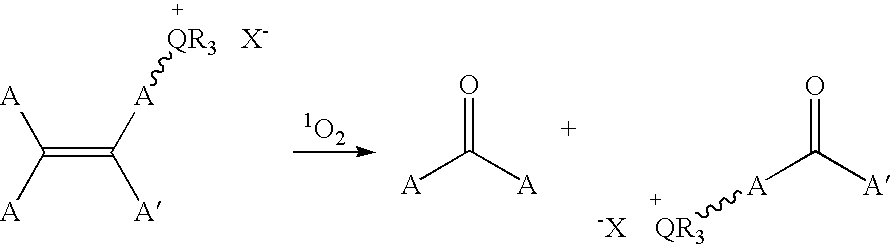
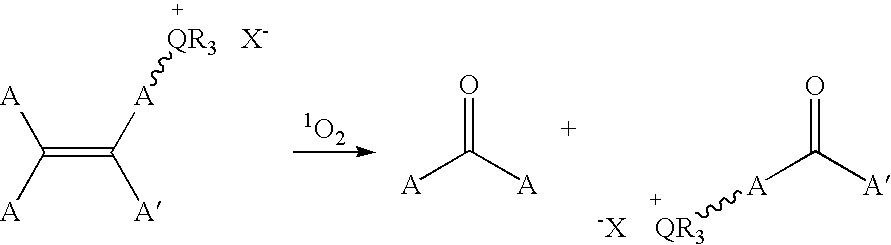
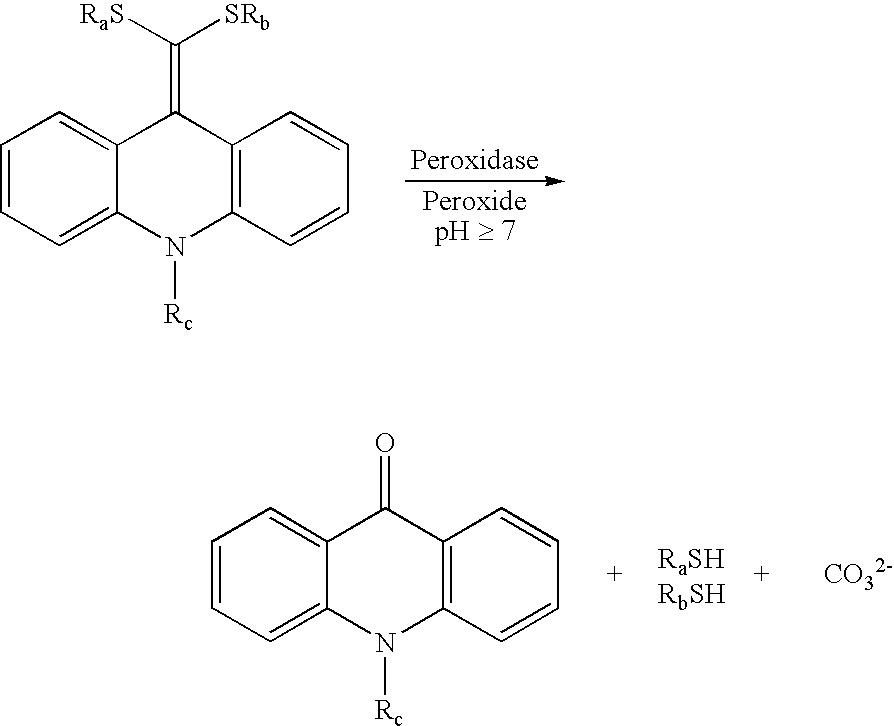
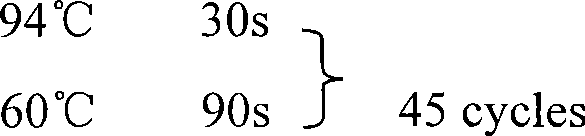Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
119 results about "Genomic rna" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
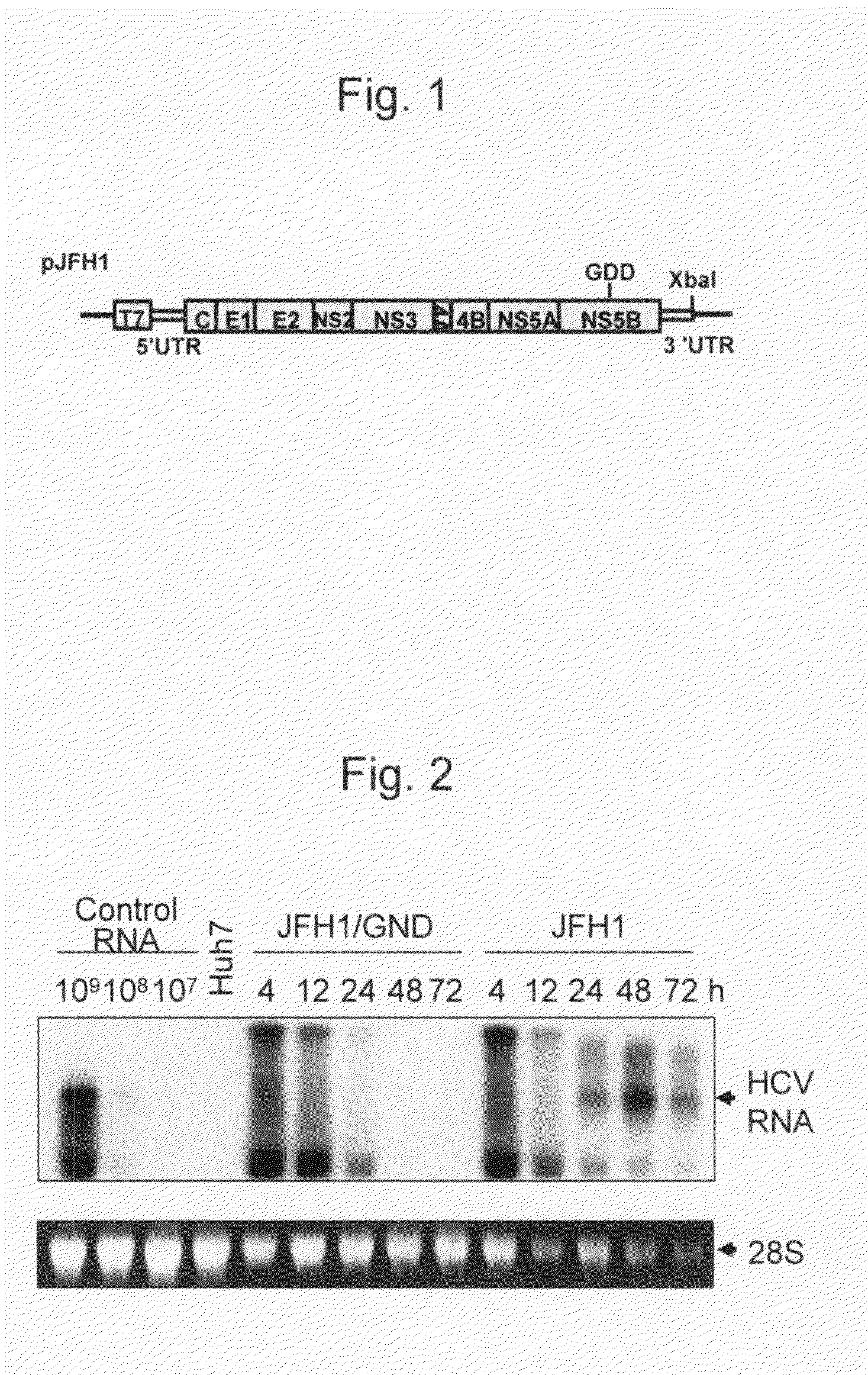
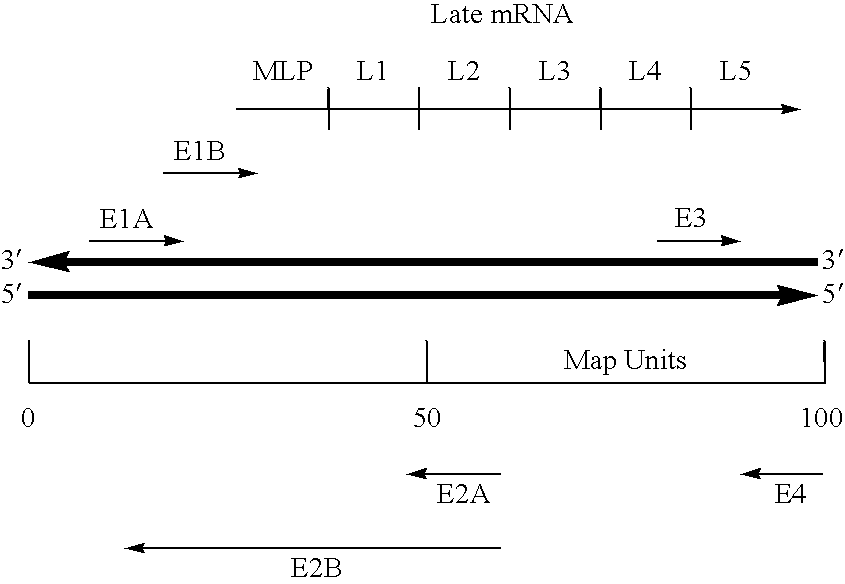
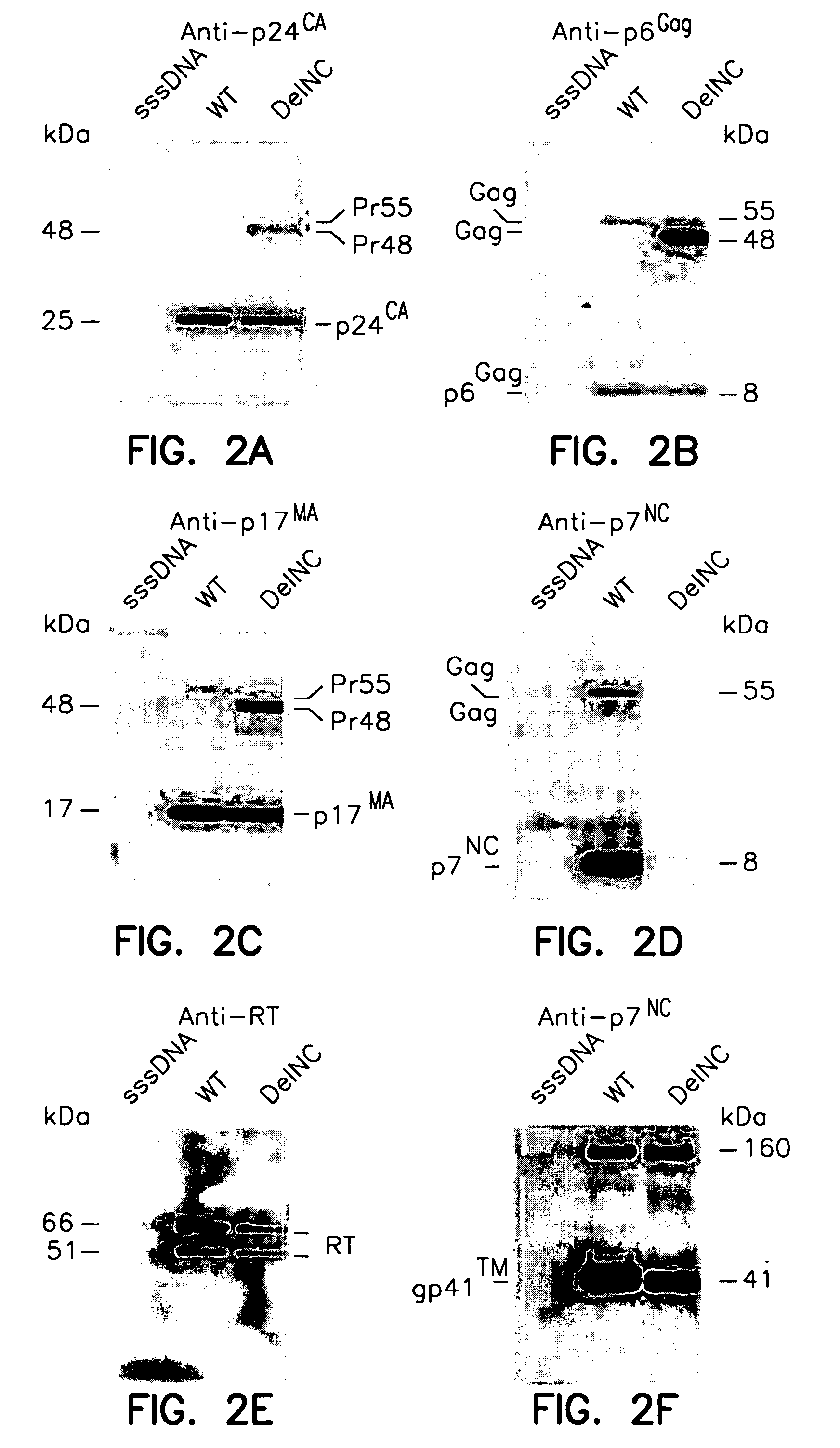
The genomic RNA is about 4.0 kb in size and contains four ORFs. Translation of the genome yields a polypeptide of about 28 kDa encoded by ORF1 and a polypeptide of about 88 kDa (ORF1RT) originating from readthrough of the amber terminator of ORF1.
