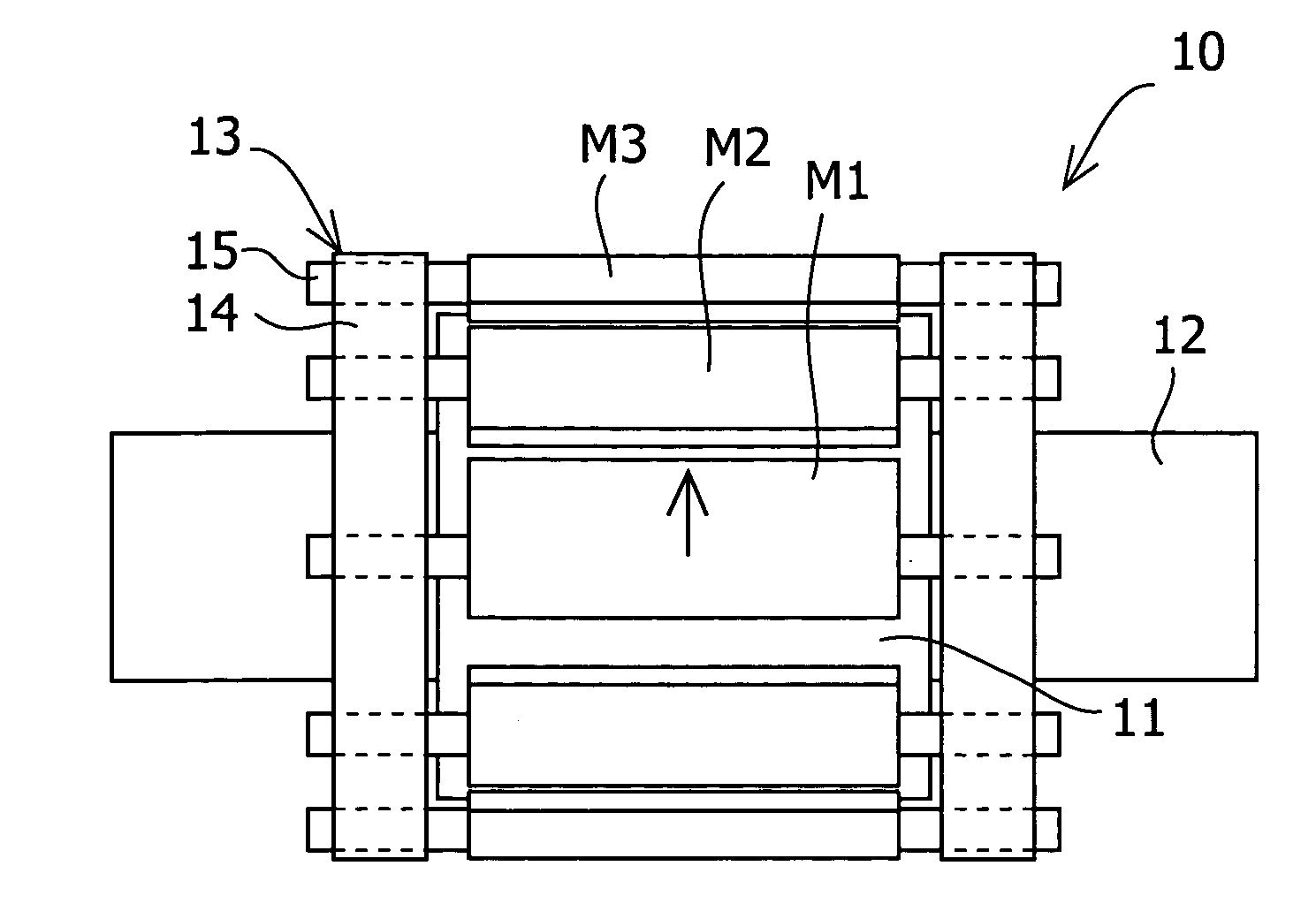
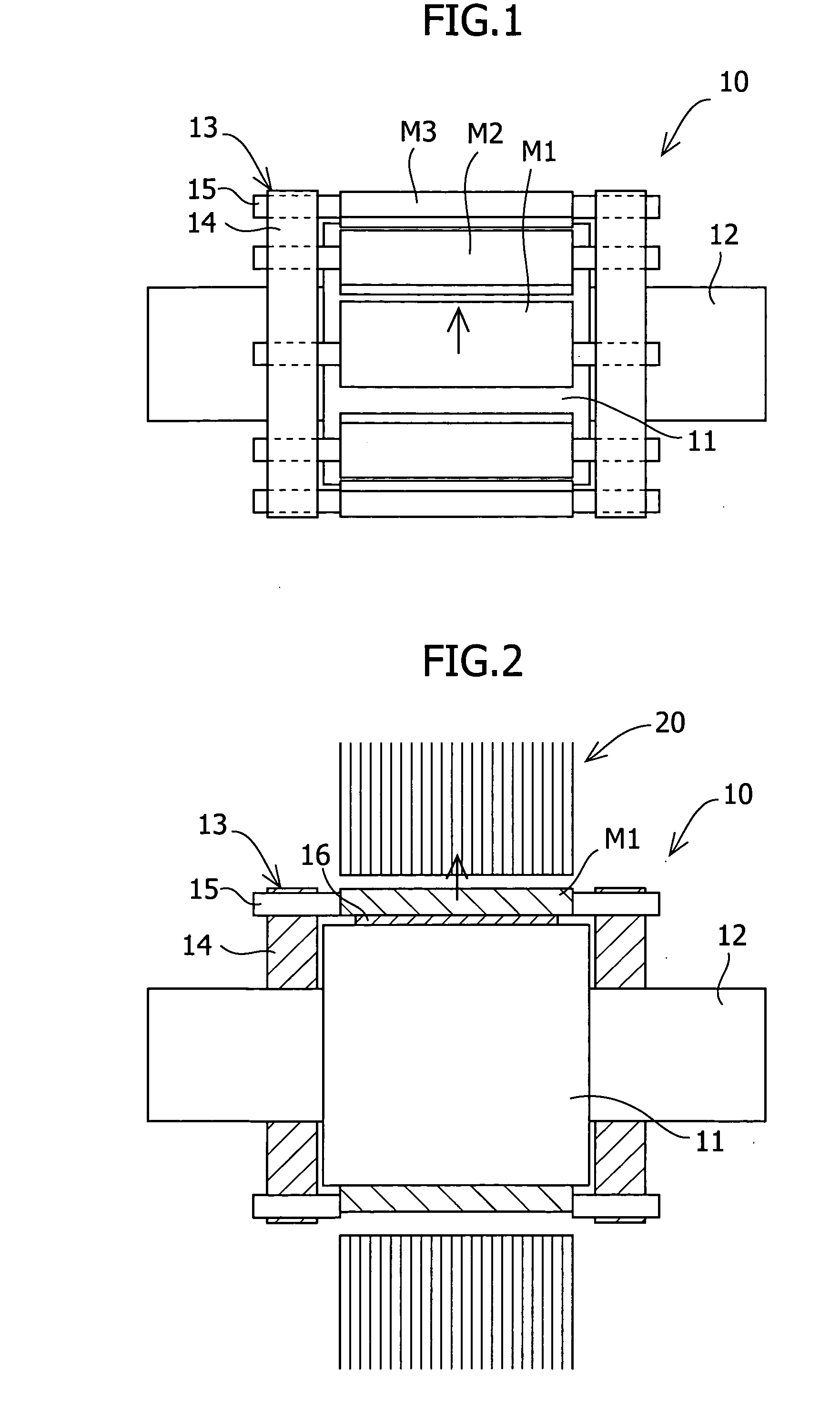
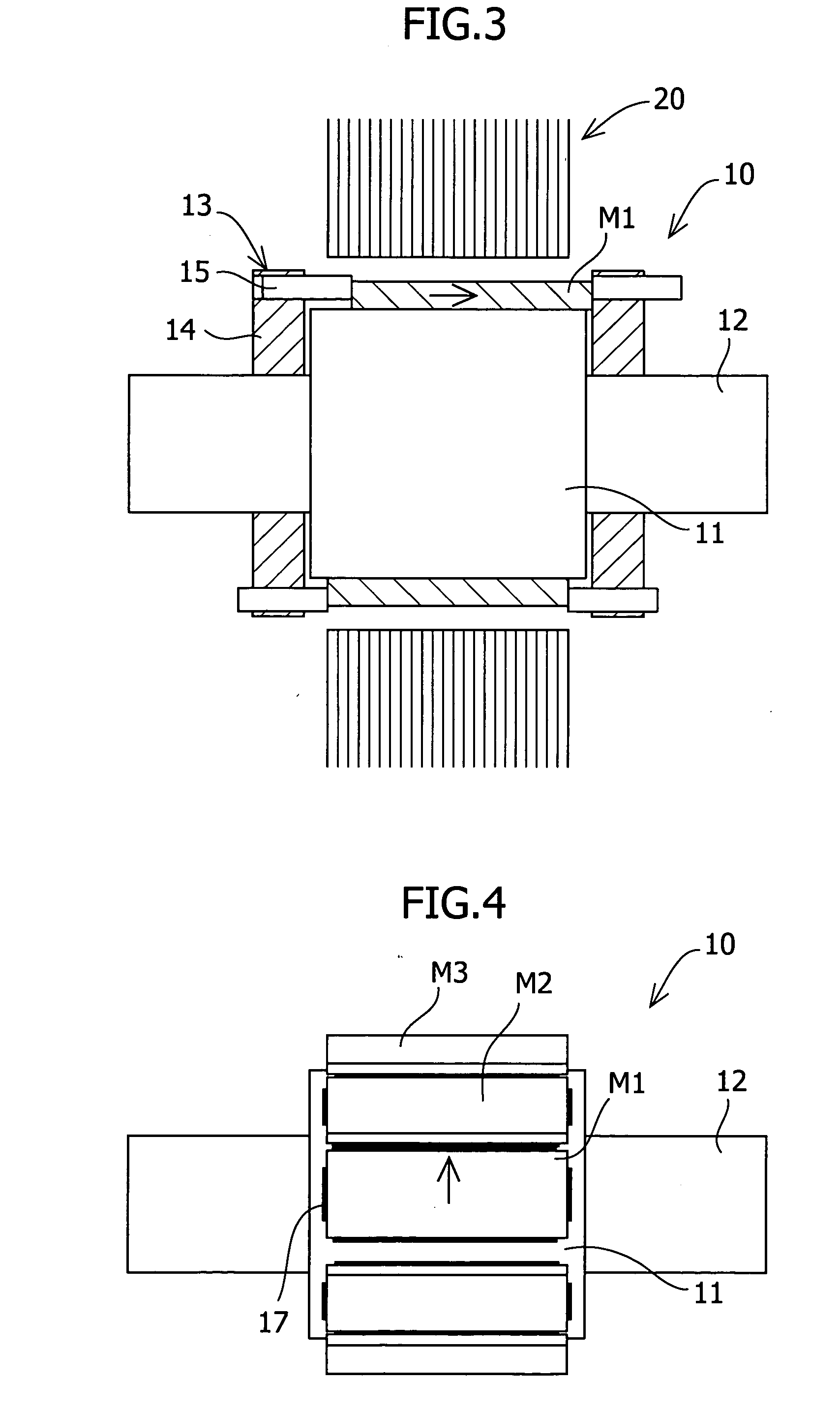
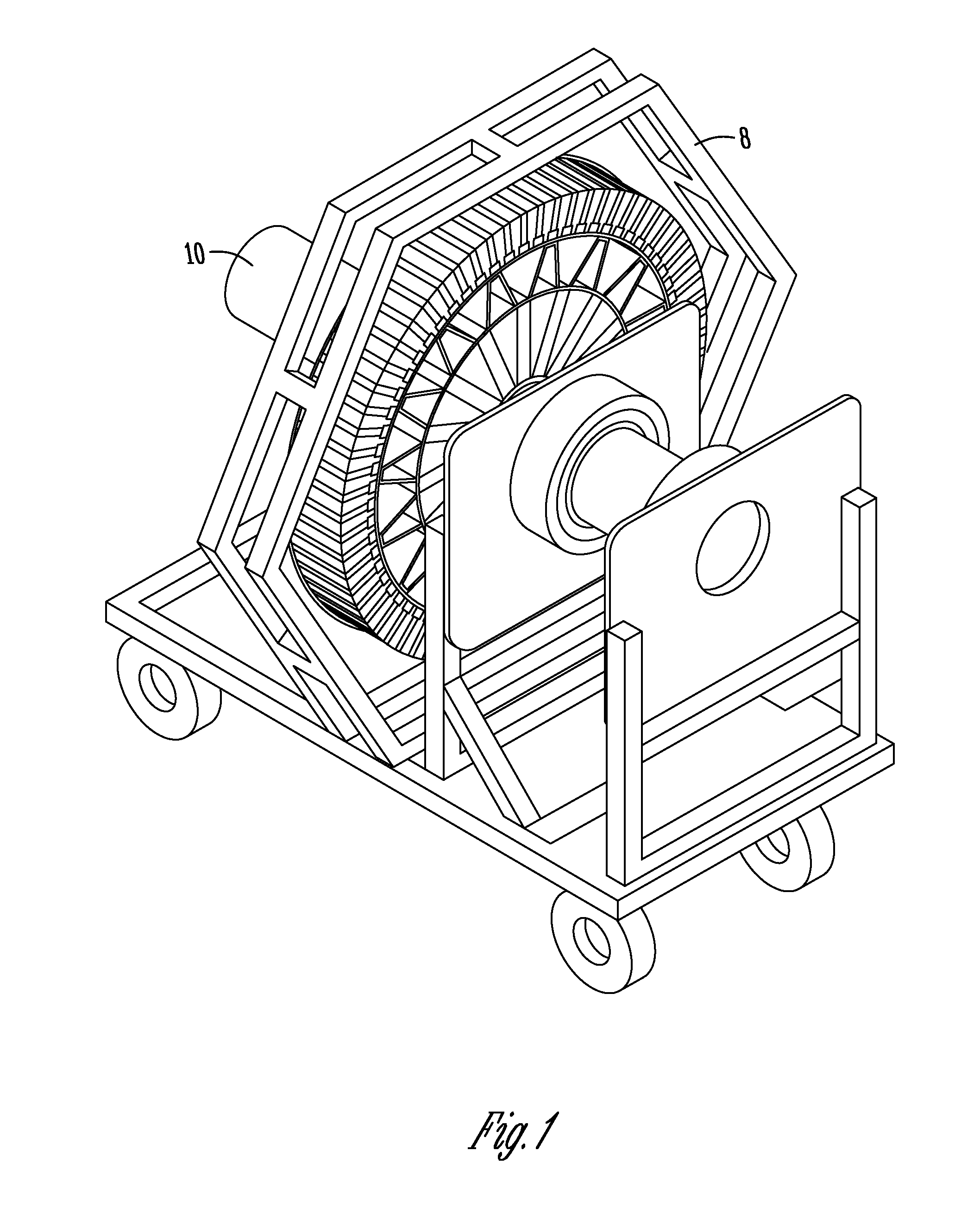
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1012 results about "Cogging torque" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
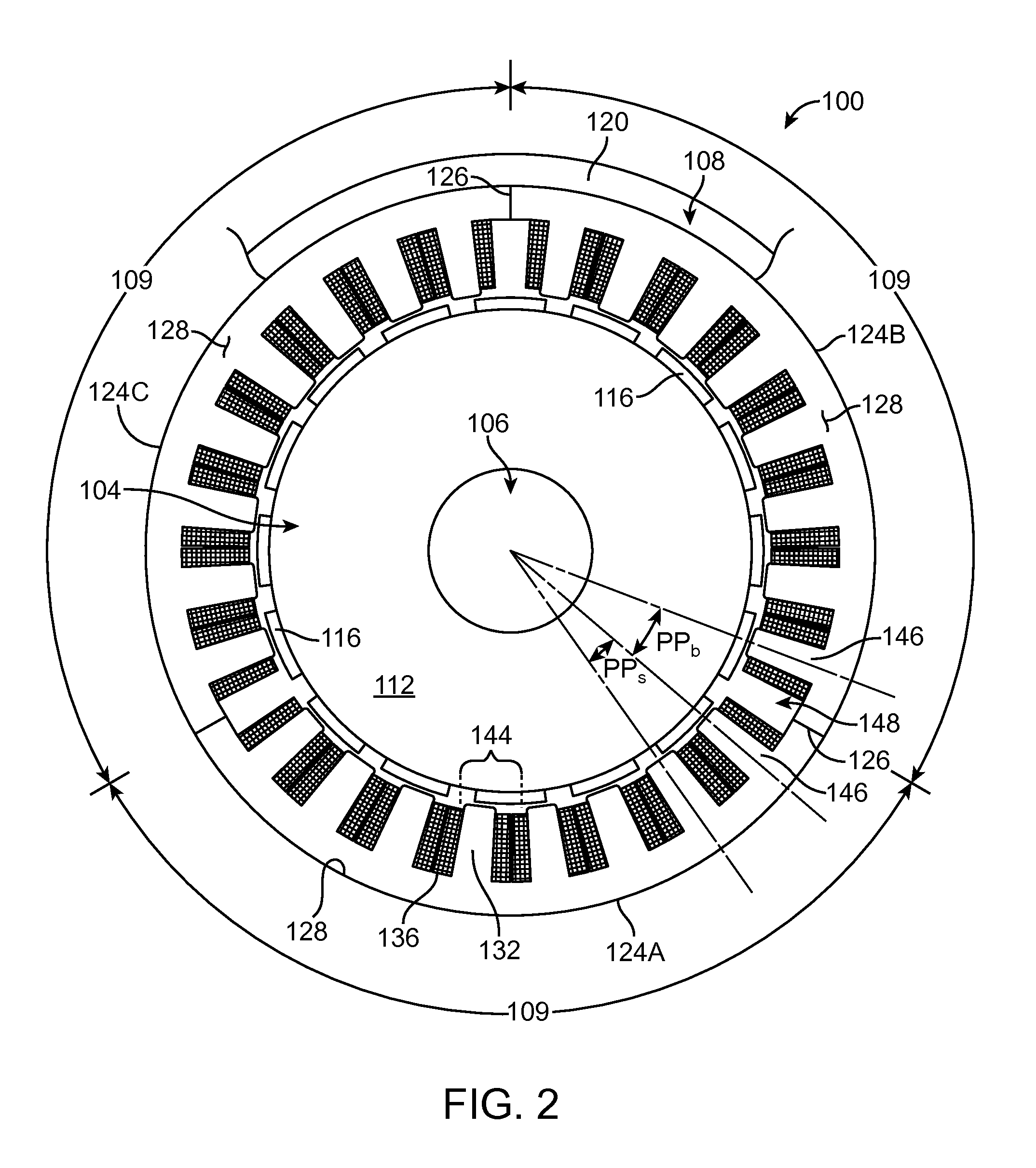
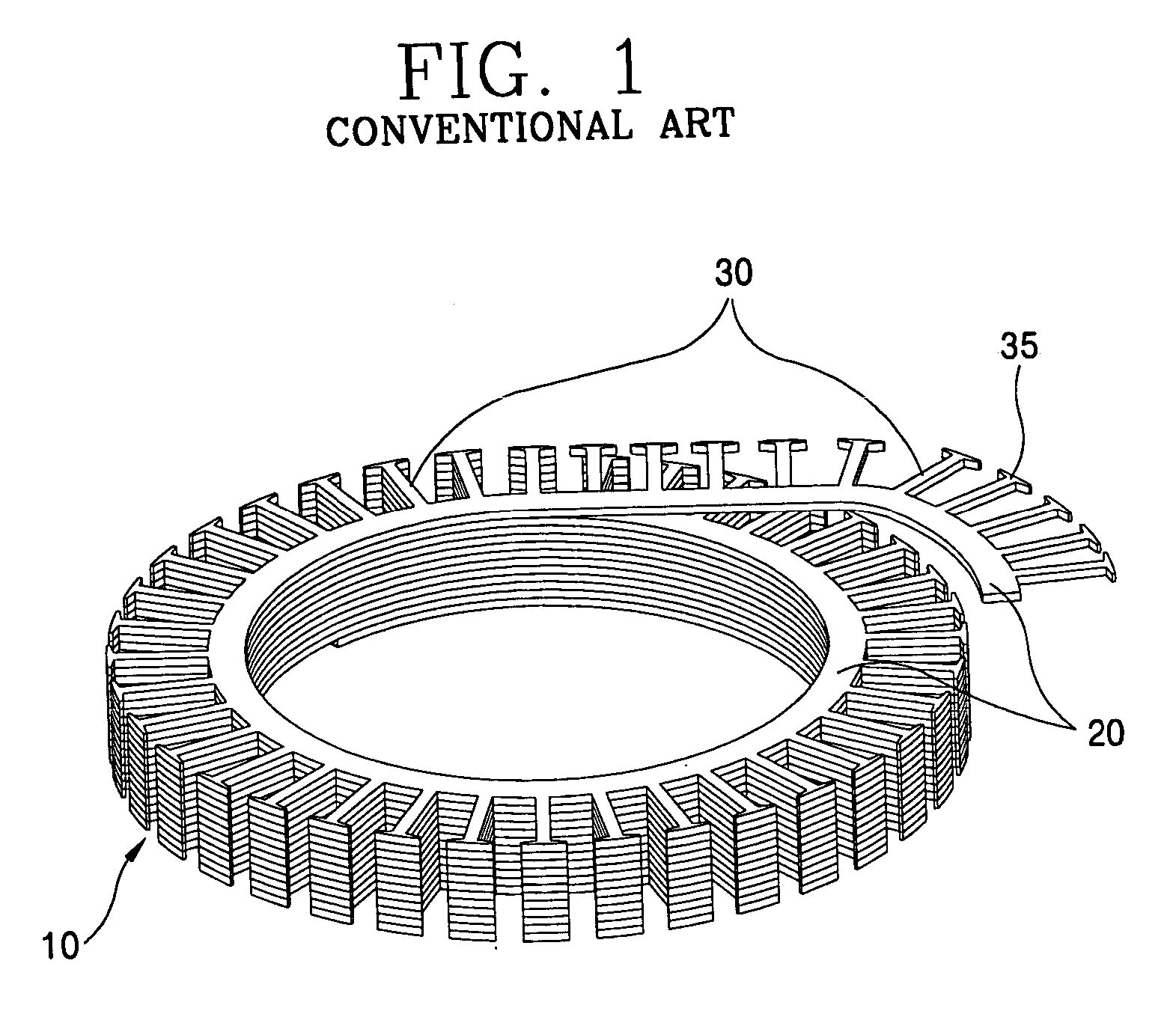
Cogging torque of electrical motors is the torque due to the interaction between the permanent magnets of the rotor and the stator slots of a Permanent Magnet (PM) machine. It is also known as detent or 'no-current' torque. This torque is position dependent and its periodicity per revolution depends on the number of magnetic poles and the number of teeth on the stator. Cogging torque is an undesirable component for the operation of such a motor. It is especially prominent at lower speeds, with the symptom of jerkiness. Cogging torque results in torque as well as speed ripple; however, at high speed the motor moment of inertia filters out the effect of cogging torque.
Permanent magnet electric rotating machine and electromotive vehicle using permanent magnet electric rotating machine
InactiveUS6208054B1Reduce pulsationMagnetic circuit rotating partsSynchronous machines with stationary armatures and rotating magnetsMagnetic polesMagnetic flux density distribution
A magnetic gap is provided between a permanent magnet of a rotor and an auxiliary magnetic pole portion which is arranged adjacent to the permanent magnet in a peripheral direction. A gradual change in a magnetic flux density distribution of a surface of the rotor is obtained and a cogging torque and a torque pulsation are restrained. By obtaining a reluctance torque according to the auxiliary magnetic pole, a permanent magnet electric rotating machine in which the cogging torque and the torque pulsation are restrained can be obtained and further an electromotive vehicle having the permanent magnet electric rotating machine can be provided.
