Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1221 results about "Vehicle acceleration" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Acceleration is the rate at which a car or other vehicle can increase its speed, often seen in terms of the time that it takes to reach a particular speed.
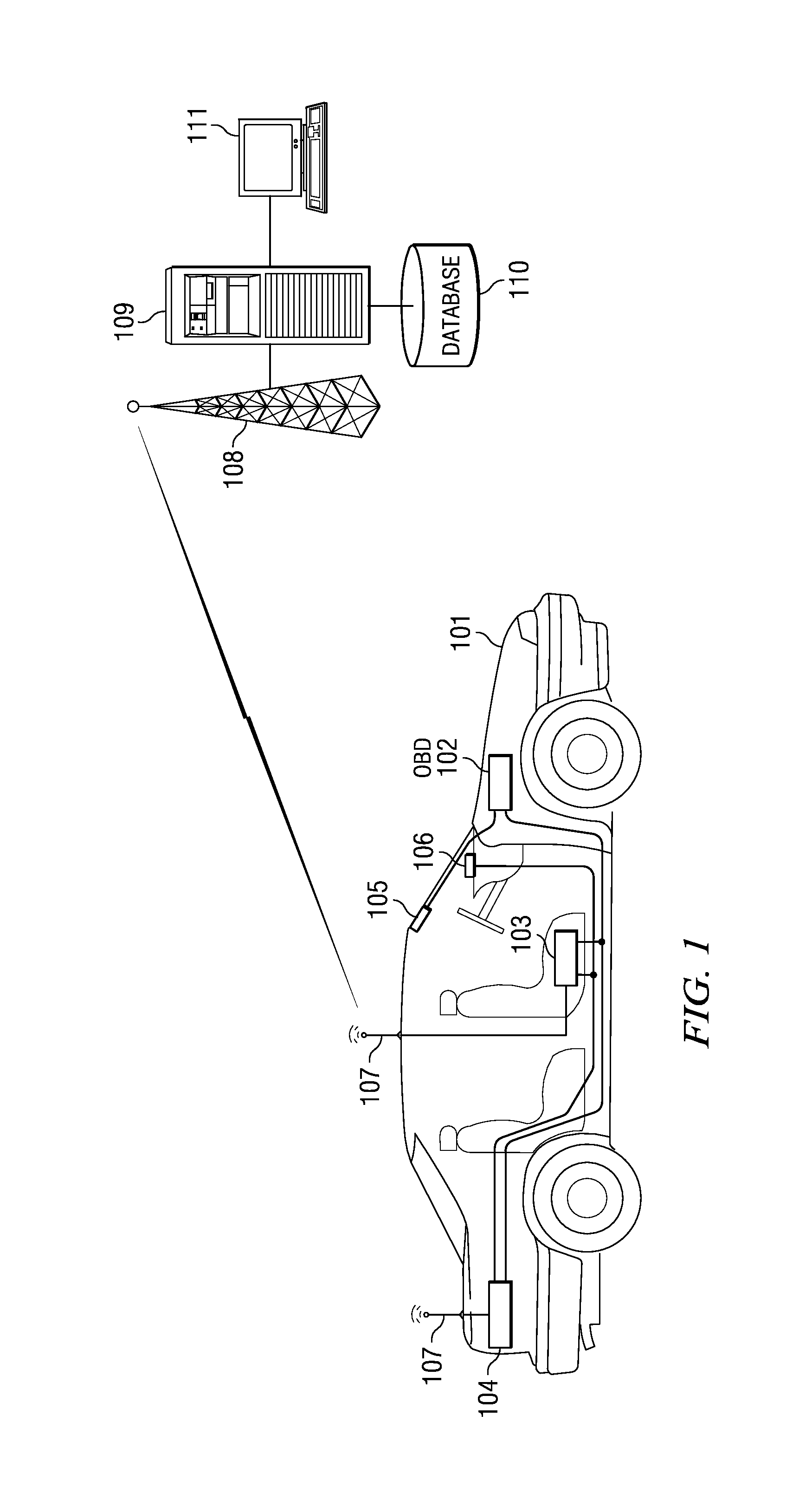
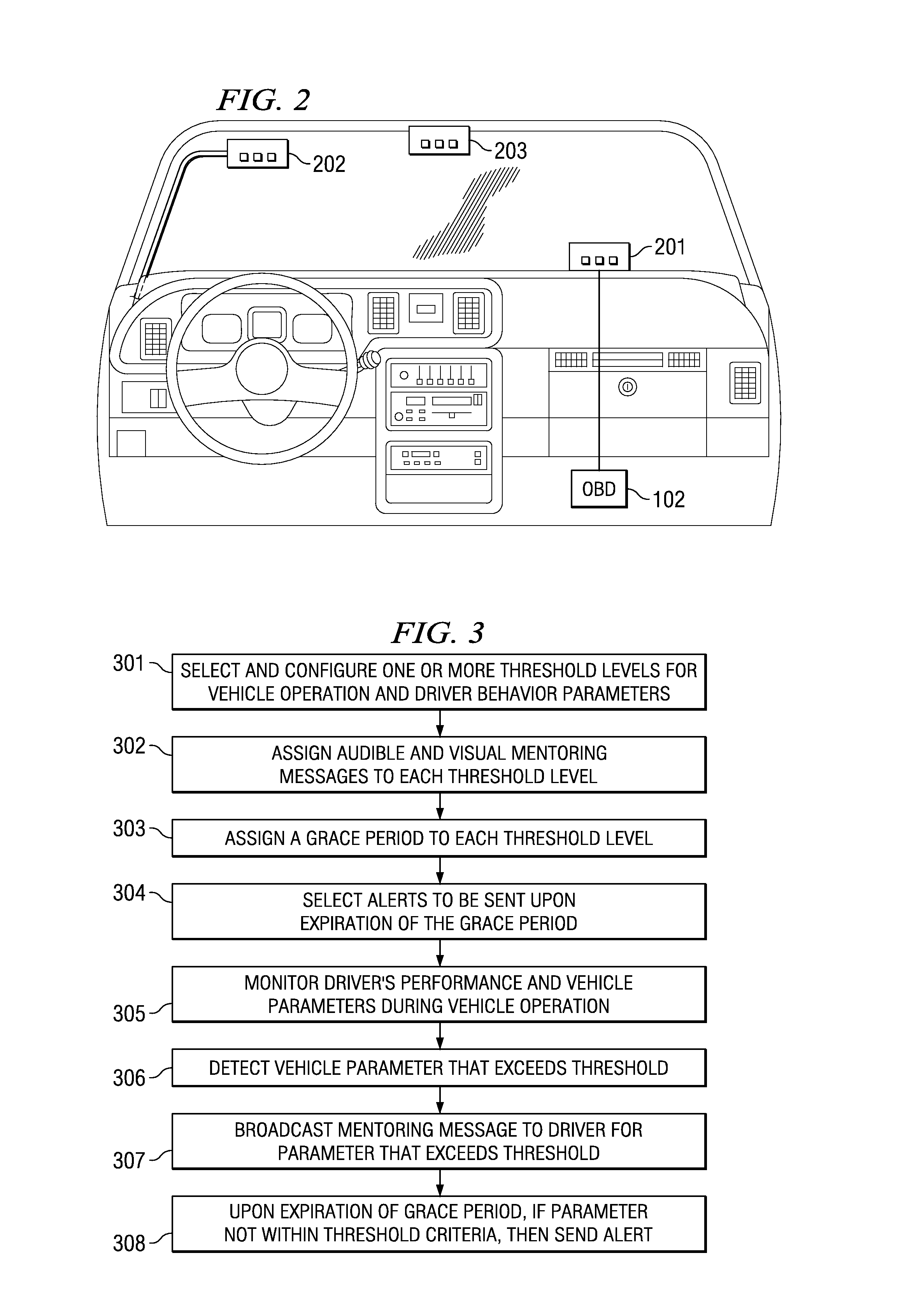
System and Method for Monitoring and Improving Driver Behavior
ActiveUS20080319602A1Reduce actionImprove securityVehicle testingRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesThird partyDriver/operator
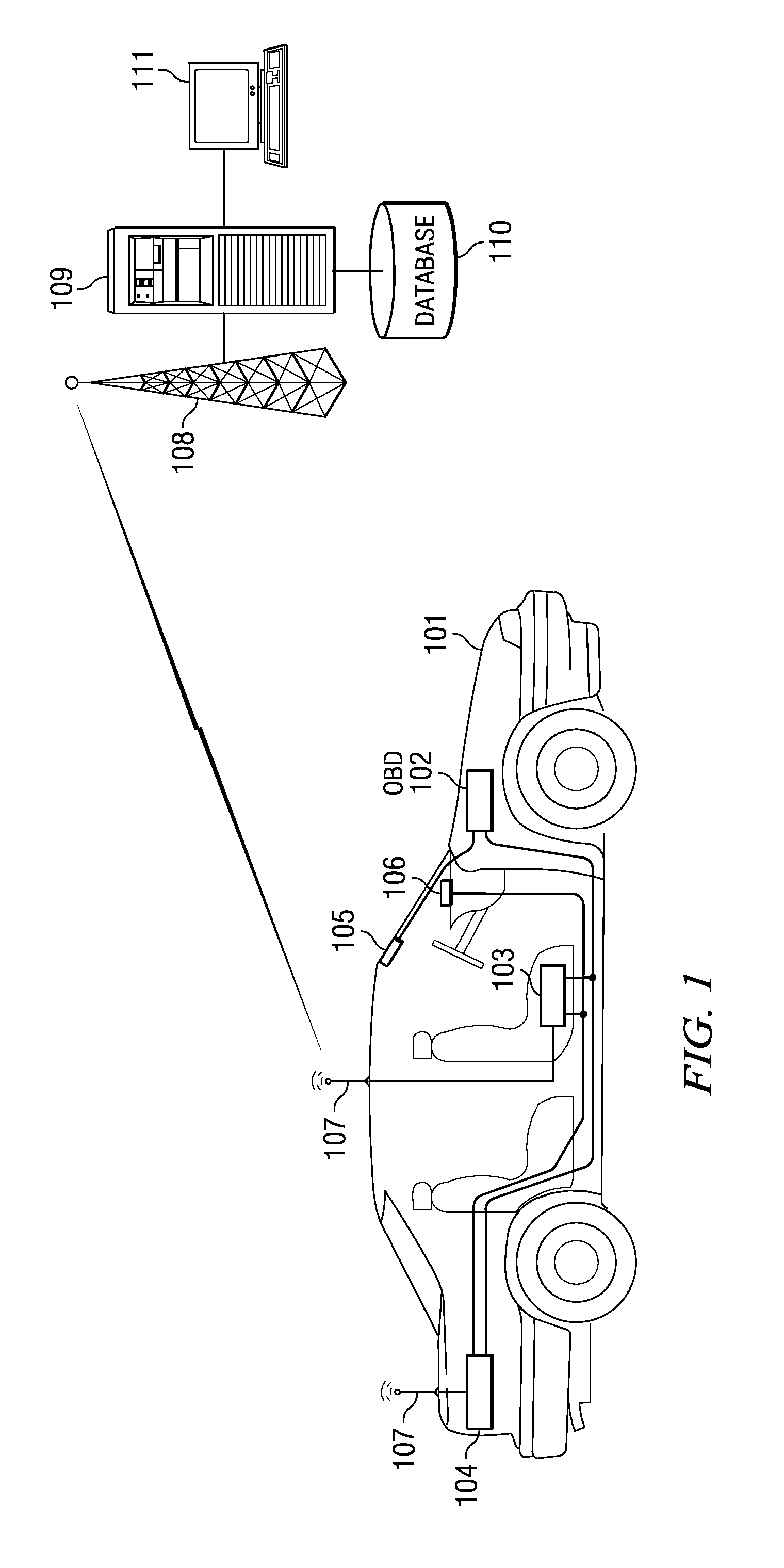
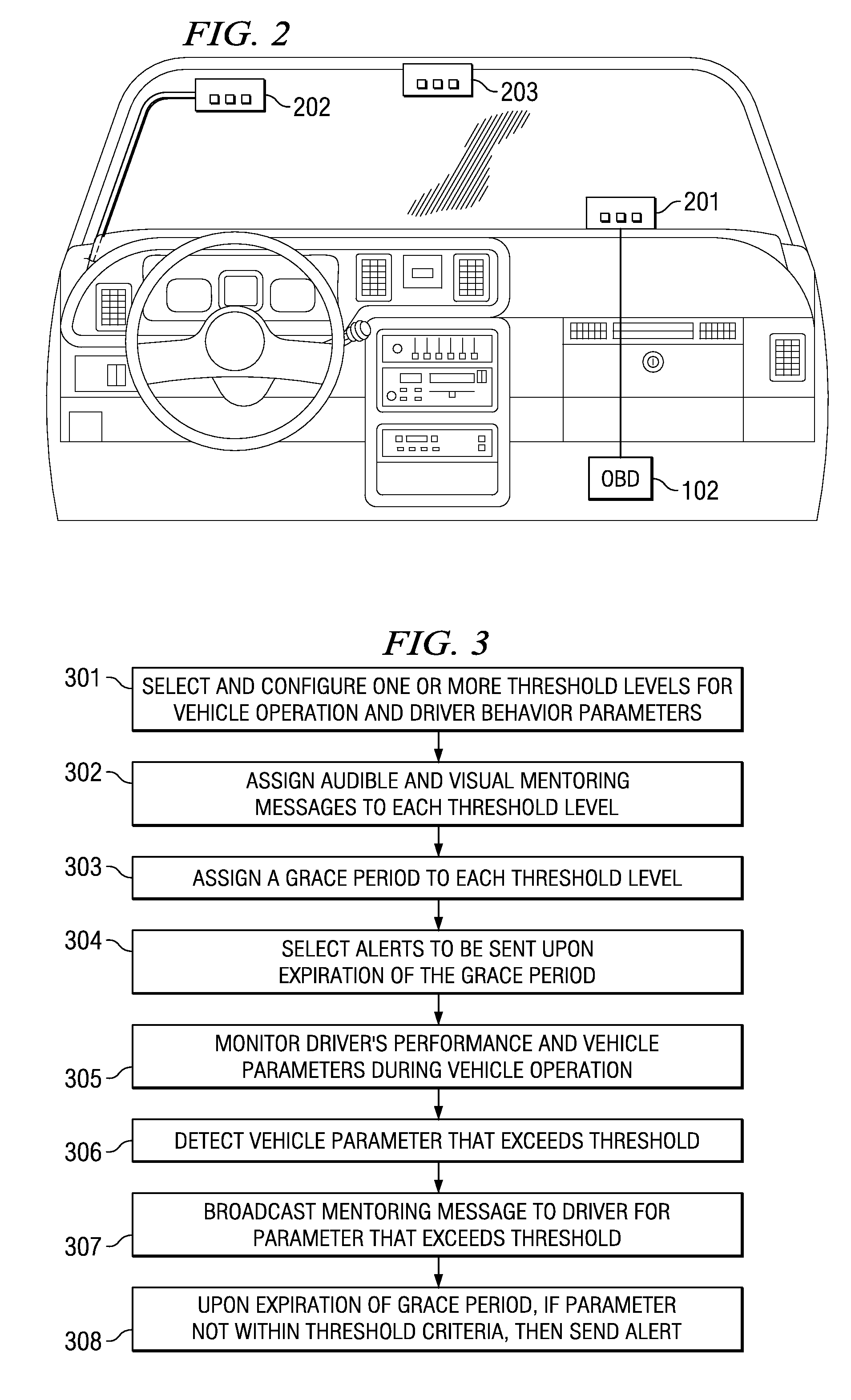
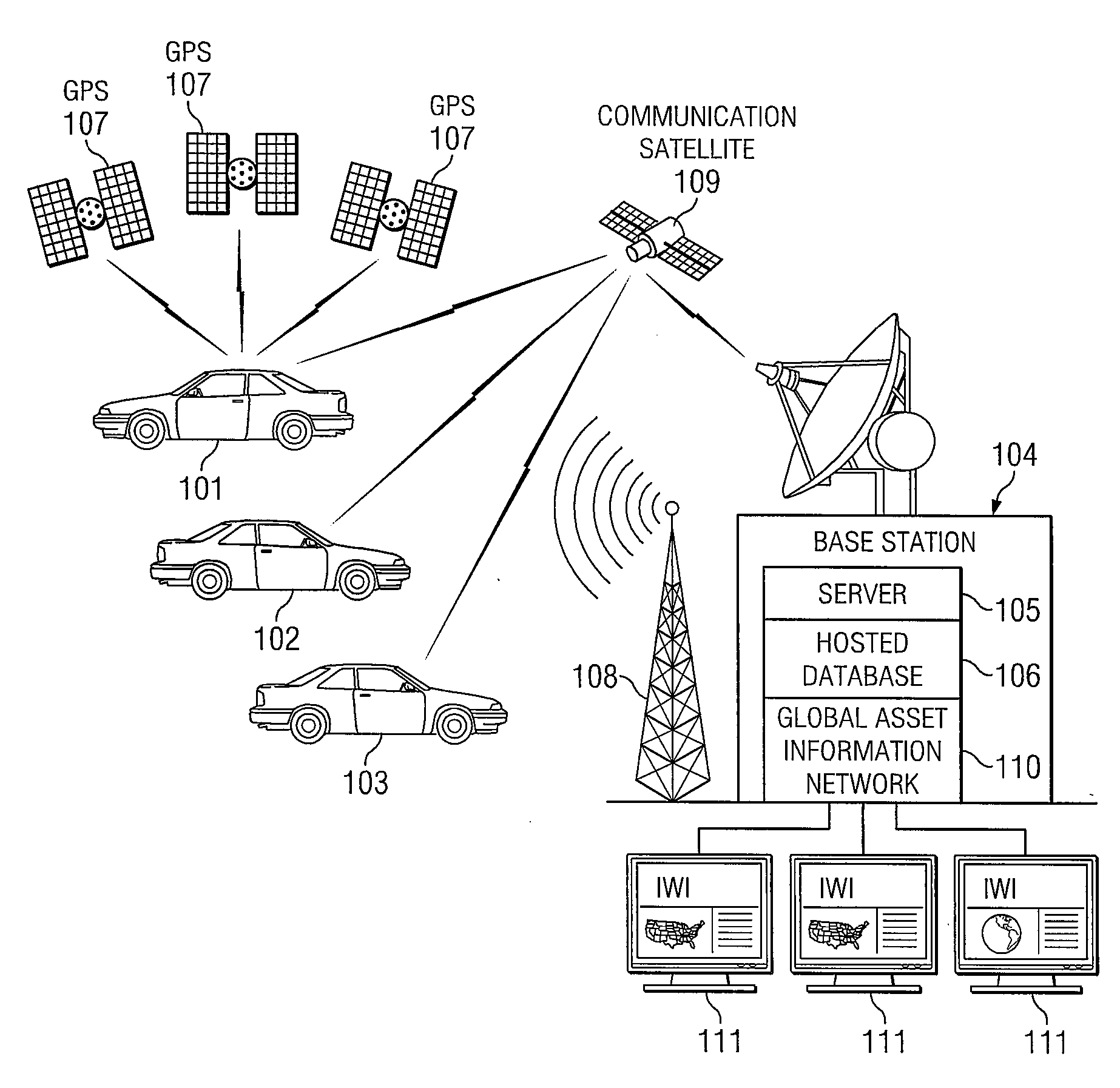
System and method for providing feedback to drivers. The system monitors selected vehicle parameters while a vehicle is being driven, and detects one or more vehicle operation violations by comparing the selected vehicle parameters to predetermined thresholds. A mentoring message is provided to the driver if the threshold is exceeded. If a vehicle operation violation has not been corrected within a preselected time period, then a violation report may be sent to a third party or a central server and / or a different mentoring message may be provided to the driver. Vehicle parameter data may be monitored from an on-board vehicle diagnostic system. The mentoring message may be an audible warning, such as a spoken message, or a visual warning, such as a text message. The selected vehicle parameters may be a vehicle speed, a vehicle acceleration, or a vehicle seatbelt use.
