Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
2641results about "Steam use" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
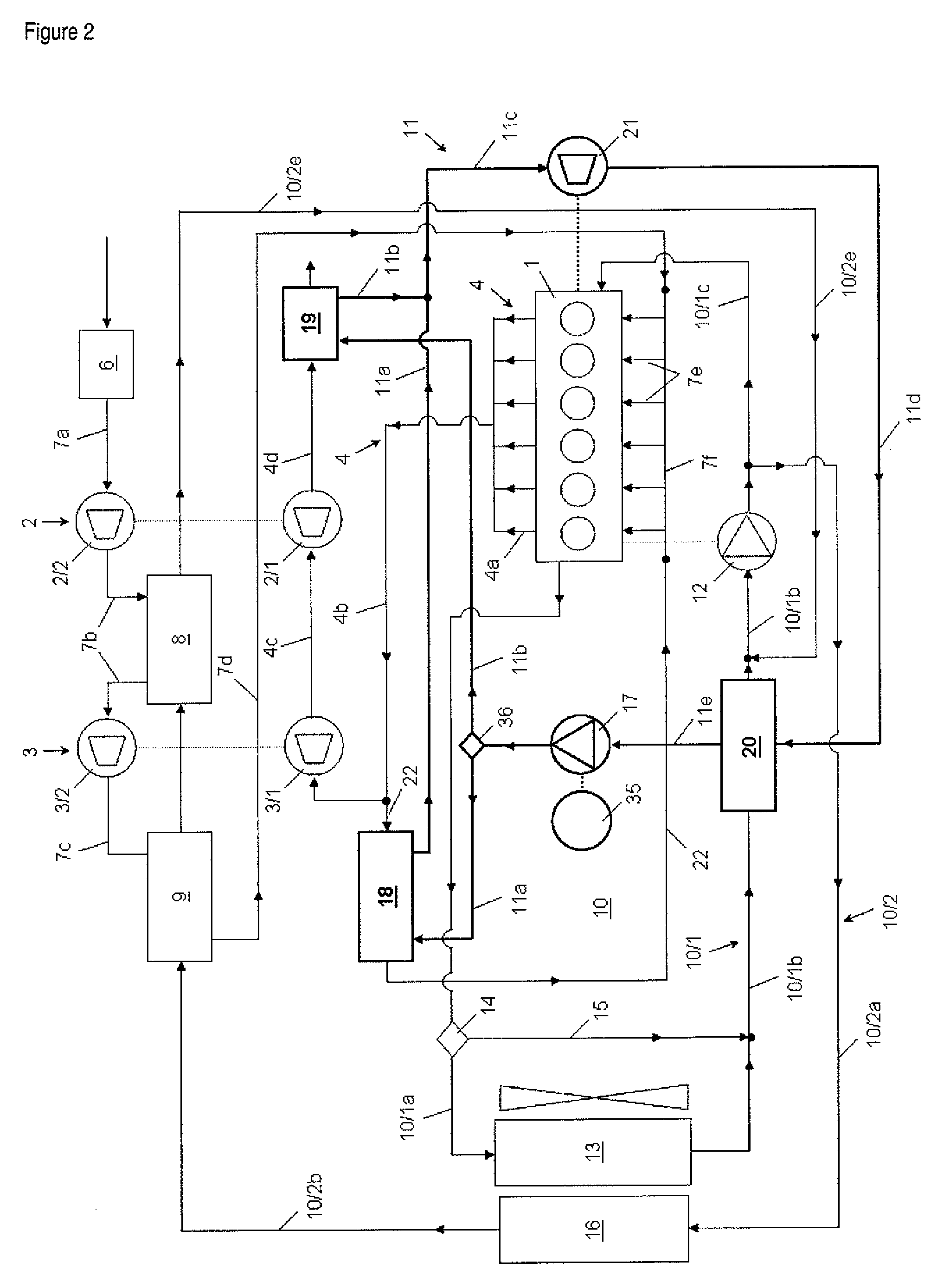
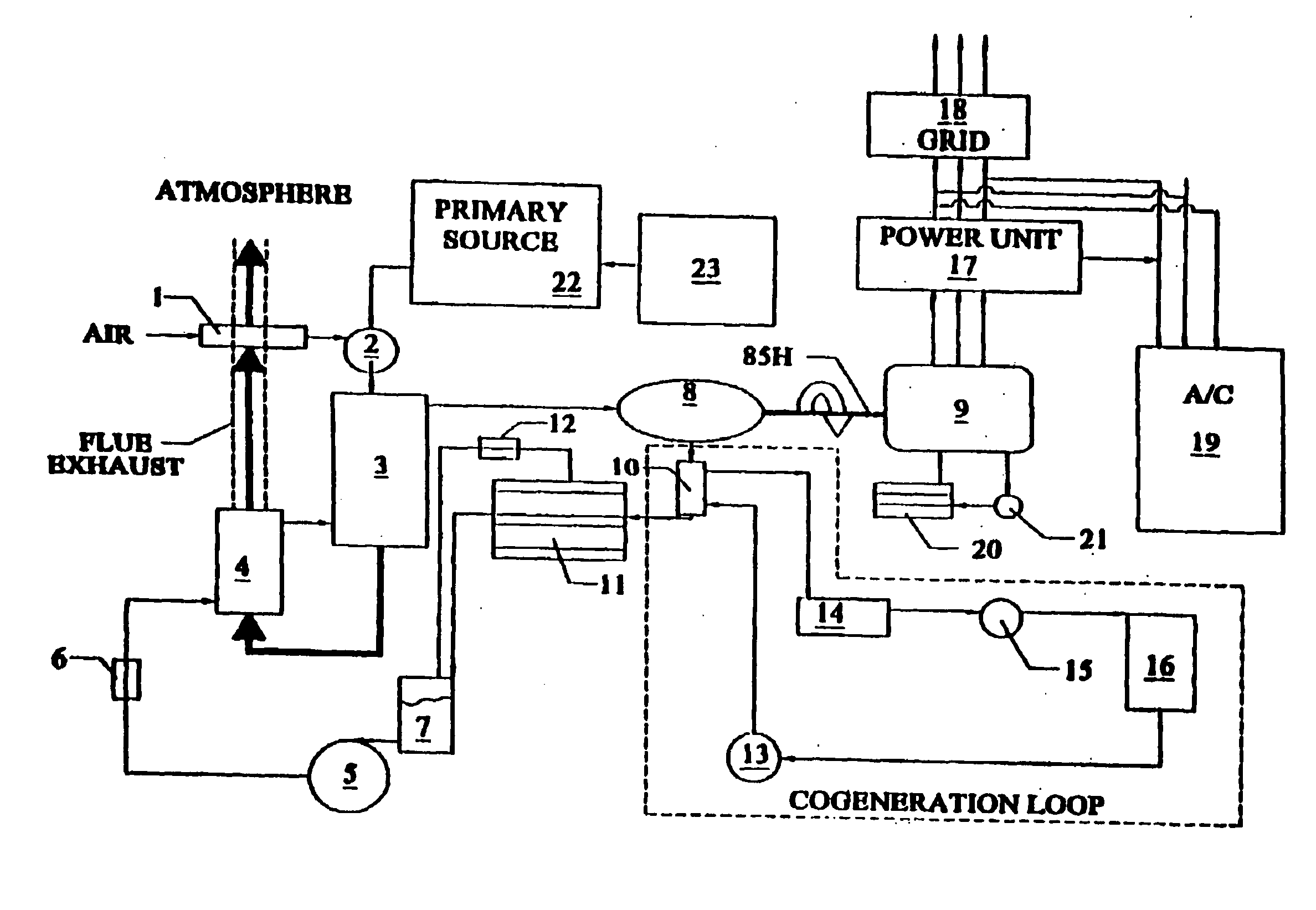
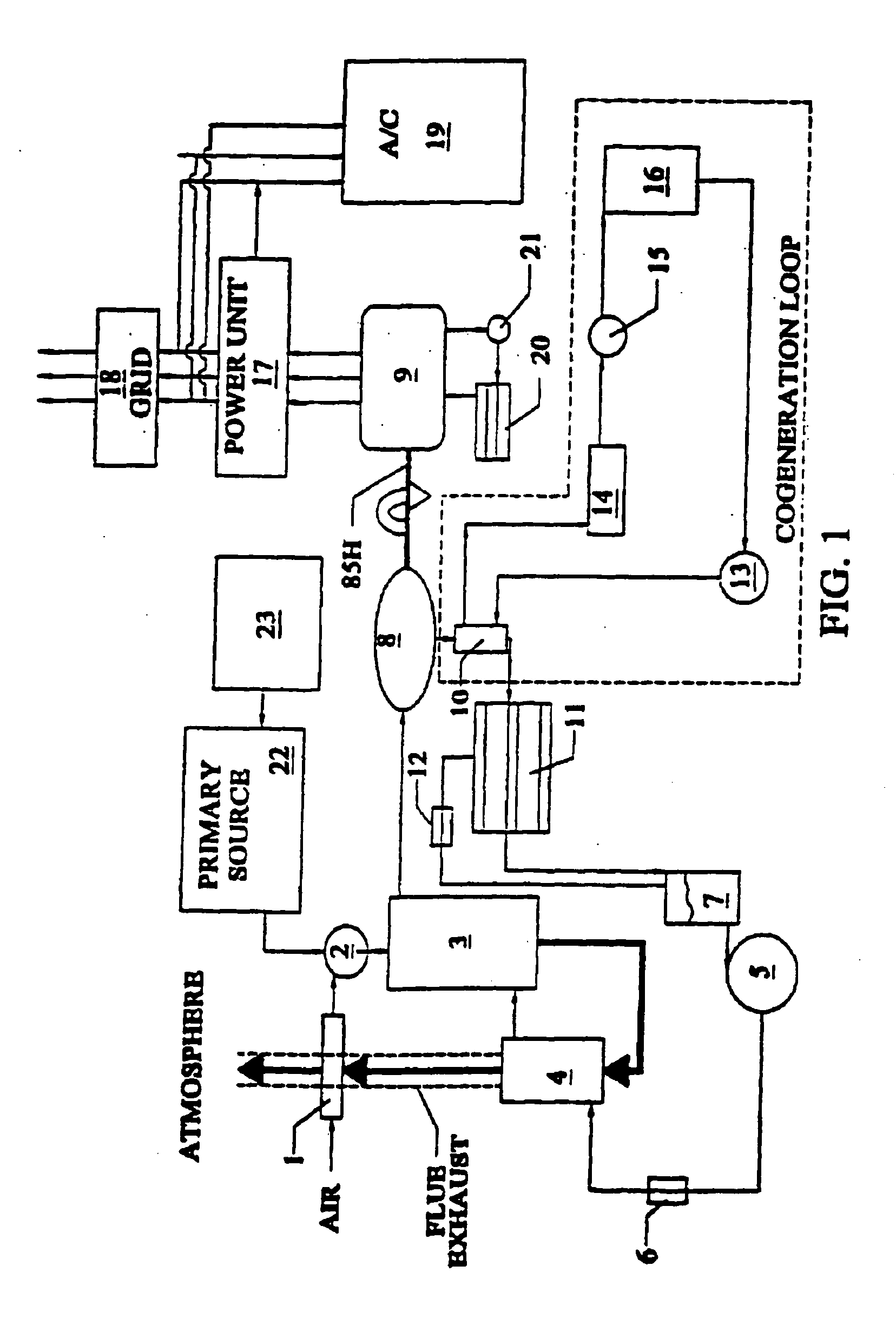
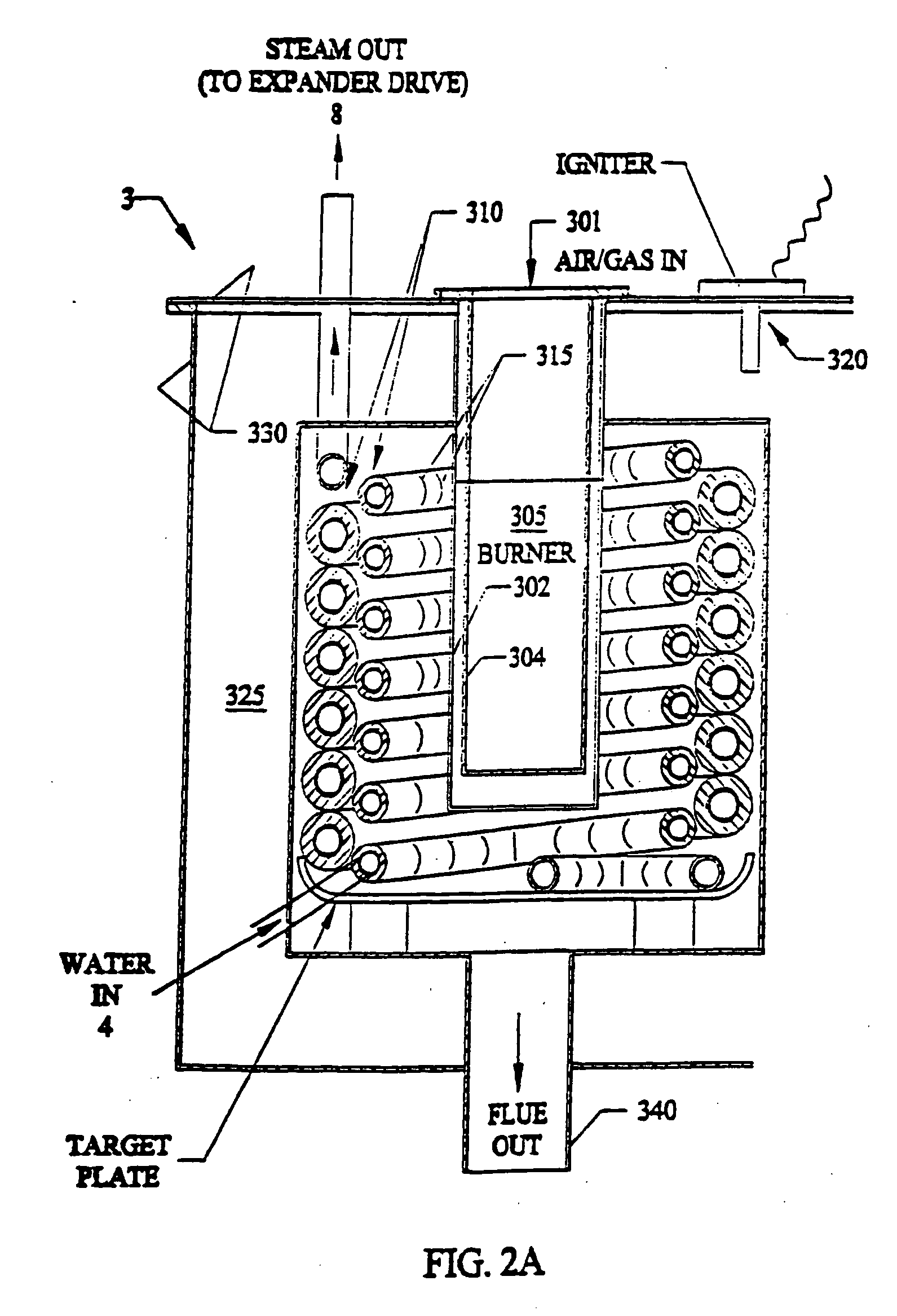
Power conversion systems
Power generation systems and methods are provided with features directed to various innovations including ones relating to the conversion of concentrated solar and biomass energy to electricity, load-shifting of electrical power supply systems, gas turbine devices and cycles, and power plant control systems.
Owner:BRAYTON ENERGY
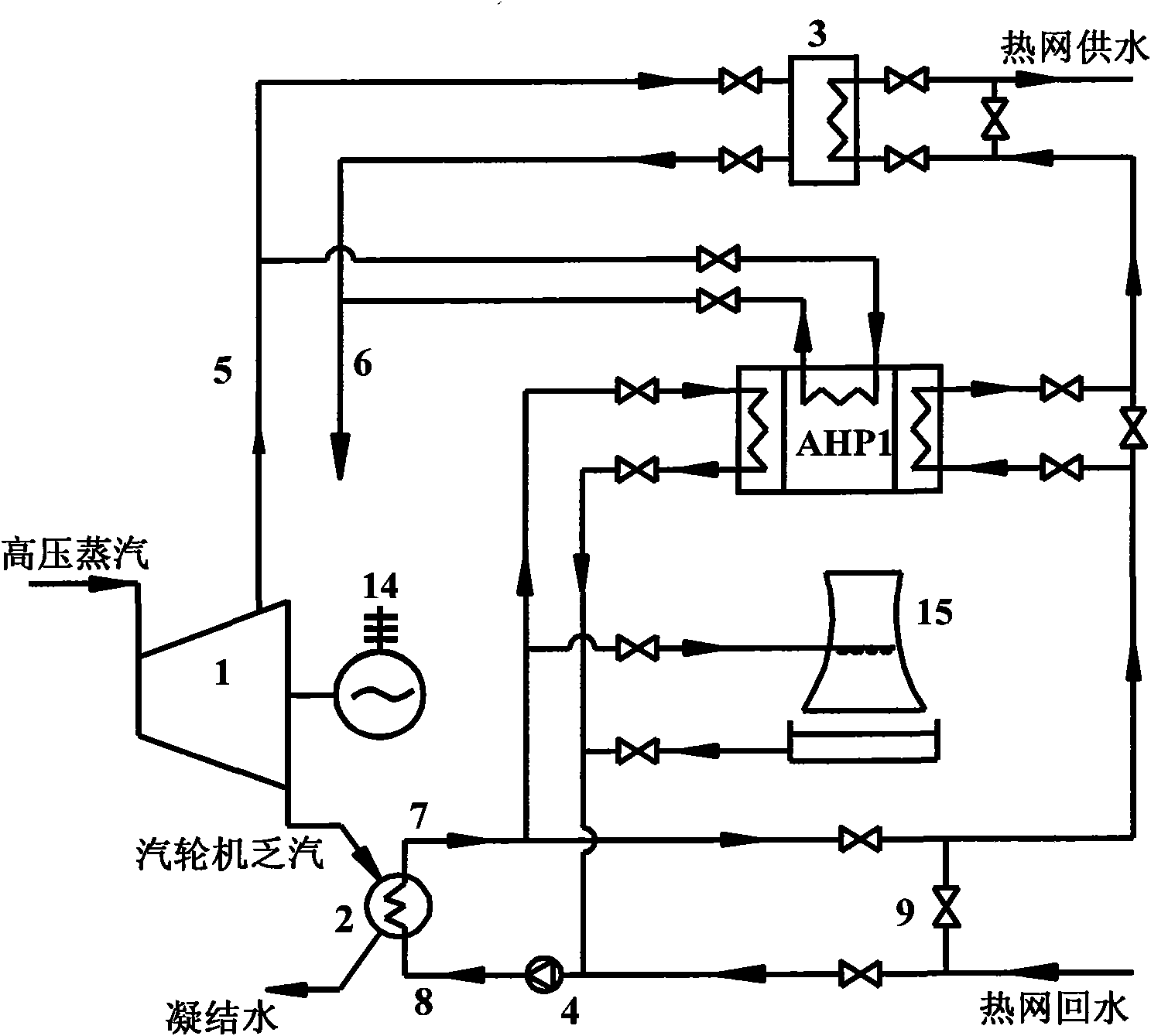
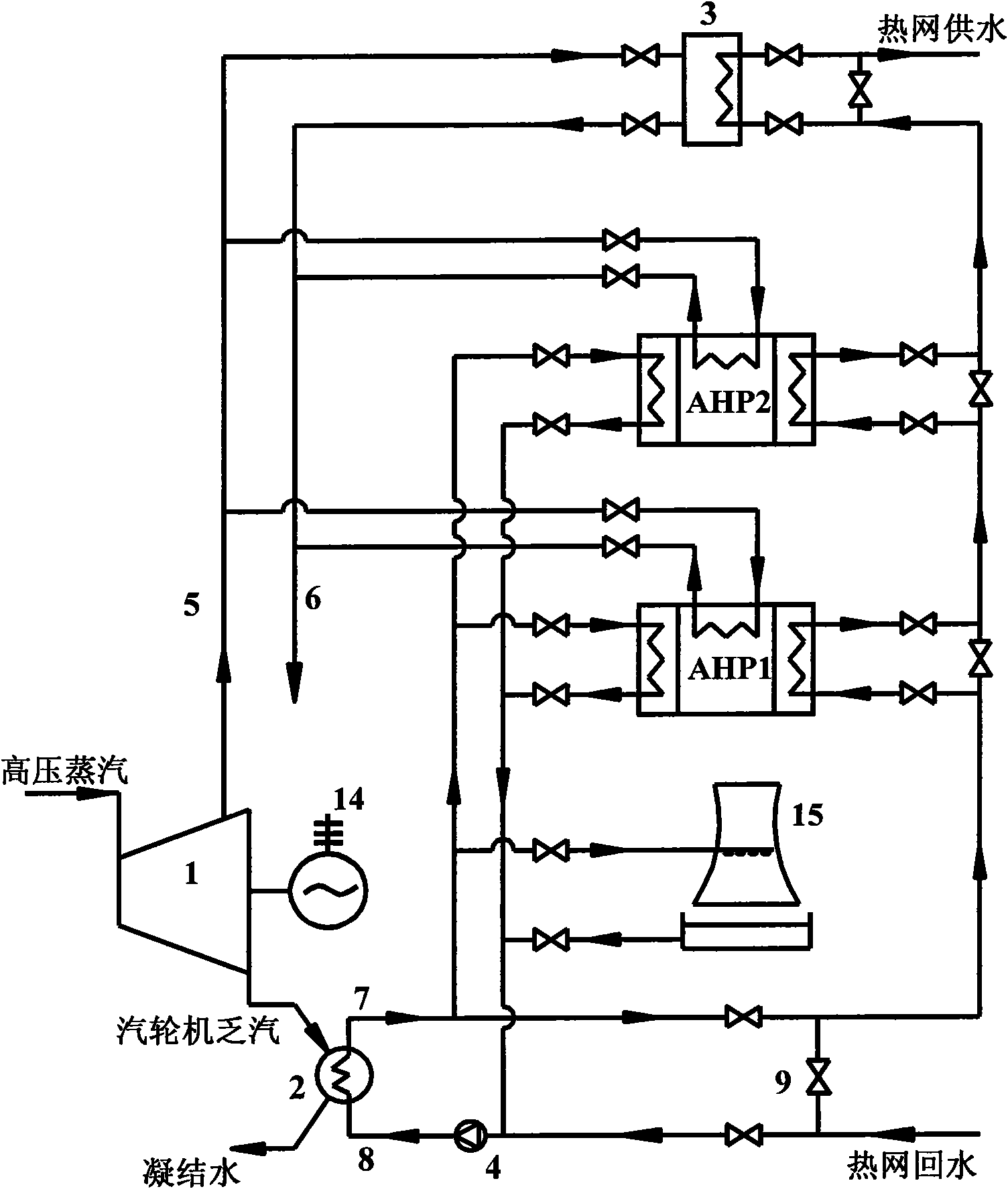
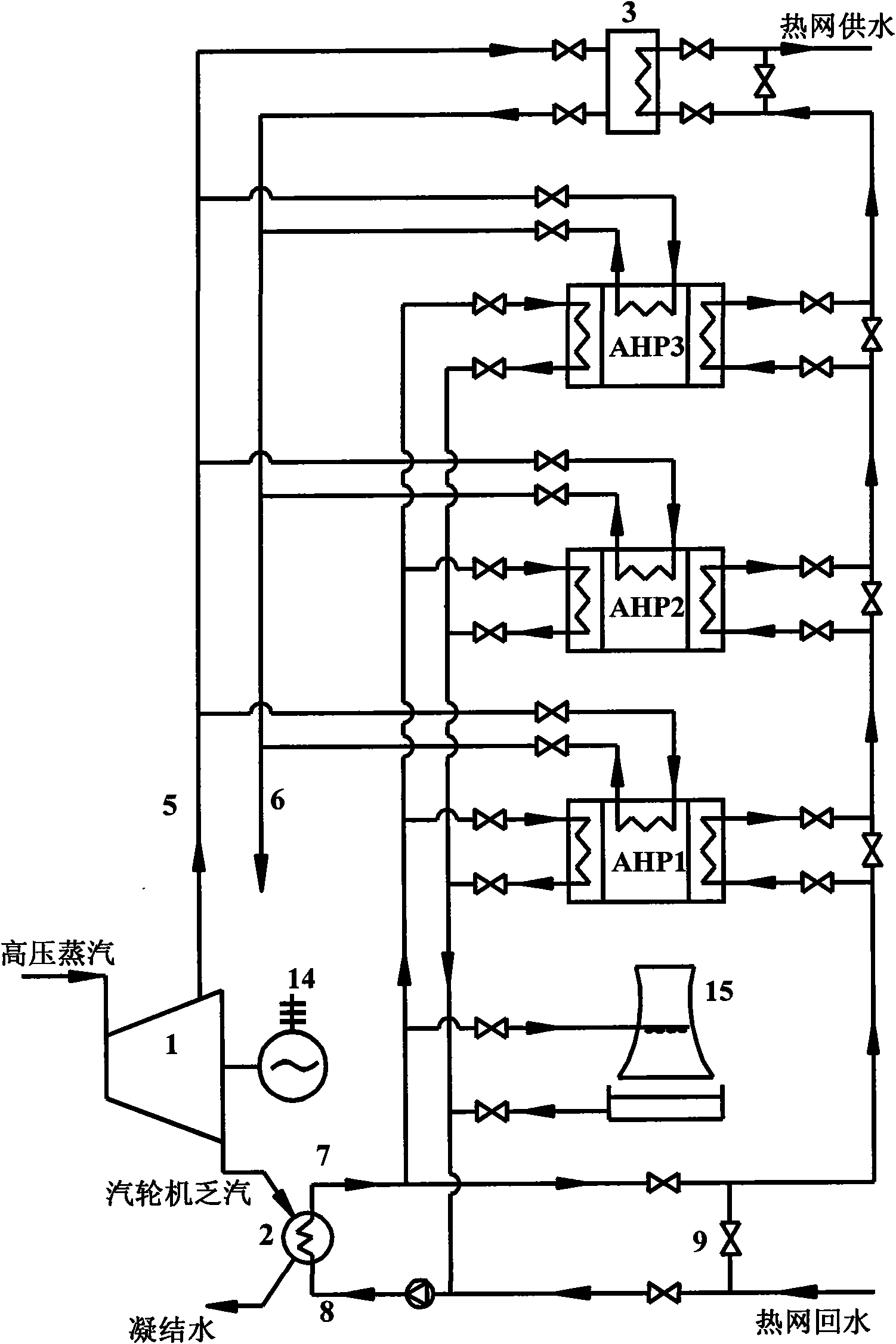
Method for recovering waste heat of thermal power plant and heating and supplying heat to hot water in a stepping way
ActiveCN101619662AImprove utilization efficiencyReduce exergy lossSteam useCombined combustion mitigationCooling towerSteam condensation
The invention discloses a method for recovering the waste heat of a thermal power plant and heating and supplying heat to hot water in a stepping way. In the method, low-temperature heat-net return water is firstly mixed with circulating cooling water positioned on an outlet of a cooling condenser or exchanges heat with the circulating cooling water positioned on the outlet of the cooling condenser to be increased in temperature and then sequentially delivered into an each-step vapour absorption type heat pump and a vapor-water heat exchanger in a series connection way to be gradually heated to be increased in temperature to heat supplying temperature and finally discharged through a water supplying pipeline; the circulating cooling water absorbs the waste steam condensation heat of a steam turbine in the cooling condenser, then one path of the circulating cooling water is directly mixed with the low-temperature heat-net return water or heats the low-temperature heat-net return water through the heat changer, the other path of the circulating cooling water is delivered into an each-step absorption type heat pump unit to be used as a low-order heat source of the absorption type heat pump unit, and the redundant heat of the circulating cooling water is discharged to the environment through a cooling tower. The invention uses the steam extraction of the steam turbine as a driving heat source of the absorption type heat pump so that the low-temperature heat-net return water is heated in a stepping way, thereby reducing the effective energy loss; the waste heat of the discharged steam of the steam turbine is sufficiently recovered in a direct heating way and an absorption type heat pump temperature increasing heating way, therefore, the comprehensive energy usage efficiency of the thermal power plant is enhanced.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
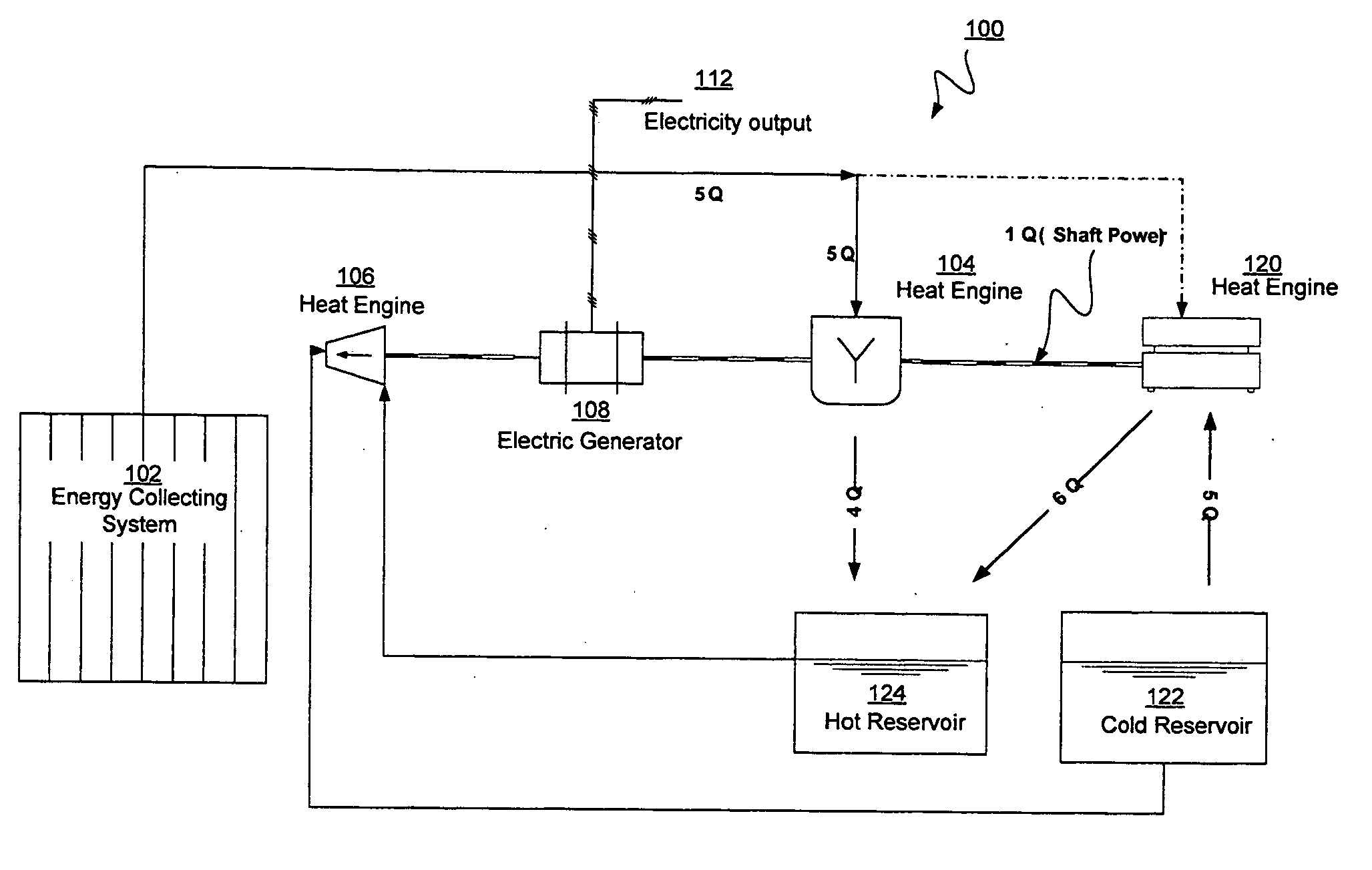
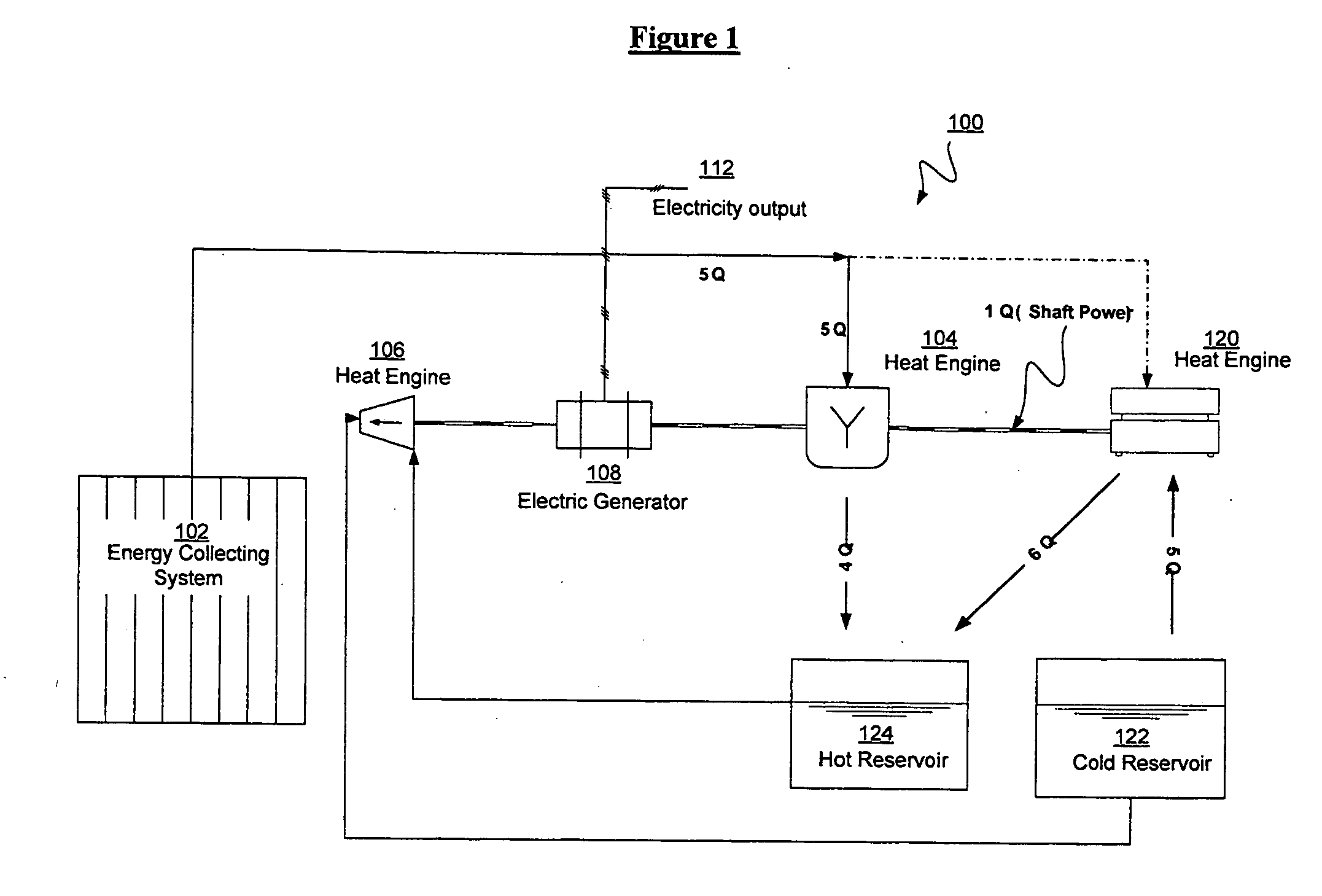
Efficient low temperature thermal energy storage
InactiveUS20090179429A1Improve heating efficiencyInternal combustion piston enginesFrom solar energyThermal energyWorking fluid
Thermal energy derived from a low temperature heat source is stored in one reservoir above ambient temperature and in another reservoir below ambient temperature for use in driving an organic Rankine cycle engine to produce electricity. The organic Rankine cycle engine may utilize an organic working fluid that boils below or near ambient temperature. Solar energy may be used to power a heat pump or chiller that provides the hot and cold storage fluids stored in hot and cold reservoirs for use in the organic Rankine cycle engine.