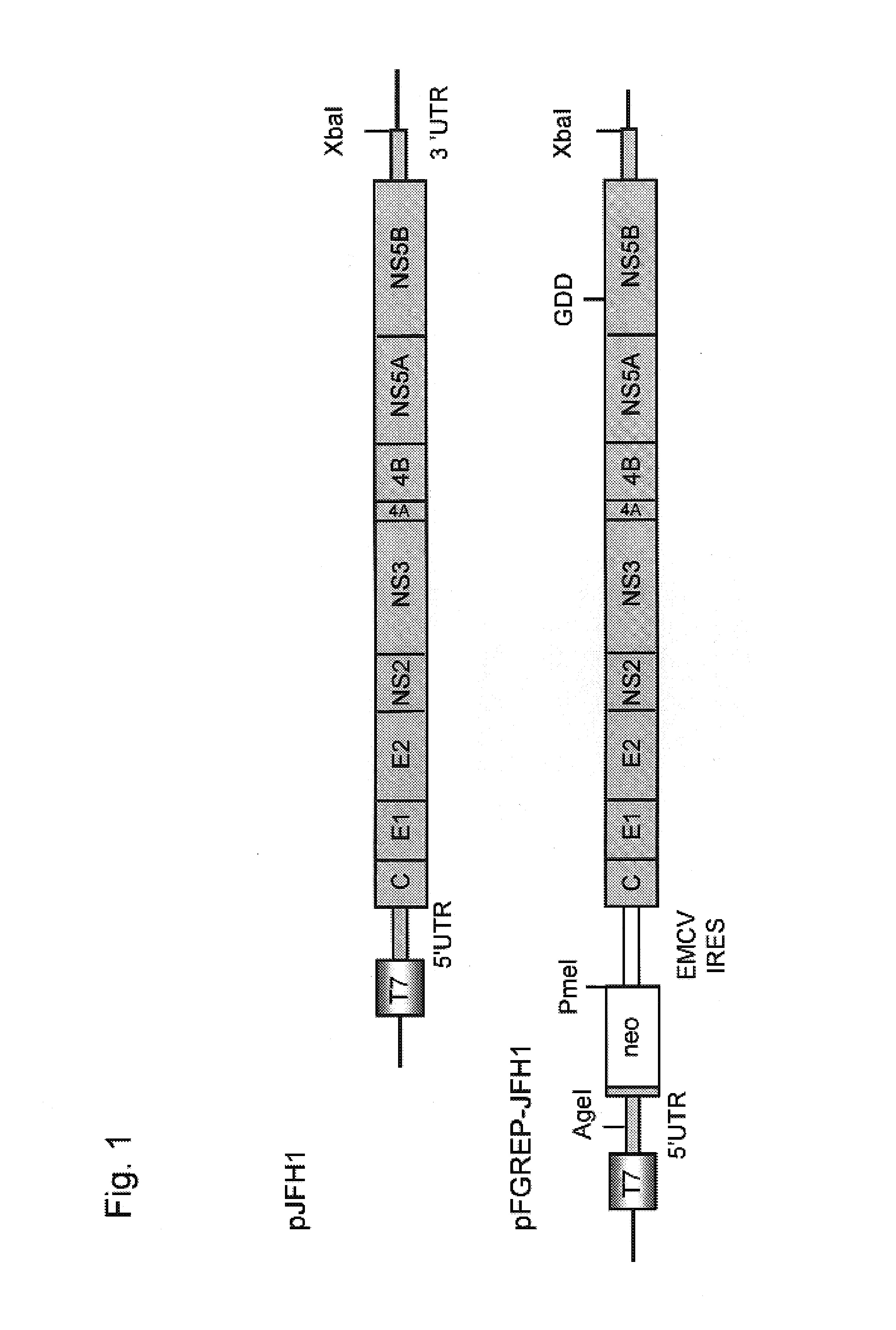
Modified Human Hepatitis C Virus Genomic RNA That can be Autonomously Replicated
ActiveUS20090176200A1Easy to useSsRNA viruses positive-senseGenetic material ingredientsNucleotideGenetics
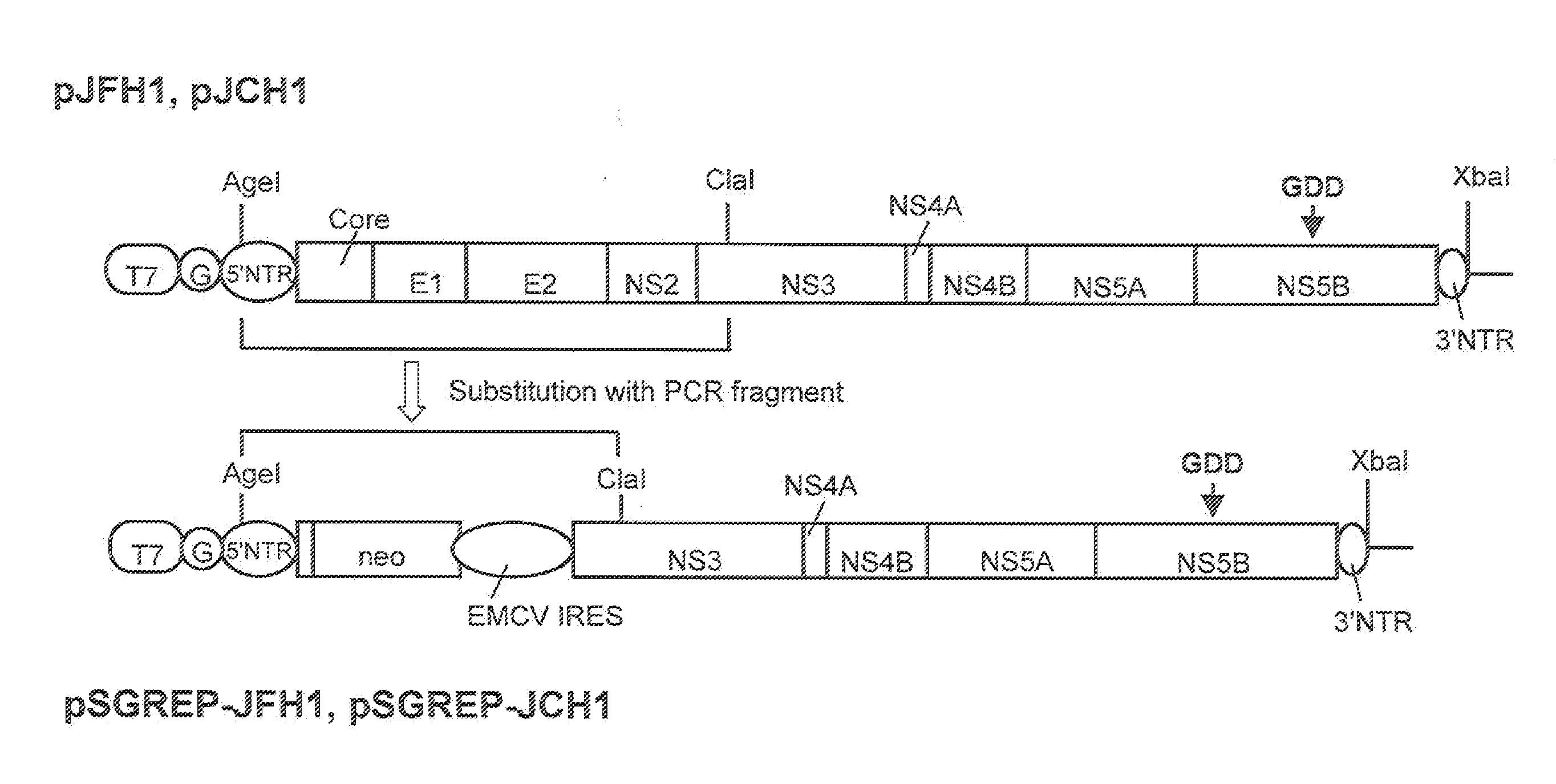
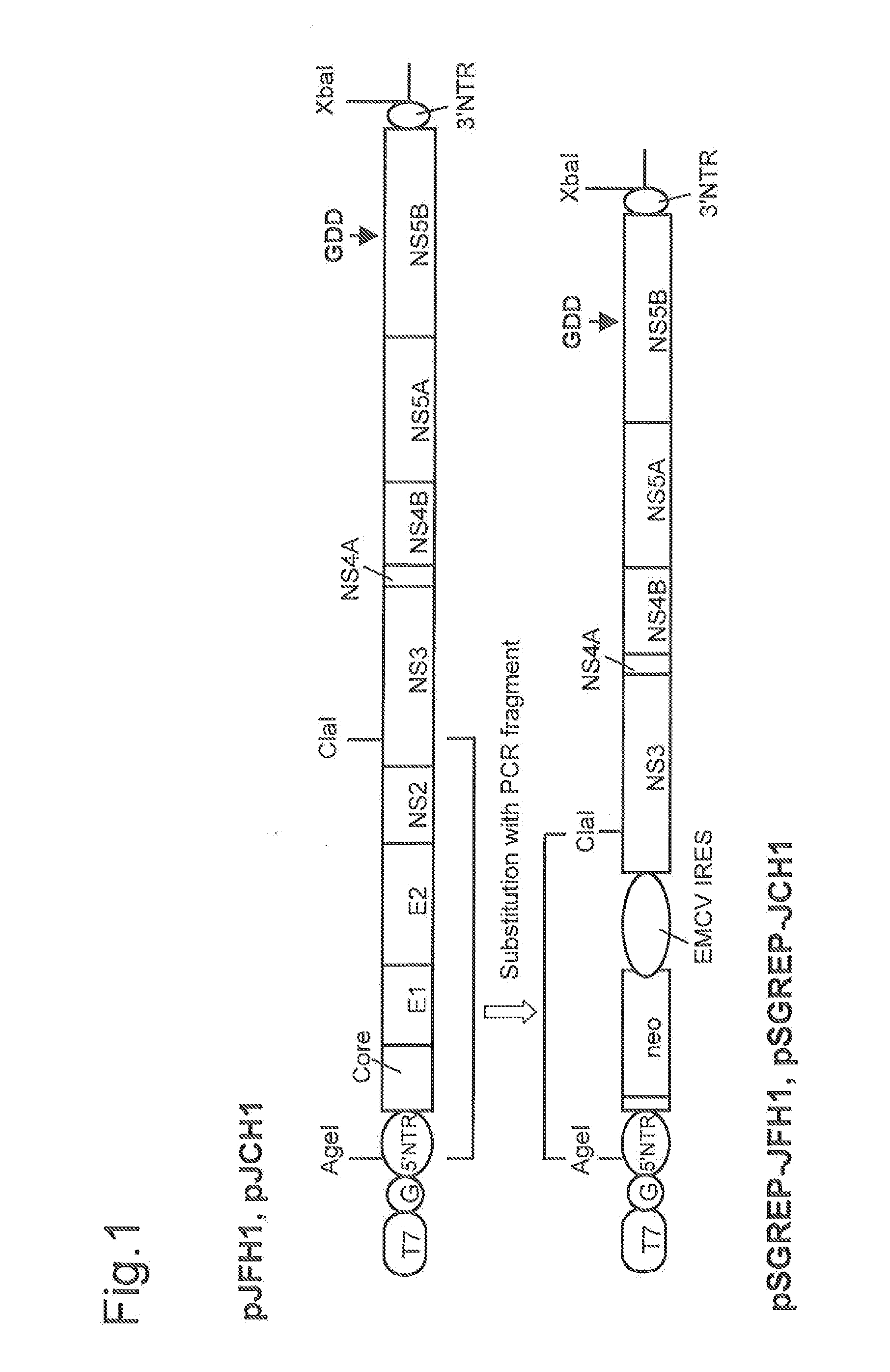
The present invention provides modified hepatitis C virus genomic RNA, comprising nucleotide sequences of genomic RNA portions of two or more types of hepatitis C viruses, which comprises a 5′ untranslated region, a core protein coding sequence, an E1 protein coding sequence, a p7 protein coding sequence, an E2 protein coding sequence, an NS2 protein coding sequence, an NS3 protein coding sequence, an NS4A protein coding sequence, an NS4B protein coding sequence, an NS5A protein coding sequence, an NS5B protein coding sequence, and a 3′ untranslated region, and which can be autonomously replicated. In particular, the present invention relates to modified hepatitis C virus genomic RNA, which can be autonomously replicated by substitution of the RNA sequence portion encoding NS3, NS4, NS5A, and NS5B proteins of hepatitis C virus genomic RNA with a partial RNA sequence encoding NS3, NS4, NS5A, and NS5B proteins of a JFH1 strain shown in SEQ ID NO: 1.
Owner:TORAY IND INC +1
Oxazolidinones Bearing Antimicrobial Activity Composition and Methods of Preparation
The present invention concerns recombinant DNA's comprising cDNA of genomic RNA of a Salmonidae alphavirus preceded by a spacer sequence, under the control of a suitable promoter. Said recombinant DNA's are useful for obtaining expression vectors, producing recombinant Salmonidae alphavirus, and for obtaining vaccines.
Owner:SINDKHEDKAR MILIND D +4
Characterization of the earliest stages of the severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) virus and uses thereof
InactiveUS20050112554A1Insufficient infectivitySsRNA viruses positive-senseSugar derivativesVirulent characteristicsMortality rate
Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome (“SARS”) is a human respiratory disease of recent origin, widespread infectivity, recurring incidence, and significant mortality. Although there is abundant evidence suggesting that the coronavirus responsible for the disease (“SARS-CoV”) evolves during an outbreak, there is currently little data on the earliest strains of this coronavirus. The present invention is directed to the characterization of the genomic RNA sequences of these earliest SARS coronaviruses, to the identification of nucleotide positions within the SARS-CoV genomic RNA that are characteristic of the different evolutionary stages of the coronavirus, to kits based on these positions for use in diagnosis of the disease in patients, and for the development of vaccines to the disease based on the lowered virulence and contagiousness of these earliest strains of SARS-CoV.
Owner:CHINESE HUMAN GENOME CENT AT SHANGHAI
Viral vector
InactiveUS20050106559A1Level of genomic RNA availableImprove the level ofVectorsSugar derivativesNucleic acid sequencingViral vector
Provided is a multicistronic retroviral vector genome having a first nucleic acid sequence upstream of at least one internal regulatory element, such that the level of genomic RNA available for packaging in the absence of rev, or a functional equivalent thereof, is increased.
Owner:OXFORD BIOMEDICA (UK) LTD
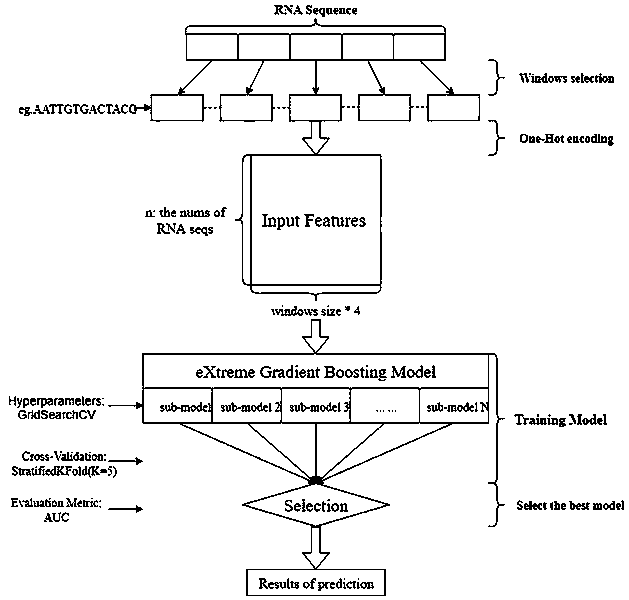
Xgboost-based whole-genome RNA secondary structure prediction method
The invention provides an Xgboost-based whole-genome RNA secondary structure prediction method. The method includes the following steps that: an RNA sequence and the probability values of the pairingof base sites in the RNA sequence are obtained; a base with a high probability of pairing, and bases of a certain length at the upstream and downstream of the bases with the high probability are combined to form sequence fragments, and the sequence fragments are adopted as positive samples; a base with a low probability of pairing, and bases of a certain length at the upstream and downstream of the bases with the low probability are combined to form sequence fragments, and the sequence fragments are adopted as negative samples; the positive samples and the negative samples are combined into sample data sets, and the sample data sets are divided into a training set and a test set, and the training set and the test set are loaded into a machine learning model established based on the Xgboostalgorithm, and the machine learning model is trained and tested; and the trained and tested machine learning model is used to predict an RNA secondary structure. With the method adopted, when the RNAforms the secondary structure, the probability scores of the paring of each base site are obtained; and with the probability scores adopted, a judgment basis can be provided for the formation of thesecondary structure in the next step.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Computational strategy for discovering druggable gene networks from genome-wide RNA expression profiles
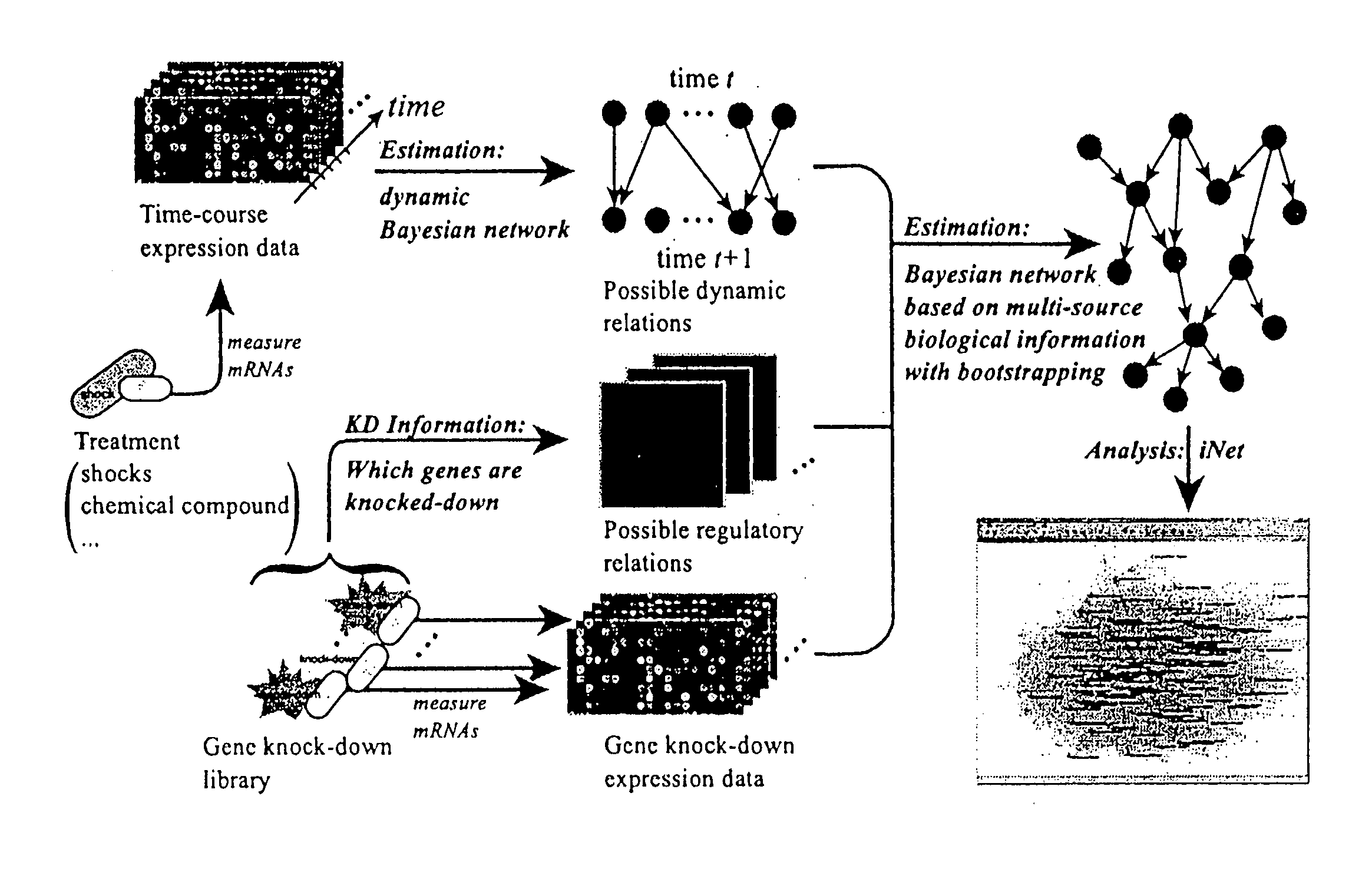
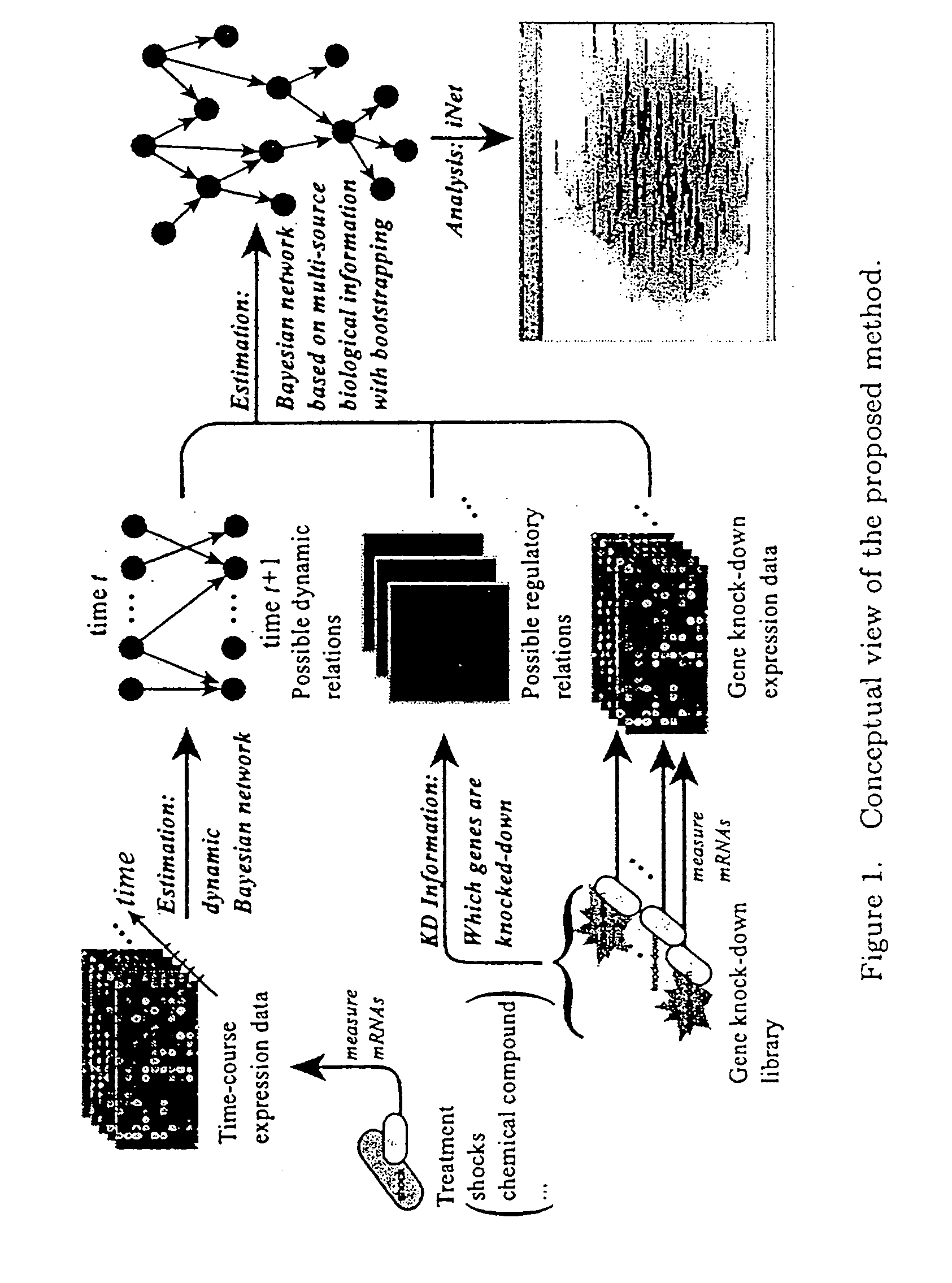
Embodiments of this invention include application of new inferential methods to analysis of complex biological information, including gene networks. New methods include modifications of Bayesian inferential methods and application of those methods to determining cause and effect relationships between expressed genes, and in some embodiments, for determining upstream effectors of regulated genes. Additional modifications of Bayesian methods include use of time course data and use of gene disruption data to infer causal relationships between expressed genes. Other embodiments include the use of bootstrapping methods and determination of edge effects to more accurately provide network information between expressed genes. Information about gene networks can be stored in a memory device and can be transmitted to an output device, or can be transmitted to remote location.
