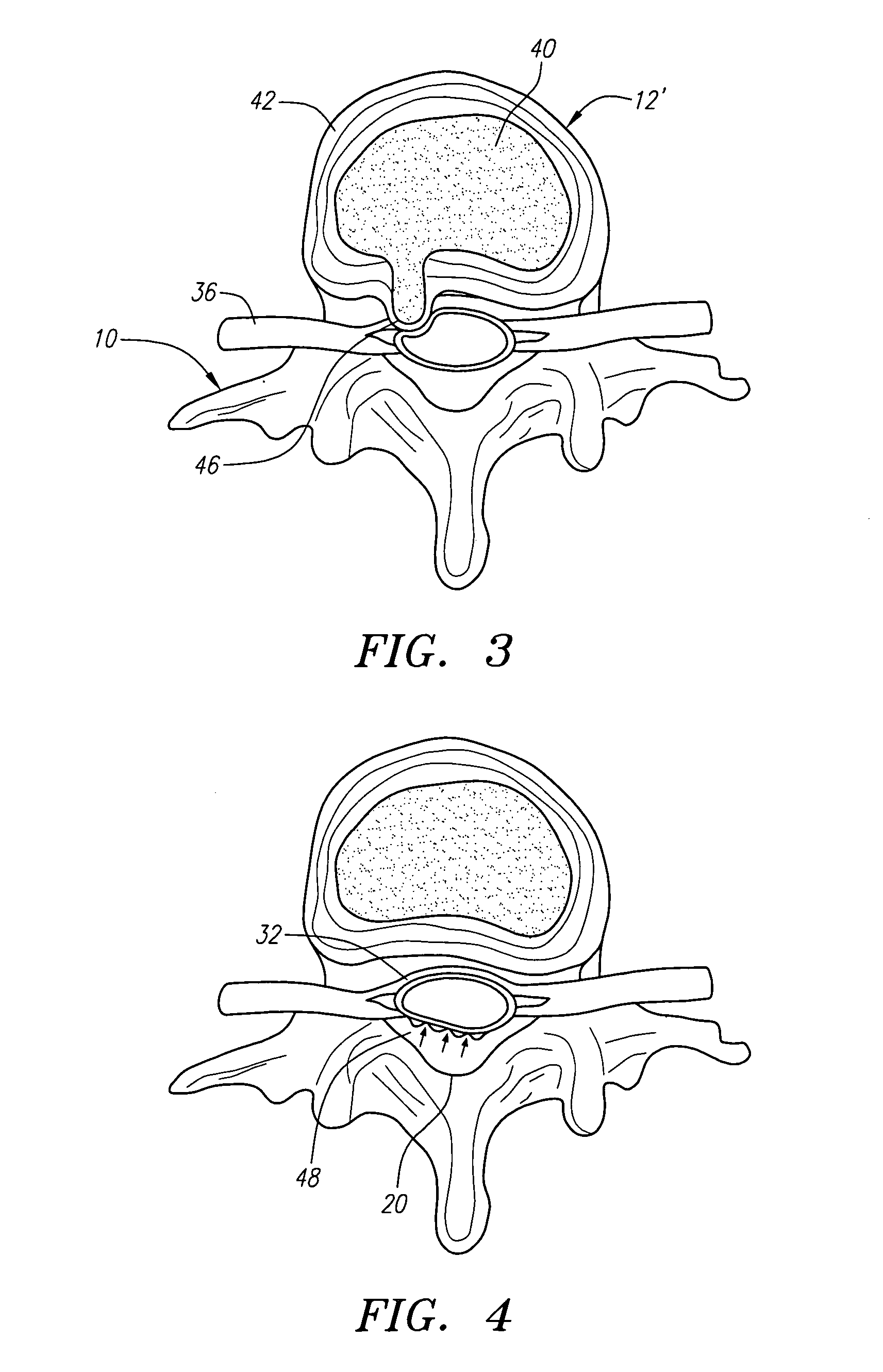
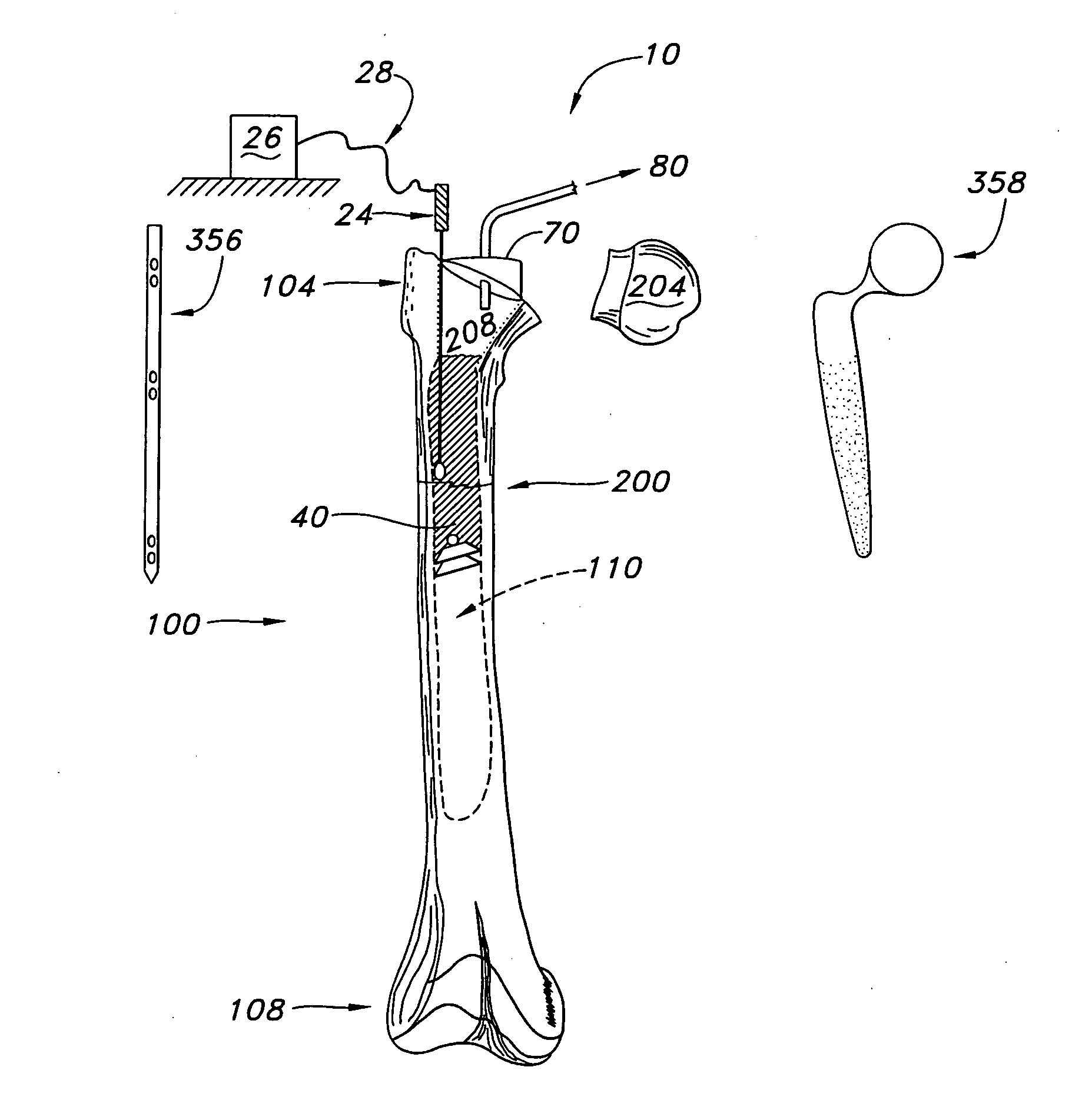
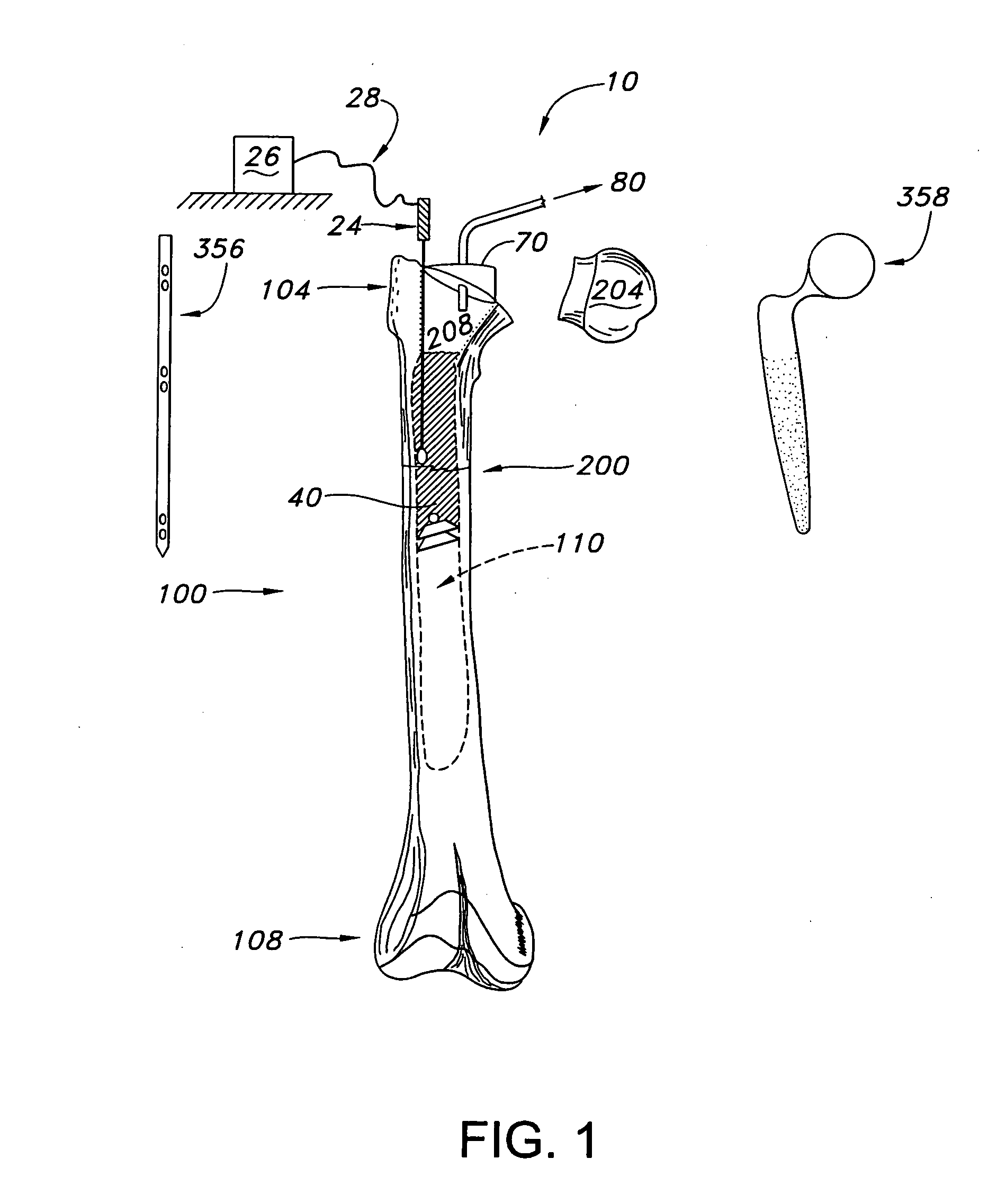
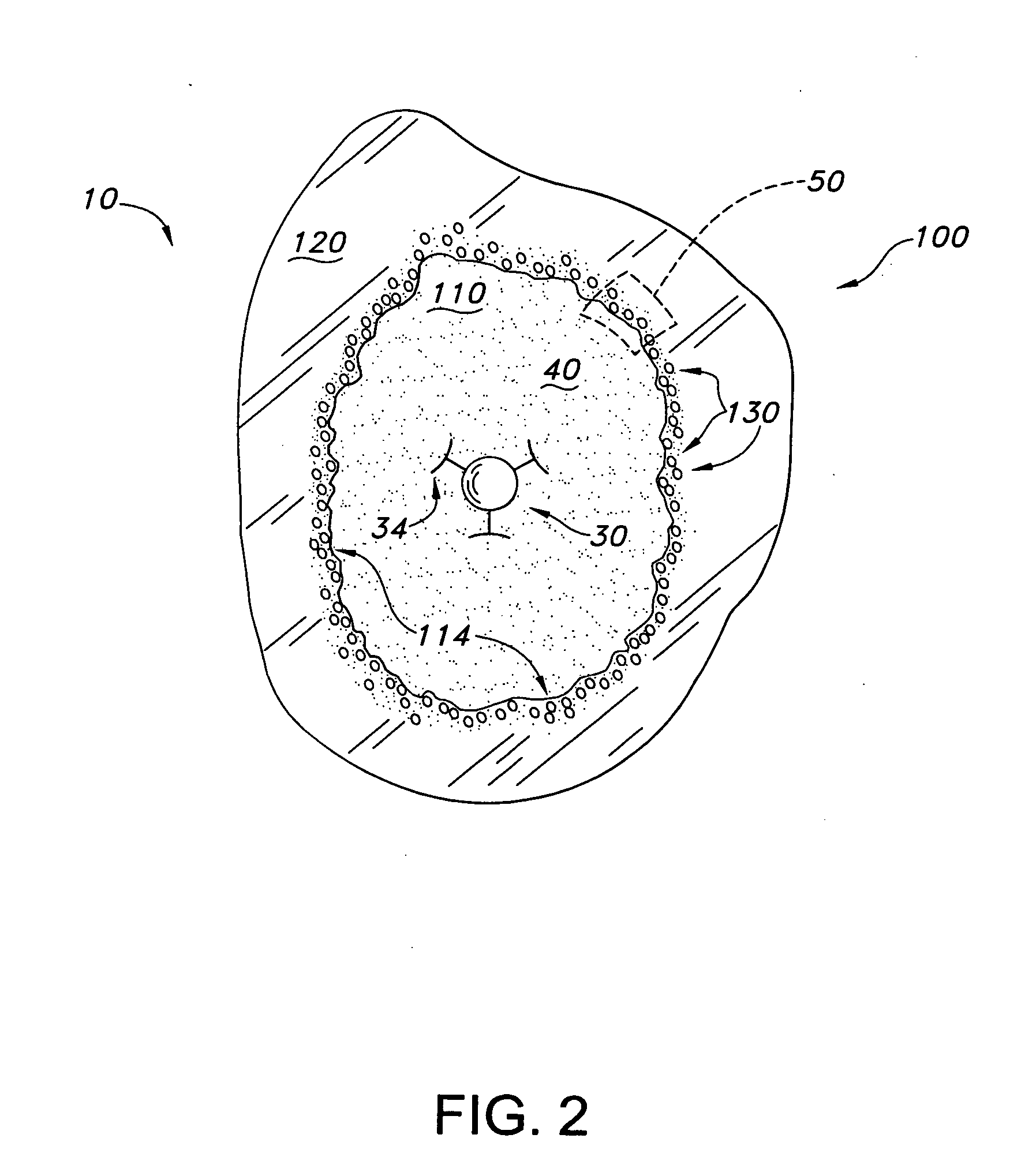
InactiveUS20050010231A1Add depthImproves Structural IntegrityInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsBiomechanicsSubject matter
A method for agitating a surgical fluid using a vibrating probe is disclosed. The agitation method drives entrapped air voids out of the surgical fluid and forces the fluid into a plurality of pores of various sizes in the adjacent bone. The vibrating apparatus in one embodiment includes a probe tip disposed upon a graspable elongate shaft and a series of fins extending into the fluid. The apparatus in one embodiment may include a set of probe tips of different shapes and sizes. The agitation and interdigitation method may facilitate any procedure involving any type of surgical fluid, with or without a prosthetic device such as an intramedullary nail or femoral prosthesis. This Abstract is provided to quickly inform a reader about the subject matter, and not for use interpreting the scope or meaning of the claims.
Owner:MYERS SURGICAL SOLUTIONS LLC
Radio frequency lens and method of suppressing side-lobes
ActiveUS7777690B2Weaken energyImproves Structural IntegrityAntennasPhotonic crystal structureCrystal structure
An RF lens according to the present invention embodiments collimates an RF beam by refracting the beam into a beam profile that is diffraction-limited. The lens is constructed of a lightweight mechanical arrangement of two or more materials, where the materials are arranged to form a photonic crystal structure (e.g., a series of holes defined within a parent material). The lens includes impedance matching layers, while an absorptive or apodizing mask is applied to the lens to create a specific energy profile across the lens. The impedance matching layers and apodizing mask similarly include a photonic crystal structure. The energy profile function across the lens aperture is continuous, while the derivatives of the energy distribution function are similarly continuous. This lens arrangement produces a substantial reduction in the amount of energy that is transmitted in the side-lobes of an RF system.
Owner:HARRIS CORP
Tissue scaffold having aligned fibrils, apparatus and method for producing the same, and artificial tissue and methods of use thereof
ActiveUS20050009178A1Improve structural strengthMinimal immunological responsePeptide/protein ingredientsHollow filament manufactureFiberRadial position
A tubular tissue scaffold is described which comprises a tube having a wall, wherein the wall includes biopolymer fibrils that are aligned in a helical pattern around the longitudinal axis of the tube where the pitch of the helical pattern changes with the radial position in the tube wall. The scaffold is capable of directing the morphological pattern of attached and growing cells to form a helical pattern around the tube walls. Additionally, an apparatus for producing such a tubular tissue scaffold is disclosed, the apparatus comprising a biopolymer gel dispersion feed pump that is operably connected to a tube-forming device having an exit port, where the tube-forming device is capable of producing a tube from the gel dispersion while providing an angular shear force across the wall of the tube, and a liquid bath located to receive the tubular tissue scaffold from the tube-forming device. A method for producing the tubular tissue scaffolds is also disclosed. Also, artificial tissue comprising living cells attached to a tubular tissue scaffold as described herein is disclosed. Methods for using the artificial tissue are also disclosed.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF SOUTH CAROLINA
Self-supporting unitary feed assembly
InactiveUS7907097B2Minimize impedance mismatchRepeatedly cost efficiently manufacturedAntenna supports/mountingsEngineeringMachining
A feed assembly for a reflector antenna having a unitary portion of dielectric material, a proximal end of the unitary portion configured for connection with the reflector antenna. The unitary portion having a waveguide portion extending between the proximal end and a sub reflector support having a sub reflector surface at a distal end. The waveguide portion and the sub reflector surface covered with an RF reflective material. The unitary portion may be cost effectively formed via, for example injection molding and or machining. Alternatively, the feed assembly may be formed as a horn feed, without a sub reflector.