Owner:AREVA SOLAR
System and Method for Rapid Isothermal Gas Expansion and Compression for Energy Storage
InactiveUS20090301089A1Overcome disadvantagesInhibit migrationElectrical storage systemFluid couplingsCounter flowEngineering
The invention relates to systems and methods for rapidly and isothermally expanding gas in a cylinder. The cylinder is used in a staged hydraulic-pneumatic energy conversion system and includes a gas chamber (pneumatic side) and a fluid chamber (hydraulic side) and a piston or other mechanism that separates the gas chamber and fluid chamber while allowing the transfer of force / pressure between each opposing chamber. The gas chamber of the cylinder includes ports that are coupled to a heat transfer subassembly that circulates gas from the pneumatic side and exchanges its heat with a counter flow of ambient temperature fluid from a reservoir or other source.
Owner:SUSTAINX
Method and system for control of turbogenerator power and temperature
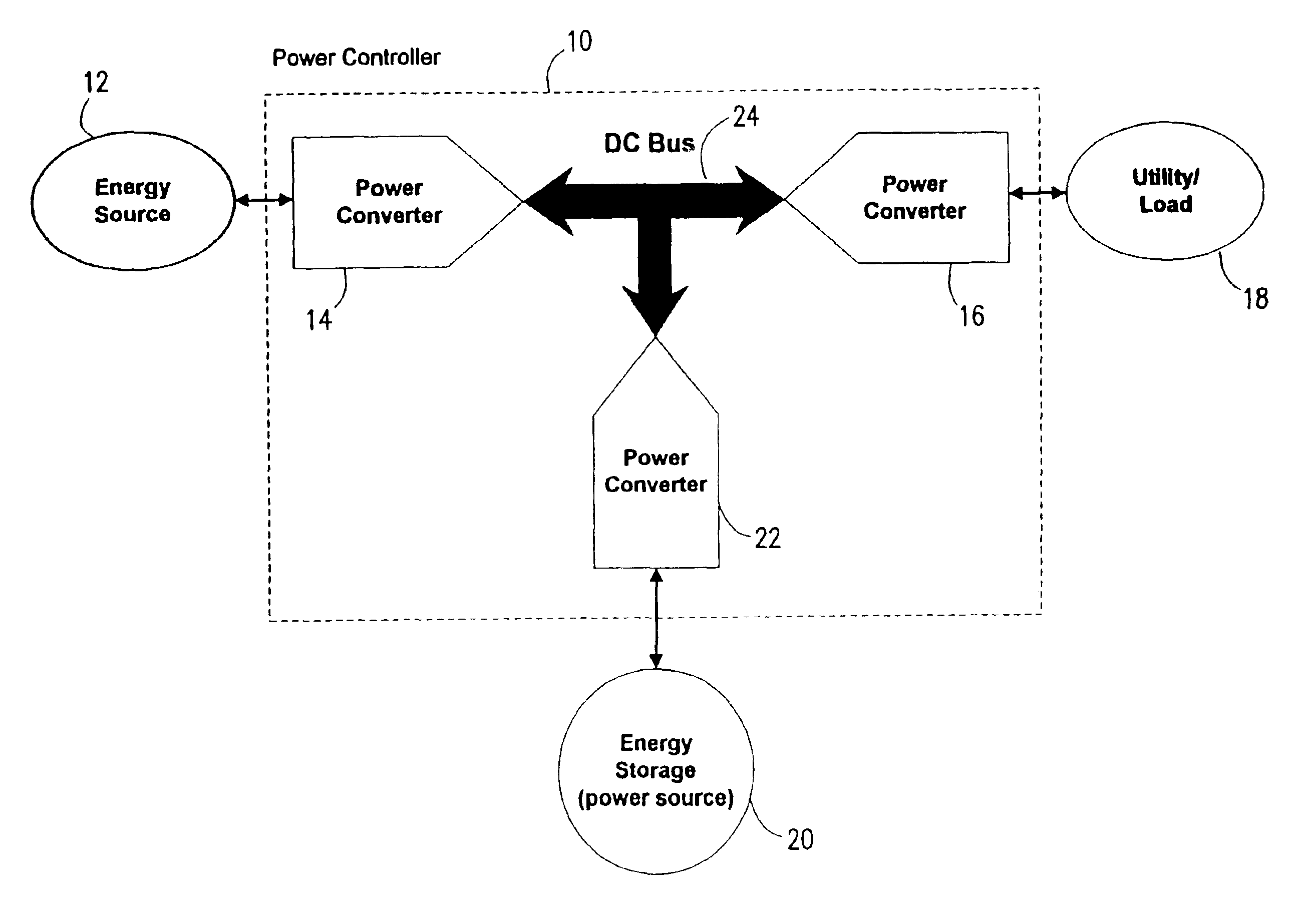
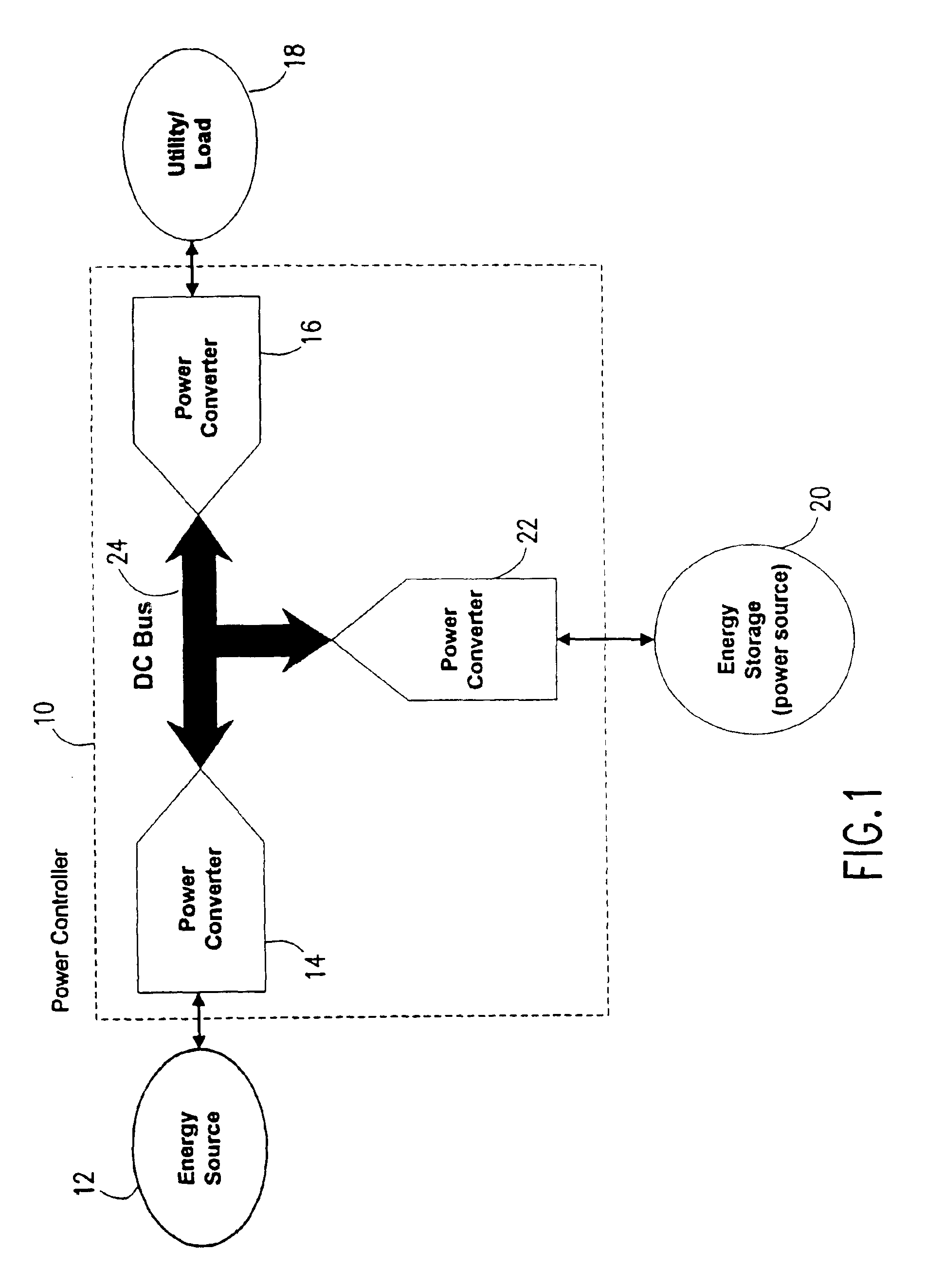
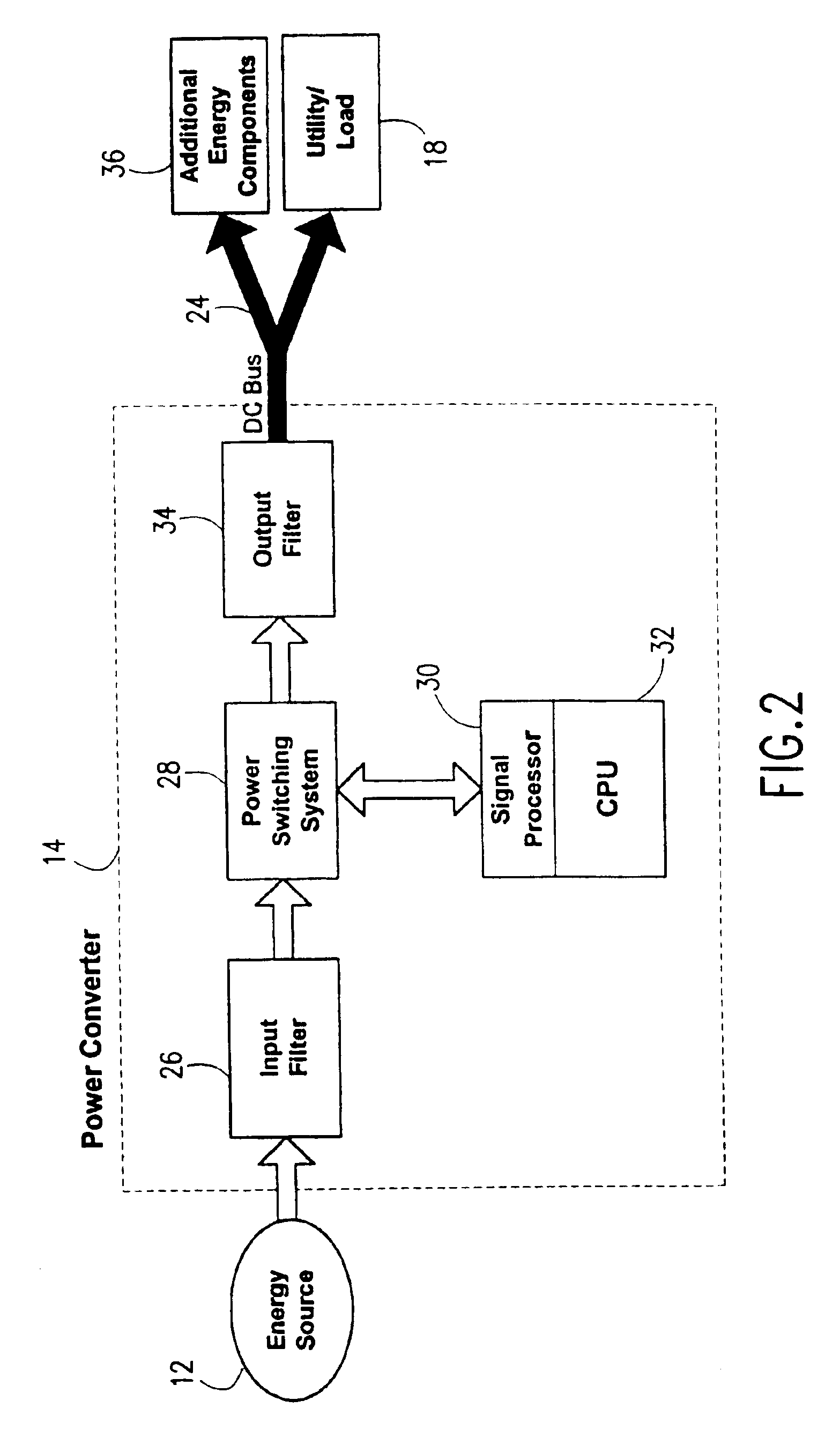
InactiveUS6958550B2Efficiency of turbine is maximizedIncrease speedLoad balancing in dc networkSteam usePower controllerEngineering
A power controller controls the turbine of a turbine powered generating system regardless of the load on the system to maximize the efficiency of the turbine and maintains the turbine at a substantially constant temperature during a system load change by using an energy storage device to provide power to the load while the turbine is changing speed to meet the new load demand.
Owner:CAPSTONE TURBINE
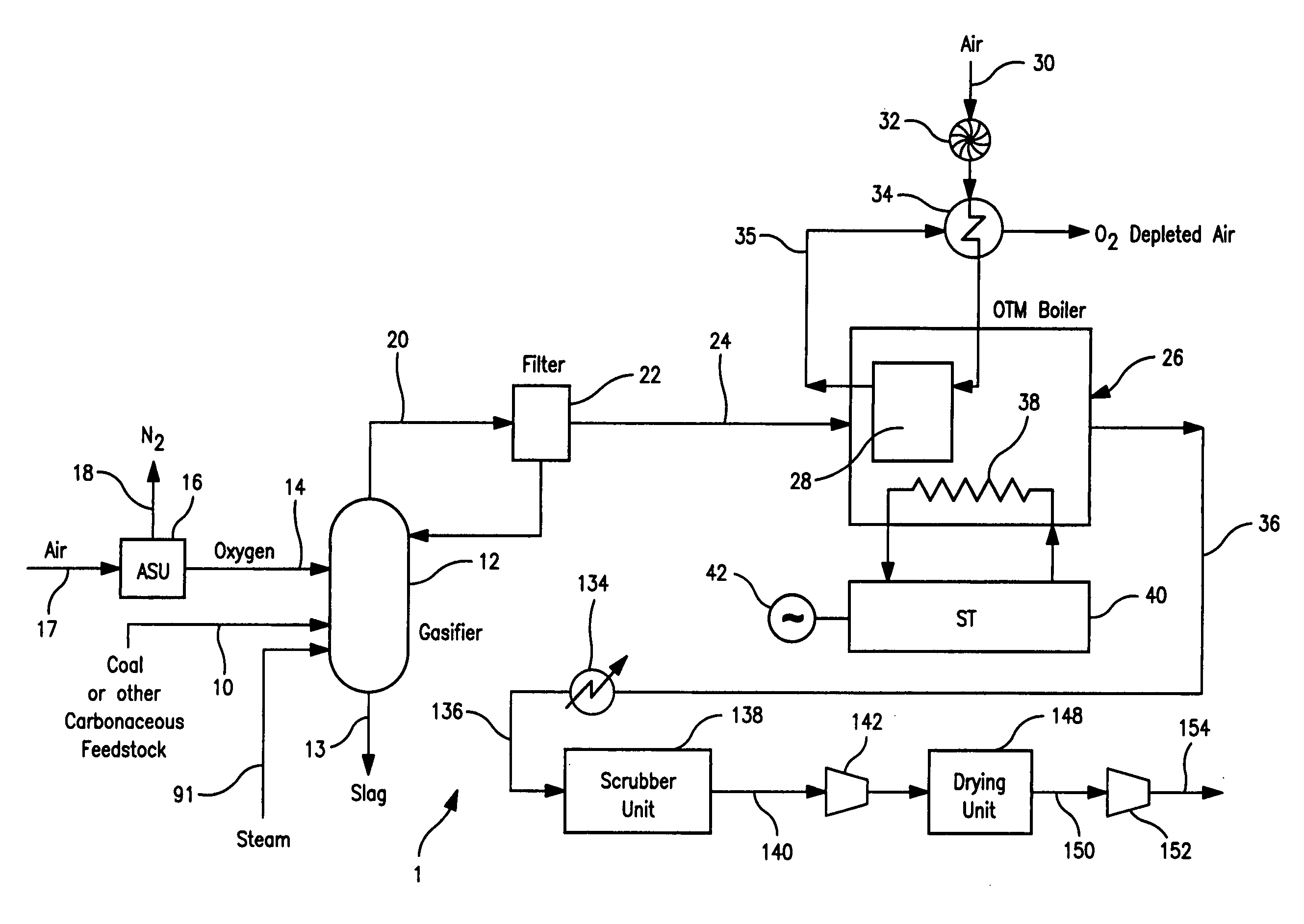
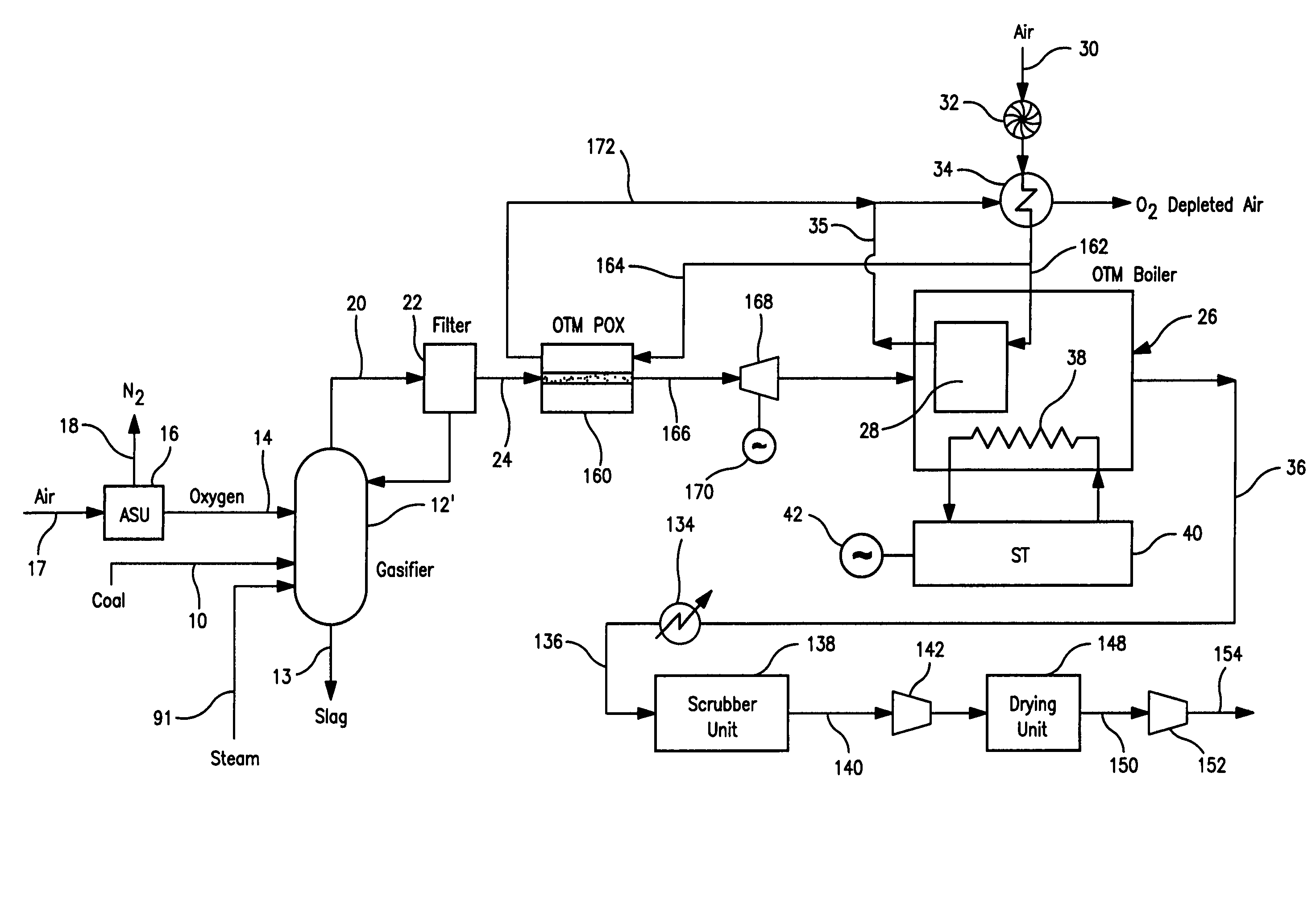
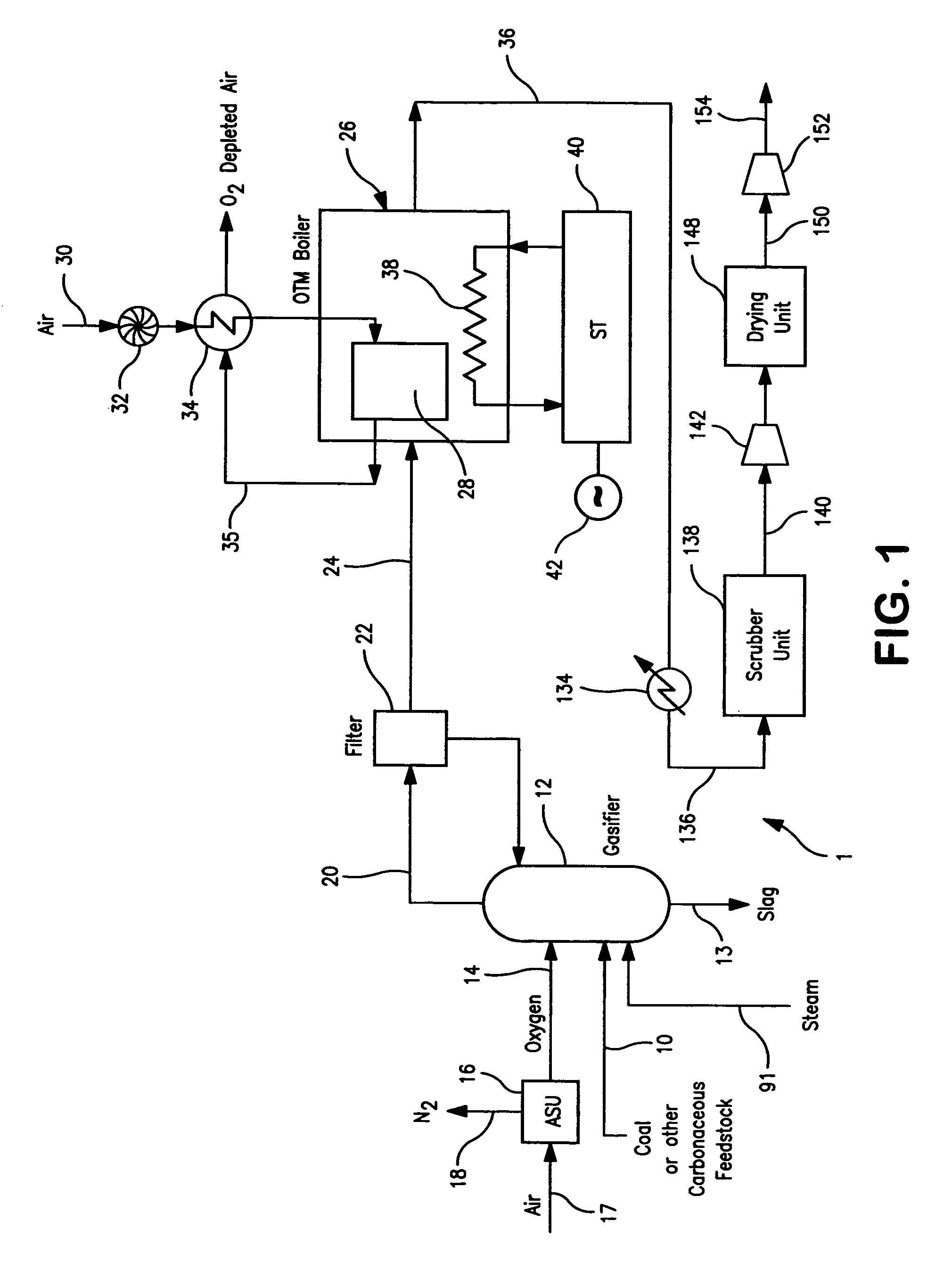
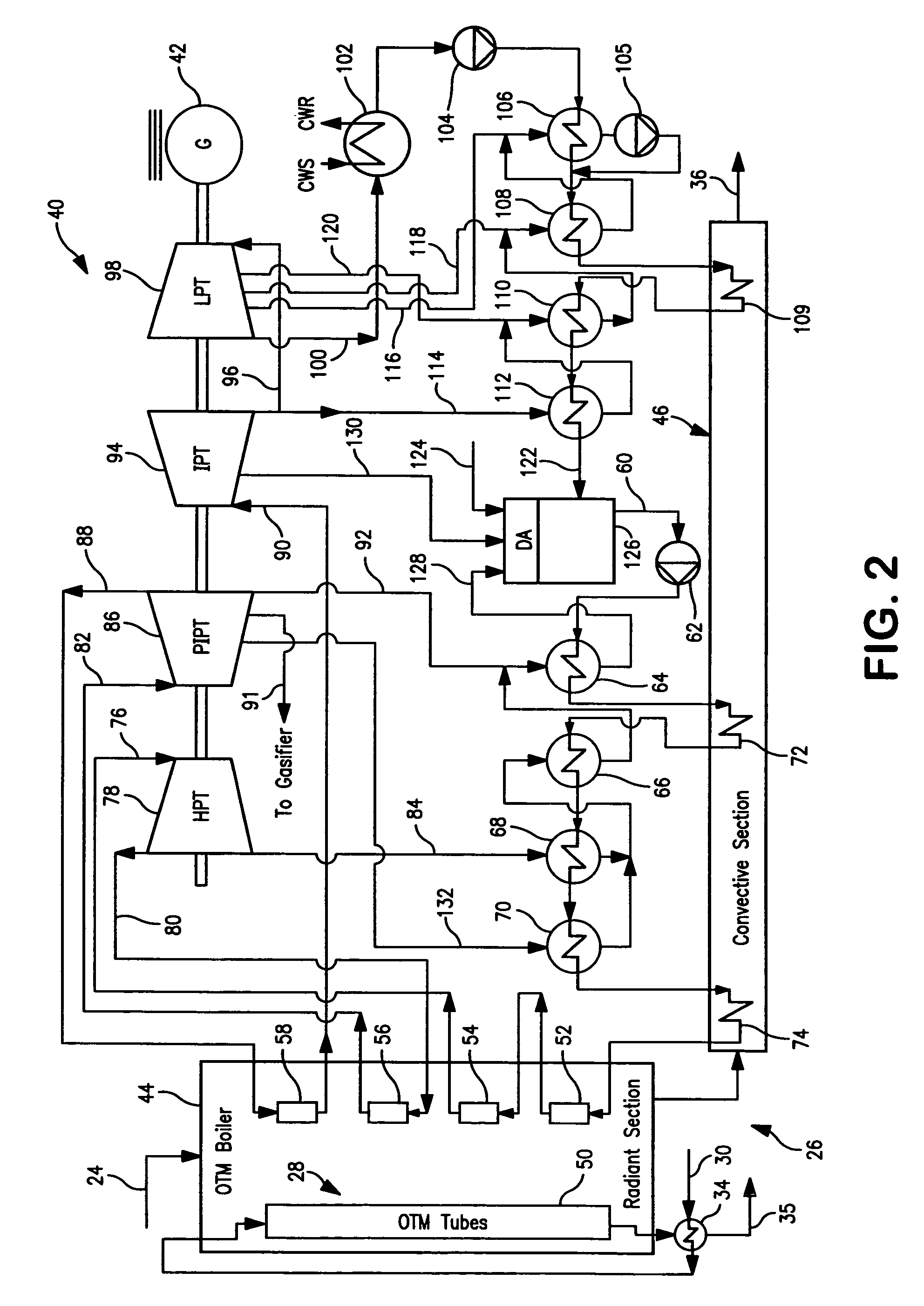
Electrical power generation method
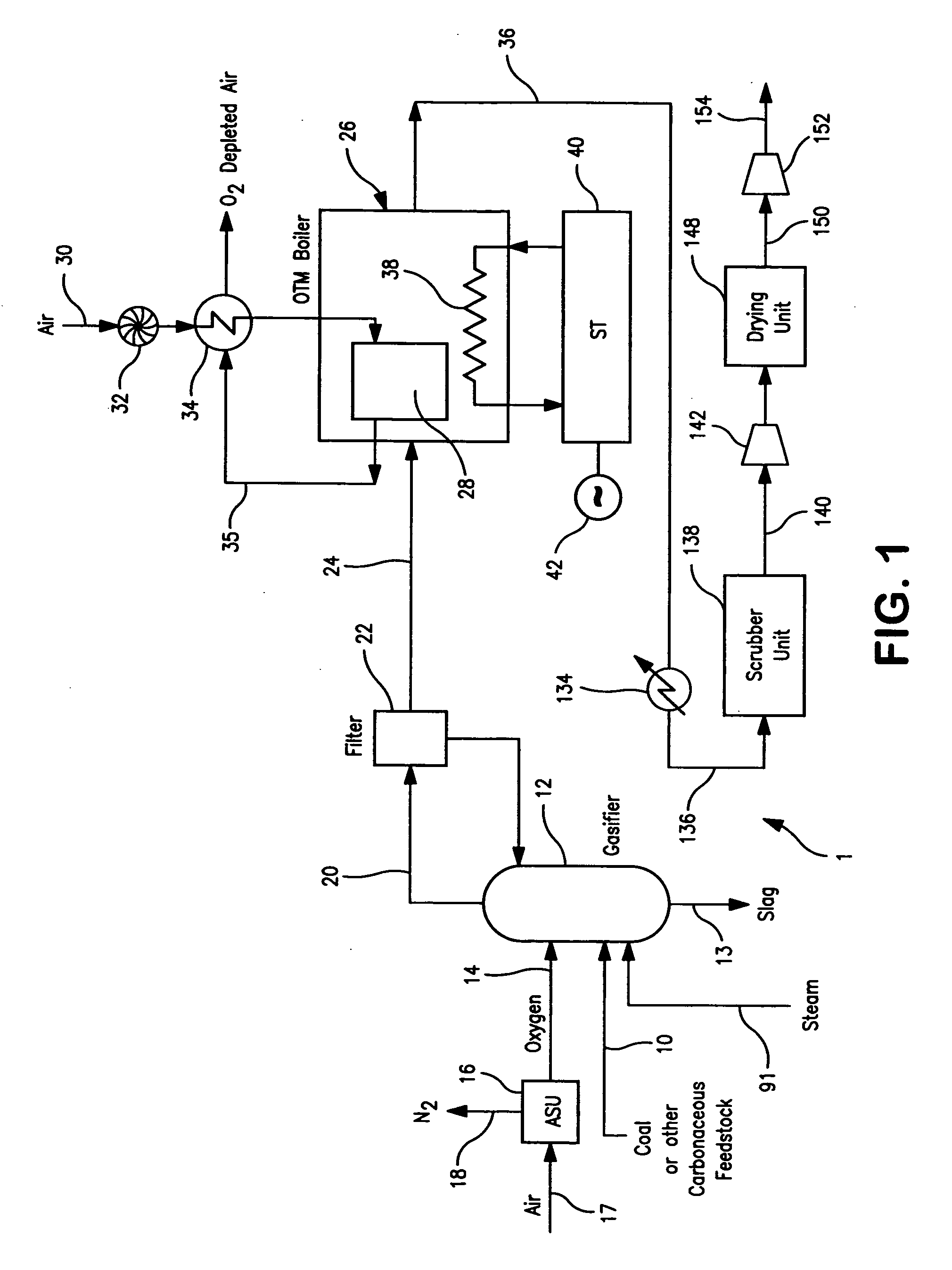
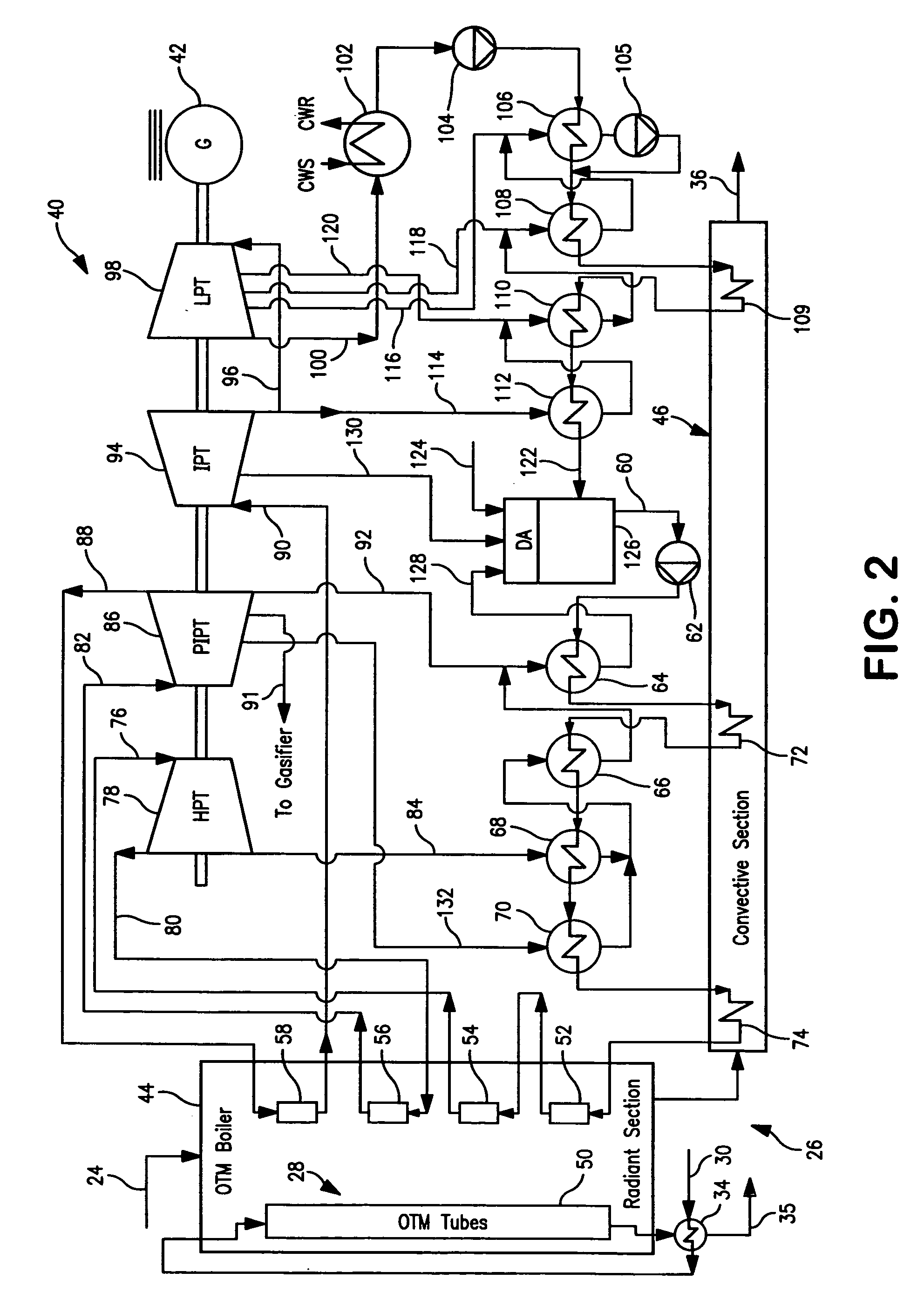
A method of generating electrical power in which a synthesis gas stream generated in a gasifier is combusted in an oxygen transport membrane system of a boiler. The combustion generates heat to raise steam to in turn generate electricity by a generator coupled to a steam turbine. The resultant flue gas can be purified to produce a carbon dioxide product.
