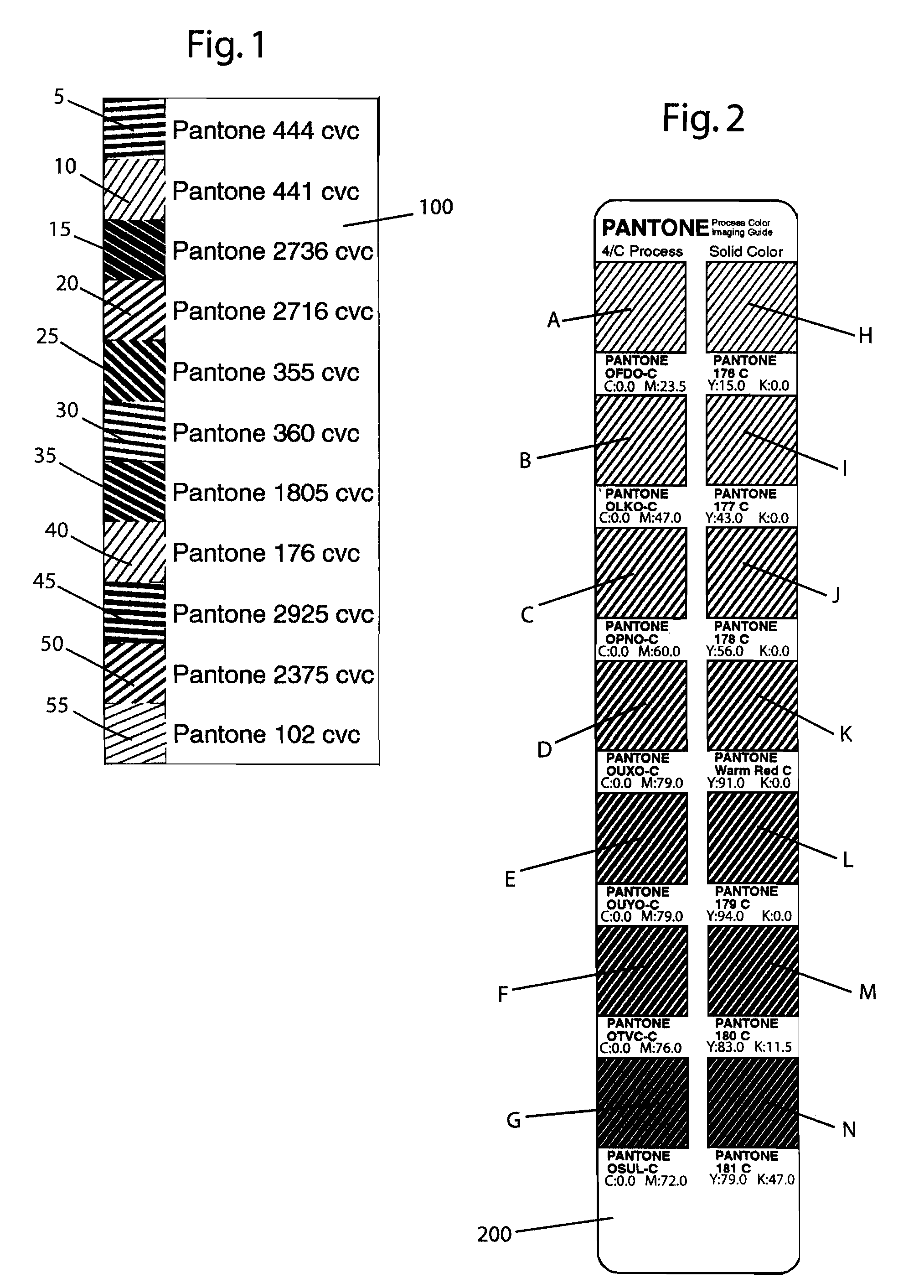
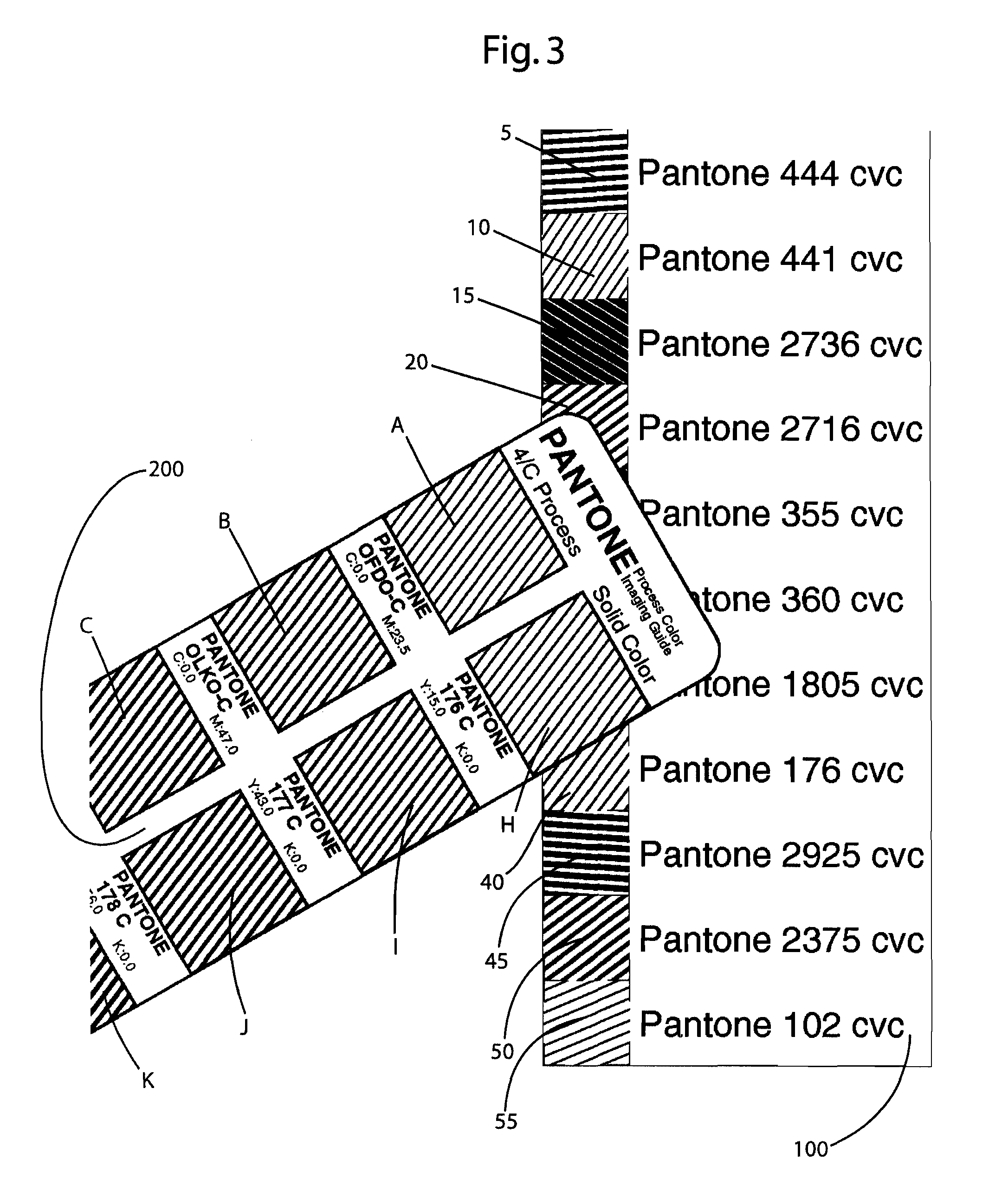
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
97 results about "Test patch" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A patch test is a method used to determine whether a specific substance causes allergic inflammation of a patient's skin. Any individual suspected of having allergic contact dermatitis or atopic dermatitis needs patch testing.
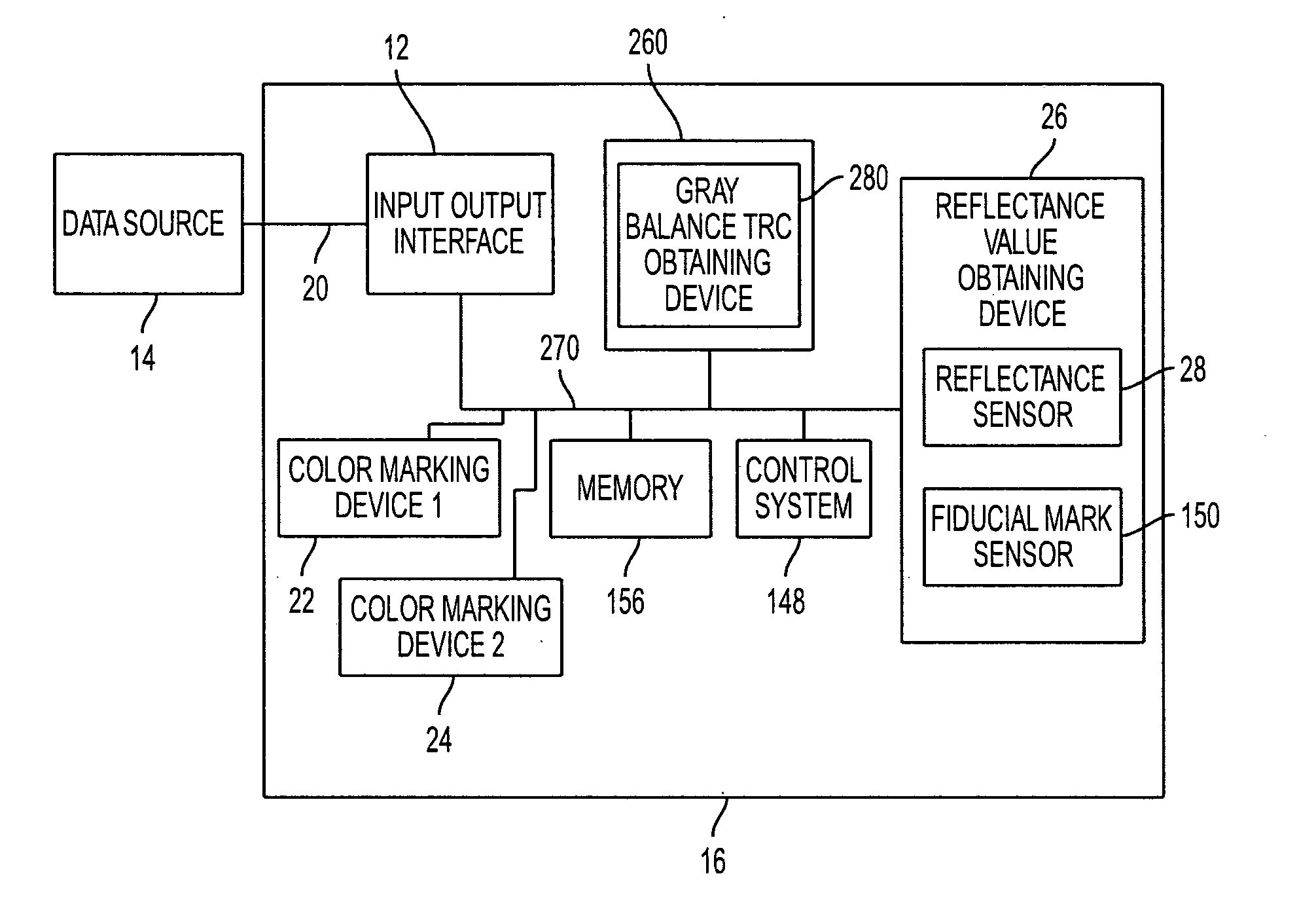
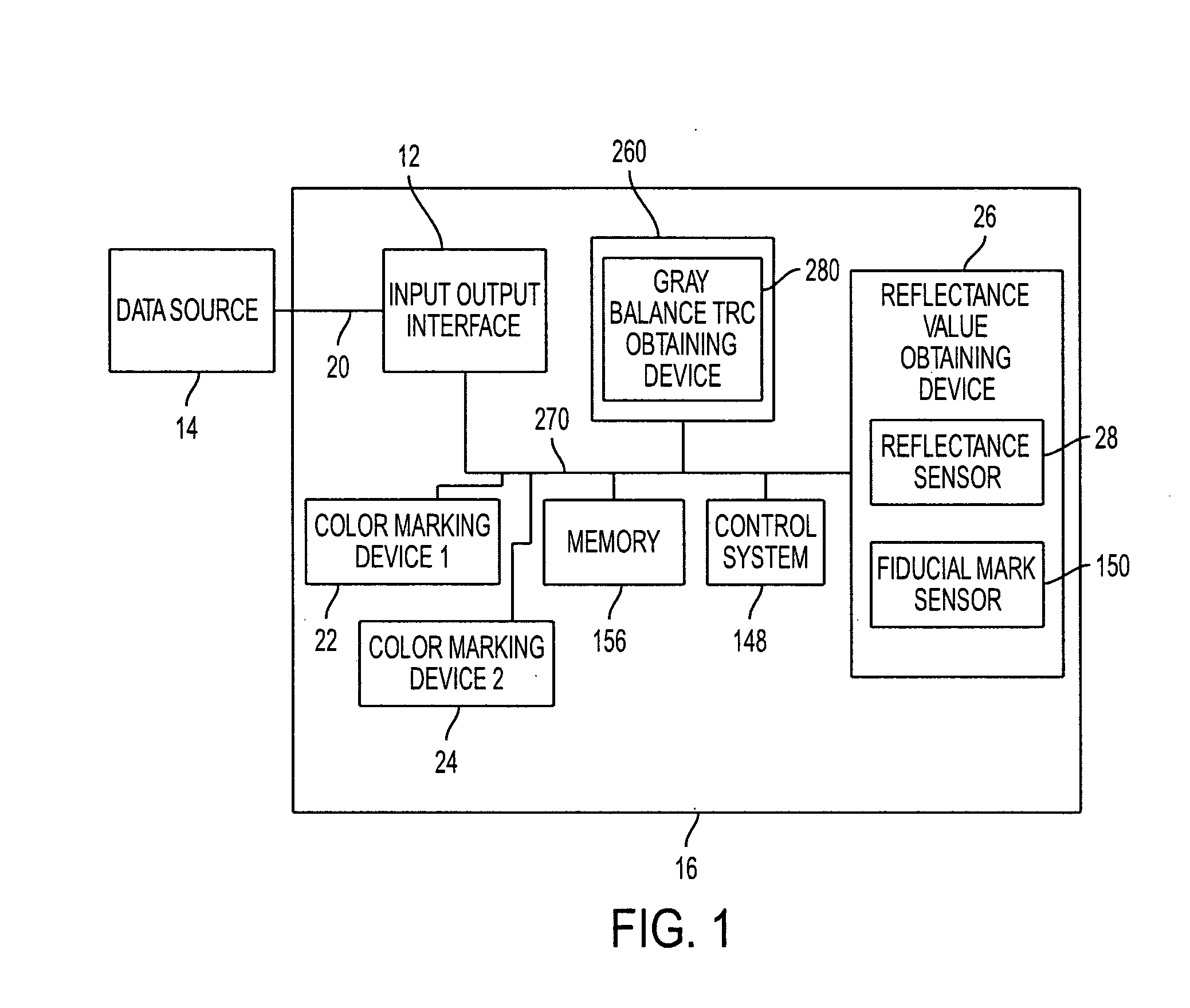
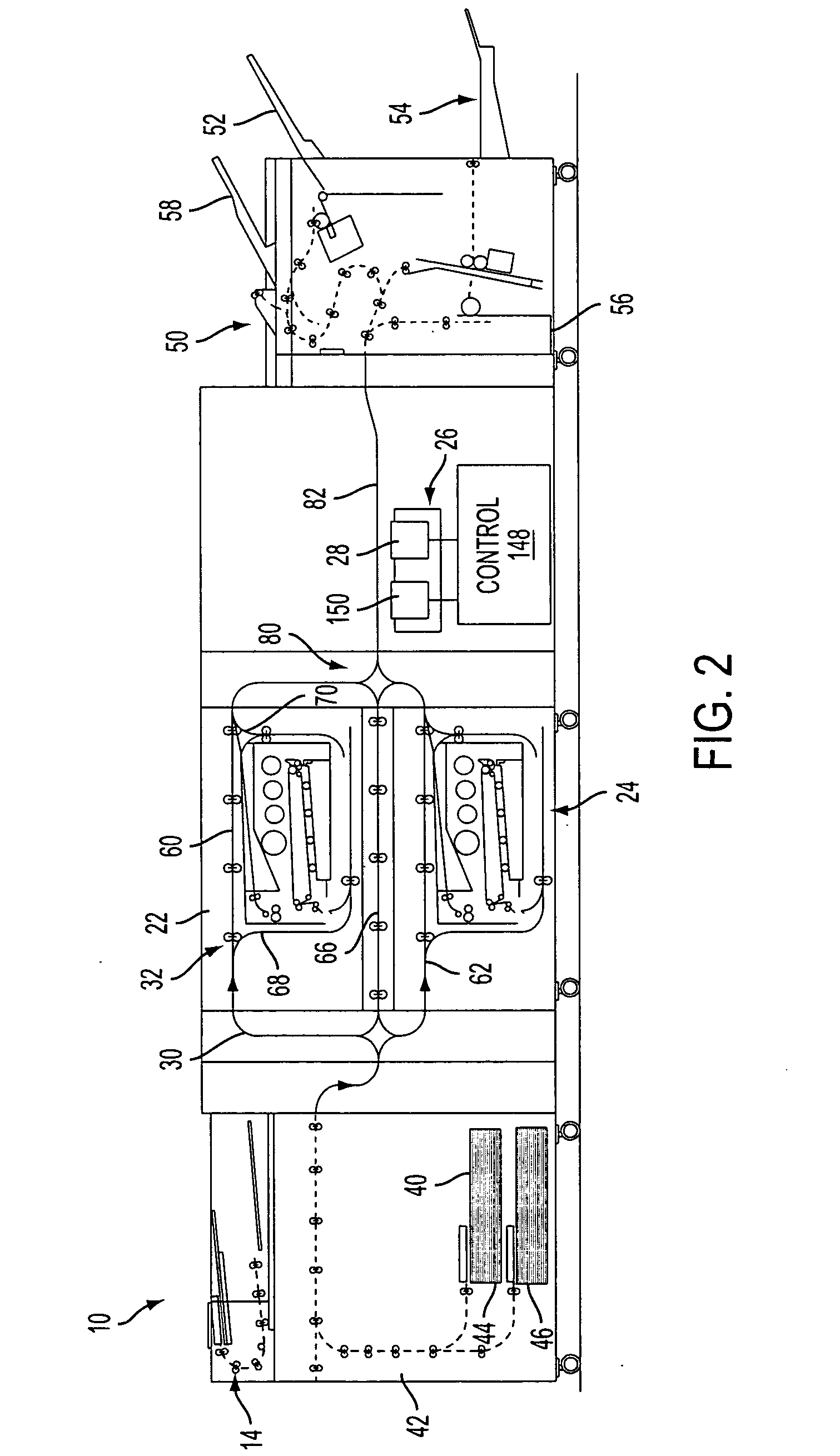
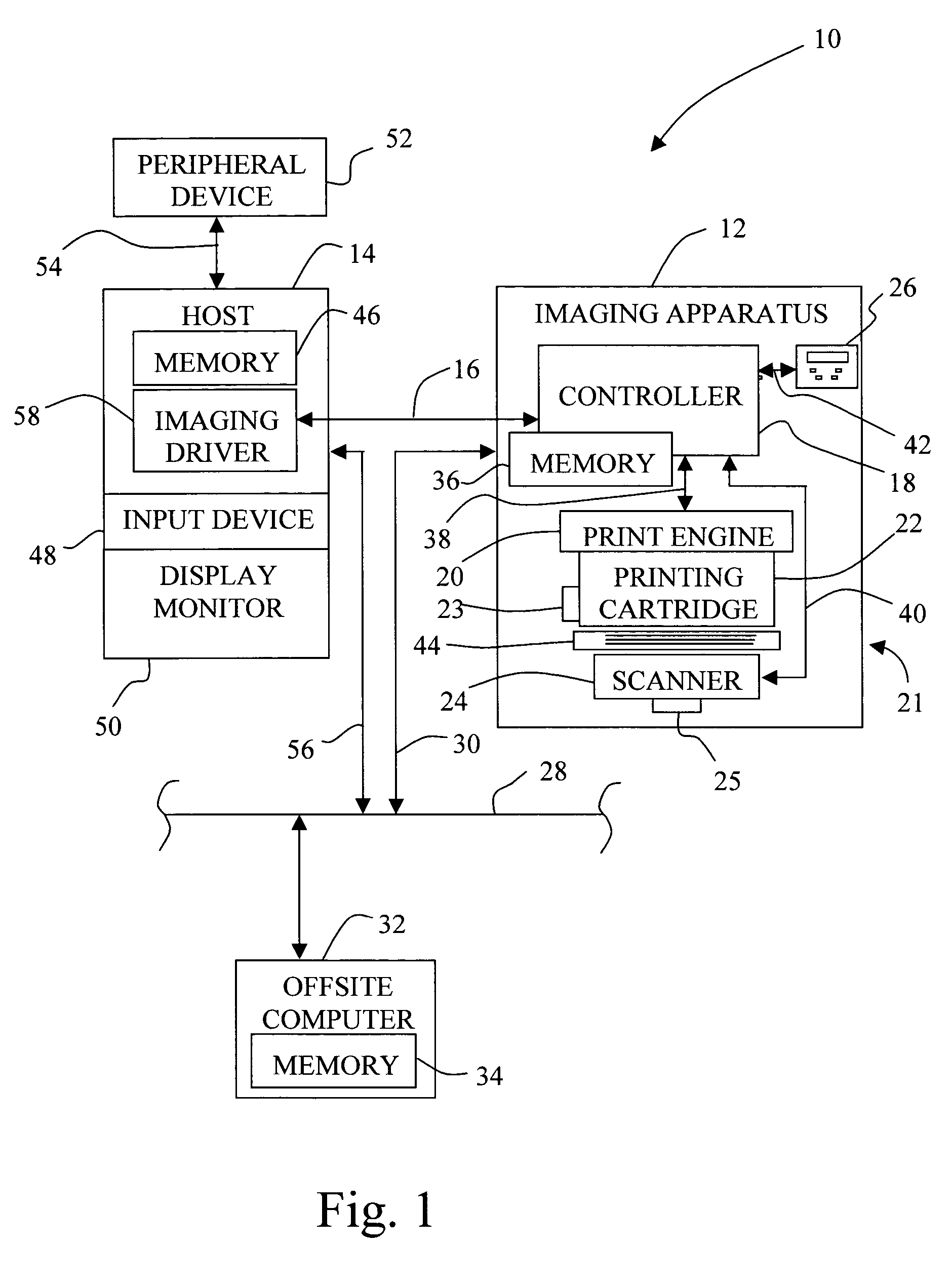
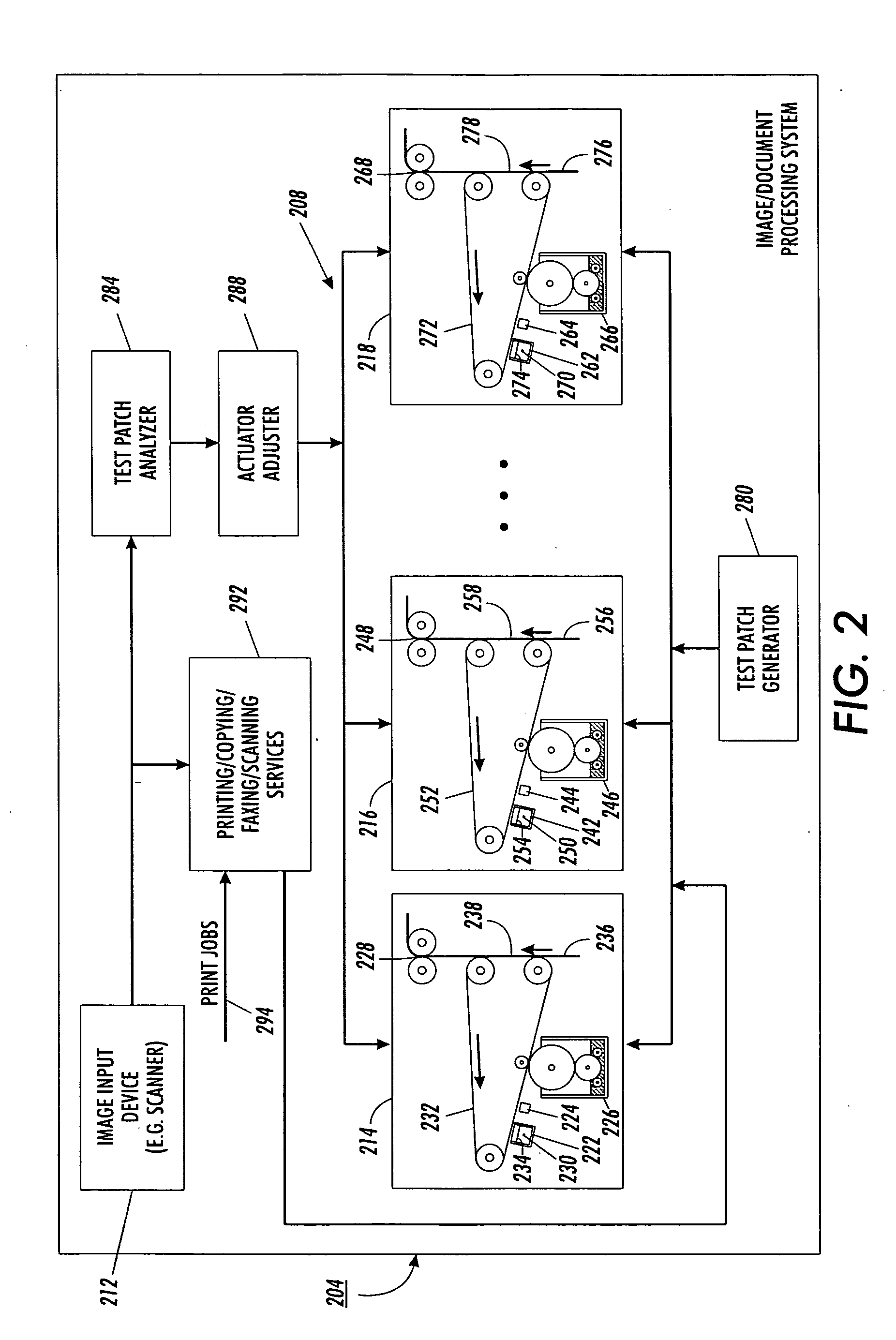
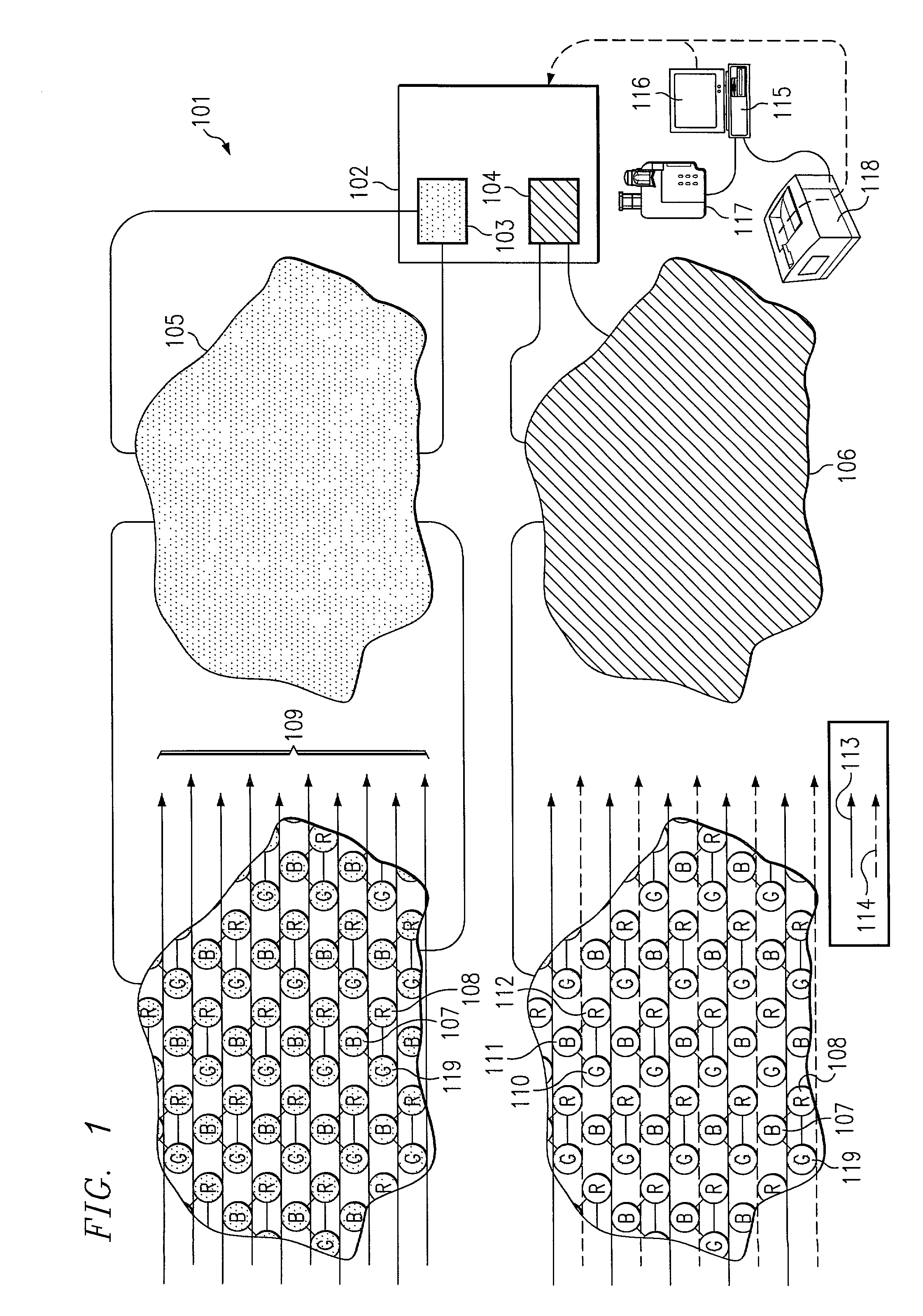
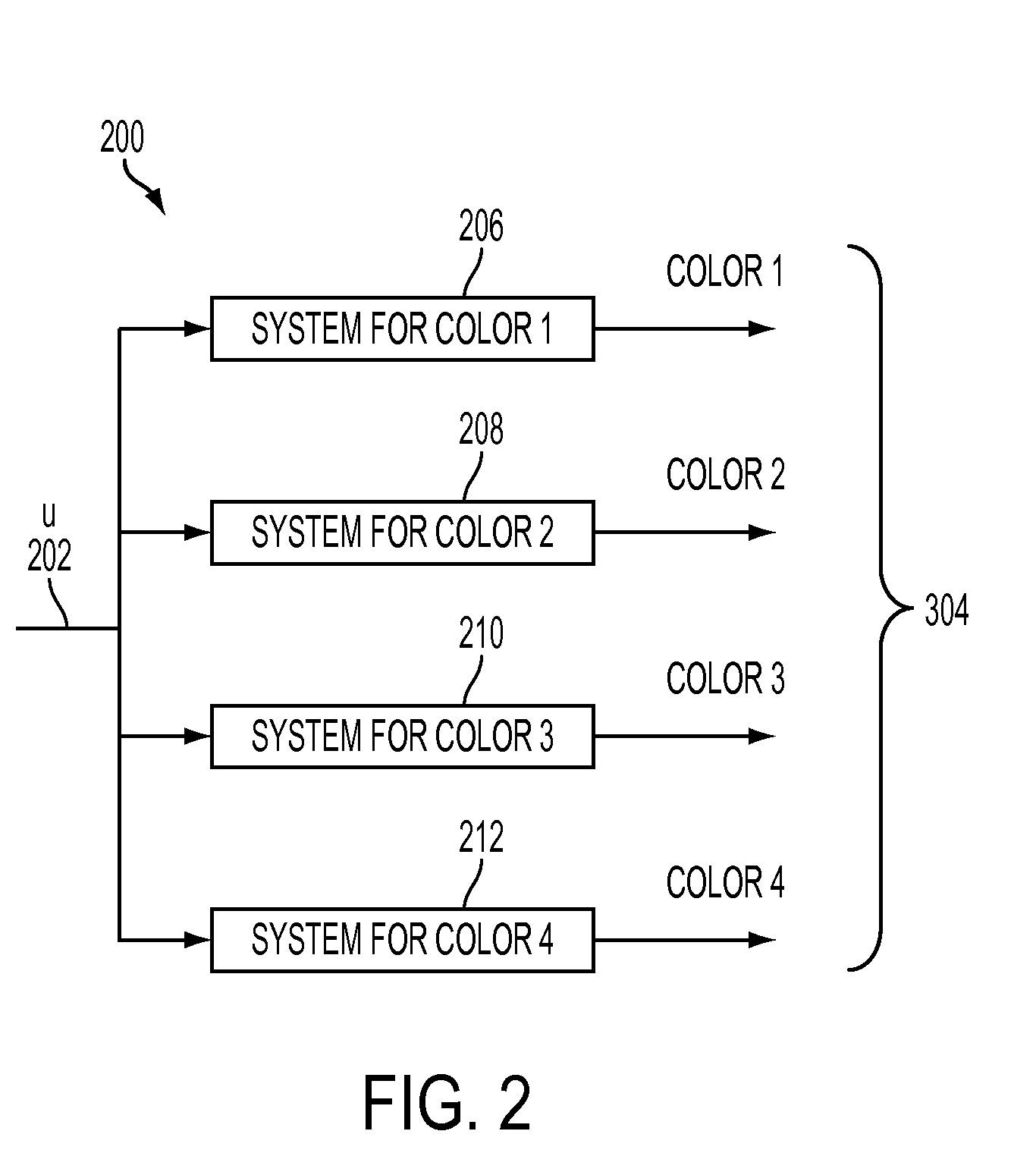
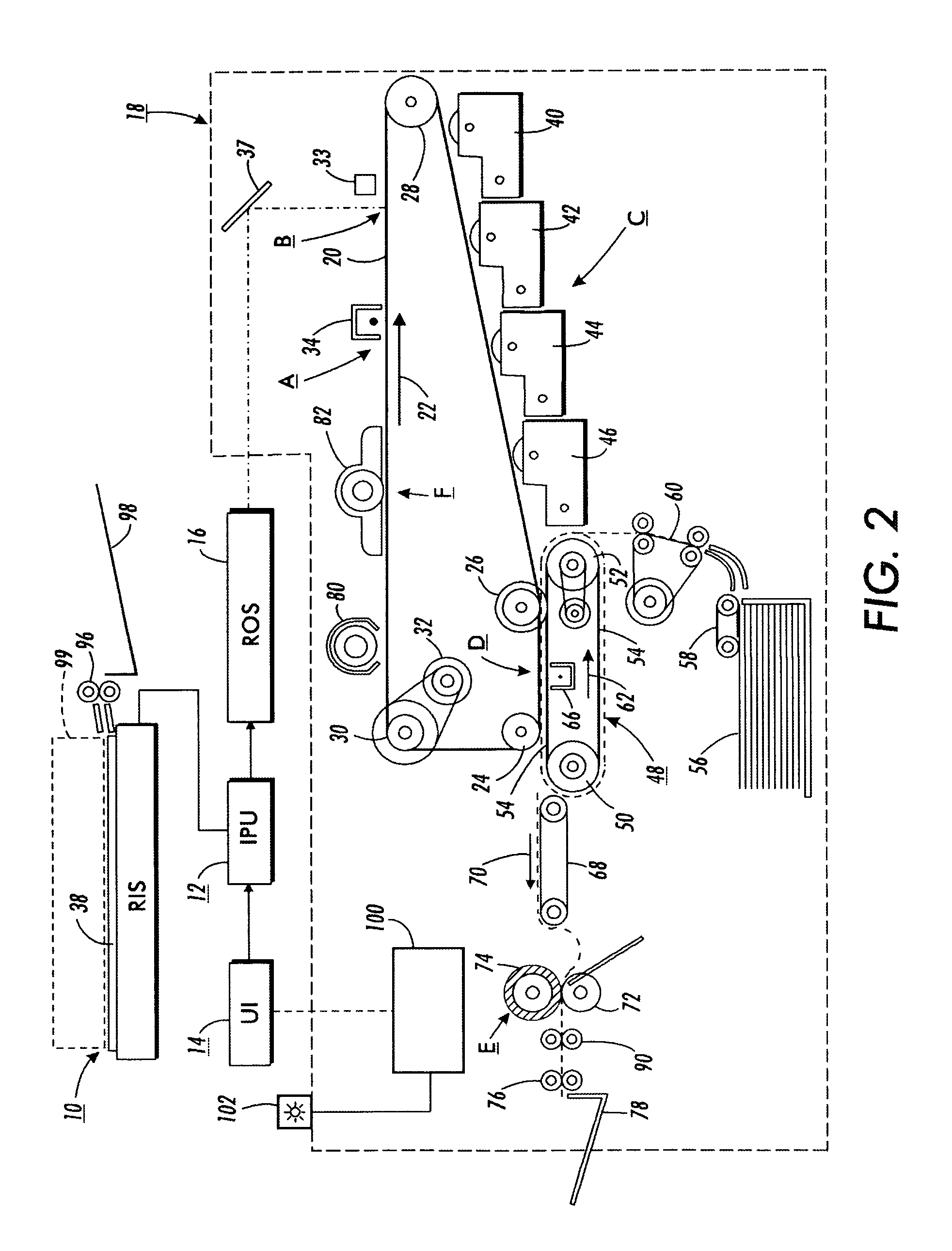
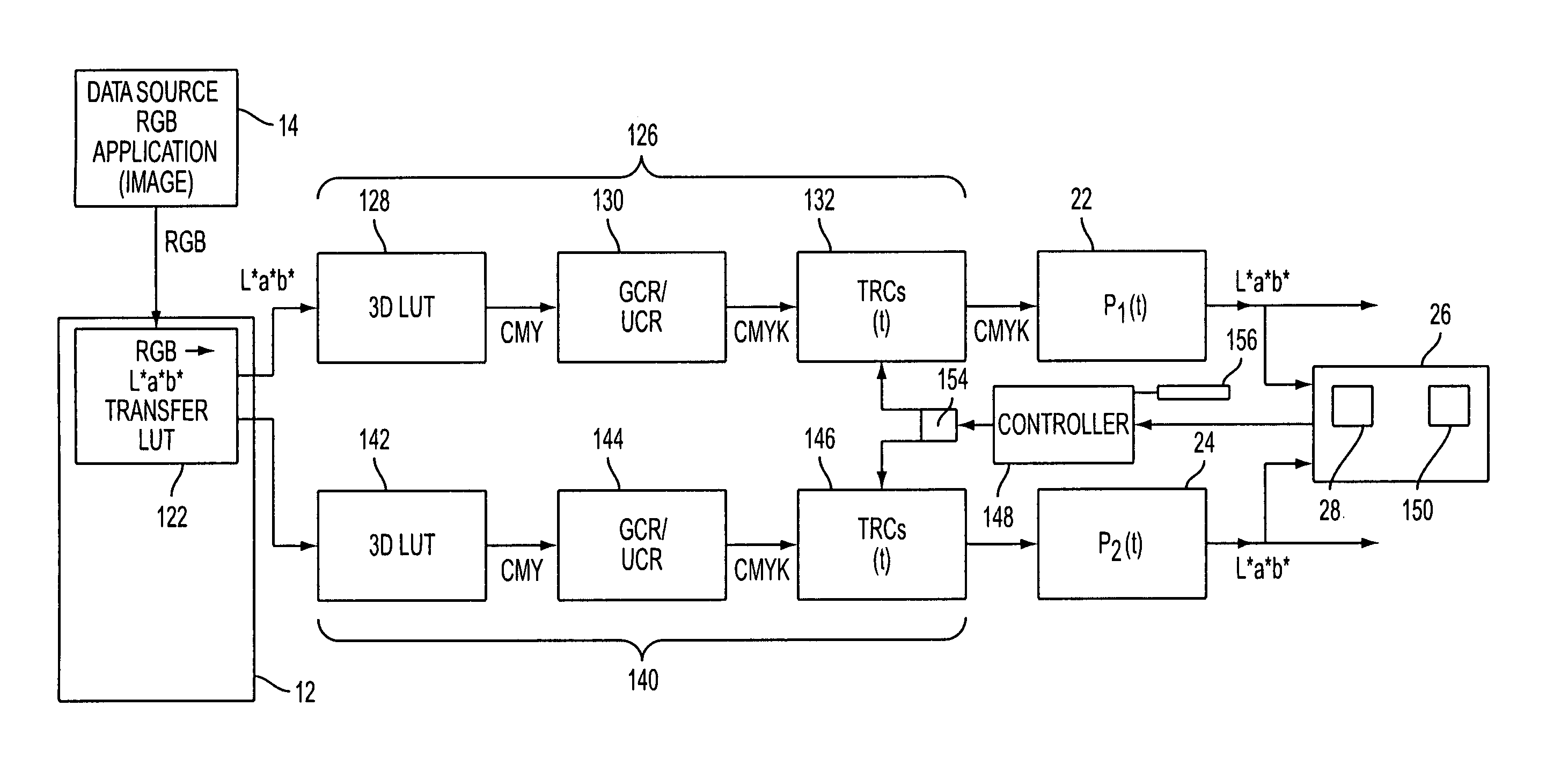
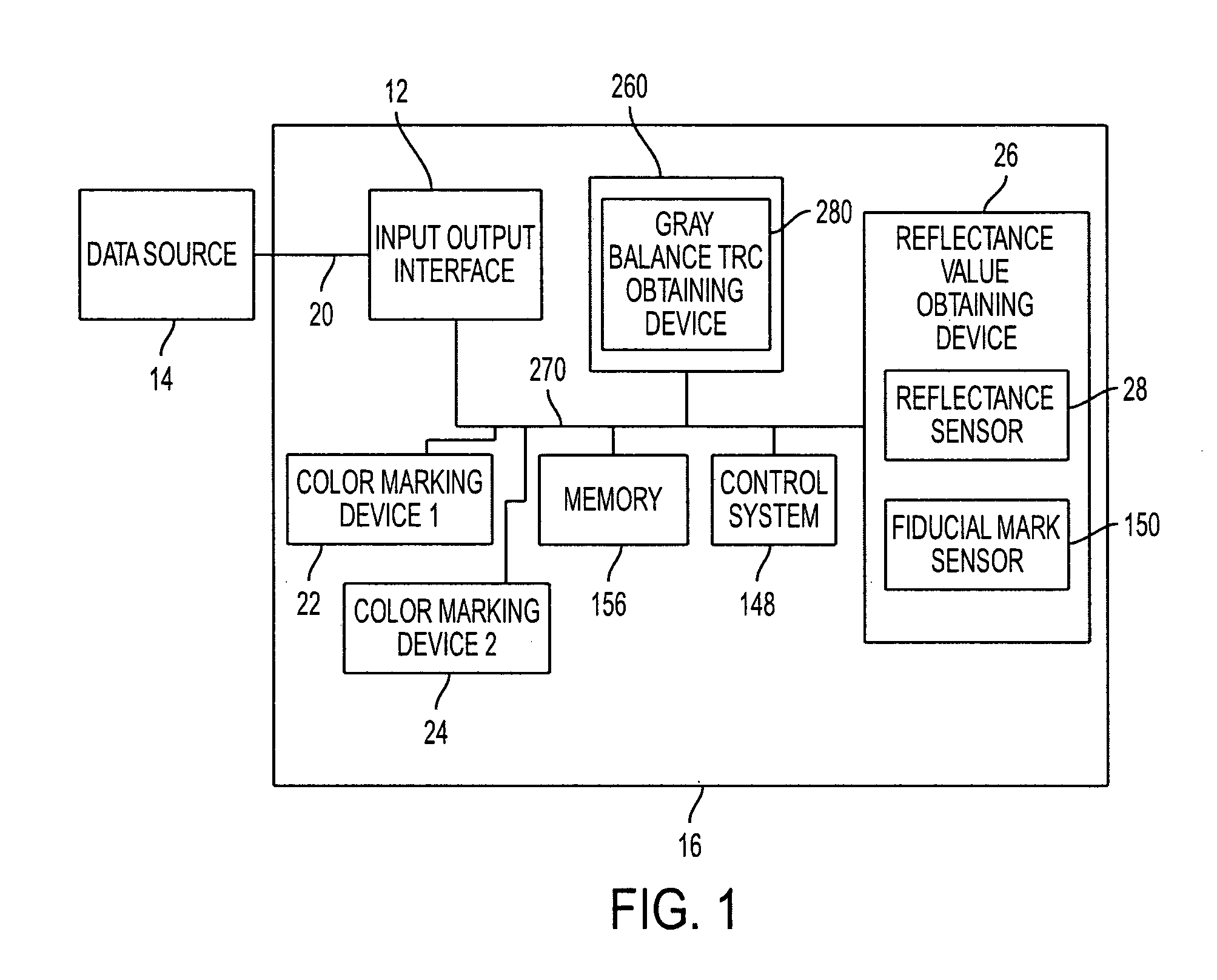
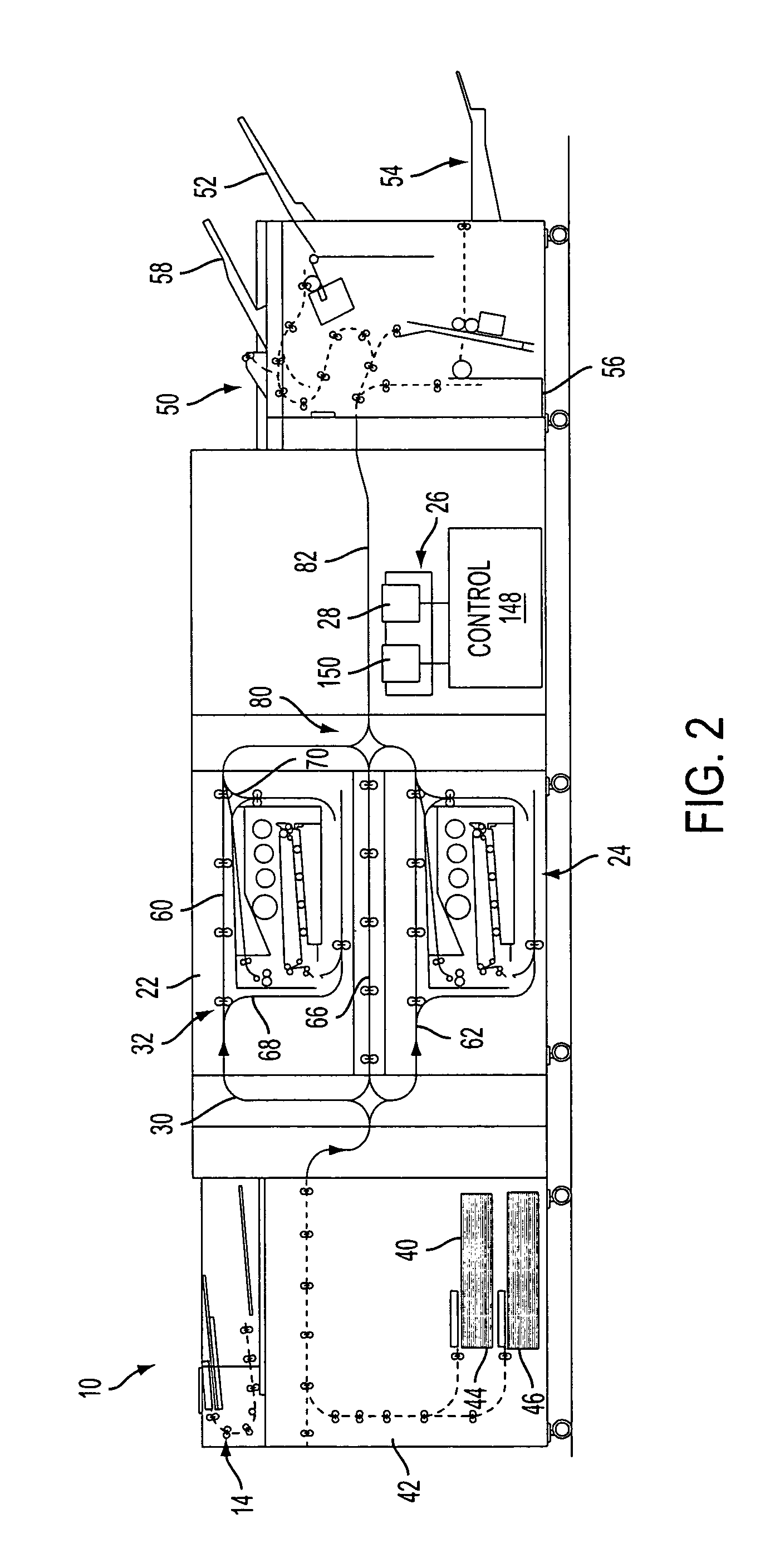
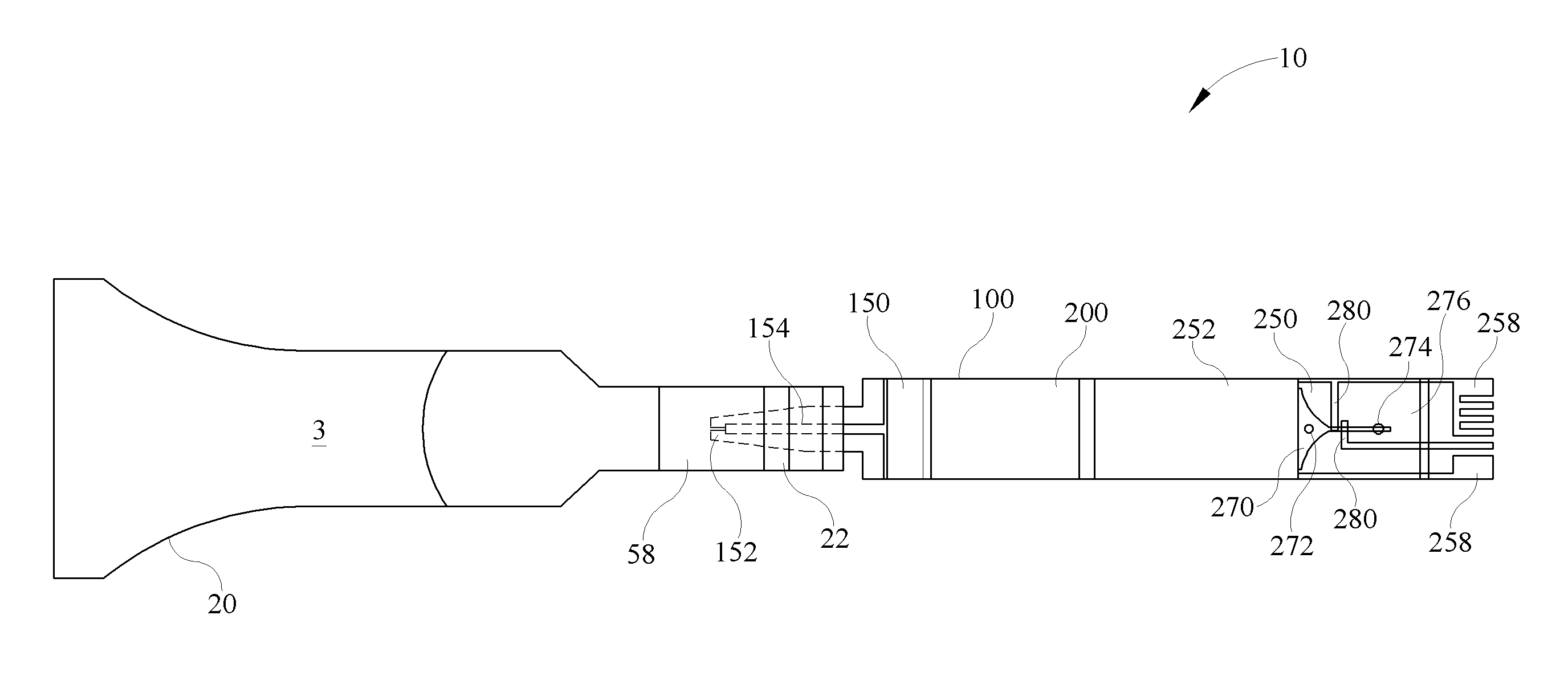
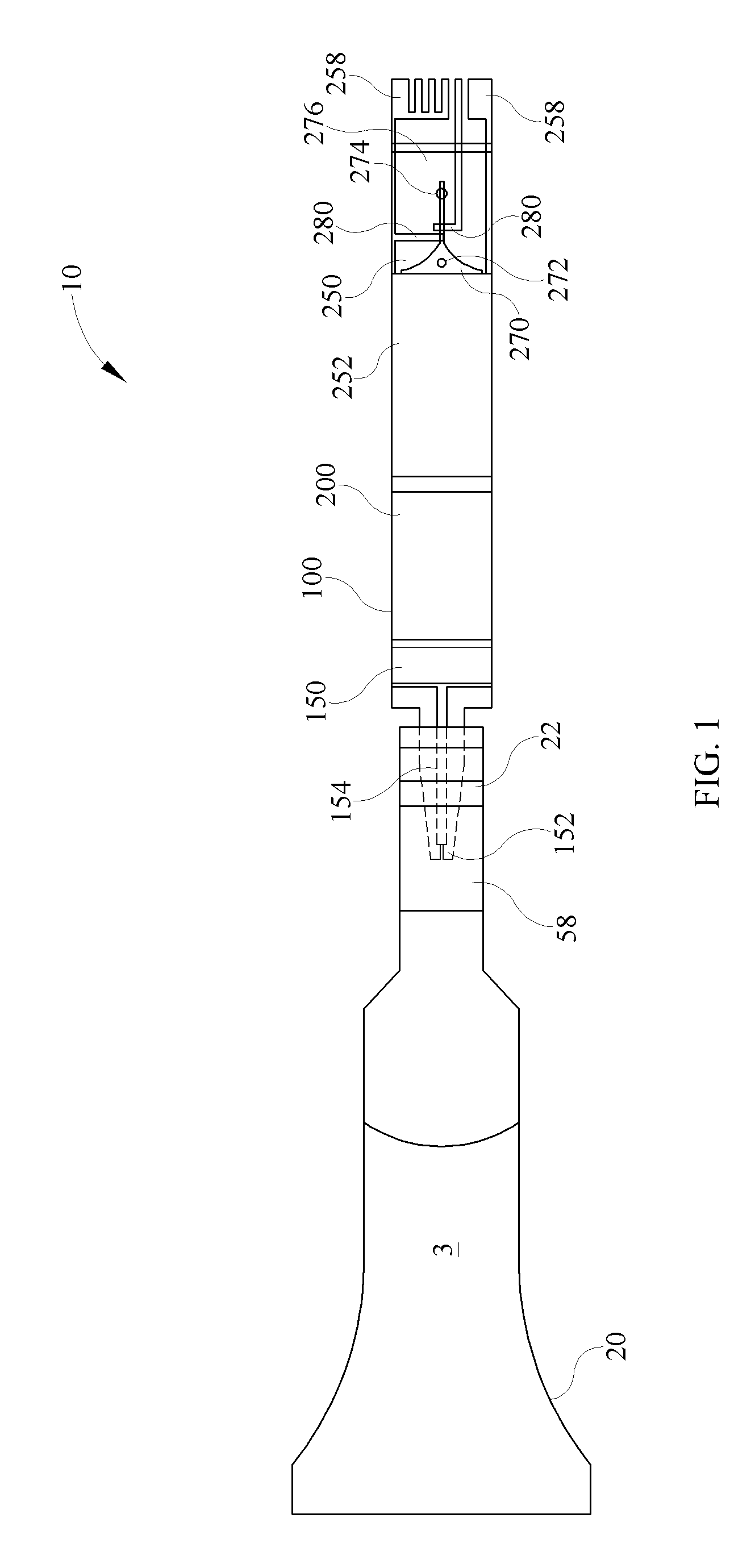
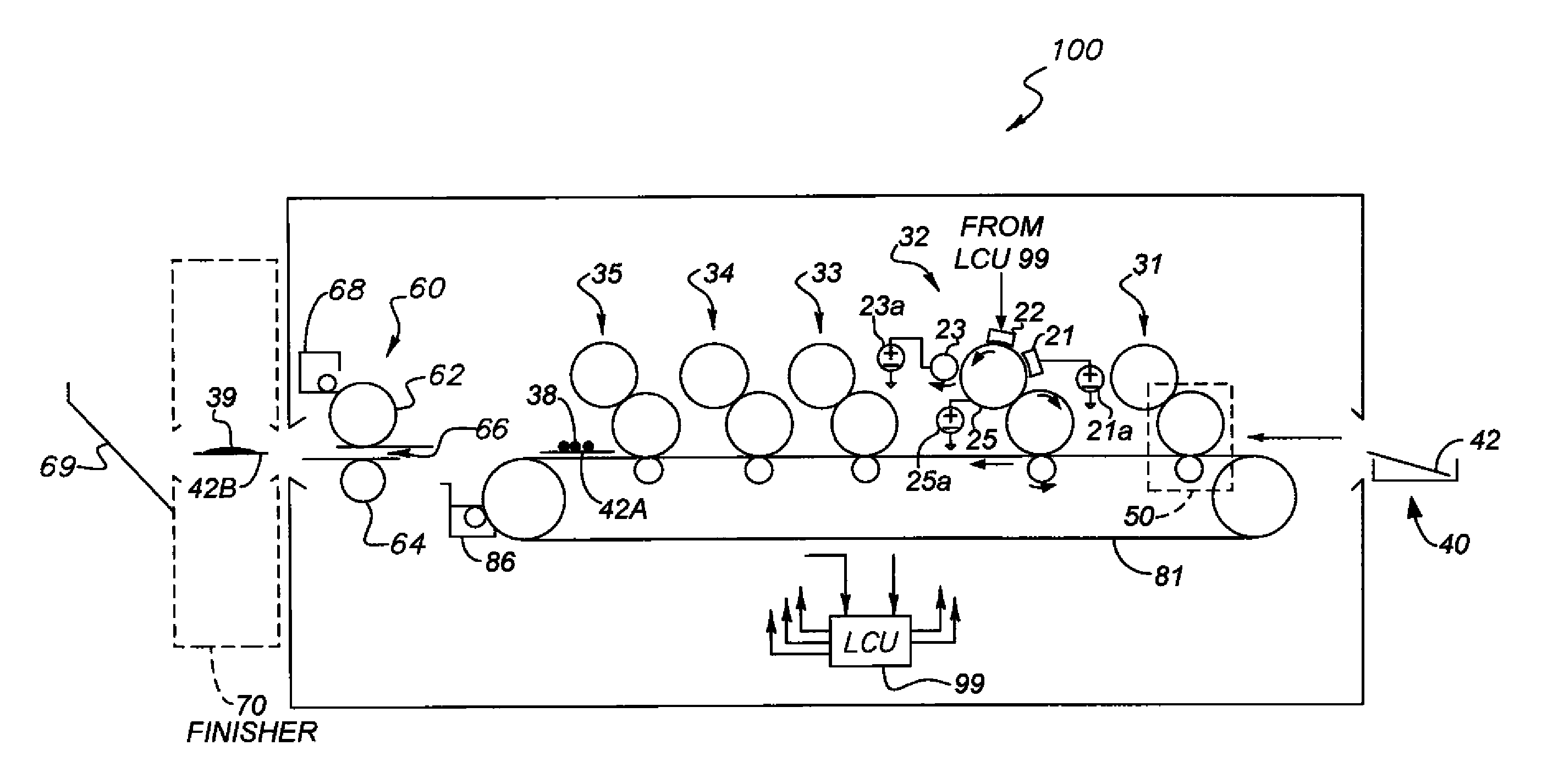
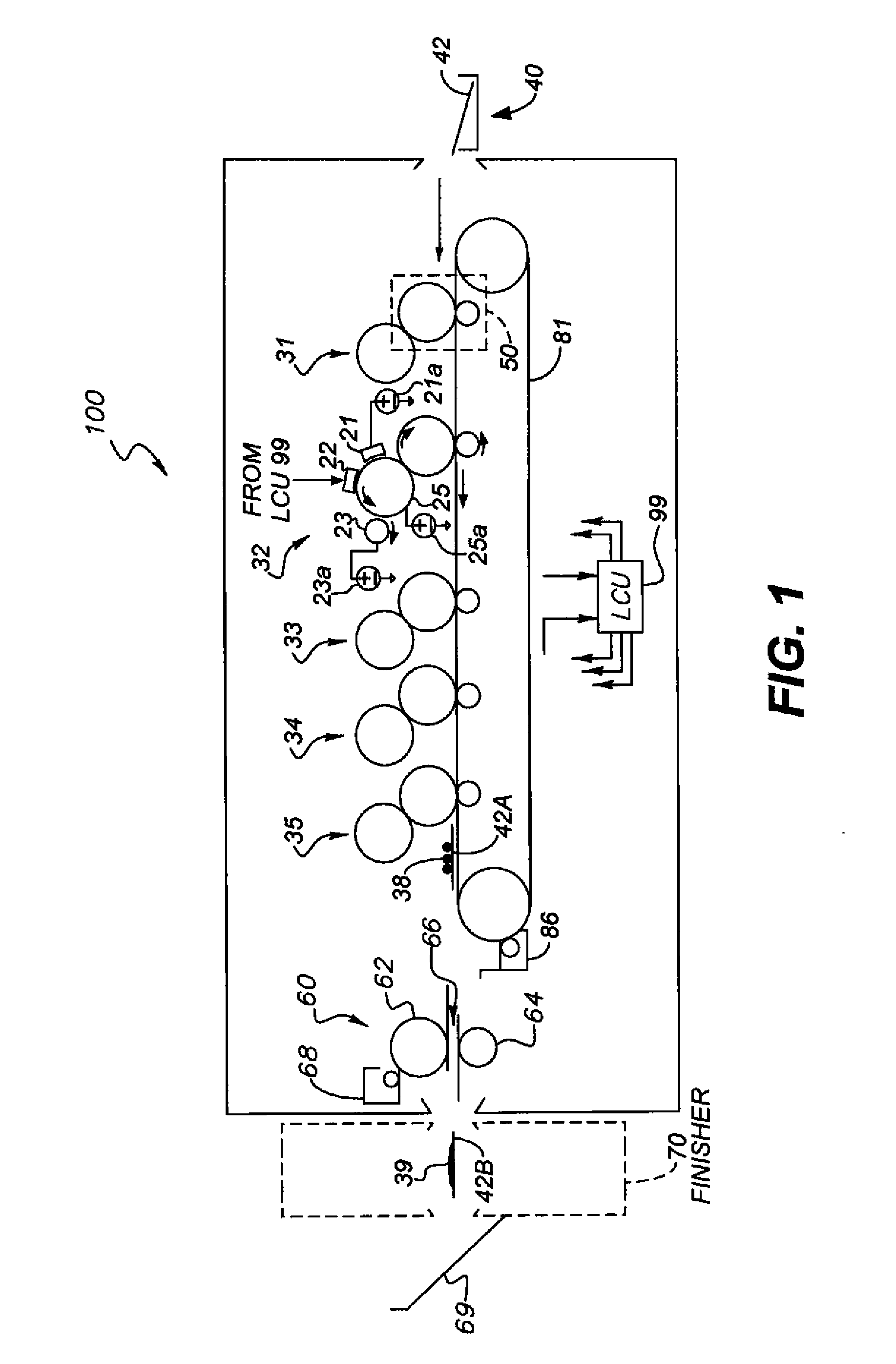
Gray balance for a printing system of multiple marking engines
InactiveUS20060197966A1Digitally marking record carriersDigital computer detailsTest patchElectrical and Electronics engineering
A method for calibrating a printing system including a plurality of printers includes designating one of the plurality of printers as a reference printer and defining color values for a desired response for one or more printed test patches on a control page. Through a first process aimed toward achieving the desired response, a printed control page is generated with the reference printer, the control page including one or more of the test patches which, when measured, has a measured response which approaches the desired response. Through a second process aimed toward achieving a desired response, the desired response being the measured response of the reference printer, a printed control page is generated with a second of the printers, the control page including one or more of the test patches which, when measured, has a response which approaches the measured response of the reference printer.
