Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
74 results about "Liquid meniscus" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
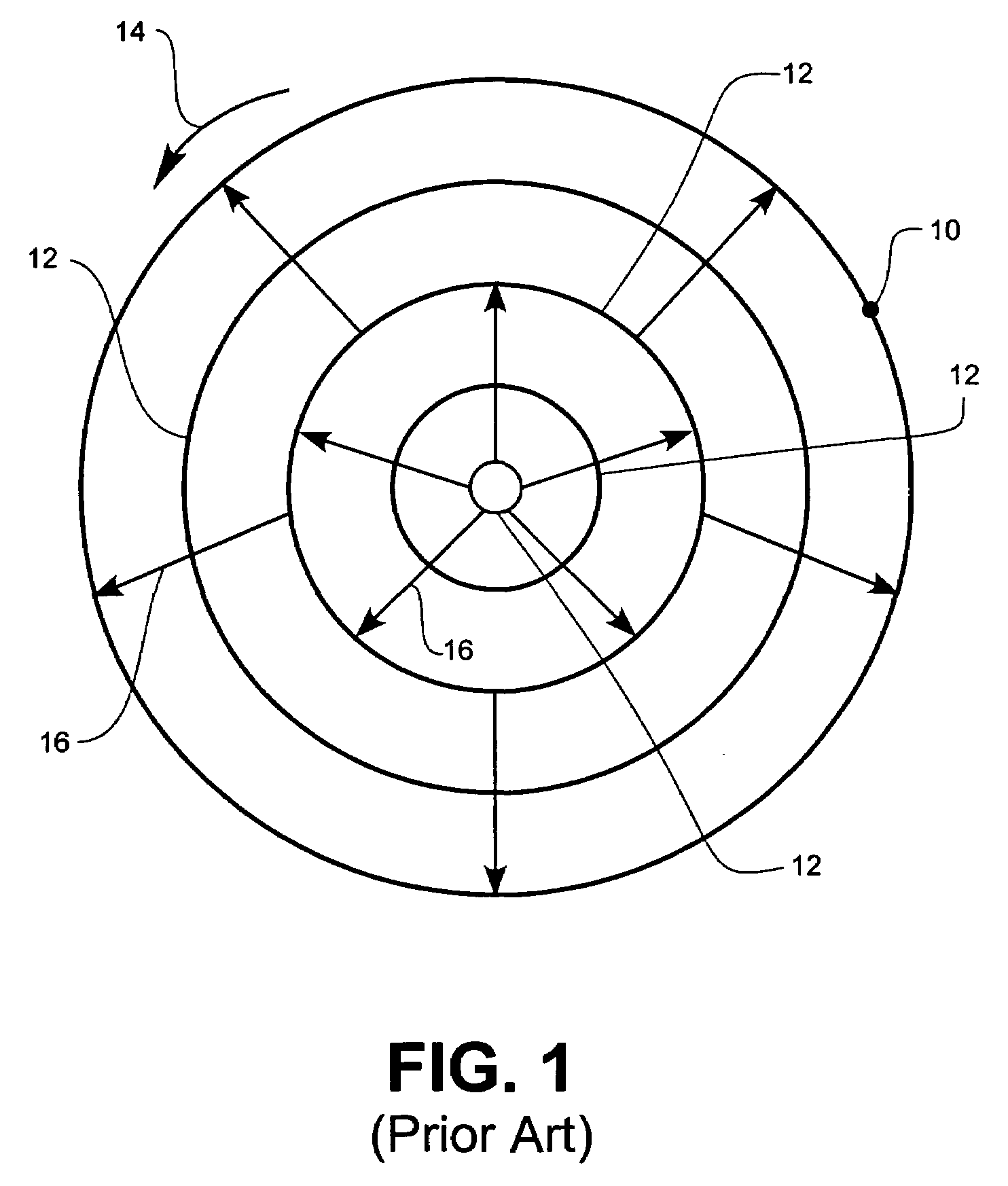
Meniscus (liquid) A: The bottom of a concave meniscus. B: The top of a convex meniscus. The meniscus (plural: menisci, from the Greek for "crescent") is the curve in the upper surface of a liquid close to the surface of the container or another object, caused by surface tension.
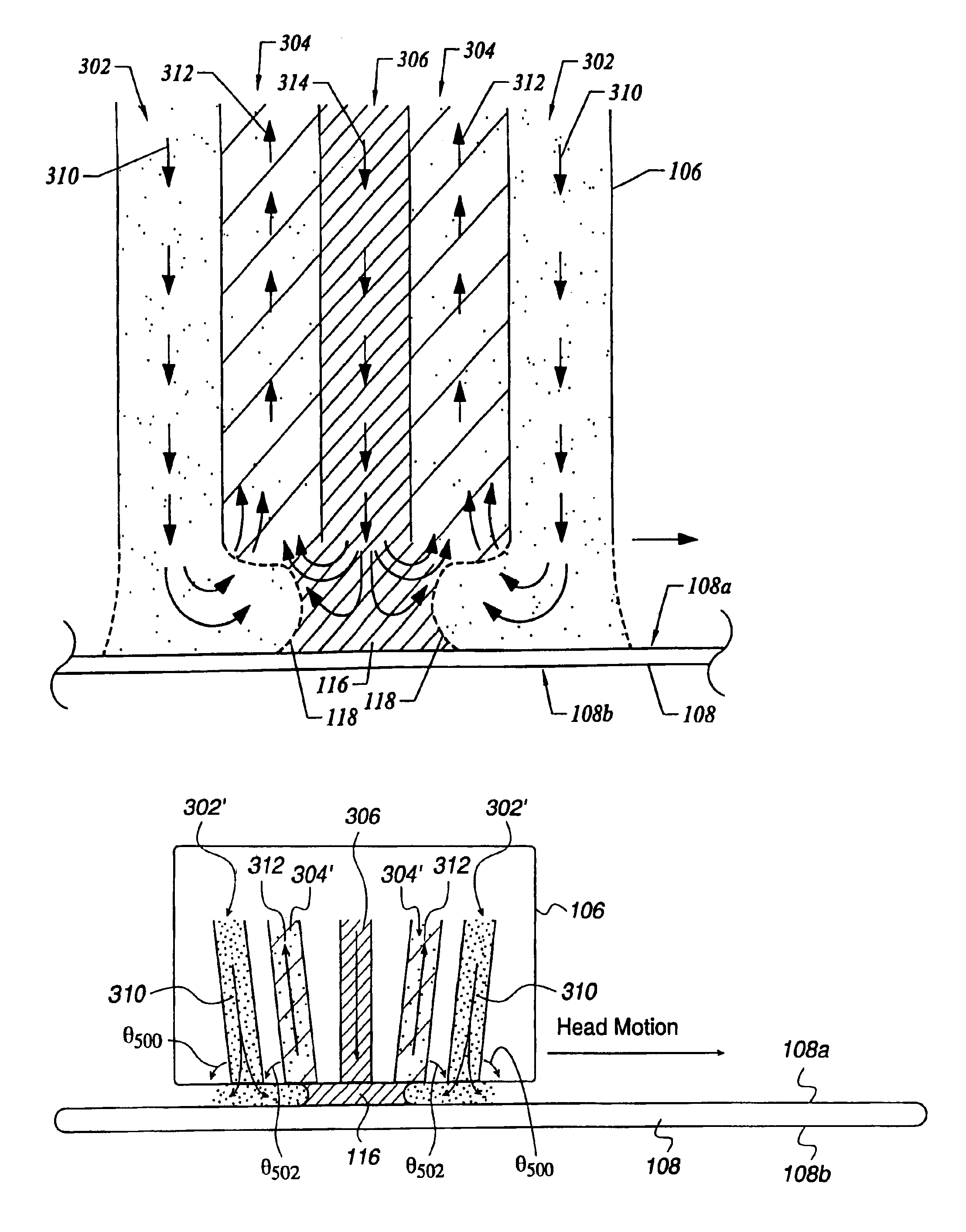