Owner:PRAXAIR TECH INC
System and method for rapid isothermal gas expansion and compression for energy storage
InactiveUS7802426B2Overcome disadvantagesInhibit migrationElectrical storage systemServomotorsCounter flowEngineering
The invention relates to systems and methods for rapidly and isothermally expanding gas in a cylinder. The cylinder is used in a staged hydraulic-pneumatic energy conversion system and includes a gas chamber (pneumatic side) and a fluid chamber (hydraulic side) and a piston or other mechanism that separates the gas chamber and fluid chamber while allowing the transfer of force / pressure between each opposing chamber. The gas chamber of the cylinder includes ports that are coupled to a heat transfer subassembly that circulates gas from the pneumatic side and exchanges its heat with a counter flow of ambient temperature fluid from a reservoir or other source.
Owner:SUSTAINX
Generator with utility fault ride-through capability
InactiveUS20050122083A1Simplified generator torque command approachPowerfulBatteries circuit arrangementsWind motor controlControl systemWave shape
A wind powered turbine with low voltage ride-through capability. An inverter is connected to the output of a turbine generator. The generator output is conditioned by the inverter resulting in an output voltage and current at a frequency and phase angle appropriate for transmission to a three-phase utility grid. A frequency and phase angle sensor is connected to the utility grid operative during a fault on the grid. A control system is connected to the sensor and to the inverter. The control system output is a current command signal enabling the inverter to put out a current waveform, which is of the same phase and frequency as detected by the sensor. The control system synthesizes current waveform templates for all three-phases based on a sensed voltage on one phase and transmits currents to all three-phases of the electrical system based on the synthesized current waveforms.
Owner:UNITED TECH CORP
Method and apparatus for power generation using waste heat
InactiveUS20060112693A1High densityReduce flowSteam generation heating methodsSteam usePower stationEngineering
According to the present invention, a method and apparatus for generating power aboard a marine vessel is provided. The method comprises the steps of: (a) providing a Rankine Cycle device that includes at least one of each of an evaporator, a turbo-generator that includes a turbine coupled with an electrical generator, a condenser, and a refrigerant feed pump; (b) disposing the one or more evaporators within an exhaust duct of a power plant of the marine vessel; (c) operating the power plant; and (d) selectively pumping refrigerant through the Rankine Cycle device, wherein refrigerant exiting the evaporator powers the turbine, which in turn powers the generator to produce power.
Owner:CARRIER CORP
Energy recovery system using an organic rankine cycle
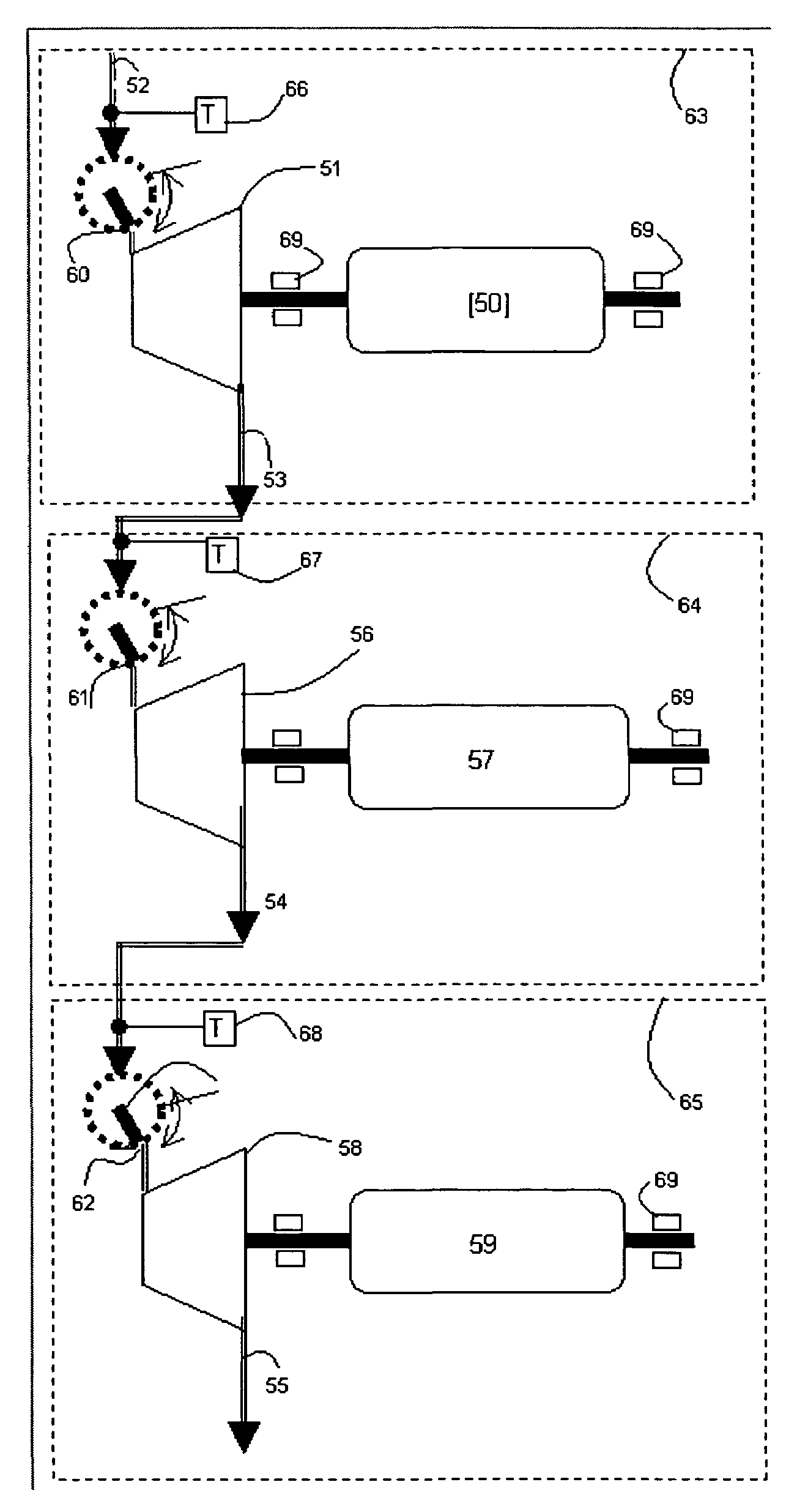
ActiveUS20110016863A1Improve energy recoveryDifferent temperatureSteam useGas turbine plantsThermal energyHeat flow
A thermodynamic system for waste heat recovery, using an organic rankine cycle is provided which employs a single organic heat transferring fluid to recover heat energy from two waste heat streams having differing waste heat temperatures. Separate high and low temperature boilers provide high and low pressure vapor streams that are routed into an integrated turbine assembly having dual turbines mounted on a common shaft. Each turbine is appropriately sized for the pressure ratio of each stream.
Owner:CUMMINS INTPROP INC
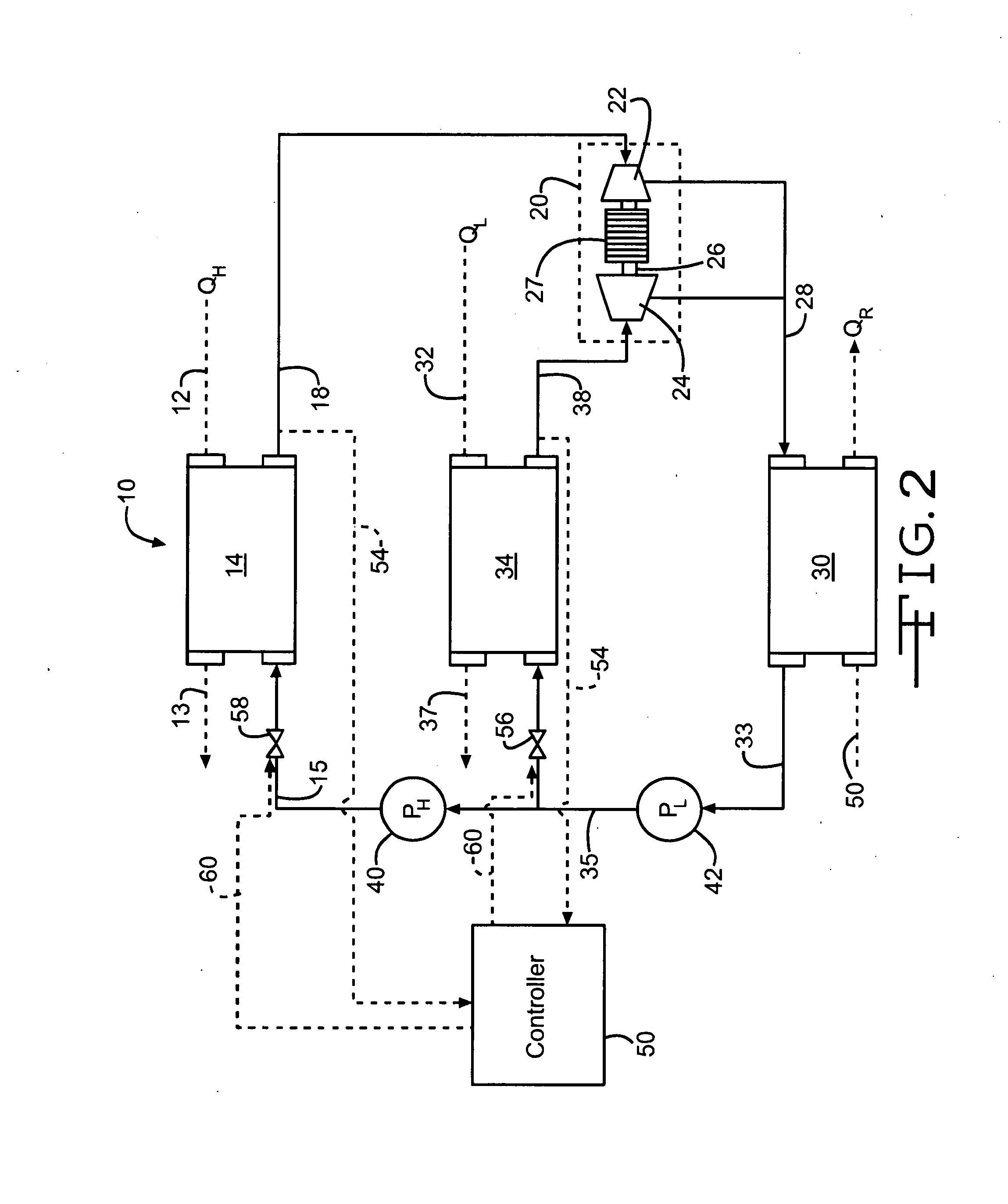
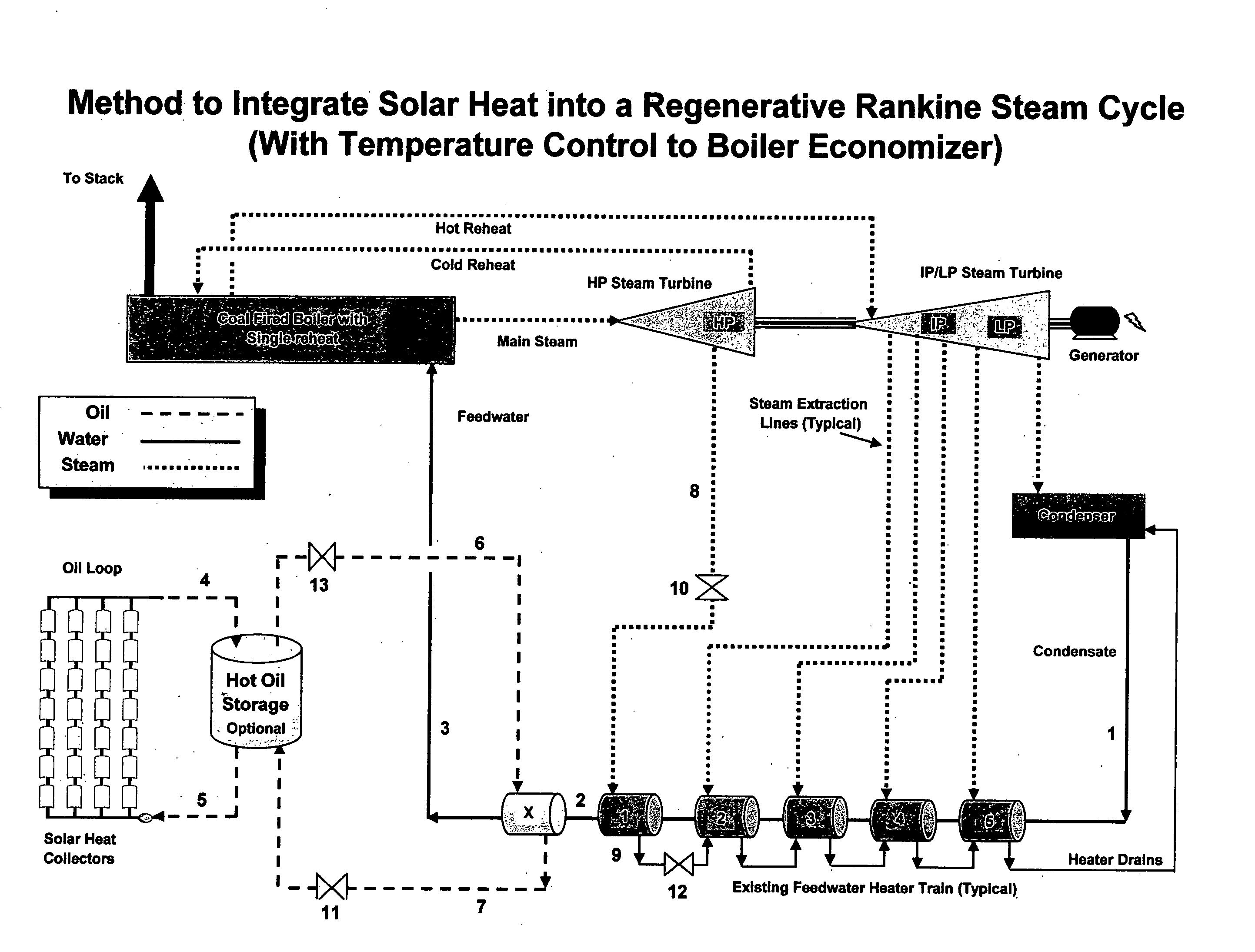
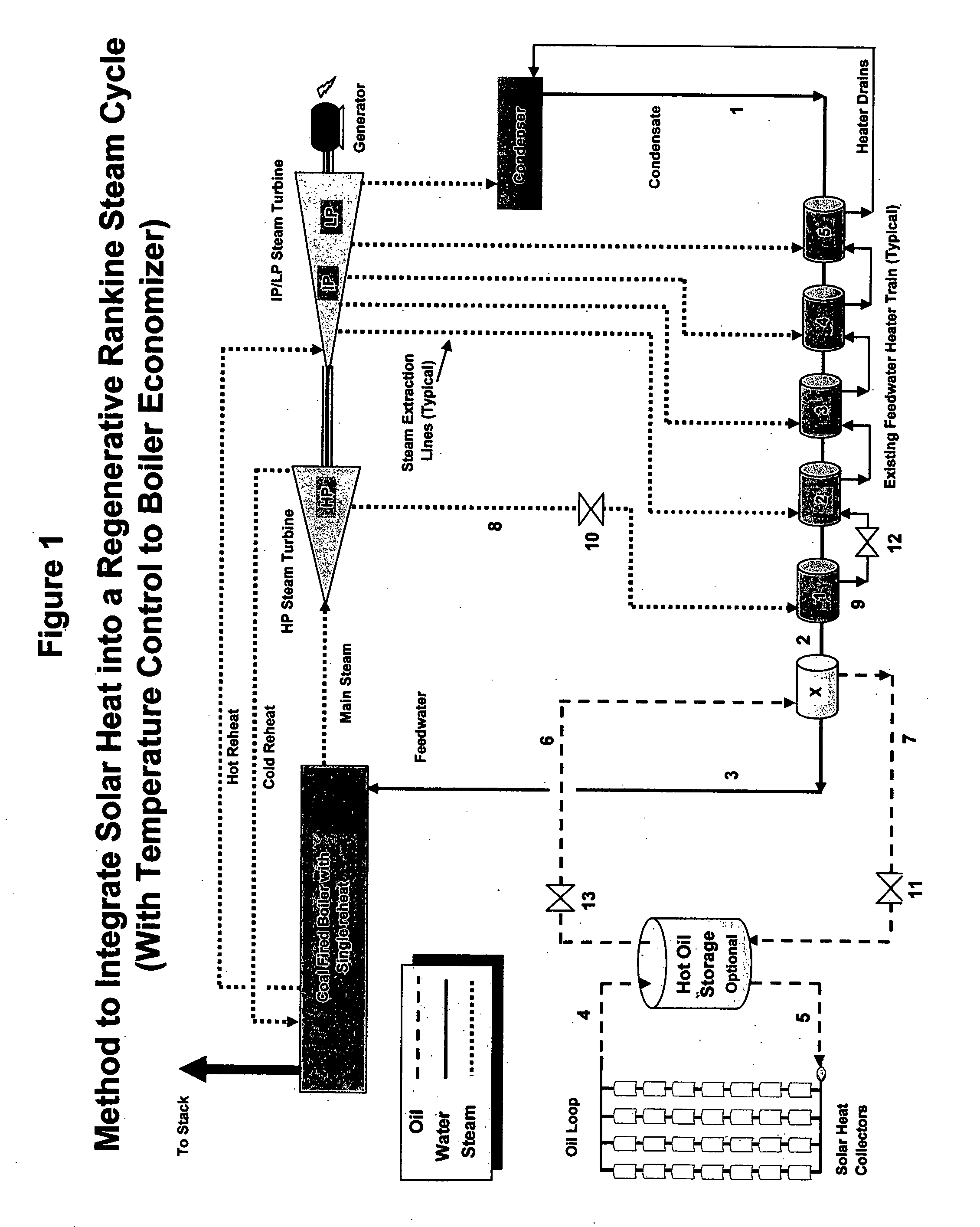
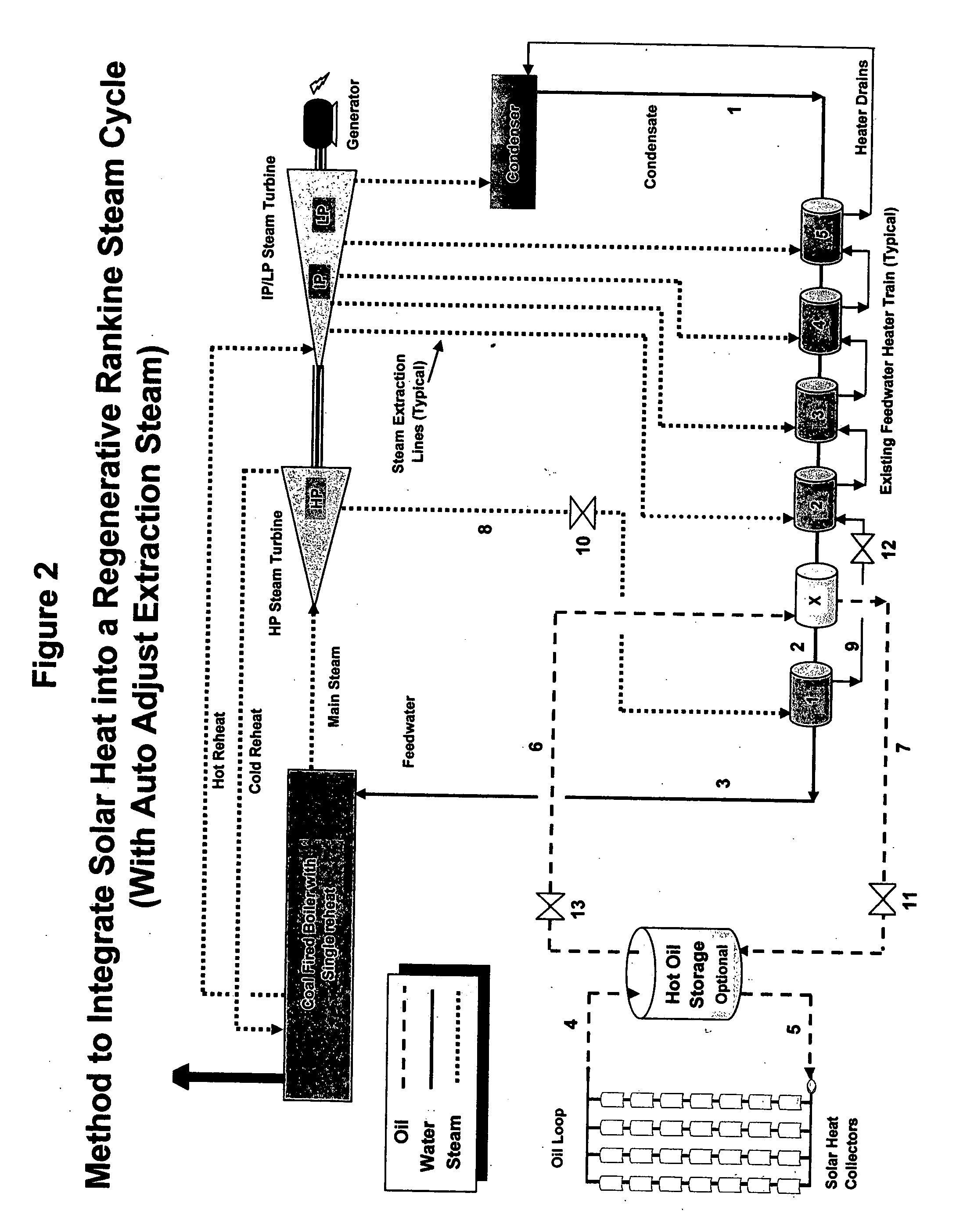
Method and system integrating solar heat into a regenerative rankine steam cycle
InactiveUS20060266039A1High solar system efficiencySmall temperature differenceAuxillary drivesFrom solar energyThermal energyClosed loop
A method to integrate collected solar thermal energy into the feedwater system of a Rankine cycle power plant is disclosed. This novelty uses a closed loop, single phase fluid system to collect both the solar heat and to provide the heat input into the feedwater stream of a regenerative Rankine cycle. One embodiment of this method of integrating solar energy into a regenerative Rankine power plant cycle, such as a coal power plant, allows for automatic balancing of the steam extraction flows and does not change the temperature of the feedwater to the boiler. The concept, depending on the application, allows for the spare turbine capacity normally available in a coal plant to be used to produce incremental capacity and energy that is powered by solar thermal energy. By “piggybacking” on the available components and infrastructure of the host Rankine cycle power plant, considerable cost savings are achieved resulting in lower solar produced electricity costs.
