Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
467 results about "Microscope slide" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
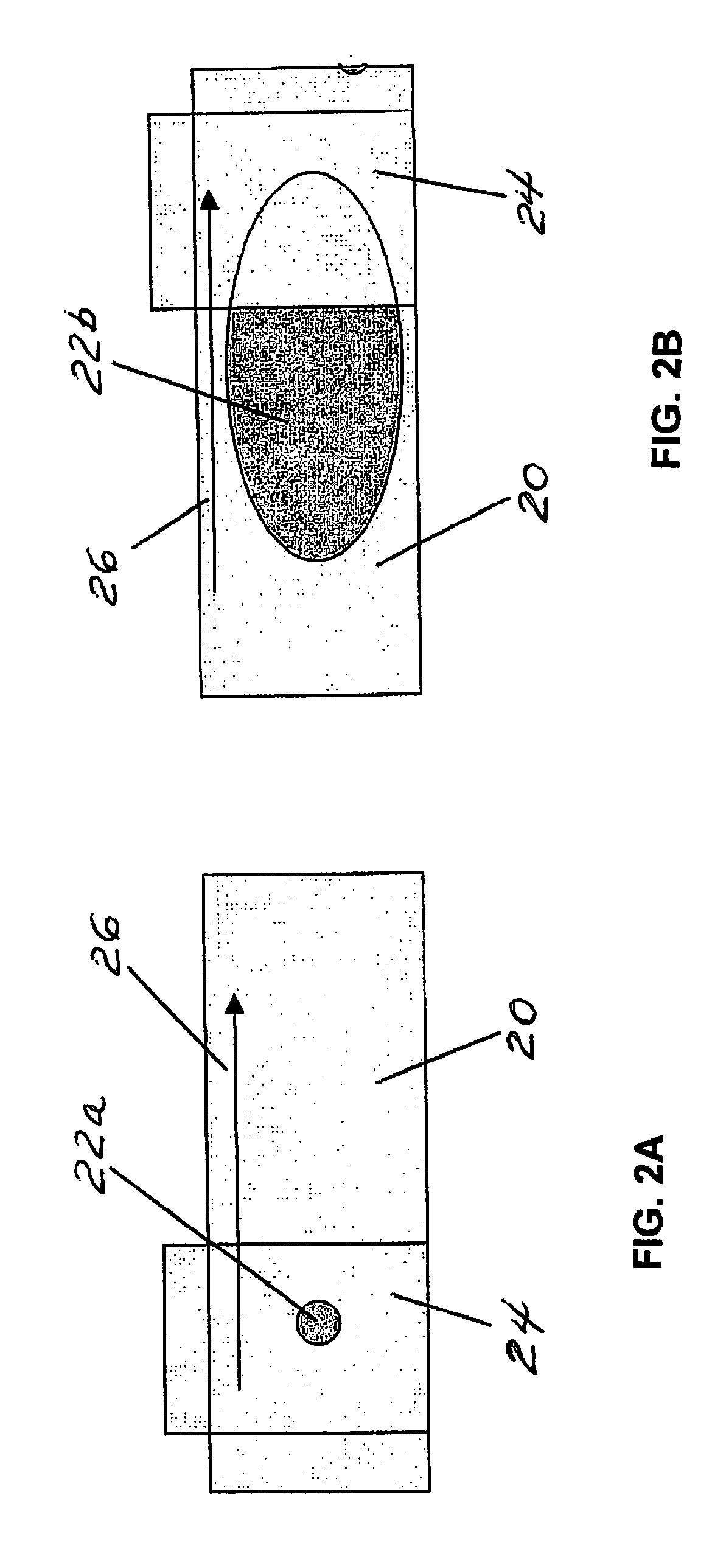
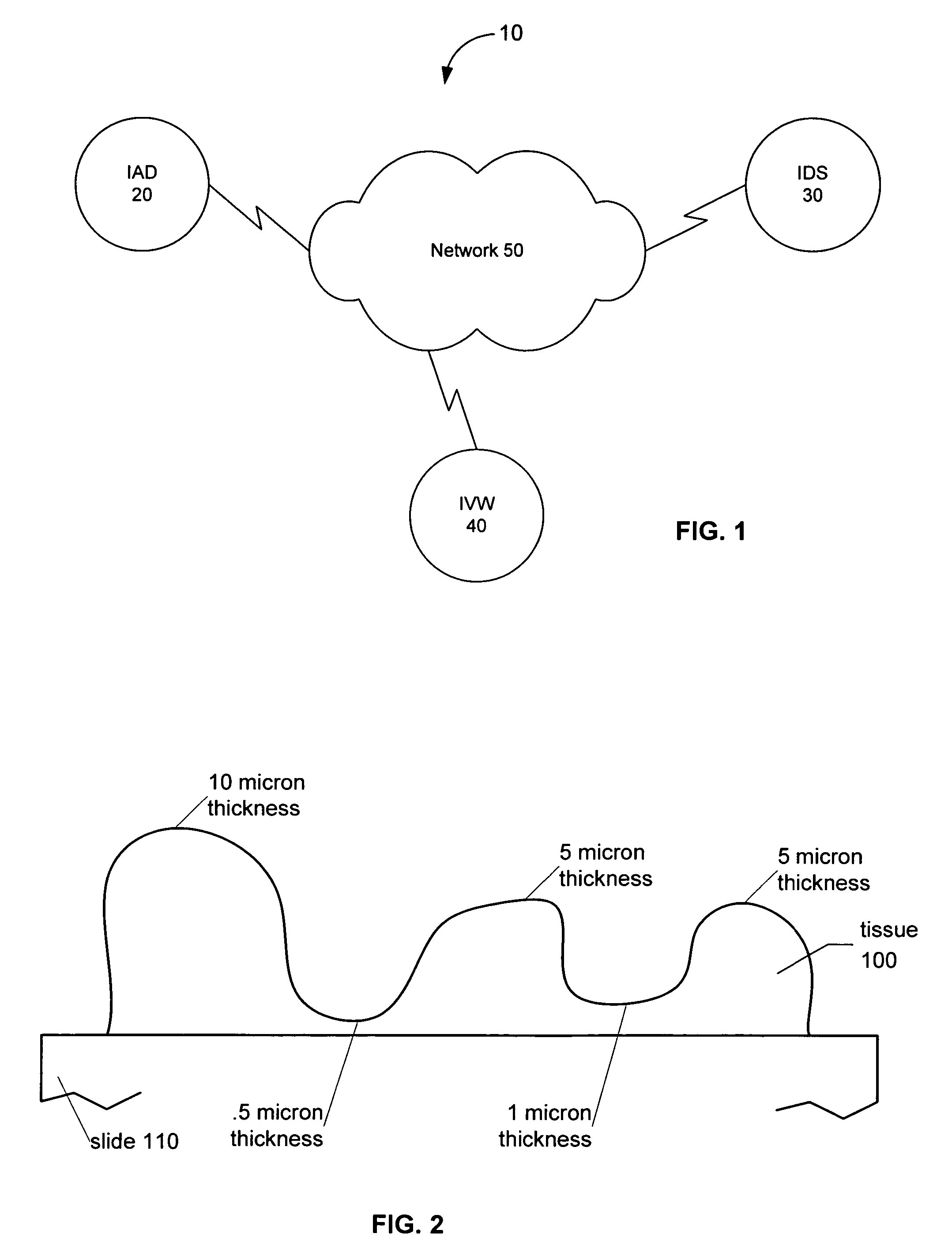
A microscope slide is a thin flat piece of glass, typically 75 by 26 mm (3 by 1 inches) and about 1 mm thick, used to hold objects for examination under a microscope. Typically the object is mounted (secured) on the slide, and then both are inserted together in the microscope for viewing. This arrangement allows several slide-mounted objects to be quickly inserted and removed from the microscope, labeled, transported, and stored in appropriate slide cases or folders etc.
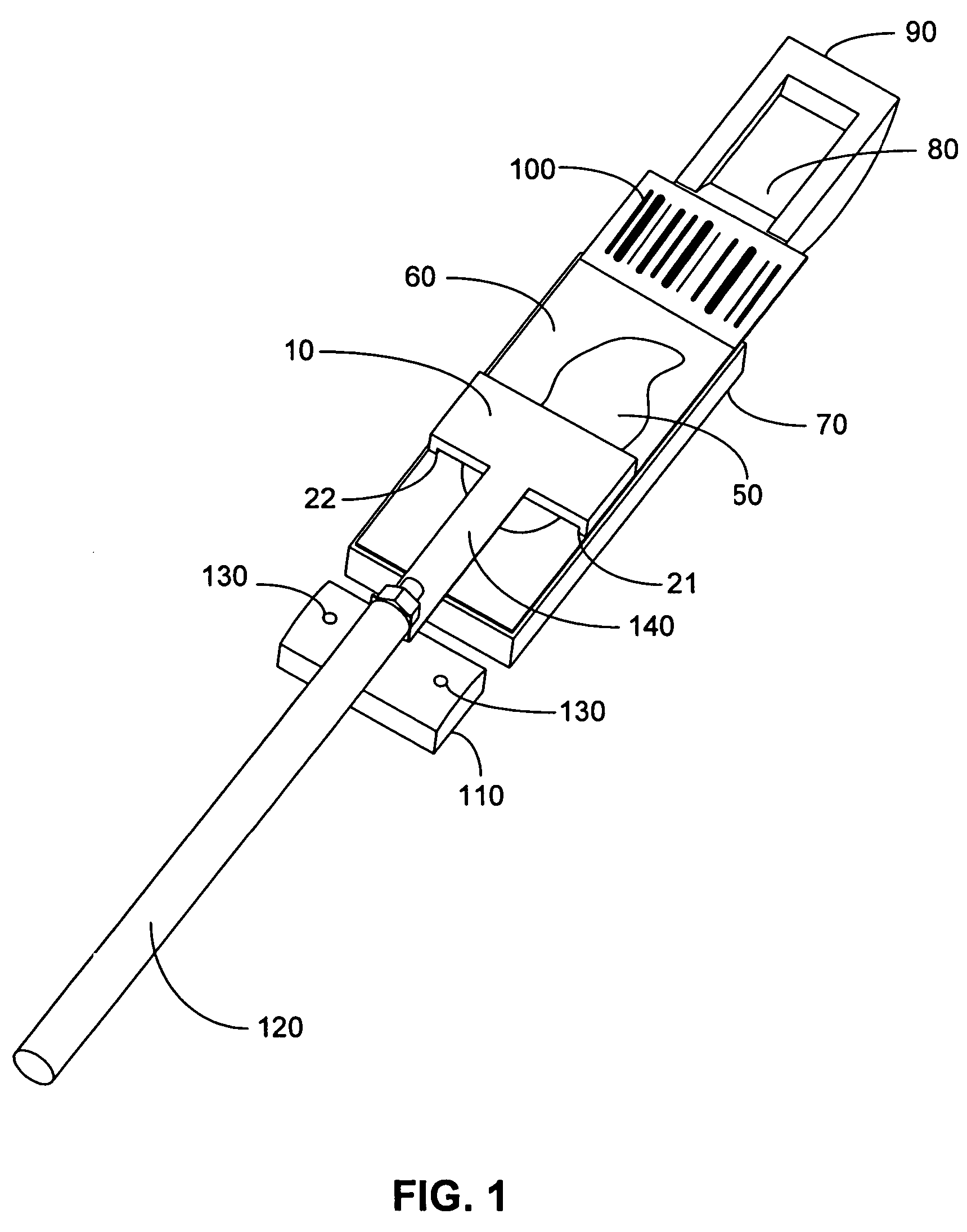
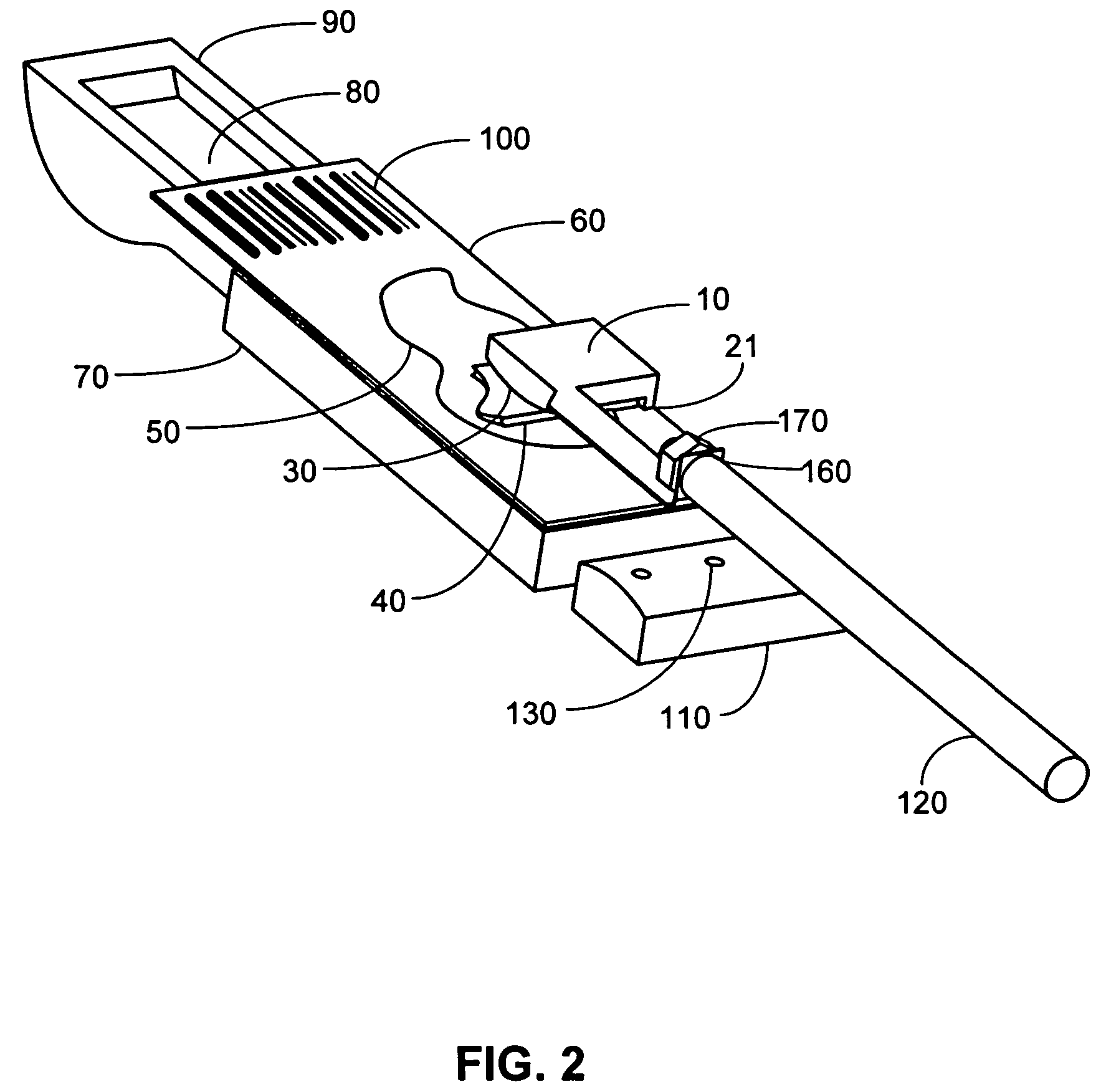
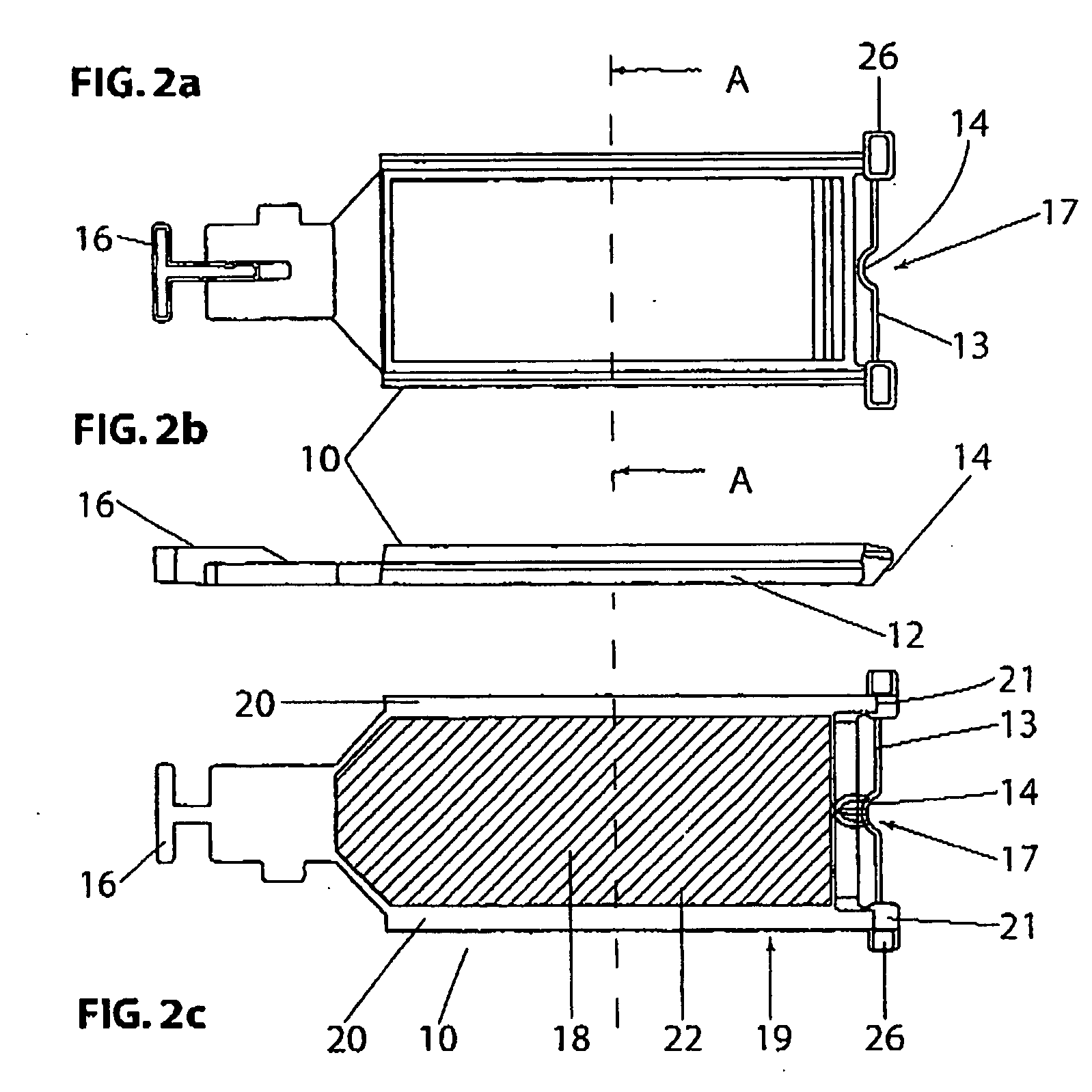
Method and apparatus for rinsing a microscope slide
InactiveUS6093574AEfficient and reliableEasy to manufactureWithdrawing sample devicesPreparing sample for investigationMicroscope slideModularity
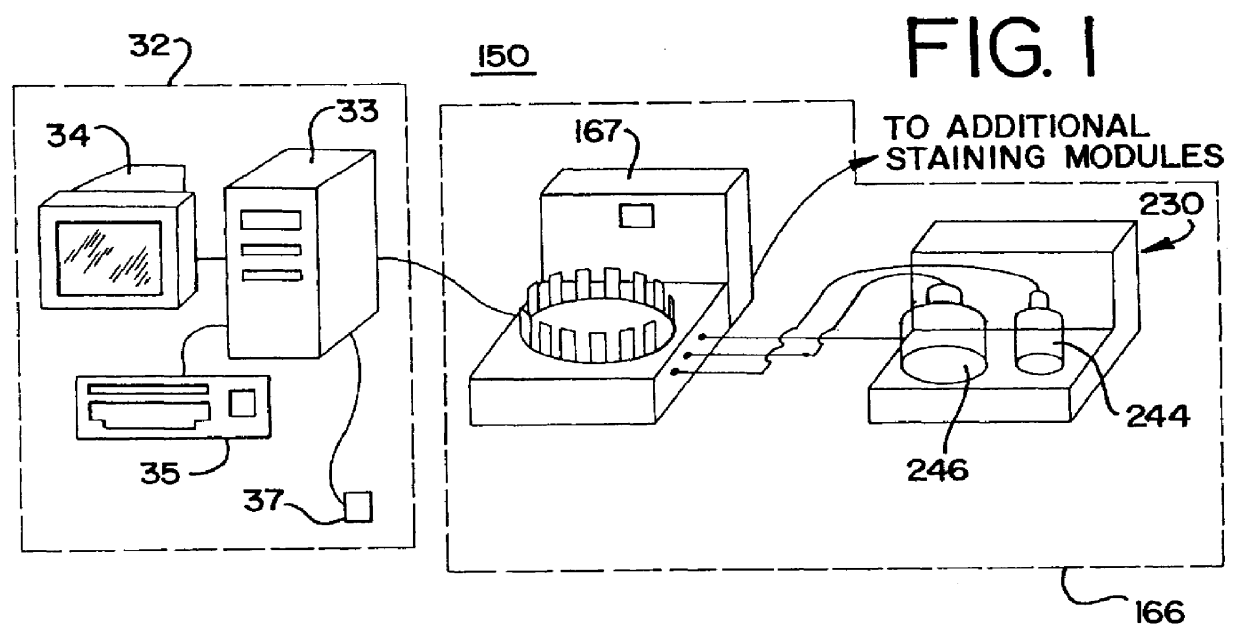
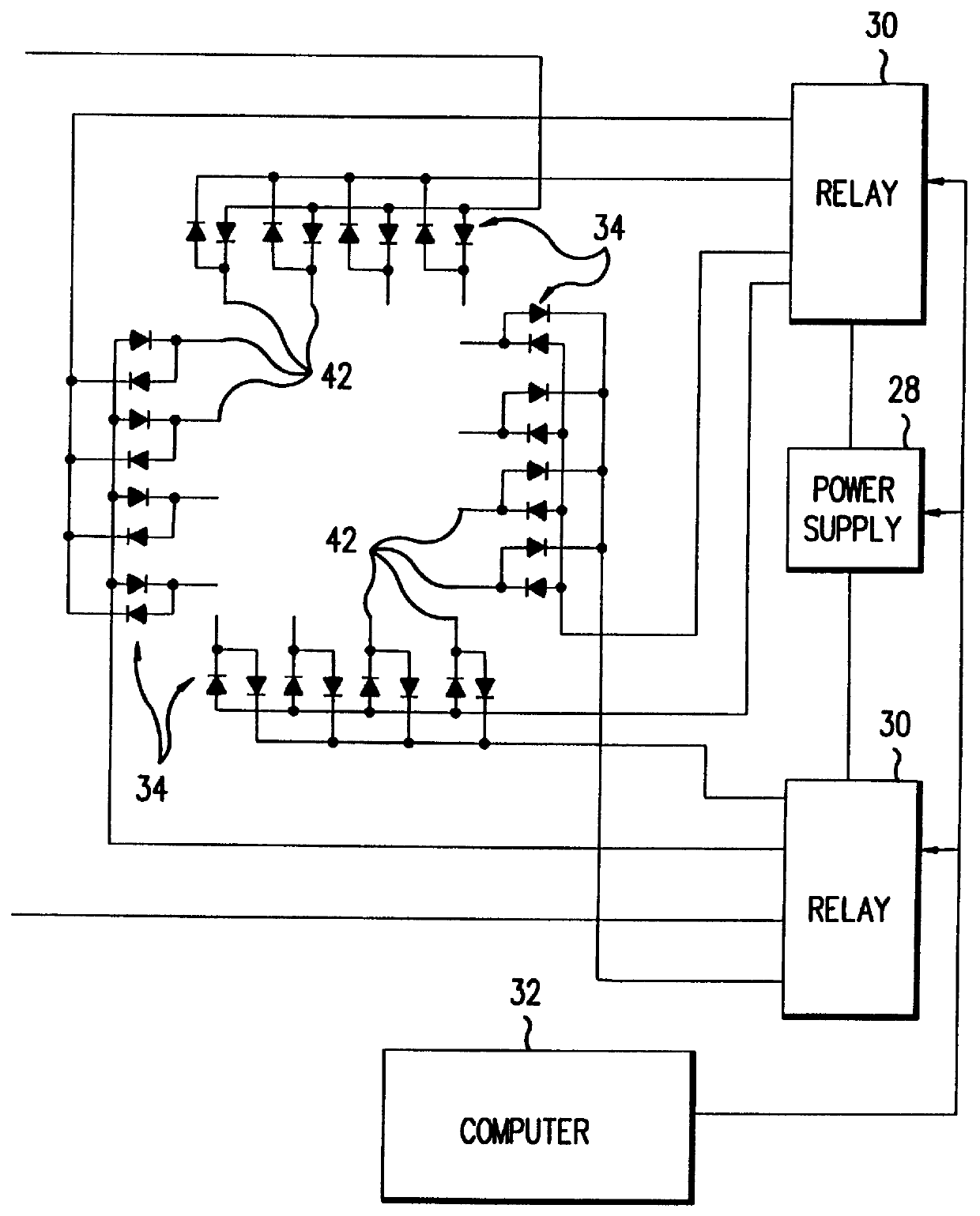
A method and apparatus for an automated biological reaction system is provided. In the processing of a biological reaction system, there is a need for consistently placing an amount of liquid on a slide. In order to accomplish this, several methods are used including a consistency pulse and a volume adjust means. Moreover, in order to reliably operate an automated biological reaction system, the dispenser must be reliable, easy to assemble and accurate. Among other things, in order to accomplish this, the dispense chamber is substantially in line with the reservoir chamber, the reservoir chamber piston is removed, and the flow of liquid through the dispenser is simplified. Further, in order to operate the automated biological reaction system more reliably, the system is designed in modular pieces with higher functions performed by a host device and the execution of the staining operations performed by remote devices. Also, to reliably catalog data which is used by the automated biological reaction system, data is loaded to a memory device, which in turn is used by the operator to update the operator's databases. The generation of the sequence of steps for the automated biological reaction device based on data loaded by the operator, including checks to determine the ability to complete the run, is provided.