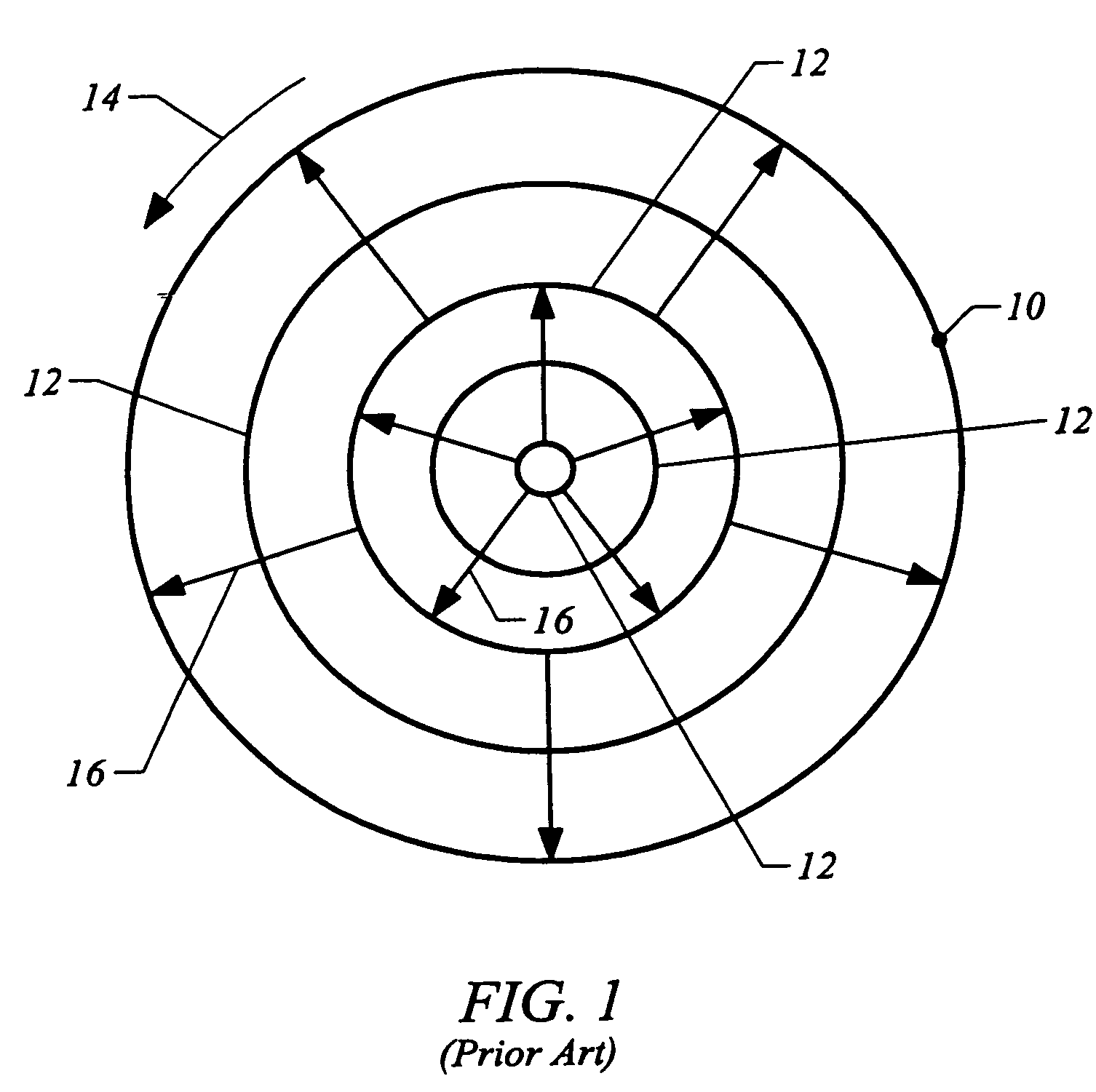
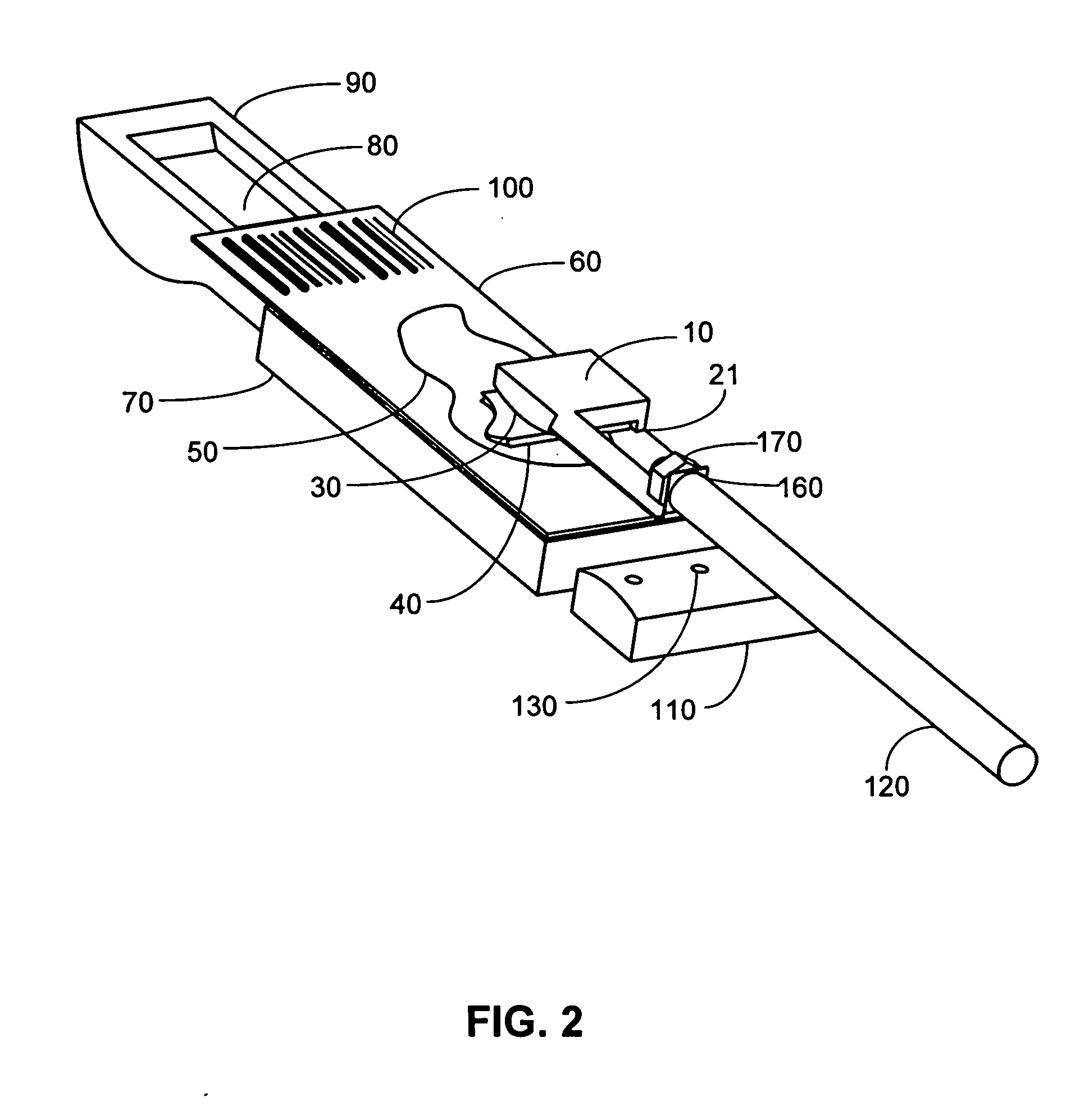
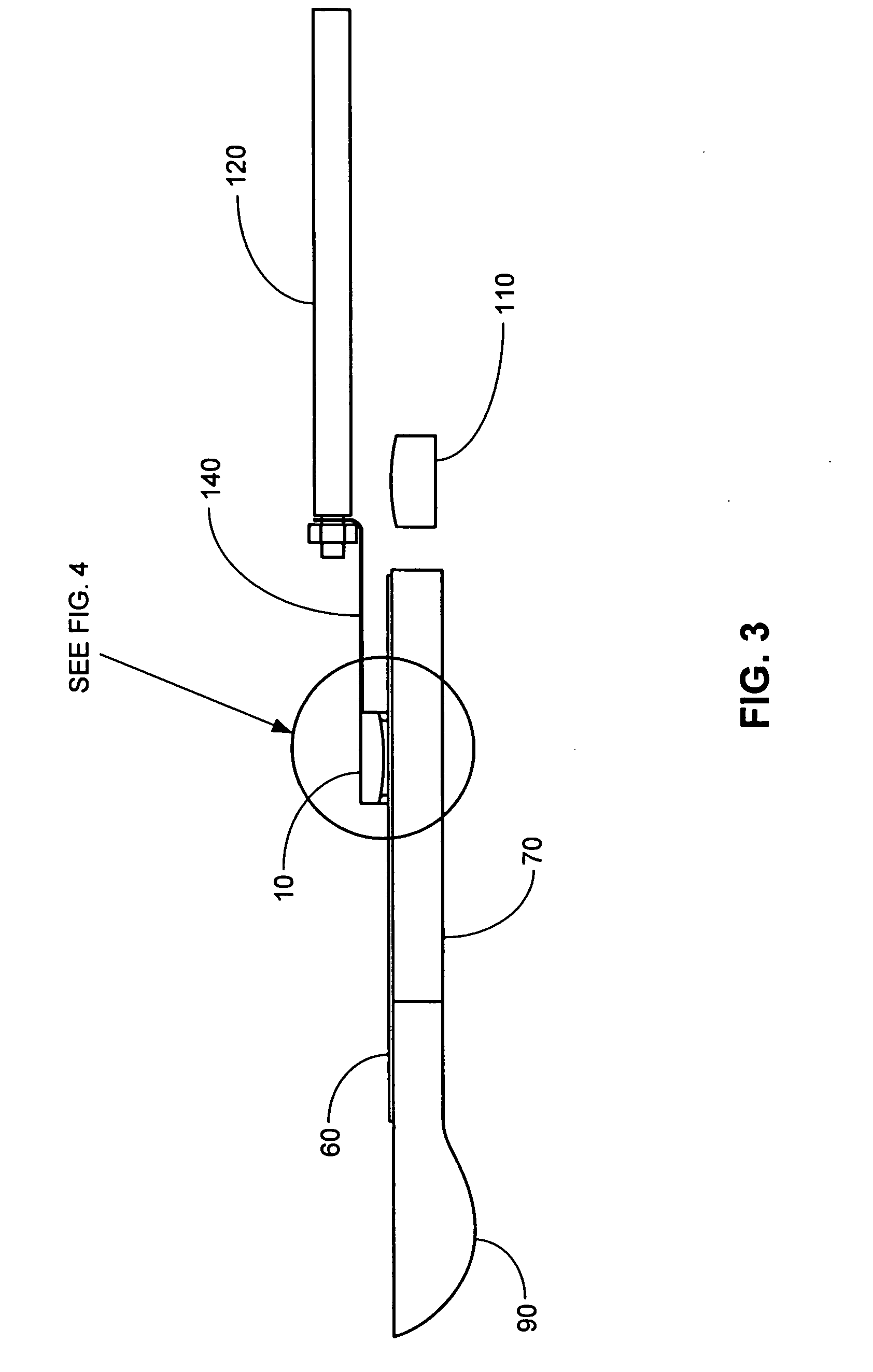
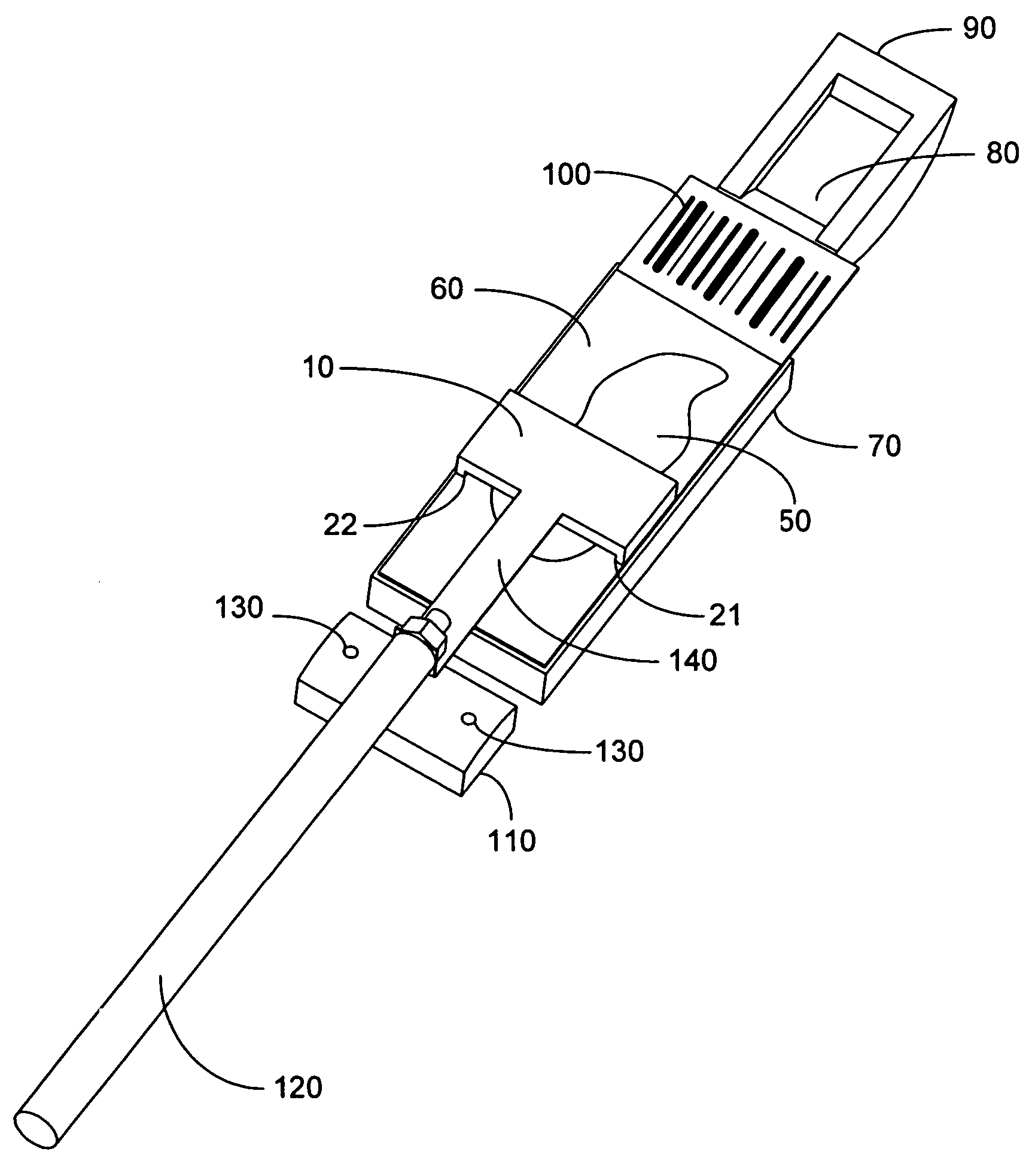
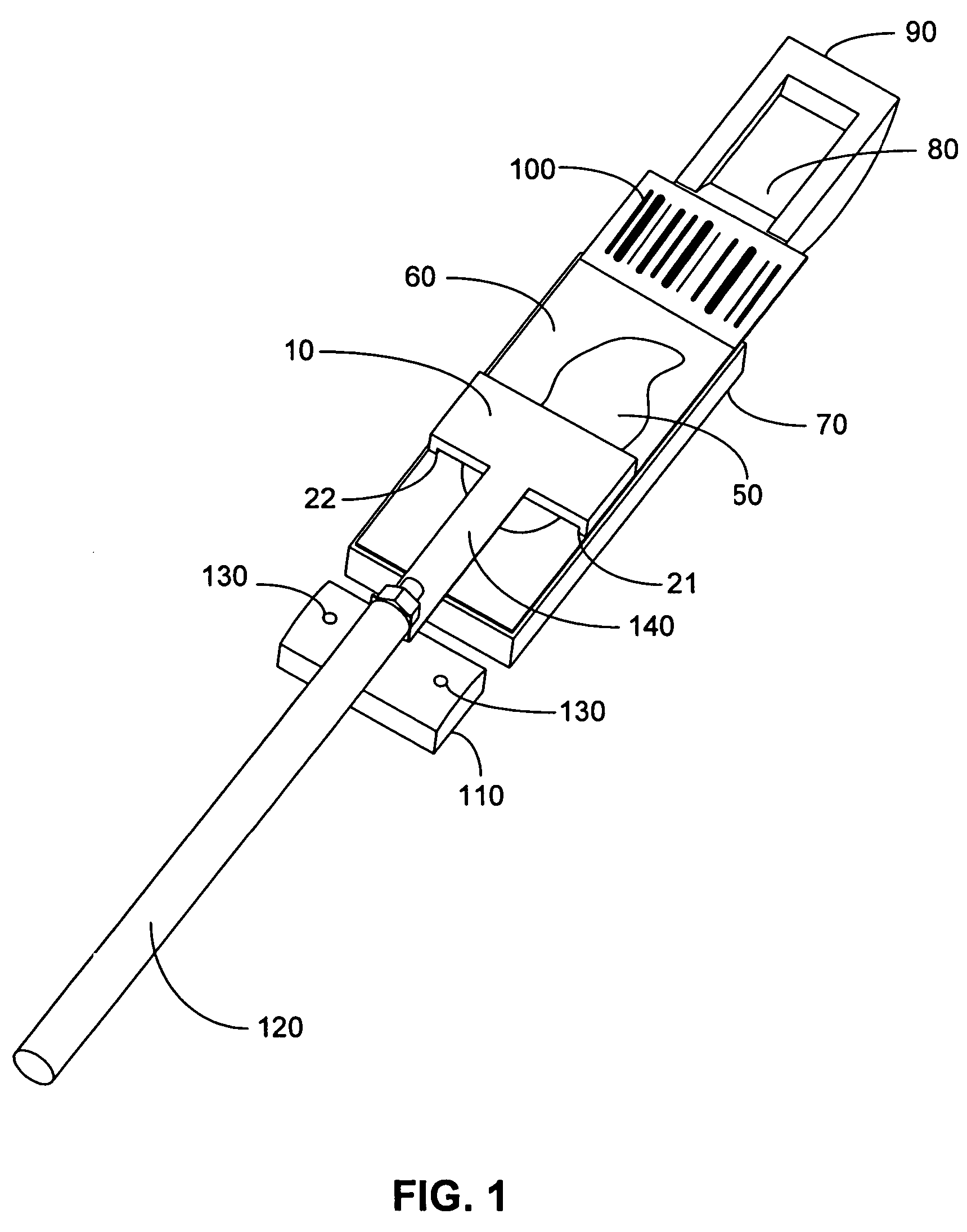
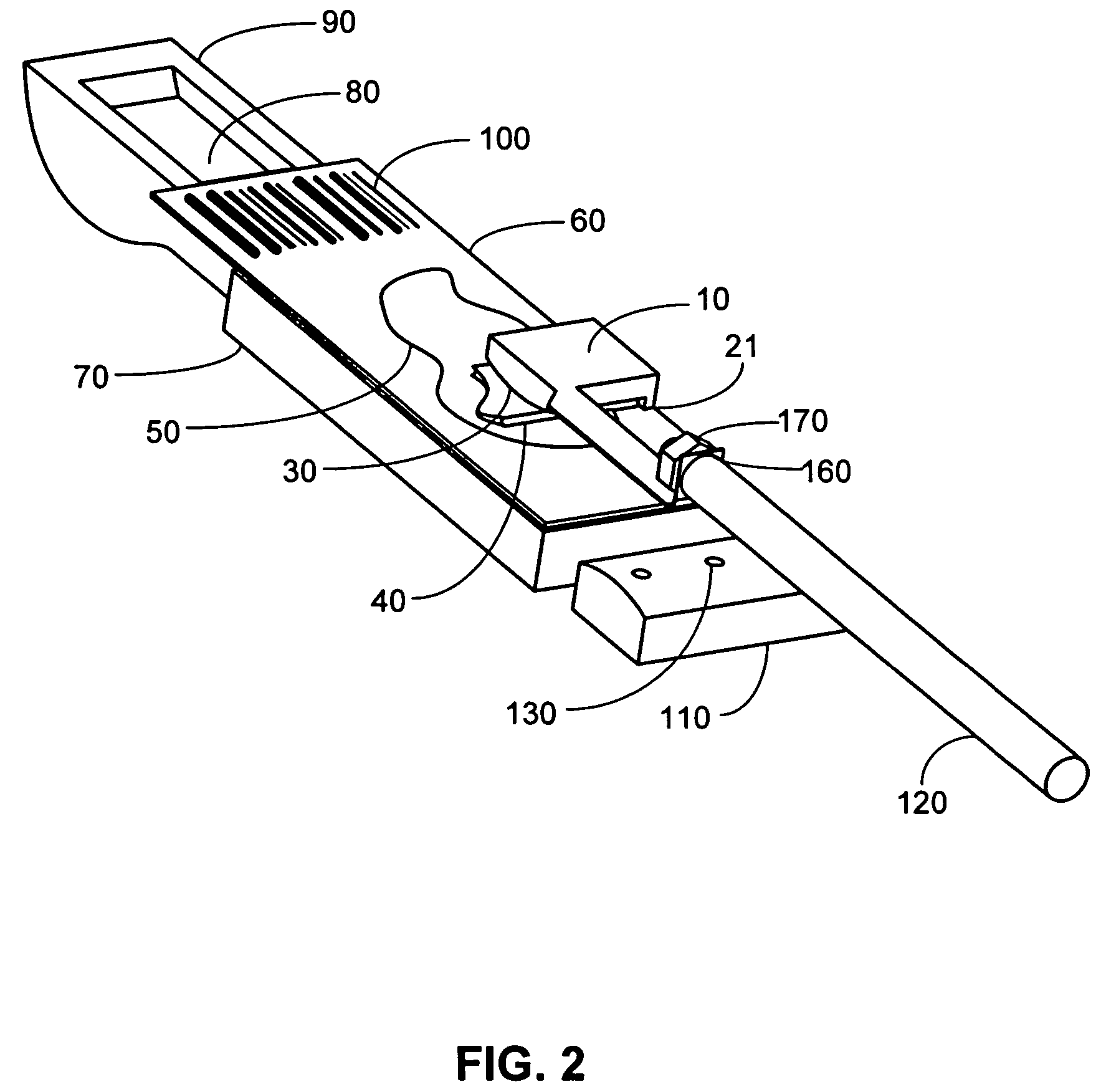
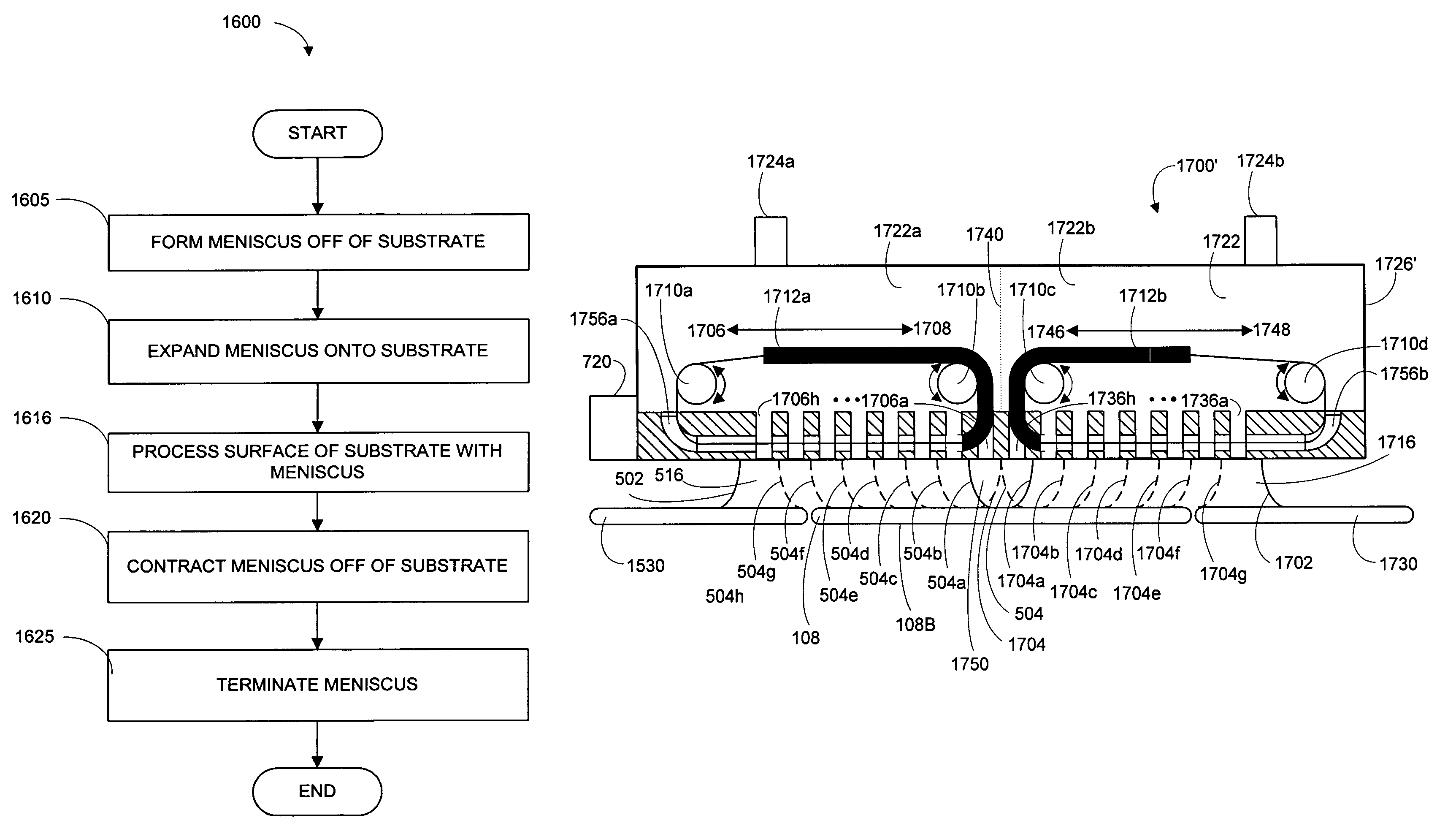
Methods and systems for processing a substrate using a dynamic liquid meniscus
InactiveUS6988327B2Increase in sizeHigh gradientDrying solid materials with heatDrying solid materials without heatEngineeringLiquid meniscus
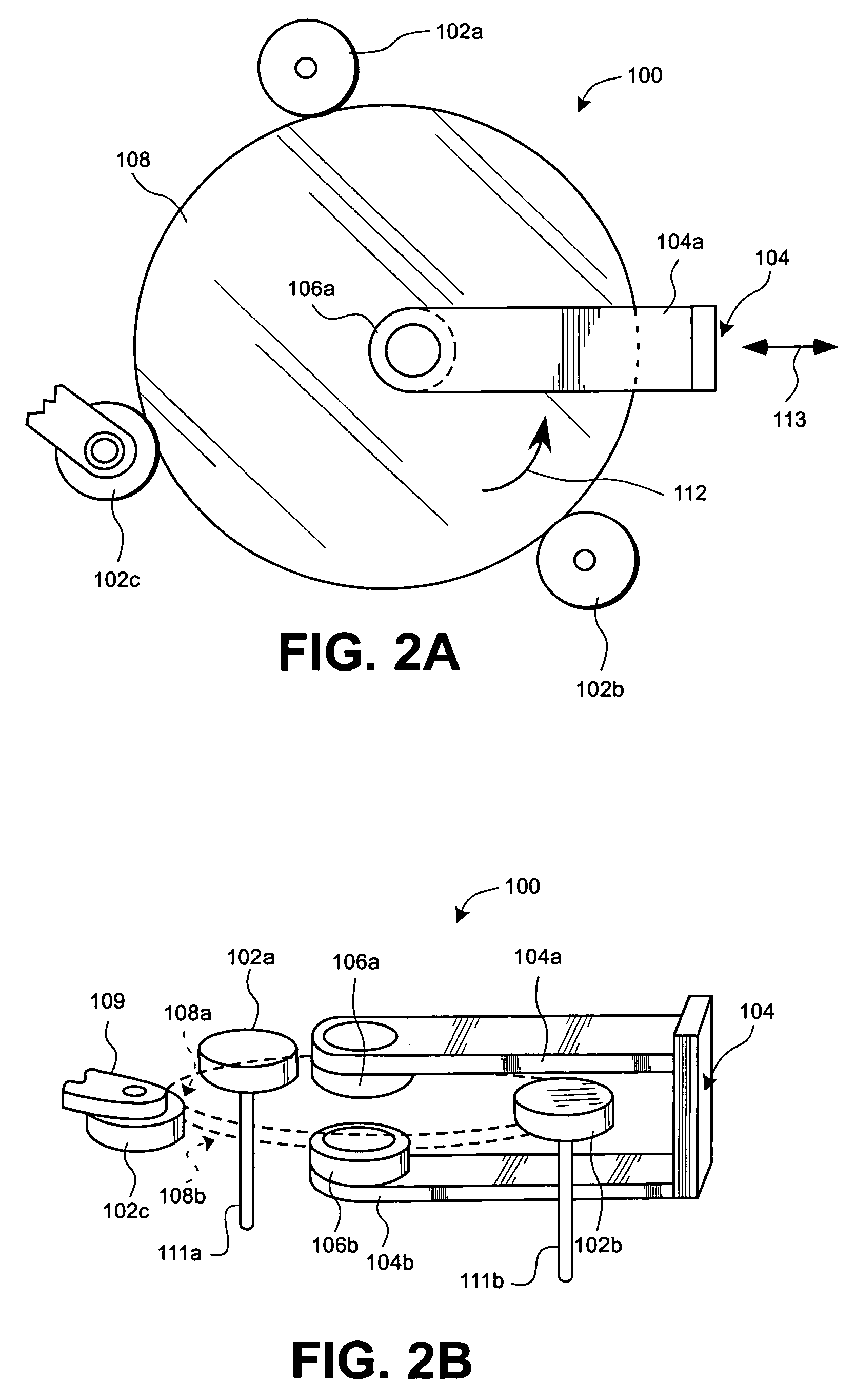
A system and method of moving a meniscus from a first surface to a second surface includes forming a meniscus between a head and a first surface. The meniscus can be moved from the first surface to an adjacent second surface, the adjacent second surface being parallel to the first surface. The system and method of moving the meniscus can also be used to move the meniscus along an edge of a substrate.
Owner:LAM RES CORP
Methods and systems for processing a substrate using a dynamic Liquid meniscus
InactiveUS20040060195A1Drying solid materials with heatDrying solid materials without heatEngineeringLiquid meniscus
A system and method of moving a meniscus from a first surface to a second surface includes forming a meniscus between a head and a first surface. The meniscus can be moved from the first surface to an adjacent second surface, the adjacent second surface being parallel to the first surface. The system and method of moving the meniscus can also be used to move the meniscus along an edge of a substrate.