Owner:MARKRON TECH
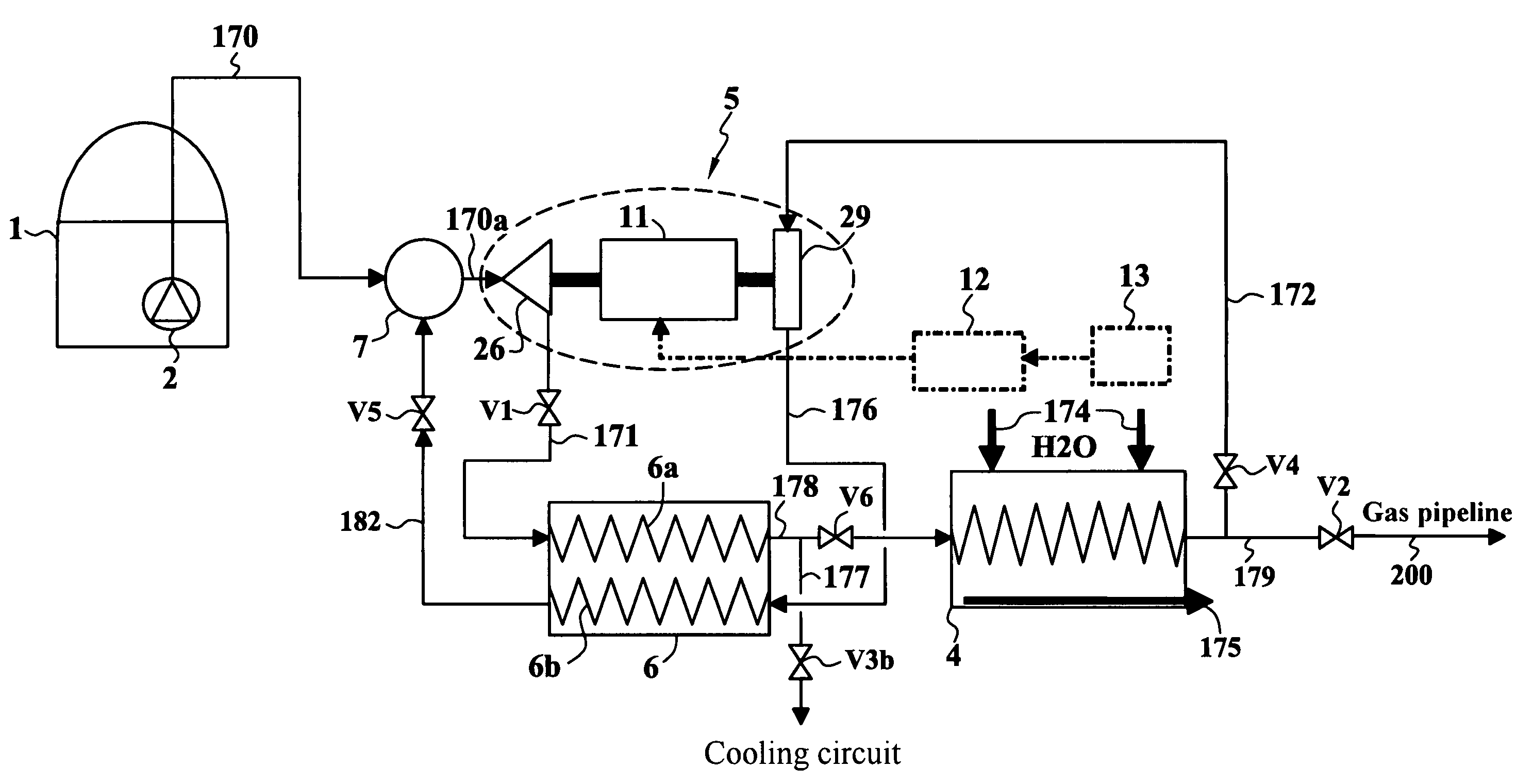
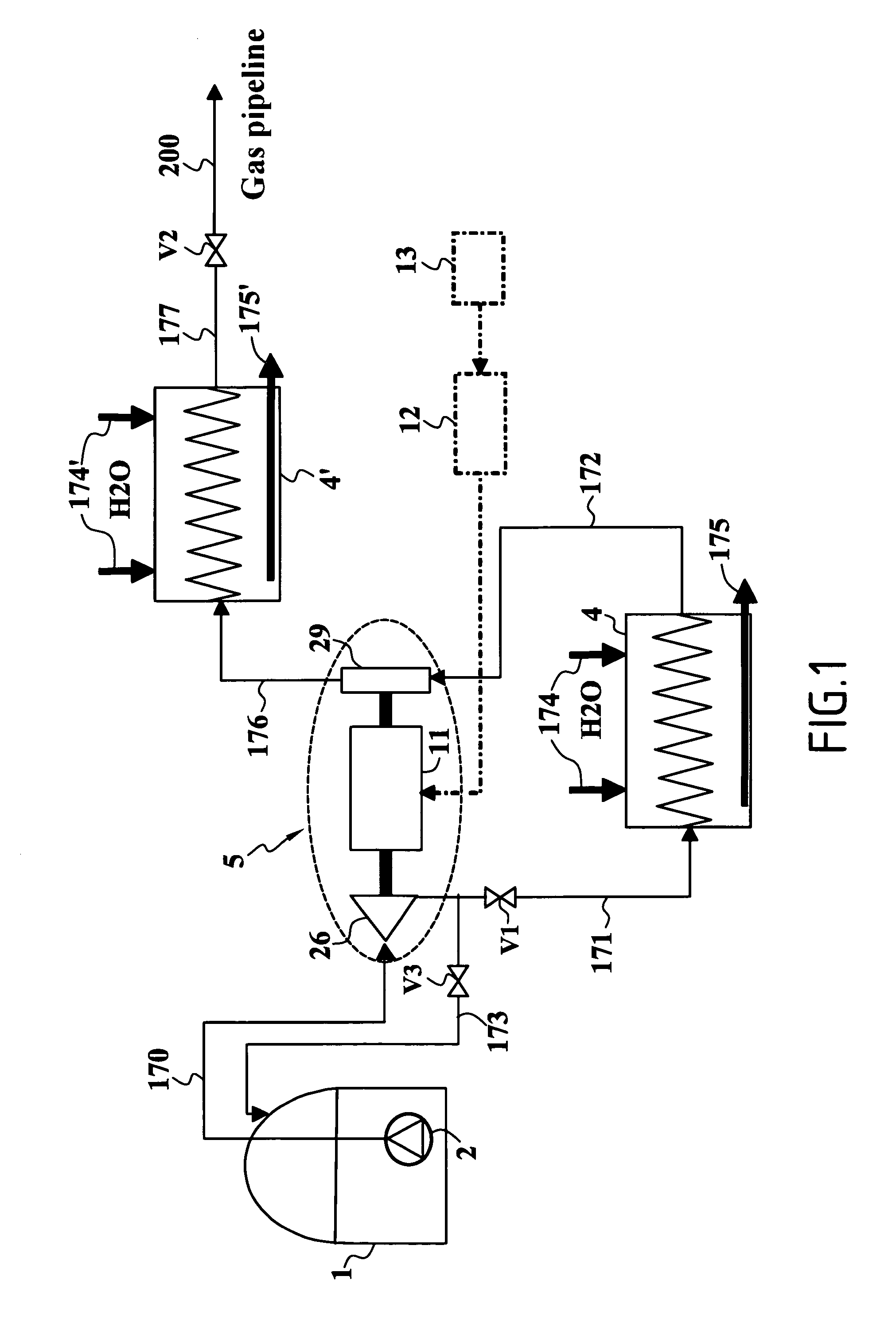
Desalination method and desalination apparatus
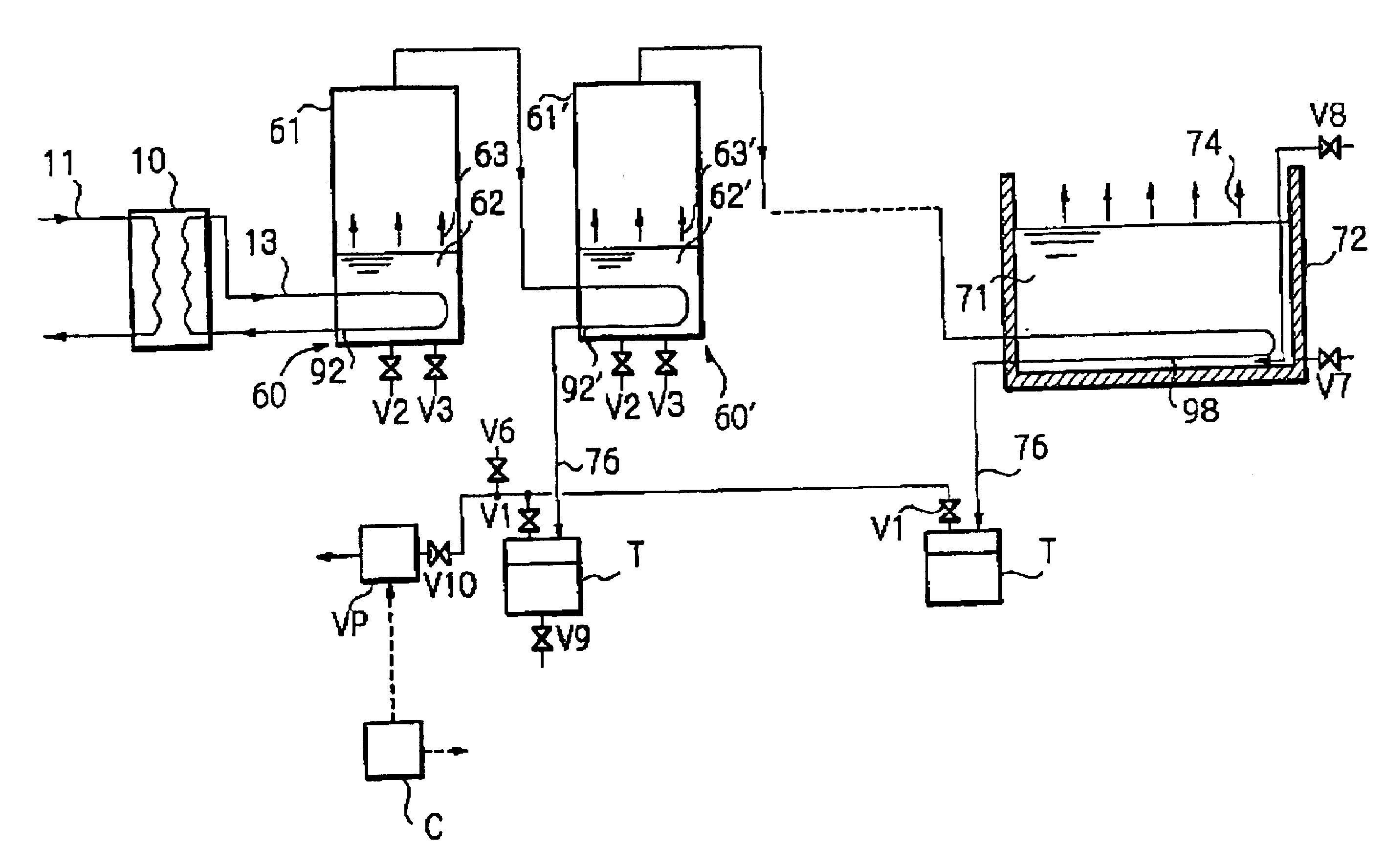
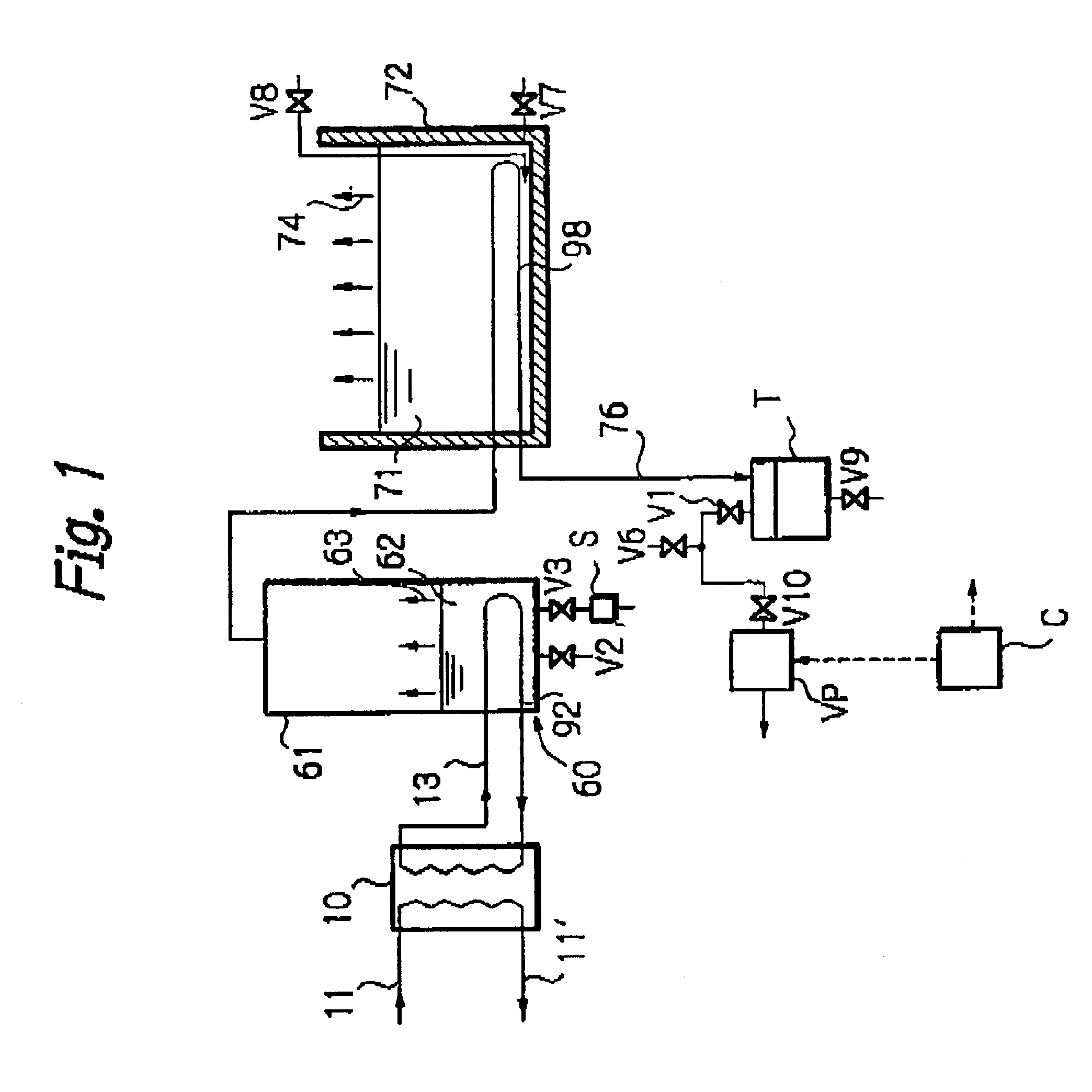
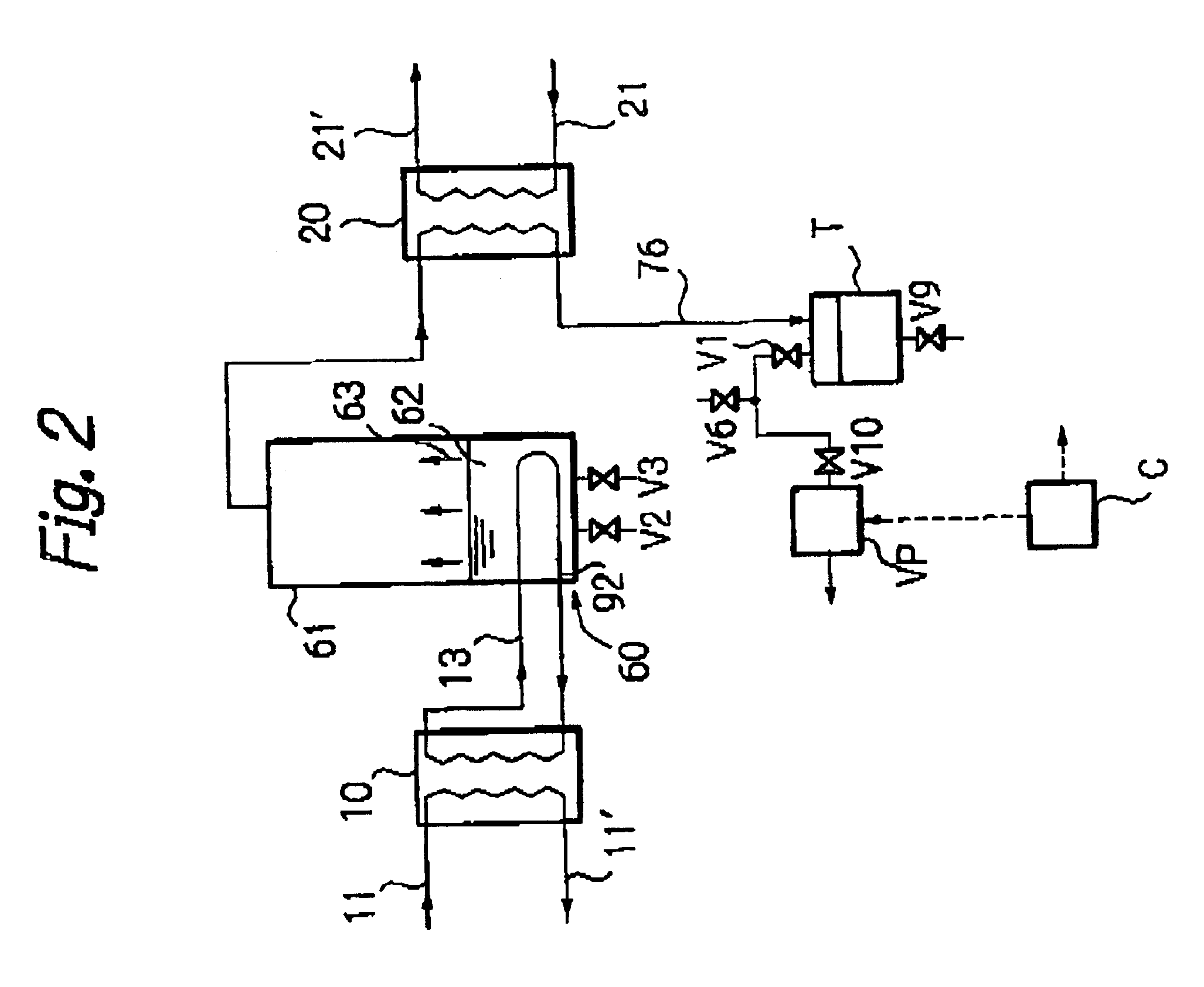
InactiveUS6833056B1Number of stage increasingIncrease the number ofAuxillariesGeneral water supply conservationDesalinationDistilled water
A desalination apparatus capable of obtaining fresh water stably at low cost by utilizing low-temperature waste, wherein the desalination apparatus including a heat exchanger 92 cooperating with an evaporation can 60 so as to subject a low-temperature waste heat 11 and raw water 62 in the evaporation can 60 to heat exchange and generate water vapor 63 in the evaporation can 60; a condenser 98 cooperating with a raw water tank 72 so as to receive the water vapor 63 from the evaporation can 60, cool the water vapor 63 by subjecting the water vapor 63 and raw water 71 in the raw water tank 72 to heat exchange and obtain distilled water 76; a distilled water tank for storing the distilled water 76; vacuum means for evacuating the evaporation can 60 and depressurizing the inside thereof so as to promote generation of water vapor 63 in the evaporation can 60; and raw water supply means for supplying raw water to the evaporation can.
Owner:EBARA CORP
High-temperature dual-source organic Rankine cycle with gas separations
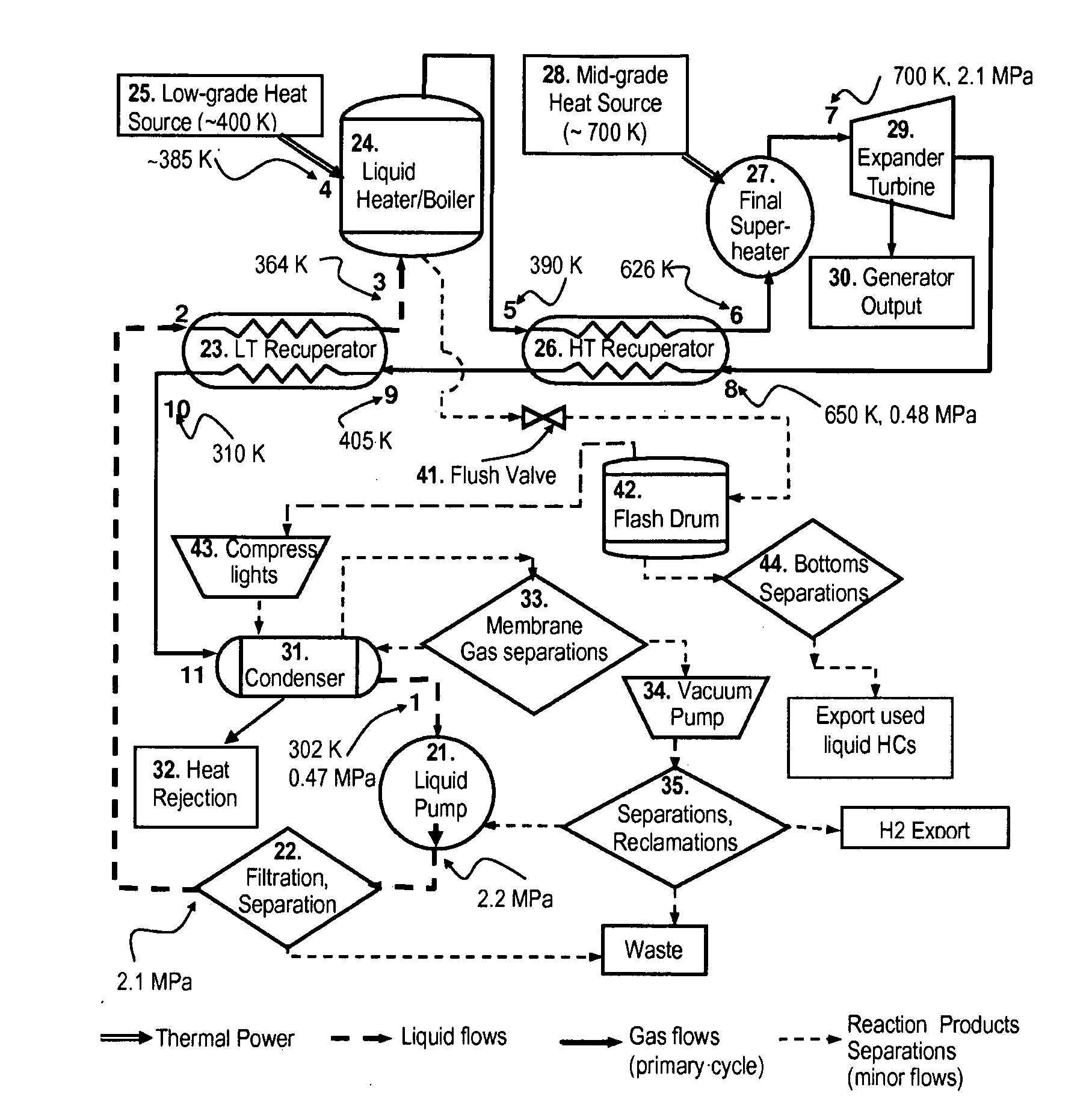
InactiveUS20100300093A1Increase temperatureMinimize timeAuxillary drivesInternal combustion piston enginesWorking fluidOrganic Rankine cycle
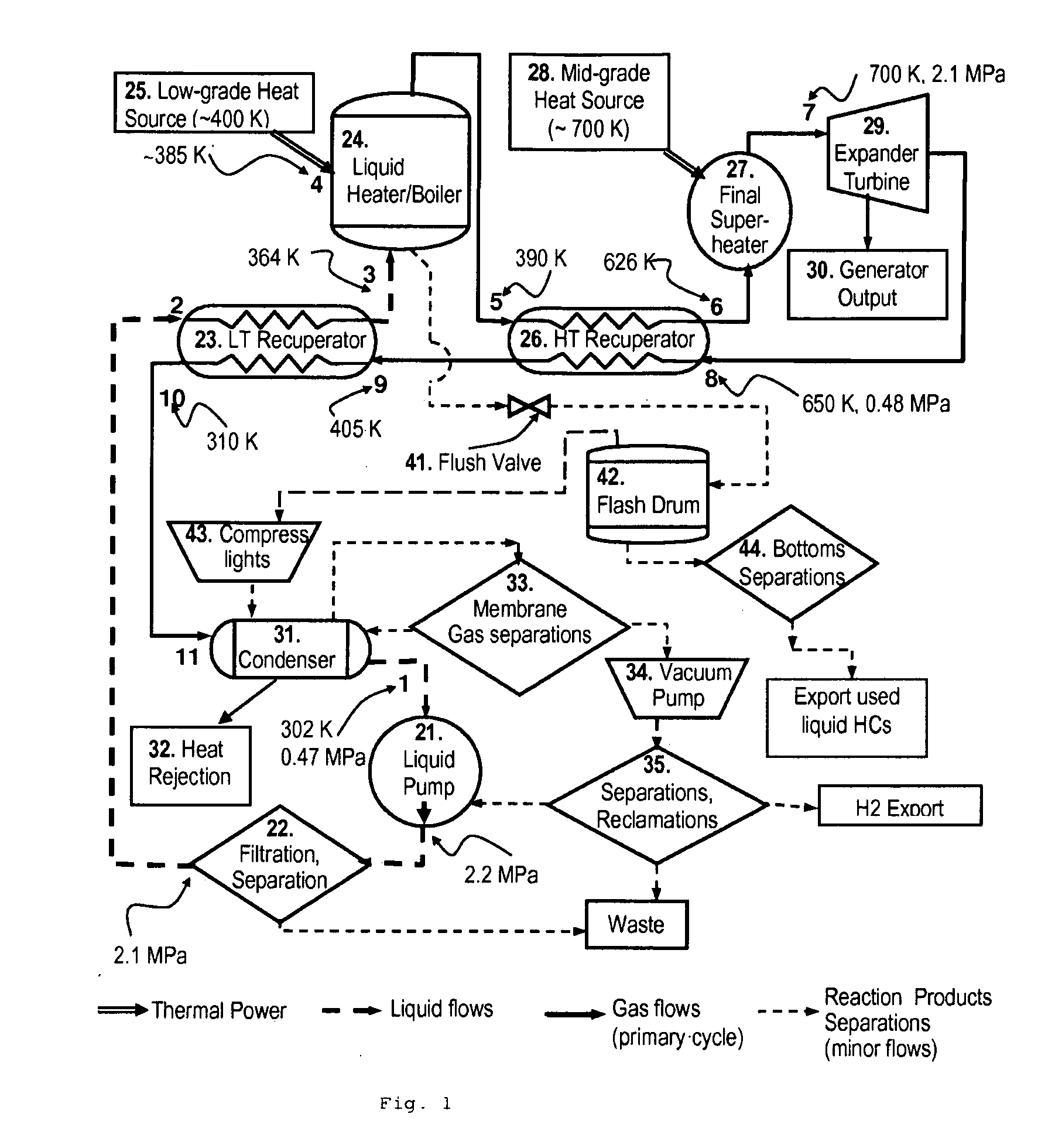
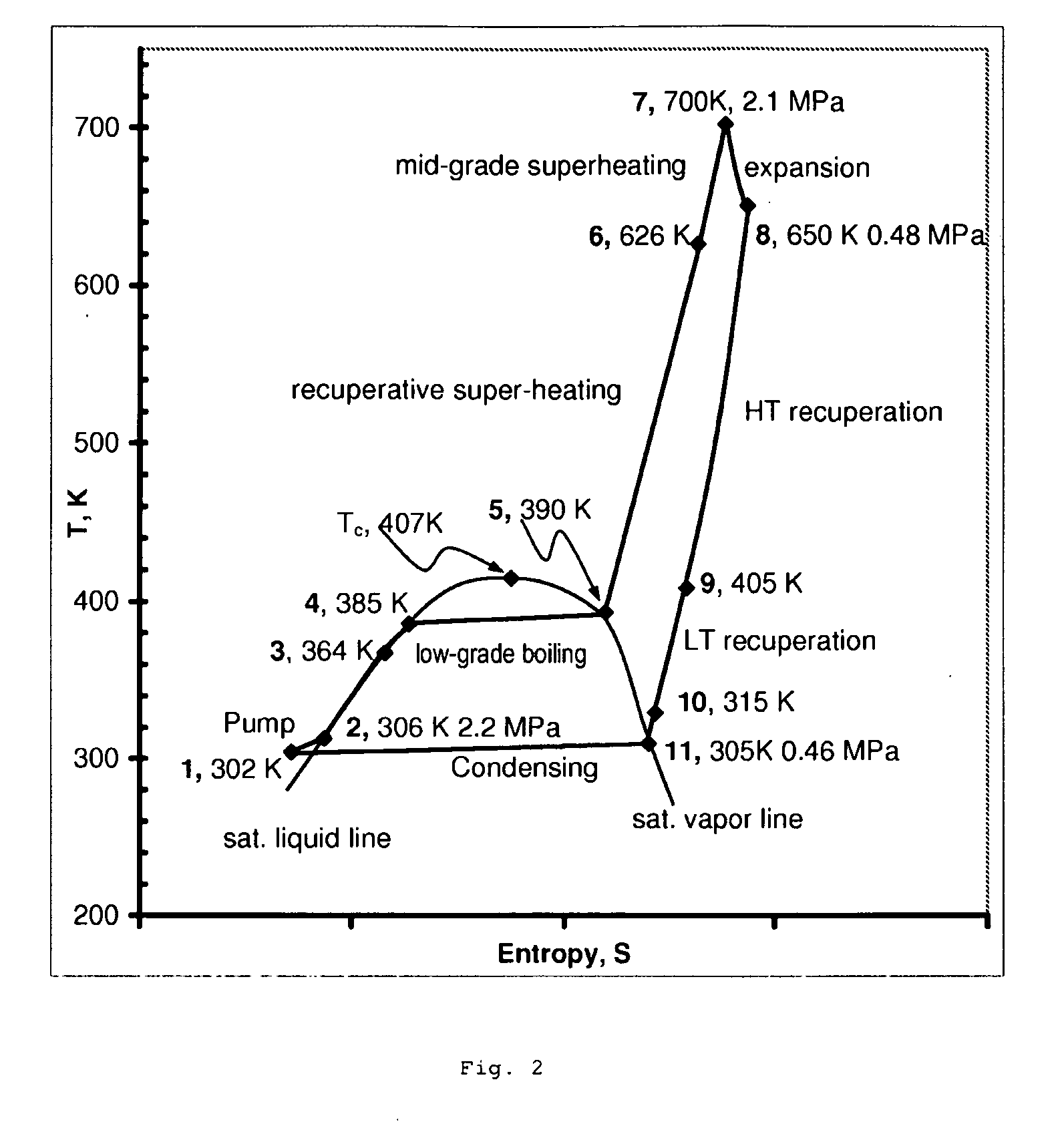
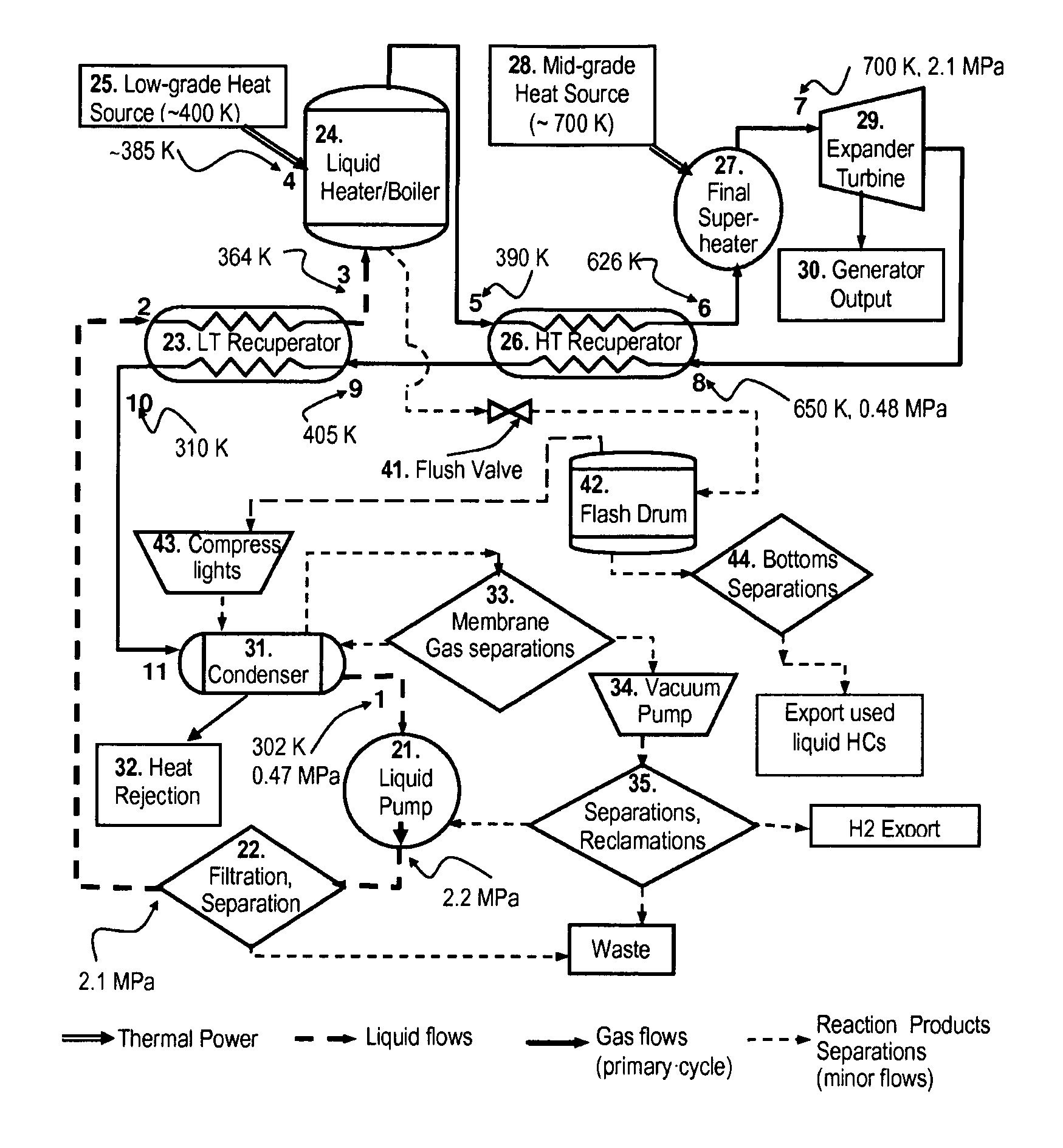
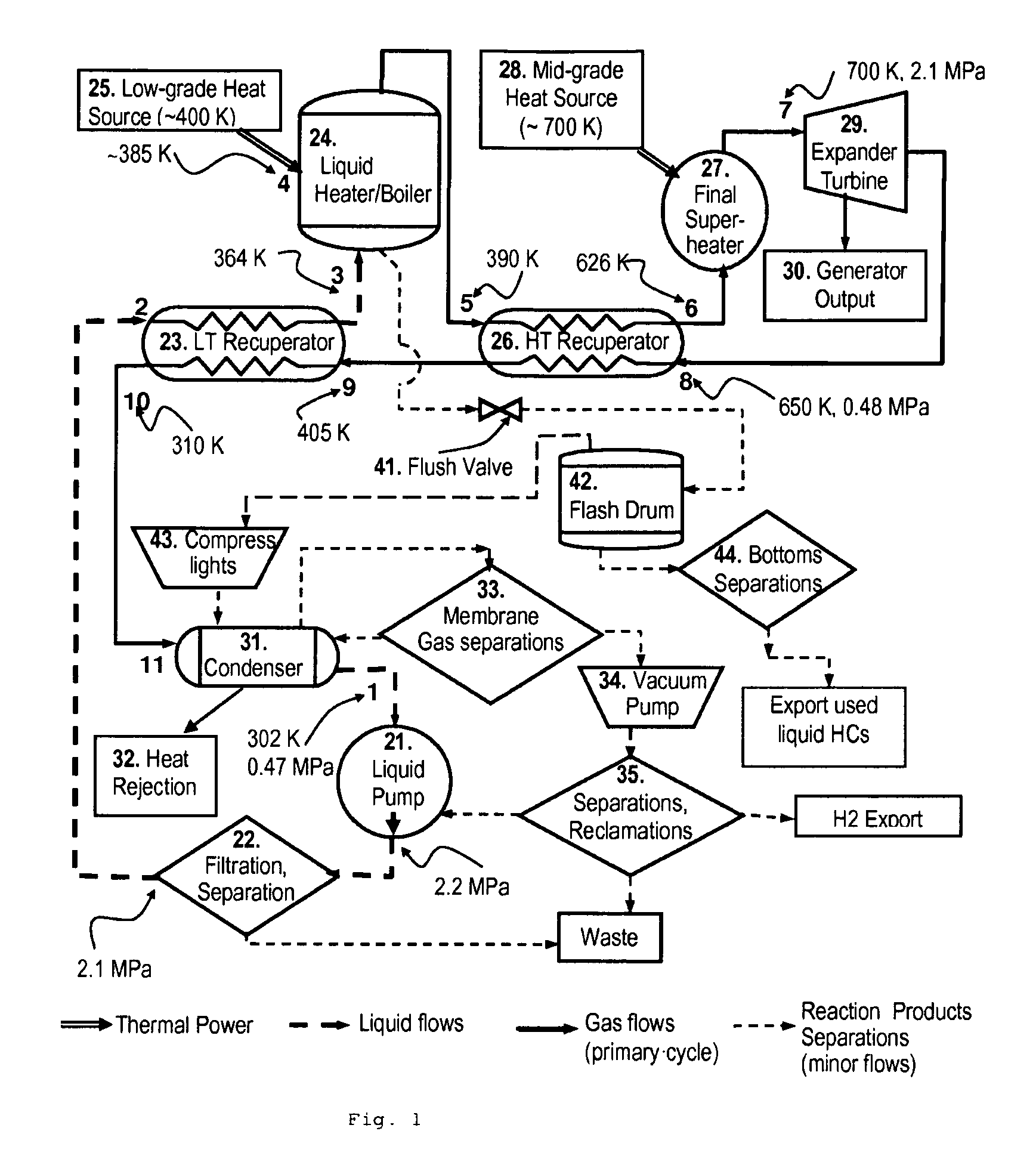
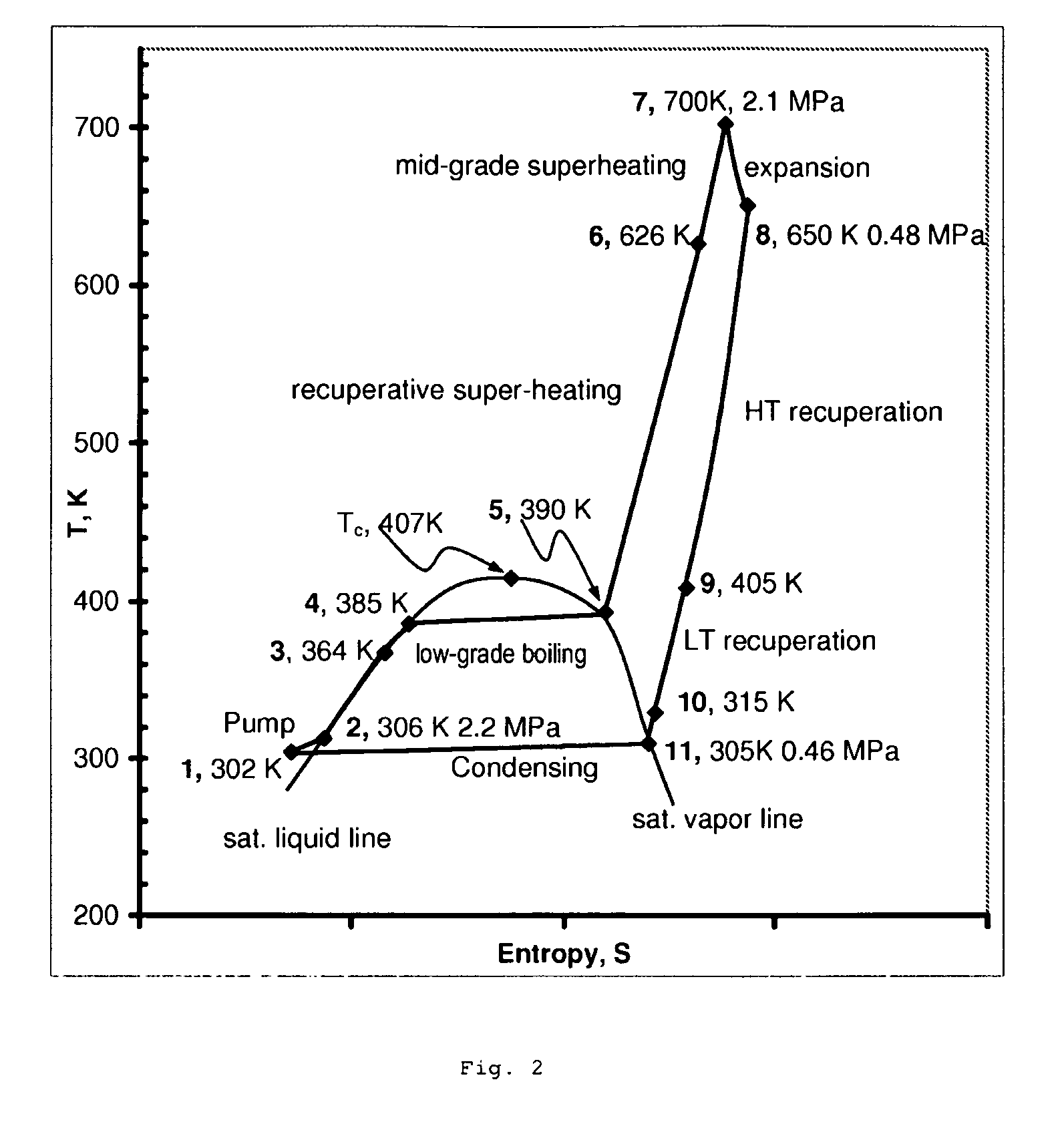
In a dual-source organic Rankine cycle (DORC), the condensed and slightly sub-cooled working fluid at near ambient temperature (˜300 K) and at low-side pressure (0.1 to 0.7 MPa) is (1) pumped to high-side pressure (0.5-5 MPa), (2) pre-heated in a low-temperature (LT) recuperator, (3) boiled using a low-grade heat source, (4) super-heated in a high-temperature (HT) recuperator to a temperature close to the expander turbine exhaust temperature using this exhaust vapor enthalpy, (5) further super-heated to the turbine inlet temperature (TIT) using a mid-grade heat source, (6) expanded through a turbine expander to the low-side pressure, (7) cooled through the HT recuperator, (8) cooled through the LT recuperator, (9) mostly liquefied and slightly subcooled in a condenser, and (10) the condensed portion is returned to the pump to repeat this cycle.
