Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
432 results about "Color calibration" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The aim of color calibration is to measure and/or adjust the color response of a device (input or output) to a known state. In International Color Consortium (ICC) terms, this is the basis for an additional color characterization of the device and later profiling. In non-ICC workflows, calibration refers sometimes to establishing a known relationship to a standard color space in one go. The device that is to be calibrated is sometimes known as a calibration source; the color space that serves as a standard is sometimes known as a calibration target. Color calibration is a requirement for all devices taking an active part of a color-managed workflow, and is used by many industries, such as television production, gaming, photography, engineering, chemistry, medicine and more.
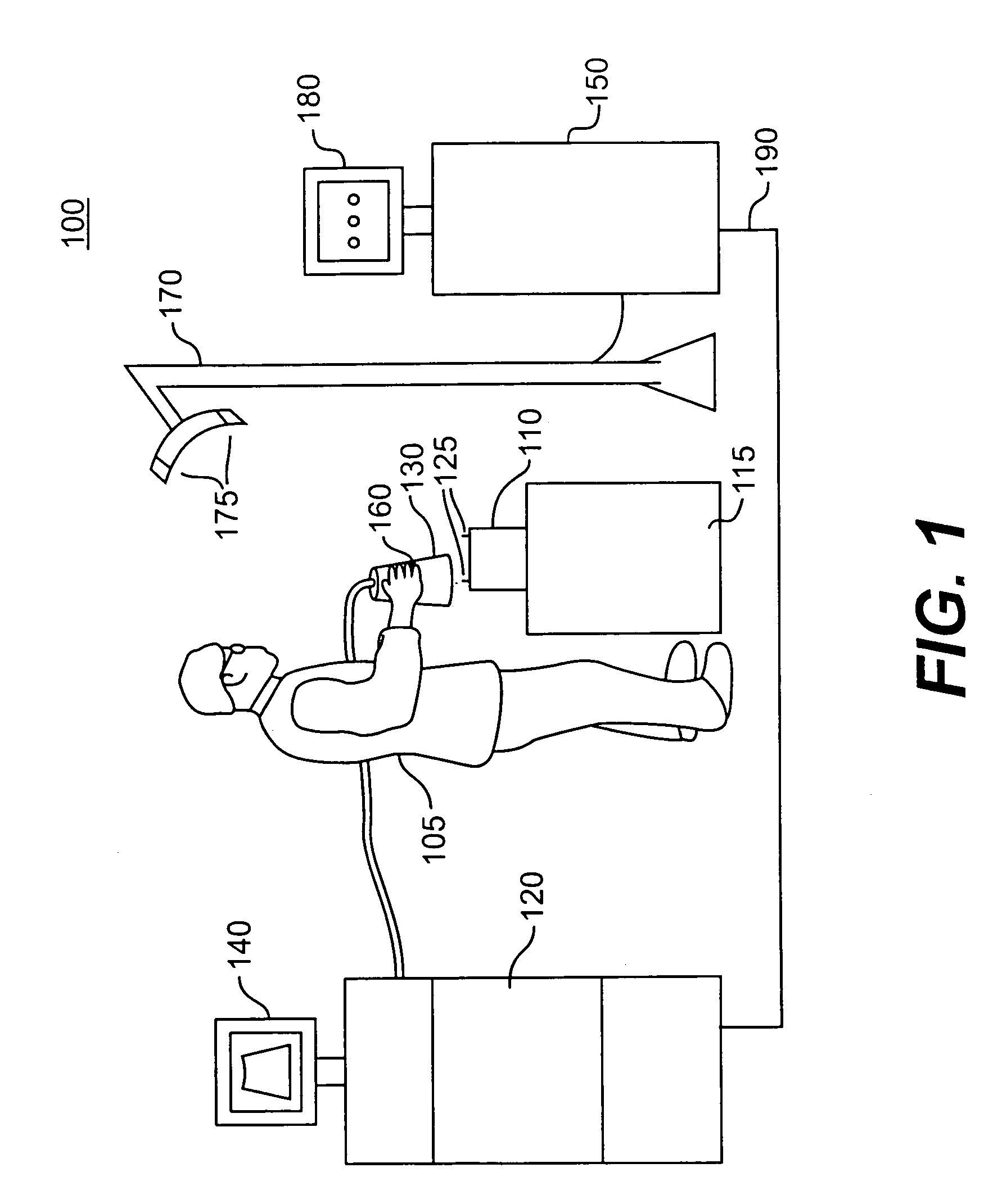
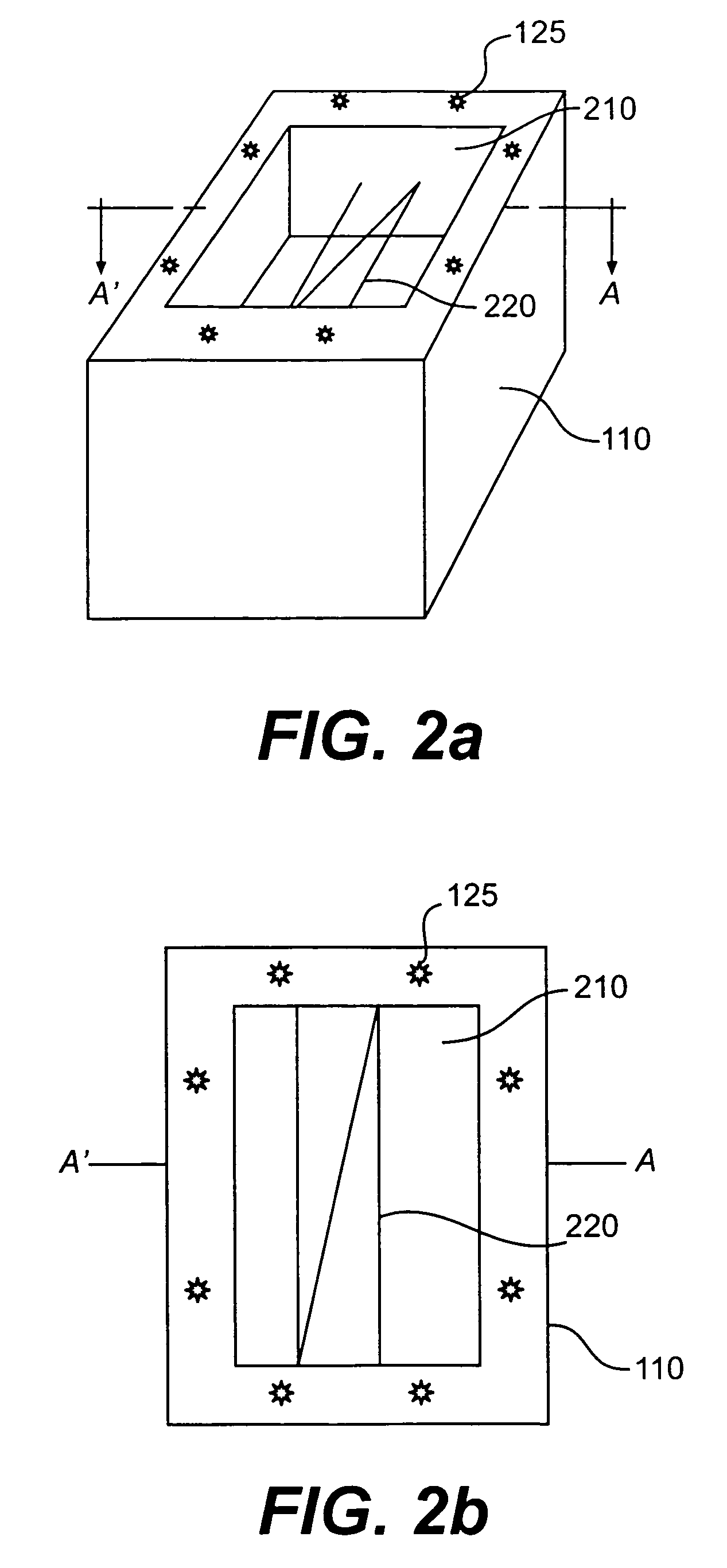
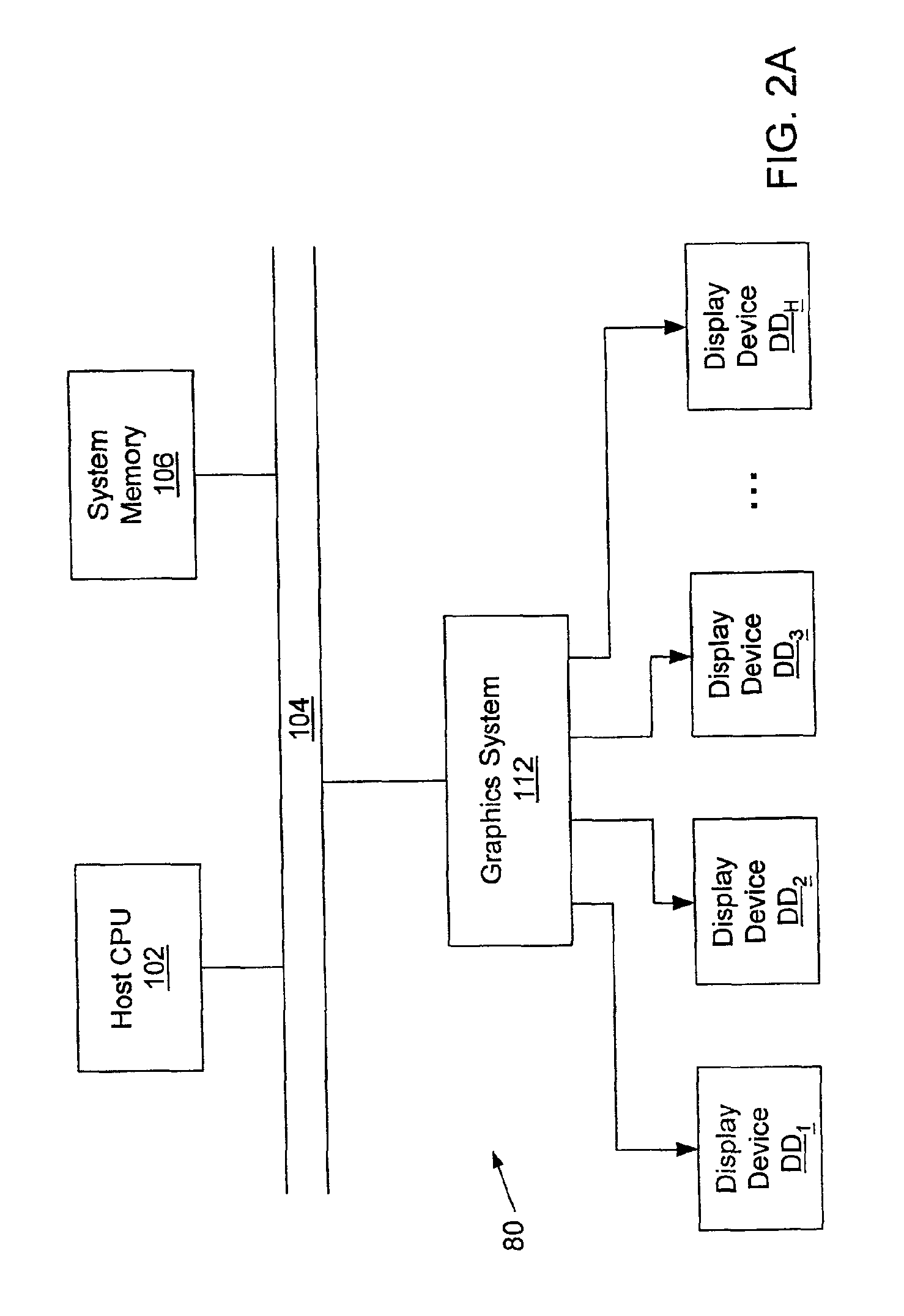
Color calibration of color image rendering devices
InactiveUS20060280360A1Increase heightImage enhancementImage analysisColor imageComputer graphics (images)
Color calibration of color image rendering devices, such as large color displays, which operate by either projection or emission of images, utilize internal color measurement instrument or external color measurement modules locatable on a wall or speaker. A dual use camera is provided for a portable or laptop computer, or a cellular phone, handset, personal digital assistant or other handheld device with a digital camera, in which one of the camera or a display is movable with respect to the other to enable the camera in a first mode to capture images of the display for enabling calibration of the display, and in a second mode for capturing image other than of the display. The displays may represent rendering devices for enabling virtual proofing in a network, or may be part of stand-alone systems and apparatuses for color calibration. Improved calibration is also provided for sensing and correcting for non-uniformities of rendering devices, such as color displays, printer, presses, or other color image rendering device.