Owner:GNI CO LTD
Methods of extracting RNA
InactiveUS20070185322A1Rapid and simple extractionRapid and simple and isolationSugar derivativesDNA preparationPresent methodLysis
Methods and materials are disclosed for rapid and simple extraction and isolation of RNA from a biological sample involving the use of an acidic solution and a solid phase binding material that has the ability to liberate nucleic acids from biological samples, including whole blood, without first performing any preliminary lysis to disrupt cells or viruses. No detergents or chaotropic substances for lysing cells or viruses are needed or used. Viral, bacterial and mammalian genomic RNA can be isolated using the method of the invention. RNA isolated by the present method is suitable for use in downstream processes such as RT-PCR.
Owner:NEXGEN DIAGNOSTICS LLC
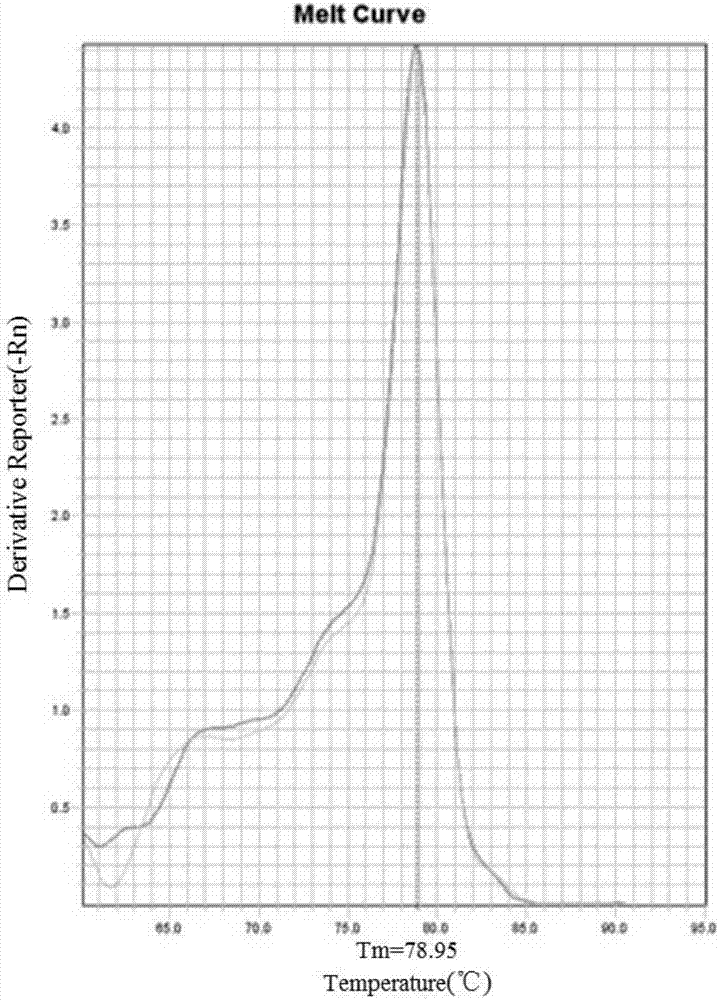
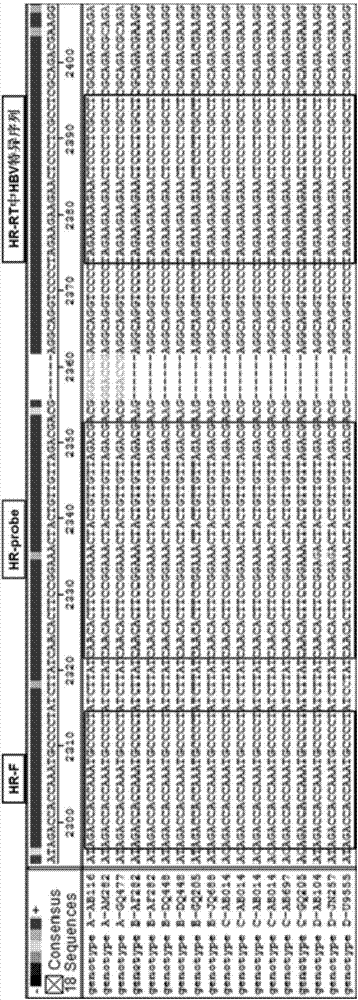
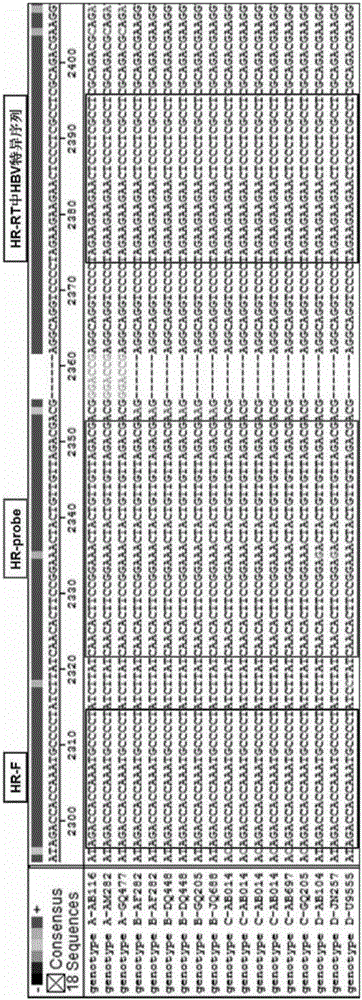
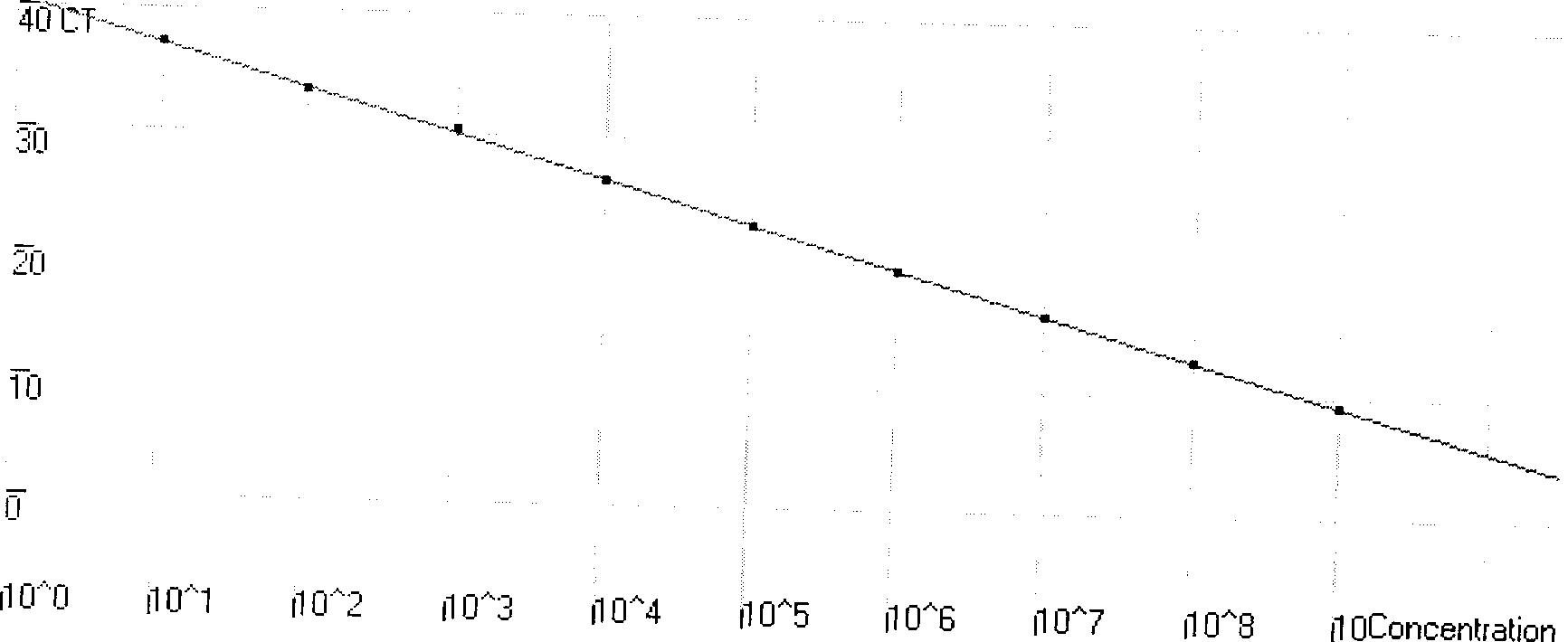
Highly sensitive and specific fluorescent quantitative PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) detection system and detection method for HBV (Hepatitis B Virus) pgRNA (pregenome Ribonucleic Acid) in blood
ActiveCN107058623AGuaranteed specificityEliminate distractionsMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationForward primerNucleotide
The invention discloses a fluorescent quantitative PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) detection system for HBV (Hepatitis B Virus) pgRNA (pregenome Ribonucleic Acid) in blood and a method for detecting the HBV pgRNA by utilizing the detection system. The detection system comprises a forward primer, a reverse primer, a reverse transcription primer with a random anchoring primer and a probe, wherein the nucleotide sequence of the forward primer is as shown in SEQ NO: 1; the nucleotide sequence of the reverse primer is as shown in SEQ NO: 2; the nucleotide sequence of the reverse transcription primer is as shown in SEQ NO: 3; the nucleotide sequence of the probe is as shown in SEQ NO: 4. The detection system and the method which are provided by the invention are adopted to be capable of being used for preparing an HBV diagnostic reagent or kit. By using the detection system and the method, the possible interference brought by HBV DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) or other RNA in a detection process is eliminated; the detection specificity of the HBV pgRNA in the blood is ensured.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
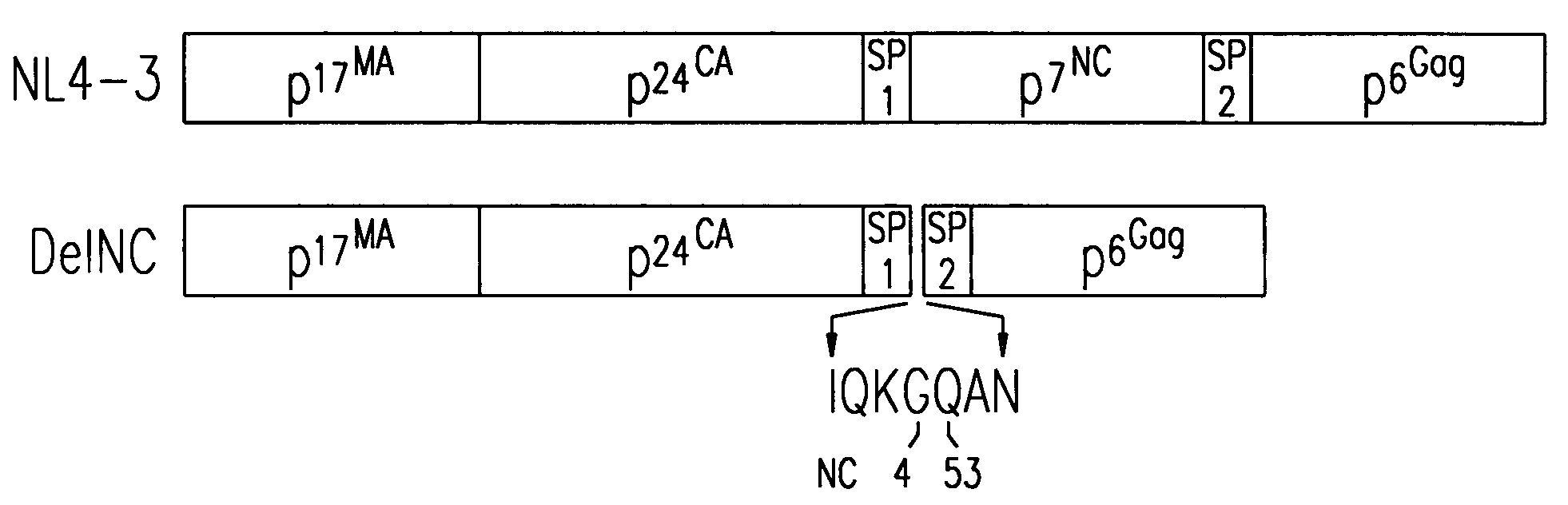
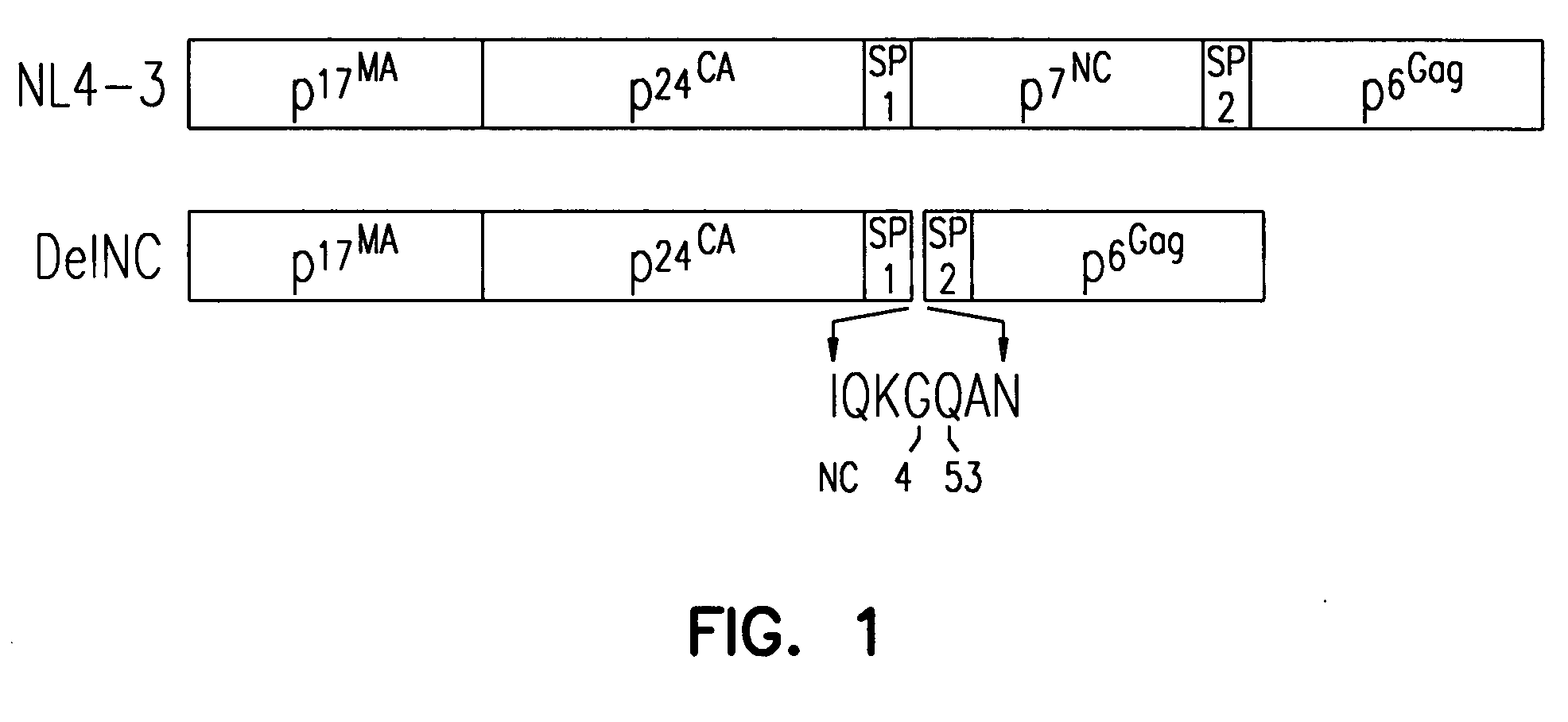
Retrovirus-like particles and retroviral vaccines
The invention relates to retrovirus-like particles having an altered nucleocapsid domain that inhibits packaging of genomic RNA into the retrovirus-like particle, and a protease having reduced enzymatic activity. The invention also provides nucleic acid constructs that encode the retrovirus-like particles. Also provided are immunological compositions, vaccines, and DNA vaccines containing the retrovirus-like particles and nucleic acid constructs that can be used to immunize a mammal against infection by a retrovirus. Methods to produce retrovirus-like particles are also provided.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA +1
3′terminal sequence of hepatitis C virus genome and diagnostic and therapeutic uses thereof
InactiveUS6943246B2Effective strikeAlter adverse consequenceOrganic active ingredientsSsRNA viruses positive-senseHCV GenotypingVaccination
The invention relates to the discovery of a novel RNA sequence at the 3′ terminal sequence of hepatitis C virus (HCV) genome RNA. Included in the invention are the 3′ sequence, its complement, and their use for nucleic-acid based diagnostics and for developing and evaluating novel anti-HCV therapies. This sequence element, which is conserved among HCV genotypes, is likely to be essential for viral replication, and required for construction of full-length HCV cDNA clones capable of yielding infectious RNA, progeny virus or replication-competent HCV replicons. Such functional clones are useful tools for evaluation of therapeutic approaches and as substrates for developing candidate attenuated or inactivated HCV derivatives for vaccination against HCV.
