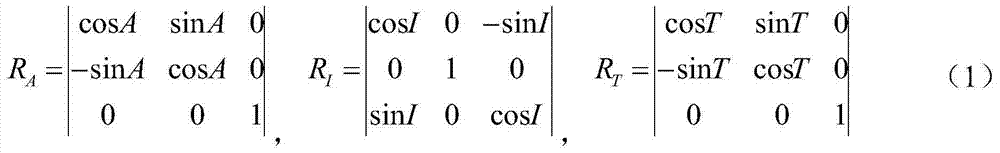Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
121 results about "Orthogonal array" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In mathematics, an orthogonal array is a "table" (array) whose entries come from a fixed finite set of symbols (typically, {1,2,...,n}), arranged in such a way that there is an integer t so that for every selection of t columns of the table, all ordered t-tuples of the symbols, formed by taking the entries in each row restricted to these columns, appear the same number of times. The number t is called the strength of the orthogonal array. Here is a simple example of an orthogonal array with symbol set {1,2} and strength 2...
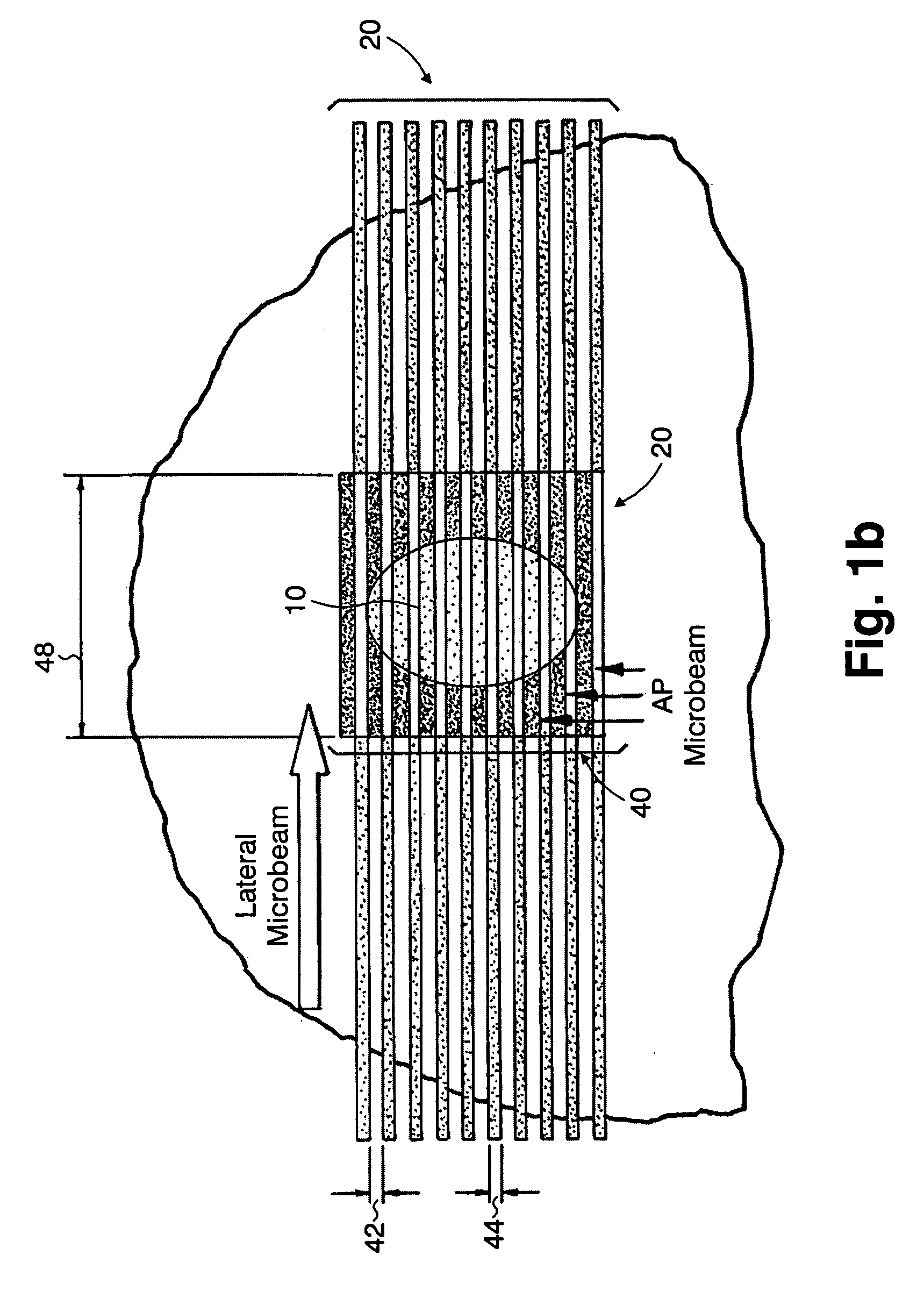
Methods for implementing microbeam radiation therapy
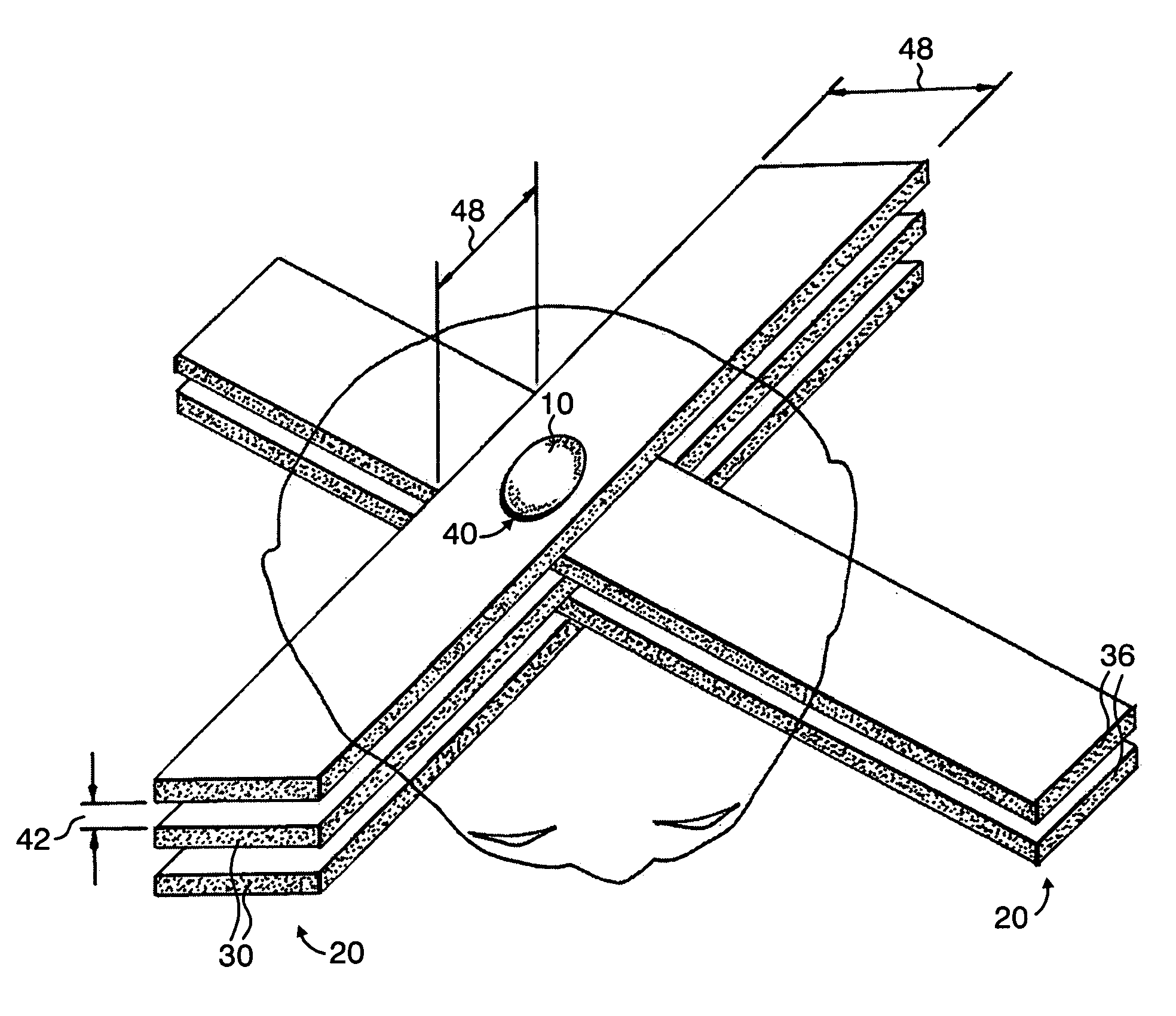
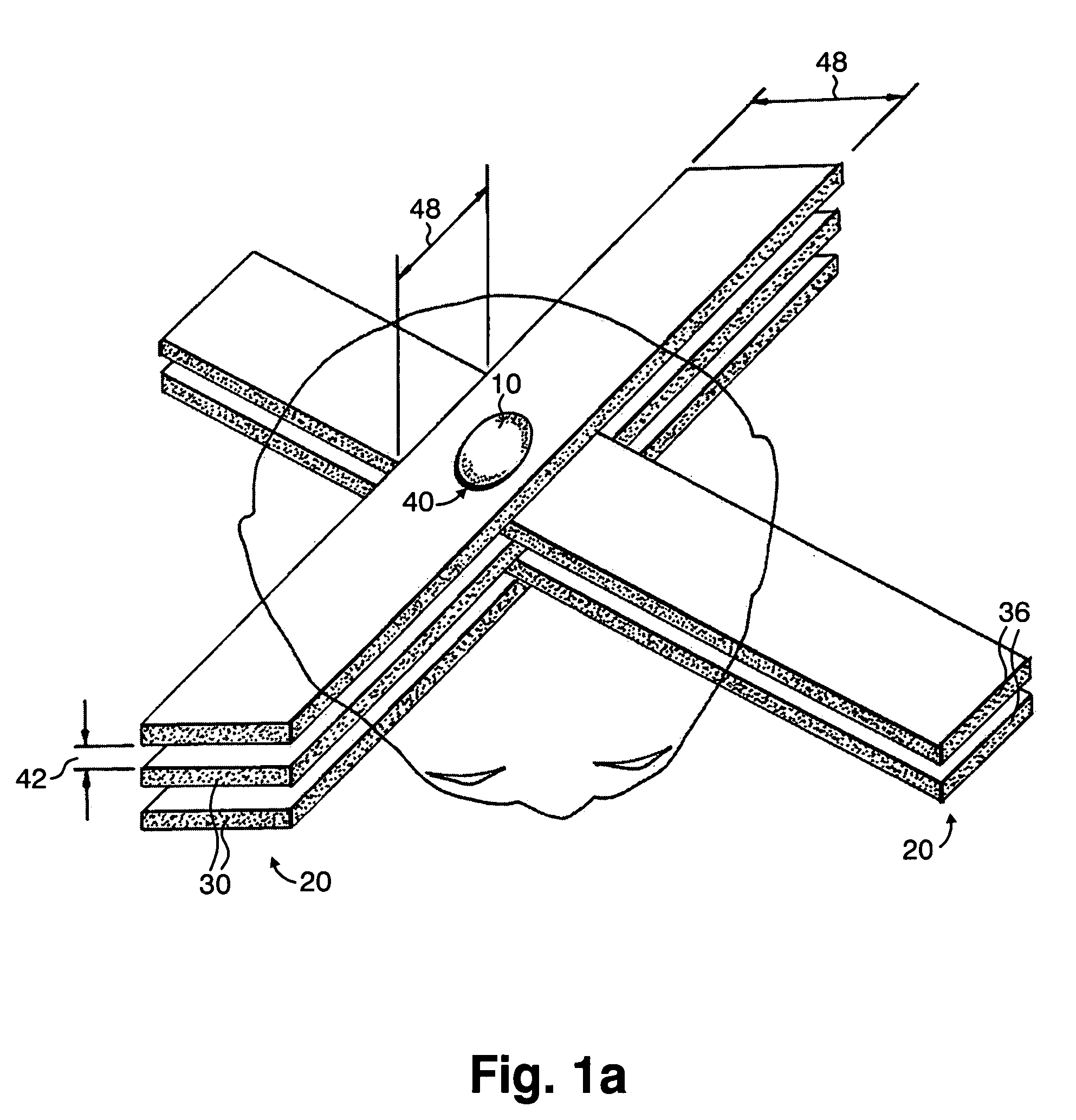
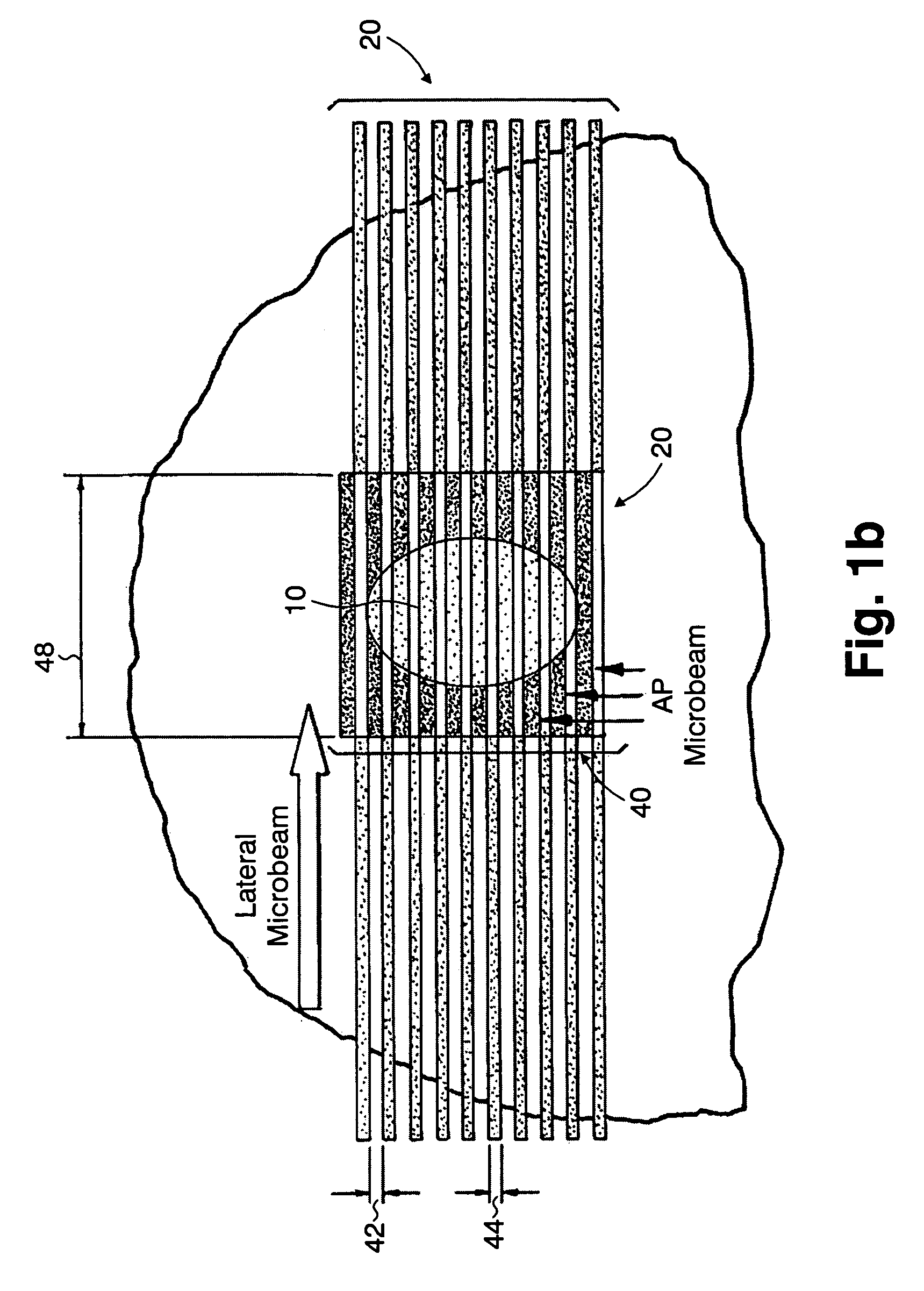
InactiveUS7194063B2Reduce harmEasily damagedIrradiation devicesX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyLight beamGadolinium
A method of performing radiation therapy includes delivering a therapeutic dose such as X-ray only to a target (e.g., tumor) with continuous broad beam (or in-effect continuous) using arrays of parallel planes of radiation (microbeams / microplanar beams). Microbeams spare normal tissues, and when interlaced at a tumor, form a broad-beam for tumor ablation. Bidirectional interlaced microbeam radiation therapy (BIMRT) uses two orthogonal arrays with inter-beam spacing equal to beam thickness. Multidirectional interlaced MRT (MIMRT) includes irradiations of arrays from several angles, which interleave at the target. Contrast agents, such as tungsten and gold, are administered to preferentially increase the target dose relative to the dose in normal tissue. Lighter elements, such as iodine and gadolinium, are used as scattering agents in conjunction with non-interleaving geometries of array(s) (e.g., unidirectional or cross-fired (intersecting) to generate a broad beam effect only within the target by preferentially increasing the valley dose within the tumor.
