Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1306 results about "Image object" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Image objects are children of axes objects, as are line, patch, surface, and text objects. Like all graphics objects, the image object has a number of properties you can set to fine-tune its appearance on the screen. The most important properties of the image object with respect to appearance are CData, CDataMapping , XData, and YData.
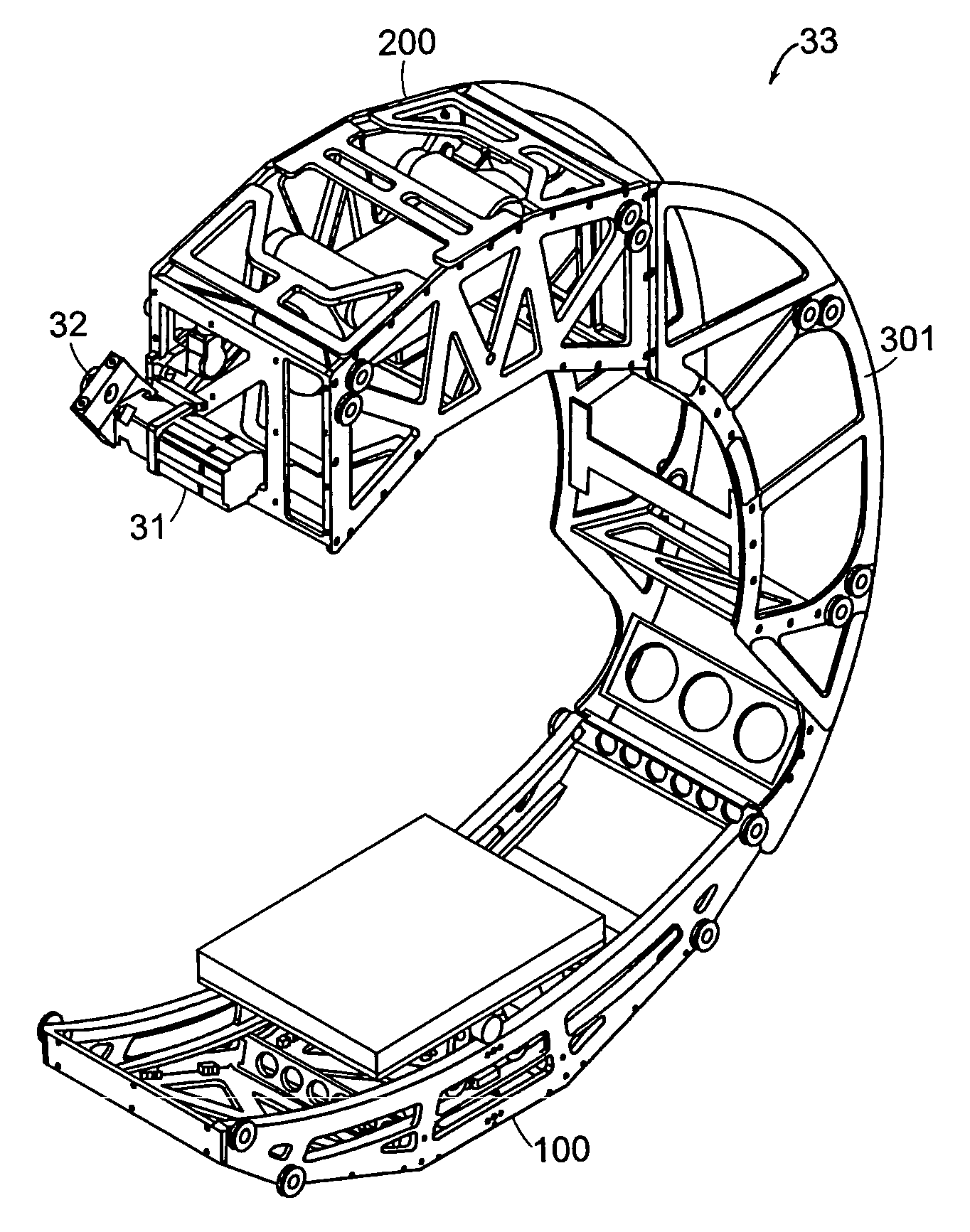
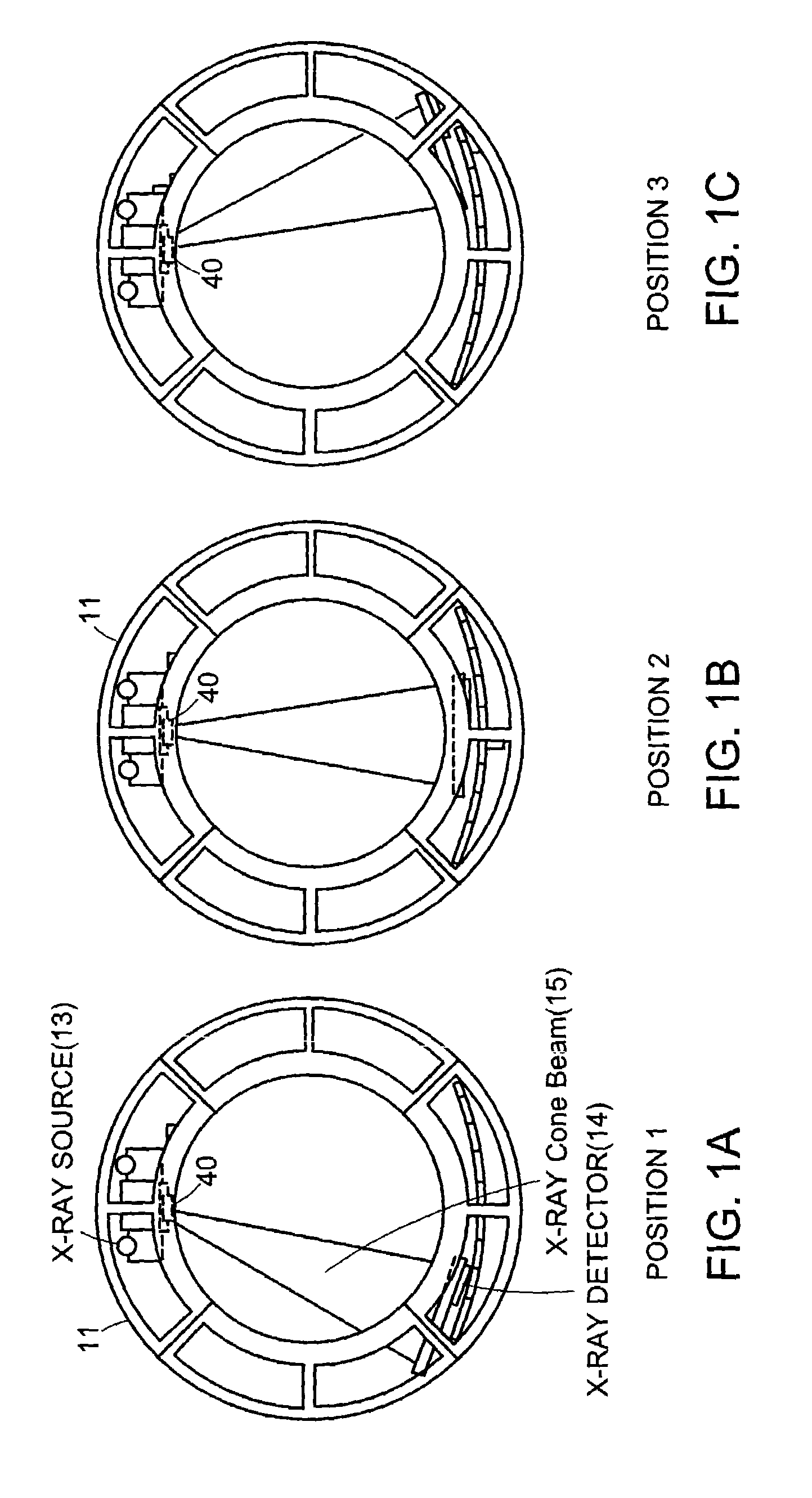
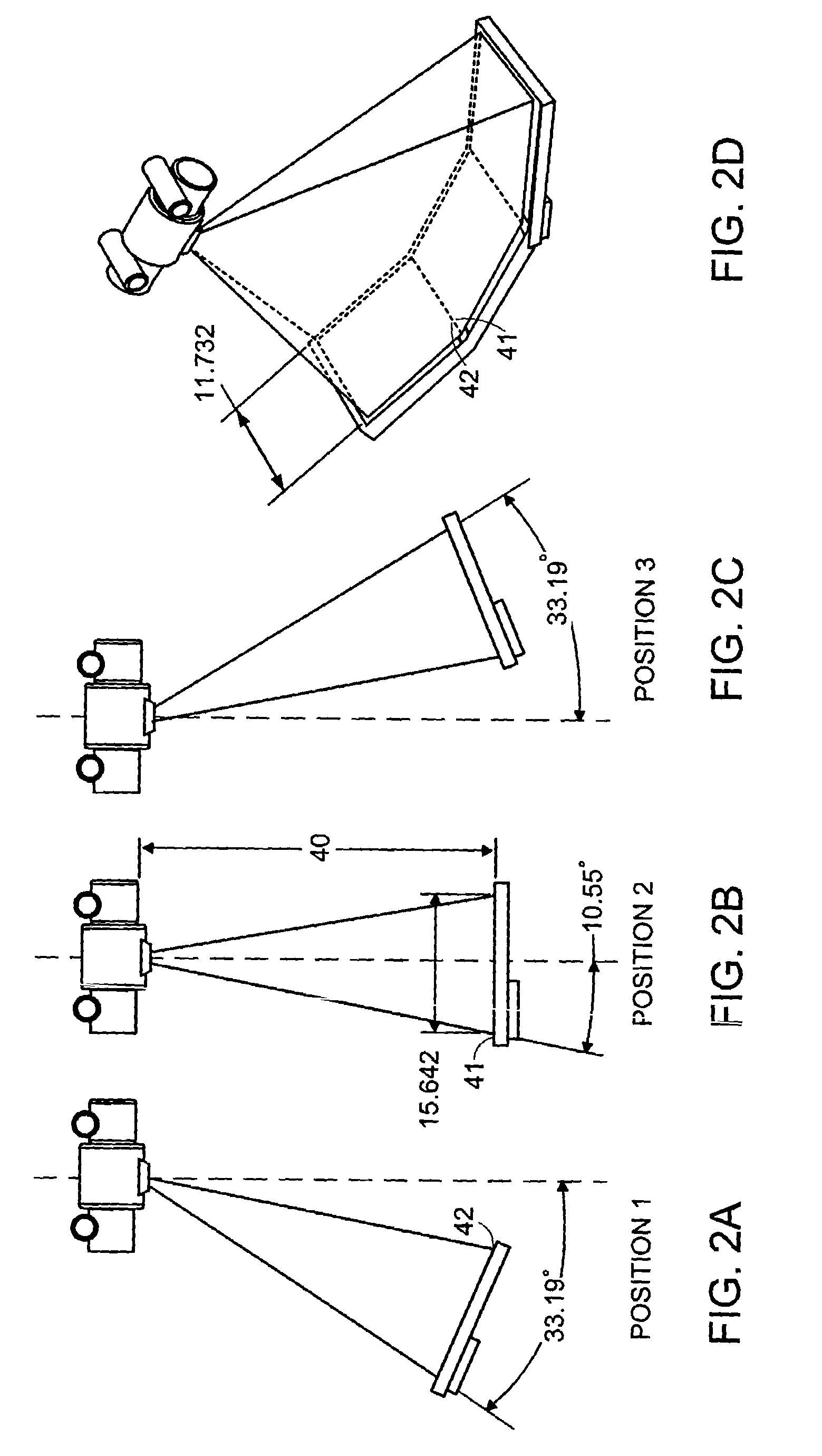
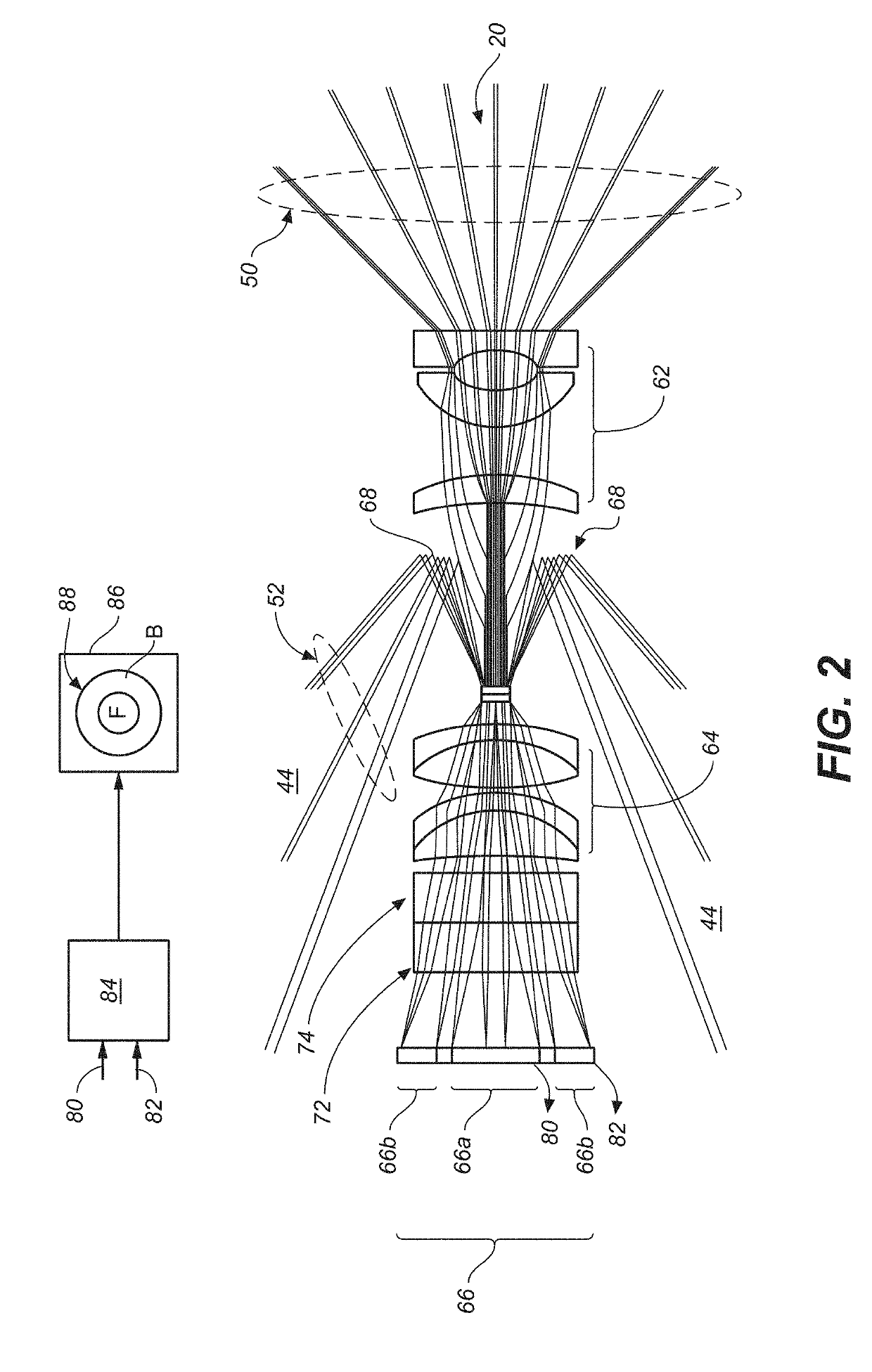
Systems and methods for imaging large field-of-view objects
InactiveUS7108421B2Quantity minimizationAvoiding corrupted and resulting artifacts in image reconstructionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingBeam sourceX-ray
An imaging apparatus and related method comprising a source that projects a beam of radiation in a first trajectory; a detector located a distance from the source and positioned to receive the beam of radiation in the first trajectory; an imaging area between the source and the detector, the radiation beam from the source passing through a portion of the imaging area before it is received at the detector; a detector positioner that translates the detector to a second position in a first direction that is substantially normal to the first trajectory; and a beam positioner that alters the trajectory of the radiation beam to direct the beam onto the detector located at the second position. The radiation source can be an x-ray cone-beam source, and the detector can be a two-dimensional flat-panel detector array. The invention can be used to image objects larger than the field-of-view of the detector by translating the detector array to multiple positions, and obtaining images at each position, resulting in an effectively large field-of-view using only a single detector array having a relatively small size. A beam positioner permits the trajectory of the beam to follow the path of the translating detector, which permits safer and more efficient dose utilization, as generally only the region of the target object that is within the field-of-view of the detector at any given time will be exposed to potentially harmful radiation.
Owner:MEDTRONIC NAVIGATION
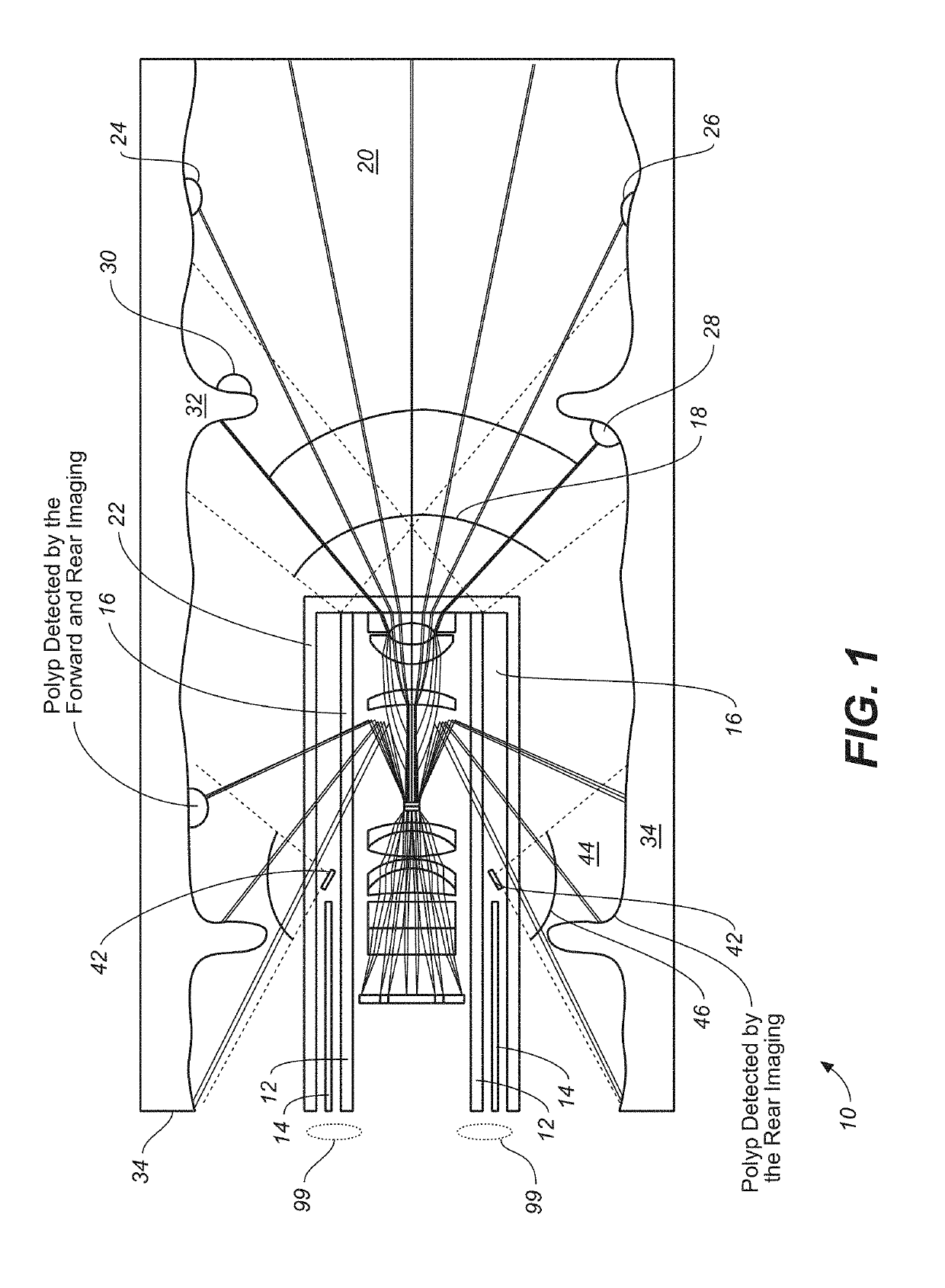
Dual-view probe for illumination and imaging, and use thereof
ActiveUS10536617B2Maximization of detectionTelevision system detailsSurgeryEngineeringElectromagnetic radiation
One embodiment of the invention is directed to an imaging probe which comprises a first element supplying electromagnetic radiation in a forward path for illuminating a forward field of view of space in front of the probe, a second element supplying electromagnetic radiation in a sideways and / or rearward path for illuminating a sideways and / or back field of view of space alongside the probe and an image sensor. The probe further includes an imaging device in imaging paths imaging the forward and sideways and / or back fields of view onto the image sensor. Preferably the forward path, the sideways and / or rearward path and the imaging paths are unobstructed by any component of the probe. Preferably the forward and sideways and / or back fields of view are registered in a fixed spatial relationship relative to one another on the image sensor. This probe can also be used with existing endoscopes or laparoscopes so that it will be easily merged into current instruments of different manufacturers, making it easier and cheaper to use this product without the expense of a totally new endoscopy or laparoscope platform. This probe can also be used to image objects in inanimate environments as well, such as in containers, buildings, rooms, engines and pipes.
Owner:THE ARIZONA BOARD OF REGENTS ON BEHALF OF THE UNIV OF ARIZONA
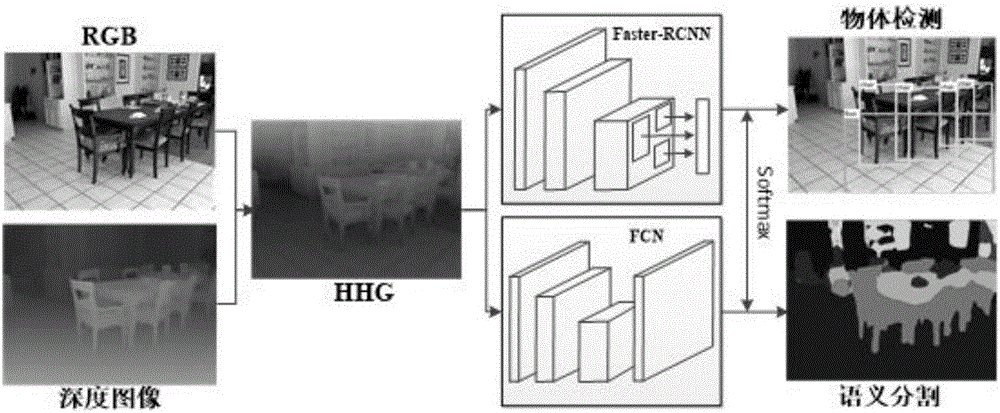
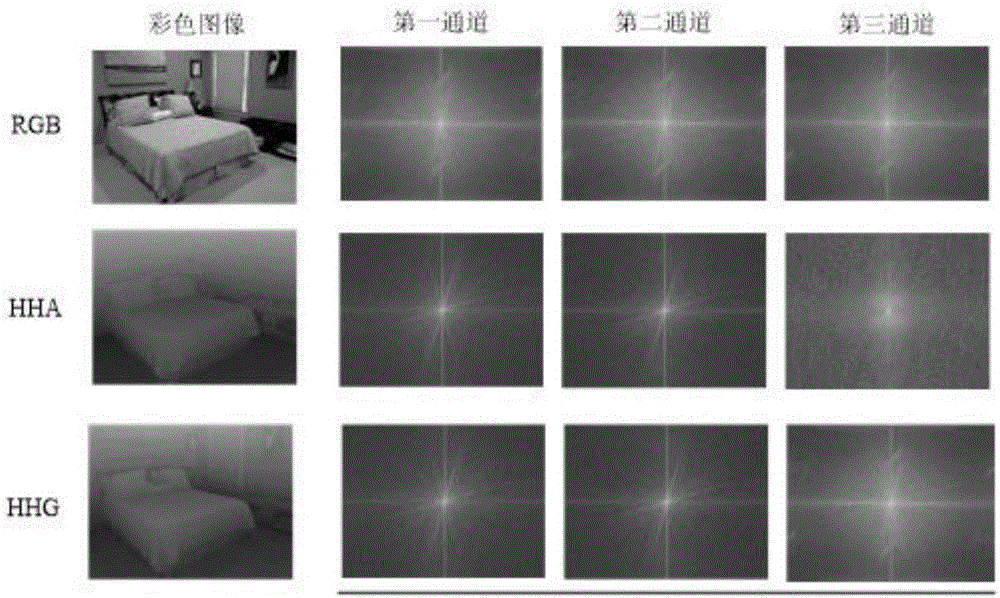
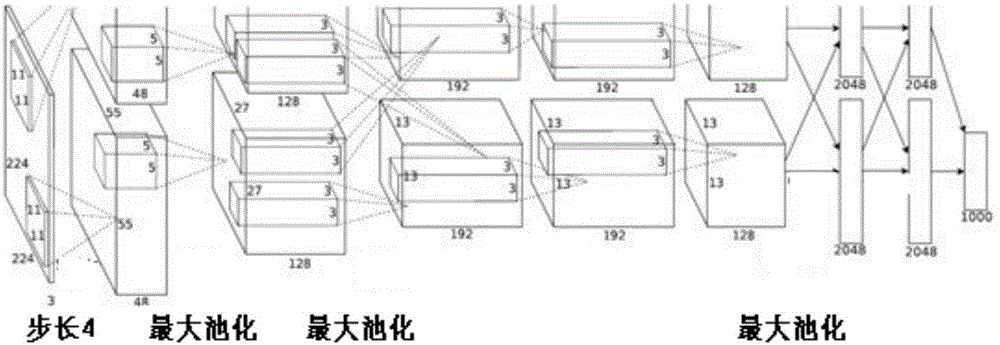
RGB-D image object detection and semantic segmentation method based on deep convolution network
ActiveCN106709568ACharacter and pattern recognitionNeural architecturesMachine visionVisual perception
The invention discloses an RGB-D image object detection and semantic segmentation method based on a deep convolution network, which belongs to the field of depth learning and machine vision. According to the method provided by the technical scheme of the invention, Faster-RCNN is used to replace the original slow RCNN; Faster-RCNN uses GPU, which is fast in the aspect of feature extracting, and at the same time generates a regional scheme in the network; the whole training process is training from end to end; FCN is used to carry out RGB-D image semantic segmentation; FCN uses a GPU and the deep convolution network to rapidly extract the deep features of an image; deconvolution is used to fuse deep features and shallow features of the image convolution; and the local semantic information of the image is integrated into the global semantic information.
Owner:深圳市小枫科技有限公司
Large-area individually addressable multi-beam x-ray system and method of forming same
A structure to generate x-rays has a plurality of stationary and individually electrically addressable field emissive electron sources with a substrate composed of a field emissive material, such as carbon nanotubes. Electrically switching the field emissive electron sources at a predetermined frequency field emits electrons in a programmable sequence toward an incidence point on a target. The generated x-rays correspond in frequency and in position to that of the field emissive electron source. The large-area target and array or matrix of emitters can image objects from different positions and / or angles without moving the object or the structure and can produce a three dimensional image. The x-ray system is suitable for a variety of applications including industrial inspection / quality control, analytical instrumentation, security systems such as airport security inspection systems, and medical imaging, such as computed tomography.