Owner:HITACHI LTD +1
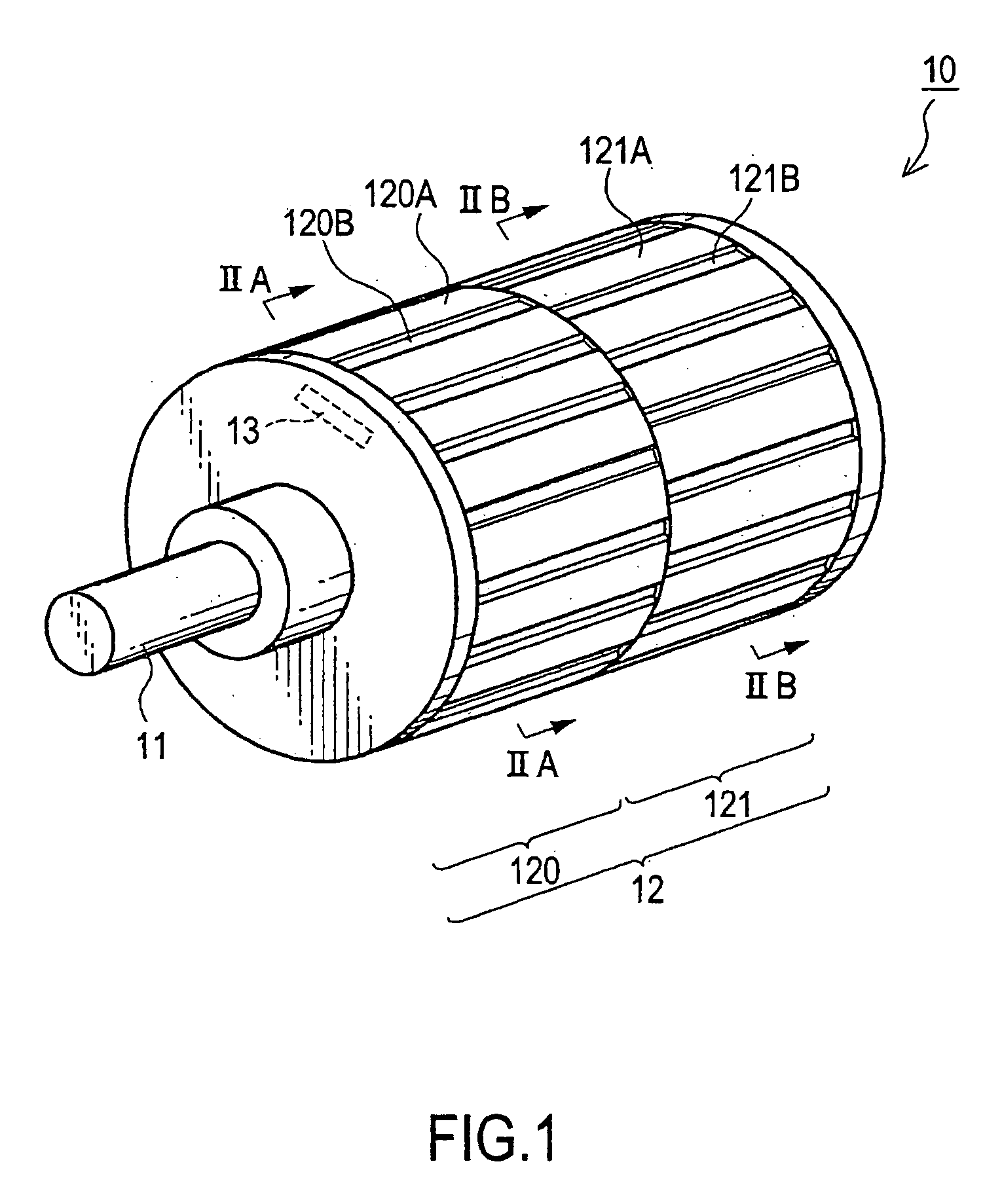
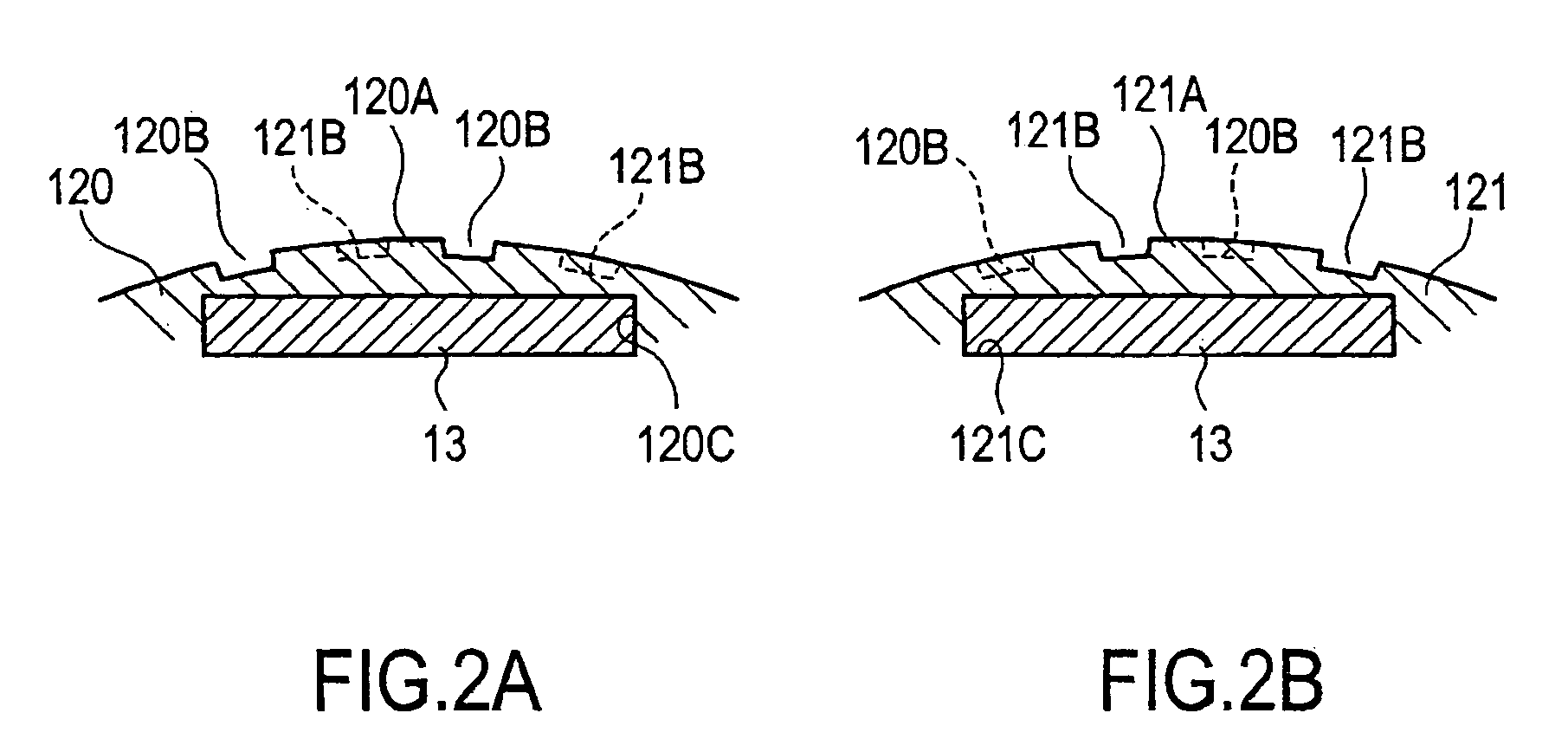
Rotor for rotary electric machine
InactiveUS20050121990A1Reduce output torqueComplicated to manufactureMagnetic circuit rotating partsSupports/enclosures/casingsElectric machineEngineering
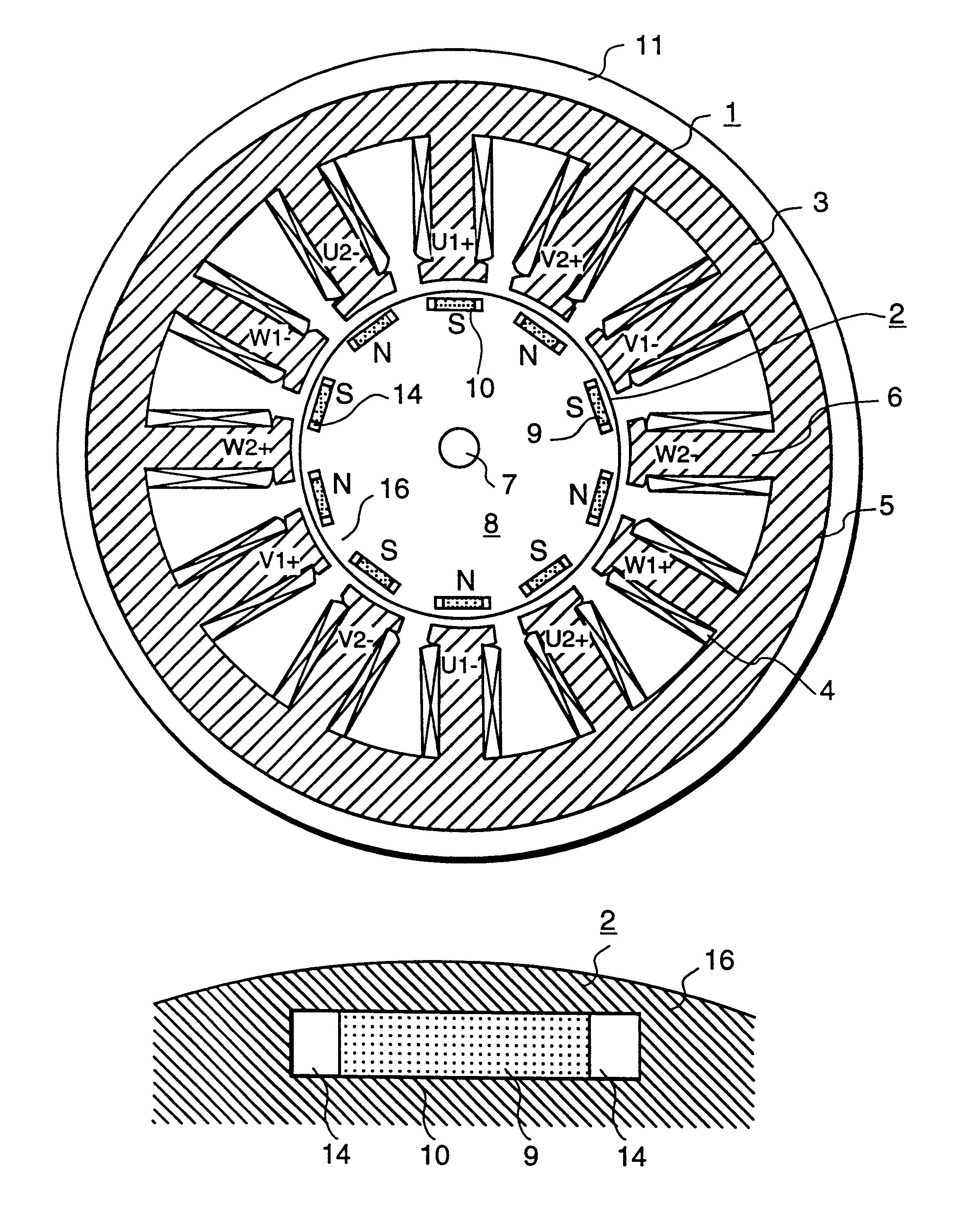
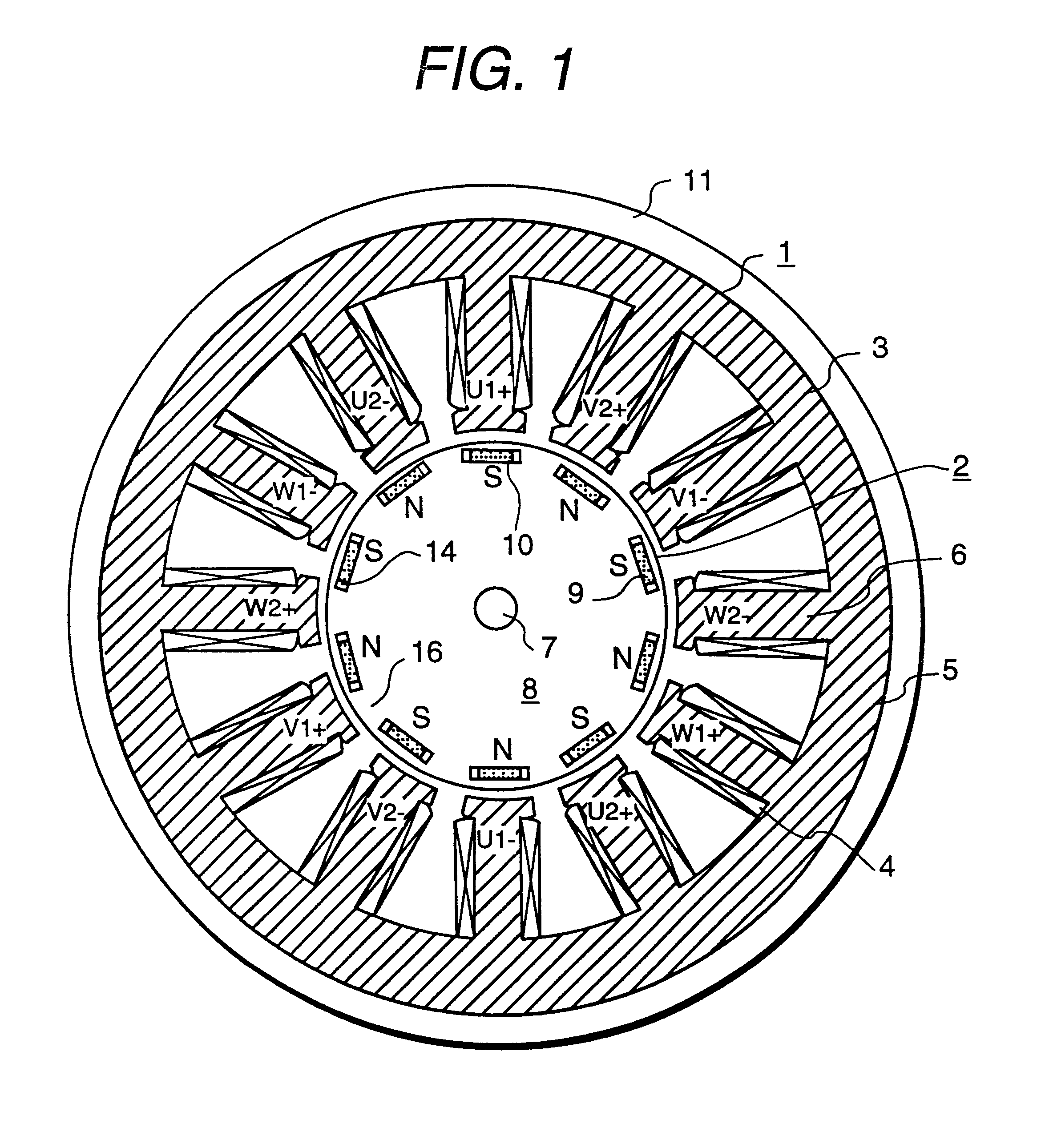
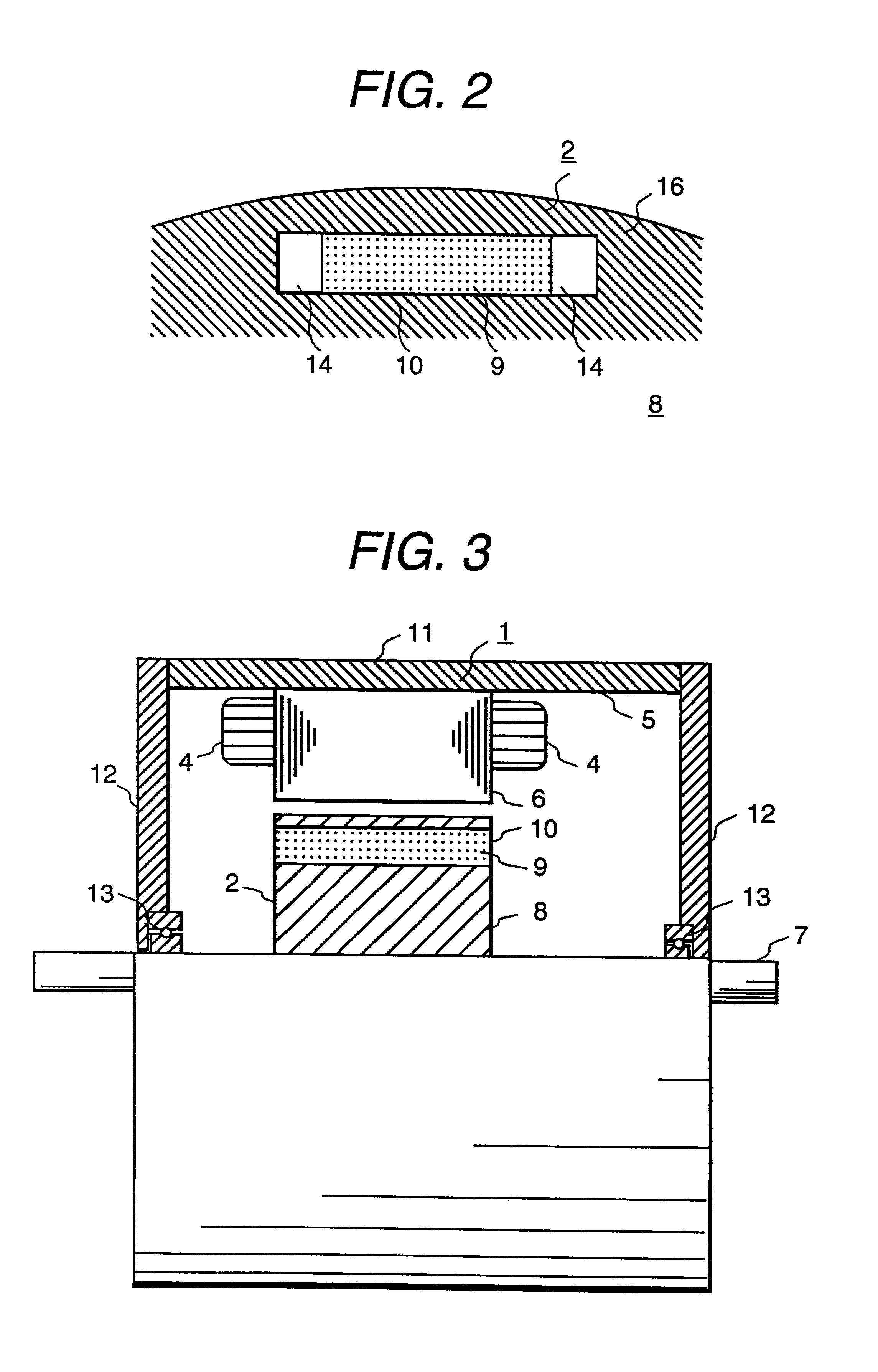
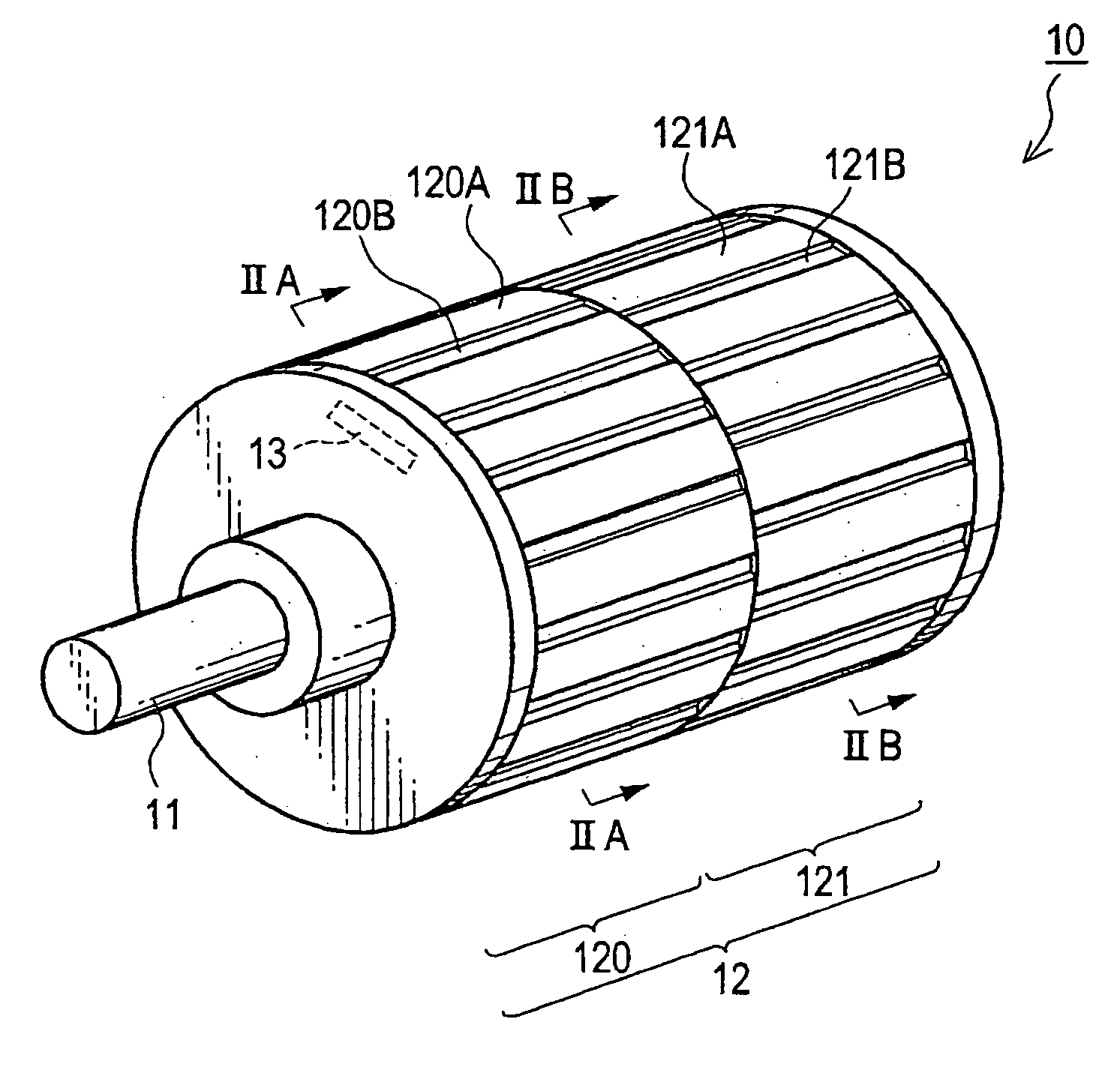
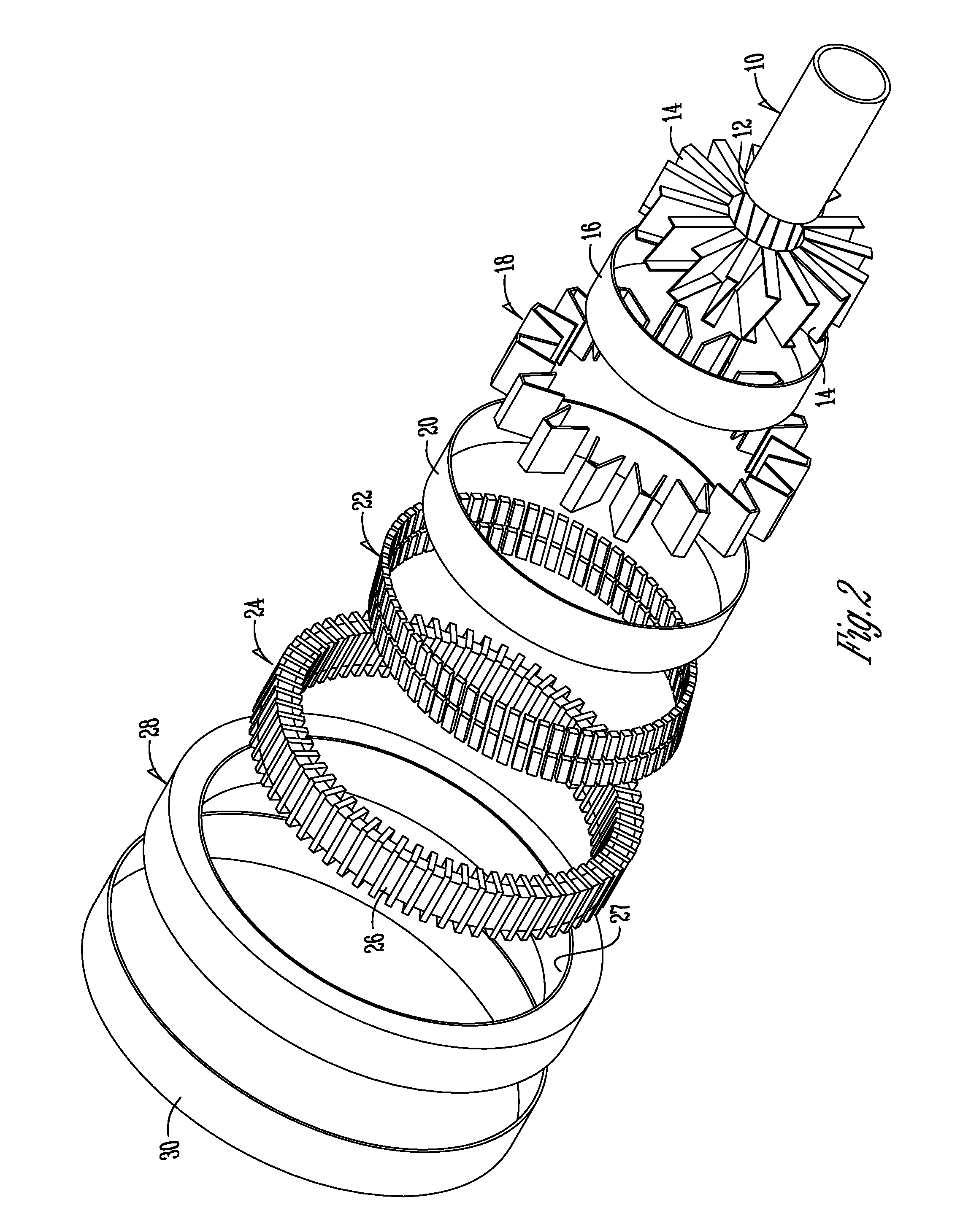
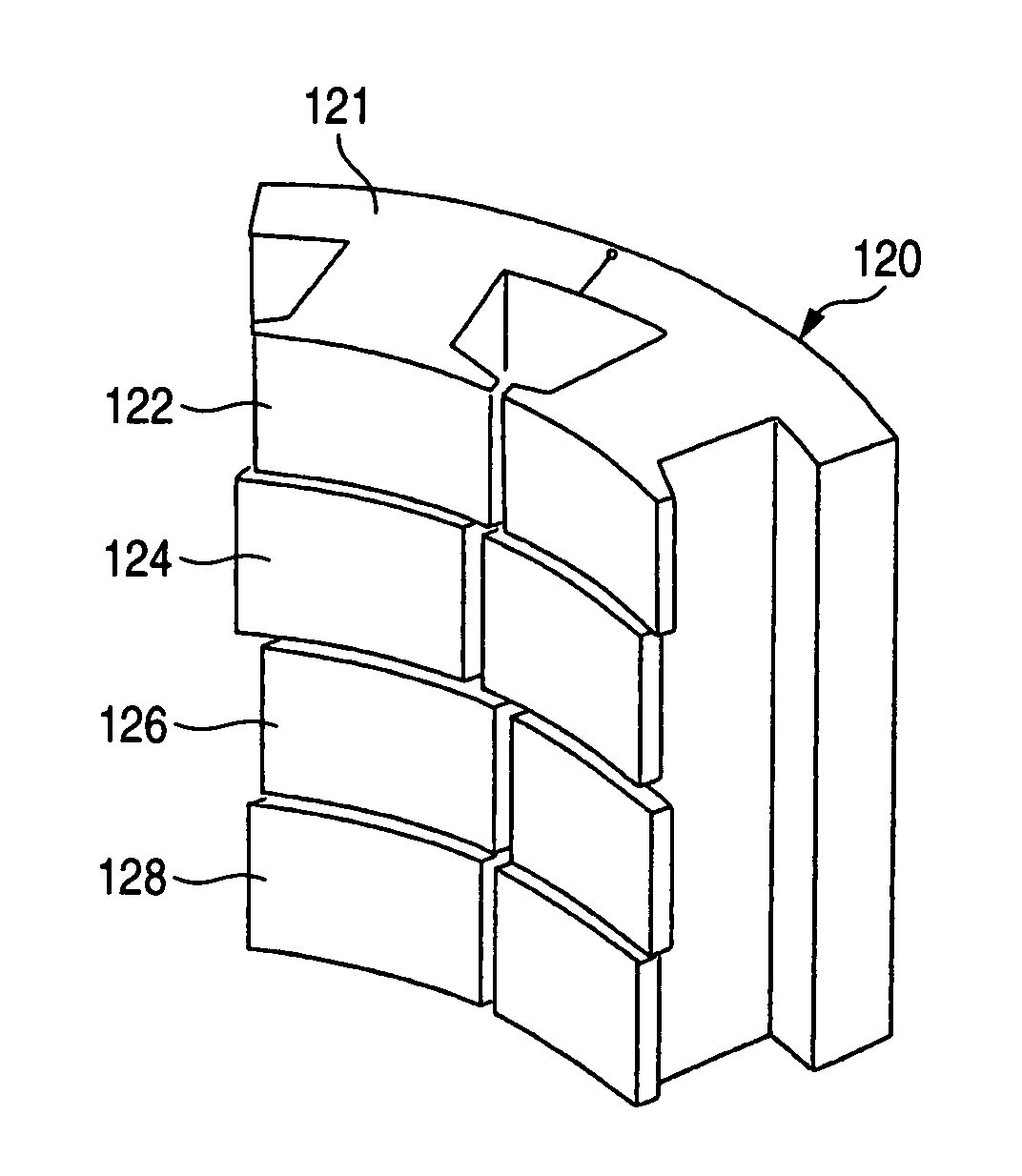
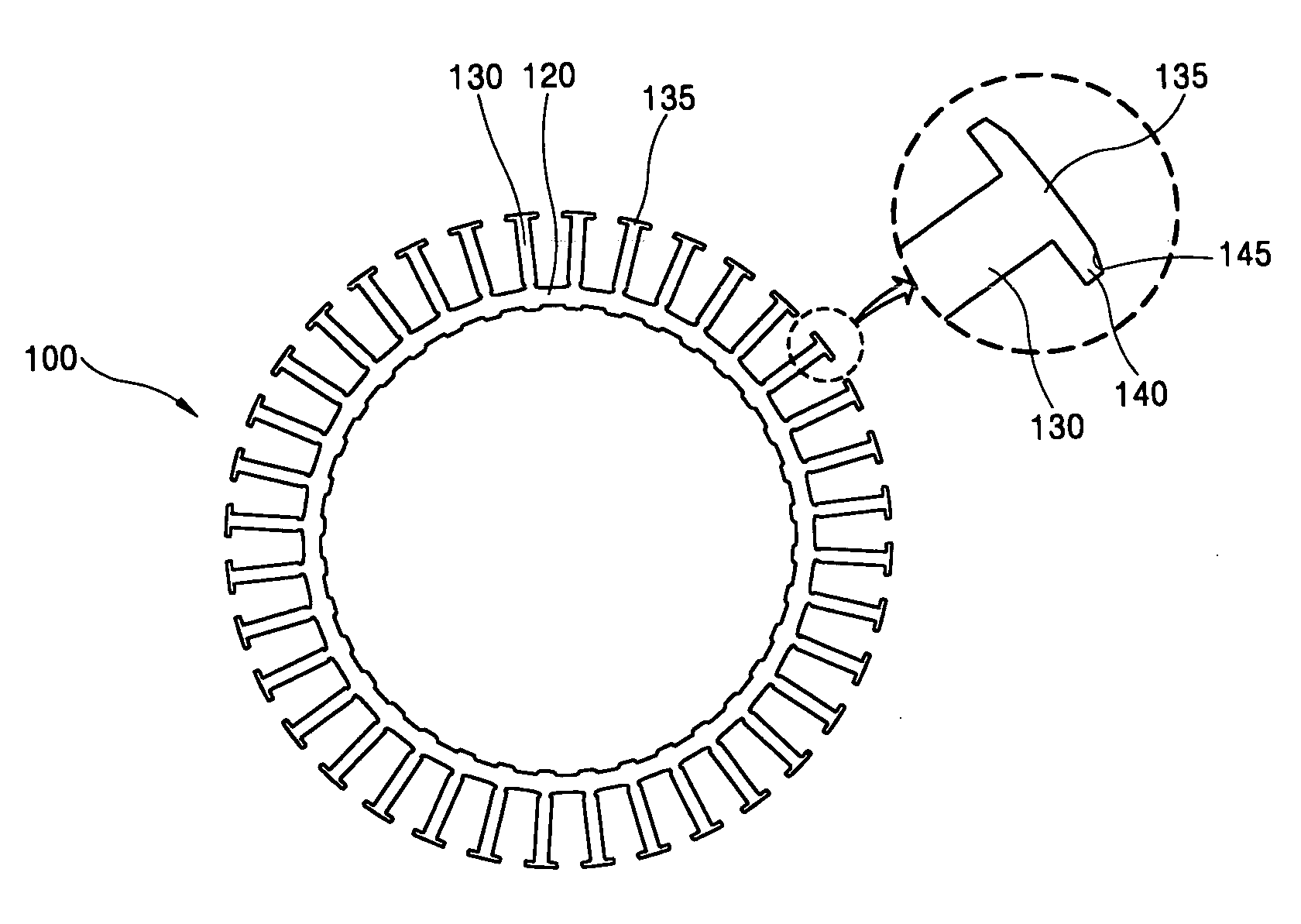
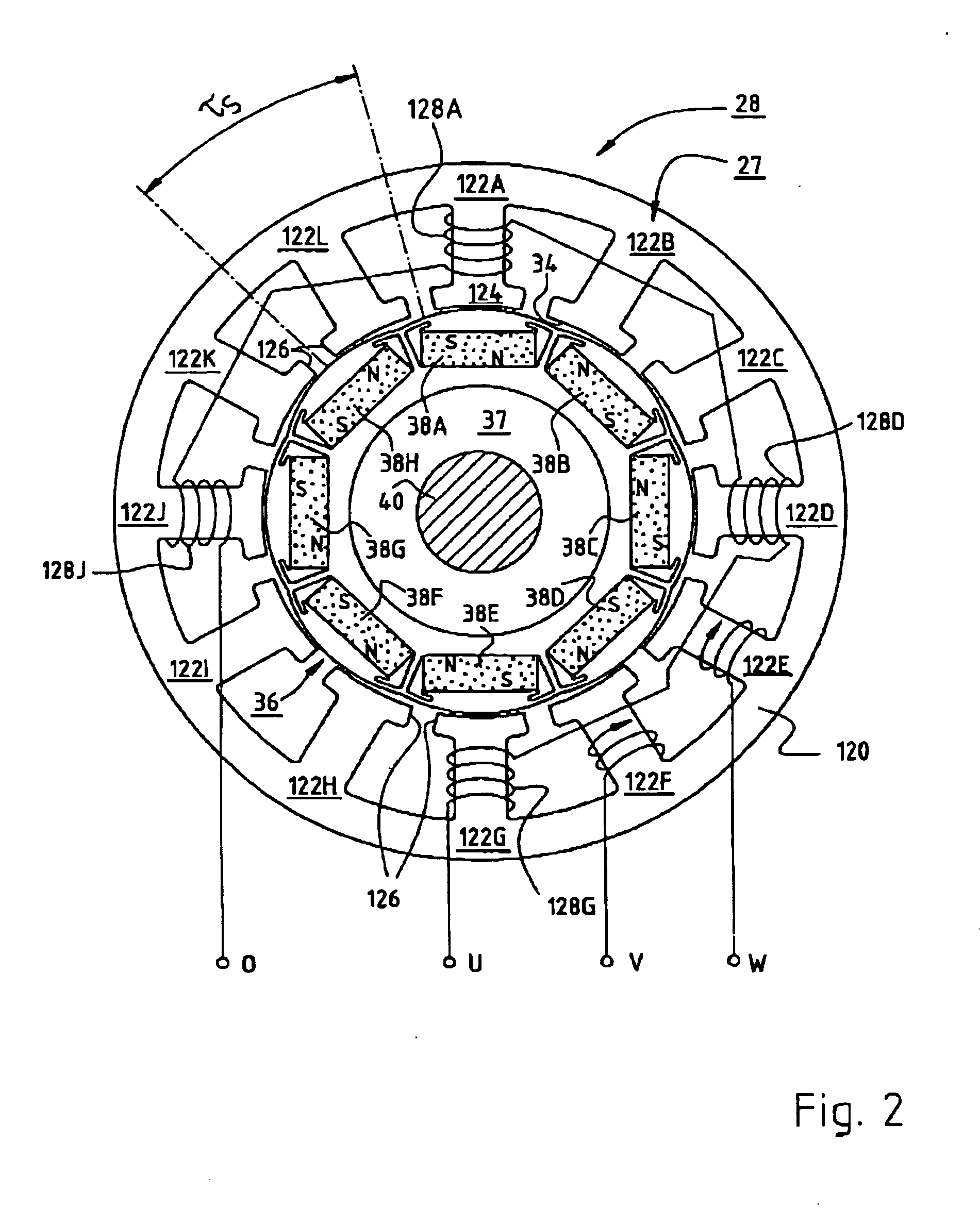
A rotor (10) for a rotary electric machine (1) comprises a rotation shaft (11), and a plurality of rotor cores (120-129) fixed to the rotation shaft (11) and axially split. The rotor cores (120-129) have outer peripheral surfaces (120A-129A) with a circular cross section. Permanent magnets (13) extending through the rotor cores (120-129) are arranged at equal circumferential intervals. Voids (120B-129B) extending axially through the rotor cores (120-129) are formed between the outer peripheral surfaces (120A-129A) and the permanent magnets (13). The voids (120B-129B) of two adjacent rotor cores (120-129) are formed at circumferentially different positions, thereby being capable of suppressing the cogging torque without introducing a reduction in output torque.
