Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
638results about "Reinforcing means" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
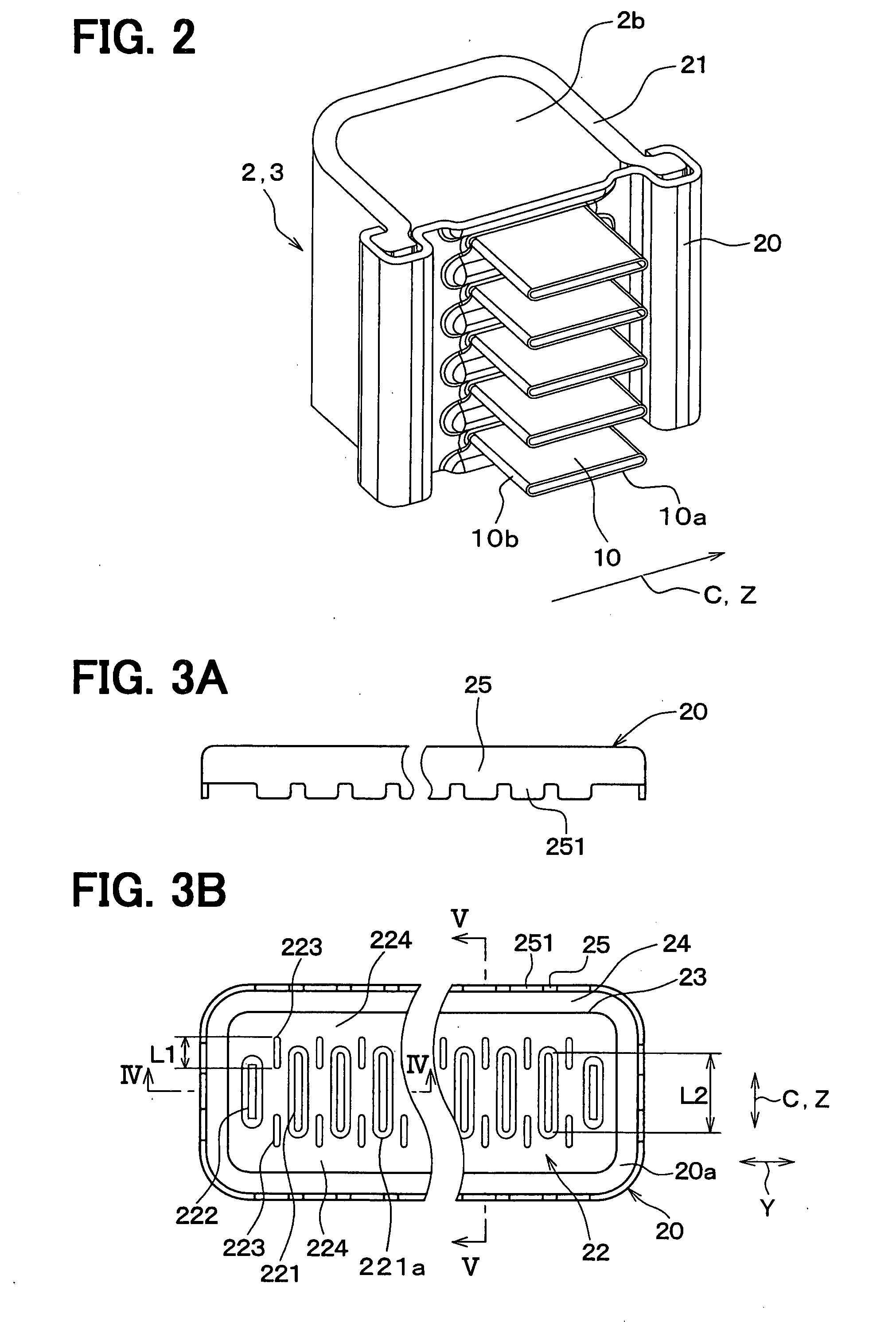
Vapor chamber structure and method for manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20090040726A1Improve structural strengthImprove sealingSpacing meansReinforcing meansWorking fluidEngineering
A vapor chamber structure includes a casing, a working fluid, a wick layer, a plurality of structure strengthening bodies, and a plurality of backflow accelerating bodies. The casing has an airtight vacuum chamber. The working fluid is filled into the airtight vacuum chamber. The wick layer is formed on a surface of the airtight vacuum chamber. The structure strengthening bodies are respectively arranged in the airtight vacuum chamber for supporting the casing. The backflow accelerating bodies are respectively arranged in the airtight vacuum chamber for increasing the backflow velocity of the working fluid. Therefore, the present invention can maintain the completeness of the vapor chamber structure and increase the backflow velocity of the working fluid due to the match of the structure strengthening bodies and backflow accelerating bodies. Because the backflow velocity of the working fluid is increased, the heat-transmitting efficiency is increased.
Owner:THERMAL TECH
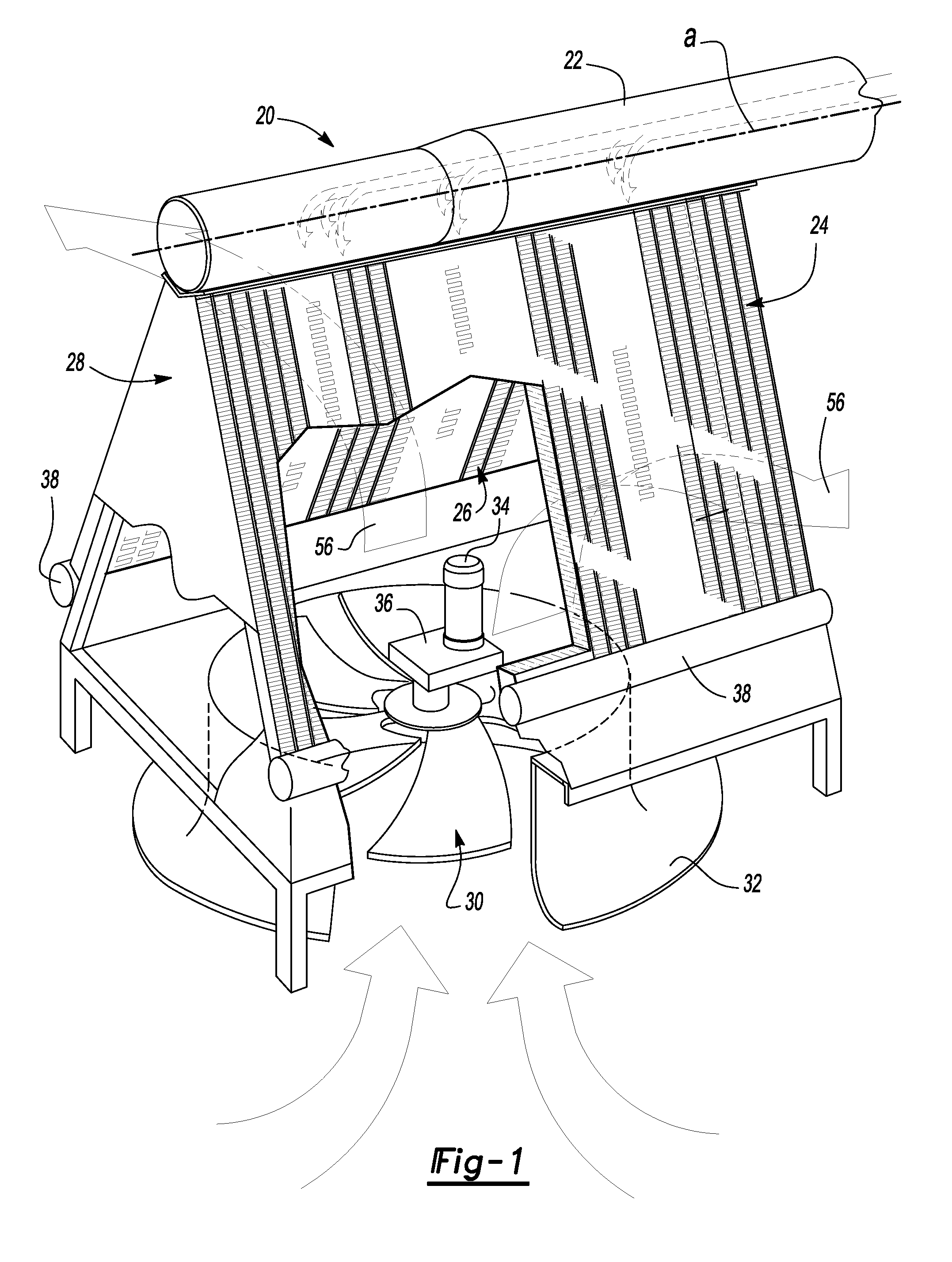
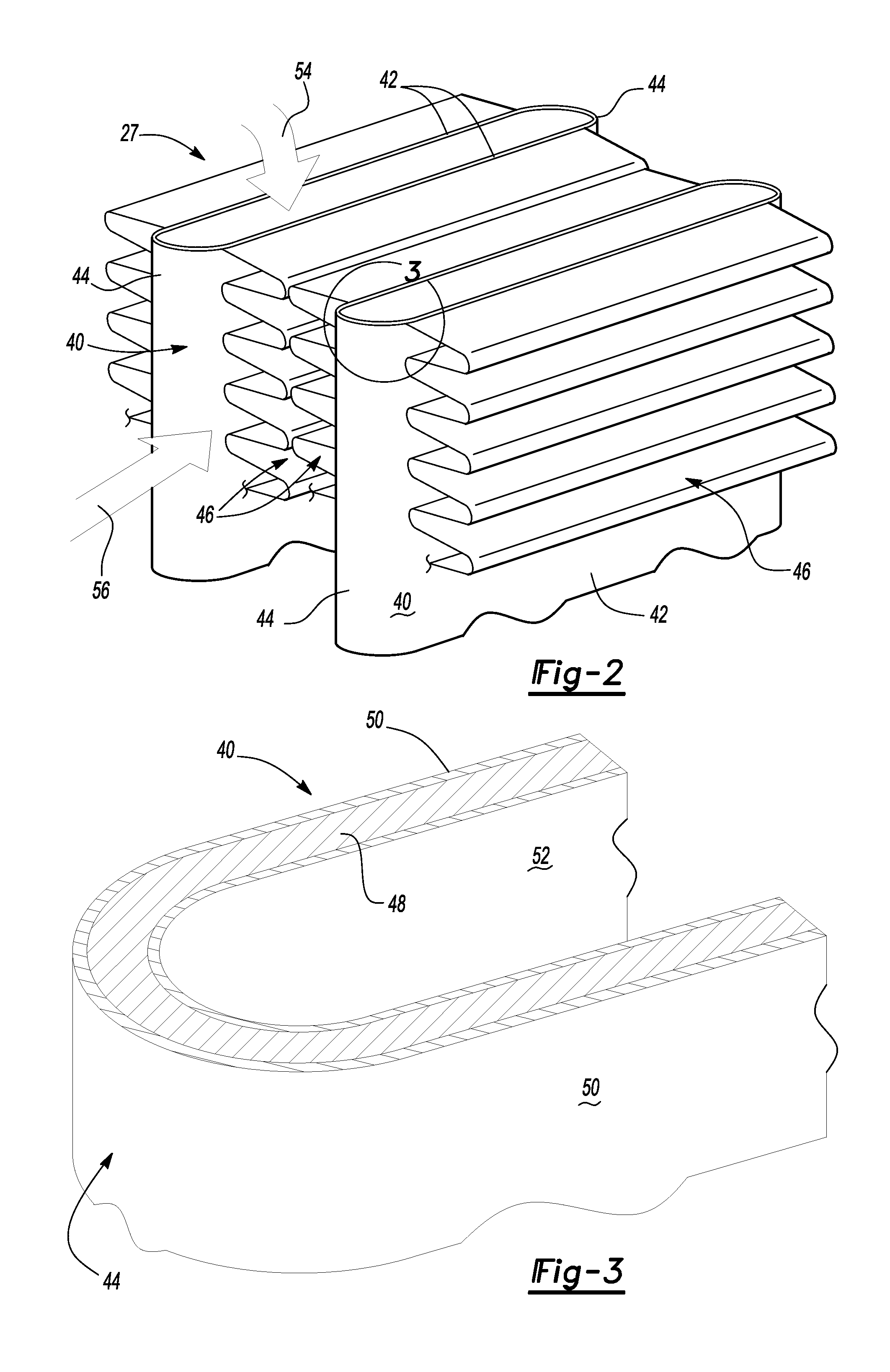
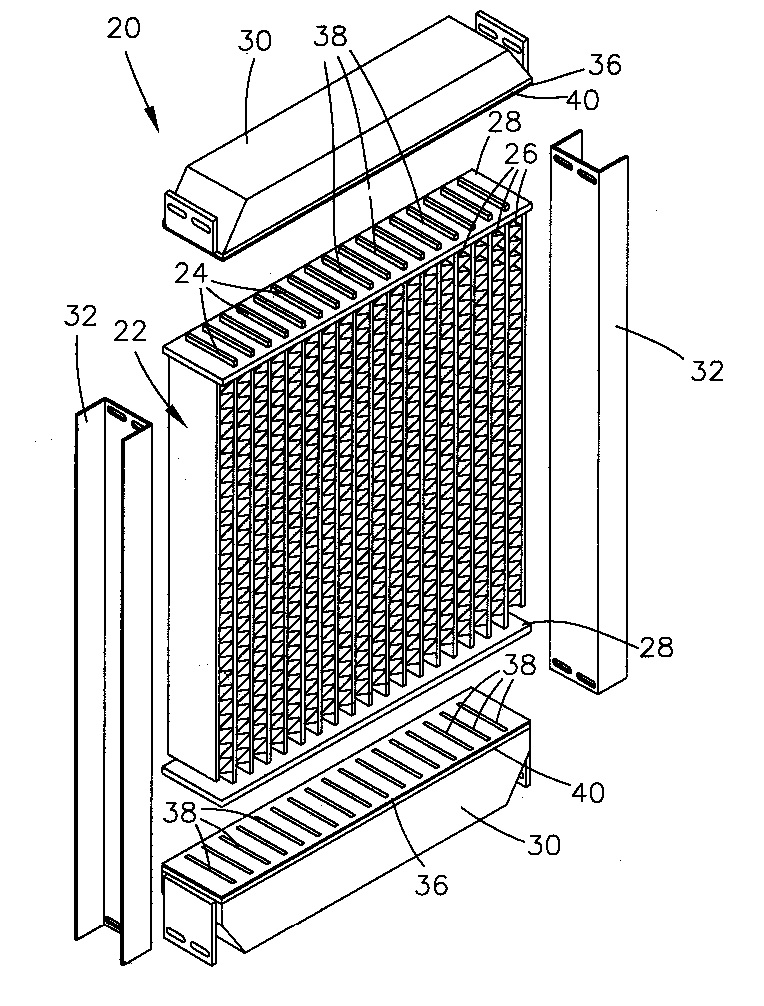
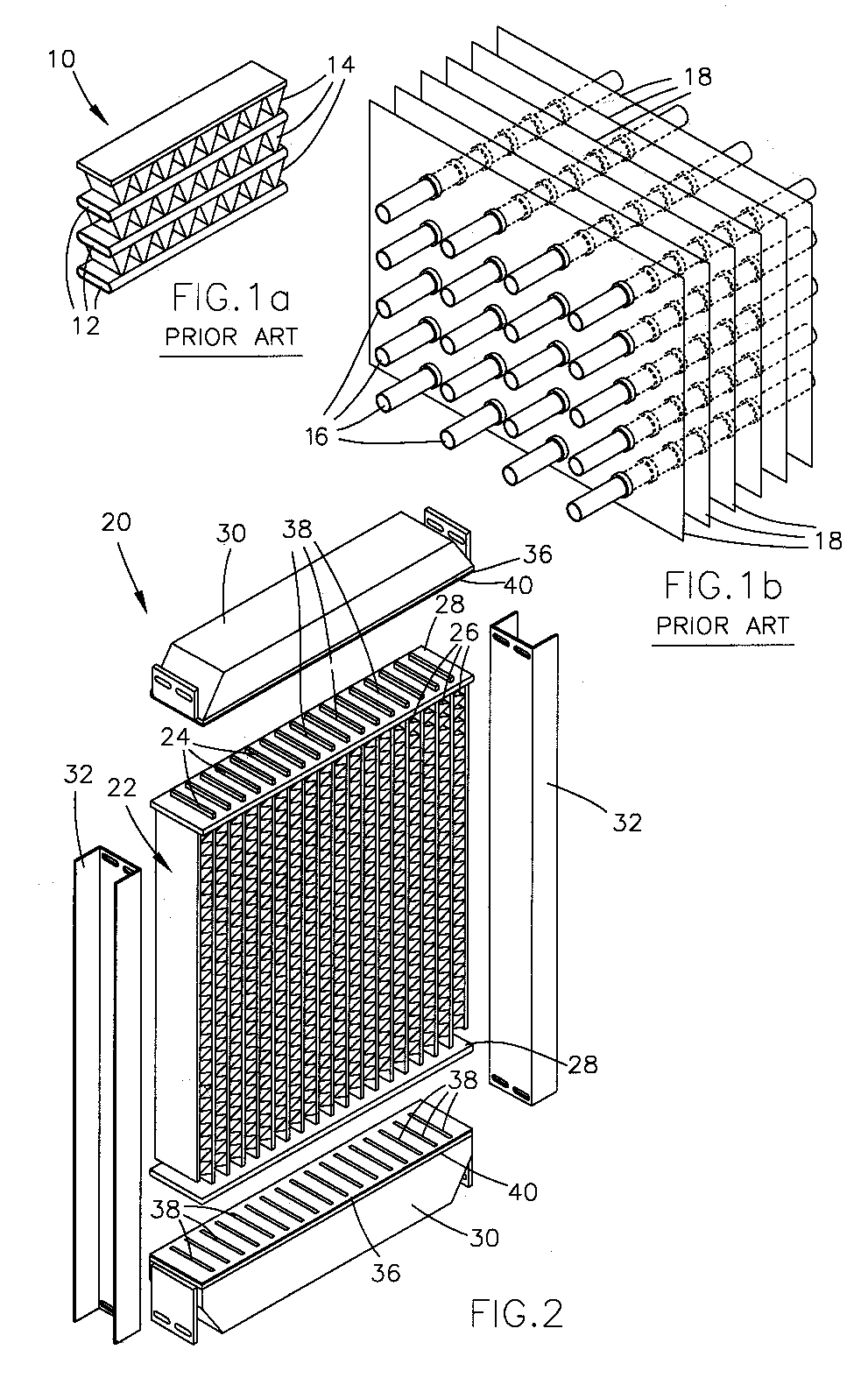
Heat exchanger with flat tubes
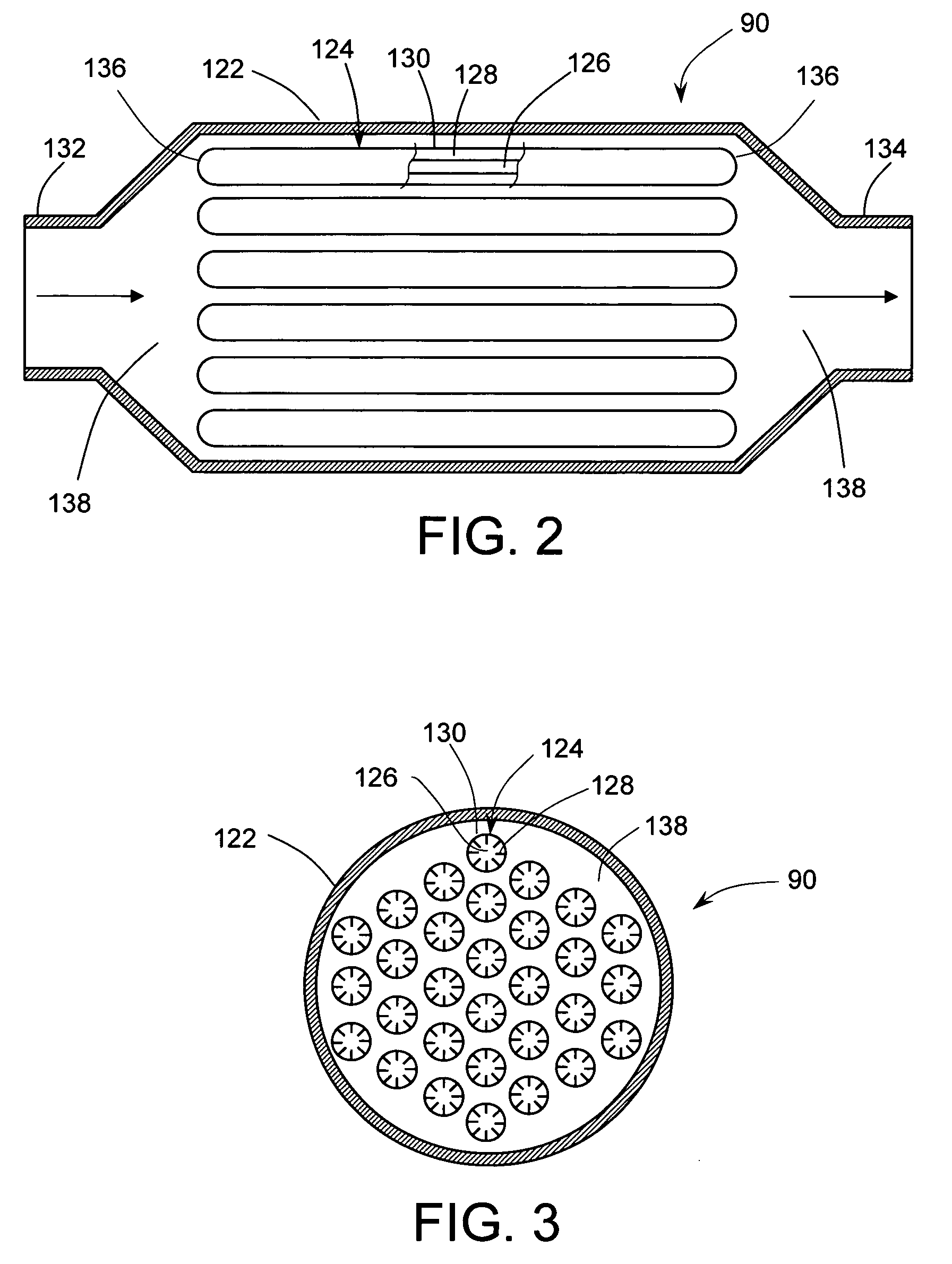
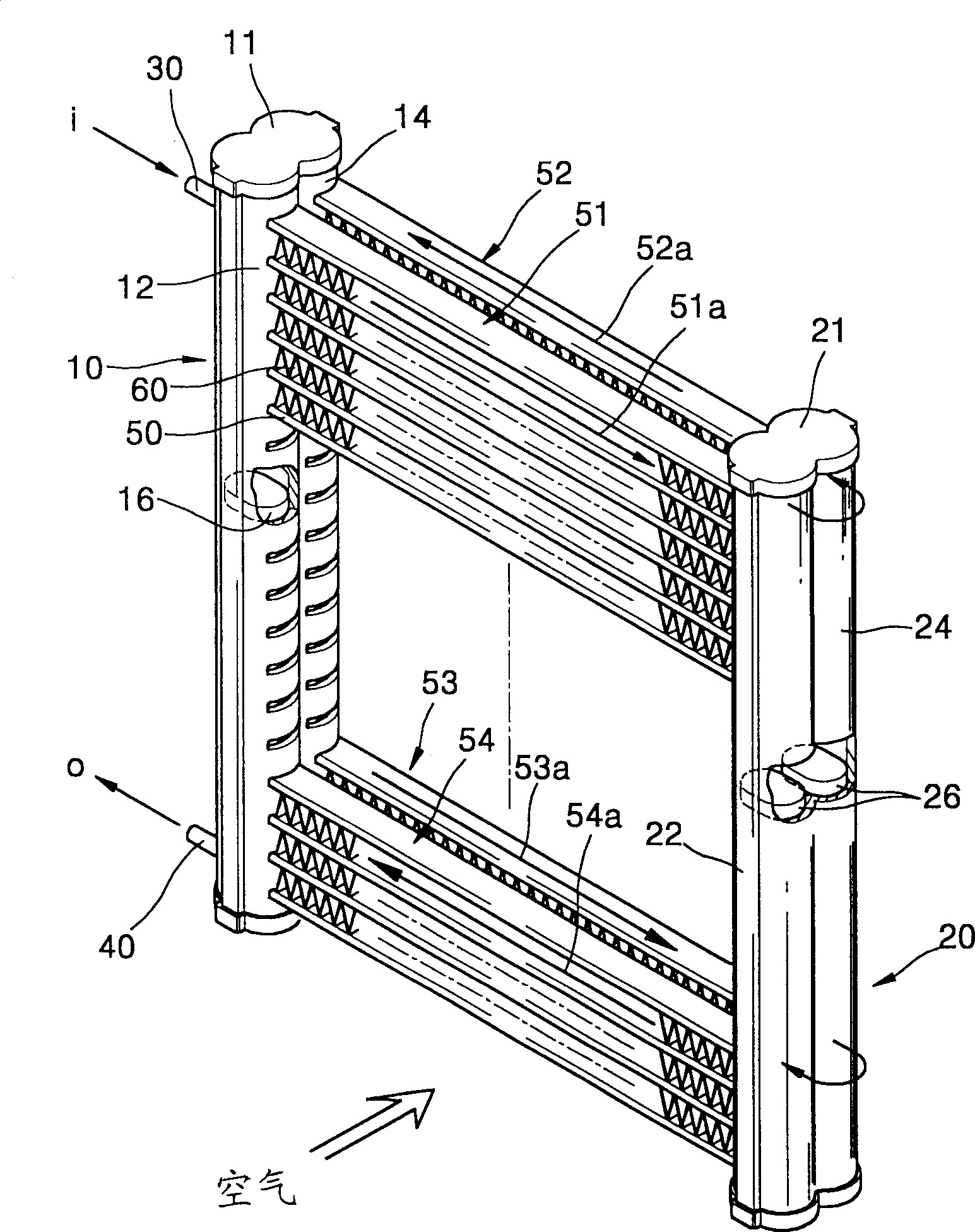
ActiveUS20050161206A1Reinforcing meansInternal combustion piston enginesElectrical and Electronics engineeringHeat exchanger
A heat exchanger with a plurality of stacked flat tubes and a collecting tank having a wall extending around the entire periphery of, and connected to, the end of the stacked flat tubes. A first medium may be distributed through the collecting tank and flat tubes. Internal inserts are in the flat tubes, with the inserts being bonded between the broad sides of the tubes and, in the region of connection of the tubes to the collecting tank, being configured to compensate for length changes in the stacking direction caused by temperature changes, as by recesses in connectors such as wave flanks or by corrugated wave flanks. The flat tubes with inserts such as described may be separately provided for use in manufacture of heat exchangers.
Owner:MODINE MFG CO
Hybrid heat exchangers
InactiveUS20070284095A1Improve mechanical durabilityLow densityReinforcing meansStationary tubular conduit assembliesCarbon compositesCore component
A light weight hybrid heat exchanger core possessing low density and improved thermal conductivity is disclosed. The hybrid core is comprised of a plurality of parting sheets and interposed by a plurality of high thermal conductivity, light weight bridging elements and enclosure bars. These core members are comprised of dissimilar materials. The parting sheets and bridging elements are interconnected by a specially tailored joint which forms form a substantially strong, high thermal conductivity bond. In particular embodiments, carbon-based bridging elements are bonded to metallic parting sheets using a brazed joint. The parting sheets, in certain embodiments, may comprise titanium or Ni-based superalloys or carbon composites, while the carbon-based bridging elements may comprise fiber-reinforced composites. The carbon-based bridging elements reduce the core weight and increase the core thermal conductivity over conventional all-metal designs, while the brazed joint provides for improved leak resistance over all-composite designs.
