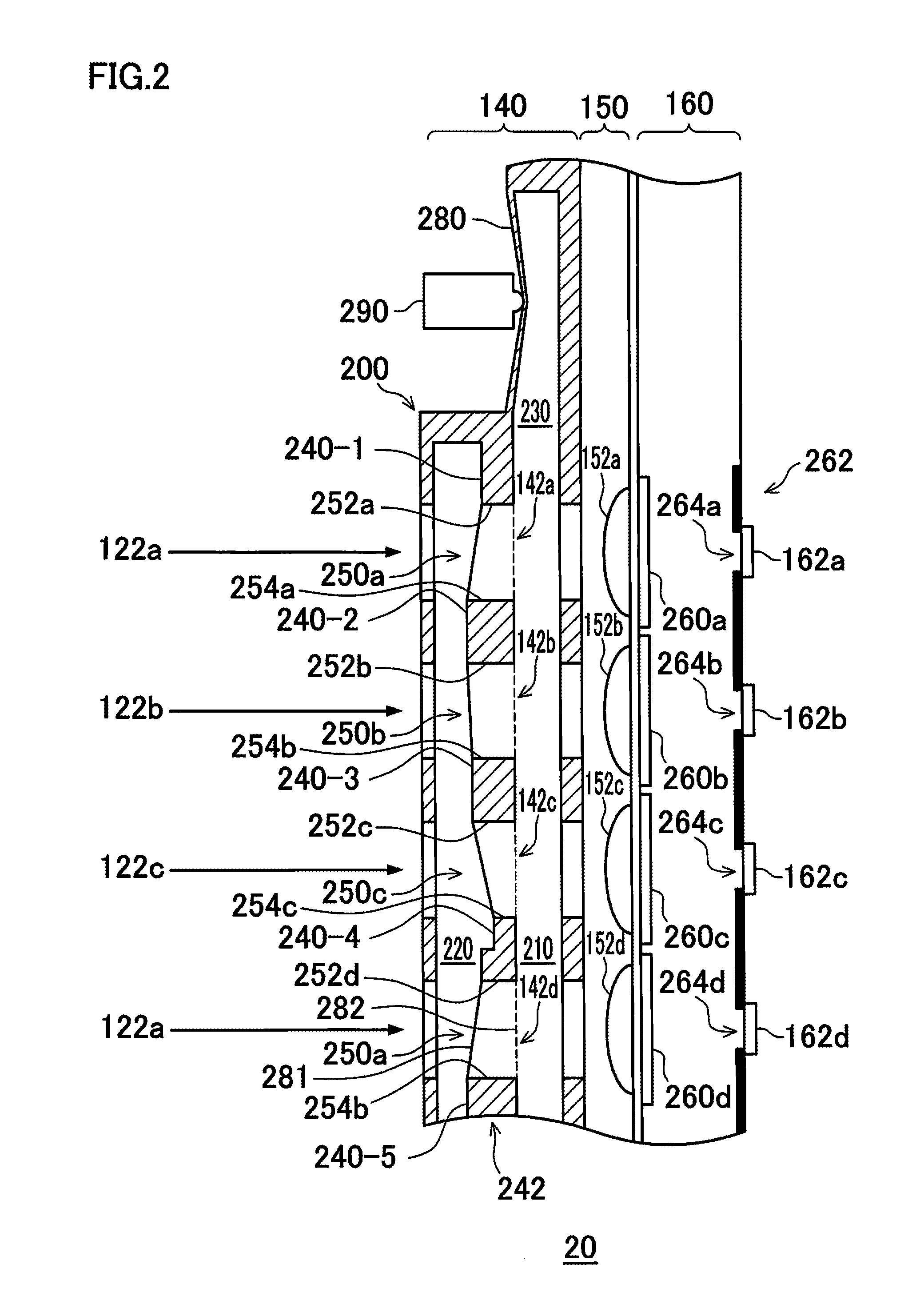
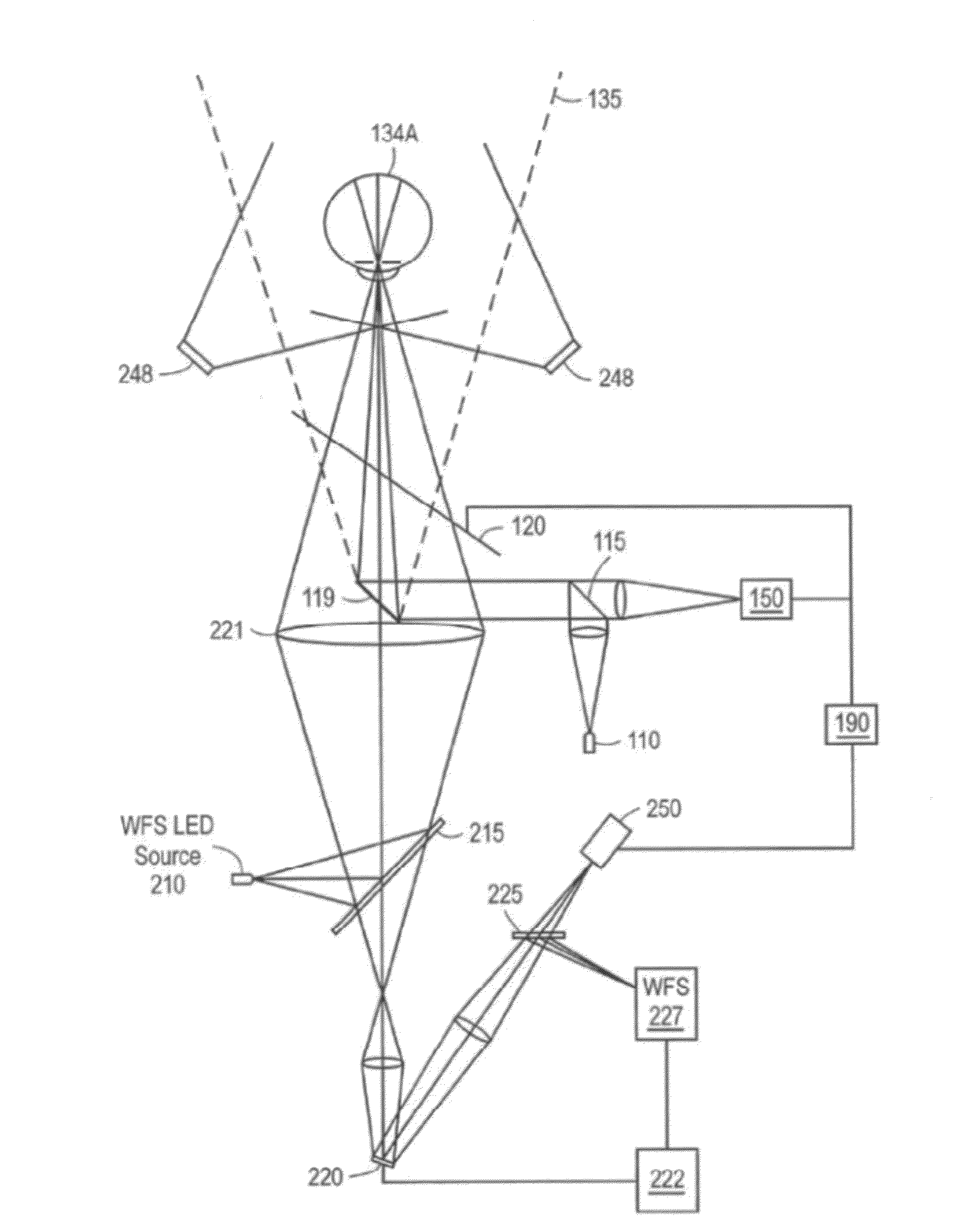
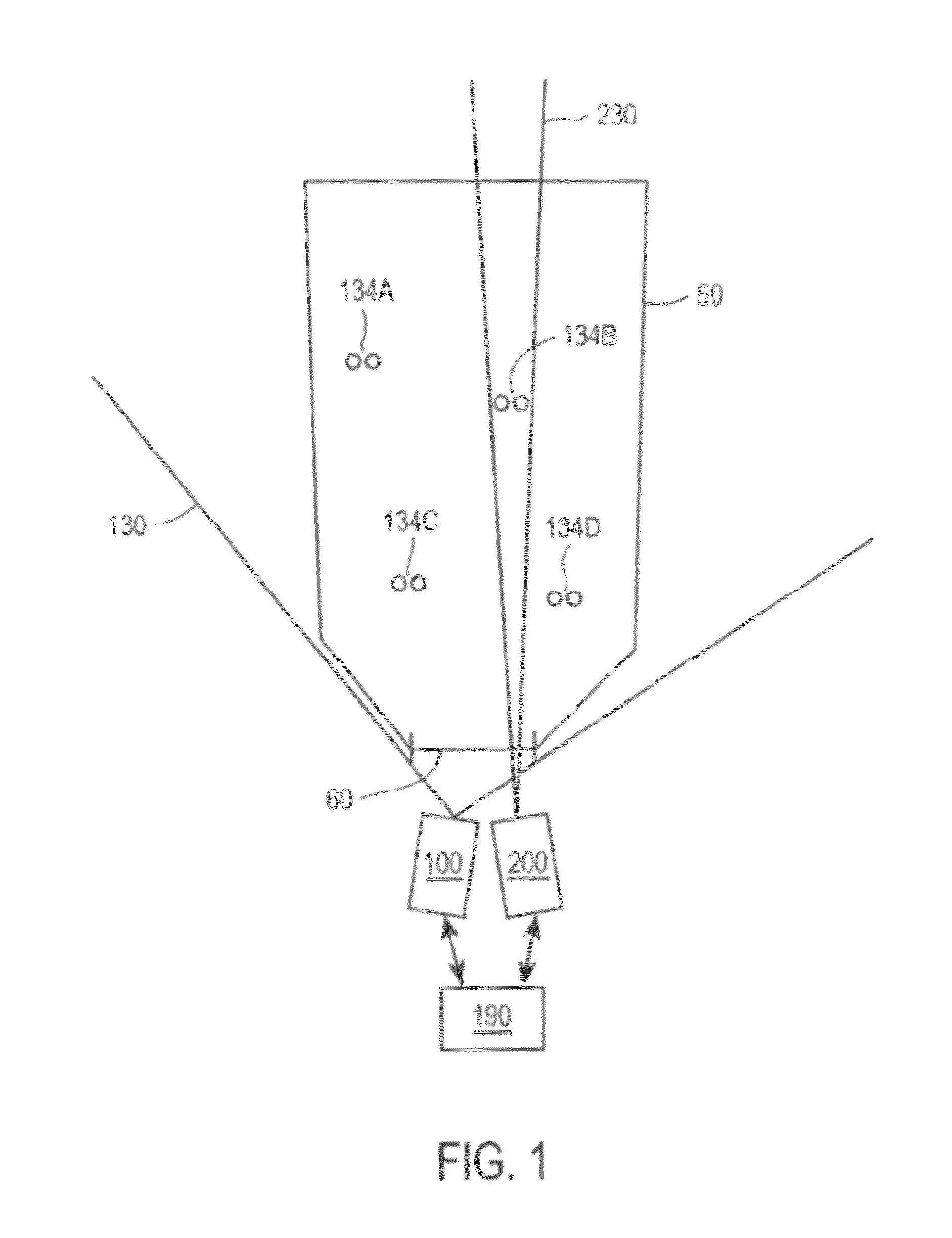
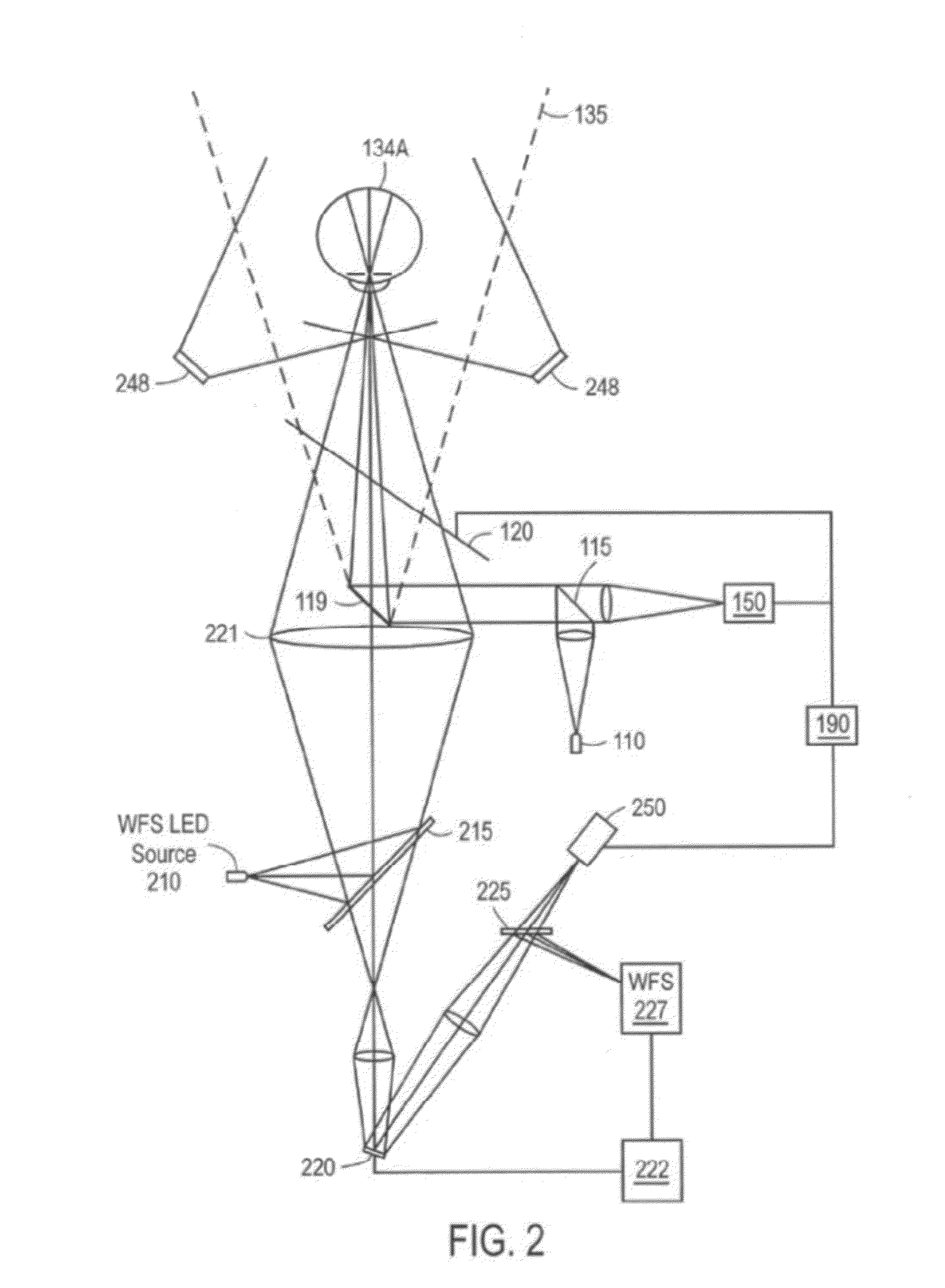
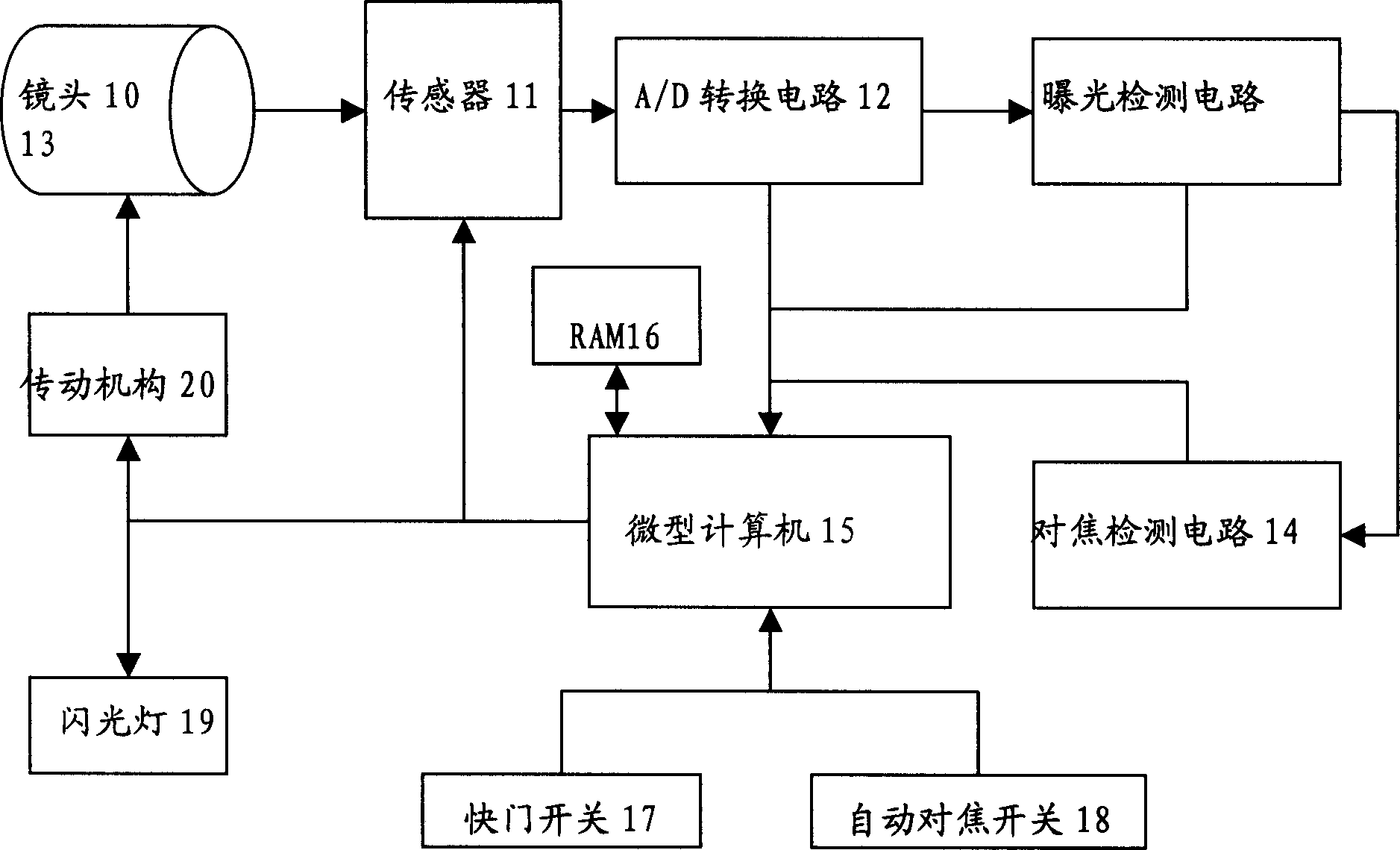
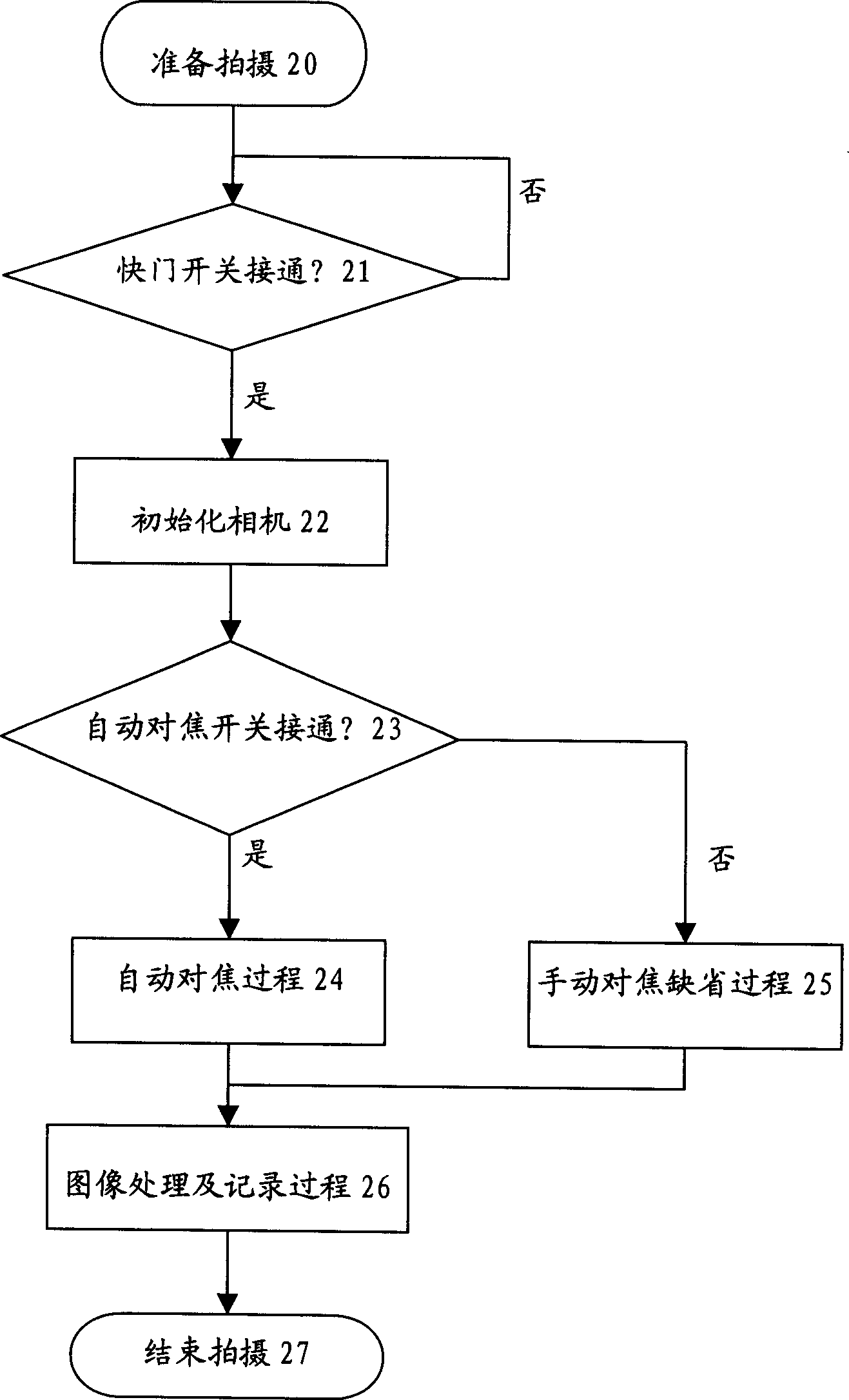
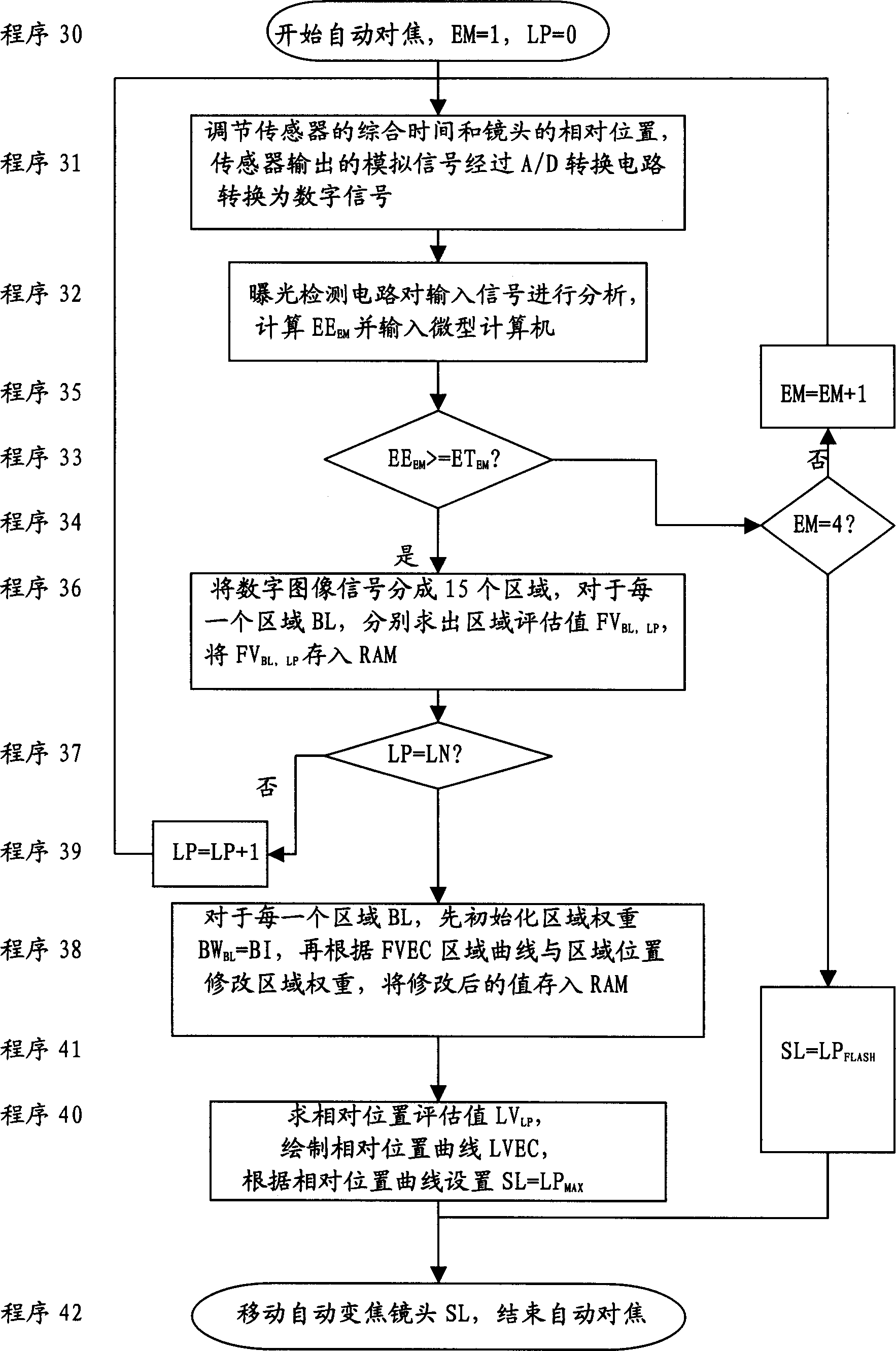
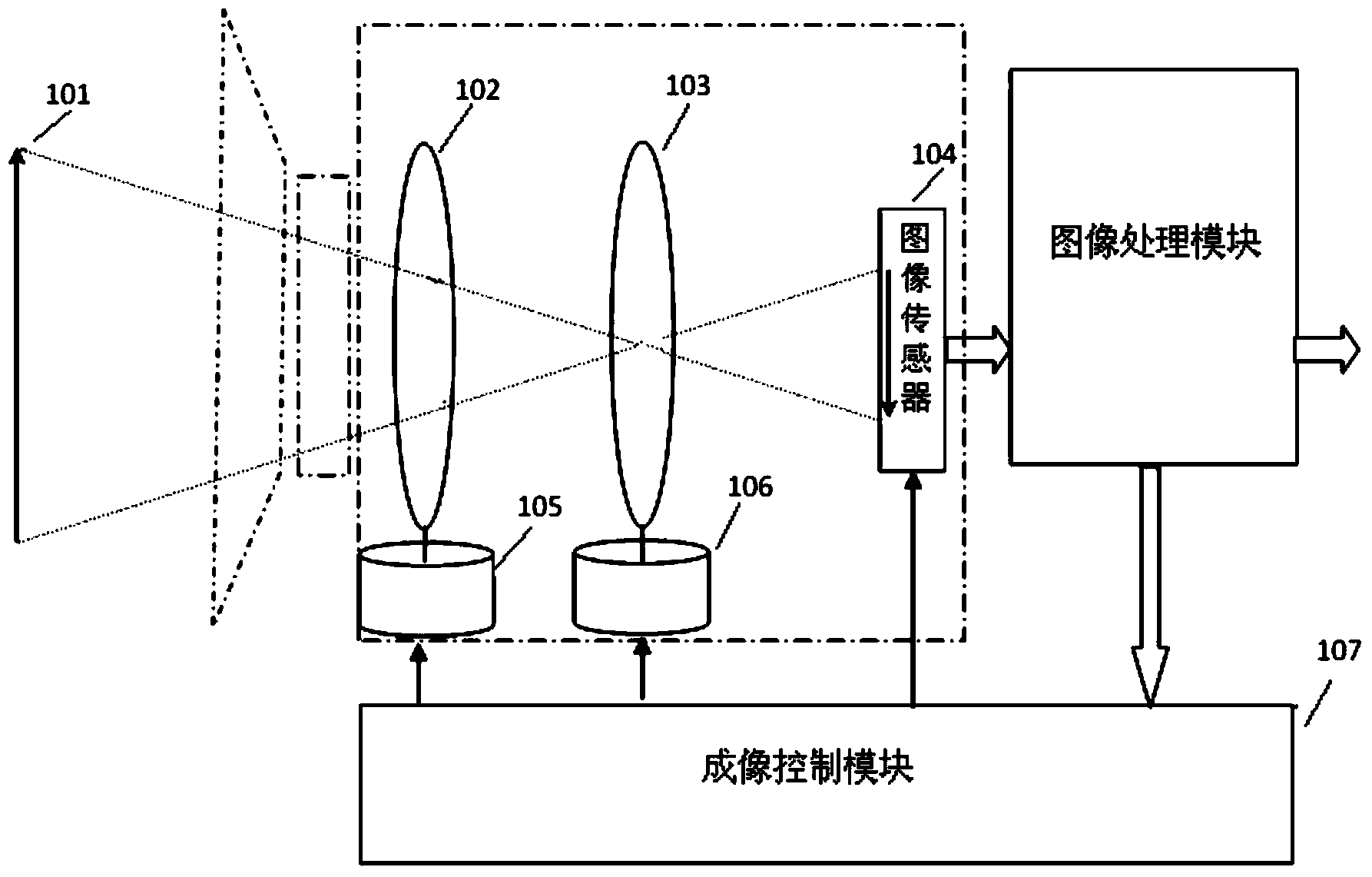