Owner:THE UNIV OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHAPEL HILL
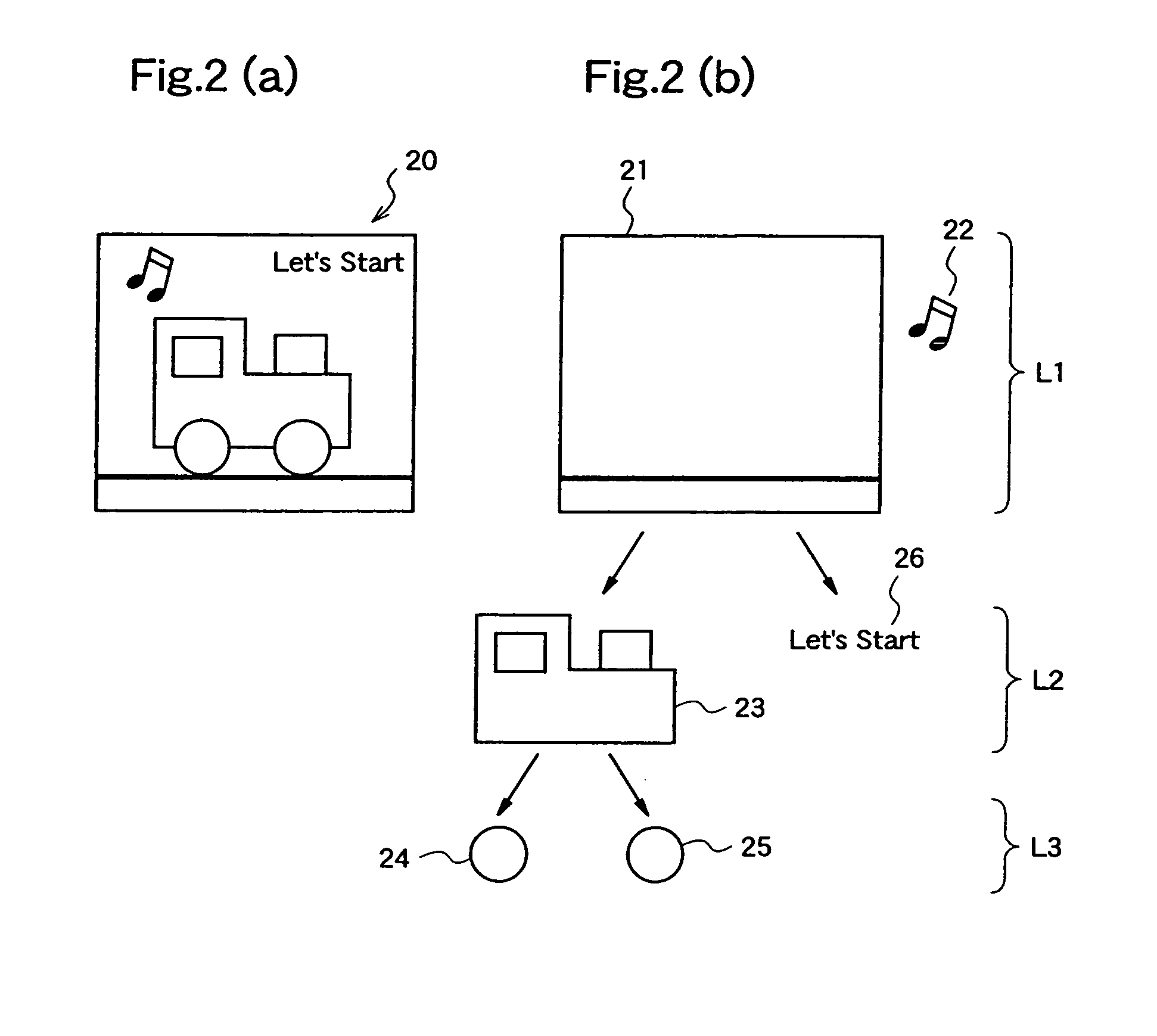
Method and system for on-screen animation of digital objects or characters
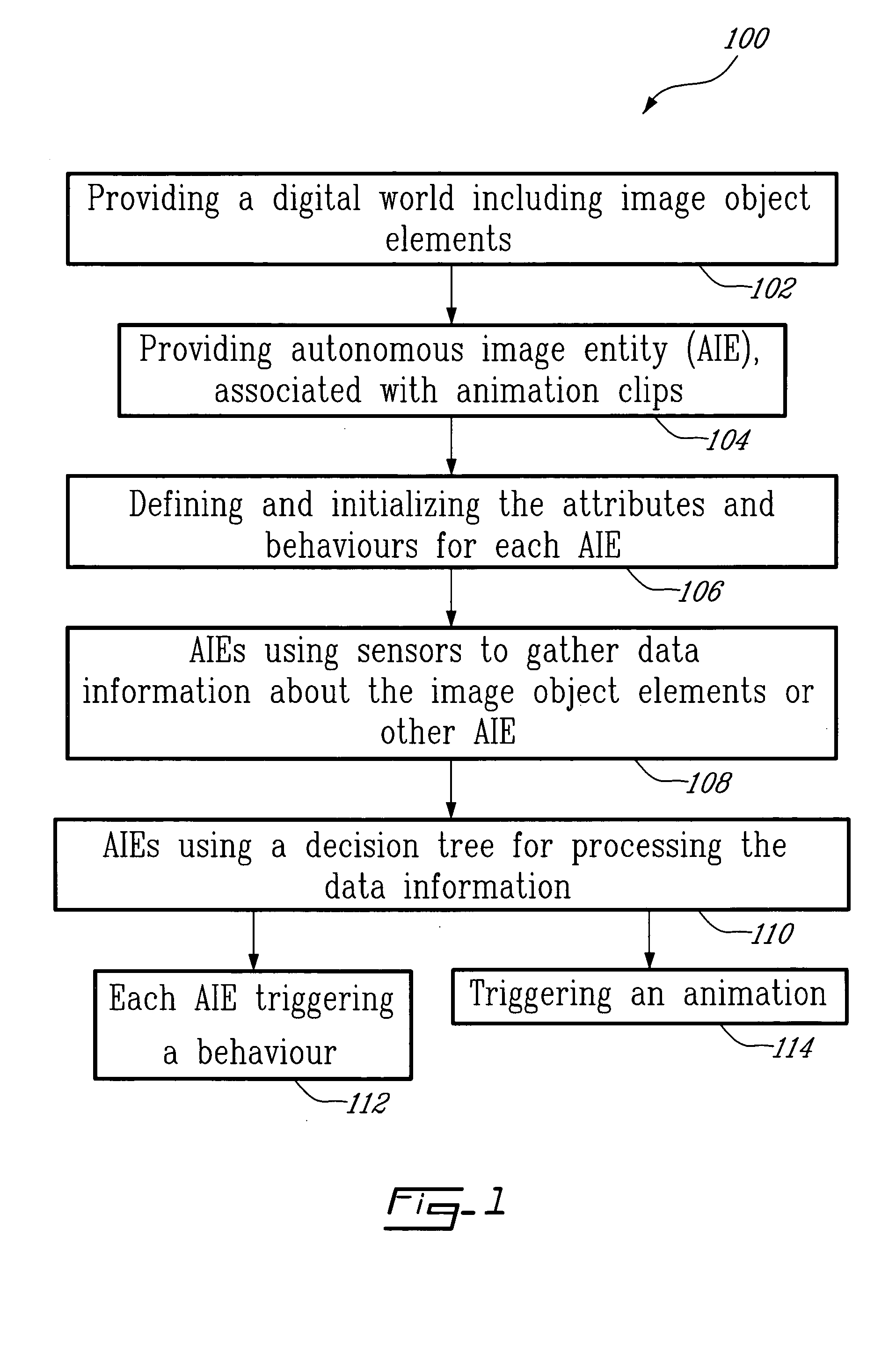
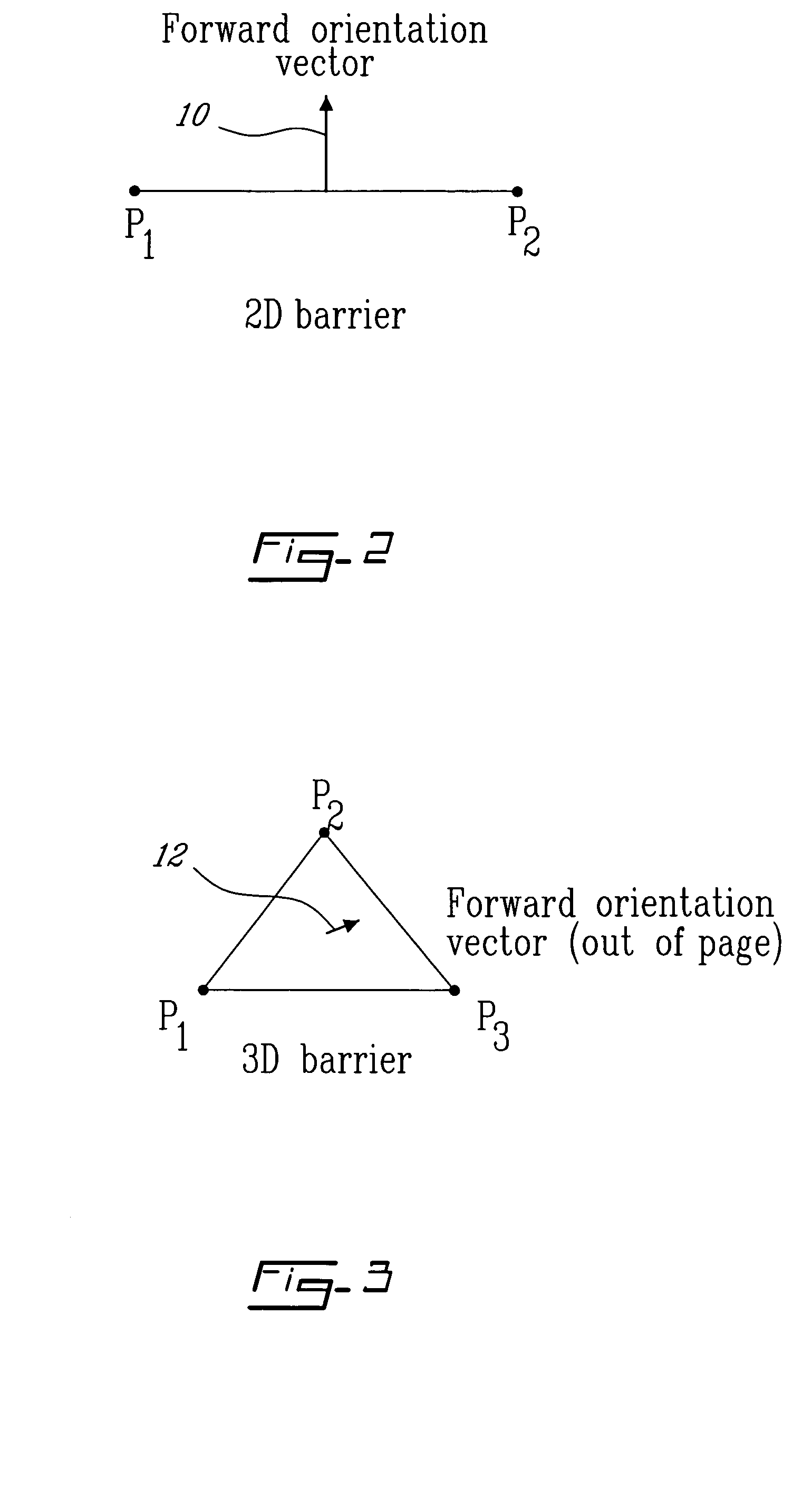
The method for on-screen animation includes providing a digital world including image object elements and defining autonomous image entities (AIE). Each AIE may represent a character or an object that is characterized by i) attributes defining the AIE relatively to the image objects elements of the digital world, and ii) behaviours for modifying some of the attributes. Each AIE is associated to animation clips allowing representing the AIE in movement in the digital world. Virtual sensors allow the AIE to gather data information about image object elements or other AIE within the digital world. Decision trees are used for processing the data information resulting in selecting and triggering one of the animation cycle or selecting a new behaviour. A system embodying the above method is also provided. The method and system for on-screen animation of digital entities according to the present invention can be used for creating animation for movies, for video games, and for simulation.
Owner:BGT BIOGRAPHIC TECH
Use of snapshots to reduce risk in migration to a standard virtualized environment
ActiveUS9092837B2Reduce risk of migrationResource allocationImage acquisitionShort termsSource system
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
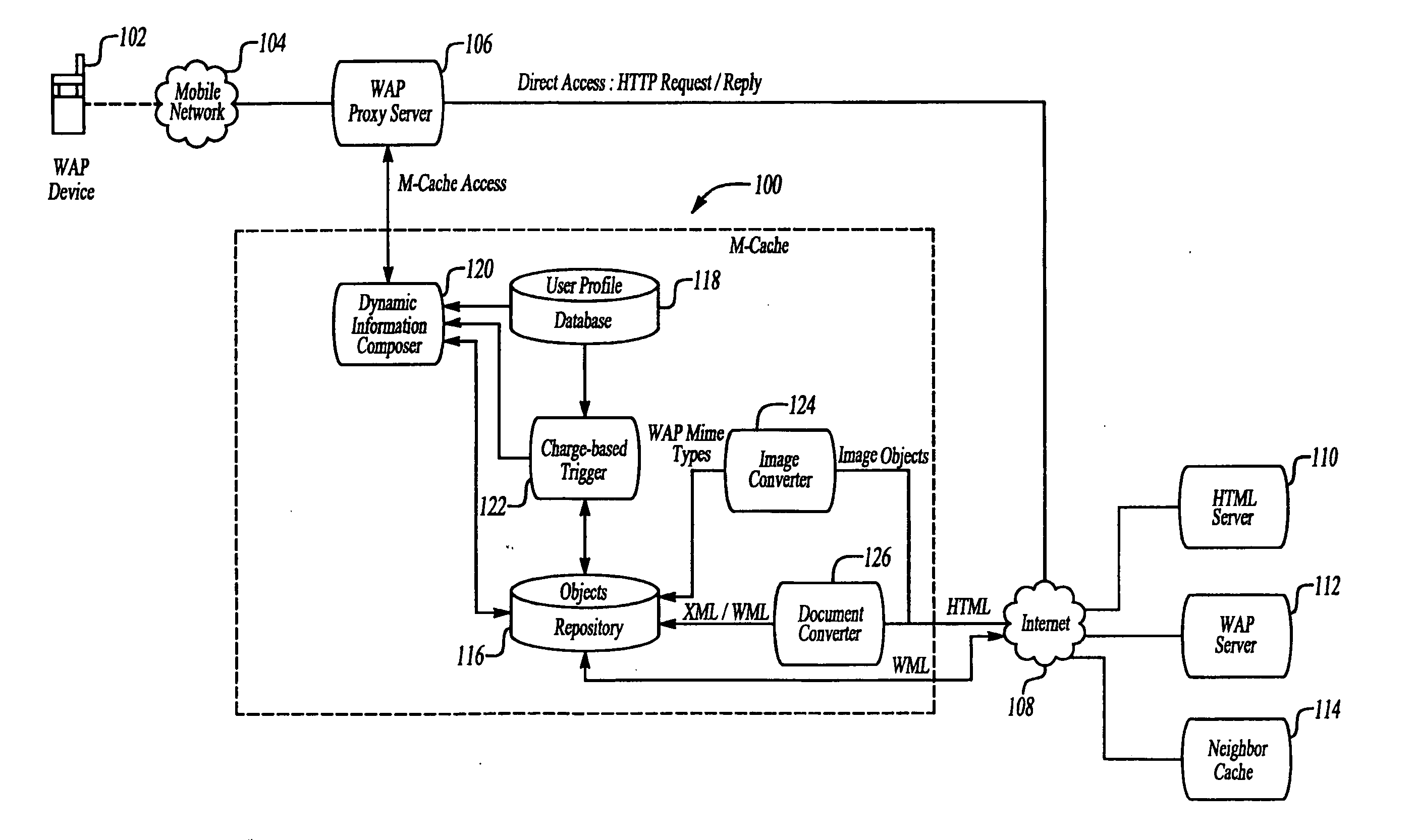
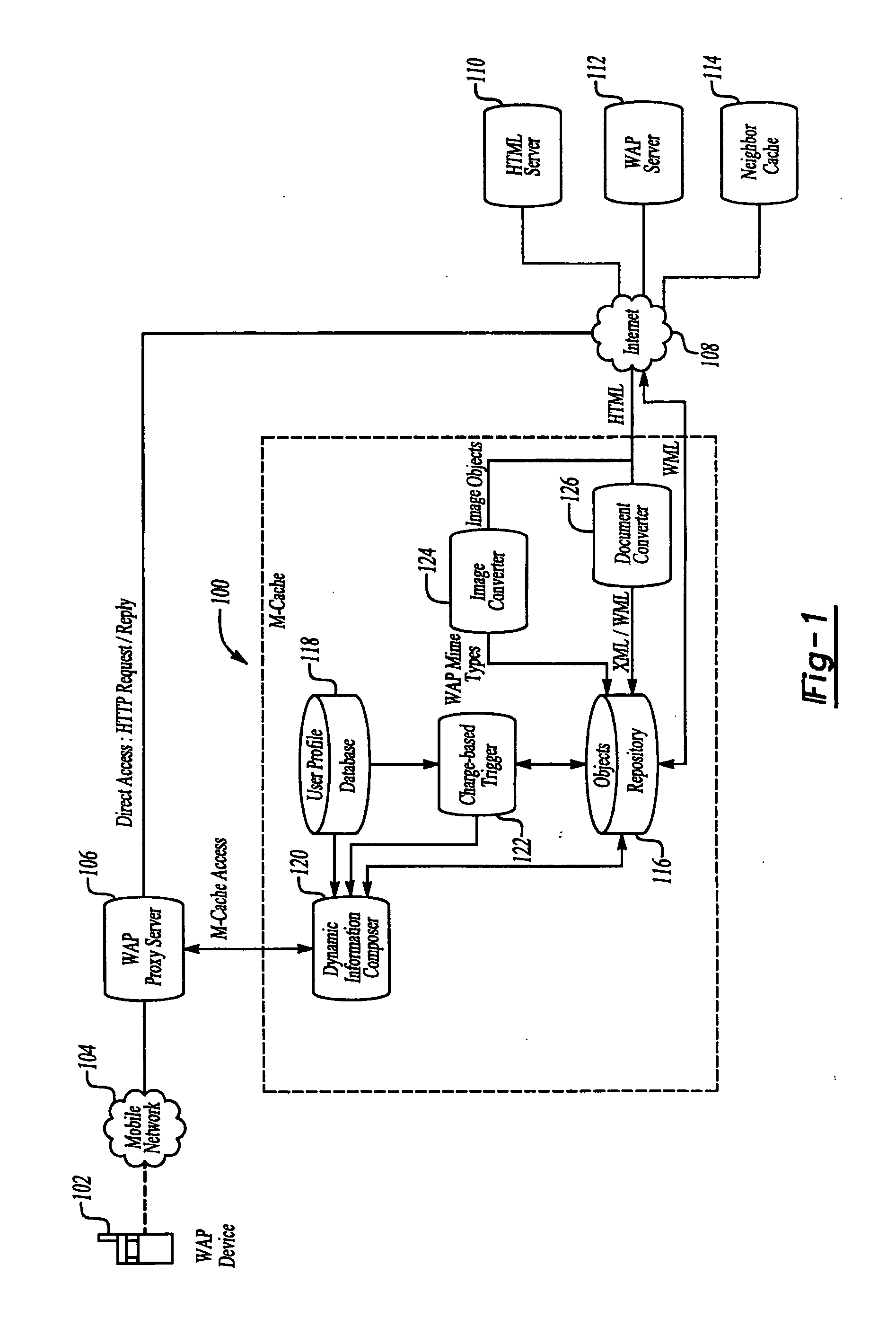
Mobile cache for dynamically composing user-specific information
InactiveUS20050210125A1Facilitate dynamic creationReduce traffic burdenMultiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionWireless Application ProtocolXML Base
A system and method for caching data in wireless application protocol (WAP) enabled services caches static data and facilitates dynamic creation of user-specific information to provide a customized output. The mobile cache generates the user-specific information in WML in real-time from cached information according to user-specified preferences. A change trigger triggers information delivery after a predetermined amount of cached information changes. The system may also include an image converter to ensure that image objects can be viewed easily on WAP-enabled devices having small display screens and a document converter to dynamically compose information from selected data based on XML-based content tagging.
Owner:UNWIRED BROADBAND INC
Use of snapshots to reduce risk in migration to a standard virtualized environment
ActiveUS20140146055A1Reduce riskReduce risk of migrationError detection/correctionDigital computer detailsSoftware engineeringSource system
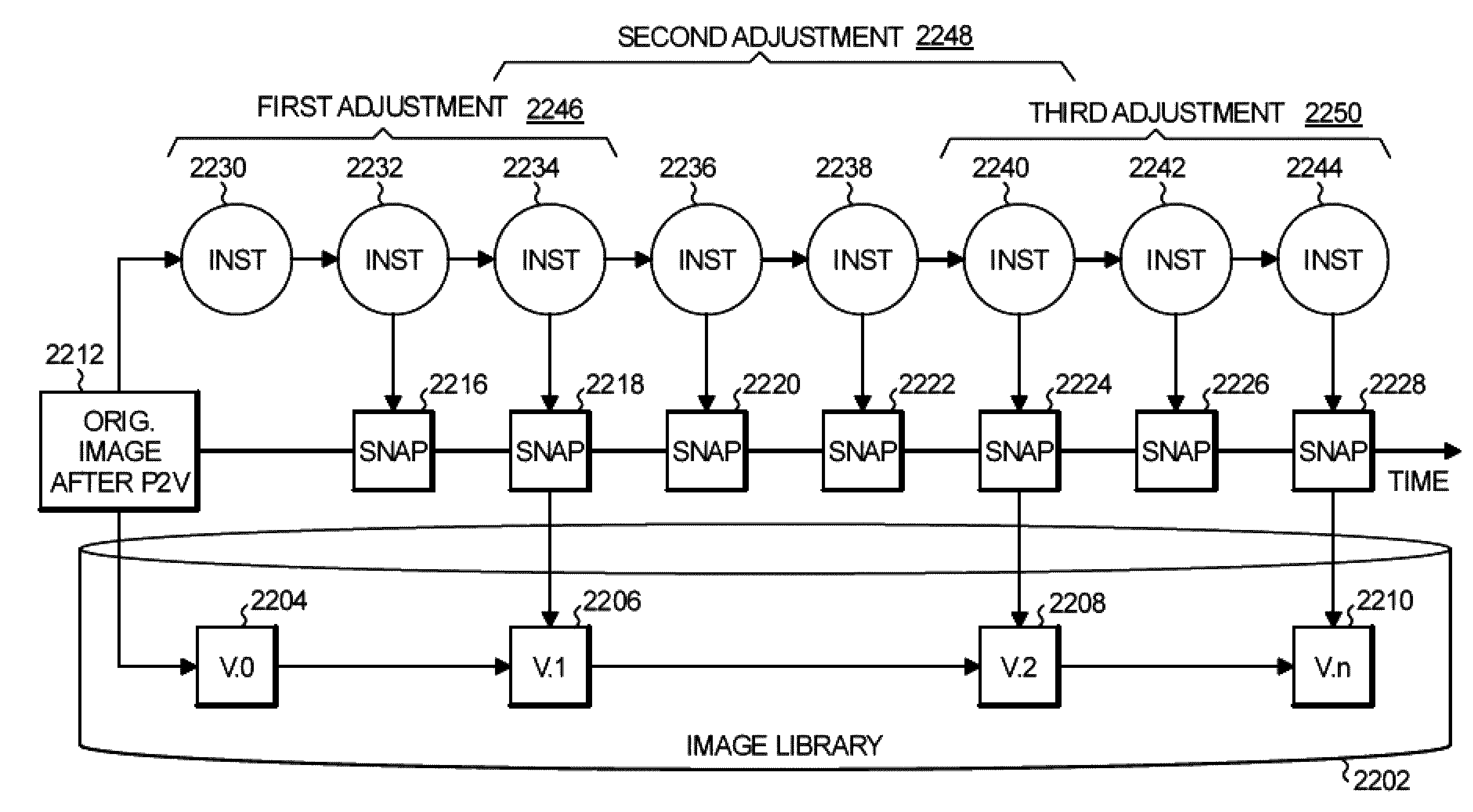
During a process of migrating a source system into a standardized virtual environment, virtual machine instances of the source system executing in a hypervisor are snapshotted as virtual machine images in an operational repository of the hypervisor. The virtual machine images in the operational repository are short-term snapshots. From time to time during the migration process, long-term snapshots of the source system are created by checking given ones of the virtual machine images from the hypervisor operational repository into an image library as image objects.
Owner:IBM CORP
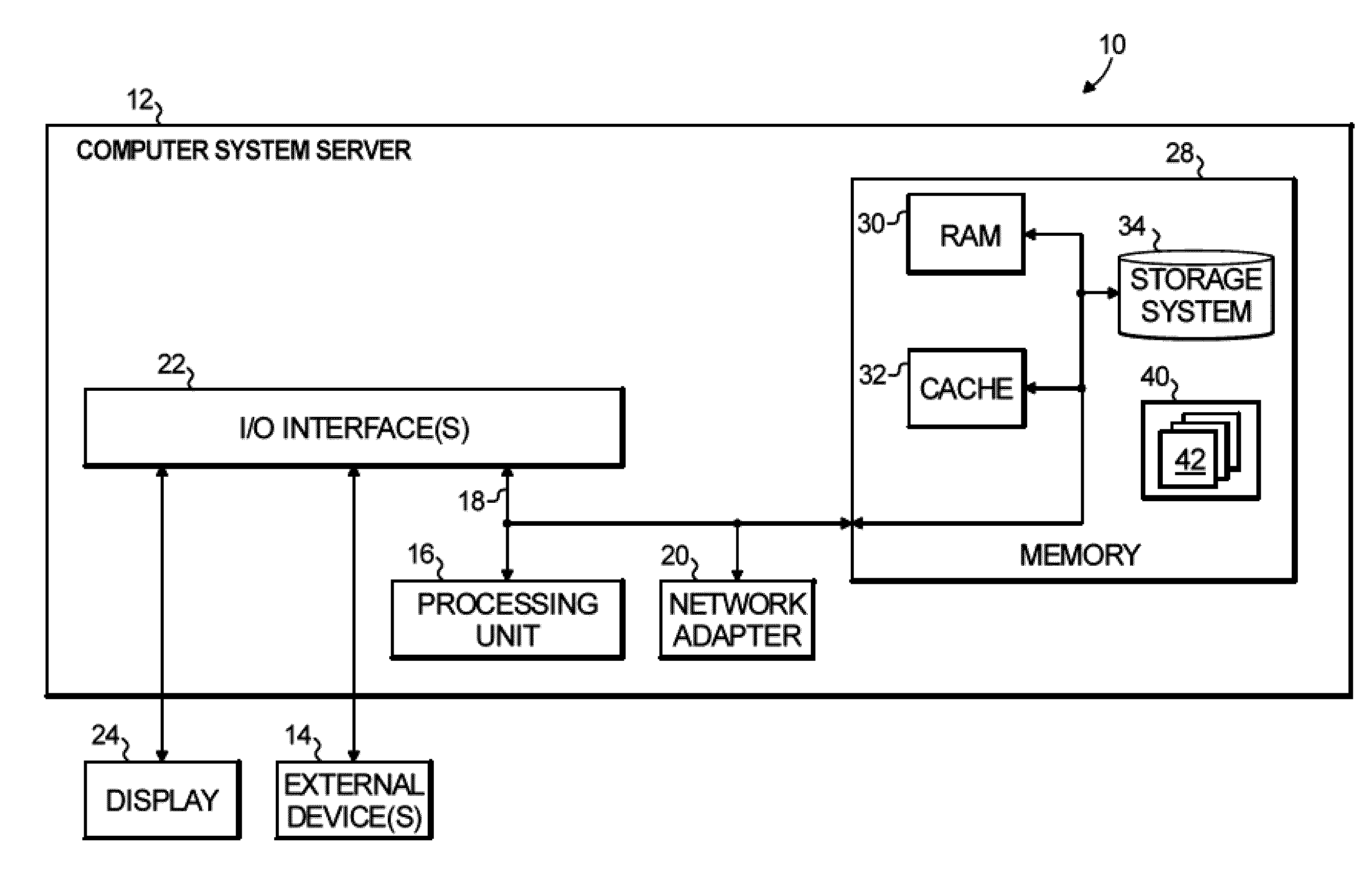
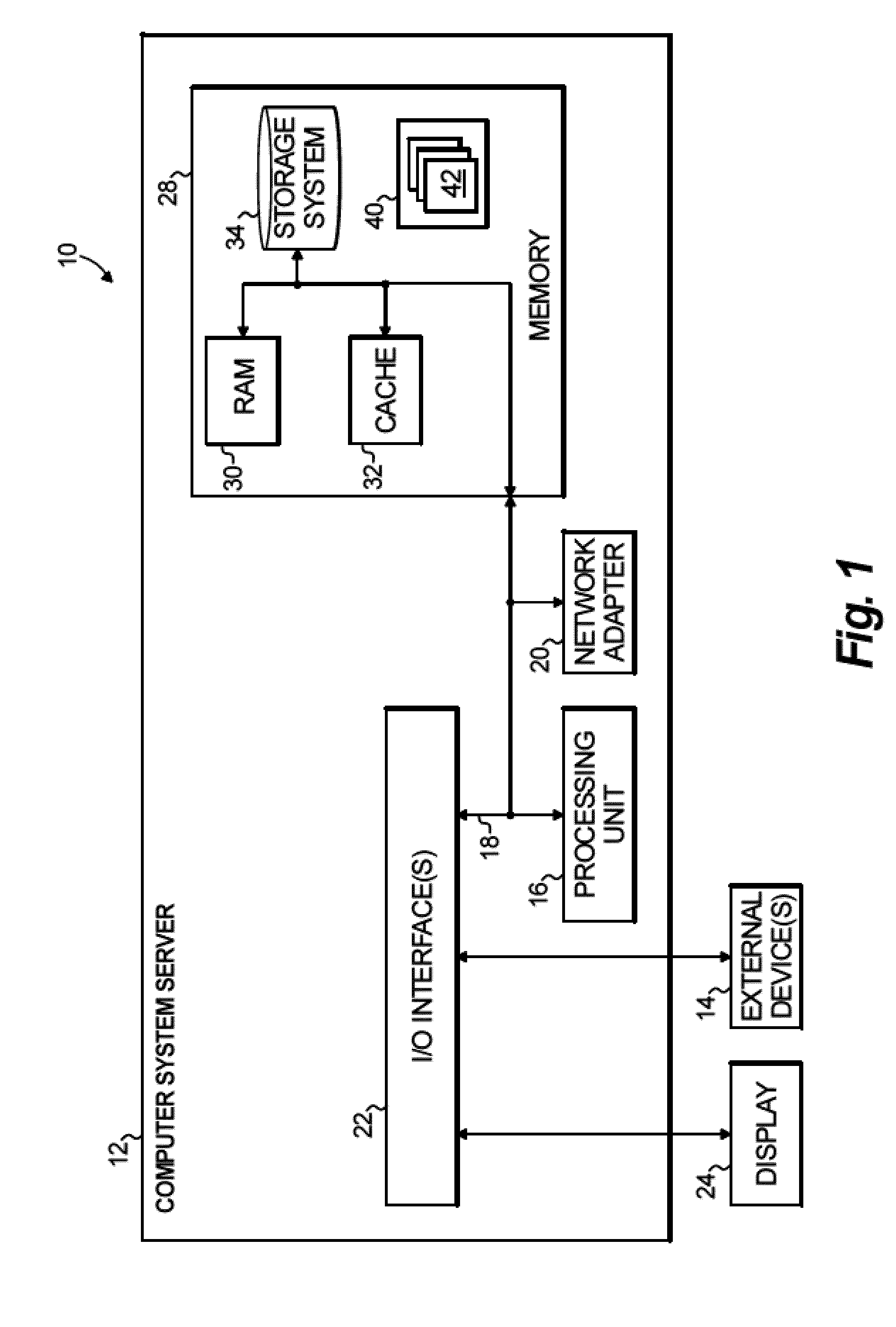
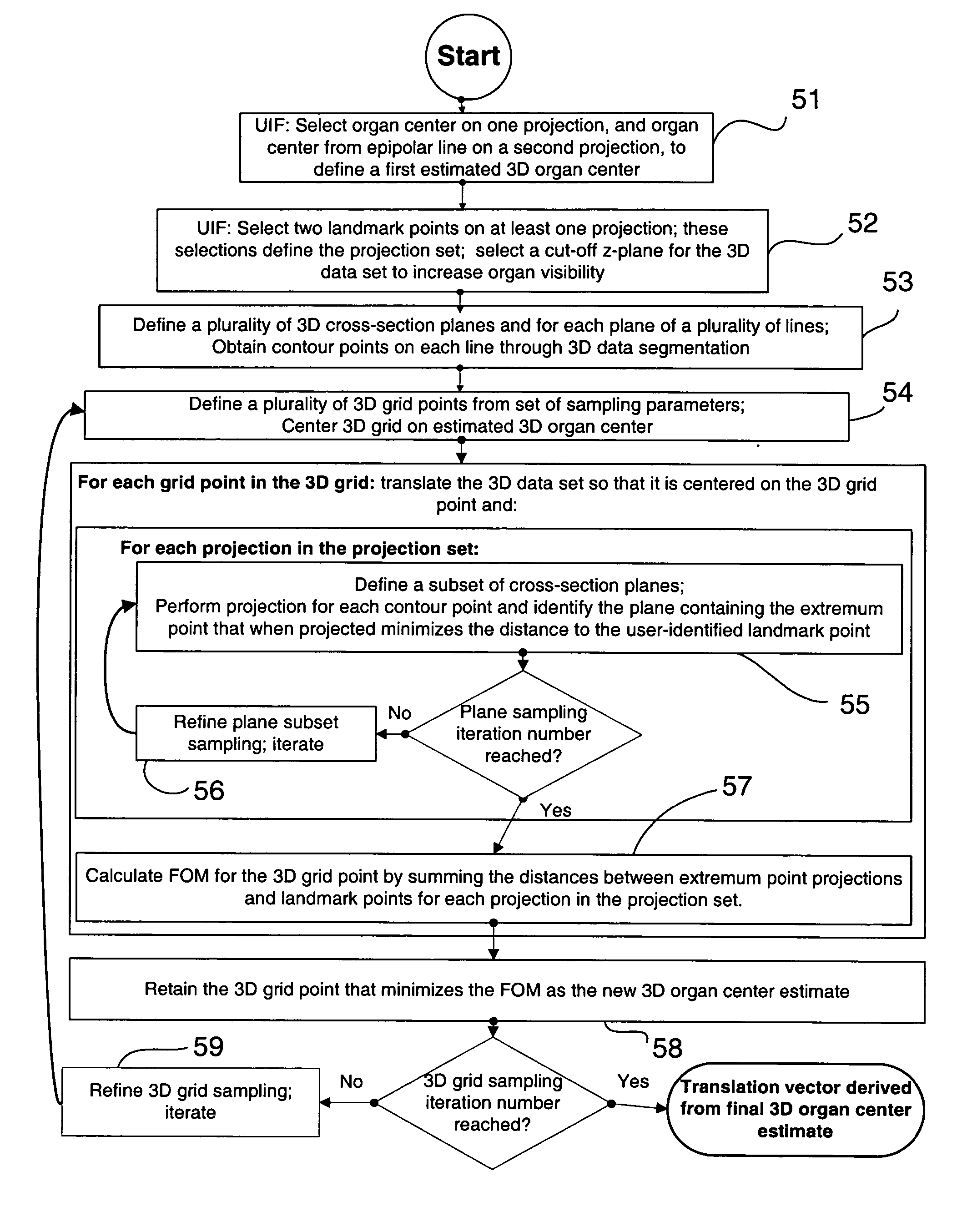
Registration of three dimensional image data with patient in a projection imaging system
A method for determining a translation of a three-dimensional pre-operative image data set to obtain a registration of the three-dimensional image data with a patient positioned in a projection imaging system. In one embodiment the user identifies an initial three-dimensional organ center from projections and extreme contour landmark points of the object on a set of projections. A set of contour points for the image object in each of a plurality of three-dimensional cross-section planes; is obtained and the points projecting nearest to the user-identified landmark points are selected. A three-dimensional grid having a predetermined number of intervals at a predetermined interval spacing centered at the user-identified organ center is defined. The three-dimensional image data contour points as centered onto each grid point are projected for evaluation and selection of the grid point leading to contour points projecting nearest to the user-identified landmark points. This selection leads to the iterative definition of a series of improved estimated three-dimensional organ centers, and associated translation vectors. Registration of a three dimensional image data to the patient positioned in a projection imaging system will allow, among other things, overlay of a visual representation of a pre-operative image object onto a projection image plane that can serve as a visual tool and a surgical navigation aid. In particular, the position and orientation of a medical device can be shown with respect to the three-dimensional image data and thus enable quicker, safer, and less invasive navigation of the medical device to and within an organ of interest.