Owner:DOTY SCI
Drive Unit with Cooling Circuit and Separate Heat Recovery Circuit
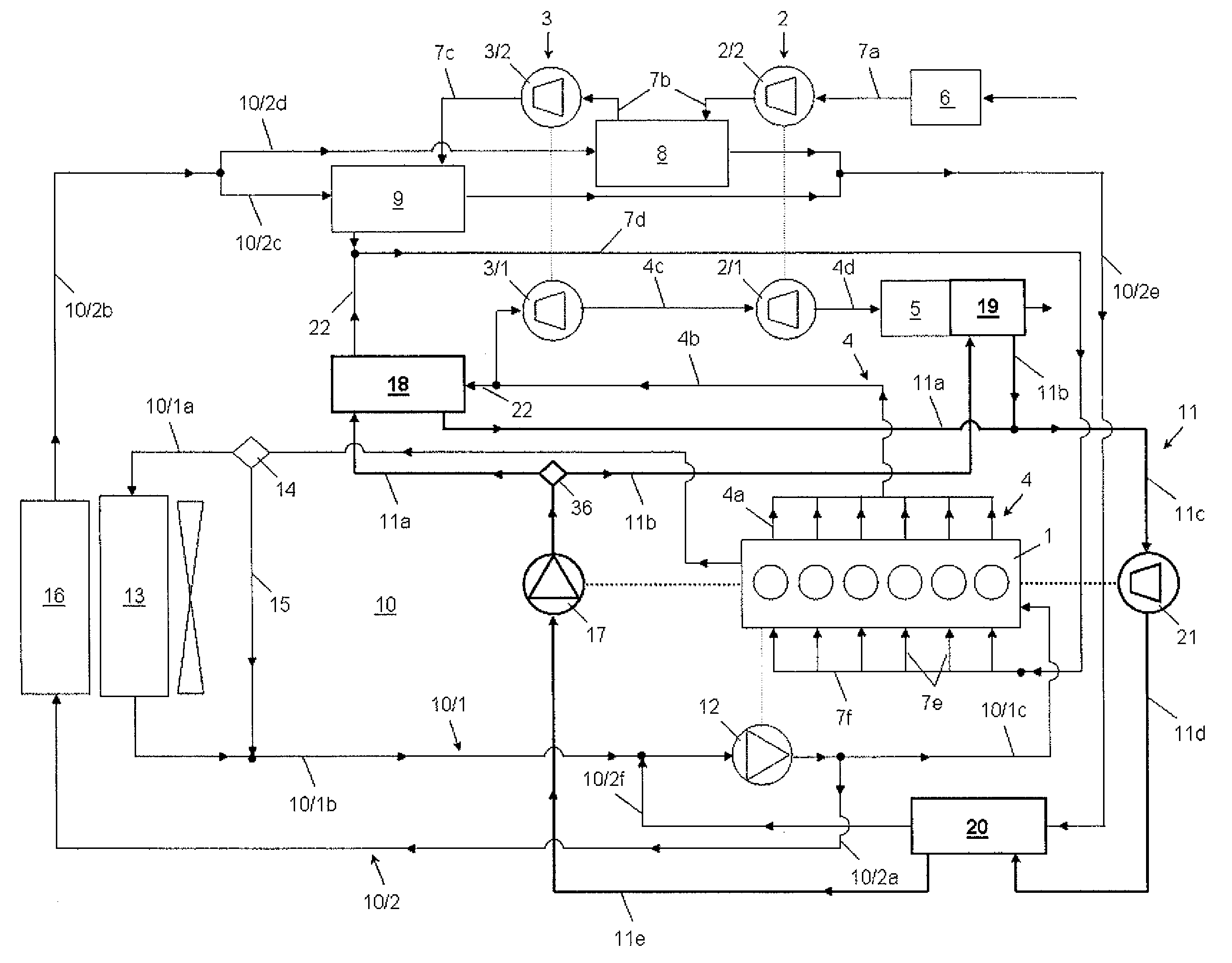
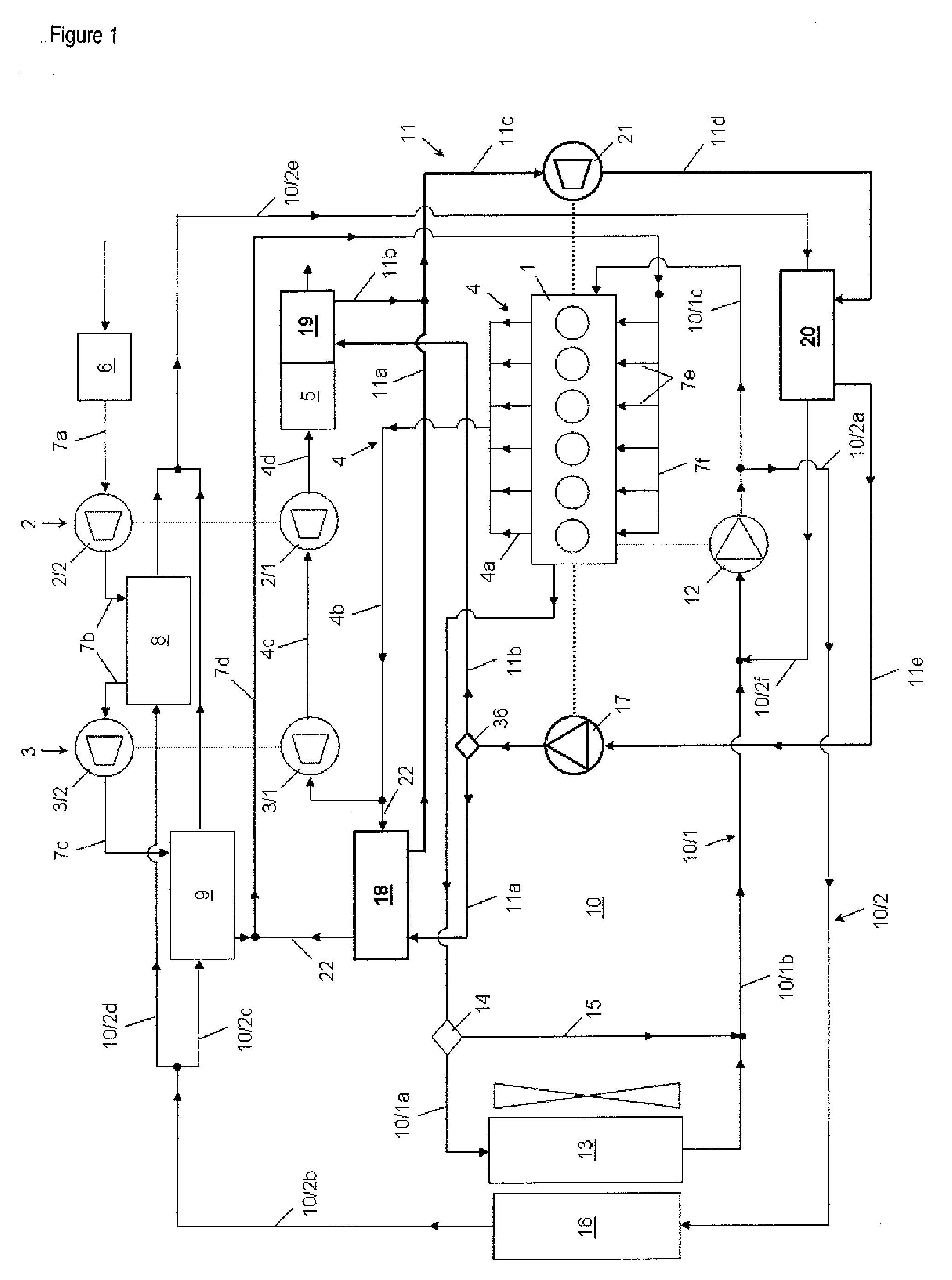
ActiveUS20100139626A1Improve cooling effectEfficient heat recoveryCoolant flow controlNon-fuel substance addition to fuelEngineeringInternal combustion engine
A cooling circuit and an independent heat recovery circuit are associated with an internal combustion engine. A coolant is circulated a pump in a first and a second cooling sub-circuit. An increase in pressure in a work medium is achieved within the heat recovery circuit by a pump. This work medium is changed from liquid aggregate state to vaporous aggregate state and back to the liquid aggregate state in heat exchangers. This work medium is divided after the pump into two parallel partial flows and is changed into vaporous state in a first parallel branch in an EGR heat exchanger through which recycle exhaust gas flows and in a second parallel branch in an exhaust gas heat exchanger through flow exhaust gas downstream of the low-pressure turbine flows. This vaporous work medium is then fed to an expander and is then conducted through a cooled condenser and, liquefied again.
Owner:MAN TRUCK & BUS AG
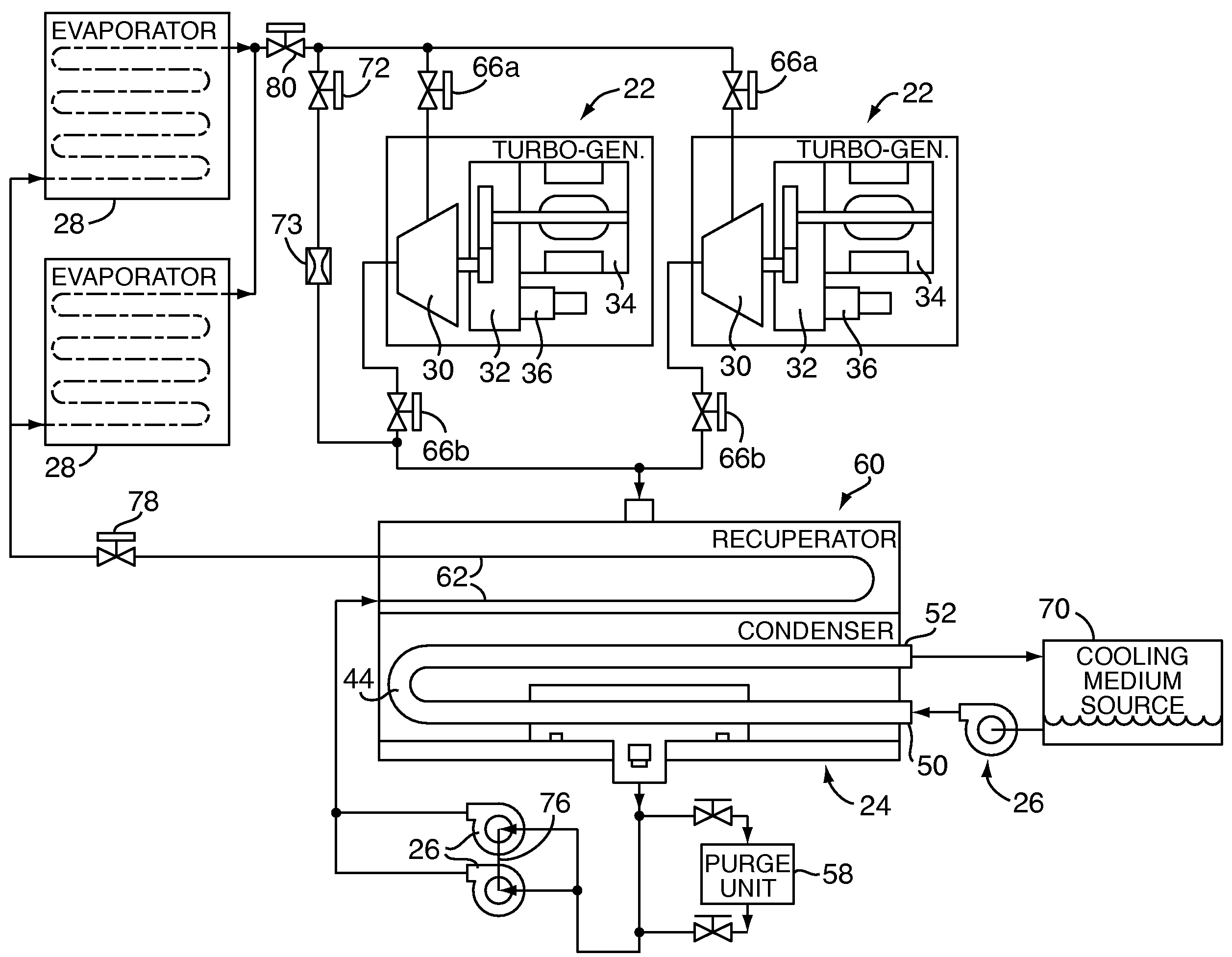
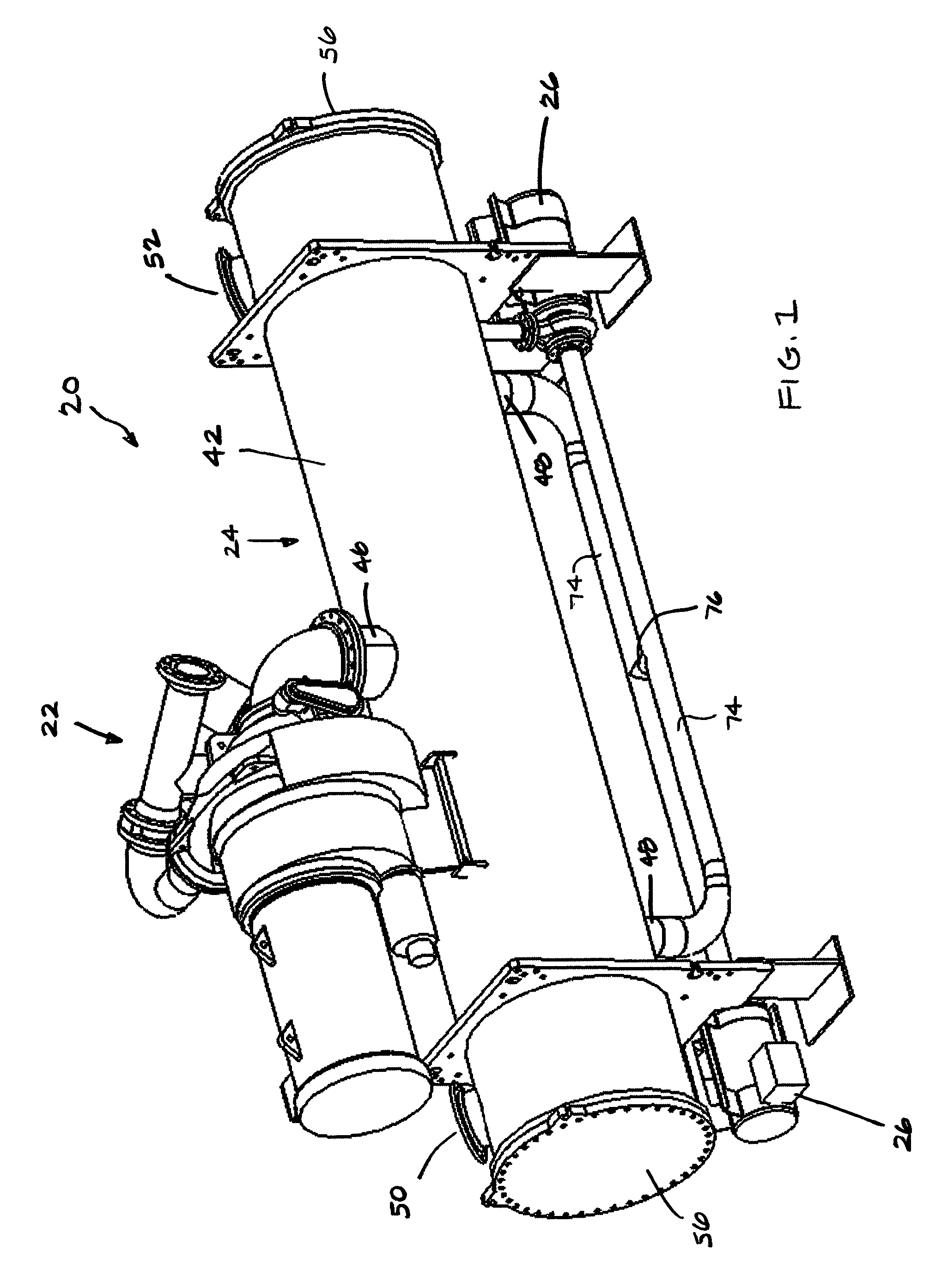
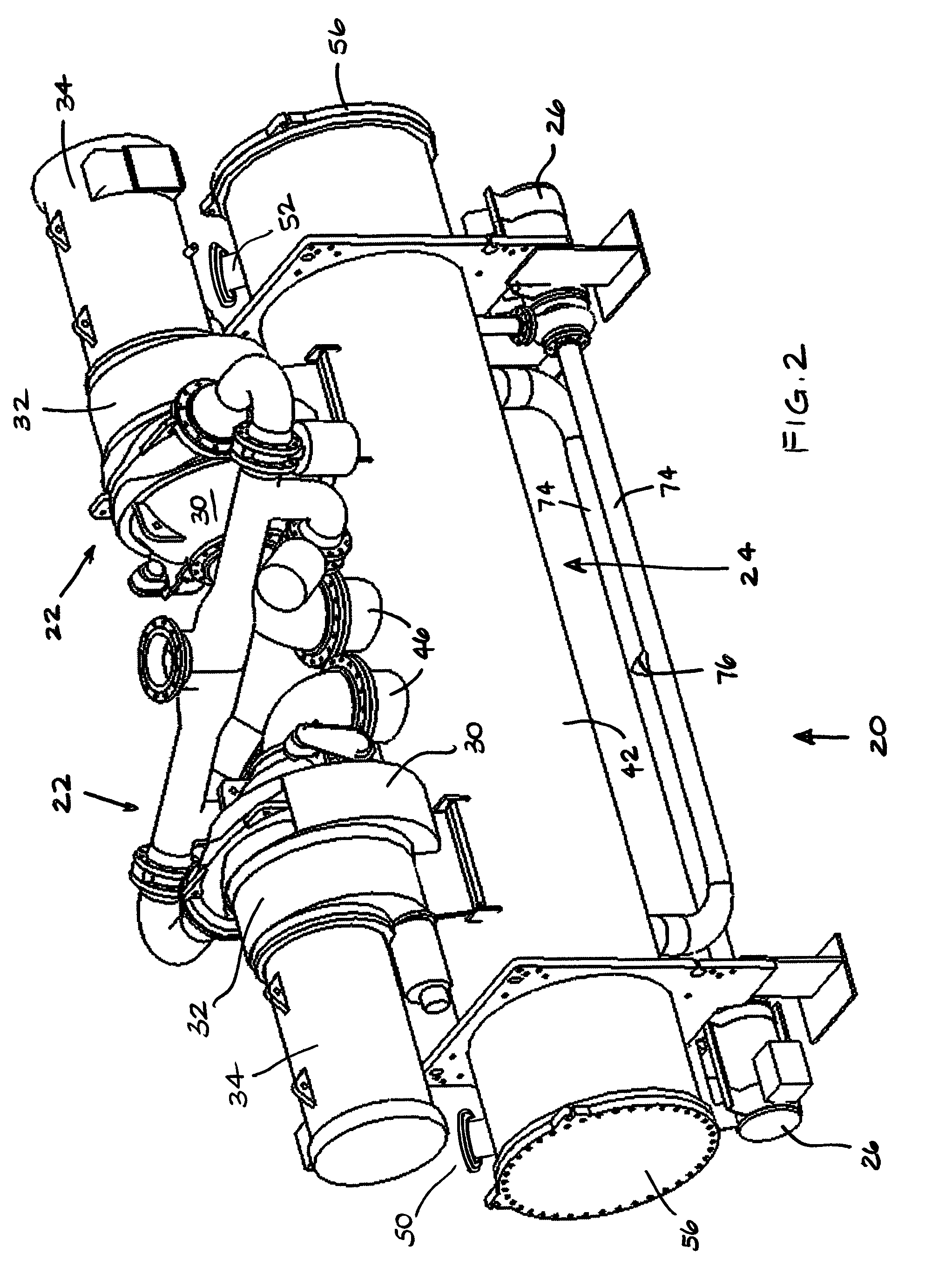
Rankine cycle device having multiple turbo-generators
A method for generating power, comprising the steps of: a) providing a Rankine Cycle device that includes a plurality of turbo-generators, each including a turbine coupled with an electrical generator, and at least one of each of an evaporator, a condenser, and a refrigerant feed pump; b) disposing the one or more evaporators within an exhaust duct of a power plant of a marine vessel; c) operating the power plant; and d) selectively pumping refrigerant through the Rankine Cycle device.
Owner:NANJING TICA AIR CONDITIONING CO LTD +1
High-temperature dual-source organic Rankine cycle with gas separations
InactiveUS8046999B2Increase temperatureMinimize timeAuxillary drivesFrom solar energyWorking fluidOrganic Rankine cycle
In a dual-source organic Rankine cycle (DORC), the condensed and slightly sub-cooled working fluid at near ambient temperature (˜300 K) and at low-side pressure (0.1 to 0.7 MPa) is (1) pumped to high-side pressure (0.5-5 MPa), (2) pre-heated in a low-temperature (LT) recuperator, (3) boiled using a low-grade heat source, (4) super-heated in a high-temperature (HT) recuperator to a temperature close to the expander turbine exhaust temperature using this exhaust vapor enthalpy, (5) further super-heated to the turbine inlet temperature (TIT) using a mid-grade heat source, (6) expanded through a turbine expander to the low-side pressure, (7) cooled through the HT recuperator, (8) cooled through the LT recuperator, (9) mostly liquefied and slightly subcooled in a condenser, and (10) the condensed portion is returned to the pump to repeat this cycle.