Owner:WASHINGTON UNIV IN SAINT LOUIS
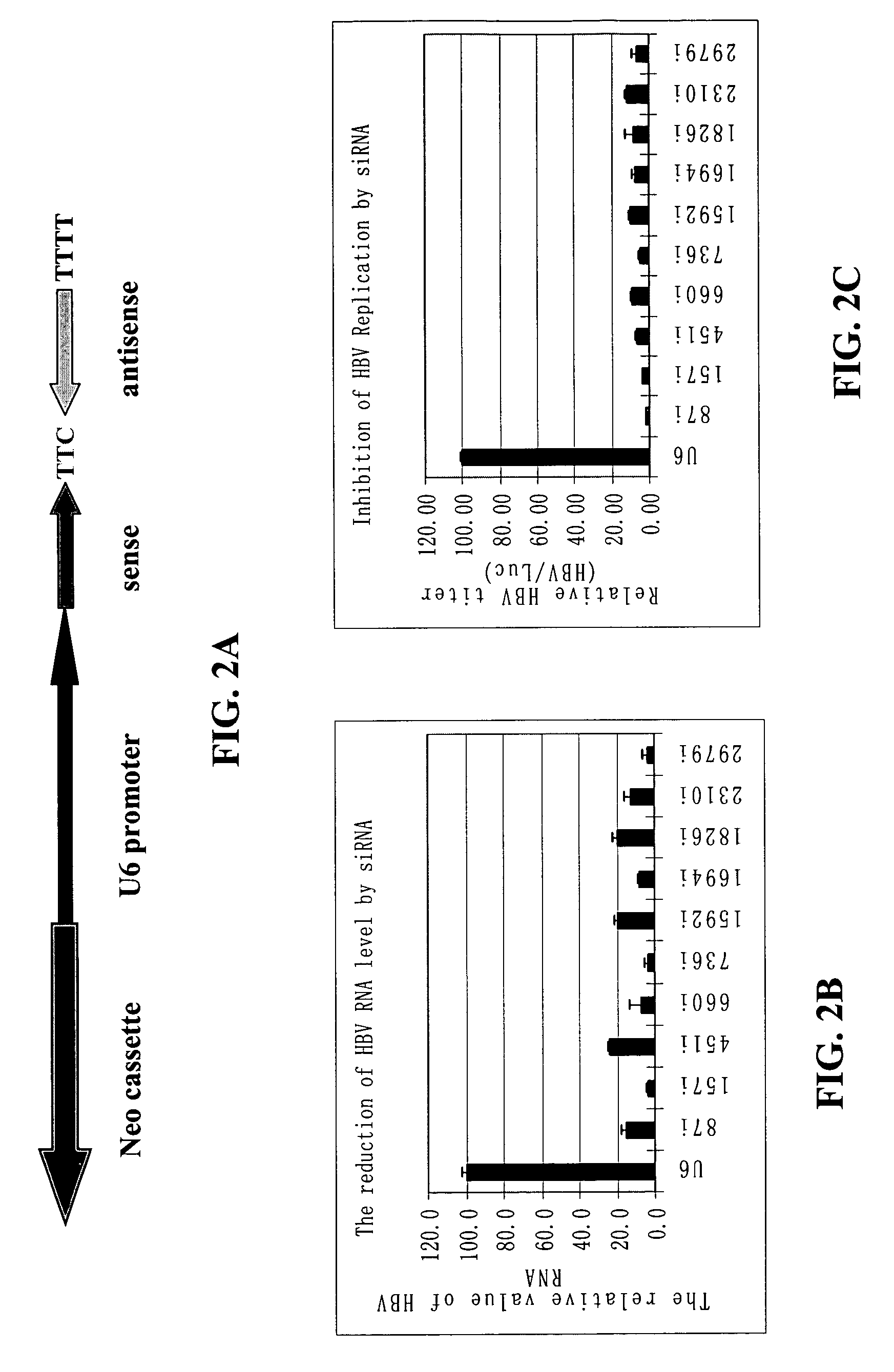
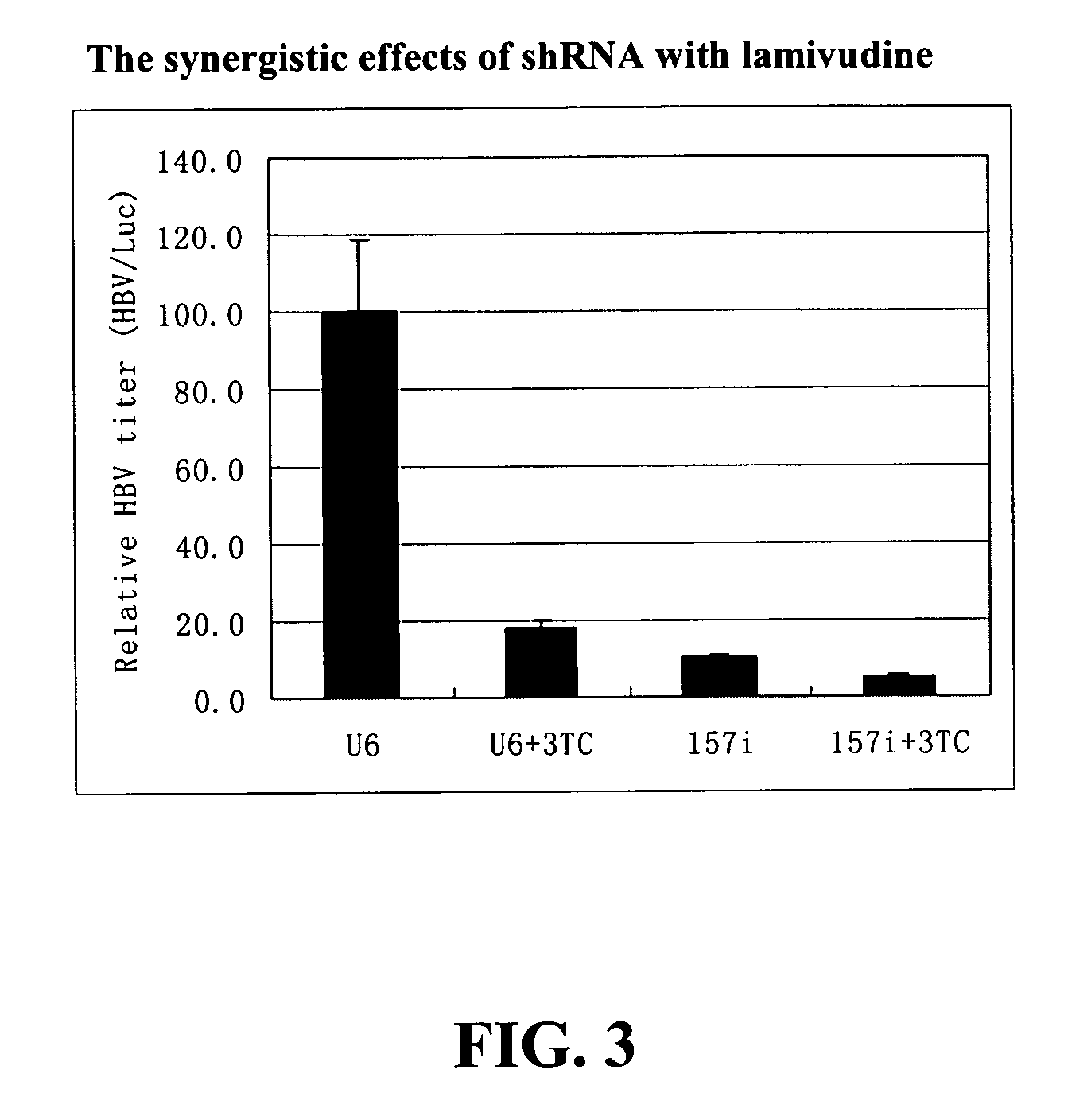
Inhibition of hepatitis B virus (HBV) replication by RNA interference
ActiveUS7067249B2Inhibit expressionObstruction is producedSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementMessenger RNARadiation therapy
The present invention relates to the inhibition of Hepatitis B virus (HBV) replication by RNA molecules of the present invention. Specifically, the RNA molecules of the present invention are double-stranded ribonucleic acid molecules (dsRNA). Specifically, the invention relates to small interfering RNAs (siRNA) which are double-stranded RNAs that direct the sequence-specific degradation of messenger RNA in mammalian cells. The invention relates to development of a new anti-HBV therapy by inhibition of Hepatitis B Virus (HBV) replication using stably-expressed short hairpin RNAs (shRNA), which degrade HBV pregenomic RNA and message RNAs. Included are methods of treatment of cancer by the administration of RNA molecules of the present invention in combination with surgery, alone or in further combination with standard and experimental chemotherapies, hormonal therapies, biological therapies / immunotherapies and / or radiation therapies.
Owner:THE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG
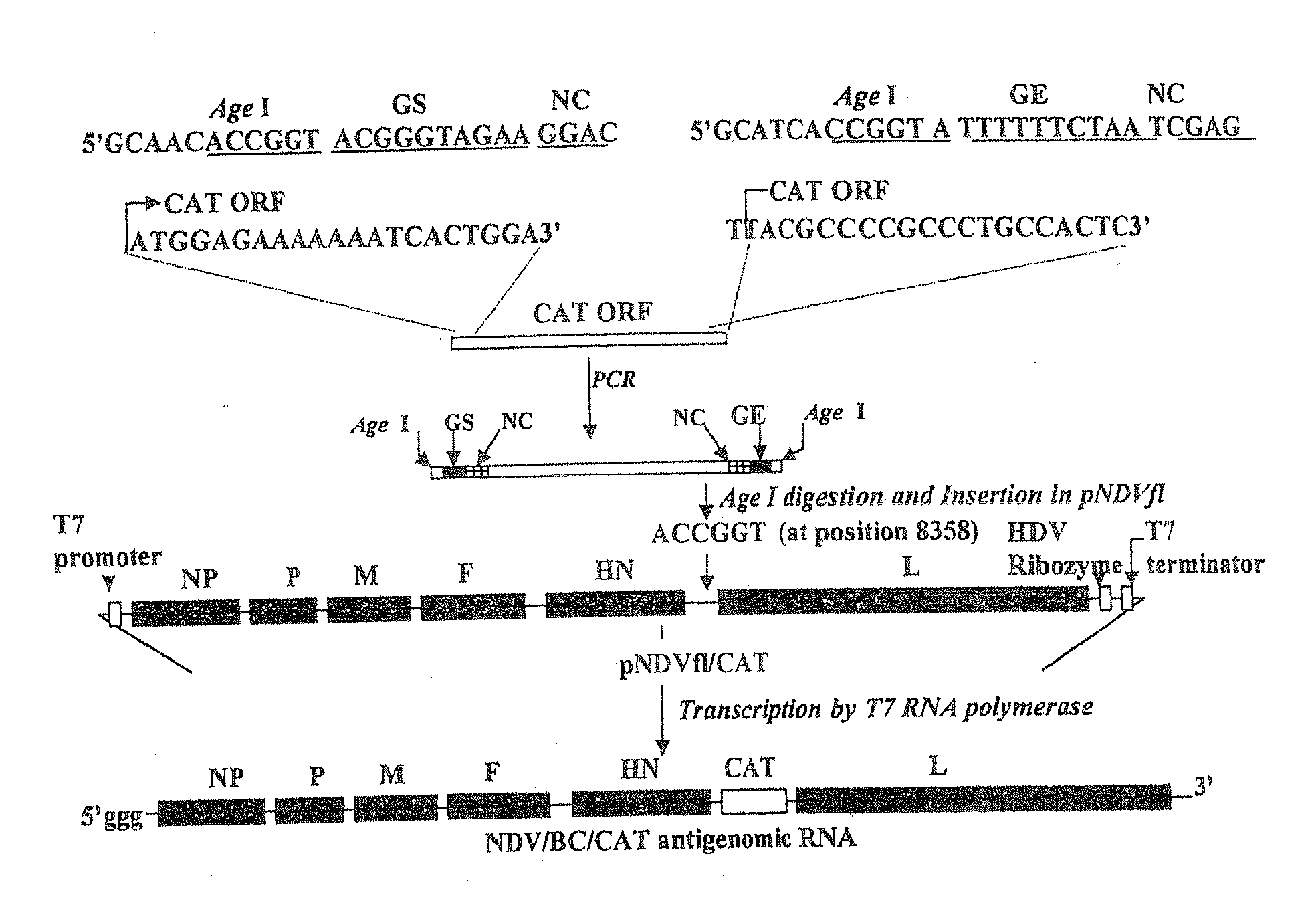
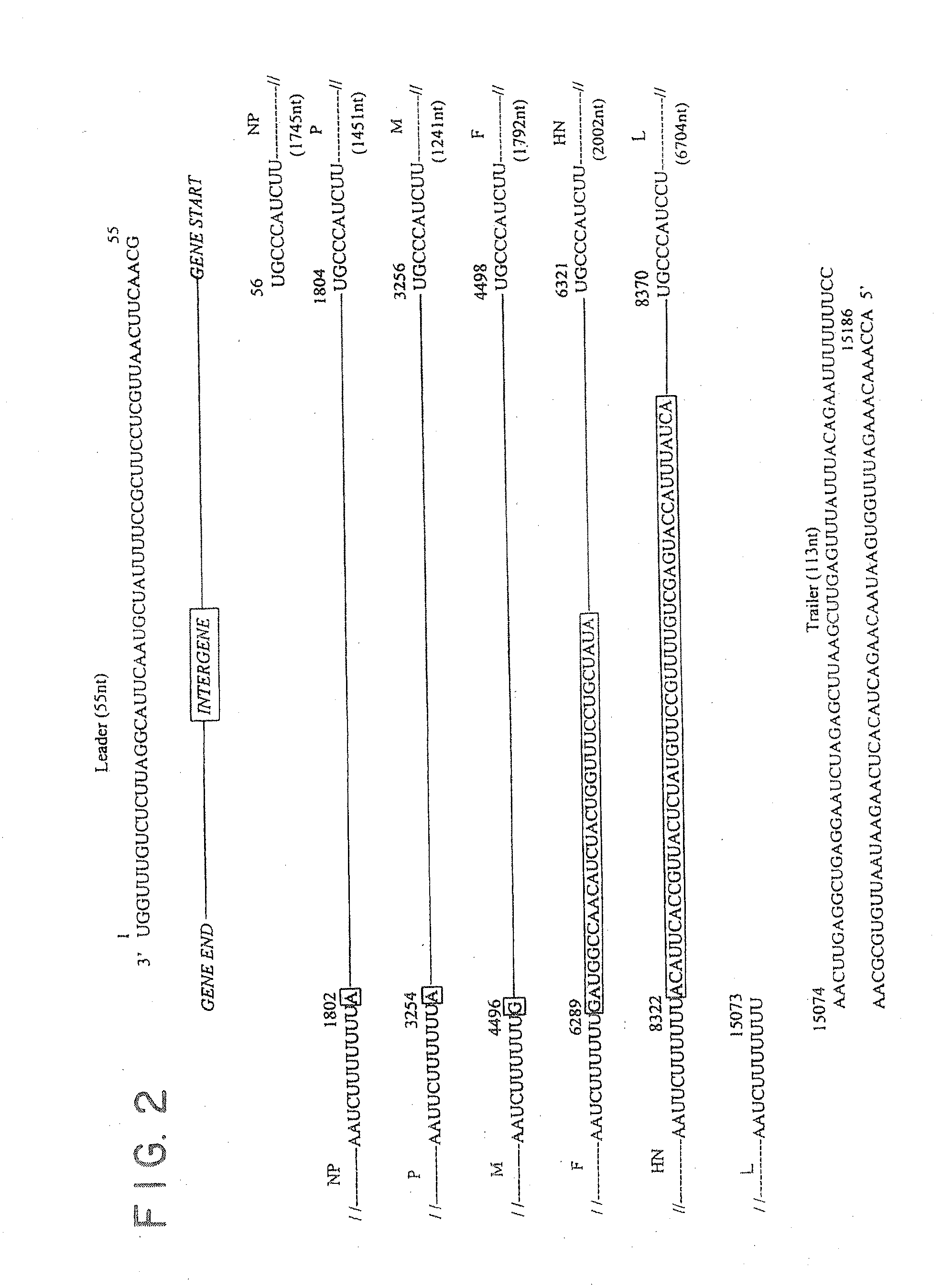
Recombinant newcastle disease viruses useful as vaccines or vaccine vectors
InactiveUS20120064112A1SsRNA viruses negative-senseAnimal cellsCompetent cellNewcastle disease virus NDV
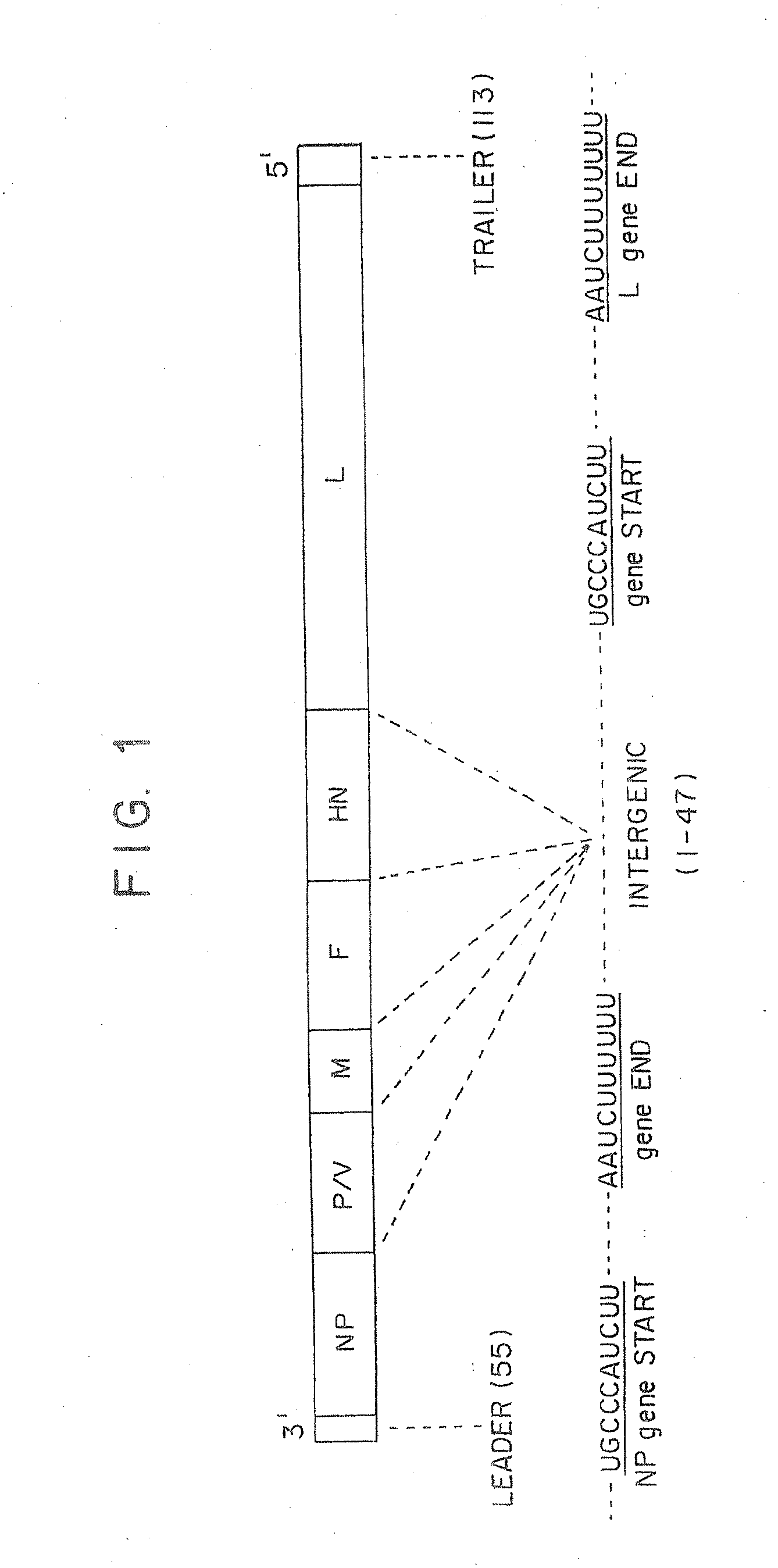
The present invention concerns an antigenomic RNA of Newcastle Disease virus (NDV) carrying one or more foreign genes inserted before NP gene, between P and M genes, and / or between HN and L genes. The invention is also directed toward a cDNA encoding a recombinant antigenomic RNA having one or more foreign genes inserted according to the invention, a cell containing the cDNA, a plasmid comprising the cDNA, a cell containing the plasmid, a cell containing the recombinant antigenomic RNA, and a recombinant NDV containing the recombinant antigenomic RNA of the invention, such as a recombinant NDV carrying one or more foreign genes recovered from transcription of the cDNA or the plasmid in a competent cell. The recombinant NDV carrying the one or more foreign genes can be used as a vaccine or vaccine vector.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND
Vectors with modified protease-dependent tropism
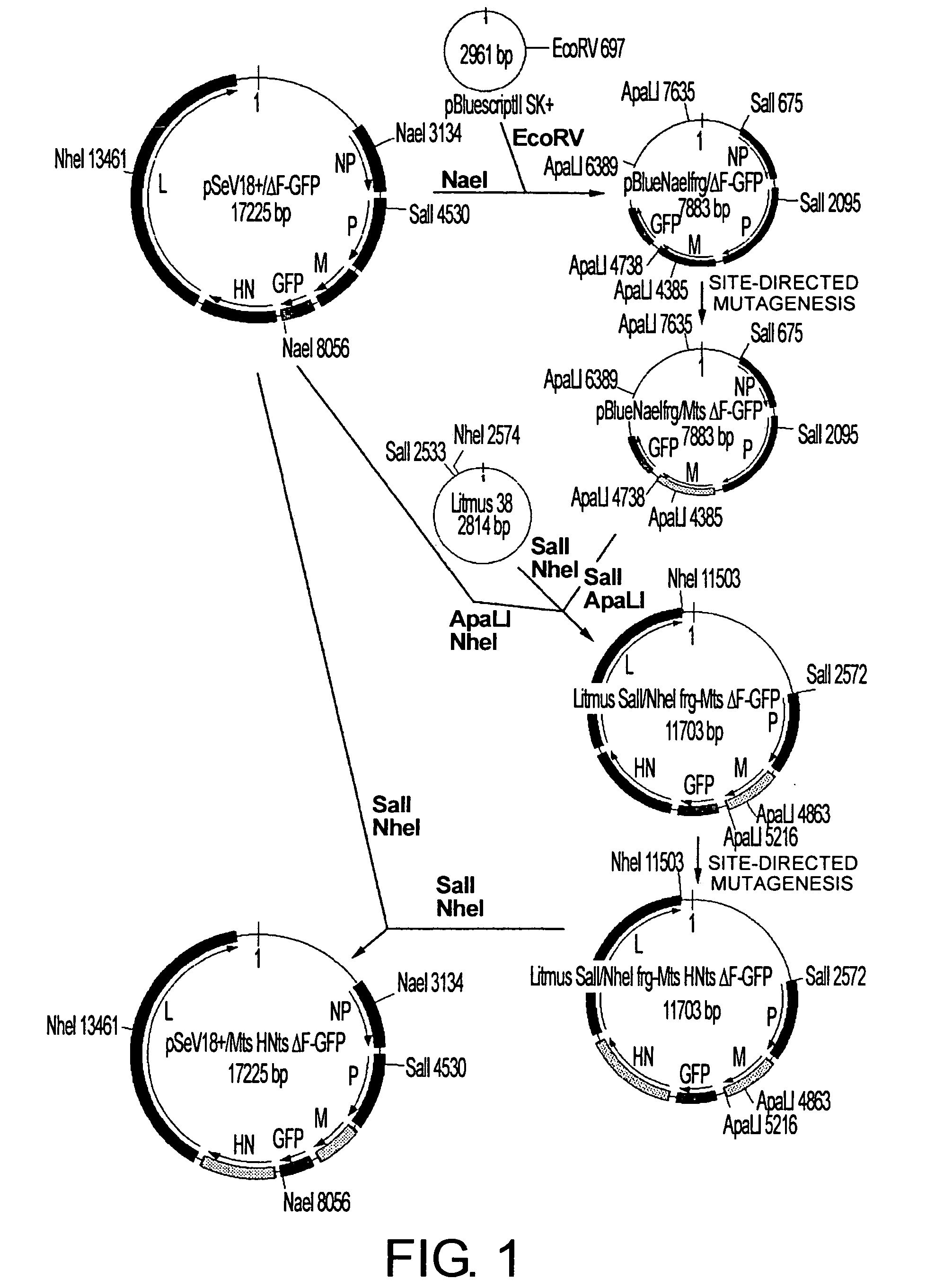