Owner:IWI
System and Method for Detecting and Reporting Vehicle Damage
InactiveUS20090051510A1Improve driver safetyLower fuel costsRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesRoad vehicles traffic controlAccelerometerEngineering
System and method for monitoring a vehicle comprising an accelerometer unit capable of monitoring vehicle accelerations, a processor adapted to receive inputs from the accelerometer unit and to compare the vehicle accelerations to predetermined parameters, wherein an attack on the vehicle is identified when one or more vehicle accelerations exceed an attack threshold, and one or more transmitter units adapted to continuously transmit messages upon occurrence of an attack, wherein the messages comprise a vehicle location.
Owner:IWI
Method for determining driving characteristics of a vehicle and vehicle analyzing system
ActiveUS20170309092A1Efficient interventionImprove securityVehicle testingRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesAcceleration UnitVehicle acceleration
A method for determining driving characteristics of a vehicle. To provide an enhanced method to determine from a driving characteristics of the vehicle a long term mechanical stress of a vehicle, it is proposed that during operation of the vehicle an acceleration of the vehicle is detected by an acceleration sensor in the vehicle and evaluated by a vehicle analyzing system in the vehicle, wherein a driving parameter occurring during an acceleration event in which the vehicle acceleration is above a predetermined threshold is used to determine a driving characteristics value of the vehicle.
Owner:ROSENBAUM WALTER STEVEN
Method and arrangement in a hybrid vehicle for improving battery state-of-charge control and minimizing driver perceptible disturbances
InactiveUS6336063B1Internal combustion piston enginesDigital data processing detailsBattery state of chargeElectric vehicle
Method for minimizing driver perceptible drive train disturbances during take-off in a hybrid electric vehicle when maximized power is often desired is disclosed. The method includes sensing an actual state-of-charge (SOC) value of a battery in a hybrid electric vehicle and a traveling velocity of the vehicle during take-off operation. The sensed actual SOC value is compared with a SOC reference value and computing a delta SOC value as a difference therebetween. A velocity-based SOC calibration factor is looked up that corresponds to the traveling velocity of the vehicle. A combination is utilized of the delta SOC value and the SOC calibration factor as a SOC feedback engine speed control instruction to an engine controller of the hybrid electric vehicle. A driver's desired vehicular acceleration is sensed based on accelerator position. Maximum possible engine power generatable at the sensed vehicle speed is determined, as is a required power value from the power train of the vehicle to meet the driver's desired vehicular acceleration. The maximum possible engine power generatable at the sensed vehicle speed is compared with the required power value and computing a delta power train requirement value as a difference therebetween. A velocity-based and accelerator position-based power calibration factor is looked-up that corresponds to the traveling velocity of the vehicle and the accelerator position. A combination of the delta power train requirement value and the power calibration factor is utilized as a power requirement feed-forward engine speed control instruction to an engine controller of the hybrid electric vehicle.
Owner:VOLOVO CAR CORP
Method for a changing safety signaling system
The present invention provides a method for a changing safety signaling system. The safety signaling system can change as a result of changing driving conditions that stem from changes in the weather or changes in vehicle velocity. As a vehicle brakes, coasts, turns, or accelerates, front-facing, side-facing, top-facing, and / or rear facing indicators can communicate vehicular acceleration, coasting, and braking to a pedestrian or other vehicles. A distance sensor can be used to trigger a signal to alert a second vehicle that the first vehicle is braking hard and slowing fast or can be used to warn the operator of the first car that a collision may be imminent and can be used to warn the operator of a second car that measures can be taken to avoid a collision or minimize damage from a collision. The instant invention can be utilized by either a first car or a second car.
Owner:SONG WON MOO
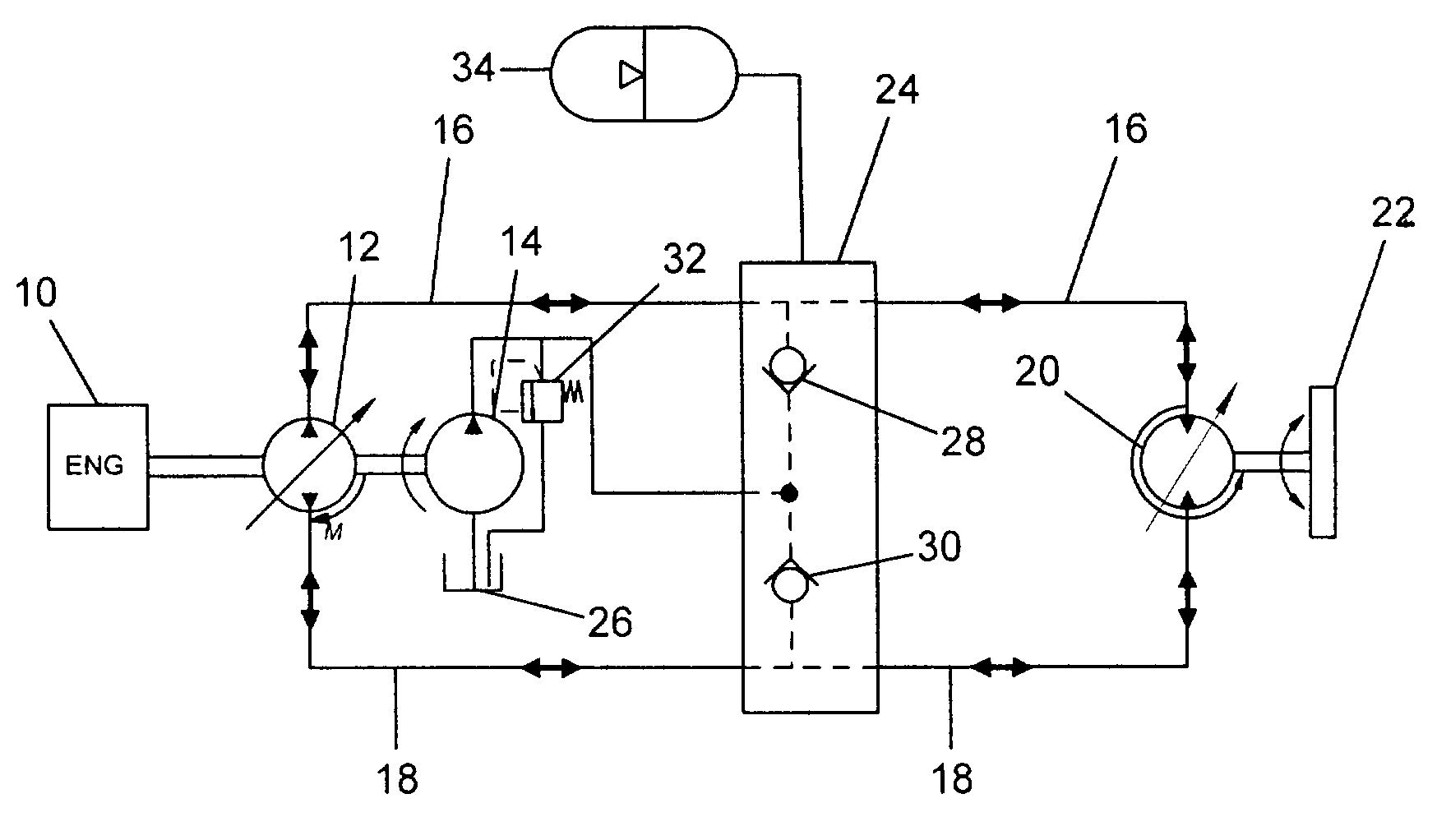
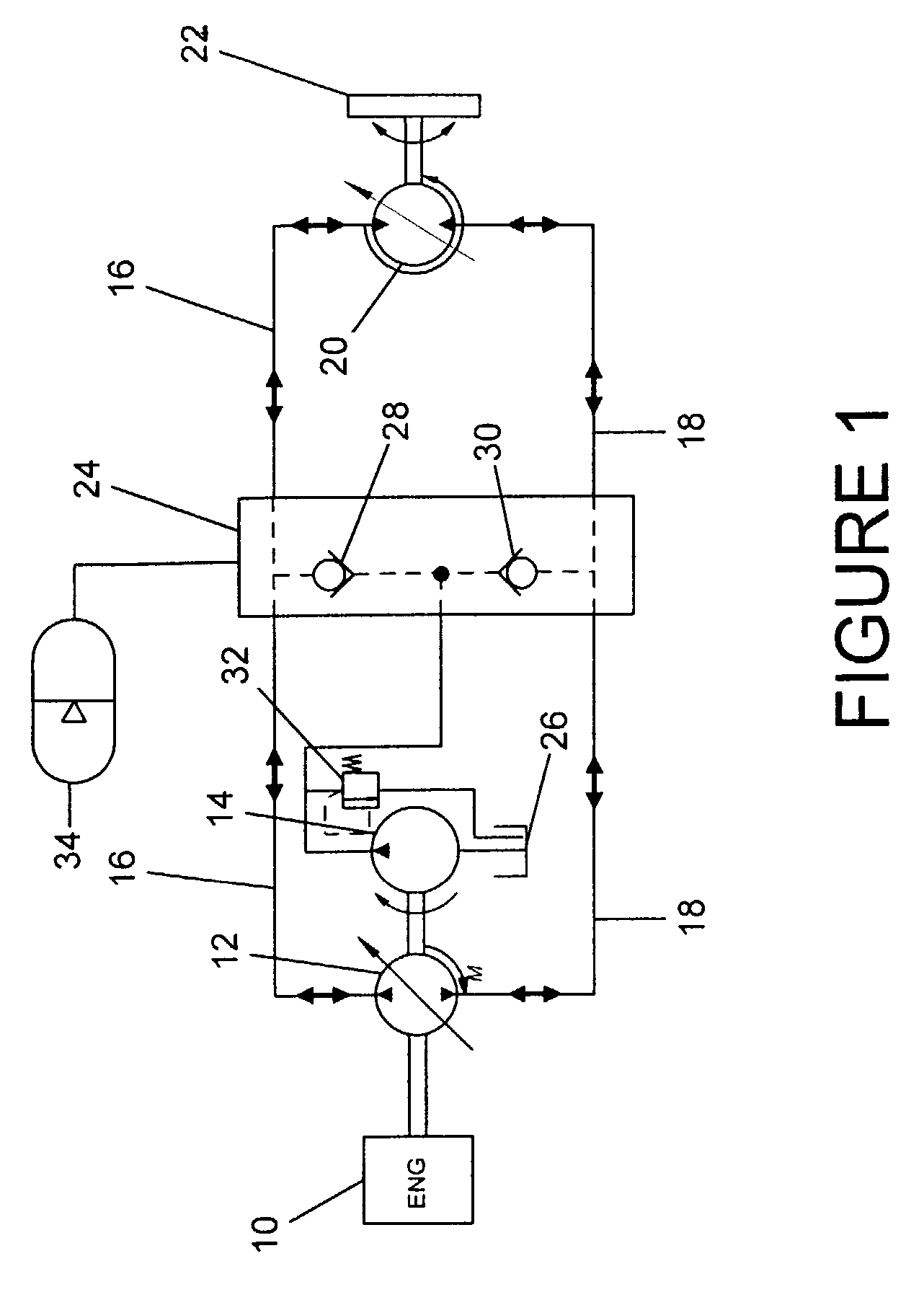
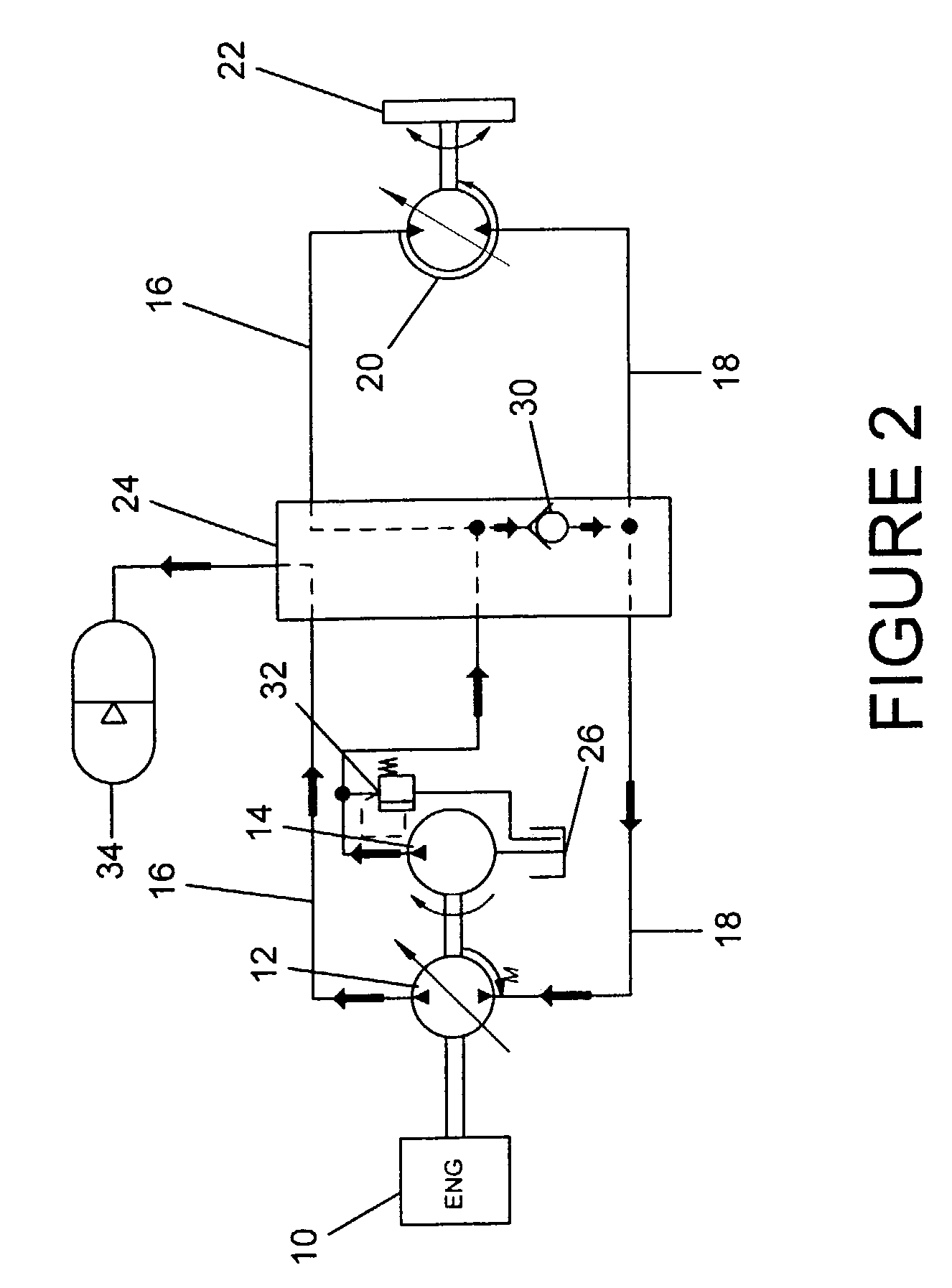
Energy recovery system for work vehicle including hydraulic drive circuit and method of recovering energy
A work vehicle having a hydrostatic drive system provides for the recovery and reuse of the vehicle's kinetic energy by conducting pressurized hydraulic fluid out of the hydrostatic drive system into an accumulator during vehicle deceleration, and conducting the pressurized fluid back into the drive system during vehicle acceleration to assist the vehicle's engine in accelerating the vehicle.
Owner:BLUE LEAF I P +1
System for controlling an internal combustion engine in a fuel efficient manner
InactiveUS6944532B2Internal combustion piston enginesDigital data processing detailsExternal combustion engineFuel efficiency
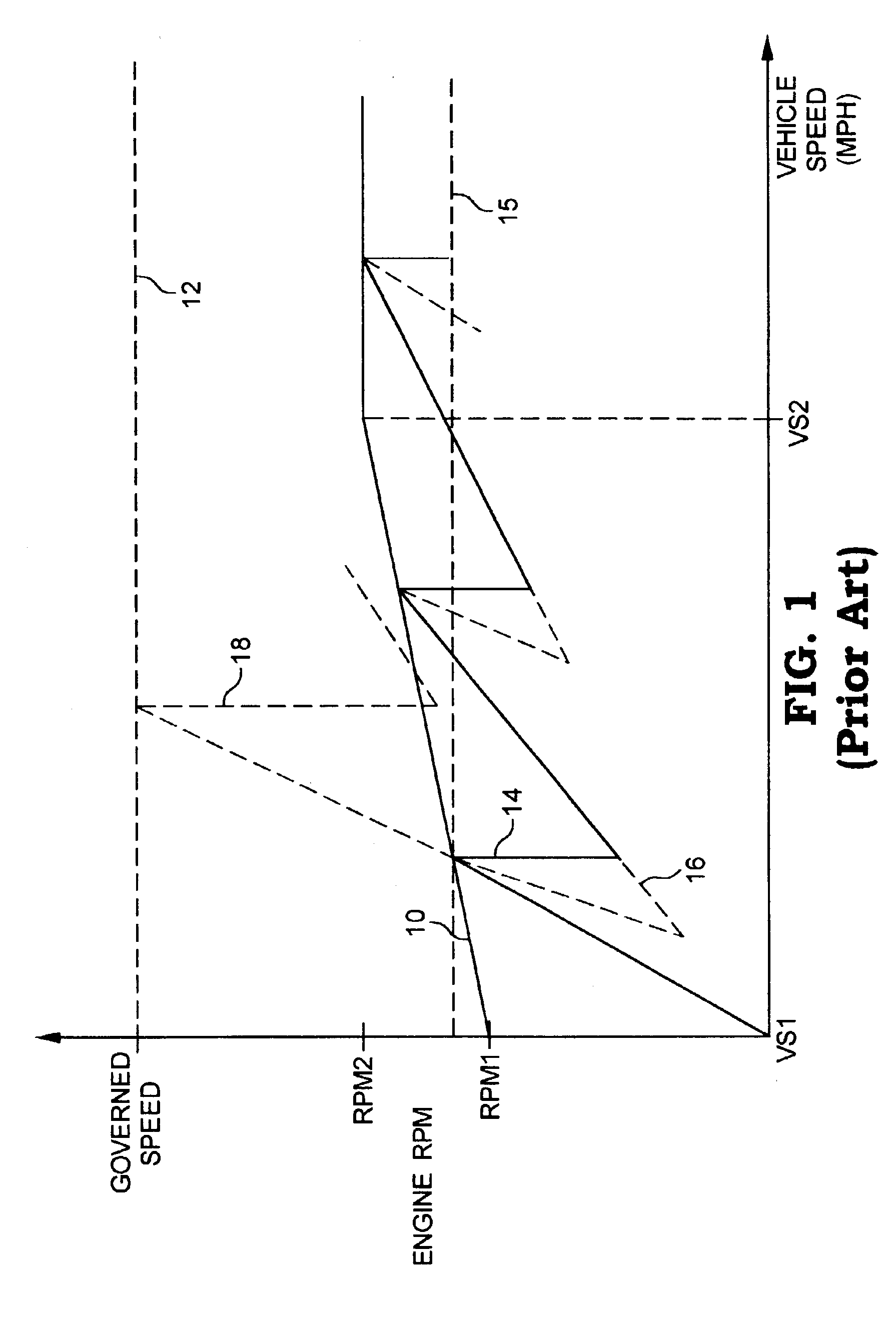
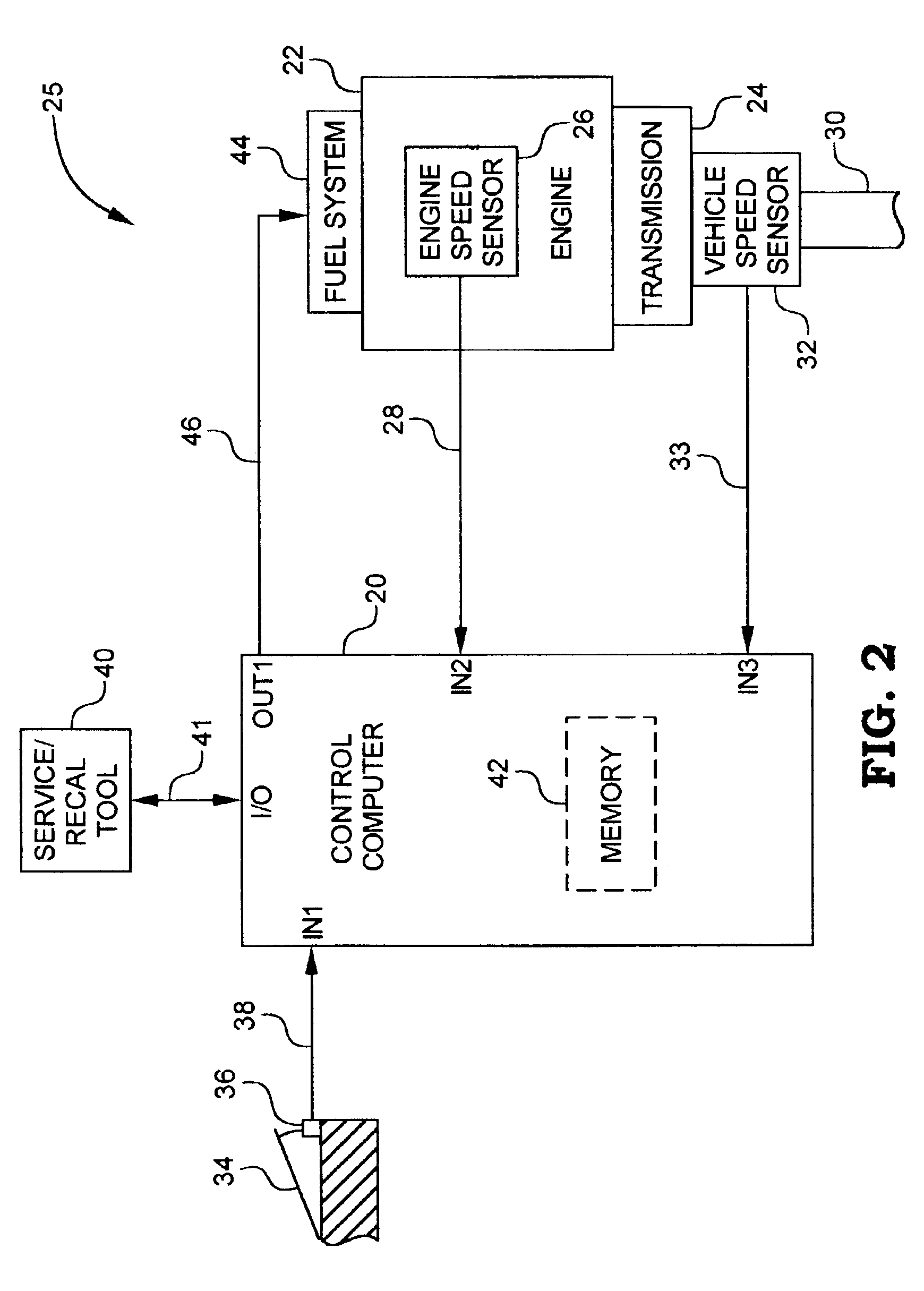
A system for controlling an engine in a fuel efficient manner includes a memory having stored therein an engine output characteristics map bounded by a maximum engine output curve. The map defines a region of undesirable operation having a first border defined as a function of engine speed and intersecting the maximum engine output curve. A control computer is configured to control engine operation in a fuel efficient manner by limiting engine operation within the map to the first border while also allowing the engine to operate anywhere on the maximum engine output curve. The control computer may be configured to so limit engine operation to the first border only if an engine or vehicle acceleration value is outside of an acceleration range, and further only if an engine work value is greater than an engine work threshold, and otherwise to allow engine operation anywhere on or within the map.