Owner:ALLCOMP
Engine cooling system with overload handling capability
InactiveUS20090205590A1Suitable for mass productionSimple and compactLiquid coolingReinforcing meansMobile vehicleInternal combustion engine
A cooling system for an internal combustion engine incorporating a heat accumulator to temporarily store heat during peak heat loads. In automotive vehicles, the heat accumulator may store excess heat generated during vehicle acceleration or hill climbing and it may dissipate stored heat during vehicle cruise, deceleration, or engine idle. The heat accumulator contains phase change material with a solid-to-liquid transition temperature higher than the normal operating temperature of the cooling system. The invention enables reducing the size and weight of engine cooling system without compromising its performance. This is particularly important for improving fuel economy and reduction of emission in automotive vehicles. In addition, the invention enables reducing the coolant inventory in the system thereby allowing for faster engine warm-up and reduced emissions of harmful pollutants during a cold engine start. The invention may be also used for thermal management of engine oil, transmission fluid, or hydraulic fluid.
Owner:AGWEST
Modular heat exchanger having a brazed core and method for forming
InactiveUS7234511B1Improve heat transfer efficiencyReadily dismantled and rebuiltReinforcing meansSafety devices for heat exchange apparatusPosition toleranceNuclear engineering
An improved modular heat exchanger suitable for automotive applications, and particularly radiators for heavy duty equipment, and methods for forming the modular heat exchanger. The modular heat exchanger construction incorporates a brazed core assembly composed of flat-type cooling tubes and sinusoidal centers. The ability to use a brazed core assembly within a modular heat exchanger construction promotes enhanced heat transfer efficiencies associated with the use of flat tubes and sinusoidal centers, as compared to mechanically-joined round tubes and fins. The required positional tolerances of the tubes for mating with the remainder of the heat exchanger are maintained within the brazed core assembly by eliminating core shrinkage attributable to the use of clad aluminum alloy components to construct the core assembly. In two embodiments, core shrinkage is physical suppressed through the use of an expandable brazing fixture or the inclusion of sub-headers in the brazed core assembly. In a third embodiment, a clad slurry containing a braze alloy is deposited prior to brazing on a core assembly composed of unclad tubes and centers.
Owner:LESAGE PHILIP GEORGE
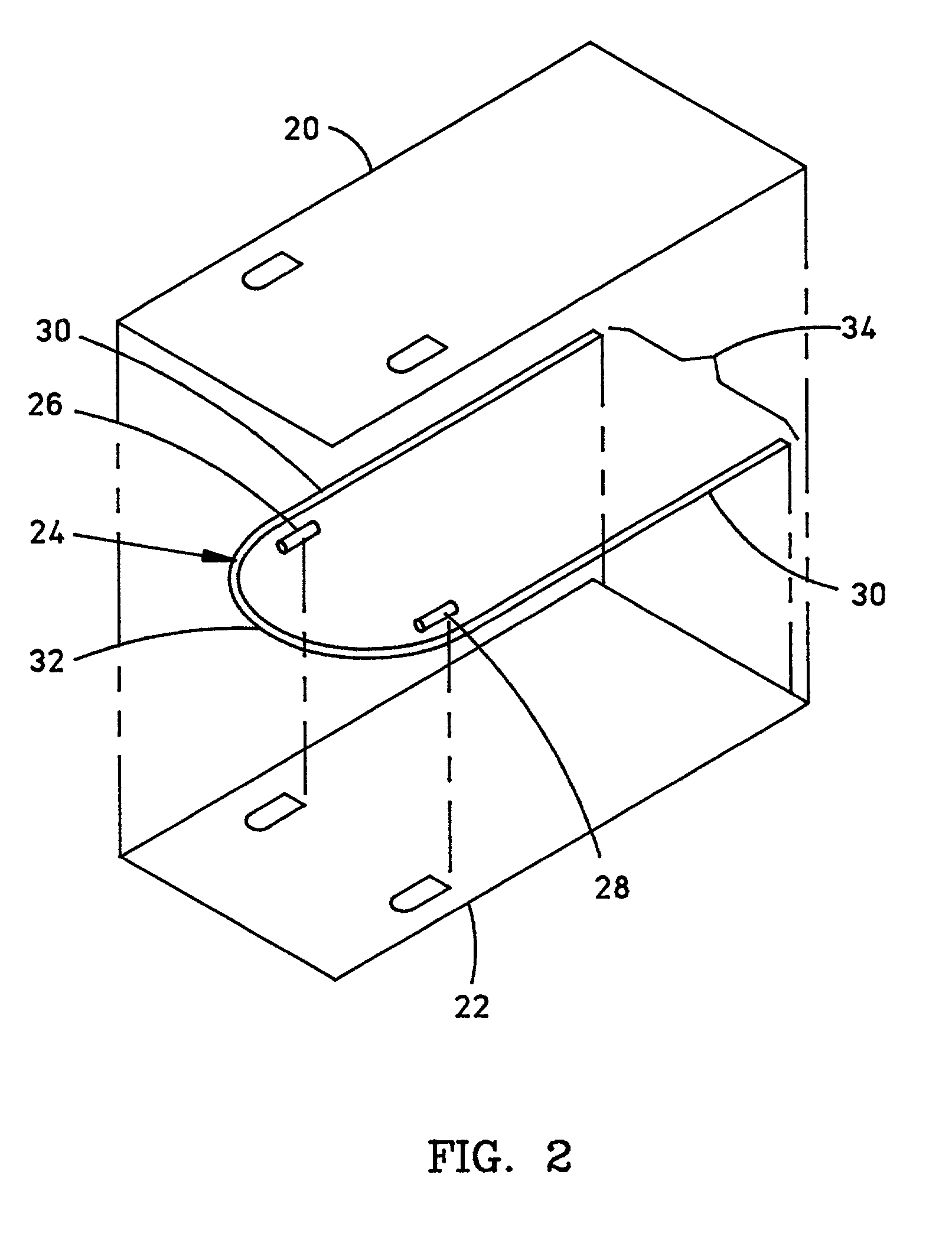
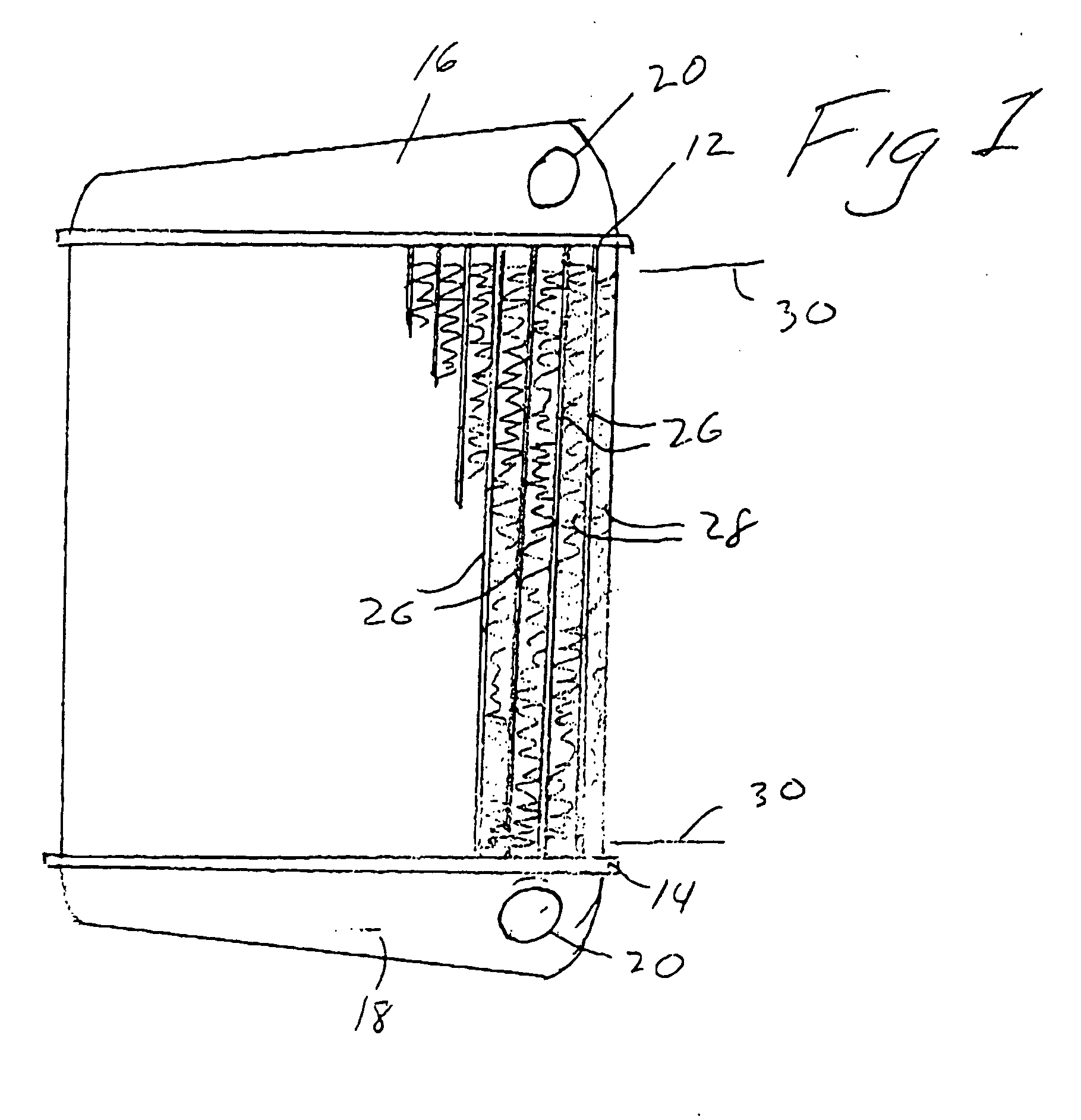
Fluid warming cassette with a tensioning rod
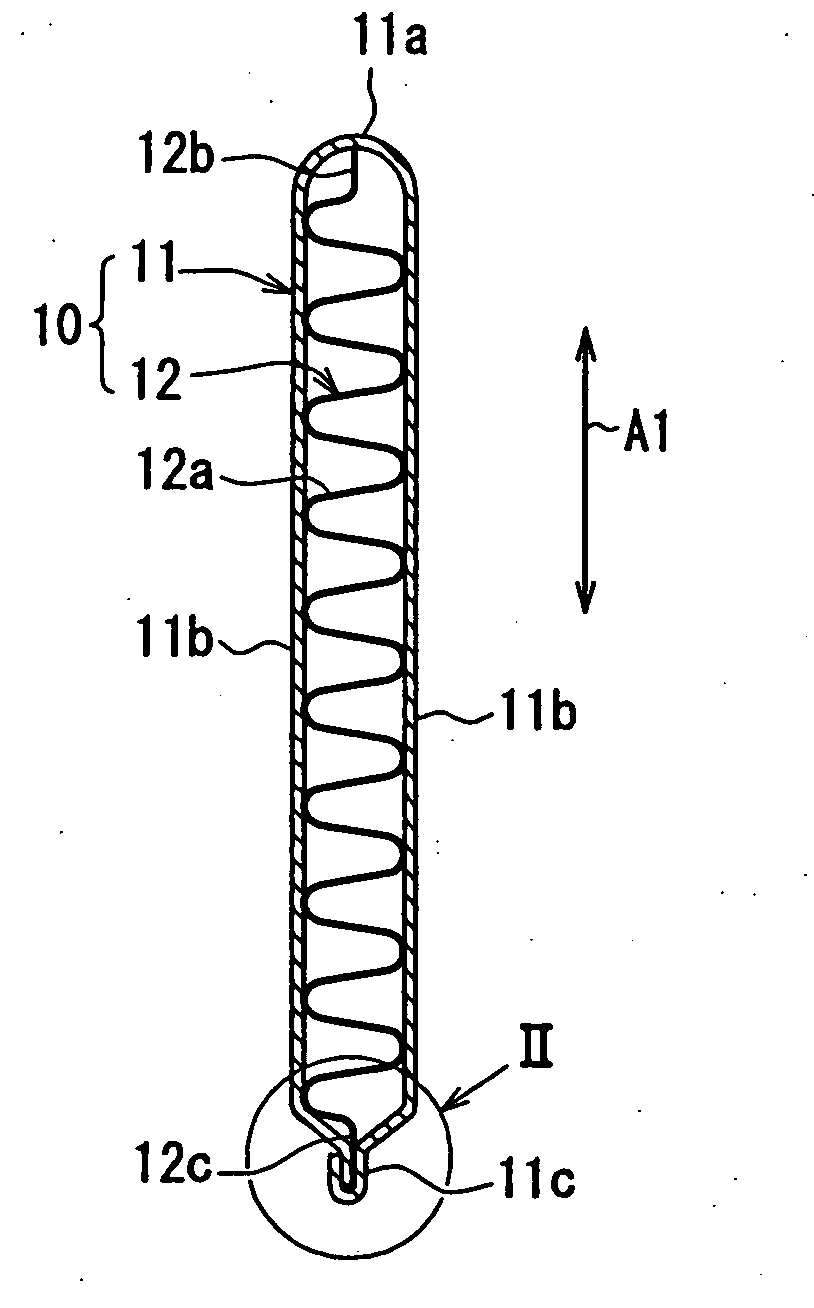
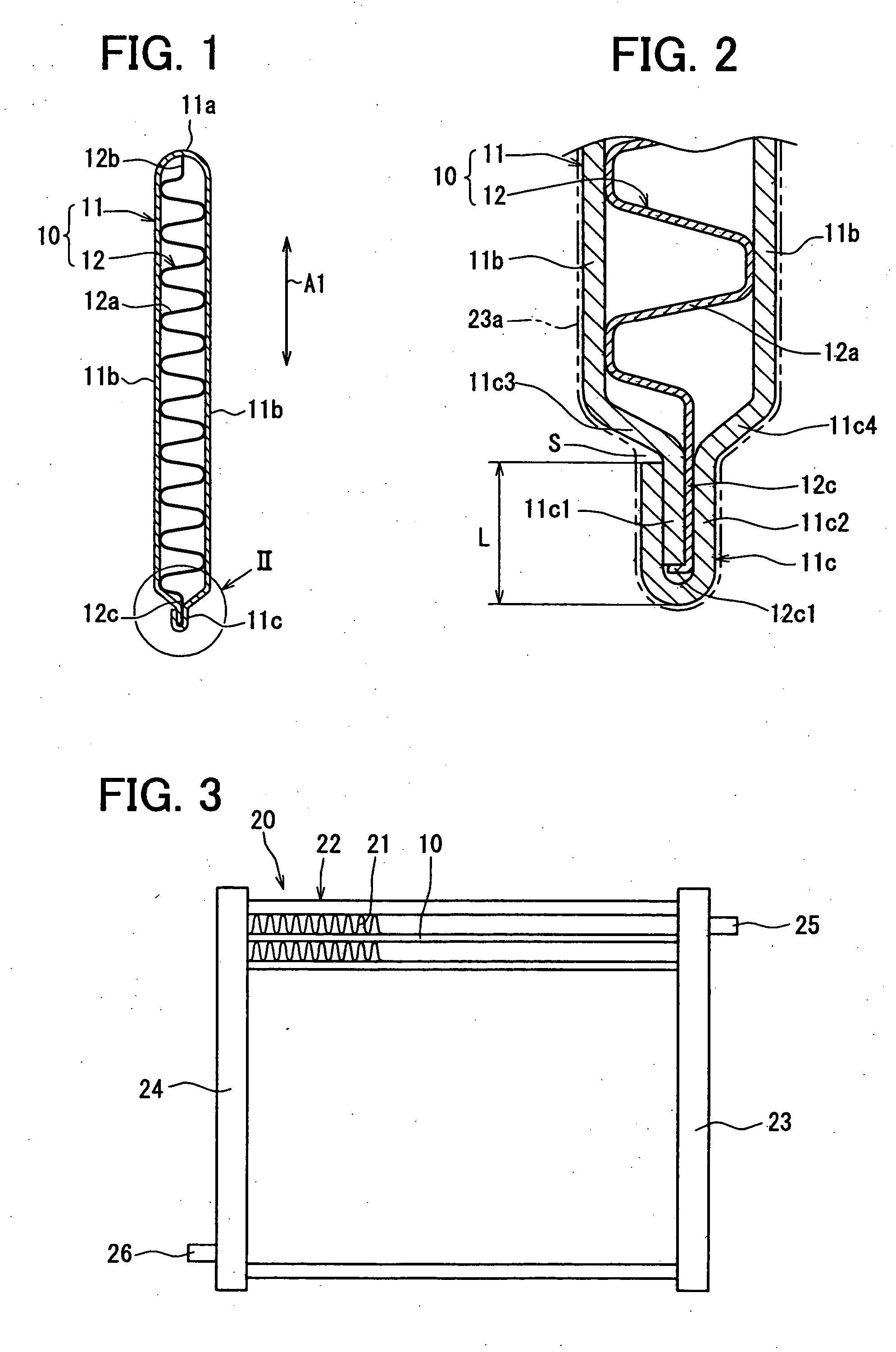
A fluid warming cassette for use in a fluid warming system includes a first sheet and second sheet joined with a flexed tensioning rod to form a fluid container with a periphery in which the flexed tensioning rod is disposed to tension the fluid container. The fluid container includes a fluid channel with inlet and outlet ports in fluid communication with the fluid channel. Preferably, the rod is flexed into an open-ended shape such as a “U” shape. So flexed, the rod tensions the fluid container, adding structural stability to the fluid warming cassette.