Owner:BROOKHAVEN SCI ASSOCS
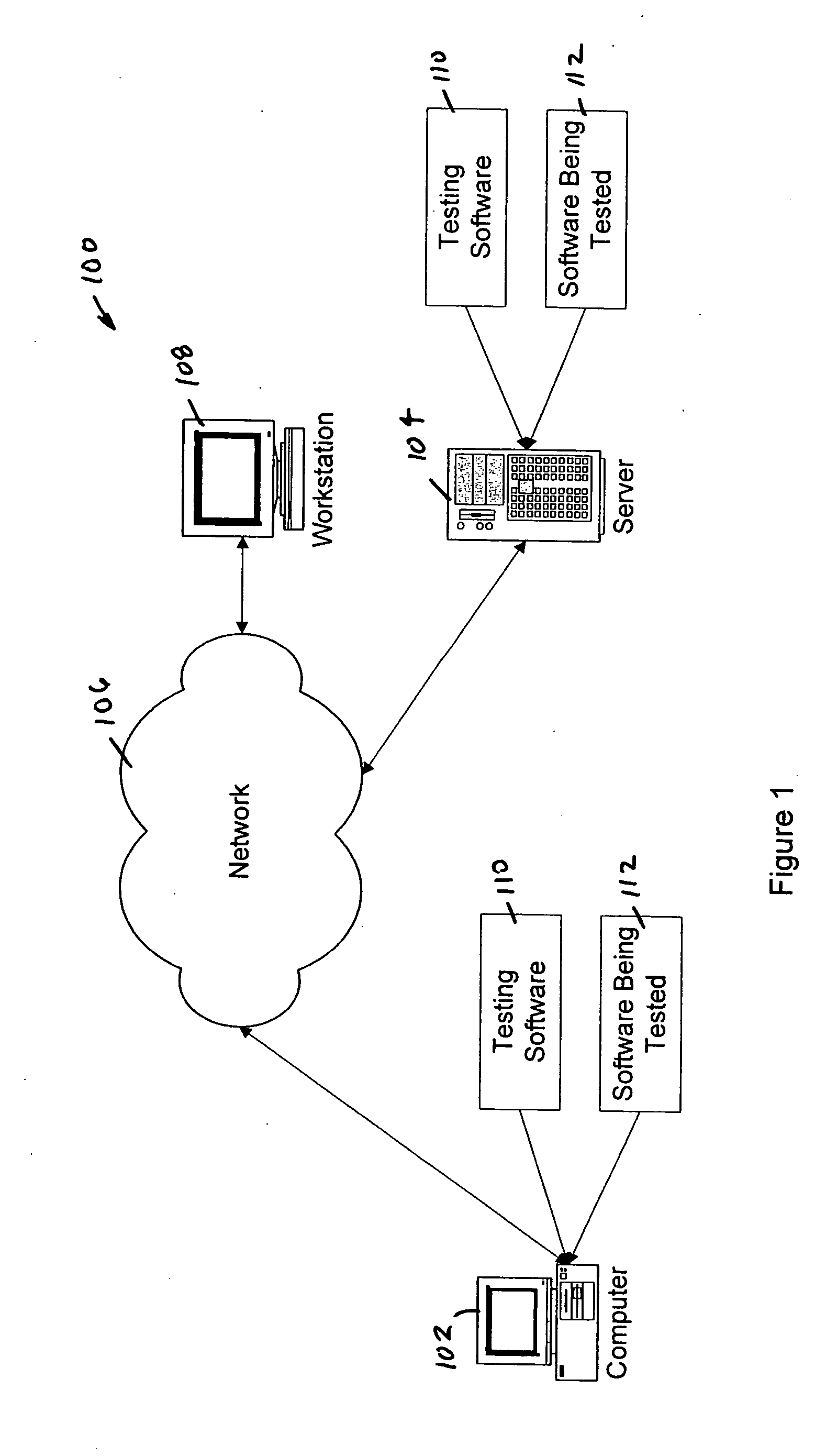
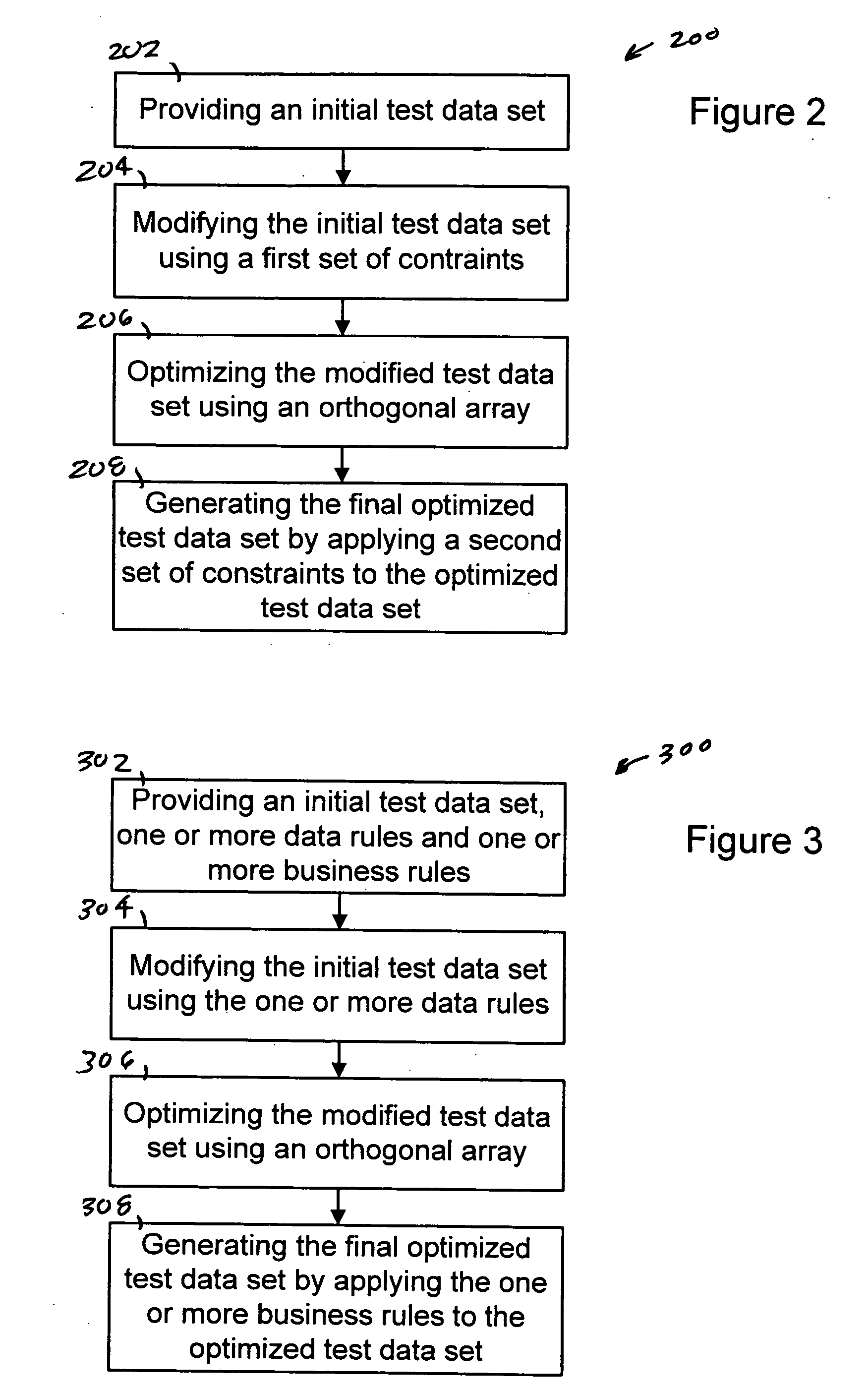
System and method for generating optimized test cases using constraints based upon system requirements
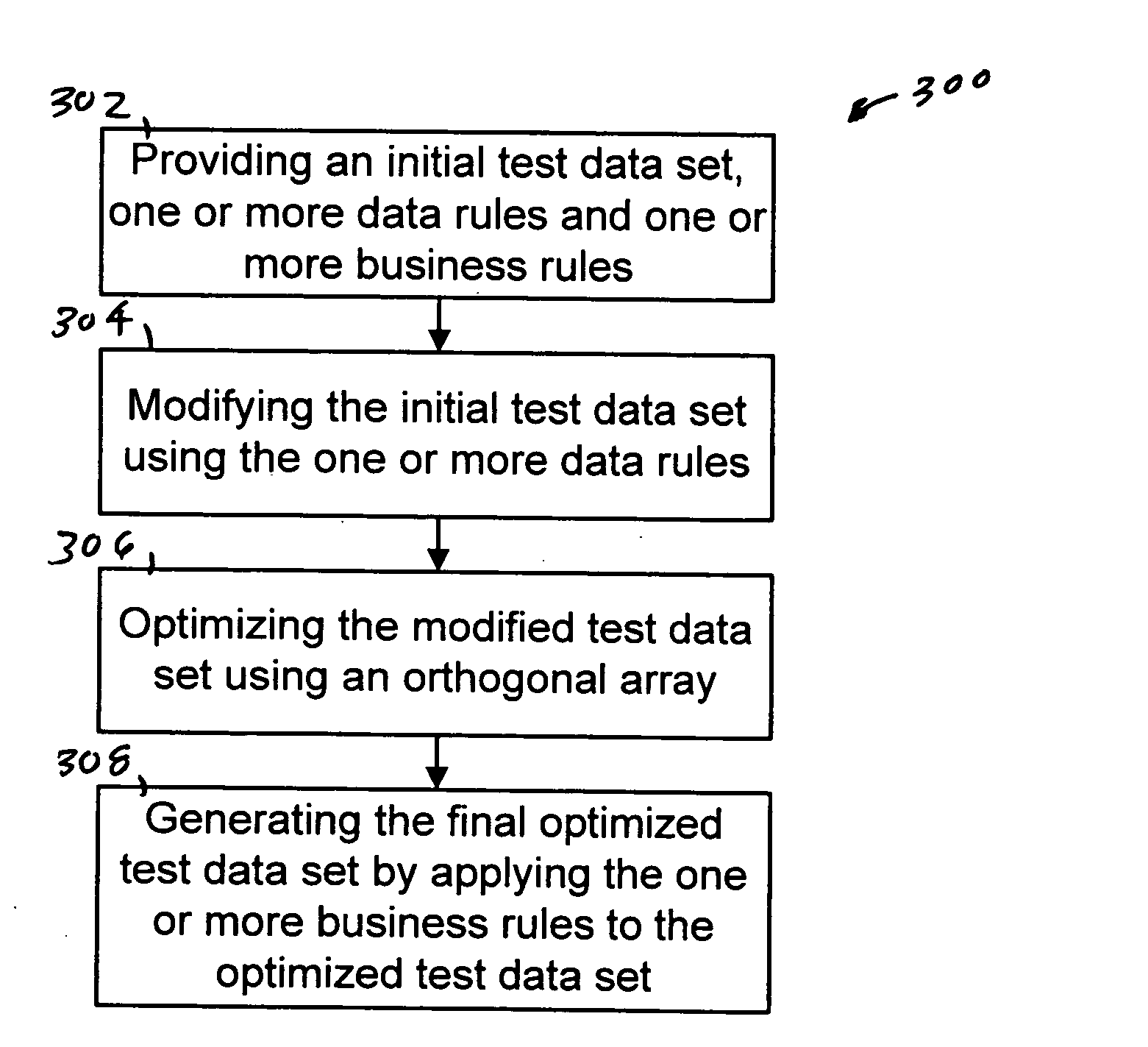
InactiveUS20060010426A1Error detection/correctionSpecific program execution arrangementsData setSystem requirements
The present invention provides a system, method and computer program for generating a final optimized test data set. An initial test data set, one or more data rules and one or more business rules are provided. The initial test data set is then modified using the one or more data rules. The modified test data set is optimized using an orthogonal array. The final optimized test data set is then generated by applying the one or more business rules to the optimized test data. The present invention can be implemented using a computer program embodied on a computer readable medium wherein each step is executed by one or more code segments. The system used to implement the present invention may include a data storage device, a processor and one or more input / output devices.
Owner:SMARTWARE TECH
Methods for implementing microbeam radiation therapy
InactiveUS20060176997A1Enhance in-beam absorptionEnhance therapeutic doseX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyIrradiation devicesAbnormal tissue growthOrthogonal array
A method of performing radiation therapy includes delivering a therapeutic dose such as X-ray only to a target (e.g., tumor) with continuous broad beam (or in-effect continuous) using arrays of parallel planes of radiation (microbeams / microplanar beams). Microbeams spare normal tissues, and when interlaced at a tumor, form a broad-beam for tumor ablation. Bidirectional interlaced microbeam radiation therapy (BIMRT) uses two orthogonal arrays with inter-beam spacing equal to beam thickness. Multidirectional interlaced MRT (MIMRT) includes irradiations of arrays from several angles, which interleave at the target. Contrast agents, such as tungsten and gold, are administered to preferentially increase the target dose relative to the dose in normal tissue. Lighter elements, such as iodine and gadolinium, are used as scattering agents in conjunction with non-interleaving geometries of array(s) (e.g., unidirectional or cross-fired (intersecting) to generate a broad beam effect only within the target by preferentially increasing the valley dose within the tumor.
Owner:BROOKHAVEN SCI ASSOCS
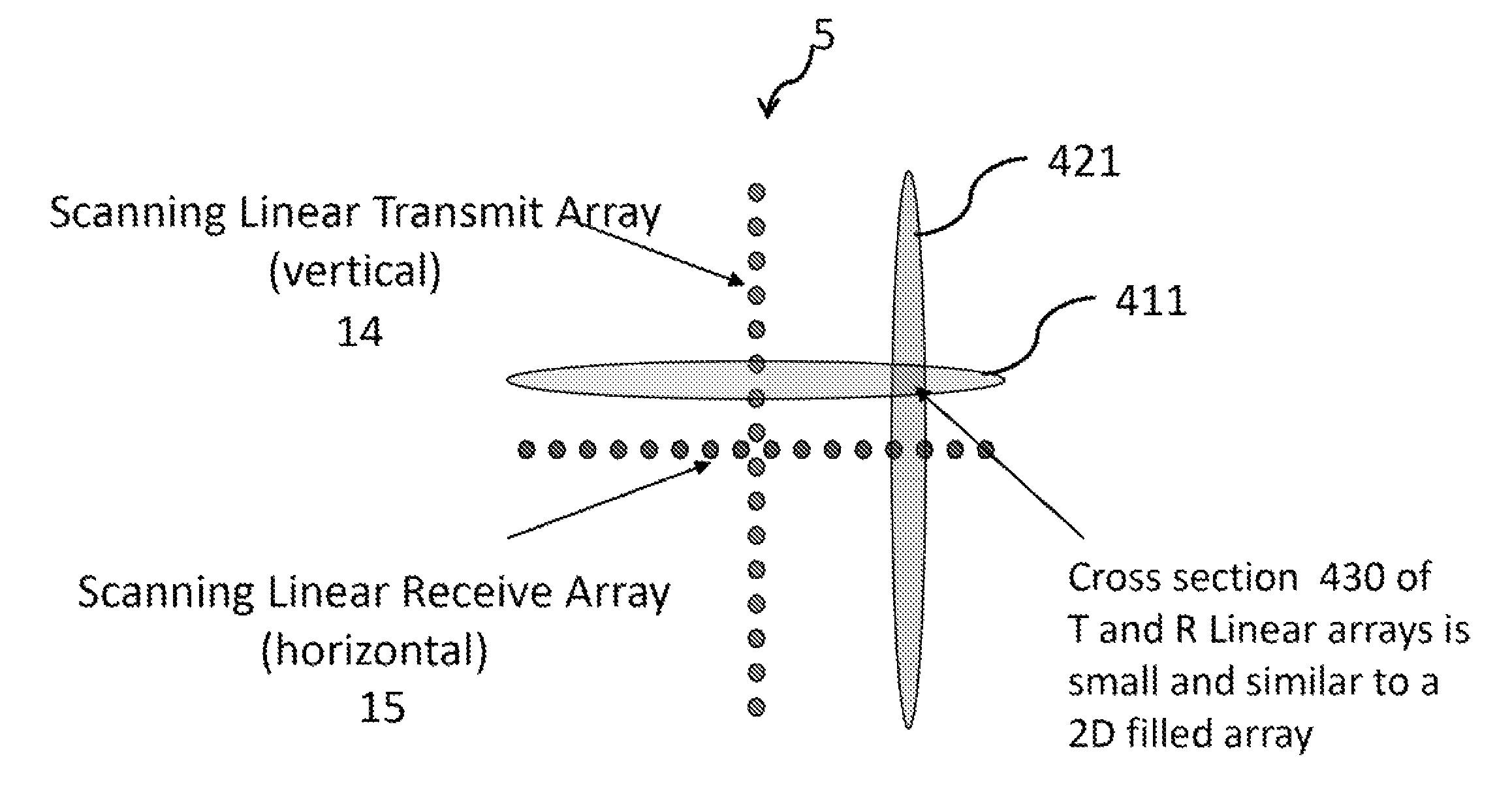
Orthogonal linear transmit receive array radar
ActiveUS8248298B2High resolution imageIndividually energised antenna arraysPolarised antenna unit combinationsRadar systemsSide lobe
A radar system having orthogonal antenna apertures is disclosed. The invention further relates to an antenna system wherein the orthogonal apertures comprise at least one transmit aperture and at least one receive aperture. The cross-product of the transmit and receive apertures provides a narrow spot beam and resulting high resolution image. An embodiment of the invention discloses orthogonal linear arrays, comprising at least one electronically scanned transmit linear array and at least one electronically scanned receive linear array. The design of this orthogonal linear array system produces comparable performance, clutter and sidelobe structure at a fraction of the cost of conventional 2D filled array antenna systems.
Owner:FIRST RF CORP
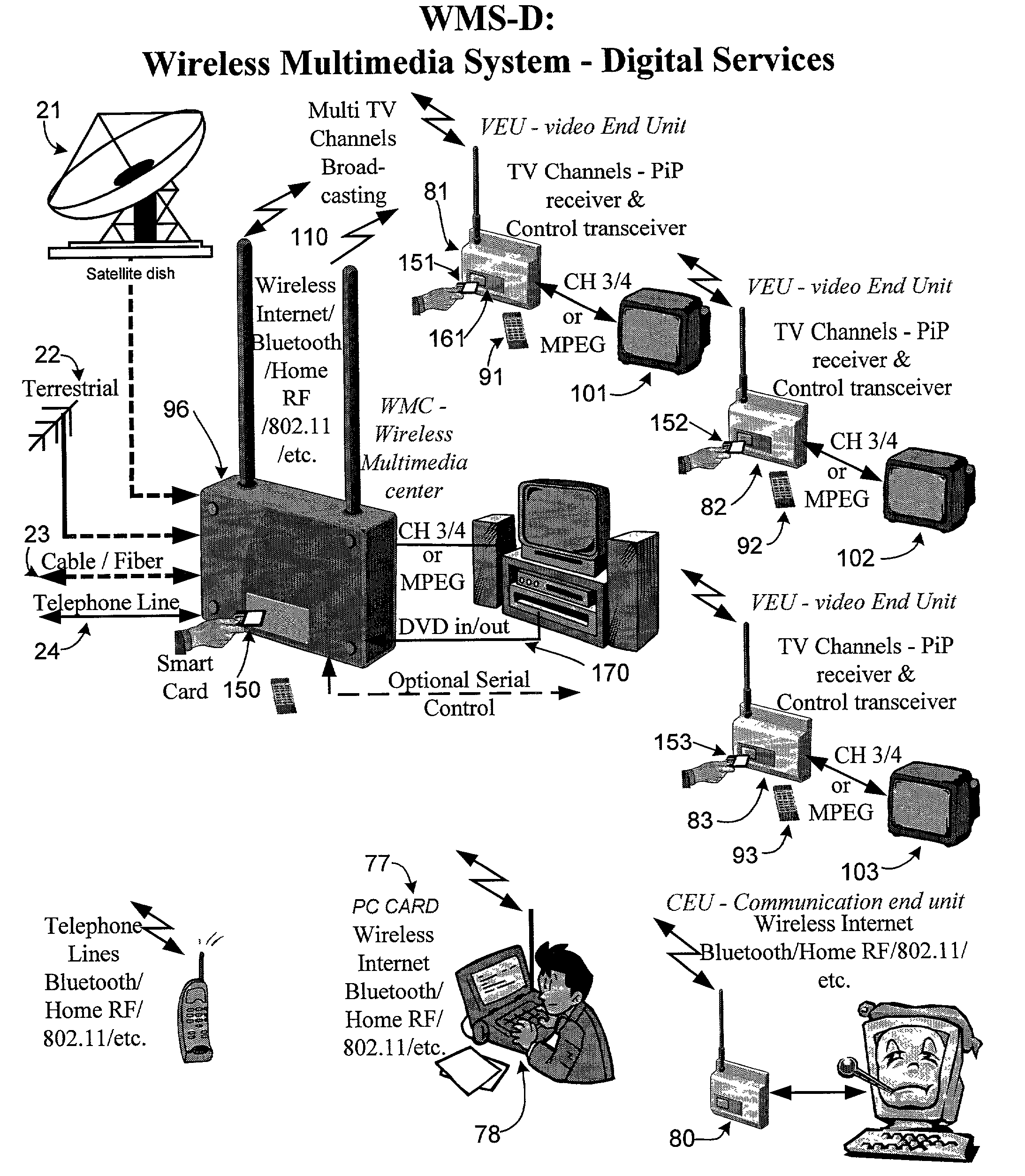
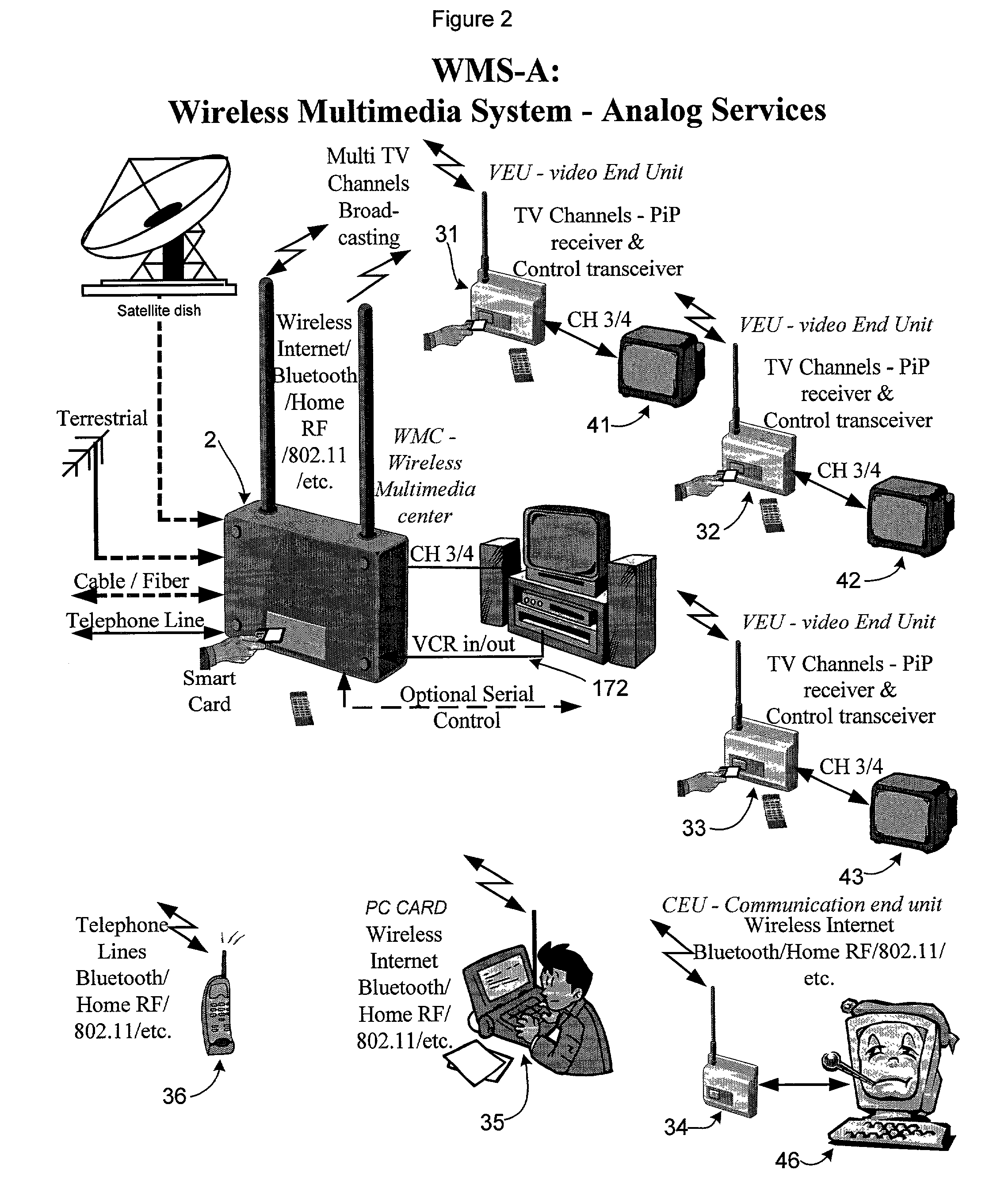
Wireless multimedia system
ActiveUS7827581B1Multiplex system selection arrangementsNetwork traffic/resource managementBroadbandOrthogonal array
A customer premises installation has a wireless multimedia center (WMC) for reception from one or more signal sources and for distribution of segments of signals from signal sources through the wireless multimedia center to a plurality of end units, in which the signals include video signals and broadband data. The wireless multimedia center receives all the signals and distributes segments of said signals via a transmitter. The video signals are transmitted by orthogonal frequency division multiplexing in which all signals are added together and summed as an orthogonal array having dimensions of time, frequency and amplitude, to transmit spread spectrum multiplexed signals. Each pulse has sufficiently long individual pulse widths to defeat multi-path, reflection and absorption phase induced losses. The video signals are distributed to one or more end units. The end units communicate with the wireless multimedia center, controlling which segments of which signals are distributed to each end unit.