Owner:RAH COLOR TECH
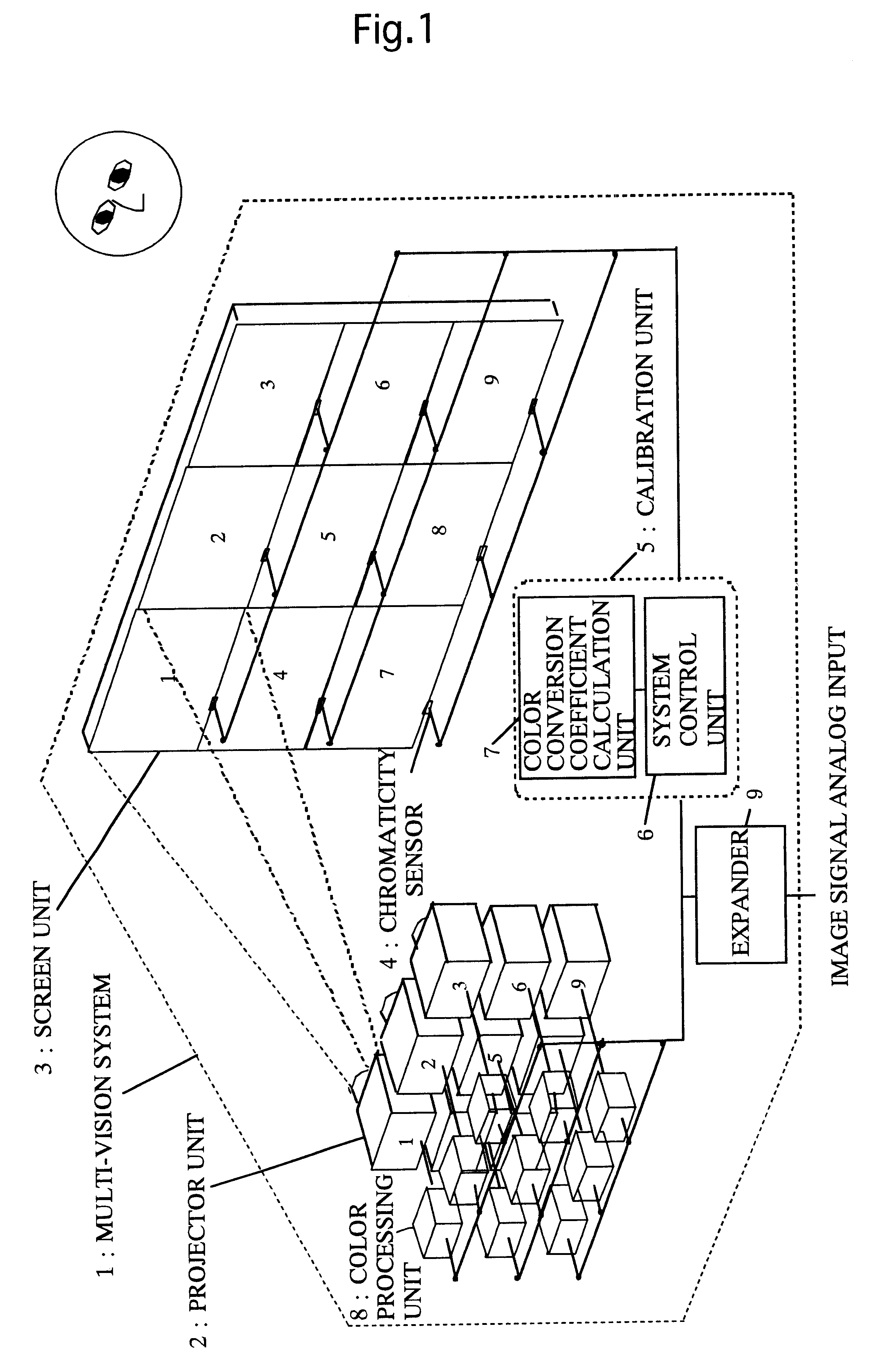
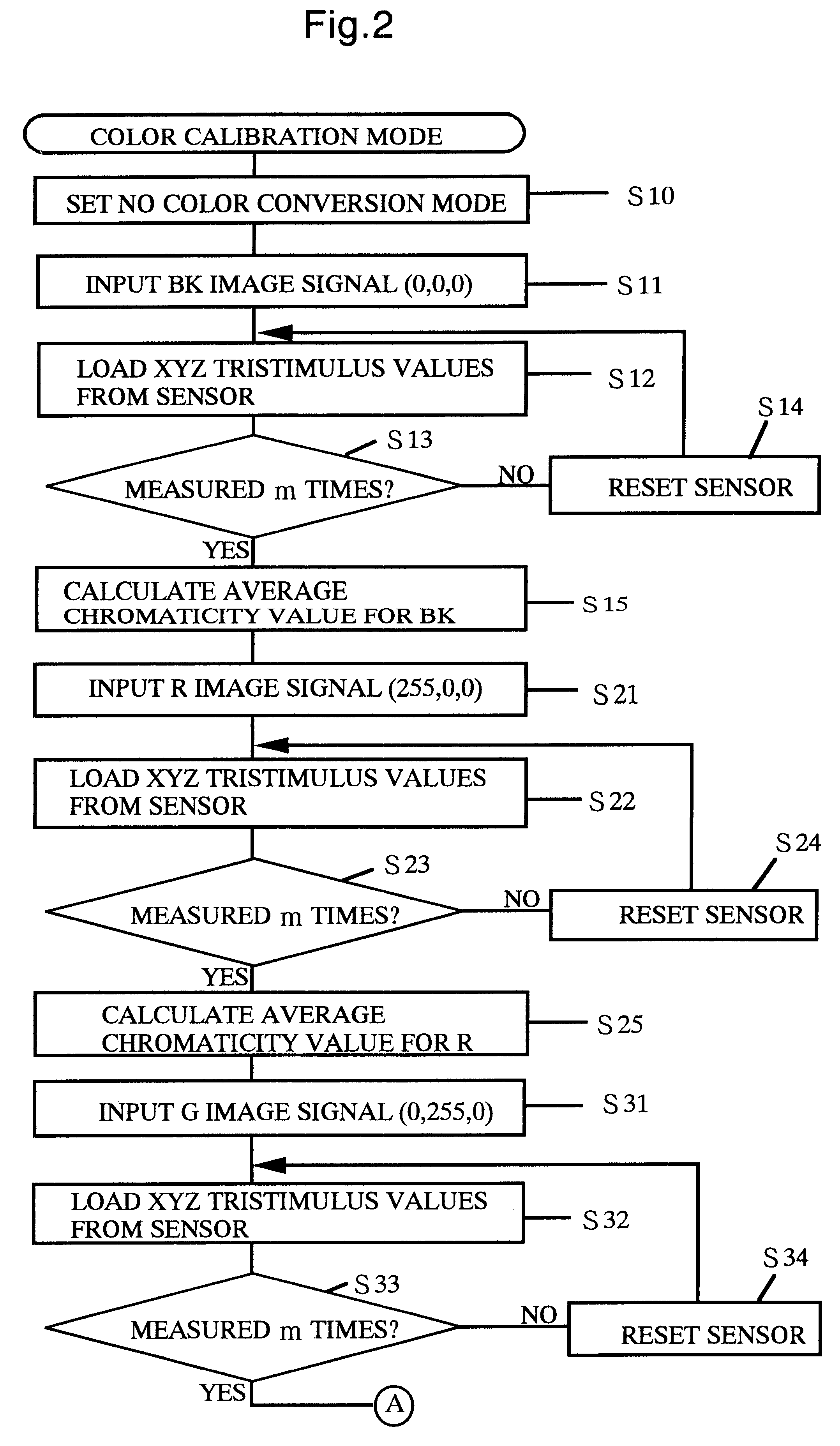
Multivision system, color calibration method and display
InactiveUS6340976B1Television system detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionColor transformationConversion coefficients
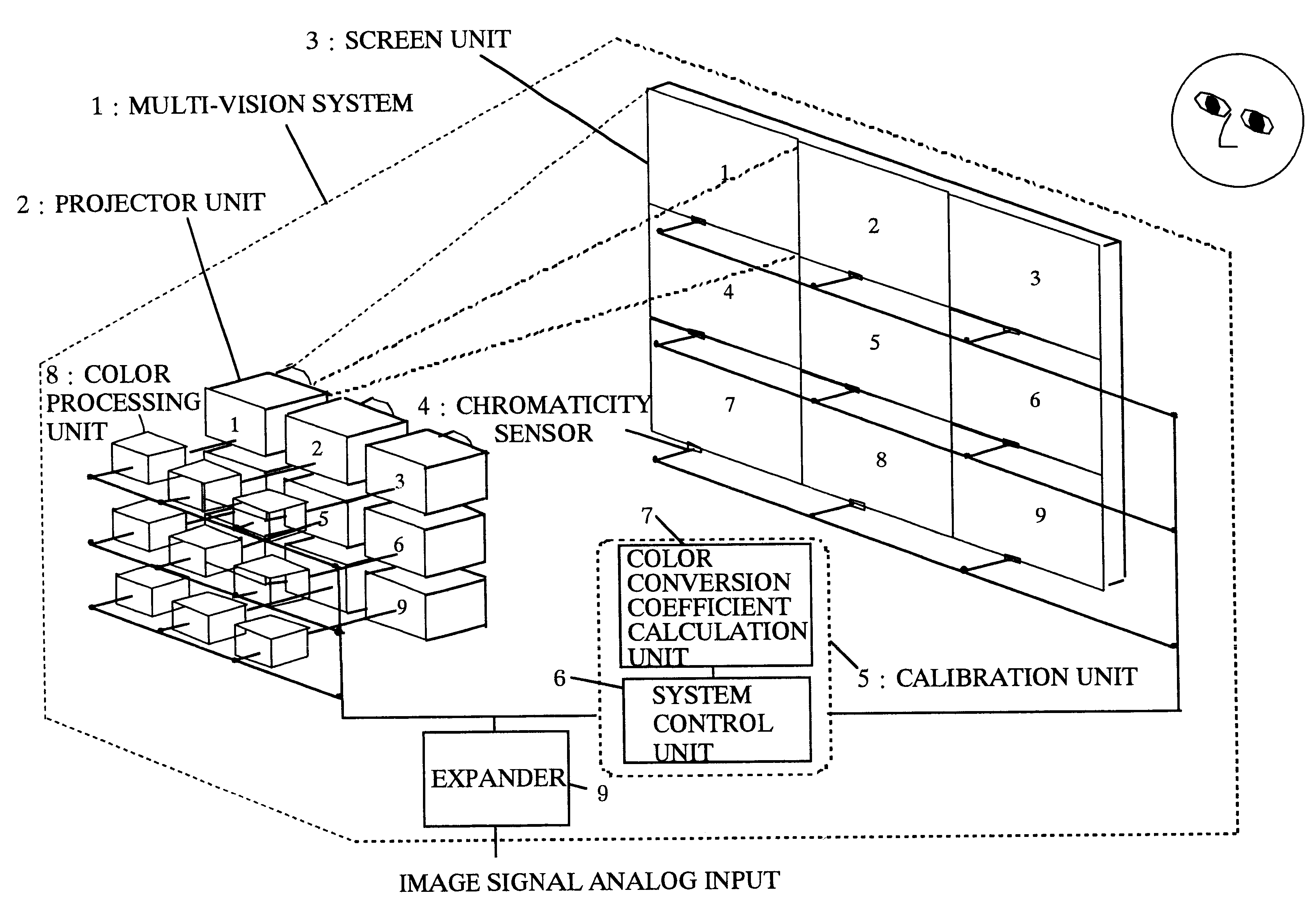
A multi-vision system includes chromaticity sensors for performing colorimetry of a plurality of display units. From colorimetry results obtained from the chromaticity sensors, a color conversion coefficient calculation unit inside a color calibration unit calculates the color conversion coefficient that is characteristic of each display unit. Calculated color conversion coefficients are stored in a color processing unit. The color calibration for this multi-vision system displays representing colors without a color conversion, and from colorimetry results of the representing colors for all the display units, a target color is decided automatically. For all display units, the color conversion coefficients are automatically calculated so that the representing colors are able to be displayed as a target color.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
System and method for image based sensor calibration
InactiveUS7085400B1Accurate and free-hand calibrationEasy to detectImage enhancementImage analysisData setImage scale
Apparatus and methods are disclosed for the calibration of a tracked imaging probe for use in image-guided surgical systems. The invention uses actual image data collected from an easily constructed calibration jig to provide data for the calibration algorithm. The calibration algorithm analytically develops a geometric relationship between the probe and the image so objects appearing in the collected image can be accurately described with reference to the probe. The invention can be used with either two or three dimensional image data-sets. The invention also has the ability to automatically determine the image scale factor when two dimensional data-sets are used.
Owner:SURGICAL NAVIGATION TECH
Color calibration of color image rendering devices
Color calibration of color image rendering devices, such as large color displays, which operate by either projection or emission of images, utilize internal color measurement instrument or external color measurement modules locatable on a wall or speaker. A dual use camera is provided for a portable or laptop computer, or a cellular phone, handset, personal digital assistant or other handheld device with a digital camera, in which one of the camera or a display is movable with respect to the other to enable the camera in a first mode to capture images of the display for enabling calibration of the display, and in a second mode for capturing image other than of the display. The displays may represent rendering devices for enabling virtual proofing in a network, or may be part of stand-alone systems and apparatuses for color calibration. Improved calibration is also provided for sensing and correcting for non-uniformities of rendering devices, such as color displays, printer, presses, or other color image rendering device.
Owner:RAH COLOR TECH
Method for spatial color calibration using hybrid sensing systems
InactiveUS20080037069A1Minimize spatial uniformity errorSpace minimizationDigitally marking record carriersDigital computer detailsOutput deviceComputer vision
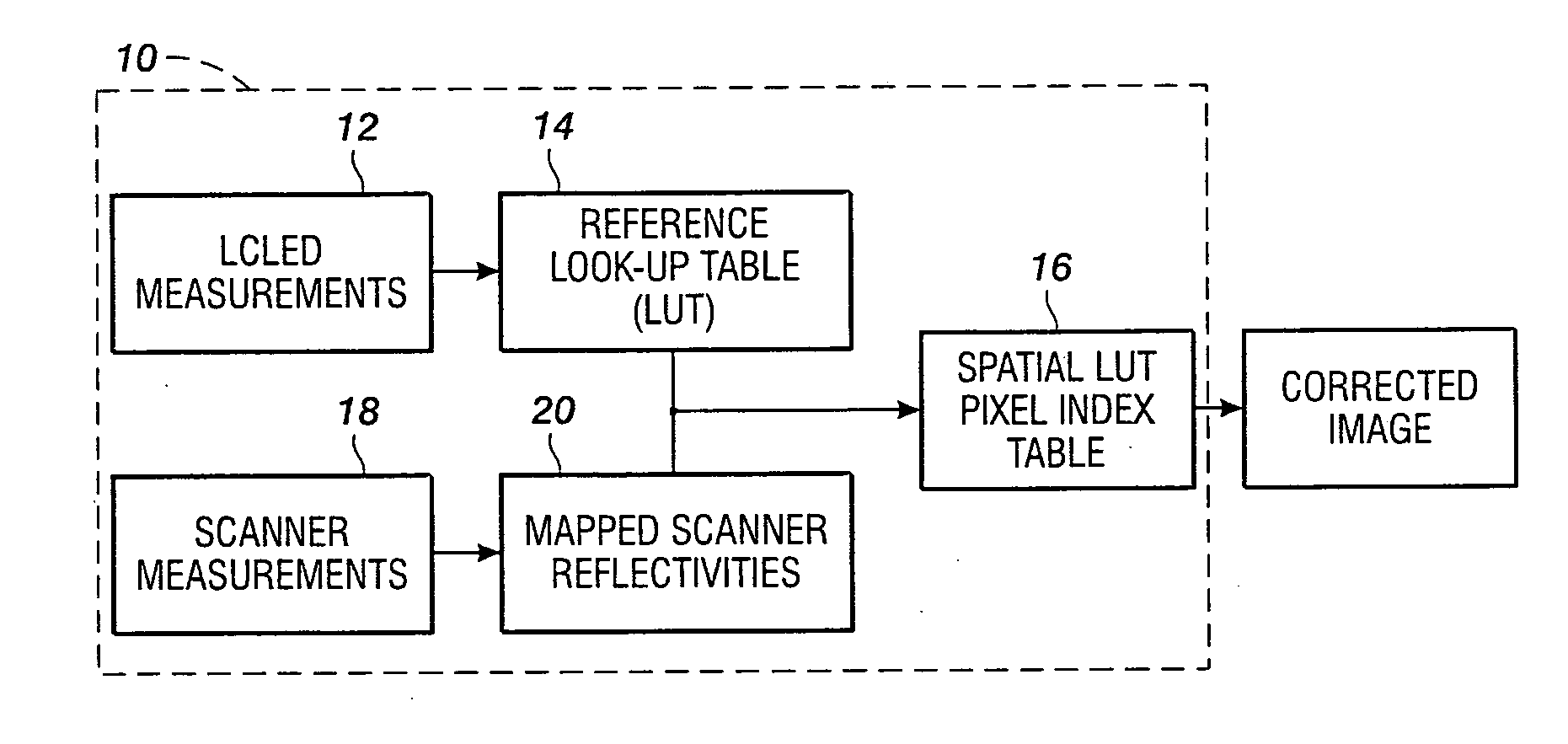
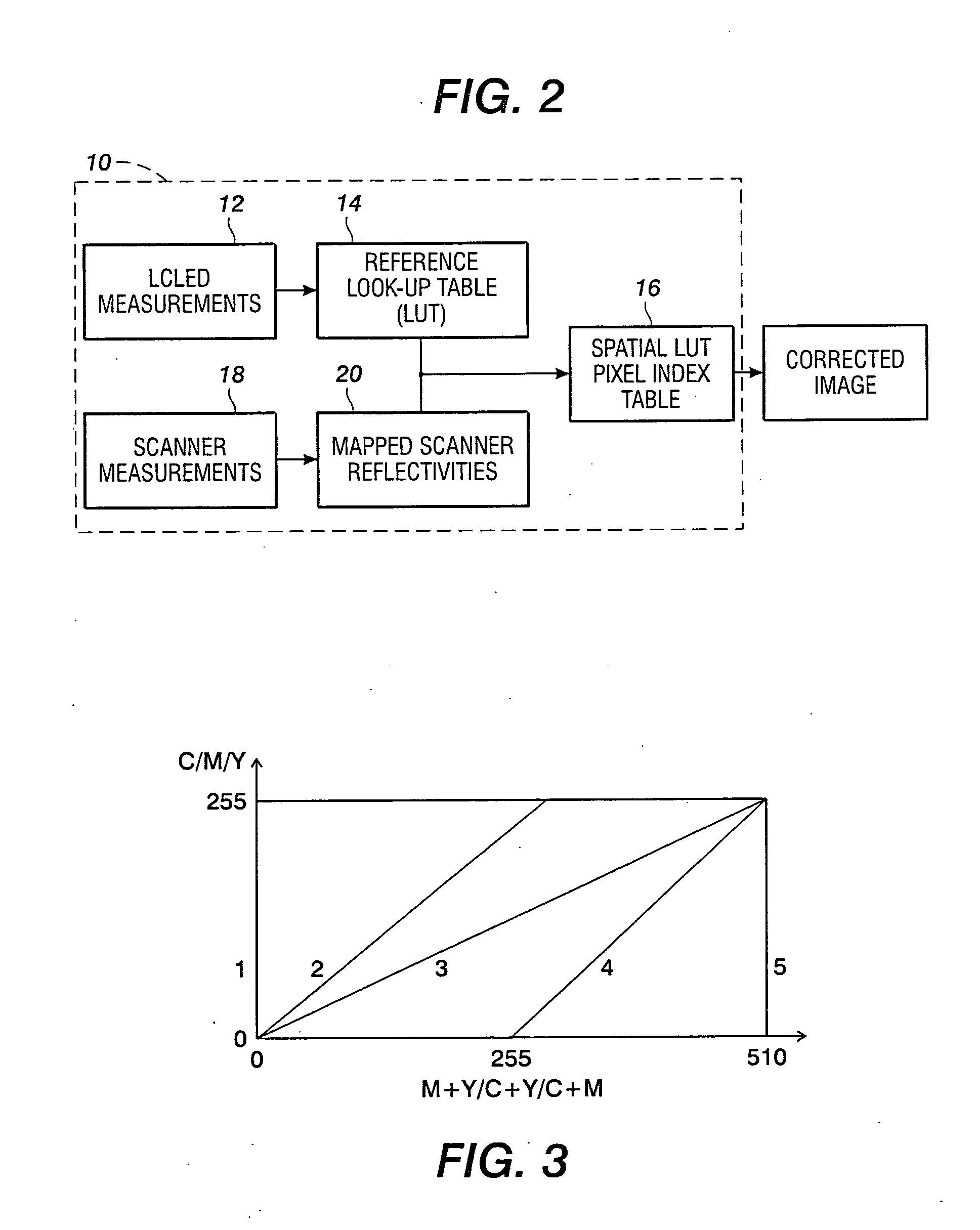
A method and system for color calibration or color output device spectrophotoically measures at test target including a preselected test color value. A multi-dimensional LUT of the device is generated representative of the color information including the at least one preselected color. Producing a second image width device including the at least one preselected color located at a plurality of spatial locations in the second image. A second sensor measures the second image and a plurality of spatial locations having the preselected color for generating reflectance information for the preselected color at the plurality of spatial locations. An error is determined between the measured color of the one preselected color and the reflectance information at the other pixel locations. A multi-dimensional LUT is adjusted to minimize spatial uniformity errors at the other pixel locations, thus calibrating device color output spatially.