Owner:STEREOTAXIS
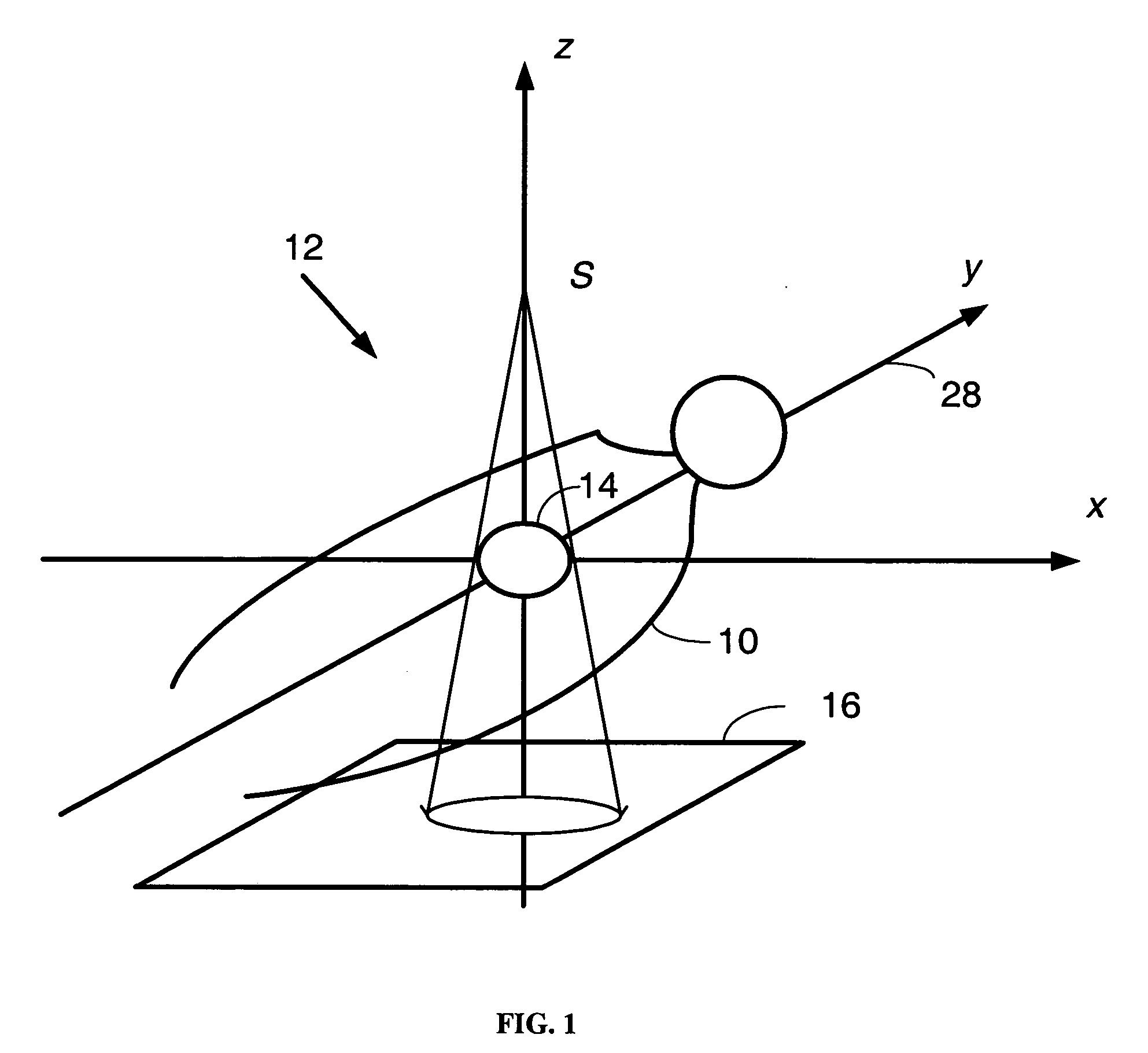
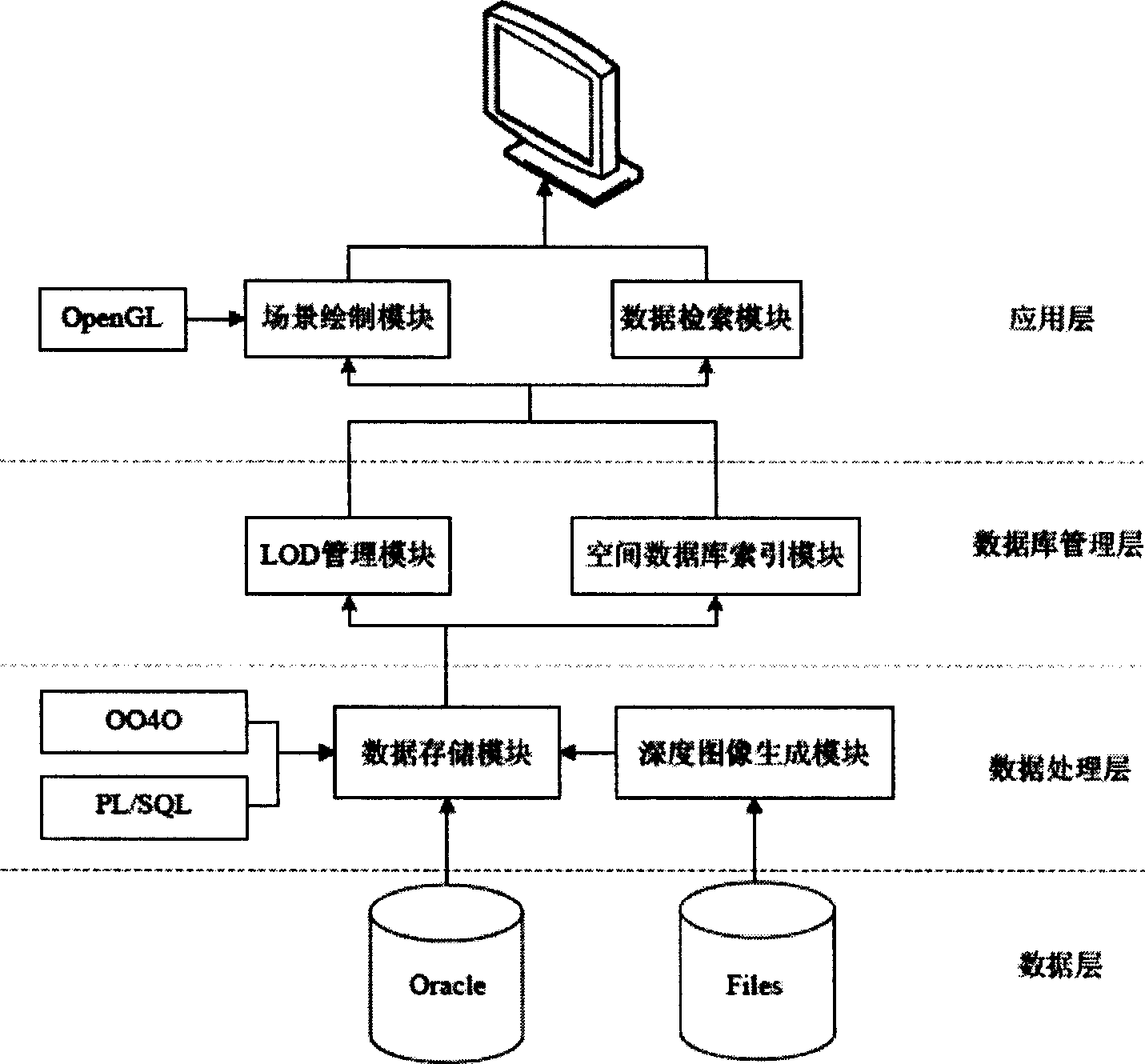
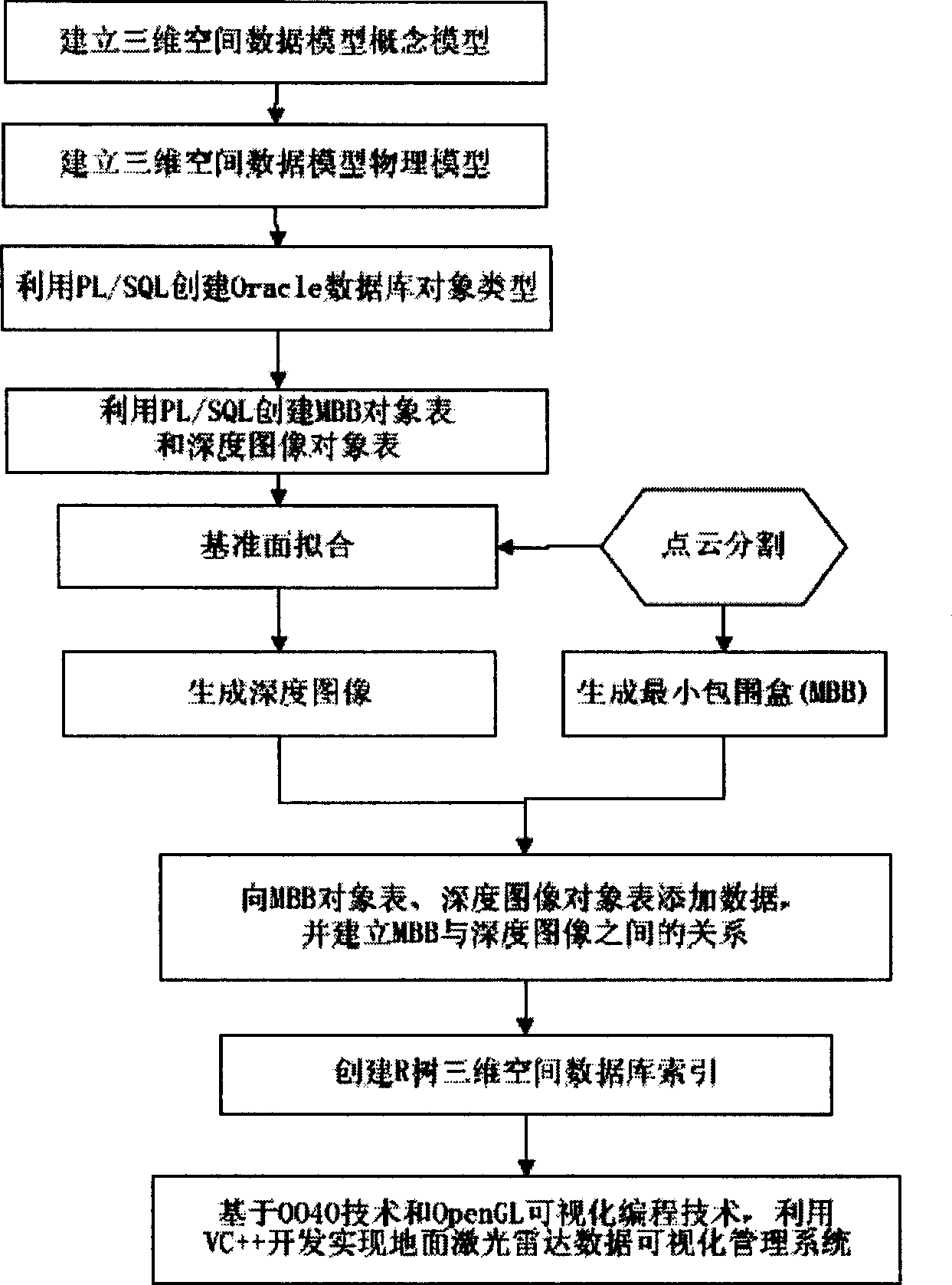
Range image-based 3D spatial data processing method and device
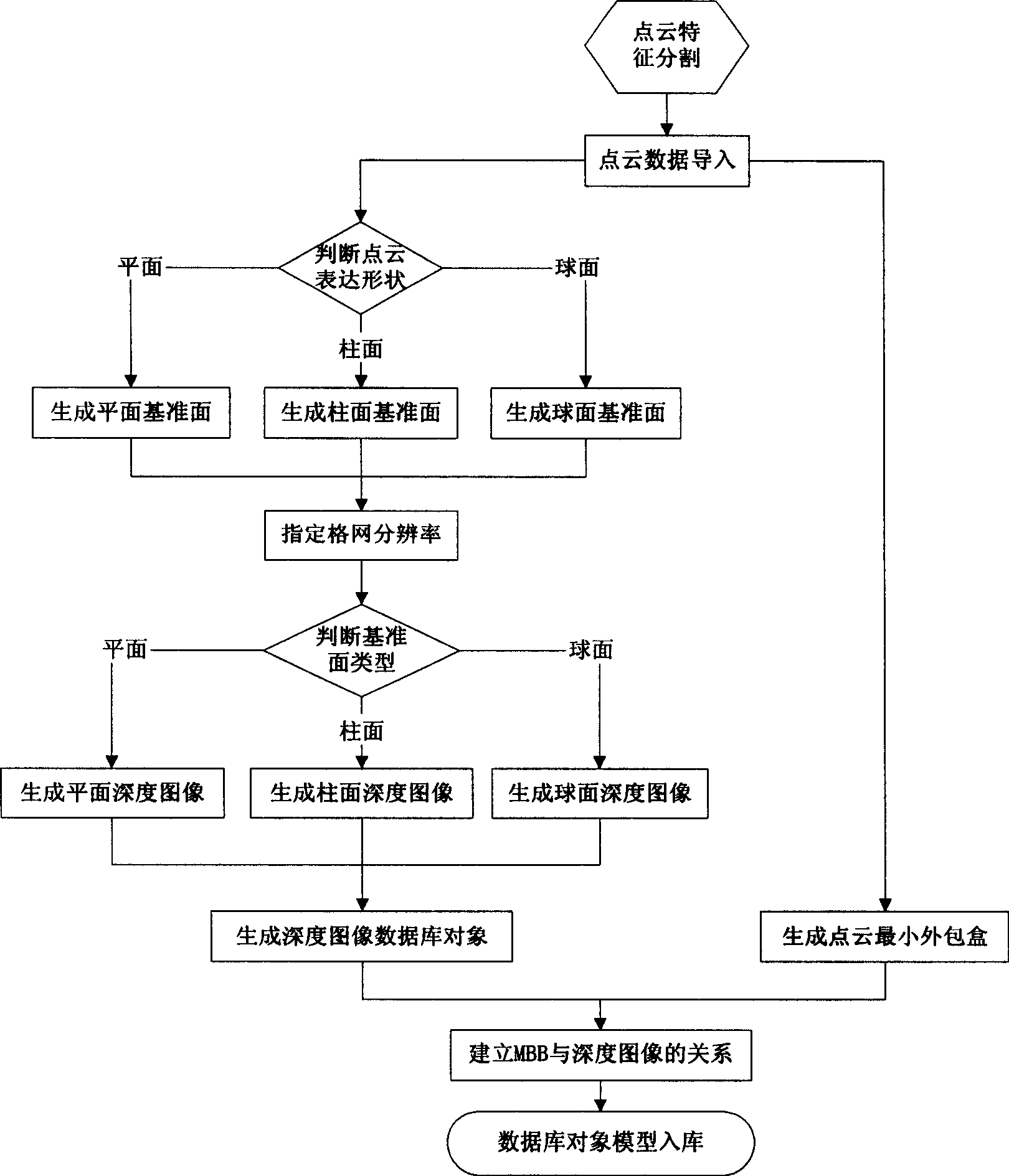
InactiveCN101533529AEfficient compressionMake up for lack of support2D-image generationSpecial data processing applicationsMinimum bounding boxR-tree
The invention relates to a range image-based 3D spatial data processing method and a device. In the method, ground laser radar is adopted to scan an object to obtain 3D point cloud data on the surface of the object; a database object table is established by a PL / SQL programming approach; a reference datum is fit according to point cloud which is segmented in advance to generate a minimum bounding box (MBB) of the point cloud and subsequently generate the range image according to the reference datum obtained by fitting. Later, data of the MBB and the range image are written into the database object table and the relation between the MBB and a range image object is established, subsequently, R tree 3D spatial database index is established for the database objects which enter the database, finally, visualization is realized based on Oracle Objects for OLE (OO4O) and OpenGL.
Owner:BEIJING UNIVERSITY OF CIVIL ENGINEERING AND ARCHITECTURE
Visual aid
InactiveUS20130250078A1Navigational calculation instrumentsWalking aidsOutput deviceVisual perception
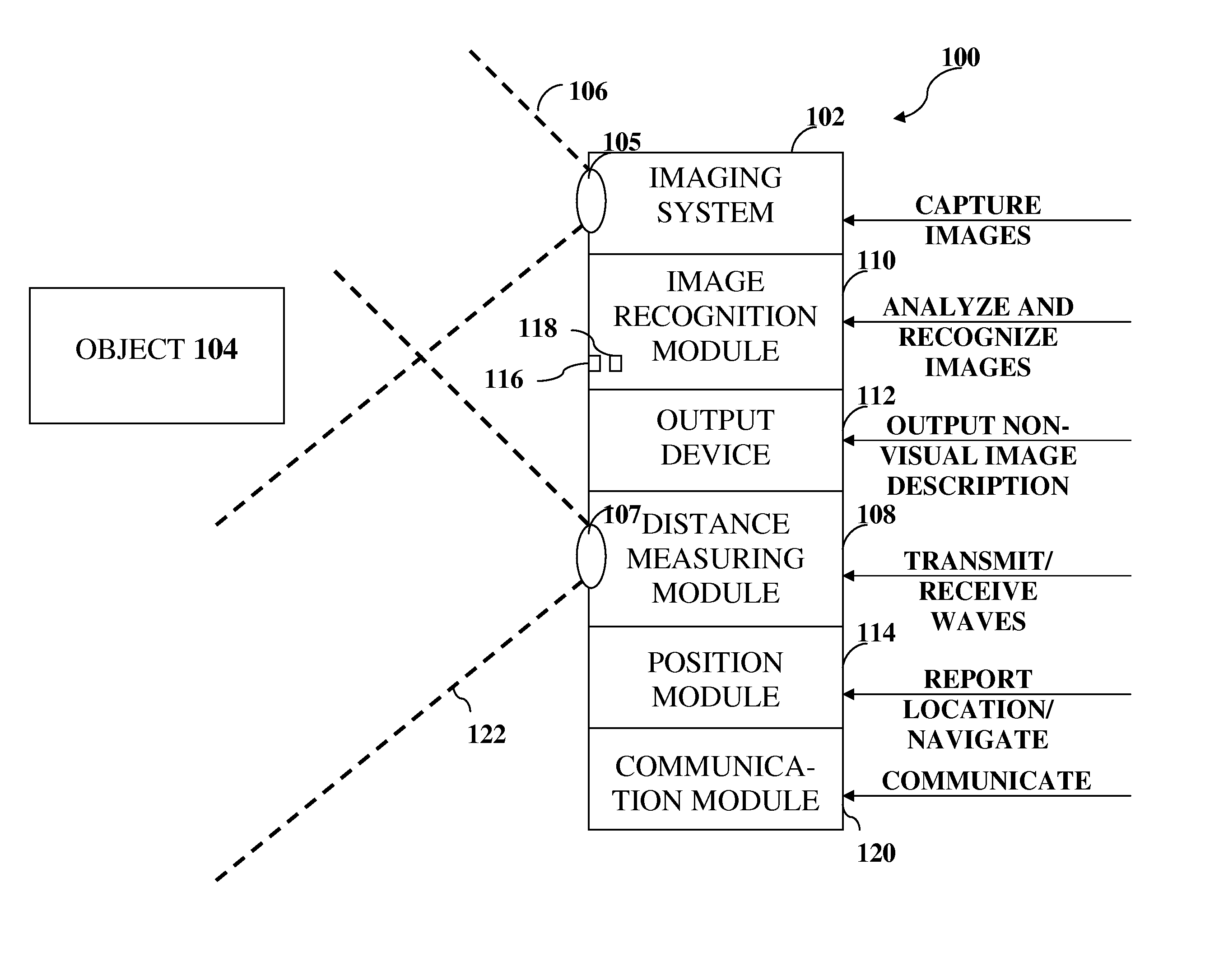
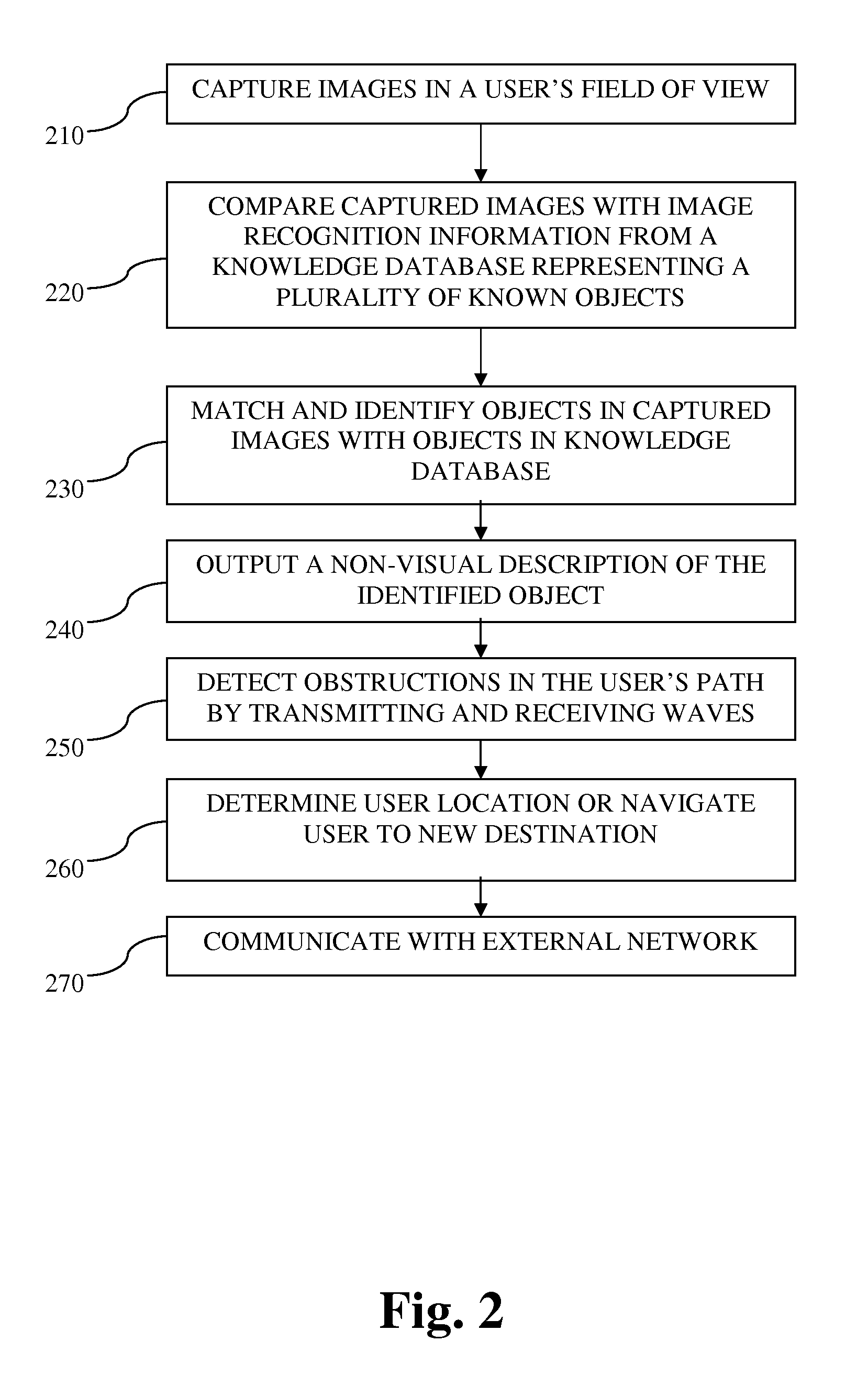
A visual aid system, device and method is provided. The visual aid system may include an imaging unit to capture images of a user's surroundings, a knowledge database to store object recognition information for a plurality of image objects, an object recognition module to match and identify an object imaged in one or more captured images with an object in the knowledge database, and an output device to output a non-visual indication of the identified object.