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1660 results about "Object distance" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
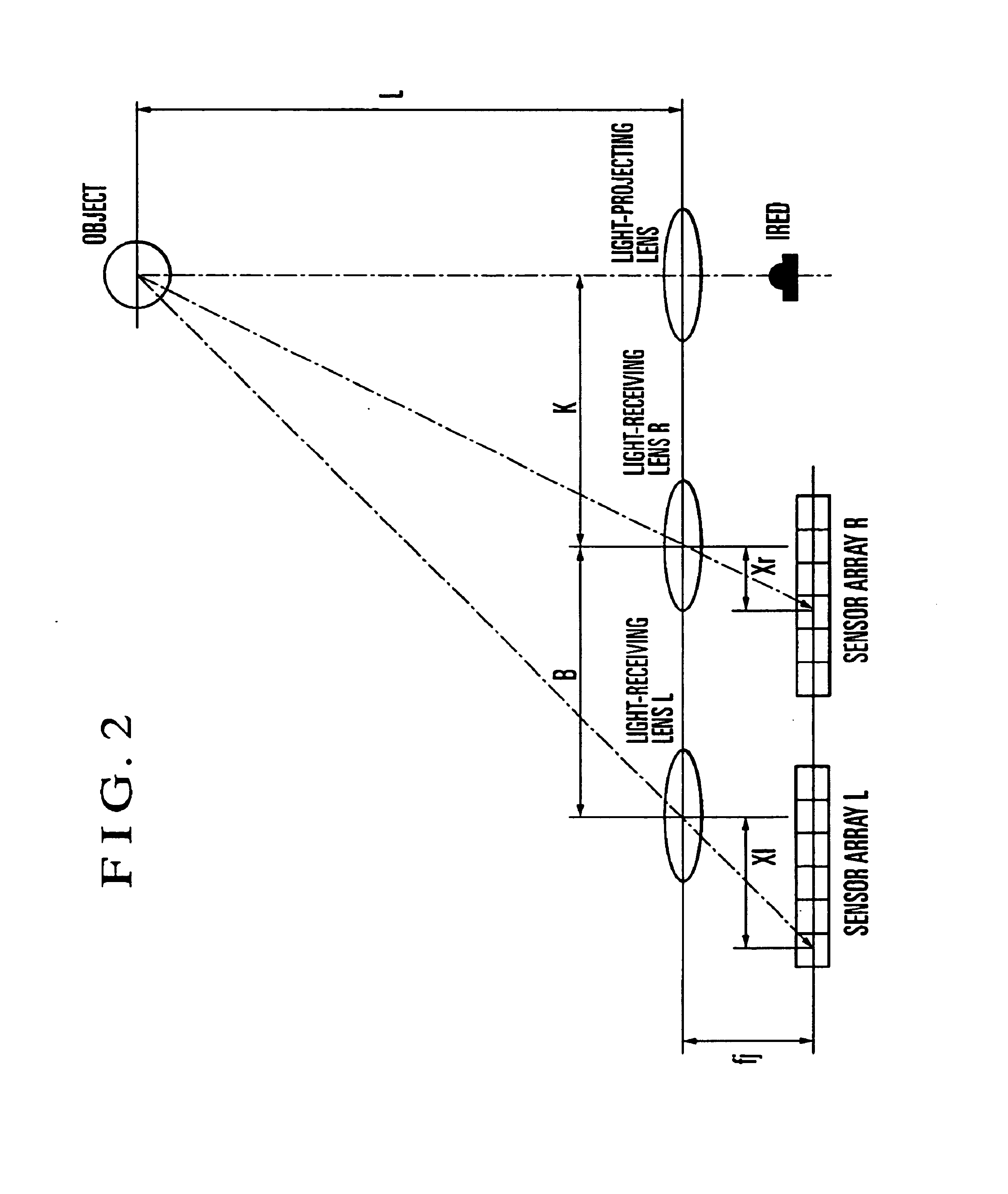
Object-film distance. About. Object-film distance (OFD) is the distance between the object (i.e. patient, phantom) and the film; the shorter the distance the sharper the image and the less the magnification.