Owner:GEN ELECTRIC CAPITAL +1
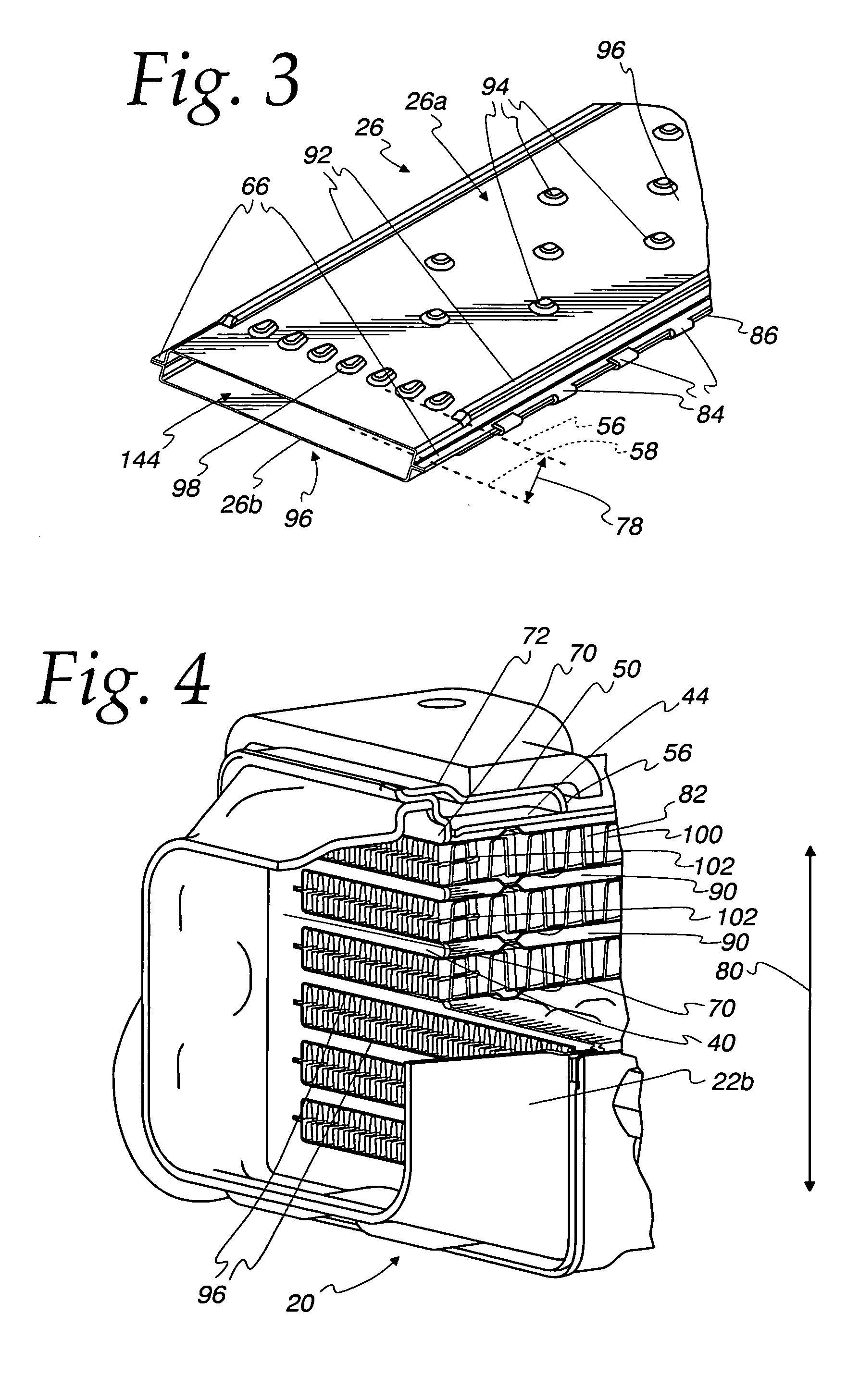
Reinforcement for dish plate heat exchangers
A reinforcing element for a heat exchanger of the type having nested dish plates with inclined, peripheral, overlapping walls, where at least one of the nested dish plates is attached to a mounting plate, the mounting plate extending beyond the outer periphery of the walls of the nested dish plates. The reinforcing element has a base flange attached to the mounting plate extending beyond the outer periphery of the walls of the nested dish plates. The reinforcing element also has a peripheral flange located in parallel, overlapping engagement with the inclined peripheral wall of the at least one dish plate attached to the mounting plate.
Owner:DANA CANADA CORP
Heat exchanger having plural tubular arrays
InactiveUS20050194120A1Reduce pressureFacilitate accurate dynamic controlHydrogenReinforcing meansEngineeringHeat exchanger
Owner:LAIR LIQUIDE SA POUR LETUDE & LEXPLOITATION DES PROCEDES GEORGES CLAUDE
Flat heat exchanger plate and bulk material heat exchanger using the same
ActiveUS7093649B2Avoid distancePrevent crashReinforcing meansVibration cleaningInternal pressurePlate heat exchanger
A flat heat exchanger plate typically used in a bulk material heat exchanger is provided. The flat heat exchanger plate is designed to operate under a negative internal pressure to eliminate depressions or dimples that are typically formed into the sides of these types of heat exchanger coils during the manufacture process. With the removal of the depressions or dimples the tendency for bulk material to accumulate to the exterior surface of the plate is reduced, thereby increasing the service period of the plate.
Owner:DAWSON & CO
Engine cooling system with overload handling capability
InactiveUS7735461B2Emission reductionReducing coolant inventoryLiquid coolingCoolant flow controlInternal combustion engineHydraulic fluid
A cooling system for an internal combustion engine incorporating a heat accumulator to temporarily store heat during peak heat loads. In automotive vehicles, the heat accumulator may store excess heat generated during vehicle acceleration or hill climbing and it may dissipate stored heat during vehicle cruise, deceleration, or engine idle. The heat accumulator contains phase change material with a solid-to-liquid transition temperature higher than the normal operating temperature of the cooling system. The invention enables reducing the size and weight of engine cooling system without compromising its performance. This is particularly important for improving fuel economy and reduction of emission in automotive vehicles. In addition, the invention enables reducing the coolant inventory in the system thereby allowing for faster engine warm-up and reduced emissions of harmful pollutants during a cold engine start. The invention may be also used for thermal management of engine oil, transmission fluid, or hydraulic fluid.
Owner:AGWEST
Tube for heat exchanger and method of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20070095514A1Joining qualityUniformly formedReinforcing meansEvaporators/condensersEngineeringHeat exchanger
A tube for a heat exchanger has a tube member and a fin inserted in the tube member. The tube member has a first wall having a first end portion and a second wall having a second end portion. The second end portion of the second wall is folded over the first end portion of the first wall. Also, an end of the fin is held between the first end portion and the second end portion of the tube member. Further, the end of the fin has a bent portion at an end of the first end portion within the folded second end portion. The bent portion of the fin is engaged with the first end portion of the tube member for positioning the fin with respect to the tube member.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Heat exchanger
InactiveCN1410738AImprove pressure resistanceEvenly distributedReinforcing meansHeat exhanger conduitsWorking pressureHigh pressure
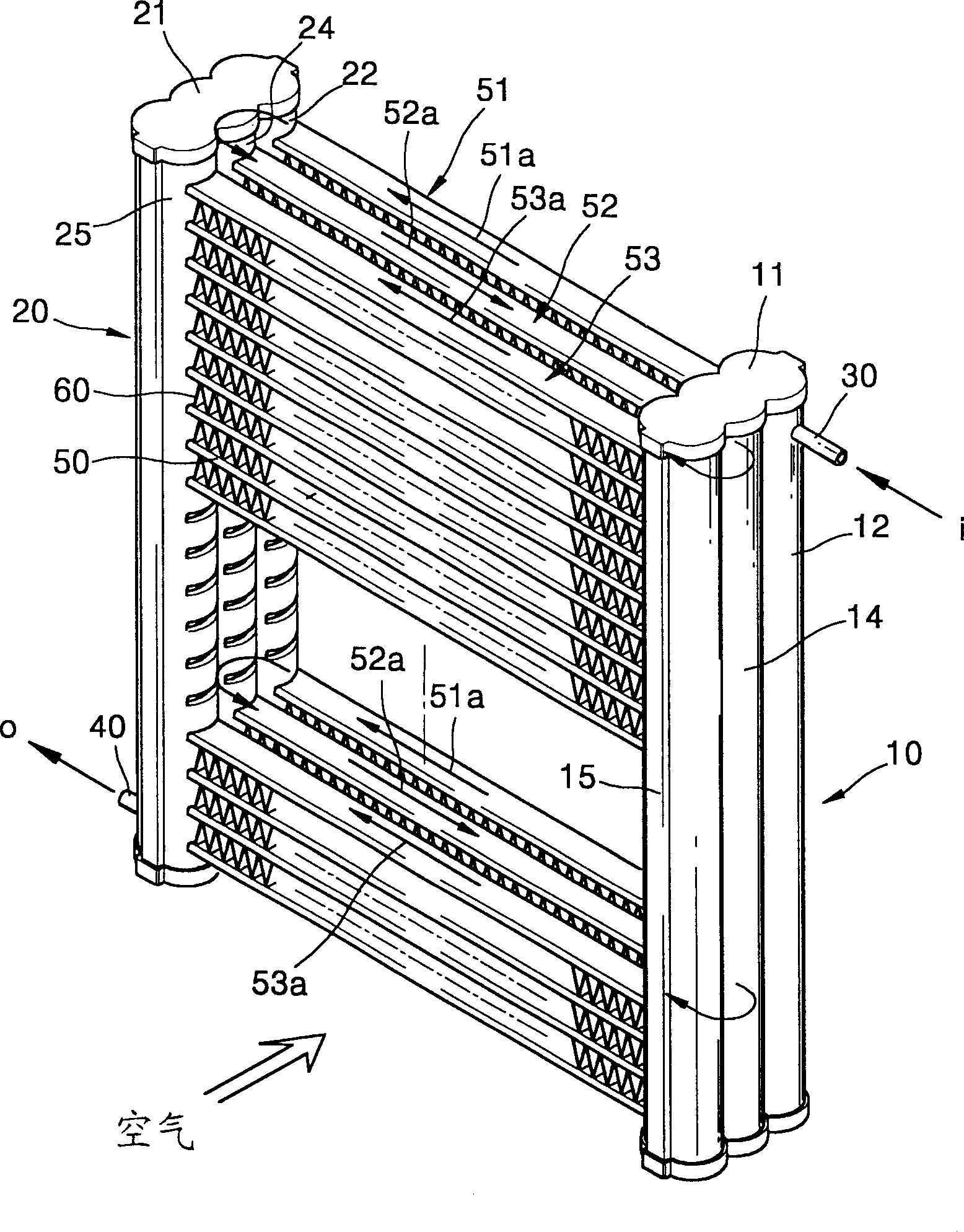
A heat exchanger uses a refrigerant acting under a high pressure, such as carbon dioxide, as a refrigerant. The heat exchanger includes first (10) and second (20) header pipes arranged a predetermined distance from each other and parallel to each other, each having at least two chambers (12,14,22,24) independently sectioned by a partition wall, a plurality of tubes (50) for separately connecting the chambers of the first (10) and second (20) header pipes, facing each other, wherein the tubes (50) are divided into at least two tube groups (51,52), each having a single refrigerant path, a refrigerant inlet pipe (30) formed at the chamber disposed at one end portion of the first header pipe (10), through which the refrigerant is supplied, a plurality of return holes (29) formed in the partition wall to connect two chambers adjacent to each other, through which the refrigerant sequentially flows the tube groups (51,52), and a refrigerant outlet pipe (40) formed at the chamber of one of the first and second header pipes connected to a final tube group of the tube groups along the flow of the refrigerant, through which the refrigerant is exhausted.