Owner:XEROX CORP
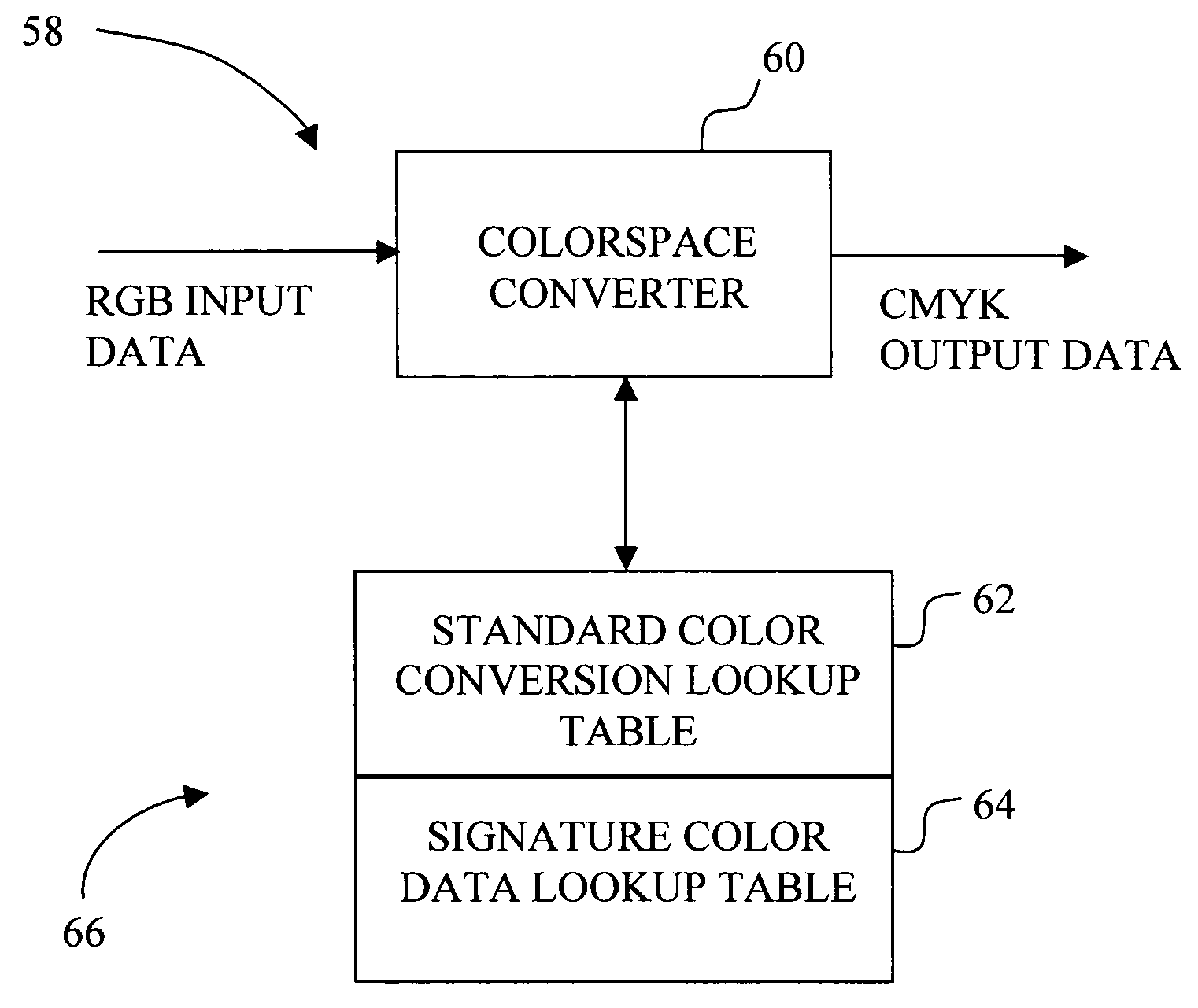
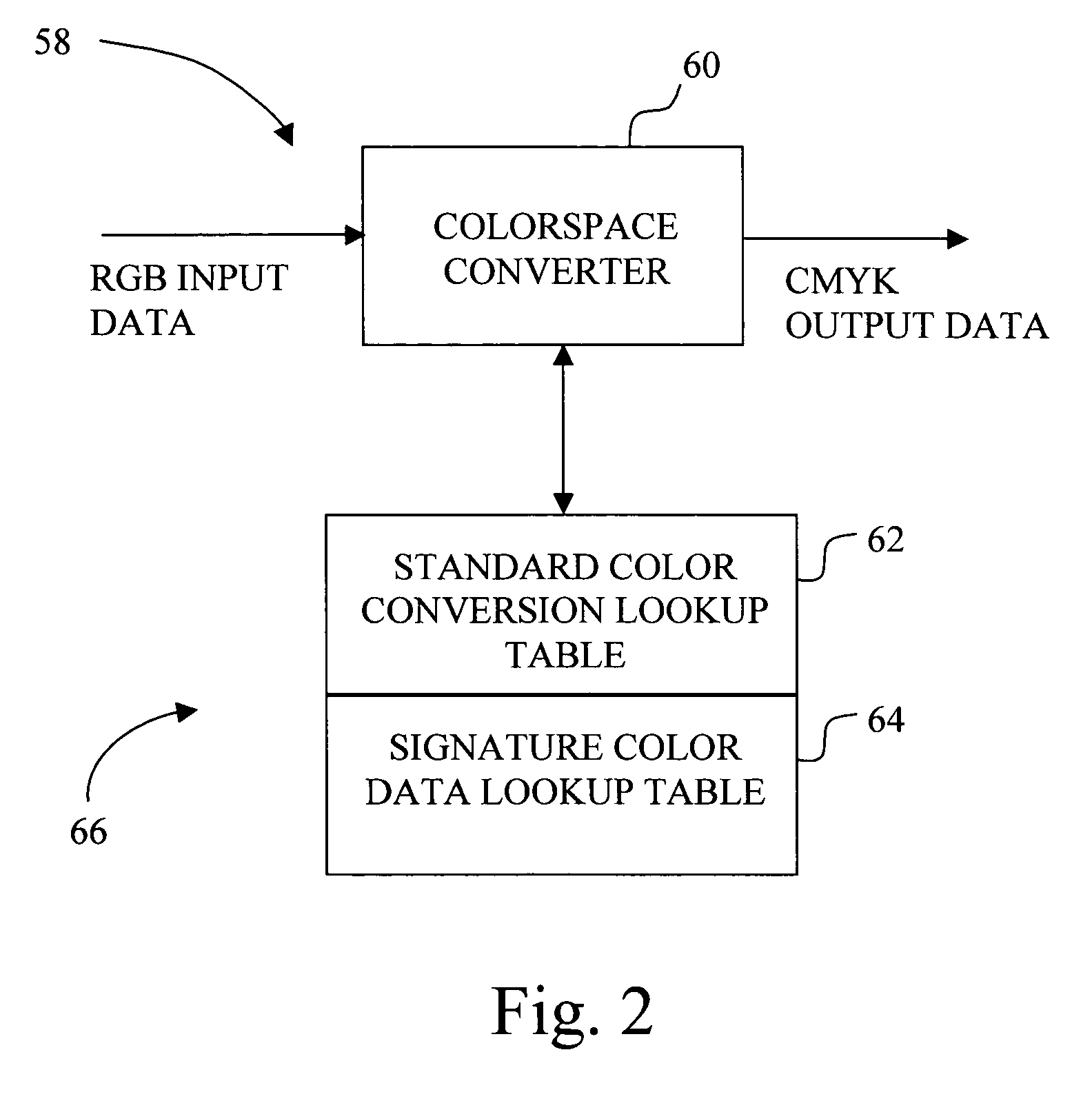
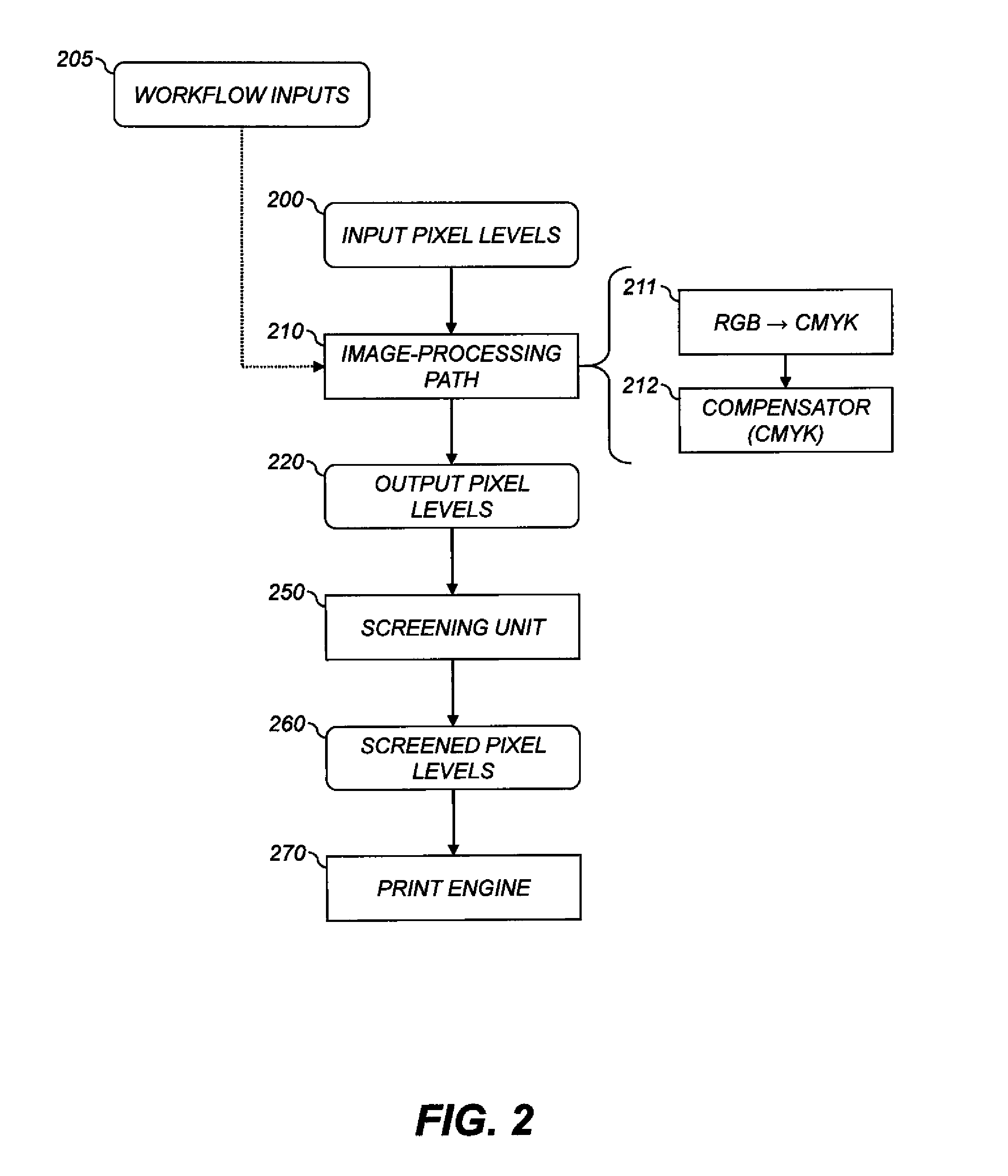
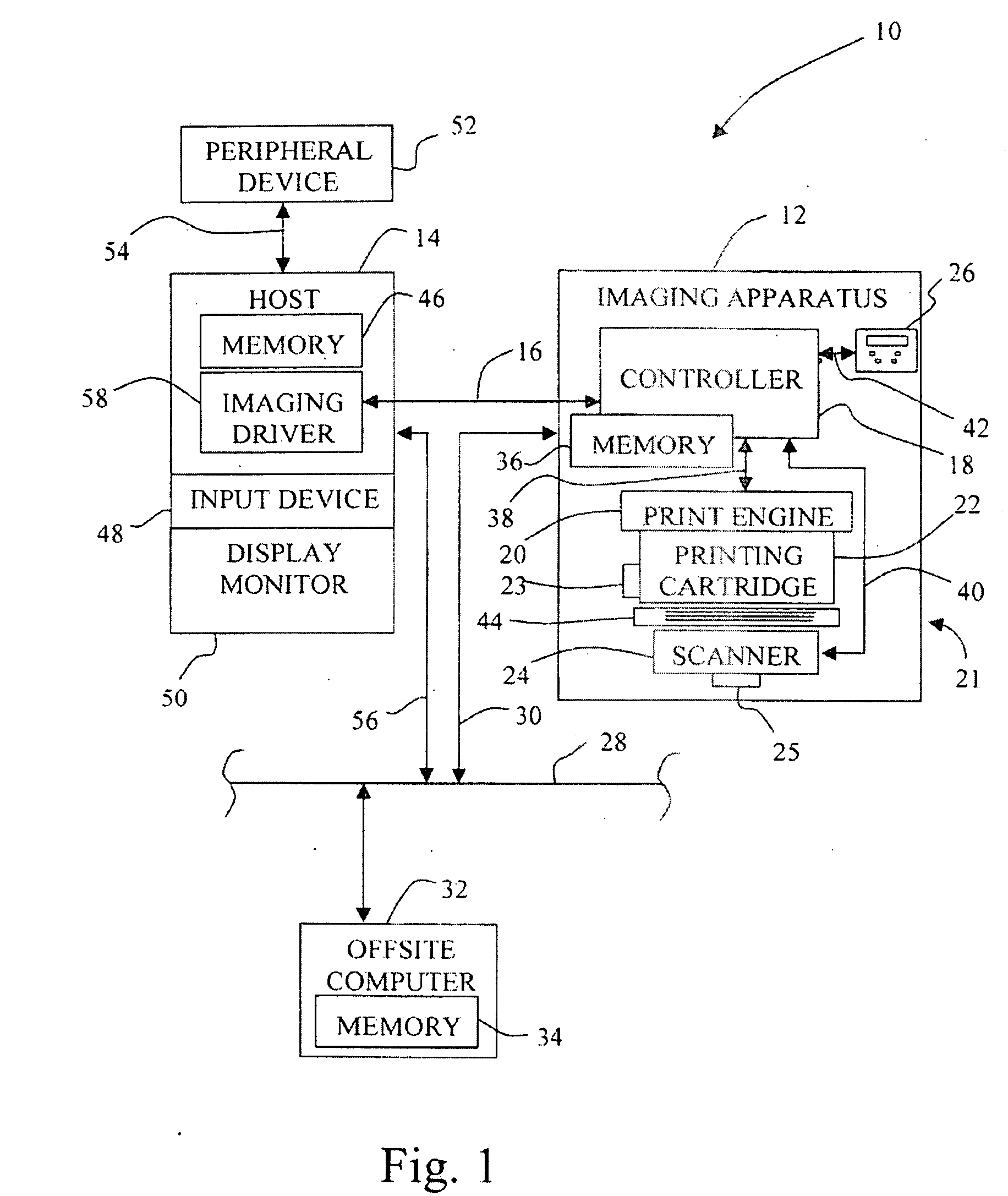
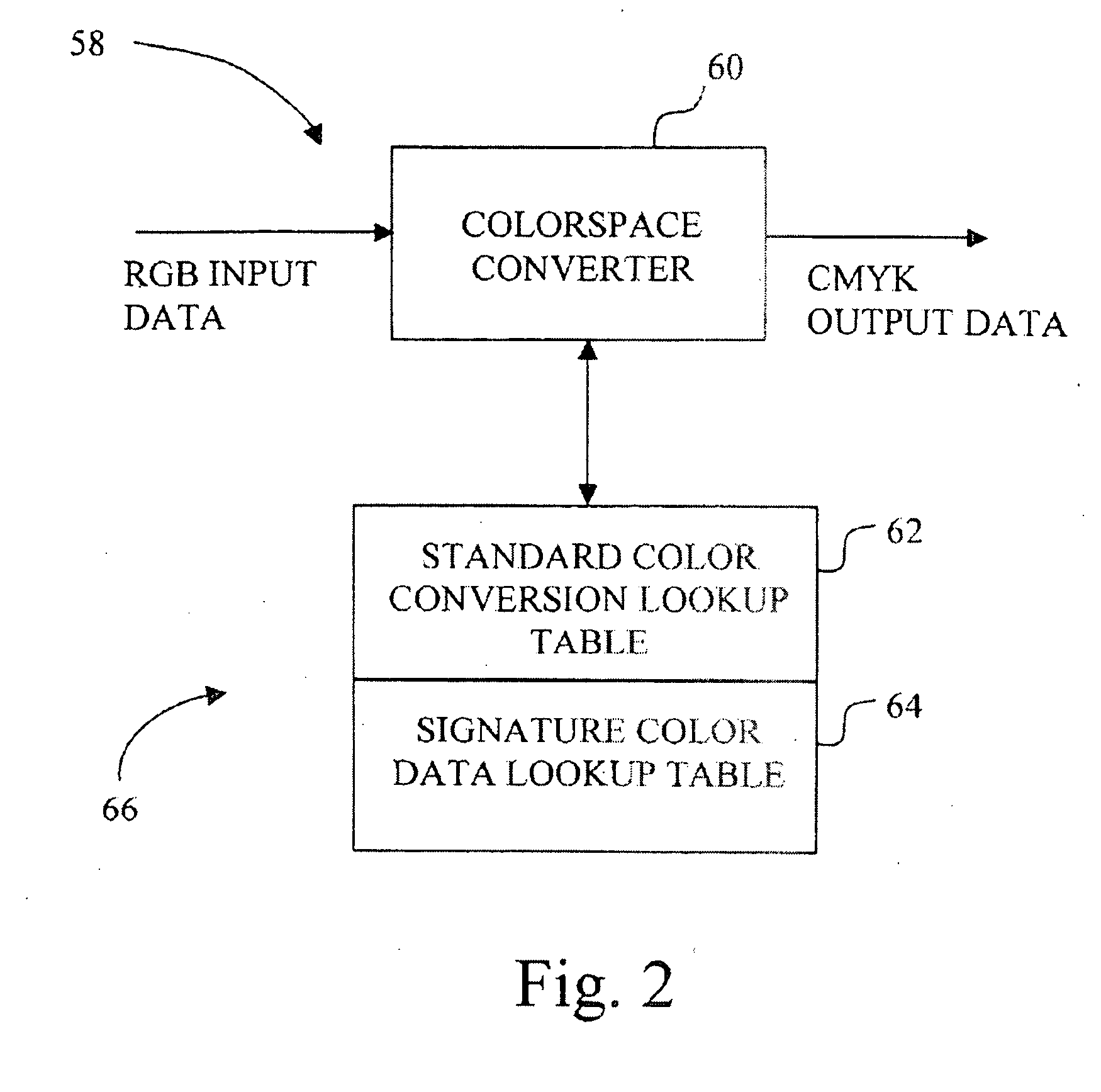
Color correction method for an imaging system
InactiveUS20050073731A1Consistent colorLower requirementDigitally marking record carriersDigital computer detailsColor shiftColor transformation
A method for correcting color shift in an imaging system, including an imaging object, and a standard color conversion lookup table associated with the imaging object, includes measuring a plurality of test patches to obtain color data associated with the imaging object. A signature color data lookup table is generated, based on the color data, and is combined with the standard color conversion lookup table to generate a composite color conversion lookup table for use with the imaging object.
