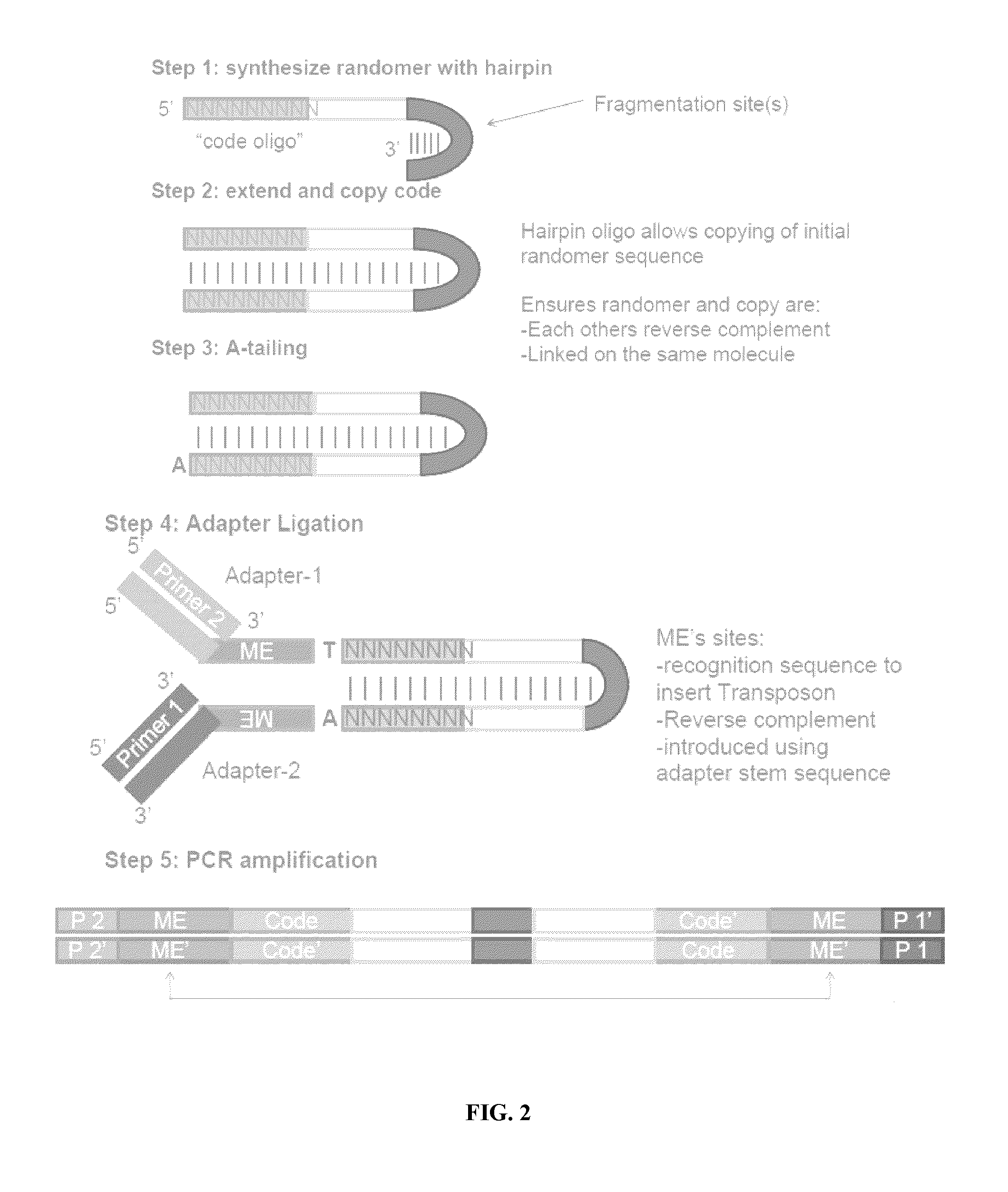
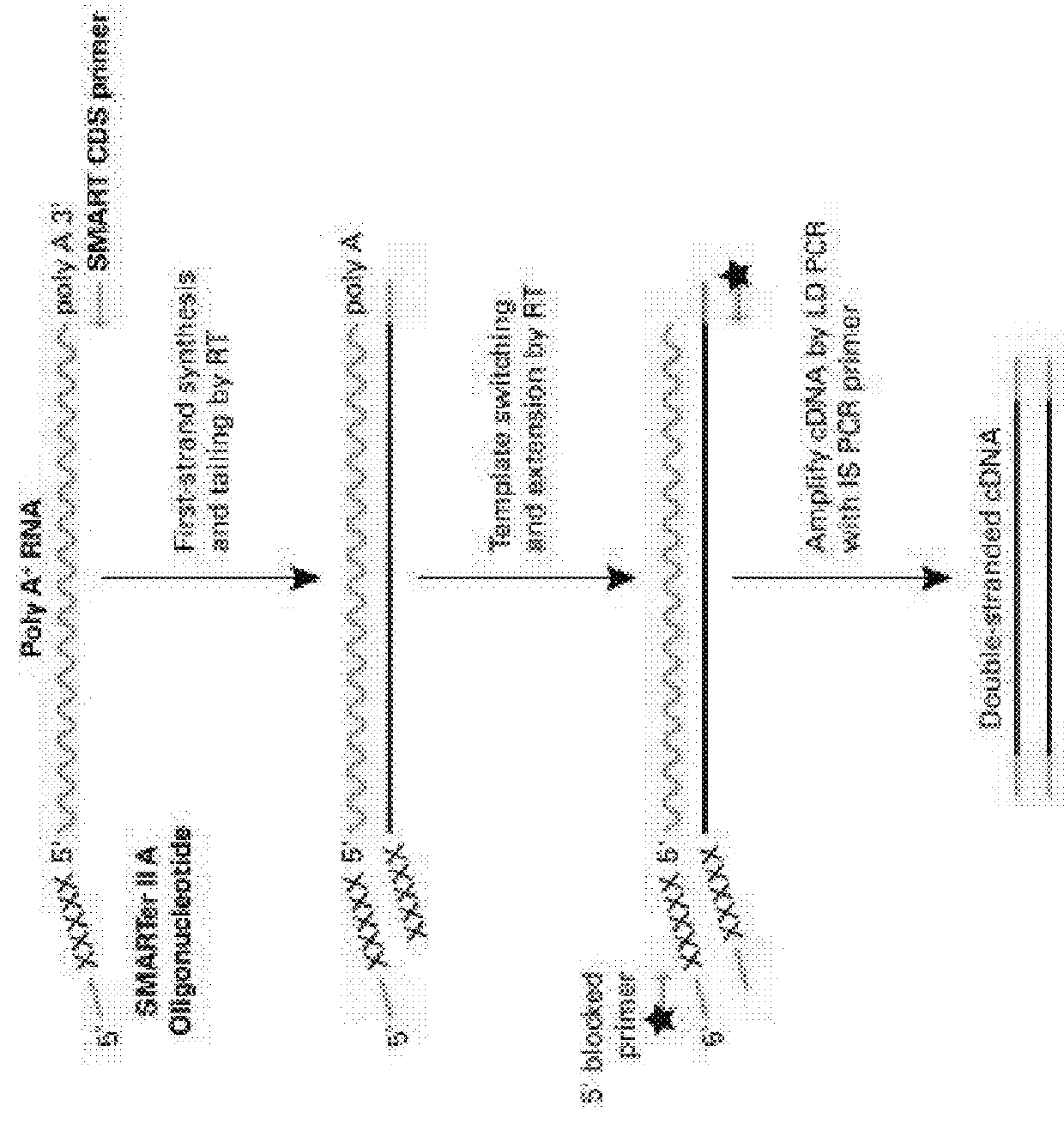
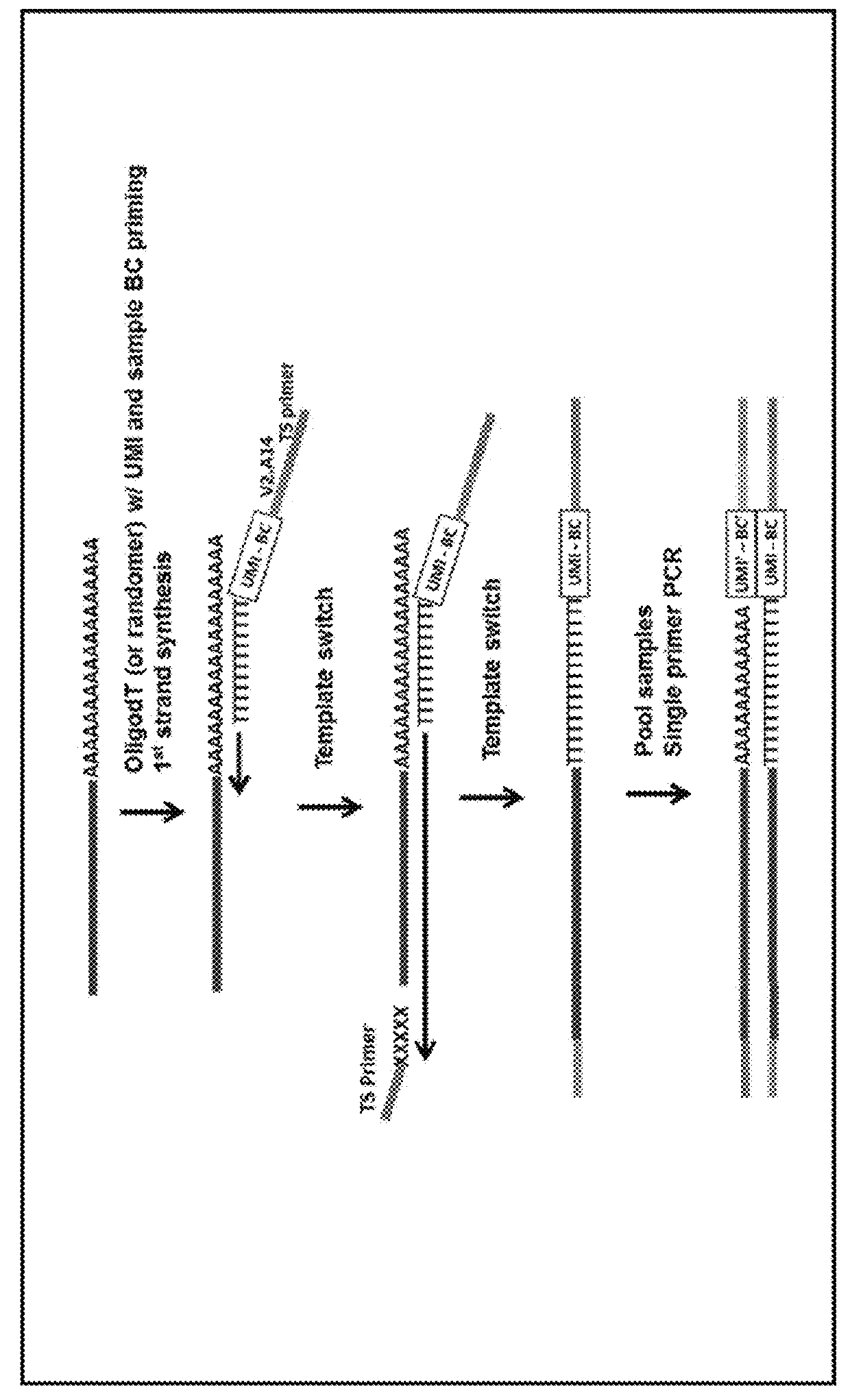
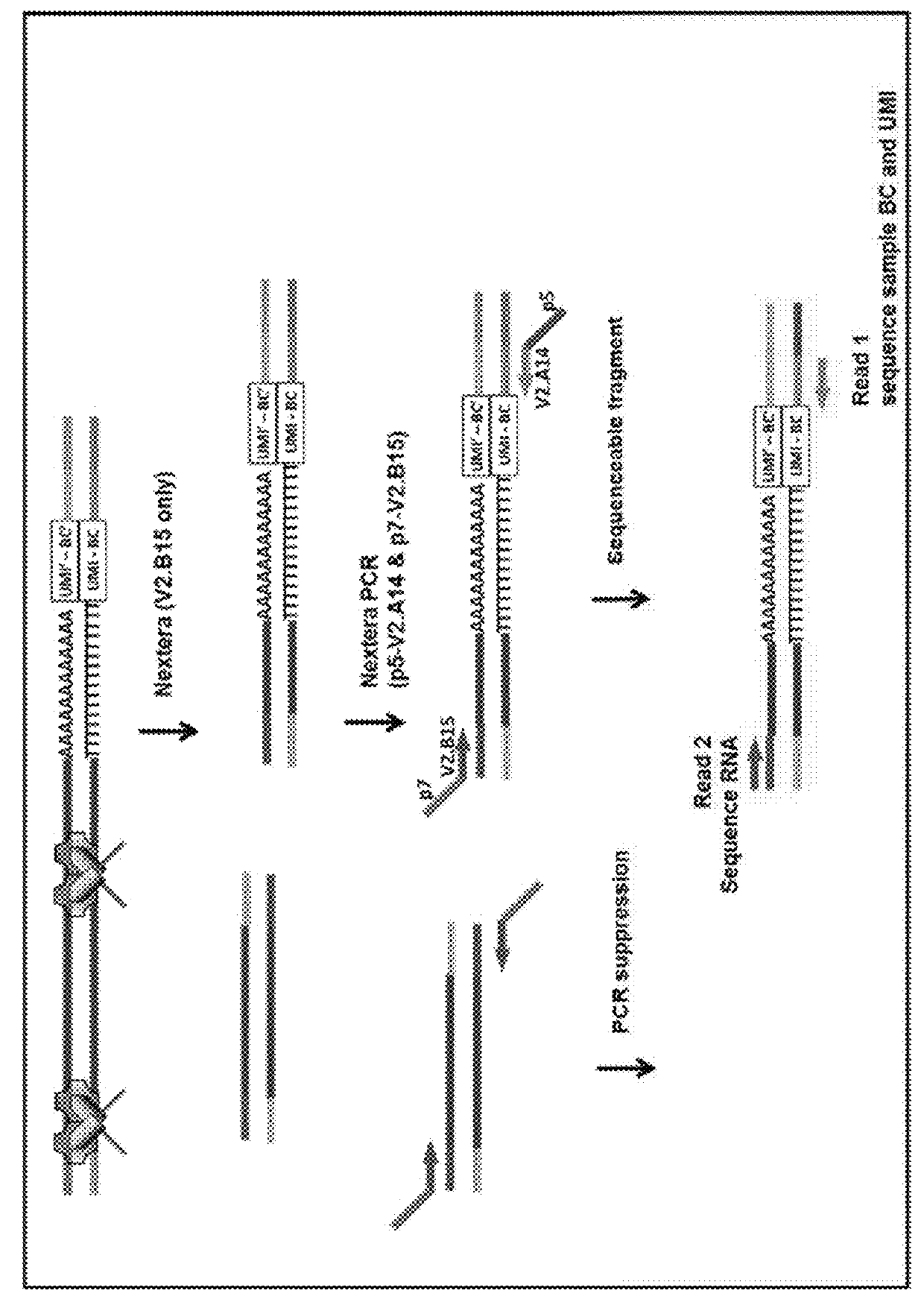
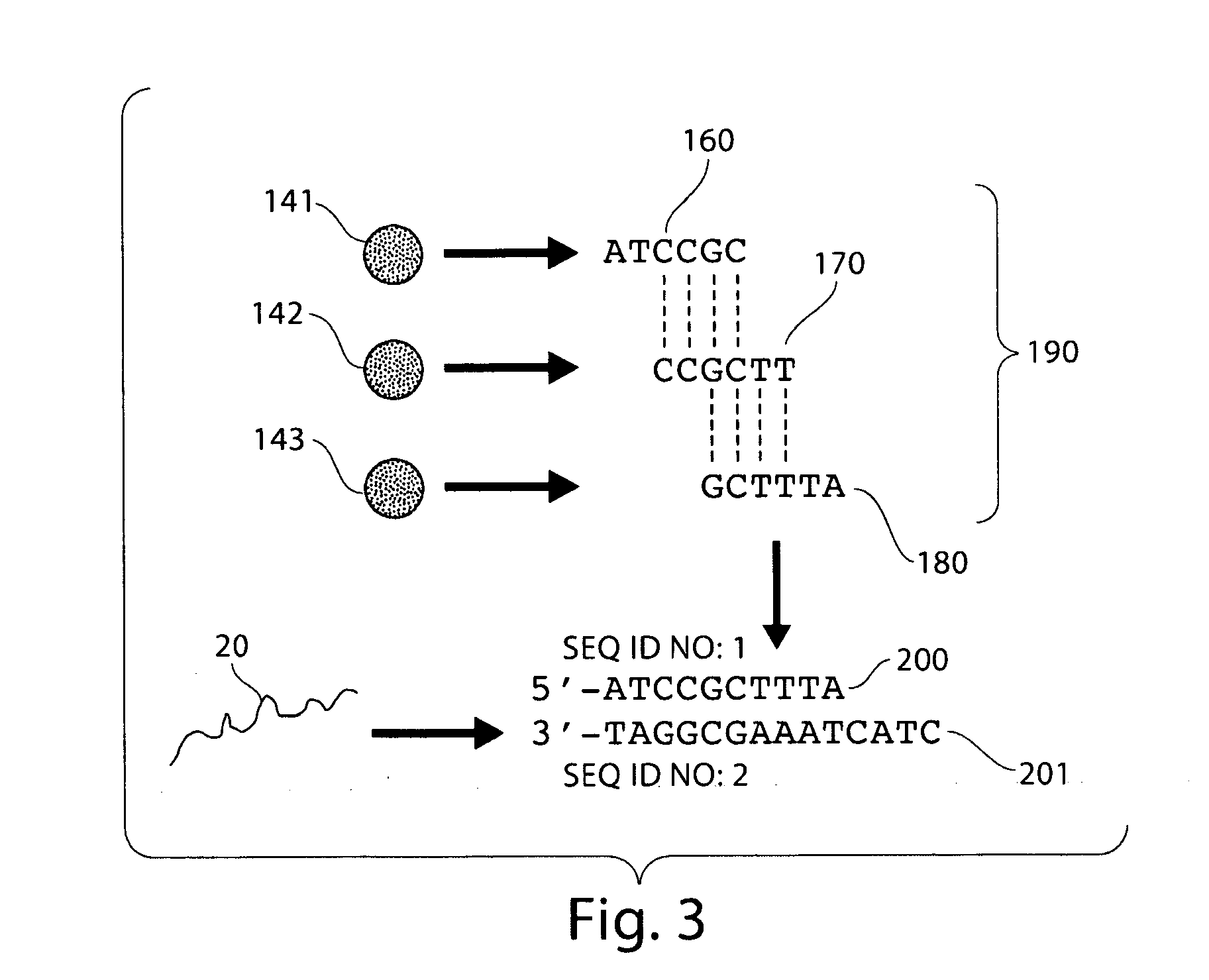
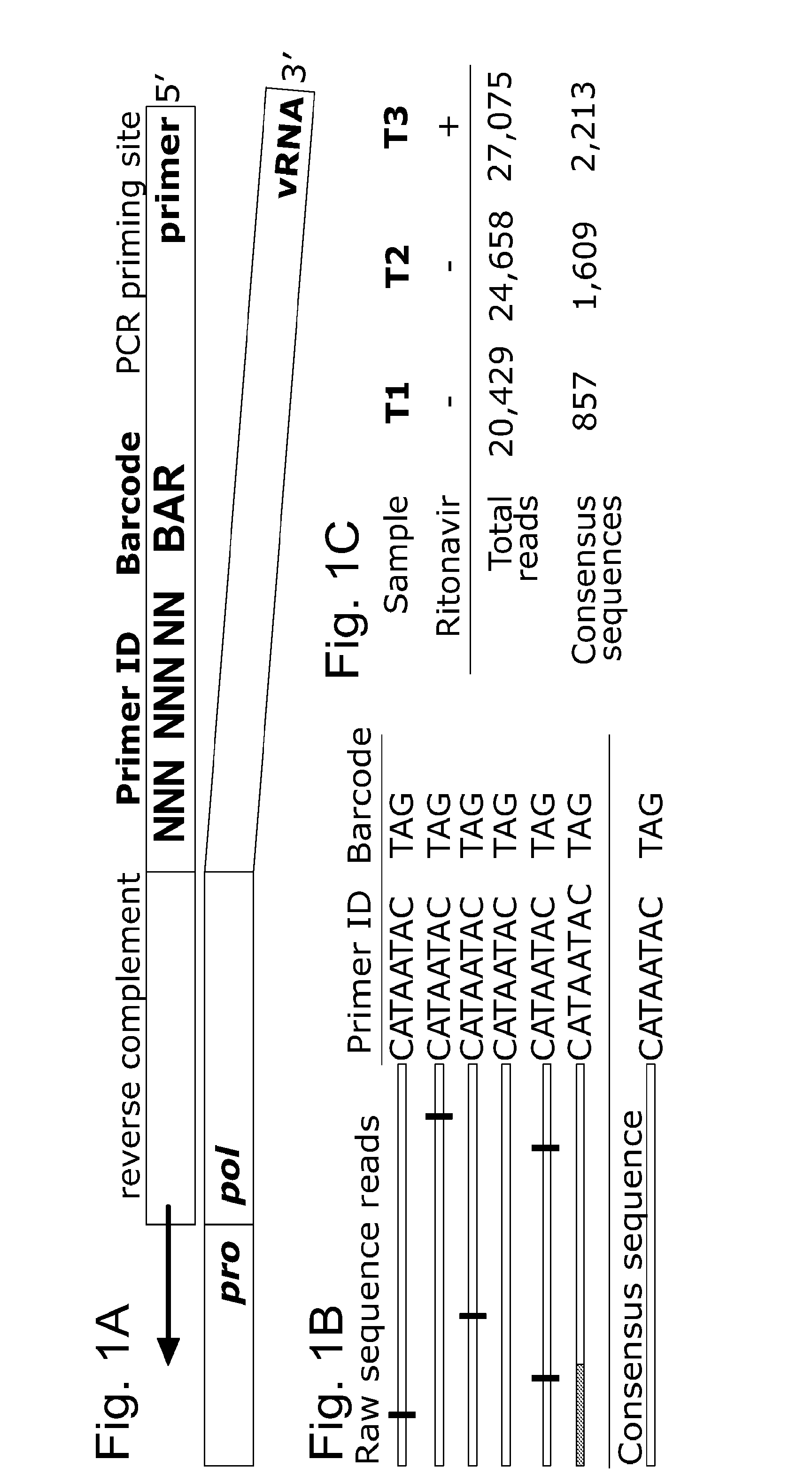
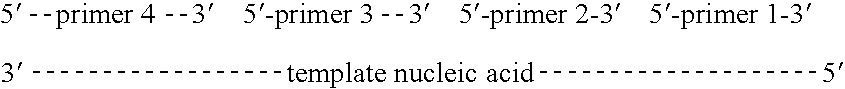Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1562results about "Library member identification" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
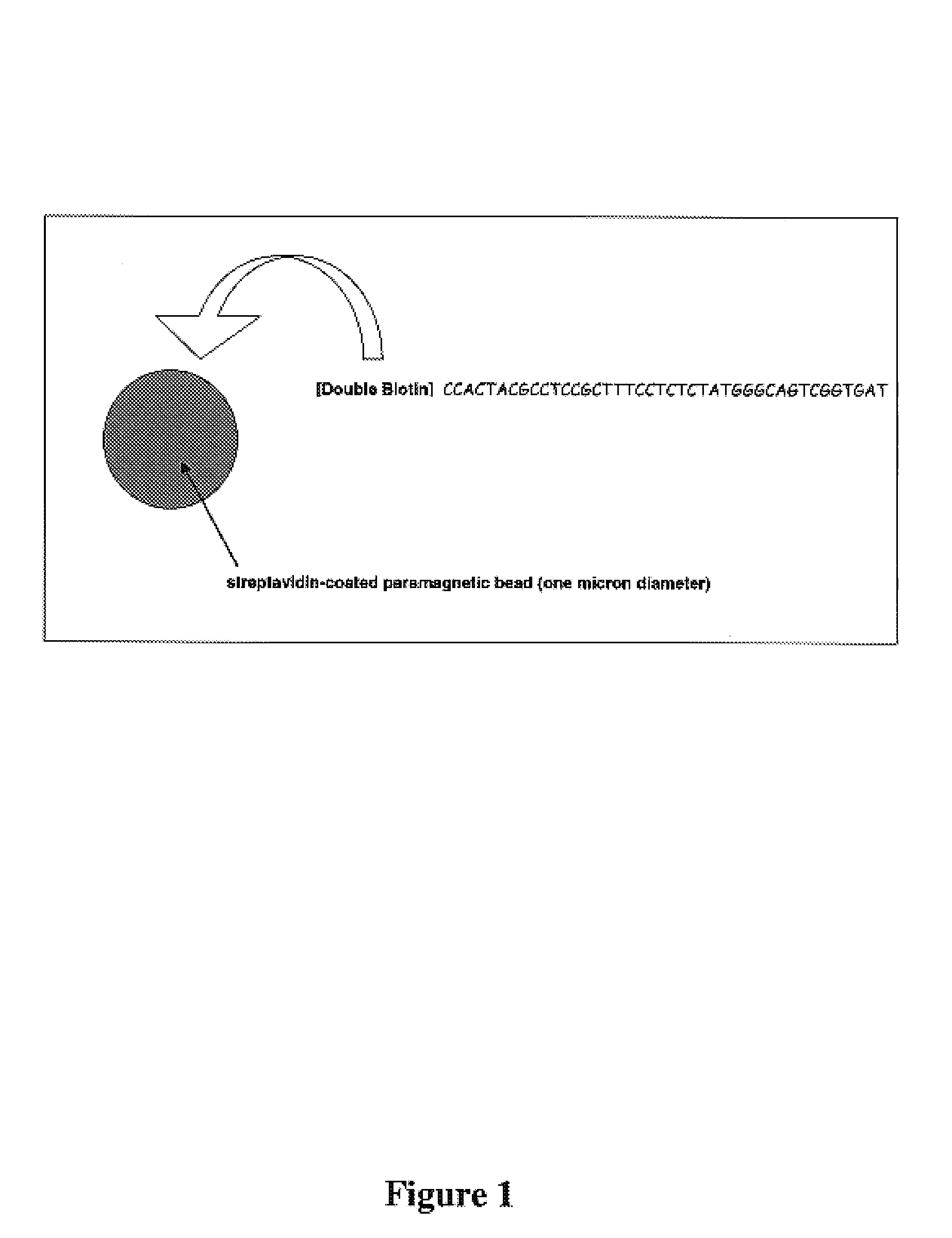
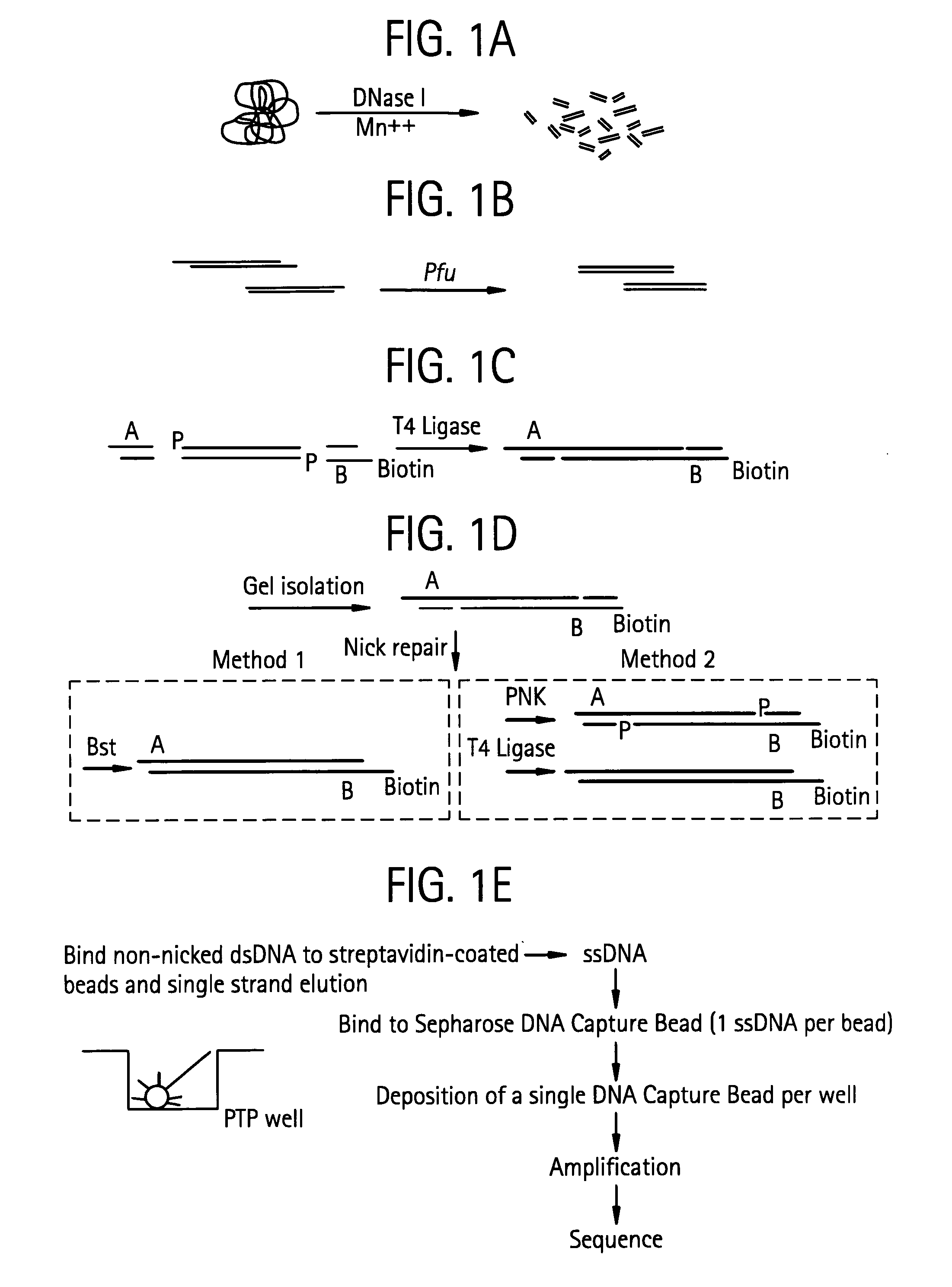
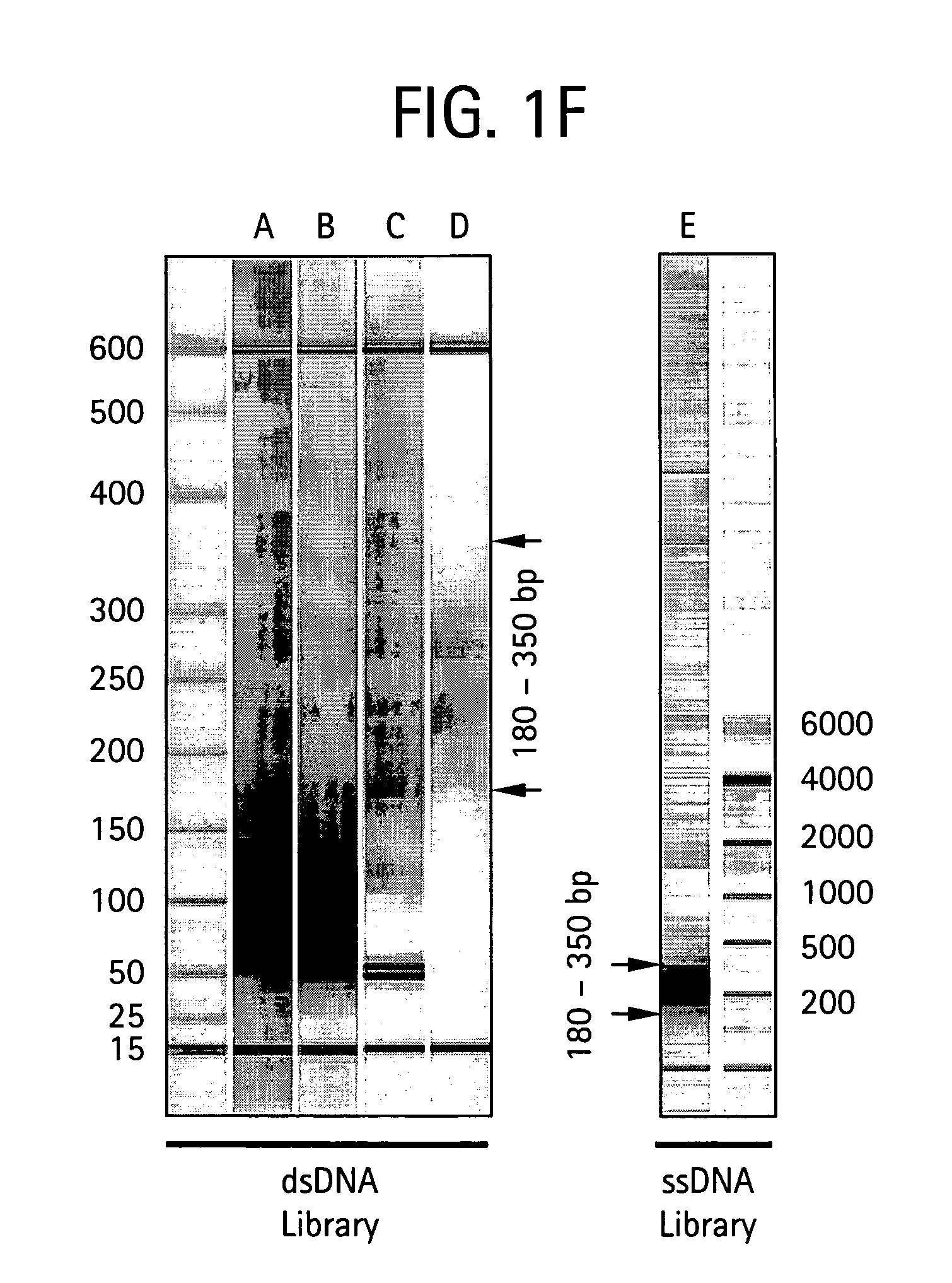
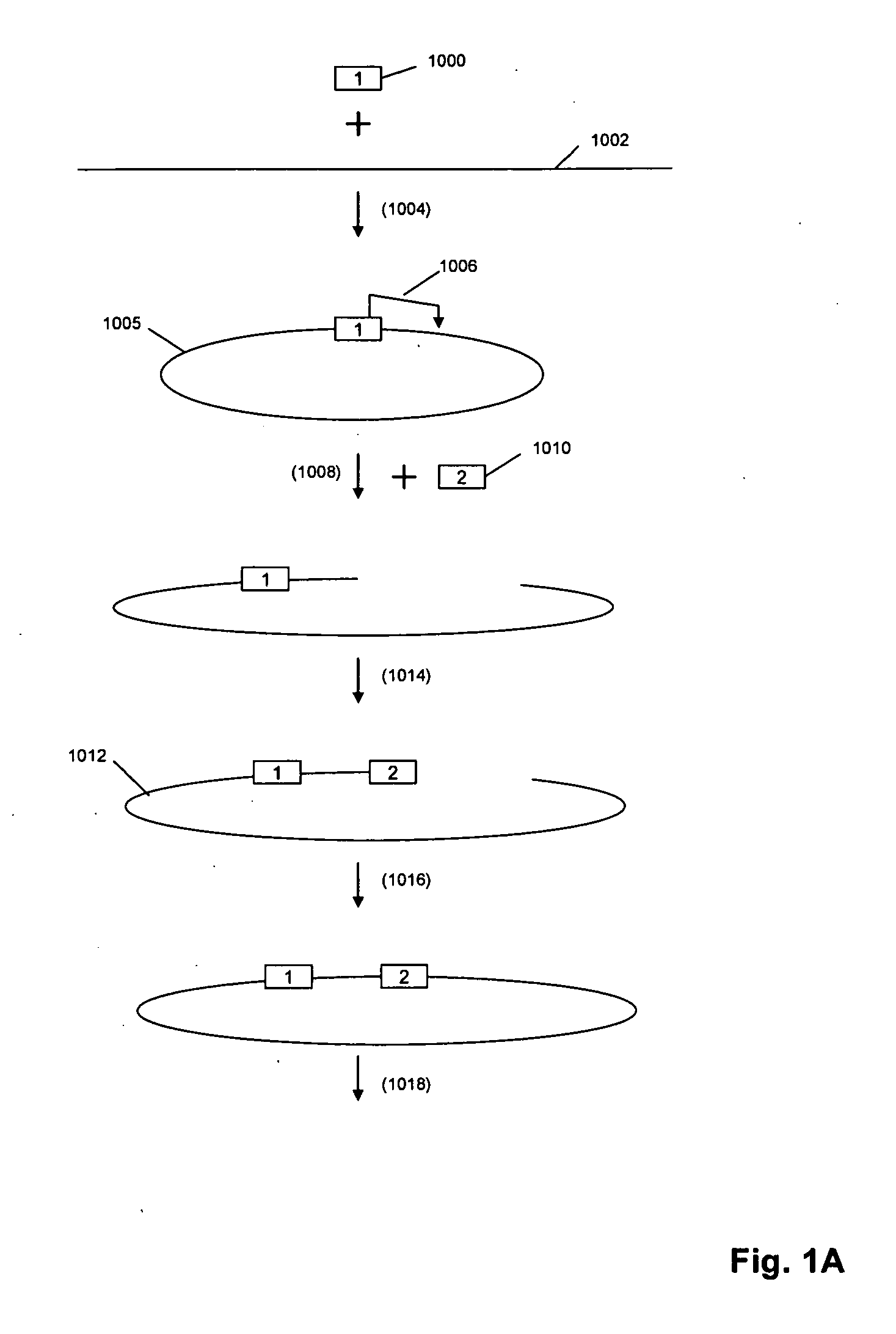
