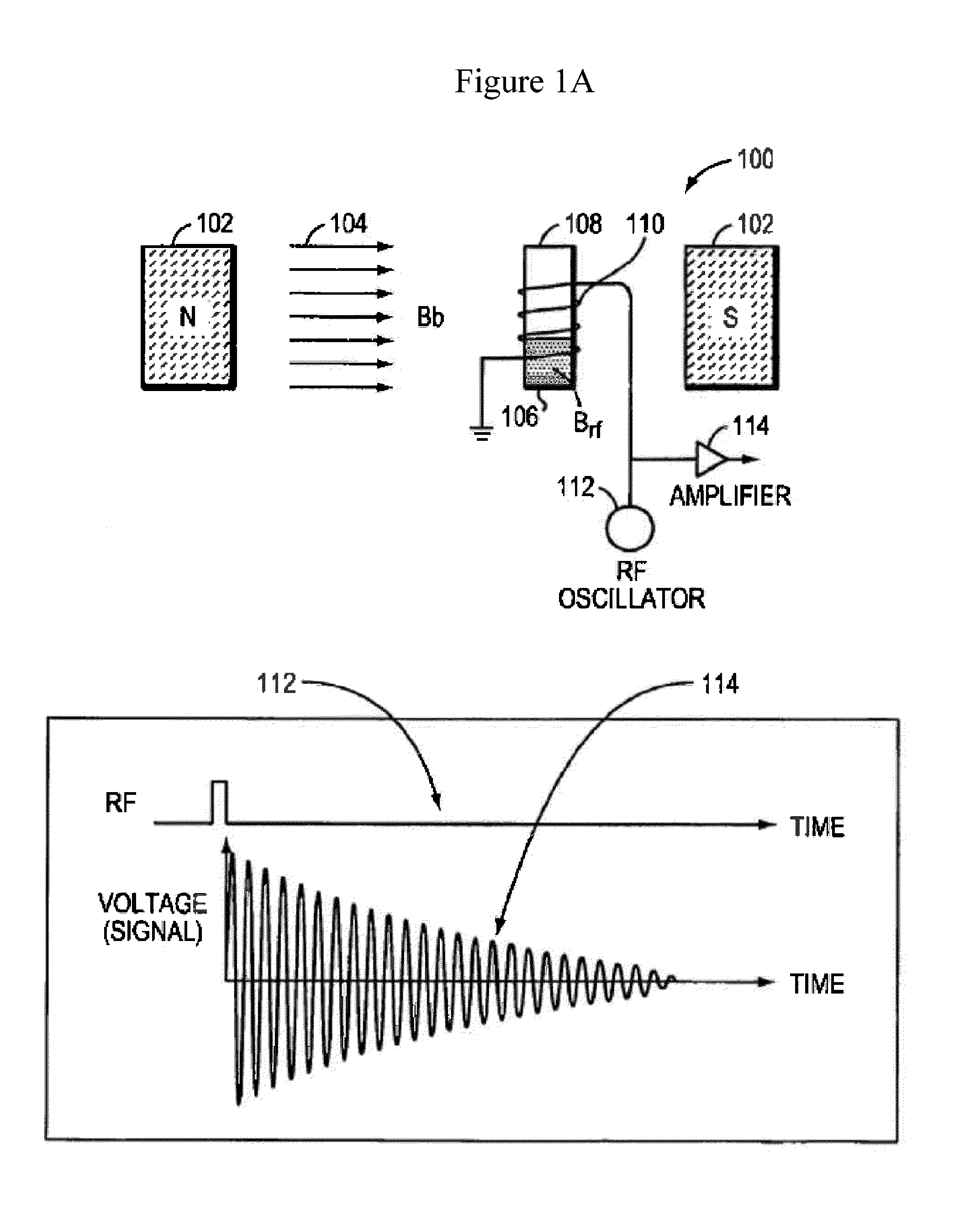
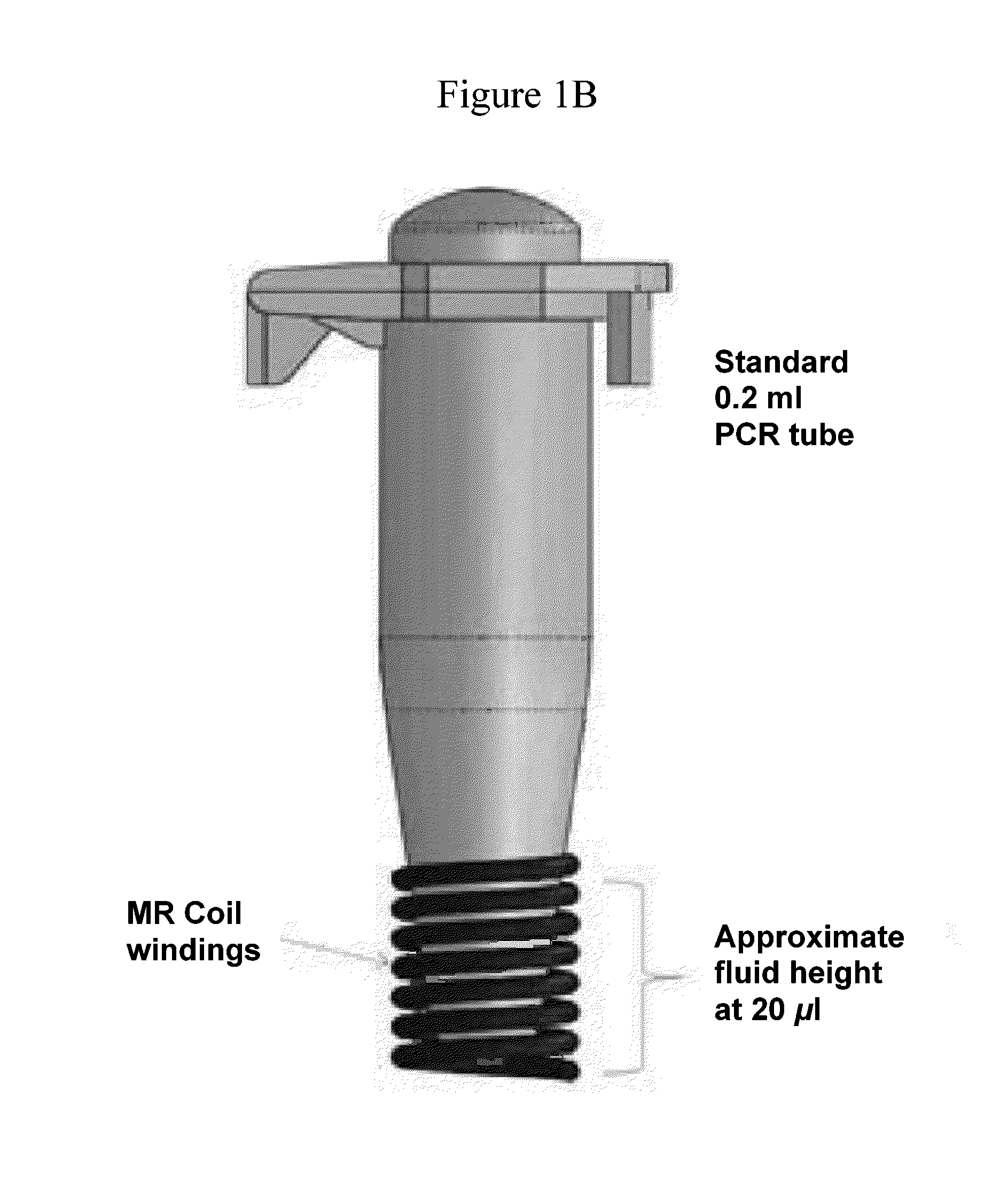
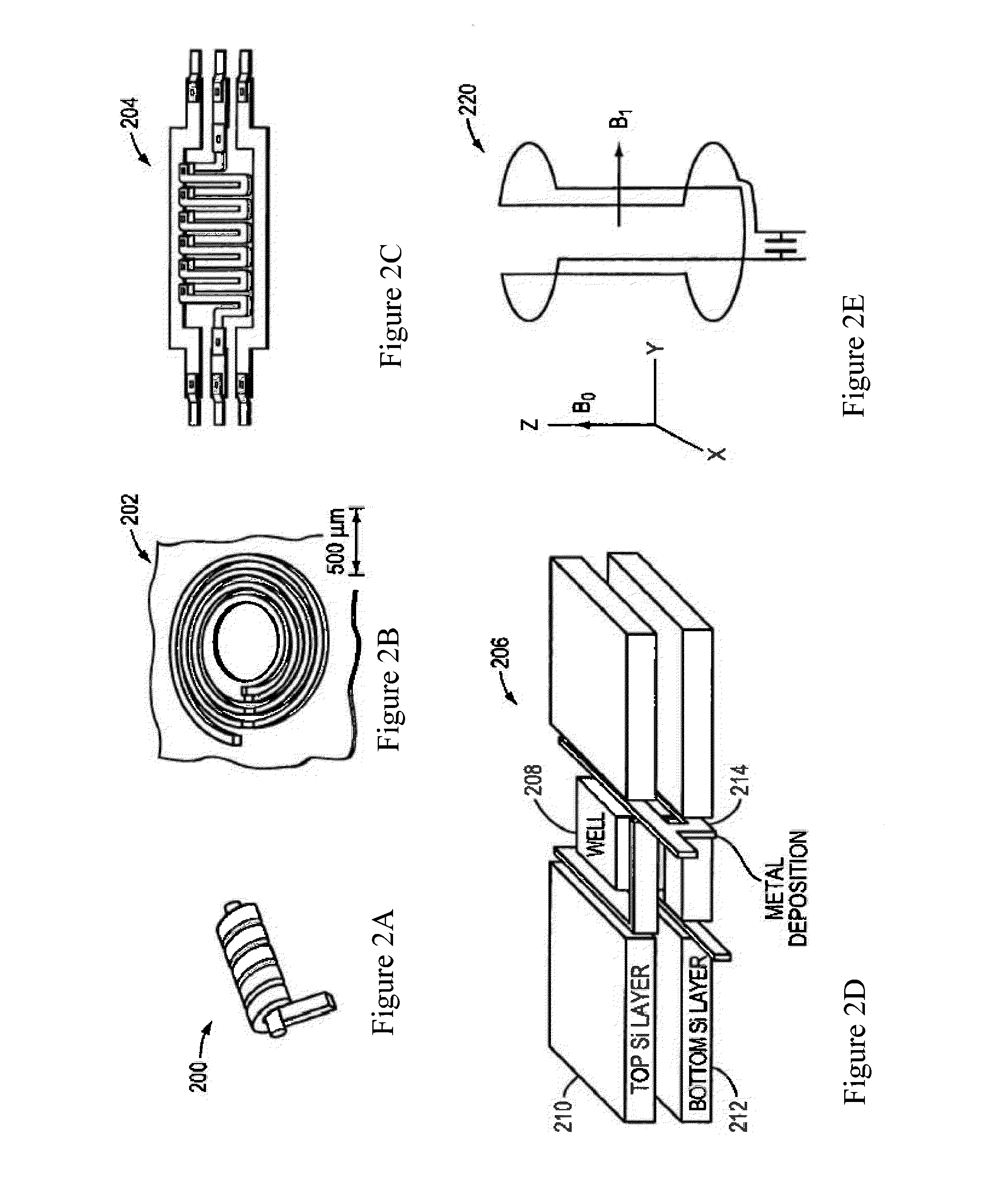
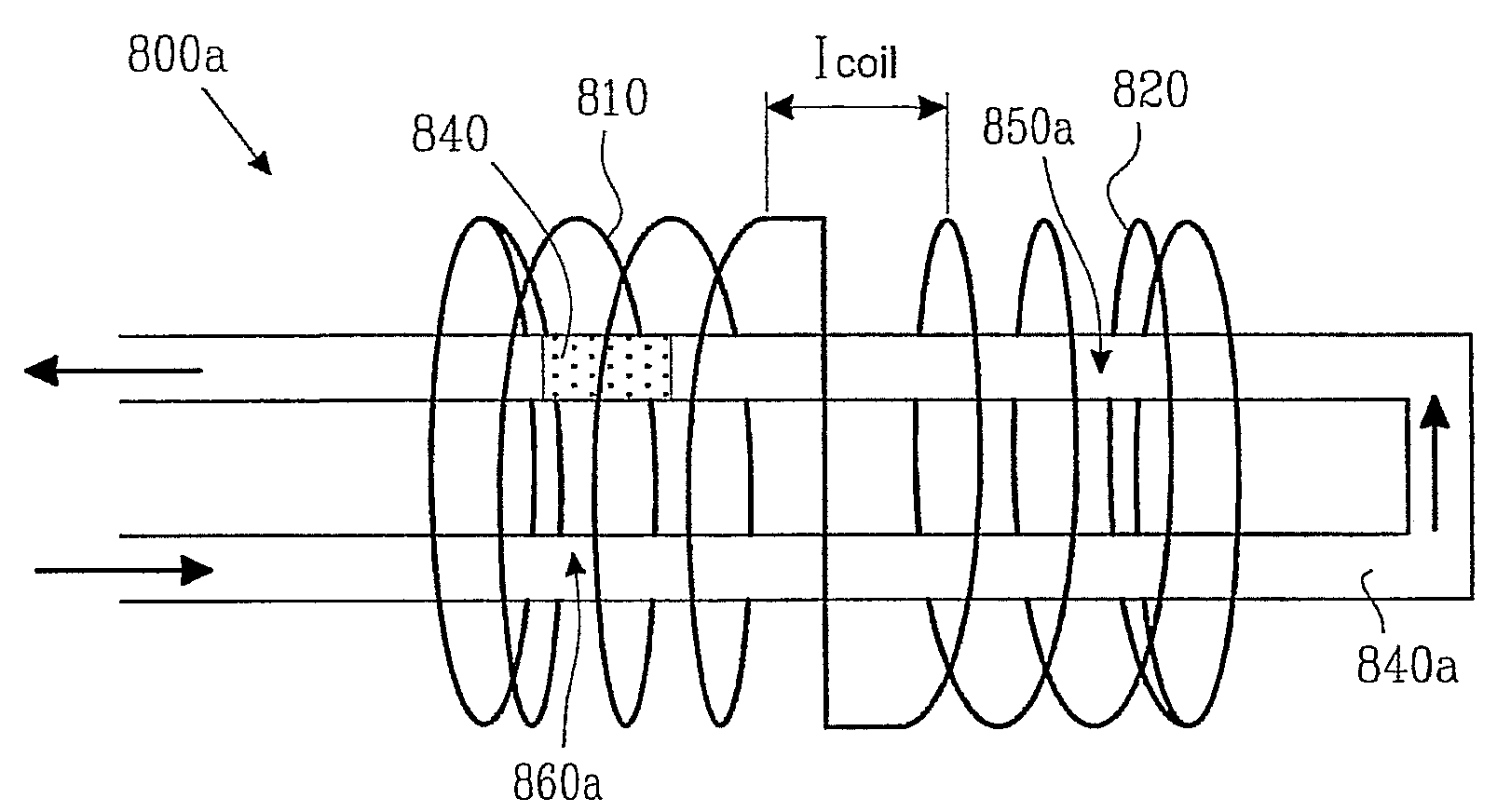
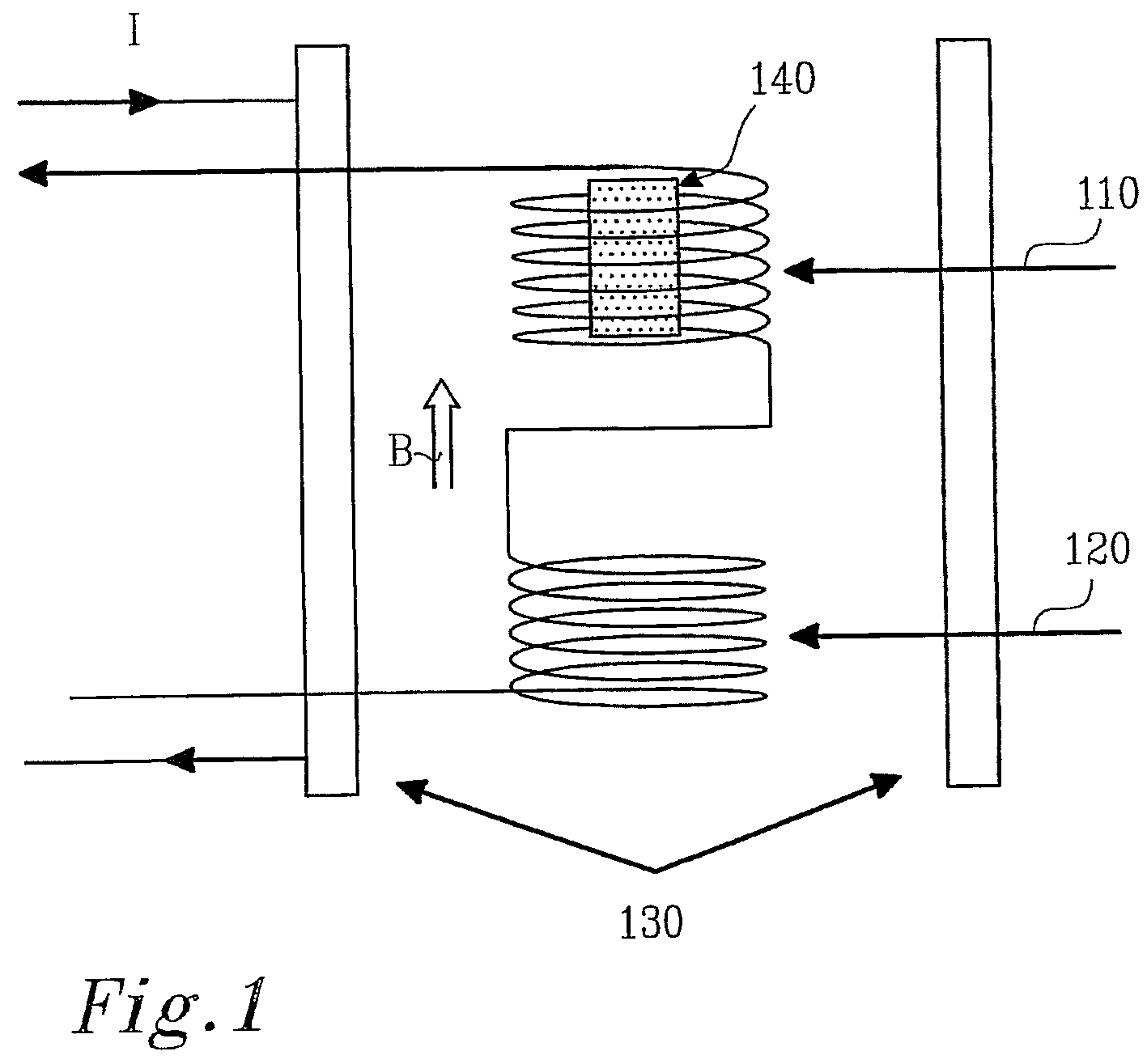
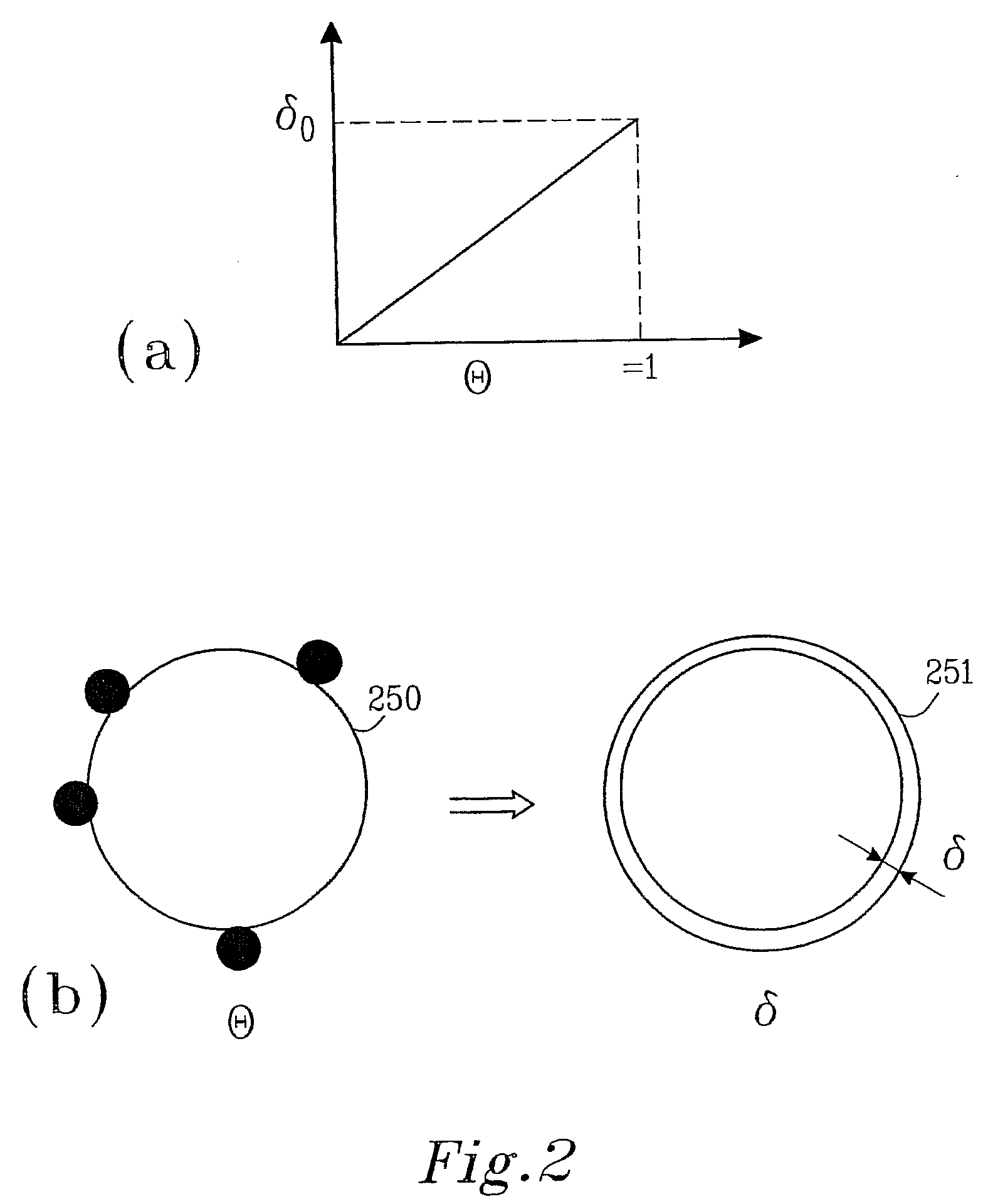
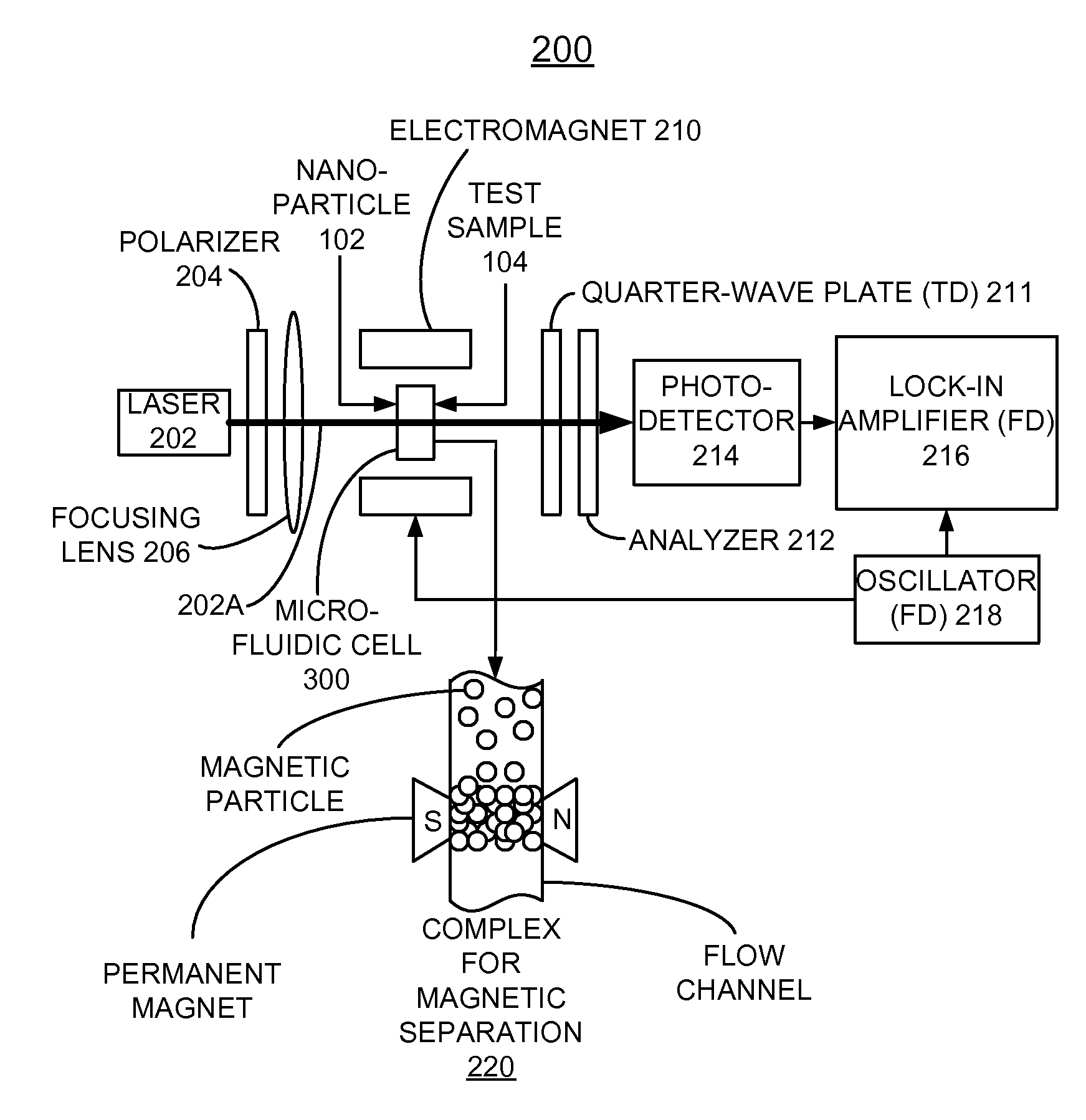
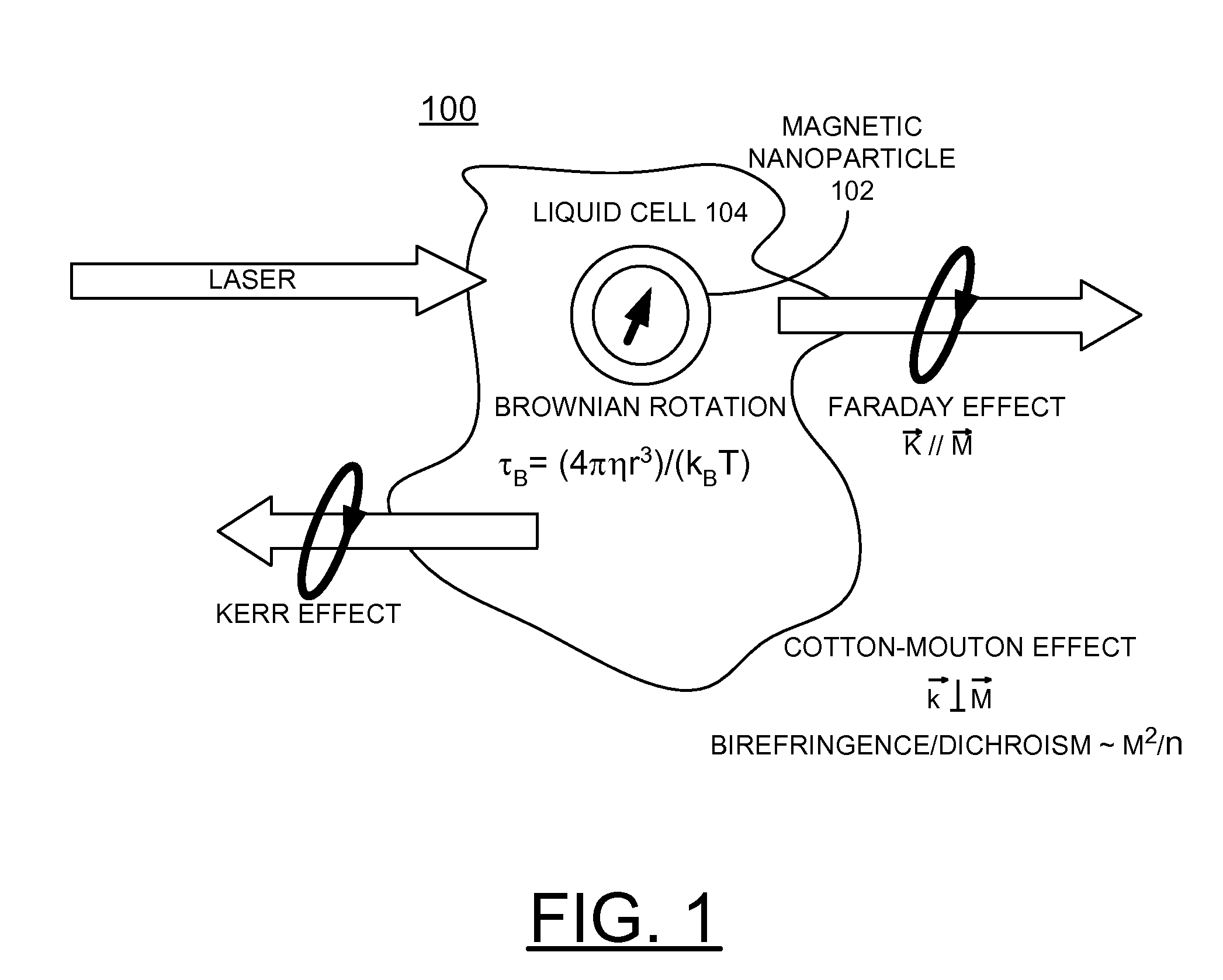
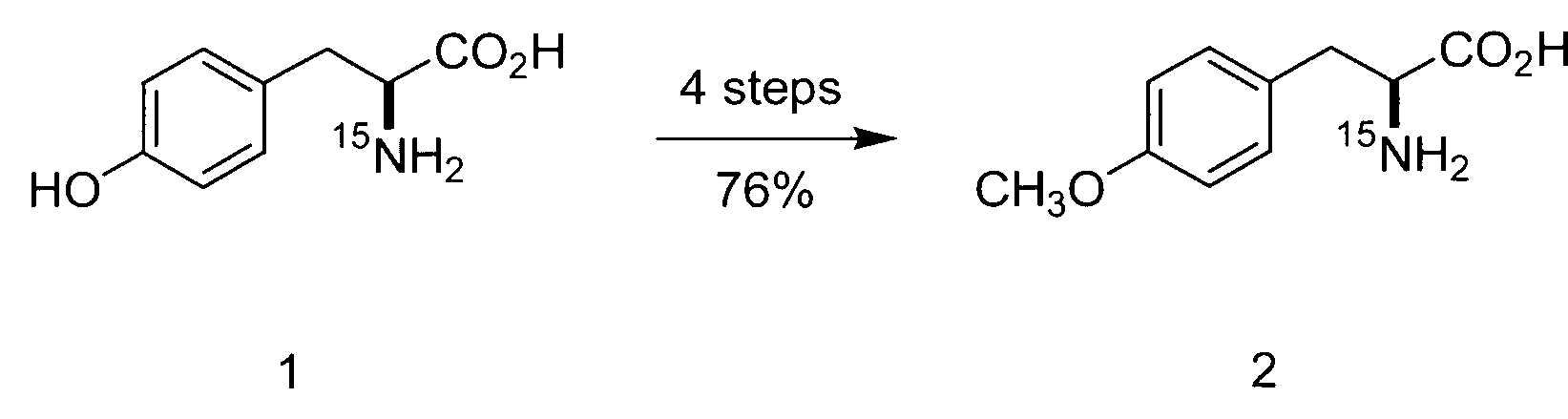
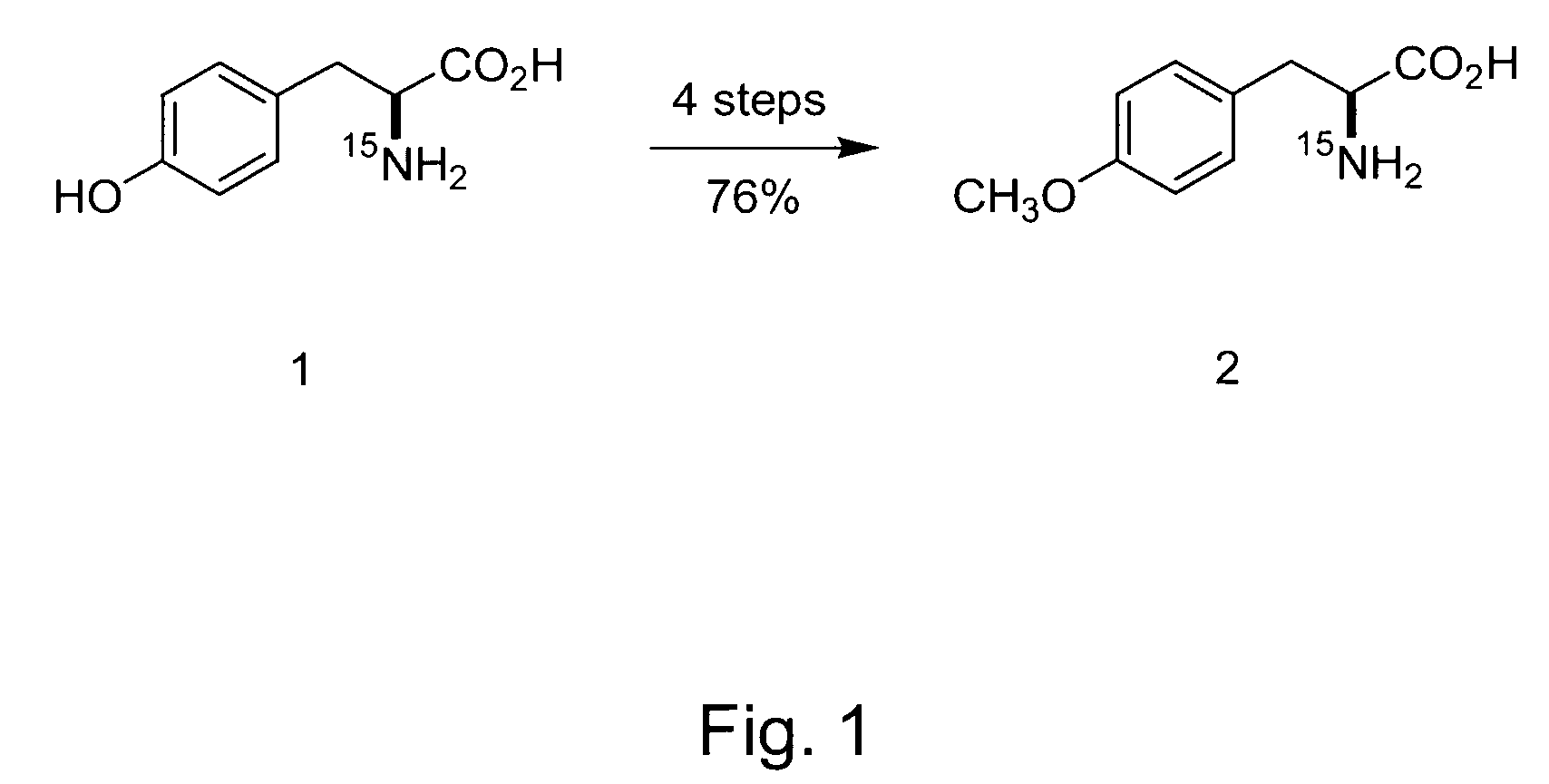
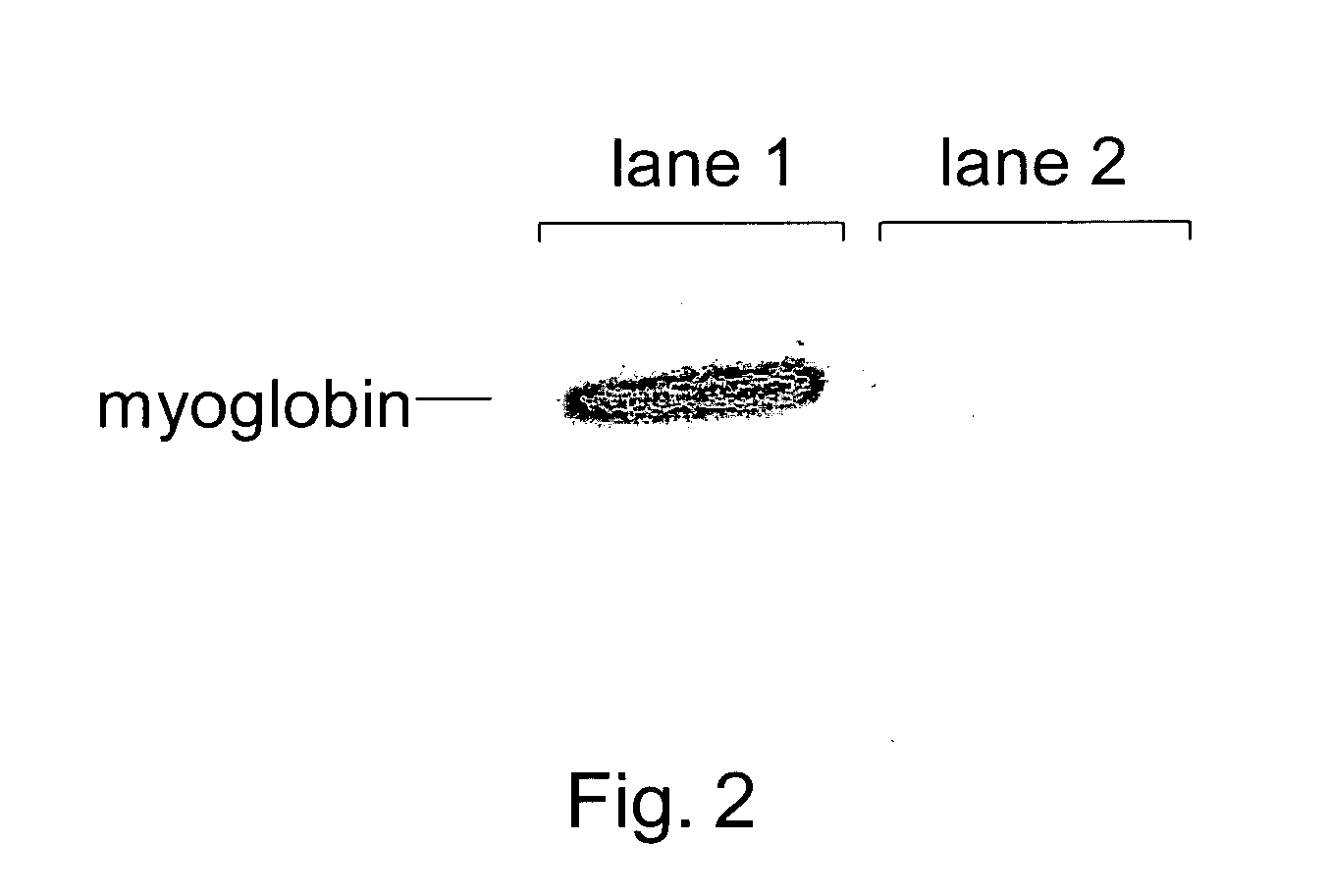
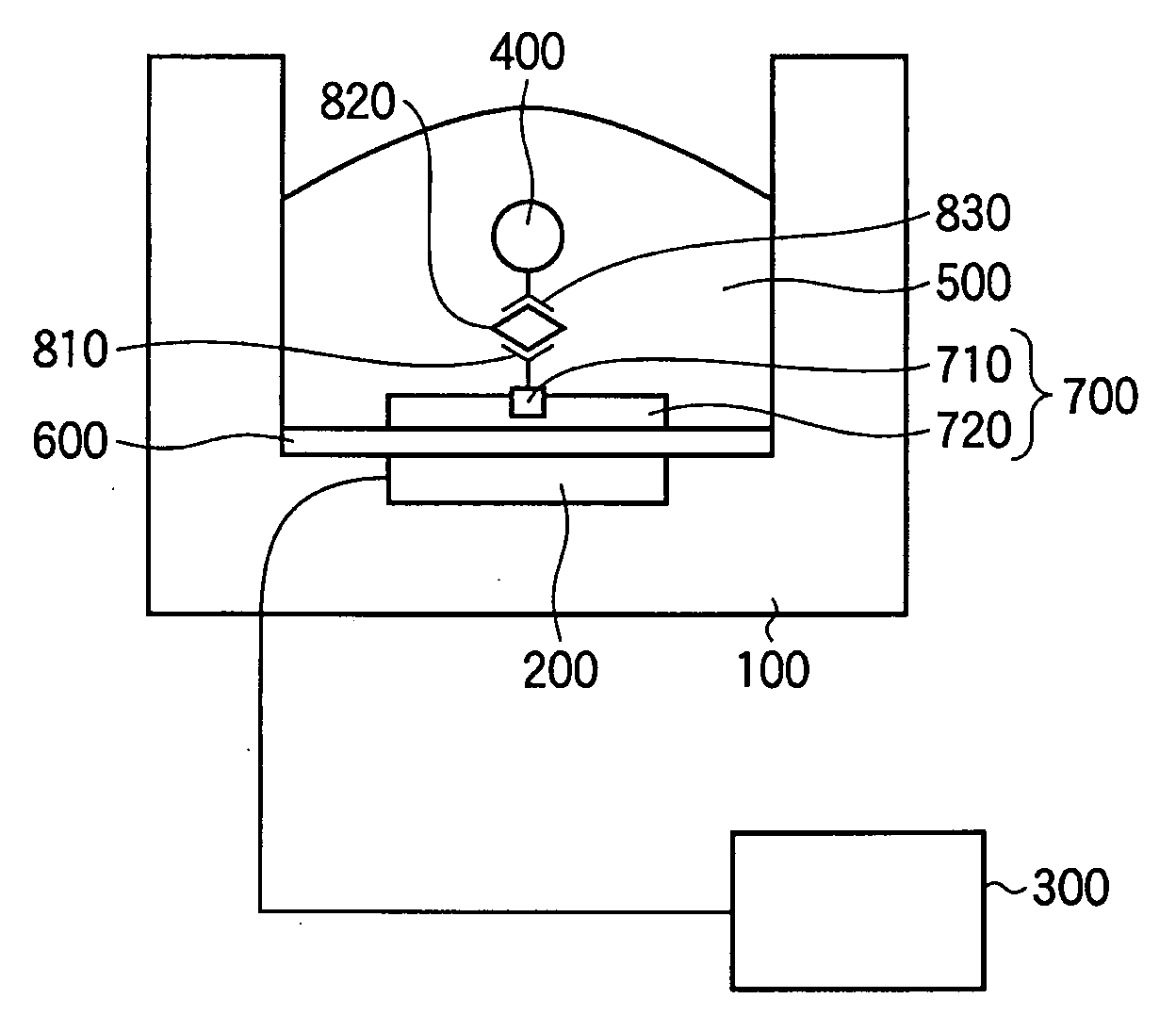
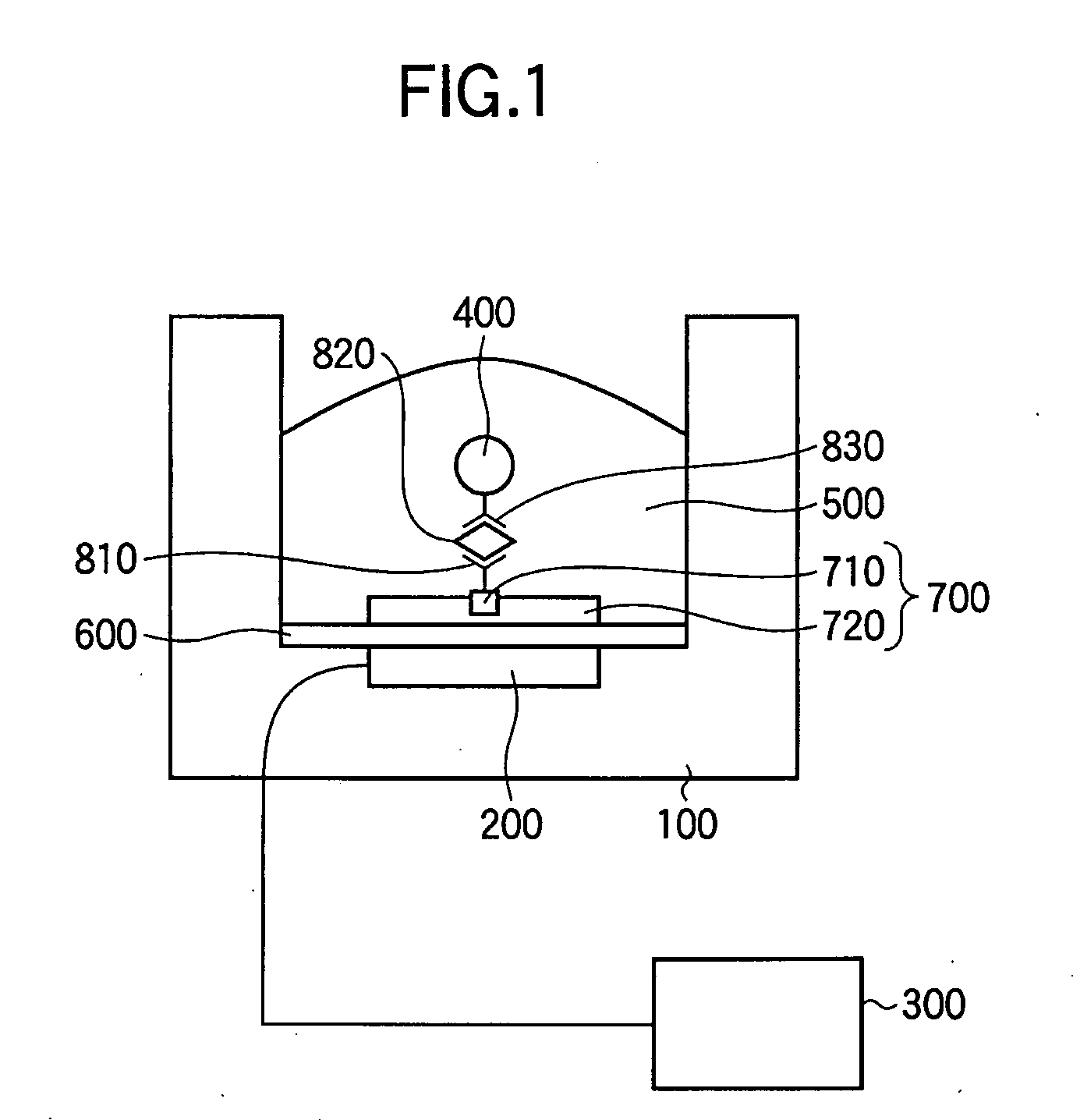
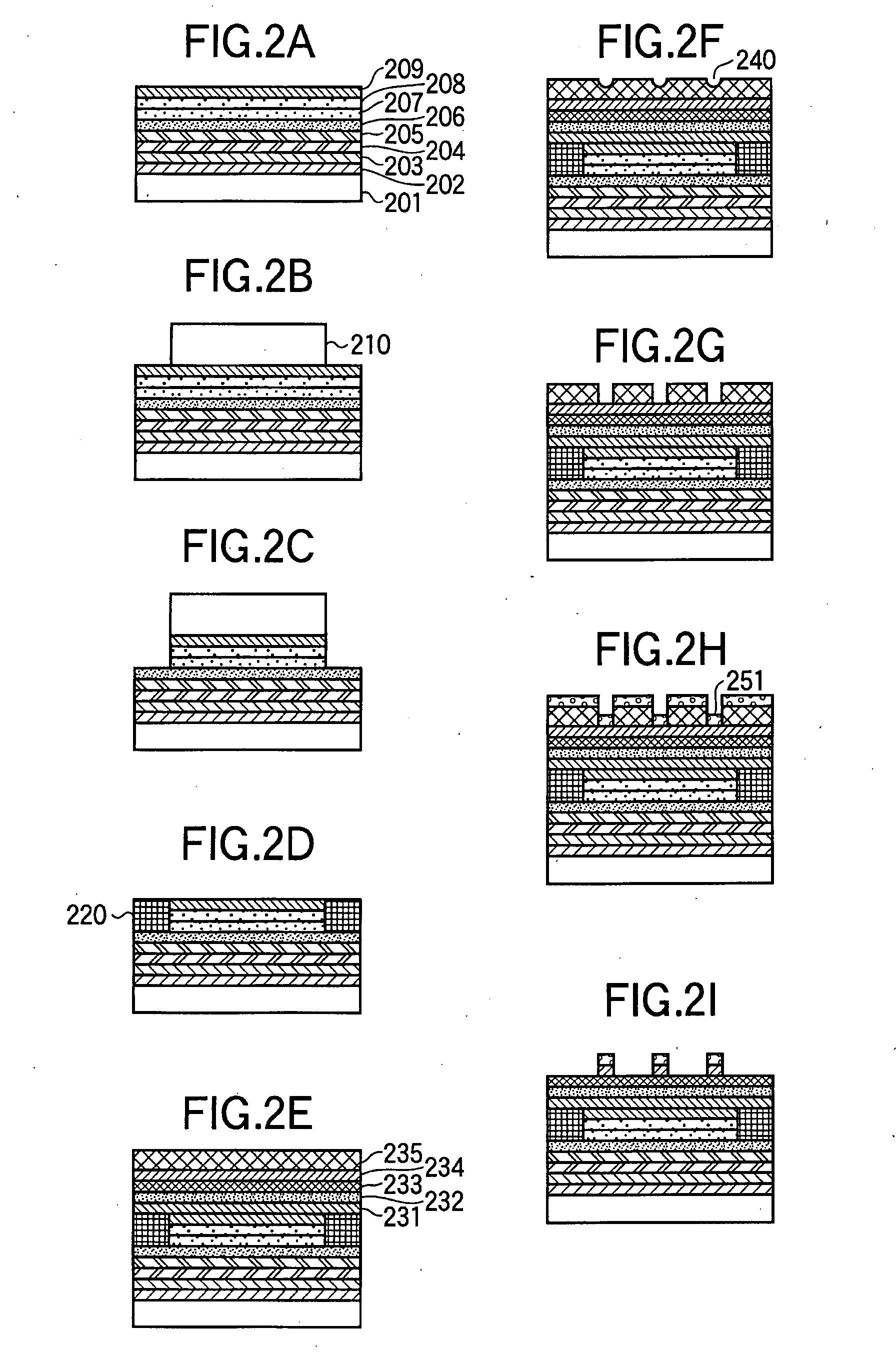
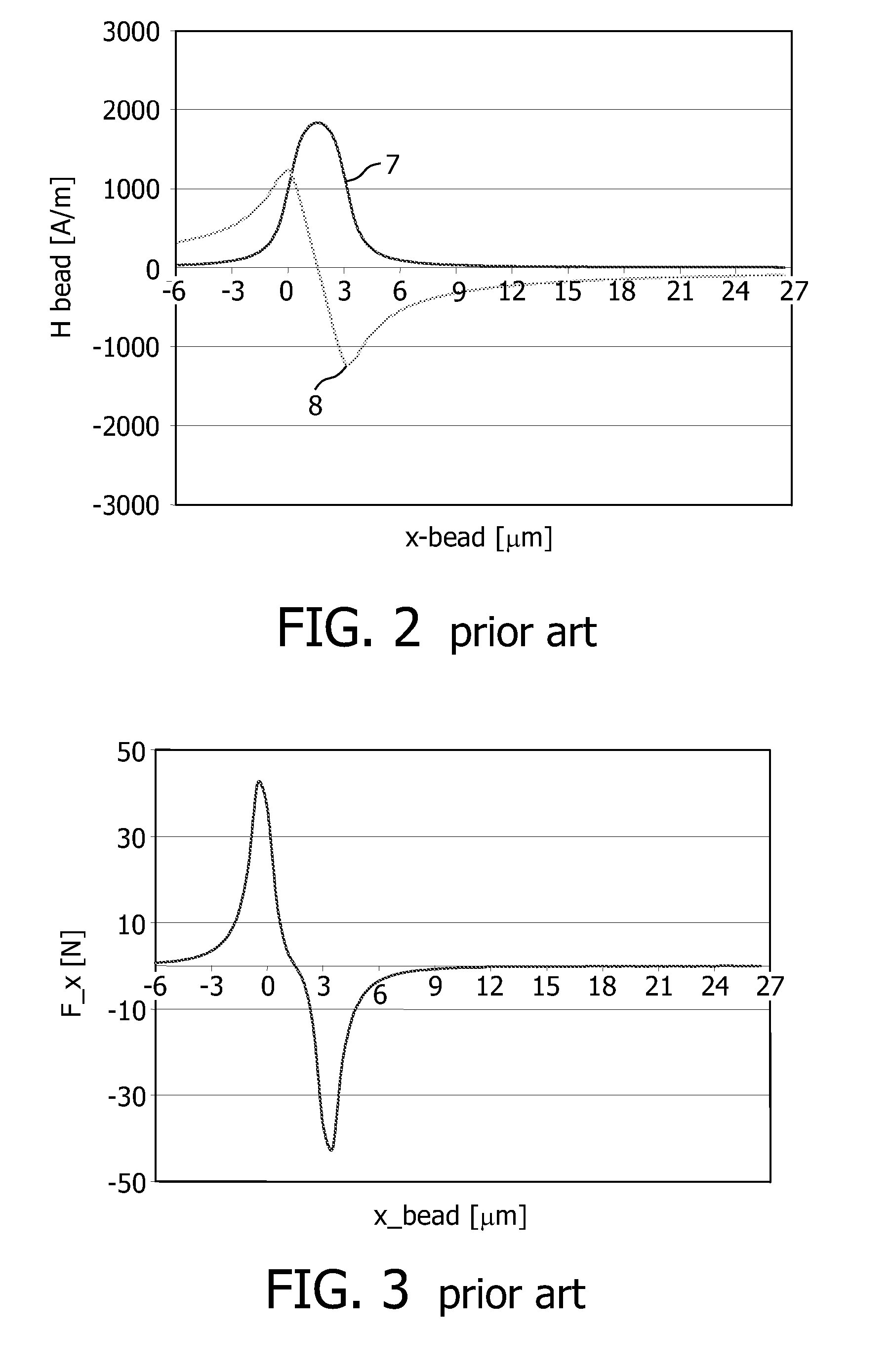
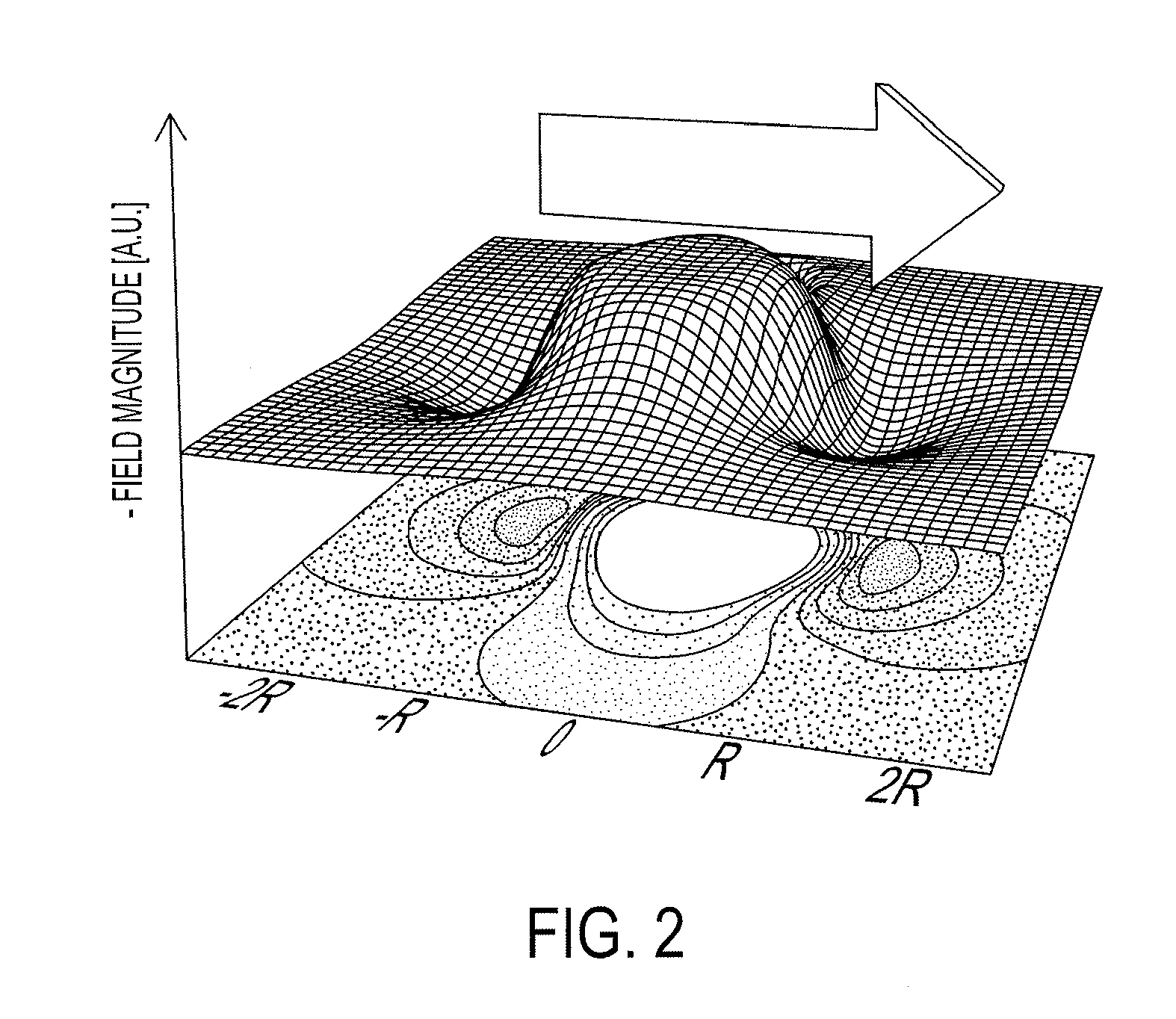