Owner:COMMSCOPE TECH LLC
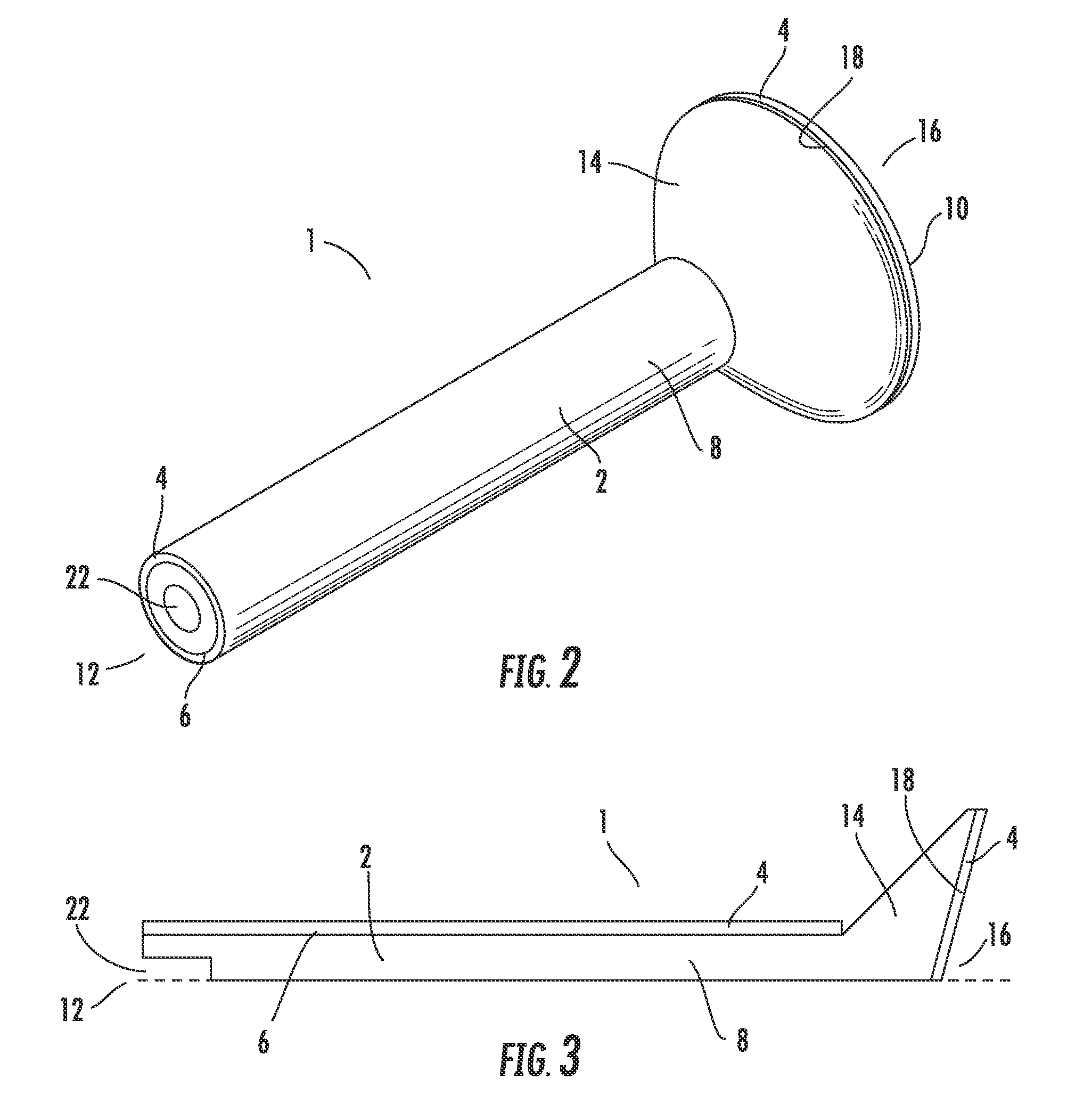
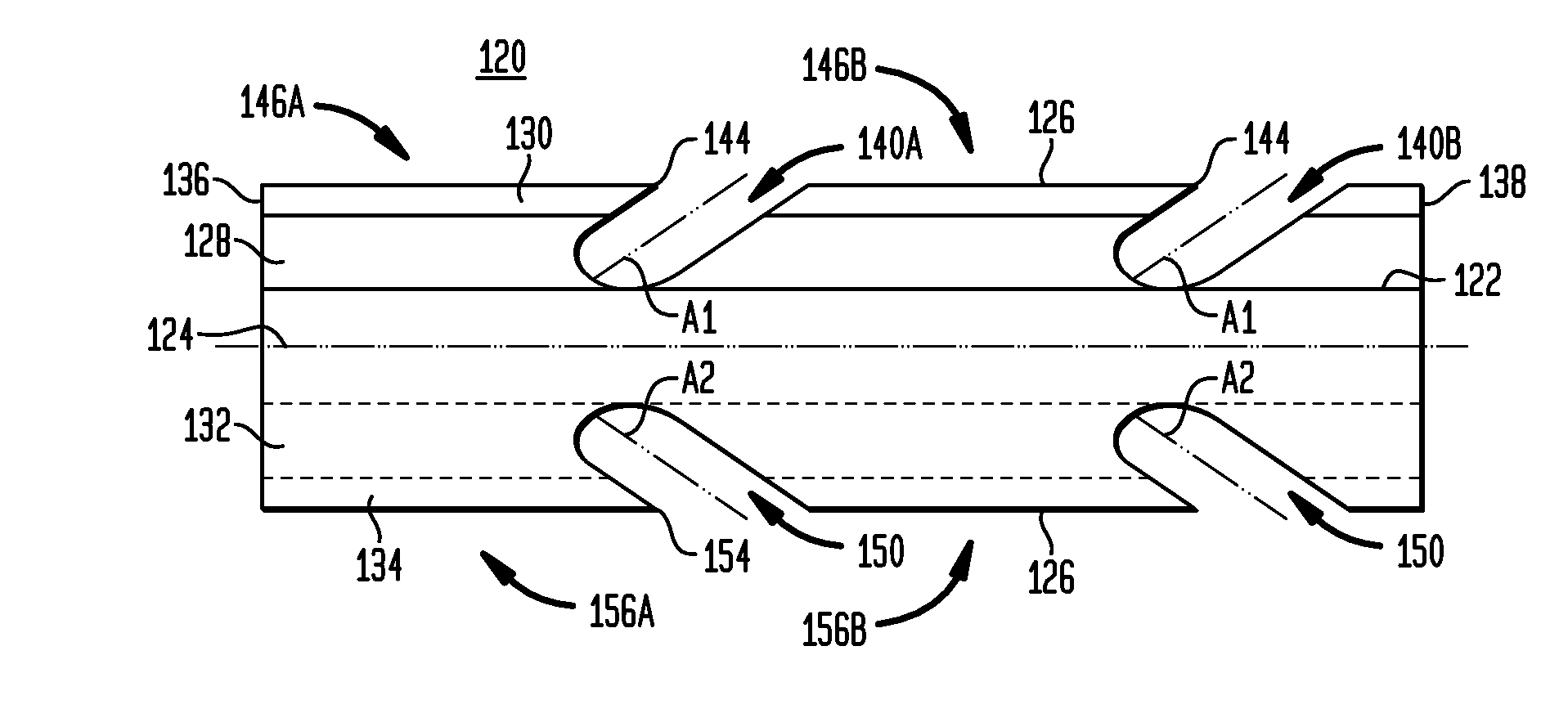
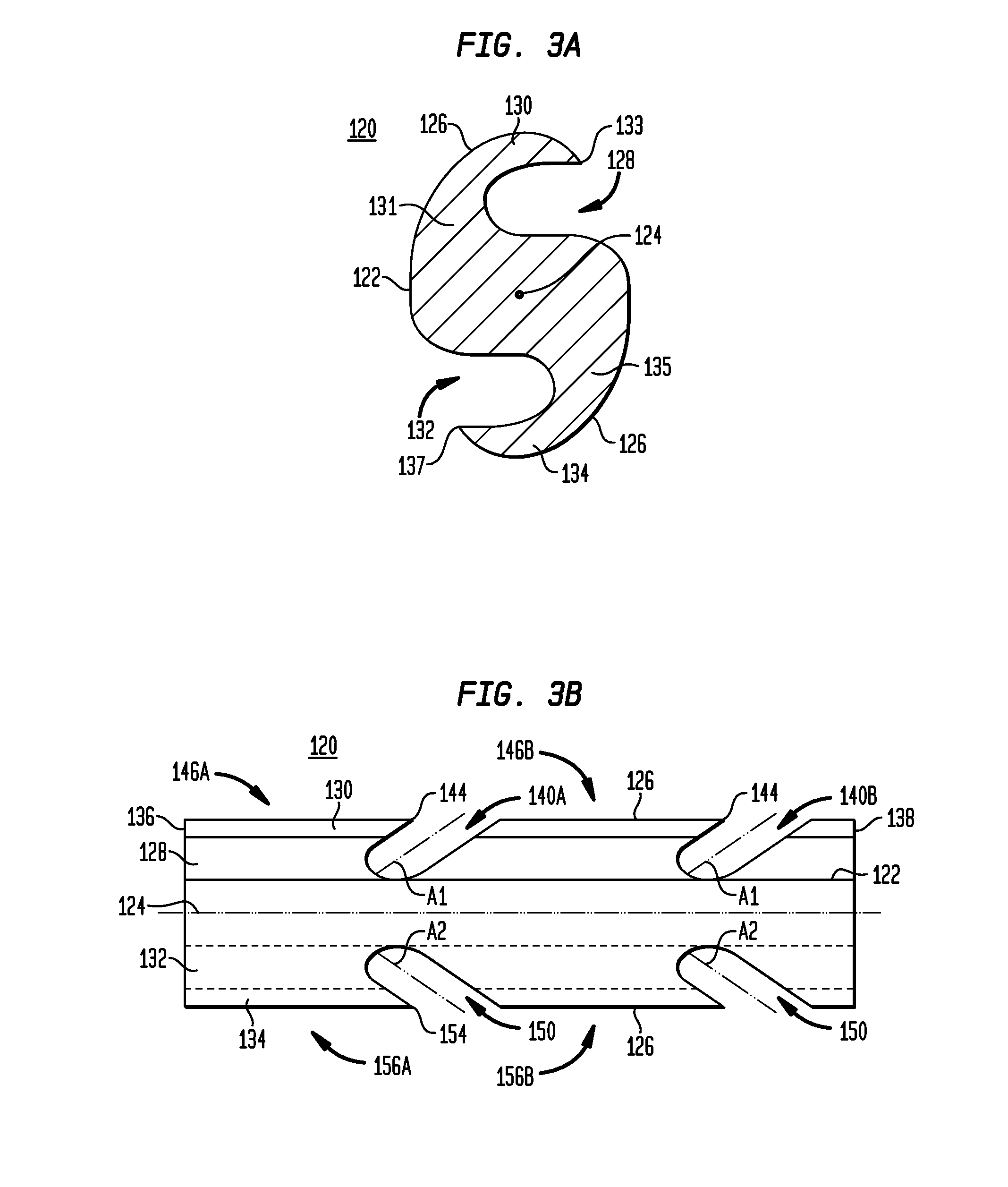
Collapsible barbed sutures having reduced drag and methods therefor
ActiveUS20100023055A1Minimize outer diameterIncrease flexibilitySuture equipmentsEngineeringMechanical engineering
A barbed suture includes a flexible thread having a core with a leading end, a trailing end, and a central axis. The barbed suture includes a first flexible flap connected to the core, the first flap extending between the leading and trailing ends of the core, and a second flexible flap connected to the core, the second flap extending between the leading and trailing ends of the core. The flexible flaps and the core have an S-shaped profile when viewed in cross-section. The barbed suture includes first and second slots formed in the respective first and second flaps for dividing the flaps into first and second barbs projecting from the core, whereby each slot extends outwardly from the core and rearwardly toward the trailing end of the core.
Owner:ETHICON INC
Methods for embolizing blood vessels
InactiveUS6017977AReduce molecular weightEasy to adjustHeavy metal active ingredientsOrganic active ingredientsPrepolymerSolvent
Disclosed are methods useful for treating vascular lesions wherein a non-particulate agent such as a metal coil is introduced into a vascular site (e.g., an aneurysm cavity) in conjunction with an embolizing composition comprising a biocompatible polymer and a biocompatible solvent. The biocompatible solvent is miscible or soluble in blood and also solubilizes the polymer during delivery. The biocompatible polymer is selected to be soluble in the biocompatible solvent but insoluble in blood. Upon contact with the blood, the biocompatible solvent dissipates from the embolic composition whereupon the biocompatible polymer precipitates. Precipitation of the polymer in the presence of the non-particulate agent permits the agent to act as a structural lattice for the growing polymer precipitate. In another embodiment, the biocompatible polymer composition can be replaced with a biocompatible prepolymer composition containing a biocompatible prepolymer.
Owner:MICRO THEREPEUTICS INC