Owner:BE LABS
Garment dispensing and receiving apparatus having a removable cartridge body and a flexible dispensing door
InactiveUS20020130135A1Cheap manufacturingInexpensive to repairShow cabinetsRacksEngineeringOrthogonal array
A dispenser for dispensing articles such as scrub garments. The dispenser includes a housing that defines an interior portion, a foldable, wheeled distribution cartridge defining an orthogonal array of receptacles for receiving items to be distributed from the dispenser; and a main door for controlling access to the interior of each of the various receptacles. The main door defines a plurality of rectangular horizontal openings, each of which aligns with a horizontal row of receptacles within the distribution cartridge. Access to each of these horizontal openings is controlled by a lockable main door. A flexible receptacle door having a vertical opening is mounted on mechanically-driven rollers on the interior of the main door. The receptacle door may be moved laterally relative to the receptacles so that the vertical opening aligns with any column of receptacles within the distribution cartridge. The dispenser allows a user access to the interior of a target receptacle while simultaneously preventing access to all other receptacles in the cartridge by laterally aligning the vertical access slot of the receptacle door with the target receptacle and then unlocking only the user door that covers the row of receptacles that includes the target receptacle. The user may then open the user door and reach through the exposed horizontal opening in the main door and through the vertical slot in the receptacle door to remove an article from within the interior of the target receptacle.
Owner:INNOVATIVE PROD ACHIEVEMENTS
Light recycling illumination systems having restricted angular output
InactiveUS20080247172A1Increase brightness efficiencyIncrease effective brightnessPoint-like light sourceSemiconductor devices for light sourcesBandpass filteringPrism
This invention is an illumination system that incorporates a light emitting diode and a partially reflecting optical element. The light emitting diode emits internally generated light having a first angular range and reflects incident light with high reflectivity. The partially reflecting optical element transmits a first portion of the internally generated light with a second angular range, smaller than the first angular range, and reflects a second portion of the internally generated light back to the light emitting diode, where the second portion is reflected by the light emitting diode. The partially reflecting optical element can be a pyramid, an array of pyramids, a first and second orthogonal arrays of prisms or a bandpass filter. Utilizing a partially reflecting optical element and light recycling can increase the effective brightness and the output efficiency of the illumination system.
Owner:GOLDENEYE
Method for robustly and optimally operating micro-grids on basis of orthogonal arrays
InactiveCN106355344AIncrease flexibilityImprove economyEnergy industryResourcesMicrogridElectricity price
The invention discloses a method for robustly and optimally operating micro-grids on the basis of orthogonal arrays. The method includes steps of extracting static data of micro grid architectures, power types, operation costs of the power types, energy storage system unit operation cots, interaction costs, time-of-use electricity prices and the like; building micro-grid uncertainty set models; screening test scenarios; building micro-grid robust and optimal operation models on the basis of the orthogonal arrays and designing solution strategies on the basis of the test scenarios so as to obtain ultimate micro-grid robust and optimal operation schemes. The method has the advantages that the grid-connection micro-grids with consideration of output of renewable energy distributed power sources and load demand uncertainty can be optimally operated by the aid of the method, and dispatching reference can be provided for operation personnel of the micro-grids.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Stacked coil array for magnetic resonance experiments
InactiveUS7474098B2Maximize SNRImprove signal-to-noise ratioDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsArray data structureCoil array
An array coil for sensing signals in magnetic resonance experiments incorporates the traditional loop-butterfly array elements at spaced positions along an axis of the sample with additional stacked twisted loops and / or twisted butterfly elements. The twisted loop and twisted butterfly elements are centered along between the standard loop-butterfly array elements. The twisted array elements are naturally isolated from both the loop and butterfly. Alternatively, for a two dimensional mesh array of loop elements, additional twisted loop array elements are added with both longitudinal and transverse orientations, again centered between loop elements. The goal is to allow separation of loop and / or butterfly elements of linear (Spine), 2D planar arrays (Cardiac) or cylindrical arrays of curved array elements (Head), for improved parallel MRI capabilities such as the SENSE or SMASH techniques, but to recover the SNR lost in between the elements and improve the g-factor of the total array with additional orthogonal array elements.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
Imaging-based bar code reader with rotated photosensor array
InactiveUS20070228176A1Easy to useVisual representatino by photographic printingSensing by electromagnetic radiationSensor arrayAcute angle
An imaging based bar code reader for imaging and decoding a target bar code. The reader features a housing including a scanning head defining a horizontal axis and an imaging system supported by the housing for imaging the target bar code. The imaging system including a 2D sensor array and focusing optics receiving reflected illumination from the target bar code through the window and focusing the reflected illumination onto the sensor array. The sensor array includes an orthogonal array of pixels and defines a horizontal axis. The reader further features a decoding system for decoding an image of the target bar code. The sensor array is oriented such that the horizontal axis of the sensor array is at an acute angle with respect to the horizontal axis of the target bar code when the target bar code is being presented to the scanning head such that the horizontal axis of the target bar code is substantially parallel to the horizontal axis of the scanning head.
Owner:SYMBOL TECH INC
Orthogonal compensation method for triaxial attitude measurement system non-orthogonal error
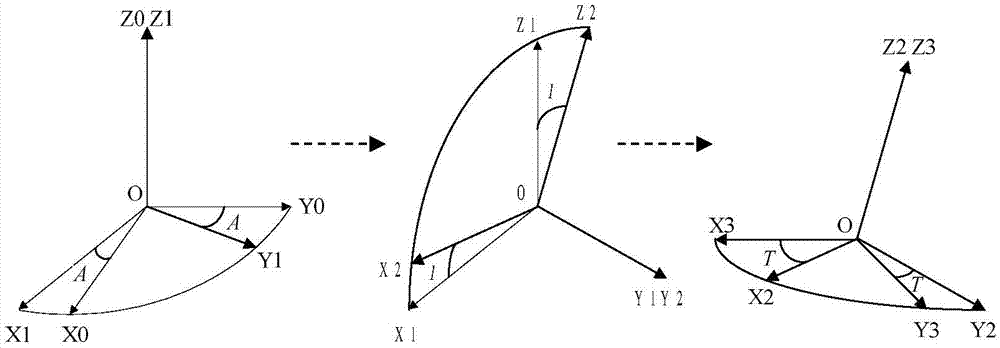
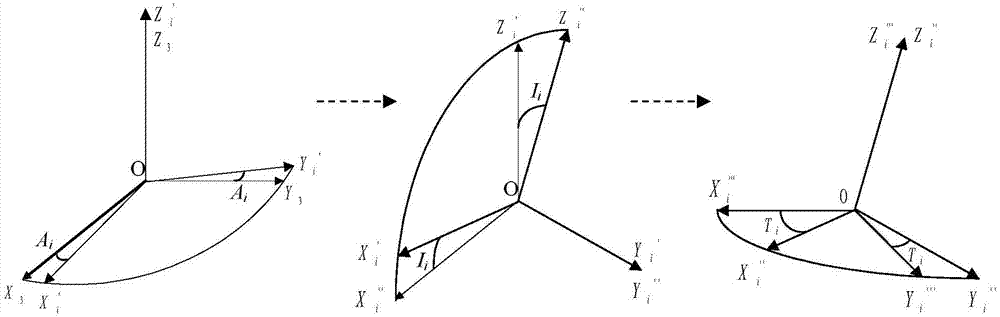
ActiveCN103591949AReduce non-orthogonalityReduce mistakesNavigational calculation instrumentsObservational errorOrthogonal array
The invention discloses an orthogonal compensation method for triaxial attitude measurement sensor non-orthogonal error. The method comprises: establishing respective independent virtual orthogonal instrument coordinate system for each measure real axis to obtain respective rotation matrix, performing fusing to obtain a triaxial non-orthogonal rotation matrix, so as to obtain an accurate non-orthogonal error model by virtual orthogonal modeling; then acquiring a compensation matrix by measure value and theory value of special positions, performing orghogonal decoupling on a measure result of a triaxial sensor so as to reduce non-orthogonality and measure error caused thereby and improve attitude measurement accuracy.
Owner:XI'AN PETROLEUM UNIVERSITY
Devices using addressable magnetic tunnel junction array to detect magnetic particles
ActiveUS20090186770A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsElectrical resistance and conductanceSuperparamagnetism
A magnetic sensor for identifying small superparamagnetic particles bonded to a substrate contains a regular orthogonal array of MTJ cells formed beneath that substrate. A magnetic field imposed on the particle, perpendicular to the substrate, induces a magnetic field that has a component within the MTJ cells that is along the plane of the MTJ free layer. If that free layer has a low switching threshold, the induced field of the particle will create resistance changes in a group of MTJ cells that lie beneath it. These resistance changes will be distributed in a characteristic formation or signature that will indicate the presence of the particle. If the particle's field is insufficient to produce the free layer switching, then a biasing field can be added in the direction of the hard axis and the combination of this field and the induced field allows the presence of the particle to be determined.
Owner:HEADWAY TECH INC
Autostereoscopic display device
ActiveUS20110164036A1Reduction in intensity modulation depthReduce unevennessSteroscopic systems3D-image renderingImage formationDisplay device
An autostereoscopic display device comprising a view forming module in registration with an image forming means. The image forming means has an orthogonal array of display pixels spatially defined by an opaque matrix. The view forming module provides at least two optical functions, namely a view forming function and a brightness non-uniformity reducing function. The view forming function modifies the direction of outputs of the display pixels such that the outputs of groups of the display pixels are projected in respective different directions as a plurality of views. The view forming function is provided by an array of parallel lenticular lenses arranged across the view forming module and having a first pitch. The brightness non-uniformity reducing function spreads the outputs of the display pixels such that brightness non-uniformities caused by imaging of the opaque matrix are reduced. The brightness non-uniformity reducing function defines a second pitch across the view forming module less than the first pitch, and further defines an effective spreading angle in a plane perpendicular to axes of the view forming elements substantially equal to or less than the angle between adjacent views projected by the view forming function. The brightness non-uniformity reducing function is provided by an array of lenses or a diffuser. In the case of an array of lenses, these lenses may be integrated with the lenticular lenses providing the view forming function in the form of lenses having a polygonal cross section.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
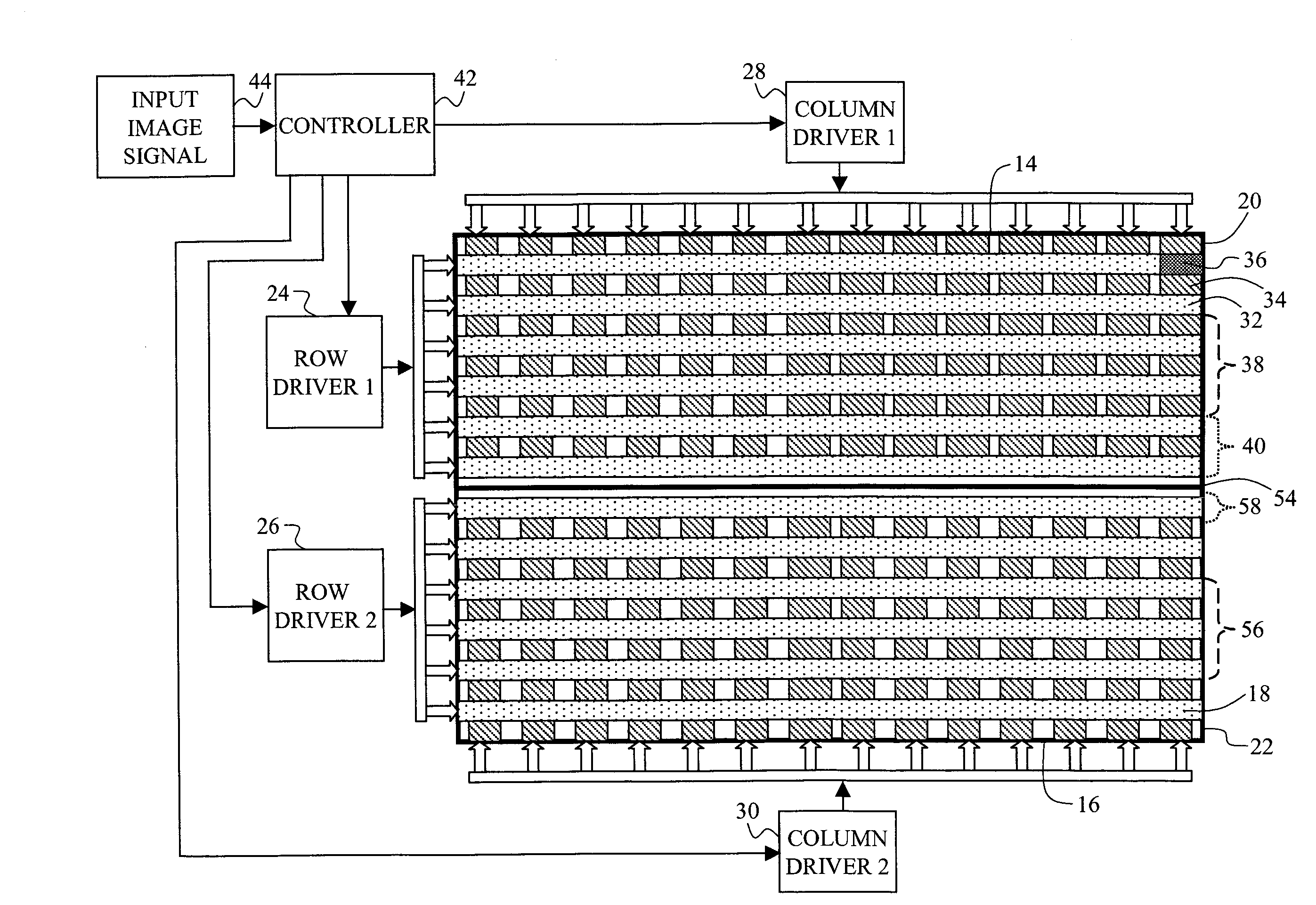
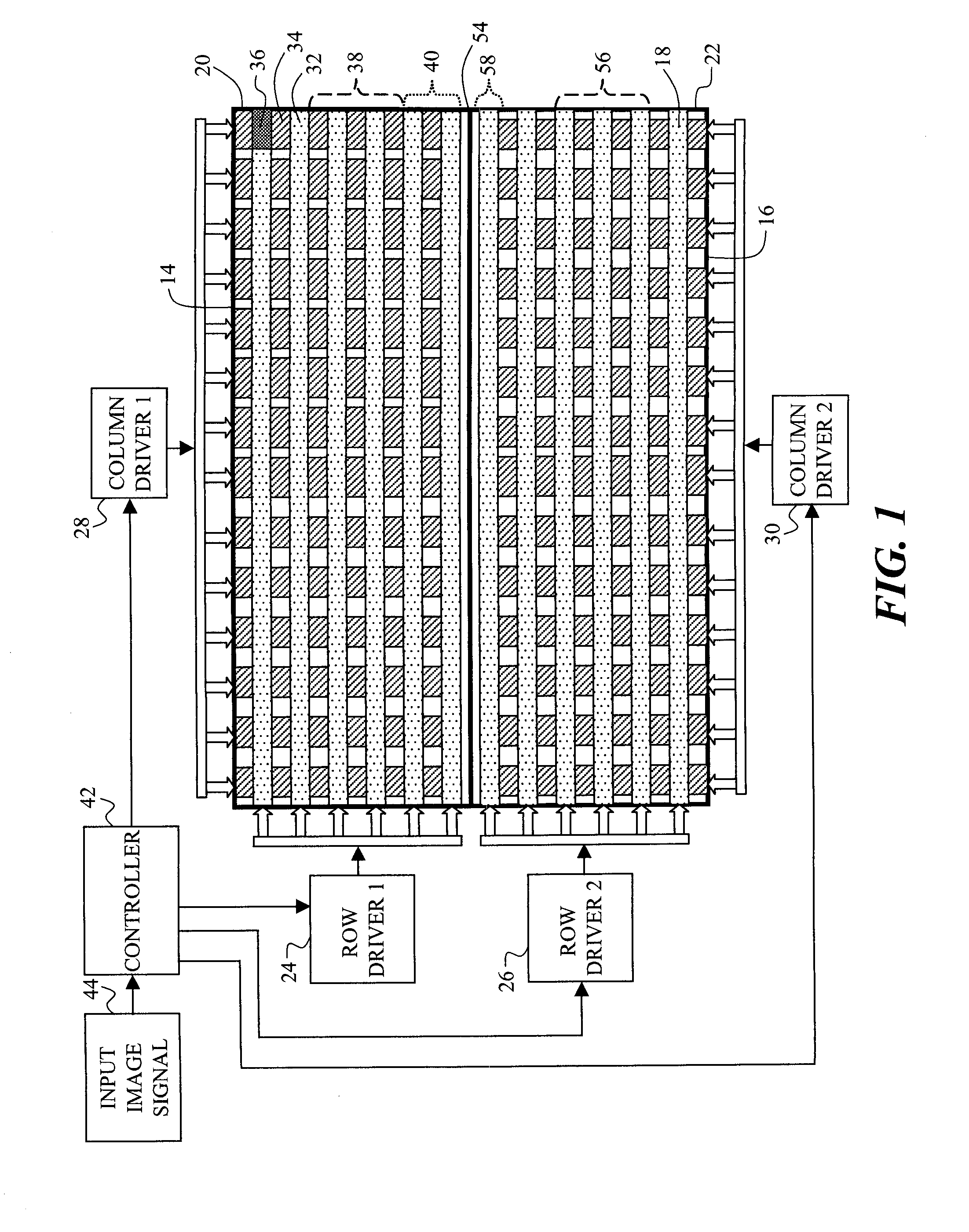
Tiled passive matrix electro-luminescent display
ActiveUS20090073079A1Less powerHigh resolutionSolid-state devicesCathode-ray tube indicatorsDisplay deviceEngineering
A tiled, passive-matrix, EL display, including two or more EL tiles, each EL tile including an array of rows and columns of light-emitting elements, each light-emitting element being formed from a light-emitting layer that is sandwiched between an orthogonal array of row and column electrodes wherein each of the two or more EL tiles further include at least one row driver; at least one column driver for operating in conjunction with each of the at least one row drivers to control the flow of electrons between the row and column electrodes to control the emission of light from each of the light-emitting elements, with a first exception that when the boundary between the two tiles is to be illuminated, then the number of rows of simultaneously illuminated rows of light-emitting elements within one tile is less than the predetermined number.
Owner:GLOBAL OLED TECH
Optical imaging element and manufacturing method thereof
PendingCN108318948ASimple structureGood optical imaging performanceOptical elementsAdhesiveEngineering
The present invention discloses an optical imaging element and a manufacturing method thereof. The optical imaging element is mainly formed by an upper layer of a light transmission stacked body and alower layer of a light transmission stacked body which are formed by binding of a plurality of long and thin transparent bars plated with single-sided or both-sided metal reflection layers, directions of the internal reflection surfaces of the two light transmission stacked bodies form an orthogonal array, and the upper layer of the light transmission stacked body and the lower layer of the lighttransmission stacked body are glued through a transparent macromolecule adhesive. The manufacturing method comprises the steps of: plating of a metal reflection layer, cutting of transparent materials, bonding of the long and thin transparent bars, forming and polishing of the light transmission stacked bodies and forming of the optical imaging element. The optical imaging element is simple in structure and has a good optical imaging performance, the manufacturing method of the optical imaging element is simple in production process and low in production cost, and compared to a manufacturingmethod in the prior art, a lot of manpower and material resources can be saved, and low-cost batch production of optical elements can be achieved.
Owner:XIANGHANG SHANGHAI TECH CO LTD
Autostereoscopic display device
ActiveUS8780188B2Reduce unevennessEfficient reductionColor television detailsSteroscopic systemsDisplay deviceImage formation
An autostereoscopic display device comprising a view forming module in registration with an image forming means. The image forming means has an orthogonal array of display pixels spatially defined by an opaque matrix. The view forming module provides at least two optical functions, namely a view forming function and a brightness non-uniformity reducing function. The view forming function modifies the direction of outputs of the display pixels such that the outputs of groups of the display pixels are projected in respective different directions as a plurality of views. The brightness non-uniformity reducing function spreads the outputs of the display pixels.
Owner:LEIA INC +1
Fiber-based field emission display
InactiveUS6917156B2Increase vacuumGas filling substance selectionCathode-ray/electron-beam tube vessels/containersFiberPhosphor
The invention relates to a field emission display constructed using an array of fibers and an orthogonal array of emitter electrodes. Each fiber in the fiber array contains an extraction electrode, spacer, a high voltage electrode and a phosphor layer. The array of emitter electrodes consists of carbon nanotube emitters attached to conductive electrodes. The emitter electrodes are separated using non-conductive fibers. A getter material in the form of a wire is placed within the array of emitter electrodes to maintain a high vacuum within the display.