Owner:NISSAN MOTOR CO LTD
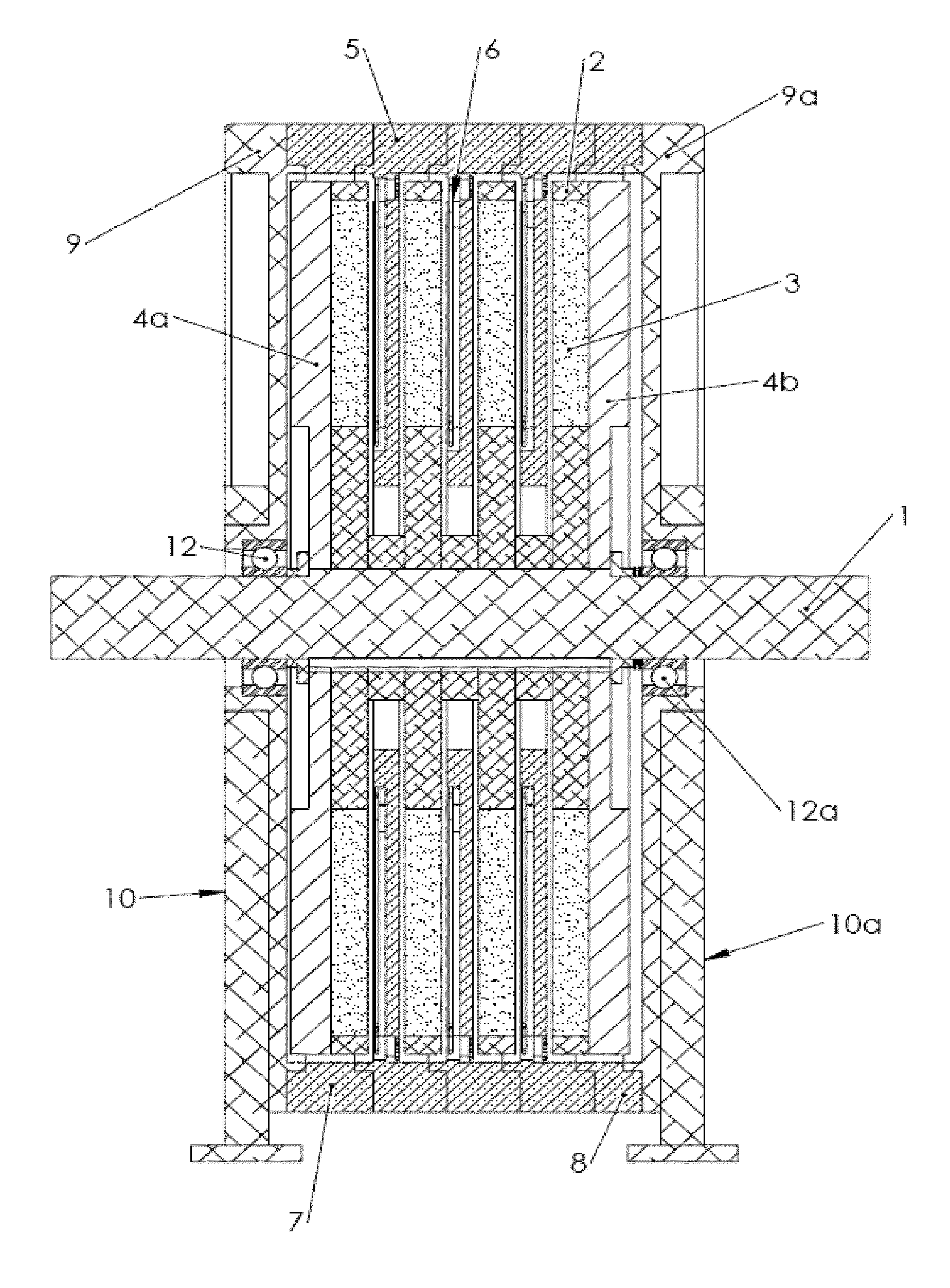
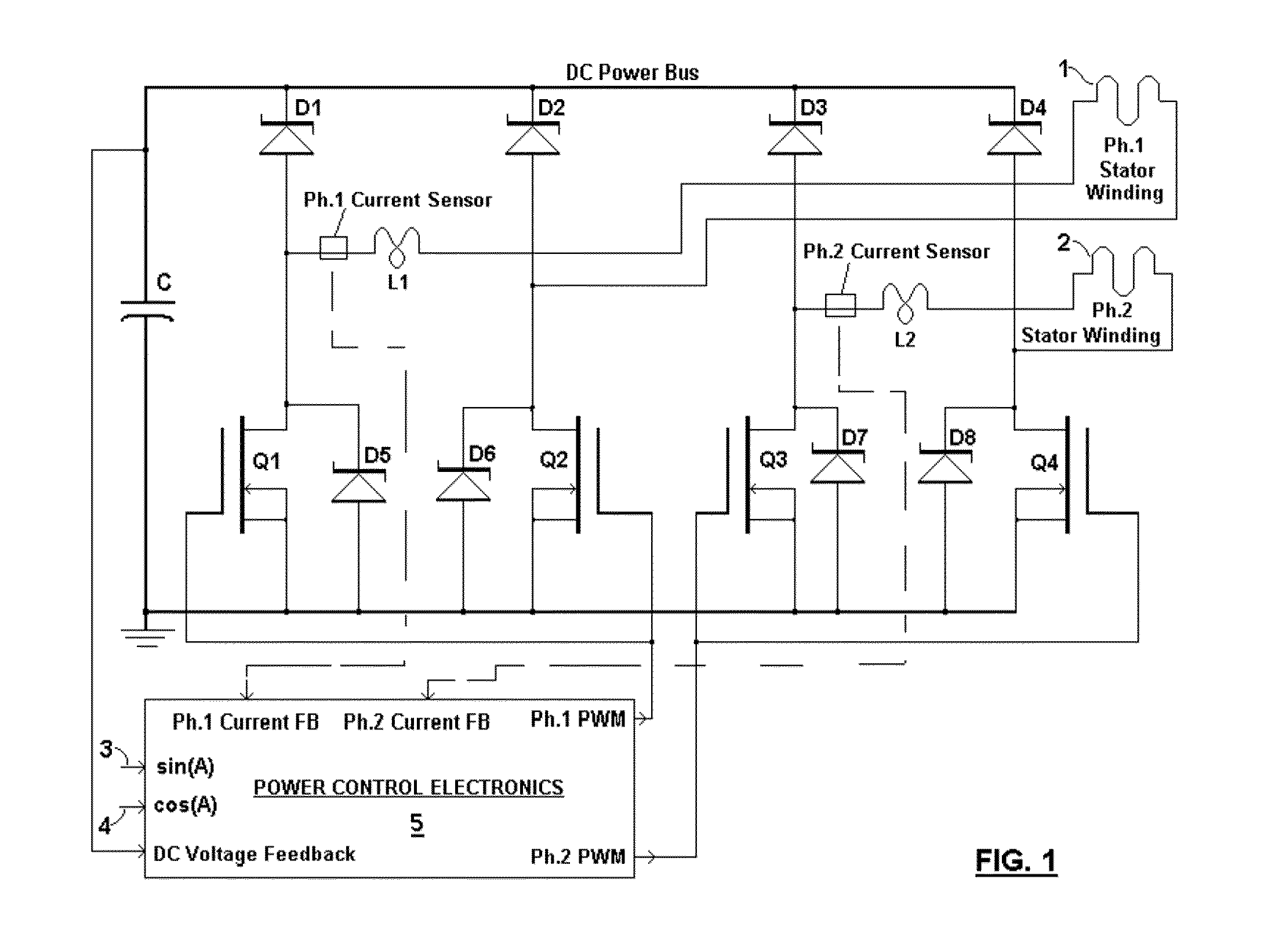
Broad speed range generator
InactiveUS20100283252A1Harvest sustainable mechanical powerWide speed rangeWindingsMagnetic circuitPower qualityDc current
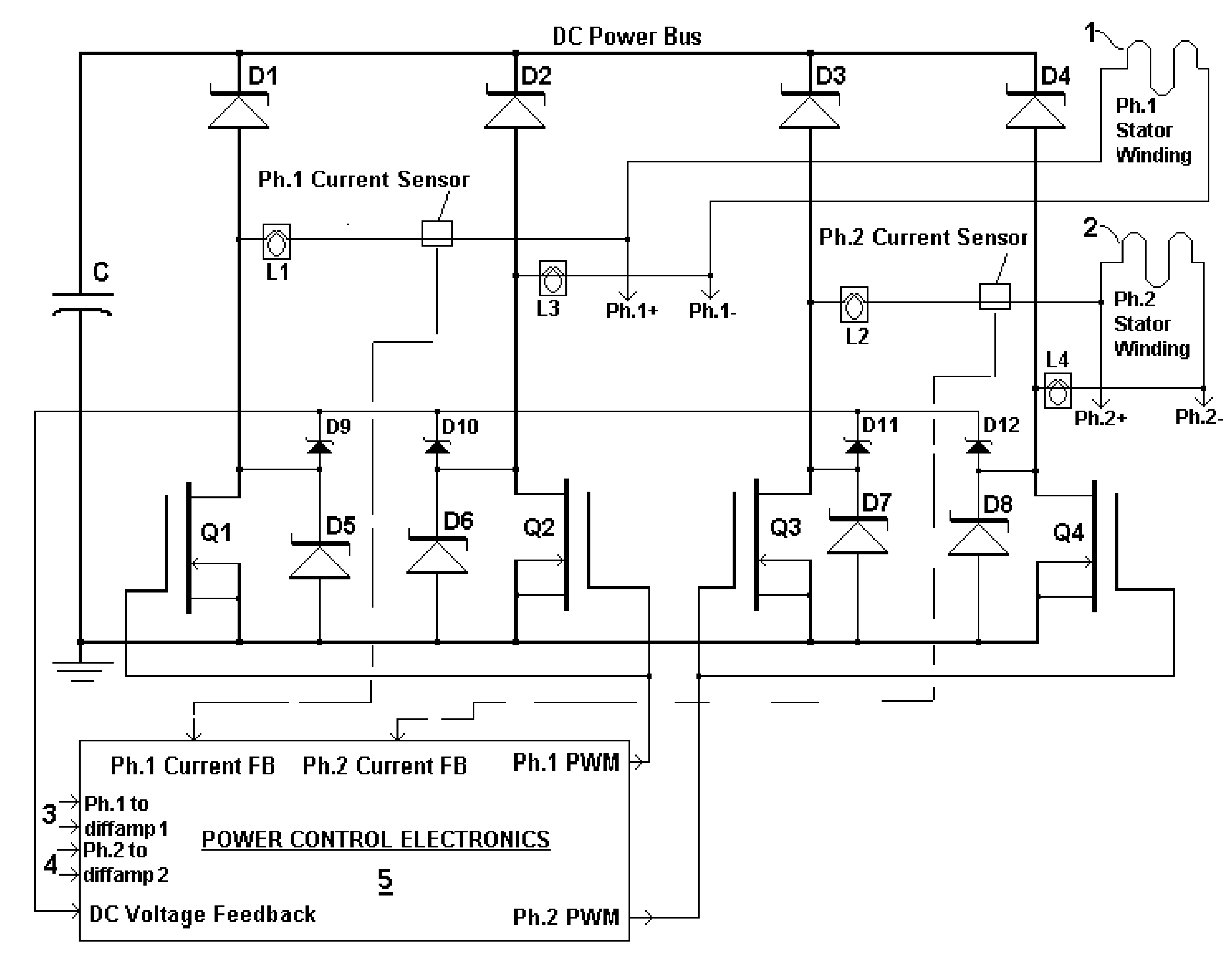
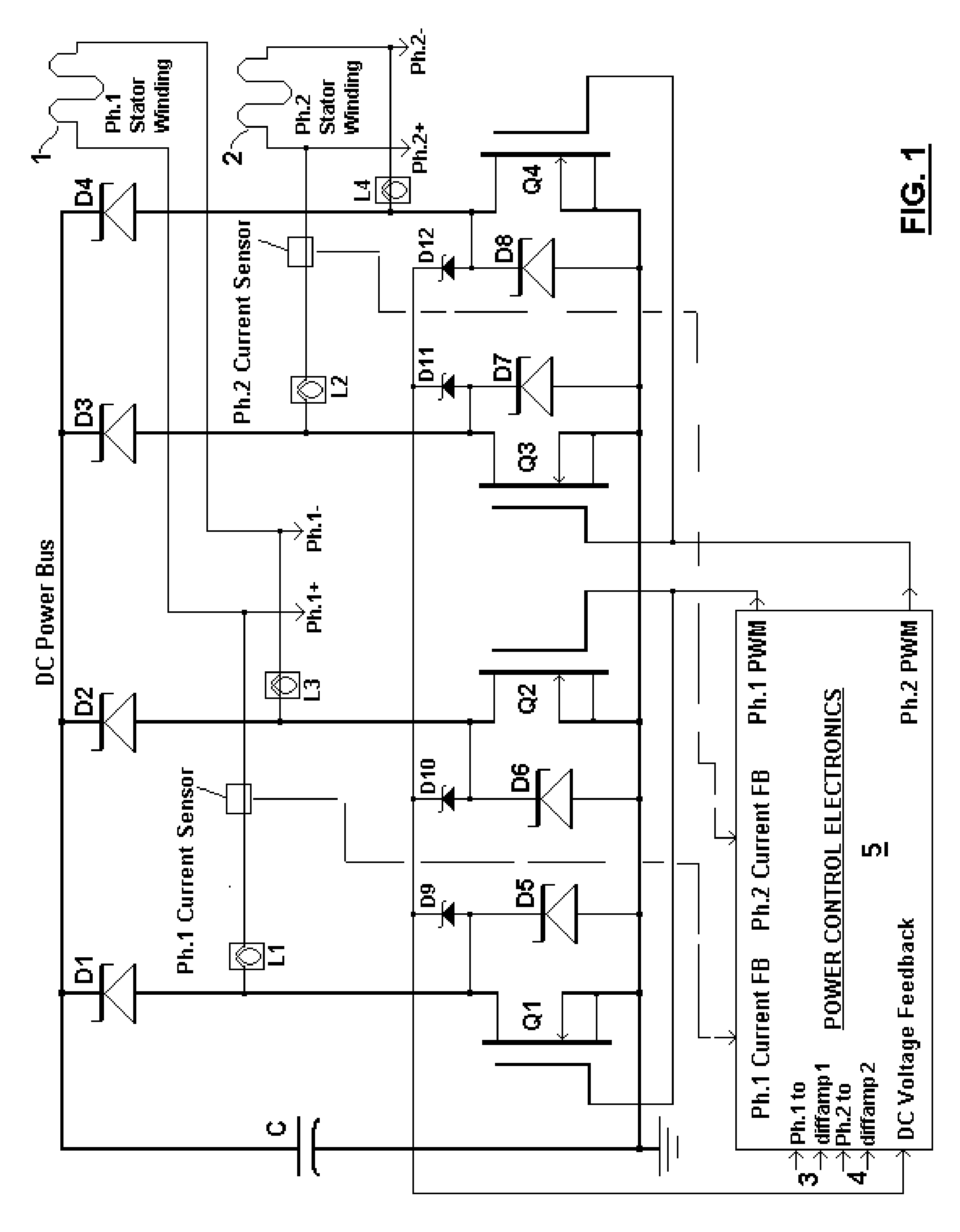
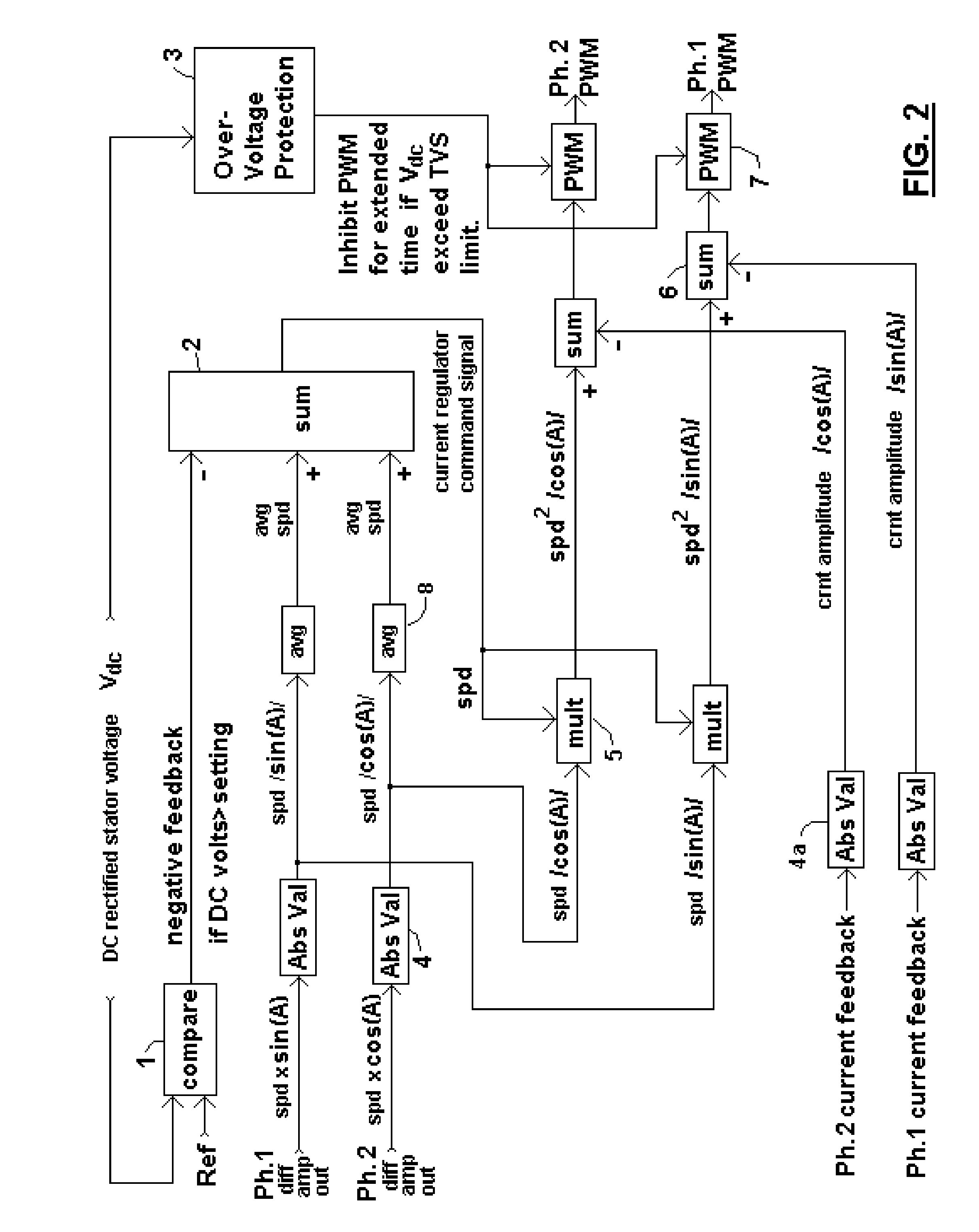
A brushless generator with permanent-magnet multi-pole rotor disks and coreless stator winding disks includes integral electronics to efficiently generate regulated DC current and voltage from shaft input power over a broad speed range. Its power rating is scalable, and it incurs no cogging torque, or friction from gearing. Integral power control electronics includes high-frequency pulse-width-modulated boost regulation, which provides regulated current at requisite voltage over its broad speed range. A main embodiment to produce DC power at widely variable speeds includes signal processing so output power varies according to the third power of speed. A version for use with vertical-axis wind turbines has a relatively large diameter to facilitate a large number of poles. Combined boost-regulation, zero cogging torque, and no gearing, enable a wide speed range, for better power quality and higher wind energy yields. An alternate embodiment is intended to produce DC power from a variety of shaft drive sources, with selectable shaft torque.
Owner:FRADELLA RICHARD B
Thin hybrid magnetization type ring magnet, yoke-equipped thin hybrid magnetization type ring magnet, and brush-less motor
ActiveUS20060113857A1Decrease in cogging torqueIncrease in torque per unit volume of magnetMagnetic circuit rotating partsPermanent magnetsBrushless motorsMagnetization
The present invention provides miniaturization of brushless motors and brush motors used in electric devices, a ring magnet which simultaneously achieves both high torque and a reduction in cogging torque, a ring magnet with yoke, and a brushless motor. The thin hybrid magnetized ring magnet of the present invention is structured of, in a ring magnet comprised of a plurality of magnetic poles, a radially magnetized main pole and an interface for which the interface of the adjoining main pole is polar anisotropic. When the thin hybrid magnetized ring magnet structured in this manner is applied to a brushless motor, in the case of radial magnetizing, the abrupt change in magnetic flux of the interface between the magnetic poles becomes smooth and cogging torque is greatly reduced due to polar anisotropic magnetization of the interface. At the same time, by polar anisotropically magnetizing the interface between the magnetic poles, magnetic flux is concentrated on the radially magnetized main pole, and in comparison to only radial magnetization, maximum surface magnetic flux improves and it is possible to attain high torque.