Owner:TECHNO DYNAMICS
System and method for editing electronic images
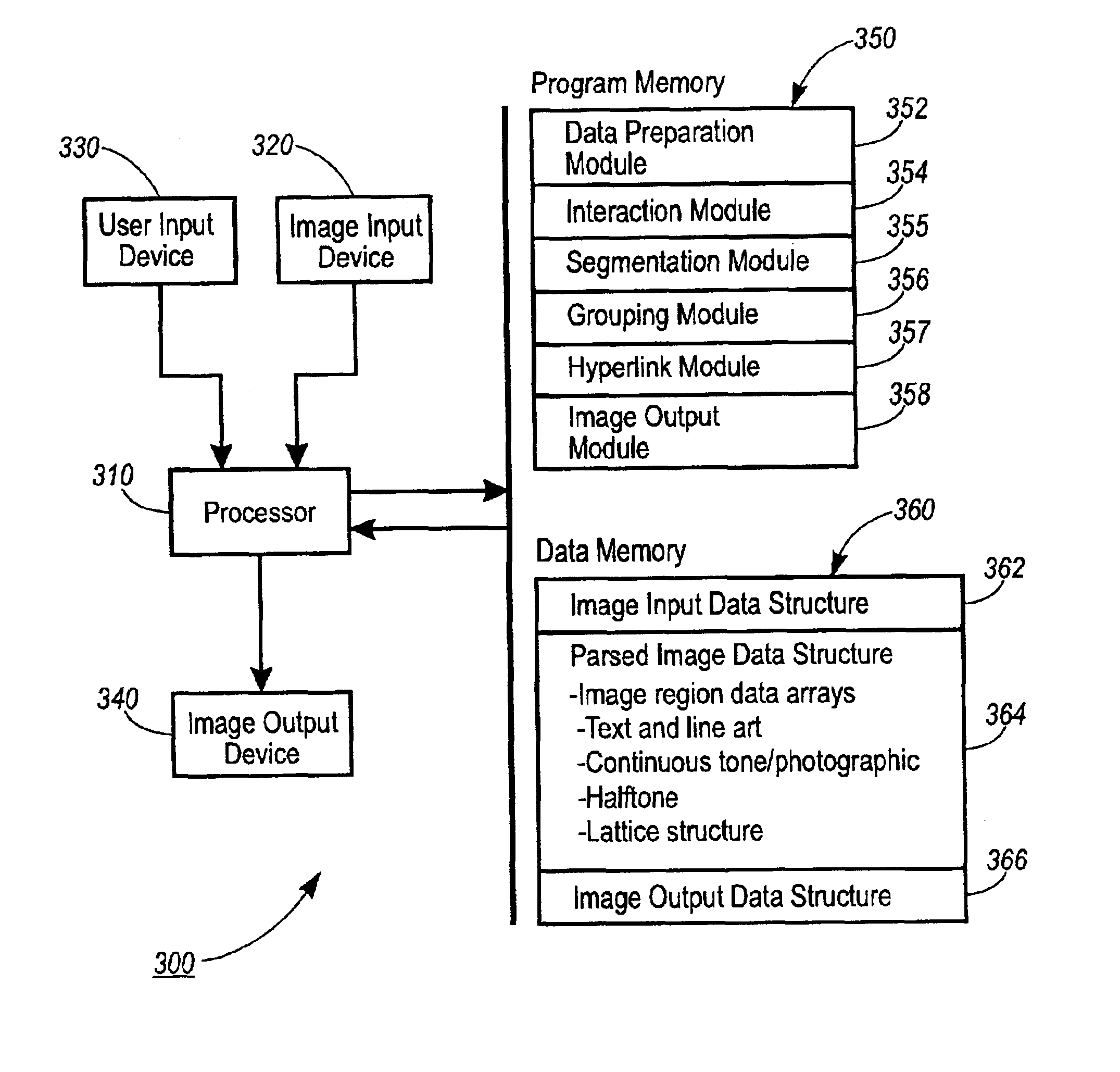
A graphical input and display system for creating and manipulating electronic images includes input devices permitting a user to manipulate elements of electronic images received from various image input sources. A processor, connected to the system, receives requests for various image editing operations and also accesses a memory structure. The system memory structure includes a user interaction module, which allows a user to enter new image material or select and modify existing image material to form primary image objects, as well as a grouping module, which maintains an unrestricted grouping structure, an output module, and data memory.
Owner:XEROX CORP
Image object recording, compression, and encryption method and system
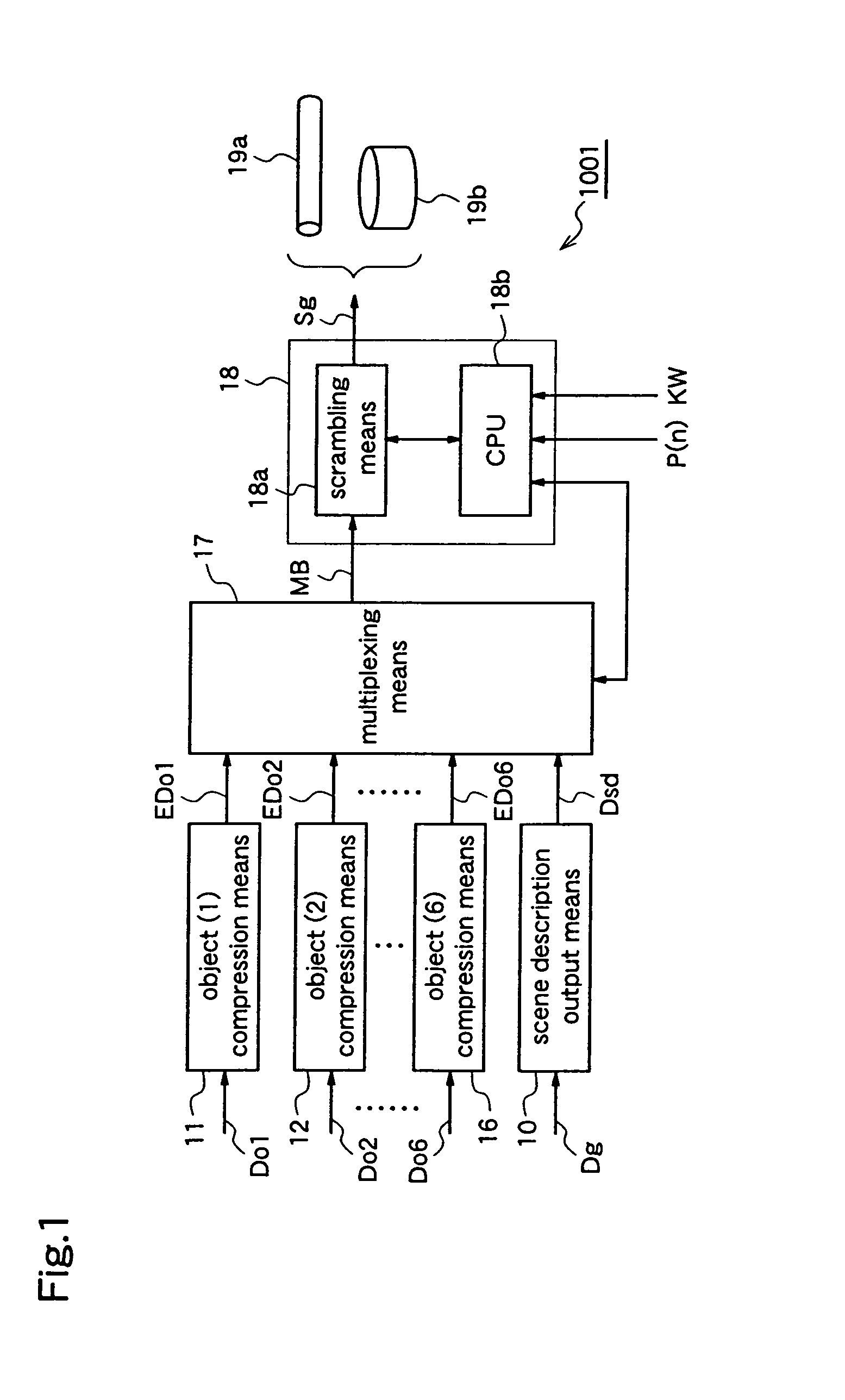
InactiveUS6931531B1Satisfactorily preventedUnauthorized useTelevision system detailsAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsComputer hardwareMultiplexing
Selective encryption for object data such that objects having copyrights to-be-protected are encrypted. There are provided a plurality of data compression devices for compressing respective object data respectively corresponding to a plurality of objects which compose a scene, a multiplexor for multiplexing scene description data and compressed object data to produce a multiplexed bit stream MB, a scrambler for encrypting (scrambling) individual streams corresponding to the objects having copyrights to-be-protected in the multiplexed bit stream MB, to produce an encrypted bit stream SB, for outputting the encrypted bit stream SB to a data storage medium or a data transmission medium.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
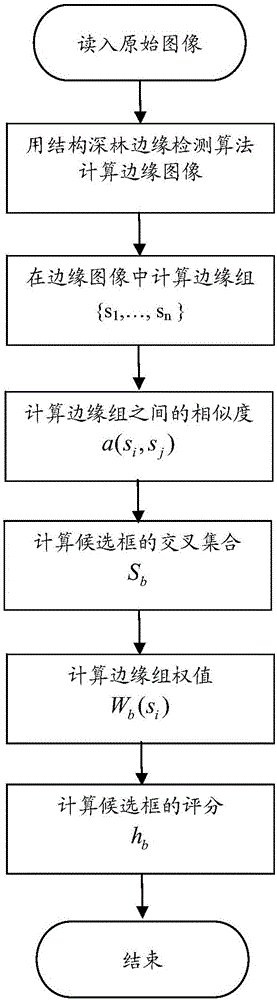
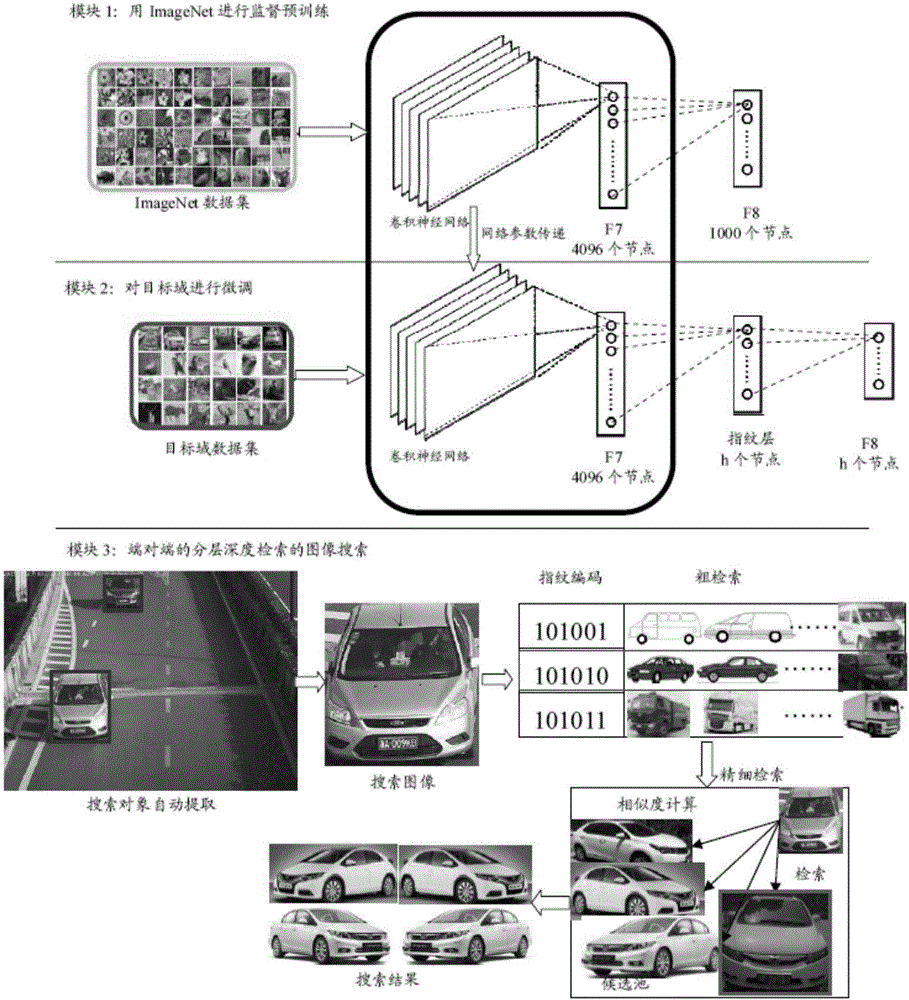
Deep convolutional neural network end-to-end based image retrieval method by layered deep searching
ActiveCN106227851ARealize automatic extractionMeet search needsCharacter and pattern recognitionSpecial data processing applicationsImage retrievalHamming distance
The invention discloses a deep convolutional neural network end-to-end based image retrieval method by layered deep searching. The method is characterized by mainly including a convolutional neural network used for deep learning, training and recognition, a rapid visual segmentation algorithm for searching image objects, a quick comparison method used for rough searching with a Hash method and Hamming distance fast images, and a precise comparison method for first k ranked images based on images from a candidate pool P. By the method, automation and intelligence level in searching images with images can be effectively heightened, search results can be acquired accurately, and demand of image retrieval in the big data era is satisfied with less storage space and high retrieval speed.
Owner:汤一平
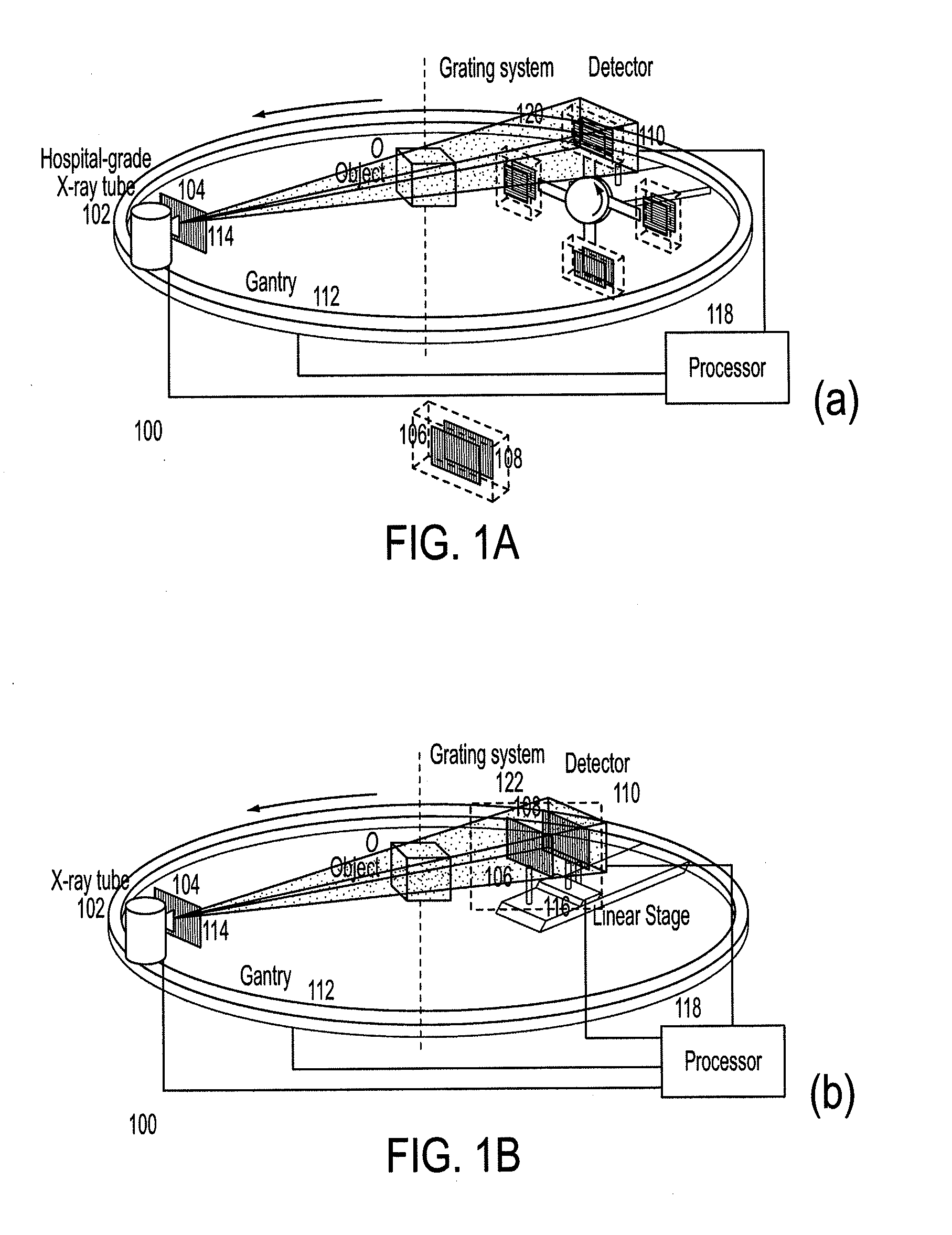
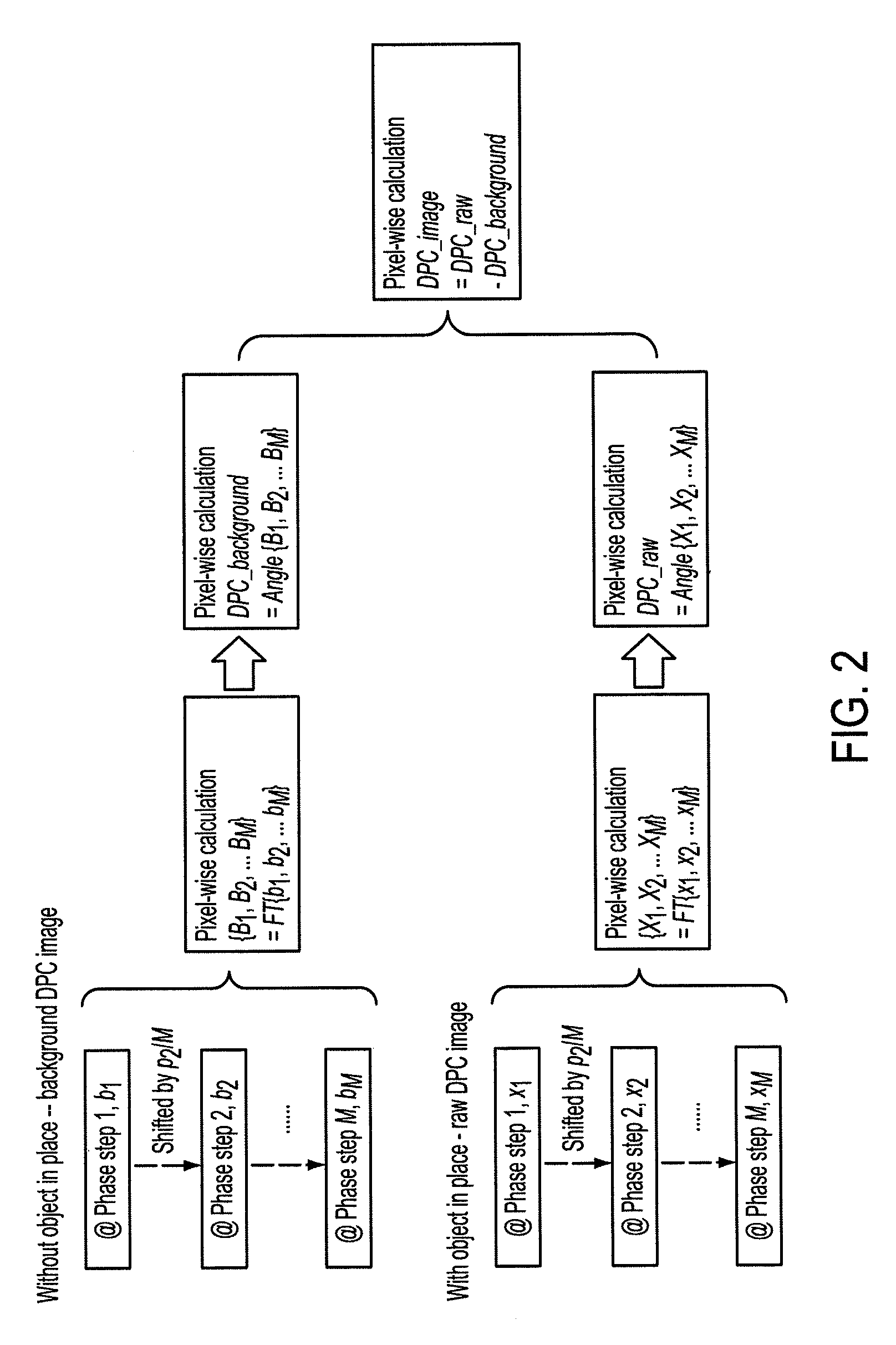
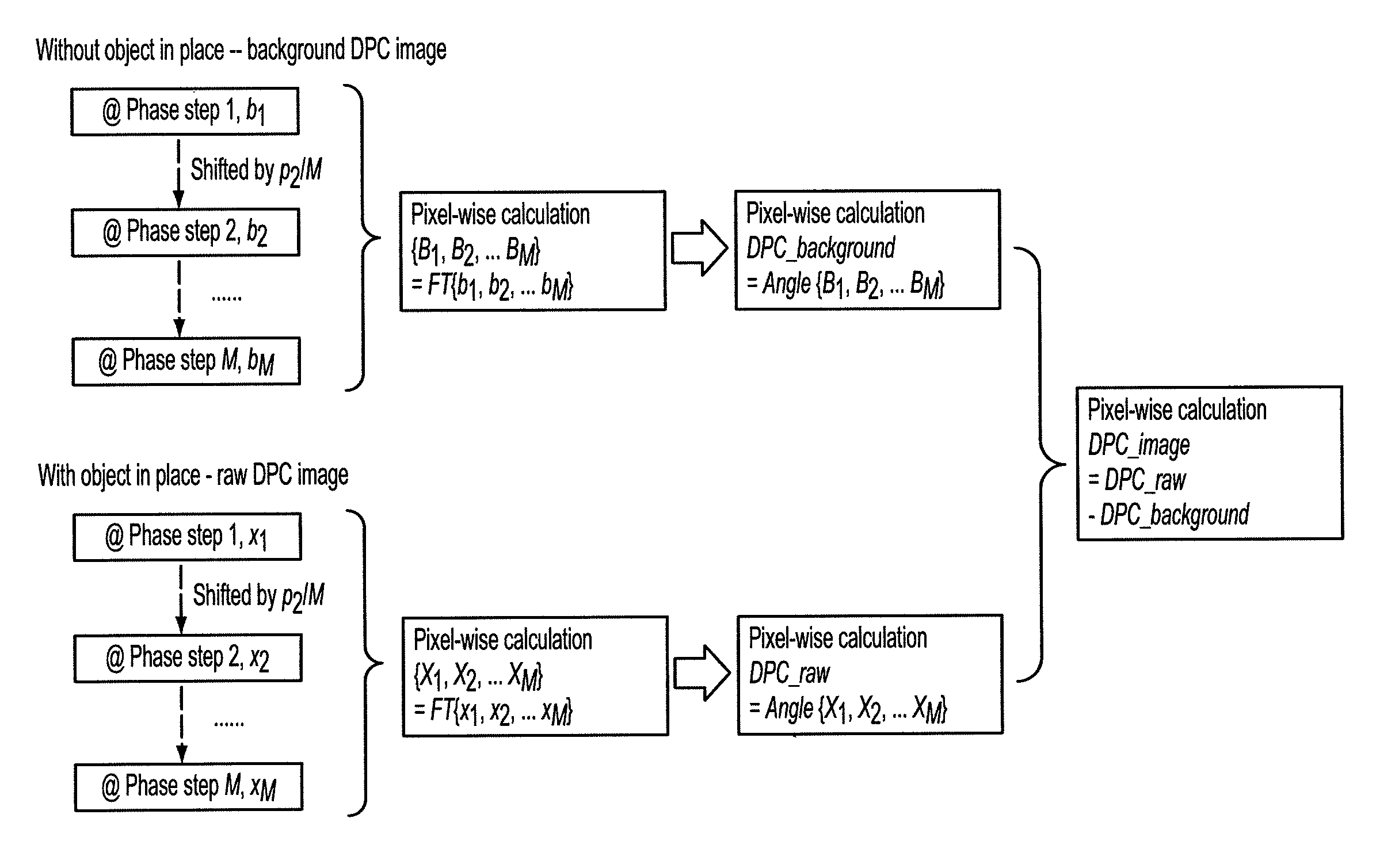
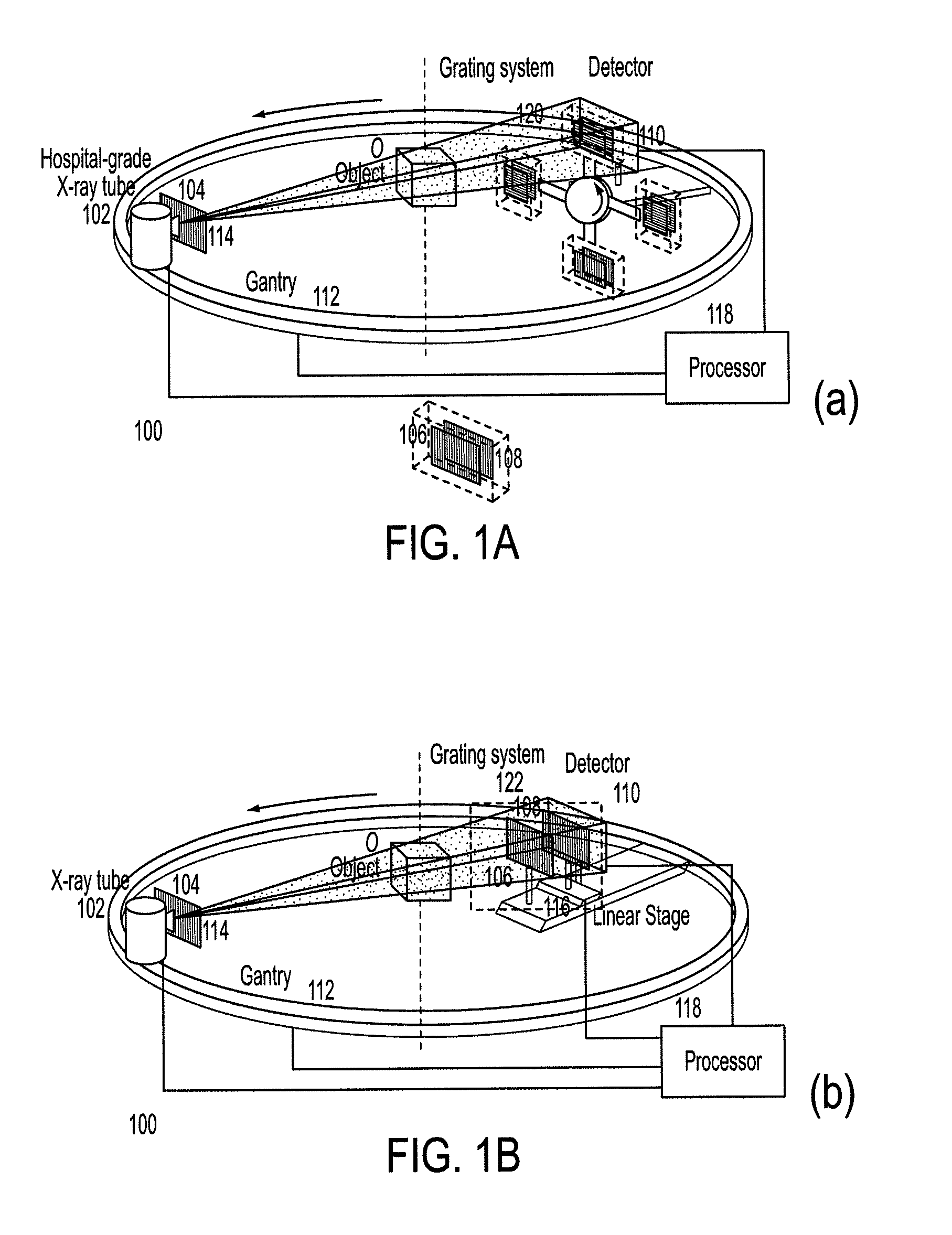
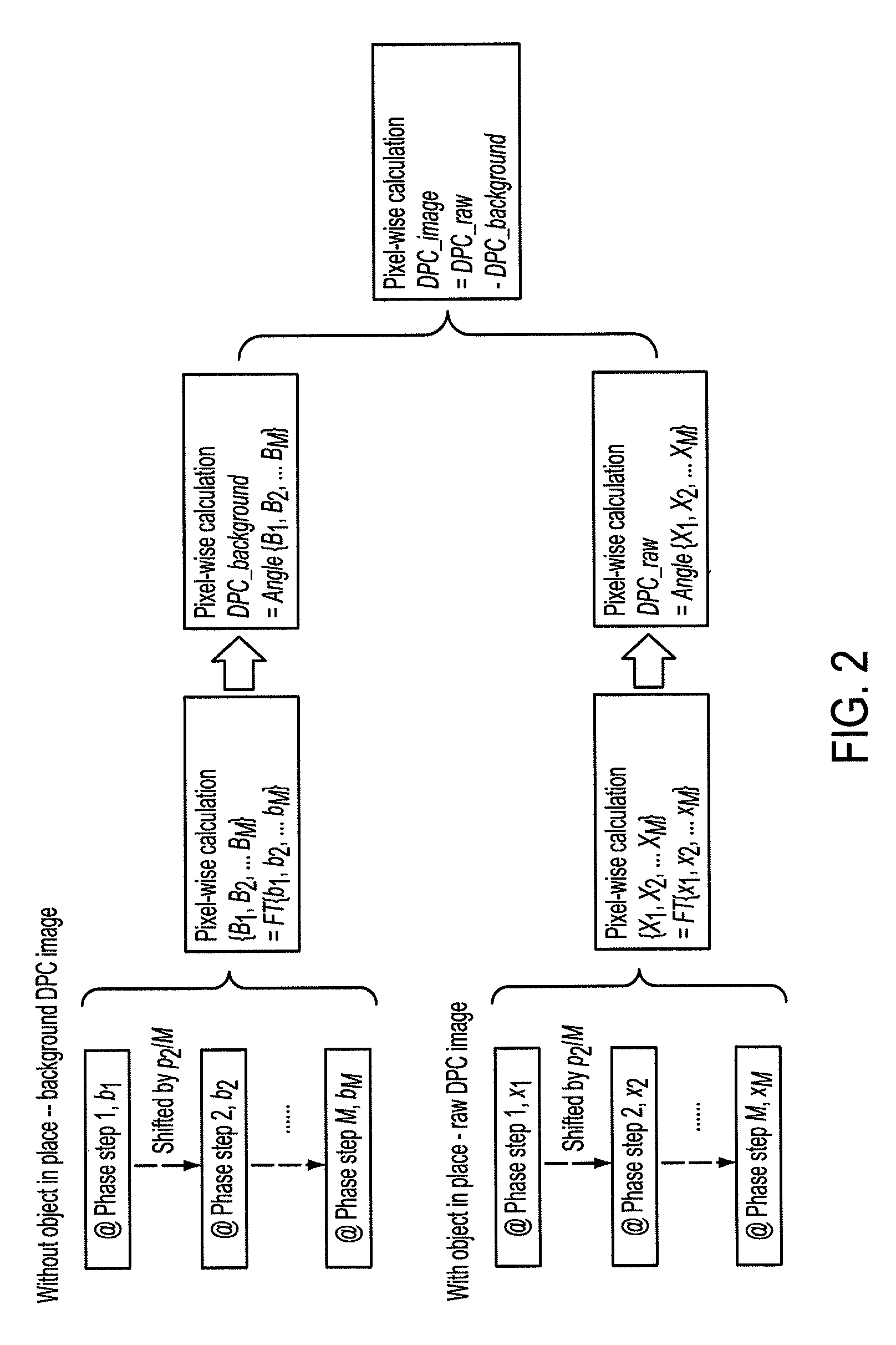
Methods and apparatus for differential phase-contrast fan beam ct, cone-beam ct and hybrid cone-beam ct
ActiveUS20100220832A1Improve spatial resolutionIncrease doseImaging devicesRadiation/particle handlingHybrid systemPhase grating