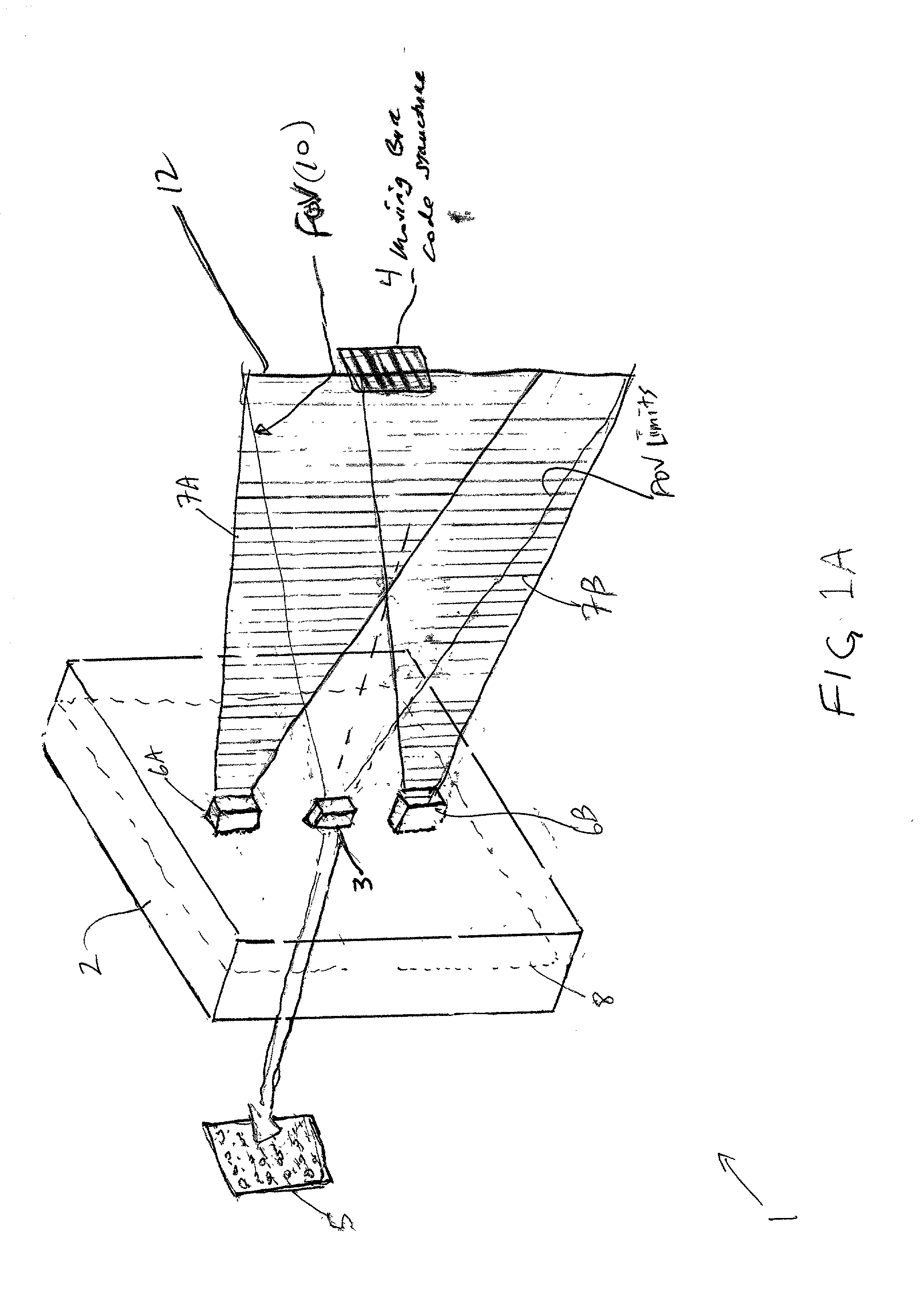
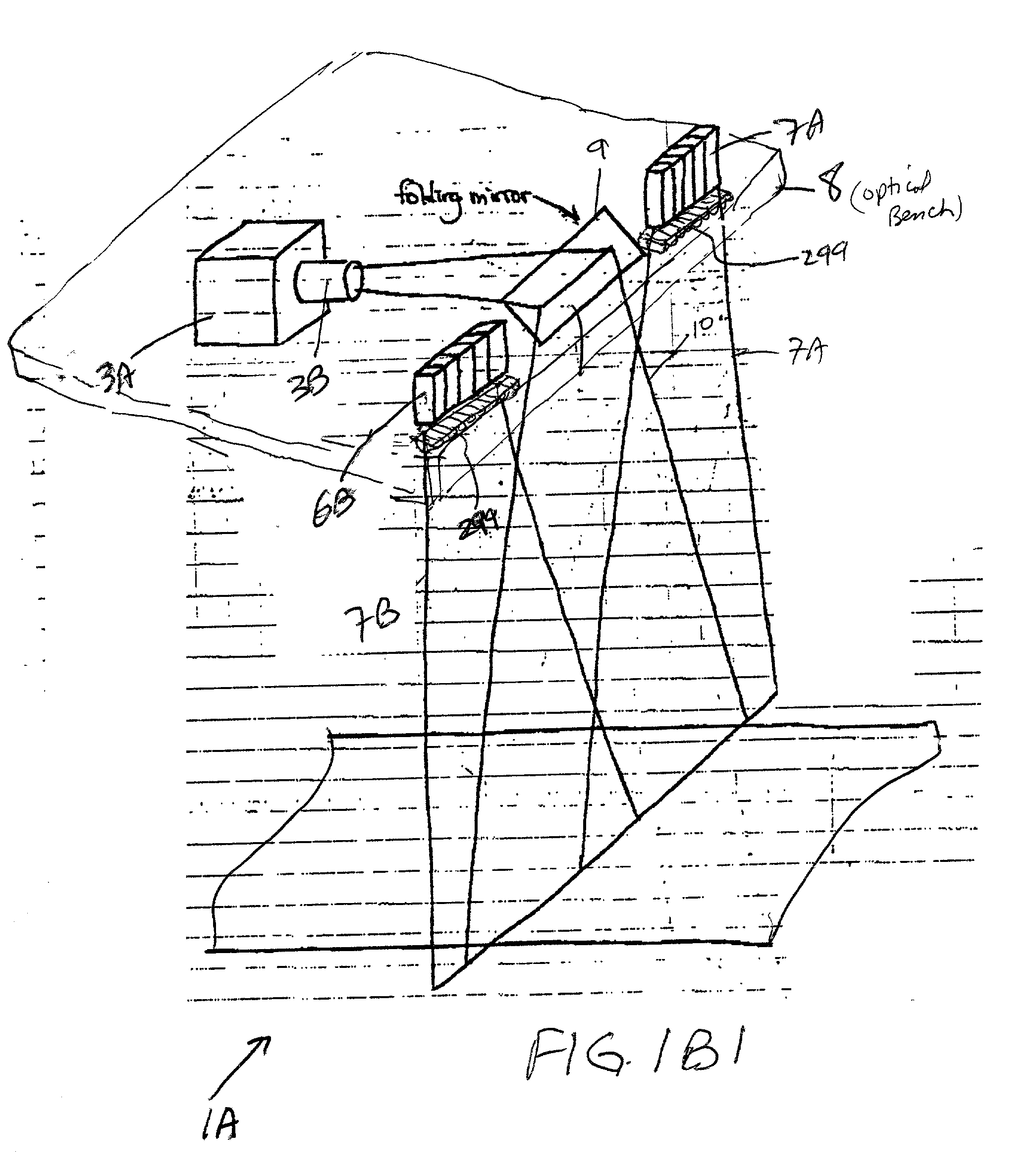
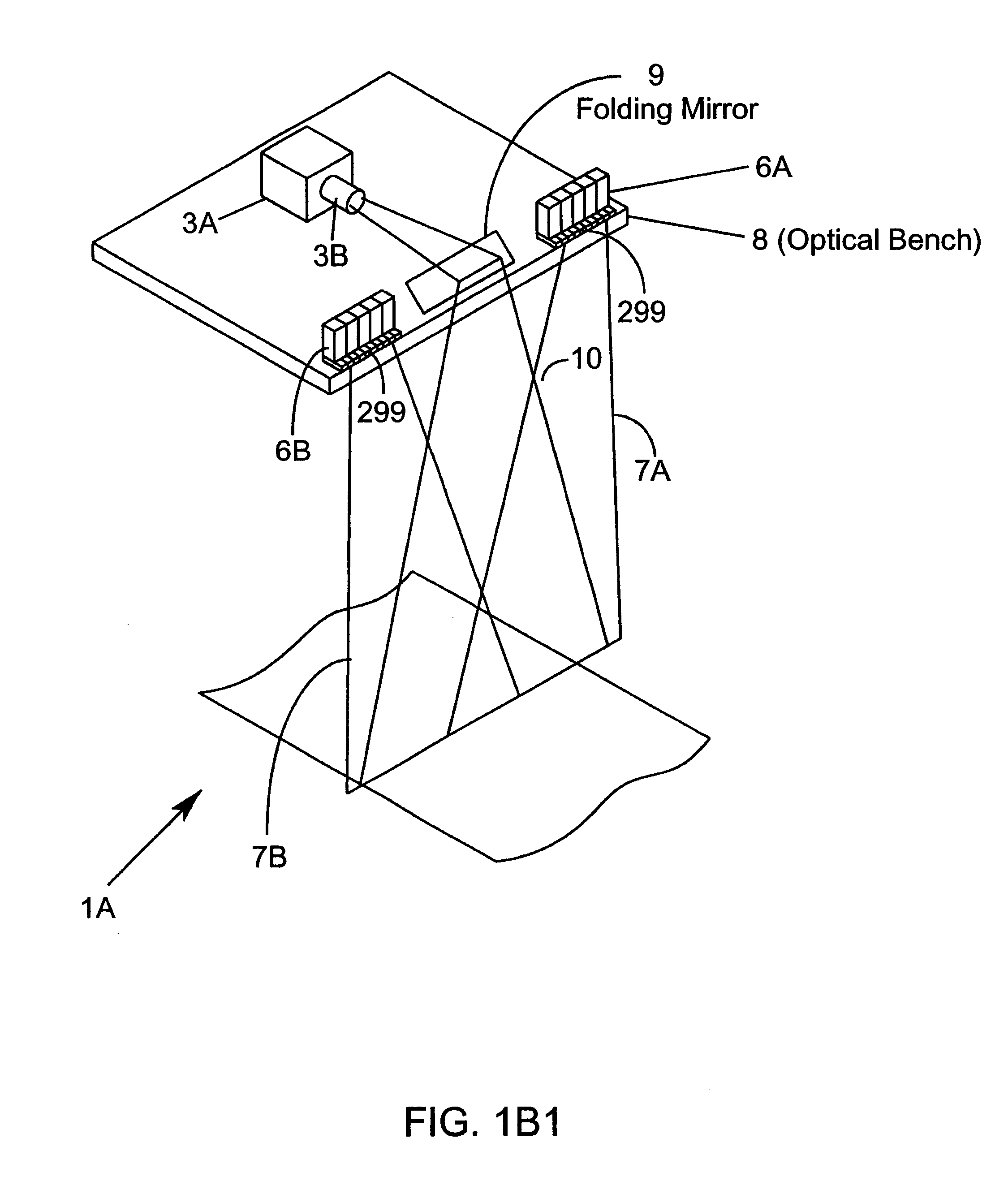
Stereoscopic Panoramic imaging system
InactiveUS20080298674A1Minimizes hyperstereoMinimizes hypostereo visual effect upon reproductionTelevision system detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionField of viewComputer science
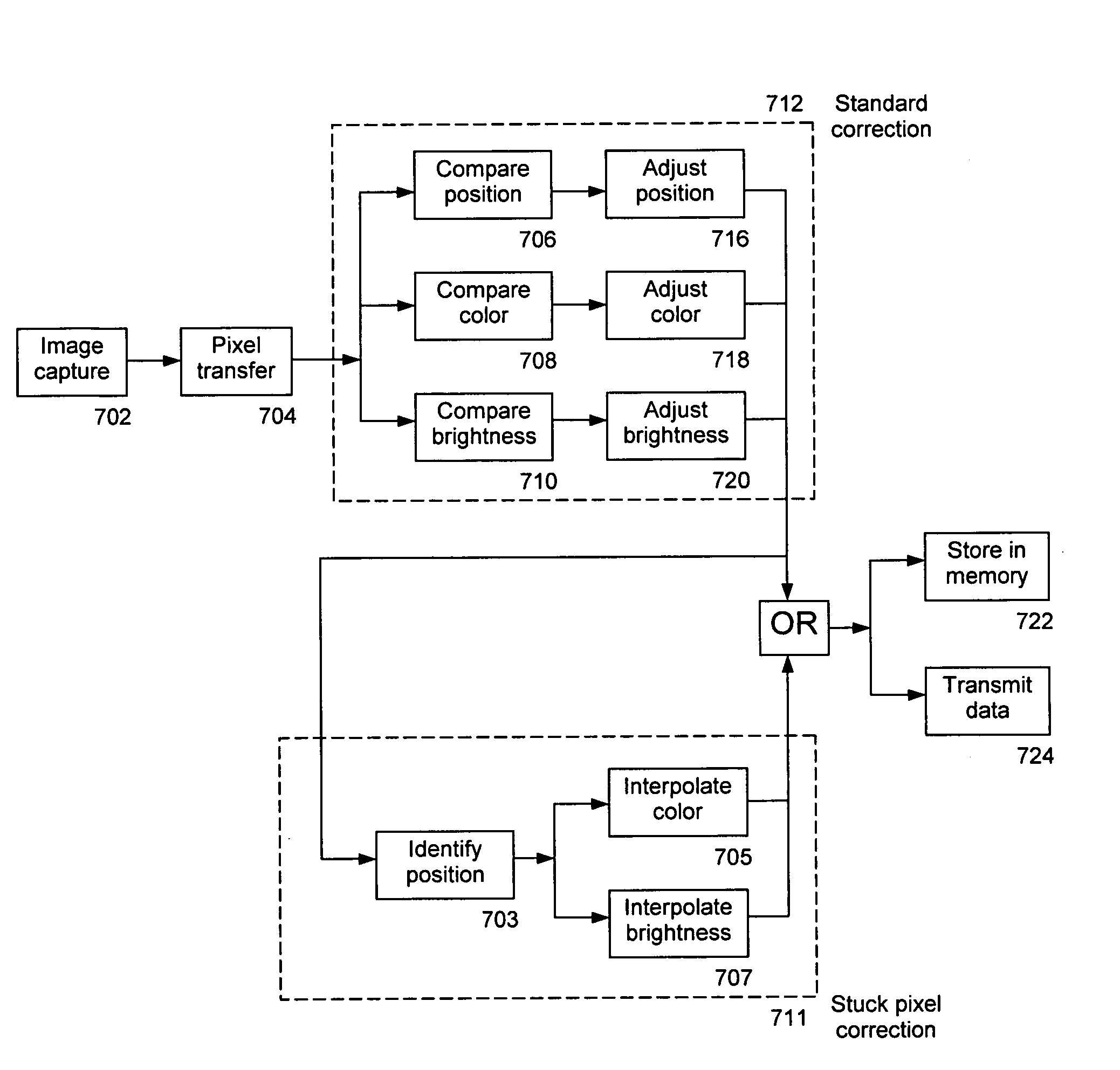
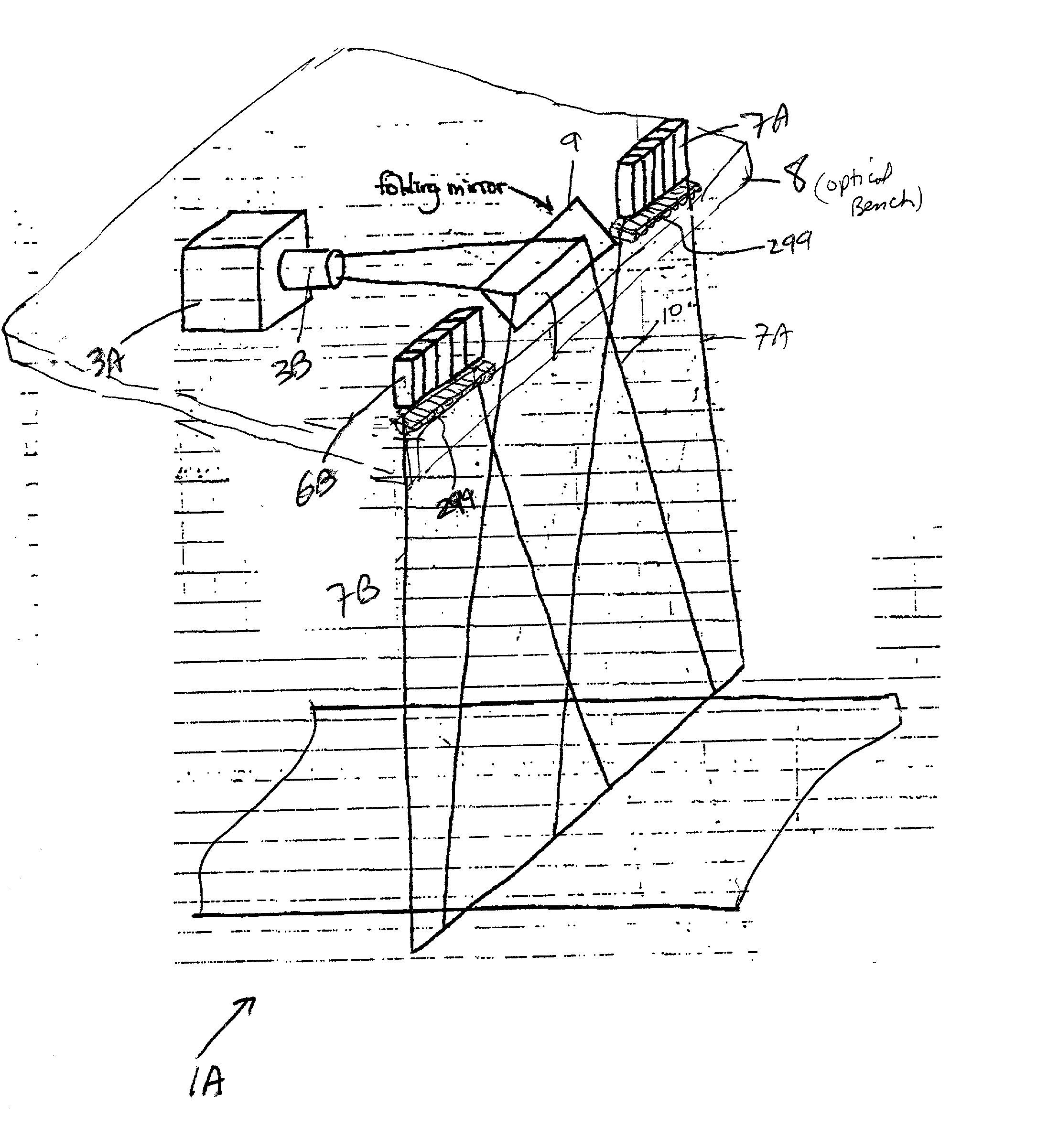
An imaging system for producing stereoscopic panoramic images using multiple coplanar pairs of image capture devices with overlapping fields of view held in a rigid structural frame for long term calibration maintenance. Pixels are dynamically adjusted within the imaging system for position, color, brightness, aspect ratio, lens imperfections, imaging chip variations and any other imaging system shortcomings that are identified during calibration processes. Correction of pixel information is implemented in various combinations of hardware and software. Corrected image data is then available for storage or display or for separate data processing actions such as object distance or volume calculations.