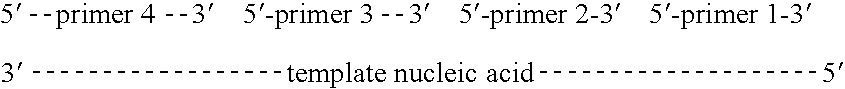Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
223results about "Measurements of magnetic beads labelled molecules" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Methods of amplifying and sequencing nucleic acids
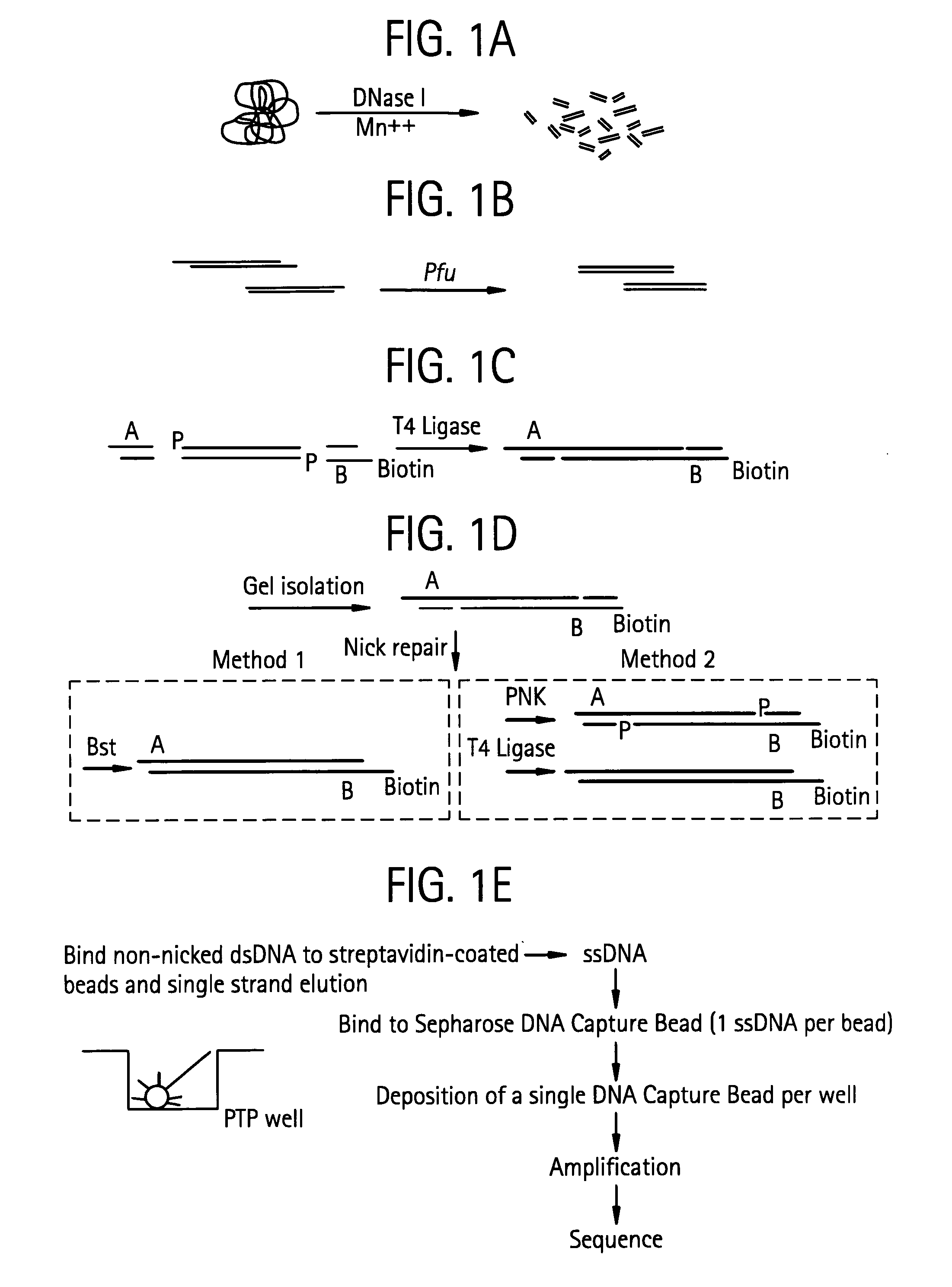
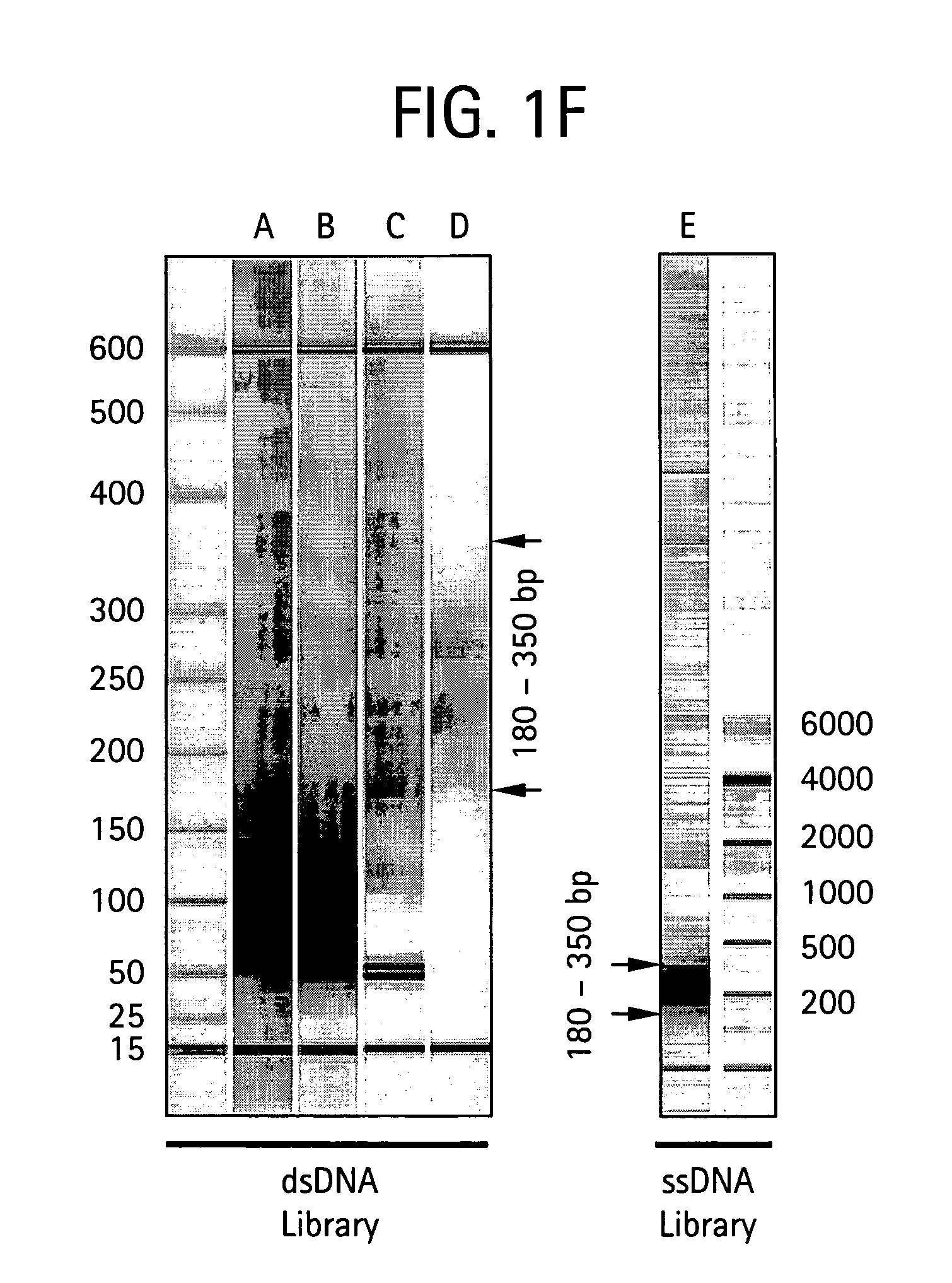
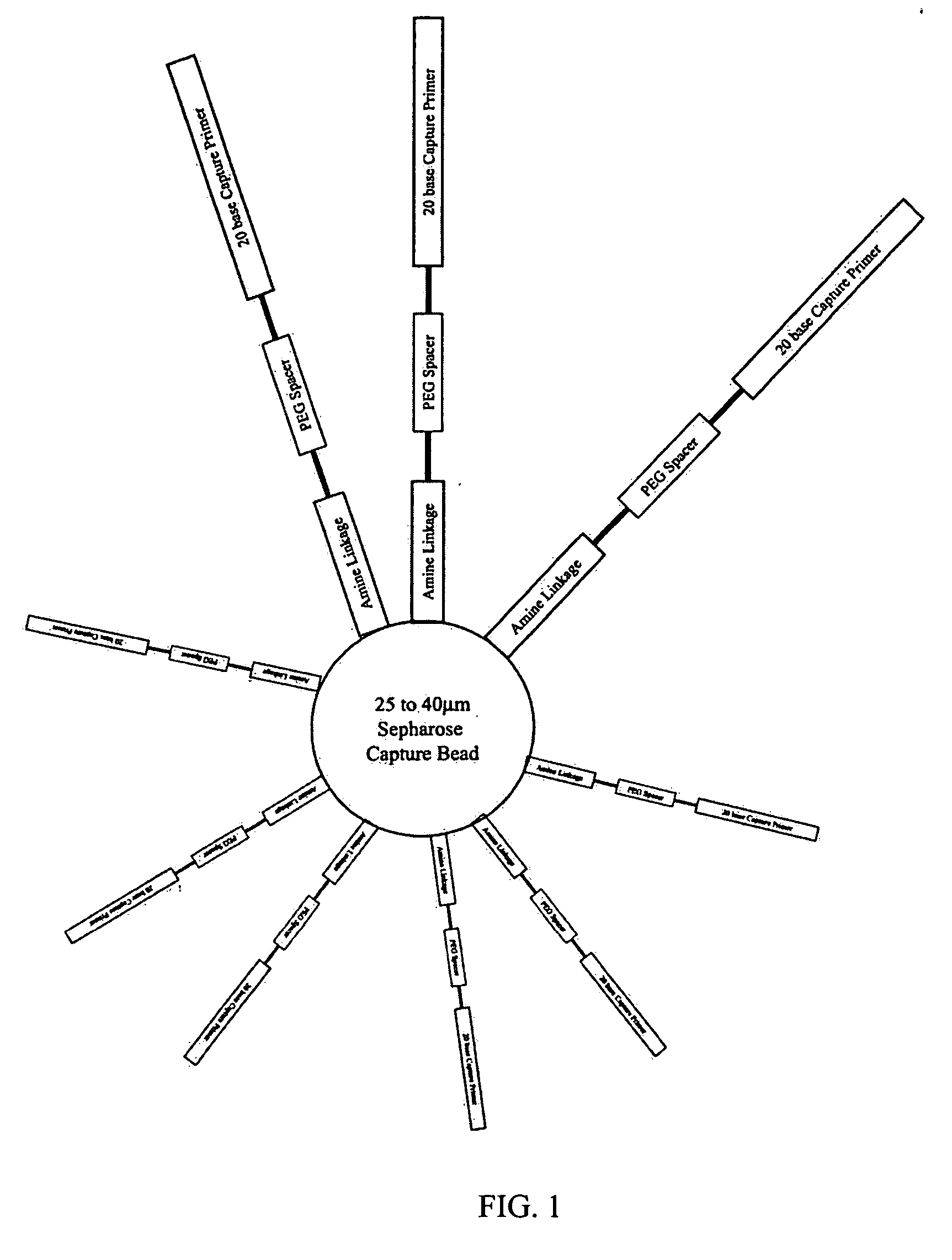
An apparatus and method for performing rapid DNA sequencing, such as genomic sequencing, is provided herein. The method includes the steps of preparing a sample DNA for genomic sequencing, amplifying the prepared DNA in a representative manner, and performing multiple sequencing reaction on the amplified DNA with only one primer hybridization step.
