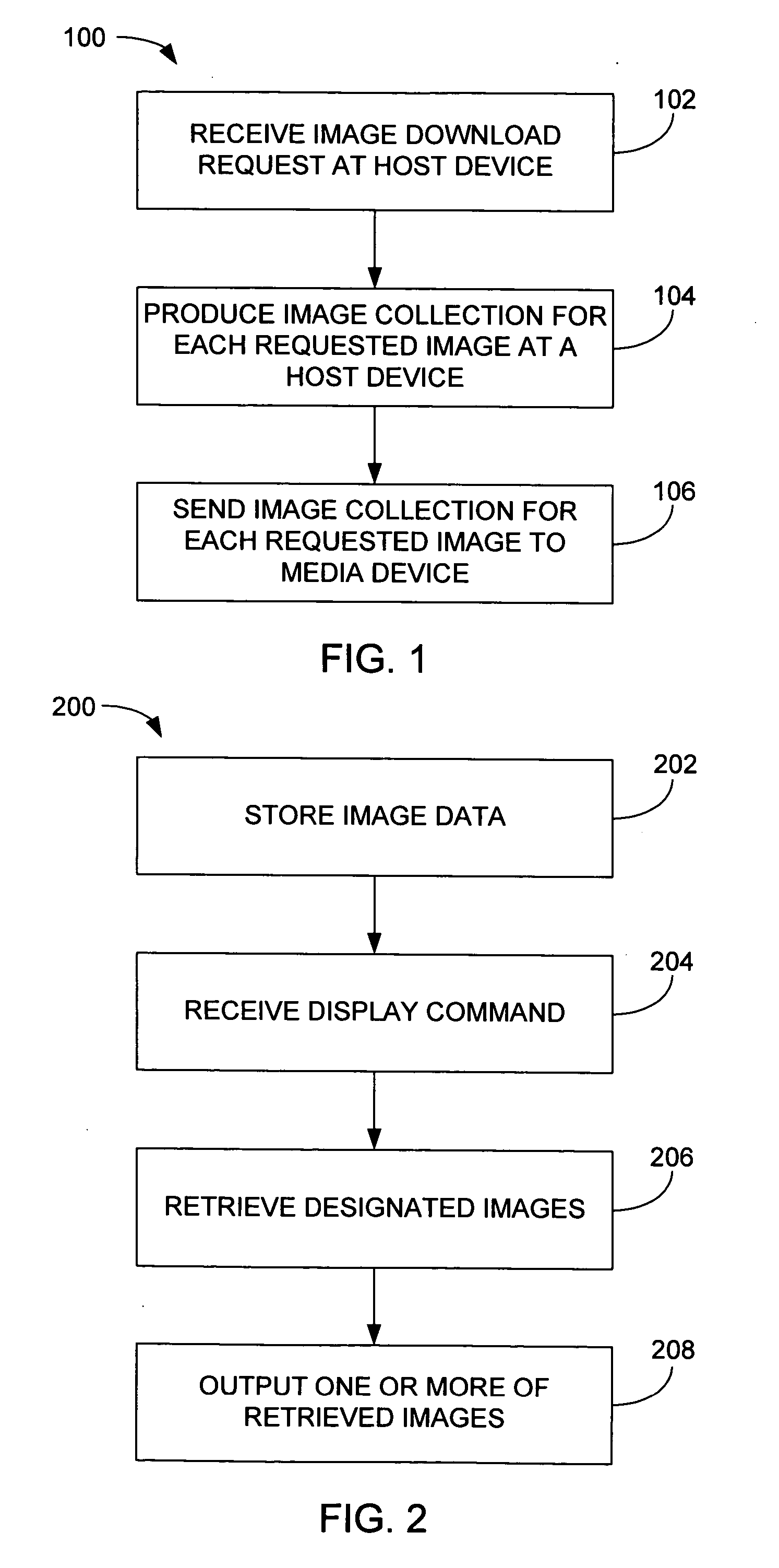
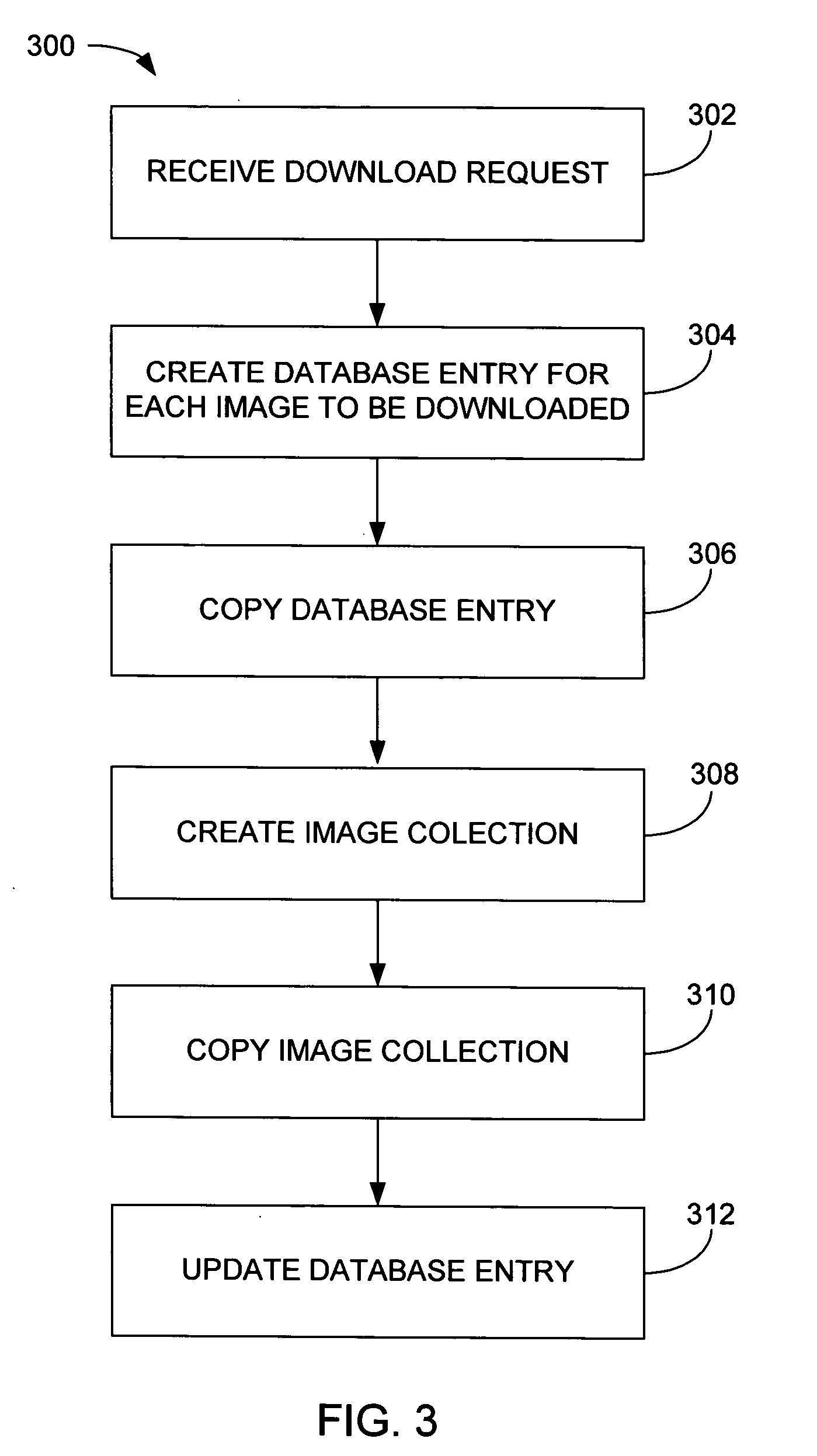
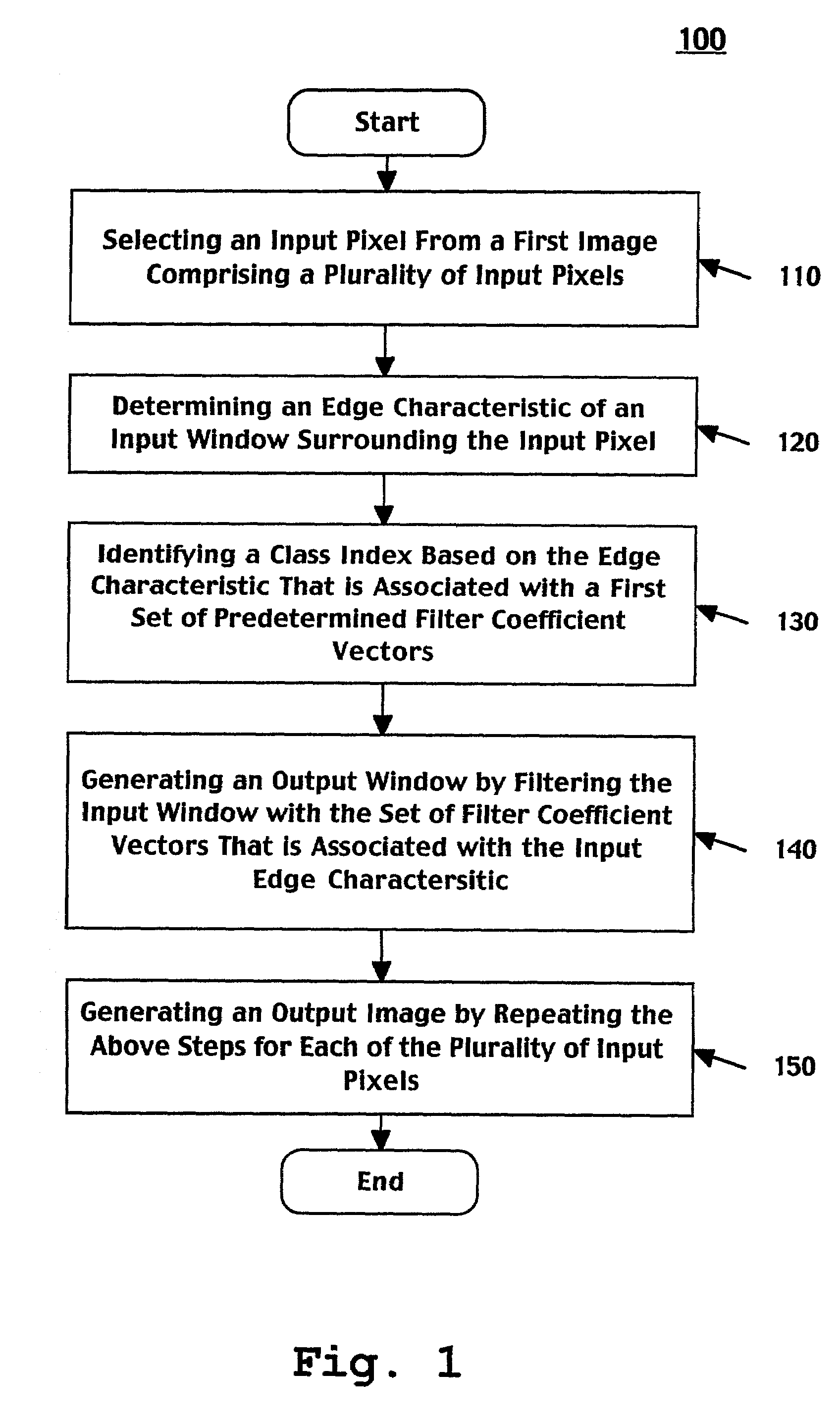
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
616 results about "Image scale" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Graphical search engine visual index
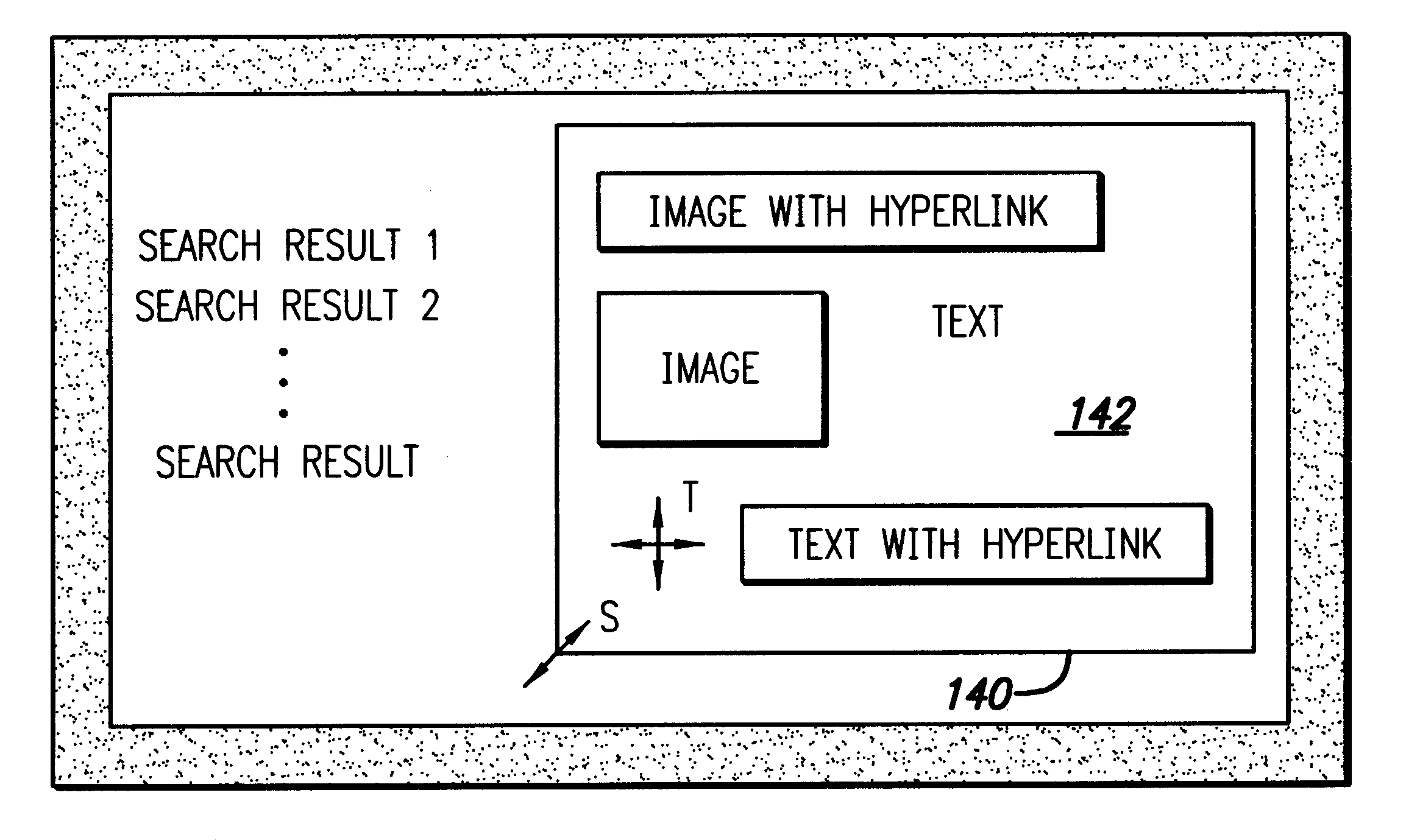
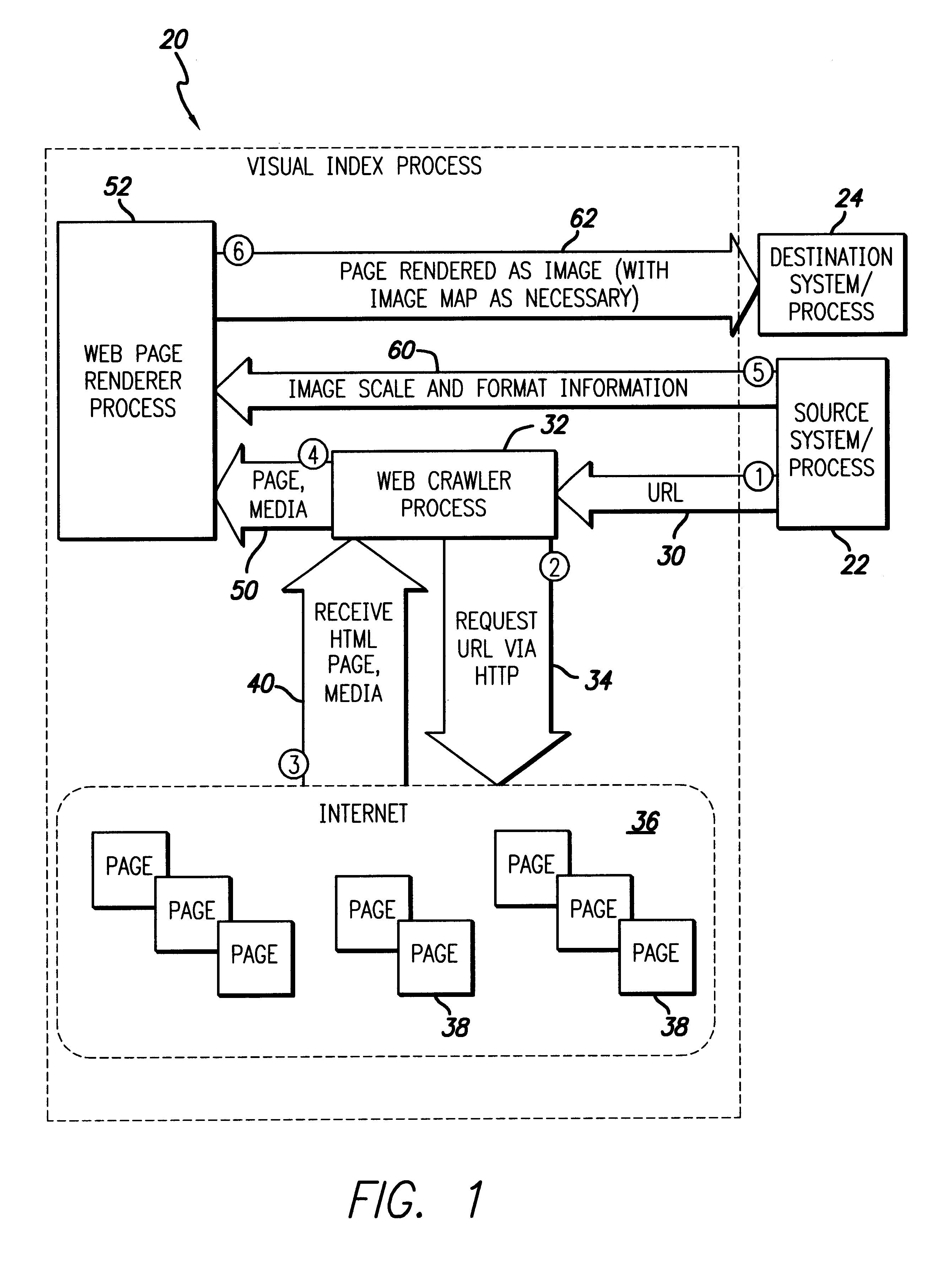
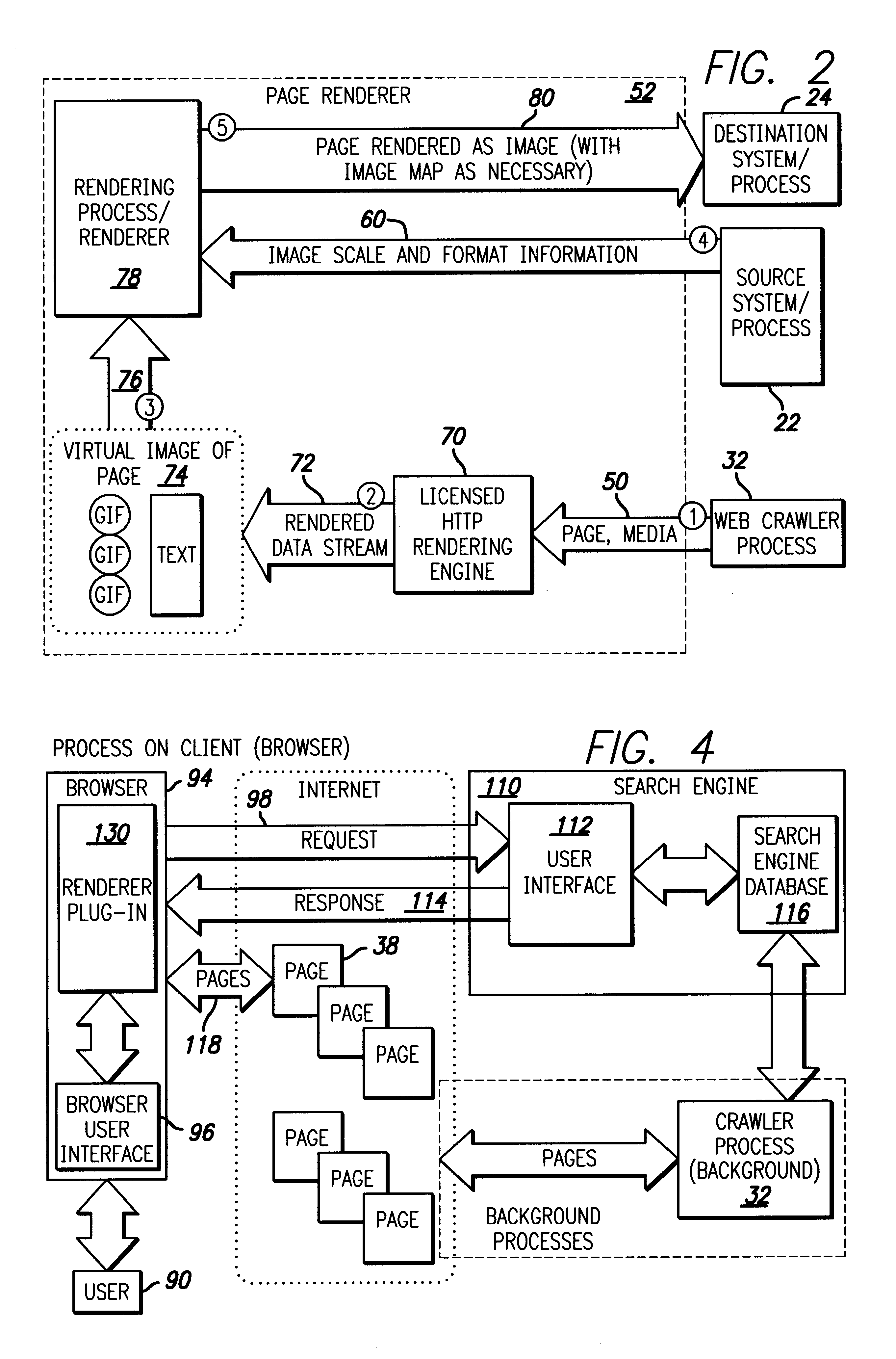
InactiveUS6271840B1Faster perusalQuick reviewWeb data indexingSpecial data processing applicationsHyperlinkGraphics
A visual index method provides graphical output from search engine results or other URL lists. Search engine results or a list of URLs are passed to a web crawler that retrieves the web page and other media information present at the associated URL. The web crawler then passes this information to a page renderer which also receives image scale and format information regarding the web pages present at the URLs. The graphical information as well as other media information is then rendered into a reduced graphical form so that the page may be summarily reviewed by the user. Media, visual, or other information may also be downwardly scaled as appropriate or rendered in its original as appropriate (such as with audio data streams). A variety of convenient formats allows the user to quickly and readily scan the presentation at the URL web pages or other data present. Image maps associated with the reduced images may also provide hyperlink access to the linked web page and / or multimedia allowing the links present on the web page in its original to be accessed through the reduced image provided by the web page renderer.