A device for imaging an object, such as for breast imaging, includes a gantry frame having mounted thereon an x-ray source, a source grating, a holder or other place for the object to be imaged, a phase grating, an analyzer grating, and an x-ray detector. The device images objects by differential-phase-contrast cone-beam computed tomography. A hybrid system includes sources and detectors for both conventional and differential-phase-contrast computed tomography.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
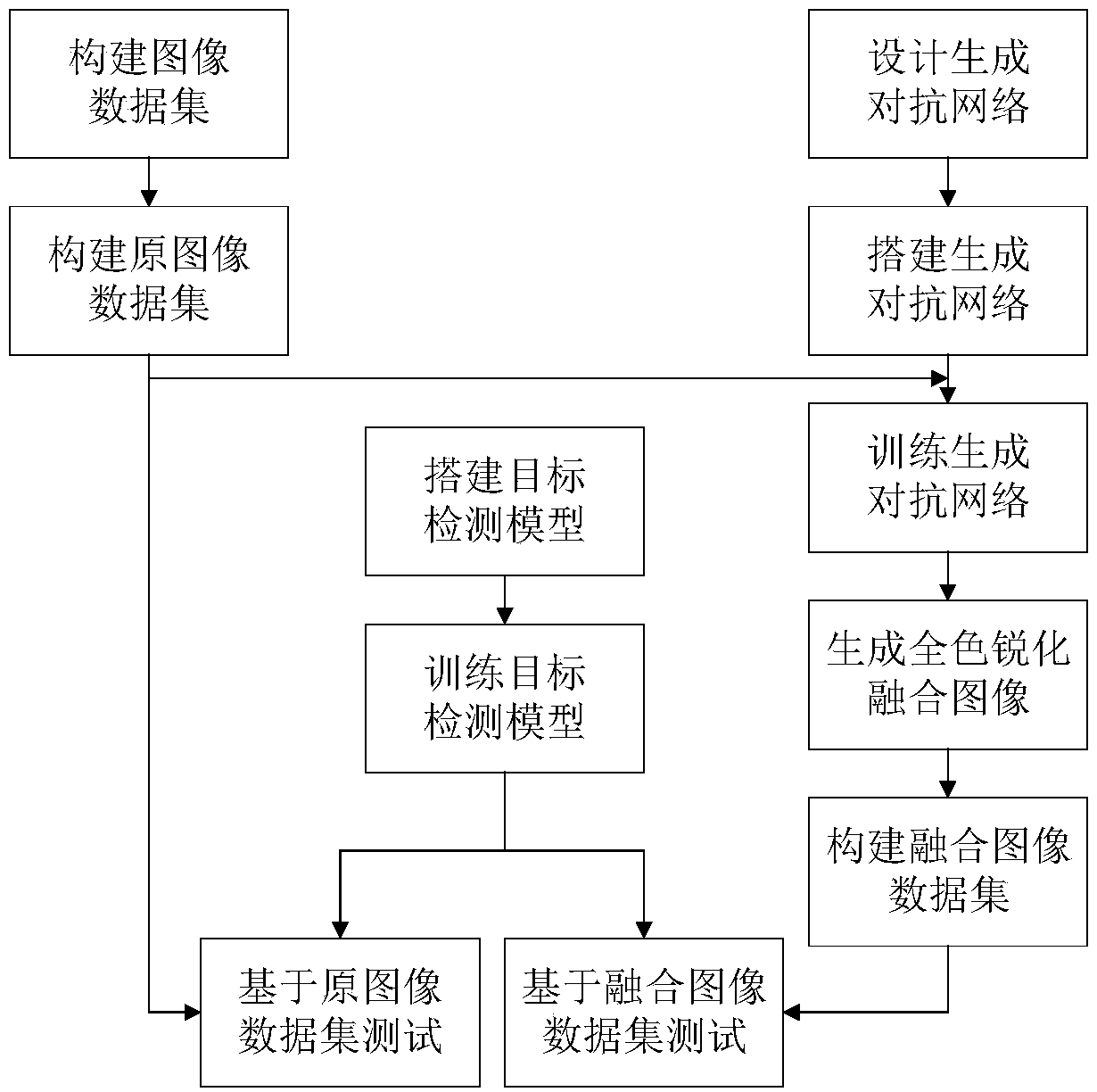
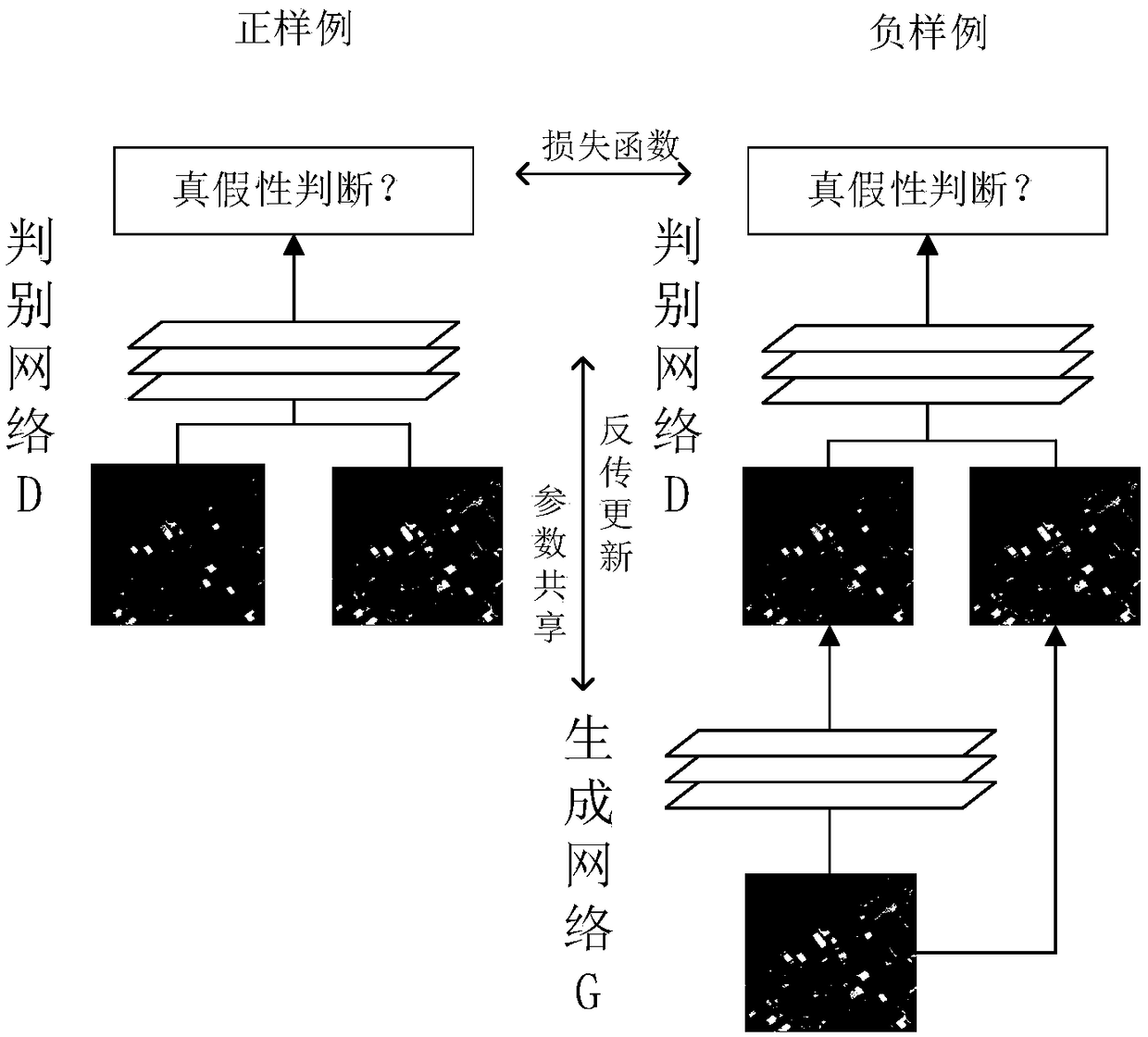
Remote-sensing image object detection method based on deep learning
ActiveCN108564109AClear Spatial DetailsReduce lossesCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural architecturesStochastic gradient descentData set
The invention relates to a remote-sensing image object detection method based on deep learning. The method comprises: using remote-sensing images to construct a related data set, namely an image dataset after classification and labeling on the remote-sensing images and class labels generated through labeling work; building a panchromatic sharpening model based on generative adversarial networks (GAN); building an object detection model based on a deep convolutional neural network, and carrying out end-to-end training on the model through methods of back propagation, random gradient descent and the like; and carrying out end-to-end testing on the built model. The method of the invention has the advantage of high accuracy.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Generation of depth map for an image
InactiveUS20100046837A1Increase varietyImprove imaging depthImage enhancementImage analysisImaging processingSelf adaptive
An image processing unit comprises a first processing unit (101) which generates a depth indication map for an image. The depth indication map may be, for example, an image object separation mask or a predetermined depth profile or background depth map. A second processing unit (103) generates a modified depth indication map by filtering the depth indication map in response to image characteristics of the image. The image adaptive filtering may, for example, provide a more accurate separation mask and / or may modify the predetermined depth profile to reflect the specific image. A third processing unit (105) generates an image depth map for the image in response to the modified depth indication map. The image depth map comprises data representing a depth of at least one image region of the image. The invention leads to the generation of an improved depth map for an image.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
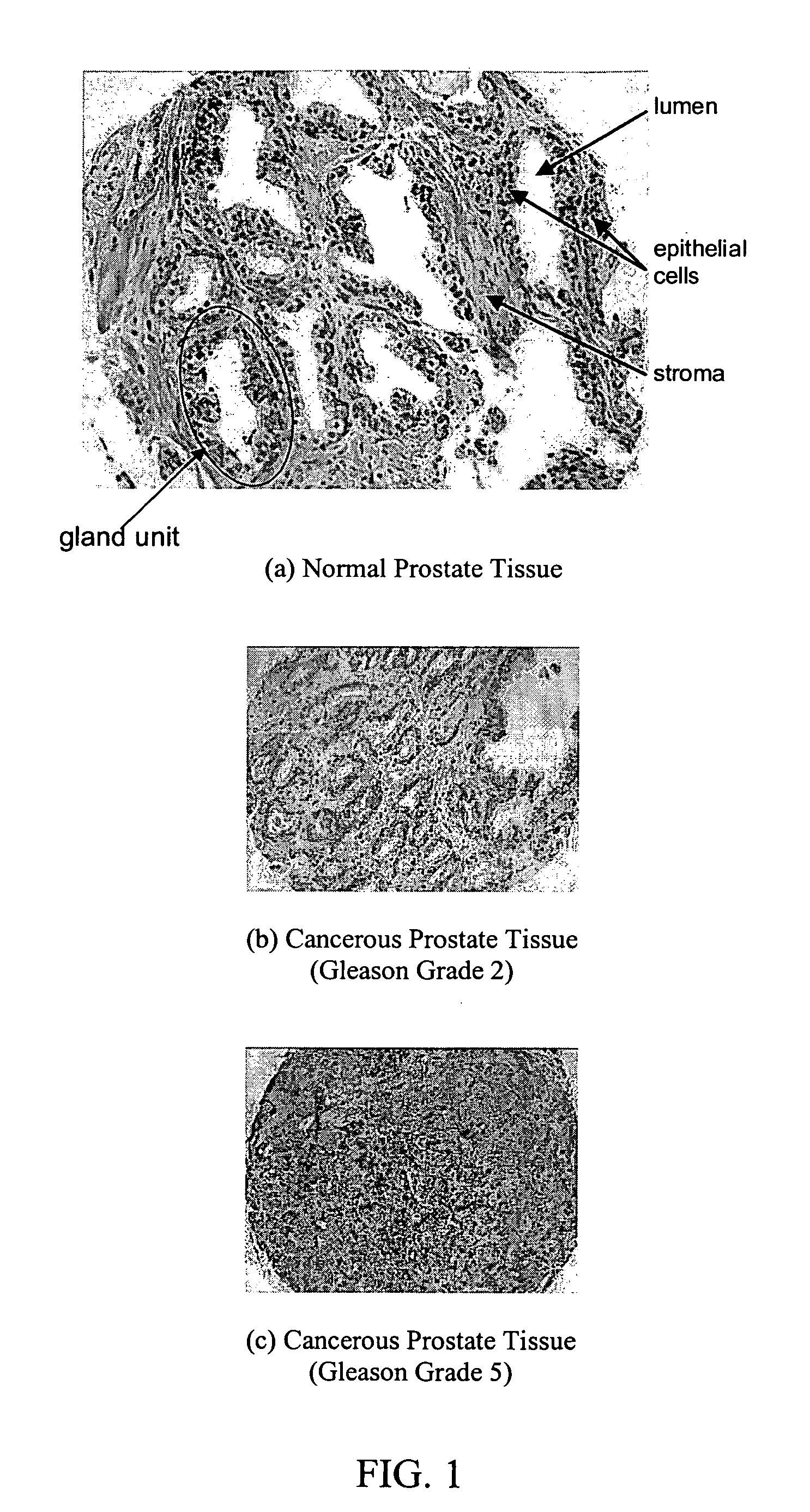
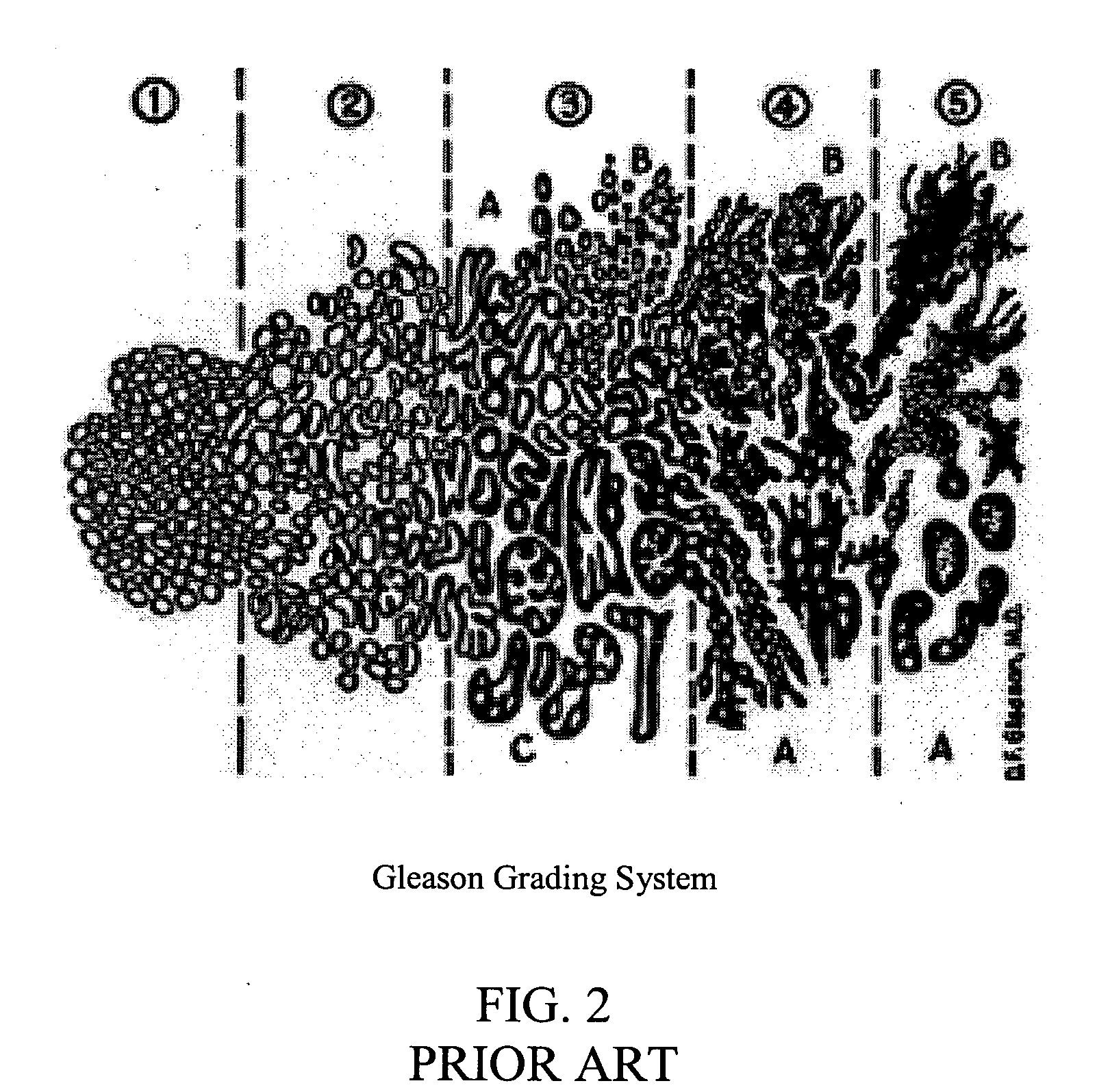
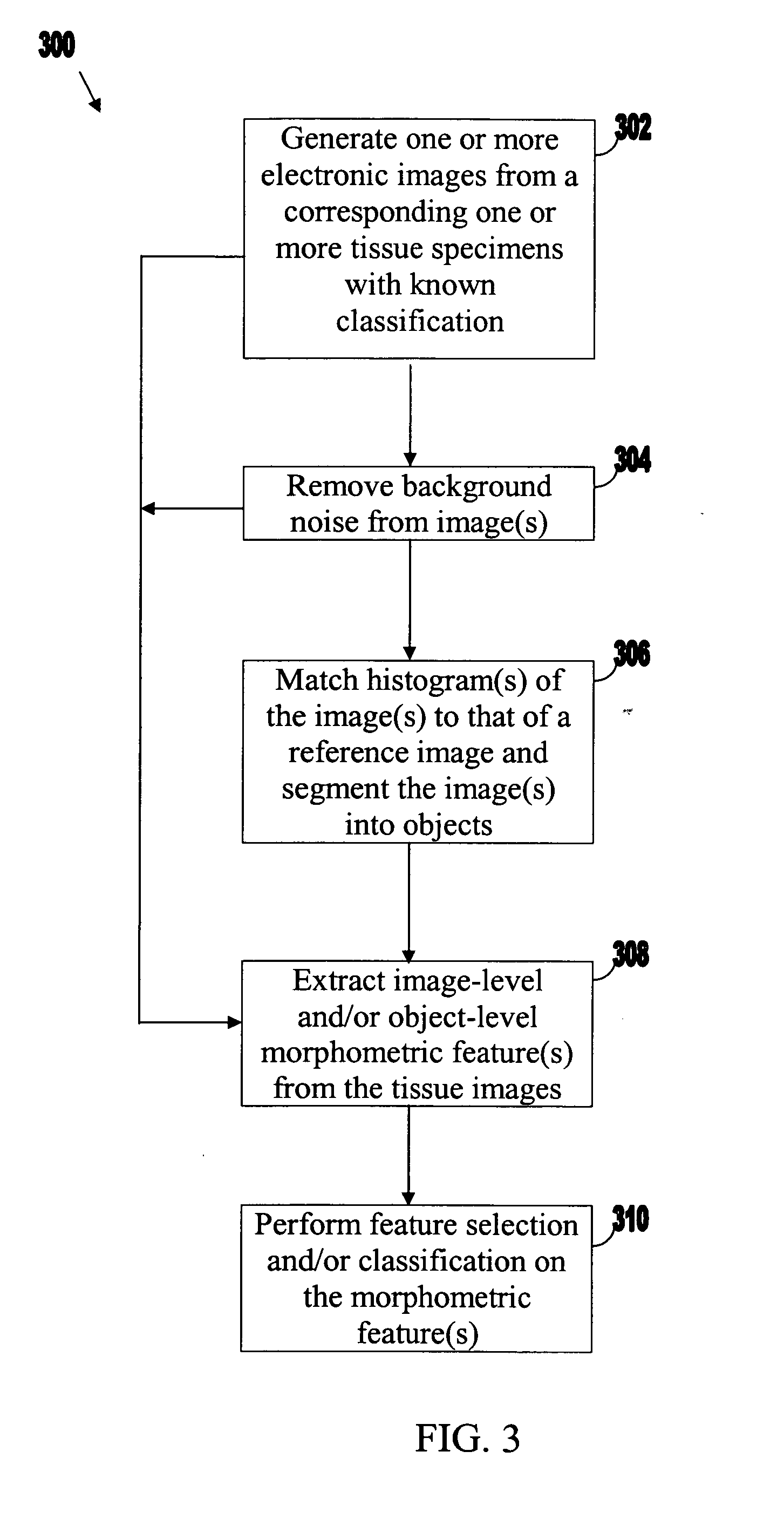
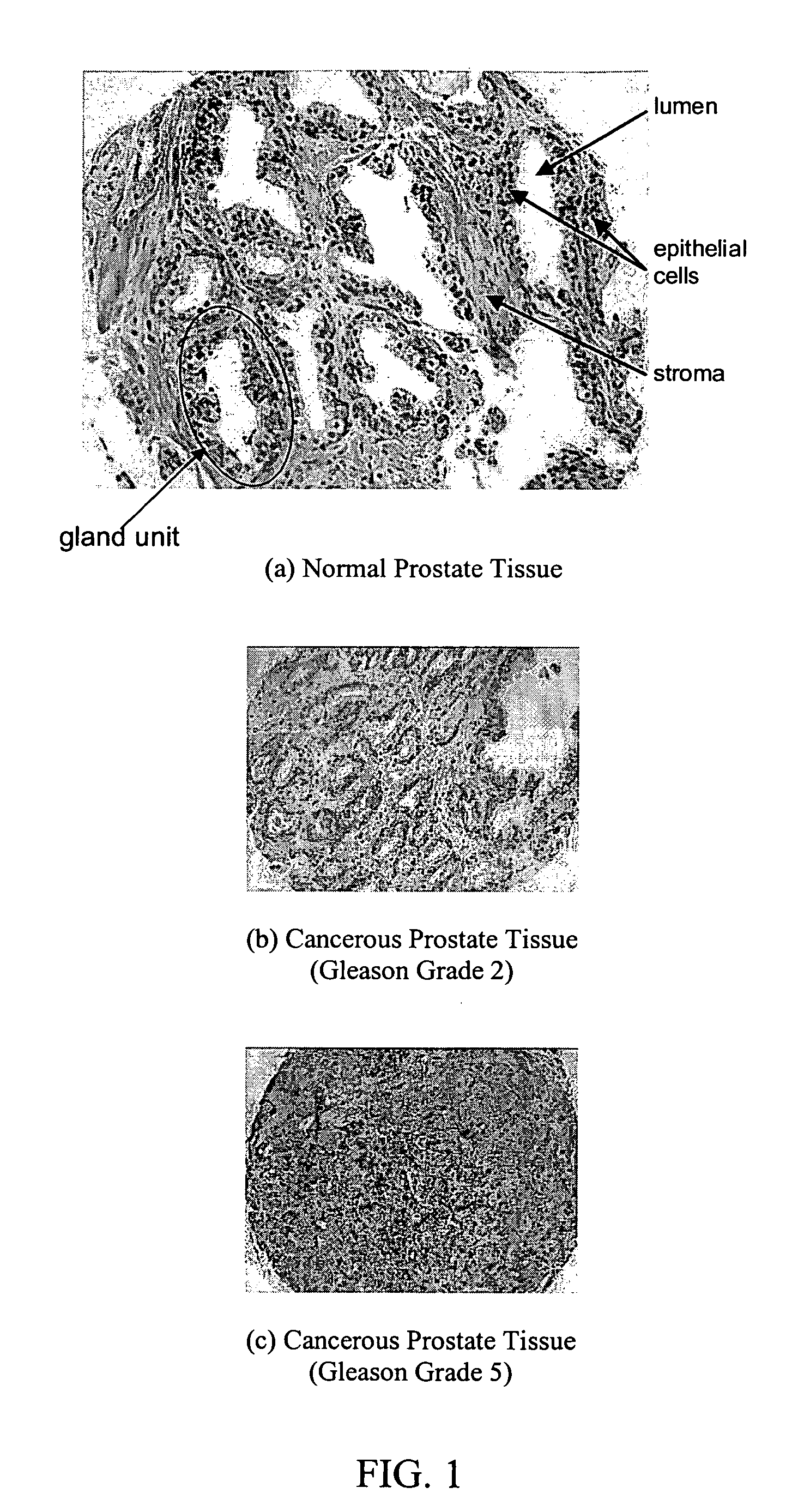
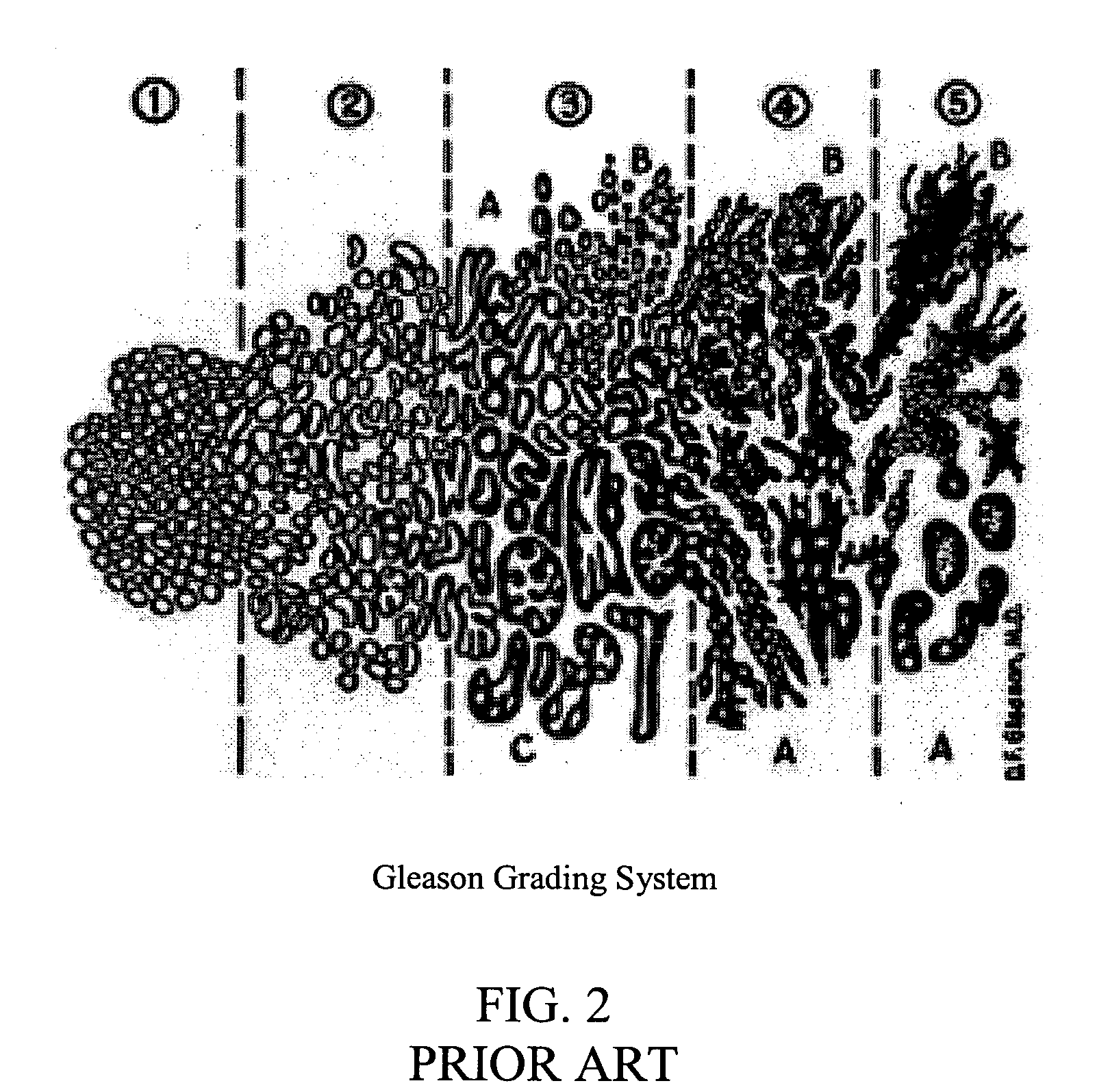
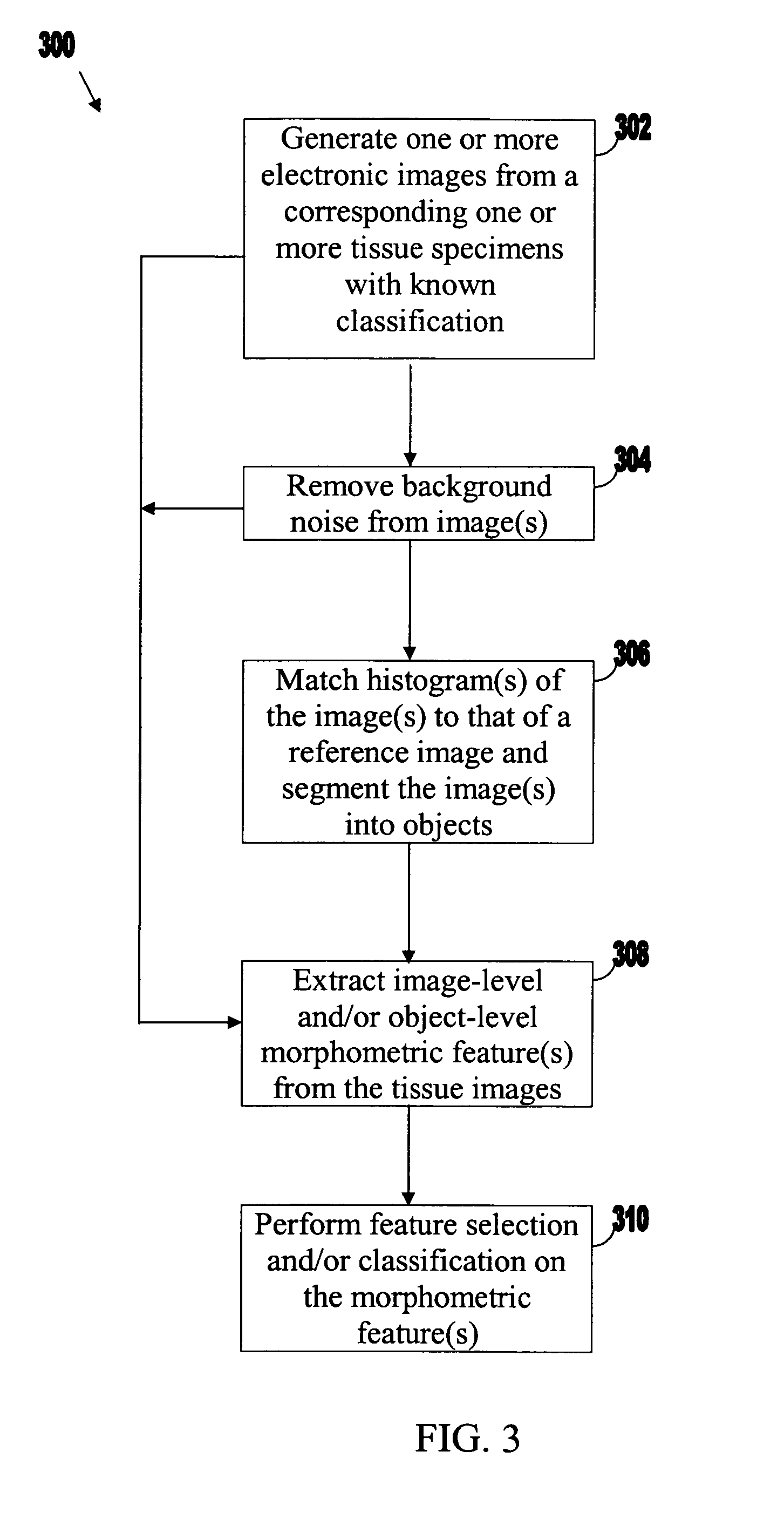
Systems and methods for automated diagnosis and grading of tissue images
Systems and methods are provided for automated diagnosis and grading of tissue images based on morphometric data extracted from the images by a computer. The morphometric data may include image-level morphometric data such as fractal dimension data, fractal code data, wavelet data, and / or color channel histogram data. The morphometric data may also include object-level morphometric data such as color, structural, and / or textural properties of segmented image objects (e.g., stroma, nuclei, red blood cells, etc.).