Owner:454 LIFE SCIENCES CORP
Bead emulsion nucleic acid amplification
Disclosed are methods for nucleic acid amplification wherein nucleic acid templates, beads, and amplification reaction solution are emulsified and the nucleic acid templates are amplified to provide clonal copies of the nucleic acid templates attached to the beads. Also disclosed are kits and apparatuses for performing the methods of the invention.
Owner:454 LIFE SCIENCES CORP
Double ended sequencing
InactiveUS20060134633A1Heating or cooling apparatusSugar derivativesPolymerase LComputational biology
This invention relates to methods of sequencing DNA. More specifically, this invention relates to methods of sequencing both the sense and antisense strands of DNA through the use of blocked and unblocked sequencing primers. In brief, these methods include the steps of annealing an unblocked primer to a first strand of nucleic acid; annealing a second blocked primer to a second strand of nucleic acid; elongating the nucleic acid along the first strand with a polymerase; terminating the first sequencing primer; deblocking the second primer; and elongating the nucleic acid along the second strand.
Owner:454 LIFE SCIENCES CORP
Magnetic resonance system and method to detect and confirm analytes
InactiveUS20070166730A1Easy to detectQuality improvementBioreactor/fermenter combinationsNanomagnetismResonance measurementAnalyte
Owner:MENON INT
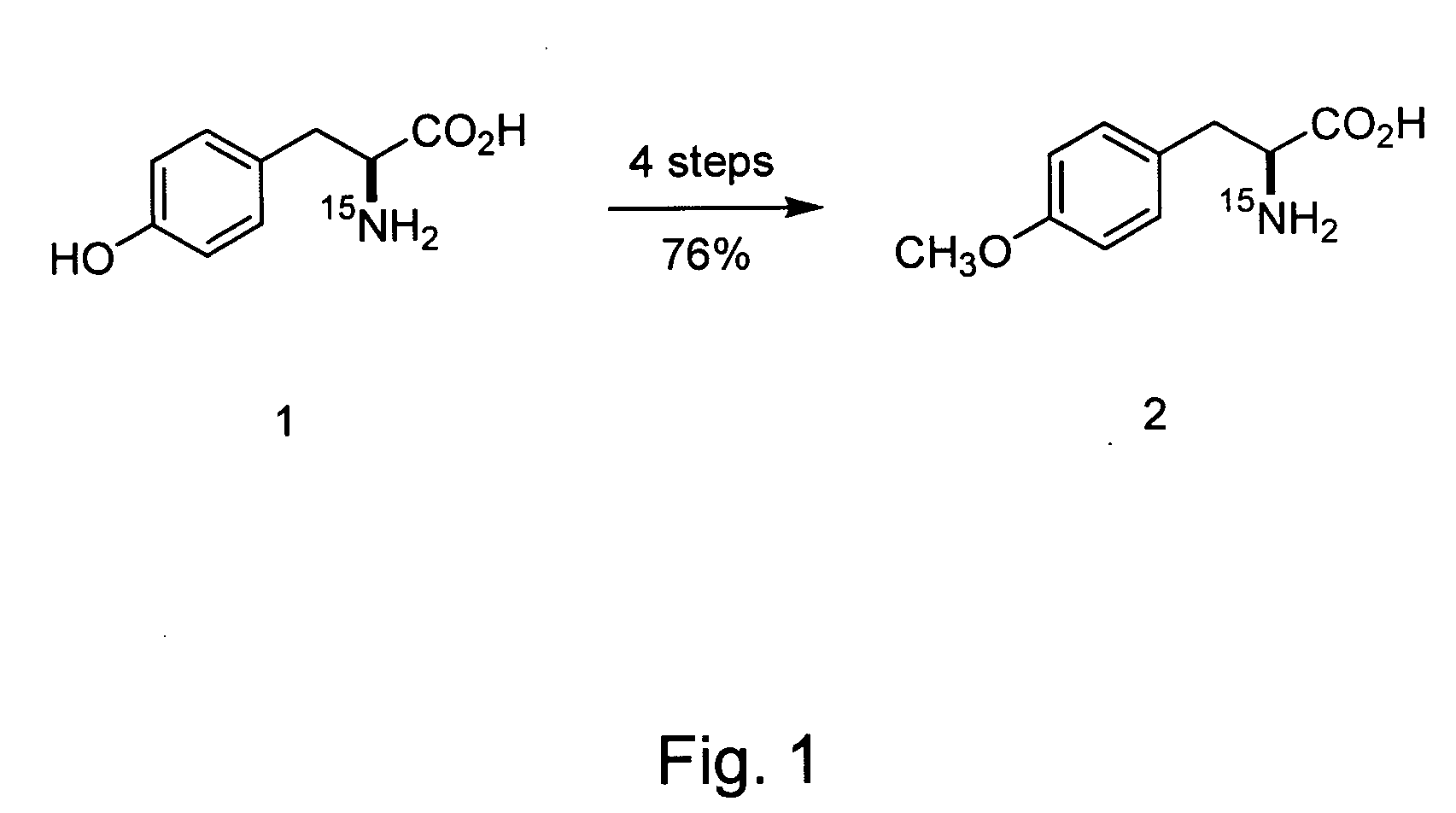
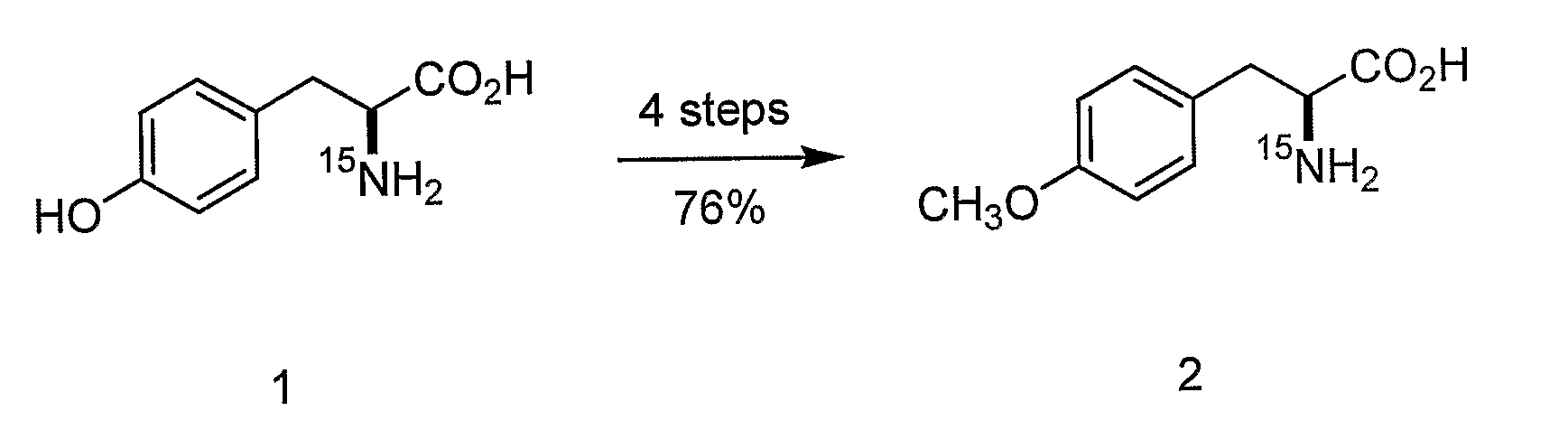
Site-specific labeling of proteins for NMR studies
Methods of producing and / or analyzing spectroscopically labeled proteins, e.g., proteins site-specifically labeled with NMR active isotopes, spin-labels, chelators for paramagnetic metals, and the like, are provided. The labeled proteins are produced in translation systems including orthogonal aminoacyl tRNA synthetase / tRNA pairs. Methods for assigning NMR resonances, e.g., methods using isotopically labeled proteins, are also provided.
Owner:THE SCRIPPS RES INST +1
Integrated Membrane Sensor
ActiveUS20080199971A1Shorten the timeFaster routingMaterial thermal conductivityMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansPhotonicsEngineering
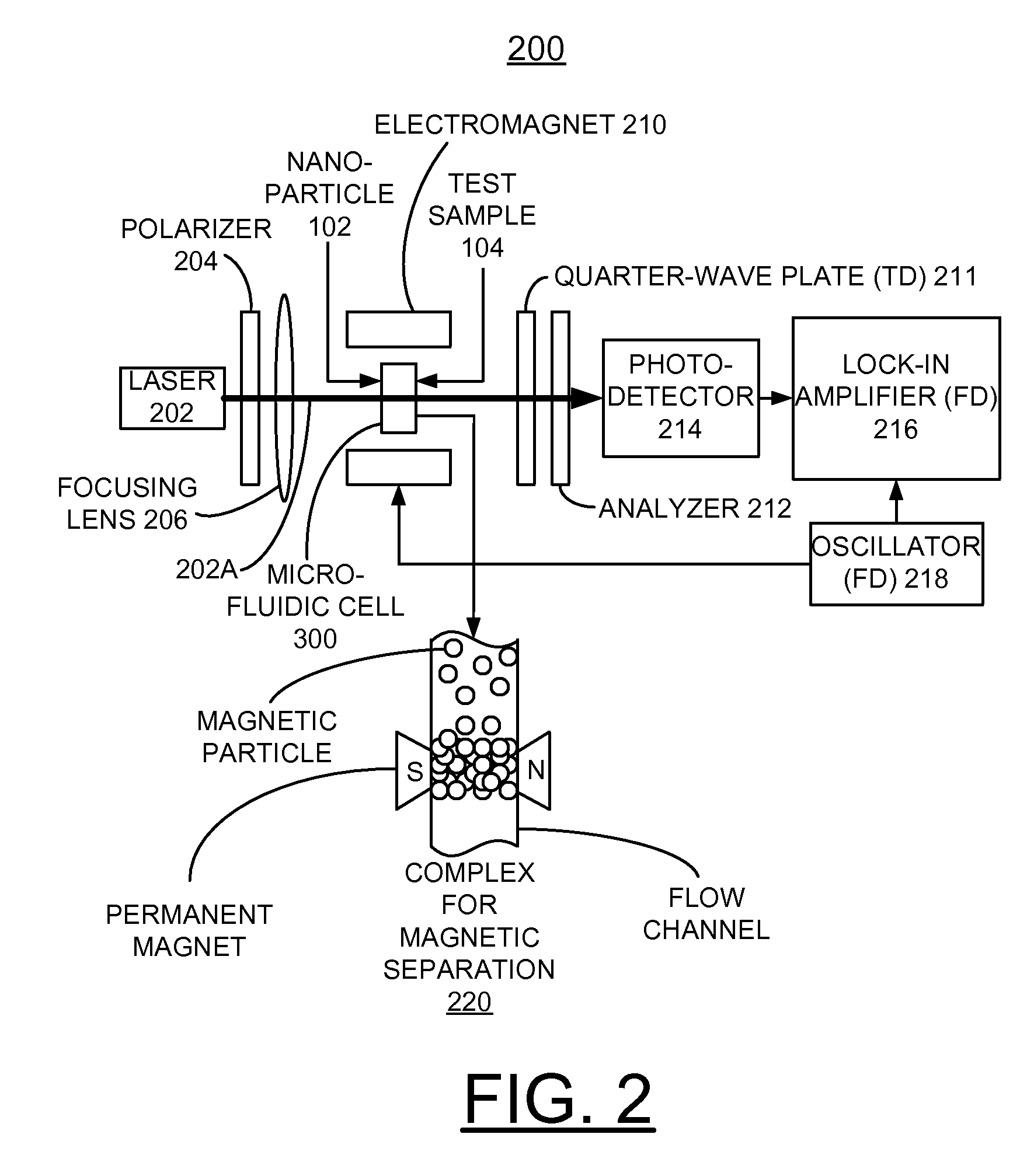
An integrated microelectronic sensor is provided in a disposable flow membrane sensing device. The integrated sensors detect electromagnetic effect labels in flow detection zones above the sensor in the membrane. The labels are small particles that give off a detectable electromagnetic signal. They are commonly used for isolating and quantifying biochemical targets of interest. The sensors are fabricated using planar integrated circuit technologies. Sensors can detect labels of several types including magnetic, electric, and photonic. These types all have in common the fact that the sensor detects the label at a distance. Magnetoresistive sensors for detecting magnetic labels, and photodiodes for detecting photonic labels are described.A system for using the sensors is described. There are disposable cartridges with a backing that supports the sensors and membrane is described. The integrated sensor in the cartridge is designed to be discarded after use. Also, label excitation sources are provided. The multi sensor array chip can be configured in order to detect labels in multiple zones, and to monitor progress of flow down a strip of membrane. These multiple label detection zones, using sandwich assay techniques, can quantify analyte concentration for many types of analytical samples. Also, the membrane can be micropatterned in order to provide multiple or unusually shaped flow paths.
Owner:DIAGNOSTIC BIOSENSORS
Method and apparatus for analyzing bioprocess fluids
InactiveUS7749445B2High fractional captureLarge gradientMaterial nanotechnologyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsAnalyteResonant sensor
Methods and apparatus for analyzing bioprocess fluids are provided. A plurality of particles coated with a plurality of capture agents having an affinity for one or more biological markers is combined with bioprocess fluid to form a plurality of analyte-particle complexes. The system also includes a transport arrangement for transporting the sample to a sensor surface, and optionally a magnetic field inducing structure constructed and arranged to establish a magnetic field at and adjacent to the sensor surface. The resonant sensor produces a signal corresponding to an amount of analyte-particle complexes that are bound to the sensor surface.