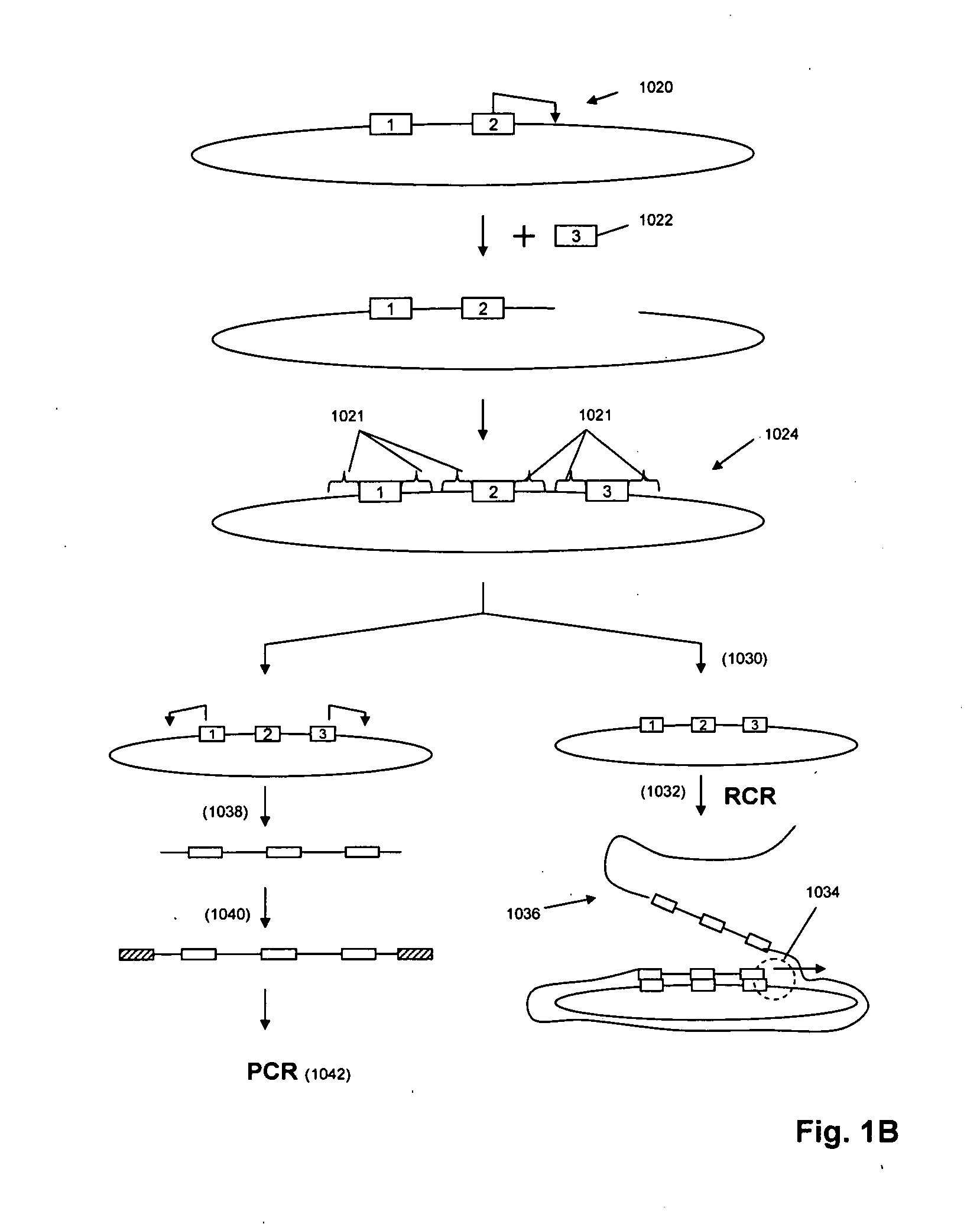
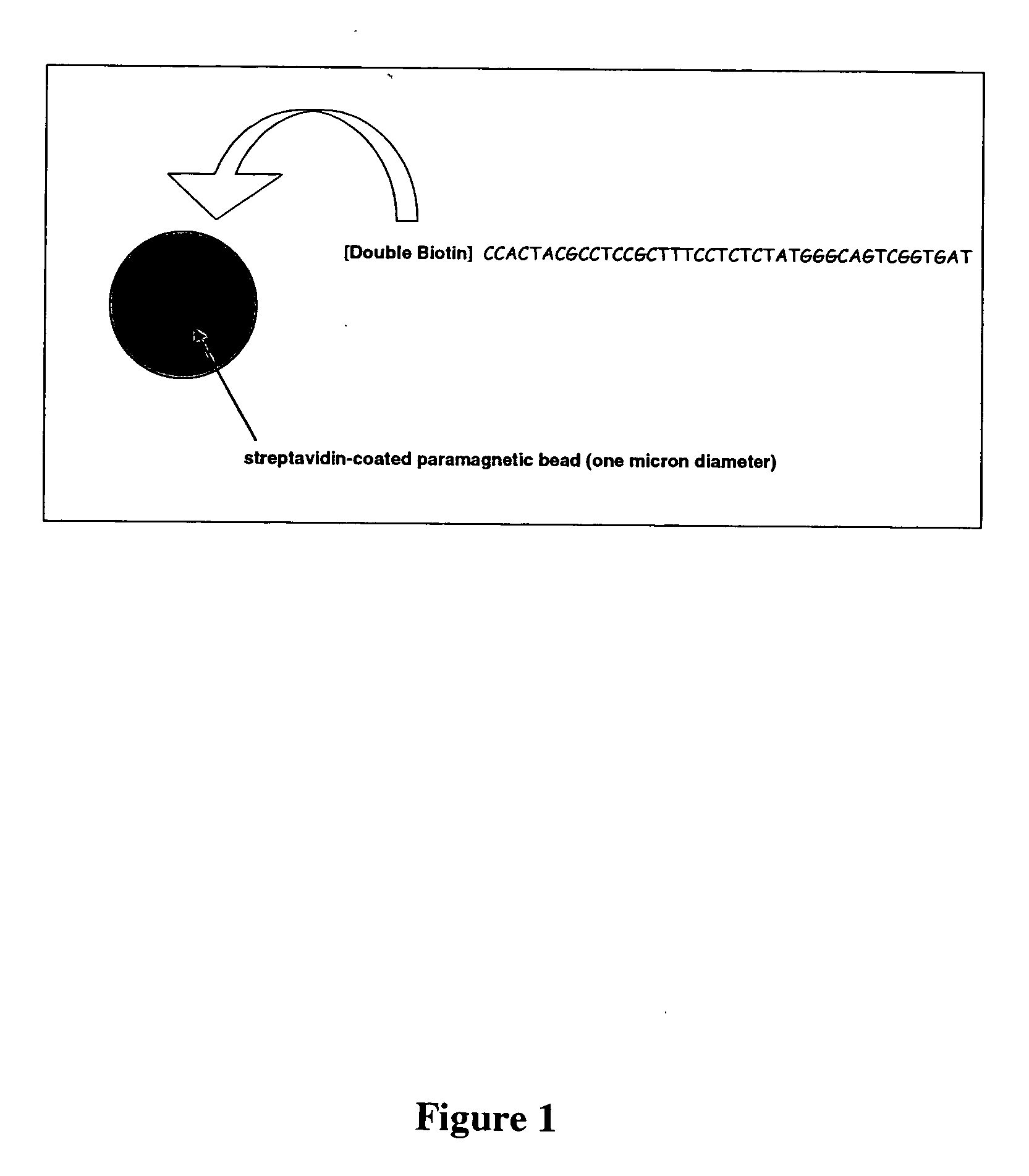
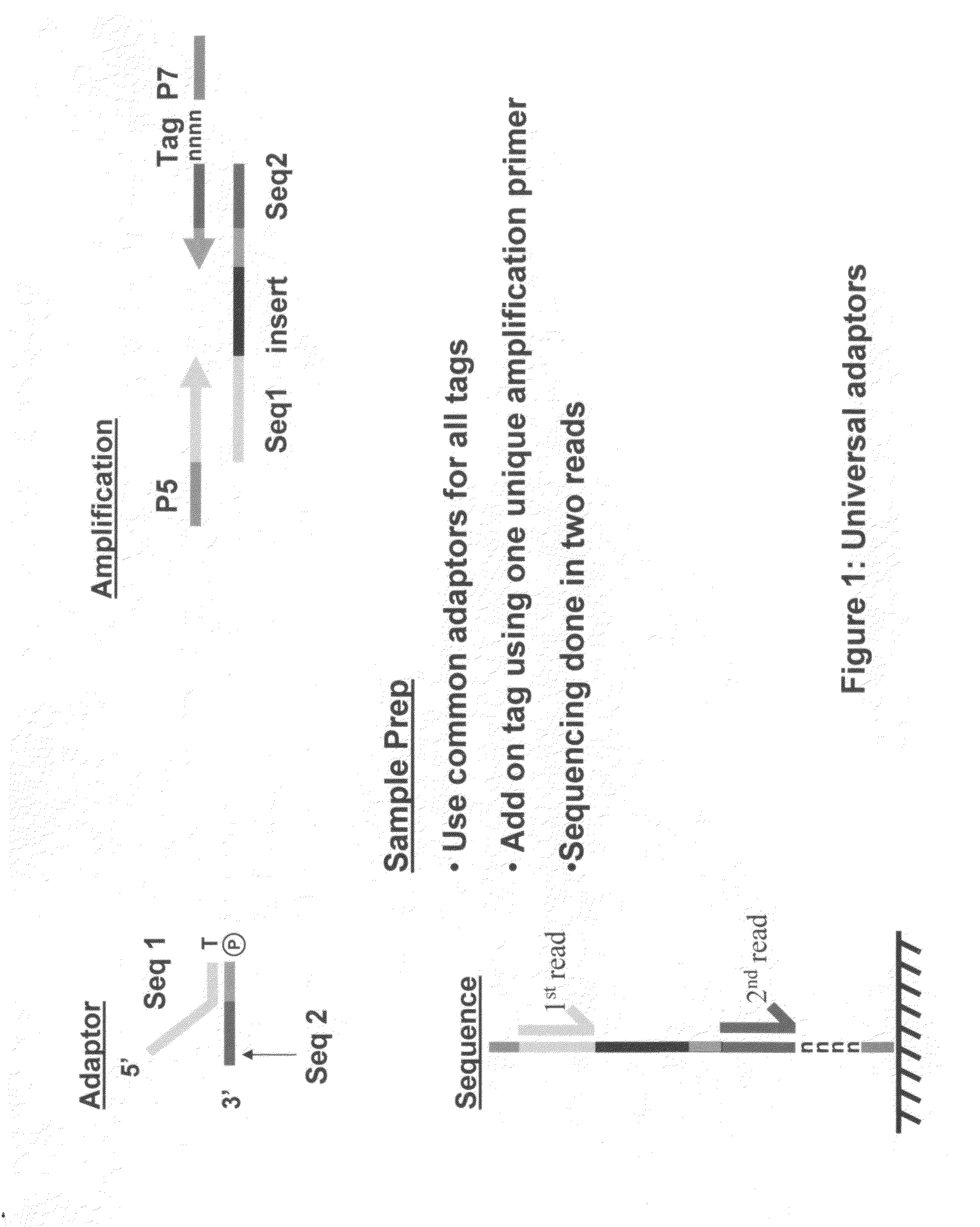
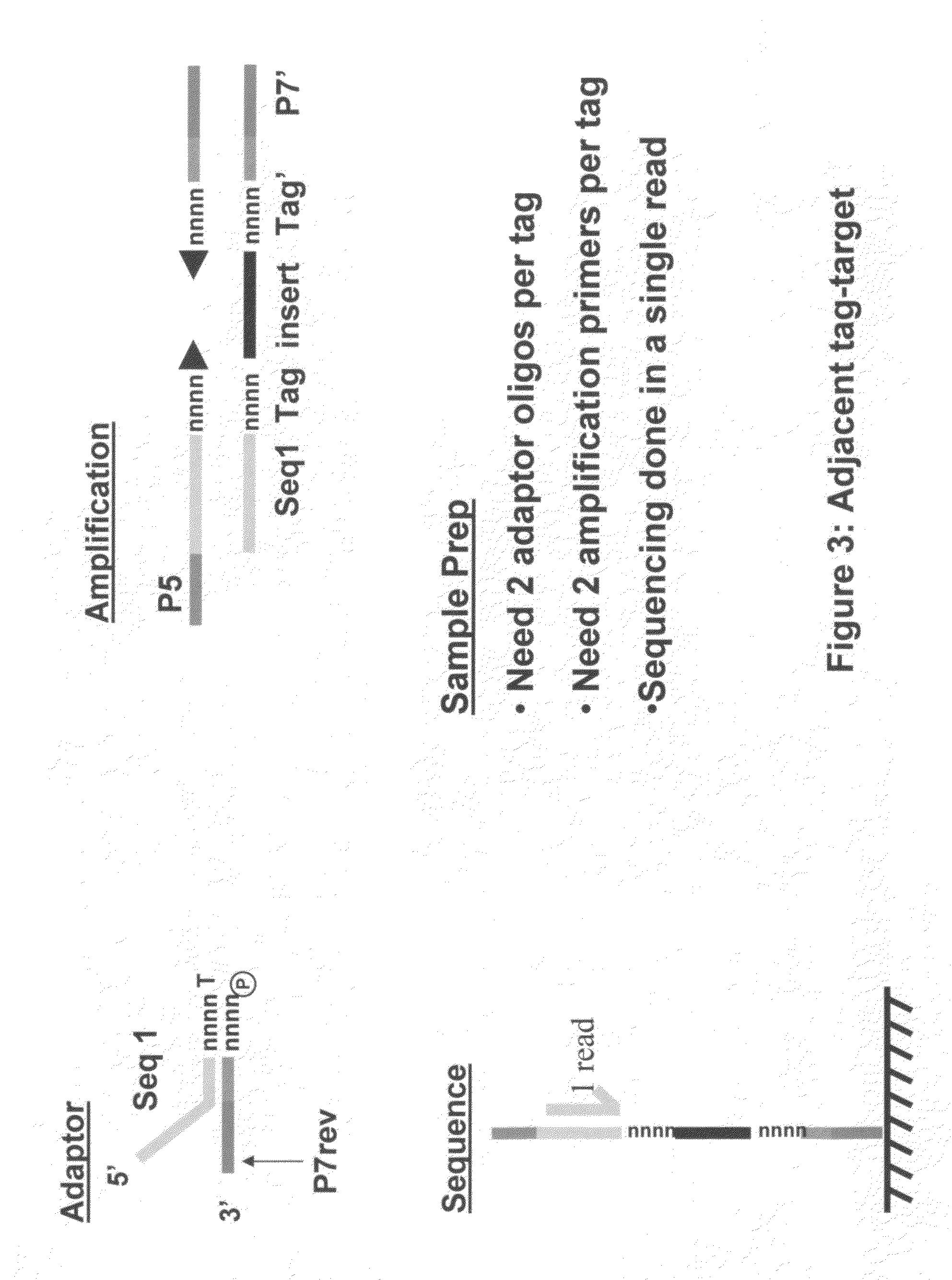
Methods of amplifying and sequencing nucleic acids
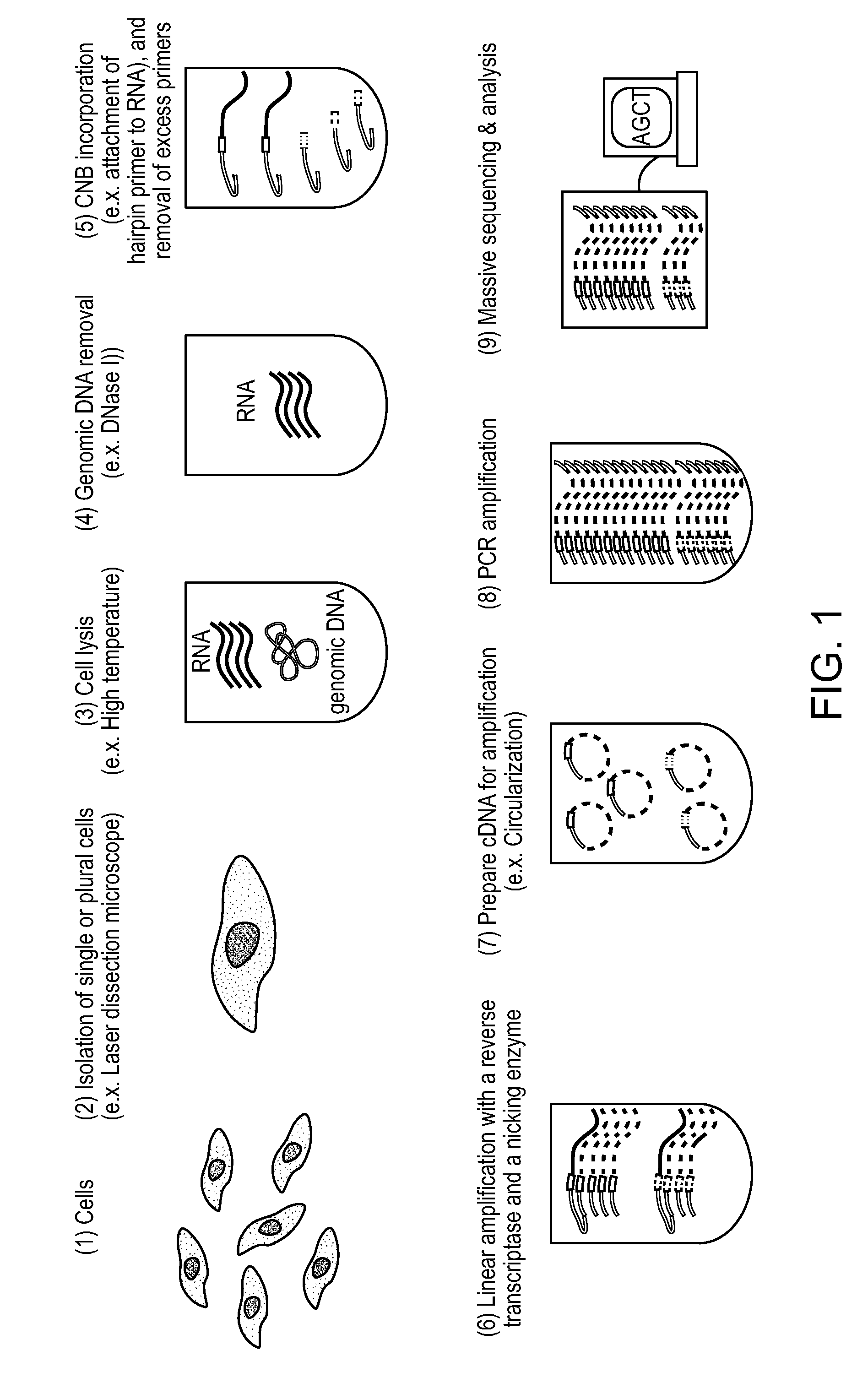
An apparatus and method for performing rapid DNA sequencing, such as genomic sequencing, is provided herein. The method includes the steps of preparing a sample DNA for genomic sequencing, amplifying the prepared DNA in a representative manner, and performing multiple sequencing reaction on the amplified DNA with only one primer hybridization step.