Owner:XEROX CORP
Medical Imaging Method and System
ActiveUS20080260218A1Accurate analysisDelayed decisionImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionHuman body
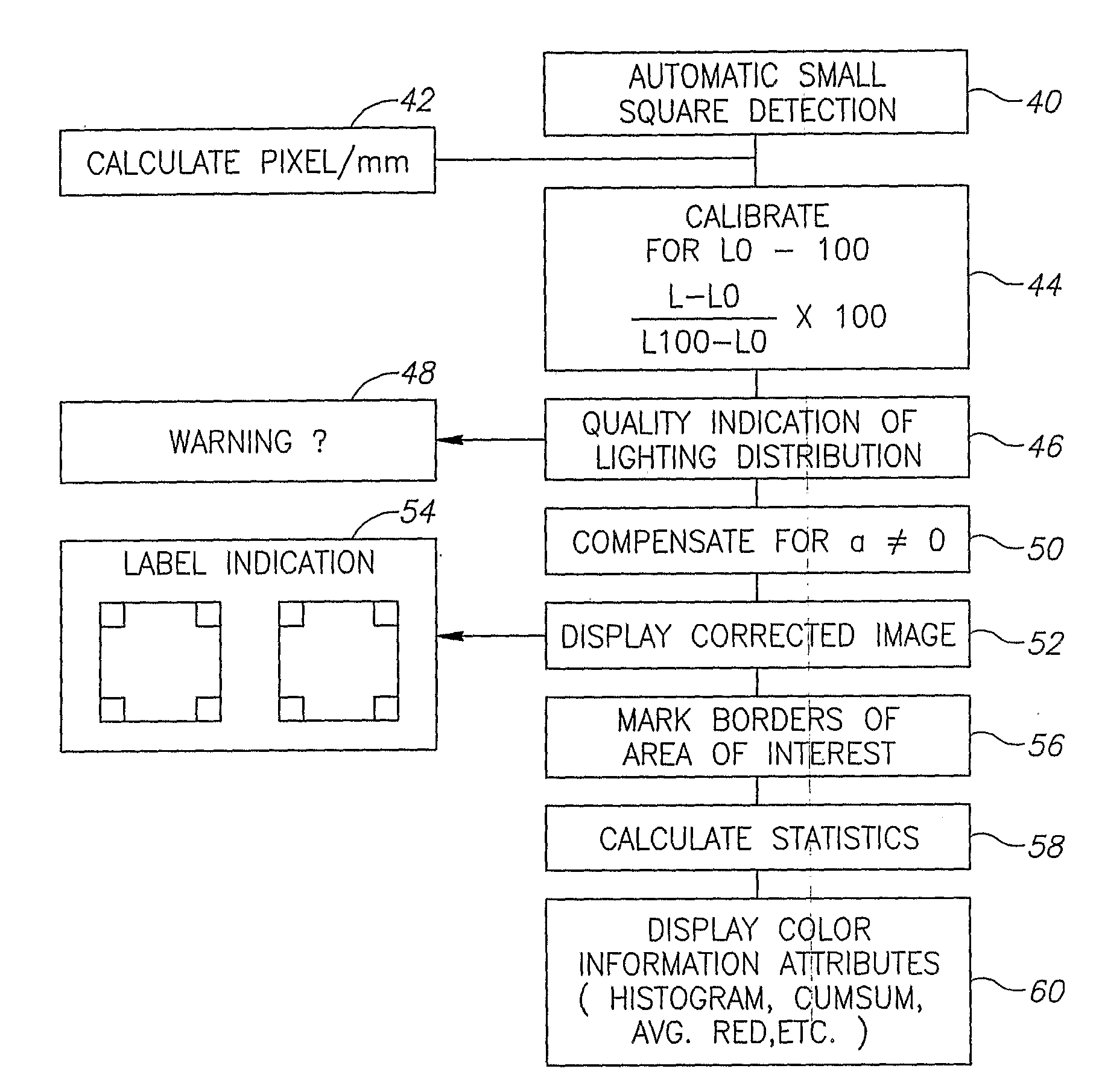
A computerized method and system for detection and quantification of changes in color on skin or internal tissue or organs within the human body. Digital images of the skin or tissue containing an area of interest are analyzed using the software of the invention, based on at least one channel of the LAB color system. The invention calculates the intensity and distribution of color present within the predetermined area of interest, and results in display of at least one color information attribute. The invention allows color calibration of the image to be performed in relation to a reference label having predetermined colors which surrounds the area of interest, prior to the analysis. The invention allows a threshold analysis to be performed, which graphically depicts the size and location of areas exhibiting significant change in color, which is a determinant factor in medical diagnosis.
Owner:YISSUM RES DEV CO OF THE HEBREWUNIVERSITY OF JERUSALEM LTD
Method and apparatus for performing and quantifying color changes induced by specific concentrations of biological analytes in an automatically calibrated environment
ActiveUS20150211987A1Accurate and precise and cost-effective measurementMinimizing user interactionImage enhancementRadiation pyrometryColor changesColor calibration
Methods and electronic devices for performing color-based reaction testing of biological materials. The method includes capturing and interpreting digital images of an unexposed and later exposed paddle at various delay times within an automatically calibrated environment. The test paddle includes a unique identification mechanism (UID), a Reference Color Bar (RCB) providing samples of standardized colors for image color calibration, compensation and corrections, and several test-specific sequences of Chemical Test Pads (CTP). The method further includes locating the paddle in the image, extracting the UID and validating the paddle, extracting the RCB and locating the plurality of CTP in each image. The method further reduces image noise in the CTP and calibrates the image automatically according to lighting measurements performed on the RCB. To determine test results, the method further determines several distances between the CTP and its possible trajectory in the color space described by the Manufacturer Interpretation Color Chart.
Owner:HEALTHY IO LTD
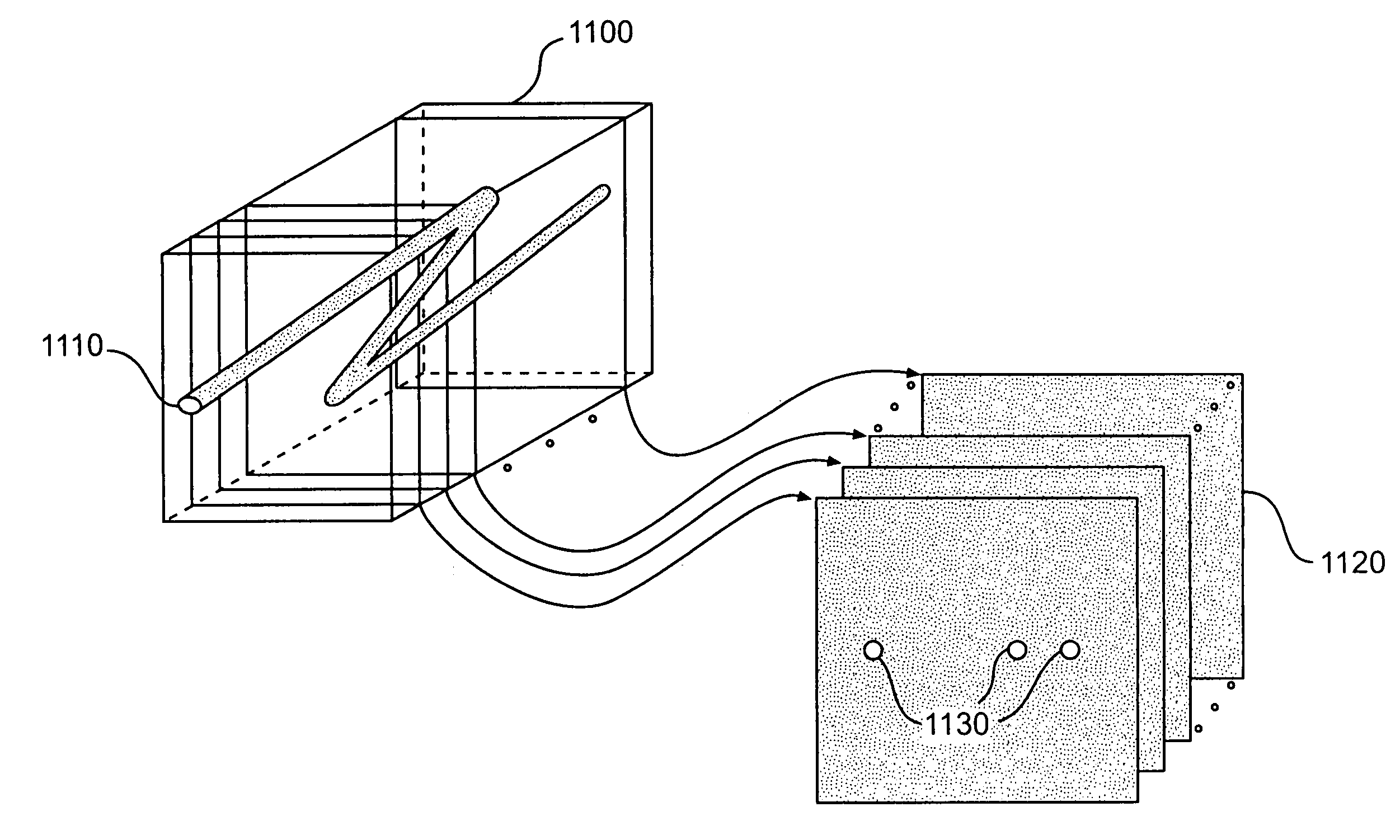
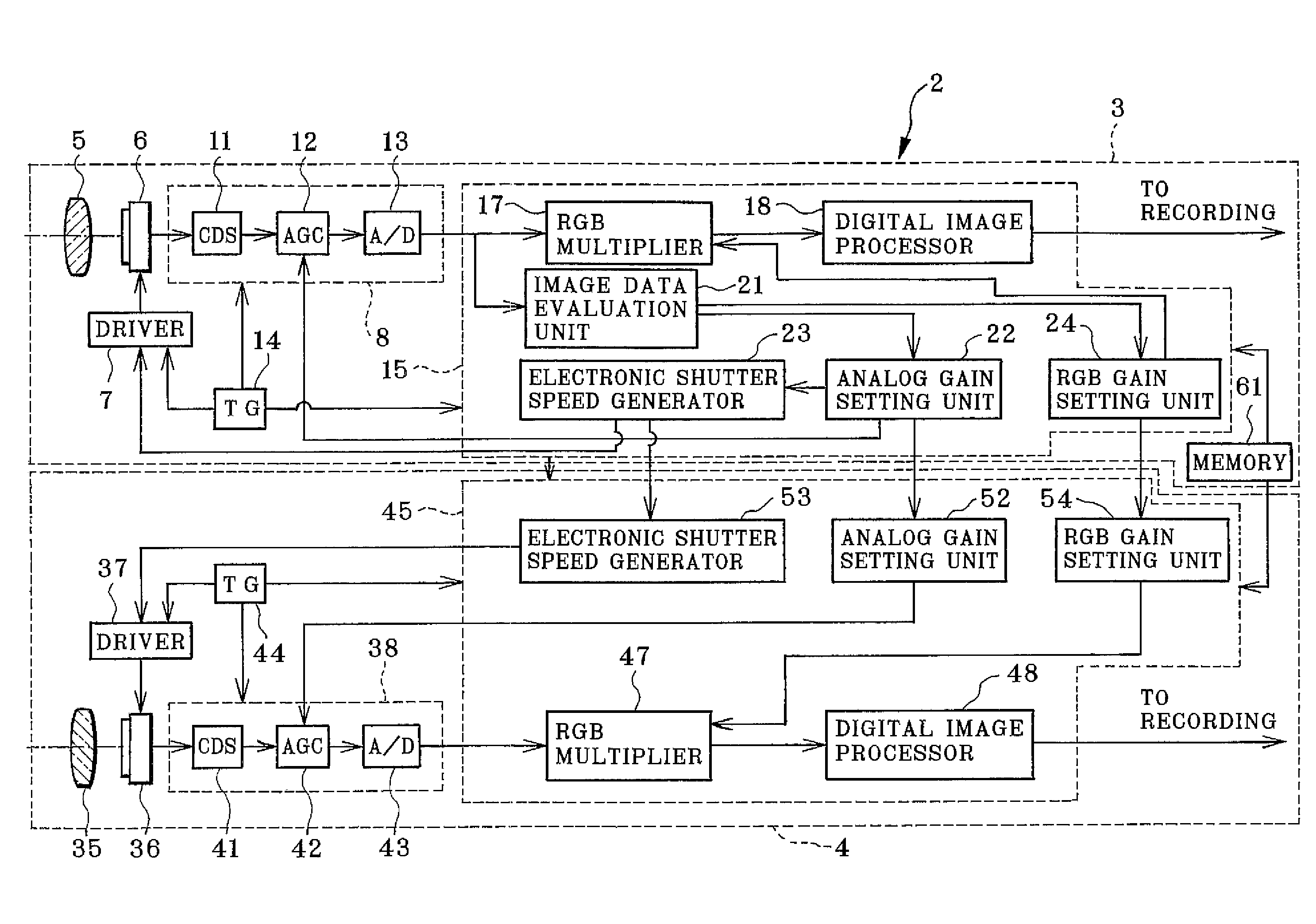
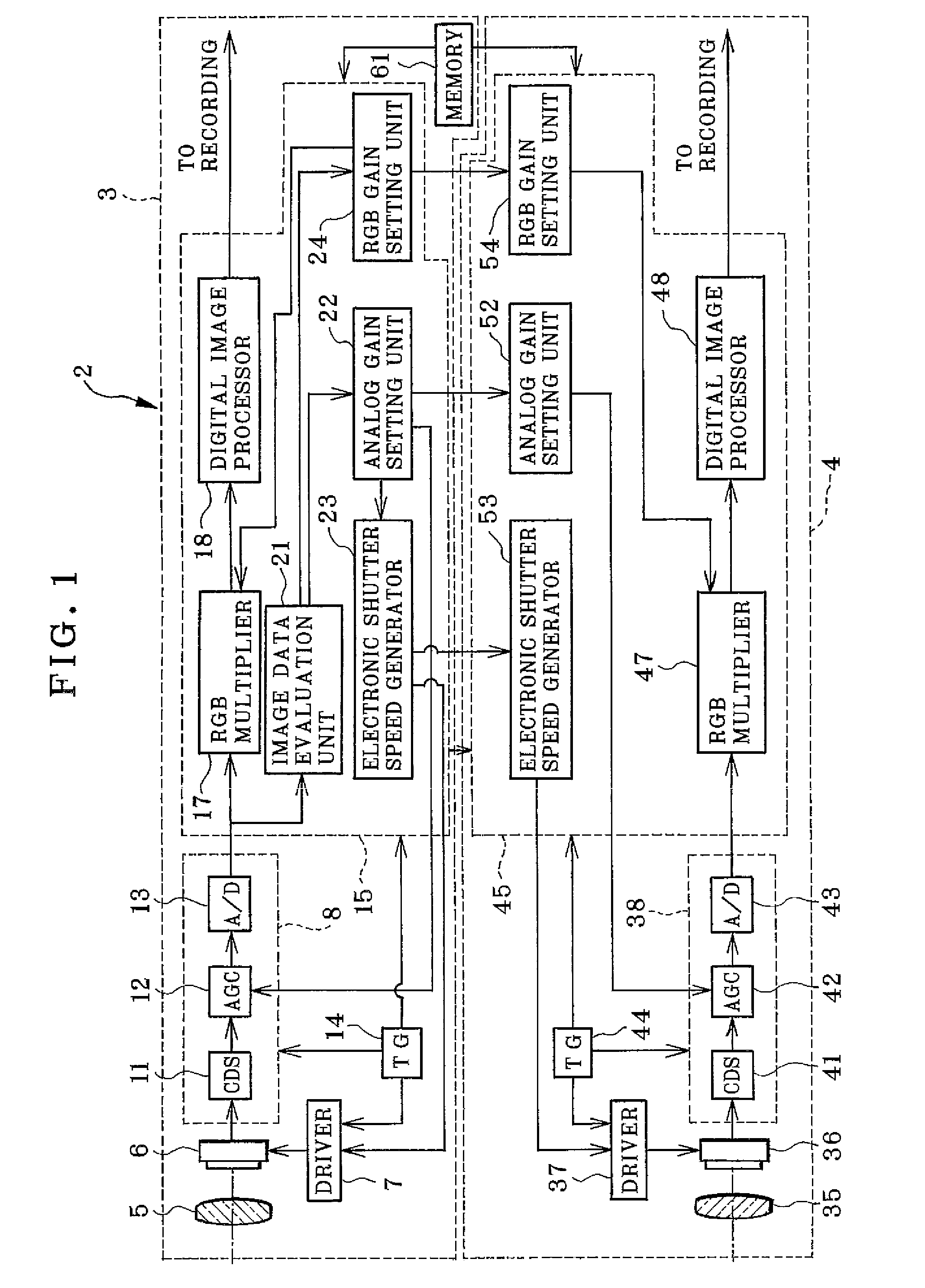
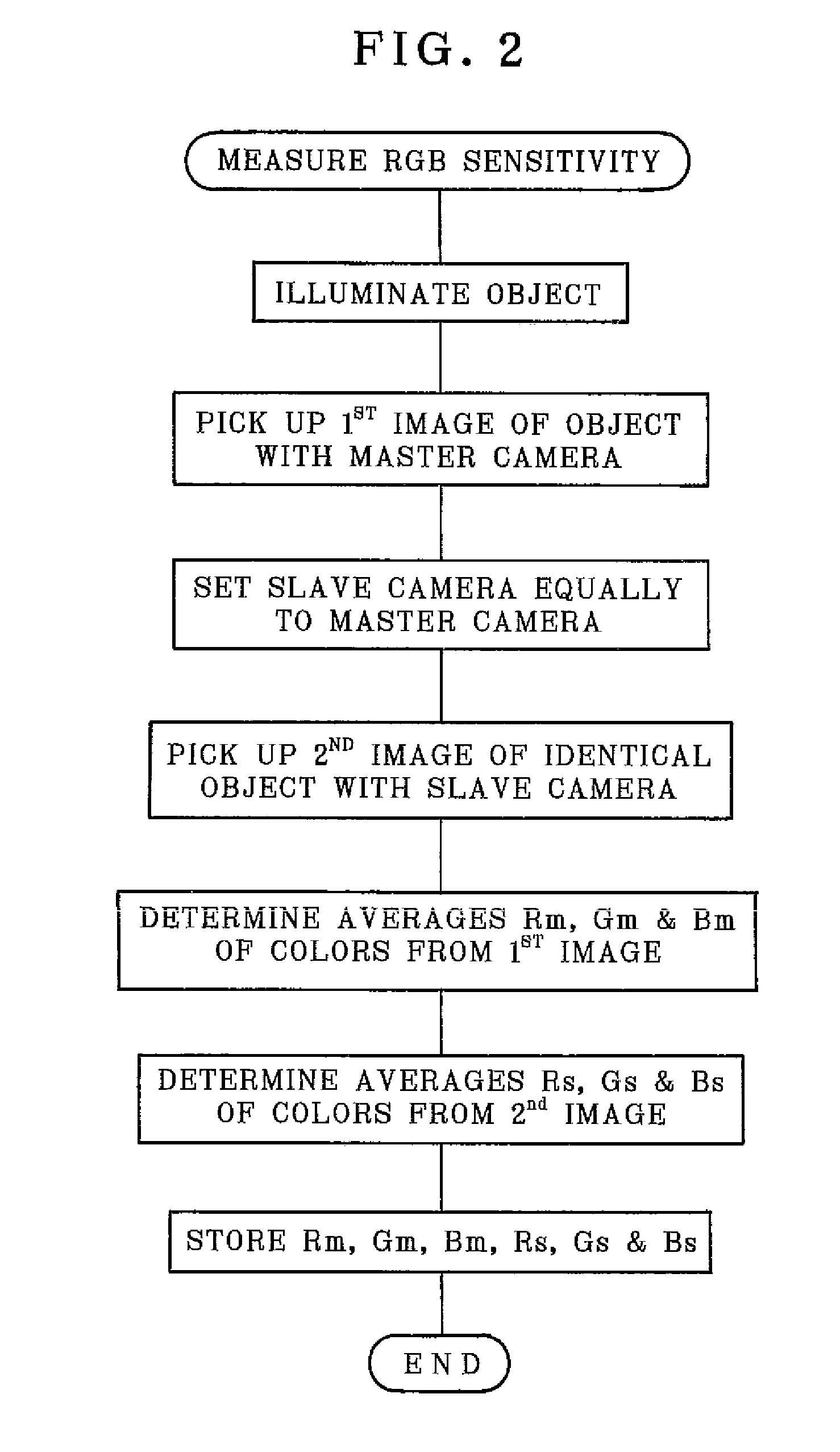
Multi-eye image pickup apparatus and adjusting method
InactiveUS20090015689A1With balanceImprove the level ofTelevision system detailsColor signal processing circuitsStereo cameraPhotoelectric conversion
A stereoscopic camera includes a master camera for photoelectric conversion of object light to generate a first image signal with three color components G, R and B. A slave camera generates a second image signal. In an adjusting method, a first gain Dmr, Dmg and Dmb of the color components is determined according to the first image signal to correct a brightness level and white balance of the master camera, to adjust the first image signal by use thereof. A second gain Dsr, Dsg and Dsb of the color components is determined according to the first gain and color calibration information predetermined according to color sensitivity of the master and slave cameras in relation to the color components. The second image signal is adjusted by use thereof, for color matching between the first and second image signals to set equal the brightness level and the white balance.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
System and method for spatial gray balance calibration using hybrid sensing systems
ActiveUS20060285134A1Minimize spatial uniformity errorUniform colorDigitally marking record carriersDigital computer detailsPattern recognitionTone reproduction
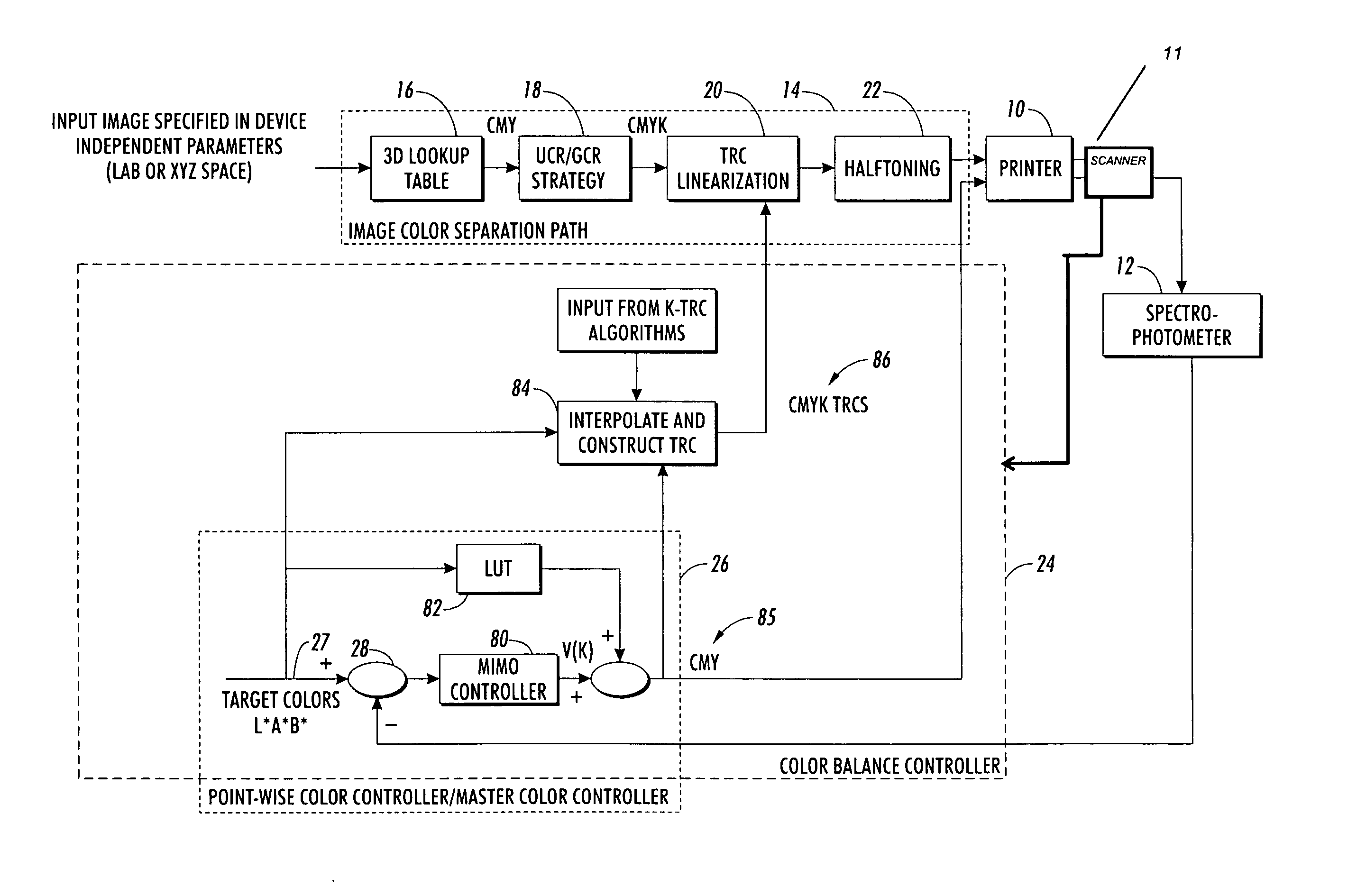
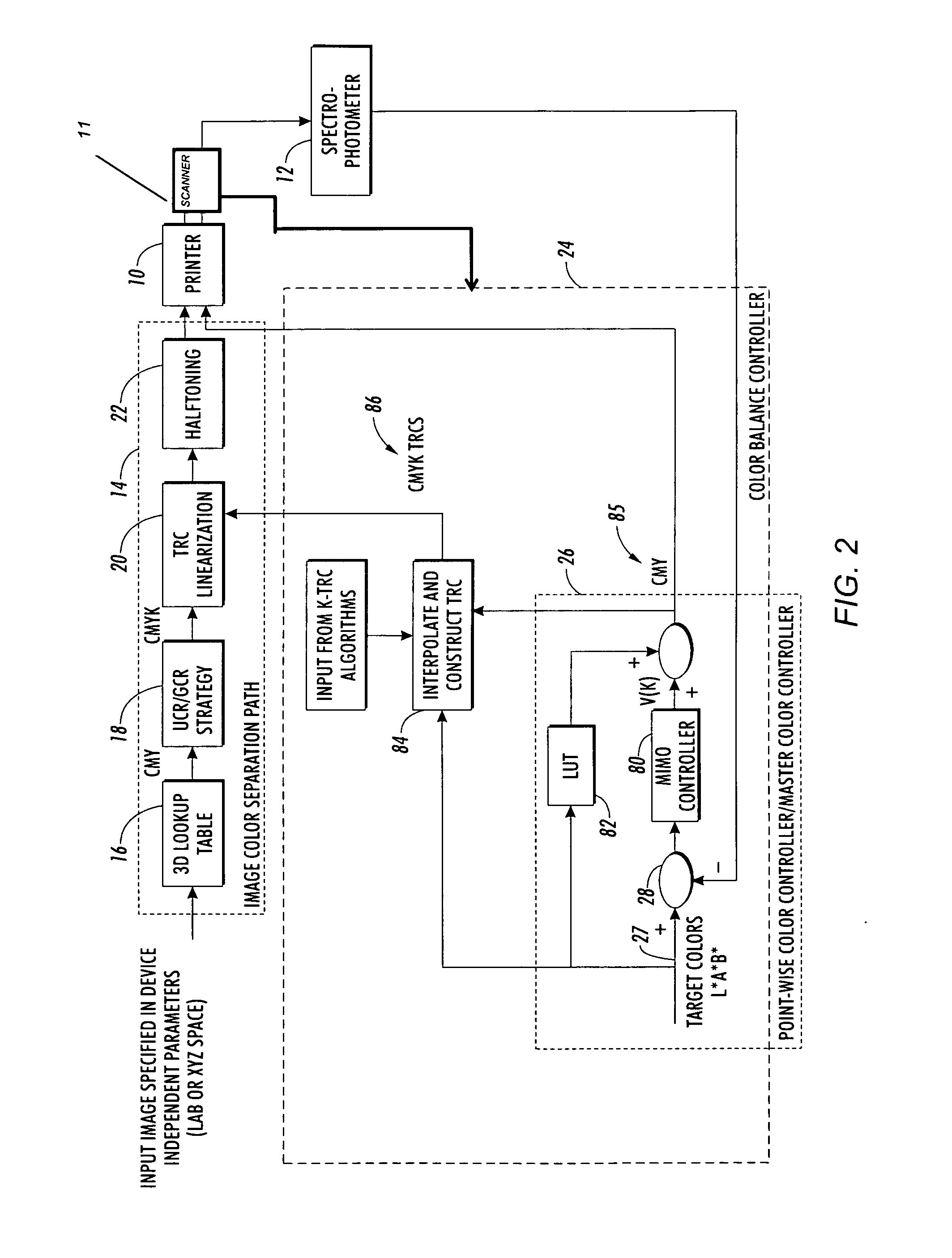
The method and system for printer color calibration use a combination of a full-width array (FWA) or similar page-scanning mechanism in conjunction with an spectrophotometer color measurement system in the output path of a color printer for measuring colors (e.g., on printed test sheets, banner / separation pages, etc.) with or without requiring any manual operations or operator involvement. The automatic color balance control system produces spatial tonal reproduction values for all four of the primary colors by printing patches, measuring colors using the sensor combination and automatically readjusting the spatial tone reproduction curves until a satisfactory level of printed color accuracy and uniformity are obtained. While producing color balanced TRCs, the system will automatically lock the printer output to some predetermined color patch targets. In one particular preferred embodiment, this output is locked to neutral gray when target colors are set to neutral gray inside the digital front end (DFE). After converging to the targets, the control system returns full TRCs for use inside the normal print path.