Owner:CUMMINS INC
Method and device for assisting a lane change of a vehicle
A method for operating an automatic speed control system of an automotive vehicle. Initially, in a normal follow mode, a setpoint distance between the vehicle and a preceding vehicle is set to a first value d1, and a setpoint vehicle acceleration is into a first value a1. Upon detection of an intention of the vehicle driver to overtake the preceding vehicle (such as switching on a turn indicator), the setpoint distance is reset to a second value d2 that is smaller than d1. The setpoint acceleration may be reset to a second value a2 greater than a1 simultaneously, or the second value a2 may be set upon detection of initiation of a lane change into an overtaking lane (such as turning a steering wheel). The method assists the driver during the execution of an overtaking process, and a safer, more comfortable and free-flowing sequence of the overtaking process is ensured.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Method for controlling creep torque of a vehicle
ActiveUS20120150384A1Efficiently prevent rolling-backVehicle testingRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesDrive motorControl theory
The present invention provides a technique for controlling creep torque to prevent a vehicle from rolling backward on an upward slope. In particular, a gradient of a road is calculated in real time from a detection value of a sensor and vehicle acceleration. A maximum creep torque for preventing roll-back caused by gravity according to the gradient is calculated using the gradient and vehicle information. A first creep torque reference is calculated based on the maximum creep torque and the vehicle speed. A second creep torque reference is calculated based on the maximum creep torque and the vehicle acceleration. A torque command value according to an operation state of a brake is calculated based on the first creep torque reference value and the second creep torque reference value and the gradient. In response, a torque output of a driving motor is controlled according to the calculated torque command value.
Owner:HYUNDAI MOTOR CO LTD
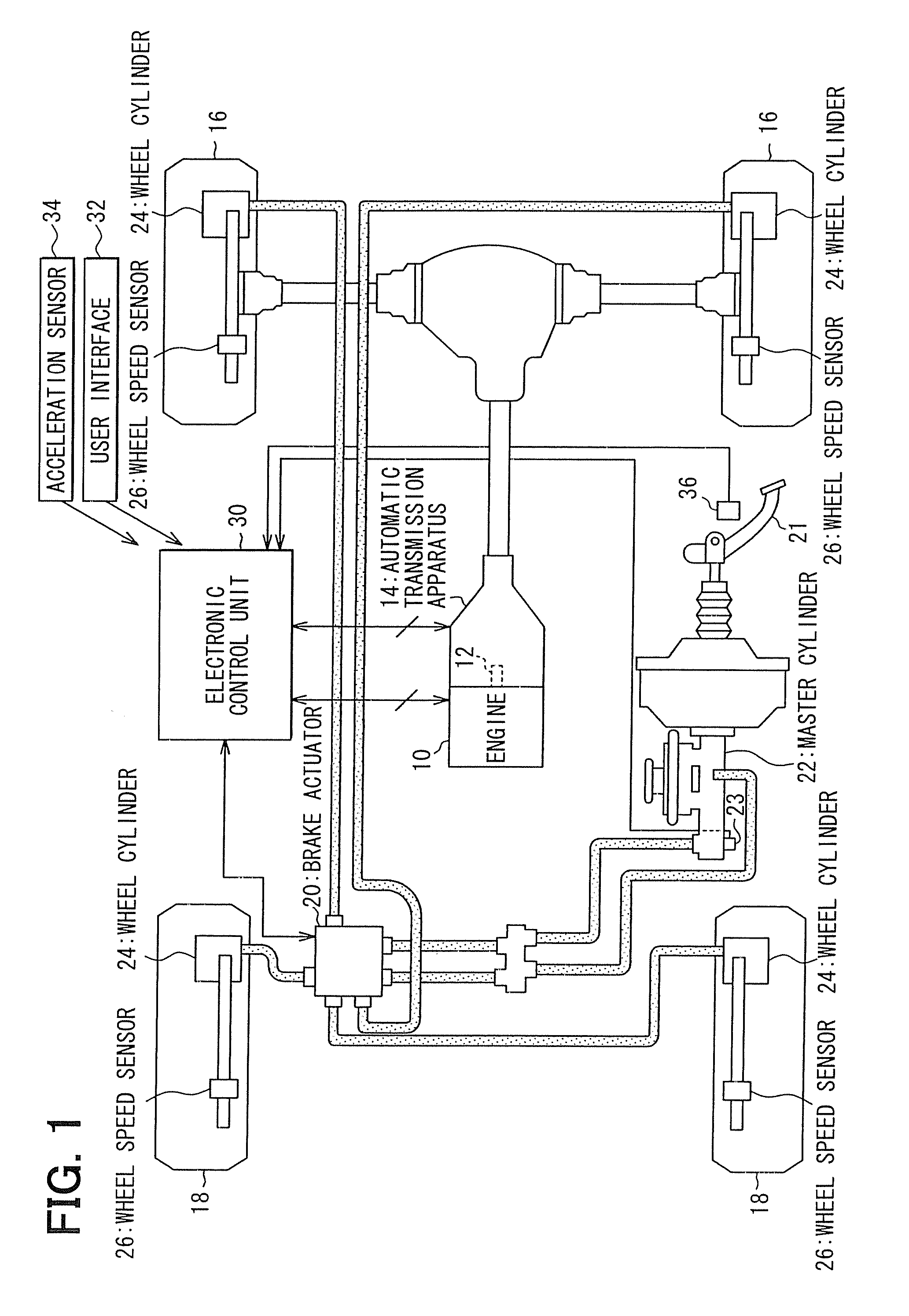
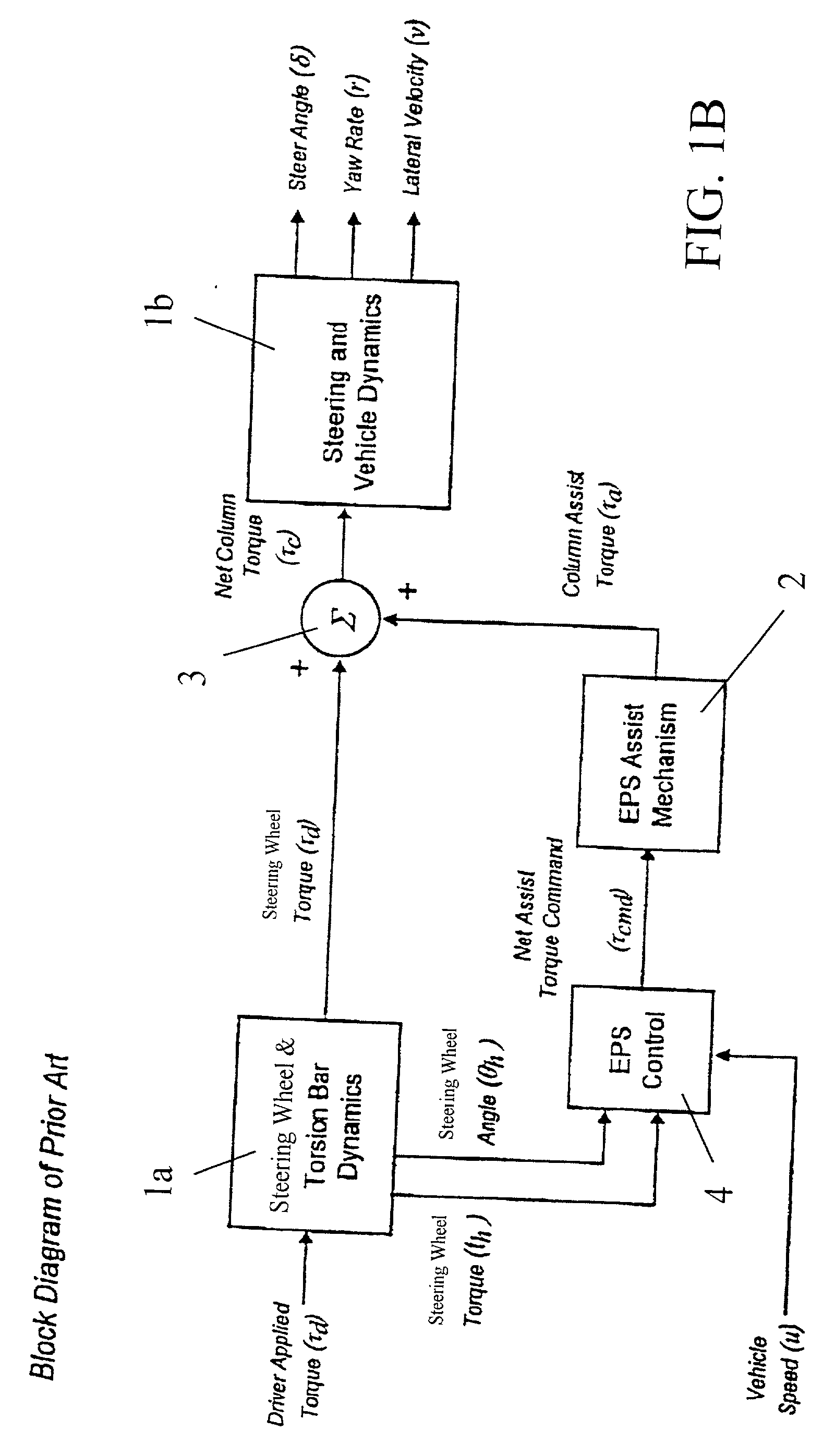
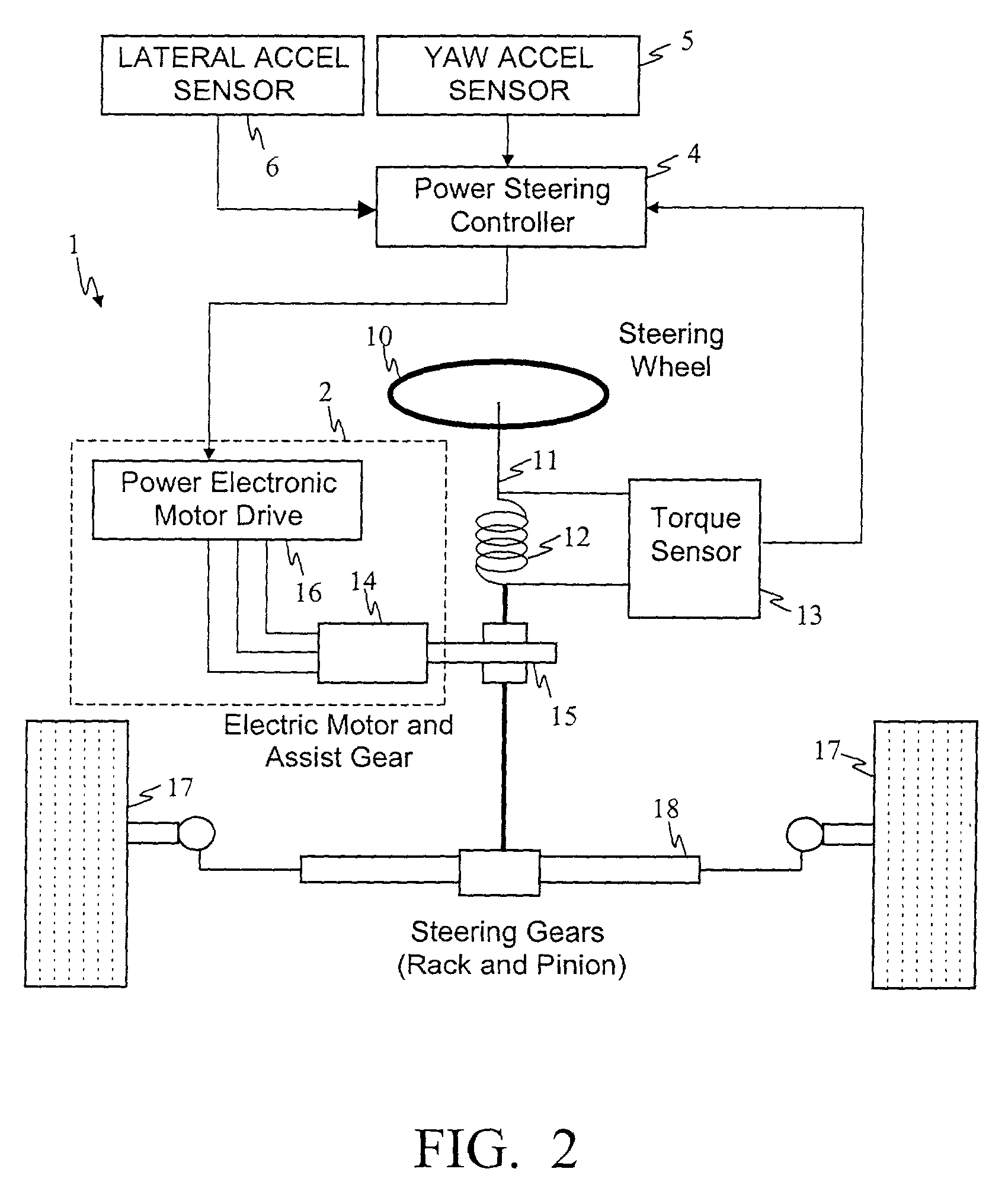
Method and system for improving motor vehicle stability incorporating an electric power steering system