Owner:AICHI STEEL
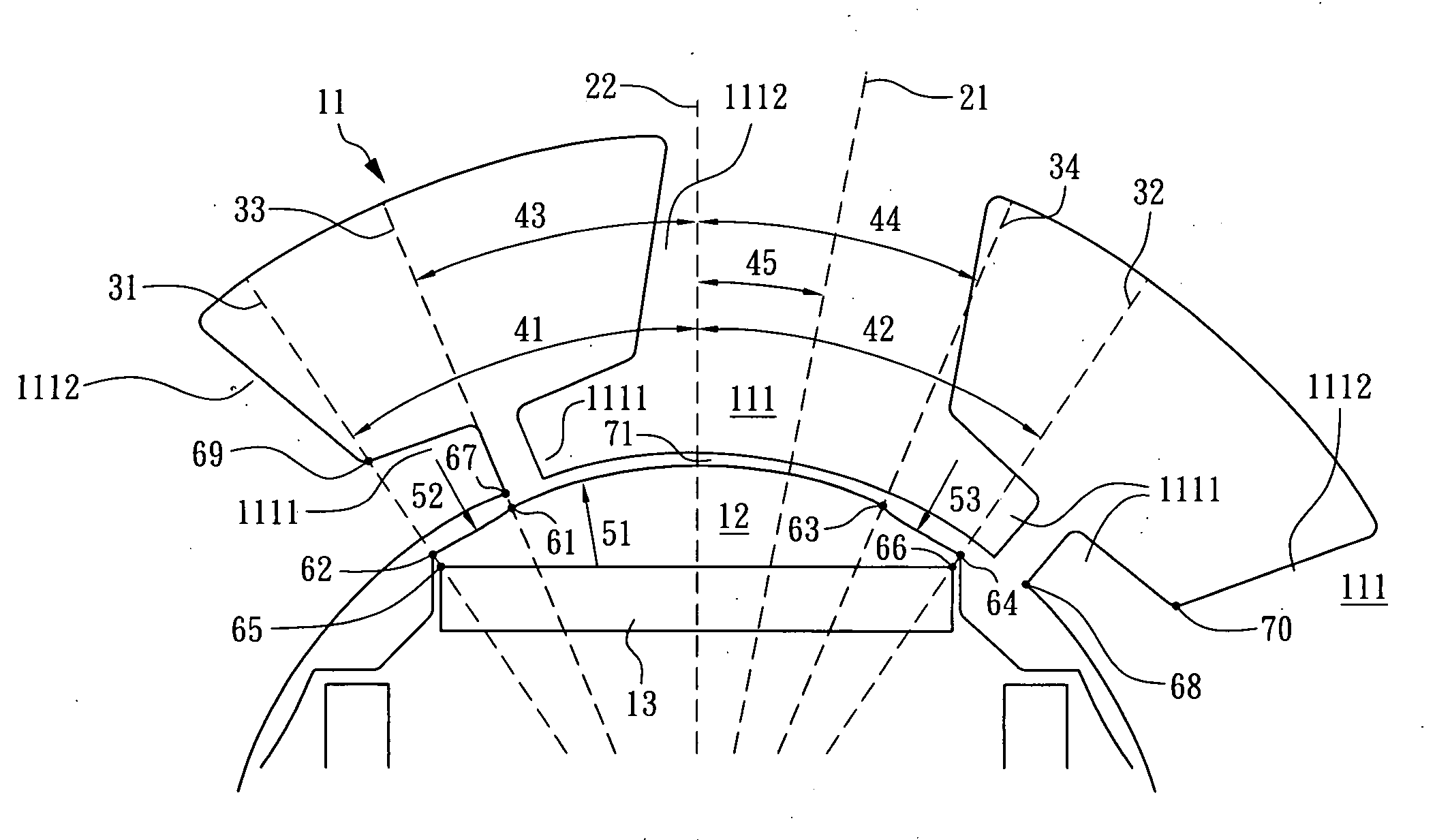
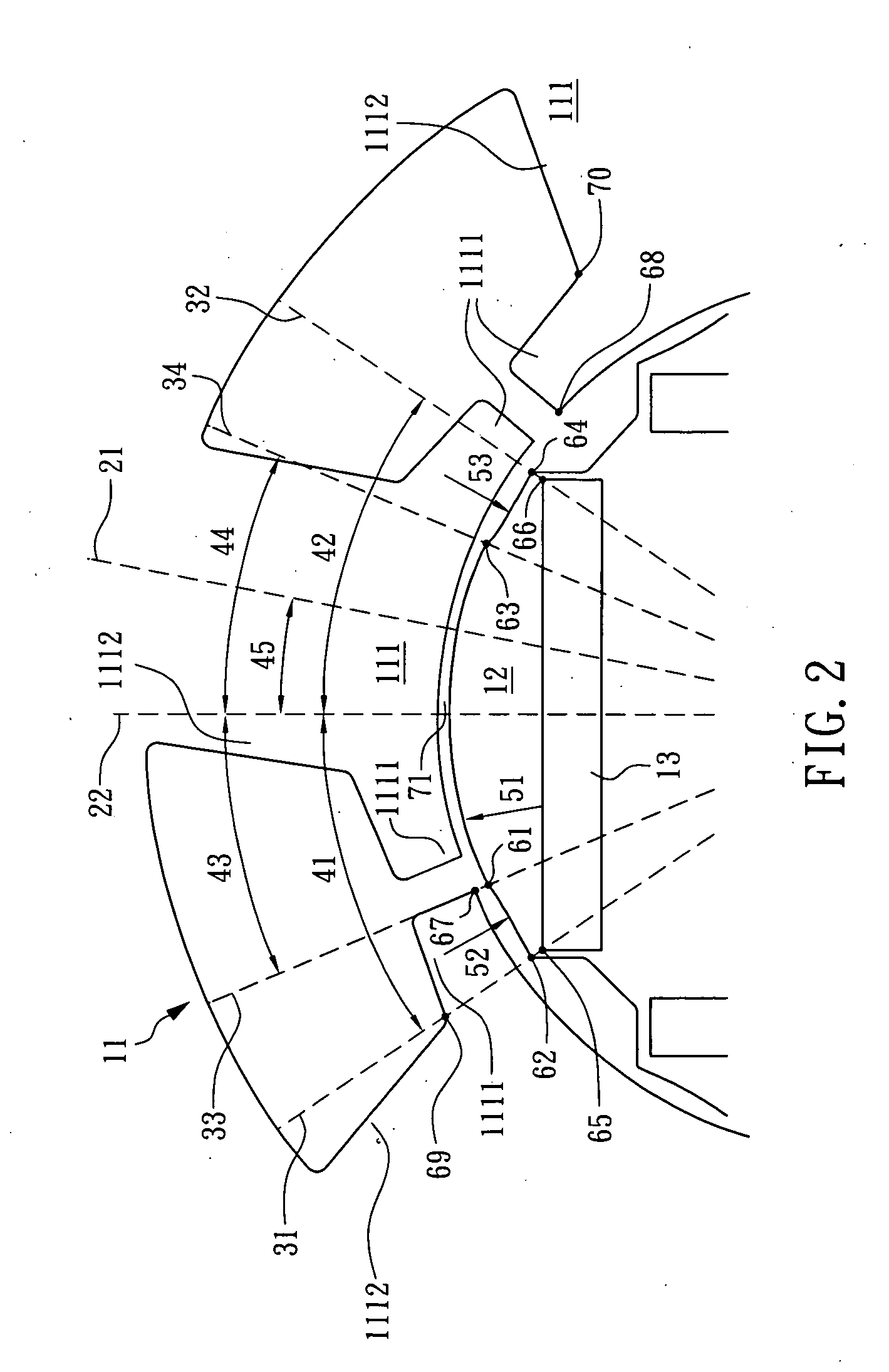
Permanent-magnet rotating machine
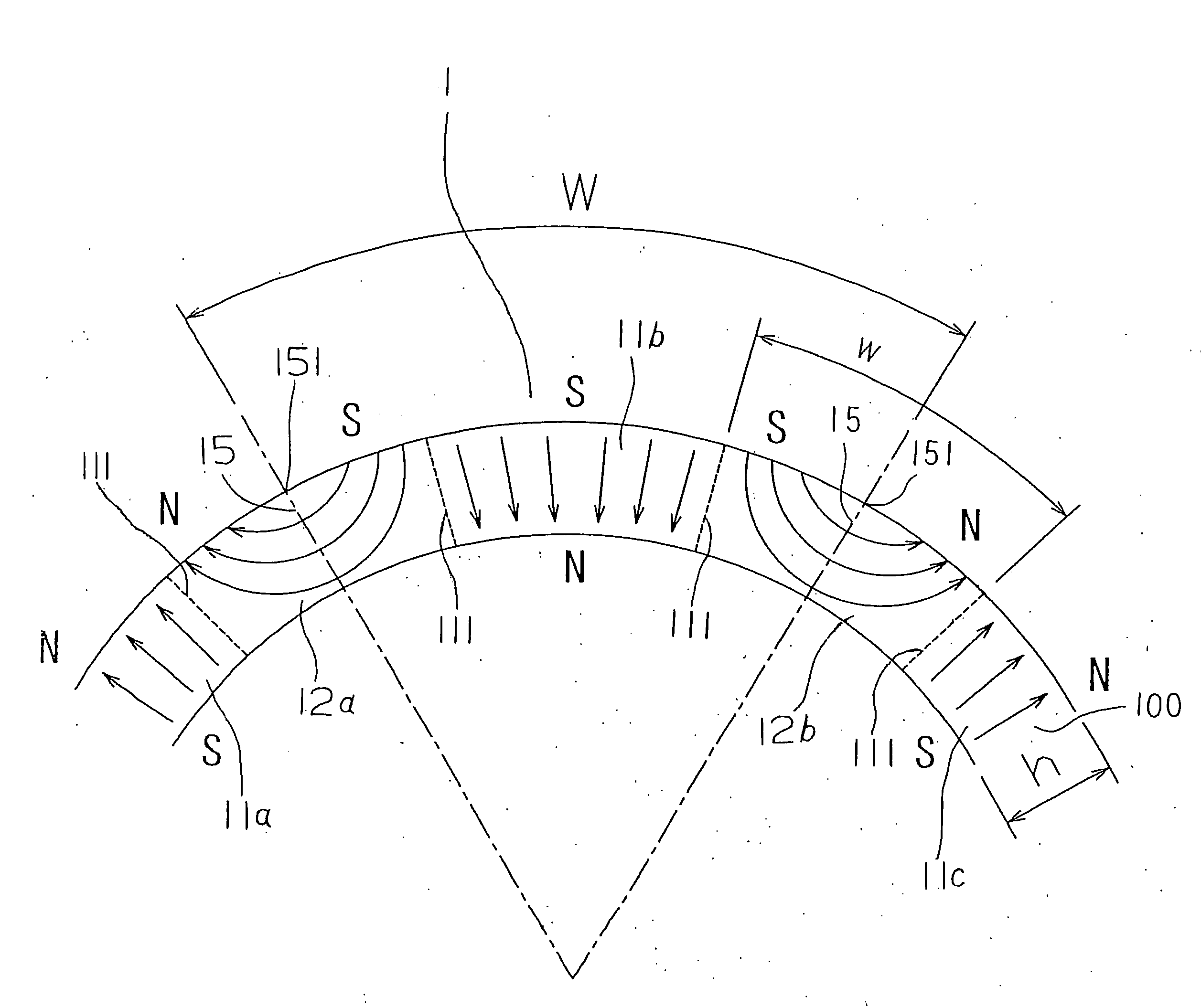
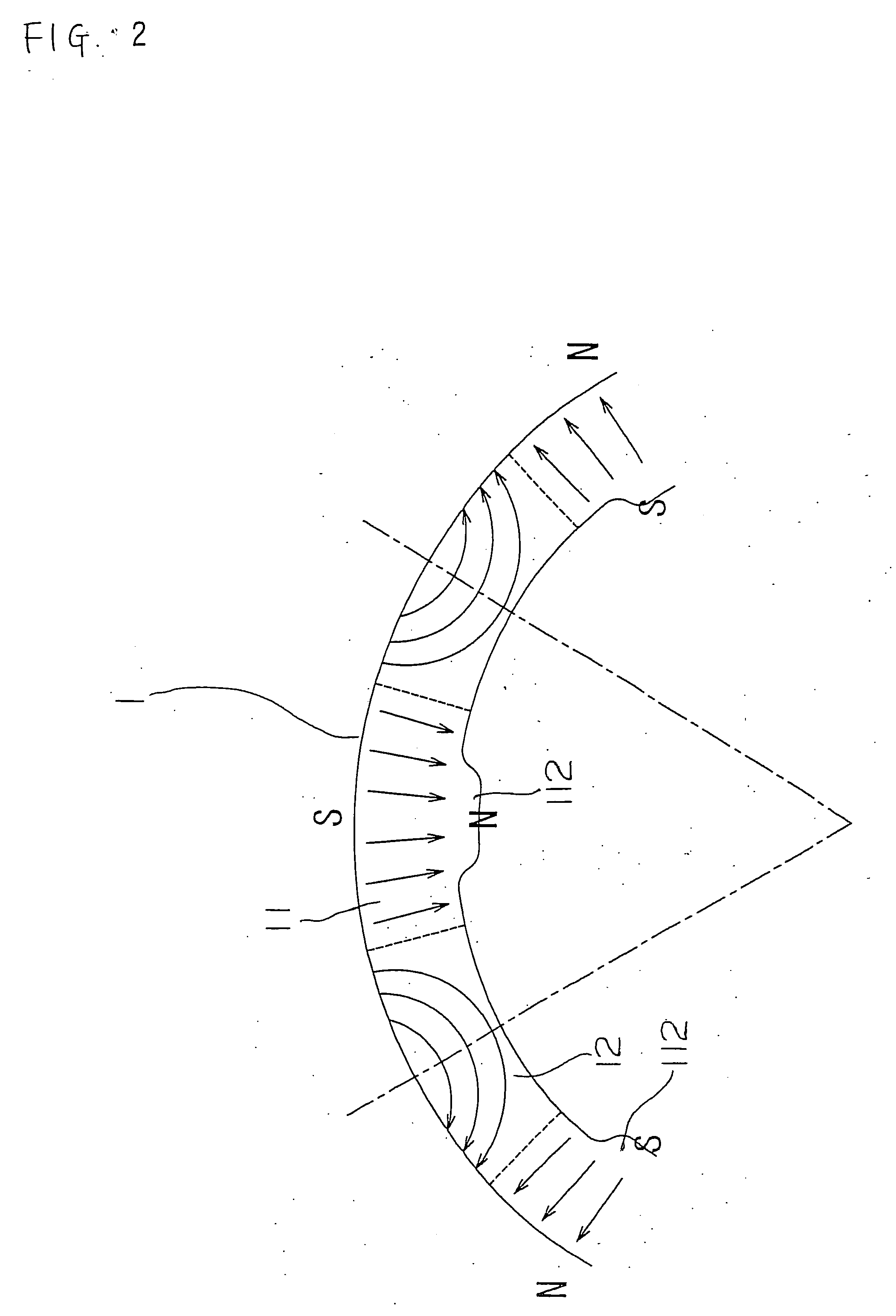
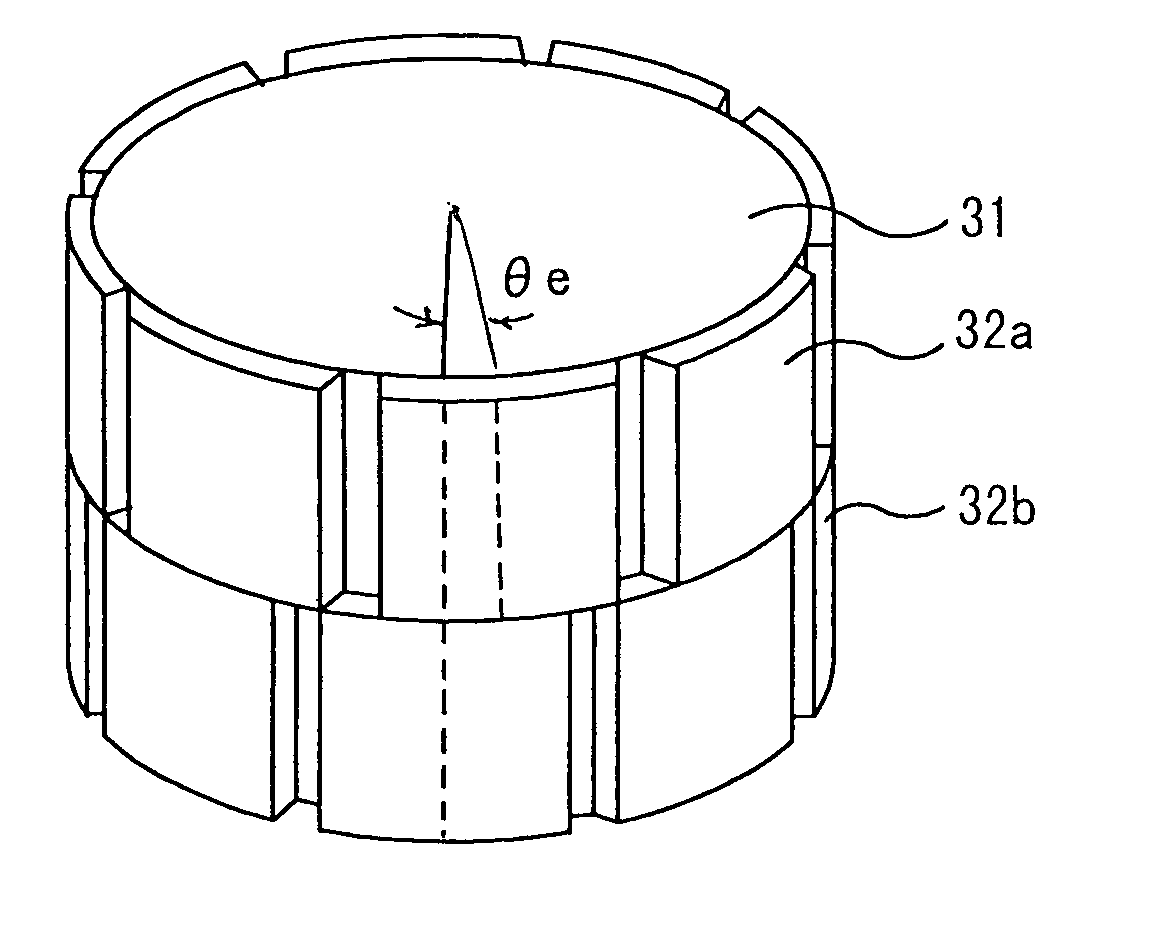
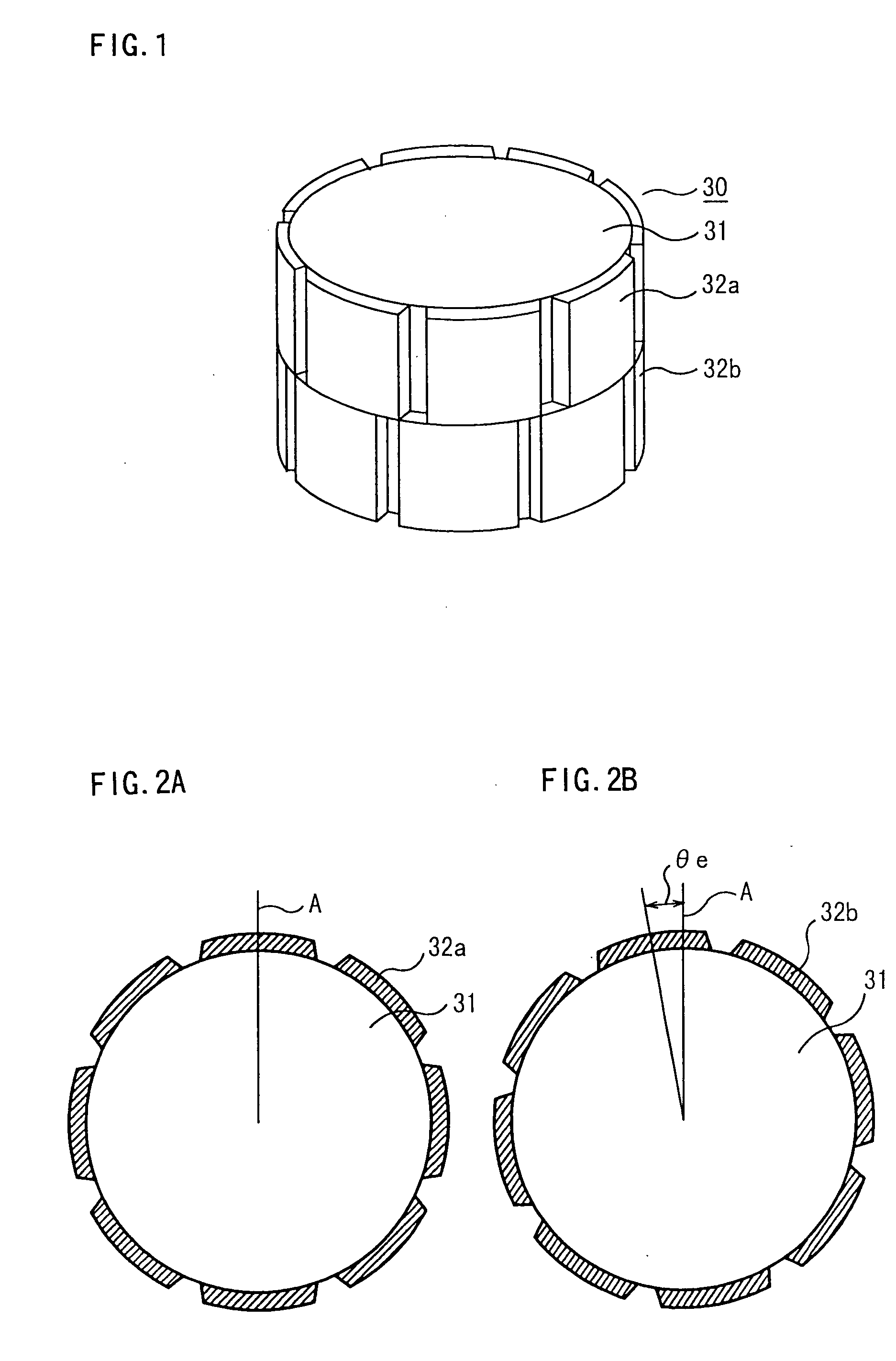
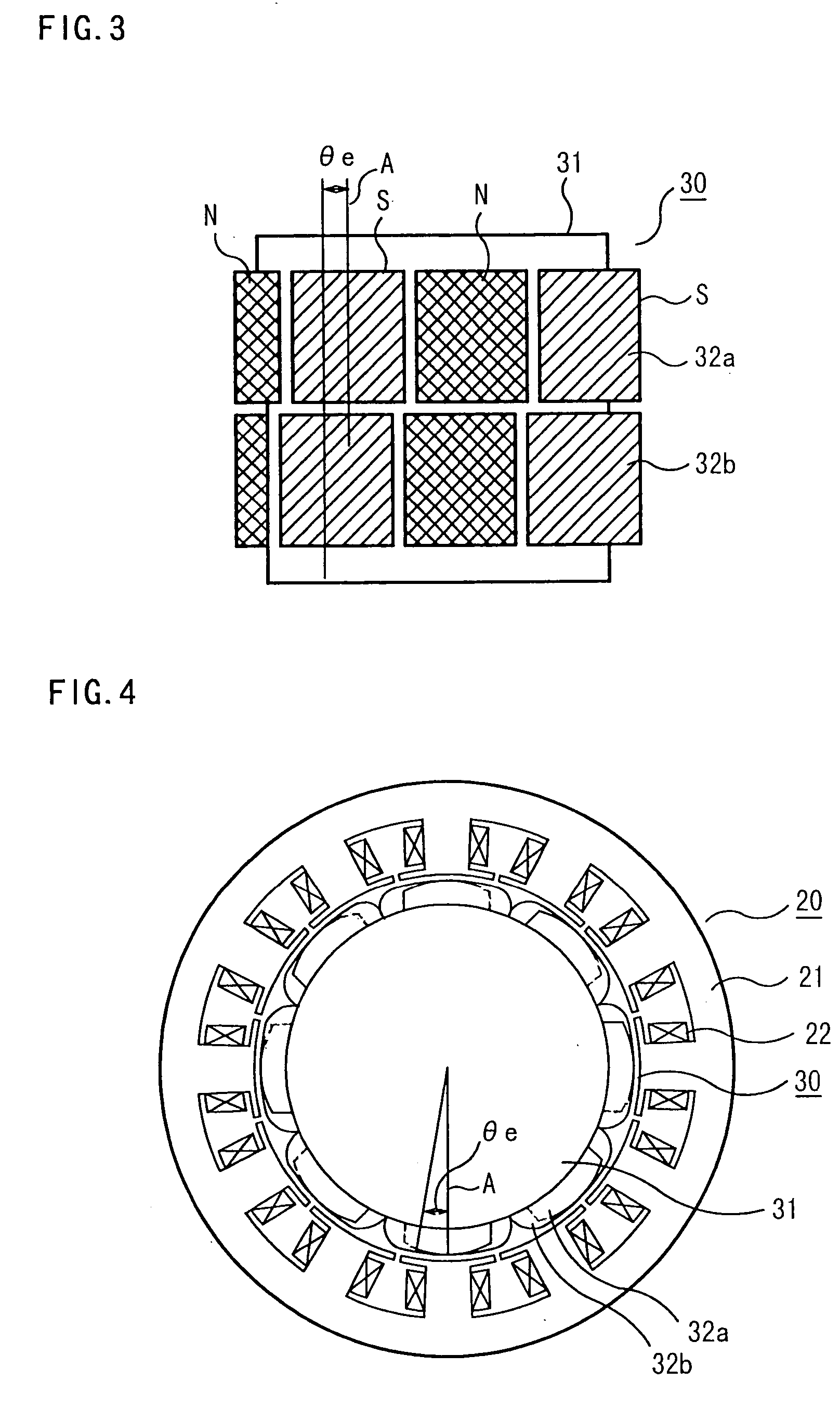
ActiveUS20040124728A1Efficiently reduce cogging torque and torque ripplesMagnetic circuit rotating partsSynchronous machines with stationary armatures and rotating magnetsLower limitSkew angle
A permanent-magnet rotating machine includes a rotor having a rotor core carrying on its curved outer surface multiple permanent magnets arranged in two rows along an axial direction in such a manner that the permanent magnets in one row are skewed from those in the other row in a circumferential direction by a row-to-row skew angle (electrical angle) thetae, and a stator having a cylindrical stator core in which the rotor is disposed, the stator core being provided with stator coils for producing a rotating magnetic field for rotating the rotor. A lower limit of the row-to-row skew angle thetae is set at a value larger than 30 degrees (electrical angle). A cogging torque ratio, or the ratio of a cogging torque occurring in the absence of skew to a cogging torque occurring when the permanent magnets are skewed, at a row-to-row skew angle of 30 degrees is calculated based on the relationship between the cogging torque ratio and the row-to-row skew angle thetae and B-H curve properties of the stator core, and an upper limit of the row-to-row skew angle thetae is set at a value not larger than its maximum value at which the cogging torque ratio does not exceed the calculated cogging torque ratio at 30 degrees.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Broad-speed-range generator variations
InactiveUS20120256422A1High energy yieldImprove global economyWindingsMagnetic circuitPower qualityDc current
A brushless generator with permanent-magnet multi-pole rotor disks and stator winding disks in their axial magnetic field includes integral electronics to efficiently generate regulated DC current and voltage from mechanical input power over a broad speed range. All power for the electronics is provided by rectifier diodes from its stator windings. Differential amplifiers provide stator voltage feedback signals. Its power rating is scalable, depending on the number of its disks. Having no iron cores and no gears, it incurs no cogging torque, and no gear friction. Integral power control electronics includes high-frequency pulse-width-modulated boost regulation, which provides regulated current at requisite voltage over its broad speed range. A main wind-powered embodiment to produce DC power for a constant voltage DC load over a broad speed range includes signal processing so output power varies according to the third power of speed. Combined boost-regulation, zero cogging torque, and no gearing, enable a wide speed range, for better power quality and higher wind energy yields.