Owner:LEXMARK INT INC
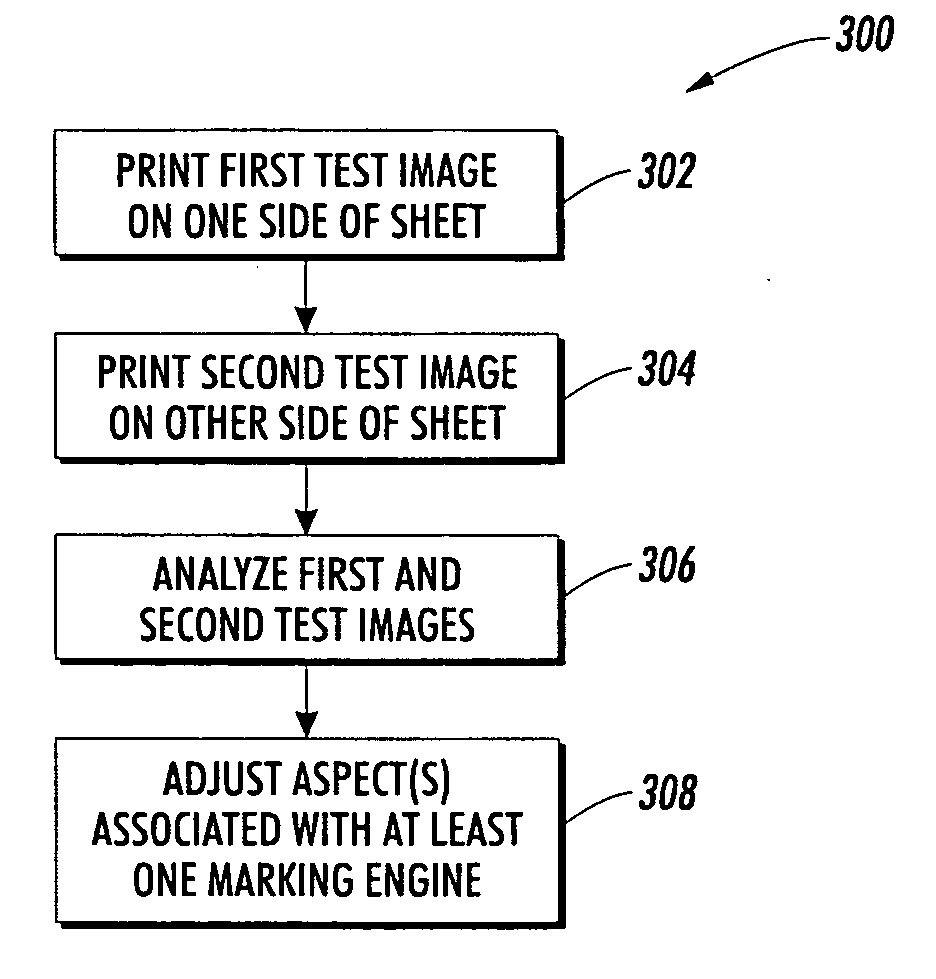
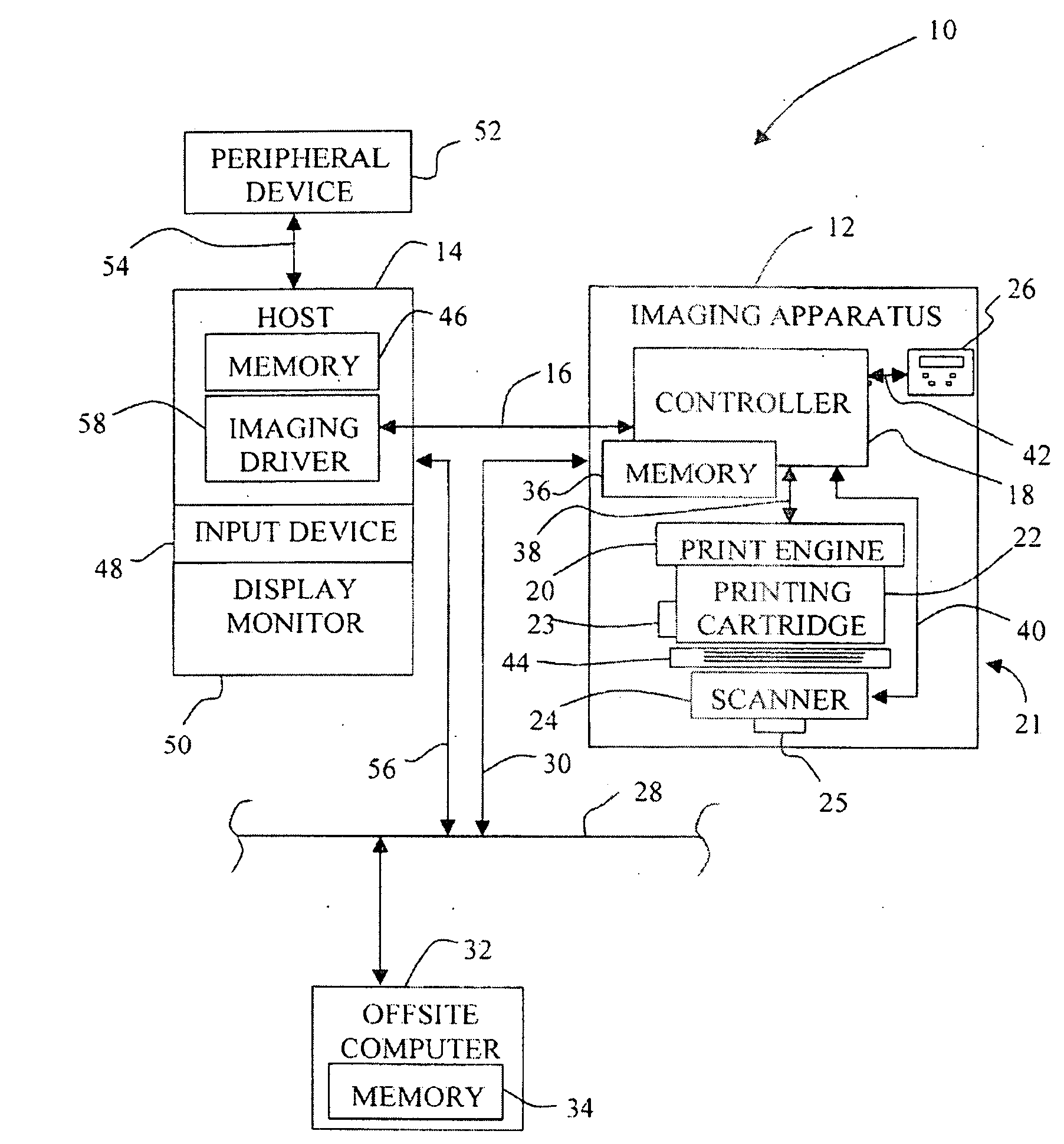
Image quality adjustment method and system
InactiveUS20060244980A1Digitally marking record carriersDigital computer detailsImaging qualityTest patch
An image rendering system periodically prints test patches on a duplex sheet from a plurality of marking engines, using a simple emitter-detector pair as a feedback means in image quality control. Image lightness is controlled by analyzing the test patches to determine updated marking engine actuator set points. For instance, ROS exposure and / or scorotron grid voltages are adjusted to maintain image lightness consistency between marking engines.
Owner:XEROX CORP
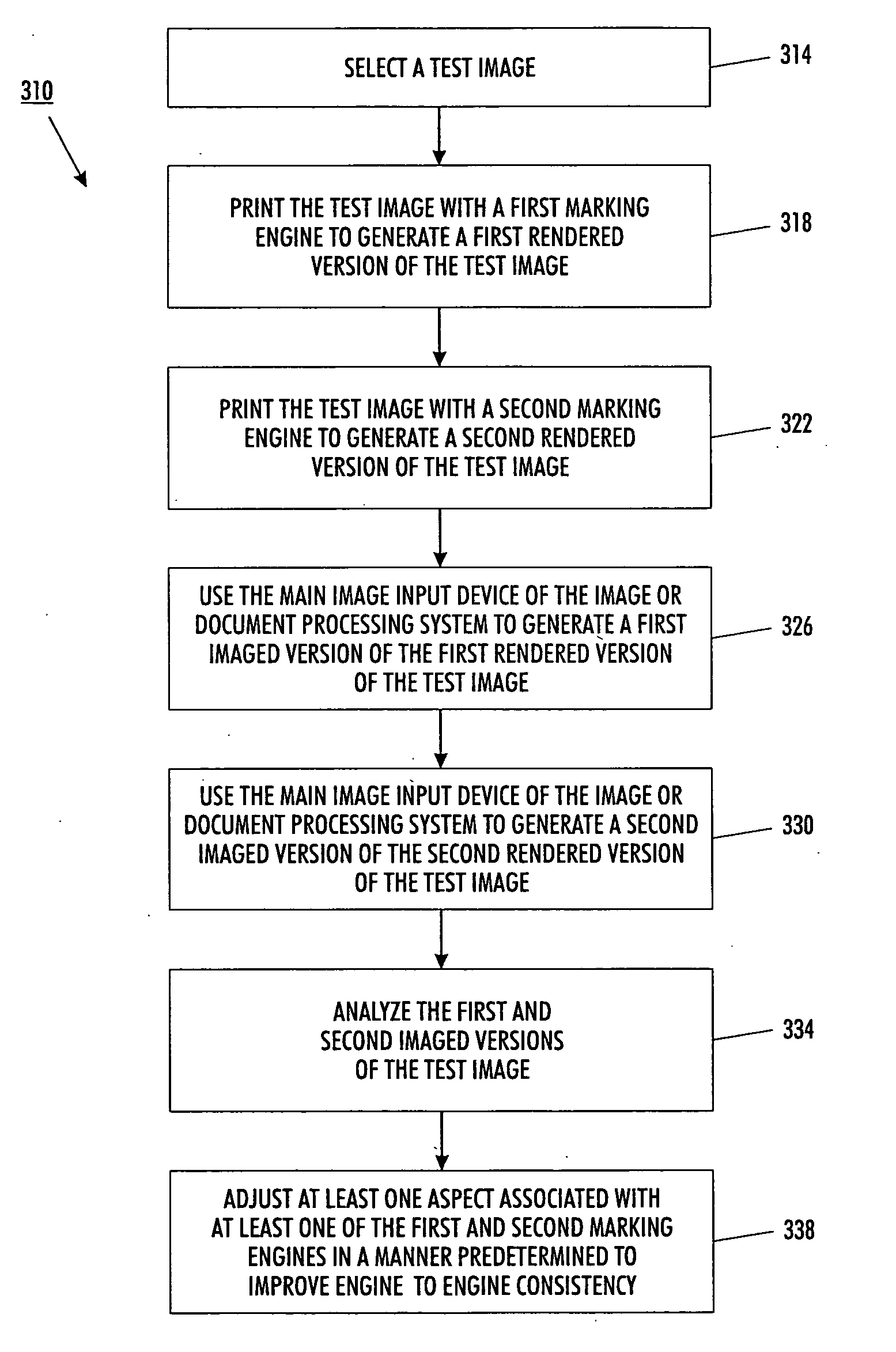
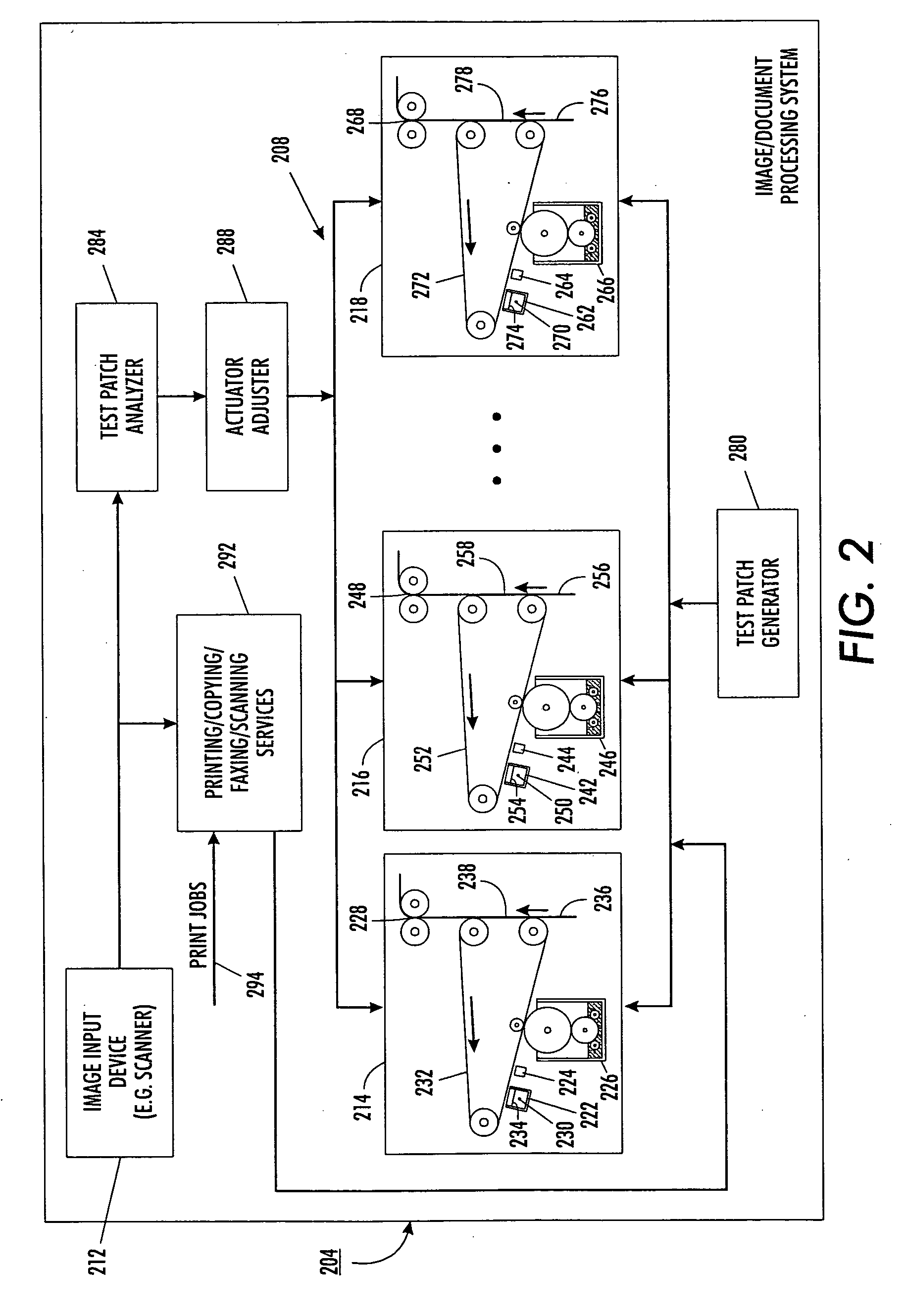
Semi-automatic image quality adjustment for multiple marking engine systems
InactiveUS20060115284A1Eliminating and reducing needEliminating and reducing and accuracy requirementElectrographic process apparatusImaging qualitySemi automatic
Using a document scanner or other image input device of an image or document processing system to periodically scan or image printed test images from a plurality of marking engines replaces internal sensors as a feedback means in image quality control. For example, image lightness (L*) is controlled by periodically printing mid-tone test patches, scanning the printed test patches with a main job document scanner and analyzing the scanned image to determine updated marking engine actuator set points. For instance, ROS exposure and / or scorotron grid voltages are adjusted to maintain image lightness consistency between marking engines.
Owner:XEROX CORP
Semi-automatic image quality adjustment for multiple marking engine systems
Using a document scanner or other image input device of an image or document processing system to periodically scan or image printed test images from a plurality of marking engines replaces internal sensors as a feedback means in image quality control. For example, image lightness (L*) is controlled by periodically printing mid-tone test patches, scanning the printed test patches with a main job document scanner and analyzing the scanned image to determine updated marking engine actuator set points. For instance, ROS exposure and / or scorotron grid voltages are adjusted to maintain image lightness consistency between marking engines.
Owner:XEROX CORP
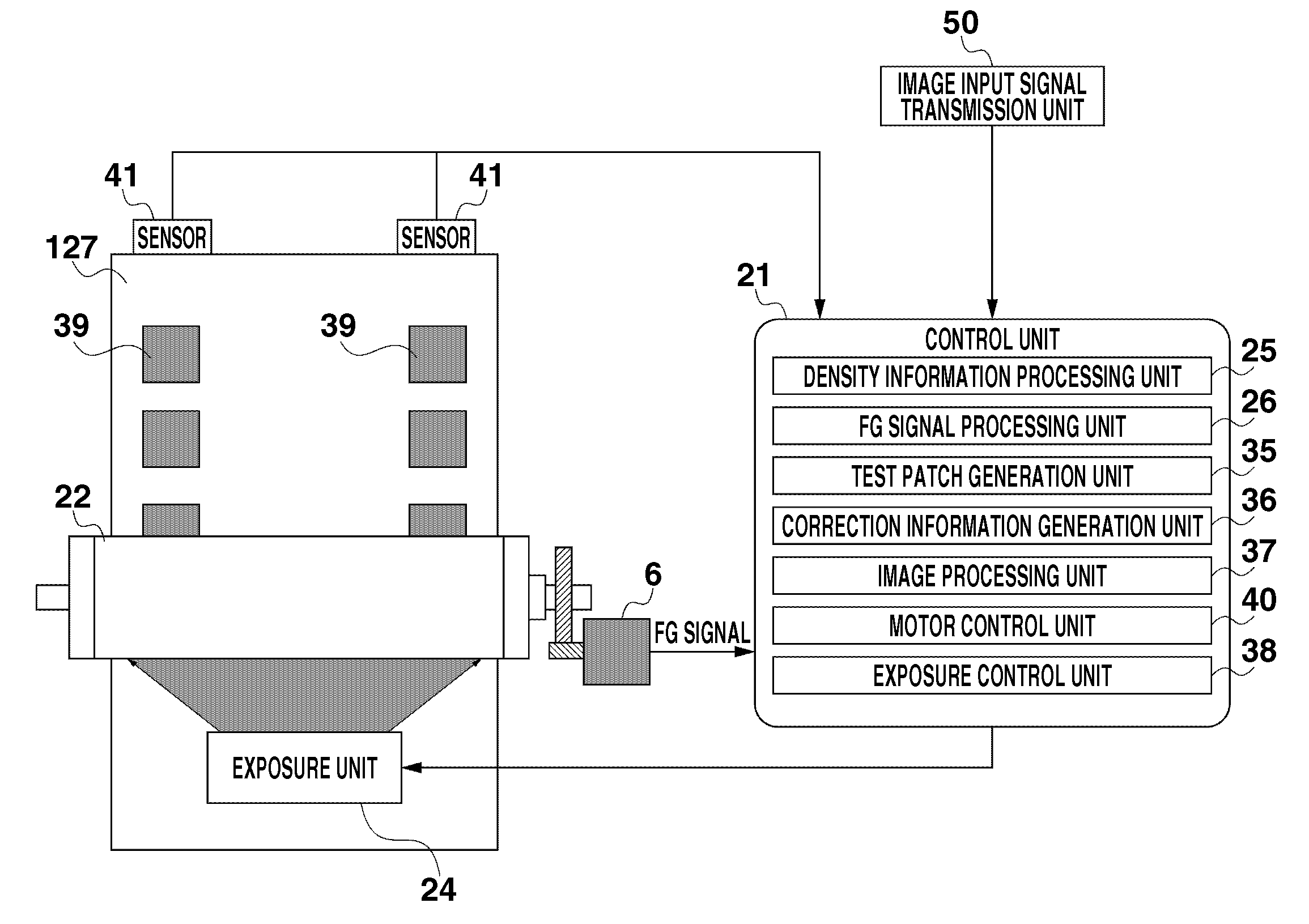
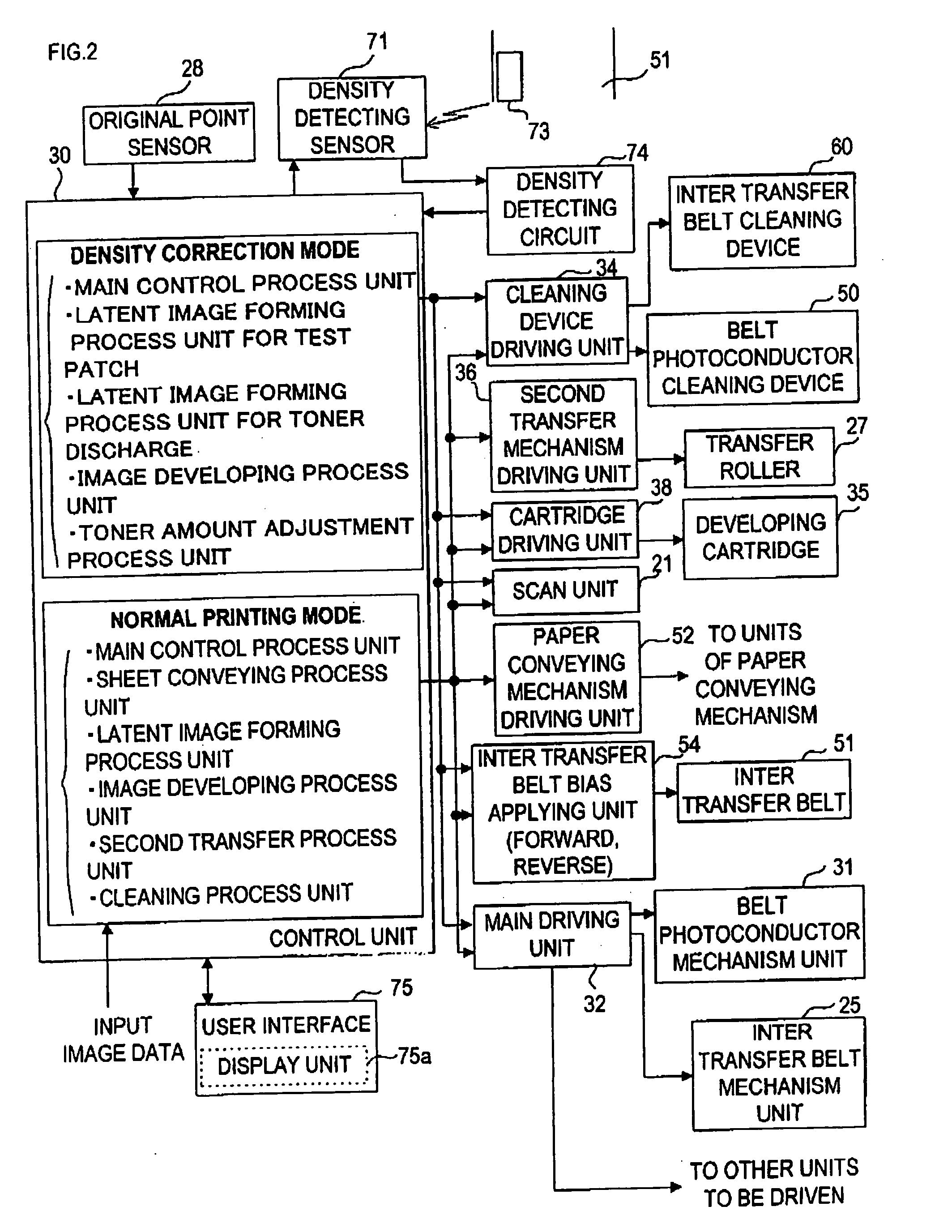
Image forming apparatus and density unevenness detection method
InactiveUS20110076040A1Accurate informationElectrographic process apparatusPhase differenceTest patch
A plurality of test patches each including a dark and light image which has density unevenness of a predetermined period in which the plurality of test patches are differentiated in phase difference relative to a phase of density unevenness induced by rotational unevenness occurring at a predetermined period in the motor for driving a photosensitive drum is formed. Then, density information of the plurality of test patches with is detected by a density sensor 41, and the phase of the density unevenness is obtained based on detection results (density information) of the plurality of test patches as well as based on a phase difference corresponding to a test patch whose density unevenness is a predetermined value in amplitude.
