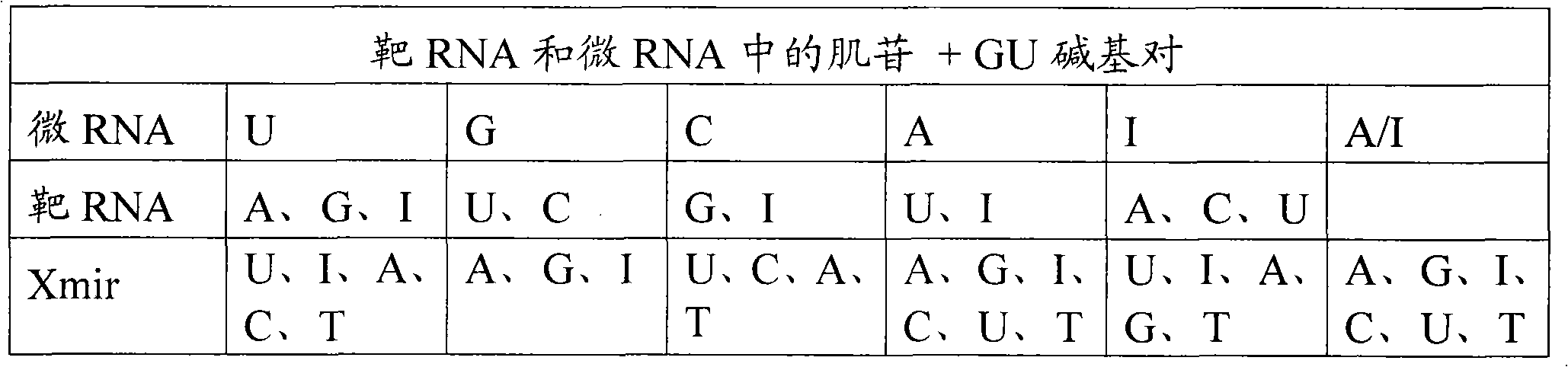
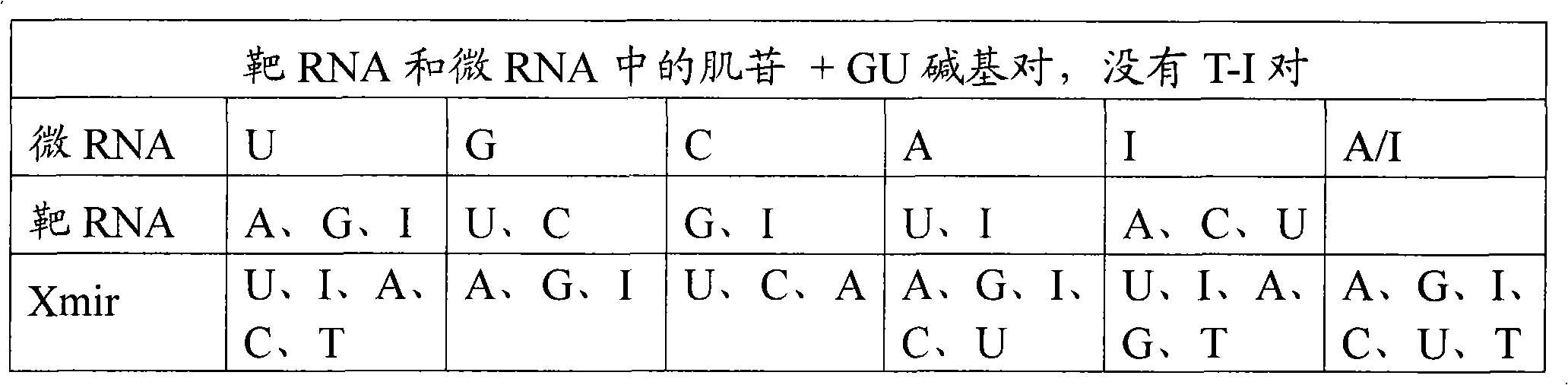
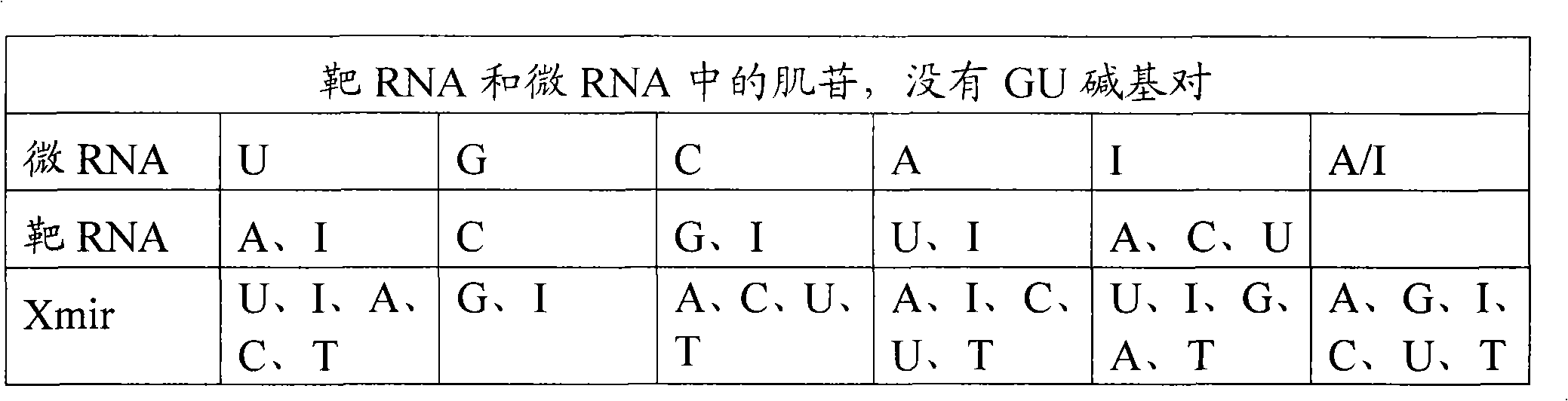
Oligonucleotides for modulating target rna activity
An oligonucleotide and RNA interference technology, which is applied in the field of oligonucleotides that affect the activity of target RNAs and regulates the activity of target RNAs, and can solve problems such as off-target effects affecting the activity of target RNAs.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0350] Blocking microRNA for the treatment of diabetes
[0351] It has been confirmed that mir-375 is a regulator of insulin secretion by pancreatic islets, and recombinant insulin-like growth factor-1 (Myotrophin (Mtpn)) is a target regulated by mir-375 (Poy MN, 2004). In addition, the inhibition of Mtpn by siRNA mimics the effect of miR-375 on glucose-stimulated insulin secretion and exocytosis. Therefore, the authors concluded that miR-375 is a regulator of insulin secretion and can thereby constitute a new pharmacological target for the treatment of diabetes.
[0352] Here, we provide a blocking microRNA that can regulate the expression of Mtpn through mir-375 regulation that inhibits the Mtpn activity in the 3'UTR of Mtpn mRNA.
[0353] The relevant part of the target mRNA is:
[0354] 5′GUGUUUUAAGUUUUGUGUUGCAA AUGGAAUAAACUUGAAU
[0355] The antisense seed sequence is shown in bold. The target region of the target RNA can be identified, for example, by looking for the target RN...
Embodiment 2
[0404] Blocking microRNA for the treatment of herpes simplex virus infection