Owner:LAM RES CORP
Modular capillary pumped loop cooling system
InactiveUS6981543B2Digital data processing detailsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsWorking fluidLiquid state
A modular capillary pump loop (CPL) cooling system and associated components. The modular CPL cooling system transfers heat from high-power circuit components, such as microprocessors disposed within computer chassis, to other locations within or external to the chassis, where the heat can be more easily removed. In various embodiments, the CPL cooling system includes one or more evaporators connected to one or more condensers via flexible liquid transport and vapor transport lines. A wicking structure, such as a volume of sintered copper, is disposed within each condenser. The wicking structure draws working fluid (e.g., water) in a liquid state into the evaporator based on a capillary mechanism and a pressure differential across a meniscus / vapor interface on an upper surface of the wicking structure. As the liquid meniscus is evaporated, additional fluid is drawn into the evaporator. The working fluid is then condensed back into a liquid in the condenser.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Method and apparatus for electrostatic dispensing of microdroplets
An apparatus and device for dispensing femtoliter to nanoliter volumes of liquid samples are disclosed. The apparatus includes a liquid-support plate, two electrodes, a substrate, and a control unit. The liquid support plate has a plurality of liquid-support regions, each capable of supporting a liquid meniscus thereon. The first electrode contains a plurality of electrode connections, each operatively connected to one of the liquid support regions, for electrical contact with a meniscus supported in such region. The substrate has a first side confronting the plate and an opposite side, and a plurality of sample-holding regions formed in the first side. The second electrode is disposed adjacent one of the two substrate sides. Thus, a selected volume of the liquid can be ejected from or to one or more of the liquid-support regions to or from one or more of the sample-holding regions.
Owner:SRI INTERNATIONAL
Method and apparatus for applying fluids to a biological sample
ActiveUS20060019302A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMicroscope slideLiquid meniscus
The invention is directed to a method of contacting a biological sample with a solution, comprising the steps of moving a curved surface wetted with the solution in proximity to the biological sample whereby the distance separating the wetted curved surface and the biological sample is sufficient to form a moving liquid meniscus layer between the two. The invention is also directed to an apparatus for contacting a biological sample suspected of containing a biomarker with a solution, comprising a platform for supporting a microscope slide having a biological sample thereon; a translating cap having a curved lower surface positioned above the platform, the curved lower surface being in proximity to a biological sample when in operation; means for moving the translating cap back and forth over the biological sample; and means for applying and removing liquid to and from the cap.
Owner:VENTANA MEDICAL SYST INC
Method and apparatus for applying fluids to a biological sample
ActiveUS7820381B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMicroscope slideLiquid meniscus
The invention is directed to a method of contacting a biological sample with a solution, comprising the steps of moving a curved surface wetted with the solution in proximity to the biological sample whereby the distance separating the wetted curved surface and the biological sample is sufficient to form a moving liquid meniscus layer between the two. The invention is also directed to an apparatus for contacting a biological sample suspected of containing a biomarker with a solution, comprising a platform for supporting a microscope slide having a biological sample thereon; a translating cap having a curved lower surface positioned above the platform, the curved lower surface being in proximity to a biological sample when in operation; means for moving the translating cap back and forth over the biological sample; and means for applying and removing liquid to and from the cap.
Owner:VENTANA MEDICAL SYST INC
Methods and systems for processing a bevel edge of a substrate using a dynamic liquid meniscus
InactiveUS7000622B2Increase in sizeSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLiquid meniscusMechanical engineering
Owner:LAM RES CORP
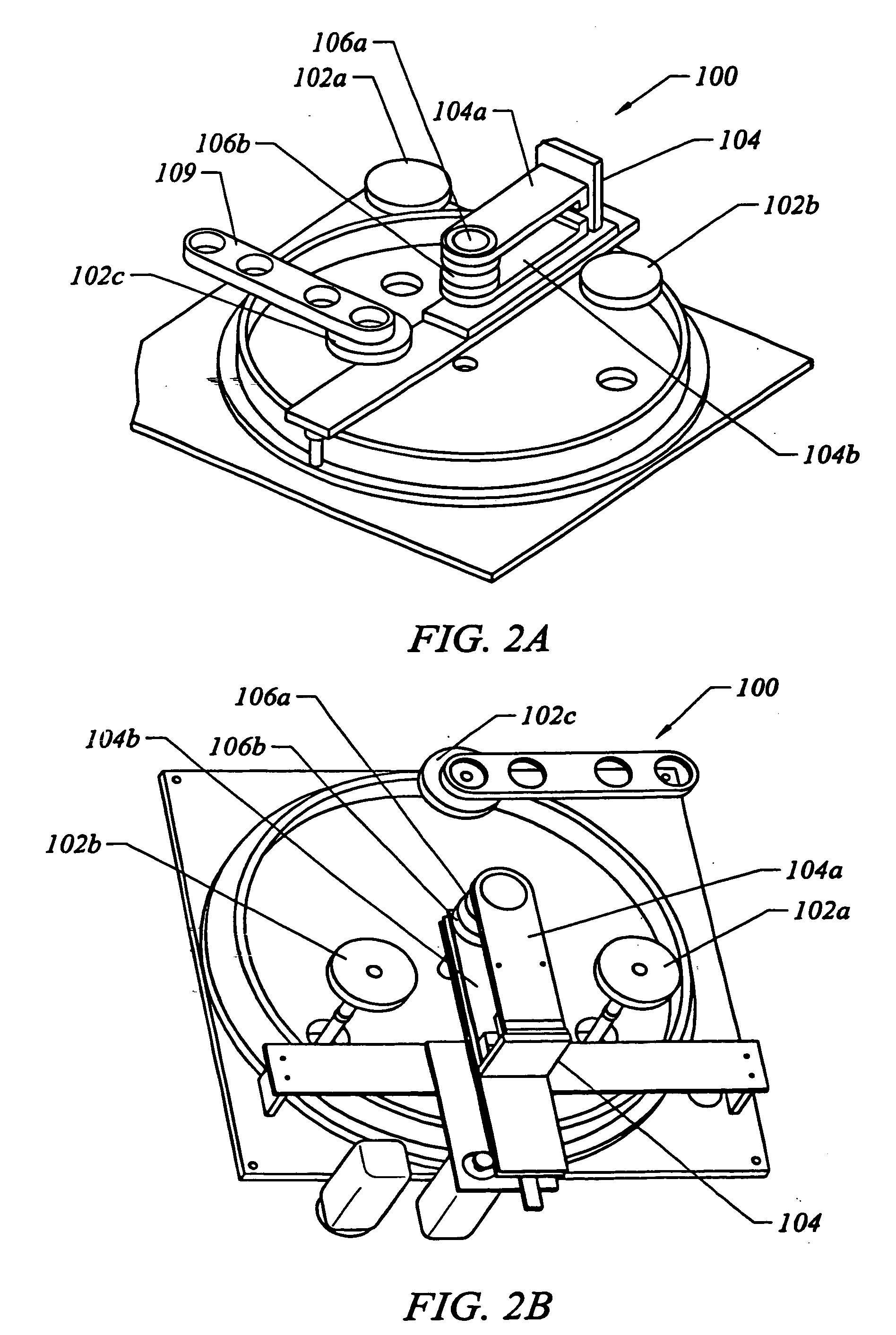
System and method for modulating flow through multiple ports in a proximity head
InactiveUS20060064895A1Drying using combination processesDrying solid materials without heatLiquid meniscusMechanical engineering
A method of forming a dynamic liquid meniscus includes forming a meniscus at a first size, the meniscus being formed between a proximity head and a first surface and changing the meniscus to a second size by modulating a flow through at least one of a set of ports on the proximity head. A system for modulating flow through the ports in a proximity head is also described.
Owner:LAM RES CORP
Modular capillary pumped loop cooling system
InactiveUS7770630B2Digital data processing detailsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsWorking fluidLiquid state
A modular capillary pump loop (CPL) cooling system and associated components. The modular CPL cooling system transfers heat from high-power circuit components, such as microprocessors disposed within computer chassis, to other locations within or external to the chassis, where the heat can be more easily removed. In various embodiments, the CPL cooling system includes one or more evaporators connected to one or more condensers via flexible liquid transport and vapor transport lines. A wicking structure, such as a volume of sintered copper, is disposed within each condenser. The wicking structure draws working fluid (e.g., water) in a liquid state into the evaporator based on a capillary mechanism and a pressure differential across a meniscus / vapor interface on an upper surface of the wicking structure. As the liquid meniscus is evaporated, additional fluid is drawn into the evaporator. The working fluid is then condensed back into a liquid in the condenser.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Image forming apparatus including recording head for ejecting liquid droplets
An image forming apparatus includes a recording head, a head driving control circuit, and a dummy ejection control circuit. The dummy ejection control circuit controls a first dummy ejection operation to eject droplets to a non-image-forming area per a constant length of a continuous medium and second dummy ejection operation to eject droplets not contributing to image formation to an image forming area. The head driving control circuit applies a first non-ejection pulse to pressure generators corresponding to a non-ejection nozzle of the plurality of nozzles to vibrate a meniscus of liquid in the non-ejection nozzle without ejecting liquid droplets, and applies a second non-ejection pulse, which vibrates the meniscus of liquid greater than the first non-ejection pulse, to pressure generators corresponding to non-ejection nozzles of the plurality of nozzles to vibrate a meniscus of liquid in the non-image-forming area.
Owner:RICOH KK
System and method for modulating flow through multiple ports in a proximity head
InactiveUS7143527B2Drying using combination processesDrying solid materials without heatLiquid meniscusMechanical engineering
A method of forming a dynamic liquid meniscus includes forming a meniscus at a first size, the meniscus being formed between a proximity head and a first surface and changing the meniscus to a second size by modulating a flow through at least one of a set of ports on the proximity head. A system for modulating flow through the ports in a proximity head is also described.
Owner:LAM RES CORP
System and method of programming an energized ophthalmic lens
A method and a system for the selection and programming of an energized ophthalmic lens are disclosed. More specifically, the energized ophthalmic lens which can include a variable state arcuate shaped liquid meniscus lens capable of changing vision correction properties upon the receipt of an activation signal. According to some aspects of the disclosure, the system and method comprise vision simulation software configured to use patient's eye related data and product design options to select the ophthalmic lens and an operational protocol for the change of optical properties.