Method and apparatus for minimally invasive delivery, tensioned deployment and fixation of secondary material prosthetic devices in patient body tissue, including hernia repair within the patient's herniation site
InactiveUS20100069930A1Reduce the possibilityRaise the possibilityProsthesisWound clampsProsthesisAbdominal wall
Apparatus and methods enable insertion and tensioned deployment of a secondary material prosthetic device into a body cavity or other tissue of a patient, such as for example hernia repair mesh into the abdominopelvic cavity of a patient through the hernia site. The present invention establishes fixation sites for the prosthetic device and tensions it against the body tissue. It may also be used implant fixation devices within the body tissue so that the prosthetic device is tensioned into firm abutting contact with the body tissue. Instrument deployment and fixation struts may be advanced in retrograde fashion in order to reduce needed deployment volume within the patient's body cavity. The prosthetic device advantageously may be flexibly coupled to the instrument via fixation devices such as sutures, so as to increase orientation flexibility.
Owner:VENTRALFIX
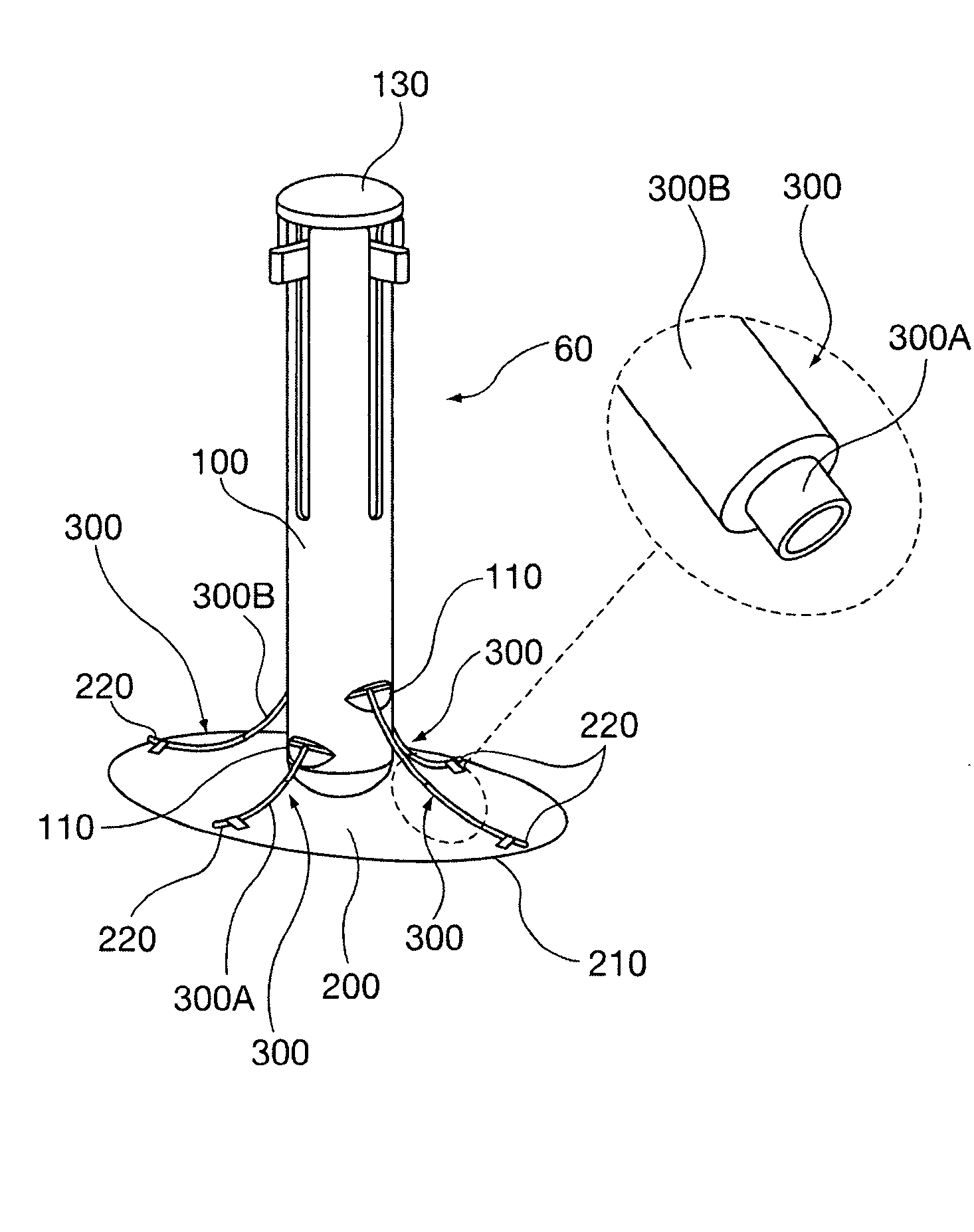
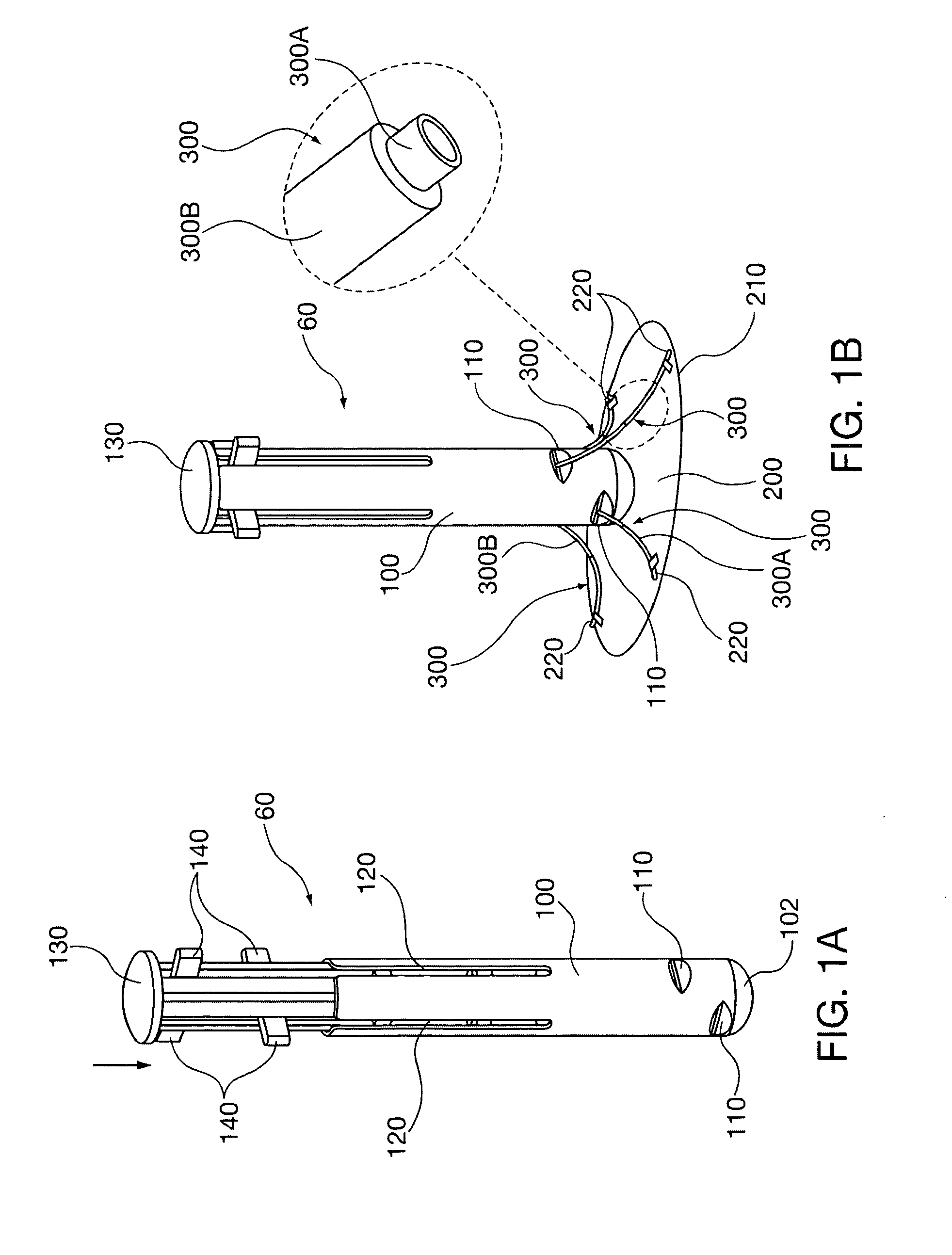
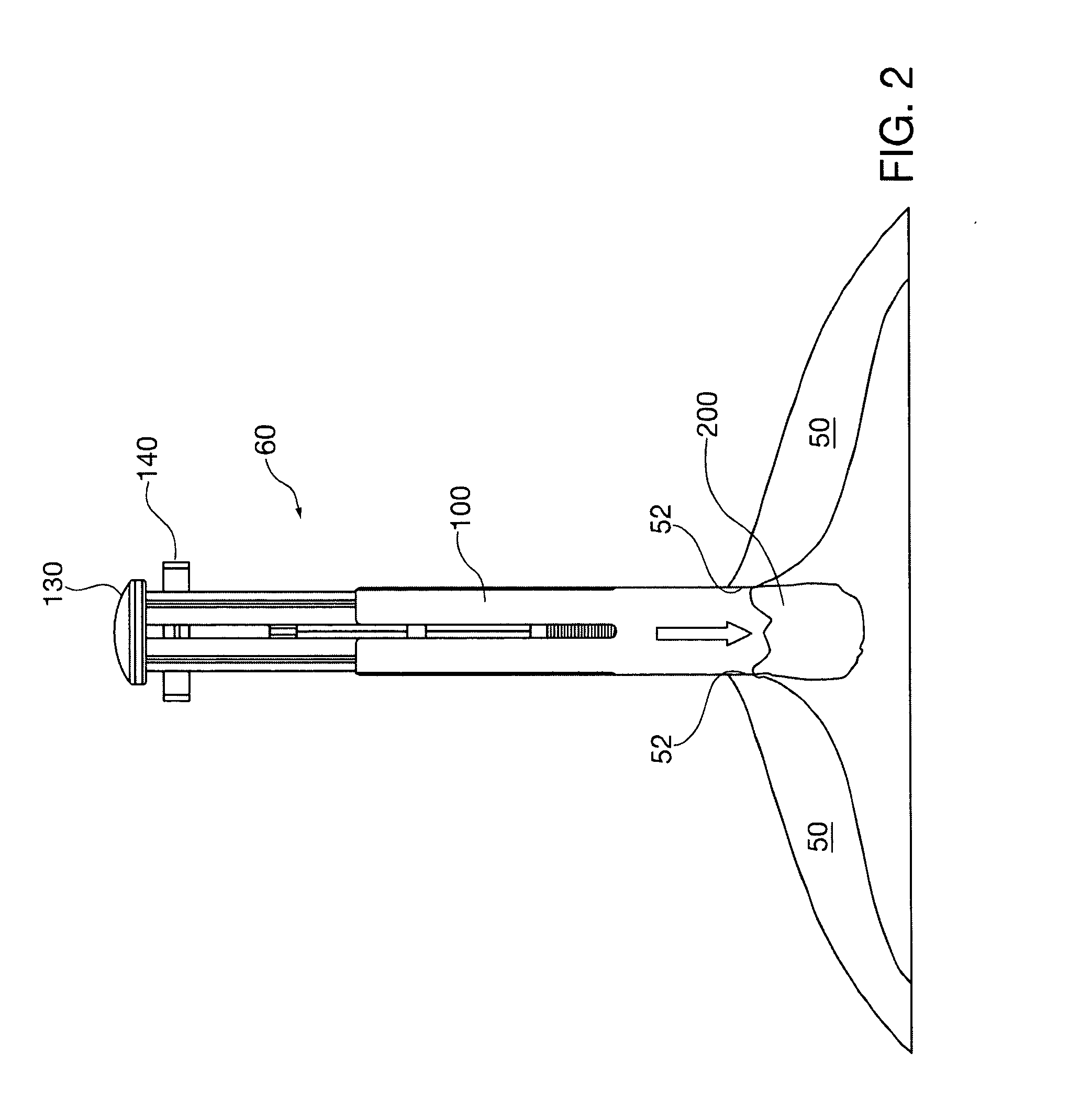
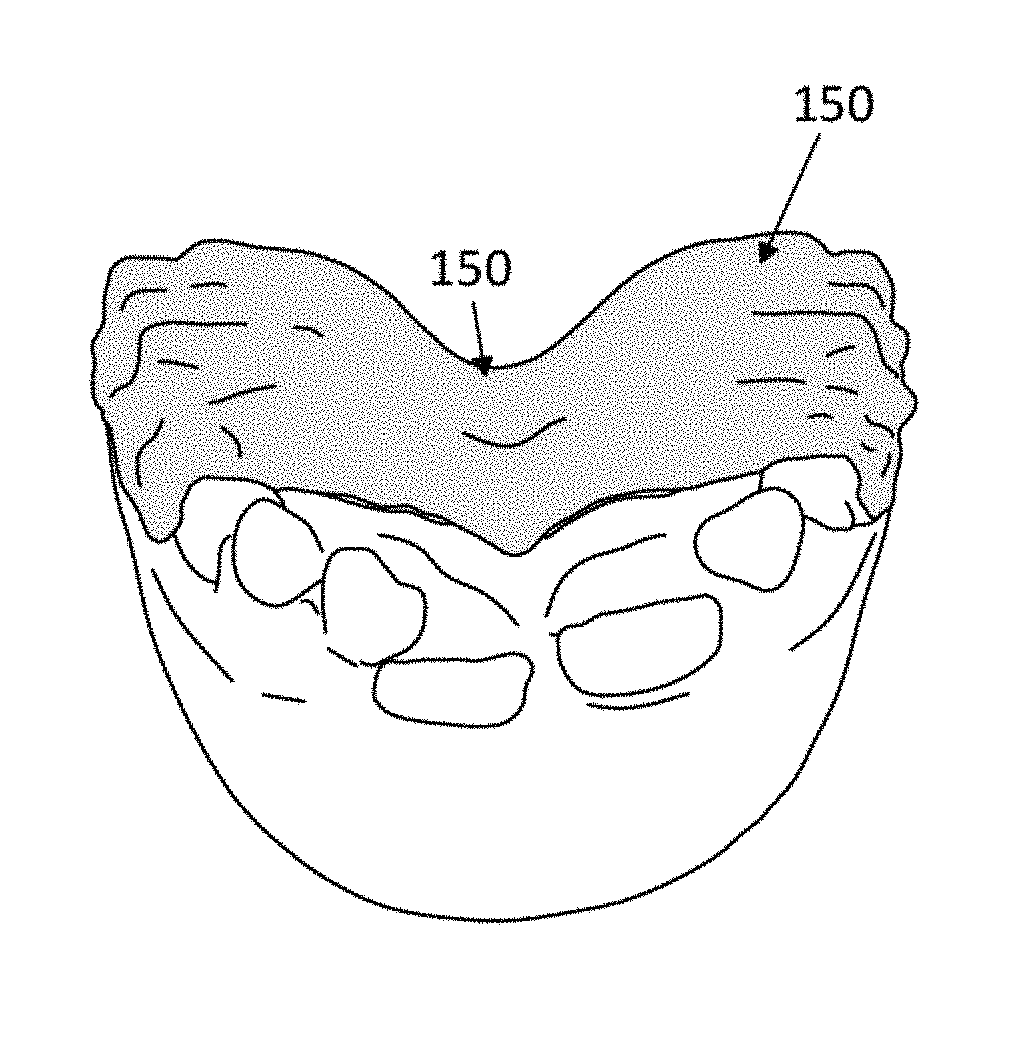
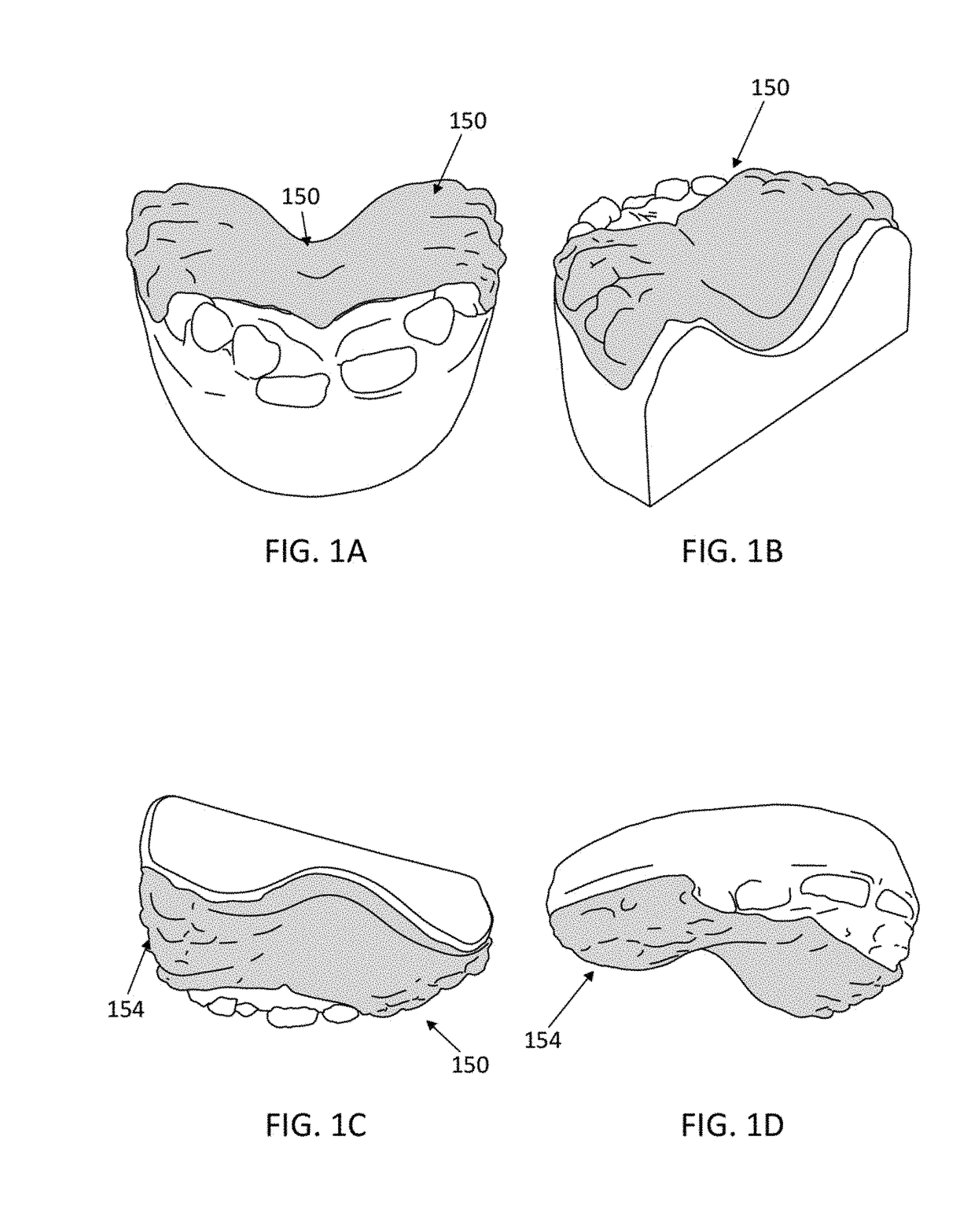
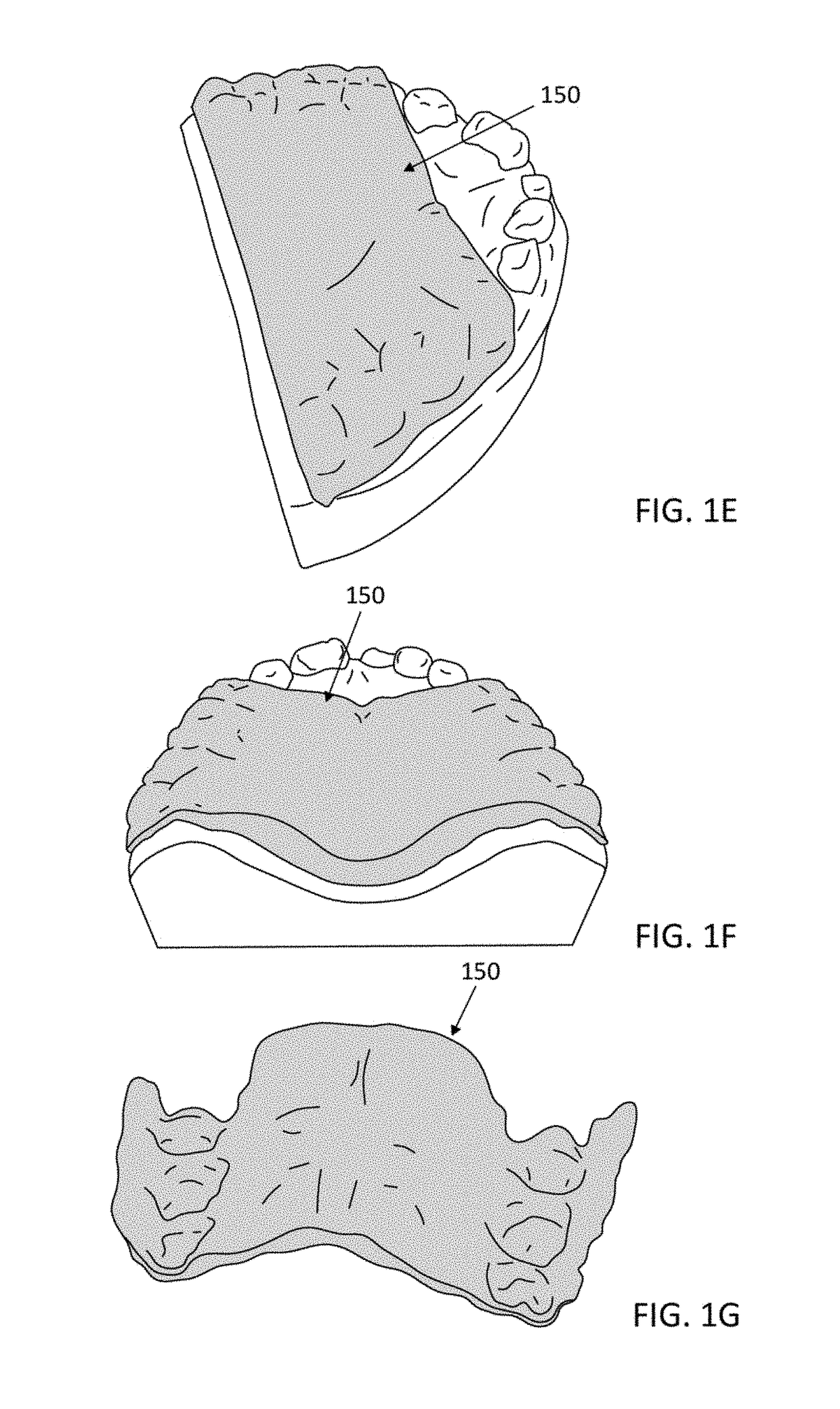
Palatal expanders and methods of expanding a palate
ActiveUS20180153648A1Reducing abilityReducing retentionAdditive manufacturing apparatusImpression capsMedicineOverbite
Palatal expander apparatuses for expanding a patient's palate (“palatal expanders”) and methods of using and making them. These palatal expanders may be configured to have a variable surface smoothness on one side (e.g., the lingual-facing surface) compared to the opposite side (e.g., the palatal-facing surface). These palatal expanders may be configured to have a varying thickness in the palatal region. These palatal expanders may be adapted for ease in removal by the patient or caregiver (e.g., including a hinged region and / or detachment region, and / or including a thinner buccal side then occlusal side, etc.).