ActiveUS20050221292A1High expressionReduced expression levelSsRNA viruses negative-senseBiocideProteinase activityF protein
The present invention provides cell fusogenic vectors having replicative ability, whose protease-dependent tropism has been modified. M gene-deficient viral vectors encoding modified F proteins, in which the cleavage site of the F protein of paramyxovirus is modified to be cleaved by different proteases, were produced. In cells transfected with these vectors, the genomic RNA present in the vectors is replicated, and cell fusogenic infection spreads to neighboring cells depending on the presence of other proteases; however, no viral particles are released. The vectors of this invention, encoding the F proteins which are cleaved by proteases whose activity is enhanced in cancer, show cancer growth suppressive effect in vivo.
Owner:DNAVEC RES
High-sensitivity and high-specificity fluorescence quantitative PCR detection system and detection method for blood HBV pgRNA
InactiveCN105734173AMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesForward primerNucleotide
Owner:PEKING UNIV
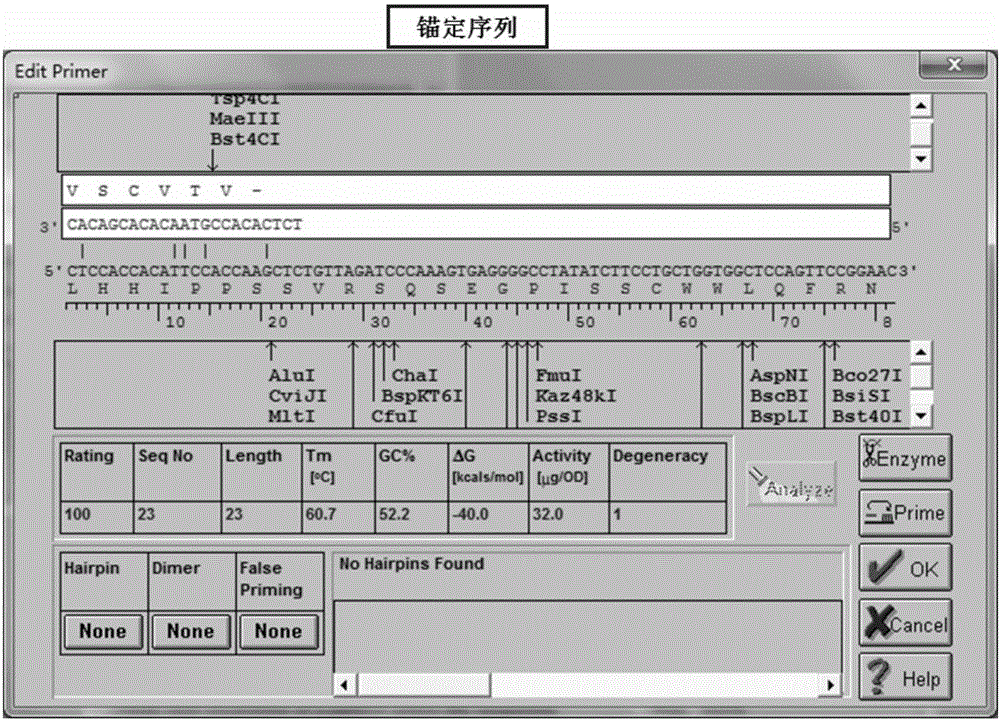
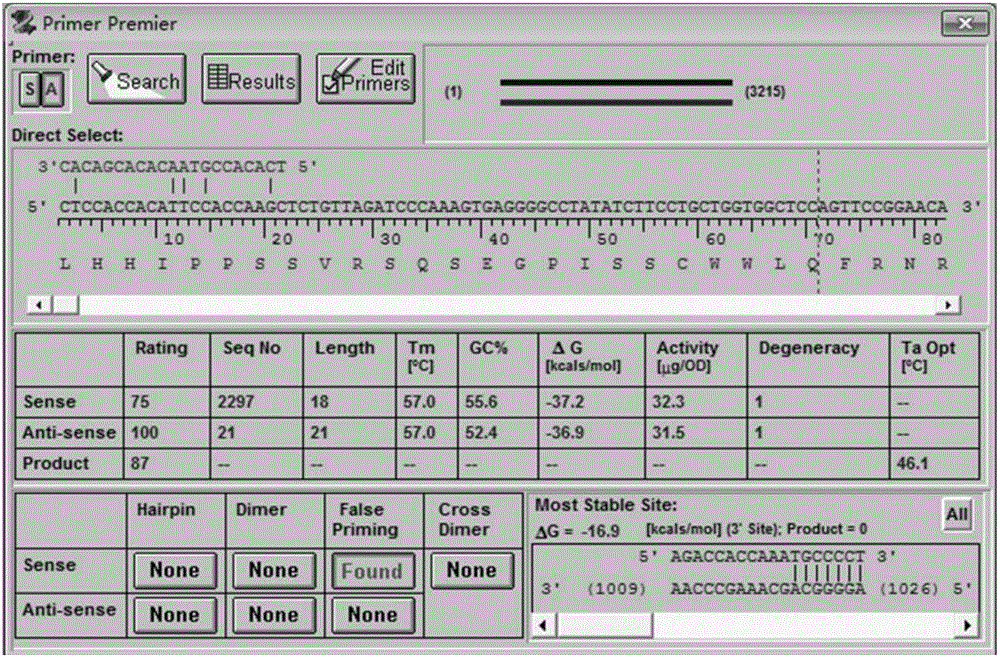
Epidemic encephalitis B/forest encephalitis hybrid virus and application of virus
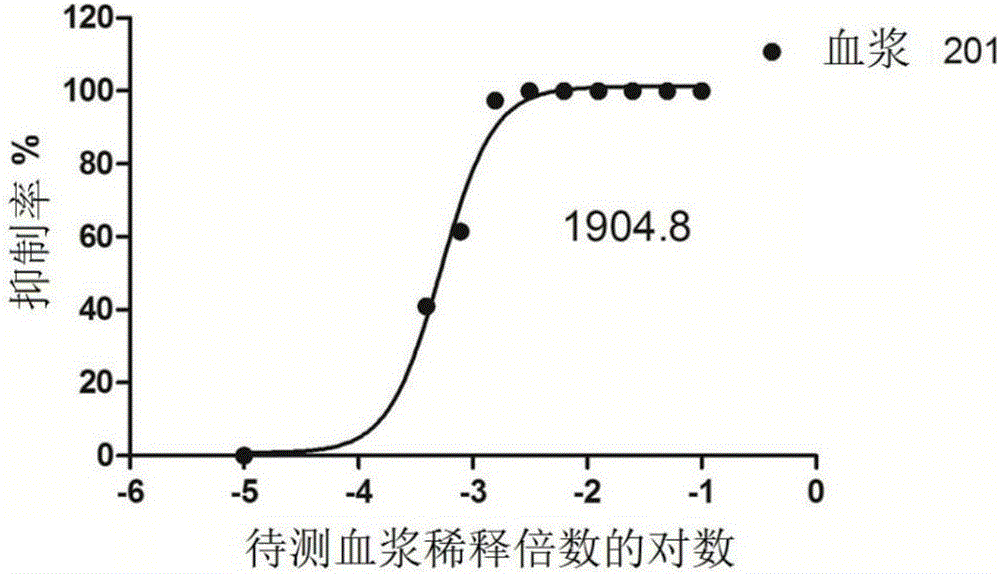
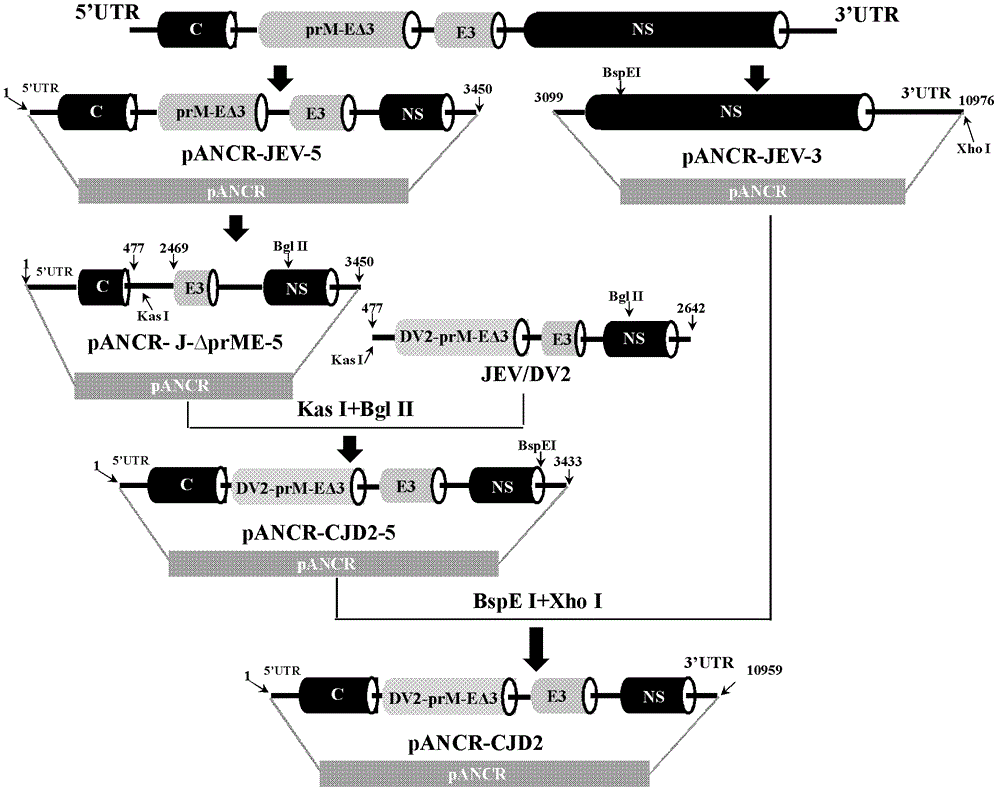
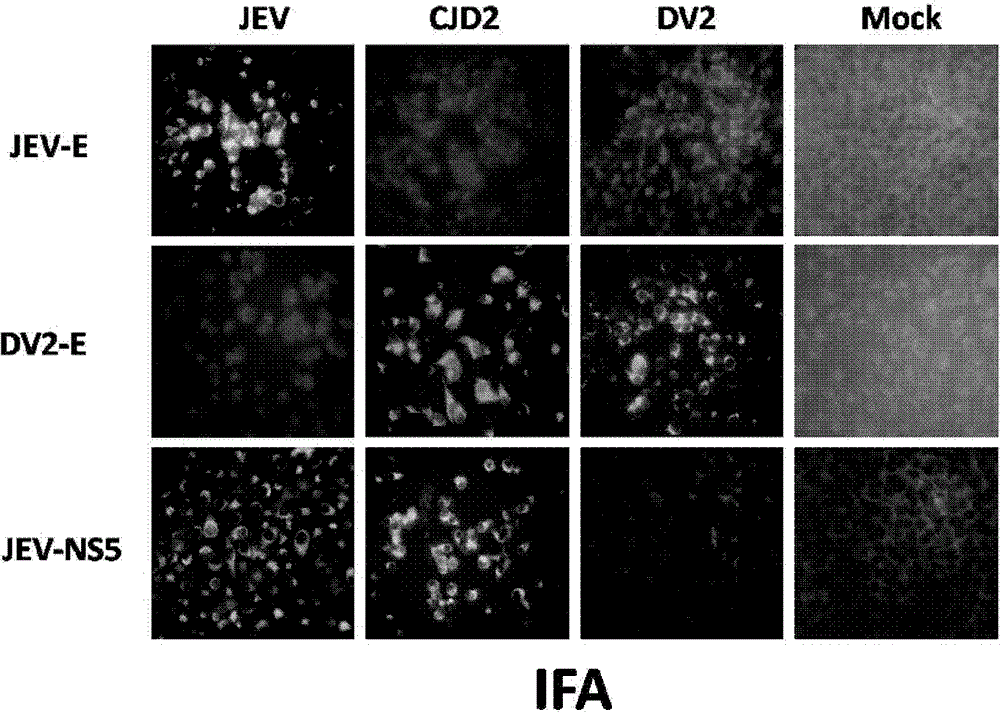
InactiveCN103352029AImprove securityStable attenuation characteristicsViral antigen ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementLethal doseEncephalitis Viruses
The invention discloses an epidemic encephalitis B / forest encephalitis hybrid virus and an application of the virus. The epidemic encephalitis B / forest encephalitis hybrid virus takes an epidemic encephalitis virus attenuated strain as a gene skeleton, and is a recombinant virus obtained by replacing a deoxyribonucleotide fragment of an encoded epidemic encephalitis virus prM-E delta 3 protein in epidemic encephalitis virus genome RNA (Ribonucleic Acid) with a deoxyribonucleotide fragment of an encoded forest encephalitis virus prM-E delta 3 protein in forest encephalitis virus genome RNA. The epidemic encephalitis B / forest encephalitis hybrid virus has the advantages that the virus is high in safety, and strong in stability, and can be induced to generate a good immune response to a forest encephalitis virus envelope protein, and protect an animal from being attacked by the exogenous forest encephalitis virus of lethal dose. The epidemic encephalitis B / forest encephalitis hybrid virus has a good application prospect in preventing and / or treating forest encephalitis virus infection as a vaccine.