Owner:JOHNSON & JOHNSON VISION CARE INC
Stress free etch processing in combination with a dynamic liquid meniscus
InactiveUS7078344B2Quantity minimizationLow down-force CMPElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsEngineeringLiquid meniscus
A system and method for planarizing and controlling non-uniformity on a patterned semiconductor substrate includes receiving a patterned semiconductor substrate. The patterned semiconductor substrate having a conductive interconnect material filling multiple features in the pattern. The conductive interconnect material having an overburden portion. A bulk of the overburden portion is removed and a remaining portion of the overburden portion has a non-uniformity. The non-uniformity is mapped, optimal solution determined and a dynamic liquid meniscus etch process recipe is developed to correct the non-uniformity. A dynamic liquid meniscus etch process, using the dynamic liquid meniscus etch process recipe, is applied to correct the non-uniformity to substantially planarize the remaining portion of the overburden portion.
Owner:LAM RES CORP
Stress free etch processing in combination with a dynamic liquid meniscus
ActiveUS20050090093A1Non-uniformity can be correctedQuantity minimizationElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsEngineeringLiquid meniscus
A system and method for planarizing and controlling non-uniformity on a patterned semiconductor substrate includes receiving a patterned semiconductor substrate. The patterned semiconductor substrate having a conductive interconnect material filling multiple features in the pattern. The conductive interconnect material having an overburden portion. A bulk of the overburden portion is removed and a remaining portion of the overburden portion has a non-uniformity. The non-uniformity is mapped, optimal solution determined and a dynamic liquid meniscus etch process recipe is developed to correct the non-uniformity. A dynamic liquid meniscus etch process, using the dynamic liquid meniscus etch process recipe, is applied to correct the non-uniformity to substantially planarize the remaining portion of the overburden portion.
Owner:LAM RES CORP
Methods and systems for processing a bevel edge of a substrate using a dynamic liquid meniscus
InactiveUS20060081270A1Increase in sizeSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLiquid meniscusMeniscus
A system and method for processing an edge of a substrate includes an edge roller and a first proximity head. The first proximity head being mounted on the edge roller. The first proximity head capable of forming a meniscus and including a concave portion and multiple ports opening into the concave portion. The concave portion being capable of receiving an edge of a substrate and the ports including at least one process liquid injection port, at least one vacuum port and at least one surface tension control port.
Owner:LAM RES CORP
Heat pipe liquid absorbing core capillary flow measuring method and device based on infrared image observation
InactiveCN103994803ASolve the problem of fuzzy and difficult positioningAccurate Capillary Flow MeasurementsMachines/enginesUsing optical meansGlass coverEmissivity
The invention discloses a heat pipe liquid absorbing core capillary flow measuring method and device based on infrared image observation. The measuring method includes the steps that one end of a liquid absorbing core is fixed through a liquid absorbing core fixing assembly, the liquid absorbing core is moved through a moving and adjusting assembly, the other end of the liquid absorbing core is immersed in a liquid working medium, the flowing process of the liquid meniscus in the liquid absorbing core is accurately monitored through a glass cover hole by the adoption of a thermal infrared imager, and a monitoring record is processed to quantitatively obtain the capillary flow distance and flow speed. By using the characteristic that display effects of infrared images are different due to the emissivity difference of the liquid working medium, a metal matrix of the liquid absorbing core and a porous medium, defects of a traditional capillary flow measuring method are overcome, the heat pipe liquid absorbing core capillary flow measuring method is particularly suitable for quantitatively and accurately monitoring the capillary flow of the colorless clear liquid in the heat pipe liquid absorbing core, experimental devices are simple, measurement accuracy is high, a reliable means is provided for testing and estimating capillary performance of the heat pipe liquid absorbing core, and the expansion of the infrared thermography from a traditional thermal measurement field to the capillary flow application field is achieved.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Device and method for measuring internal contact angle of high-temperature and high-pressure capillary tube
ActiveCN103499517AEffective simulationWide measurement rangeSurface/boundary effectCapillary TubingEngineering
The invention discloses a device and method for measuring an internal contact angle of a high-temperature and high-pressure capillary tube. The device comprises a steel body, the capillary tube and a second fluid injecting pump, wherein the steel body is provided with a through hole, and observation windows are sealed at two ends of the through hole respectively; one end of the capillary tube is arranged in the through hole of the steel body in a penetrating manner, and the other end of the capillary tube is connected with a first fluid injecting pump through a first fluid injecting pipeline; the second fluid injecting pump is connected with a second fluid injecting pipeline, and the second fluid injecting pipeline extends into the through hole of the steel body. According to the device and method for measuring the internal contact angle of the high-temperature and high-pressure capillary tube, various gases can be measured, capillary tubes with different internal diameters can be freely replaced, and the purpose of measuring the contact angle of a gas-liquid meniscus surface under the oil deposit condition is realized.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
Methods and systems for processing a substrate using a dynamic liquid meniscus
InactiveUS20060150435A1Increase in sizeHigh gradientDrying using combination processesDrying solid materials without heatEngineeringLiquid meniscus
Owner:LAM RES CORP
Liquid Ejection Apparatus
ActiveUS20080122887A1Excellent ejection stabilityImprove image qualityOther printing apparatusLiquid jetEngineering
In a liquid ejection apparatus, having: a liquid ejection head having, a nozzle plate having a nozzle to eject liquid, a cavity to reserve liquid ejected form a ejection hole of the nozzle, a pressure generating device to form a meniscus of the liquid, and a ejecting voltage applying device to apply a ejection voltage to the liquid in the nozzle; a operation control device to control application a drive voltage to drive the pressure generating device and application of the ejection voltage by the ejection voltage applying device; and a counter electrode opposite to the liquid ejection head; wherein in the liquid ejection device in which the liquid is ejected by a static electric attraction force generated between the liquid in the nozzle to which a voltage is applied by the ejection voltage applying device and the counter electrode, and by a pressure generated in the nozzle, the pressure generating device to form the liquid meniscus forms the meniscus having a height of equal to or more than 1.3 times a radius of the nozzle on the ejection hole of the nozzle.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA INC
System and method for modulating flow through multiple ports in a proximity head
InactiveUS7003899B1Drying gas arrangementsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringLiquid meniscus
A method of forming a dynamic liquid meniscus includes forming a meniscus at a first size, the meniscus being formed between a proximity head and a first surface and changing the meniscus to a second size by modulating a flow through at least one of a set of ports on the proximity head. A system for modulating flow through the ports in a proximity head is also described.
Owner:LAM RES CORP
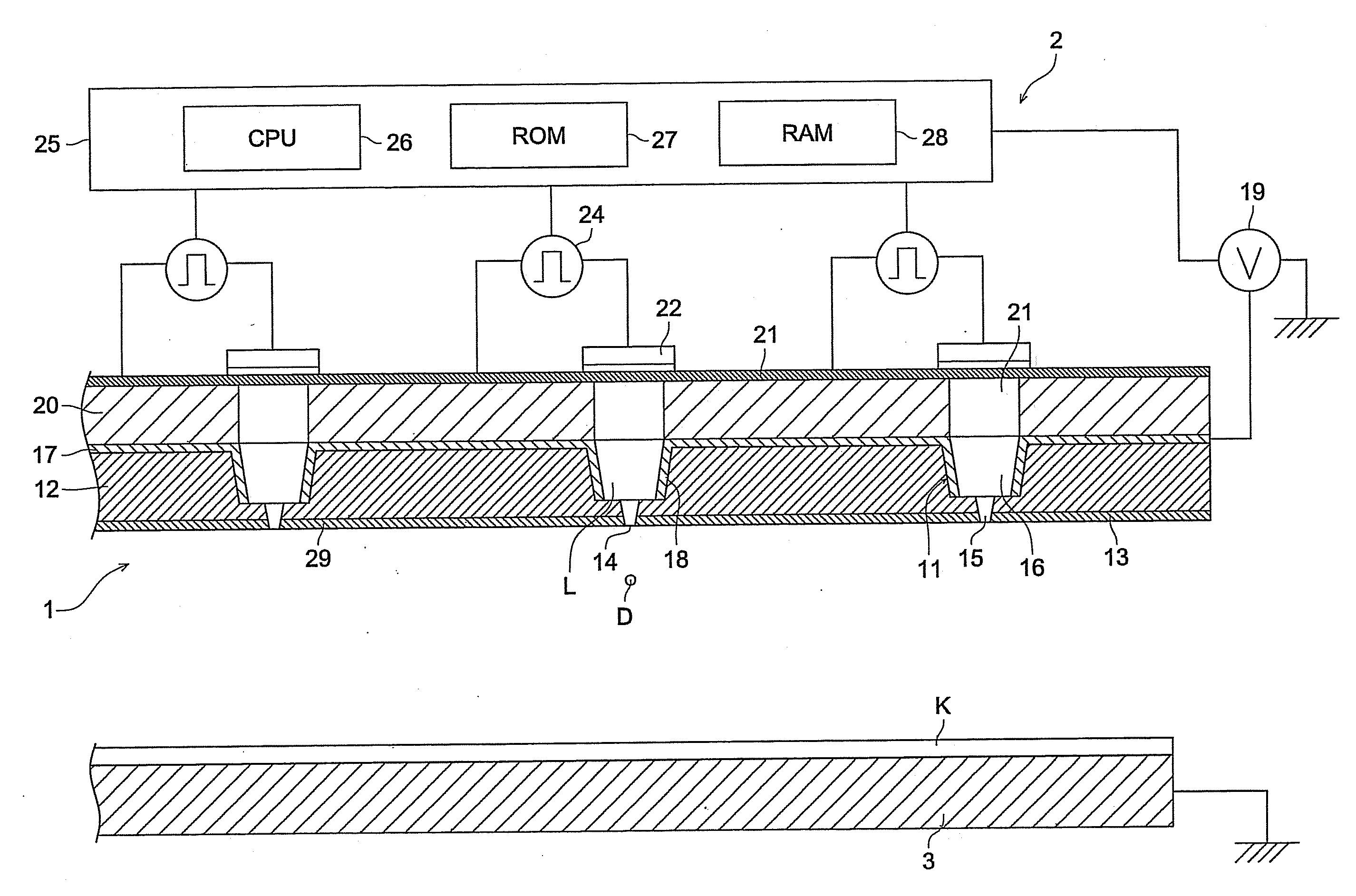
Driving method of liquid discharge head and liquid discharge apparatus
InactiveUS20110074845A1Return quicklySpeedup of drive frequencyInking apparatusOther printing apparatusLiquid meniscusActuator
A driving method of a liquid discharge head including discharge ports, flow paths communicated with the discharge ports, a first actuator provided on the flow paths, a second actuator provided at a position further from the discharge port than the first actuator of the flow paths, and a common liquid chamber communicated with the flow paths, includes: contracting the flow path and expanding the flow path by the first actuator to discharge liquid from the discharge port; starting contraction of the flow path the second actuator when or before flow of liquid from the common liquid chamber to the discharge port in the vicinity of the second actuator, disappears to allow a meniscus of liquid, located at an inner position of the flow path, to project from the discharge port; and starting expansion of the flow path by the second actuator while the meniscus projects from the discharge port.