Owner:FRADELLA RICHARD B
Cylindrical linear motor, electromagnetic suspension, and vehicle using the same
InactiveUS20060181158A1Reduce torque pulsation torqueReduce torque cogging torqueResilient suspensionsPropulsion systemsElectric machineEngineering
A cylindrical linear motor, an electromagnetic suspension, and a vehicle using the same, which can generate a large thrust and reduce torque pulsations and cogging torque. The cylindrical linear motor comprises a stator and a slider disposed with a gap left relative to the stator and being linearly movable relative to the stator. The stator comprises a stator core having stator salient poles, and 3-phase stator windings inserted in slots formed in the stator core. The slider comprises a plurality of permanent magnets fixed to a slider core. The motor satisfies τp:τs=9:9±1 where τs is a pitch of the stator salient poles and τp is a pitch of the permanent magnets.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
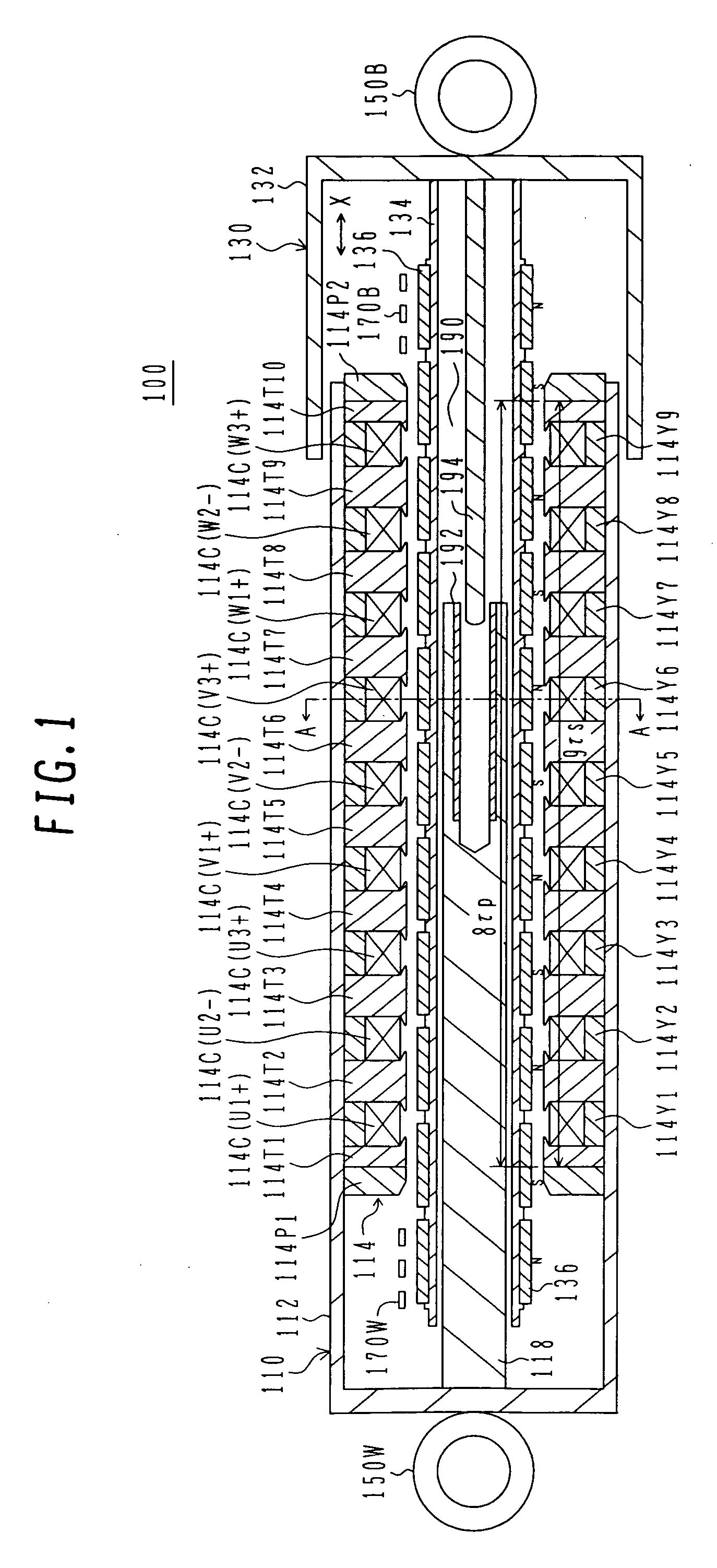
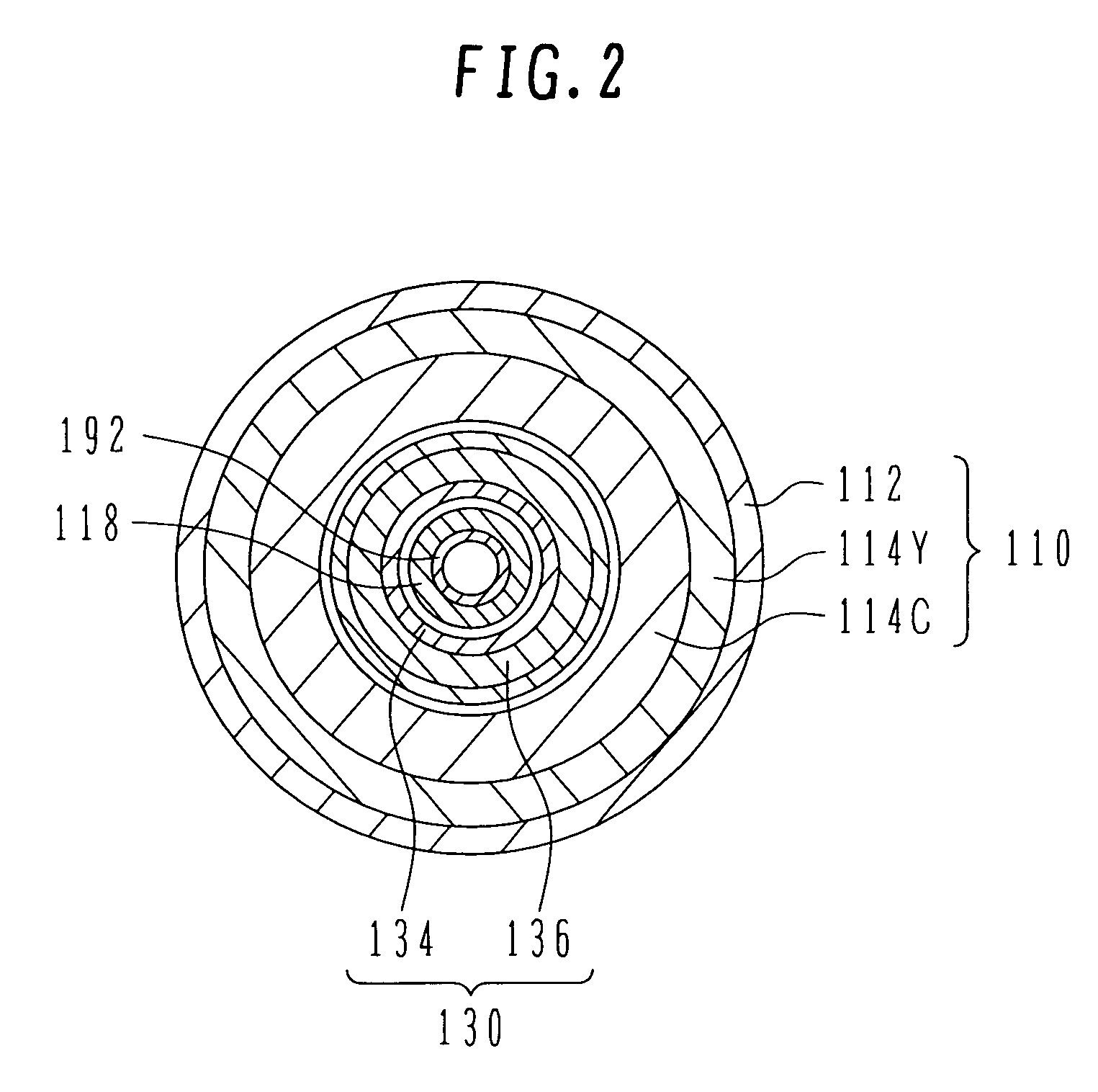
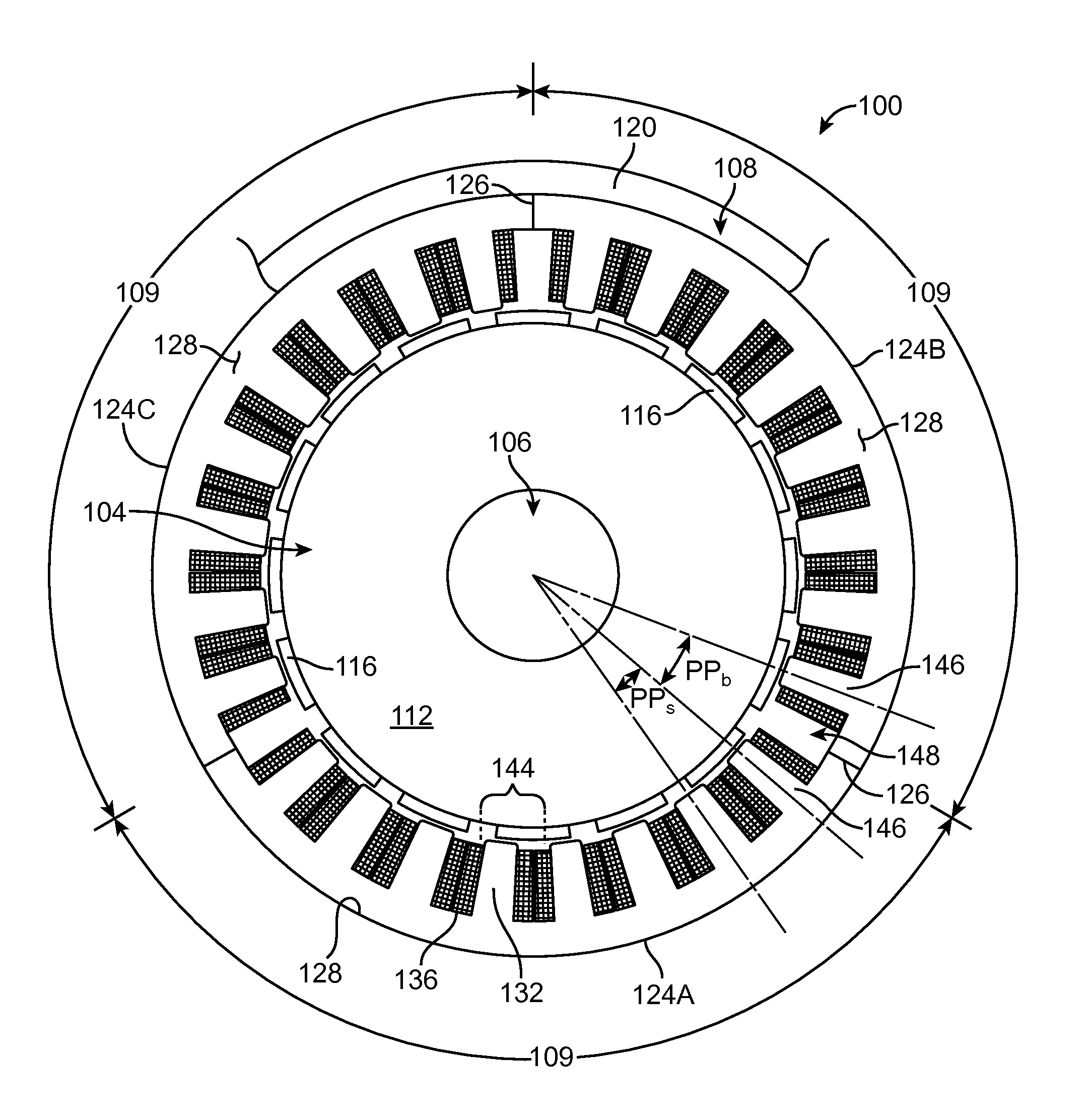
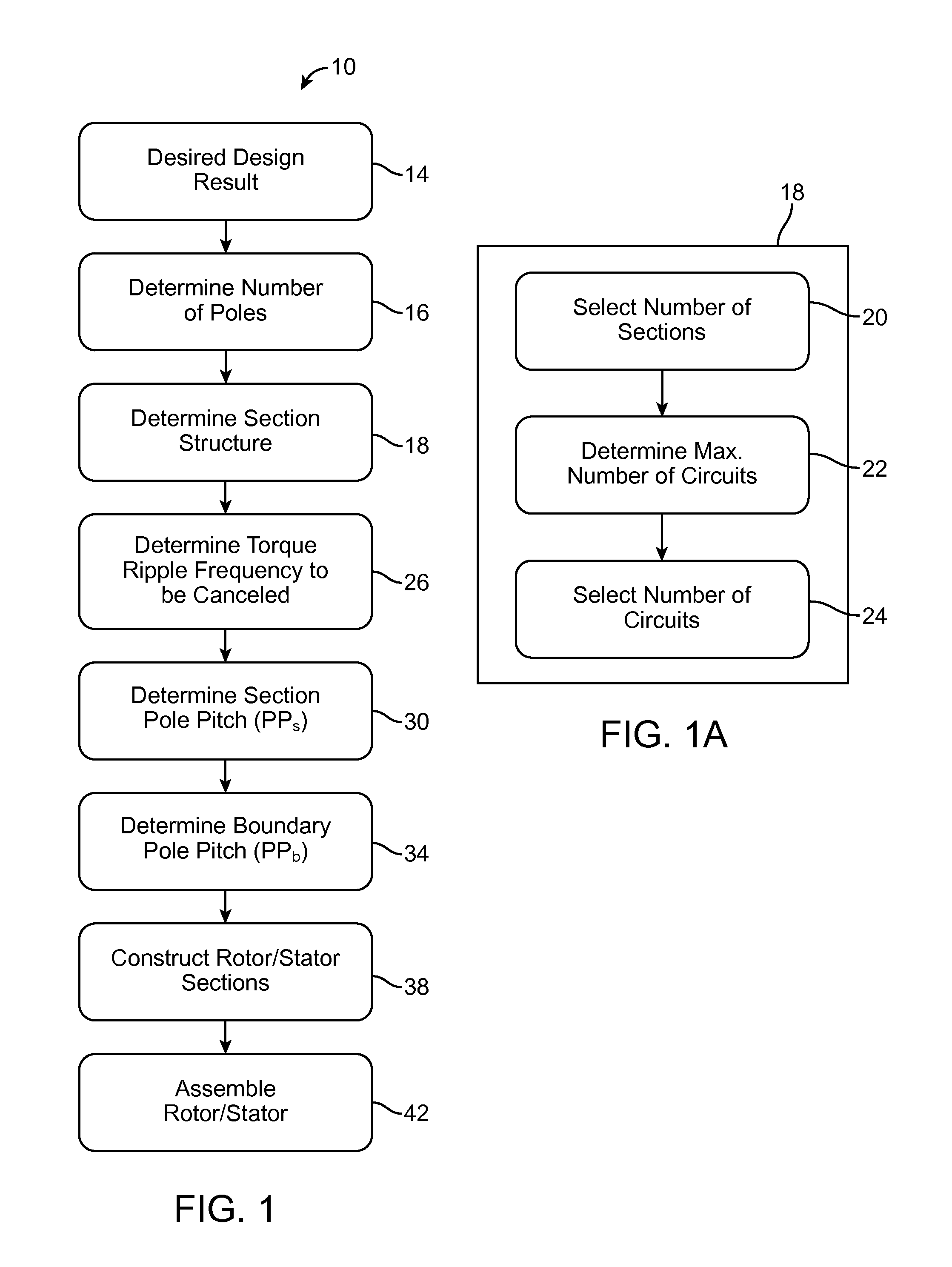
Sectionalized Electromechanical Machines Having Low Torque Ripple and Low Cogging Torque Characteristics
InactiveUS20120074797A1Reducing torque ripple torqueReducing torque cogging torqueMagnetic circuit rotating partsMagnetic circuit stationary partsRotor magnetsControl theory
A method and apparatus for reducing or eliminating the effects of torque ripple and cogging torque and otherwise improving performance in an electromechanical machine such as a motor or generator. The rotor and / or stator is conceptually sectionalized and the sections spaced apart by amount sufficient to alleviate deleterious aspects of cogging torque and torque ripple. Positioning of the stator teeth or rotor magnets is determined based on the calculated spacing. Conceptual sections may be formed as physically individual segments. Unwound teeth may be disposed in end spaces between sections occupying less than the entire area of the end space.
Owner:WEG ELECTRIC CORP
Split cores for motor stator, motor stator, permanent magnet type synchronous motor and punching method by split core punching die
ActiveUS20090026872A1Improve rigidityImprove assembly accuracyMagnetic circuit stationary partsManufacturing stator/rotor bodiesSynchronous motorPunching
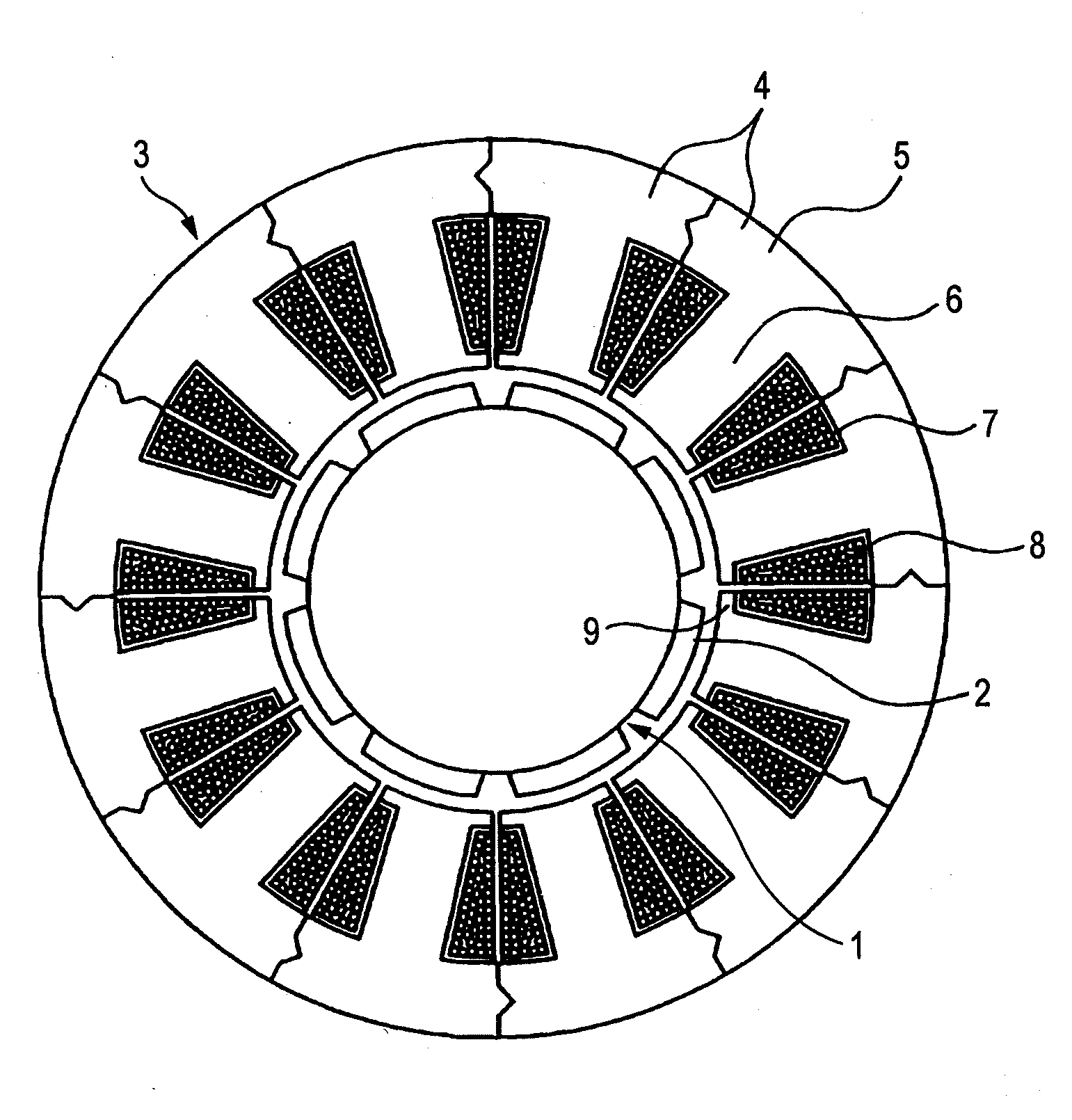
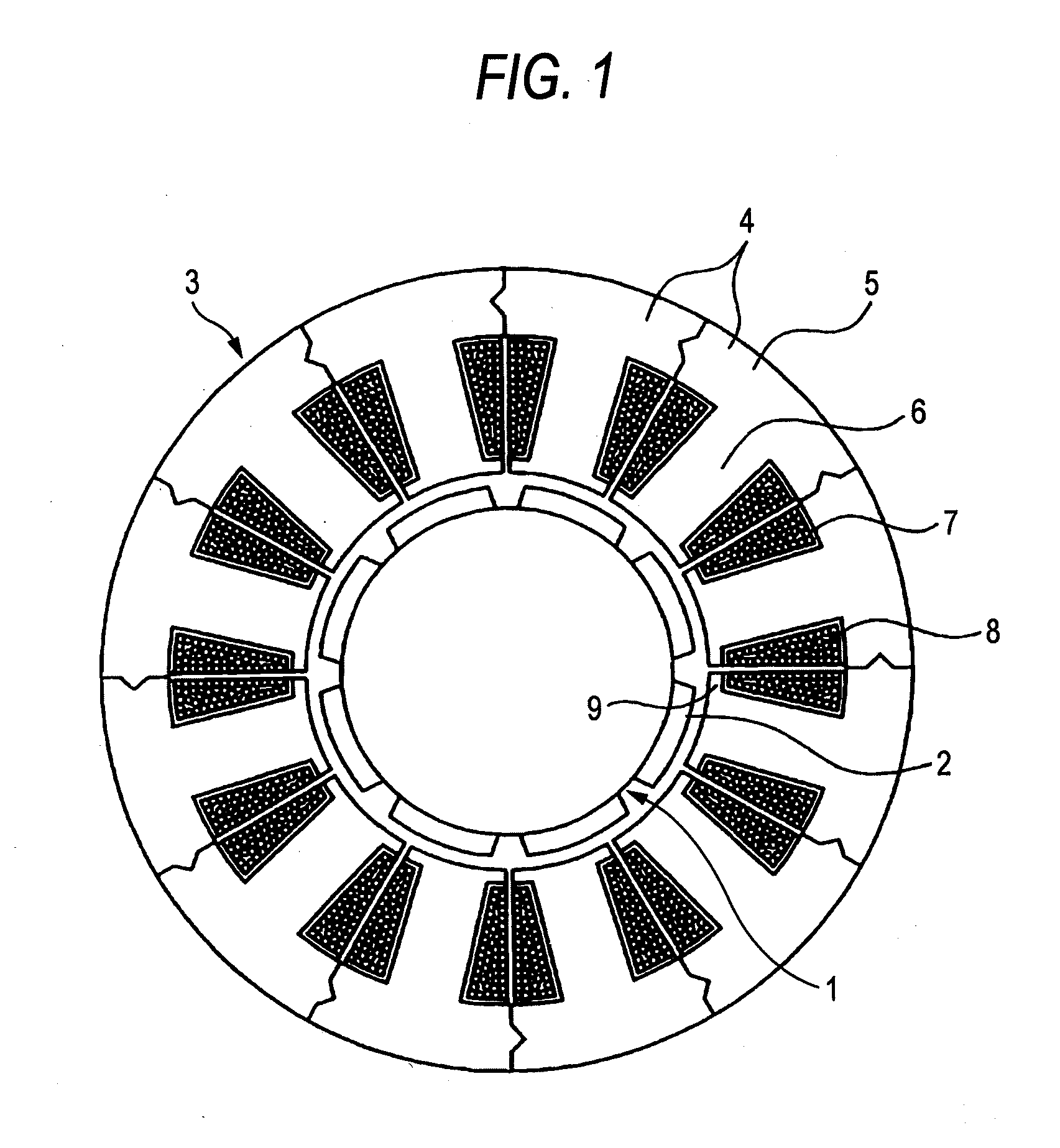
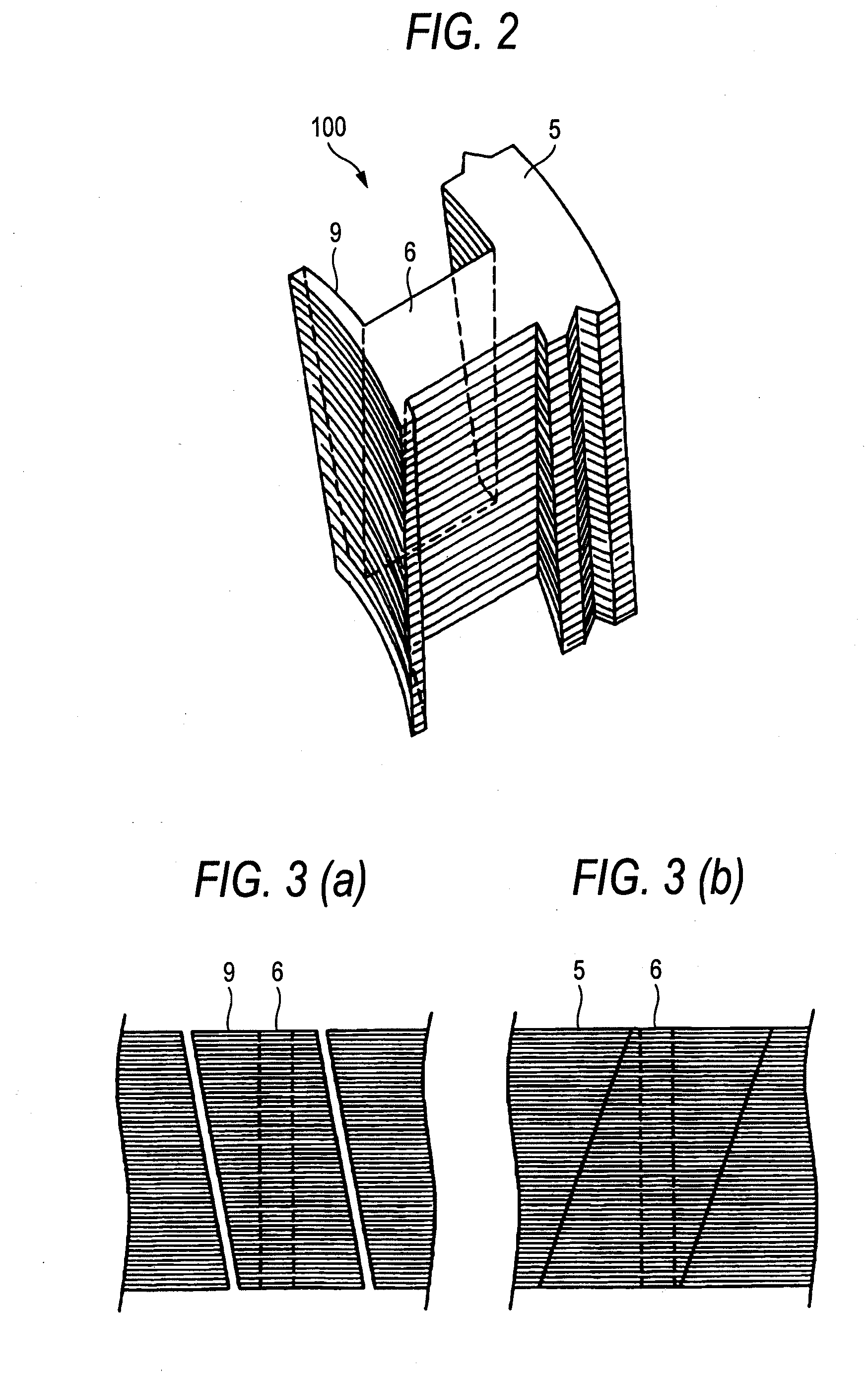
Although in a conventional permanent magnet type synchronous motor, cogging torque is reduced by displacing permanent magnets of a rotor in a circumferential direction or displacing a stator core in a circumferential direction, since the skew so produced reduces the output of the motor and moreover the winding work of windings cannot be automated to make the resulting motor highly expensive, split cores are provided which solves those problems and enables the winding work of windings to be automated so as to obtain an inexpensive and high-output motor.There are provided a plurality of split cores (100) made up of laminated iron cores each having formed thereon a tooth (6), and a yoke (5) and a pole piece (9) which are made to connect to the tooth (6) at both ends thereof, and arranged and connected together into an annular shape to make up a stator, characterized in that both ends of the yokes (5) and both ends of the pole pieces (9) are displaced in one circumferential direction by laminated iron core from a top laminated layer to a bottom laminated layer of the iron cores of the split cores.