Owner:MICROBE EPIDEMIC DISEASE INST OF PLA MILITARY MEDICAL ACAD OF SCI
Sulfamoylbenzamide derivatives as antiviral agents against hbv infection
Owner:BARUCH S BLUMBERG INST +1
Complete virus gene engineering vaccine of aftosa and its preparation method
InactiveCN1602962ANot contagiousLow costSsRNA viruses positive-senseAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsNucleic Acid ProbesViral Vaccine
The invention discloses a kind of foot-and-mouth disease genetic engineering vaccine and its the preparing method.Its structure expression is: Entire virus genetic engineering vaccine: Phage T4-Soc-Hoc-FMDV-P1; Asian unit genetic engineering vaccine: Phage T4-Soc-Hoc-FMDV-F3.The preparing method is: Takes O blood serum foot-and-mouth disease virus poisonous, extracts total gene group RNA; From blood serum poisonous DNA measure foreword to synthesizes two DNA nucleic acid probe;takes the probe as the directing thing, carries on Rt-pcr chain type DNA expand increase response, obtains the viral granule P1gene;gene recombinate the P1gene and the T4bacteriophage material particle, pRH-Soc, obtains T4bacteriophage conformity material particle pRH-Soc-P1;homology reorganizes pRH-Soc-P1with the T4bacteriophage carrier phage T4- í¸ Soc & í¸ Hoc, then enters in the backwoods coli E.coli.CR63host mycelium, obtains this invention genetic engineering vaccine phage T4-Soc-FMDV-P1.compares this invention with the deactivation entire viral vaccine, it does not have to fight fire, maintains the entire viral antigenicity but not have the infection.may inject, also may take orally, convenient, quick, the immunity effect is good.
Owner:任兆钧
Single cell real time fluorescent quantitative RT-PCR method for detecting foot-and-mouth disease virus genome RNA
InactiveCN101386893APerfect research methodWide applicabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescenceNormal cell
The invention discloses a method for detecting real-time fluorescence quantitative RT-PCR of a single cell of foot and mouth disease virus genome RNA. The method utilizes a microinjection instrument to separate single cell of a foot and mouth disease virus; and after cracking, the fluorescence quantitative RT-PCR is used to carry out quantitative analysis. Visible operation of the microinjection instrument can rapidly and accurately separate out the single cell; and the microinjection instrument is combined with the high-sensitivity fluorescence quantitative RT-PCR to realize the detection of the quantity of the virus genome RNA in the single cell. The method can be used for researching virus copying on the level of the single cell and the relation between the single cell and a host cell and provides a new method for in-depth research of virus infection cytobiology. The technology for separating and cracking the cells has wide applicability, can be directly applied to the separating pretreatment of other kinds of virus-infected cells or normal cells in order that the method can be also used for the detection of other RNA virus genomes, the copying of normal cell genomes and the research on a transcribed molecular mechanism.
Owner:广州誉嘉生物科技有限公司
Functionalized benzamide derivatives as antiviral agents against hbv infection
Owner:BARUCH S BLUMBERG INST +1
Method for detecting enterovirus neutralizing antibody and special recombinant virus for method
InactiveCN102911948ALower requirementSimple and fast operationFungiBacteriaHand-foot-and-mouth diseaseGenomic rna
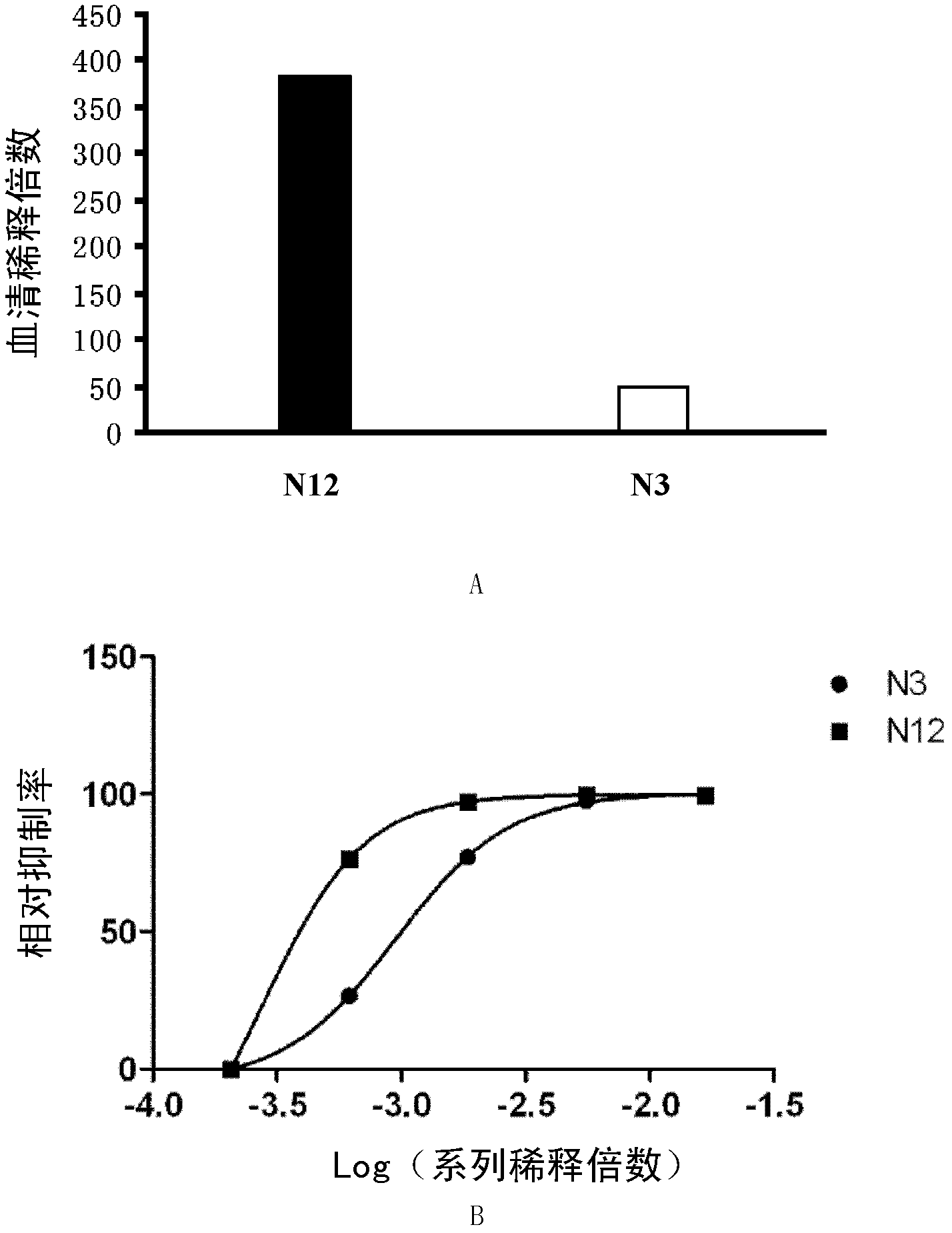
The invention discloses a method for detecting an enterovirus neutralizing antibody and a special recombinant virus for the method and provides a DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) molecule. The DNA molecule is a recombinant DNA obtained by substituting coding genes of all structural proteins in cDNA (complementary DNA) corresponding to genome RNA (ribonucleic acid) of an enterovirus for report genes. An EV71 FY pseudovirus system is used for the method for detecting the neutralizing antibody, and since pseudoviruses subjected to monocyclic infection are adopted, the safety problem during using of live viruses is avoided. After multiple tests, results show that the pseudovirus system is the method for detecting the neutralizing antibody and is safe, sensitive, rapid, specific, simple, convenient and low in cost. Based on the advantages, the pseudovirus system is extremely suitable for rapid and massive neutralizing antibody detection tests, and has important application values for virus vaccine development and detection of hand-foot-and-mouth disease specificity neutralizing antibody level of individual patients and patient populations.
Owner:NAT INST OF BIOLOGICAL SCI BEIJING
NUCLEIC ACID CONSTRUCT CONTAINING A NUCLEIC ACID DERIVED FROM THE GENOME OF HEPATITIS C VIRUS (HCV) OF GENOTYPE 2a, AND A CELL HAVING SUCH NUCLEIC ACID CONSTRUCT INTRODUCED THEREIN
The present invention relates to a replicon RNA comprising a nucleotide sequence at least containing the 5′ untranslated region, the nucleotide sequence encoding NS3 protein, NS4A protein, NS4B protein, NS5A protein and NS5B protein, and the 3′ untranslated region on the genomic RNA of hepatitis C virus of genotype 2a.
Owner:TOKYO METROPOLITAN INST OF MEDICAL SCI
Antiviral agents against HBV infection
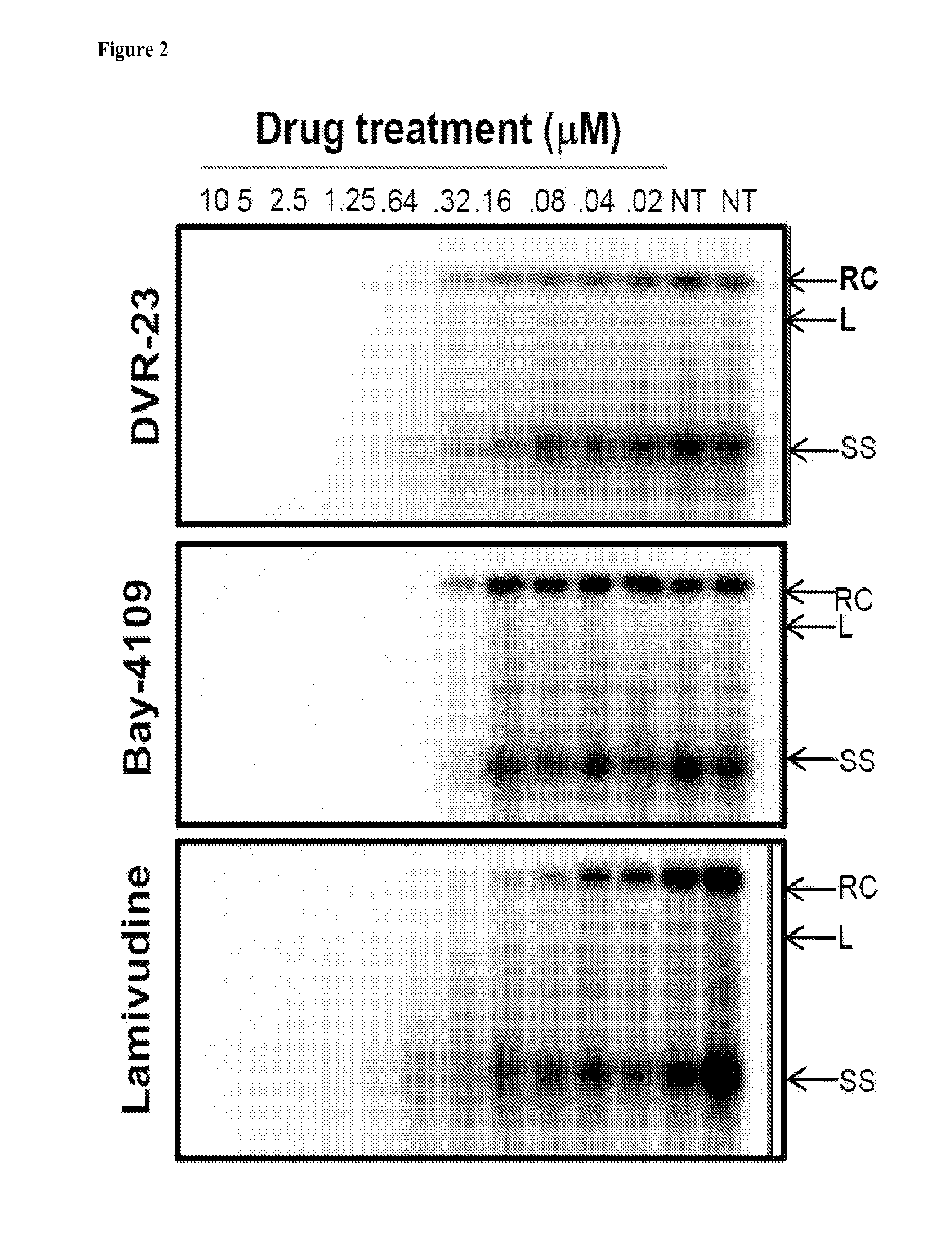
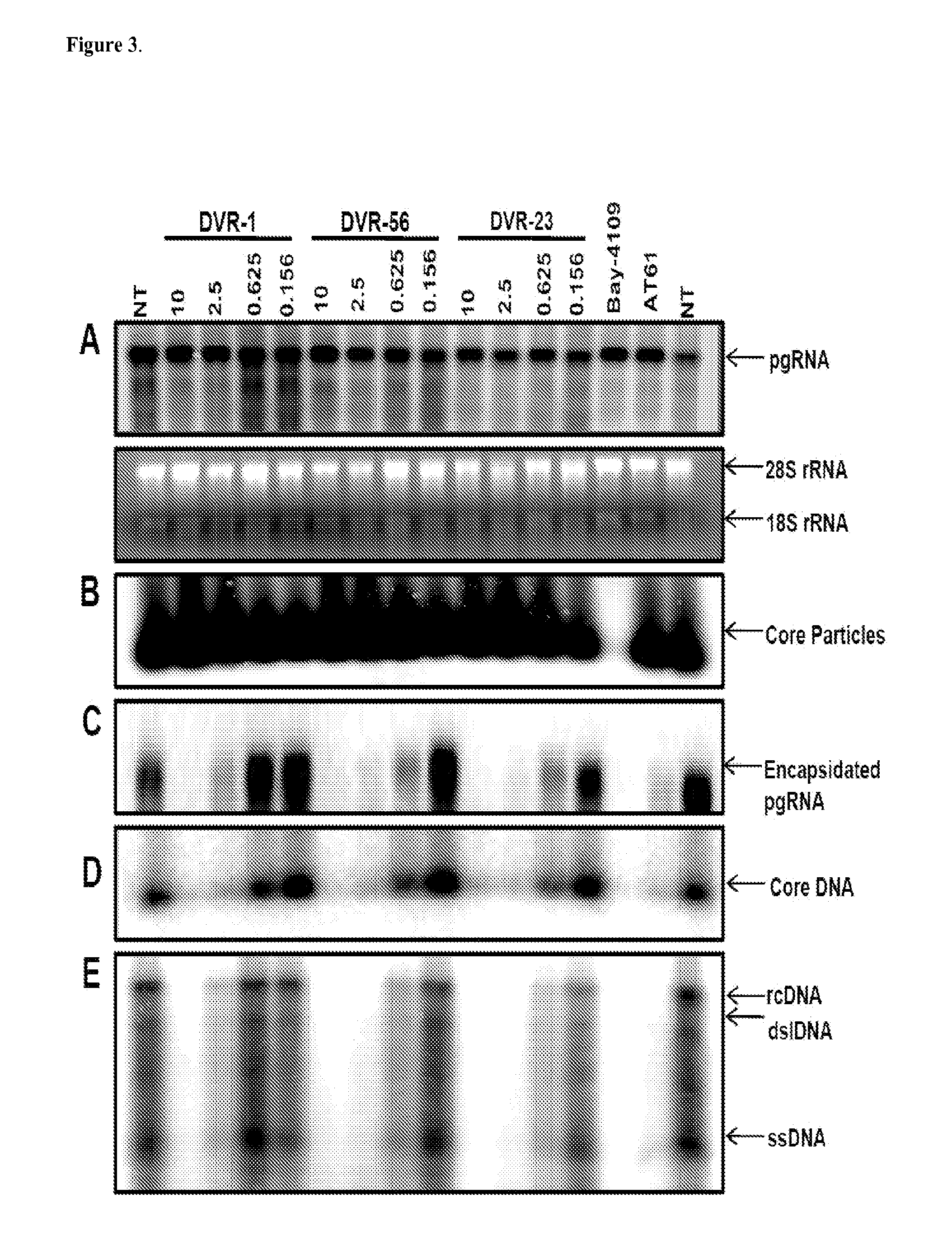
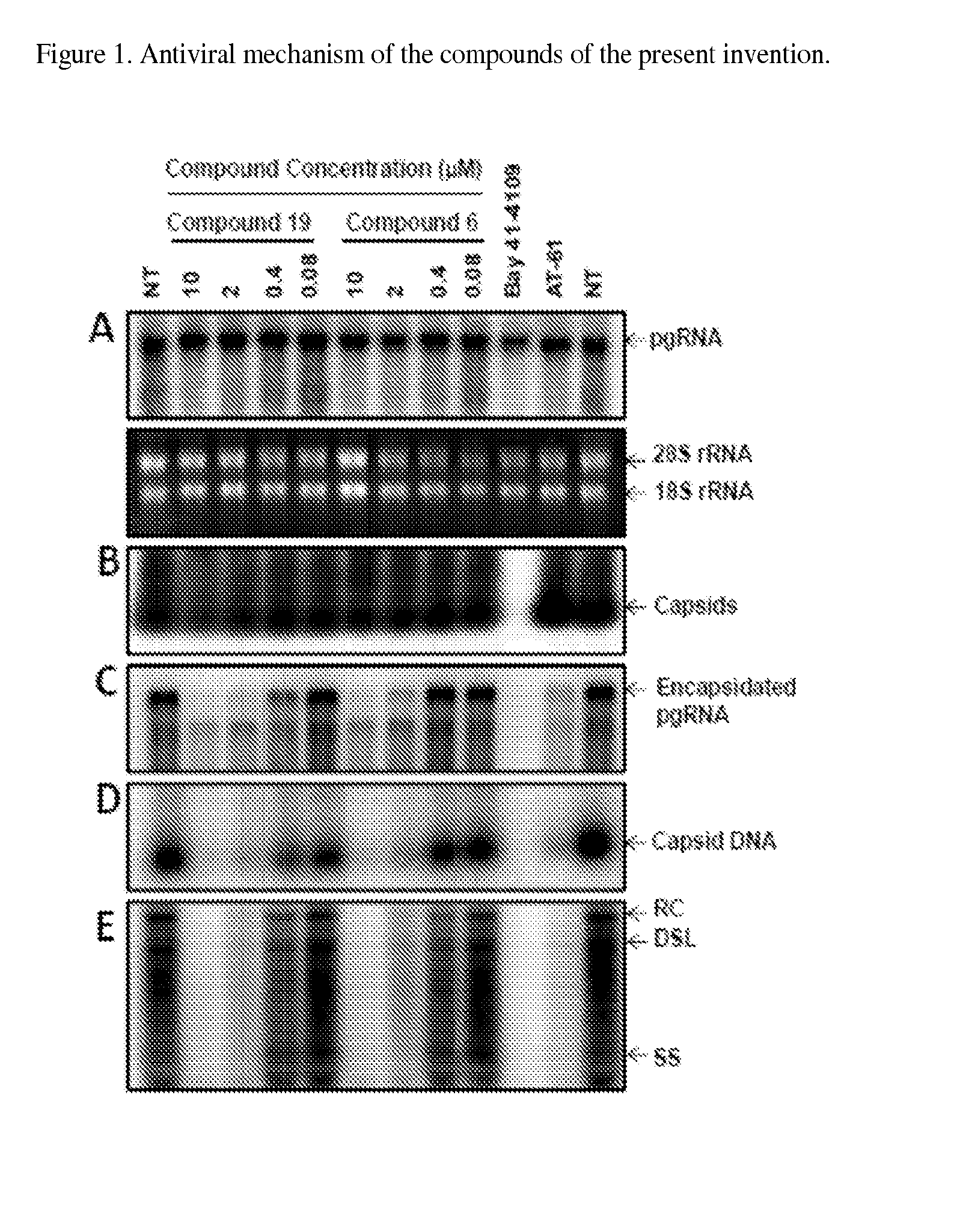
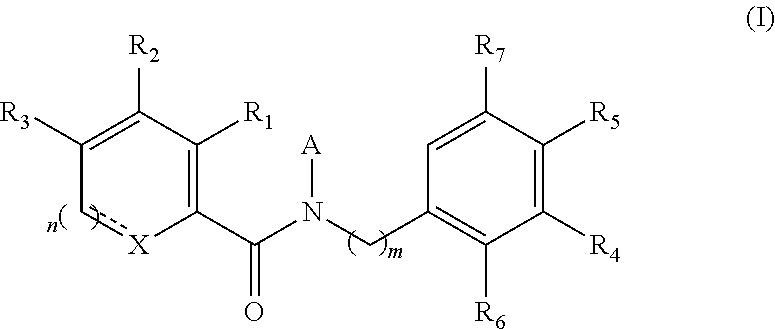
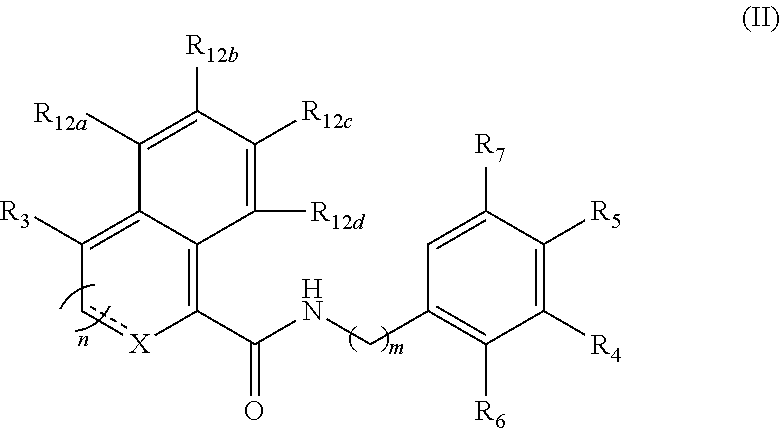
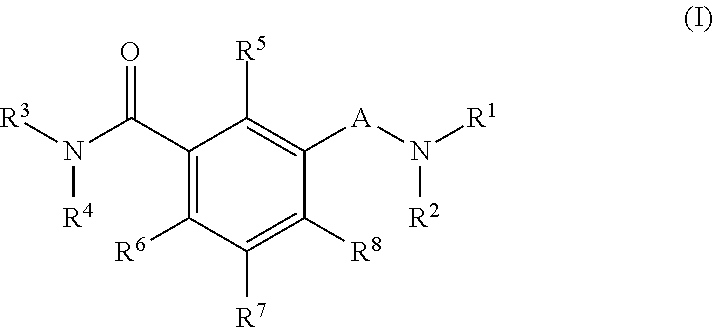
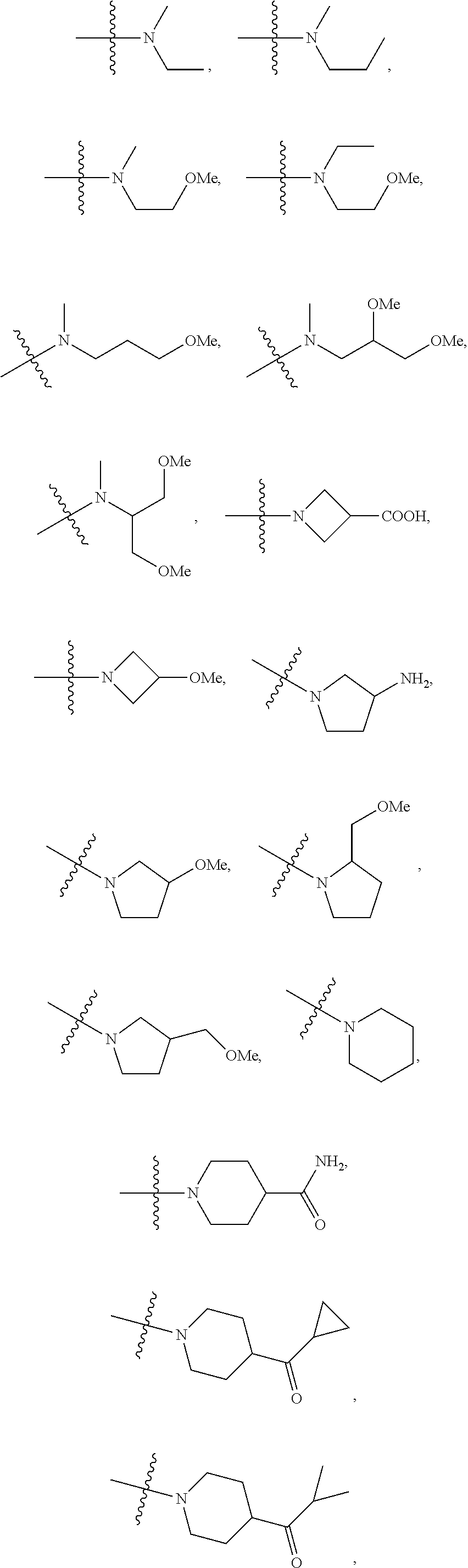
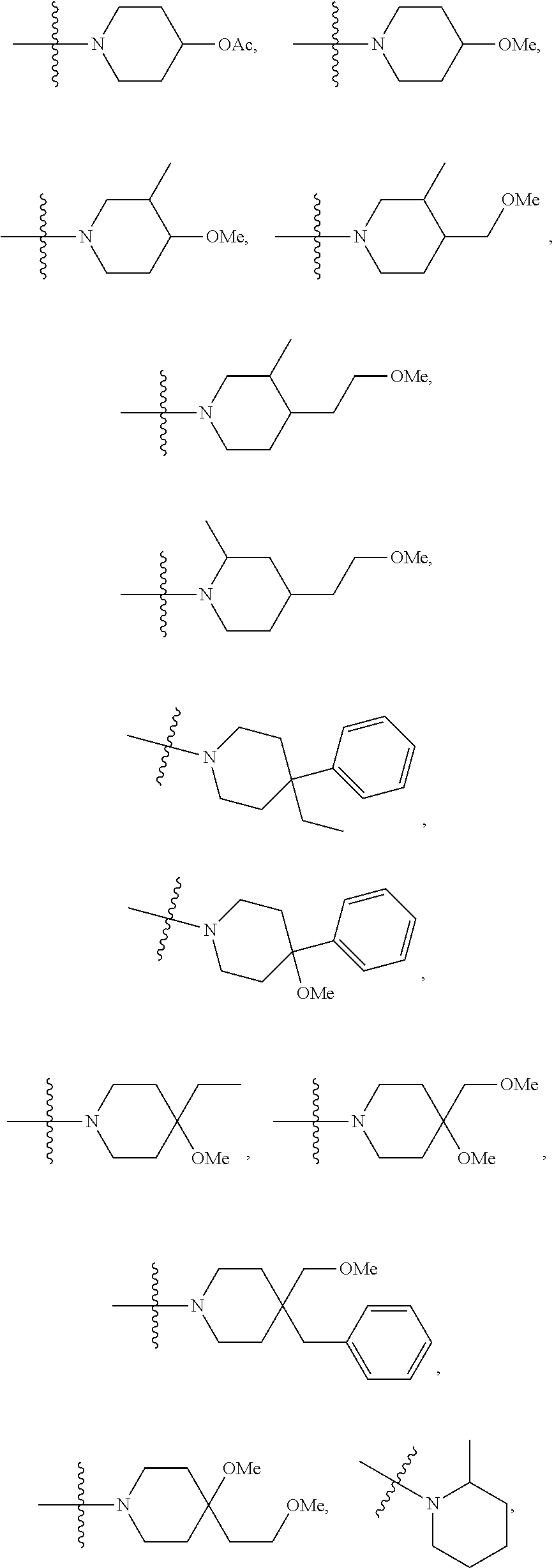