Owner:HYPER SEARCH LLC
Image scaling arrangement
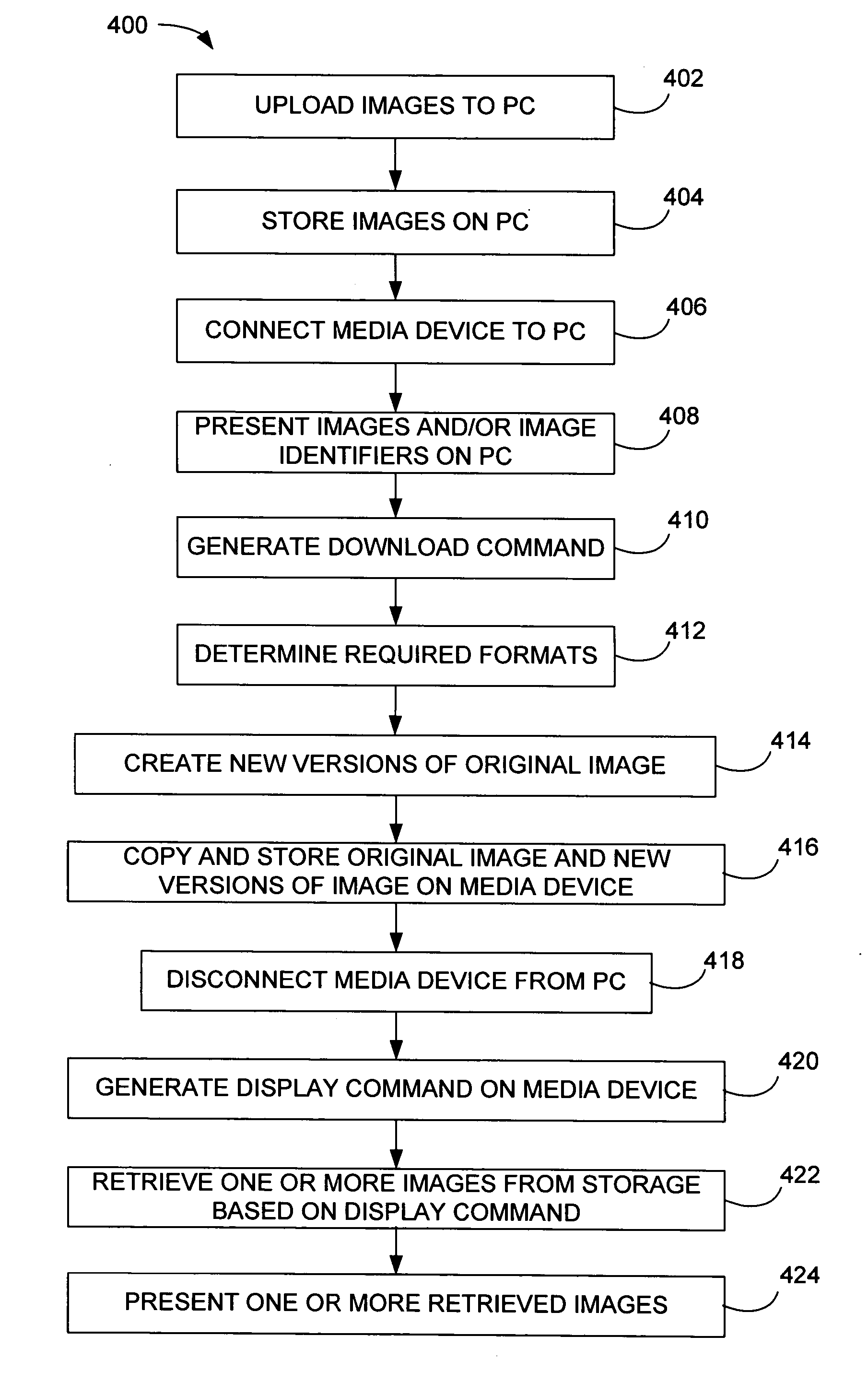
ActiveUS20060088228A1Facilitate communicationData processing applicationsRecord information storageComputer graphics (images)Computer printing
Methods and system for transferring images between devices is disclosed. For example, differently scaled images by a host device may automatically and / or selectively be transferred to a media player for display. In turn, appropriately scaled images may be transferred automatically and / or selectively to another display device for example a TV, camera or printer. The selectivity may occur either at the host level or at the player level.
Owner:APPLE INC
Resizing images to improve network throughput
InactiveUS6310601B1Digital data information retrievalCathode-ray tube indicatorsImage scaleClient-side
A method to resize an image on a server comprising the steps of: hosting multimedia content on a server, wherein said server is coupled to one or more client systems capable of rendering multimedia content, wherein said multimedia content includes at least one image; receiving user requests to transmit user selected multimedia content; determining the display size directives of each image referenced on said user selected multimedia content; scaling said image referenced to the size specified in said multimedia content; and transmitting said user selected multimedia content with said image scaled to said size directive. A server for hosting multimedia content is electrically connected to one or more client systems for rendering multimedia content.
Owner:IBM CORP
System and method for image based sensor calibration
InactiveUS7085400B1Accurate and free-hand calibrationEasy to detectImage enhancementImage analysisData setImage scale
Apparatus and methods are disclosed for the calibration of a tracked imaging probe for use in image-guided surgical systems. The invention uses actual image data collected from an easily constructed calibration jig to provide data for the calibration algorithm. The calibration algorithm analytically develops a geometric relationship between the probe and the image so objects appearing in the collected image can be accurately described with reference to the probe. The invention can be used with either two or three dimensional image data-sets. The invention also has the ability to automatically determine the image scale factor when two dimensional data-sets are used.
Owner:SURGICAL NAVIGATION TECH
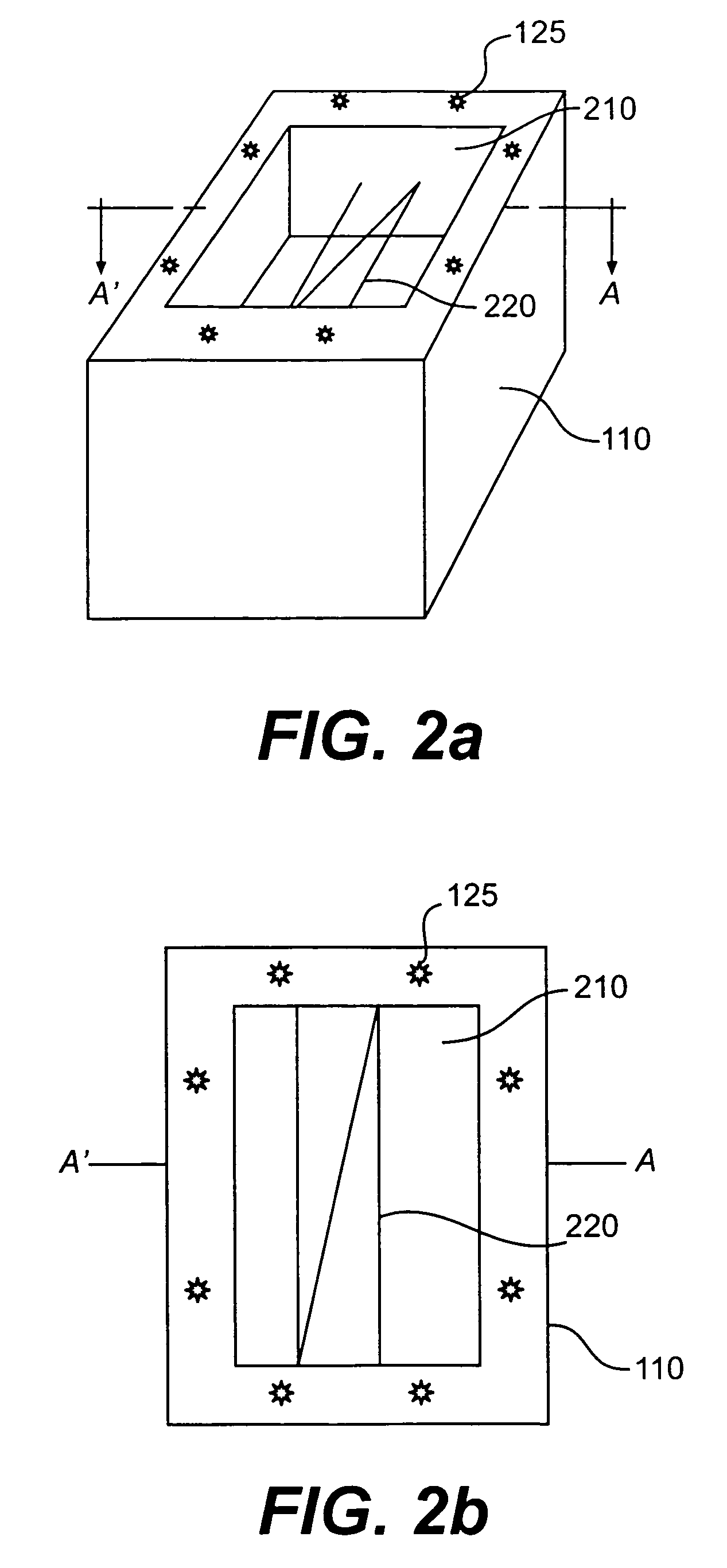
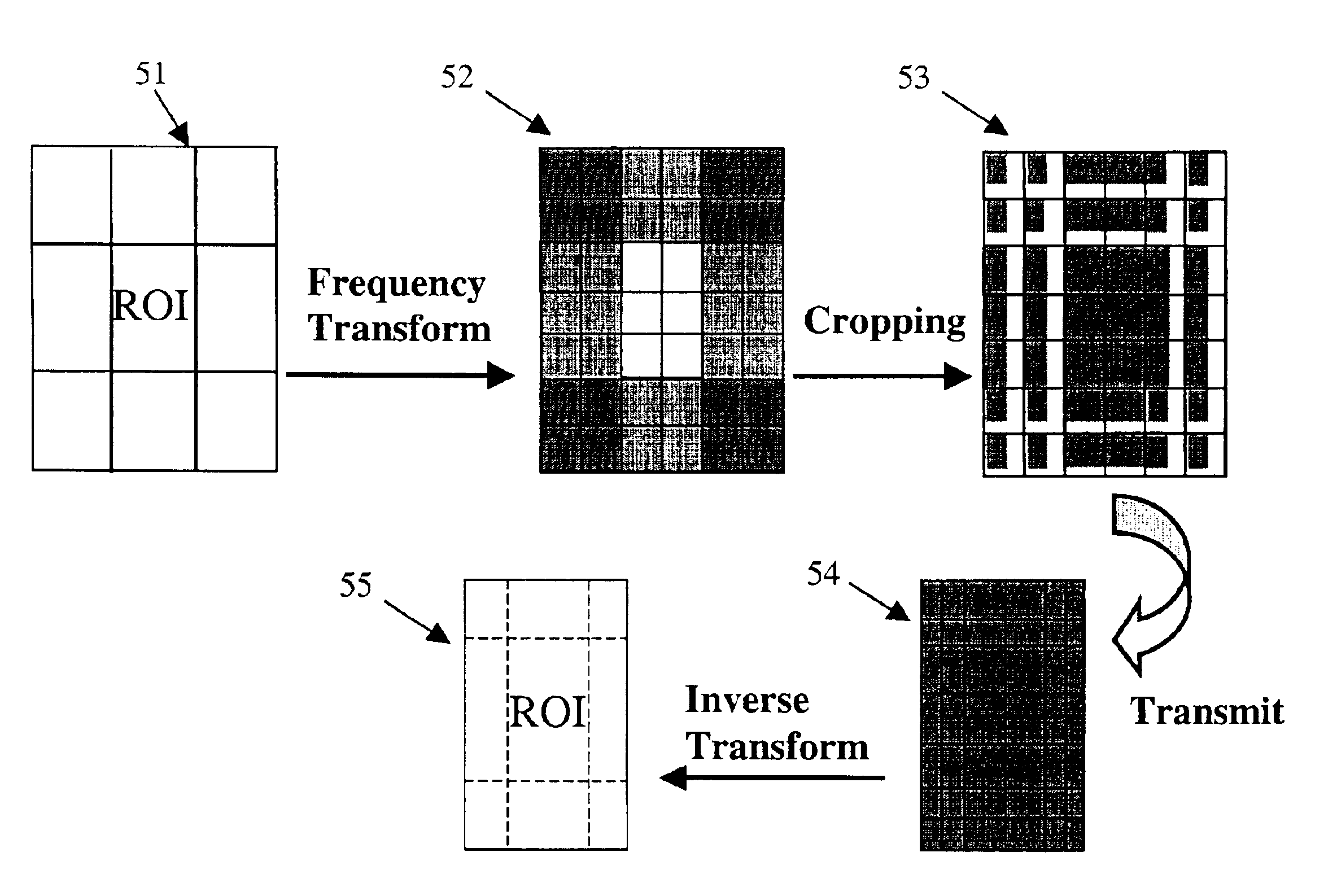
Image transmission for low bandwidth with region of interest
InactiveUS6882755B2Pulse modulation television signal transmissionCharacter and pattern recognitionImage transferImage scale
A system and method of transmitting an image adapted to a first display area size, such as a standard computer screen having a particular pixel-by-pixel resolution, to an apparatus having a smaller second display area size by scaling the image through coefficient cropping its frequency domain representation. When the cropped frequency coefficients are used to display an image within the second smaller display area, a scaled version of the image is displayed. In a specific embodiment, frequency domain coefficients are cropped such that a region of interest of the image is scaled down less than the remainder of the image when displayed in the second smaller display area. Scaling in this manner provides the user with a readable region of interest with the remainder of the image scaled down so as to facilitate easy image navigation by the user.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