Owner:IMAGE MASTERS
Object Distance Deriving Device
InactiveUS20100103259A1Accurately derivedControl lengthOptical rangefindersColor television detailsHigh resolution imageImage capture
An object distance deriving device comprises: a compound-eye imaging device having imaging units with optical lenses randomly arranged for the respective imaging units; and a distance calculation unit to calculate an object distance using images captured by the compound-eye imaging device. The distance calculation unit: sets temporary distances z (S1); calculates an imaging process matrix [Hz] according to a temporary distance z (S2); estimates a high-resolution image by super-resolution processing using the imaging process matrix [Hz] (S3); uses the estimated high-resolution image to calculate an evaluation value distribution E for evaluating the temporary distance z (S4); repeats steps S2 to S4 for all temporary distances z (S5); and determines, as an object distance, one temporary distance z giving a minimum evaluation value in the evaluation value distributions E. This makes it possible to accurately derive the object distance even if the baseline length of the compound-eye imaging device is limited.
Owner:FUNAI ELECTRIC CO LTD +1
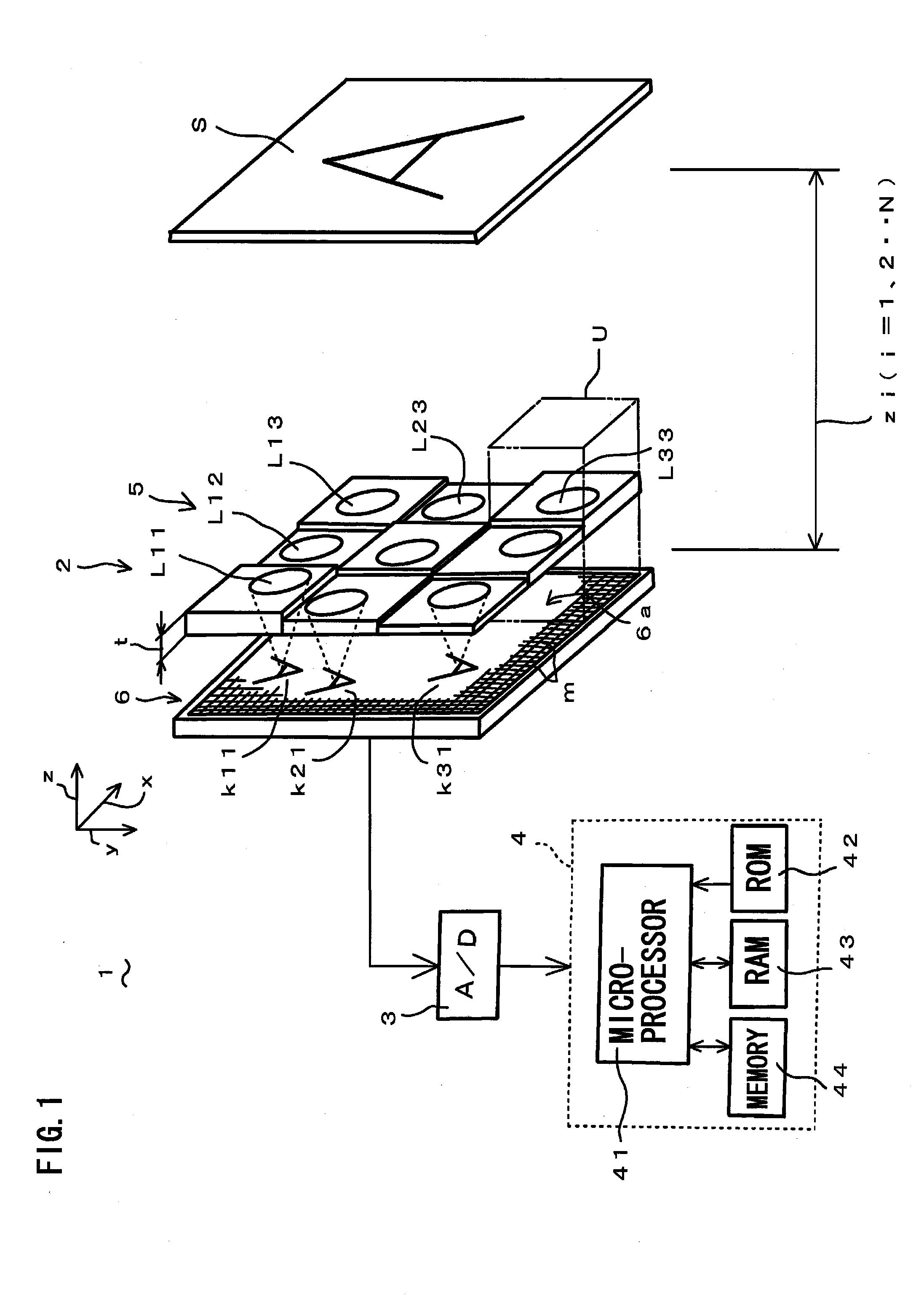
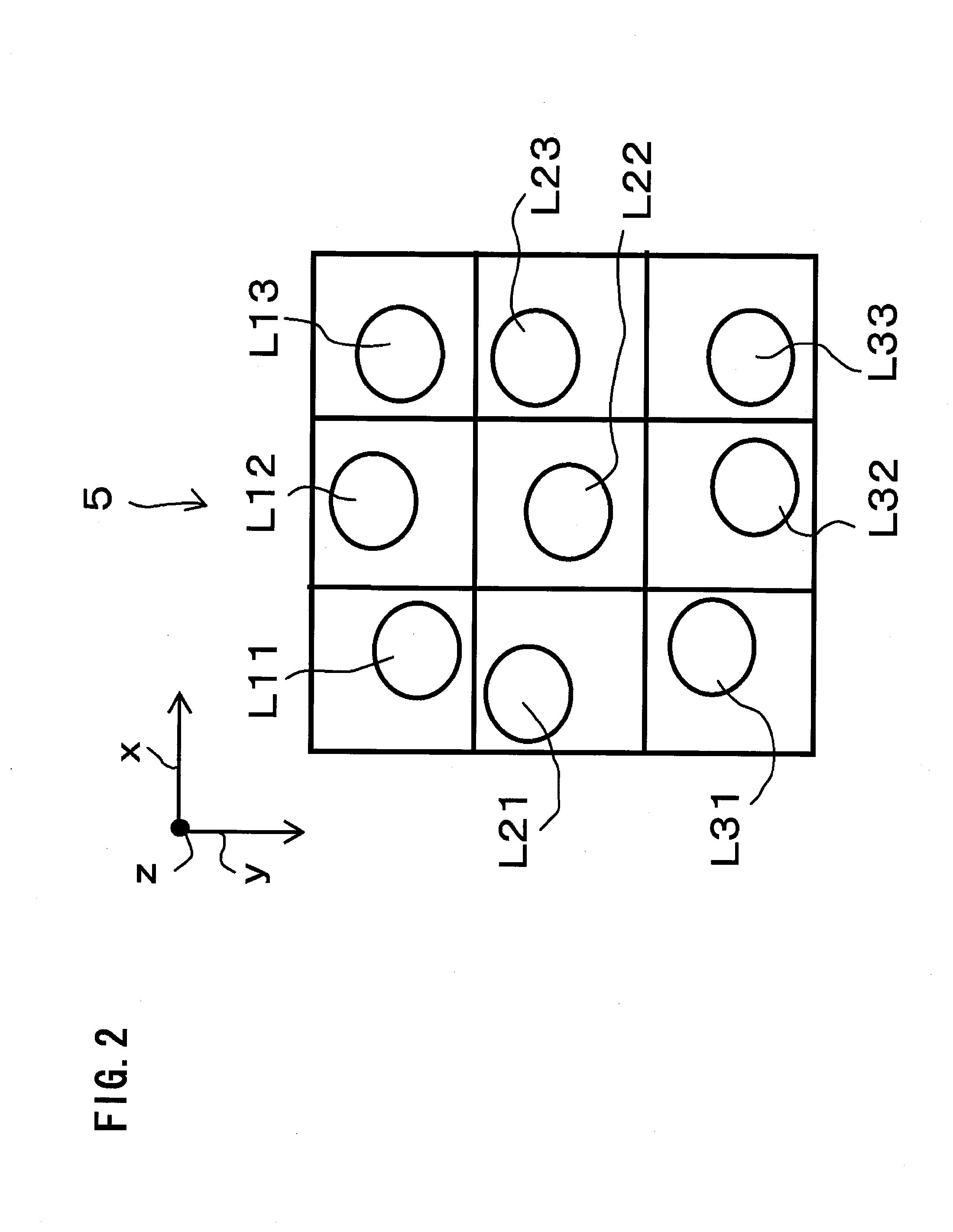
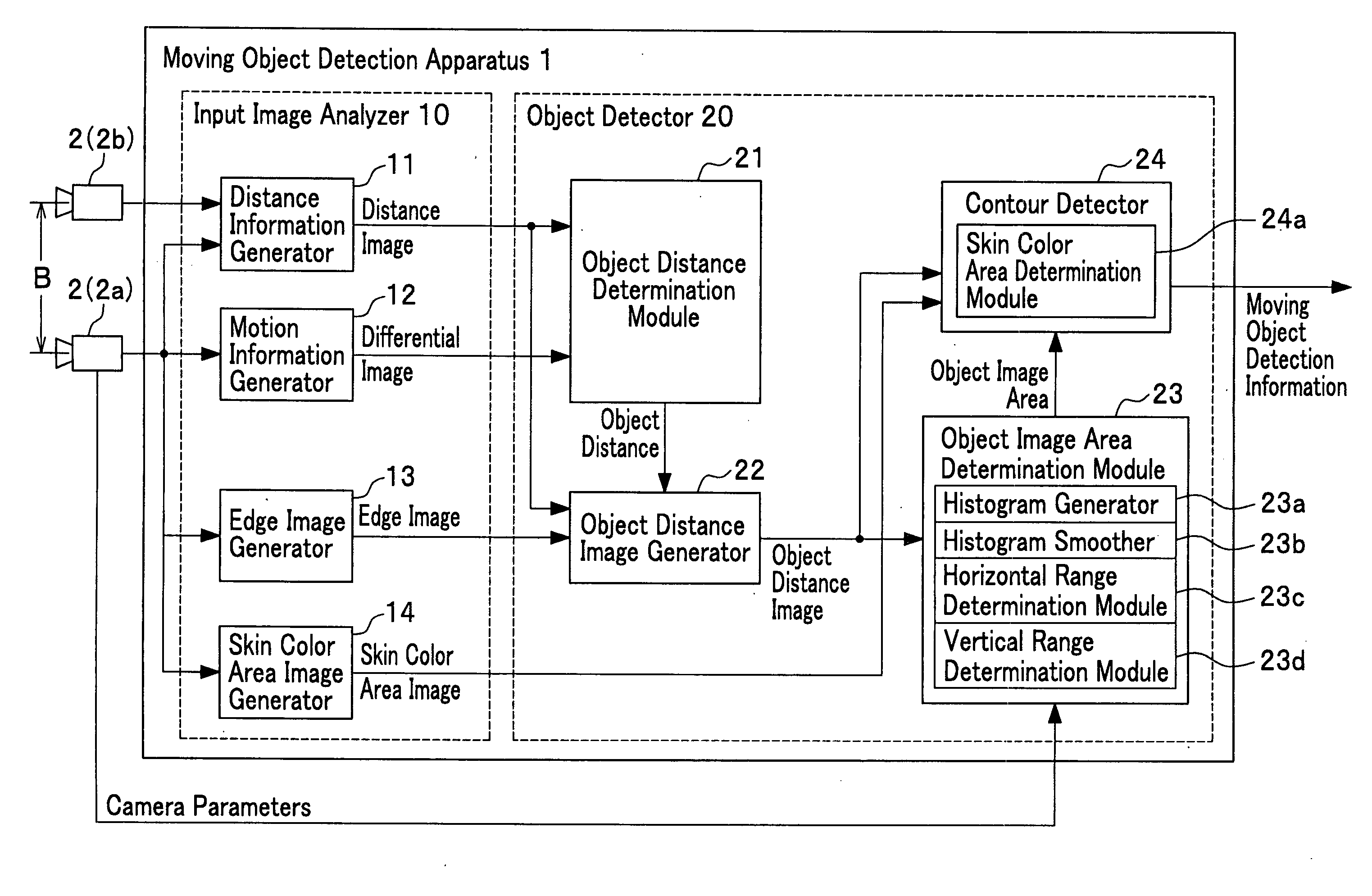
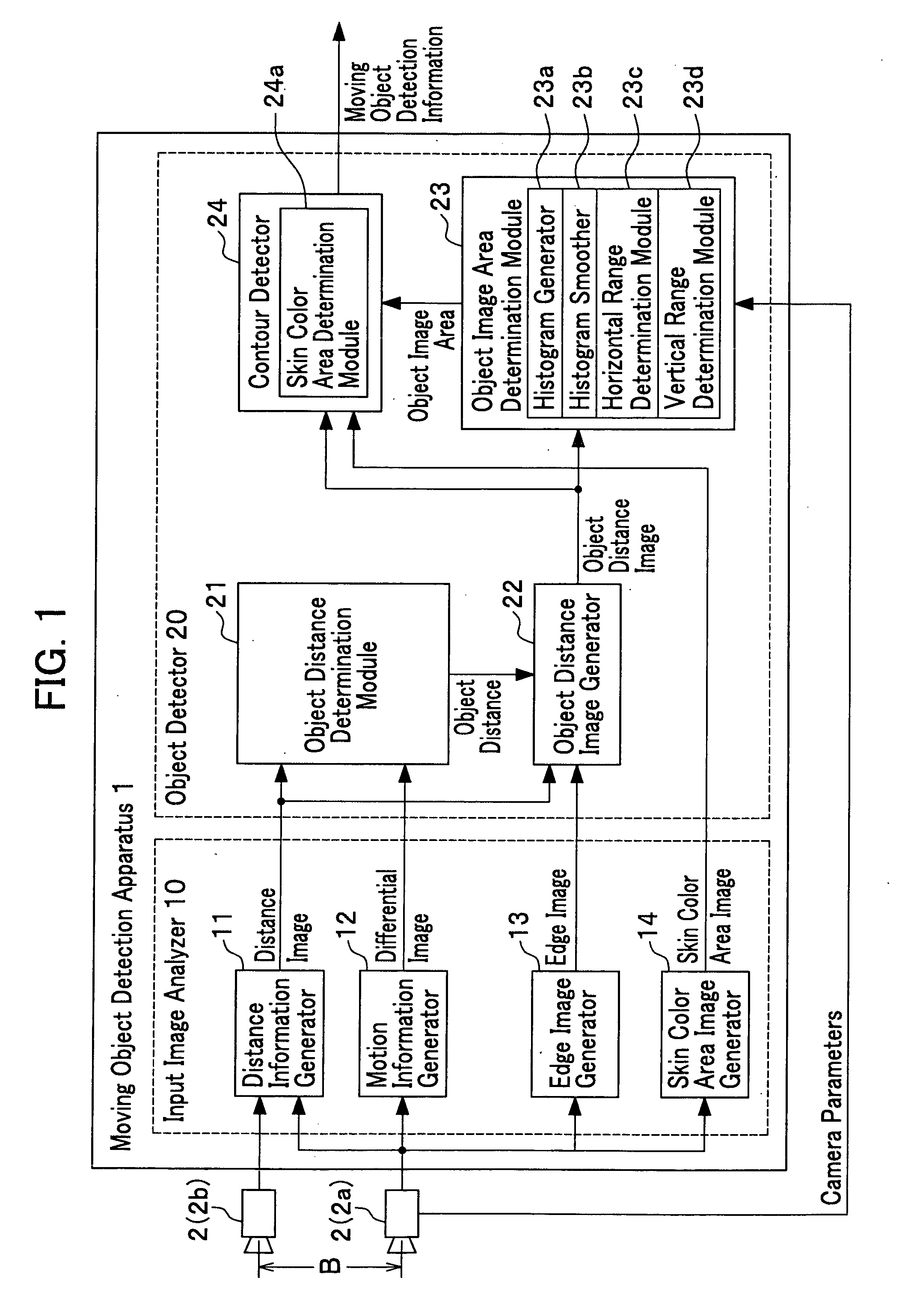
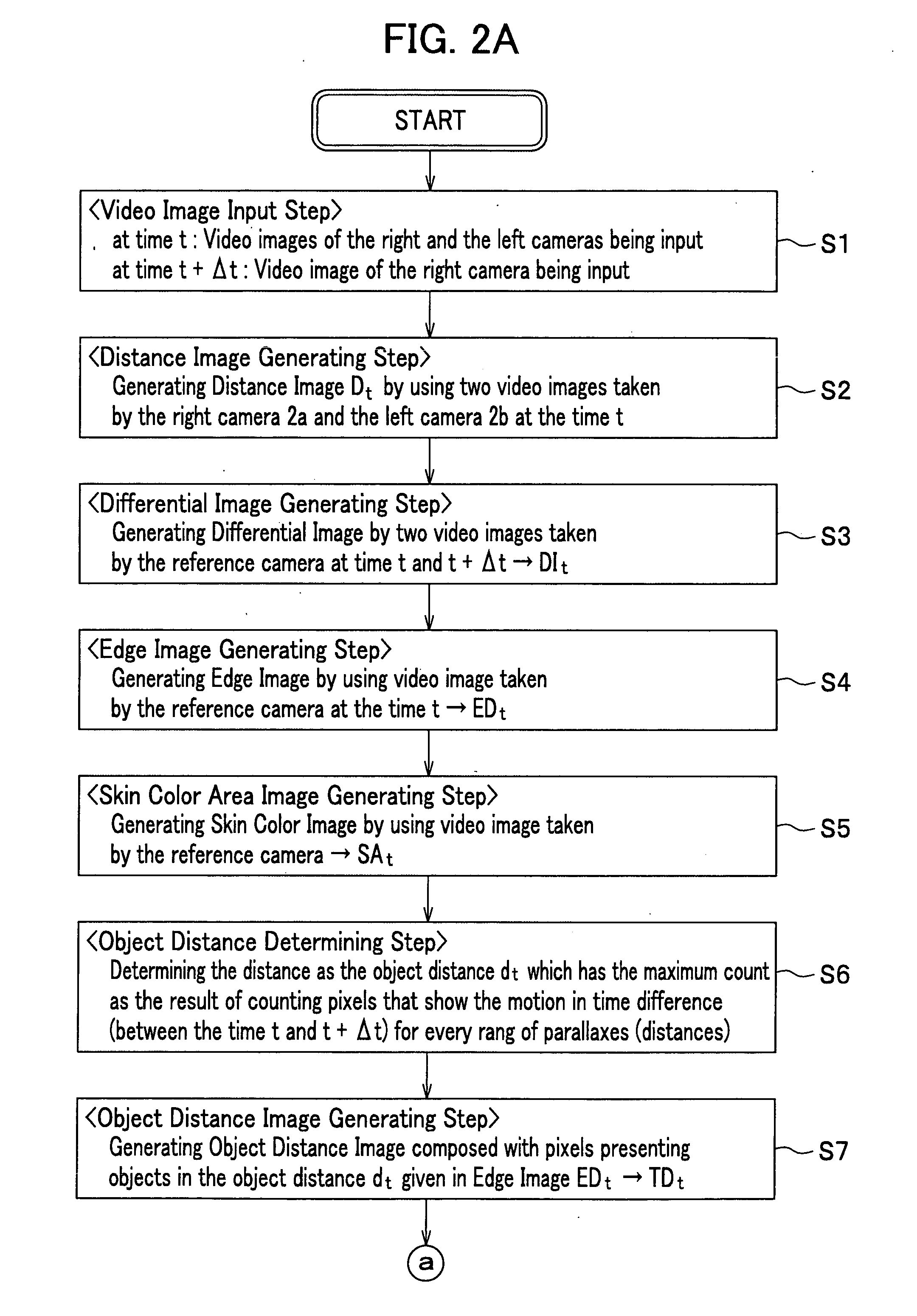
Apparatus, method and program for moving object detection
ActiveUS20050147277A1Improve accuracyEasy determine symmetryImage enhancementImage analysisObject motionVideo image
The present invention detects a moving object by generating the distance information of the moving object, detecting the object motion, determining the object distance, detecting the object image area and the object contour from the video image that includes the object image and contour, and provides a moving object detection apparatus to carry out such detection as well as detecting a contour of the specific moving object by detecting the center of the moving object in high precision.