Owner:XEROX CORP
Mobile imaging platform calibration
ActiveUS20140368651A1Faster and accurate techniqueLow efficiencyImage analysisOptical rangefindersLaser scanningComputer vision
Mobile platforms are used to capture an area using a variety of sensors (e.g., cameras and laser scanners) while traveling through the area, in order to create a representation (e.g., a navigable set of panoramic images, or a three-dimensional reconstruction). However, such sensors are often precisely calibrated in a controlled setting, and miscalibration during travel (e.g., due to a physical jolt) may result in a corruption of data and / or a recalibration that leaves the platform out of service for an extended duration. Presented herein are techniques for verifying sensor calibration during travel. Such techniques involve the identification of a sensor path for each sensor over time (e.g., a laser scanner path, a camera path, and a location sensor path) and a comparison of the paths, optionally after registration with a static coordinate system, to verify that the continued calibration of the sensors during the mobile operation of the platform.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Multi-spectral color correction
InactiveUS6950109B2Effective color correctionIncrease memory storageColor signal processing circuitsCharacter and pattern recognitionTransformation parameterDisplay device
A system and method for performing color correction based on physical measurements (or estimations) of color component spectra (e.g. red, green, blue color component spectra). A color correction system may comprise a spectrum sensing device, a color calibration processor, and a calculation unit. The spectrum sensing device may be configured to measure color component power spectra for pixels generated by one or more display devices on a display surface. The color calibration processor may receive power spectra for a given pixel from the spectrum sensing device and compute a set of transformation parameters in response to the power spectra. The transformation parameters characterize a color correction transformation for the given pixel. The color calibration processor may compute such a transformation parameter set for selected pixels in the pixel array. The calculation unit may be configured to (a) compute initial color values for an arbitrary pixel in the pixel array, (b) compute modified color values in response to the initial color values and one or more of the transformation parameter sets corresponding to one or more of the selected pixels, and (d) transmit the modified color values to the display device.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Color printer calibration
InactiveUS7050196B1Promote generationDigitally marking record carriersDigital computer detailsGraphicsPattern recognition
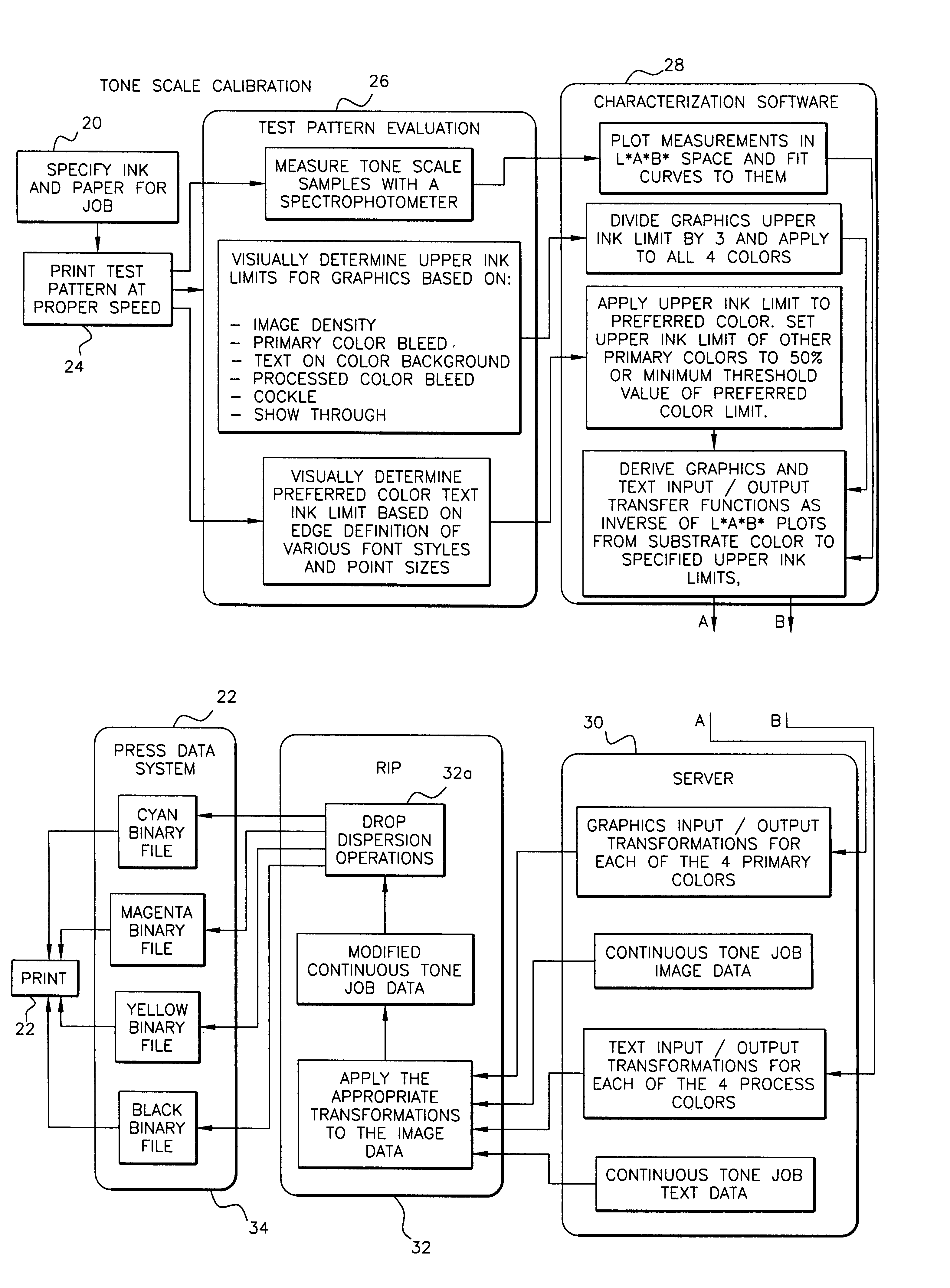
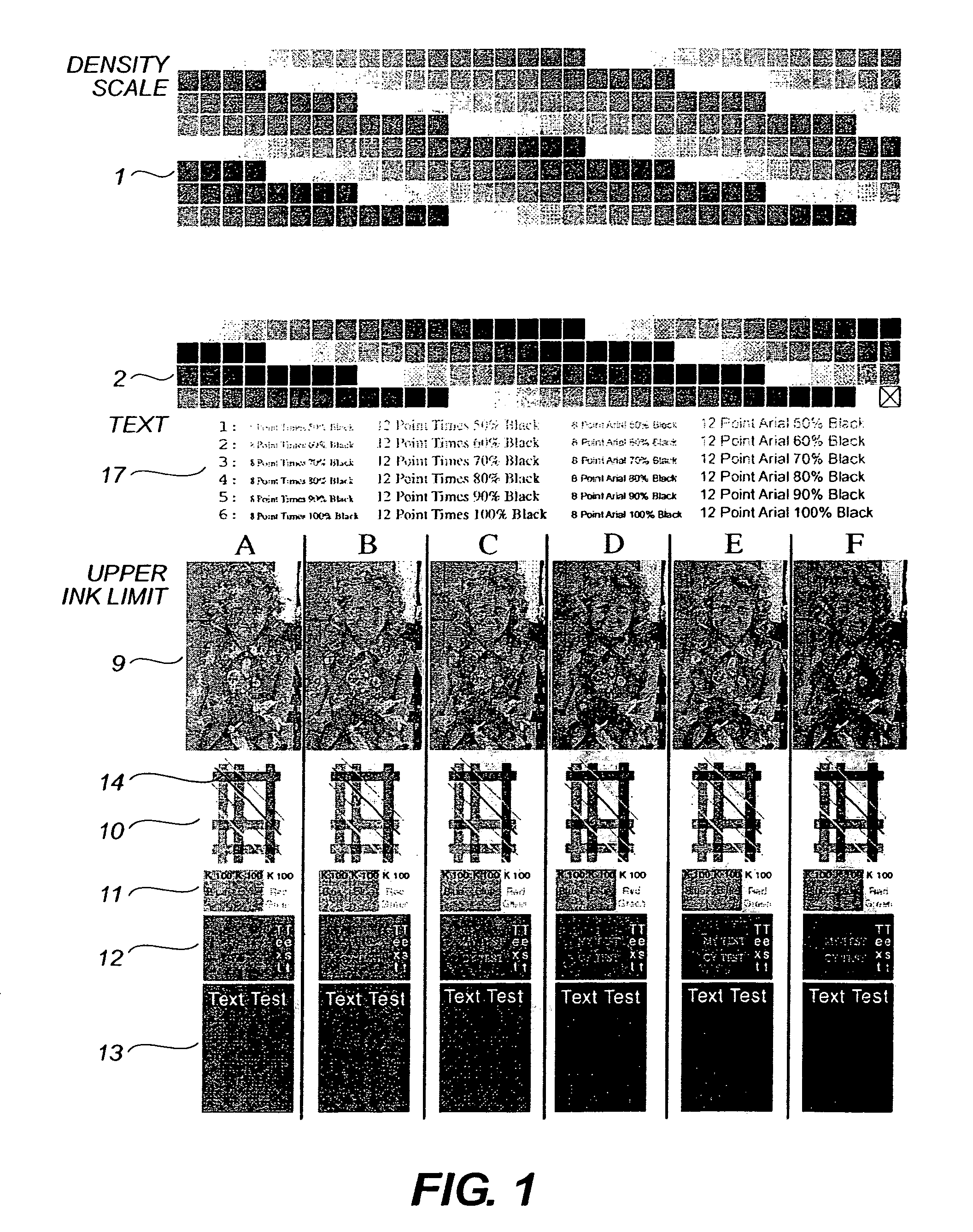
The present invention addresses the quantification of a printed tone scale for each individual color in a printing system, developing a linear tone scale derived in an independent color space and referenced from the shade of the unprinted substrate. The present invention determines the threshold for excessive ink coverage of a printing system on a specified substrate. This determination is based on a subjective evaluation of acceptable thresholds for bleed, cockle, show through, and image density. The method works in conjunction with a predefined test pattern printed on the specified substrate at fixed printing parameters, such as speed, dryer temperature, and web tension. This invention also includes an ability to limit the ink of each independent color in the system as a fraction of the total upper ink limit. Furthermore, this invention allows calibration of the tone scale of each color in the system using the color of the paper as a reference point. In addition, this invention facilitates the generation of separate sets of tone scale transformations for both graphics and text for each color in the system.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
Scanner with color profile matching mechanism
Scanner with light source calibration mechanism. The scanner includes a light source that generates a white light utilized to scan an image. The light source calibration mechanism includes a calibration color sensor that generates a calibration color sensor output. The light source calibration mechanism receives a predetermined color profile that can be, for example, the amount of red, green light, and blue light expected from the light source utilized by the scanner for scanning. The color calibration mechanism calibrates the light source of the scanner based on the output of the calibration color sensor and the predetermined color profile.