Owner:CHAMPALIMAUD FOUND +2
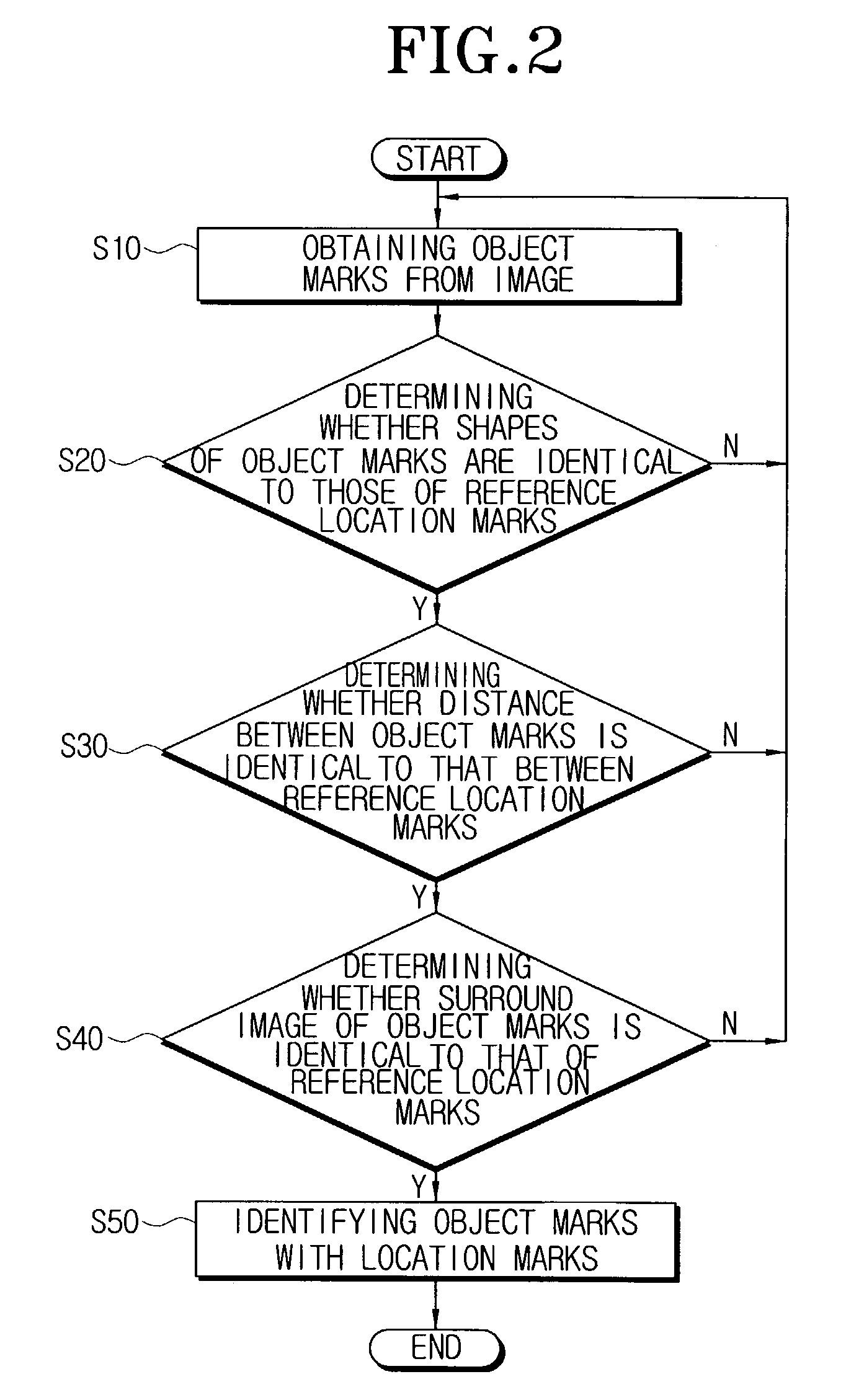
Location mark detecting method for robot cleaner and robot cleaner using the method
InactiveUS7184586B2Accurate detectionAutomatic obstacle detectionImage analysisImage capturePeripheral
A location mark detecting method of a robot cleaner capable of accurately detecting location marks from an image captured by an upwardly looking camera. The location mark detecting method comprises the steps of obtaining from the image object marks to be compared with the reference location marks, determining whether shapes of the object marks are identical to those of the reference location marks, determining whether a distance separating the object marks is identical to that between the reference location marks if it is determined that the shapes are identical, determining whether a surrounding image of the object marks is identical to that of the reference location marks if it is determined that the distances are identical, and identifying the object marks as the location marks if it is determined that the surrounding images are identical. A robot cleaner capable of wirelessly communicating with an external device comprises a driving unit, an upwardly-looking camera for capturing an image of a ceiling above an area to be cleaned on which location marks are disposed, and a control unit for detecting the location marks from the image captured by the upwardly-looking camera, the control unit commanding the driving unit utilizing information of the current location to perform a work command.
Owner:SAMSUNG GWANGJU ELECTRONICS CO LTD
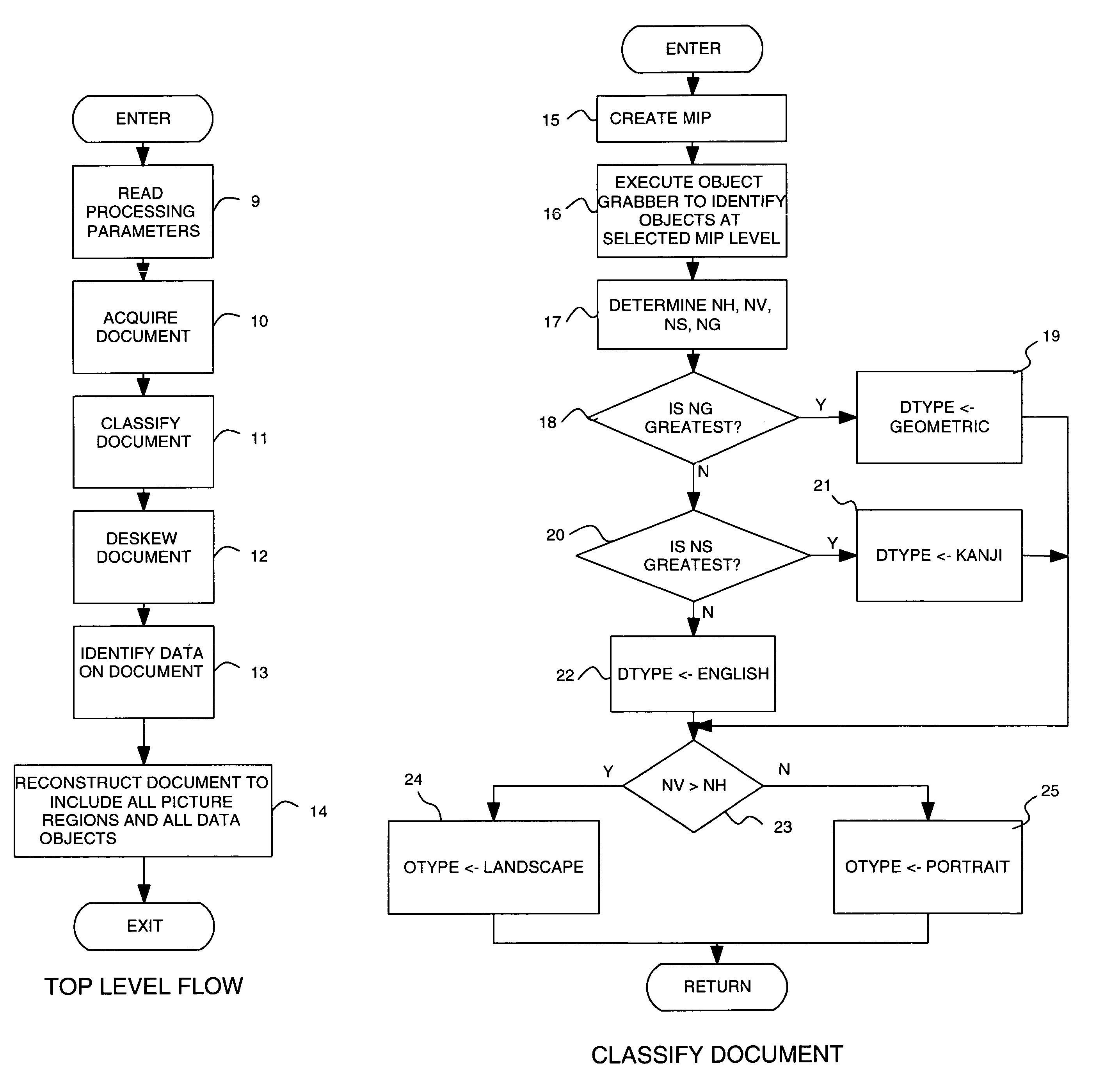
Method and apparatus for automatic cleaning and enhancing of scanned documents
InactiveUS7016536B1Fast informationFast noiseImage enhancementImage analysisImage resolutionDocument preparation
A method and apparatus are provided for removing noise from a first digital representation of data images and noise images of a document, including digitally scanning the document so as to produce the first digital representation of all the images of the document, including the data images and the noise images. After de-skewing the image representation, objects are built from a reduced-resolution representation of the scanned representation. Objects identified as picture objects are included in a mask which is logically ANDed with the de-skewed representation of the scanned document. All objects are added to an object list and initially marked as noise. Objects identified as text objects or geometric objects are marked as data objects. Objects identified as picture objects are included in a mask which is logically ANDed with the de-skewed representation to eliminate all other objects. Objects marked as data objects are added to that representation to provide the de-skewed, de-speckled representation of the scanned document.
Owner:GTX EURO LTD
Automated document layout design
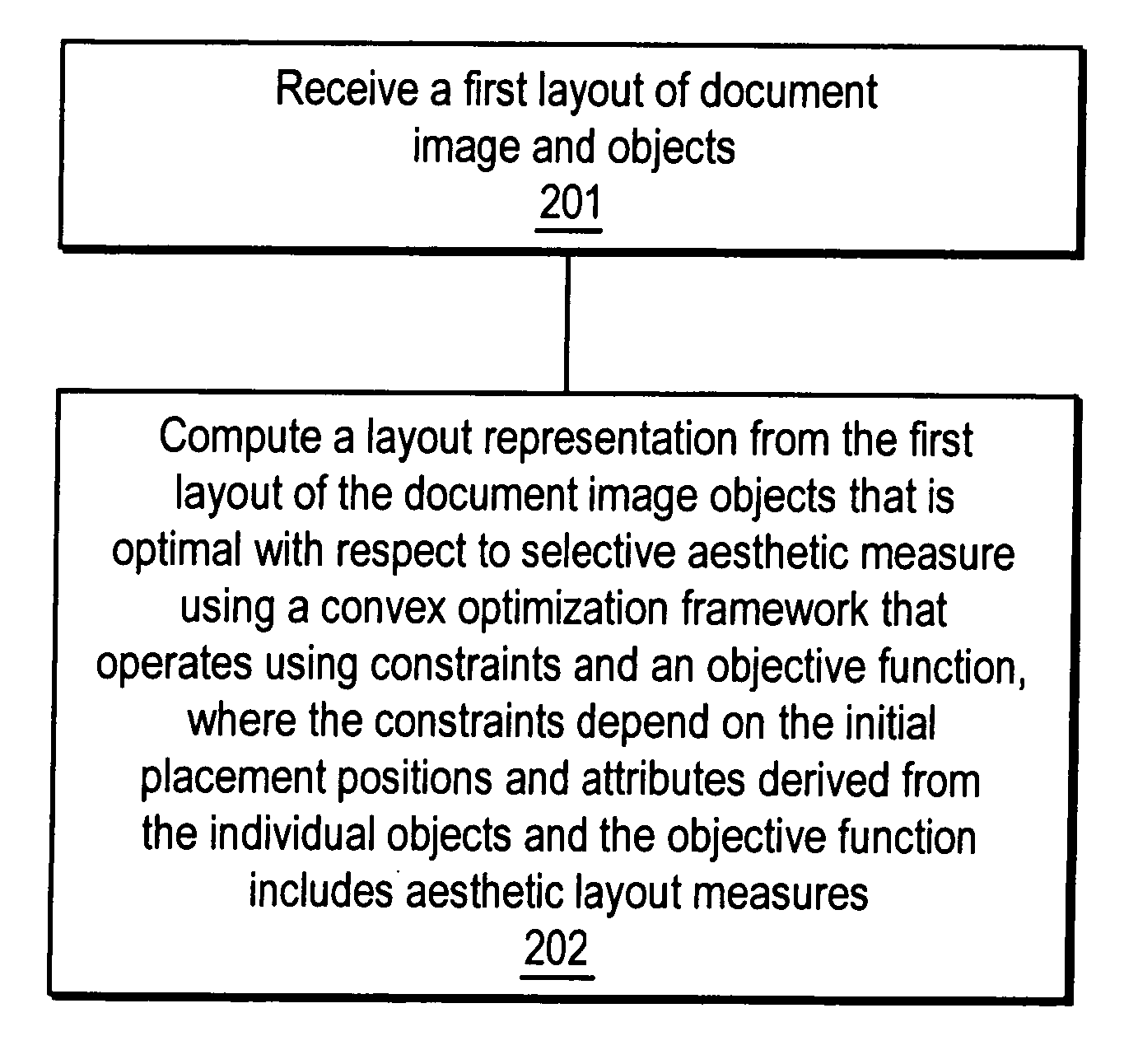
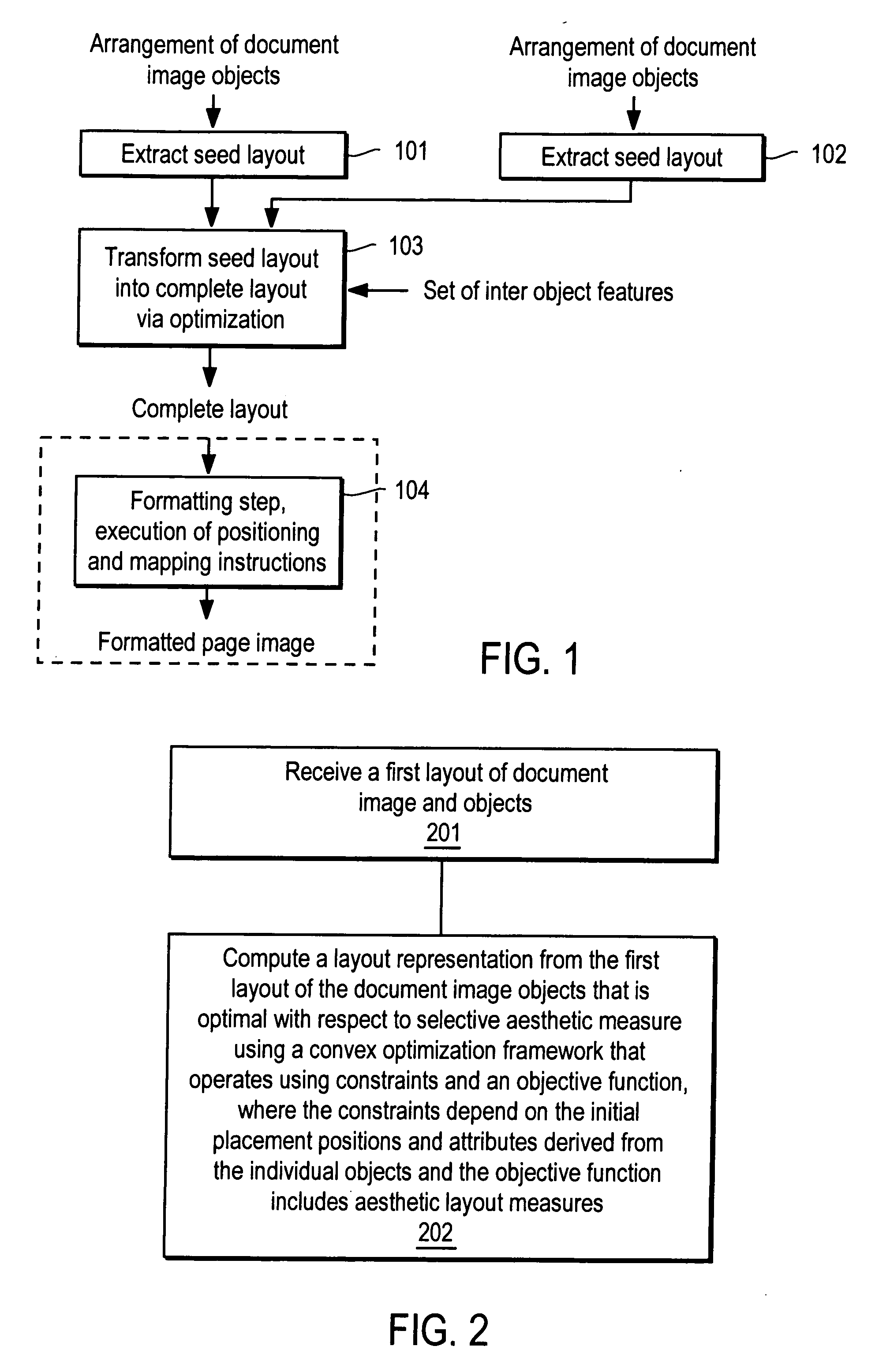
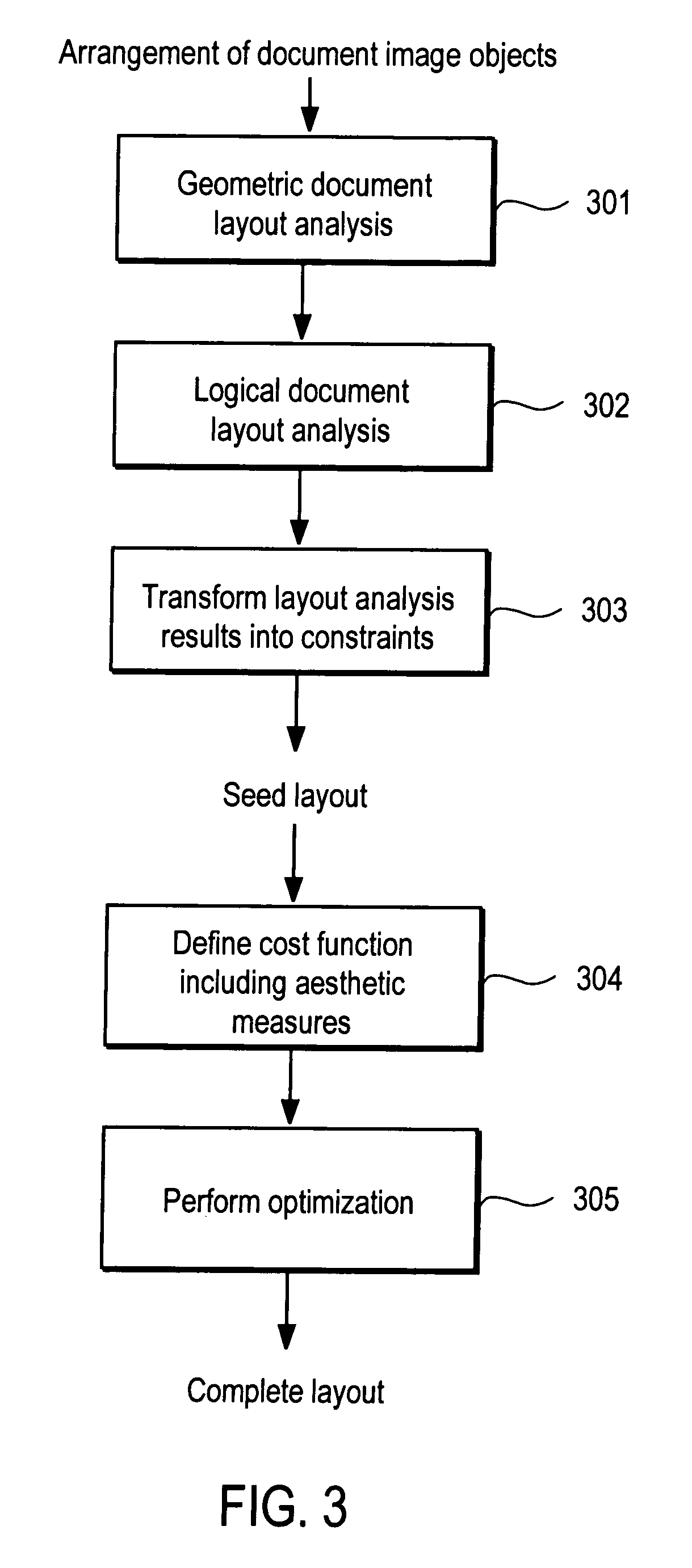
ActiveUS20070208996A1Digital computer detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionPaper documentDocument preparation
A method and apparatus for automated document layout creation is disclosed. In one embodiment, the method comprises receiving a first layout of document image objects and creating a second layout of document image objects subject to placement constraints corresponding to placement of document image objects, at least one of the placement constraints being based on object content in one or more of the document image objects.
Owner:RICOH KK
Video system with de-motion-blur processing
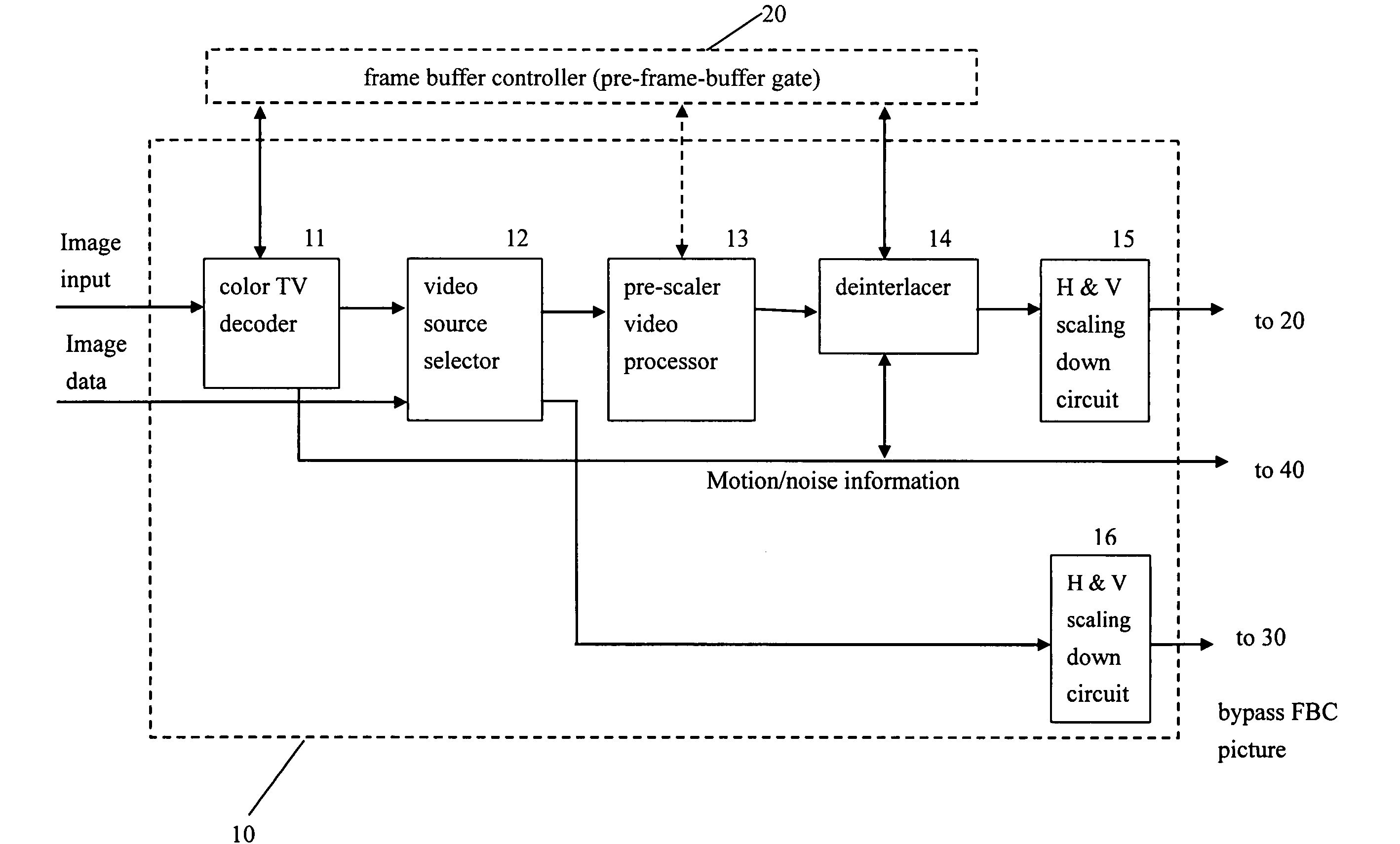
ActiveUS20050162566A1Short response timeQuality improvementImage enhancementTelevision system detailsProgressive scanImage resolution
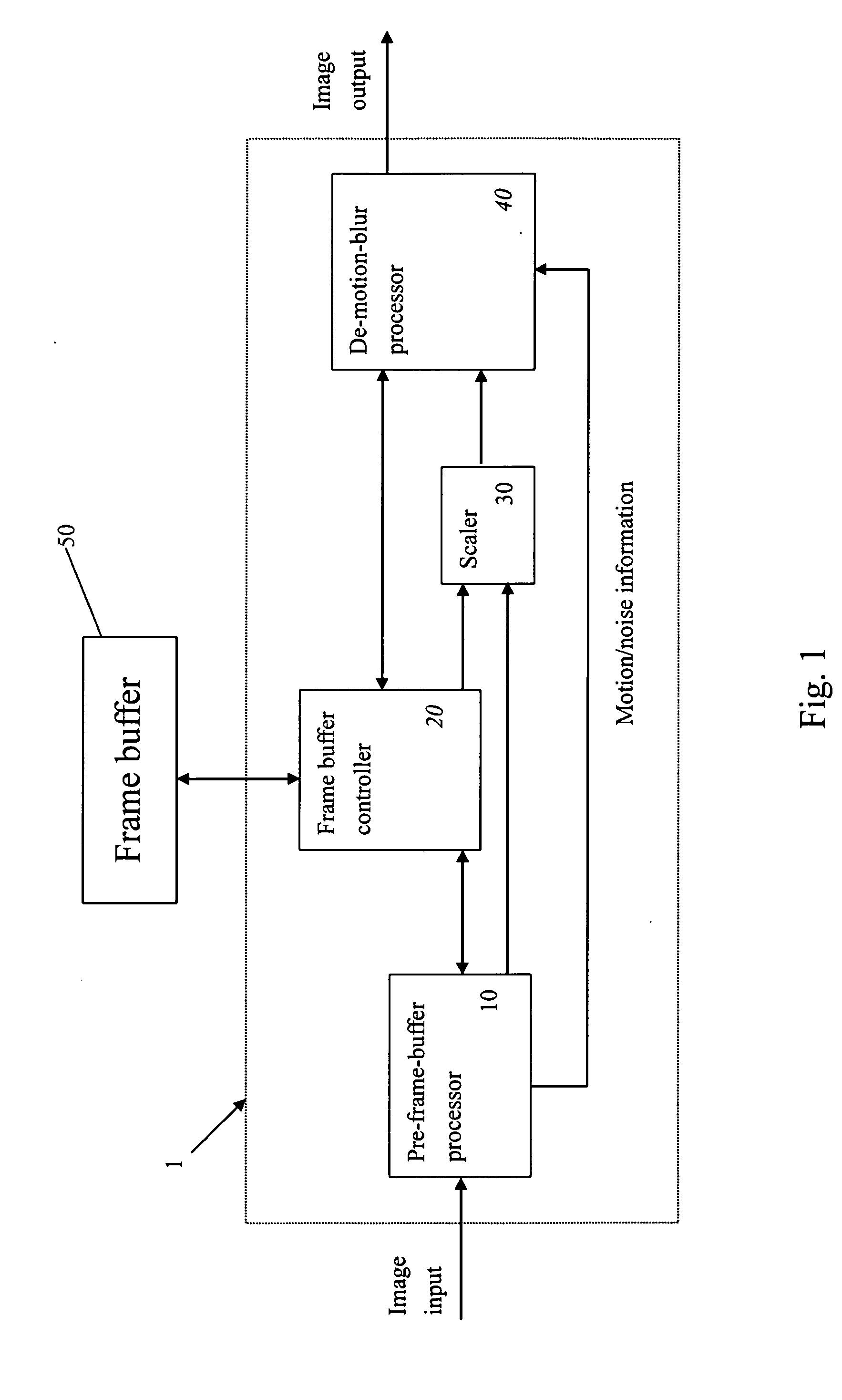
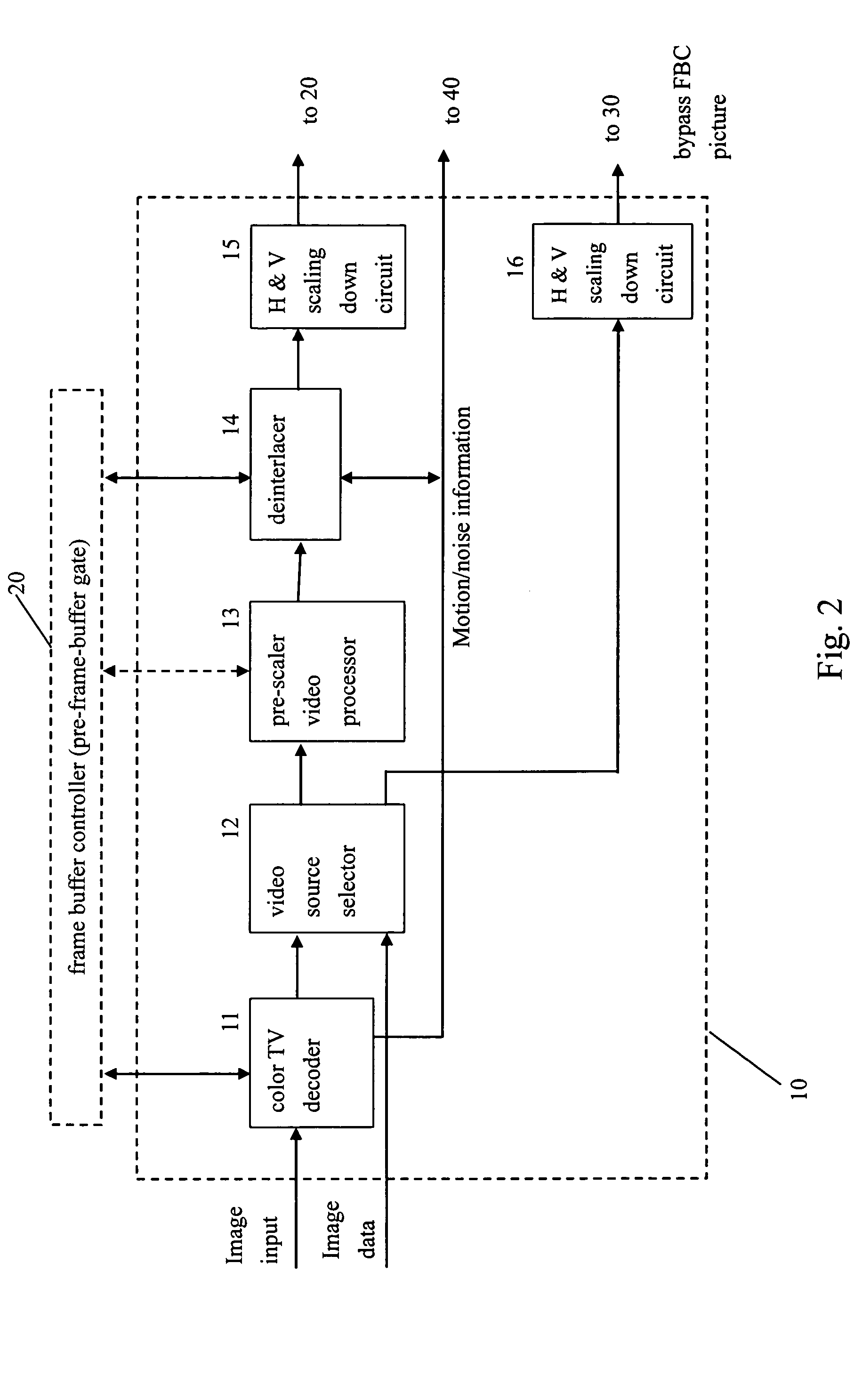
A video system that performs TV signal decoding, deinterlacing, and de-motion-blurring for progressive scan flat panel display is introduced. The system embeds a frame buffer and a scaler for conducting format and resolution conversions for display panels of different sizes. The output of the scaler is sent to a de-motion-blur processor for reducing the blurriness due to the motion of image objects and the slow response time of flat panel display devices. The de-motion-blur processor gets the motion and noise indication signal from scaler or the pre-frame-buffer video processor. Based on the motion and noise information and the information of temporal difference, the de-motion-blur processor performs over driving for the display panel interface and improves the rising and falling response time of the flat panel display. The decoding, deinterlacing, and de-motion-blur processing share the same frame buffer controller so the entire system can be optimized in cost and performance.