Owner:HANON SYST
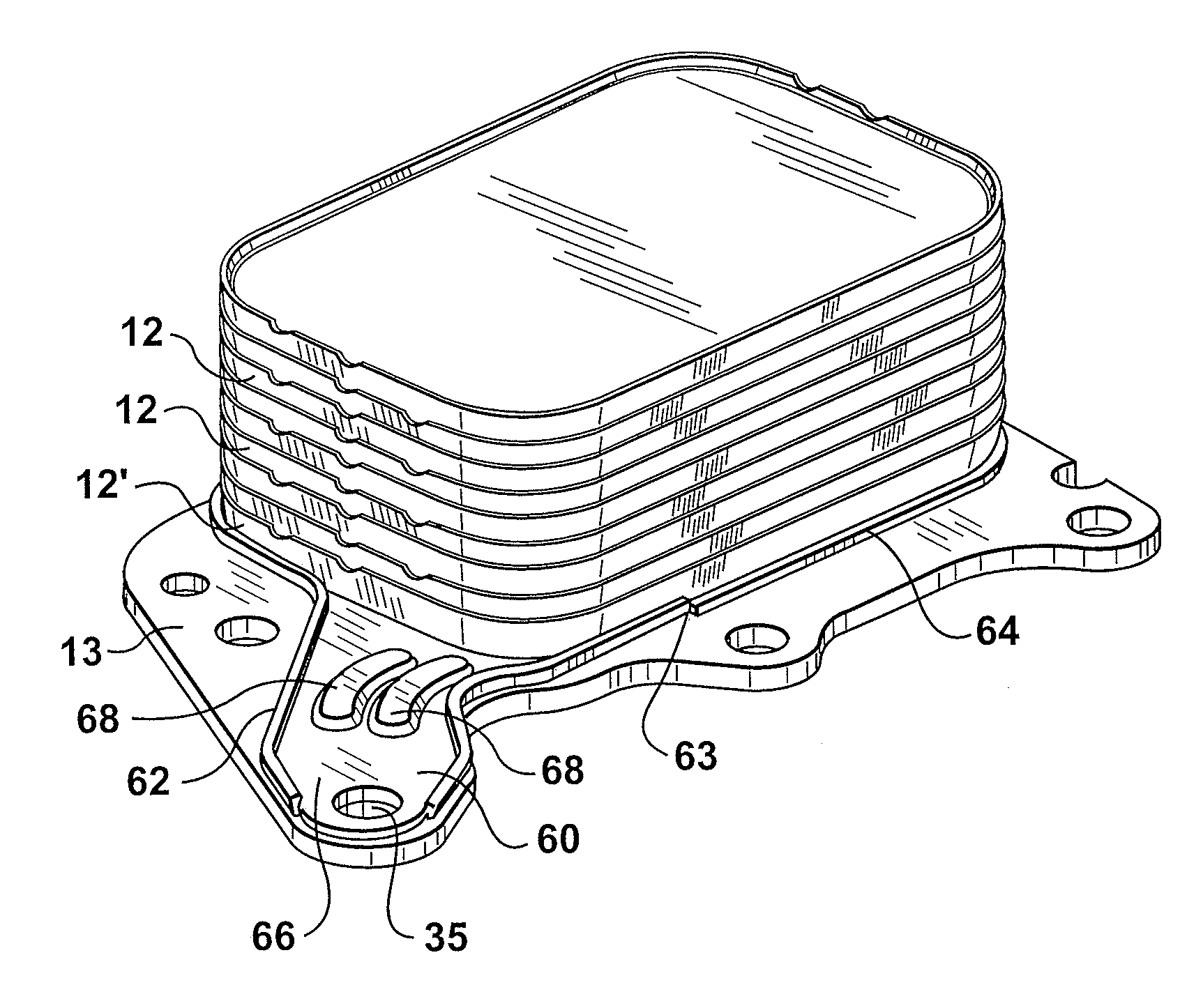
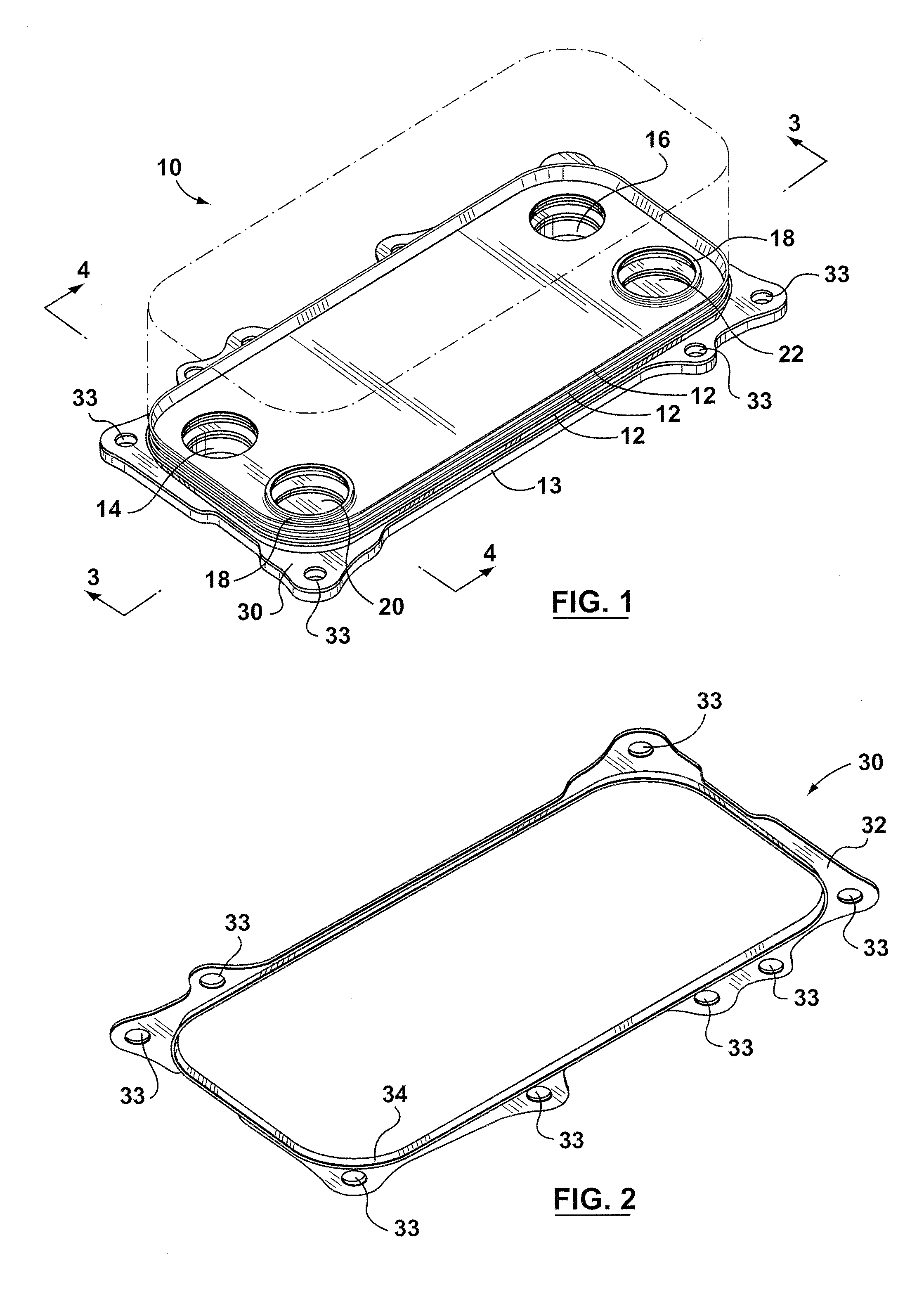
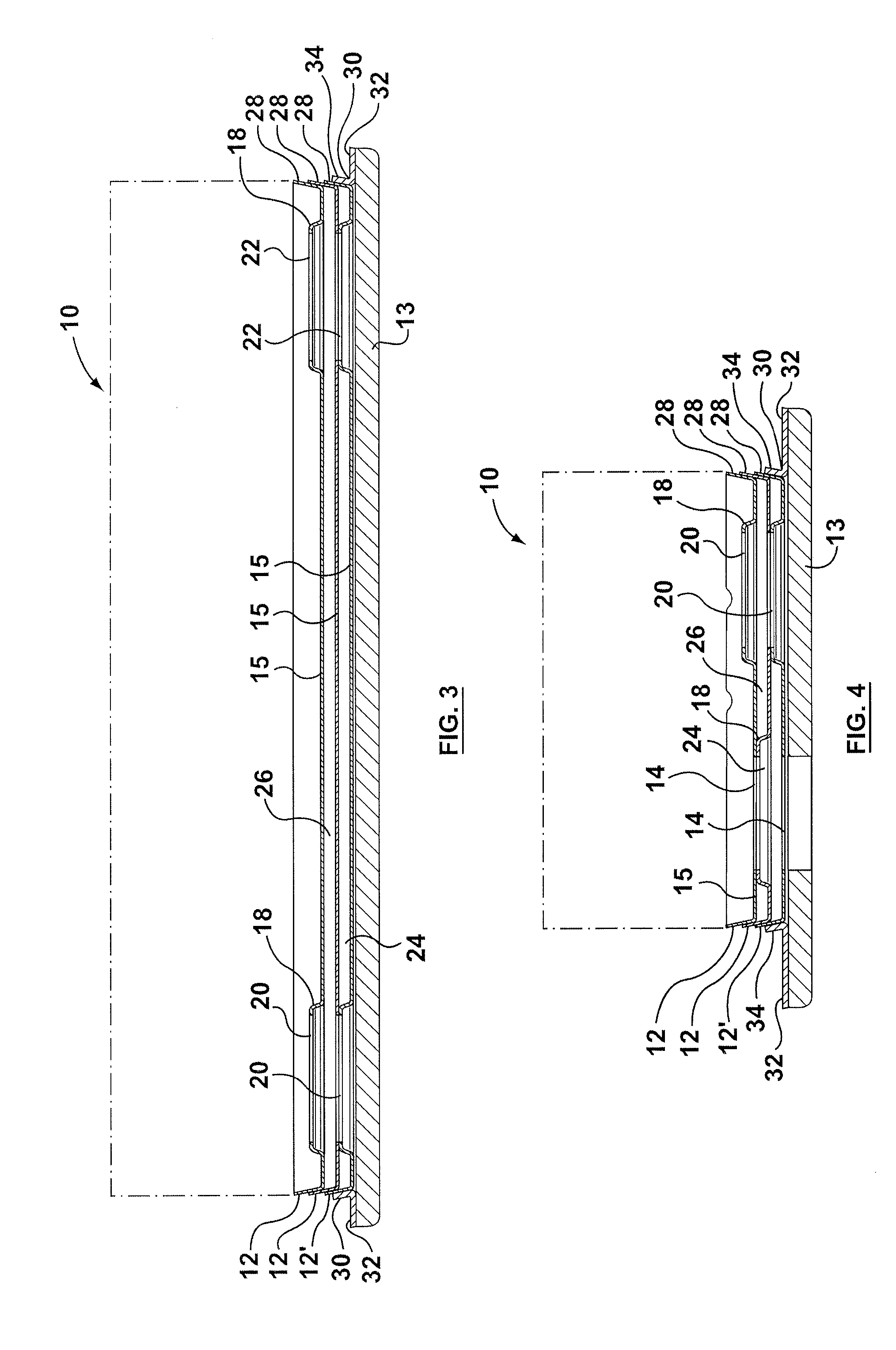
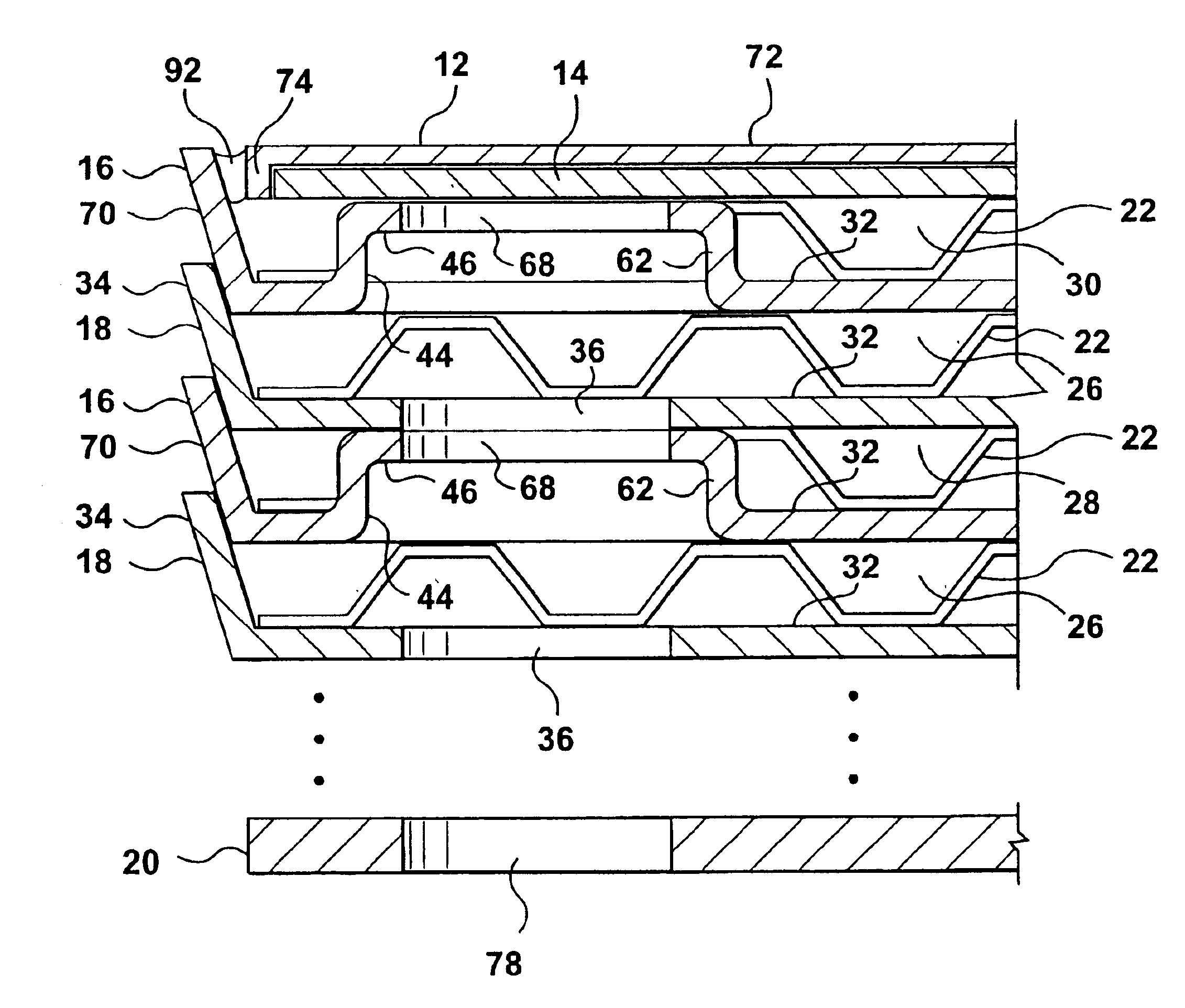
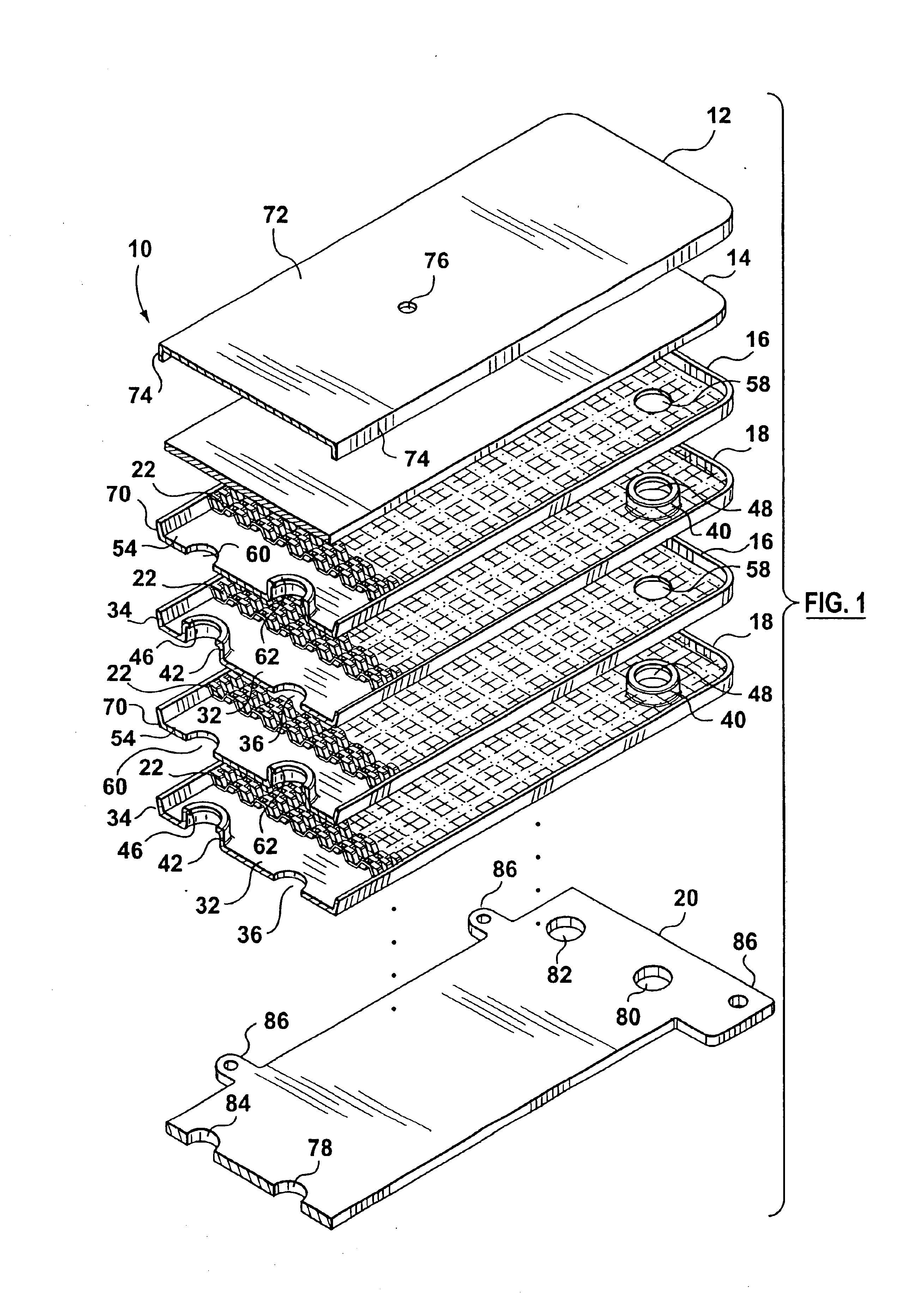
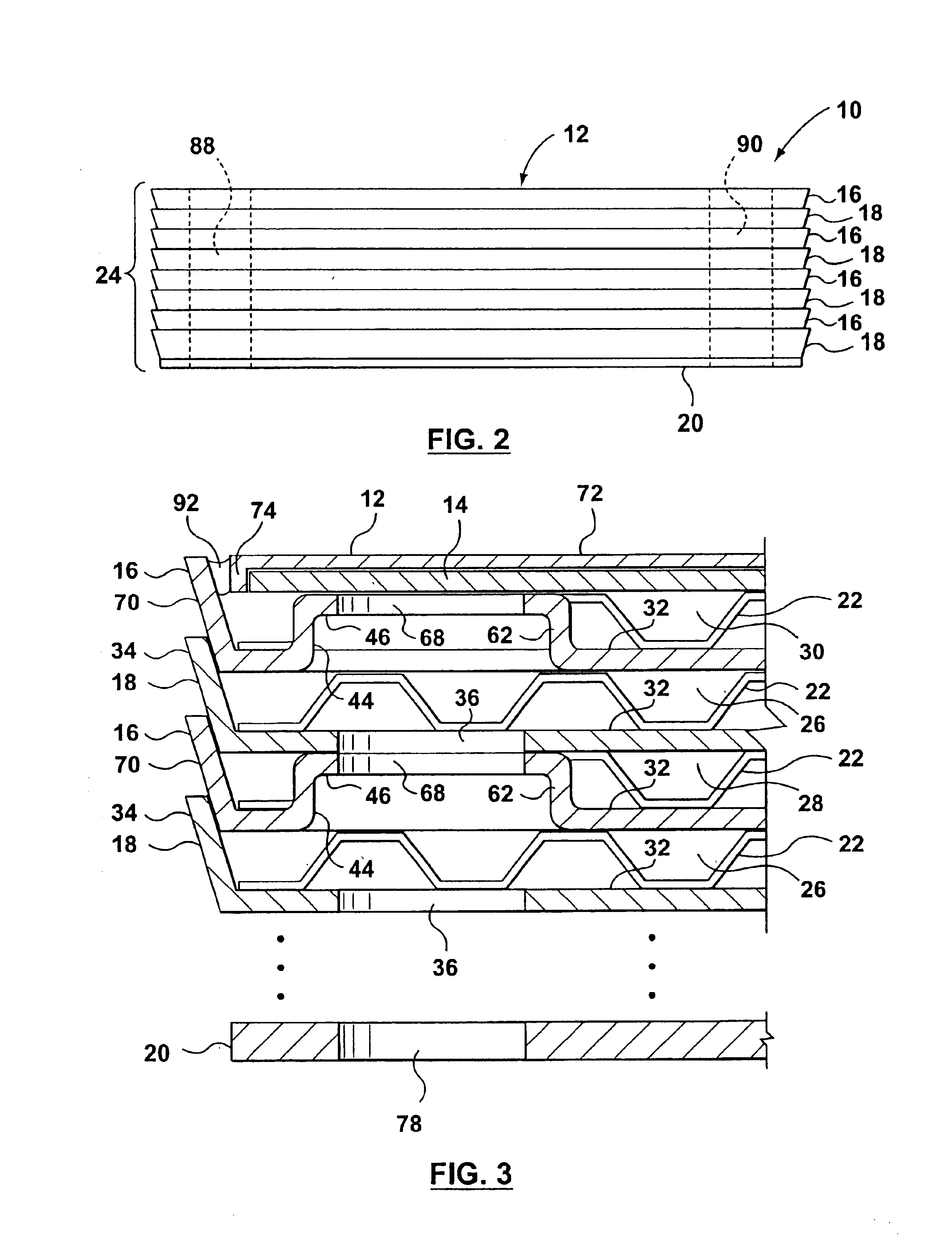
Inverted lid sealing plate for heat exchanger
InactiveUS6843311B2Reduce unused spaceReducing the extent to which the flangeReinforcing meansHeat exchanger casingsEngineeringFlange
A stacked plate-type heat exchanger including a plurality of dish-shaped heat exchanger plates arranged one next to the other to form a nested heat exchanger plate stack. A plurality of first and second fluid flow channels are formed between the heat exchanger plates for first and second fluids respectively, and first fluid and second fluid chambers are formed in the stack in communication with the first and second fluid channels respectively. An end plate for the heat exchanger has an end plate central planar portion and a peripheral flange projecting from the end plate central planar portion, the peripheral flange of the end plate projecting in an opposite direction and sealably nested within the peripheral flange of a final heat exchanger plate in the plate stack. A planar reinforcing plate is secured to an inner surface of the end plate central planar portion between the end plate central planar portion and the final heat exchanger plate, a further fluid channel for one of the first and second fluids being located between the planar reinforcing plate and the final heat exchanger plate.
Owner:DANA CANADA CORP
Heat exchanger and method of producing
A heat exchanger including a collecting tank having an outwardly extending flange around an edge, a tube plate having a connection edge, tubes having ends extending into openings in the tube plate, and an intermediate plate having an edge lying against the connection edge of the tube plate. The connection edges of the intermediate plate and the tube plate are both mechanically connected to the flange of the collecting tank. Pins in the corners of one of the tube plate and the intermediate plate secure the tube plate and intermediate plate together. The connection edge of the plates include protrusions bendable onto the edge flange of the collecting tank.
Owner:MODINE MFG CO
Heat exchanger with manifold strengthening protrusion
ActiveUS20090126911A1Improve abilitiesPreventing undesirable bypass flowReinforcing meansStationary conduit assembliesPlate heat exchangerEngineering
A plate type heat exchanger is disclosed having a plurality of stacked plate pairs made up of first and second plates. Each plate pair has opposed manifold members with respective inlet and outlet openings that are in registration to form respective inlet and outlet manifolds for the flow of a first fluid through a first set of fluid channels formed by the plate pairs, the manifold members spacing the plate pairs apart to form a second set of transverse flow channels for the flow of a second fluid. Each plate has a peripheral edge portion which seals the plates together to form the first set of fluid channels therebetween. A protrusion member is formed proximal to each of the manifold members, each protrusion member having a mating surface such that the protrusion members on the second plate of one plate pair align and abut with the protrusion members on the first plate of an adjacent plate pair thereby reinforcing and strengthening the manifold region of the heat exchanger to prevent the deformation or accordion of the manifold under pressure.
Owner:DANA CANADA CORP
Automotive heat exchanger assemblies having internal fins and methods of making the same
ActiveUS7487589B2Improved thermal/pressure resistant heat exchangerImprove heat resistanceReinforcing meansHeat exchanger casingsEngineeringHigh stress
The present invention relates to automotive heat exchanger assemblies that can withstand high environmental temperature and pressures conditions. By providing a tube strengthener inserted into the tubes at the areas of highest stress, the heat exchanger assembly is strengthened to be efficient under typical operating conditions.