Owner:VENTANA MEDICAL SYST INC
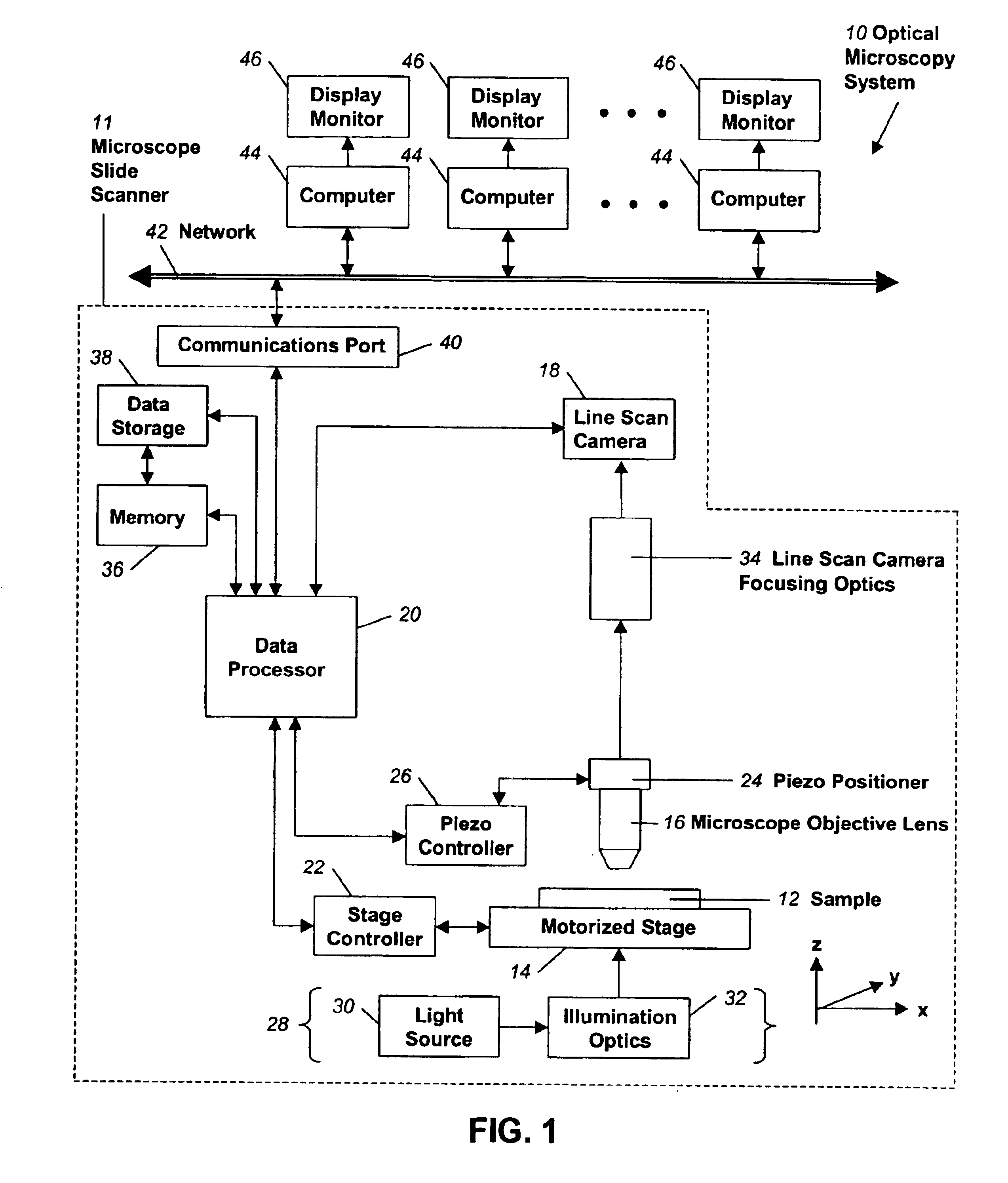
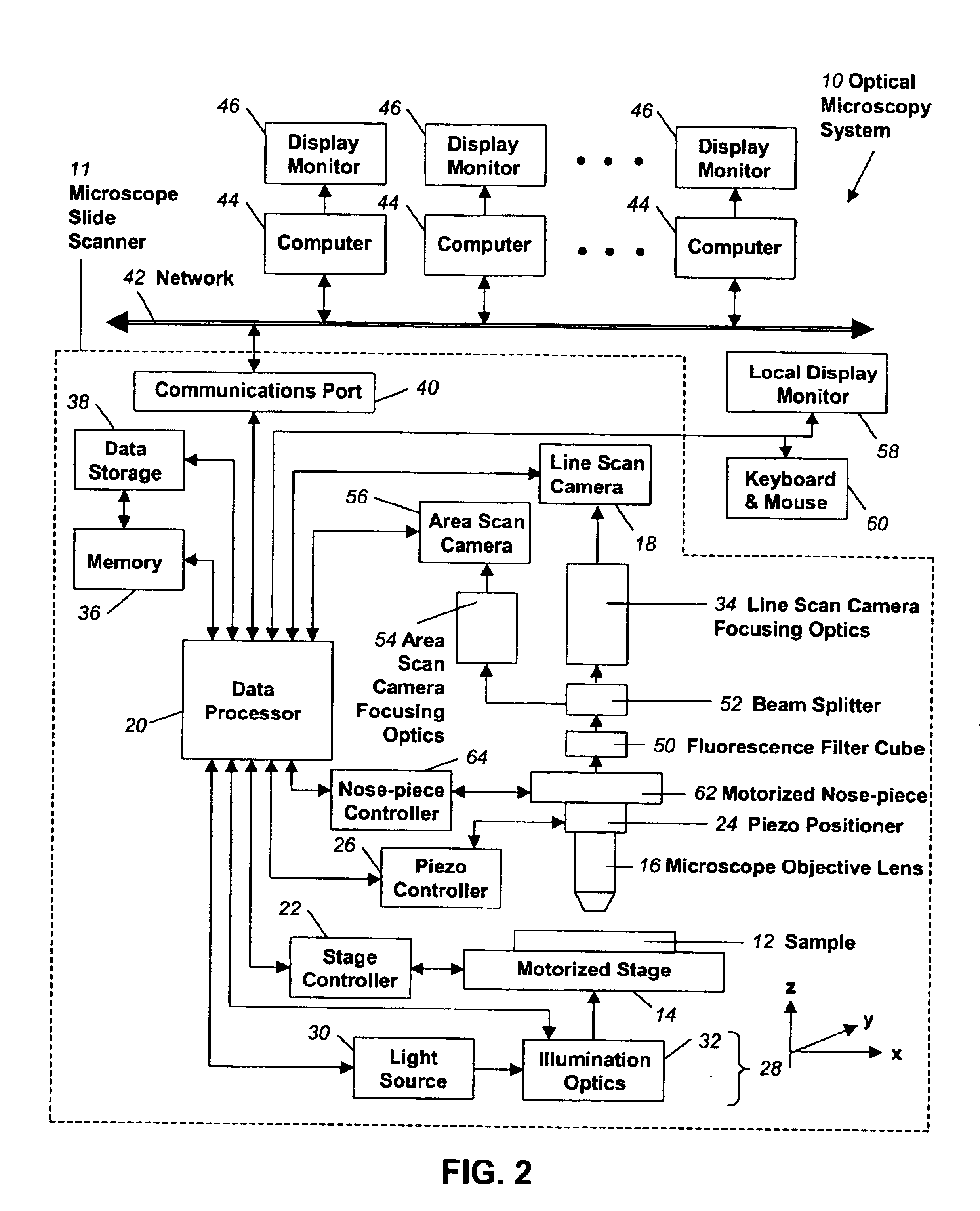
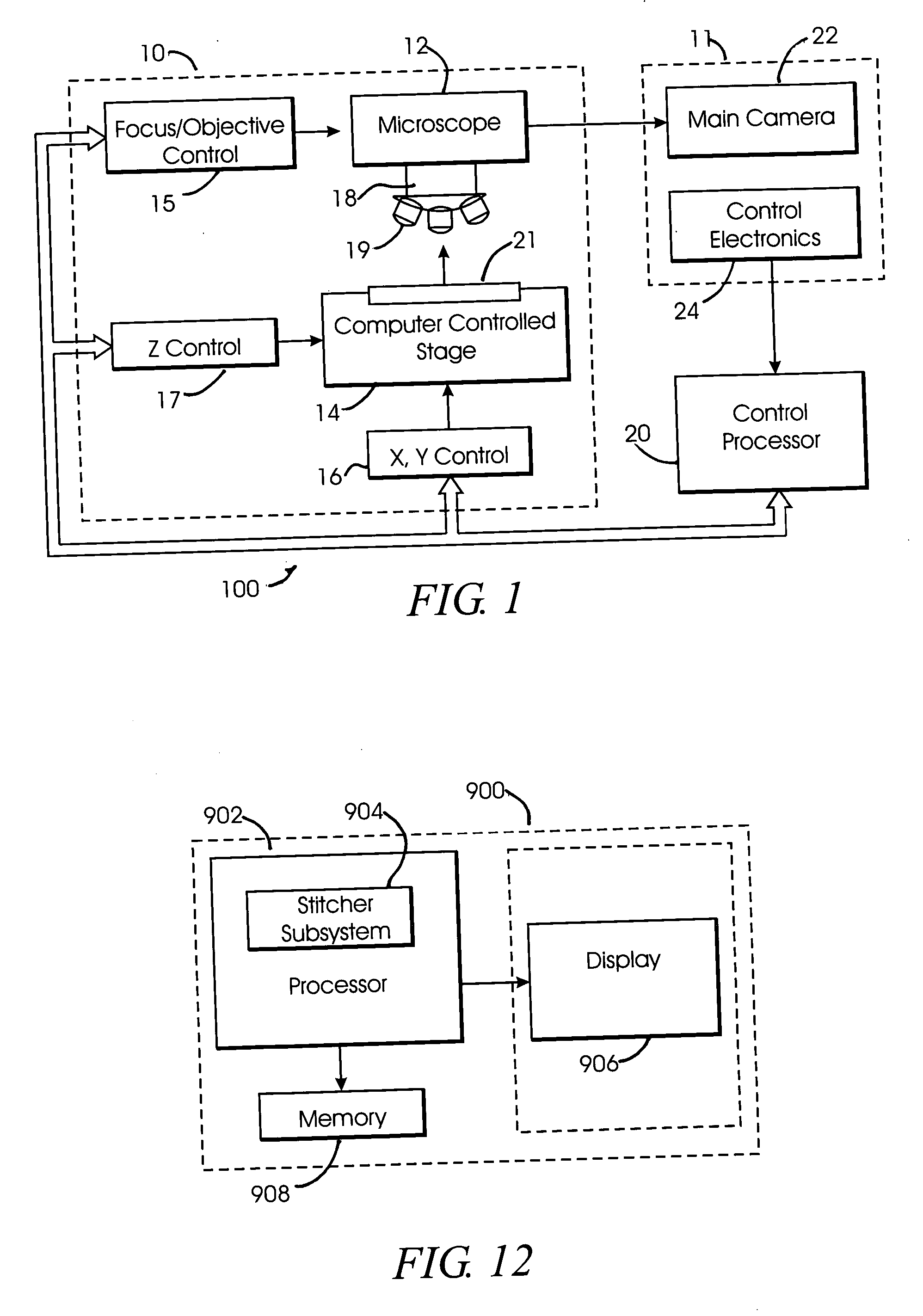
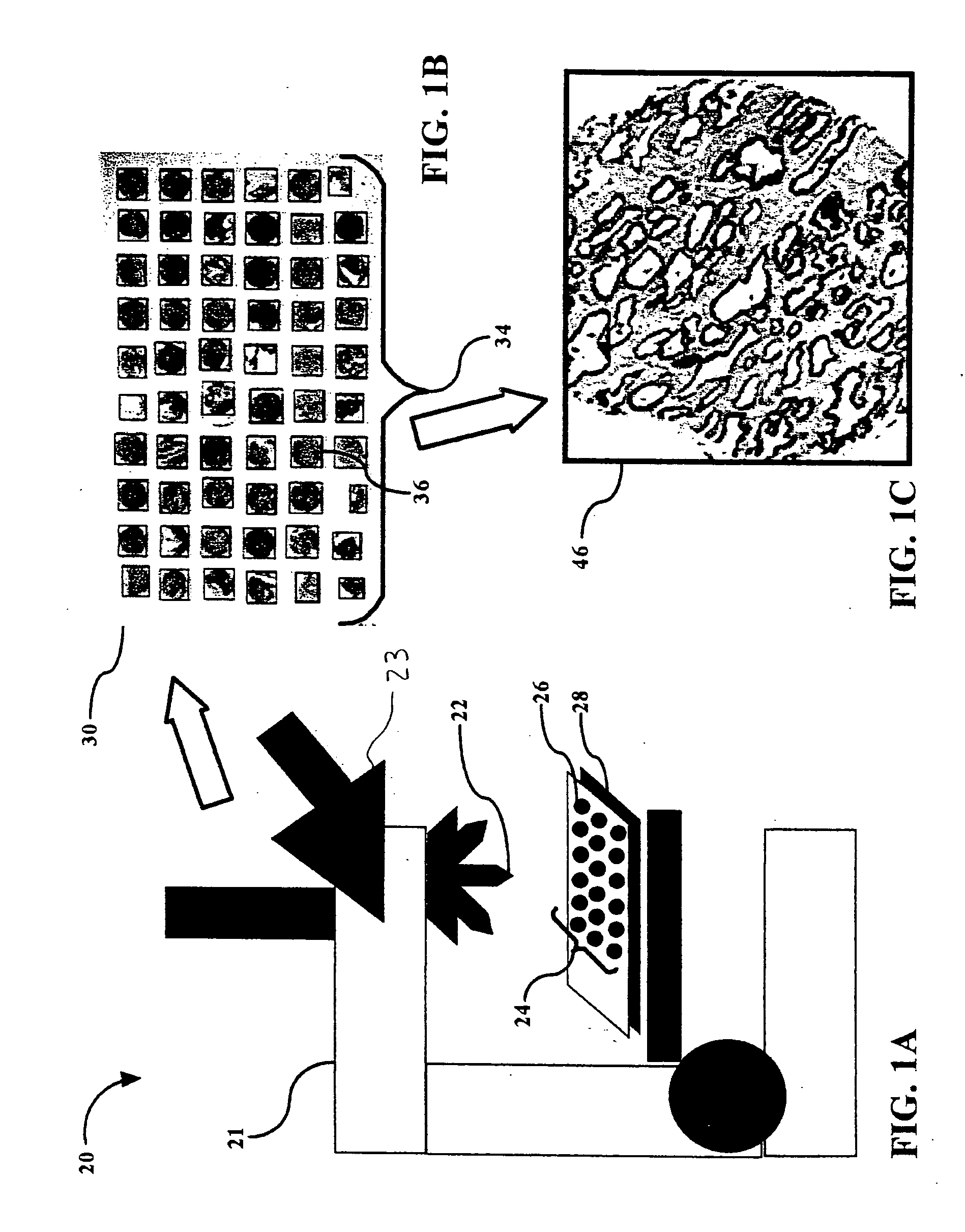
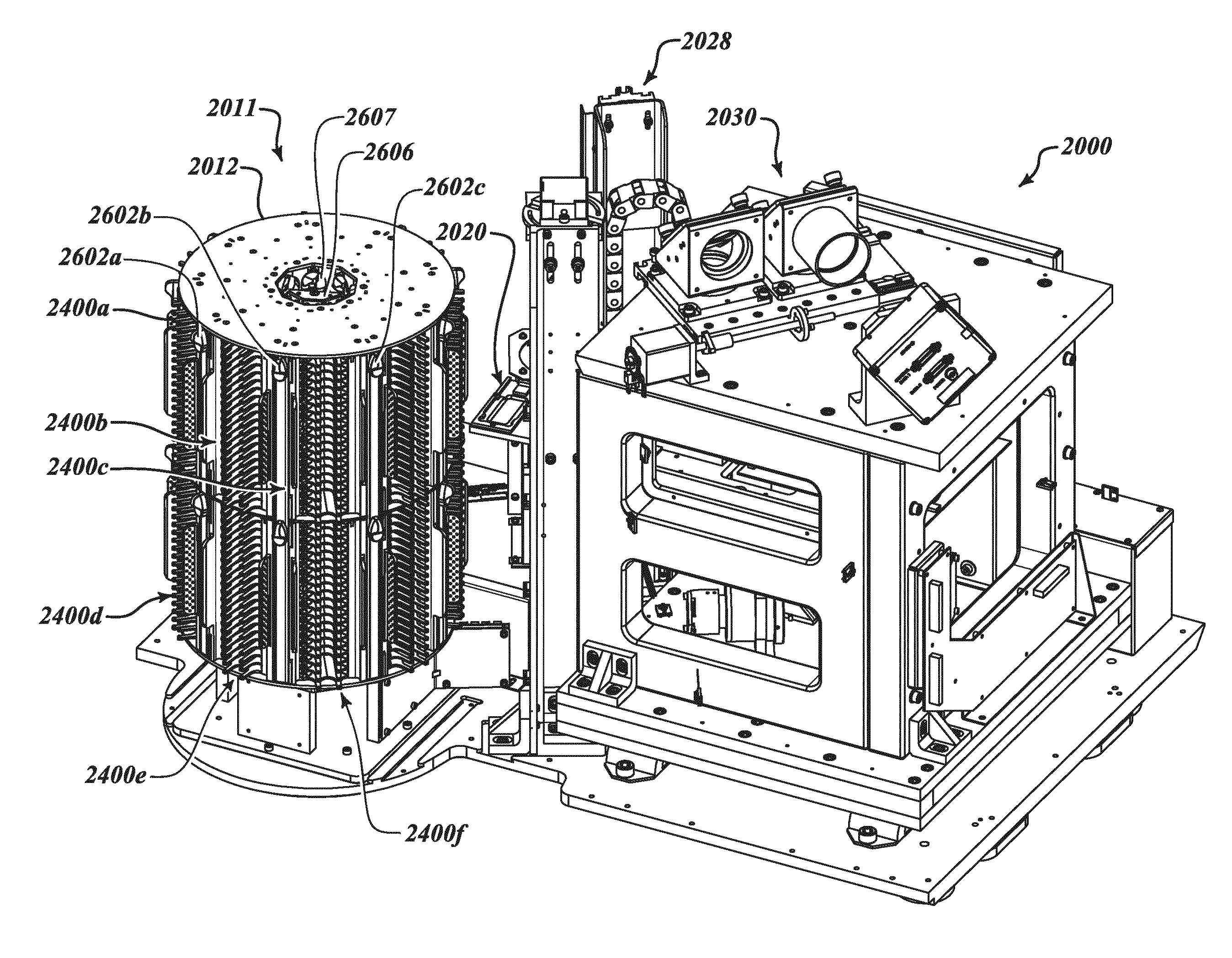
Fully automatic rapid microscope slide scanner
InactiveUS6917696B2Television system detailsMaterial analysis by optical meansMicroscope slideContinuous scanning
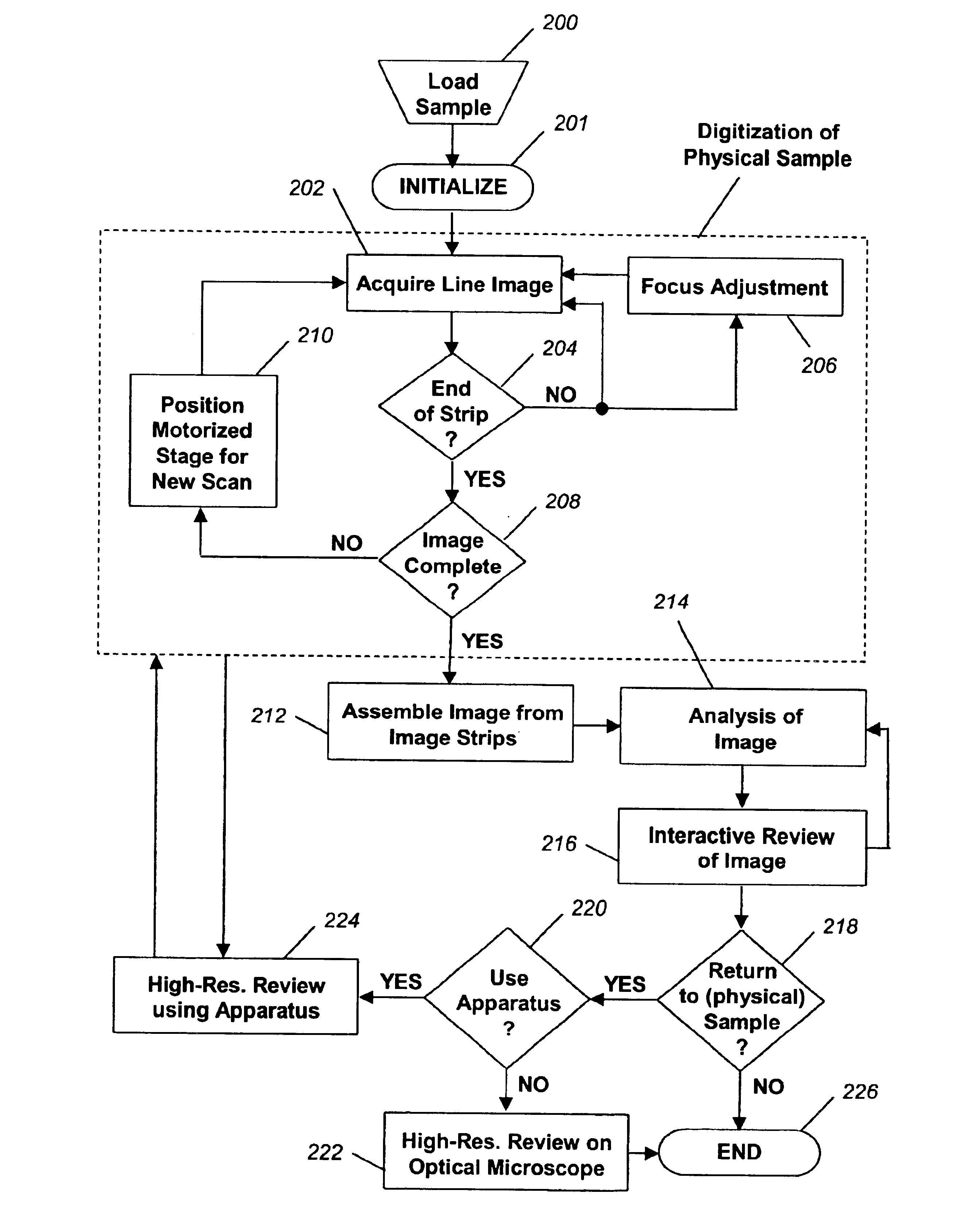
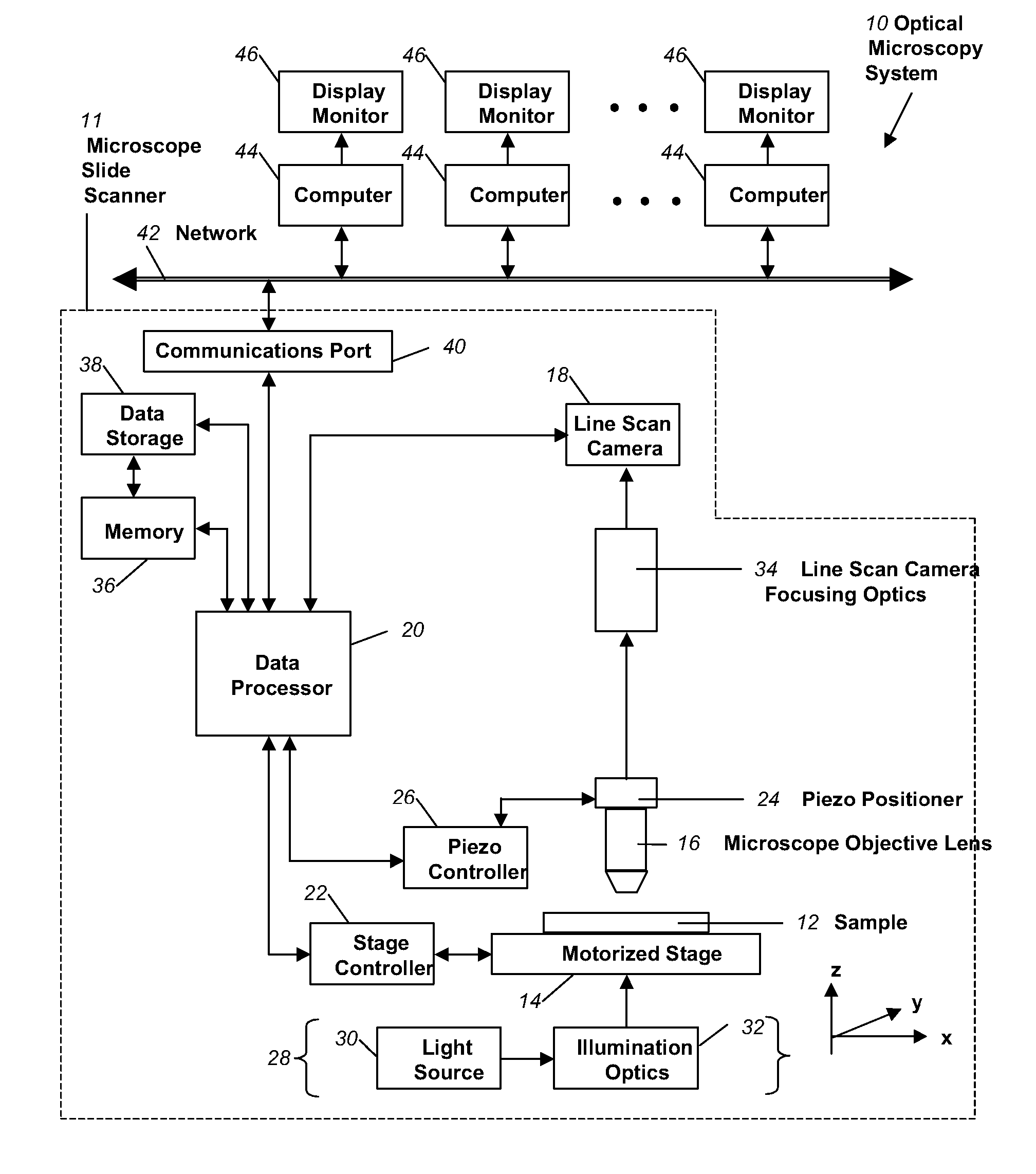
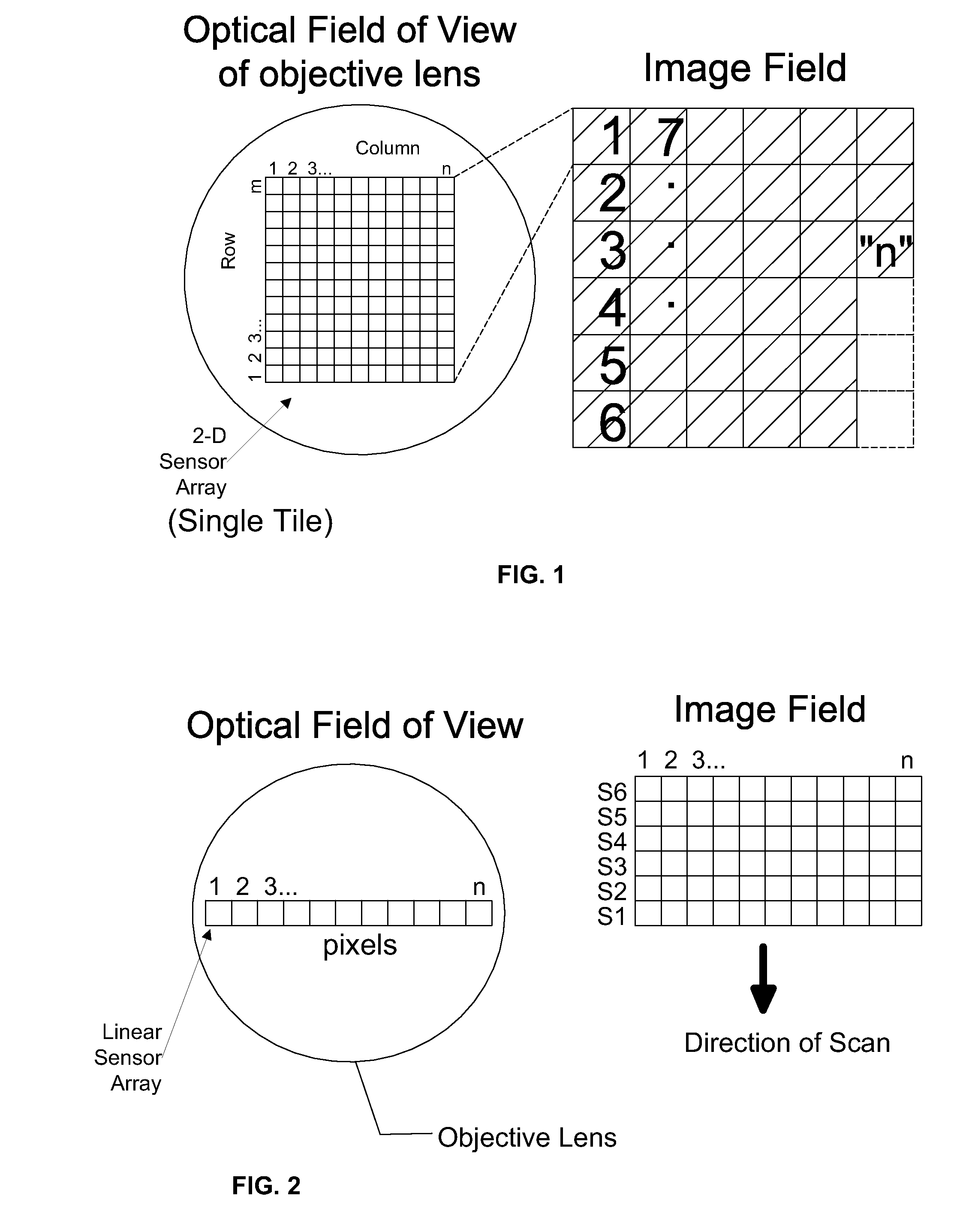
Apparatus for and method of fully automatic rapid scanning and digitizing of an entire microscope sample, or a substantially large portion of a microscope sample, using a linear array detector synchronized with a positioning stage that is part of a computer controlled microscope slide scanner. The invention provides a method for composing the image strips obtained from successive scans of the sample into a single contiguous digital image. The invention also provides a method for statically displaying sub-regions of this large digital image at different magnifications, together with a reduced magnification macro-image of the entire sample. The invention further provides a method for dynamically displaying, with or without operator interaction, portions of the contiguous digital image. In one preferred embodiment of the invention, all elements of the scanner are part of a single-enclosure that has a primary connection to the Internet or to a local intranet. In this embodiment, the preferred sample type is a microscope slide and the illumination and imaging optics are consistent with transmission mode optics optimized for diffraction-limited digital imaging.
Owner:LEICA BIOSYST IMAGING
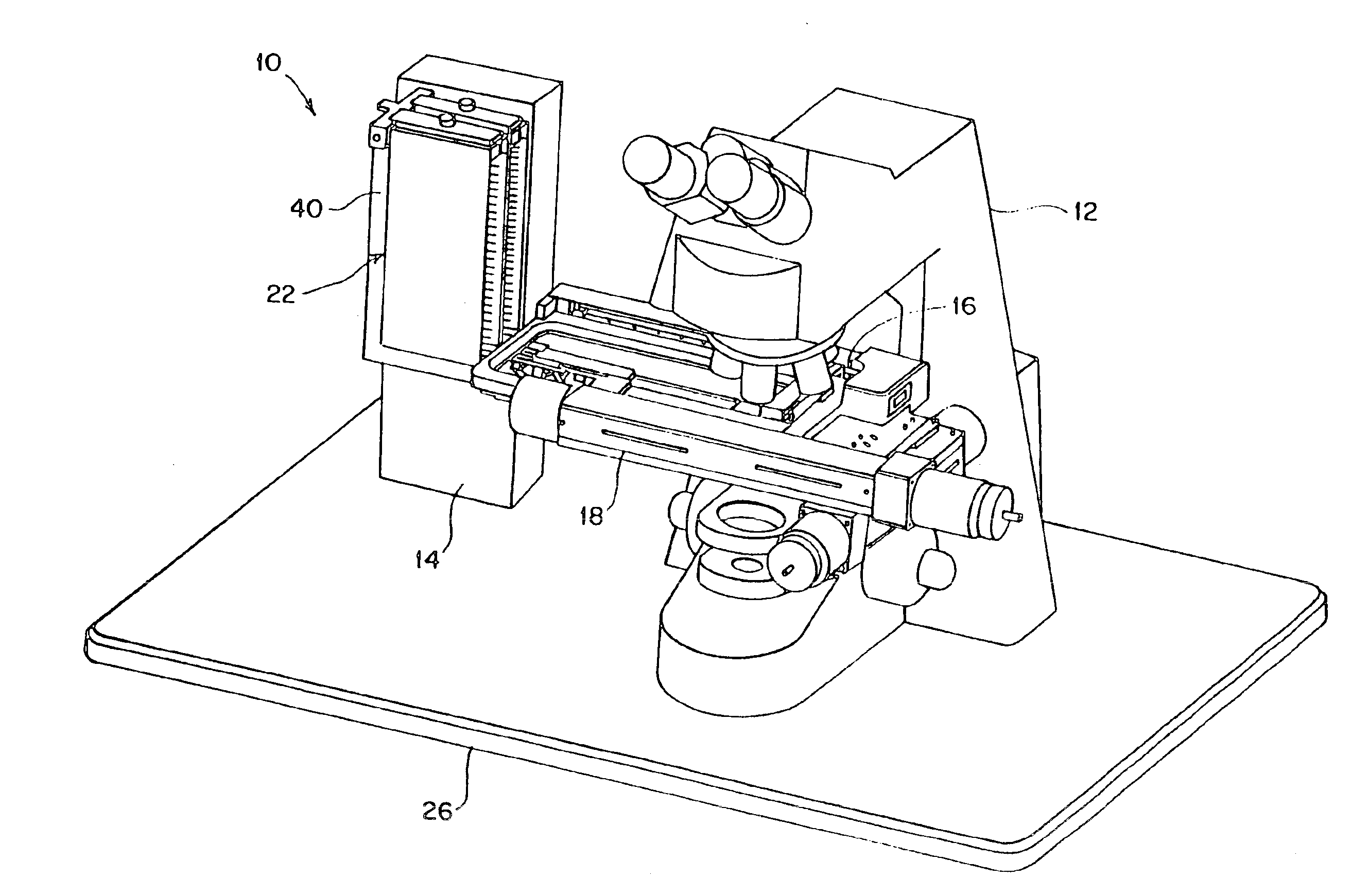
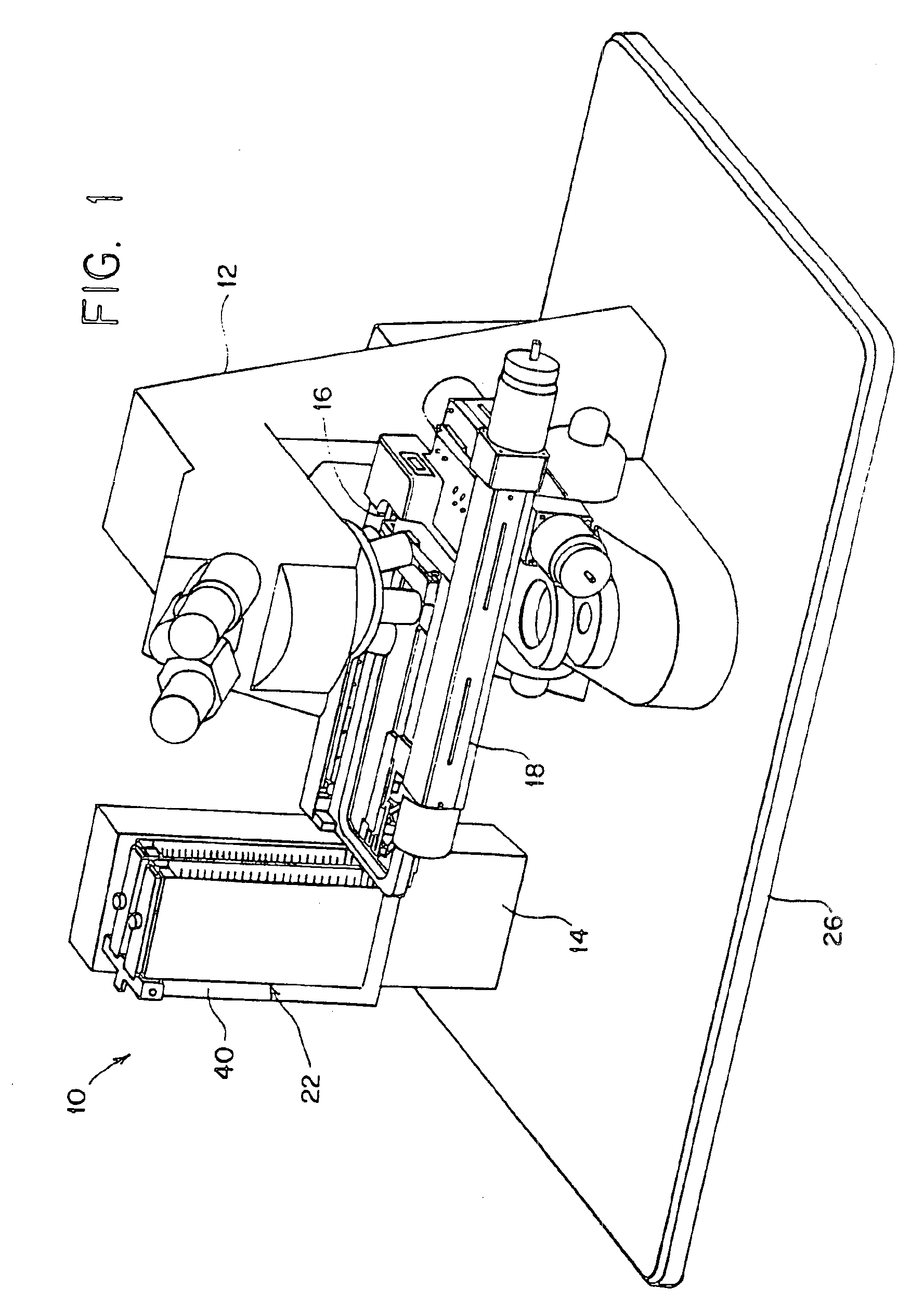
Automated slide loader cassette for microscope
InactiveUS6847481B1Enhance intrinsic valuePrecise positioningArticle unpackingMicroscopesMicroscope slideMagnetic tape
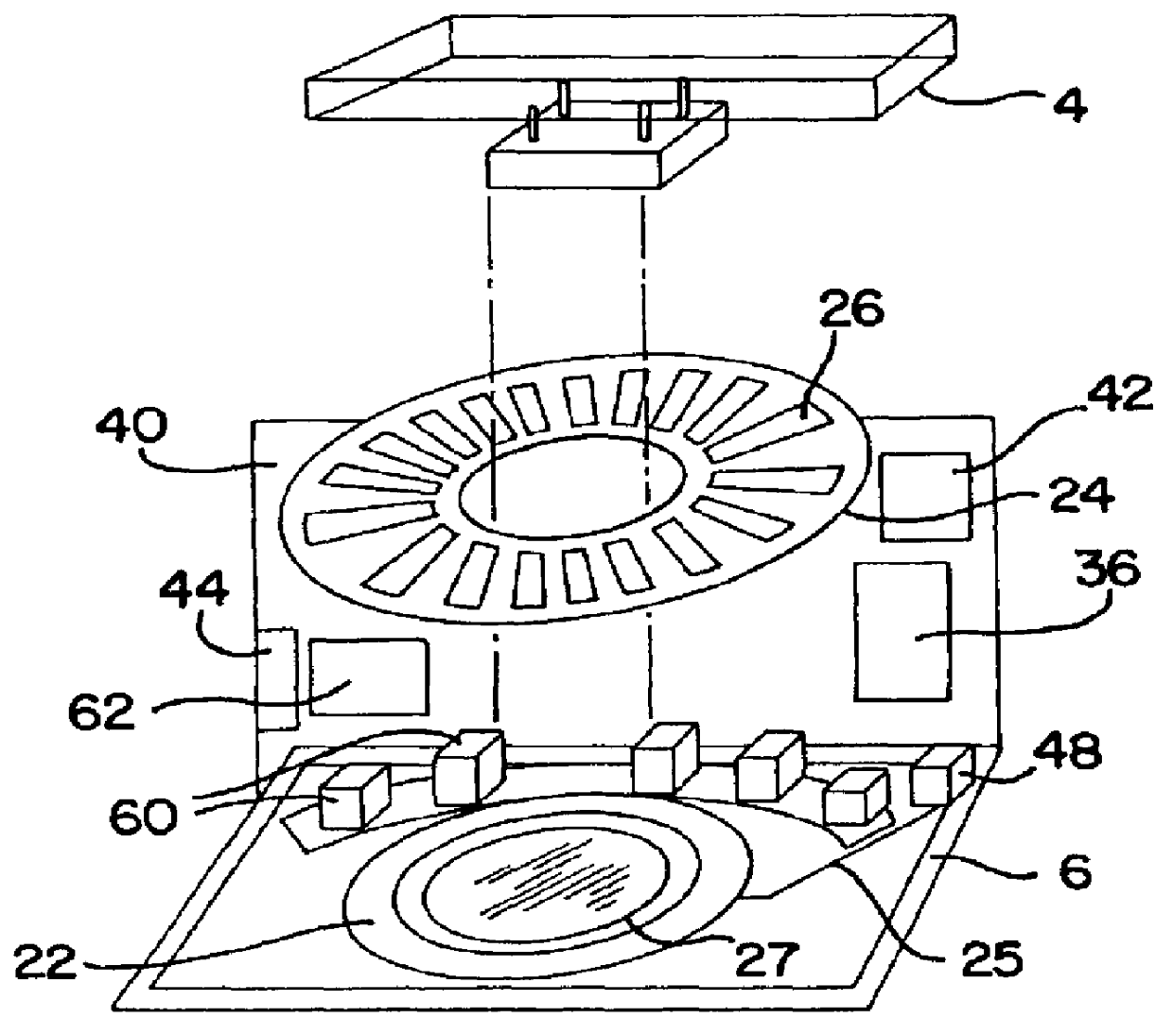
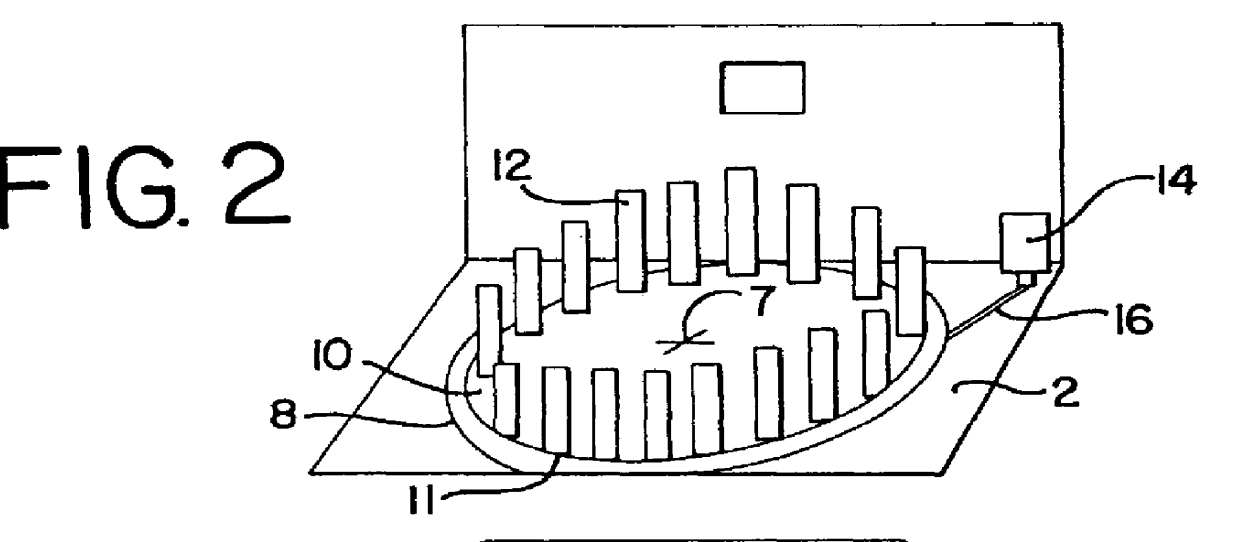
The slide handler is an instrument that automatically transfers glass microscope slides from a cassette or magazine to a motorized microscope stage and then returns the slide back into the second cassette. The use of this instrument permits the unattended computer control, measurement and inspection of specimens mounted to the slides. Full modular integration of the system components allows for the slide handler instrument to be utilized with any microscope. The instrument system has a minimum of three components; namely a slide cassette indexer, an XY-stage, and a slide exchange arm. The indexer, the arm and the XY-stage are connected together and integrated into one unitary modular instrument that can be moved from one microscope to another.