Owner:AVAGO TECH ECBU IP (SINGAPORE) PTE LTD
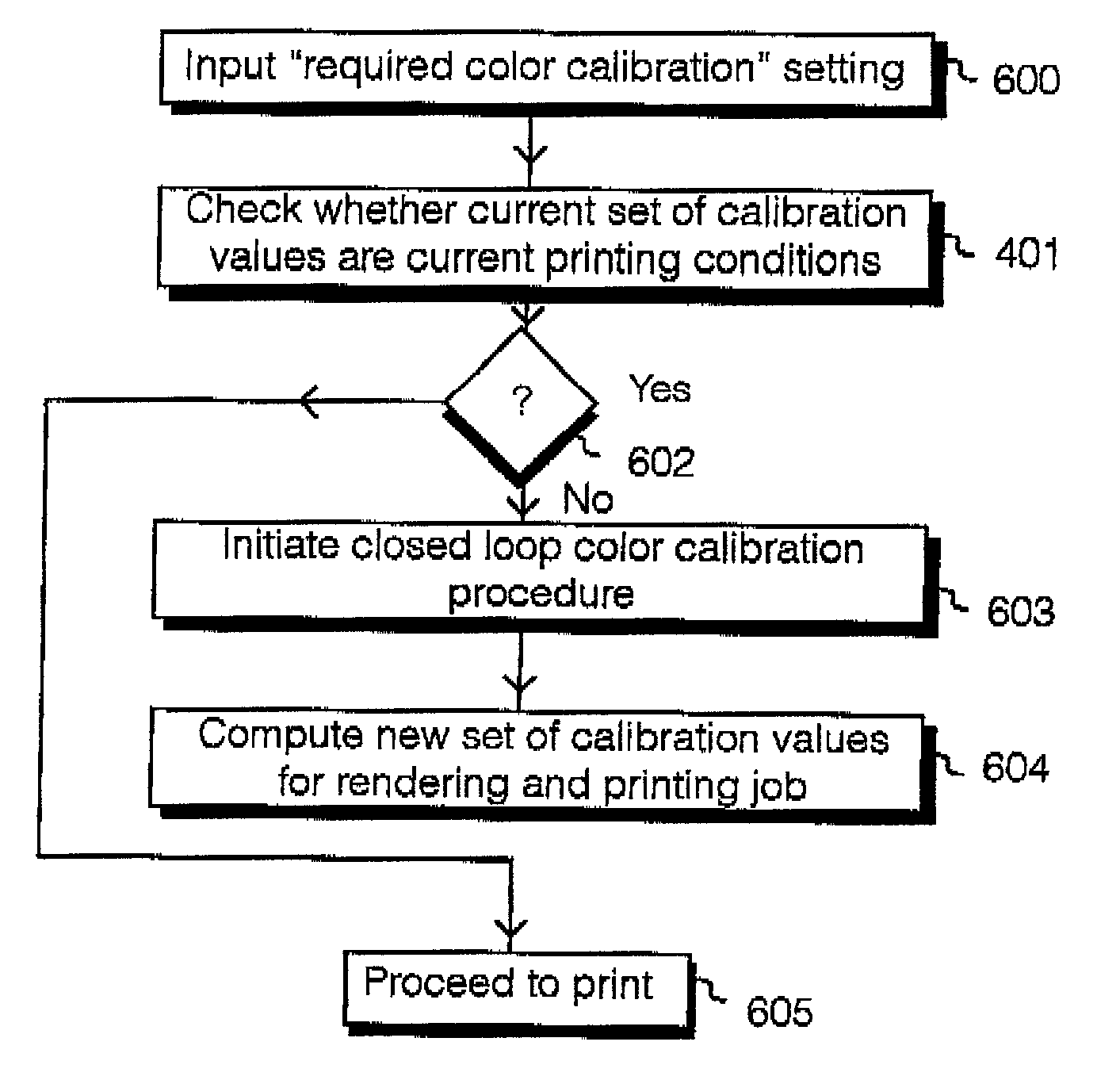
Automatic triggering of a closed loop color calibration in printer device
InactiveUS20040207862A1Digitally marking record carriersDigital computer detailsComputer printingClosed loop
There is disclosed a format used in a remote proofing system to ensure that a printer device to which a print job is sent, operates within pre-determined calibration criteria for printing an image. Each job file has a job ticket, which defines a plurality of data types, which are to be checked for a printer device which is assigned to perform the printing. The parameters include ink level, environmental conditions (temperature, humidity), and media type. A printer device operates an algorithm to implement checks on the various parameters to determine whether a re-calibration process is required prior to printing an image. By sending a job file having no image data, a calibration of a printer can be achieved remotely, without necessarily printing an image.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
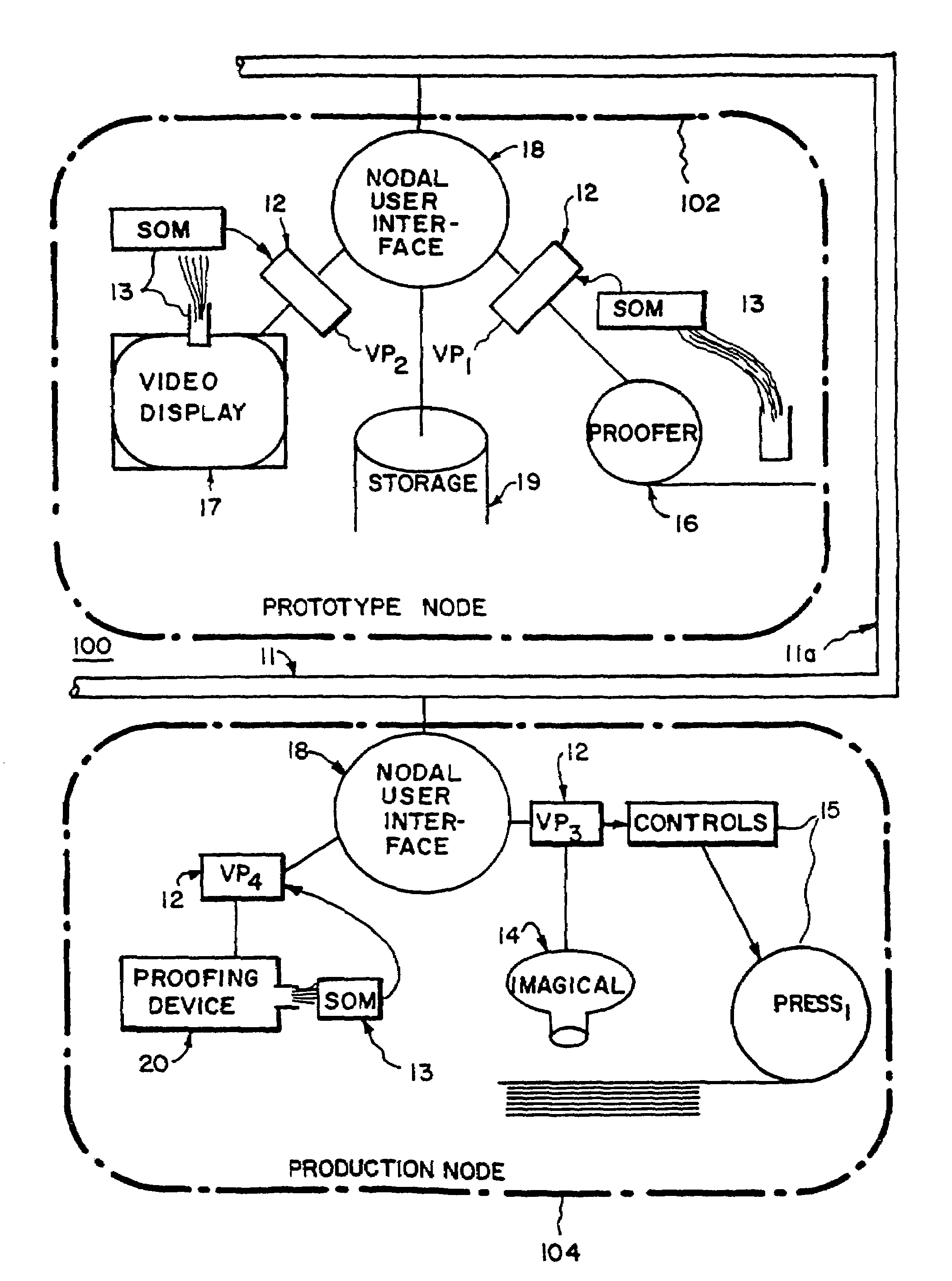
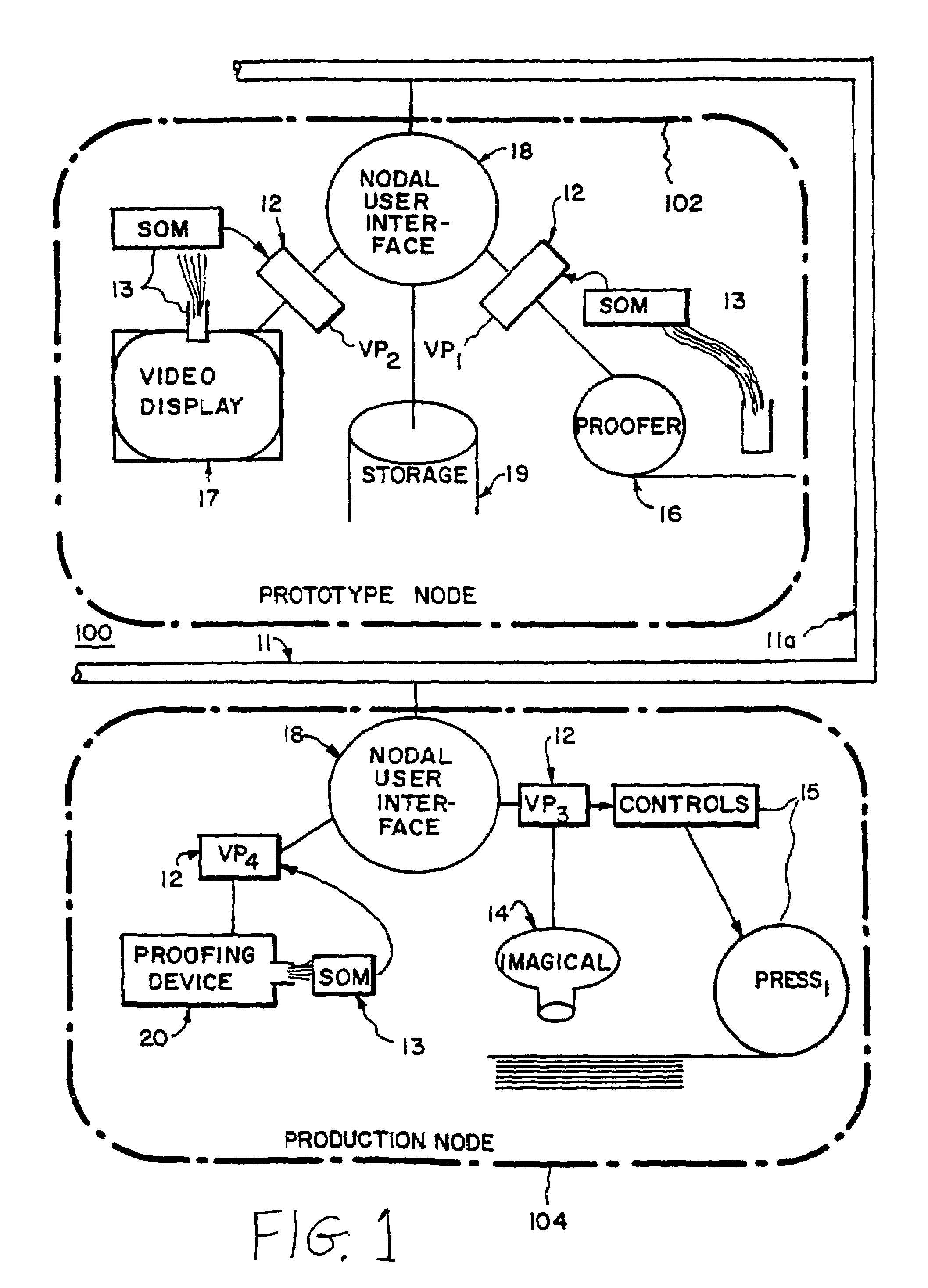
System for distributing and controlling color reproduction at multiple sites
InactiveUS6995870B2True colorGood user interfaceDigitally marking record carriersDigital computer detailsColor imageOperational system
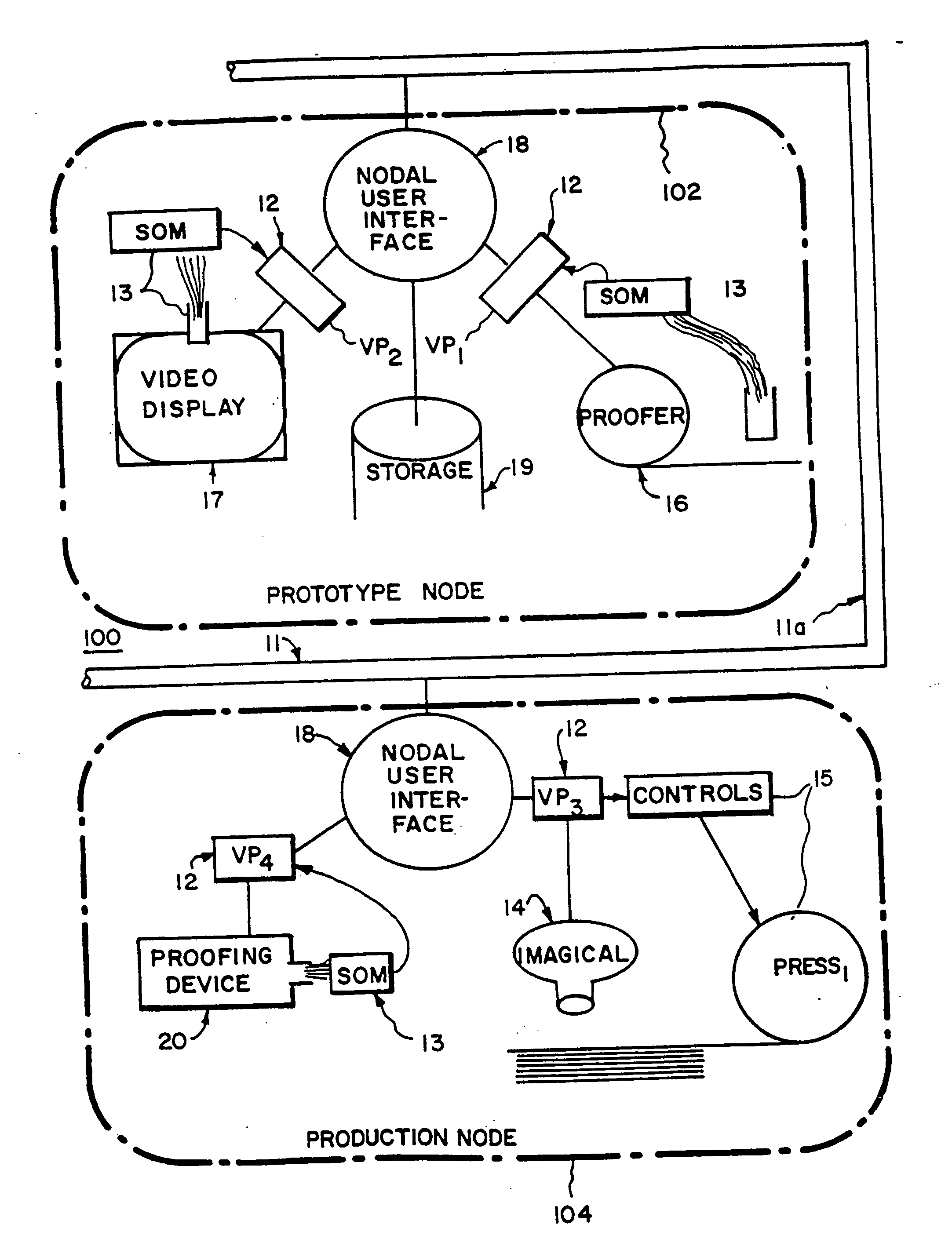
The system provides for controlling color reproduction of input color image data representing one or more pages or page constituents in a network having nodes (or sites). Each one of the nodes comprises at least one rendering device. The system distributes the input color image data from one of the nodes to other nodes, and provides a data structure (virtual proof) in the network. This data structure has components shared by the nodes and other components present only at each node. Next, the system has means for providing color calibration data at each node characterizing output colors (colorants) of the rendering device of the node, and means for producing at each node, responsive to the color calibration data of the rendering device of the node, information for transforming the input color image data into output color image data at the rendering device of the node. The information is then stored in the data structure in different ones of the shared and other components. Means are provided in the system for transforming at each node the input color image data into output color image data for the rendering device of the node responsive to the information in the data structure. The rendering device of each node renders a color reproduction of the page constituents responsive to the output color image data, wherein colors displayed in the reproduction at the rendering device of each node appear substantially the same within the output colors attainable by the rendering devices. The system further has means for verifying at each node that the information for the rendering device of the node properly transformed the input color image data into the output color image data, and means for revising the information stored in the data structure at the node responsive to results of the verifying means. Shared components of the data structure may also store color preferences selected by a user. The information producing means of the system may further operate responsive to both the color calibration data and the color preferences. The rendering devices in the system can provide color reproductions having three or four colorants, and may provide more than four output colors (color inks).
