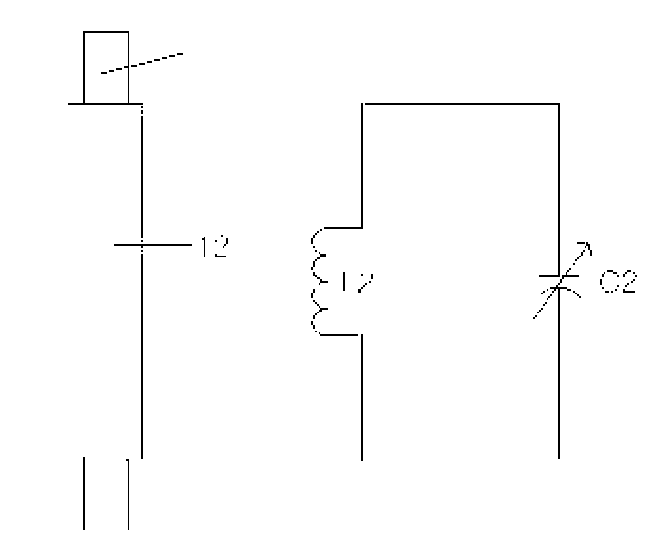Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1805 results about "Rectifier diodes" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
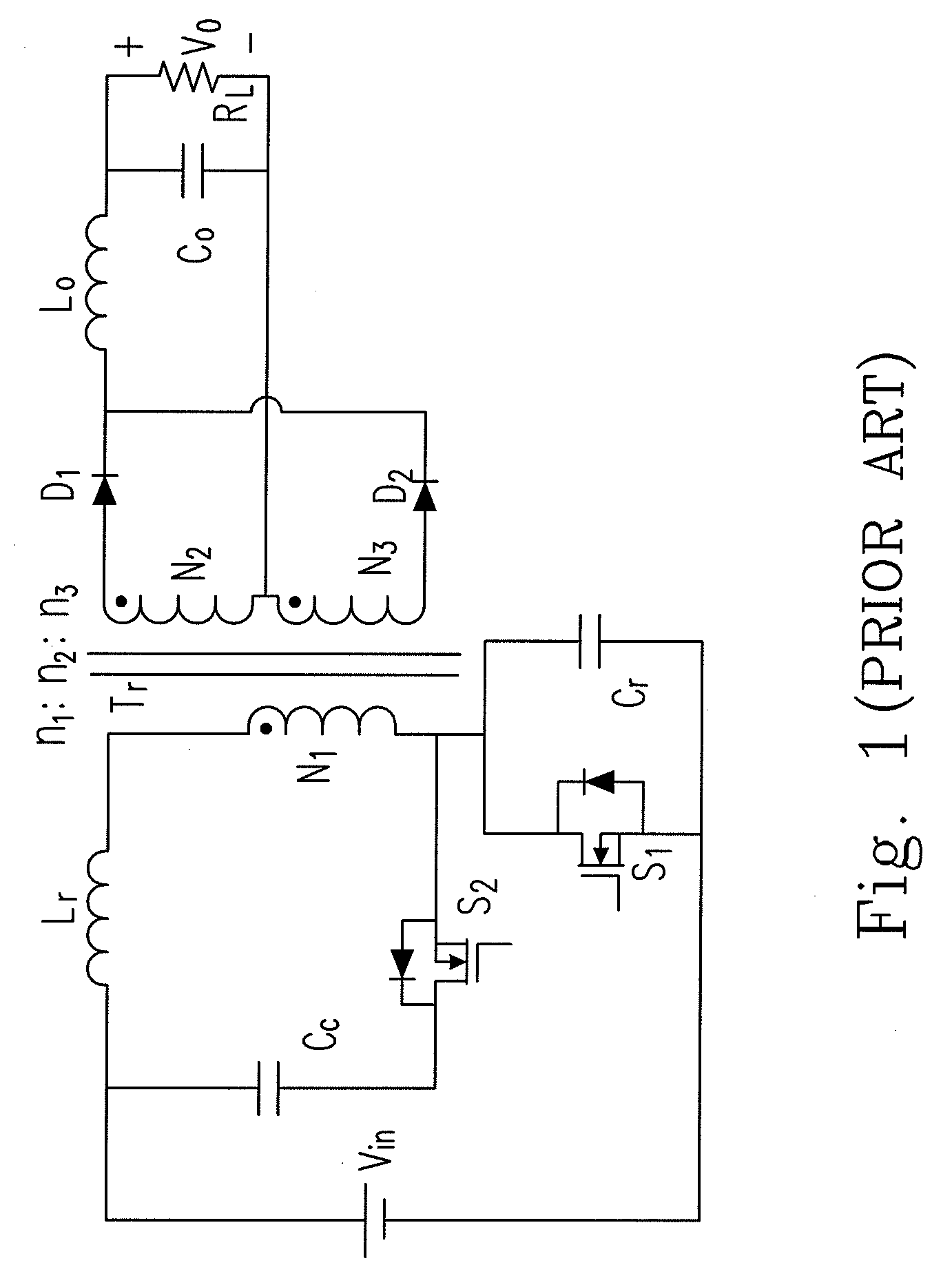
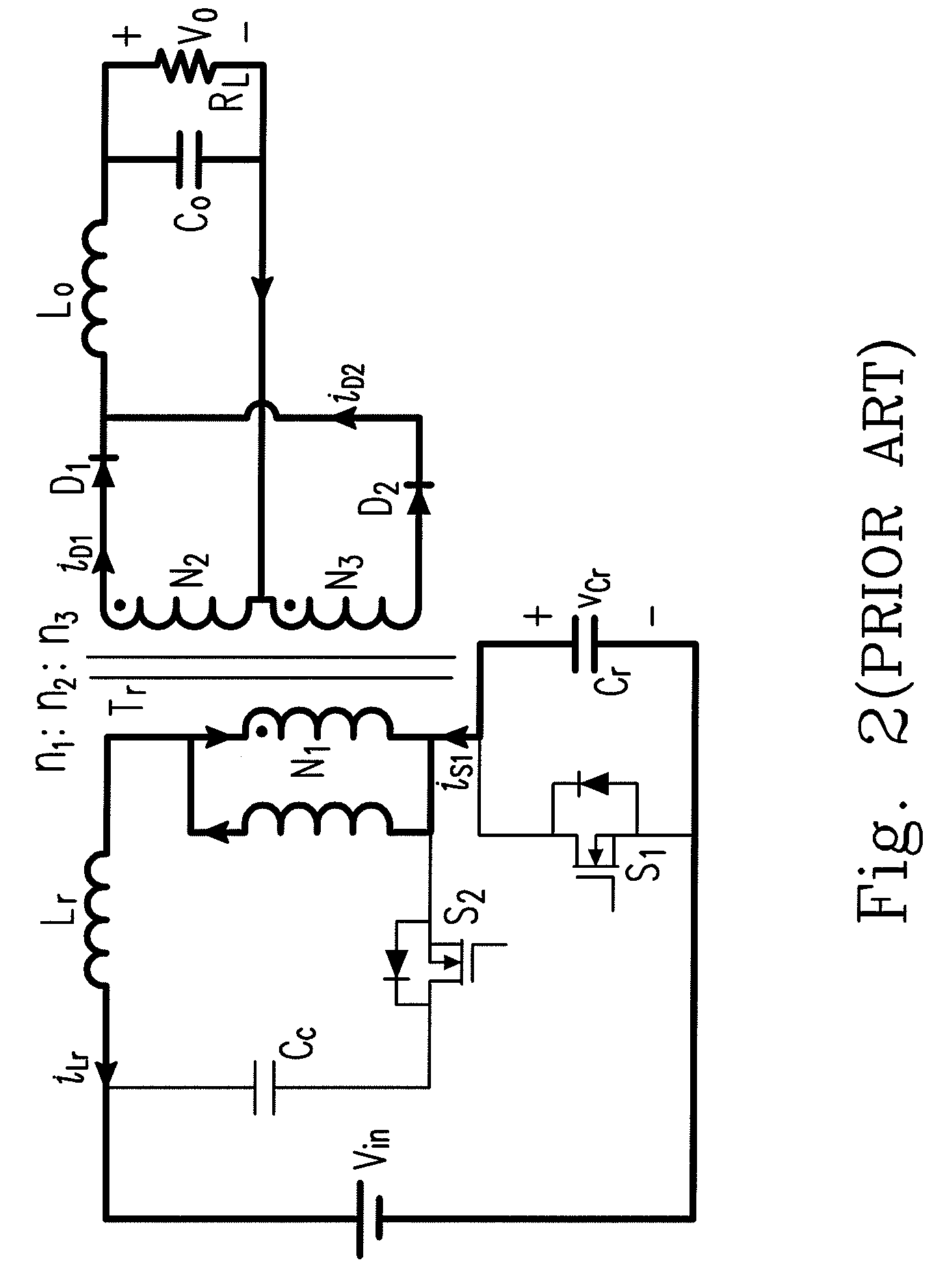
A rectifier is an electrical device composed of one or more diodes that converts alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC). A diode is like a one-way valve that allows an electrical current to flow in only one direction. This process is called rectification. A rectifier can take the shape...
Amplification Relay Device of Electromagnetic Wave and a Radio Electric Power Conversion Apparatus Using the Above Device
ActiveUS20080266748A1Improve throughputMultiple-port networksNear-field transmissionElectric power transmissionImpedance matching
The present invention provides an amplifying repeater, which is constructed in such a manner that a ferrite core is inserted into a coil with a pre-determined number of winds to increase an induced electromotive force caused by an increase in flux linkage using a time-varying magnetic field of electromagnetic waves at a position distant from various electromagnetic wave generating sources by a predetermined distance and the induction coil and a variable condenser for inducing resonance are connected to each other to increase current while reducing a resistant component existing in the induction coil to intensify and amplify the magnetic field of electromagnetic waves. Furthermore, the present invention provides a wireless power conversion charging device using the magnetic field of electromagnetic waves, which is located between an electromagnetic wave generating source transmitter and a receiving coil or attached to the transmitter and receiving coil. The wireless power conversion charging device includes a rectifying diode for rectifying an electromotive force induced in a construction in which a resonance and impedance matching variable condenser is connected to a coil in series or in parallel in order to transmit maximum induced power to a charging battery that is a load using electromagnetic waves amplified by the amplifying repeater, and a smoothing condenser for smoothing the rectified voltage. Accordingly, charging power required for various small power electronic devices can be provided and power can be supplied to various loads.
Owner:JC PROTEK +1
Amplification relay device of electromagnetic wave and a radio electric power conversion apparatus using the above device
ActiveUS7885050B2Increase forceGuaranteed normal transmissionNear-field transmissionBatteries circuit arrangementsElectric power transmissionImpedance matching
The present invention provides an amplifying repeater, which is constructed in such a manner that a ferrite core is inserted into a coil with a pre-determined number of winds to increase an induced electromotive force caused by an increase in flux linkage using a time-varying magnetic field of electromagnetic waves at a position distant from various electromagnetic wave generating sources by a predetermined distance and the induction coil and a variable condenser for inducing resonance are connected to each other to increase current while reducing a resistant component existing in the induction coil to intensify and amplify the magnetic field of electromagnetic waves. Furthermore, the present invention provides a wireless power conversion charging device using the magnetic field of electromagnetic waves, which is located between an electromagnetic wave generating source transmitter and a receiving coil or attached to the transmitter and receiving coil. The wireless power conversion charging device includes a rectifying diode for rectifying an electromotive force induced in a construction in which a resonance and impedance matching variable condenser is connected to a coil in series or in parallel in order to transmit maximum induced power to a charging battery that is a load using electromagnetic waves amplified by the amplifying repeater, and a smoothing condenser for smoothing the rectified voltage. Accordingly, charging power required for various small power electronic devices can be provided and power can be supplied to various loads.
Owner:JC PROTEK +1
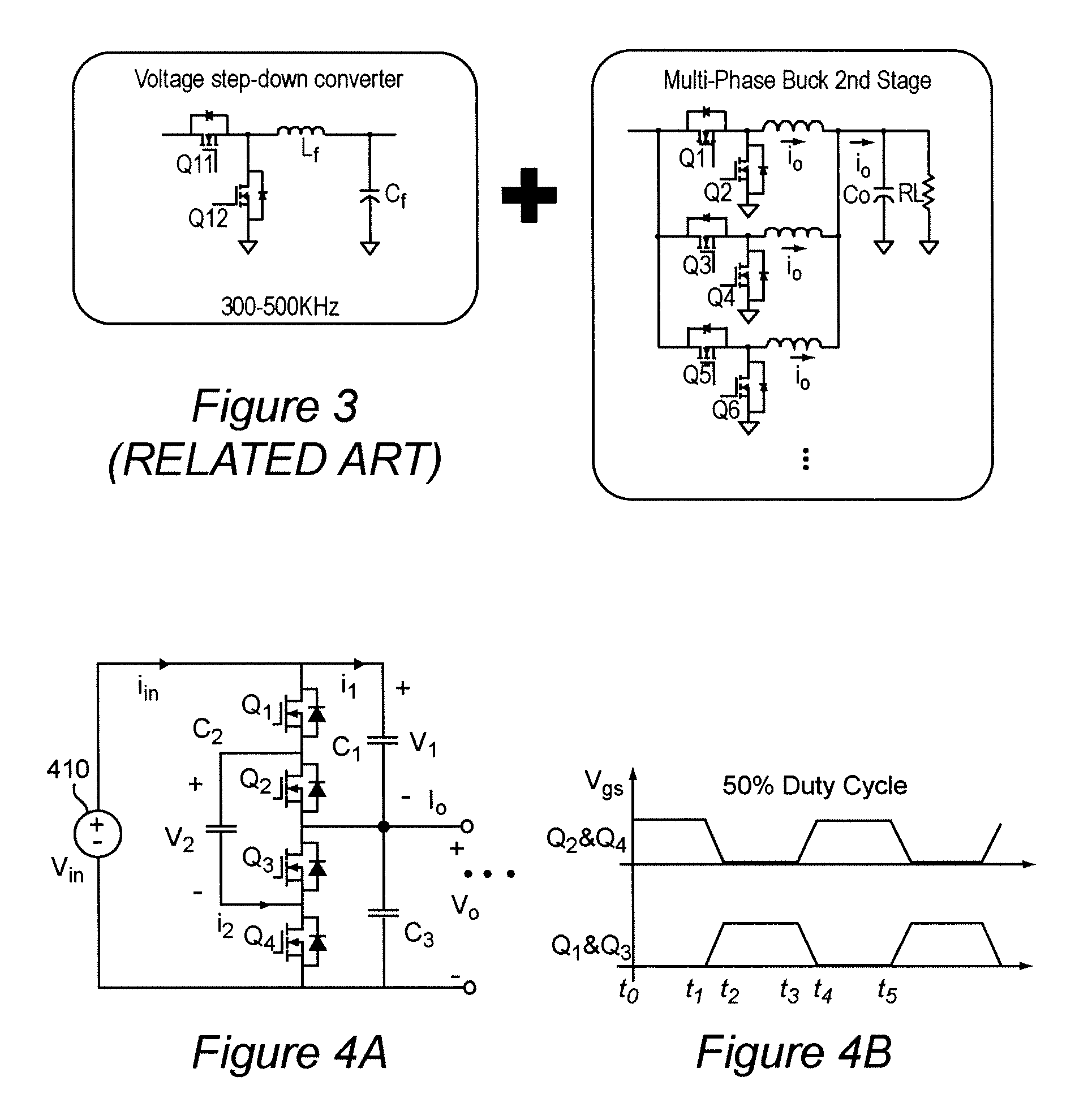
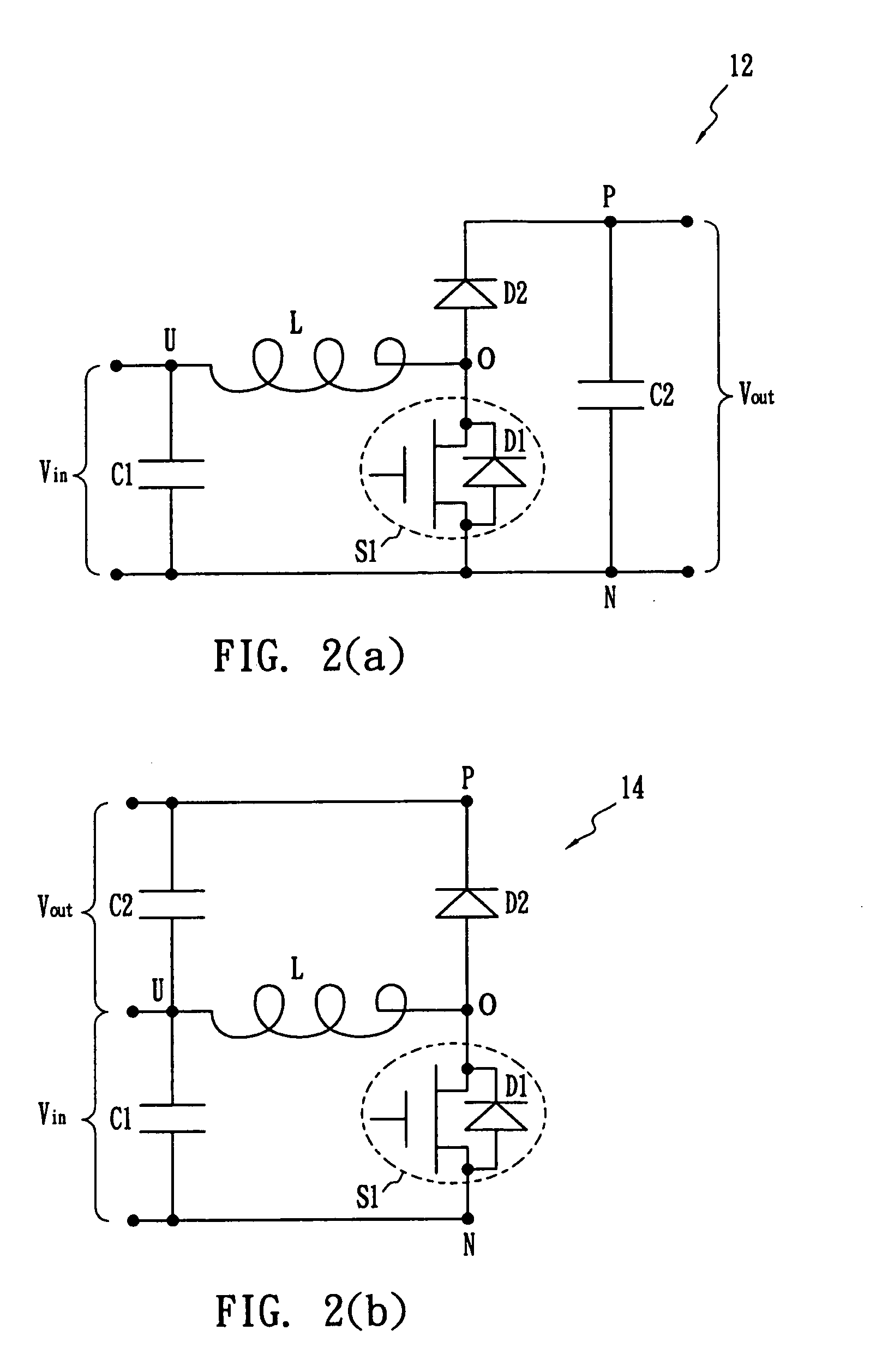
Non-Isolated Bus Converters with Voltage Divider Topology
InactiveUS20070296383A1Filter capacitors can be reduced or eliminatedEasy to controlAc-dc conversionDc-dc conversionCapacitanceVoltage converter
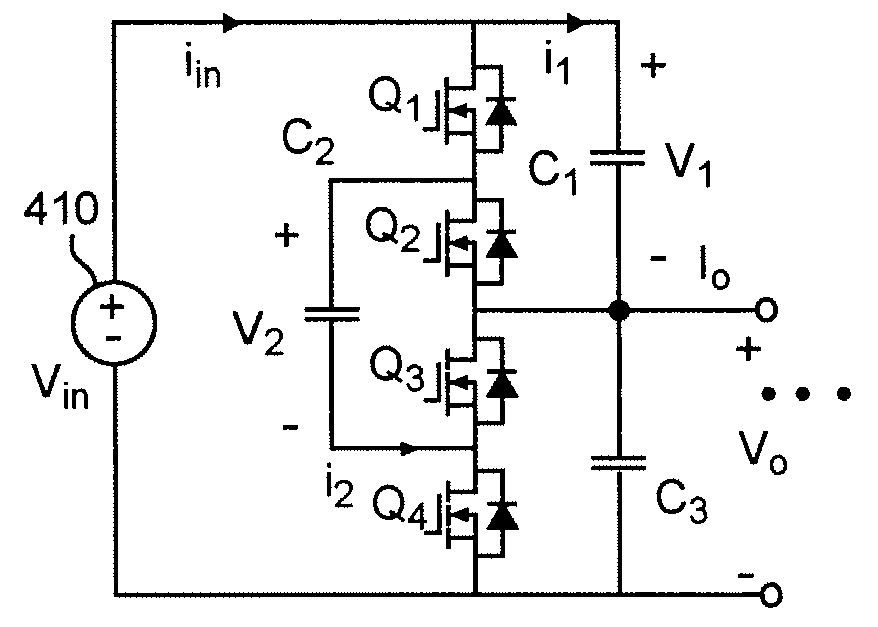
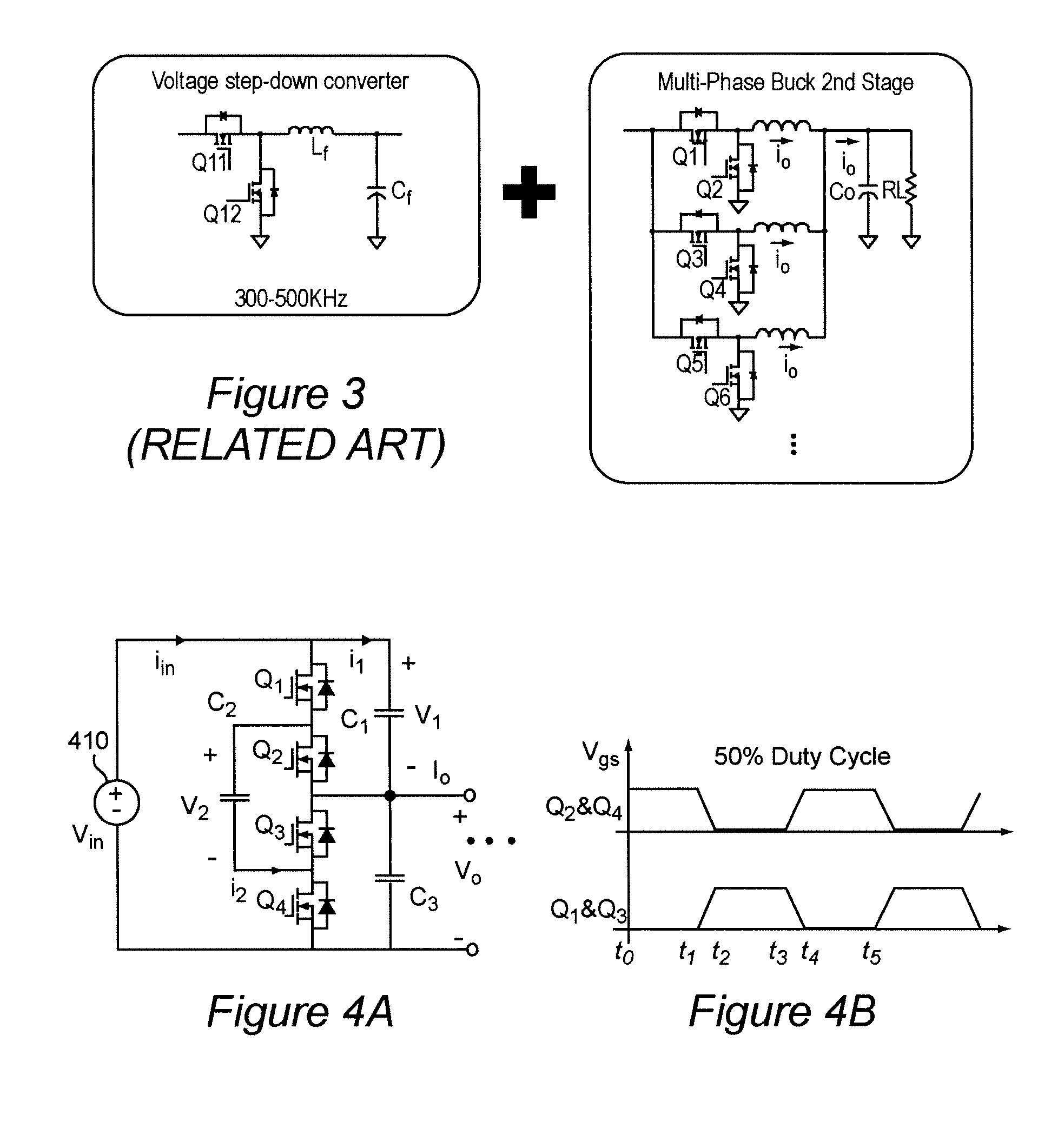
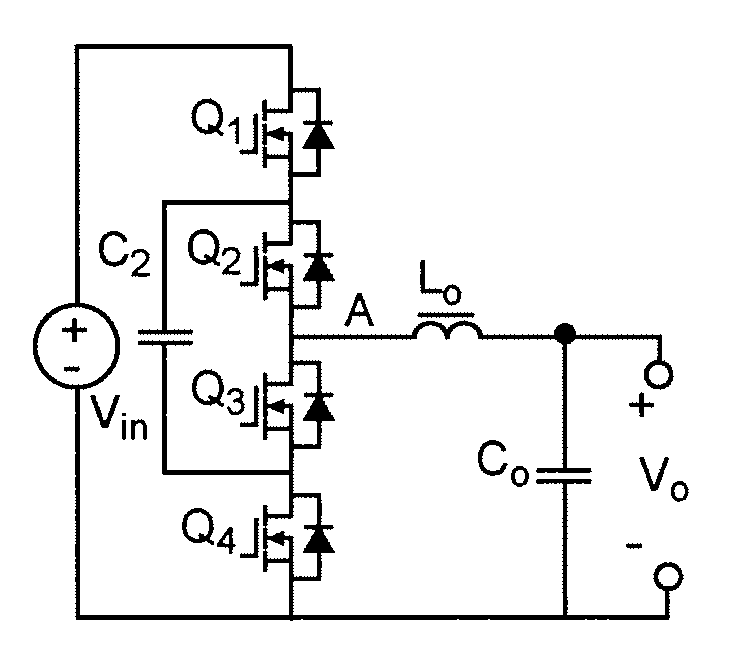
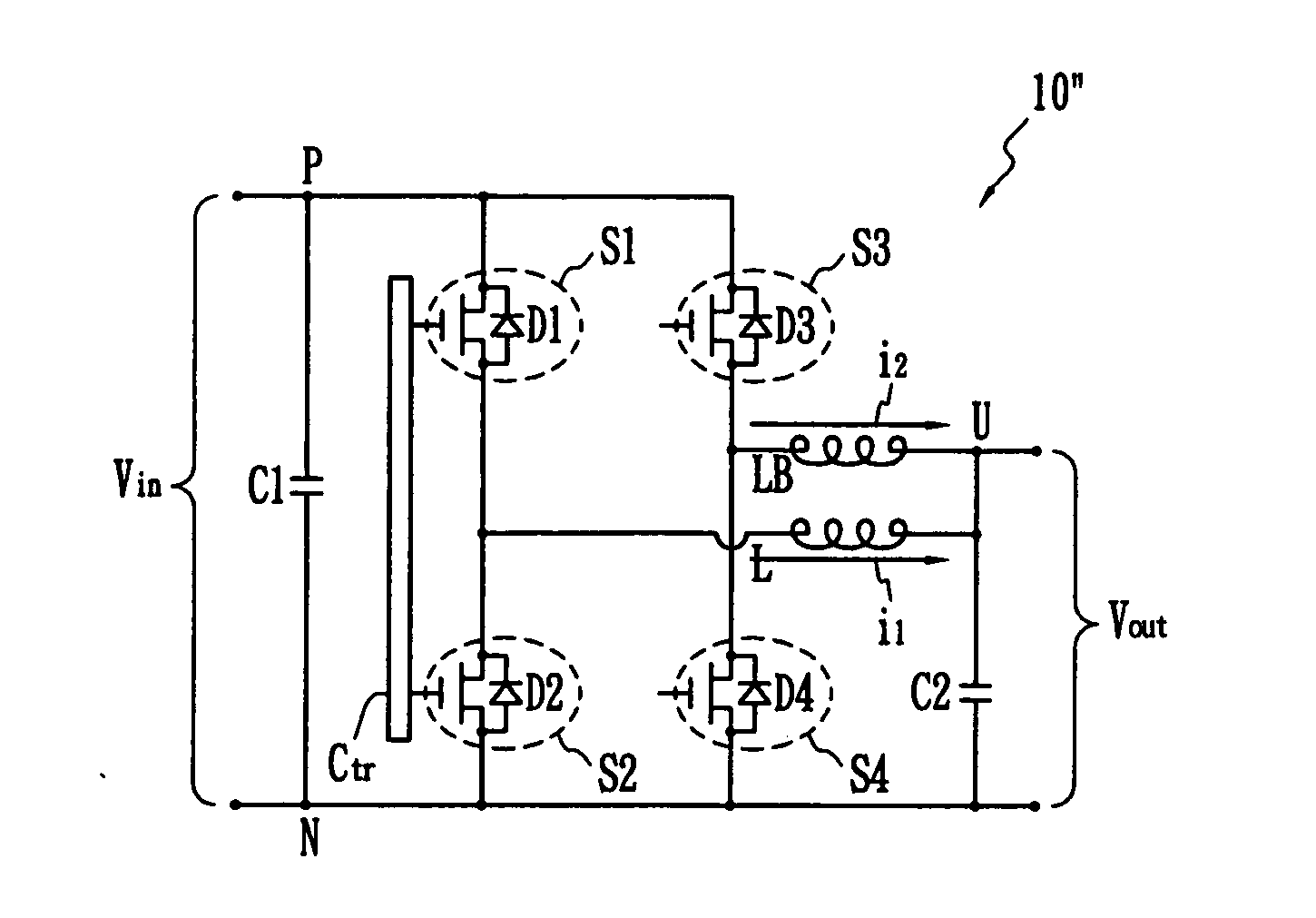
A voltage converter having four switches Q1, Q2, Q3, Q4, connected in series and operated in pairs in a complementary fashion. An input voltage is provided across the four switches. A middle capacitor is connected in parallel with two middle switches Q2, Q3. Voltage output is provided across switches Q3 and Q4 (i.e. at a midpoint of the four switches). Series-connected output capacitors can be connected in parallel with the set of four switches. The middle capacitor alone or in combination with parallel connected capacitors, when connected to the input voltage or output terminals functions as a capacitive voltage divider for voltage conversion and / or regulation with extremely high efficiency and which can provide either step-down or step-up function. Also, an output inductor can be provided as a perfecting feature to further increase efficiency. Alternatively, two of the four switches can be replaced with rectifying diodes. Alternatively, the voltage converter has two or more sets of four switches connected in parallel. The two sets can be connected by resistor-capacitor ladder, or an inductor-capacitor ladder for charge / voltage sharing to reduce voltage ripple.