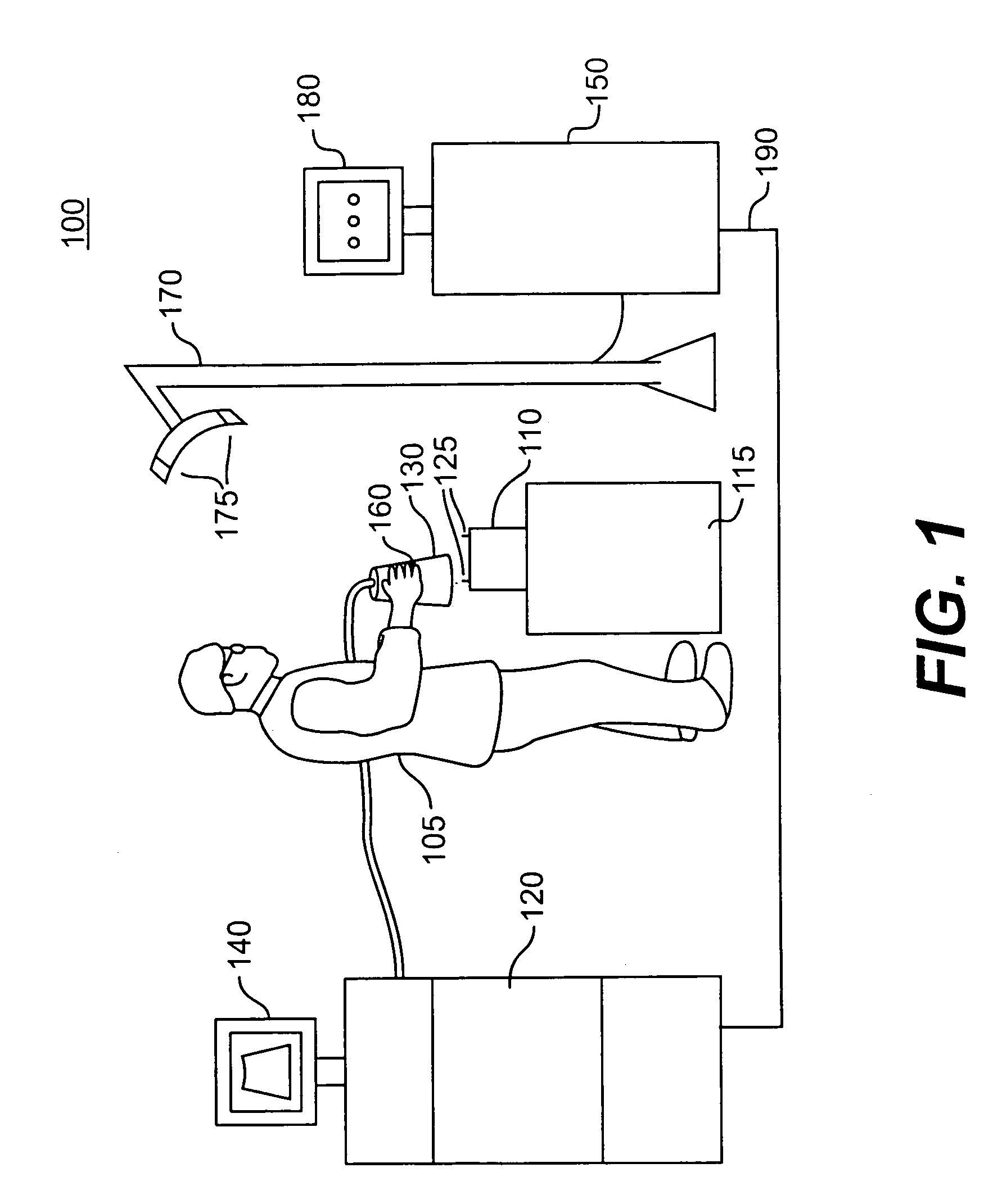
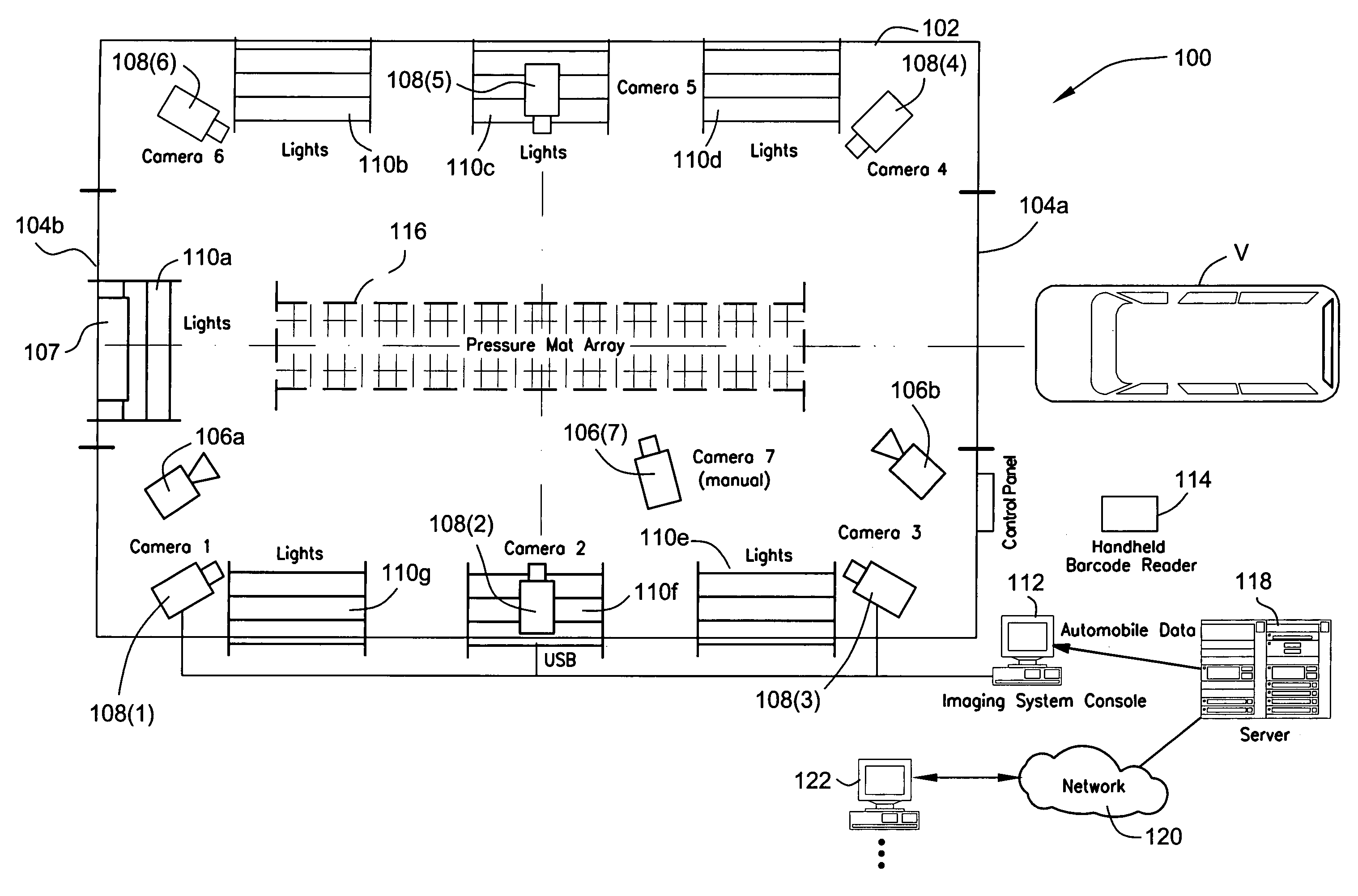
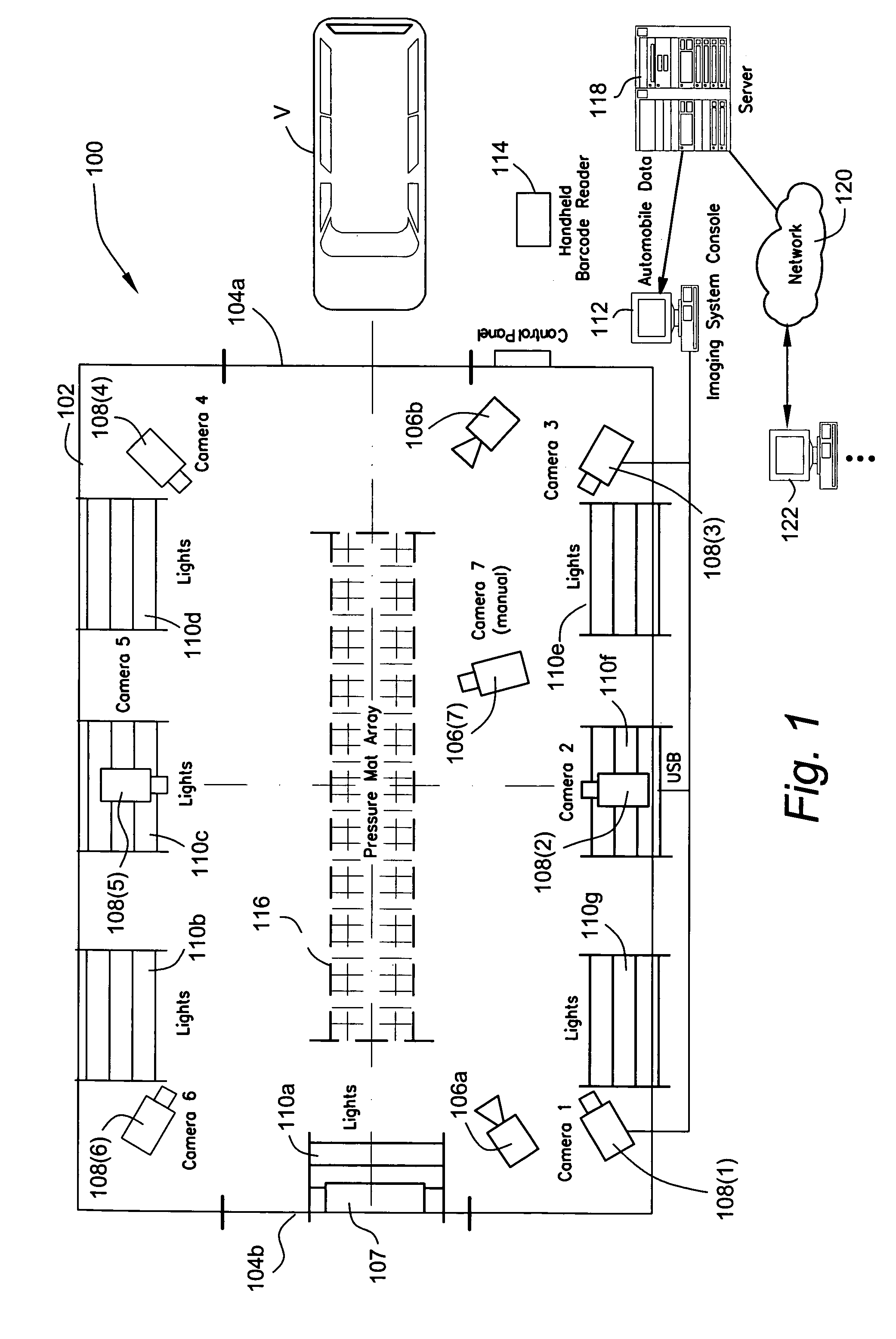
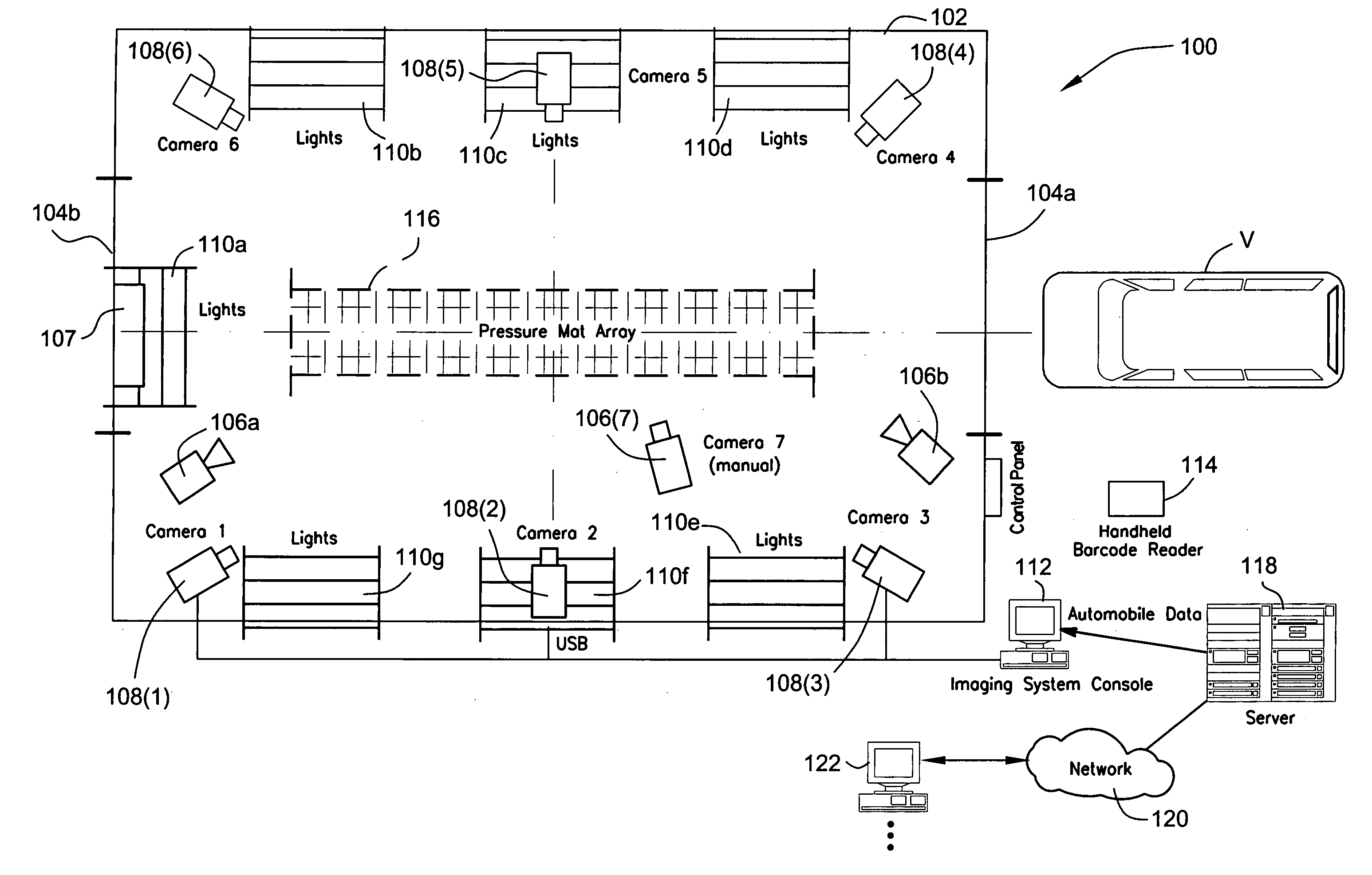
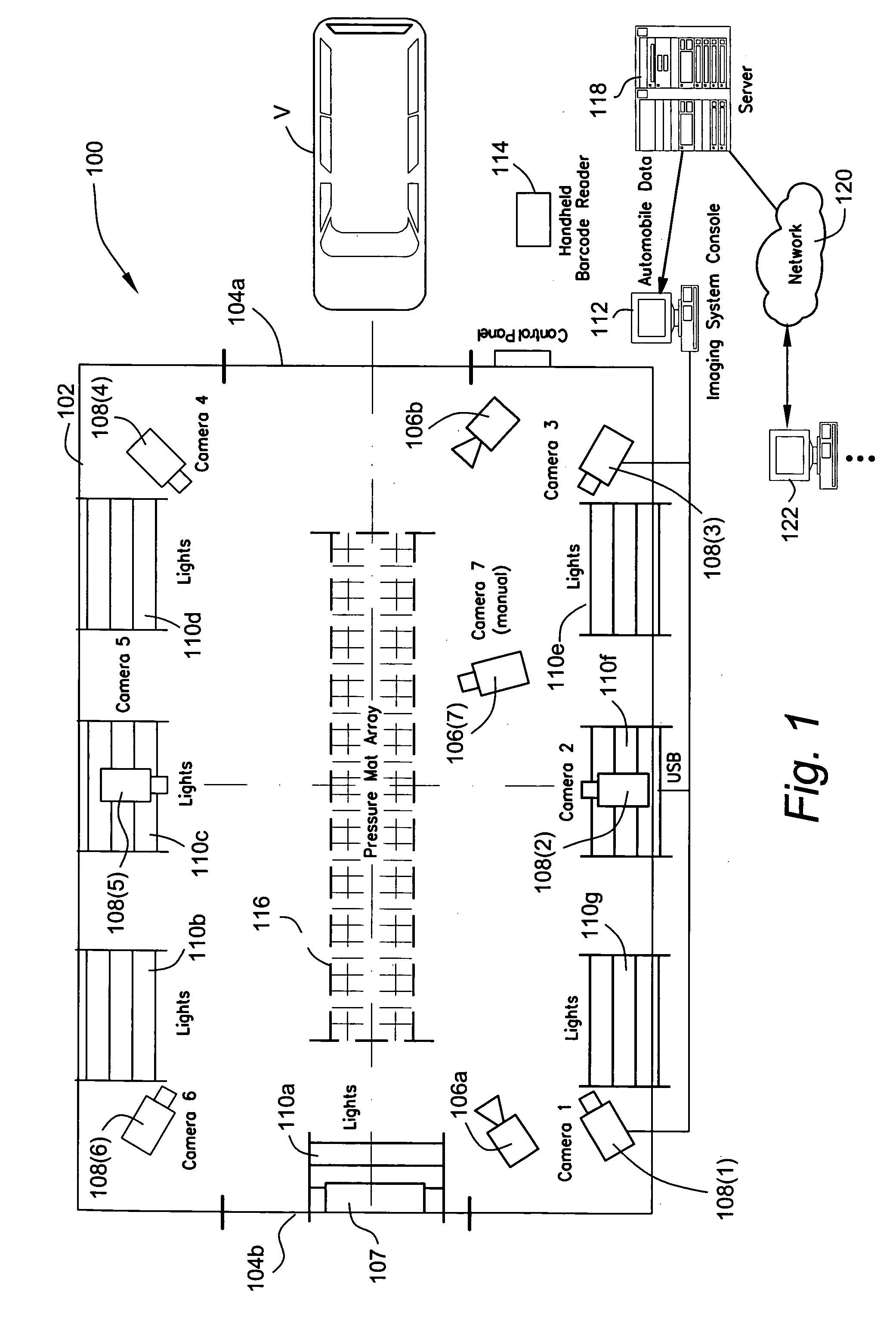
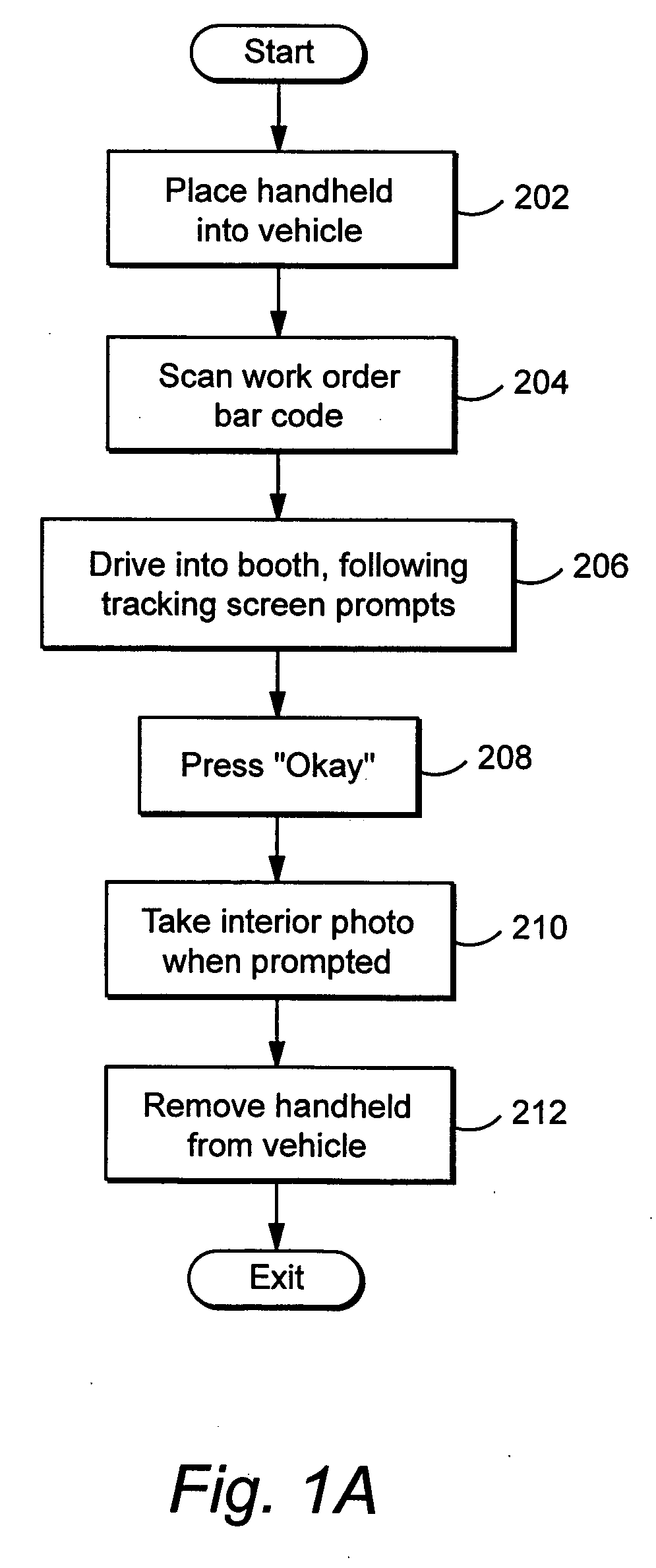
Method and apparatus for automatically capturing multiple images of motor vehicles and other items for sale or auction
ActiveUS8112325B2Value maximizationHigh resolutionTelevision system detailsArrangements for variable traffic instructionsInterior spaceUltrasonic sensor
An automatic “photo booth” for capturing images of objects including but not limited to motor vehicles provides consistent and rapid image capture from multiple viewpoints. Ultrasonic sensors or other positional sensing devices are used to both position the object with the photo booth enclosure and calculate field of view parameters controlling digital cameras to provide appropriate image scaling / cropping at time of image capture. The enclosure provides automatic entry / exit door opening / closure and a controlled interior space to provide a controlled environment for image capture. Captured images may be rapidly uploaded to a server for electronic distribution over the World Wide Web or other appropriate network.
Owner:MANHEIM INVESTMENTS
Dynamic image presentation
ActiveUS20110074824A1Reduce white spaceFacilitate intuitiveGeometric image transformationCathode-ray tube indicatorsDisplay deviceImage scale
One or more techniques and / or systems are disclosed for efficiently organizing images in a display. A size of an image is scaled by an image scale factor, while an aspect ratio for the image is maintained, where the image scale factor comprises a combination of a first scale distance and a second scale distance. The scaled image is filled into a first display line, if the size of the scaled image is not greater than an amount of display space remaining in the first display line; otherwise the scaled image is filled into a second display line. The image is expanded to mitigate white space in the display after the scaling, while maintaining the image's aspect ratio. This can be performed for a collection of images presented on a display to provide an enhanced user experience.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
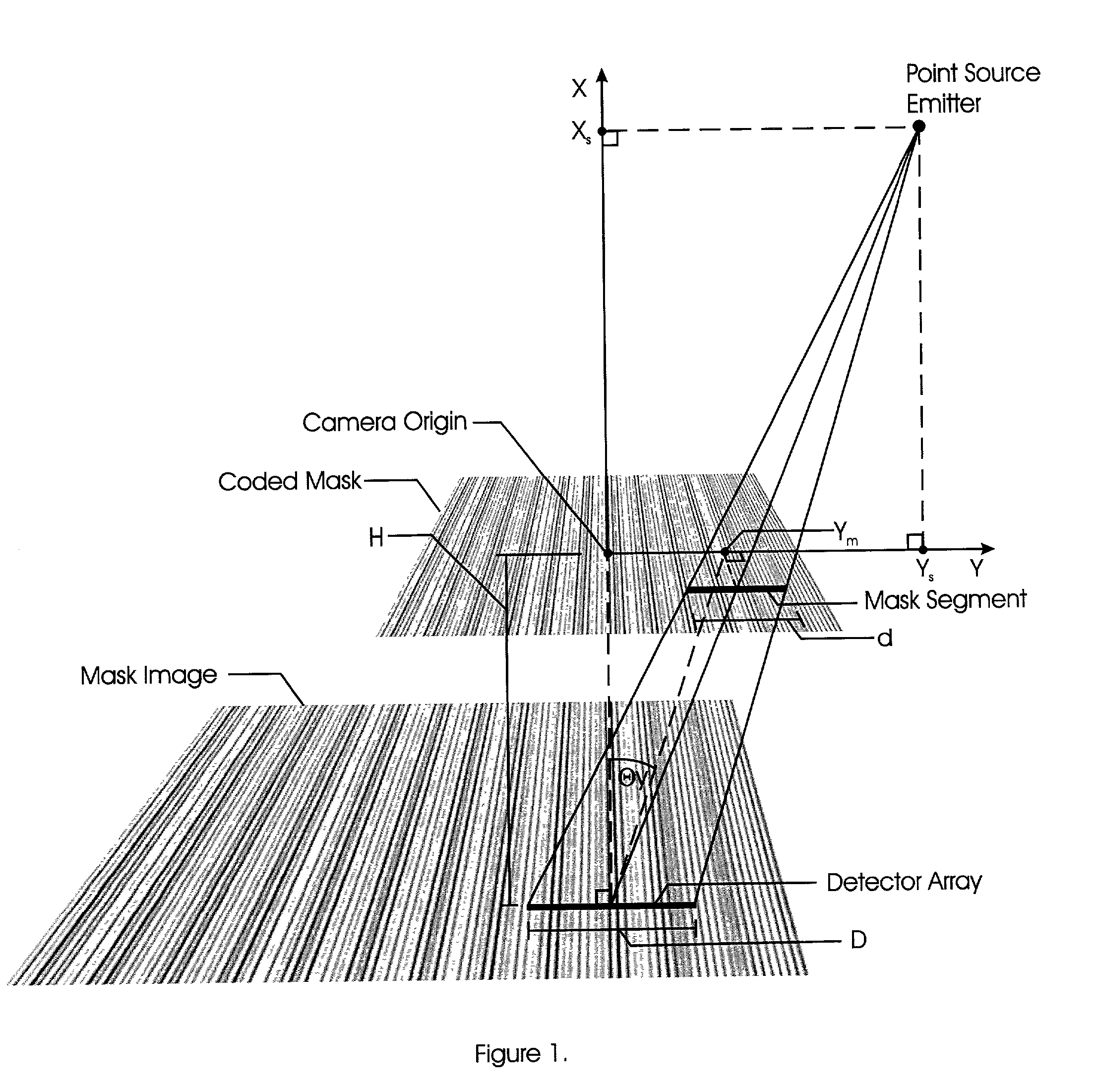
Range adaptable system for determining the angular position and distance of a radiating point source and method of employing
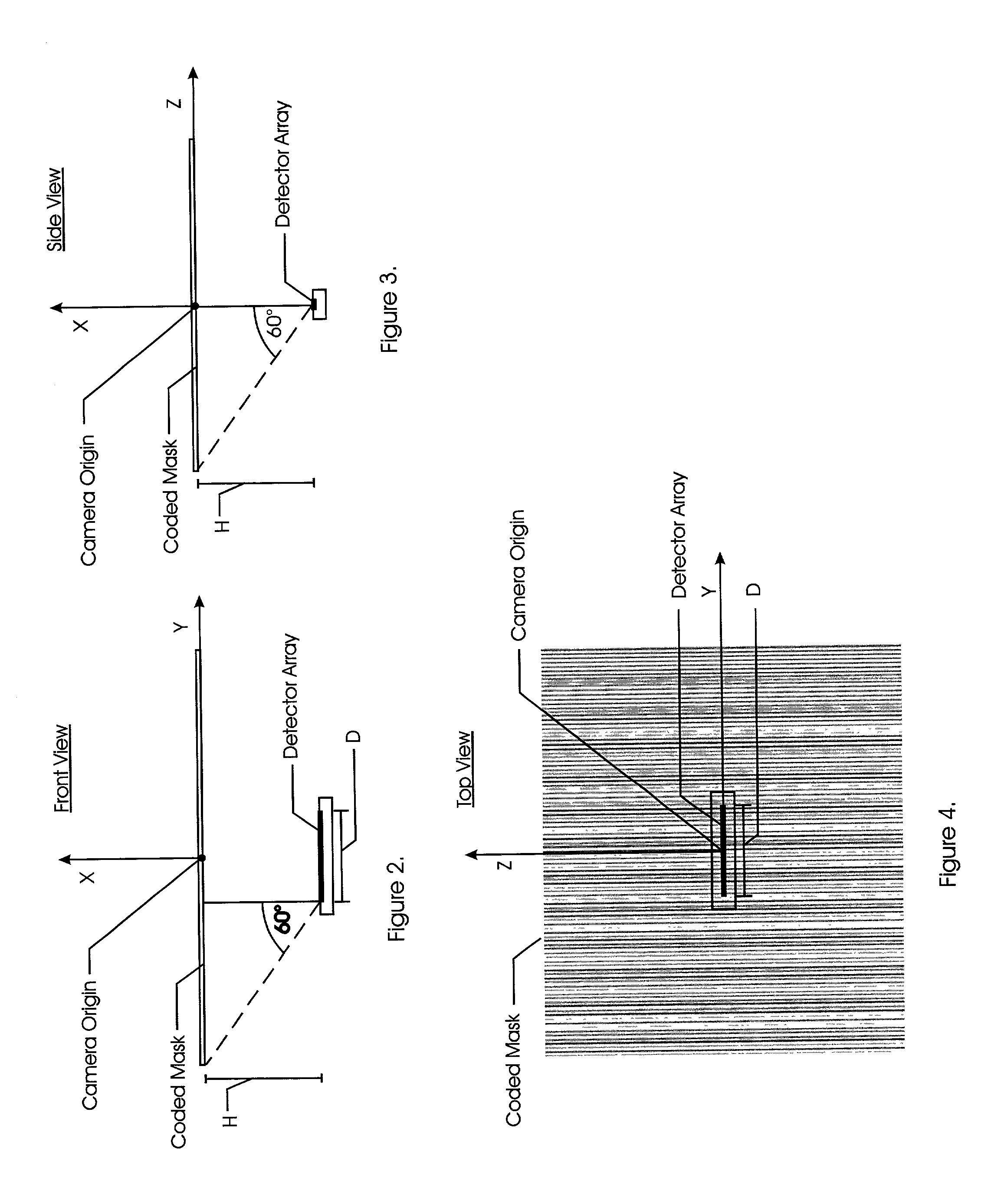
ActiveUS7027634B2Accurate measurementMaterial analysis by optical meansPosition fixationDetector arrayImage scale
A patterned mask is located at a distance from a linear detector array. A point radiating source illuminates the aperture to cast an image onto the array. A computer is employed to identify frequencies in the frequency domain to determine the image scale and shift along the detector array axis. Determination of the magnification of the aperture image is made employing frequency domain techniques, the aperture pattern being re-scaled to match that of the actual image, so that determination of pattern shift can be made. A first embodiment of the present invention has two variations, one of which employs the use of multiple single frequency components and phase methodology, the second of which uses multiple single frequency components as well as a variable frequency component. In a second embodiment, a composite image is also used except that only one single frequency component is used in addition to a non-periodic function.