Owner:454 LIFE SCIENCES CORP
Methods of Analyzing Nucleic Acids from Individual Cells or Cell Populations
InactiveUS20150376609A1Facilitate hybridizationMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary member identificationReagentNucleic acid
Methods, compositions and systems for analyzing individual cells or cell populations through the partitioned analysis of contents of individual cells or cell populations. Individual cells or cell populations are co-partitioned with processing reagents for accessing cellular contents, and for uniquely identifying the contents of a given cell or cell population, and subsequently analyzing the cell's contents and characterizing it as having derived from an individual cell or cell population, including analysis and characterization of the cell's nucleic acids through sequencing.
Owner:10X GENOMICS
High throughput genome sequencing on DNA arrays
ActiveUS20090005252A1Simple processMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary member identificationRe sequencingNucleotide
The present invention is directed to methods and compositions for acquiring nucleotide sequence information of target sequences using adaptors interspersed in target polynucleotides. The sequence information can be new, e.g. sequencing unknown nucleic acids, re-sequencing, or genotyping. The invention preferably includes methods for inserting a plurality of adaptors at spaced locations within a target polynucleotide or a fragment of a polynucleotide. Such adaptors may serve as platforms for interrogating adjacent sequences using various sequencing chemistries, such as those that identify nucleotides by primer extension, probe ligation, and the like. Encompassed in the invention are methods and compositions for the insertion of known adaptor sequences into target sequences, such that there is an interruption of contiguous target sequence with the adaptors. By sequencing both “upstream” and “downstream” of the adaptors, identification of entire target sequences may be accomplished.
Owner:COMPLETE GENOMICS INC
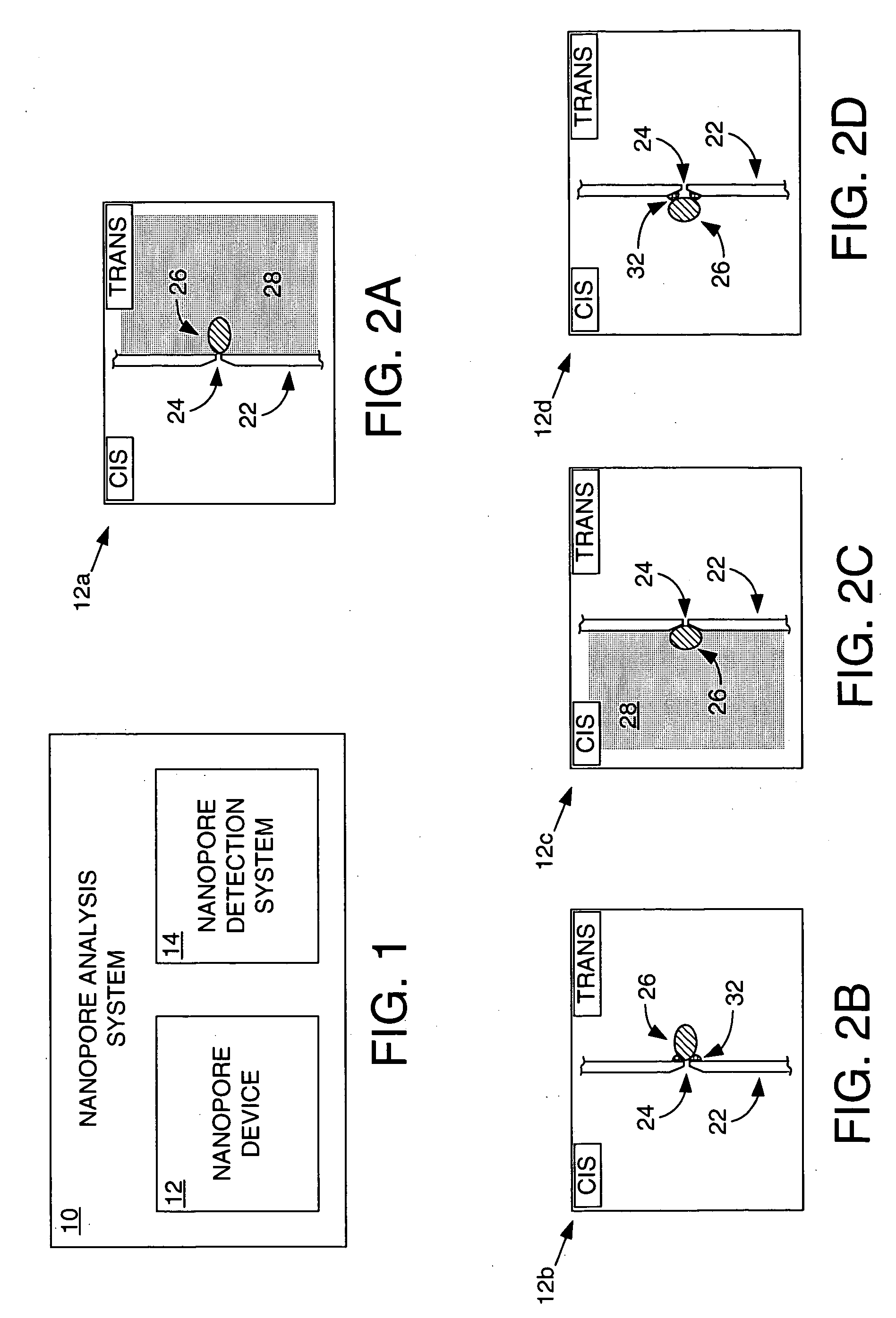
Nanopore sequencing devices and methods
ActiveUS20100331194A1Microbiological testing/measurementMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansCMOSElectrical resistance and conductance
The invention relates to devices and methods for nanopore sequencing. The invention includes arrays of nanopores having incorporated electronic circuits, for example, in CMOS. In some cases, the arrays of nanopores comprise resistive openings for isolating the electronic signals for improved sequencing. Methods for controlling translocation of through the nanopore are disclosed.
Owner:PACIFIC BIOSCIENCES
Nucleotide sequences and corresponding polypeptides conferring modulated plant characteristics
ActiveUS20090094717A1Modulation characteristicLibrary member identificationVector-based foreign material introductionBiotechnologyNucleotide
The present invention relates to isolated nucleic acid molecules and their corresponding encoded polypeptides able confer the trait of modulated plant size, vegetative growth, organ number, plant architecture, sterility or seedling lethality in plants. The present invention further relates to the use of these nucleic acid molecules and polypeptides in making transgenic plants, plant cells, plant materials or seeds of a plant having such modulated growth or phenotype characteristics that are altered with respect to wild type plants grown under similar conditions.
Owner:CERES INC
High throughput genome sequencing on DNA arrays
ActiveUS20090011943A1Microbiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningRe sequencingNucleotide sequencing
The present invention is directed to methods and compositions for acquiring nucleotide sequence information of target sequences using adaptors interspersed in target polynucleotides. The sequence information can be new, e.g. sequencing unknown nucleic acids, re-sequencing, or genotyping. The invention preferably includes methods for inserting a plurality of adaptors at spaced locations within a target polynucleotide or a fragment of a polynucleotide. Such adaptors may serve as platforms for interrogating adjacent sequences using various sequencing chemistries, such as those that identify nucleotides by primer extension, probe ligation, and the like. Encompassed in the invention are methods and compositions for the insertion of known adaptor sequences into target sequences, such that there is an interruption of contiguous target sequence with the adaptors. By sequencing both “upstream” and “downstream” of the adaptors, identification of entire target sequences may be accomplished.