Owner:VIRGINIA TECH INTPROP INC
PFC apparatus for a converter operating in the borderline conduction mode
InactiveUS6469917B1Ac-dc conversion without reversalEfficient power electronics conversionHemt circuitsEngineering
Power factor correction apparatus, for a switching power supply fed by an array of rectifying diodes and consisting of at least an input inductor, a contact of which is connected in series with a contact of the array, and of a power switch connected between the other contact of the array and the other contact of the input inductor that comprises circuitry for identifying, in each cycle determined by the switching frequency of the power supply, whenever the instantaneous value of the current through the inductor reaches a minimal value; circuitry for switching the power switch to its conducting state in response to the minimal current through the inductor; circuitry for reflecting the current flowing through the inductor by a measurable or simulated parameter; and circuitry for providing indication, in each cycle, by using the parameter, the indication being related to the timing until the peak value of the current, that corresponds to a specific load, has been essentially reached, or to the time from the moment that the current reaches the minimal value until the timing, and for switching the power switch to its non-conducting state in response to the indication.
Owner:GREEN POWER TECH LTD
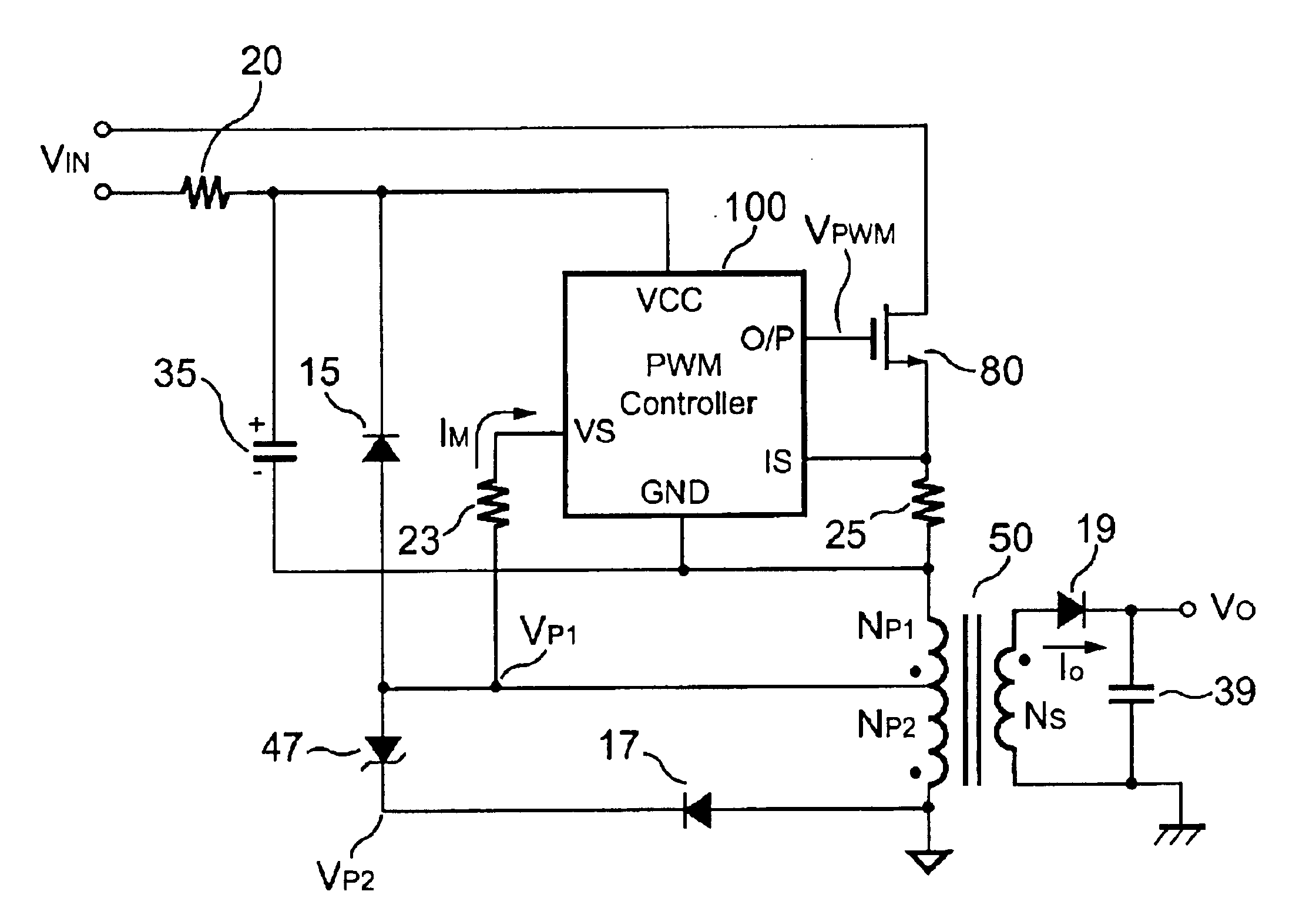
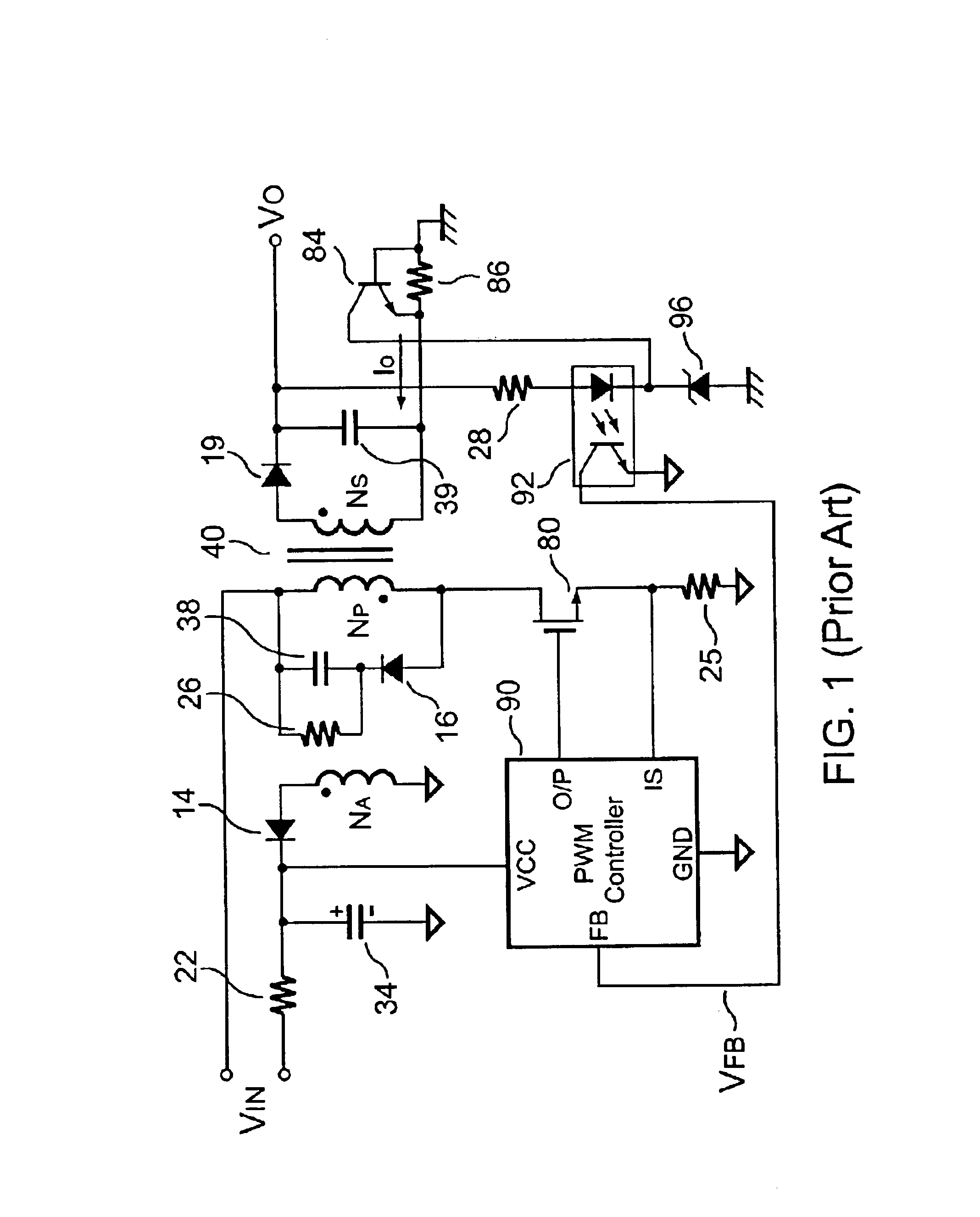
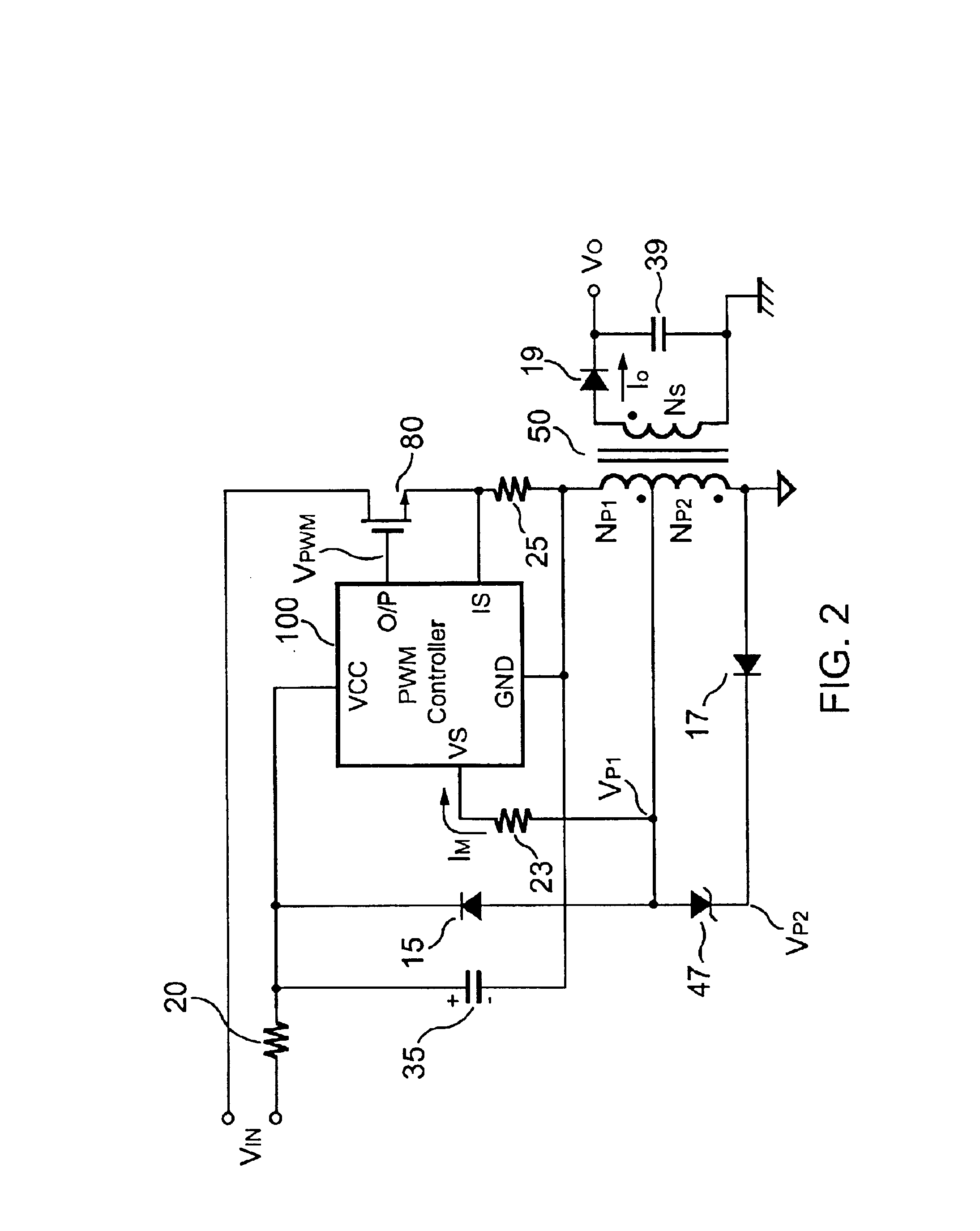
Flyback power converter having a constant voltage and a constant current output under primary-side PWM control
InactiveUS6862194B2Accurate supervisionSmall sizeAc-dc conversion without reversalEmergency protective circuit arrangementsConductor CoilPwm signals
A primary-side flyback power converter supplies a constant voltage and a constant current output. To generate a well-regulated output voltage under varying load conditions, the power converter includes a PWM controller. The PWM controller generates a PWM signal to control a switching transistor in response to a flyback voltage detected from the first primary winding of the power supply transformer. To reduce power consumption, the flyback energy of the first primary winding is used as a DC power source for the PWM controller. The flyback voltage is sampled following a delay time to reduce interference from the inductance leakage of the transformer. To generate a more accurate DC output voltage, a bias current is pulled from the detection input to form a voltage drop across a detection resistor for compensating for the voltage drop of the output rectifying diode.
Owner:FAIRCHILD TAIWAN
Forward-flyback converter with active-clamp circuit
ActiveUS20100067259A1Improve conversion efficiencyAdditional drawbackEfficient power electronics conversionEmergency protective circuit arrangementsHeavy loadCenter tap
The present invention discloses a forward-flyback converter with active-clamp circuit. The secondary side of the proposed converter is of center-tapped configuration to integrate a forward circuit and a flyback circuit. The flyback sub-circuit operating continuous conduction mode is employed to directly transfer the reset energy of the transformer to the output load. The forward sub-circuit operating discontinuous conduction mode can correspondingly adjust the duty ratio with the output load change. Under the heavy load condition, the mechanism of active-clamp flyback sub-circuit can provide sufficient resonant current to facilitate the parasitic capacitance of the switches to be discharged to zero. Under the light load condition, the time interval in which the resonant current turns from negative into positive is prolonged to ensure zero voltage switching function. Meanwhile, the flyback sub-circuit wherein the rectifier diode is reverse biased is inactive in order to further reduce the power losses.
Owner:DELTA ELECTRONICS INC
Non-isolated bus converters with voltage divider topology
InactiveUS7746041B2Filter capacitors can be reduced or eliminatedEasy to controlAc-dc conversionDc-dc conversionCapacitanceVoltage converter
A voltage converter having four switches Q1, Q2, Q3, Q4, connected in series and operated in pairs in a complementary fashion. An input voltage is provided across the four switches. A middle capacitor is connected in parallel with two middle switches Q2, Q3. Voltage output is provided across switches Q3 and Q4 (i.e. at a midpoint of the four switches). Series-connected output capacitors can be connected in parallel with the set of four switches. The middle capacitor alone or in combination with parallel connected capacitors, when connected to the input voltage or output terminals functions as a capacitive voltage divider for voltage conversion and / or regulation with extremely high efficiency and which can provide either step-down or step-up function. Also, an output inductor can be provided as a perfecting feature to further increase efficiency. Alternatively, two of the four switches can be replaced with rectifying diodes. Alternatively, the voltage converter has two or more sets of four switches connected in parallel. The two sets can be connected by resistor-capacitor ladder, or an inductor-capacitor ladder for charge / voltage sharing to reduce voltage ripple.
Owner:VIRGINIA TECH INTPROP INC
Gallium nitride material devices and methods of forming the same
The invention provides gallium nitride material devices, structures and methods of forming the same. The devices include a gallium nitride material formed over a substrate, such as silicon. Exemplary devices include light emitting devices (e.g., LED's, lasers), light detecting devices (such as detectors and sensors), power rectifier diodes and FETs (e.g., HFETs), amongst others.
Owner:NITRONEX
Illumination apparatus and image display apparatus
InactiveUS20060158130A1Small sizeReduce weightStatic indicating devicesElectroluminescent light sourcesDriving currentRectifier diodes
An illumination apparatus is configured simply in a reduced scale while a light emitting diode is used as a light emitting source for illumination. The illumination apparatus includes an LED driving block including an LED bridge circuit formed from a bridge connection of a plurality of diode series circuits each of which is formed from a series connection of a plurality of light emitting diodes and a rectifying diode. A load resistor is connected to a rectification output of the LED bridge circuit. When an AC voltage is input to the LED driving block, the LED bridge circuit rectifies the AC voltage, and the resulting rectification current is used as driving current to drive the light emitting diodes to emit light.
Owner:SONY CORP
Gallium nitride material devices and methods of forming the same
The invention provides gallium nitride material devices, structures and methods of forming the same. The devices include a gallium nitride material formed over a substrate, such as silicon. Exemplary devices include light emitting devices (e.g., LED's, lasers), light detecting devices (such as detectors and sensors), power rectifier diodes and FETs (e.g., HFETs), amongst others.