The present invention provides novel compounds of formula (I) and methods of use thereof. In certain embodiments, the compounds of the invention are useful as nucleocapsid assembly inhibitors. In other embodiments, the compounds of the invention are useful as pregenomic RNA encapsidation inhibitors of Hepatitis B virus (HBV). In yet other embodiments, the compounds of the invention are useful for the treatment of viral infection, including HBV and related viral infections.
Owner:BARUCH S BLUMBERG INST +2
Nucleic acid construct containing fulllength genome of human hepatitis C virus, recombinant fulllength virus genome-replicating cells having the nucleic acid construct transferred thereinto and method of producing hepatitis C virus Particle
The present invention provides a method for replicating efficiently an RNA containing fulllength HCV genomic sequence and a method for producing HCV virus particles containing fulllength HCV replicon RNA or fulllength HCV genomic RNA by using a cell culture system. Further, the present invention relates to a method for producing hepatitis C virus particles which comprises culturing a cell, into which a replicon RNA comprising a nucleotide sequence comprising a fulllength genomic RNA sequence of hepatitis C virus of the genotype 2a, at least one selectable marker gene and / or at least one reporter gene and at least one IRES sequence or the fulllength genomic RNA of hepatitis C virus of the genotype 2a is introduced, and generating virus particles in the culture medium. Still further the present invention relates also to a hepatitis C vaccine and an antibody against hepatitis C virus particles.
Owner:TORAY IND INC +1
Recombinant expression plasmids used for packaging coxsackievirus B5 (CV-B5) pseudovirus, pseudovirus, kit and method
PendingCN106884017ADetection securityQuick checkViruses/bacteriophagesFermentationCoxsackievirusStructural protein
The invention relates to recombinant expression plasmids used for packaging a coxsackievirus B5 (CV-B5) pseudovirus, the pseudovirus, a kit and a method. The recombinant expression plasmids used for packaging the coxsackievirus B5 pseudovirus are respectively named as the pEGFP-CV-B5 (417) plasmid and the pCVB3-replicon, the CV-B5 structural protein expressed by the pEGFP-CV-B5 (417) plasmid can be used for packaging CV-B3 subgenome RNA transcribed by the pCVB3-replicon in the cell, thus the CV-B5 pseudovirus is generated, the pseudovirus can be used for detecting the neutralizing antibody, and since the pseudovirus with single-cycle infection is adopted, the safety problem caused when the live virus is used is avoided. After a plurality of experiments, the result shows that the invention provides the method for detecting the CV-B5 neutralizing antibody which is safe, sensitive, rapid, specific, simple and convenient, and is low in cost. Based on the abovementioned features, the method is particularly suitable for the experiment for rapidly detecting the neutralizing antibody in large scale, and thus the method has the significant application value in developing viral vaccines and detecting the level of the CV-B5 specific neutralizing antibody of individual and group patients.
Owner:NAT INST FOR FOOD & DRUG CONTROL
Epidemic encephalitis B/dengue chimeric virus with epidemic encephalitis B virus attenuated strain as gene framework and application of epidemic encephalitis B/dengue chimeric virus
ActiveCN102796749AImprove securityStable attenuation characteristicsFungiBacteriaDengue vaccineTGE VACCINE
The invention discloses a pidemic encephalitis B / dengue chimeric virus with an epidemic encephalitis B virus attenuated strain as a gene framework and application of the epidemic encephalitis B / dengue chimeric virus. The invention provides a deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) molecule, and the DNA molecule is recombinant DNA which is obtained by replacing an encoding gene of protein A in complementary DNA (cDNA) corresponding to genome ribonucleic acid (RNA) of an epidemic encephalitis B virus by using an encoding gene of protein B; the protein A consists of an amino acid sequence shown as a sequence 1 in a sequence table; and the protein B consists of an amino acid sequence shown as a sequence 2 in the sequence table. The pidemic encephalitis B / dengue chimeric virus with the epidemic encephalitis B virus attenuated strain as the gene framework is a recombinant virus containing the DNA molecule. The pidemic encephalitis B / dengue type II chimeric virus also has a good application prospect when taken as a dengue vaccine and used for preventing dengue virus infection.
Owner:MICROBE EPIDEMIC DISEASE INST OF PLA MILITARY MEDICAL ACAD OF SCI +1
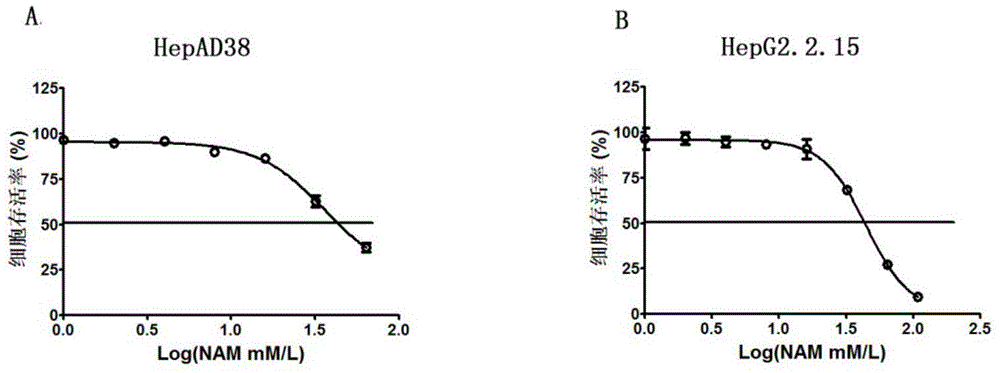
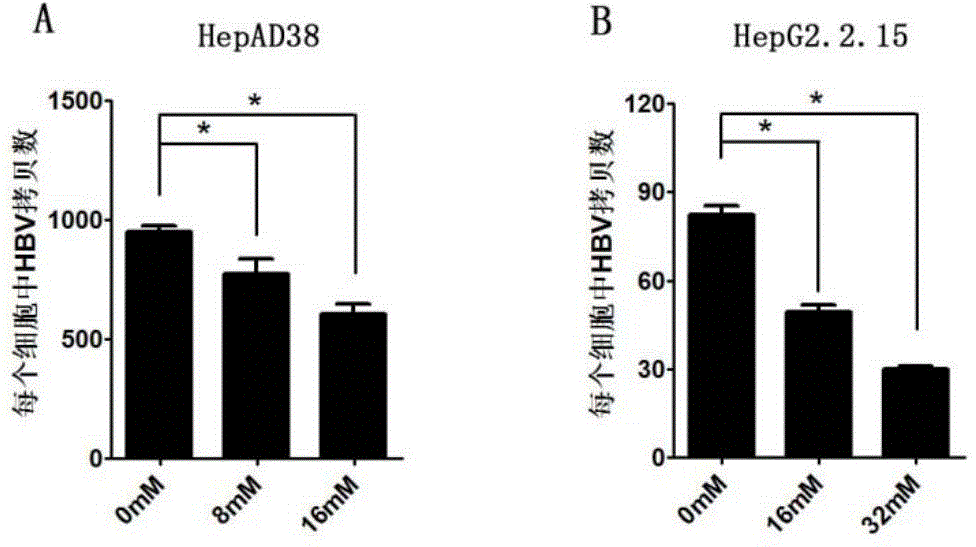
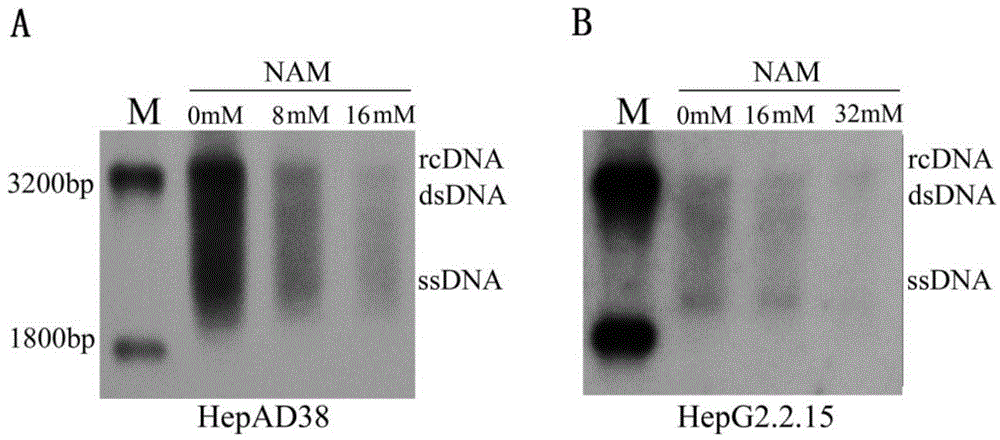
Application of niacinamide as effective component in preparation of medicine for treating hepatitis B
ActiveCN104784178AInhibit expressionInhibition of secretionOrganic active ingredientsAntiviralsNiacinamideRna expression
The invention relates to the field of drug research and development and particularly discloses application of niacinamide as an effective component in preparation of a medicine for treating hepatitis B. The experiment firstly reveals that the niacinamide is capable of inhibiting the expression level of the hepatitis B (HBV), including inhibiting the formation of the HBV replication intermediate, inhibiting the pregenome RNA expression, inhibiting the expression of a core protein and inhibiting the secretion of HBeAg and HbsAg. The niacinamide has a function of obviously treating the hepatitis B, can be used for preparing the medicine for treating the hepatitis B and has a wide application future.