Owner:DOTY SCI
Apparatus for producing water onboard of a craft driven by a power plant
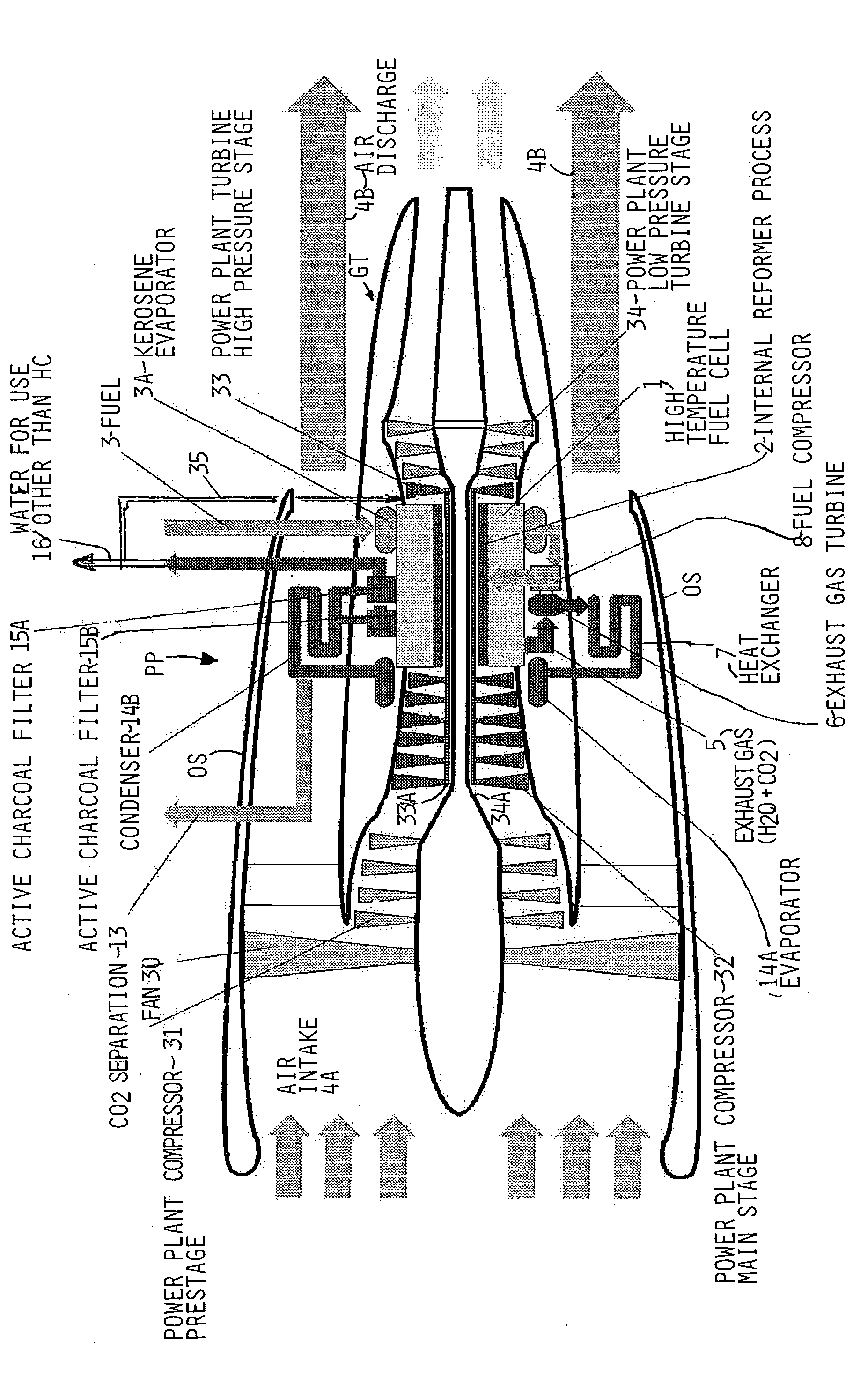
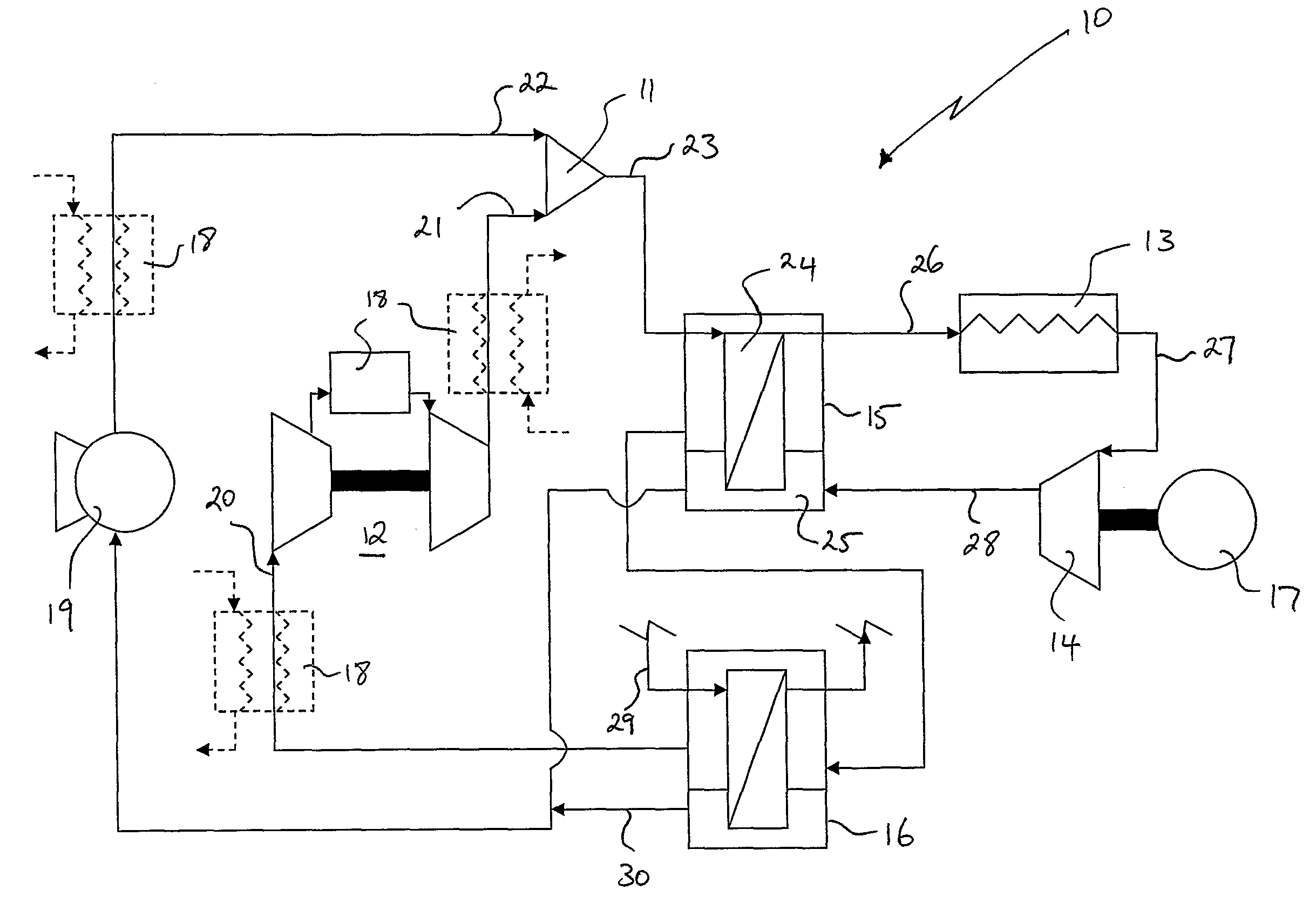
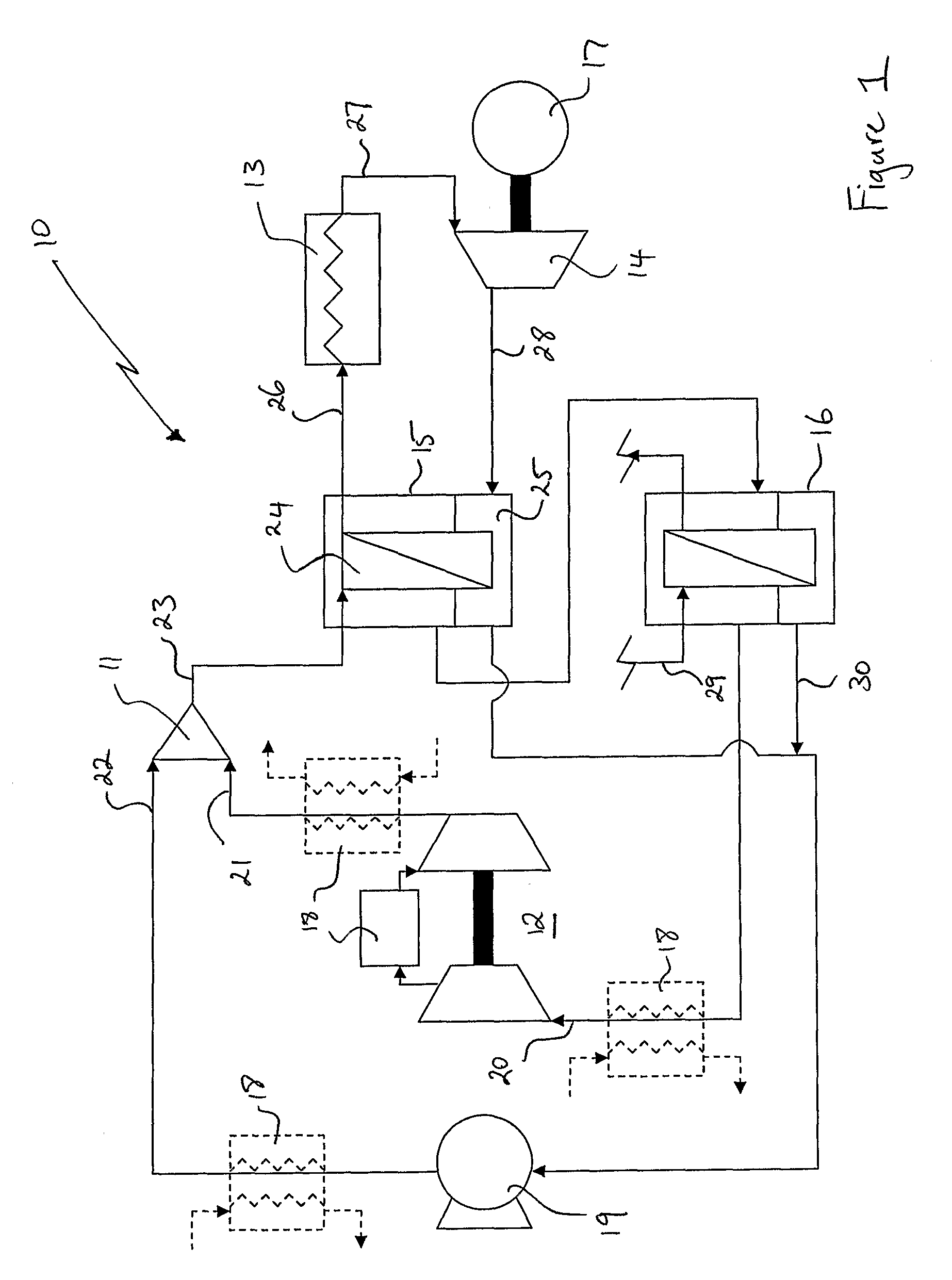
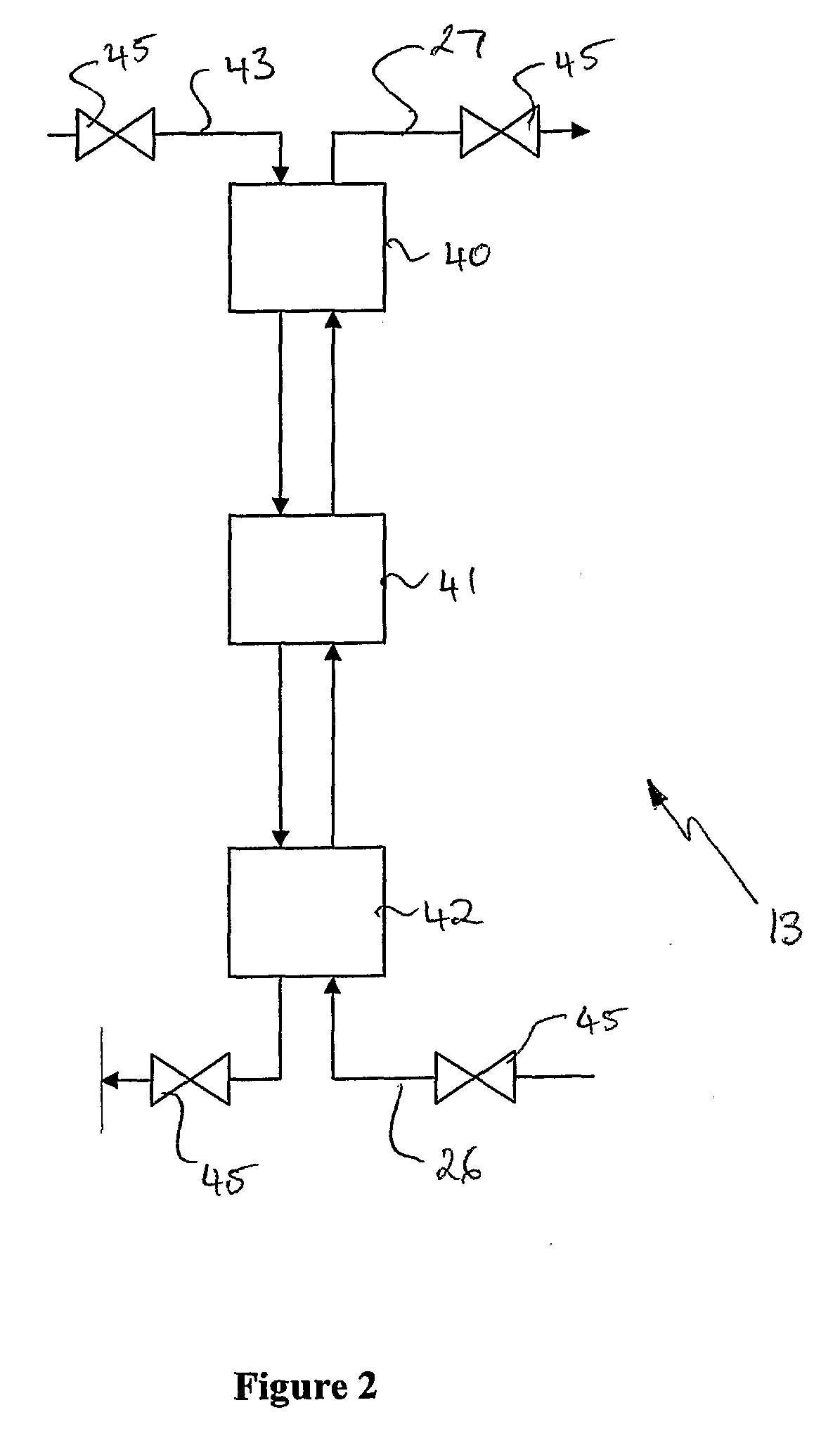
InactiveUS20040040312A1Improve overall utilizationFlexibility in distributionFuel cells groupingFuel cell auxillariesCombustion chamberEngineering
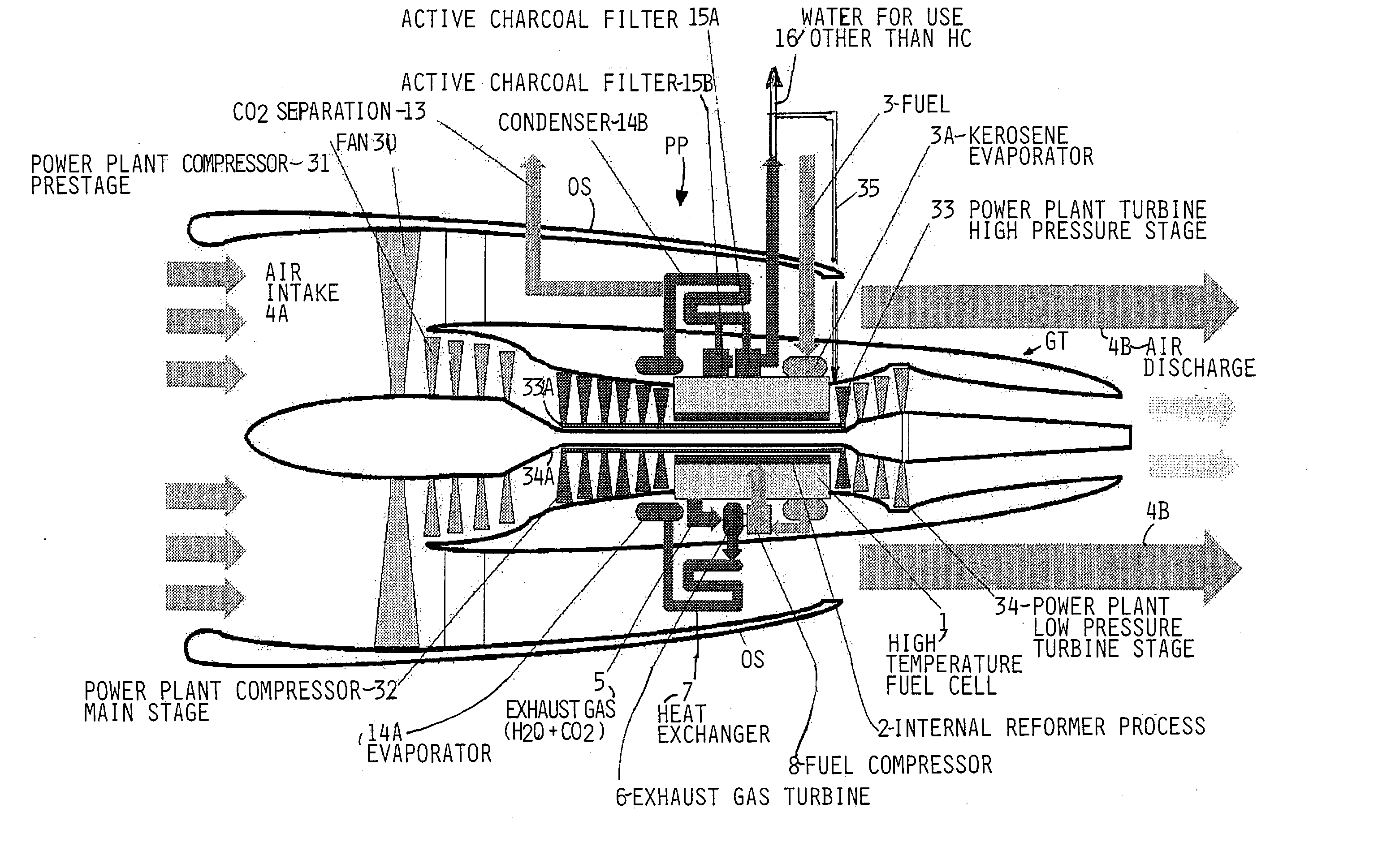
Water is generated onboard of a craft such as an aircraft or in a self-contained stationary system by partially or completely integrating a water generating unit into a power plant of the craft or system. The water generating unit includes one or more high temperature fuel cells which partially or completely replace the combustion chamber or chambers of the power plant. A reformer process is integrated into the high temperature fuel cell which is arranged between, on the one hand, a fan (30) and power plant compressor stages (31, 32) and, on the other hand, power plant turbine stages (33, 34). These power plant stages may be provided in such redundant numbers that safety and redundancy requirements are satisfied.
Owner:AIRBUS OPERATIONS GMBH
Heat Engine System
InactiveUS20100287934A1Increase temperatureImprove heat transfer performanceHeat storage plantsSteam useEnergy transferWorking fluid
A heat engine system for producing work by expanding a working fluid comprising first and second components, the system comprising, an apparatus for combining the second component of the working fluid as a liquid with the first component, the first component being a gas throughout the system, a compressor for compressing the first component, a pump for compressing at least most of the second component, a heater for heating the first and second components, an expander for expanding the first and second components to produce the work, and a recuperator for transferring at least some of the energy of the working fluid from the outlet of the expander, to the working fluid from the outlet of the apparatus, wherein a substantial portion of the energy transferred in the recuperator is at least a portion of the latent heat of the second component from the outlet of the expander.
Owner:COMMONWEALTH SCI & IND RES ORG +1
Power generation methods and systems
A closed loop system for generating mechanical energy at high efficiencies from hydrogen, fossil fuels, bio-fuels, solar or other renewable and recoverable energy sources. The system can have a heating source, a superheater, an expander, a receiver, a condenser, vacuum pump, or absorber, a desorber, and regenerator with pumps and controls. The heating source and superheater are used to heat a working fluid (including ammonia, other refrigerants, a combination of refrigerants, or steam). A positive displacement liquid / vapor expander expands the heated working fluid to the near saturated or saturated state utilizing a reduced pressure, low-pressure, or sub-atmospheric exhaust sink. A condenser, vacuum pump, or absorber is used to generate the reduced pressure, low pressure, or sub-atmospheric sink. The desorber is used to reconstitute inlet vapor (for reuse) and the regenerator recovers heat generated by the process. The system can generate mechanical energy (or power) which can be used to drive a wide range of mechanical systems (including pumps, compressors, vehicles, conveyances, or other similar mechanical devices); or used to drive an electrical generator to meet electrical power needs-for residences, businesses or office buildings, or commercial and industrial applications. The system can supply electrical energy to power grids, and can be an alternative to power generation plants.
Owner:RES SCI
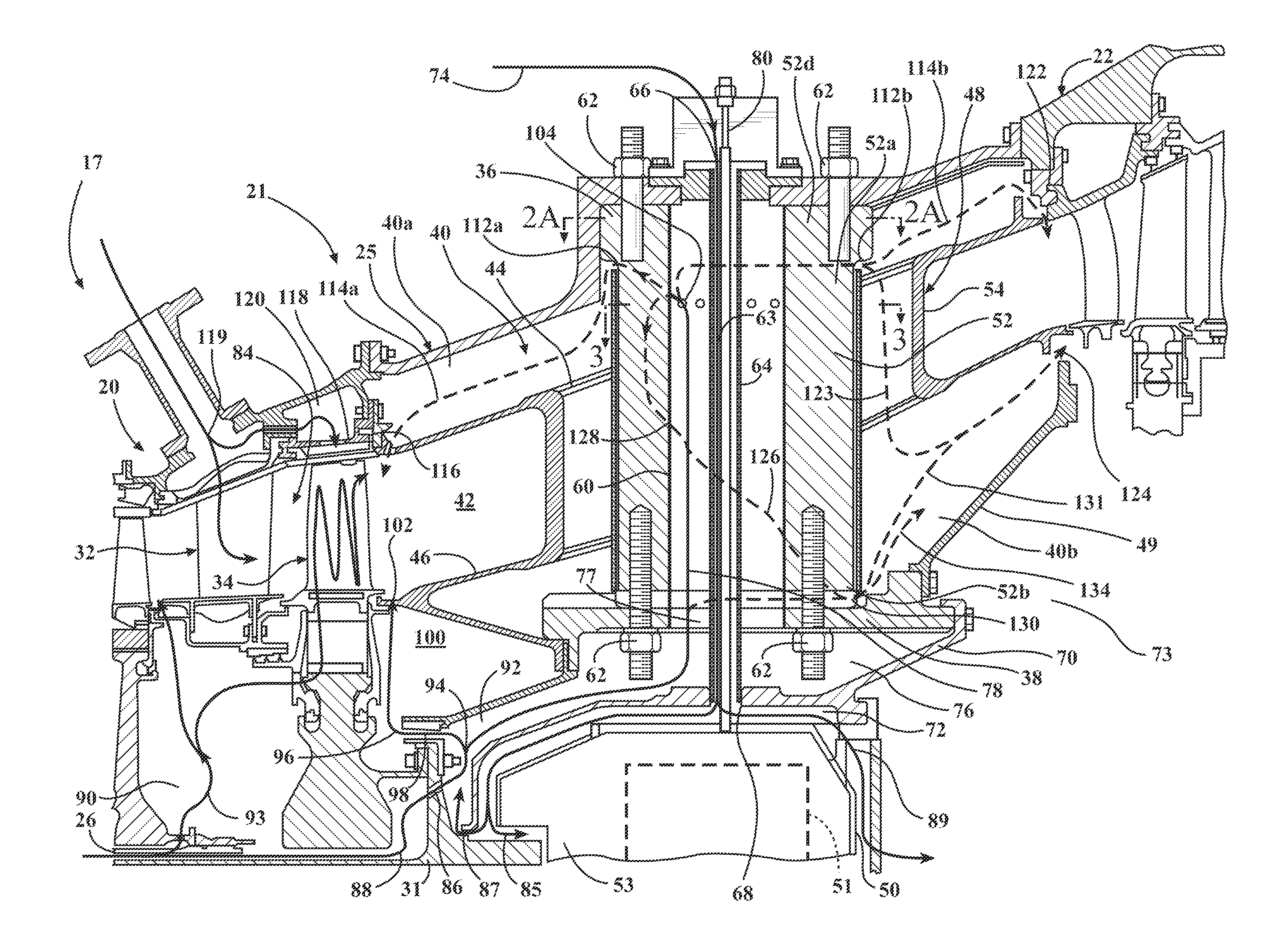
Purge and cooling air for an exhaust section of a gas turbine assembly
A turbine exhaust casing having an outer casing, an inner casing, an annular exhaust gas path defined between outer and inner flow path walls, and a turbine exhaust casing cavity located radially outward and radially inward from the gas path. A plurality of structural struts support the inner casing to the outer casing, and a fairing surrounds each of the struts in an area extending between the outer and inner flow path walls. A first purge air path extends through at least one of the struts for conducting purge cooling air radially inward to the inner casing, and a second purge air path extends through the strut for further conducting the purge cooling air radially outward to provide a flow of purge air to a location of the exhaust casing cavity radially outward from the outer flow path wall.
Owner:SIEMENS ENERGY INC
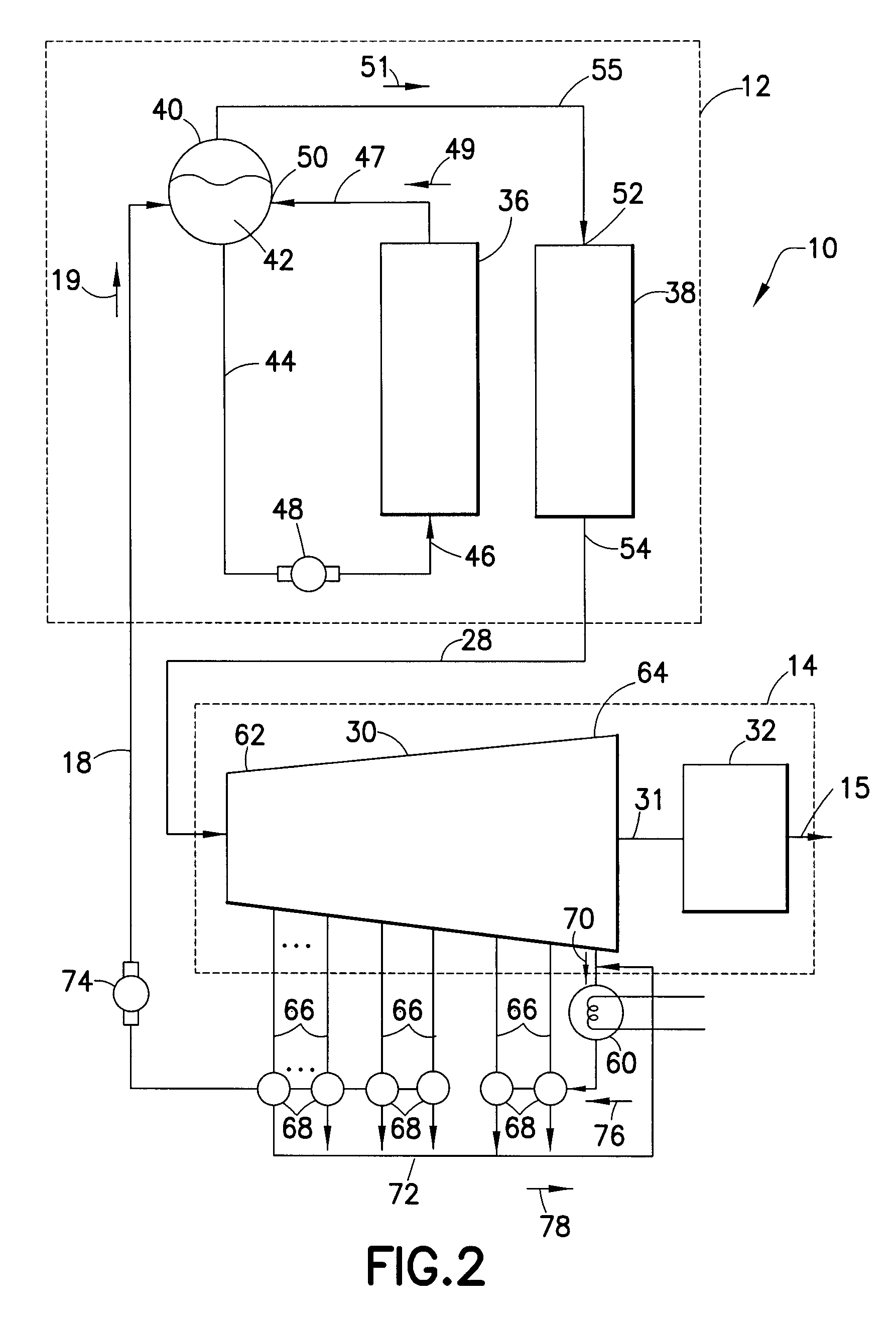
Solar thermal power plant
A solar thermal power plant 10 includes a steam generation portion 12 and a turbine 30. The steam generation portion 12 includes a steam drum 50 that separates water and steam, and an evaporator 36 and super heater 38 in fluid communication with the steam drum. The evaporator 36 receives and heats a portion of a flow of water from the steam drum 50 to provide the steam using solar energy provided thereto. The super heater 38 heats the steam from the evaporator 36 to provide super heated steam. A turbine 30 receives the super heated steam from the steam generation portion 12 to rotate the turbine. A plurality of extraction stages 66 extracts steam from the turbine 30 and provides the steam to a plurality of feedwater heaters 68. The feedwater heaters 68 heat the feedwater provided by the turbine 30, wherein the heated feedwater is provided to the steam generation portion 12.
Owner:ALSTOM TECH LTD
Apparatus and method for producing sustainable power and heat
InactiveUS20080163625A1Maximize energy efficiencyEasy to convertSteam useCombined combustion mitigationWorking fluidWater production
An integrated system provides electricity and heat from solar, waste heat, biomass and fossil fuel energy. The system operates with a volatile organic working fluid that circulates in a variable speed heat engine type cycle, that is heated either to its boiling point, to a saturated state or above its boiling point, or to a superheated gas state, expanded through an expander, with working fluid injected therein such that the fluid exiting the expander is cooled in a condenser in thermal communication with a facility's domestic hot water, space heating or process heating systems, and circulated by a pump. Heat exchange loops define hot water production capability for use in a facility while a generator is coupled to the expander to produce electricity and is connected to the utility grid at fixed frequency and voltage in either a paralleling or island mode.
Owner:OBRIEN KEVIN M
Heat/electric power supply system having power storage unit
InactiveUS20050062289A1Low costSave spaceBatteries circuit arrangementsSteam useElectricityPeak value
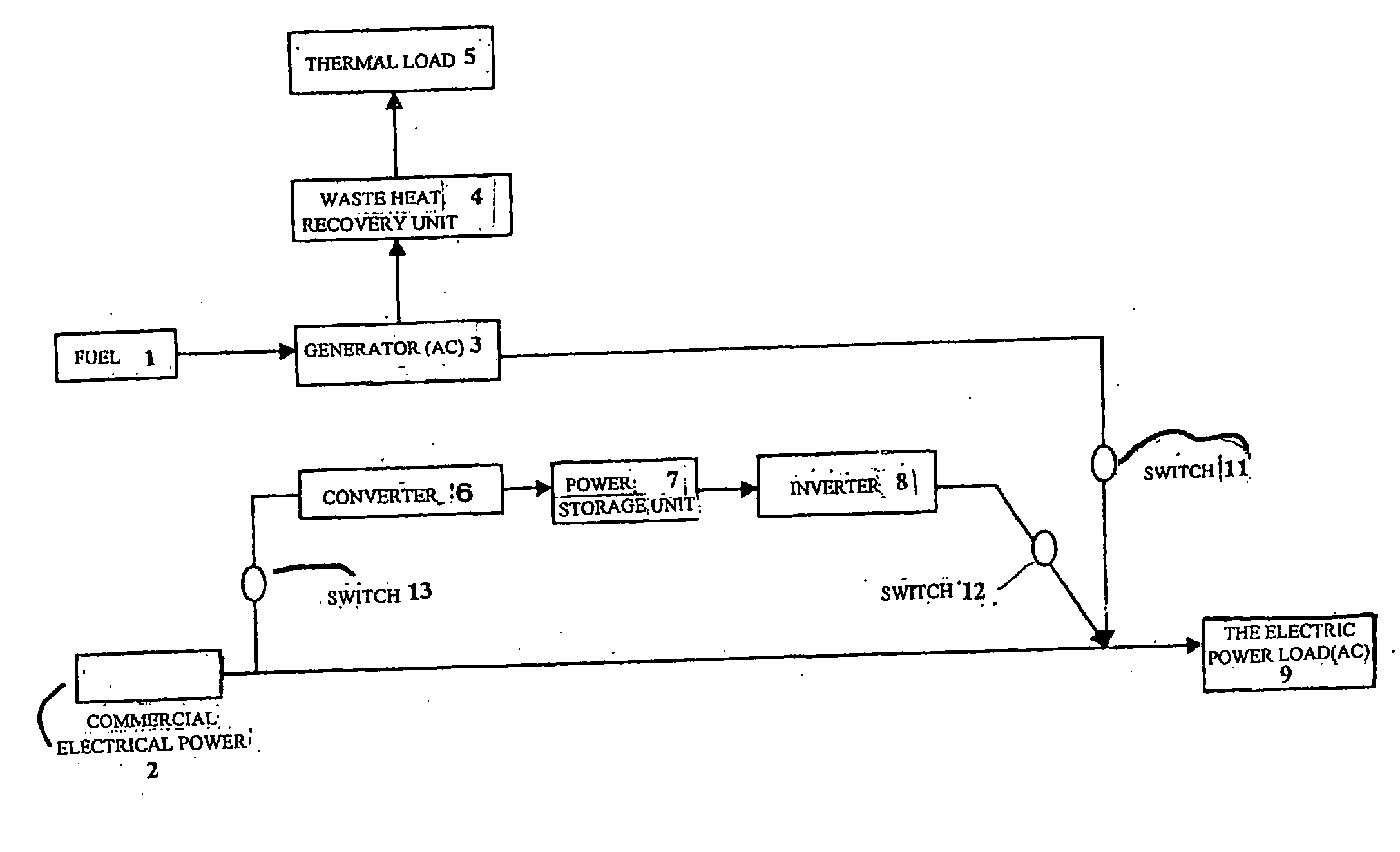
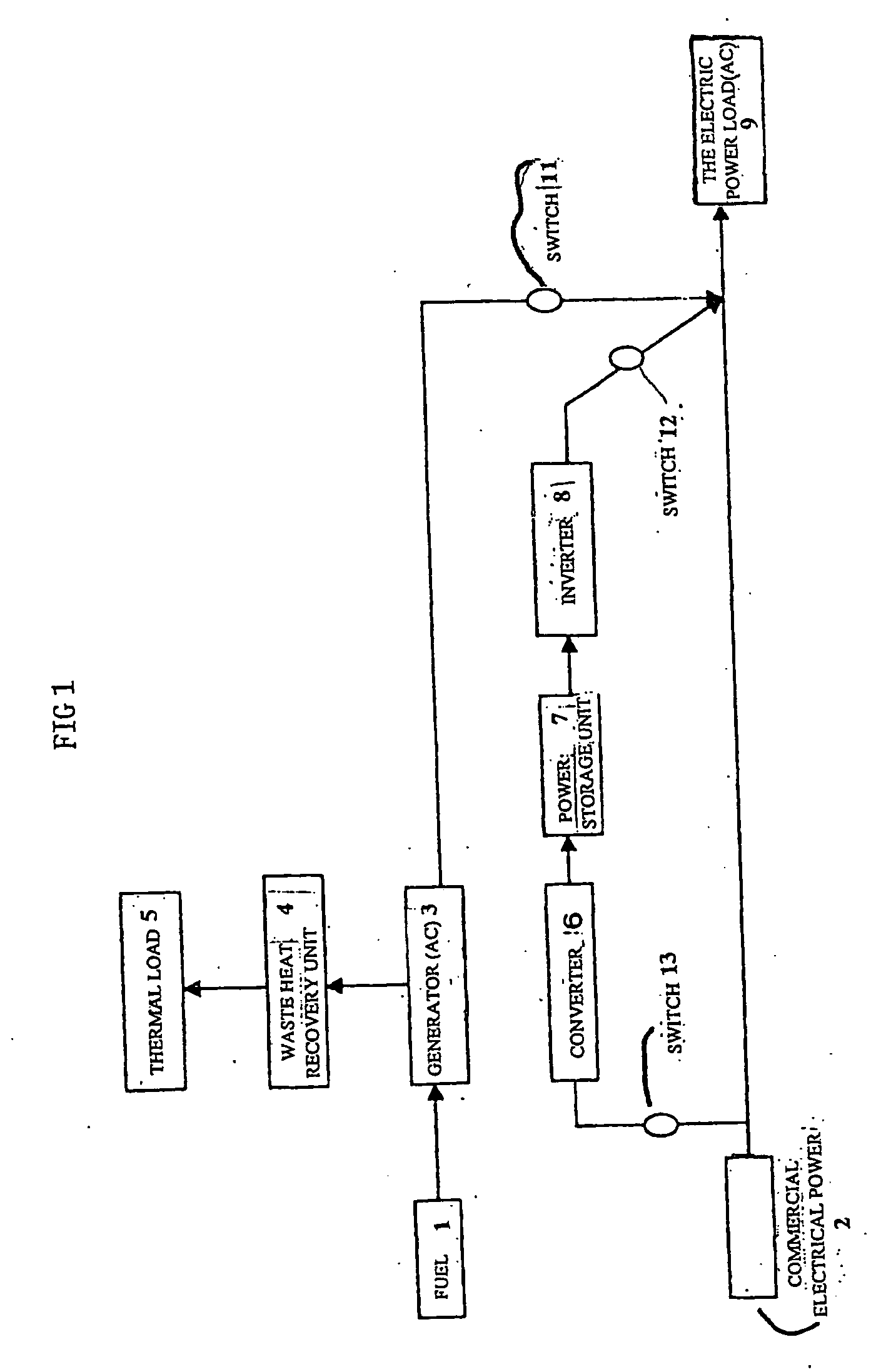
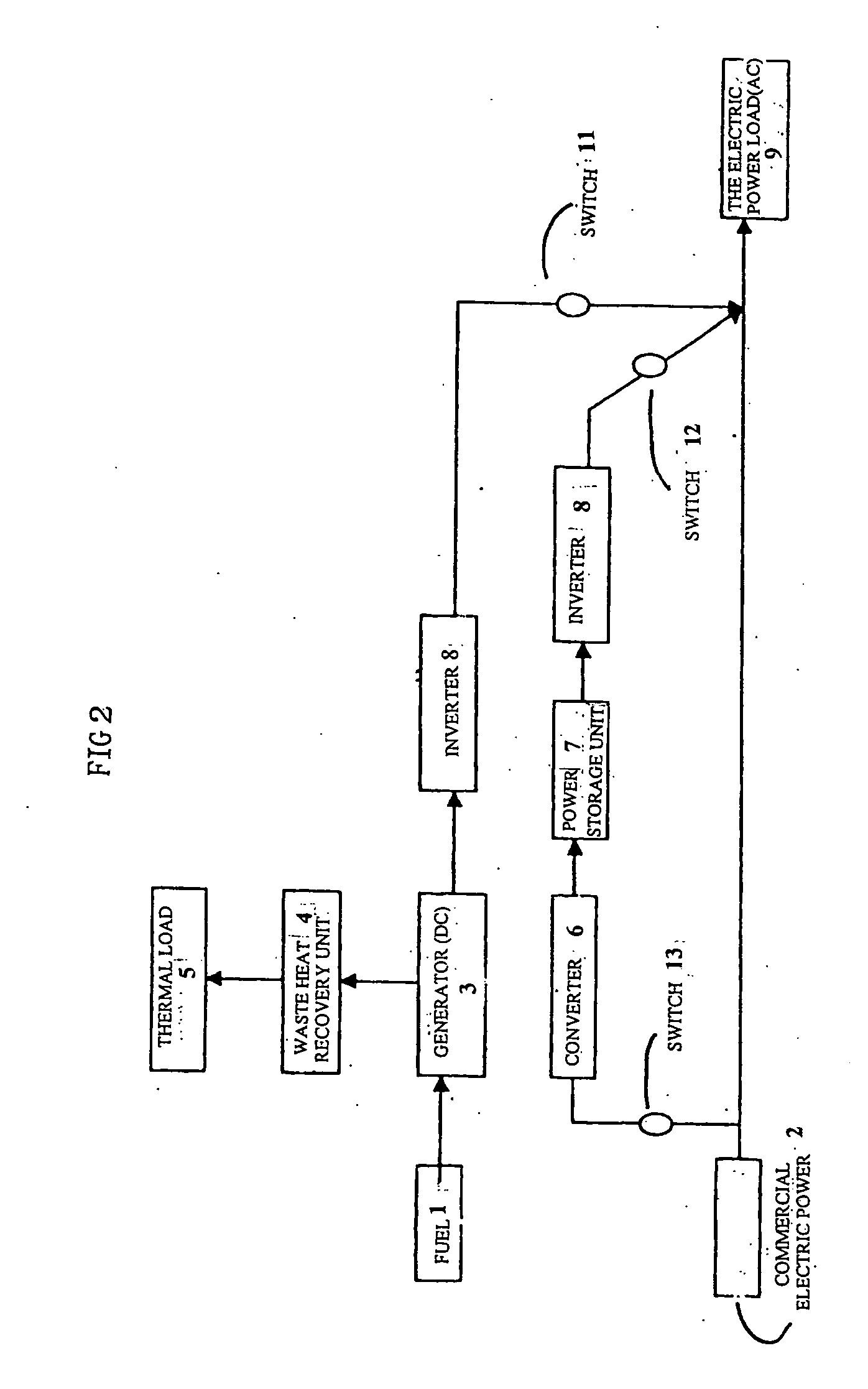
A heat / electric supply system the entire efficiency of which is enhanced while reducing the capacity of facility. The heat / electric supply system is characterized in that electric power is supplied from a generator, a commercial power supply and a power storage unit in the time zone when power consumption by the power load is higher than a specified output C1 and commercial power is stored in a power storage unit in the night time zone can be utilized at the time of peak power demand, the backup power at the time of peak power demand can be reduced.