Owner:BIOSCALE
Method and apparatus for analyzing bioprocess fluids
InactiveUS20070224700A1Low level of analyteLess timeBioreactor/fermenter combinationsMaterial nanotechnologyAnalyteResonant sensor
Owner:BIOSCALE
Improved techniques for magnetic particle imaging
ActiveUS20110089942A1Prevents phaseHarmonic suppressionDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsMagnetic particle imagingMagnetite Nanoparticles
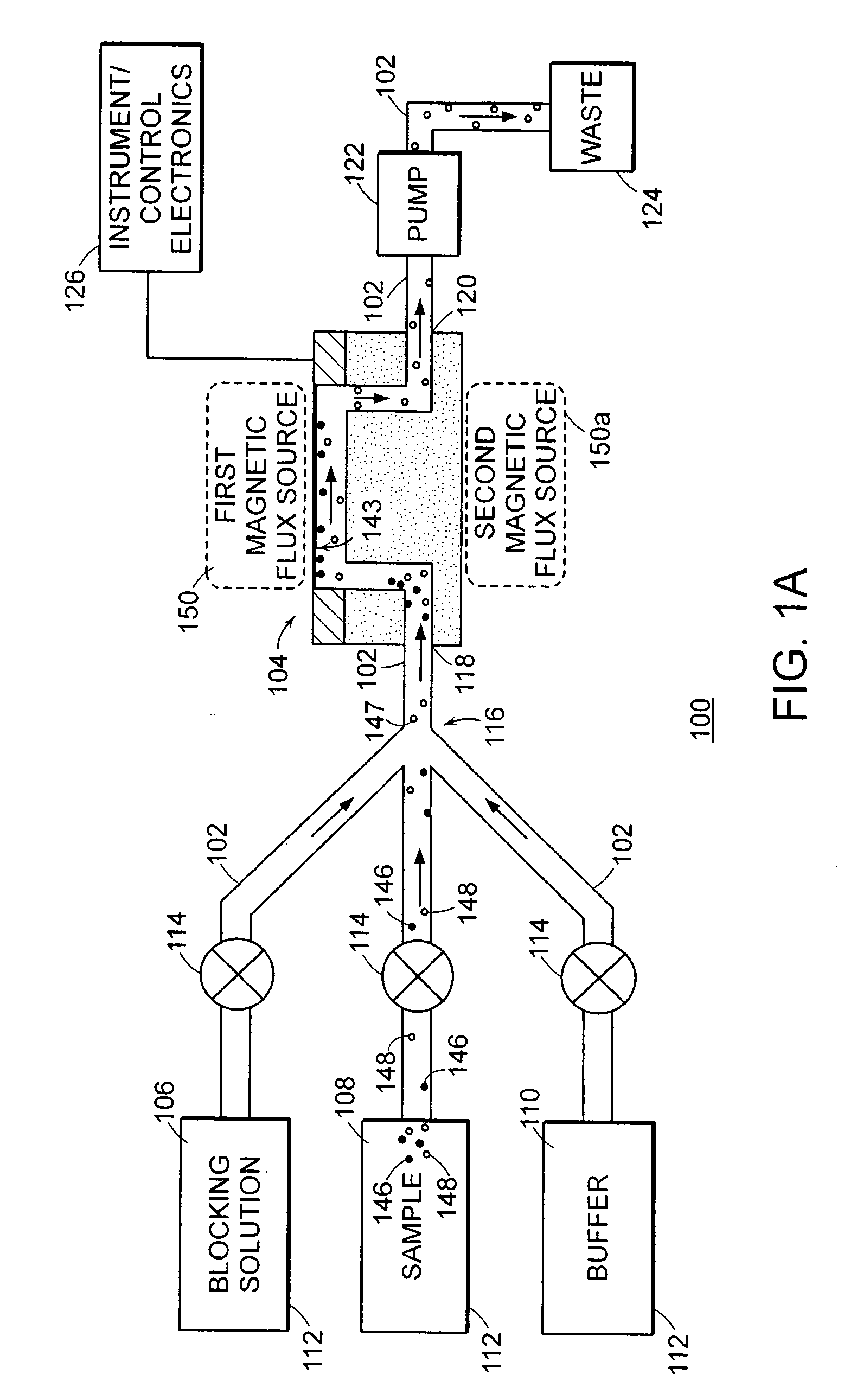
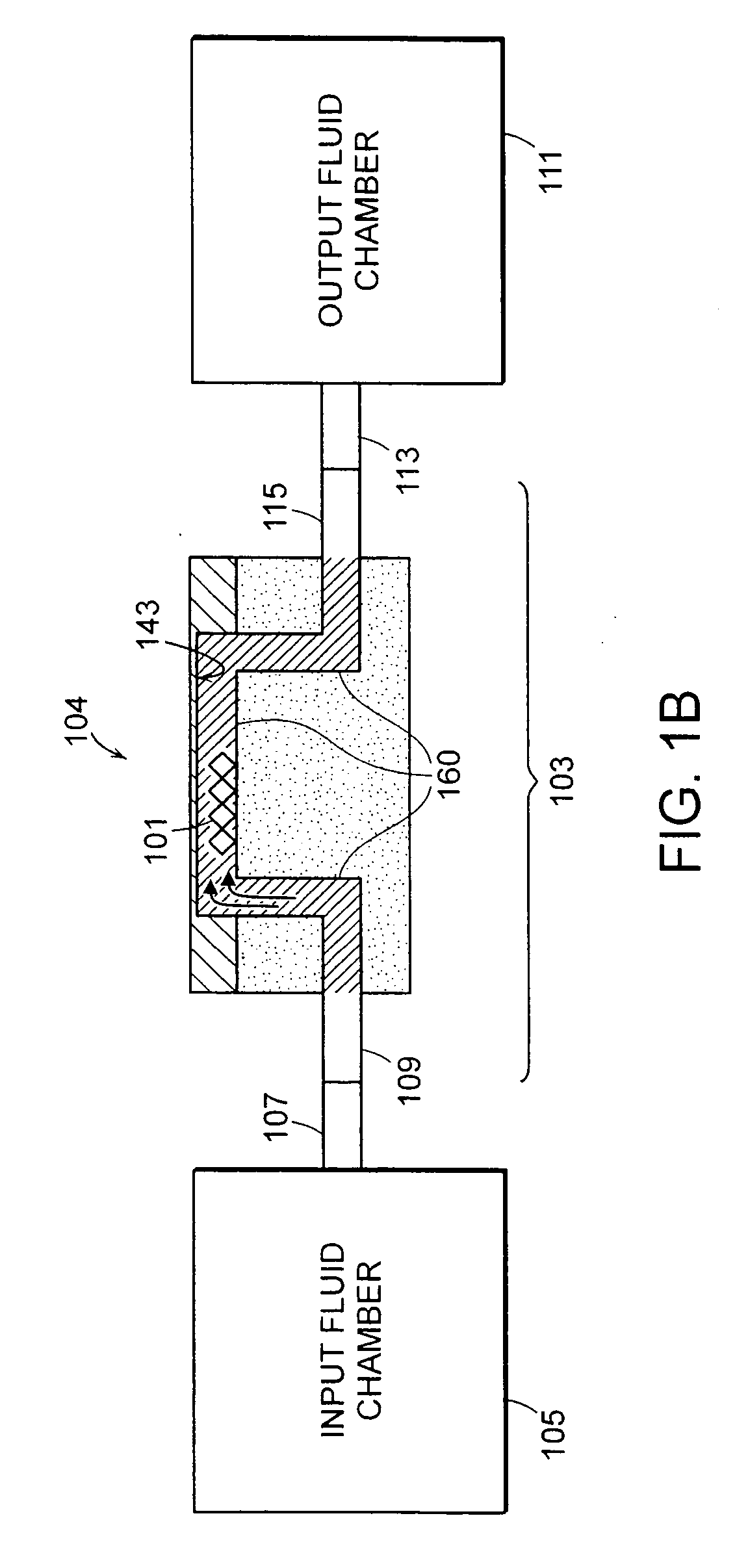
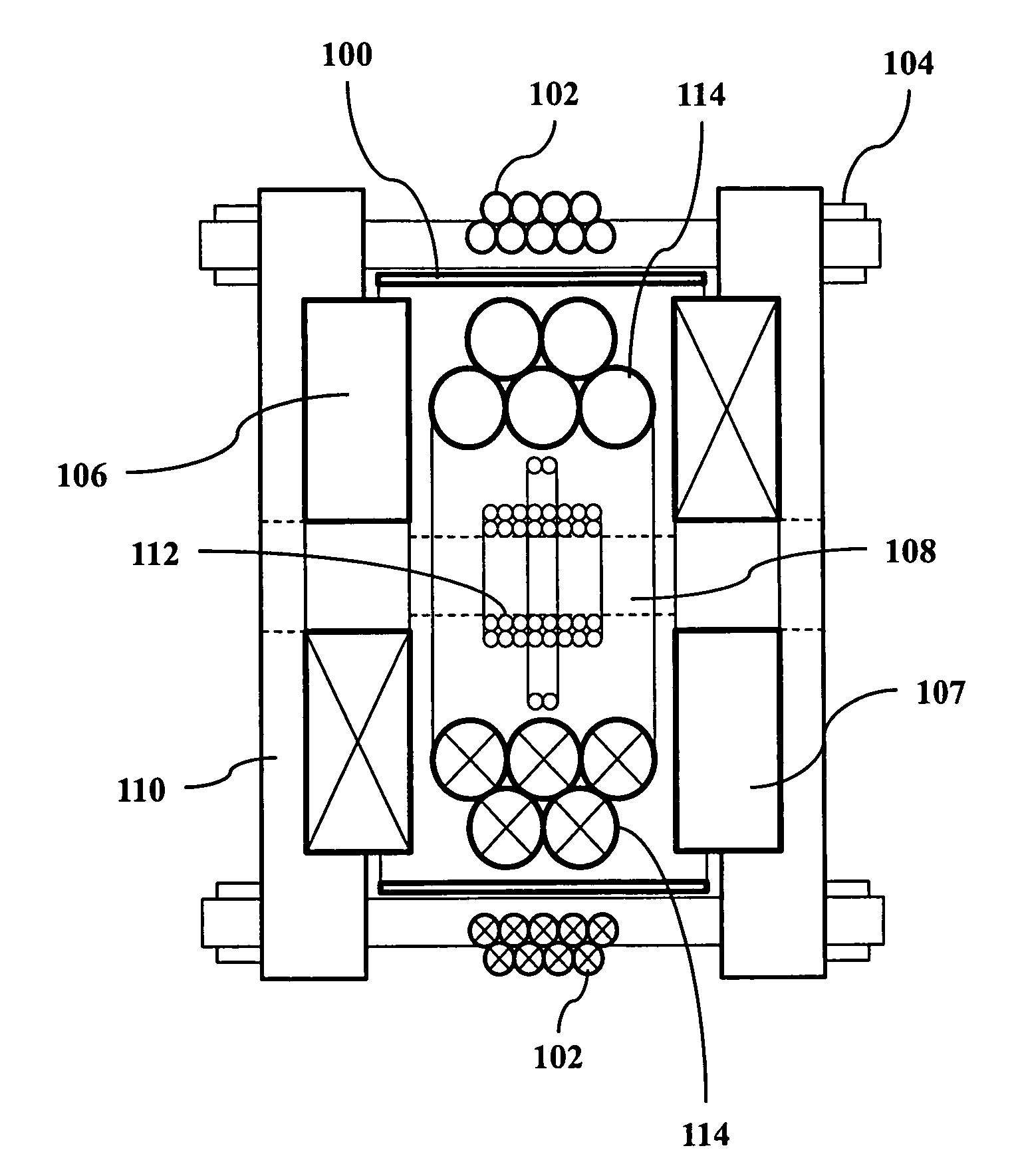
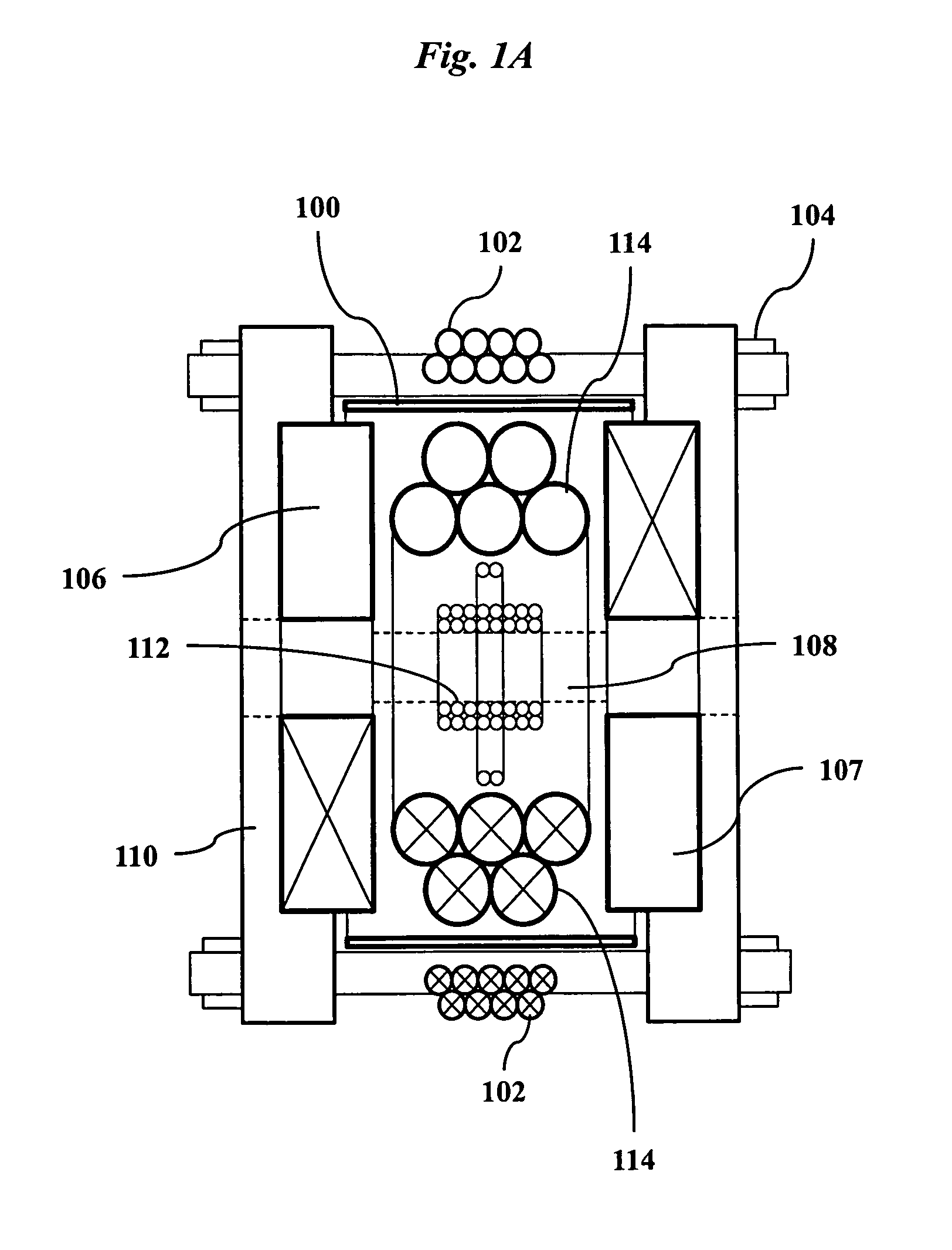
A magnetic particle imaging apparatus includes magnets [106,107] that produce a gradient magnetic field having a field free region (FFR), excitation field electromagnets [102,114] that produce a radiofrequency magnetic field within the field free region, high-Q receiving coils [112] that detect a response of magnetic particles in the field free region to the excitation field. Field translation electromagnets create a homogeneous magnetic field displacing the field-free region through the field of view (FOV) allowing the imaging region to be scanned to optimize scan time, scanning power, amplifier heating, SAR, dB / dt, and / or slew rate. Efficient multi-resolution scanning techniques are also provided. Intermodulated low and radio-frequency excitation signals are processed to produce an image of a distribution of the magnetic nanoparticles within the imaging region. A single composite image is computed using deconvolution of multiple signals at different harmonics.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Magnetic Probe Apparatus
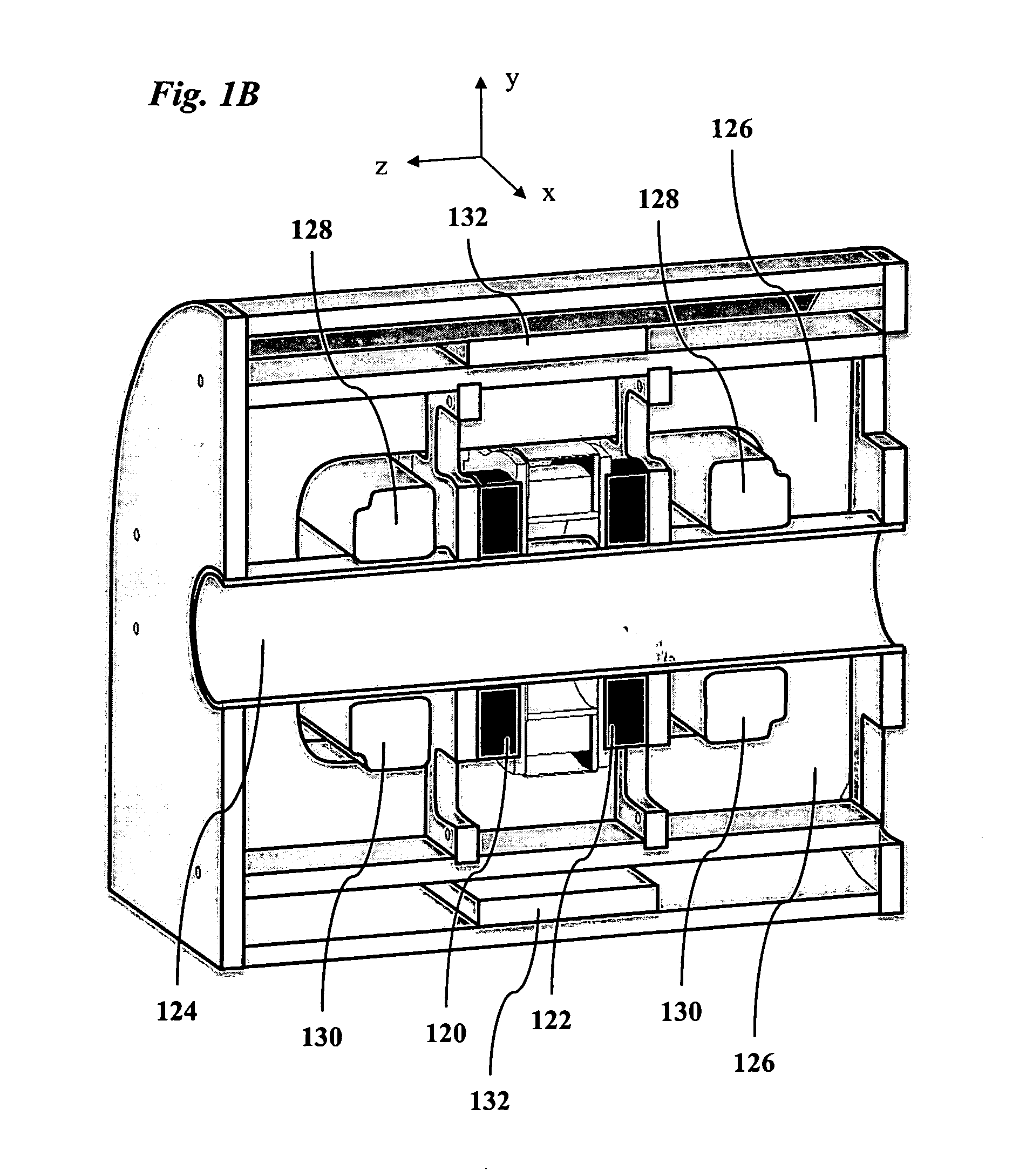
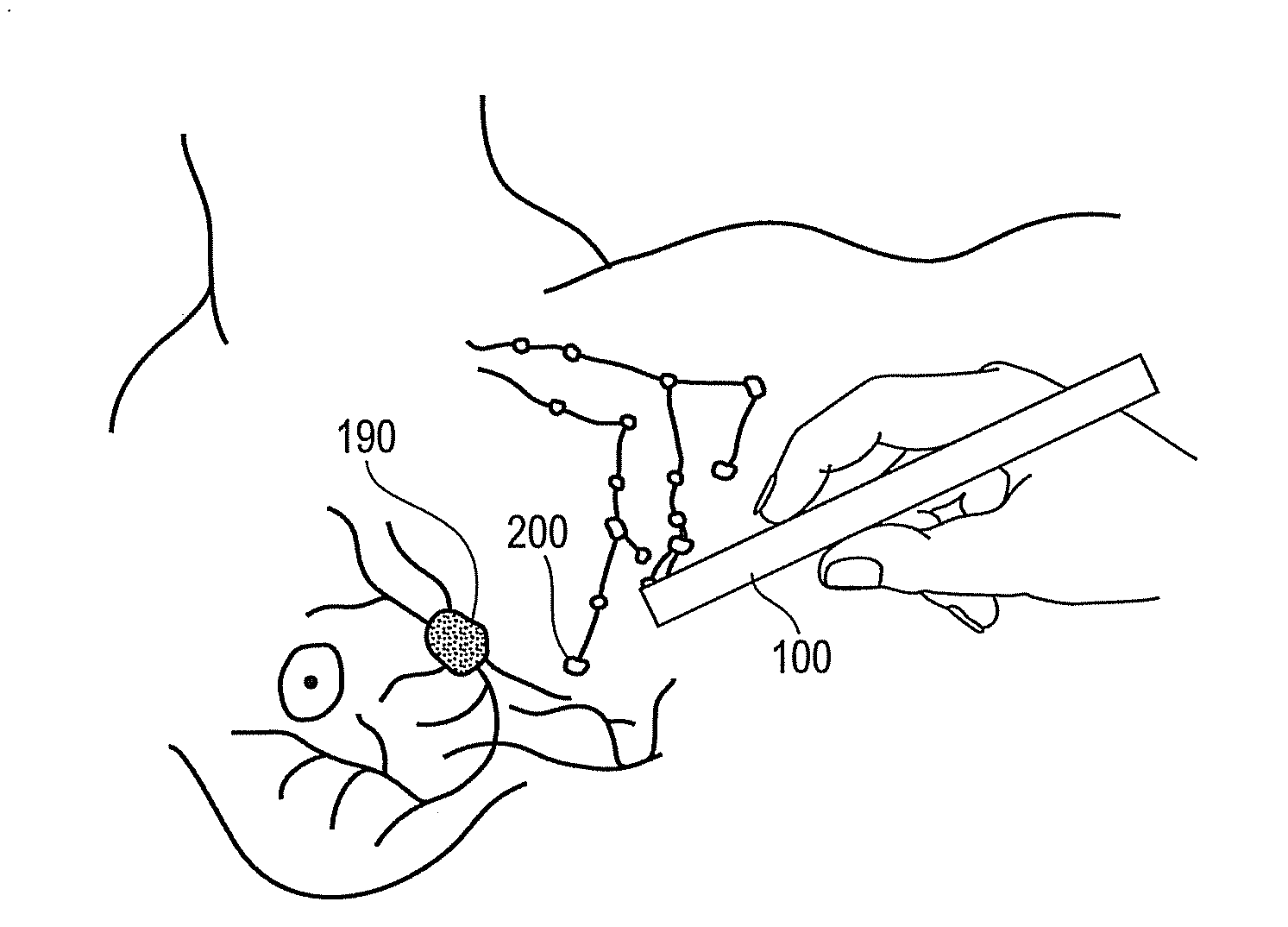
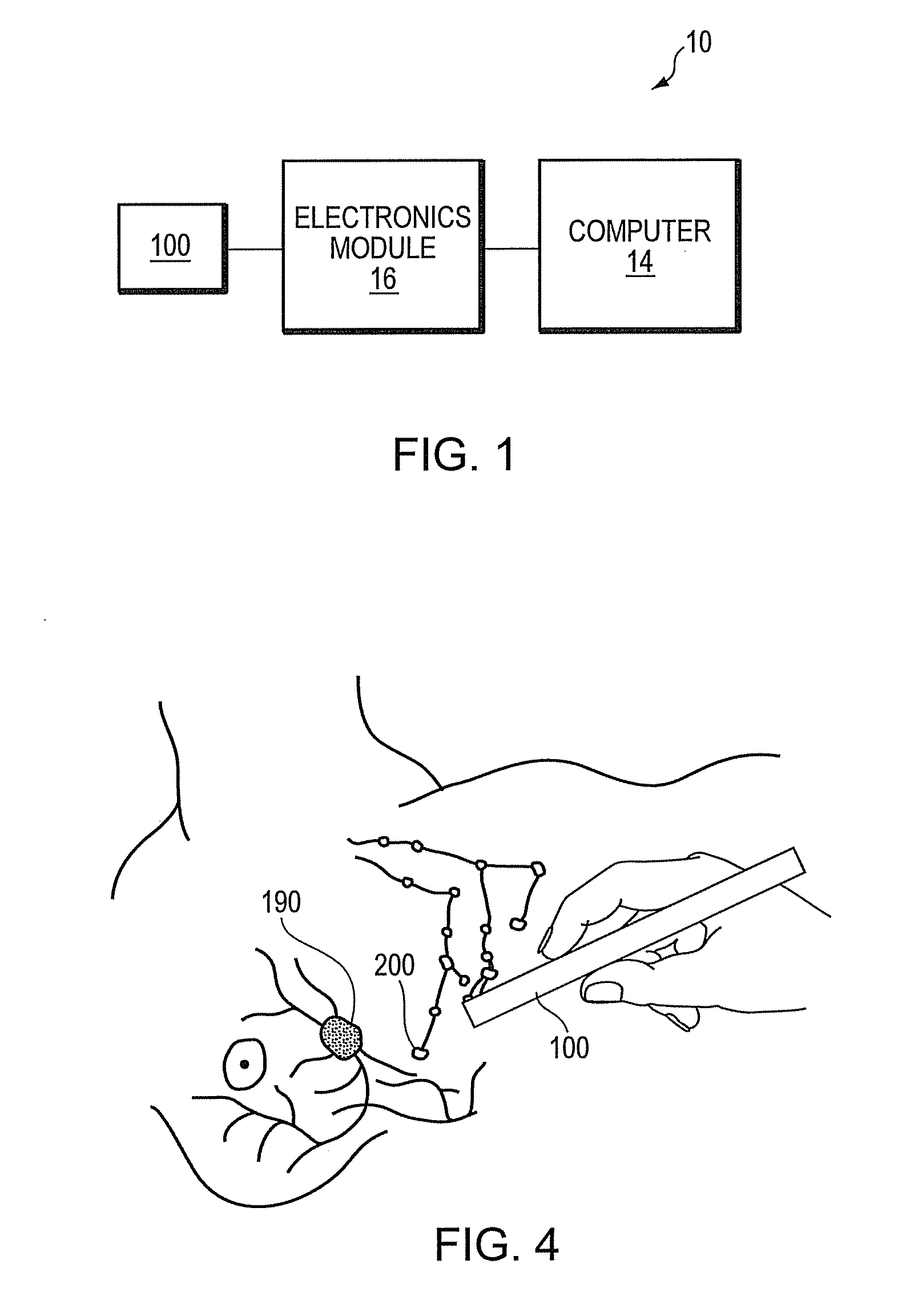
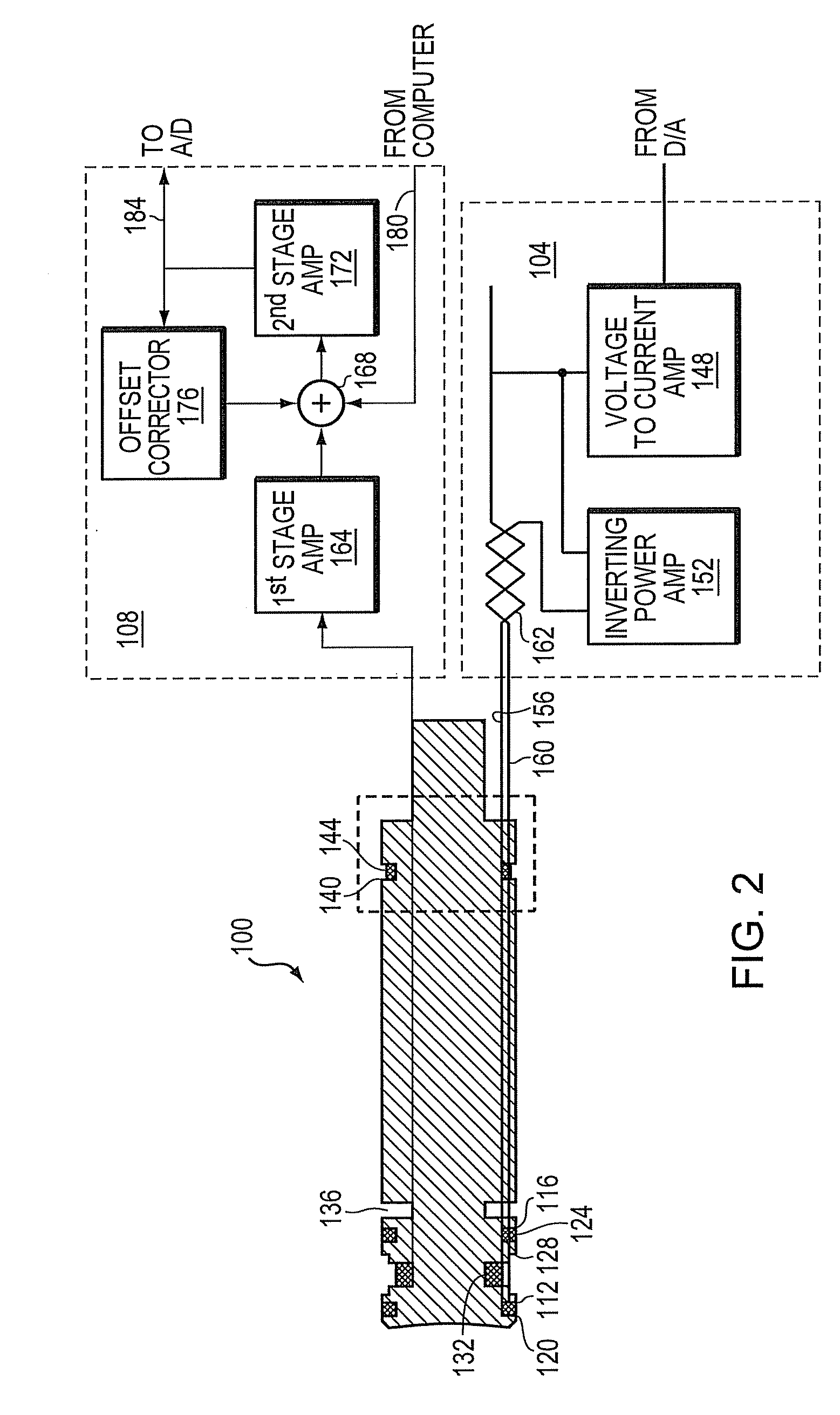
A system and method for locating magnetic material. In one embodiment the system includes a magnetic probe; a power module in electrical communication with the magnetic probe to supply current to the magnetic probe; a sense module in electrical communication with the magnetic probe to receive signals from the magnetic probe; and a computer in electrical communication with the power module and the sense module. The computer generates a waveform that controls the supply of current from the power module and receives a signal from the sense module that indicates the presence of magnetic material. The magnetic probe is constructed from a material having a coefficient of thermal expansion of substantially 10−6 / ° C. or less and a Young's modulus of substantially 50 GPa or greater. In one embodiment magnetic nanoparticles are injected into a breast and the lymph nodes collecting the particles are detected with the probe and deemed sentinel nodes.
Owner:ENDOMAGNETICS LTD
Nmr systems and methods for the rapid detection of analytes
ActiveUS20130244238A1Spin easilyFacilitate insertion intoNanomagnetismMicrobiological testing/measurementDiseaseAnalyte
This invention features systems and methods for the detection of analytes, and their use in the treatment and diagnosis of disease.
Owner:T2 BIOSYST
Detection device and method
ActiveUS20090085557A1High magnetizationDecrease of magnetisationElectrical measurementsSusceptibility measurementsCarrier fluidMagnetic response
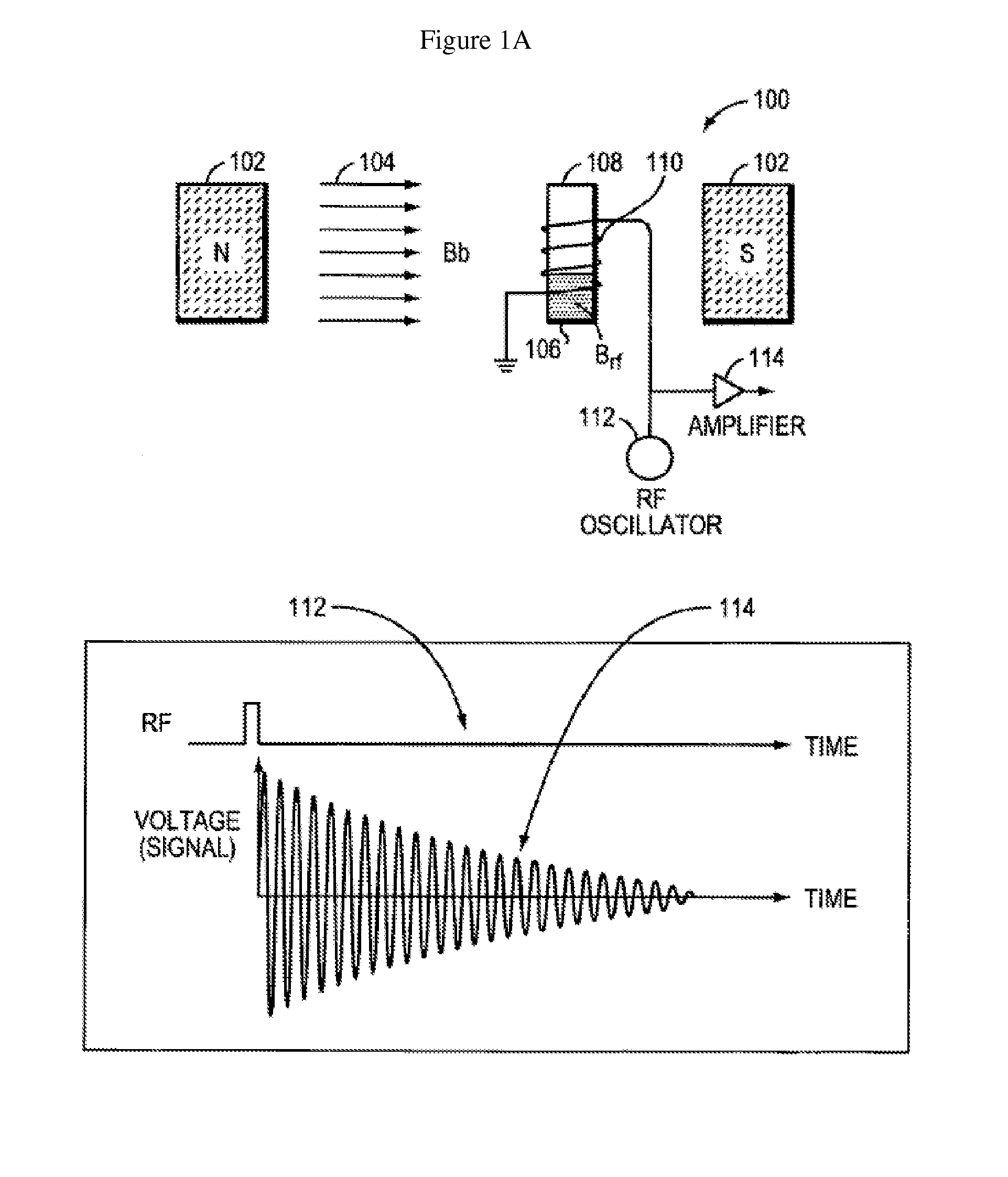
The present invention relates to method and device for detecting changes of a magnetic response of at least one magnetic particle in a carrier fluid. The method comprises: using a measuring procedure comprising measuring the characteristic rotation time of said magnetic particle, said measuring procedure further involving measuring Brownian relaxation in said carrier fluid under influence of an external pulsed excitation magnetic field, and based on said influence of said external pulsed excitation magnetic field measuring a hydrodynamic volume of a particle or a change in a hydrodynamic volume of the particle change upon modification of an effective volume of the particle or its interaction with said carrier fluid by detecting change of magnetization of the particle with time by monitoring change of an output signal in detection coil.