Owner:COMPLETE GENOMICS INC
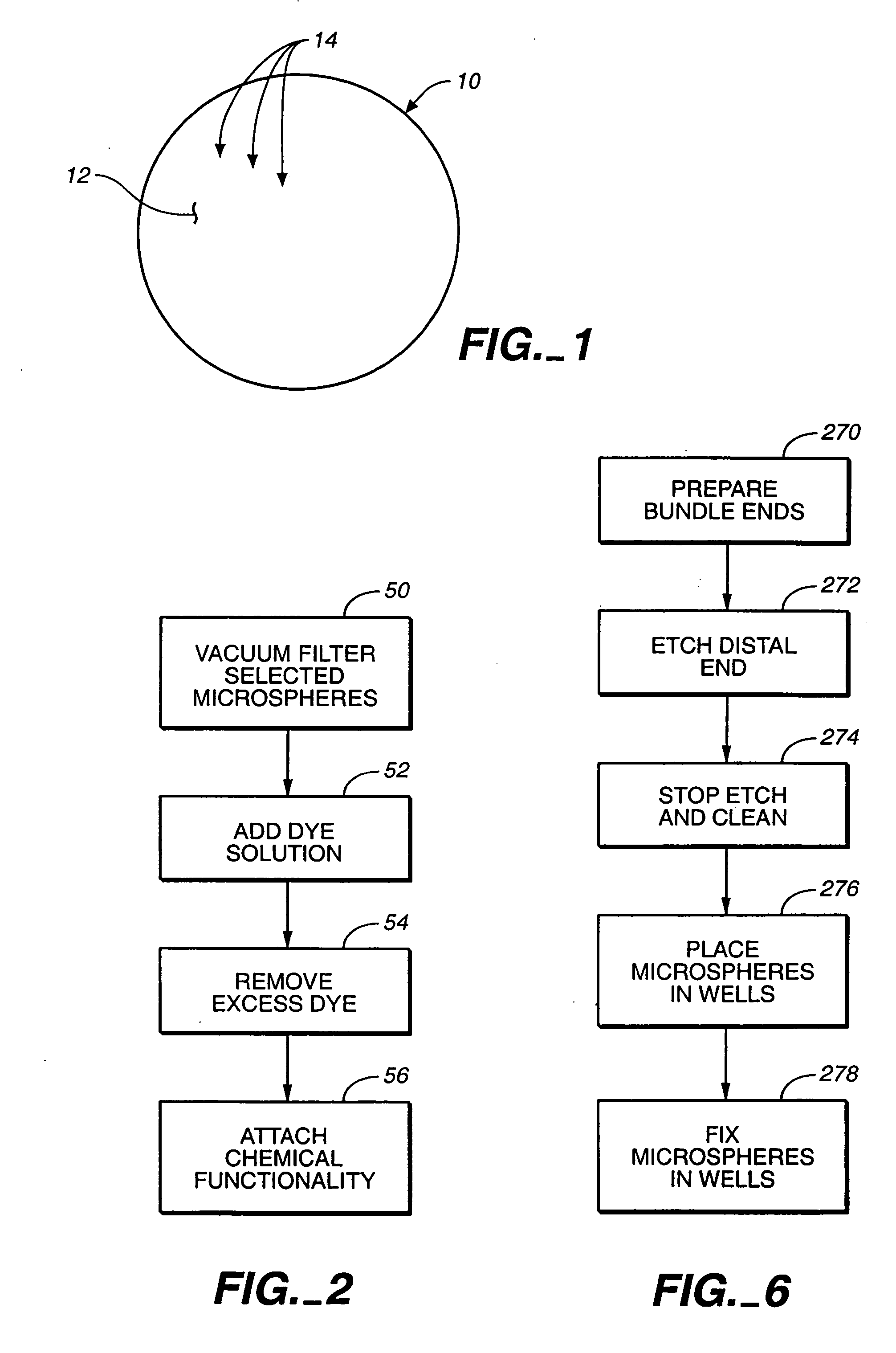
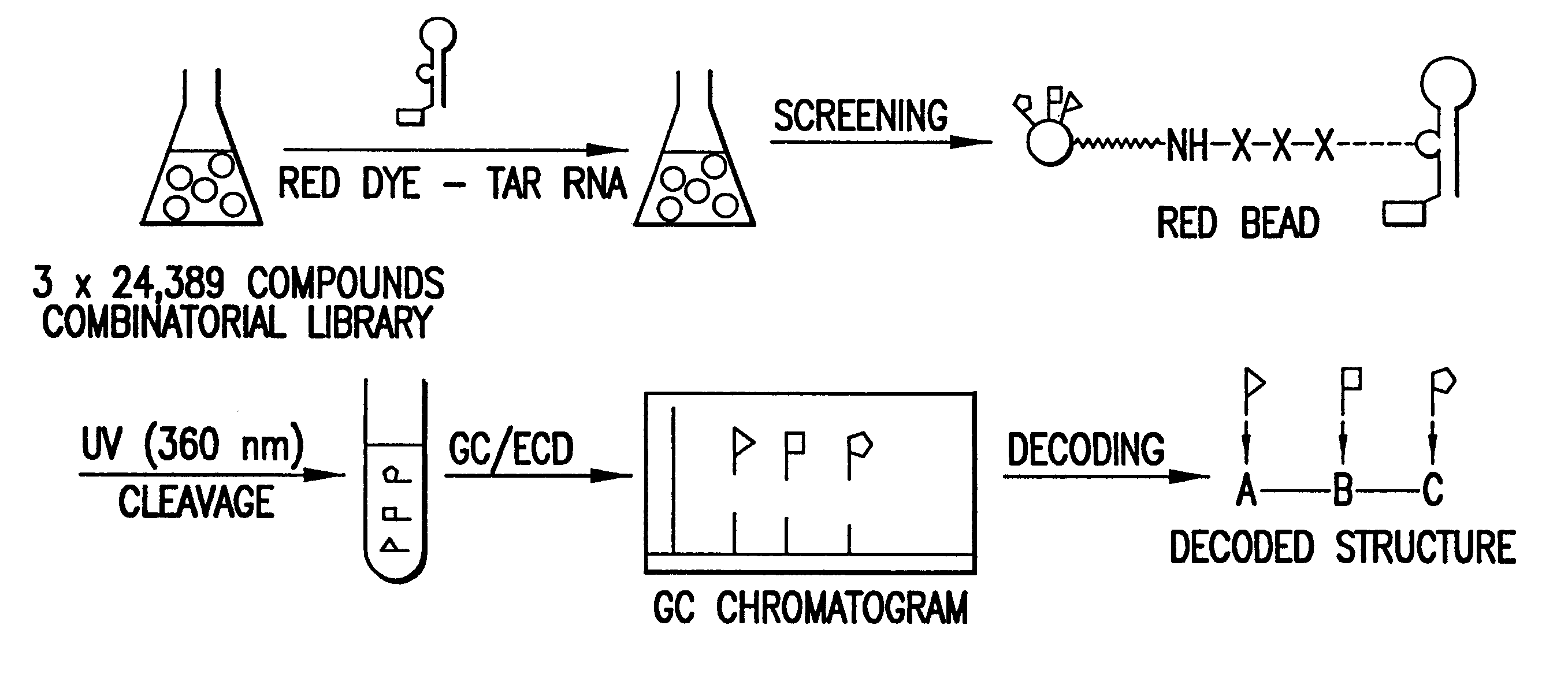
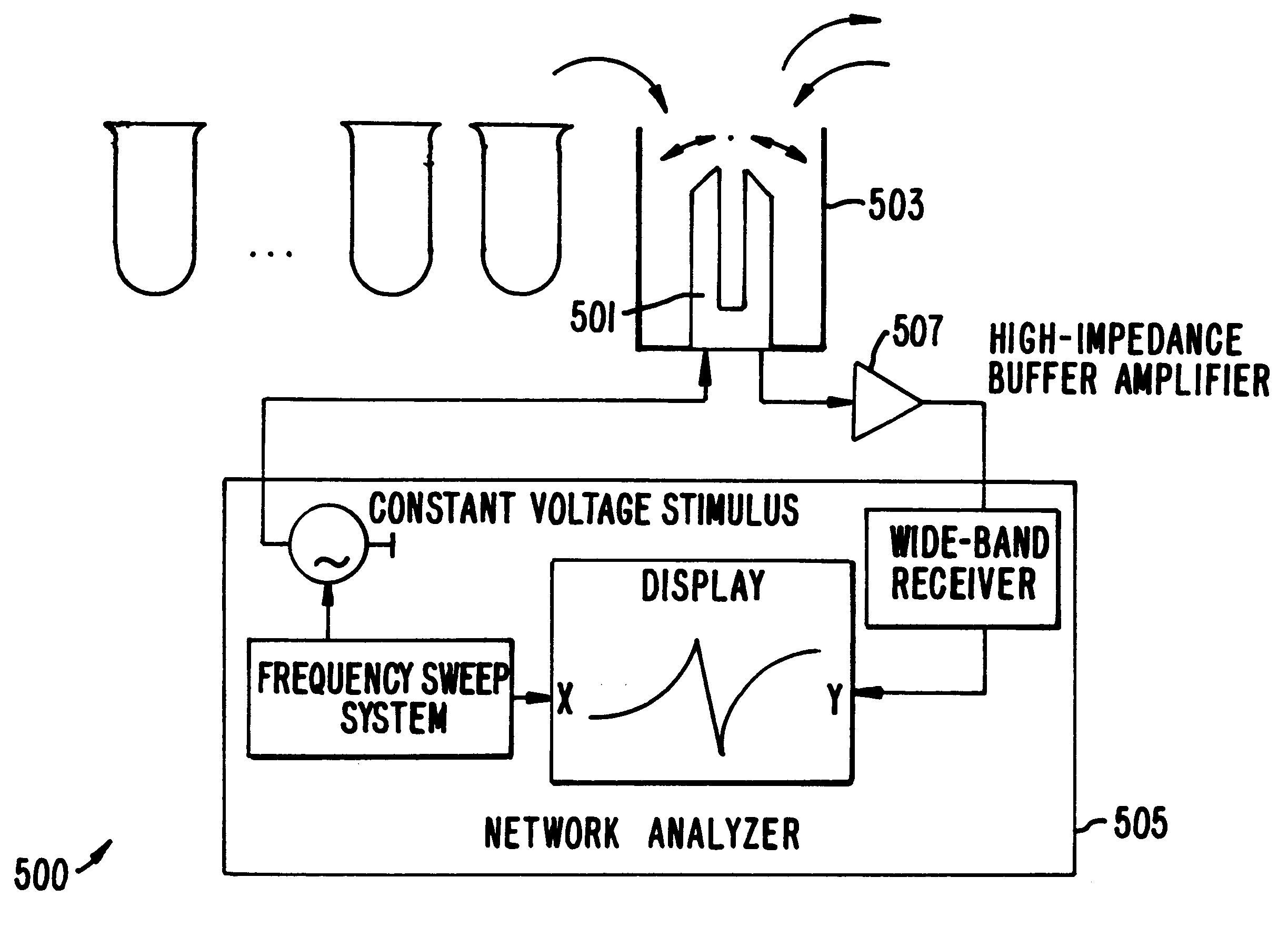
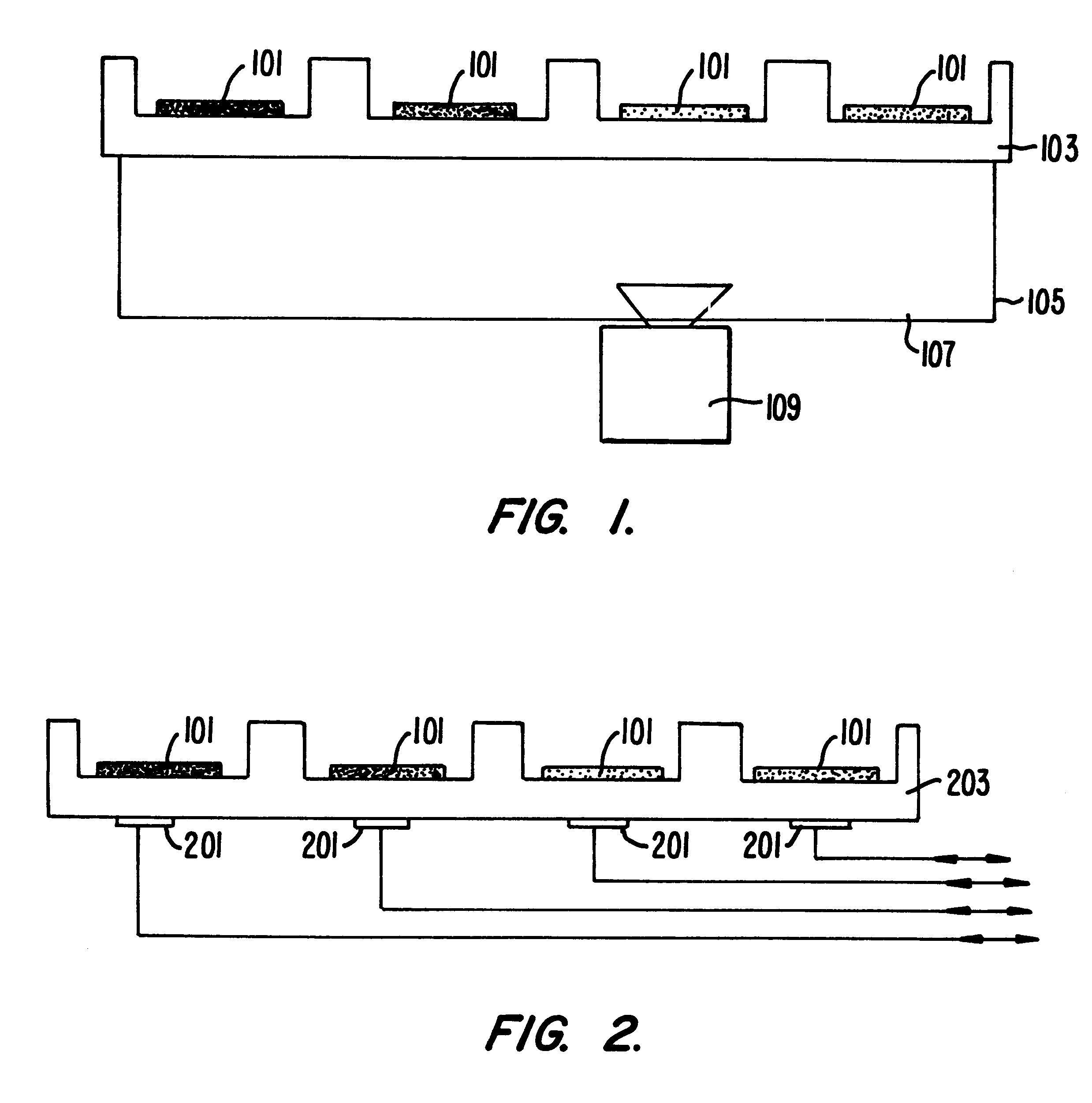
Methods for detecting target analytes and enzymatic reactions
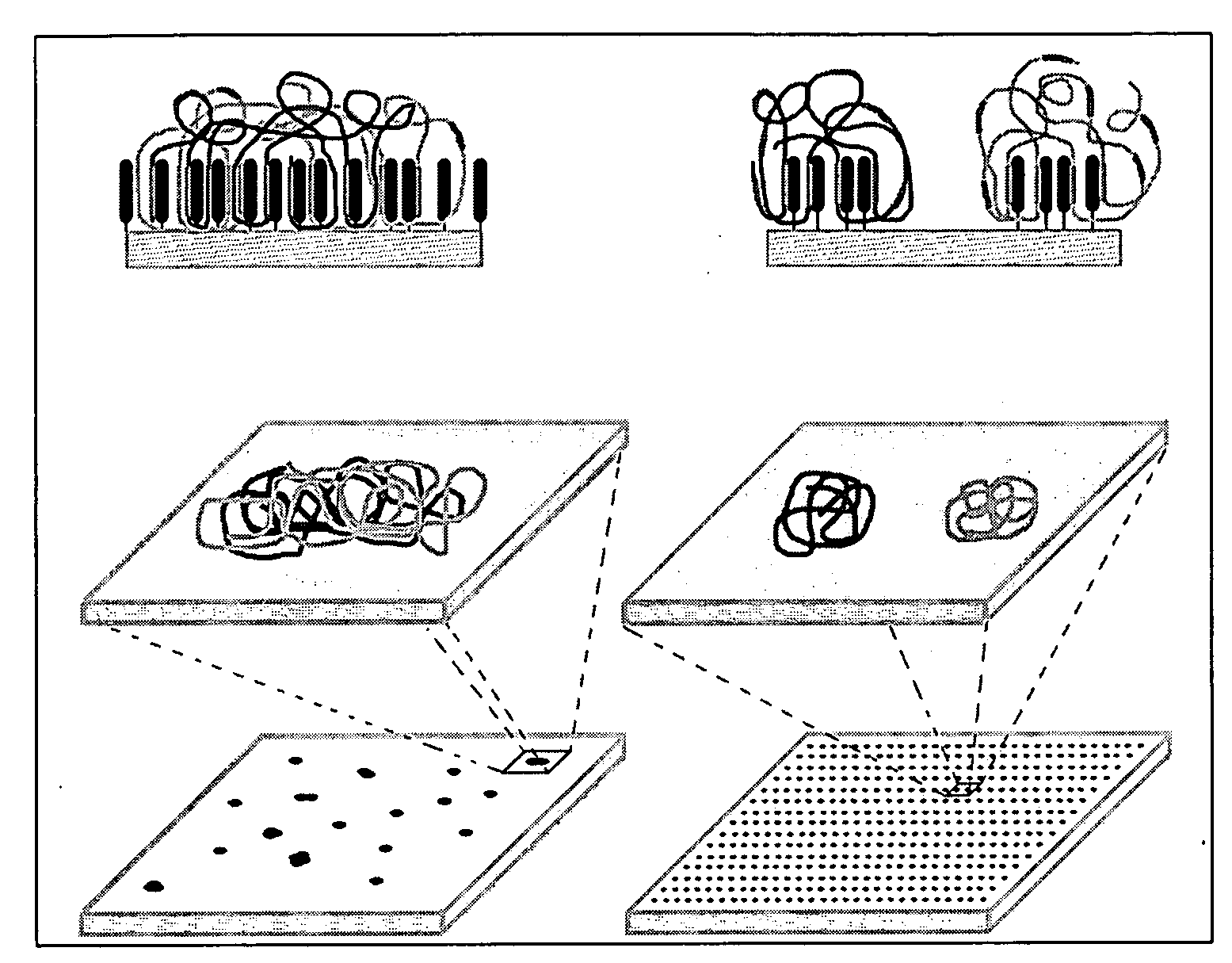
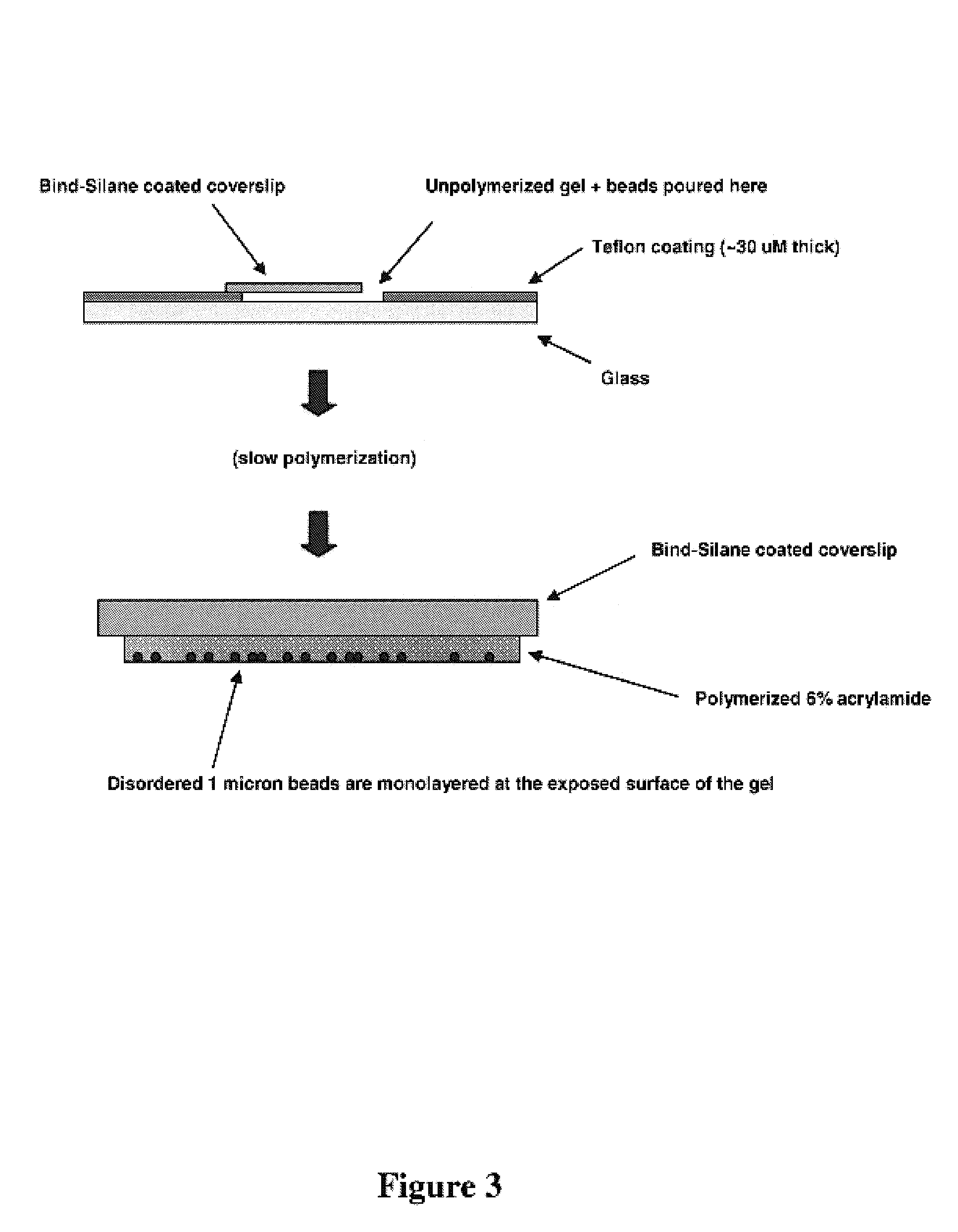
A microsphere-based analytic chemistry system and method for making the same is disclosed in which microspheres or particles carrying bioactive agents may be combined randomly or in ordered fashion and dispersed on a substrate to form an array while maintaining the ability to identify the location of bioactive agents and particles within the array using an optically interrogatable, optical signature encoding scheme. A wide variety of modified substrates may be employed which provide either discrete or non-discrete sites for accommodating the microspheres in either random or patterned distributions. The substrates may be constructed from a variety of materials to form either two-dimensional or three-dimensional configurations. In a preferred embodiment, a modified fiber optic bundle or array is employed as a substrate to produce a high density array. The disclosed system and method have utility for detecting target analytes and screening large libraries of bioactive agents.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF TUFTS COLLEGE TUFTS UNIV
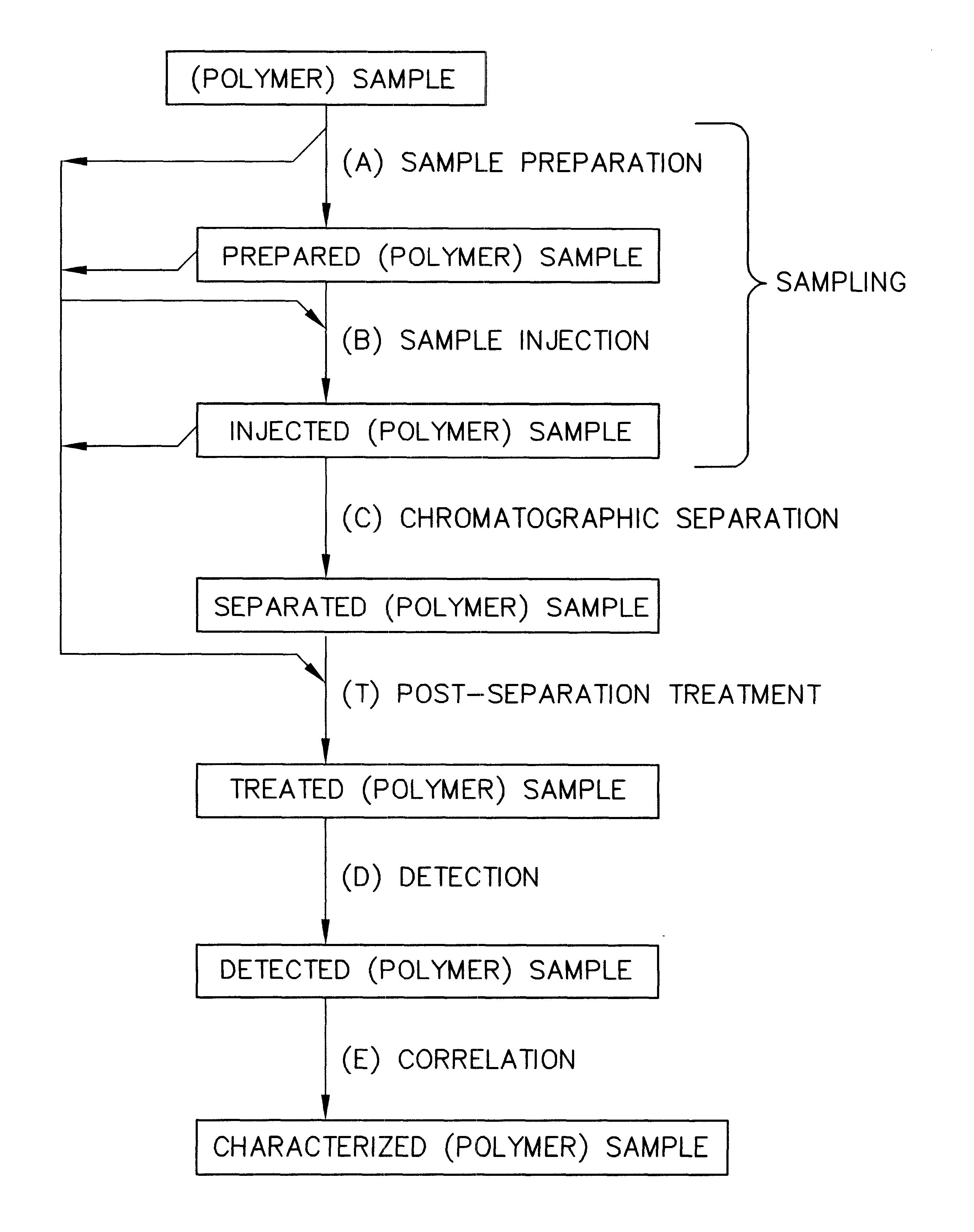
Parallel high-performance liquid chromatography with post-separation treatment
InactiveUS6436292B1High sample throughputEasy to findIon-exchange process apparatusSamplingChromatographic separationCombinatorial synthesis
High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) methods and systems are disclosed that combine parallel chromatographic separation of a plurality of samples with a detection technique that involves post-separation treatment of the plurality of samples to enhance one or more properties of the sample or of a component thereof, followed by detection of the one or more enhanced properties. Selective, tunable detection schemes are achievable, and are particularly advantageous as applied in connection with combinatorial chemistry, combinatorial material science and more particularly, combinatorial synthesis and screening of polymeric materials.
Owner:FREESLATE
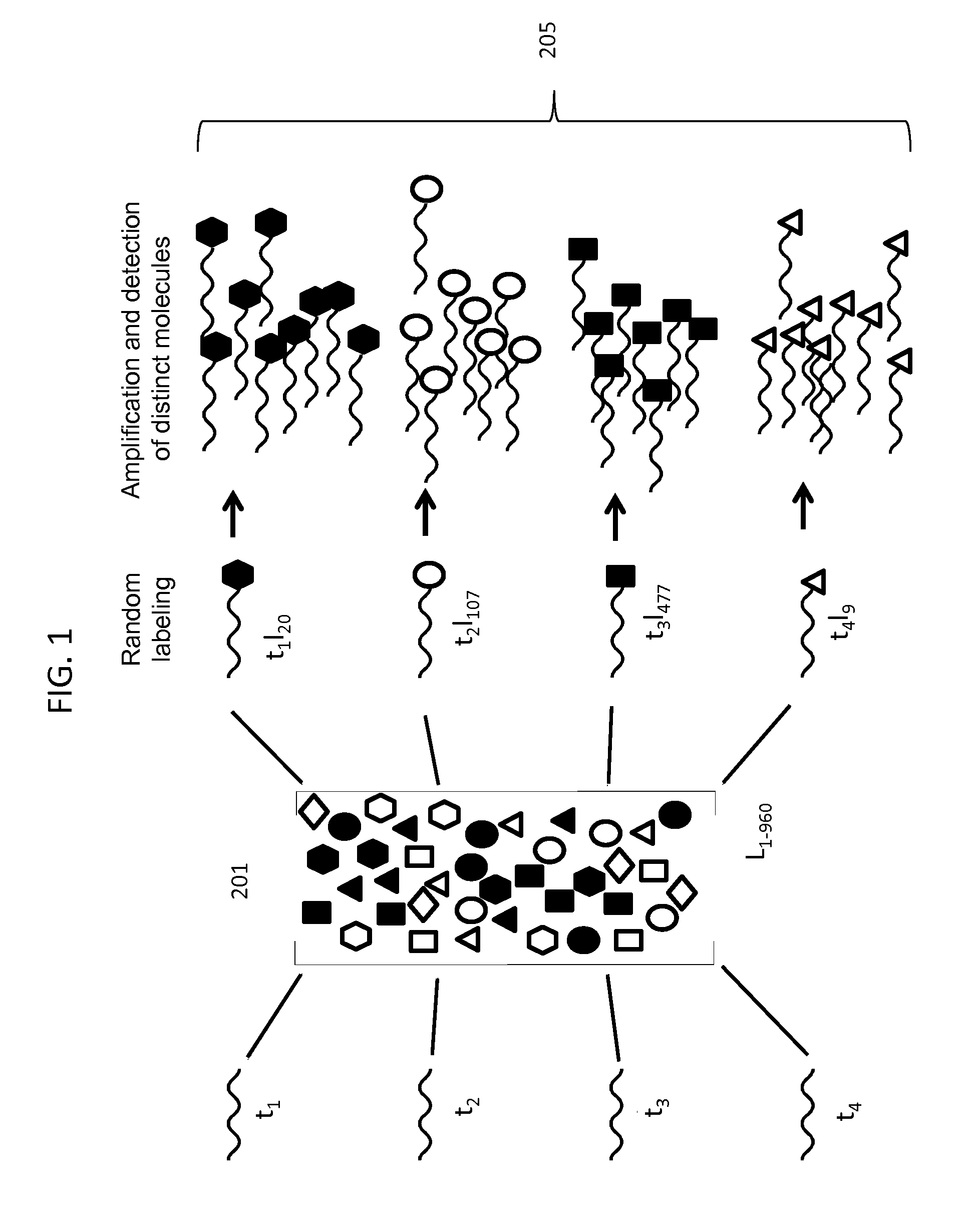
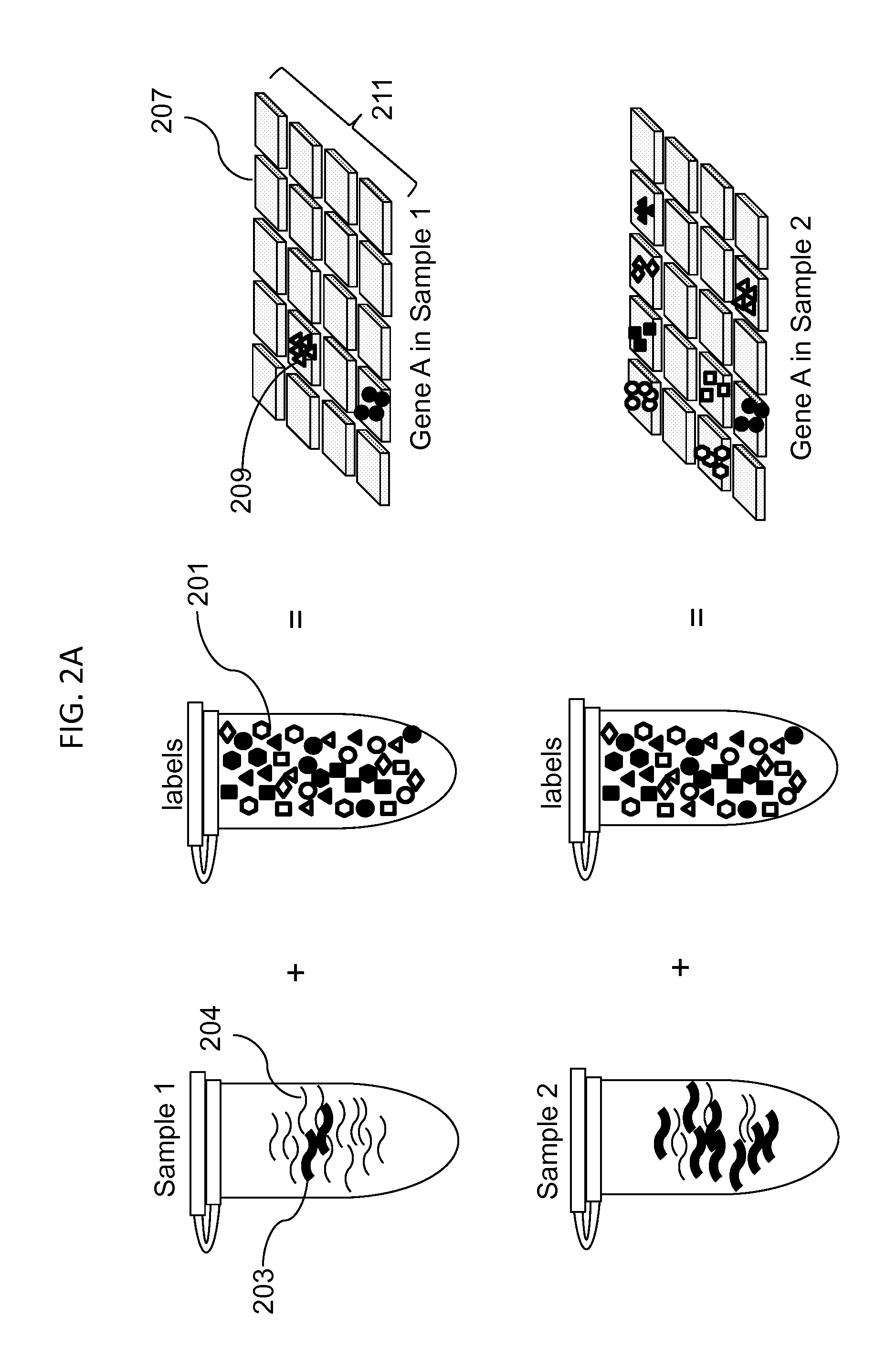
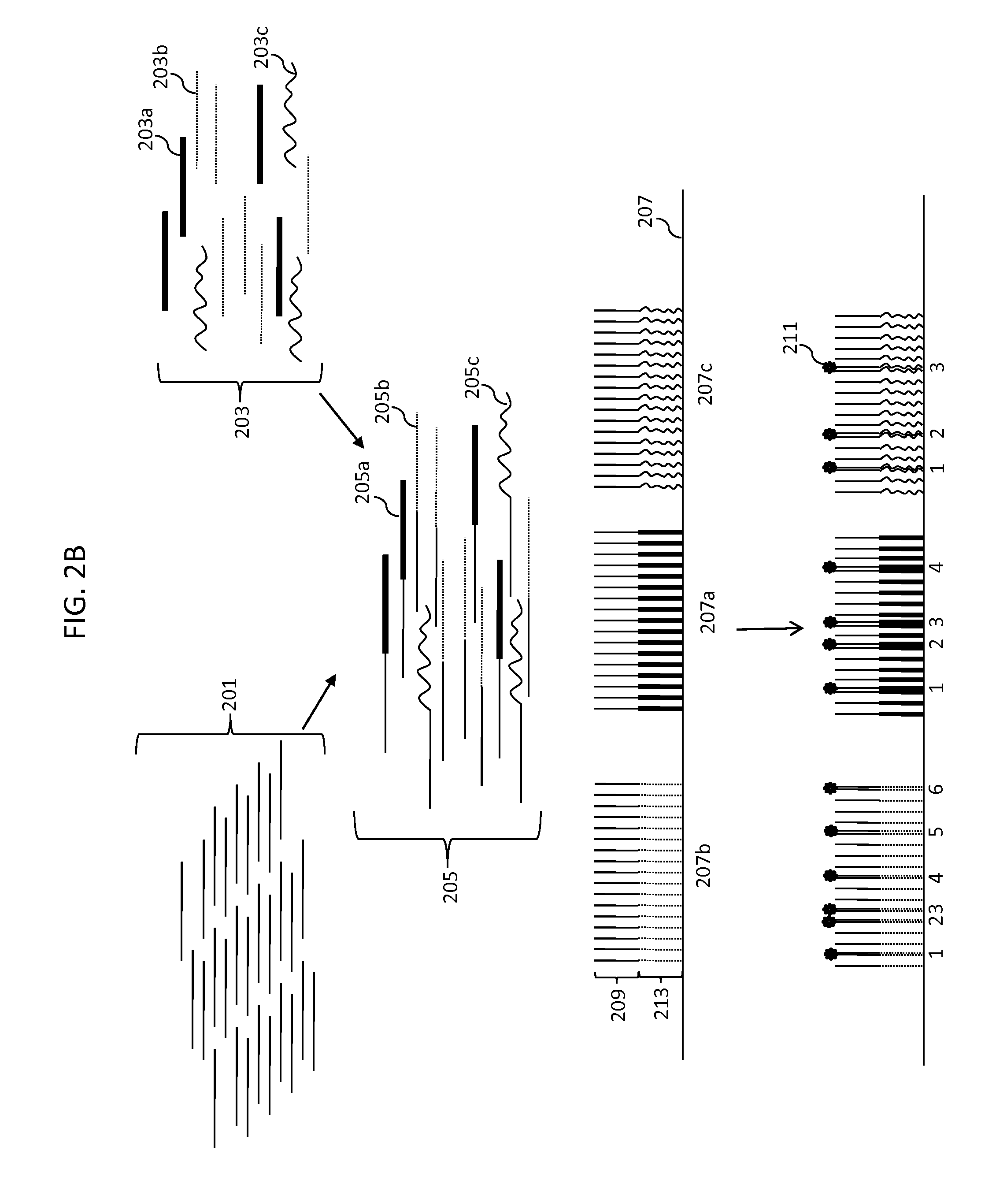
Digital Counting of Individual Molecules by Stochastic Attachment of Diverse Label-Tags
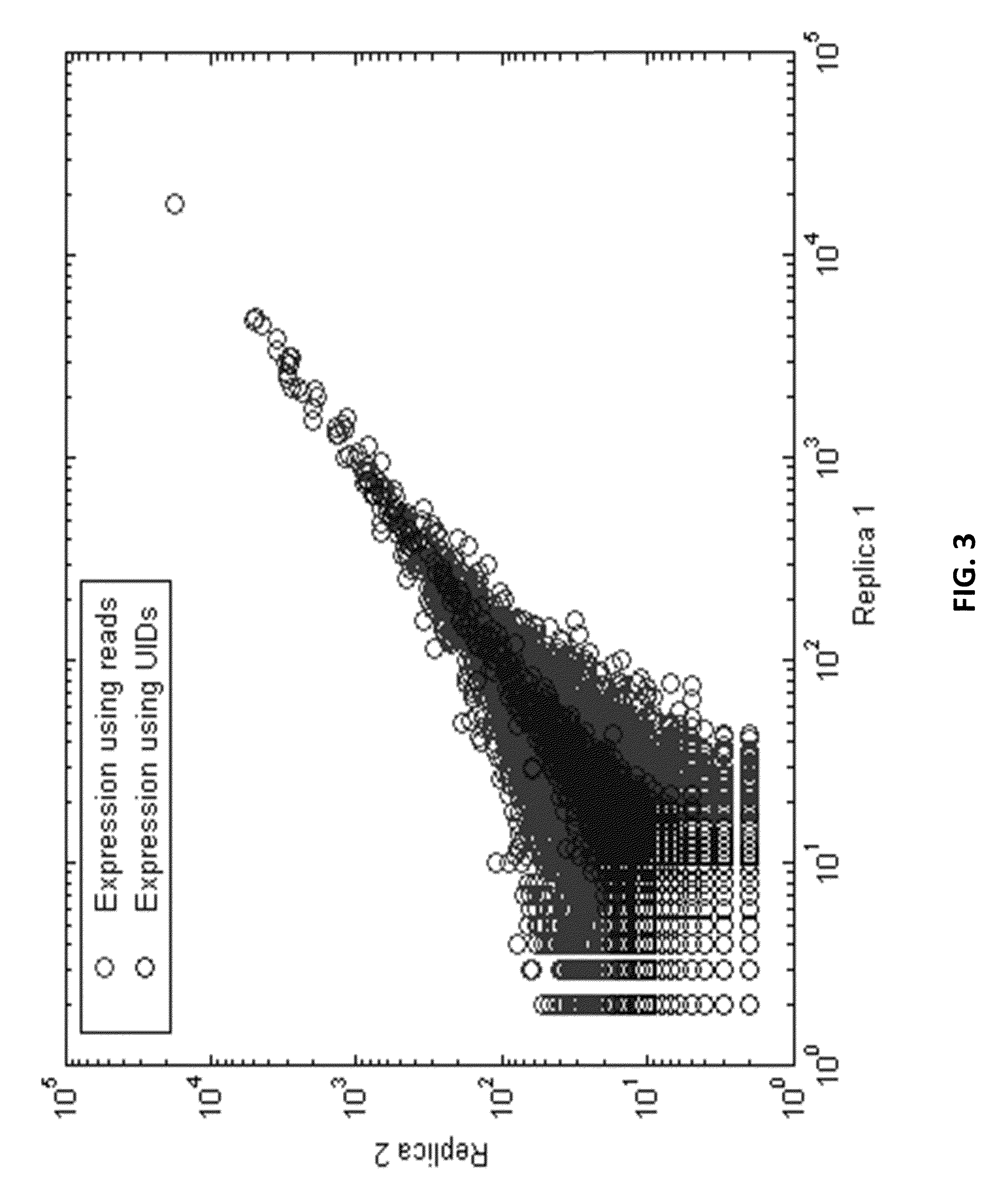
ActiveUS20130116130A1Highly precise relative and absolute counting statisticRaise countNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementBiology
Compositions, methods and kits are disclosed for high-sensitivity counting of individual molecules by stochastic labeling of a identical molecules in mixtures of molecules by attachment of a unique label-tags from a diverse pool of label tags to confer uniqueness to otherwise identical or indistinguishable events. Individual occurrences of target molecules randomly choose from a non-depleting reservoir of diverse label-tags. Labeled molecules may be detected by hybridization or sequencing based methods. Molecules that would otherwise be identical in information content are labeled to create a separately detectable product that can be distinctly detected. The disclosed stochastic transformation methods reduce the problem of counting molecules from one of locating and identifying identical molecules to a series of binary digital questions detecting whether preprogrammed label-tags are present. The methods may be used, for example, to count a given species of molecule within a sample.