Owner:CANON KK
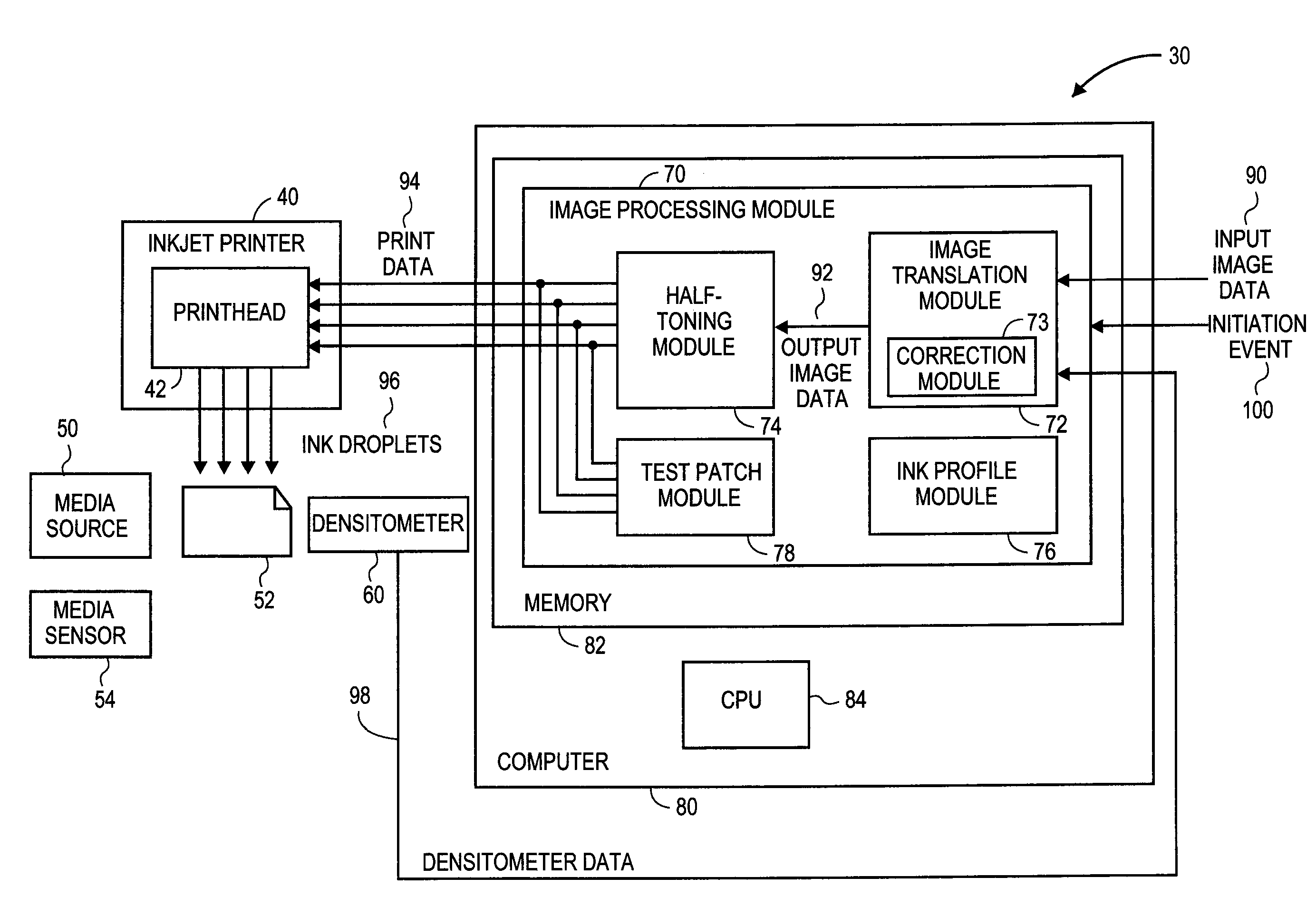
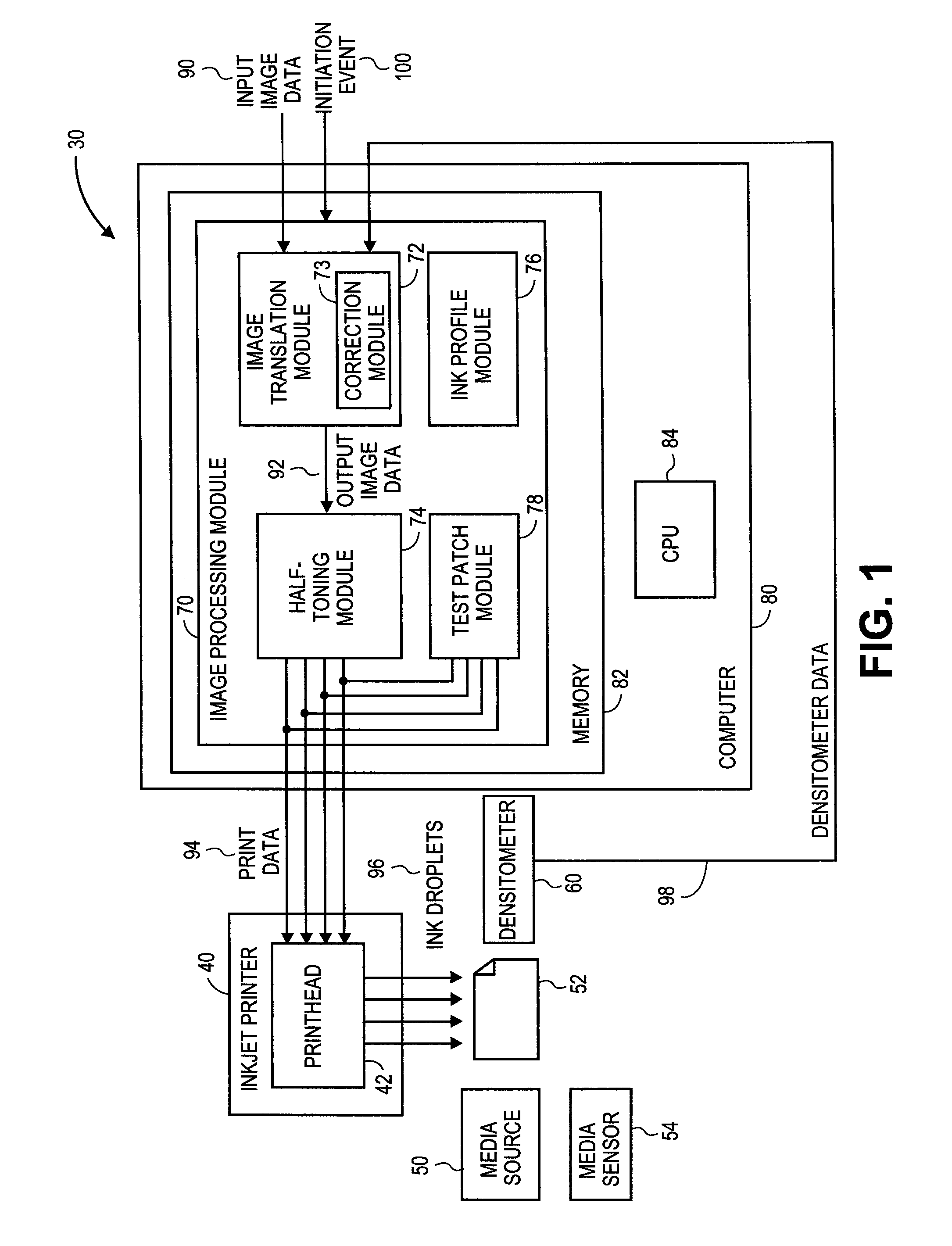
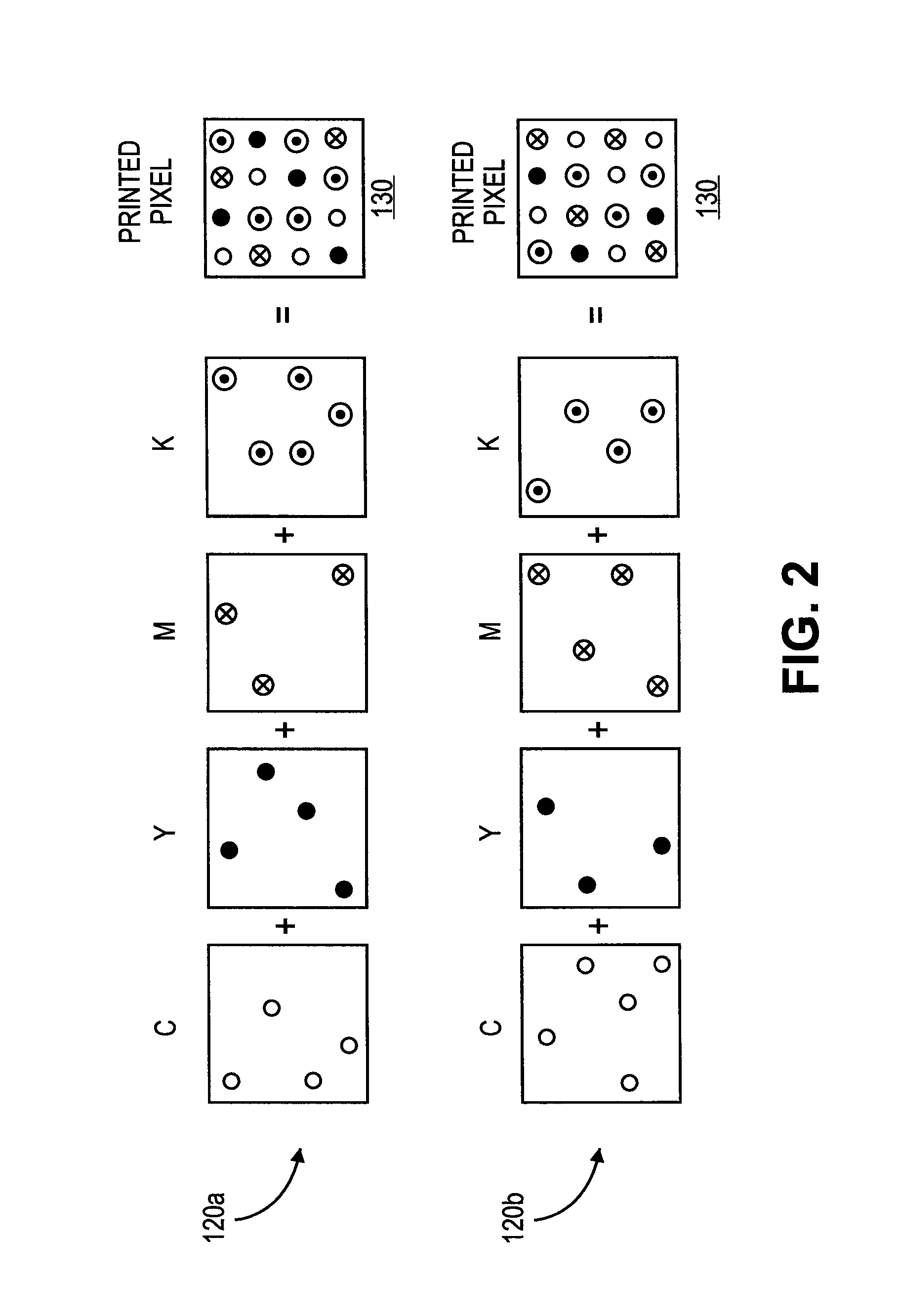
Inkjet print calibration using test patches and densitometer
InactiveUS20130222461A1Affect qualityOther printing apparatusPictoral communicationTest patchVolumetric Mass Density
An inkjet printing system including a media source supplying sheets of transparent film. An image processing module receives and converts input image data to output image data comprising a plurality of output pixels configured to select an ink profile. Predetermined ink profiles are selected representative of a series of test patches each having an expected density. A printhead is configured to eject droplets of available colors of ink onto a sheet of transparent film based on the selected ink profiles to produce the output pixels and an output image thereon, including the series of test patches. A transmissive densitometer measures the actual density value of each of the test patches, wherein the image processing module adjusts the output pixel values based on a deviations between the expected and actual density values of the series of test patches.
Owner:CARESTREAM HEALTH INC
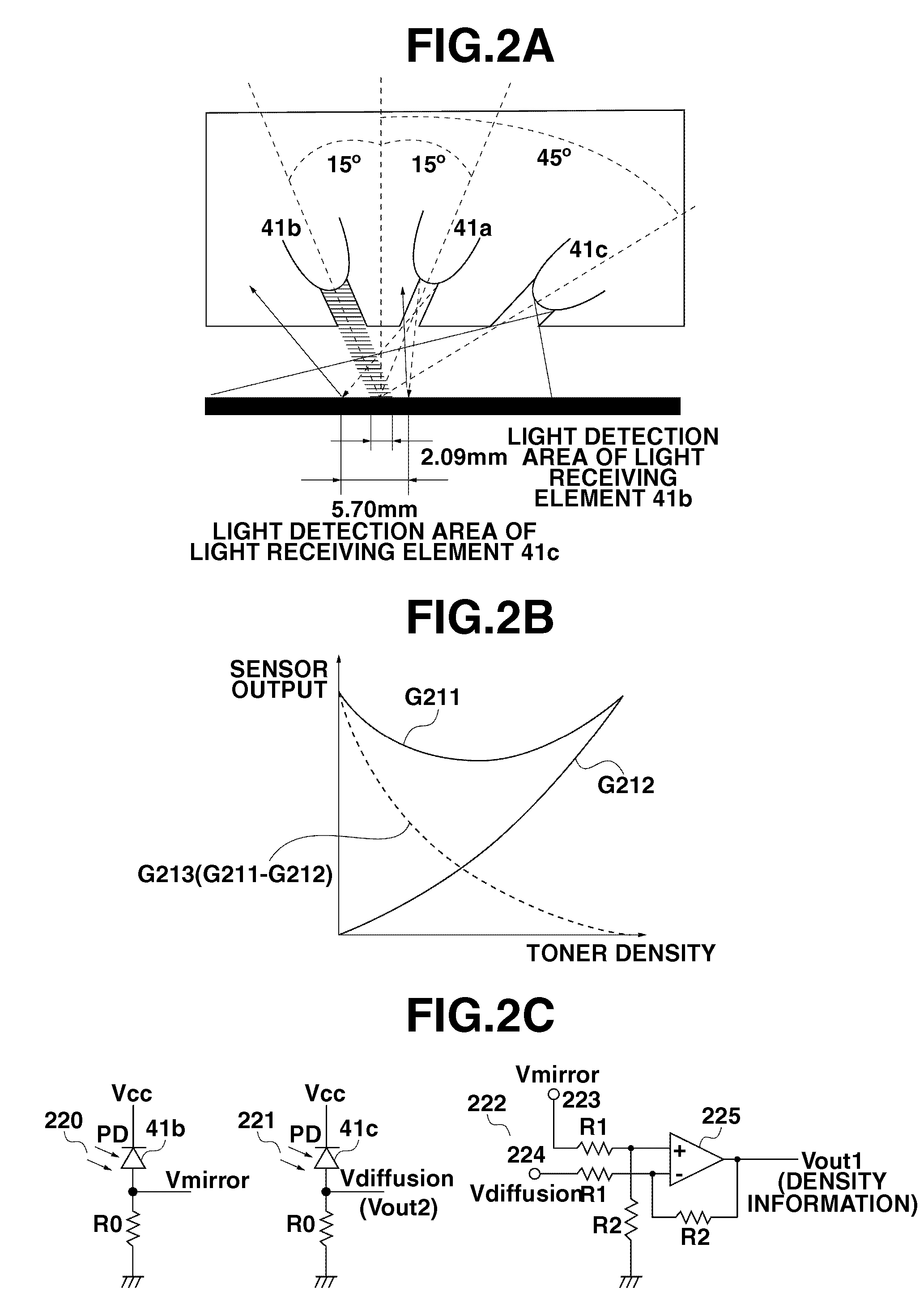
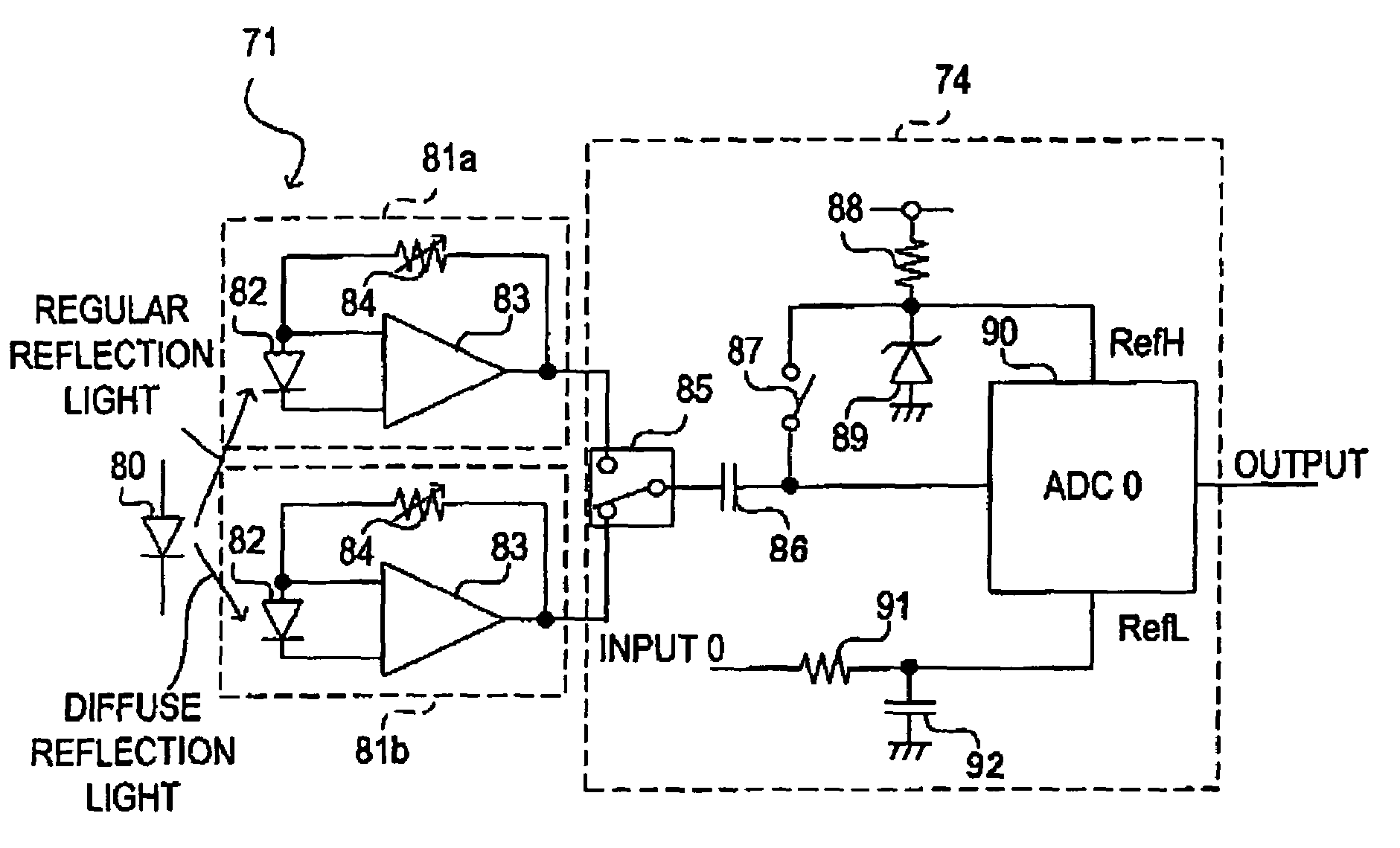
Patch density measuring apparatus and image forming apparatus
ActiveUS20050163519A1Avoiding improper density correctionReduce image qualityPhotometry using reference valueScattering properties measurementsTest patchZener diode
When a regular reflection light receiving unit is receiving a reflected light in a non-image area where the test patches are not formed, a clamp switch is closed. Then, a first reference voltage generated by a pull-up resistor and a zener diode is corresponded to an electric potential of a terminal of a capacitor on the side of an A / D converter. The capacitor is charged by the difference in electric potential between the first reference voltage and an output voltage from the regular reflection light receiving unit. Next, the clamp switch is opened. After the regular reflection light receiving unit receives the reflected light from an image area where the test patches are formed with this state of things, the output voltage from the regular reflection light receiving unit is changed. The difference in density between the image area and the non-image area can be quantified by the A / D converter.
Owner:BROTHER KOGYO KK
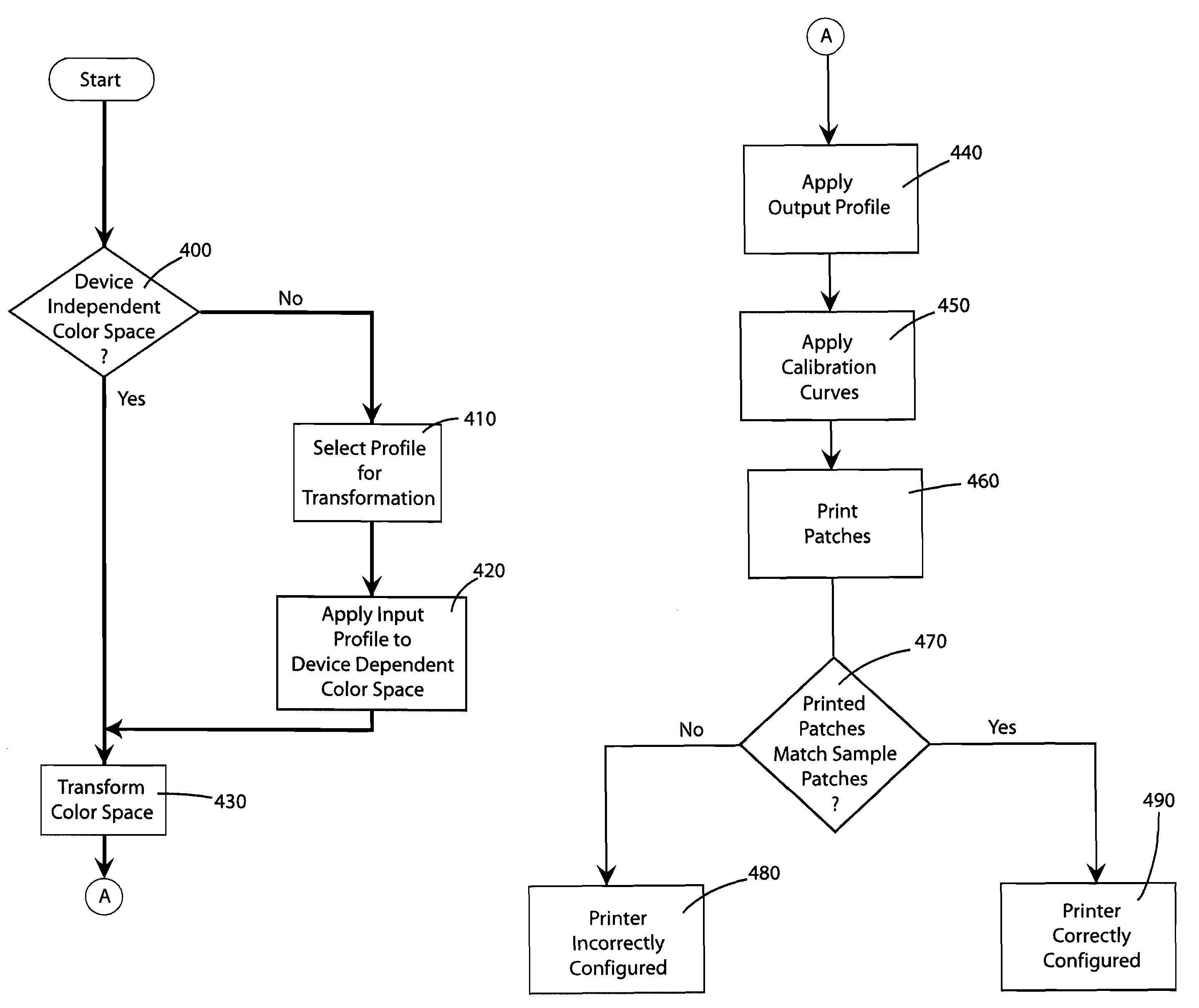
Method for confirming correct selection of an output profile of a printer
ActiveUS20040184051A1Digitally marking record carriersDigital computer detailsPattern recognitionTest patch
A method for using a page description language to electronically express colored patches on the border of contract proofs, such that a user can quickly and easily evaluate whether the color of prints produced using a color printer are correct. The verification is performed by visually comparing the test patches added to a print with color patches in publicly available standard color sample swatches.
Owner:GLOBAL GRAPHICS SOFTWARE
Digital camera for image device calibration
InactiveUS7133148B2Electric signal transmission systemsDigitally marking record carriersGraphicsGrating
The invention is directed to an apparatus for calibrating an output of an image output device, comprising an image input device configured to image an output of the image output device; and a test pattern generator having an output of a dynamic test patch area and a grating area connected to an input of the image output device and responsive to the image input device for adjusting an intensity level of the dynamic test patch area to match an average intensity level of the grating area.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Reprinting
InactiveUS20070268502A1Improve consistencyDigitally marking record carriersDigital computer detailsTest patchDocument preparation
Consistency of document reprints is improved by recording characteristics of a reference printing system used to produce a reference printing of a document, determining related characteristics of a reprint printing system, retrieving the recorded characteristics and compensating for differences between the reference system and the reprint system in the reprint system prior to using the reprint system to produce reprints of the document. Analytical test prints (TPs) are produced with the respective printing systems in close temporal association to the production of the respective reference prints and reprints. TPs can be customized according to aspects of the document. TP customization allows the compensation to address aspects of the printing systems that have a bearing on perceived consistency in the reprints. TPs can be customized with regard to colors in test patches or both the colors and locations of test patches on a page. Compensation is based on measurements of the TPs.
Owner:XEROX CORP
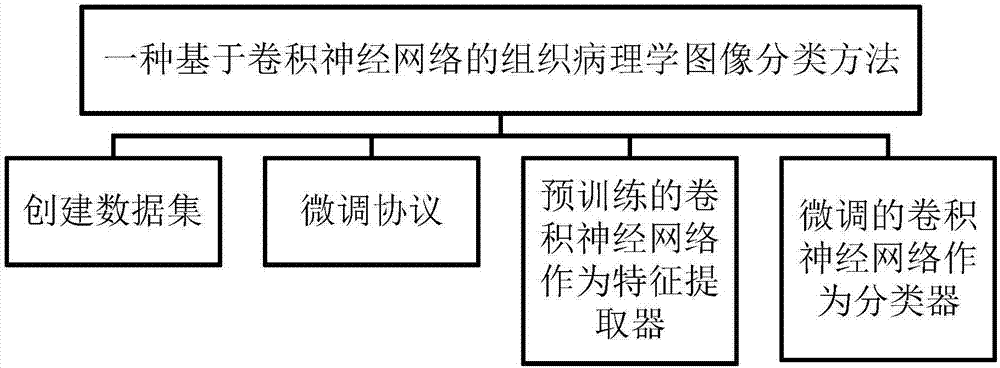
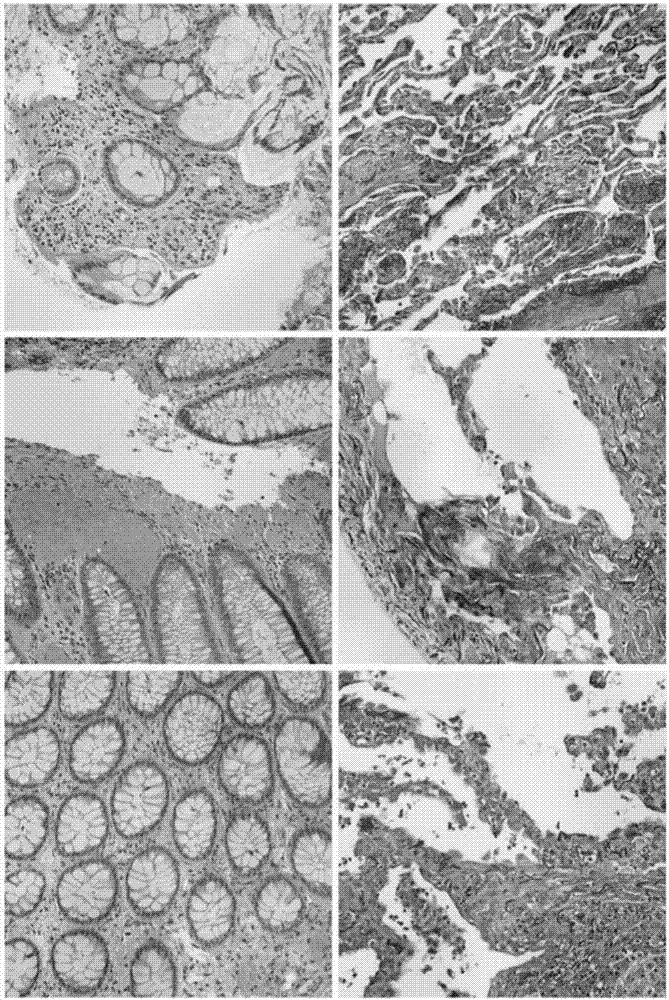
Histopathological image classification method based on convolutional neural network
InactiveCN107886127ACharacter and pattern recognitionNeural architecturesSupport vector machineData set
The invention provides a histopathological image classification method based on the convolutional neural network. The method mainly comprises steps that a data set is established, a fine-tuning protocol is adopted and carried out, a pre-trained convolutional neural network is taken as a characteristic extractor and a fine-tuned CNN is taken as a classifier, for the process, firstly, images of different body parts with different texture patterns are manually selected from the scan, patch selection and accuracy calculation are carried out, secondly, a specific single-layer complete connection layer is selected for network training, thirdly, the pre-trained CNN is taken as the characteristic extractor, depth characteristics are utilized to train the linear support vector machine (SVM) for classification, and lastly, the fine-tuned CNN is taken as the classifier, and the acquired network is utilized to classify test patches. The method is advantaged in that the data set is utilized to design and train the deep network, details are richer, the data is more perfect, retrieval and classification accuracy is significantly improved, and classification of histopathological images is effectively realized.