Owner:ALIGN TECH
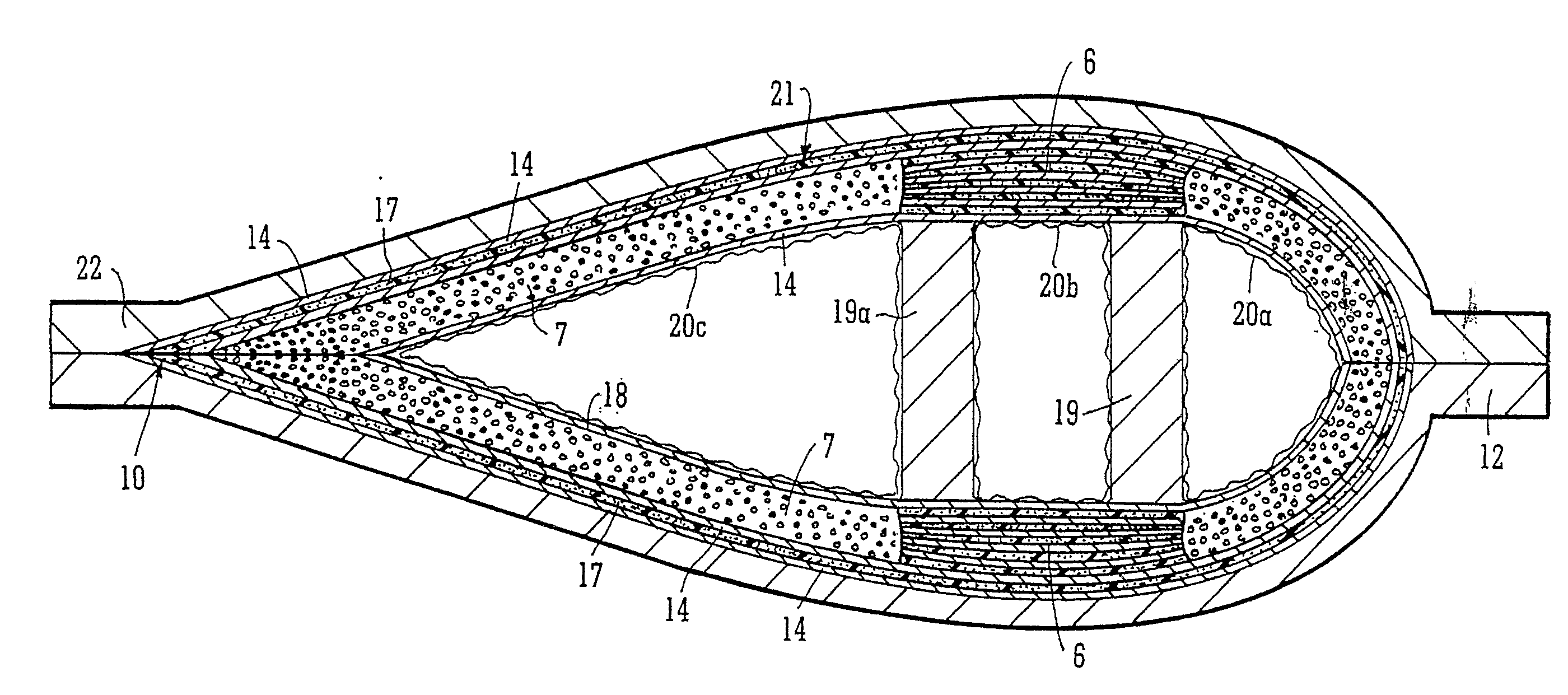
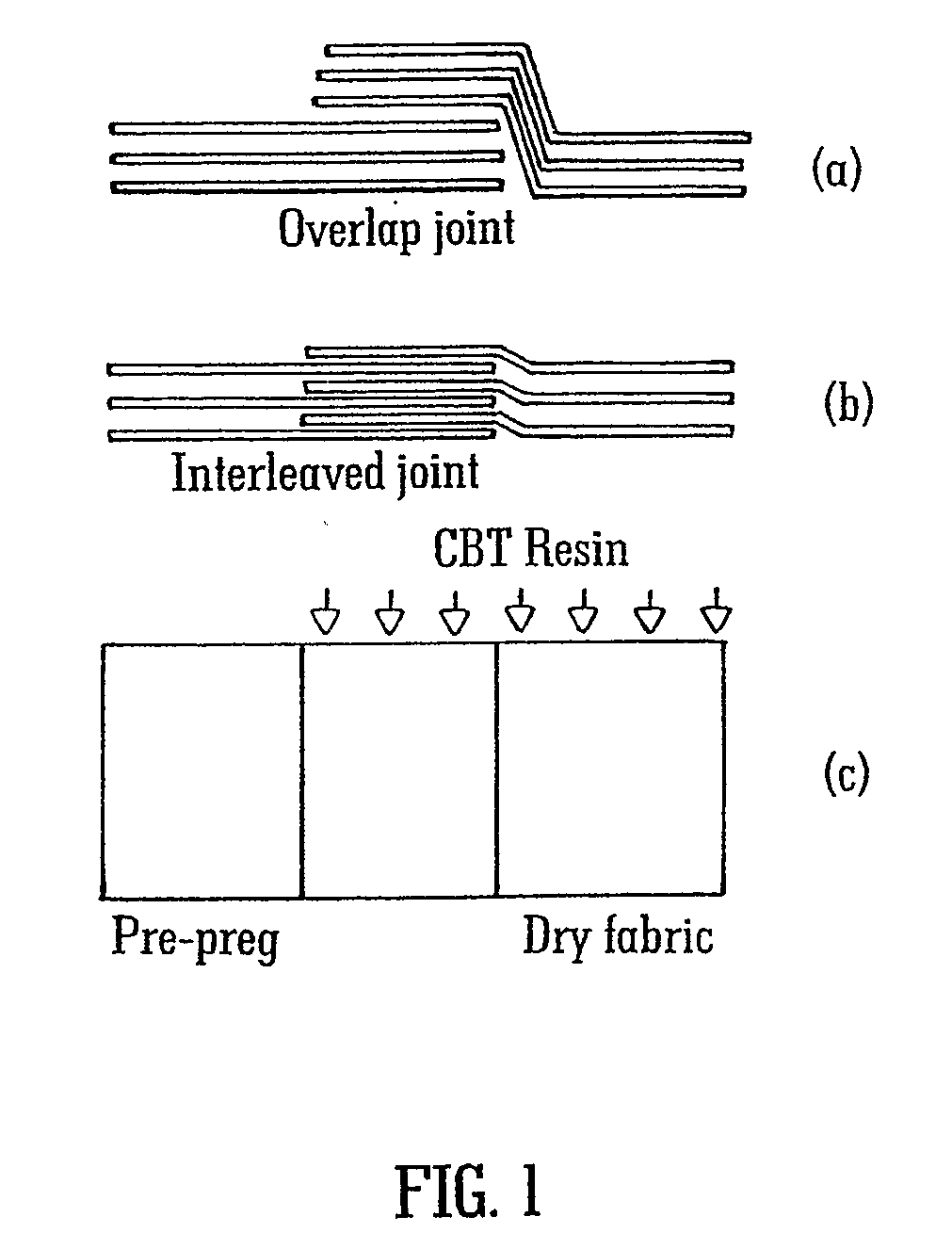
Composite Articles Comprising In-Situ-Polymerisable Thermoplastic Material and Processes for their Construction
InactiveUS20100062238A1Reliable constructionLow costFinal product manufacturePretreated surfacesTurbine bladeIn situ polymerization
A process for the manufacture of a composite article is described wherein the process comprises the steps of (i) providing on a tool (22) a fibrous material (14) having associated therewith in at least one region thereof an in-situ polymerisable non-fibrous form of a thermoplastic material; (ii) applying heat and a vacuum to said material; and additionally (iii) drawing into the fibrous material, from a source external to the tool, additional thermoplastic pre-polymer material. The process described is particularly useful for the manufacture of a large composite structure such as thermoplastic composite wind turbine blade, for example.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF LIMERICK +2
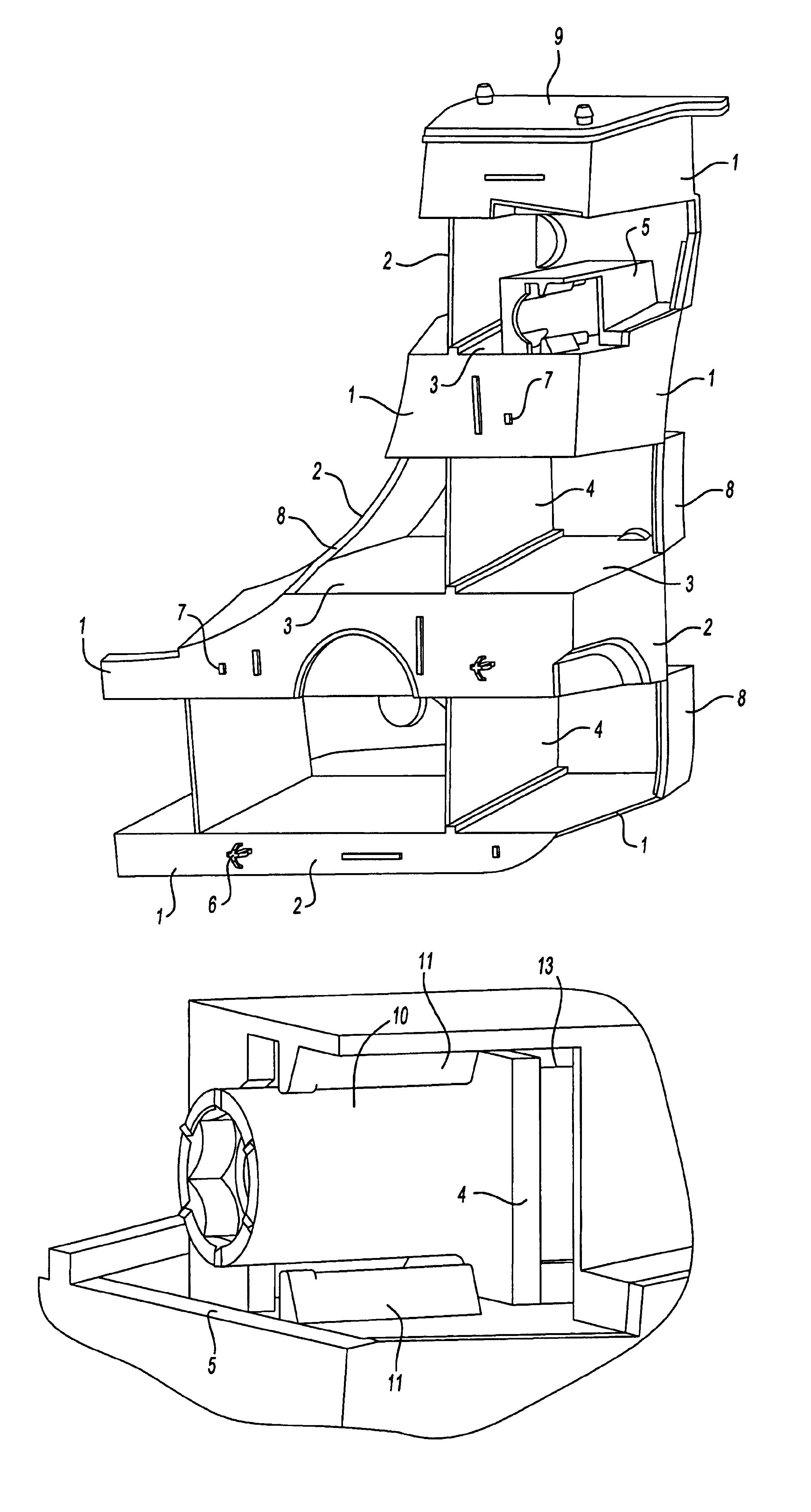
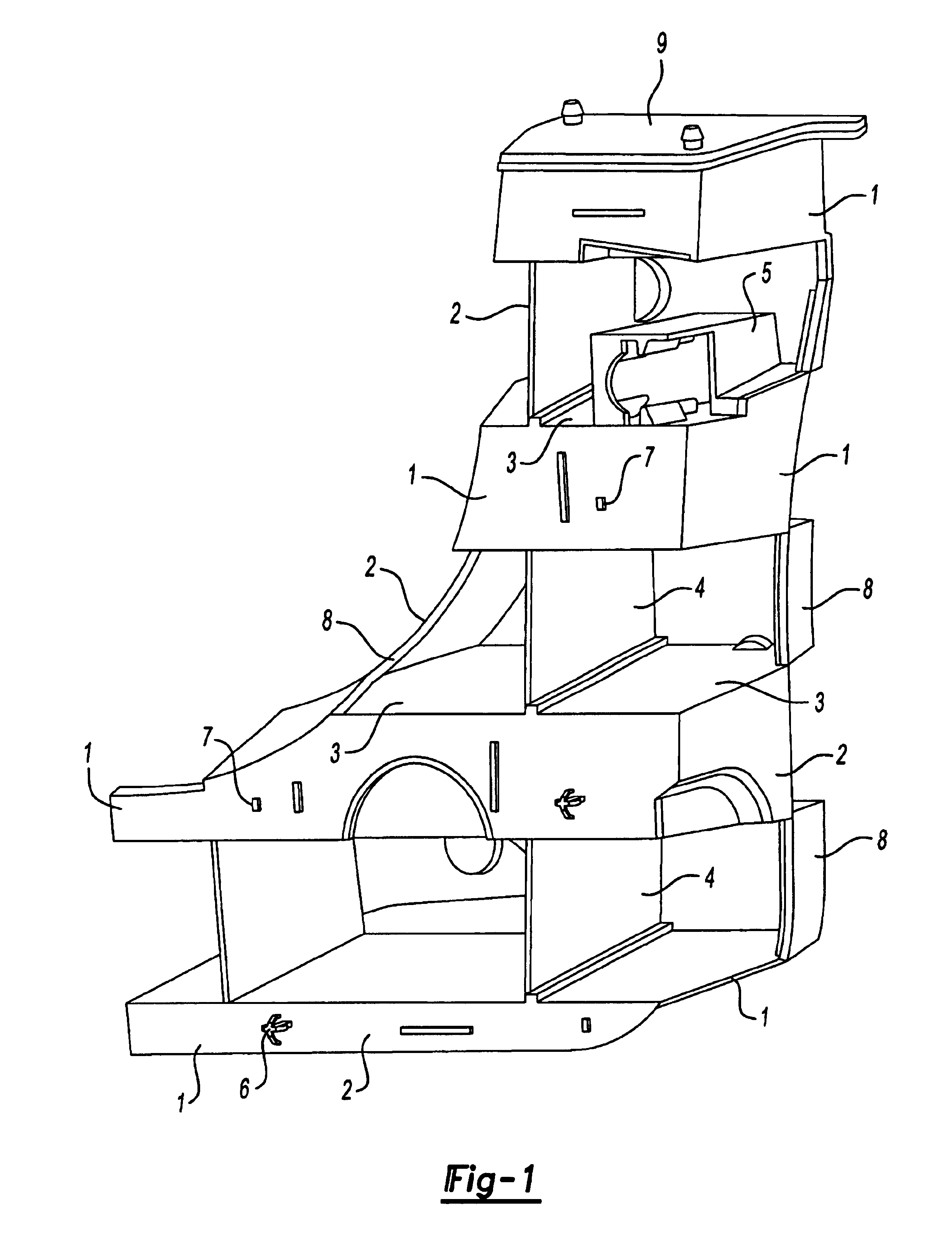
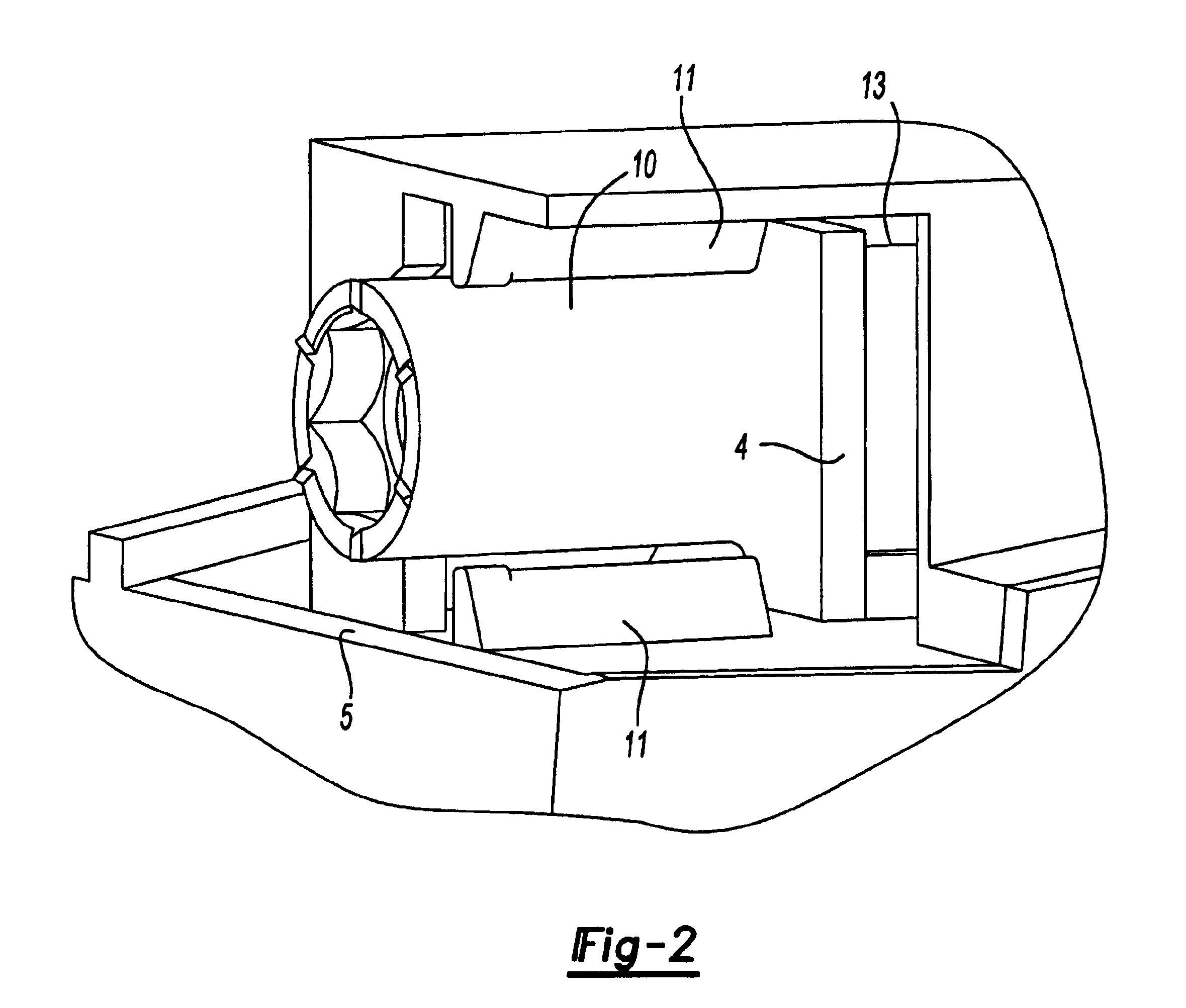
Reinforcing members
ActiveUS6953219B2Light weightHigh strengthVehicle seatsSuperstructure subunitsEngineeringMechanical engineering
Parts are provided which combine structural reinforcement of hollow profiles and light weight means of attachment. Optionally, the part may also provide an acoustic baffle. The parts consists of a core coated with expandable structural reinforcing foam on at least part of its surface the core being provided with means for receipt of a nut and means to prevent rotation of the nut. Optionally, a piece of a second expandable material is provided on at least one extremity which can expand to fill the entire cross section of the hollow profile. In a preferred embodiment, the hollow profile is the A, B or C pillar of a vehicle and the nut is used for attaching doors.
Owner:ZEPHYROS INC
Nonabsorbent surge layer having discrete regions of superabsorbent and method for making
InactiveUS7189888B2Increase fluid intake and absorption capacityIncreased structural integrityBaby linensTamponsPolymer chemistryPolymer
Owner:KIMBERLY-CLARK WORLDWIDE INC
Contoured golf club face
InactiveUS6471603B1Increased structural integrityLow weightGolf clubsRacket sportsIt designEngineering
A contoured golf club face provides increased structural integrity for a given weight and size is described and shown along with a method for its design. The contoured golf club face includes a vertical stiffening region, a tapered horizontal stiffening region, four similar contoured quadrants of increasingly thinning material toward the center of each quadrant, and thickening regions at face / sole and face / crown intersection regions. The thicknesses of adjoining regions are gradually blended to provide a smooth contoured surface. The present golf club face is light weight, is structurally resistant to impact deformation, is resistant to initial and long-term failure, has its mass center located at its sweet spot, exhibits inertial axes which are aligned with vertical and horizontal axes (i.e. primary club force directions: ball impact force and club centrifugal force directions), and produces acoustical tones. A club incorporating the present contoured golf club face may be provide a certain first acoustical sound when used to hit a ball with a certain first specific area of the face (e.g. the sweet spot or sweet spot region) and to provide a different second acoustical sound when used to hit a ball with an area of the face other than that first area (e.g. other than the sweet spot or sweet spot region). Thus, the present invention may be used to provide an educational tool for use in teaching and / or learning to consistently impact a ball on the optimal region of the club face.
Owner:CALLAWAY GOLF CO
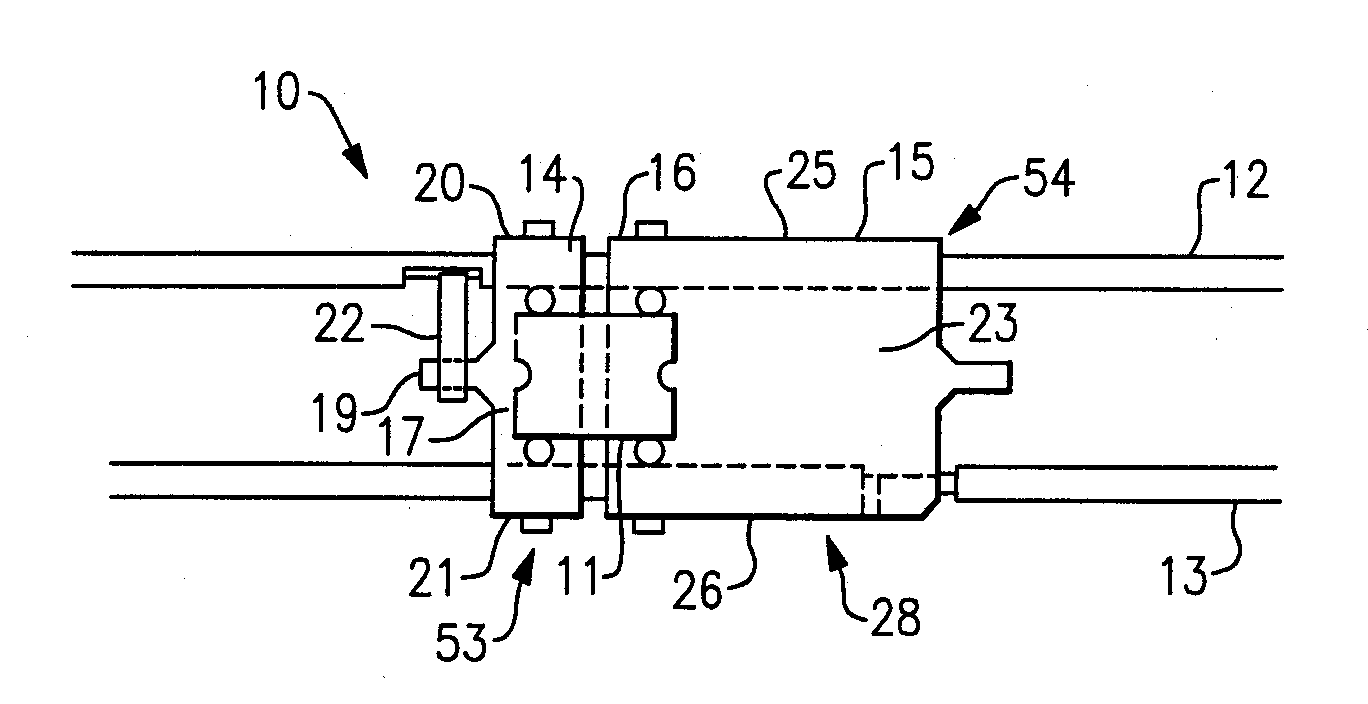
Shielded cage assembly for electrical connectors
ActiveUS20060003632A1Improve abilitiesImproves Structural IntegrityElectrically conductive connectionsMagnetic/electric field screeningEngineeringElectrical connector
An integrated wall stacked shielded cage assembly is provided for electrical connectors. The cage assembly has multiple bays for receiving electrical components. At least two arrays of bays are provided, and the arrays are separated by an intervening space. Assembly is carried out with a plurality of spacers which interlock with a plurality of intermediate walls, and cover structures are provided in order to complete EMI shielding.