Owner:BECTON DICKINSON & CO
Single Cell Nucleic Acid Detection and Analysis
ActiveUS20140155274A1High amplification efficiencyEasy to detectMicrobiological testing/measurementScreening processNucleic acid detectionNucleic acid sequencing
Methods and compositions for digital profiling of nucleic acid sequences present in a sample are provided.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
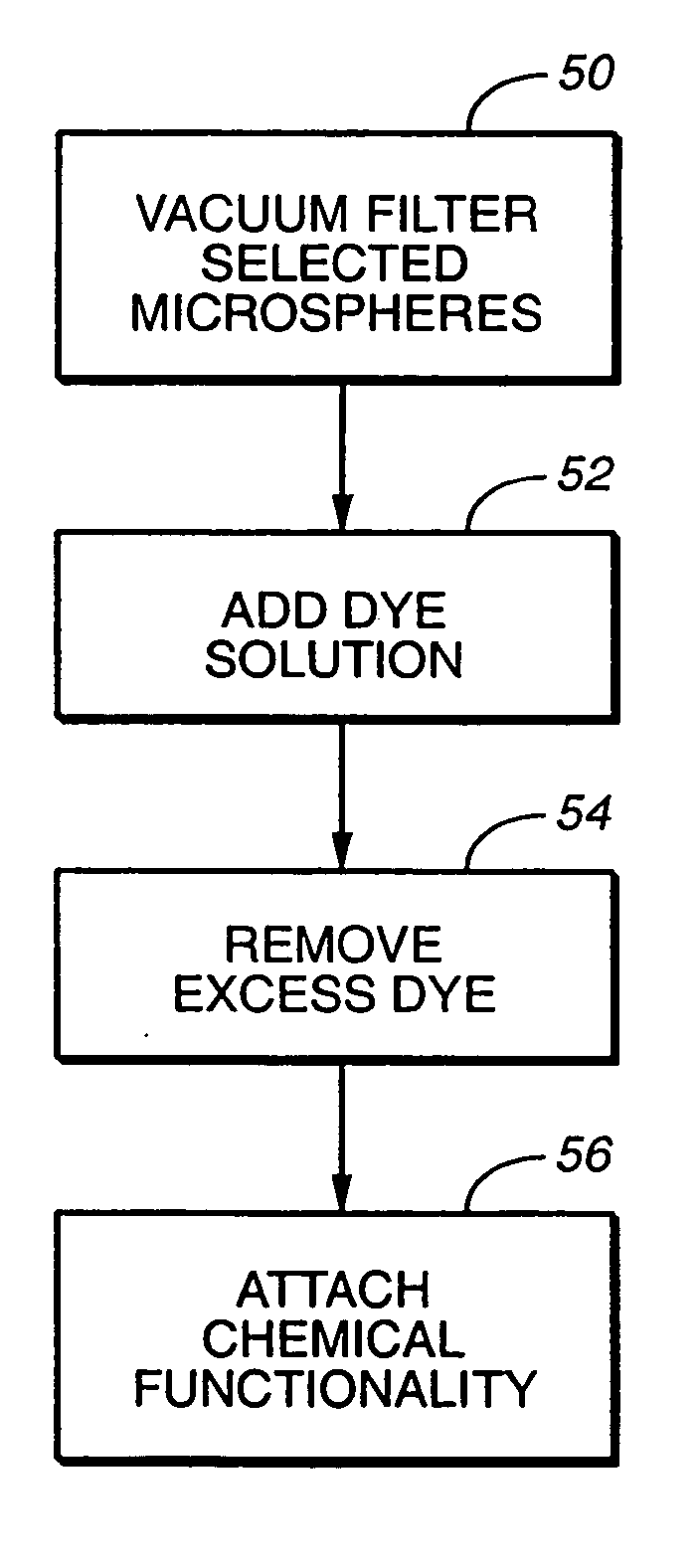
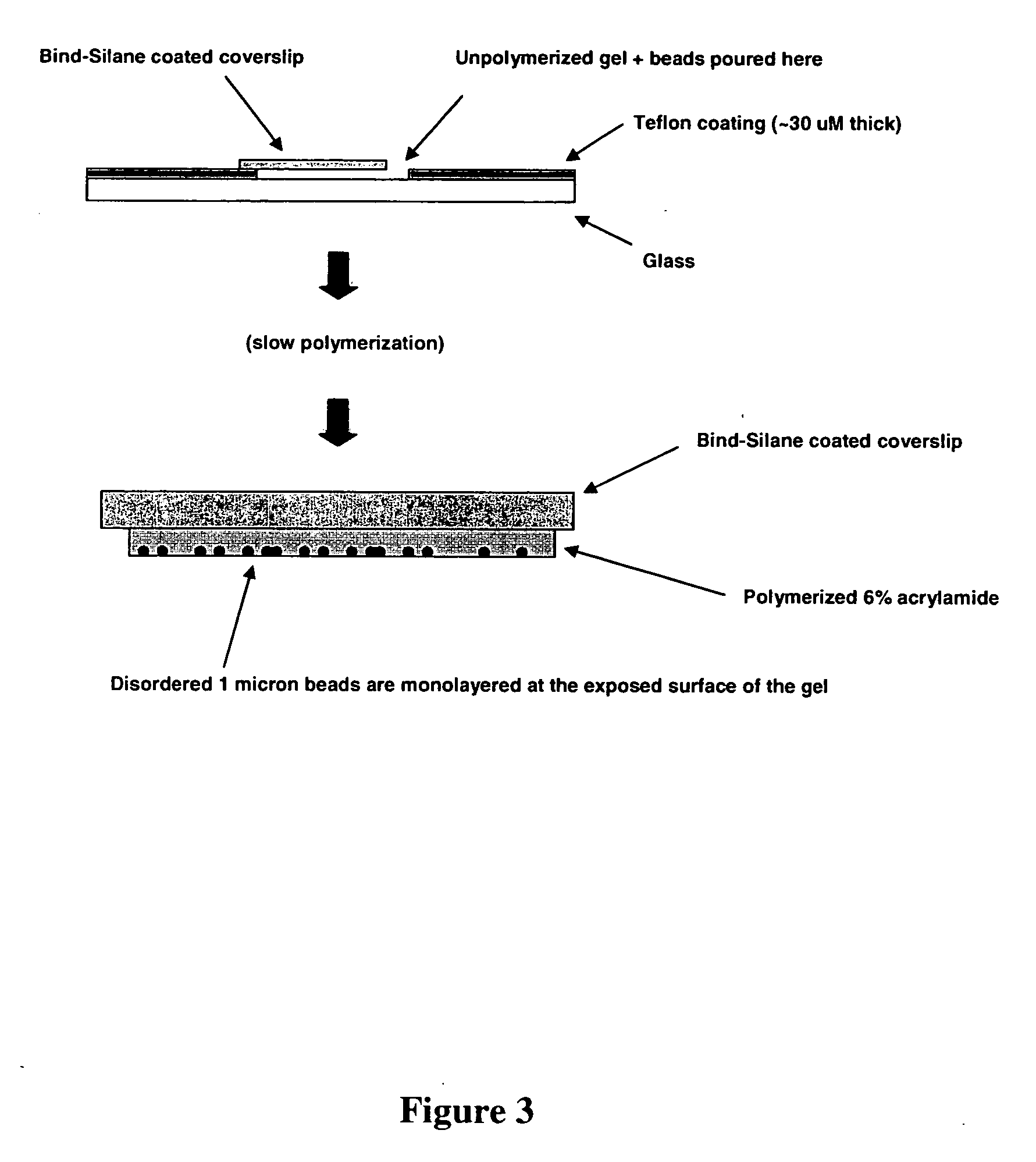
Polony fluorescent in situ sequencing beads
ActiveUS7425431B2Efficient and cost-effective productionBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsHigh densityFluorescent in situ sequencing
Miniaturized, high-density, bead-based arrays are provided. Methods of producing and using clonal beads and producing and using miniaturized, high density, bead-based arrays are also provided.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
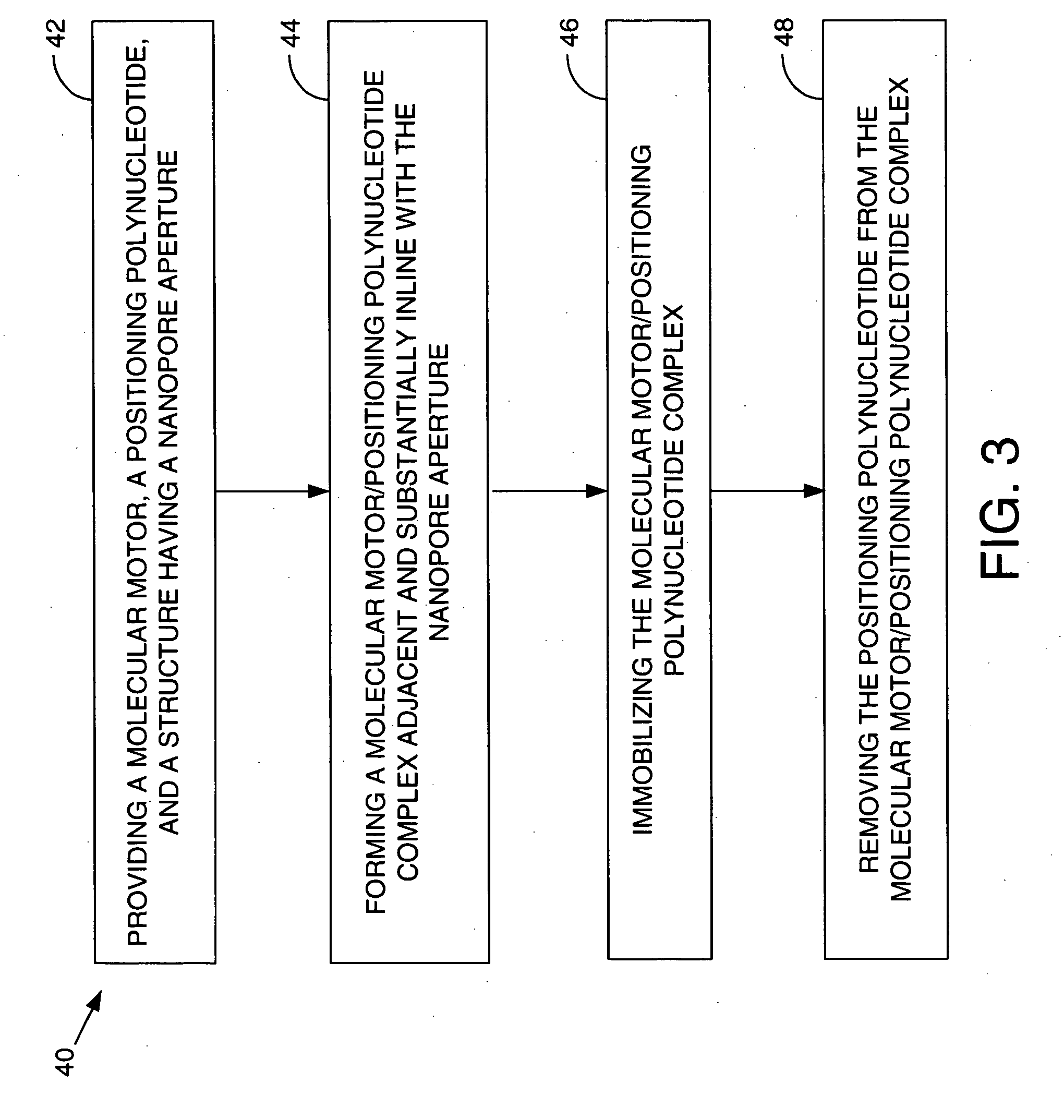
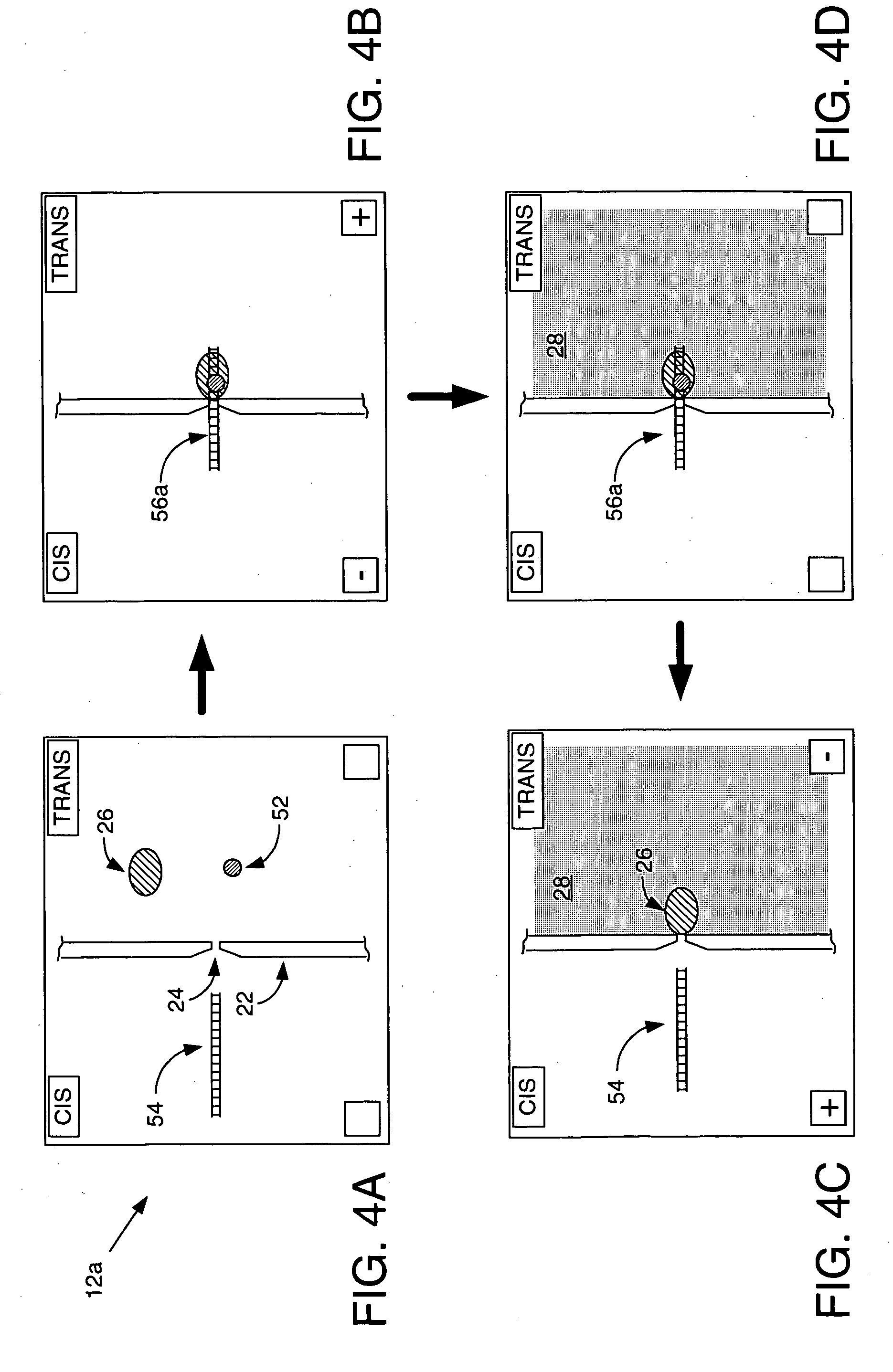
Methods and apparatus for characterizing polynucleotides
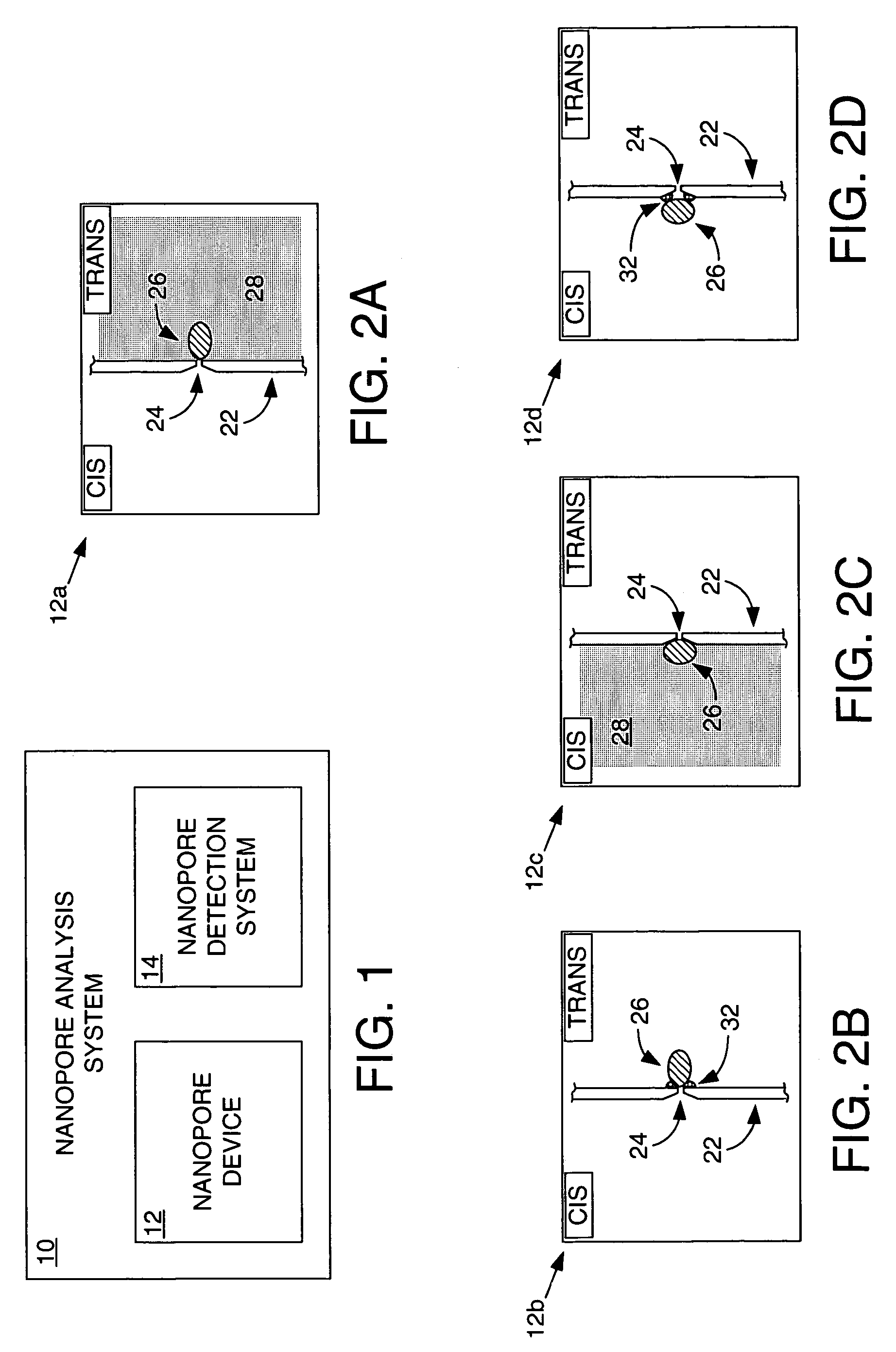
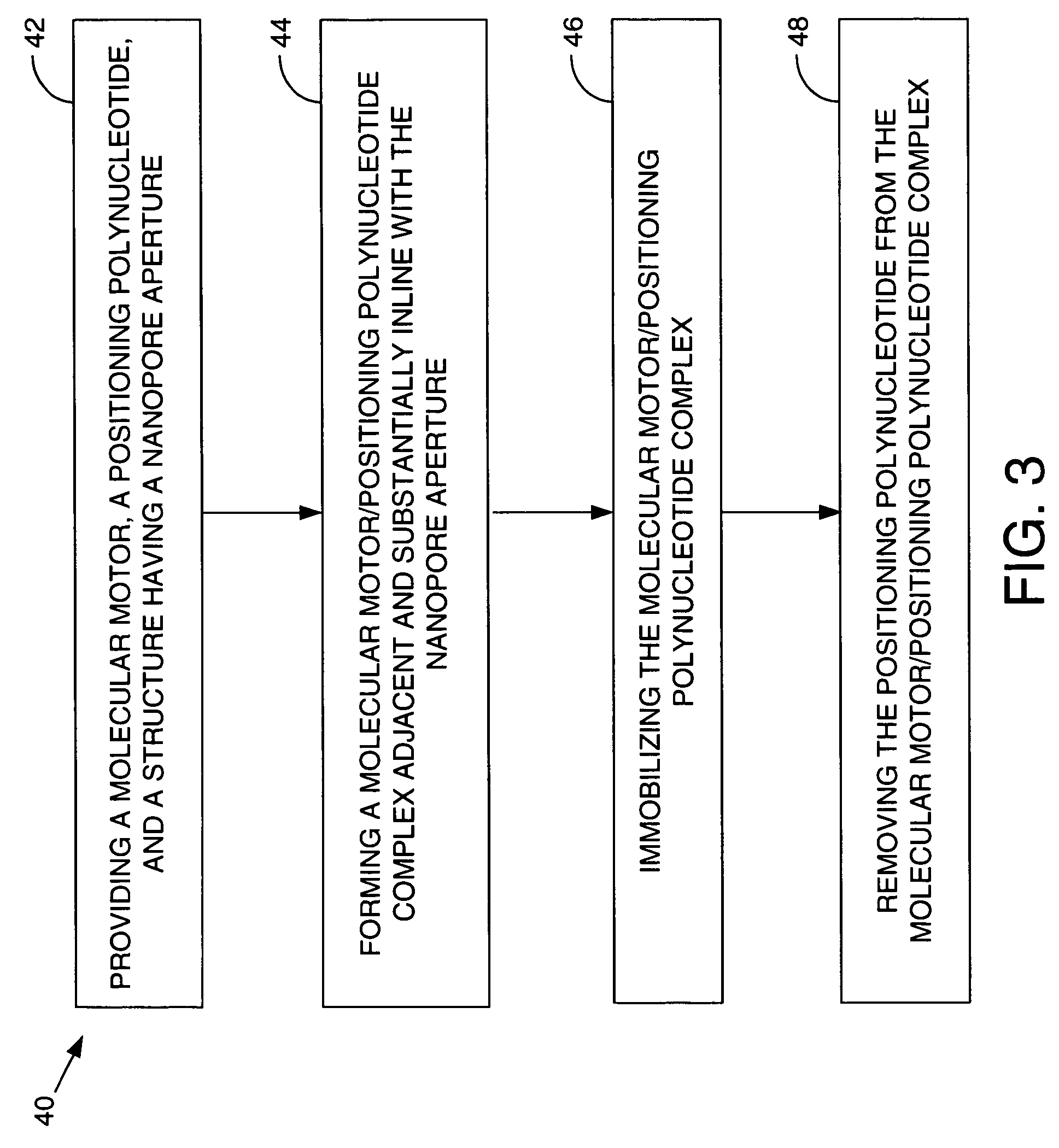
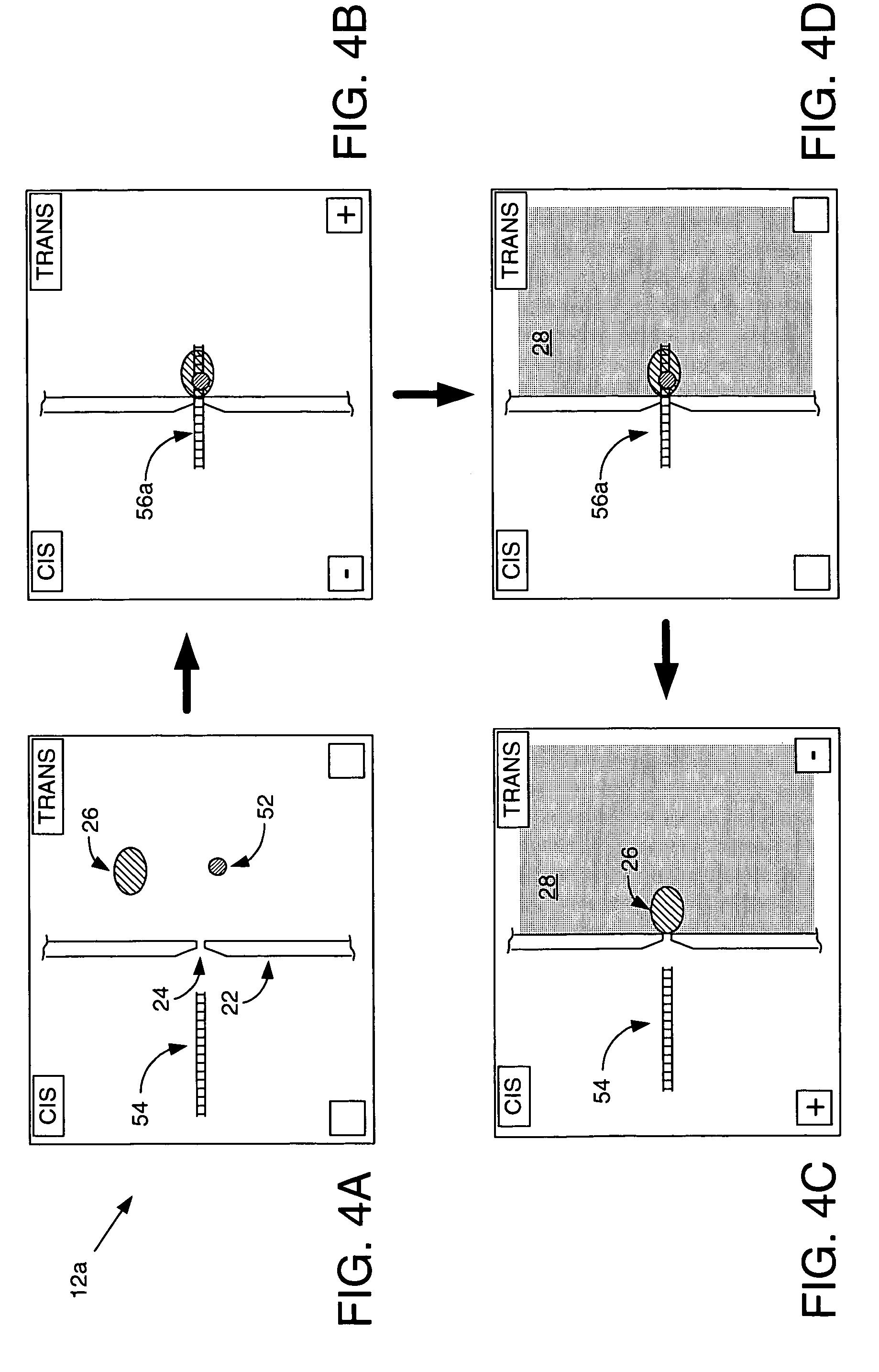
ActiveUS7238485B2Reduce probabilityMaterial nanotechnologyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsCrystallographyMolecular motor
Systems and methods for analysis of polymers, e.g., polynucleotides, are provided. The systems are capable of analyzing a polymer at a specified rate. One such analysis system includes a structure having a nanopore aperture and a molecular motor, e.g., a polymerase, adjacent the nanopore aperture.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE +2
Methods for detection and quantification of analytes in complex mixtures
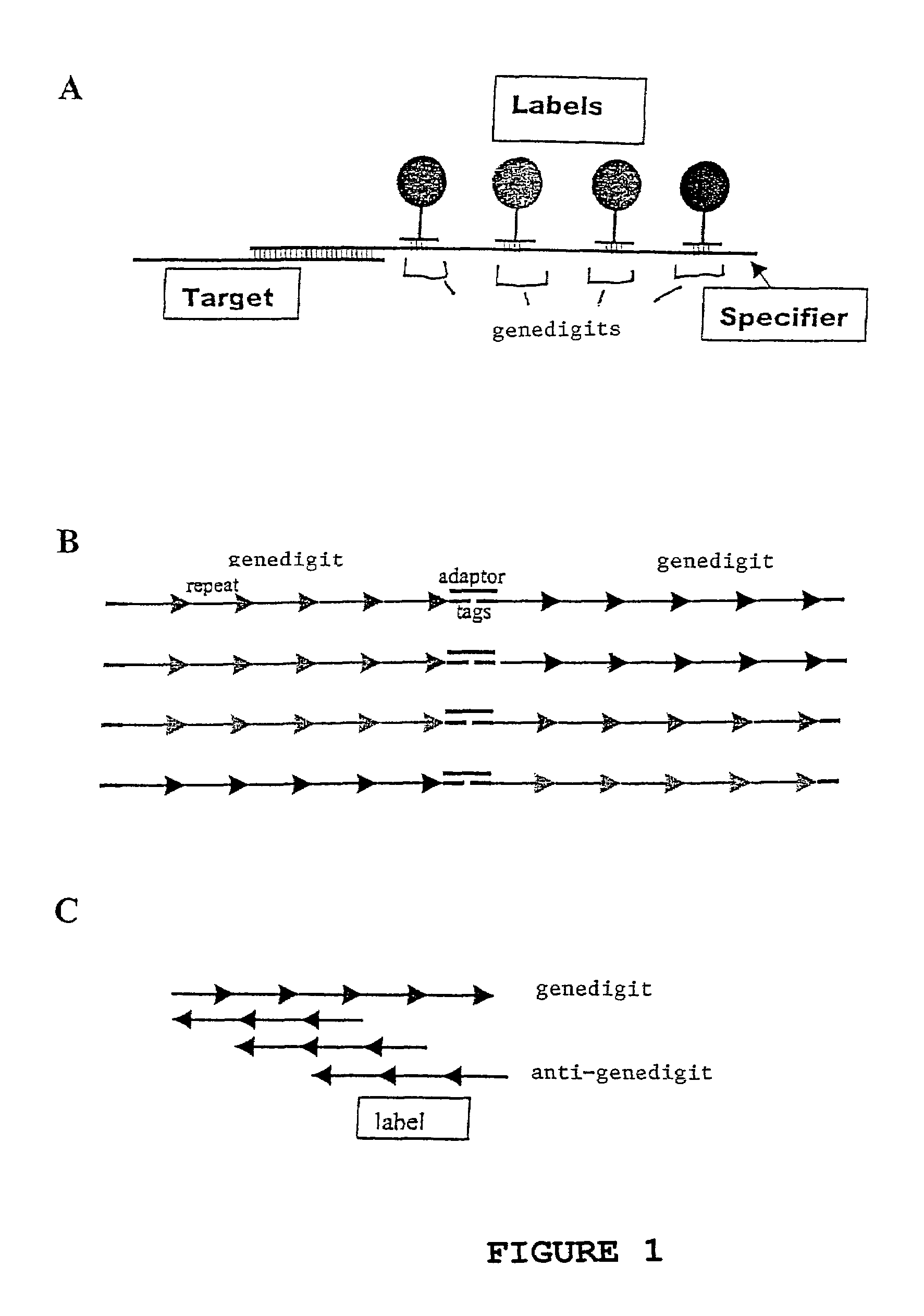
InactiveUS7473767B2Sugar derivativesMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorAnalyteNucleic Acid Probes
The invention provides a diverse population of uniquely labeled probes, containing about thirty or more target specific nucleic acid probes each attached to a unique label bound to a nucleic acid. Also provided is a method of producing a population of uniquely labeled nucleic acid probes. The method consists of (a) synthesizing a population of target specific nucleic acid probes each having a different specifier; (b) synthesizing a corresponding population of anti-genedigits each having a unique label, the population having a diversity sufficient to uniquely hybridize to genedigits within the specifiers, and (c) hybridizing the populations of target nucleic acid probes to the anti-genedigits, to produce a population in which each of the target specific probes is uniquely labeled. Also provided is a method of detecting a nucleic acid analyte.