Owner:ACREO SWEDISH ICT
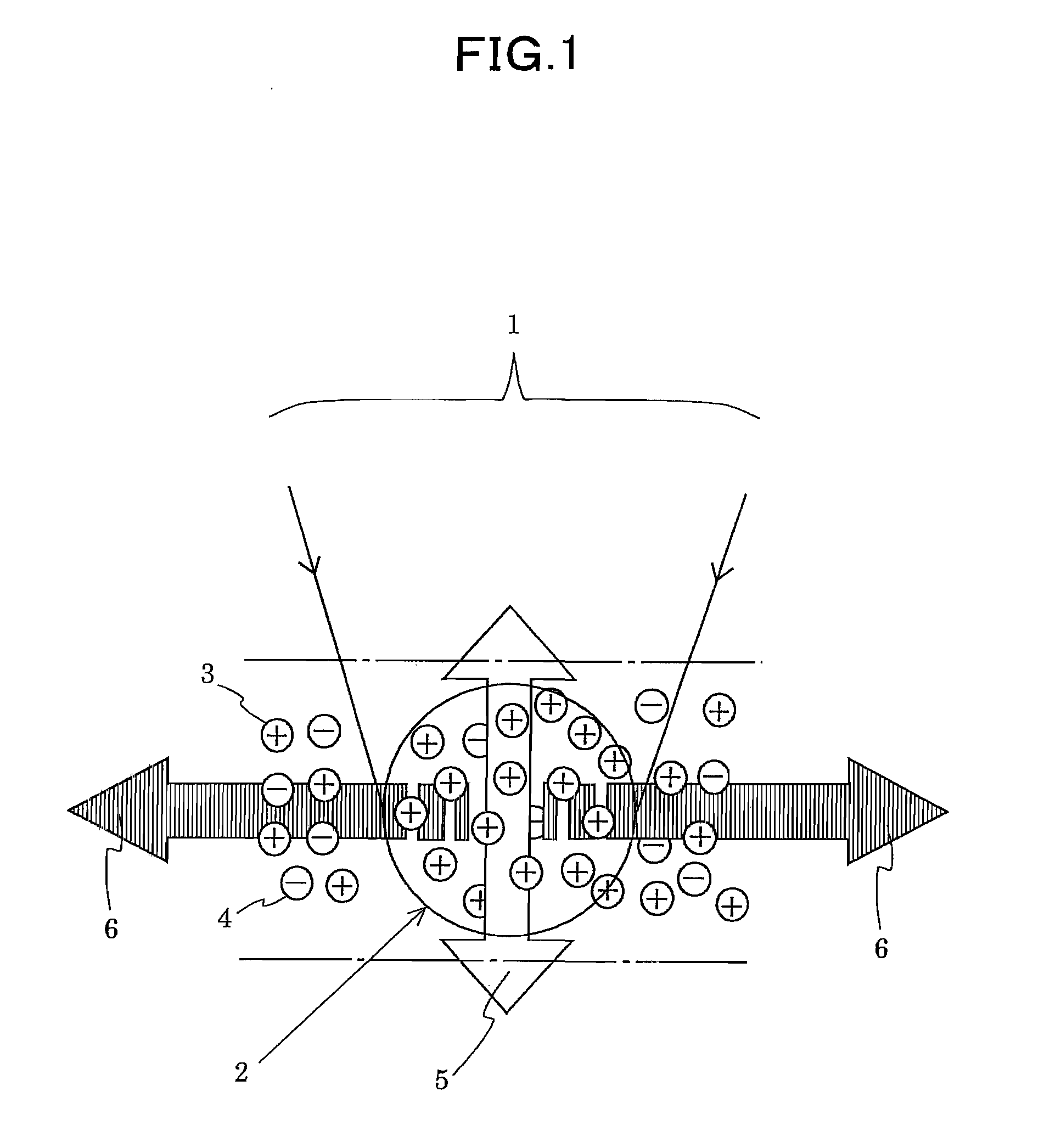
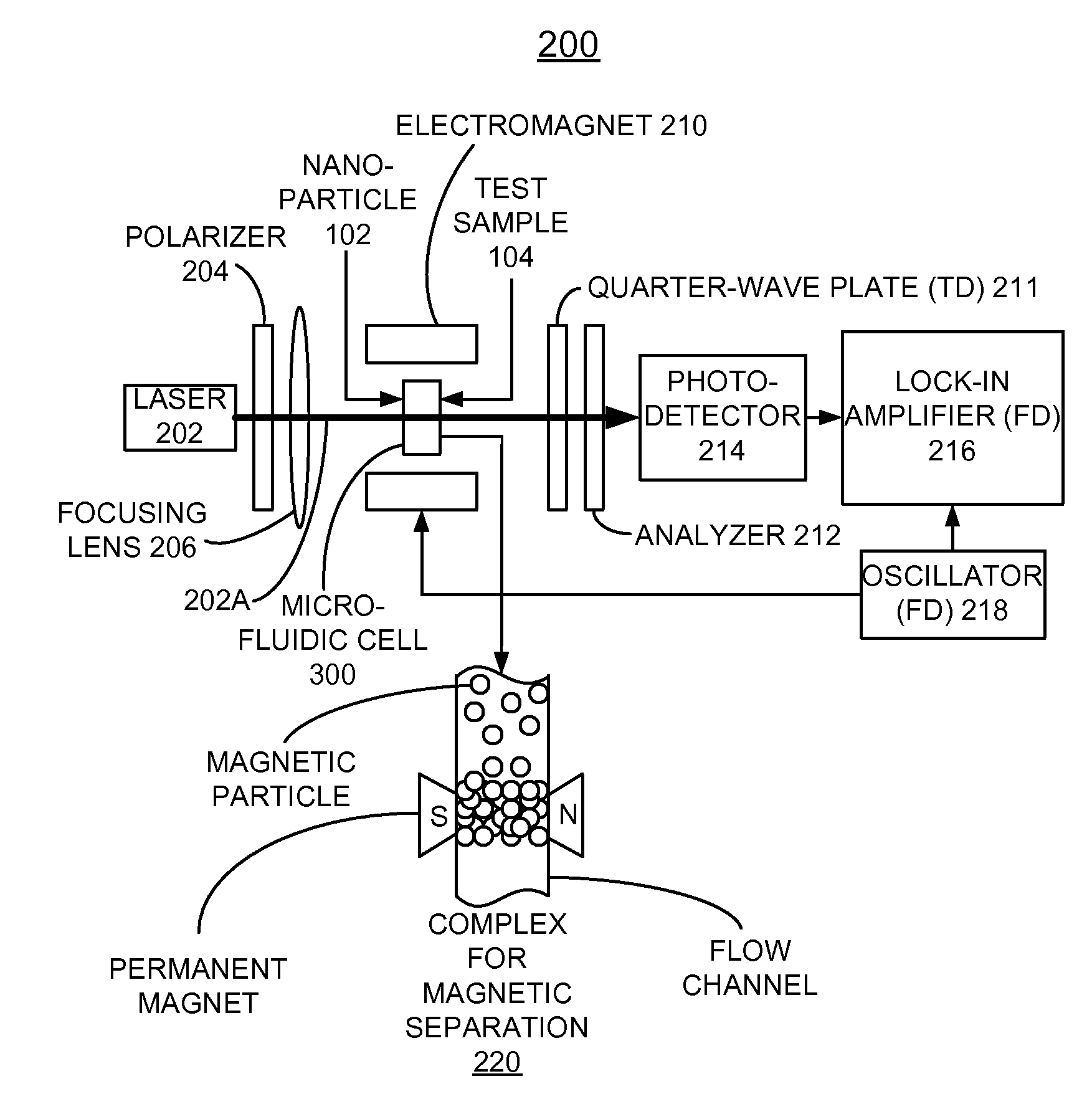
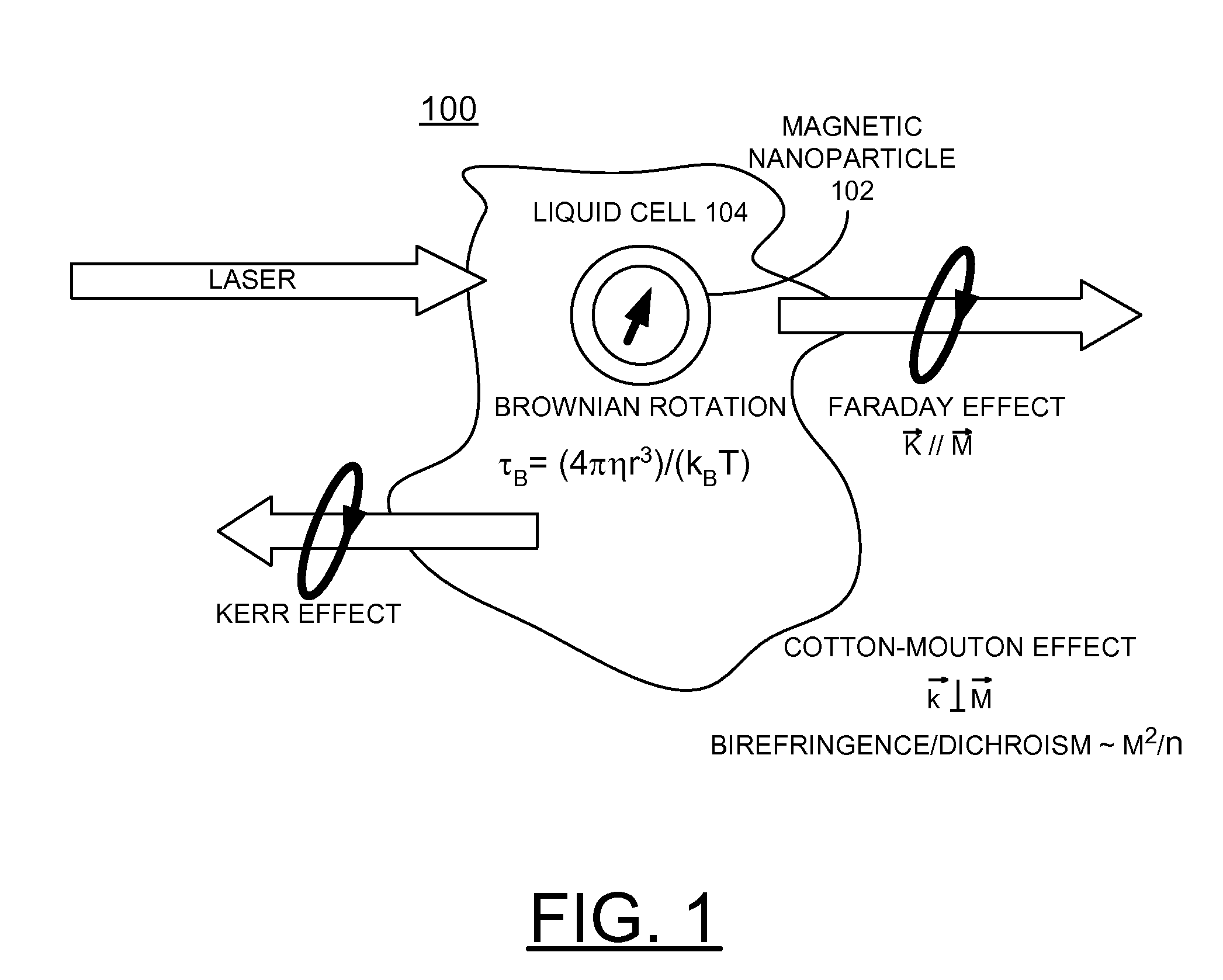
Magneto-optic biosensor using bio-functionalized magnetized nanoparticles
InactiveUS7639359B2Quick changeHigh signal sensitivityMaterial analysis by optical meansNanosensorsSmall sampleMagnetite Nanoparticles
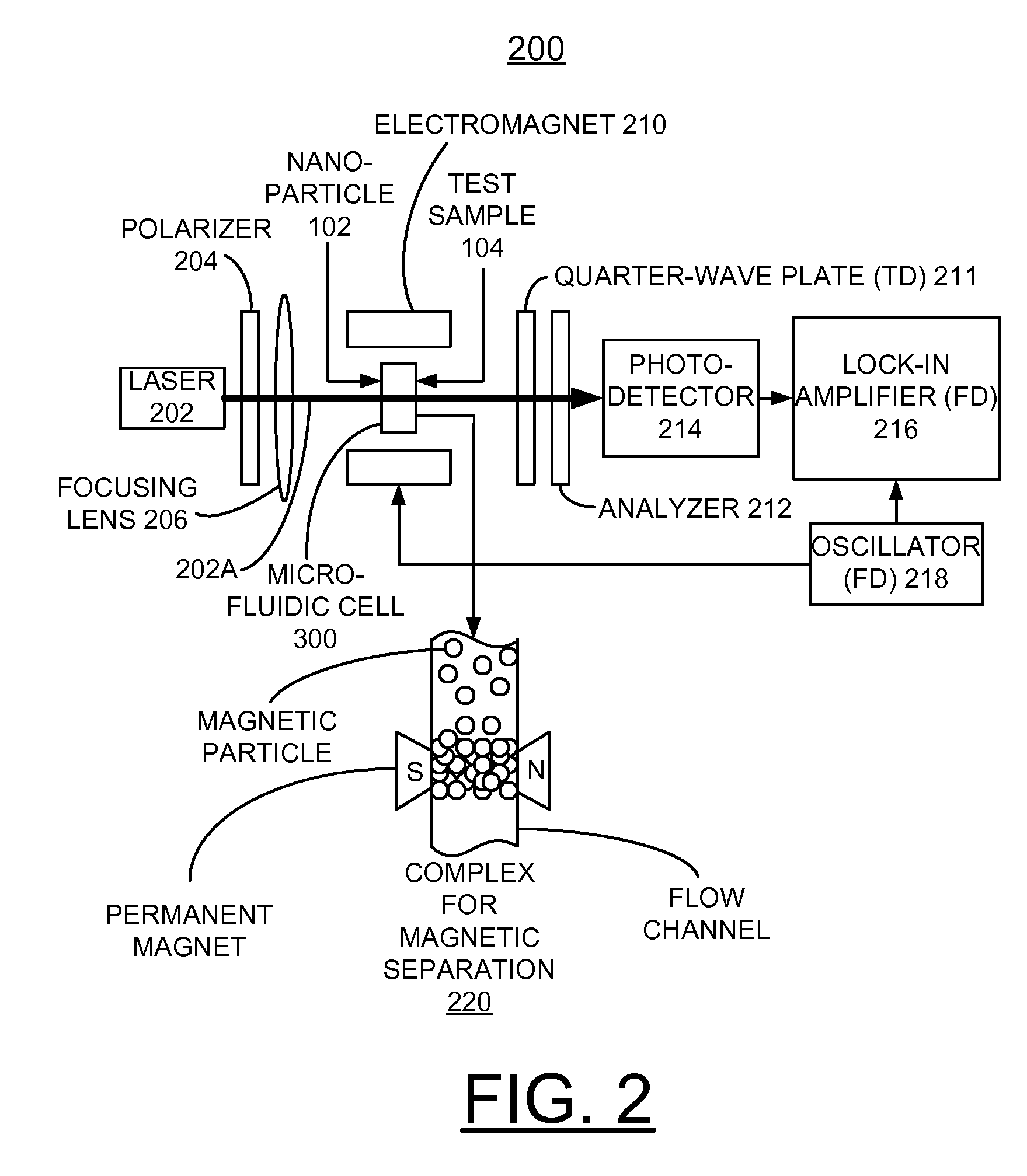
A biosensor utilizing bio-functionalized magnetic nanoparticles is provided. An external magnetic field is applied to a suspension of magnetic nanoparticles. A linearly polarized incident light is applied to the suspension of magnetic nanoparticles. A photocurrent from polarized light scattering by bio-functionalized magnetic nanoparticles in liquid is detected. The magneto-optic sensing technique is applied to a micro-fluidic channel for rapid and sensitive detection with a small sample amount, and subsequent magnetic separation for detoxification. This technique is used for the detection of Brownian relaxation with time sweep as well as frequency sweep. The magneto-optical sensor enables rapidly detecting changes in local dynamic properties of the magnetic nanoparticles in liquids and magnetic modulation of ferromagnetic particles in liquid provides increased signal sensitivity.
Owner:UCHICAGO ARGONNE LLC
Magnetic sensor device for and a method of sensing magnetic particles
InactiveUS20100052665A1Robust readoutRobust sensor readout topologyNanomagnetismMaterial magnetic variablesMagnetic fieldNuclear magnetic resonance
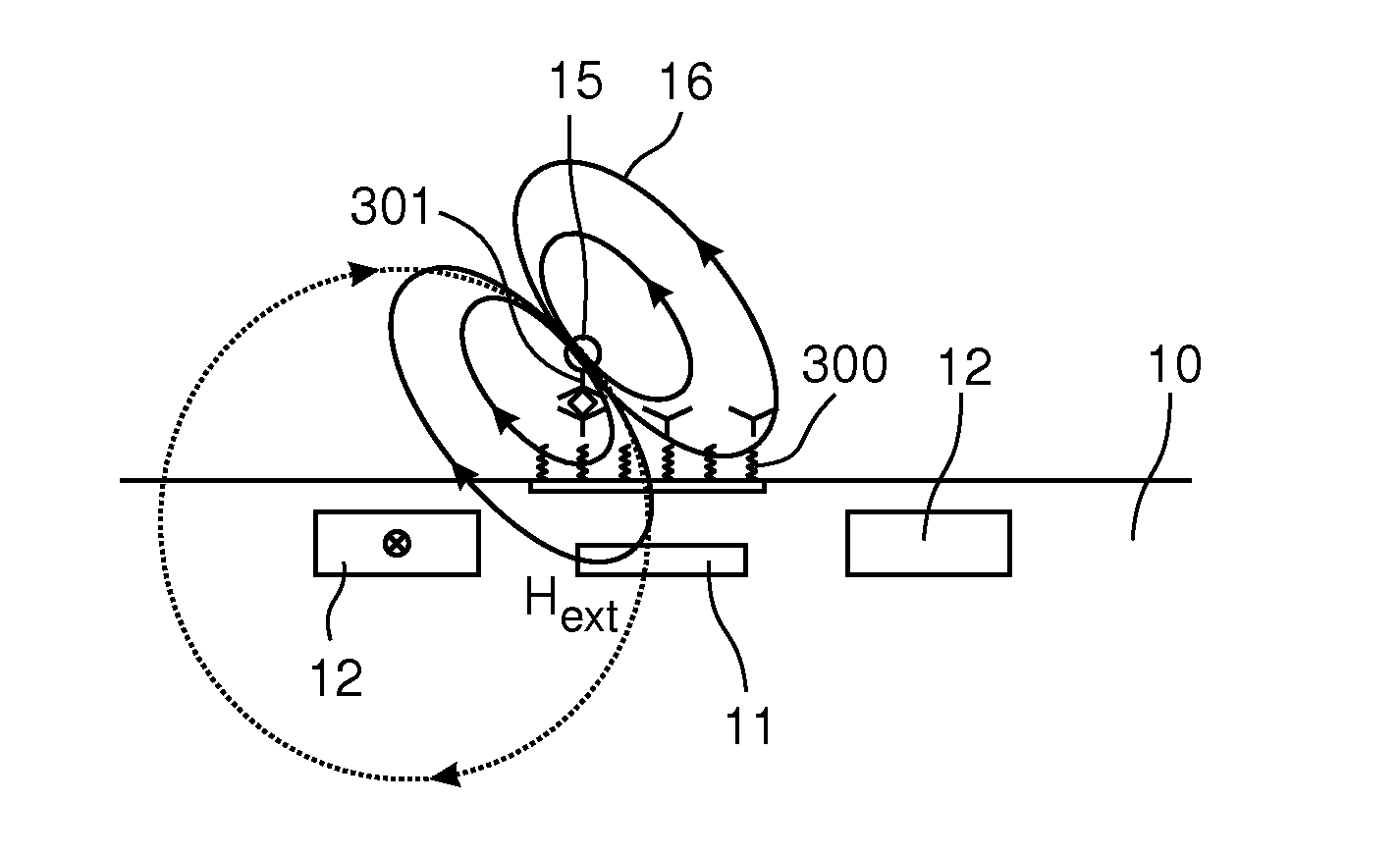
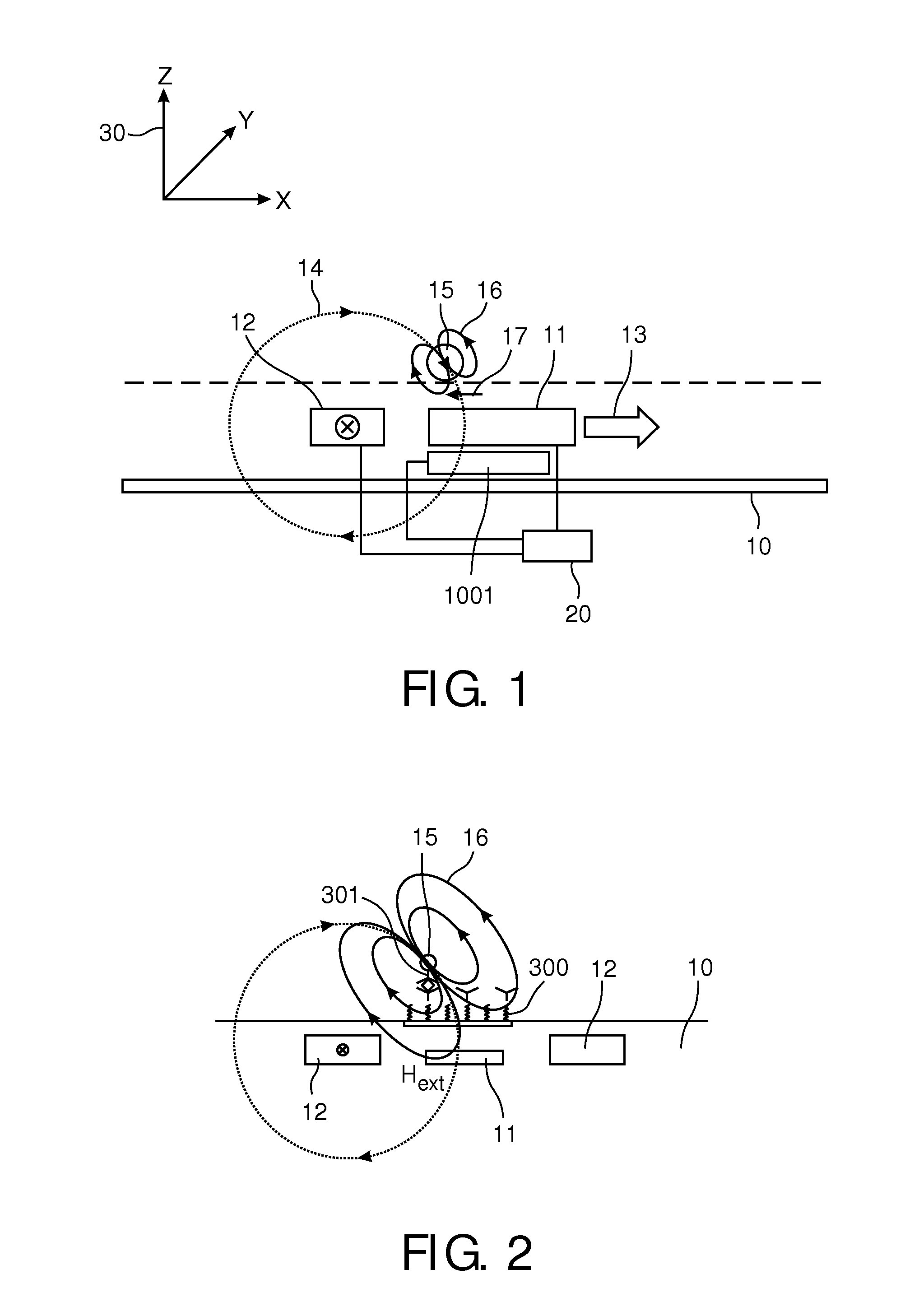
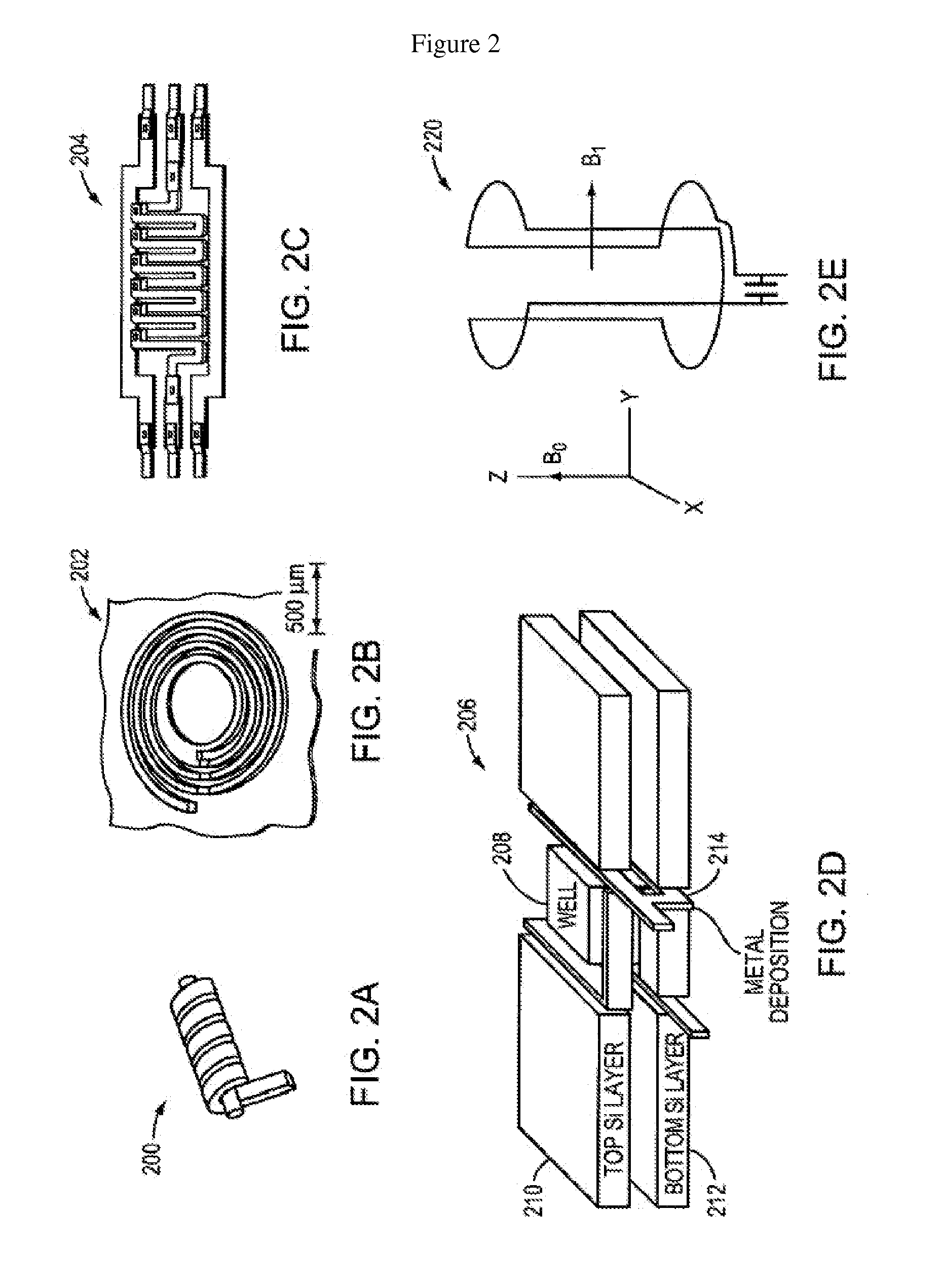
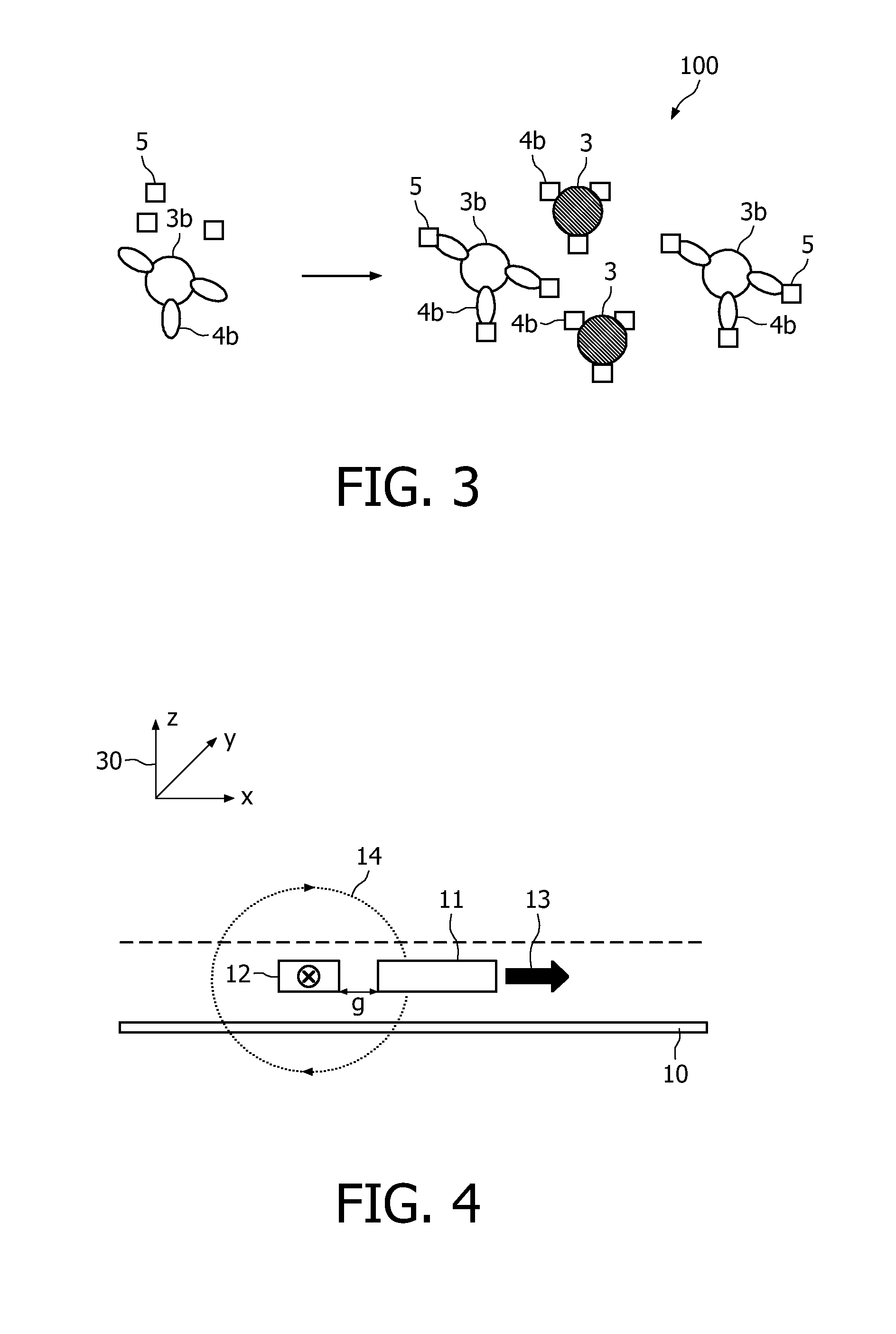
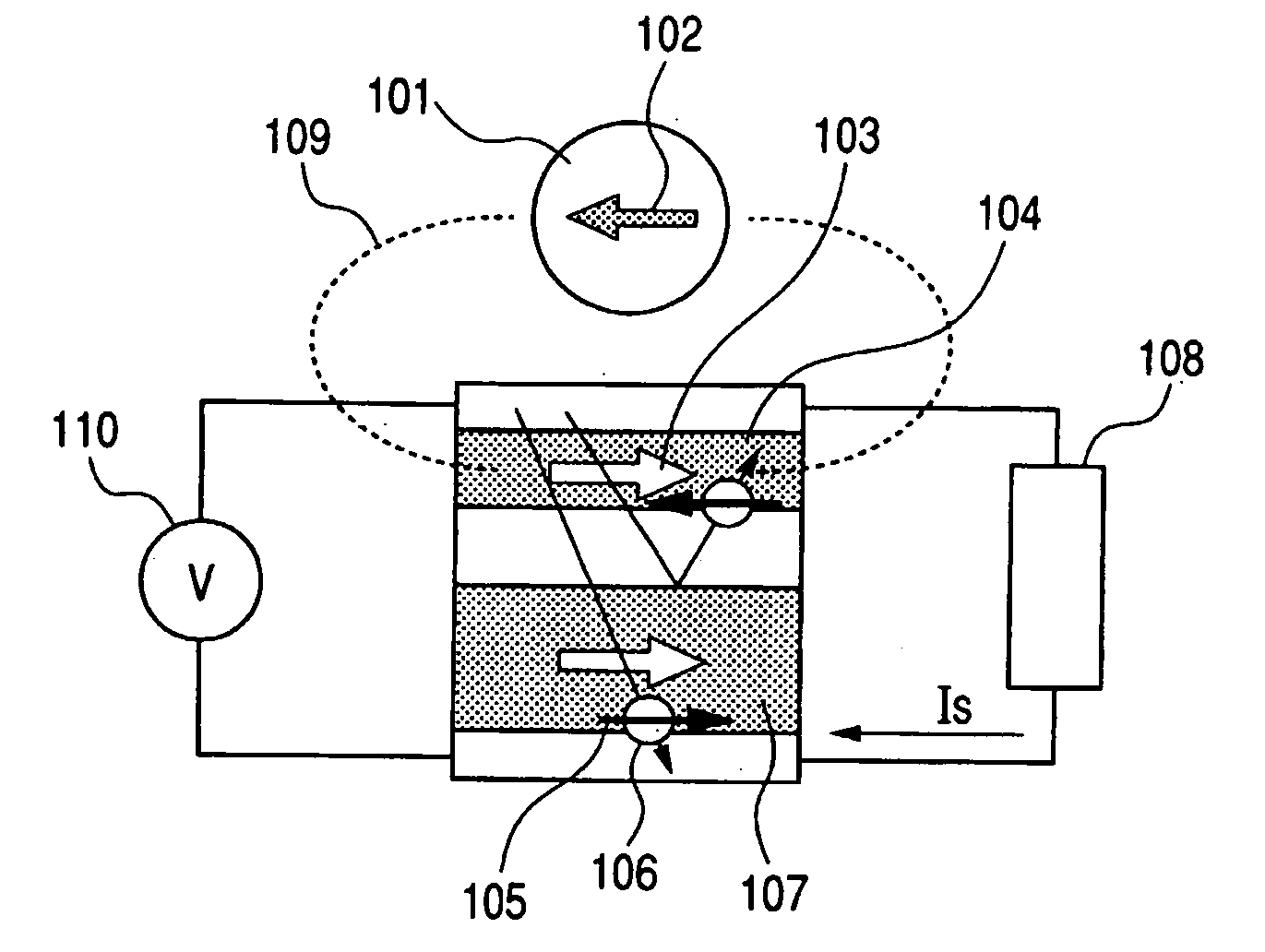
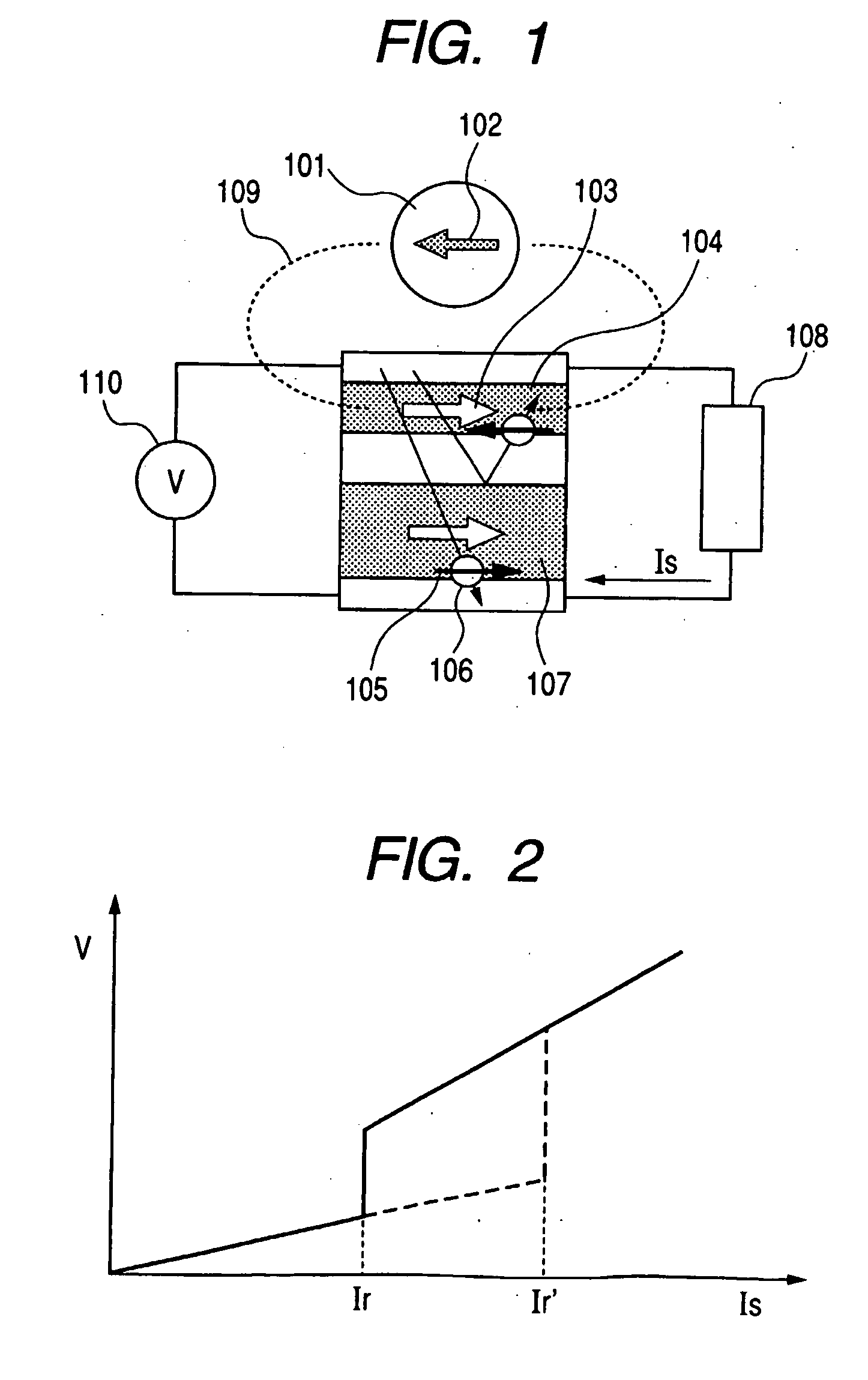