Owner:NORTHERN DIGITAL
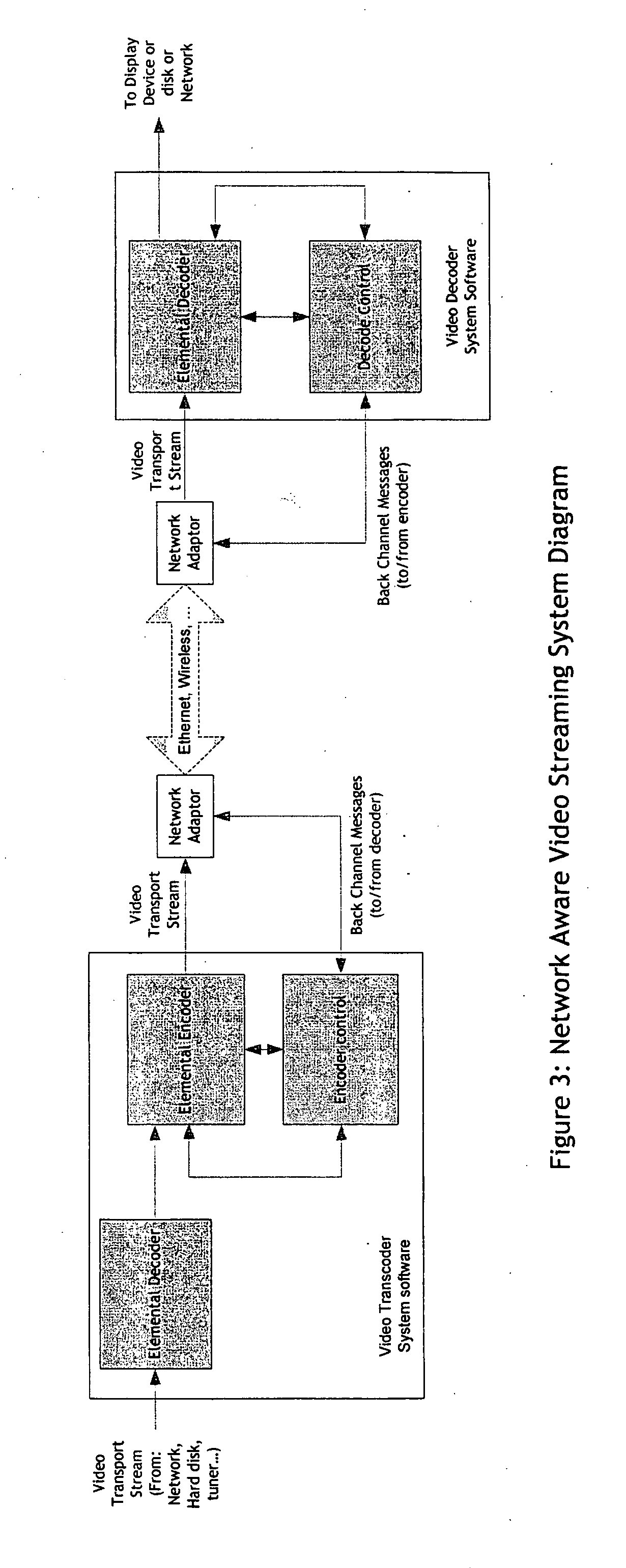
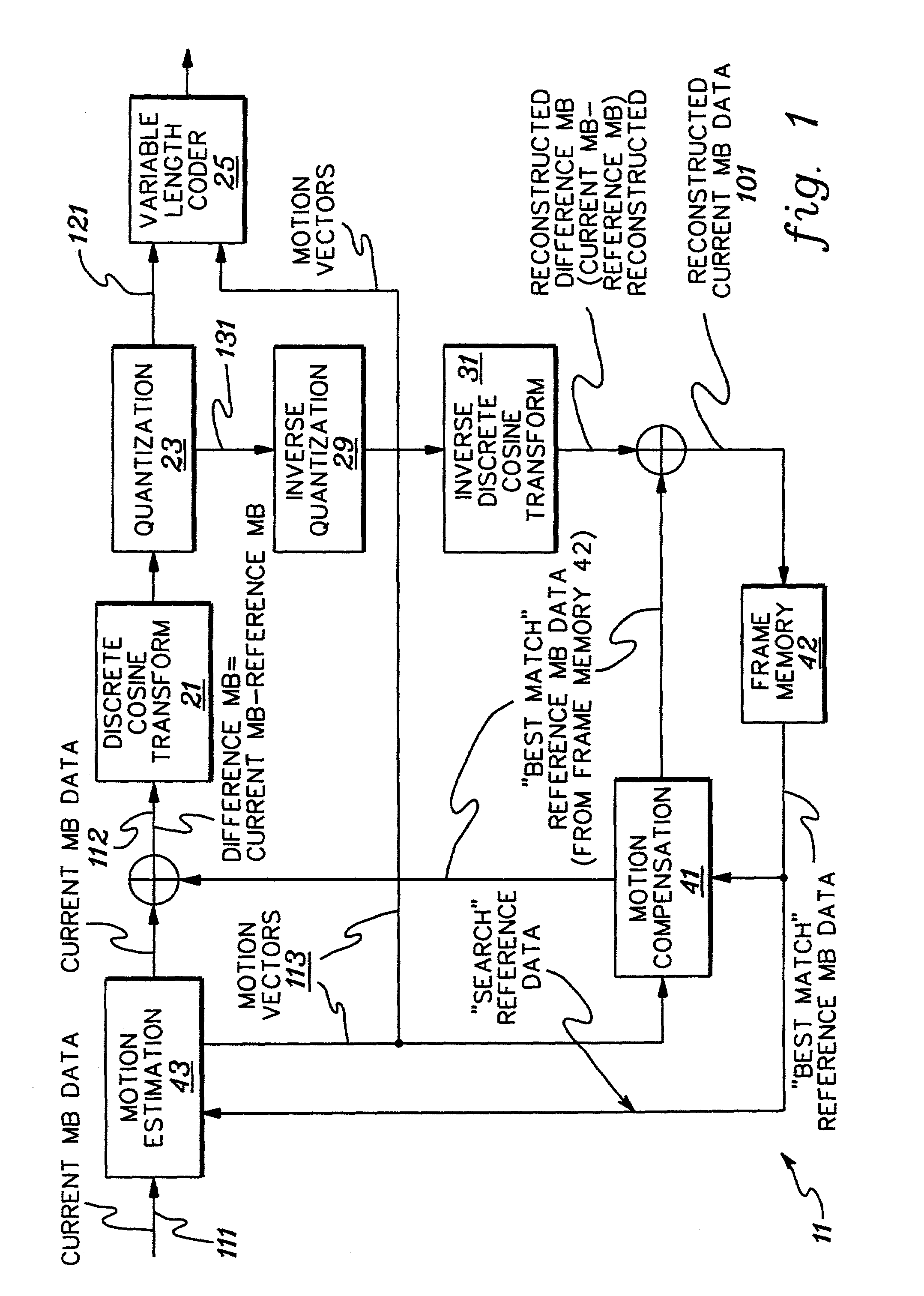
Real-time network adaptive digital video encoding/decoding
ActiveUS20080084927A1Lowering scale factorLow data ratePulse modulation television signal transmissionPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesDigital videoImaging quality
A method for real time video transmission over networks with varying bandwidth is described. Image quality is maintained even under degrading network performance conditions through the use of image scaling in conjunction with block based motion compensated video coding (MPEG2 / 4, H.264, et. Al.). The ability to quickly switch resolutions without decreasing reference frame correlation is shown enabling a fast switch to reduce the required bandwidth for stable image quality.
Owner:ELEMENTAL TECH LLC
Method and apparatus for automatically capturing multiple images of motor vehicles and other items for sale or auction
ActiveUS20070057815A1Uniform contrastValue maximizationTelevision system detailsArrangements for variable traffic instructionsInterior spaceMobile vehicle
An automatic “photo booth” for capturing images of objects including but not limited to motor vehicles provides consistent and rapid image capture from multiple viewpoints. Ultrasonic sensors or other positional sensing devices are used to both position the object with the photo booth enclosure and calculate field of view parameters controlling digital cameras to provide appropriate image scaling / cropping at time of image capture. The enclosure provides automatic entry / exit door opening / closure and a controlled interior space to provide a controlled environment for image capture. Captured images may be rapidly uploaded to a server for electronic distribution over the World Wide Web or other appropriate network.
Owner:MANHEIM INVESTMENTS
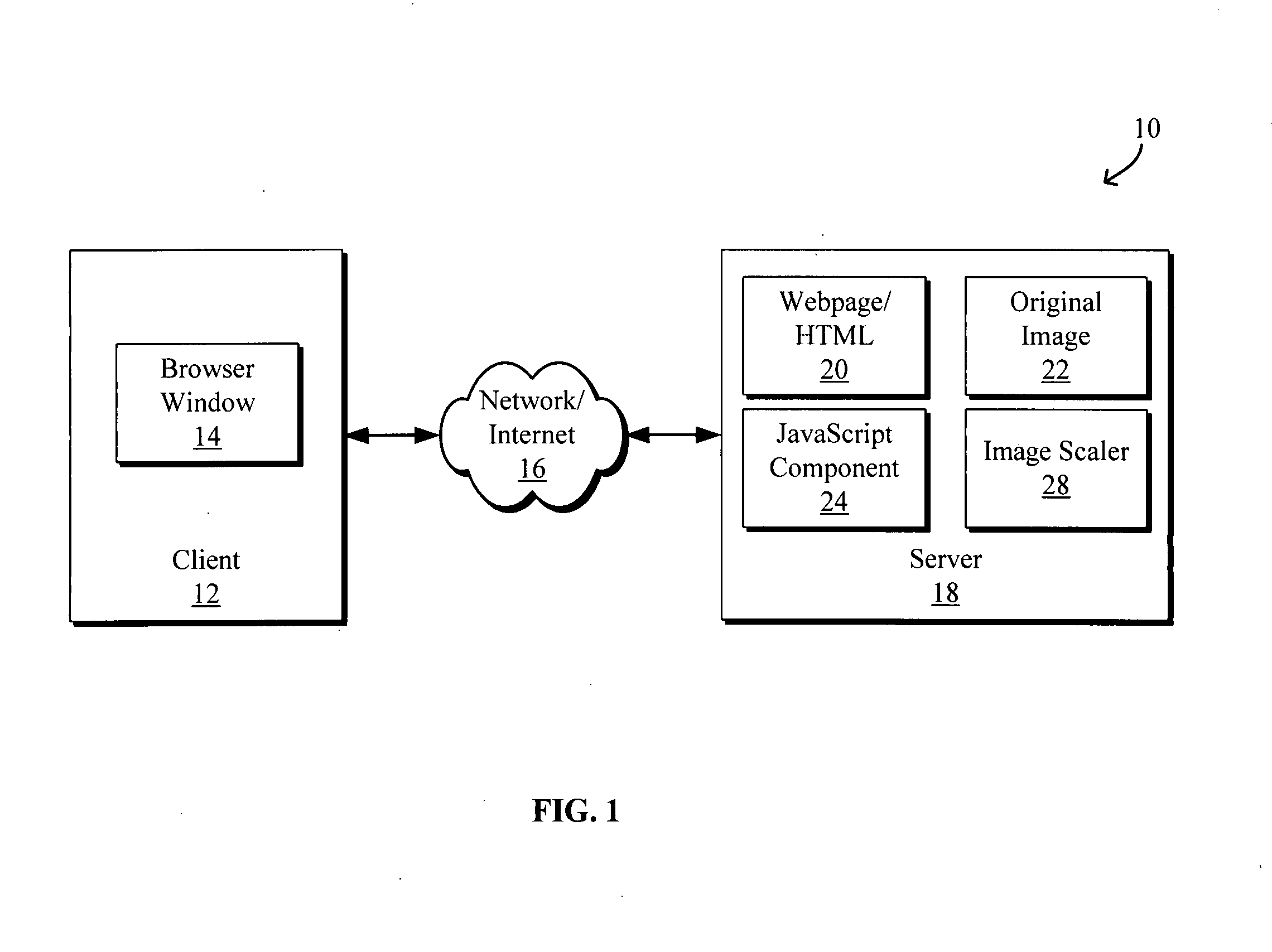
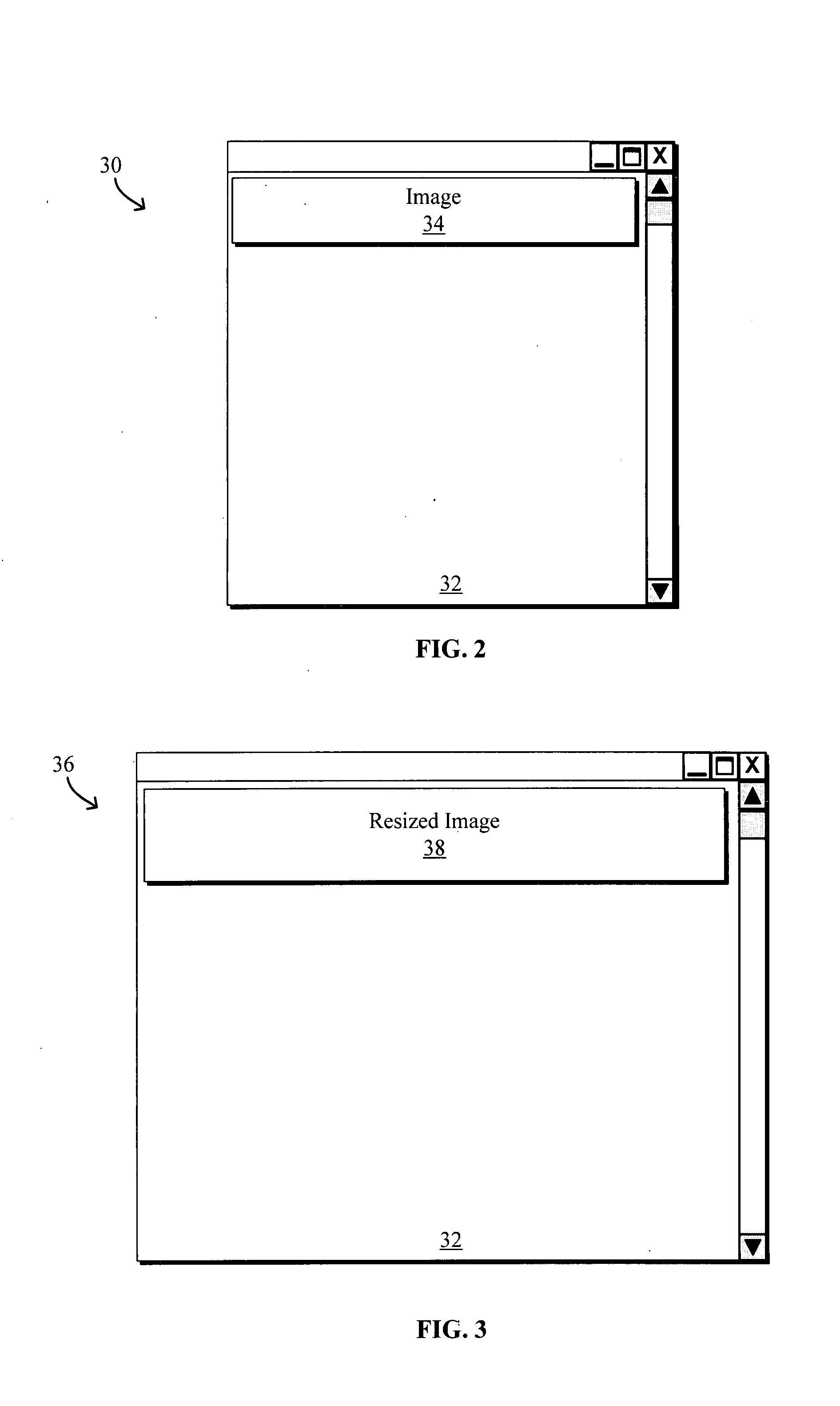
Automatic display of resized images
ActiveUS20070283247A1Digital data information retrievalNatural language data processingWeb browserImage scale
Systems and methods for automatic display of scaled and / or resized images that fit within pre-defined areas in a web browser are disclosed. The method may be implemented using an image scaling JavaScript component embedded within a HTML document. Upon resizing the a client document browser in which the document is displayed, the component is resized and requests, receives and redisplays a resized image within the resized component from a server. By having the server perform the resizing, the resized image not only fits within the resized component but also maintains the quality of the image without the need for special client-side software.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
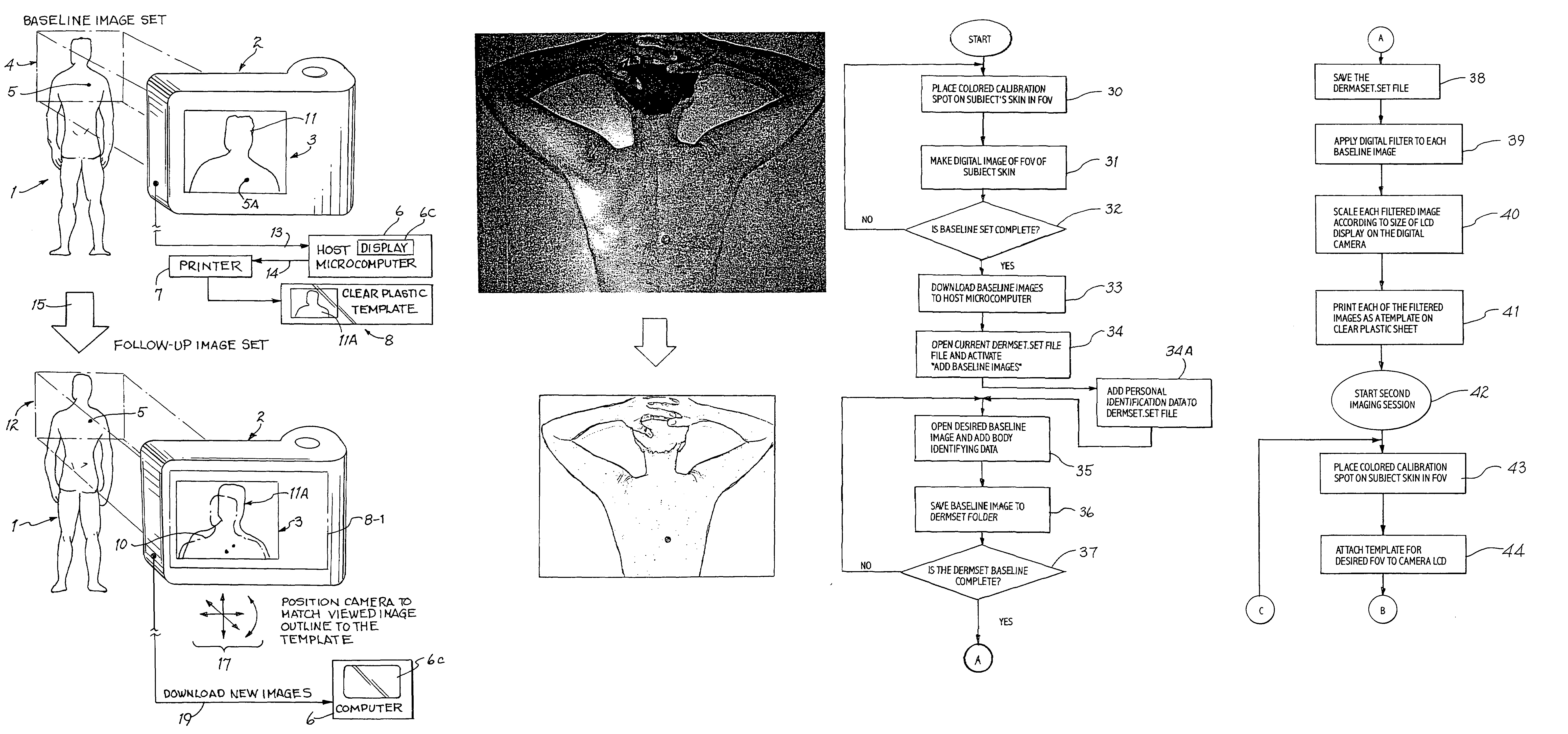
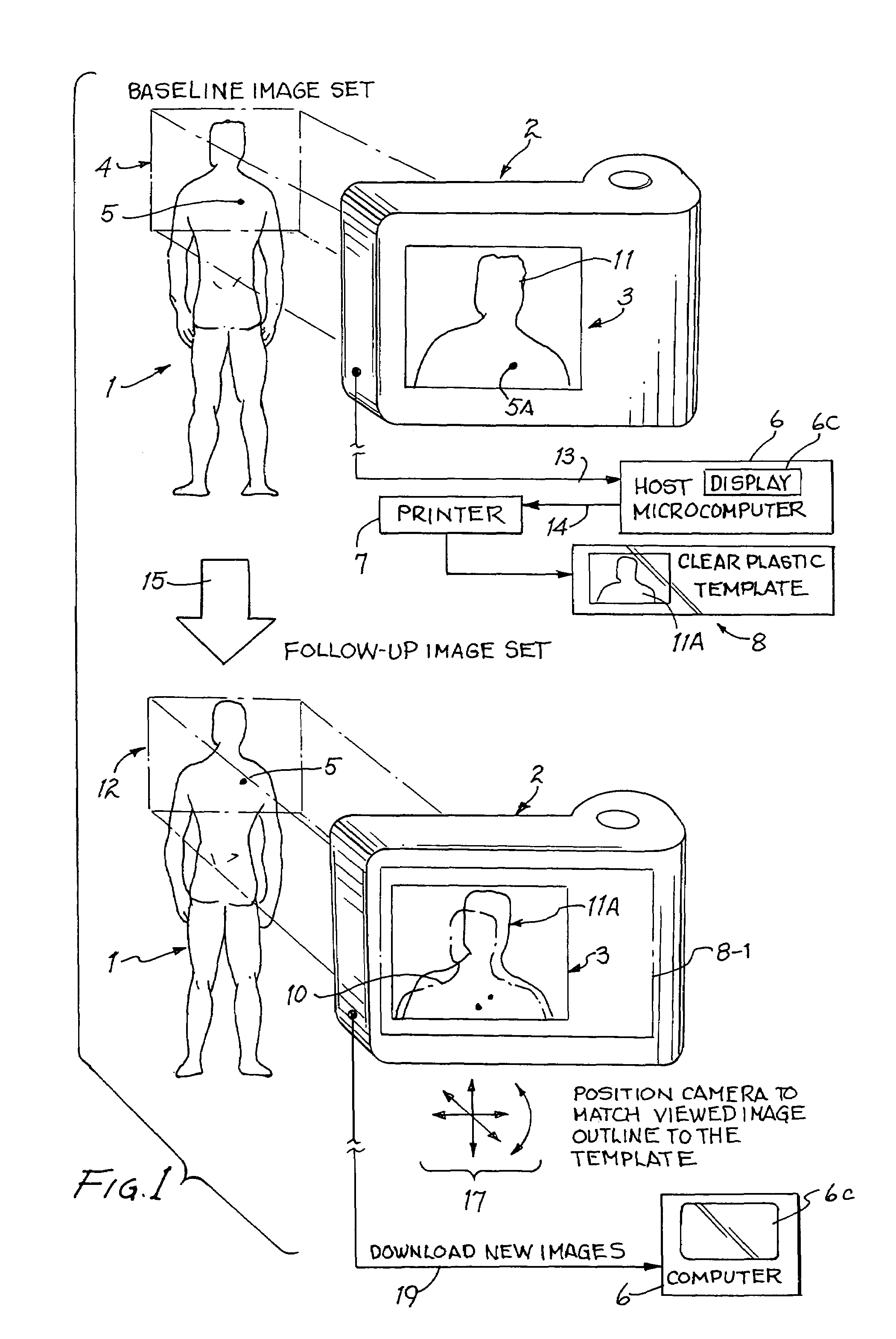
Digital skin lesion imaging system and method
InactiveUS7162063B1Easy to useReadily accurately identifyImage enhancementImage analysisDisplay deviceImage scale
New or significantly changed skin lesions are detected by providing digital baseline image data of an area of a subject's skin by placing a calibration piece on the area and then positioning a digital camera to frame the area within a field of view of the camera and digitally photographing the area to produce a digital baseline image of the area. The digital baseline image is downloaded from the camera to a computer, which digitally filters the baseline image to produce a partially transparent baseline image scaled to fit over a viewfinder display of the camera. The filtered baseline image is printed on a transparent sheet to produce template. Substantially later, a calibration piece is placed on the area, and the template is placed over the viewfinder display of the camera. The camera is positioned to frame that area within the field of view so as to align a live image of the area with the baseline image on the template. The area is photographed to produce a digital current image thereof. The current image is downloaded to the computer, which is operated to alternately display the aligned current image data and the baseline image data to allow visual identification of lesions which changed enough in the “alternating image comparison display” to identify a new or significantly growing lesion.