Owner:INSTITUTE FOR SYSTEMS BIOLOGY
Increasing confidence of allele calls with molecular counting
ActiveUS20120071331A1Easy to analyzeMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary member identificationSequence analysisAllele
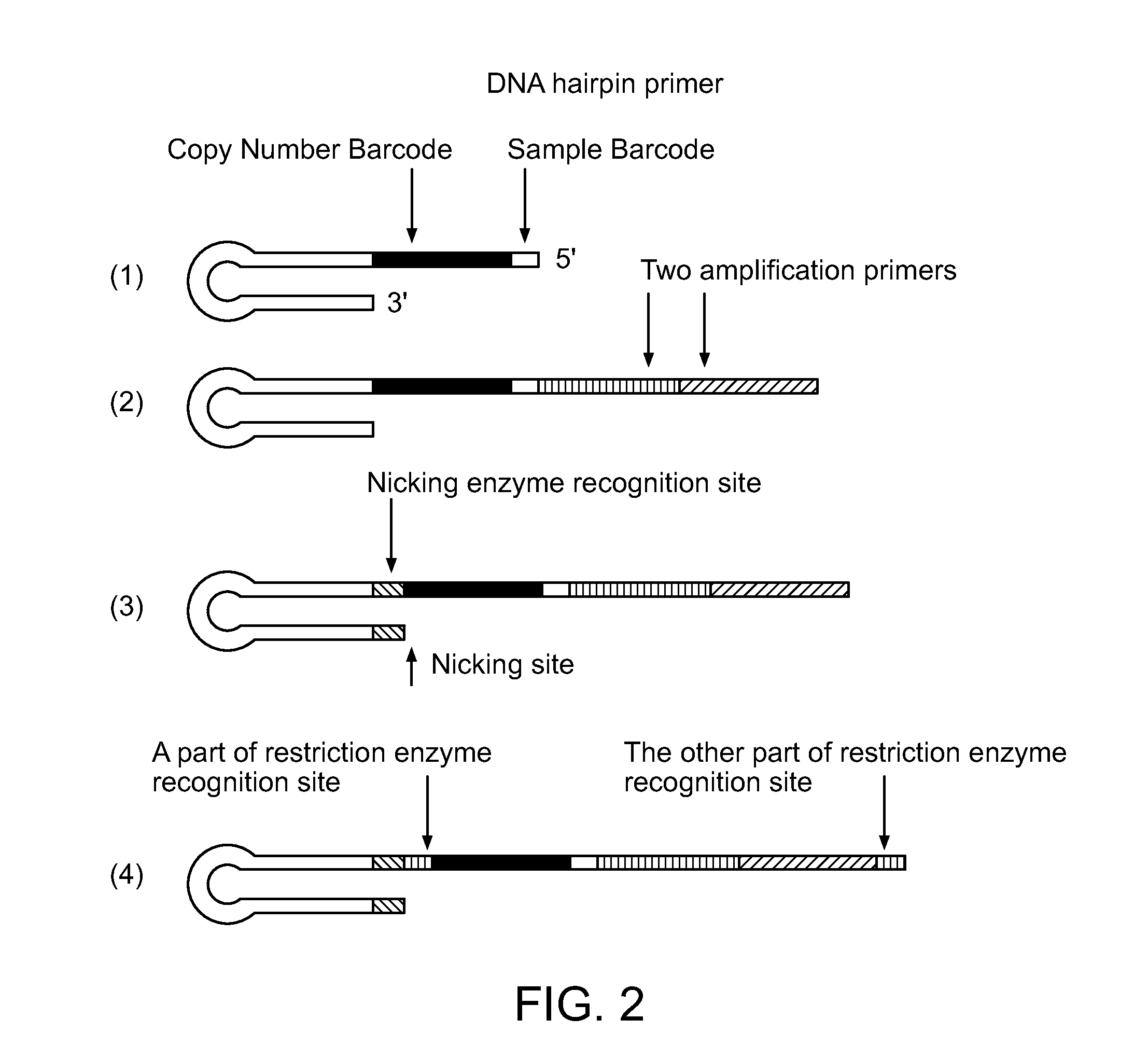
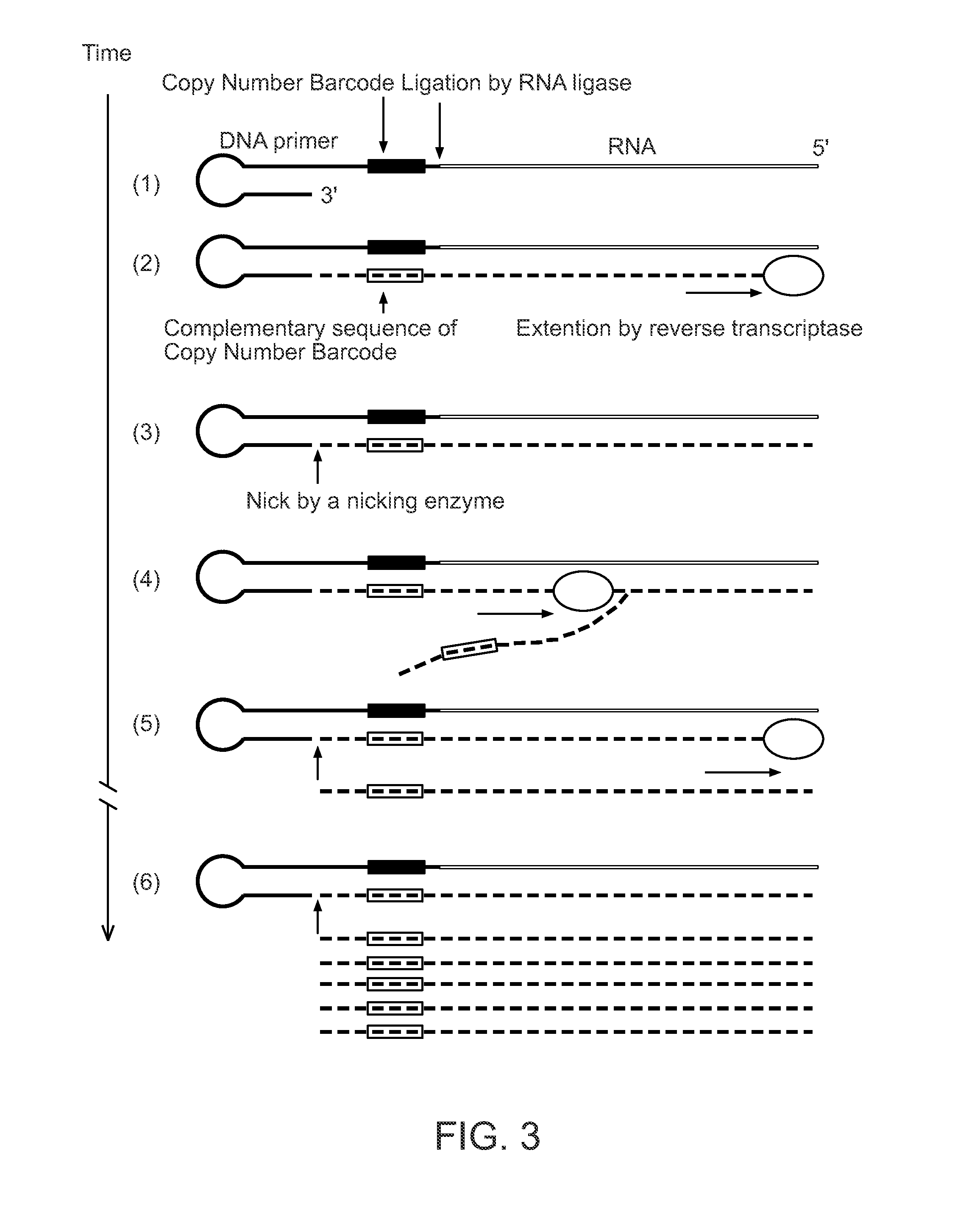
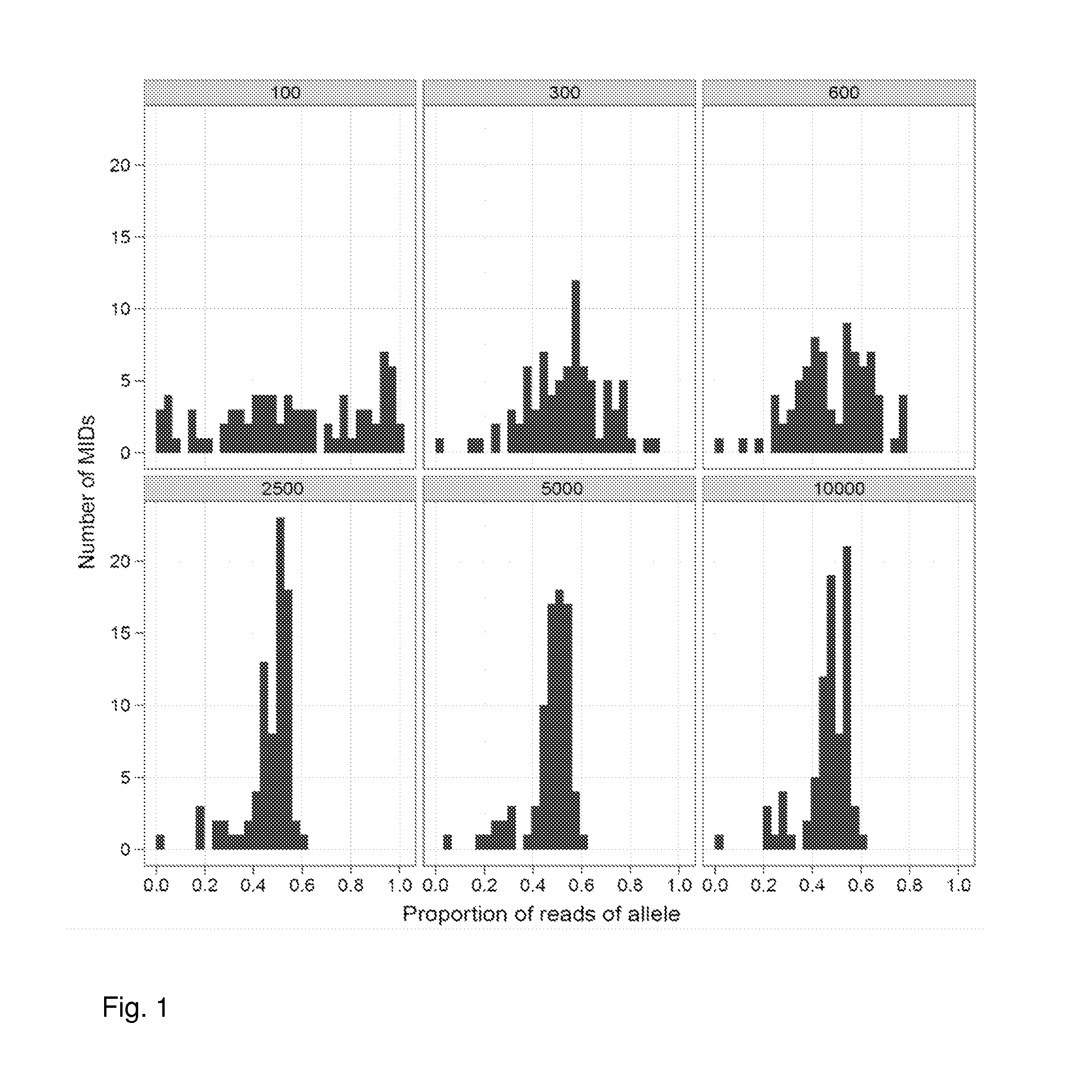
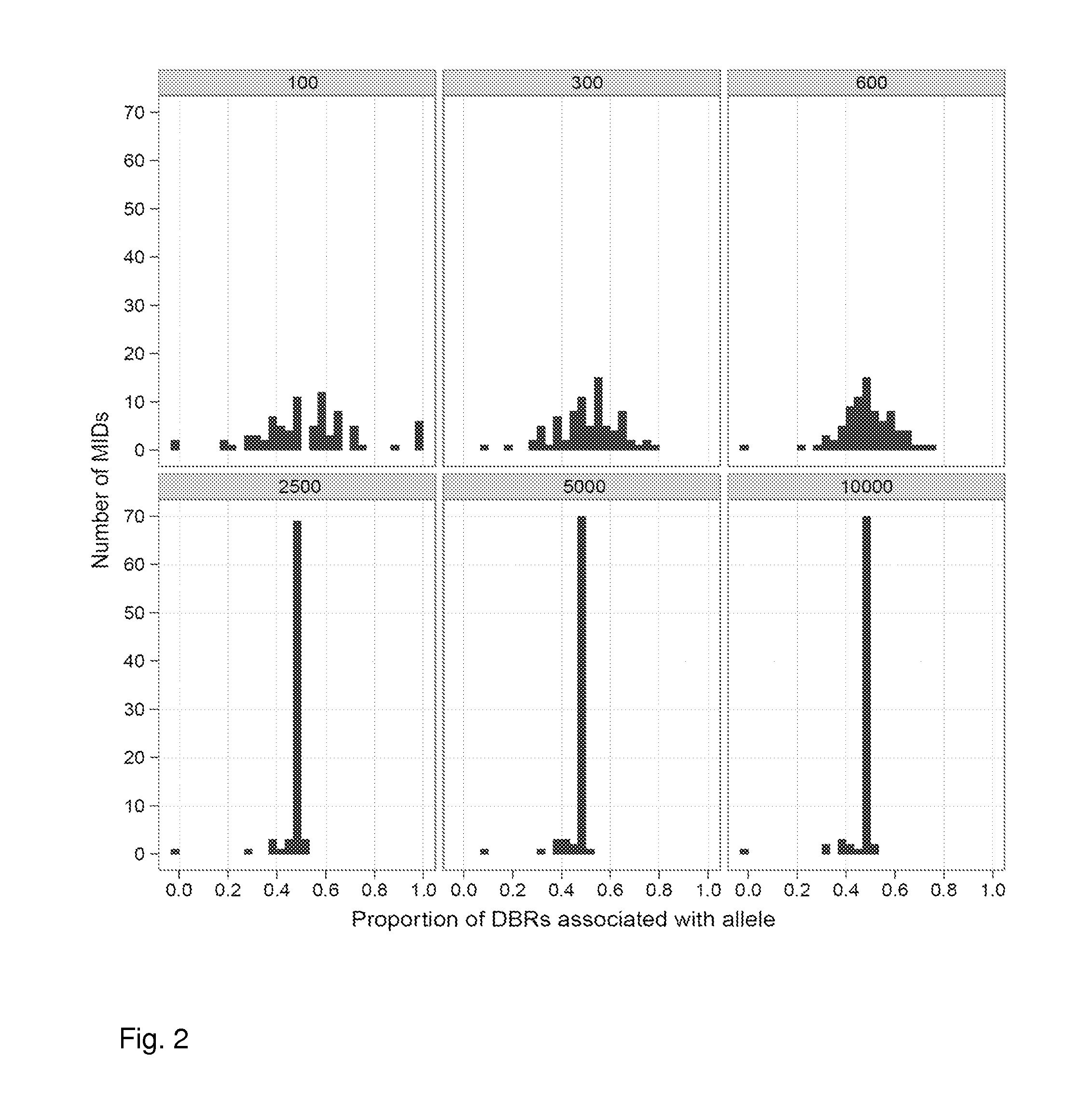
Aspects of the present invention include methods and compositions for determining the number of individual polynucleotide molecules originating from the same genomic region of the same original sample that have been sequenced in a particular sequence analysis configuration or process. In these aspects of the invention, a degenerate base region (DBR) is attached to the starting polynucleotide molecules that are subsequently sequenced (e.g., after certain process steps are performed, e.g., amplification and / or enrichment). The number of different DBR sequences present in a sequencing run can be used to determine / estimate the number of different starting polynucleotides that have been sequenced. DBRs can be used to enhance numerous different nucleic acid sequence analysis applications, including allowing higher confidence allele call determinations in genotyping applications.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Nucleic acid encoding reactions
ActiveUS20130005585A1Avoid substantial annealingNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleotideBarcode
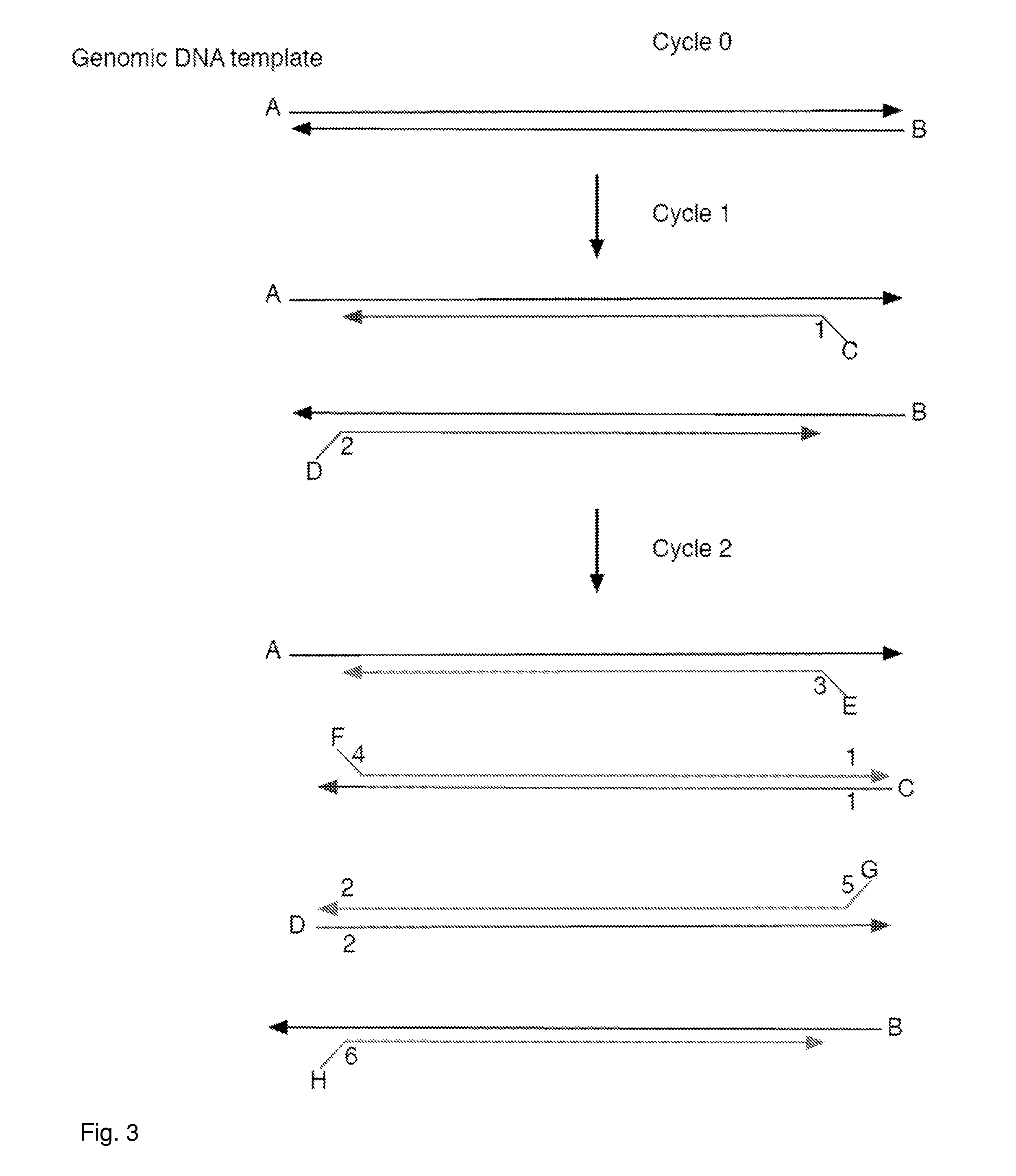
Described herein are methods useful for incorporating one or more adaptors and / or nucleotide tag(s) and / or barcode nucleotide sequence(s) one, or typically more, target nucleotide sequences. In particular embodiments, nucleic acid fragments having adaptors, e.g., suitable for use in high-throughput DNA sequencing are generated. In other embodiments, information about a reaction mixture is encoded into a reaction product. Also described herein are methods and kits useful for amplifying one or more target nucleic acids in preparation for applications such as bidirectional nucleic acid sequencing. In particular embodiments, methods of the invention entail additionally carrying out bidirectional DNA sequencing. Also described herein are methods for encoding and detecting and / or quantifying alleles by primer extension.