Owner:RAH COLOR TECH
Image processing
ActiveUS20150248775A1Improve accuracyTerminate calibrationImage enhancementImage analysisImaging processingFrequency of occurrence
There is described an image processing method in which a scene is repeatedly imaged to form a series of input images. For at least a subset of the input images, a colour calibration procedure is conducted which populates a foreground colour histogram with the frequency of occurrence of colour values in a stencil area of the input image, and populates a background colour histogram with the frequency of occurrence of colour values outside of the stencil portion of the input image. For at least a subset of the input images, a colour replacement procedure is conducted which updates the stencil area based on a determination, from the colour values of pixels within the input image, of likelihood values representing the likelihood of pixels belonging to an image area of interest, the likelihood value for each colour value being determined from a combination of the foreground and background colour histograms, replaces the original colour values of pixels within the updated stencil area of the input image with replacement colour values, and displays the image on which colour replacement processing has been conducted. In this way, a stencil area is determined based on foreground / background histogramming, and used both to define an area to which colour replacement processing is to be conducted, and also an area for use in further populating the colour histograms to calibrate the colour replacement processing.
Owner:HOLITION
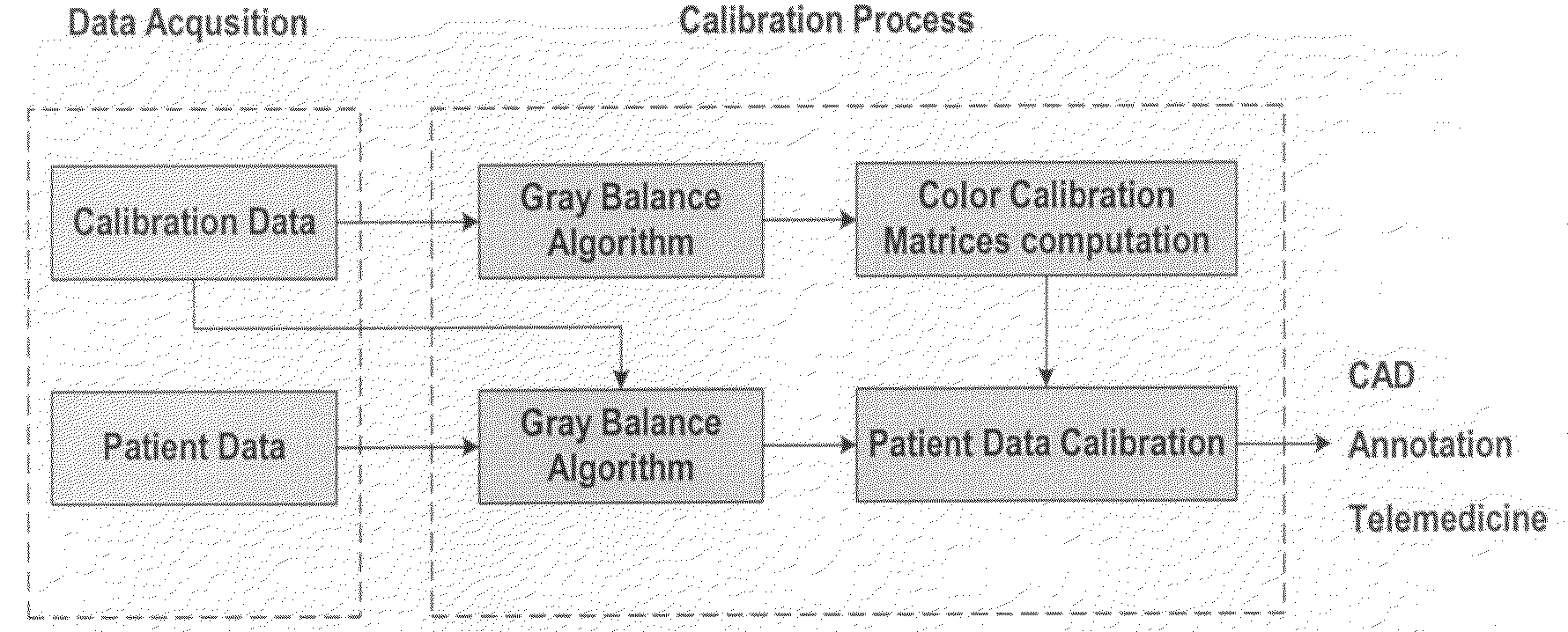
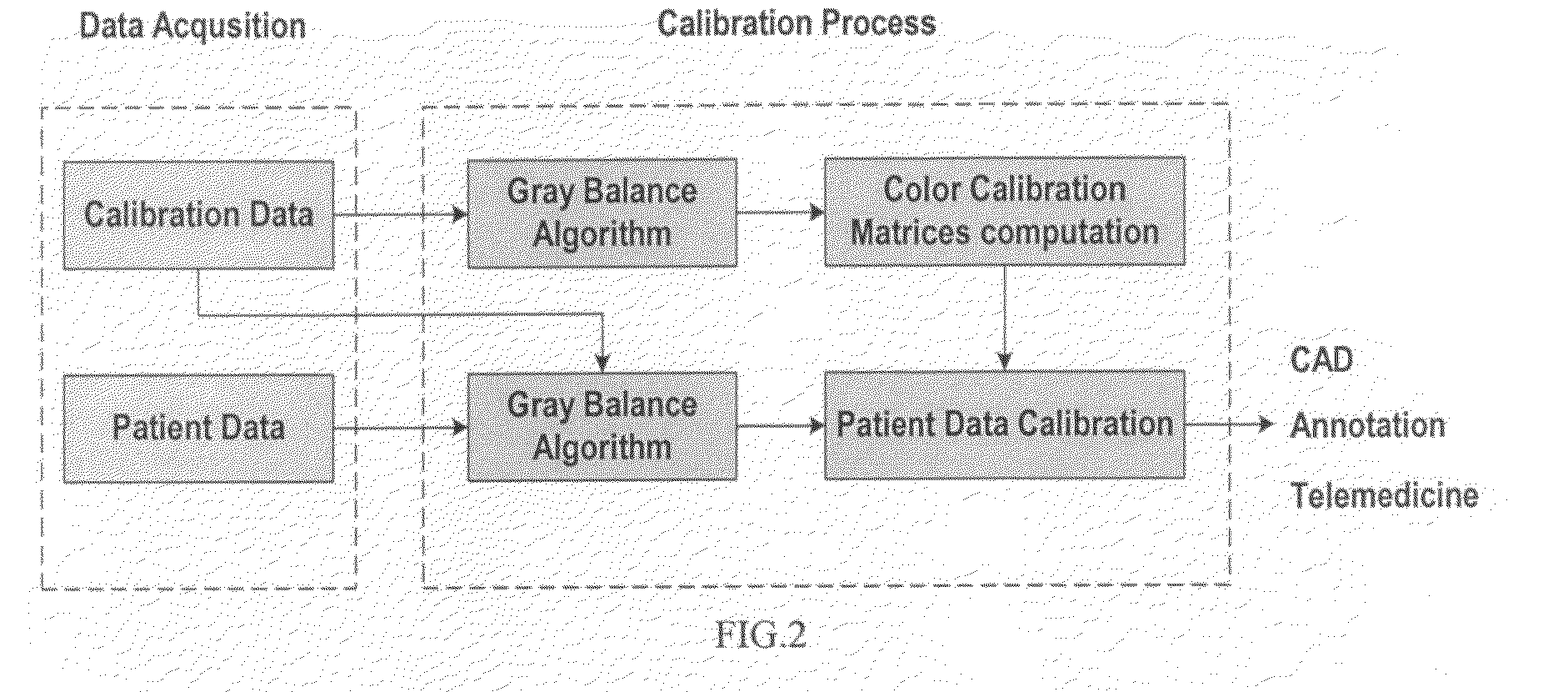
Method of automated image color calibration
A method of automated image calibration that corrects for non-uniform illumination and calibrates color that is simple, fast, automated, accurate and reliable. A gray balance algorithm is applied to correct for non-uniform illumination and a color calibration algorithm is then applied to calibrate the human subject data. The system has been applied in multiple clinical sites with different instruments.
Owner:STI MEDICAL SYST
Compact flat panel color calibration system
InactiveUS20050157298A1Eliminates and greatly reduces disadvantageEliminates and greatly reduces and problemTelevision system detailsRadiation pyrometryPhotovoltaic detectorsPhotodetector
A compact flat panel color calibration system includes a lens prism optic able to pass a narrow, perpendicular, and uniform cone angle of incoming light to a spectrally non-selective photodetector. The calibration system also includes a microprocessor operable to determine the luminance of the display based upon the information gathered by the photodetector. A software module included in the calibration system is then operable to process the luminance information in order to adjust the flat panel display.
Owner:RPX CORP +1
Method and apparatus for performing and quantifying color changes induced by specific concentrations of biological analytes in an automatically calibrated environment
ActiveUS9311520B2Minimizing user interactionAccurate and precise and cost-effective measurementImage enhancementRadiation pyrometryColor calibrationColor changes
Owner:HEALTHY IO LTD
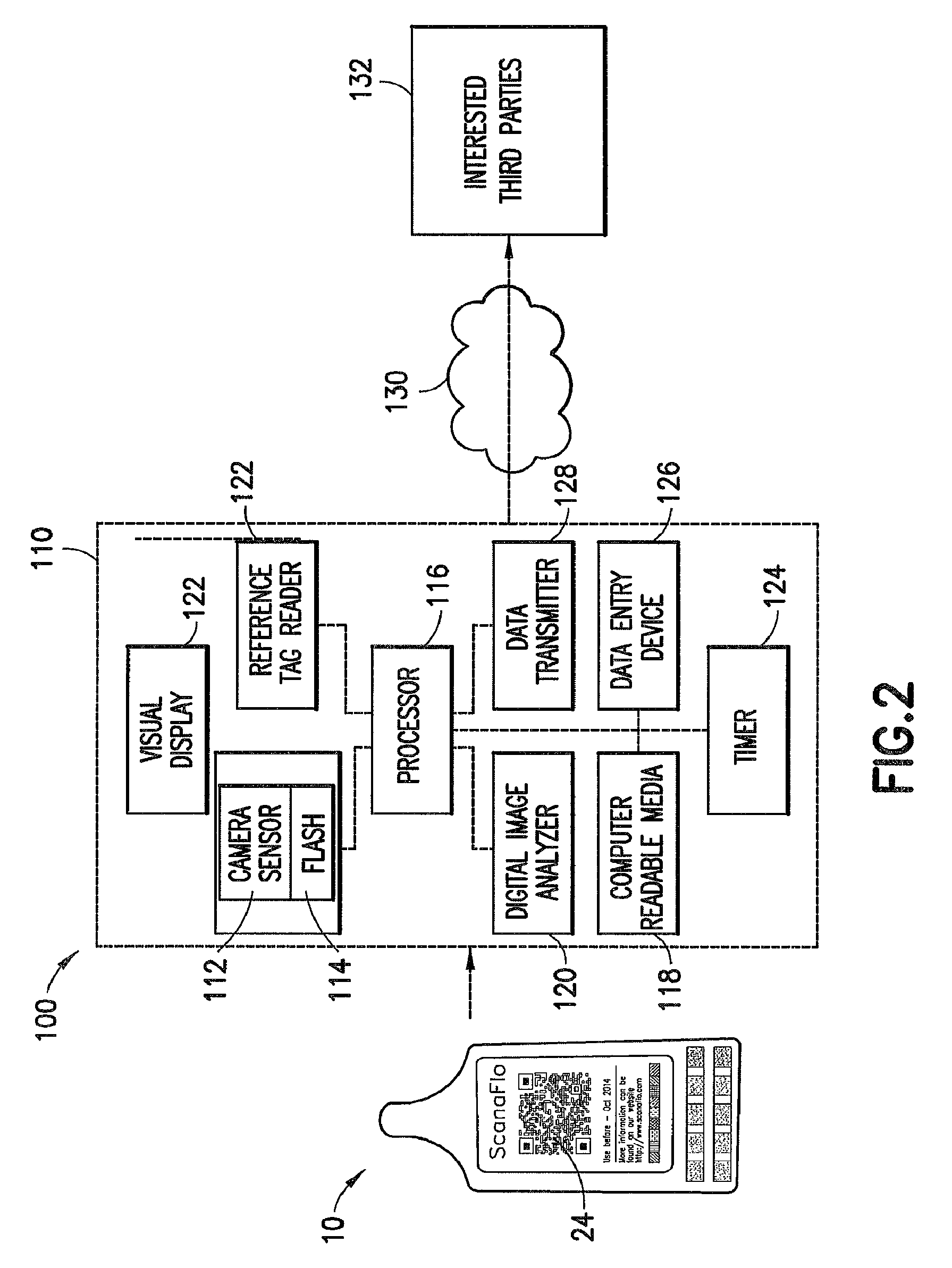
Color calibration for color bar codes
InactiveUS20050023354A1Record carriers used with machinesSensing by electromagnetic radiationBarcodeColor calibration
A color bar code system includes a camera reader to read at least one color bar code having a subset of N bar code colors, a color association unit and an identifier. The color association unit associates each point in a color space with one of the bar code colors. The color association unit is calibratable to the range of colors that the camera reader is expected to produce given at least one environmental condition in which it operates. The identifier uses the color association unit to identify an item associated with the bar code from the output of the camera reader.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC +1
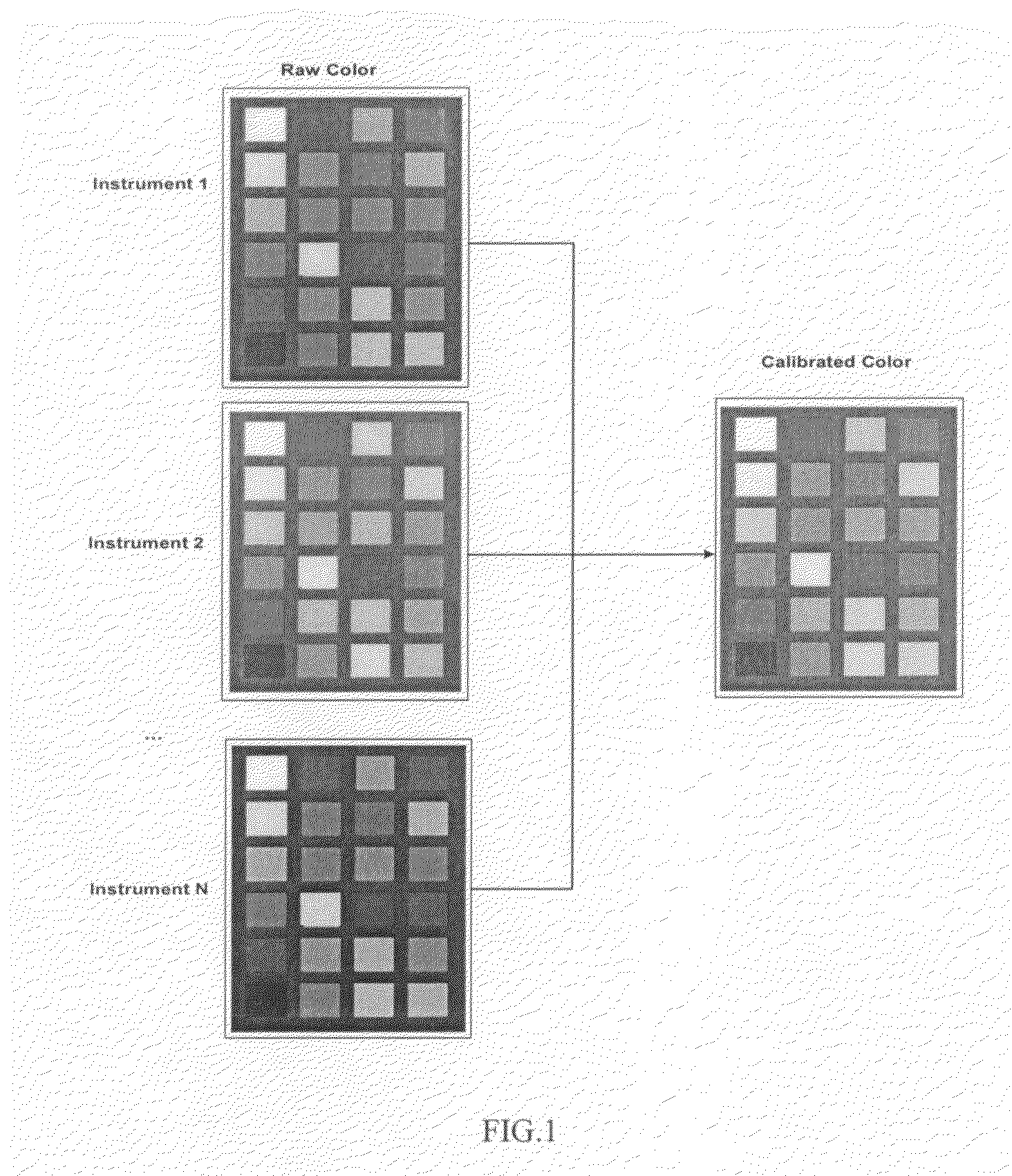
Method for calibrating colors of multiple cameras in open environment
InactiveCN102137272AColor Calibration ImplementationColor signal processing circuitsTelevision systemsColor mappingMonitoring system
The invention discloses a method for calibrating colors of multiple cameras in an open environment, comprising the specific steps as follows: firstly, the white balance of a single camera is calibrated by adopting an X-Rite 24 color standard color card so as to solve the problem that physical parameters of the cameras are inconsistent with one another; secondly, data of the X-Rite 24 color standard color card of different cameras under different monitoring scenes is obtained, the position of the color card is obtained in a man-machine interaction way, the position and the color average value of each color lump in the color card are calculated to obtain 24 color values in two scenes with multiple cameras, color mapping relation among the cameras is calculated in a polynominal regression method, and each camera is subjected to color calibration; and finally, areas with similar colors in the two scenes are found according to an H-S color matching method, and color calibration parameters are adjusted in a self-adaption way by detecting the change of pixel colors in the matched areas with the similar colors through on-line detection, thereby ensuring that the multiple cameras in a monitoring system are consistent in color in the open environment.