Owner:WESTERN RES
Method, Terminal Device and Program for Dynamic Image Scaling Display in Browsing
InactiveUS20070250768A1Increase awarenessDifficult to viewDigital data information retrievalMultiple digital computer combinationsTerminal equipmentImage scale
Owner:ACCESS
Image scaling arrangement
ActiveUS7433546B2Data processing applicationsRecord information storageComputer graphics (images)Display device
Methods and system for transferring images between devices is disclosed. For example, differently scaled images by a host device may automatically and / or selectively be transferred to a media player for display. In turn, appropriately scaled images may be transferred automatically and / or selectively to another display device for example a TV, camera or printer. The selectivity may occur either at the host level or at the player level.
Owner:APPLE INC
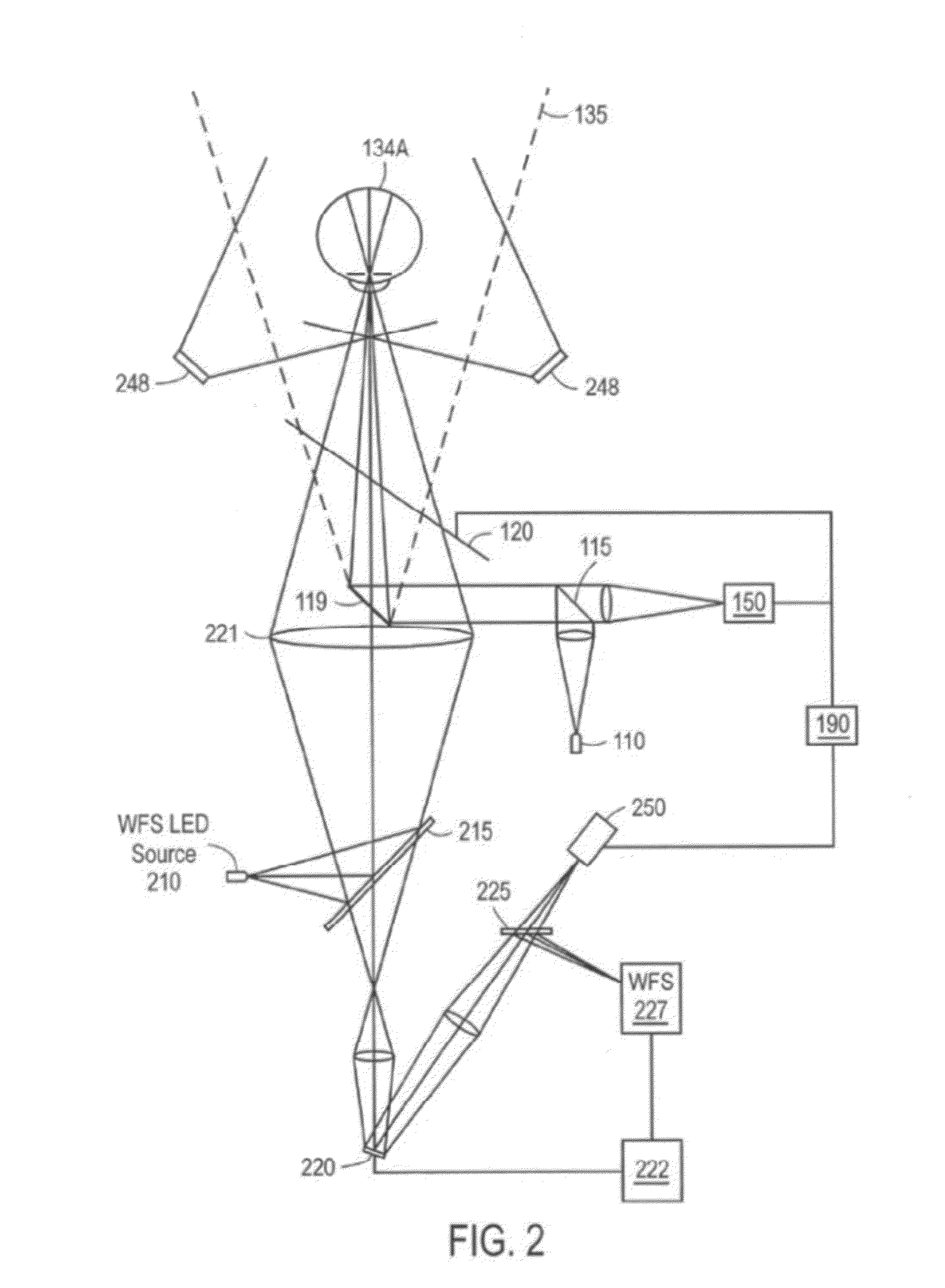
Scale-invariant, resolution-invariant iris imaging using reflection from the eye
ActiveUS8243133B1Reduce sensitivityAcquiring/recognising eyesColor television detailsImage resolutionImage scale
An optical system includes an active focus element that maintains an image in focus over a range of object distances. The active focus element and aperture stop are positioned such that the image scale and the image spatial resolution are also invariant (or at least have a reduced sensitivity) with respect to object distance.
Owner:TASCENT INC
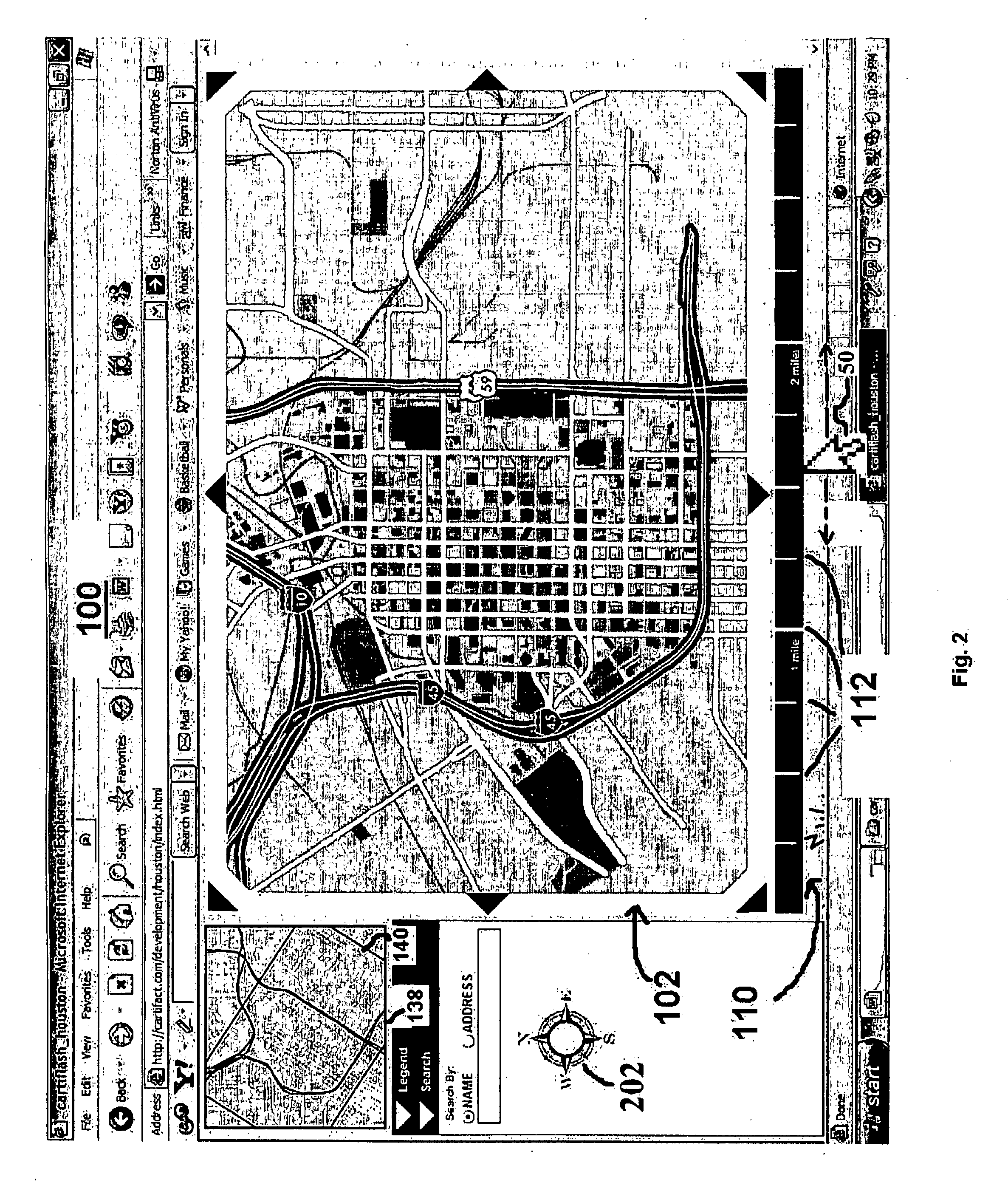
Interactive scaling feature having scalability in three dimensional space
InactiveUS20060293847A1Instruments for road network navigationRoad vehicles traffic controlGraphicsGraphical user interface
A system and method for controlling the scale of an image is disclosed, which comprises an image object in a graphical user interface. A ruler object provides a ruler display for distance measurement in the image. A button object comprising the ruler detects a cursor event that is sent to the image object for processing changes in the scale of the image responsive to the cursor event. Further disclosed is a system and method to provide directional orientation in an electronic map. Data is stored that indicates local perceptions of north, south, east and west for regions on the map. When each region is displayed, the system provides a toggle for switching between displaying the region with true north at an angle of 0 degrees orientation, or displaying the region at an angle with the local perception of north at an angle of 0 degrees orientation.
Owner:CARTIFACT
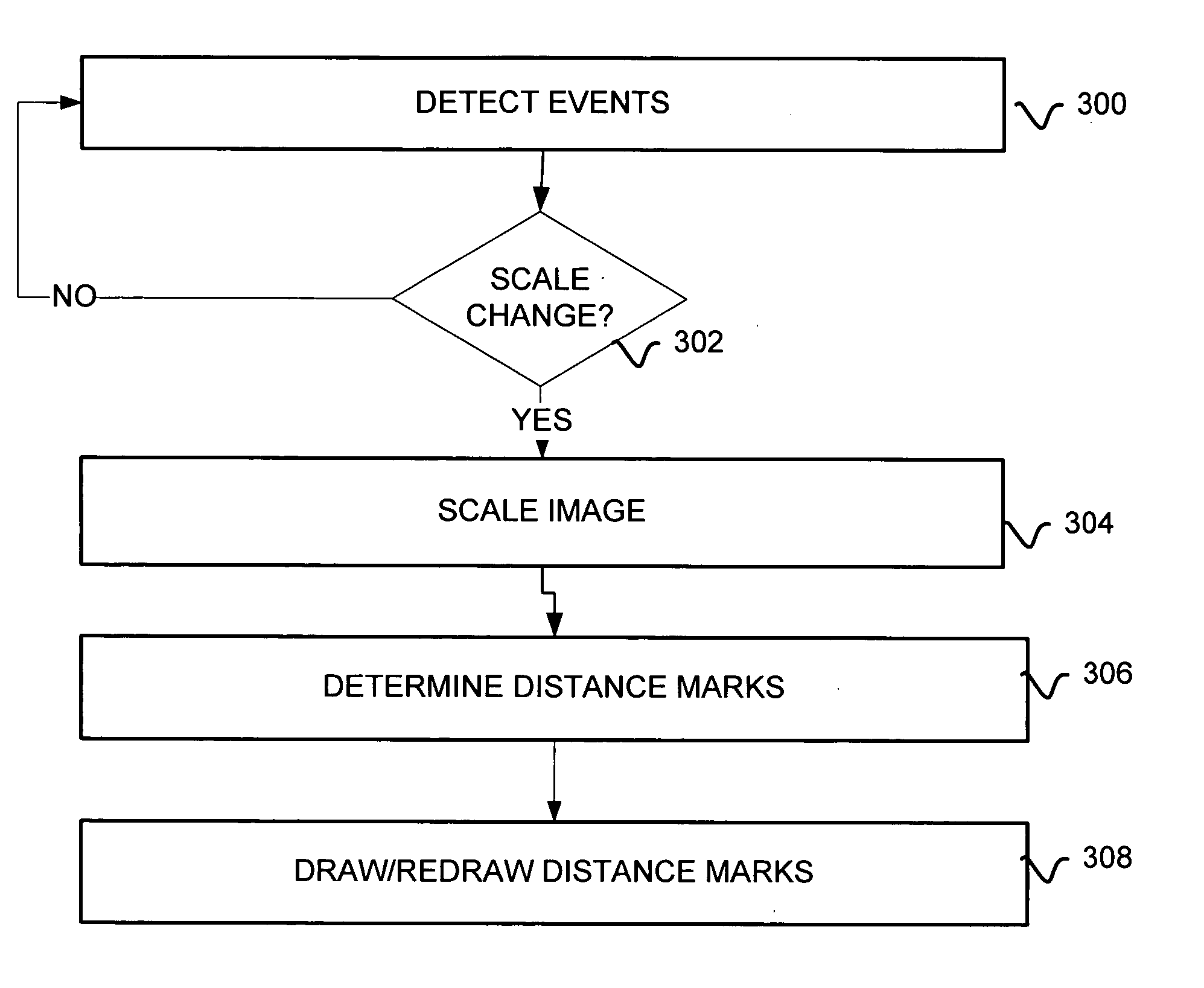
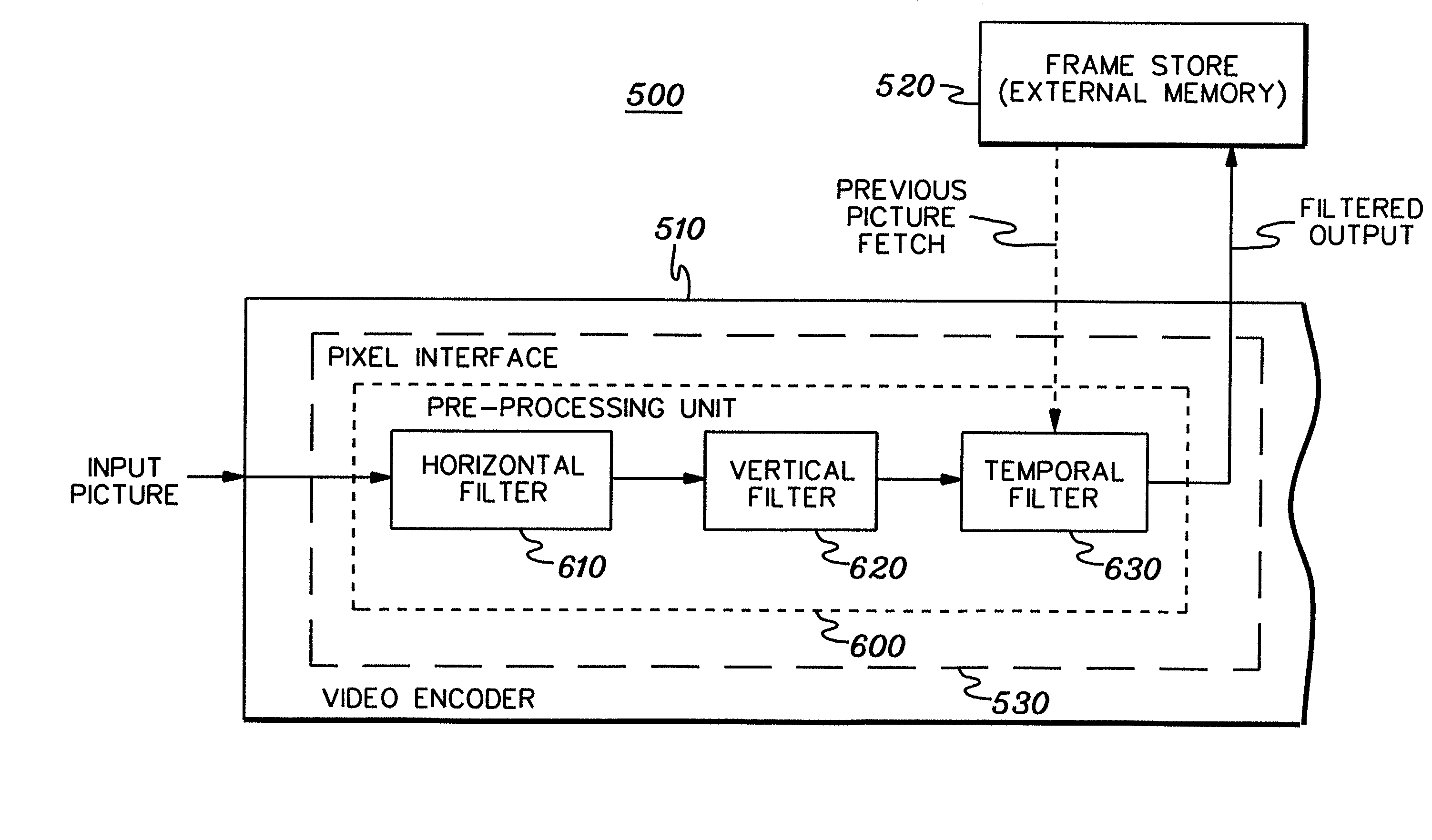
Programmable horizontal filter with noise reduction and image scaling for video encoding system
InactiveUS6996186B2Improve video qualityInherent noiseTelevision system detailsPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesSpatial noiseVideo encoding
A technique is provided for programmably horizontally filtering pixel values of frames of a plurality of video frames. The technique includes, in one embodiment, passing pixel values through a real-time horizontal filter disposed as preprocessing logic of a video encode system. The horizontal filter is programmable and includes a filter coefficients buffer for holding multiple sets of filter coefficients. The horizontal filter programmably employs the multiple sets of filter coefficients to selectively perform spatial noise filtering, or spatial noise filtering and image scaling on the pixels. The filter coefficients are also programmable and may be changed dynamically and repeatedly, with changes being applied at frame boundaries. When performing image scaling, multiple sets of filter coefficients are employed.