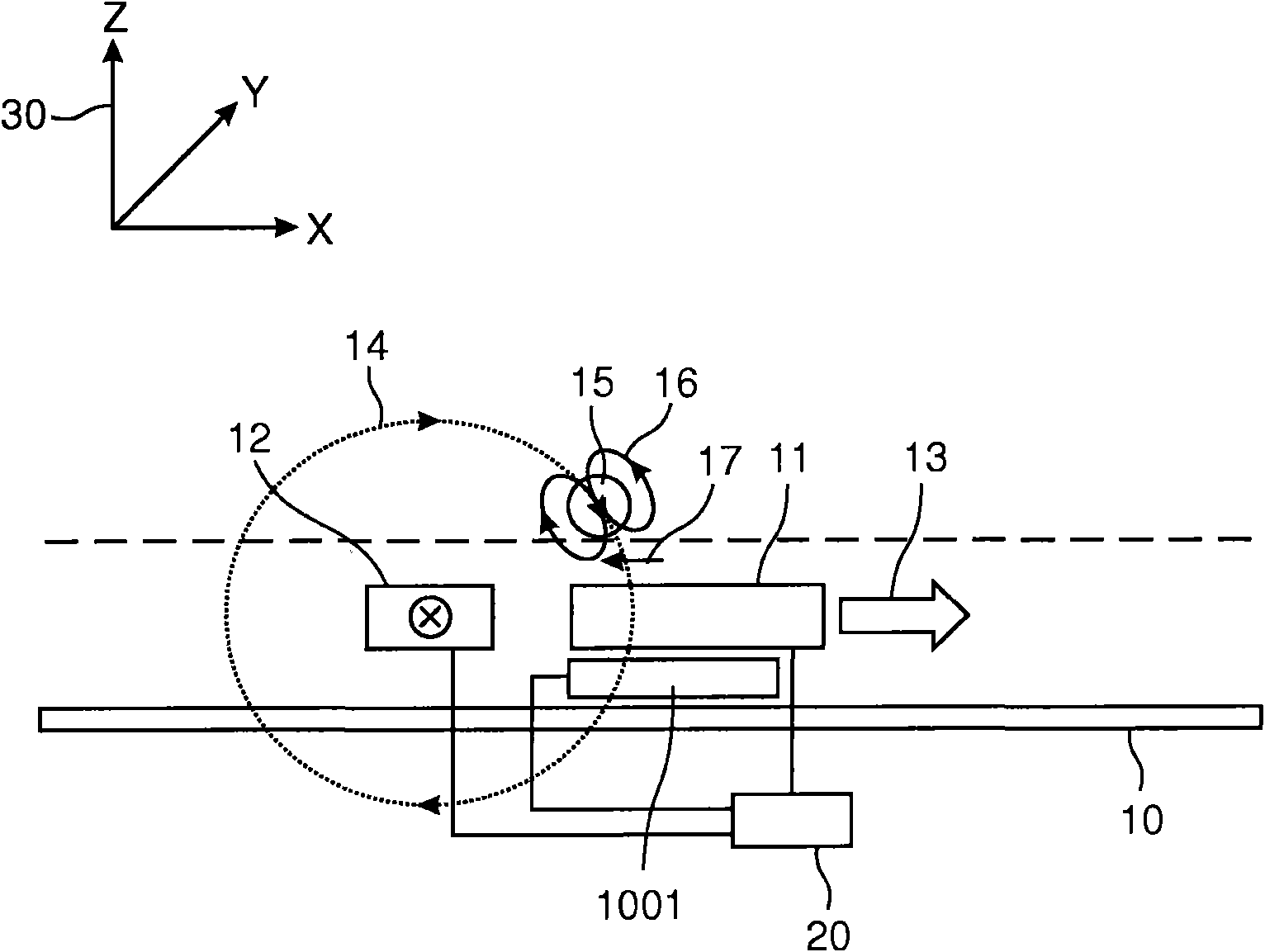
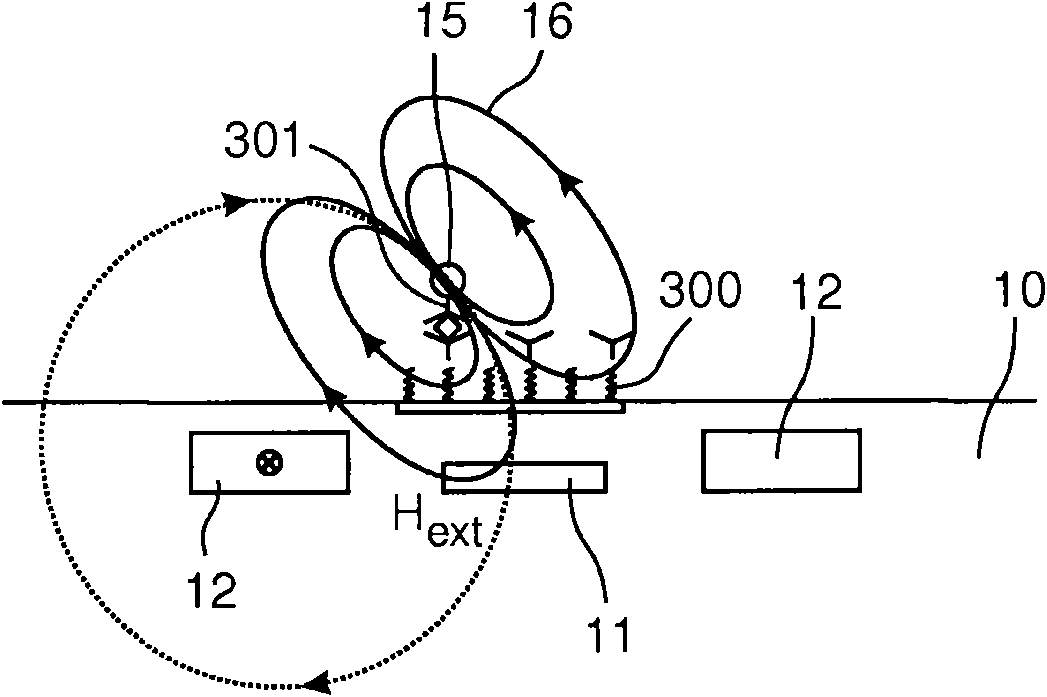
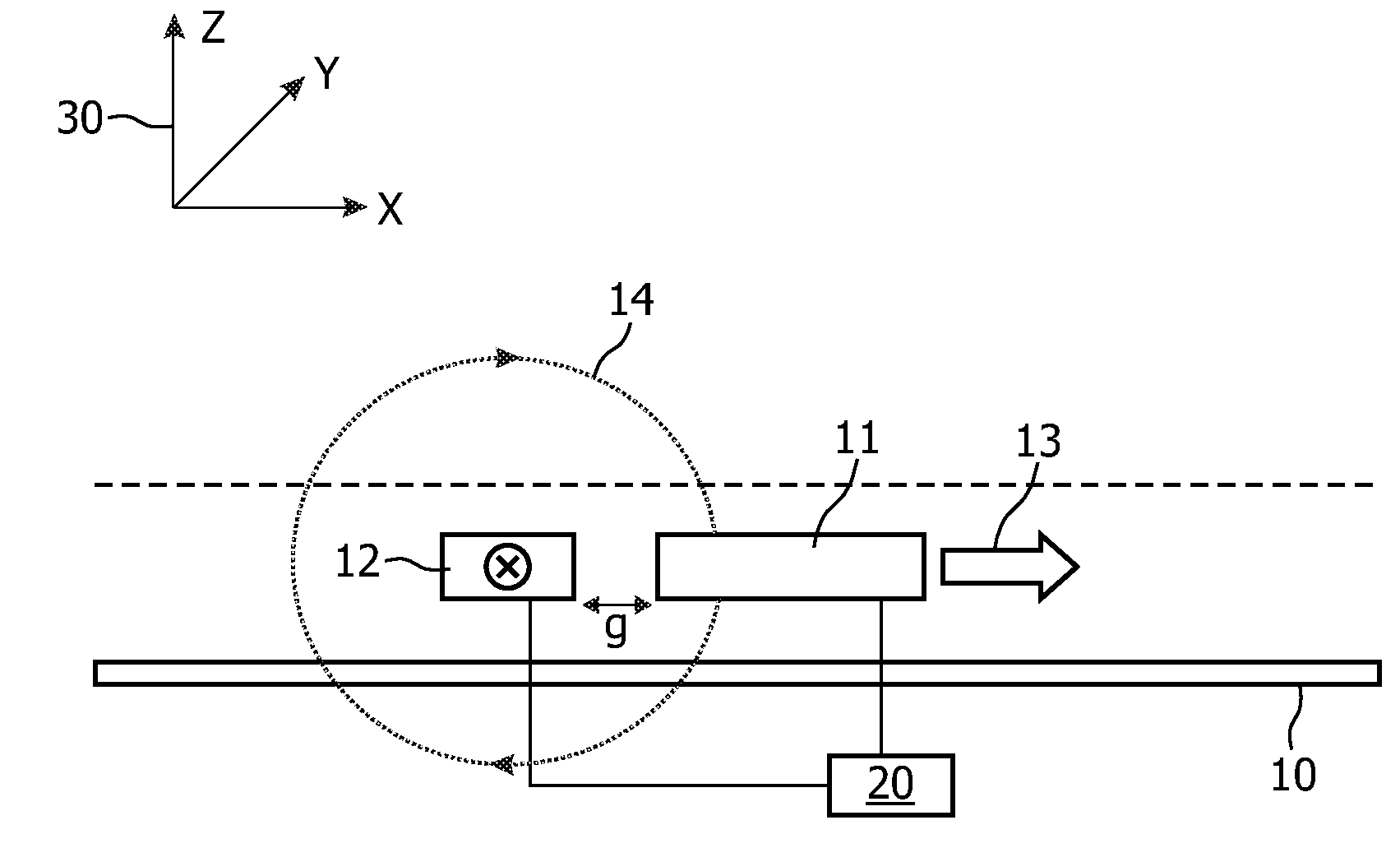
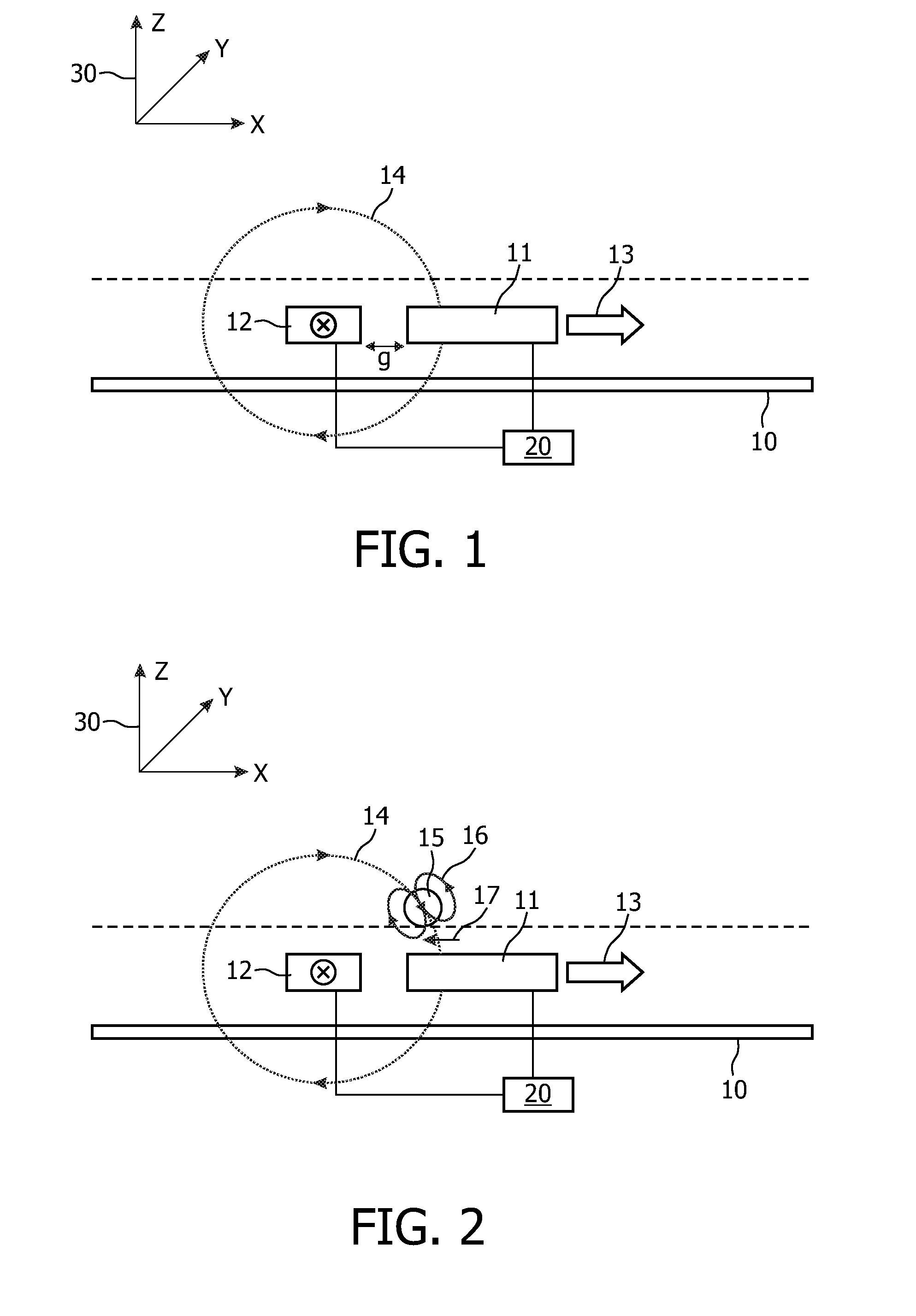
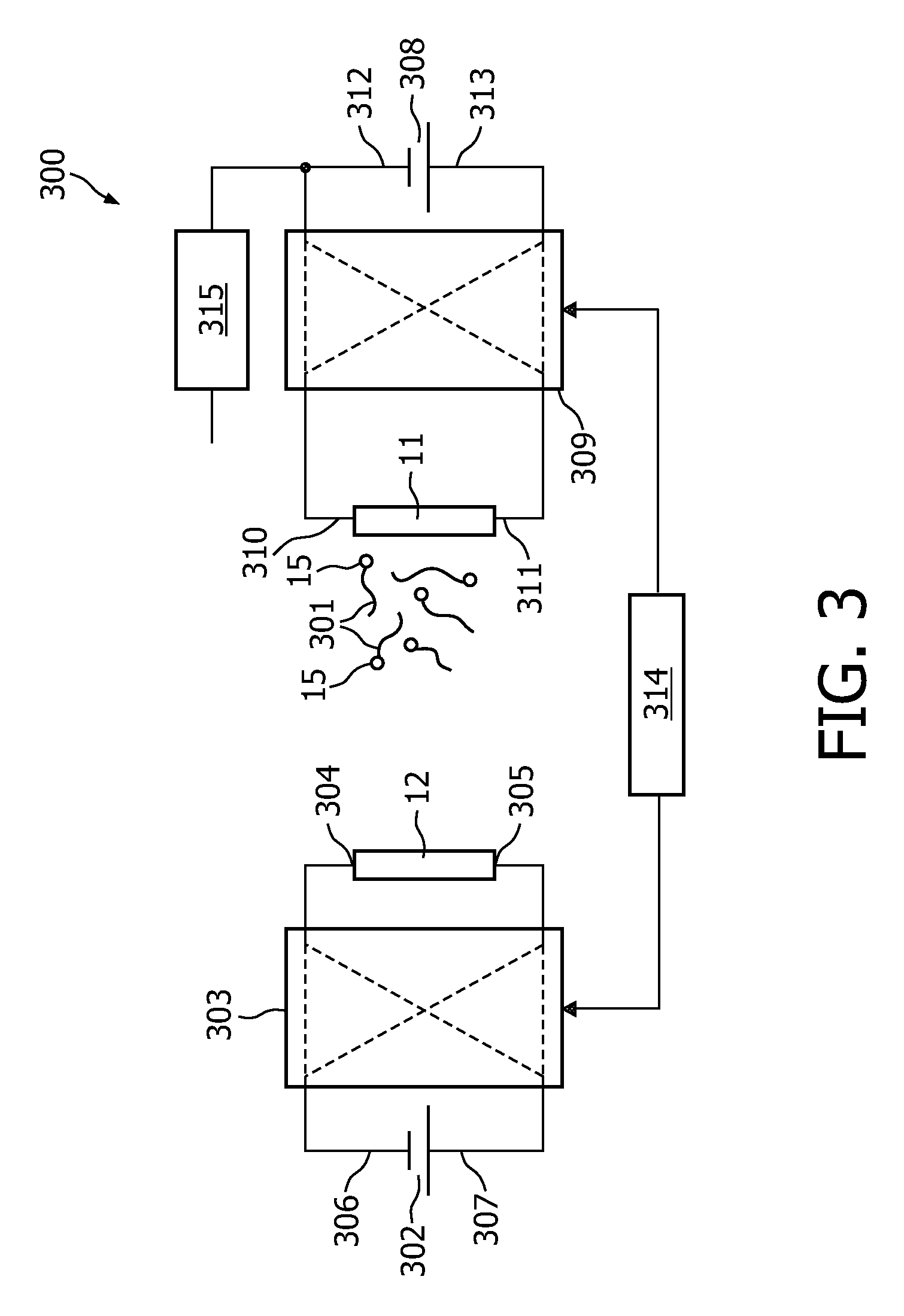
A magnetic sensor device (1000) for sensing magnetic particles (15), the magnetic sensor device (1000) comprising a first magnetic field generator unit (12) excitable for generating a first magnetic field, a sensing unit (11) adapted for sensing a signal indicative of the presence of the magnetic particles (15) in the first magnetic field, a second magnetic field generator unit (1001) adapted for generating a second magnetic field affecting the sensing unit (11), and a processing circuitry (1002) adapted for processing the signal to form a digitized signal and adapted for feeding back the processed signal to the second magnetic field generator unit (1001).
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Calibration of a magnetic sensor device
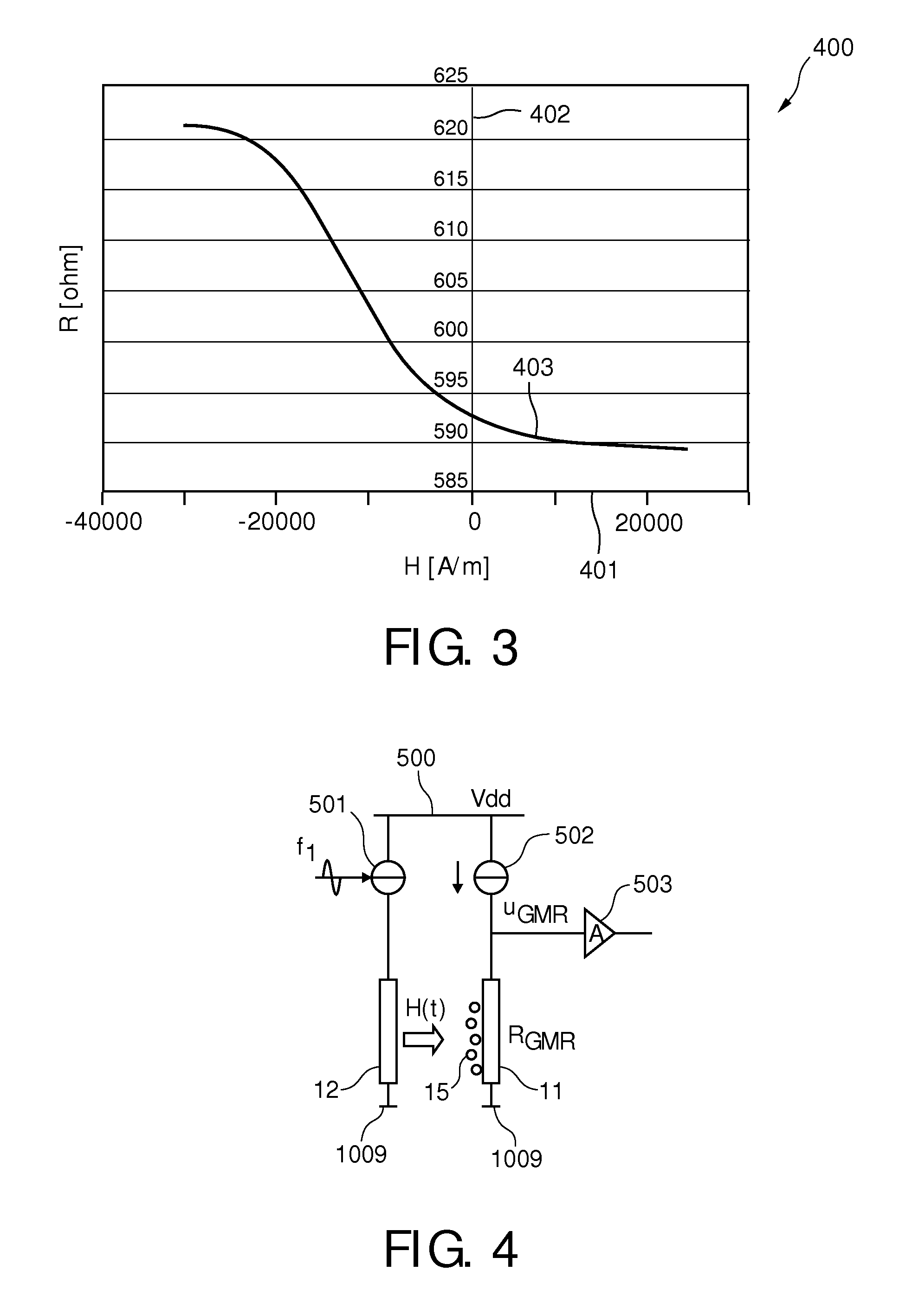
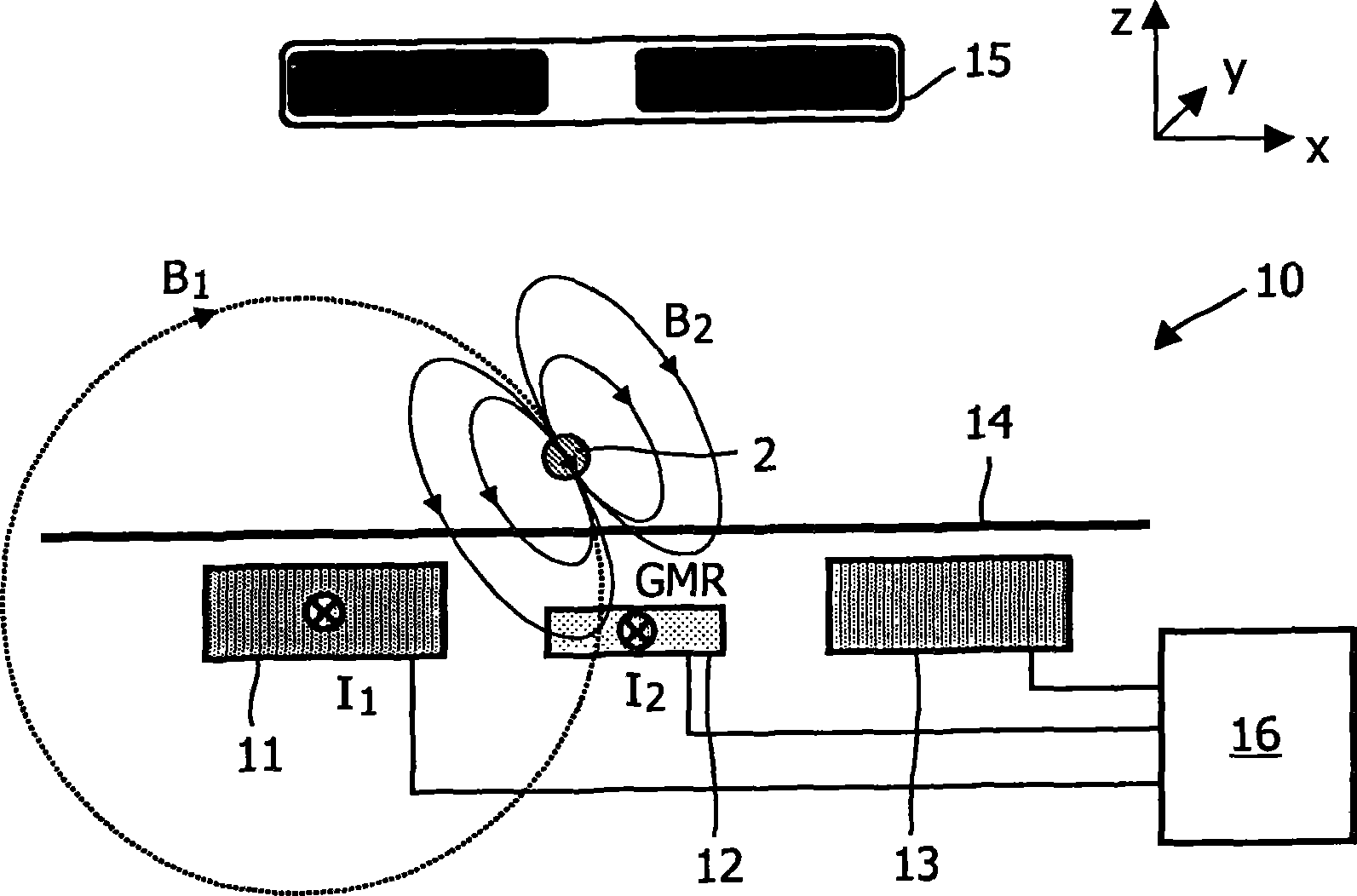
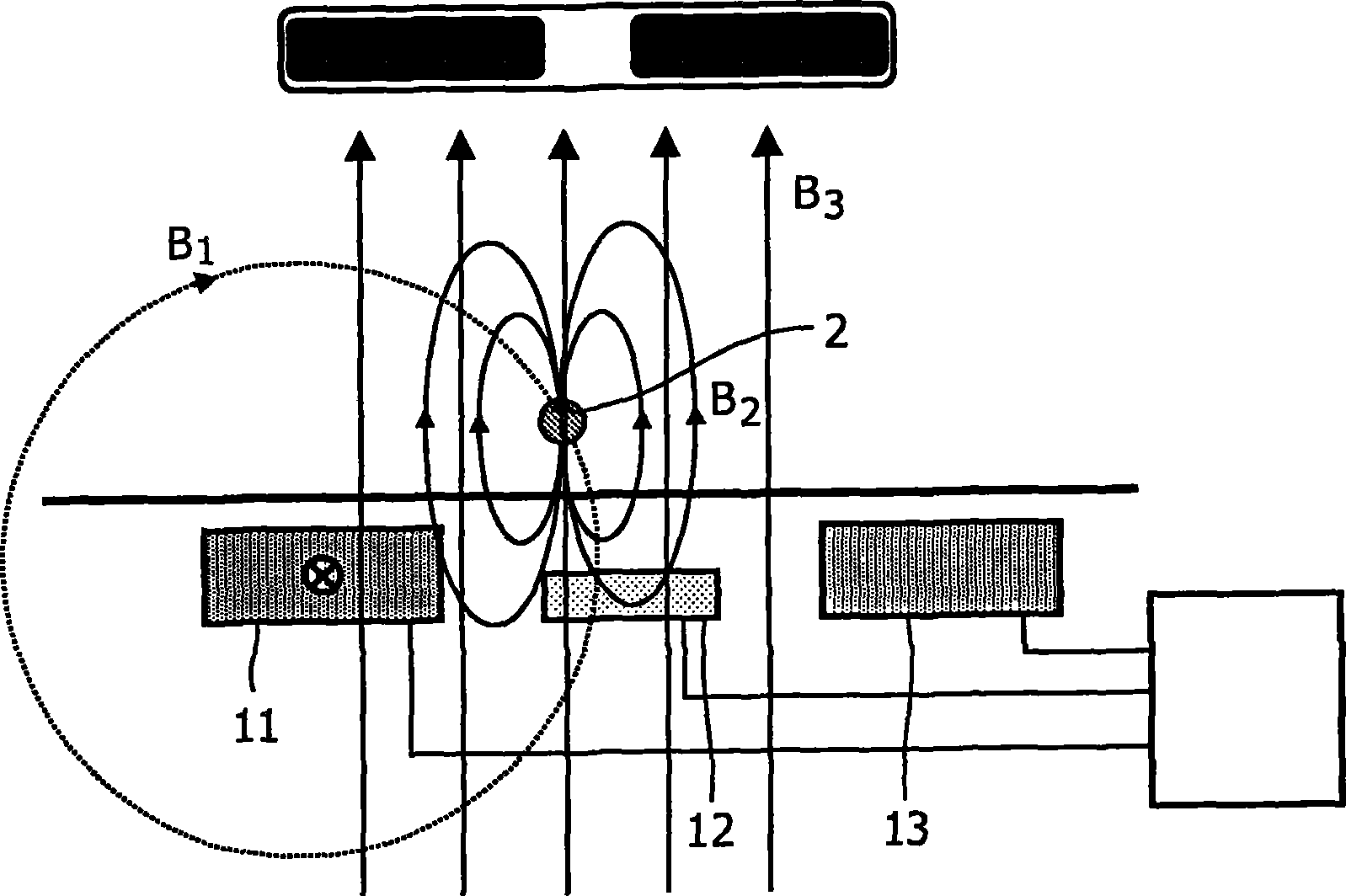
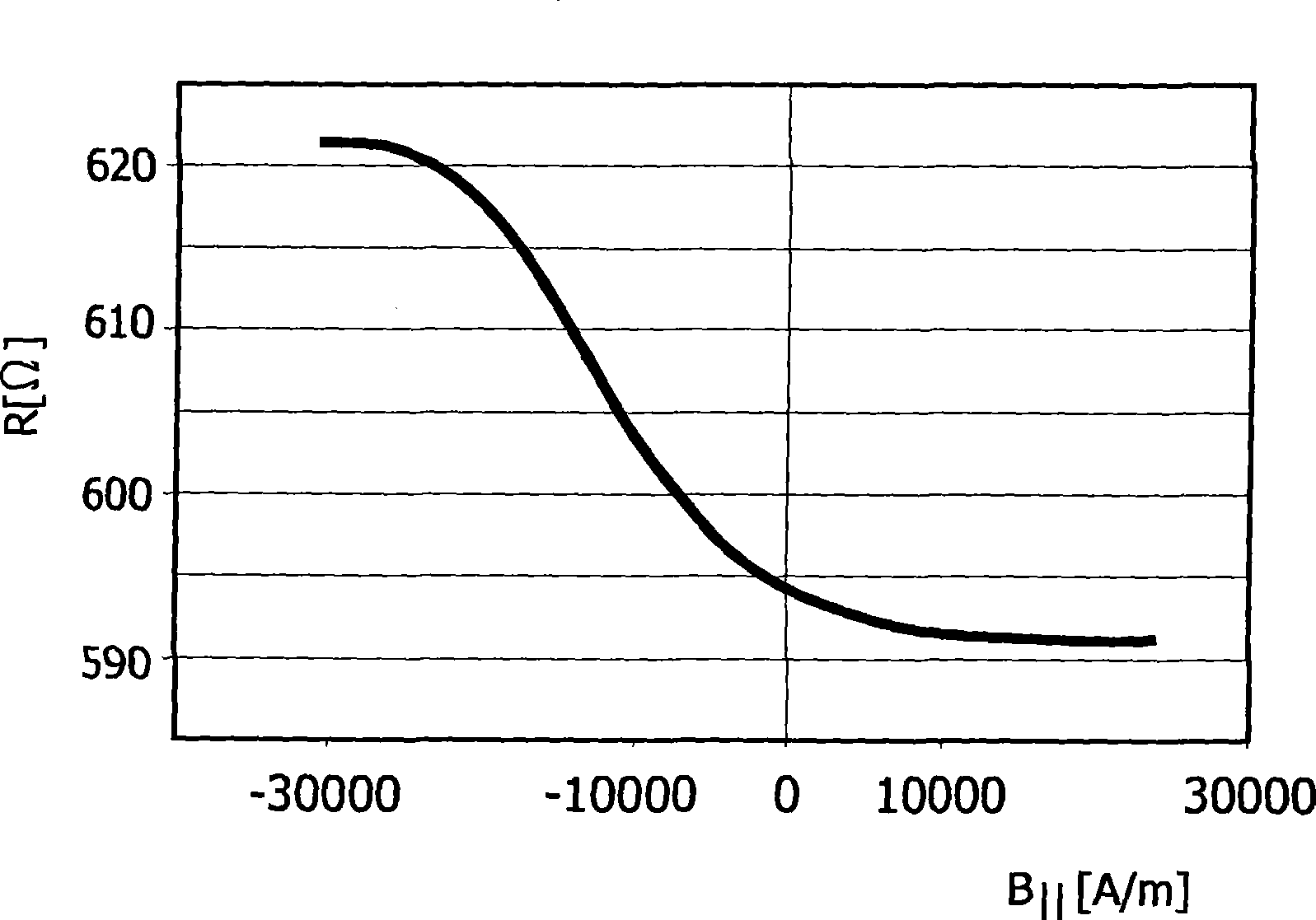
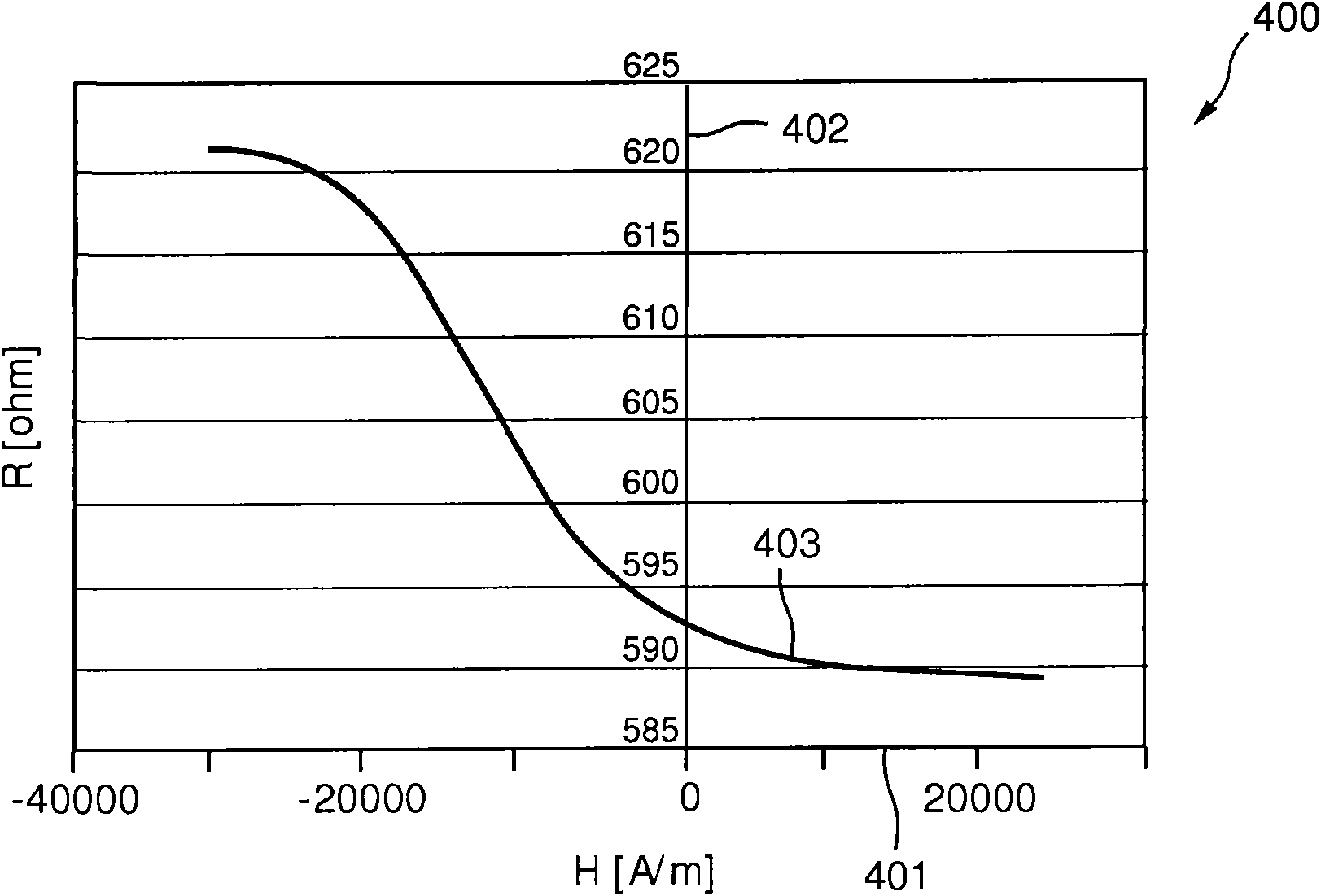
The invention relates to the calibration of the magnetic sensor device comprising magnetic excitation wires (11, 13) and a magnetic sensor element, for example a GMR sensor (12), for measuring reaction fields (B2) generated by magnetic particles (2) in reaction to an excitation field (B1) generated by the excitation wires. The magnetic sensor element (12) can be calibrated by saturating the magnetic particles (2) with a magnetic calibration field (B3). Thus the direct (crosstalk) action of the excitation field (B1) on the magnetic sensor element (12) can be determined without disturbing contributions of the magnetic particles (2).