Owner:FLUIDIGM CORP
Polony fluorescent in situ sequencing beads
ActiveUS20070087362A1Efficient and cost-effective productionBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsHigh densityFluorescent in situ sequencing
Miniaturized, high-density, bead-based arrays are provided. Methods of producing and using clonal beads and producing and using miniaturized, high density, bead-based arrays are also provided.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Methods and apparatus for characterizing polynucleotides
ActiveUS20060063171A1Reduce probabilityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsMaterial nanotechnologyCrystallographyMolecular motor
Systems and methods for analysis of polymers, e.g., polynucleotides, are provided. The systems are capable of analyzing a polymer at a specified rate. One such analysis system includes a structure having a nanopore aperture and a molecular motor, e.g., a polymerase, adjacent the nanopore aperture.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE +2
Method for differentially quantifying naturally processed hla-restricted peptides for cancer, autoimmune and infectious diseases immunotherapy development
ActiveUS20130096016A1Efficient use ofBiological material analysisLibrary member identificationDiseaseAntigen
The invention relates to a method for quantitatively identifying relevant HLA-bound peptide antigens from primary tissue specimens on a large scale without labeling approaches. This method can not only be used for the development of peptide vaccines, but is also highly valuable for a molecularly defined immunomonitoring and the identification of new antigens for any immunotherapeutic strategy in which HLA-restricted antigenic determinants function as targets, such as a variety of subunit vaccines or adoptive T-cell transfer approaches in cancer, or infectious and autoimmune diseases.
Owner:IMMATICS BIOTECHNOLOGIES GMBH
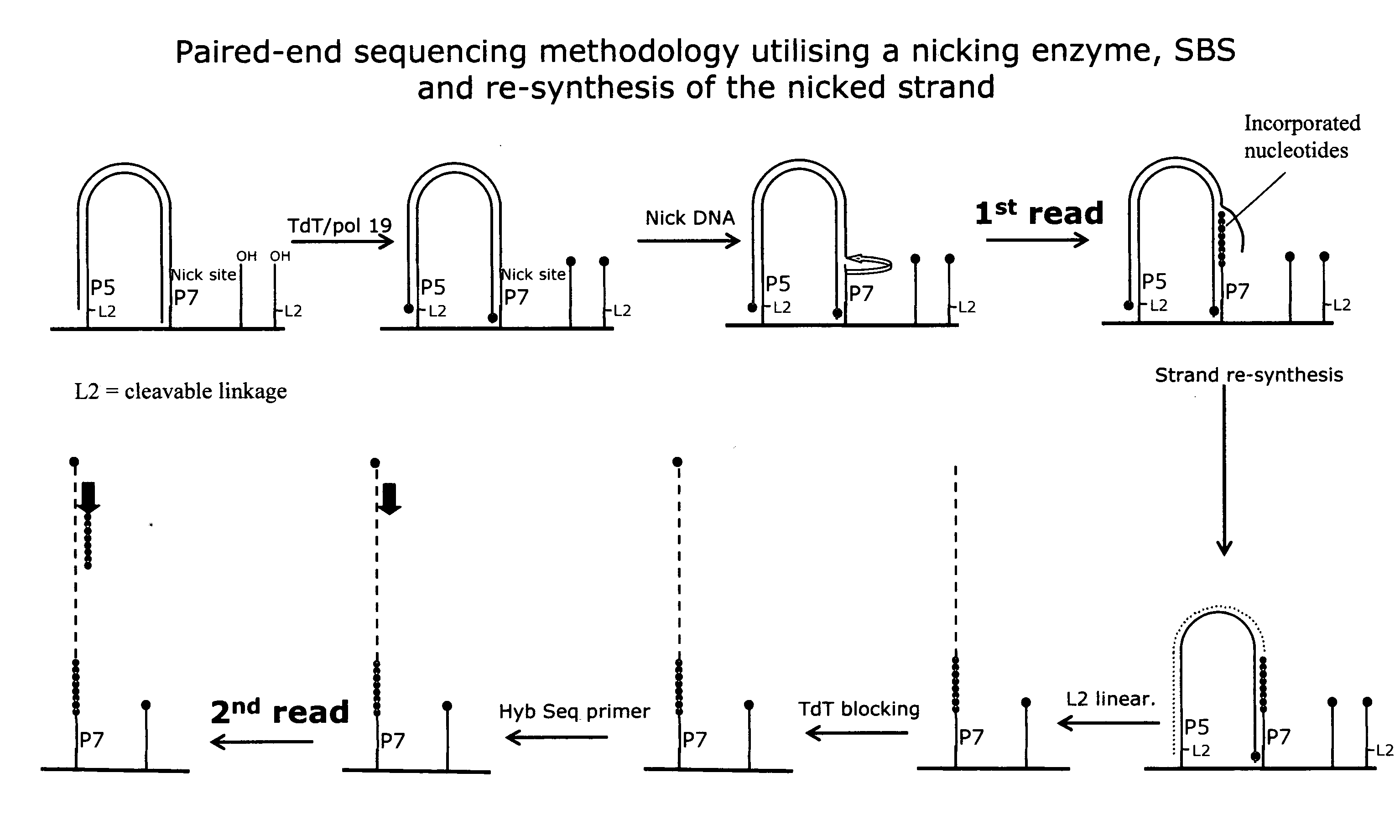
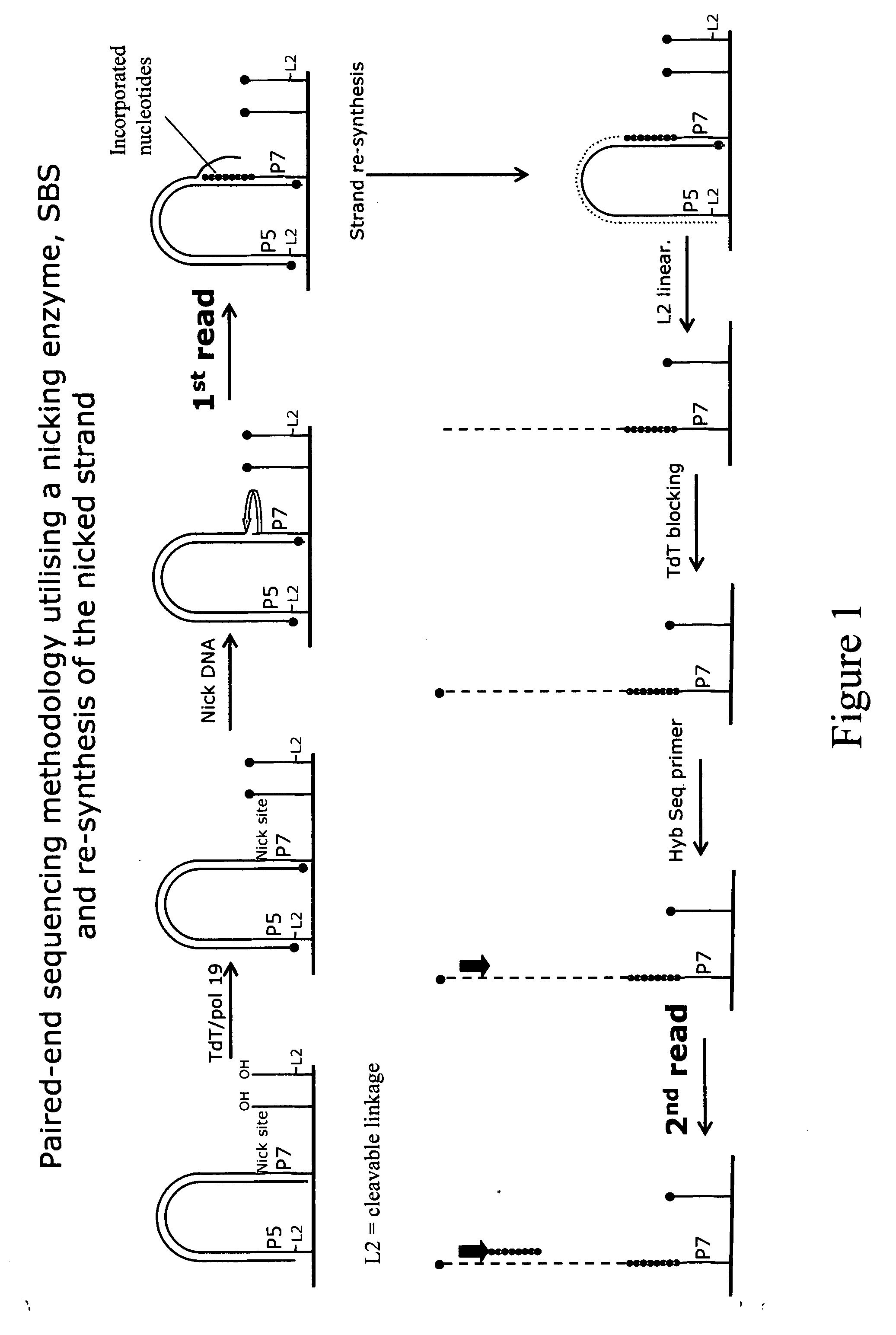
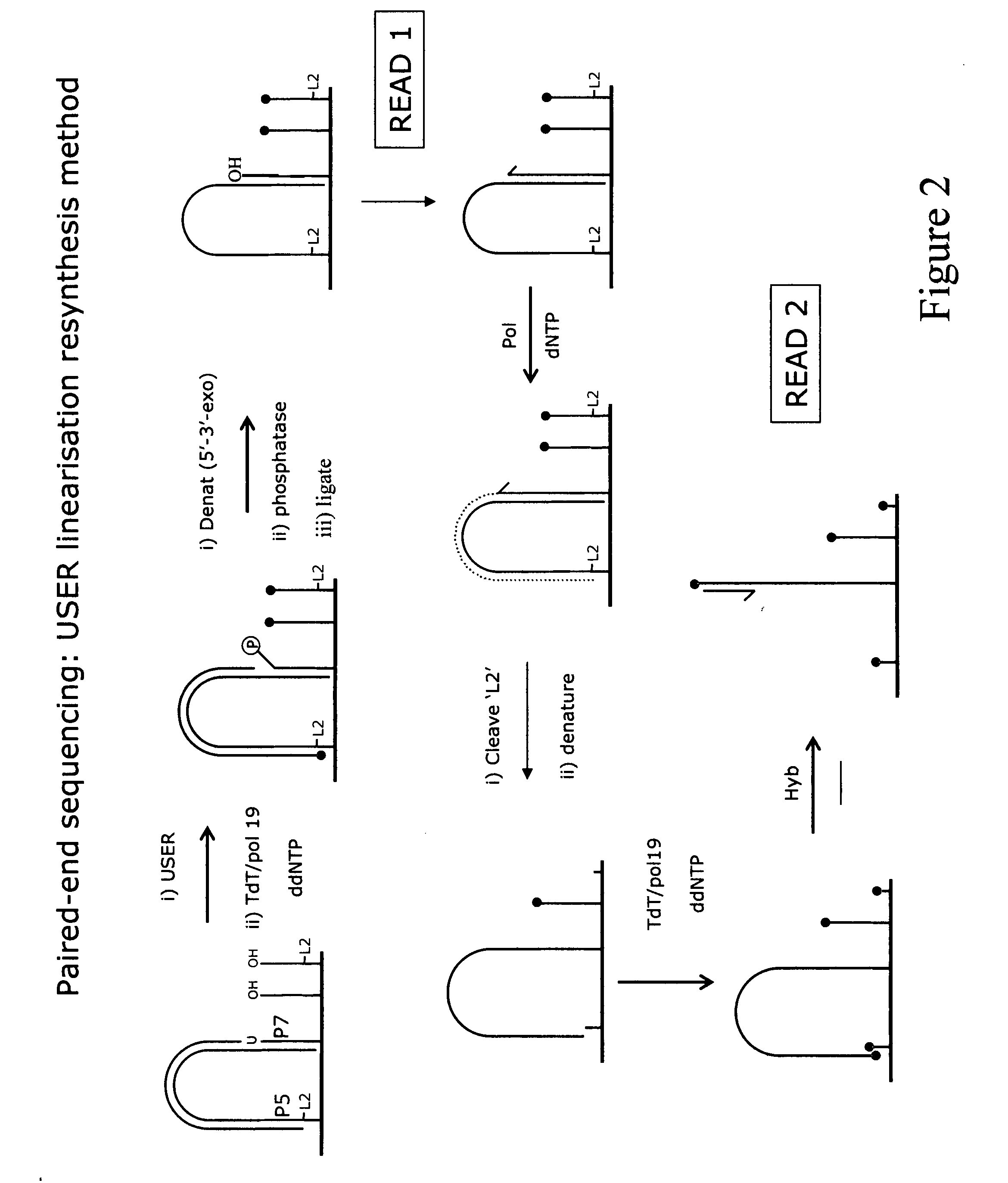
Method for sequencing a polynucleotide template
ActiveUS20090088327A1Improve data qualityMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary member identificationNucleotide sequencingPolynucleotide
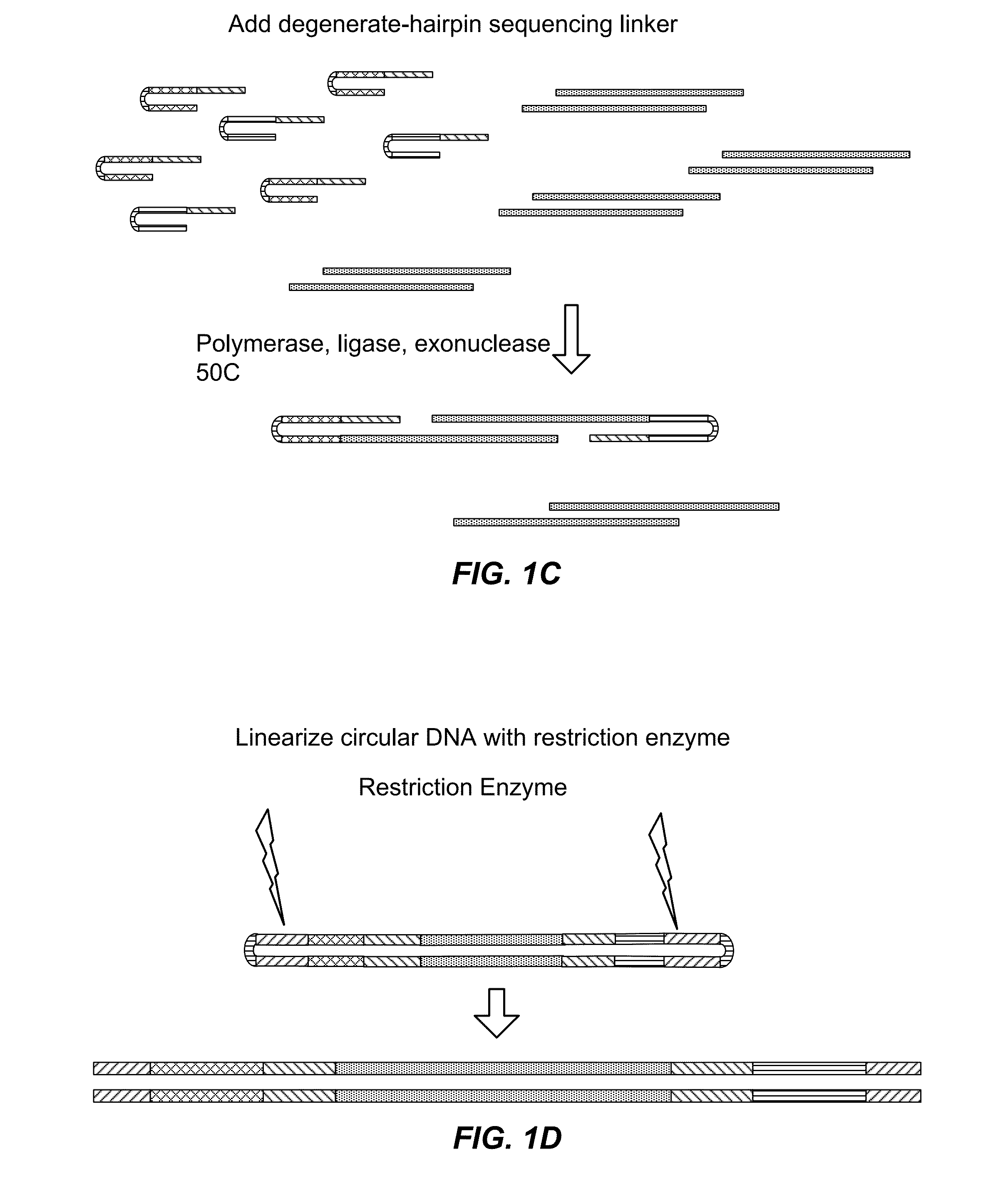
The invention relates to methods for pairwise sequencing of a double-stranded polynucleotide template, which methods result in the sequential determination of nucleotide sequences in two distinct and separate regions of the polynucleotide template. Using the methods of the invention it is possible to obtain two linked or paired reads of sequence information from each double-stranded template on a clustered array, rather than just a single sequencing read from one strand of the template.