Owner:IBM CORP +1
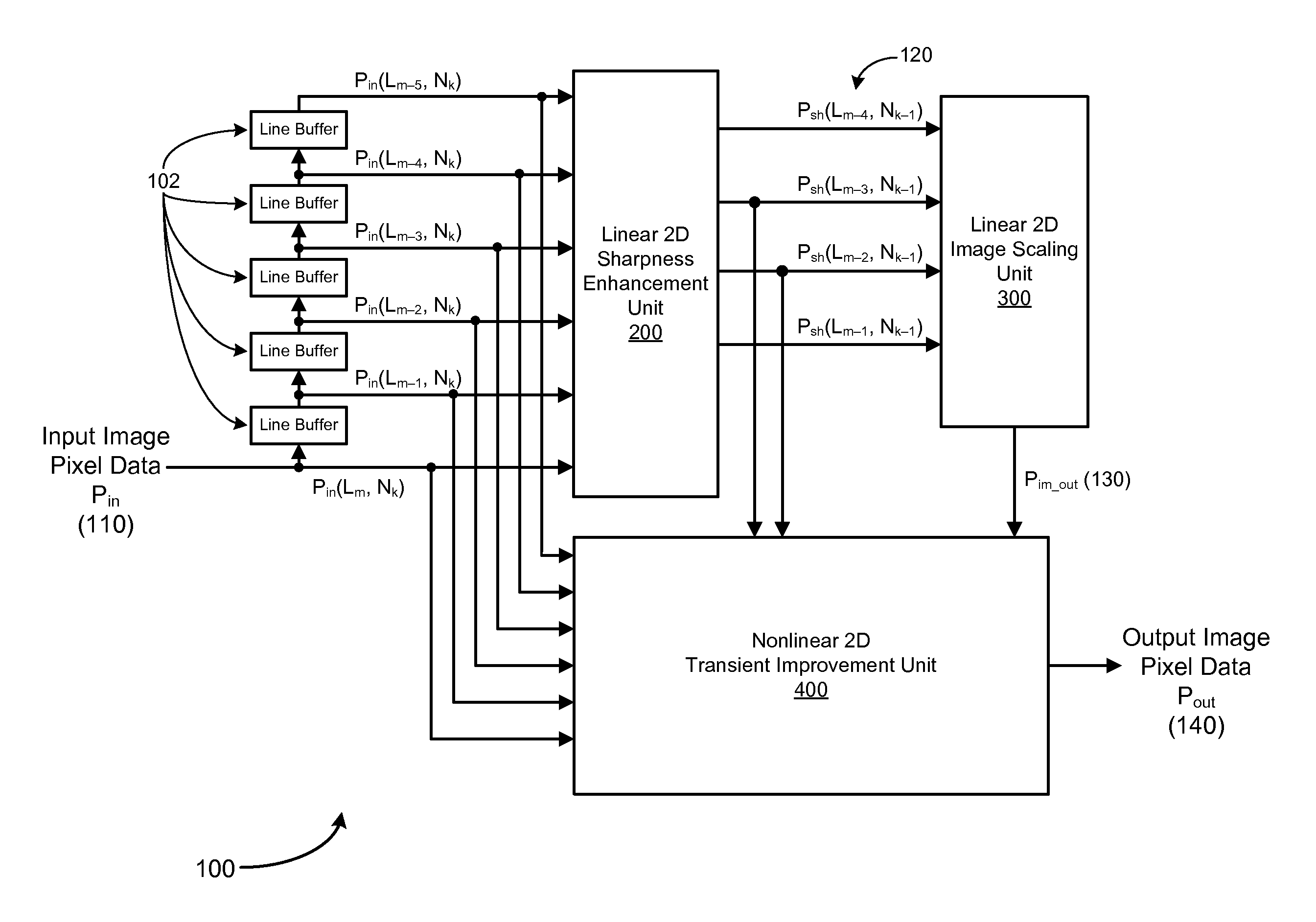
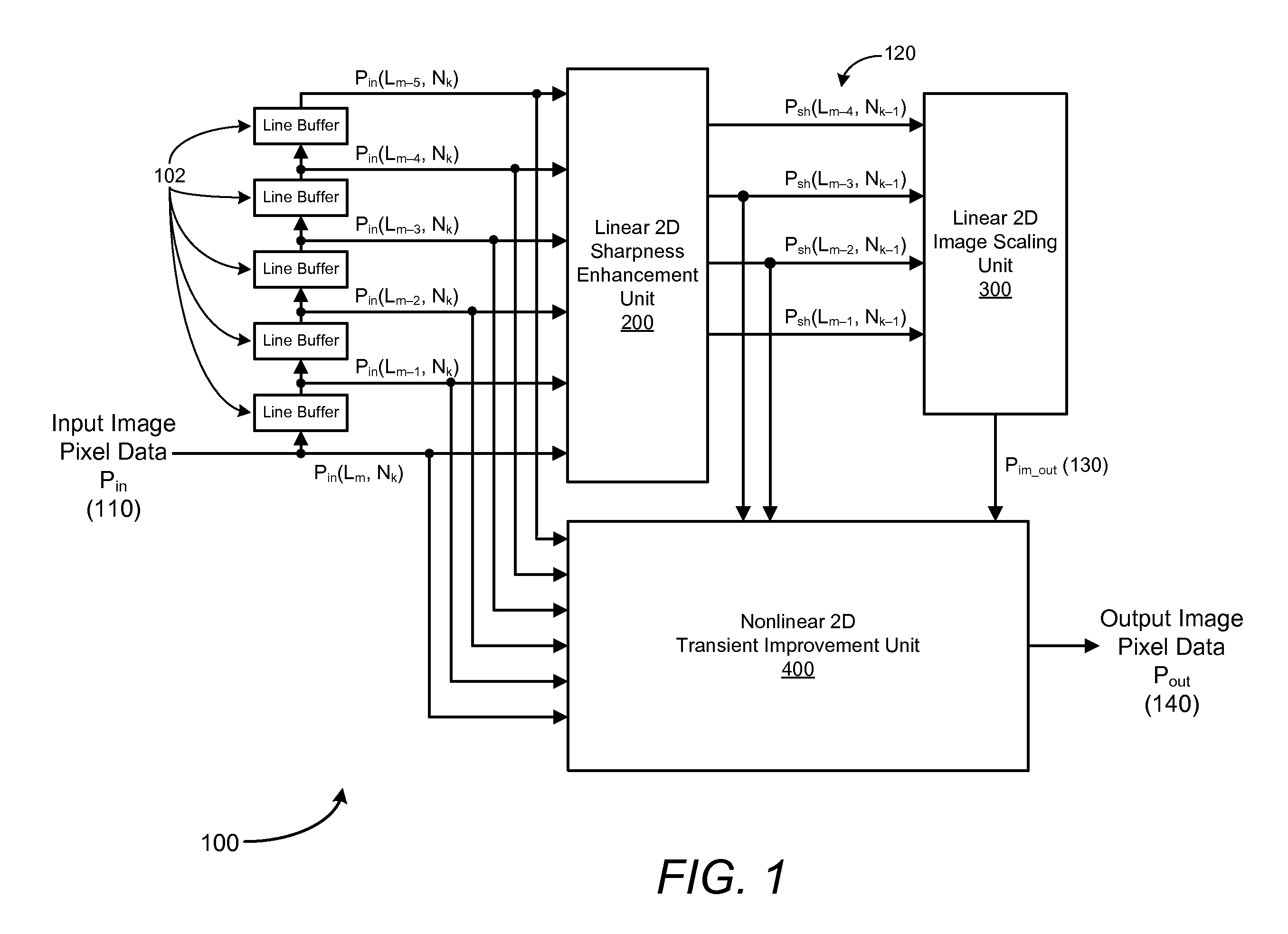
Method and system for digital image scaling with sharpness enhancement and transient improvement
InactiveUS7782401B1Low costReduce complexityTelevision system detailsColor signal processing circuitsImage resolutionImage scale
An image scaling system includes a single set of line buffers that receive and store input image pixel data in an input video frame. The scaling system also includes a linear two-dimensional sharpness enhancement unit configured to receive input pixel data from the line buffers and to generate sharpened pixel data by enhancing high frequency components of the input pixel data at an input image resolution, a linear two-dimensional image scaling unit configured to receive the sharpened pixel data and to convert the sharpened pixel data into scaled sharpened pixel data at an output image resolution, and a transient improvement unit configured to receive the input pixel data from the line buffers, sharpened pixel data and scaled sharpened pixel data to improve transient responses at edges in an output image, and to generate output image pixel data at the output image resolution.
Owner:CORONA
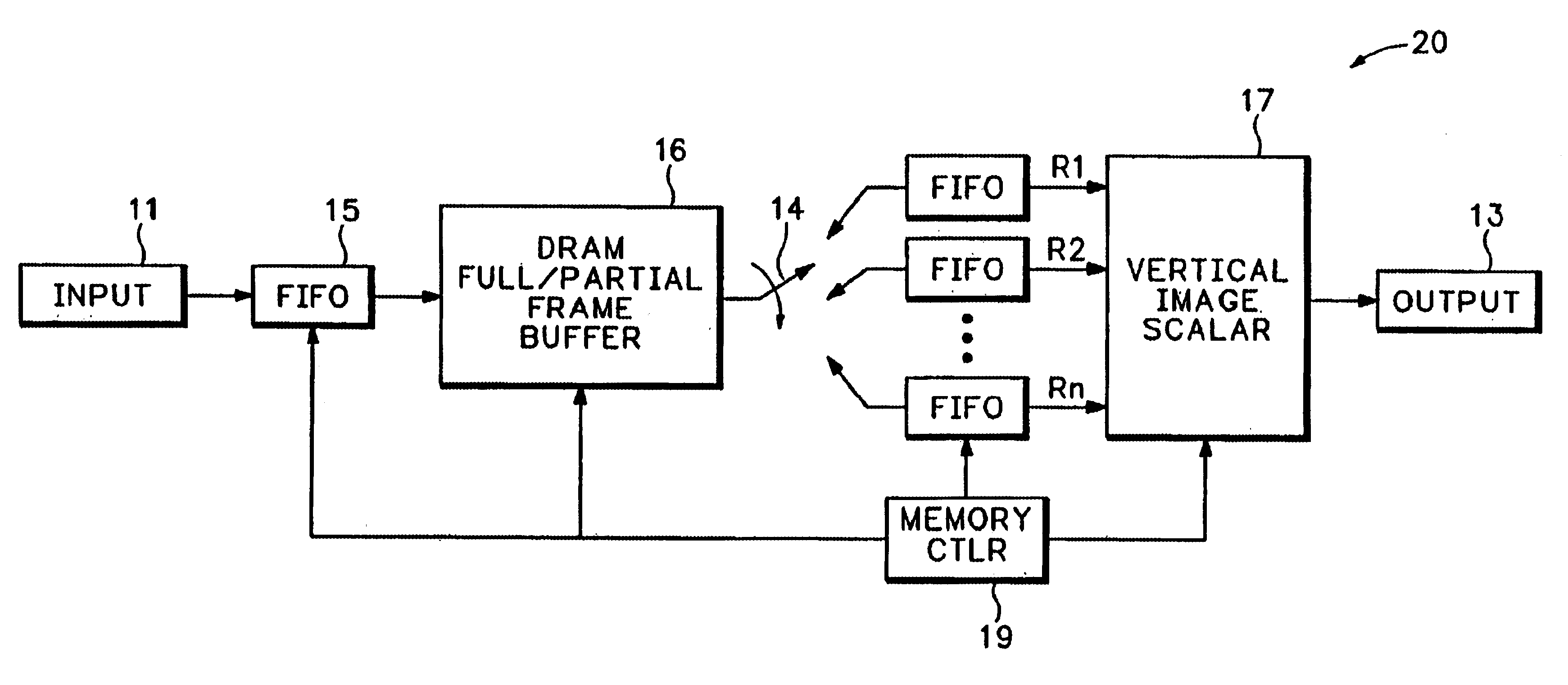
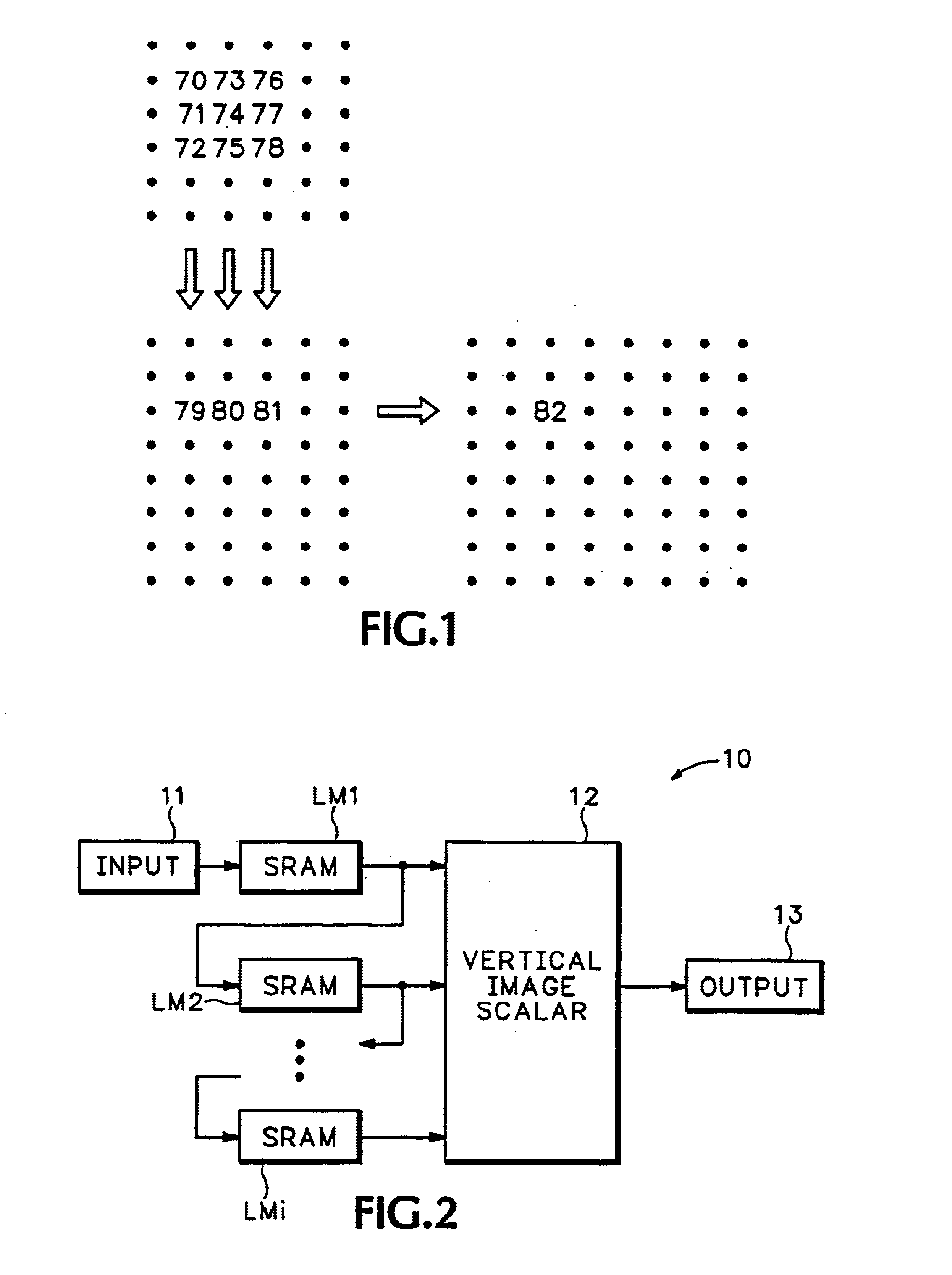
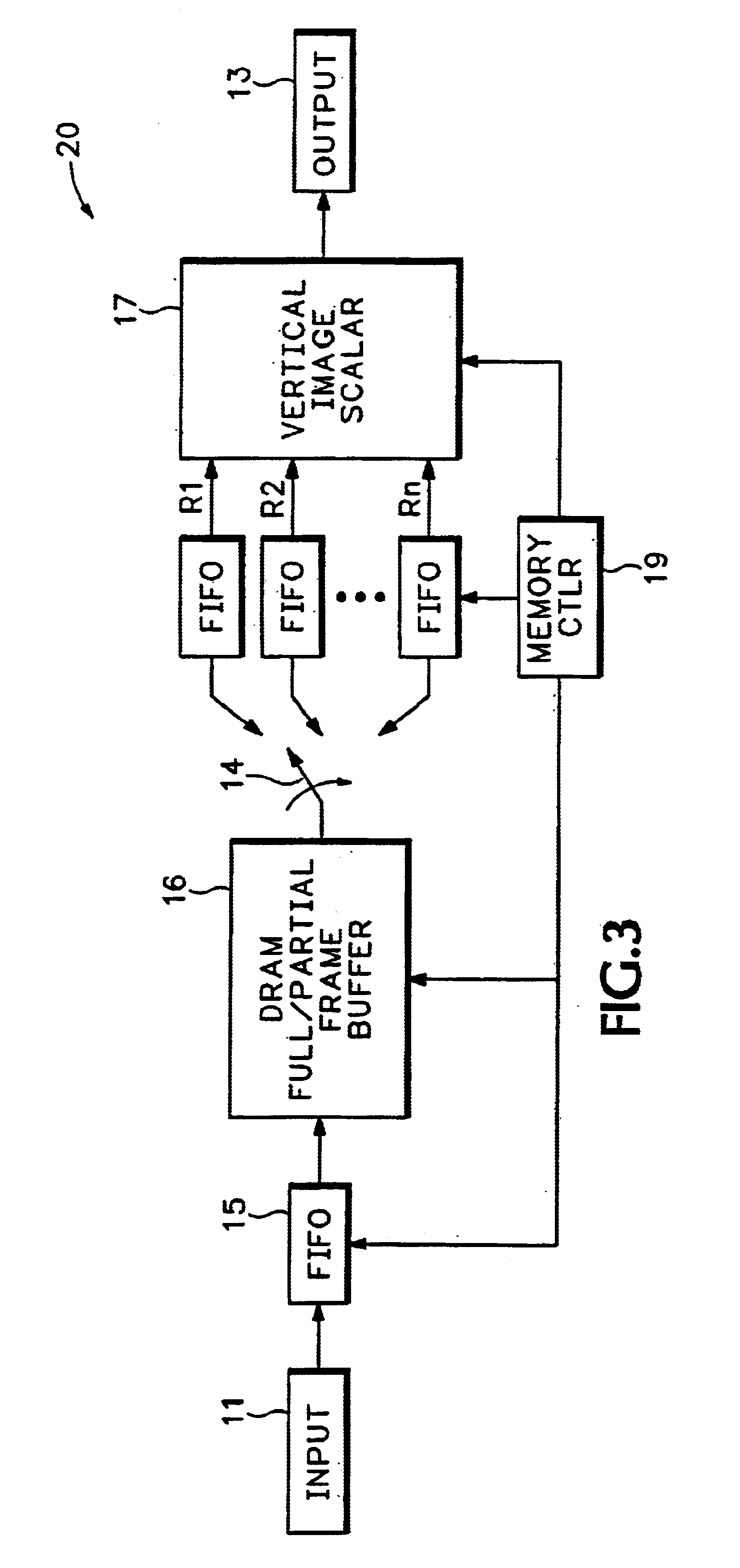
Ultra-high bandwidth multi-port memory system for image scaling applications
InactiveUS6903733B1Improve reliabilityLow costGeometric image transformationCathode-ray tube indicatorsSample rate conversionParallel computing
The image scaling memory system of the present invention eliminates the use of internal or external line memories by using an existing frame memory coupled with an input buffer and a plurality of output buffers for providing a vertical scalar with simultaneous parallel access to multiple lines of data. Additionally, the image scaling memory system of the present invention, including the frame memory, is embedded into an integrated circuit. Thus, the image scaling circuit of the present invention improves reliability, lowers cost, and improves silicon area usage. The frame memory is coupled to an input buffer at an input side and a plurality of output buffers at an output side. The plurality of output buffers is positioned between the frame memory and the vertical scalar. Each output buffer sequentially gains access to and transfers portions of image lines from the frame buffer. Each output buffer stores only a portion of an image line resulting in relatively small output buffers. The plurality of output buffers provides the vertical scalar with simultaneous parallel access to multiple lines of buffered digital image data. The frame memory preferably comprises DRAM that stores the image data such that row faults are minimized. The DRAM frame memory preferably includes at least two memory banks, each including a plurality of rows and a plurality of columns. The DRAM frame memory has multiple purposes including storing digital image data frames for sample rate conversion, as well as, storing bitmaps for access by an On Screen Display controller and storing microprocessor data for access by a microprocessor.
Owner:PIXELWORKS
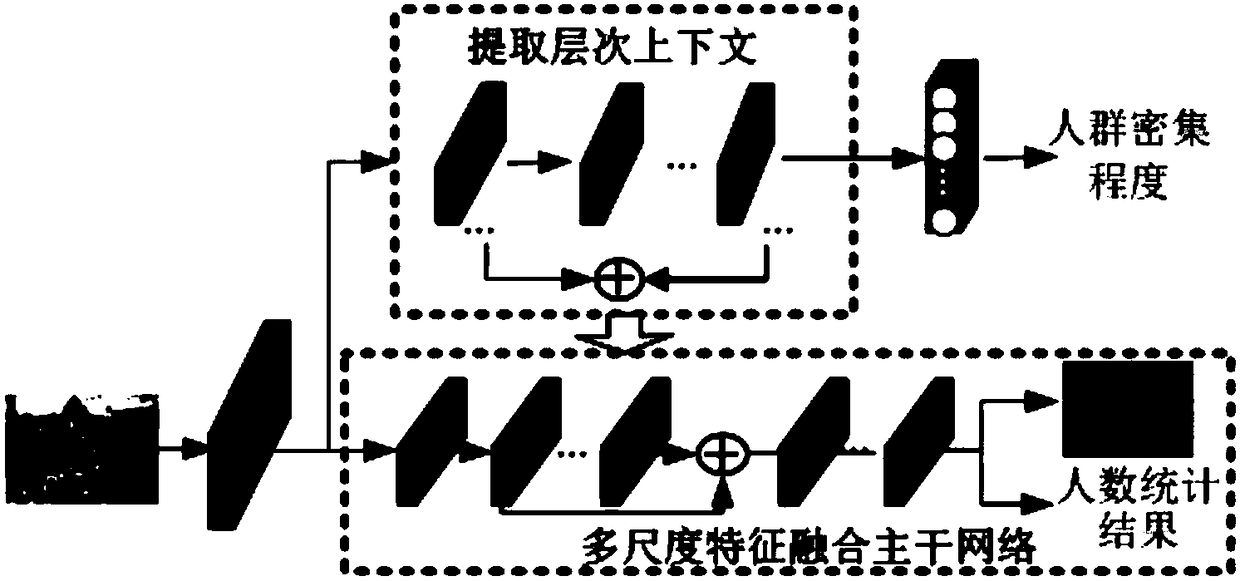
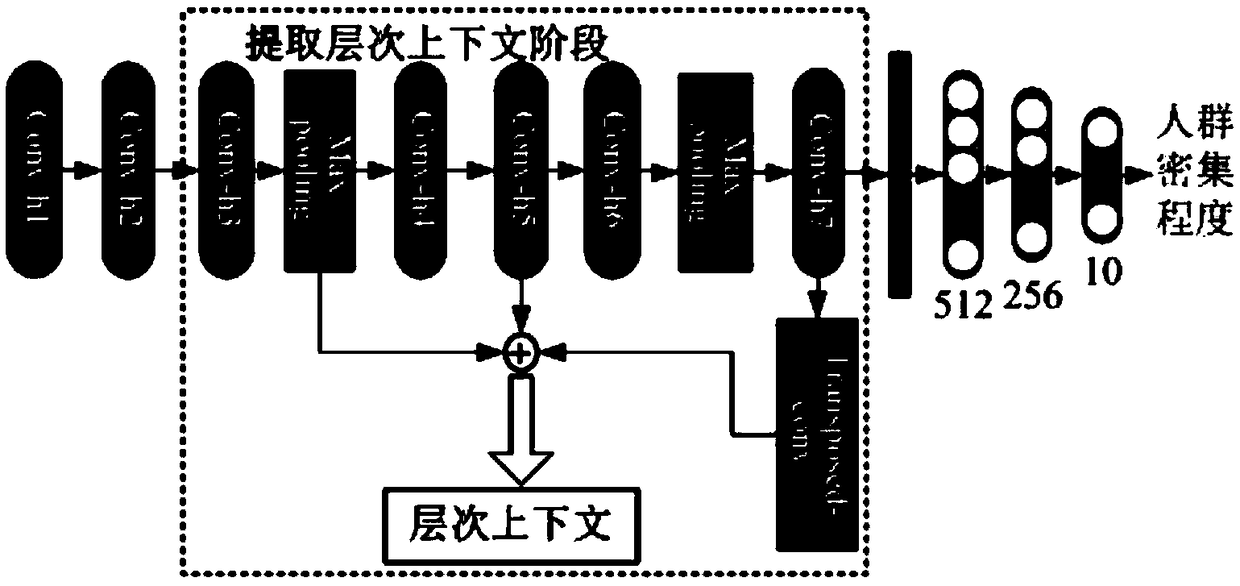
A method for counting the number of people based on a convolution neural network
ActiveCN109271960AReduce the defect that the accuracy rate dropsImprove universalityCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural architecturesCrowdsImage scale
The invention discloses a method for counting the number of people based on a convolution neural network, which relates to the field of computer vision. Firstly, the image sample data is processed andthe actual crowd density map of the sample image is generated. Then, a hierarchical context and multi-scale feature fusion network is established by extracting and processing the feature maps in thebranch network to obtain the hierarchical context information and transferring it to the backbone network, which selectively fuses the low-level and high-level feature maps in the backbone network. The network is trained by using the processed sample data. Finally, the trained model is used to count the number of people in any image. The invention effectively solves the problem that the accuracy rate drops due to the inconsistent image scale in the number of people counting task, and improves the universality of the method in different scenes.