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
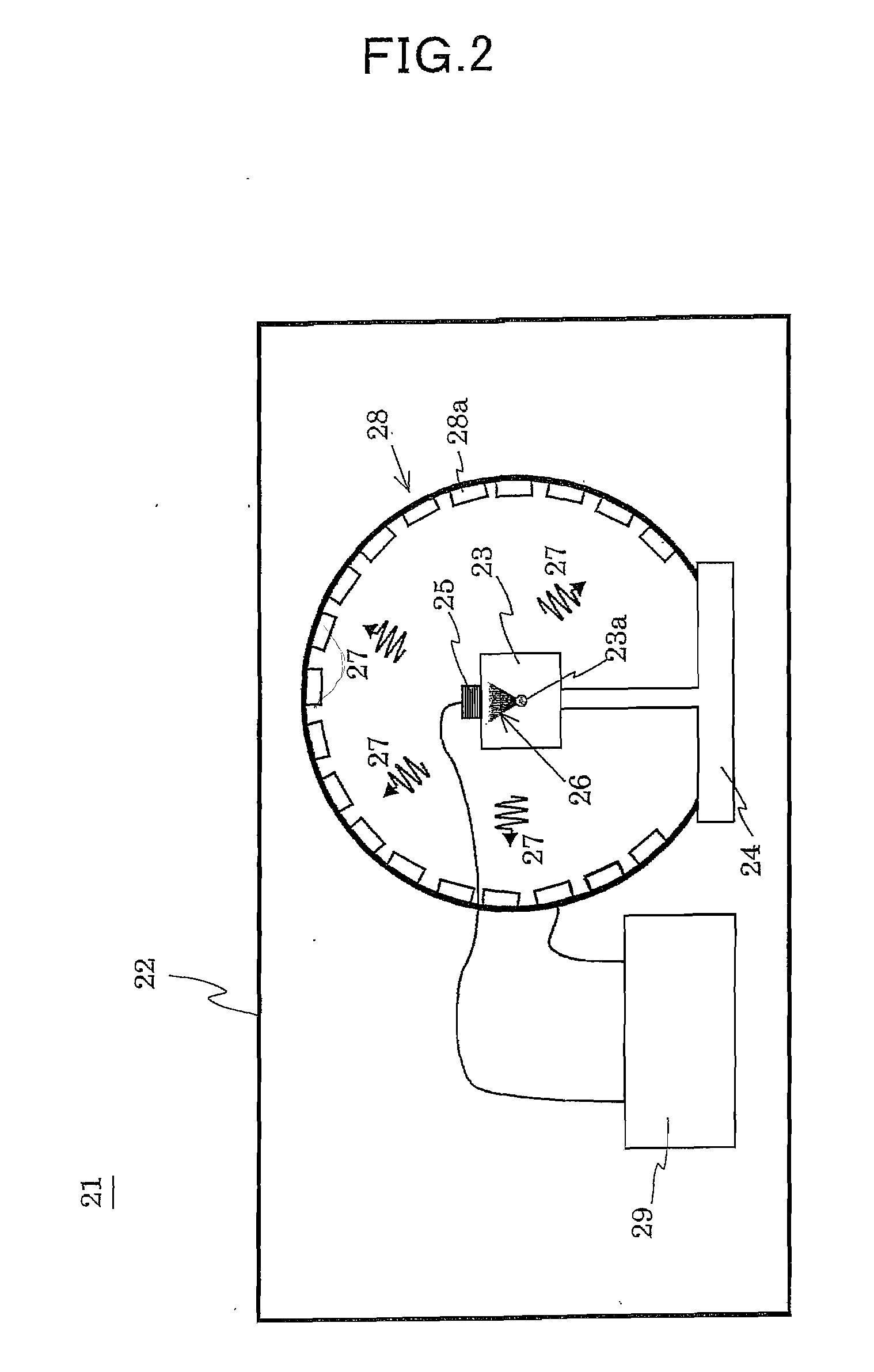
Method of and apparatus for measuring properties of an object with acoustically induced electromagnetic waves
ActiveUS20090221900A1High position resolutionUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsMagnetic field measurement using superconductive devicesElectromagnetic electron waveProperty value
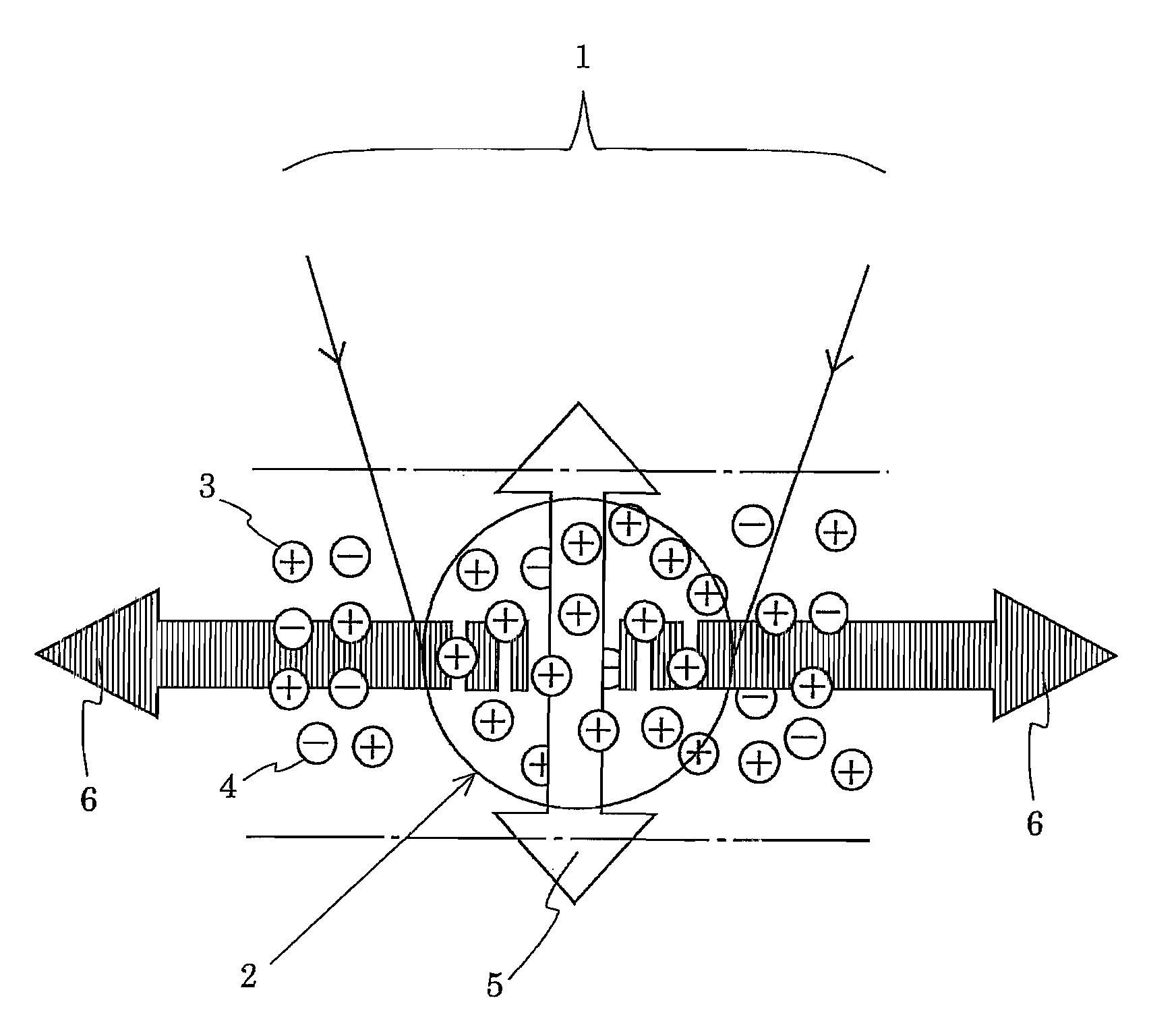
A measuring method and apparatus in which a measurable object (23) is irradiated with acoustic waves to measure a change in property value of charged particles in the object from electromagnetic waves induced thereby. A part (2) of the measurable object irradiated with an acoustic focused beam (1) is in a charge distribution state in which positive charged particles (3) are greater in number in the part (2) where electromagnetic waves induced by positive charged particles (3) are not canceled by those induced by negative charged particles (4) and where net electromagnetic waves (6) are induced. Since a change in concentration of positive charged particles (3) and / or negative charged particles (4) changes the intensity of electromagnetic waves (6), it is possible to know such a change in concentration of the charged particles from a change in intensity of electromagnetic waves (6).
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP
Magneto-optic biosensor using bio-functionalized magnetized nanoparticles
InactiveUS20090033935A1Quick changeHigh signal sensitivityScattering properties measurementsNanosensorsSmall sampleMagnetite Nanoparticles
A biosensor utilizing bio-functionalized magnetic nanoparticles is provided. An external magnetic field is applied to a suspension of magnetic nanoparticles. A linearly polarized incident light is applied to the suspension of magnetic nanoparticles. A photocurrent from polarized light scattering by bio-functionalized magnetic nanoparticles in liquid is detected. The magneto-optic sensing technique is applied to a micro-fluidic channel for rapid and sensitive detection with a small sample amount, and subsequent magnetic separation for detoxification. This technique is used for the detection of Brownian relaxation with time sweep as well as frequency sweep. The magneto-optical sensor enables rapidly detecting changes in local dynamic properties of the magnetic nanoparticles in liquids and magnetic modulation of ferromagnetic particles in liquid provides increased signal sensitivity.
Owner:UCHICAGO ARGONNE LLC
Nmr systems and methods for the rapid detection of analytes
ActiveUS20130260367A1Improve accuracyNoise minimizationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsNanomagnetismAnalyteBiochemistry
This invention features systems and methods for the detection of analytes, and their use in the treatment and diagnosis of disease.
Owner:T2 BIOSYST
Site-Specific Labeling of Proteins for Nmr Studies
Methods of producing and / or analyzing spectroscopically labeled proteins, e.g., proteins site-specifically labeled with NMR active isotopes, spin-labels, chelators for paramagnetic metals, and the like, are provided. The labeled proteins are produced in translation systems including orthogonal aminoacyl tRNA synthetase / tRNA pairs. Methods for assigning NMR resonances, e.g., methods using isotopically labeled proteins, are also provided.
Owner:THE SCRIPPS RES INST +1
Magnetic field detector
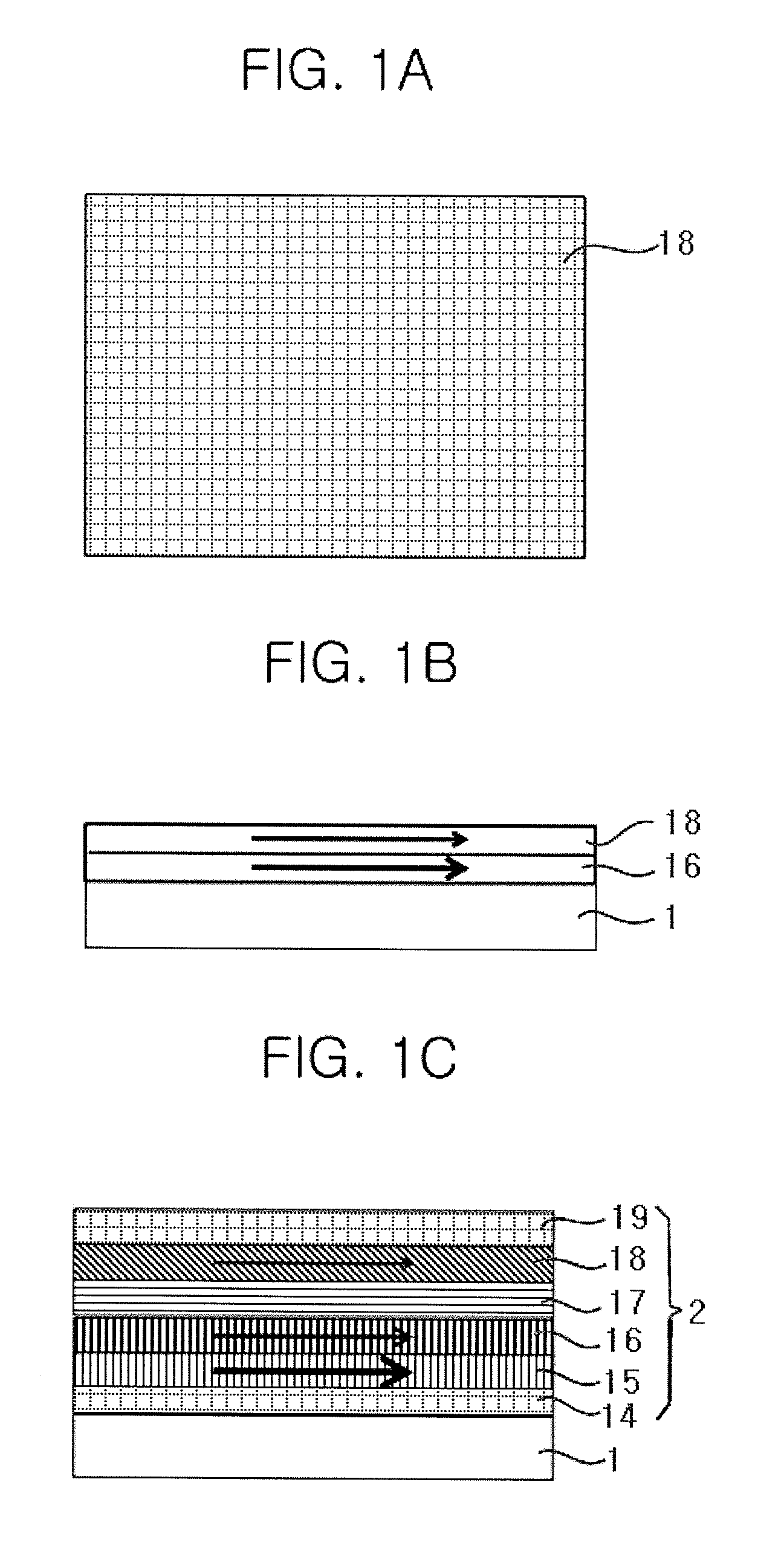
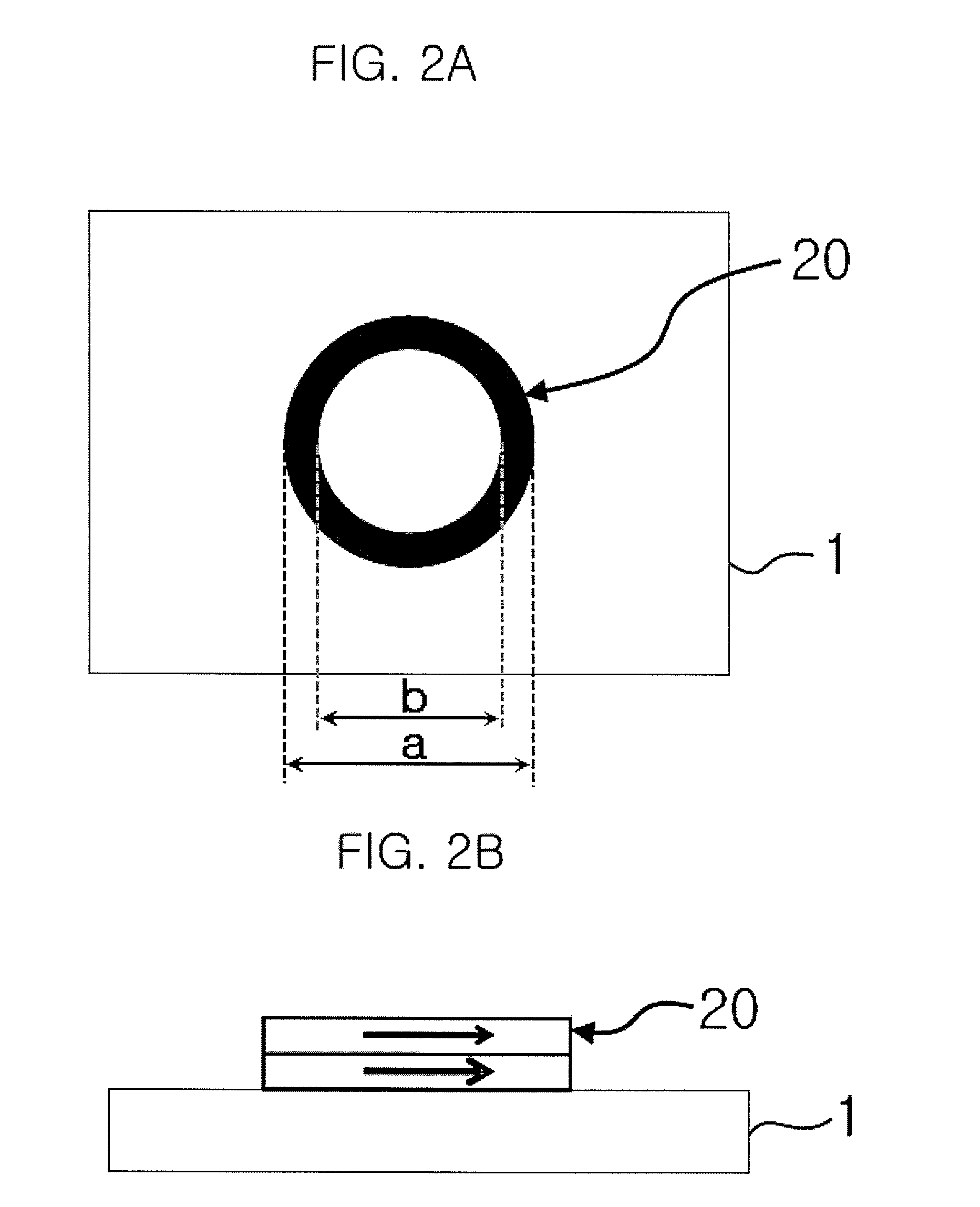
InactiveUS20090152657A1Improve magnetismSemiconductor devicesMeasurements of magnetic beads labelled moleculesHigh densityMagnetic bead
Disclosed is a magnetic field detector having various structures that can be used as a high-density magnetic biosensor. An embodiment of the invention provides a magnetic field detector using a thin film for detecting magnetic beads. The magnetic field detector includes: a substrate; a magnetoresistive element that is formed on an upper surface of the substrate in a ring shape using the thin film; electrodes that are formed on the upper surface of the substrate to be connected to the magnetoresistive element; a protective layer that is formed on the magnetoresistive element and the electrodes; and a magnetic bead limiting layer that is formed on an upper surface of the protective layer to cover the entire surface of the magnetoresistive element and portions of the electrodes.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
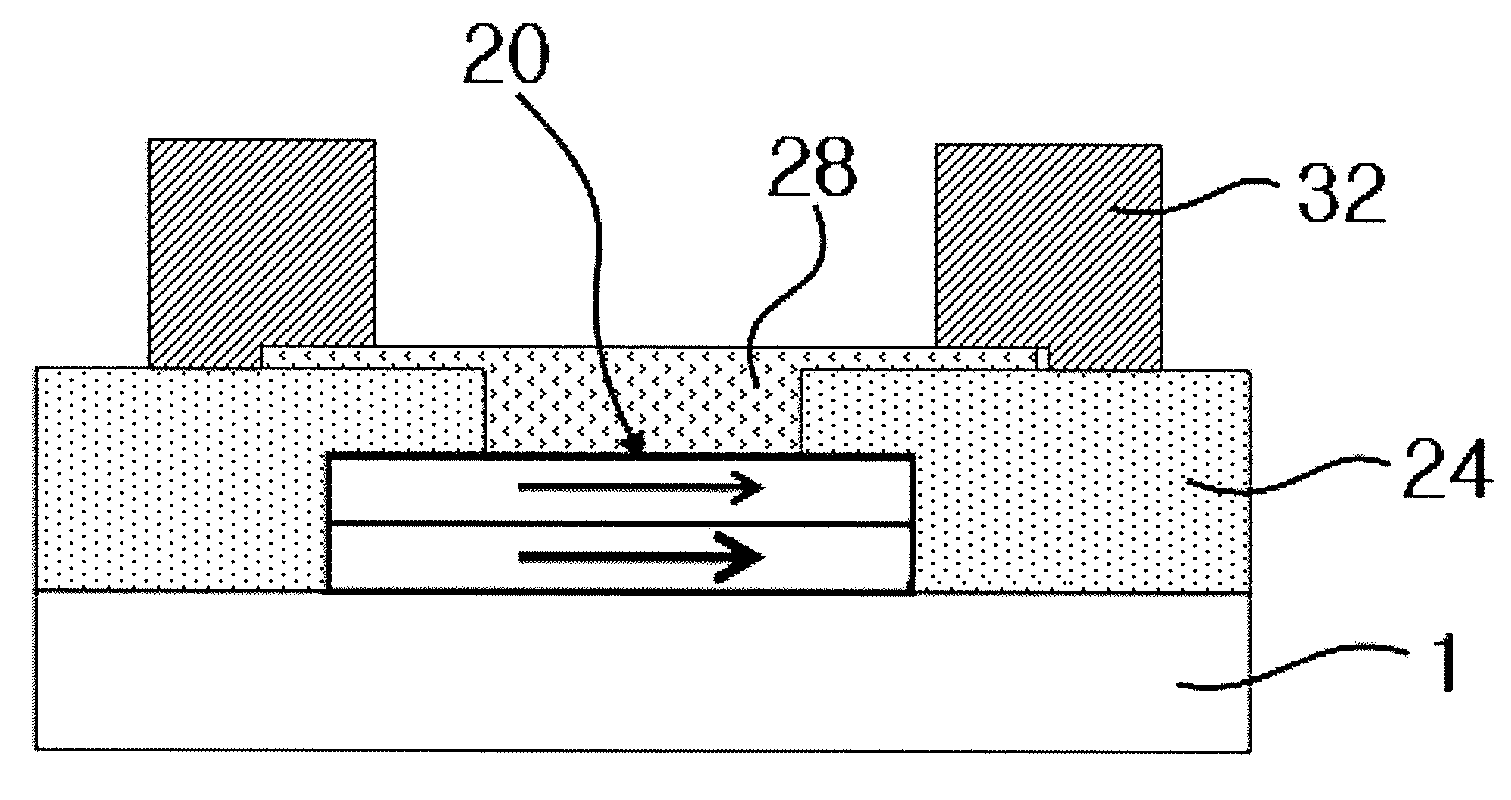
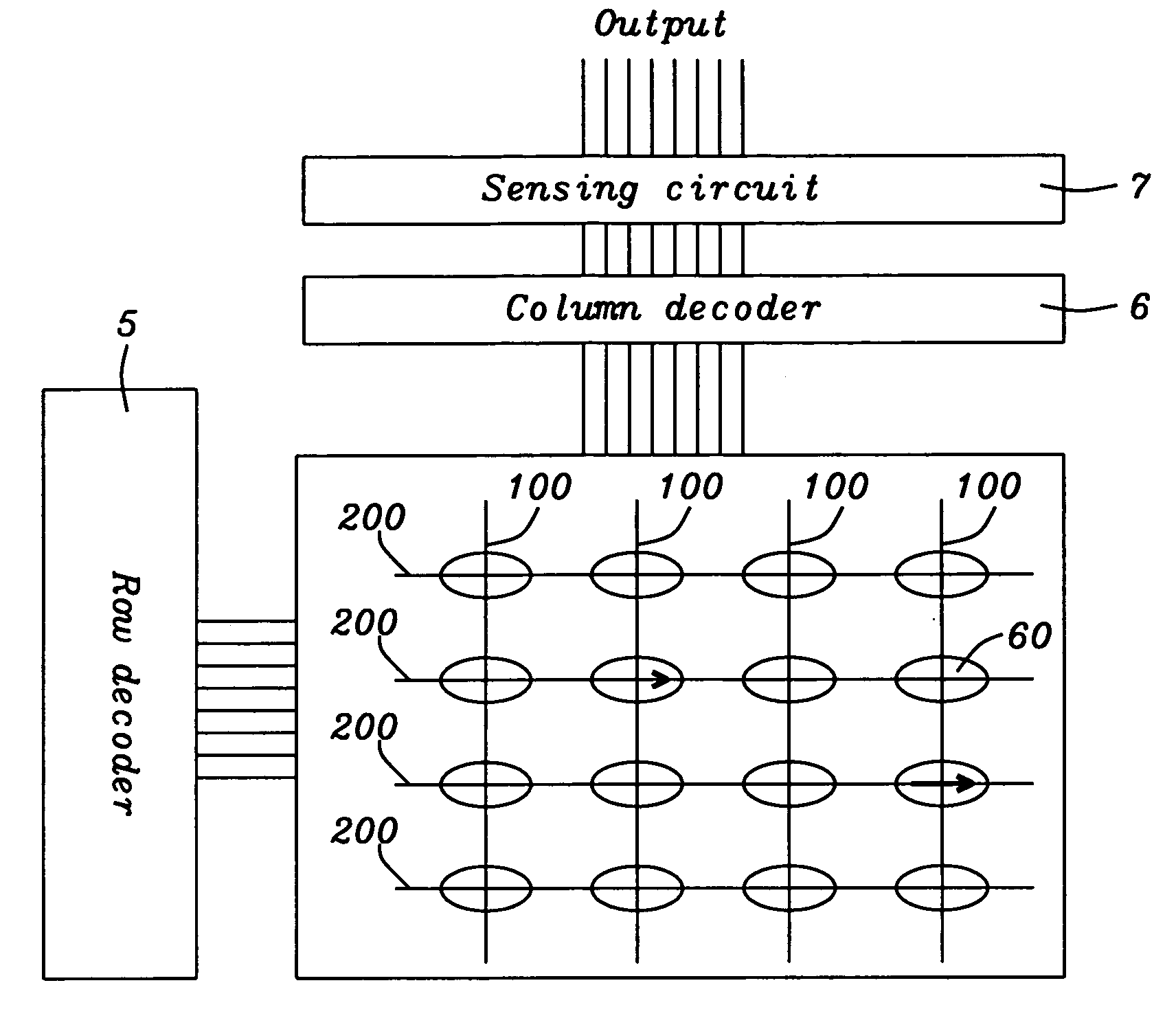
Devices using addressable magnetic tunnel junction array to detect magnetic particles
ActiveUS20090186770A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsElectrical resistance and conductanceSuperparamagnetism
A magnetic sensor for identifying small superparamagnetic particles bonded to a substrate contains a regular orthogonal array of MTJ cells formed beneath that substrate. A magnetic field imposed on the particle, perpendicular to the substrate, induces a magnetic field that has a component within the MTJ cells that is along the plane of the MTJ free layer. If that free layer has a low switching threshold, the induced field of the particle will create resistance changes in a group of MTJ cells that lie beneath it. These resistance changes will be distributed in a characteristic formation or signature that will indicate the presence of the particle. If the particle's field is insufficient to produce the free layer switching, then a biasing field can be added in the direction of the hard axis and the combination of this field and the induced field allows the presence of the particle to be determined.