InactiveUS6499559B2Improve stabilityImprove responseSteering initiationsDigital data processing detailsElectric power steeringSteering wheel
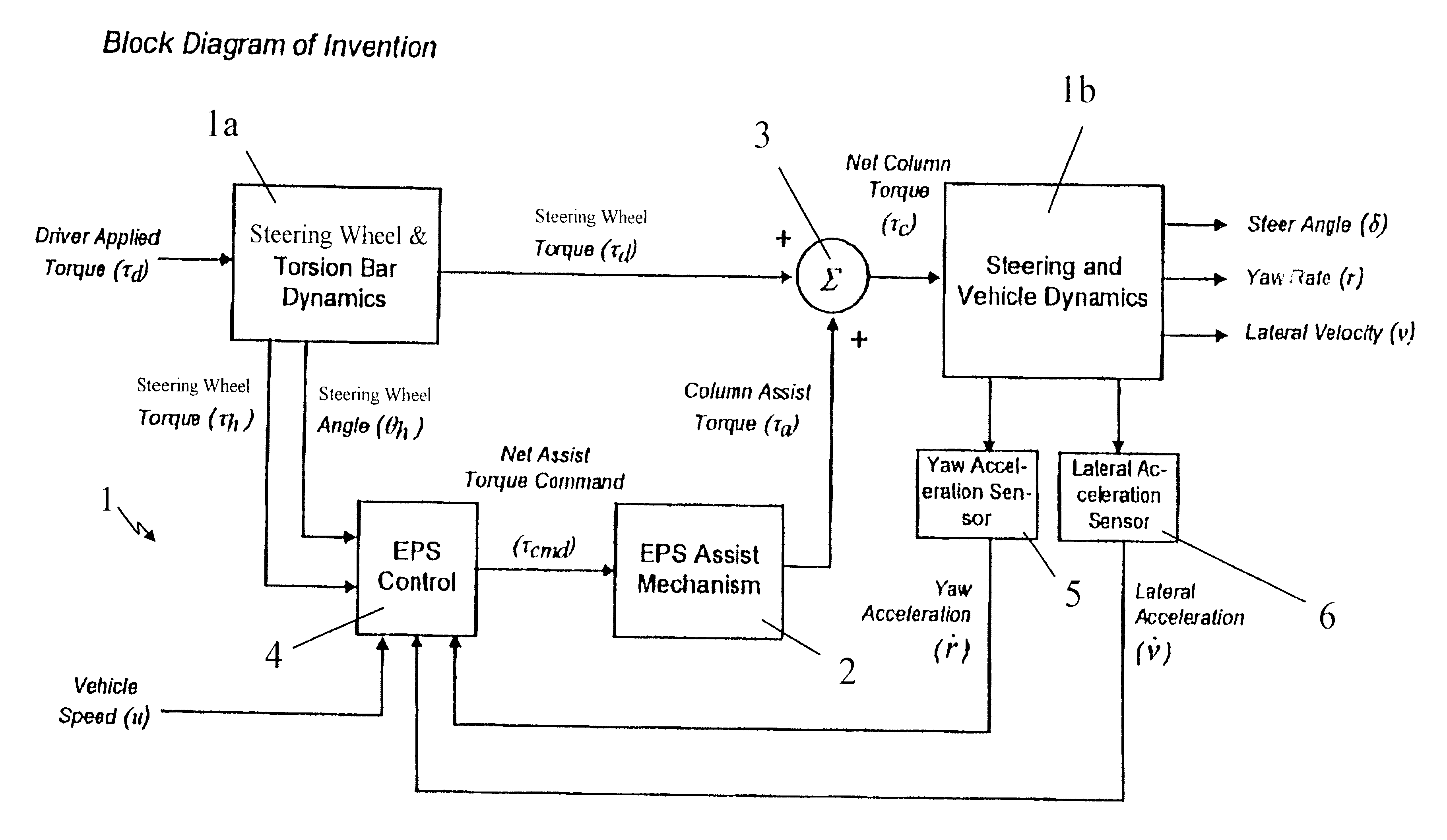
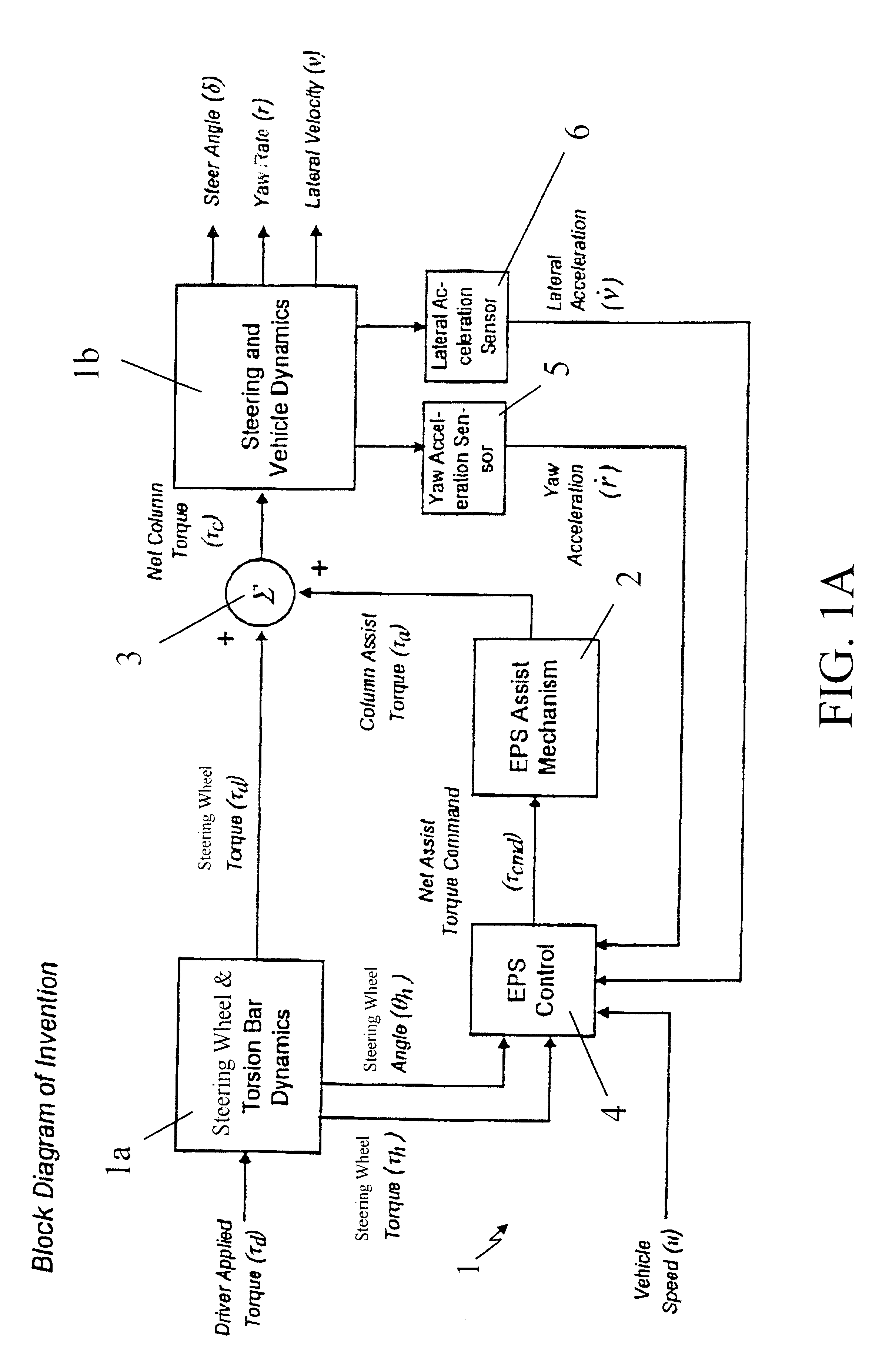
A method and system for stabilizing a vehicle employing an electric power steering system is disclosed. The method includes receiving as inputs, a desired torque command representative of a steering wheel torque and a vehicle speed signal. The method also includes acquiring an acceleration signal representative of vehicle acceleration. The method further comprises generating an assist torque command, which is a combination of the desired torque command and a compensating torque command where the compensating torque command is responsive to the vehicle speed signal and the acceleration signal.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC +1
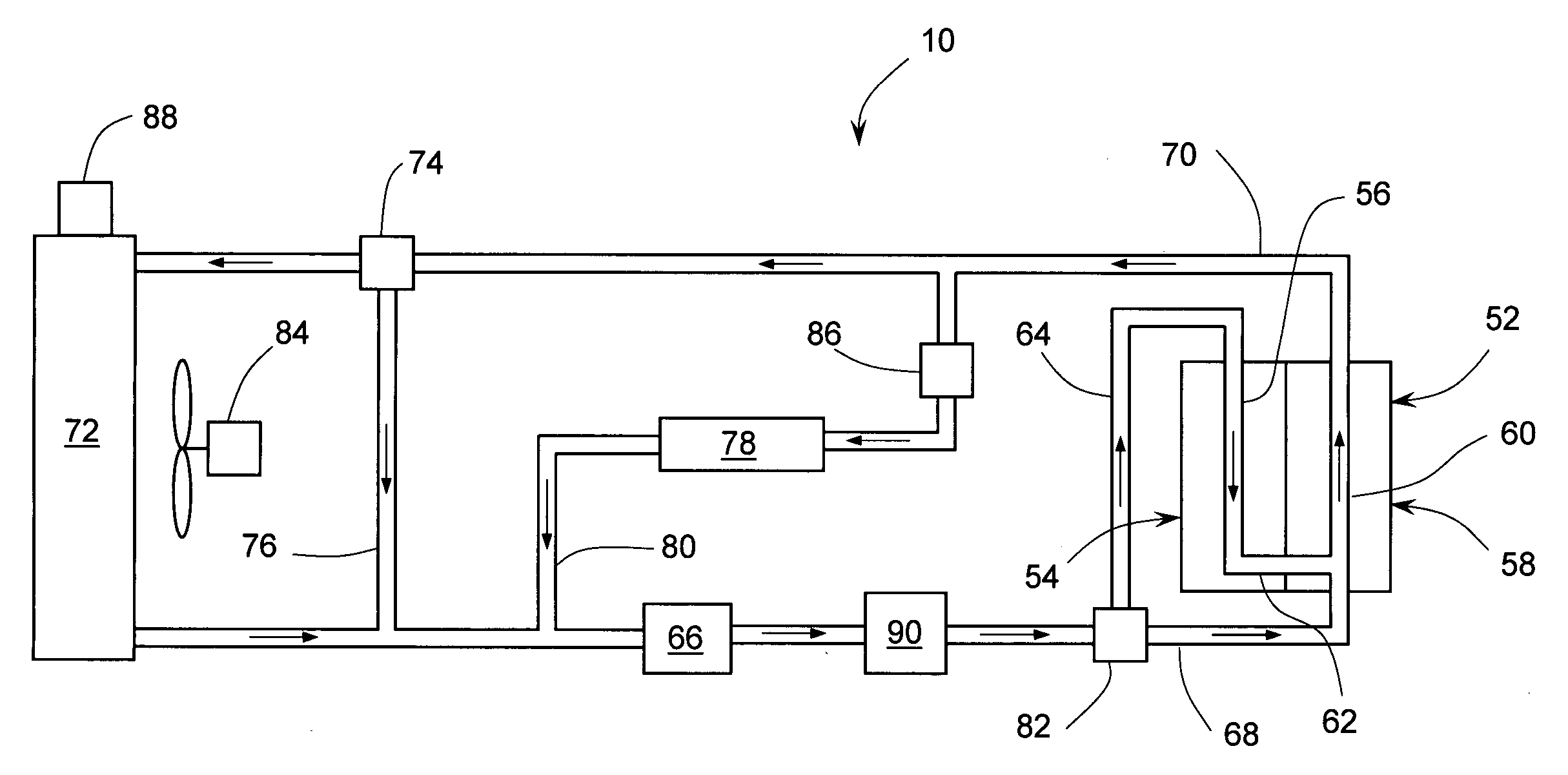
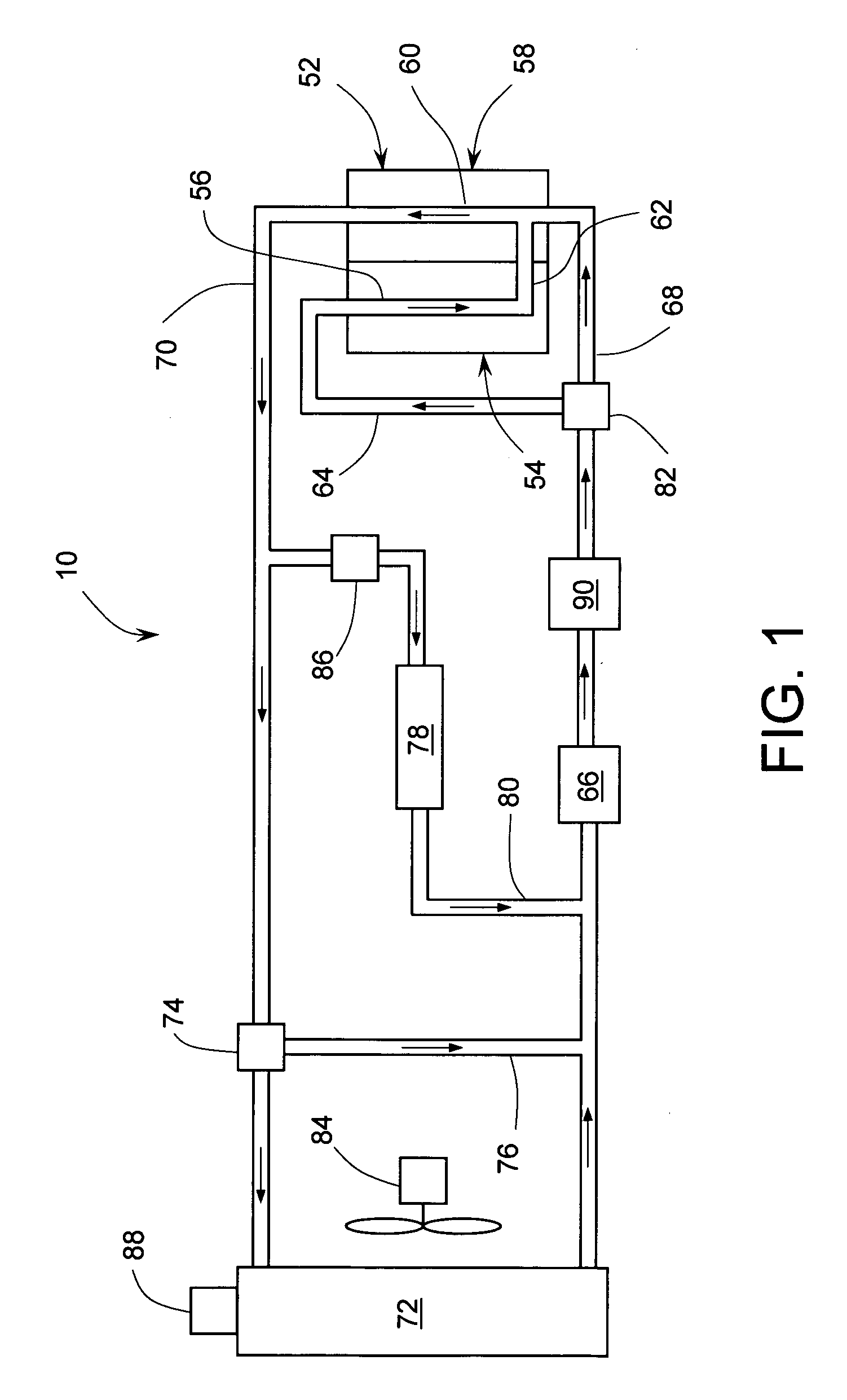
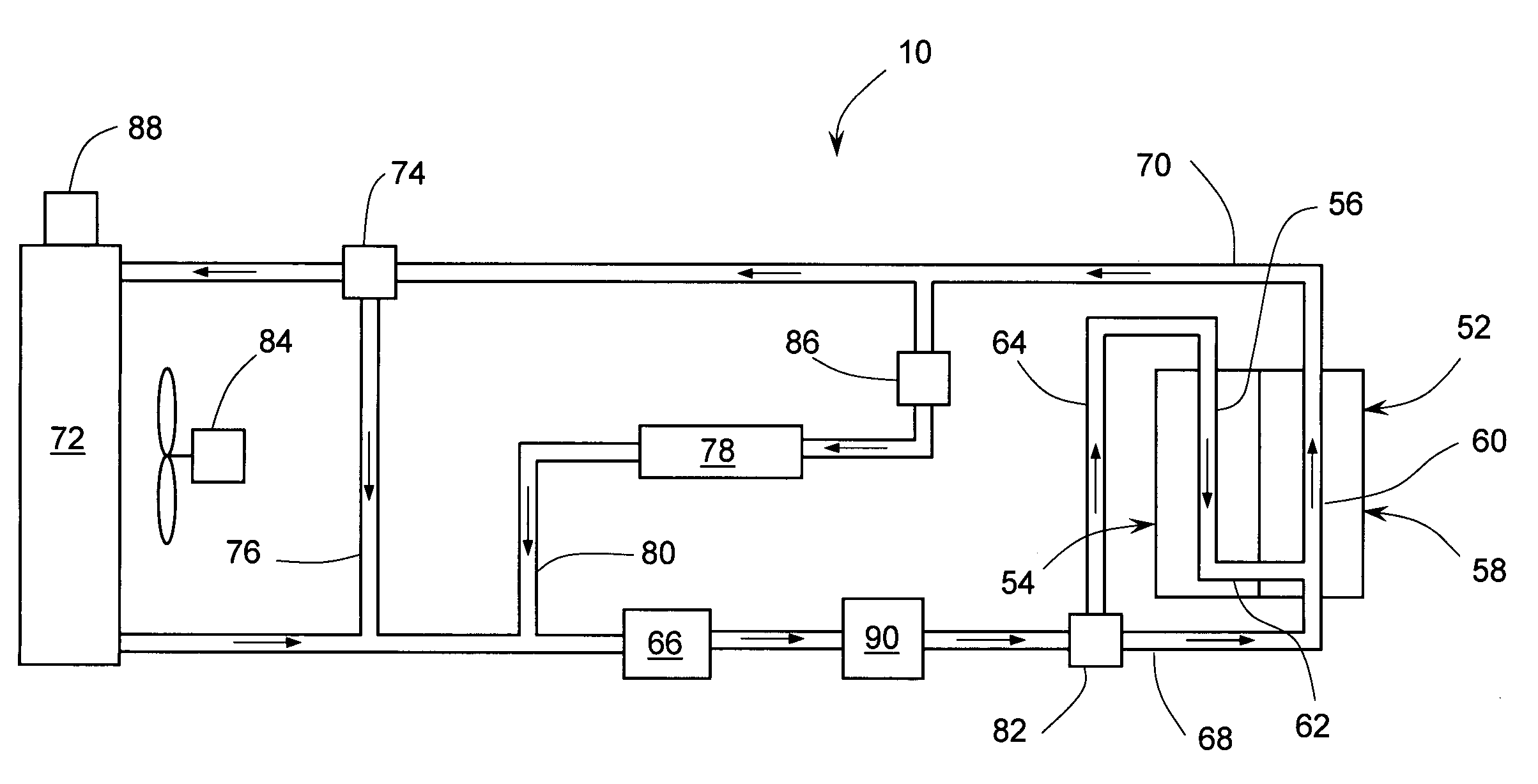
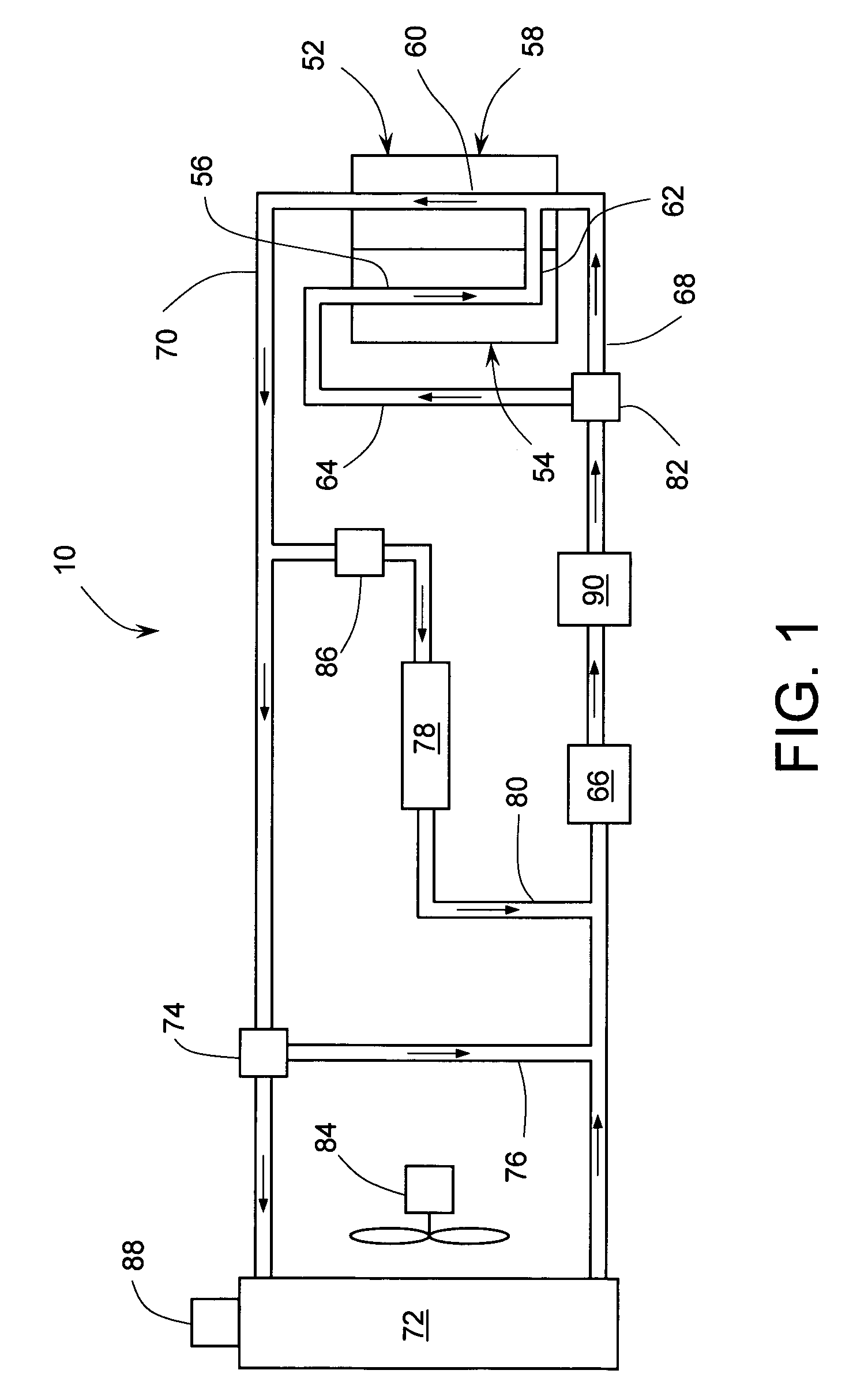
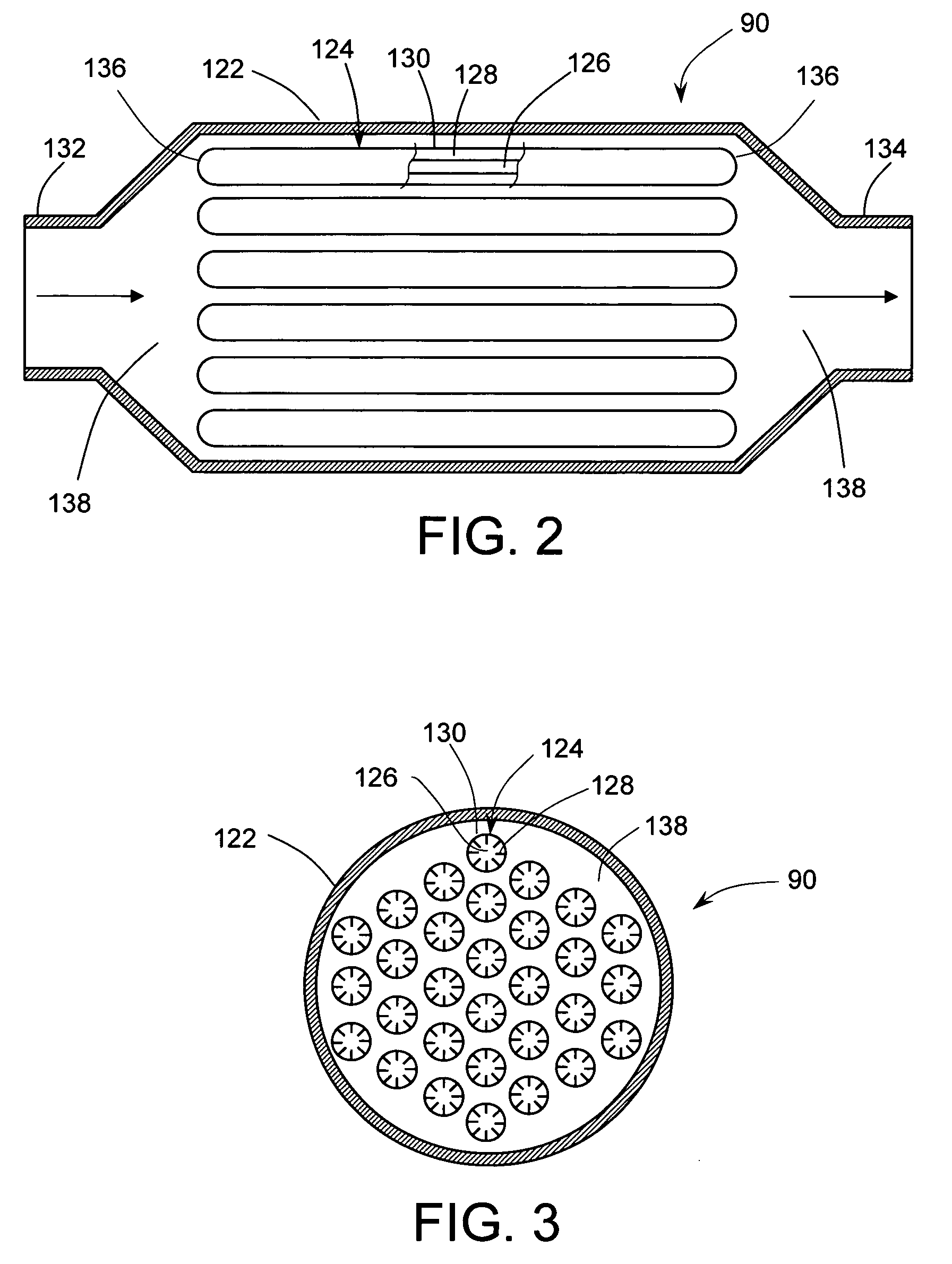
Engine cooling system with overload handling capability
InactiveUS20090205590A1Suitable for mass productionSimple and compactLiquid coolingReinforcing meansMobile vehicleInternal combustion engine
A cooling system for an internal combustion engine incorporating a heat accumulator to temporarily store heat during peak heat loads. In automotive vehicles, the heat accumulator may store excess heat generated during vehicle acceleration or hill climbing and it may dissipate stored heat during vehicle cruise, deceleration, or engine idle. The heat accumulator contains phase change material with a solid-to-liquid transition temperature higher than the normal operating temperature of the cooling system. The invention enables reducing the size and weight of engine cooling system without compromising its performance. This is particularly important for improving fuel economy and reduction of emission in automotive vehicles. In addition, the invention enables reducing the coolant inventory in the system thereby allowing for faster engine warm-up and reduced emissions of harmful pollutants during a cold engine start. The invention may be also used for thermal management of engine oil, transmission fluid, or hydraulic fluid.