Owner:MACOM TECH SOLUTIONS HLDG INC
Structure for LED lighting chain
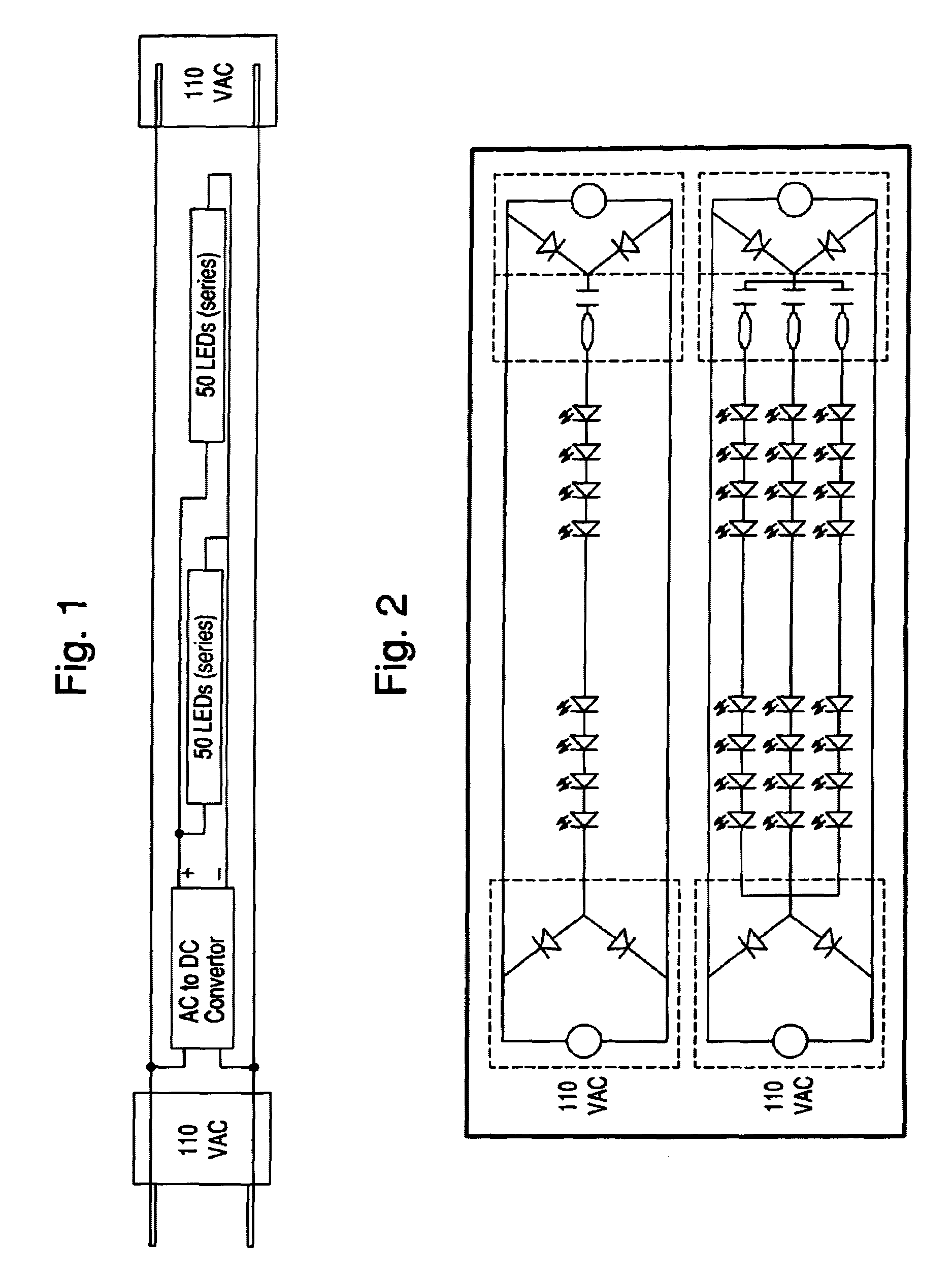
ActiveUS6972528B2Simple structureShorten the counting processLighting support devicesElectrical apparatusRectifier diodesEffect light
Owner:DENG JINHONG
Switching power supply device
InactiveUS6061252AConversion with intermediate conversion to dcApparatus with intermediate ac conversionRectifier diodesInductor
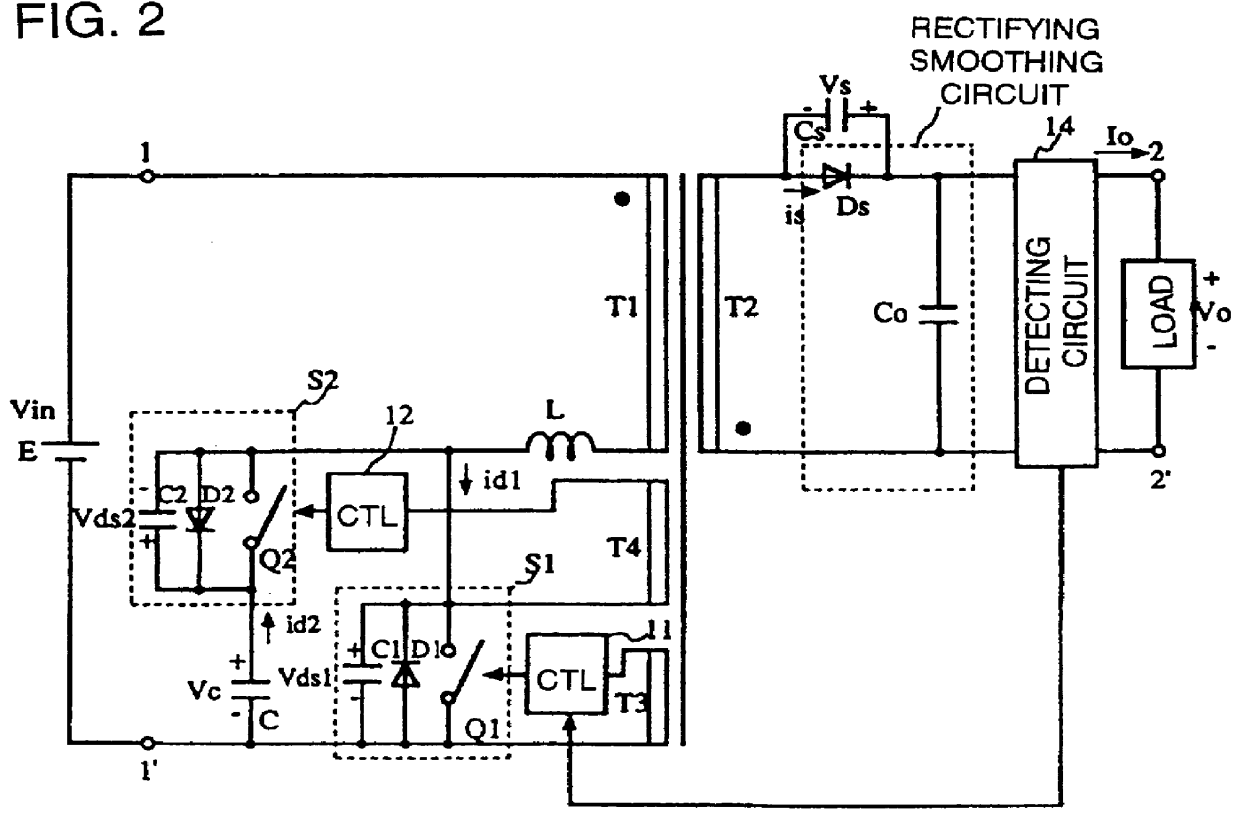
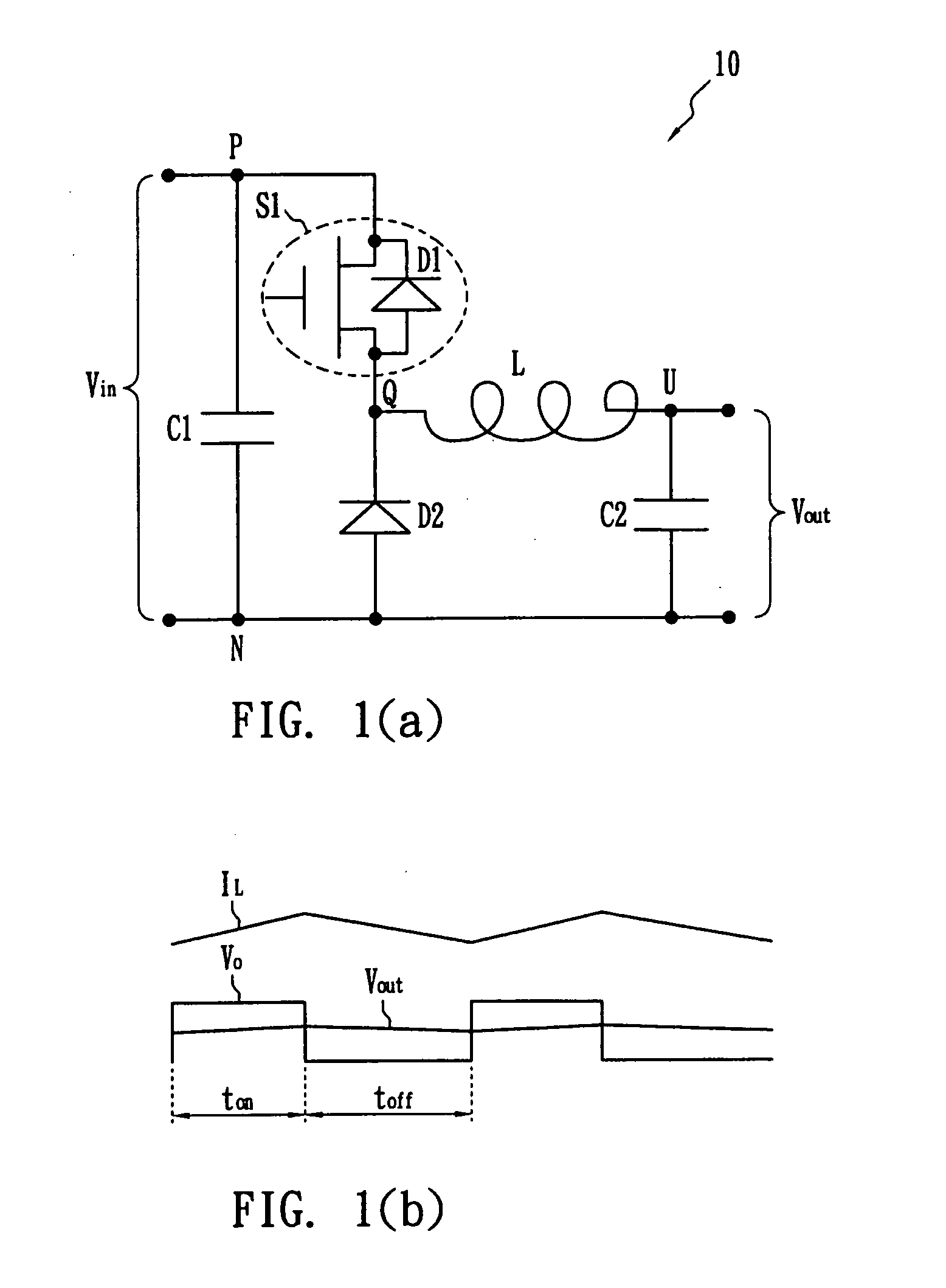
A switching power supply device has a configuration in which a series combination of a first switching circuit and an input power source is connected in series with a series combination of a primary winding of a transformer and an inductor, a series combination of a second switching circuit and a capacitor is connected in parallel to the series combination of the primary winding of the transformer and the inductor, and the secondary winding of the transformer is provided with a rectifying smoothing circuit including a rectifying element. The first switching circuit is made up of a parallel connection circuit including a first switching element, a first diode, and a first capacitor. The second switching circuit is made up of a parallel connection circuit including a second switching element, a second diode, and a second capacitor. A switching controlling circuit is provided adapted to turn the first and second switching elements on and off alternately, with a period of time when both switching elements are off is interposed, and a capacitor is connected in parallel to the rectifying diode in the rectifying smoothing circuit.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
Method and apparatus for controlling a constant current output in a switching mode power supply
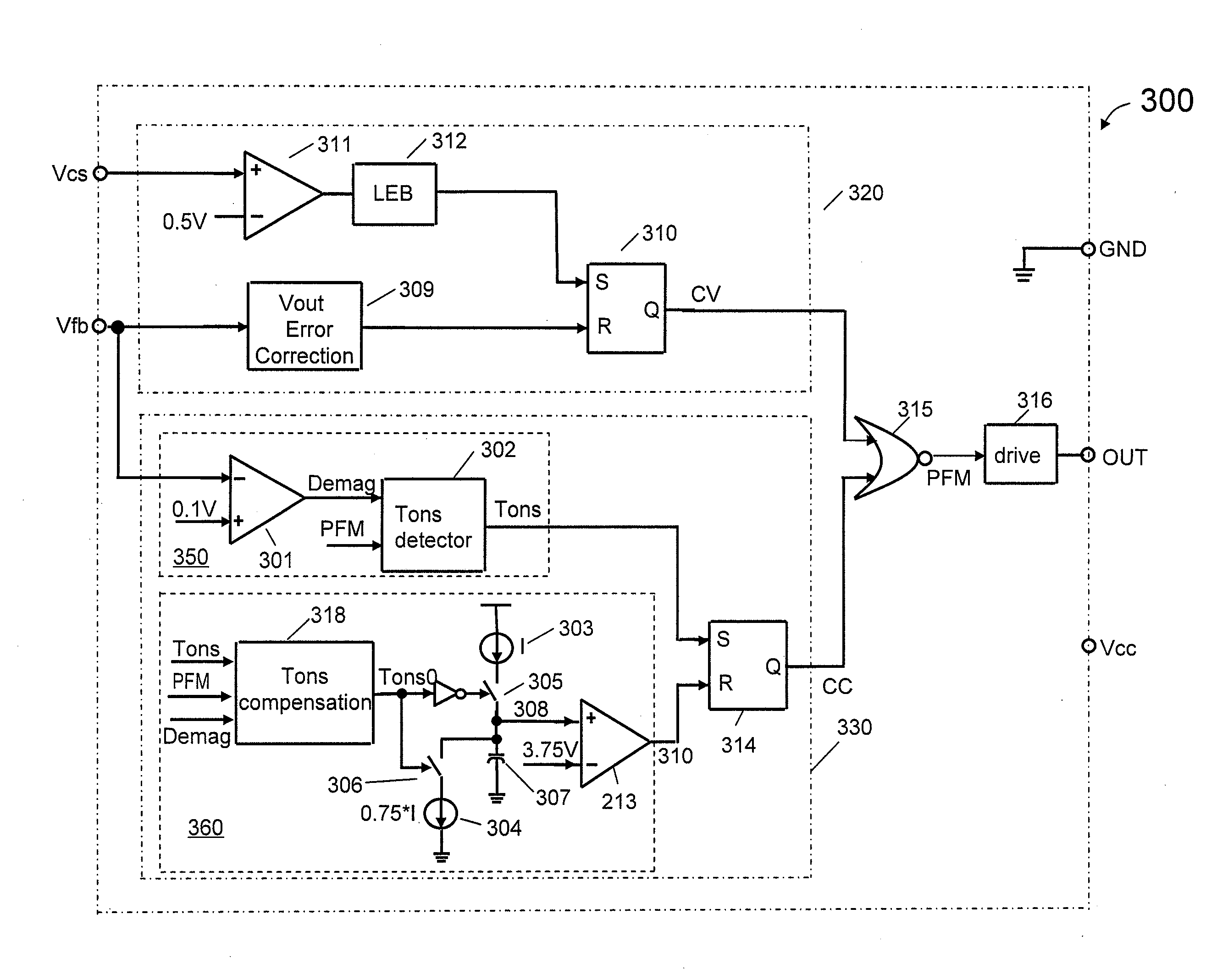
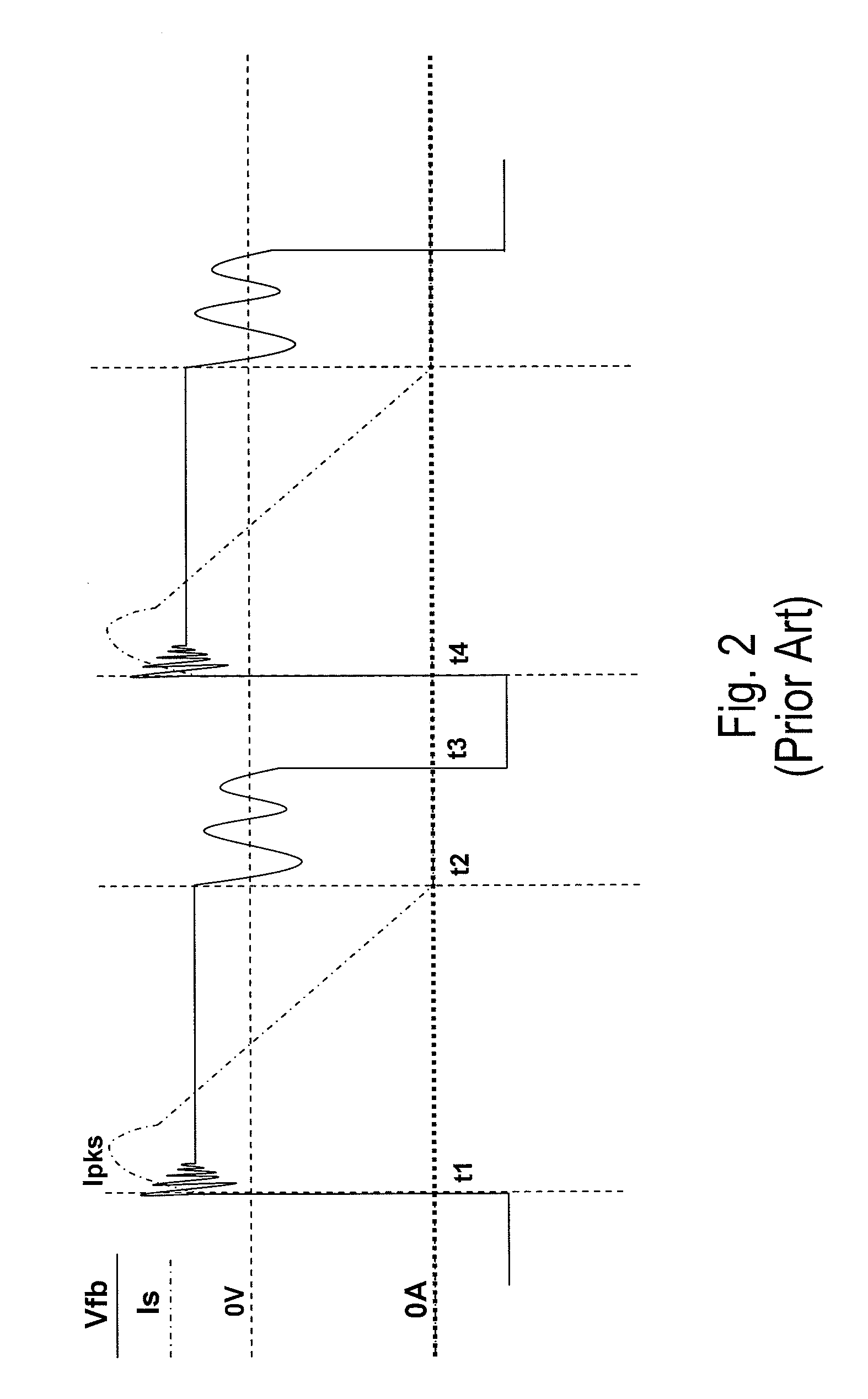
ActiveUS20100238689A1Reduces and eliminates errorAc-dc conversionDc-dc conversionControl signalRectifier diodes
A controller for providing a constant output current control signal in a switched mode power supply (SMPS) includes a conduction time compensation circuit that is configured to produce a compensated conduction time interval signal that includes compensation for a ringing waveform of a feedback signal. The compensated signal reflects more accurately the actual conductive time of a rectifying diode in a secondary winding of the switched mode power supply. In one embodiment, the compensated conduction time interval signal is used to generate a fixed ratio between the conduction time and the non-conduction time of the rectifying diode. In another embodiment, the controller also provides a constant voltage control signal.
Owner:BCD SHANGHAI MICRO ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Lighting strip
InactiveUS20060221609A1Improves Structural IntegrityCoupling device connectionsPoint-like light sourceFull waveRectifier diodes
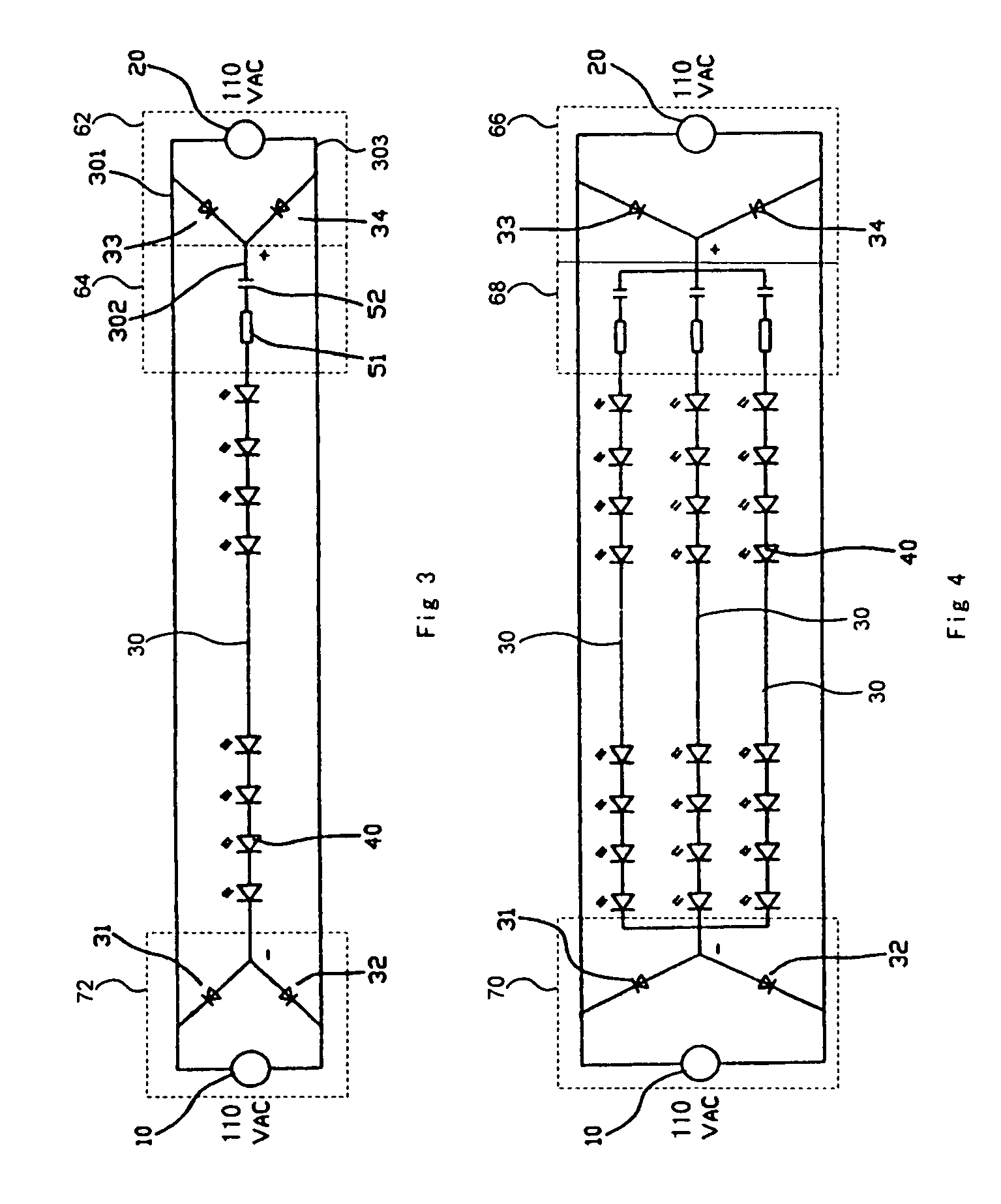
The lighting strip has two elongated flexible conductors for carrying primary power to a plurality of modules. Each module has rectification diodes and a series lighting element. The series lighting element has at least one resistor and at least one light emitting diode (LED). The LED operates using the full-wave rectified power. The lighting strip may be provided in a spool which can be easily cut to the desired length. The number of light emitting diodes in a module, the spacing between components in a module, and the use of multiple lighting strips, can be selected to provide the desired illumination level or effect.