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
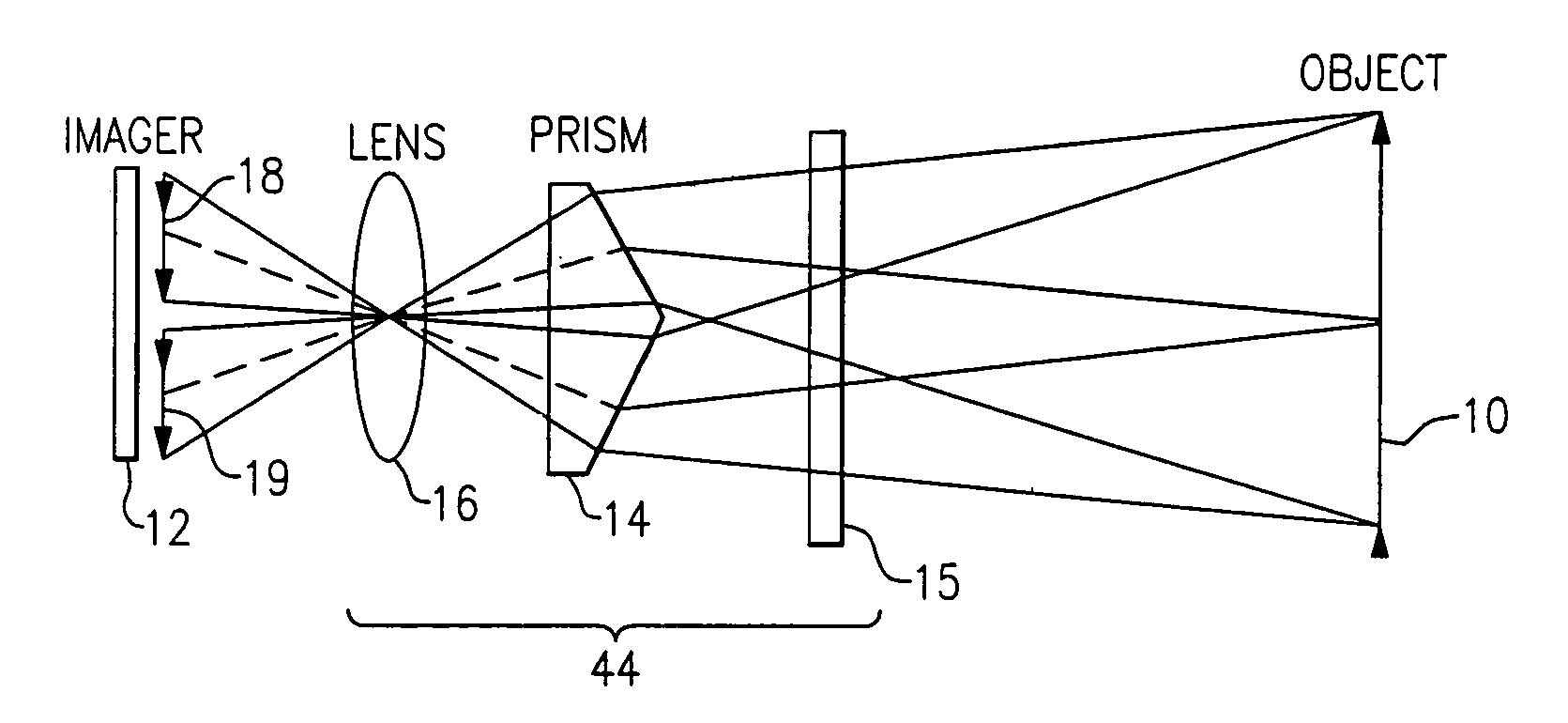
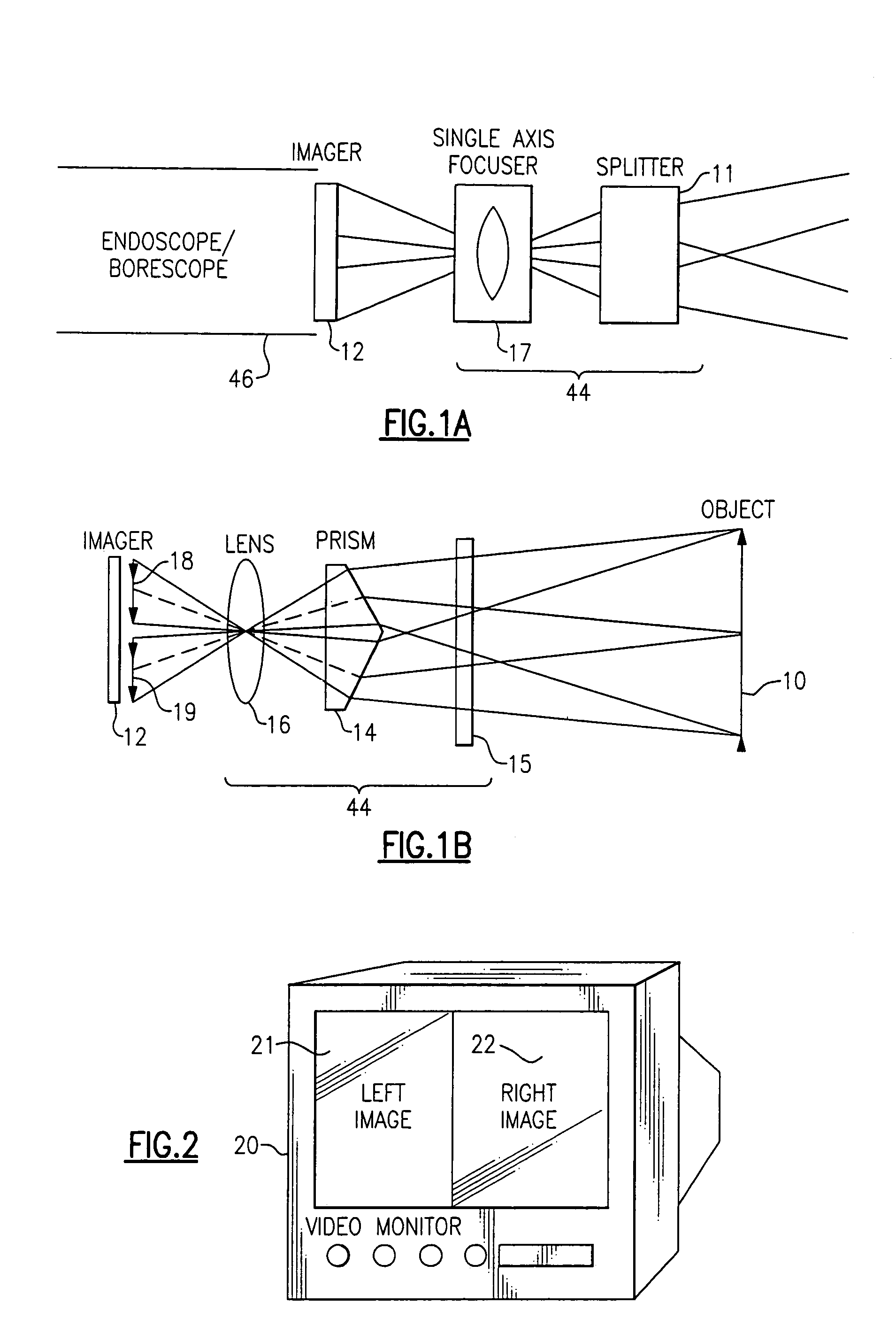
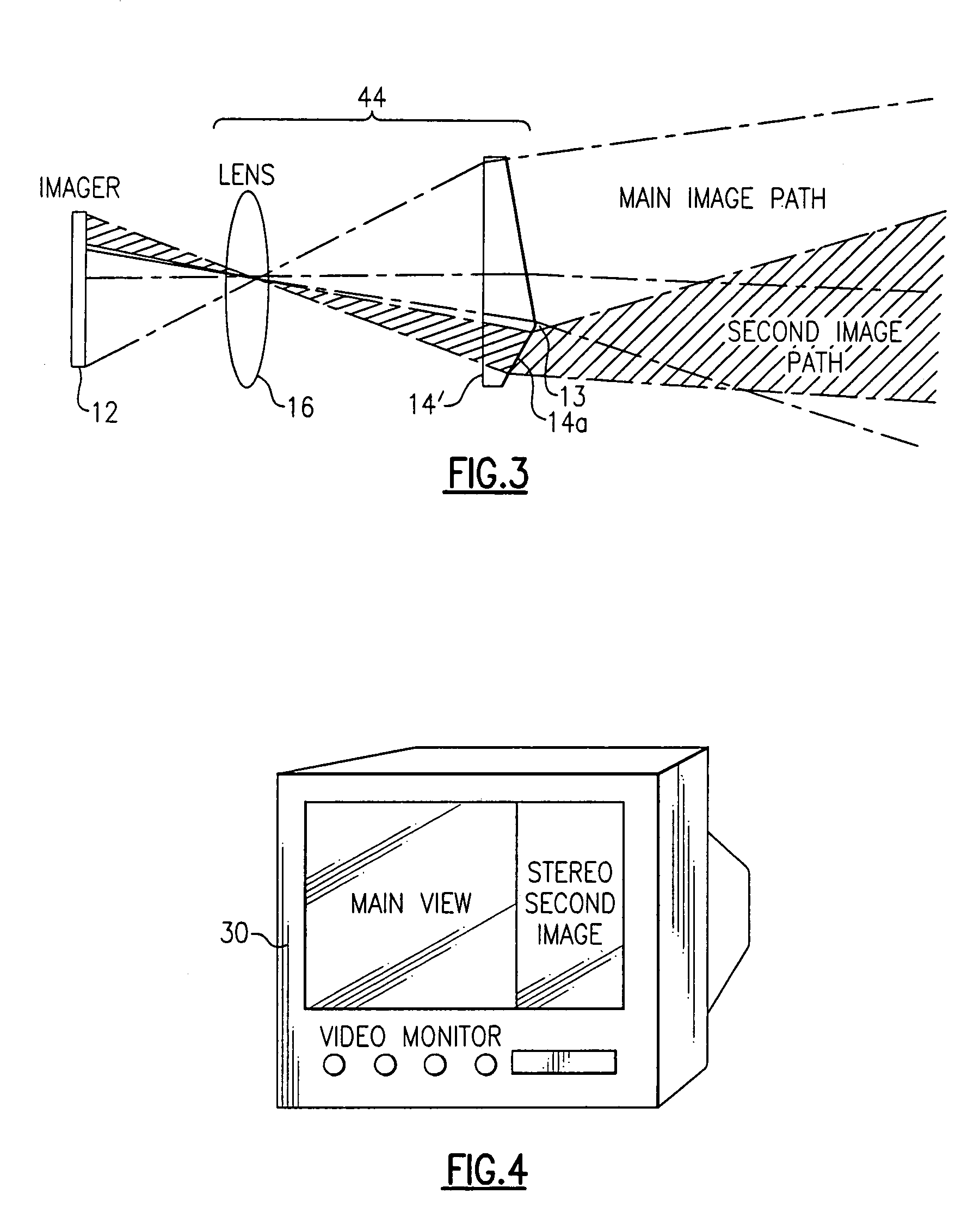
Stereo-measurement borescope with 3-D viewing
Two stereo images are created by splitting a single image into two images using a field of view dividing splitter. The two images can be displayed side by side so that they can be viewed directly using stereopticon technology, heads-up display, or other 3-D display technology, or they can be separated for individual eye viewing. The two images focus on one imager such that the right image appears on the right side of the monitor and the left image appears on the left side of the monitor. The view of the images is aimed to converge at a given object distance such that the views overlap 100% at the object distance. Measurement is done with at least one onscreen cursor.