Owner:NOVATEK MICROELECTRONICS CORP
Method and device for synthesizing image
A method and device for synthesizing an image for audiovisual communication includes: generating, if a request for synthesizing a sensor image input through a camera sensor and an image designated by a user is input, a synthesis image of the sensor image and the designated image. The method also includes storing, when the synthesis image is generated, object information of an object of the sensor image and object information of an object of the designated image; and changing, if a sensor image is input in which object information of the sensor image object has changed, object information of the designated image object according to the changed object information of the sensor image object and synthesizing the sensor image and the designated image in which object information has changed.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
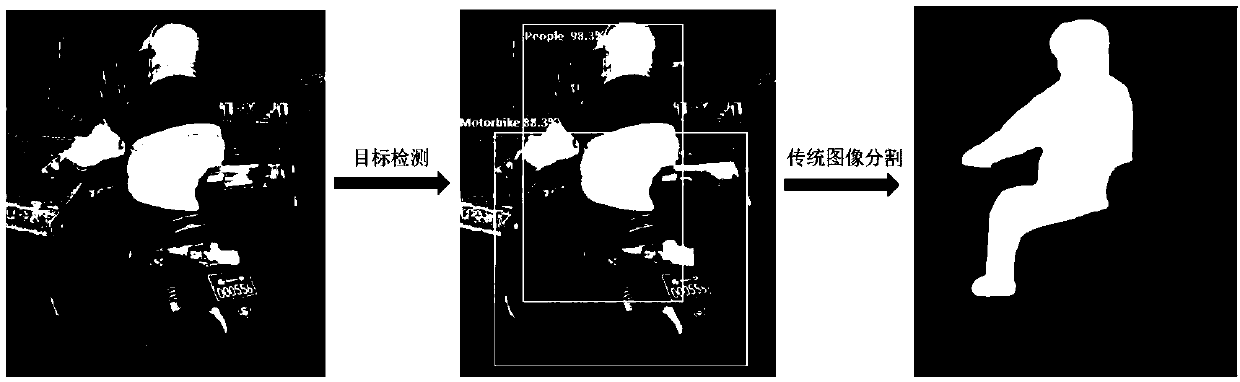
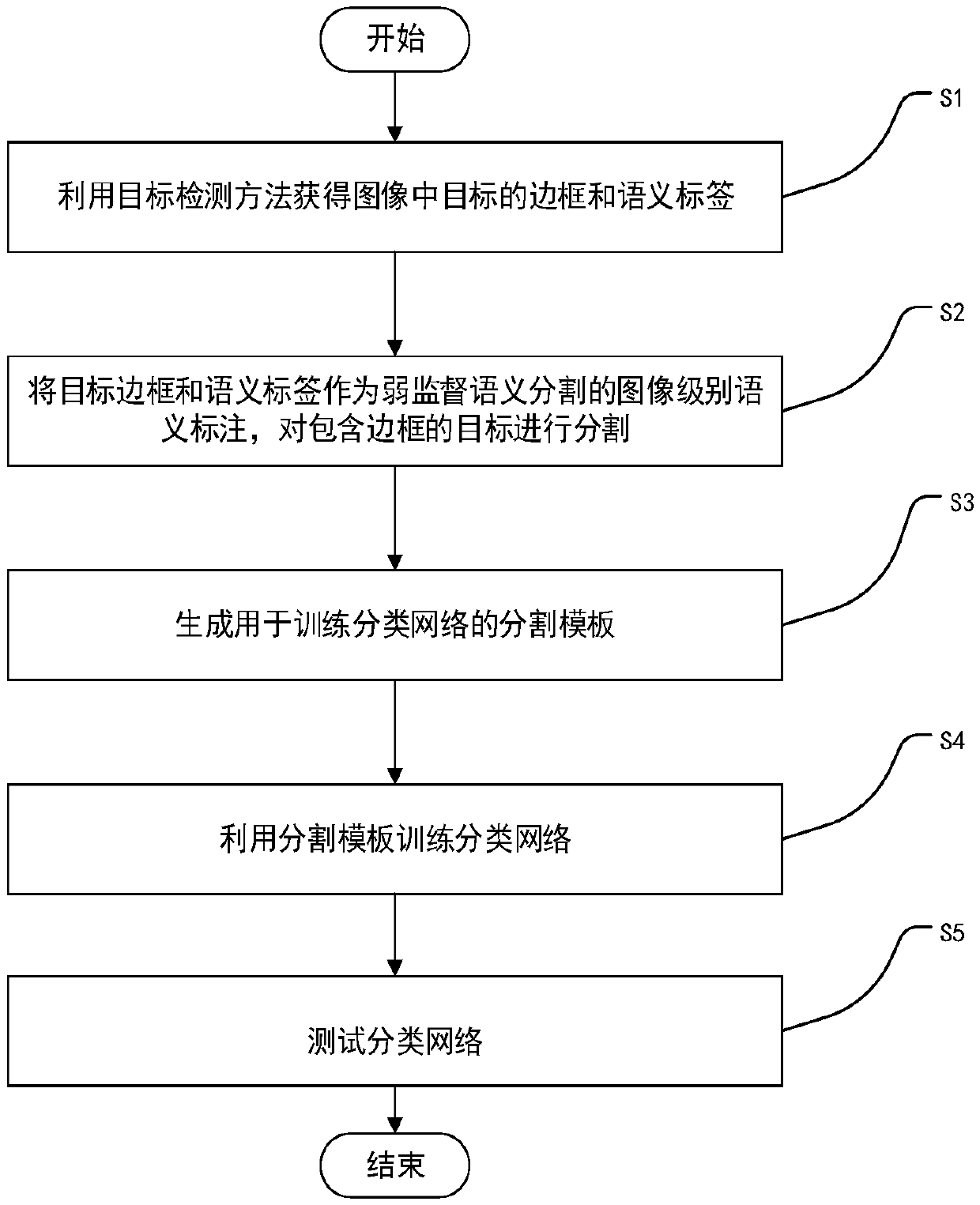
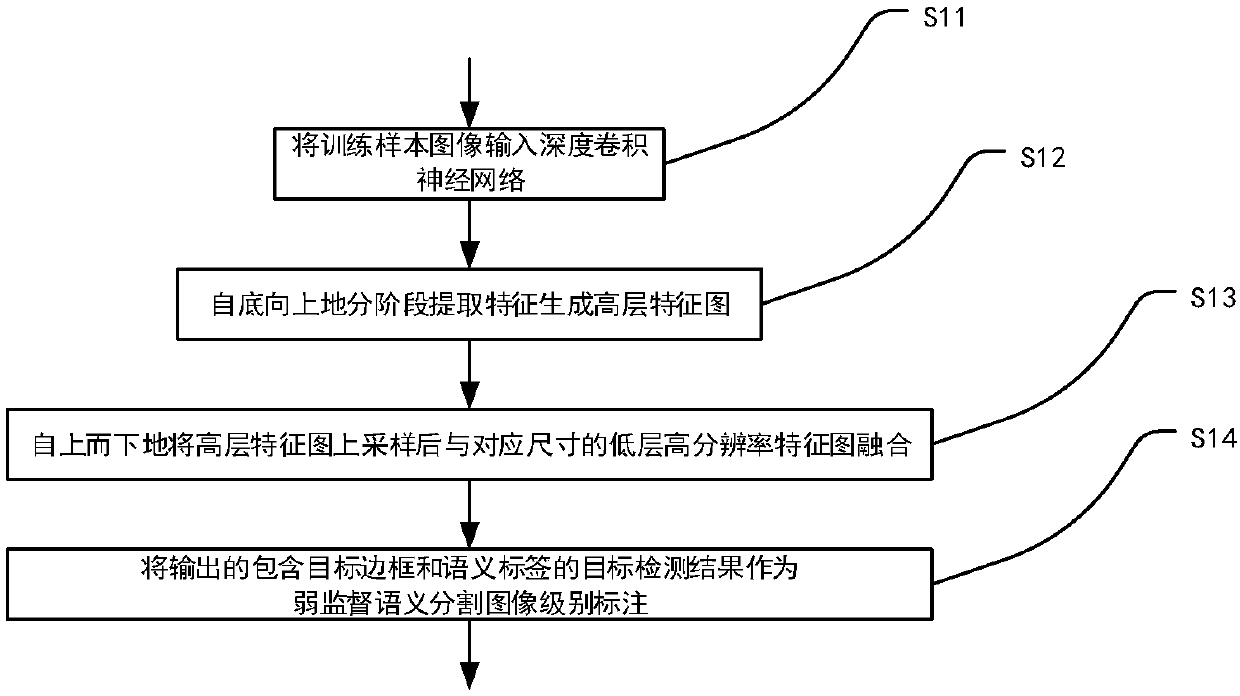
An automatic image annotation method for weakly supervised semantic segmentation
An automatic image annotation method for weakly supervised semantic segmentation. The object border is located by an image object detection method, and the semantic label is given. The object border and the semantic label are regarded as a kind of weak supervised semantic label of image level. By using traditional image segmentation method, the whole object region is segmented out, and the segmentation template for training classification network is generated. Then, the segmentation template is used as a supervisory signal to train the classification network. Finally, the trained classification network is used to segment the test image semantically. The technical proposal of the invention utilizes an object detection method to obtain a border and a semantic tag of an object in an image, utilizes a traditional image segmentation method to segment an object region, and combines the semantic tag to serve as a training sample for weak supervision semantic segmentation. The method to automatically generate training samples for weak supervised semantic segmentation, solves the problem of time-consuming and laborious manual labeling of a large number of images.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Methods and apparatus for differential phase-contrast fan beam CT, cone-beam CT and hybrid cone-beam CT
ActiveUS7949095B2Increase doseImprove spatial resolutionImaging devicesRadiation/particle handlingPhase gratingHybrid system
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
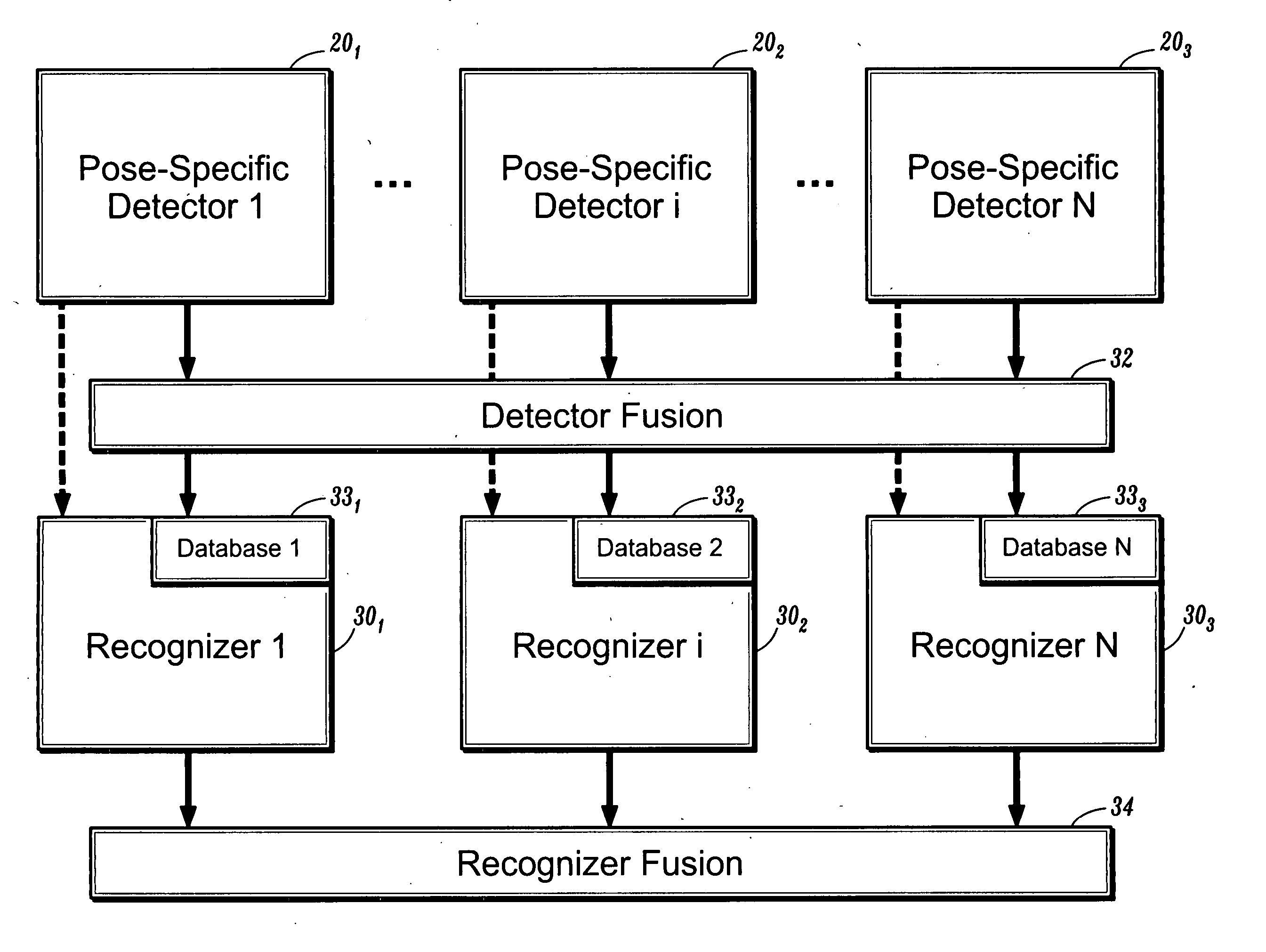
Systems and methods for face detection and recognition using infrared imaging
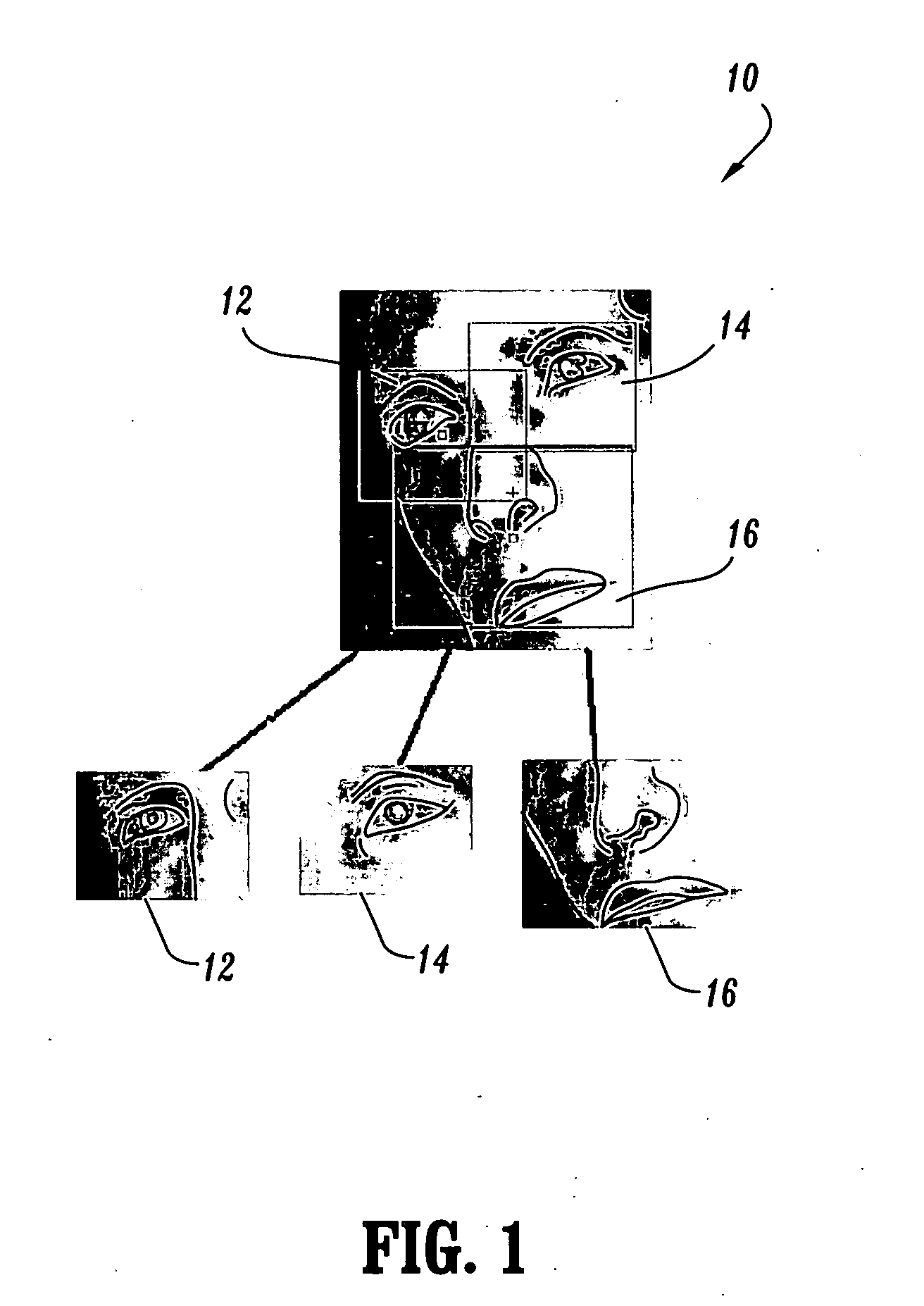
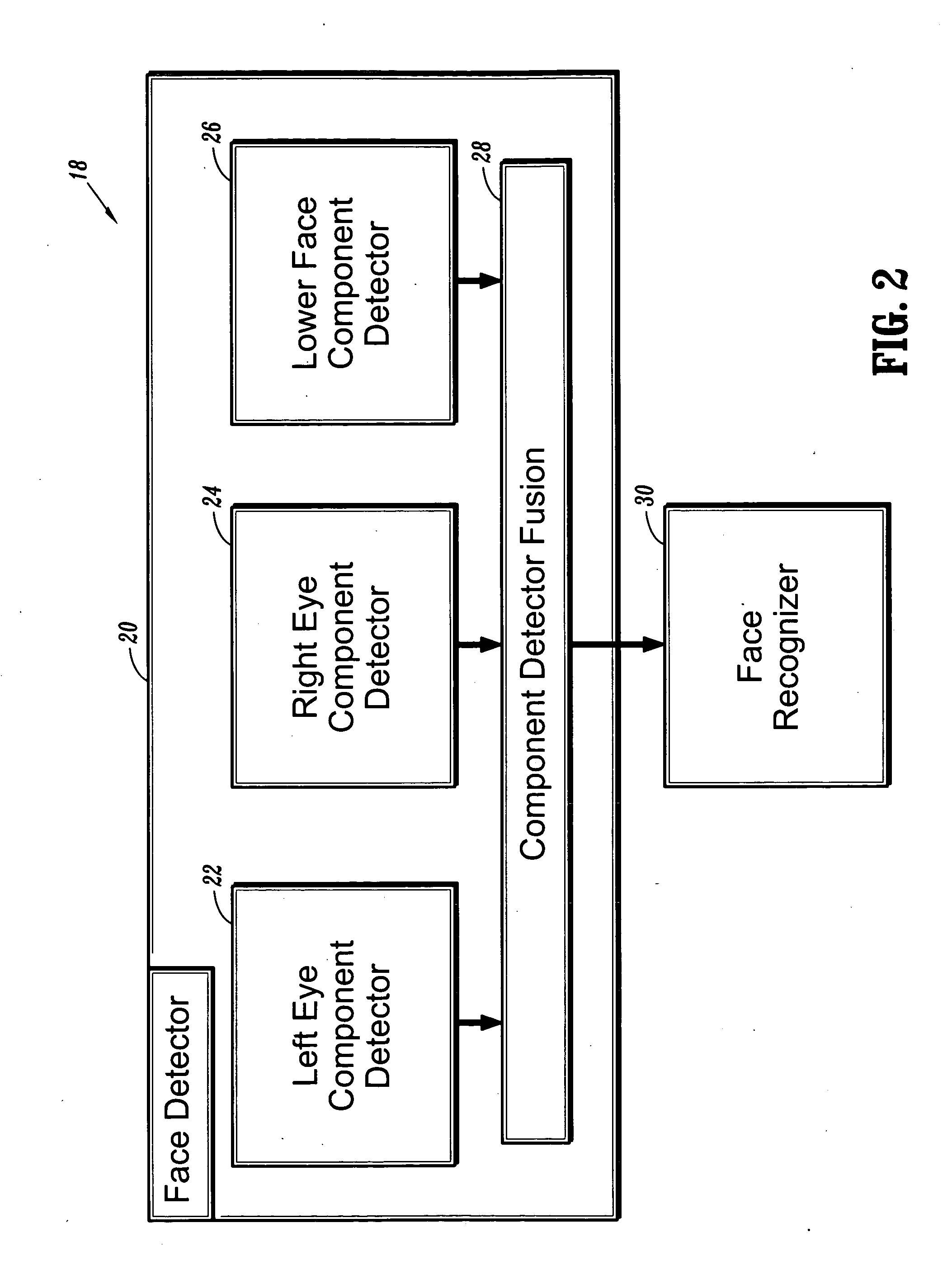
ActiveUS20050226471A1Promote resultsHigh positioning accuracyTelevision system detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionFace detectionImaging processing
Methods for image processing for detecting and recognizing an image object include detecting an image object using pose-specific object detectors, and performing fusion of the outputs from the pose-specific object detectors. The image object is recognized using pose-specific object recognizers that use outputs from the pose-specific object detectors and the fused output of the pose-specific object detectors; and by performing fusion of the outputs of the pose-specific object recognizers to recognize the image object.