Owner:AGWEST
System and method for monitoring and improving driver behavior
ActiveUS9129460B2Reduce actionImprove securityVehicle testingRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesThird partyDriver/operator
Owner:IWI
Vehicle control system
ActiveUS20090063000A1Small valuePrevent slippingDigital data processing detailsEngine controllersControl systemRoad surface
When a vehicle is started on an uphill road, slip may easily occur between vehicle wheels and a sloping road surface. When vehicle condition is changed from its stopping condition to its traveling condition on the uphill road, vehicle acceleration is controlled in a feed-back operation in such a manner that a target acceleration is made smaller as road gradient becomes larger or coefficient of friction becomes smaller.
Owner:ADVICS CO LTD
Method and system for improving motor vehicle stability incorporating an electric power steering system
InactiveUS20010041957A1Expands available torque-speed envelopeImprove vehicle-handling characteristicSteering initiationsDigital data processing detailsElectric power steeringSteering wheel
A method and system for stabilizing a vehicle employing an electric power steering system is disclosed. The method includes receiving as inputs, a desired torque command representative of a steering wheel torque and a vehicle speed signal. The method also includes acquiring an acceleration signal representative of vehicle acceleration. The method further comprises generating an assist torque command, which is a combination of the desired torque command and a compensating torque command where the compensating torque command is responsive to the vehicle speed signal and the acceleration signal.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC +1
Physical activity control system for moter vehicles
A control system for motor vehicles that uses physical activity to operate the acceleration of a vehicle comprising a mechanical controller that proportionally converts kinetic movement into an electronic signal. An electronic controller uses this signal as well as the current vehicle speed and user preferences to calculate a new pattern of energy flow to the engine. The controller then drives a system that manipulates the vehicle's acceleration or deceleration.
Owner:CHAMBERLIN BRIAN
Vehicle control system
ActiveCN101020453AConsistent decelerationPedestrian/occupant safety arrangementAnti-collision systemsControl systemVehicle control
When a vehicle travels along a curve of a road, a target vehicle acceleration / deceleration (dV s0 / dt) that is used for accelerating / decelerating the vehicle to a target vehicle speed (V s0_t), which is set for the curve, is calculated. Based on a comparison between a present vehicle speed (V s0) of the vehicle and the target vehicle speed (V s0_t ) the vehicle is controlled such that an acceleration / deceleration of the vehicle coincides with the target vehicle acceleratio / deceleration (dV s0 / dt).
Owner:DENSO CORP
Vehicle control system
ActiveUS20070191997A1Safe travelAnalogue computers for trafficPedestrian/occupant safety arrangementControl systemVehicle control
When a vehicle travels along a curve of a road, a target vehicle acceleration / deceleration that is used for accelerating / decelerating the vehicle to a target vehicle speed, which is set for the curve, is calculated. Based on a comparison between a present vehicle speed of the vehicle and the target vehicle speed, the vehicle is controlled such that an acceleration / deceleration of the vehicle coincides with the target vehicle acceleration / deceleration.
Owner:DENSO CORP
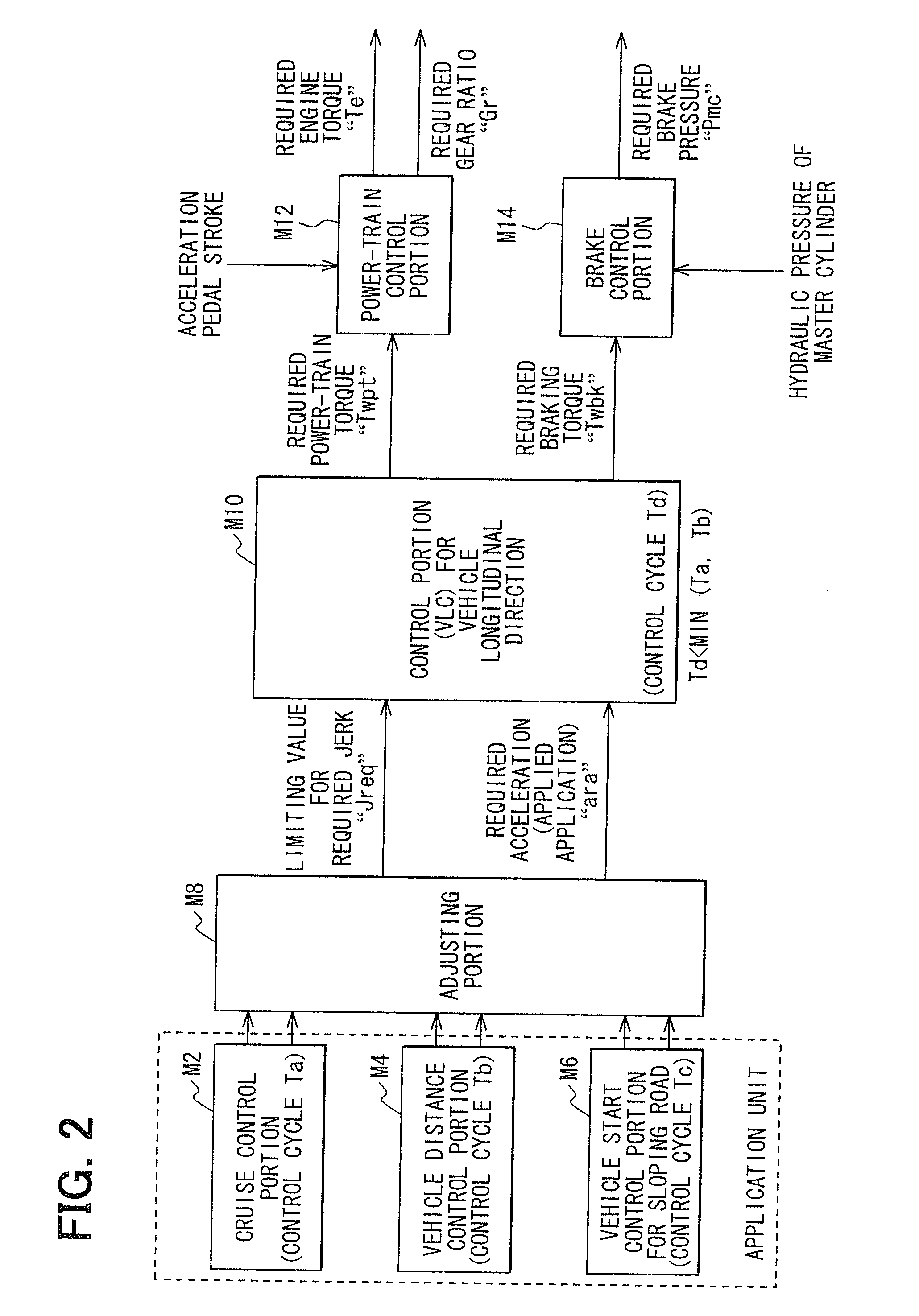
Adaptive cruise control method on incline
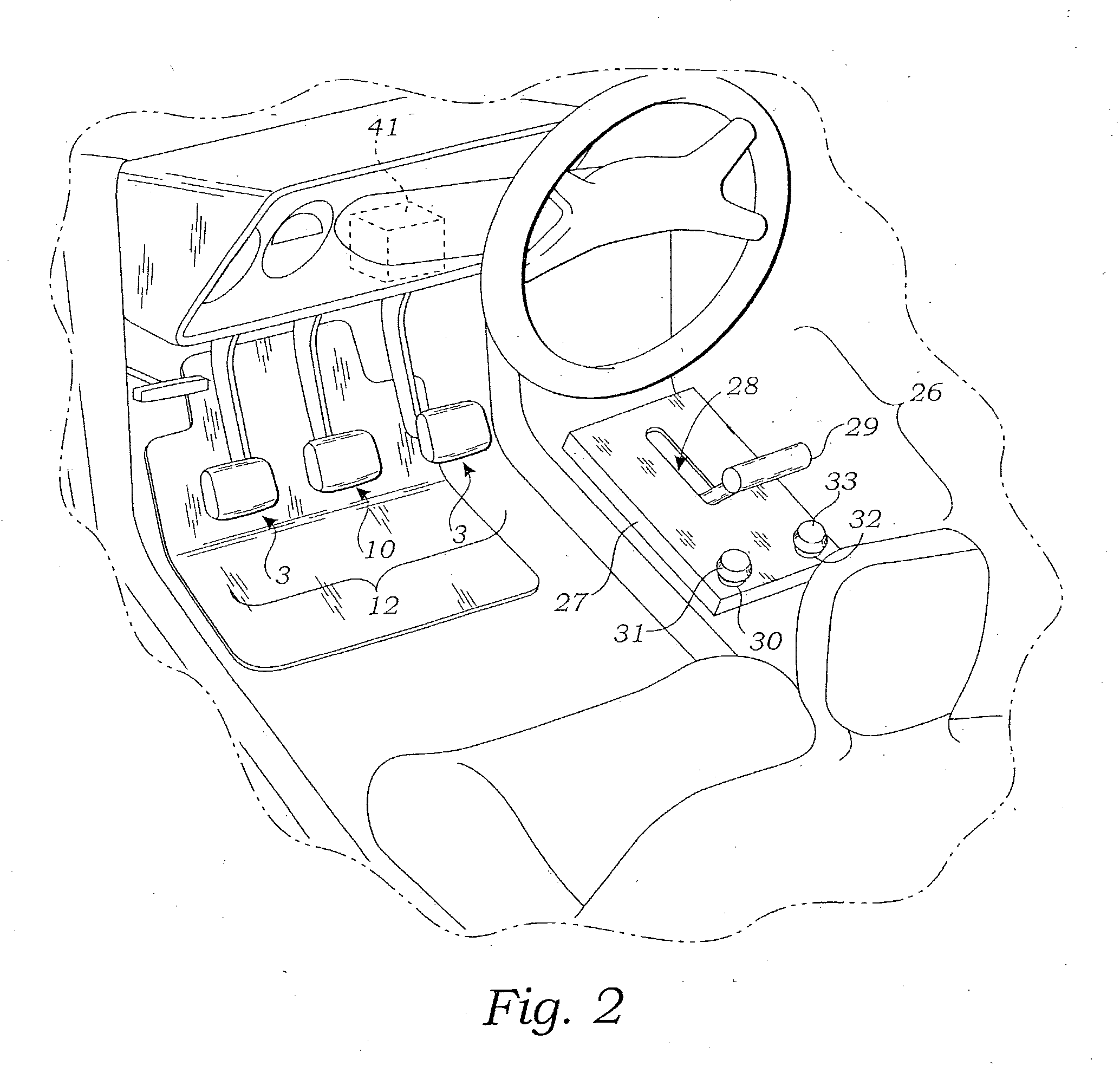
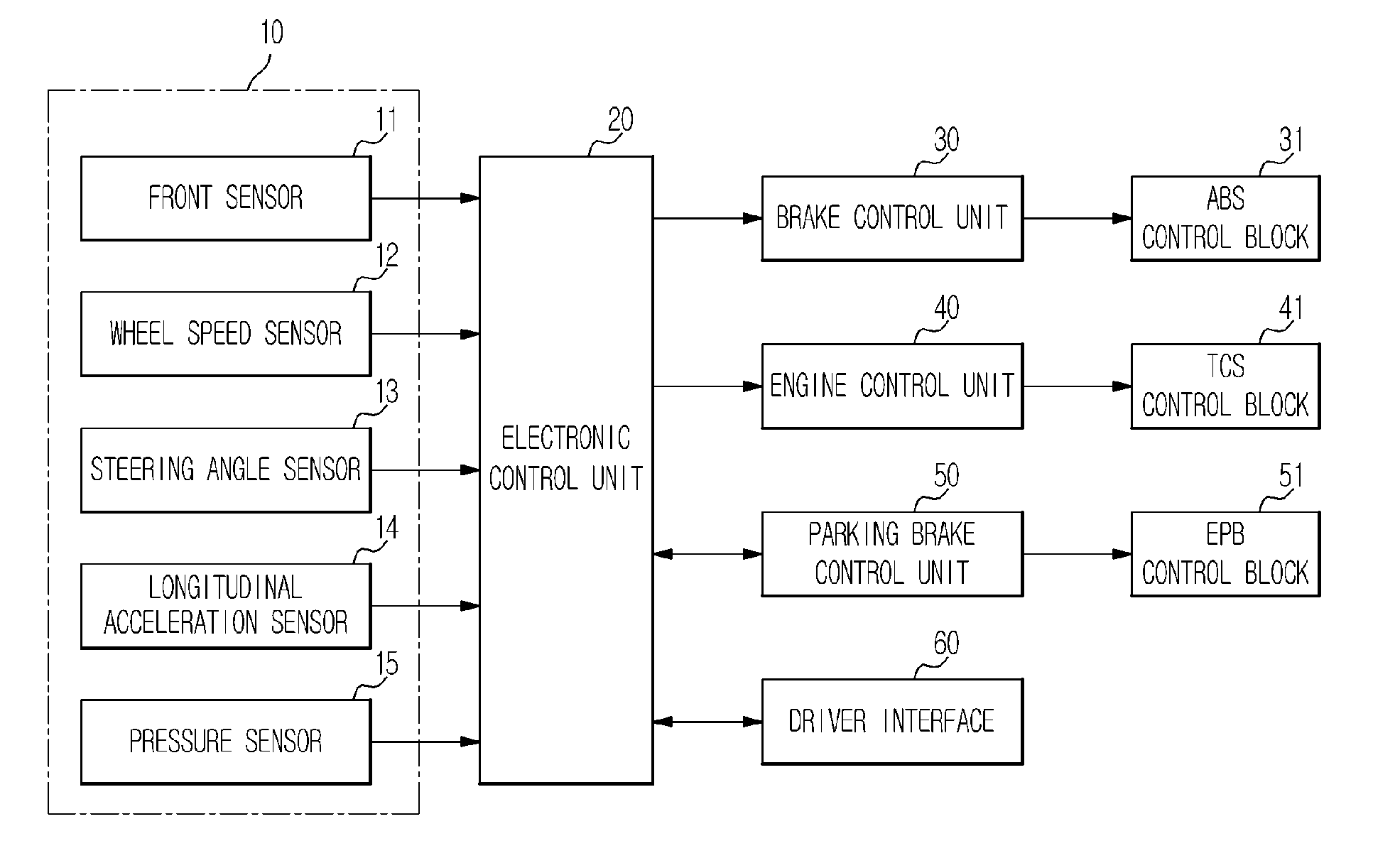
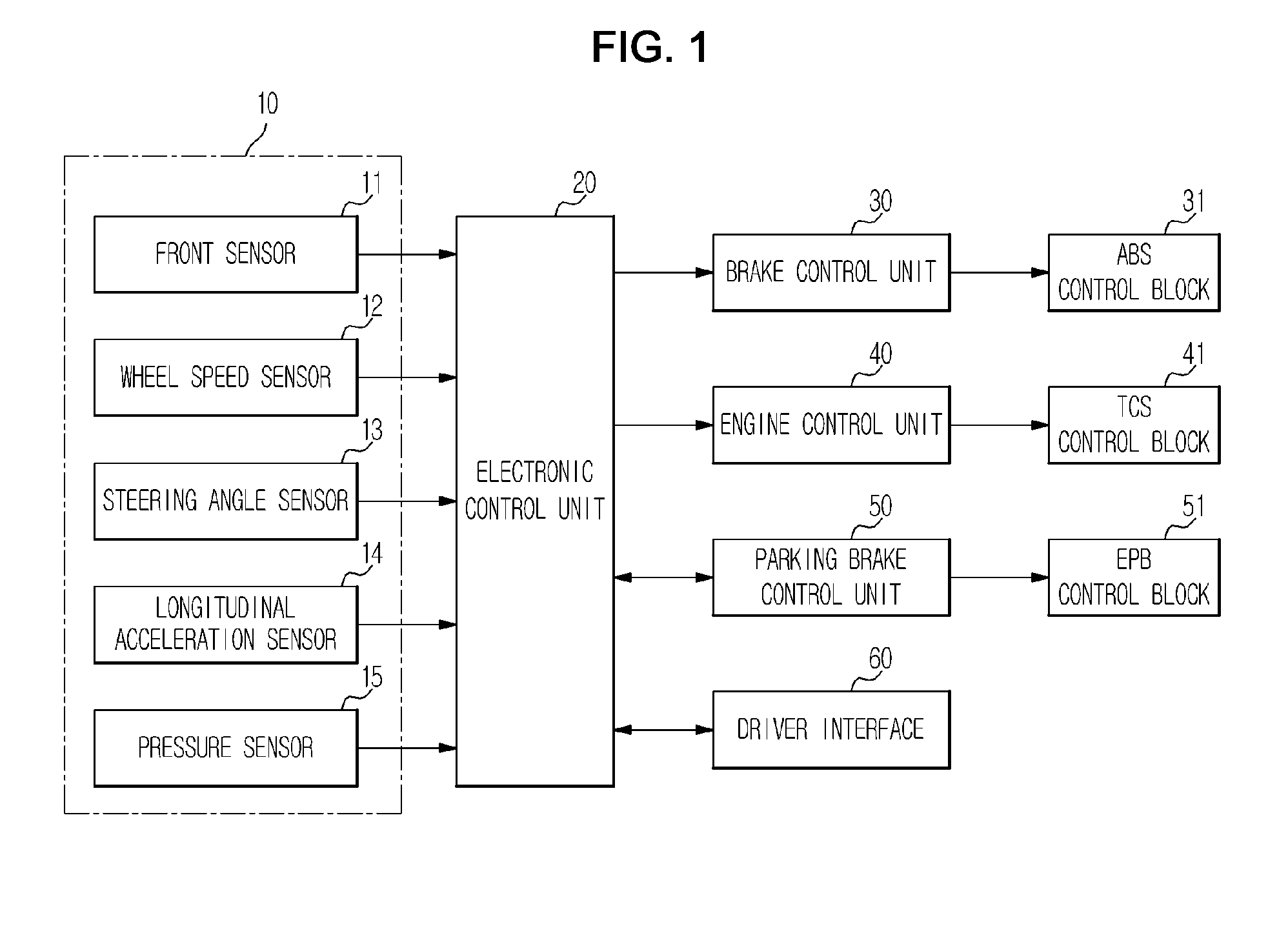
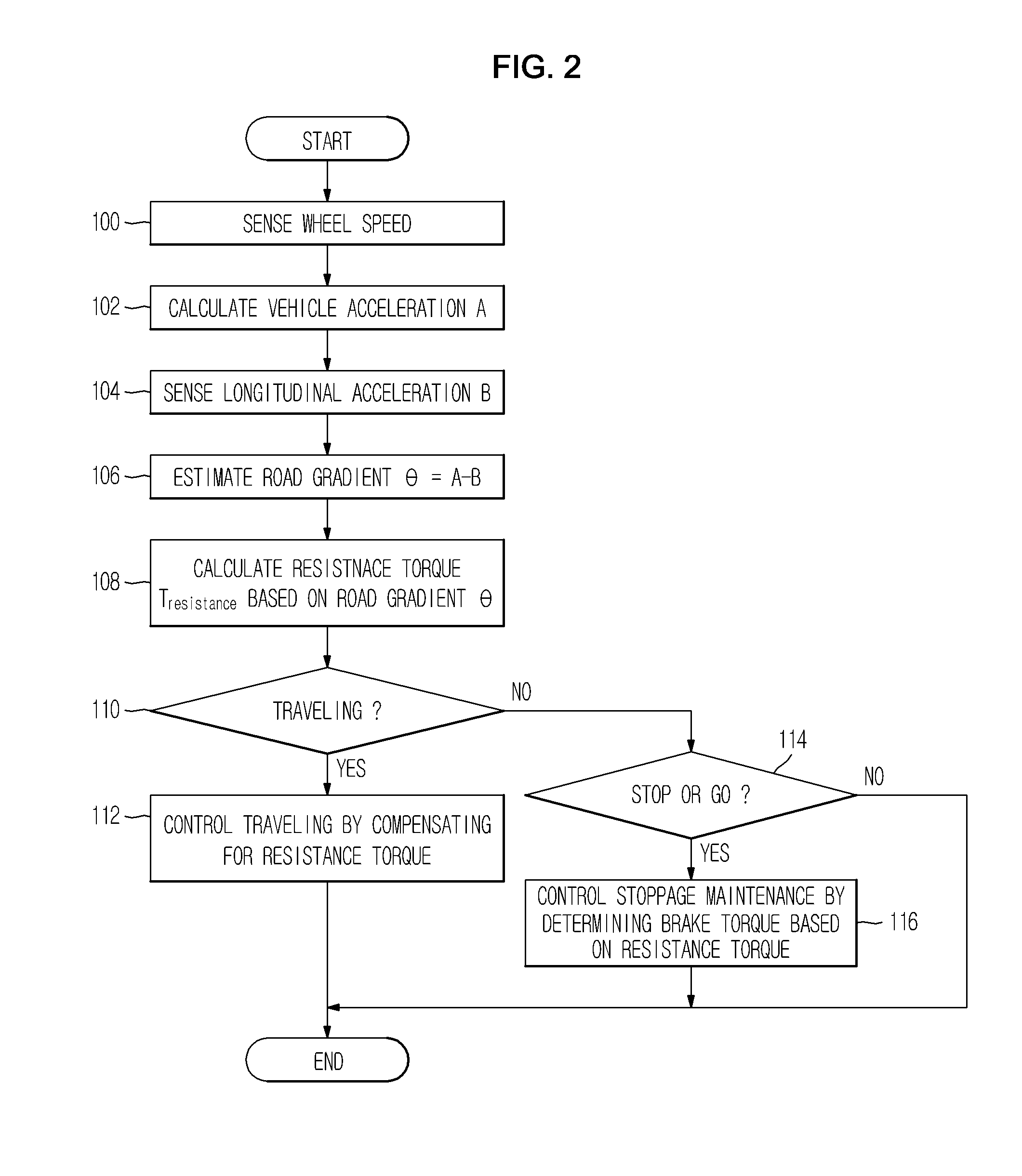
ActiveUS20110282558A1Improve traveling performanceImprove performance stoppage maintenanceVehicle fittingsDigital data processing detailsBrake torqueCruise control
Disclosed herein is an adaptive cruse control method on an incline to improve traveling performance and stoppage maintenance performance on an incline. During adaptive cruise control, a gradient of a road is estimated based on a vehicle acceleration and longitudinal acceleration to enable compensation of a resistance torque with respect to the gradient of the road, which prevents deterioration of a traveling speed of a vehicle on an incline. Also, compensating for a brake torque to prevent the vehicle from being pushed rearward when the vehicle is stopped or starts to go on an incline may prevent deterioration of performance on an incline.