[0405] It has recently been confirmed that the microRNA encoded by herpes simplex virus-1 can make the virus develop into a latent infection (Gupta A, 2006). It was discovered that the microRNA called mir-LAT regulates TGF-β and SMAD3, thereby affecting the ability of cells to undergo apoptosis. The infected cells are self-destructed by usual methods to prevent the generation of virus progeny. Therefore, it is interesting to be able to block the mir-LAT regulatory activity in the expression of TGF-β and SMAD3.
[0406] The sequence of the target region of TGF-β mRNA is:
[0407] 5′AGGTCCCGCCCCGCCCCGCCCCGCCCCGGCAGGCCCG CC
[0408] The sequence of mir-LAT is:
[0409] 5′ CCCGGCCCGGGGCC
[0410] Therefore, the following complexes can be formed:
[0411] 5′CGCCCCGGCAGGCCCG
[0412] ||||||| ||| |||| |||
[0413] 3′CCGGGGCC---CGGCCCGGCGGU
[0414] A series of blocking microRNAs can be designed according to the ...
Embodiment 3
[0441] Identify oligonucleotides that regulate Mtpn expression
[0442] The following is a non-limiting example of how this method will proceed. In fact, no wet experiment (wetexperiment) was performed.
[0443] The following sequence is part of the estimated target region of Mtpn mRNA:
[0444] 5′UUUGACGCAGUUGGGUUUCUCAUAAGUAUCCUAGUUCAUGUACAUCCGAAUGCUAAAU
[0445] AAUACUGUGUUUUAAGUUUUGUGUUGCAA GGAAUAAACUUGAAUUGUGCUAC
[0446] It involves a series of potential blocking microRNAs with 50% overlap for this region. Potential blocking microRNAs are shown in italics, and the reference sequence and complementary strand of Mtpn mRNA are shown for comparison:
[0447] 5′UUUGACGCAGUUGGGUUUCUCAUAAGUAUCCUAGUUCAUGUACAUCCGAAUGCUAAAUAAU-
[0448] ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||| |||||||||||
[0449] 3′AAACUGCGUCAACCCAAAGAGUAUUCAUAGGAUCAAGUACAUGUAGGCUUACGAUUUAUUA-
[0450]
[0451]
[0452]
[0453]
[0454]
[0455] -
[0456] 5′-ACUGUGUUUUAAGUUUUGUGUUGCAA UGGAAUAAACUUGAAUUGUGCUAC
[0...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com