Owner:XIAN UNIV OF TECH
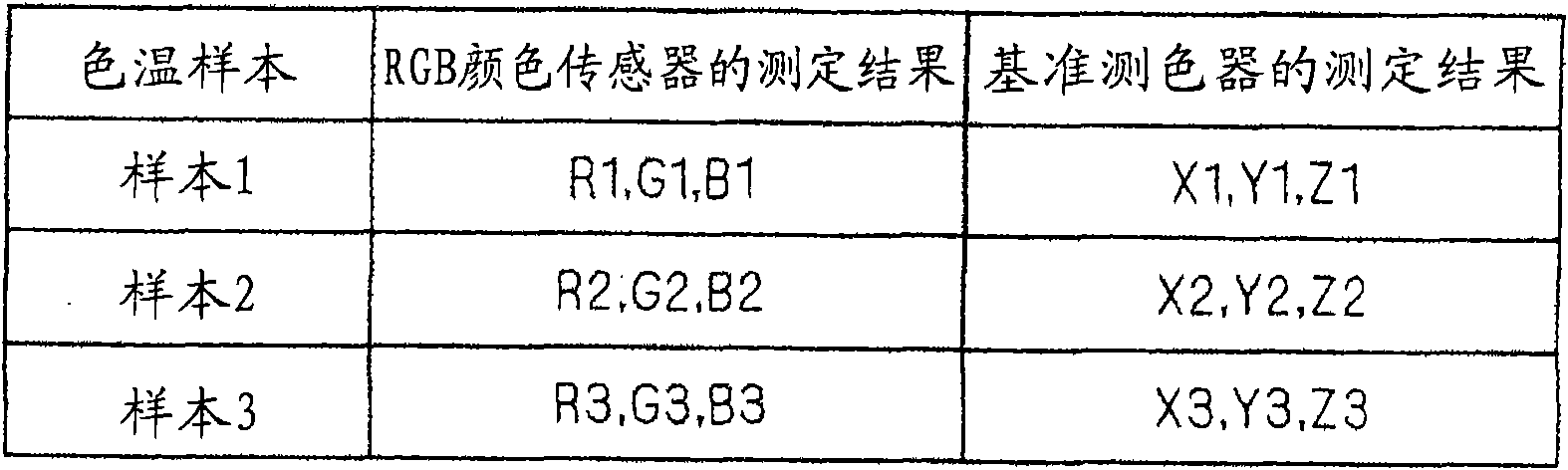
Color calibration system
InactiveCN101788342AHigh precisionEasy Color CalibrationRadiation pyrometryPhotometryMicrocomputerIlluminance
The invention provides a color calibration system capable of performing color calibration with high accuracy and simply. The color calibration system (100) in accordance with a preferred embodiment of the present invention comprises a display device (12) provided with a color sensor (12c) for detecting a color temperature and illuminance of ambient light (14), a microcomputer (12b), and a colorimeter (13) for performing colorimetry on a display screen (12a) of the display device (12) from the outside. The microcomputer (12b) calculates a target value by using a preset calculation equation and a detection result on the ambient light (14) detected by the color sensor(12c). Then, the microcomputer (12b) automatically performs color calibration of the display device so that a colorimetry result obtained by the colorimeter (13) may agree with the target value.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
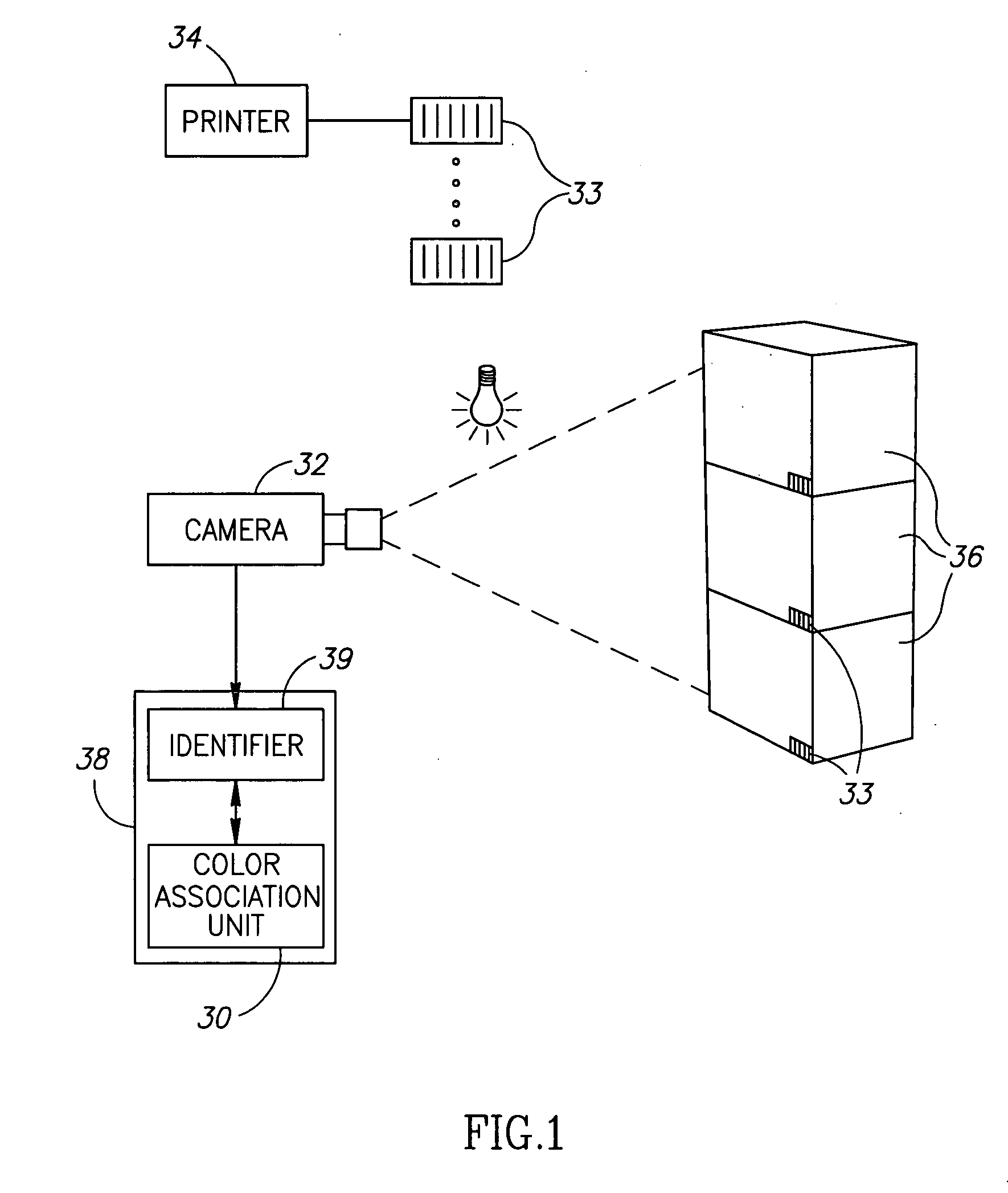
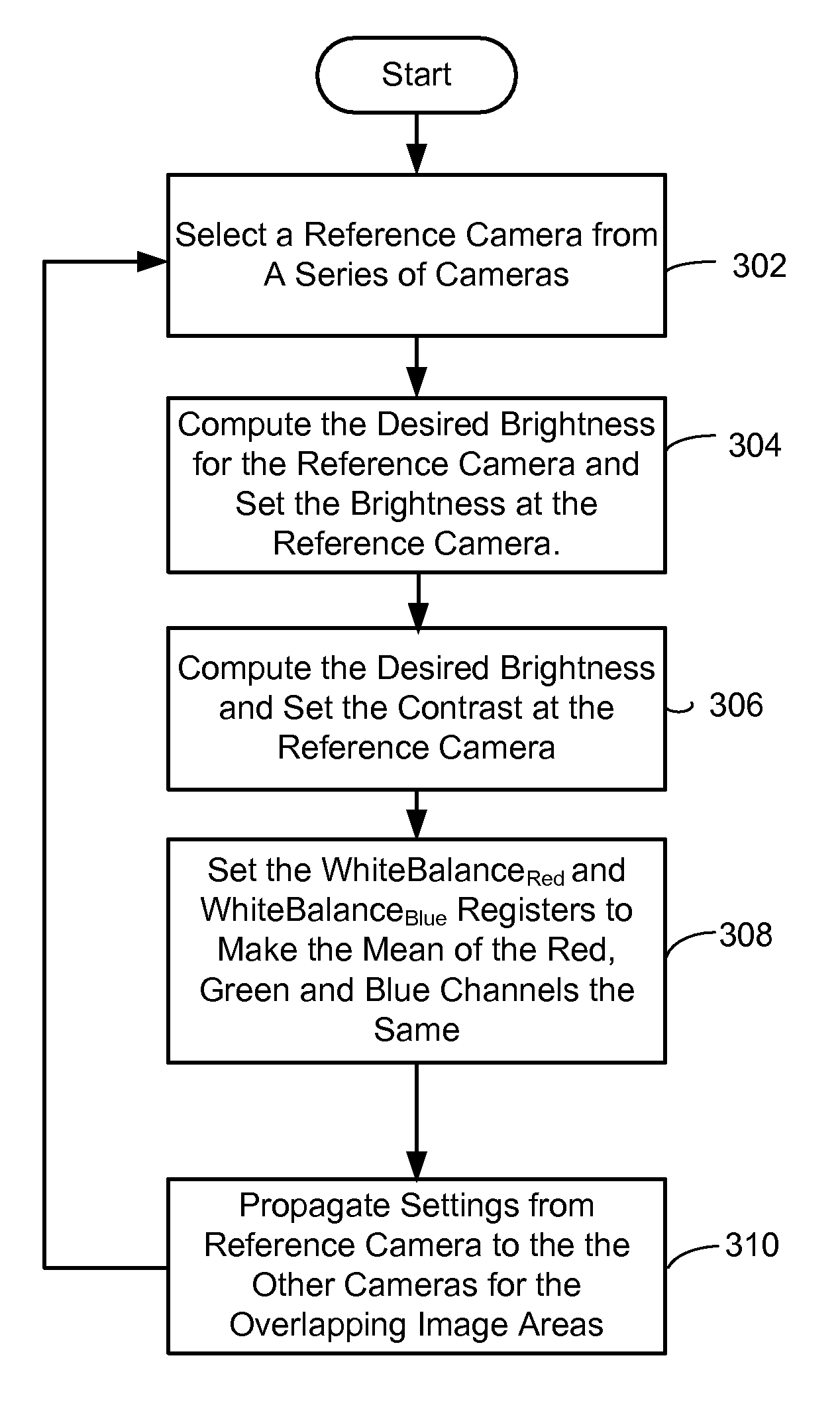
System and method for camera color calibration and image stitching
InactiveUS7259784B2Low costImprove image qualityImage enhancementTelevision system detailsVignettingCamera auto-calibration
A practical, real-time calibration of digital omnidirectional cameras in the areas of de-vignetting, brightness, contrast, and white balance control. Novel solutions for the color calibration of an omnidirectional camera rig, and an efficient method for devignetting images are presented. Additionally, a context-specific method of stitching images together into a panorama or a mosaic is provided.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
System and apparatus for the calibration and management of color in microscope slides
InactiveUS20130044200A1Character and pattern recognitionColor television detailsMicroscope slideImage calibration
A system and apparatus for the color calibration of images recorded through a microscope. An integrated color calibration target microscope slide device and specimen are recorded with an imaging device that acquires both the color values of the specimen and the color values of the color calibration target under a plurality of illuminations and trans-illuminations. A composite image is formed to provide a spectral estimation of the relevant color values of the image. The image is converted into multi-stimulus values governed by a plurality of illuminating conditions. The multi-stimulus values are used to provide image calibration data so that color values of the image, when displayed on a display devices, are faithfully reproduced.