Owner:HL KLEMOVE CORP
Vehicle control apparatus
InactiveUS20050001480A1Improve drivabilityEngine torqueElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesExhaust valveInlet valve
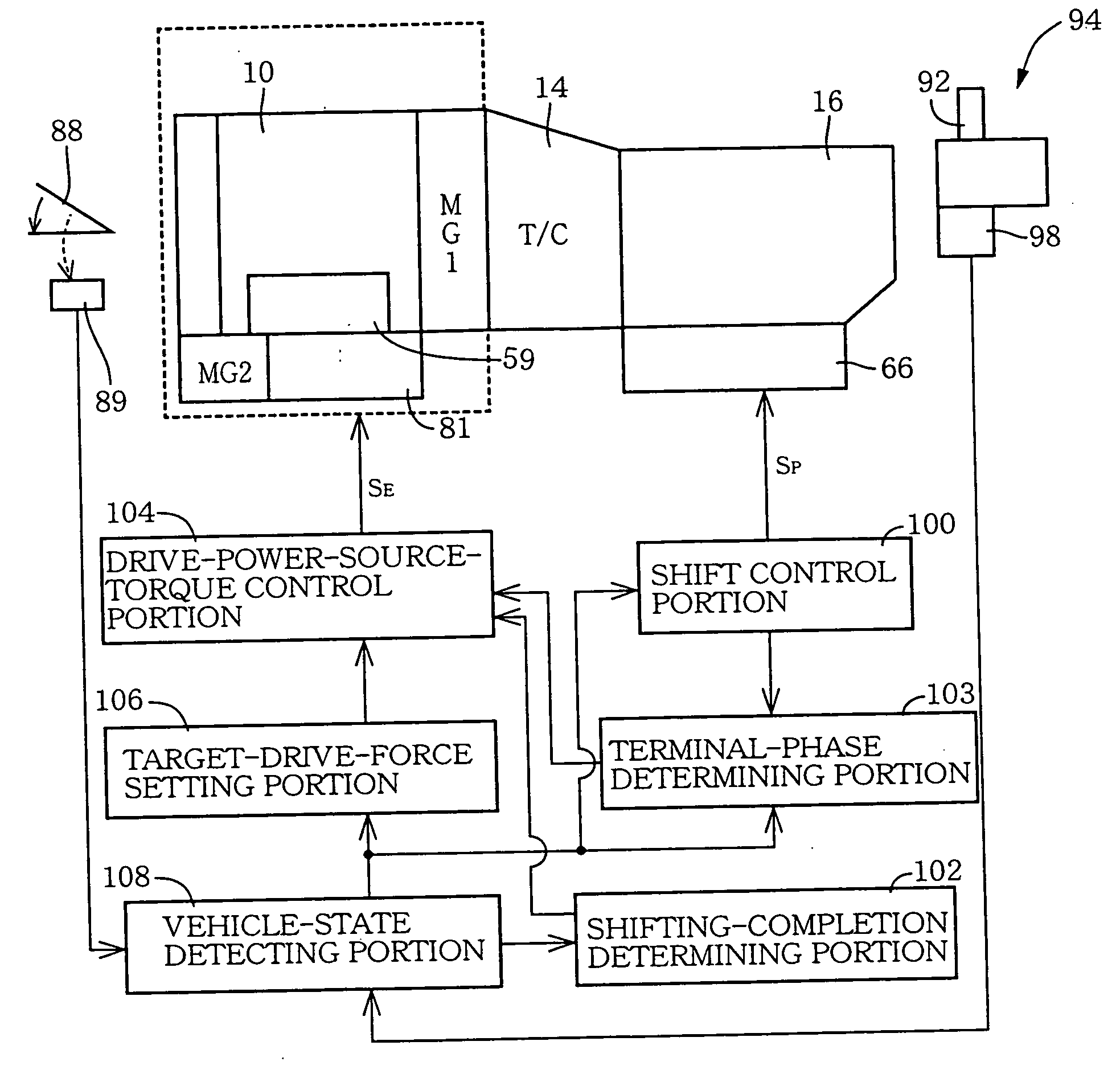
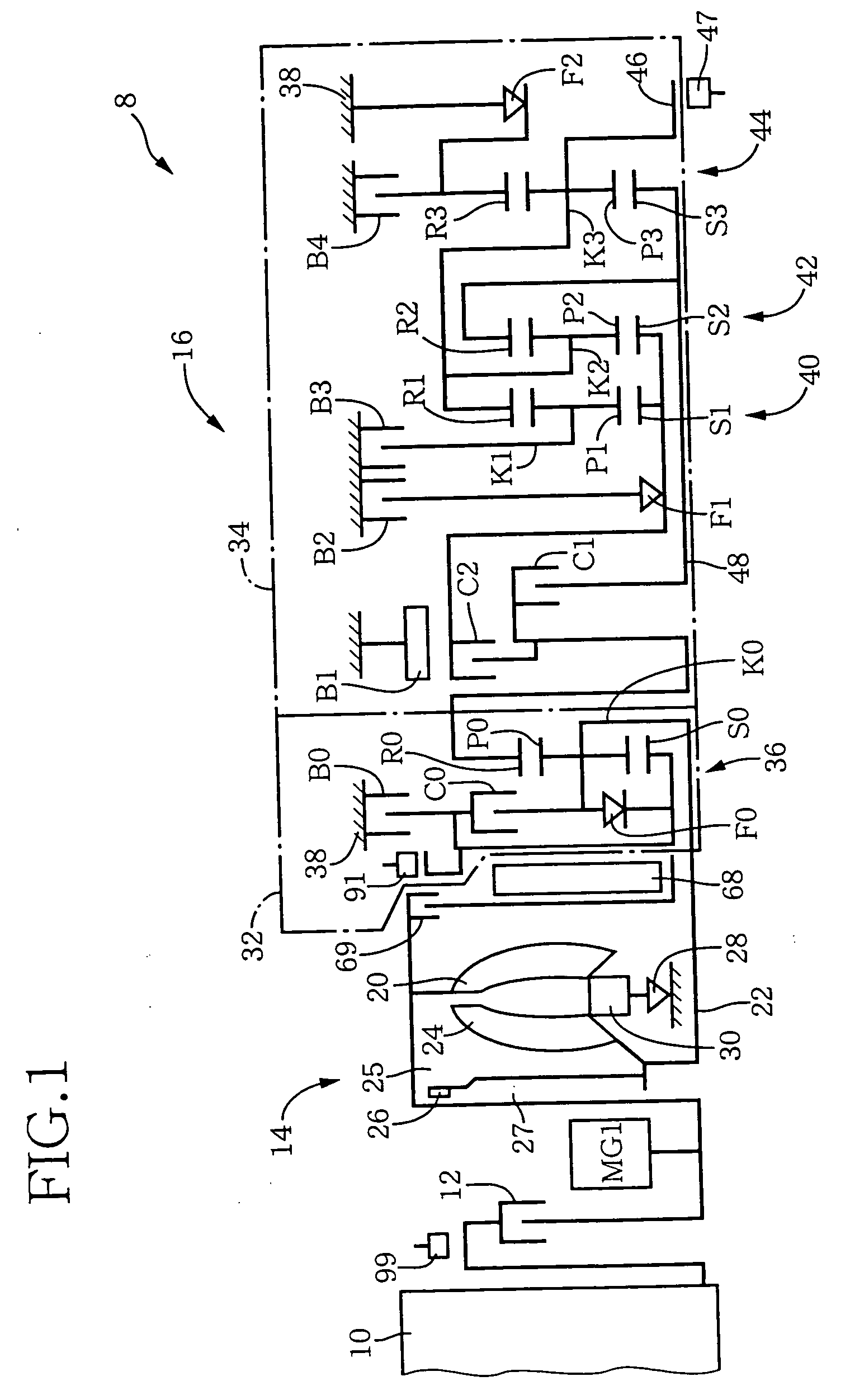
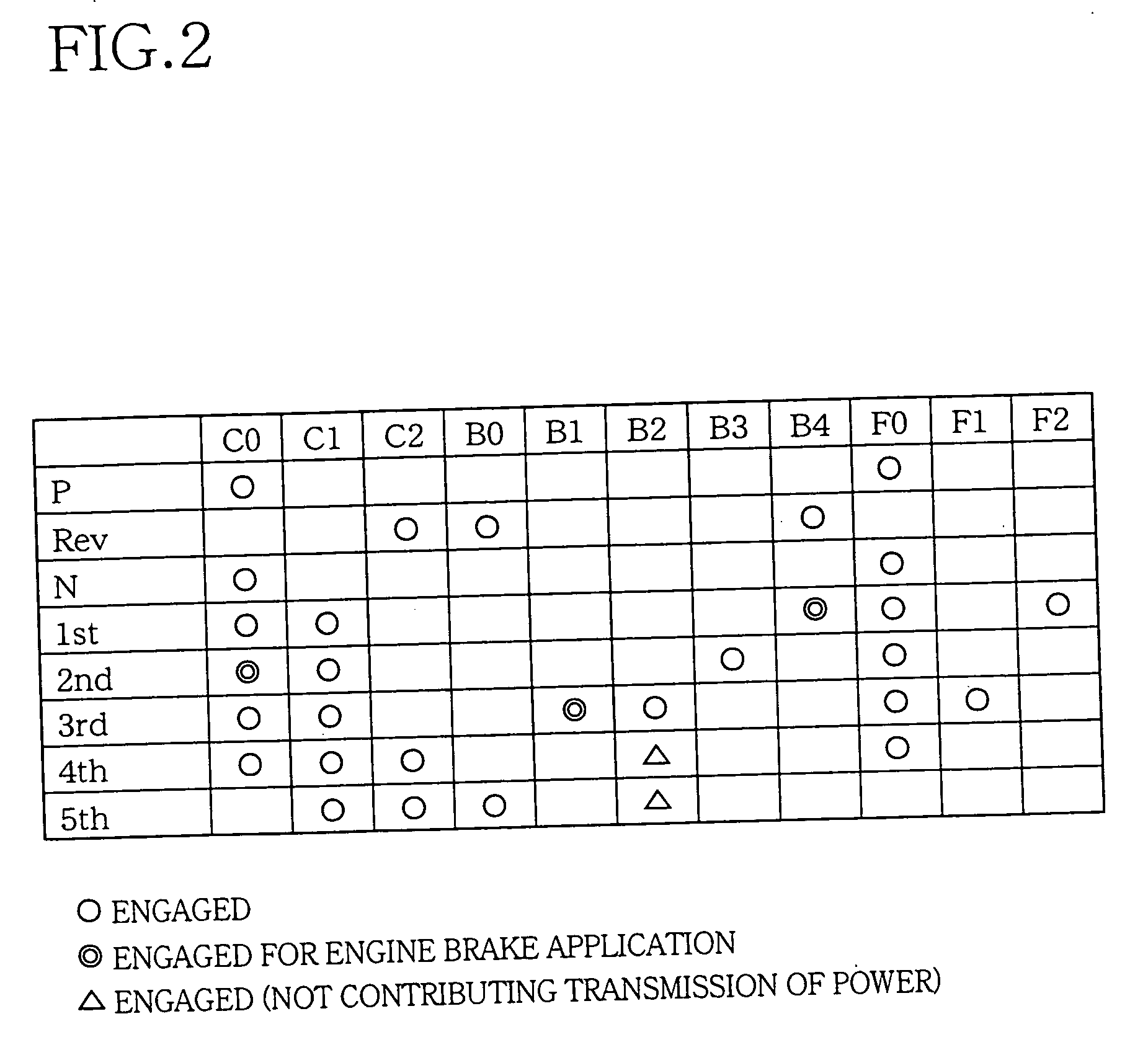
An apparatus for controlling an automotive vehicle including an engine with an intake valve and / or an exhaust valve having a variable operating characteristic, a transmission having a plurality of operating positions that are selectively established, and a manually operable vehicle accelerating member, the apparatus including a target-drive-force setting portion operable to determine a target vehicle drive force on the basis of an operating amount of the accelerating member and a presently selected one of the operating positions of the transmission, such that the determined target vehicle drive force permits a smooth change of an actual vehicle drive force with a change of the operating amount of the vehicle accelerating member, irrespective of a shifting action of the transmission, and a drive-power-source-torque control portion (104) operable to control a torque of the engine, by controlling at least one of a lift amount, an operating period of an opening and closing action and an operating timing of the intake valve (74) and / or the exhaust valve (75), so that the actual vehicle drive force coincides with the target vehicle drive force after the shifting action of the transmission.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
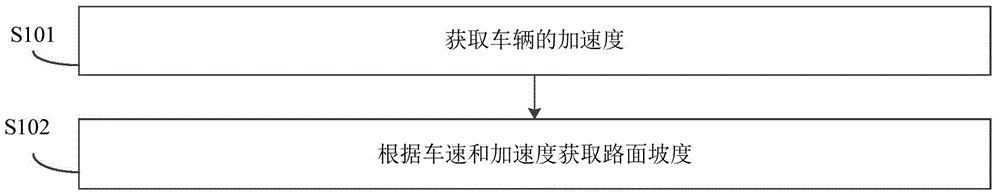
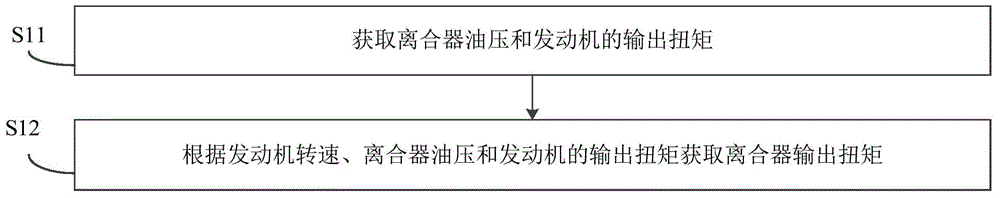
Vehicle and vehicle hill starting control method and hill starting control apparatus
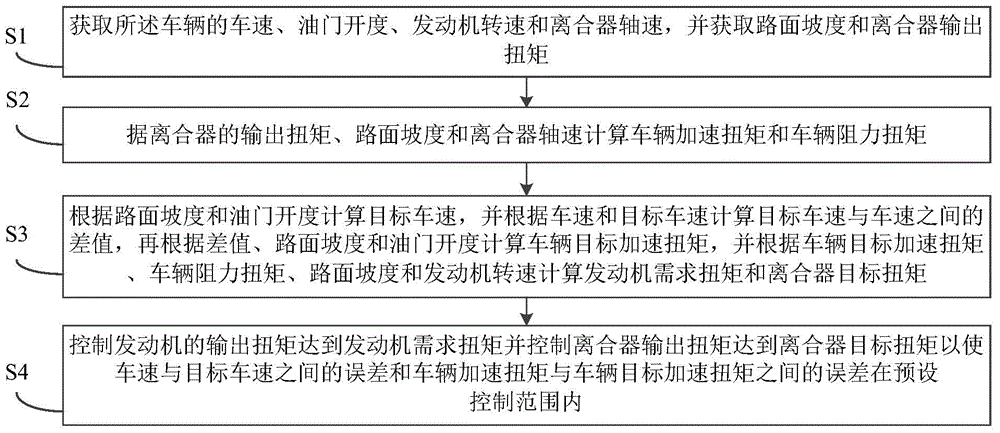
The invention discloses a vehicle and a vehicle hill starting control method and a hill starting control apparatus, wherein the method comprises: acquiring vehicle speed, an accelerator opening degree, engine rotation speed, clutch shaft speed, road slope and clutch output torque; calculating vehicle acceleration torque and vehicle resistance torque based on the clutch output torque, the road slope and the clutch shaft speed; calculating the target vehicle speed based on the road slope and the accelerator opening degree; calculating the target acceleration torque of a vehicle based on the difference value between the calculated target vehicle speed and the vehicle speed, the road slope and the accelerator opening degree; calculating the torque that an engine needs and the clutch target torque based on the target acceleration torque of the vehicle, the vehicle resistance torque and the engine rotation speed; and controlling the engine output torque to reach the torque that the engine needs and the clutch output torque reach the clutch target acceleration torque so as to make the vehicle speed reach the target vehicle speed and the vehicle acceleration torque reach the target acceleration torque of the vehicle, thus controlling the vehicle speed and the vehicle acceleration speed and rapidly realizing the intention of a driver.