Owner:GE INSPECTION TECH LP
Stereo camera
InactiveUS7190389B1Quality improvementEasy to operateTelevision system detailsPrintersOptical axisStereo cameras
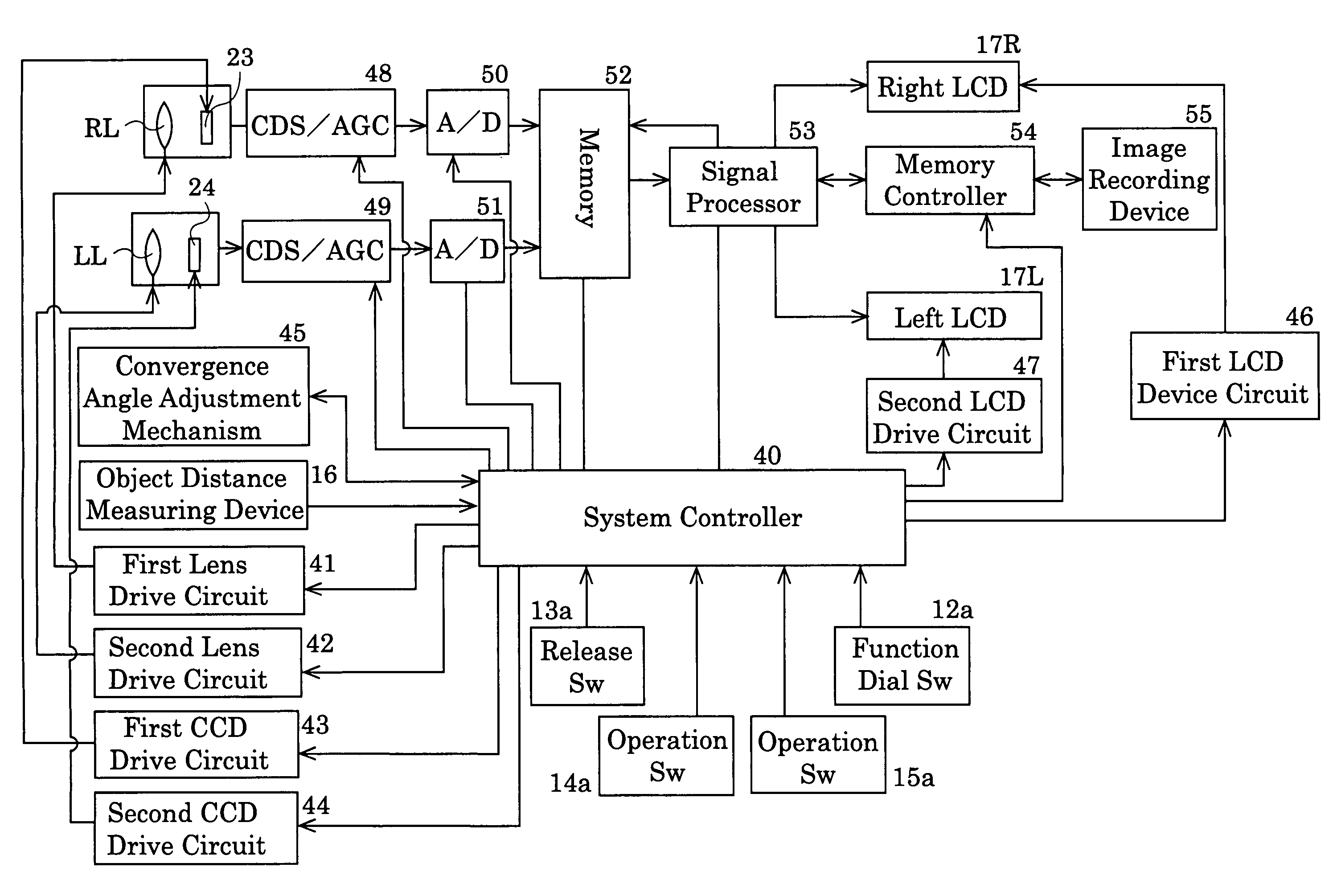
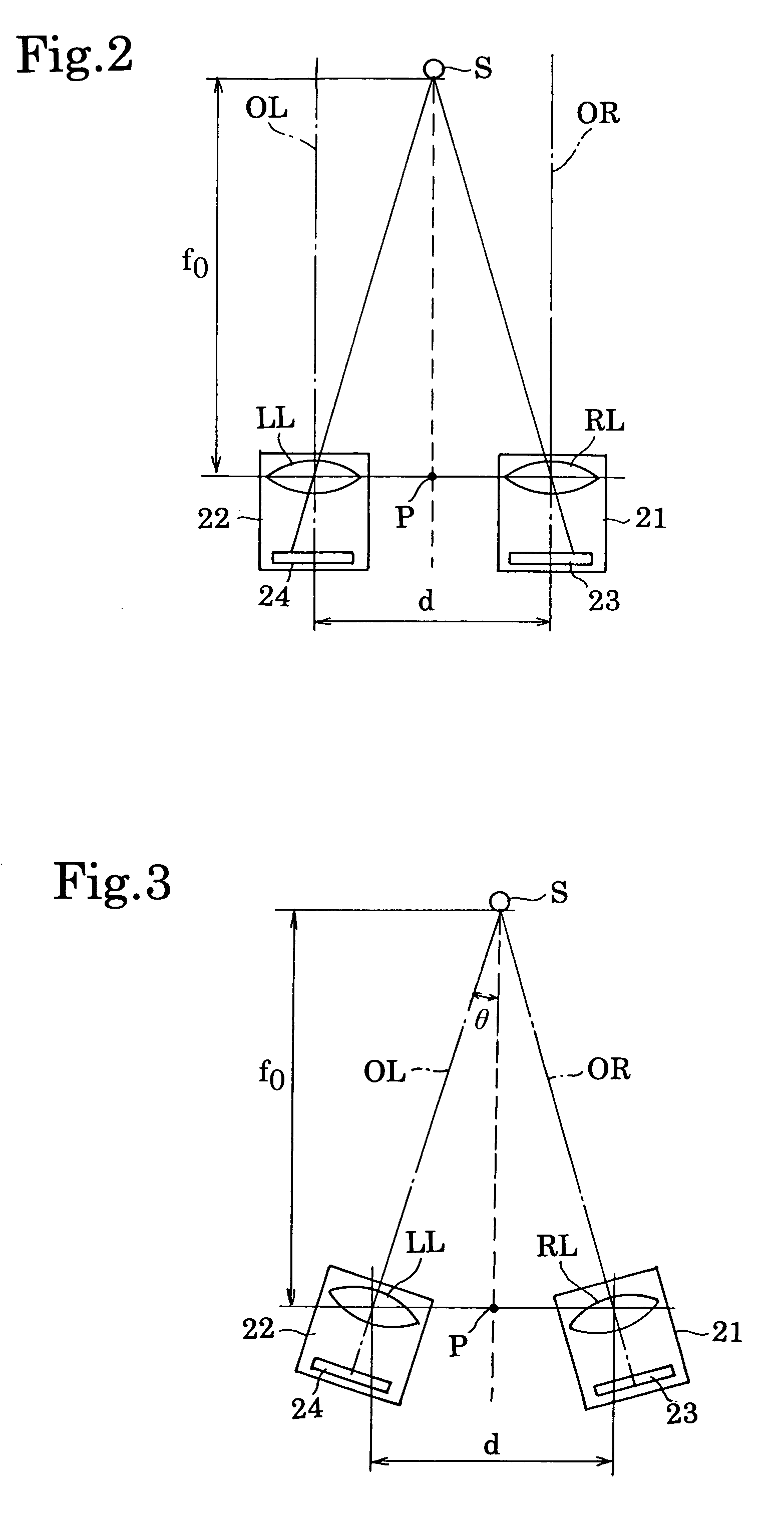
A stereo camera includes a pair of photographing optical systems arranged in a common plane so that a common photographing coverage occurs between a pair of photographing areas taken by the pair of photographing optical systems, an object distance measuring device, a convergence angle adjustment mechanism adapted to vary an angle of convergence defined by, and between, the optical axes of the pair of photographing optical systems, so as to adjust an amount of common photographic coverage of the pair of photographing optical systems, and a controller adapted to control the convergence angle adjustment mechanism in accordance with object distance data obtained by the object distance measuring device.
Owner:RICOH IMAGING COMPANY
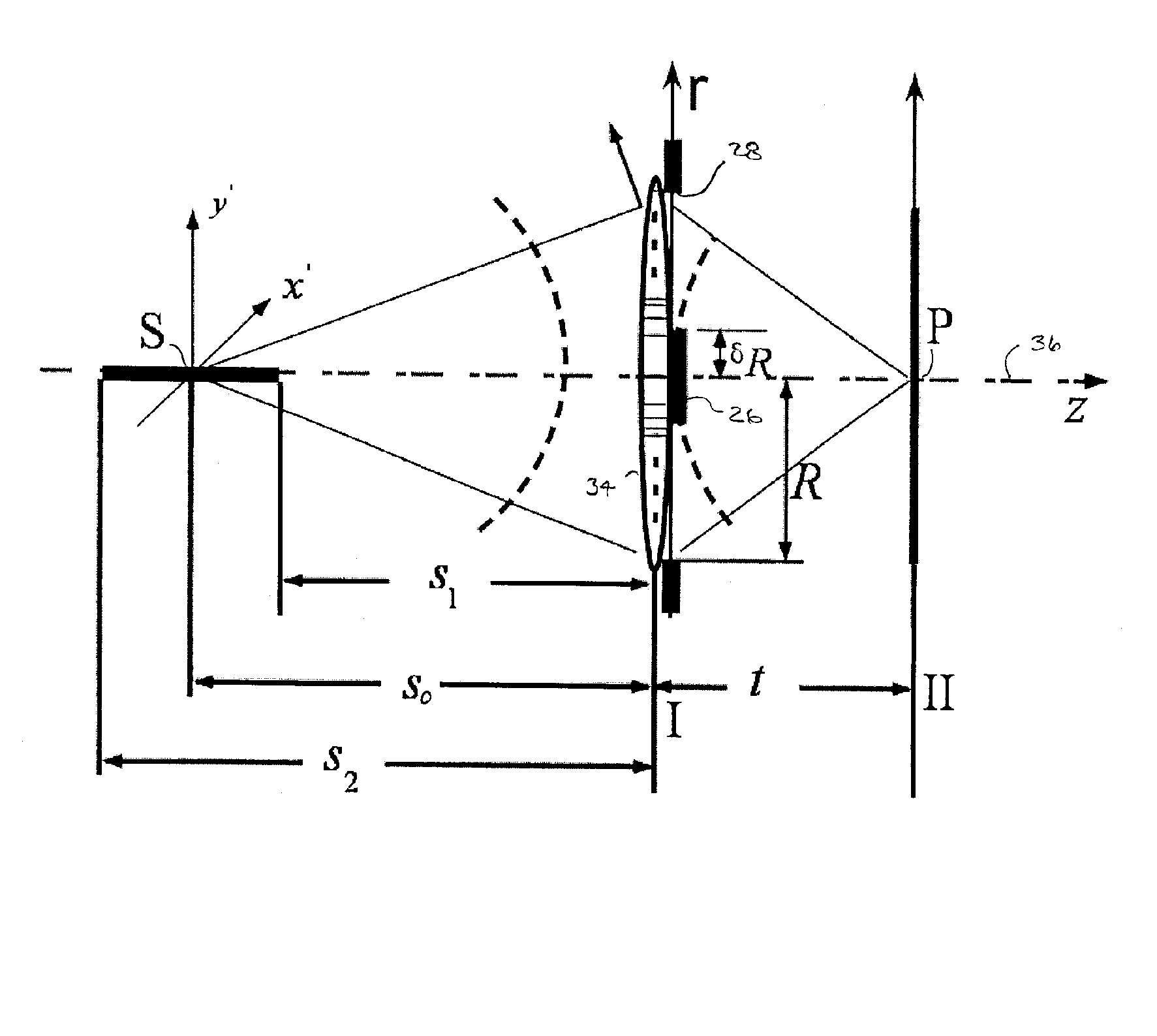
Extended depth of field using a multi-focal length lens with a controlled range of spherical aberration and a centrally obscured aperture
ActiveUS7336430B2Easy to manufactureUniform responseImage enhancementTelevision system detailsIntermediate imageImaging quality
An extended depth of field is achieved by a computational imaging system that combines a multifocal imaging subsystem for producing a purposefully blurred intermediate image with a digital processing subsystem for producing a recovered image having an extended depth of field. The multifocal imaging system preferably exhibits spherical aberration as the dominant feature of the purposeful blur. A central obscuration of the multifocal imaging subsystem renders point-spread functions of object points more uniform over a range of object distances. An iterative digital deconvolution algorithm for converting the intermediate image into the recovered image contains a metric parameter that speeds convergence, avoids stagnations, and enhances image quality.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
Short-range frequency-modulation continuous wave FMCW radar anti-interference method
ActiveCN101089653AWork reliablyEasy to implementRadio wave reradiation/reflectionContinuous waveFrequency modulation
An anti-interfering method of short-range FMCW radar includes designing a set of pseudo-random code according to occasion of radar, distributing different pseudo-random code to different radar operated at different area, applying different pseudo-random code to modulate frequency start-point of FM emission signal for the same radar on each cycle, making frequency-mixture on received echo signal by utilizing emission signal, using filter to filter off interference signal and applying FM signal processing means to treat reserved usable signal for obtaining object distance and speed information in high resolution.
Owner:南京精益安防系统科技有限公司
Extended depth of field using a multi-focal length lens with a controlled range of spherical aberration and a centrally obscured aperture
ActiveUS20060050409A1Increase contrastReduce image contrastImage enhancementTelevision system detailsPoint spreadIntermediate image
An extended depth of field is achieved by a computational imaging system that combines a multifocal imaging subsystem for producing a purposefully blurred intermediate image with a digital processing subsystem for producing a recovered image having an extended depth of field. The multifocal imaging system preferably exhibits spherical aberration as the dominant feature of the purposeful blur. A central obscuration of the multifocal imaging subsystem renders point-spread functions of object points more uniform over a range of object distances. An iterative digital deconvolution algorithm for converting the intermediate image into the recovered image contains a metric parameter that speeds convergence, avoids stagnations, and enhances image quality.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
Locating and tracking method and apparatus based on sound source array
InactiveCN104991573AImprove accuracyPosition fixationControl using feedbackSound sourcesArrival time
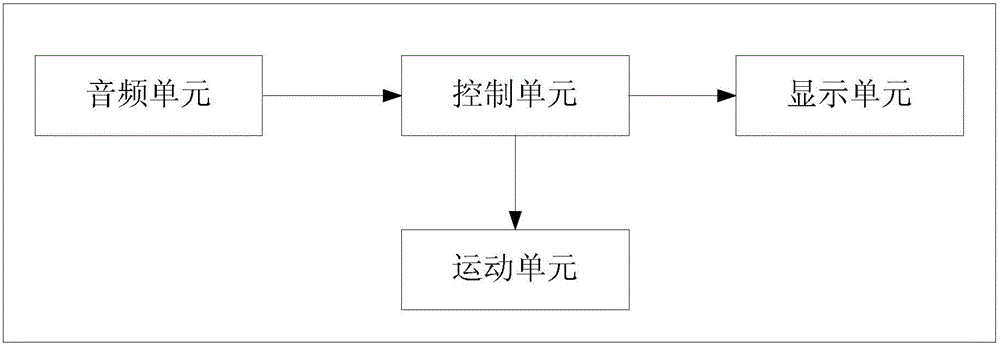
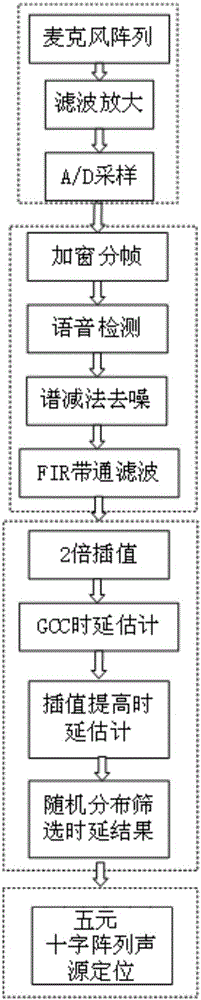
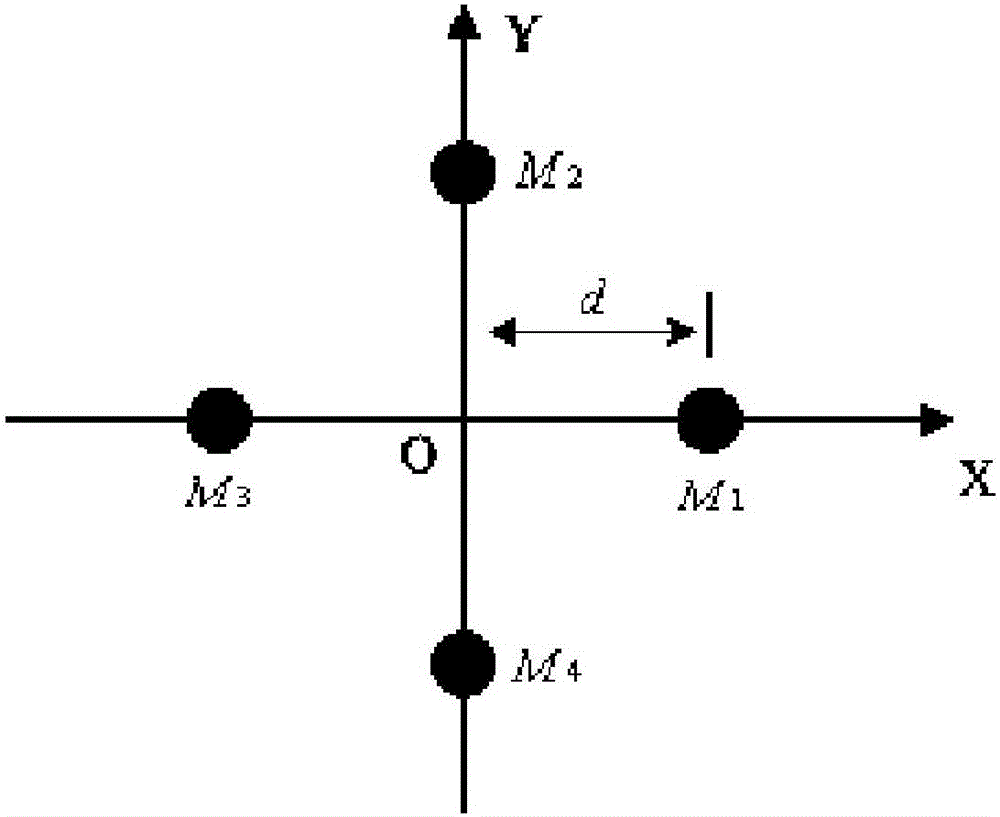
The present invention discloses a locating and tracking method based on a sound source array, comprising the following steps: S1, acquiring on-site sound through a quintuple microphone array, and pre-processing a sound signal acquired by each microphone in the quintuple microphone array to obtain an audio signal; S2, performing sound source locating for the audio signals according to arrival time delay of the audio signals between the microphones and positional information of the microphone array, so as to calculate a pitch angle, an azimuth angle and an object distance; and S3, moving and turning a locating and tracking apparatus to arrive to a sound source position. The locating and tracking method of the present invention performs related processing for influences of non-gauss noises, coherent noises and indoor reverberation of the sound source on accurate locating, thereby improving accuracy of locating of the sound source.