Owner:LUDL ELECTRONICS PRODS
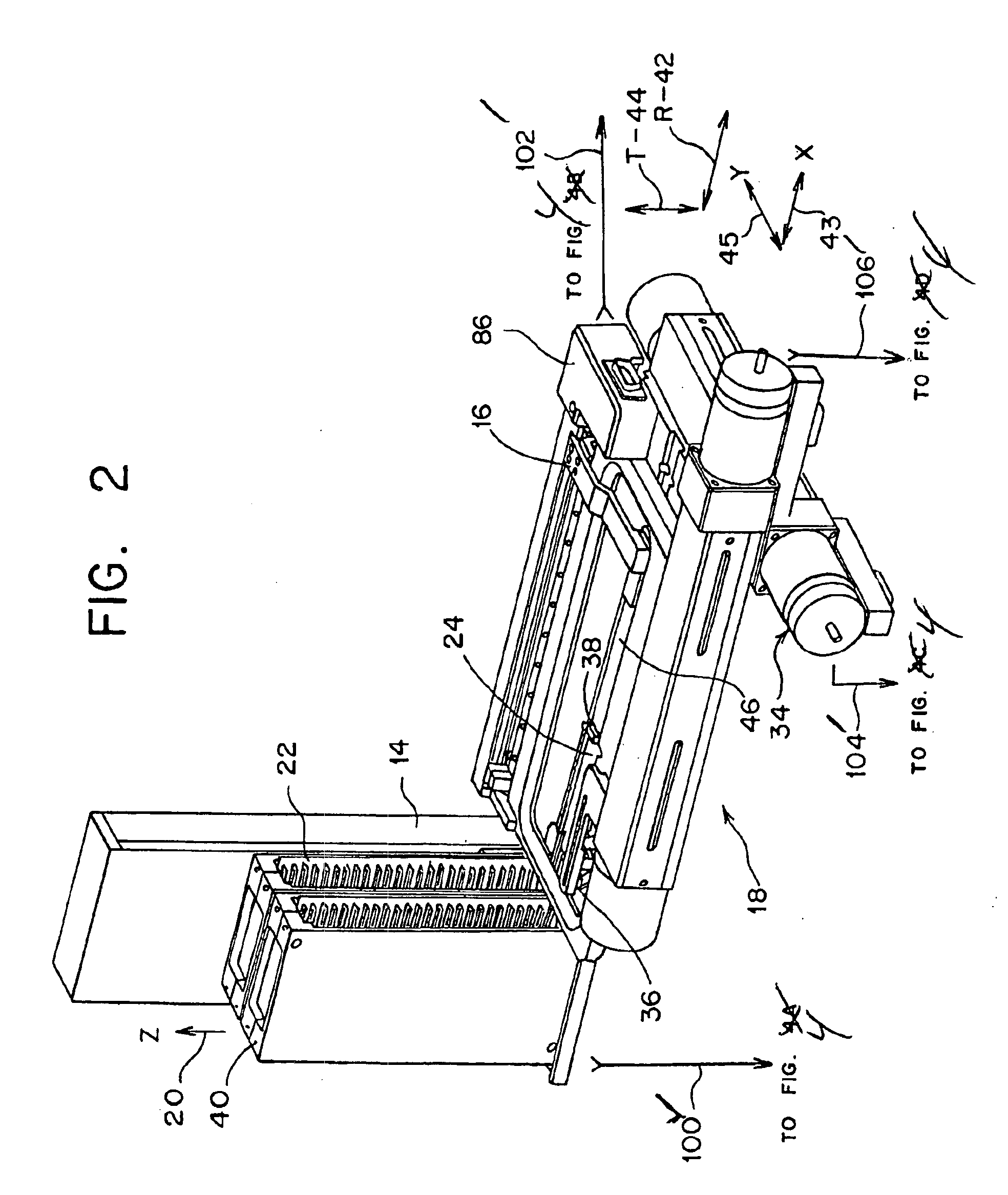
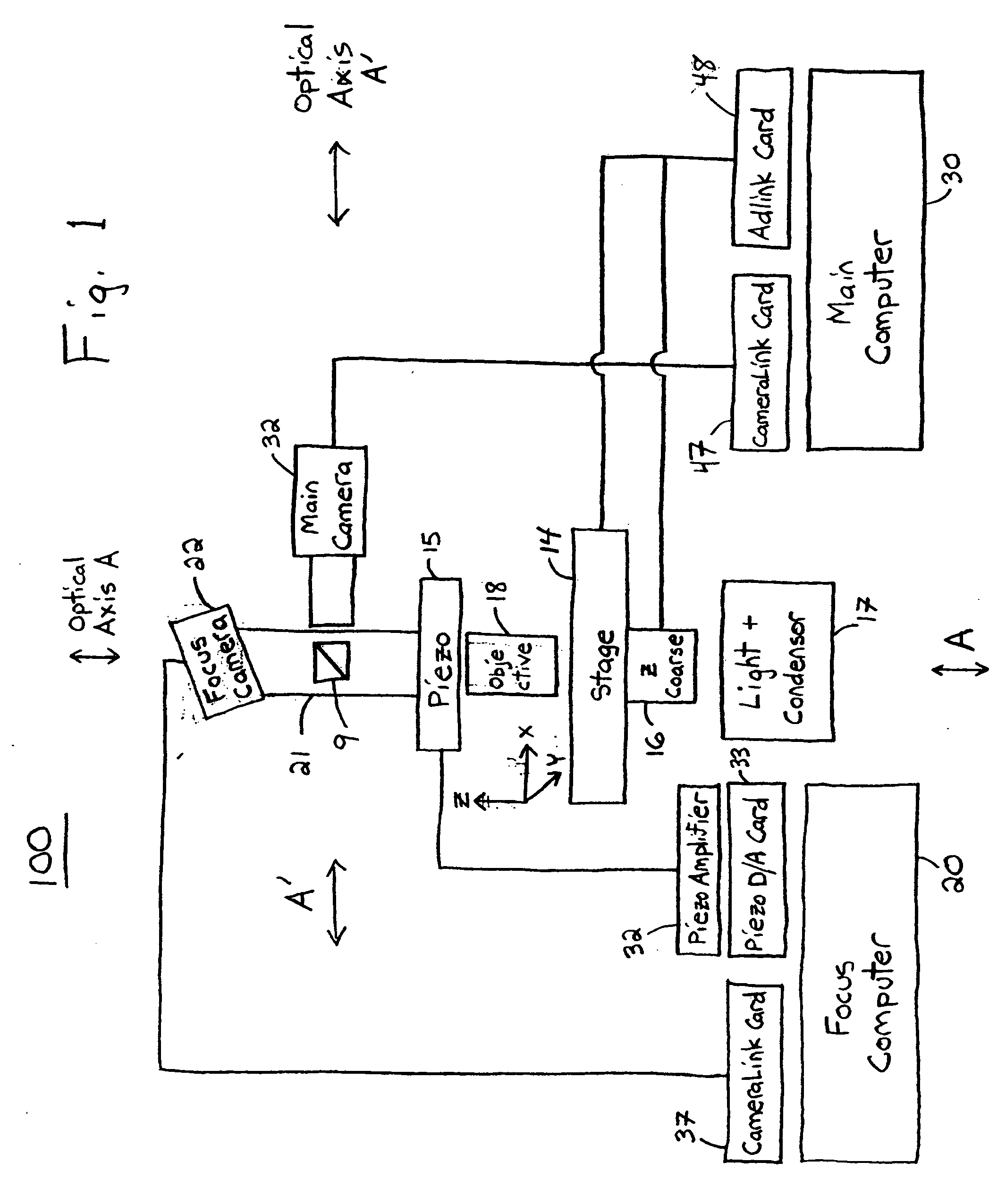
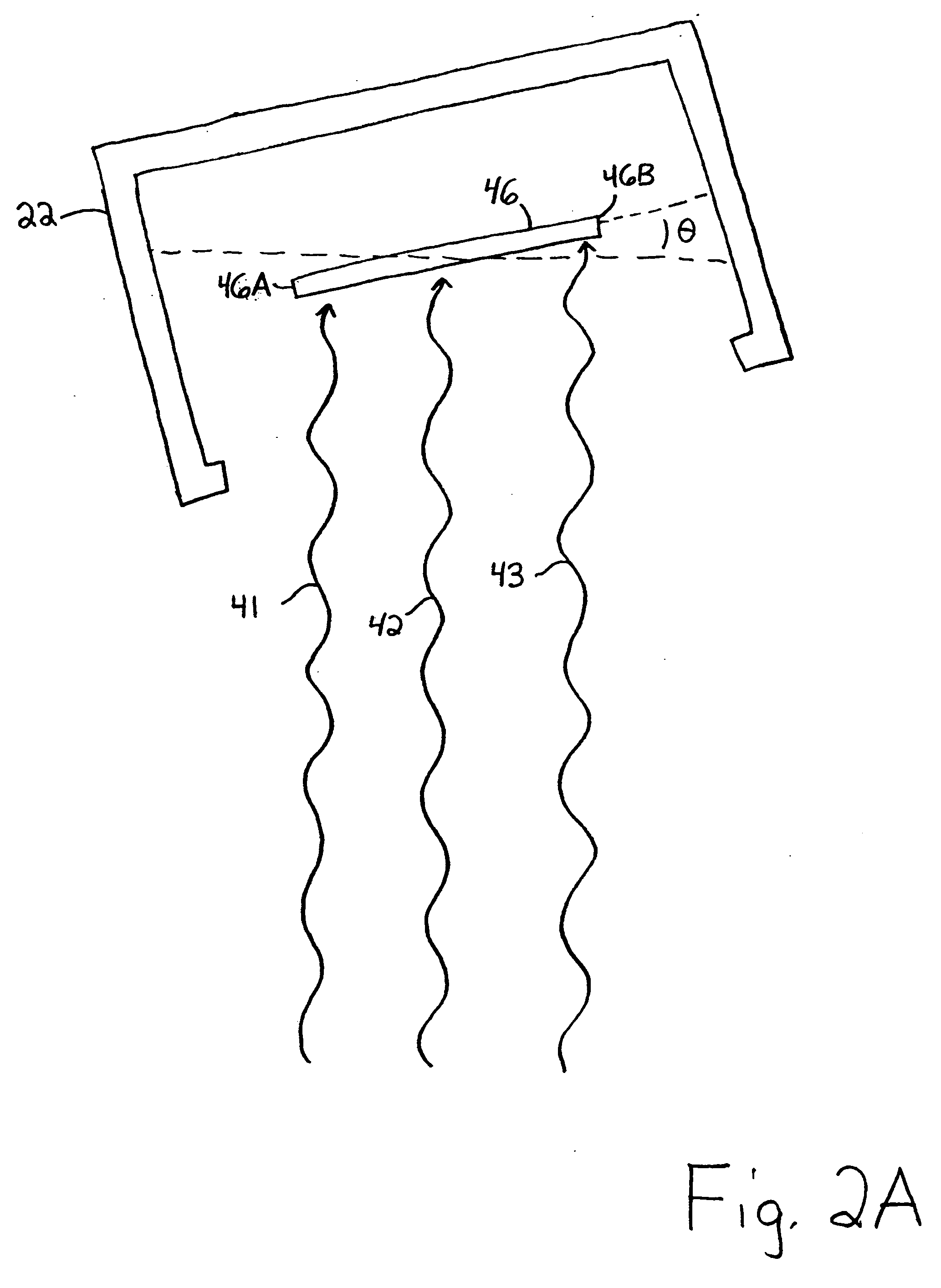
System and method for generating digital images of a microscope slide
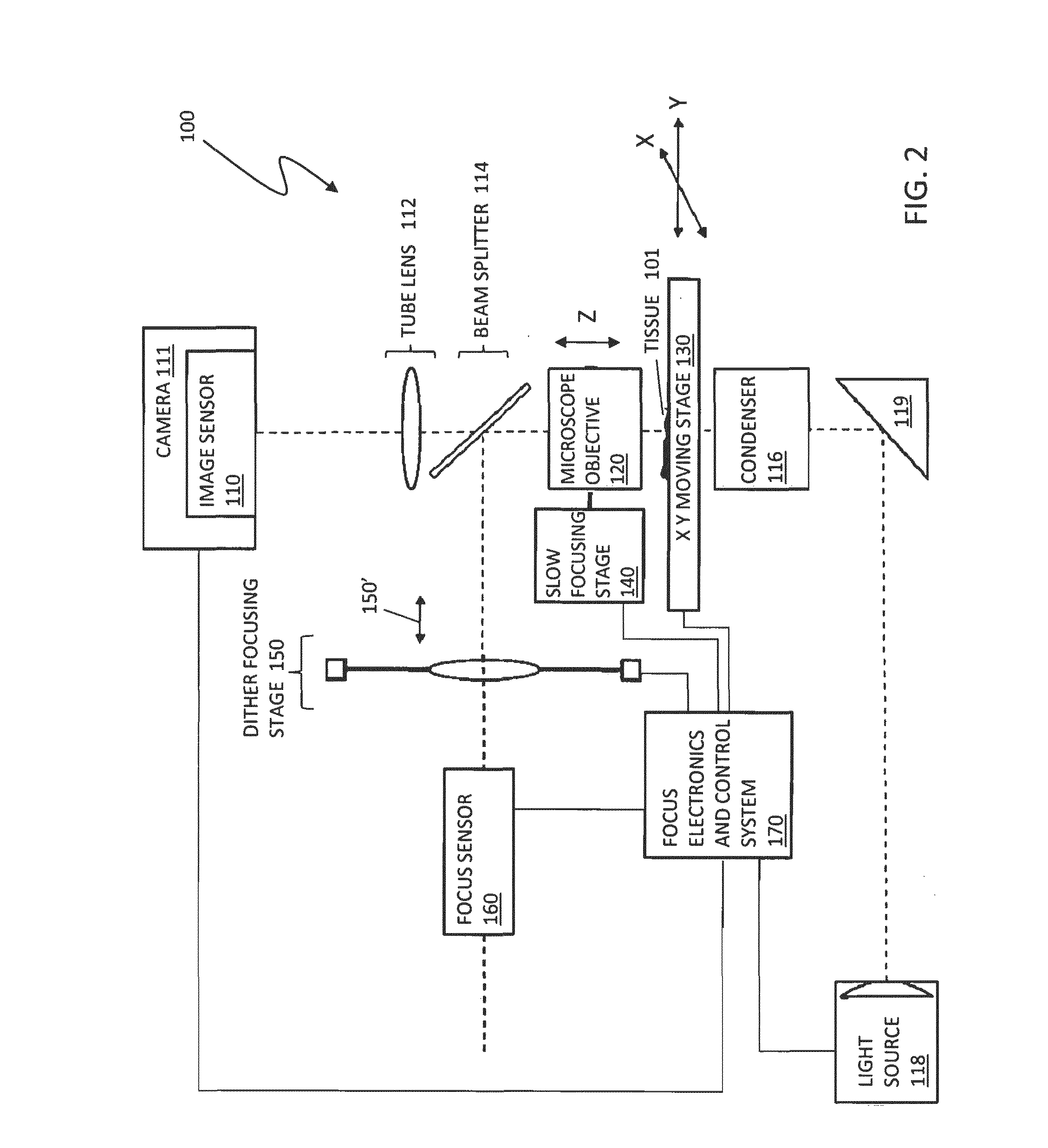
An improved system and method for obtaining images of a microscope slide are provided. In one embodiment, a focus camera includes an optical sensor that is tilted relative to the focal plane of a scanning camera. A scan of a target region is performed, and multiple overlapping images of the target region are captured from a plurality of x-y positions. Each image contains information associated with multiple focal planes. Focus information is obtained from the images, and a desired-focus position is determined for the target region based on the focus information. The scanning camera then captures an image of the target region from the desired-focus position. This procedure may be repeated for selected regions on the microscope slide and the resulting images of the respective regions are merged to create a virtual slide.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MICROIMAGING AIS
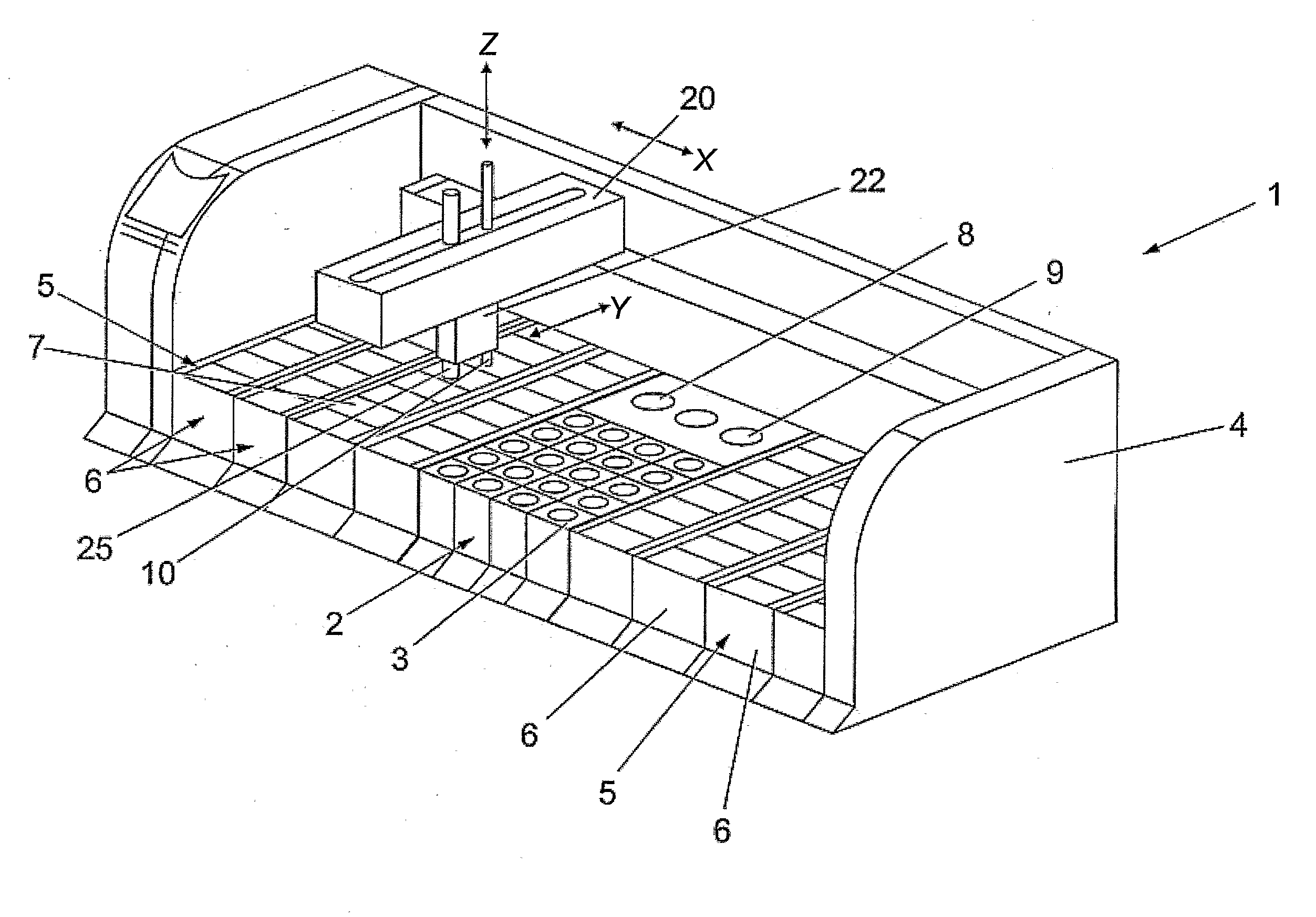
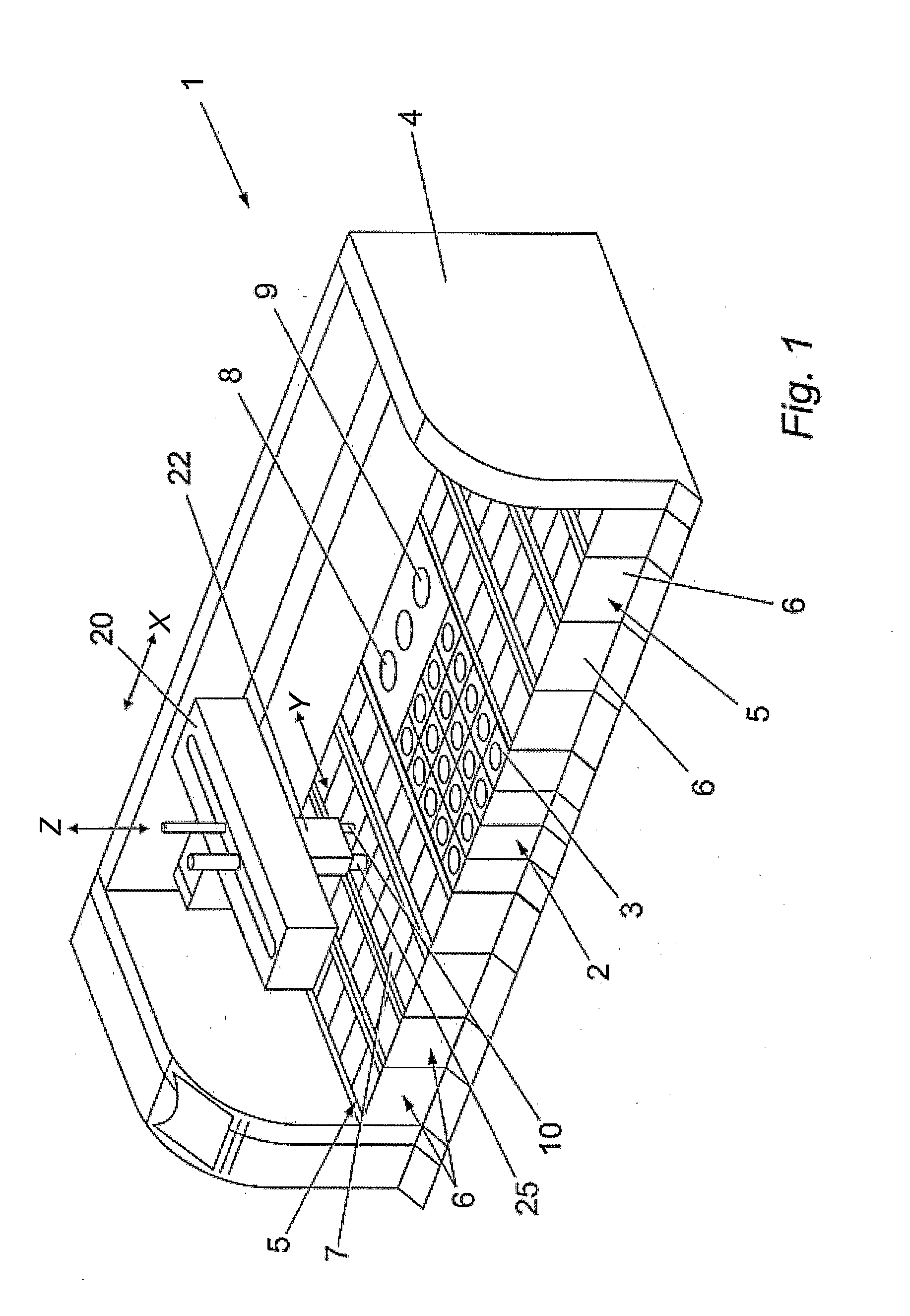
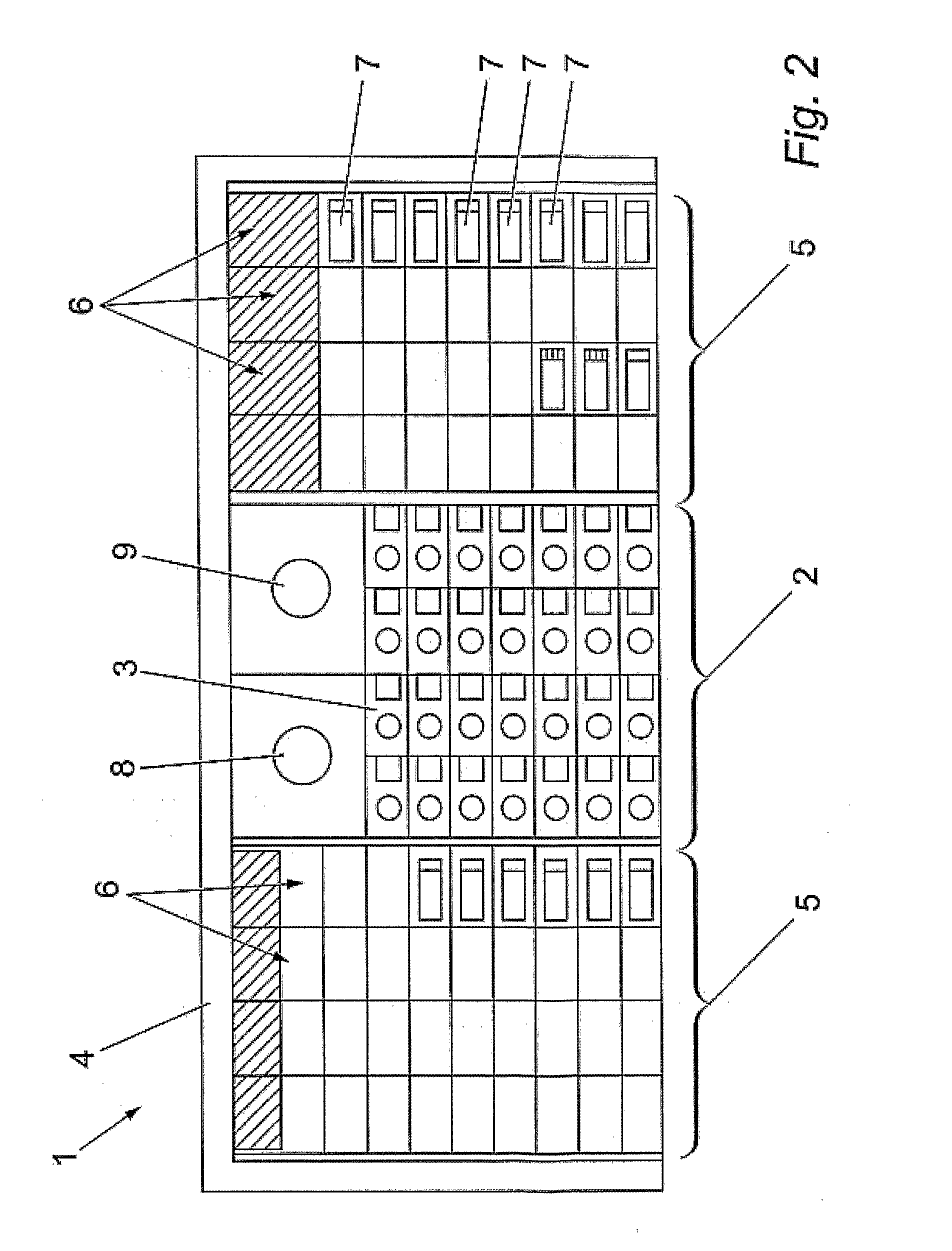
System and Method for Single Optical Axis Multi-Detector Microscope Slide Scanner
ActiveUS20070147673A1Improve scan performanceQuality improvementLaser using scattering effectsCharacter and pattern recognitionSensor arrayMicroscope slide
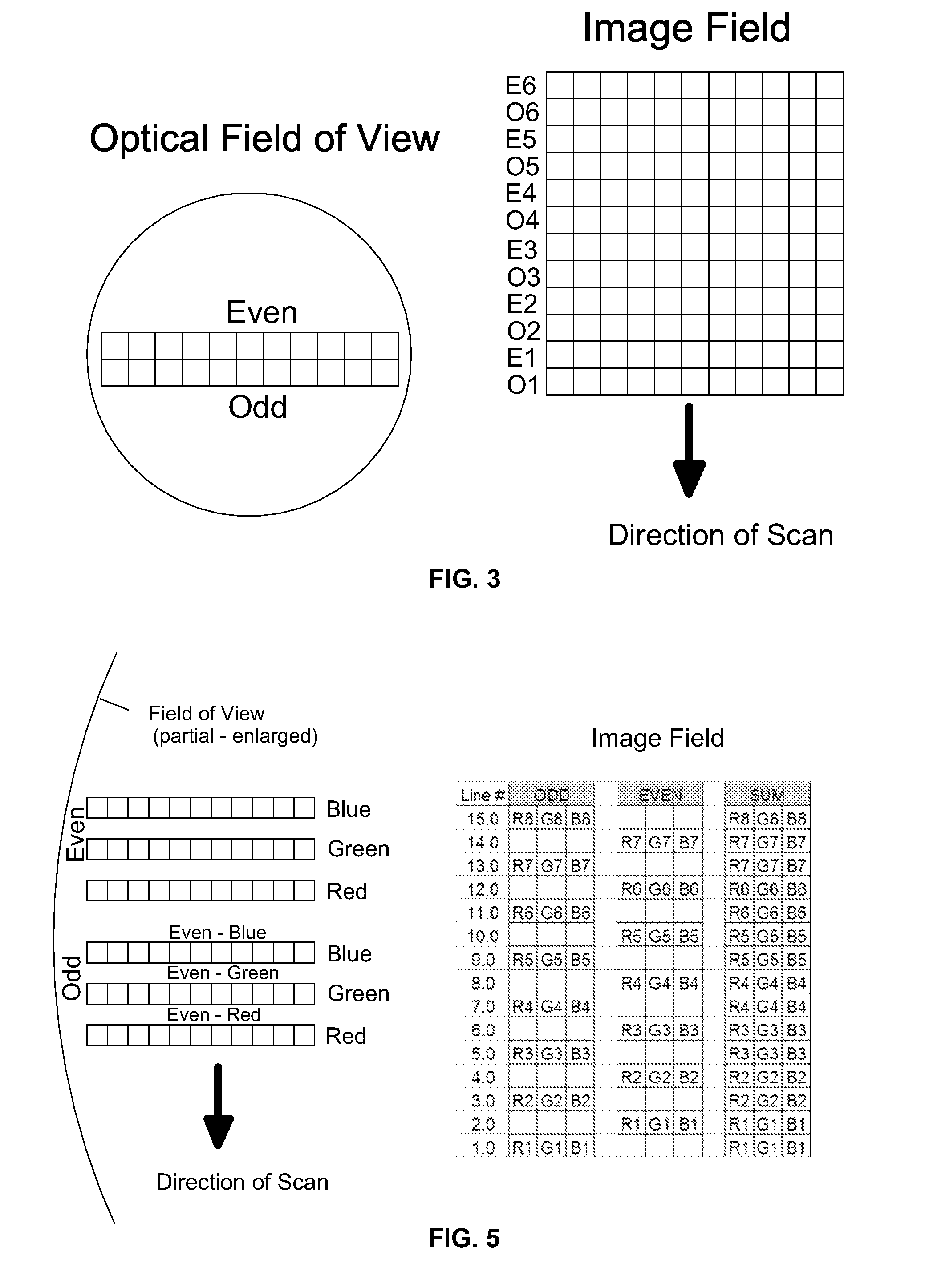
Systems and methods for microscope slide scanning using multiple sensor arrays that receive imagery data from a single optical axis are provided. A single, high quality, easily obtained microscope objective lens is used to project an image onto two or more sensor arrays. The sensor arrays can be linear or two dimensional and imaging takes place along a single optical axis. Simultaneous sensor acquisition and parallel data processing reduce the image acquisition time by a factor of N, where N represents the number of sensors employed.