Owner:BYD CO LTD
Anti-rollback control for hybrid and conventional powertrain vehicles
InactiveUS20070073466A1Internal combustion piston enginesAnalogue computers for trafficControl systemVehicle driving
An anti-rollback vehicle control system reduces vehicle rollback by restarting an engine based on a grade, a brake signal, and a calculated brake release rate. In a hybrid vehicle, the control system restarts the vehicle engine and electric motor. In a conventional powertrain vehicle that utilizes a transmission with a neutral-idle mode, the control system directs the transmission to exit neutral-idle mode. The grade may be estimated based on a vehicle acceleration rate, a vehicle driving force, and resistance factors.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Noise source recognition method for vehicle acceleration noise
InactiveCN101464168AImproves acceleration noiseSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementUsing electrical meansNoise controlTransfer function matrix
The invention relates to a method for indentifying a noise source that produces noise when a vehicle accelerates, and belongs to the technical field of vehicle noise control. The method comprises the following steps: when the vehicle accelerates or travels at a uniform speed, the noise source signal, the vibration source signal, the speed signal, the response point sound pressure signal, the vehicle position signal and the like are collected; the transfer function matrix from the noise source and the vibration source to the response point is calculated; the changing response point sound pressure during the process of acceleration is synthesized and computed; and the sensitivity and the contribution degree of each noise source and vibration source are calculated. The invention has the following advantages: the noise source signal, the vibration source signal, the vehicle travelling state signal, and the ground response point sound pressure signal, which are collected during the running of the vehicle, can be utilized for accurately identifying the noise source that produces noise during the acceleration; and the quantitative relationship between the response point noise signal and each noise source is obtained and can provide a reliable basis for the reduction of noise produced by the acceleration of a running vehicle.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
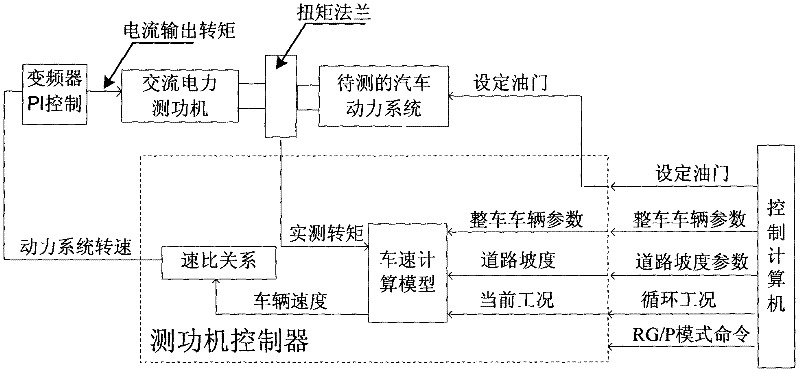
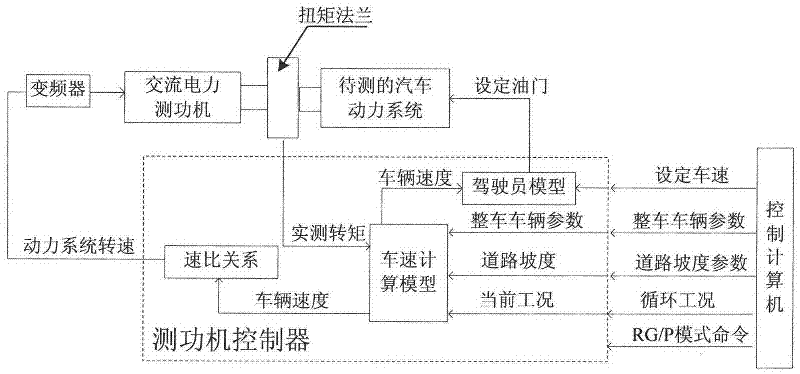
Dynamic load simulating device and method for automobile power system test
InactiveCN102305715AAvoid Differential ValuesImprove dynamic stabilityMachine gearing/transmission testingEngine testingRolling resistanceDynamometer
The invention relates to a dynamic load simulating device and a dynamic load simulating method for an automobile power system test, and belongs to the technical field of vehicle power system tests. The dynamic load simulating device comprises a control computer, a dynamometer controller, a frequency converter, an alternating current (AC) power dynamometer and a torque flange with a controller. A virtual automobile model-based control algorithm is adopted, a virtual automobile model is driven by an actual measurement torque, and the simulation of the rolling resistance, wind resistance and the inertia resistance of a vehicle is realized under the conditions of not calculating angular acceleration of the dynamometer. The dynamic load simulating device and the dynamic load simulating method have high stability and high simulation precision, are favorable for shortening the development cycle of an automobile power system and providing convenient test environment for the development of the power system. A process that the vehicle acceleration is acquired by differentiating the rotation speed of the automobile power system is avoided in the calculation process, and a phenomenon that accurate differential values are difficult to acquire due to relatively large noise caused by the process of differentiating the rotation speed is prevented.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Engine cooling system with overload handling capability
InactiveUS7735461B2Emission reductionReducing coolant inventoryLiquid coolingCoolant flow controlInternal combustion engineHydraulic fluid
A cooling system for an internal combustion engine incorporating a heat accumulator to temporarily store heat during peak heat loads. In automotive vehicles, the heat accumulator may store excess heat generated during vehicle acceleration or hill climbing and it may dissipate stored heat during vehicle cruise, deceleration, or engine idle. The heat accumulator contains phase change material with a solid-to-liquid transition temperature higher than the normal operating temperature of the cooling system. The invention enables reducing the size and weight of engine cooling system without compromising its performance. This is particularly important for improving fuel economy and reduction of emission in automotive vehicles. In addition, the invention enables reducing the coolant inventory in the system thereby allowing for faster engine warm-up and reduced emissions of harmful pollutants during a cold engine start. The invention may be also used for thermal management of engine oil, transmission fluid, or hydraulic fluid.
Owner:AGWEST
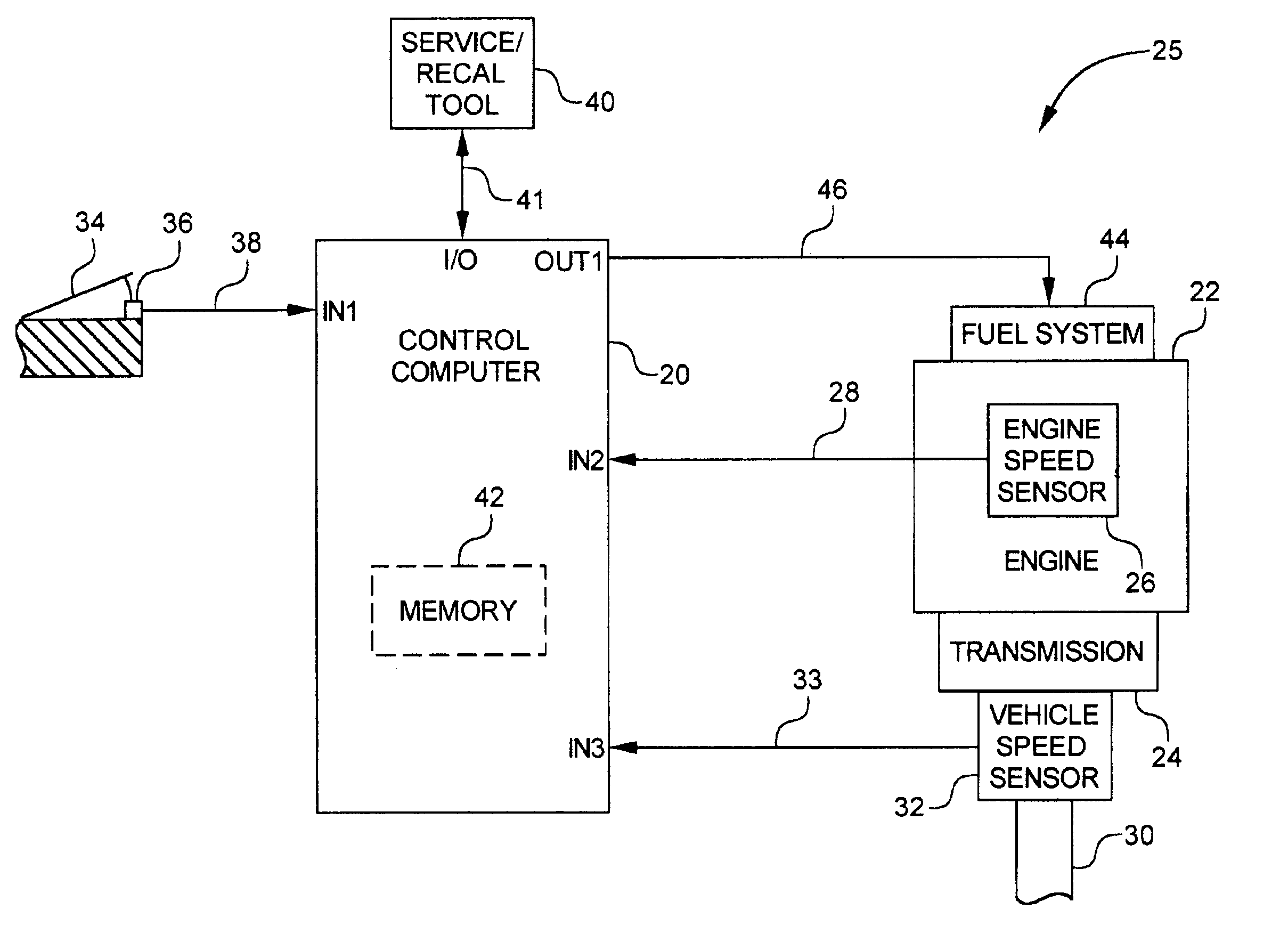
Engine control monitor for vehicle equipped with engine and transmission
InactiveUS6304809B1Low costReduce system complexityVehicle fittingsDigital data processing detailsEngineeringAcceleration Unit
A method for monitoring an electronically controlled drive unit of a vehicle uses actual vehicle acceleration and a preselected vehicle acceleration. Actual acceleration is determined from any of an acceleration sensor or vehicle speed sensors. When actual acceleration is greater than the preselected acceleration, a reaction is initiated to reduce vehicle acceleration.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
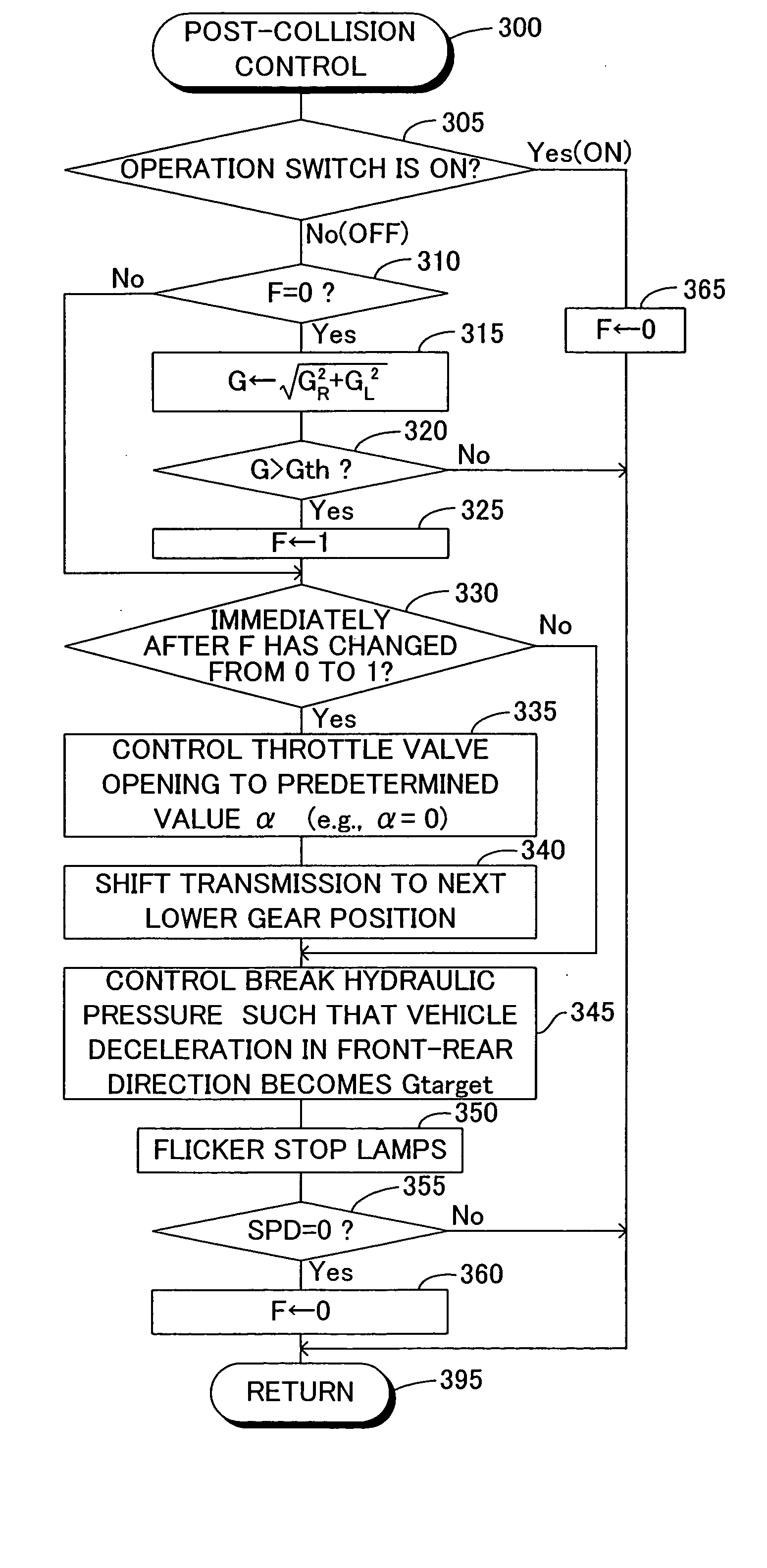
Vehicle control apparatus
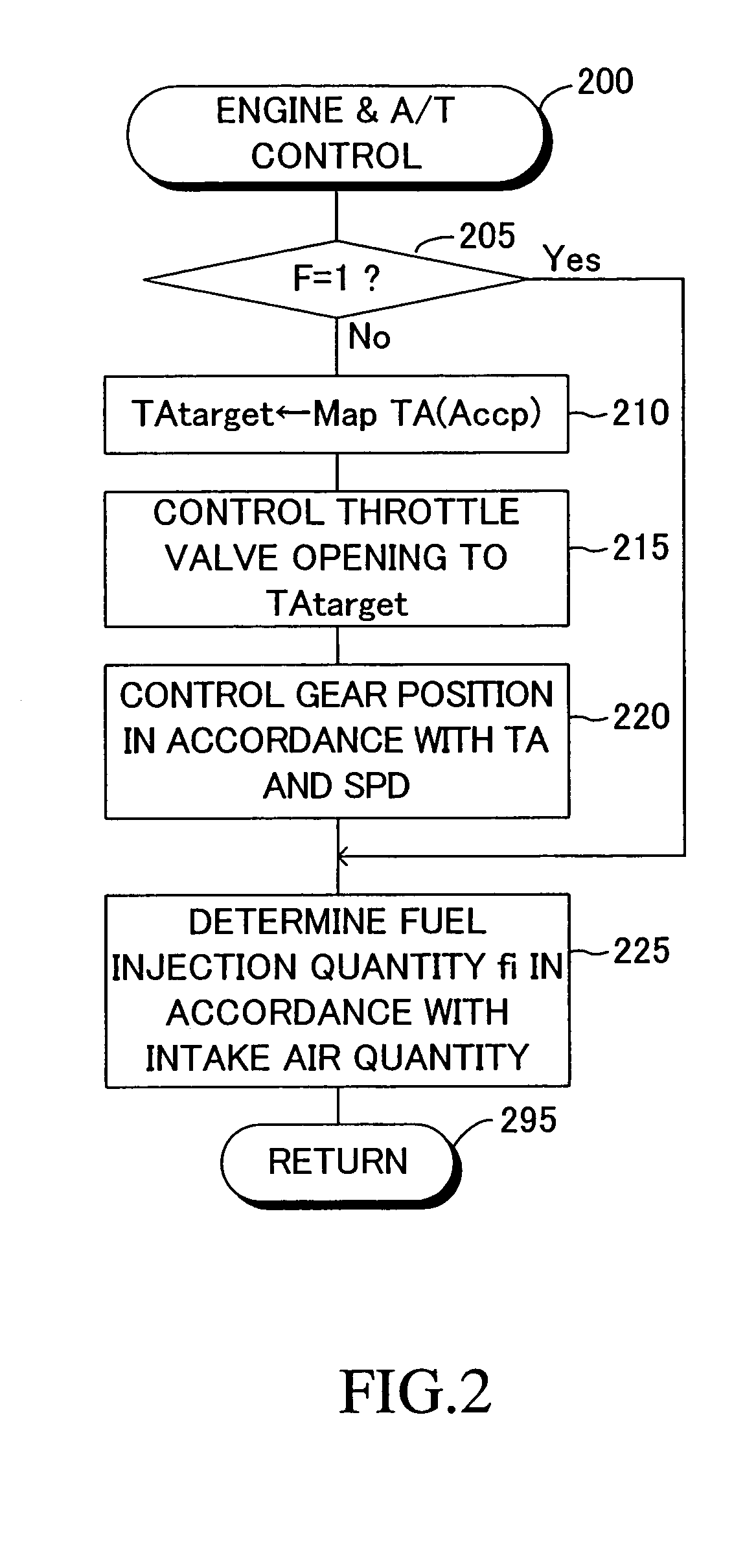
InactiveUS20050071071A1Safely stoppedEnsure safetyAnalogue computers for trafficPedestrian/occupant safety arrangementPost collisionControl theory
An electric controller starts post-collision control when an acceleration of the vehicle detected by means of sensors mounted on the vehicle is greater than an acceleration threshold (i.e., after occurrence of a collision of a vehicle). In the post-collision control, the electric controller fixes the throttle valve opening to a predetermined value, and shifts the transmission from the present gear position to an adjacent lower-side gear position. Moreover, the electric controller controls the hydraulic pressure of the brake such that the vehicle deceleration in the front-rear direction detected by means of the sensors becomes a target deceleration.