Owner:MOLEX INC
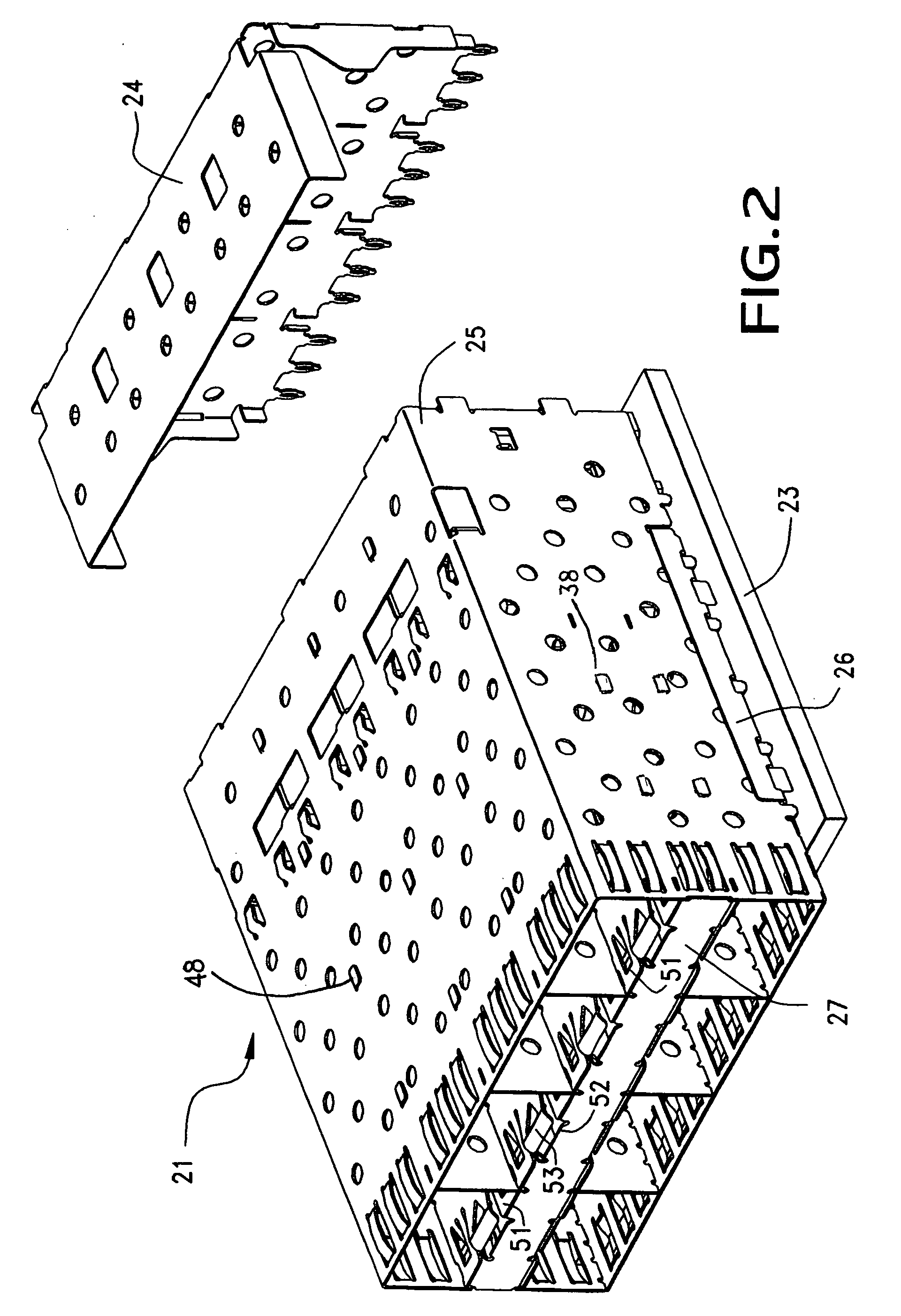
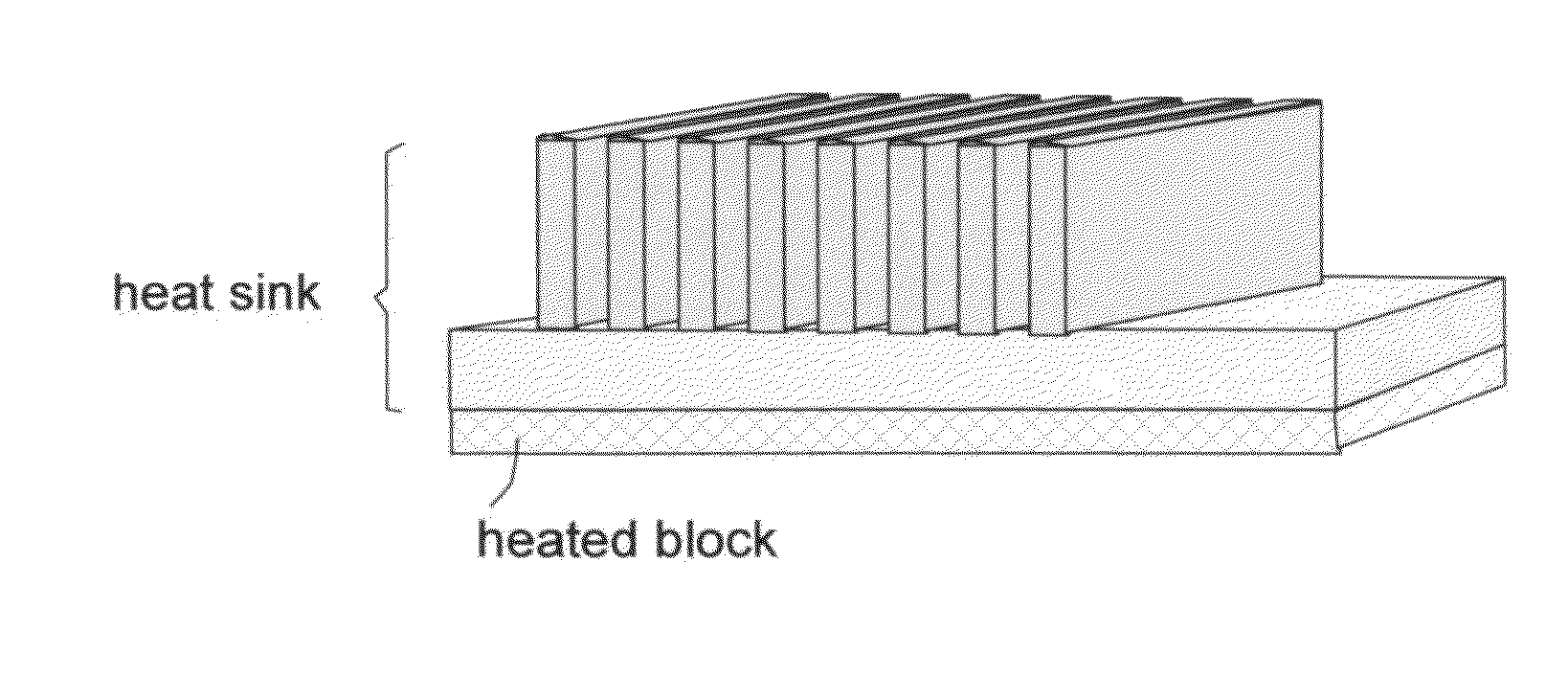
Nano graphene platelet-reinforced composite heat sinks and process for producing same
ActiveUS20140224466A1Improve surface scratch resistanceReduced/eliminated possibilityMaterial nanotechnologySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsEngineeringGraphite
An integrated heat sink article composed of a heat collection member and at least one heat dissipation member integral to the heat collection member, wherein the heat collection member is configured to be in thermal contact with a heat source, collects heat from the heat source, and dissipates heat through the at least one heat dissipation member, and further wherein the heat sink is formed of a nano graphene platelet-reinforced composite having nano graphene platelets or sheets (NGPs) as a first reinforcement phase dispersed in a matrix material and the first reinforcement phase occupies a weight fraction of 1-90% based on the total composite weight. Preferably, these NGPs, alone or in combination with a second reinforcement phase, are bonded by an adhesive and constitute a continuous 3-D network of electron- and phonon-conducting paths.
Owner:GLOBAL GRAPHENE GRP INC
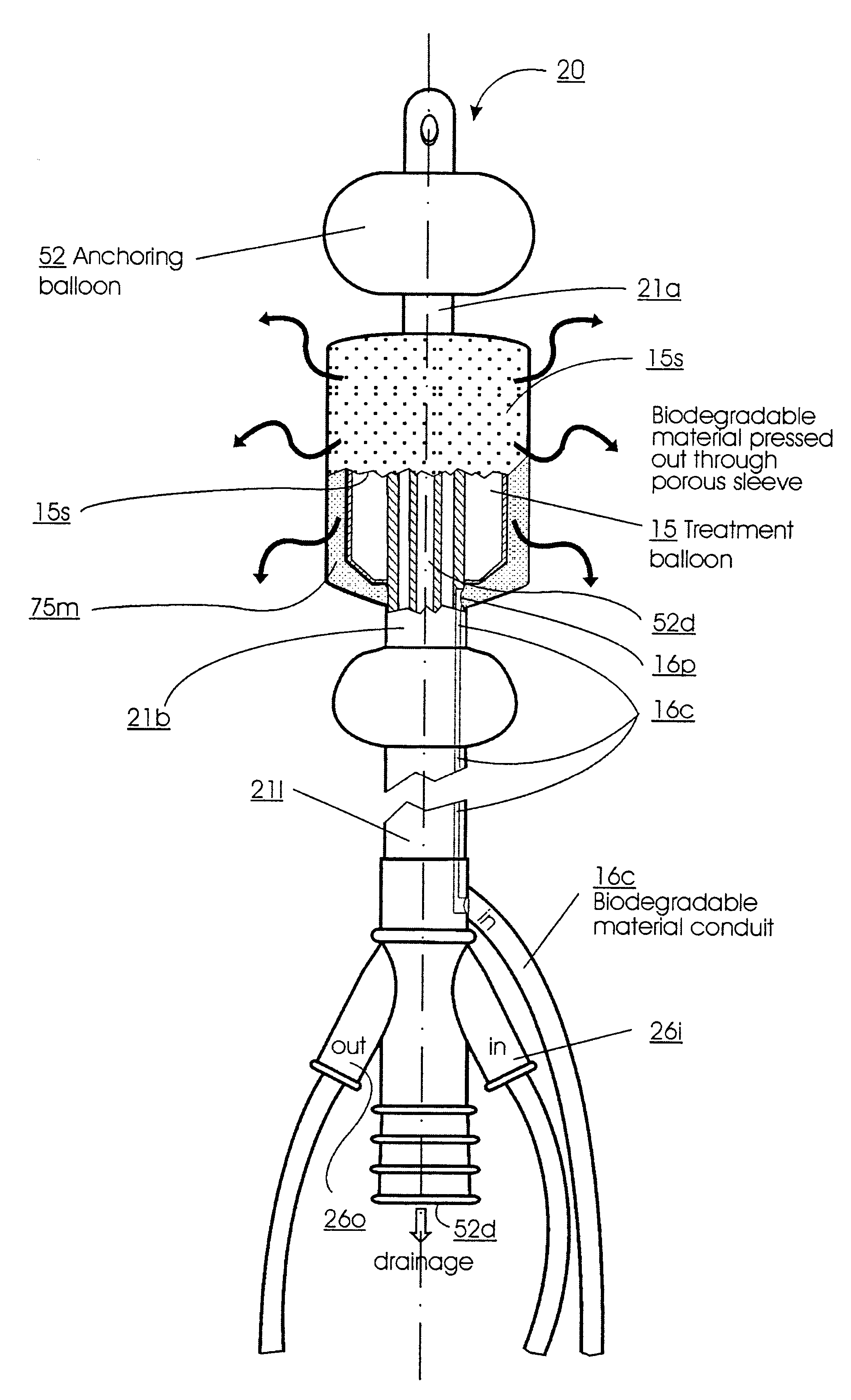
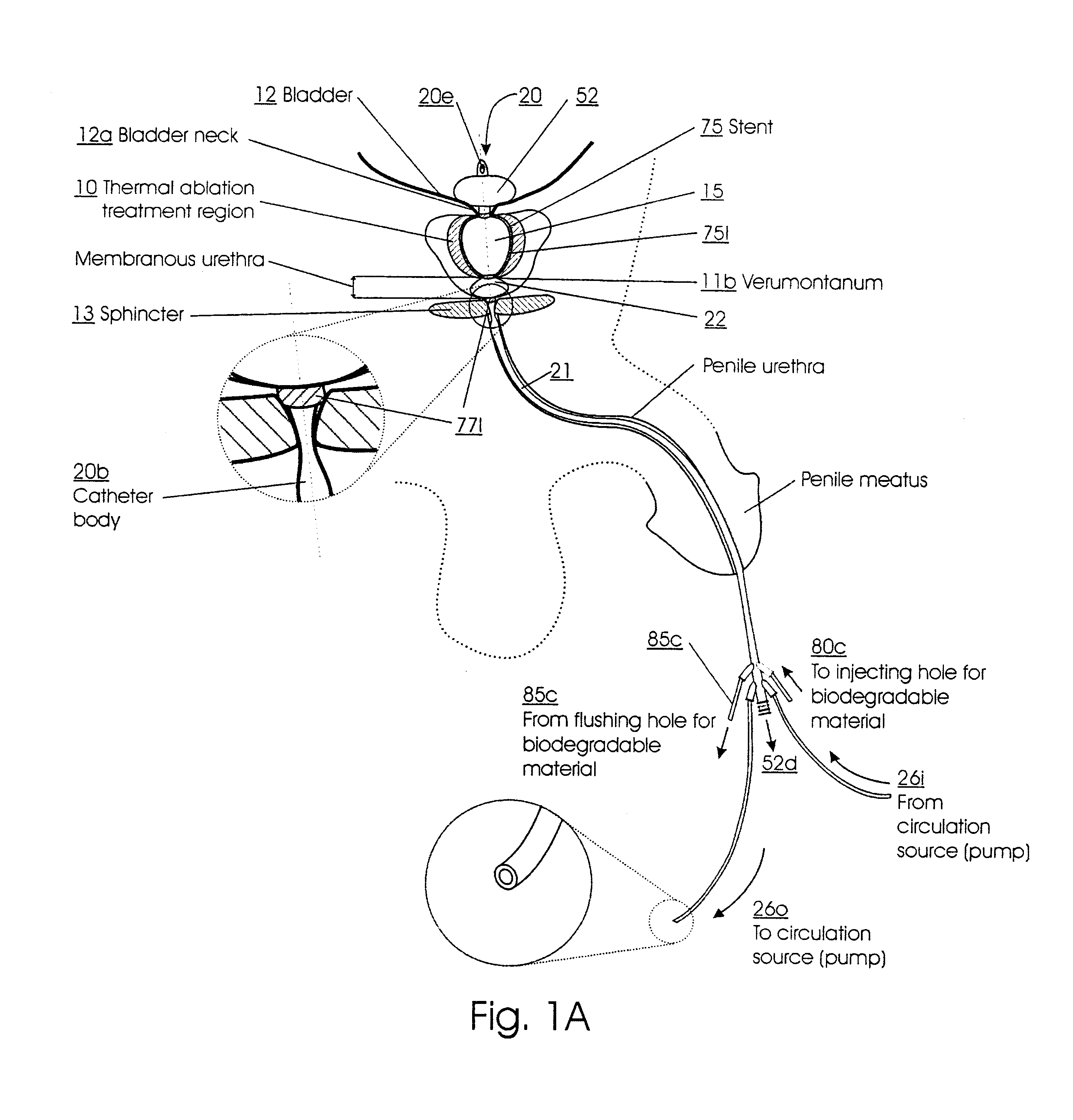
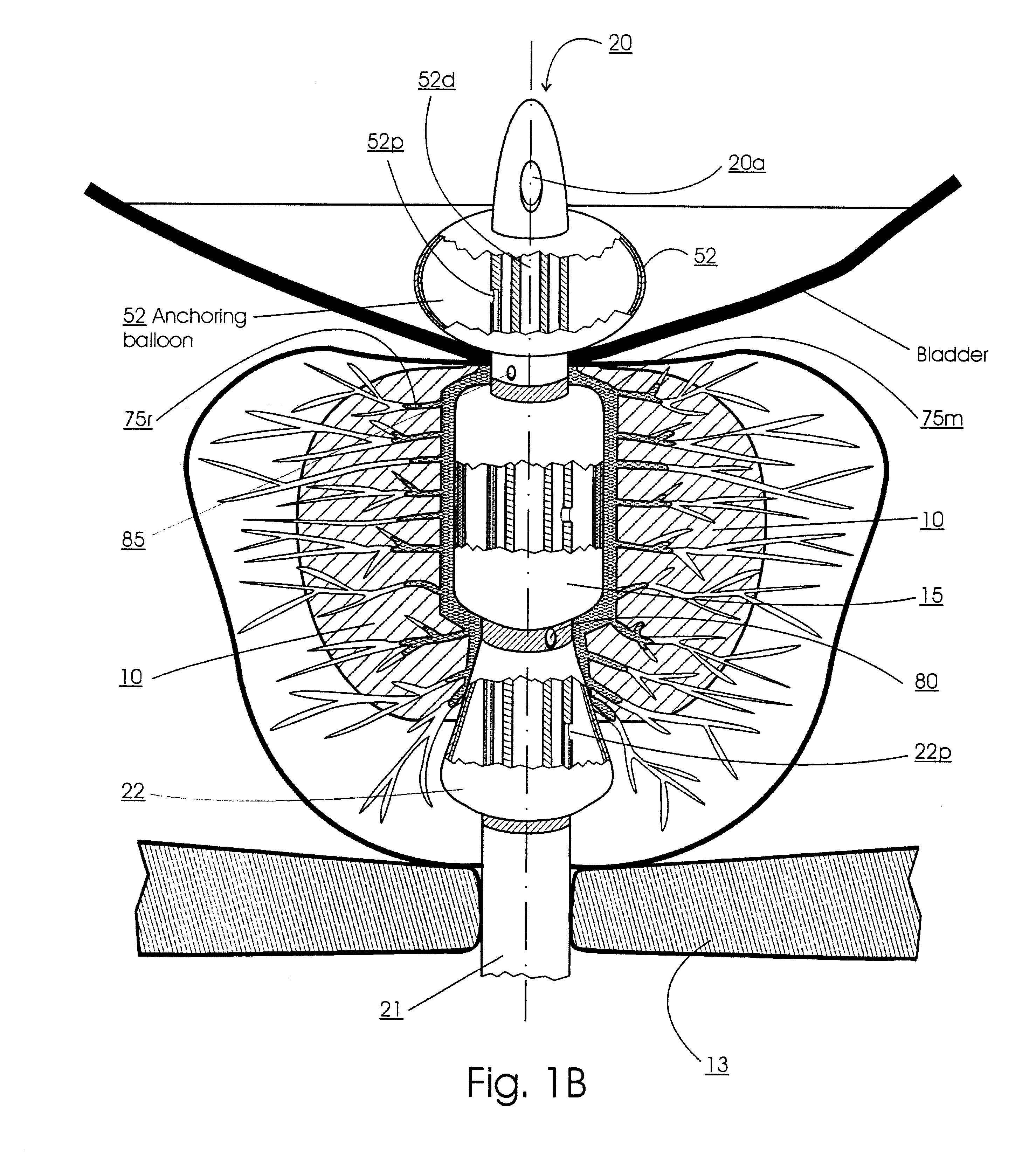
Methods for treating the prostate and inhibiting obstruction of the prostatic urethra using biodegradable stents
InactiveUS6682555B2Improves Structural IntegrityEar treatmentMedical devicesUrethraBiodegradable scaffold
Owner:JPMORGAN CHASE BANK AS ADMINISTATIVE AGENT
Semiconductor flip-chip package and method for the fabrication thereof
InactiveUS20020031868A1Simple chip placementLow cost methodSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesElastic modulusSemiconductor
A flip-chip device and process for fabricating the device employs a multilayer encapsulant that includes a first portion encapsulant having a coefficient of thermal expansion of at most 30 ppm / .degree. C. and an elastic modulus of 2-20 GPa and a second portion comprising a polymer flux having a coefficient of thermal expansion that may exceed 30 ppm / .degree. C.