Owner:LEICA BIOSYST IMAGING
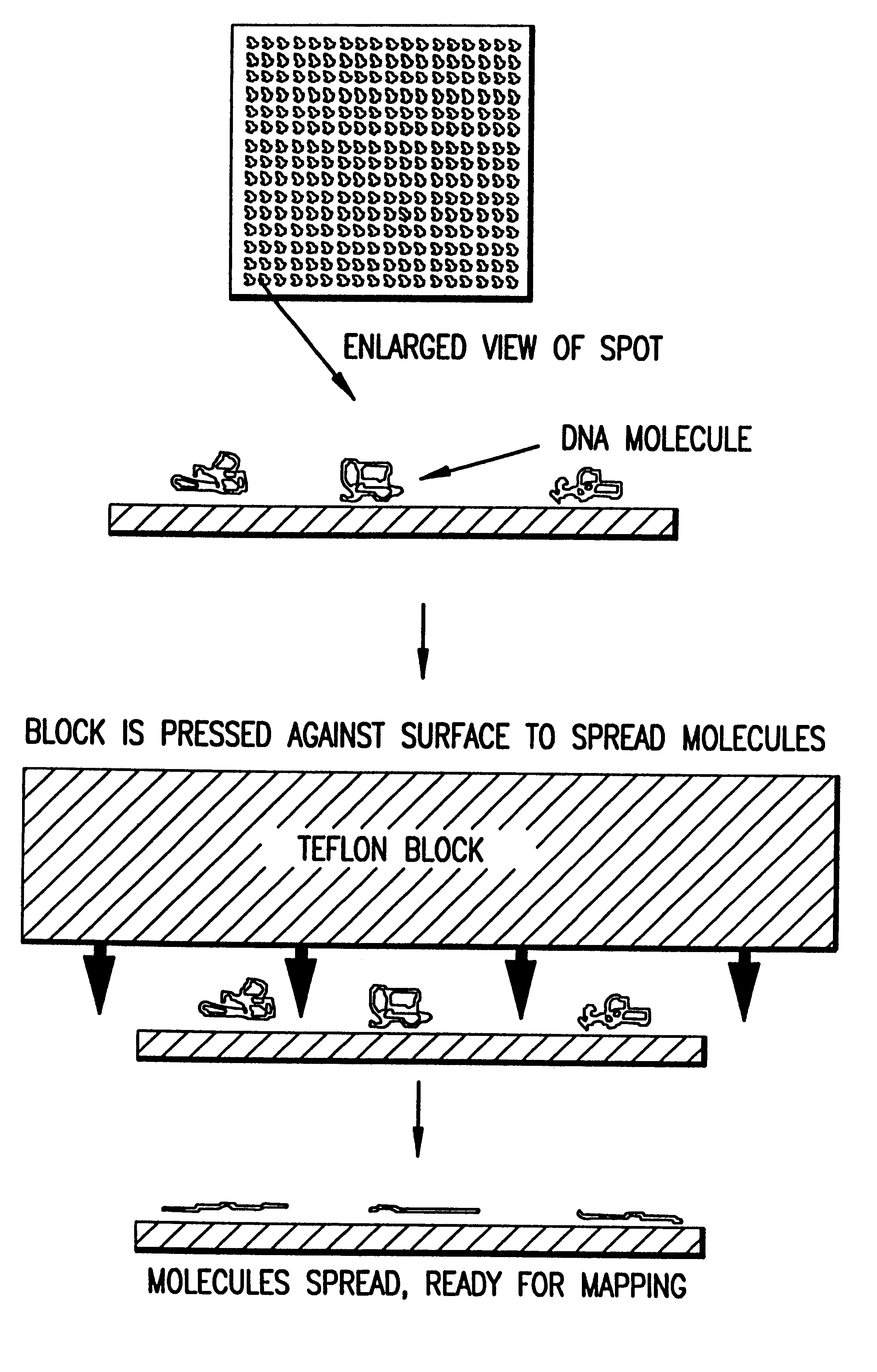
Methods and compositions for the manipulation and characterization of individual nucleic acid molecules
InactiveUS6147198AQuick analysisQuick buildSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroscope slideMap Location
A method for observing and determining the size of individual molecules and for determining the weight distribution of a sample containing molecules of varying size, which involves placing a deformable or nondeformable molecule in a medium, subjecting the molecule to an external force, thereby causing conformational and / or positional changes, and then measuring these changes. Preferred ways to measure conformational and positional changes include: (1) determining the rate at which a deformable molecule returns to a relaxed state after termination of the external force, (2) determining the rate at which a molecule becomes oriented in a new direction when the direction of the perturbing force is changed, (3) determining the rate at which a molecule rotates, (4) measuring the length of a molecule, particularly when it is at least partially stretched, or (5) measuring at least one diameter of a spherical or ellipsoidal molecule. Measurements of relaxation, reorientation, and rotation rates, as well as length and diameter can be made using a light microscope connected to an image processor. Molecule relaxation, reorientation and rotation also can be determined using a microscope combined with a spectroscopic device. The invention is particularly useful for measuring polymer molecules, such as nucleic acids, and can be used to determine the size and map location of restriction digests. Breakage of large polymer molecules mounted on a microscope slide is prevented by condensing the molecules before mounting and unfolding the molecules after they have been placed in a matrix.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Image processing and analysis of individual nucleic acid molecules
InactiveUS6294136B1Improve throughputQuick buildMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansLaboratory glasswaresMicroscope slideMap Location
A method for observing and determining the size of individual molecules and for determining the weight distribution of a sample containing molecules of varying size, which involves placing a deformable or nondeformable molecule in a medium, subjecting the molecule to an external force, thereby causing conformational and / or positional changes, and then measuring these changes. Preferred ways to measure conformational and positional changes include: (1) determining the rate at which a deformable molecule returns to a relaxed state after termination of the external force, (2) determining the rate at which a molecule becomes oriented in a new direction when the direction of the perturbing force is changed, (3) determining the rate at which a molecule rotates, (4) measuring the length of a molecule, particularly when it is at least partially stretched, or (5) measuring at least one diameter of a spherical or ellipsoidal molecule. Measurements of relaxation, reorientation, and rotation rates, as well as length and diameter can be made using a light microscope connected to an image processor. Molecule relaxation, reorientation and rotation also can be determined using a microscope combined with a spectroscopic device. The invention is particularly useful for measuring polymer molecules, such as nucleic acids, and can be used to determine the size and map location of restriction digests. Breakage of large polymer molecules mounted on a microscope slide is prevented by condensing the molecules before mounting and unfolding the molecules after they have been placed in a matrix.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
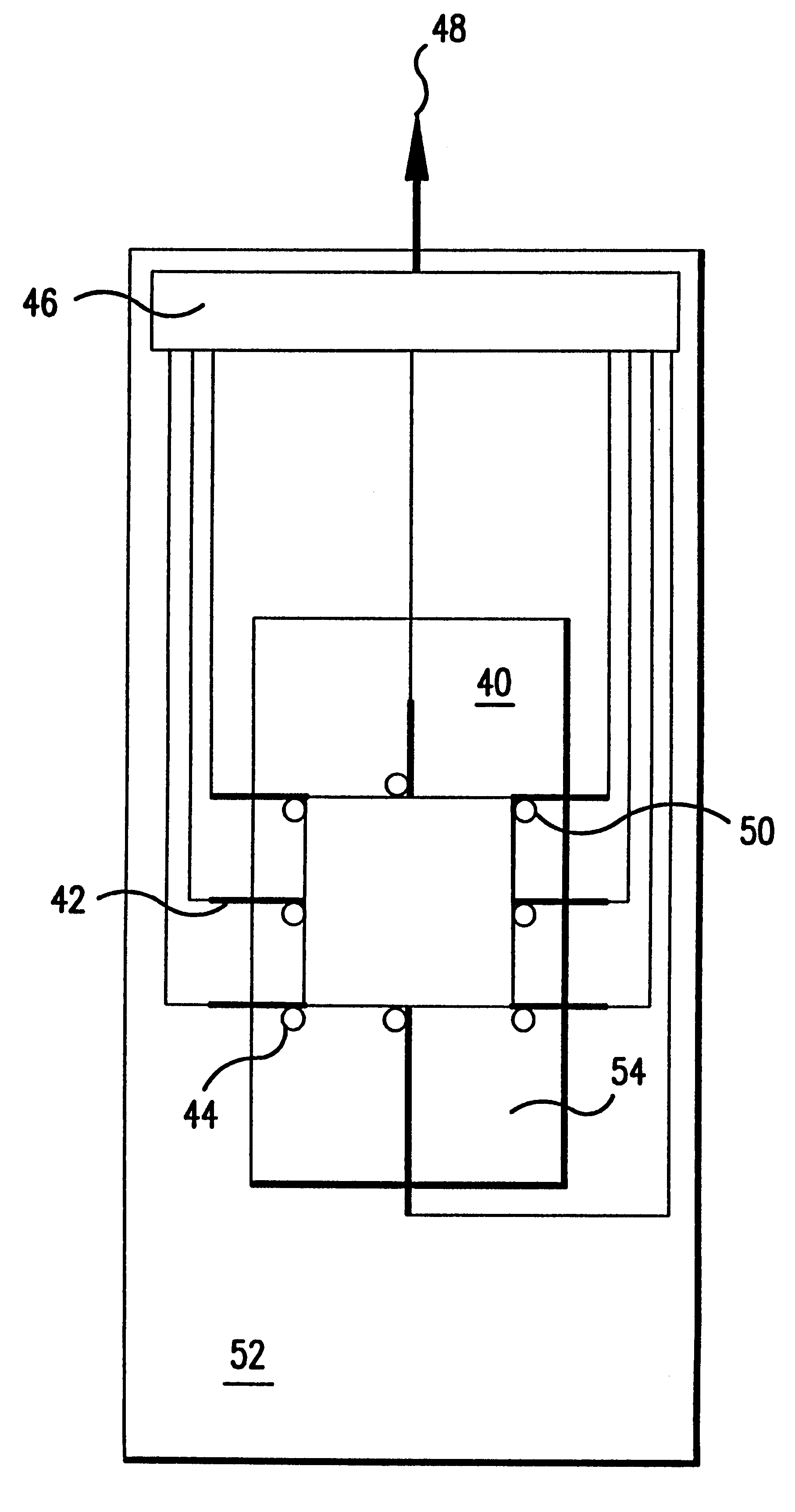
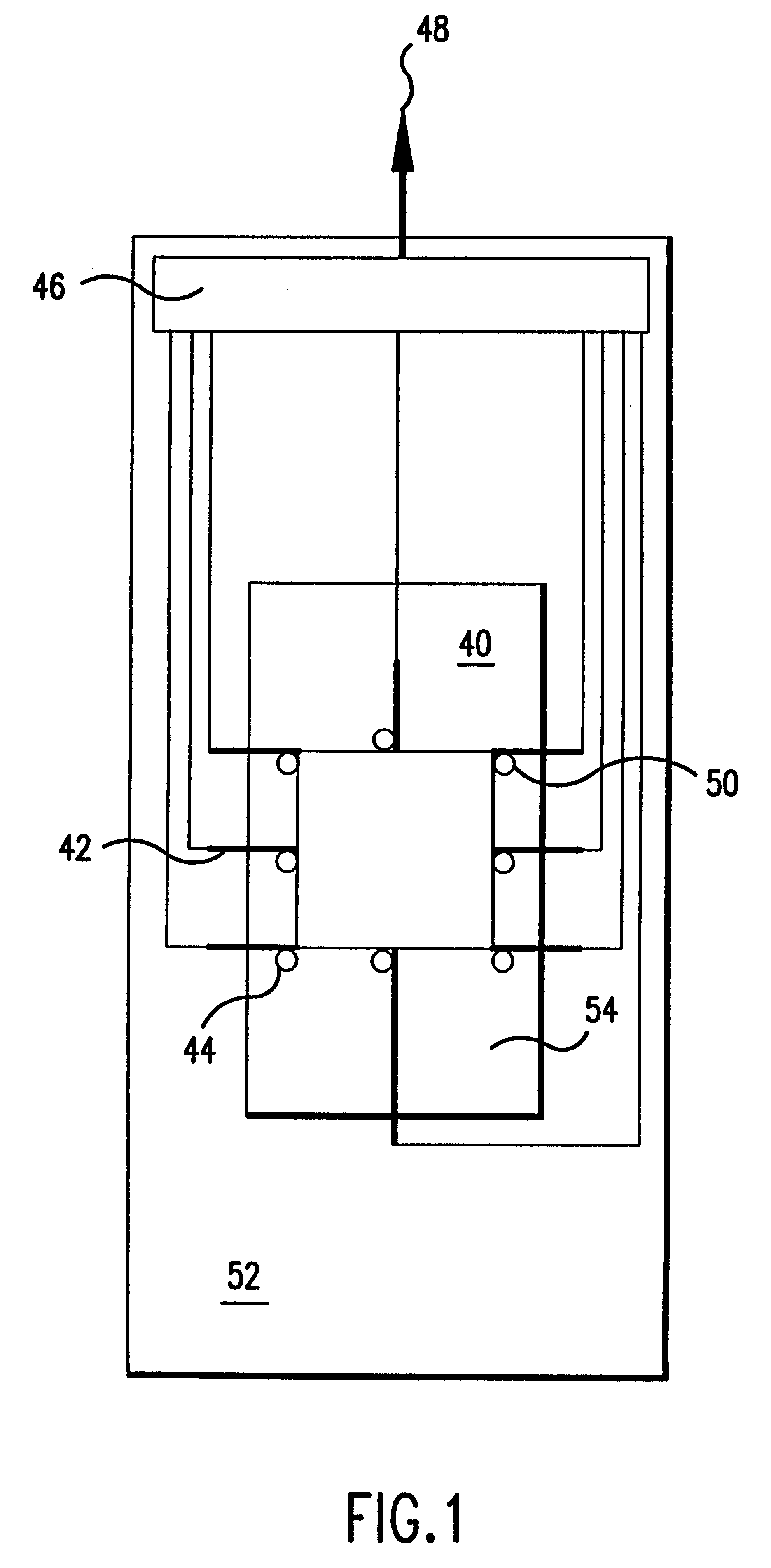
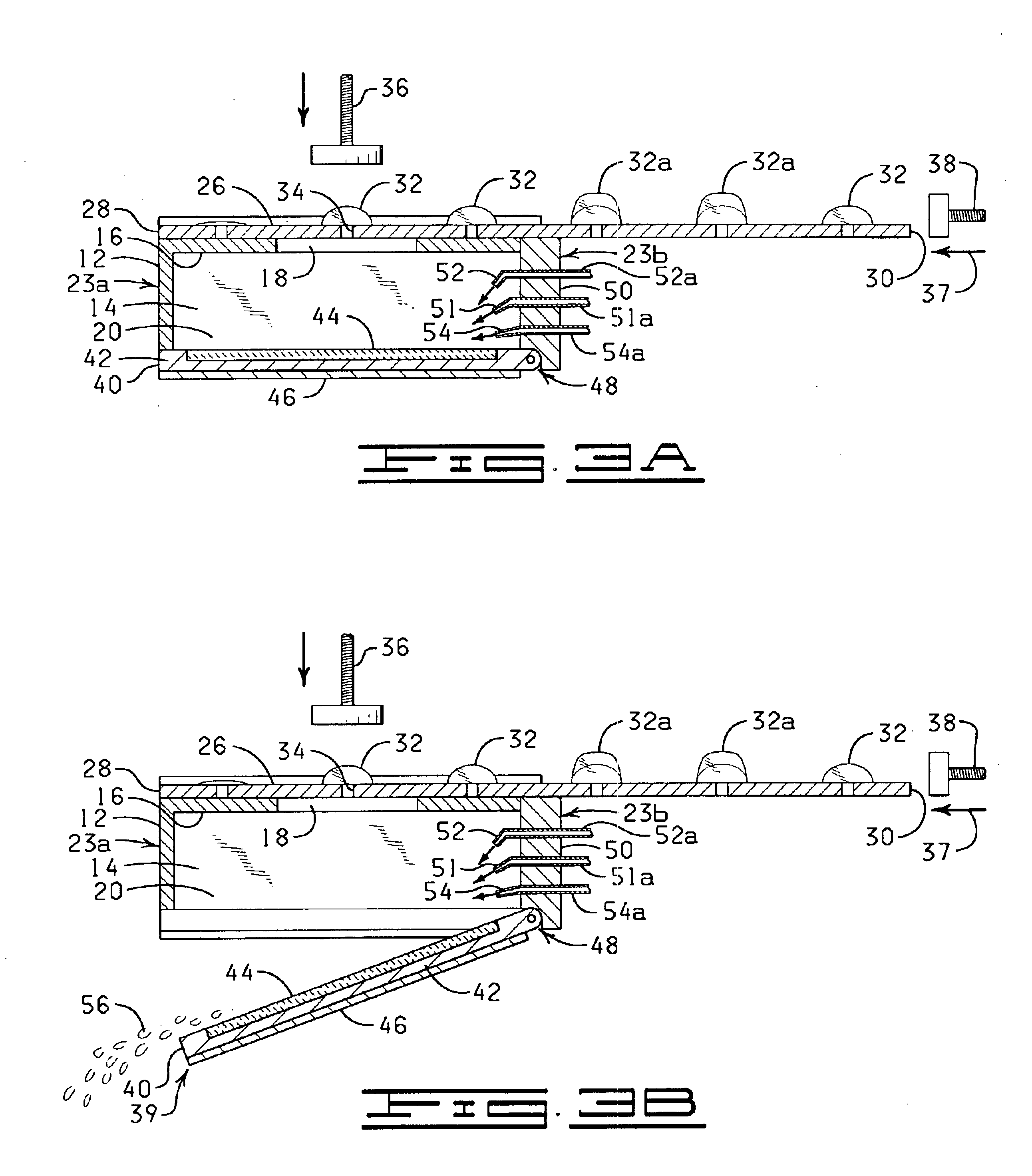
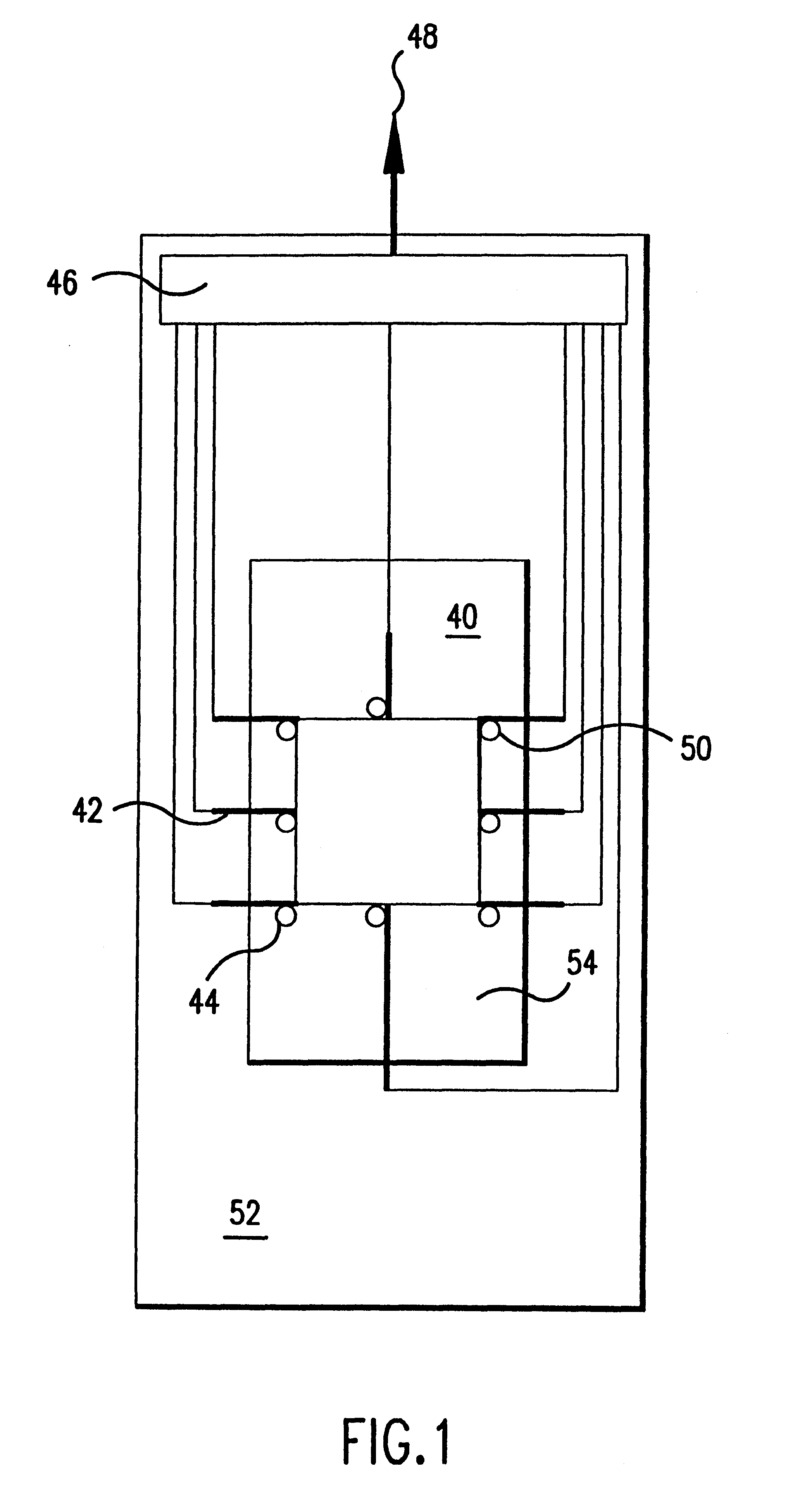
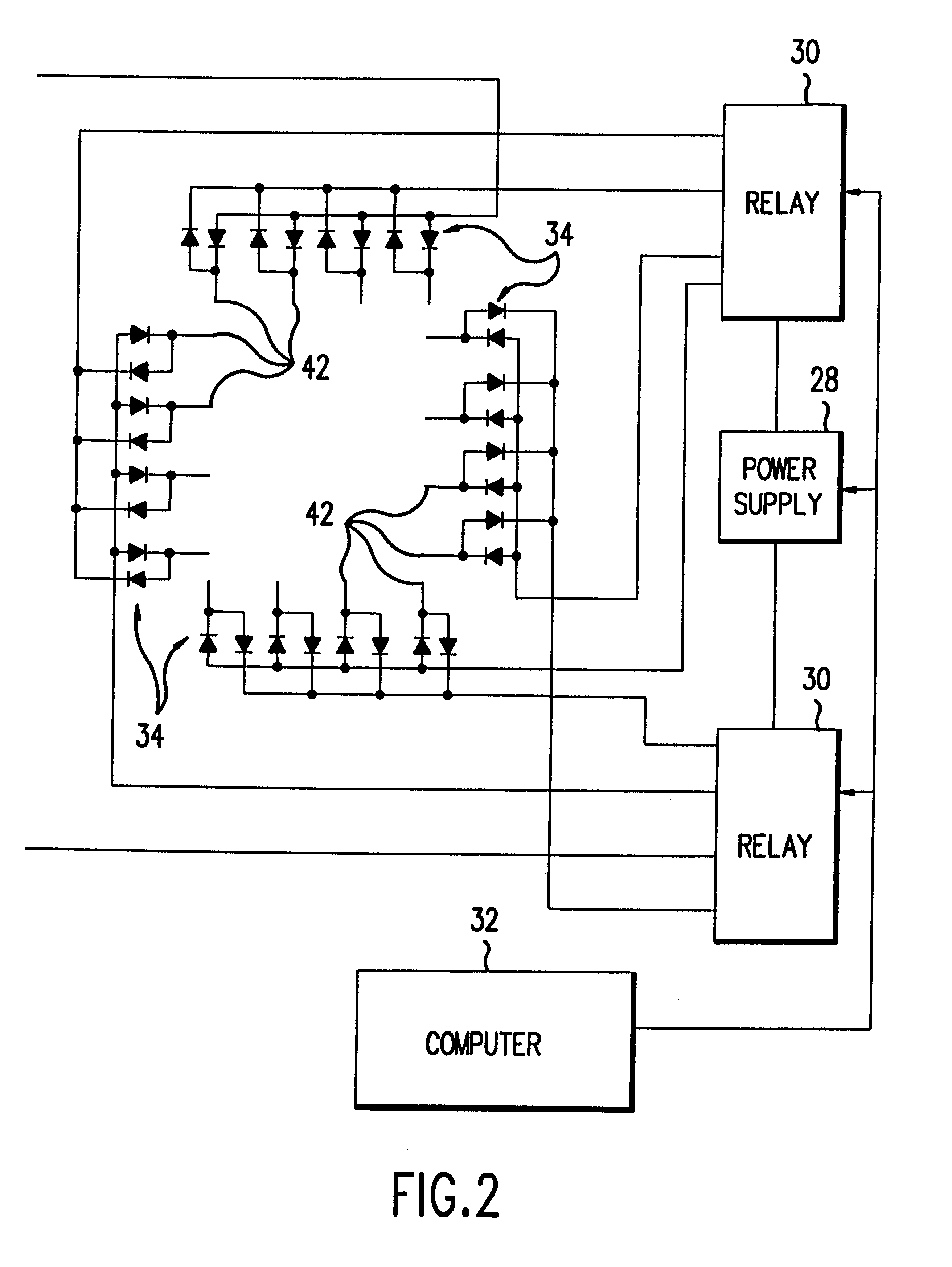
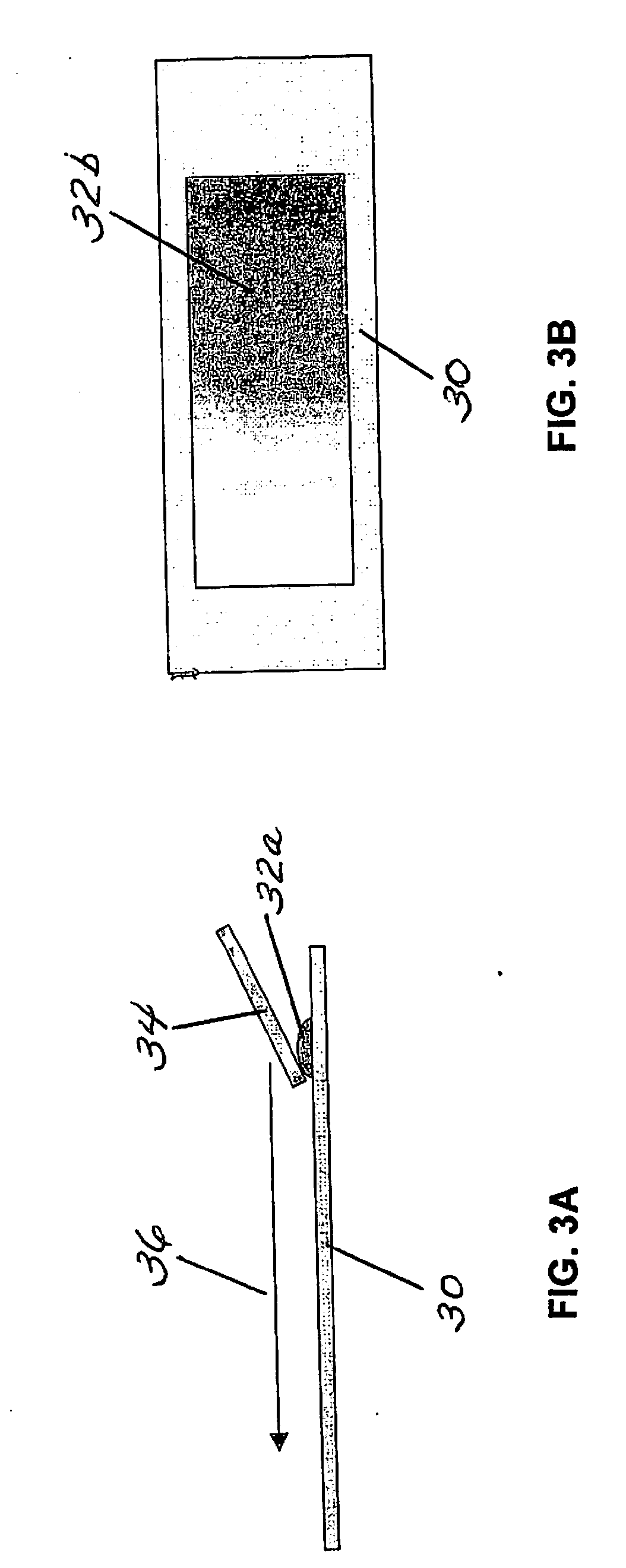
Fluid exchange in a chamber on a microscope slide
InactiveUS7318913B2Prevent evaporationOperating means/releasing devices for valvesPreparing sample for investigationMicroscope slideEngineering
A sample chamber is formed by a housing sealed against a microscope slide. The housing has fluid ports, including a well formed over at least one port. In a rinse station, rinse solution is drawn from a reservoir through the chamber to a waste reservoir. At a fill station, an aliquot of reagent already placed in the well is driven into the chamber. The reagent may be driven into the chamber by first drawing a vacuum on the chamber through the aliquot of reagent and then releasing the reagent to be drawn into the chamber by the vacuum.