Owner:MOORE CHAD BYRON
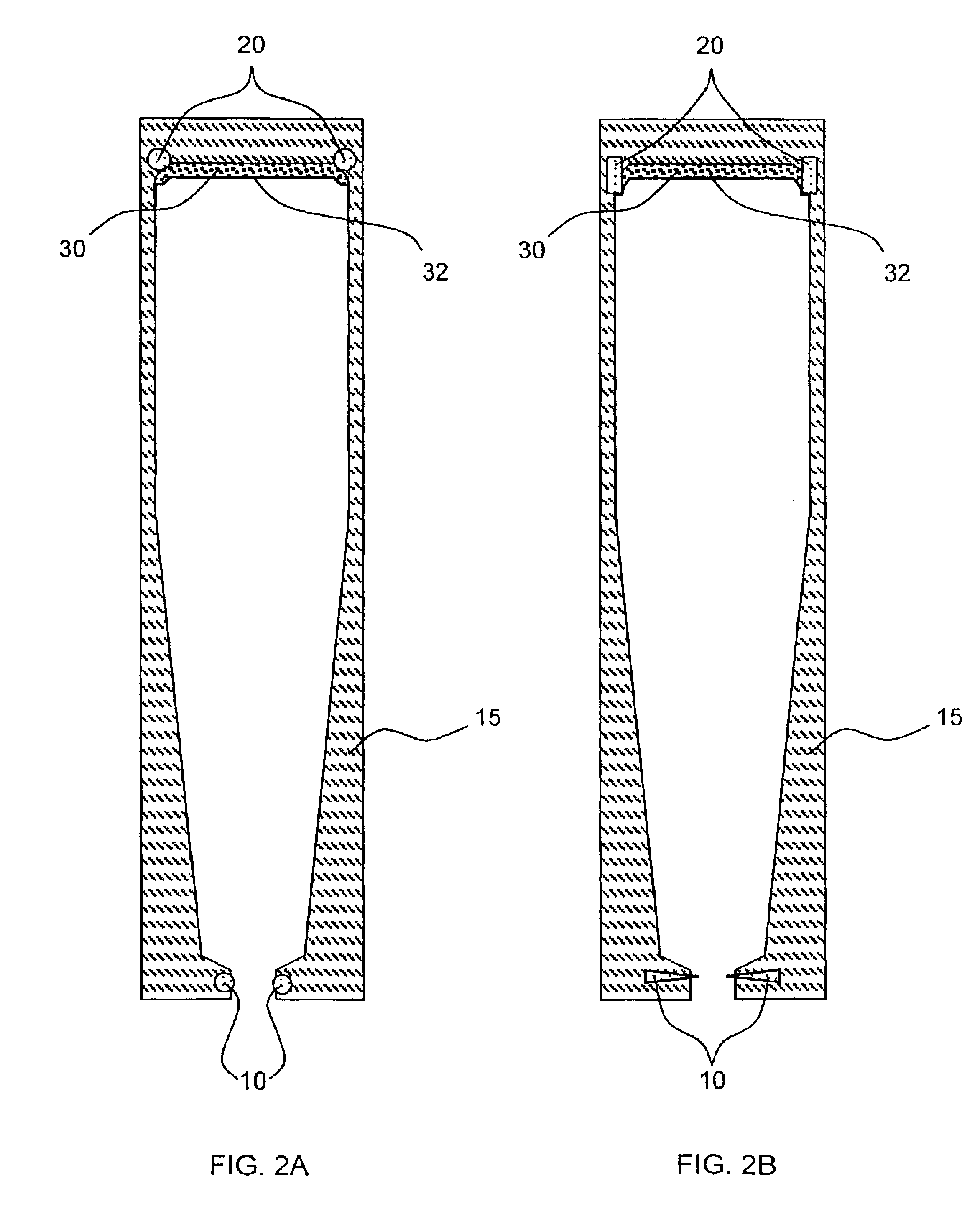
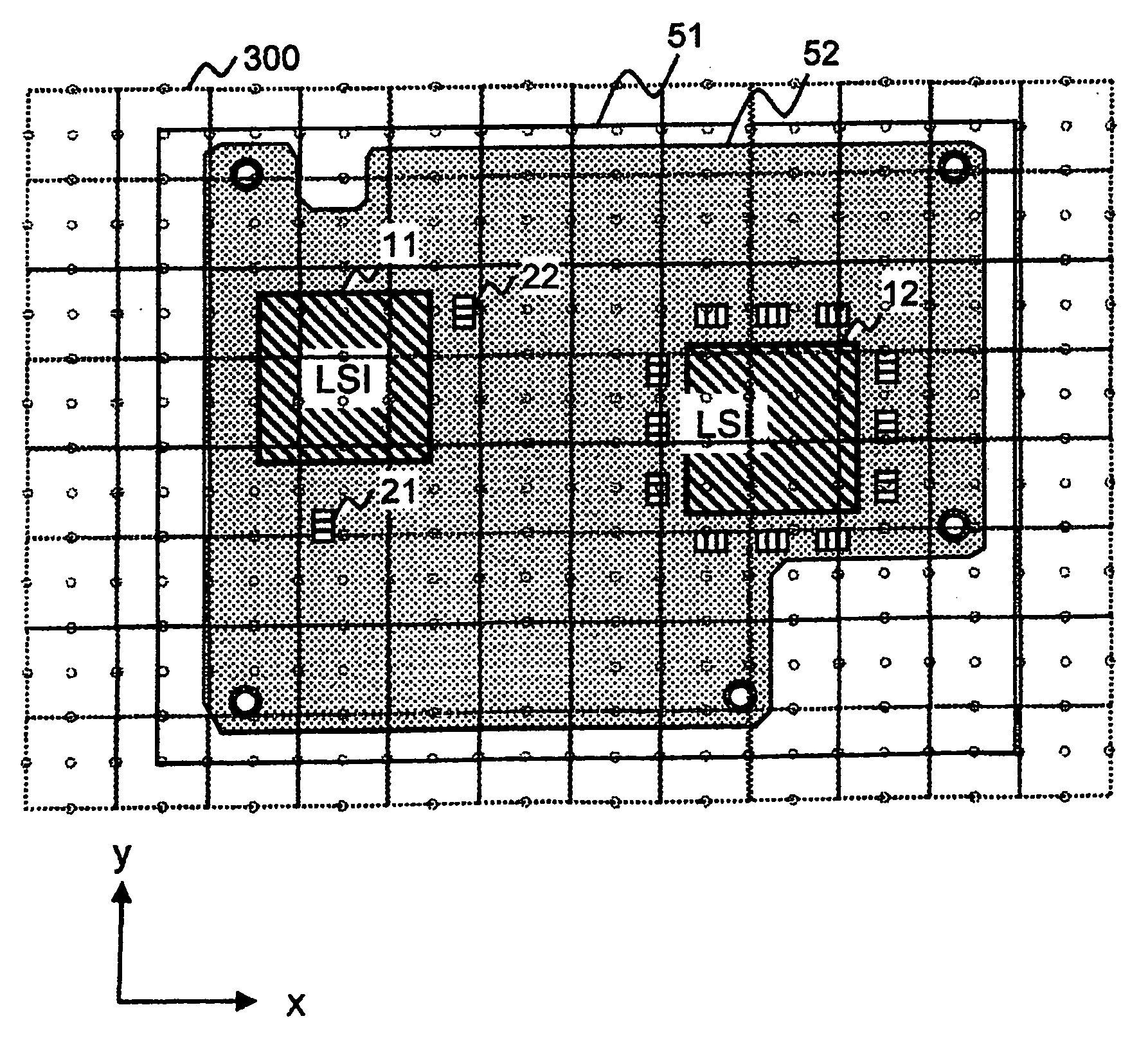
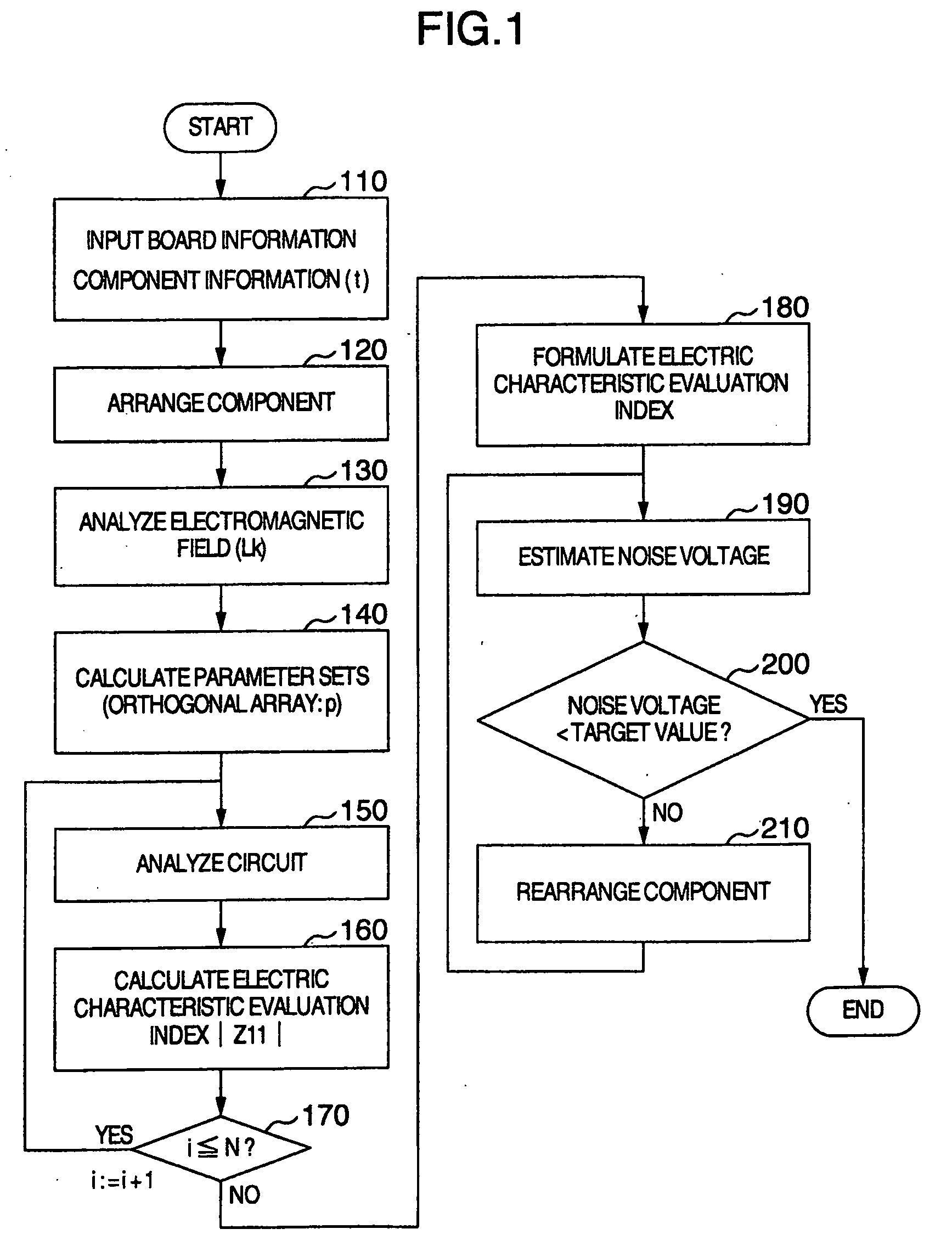
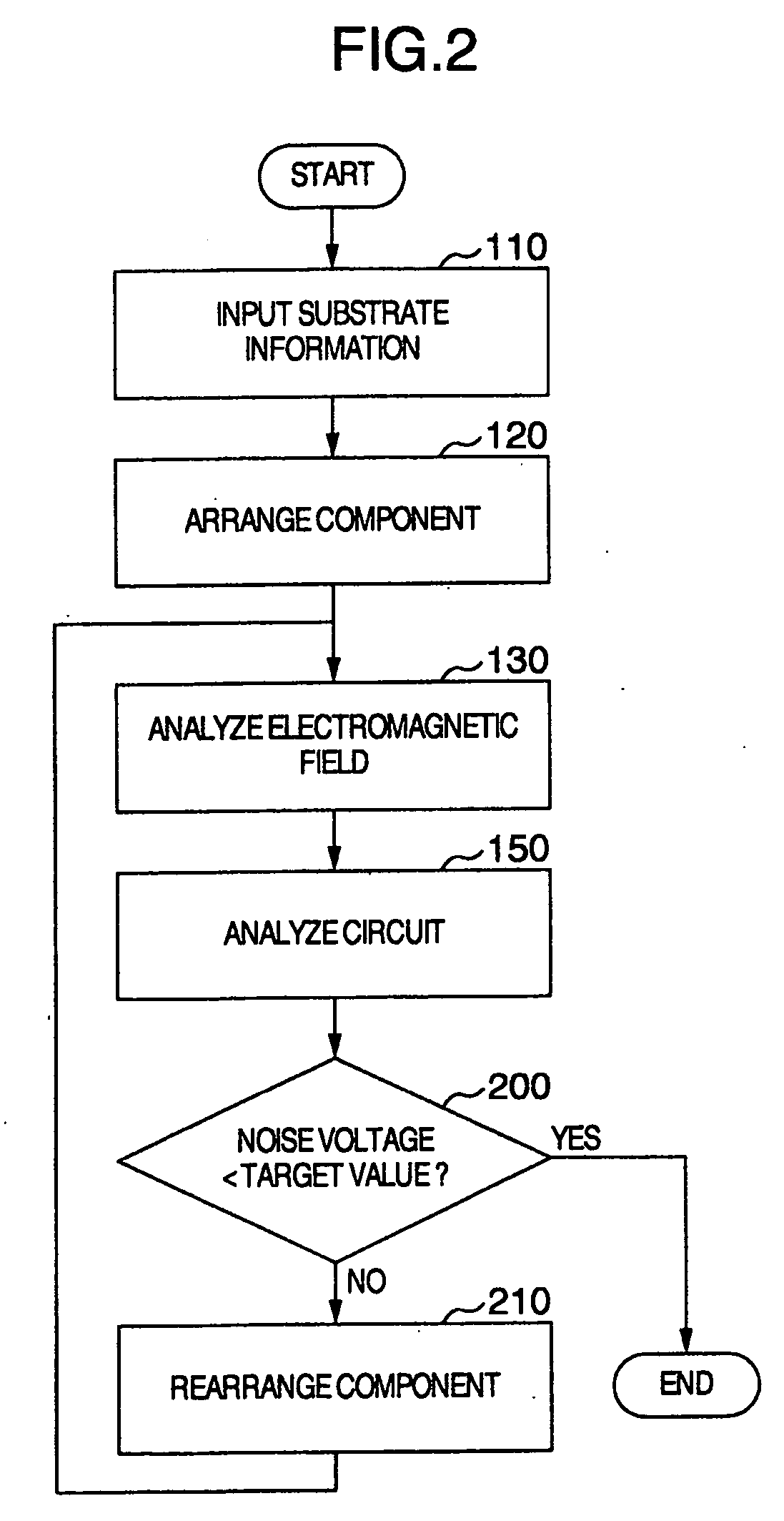
Support method and apparatus for printed circuit board
InactiveUS20090213558A1Guaranteed uptimeReduce design costResistance/reactance/impedenceCross-talk/noise/interference reductionOrthogonal arrayElectromagnetic field
An orthogonal array is formed by performing electromagnetic field analysis only once and determining a range by using the mount position and type of a capacitor and the number of capacitors as parameters to perform circuit analysis a small number of times. An estimation equation is formed by using as an index a result of the absolute value of the calculated power source impedance, and a capacitor is disposed to reduce noises by using the estimation equation.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
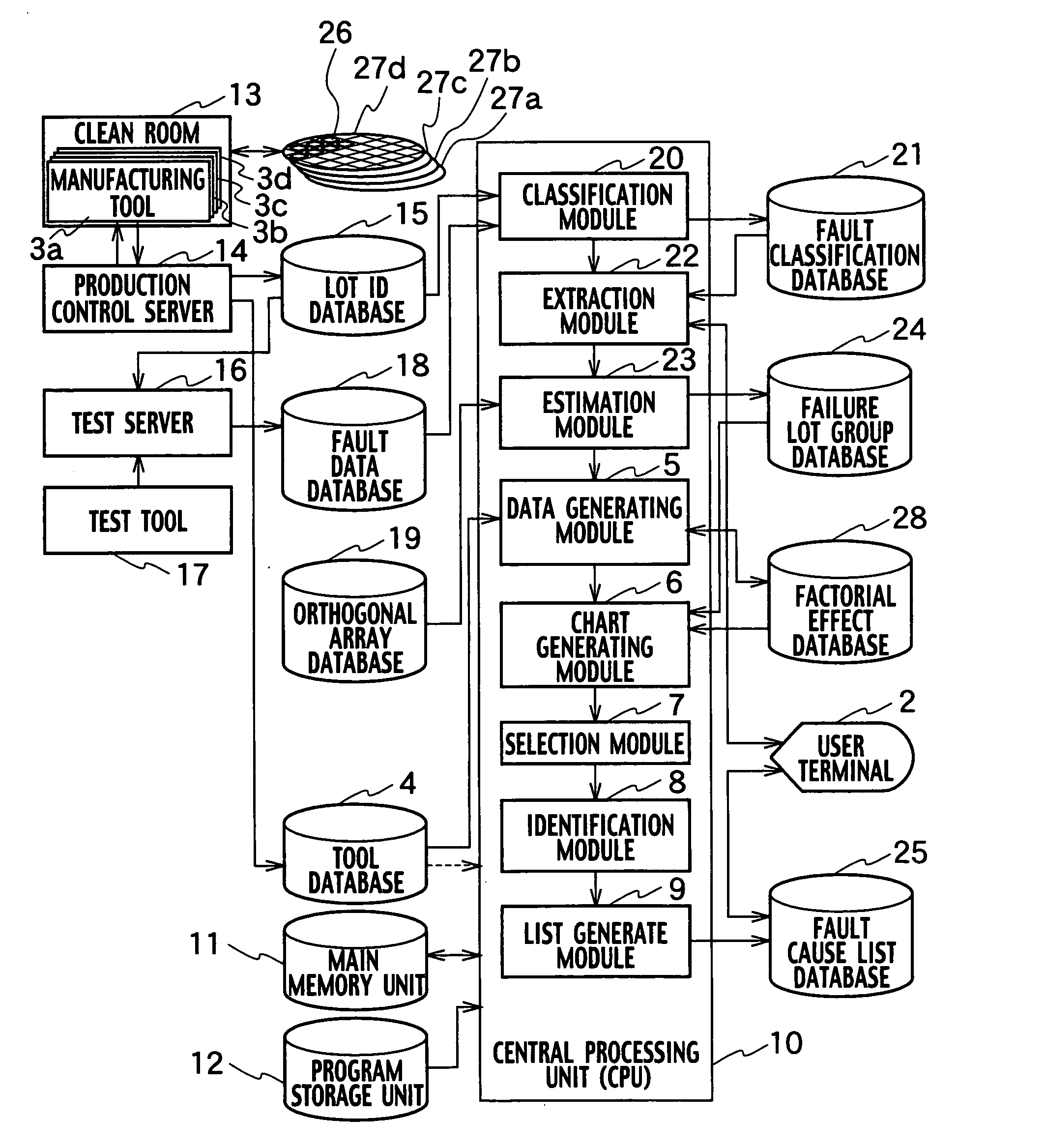
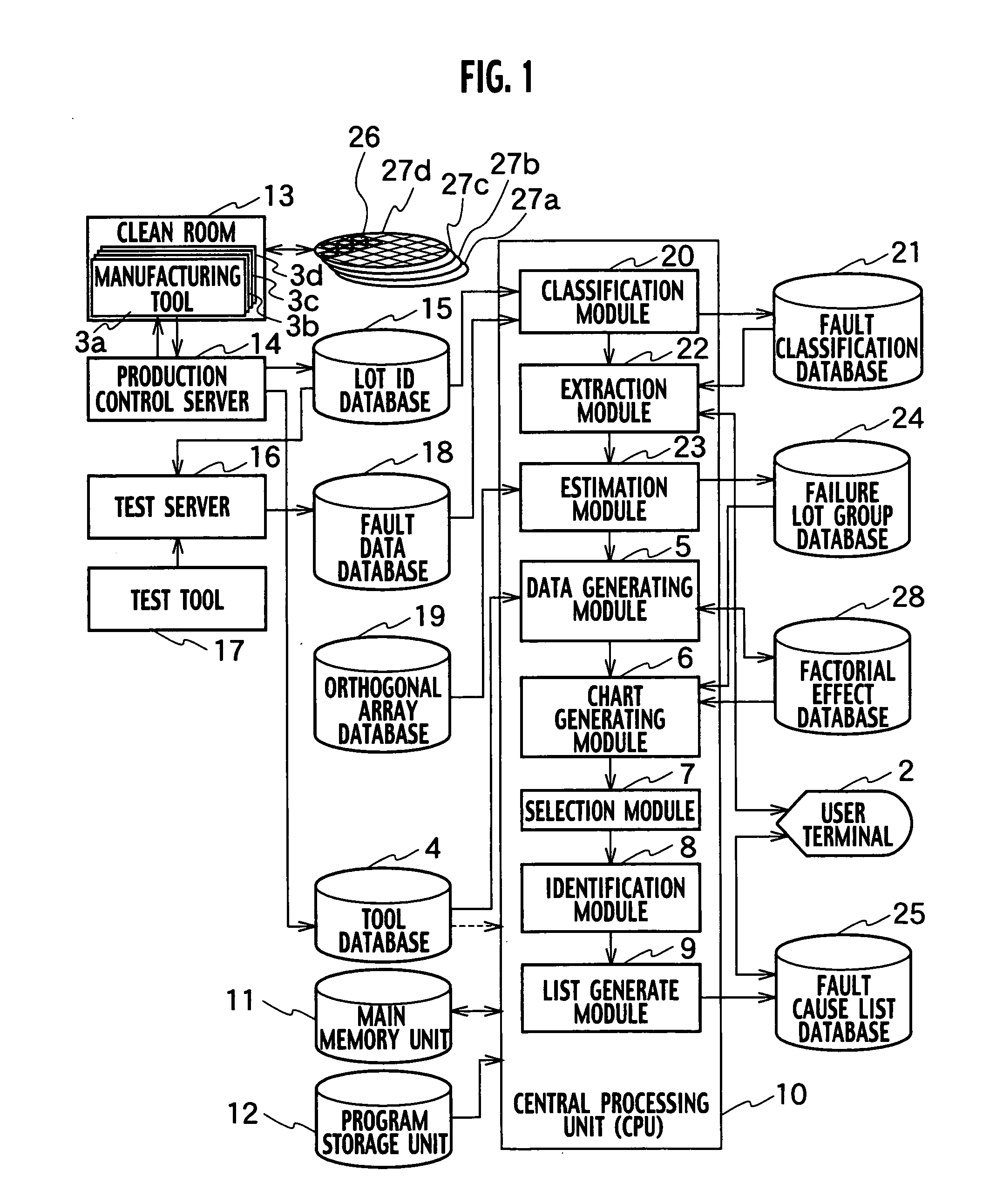
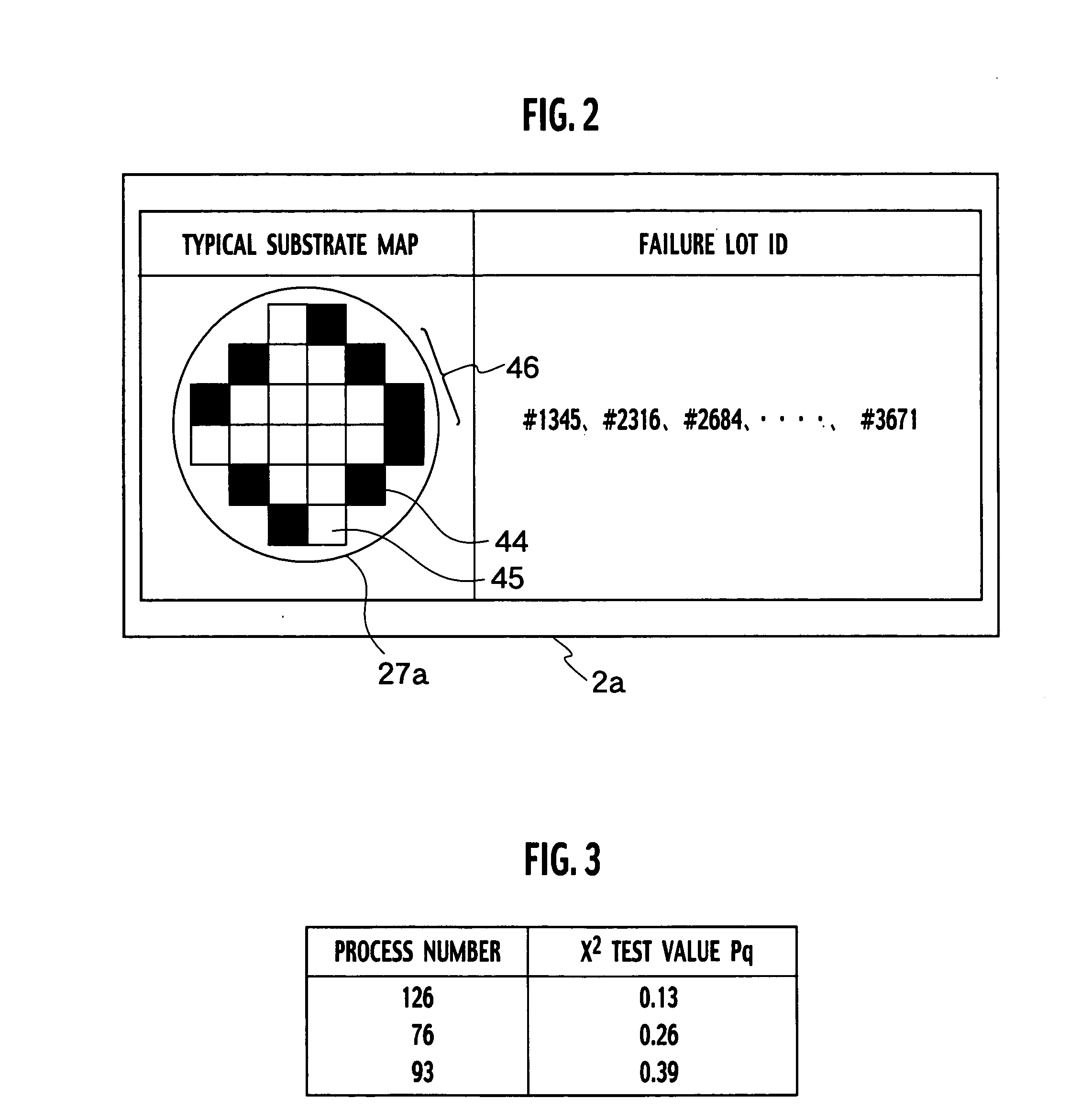
System and method for identifying a manufacturing tool causing a fault
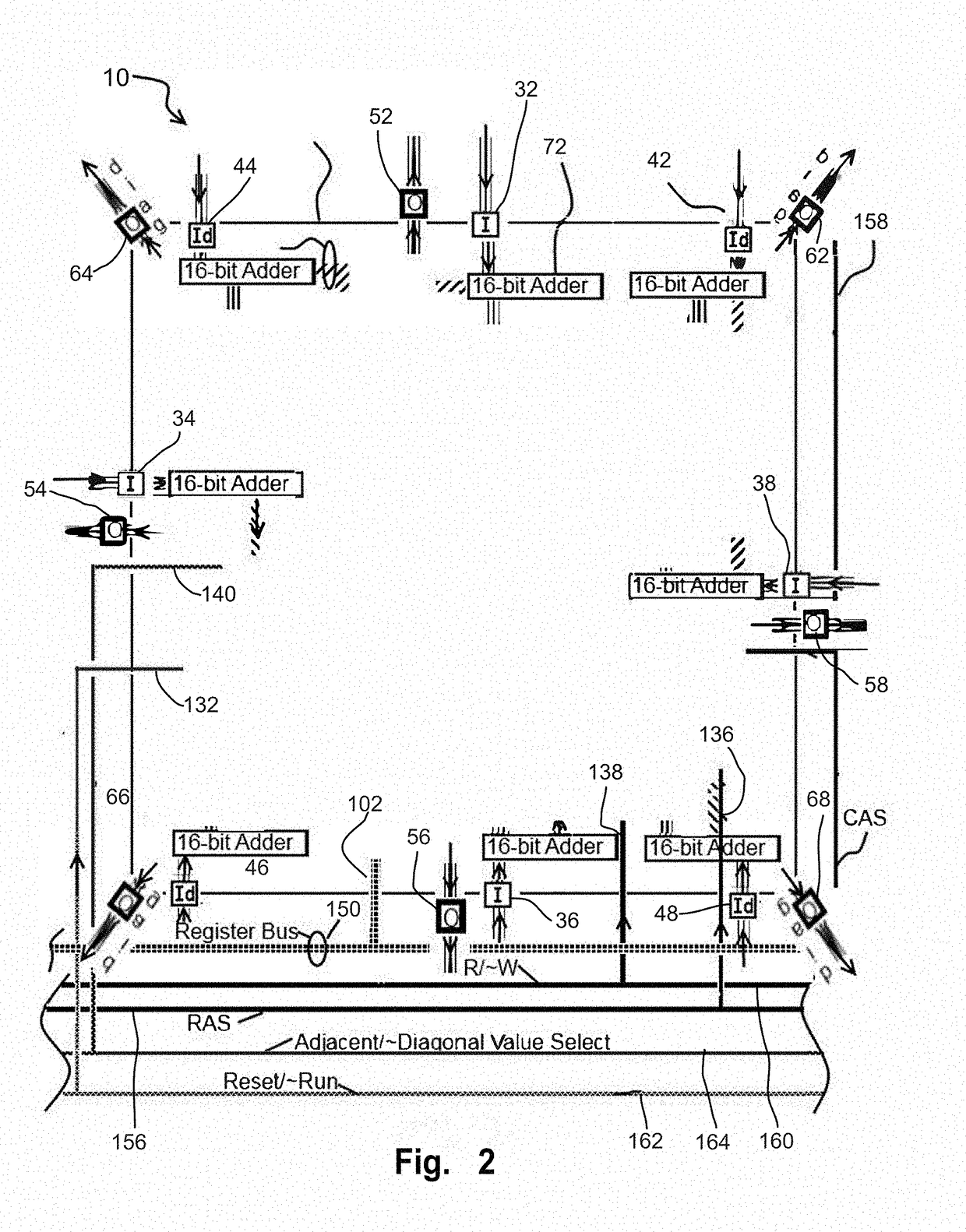
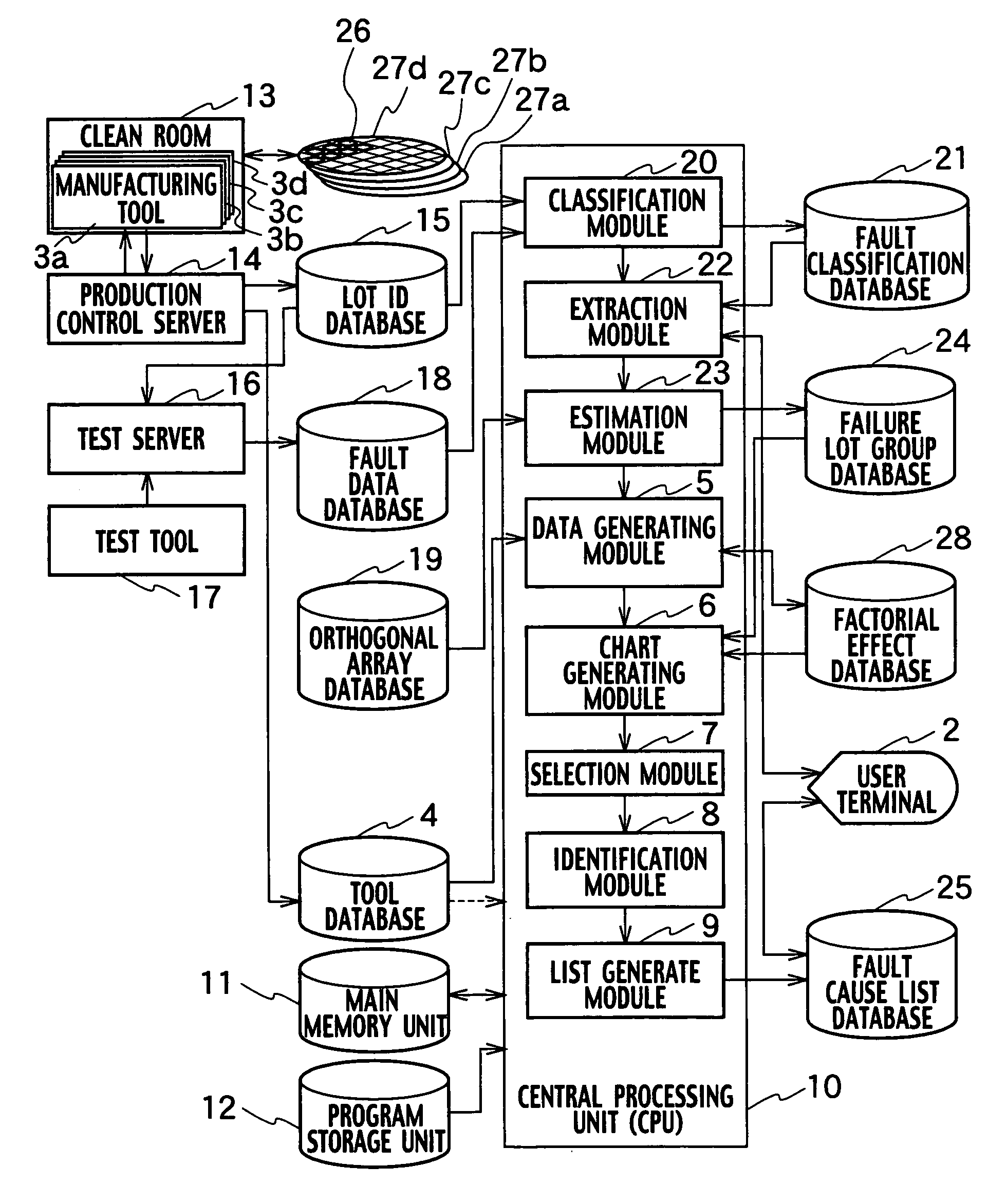
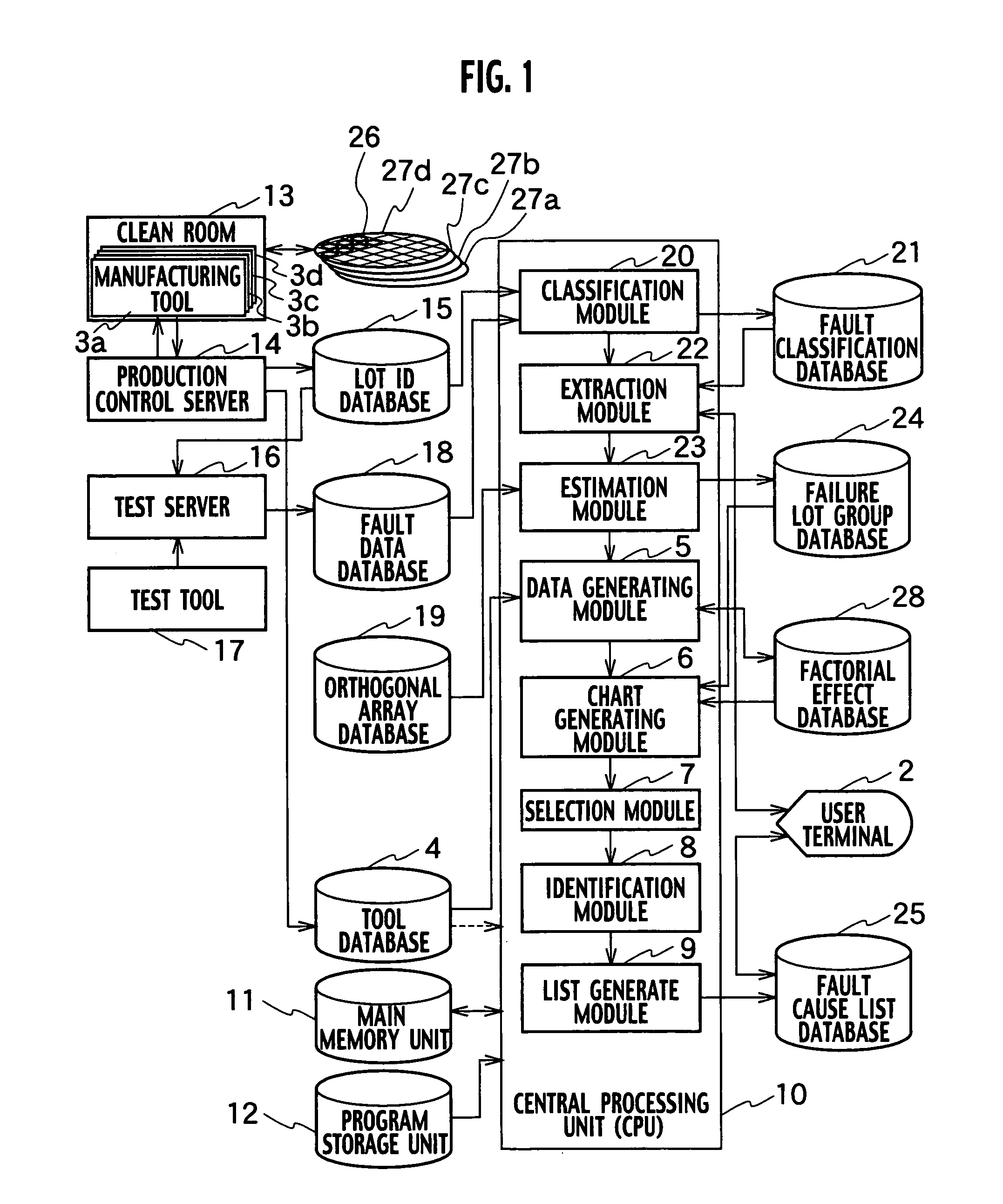
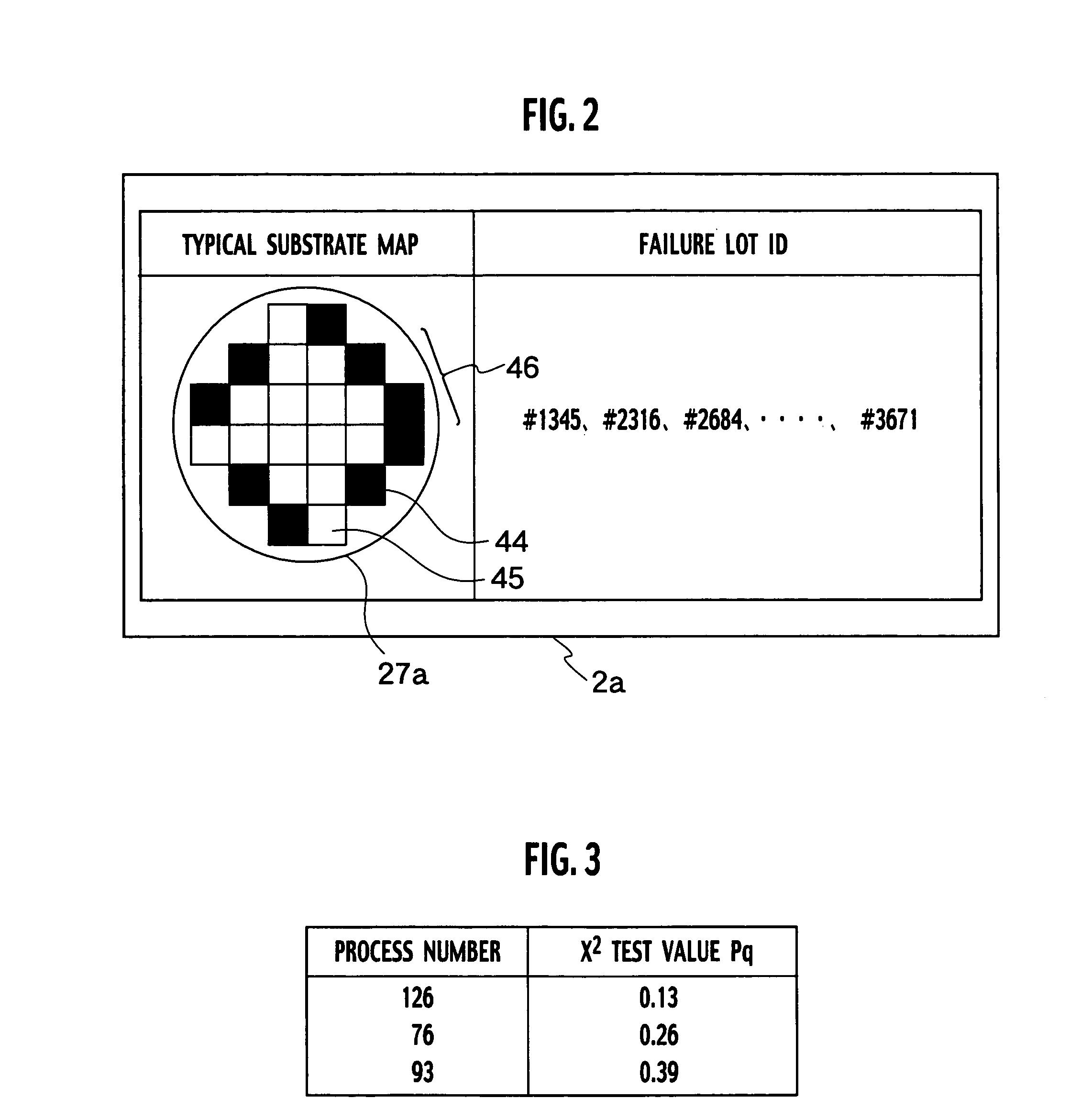