Owner:RYAN PATRICK H JR
Electronic power supply device
InactiveUS6219263B1Efficient power electronics conversionAc-dc conversionOvervoltageElectronic switch
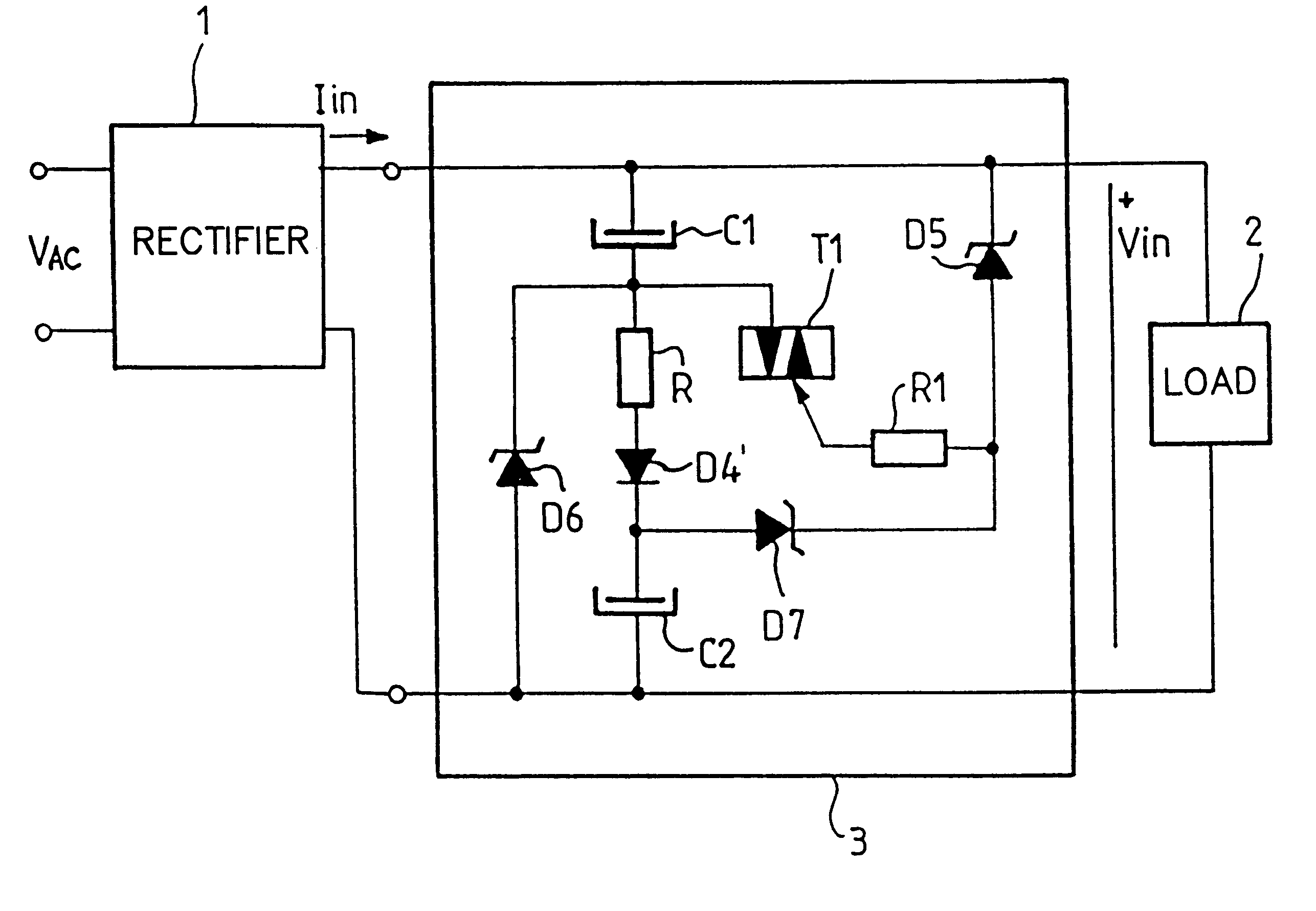
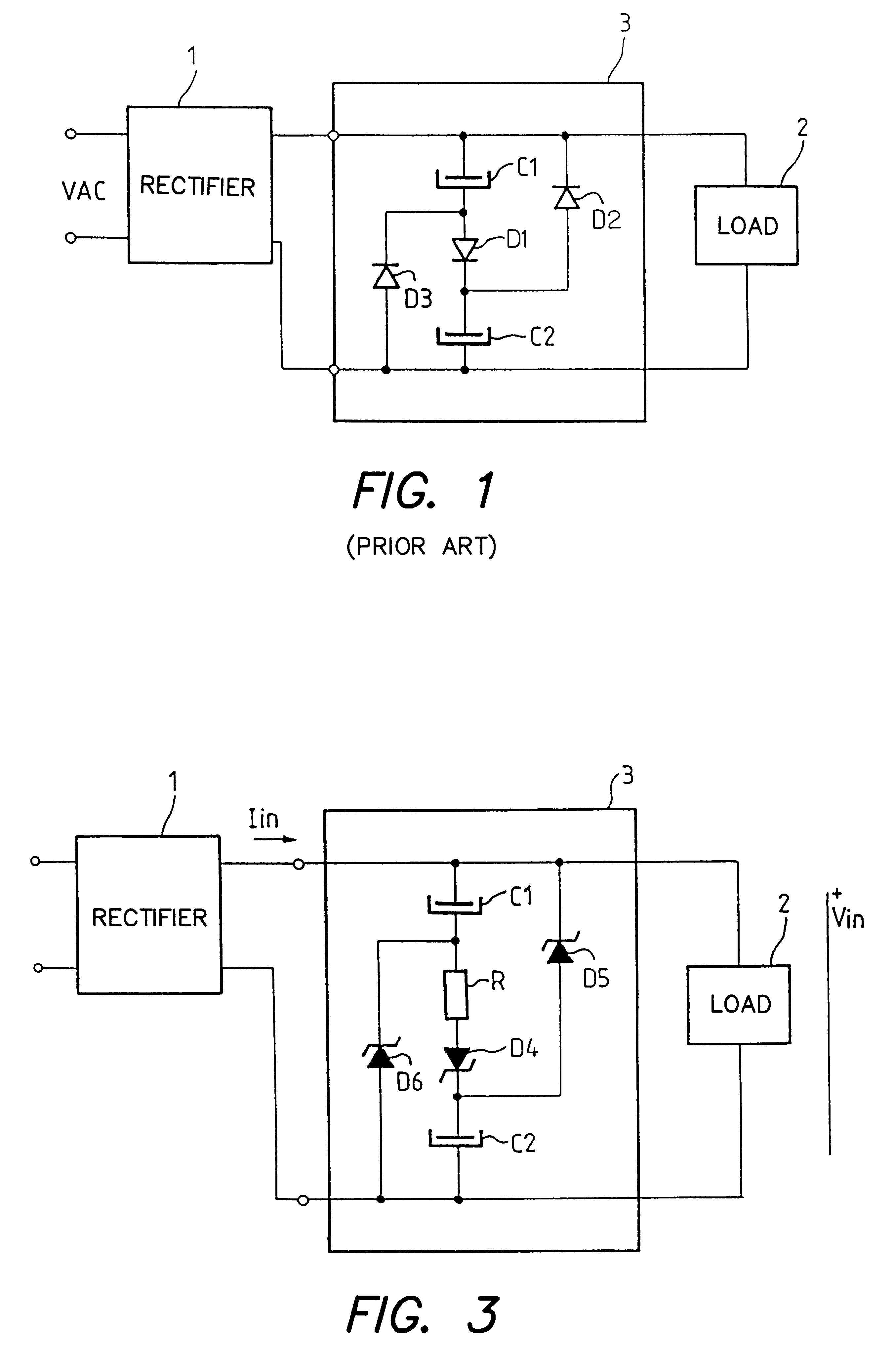
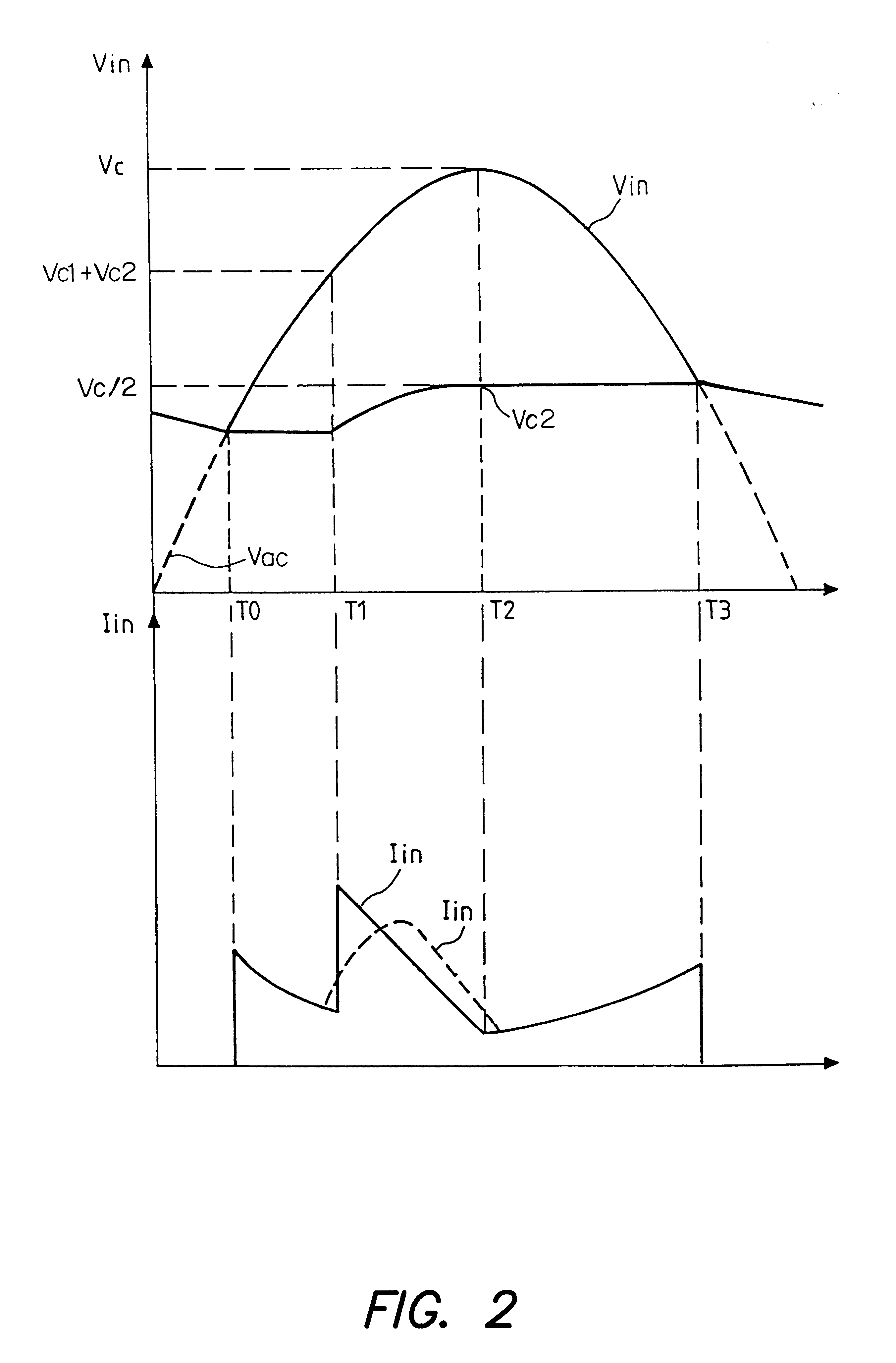
A power factor correction circuit using a first rectifier diode to control the series charging of two capacitors and two rectifier diodes to control the parallel discharging of the two capacitors. The power factor correction circuit further includes a resistor that is series-connected with the first diode to improve the power factor and to reduce the current drawn when the voltage is turned on. The rectifier diodes are advantageously voltage limiting diodes to protect the downline circuitry against overvoltages. In one improvement, a current-controlled electronic switch is used for protection against overvoltages that are just above the peak value of the line voltage.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
Flexible direct current transmission converter valve steady-state high-power running testing device and testing method
ActiveCN103033701ARealize power loop steady-state performance testMeet the requirements for concurrent testingElectrical testingElectrical resistance and conductanceRectifier diodes
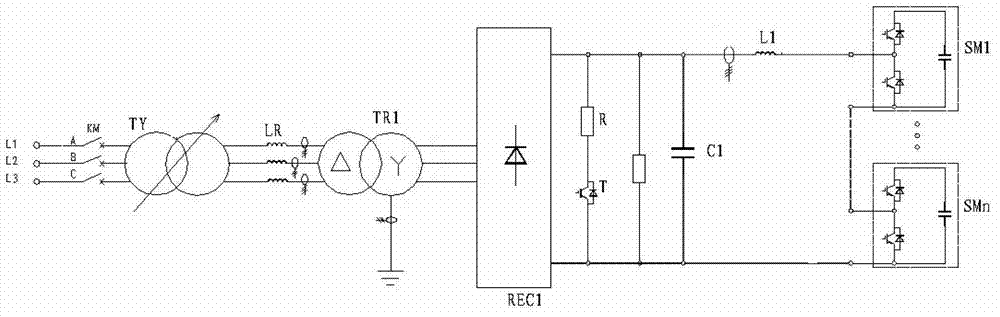
The invention relates to a flexible direct current transmission converter valve steady-state high-power running testing device and a testing method. The testing device comprises an isolation transformer (TR1), a rectifier bridge (REC1) and a converter valve group. An alternating current input end of the rectifier bridge is connected with the isolation transformer. A direct current output end of the rectifier bridge is connected with the converter valve group. The testing device further comprises a BUCK-BOOST circuit which comprises an insulated gate bipolar translator (IGBT) module formed by an IGBT and an antiparallel diode, a resistor (R), a direct current bus support capacitor (C1) and a load electric reactor (L1). The resistor (R) and the IGBT module are connected in series and then connected with a direct current output end of rectifier bridge (REC1) in parallel. The direct current bus support capacitor (C1) is connected with two ends of a series branch circuit of the resistor (R) and the IGBT module in parallel and is connected with the converter valve group through the load electric reactor (L1). Through construction of a test platform which accords with the actual steady-state operation condition, the flexible direct current transmission converter valve steady-state high-power running testing device carries out steady-state power operation tests of a converter valve, carries out detection to current, voltage and temperature rising of components, and checks the correctness of design of the converter valve.
Owner:XJ ELECTRIC +1
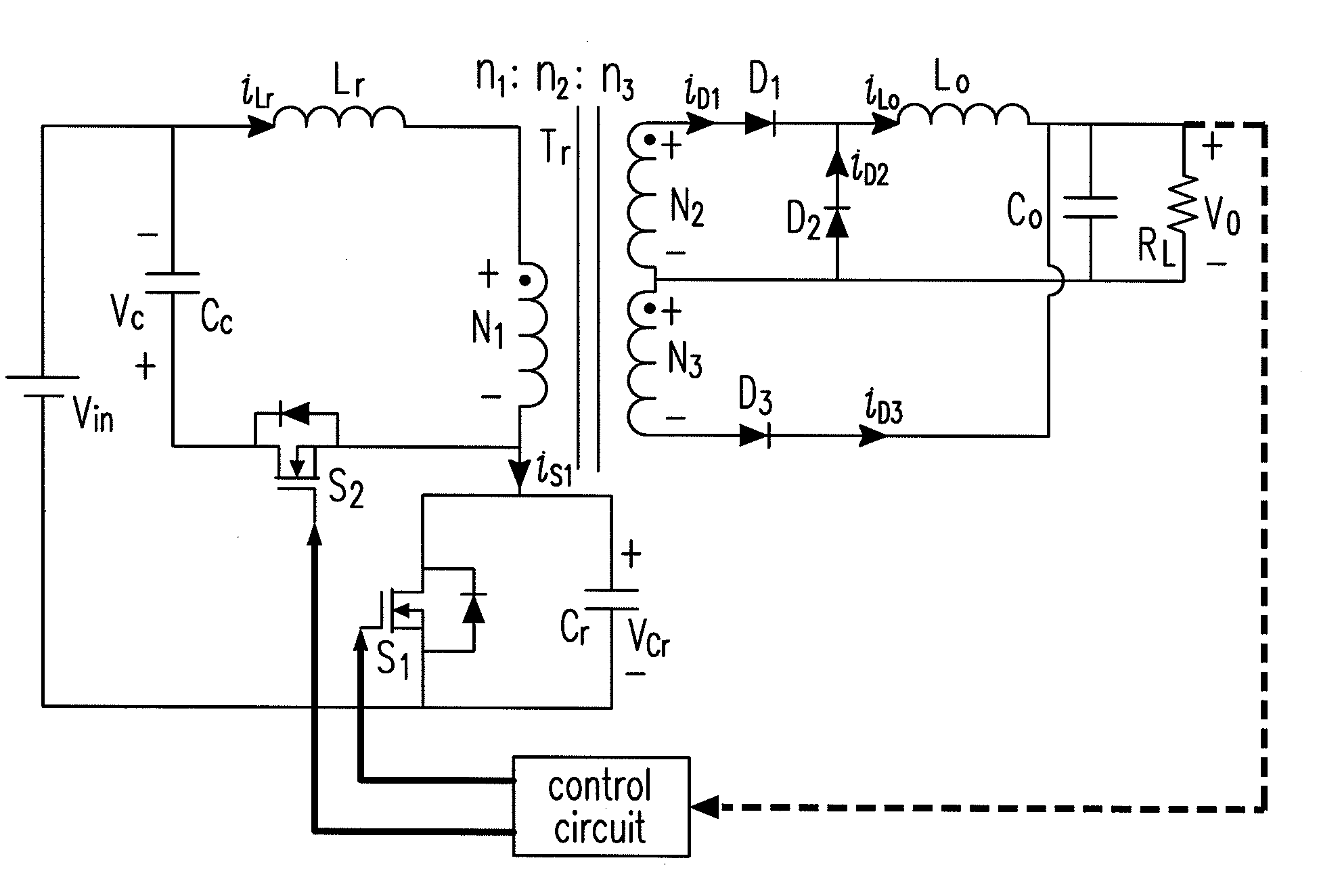
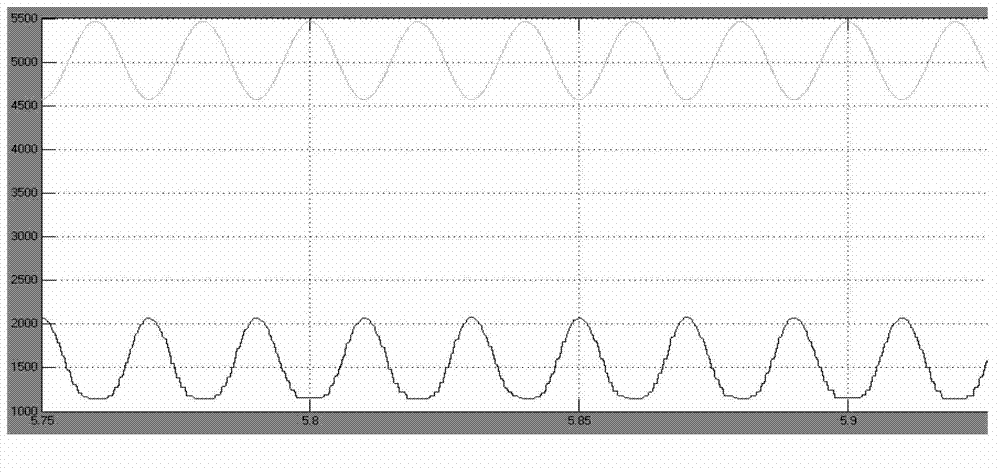
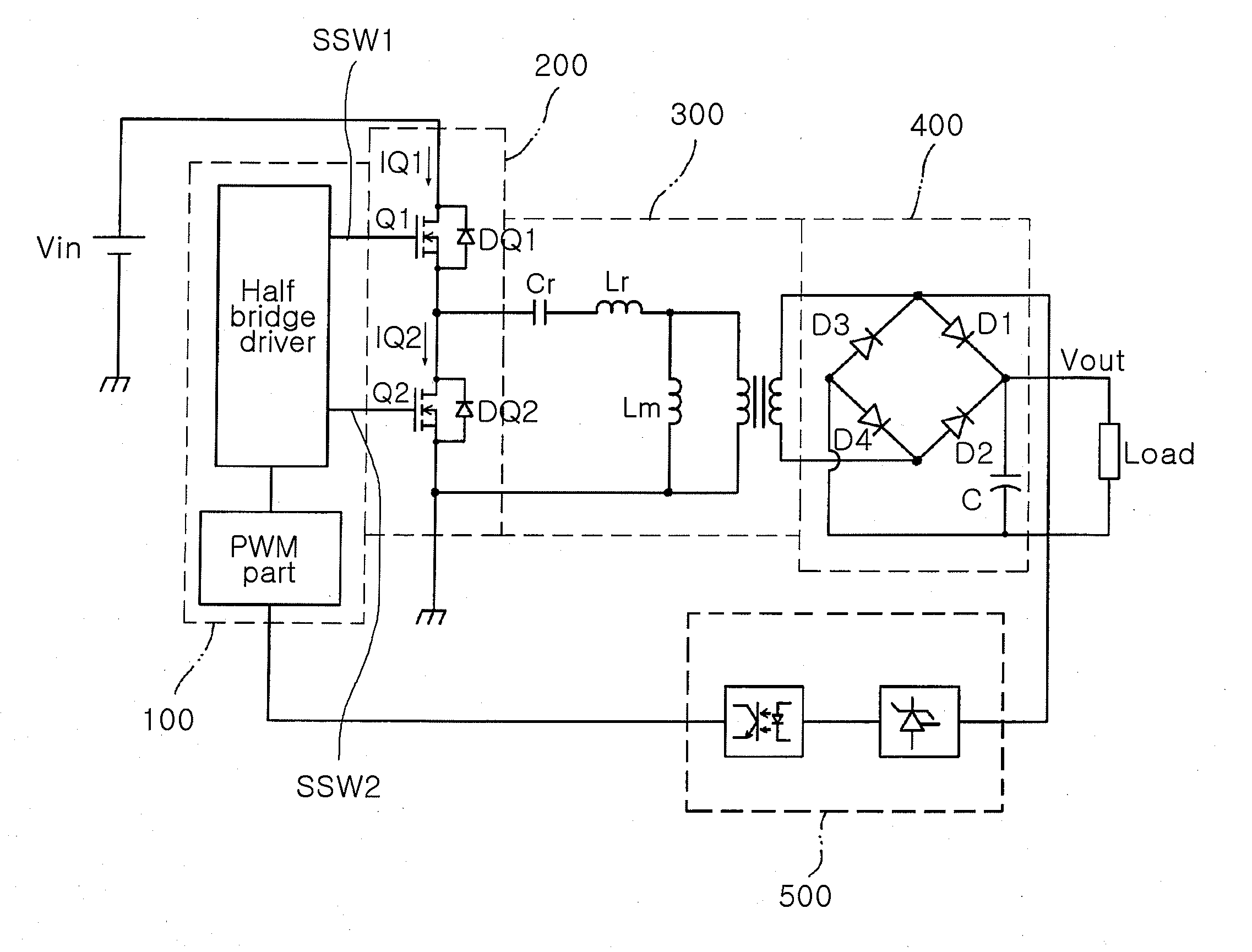
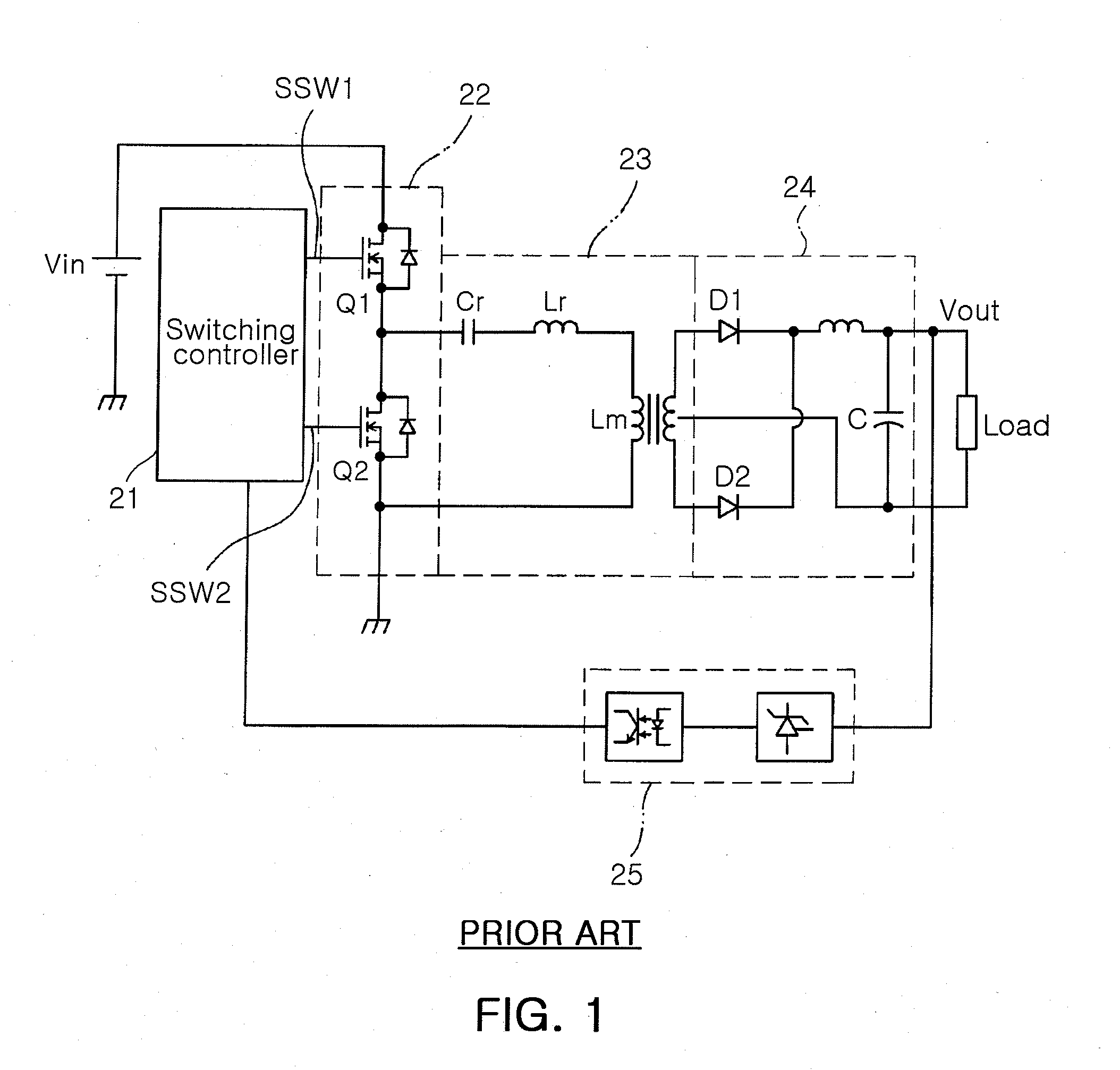
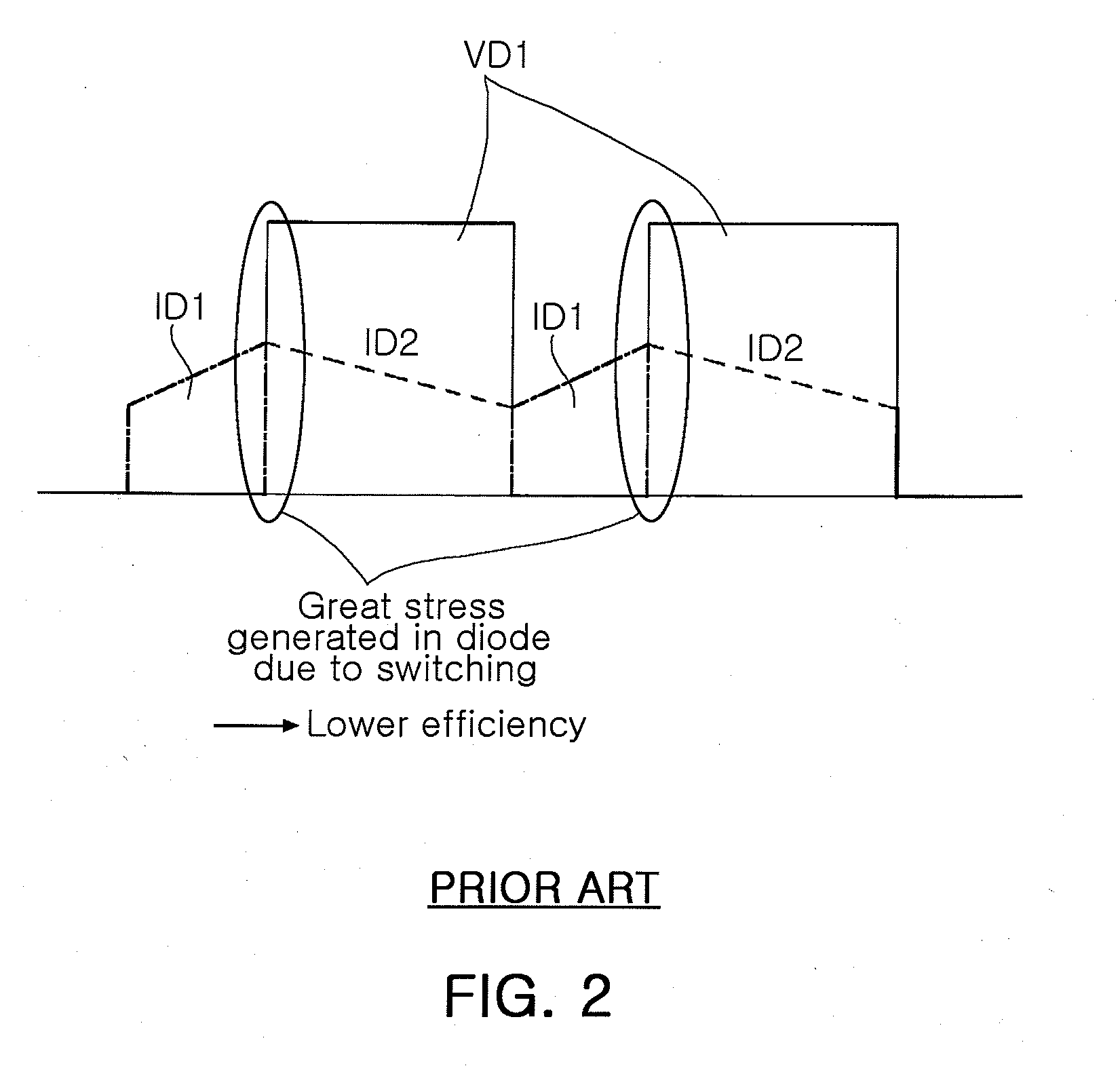
High efficiency half-bridge dc/dc convertor
InactiveUS20070008744A1Reduce switch stressImprove efficiencyAc-dc conversionDc-dc conversionSwitching signalRectifier diodes