Owner:CHO TONG RAE +1
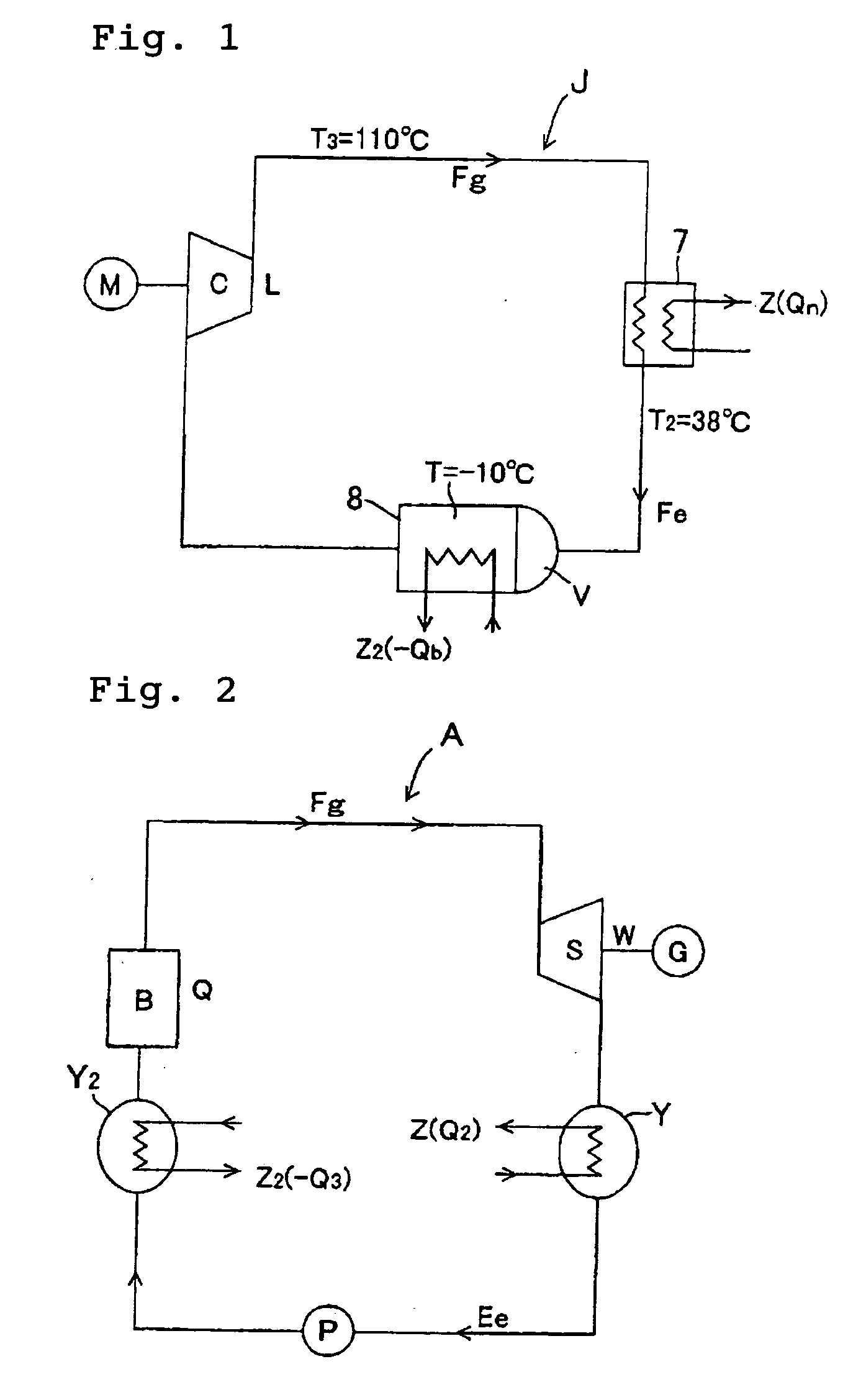
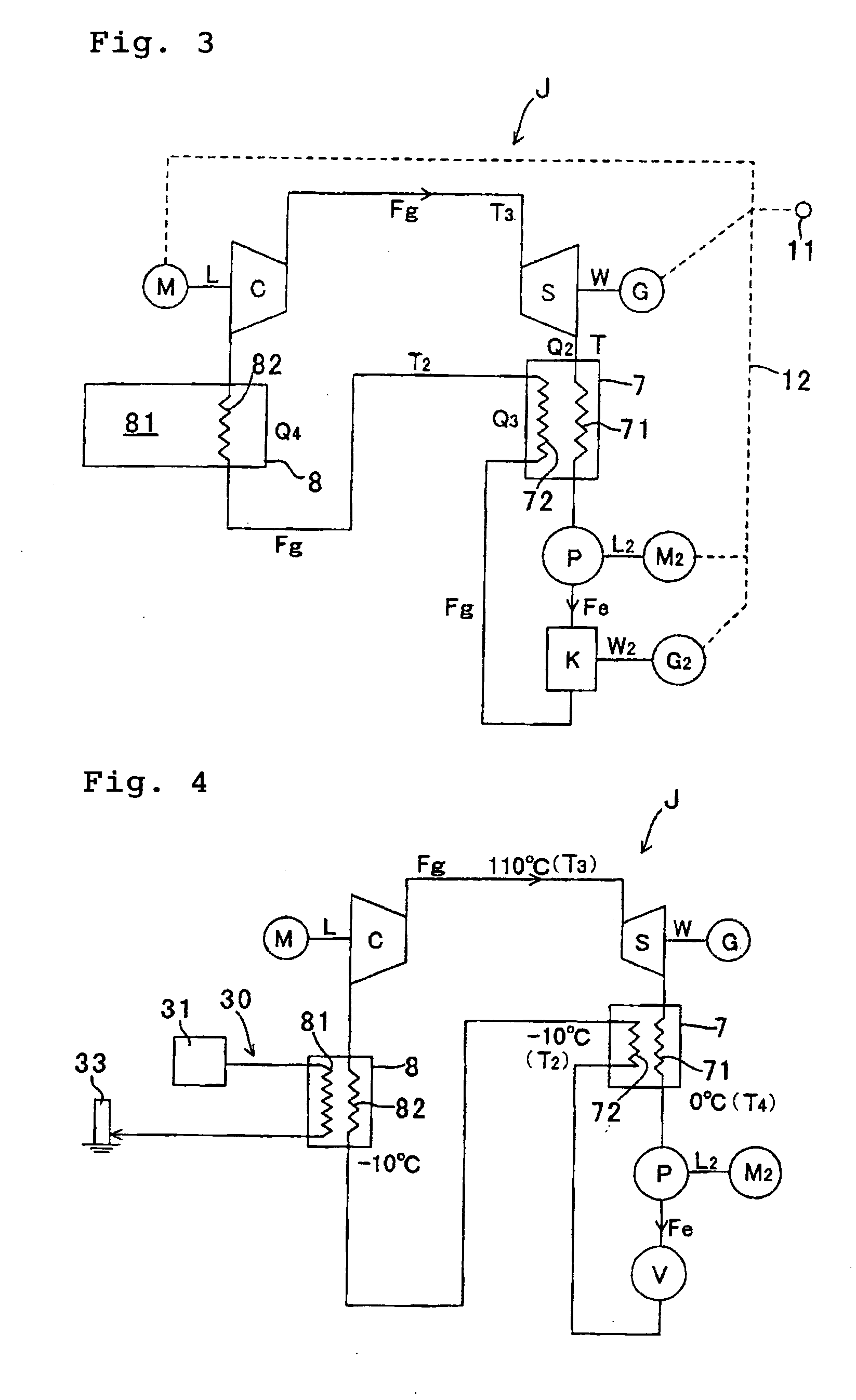
Heat Cycle System and Composite Heat Cycle Electric Power Generation System
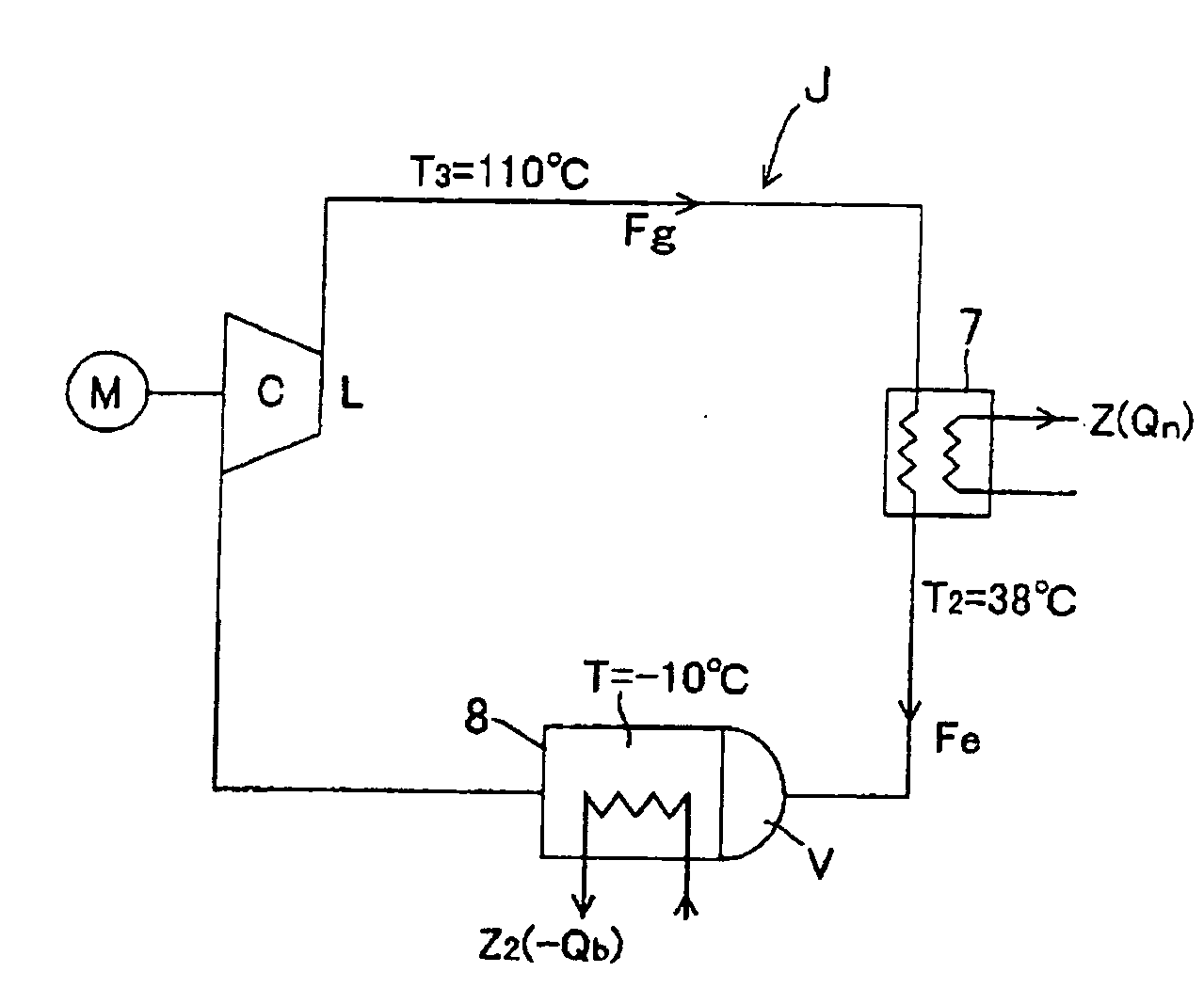
InactiveUS20090165456A1Improve thermal efficiencyImprove heating efficiencyWorking fluid for enginesSteam useEngineeringHeat recirculation
A high-efficiency heat cycle system including a compressor, a first turbine, first and second heat exchangers 7 and 8, a first pump, and an expander, and a composite heat cycle power generator using the high-efficiency heat cycle system. Working gas Fg compressed in the compressor (C) drives a first turbine (S) and is thereafter cooled by passing through a heat dissipating side of a first heat exchanger (7) and then raised in pressure by a first pump (P) to form high-pressure working liquid Fe, the high-pressure working liquid is expanded and evaporated in a expander (K) to form working gas Fg, said working gas Fg is heated by passing through a heat receiving side 82 of the second heat exchanger before being introduced into the compressor C. A heat dissipating side 81 of the second heat exchanger comprises a heat dissipating portion of a refrigerating machine or a heat dissipating portion for waste heat from a heating machine.
Owner:MASADA NOBORU
Compression-evaporation system for liquefied gas
InactiveUS7406830B2Reduce and even eliminate consumptionGas handling applicationsGas handling/storage effectsEvaporationEngineering
The compressor-evaporator system for liquefied gas contained in a tank comprises, in addition to a deice for evaporation by heat exchange with a liquid and devices for conditioning and transferring gas to a pipeline, a motor-driven turbopump comprising a rotary assembly of high bending stiffness on a common shaft line, with at least one high pressure pump, a turbine, and a central electrical machine capable of being used in motor mode or in generator mode. The rotary assembly of the motor-driven turbopump is adapted to present a high speed of rotation, greater than 12,000 rpm, while remaining outside ranges for exciting critical speeds in rotation. All of the internal portions of the motor-driven turbopump are immersed in a cryogenic fluid that is the same as the liquefied gas contained in the tank. The internal cavities of the motor-driven turbopump that are under different thermodynamic conditions are separated by contactless dynamic seals. Electronic power circuits connected to an electricity network control the central electrical machine in motor mode or generator mode.
Owner:SN DETUDE & DE CONSTR DE MOTEURS DAVIATION S N E C M A
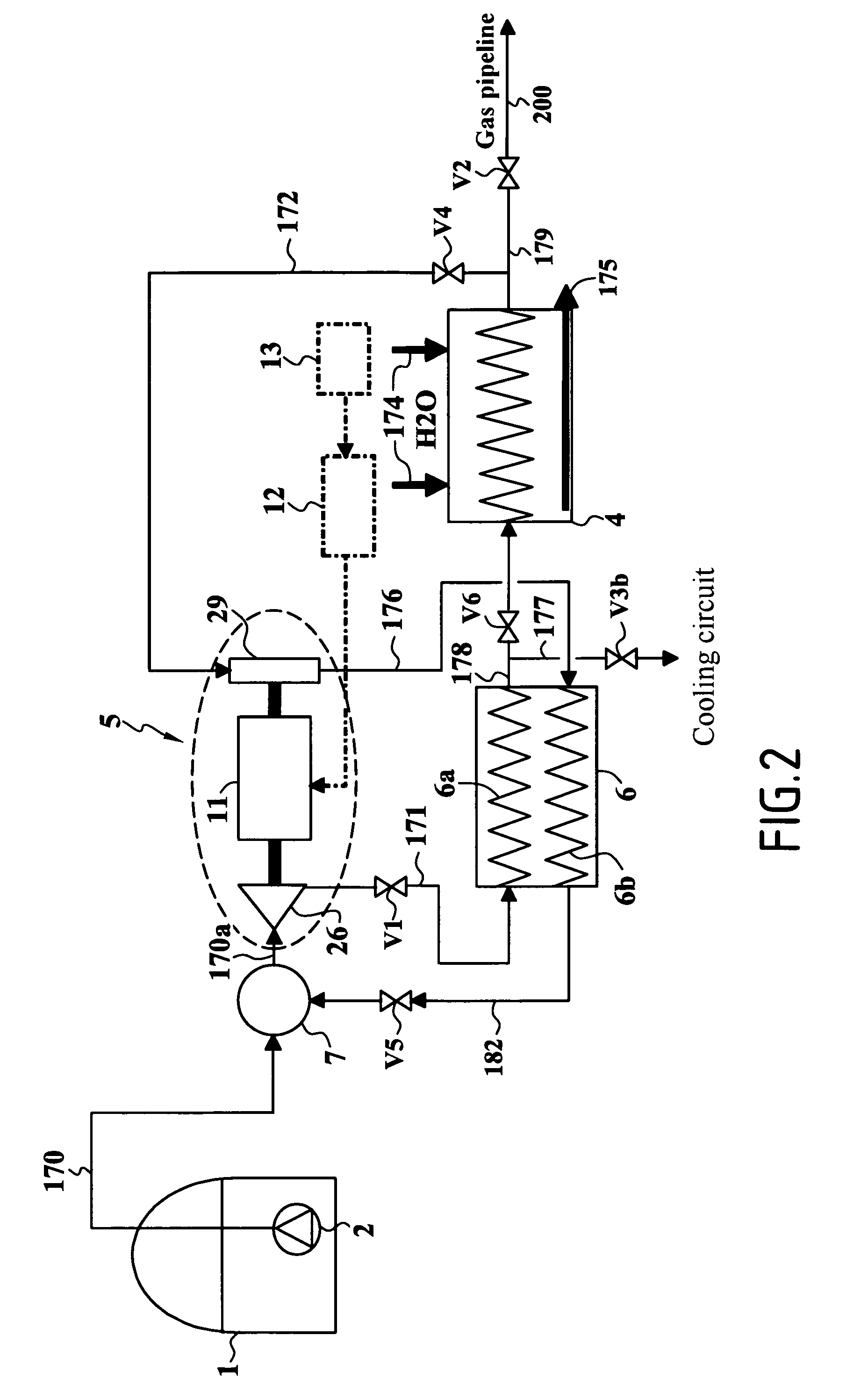
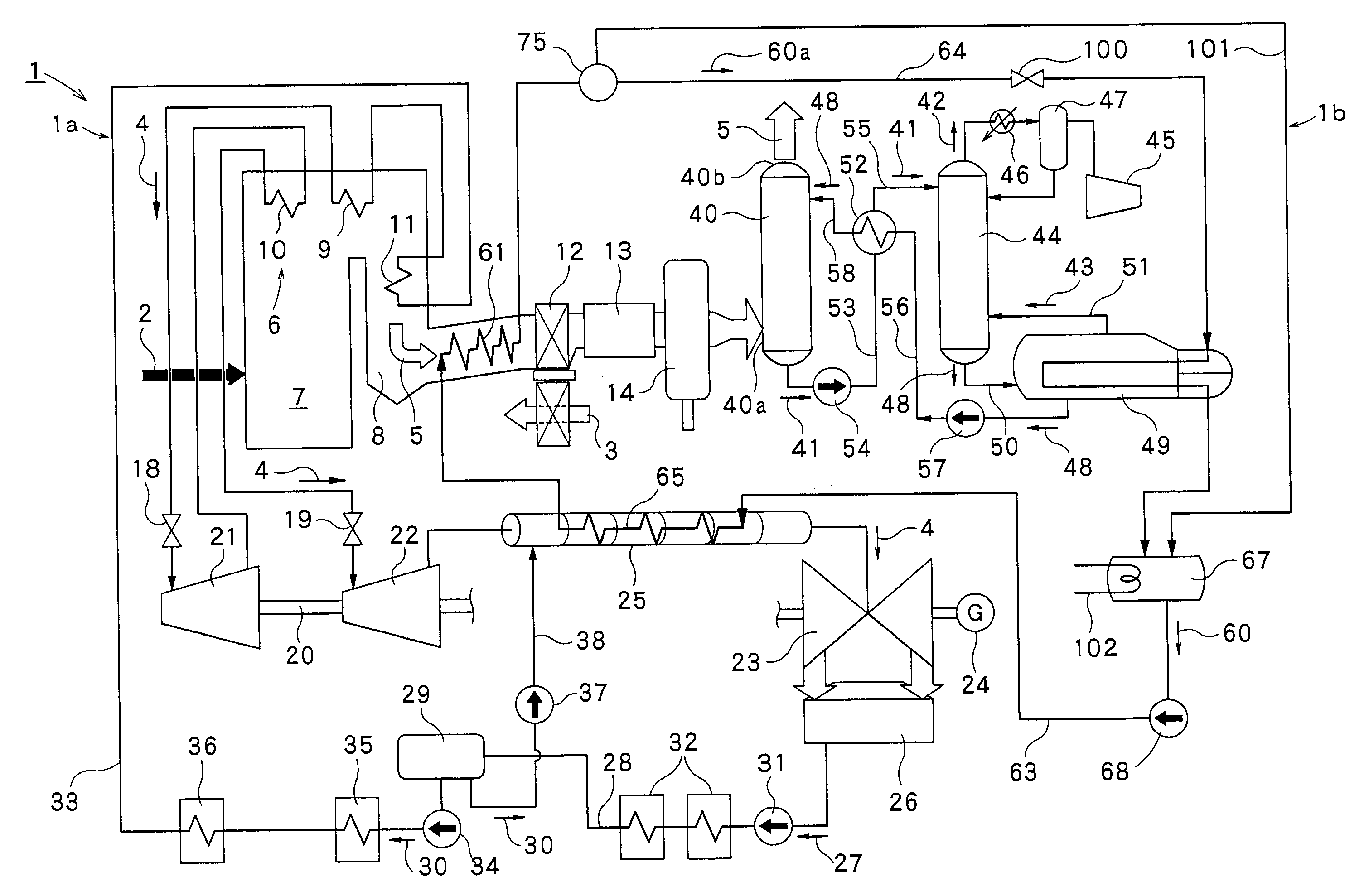
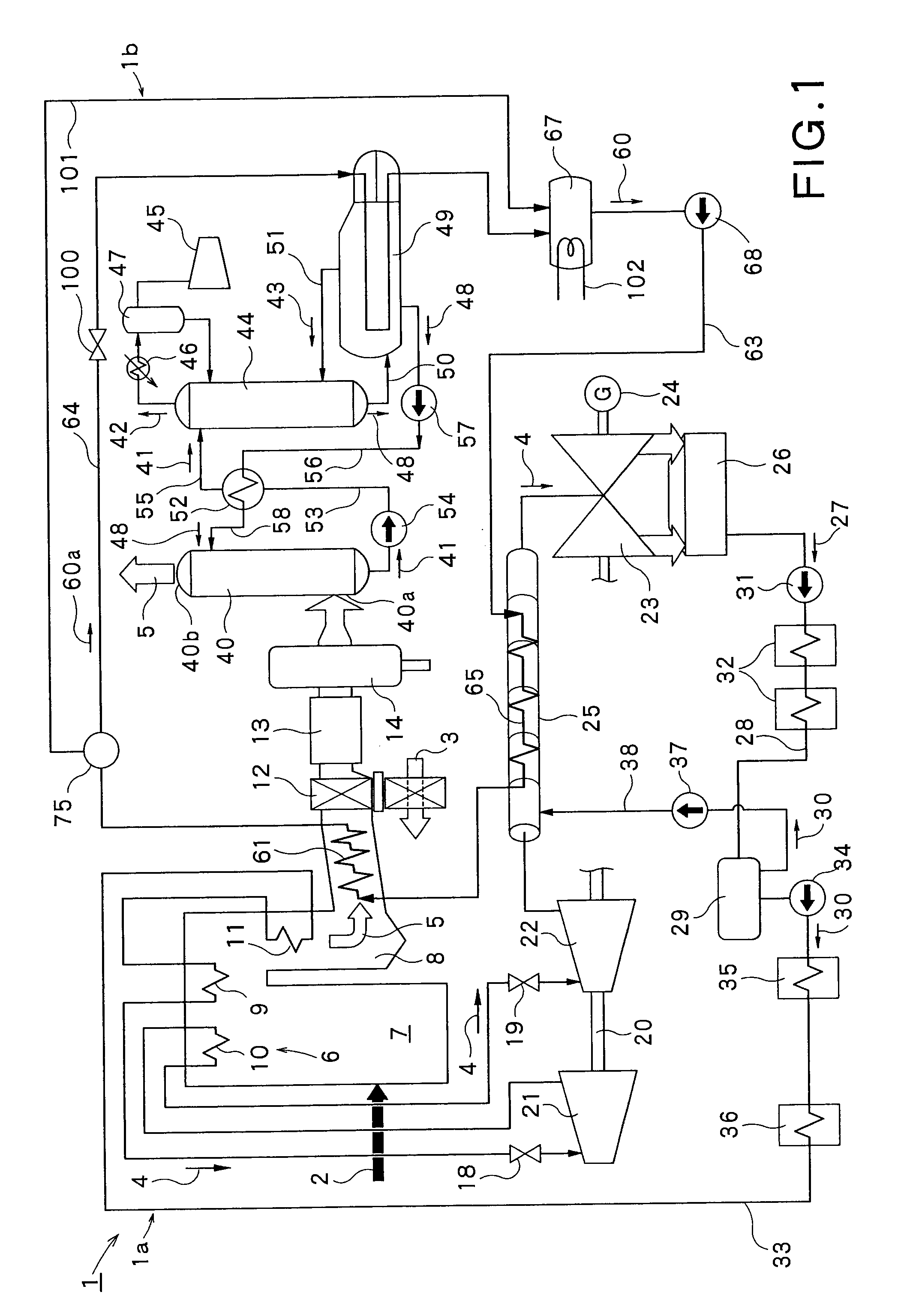
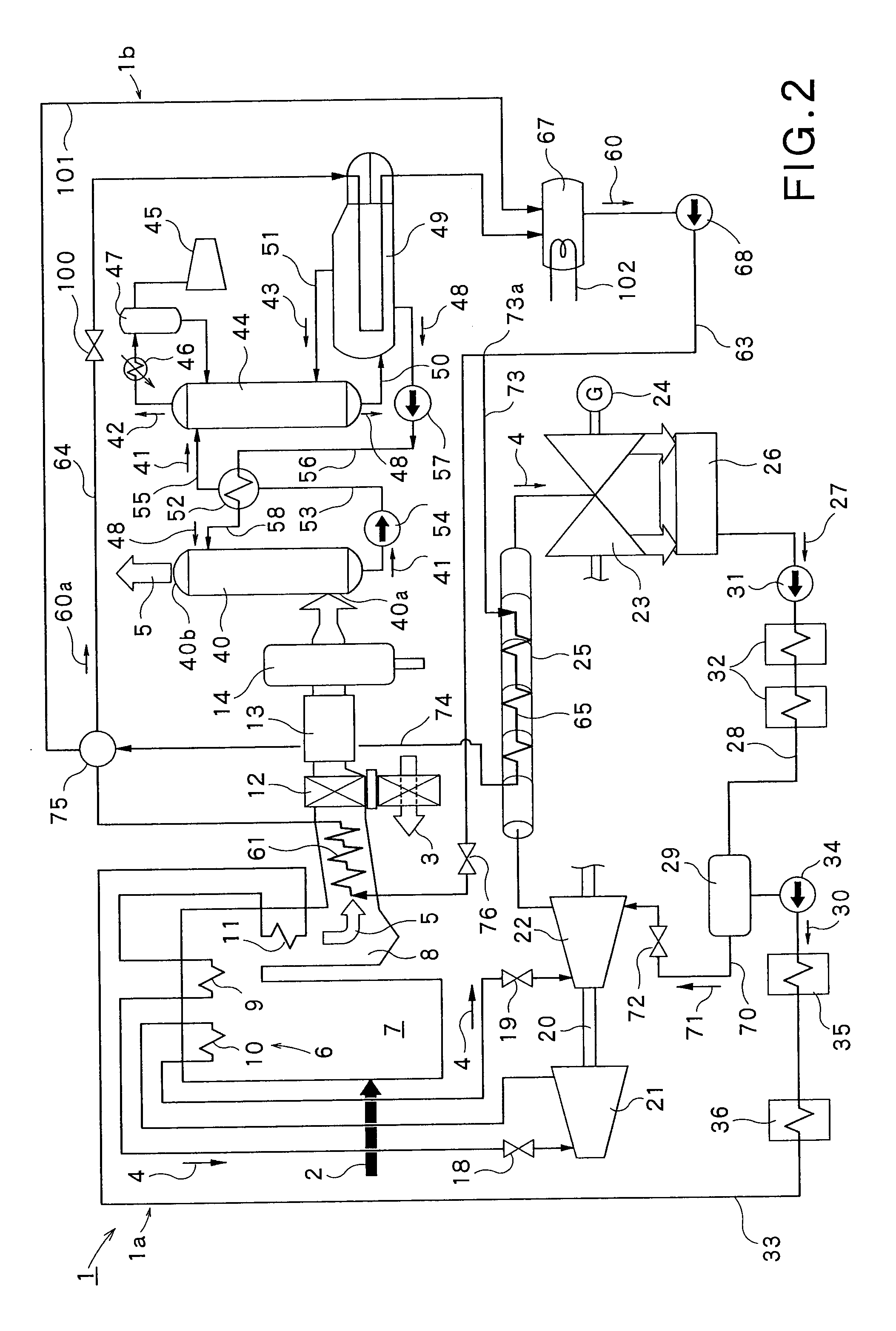
Carbon-dioxide-capture-type steam power generation system
InactiveUS20100050637A1Avoid power generation efficiencyImprove efficiencyLiquid degasificationCarbon compoundsCo2 absorptionReboiler
A carbon-dioxide-capture-type steam power generation system 1 according to the present invention comprises a boiler 6 producing an exhaust gas 5 by combusting a fuel 2 and having a flue 8; an absorbing unit 40 being configured to absorb the carbon-dioxide contained in the exhaust gas 5 into an absorbing solution; and a regenerating unit 44 being configured to release the carbon dioxide gas from the absorbing solution absorbing the carbon dioxide and discharge the released carbon dioxide gas. Further, in this system, a reboiler 49 is provided for receiving a heating-medium as heat source, producing a steam 43 and supplying the produced steam 43 to the regenerating unit 44. Additionally, in the flue 8 of the boiler 6, a boiler-side heat exchanger 61 is provided for heating the heating-medium by the exhaust gas 5 passing therethrough.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Dual-rotor, single input/output starter-generator