Owner:CHONGQING MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Type H5 and H9 avian influenza virus and multiple detection method for newcastle disease virus
The invention discloses a method of detecting whether the birds and the related products are infected with H5 type or H9 type bird-flu virus or Newcastle disease virus. In the method of the invention, the trachea, cloacal swabs, blood, dung, or organs and tissues of dead birds are sterilely taken, and then milled into milk suspension by sterile physiological saline; the genomic RNA are extracted, and the RNA is used as template; the H5A, H9A and F are used as the primer for the targeted gene to undergo RT-PCR; the product obtained is electrophoresed; whether the birds detected are infected with H5, H9 type bird-flu virus or Newcastle disease virus are analyzed according to the electrophoretogram.
Owner:LANZHOU INST OF VETERINARY SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
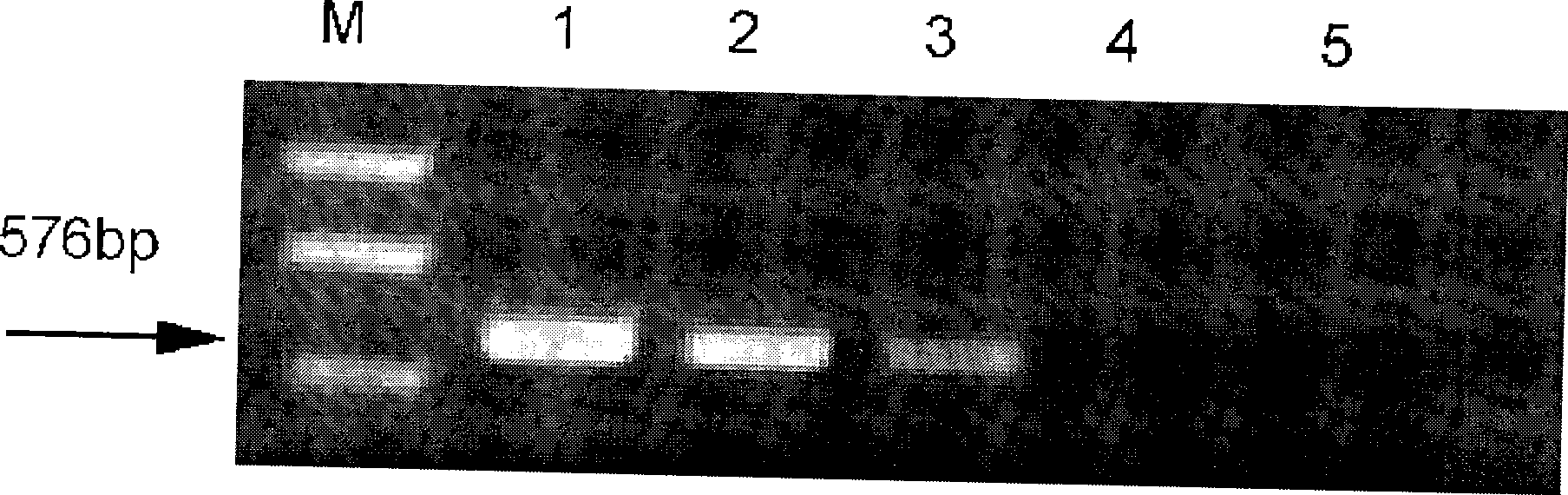
Multiplex RT-PCR (reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction) detection primer and reagent for swine fever virus (SFV) and porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus (PRRSV)
InactiveCN103397109ASolve the problem of multiplex RT-PCR detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationAgricultural scienceHighly pathogenic
The invention relates to a multiplex RT-PCR (reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction) detection primer and reagent for swine fever virus (SFV) and porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus (PRRSV), which can effectively solve the multiplex RT-PCR detection problem of the SFV and the PRRSV. The technical scheme of the invention is as follows: the invention provides the multiplex RT-PCR detection primer for the SFV and the PRRSV, which comprises primer pairs C1 / C2 and P1 / P2, wherein the primer pair C1 / C2 comprises a primer C1 and a primer C2, the primer pair P1 / P2 comprises a primer P1 and a primer P2, and the nucleotide sequences of the primer C1, the primer C2, the primer P1 and the primer P2 are SEQ (sequence) ID (identity) NO: 1, SEQ ID NO: 2, SEQ ID NO: 3 and SEQ ID NO: 4 in a sequence table respectively; and after the primer pairs C1 / C2 and P1 / P2 are used for performing RT-PCR amplification on RNA (ribonucleic acid) of genomes of CSFV (classical swine fever virus) cytotoxicity, PRRSV cytotoxicity and HP-PRRSV (highly pathogenic-porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus) cytotoxicity, CSFVPCR product 294bpSEQ ID NO: 7, PRRSVPCR product 536bpSEQ ID NO: 5 and HP-PRRSVPCR product 452bpSEQ ID NO: 6 are obtained. The invention further provides an application of the primer pairs C1 / C2 and P1 / P2 in the multiplex RT-PCR detection and testing of the SFV and the PRRSV.
Owner:曲哲会
Recombinant newcastle disease viruses useful as vaccines or vaccine vectors
InactiveUS9476033B2SsRNA viruses negative-senseAnimal cellsCompetent cellNewcastle disease virus NDV
The present invention concerns an antigenomic RNA of Newcastle Disease virus (NDV) carrying one or more foreign genes inserted before NP gene, between P and M genes, and / or between HN and L genes. The invention is also directed toward a cDNA encoding a recombinant antigenomic RNA having one or more foreign genes inserted according to the invention, a cell containing the cDNA, a plasmid comprising the cDNA, a cell containing the plasmid, a cell containing the recombinant antigenomic RNA, and a recombinant NDV containing the recombinant antigenomic RNA of the invention, such as a recombinant NDV carrying one or more foreign genes recovered from transcription of the cDNA or the plasmid in a competent cell. The recombinant NDV carrying the one or more foreign genes can be used as a vaccine or vaccine vector.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND
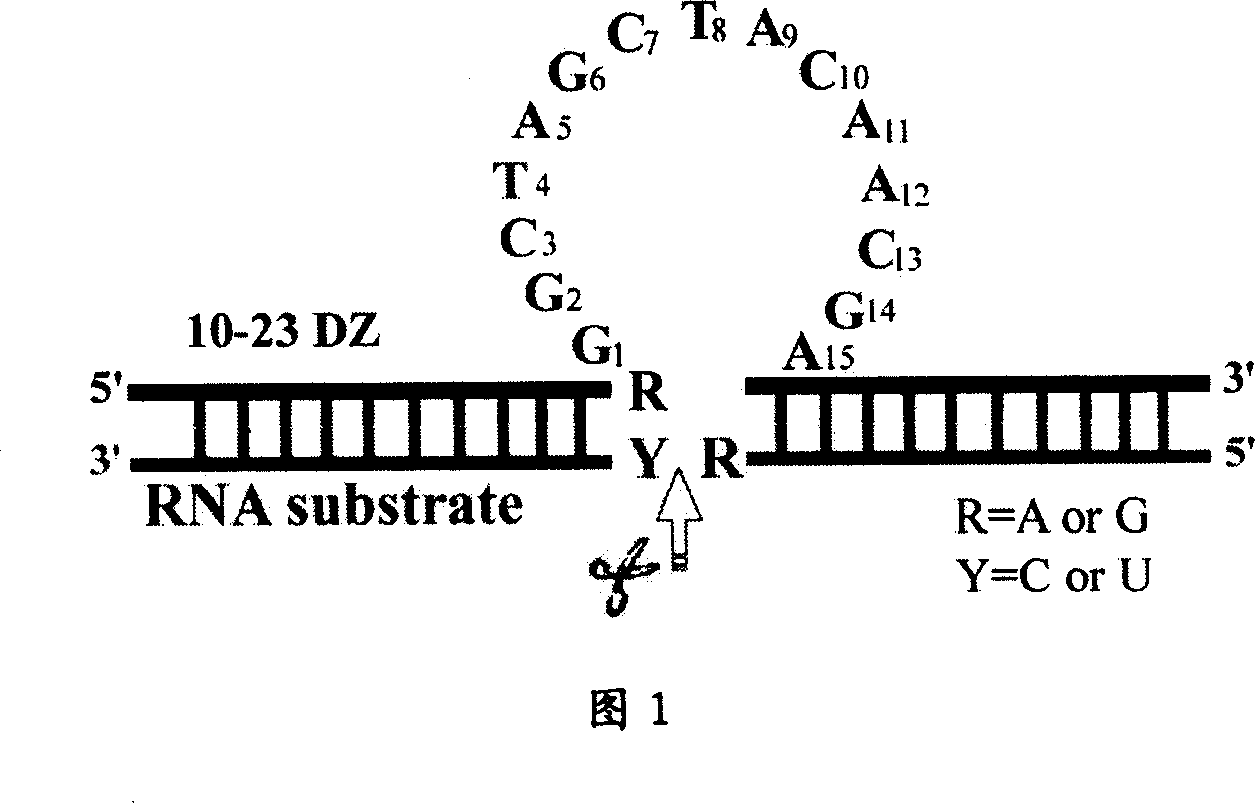
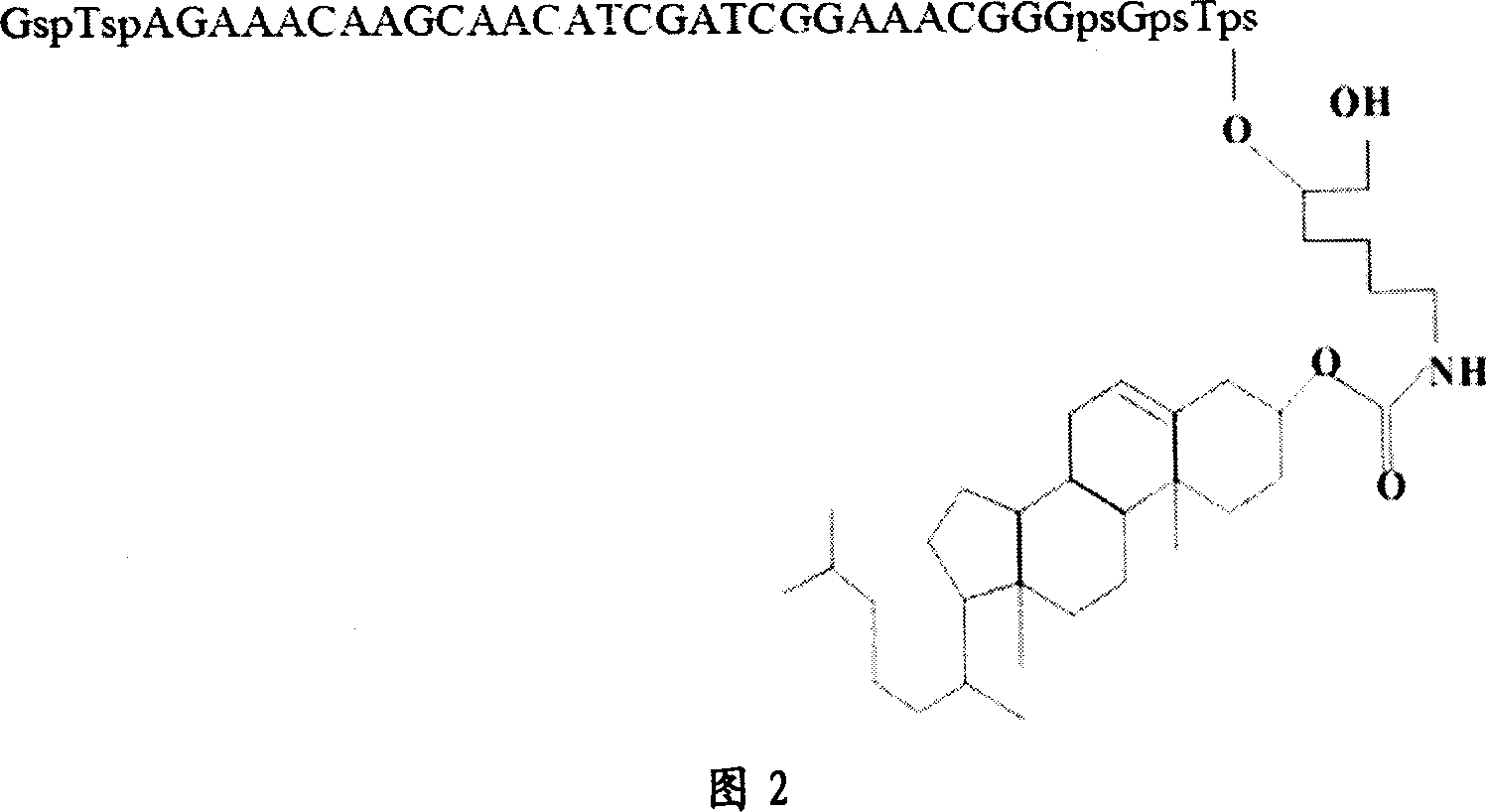
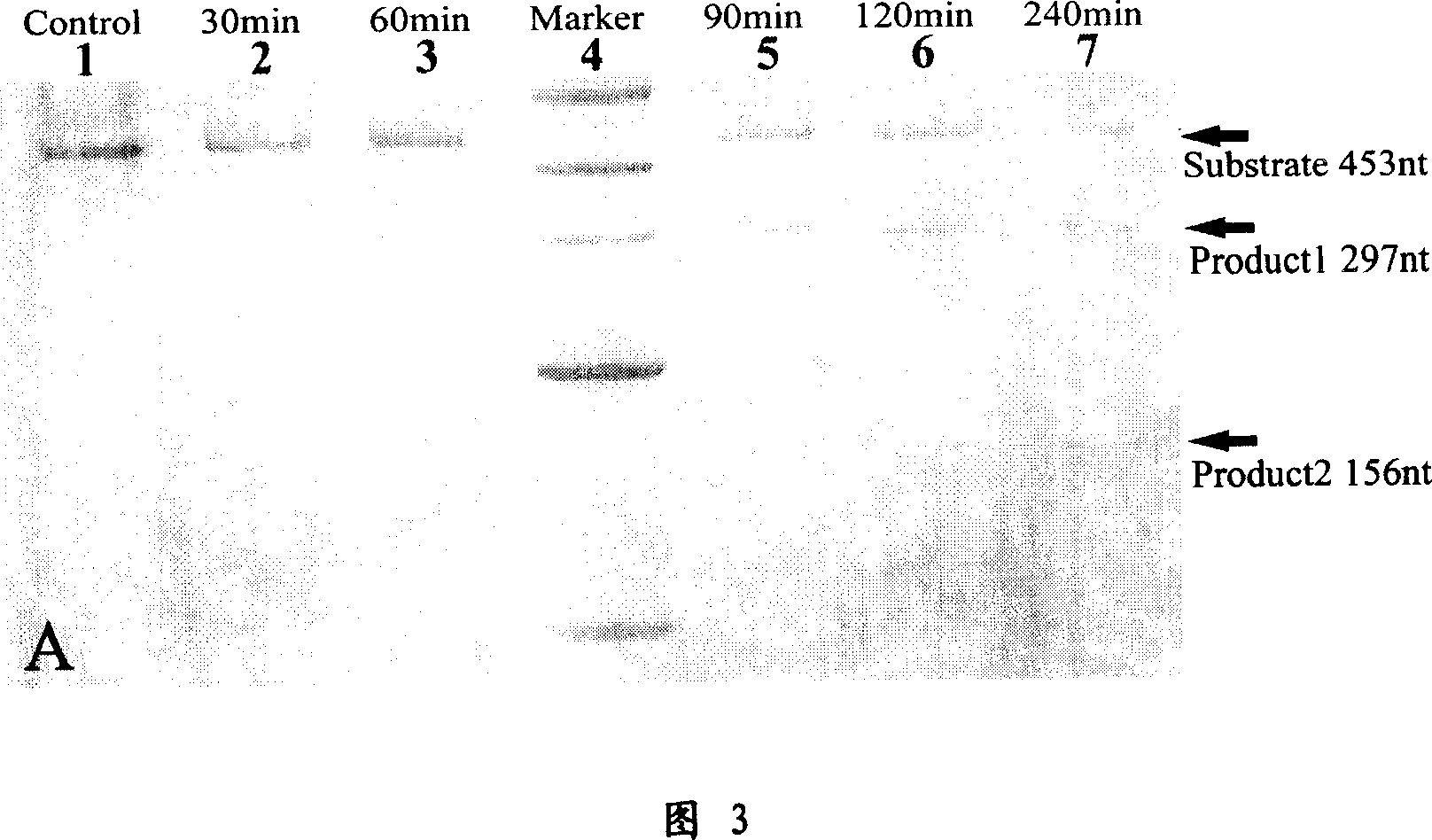
Deoxyzyme of anti-respiratory syncytial viruses and its medicinal use
InactiveCN101029313AInhibition of replicationIncreased sensitivityHydrolasesGenetic engineeringIncision SiteRespiratory syncytial virus (RSV)
A deoxyribonse of anti-respiratory tract syncytium virus and its medicinal use are disclosed. The deoxyribonse has purine in RSV RNA nucleotide sequence; pyramine site cracks RNA catalytic active domain specially, the No.1 combined domain adjacent to catalytic domain 5' end is supplemented combined with base sequence specificity at one side of RSV RNA incision site; the No.2 combined domain adjacent to catalytic domain 3' end is supplemented combined with base sequence specificity at one side of RSV RNA incision site. It contains 0.01mg-20mg / 50 mu l anti-respiratory tract syncytium virus deoxyribonse solution. It is non-toxic, has better medicine sensitivity and can inhibit respiratory tract syncytium virus duplication specially.
Owner:CHILDRENS HOSPITAL OF CHONGQING MEDICAL UNIV
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com