In the DC / DC converter, a switching part has first and second switches serially connected from a power supply to a ground. The first and second switches switch on / off in response to first and second switching signals having a fixed frequency. The first switching signal has a phase level that does not overlap a corresponding phase level of the second switching signal. A transformer transforms a voltage applied to a first winding into a second winding in response to switching operation of the switching part, and resonates by an inductor and a capacitor of the first winding. Also, a rectifier includes a rectifying diode for rectifying the voltage from the transformer into a direct voltage. A feedback circuit detects the voltage outputted via the rectifier. Additionally, a controller controls pulse width of the first and second switching signals in a PWM mode according to the voltage detected by the feedback circuit.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRO MECHANICS CO LTD
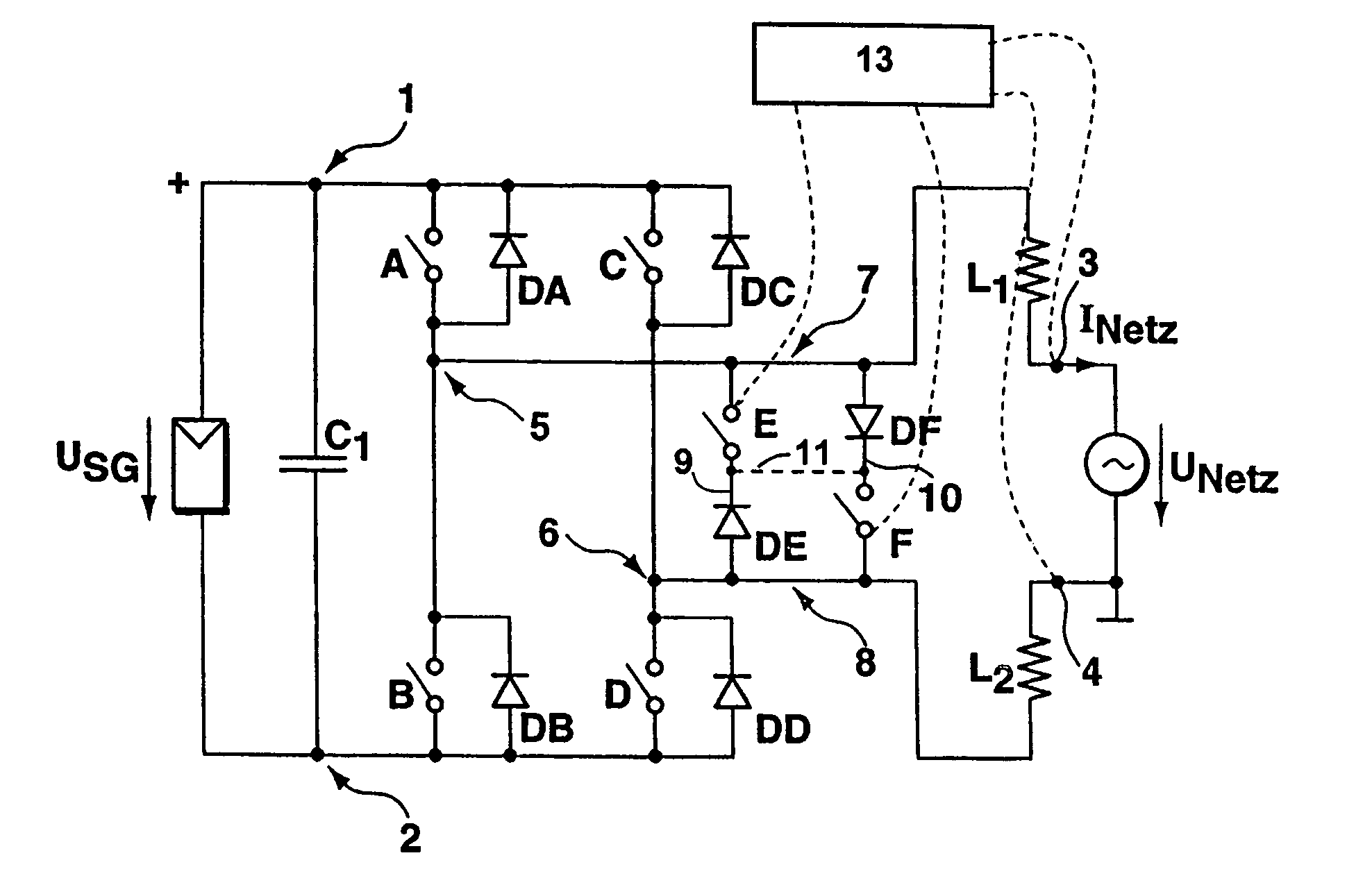
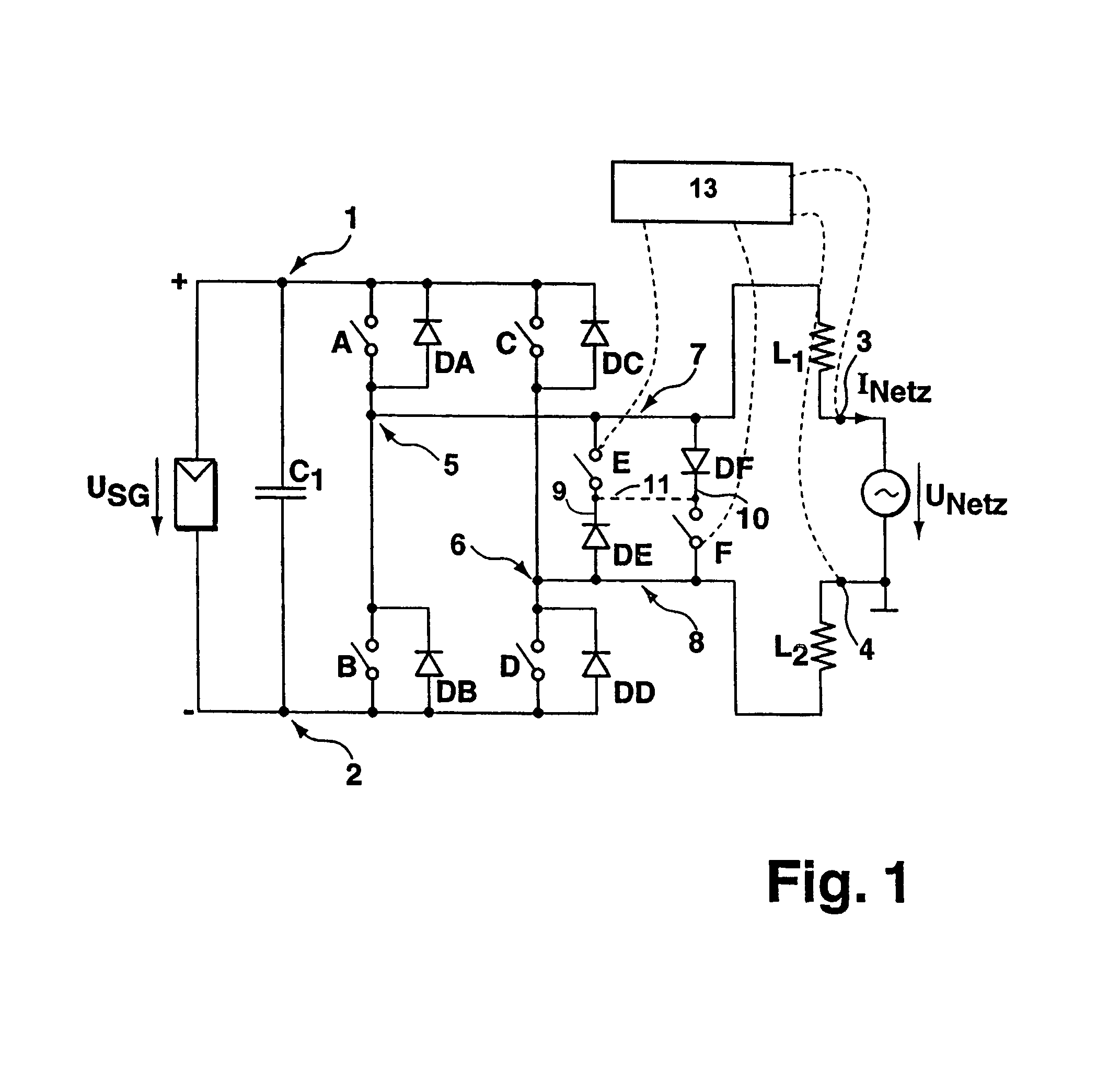
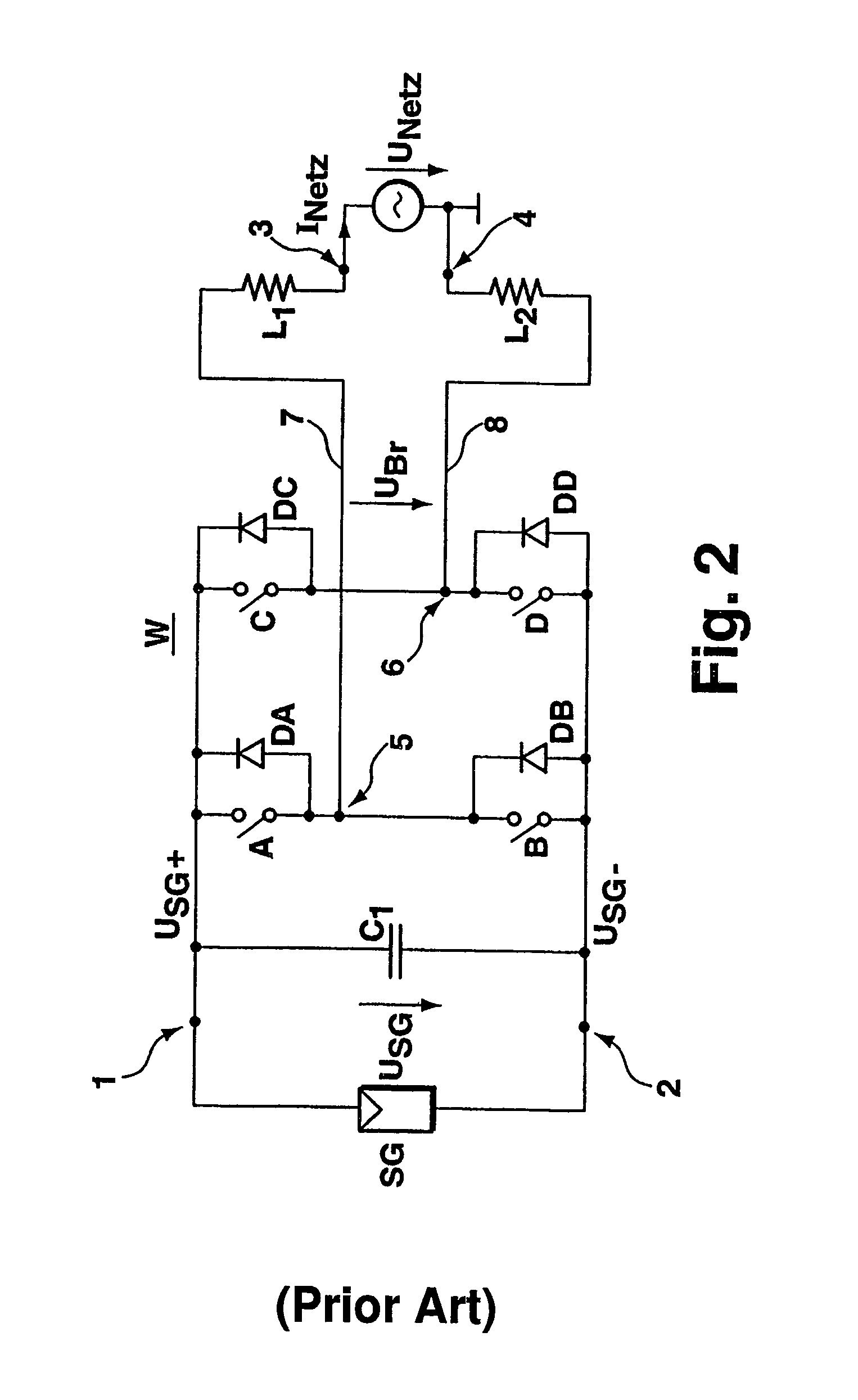
DC/AC converter to convert direct electric voltage into alternating voltage or into alternating current
ActiveUS7046534B2Improve efficiencyAvoid complicationsConversion with intermediate conversion to dcDc-dc conversionRectifier diodesInductor
A DC / AC converter is disclosed having two DC voltage connections (1,2), between which are provided in a parallel circuit configuration, an intermediate energy storage (C1) and a bridge circuit providing at least two parallel branches, each branch providing two in-series-connected switch units (A,B and C,D), to each of which a rectifier diode (DA,DB,DC DD) is connected in parallel, and having at least two AC connections, of which each single AC connection is connected via a connecting line, in each of which an inductor (L1 respectively L2) is provided, to one of the parallel branches of the bridge circuit between two the switch units (A,B respectively C,D) via one connecting node. In at least two connecting lines, two separate electrical connecting paths are provided, in each of which a switch (E respectively F) and an in-series-switched rectifier diode (DE respectively DF) are provided. The rectifier diodes (DE,DF) in the single connecting paths are switched in an opposite conducting direction.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
High efficiency AC LED driver circuit
ActiveUS20080252229A1Electrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesCurrent limitingRectifier diodes
In an AC drive circuit for LEDs, a current limiting capacitor connects to an AC source, a first circuit portion, including a first rectifying diode and a first power capacitor, connects between the current limiting capacitor and the source and a second circuit portion, including a second rectifying diode in series with a second power capacitor, is in parallel with the first circuit portion. A first LED is in the first circuit portion in parallel with the first power capacitor, while a second LED in the second circuit portion is in parallel with the second power capacitor. During positive half cycles, the first rectifying diode charges the first power capacitor and drives the first LED. During negative half cycles, the second rectifying diode charges the second power capacitor and drives the second LED.