Owner:INVENSAS CORP
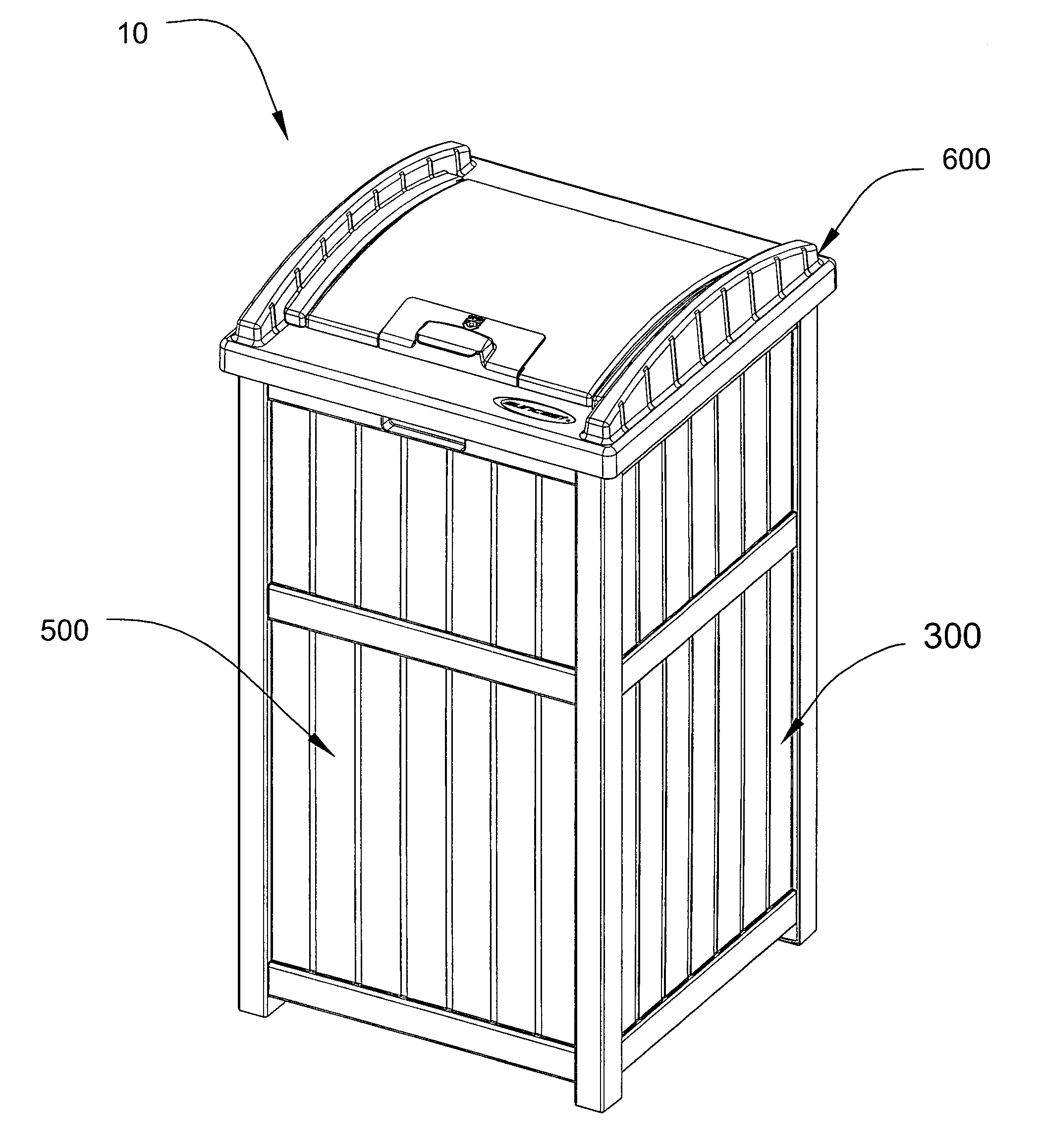
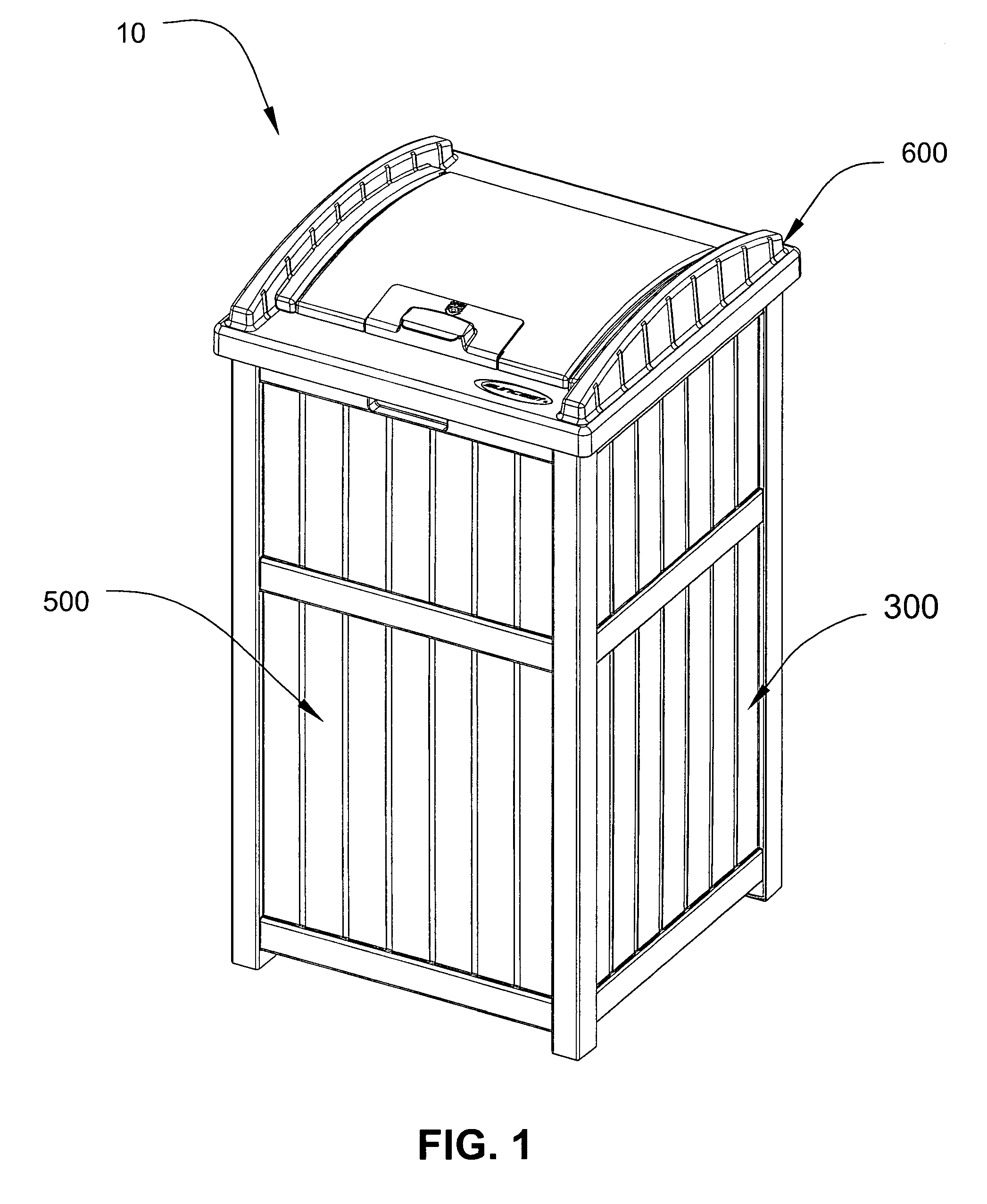
Secure trash container assembly
Owner:SUNCAST
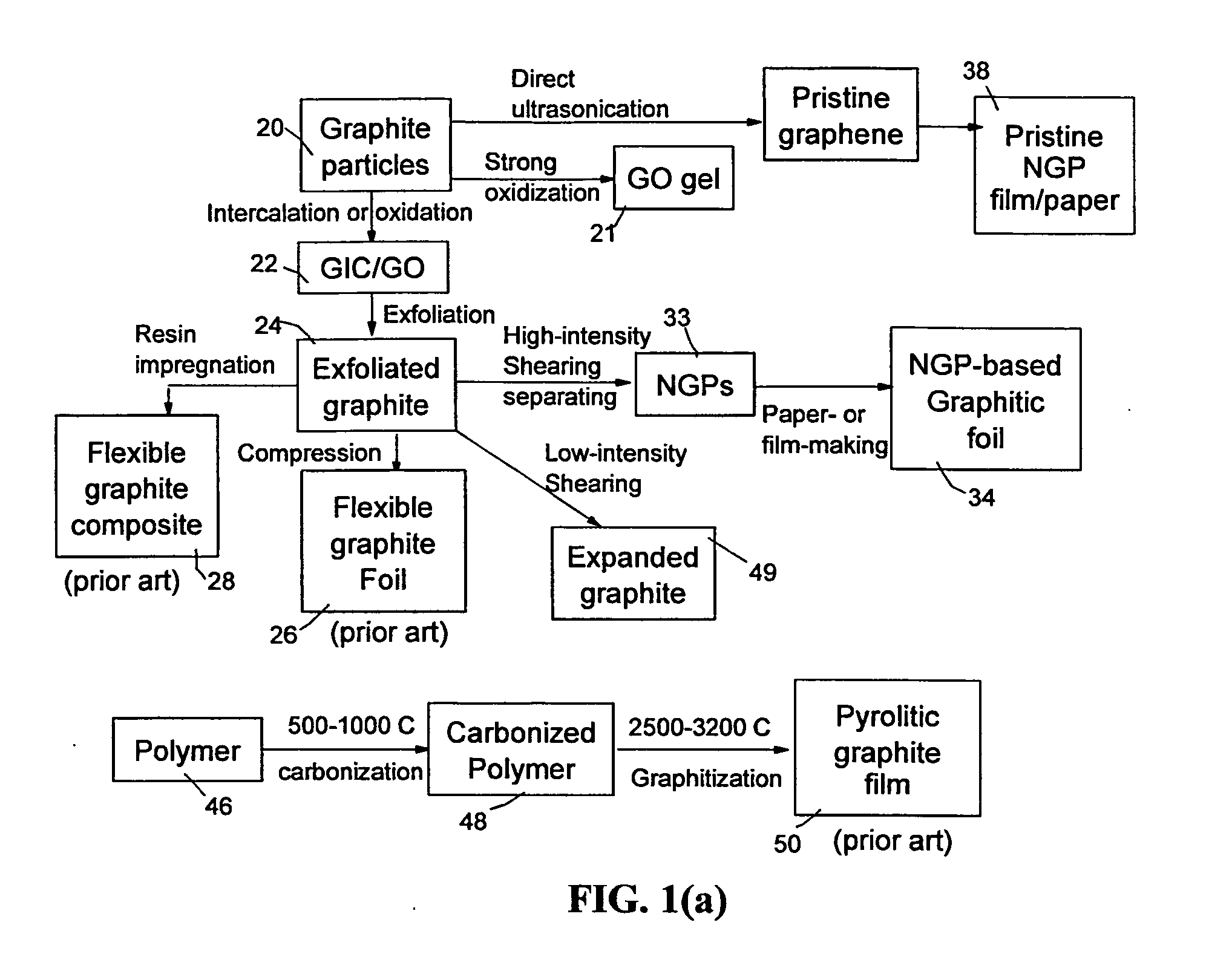
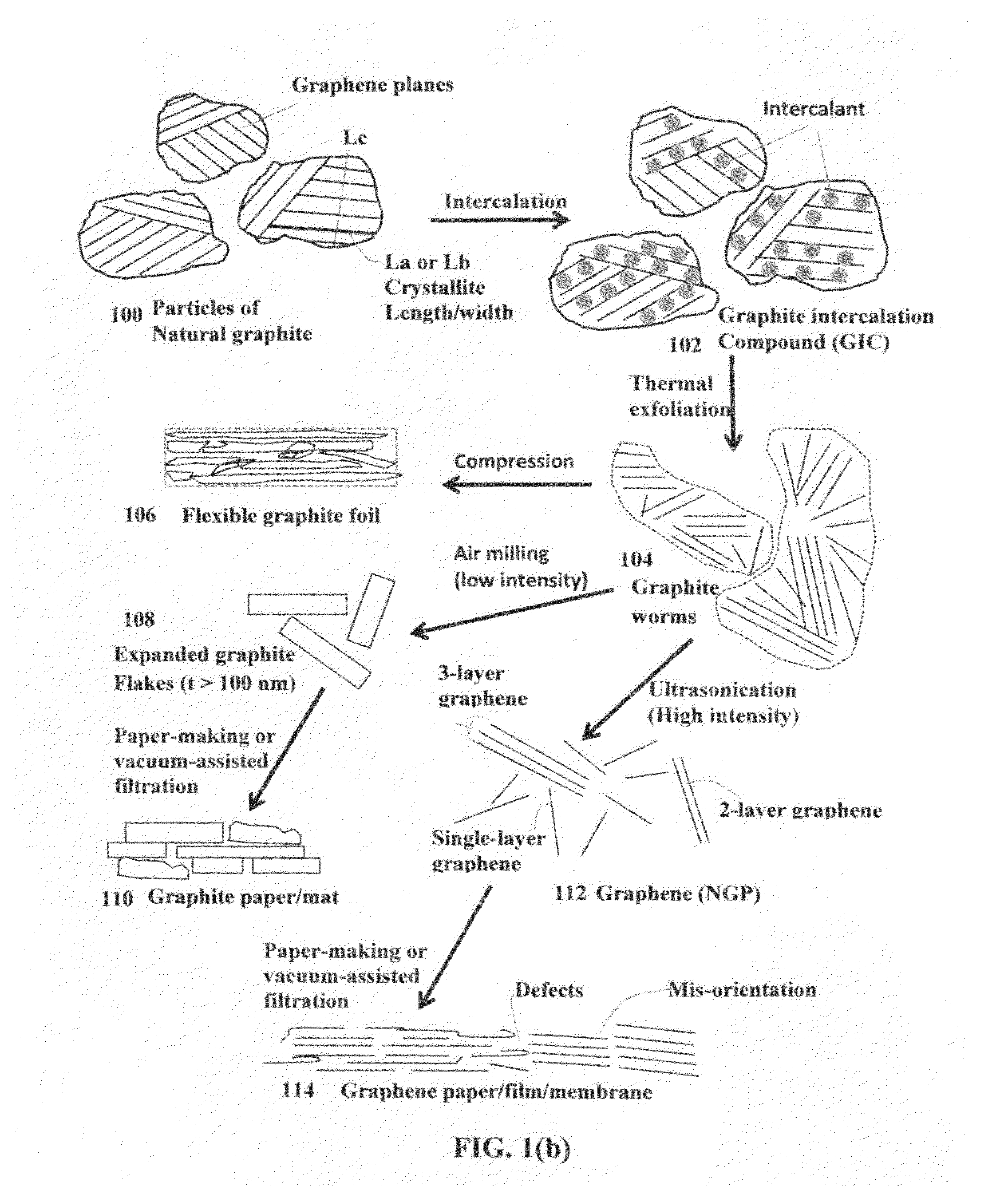
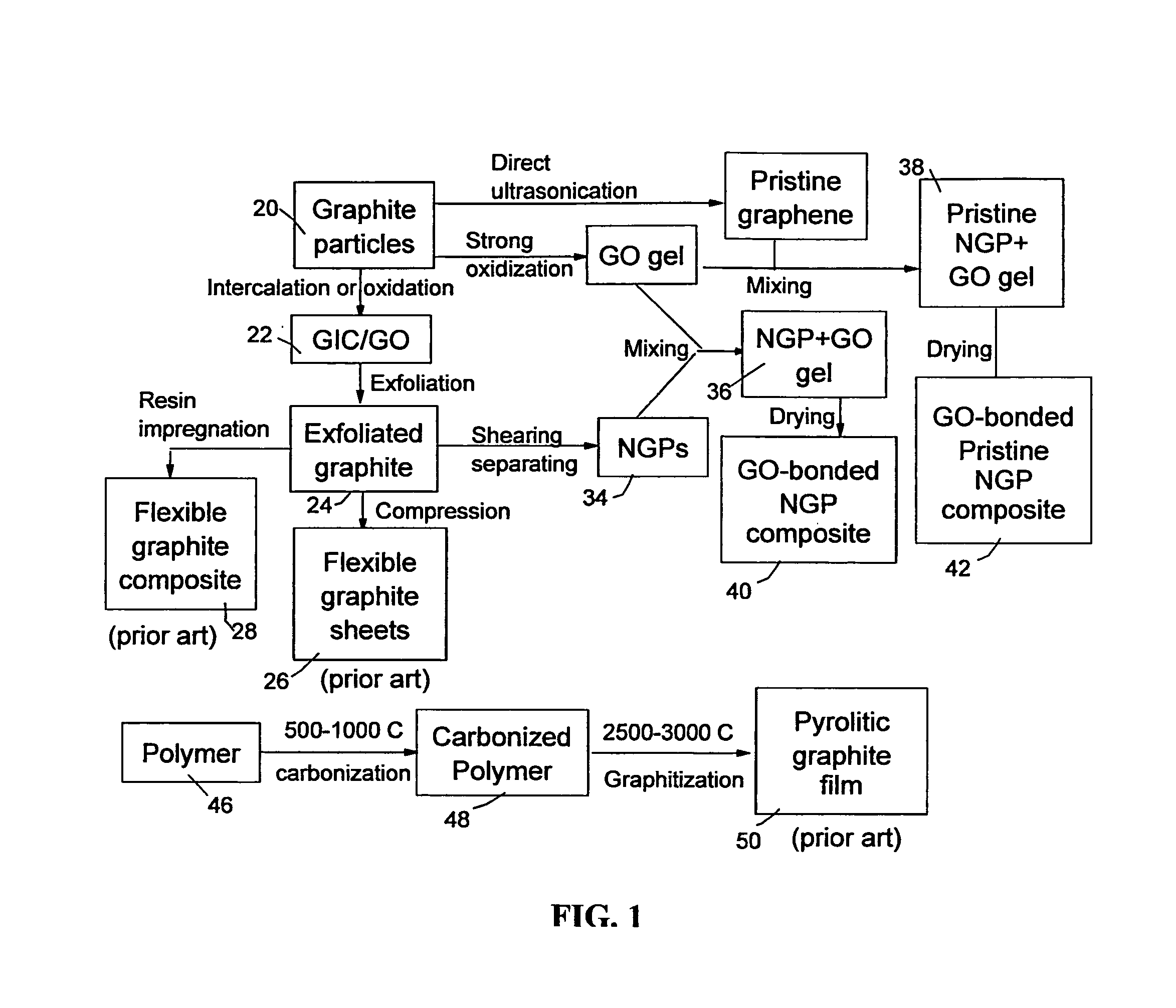
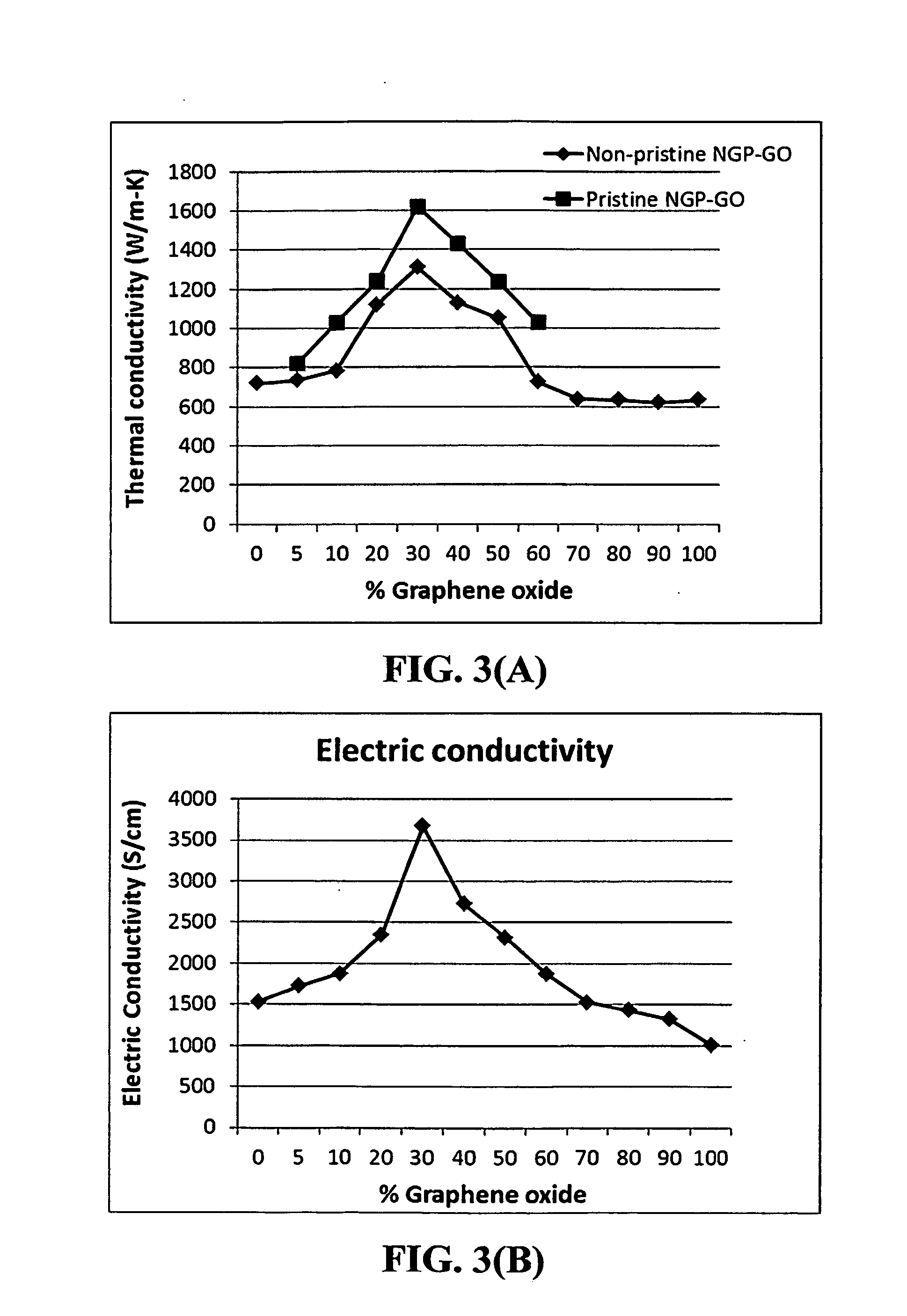
Graphene oxide gel bonded graphene composite films and processes for producing same
ActiveUS20130236715A1Low densityThermal conductivityMaterial nanotechnologyNon-metal conductorsPhysical chemistryThin membrane
Disclosed is a graphene composite thin film composition composed of nano graphene platelets (NGPs) bonded by a graphene oxide binder, wherein the NGPs contain single-layer graphene or multi-layer graphene sheets having a thickness from 0.335 nm to 100 nm. The NGPs occupy a weight fraction of 1% to 99.9% of the total composite weight. The graphene oxide binder, having an oxygen content of 1-40% (preferably <10%) by weight based on the total graphene oxide weight, is obtained from a graphene oxide gel. The composite forms a thin film with a thickness no greater than 1 mm, but preferably no greater than 100 μm and no less than 10 μm. This composition has a combination of exceptional thermal conductivity, electrical conductivity, and mechanical strength unmatched by any thin-film material of comparable thickness range.