Owner:ILLUMINA CAMBRIDGE LTD
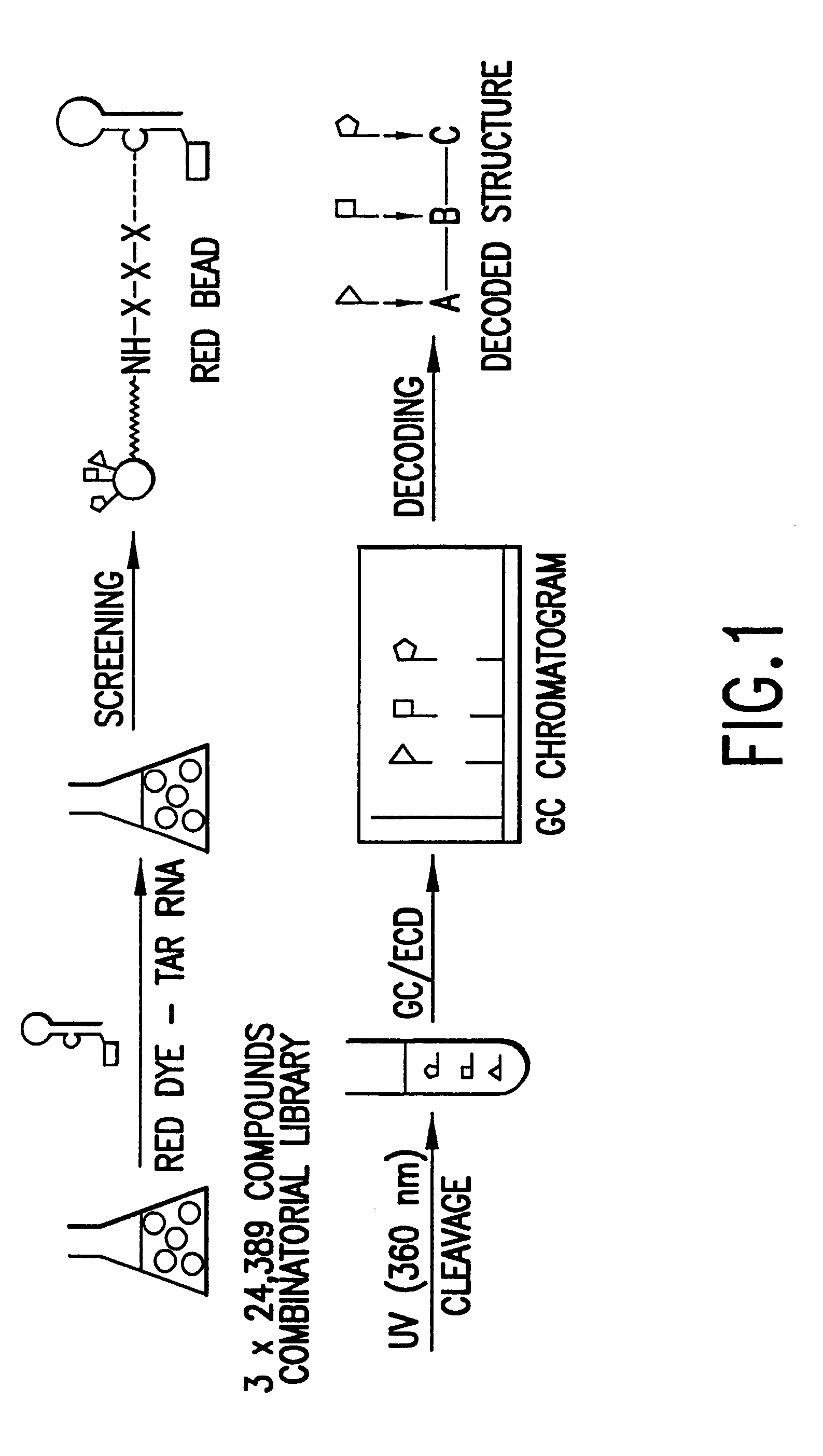
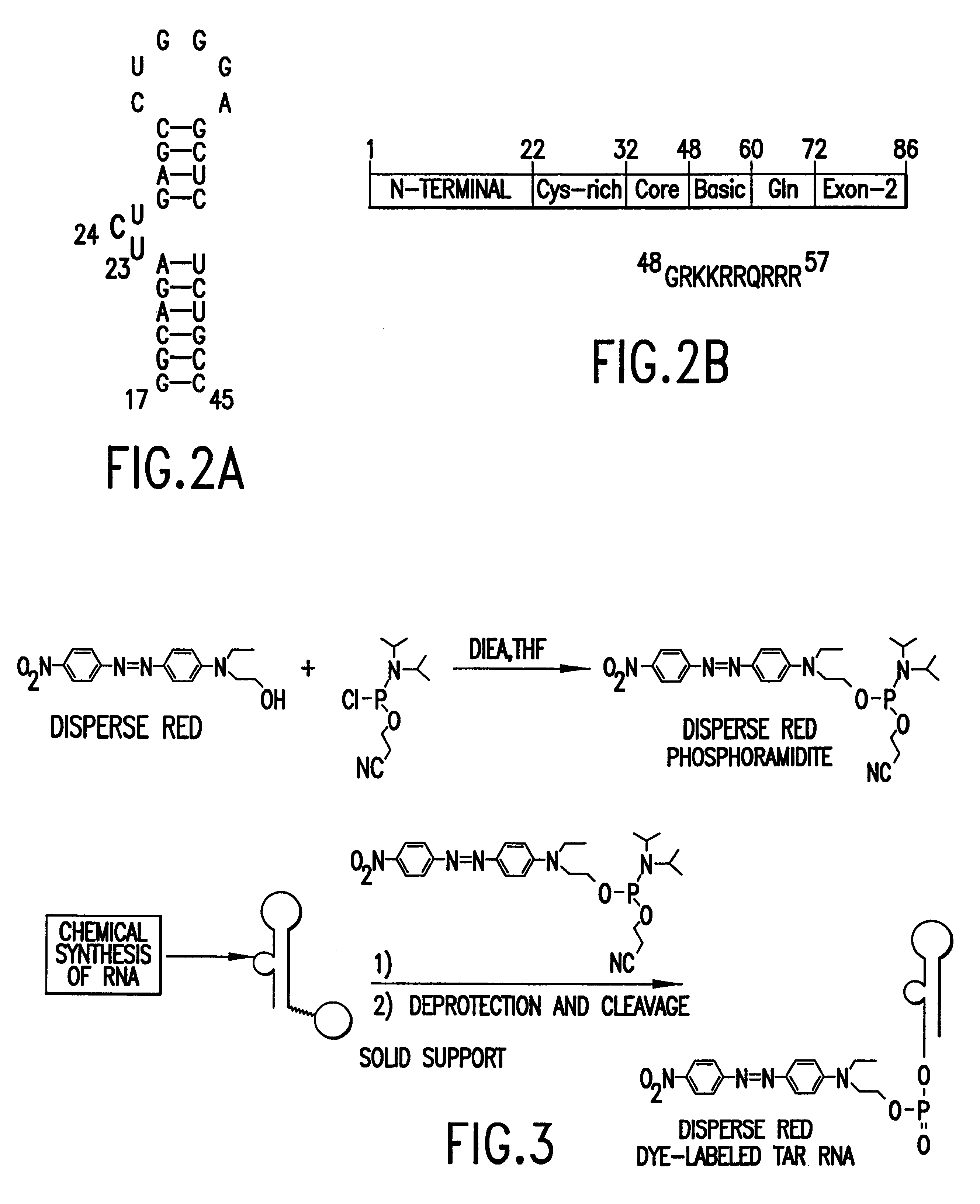
Methods for identifying RNA binding compounds
Owner:RUTGERS THE STATE UNIV
Single cell bar-coding for antibody discovery
Provided herein are methods and composition for immune repertoire sequencing and single cell barcoding for heavy and IgL pairing if antibodies.
Owner:ABVITRO LLC
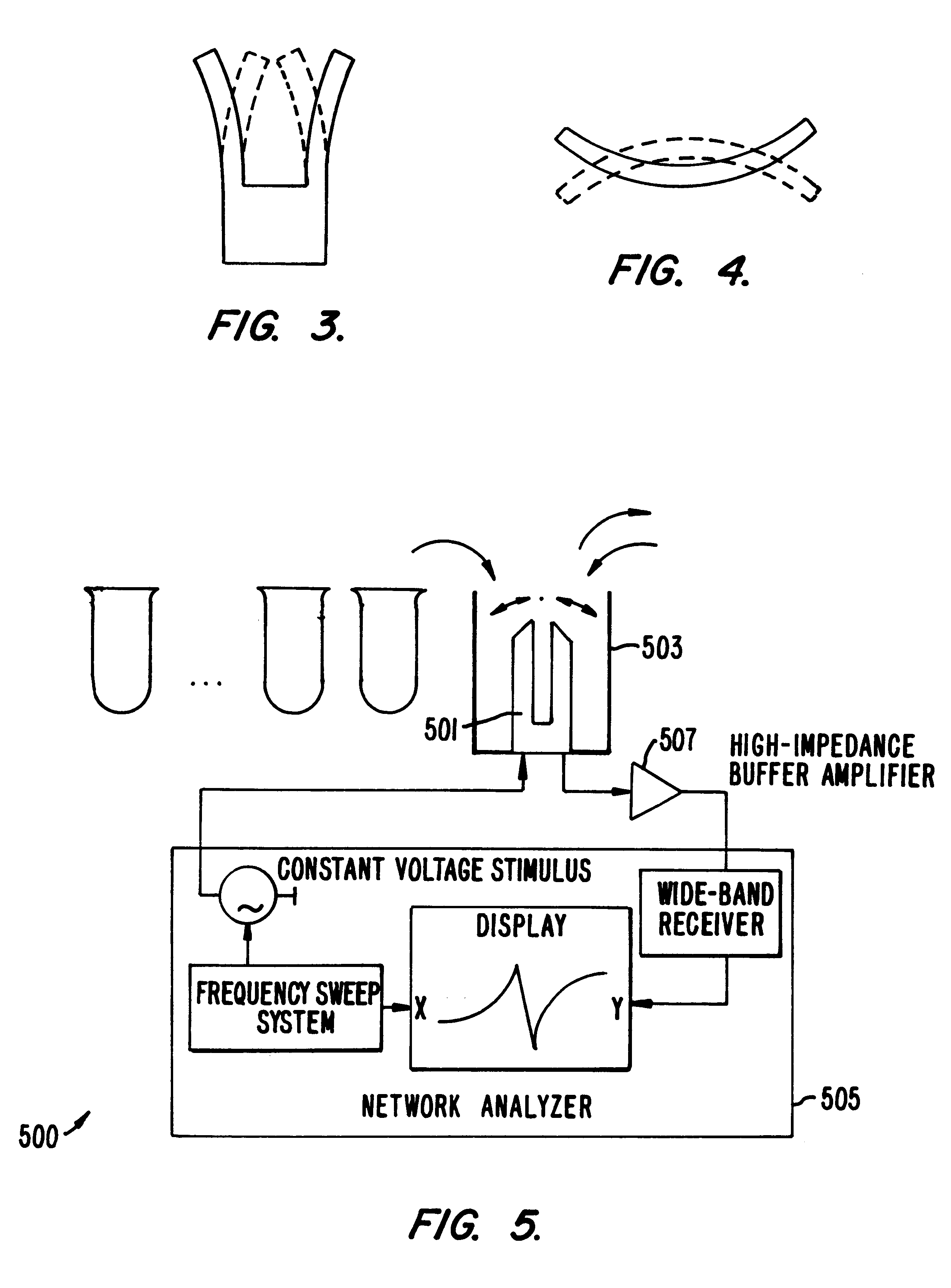
Systems and methods for characterization of materials and combinatorial libraries with mechanical oscillators
InactiveUS6182499B1Optical radiation measurementMaterial nanotechnologySonificationVisual perception
Methods and apparatus for screening diverse arrays of materials are provided. In one aspect, systems and methods are provided for imaging a library of materials using ultrasonic imaging techniques. The system includes one or more devices for exciting an element of the library such that acoustic waves are propagated through, and from, the element. The acoustic waves propagated from the element are detected and processed to yield a visual image of the library element. The acoustic wave data can also be processed to obtain information about the elastic properties of the library element. In another aspect, systems and methods are provided for generating acoustic waves in a tank filled with a coupling liquid. The library of materials is then placed in the tank and the surface of the coupling liquid is scanned with a laser beam. The structure of the liquid surface disturbed by the acoustic wave is recorded, the recorded disturbance being representative of the physical structure of the library. In another aspect of the invention, a mechanical resonator is used to evaluate various properties (e.g., molecular weight, viscosity, specific weight, elasticity, dielectric constant, conductivity, etc.) of the individual liquid elements of a library of materials. The resonator is designed to ineffectively excite acoustic waves. The frequency response of the resonator is measured for the liquid element under test, preferably as a function of time. By calibrating the resonator to a set of standard liquids with known properties, the properties of the unknown liquid can be determined. An array of library elements can be characterized by a single scanning transducer or by using an array of transducers corresponding to the array of library elements. Alternatively, multiple resonators of differing design may be used to evaluate each element of a library of elements, thus providing improved dynamic range and sensitivity.
Owner:FREESLATE
Methods for indexing samples and sequencing multiple polynucleotide templates
ActiveUS20090233802A1Microbiological testing/measurementLibrary member identificationHuman DNA sequencingPolynucleotide
The invention relates to methods for indexing samples during the sequencing of polynucleotide templates, resulting in the attachment of tags specific to the source of each nucleic acid sample such that after a sequencing run, both the source and sequence of each polynucleotide can be determined. Thus, the present invention pertains to analysis of complex genomes (e.g., human genomes), as well as multiplexing less complex genomes, such as those of bacteria, viruses, mitochondria, and the like.
Owner:ILLUMINA CAMBRIDGE LTD
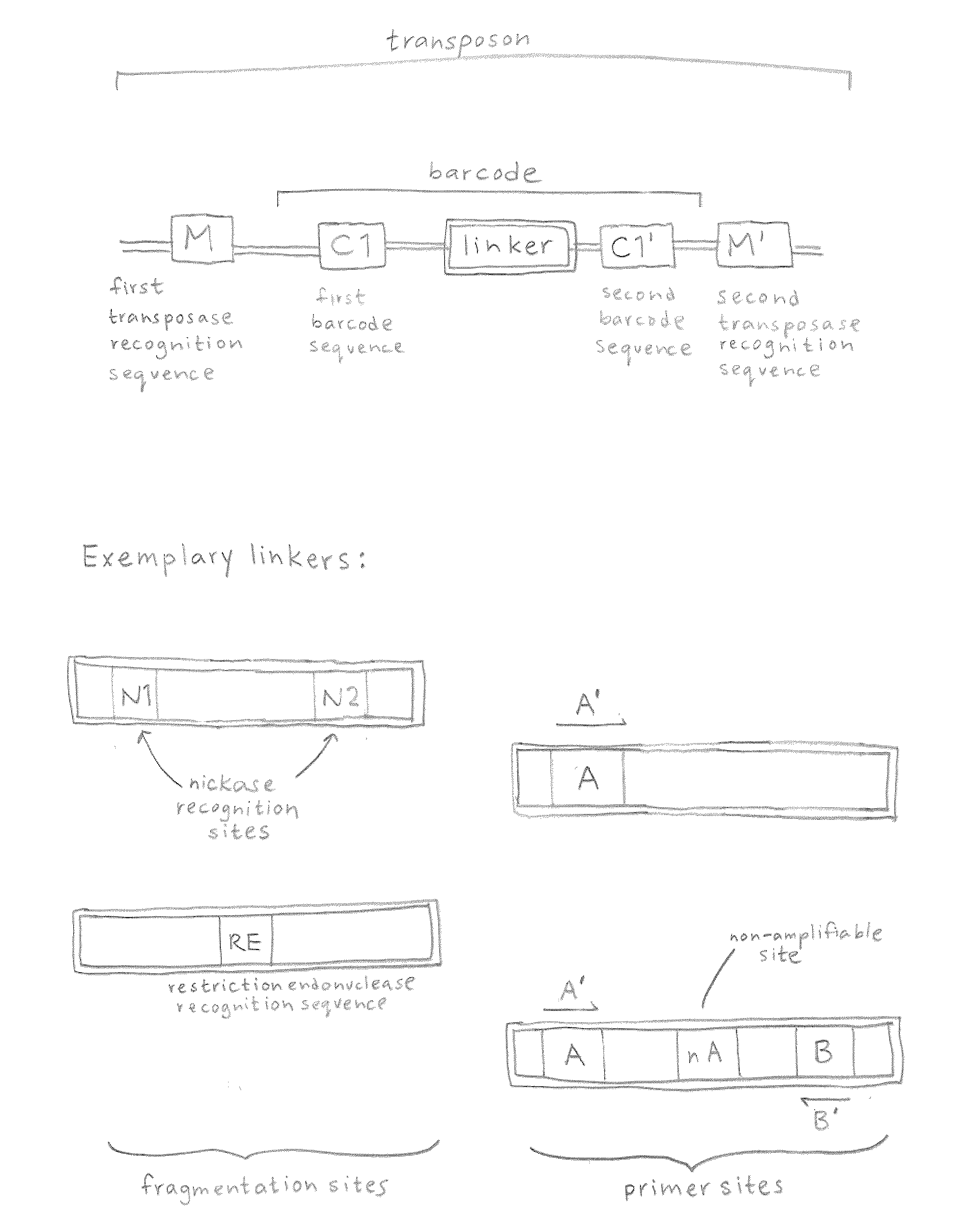
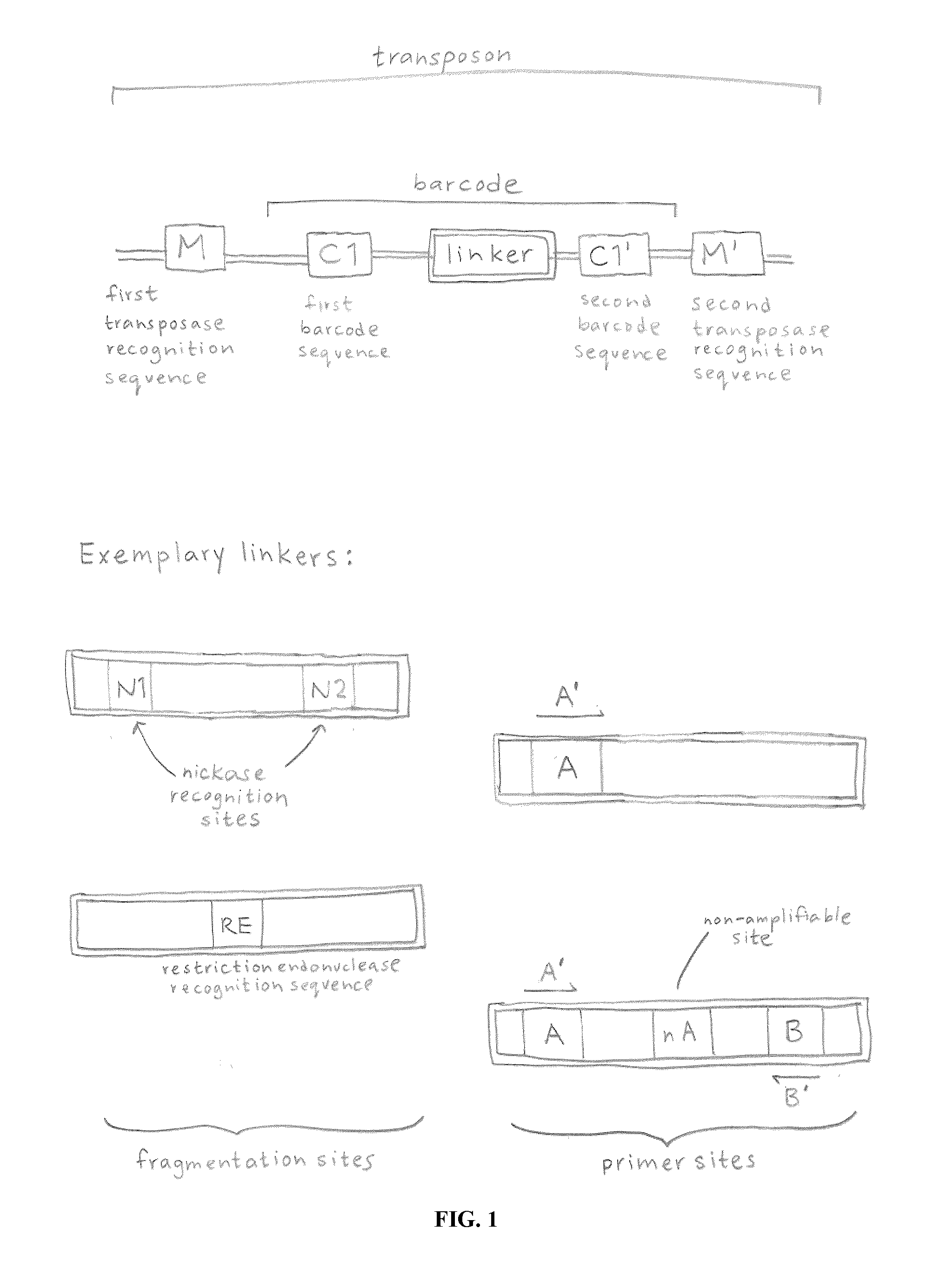
Linking sequence reads using paired code tags
ActiveUS20120208705A1Reduce in quantitySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementComputational biologyTransposon element
Owner:ILLUMINA INC
Nucleic acid sequence analysis from single cells
ActiveUS20160053253A1Reduce cascadeNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementBarcodeNucleic acid sequencing
Presented herein are methods and compositions for multiplexed single cell gene expression analysis. Some methods and compositions include the use of droplets and / or beads bearing unique barcodes such as unique molecular barcodes (UMI).
Owner:ILLUMINA INC
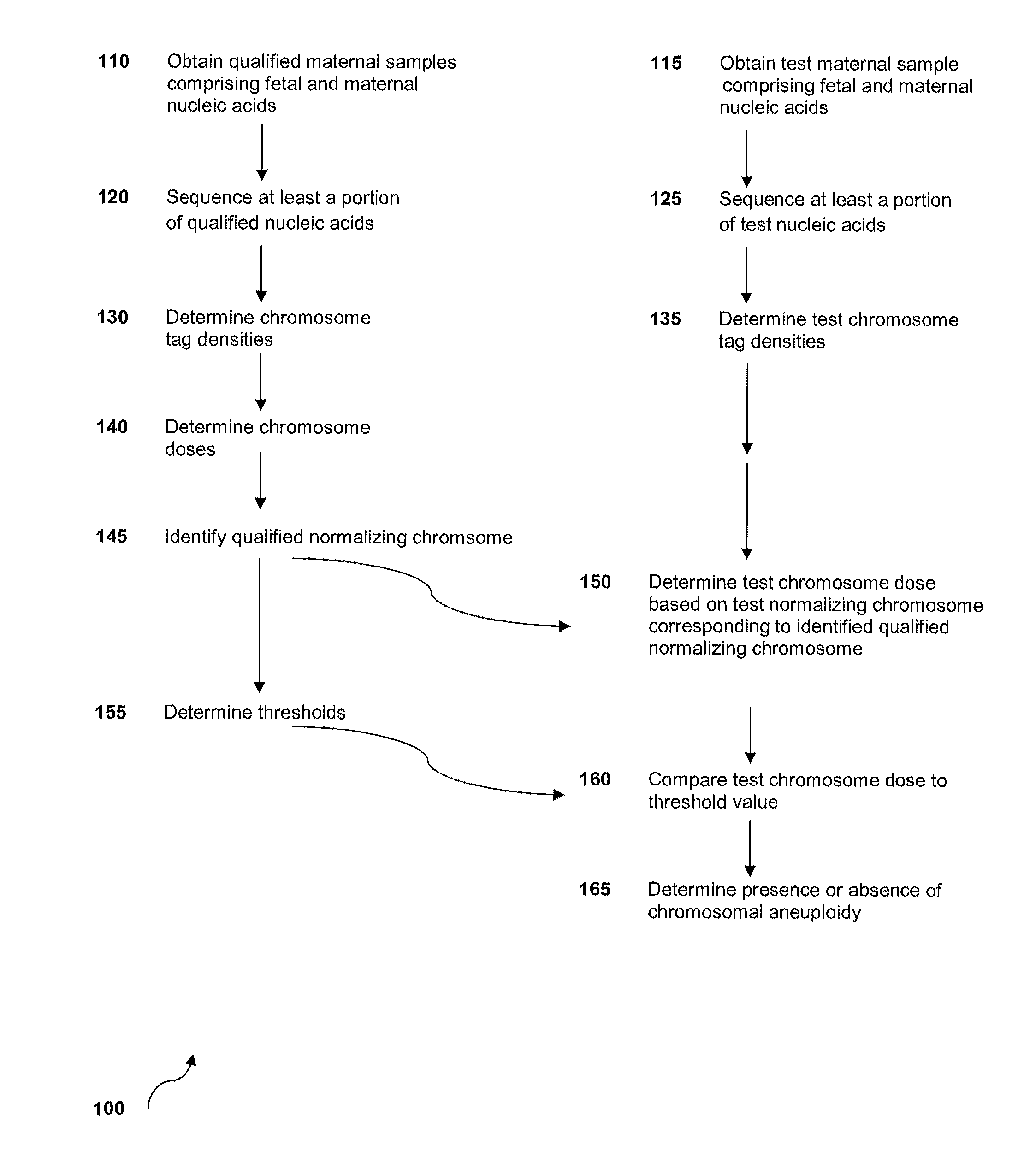
Method for sample analysis of aneuploidies in maternal samples
InactiveUS20120270739A1Decreases sequencing biasQuality improvementMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary member identificationPrenatal diagnosisAnalysis method
The invention provides methods for determining aneuploidy and / or fetal fraction in maternal samples comprising fetal and maternal cfDNA by massively parallel sequencing. The method comprises a novel protocol for preparing sequencing libraries that unexpectedly improves the quality of library DNA while expediting the process of analysis of samples for prenatal diagnoses. The novel protocol can be performed in solution or on a solid surface.
Owner:VERINATA HEALTH INC
Massively parallel contiguity mapping
ActiveUS20130203605A1Reducing sequenceLimited to sequenceLibrary member identificationChemical recyclingHuman DNA sequencingMammalian genome
Contiguity information is important to achieving high-quality de novo assembly of mammalian genomes and the haplotype-resolved resequencing of human genomes. The methods described herein pursue cost-effective, massively parallel capture of contiguity information at different scales.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON CENT FOR COMMERICIALIZATION
Particle-assisted nucleic acid sequencing
ActiveUS20120015822A1Microbiological testing/measurementLaboratory glasswaresNucleic Acid ProbesNucleic acid sequencing
This invention generally relates to particle-assisted nucleic acid sequencing. In some embodiments, sequencing may be performed in a microfluidic device, which can offer desirable properties, for example, minimal use of reagents, facile scale-up, and / or high throughput. In one embodiment, a target nucleic acid may be exposed to particles having nucleic acid probes. By determining the binding of the particles to the target nucleic acid, the sequence of the target nucleic acid (or at least a portion of the target nucleic acid) can be determined. The target nucleic acid may be encapsulated within a fluidic droplet with the particles having nucleic acid probes, in certain instances. In some cases, the sequence of the target nucleic acid may be determined, based on binding of the particles, using sequencing by hybridization (SBH) algorithms or other known techniques.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Methods and uses for molecular tags
ActiveUS20160026758A1Overcome limitationsImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary member identificationGenetic analysisComputational biology
Methods and uses for molecular tags are disclosed. Molecular tags may be attached to nucleic acid molecules. The attachment of the nucleic acid molecules prior to PCR amplification and sequencing improves the accuracy of genetic analysis and detection of genetic variations and diversity. Molecular tags may also be used for detection of drug-resistant variants. Methods for using molecular tags for determining and correcting PCR errors and / or sequencing error are also disclosed.
Owner:THE UNIV OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHAPEL HILL
Field-switch sequencing
ActiveUS7462452B2Low costImprove reuseSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementPhosphatePolymerase L
Owner:PACIFIC BIOSCIENCES
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com