Owner:IDEAL IND LLC
Light emitting diode driving circuit for backlight having constant current control function
ActiveUS20070001625A1Improvement in driving current detectionIncrease currentStatic indicating devicesElectroluminescent light sourcesVoltage referenceVoltage control
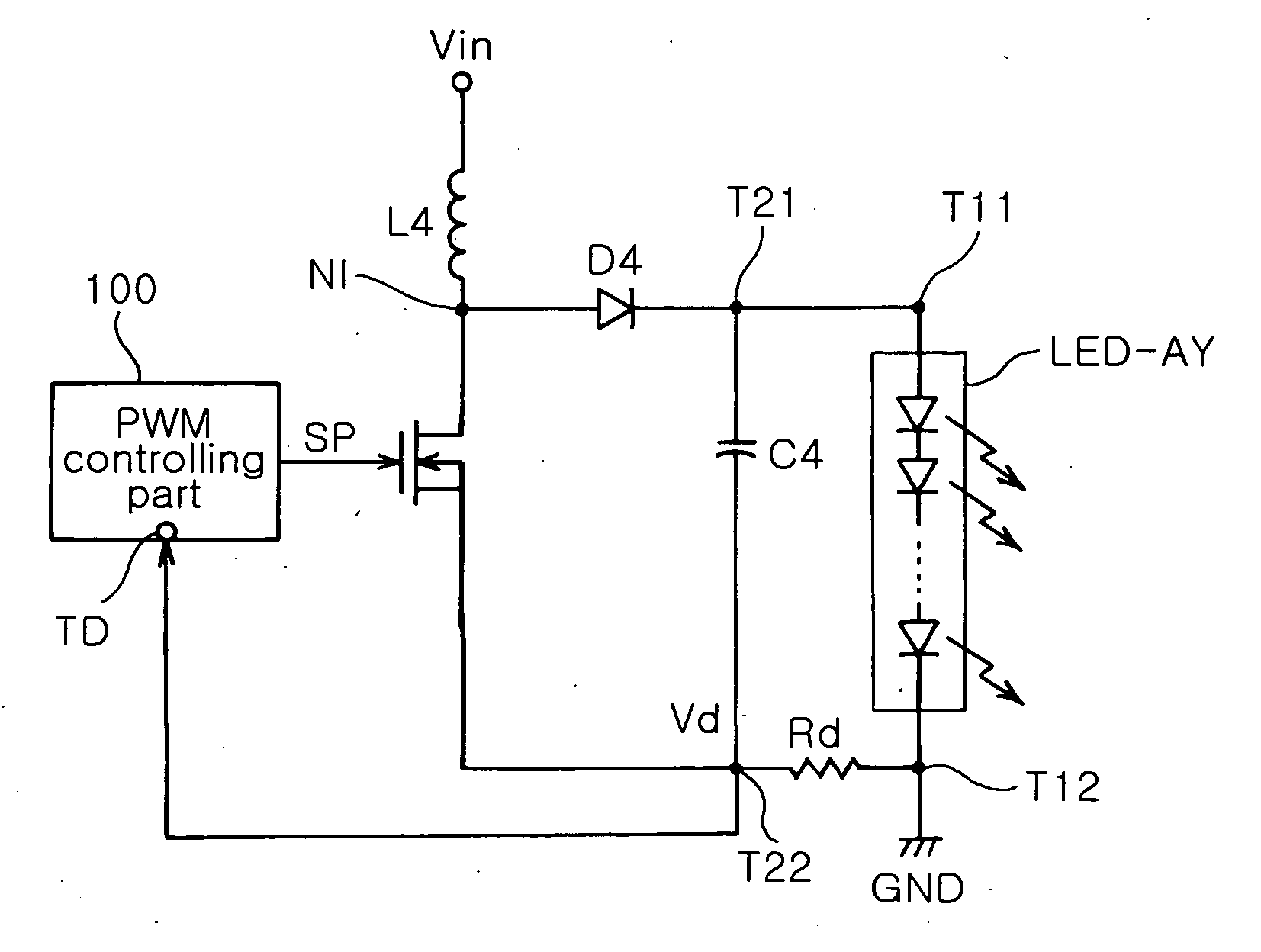
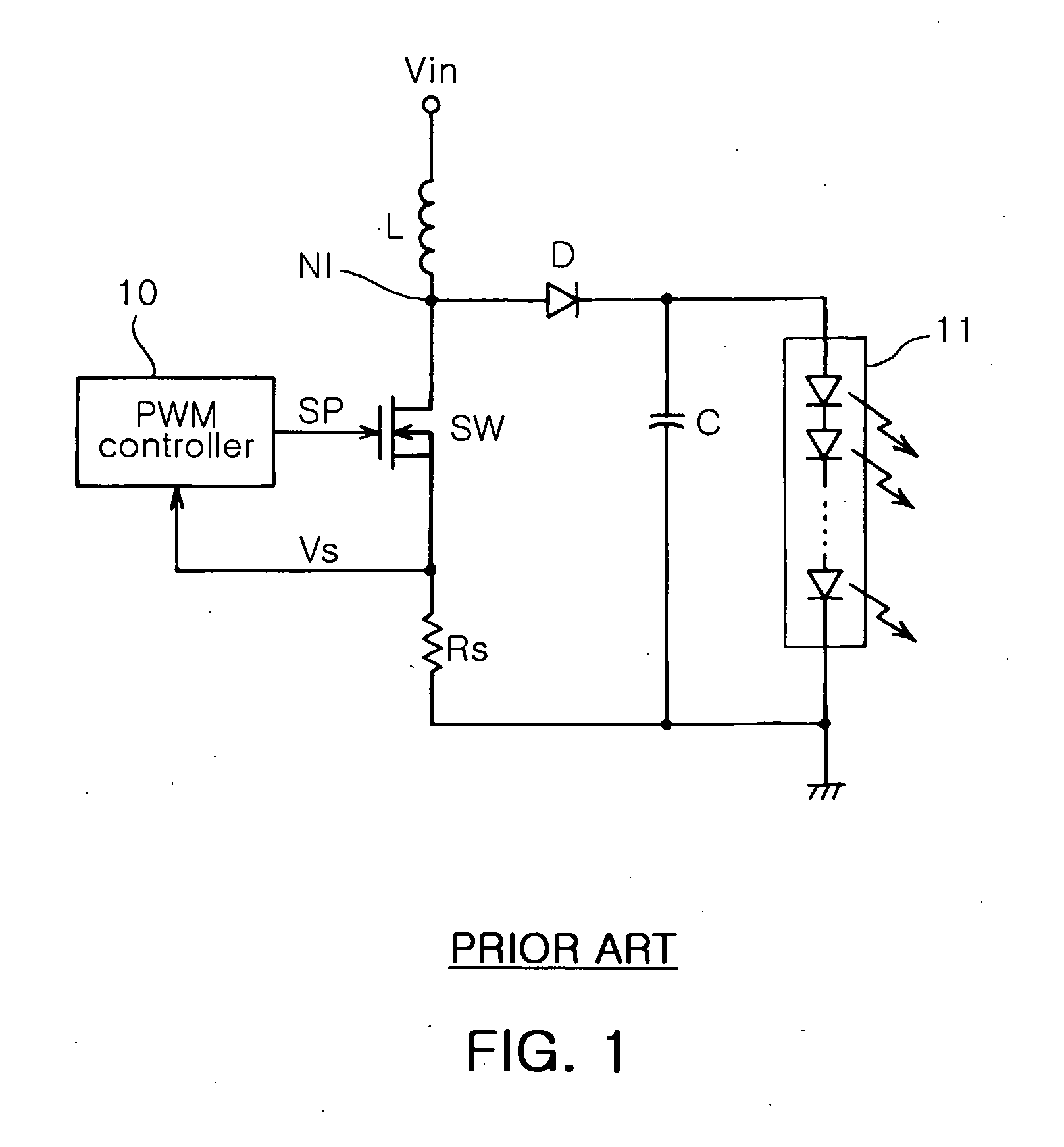
An LED driving circuit of a backlight unit includes a switch connected between an input of direct voltage and a ground to switch the direct voltage according to a switching pulse; a rectifying diode connected between a connecting node and one terminal of the LED array to rectify driving voltage supplied according to switching operation of the switch; a smoothing capacitor having one terminal connected to a cathode of the rectifying diode and the other terminal connected to a ground; a voltage detecting resistor connected between the other terminal of the LED array connected to the ground and the other end of the smoothing capacitor to detect voltage from the current flowing to the ground; and a PWM controlling part for controlling on / off status of the switching according to the switching pulse, wherein the switching pulse has a duty ratio determined according to a preset internal reference voltage and the voltage detected by the voltage detecting resistor. The driving current of can be controlled at a constant current and thus be stabilized.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Decorative lighting string with stacked rectification
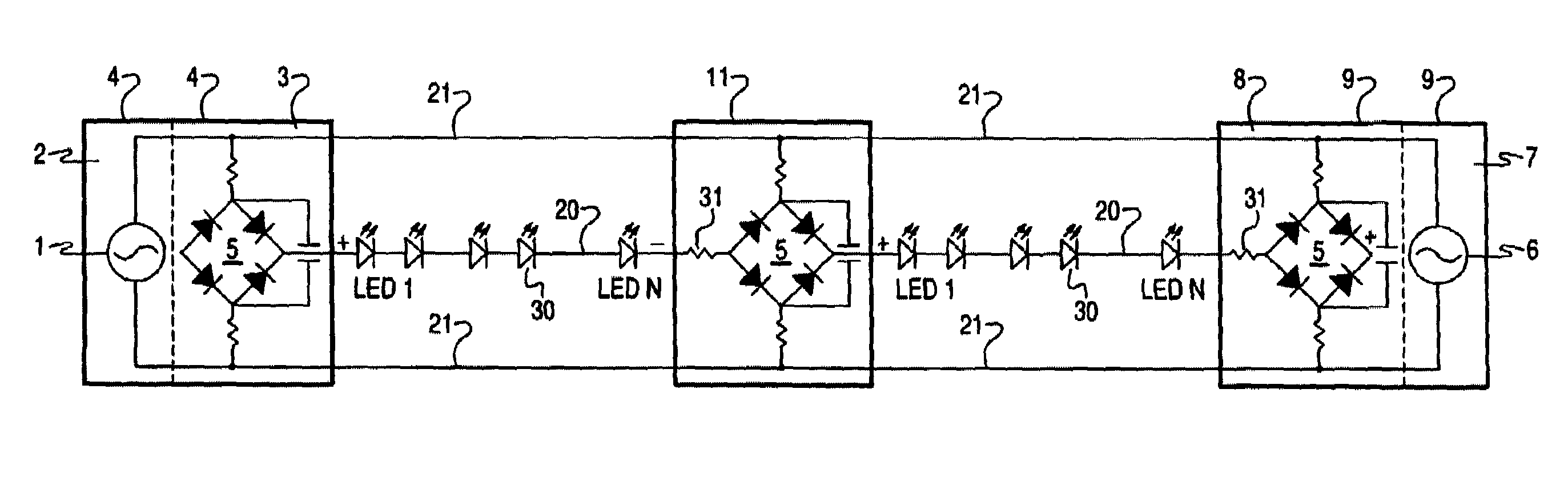
ActiveUS7276858B2Reduce or limit LED drive currentReduce (filter) DC rippleElectrical apparatusLighting elementsDriving currentFull bridge
An improved decorative light string circuit comprises full bridge rectification located in or downstream of the front plug, wherein the rectification circuit contains one or more voltage reducing and / or filtering elements in order to reduce or limit LED drive current and reduce (filter) DC ripple and 1 or 2 LED series sets. Additional rectification circuits and LED series sets can be added in parallel to the first in “stacked mode”, with each rectification circuit and LED series set electrically independent of prior and subsequent circuits. This eliminates the rectifying diode current summation load restrictions imposed by prior art and associated safety hazard due to diode overheating.
Owner:FIBER OPTIC DESIGNS
Zero voltage switch method for synchronous rectifier and inverter
InactiveUS20070109822A1Reduce switching lossesWithout compromising efficiencyEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionLower limitReverse current
The zero voltage switch (ZVS) method for the synchronous rectifiers and inverter. The ZVS method for synchronous rectifier, in which the rectifier diode is replaced by a bi-directional-current one directional-voltage blocking capability switch, by allowing and terminating current flow in a reverse direction, achieves zero voltage turn-on on both inverter and rectifier switches. The ZVS method of the present invention includes: increasing an inductor current to a current upper limit with a first switch module active; decreasing the inductor current with the first switch module open and a second switch module passive; decreasing the inductor current with a second switch module active; turning the second switch module open when the inductor current turns negative; increasing the inductor current from a current lower limit with the first switch module passive; and increasing the inductor current with the first switch module active with zero voltage.
Owner:KUAN KAN SHENG
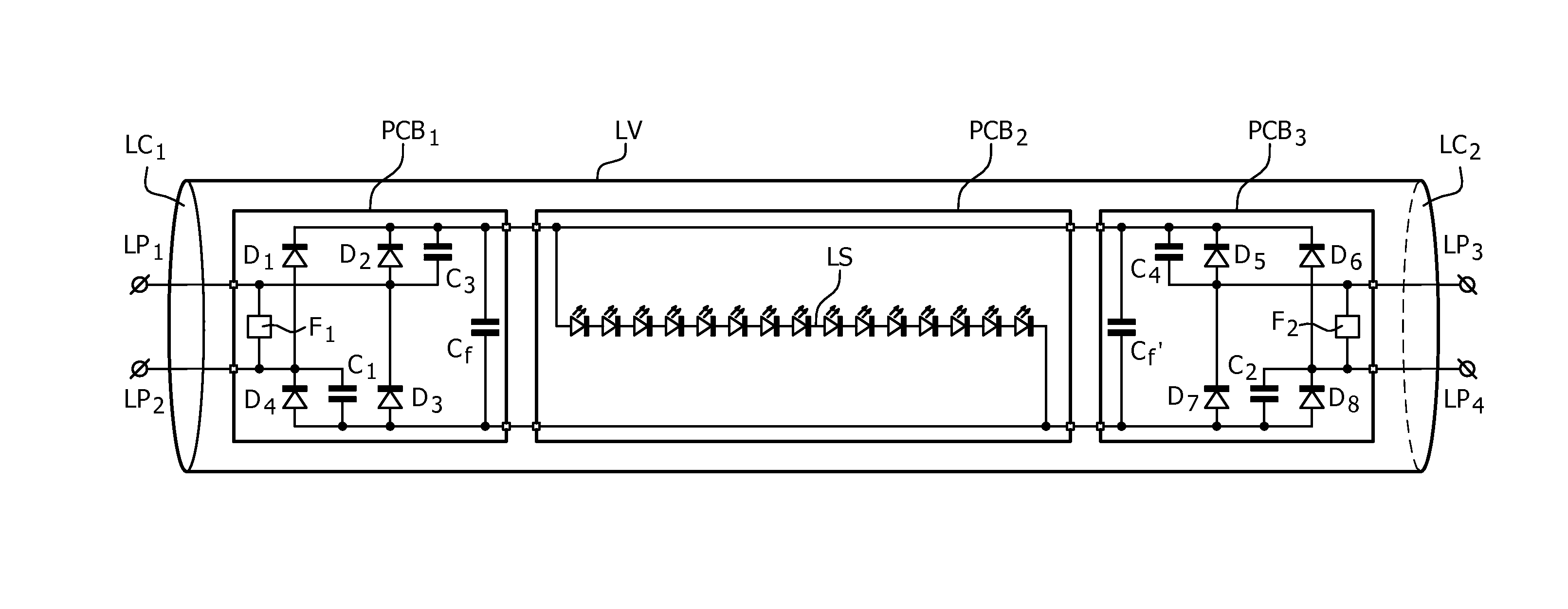
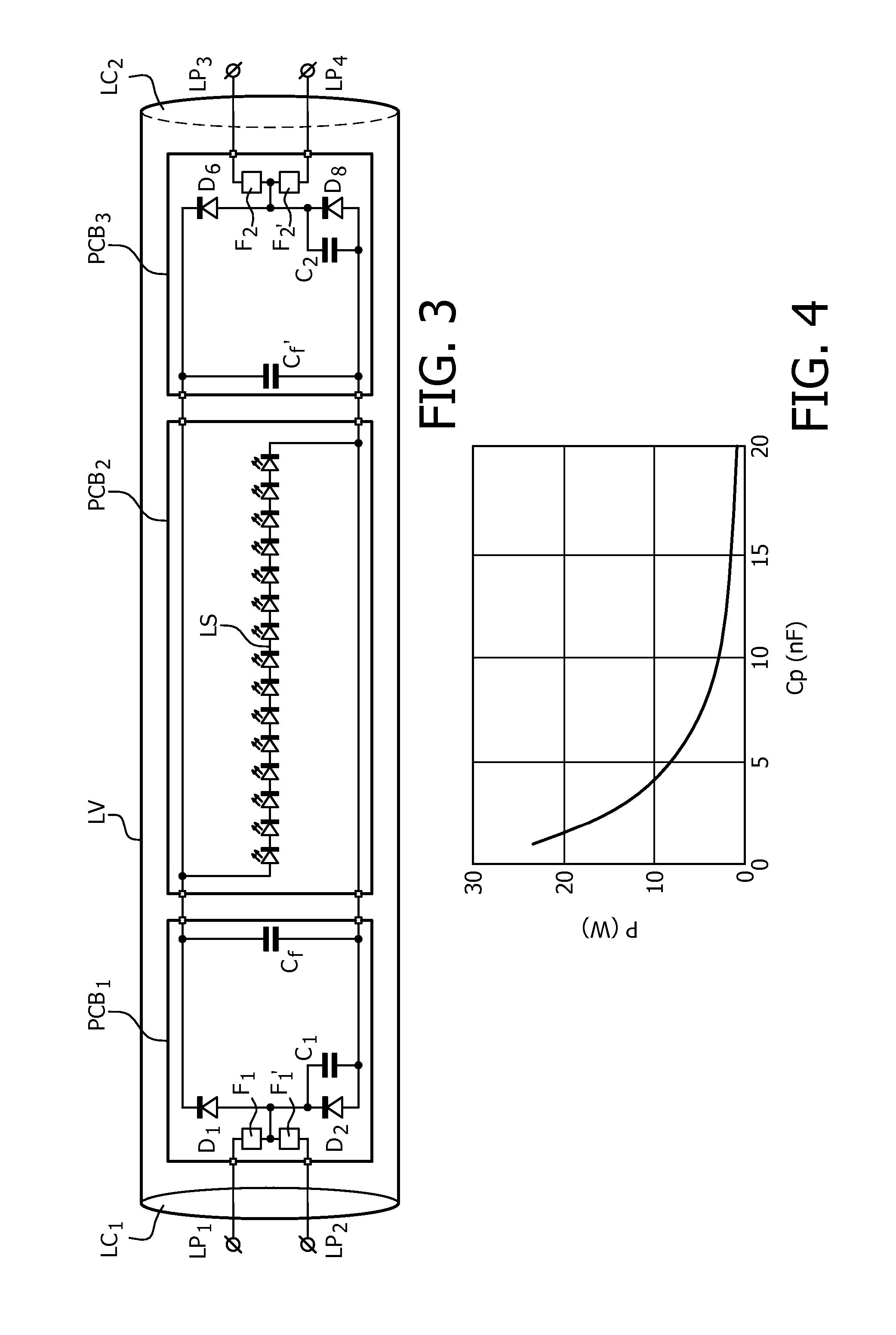
LED retrofit lamp with shunt capacitors across rectifier diodes for use with a ballast
ActiveUS20150351171A1Extend lamp lifeSave energyElectrical apparatusElectric circuit arrangementsShunt capacitorsRectifier diodes
The invention relates to LED replacement lamp suitable for operation with a high frequency fluorescent lamp ballast, comprising—a LED load (LS) comprising a series arrangement of LEDs,—a first lamp end circuit comprising—a first lamp pin (LP1) and a second lamp pin (LP2) for connection to a first lamp connection terminal comprised in the high frequency fluorescent lamp ballast,—a first rectifier (D1-D4; D1,D2) equipped with at least one input terminal coupled to the second lamp pin and with first and second output terminals coupled to respective ends of the LED load, the first rectifier comprising at least two diodes, one of which is shunted by a first capacitor (C1),—a second lamp end circuit comprising—a third lamp pin (LP3) and a fourth lamp pin (LP4) for connection to a second lamp connection terminal comprised in the high frequency fluorescent lamp ballast,—a second rectifier (D5-D8, D5, D6) equipped with at least one input terminal coupled to the fourth lamp pin and with first and second output terminals coupled to respective ends of the LED load, the second rectifier comprising at least two diodes, one of which is shunted by a second capacitor (C2), wherein the first capacitor and the second capacitor form a series arrangement coupled between the second lamp pin and the fourth lamp pin.
Owner:SIGNIFY HLDG BV
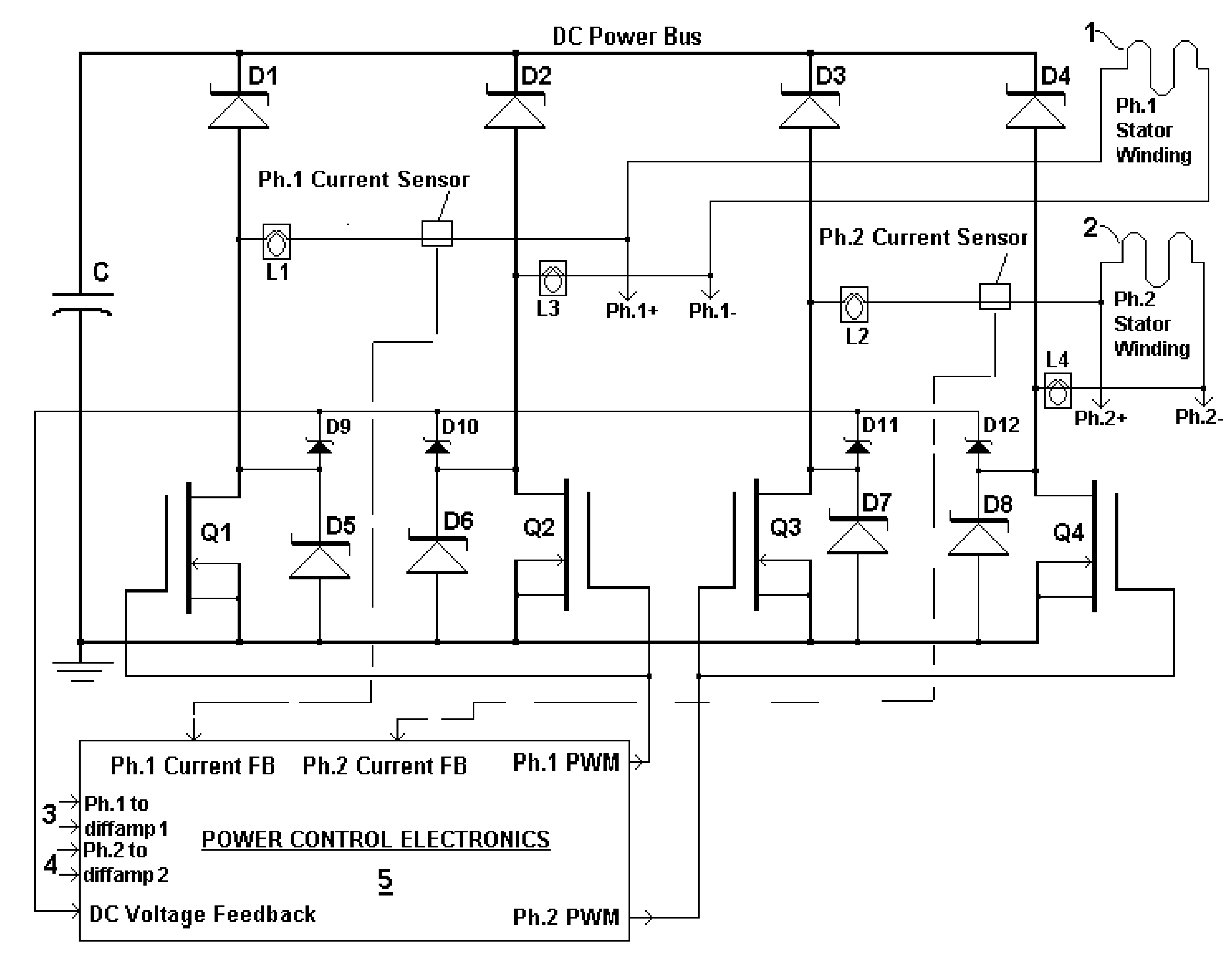
Broad-speed-range generator variations
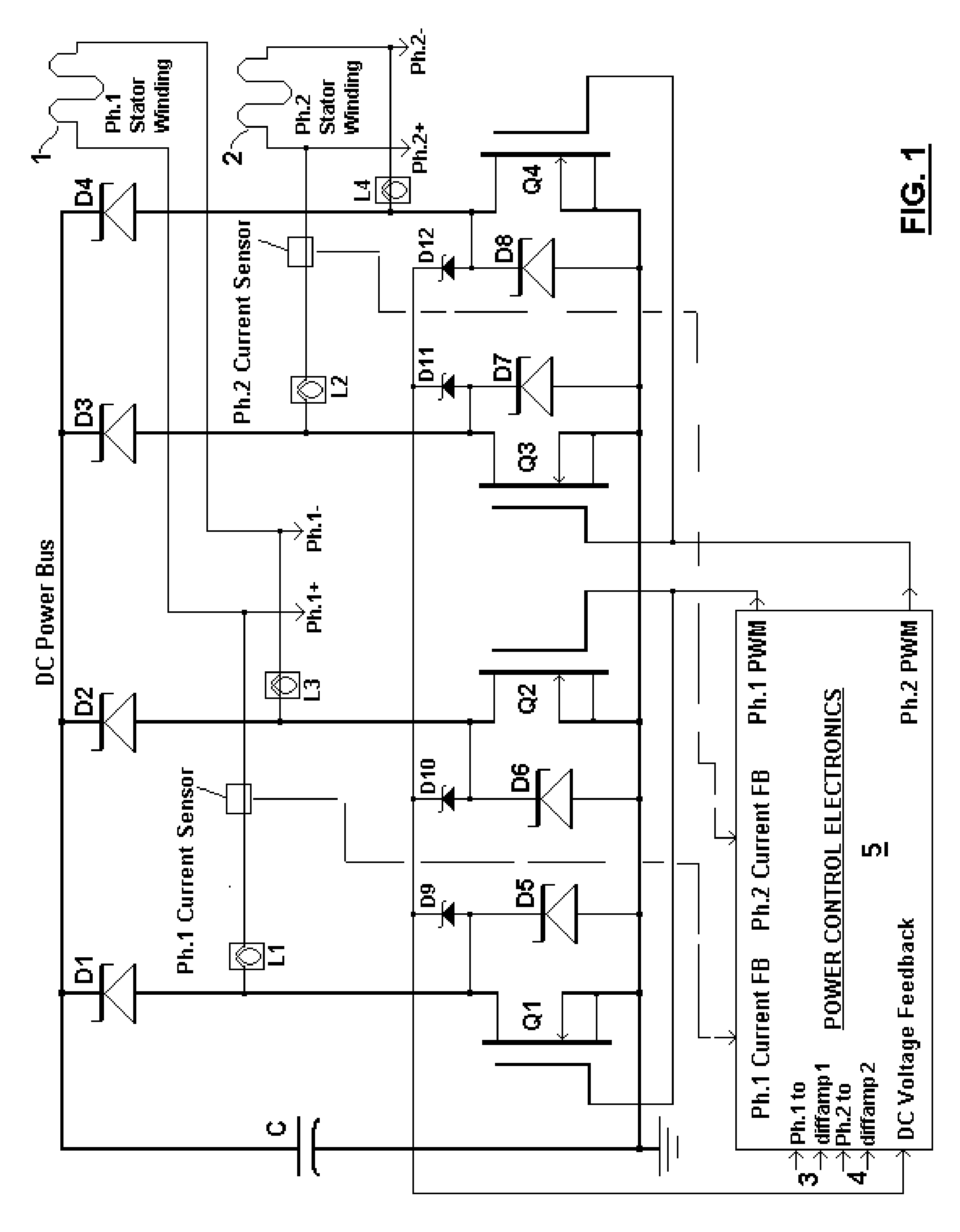
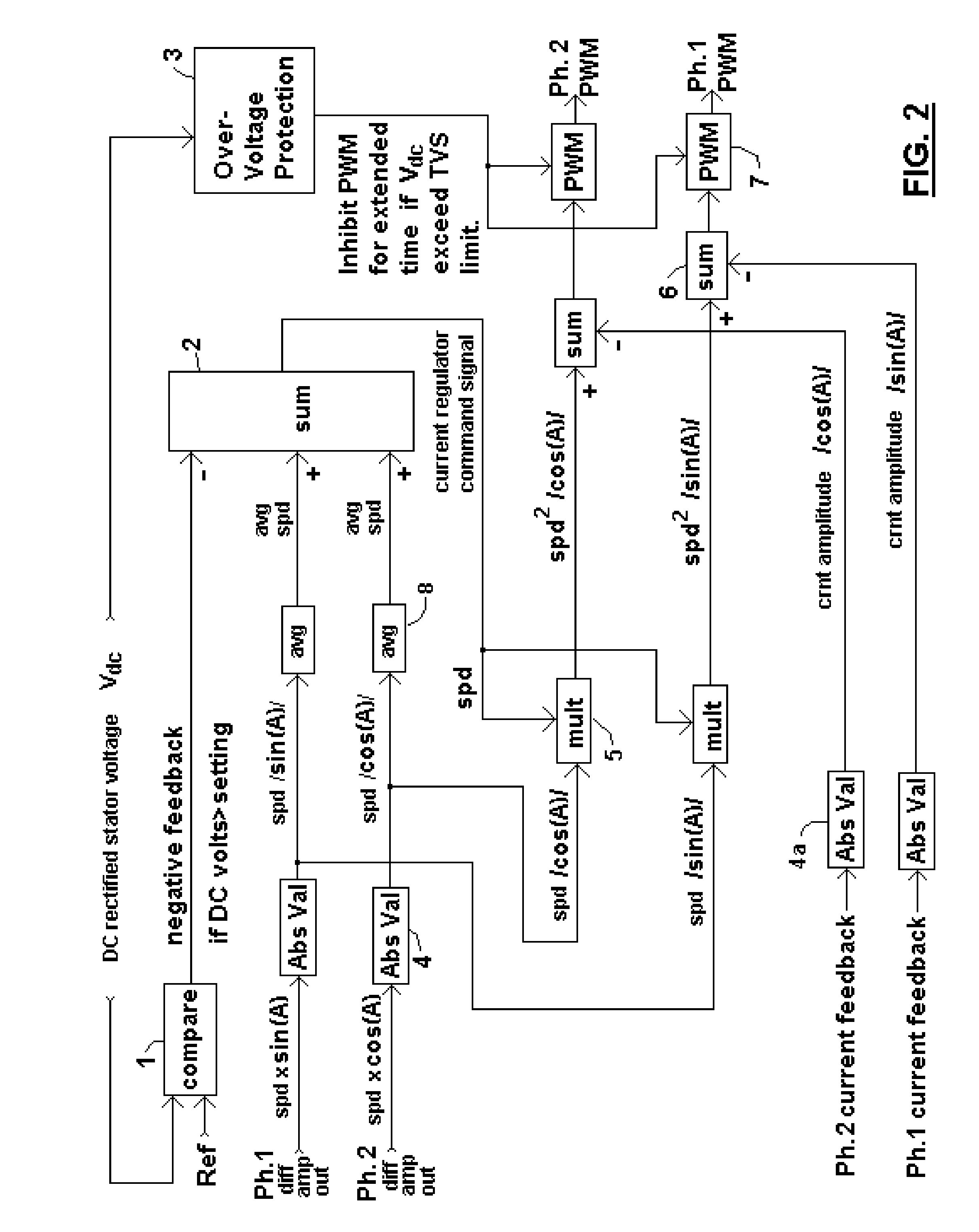
InactiveUS20120256422A1High energy yieldImprove global economyWindingsMagnetic circuitPower qualityDc current
A brushless generator with permanent-magnet multi-pole rotor disks and stator winding disks in their axial magnetic field includes integral electronics to efficiently generate regulated DC current and voltage from mechanical input power over a broad speed range. All power for the electronics is provided by rectifier diodes from its stator windings. Differential amplifiers provide stator voltage feedback signals. Its power rating is scalable, depending on the number of its disks. Having no iron cores and no gears, it incurs no cogging torque, and no gear friction. Integral power control electronics includes high-frequency pulse-width-modulated boost regulation, which provides regulated current at requisite voltage over its broad speed range. A main wind-powered embodiment to produce DC power for a constant voltage DC load over a broad speed range includes signal processing so output power varies according to the third power of speed. Combined boost-regulation, zero cogging torque, and no gearing, enable a wide speed range, for better power quality and higher wind energy yields.