InactiveUS20060087123A1Shorten the lengthOverhung momentSteam useEfficient propulsion technologiesStarter generatorTorsional load
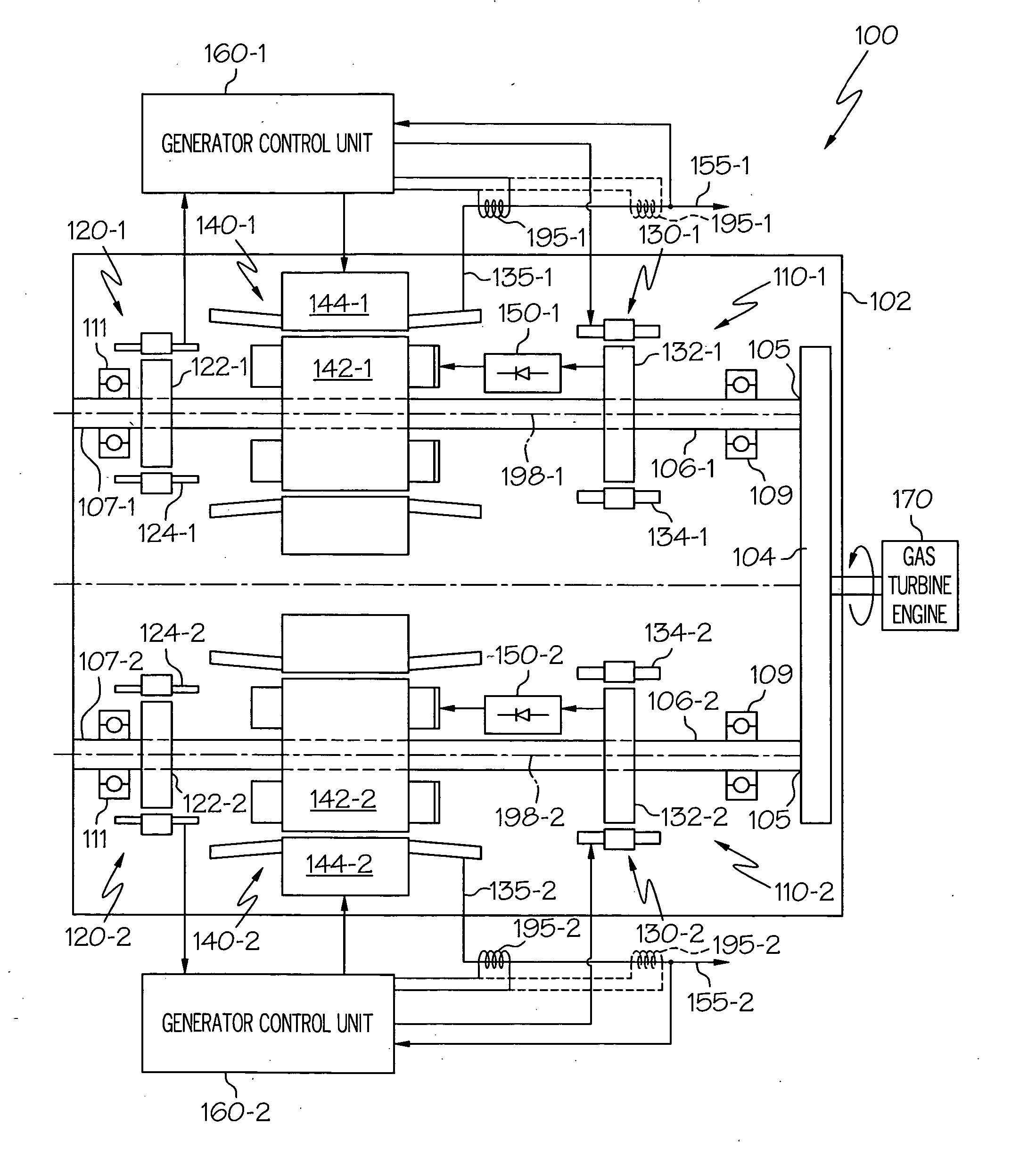
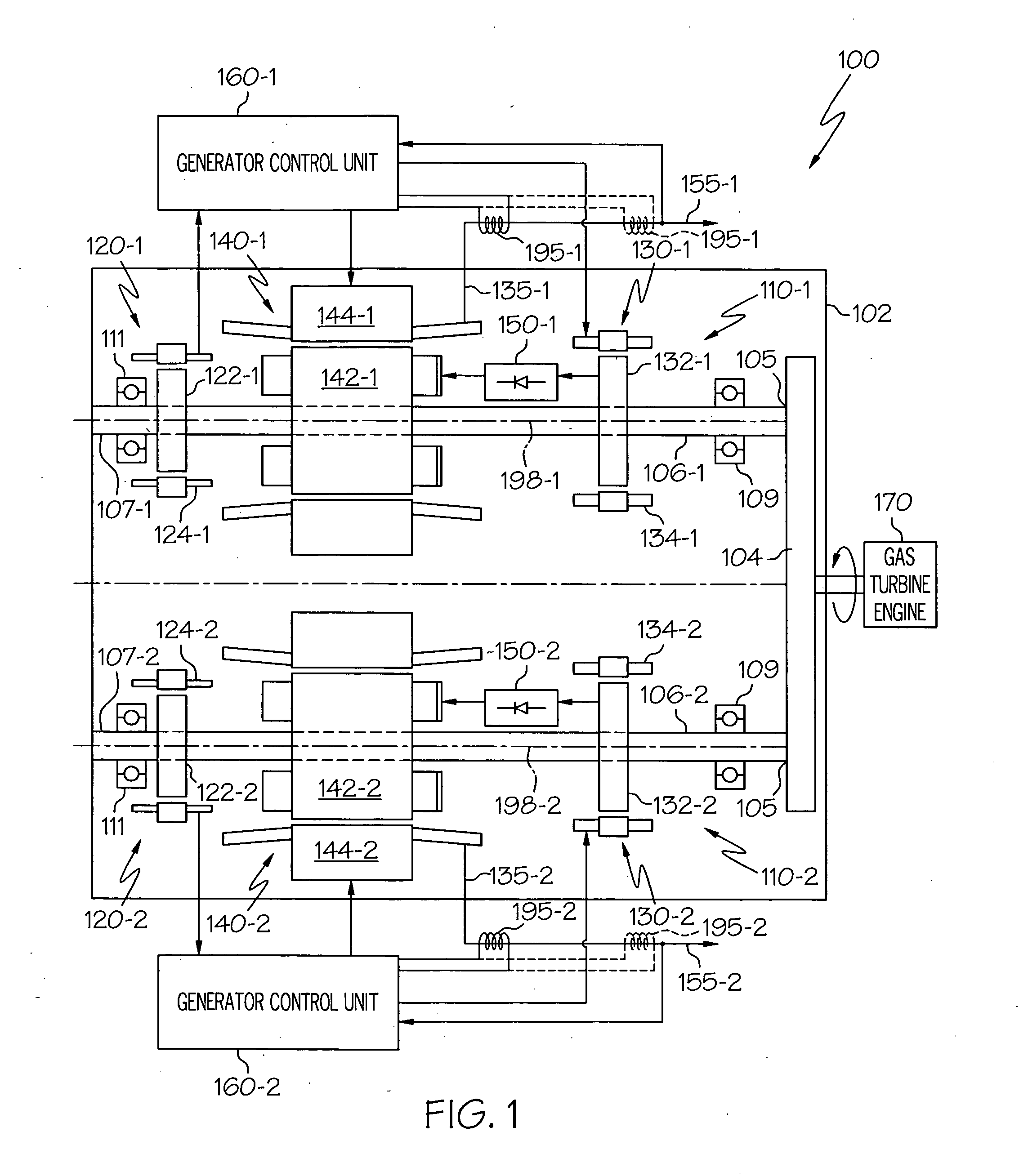
A starter-generator includes redundant motor / generator sets disposed within a common housing. Each motor / generator set is electrically and mechanically independent of one another, with the exception of a common input / output gear. The starter-generator is configured such that if one of the motor / generator sets experiences a predetermined torsional load, it will decouple from the input / output gear, allowing the other motor / generator set to continue operation uninterrupted.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
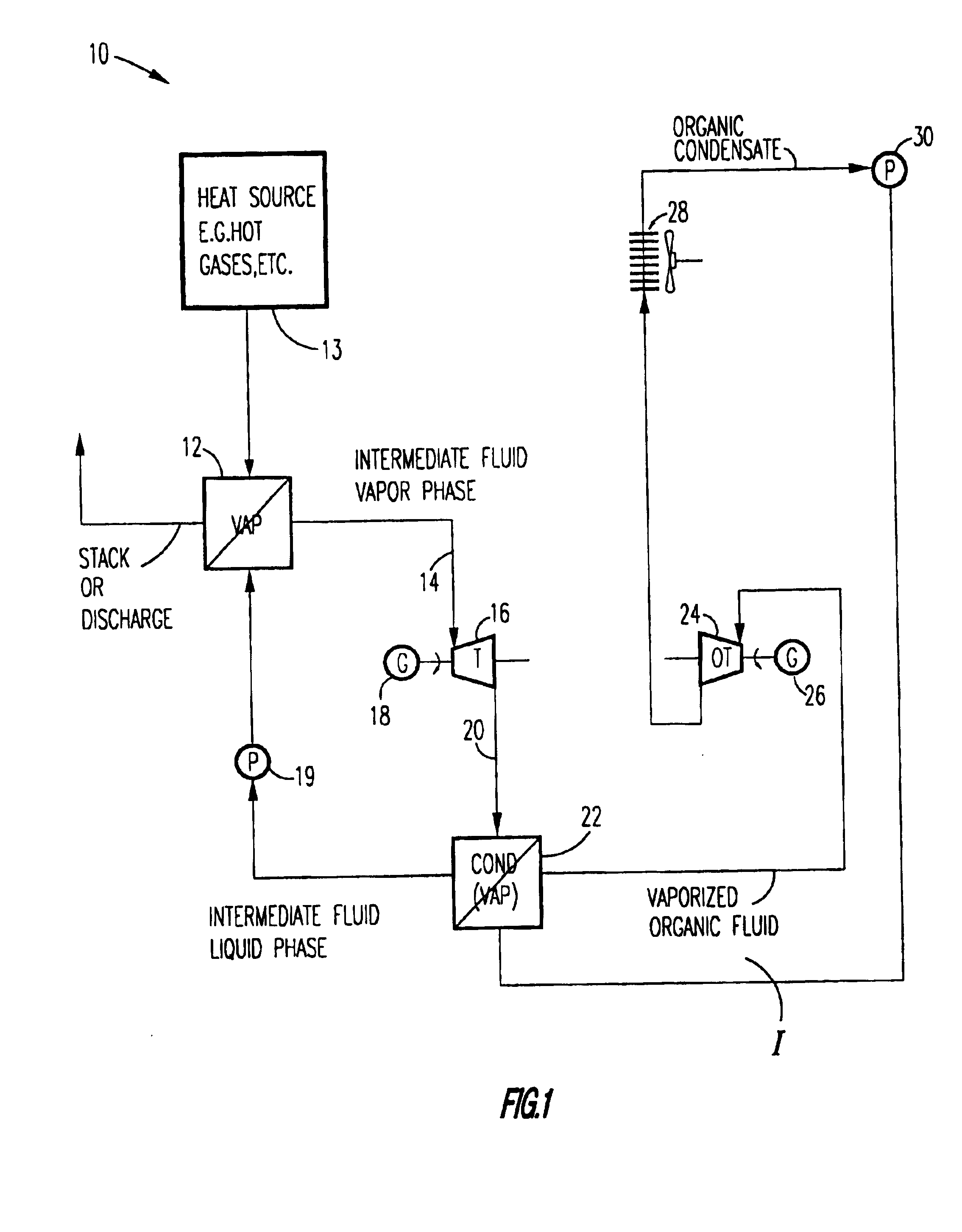
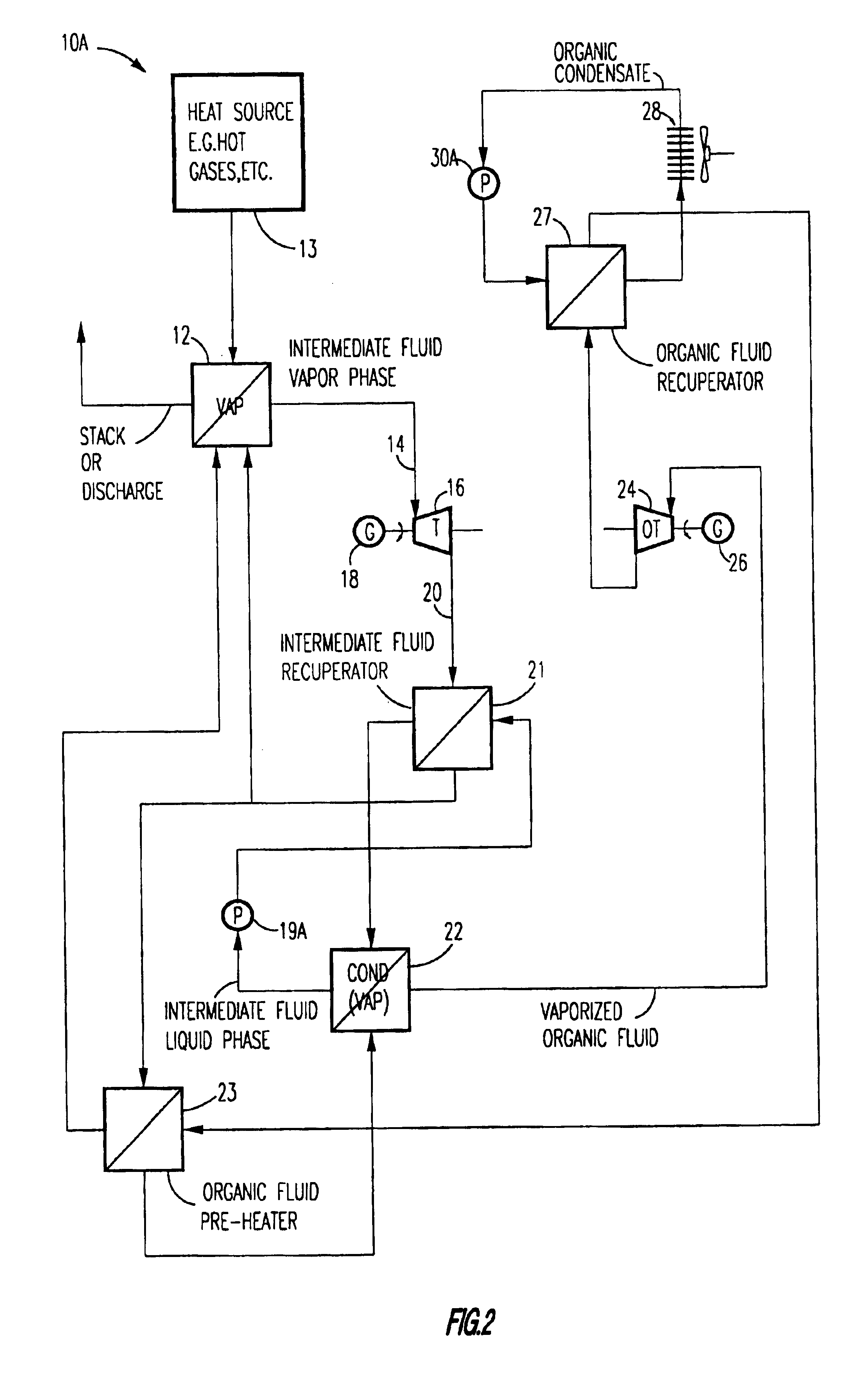
Method of and apparatus for producing power from a heat source
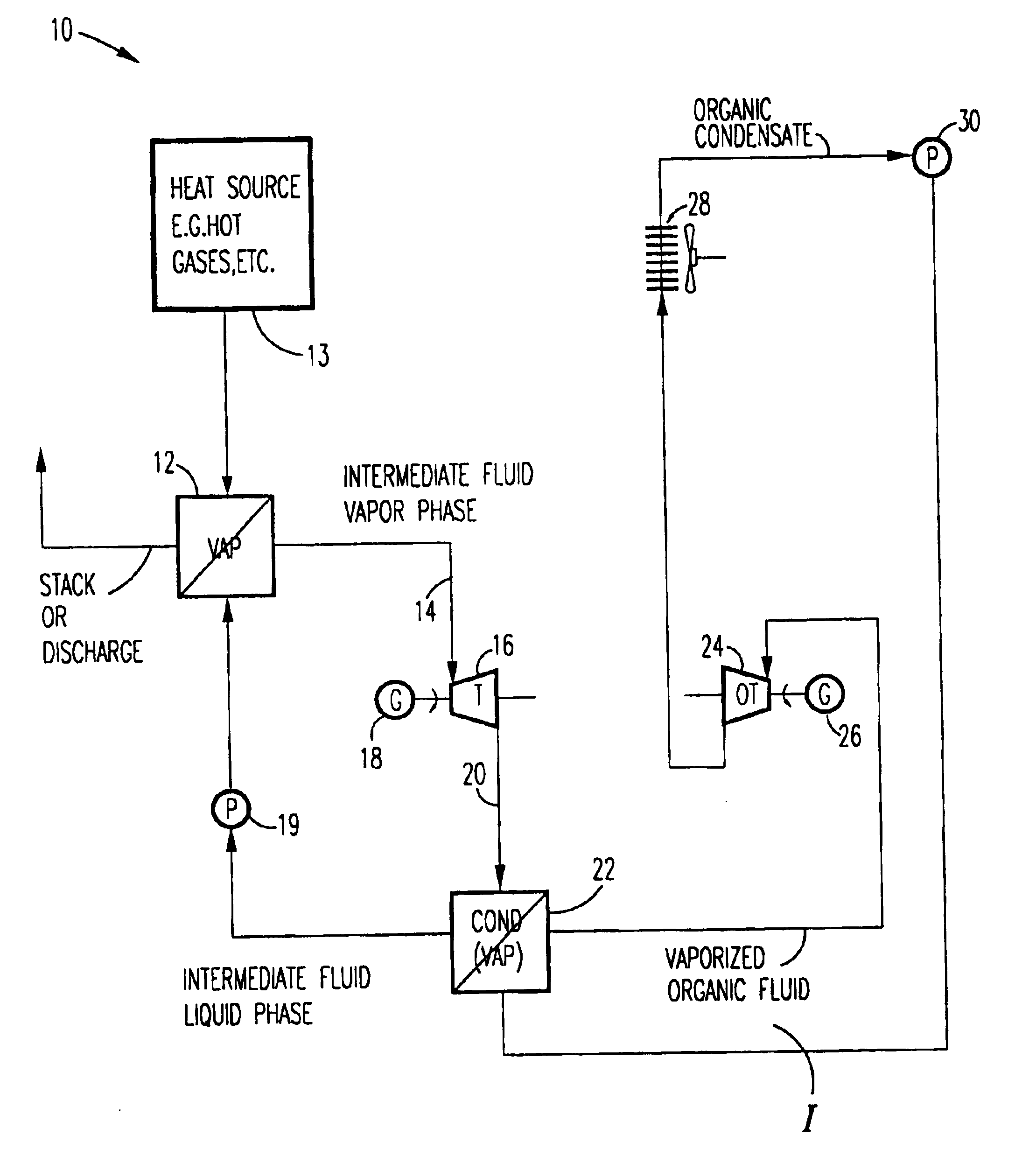
A method for producing power from a heat source comprises the steps of: heating an intermediate fluid with heat from the heat source and producing a vaporized intermediate fluid in an intermediate fluid heater / vaporizer. Heat from the vaporized intermediate fluid vaporizes an organic liquid working fluid present in an organic working fluid vaporizer to form a vaporized organic working fluid and intermediate fluid condensate. The vaporized organic working fluid is expanded in an organic vapor turbine for generating power and producing expanded vaporized organic working fluid; the expanded organic vaporized working fluid being condensed to produce an organic fluid condensate with the organic fluid condensate being supplied to the organic fluid vaporizer. According to the present invention, prior to supplying the vaporized intermediate fluid to the organic fluid vaporizer the vaporized intermediate fluid is expanded in an intermediate fluid vapor turbine and power is produced.
Owner:ORMAT TECH INC
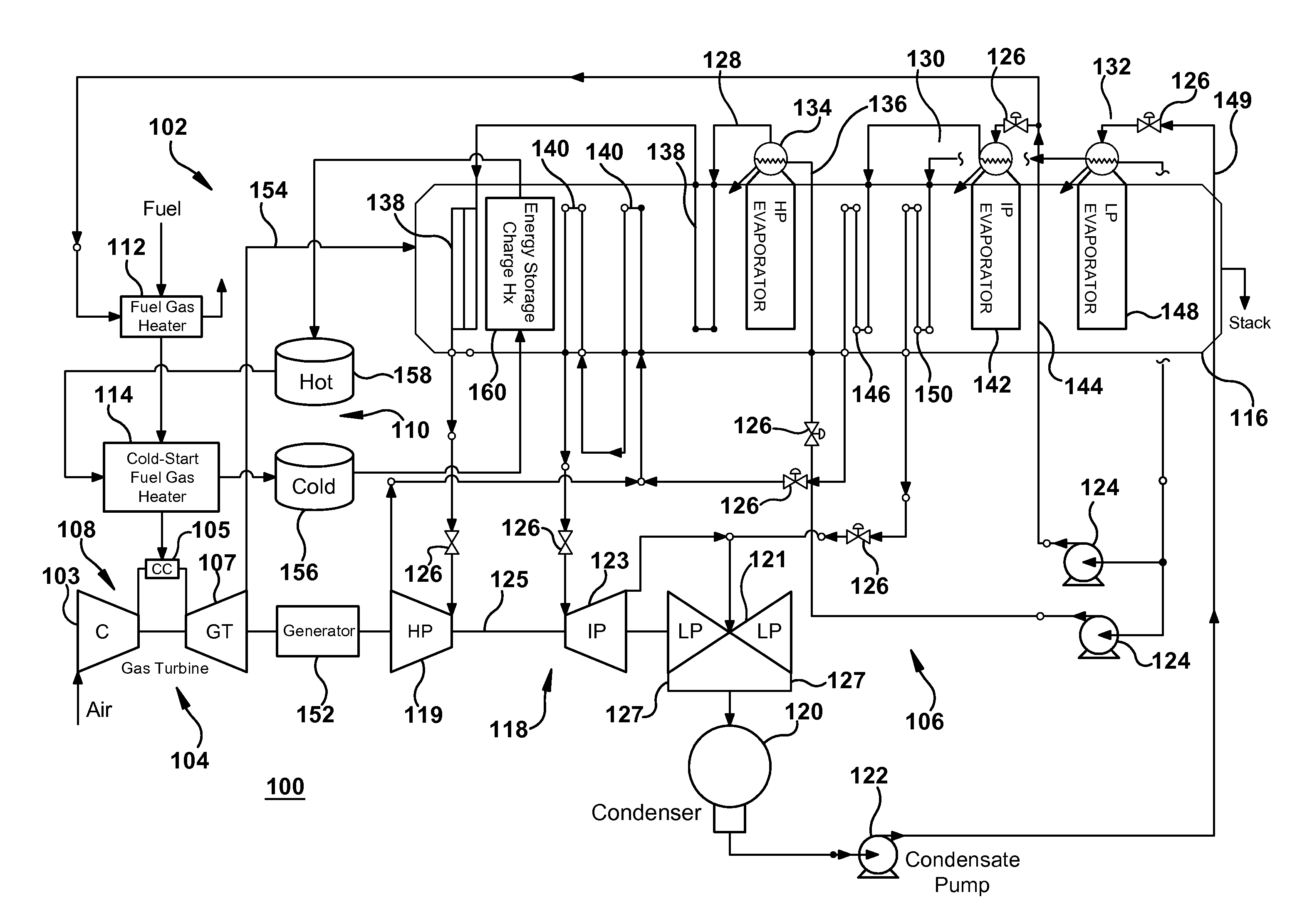
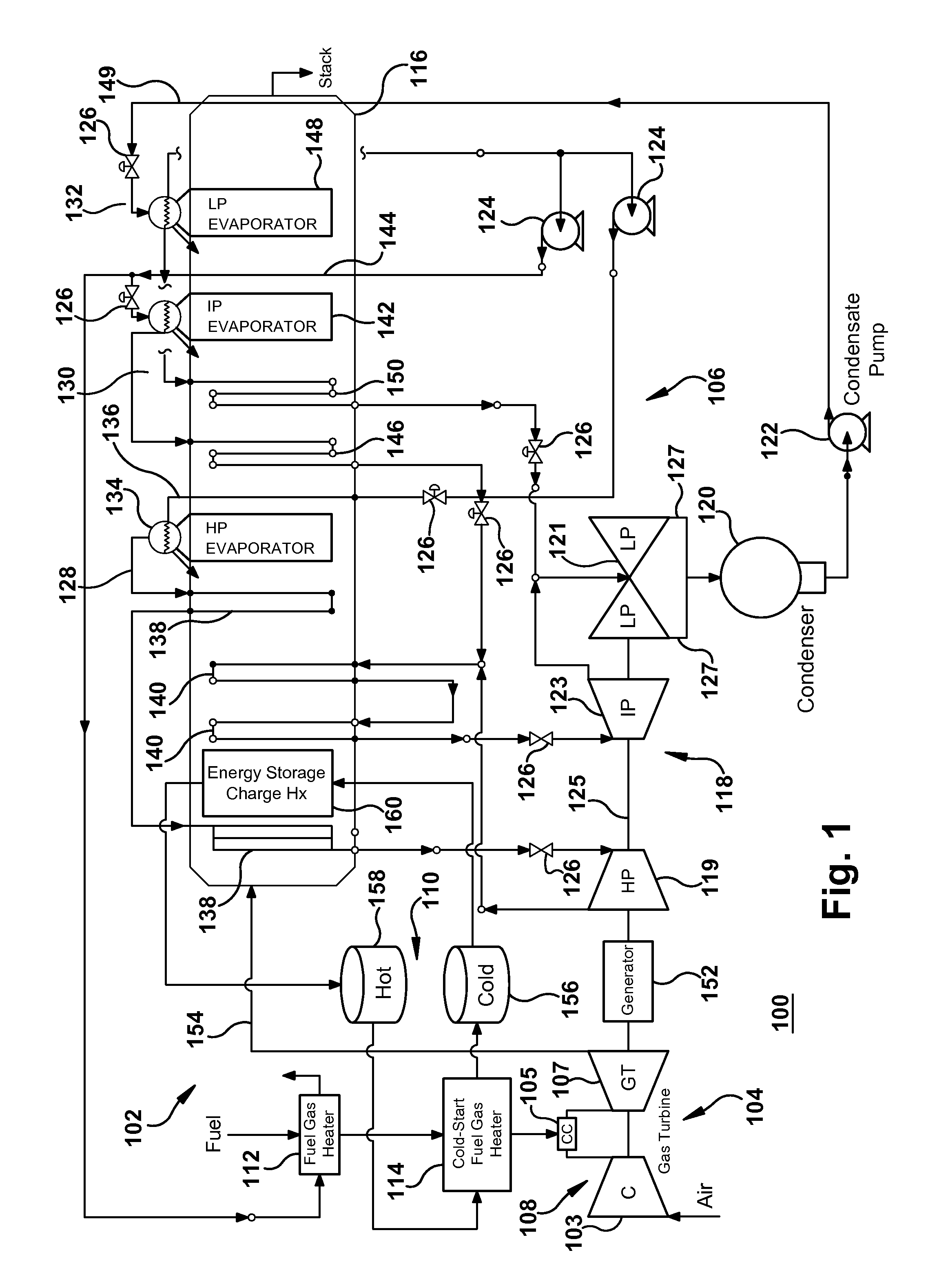
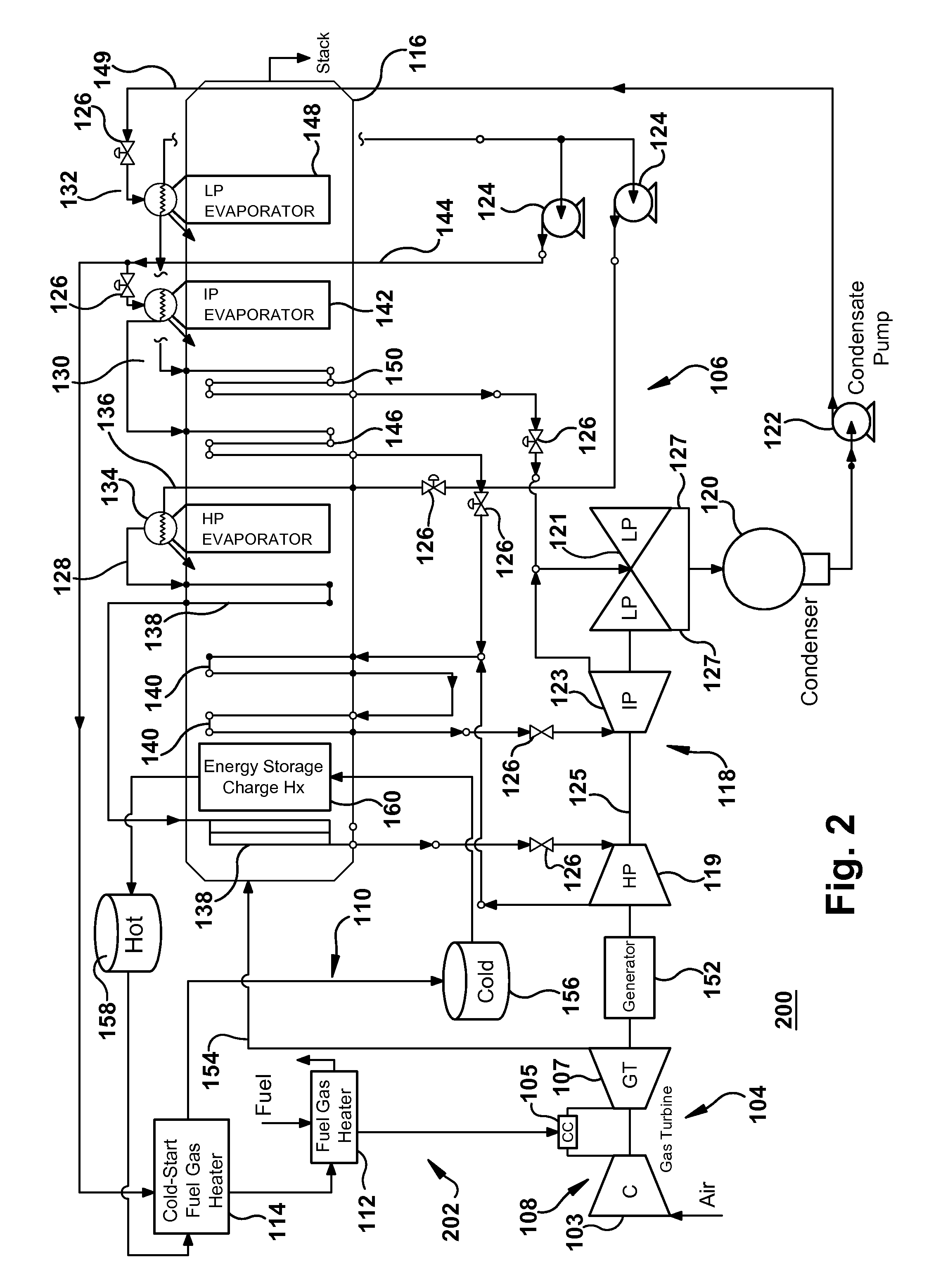
Fuel gas heating with thermal energy storage
Thermal energy storage containing thermal energy extracted from a bottom cycle heat engine is leveraged to heat fuel gas supplied to a gas turbine engine operating in a top cycle heat engine. Further, an extracted portion of a working fluid generated in a steam generation source of the bottom cycle heat engine can be used along with the thermal energy storage to heat fuel gas.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Electrical power generation method
A method of generating electrical power in which a synthesis gas stream generated in a gasifier is combusted in an oxygen transport membrane system of a boiler. The combustion generates heat to raise steam to in turn generate electricity by a generator coupled to a steam turbine. The resultant flue gas can be purified to produce a carbon dioxide product.
Owner:PRAXAIR TECH INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com