Owner:SHENZHEN WEITESHI TECH
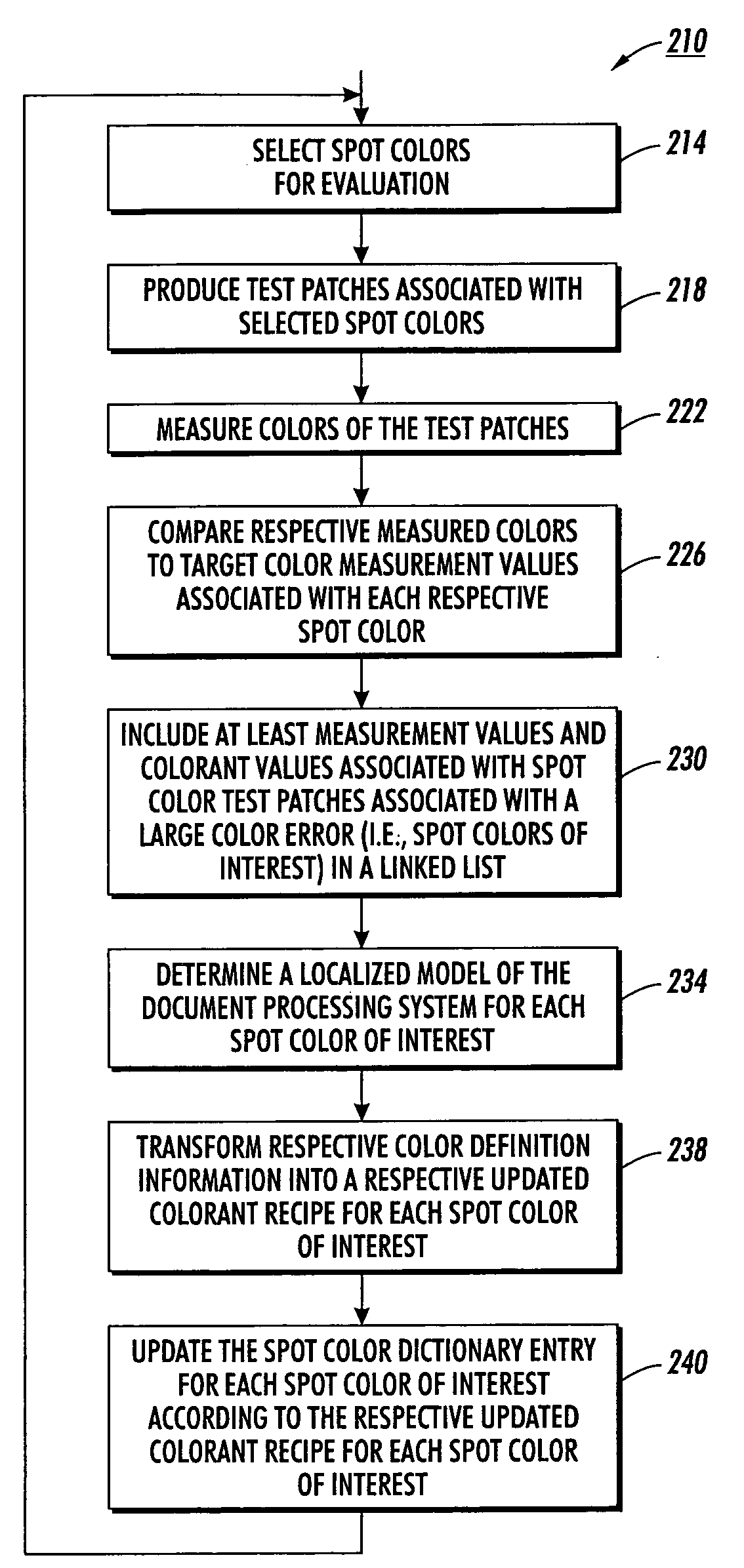
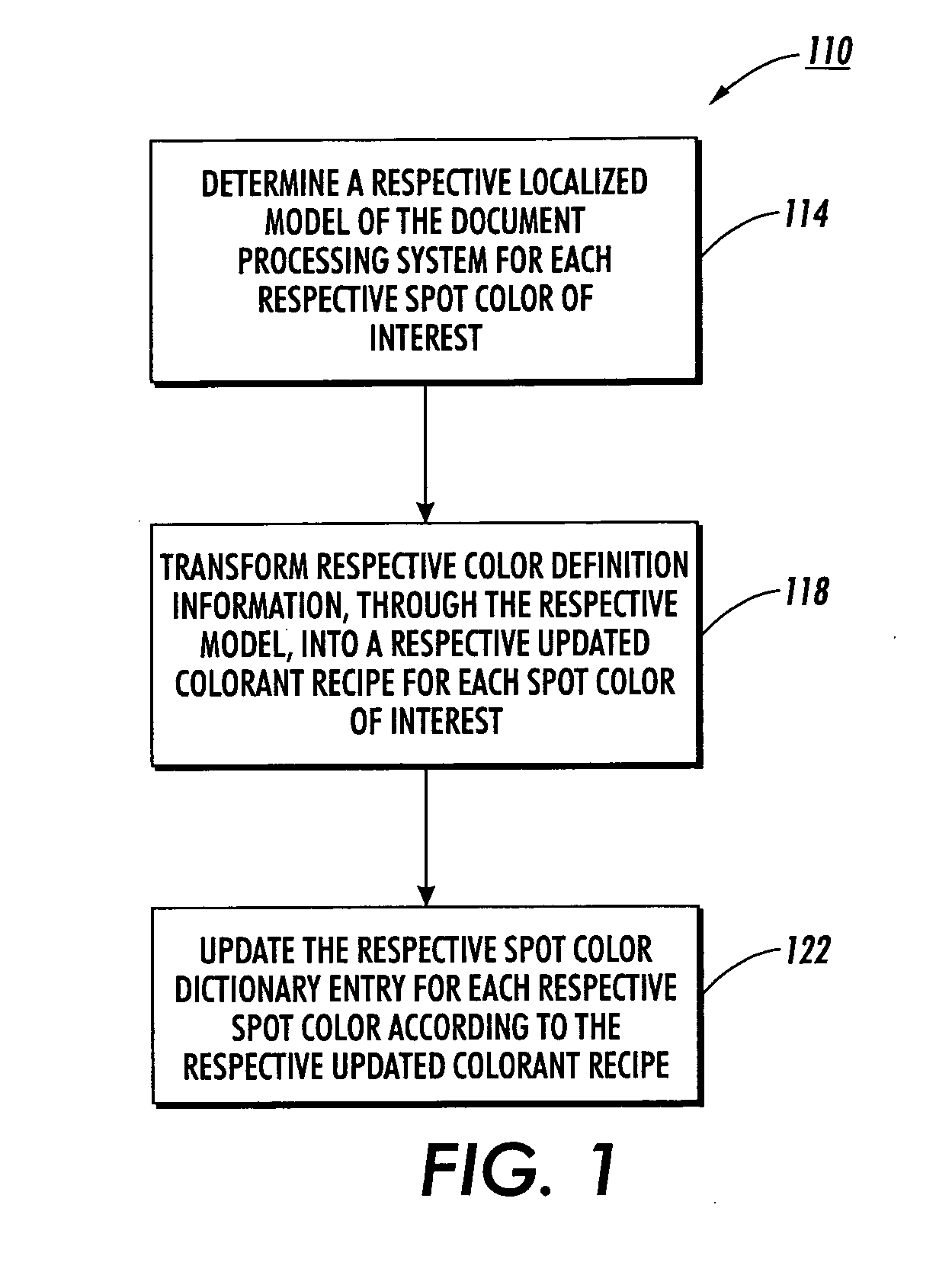
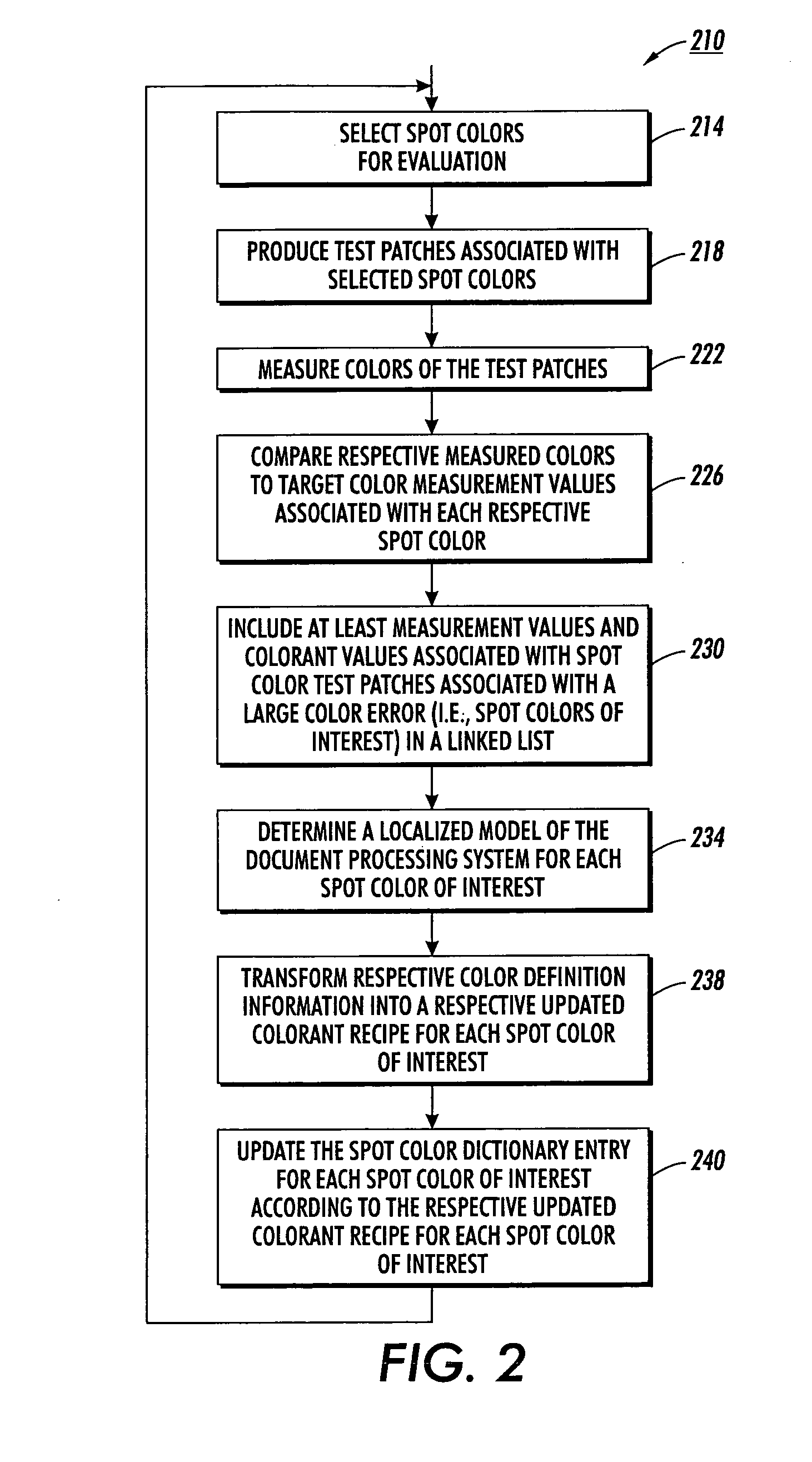
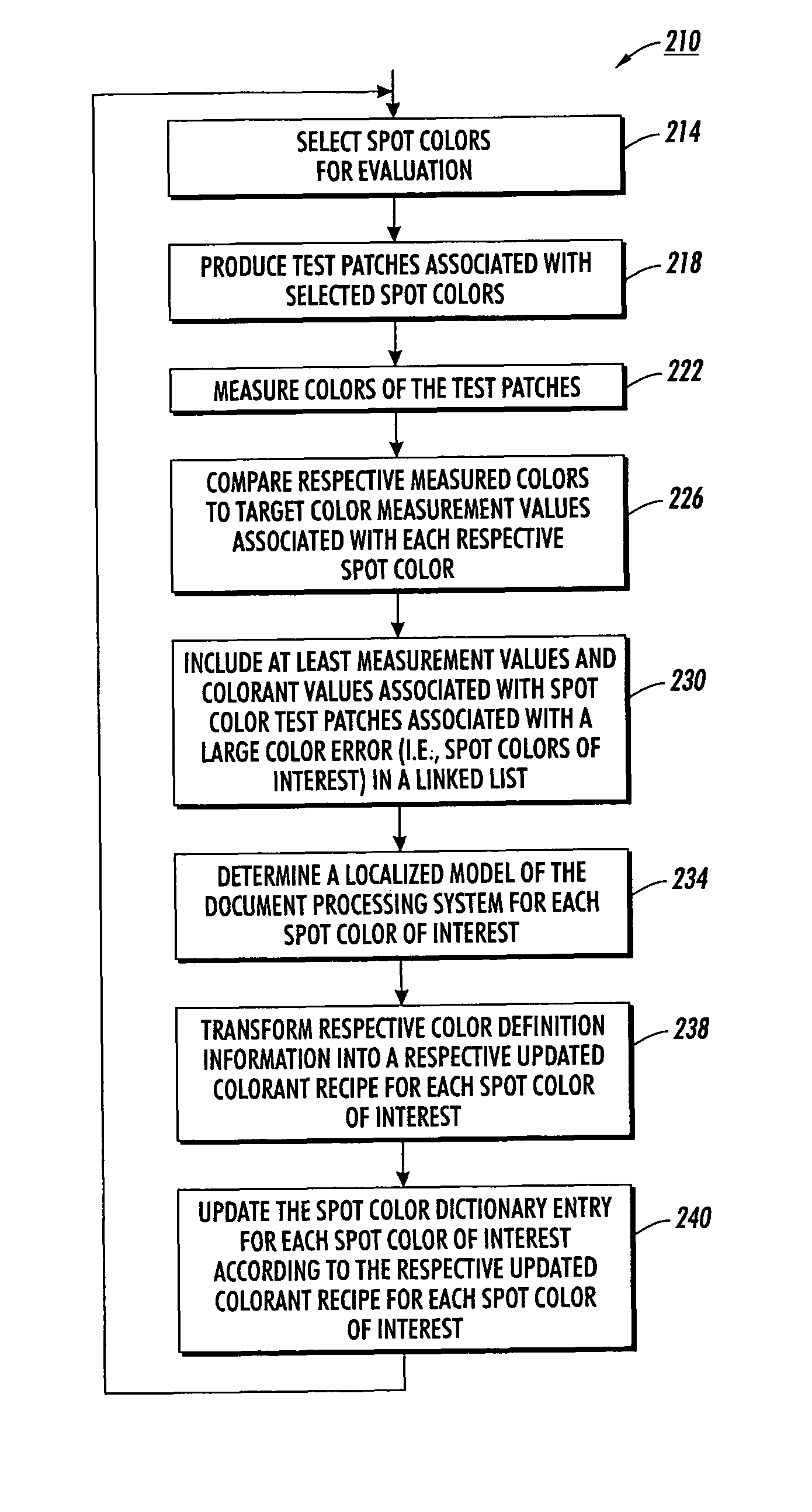
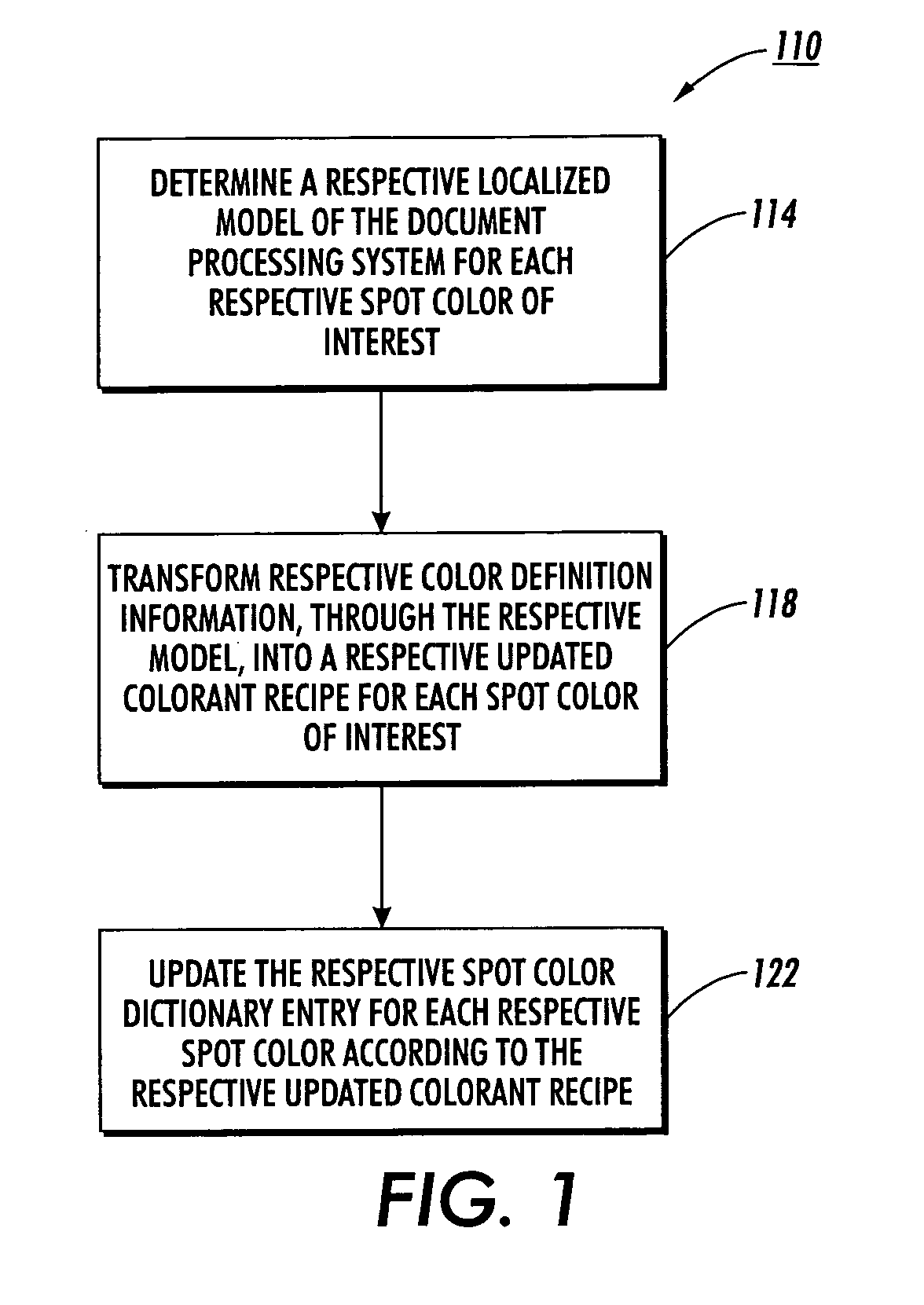
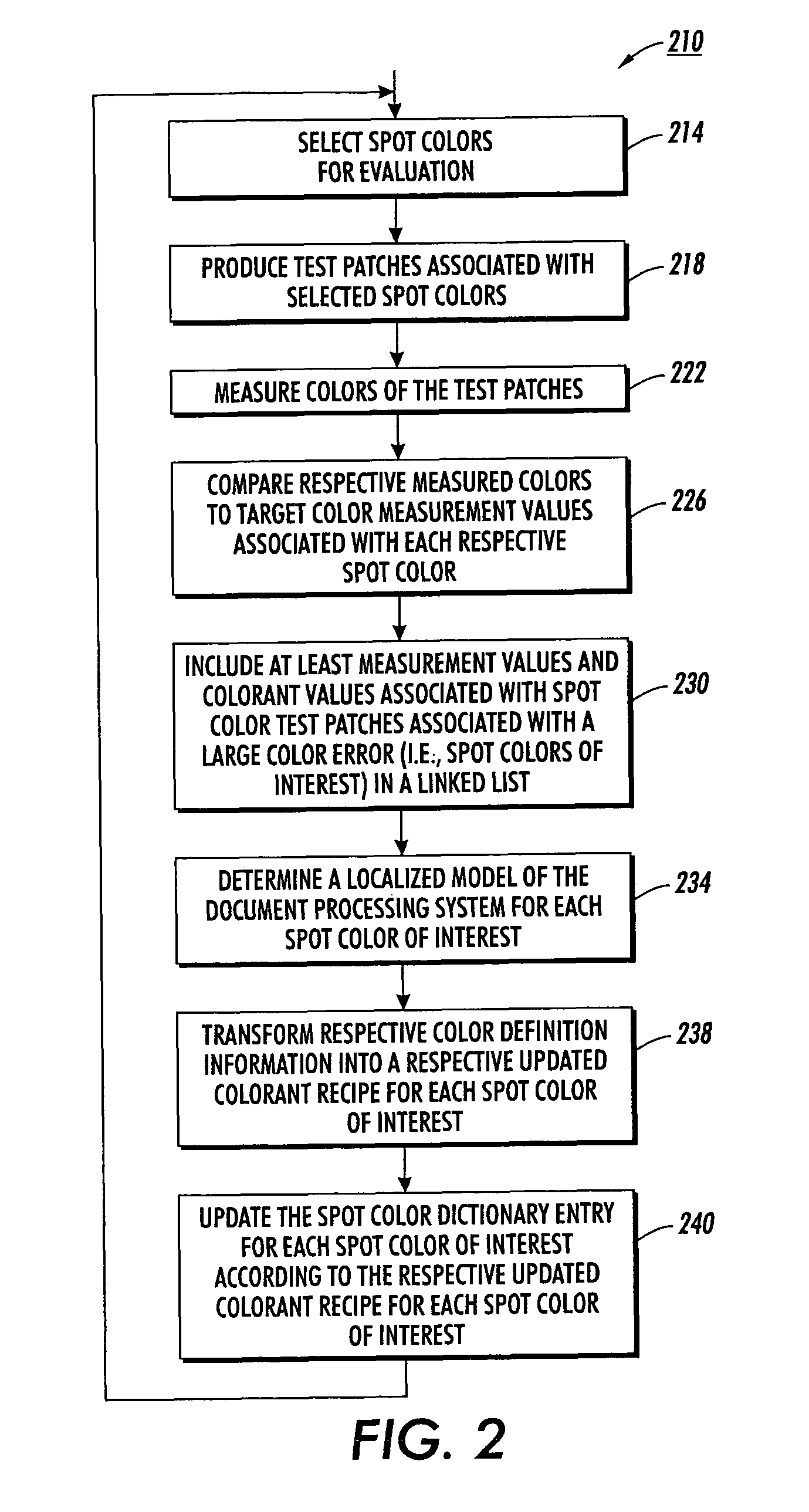
Fine tuning color dictionaries
InactiveUS20080130022A1Increase weightReduce weightDigitally marking record carriersDigital computer detailsProduction modelPattern recognition
A spot color dictionary is fine tuned or updated. Localized color production models are determined for spot colors of interest to be produced by an associated document processing system or printer. Measurements are made of colors of produced spot colors. Optionally, measurements are made of colors of test patches that are based on perturbations from the colors of the spot colors. In determining a model for the production of a target spot color, measurement data related to colors that are closer in color space to a given target color is given a higher weight than is measurement data related to colors that are further in color space from the target color. Accordingly, the model is localized to the region of color space about the target color and therefore, more accurately predicts a colorant recipe for the target color than would interpolation based on a full gamut, or more general model.
Owner:XEROX CORP
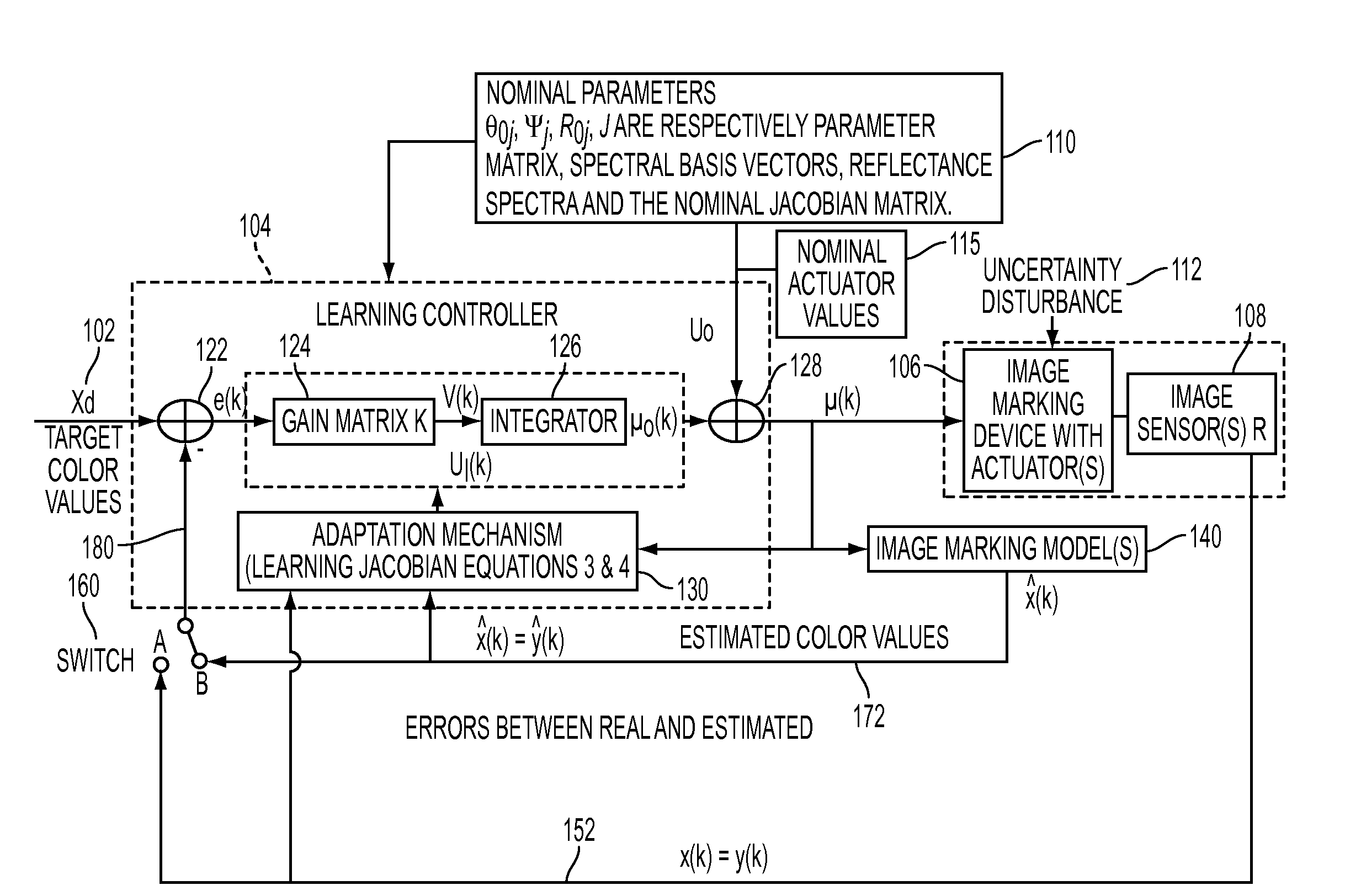
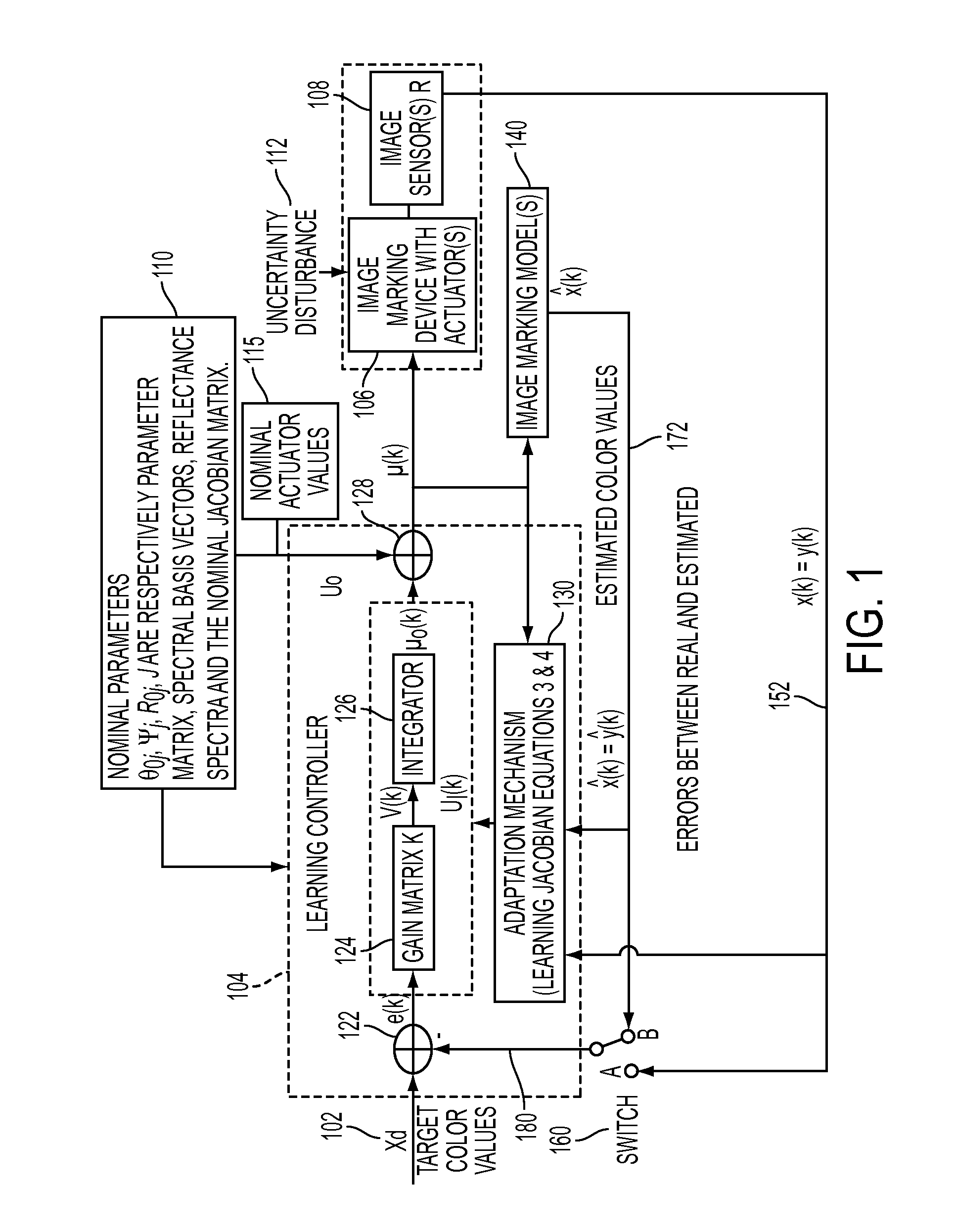
Controlling process color in a color adjustment system
InactiveUS20110032545A1Reduce sensitivity to noiseReduce offsetDigitally marking record carriersDigital computer detailsFeedback controllerControl system
What is disclosed is a novel system and method for controlling process color in a color adjustment system in an image marking device. A control parameter, such as a gain matrix, forms a basis of an adaptive closed-loop controller. A sensitivity matrix is used to calculate the gain matrix. This permits complex color adjustments at a customer location. The present system and method is well suited for long production runs because, as the system moves (or drifts) away from nominal, the color control system will learn the changes in the system (e.g., new input-output sensitivity) with print, measure, and prediction processes, operating on the test patches, and effectively adapt to these changes by re-computing the feedback controller gains and revising the current actuator values to follow desired target color values. The present system and method can also be used for adjusting or developing a CMYK recipe in color management LUTs.