InactiveUS20050251365A1Data processing applicationsSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementOrthogonal arrayManufacturing engineering
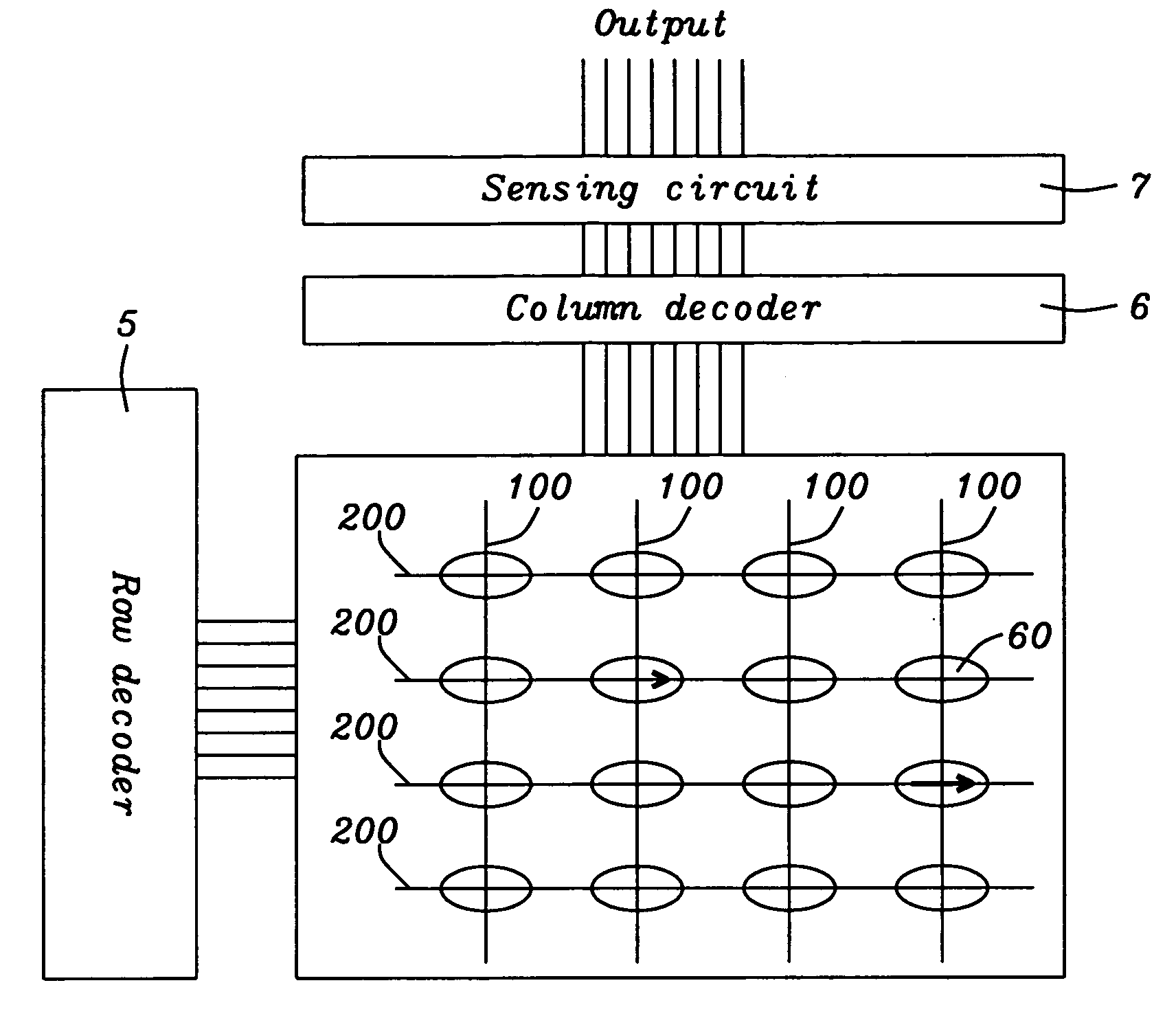
A system for identifying a manufacturing tool causing a failure, includes a data generating module generating factorial effect data, based on information on a failure lot group by using an orthogonal array, a chart generating module generating a factorial effect chart based on the factorial effect data, a selection module selecting failure lots caused by the same reason for a failure from among the failure lot group, based on the factorial effect chart, and an identification module identifying a manufacturing tool used as a common tool for the selected plurality of failure lots, based on history information of the manufacturing tool group.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Compositions of tRNA and uses thereof
Compositions and methods of producing components of protein biosynthetic machinery that include orthogonal tRNA's, orthogonal aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases, and orthogonal pairs of tRNA's / synthetases are provided. Methods for identifying these orthogonal pairs are also provided along with methods of producing proteins using these orthogonal pairs.