Owner:YASKAWA DENKI KK
Permanent magnet motor
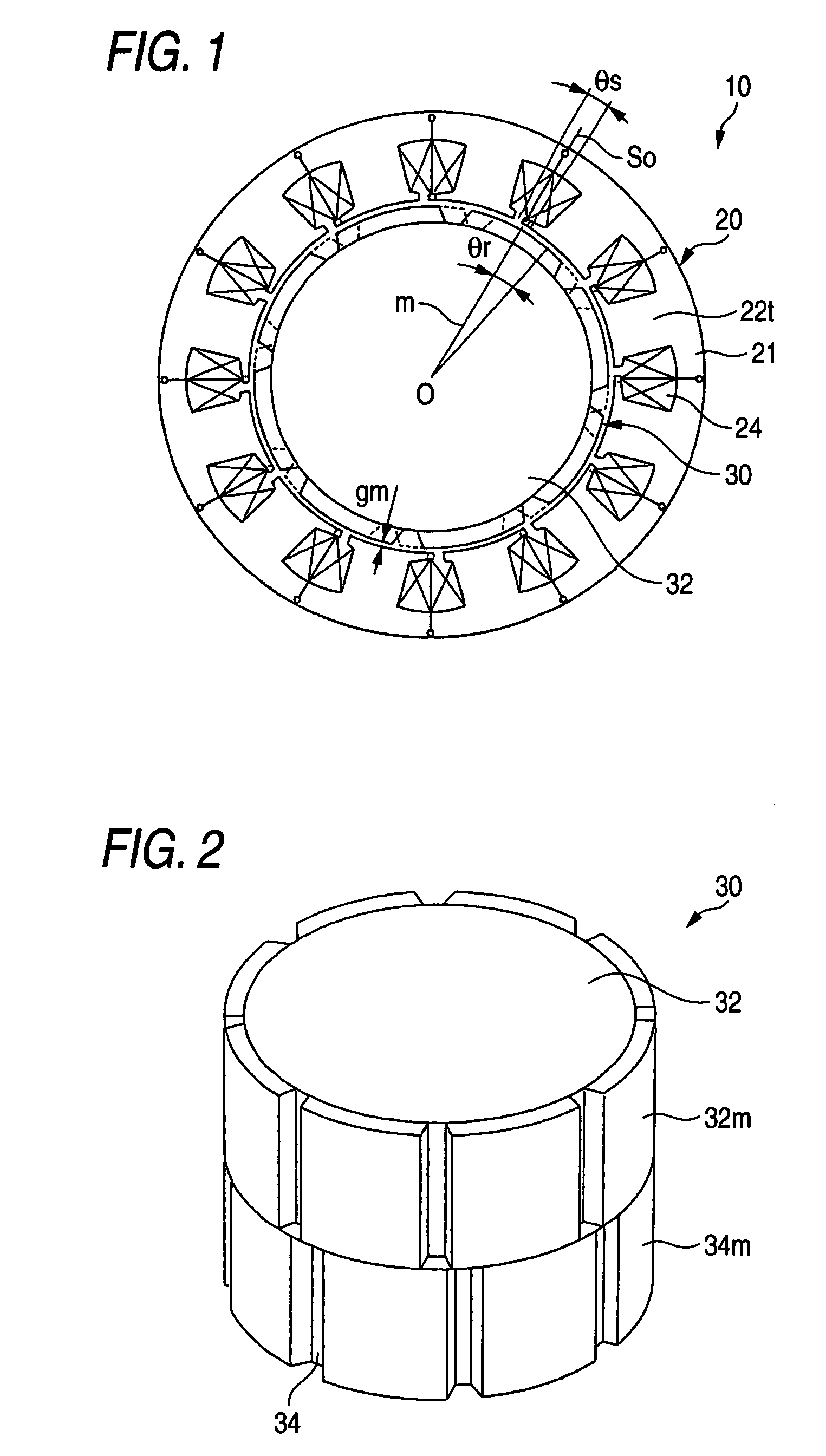
InactiveUS20060038457A1Reduce the cogging torque of servomotorsImprove accuracyMagnetic circuit rotating partsManufacturing stator/rotor bodiesElectric power steeringElectric machine
To reduce the cogging torque of servomotors, electric power steering motors, and others, there is provided a permanent magnet motor comprising: a rotor 10 comprising a rotor yoke 11 and a plurality of permanent magnets (M1-M10); and a stator 20 comprising a stator yoke 22, salient magnetic poles 21, and armature windings 23, wherein at least one of the permanent magnets is disposed in an adjustment position that is displaced from a corresponding reference position in at least one of the circumferential, radial, and axial directions of the rotor yoke, and the plurality of permanent magnets excluding the permanent magnet disposed in the adjustment position is disposed in the reference positions, and wherein the adjustment position is set so that the permanent magnet motor in which at least one of the plurality of permanent magnets is disposed in the adjustment position has a smaller cogging torque than a permanent magnet motor in which all of the plurality of permanent magnets are disposed in the reference positions; and a method for adjusting a cogging torque of a permanent magnet motor.
Owner:SHIN ETSU CHEM IND CO LTD
Direct drive wind turbine and blade assembly
Owner:TODOROF BILL
Permanent magnet electric motor with reduced cogging torque
ActiveUS7342338B2Simple constitutionEasy constructionSynchronous generatorsMagnetic circuit rotating partsSkew anglePermanent magnet motor
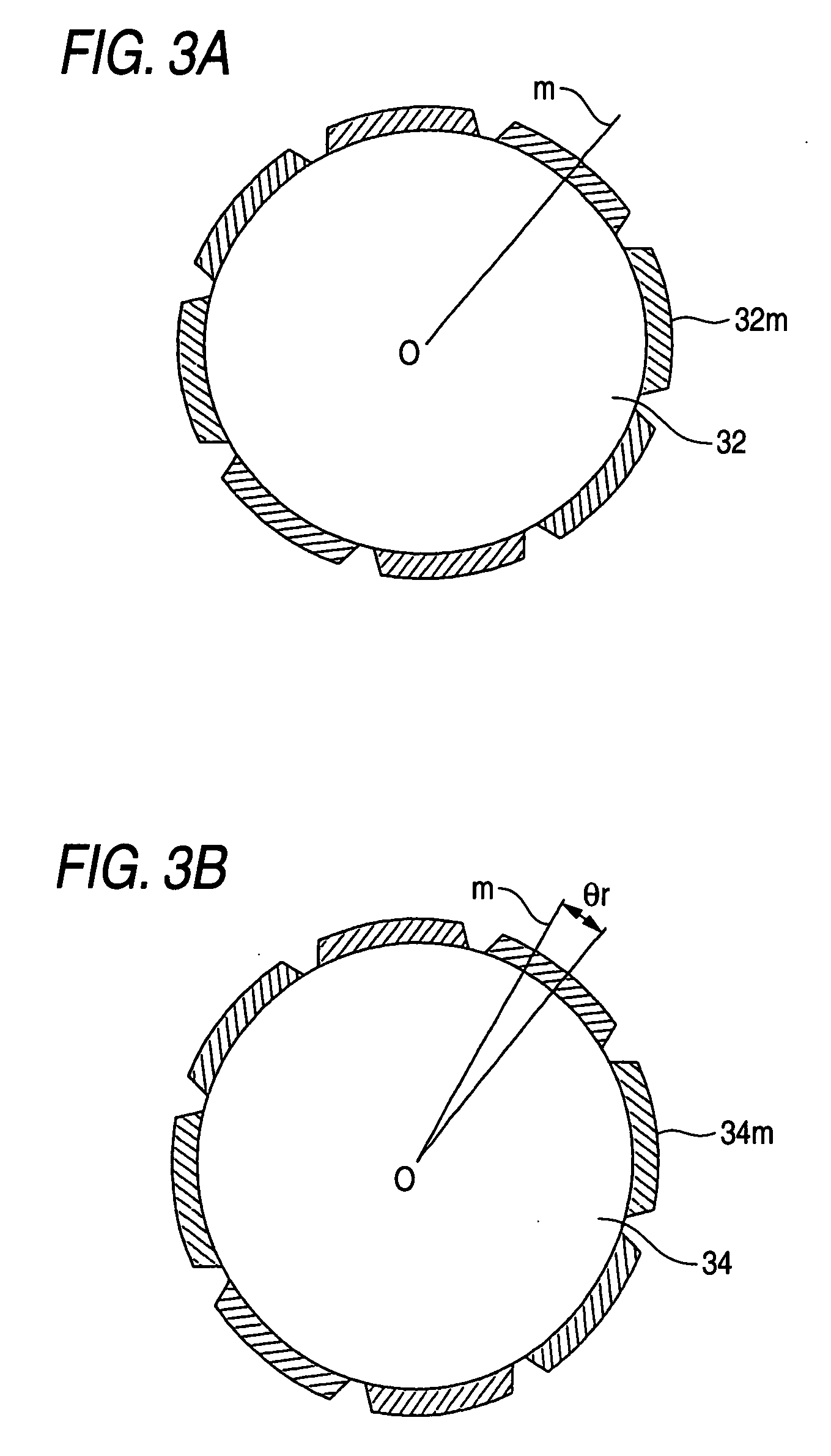
A permanent magnet electric motor 10 comprises a rotor 30 provided with two stages of permanent magnets in the axial direction on an outer circumferential face of a rotor iron core, and having a shaft shifted by a stage skew angle θr in electrical angle to decrease a first frequency component of cogging torque in the circumferential direction of the rotor iron core between two stages of the permanent magnets, a stator iron core 21 of cylindrical shape provided with the stator winding for producing a rotating magnetic field causing the rotor 30 to be rotated, and a stator 20 dividing the stator iron core 21 into plural blocks in the axial direction, and shifted by a stage skew angle θs in electrical angle to decrease a second frequency component of the cogging torque in the circumferential direction of the stator iron core 21.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Electric motor with poles shaped to minimize cogging torque
InactiveUS7230359B2Minimized cogging torqueGood sinusoidal formMagnetic circuit rotating partsSynchronous machines with stationary armatures and rotating magnetsMagnetic polesEngineering
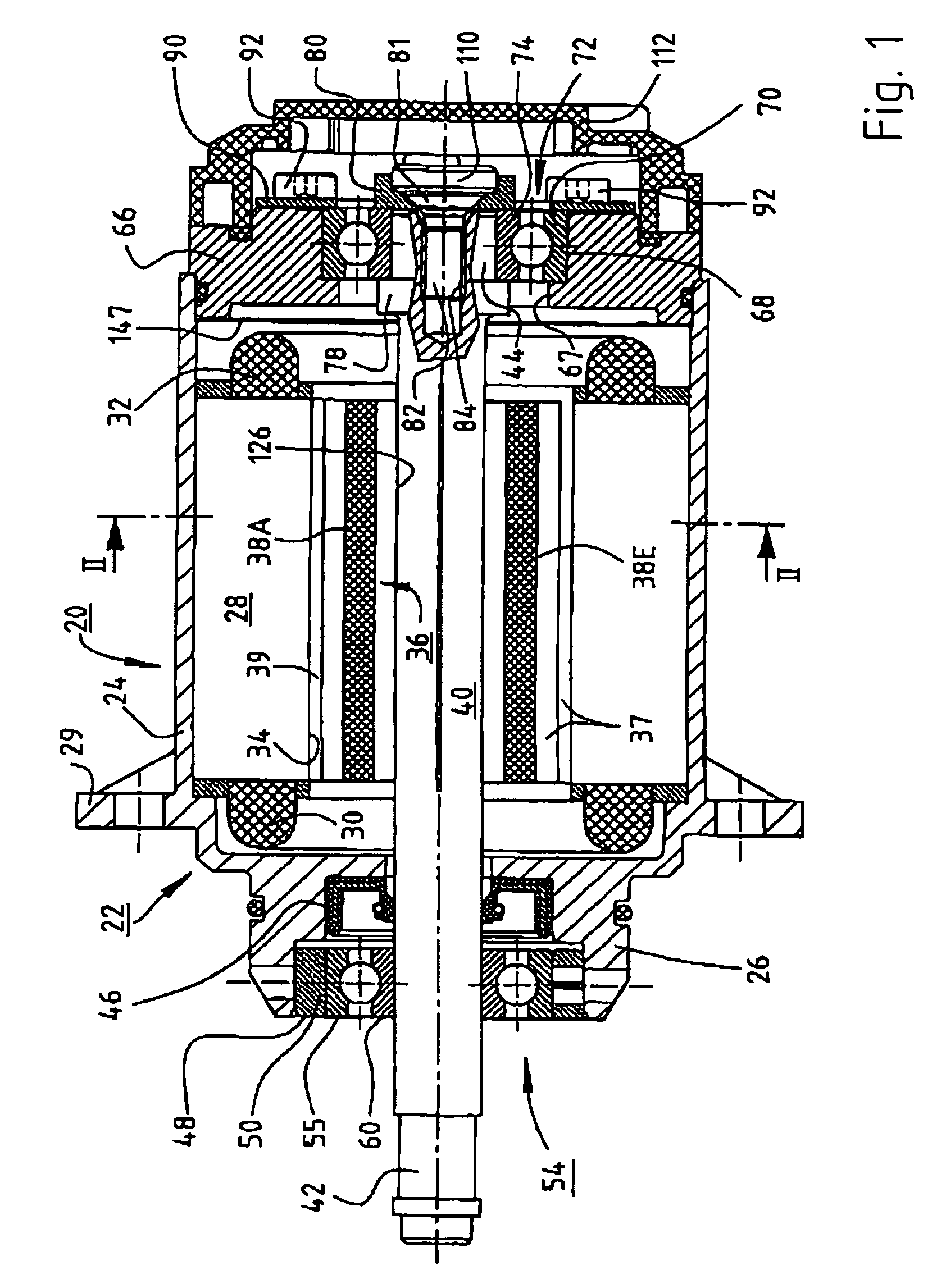
An electric motor has a rotor (36) and a stator (28) having a lamination stack formed with slots (126). The slots have a predetermined slot pitch (τs), and a multi-phase stator winding is arranged in them. The rotor (36) has salient poles having pole shoes (136) and a magnetic return path (130). Between the return path (130) and each pole shoe (136), a recess (138, 140) is formed for receiving a permanent magnet (38). On each side of such a permanent magnet (38), a region (146a, 146b) of poor magnetic conductivity is arranged, in order to make the flux distribution in the air gap more sinusoidal. Measuring in a circumferential direction, the width (β) of a pole shoe (136) decreases with increasing distance from an interface (138) between said return path and said permanent magnet (38), and, at a place of lowest width, the pole shoe has an angular extent (βc) which has, with respect to the slot pitch (τs) between said stator slots (126), the following relationship:βc=n*τs*(1−0.02) . . . n*τs*(1−0.2),where n=1, 2, 3 . . . andβc and τs are measured in mechanical degrees.
Owner:EBM PAPST ST GEORGEN & -
Motor and Recording Disk Drive Device Provided with the Same
InactiveUS20060197402A1Easy to adjustCombined cogging waveform can be reducedMagnetic circuit shape/form/constructionSynchronous machines with stationary armatures and rotating magnetsRotor magnetsEngineering
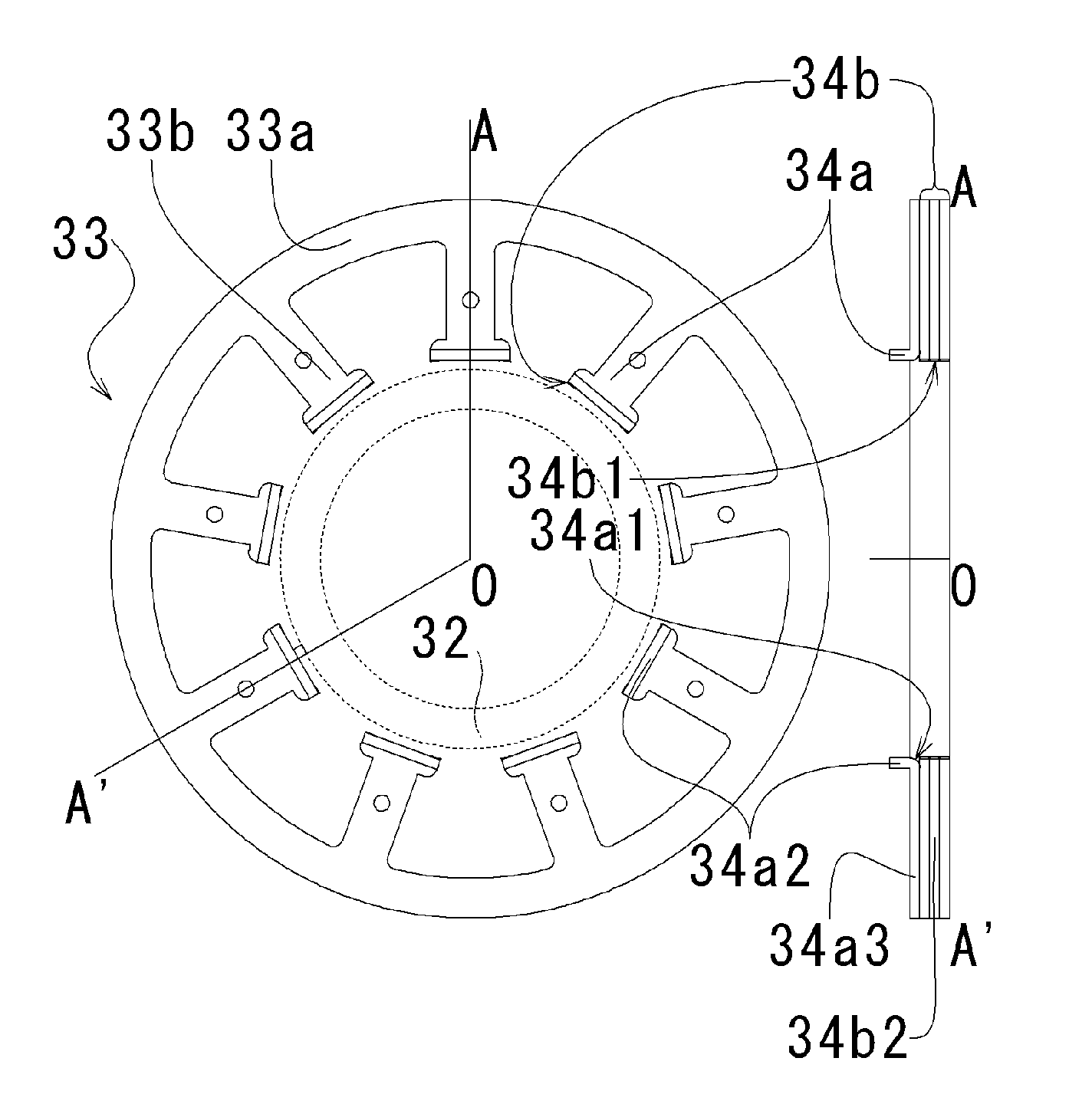
In a spindle motor, a core (33) includes a plurality of core plates (34), which are laminated one on another. The core (33) is constituted by laminating two cores, that is, a first core (34a) and a second core (34b), which are different from each other in shape of a surface facing to a rotor magnet (32). At least a part of a cogging torque generated at the second core (34b) can be cancelled by a cogging torque generated at the first core (34a).
Owner:NIPPON DENSAN CORP
Permanent-magnet rotating machine
ActiveUS7067948B2Efficiently reduce cogging torque and torque ripplesMagnetic circuit rotating partsSynchronous machines with stationary armatures and rotating magnetsLower limitSkew angle
A permanent-magnet rotating machine includes a rotor having a rotor core carrying on a curved outer surface multiple permanent magnets arranged in two rows along an axial direction. The permanent magnets in one row are skewed from those in the other row in a circumferential direction by a row-to-row skew angle (electrical angle) θe. A stator having a tubular stator core in which the rotor disposed includes stator coils for producing a rotating magnetic field for rotating the rotor. A lower limit of the row-to-row skew angle θe larger than 30 degrees (electrical angle). A ratio of cogging torque occurring in the absence of skew to cogging torque occurring when the permanent magnets are skewed, at a row-to-row skew angle of 30 degrees is calculated based on the cogging torque ratio, the row-to-row skew angle θe, and B-H curve properties of the stator core. An upper limit of the row-to-row skew angle θe is not larger than the maximum value at which the cogging torque ratio does not exceed the calculated cogging torque ratio at 30 degrees.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Laminated body of motor and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveUS20050073211A1Reducing cogging torque in operation of motorNo thermal deformationMagnetic circuit stationary partsManufacturing stator/rotor bodiesConductor CoilTooth part
A laminated body of a motor includes: a yoke part having a belt shape with a long length in comparison with its width and spirally laminated to form a hollow cylindrical shape; a plurality of teeth parts protruding from one side edge of the yoke part in a width direction and disposed along a longitudinal direction in an isolated manner at a predetermined distance; a stopping protrusion extendingly formed at a protruding end of the teeth part in a longitudinal direction of the yoke part; and an inclined portion having an inclined surface formed by decreasing a width of the stopping protrusion toward its end so as to reduce cogging torque, so that a minimum passage for a winding nozzle is provided while cogging torque is reduced. A laminated body of a motor includes: a yoke part having a belt shape with a long length in comparison with its width and spirally laminated to form a hollow cylindrical shape; a plurality of teeth parts protruding from one side edge of the yoke part in a width direction and disposed along a longitudinal direction in an isolated manner at a predetermined distance; and a protrusion receiving groove recessed in one side of the teeth part along a thickness direction and a coupling protrusion protruding from its other side along the thickness direction of the teeth part to be inserted and fixed by each other, so that defective measurement and an increase in production time caused by welding operation are prevented.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Permanent magnet type motor
ActiveUS20060244335A1Reduce leakage fluxSimple constitutionMagnetic circuit rotating partsMagnetic circuit stationary partsSkew anglePermanent magnet motor
A permanent magnet electric motor 10 comprises a rotor 30 provided with two stages of permanent magnets in the axial direction on an outer circumferential face of a rotor iron core, and having a shaft shifted by a stage skew angle θr in electrical angle to decrease a first frequency component of cogging torque in the circumferential direction of the rotor iron core between two stages of the permanent magnets, a stator iron core 21 of cylindrical shape provided with the stator winding for producing a rotating magnetic field causing the rotor 30 to be rotated, and a stator 20 dividing the stator iron core 21 into plural blocks in the axial direction, and shifted by a stage skew angle θs in electrical angle to decrease a second frequency component of the cogging torque in the circumferential direction of the stator iron core 21.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Permanent magnet type magnetic pole core structure capable of minimizing cogging torque for rotating electric machine
InactiveUS20090140590A1Minimizing cogging torqueMagnetic circuitSynchronous machines with stationary armatures and rotating magnetsElectric machineMagnetic poles
A permanent magnet type magnetic pole core structure capable of minimizing the cogging torque for a rotating electric machine such as an electric motor or a power generator is disclosed. The rotating electric machine comprises: a magnetic pole core and an armature core. The magnetic pole core comprises a plurality of magnetic pole structures in a number of M, while each magnetic pole structure comprises at least one permanent magnet and can be used for defining two reference lines with an expanding angle sandwiched therebetween, and a periphery of the magnetic pole core enclosing the pole structure defining between the two reference lines is divided into a first arc surface, a second arc surface and a third arc surface. In an exemplary embodiment, the armature core comprises a plurality of slot structures in a number of S. The ratio of the amount of slot structure to the amount of the magnetic pole structure, i.e. S / M, is 3 / 2. With the aforesaid permanent magnet type magnetic pole core structure, the cogging torque of the rotating electric machine can be minimized.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Permanent magnet rotary structure of electric machine
InactiveUS20080157619A1Reduce the cogging torqueMagnetic circuitSynchronous machines with stationary armatures and rotating magnetsElectric machinePermanent magnet motor
A permanent magnet motor is provided. The permanent magnet motor includes a stator having a stator shaft having an outer surface, K salient teeth formed upon the outer surface, and K winding slots formed among the K salient teeth, and a rotor having a first inner surface facing the outer surface, and P pairs of permanent magnets formed on the first inner surface, each of which has a second inner surface facing the outer surface and at least a groove formed on the second inner surface to reduce a cogging torque.