Owner:CANON KK
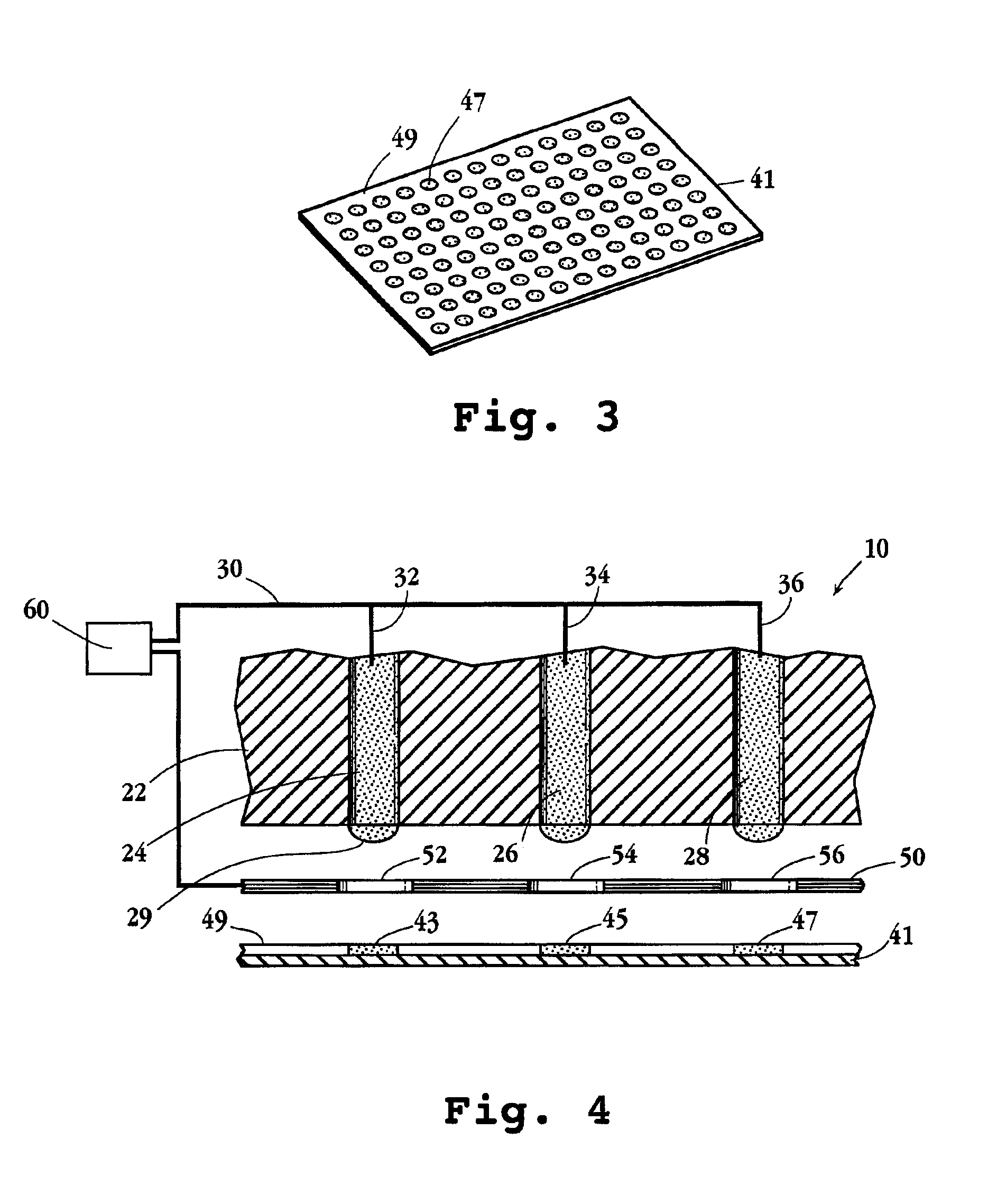
Method and Apparatus for Physical Confinement of a Liquid Meniscus over a Semiconductor Wafer
InactiveUS20100300492A1Preserve confinement characteristicSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCleaning using liquidsLeading edgeLiquid medium
Apparatus, methods and systems for physically confining a liquid medium applied over a semiconductor wafer include a first and a second chemical head that are disposed to cover at least a portion of a top and an underside surface of the semiconductor wafer. Each of the first and the second chemical heads include an angled inlet conduit at a leading edge of the respective chemical heads to deliver liquid chemistry into a pocket of meniscus in a single phase. The pocket of meniscus is defined over the portion of the top and underside surface of the semiconductor wafer covered by the chemical heads and is configured to receive and contain the liquid chemistry applied to the surface of the semiconductor wafer as a meniscus. A step is formed at a leading edge of the first and second chemical heads along an outer periphery of the pocket of meniscus to substantially confine the meniscus of the liquid chemistry within the pocket of meniscus. The step covers at least a portion of the pocket of meniscus and the step's height is sufficient to preserve confinement characteristic of the meniscus. An inner return conduit is defined within the pocket of meniscus at a trailing edge of the respective chemical heads and is used to remove the liquid chemistry from the surface of the semiconductor wafer in a single phase after the cleaning process.
Owner:LAM RES CORP
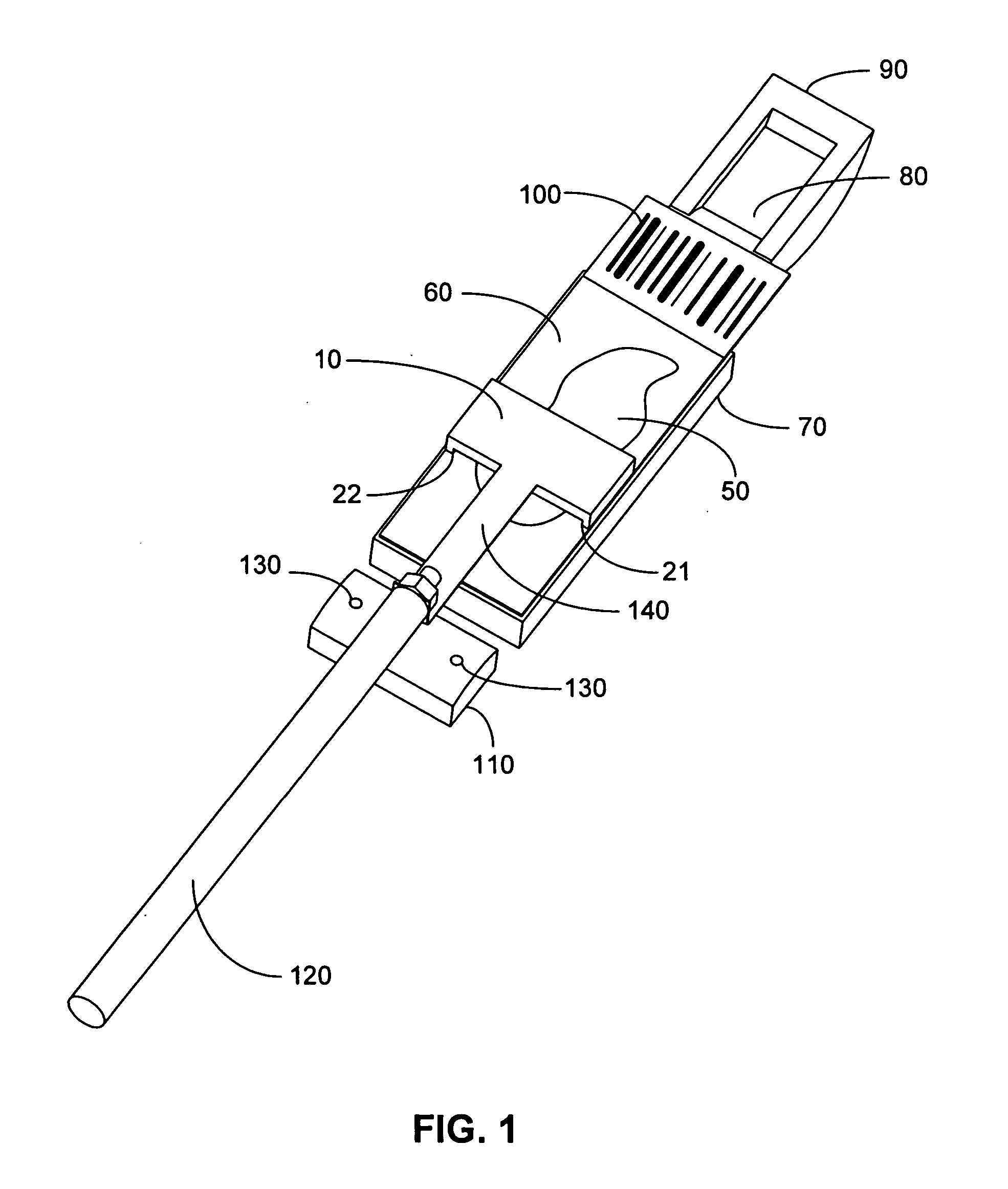
Device and method for holding a substrate
InactiveUS20070116551A1Big contactAvoid contactLiquid surface applicatorsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringLiquid meniscus
A device and method for holding a substrate, e.g., a semiconductor wafer, during a process, e.g., a liquid meniscus process, the substrate having a first side and a second side. The device includes one or more holding components, e.g., fingers, configured to contact a second side of the substrate without significantly contacting the first side of the substrate. At least one of the holding components may be configured to be moved during the process so as to prevent the at least one holding components from effecting the process, e.g., contacting the liquid meniscus. Such an arrangement may be employed when the substrate includes a top side having at least one structure or feature thereon, it being desirable that the holding components avoid contact with the structures or features during the process.