Owner:GLOBAL GRAPHENE GRP INC
Robust interconnect structure
InactiveUS6133136AImproves Structural IntegritySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesOptoelectronicsCopper
A structure comprising a layer of copper, a barrier layer, a layer of AlCu, and a pad-limiting layer, wherein the layer of AlCu and barrier layer are interposed between the layer of copper and pad-limiting layer.
Owner:INVENSAS CORP
Method for preparing and processing a sample for intensive analysis
ActiveUS20050012244A1Accurate measurementReduce concentrationRadiation pyrometryLaser detailsEpoxyComposition analysis
A method for pelletizing and taking intensive measurements of a raw sample is disclosed. The method includes homogenizing and pelletizing the sample that is to be subjected to compositional or intensive analysis. The raw sample is mixed with several solutions containing epoxies and activators based in carrier solutions or solvents, and ground to a fine powder or gel. The gel is partially dried and conformed to a pellet shape. The pellet is then cured such that the epoxy and activator solutions react and form a binding agent capable of maintaining the structural integrity of the sample pellet during intensive analysis. An intensive analysis instrument, such as LIBS, may then be used to ablate the surface of the pellet. The pellet provides consistent ablation of the sample material for accurate intensive measurements.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
Method for preparing supported catalysts from metal loaded carbon nanotubes
InactiveUS20060142149A1Improves Structural IntegrityMaterial nanotechnologyOrganic compound preparationPtru catalystNanotube
A new method for preparing a supported catalyst is herein provided. Carbon nanotubes are functionalized by contacting them with an oxidizing agent to form functionalized carbon nanotubes. A metal catalyst is then loaded or deposited onto the functionalized carbon nanotubes. The mixture is then extruded to form the supported catalyst comprising a carbon nanotube structure containing metal catalyst more evenly dispersed within the internal structure of the carbon nanotube structure.
Owner:HYPERION CATALYSIS INT
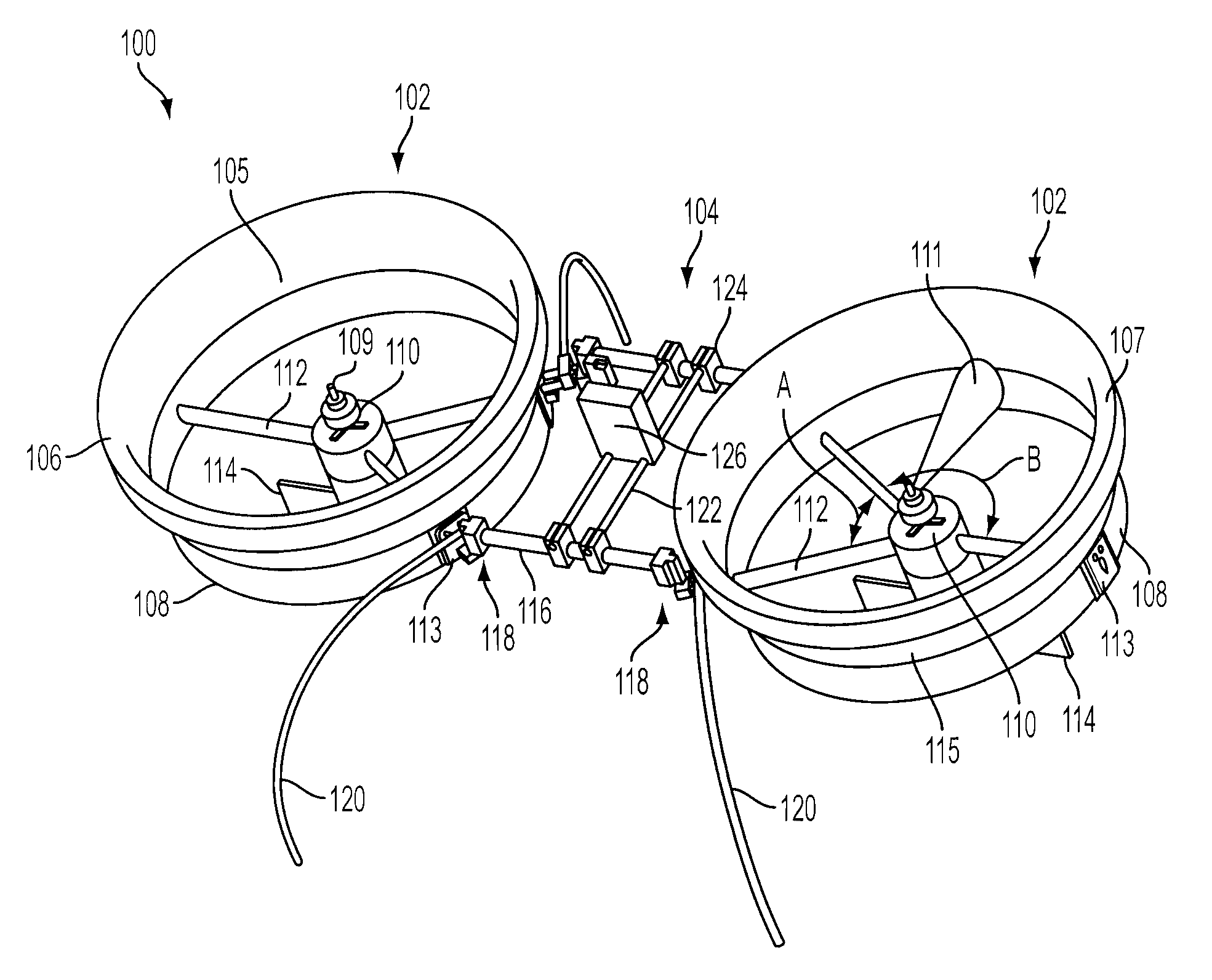
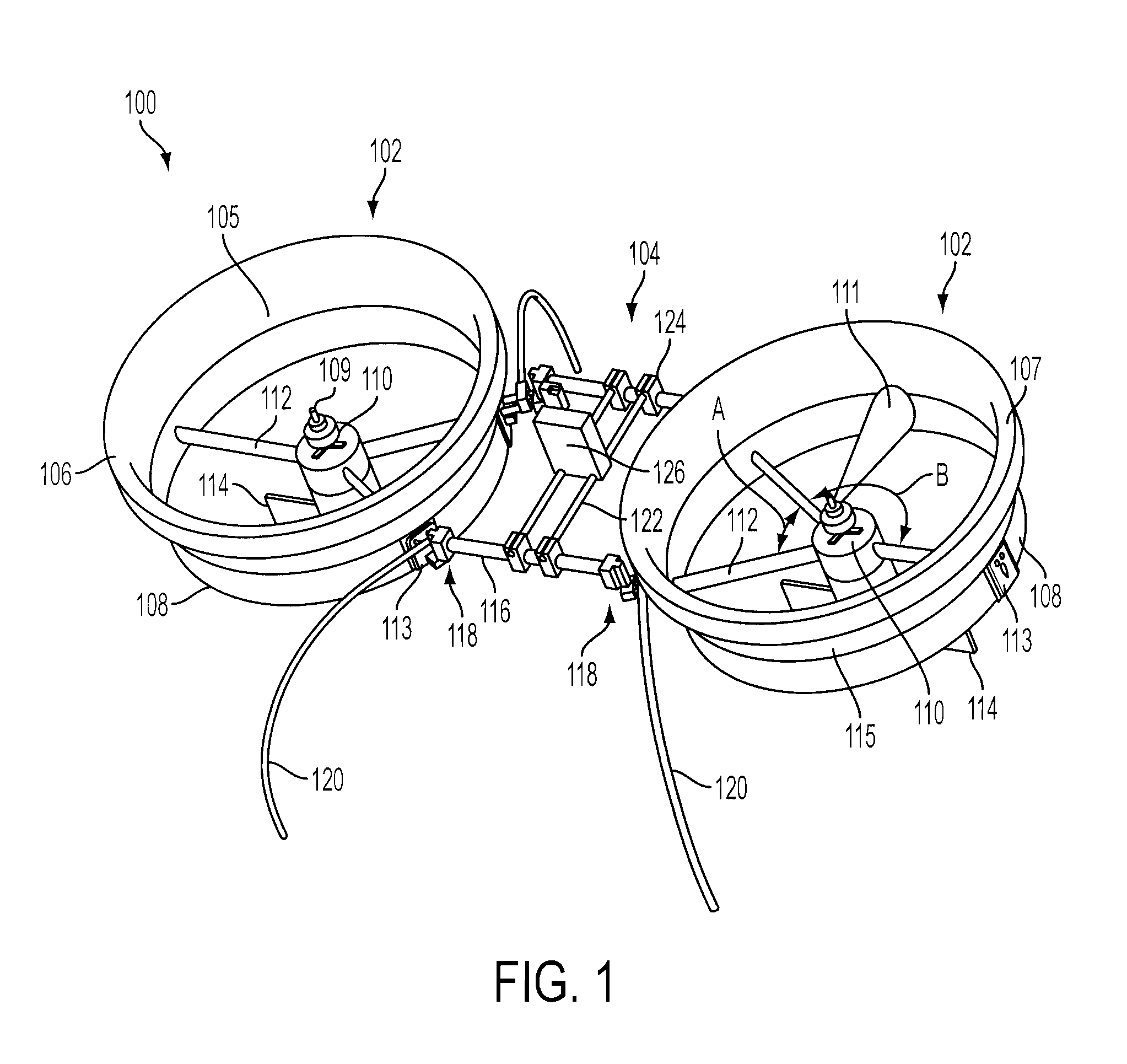
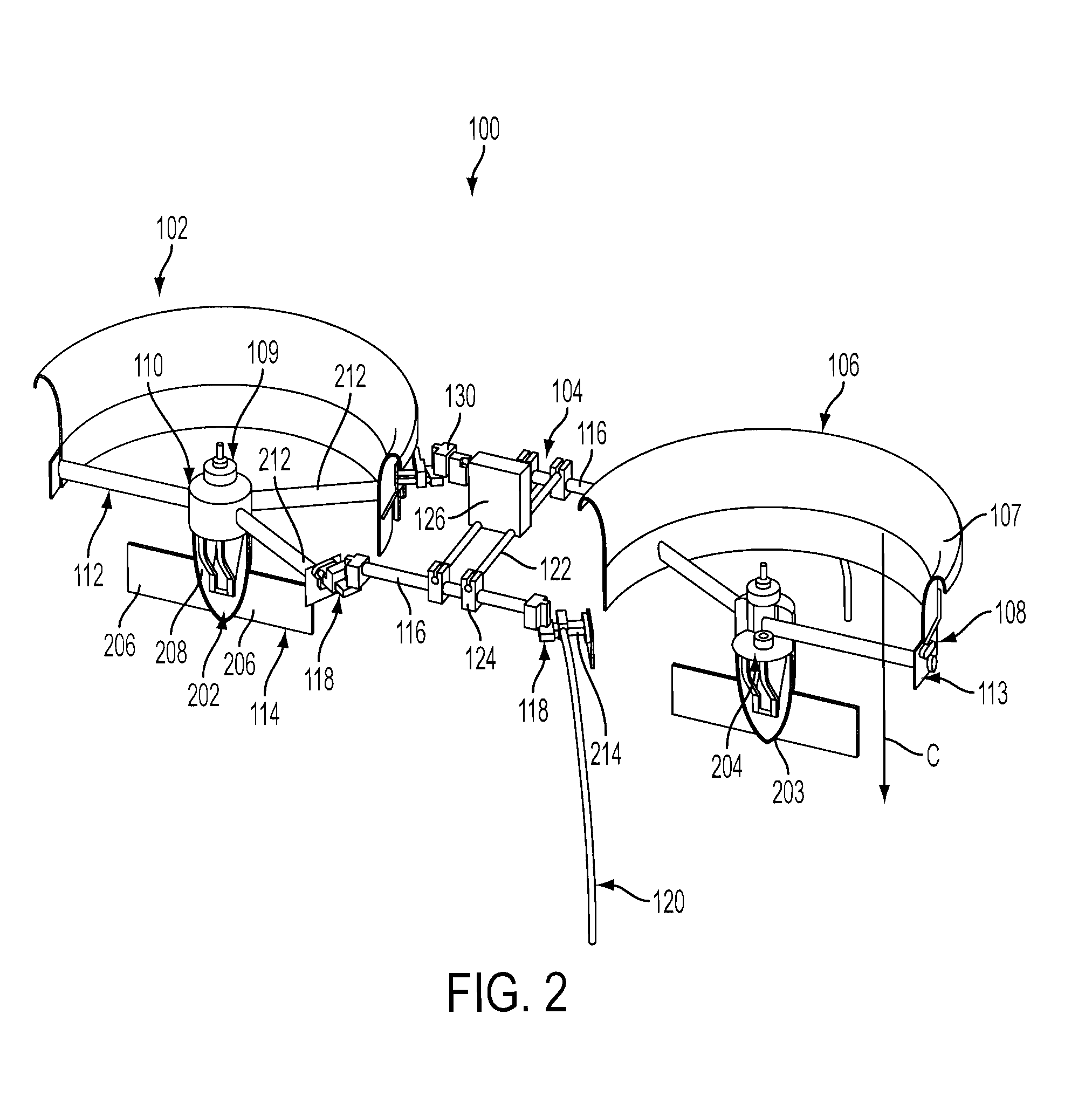
Vertical take off and landing unmanned aerial vehicle airframe structure
InactiveUS8328130B2Low costReduce weightAdditive manufacturing apparatusUnmanned aerial vehiclesEngineeringHigh intensity
An unmanned aerial vehicle selectively formed of high strength composite structural part portions and lightweight aerodynamic foam portions to provide a low-cost and lightweight UAV that comports with export, civil airspace, and safety regulations. To further to reduce an overall weight of the UAV, mechanical elements are designed to provide multiple functionalities. Structural elements may be manufactured in same or similar non-specialized processes, and non-structural elements manufactured in same or similar non-specialized processes, reducing overall manufacturing costs. Materials and bonding elements are selected to provide frangibility and yet maintain normal flight structural integrity.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
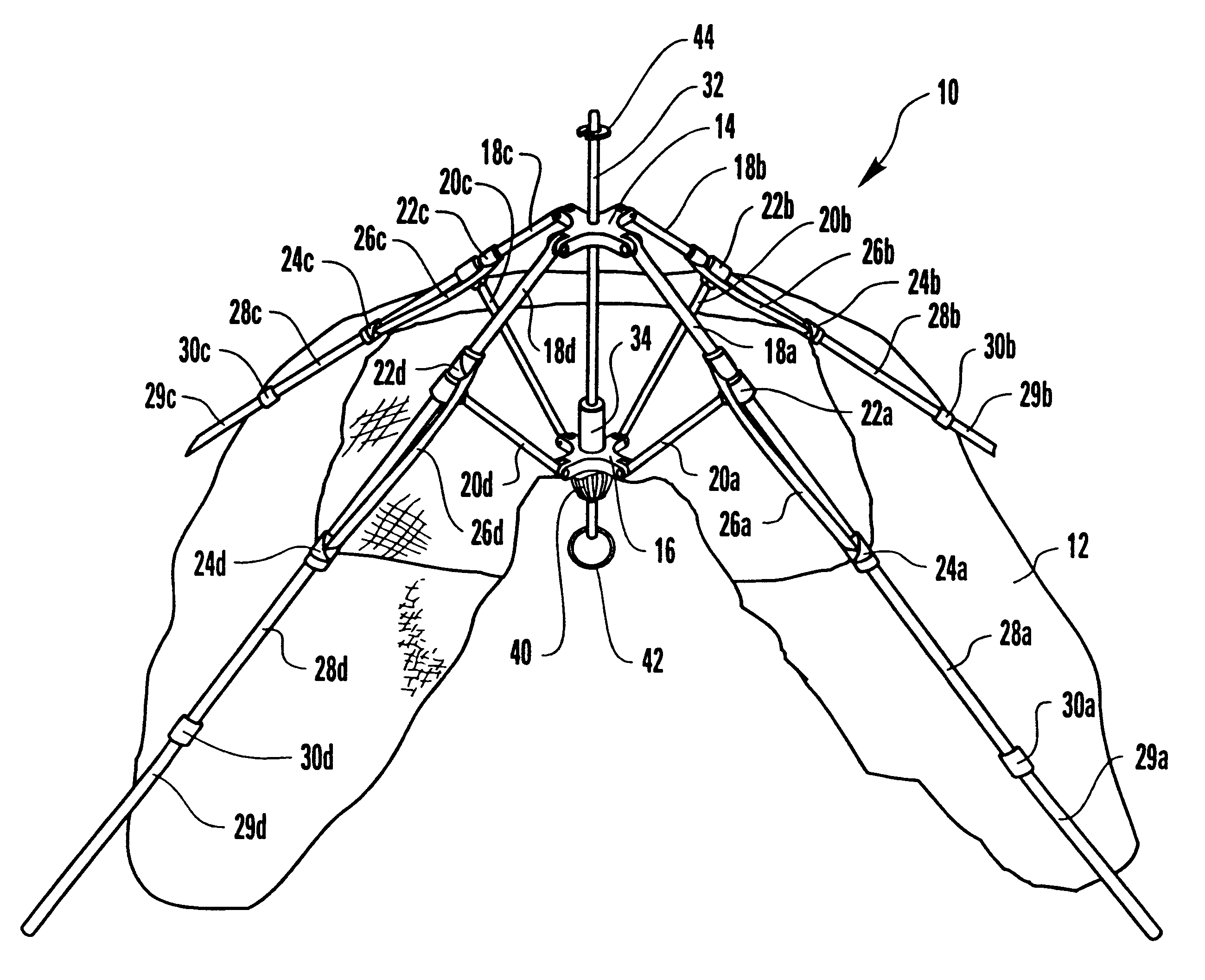
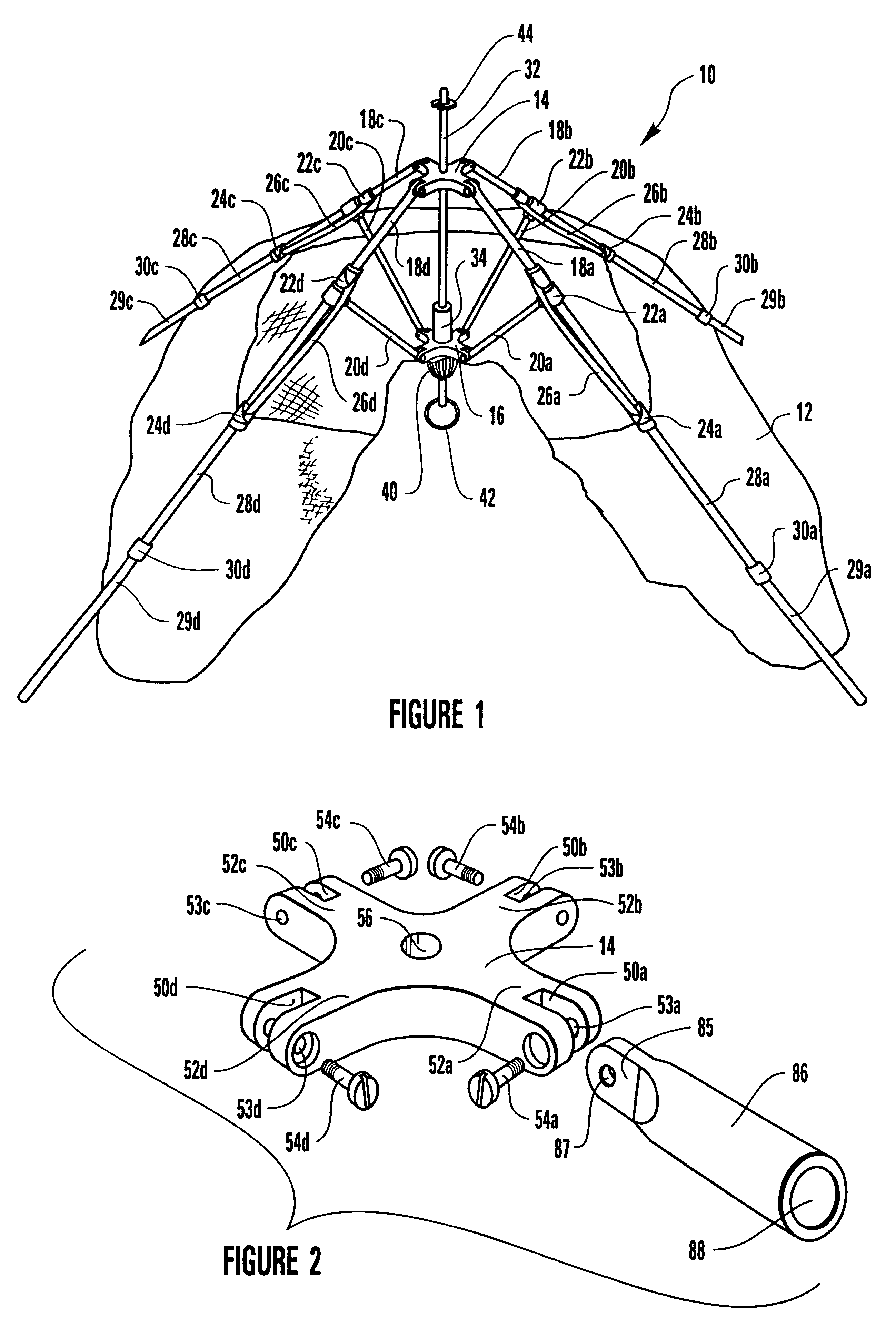
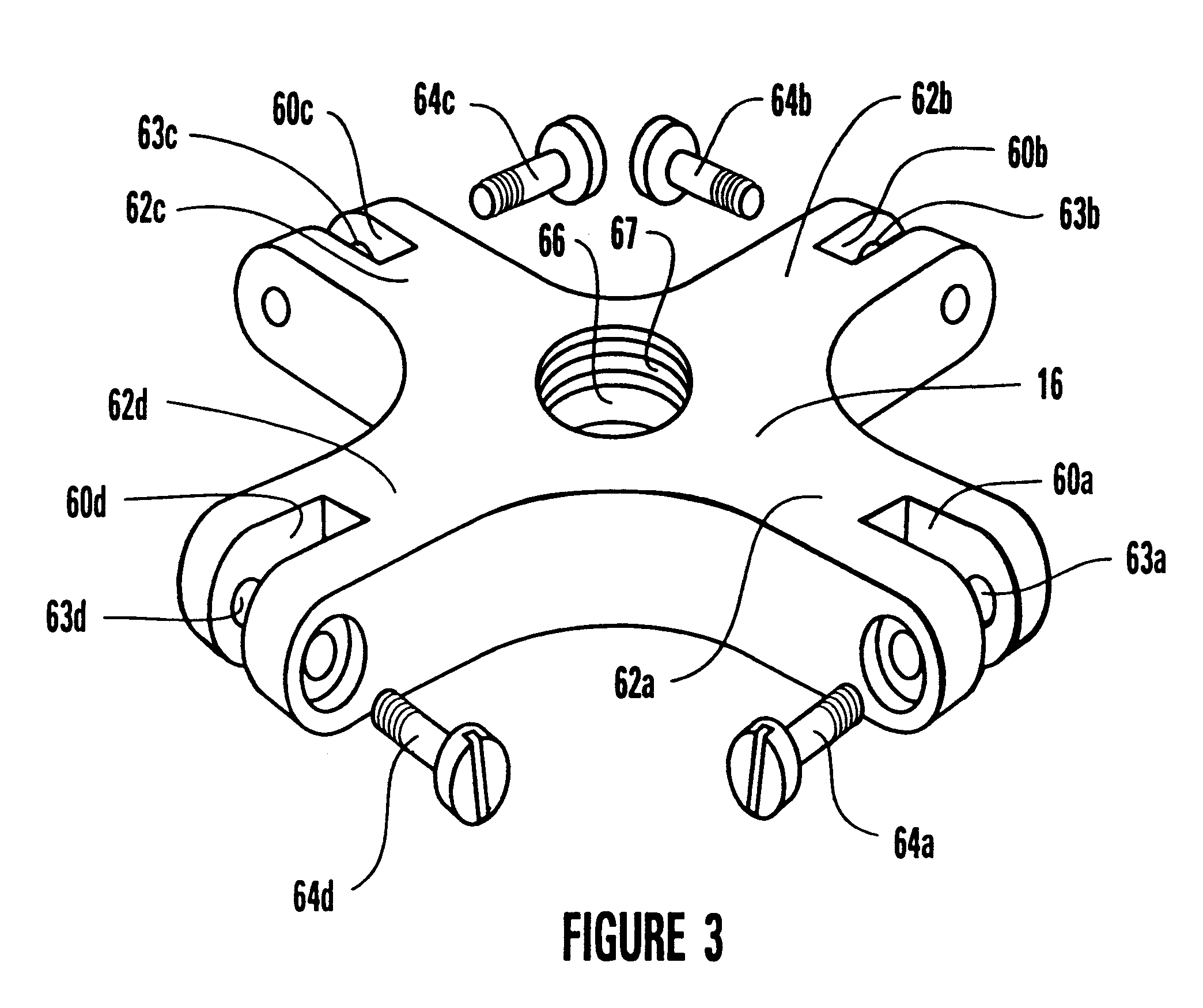