Owner:DELTA ELECTRONICS INC
Permanent magnet motor
InactiveUS20050264122A1Decrease cogging torqueCogging torque can be decreasedMagnetic circuit rotating partsSynchronous machines with stationary armatures and rotating magnetsMagnetic polesPermanent magnet motor
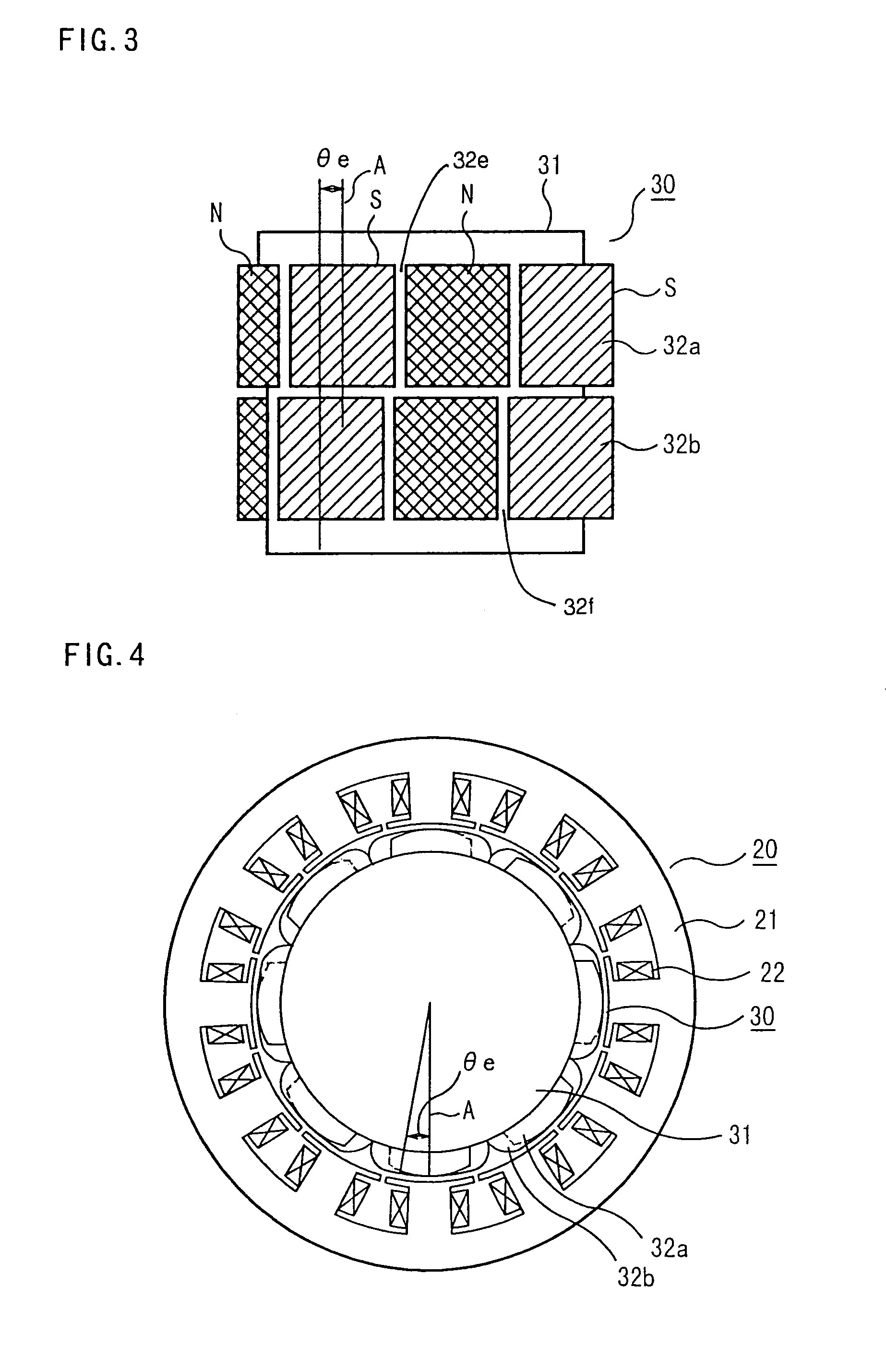
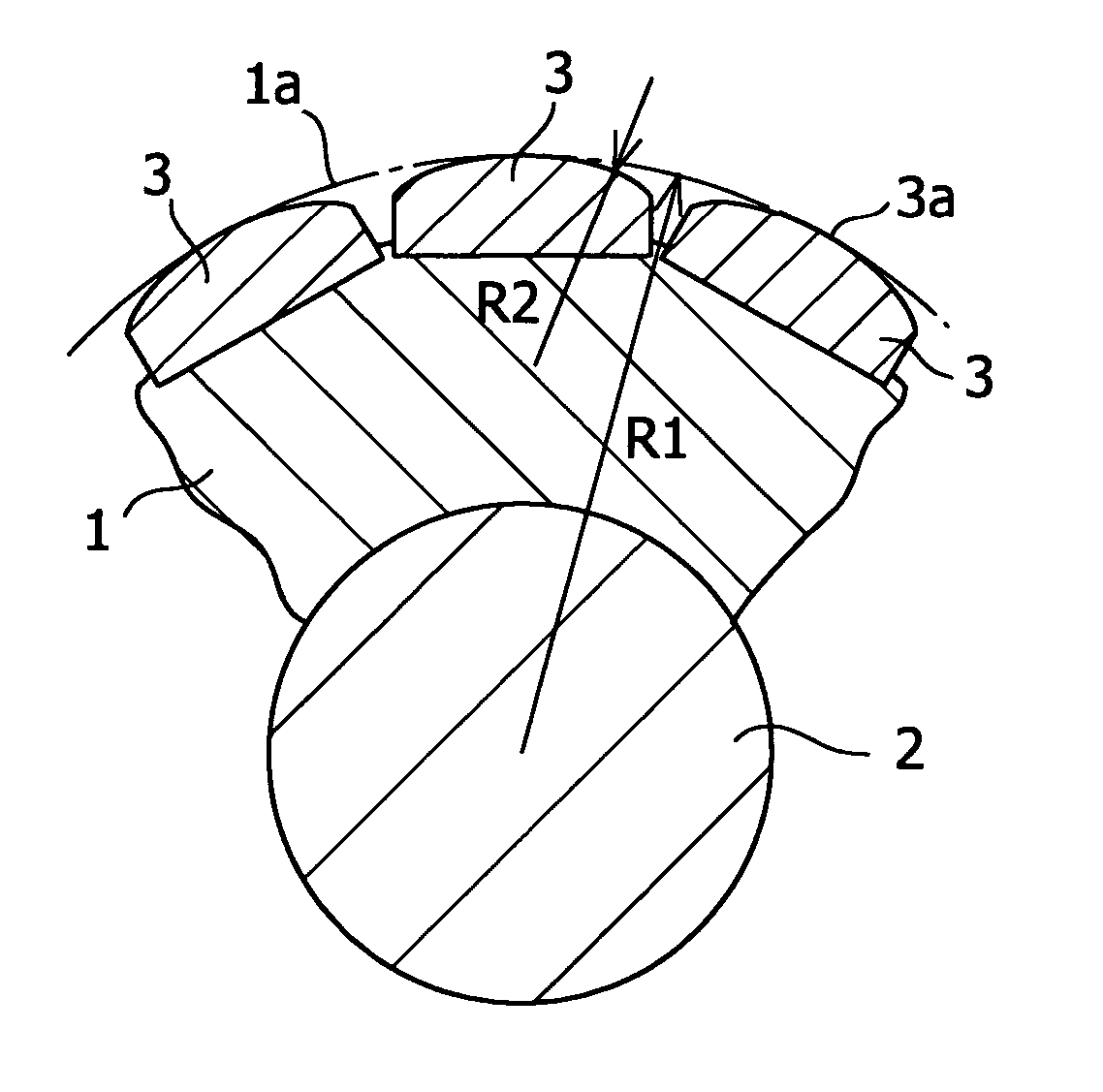
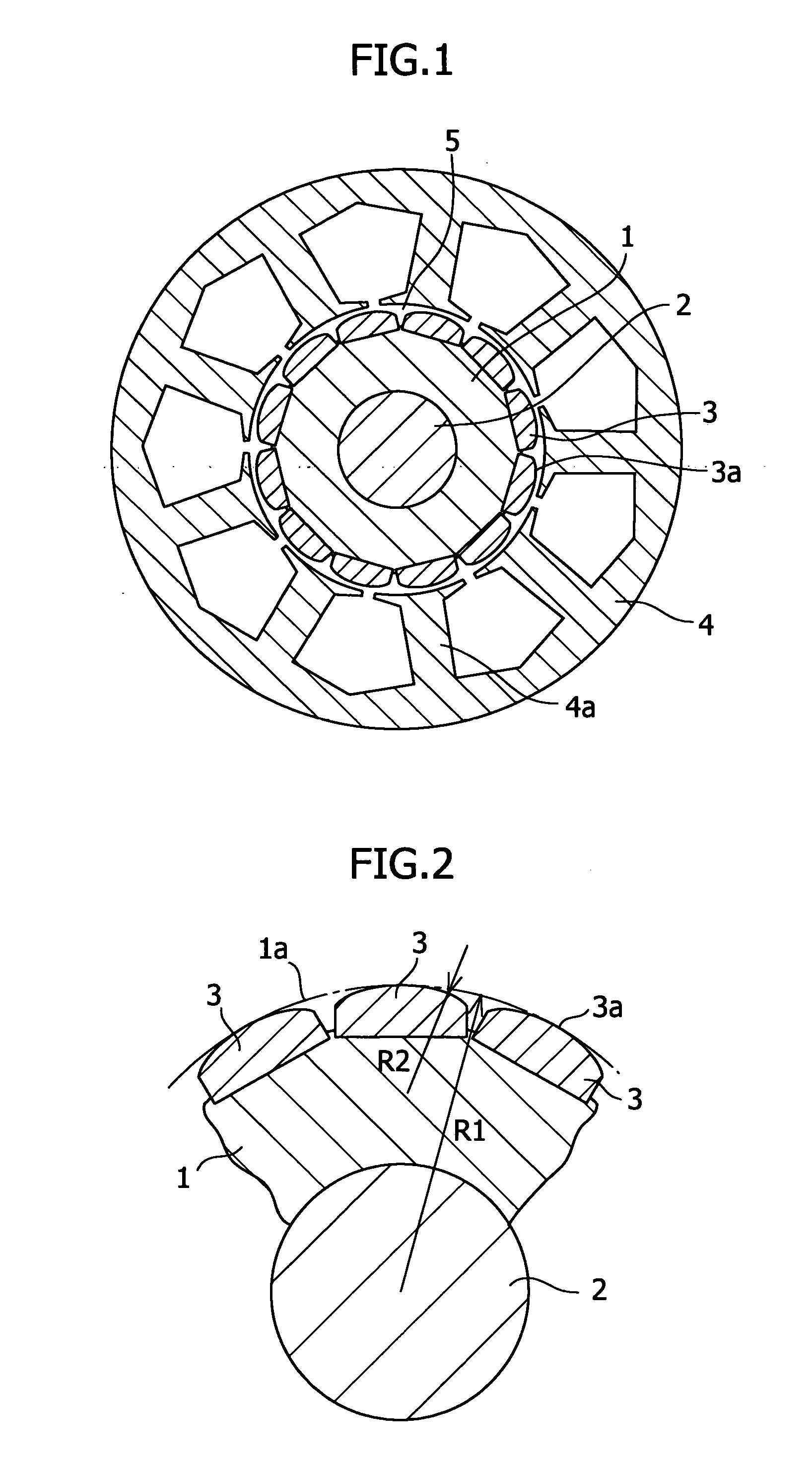
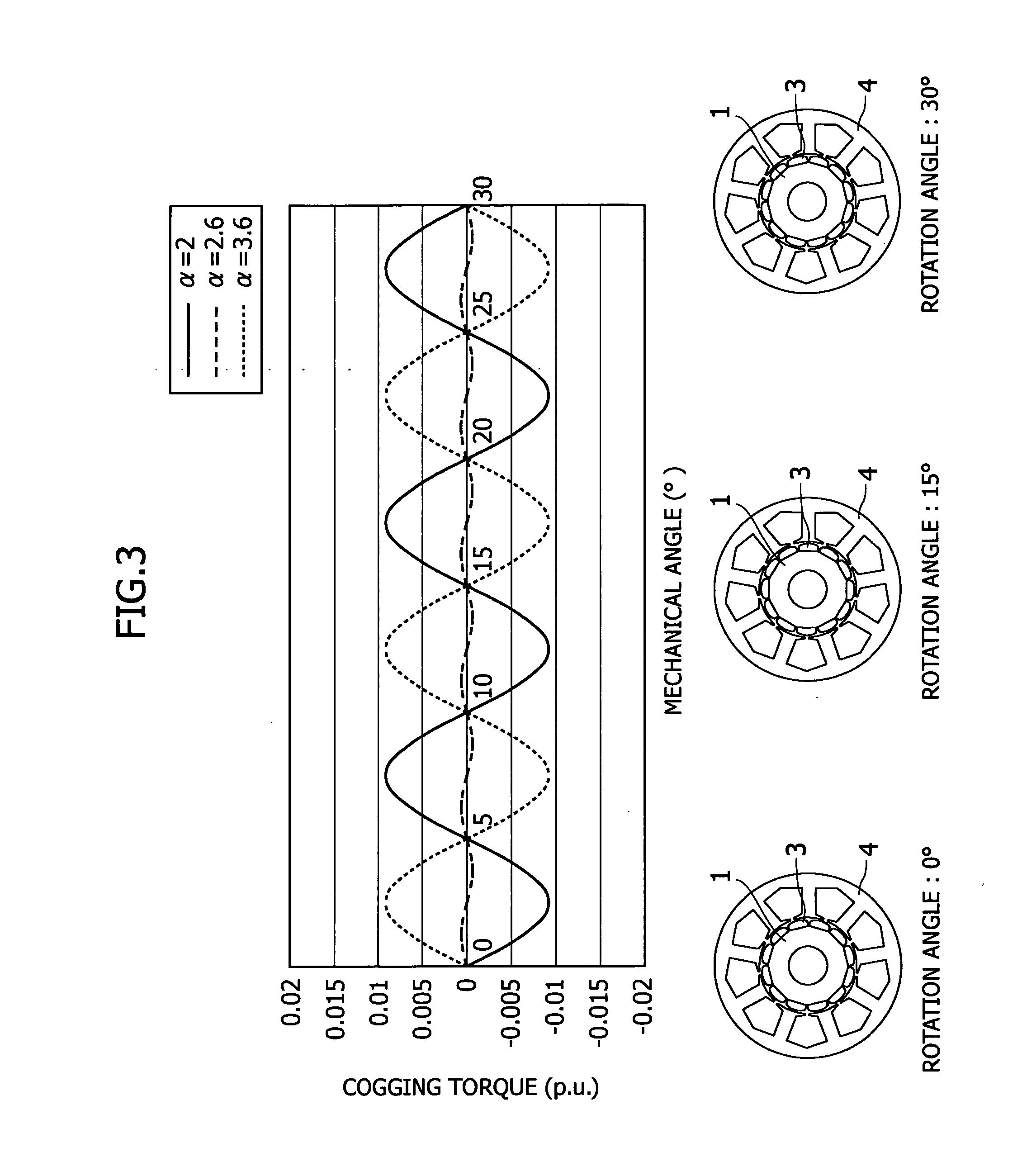
In a permanent magnet motor consisting of a rotor 1, which is supported on a rotating shaft 2 and has twelve permanent magnets 3 arranged at fixed intervals in the circumferential direction in the peripheral edge portion thereof, and a stator 4, which is disposed around the rotor 1 with a gap being provided with respect to the rotor 1 and has nine magnetic poles 4a, each having a coil wound thereon, arranged at fixed intervals in the circumferential direction so as to face towards the outer peripheral surface of the rotor 1, a value obtained by dividing the radius of the rotor 1 by the radius of curvature of a permanent magnet surface facing towards the stator is set at a value such as to decrease cogging torque. Thereby, there is provided a permanent magnet motor in which the radius of an arcuate shape which can minimize cogging torque is theoretically verified, by which the optimum radius can be determined limitedly for a permanent magnet motor consisting of a rotor having twelve permanent magnets and a stator having nine magnetic poles.
Owner:ORIENTAL MOTOR
Application method of mixed permanent magnets in flux-switching permanent magnet motor
InactiveCN104242501ASignificant progressHighlight substantiveMagnetic circuit stationary partsMagnetic circuit characterised by magnetic materialsRare earthPermanent magnet motor
Owner:HEBEI UNIV OF TECH
Single phase brushless motor and power tool utilizing same
InactiveUS10199886B2Large peak valueIncreases startup torqueMagnetic circuit rotating partsMagnetic circuit stationary partsBrushless motorsPeak value
A single phase brushless motor and a power tool are provided. The single phase brushless motor includes a stator and a rotor. The stator includes a stator core and windings wound around the stator core. The stator core includes a yoke and at least two teeth. The tooth includes a tooth body and a tooth tip. The tooth tip includes first and second pole shoes. The two pole shoes of each tooth are symmetrical about a center line of the tooth body. Each tooth defines a positioning groove facing the rotor between the two pole shoes. Pole shoes of adjacent two of the at least two teeth are spaced apart by a slot opening. A width of the positioning groove is greater than a width of the slot opening. The peak value of the cogging torque of the motor is increased, and the motor has a large startup torque.
Owner:JOHNSON ELECTRIC SA
Method of determining pole arc ratio of interior permanent magnet rotary motor and interior permanent magnet rotary motor
InactiveUS20050168089A1Reduce the amount requiredReduce torqueMagnetic circuit rotating partsManufacturing dynamo-electric machinesMagnetic polesControl theory
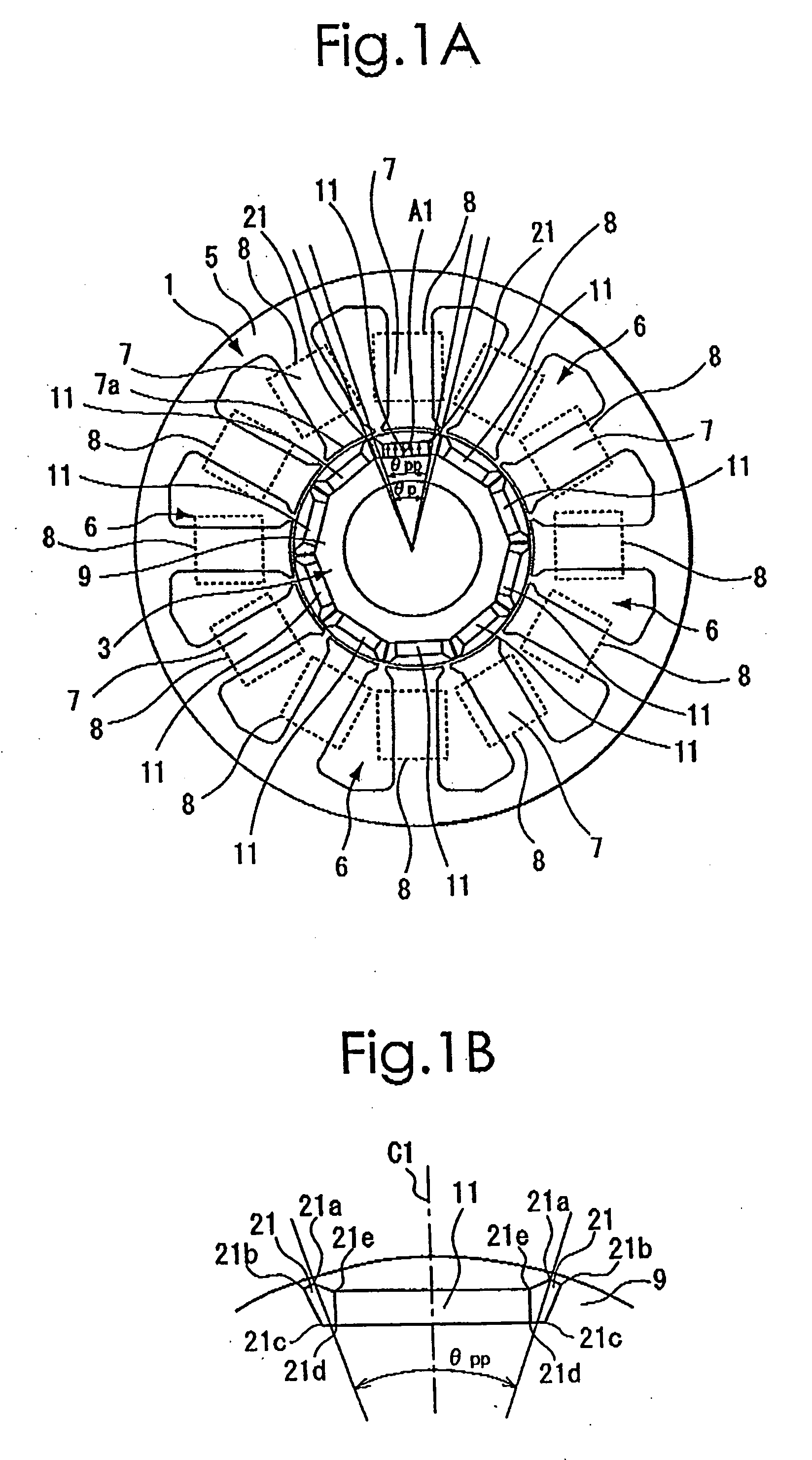
There is provided an interior permanent magnet rotary motor that can reduce cogging torque and can also reduce the amount of permanent magnet used, without reducing torque. In an interior permanent magnet rotary motor of the present invention having N slots 6 and P permanent magnet magnetic pole sections 11, in which P / N is set in the range of ⅔ to 43 / 45 and Po in a irreducible fraction Po / No of the P / N is set to be an odd number, an pole arc ratio ψp is defined to be the ratio of θpp / θp where an angle between two line segments assumed for a pair of flux barriers 21, each of which connects the center of a rotor core and one of a plurality of corners of the section of each flux barrier that is closest to the surface of the rotor core 9 is indicated by the θpp and an angle obtained by dividing the full circumference angle (360°) of the rotor core by the number of the permanent magnet pole sections is indicated by the θp. Then, the pole arc ratio indicated by Ψp is determined is so as to satisfy the relation of Ψp=2mP / N+P / 4LCM (P, N)−2n, in which LCM (P, N) is the least common multiple between P and N, m and n are arbitrary natural numbers, and the Ψp is larger than zero but smaller than one.
Owner:SANYO DENKI CO LTD
Drive apparatus for vehicle
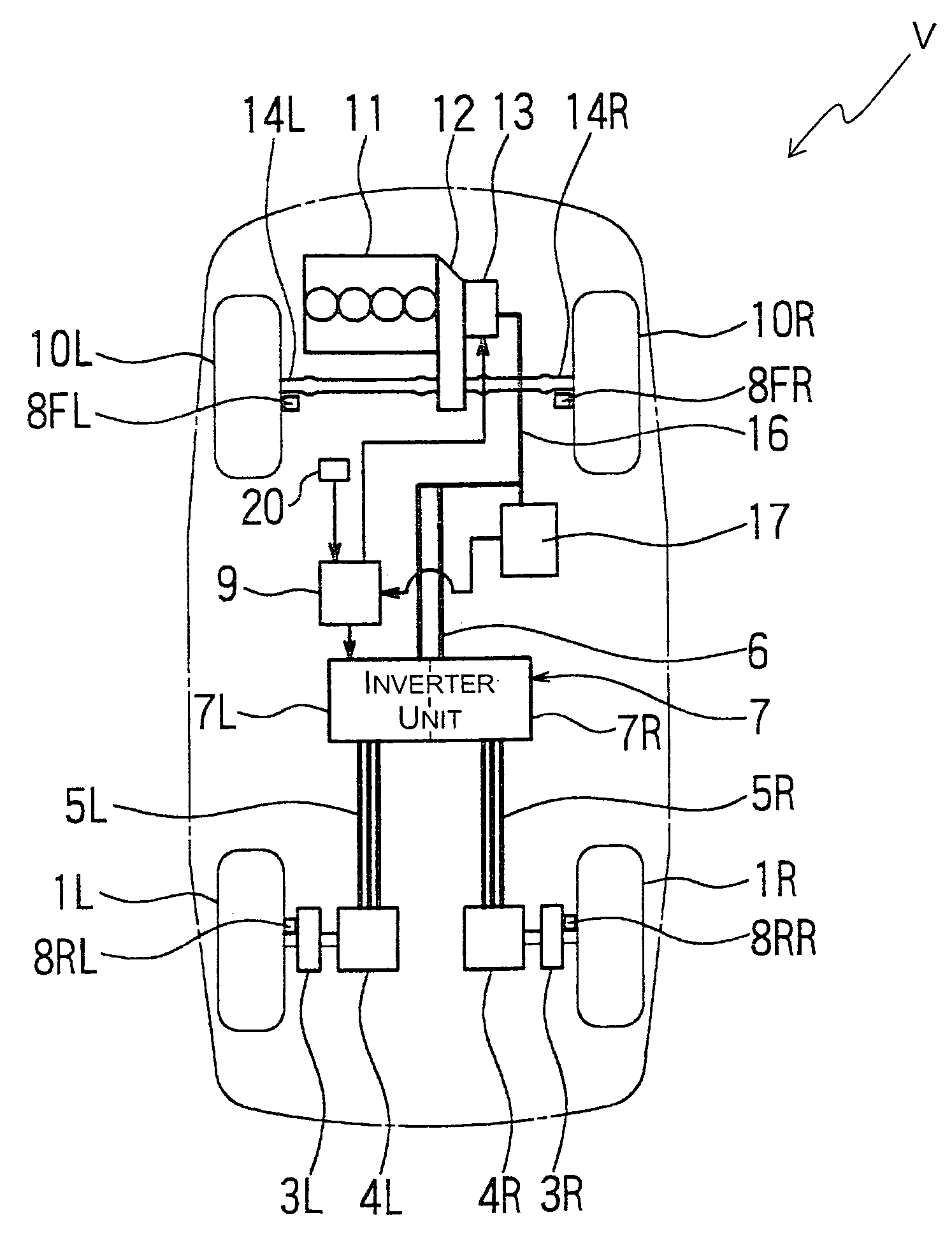
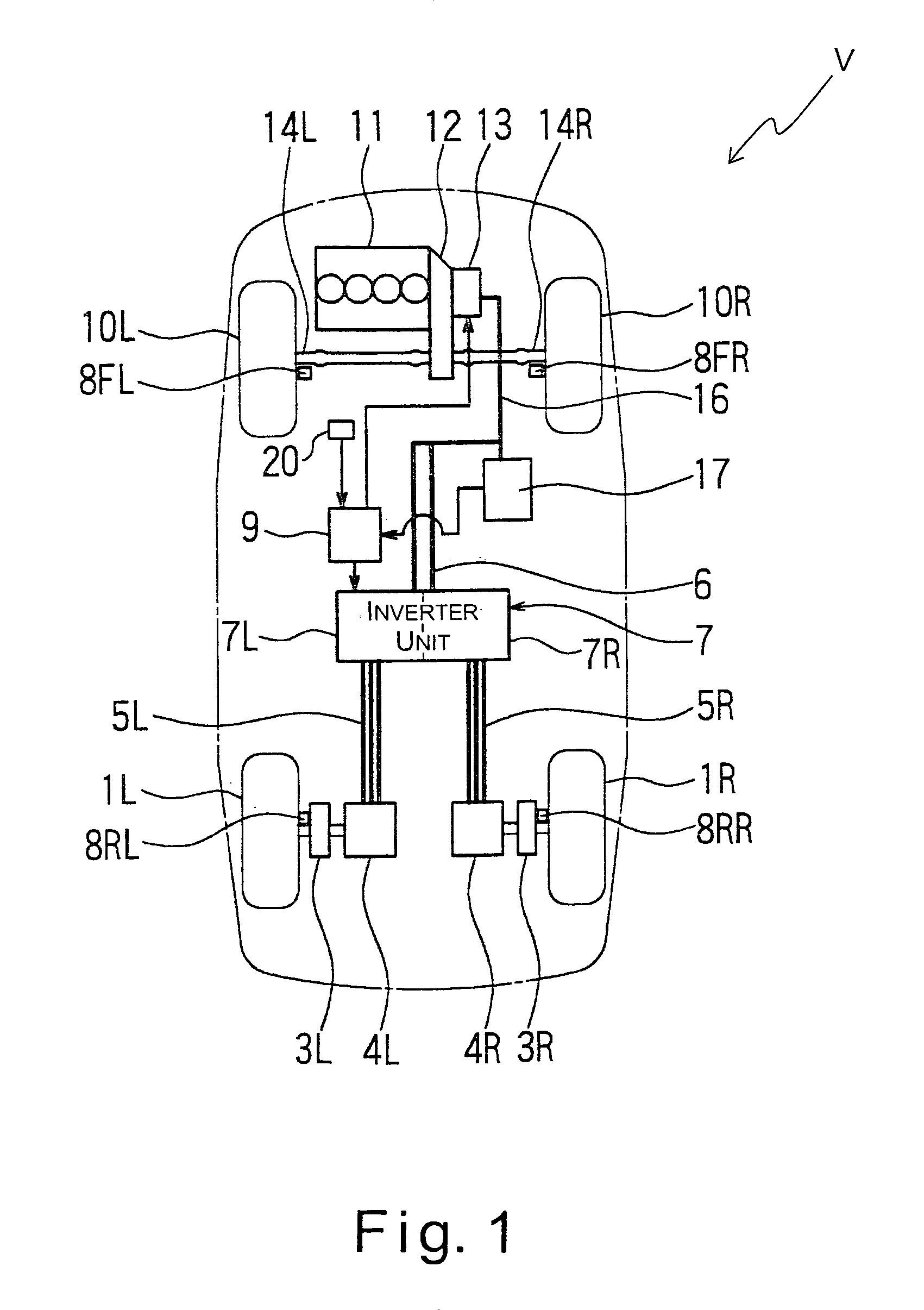
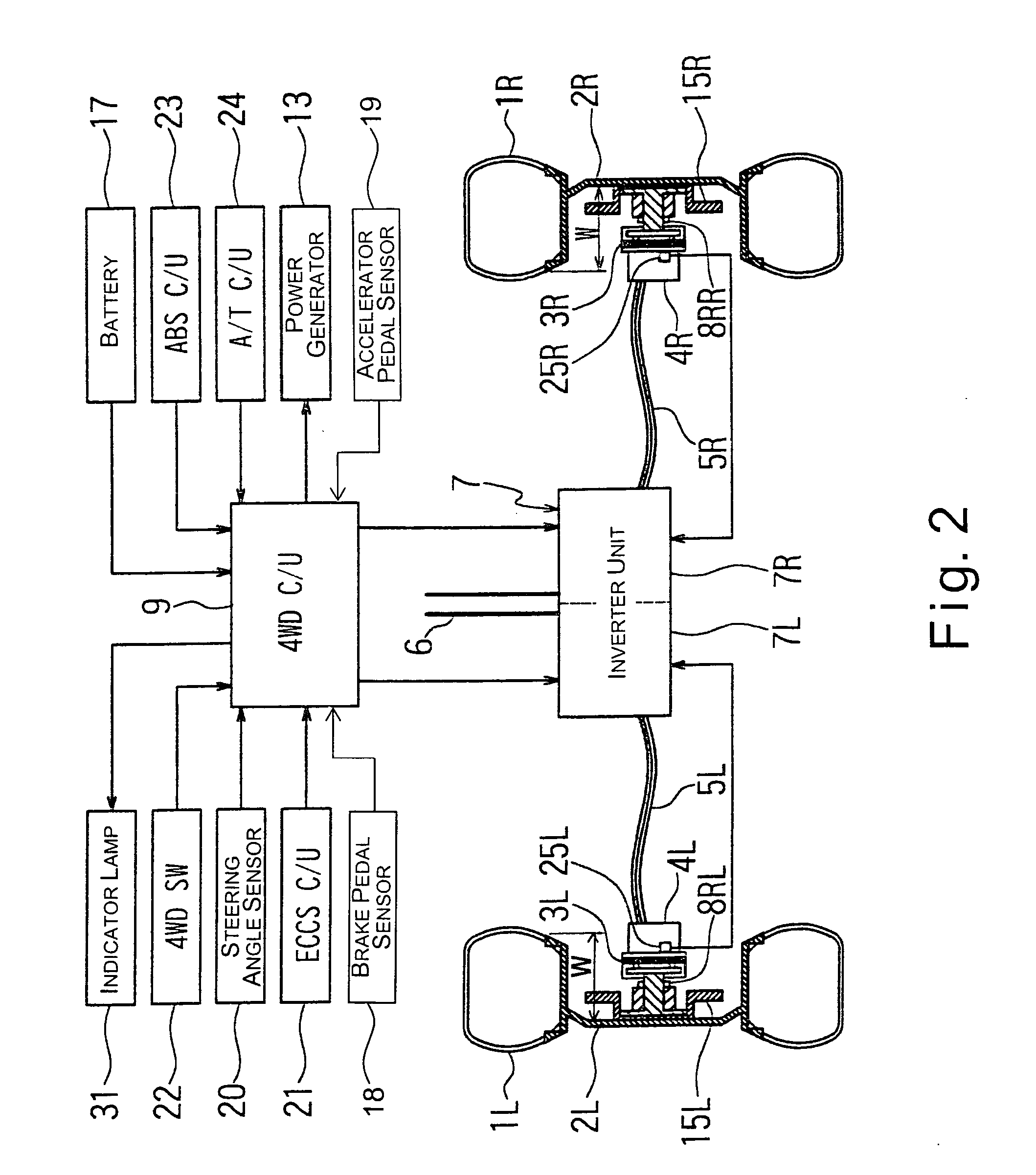
InactiveUS7195087B2Weight increaseImprove fuel efficiencyInternal combustion piston enginesPropulsion using ac induction motorsDrive wheelFriction loss
A drive apparatus basically comprises left and right drive units each including at least a reduction gear, an electric motor without a permanent magnet, and a brake disc. Each of the left and right drive units is housed substantially within a rim of each of rear wheels which are driven wheels. A 4WD control unit is configured to control a pair of inverters to separately drive the electric motors when a vehicle speed is in a range between a standing start speed and a prescribed vehicle speed, and to stop driving the electric motors when the vehicle speed is equal to or greater than the prescribed vehicle speed to place the rear wheels in a driven state. Accordingly, a friction loss due to a cogging torque encountered in a conventional permanent magnet-type motor is eliminated, and a lightweight drive apparatus is obtained. Fuel efficiently is accordingly improved.