Owner:FRADELLA RICHARD B
Synchronous rectifier circuit
InactiveUS6151233AEfficient power electronics conversionAc-dc conversionReverse currentHemt circuits
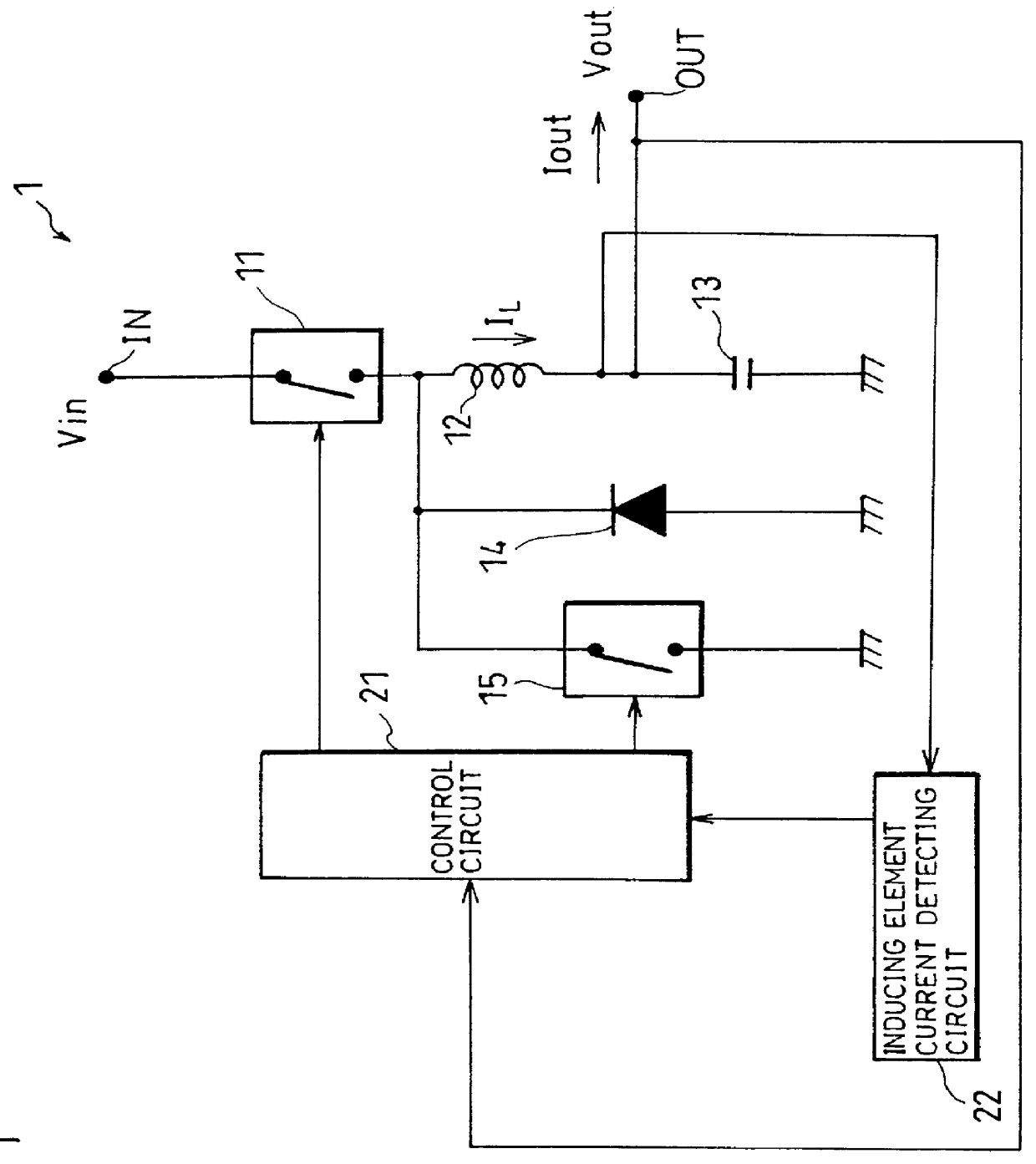
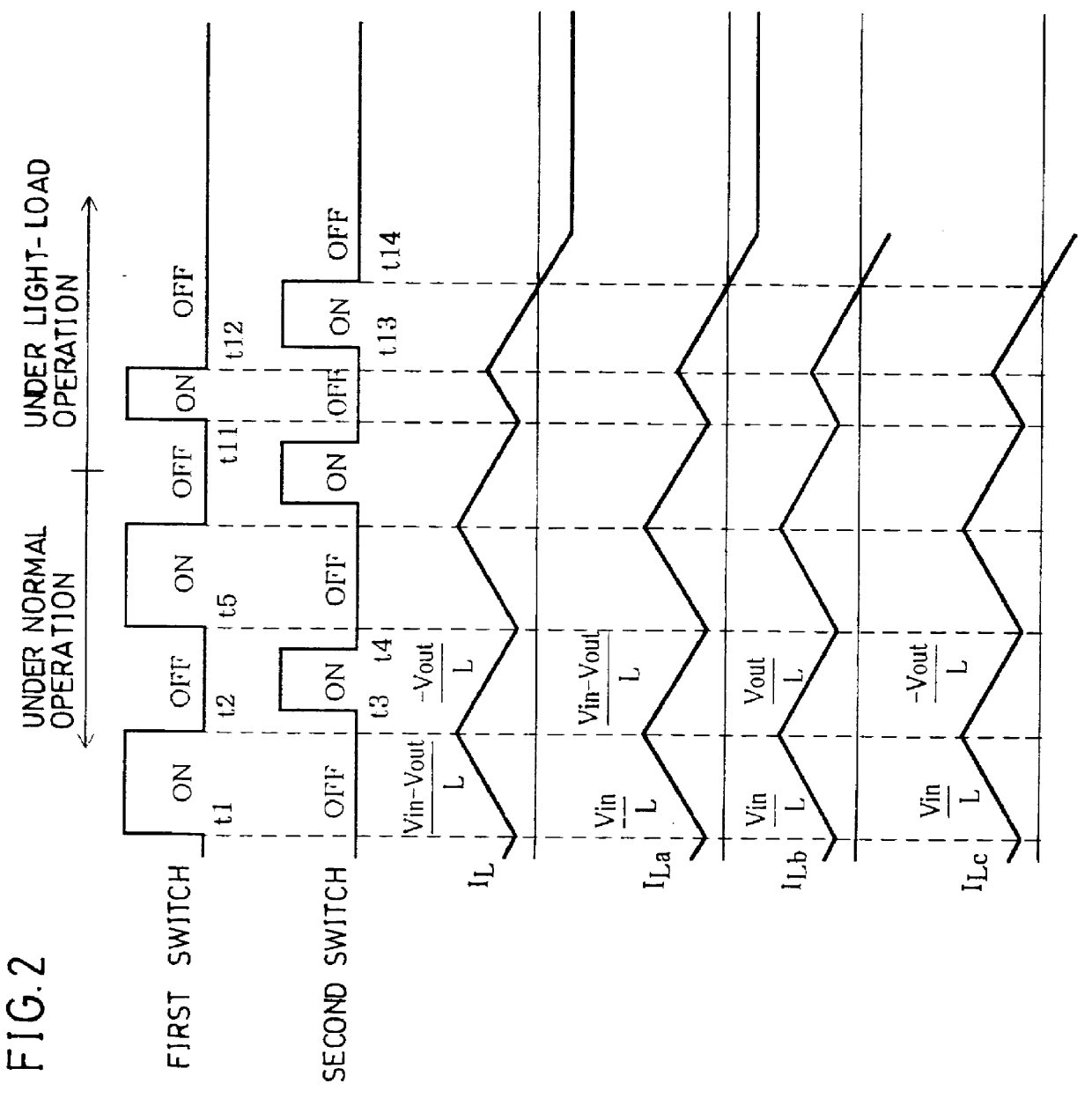
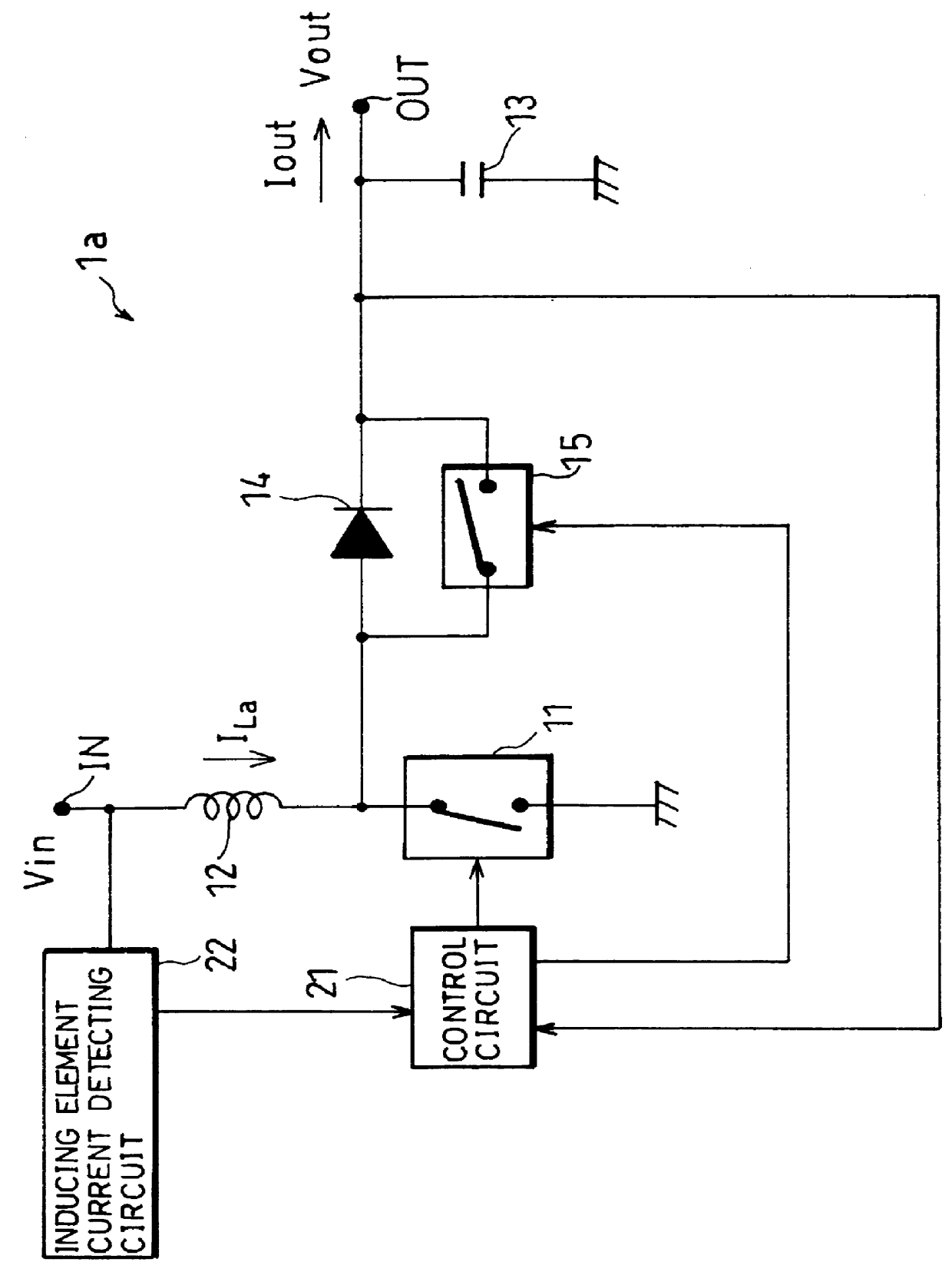
In a switching power circuit adopting the synchronous rectifying system, when a first switch is cut-off, current IL of an inducing element is maintained by a commutating diode, and the inducing element releases an energy which was stored in a conduction period of the first switch. A second switch connected in parallel to the commutating diode is conducted so as not to be overlapped with the conduction period of the first switch. In the conduction period of the second switch, the current IL does not flow through the commutating diode, and it is possible to prevent lowering of efficiency caused by forward voltage drop. An inducing element current detecting circuit monitors the current IL and, when the current IL is reversing its direction, instructs a control circuit to cut-off the second switch. As a result, no reverse current flows through the inducing element even when the load is small, thus realizing a switching power circuit always having high efficiency.
Owner:SHARP KK
Transient voltage suppression device
InactiveUS6867436B1Lower clamping voltageOvercome disadvantagesThyristorSolid-state devicesRectifier diodesHigh resistivity
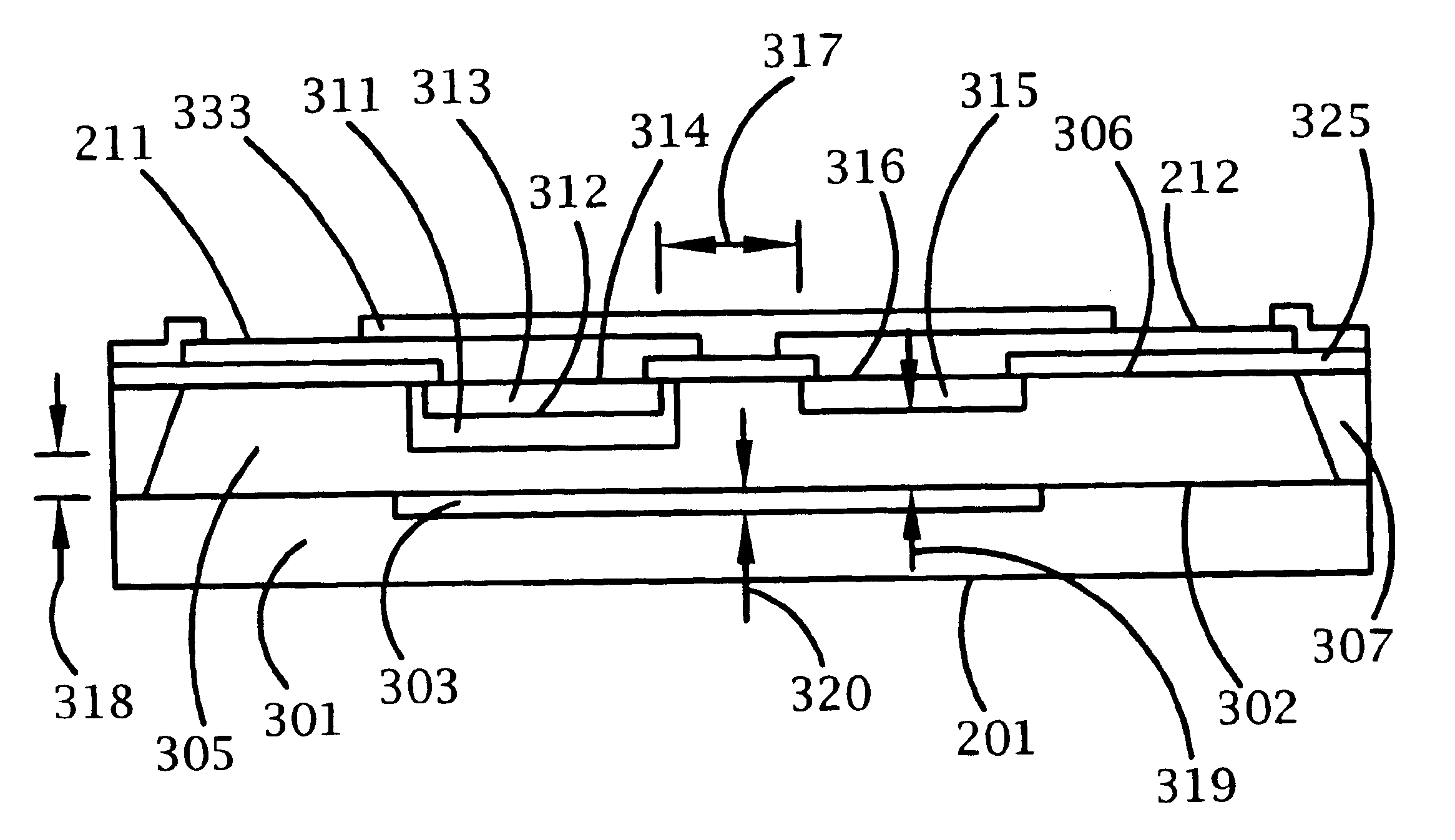
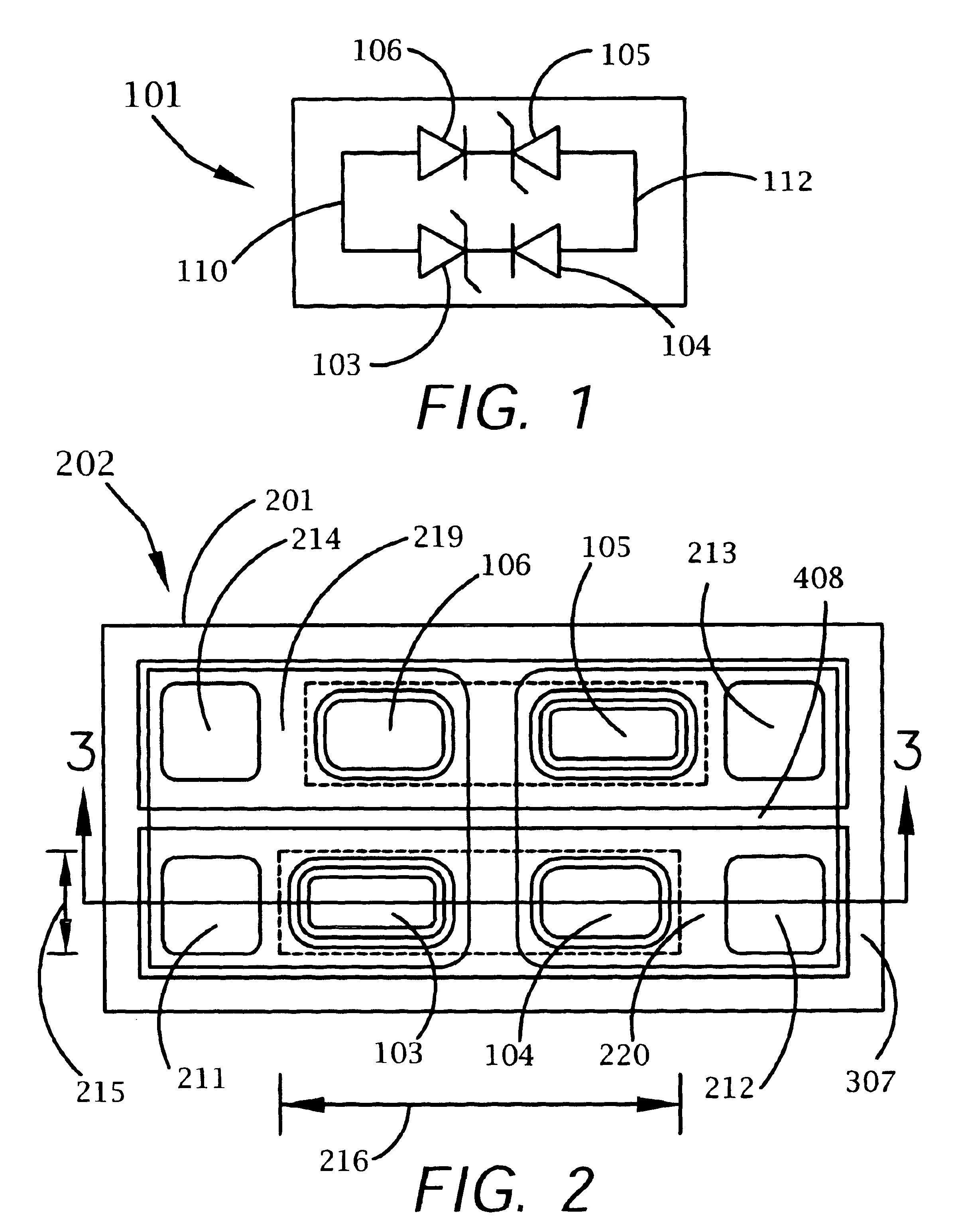
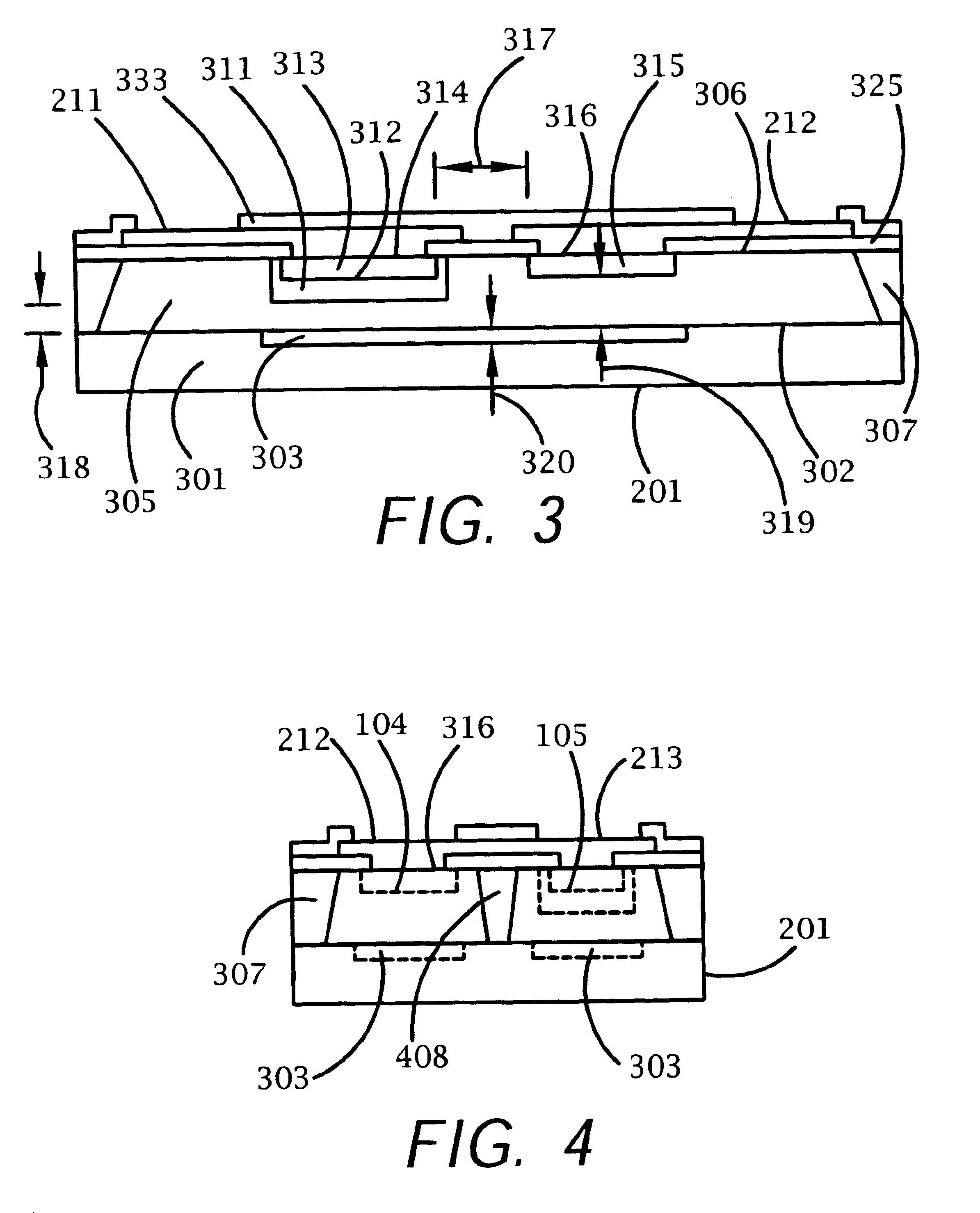
A bi-directional transient voltage suppression (“TVS”) device (101) includes a semiconductor die (201) that has a first avalanche diode (103) in series with a first rectifier diode (104) connected cathode to cathode, electrically coupled in an anti-parallel configuration with a second avalanche diode (105) in series with a second rectifier diode (106) also connected cathode to cathode. All the diodes of the TVS device are on a single semiconductor substrate (301). The die has a low resistivity buried diffused layer (303) having a first conductivity type disposed between a semiconductor substrate (301) having the opposite conductivity type and a high resistivity epitaxial layer (305) having the first conductivity type. The buried diffused layer shunts most of a transient current away from a portion of the epitaxial layer between the first avalanche diode and the first rectifier diode, thereby reducing the clamping voltage relative to the breakdown voltage. The TVS device is packaged as a flip chip (202) that has four solder bump pads (211-214). The abstract is submitted with the understanding that it will not be used to interpret or limit the scope or meaning of the claims pursuant to 37 C.F.R. §1.72(b).