Owner:CONTINENTAL AUTOMOTIVE GMBH +1
Information output apparatus
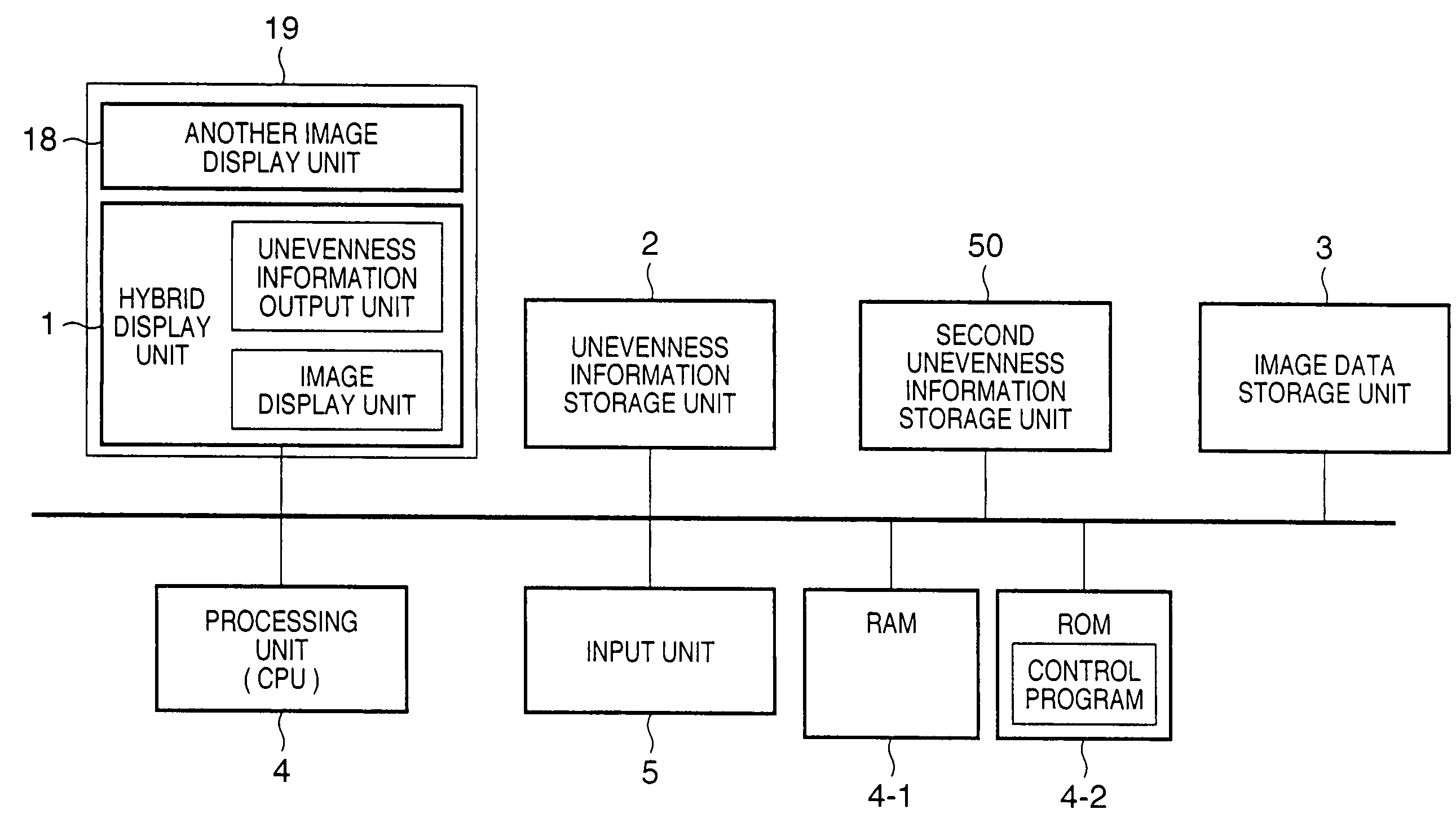
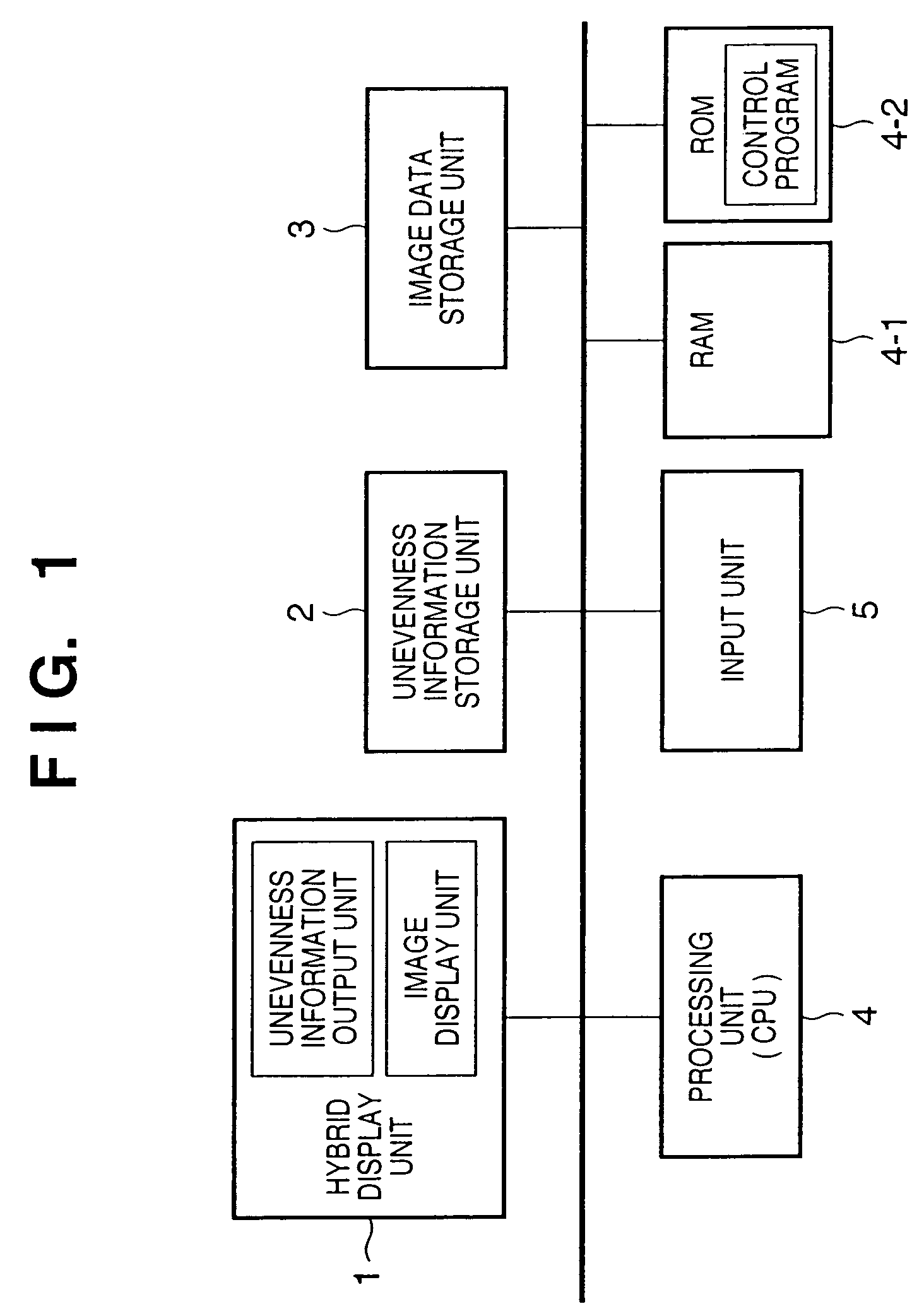
InactiveUS7202837B2Easily discriminatedInput/output for user-computer interactionCathode-ray tube indicatorsOutput deviceSurface states
This invention provides an information output apparatus which outputs tactile information or the like corresponding to the surface state of an object as three-dimensional information together with image information, and allows the user to easily discriminate the surface material or the like of an image object in the image information.A hybrid display unit of the information display apparatus of this invention has a structure formed by overlaying, e.g., a display panel used to display an image, and an unevenness output element group used to output the unevenness level of that image, and voltage values to be applied to respective unevenness output elements of the unevenness output element group are determined on the basis of, e.g., unevenness information stored in a memory. Therefore, material differences (smooth or rough touch) of images displayed on the display panel can be felt by touching unevenness output by the unevenness output elements.
Owner:CANON KK
Systems and methods for automated diagnosis and grading of tissue images
Systems and methods are provided for automated diagnosis and grading of tissue images based on morphometric data extracted from the images by a computer. The morphometric data may include image-level morphometric data such as fractal dimension data, fractal code data, wavelet data, and / or color channel histogram data. The morphometric data may also include object-level morphometric data such as color, structural, and / or textural properties of segmented image objects (e.g., stroma, nuclei, red blood cells, etc.).
Owner:CHAMPALIMAUD FOUND +2
Apparatus and method for providing three-dimensional air-touch feedback
InactiveUS20150277610A1Improve spatial resolutionSmall sizeInput/output processes for data processingMobile deviceHuman–computer interaction
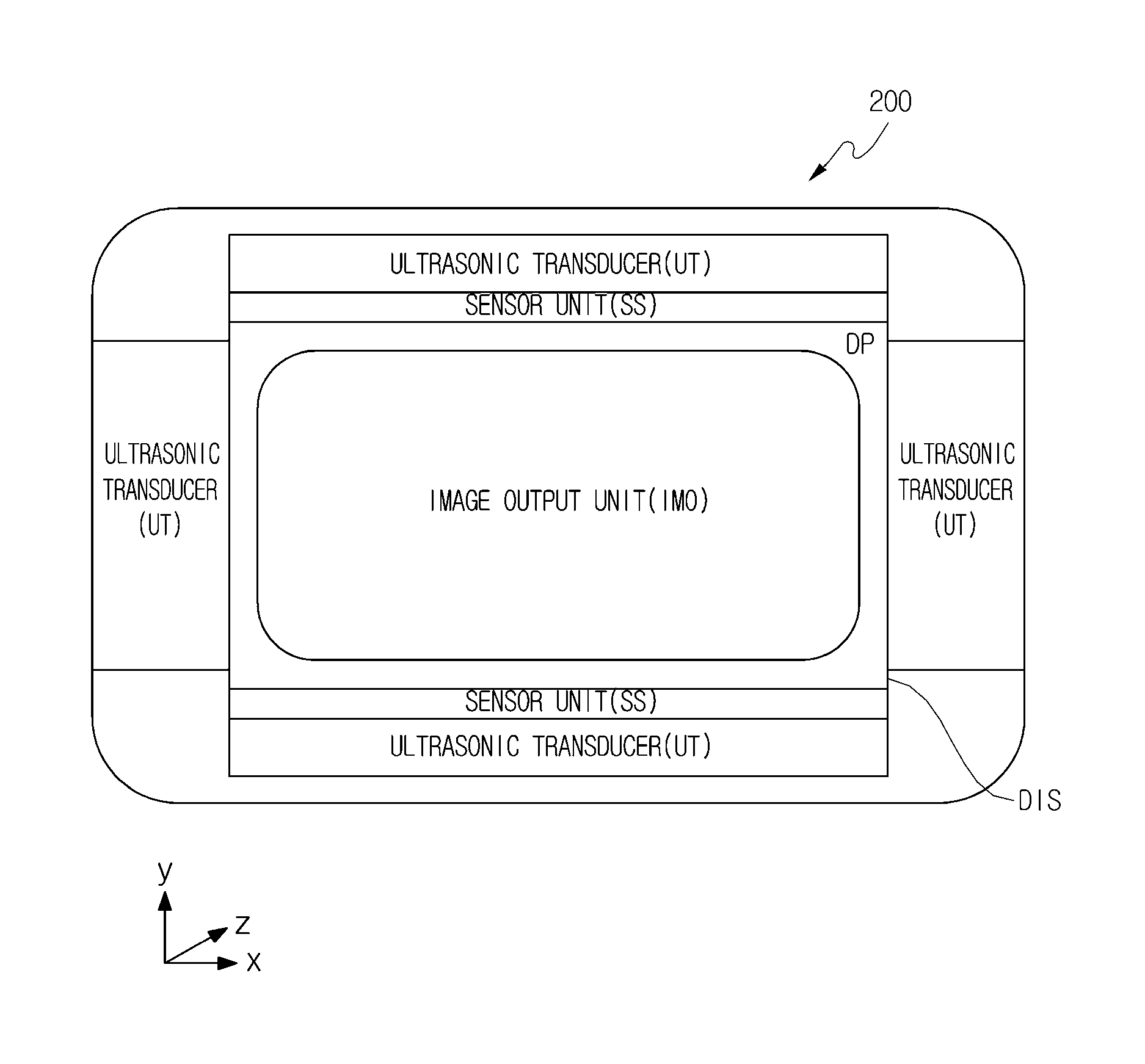
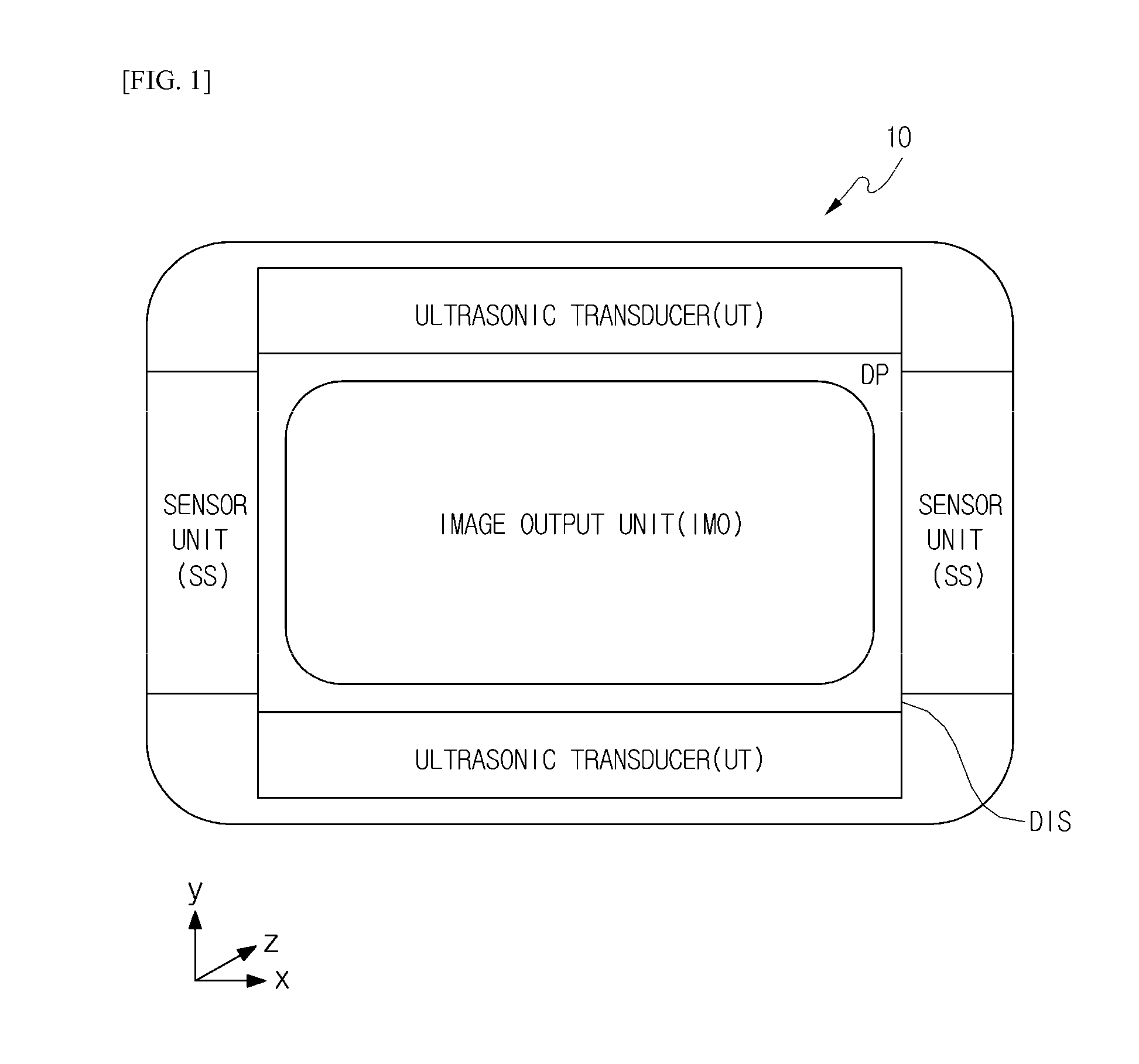
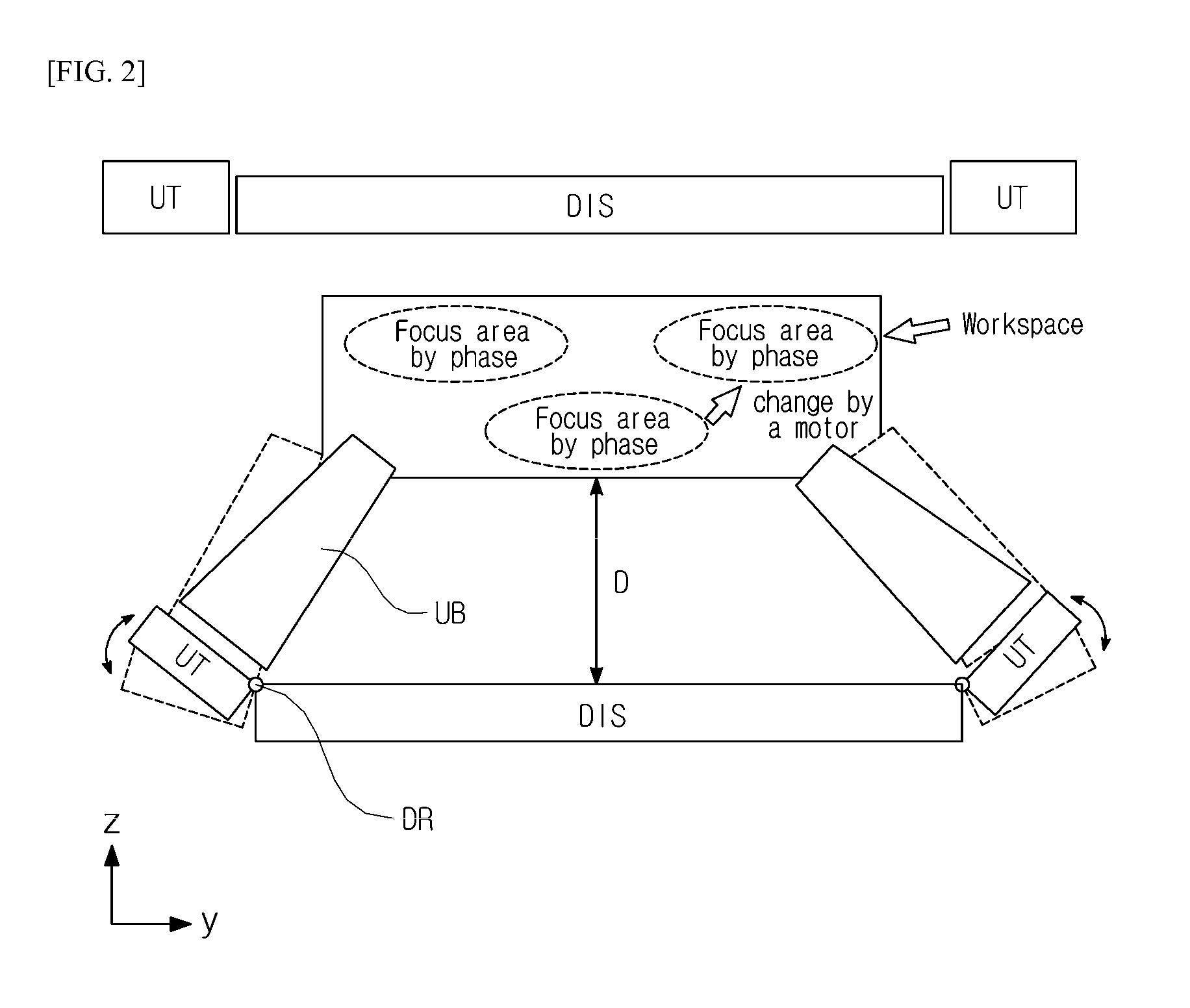
Provided are three-dimensional air touch feedback apparatus and method for a mobile apparatus. The present invention provides an air touch feedback apparatus, including: a display unit which outputs a 3D floating image; a touch detecting unit which is disposed at a side edge of a display unit and includes a plurality of sensors to detect a body of a user and receives position information on at least one image object of the 3D floating image from the display unit to determine an air touch position where the body of the user is in contact with the image object; and a feedback providing unit which receives air touch position information from the touch detecting unit and radiates an ultrasonic wave to the air touch position at the side edge of the display unit.
Owner:IND ACADEMIC CORP FOUND YONSEI UNIV
Image description system and method
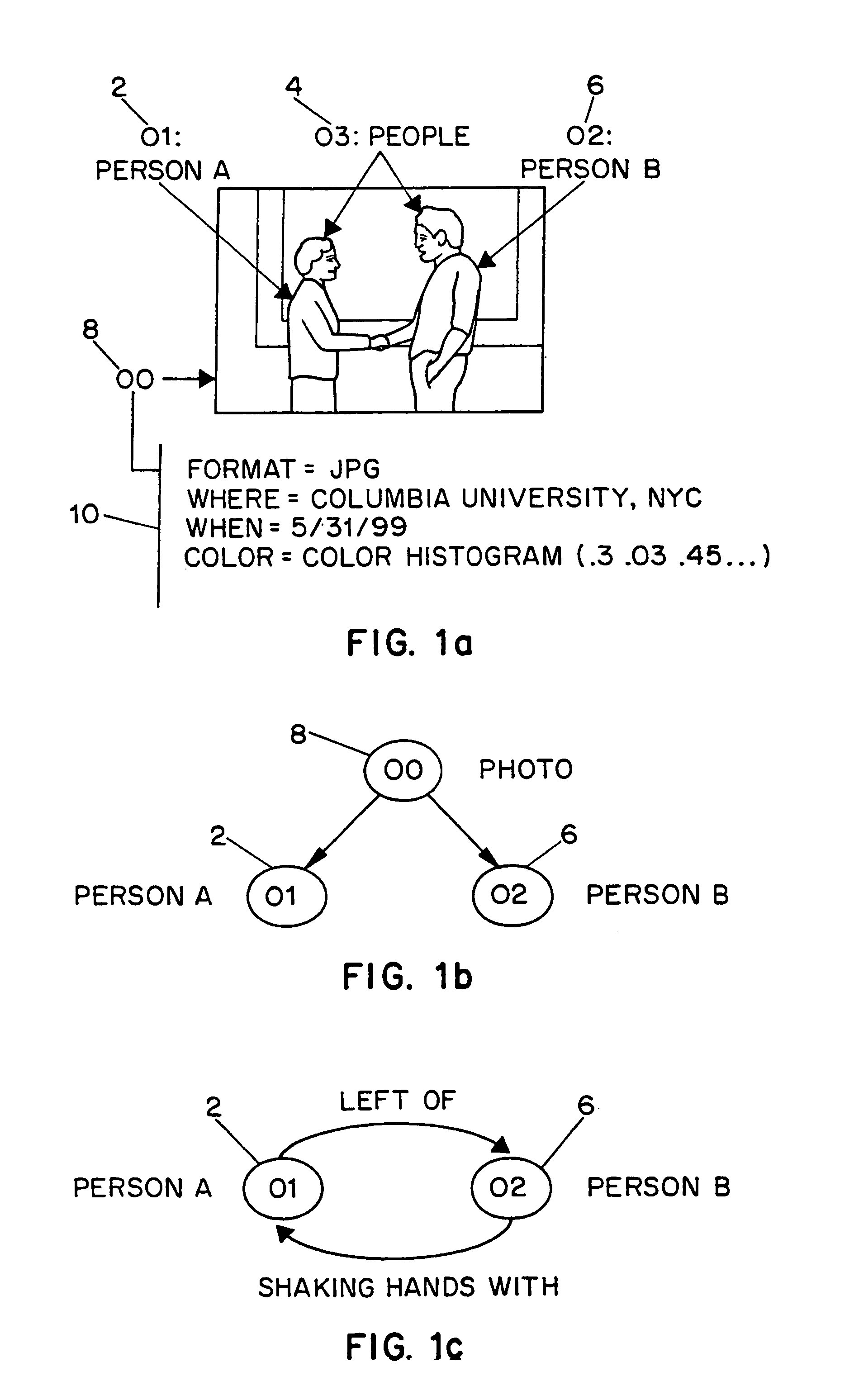
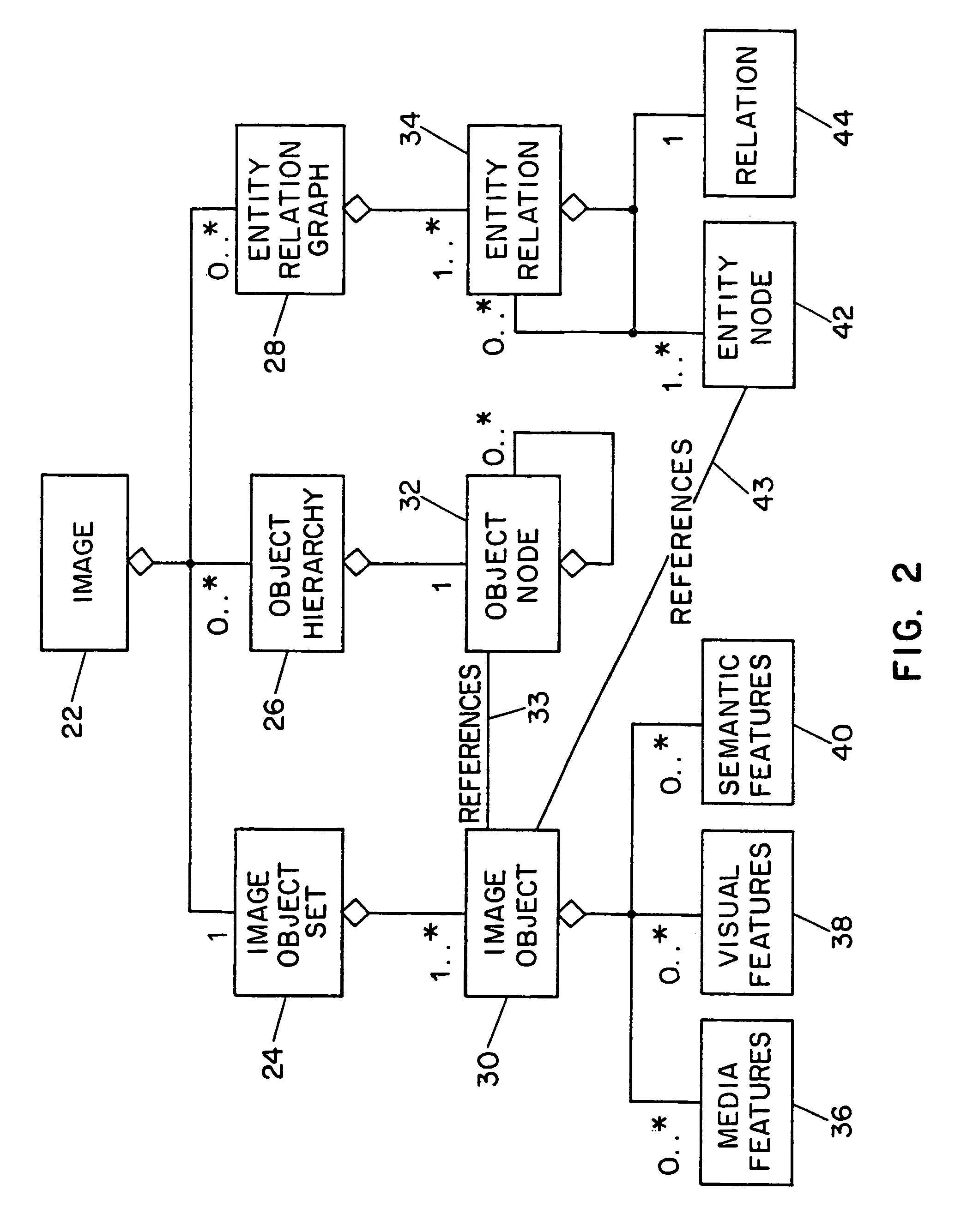
InactiveUS7254285B1Character and pattern recognitionPictoral communicationImage objectFeature descriptor
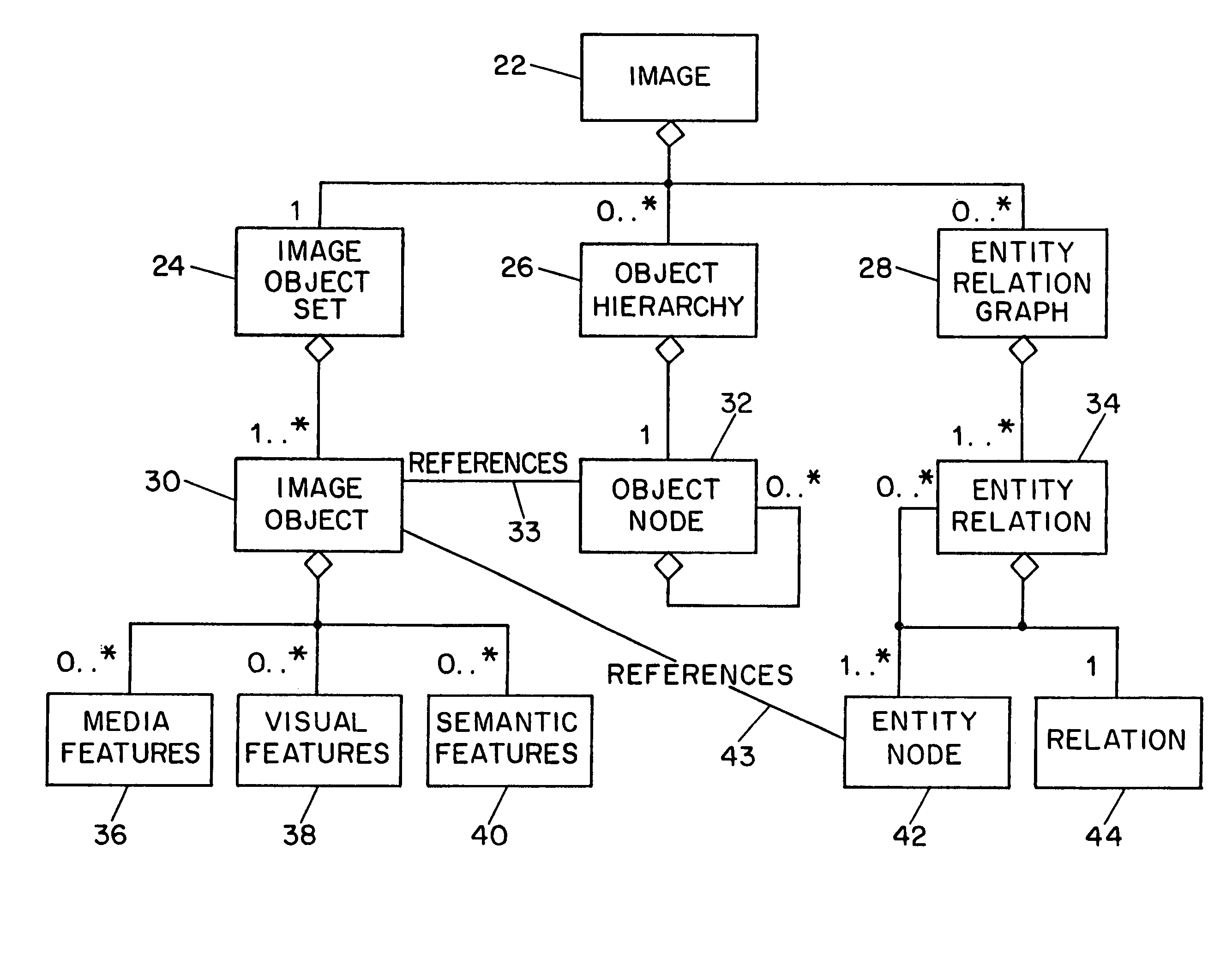
Systems and methods for describing image content establish image description records which include an object set (24), an object hierarchy (26) and entity relation graphs (28). For image content, image objects can include global objects (O0 8) and local objects (O1 2 and O2 6). The image objects are further defined by a number of features of different classes (36, 38 and 40), which in turn are further defined by a number of feature descriptors. The relationships between and among the objects in the object set are defined by the object hierarchy (26) and entity relation graphs (28). The image description records provide a standard vehicle for describing the content and context of image information for subsequent access and processing by computer applications such as search engines, filters, and archive systems.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com