Owner:AMBRX
Underwater exterior ship hull imaging system employing a remote microprocessor controlled acoustic transducer array
InactiveUS20060114748A1Optimal and redundant coverageHigh resolutionAcoustic wave reradiationSonarVertical plane
A multi-beam acoustic transducer array system for producing color enhanced, three dimensional, high resolution images of a ship's underwater hull, wherein the acoustic transducers can be mounted in orthogonal pairs, each pair being positioned opposite from another pair within a shipping channel. The array can be utilized either in a stationary configuration within a controlled shipping lane or suspended in the water column from a mobile support vessel, with at least one array being orthogonally mounted and suspended in the water column from the mobile support vessel, wherein the mobile configuration obviates the need for multiple orthogonal arrays, for purposes of performing acquisition and imaging of a ship's hull. Each orthogonal array consists of a first transducer transmitting sonar pulses along a horizontal plane and a second transducer transmitting sonar pulses along a vertical plane, such that the two beaming sonar pulses are orthogonal, thereby providing optimal coverage.
Owner:HULL UNDERWATER IMAGING SYST
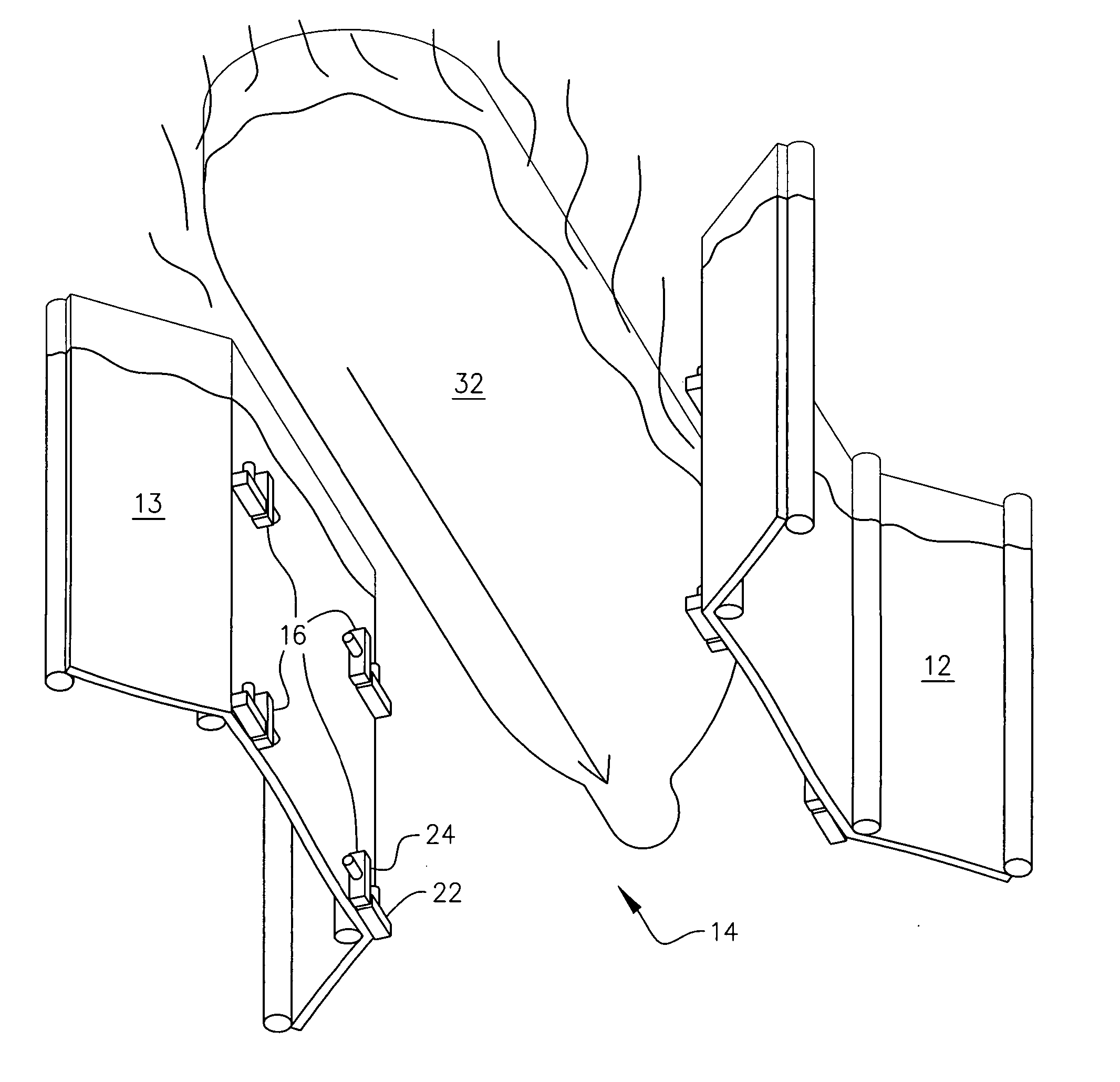
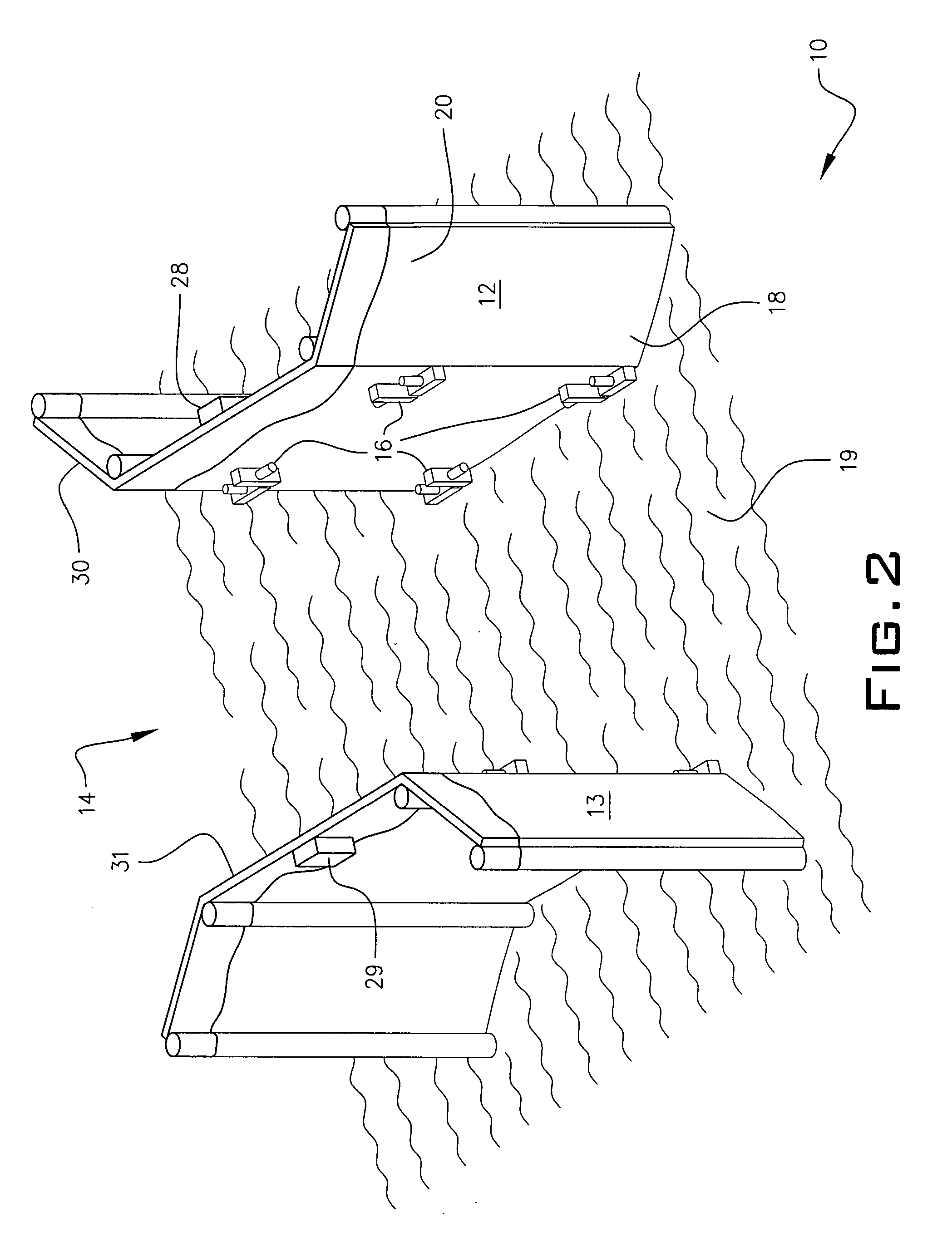
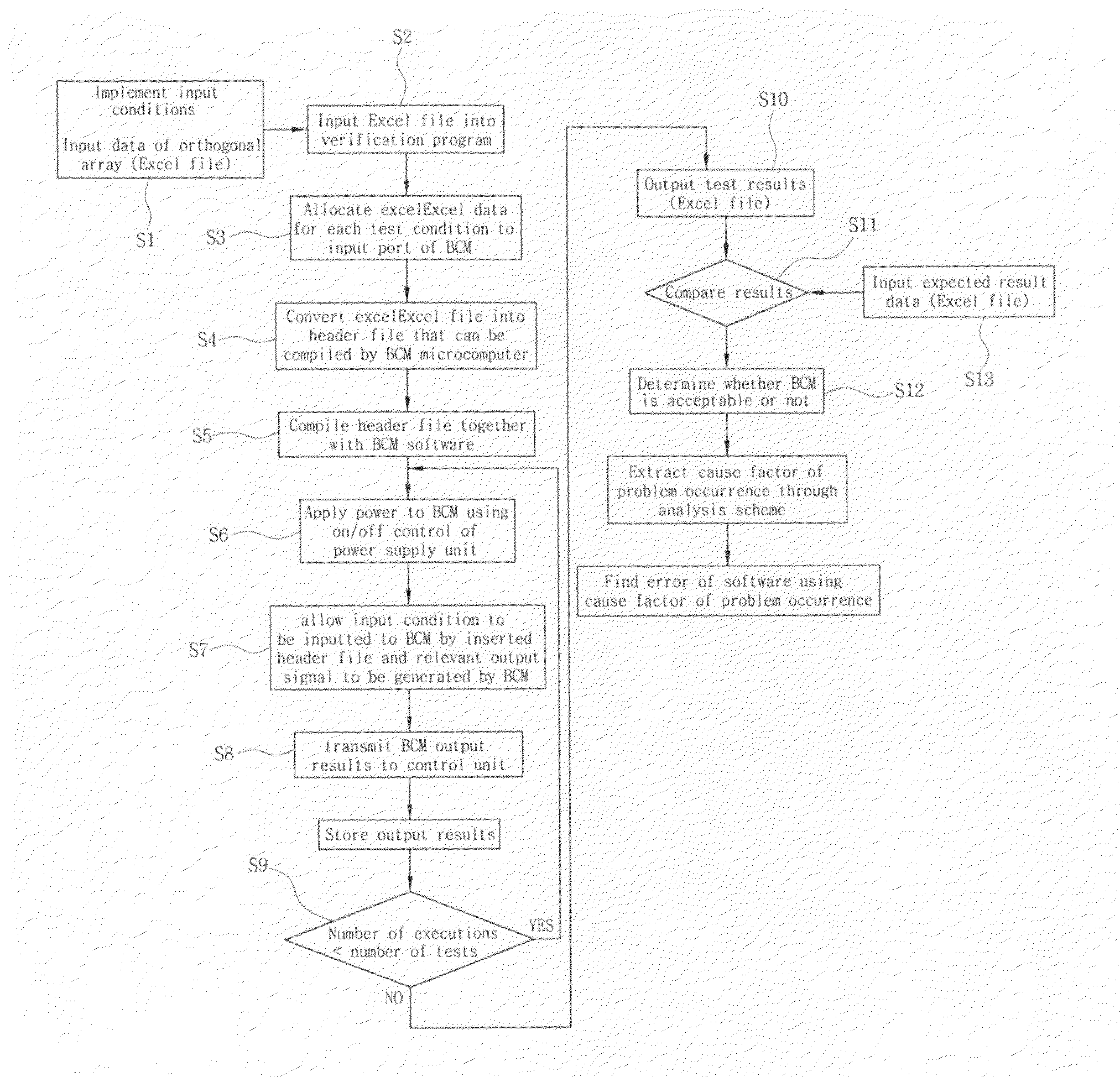
Verification system and method for body control module software
InactiveUS20080178045A1Reduce in quantityEliminate errorsDigital data processing detailsSoftware testing/debuggingComputer architectureSoftware error
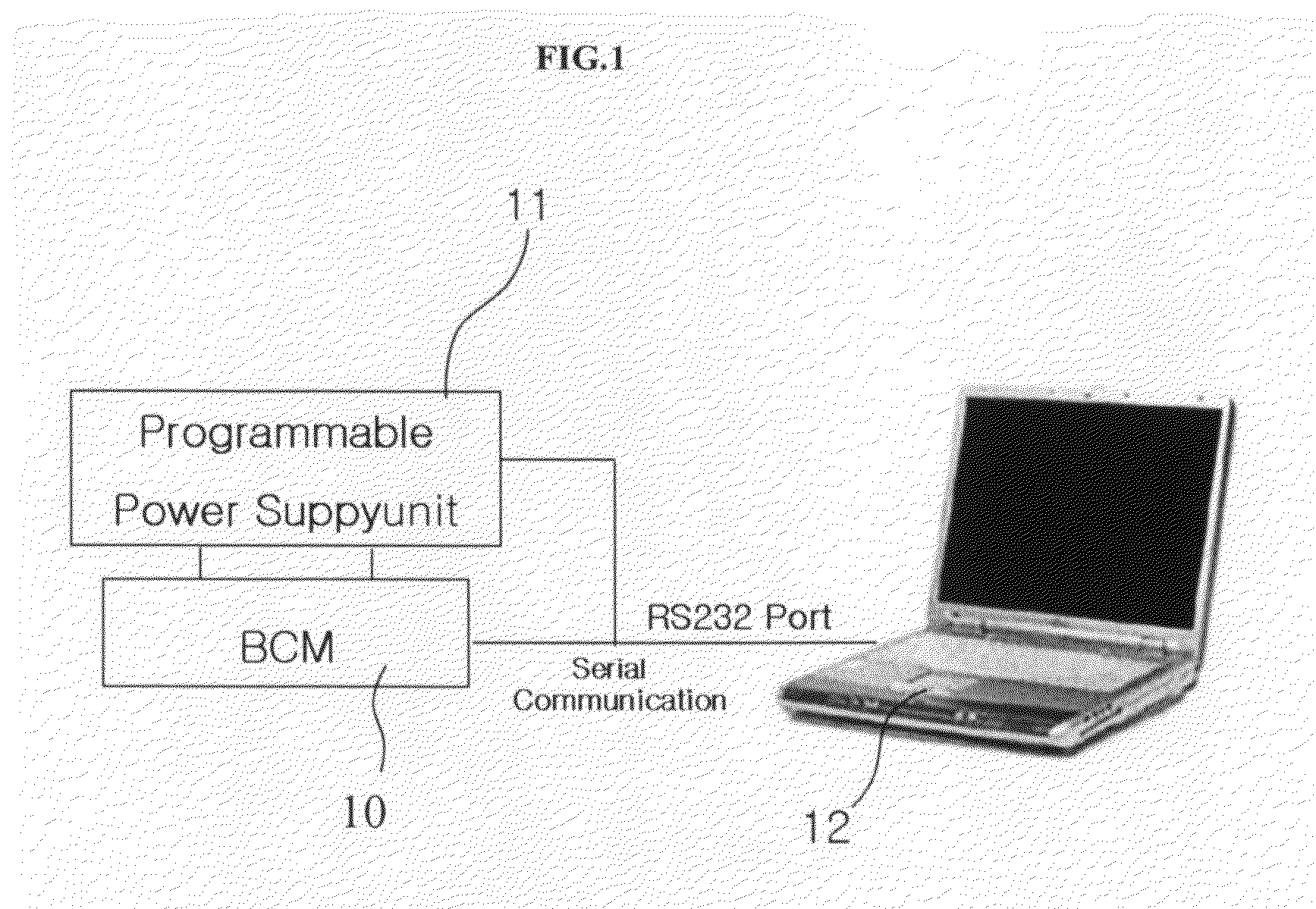
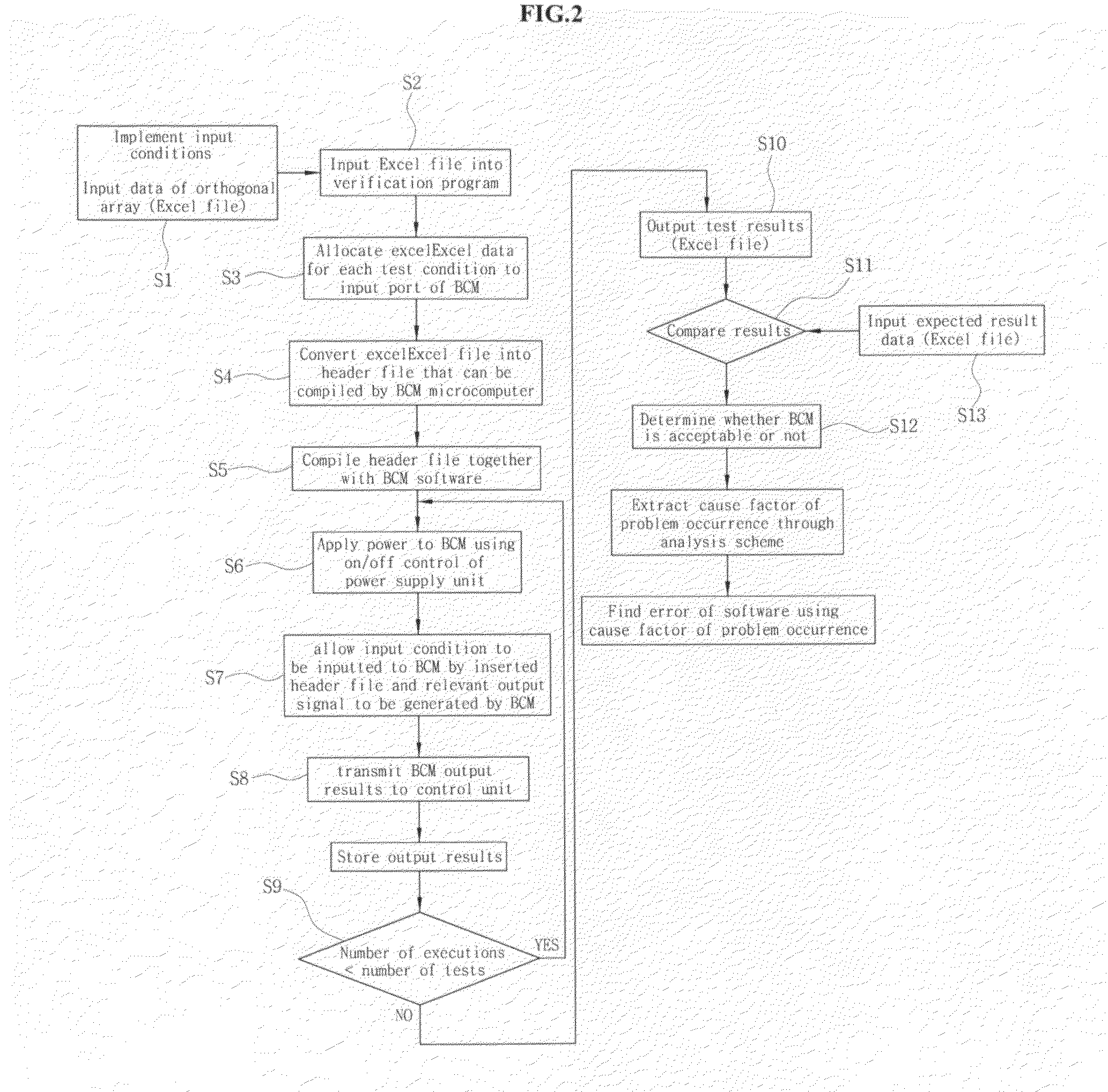
The present invention relates to a verification system and method for BCM software wherein data extracted from an orthogonal array are applied to verification for BCM software to reduce the number of tests such that verification for each BCM can be performed in a short period of time before manufacturing a prototype, reliability of verification results can be improved using a verification program regardless of an evaluator, and errors in the software for each BCM can be found and corrected at an early stage.To this end, the present invention provided a verification system for BCM software which comprises a BCM for controlling functions of convenience equipment in a vehicle; a computer equipped with a verification program and capable of exchanging information with the BCM through serial communication; and a power supply unit for applying power to the computer and the BCM.