Owner:DAKOAS
Image processing and analysis of individual nucleic acid molecules
InactiveUS6509158B1Quick analysisQuick buildMicrobiological testing/measurementChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceMicroscope slideMap Location
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Systems and methods for stitching image blocks to create seamless magnified images of a microscope slide
Scanned image portions of a virtual slide are stored in accord with a positional index metric associated to each image's location in a mosaic representation of the entire physical slide and a normalized correlation search is performed on next neighbor regional image blocks. A set of relative positional offset values and a correlation coefficient is determined for a regional image block and a next neighbor regional image block. A portion of the regional image blocks is viewed as a field of view of a display and a composite of the portion of regional image blocks is stitched together in accord with the set of relative positional offset values and the correlation coefficient, such that only the blocks comprising the portion are stitched. Moving the field of view of the display causes additional regional image blocks to be displayed, where image stitching is subsequently performed only with respect to the additional regional image blocks brought into the new field of view.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MICROIMAGING AIS +1
In situ heat induced antigen recovery and staining apparatus and method
InactiveUS6855292B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAntigenMicroscope slide
An automated in situ heat induced antigen recovery and staining method and apparatus for treating a plurality of microscope slides. The process of heat induced antigen recovery and the process of staining the biological sample on the microscope slide are conducted in the same apparatus, wherein the microscope slides do not need to by physically removed from one apparatus to another. Each treatment step occurs within the same reaction compartment. The reaction conditions of each reaction compartment for treating a slide can preferably be controlled independently, including the individualized application of reagents to each slide and the individualized treatment of each slide. The reagents are preferably held in a reagent dispensing strip similar to a “blister pack”.
Owner:ANGROS LEE
Image processing and analysis of individual nucleic acid molecules
InactiveUS6610256B2Quick analysisQuick buildBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMicroscope slideImaging processing
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
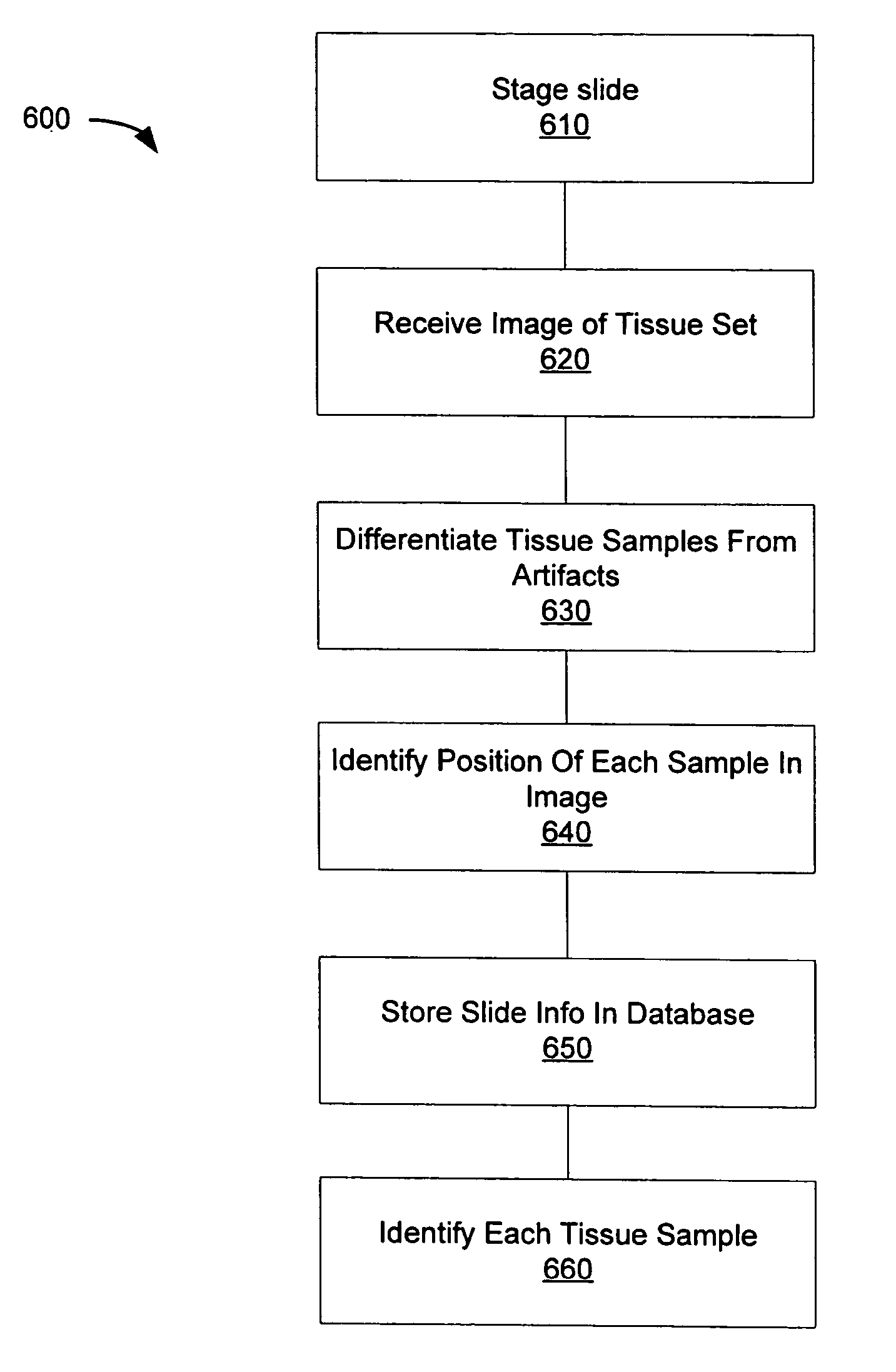
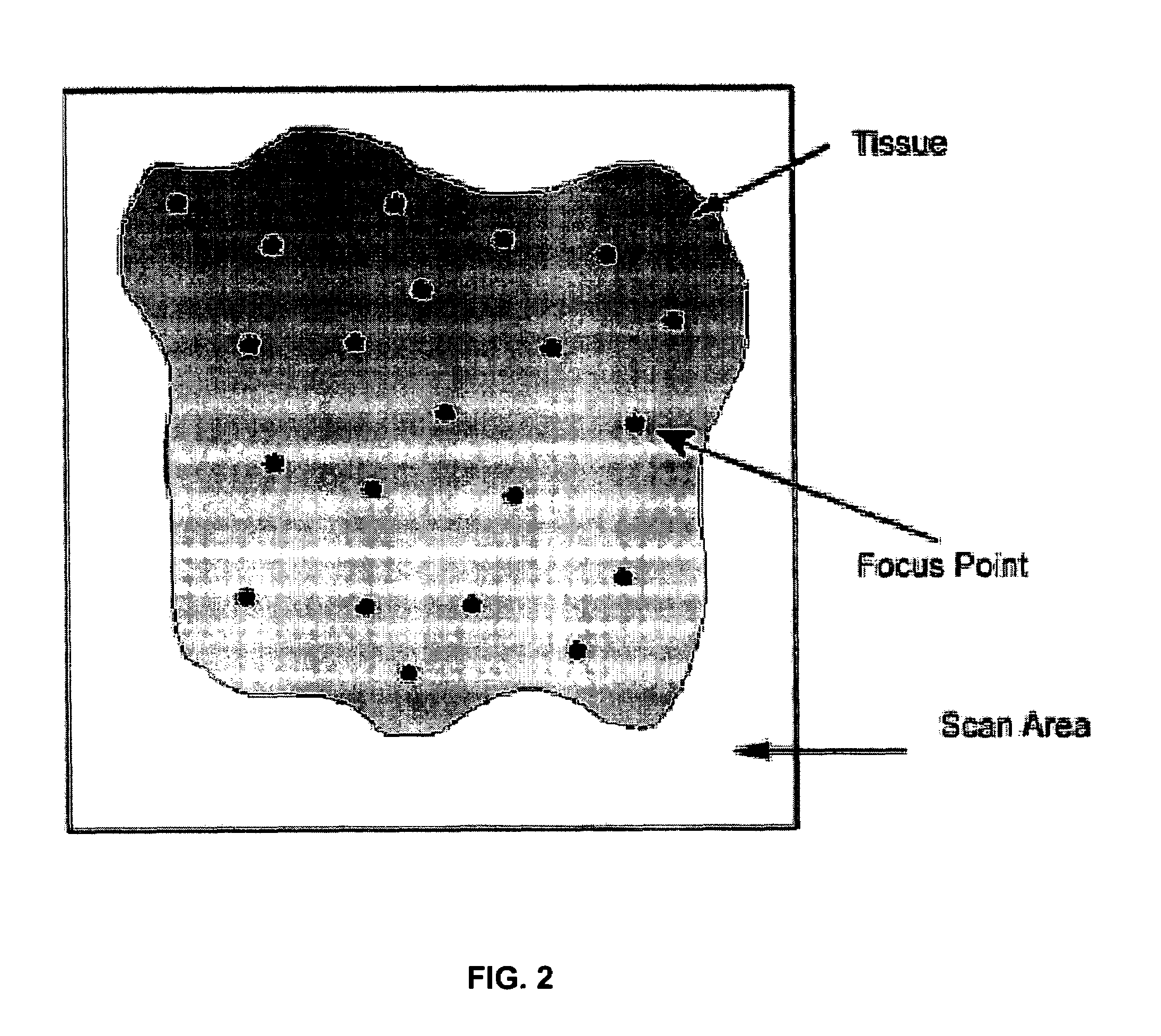
Automated microscope slide tissue sample mapping and image acquisition
A method comprises receiving an image of a tissue-sample set. A position in the image of each tissue sample relative to at least one other tissue sample is electronically identified. Each tissue sample is electronically identified based on the tissue sample position identification.
Owner:THE CHAMBERLAIN GRP INC +1
Method for performing a blood count and determining the morphology of a blood smear
InactiveUS20110151502A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMicroscope slideStaining
A method for counting blood cells in a sample of whole blood. The method comprises the steps of:(a) providing a sample of whole blood;(b) depositing the sample of whole blood onto a slide, e.g., a microscope slide;(c) employing a spreader to create a blood smear;(d) allowing the blood smear to dry on the slide;(e) measuring absorption or reflectance of light attributable to the hemoglobin in the red blood cells in the blood smear on the slide;(f) recording a magnified two-dimensional digital image of the area of analysis identified by the measurement in step (e) as being of suitable thickness for analysis; and(g) collecting, analyzing, and storing data from the magnified two-dimensional digital image.Optionally, steps of fixing and staining of blood cells on the slide can be employed in the method.
Owner:ABBOTT LAB INC
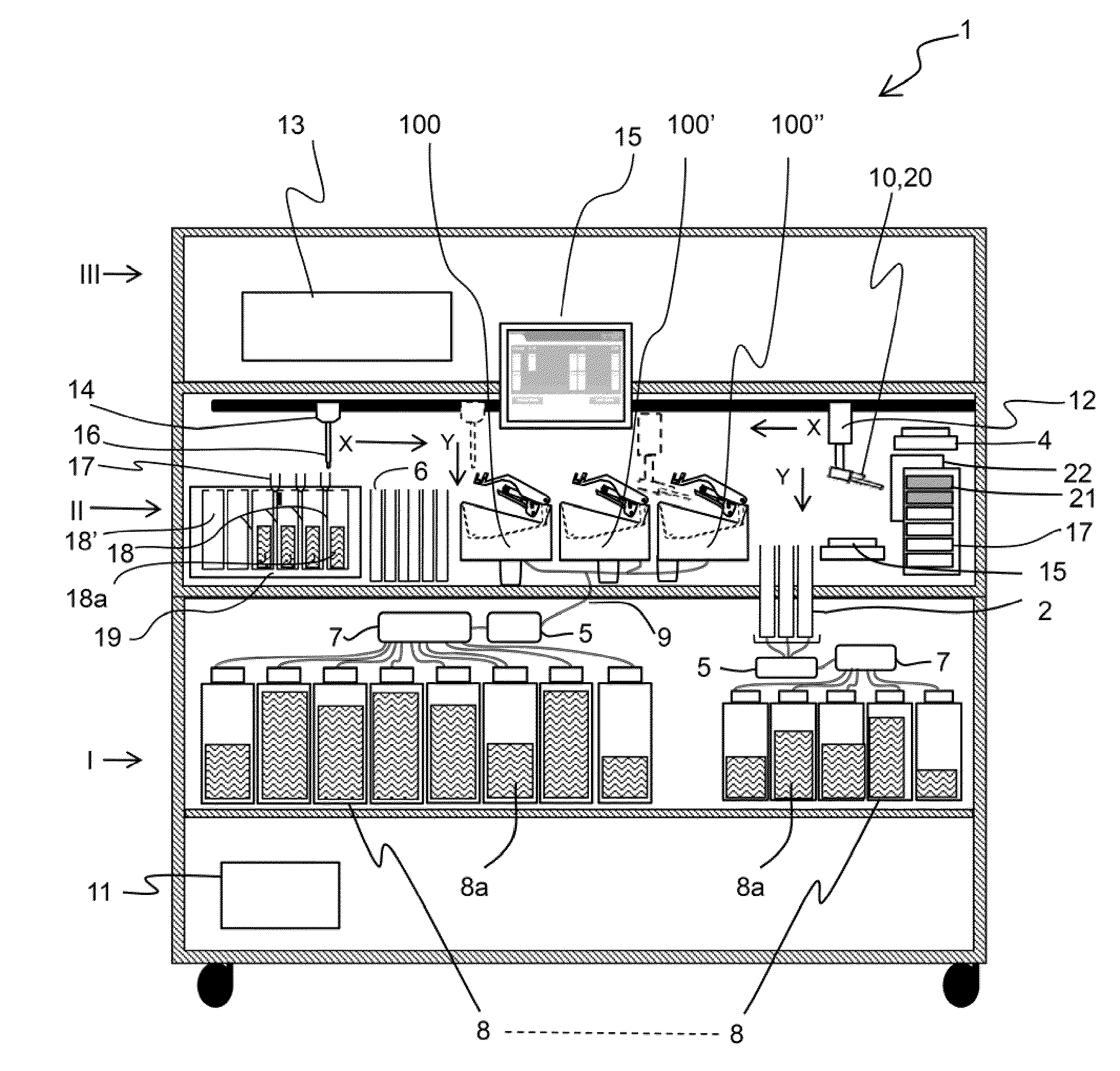
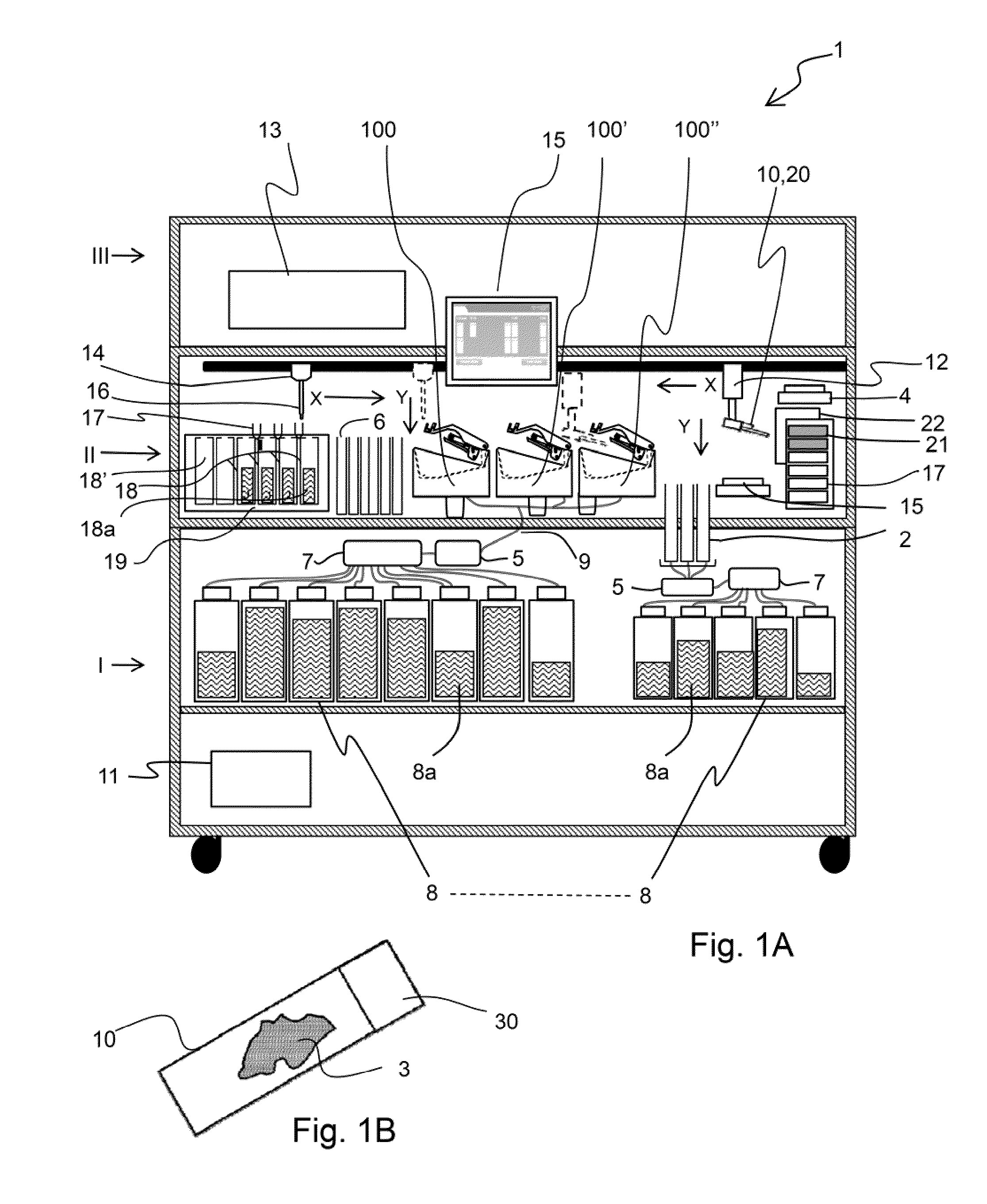
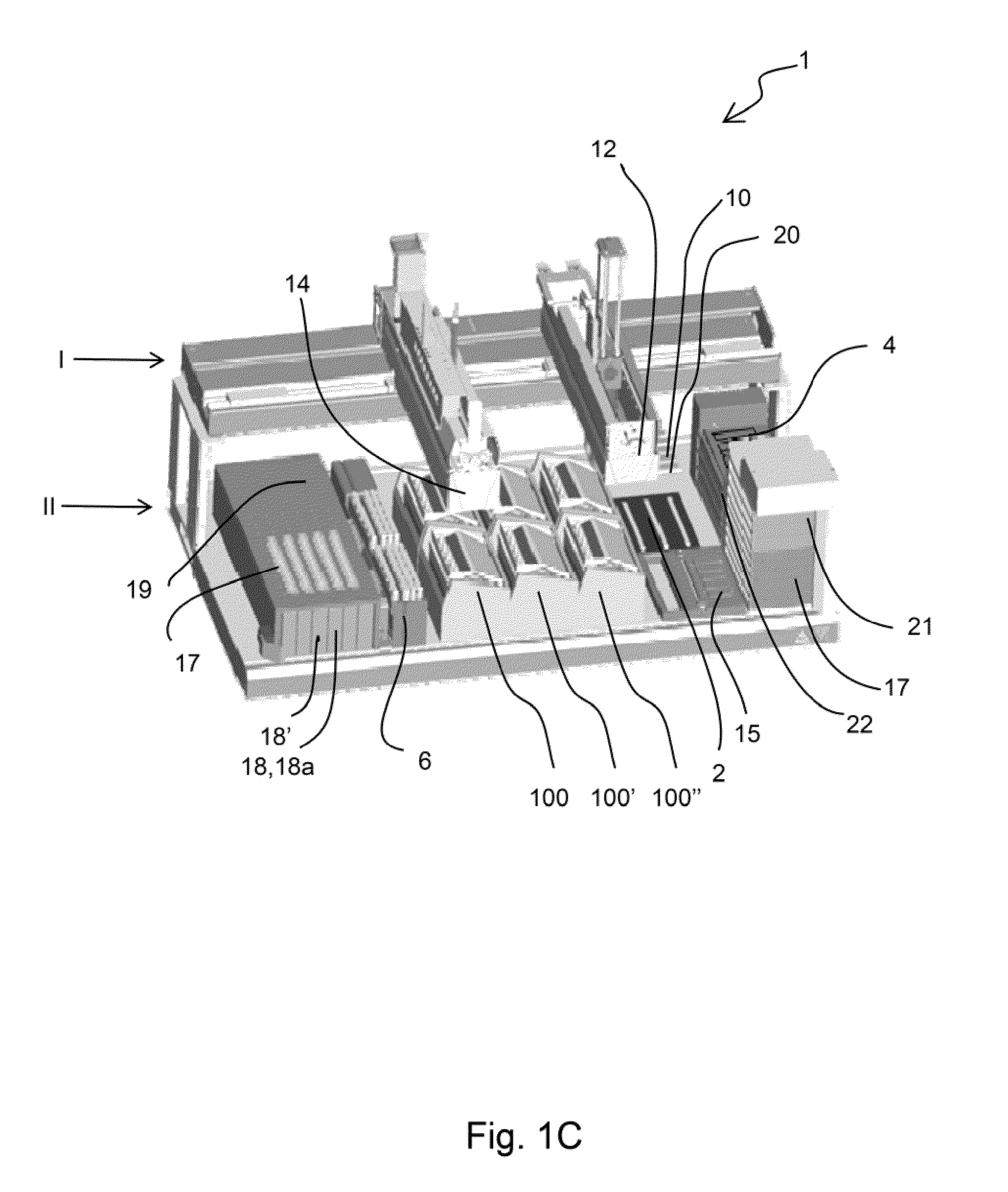
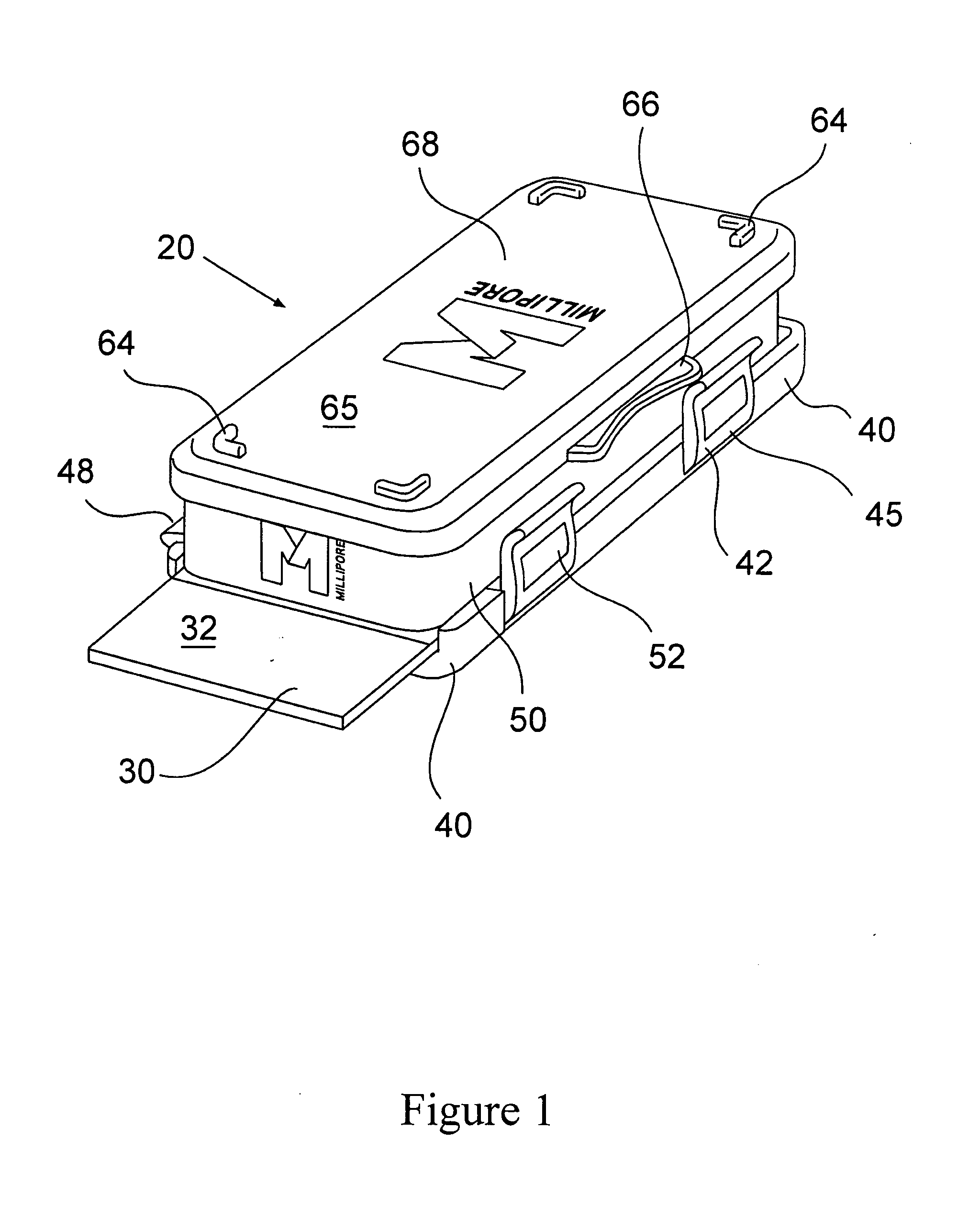
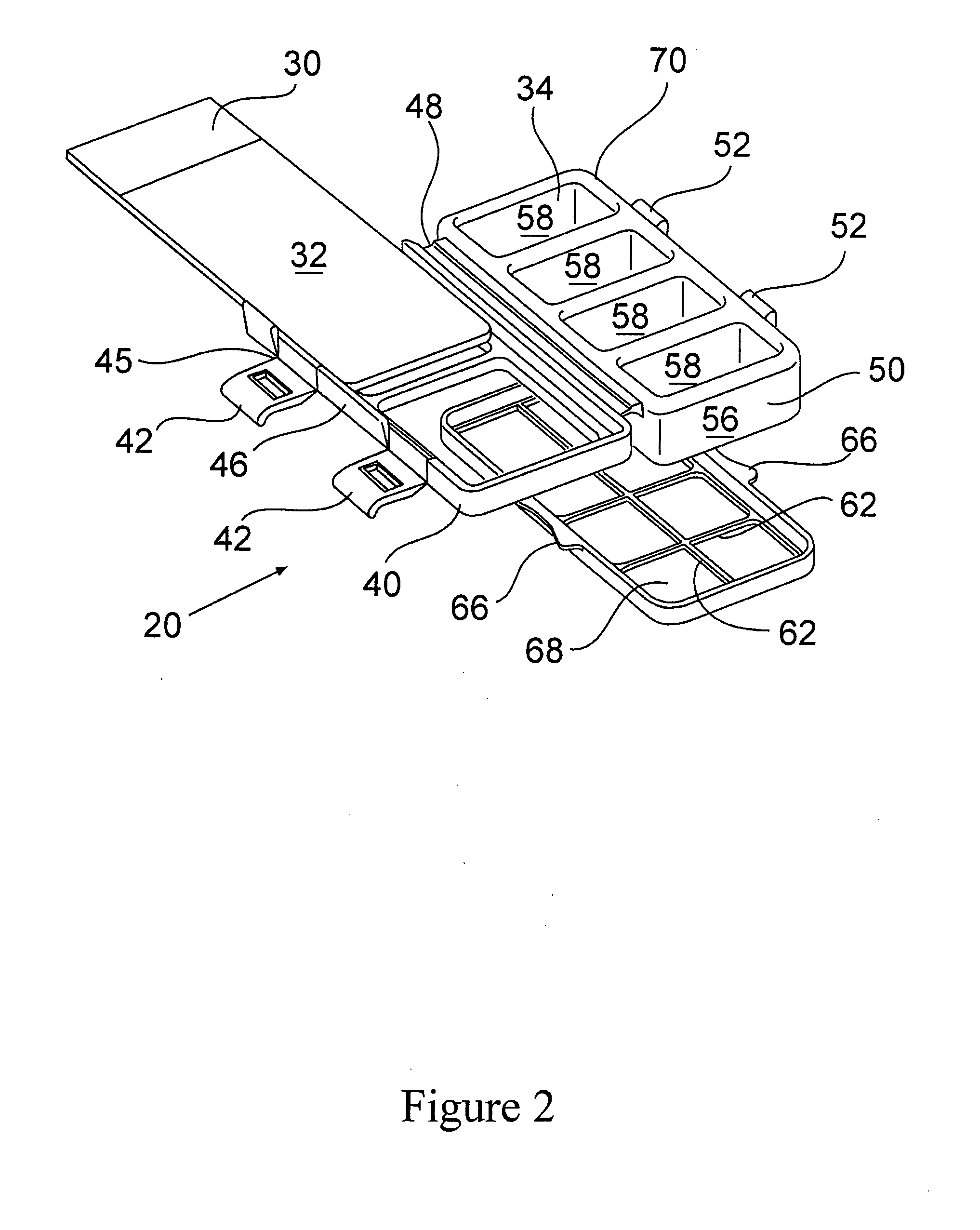
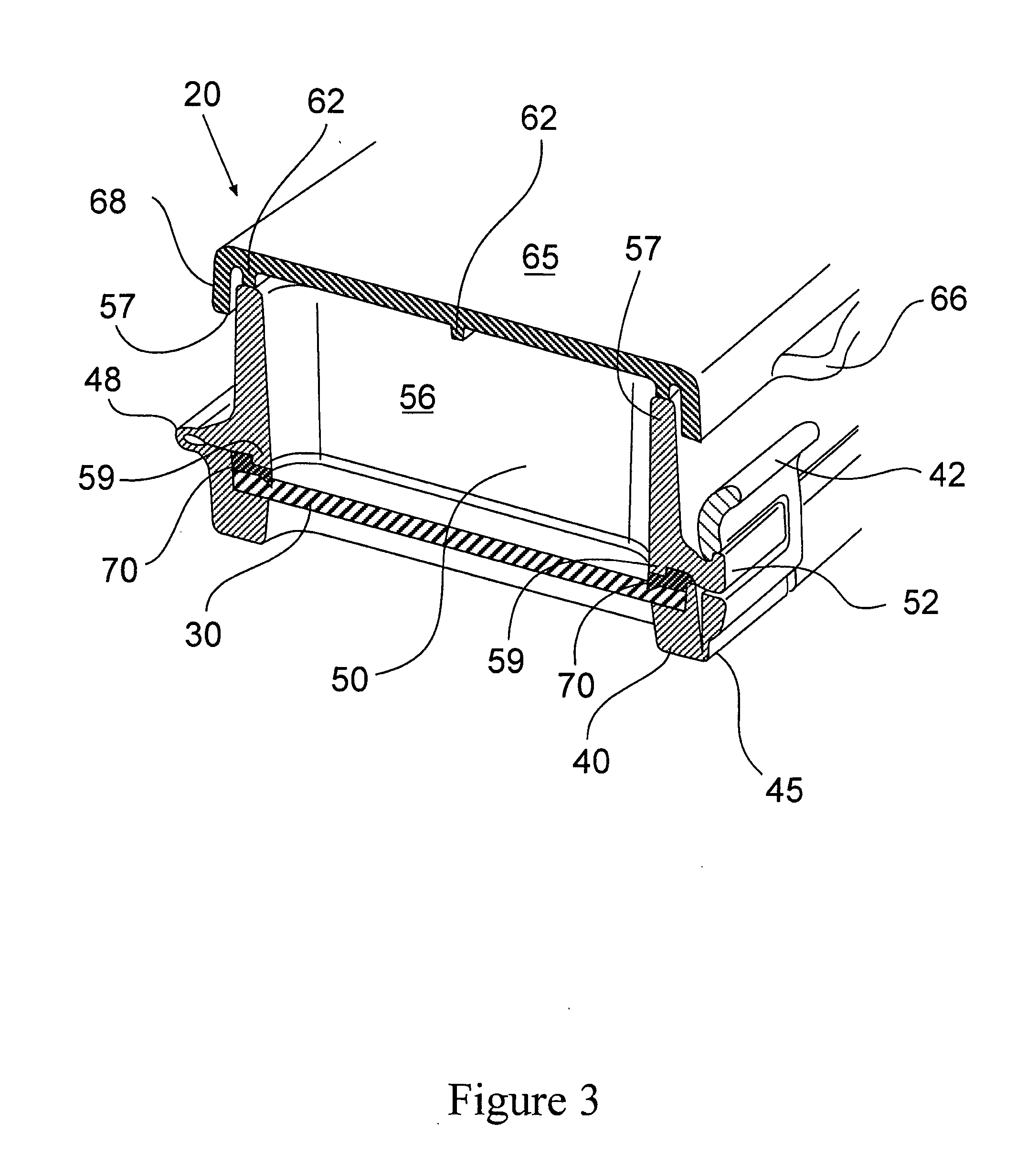
Imaging systems, cassettes, and methods of using the same
InactiveUS20140178169A1Restrict movementOther accessoriesContainer/bottle contructionMicroscope slideWorkstation
A microscope slide holding cassette includes a main body for surrounding and protecting microscopes, and shelves capable of holding the microscope slides. The shelves have support members that extend outwardly in order to support label ends of slides. Catches carried at the end of the support members are capable of limiting movement of the slides during transport of the cassette. To transport slides to different workstations, a pickup device can use a vacuum to pick up a slide without contacting areas of the slide that may have glue. The pickup device can load and unload the cassette. The pickup device can have a low-profile configuration in order to access relatively small spaces for processing flexibility.