Owner:YANSHAN UNIV
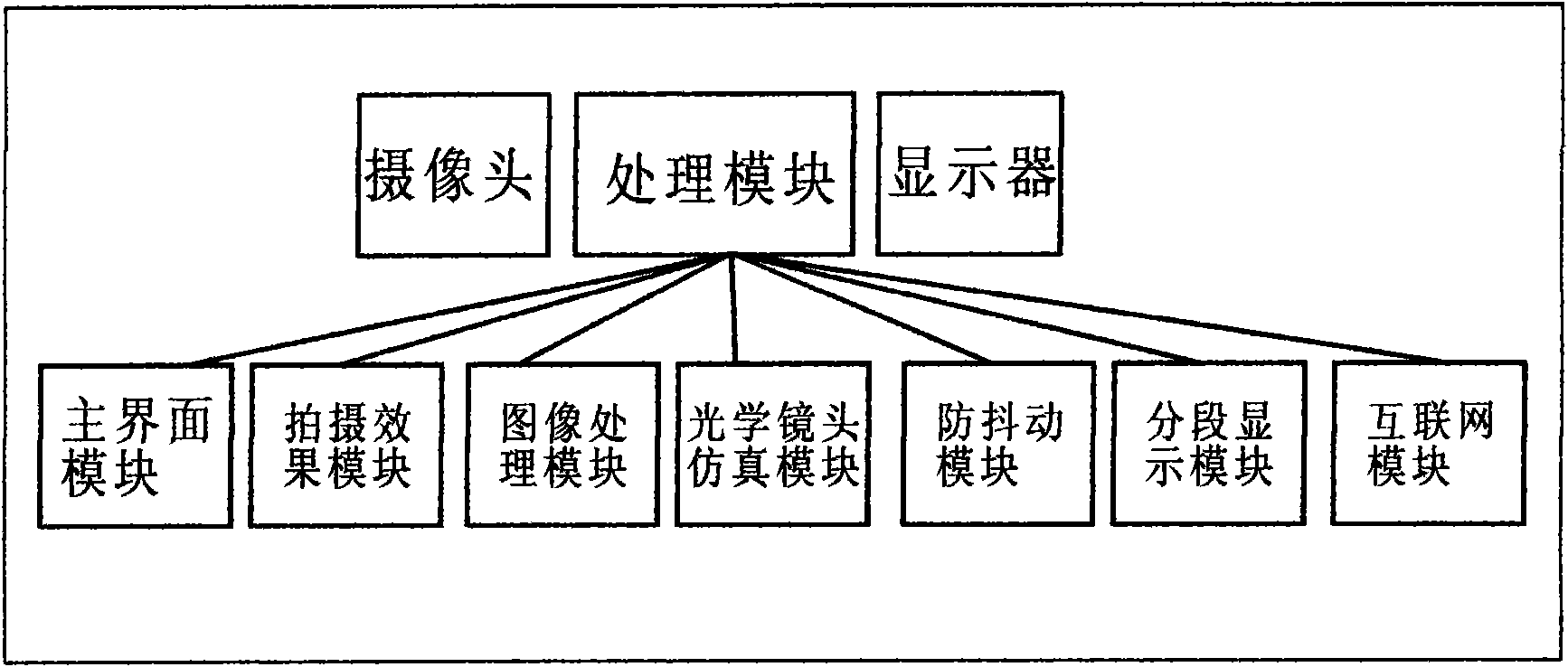
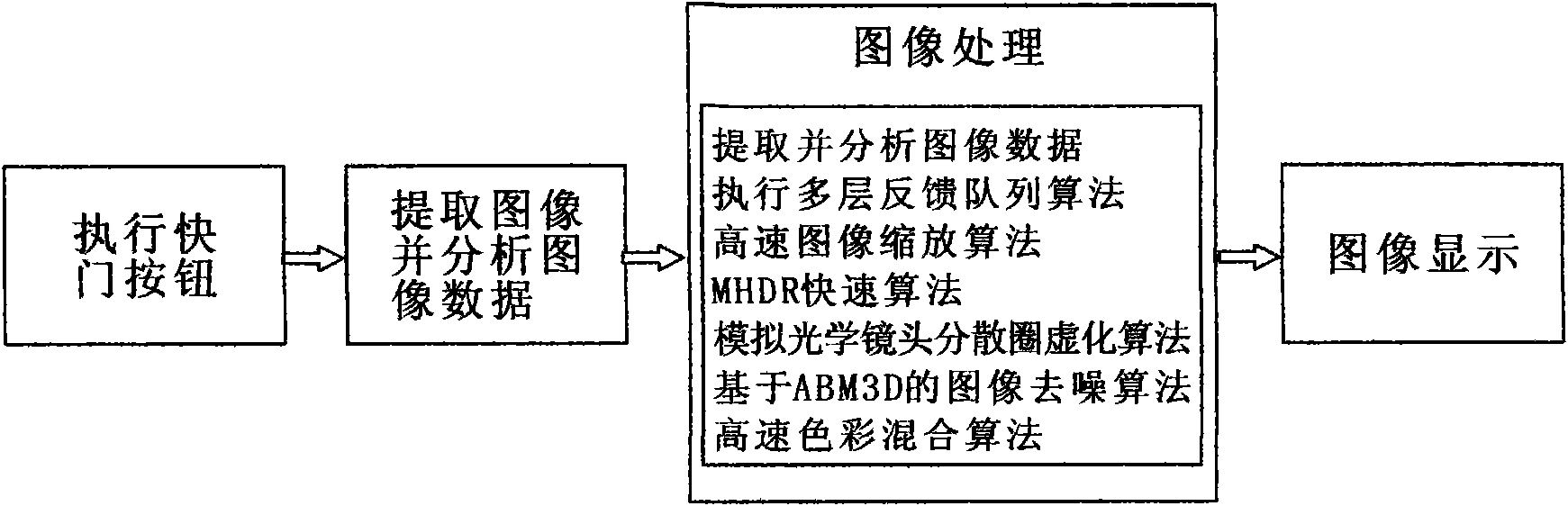
Camare360 mobile phone photographic platform and instant processing method
ActiveCN102082864AQuality improvementAvoid jitterSubstation equipmentPhotographyImage denoisingImaging processing
The invention discloses a Camare360 mobile phone photographic platform and an instant processing method. The Camare360 mobile phone photographic platform comprises a main interface module, a photographic effect module, an image processing module, an optical lens simulation module, an anti-vibration module, a segmental shrinking developing instant image processing module and an internet service module. A method for instantly processing a photo comprises the following steps of: executing a shutter button module; extracting and analyzing image data; and executing a multi-layer feedback queue algorithm, a high-speed image scaling algorithm, an MHDR fast algorithm, a simulated optical lens scattered aperture visual algorithm, an ABM3D-based image denoising algorithm and a high-speed color mixing algorithm. By a platform for instantly processing the photo by using a third generation (3G) mobile phone, the quality of mobile phone photos is greatly improved; artistic representation and artistic impact of mobile phone photography are greatly enriched; the complex processes are simplified to be integrated fully automatic operation; and a user can take various types of high-quality artistic photos as the user wishes.
Owner:CHENDU PINGUO TECH
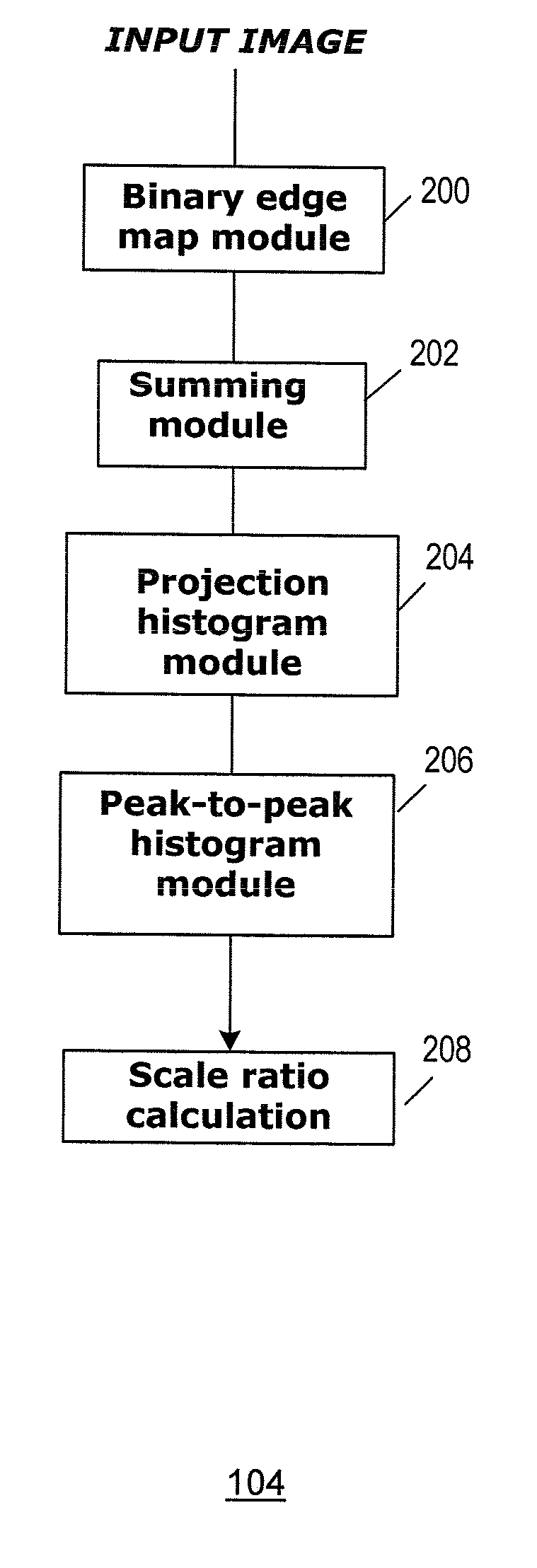
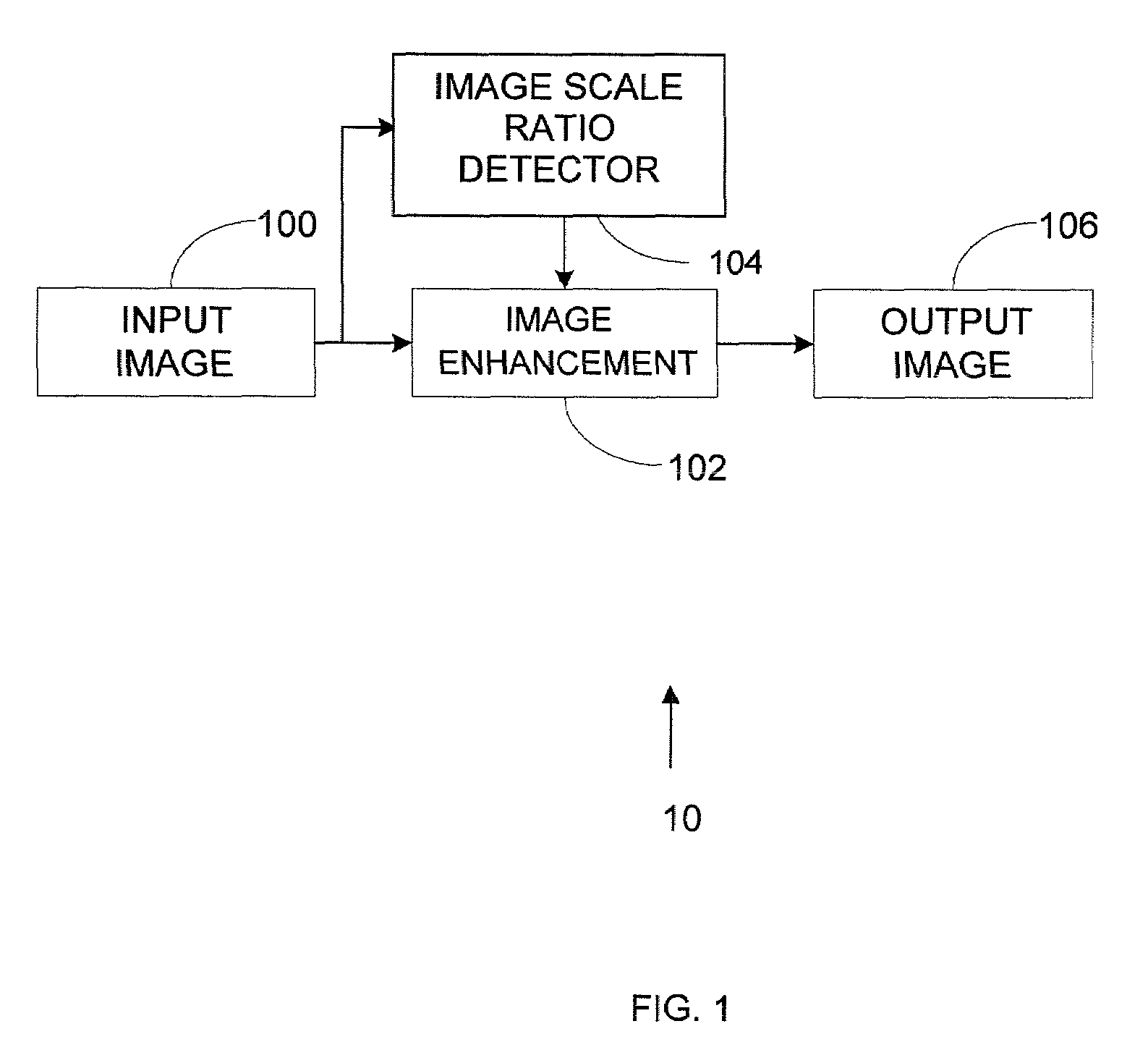
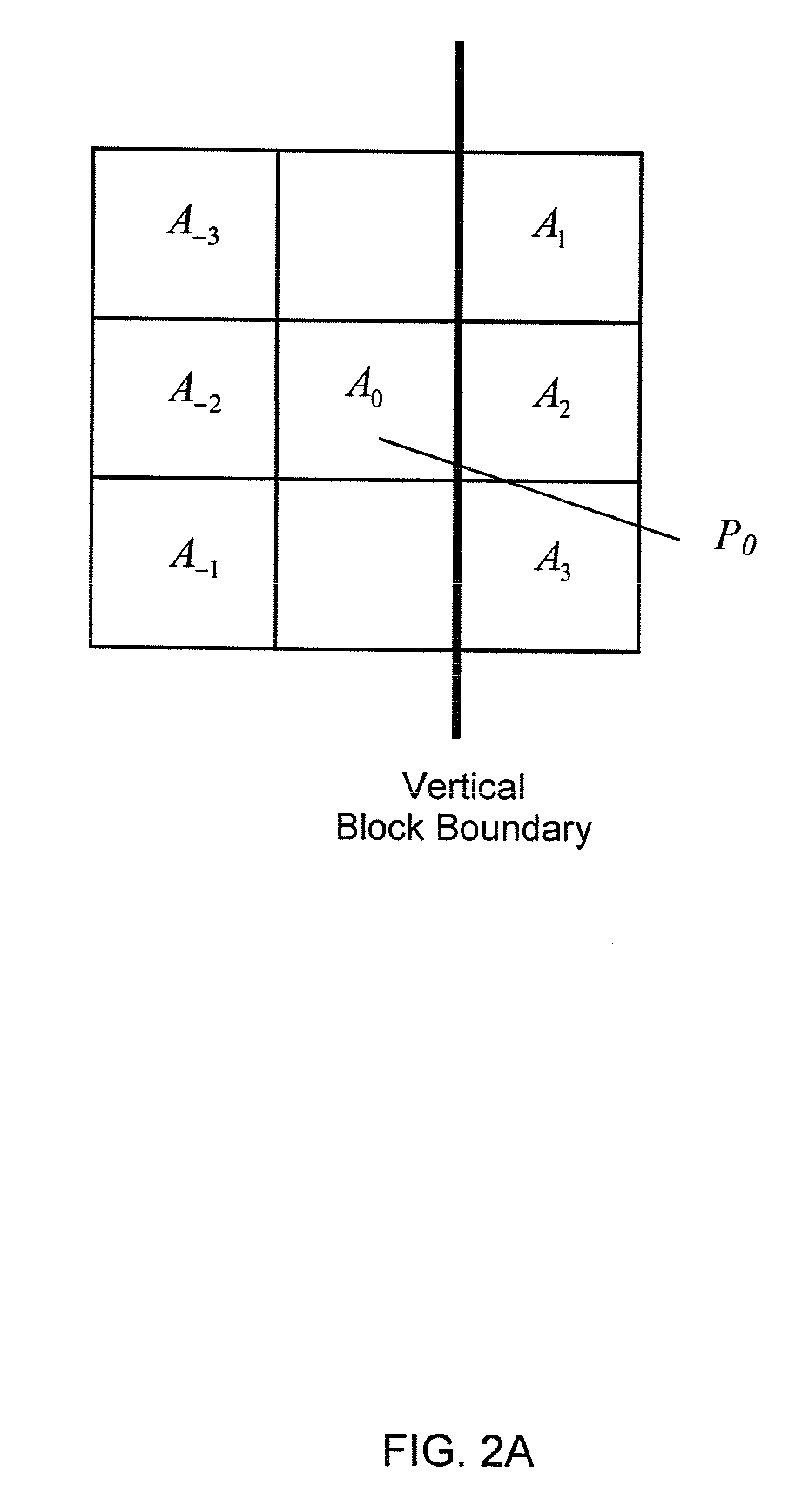
Method and system for image scaling detection
InactiveUS20090245755A1Television system detailsColor television signals processingPattern recognitionImage scale
A method and system for image scaling detection is provided. Image scaling detection involves receiving a decoded scaled input image having a plurality of pixels, wherein the input image has a scaling ratio relative to an original image; detecting blocking boundary artifact pixels in the image; determining a sum of pixel values for each blocking boundary artifact; detecting the pixel distance value between each pair or neighboring block boundaries; and determining the scaling ratio based on a distance value and said sum of pixel values.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Image scaling employing horizontal partitioning
InactiveUS20050122347A1Less real estateLow costGeometric image transformationImage memory managementComputational scienceImage scale
An apparatus, circuit arrangement, program product and method of scaling an image horizontally partition a source image into a plurality of partitions, with each partition having a width that is no greater than the width of a line buffer used to scale the image. By partitioning an image into a plurality of partitions, the overall width of the scaled image is not constrained by the width of the line buffer. As a result, in many instances line buffers that are significantly smaller than conventional full-width line buffers may be used to generate scaled images that are substantially wider than may be generated by conventional buffers. Moreover, when implemented in hardware, the line buffers typically occupy significantly less real estate on an integrated circuit, thus reducing both cost and power consumption.