Owner:NISSAN MOTOR CO LTD
Rotor of rotating electrical machine and manufacturing method there for
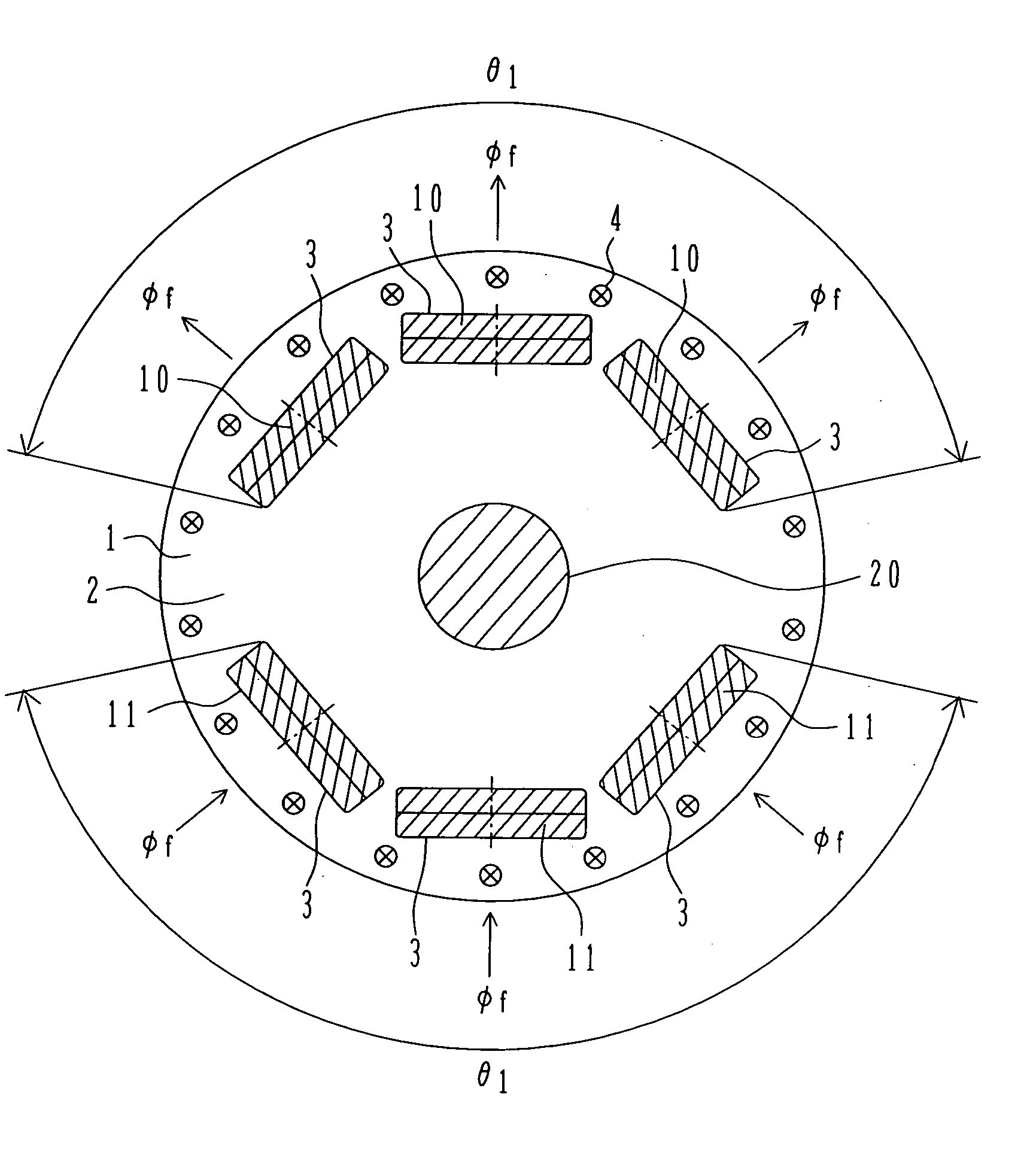
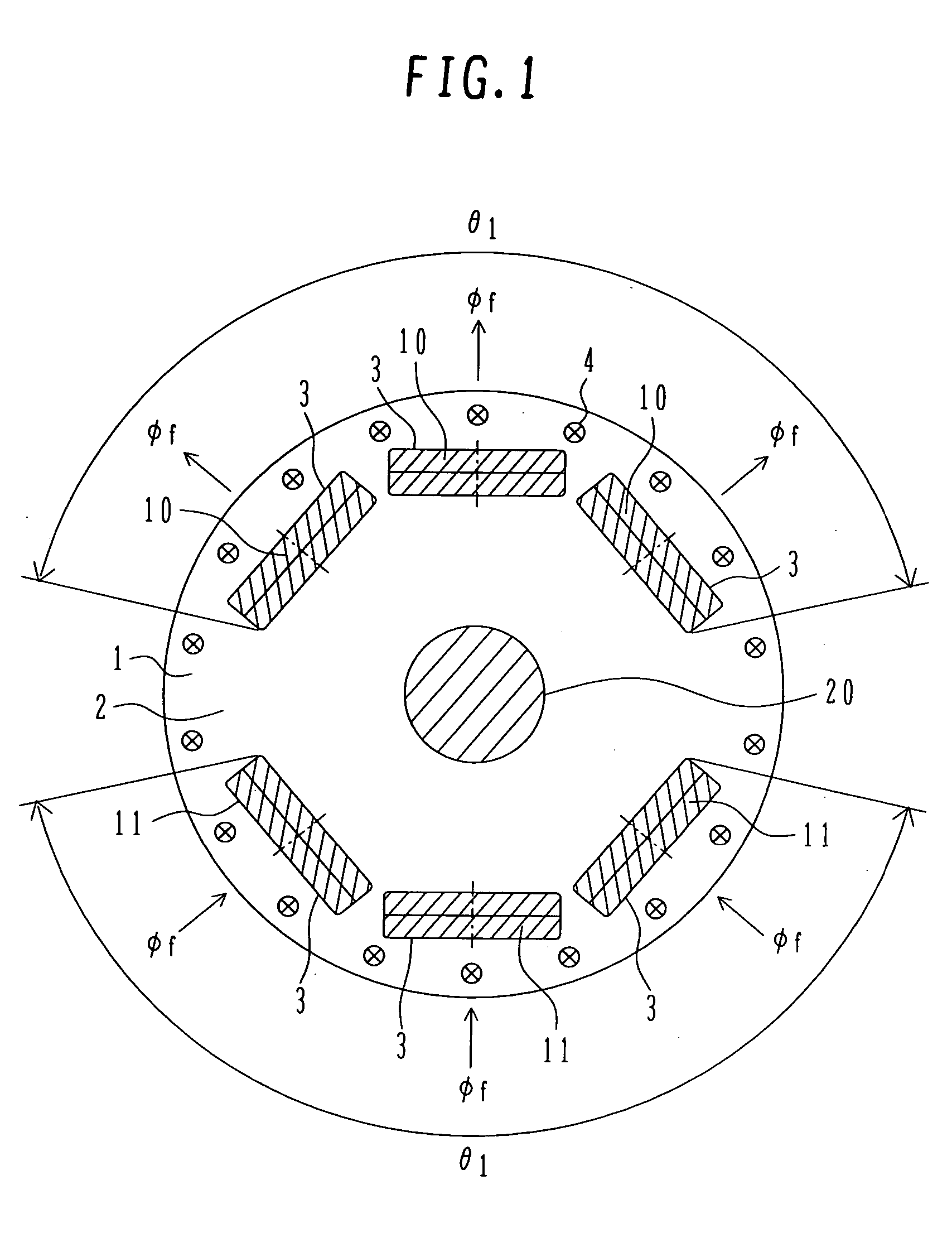
ActiveUS20090102304A1Increase costFixed securityMagnetic circuit rotating partsManufacturing stator/rotor bodiesElectric machineMagnetic poles
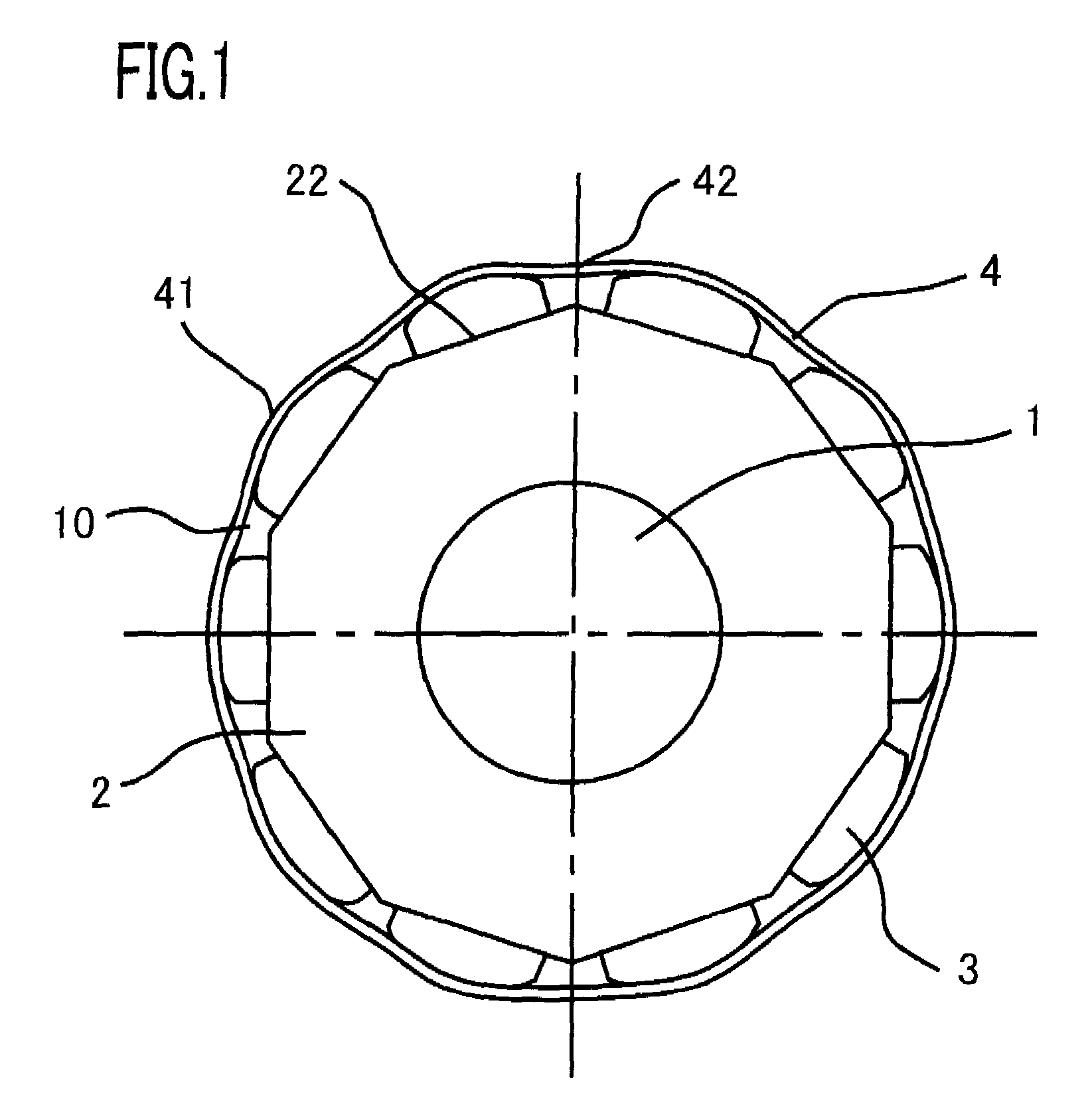
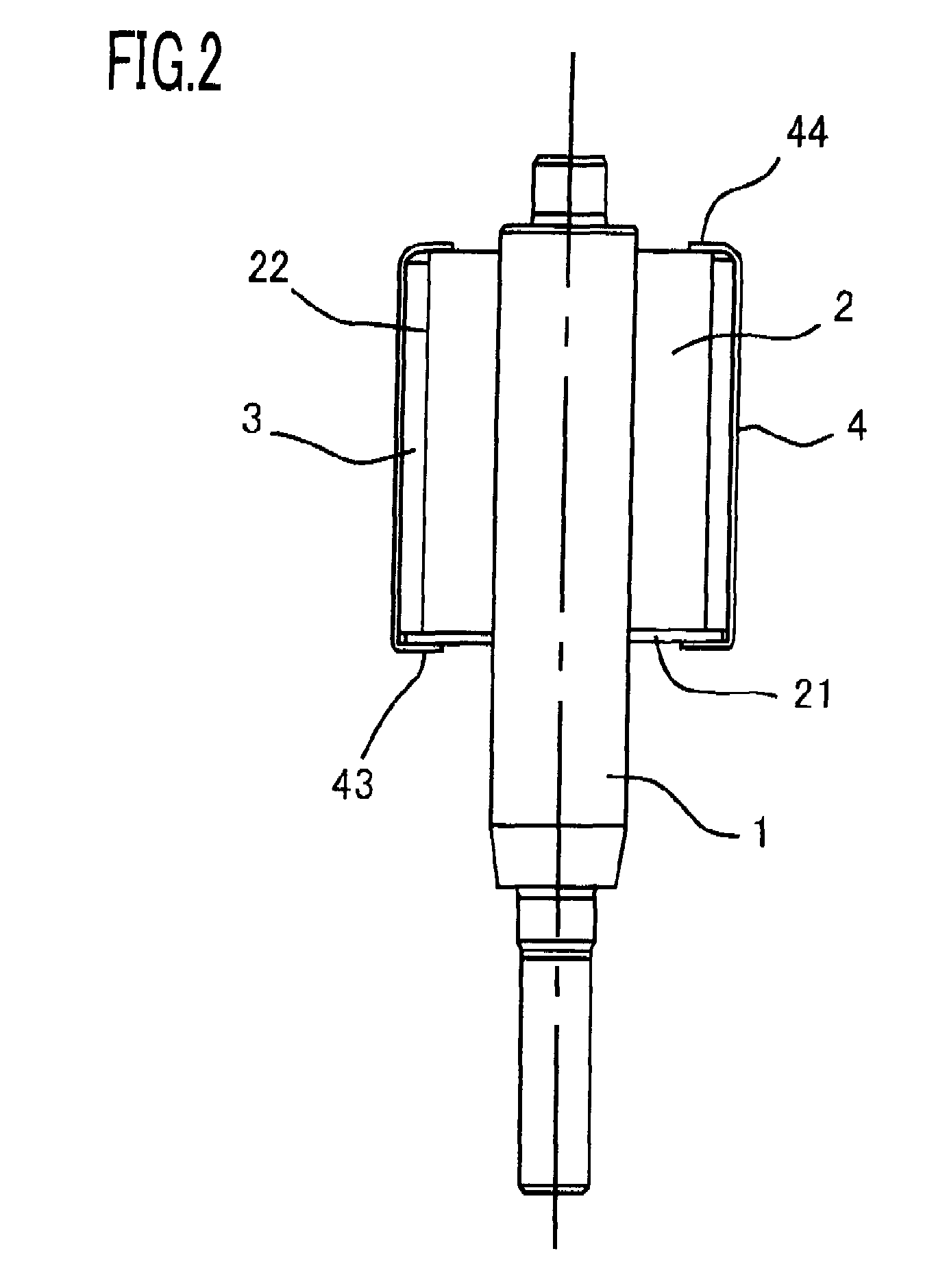
A rotor of a rotating electrical machine is provided in which neither deterioration nor fluctuation in the cogging torque is caused and that causes neither physical enlargement nor cost increase. The rotor of a rotating electrical machine, provided with a plurality of magnetic poles 3 that are fixed on a rotor iron core 2 and arranged spaced apart from one another in the circumferential direction of the rotor iron core 2, is characterized by including a tube-shaped non-magnetic ring 4 mounted on the outer circumferential surfaces of the plurality of magnetic poles 3, and characterized in that the non-magnetic ring has a plurality of inner-diameter bulging portions 41 that abut on the corresponding outer circumferential surfaces of the plurality of magnetic poles.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Rotor of permanent magnet rotating electric machine
InactiveUS20060103251A1Satisfactory magnetic flux distributionIncreasing fundamental wave effective valueMagnetic circuit rotating partsSynchronous machines with stationary armatures and rotating magnetsElectric machineMagnetic poles
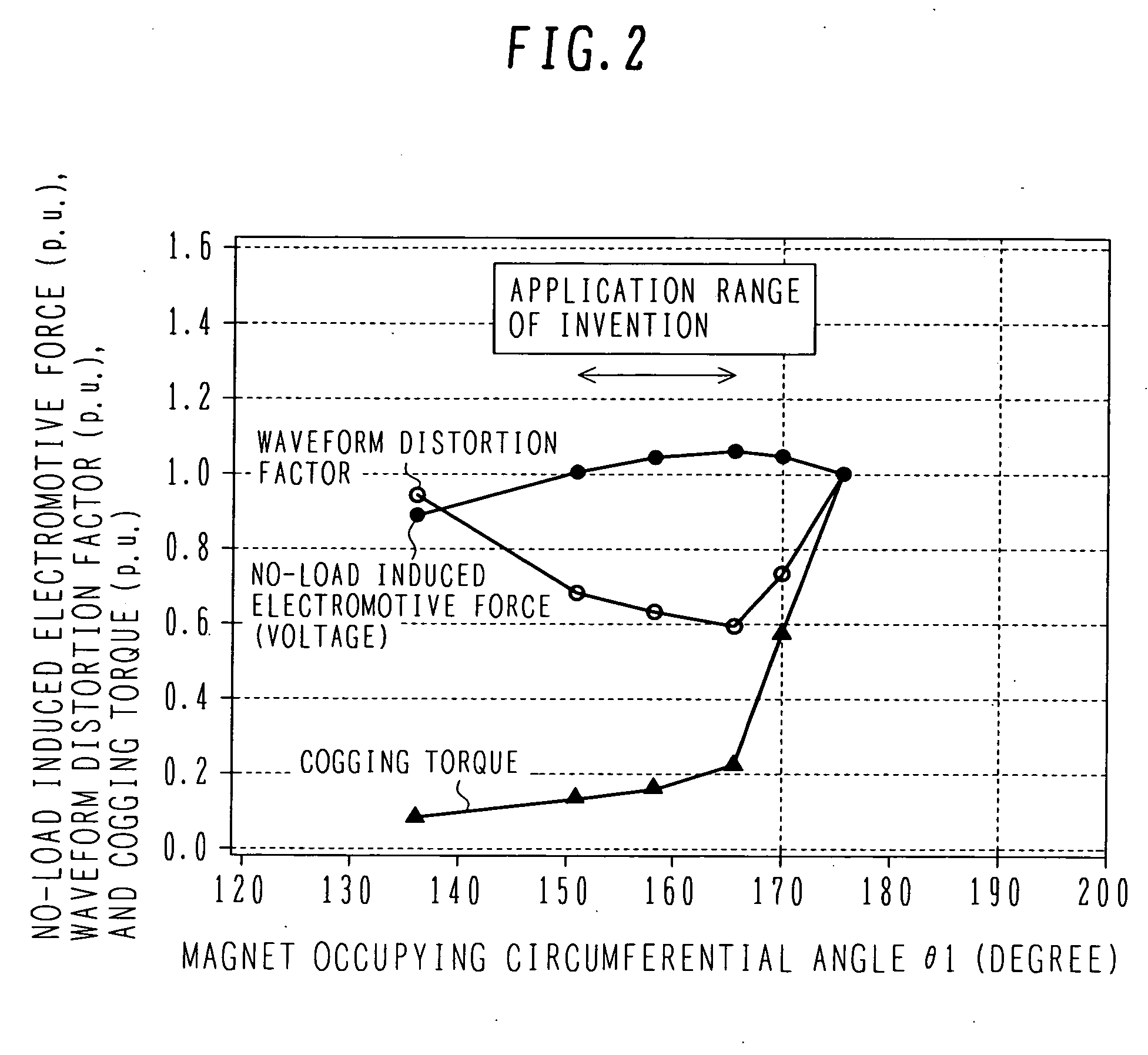
In the prior art in which permanent magnets are regularly arranged over the whole circumference of a rotor core, a satisfactory magnetic flux distribution is hard to obtain, and the cogging torque and the distortion factor of the induced electromotive force waveform are large, whereby characteristics of a rotating electric machine are poor. Also, because the permanent magnets are arranged over the whole circumference, a large number of permanent magnets are required and cost reduction is difficult. A permanent magnet rotating electric-machine of the invention comprises a stator provided with a plurality of windings, and a rotor in which magnets are disposed in slots formed in a rotor core along an outer circumference thereof, the rotor core being fixed on a rotary shaft rotating inside the stator, and in which one magnetic pole is constituted by each group of three or more of the magnets. A total angle occupied by the group of magnets constituting one magnetic pole is in the range of 150 to 165 degrees in terms of an electrical angle.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Electric motor with poles shaped to minimize cogging torque
InactiveUS20050062354A1Minimized cogging torqueGood sinusoidal formMagnetic circuit rotating partsSynchronous machines with stationary armatures and rotating magnetsEngineeringFlux distribution
An electric motor has a rotor (36) and a stator (28) having a lamination stack formed with slots (126). The slots have a predetermined slot pitch (τS), and a multi-phase stator winding is arranged in them. The rotor (36) has salient poles having pole shoes (136) and a magnetic return path (130). Between the return path (130) and each pole shoe (136), a recess (138, 140) is formed for receiving a permanent magnet (38). On each side of such a permanent magnet (38), a region (146a, 146b) of poor magnetic conductivity is arranged, in order to make the flux distribution in the air gap more sinusoidal. Measuring in a circumferential direction, the width (β) of a pole shoe (136) decreases with increasing distance from an interface (138) between said return path and said permanent magnet (38), and, at a place of lowest width, the pole shoe has an angular extent (βC)which has, with respect to the slot pitch (τS) between said stator slots (126), the following relationship: βC=n*τS*(1−0.02) . . . n*τS*(1−0.2), where n=1, 2, 3 . . . and βC and τS are measured in mechanical degrees.
Owner:EBM PAPST ST GEORGEN & -
Stator of outer rotor type motor for drum type washing machine
ActiveUS7138741B2Reduce materialReduce weightSynchronous generatorsWindings insulation shape/form/constructionEngineeringMechanical engineering
The present invention provides an outer rotor type motor for a drum type washing machine to reduce material and weight for fabrication, simplify fabrication process, provide stable assembly of a stator to a fixing side, such as a tub or a bearing housing, prevent unwinding of stacked steel plates in assembling a helical core, and reduce stress on the steel plates of the core. The present invention includes a helical core having multiple layers formed by winding steel plates in a helix starting from a bottom layer to a top layer, the steel plate having a base portion with teeth projected from the base portion, wherein the teeth have arched shape tips for reducing vibration and noise generated by cogging torque of the helical core, an upper insulator of an electric insulating material covered on an upper side of the helical core in a shape complementary to a shape of the helical core, and a lower insulator of an electric insulating material covered on a lower side of the helical core at the time of assembly with the upper insulator having a shape complementary to a shape of a helical core.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Electric machine, in particular brushless synchronous motor
InactiveUS7233090B2Degree of reductionReduced cogging torqueMagnetic circuit rotating partsMagnetic circuit characterised by magnetic materialsMagnetic anisotropySynchronous motor
An electrical machine, in particular a brushless synchronous motor has a stator (14) and a rotor (12) with salient poles (18) disposed distributed over its circumference, each of which poles has an enclosed permanent magnet (11) and a pole shoe (19) that extends radially outward from the permanent magnet and defines an air gap (13) between the stator (14) and rotor (12). In order to achieve a low cogging torque and a low torque undulation, the pole shoes (19) are embodied as magnetically anisotropic, with a preferred direction of the greater magnetic conductivity extending parallel to the radial salient pole axis.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Rotor of rotating electrical machine and manufacturing method there for
ActiveUS7741747B2Easy to manufactureNeither deterioration nor fluctuation in the cogging torque is causedMagnetic circuit rotating partsManufacturing dynamo-electric machinesElectric machineMagnetic poles
A rotor of a rotating electrical machine is provided in which neither deterioration nor fluctuation in the cogging torque is caused and that causes neither physical enlargement nor cost increase. The rotor of a rotating electrical machine, provided with a plurality of magnetic poles 3 that are fixed on a rotor iron core 2 and arranged spaced apart from one another in the circumferential direction of the rotor iron core 2, is characterized by including a tube-shaped non-magnetic ring 4 mounted on the outer circumferential surfaces of the plurality of magnetic poles 3, and characterized in that the non-magnetic ring has a plurality of inner-diameter bulging portions 41 that abut on the corresponding outer circumferential surfaces of the plurality of magnetic poles.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com