Owner:VENTANA MEDICAL SYST INC
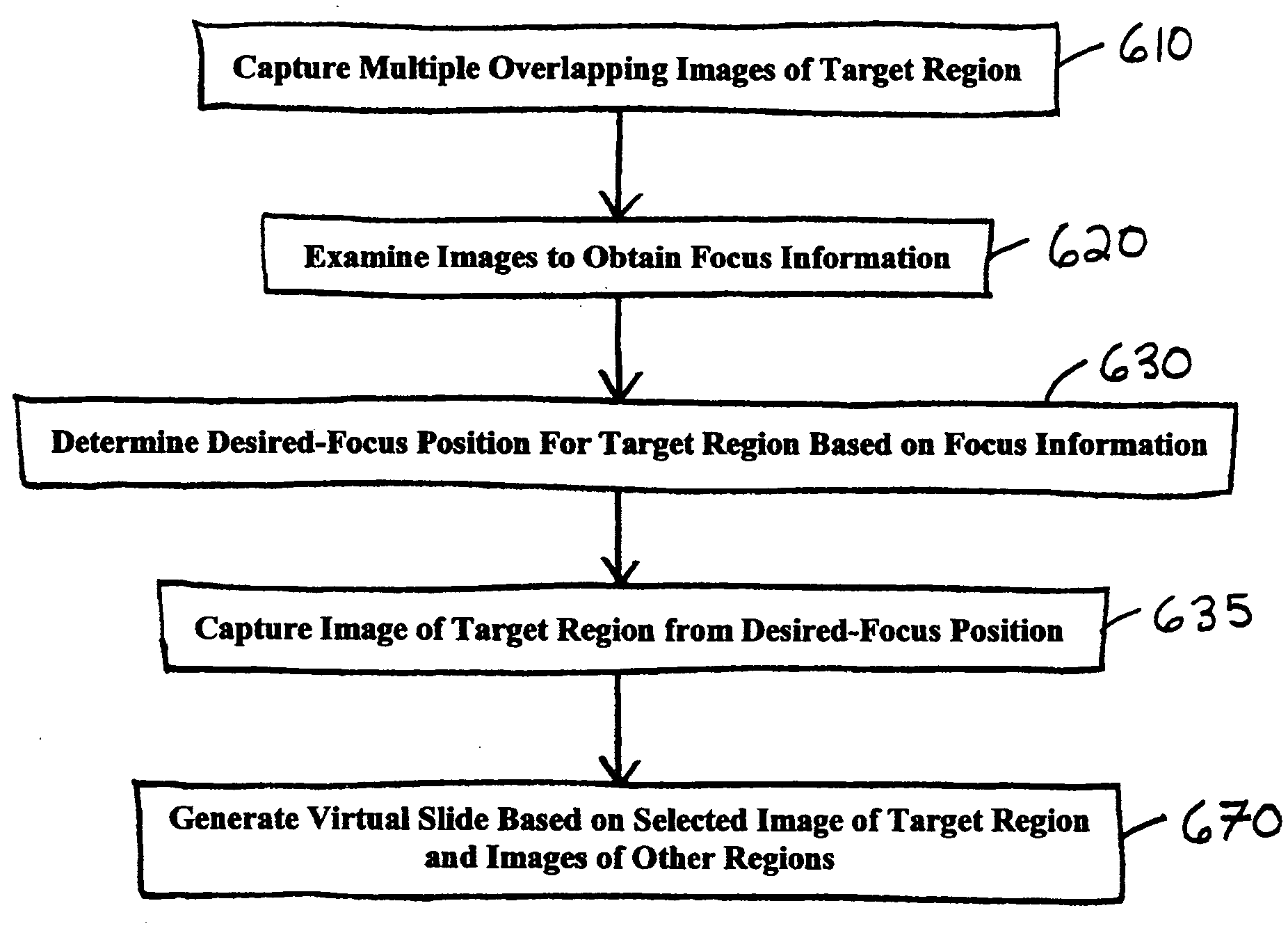
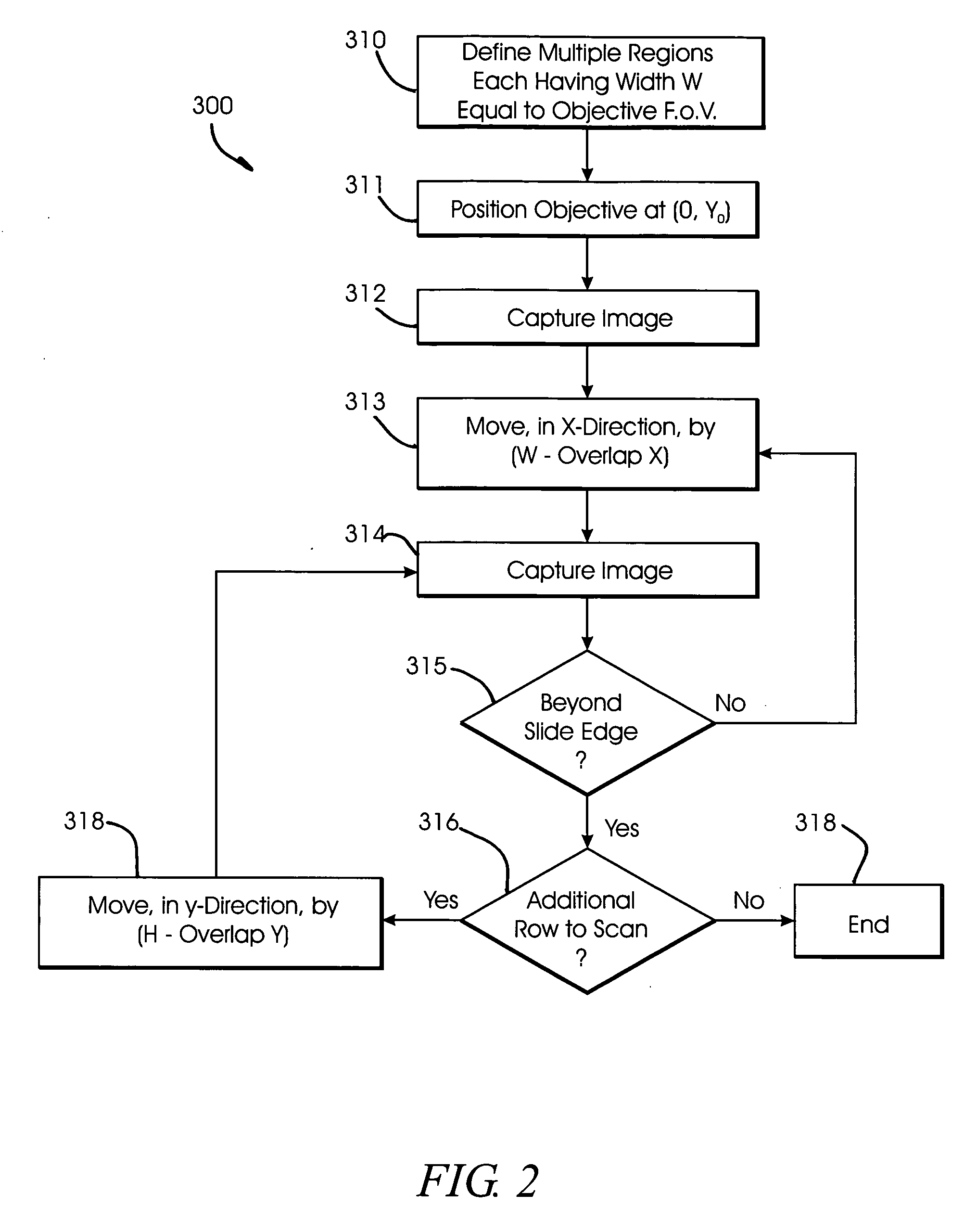
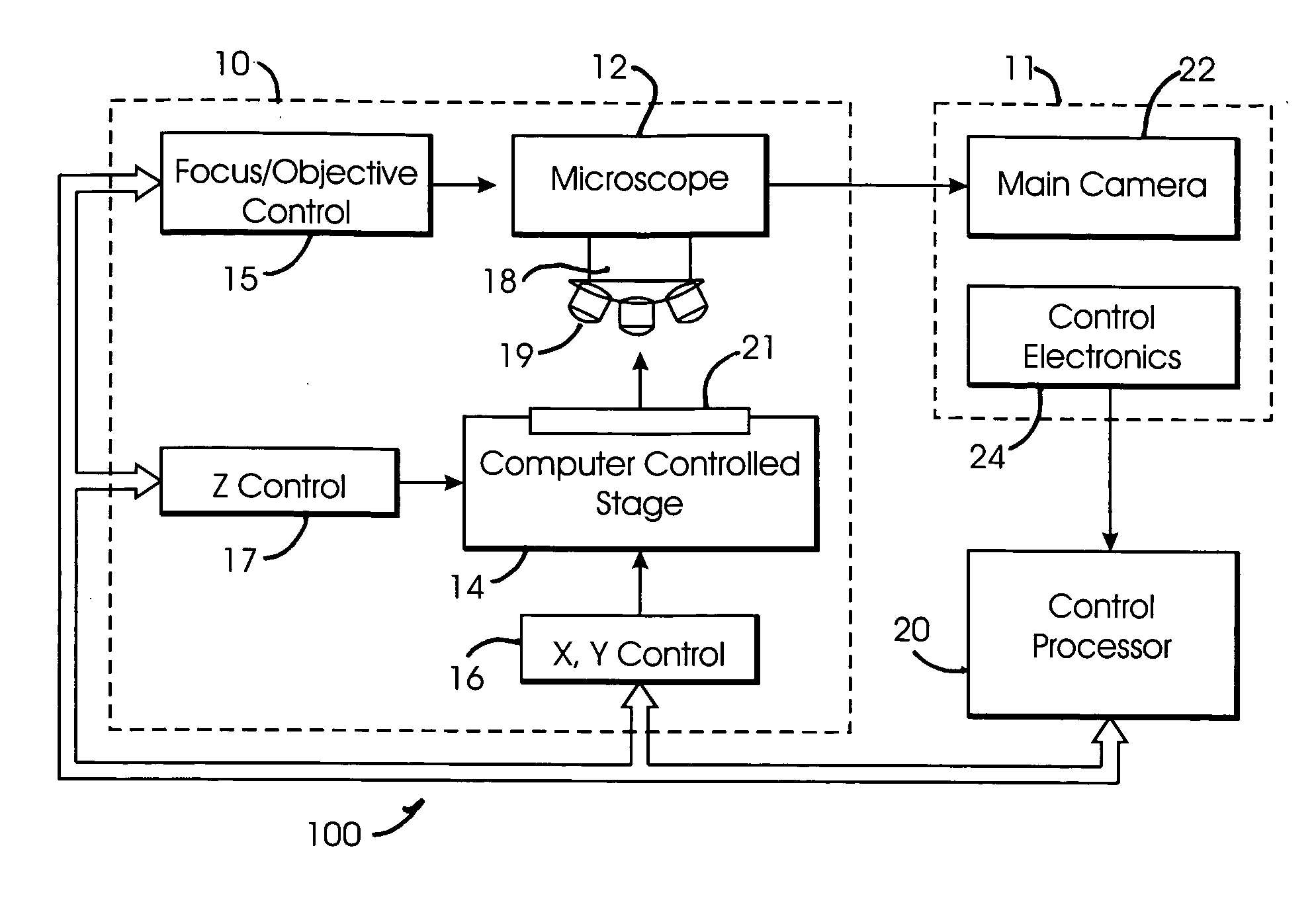
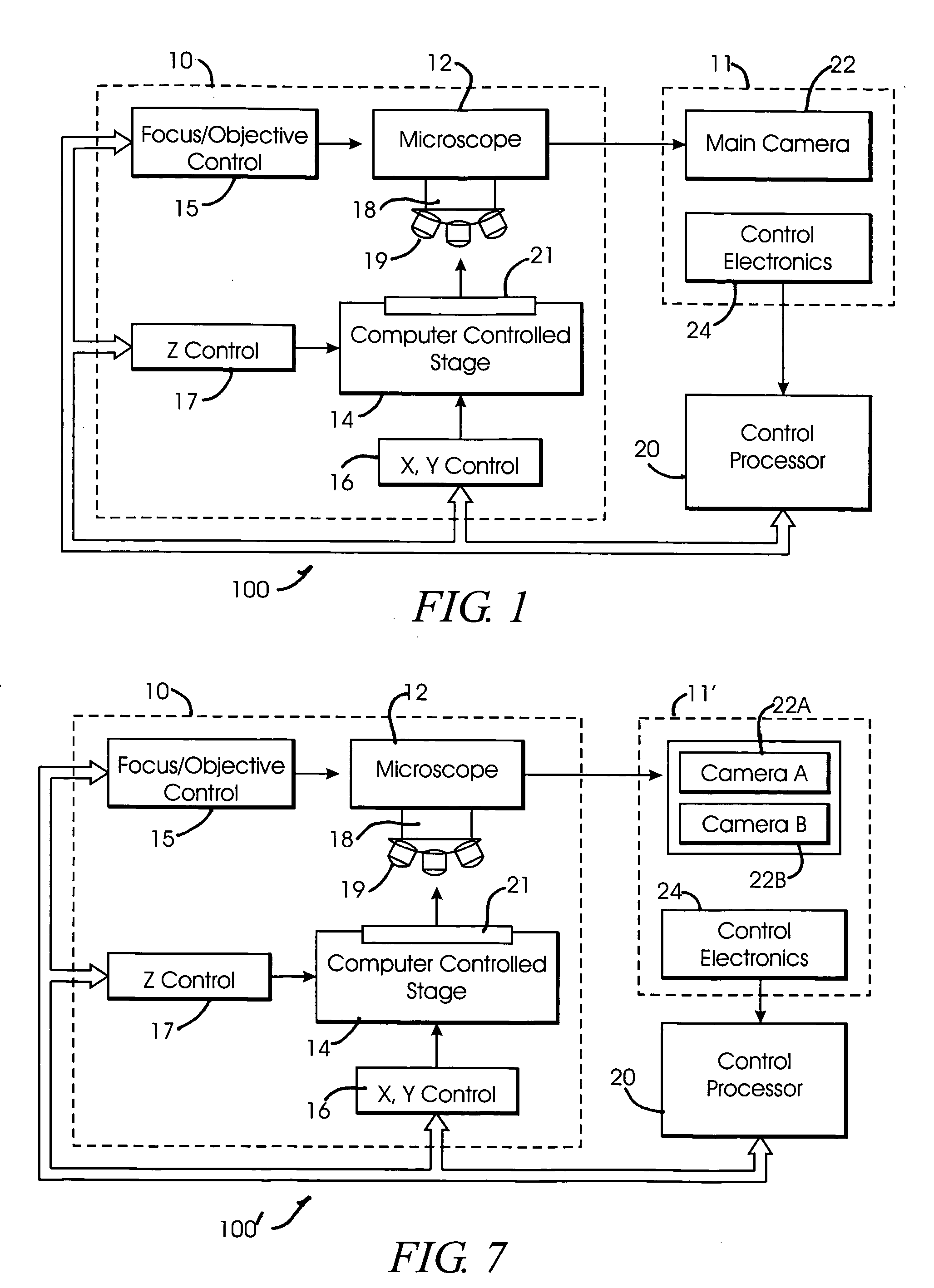
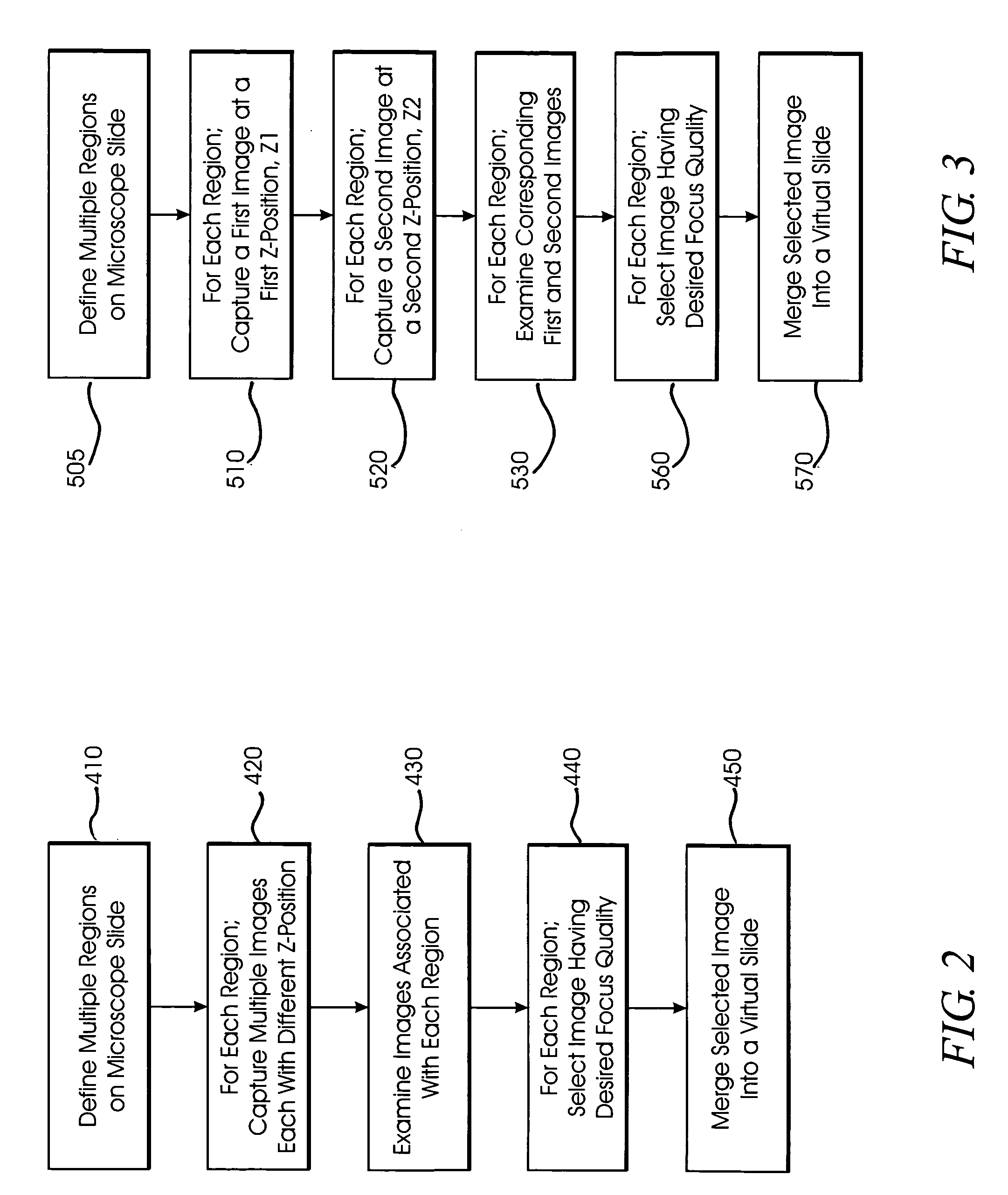
System and method for creating magnified images of a microscope slide
InactiveUS20060045505A1Optimum image quality characteristicImage enhancementImage analysisMicroscope slideRegion selection
A method and system for creating a digital, virtual slide having optimum image quality characteristics. Multiple regions of a physical slide are identified as well as at least two focus z-positions z1, and z2. Each region of the physical slide is scanned (imaged) at the first z position, so as to produce a first set of digital images of each defined region. Each region of the physical slide is also scanned (imaged) at the second z position, so as to produce a second set of digital images of each defined region. Each image of each set is evaluated against a focus quality metric and, for each region, either the first or second image, corresponding to that region, is selected that exhibits a focus quality metric corresponding to a desired focus quality. These images are then merged into a digital virtual slide. Additional focus z-positions may be included, and the multiple z-positions may be scanned seriatim, sequentially, and / or in overlapping fashion.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MICROSCOPY GMBH
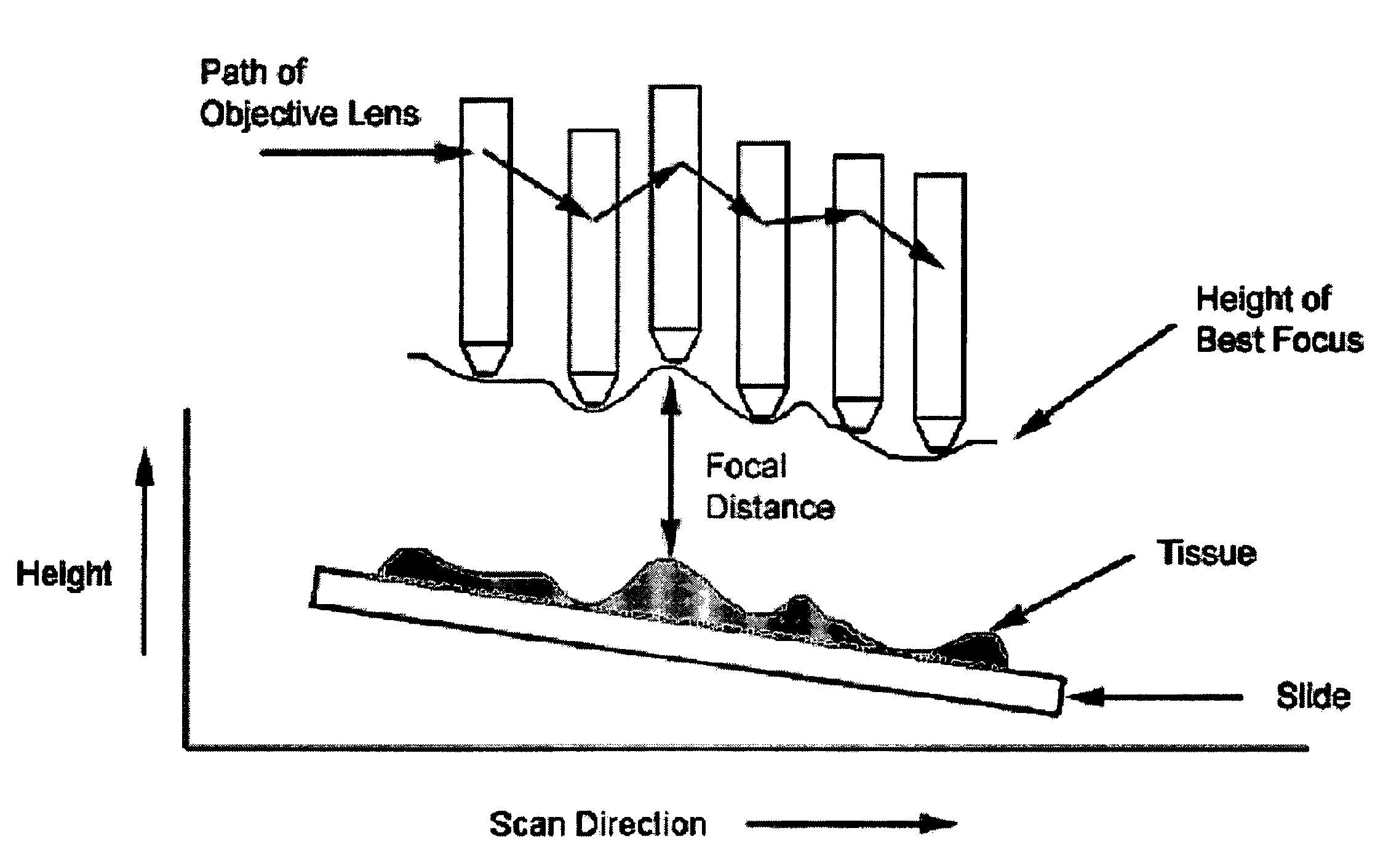
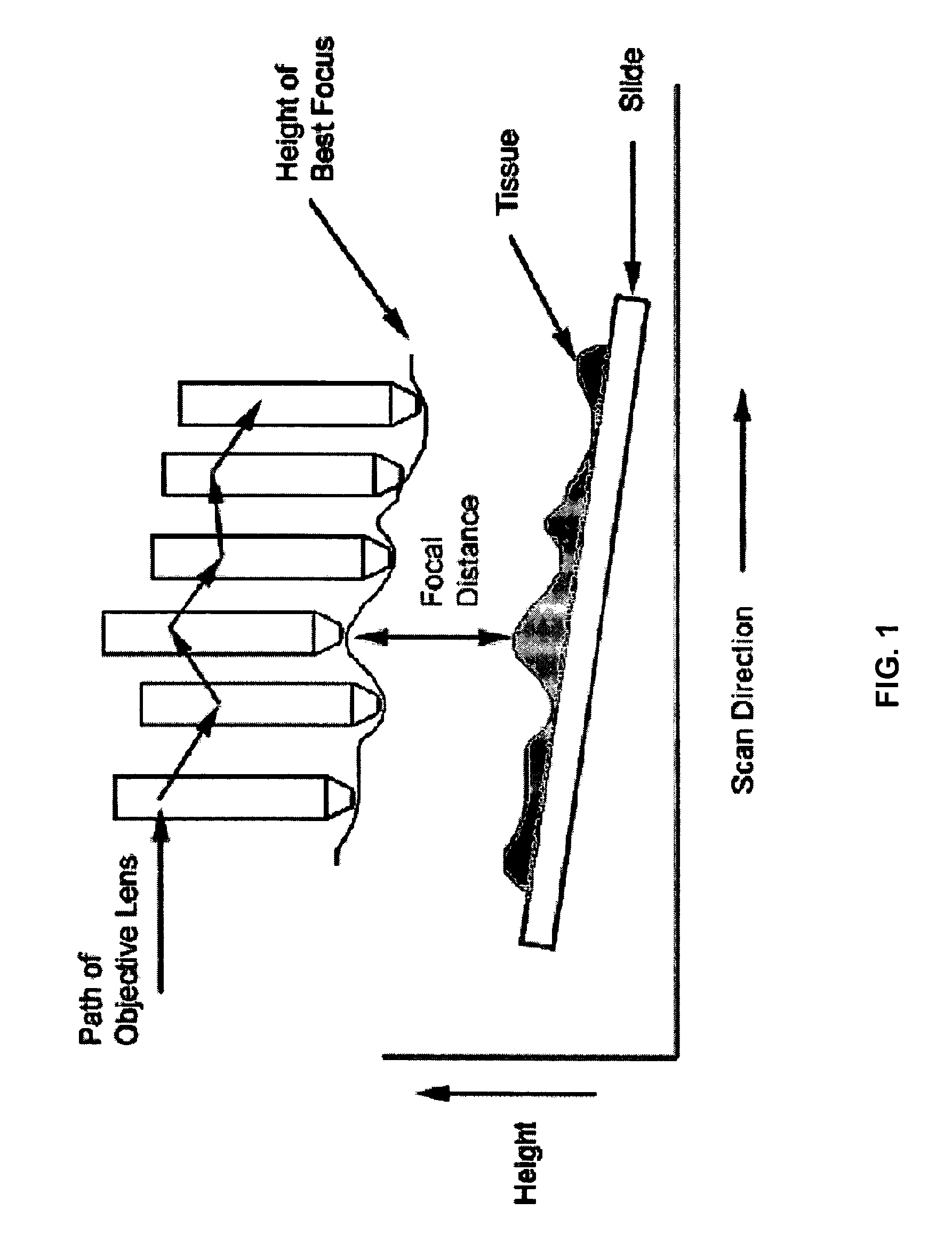
Method and apparatus for pre-focus in a linear array based slide scanner
InactiveUS7518652B2Television system detailsMaterial analysis by optical meansMicroscope slideBand pattern
Methods and apparatus are provided for computing focus information prior to scanning microscope slides with a line scan camera. The methods include a point-focus procedure that works by moving the slide to the desired measurement location, moving the objective lens through a predefined set of height values, acquiring imagery data at each height, and determining the height of maximum contrast. The methods also include a ribbon-focus procedure whereby imagery data are acquired continuously, while the slide and objective lens are in motion. Both methods may be applied with either a static or a dynamic implementation.