Owner:XEROX CORP
Providing calibration data for printer
InactiveUS20120133960A1Shorten the timeImprove image qualityImage enhancementDigitally marking record carriersTest patchData value
A method of providing calibration data for a printer includes printing a calibration target using the printer. The target includes a plurality of patch sets, each including a plurality of test patches, each patch having a respective color. Scanned patch data for one of the sets are received from a spot scanner. The scanned patch data values are compared to respective aims to determine a reproduction error value for the scanned patch set. A processor automatically determines which of the sets should be scanned next using the calculated reproduction error value. The process is repeated until all sets have been scanned, or until the reproduction error value is less than or equal to a selected threshold. Calibration data are automatically generated using the scanned patch data.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
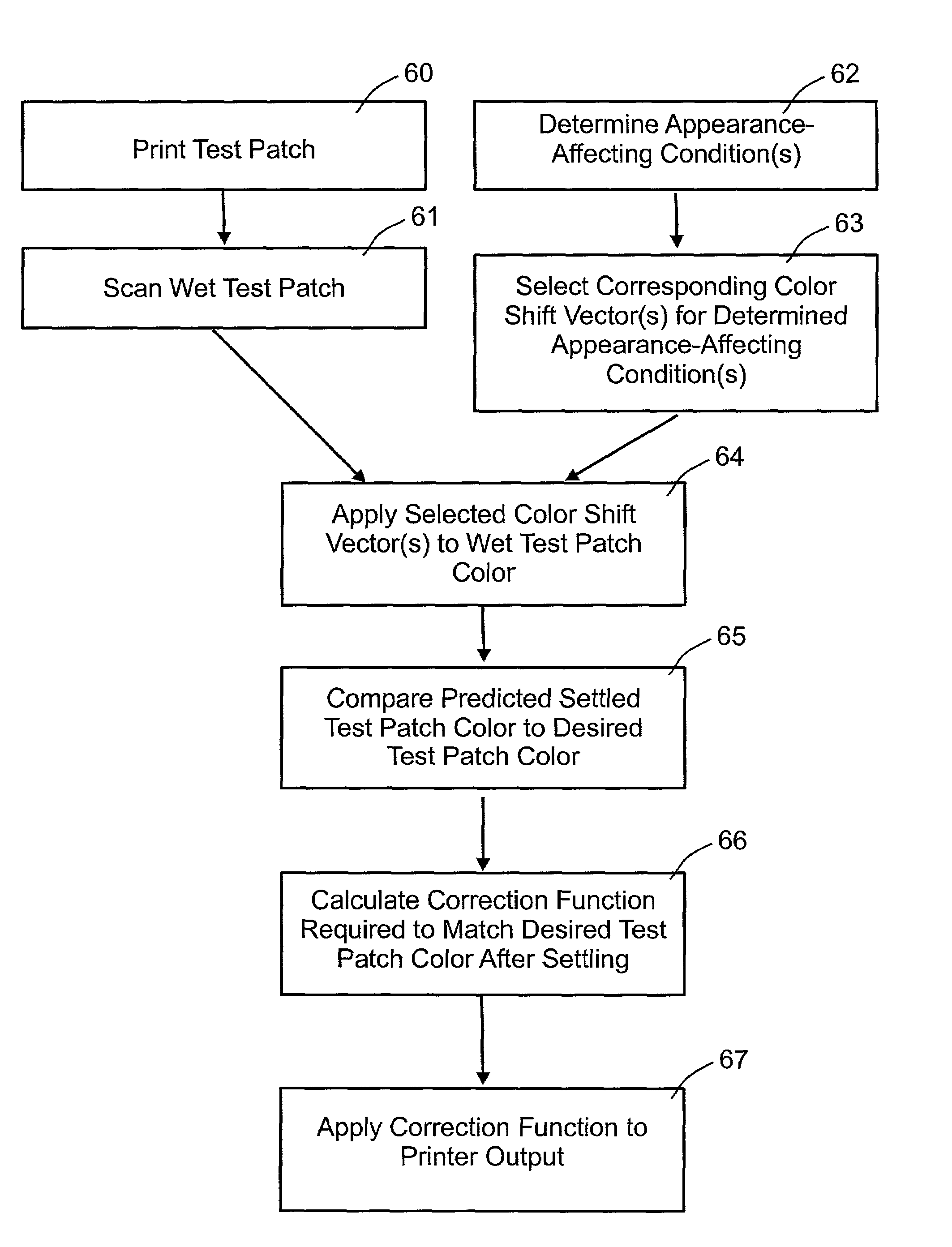
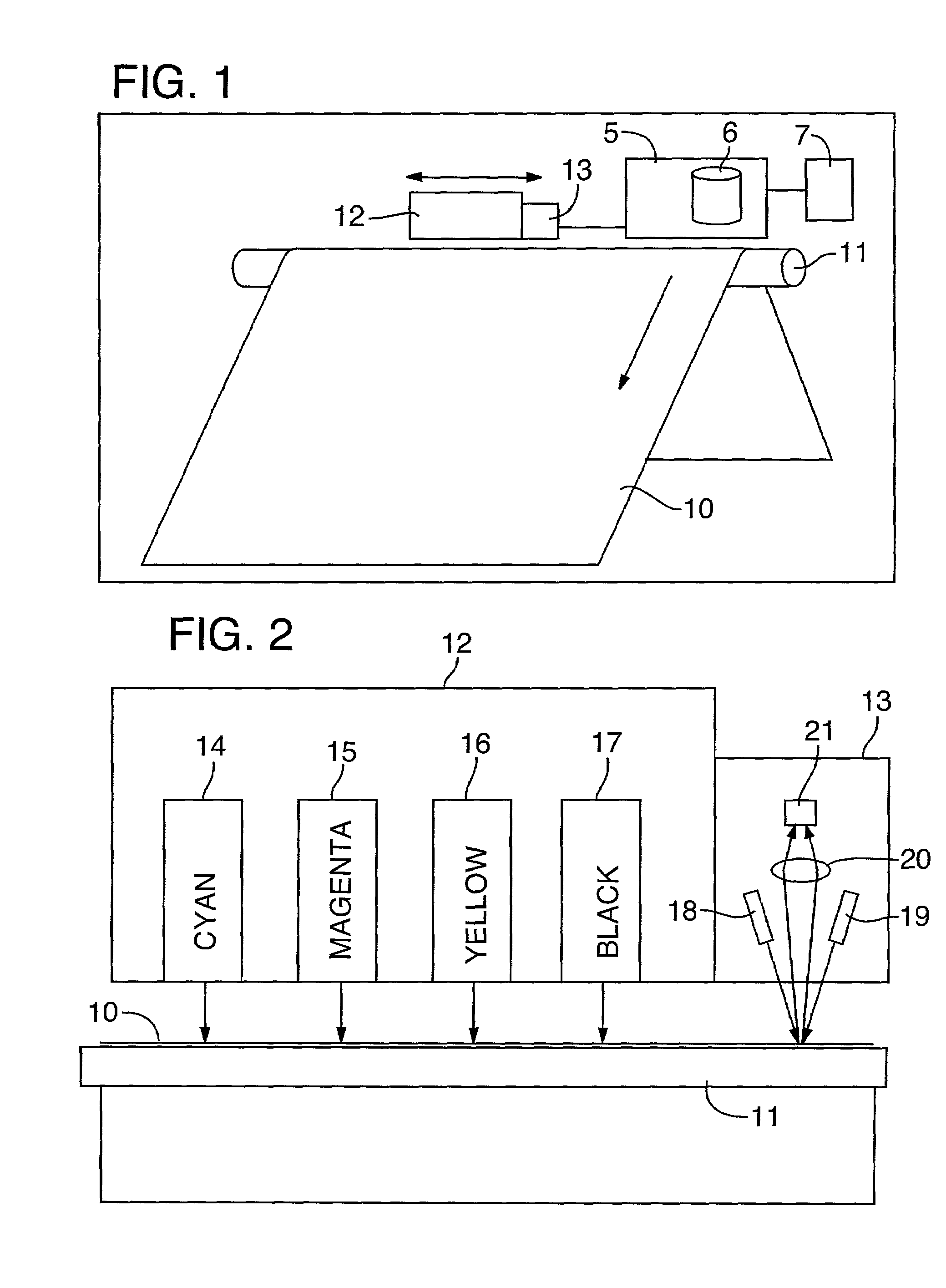
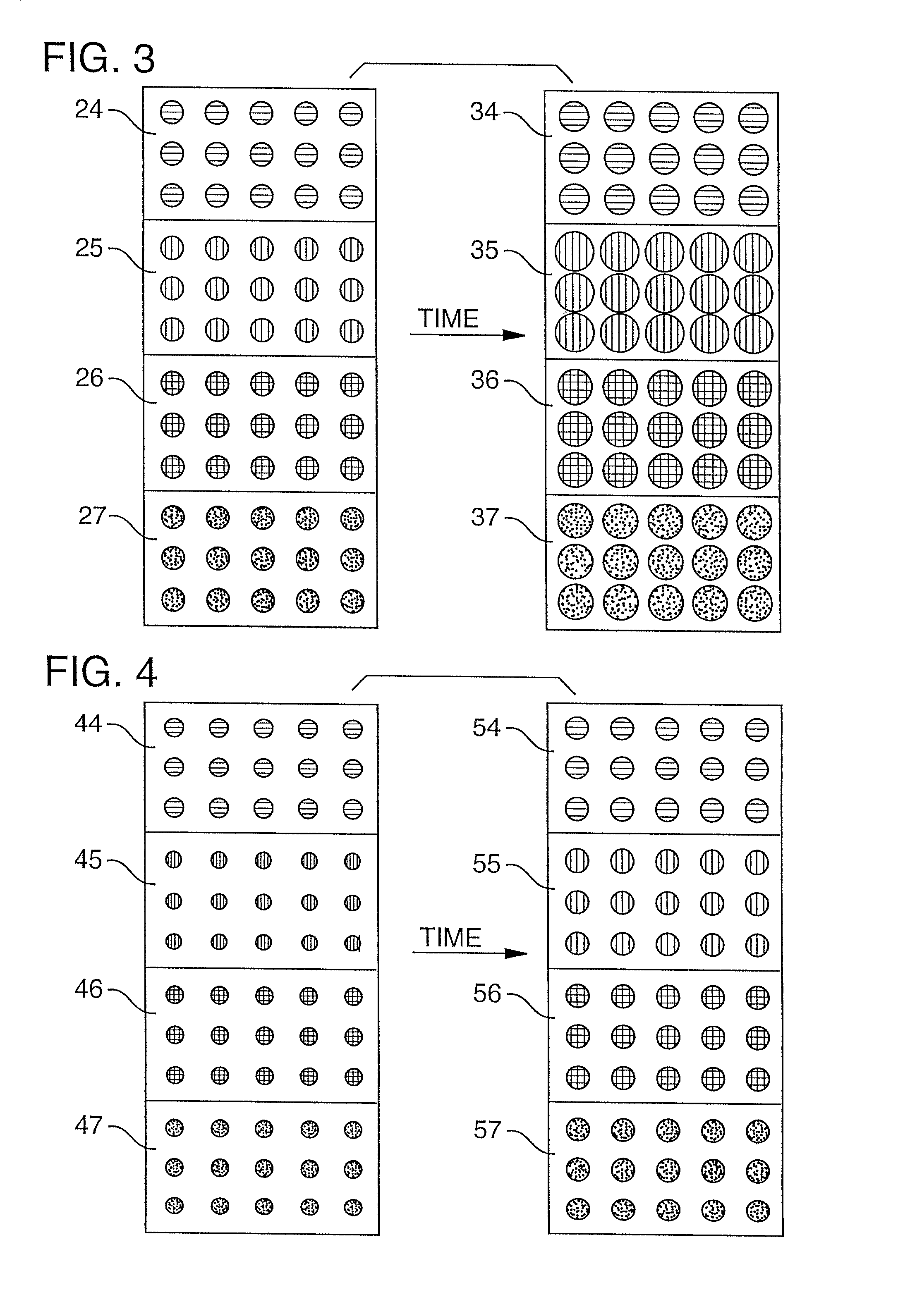
Calibration of a multi color imaging system using a predicted color shift
InactiveUS6985254B2Digitally marking record carriersDigital computer detailsPattern recognitionColor shift
A method for predicting the settled appearance of a test patch printed by an imaging system by applying a transfer function to the color of a freshly printed test patch. The transfer function may be formulated to take into account a variety of environmental conditions, such as humidity or temperature, or post-printing processes, such as lamination. The predicted settled test patch color may be exported to an external image processor, or the imaging system processor may internally compare the predicted settled test patch color with the desired test patch color in order to calibrate the color map used by the imaging system.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
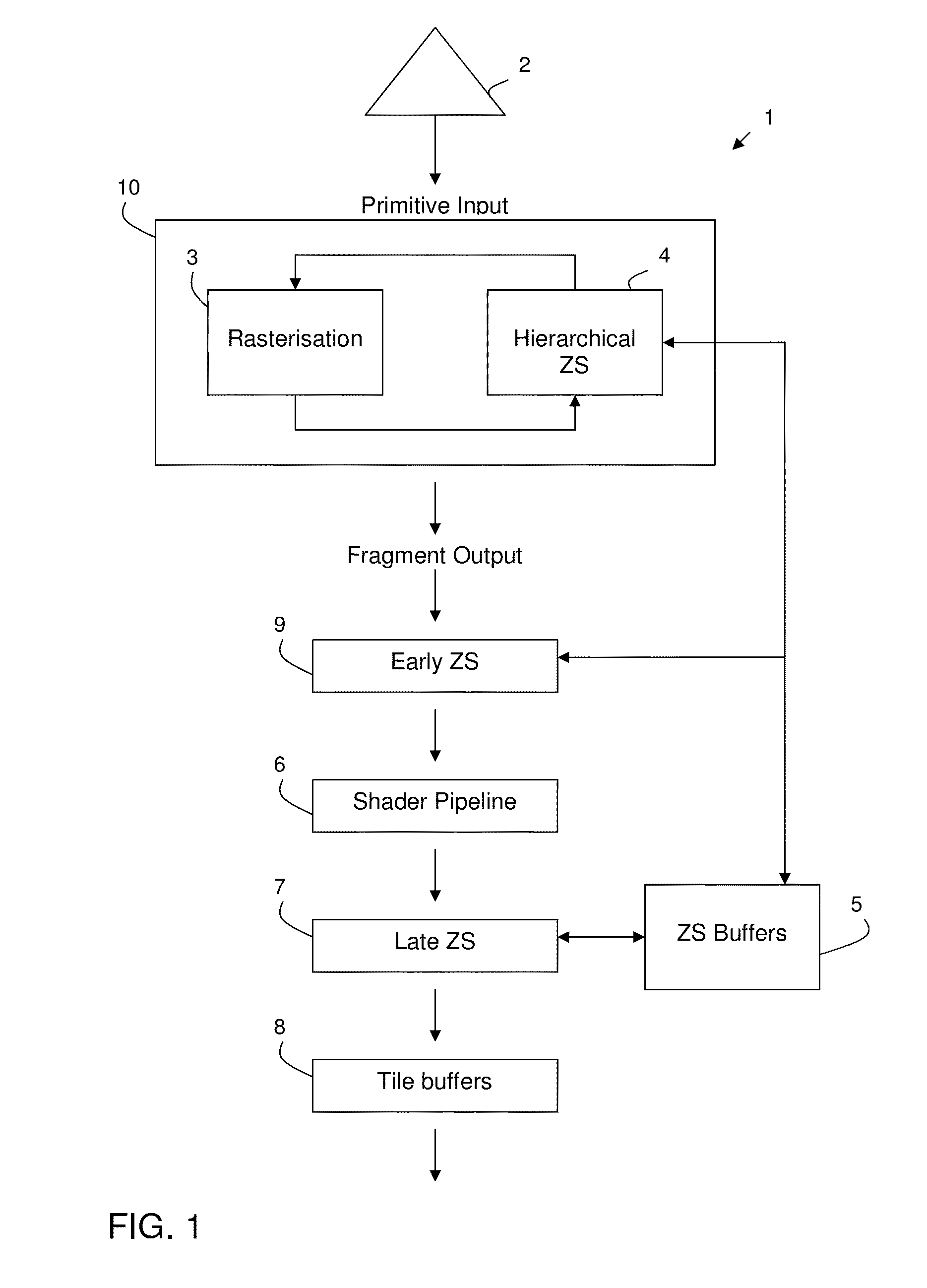
Hidden surface removal in graphics processing systems
A graphics processing pipeline 1 includes a rasteriser 3 that tests patches representing respective different regions of a render output against the edges of primitives 2 to determine if the primitive at least partially covers the patch and an early depth test stage 4 that performs early depth tests for primitives in respect of patches of the render output that the primitive has been found by the rasteriser at least partially to cover, by using depth test information 5 associated with a patch indicating the number and distribution of different depth value regions associated with the patch to determine the depth value region or regions associated with the patch that the primitive should be depth tested against, and then performing a depth test or tests for the primitive in respect of the respective determined depth value region or regions associated with the patch.
Owner:ARM LTD
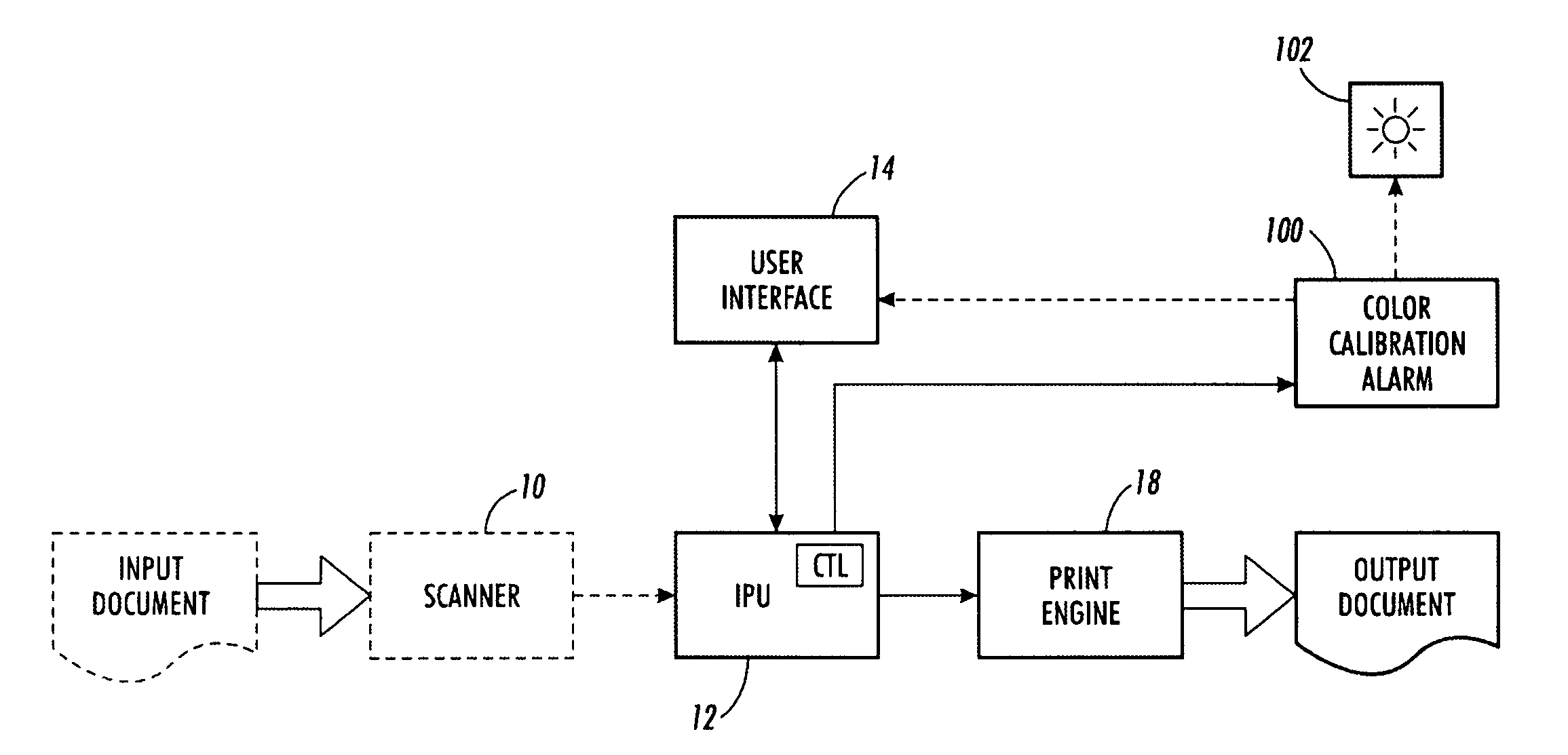
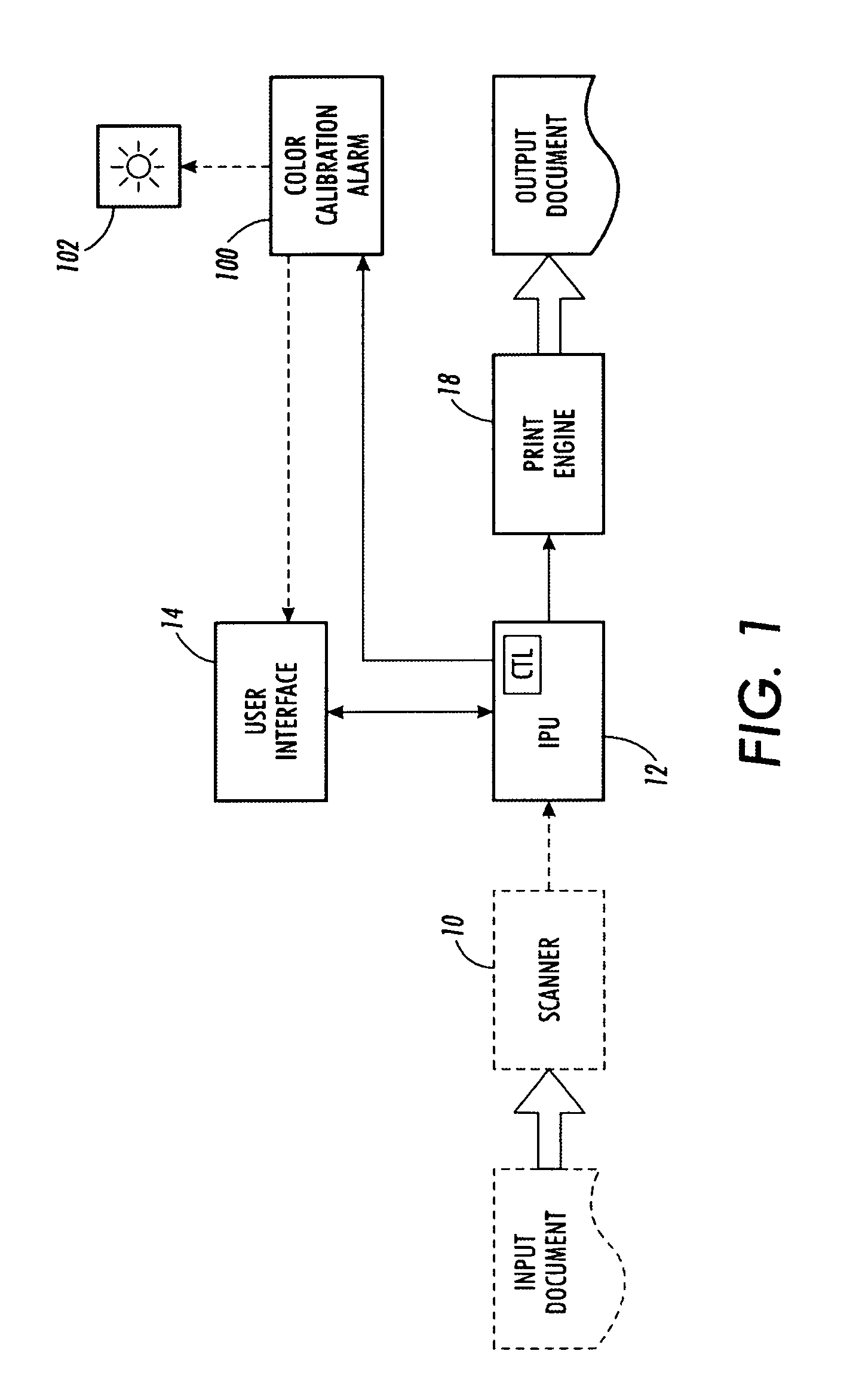
Color calibration alarm apparatus and method for use in an image-rendering device
This invention relates to a color calibration alarm apparatus and method for use in an image-rendering device. The alarm apparatus, and associated method, make use of a sensor device that compares printed or measured color values with expected or ideal color values. With the measured values differ sufficiently from the ideal color values, the alarm apparatus signals to the user that a calibration should be performed. The printed or measured color values are obtained from a test patch that is printed, preferably, on a break page between print jobs. The alarm device is placed at the output tray of an image rendering device in one embodiment that may also be a separate stand alone hand-held unit in other embodiments where it is manually used.