Owner:IBM CORP
Method and system for image scaling
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
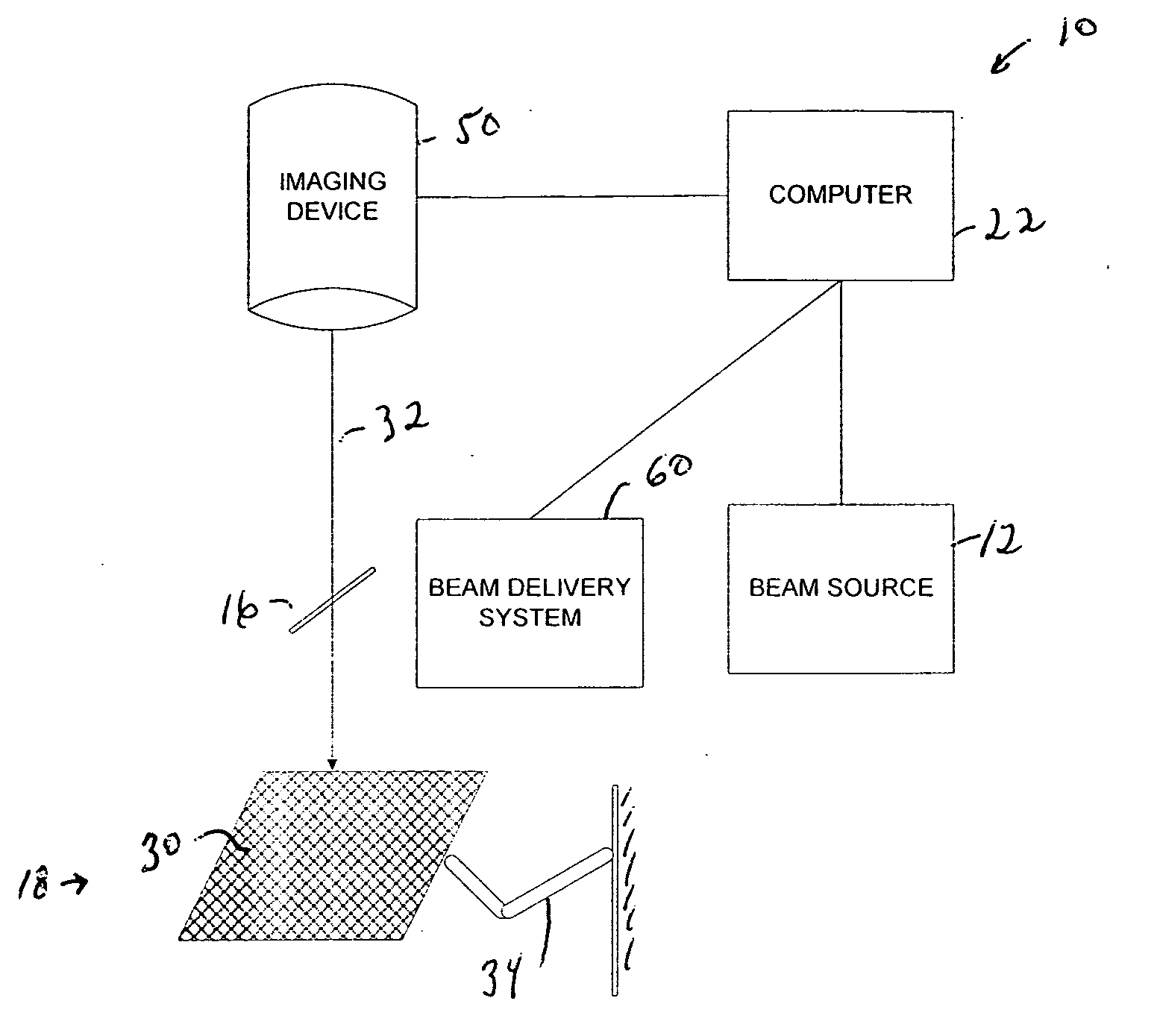
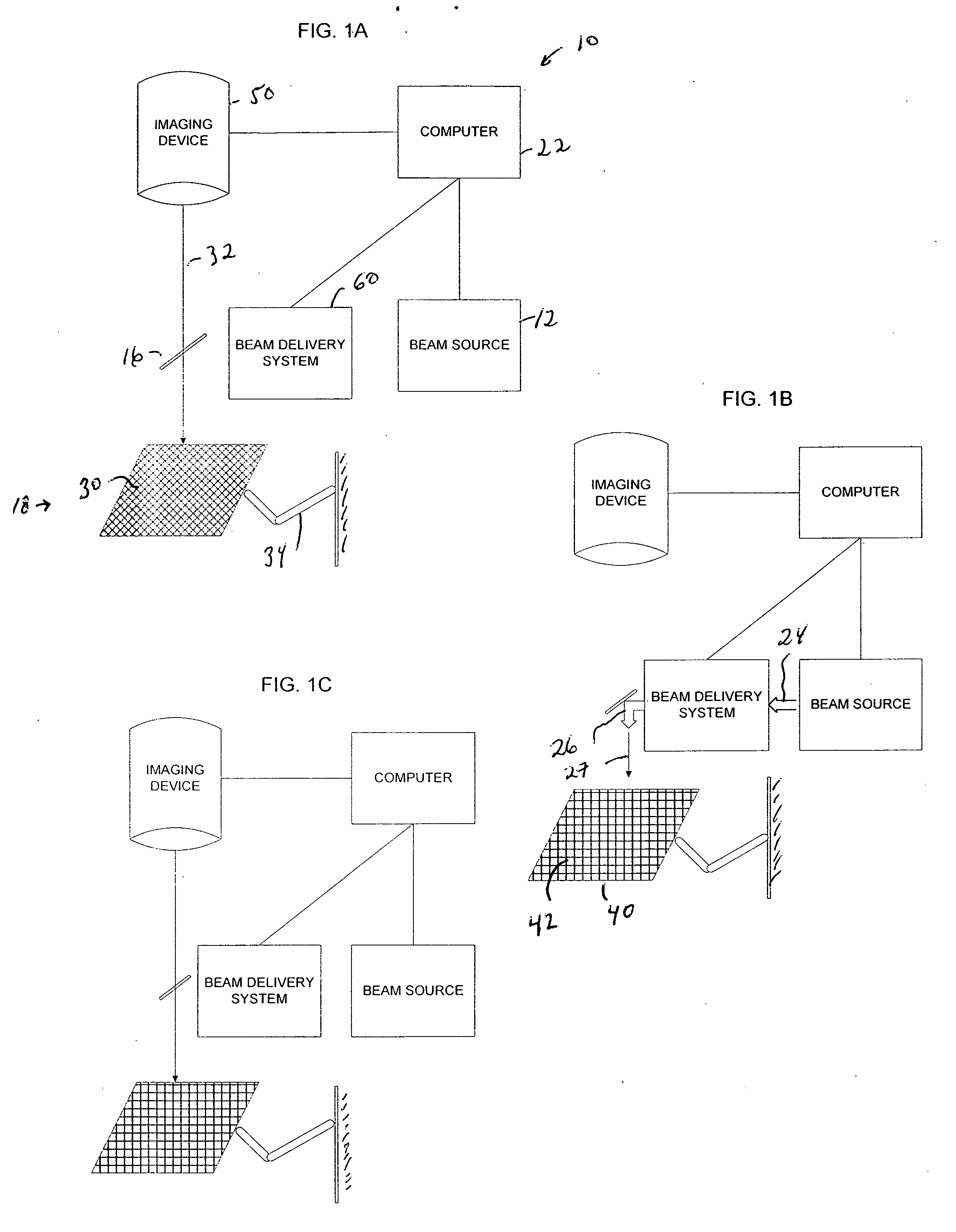
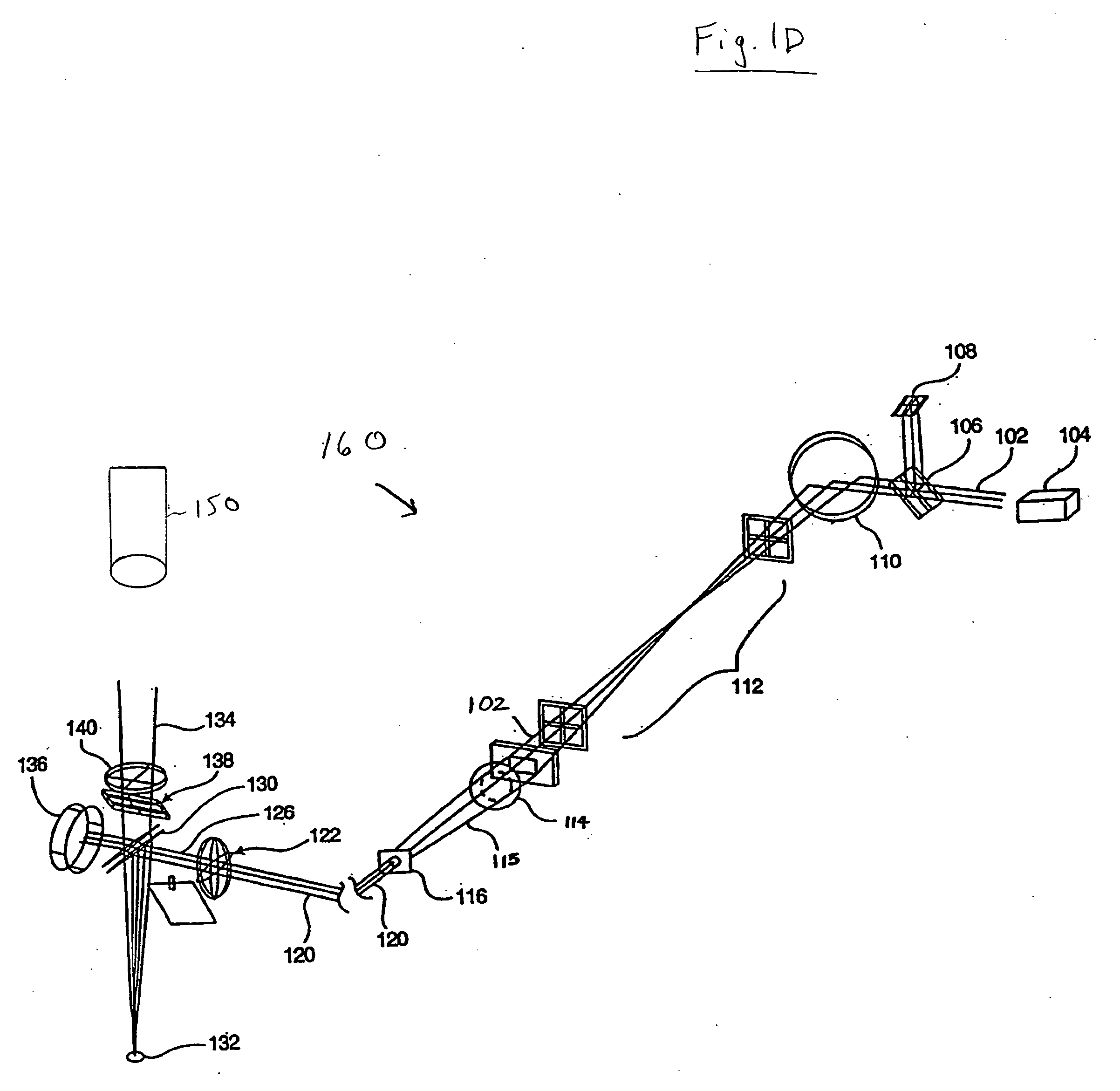
Systems and methods for qualifying and calibrating a beam delivery system
ActiveUS20070173792A1Improve qualificationImprove calibration accuracyLaser surgerySurgical instrument detailsLight beamImage scale
Systems and methods for testing a laser eye surgery system are provided. Methods include establishing an image scale based on a calibration pattern, imageably altering a series of regions of a test surface with the laser system, laterally redirecting a laser beam to form a test pattern, imaging the test pattern, determining a lateral redirecting characteristic of the beam delivery system, and qualifying or calibrating the beam delivery system. Systems can include an input module that accepts an input member such as a calibration pattern parameter, a calibration pattern image, an intended pattern parameter, a test pattern image, an imaging device position, a calibration pattern position, a test pattern position, and a beam delivery system position, a characterization module that determines a beam delivery system characteristic, and an output module that generates a calibration for the beam delivery system of the laser eye surgery system.
Owner:AMO MFG USA INC
Methods, systems, and programming for producing and displaying subpixel-optimized images and digital content including such images
InactiveUS20050062758A1Reduce color imbalanceSuitable displayDigital data information retrievalDetails involving antialiasingDigital contentLuminosity
The invention relates to methods, systems, and programming for producing and displaying subpixel-optimized images and digital content including such images. Some embodiments access digital content represented by a mark-up language and display it with its images scaled down in a subpixel-optimized manner in a format dictated by the mark-up language. Some embodiments produce subpixel-optimized images by calculating the luminosity of a subpixel in such an image as a function of the length of a plurality of coverage lines within a window in a source image corresponding to the subpixel that is covered by source image pixels having the subpixel's color. Some embodiments calculate the luminosity of a subpixel in a subpixel-optimized image as a function both of the average luminosity of pixels in the subpixel's source image window and as a function of any color balancing distribution between resulting subpixel luminosities necessary to reduce color imbala
Owner:MARLBOROUGH SOFTWARE DEV HLDG
Image salient region detection method based on joint sparse multi-scale fusion
InactiveCN104392463AOvercome the shortcomings of observing different salient regionsOvercoming the disadvantages of different salient areasImage enhancementImage analysisImage scaleComputer science
The invention belongs to the technical field of image salient region detection and particularly discloses an image salient region detection method based on joint sparse multi-scale fusion. The image salient region detection method comprises the following steps: (1) constructing a multilayer Gaussian pyramid for a training image to realize multi scales and training to obtain a dictionary under each scale; (2) obtaining an image block of each pixel point in a test image and carrying out joint sparse solution of a sparse representation coefficient of the image block under each scale; (3) taking the sparse representation coefficient as a feature to carry out saliency calculation; (4) fusing salient results under the multi sales to obtain a final salient image. The image salient region detection method has the benefits that the purpose of extracting a region capable of catching people's eyes in any given image is realized; the image salient region detection method has the advantages that firstly, the effect under different image scales is overcome under multi-scale operation; secondly, a joint sparse framework is very beneficial to saliency calculation; experiments show that the results obtained by the method have better robustness and are inferior to those obtained according to most of the conventional methods.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Method and system for digital image magnification and reduction
InactiveUS20070104394A1Enhance the imageLowering scale factorColor signal processing circuitsGeometric image transformationSingle stagePhase filter
An image scaling system for converting a sampling rate of an input video signal comprising input pixel data to produce a magnified or reduced output video image comprising output pixel data includes a first one-dimensional image scaler comprising a single-stage finite-duration impulse response (FIR) filter structure with poly-phase filter responses that receives and scales the input pixel data by a scaling factor in either a horizontal or vertical direction to produce output pixel data and a second one-dimensional image scaler comprising a single-stage FIR filter structure that is coupled in tandem to the first one-dimensional image scaler and scales by the scaling factor the output pixel data from the first one-dimensional image scaler in a direction perpendicular to that of the first one-dimensional image scaler to produce the magnified or reduced output video image. Each of the first and second one-dimensional image scalers includes a reconfigurable interpolation unit that allows each single-stage FIR filter structure to switch back and forth between operating in a direct-form FIR filter mode and a transposed-form FIR filter mode while using a fixed set of system resources such that a wide range of image magnification and reduction scaling factors can be achieved using the fixed set of system resources.
Owner:CORONA
Multi-dimensional keystone correction projection system and method
InactiveUS20060203207A1Good lookingReduce calculationTelevision system detailsProjectorsGratingProjection image
A digital circuit, system, and method for keystone correction of a projected image utilize a digital keystone correction engine to resize a raster-scanned input image prior to projection. An image keystone correction engine uses coordinates of the corners of the image on the display device that are modified to produce a resized image for projection onto a screen. Scaling factors are generated at the corners of the image to represent image scaling along two image axes that span the area of the image to form a resized image on the display device by repositioning pixels from an uncorrected or previously resized image. The variation of the scaling factors across the image can be assumed to be linear.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
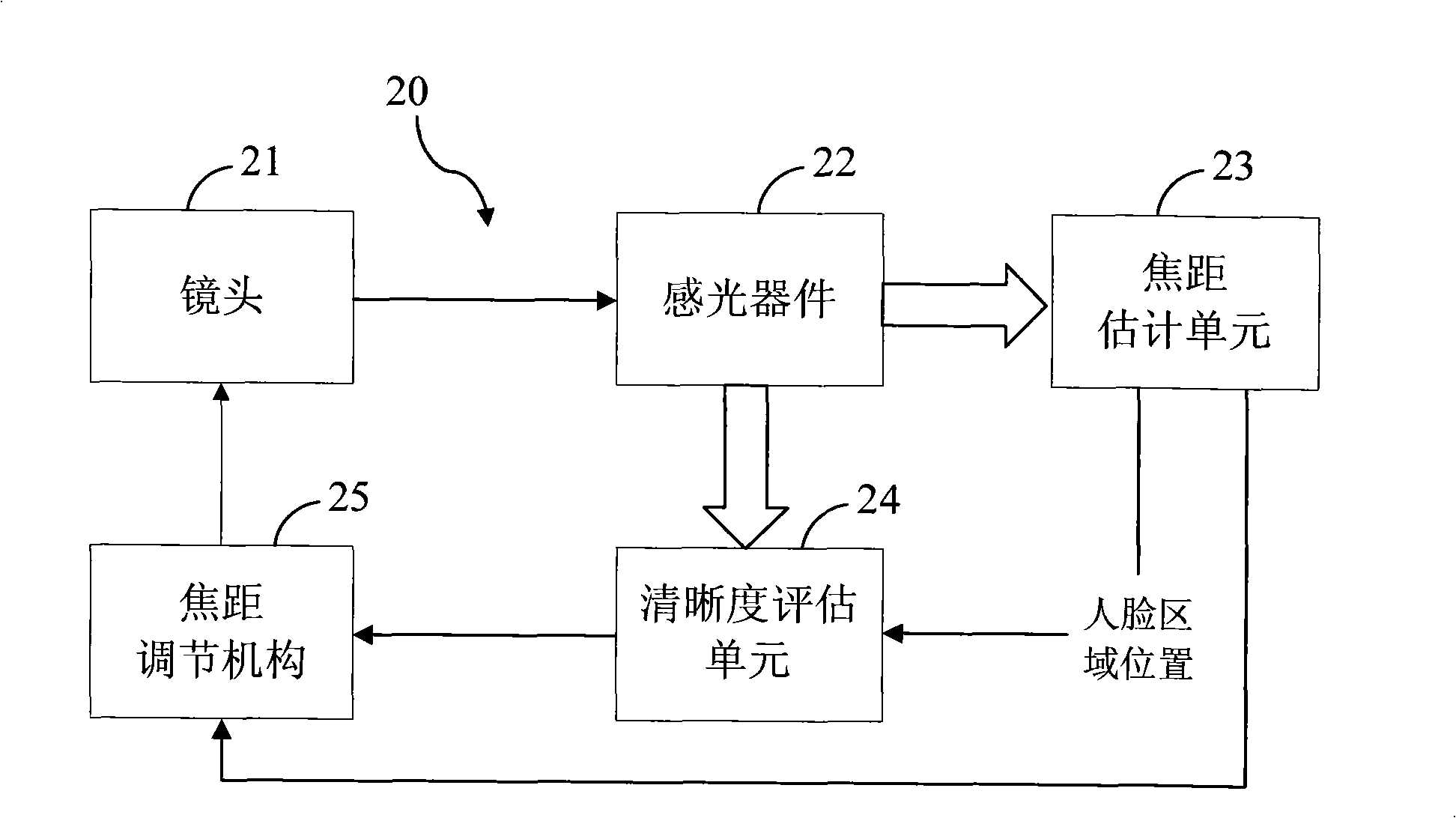
Automatic focusing method and image collecting device
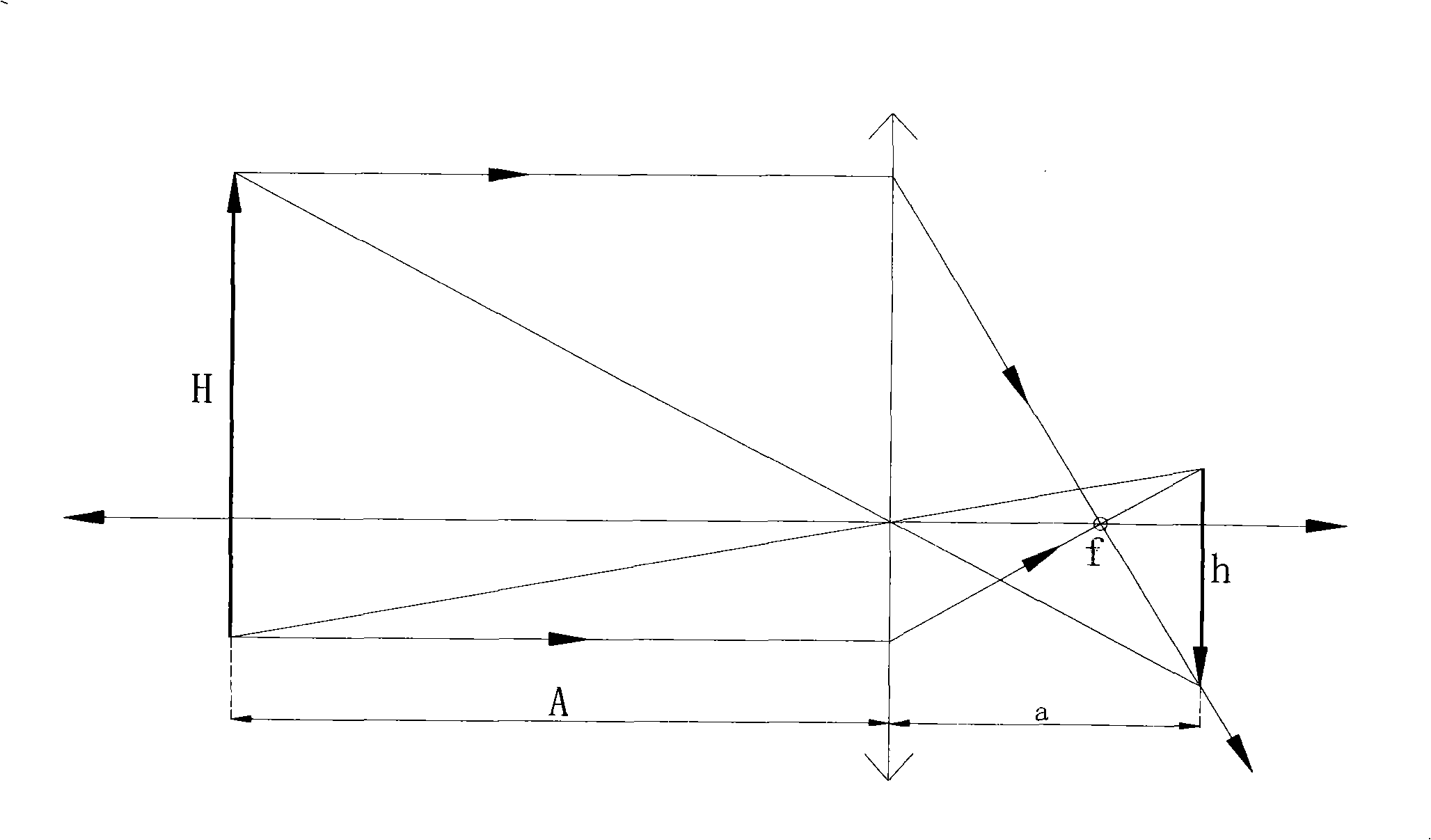
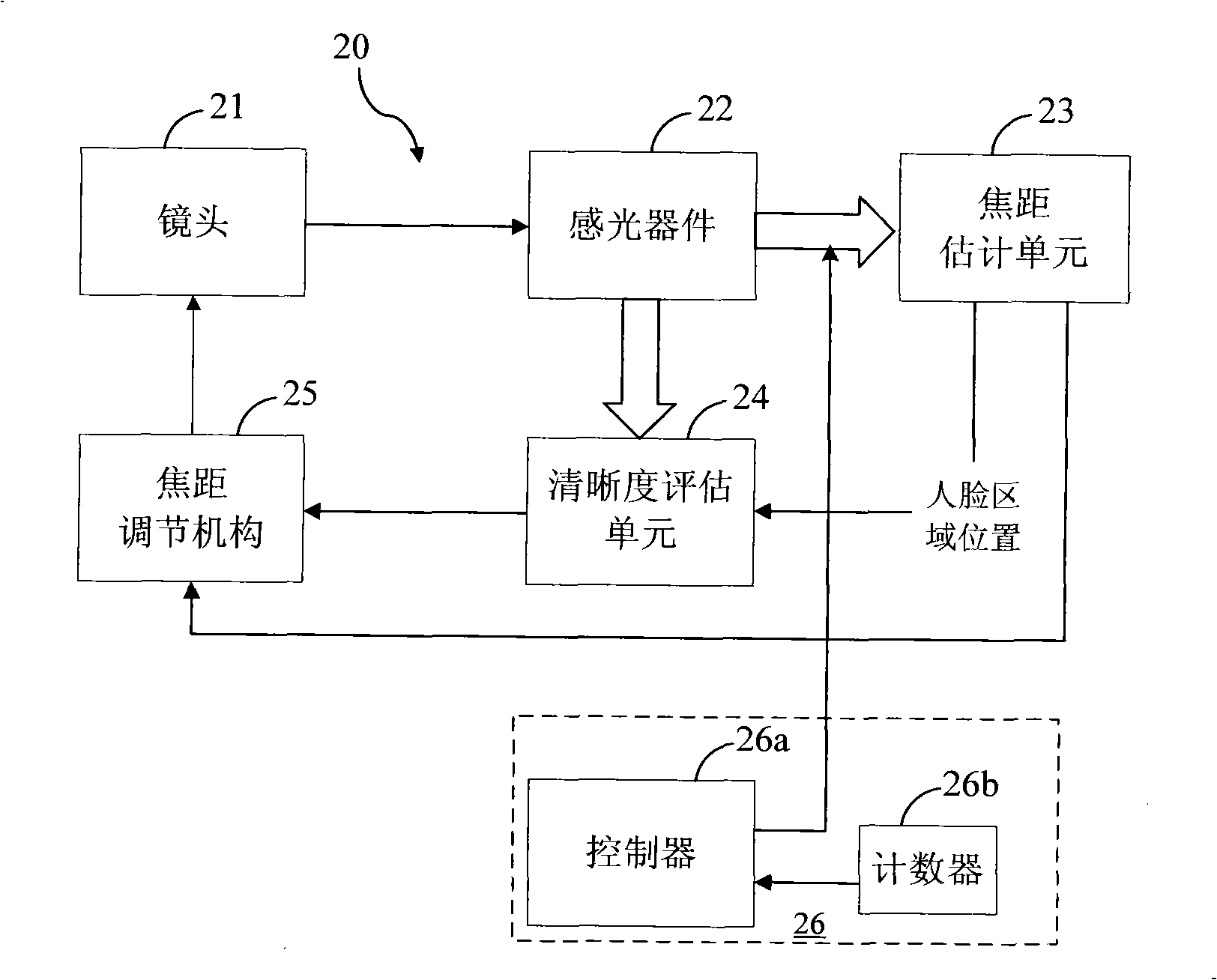
ActiveCN101290388AImprove accuracyEliminate the effects ofTelevision system detailsColor television detailsImage scaleImaging lens
The invention discloses an automatic focusing method and an image acquisition device, wherein the device comprises at least one imaging lens, at least one focusing lens, a photosensitive device and a focal length regulation mechanism. The method comprises the following steps that: A. according to the actual scale of an object, the actual scale of an image formed on the photosensitive device by the object and the distance between the photosensitive device and the imaging lens, the product of the distance between the photosensitive device and the imaging lens and the actual object scale divided by the sum of the actual object scale and the actual image scale equals a focusing focal length estimation value FF; B. the focal length regulation mechanism is regulated to allow the focal length to reach the focusing focal length estimation value FF; C. the focal length is fine-adjusted to a plurality of focal length positions around the focusing focal length estimation value FF; the focusing estimation value of the image formed on each focal length position is calculated, and the focal length corresponding to the maximum focusing estimation value is taken as an accurate focusing focal length MF; D. the focal length regulation mechanism is regulated to allow the focal length to reach the accurate focusing focal length MF, and then the automatic focusing process is accomplished.
Owner:BEIJING VIMICRO ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE CHIP TECH CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com