Owner:LEICA BIOSYST IMAGING
System and method for automatically processing tissue samples
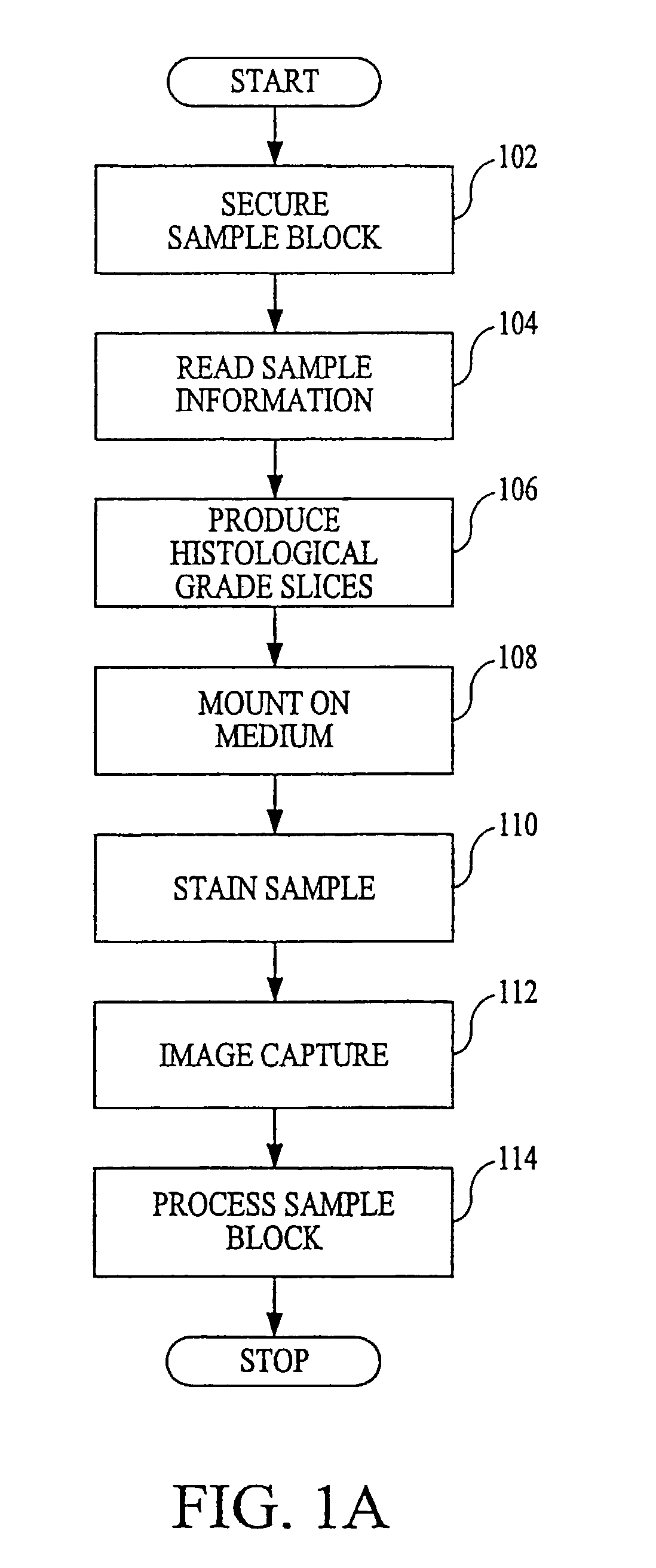
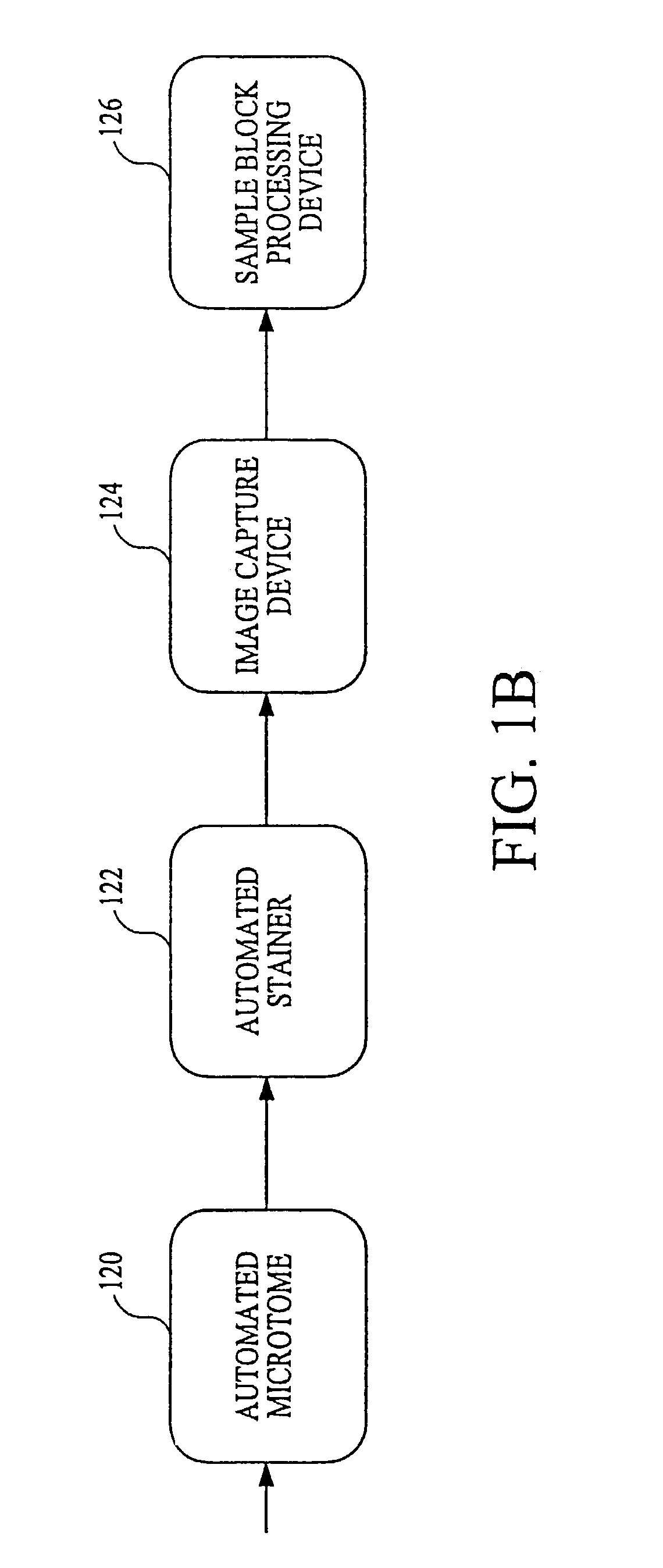
An apparatus and method for producing tissue slides is disclosed. The apparatus includes a holding assembly for manipulating the sample block, a blade assembly for preparing a thin section from the sample block, and a transfer roller mechanism for transferring the thin section to a receiving medium. The apparatus further includes a controller that may track the sample block and thin section. The method includes the steps of first locating a sample embedded within a support medium, which may be paraffin or a similar medium. Next, the embedded sample is oriented in such a way that its working surface is presented. This orientation may entail determining the orientation of the embedded sample with respect to the blade that will produce the largest cross-sectional area. Next, a slice of the sample from said embedded sample is removed and subsequently transferred to a suitable receiving medium, which may include a microscope slide. The slices may be stained, and a representation of the slice may be captured by an image capture device. The sample blocks may be transferred to a holding device, where they may be indexed and stored.
Owner:VONEIFF JOHN +2
Image processing and analysis of individual nucleic acid molecules
InactiveUS20030036067A1Improve throughputQuick buildBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMicroscope slideImaging processing
A method for observing and determining the size of individual molecules and for determining the weight distribution of a sample containing molecules of varying size, which involves placing a deformable or nondeformable molecule in a medium, subjecting the molecule to an external force, thereby causing conformational and / or positional changes, and then measuring these changes. Preferred ways to measure conformational and positional changes include: (1) determining the rate at which a deformable molecule returns to a relaxed state after termination of the external force, (2) determining the rate at which a molecule becomes oriented in a new direction when the direction of the perturbing force is changed, (3) determining the rate at which a molecule rotates, (4) measuring the length of a molecule, particularly when it is at least partially stretched, or (5) measuring at least one diameter of a spherical or ellipsoidal molecule. Measurements of relaxation, reorientation, and rotation rates, as well as length and diameter can be made using a light microscope connected to an image processor. Molecule relaxation, reorientation and rotation also can be determined using a microscope combined with a spectroscopic device. The invention is particularly useful for measuring polymer molecules, such as nucleic acids, and can be used to determine the size and map location of restriction digests. Breakage of large polymer molecules mounted on a microscope slide is prevented by condensing the molecules before mounting and unfolding the molecules after they have been placed in a matrix.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Apparatus and method for processing biological samples
ActiveUS20110136135A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMicroscope slideCapillary Tubing
A method and an automated apparatus for processing at least one biological sample arranged on a slide. At least one capillary staining module has a slide rack holder configured to detachably hold a slide rack configured to hold slides, and a capillary lid rack holder configured to detachably hold a capillary lid rack configured to hold capillary lids, wherein the slide rack can be removed independently of removing the capillary lid rack. A first fluid container has a first fluid. The apparatus being configured to automatically rotate the one or more slides, and to move the lids towards the slides to automatically form a capillary gap between each slide and each capillary lid, said capillary gap functioning as a capillary chamber; and to supply an amount of the first fluid to the slide.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
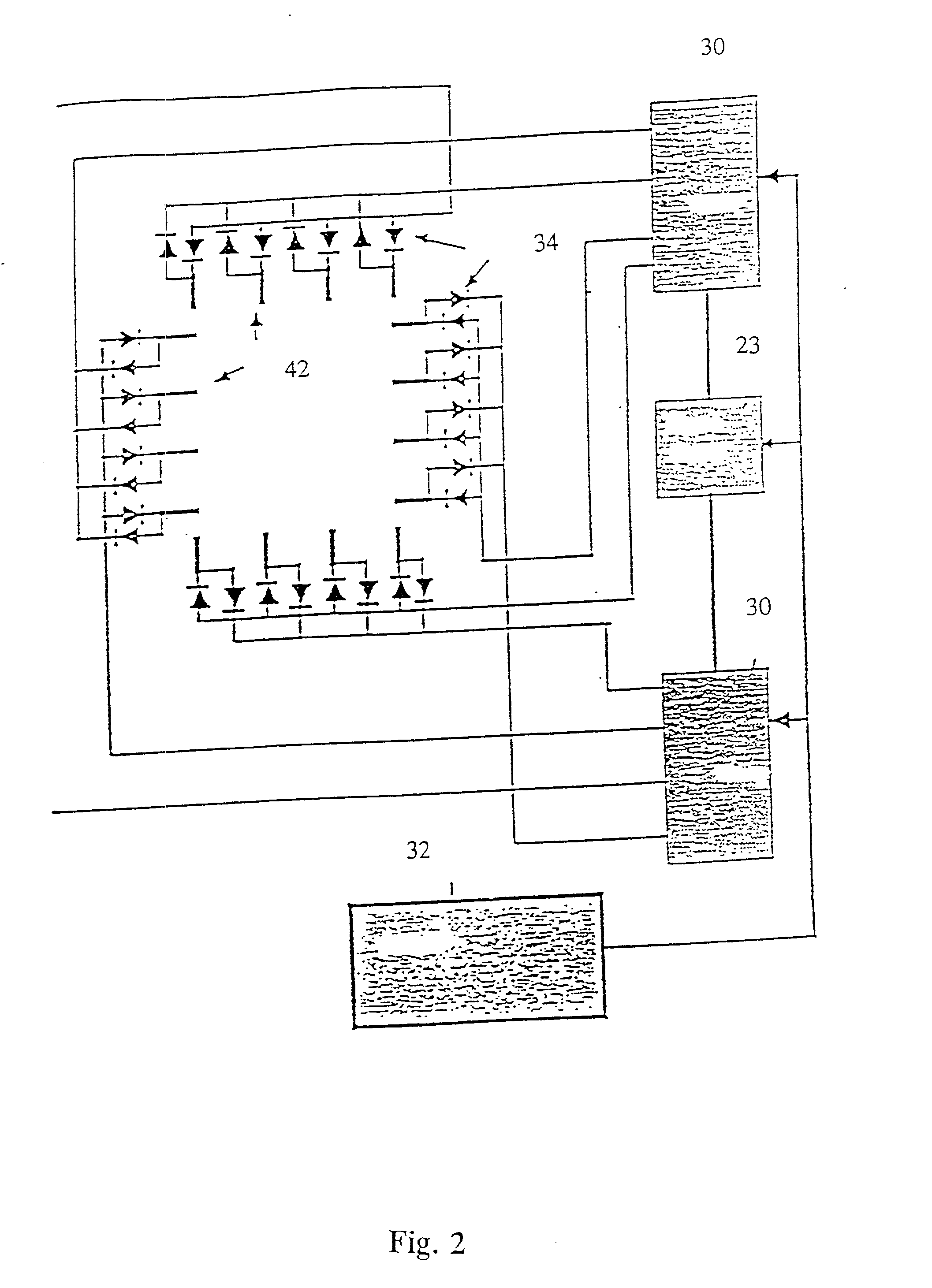
Reagent Delivery System, Dispensing Device and Container for a Biological Staining Apparatus
ActiveUS20090325309A1Allocation is accurateEliminate cross-contaminationAnalysis using chemical indicatorsTesting/calibration apparatusMicroscope slideStaining
The invention concerns reagent delivery system for an apparatus for processing of biological samples arranged on microscope slides, comprising a reagent section having one or more reagent containers; a slide section in which at least one microscope slide is arranged; a probe for dispensing a portion of reagent onto a predetermined microscope slide, and means for handling the probe. The probe comprises a continuous prove tubing element extending through a rigid probe member and connecting the probe tip to a pneumatic pressure regulation device. The reagent containers are adapted for cooperation with the probe tip. In this manner a high though-put and a very low carry over of fluid residues is achieved since there is no assembled parts making up the inside volume of the probe in which the fluid may be retained.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Biological culture assembly
ActiveUS20100151511A1Speeding up biological sample testingSpeeding up culturingBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMicroscope slideEngineering
The invention relates to a resealable or a single use cell culture assembly for use in growing, storing and transporting, cell and tissue cultures. The assembly includes a support frame for receiving a base member insert having an upper surface, such as a microscope slide, and a well frame, preferably partitioned into a plurality of well compartments having sidewalls with upper and lower surfaces, upper and lower edges, and upper and lower well openings. The well frame is adapted to be operatively positioned on the upper surface of the base member, and includes a sealing means positioned on or within the lower edge of the well frame. The sealing means is adapted to operatively create a liquid-impermeable releasable seal or barrier when the lower surface of the well frame is positioned on the upper surface of the base member, such that the sealing means is releasably positioned on the upper surface of the base member for maintaining a liquid-impermeable barrier between well compartments. The assembly may include a cover or lid positioned over the upper opening of the well frame. When the assembly is in a closed position, the well frame can be secured to the support frame by a variety of closure means.
Owner:MILLIPORE CORP
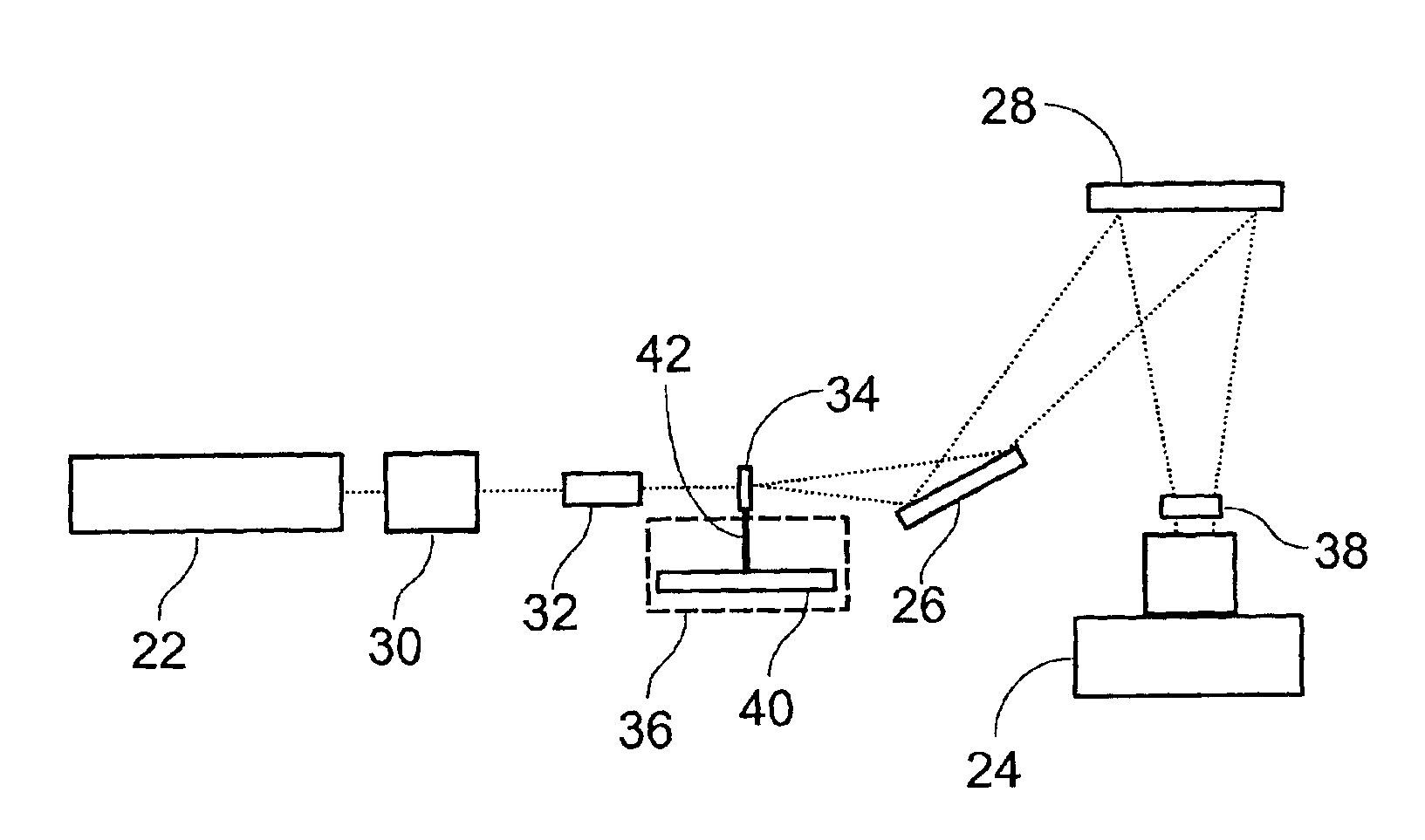
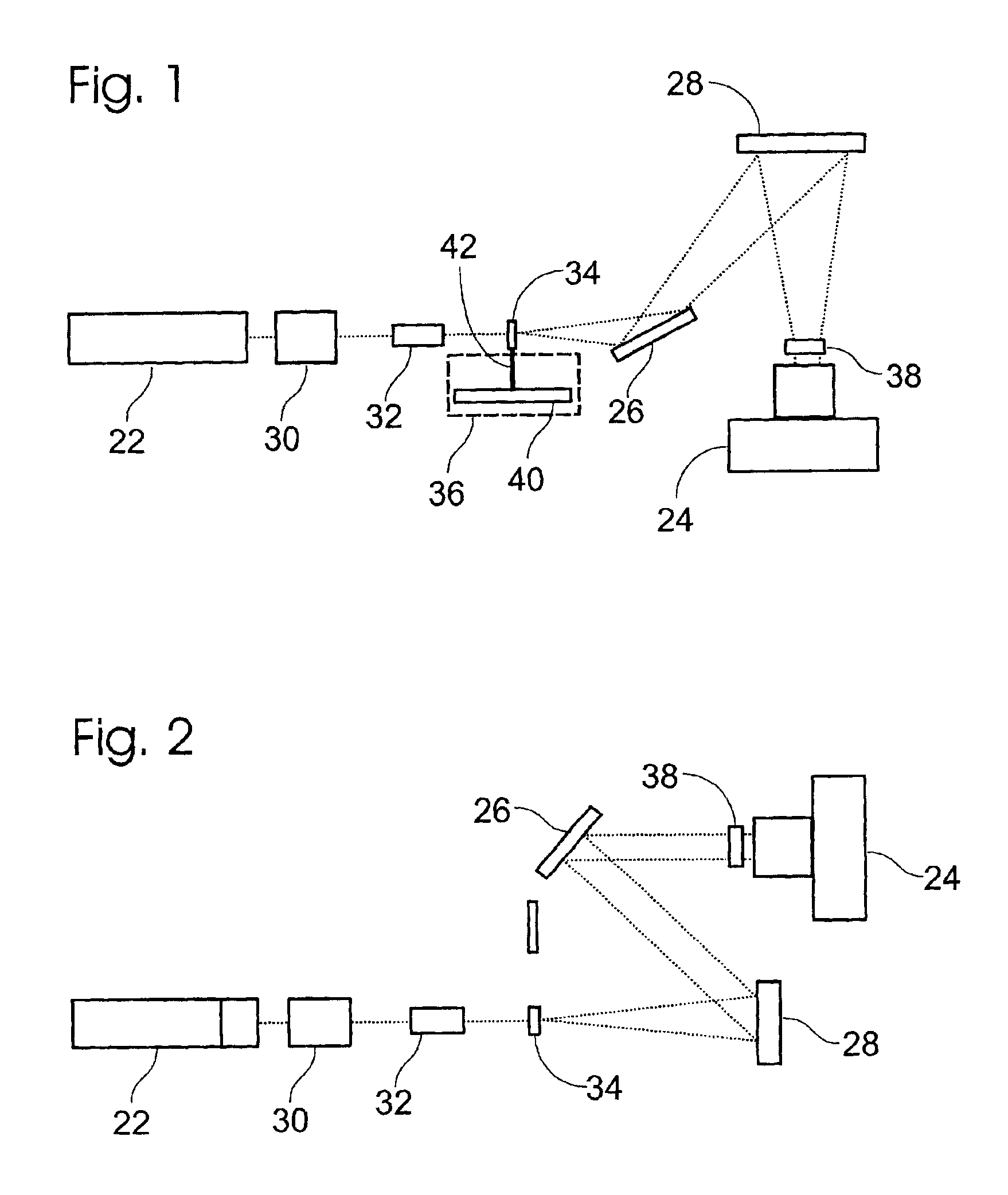
Light detection device
InactiveUS6930314B2Increase flexibilityImprove reading speedSpectrum investigationScattering properties measurementsGenomicsMicroscope slide
Apparatus and methods for optical illumination and / or detection with improved flexibility and / or read speed. The apparatus and methods may include mechanisms for selecting and switching between multiple excitation wavelengths and / or simultaneously reading from a plurality of sample sites. The apparatus and methods may be used with microplates, PCR plates, cell culture plates, biochips, chromatography plates, microscope slides, and other substrates for high-throughput screening, genomics, SNPs analysis, pharmaceutical research and development, life sciences research, and other applications.
Owner:MOLECULAR DEVICES
Method and apparatus for applying fluids to a biological sample
ActiveUS20060019302A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMicroscope slideLiquid meniscus
The invention is directed to a method of contacting a biological sample with a solution, comprising the steps of moving a curved surface wetted with the solution in proximity to the biological sample whereby the distance separating the wetted curved surface and the biological sample is sufficient to form a moving liquid meniscus layer between the two. The invention is also directed to an apparatus for contacting a biological sample suspected of containing a biomarker with a solution, comprising a platform for supporting a microscope slide having a biological sample thereon; a translating cap having a curved lower surface positioned above the platform, the curved lower surface being in proximity to a biological sample when in operation; means for moving the translating cap back and forth over the biological sample; and means for applying and removing liquid to and from the cap.
Owner:VENTANA MEDICAL SYST INC
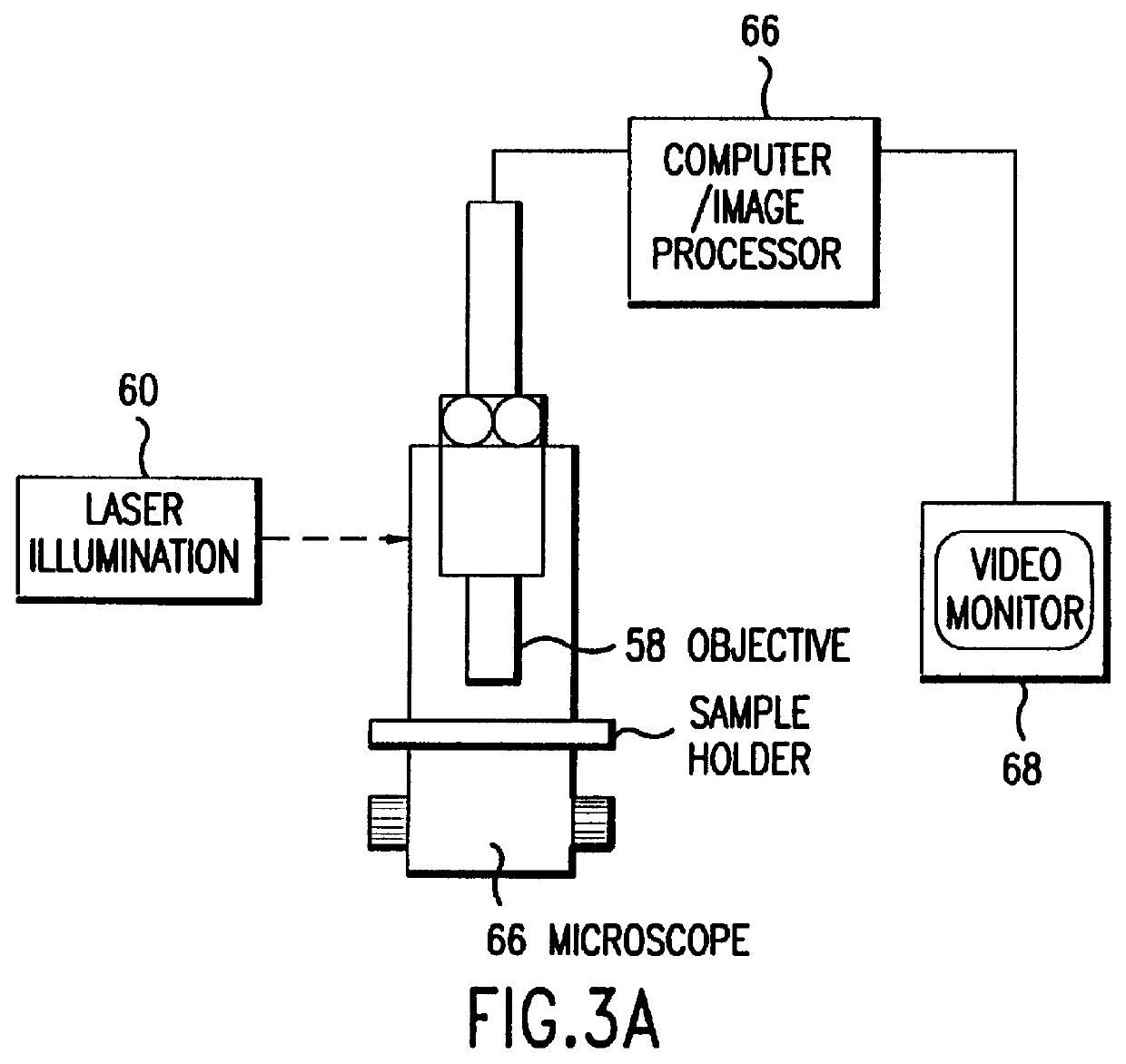
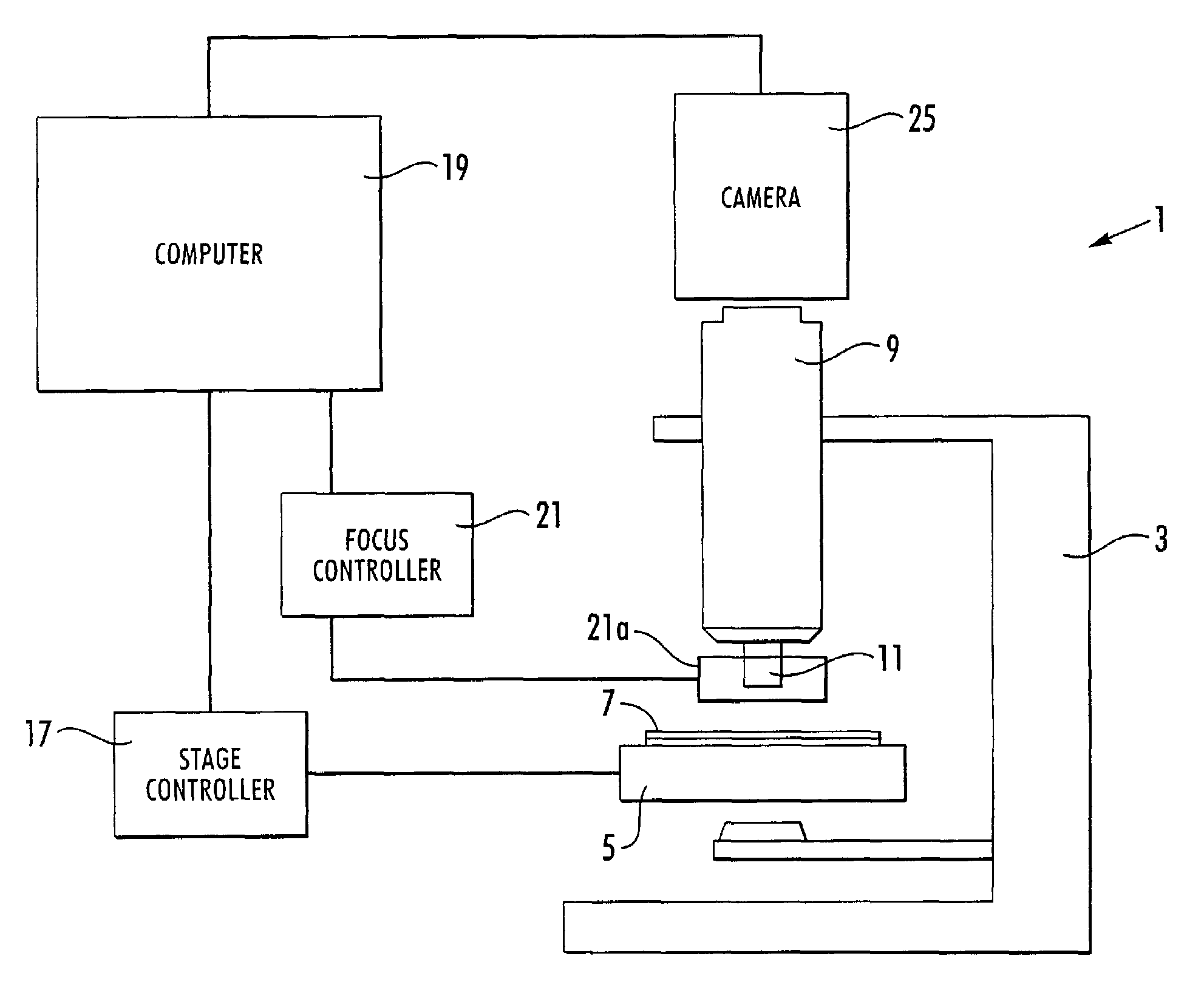
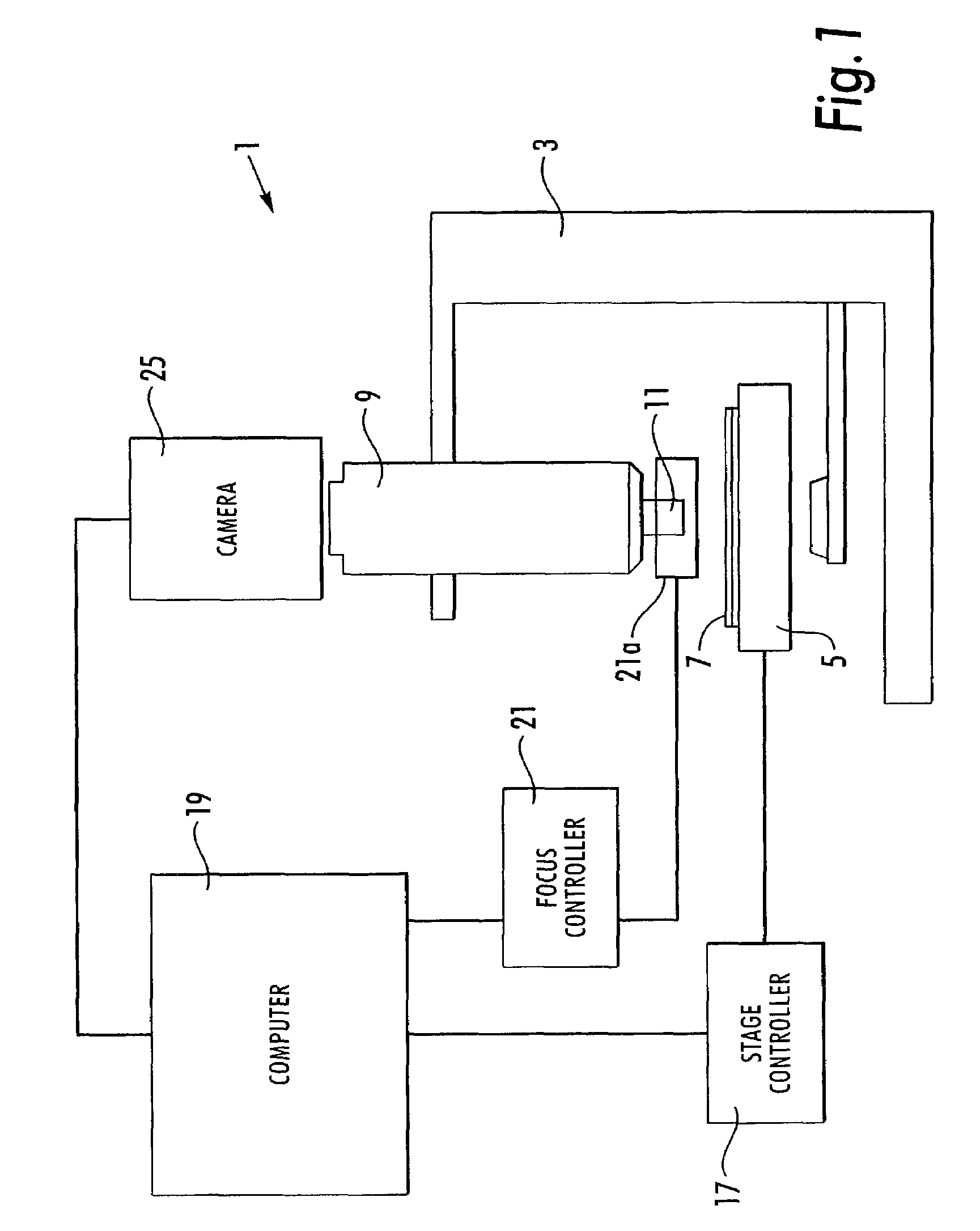
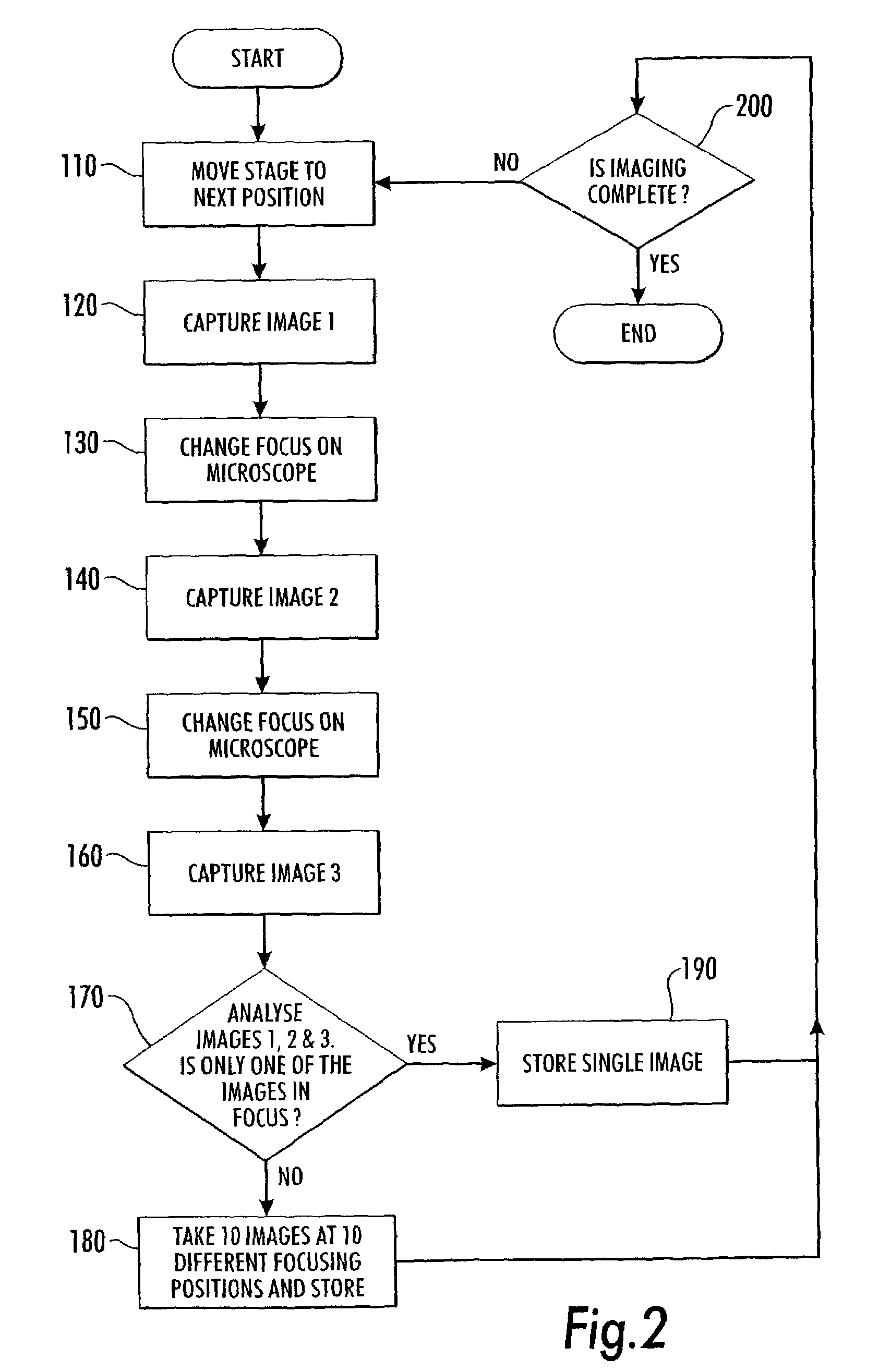
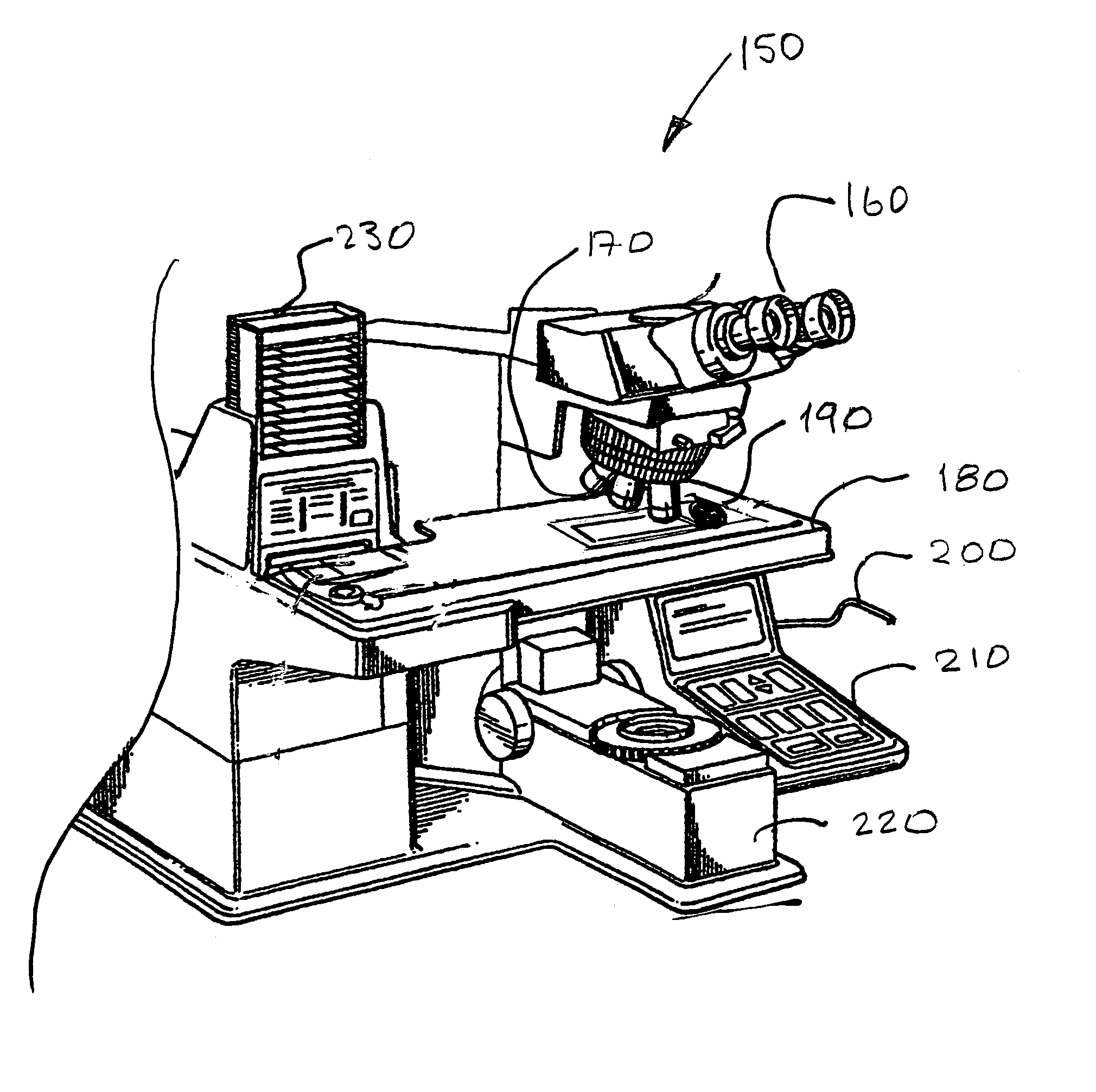
Microscopy imaging system and method
InactiveUS7248282B2Minimize timeCharacter and pattern recognitionColor television detailsMicroscope slideDigital camera
A microscopy imaging system and method acquires digital images of a microscope specimen using a computer-controlled microscope and digital camera. A specimen on a microscope slide is placed within the microscope. The method comprises the steps of determining whether an area of the specimen contained within a microscope field of view has a thickness, and, if so, capturing digital images of the field of view at a plurality of depths of focus. In a preferred embodiment, the step of determining whether an area of the specimen contained within a microscope field of view has a thickness comprises the steps of: capturing a digital image of the field of view at two or more depths of focus; comparing the captured digital images, and determining that the specimen has a thickness, if the comparing step finds that the images are different. The method may be implemented in the form of a computer program.