Owner:XEROX CORP
Method for confirming correct selection of an input profile for a color printer
InactiveUS20050275854A1Rapid and accurate visual checkDigitally marking record carriersVisual presentation using printersPattern recognitionVia rectum
Owner:GLOBAL GRAPHICS SOFTWARE
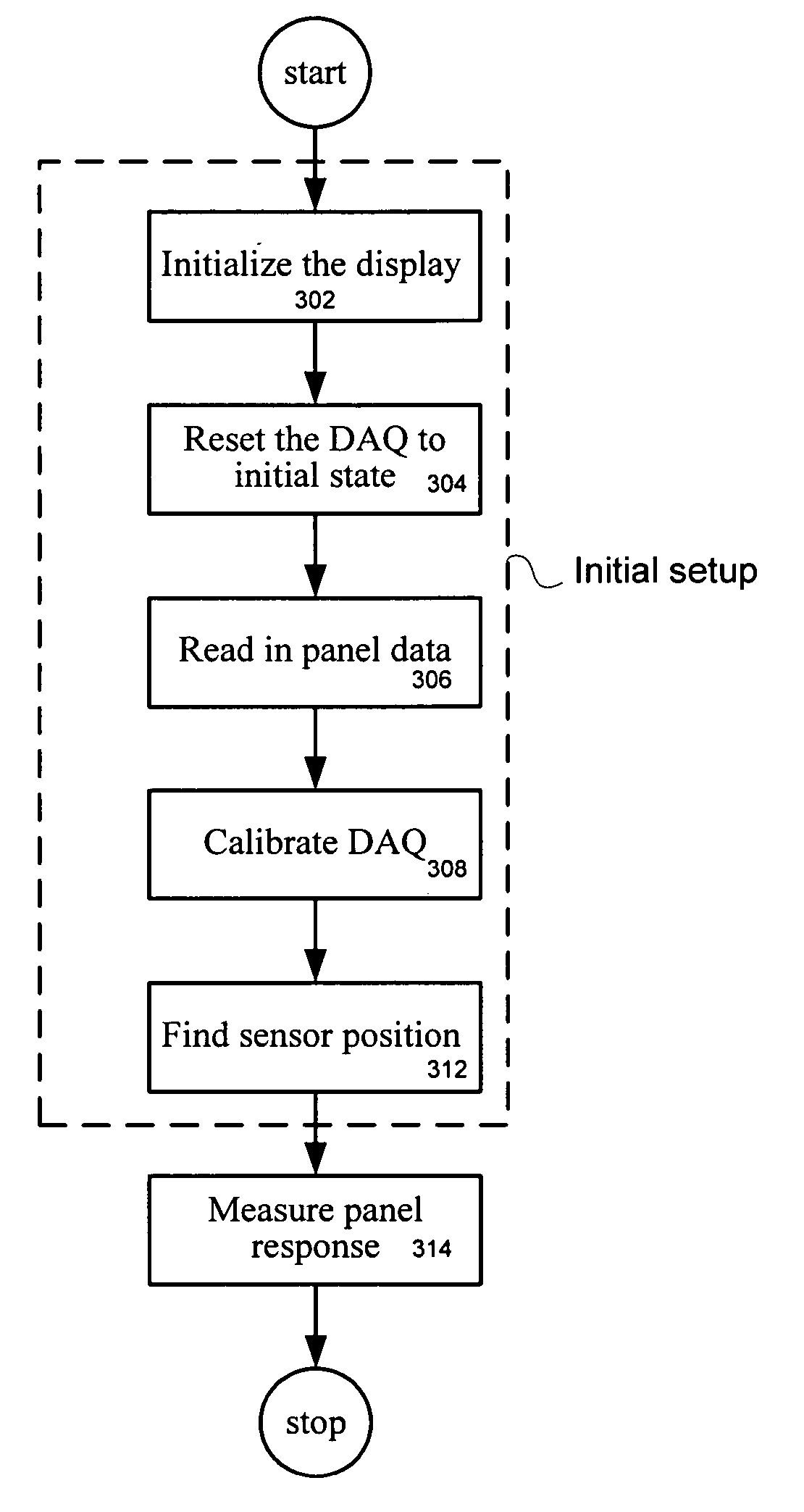
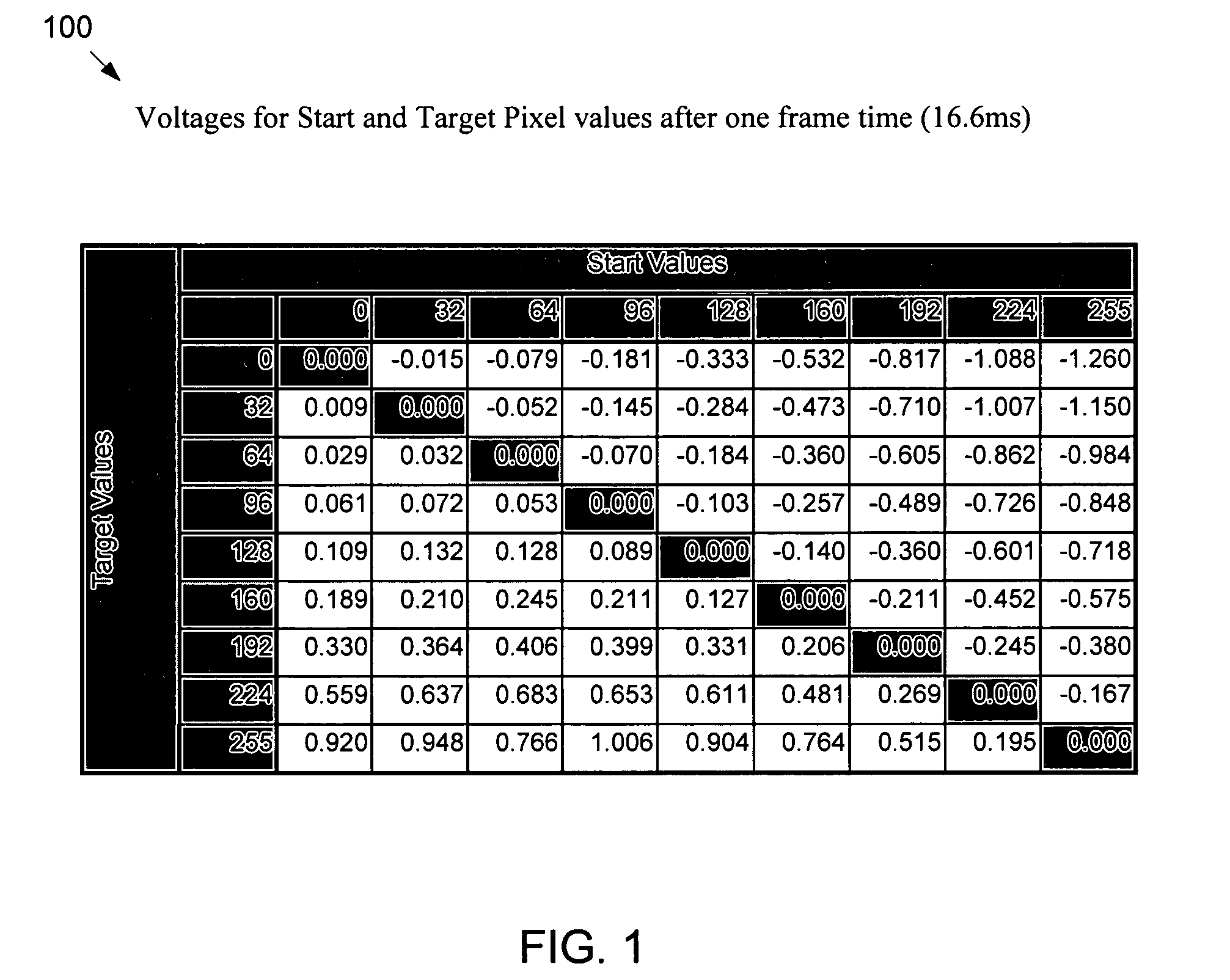
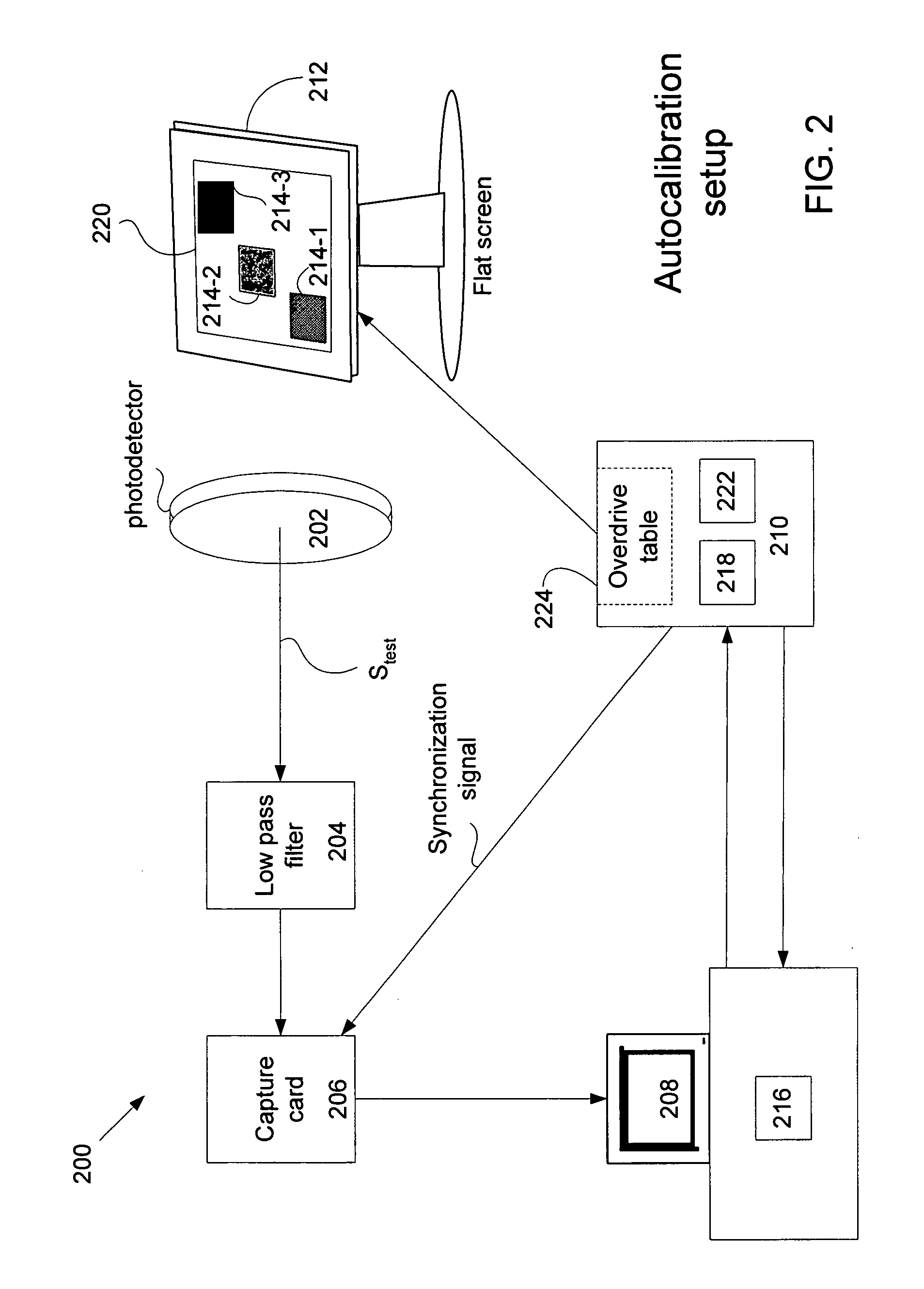
LCD overdrive auto-calibration apparatus and method
InactiveUS20050125179A1Cathode-ray tube indicatorsElectrical measurementsLiquid-crystal displayGray level
A method of auto-calibration of a liquid crystal display (LCD) is described. The method is carried out by generating and displaying on the LCD a test patch at a first grey level, generating a first signal based upon the test pattern at the first grey level, generating and displaying a second test patch at a second grey level, generating a second signal based upon the test pattern at the second grey level, and calculating an entry to an LCD overdrive table based upon the first and the second signal.
Owner:GENESIS MICROCHIP
Gray balance for a printing system of multiple marking engines
A method for calibrating a printing system including a plurality of printers includes designating one of the plurality of printers as a reference printer and defining color values for a desired response for one or more printed test patches on a control page. Through a first process aimed toward achieving the desired response, a printed control page is generated with the reference printer, the control page including one or more of the test patches which, when measured, has a measured response which approaches the desired response. Through a second process aimed toward achieving a desired response, the desired response being the measured response of the reference printer, a printed control page is generated with a second of the printers, the control page including one or more of the test patches which, when measured, has a response which approaches the measured response of the reference printer.
Owner:XEROX CORP
Test Patch System and Method
InactiveUS20090015273A1Resistance/reactance/impedenceWithdrawing sample devicesTest patchEnvironmental geology
A test system for taking a sample of a constituent on a surface utilizing a fluid source includes a transition region having a capillary layer for delivering a fluid from said fluid source, an extraction region having a collection material in contact with said surface, and a collection region having a sensor reservoir therein for collecting the fluid for analysis.
Owner:UNSQARE LLC
Calibration method for an imaging device
ActiveUS7315394B2Reduce adverse effectsReduce impactImage enhancementDigitally marking record carriersTest patchEquivalent input
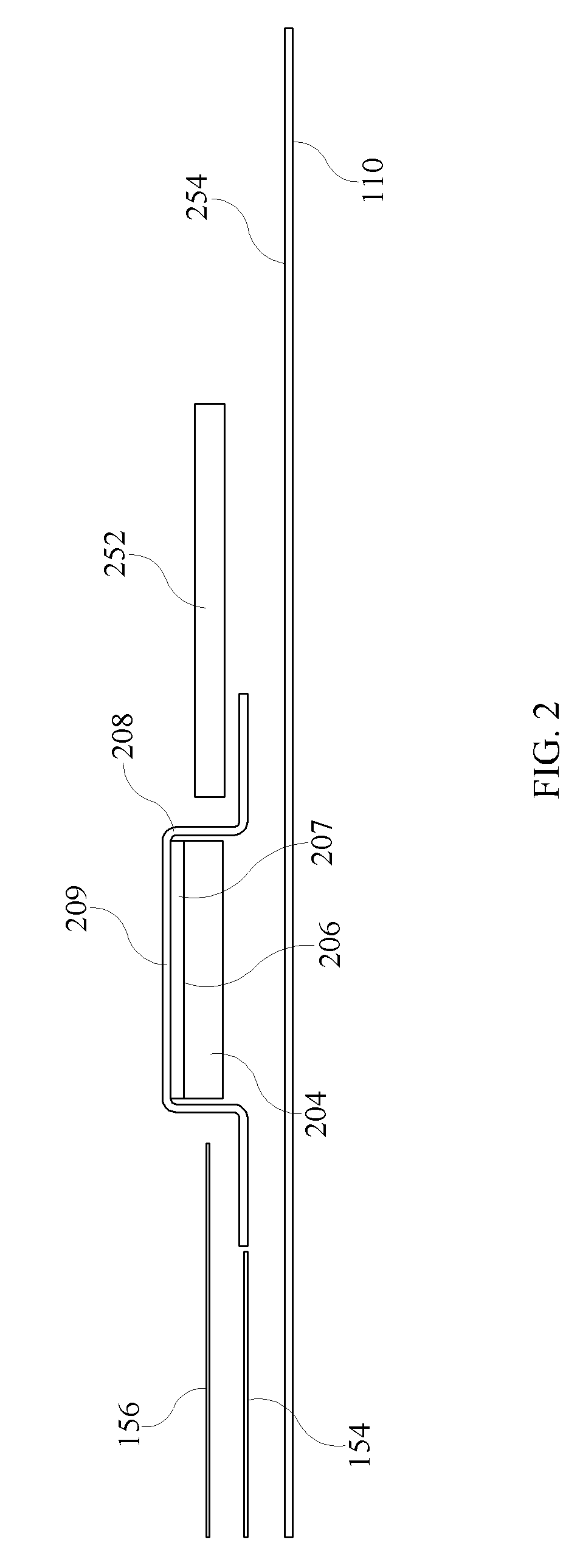
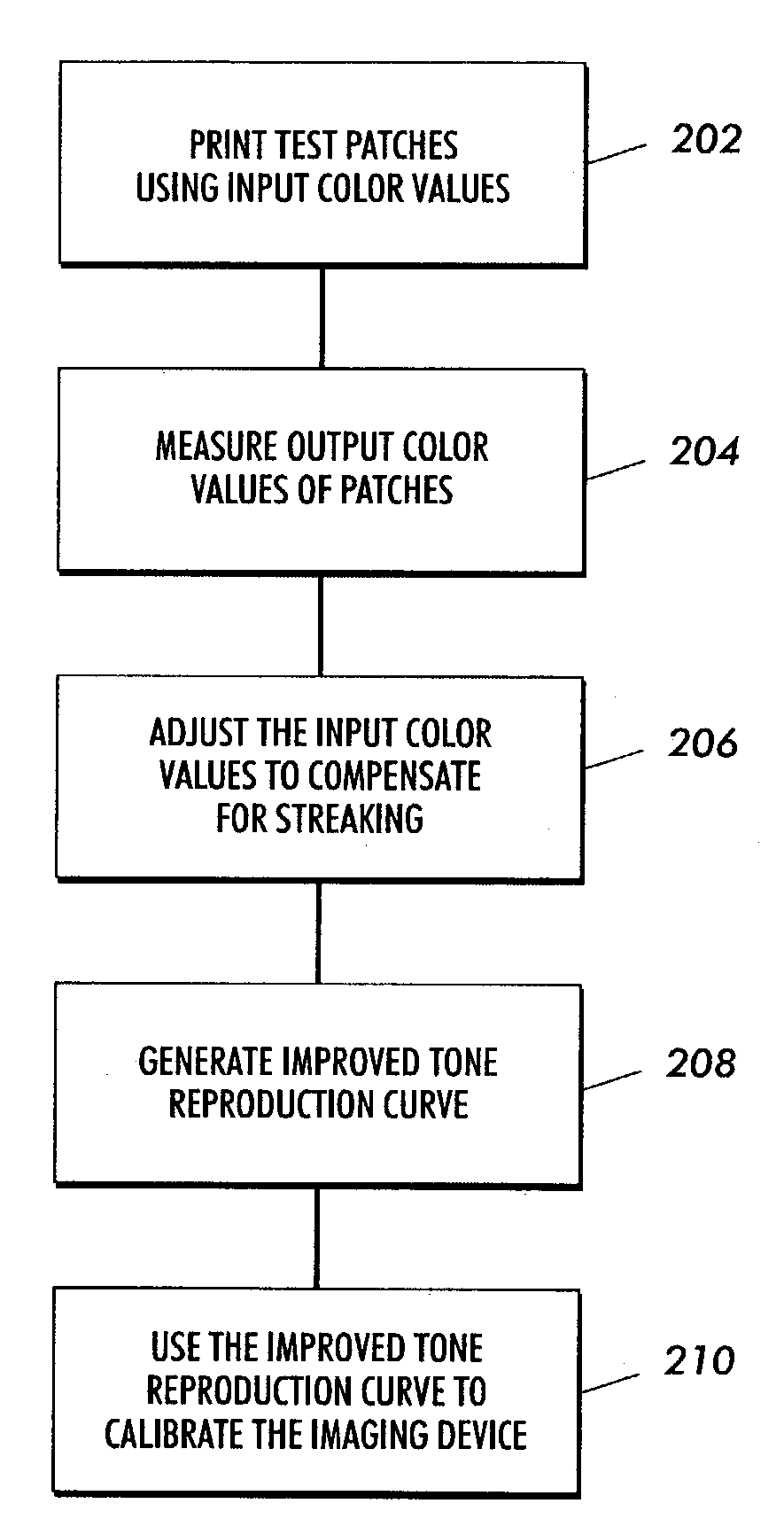
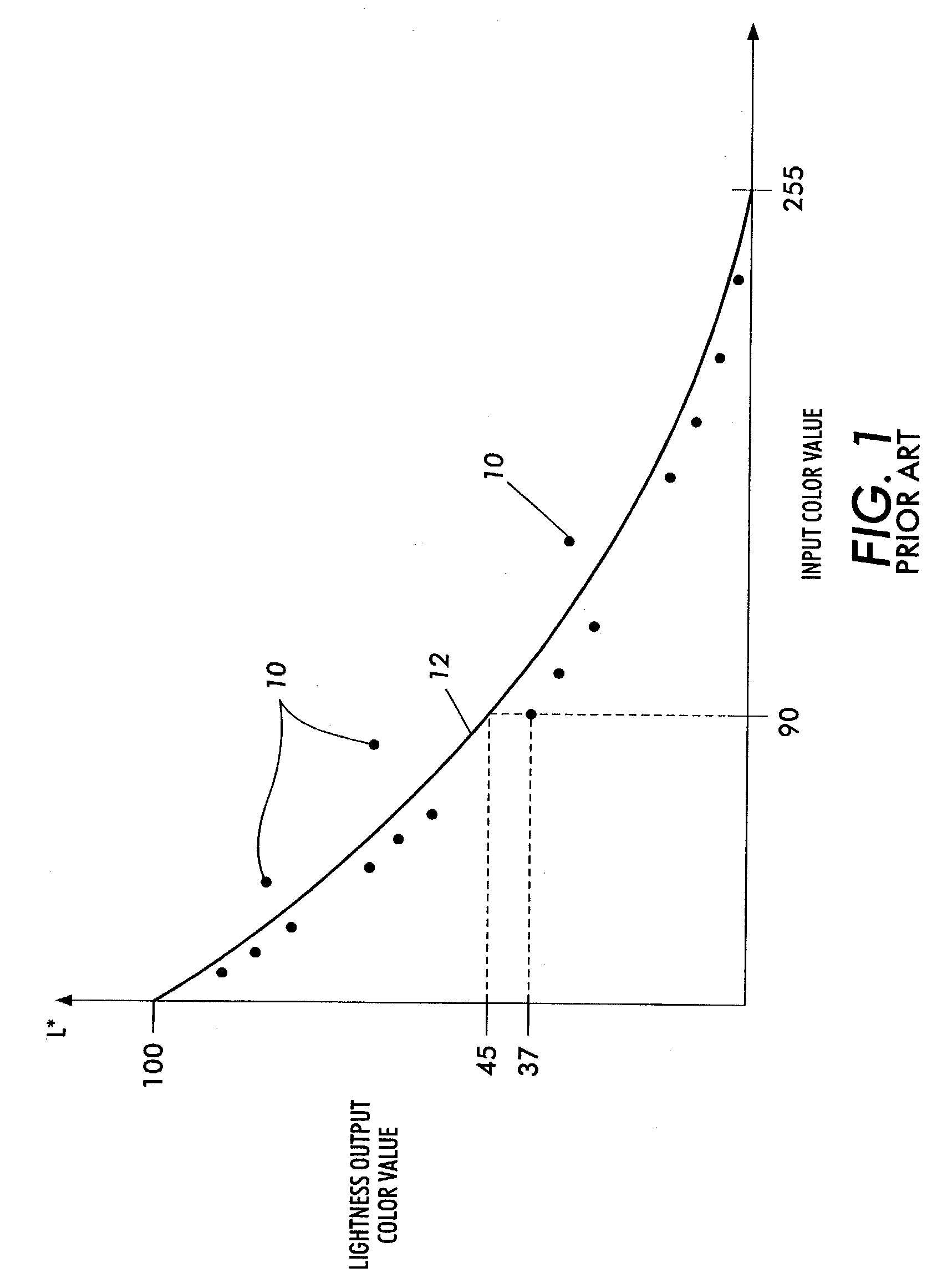
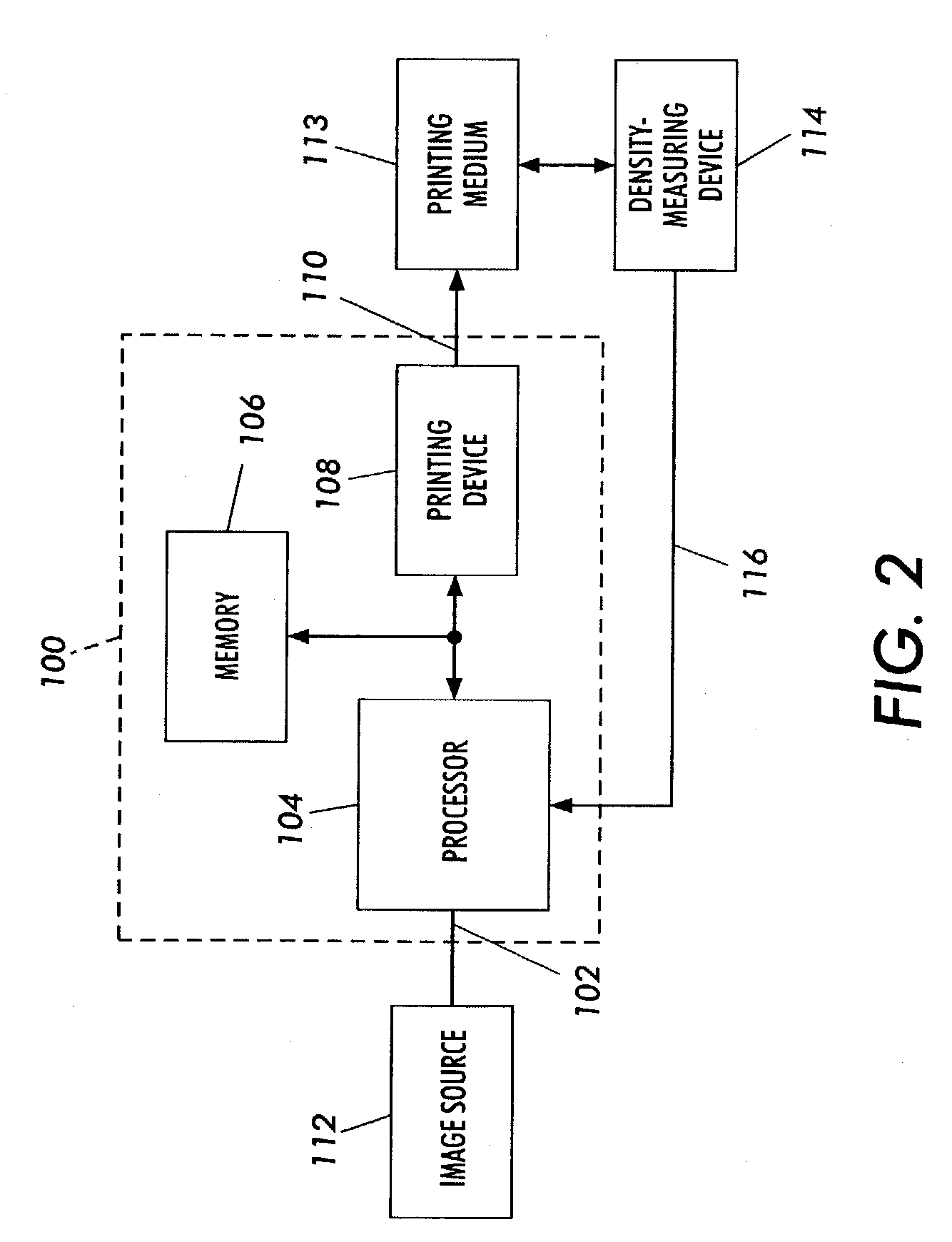
A method includes forming a plurality of test patches in an array of orthogonal rows. The test patches are formed by using at least one printhead in an imaging machine. Each of the test patches is associated with a respective one of a plurality of initial input color values. The array of test patches includes a plurality of rows of varied-input test patches and at least one row of first equivalent-input test patches. A respective output color value of each of the test patches is measured. At least one first mathematical relationship is generated based on the output color values of the at least one row of first equivalent-input test patches. A plurality of adjusted input color values are calculated for respective ones of the varied-input test patches. Each adjusted input color value is calculated based upon the generated at least one first mathematical relationship. A second mathematical relationship is computed between the adjusted input color values and the output color values. The imaging machine is calibrated by using the second mathematical relationship.
Owner:XEROX CORP
Scanning patches to provide printer calibration data
InactiveUS20120120428A1Good flexibilityShorten the timeVisual presentationPictoral communicationComputer graphics (images)Test patch
A method of providing calibration data for a printer includes printing a calibration target using the printer, the target including first and second patch sets, each patch set including a plurality of test patches. An operator scans one or both sets using an external scanner to provide scanned patch data. A processor automatically determines which set(s) have been scanned. Calibration data are automatically generated for the printer using the scanned patch data.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
Color Correction Method for an Imaging System
InactiveUS20090190194A1Consistent colorLower requirementDigital computer detailsColour-separation/tonal-correctionColor shiftTest patch
A method for correcting color shift in an imaging system, including an imaging object, and a standard color conversion lookup table associated with the imaging object, includes measuring a plurality of test patches to obtain color data associated with the imaging object. A signature color data lookup table is generated, based on the color data, and is combined with the standard color conversion lookup table to generate a composite color conversion lookup table for use with the imaging object.
Owner:DEER ANNA Y +3
Image forming apparatus, control method of image forming apparatus, and computer program product
InactiveUS20100238509A1Digitally marking record carriersDigital computer detailsImage formationTest patch
Owner:RICOH KK
Sweat analyte testing components and methods
InactiveUS20140257064A1Increase distanceElectrotherapyDiagnostic recording/measuringElectricityAnalyte
Embodiments of the invention include adhesive electrode sets and related methods. In an embodiment, the invention includes an adhesive electrode set. The adhesive electrode set can include a first pad, a first electrode, a first electrical contact, a first conductive lead, a second pad, a second electrode, a second electrical contact, a second conductive lead, a flexible strip, and an adhesive material. The flexible strip can include a fold. The flexible strip can be configured to allow the distance between the first pad and the second pad to increase through flexion of the flexible strip. In an embodiment, the invention includes an analyte receiving test patch. The analyte receiving test patch can include a skin contact layer, a wick, an absorbent layer, a barrier film layer, and an adhesive frame. Other embodiments are also included herein.
Owner:BIRCHWOOD LAB
Fine tuning color dictionaries
InactiveUS7933053B2Increase weightReduce weightDigitally marking record carriersDigital computer detailsPattern recognitionProduction model
A spot color dictionary is fine tuned or updated. Localized color production models are determined for spot colors of interest to be produced by an associated document processing system or printer. Measurements are made of colors of produced spot colors. Optionally, measurements are made of colors of test patches that are based on perturbations from the colors of the spot colors. In determining a model for the production of a target spot color, measurement data related to colors that are closer in color space to a given target color is given a higher weight than is measurement data related to colors that are further in color space from the target color. Accordingly, the model is localized to the region of color space about the target color and therefore, more accurately predicts a colorant recipe for the target color than would interpolation based on a full gamut, or more general model.
Owner:XEROX CORP
Method for confirming correct selection of an output profile of a printer
ActiveUS7298526B2Digitally marking record carriersDigital computer detailsPattern recognitionTest patch
A method for using a page description language to electronically express colored patches on the border of contract proofs, such that a user can quickly and easily evaluate whether the color of prints produced using a color printer are correct. The verification is performed by visually comparing the test patches added to a print with color patches in publicly available standard color sample swatches.
Owner:GLOBAL GRAPHICS SOFTWARE
Patch density measuring apparatus and image forming apparatus
ActiveUS7194214B2Without complicating configuration and processImprove accuracyPhotometry using reference valueScattering properties measurementsMeasurement devicePotential difference
When a regular reflection light receiving unit is receiving a reflected light in a non-image area where the test patches are not formed, a clamp switch is closed. Then, a first reference voltage generated by a pull-up resistor and a zener diode is corresponded to an electric potential of a terminal of a capacitor on the side of an A / D converter. The capacitor is charged by the difference in electric potential between the first reference voltage and an output voltage from the regular reflection light receiving unit. Next, the clamp switch is opened. After the regular reflection light receiving unit receives the reflected light from an image area where the test patches are formed with this state of things, the output voltage from the regular reflection light receiving unit is changed. The difference in density between the image area and the non-image area can be quantified by the A / D converter.
Owner:BROTHER KOGYO KK
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com