Owner:PROTEK DEVICES
Switching power supply circuit
InactiveUS20060192774A1Improve conversion efficiencyImprove power factorAc-dc conversion without reversalEfficient power electronics conversionFull wavePower factor
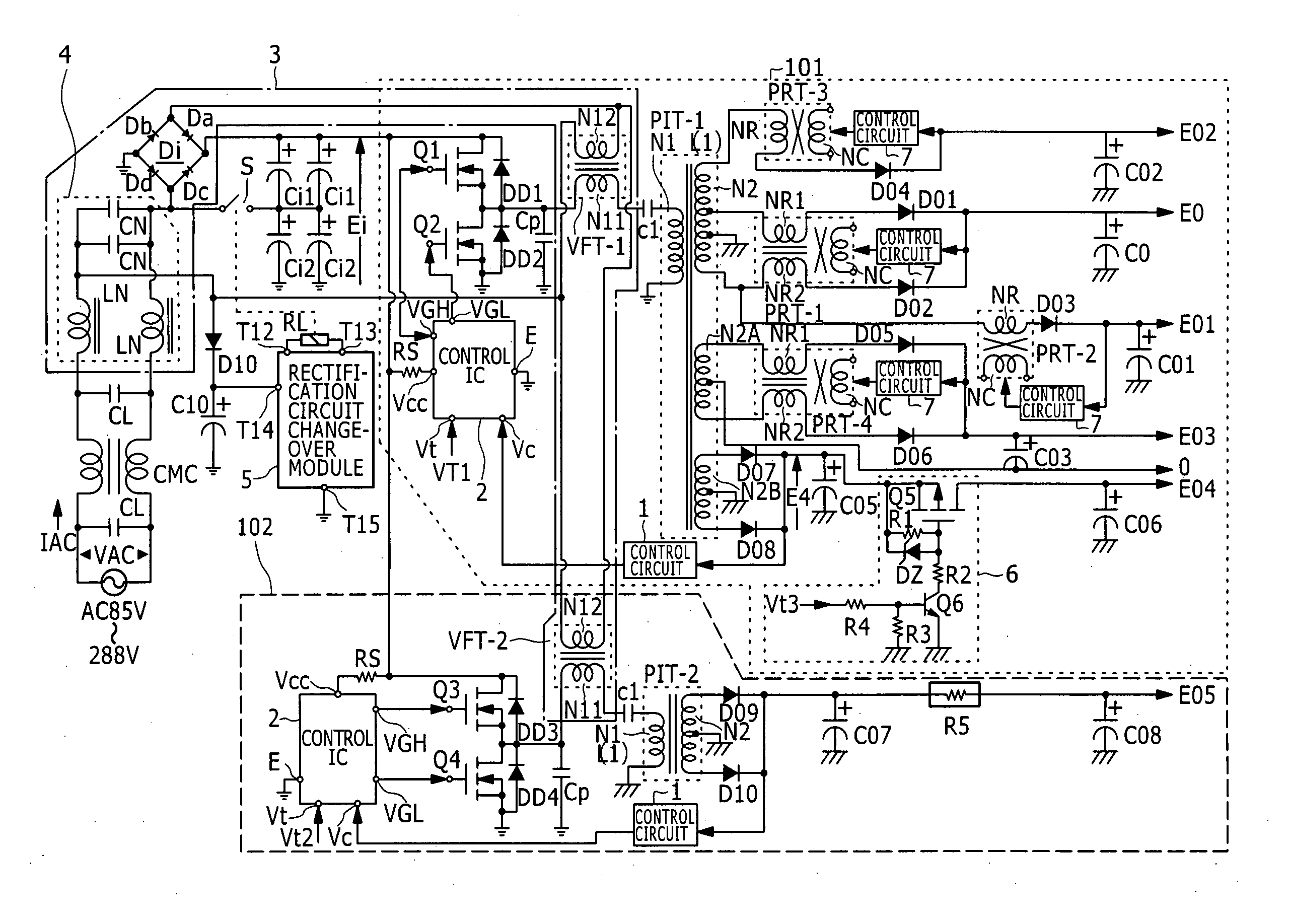
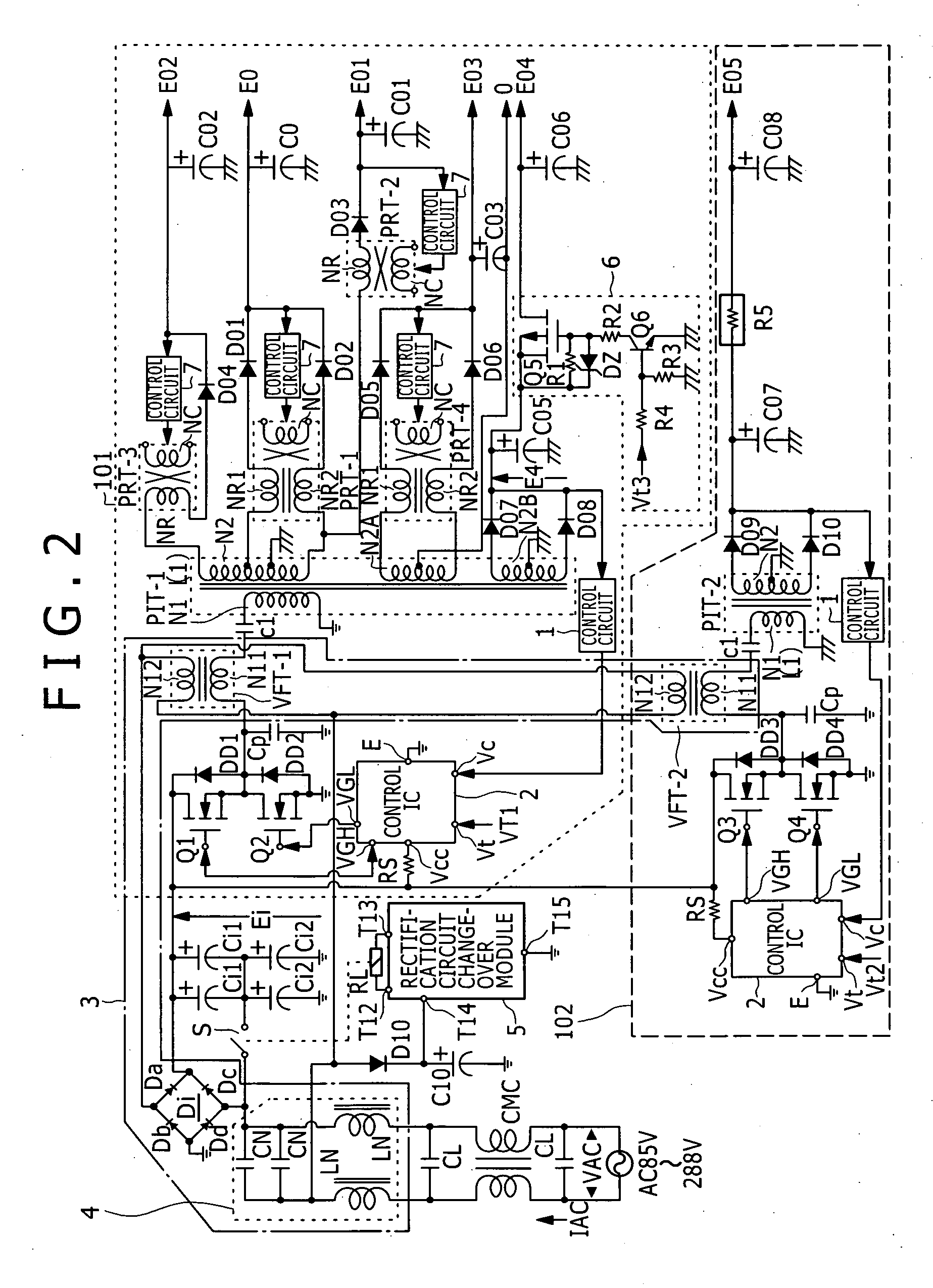
A switching power supply circuit ready for a wide range and including a power factor improving function is disclosed which can achieve reduction in cost, reduction in size and weight of the circuit and reduction of the power loss by reducing the number of converter sections with respect to the number of stages in a starting order of secondary side DC output voltages. A plurality of switching converters (101), (102) are of the composite resonance type wherein a partial resonance voltage circuit is combined with a switching converter of the current resonance type according to a half-bridge connection system. Changeover control is performed such that a rectification circuit serves as a voltage doubler rectification circuit at an AC voltage equal to or lower than 150 V, but serves as a full-wave rectification circuit at another AC voltage equal to or higher than 150 V. Power factor improvement is implemented by feeding back the voltages of outputs of the converters to a rectification current path by a power factor improving transformer (VFT) and interrupting the rectification current by means of a rectification diode to expand the
Owner:SONY CORP
Gate-tunable p-n heterojunction diode, and fabrication method and application of same
ActiveUS20150034907A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesCarbon nanotubeRectifier diodes
One aspect of the invention relates to a gate-tunable p-n heterojunction diode including a vertical stacked heterojunction of two ultrathin semiconductors. In one embodiment, single-layer molybdenum disulphide of an n-type semiconductor are stacked below semiconducting single-walled carbon nanotubes of a p-type semiconductor with each of them connected to a gold electrodes to form a p-n heterojunction. The electrical properties of the p-n heterojunction can be modulated by a gate voltage applied to a gate electrode and range from an insulator to a linear-response resistor to a highly rectifying diode. The gate tunability of the p-n heterojunction also allows spectral control over the photoresponse.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN UNIV
Forward-flyback converter with active-clamp circuit
ActiveUS8009448B2Improve conversion efficiencyAdditional drawbackEfficient power electronics conversionEmergency protective circuit arrangementsEngineeringHeavy load
Owner:DELTA ELECTRONICS INC
Pulsed power generator
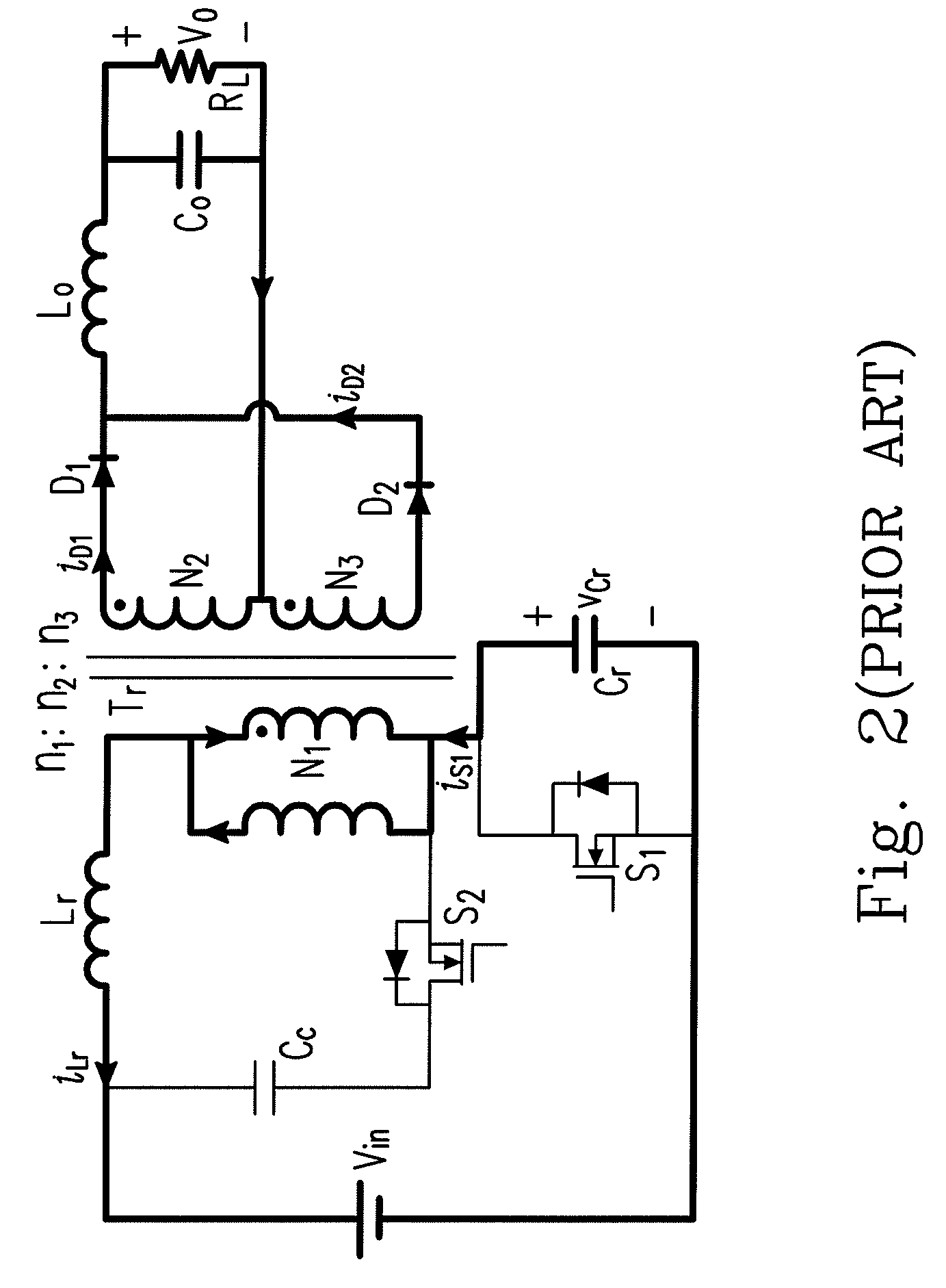
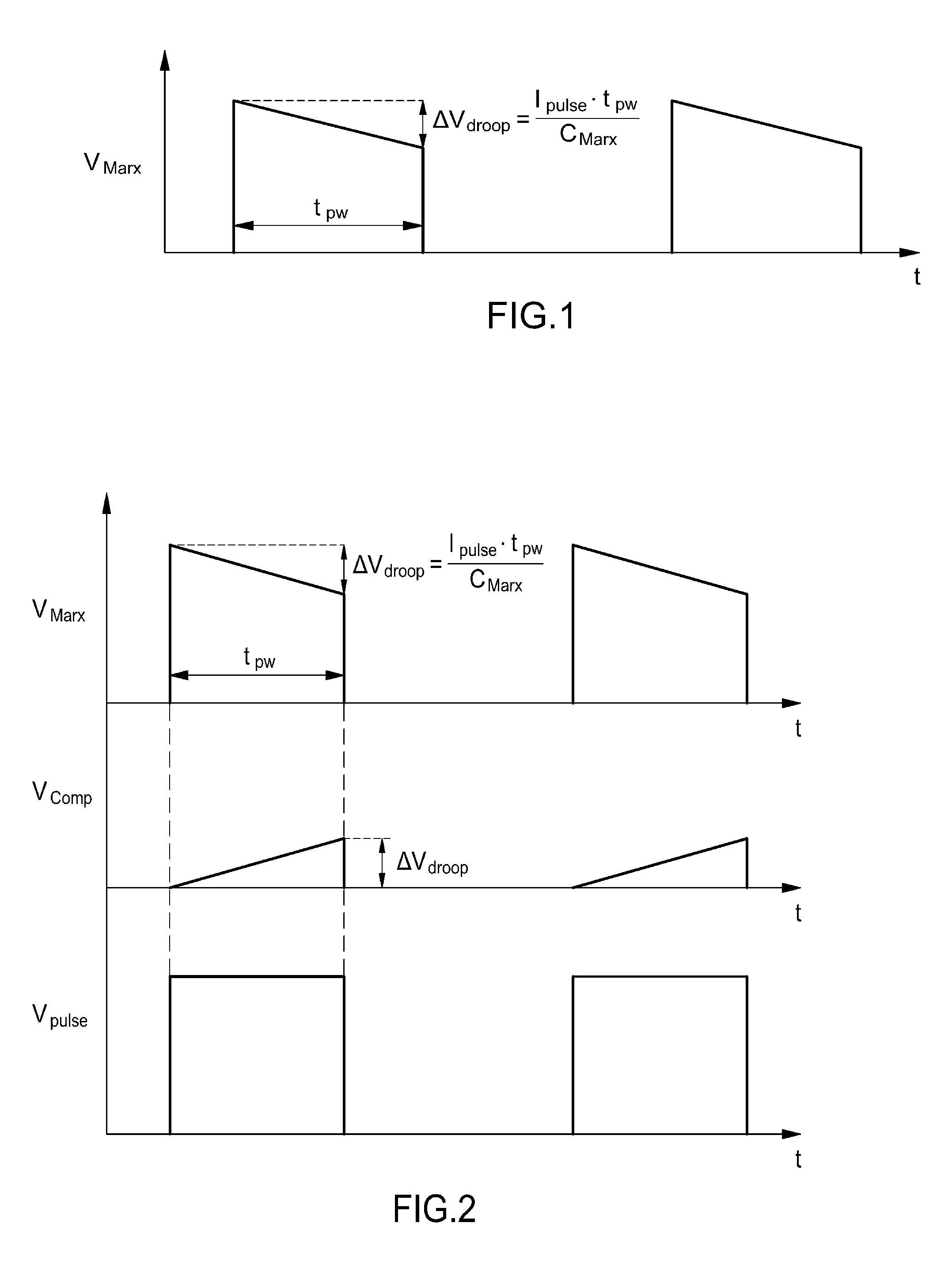
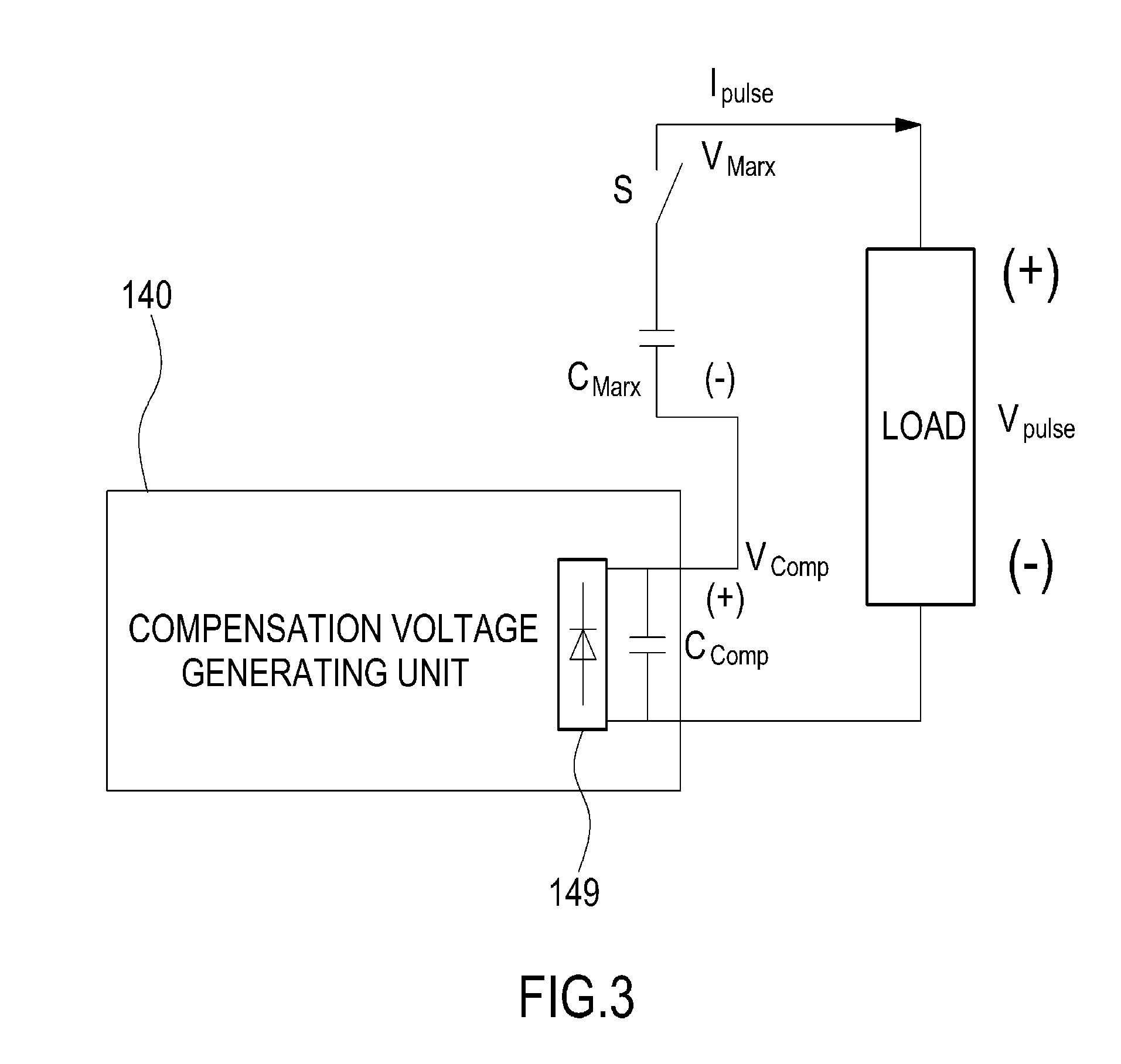
ActiveUS20140146571A1Minimizing voltage droopSimple circuit configurationAc-dc conversion without reversalApparatus with intermediate ac conversionPower inverterControl signal
An active voltage drop control-type pulse power generator includes power stages, a power inverter, a power loop, a control inverter, a control loop, and a compensation unit. The power stages include power cells connected in series. Each power cell includes a switch and a capacitor connected in series, a driver for driving the switch, a bypass diode connected to both ends of the switch, and a rectifying diode connected to both ends of the capacitor. The power inverter charges the capacitor via the power loop and the rectifying diode inside each power cell. The control inverter provides a control signal for the switch via the control loop and the driver inside each power cell. The compensation unit is connected to one of the power cells and generates a compensation voltage for compensating for a voltage drop at a load according to a voltage detected in real-time from the power cell.
Owner:KOREA ELECTROTECH RES INST
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com