Owner:ADVICS CO LTD
System and method for identifying a spatial relationship for use in calibrating accelerometer data
ActiveUS20120253585A1Improve accuracyReduce the possibilityVehicle testingRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesAccelerometer dataEngineering
Methods and systems for identifying a spatial relationship between a frame of reference associated with an accelerometer mounted in a vehicle and a frame of reference associated with the vehicle Accelerometer data is received from an accelerometer and vehicle data is received from a vehicle network of the vehicle, a long term average of the accelerometer data is used to determine the direction of gravity in the frame of reference of the vehicle. In addition the vehicle date is used to determine changes in speed of the vehicle, and thus to determine the direction of the longitudinal axis of the vehicle in the frame of reference of the vehicle. From these determined directions, the spatial relationship between the frames of reference may be determined.
Owner:TRIMBLE NAVIGATION LTD
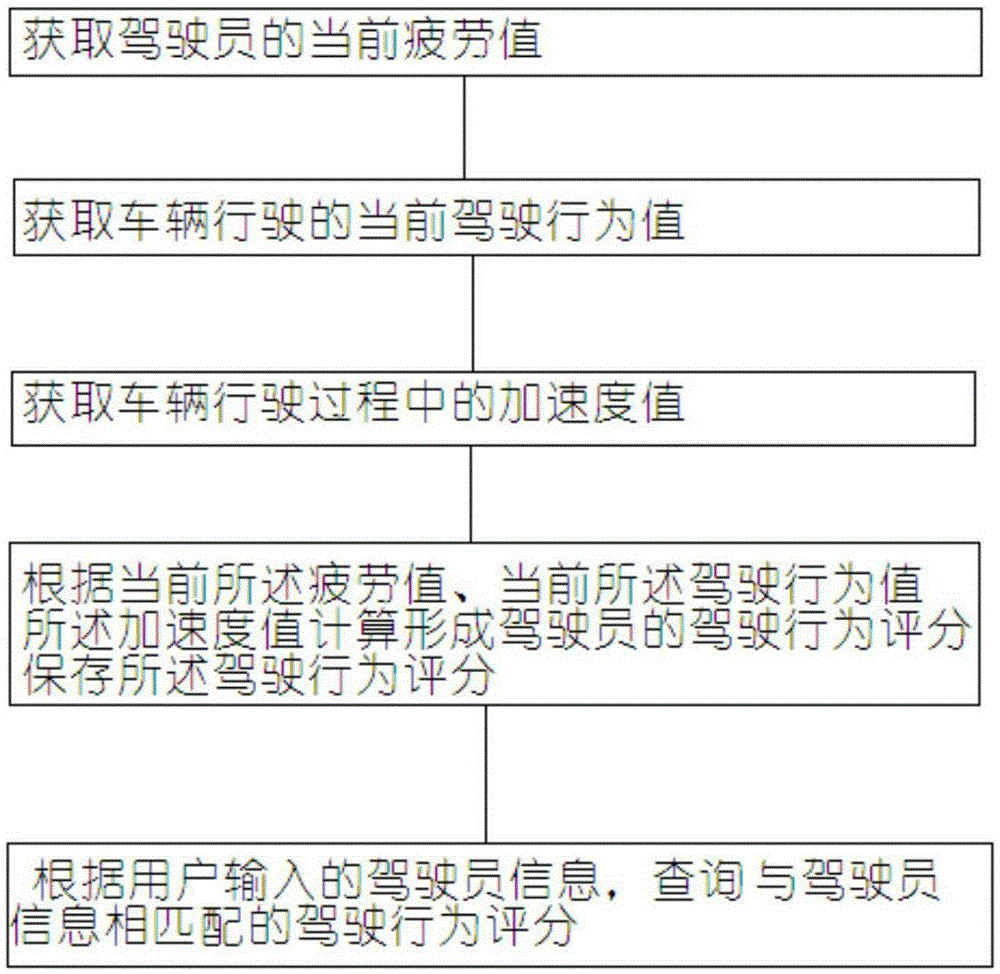
Driving behavior analysis system and analysis method
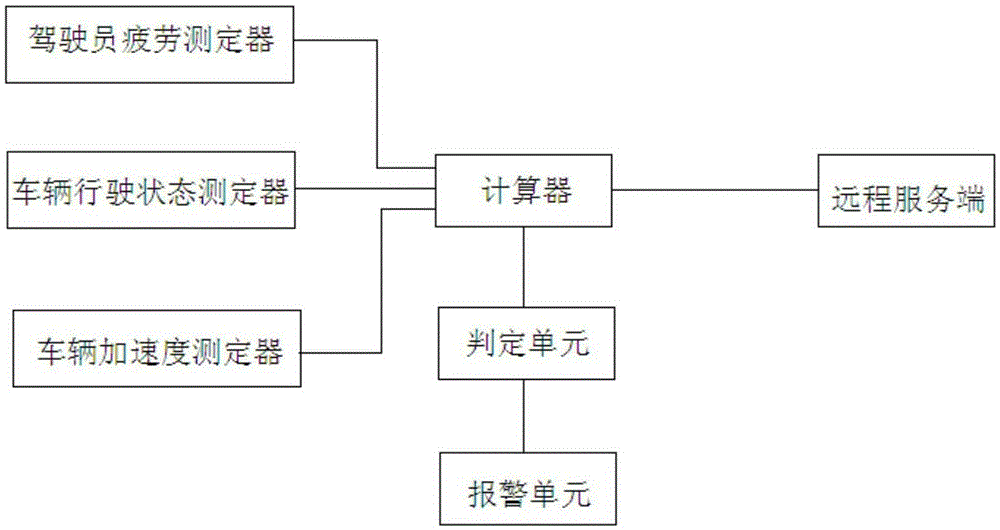
InactiveCN105303830AEasy to drive safelyDetection of traffic movementAlarmsEngineeringVehicle driving
The invention relates to the field of vehicle safety driving control, and particularly relates to a driving behavior analysis system and analysis method. The system comprises a driver fatigue tester which acquires the current fatigue value of a driver, a vehicle driving state tester which acquires the current driving behavior value of a driving vehicle, a vehicle acceleration tester which acquires an acceleration value in the vehicle driving process, a calculator which calculates the driving behavior score of the driver according to the current fatigue value, the current driving behavior value and the acceleration value, and a remote server which receives and stores the driving behavior score, and reminds the driver to avoid fatigue driving or violation driving when the driving behavior score is low. The remote server receives and stores the driving behavior score, and stores each time of driving behavior score record of the driver. The analysis system and the analysis method are conducive to safe driving of the driver.
Owner:CHENGDU TOPPLUSVISION TECH CO LTD
Apparatus for estimating road surface gradient and vehicular control apparatus using the same
InactiveUS20090043473A1Improve travel conditionsImprove ride qualityAnalogue computers for trafficExternal condition input parametersEngineeringRoad surface
An apparatus is provided to estimate a gradient of a road surface on which a vehicle travels. The apparatus comprises acquisition, estimation, and compensation members. The acquisition member acquires at least one of acceleration of the vehicle calculated on changes in a travel speed of the vehicle and acceleration sensed from a force applied to the vehicle. The estimation means estimates the gradient of the road surface based on the acquired acceleration. The compensation member compensates the acquired acceleration in terms of influence of noise superposed on the acceleration, depending on an operational condition of the vehicle. The compensated acceleration is used by the estimation. The compensation is carried out by cutting off the noise by a filter, for example.
Owner:DENSO CORP
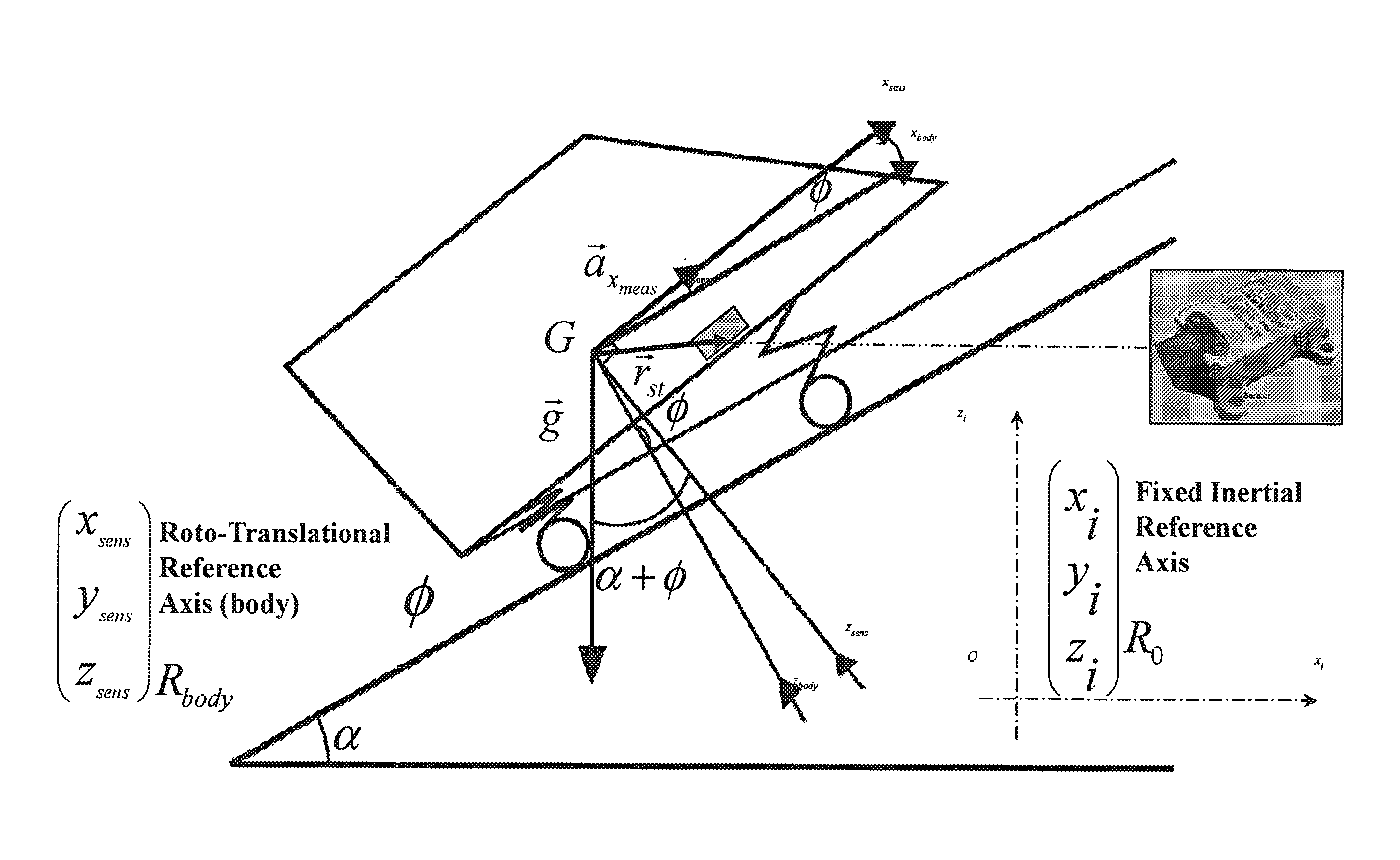
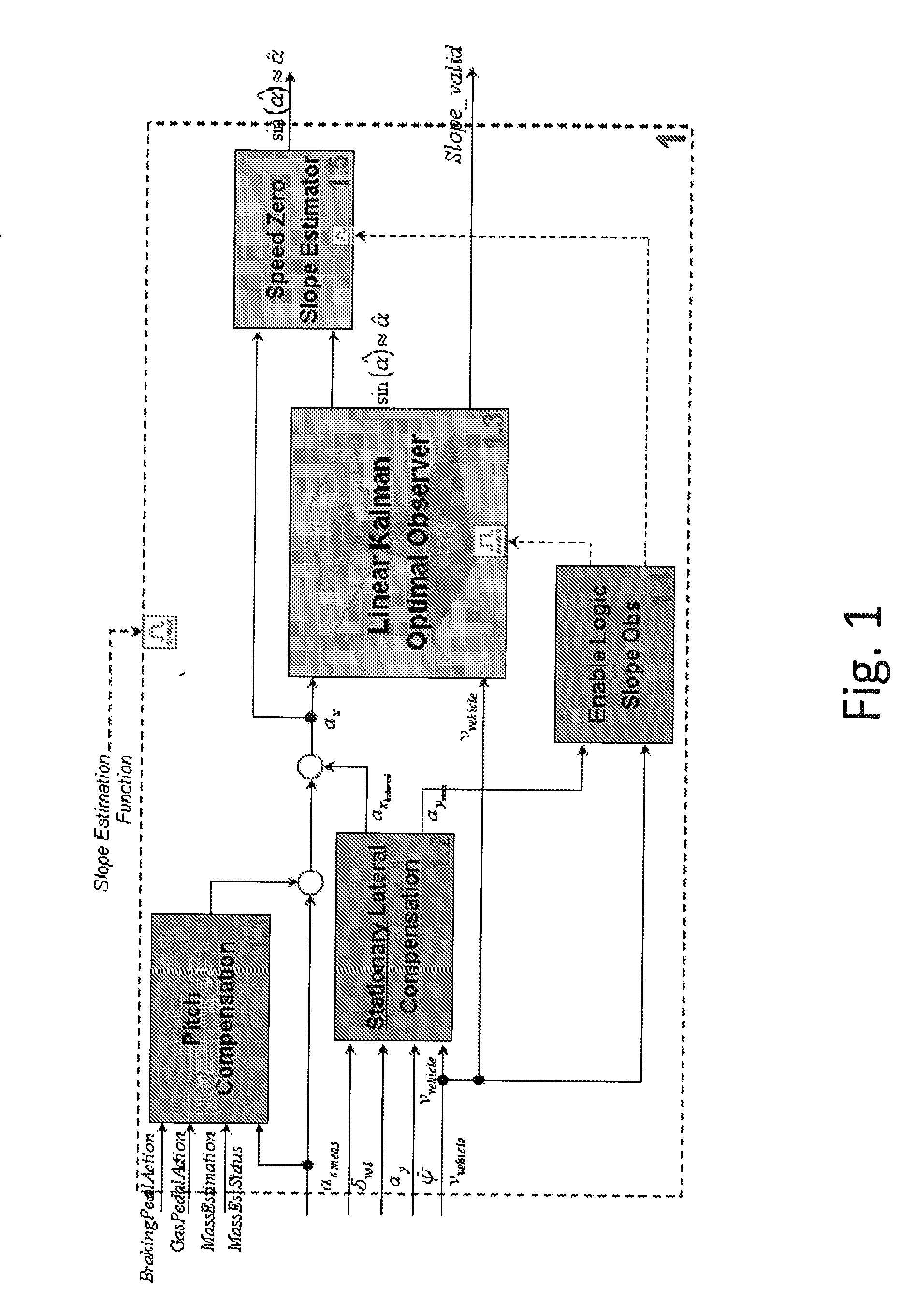
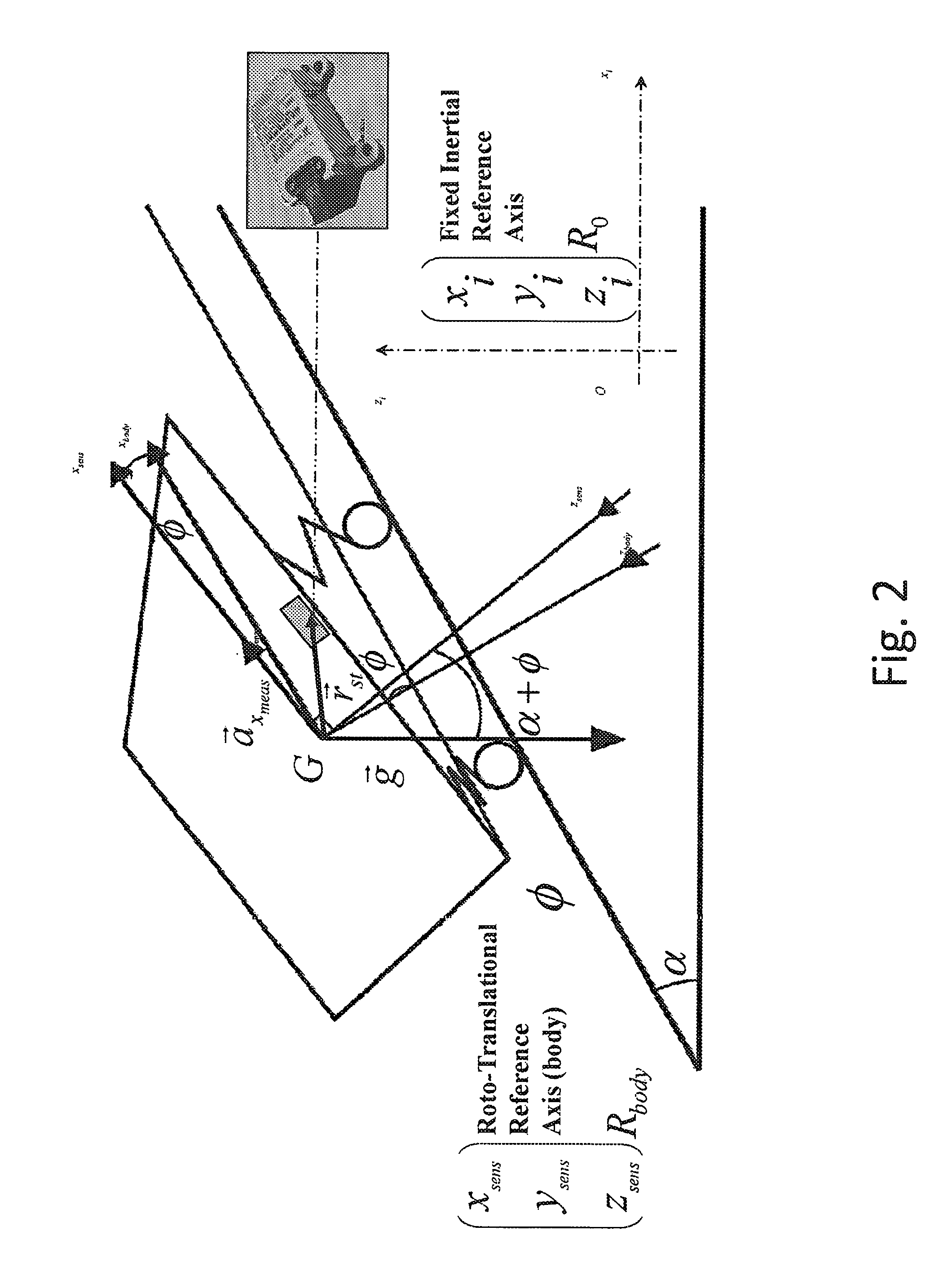
Automotive control unit programmed to estimate road slope and vehicle mass, vehicle with such a control unit and corresponding program product
ActiveUS20160332633A1Gearing controlExternal condition input parametersVehicle dynamicsAccelerometer
Automotive electronic control unit programmed to realtime estimate either or both of vehicle mass and road slope, wherein; a. road slope, is estimated; a1. when vehicle is considered stopped based on an accelerometer signal indicative of vehicle acceleration, wherein the vehicle is considered stopped in the presence of substantially zero values of a speed signal indicative of vehicle speed, and a2. when vehicle is in rectilinear and curvilinear motion by implementing a road slope observer based on a linear Kalman filter, which is designed to: a21. operate based on signals indicative of vehicle speed and acceleration, and a22. compensate for accelerometric disturbances due to; a221. vehicle static pitch resulting from vehicle load distribution, and a222. vehicle dynamic pitch due to acceleration to which vehicle is subjected during motion, and a223. accelerometric disturbance components due to vehicle lateral dynamics; b. vehicle mass is estimated: b1. when vehicle is in motion, and b2. based on a recursive least square algorithm with forgetting factor, and b3. based on an accelerometric signal indicative of vehicle acceleration, on a vehicle speed signal, and other signals representing a vehicle propulsive / resistive torque, and b4. at different low gears, to provide a mass estimation and an associated variance for each gear, and b5. based on mass estimations and corresponding variances for each gear, and b6. compensating for accelerometer disturbances due to: b61, vehicle dynamic pitch; and b62. accelerometrie disturbance components due to vehicle lateral dynamics; and b7. minimizing uncertainties on propulsive / resistive torque due to gear efficiency and roiling resistance.
Owner:CENT RICERCHE FIAT SCPA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com