Owner:HYUNDAI MOTOR CO LTD
Finite differences methods
ActiveUS20090083356A1Improved accuracy in the calculation of the function fMeet growth requirementsDigital differential analysersDesign optimisation/simulationBoundary valuesDiscretization
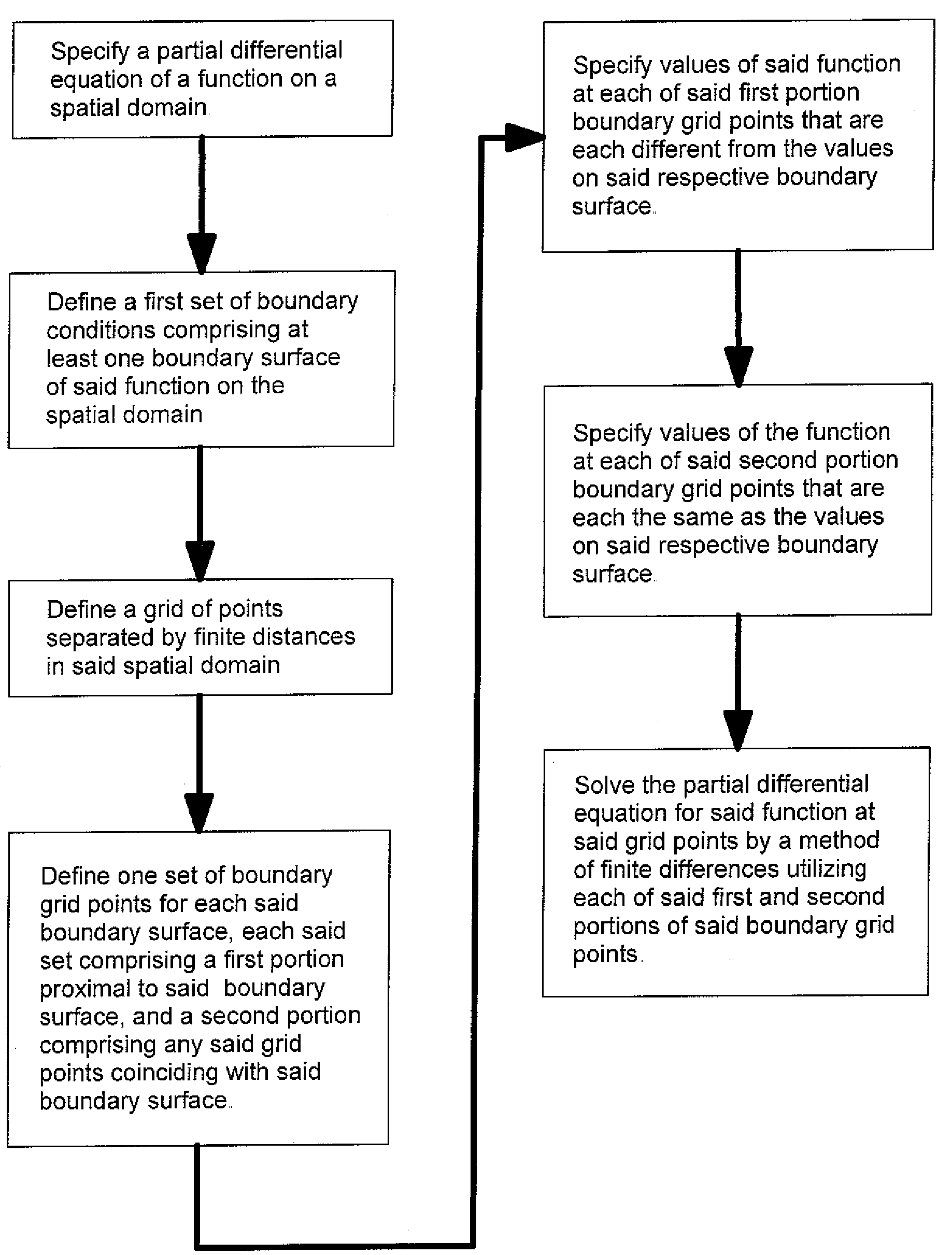
The application of finite differences methods to solve boundary value problems typically involves a discretization of such a problem across an orthogonal array of discrete grid points. This leads to an array of difference equations which is solved numerically within the constraints of the boundary conditions to yield solutions at the grid point locations. However, the accuracy of the solutions is limited with conventional finite differences methods when the boundary conditions are not represented exactly within the orthogonal array of discrete grid points, as when the boundary conditions are curved or slanted surfaces. The invention described herein provides finite differences methods for solving boundary value problems more accurately than with conventional finite differences methods, particularly when curved or slanted boundary surfaces correspond to terminations of a known analytical function.
Owner:PERKINELMER U S LLC
Relieved-channel, bonded heat exchanger
InactiveUS20090250196A1Minimal temperature differentialImprove structural strengthCosmonautic environmental control arrangementIncreasing energy efficiencyPlate heat exchangerEngineering
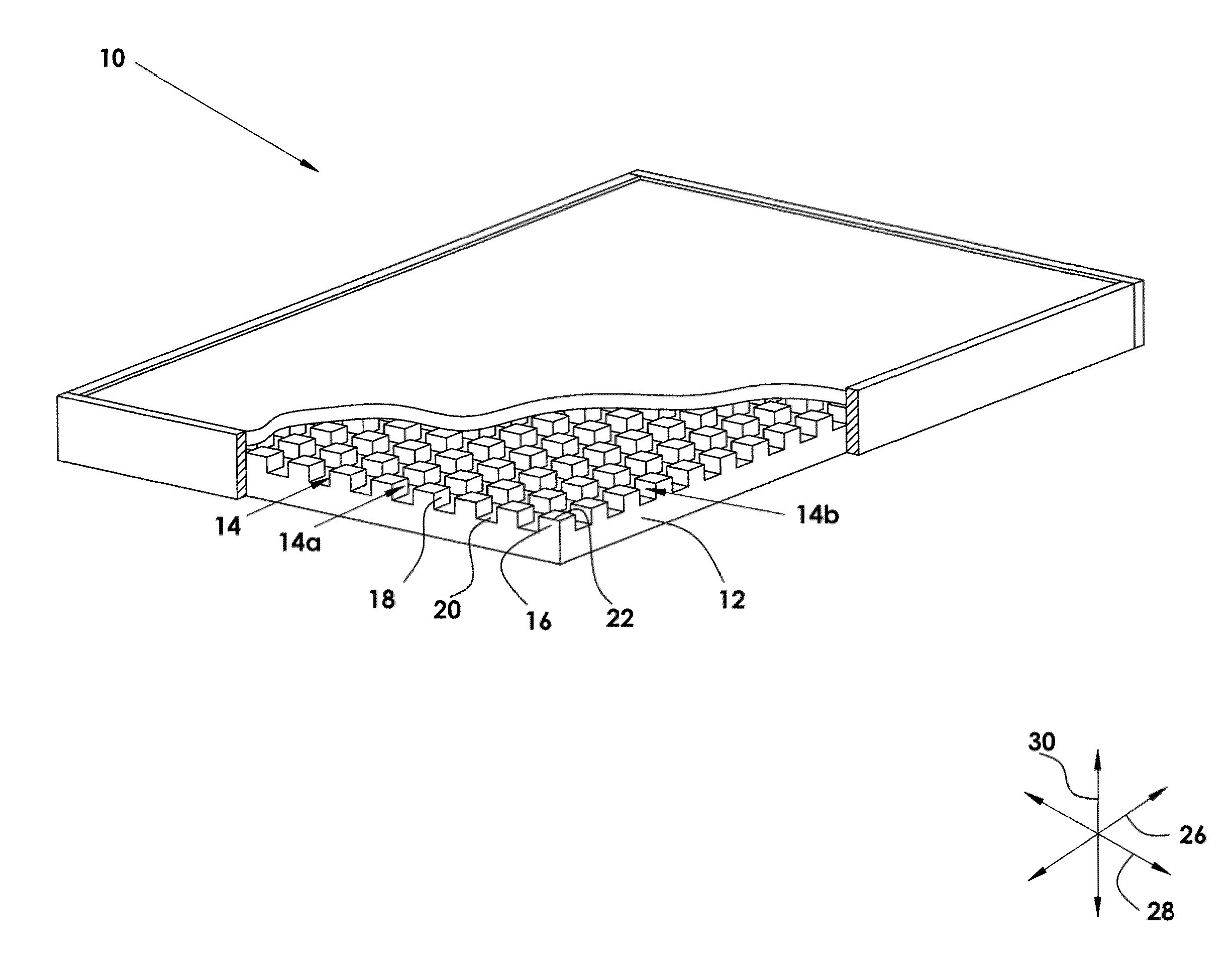
A panel assembly for exchanging heat with an ambient environment maintains minimal temperature differential by virtue of operation as a heat pipe apparatus. Panels of a composite material having excellent structural strength and structural stiffness but comparatively modest thermal conductivity are machined as mirror images of one another. Two orthogonal arrays of parallel channels are machined in the faces of two panels, each intersection of channels forming and bounded by pedestals having a lower, broader base with a narrower upper portion extending from a shoulder of the base portion of the pedestals. The pedestals, in turn, form the bounds of the channels, each having a deeper and a narrower aspect extending along the bases of all the pedestals. Channels have a broader aspect extending along near the tops of the pedestals.
Owner:UTAH STATE UNIVERSITY
Tiled passive matrix electro-luminescent display
ActiveCN101809644AHigh resolutionLuminance artifacts are annoyingStatic indicating devicesSolid-state devicesDisplay deviceEngineering
A tiled, passive-matrix, EL display, including two or more EL tiles, each EL tile including an array of rows and columns of light-emitting elements, each light-emitting element being formed from a light-emitting layer that is sandwiched between an orthogonal array of row and column electrodes wherein each of the two or more EL tiles further include at least one row driver; at least one column driver for operating in conjunction with each of the at least one row drivers to control the flow of electrons between the row and column electrodes to control the emission of light from each of the light-emitting elements, with a first exception that when the boundary between the two tiles is to be illuminated, then the number of rows of simultaneously illuminated rows of light-emitting elements within one tile is less than the predetermined number.
Owner:GLOBAL OLED TECH
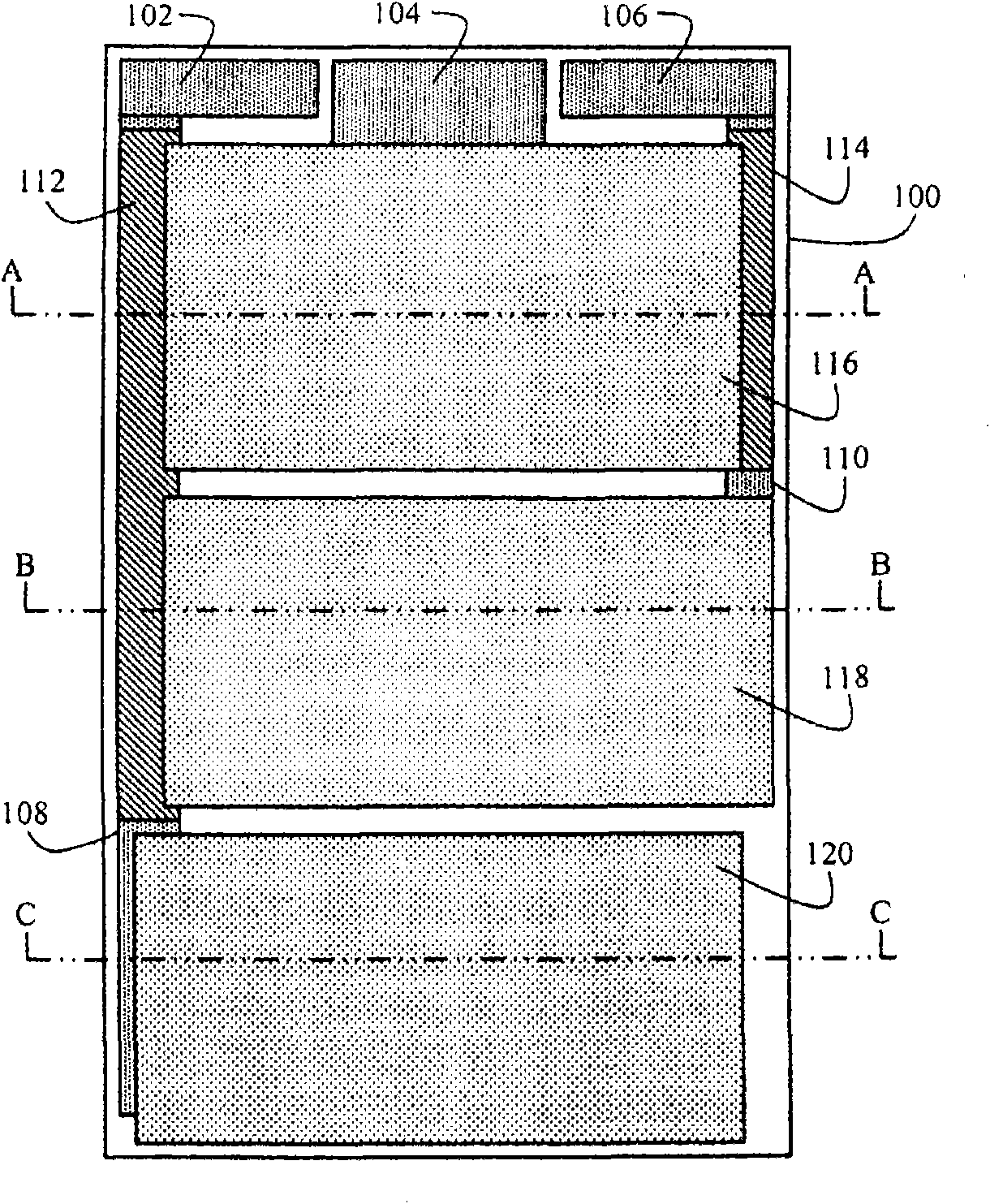
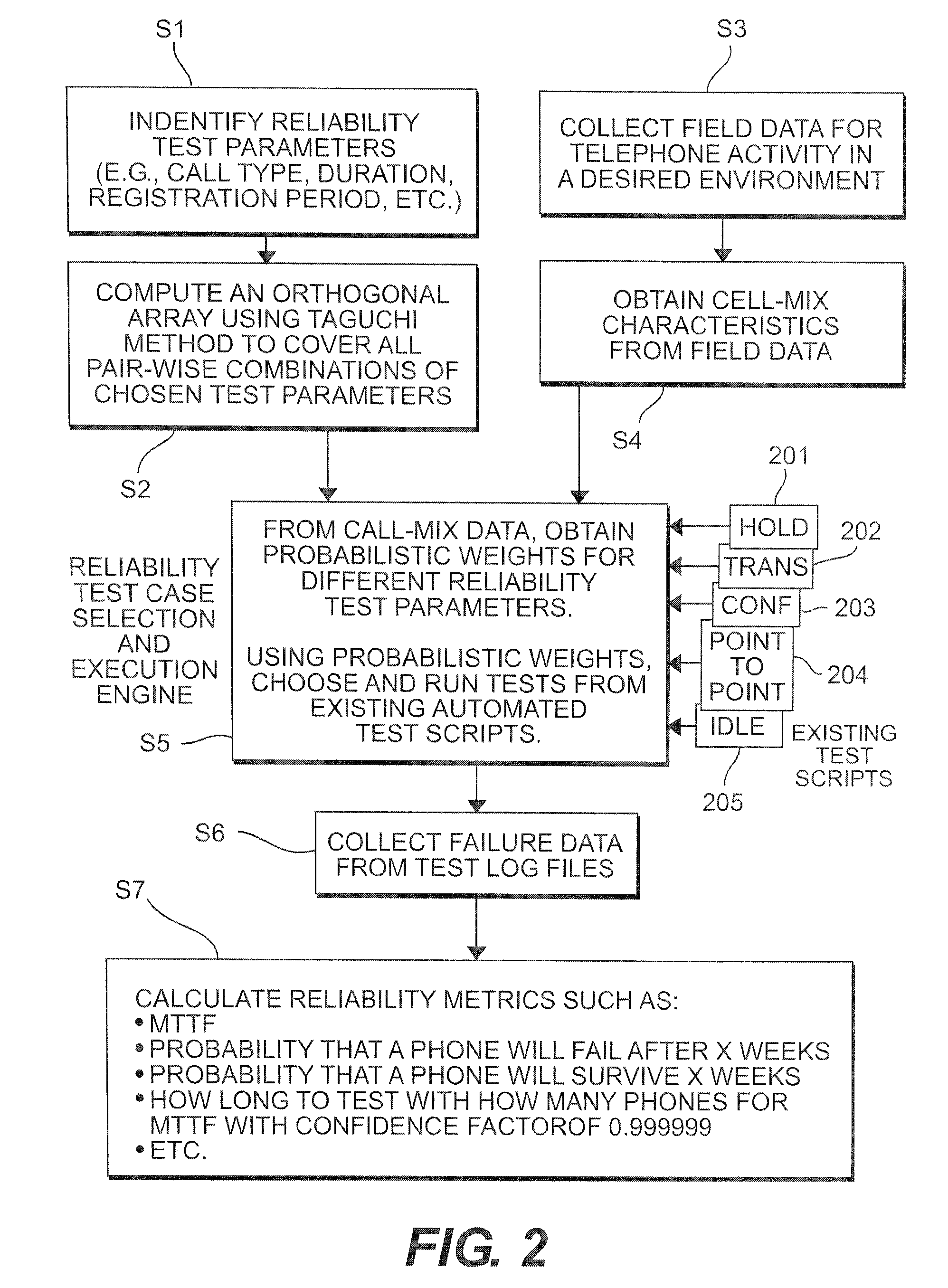
Method for generating reliability tests based on orthogonal arrays and field data
ActiveUS8019049B2Efficient testingEfficient combinationElectronic circuit testingResistance/reactance/impedenceTest scriptField data
A method for generating reliability tests for a telephone system is based upon sampling an orthogonal array which covers various combinations of test parameters. Field data is collected of actual telephone activity on a telephone system. The field data is evaluated so as to determine call-mix characteristics. Probabilistic weights for the different call-mix characteristics are obtained, and then the probabilistic weights are used to sample the test case scenarios generated in the orthogonal array which have the same call-mix characteristics. These test case scenarios are used to run tests on the telephone system. These tests are preferably performed using automated test scripts. After the test data is collected, reliability metrics are calculated from the test data.