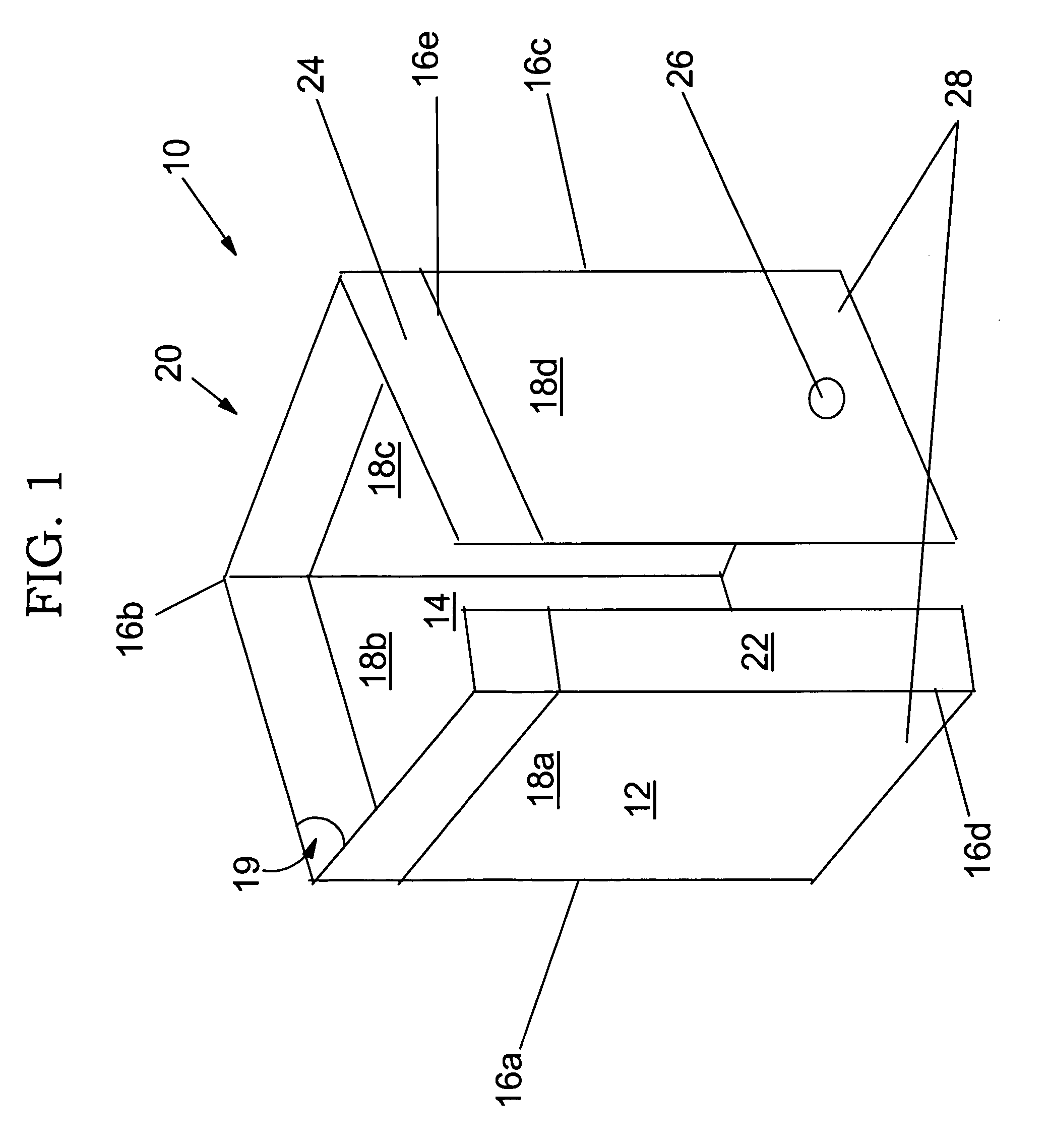
Umbrella-type tent apparatus and method
A support framework for an umbrella-type tent, the tent including a fabric tent shell suspended from the support framework. The top and center hubs for the support framework are fabricated from a suitable material so as to provide increased strength to the top hub and the center hub. The fabric tent shell is tethered to the support framework to limit slippage of the fabric tent shell down the tent poles. The tent poles are segmented so as to provide foldable tent poles. A bungee cord keeper system is incorporated into the upper coupling for the segmented tent pole.
Owner:OUTDOOR SPORTS PROD
Minimally invasive instrumentation for recovering tissue
ActiveUS20050033286A1Improve tissue performanceHigh strengthSurgical needlesSurgical instruments for heatingUltimate tensile strengthBiomedical engineering
The capture component of tissue retrieval apparatus is strengthened to improve its structural integrity when utilized within very dense tissue. Eyelet structures carrying pursing cable are improved through the utilization of slightly expanded constant widths with diminished lengths to avoid fold back phenomena. The pursing cables employed with the capture component exhibit more than a 100% improvement in tensile strength at high electrosurgical cutting temperatures through the utilization of strands having about a 1.4 mil diameter formed with a type 316 stainless steel.
Owner:COVIDIEN AG
Support for cage and bottle style intermediate bulk container
InactiveUS20060027582A1Improves Structural IntegrityAvoid squeezingLarge containersLinings/internal coatingsIntermediate bulk containerCombined use
The present invention provides a system and method for using a liner in conjunction with the cage of a bottle and cage type IBC. The invention involves use of a support that is placed inside the cage of a bottle and cage type IBC. In one embodiment, the support may be a thin sheet of material that conforms to the inner surface of the cage. In an alternative embodiment, the support may be a bottle from a cage and bottle type IBC that has been modified by removing the discharge valve spout. In the case that a liner is used in conjunction with the cage, the support forms a barrier between the liner and the cage to prevent the liner from extruding through the bars of the cage. An aperture in the support may allow a discharge valve of a liner to extend outwardly for easy access to the item.
Owner:BEACH JOHN E
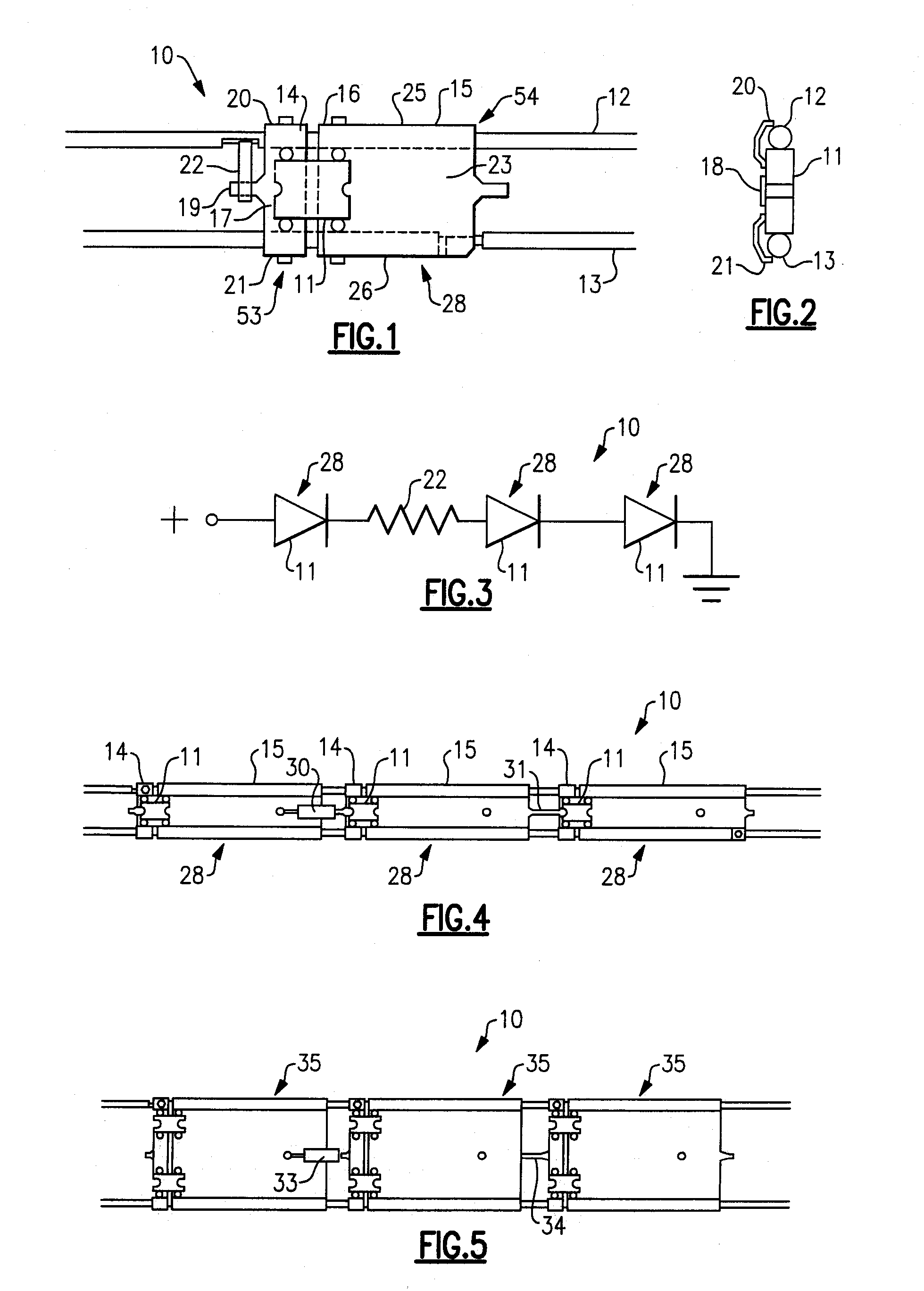
Lighting strip
InactiveUS20060221609A1Improves Structural IntegrityCoupling device connectionsPoint-like light sourceFull waveRectifier diodes
The lighting strip has two elongated flexible conductors for carrying primary power to a plurality of modules. Each module has rectification diodes and a series lighting element. The series lighting element has at least one resistor and at least one light emitting diode (LED). The LED operates using the full-wave rectified power. The lighting strip may be provided in a spool which can be easily cut to the desired length. The number of light emitting diodes in a module, the spacing between components in a module, and the use of multiple lighting strips, can be selected to provide the desired illumination level or effect.
Owner:RYAN PATRICK H JR
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com