Owner:DATACOLOR HOLDING AG
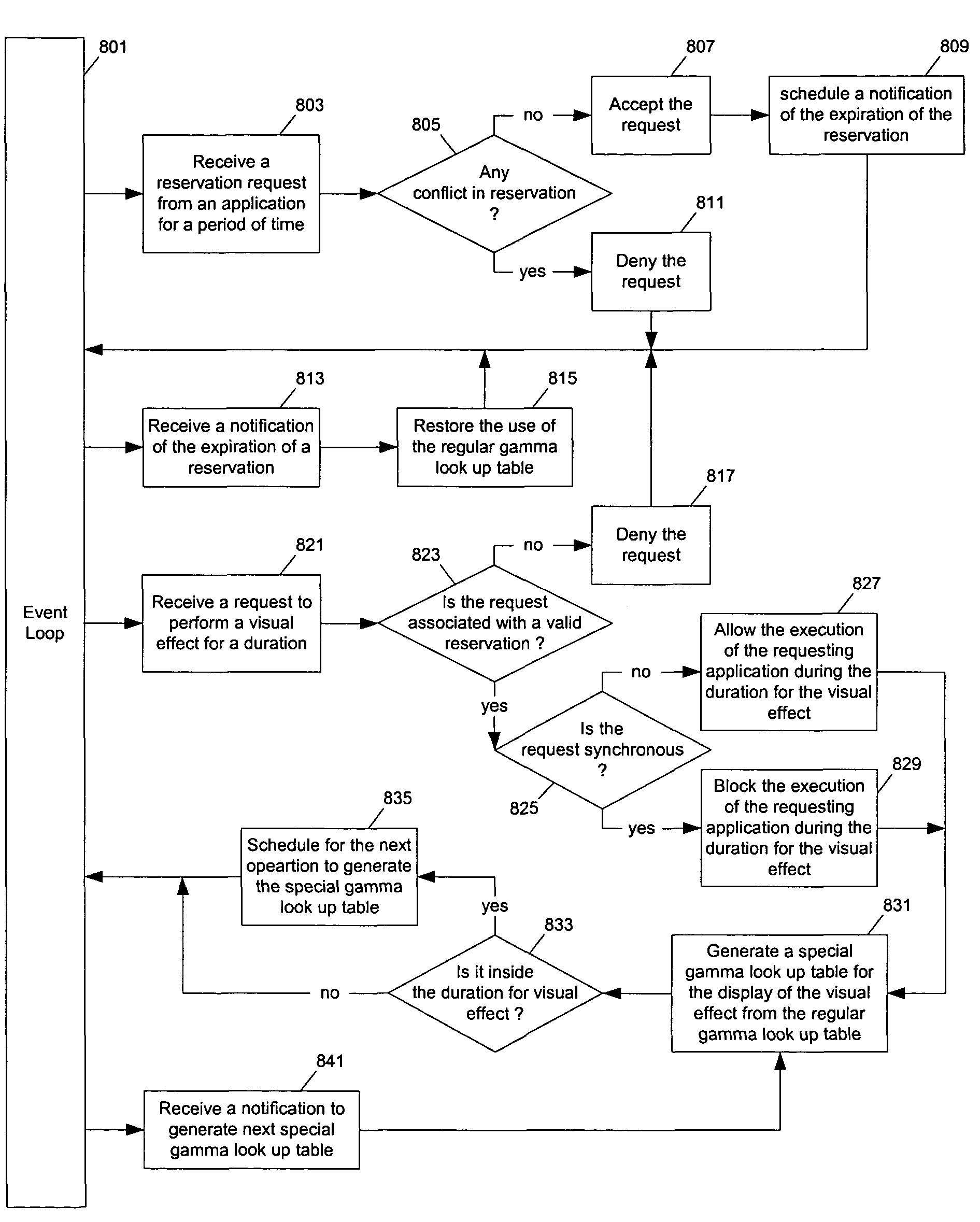
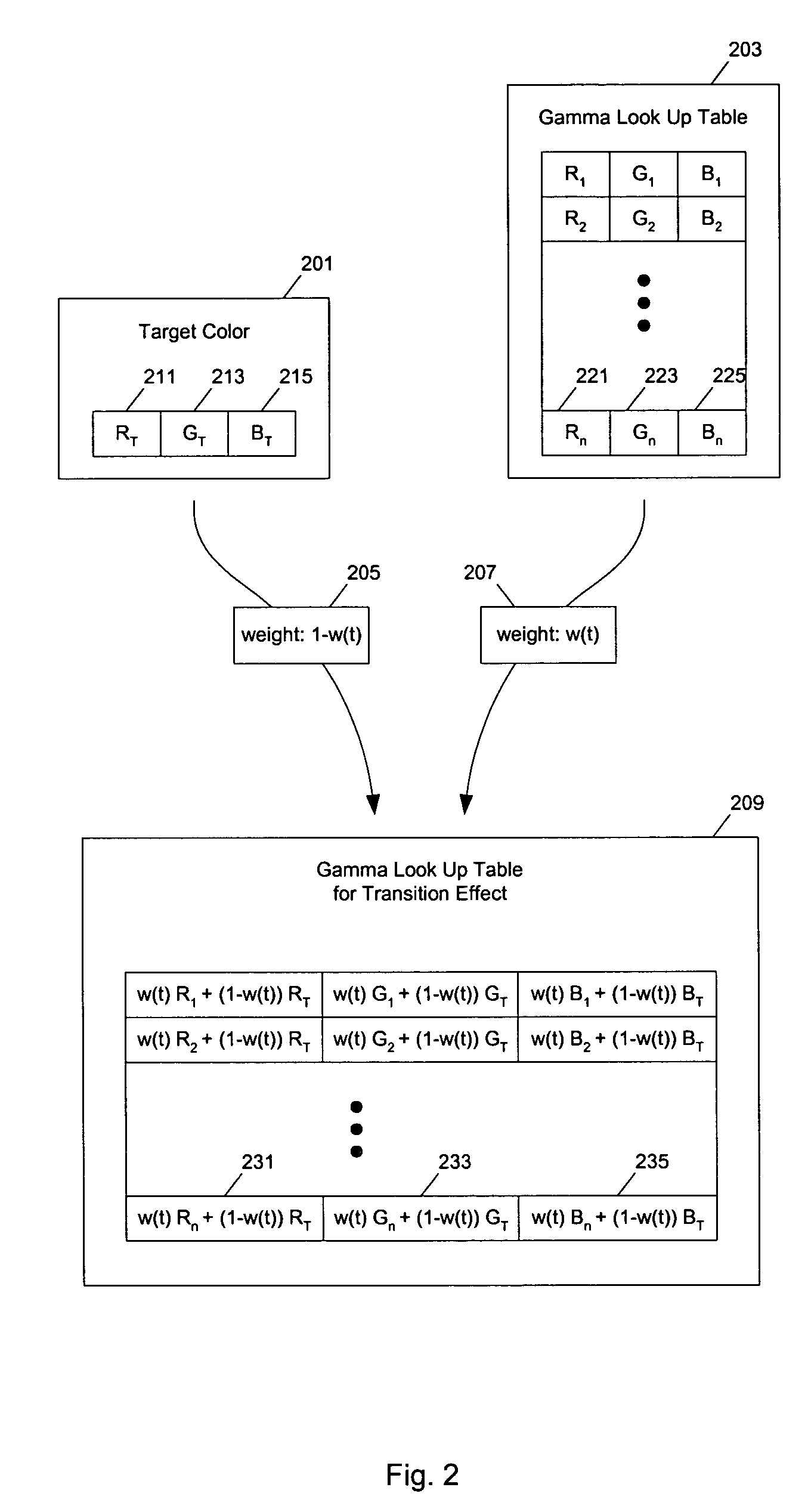
Methods and apparatuses for the automated display of visual effects
InactiveUS7042464B1Simplify the codeProvide consistencyTelevision system detailsColor signal processing circuitsOperational systemDisplay device
Methods and apparatuses for the generation of visual effects according to the elapsed time for real time display. One embodiment of the present invention provides an automated mechanism for displaying visual effects (e.g., fade to or from a target color) through adjusting color correction parameters (e.g., the look up table for gamma correction) without disturbing display color calibration settings for the current display device. Time-based adjustments are made in small steps in the beginning and end and large steps in the middle of the transition to provide perceptually smooth transition effect. In one embodiment, a operating system resource is provided to manage, synchronously or asynchronously, the visual effect on behalf of requesting applications, simplifying the coding of the application programs and providing consistency across application programs. In one embodiment, the operating system resource uses a reservation system to prevent conflict and interference between application programs.
Owner:APPLE INC
Color calibration for object tracking
To calibrate a tracking system a computing device locates an object in one or more images taken by an optical sensor. The computing device determines environment colors included in the image, the environment colors being colors in the one or more images that are not emitted by the object. The computing device determines one or more trackable colors that, if assumed by the object, will enable the computing device to track the object.
Owner:SONY COMPUTER ENTERTAINMENT INC
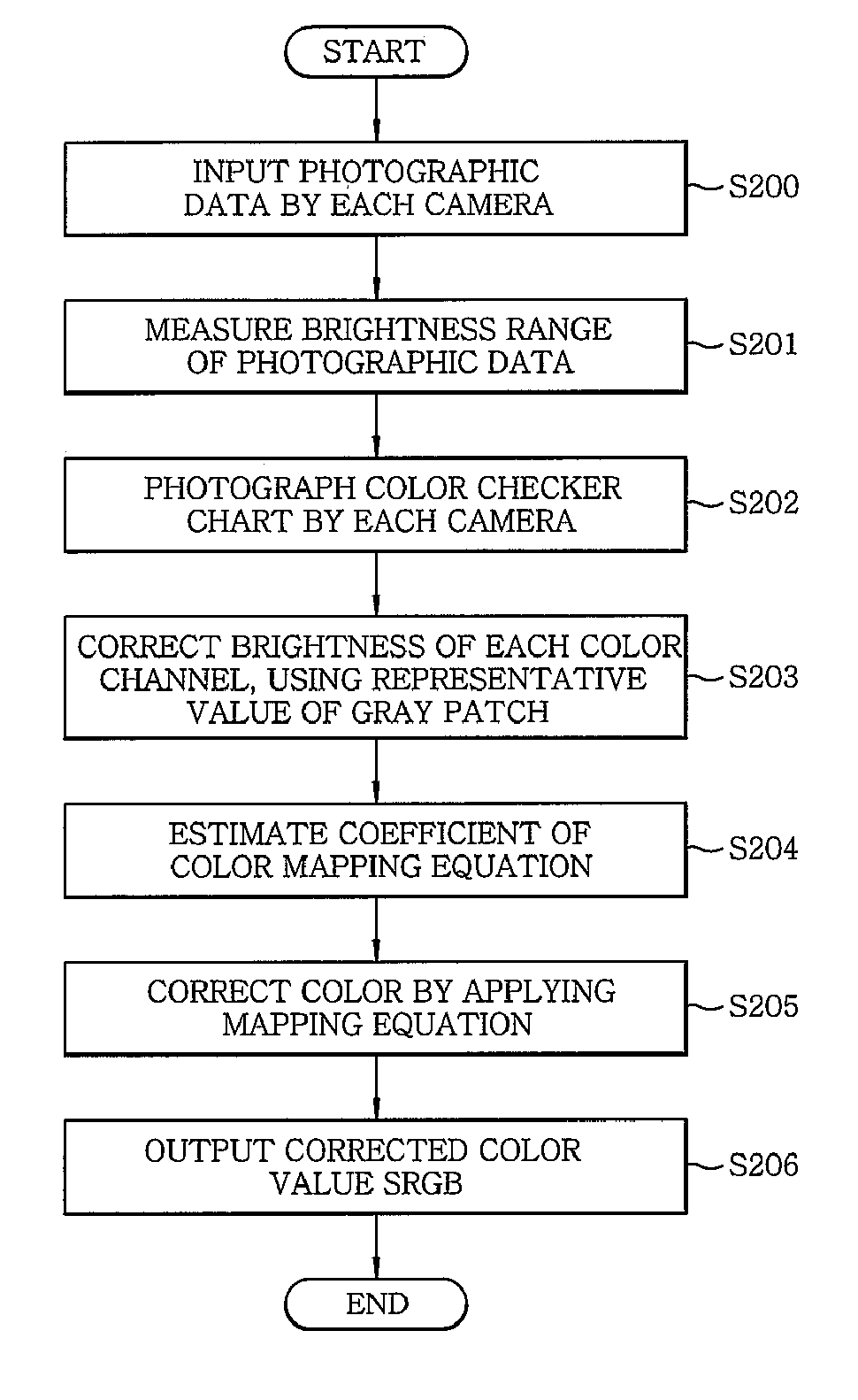
Multi-view camera color calibration method using color checker chart
A multi-view camera color calibration method using a color checker chart, includes measuring a brightness range of photographic data being input from multiple cameras; photographing the color checker chart for each camera and adjusting a brightness value of the chart to be within the brightness range of an input image of each camera; correcting brightness of each camera by using a gray patch of the checker chart; modeling a relationship between a color value of the checker chart obtained by each camera and a standard color value provided by the color checker chart; and correcting differences in color as a result of the modeling, to calibrate colors among the multiple cameras. Therefore, the three-dimensional information of a moving object for photography which cannot be photographed by moving only one camera is capable of being restored.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Colour calibration of emissive display devices
ActiveUS20050174309A1Extend potential colour gamutImprove color gamutCathode-ray tube indicatorsDriving currentVirtual target
A calibration method for calibrating a fixed format emissive display device having a plurality of pixels is described In the display each pixel comprises at least three sub-pixels for emitting light of different real primary colours. The method comprises determining, for each real primary colour separately, a virtual target primary colour which can be reached by at least 80% of the pixels of the display, determining a colour gamut defined by the determined virtual target primary colours, and adjusting the drive currents to the sub-pixels to achieve a colour inside the determined colour gamut. A display having an extended range of colours is described, i.e. a gamut of colours that is more than the gamut provided by an n virtual primary colour based electronic multicolour display, as measured on a chromaticity diagram, for example. A color and / or brightness uniform image can be produced with this fixed format emissive display device.
Owner:BARCO NV
Color management and calibration using a scanner or camera
InactiveUS20120044540A1Radiation pyrometryCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionMeasurement test
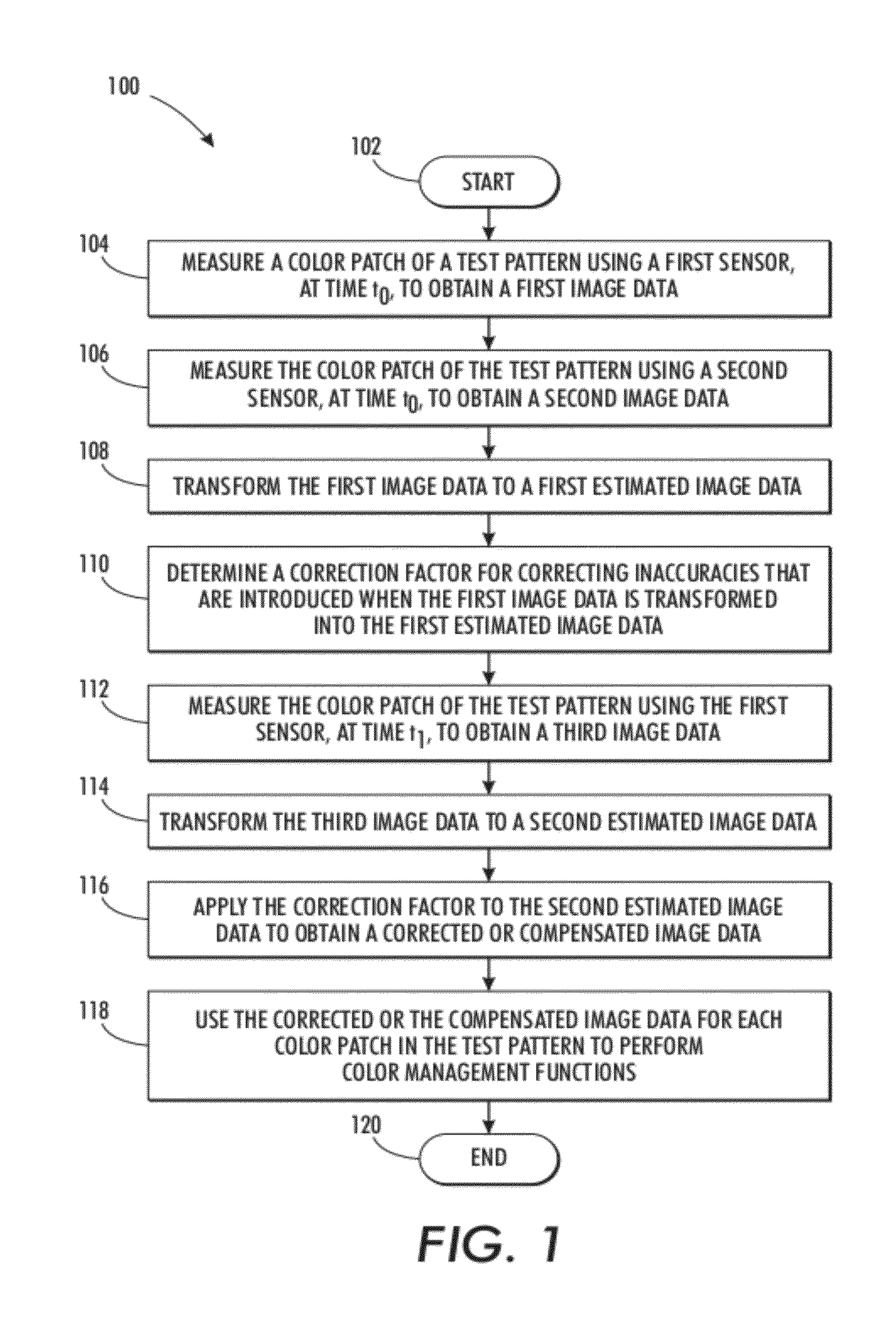
A computer-implemented method for color calibration and profiling of an output device includes measuring a color patch in a test pattern, which comprises a plurality of color patches, to obtain first image data; measuring the color patch in the test pattern to obtain second image data; transforming the first image data to a first estimated image data; determining a difference between the second image data and the first estimated image data to obtain a correction factor; and calculating, for each patch in the test pattern, a corrected image data by applying the correction factor to a subsequent estimated image data from the first sensor. The correction factor is used for correcting inaccuracies introduced when the first image data is transformed into the first estimated image data. The first image data and the second image data provide a measured color representation of the color patch in a device dependent color space and a device independent color space, respectively.
Owner:XEROX CORP
Method and apparatus for determining analyte concentration by quantifying and interpreting color information captured in a continuous or periodic manner
ActiveUS20150241358A1Eliminate errorsTelevision system detailsAnalysis using chemical indicatorsAnalyteDisplay device
In one embodiment, an apparatus for automatic test diagnosis of a test paddle is disclosed. The apparatus comprises a personal computing device including: a camera to capture images over time of test pads of a test paddle, a processor coupled to the camera, and a display device coupled to the processor. The processor analyzes the color changes over time of each test pad to determine a color trajectory over time for each test pad. The processor compares the color evolution trajectory for each test pad with color calibration curves for each test pad to determine an analyte concentration of a test biological sample, such as urine. During the analysis by the processor, the display device displays a user interface with results of the analyte concentration in response to the analysis over time.
Owner:HEALTHY IO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com