Owner:AVAYA INC
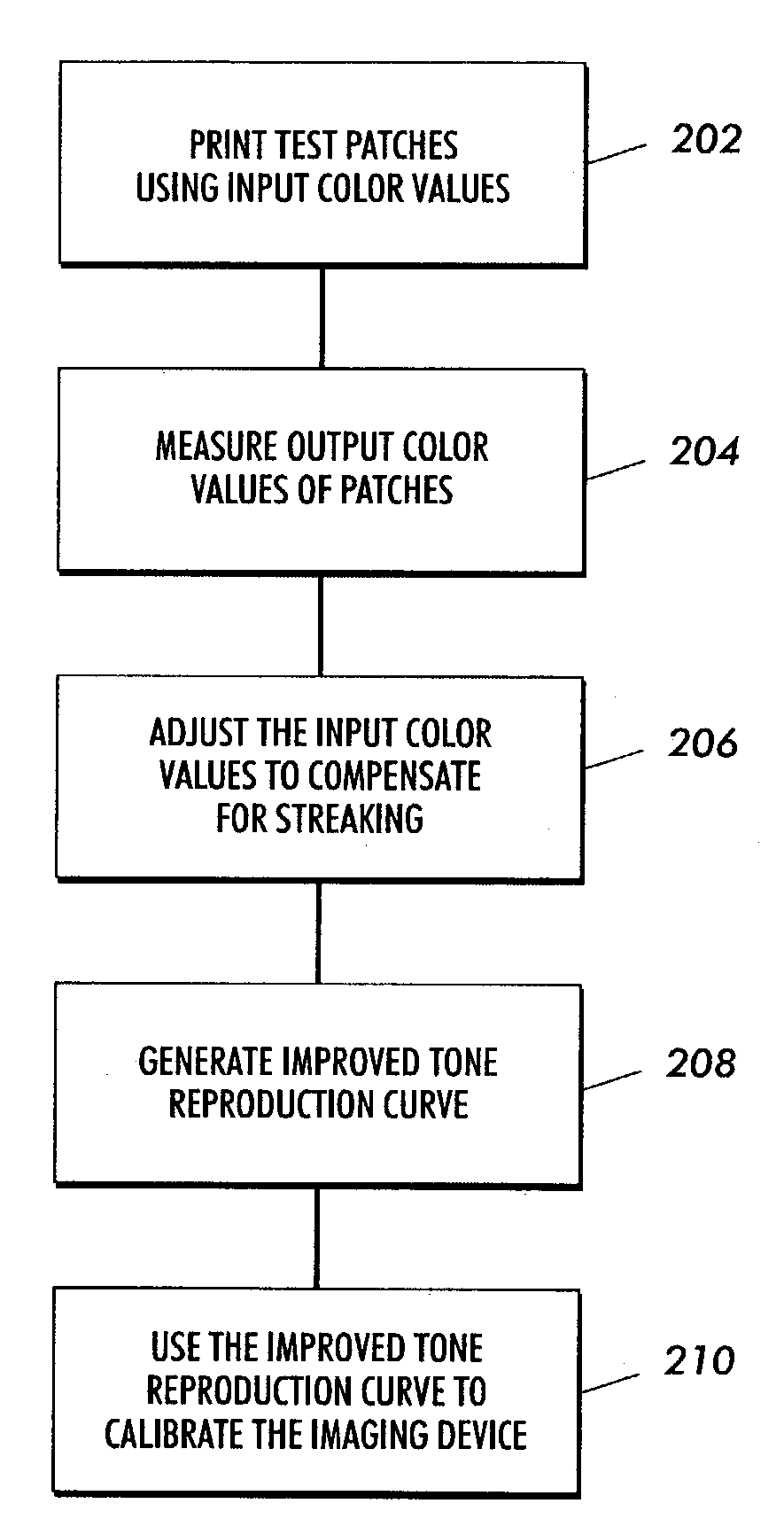
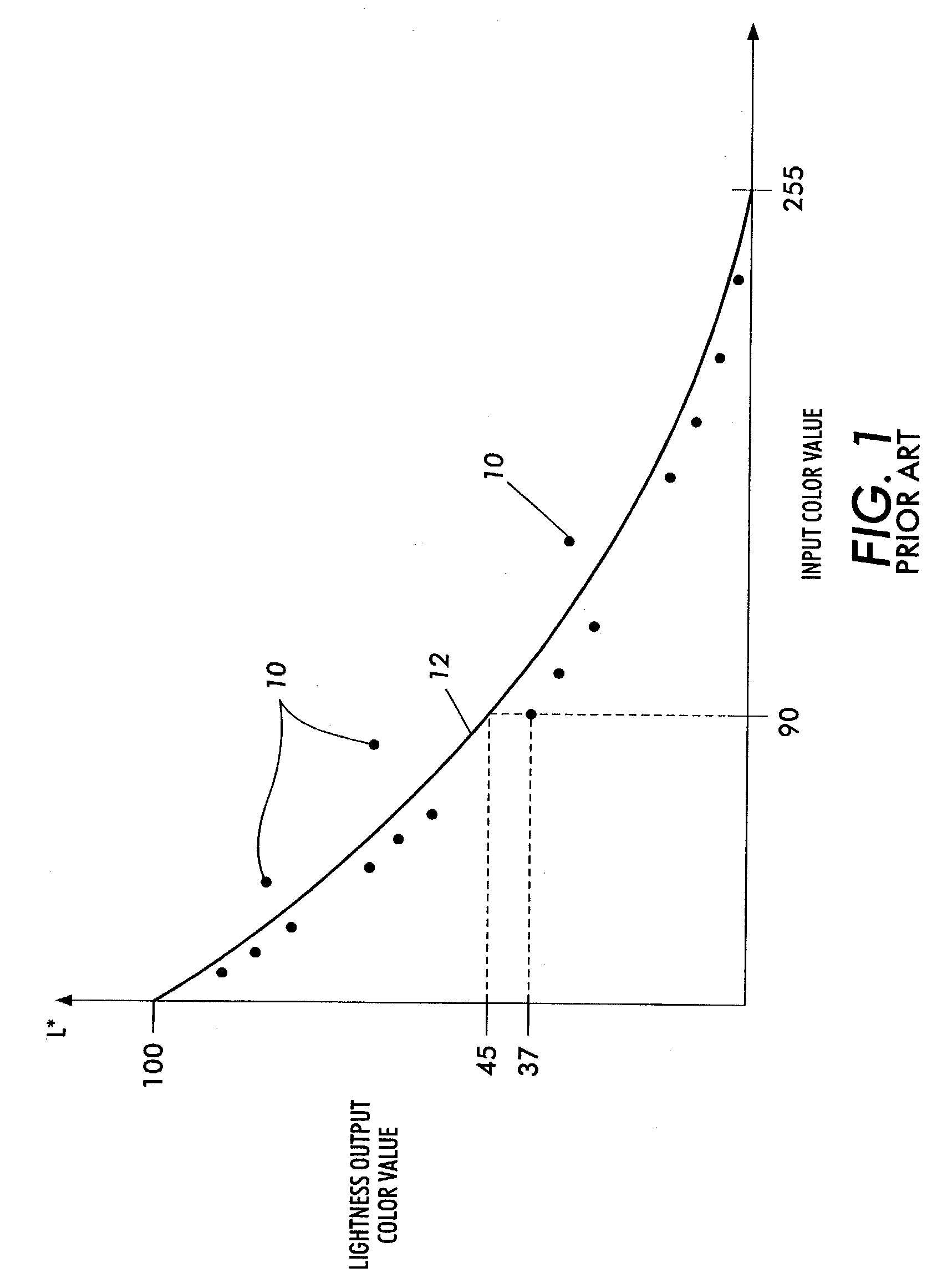
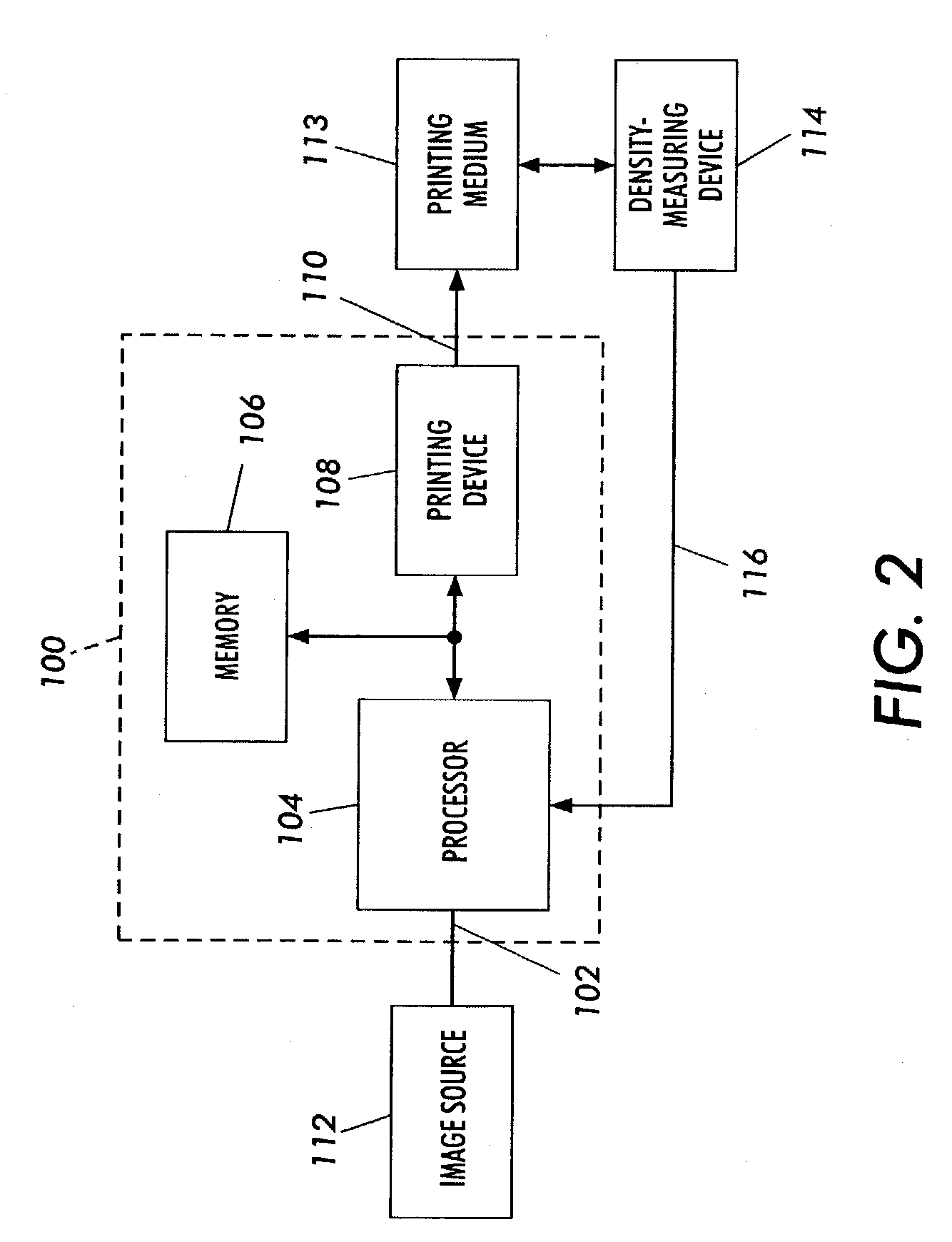
Calibration method for an imaging device
ActiveUS7315394B2Reduce adverse effectsReduce impactImage enhancementDigitally marking record carriersTest patchEquivalent input
A method includes forming a plurality of test patches in an array of orthogonal rows. The test patches are formed by using at least one printhead in an imaging machine. Each of the test patches is associated with a respective one of a plurality of initial input color values. The array of test patches includes a plurality of rows of varied-input test patches and at least one row of first equivalent-input test patches. A respective output color value of each of the test patches is measured. At least one first mathematical relationship is generated based on the output color values of the at least one row of first equivalent-input test patches. A plurality of adjusted input color values are calculated for respective ones of the varied-input test patches. Each adjusted input color value is calculated based upon the generated at least one first mathematical relationship. A second mathematical relationship is computed between the adjusted input color values and the output color values. The imaging machine is calibrated by using the second mathematical relationship.
Owner:XEROX CORP
Asynchronous clock-less digital logic path planning apparatus and method
A hybrid of initial time consuming phase of a Single Directional Dijkstra's Algorithm is embodied on an unclocked CMOS logic chip using a parallelized approach with Asynchronous Digital Logic (ADL). The chip includes a a plurality of addressable configurable cells arranged as a multidimensional orthogonal array. The cell array only executes mathematical operations based on a communication between immediately adjacent cells.
Owner:NOKOMIS
System and method for identifying a manufacturing tool causing a fault
InactiveUS7197414B2Data processing applicationsSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementComputer moduleOrthogonal array
A system for identifying a manufacturing tool causing a failure, includes a data generating module generating factorial effect data, based on information on a failure lot group by using an orthogonal array, a chart generating module generating a factorial effect chart based on the factorial effect data, a selection module selecting failure lots caused by the same reason for a failure from among the failure lot group, based on the factorial effect chart, and an identification module identifying a manufacturing tool used as a common tool for the selected plurality of failure lots, based on history information of the manufacturing tool group.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
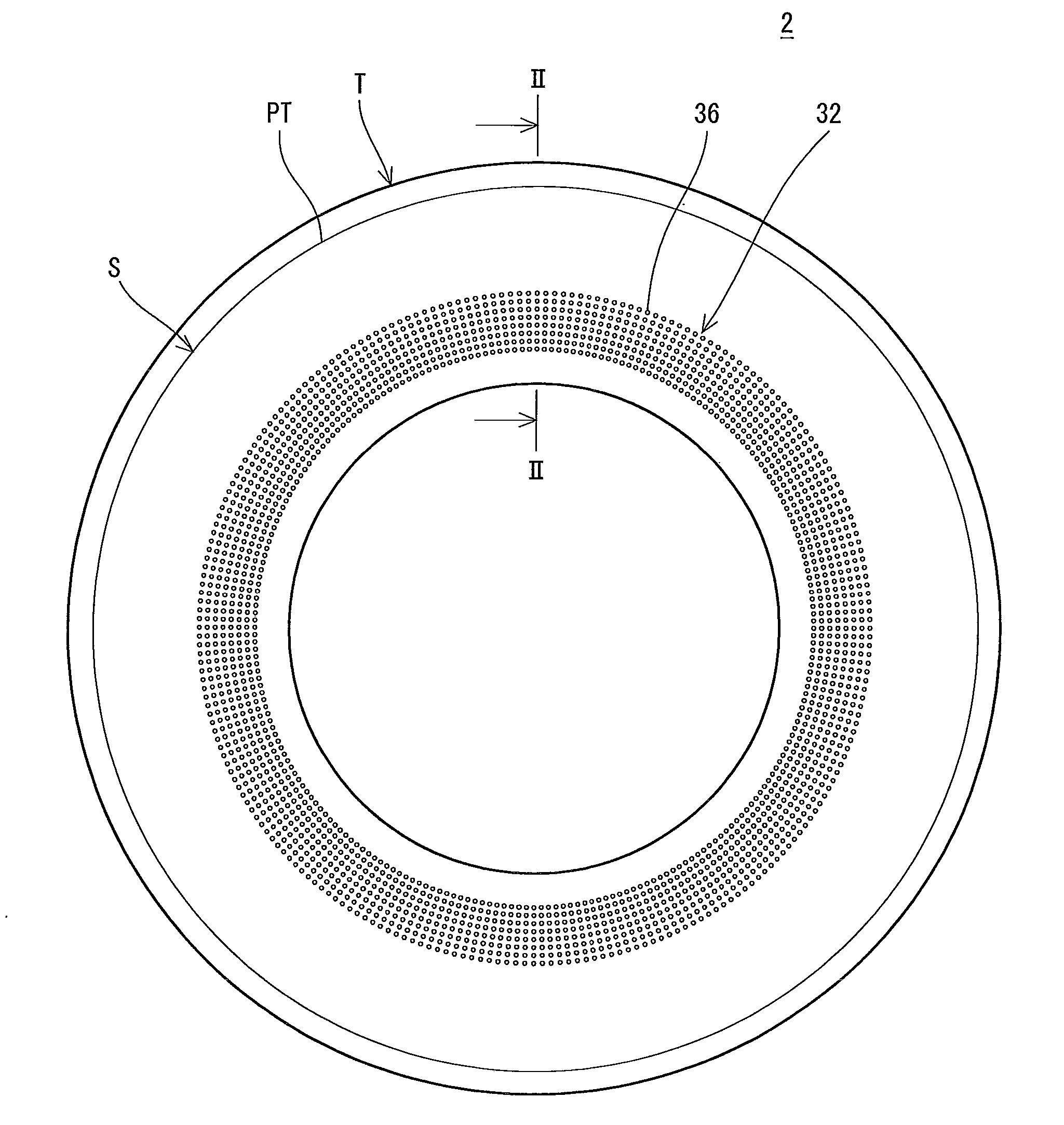
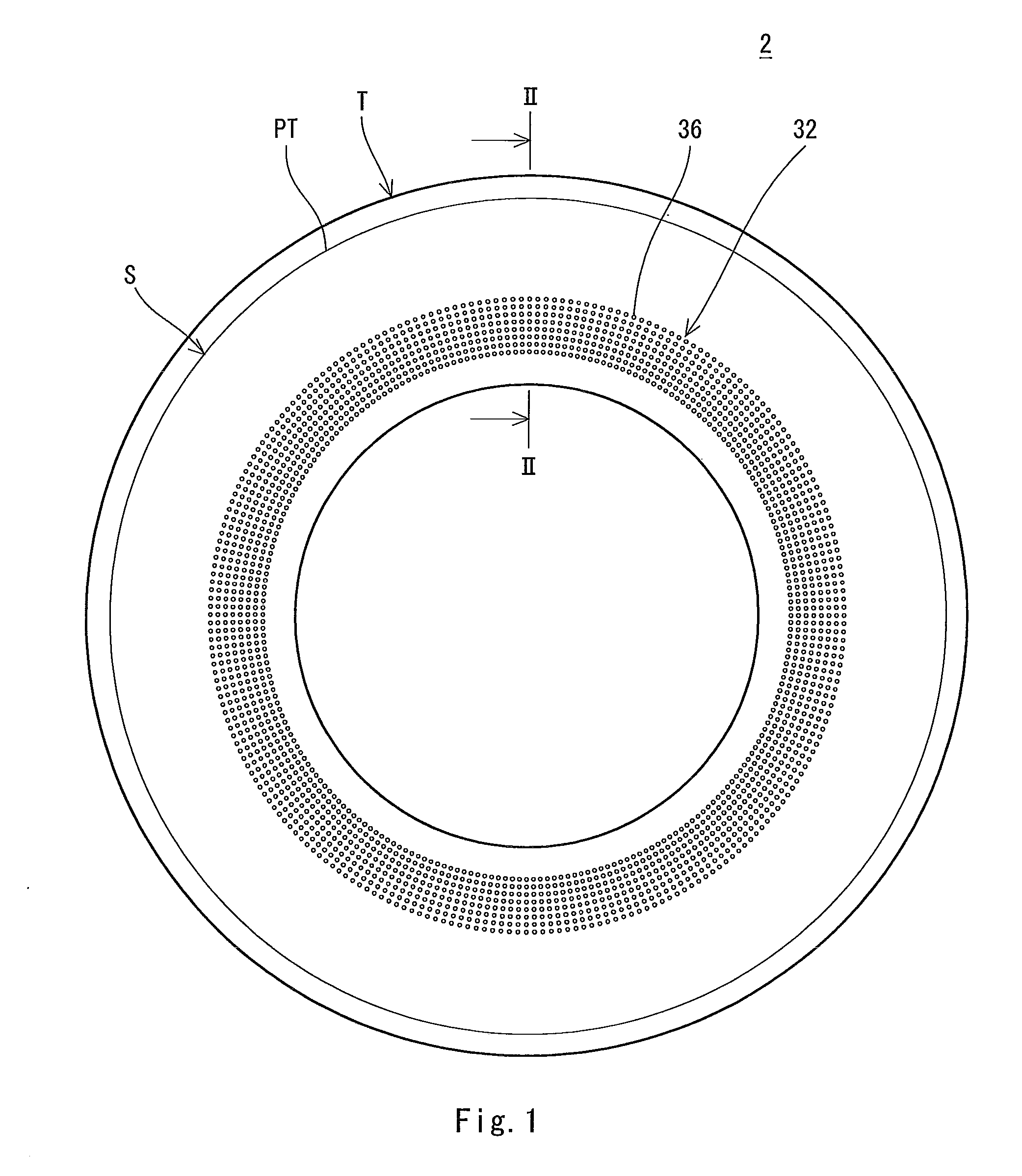
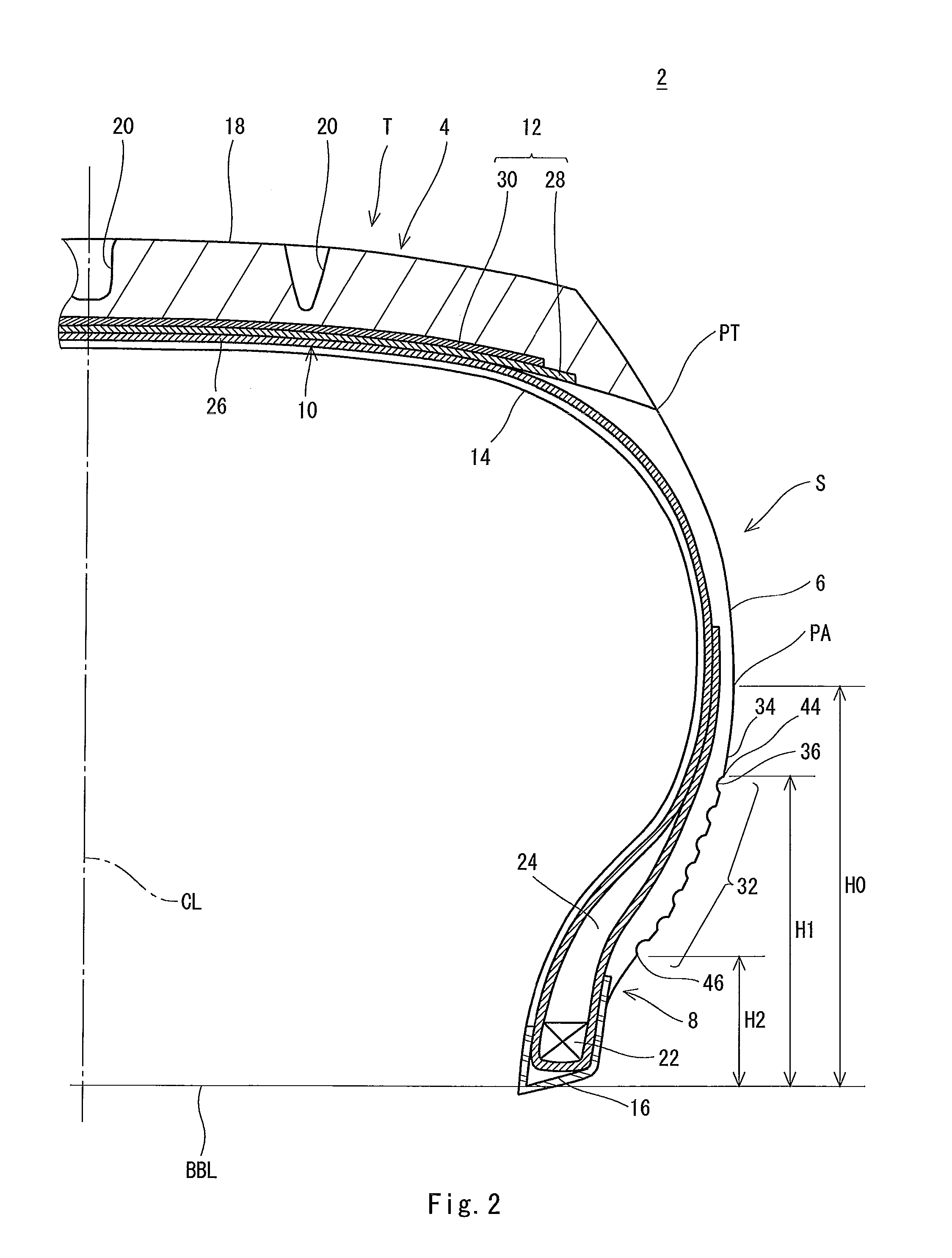
Pneumatic tire
InactiveUS20110108174A1Curb riseIncreased durabilityWithout separate inflatable insertsTyre measurementsEngineeringOrthogonal array
A tire (2) includes a tread portion (T) and a pair of side portions (S). An agitating portion (32) is provided on an inner part in a radial direction with respect to a position (PA) indicative of a maximum width over an external surface (34) of each of the side portions (S). The agitating portion (32) includes a large number of dimples (36) which are dented inward from the external surface. An edge of the dimple (36) has a circular contour. A ratio of a depth of the dimple (36) to an outside diameter of the dimple (36) is equal to or higher than 0.2 and is equal to or lower than 0.5. A ratio of a distance between a center of one of the dimples (36) and a center of the other dimple (36) which is close to the one of the dimples 36 to the outside diameter is equal to or higher than 1.2 and is equal to or lower than 2. It is preferable that the outside diameter of the dimple (36) should be equal to or greater than 3 mm and be equal to or smaller than 5 mm in the tire (482). It is preferable that an array pattern of the large number of dimples (36) should be an orthogonal array in the tire (2).
Owner:SUMITOMO RUBBER IND LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com