Owner:HEADWAY TECH INC
Measuring agglutination parameters
ActiveUS20100033158A1Mitigate, alleviate or eliminate one or moreImprove throughputBioreactor/fermenter combinationsNanomagnetismAgglutination assayAgglutination
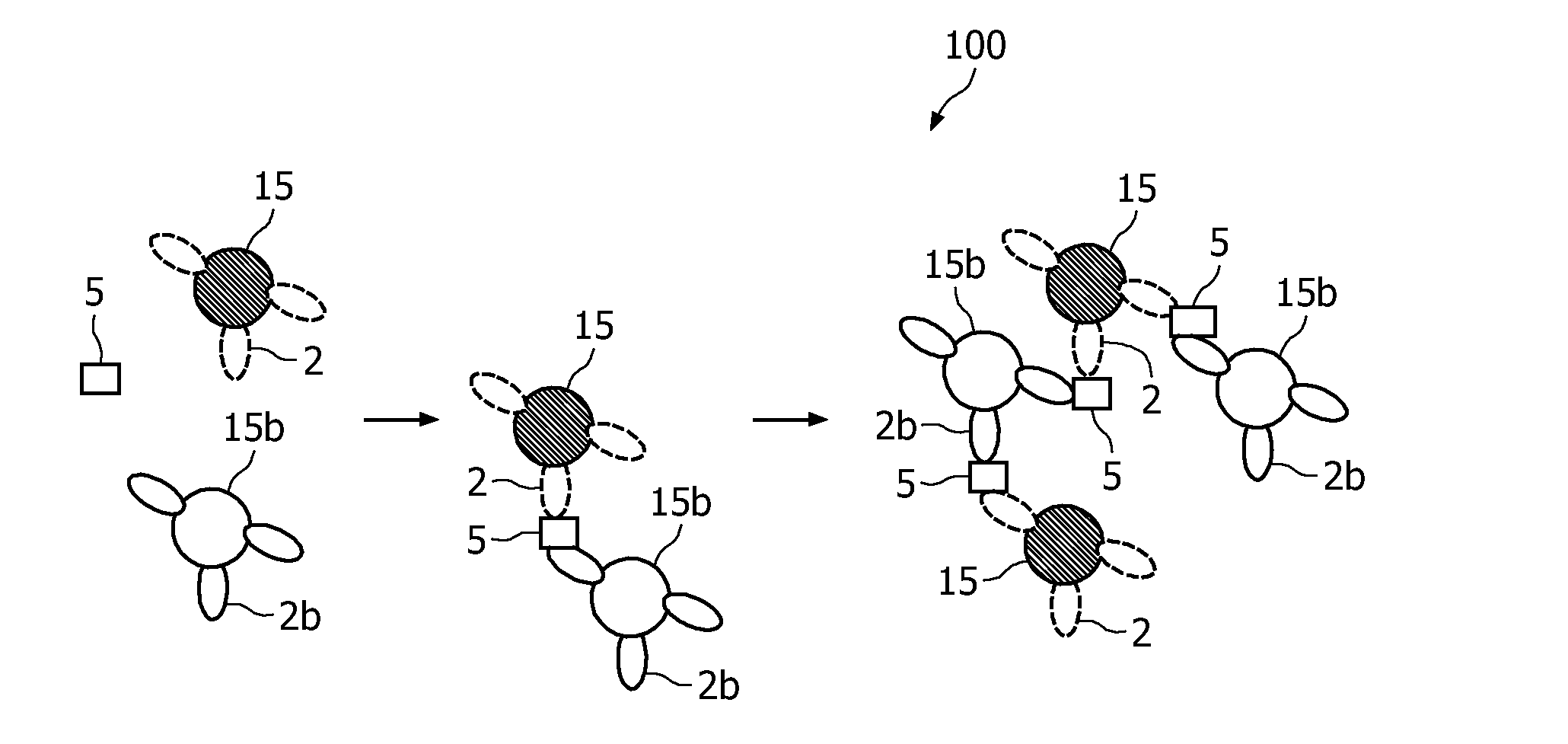
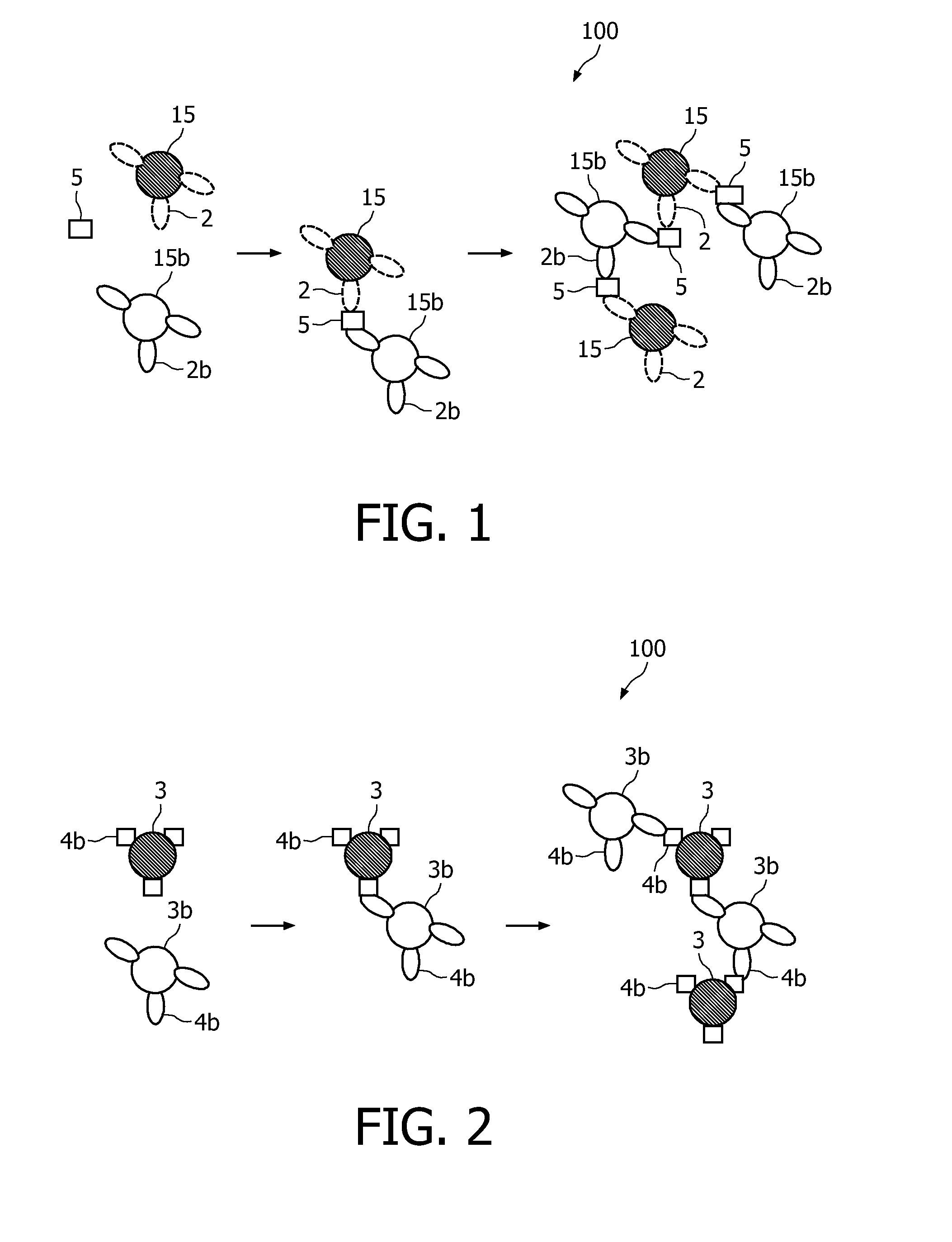
A method and system are described for measuring agglutination in a target-induced agglutination assay with one or more magnetic particles performed in a reaction chamber. After the magnetic particles (3, 15), which are capable of binding to a target (5) are provided in the assay, an agglutination process resulting in agglutinated particles (100) comprising at least one magnetic particle is performed. The method then further comprises applying an alternating current magnetic field (HAC) to the assay and—measuring an effect of the HAC on the one or more magnetic particles (3,15) unattached to any surface. The measured effect is indicative of one or more agglutination parameters.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Site-specific labeling of proteins for NMR studies
Methods of producing and / or analyzing spectroscopically labeled proteins, e.g., proteins site-specifically labeled with NMR active isotopes, spin-labels, chelators for paramagnetic metals, and the like, are provided. The labeled proteins are produced in translation systems including orthogonal aminoacyl tRNA synthetase / tRNA pairs. Methods for assigning NMR resonances, e.g., methods using isotopically labeled proteins, are also provided.
Owner:THE SCRIPPS RES INST & IRM
Magnetic sensor, production method of the same, and target substance detecting apparatus and biosensor kit using the same
InactiveUS20070237673A1Solve the real problemNanomagnetismAnalysis using chemical indicatorsBiosensorAmount of substance
Owner:CANON KK
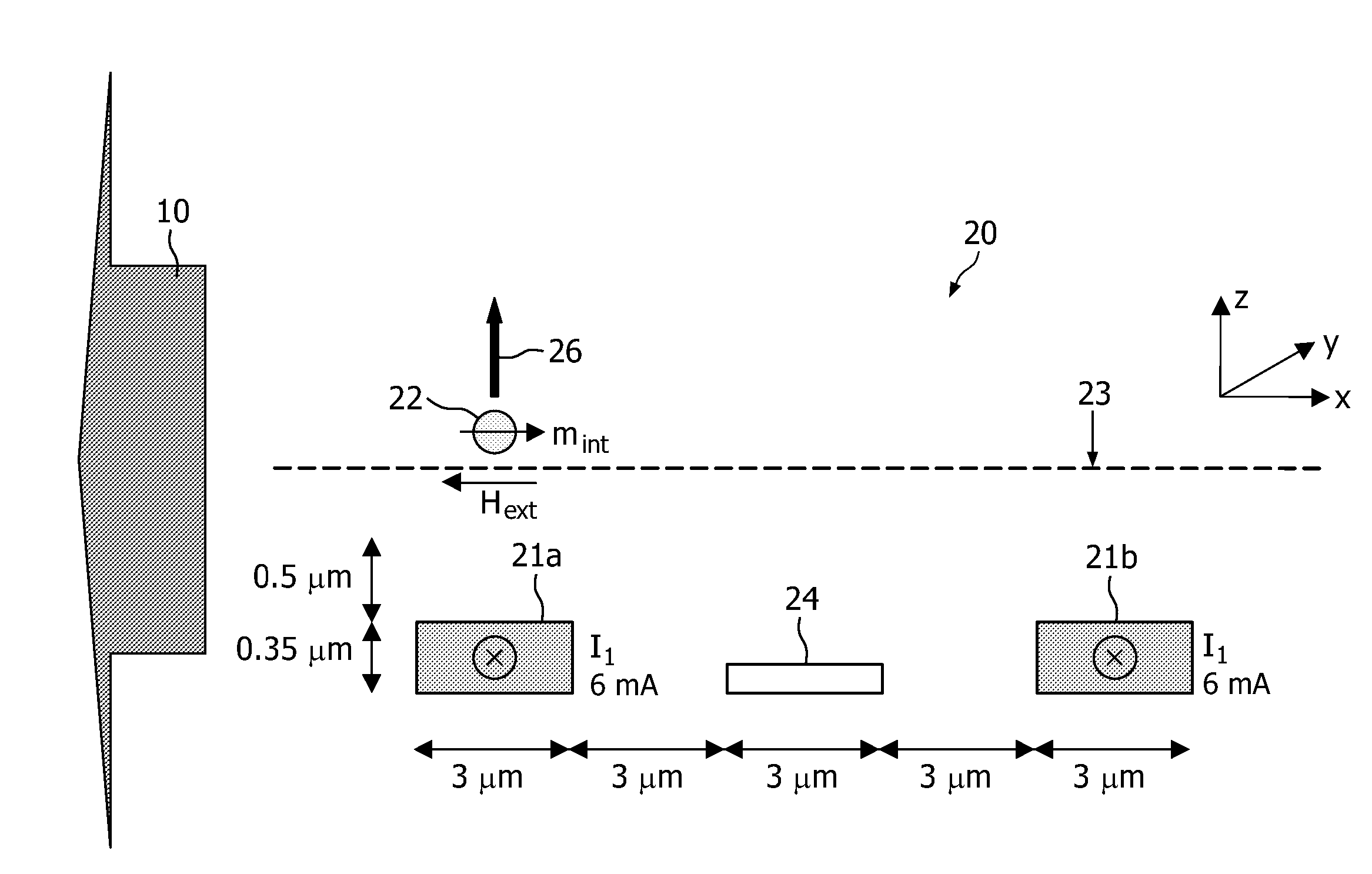
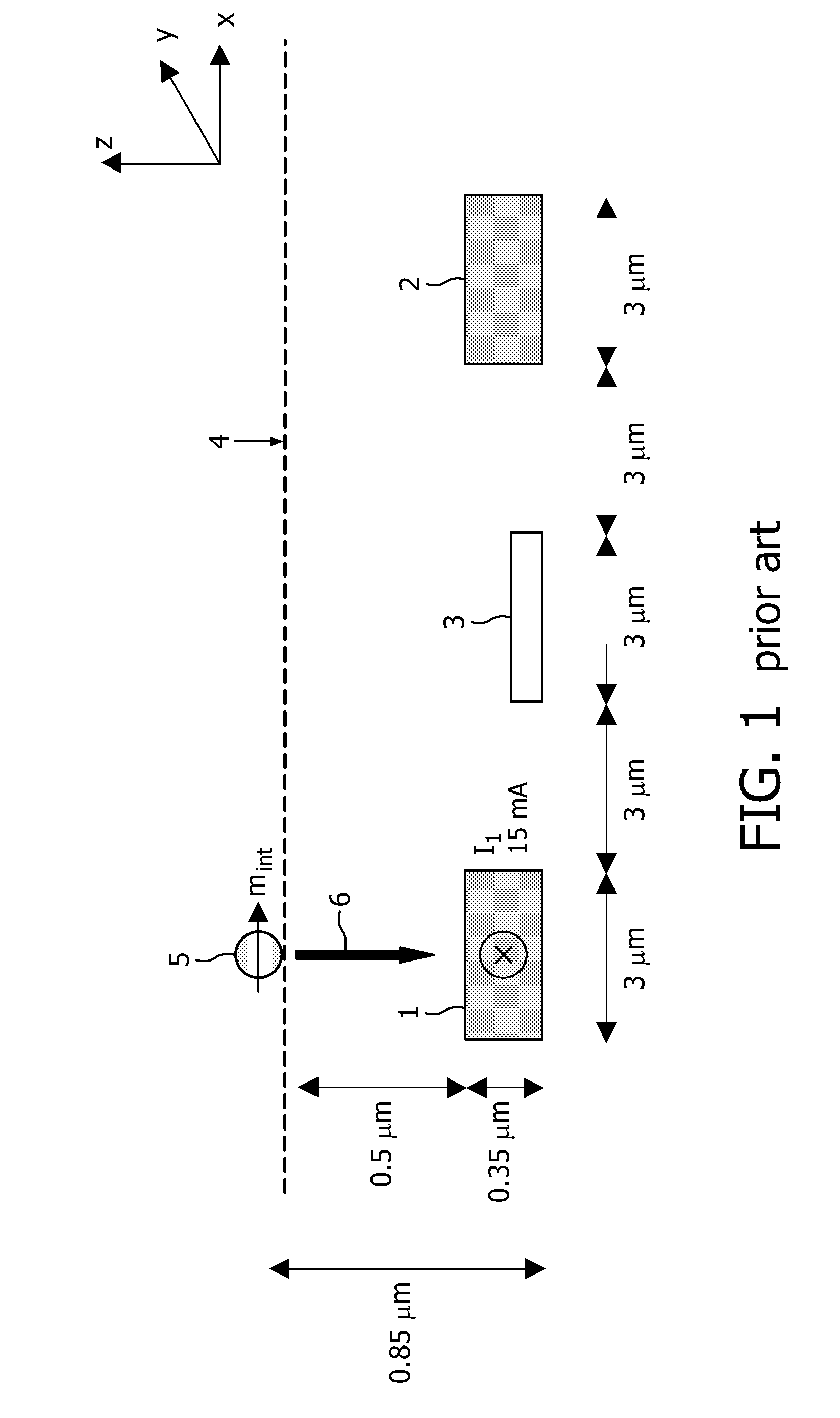
Attraction and repulsion of magnetic of magnetizable objects to and from a sensor surface
InactiveUS20090251136A1Easy to optimizeSimple methodNanomagnetismRelaysMagnetic fieldNuclear magnetic resonance
The present invention provides a magnetic sensor device a first magnetic field generating means (21a, 21b) for attracting magnetic or magnetizable objects (22), e.g. magnetic particles, to a sensor surface (23) and a second magnetic field generating means (25) for, in combination with the first magnetic field, repelling magnetic or magnetizable objects (22), e.g. magnetic particles, from the sensor surface (23). The magnetic fields generated by the first and second magnetic field generating means have substantially anti-parallel directions. The present invention furthermore provides a method for attracting and repelling magnetic or magnetizable objects (22), e.g. magnetic particles, to and from a sensor surface (23).
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Magnetic microstructures for magnetic resonance imaging
ActiveUS20110144478A1NMR/MRI constrast preparationsDiagnostic recording/measuringResonanceMagnetic field
A magnetic resonance contrast agent has a medium, and a contrast structure dispersed in the medium. The contrast structure comprises a magnetic material arranged to create a local region of a local magnetic field such that nuclear magnetic moments of a material when arranged within said local region precess at a characteristic Larmor frequency about a total magnetic field in the local region while in use, the characteristic Larmor frequency being identifiable with the contrast structure, and the total magnetic field in the local region being a substantially spatially uniform magnetic field.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE COMMERCE +1
Magnetic Material Sensor and Detection Method Employing this Sensor, and Target Material Detection Sensor and Target Material Detection Kit
InactiveUS20080284419A1Production compactVoltage changeNanomagnetismMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsMagnetizationElectrical current
The present invention provides an appropriately produced magnetic material sensor having a small size.The magnetic material sensor of this invention includes: a magnetoresistive effect film, formed using magnetic films; a current source, for supplying to the magnetoresistive effect film a current having a magnitude and a direction that can change the magnetization directions of the magnetic films; and a detector, for detecting the resistance of the magnetoresistive effect film.
Owner:CANON KK
A magnetic sensor device for and a method of sensing magnetic particles
InactiveCN101611316AOvercome or reduce gain variationEffective powerNanomagnetismMagnetic field measurement using galvano-magnetic devicesMagnetic fieldNuclear magnetic resonance
A magnetic sensor device (1000) for sensing magnetic particles (15), the magnetic sensor device (1000) comprising a first magnetic field generator unit (12) excitable for generating a first magnetic field, a sensing unit (11) adapted for sensing a signal indicative of the presence of the magnetic particles (15) in the first magnetic field, a second magnetic field generator unit (1001) adapted for generating a second magnetic field affecting the sensing unit (11), and a processing circuitry (1002) adapted for processing the signal to form a digitized signal and adapted for feeding back the processed signal to the second magnetic field generator unit (1001).
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Magnetic sensor device for and a method of sensing magnetic particles
InactiveUS20090237844A1Improve sensor performanceReduce resistanceBiological particle analysisRecord information storageExcitation signalSignal source
A magnetic sensor device (300) for sensing magnetic particles (15), the magnetic sensor device (300) comprising a magnetic field generator unit (12) adapted for generating a magnetic field, an excitation signal source (302) adapted for supplying the magnetic field generator unit (12) with a static electric excitation signal, an excitation switch unit (303) adapted for switching between different modes of electrically coupling the excitation signal source (302) to the magnetic field generator unit (12), and a sensing unit (11) adapted for sensing a signal indicative of the presence of the magnetic particles (15) in the generated magnetic field.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
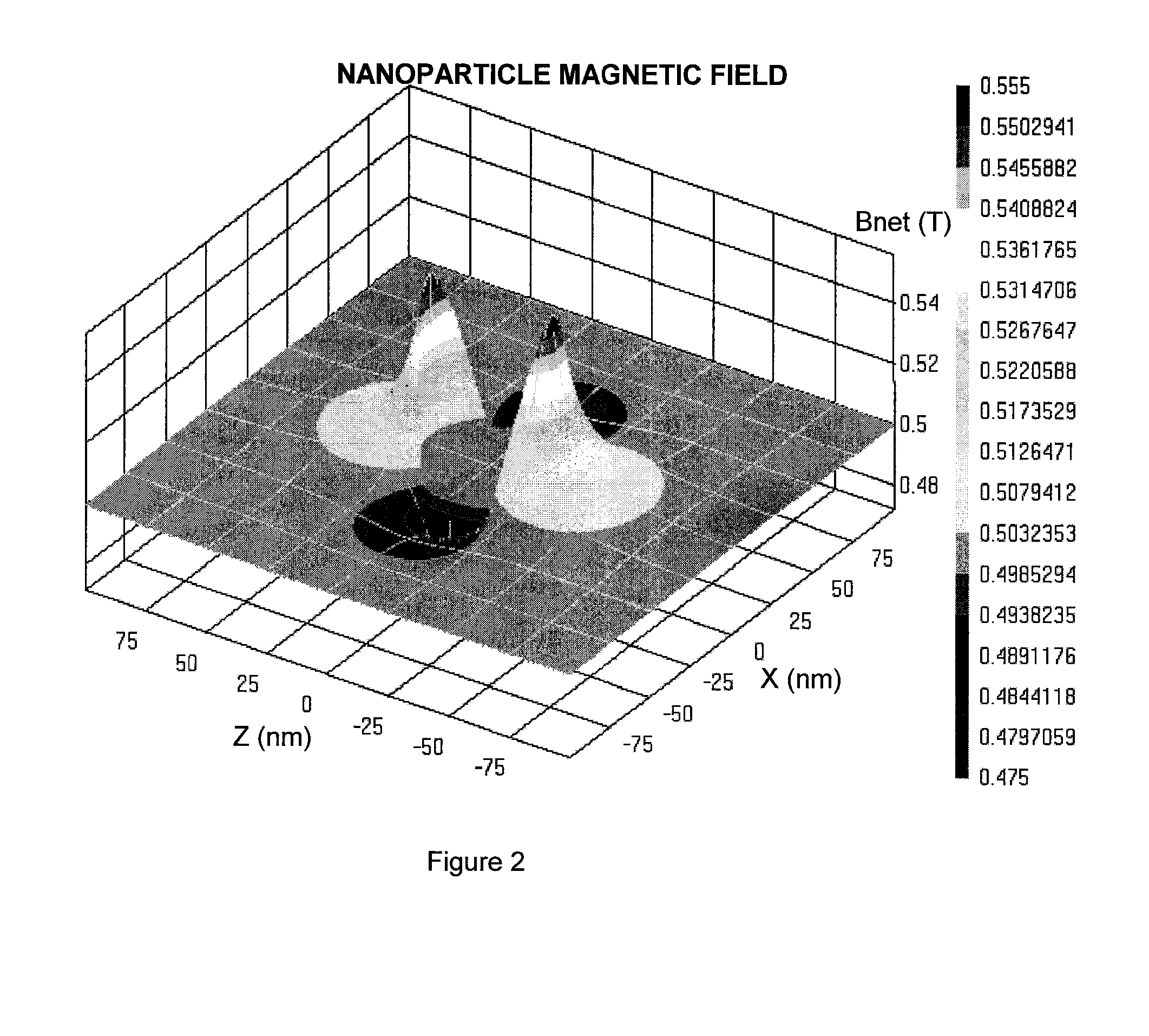
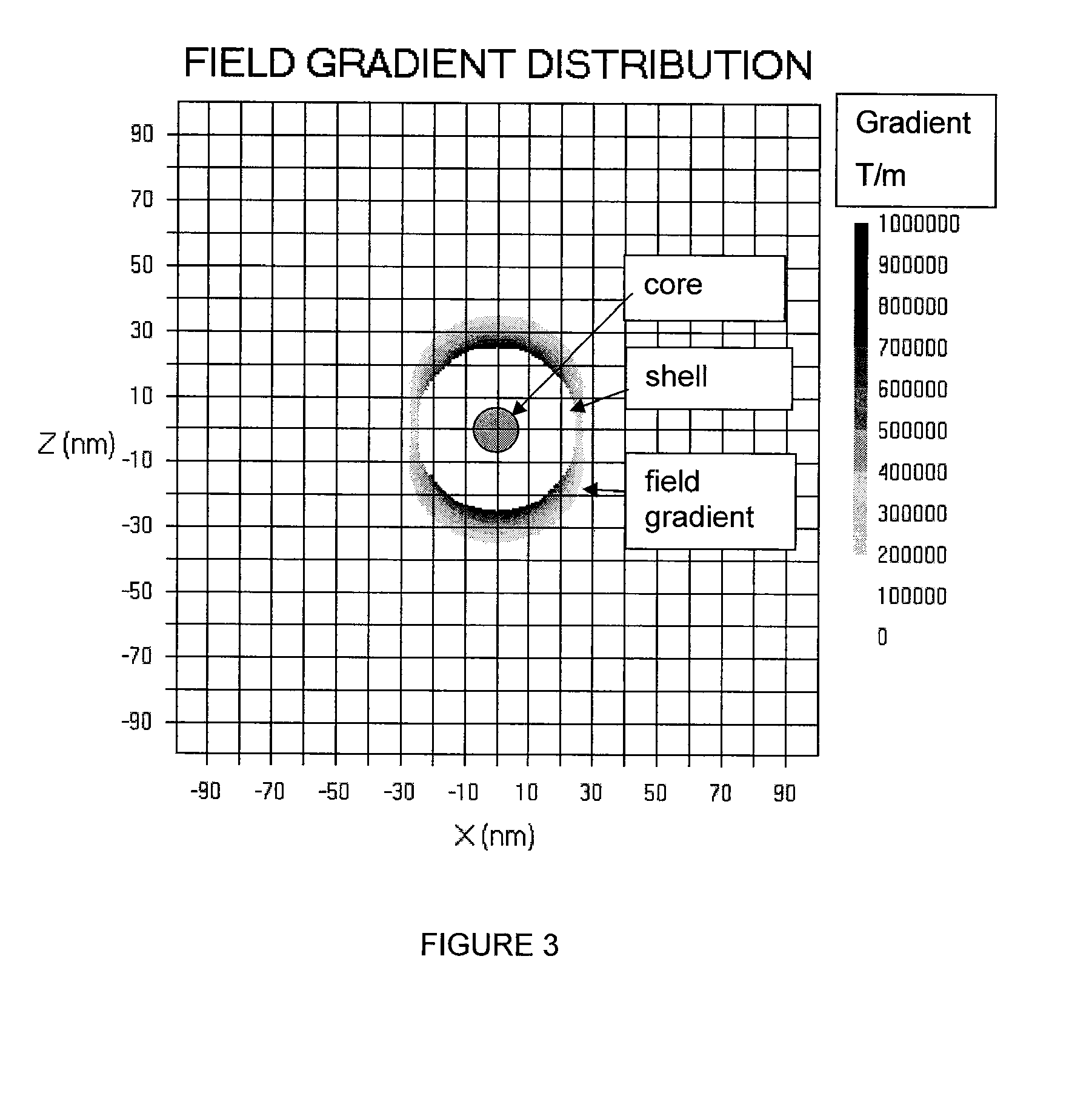
Detection, measurement, and imaging of cells such as cancer and other biologic substances using targeted nanoparticles and magnetic properties thereof
ActiveUS20120035458A1Useful propertyDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsSubstance useParamagnetic nanoparticles
The present invention can provide a method of determining the presence, location, quantity, or a combination thereof, of a biological substance, comprising: (a) exposing a sample to a plurality of targeted nanoparticles, where each targeted nanoparticle comprises a paramagnetic nanoparticle conjugated with one or more targeting agents that preferentially bind with the biological substance, under conditions that facilitate binding of the targeting agent to at least one of the one or more biological substances; (b) subjecting the sample to a magnetic field of sufficient strength to induce magnetization of the nanoparticles; (c) measuring a magnetic field of the sample after decreasing the magnetic field applied in step b below a threshold; (d) determining the presence, location, quantity, or a combination thereof, of the one or more biologic substances from the magnetic field measured in step (c).
Owner:IMAGION BIOSYST INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com