Owner:VALEO INC
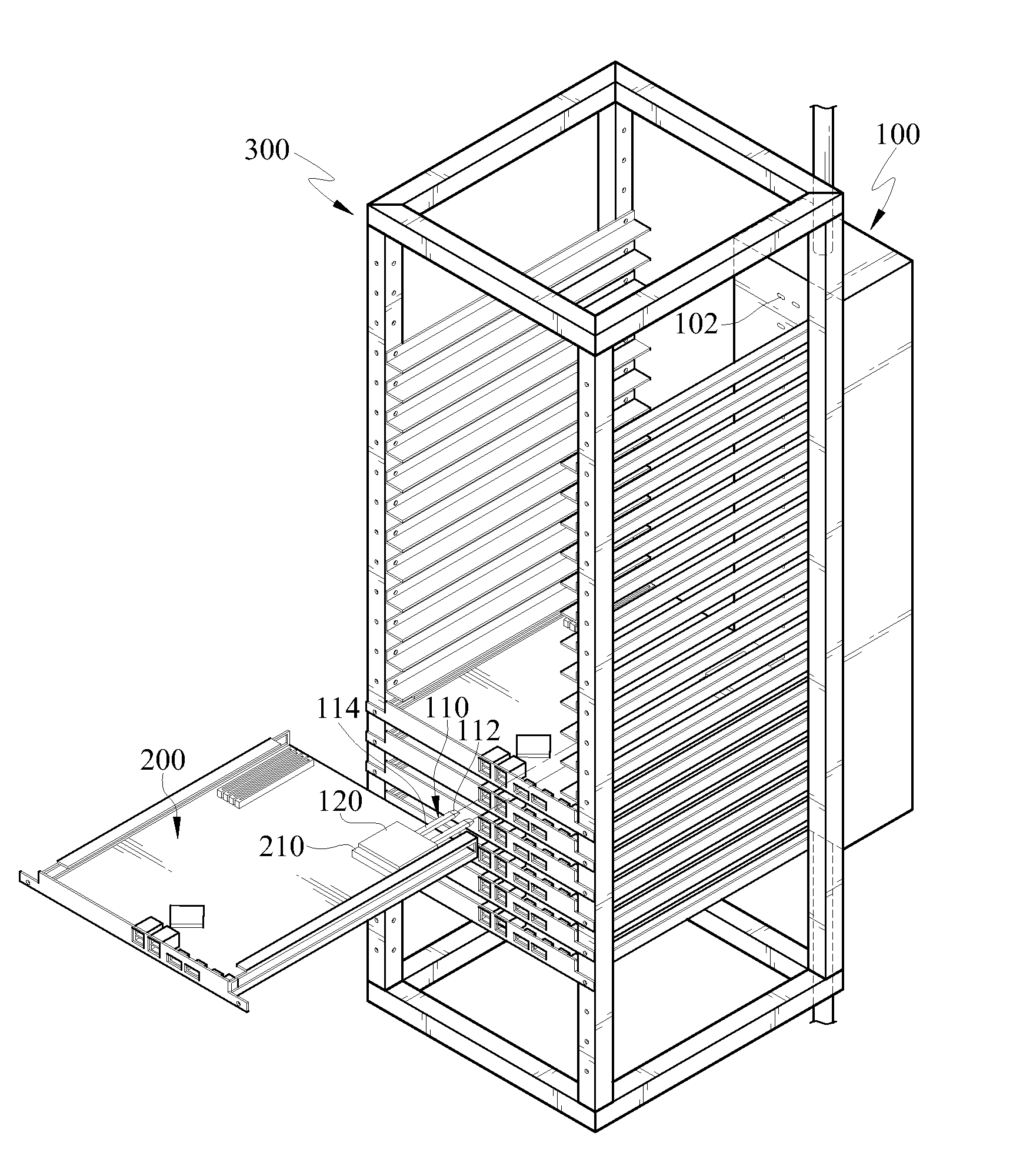
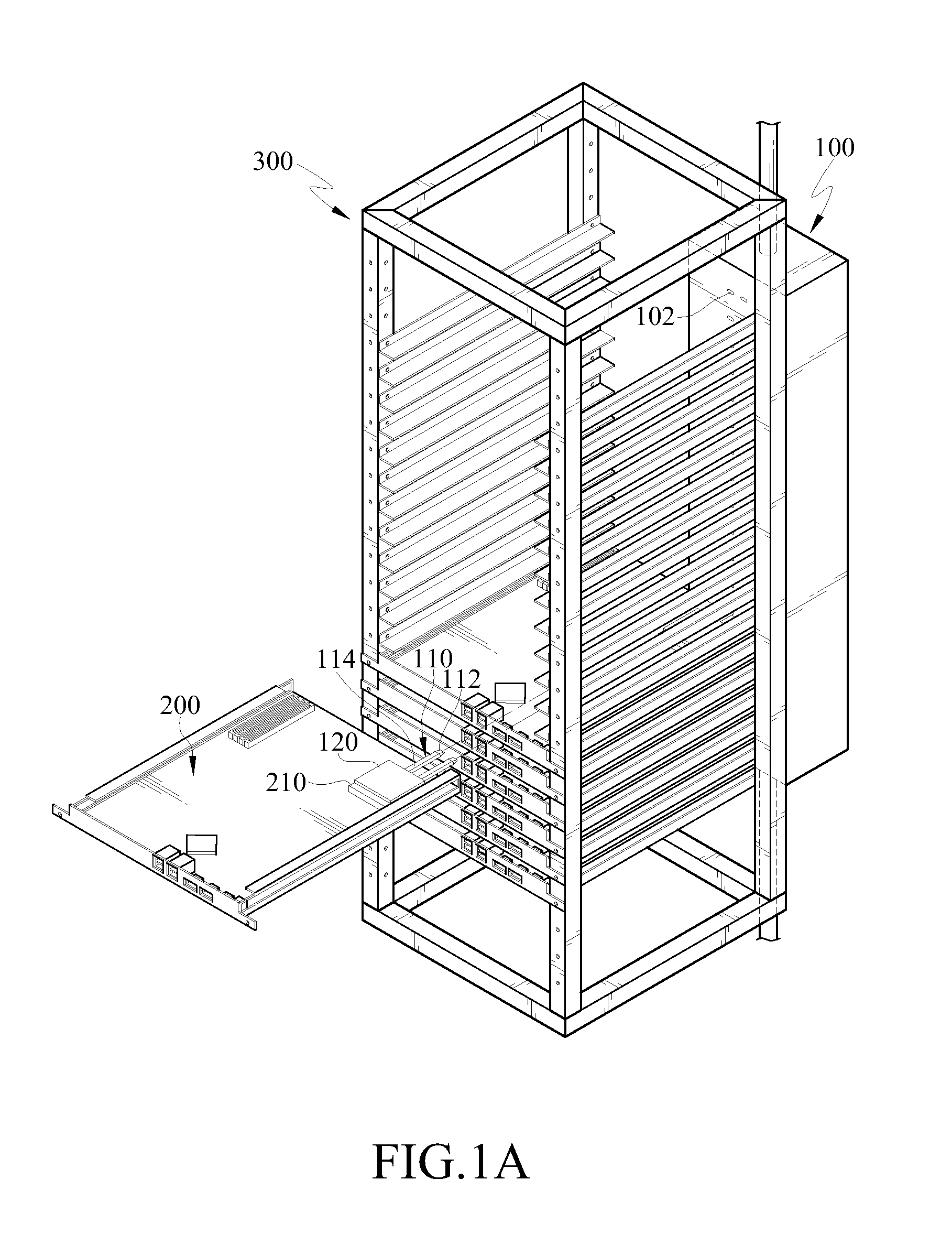
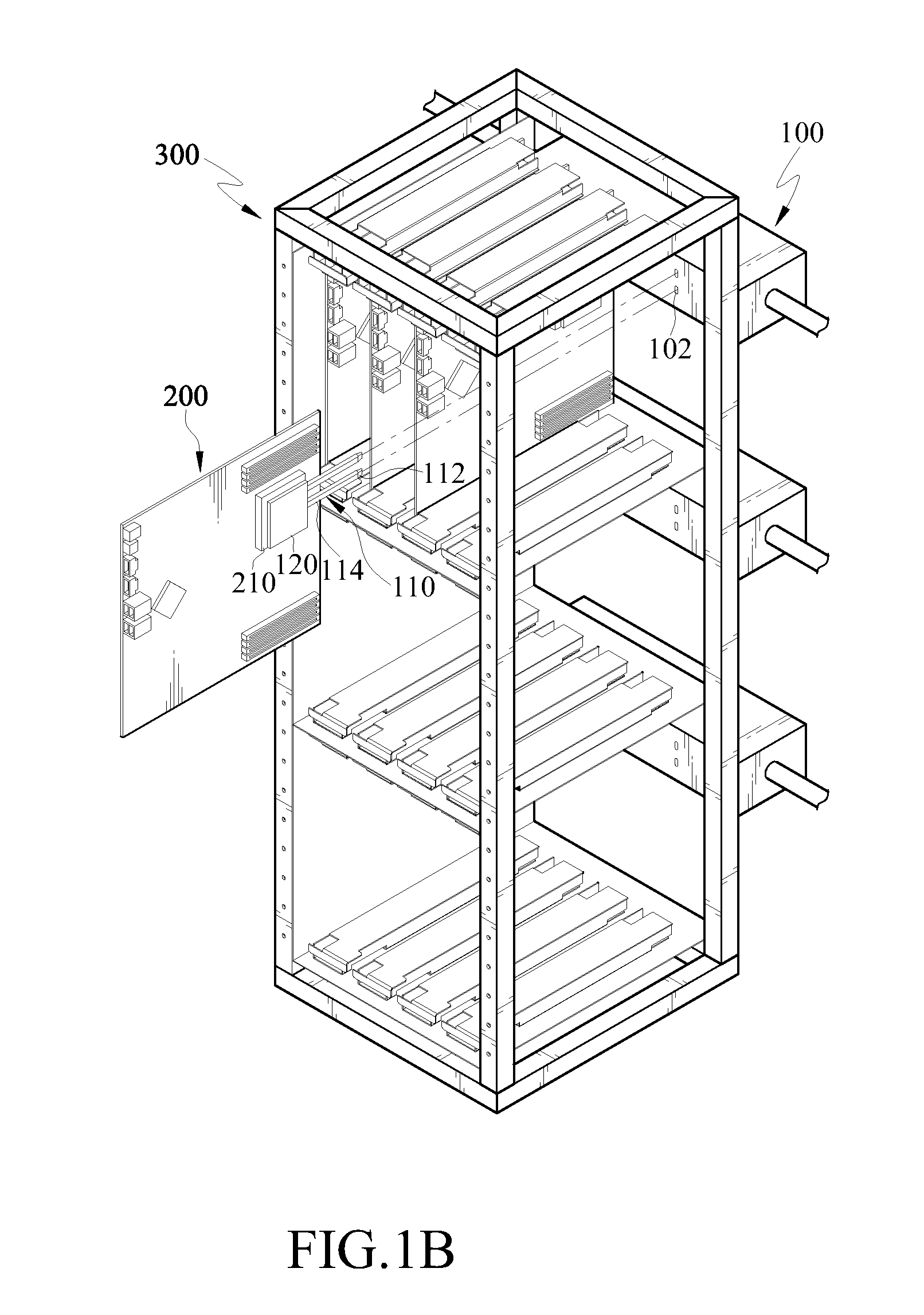
Heat dissipation structure of electronic device
ActiveUS8305754B2Effective coolingEfficient solutionReinforcing meansDigital data processing detailsEvaporationEngineering
A structure of heat dissipation of an electronic device includes at least one heat pipe and a cooler. The heat pipe has a condensation end and an evaporation end opposite to each other, and the evaporation end is disposed on a heat generating element of the electronic device. The cooler is disposed on a rack and has a chamber therein, and the chamber has an inner shell having a cooling fluid therein. When the electronic device is mounted in the rack, the condensation end of the heat pipe is inserted into the cooler and positioned into the inner shell. The evaporation end absorbs the heat energy of the heat generating element, and transfers the heat energy to the condensation end, such that the cooling fluid dissipates the heat energy of the condensation end.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
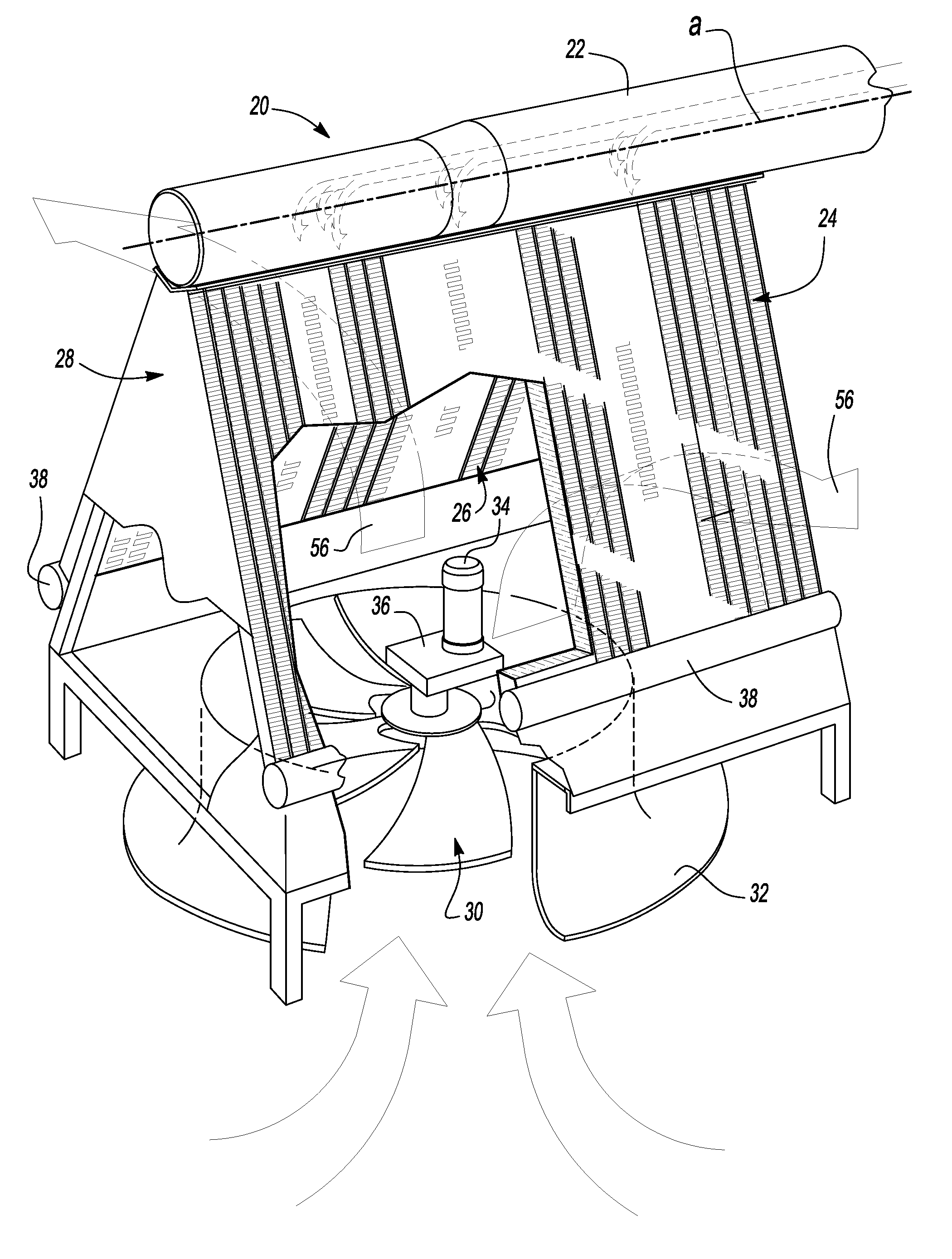
Turbine exhaust condenser
InactiveUS20100263840A1Improve efficiencyReduce back pressureReinforcing meansSteam useEngineeringTurbine
An air cooled steam condenser for condensing exhaust steam from a steam turbine including a steam delivery manifold, first and second bundles of aligned elongated tubes extending downwardly at an angle to the axis of the steam delivery manifold, each bundle containing a plurality of elongated tubes having exterior aluminum fins, an exterior coating of aluminum and an interior cladding of stainless steel having a thickness between about 45 and 125 microns, wherein a height measured between the rounded ends of the tubes is greater than 220 mm or between 220 and 280 mm and the length of the tubes is greater than 11 m, preferably between 12 and 14 m or greater.
Owner:RES COTTRELL DRY COOLING
Modular heat exchanger having a brazed core and method for forming
InactiveUS20060196052A1Improve heat transfer efficiencyReadily dismantled and rebuiltReinforcing meansSafety devices for heat exchange apparatusPosition toleranceNuclear engineering
A modular heat exchanger suitable for automotive applications, and methods for forming the modular heat exchanger. The modular heat exchanger construction incorporates a monolithic brazed core assembly composed of flat-type cooling tubes and sinusoidal centers. The required positional tolerances of the tubes for mating with the remainder of the heat exchanger are maintained within the brazed core assembly by minimizing core shrinkage resulting from the brazing operation during which the tubes are brazed to the centers.
Owner:LESAGE PHILIP GEORGE
Compressed gas cooling apparatus
InactiveUS20140000841A1Lower overall pressure dropReduced flow separationReinforcing meansPump componentsEngineeringGas cooling
A compressed gas cooling apparatus in which gas from an upstream compression stage enters an inlet section from an inlet opening and flows to a heat exchanger that cools the gas. The cooled gas then flows from the heat exchanger to the outlet section where the gas is discharged from an outlet opening. Pressure drop within the apparatus is decreased by providing the inlet and outlet sections with ever increasing and decreasing cross-sectional flow areas. In order to further decrease pressure drop due to a swirl within the gas flow imparted from the upstream compression stage, the inlet section is provided with first and second subsections wherein the cross-sectional flow area of the first subsection increases at lesser rate than the second subjection. Alternatively, or in addition, the inlet section can be provided with partitions to divide the gas flow into subflows in order to lessen pressure drop from swirl.