Owner:SOURCE BIOSCI
Method and apparatus for applying fluids to a biological sample
ActiveUS7820381B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMicroscope slideLiquid meniscus
The invention is directed to a method of contacting a biological sample with a solution, comprising the steps of moving a curved surface wetted with the solution in proximity to the biological sample whereby the distance separating the wetted curved surface and the biological sample is sufficient to form a moving liquid meniscus layer between the two. The invention is also directed to an apparatus for contacting a biological sample suspected of containing a biomarker with a solution, comprising a platform for supporting a microscope slide having a biological sample thereon; a translating cap having a curved lower surface positioned above the platform, the curved lower surface being in proximity to a biological sample when in operation; means for moving the translating cap back and forth over the biological sample; and means for applying and removing liquid to and from the cap.
Owner:VENTANA MEDICAL SYST INC
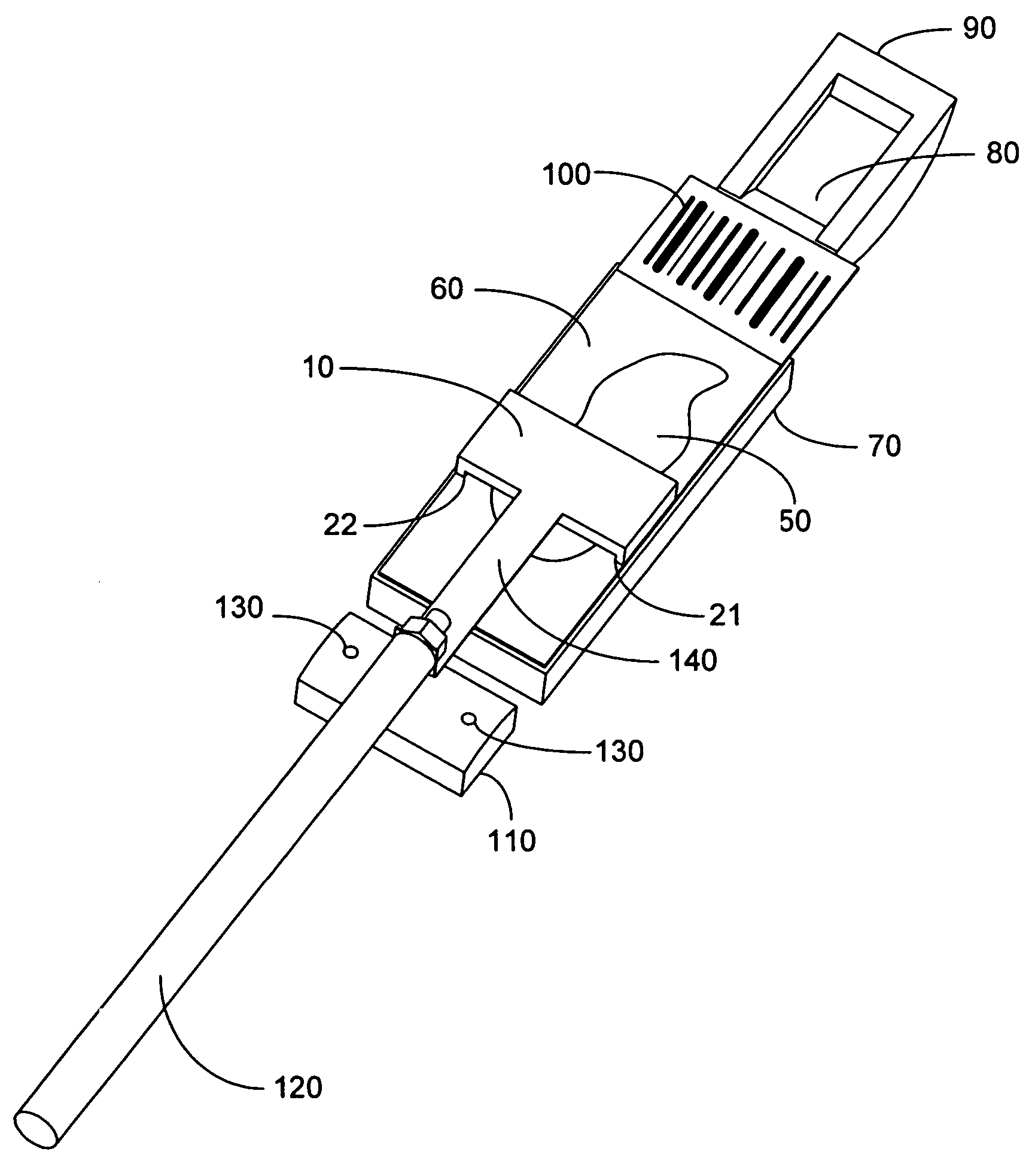
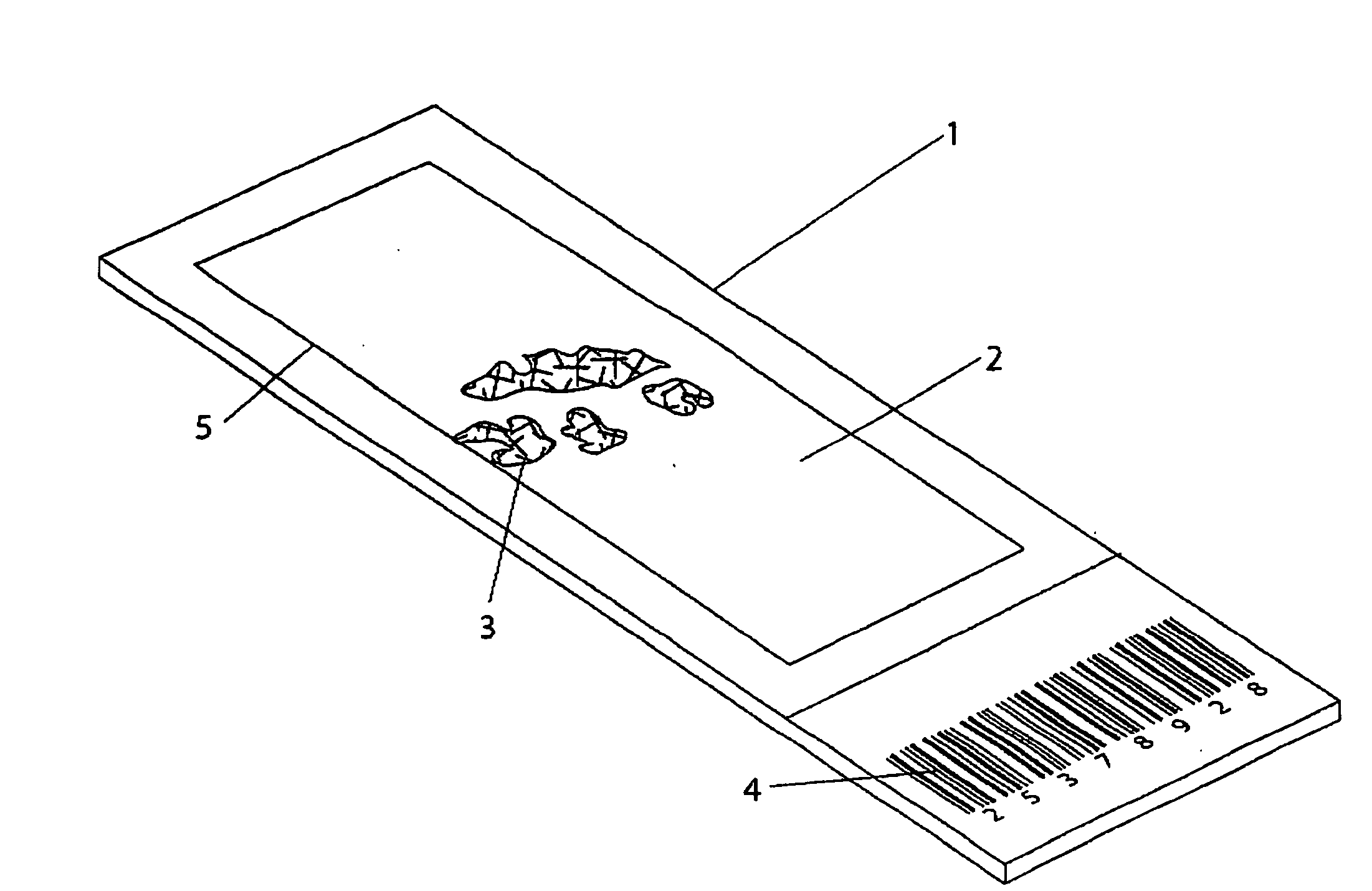
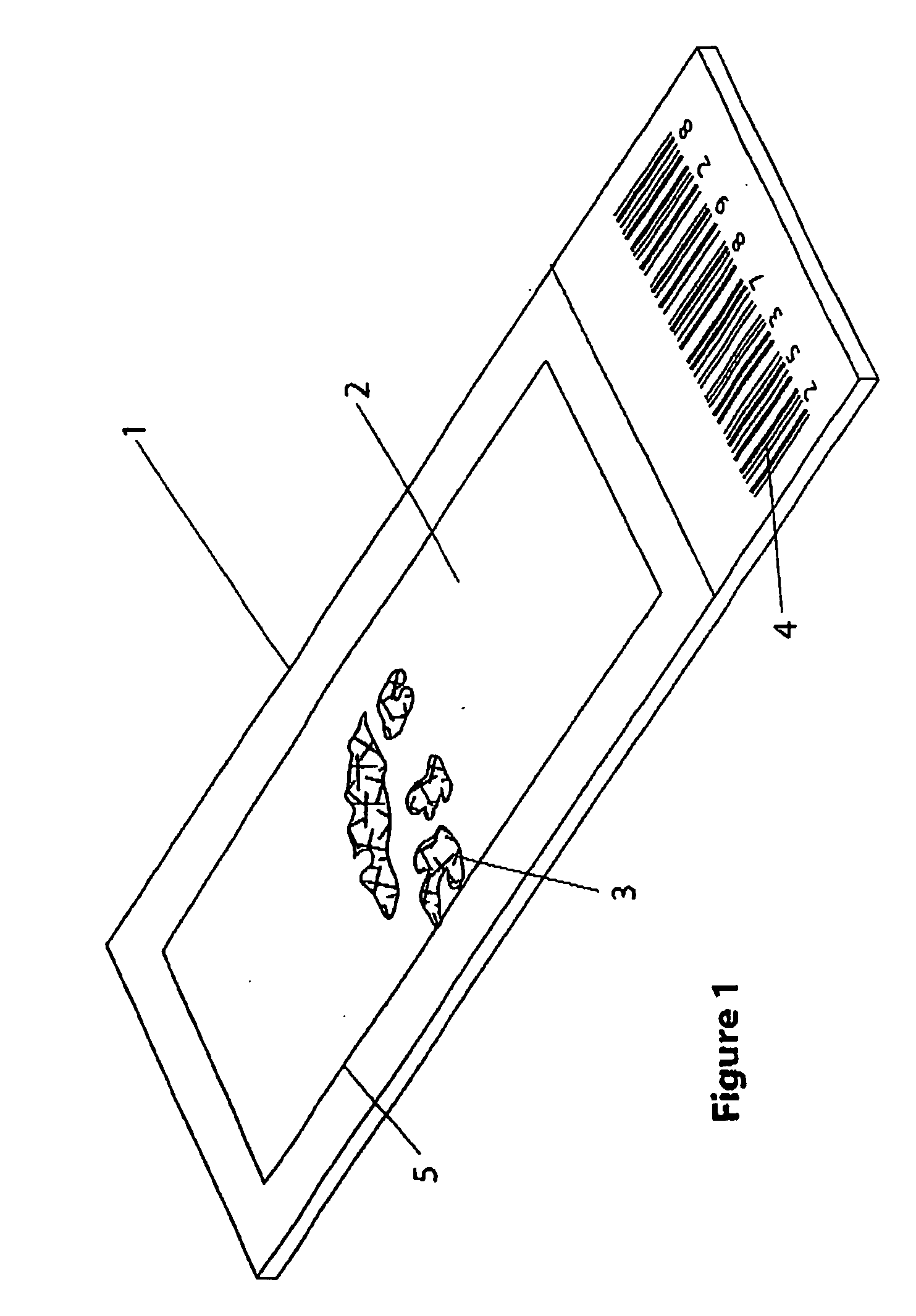
Microscope slide cover with integrated reservoir
InactiveUS20050270642A1Improve contact effectPreparing sample for investigationLaboratory glasswaresBiomedical engineeringMicroscope slide
A cover (10) for substrate (not shown) including: a body (12) defining a cavity (18), for positioning over the substrate (not shown) to form a reaction chamber (18); and a projection (13) extending from the body (12) to define a fluid reservoir (14), when the cover (10) is fitted to the substrate (not shown), the fluid reservoir (14) being in fluid communication with the cavity (18).
Owner:VISION BIOSYST
System for automatically locating and manipulating positions on an object
A system for automatically locating positions on an object and uniquely identifying the object employing an electronic tag positioned in or on the object. The system utilizes a plurality of sensors to locate the electronic tag and identify the object, and triangulation techniques to locate positions on the object where the object may be manipulated according to instructions coded with respect to the positions. Advantageously, the present invention may be used for automatically locating specimens on a microscope slide without regards to their positions on the slide, and for uniquely labeling a microscope slide.
Owner:TAFAS TRIANTAFYLLOS P +1
Currency dispenser service method
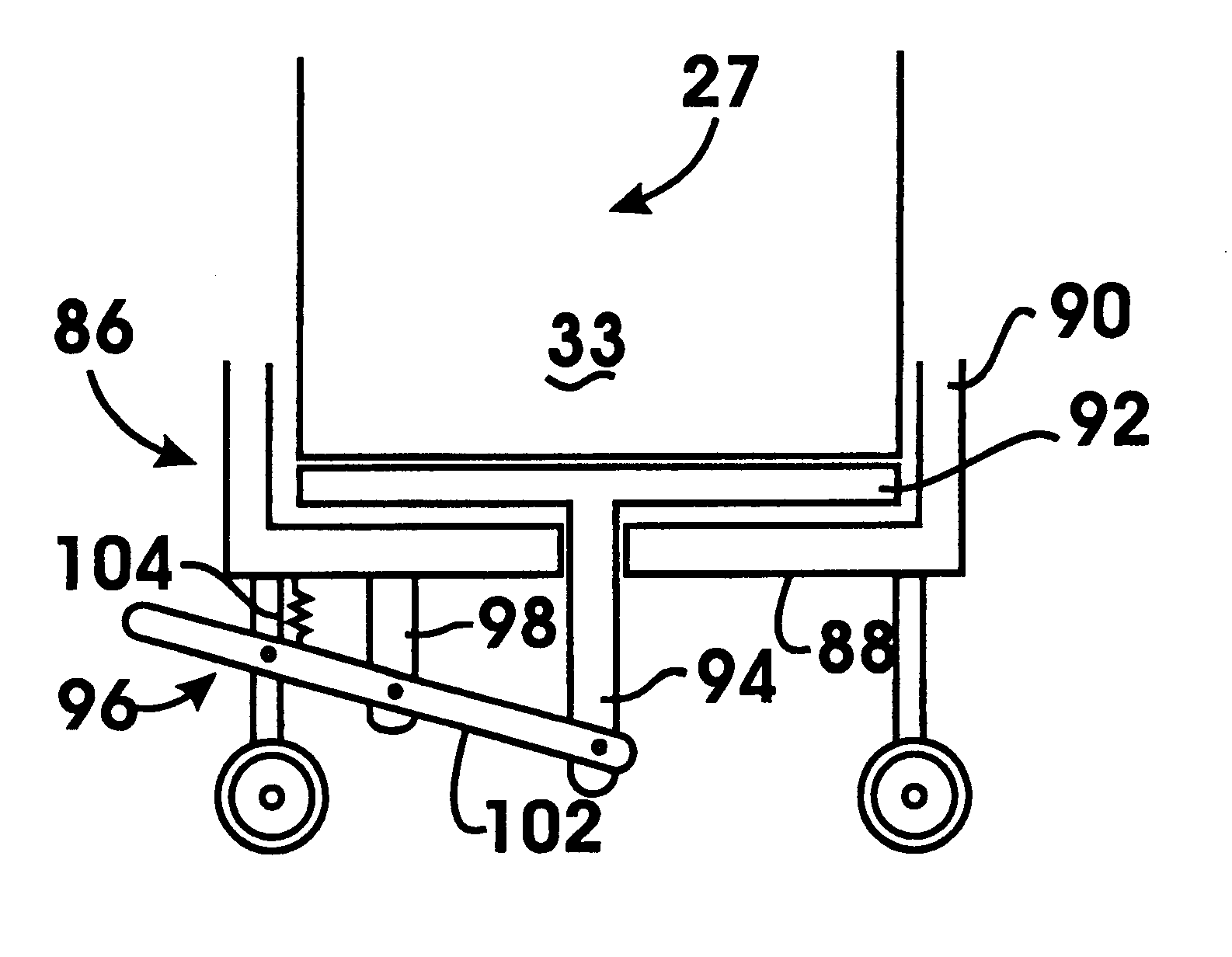
InactiveUS6293540B1Facilitates of componentPromote repairCoin/currency accepting devicesArticle separationMicroscope slideEngineering
An automated banking machine (10) has a secure chest (20). A sheet dispenser assembly is supported on the chest through movable slides (40). The dispenser may be moved outward through an opening (26) in the chest by extending the slides. The dispenser may be disengaged from the slides through use of a portable carrier (50). The portable carrier has a lifting device which is operated to lift the dispenser relative to the slides enabling disengagement therefrom. The dispenser is then movable away from the chest for servicing on the carrier. The dispenser may be re-engaged with the slides after servicing using the portable carrier.
Owner:DIEBOLD NIXDORF
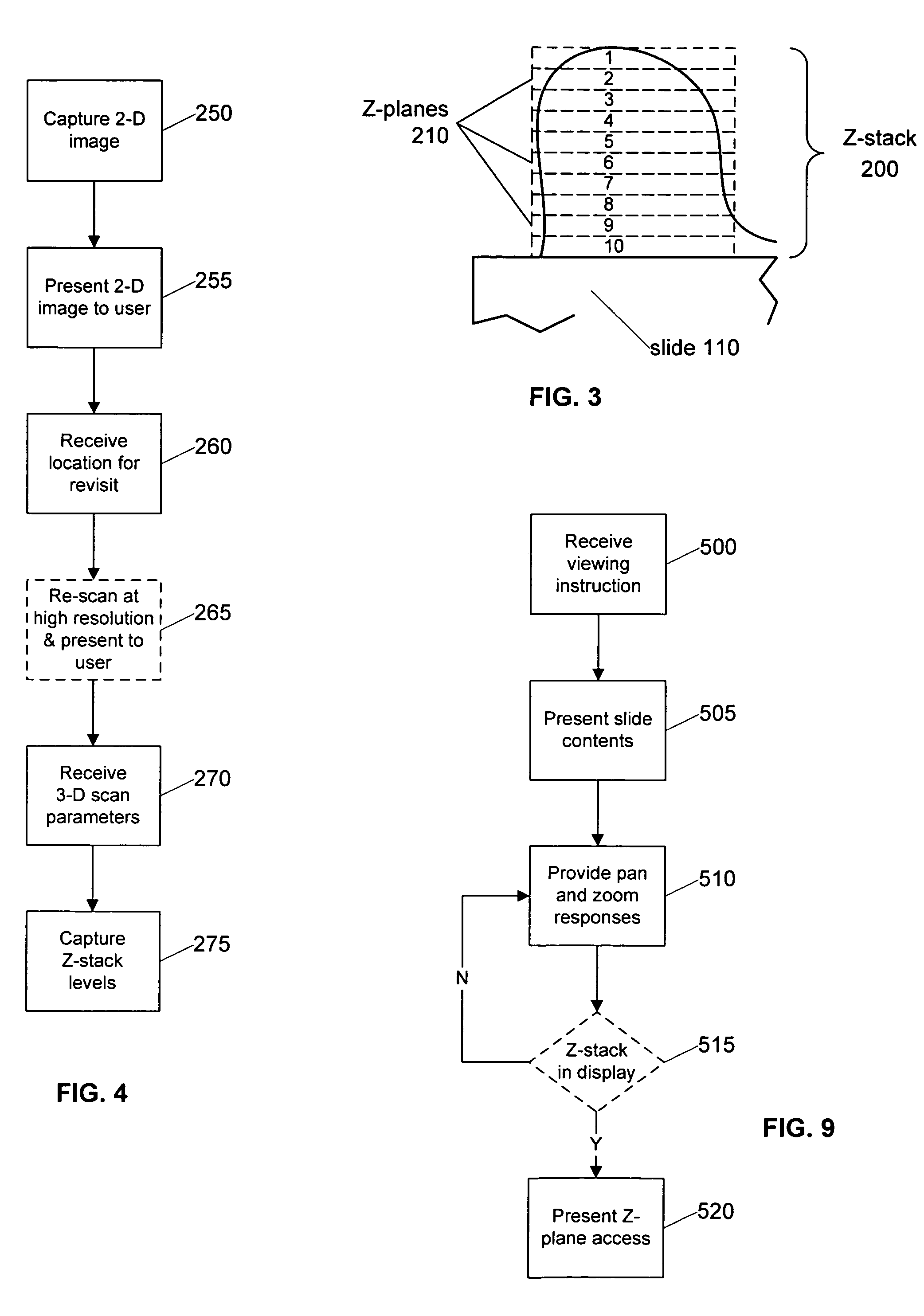
Systems and methods for creating and viewing three dimensional virtual slides
ActiveUS7463761B2High bandwidthQuick ViewMicroscopesSteroscopic systemsMicroscope slideAcquisition apparatus
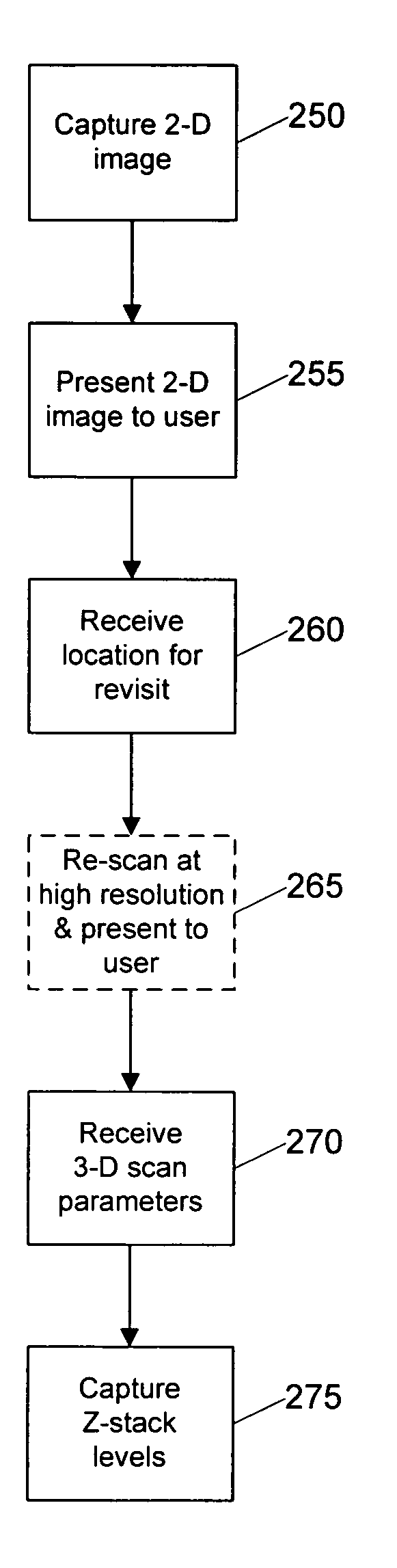
Systems and methods for creating and viewing three dimensional virtual slides are provided. One or more microscope slides are positioned in an image acquisition device that scans the specimens on the slides and makes two dimensional images at a medium or high resolution. This two dimensional images are provided to an image viewing workstation where they are viewed by an operator who pans and zooms the two dimensional image and selects an area of interest for scanning at multiple depth levels (Z-planes). The image acquisition device receives a set of parameters for the multiple depth level scan, including a location and a depth. The image acquisition device then scans the specimen at the location in a series of Z-plane images, where each Z-plane image corresponds to a depth level portion of the specimen within the depth parameter.
Owner:LEICA BIOSYST IMAGING
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com