Owner:MATERIALS & TECH
Immersion lithographic process using a variable scan speed
InactiveUS20080297749A1Speed of can varyPhotomechanical apparatusPhotographic printingLithographic artistEngineering
A lithography system and a lithography method is provided for increasing reliability and efficiency of immersion lithography. By varying a scan speed between a wafer and an optical component depending on at least one process parameter during exposure of the wafer, loosening of a fluid meniscus during the relative movement of the optical component and the wafer is avoided.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Method and apparatus for manufacturing electronic assemblies, electronic assemblies manufactured by the method or in the apparatus
InactiveCN102272909ASolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectronic componentLiquid meniscus
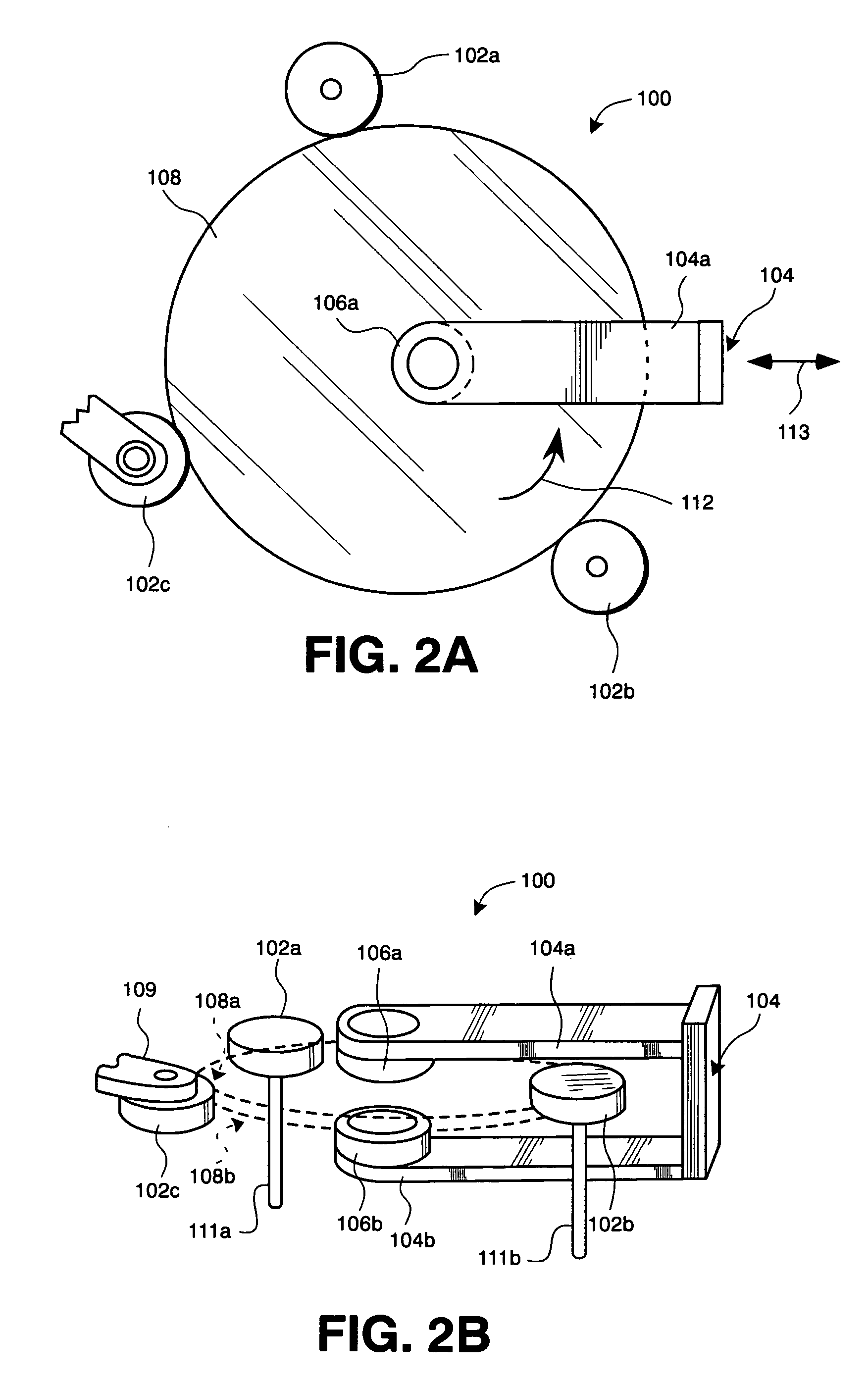
A method of producing an electronic module with at least one electronic component and one carrier. A structure is provided on the carrier so that the electronic component can take a desired target position relative to the structure. The structure is coated with a liquid meniscus suitable for receiving the electronic component. Multiple electronic components are provided at a delivery point for the electronic components. The carrier, with the structure, is moved nearby and opposite to the delivery point, where the delivery point delivers one of the electronic components without contact, while the structure on the carrier is moving near the delivery point, so that after a phase of free movement the electronic component at least partly touches the material, and the carrier, with the structure, is moved to a downstream processing point, while the electronic component aligns itself to the structure on the liquid meniscus.
Owner:MUEHLBAUEHR AG
Post etch wafer surface cleaning with liquid meniscus
InactiveCN101479831ASemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCleaning using liquidsSurface cleaningLiquid meniscus
Owner:LAM RES CORP
Liquid ejector cleaning method and liquid ejector
Recording head of a printer is sealed by a cap connected with a gear pump. Fluid is discharged from a nozzle through the cap by a negative pressure being generated by the gear pump. The gear pump is driven at a first rotational speed to suck the fluid in the cap and to discharge the fluid from the nozzle. Subsequently, the gear pump is driven at a second rotational speed lower than the first rotational speed and then it is stopped. This prevents backflow of the fluid to a liquid ejection head and breakage of a liquid meniscus in the nozzle of the liquid ejection head occurring when cleaning of the liquid ejection head is ended.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Method for nano-dripping 1d, 2d or 3D structures on a substrate
InactiveUS20140205761A1Improve accuracyExtreme precisionSpecific nanostructure formationLiquid surface applicatorsChemical physicsPotential difference
A method for the production of nano- or microscaled ID, 2D and / or 3D depositions from an solution (6), by means of a liquid reservoir (2) for holding the ink with an outer diameter (3,D) of at least 50 nm, is proposed, wherein there is provided an electrode (7,8 or 9) in contact with said ink (6) in said capillary (2), and wherein there is a counter electrode in and / or on and / or below and / or above a substrate (15) onto which the depositions are to be produced, including the steps of: i) keeping the electrode (7, 8, 9) and the counter electrode (15, 18) on an essentially equal potential; ii) establishing a potential difference between the electrode (7, 8, 9) and the counter electrode (15, 18) leading to the growth of an ink meniscus (1) at the nozzle (3) and to the ejection of droplets (13) at this meniscus with a homogeneous size smaller than the meniscus size (11) at a homogenous ejection frequency; keeping the voltage applied while the continuously dried droplets leave behind the dispersed material which leads a structure to emerge with essentially the same diameter as a single droplet, wherein the distance between the substrate (1) and the nozzle (3) is smaller than or equal to 20 times the meniscus diameter at least at the moment of nano-droplet ejection (12); wherein the conductivity of the ink (6) is high enough to stabilize the liquid meniscus during droplet ejection;
Owner:ETH ZZURICH
Post etch wafer surface cleaning with liquid meniscus
InactiveUS7597765B2Improve cleaning methodsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCleaning using liquidsSurface cleaningLiquid meniscus
A method for cleaning the surface of a semiconductor wafer is disclosed. A first cleaning solution is applied to the wafer surface to remove contaminants on the wafer surface. The first cleaning solution is removed with some of the contaminants on the wafer surface. Next, an oxidizer solution is applied to the wafer surface. The oxidizer solution forms an oxidized layer on remaining contaminants. The oxidizer solution is removed and then a second cleaning solution is applied to the wafer surface. The second cleaning solution is removed from the wafer surface. The cleaning solution is configured to substantially remove the oxidized layer along with the remaining contaminants.
Owner:LAM RES CORP
Substrate preparation using megasonic coupling fluid meniscus
InactiveUS20100319726A1Improve operationEasy to prepareElectrostatic cleaningSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringAcoustic wave
A method for cleaning a substrate is provided. The method includes receiving the substrate using a carrier that forms a circular opening, the substrate being positioned in the circular opening of the carrier. The holding of the substrate enables exposure of both a first side and a second side of the substrate at a same time. Then, moving the substrate along a direction, and while moving the substrate: (i) applying a chemistry onto the first side of the substrate, where the first side of the substrate having material to be removed; (ii) forming a fluid meniscus against the second side of the substrate at a location that is opposite a location onto which the chemistry is applied; and (iii) applying megasonic energy to the fluid meniscus while the fluid meniscus is applied against the second side. The megasonic energy increases mass transport of the chemistry to enhance removal of the material to be removed from the first side.
Owner:BOYD JOHN M +2
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com