Owner:PRAXAIR TECH INC
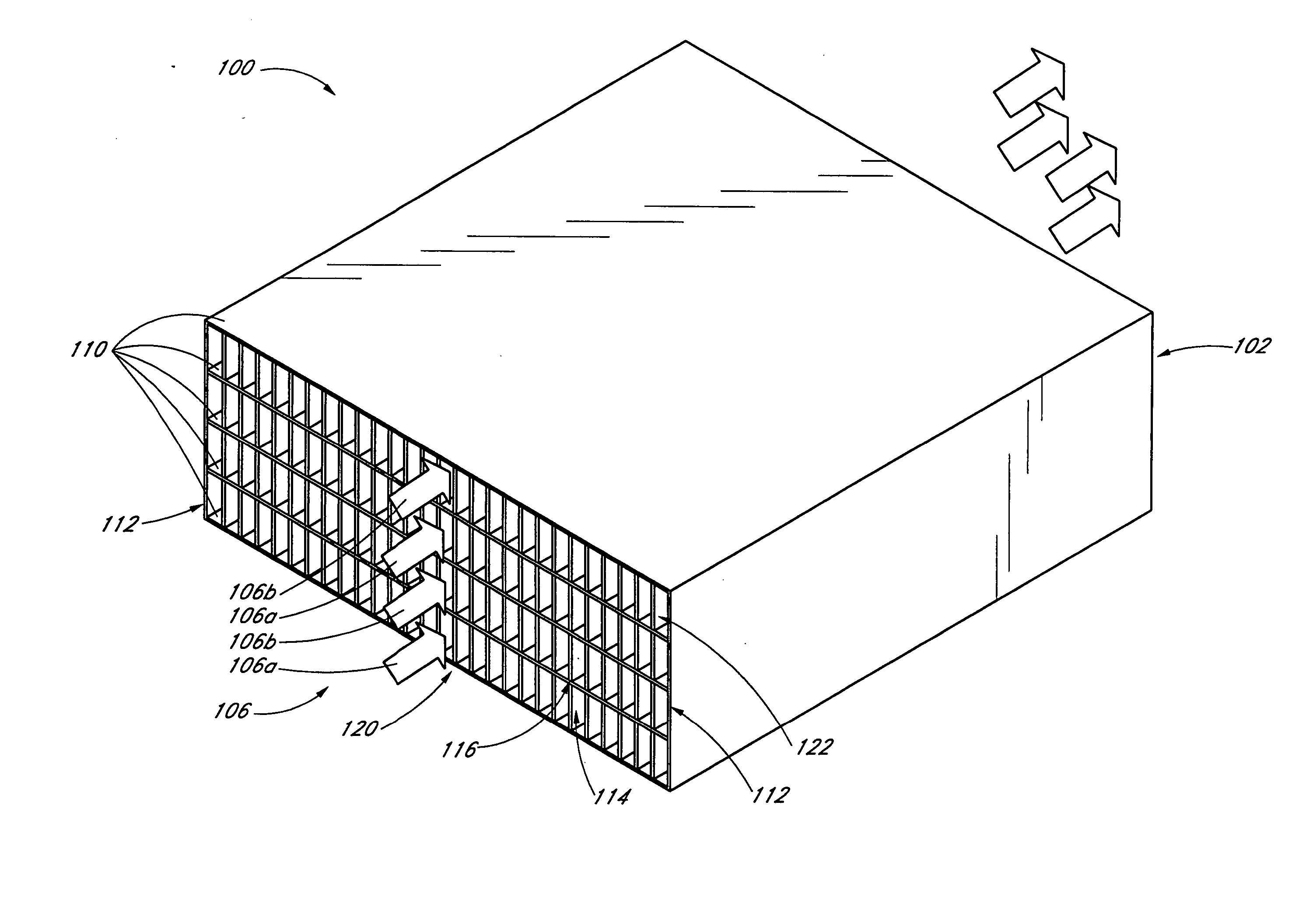
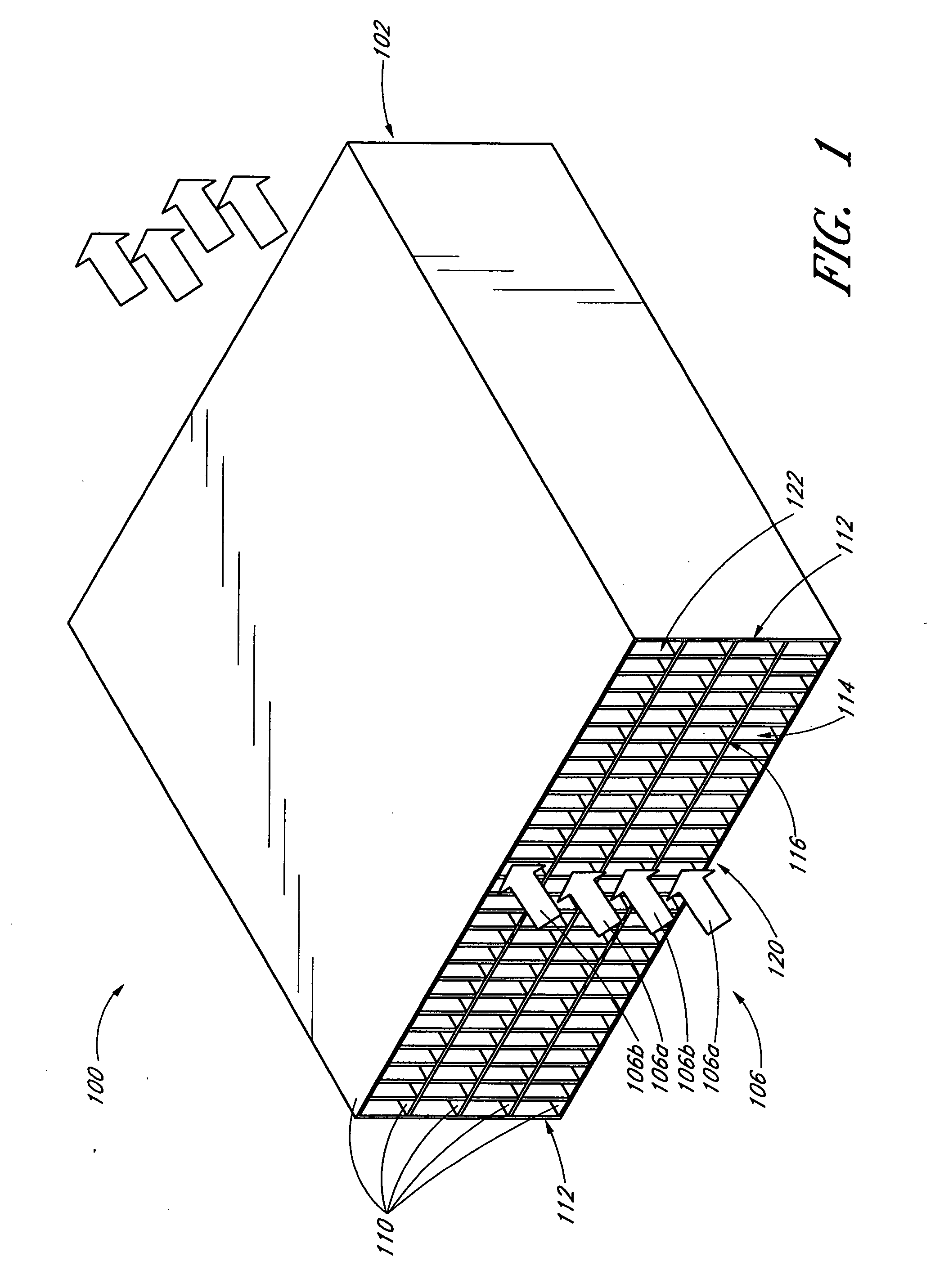
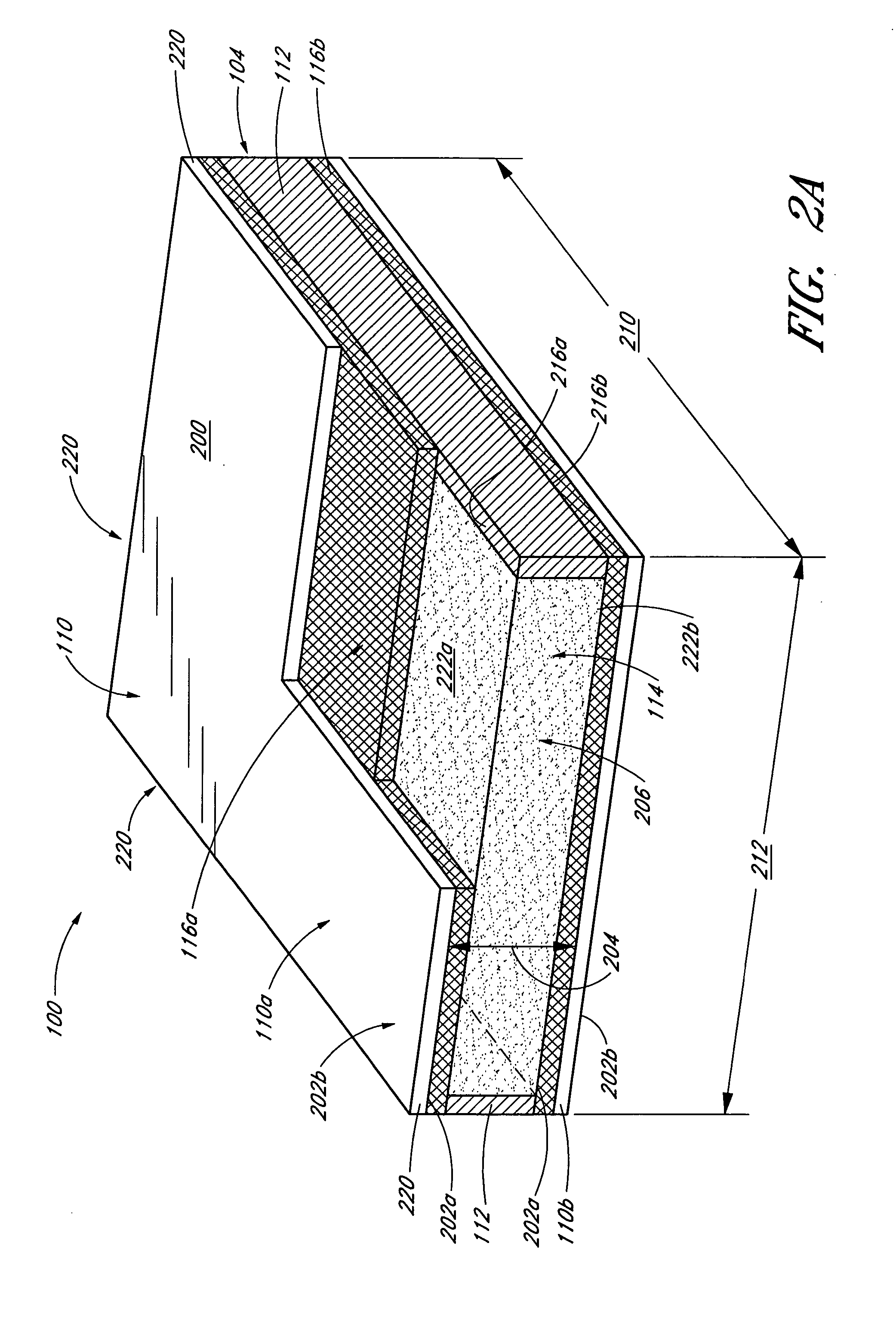
Gas Turbine Regenerator Apparatus and Method of Manufacture
A regenerator core for use in a gas turbine regenerator has integral manifold openings formed in the tube plates used to make up the core and has special reinforcing elements which provide high pressure containment in critical portions of the plate-and-fin heat exchanger construction. The reinforcing elements include a series of hoops of U-shaped cross section which are used to bridge the juncture lines of the heat exchanger manifolds. An outer channel region of the hoops is provided with a reinforcing strip of gusset material. The hoops with their reinforcing strips provide structural reinforcement in the region between the manifolds and the conventional side bar reinforcing members in the central core section.
Owner:MUND 2013 FAMILY TRUST +2
Heat dissipation structure of electronic device
ActiveUS20120103571A1Desired heat dissipation efficiencyEfficient solutionReinforcing meansDigital data processing detailsEvaporationEngineering
A structure of heat dissipation of an electronic device includes at least one heat pipe and a cooler. The heat pipe has a condensation end and an evaporation end opposite to each other, and the evaporation end is disposed on a heat generating element of the electronic device. The cooler is disposed on a rack and has a chamber therein, and the chamber has an inner shell having a cooling fluid therein. When the electronic device is mounted in the rack, the condensation end of the heat pipe is inserted into the cooler and positioned into the inner shell. The evaporation end absorbs the heat energy of the heat generating element, and transfers the heat energy to the condensation end, such that the cooling fluid dissipates the heat energy of the condensation end.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Heat exchanger
ActiveUS20080000626A1Good molding effectAvoid stress concentrationReinforcing meansStationary conduit assembliesMechanical engineeringRib cage
A heat exchanger includes tubes and a tank. The tubes extend in a first direction, and are stacked in a second direction. The tank has a tube insertion plate part, and is arranged at an end portion of the tubes. The tube insertion plate part has tube holes in which the tubes are inserted, and ribs extending in a third direction that is approximately perpendicular to the first direction and the second direction. The tube hole has end portions in the third direction. The rib are arranged to overlap with the end portion of the tube hole in the second direction, and to provide a deformable part to be deformable in the first direction. The deformable part is located in the tube insertion plate part outside of the ribs in the third direction.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Slim vapor chamber
ActiveUS20170023308A1Improve thermal conductivitySmall sizeReinforcing meansIndirect heat exchangersEngineeringMechanical engineering
A slim vapor chamber includes a first plate, a second plate and a capillary structure. The periphery of the second plate is connected with that of the first plate to form a chamber. The capillary structure is disposed in the chamber. At least one of a side of the first plate facing the second plate and a side of the second plate facing the first plate is formed with a plurality of supporting structures, which include a plurality of supporting pillars and a plurality of supporting plates, by an etching process.
Owner:DELTA ELECTRONICS INC
Flat loop Heat pipe
InactiveUS20100163212A1Improve cooling effectPrevent circulation of thermal dissipation from difficult activationReinforcing meansIndirect heat exchangersEvaporationEngineering
A flat loop heat pipe is formed of a first capillary core, a second capillary core, a first support member, and a second support member. The first capillary core and the first support member constitute an evaporation room. The second capillary core and the second support member constitute a compensation room. In light of this structure, it is not difficult to activate circulation of thermal dissipation under low-watt heat source and the first capillary core can avoid dry-out phenomenon.
Owner:CHIN CHI TE
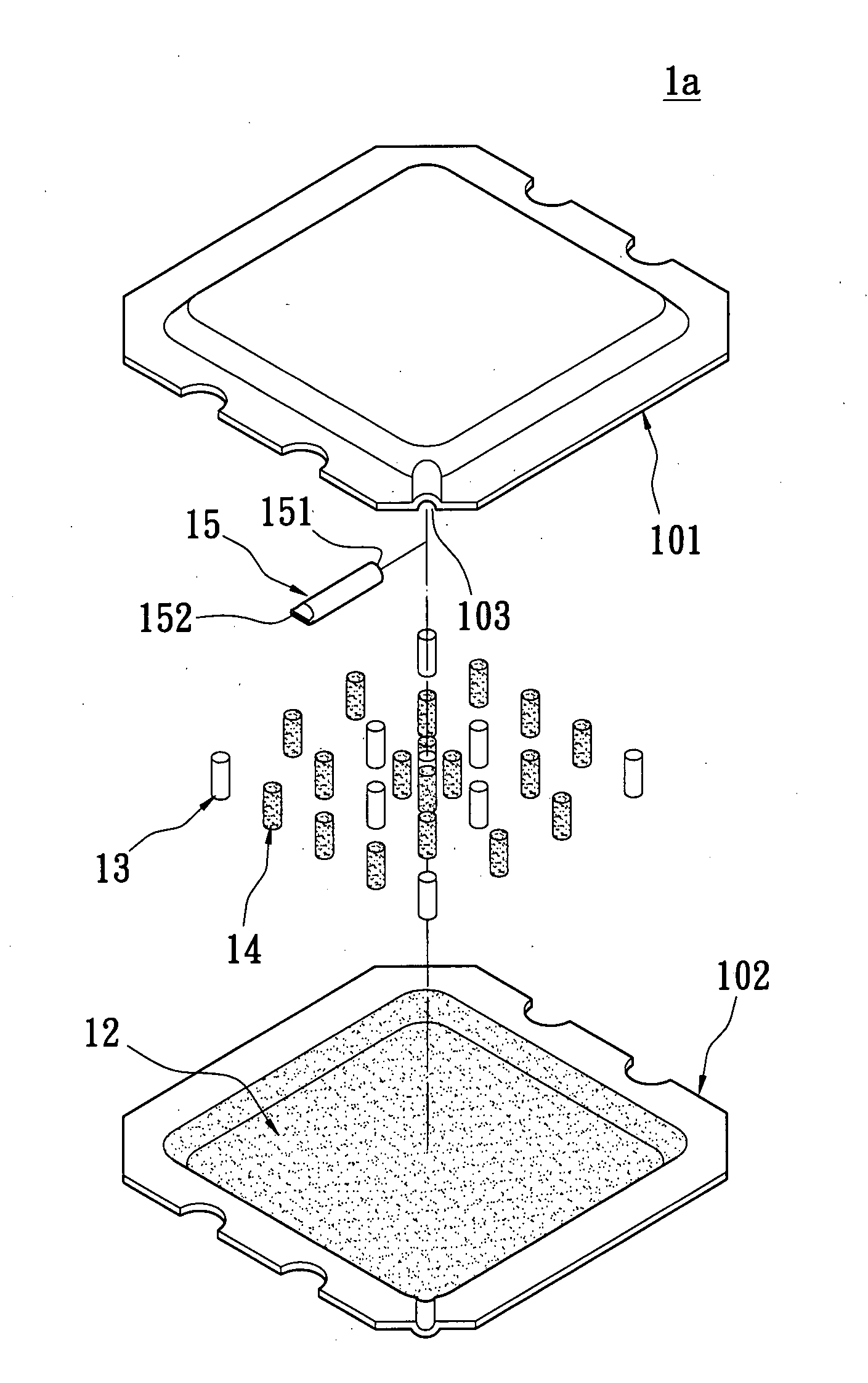
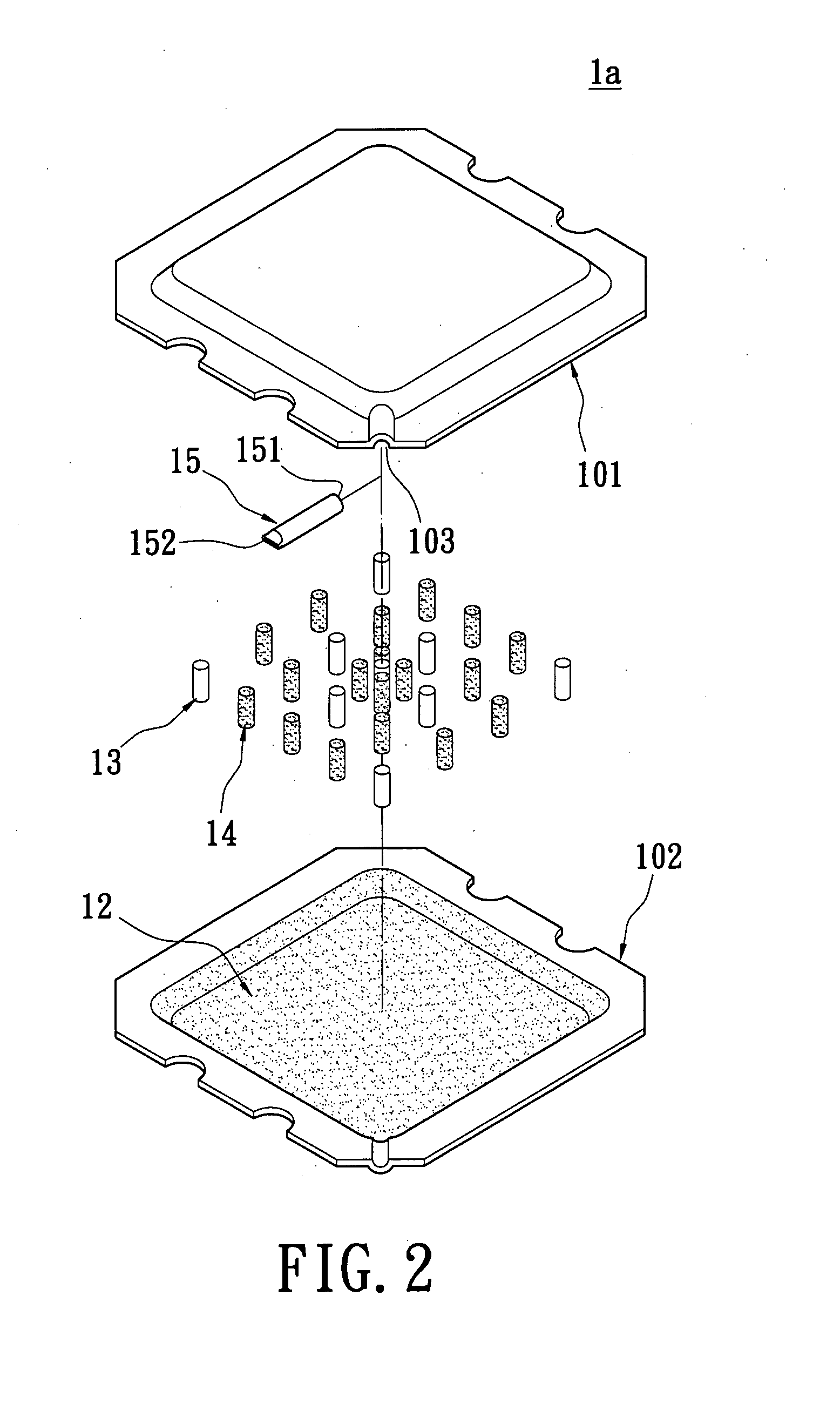
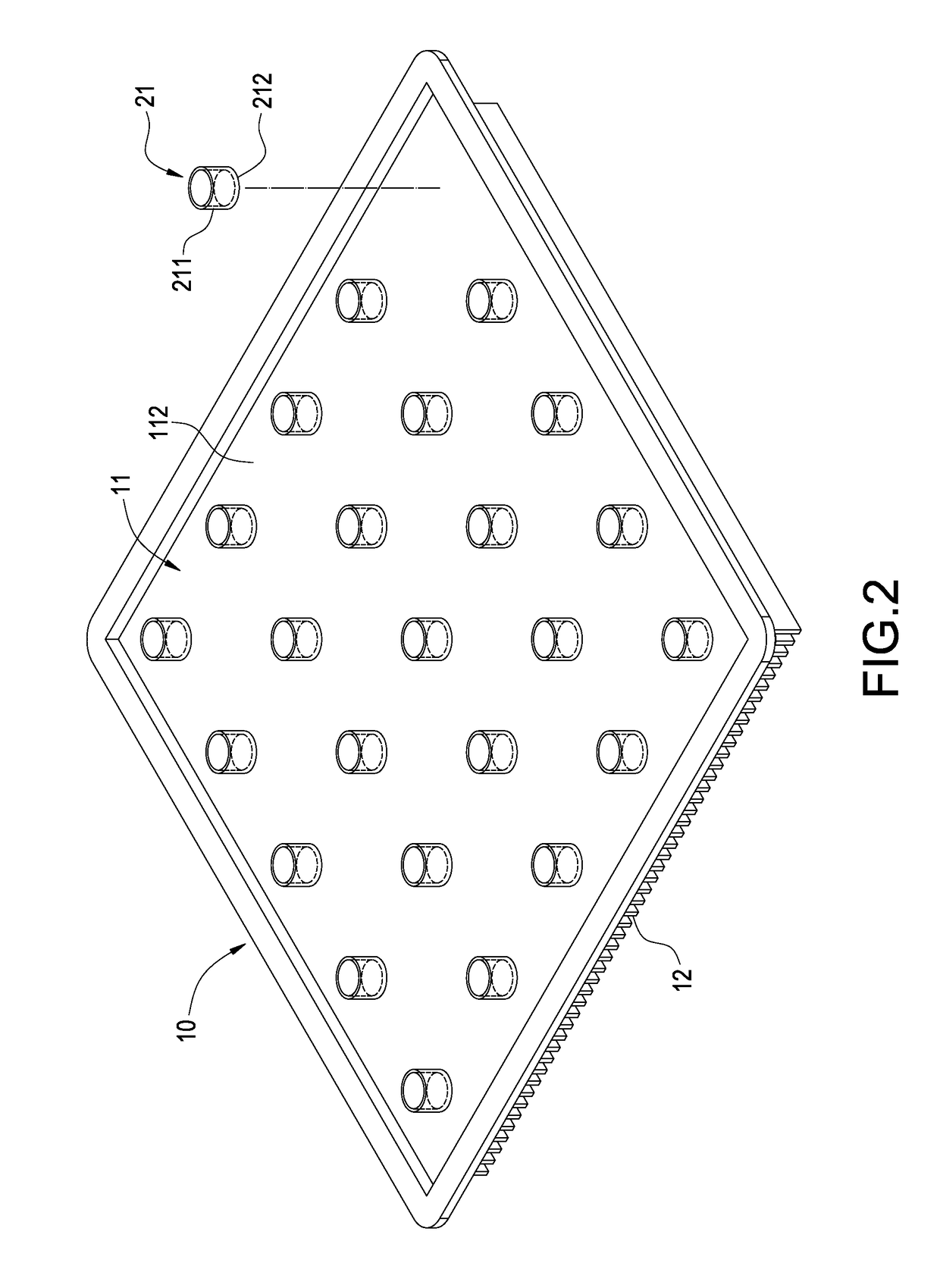
Vapor chamber and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveUS20170122672A1Work fasterIncrease return speedSpacing meansReinforcing meansWorking fluidManufacturing technology
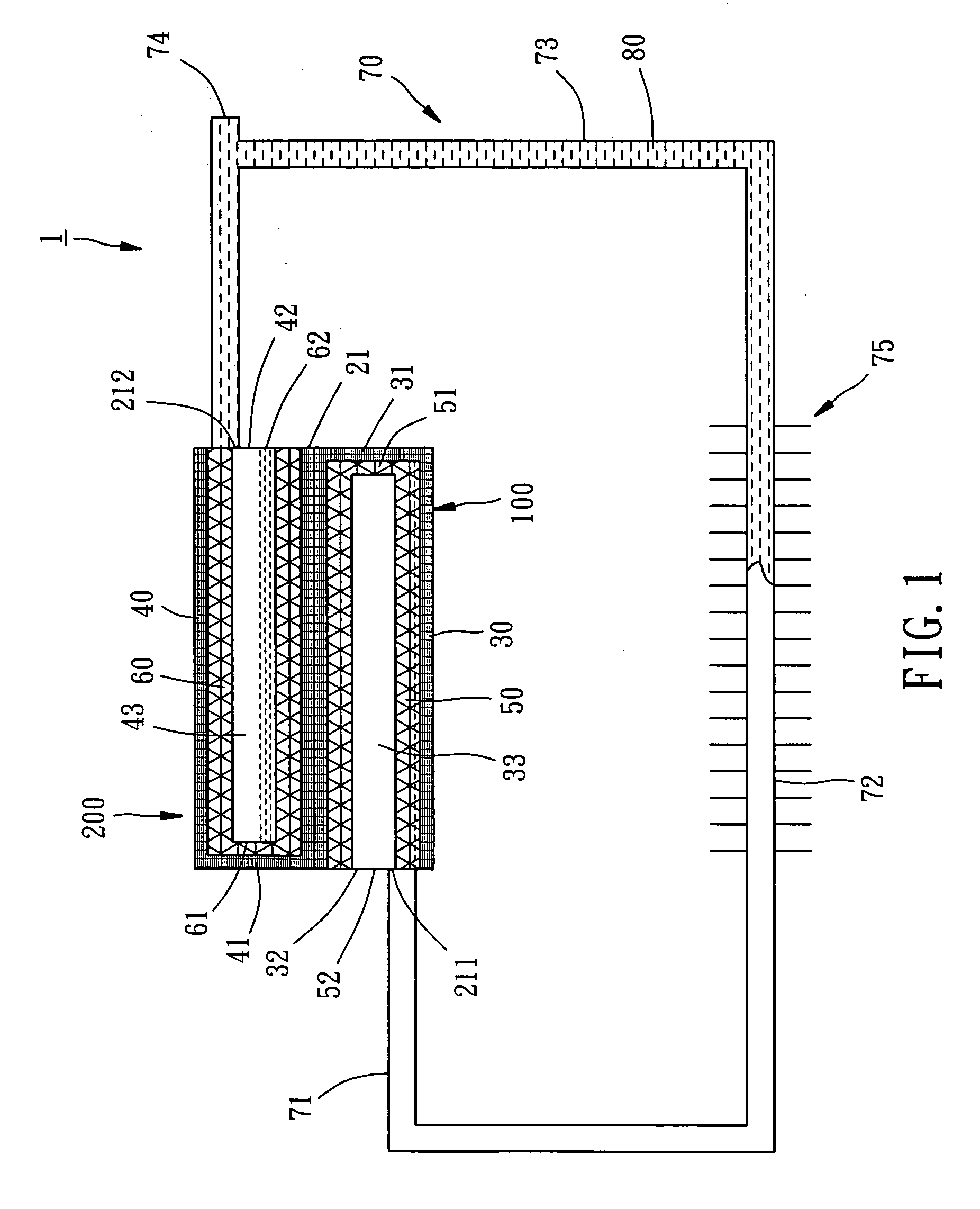
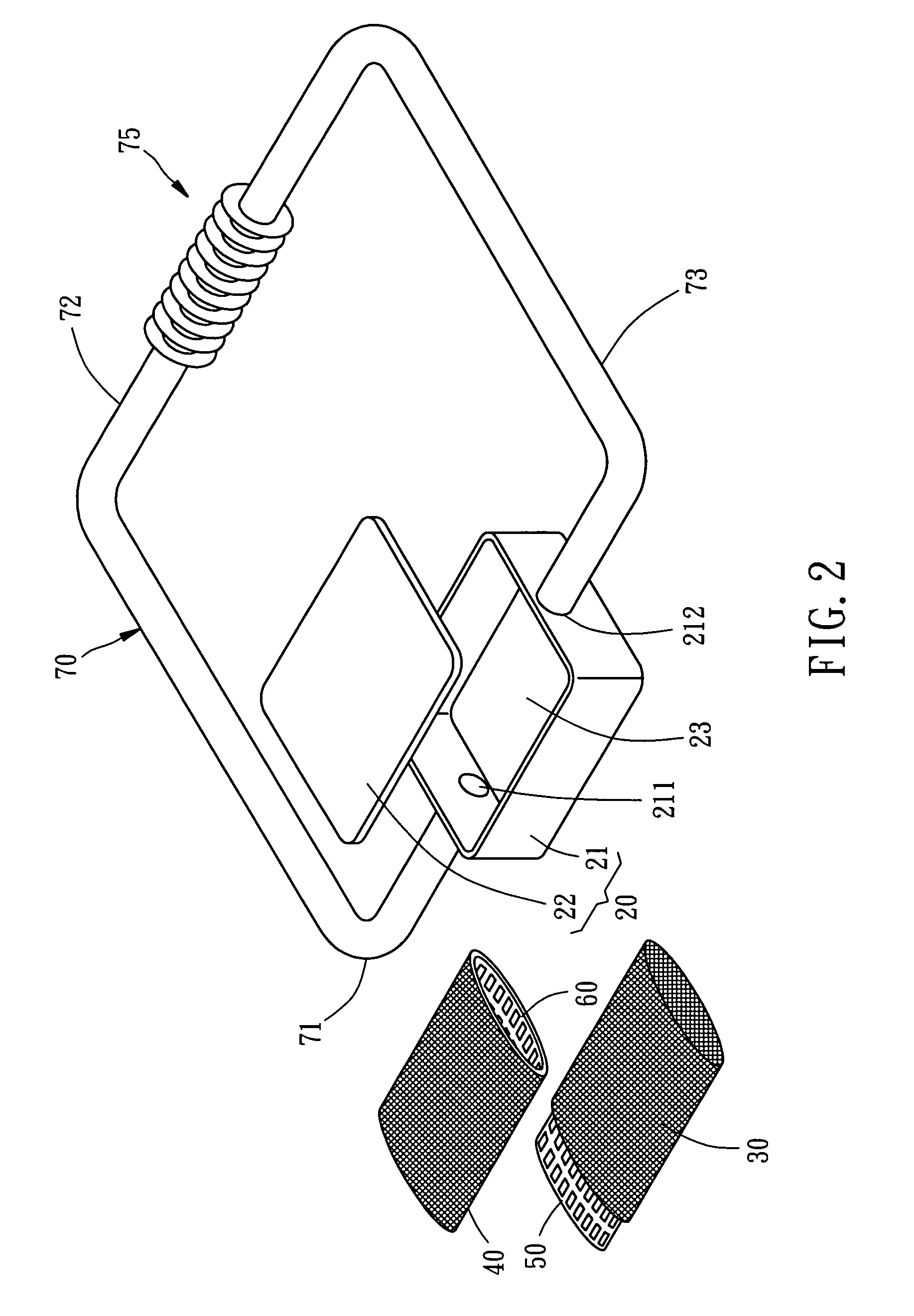
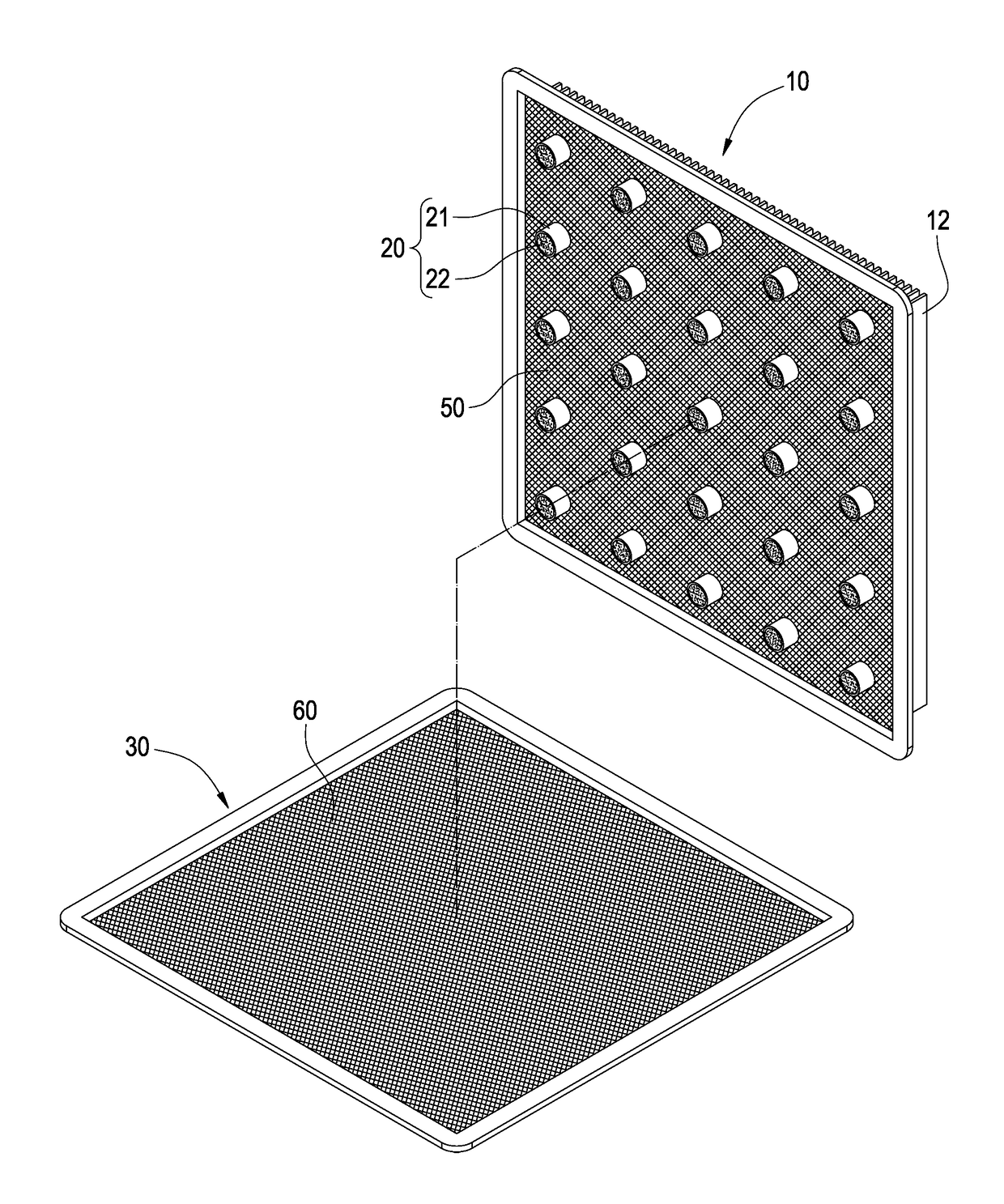
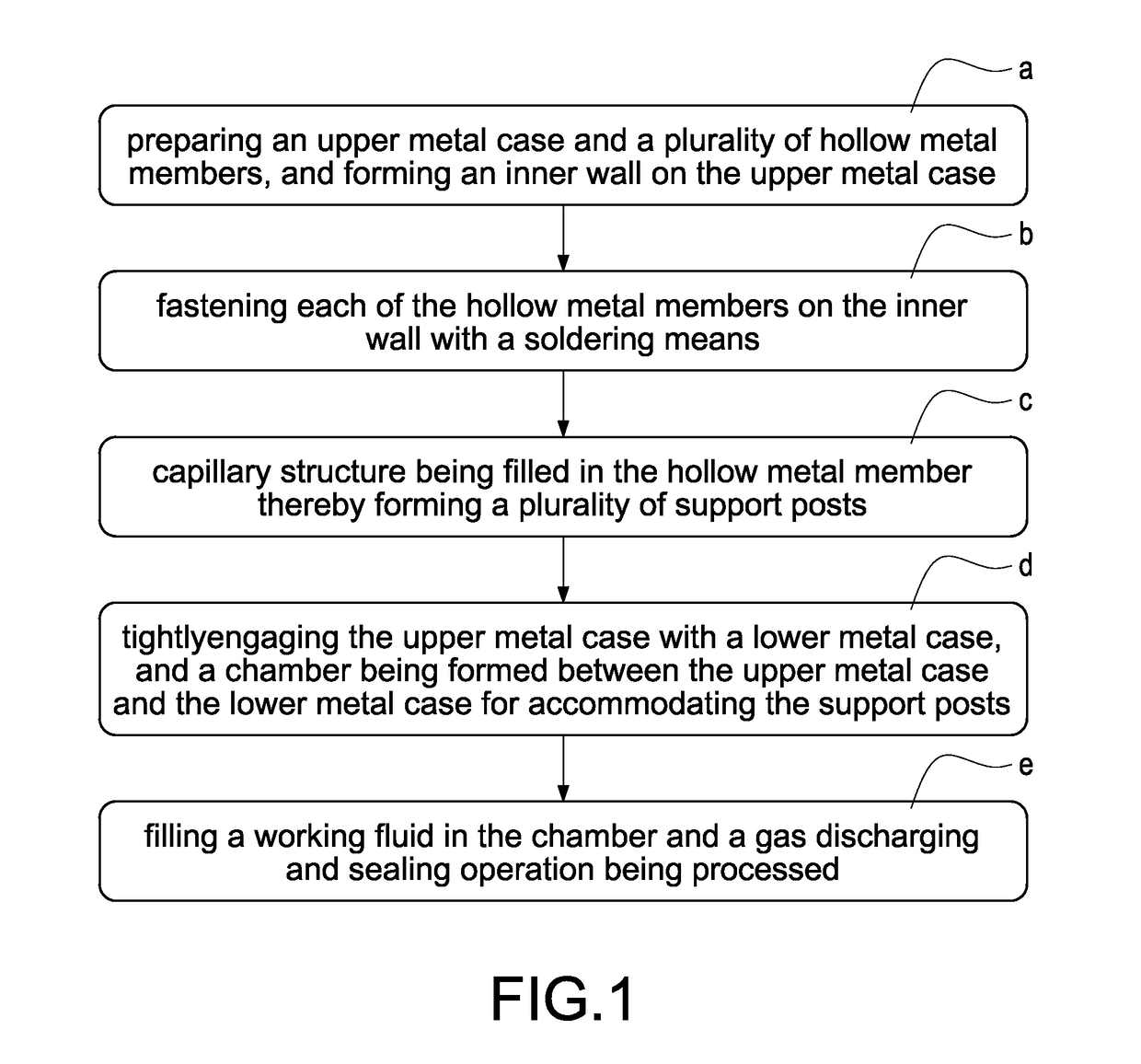
In a vapor chamber and a manufacturing method thereof, the vapor chamber includes a lower metal case, an upper metal case, a plurality of support posts and a working fluid; the upper metal case is tightly engaged with the lower metal case, and a chamber is formed between the upper metal case and the lower metal case; the support posts are accommodated in the chamber and disposed between the upper metal case and the lower metal case, each of the support posts includes a hollow metal member and a capillary structure disposed inside the hollow metal member, and one end of the hollow metal member is soldered and fastened on the upper metal case; and the working fluid is filled in the chamber. Accordingly, advantages of simplifying manufacturing process, shortening manufacturing time and ensuring the quality of the vapor chamber to be stable can be achieved.
Owner:TAIWAN MICROLOOPS CORP
Thermal cycling resistant tube to header joint for heat exchangers
InactiveUS20050263263A1Improve thermal cycle lifeMinimizes material requirementReinforcing meansCorrosion preventionEngineeringMechanical engineering
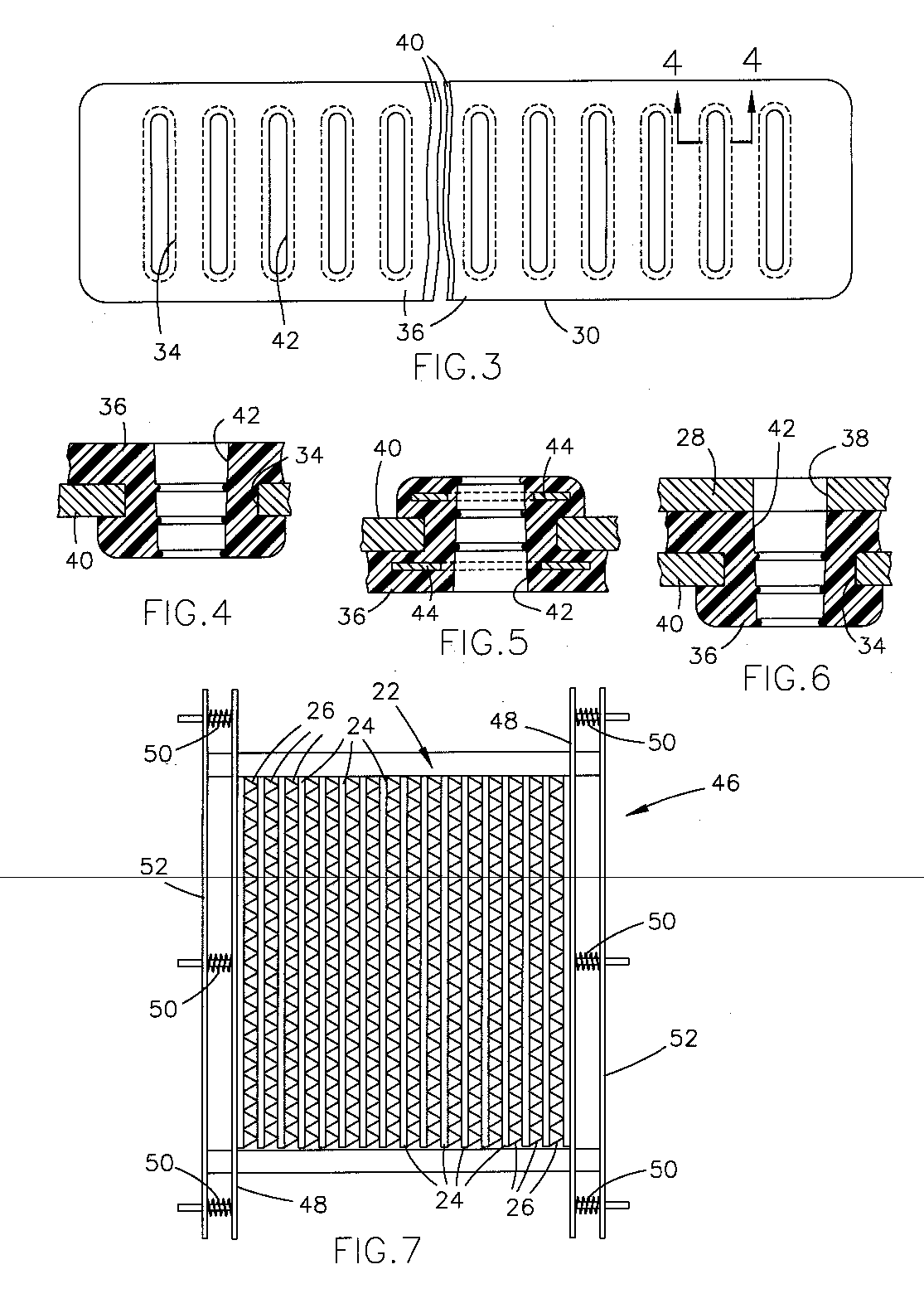
A reduction in tube to header joint failures in a heat exchanger having spaced headers (12,14), elongated, side-by-side parallel spaced tube slots (22) in the headers (12,14) along the length thereof and a plurality of flattened tubes (26) having ends (24) received in the tube slots (22) and metallurgically bonded to the header (12,14) thereat was achieved through the use of a reinforcing structure (38) having at least two projections (40) having a cross sectional shape complimentary to at least a part of the surface of the tubes (26) at their ends (24) and a length sufficient to extend along the tube ends (24) to a location past the metallurgical bonds between the tube ends (24) and a header (12,14), and a spine (44) extending transverse to the projection. Also disclosed is a reinforcing structure (38) and a method of reinforcing the tube to header joints in a heat exchanger.
Owner:MODINE MFG CO
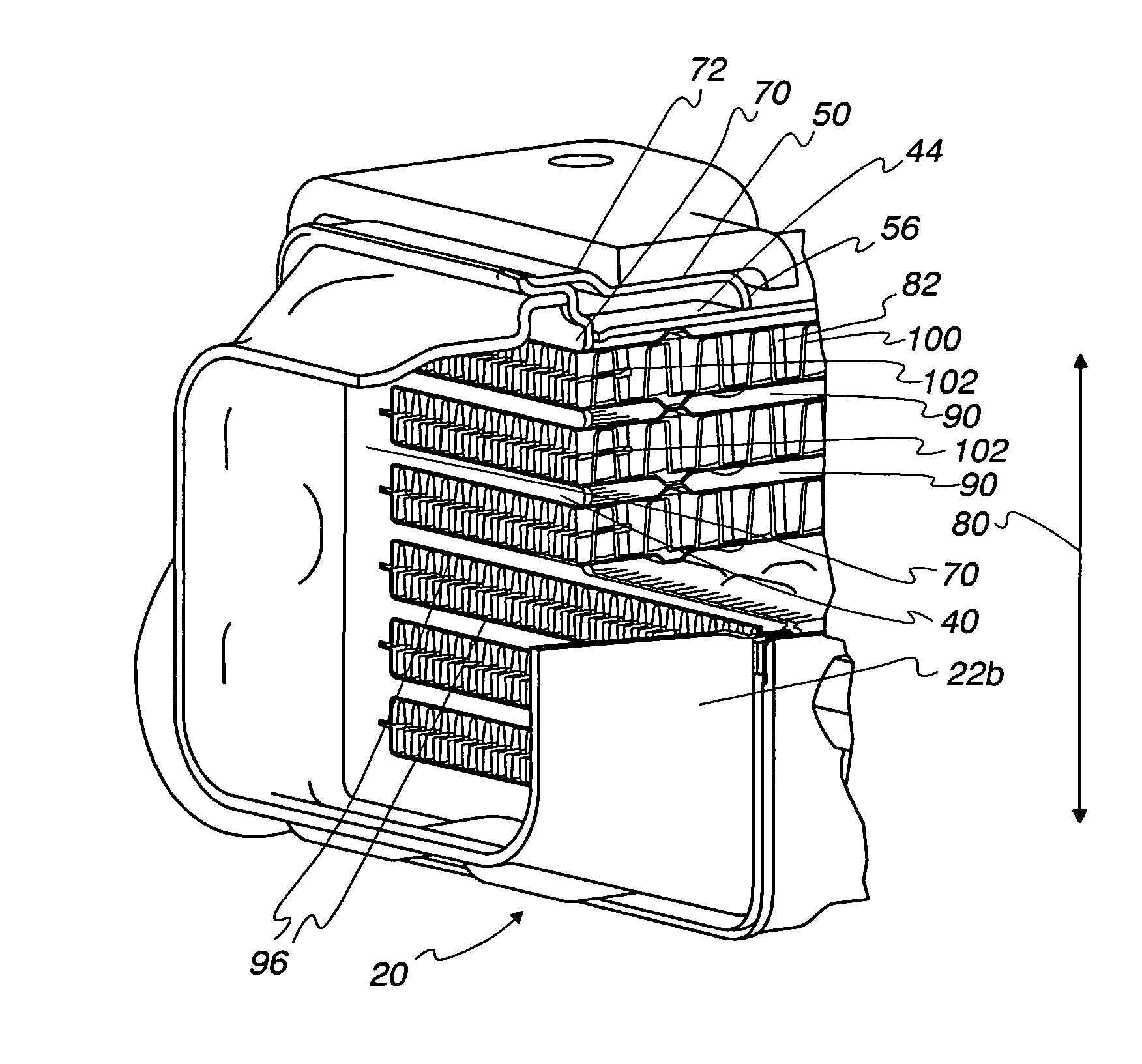
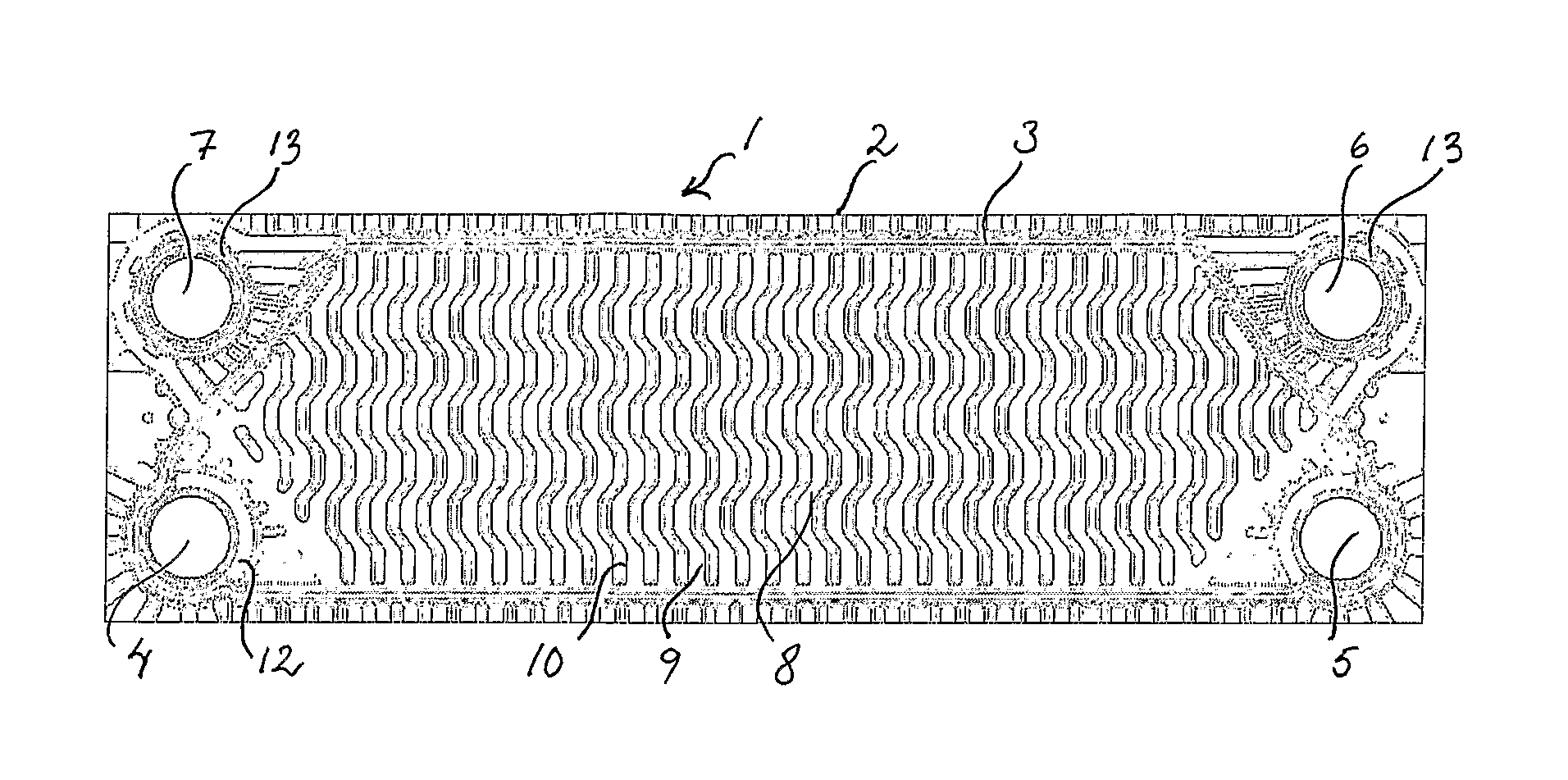
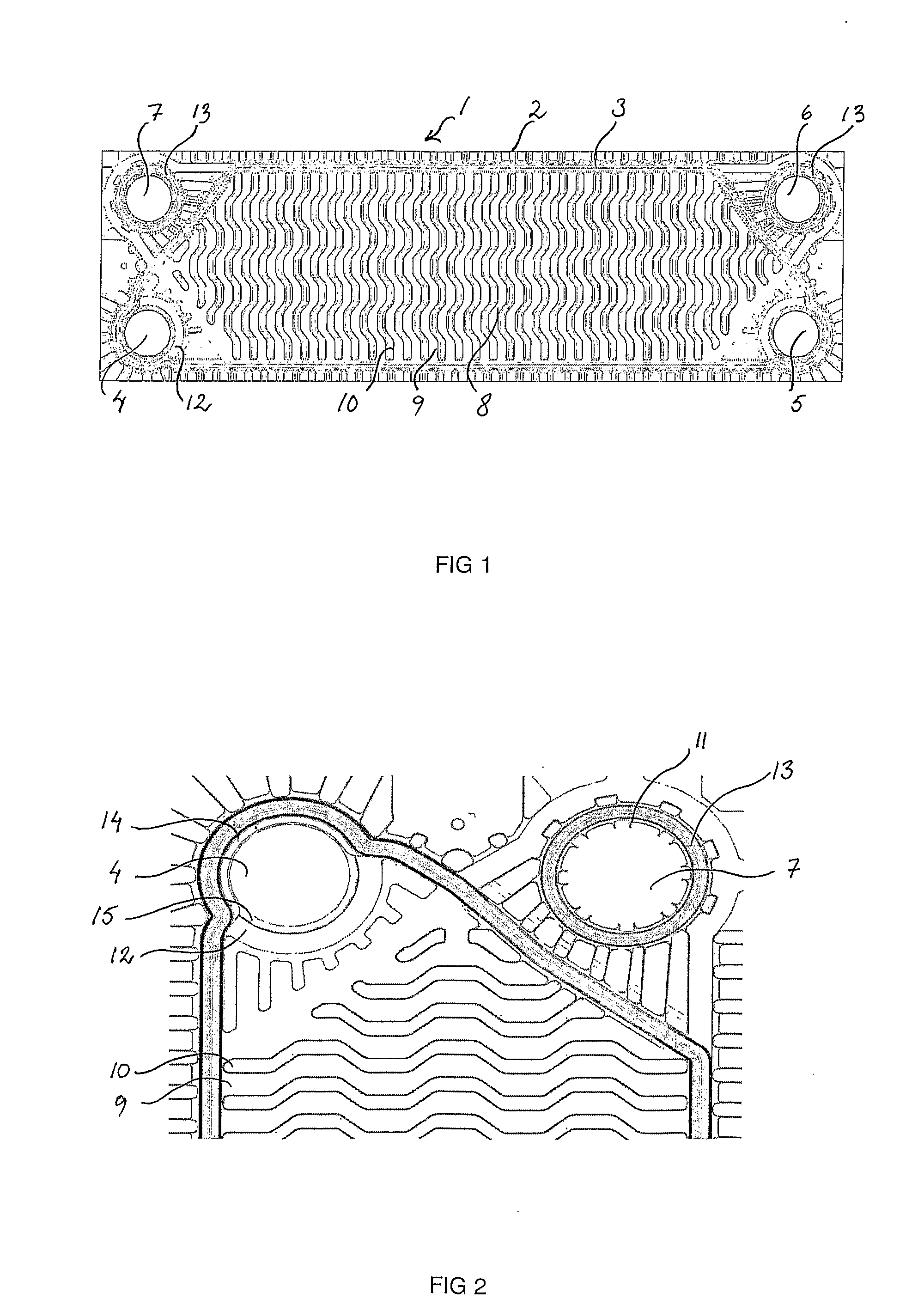
Gasket Assembly for Plate Heat Exchanger
InactiveUS20080196873A1Easy to solveReduce riskReinforcing meansLaminated elementsPlate heat exchangerGasket
A gasket assembly of a plate heat exchanger, comprising at least one gasket (3) and a package of heat exchanger plates (2) which are provided with inlet and outlet ports (4, 5, 6, 7) which constitute channels through the package and between the heat exchanger plates, whereby the heat exchanger plates are permanently joined in pairs to constitute cassettes (1), the gasket is disposed between the cassettes in a groove (12) in the heat exchanger plates and delimits in combination with the cassettes in every second space between plates a first flow passage for a first fluid, and the cassettes delimit a second flow passage for a second fluid. The gasket in the area around the ports comprises along its side facing the porthole a circumferential protruding bead (14). The invention also relates to a plate heat exchanger comprising the gasket unit, a heat exchanger plate and a gasket according to the invention.
Owner:ALFA LAVAL CORP AB
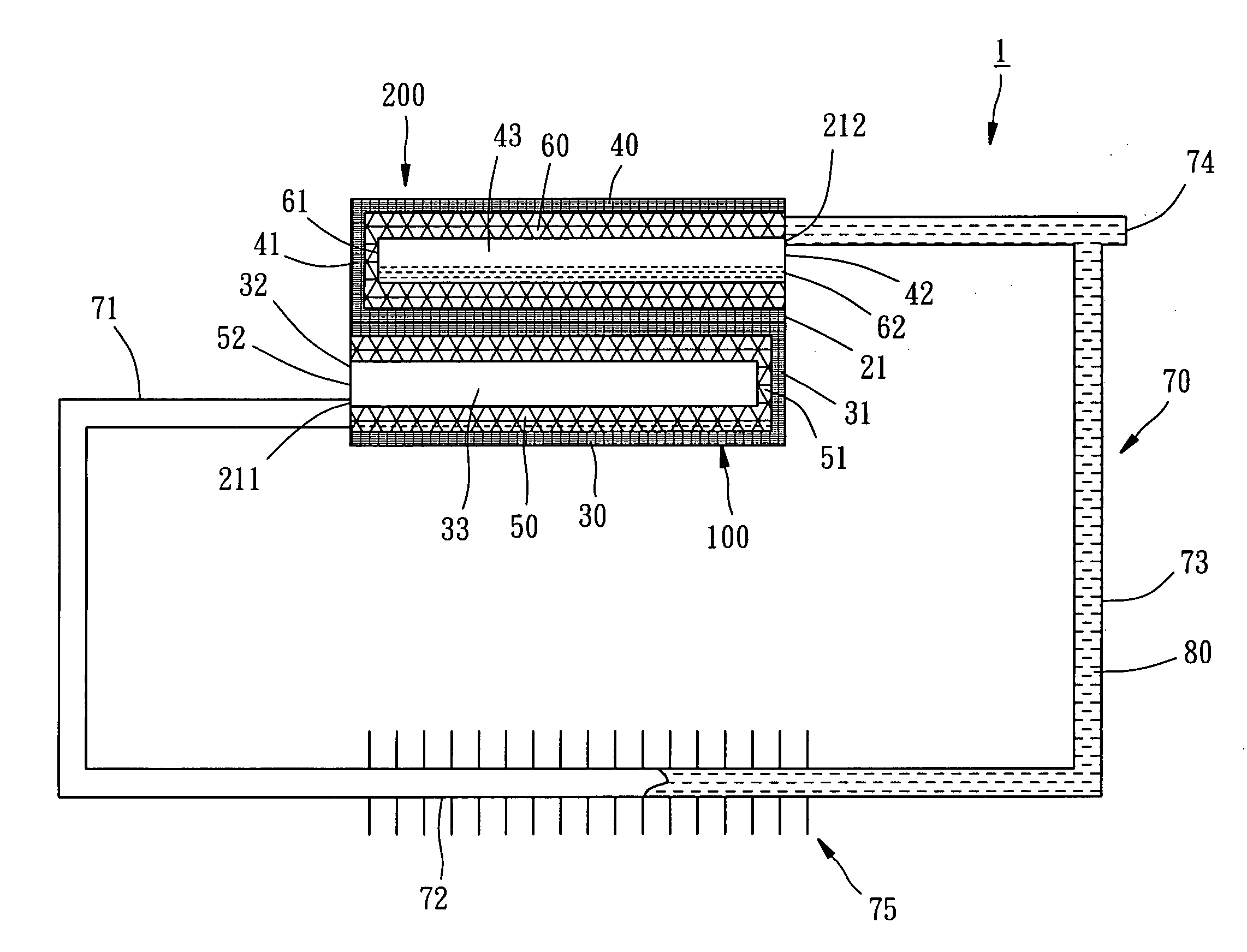
Method for heat transfer and device therefor
A heat transfer device comprising at least an aggregate of fibres or sheet of fibres (60) with internal passages and holes capable of capillary transport of liquids capable of capillary convection of coolant fluid from a heat source region (54) to heat dissipation region (56) and vice versa. A supply of coolant fluid in sufficient amount is provided to be absorbed or contained by said fibres or sheet of fibres (60) with internal passages and holes capable of capillary transport of liquids. A pressure tension member (70) comprising a strong yet resilient structure placed within said confined space and exerting pressure on said aggregate of fibres or sheet of fibres (60) with internal passages and holes capable of capillary transport of liquids against said heat source region (54) and / or heat dissipation region (57). A plurality of undulations are provided on said pressure tension member, including laterally extending ribs or protuberance (84) and protrusions (82) to accentuate the pressure exerted by the pressure tension member (70). A casing then encloses hermetically the above components.
Owner:NEXCHIP TECH
Tube in cross-flow conduit heat exchanger
A heat exchanger that includes an input cavity defined by inlet cavity walls; a heat exchanger portion in fluid communication with the input cavity and defined between a first side and a second side, and wherein a plurality of baffles are positioned within the heat exchanger portion; and an outlet cavity in fluid communication with the heat exchanger portion and defined by outlet cavity walls. The heat exchanger portion comprises: a plurality of first fluid paths defined between the baffles and extending from the input cavity to the outlet cavity, and a plurality of tubes extending through the heat exchanger portion from the first side to the second side. Each tube extends through the baffles so as to define a second fluid path through the heat exchanger portion. Heat exchanger systems are also generally provided, along with methods for cooling a hot fluid input with a heat exchanger.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com