Owner:北京品创智能科技有限公司
Method of and system for producing digital images of objects with subtantially reduced speckle-noise patterns by illuminating said objects with spatially and/or temporally coherent-reduced planar laser illumination
InactiveUS20020043561A1Reducing speckle-noise patternSemiconductor laser arrangementsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSystems designHand held
Methods of and systems for illuminating objects using planar laser illumination beams having substantially-planar spatial distribution characteristics that extend through the field of view (FOV) of image formation and detection modules employed in such systems. Each planar laser illumination beam is produced from a planar laser illumination beam array (PLIA) comprising an plurality of planar laser illumination modules (PLIMs). Each PLIM comprises a visible laser diode (VLD, a focusing lens, and a cylindrical optical element arranged therewith. The individual planar laser illumination beam components produced from each PLIM are optically combined to produce a composite substantially planar laser illumination beam having substantially uniform power density characteristics over the entire spatial extend thereof and thus the working range of the system. Preferably, each planar laser illumination beam component is focused so that the minimum beam width thereof occurs at a point or plane which is the farthest or maximum object distance at which the system is designed to acquire images, thereby compensating for decreases in the power density of the incident planar laser illumination beam due to the fact that the width of the planar laser illumination beam increases in length for increasing object distances away from the imaging optics. Advanced high-resolution wavefront control methods and devices are disclosed for use with the PLIIM-based systems in order to reduce the power of speckle-noise patterns observed at the image detections thereof. By virtue of the present invention, it is now possible to use both VLDs and high-speed CCD-type image detectors in conveyor, hand-held and hold-under type imaging applications alike, enjoying the advantages and benefits that each such technology has to offer, while avoiding the shortcomings and drawbacks hitherto associated therewith.
Owner:METROLOGIC INSTR
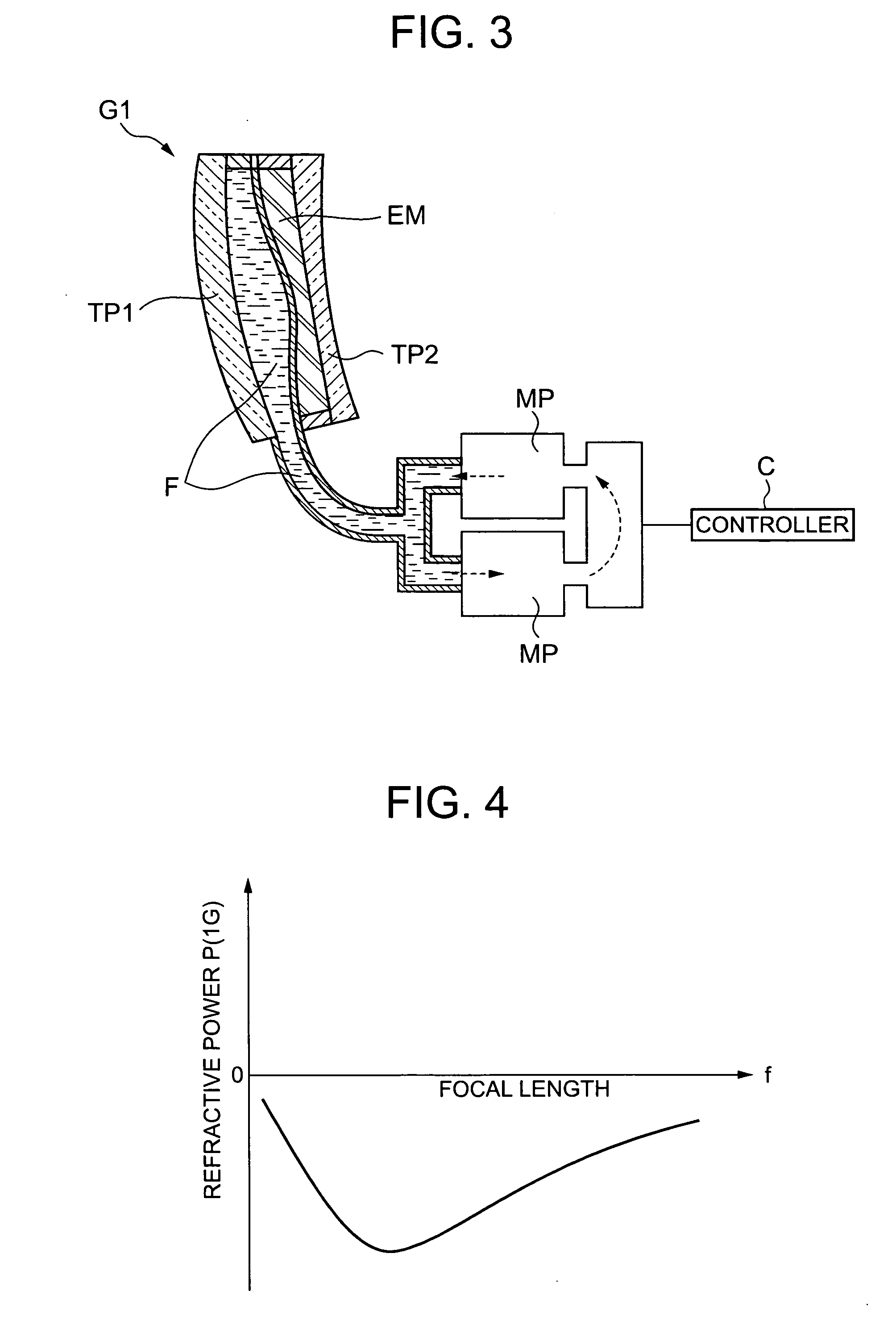
Zoom lens
InactiveUS20050200973A1Reduce the numberSimplify the movement mechanismLensElectrical polarityZoom lens
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA OPTO
Augmenting panoramic lidar results with color
Methods and systems can augment 360 degree panoramic LIDAR results (e.g., from a spinning LIDAR system) with color obtained from color cameras. A color-pixel-lookup table can specify the correspondence between LIDAR pixels (depth / ranging pixels) and color pixels, which may be done at different viewing object distances. The operation of the color cameras can be triggered by the angular positions of the LIDAR system. For example, a color image of a particular camera can be captured when the LIDAR system is at a particular angular position, which can be predetermined based on properties of the cameras (e.g., shutter speed). Alternatively or in addition, a common internal clock can be used to assign timestamps to LIDAR and color pixels as they are captured. The corresponding color pixel(s), e.g., as determined using a color-pixel-lookup table, with the closest timestamp can be used for colorization.
Owner:OUSTER INC
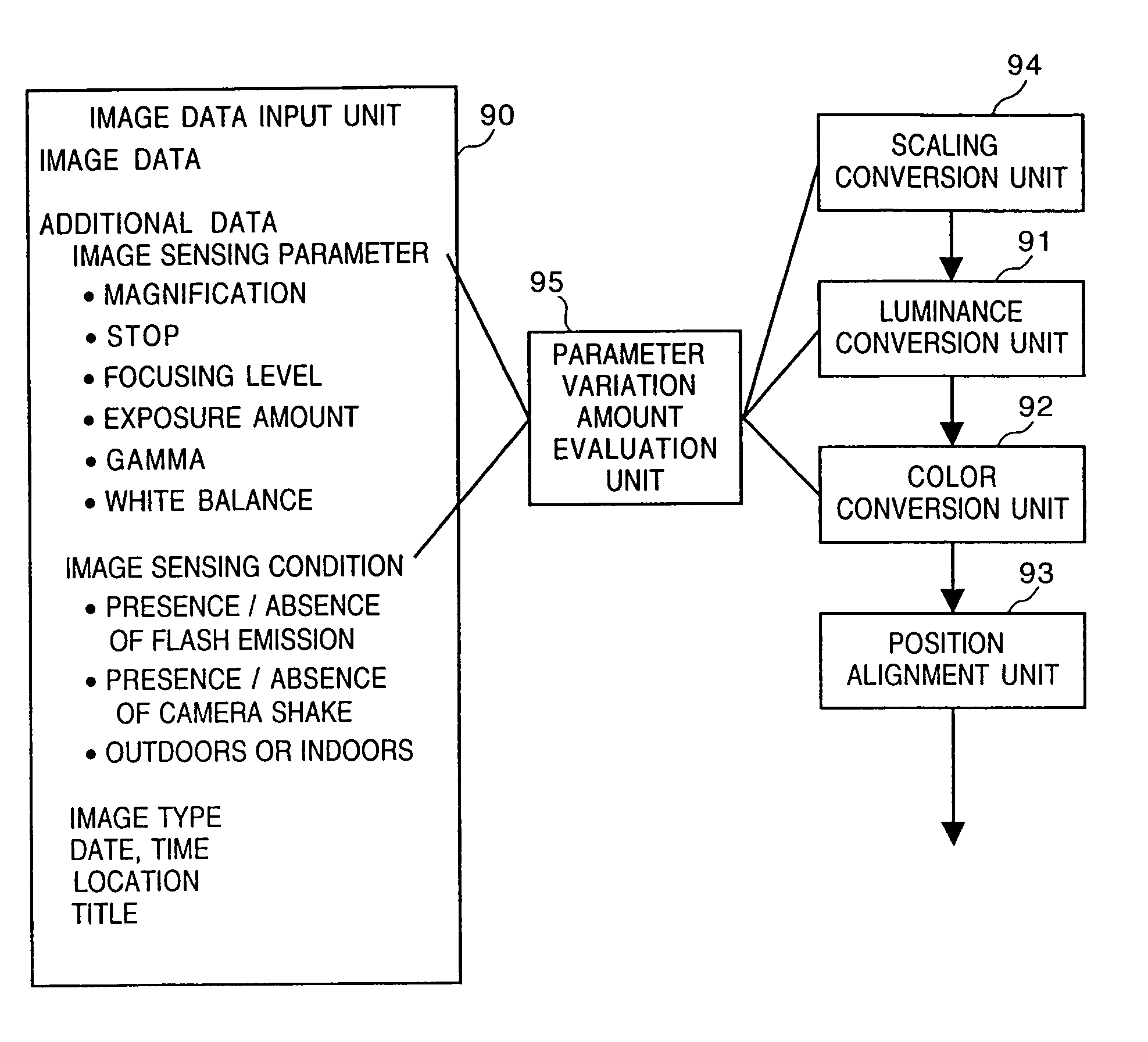
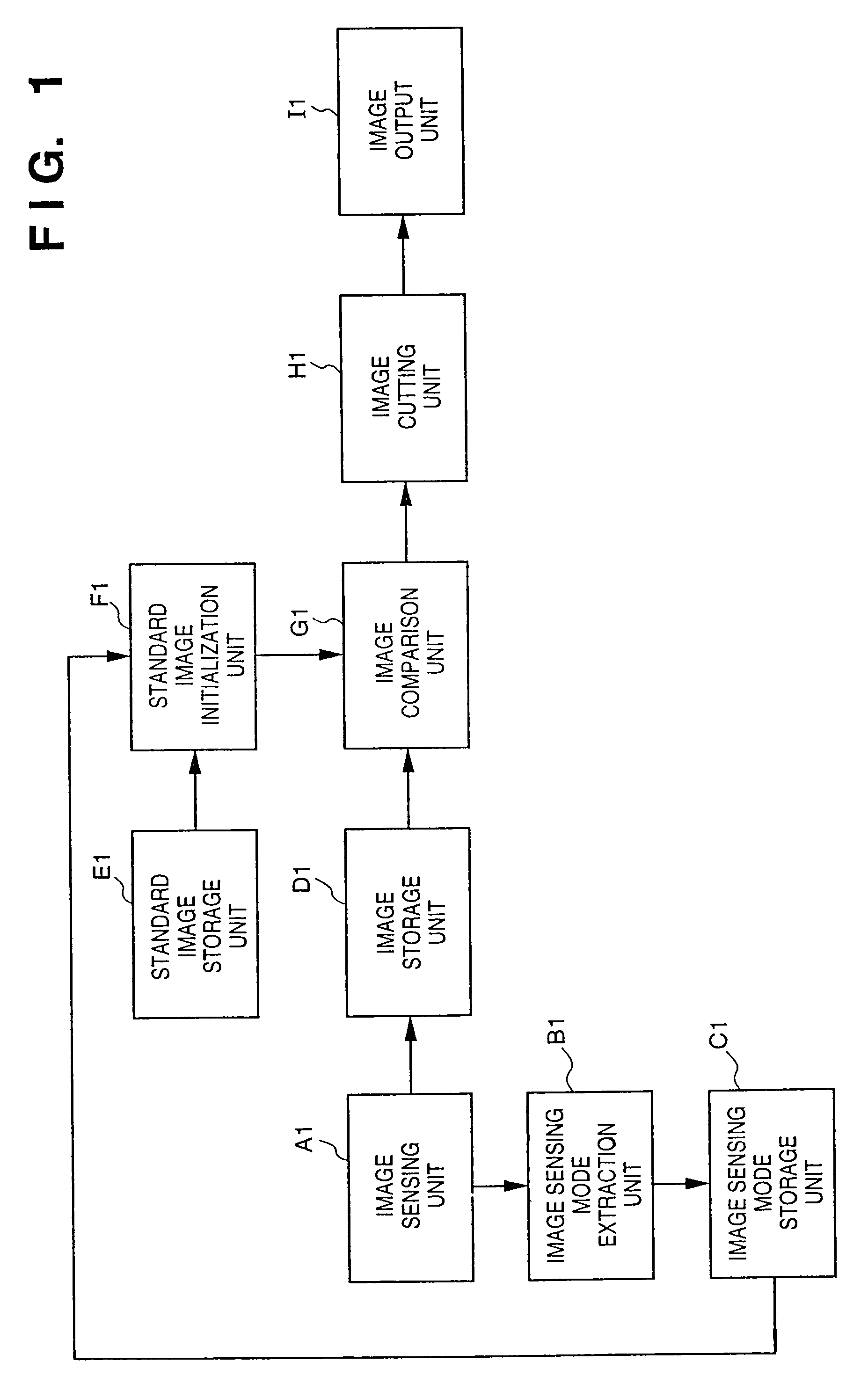
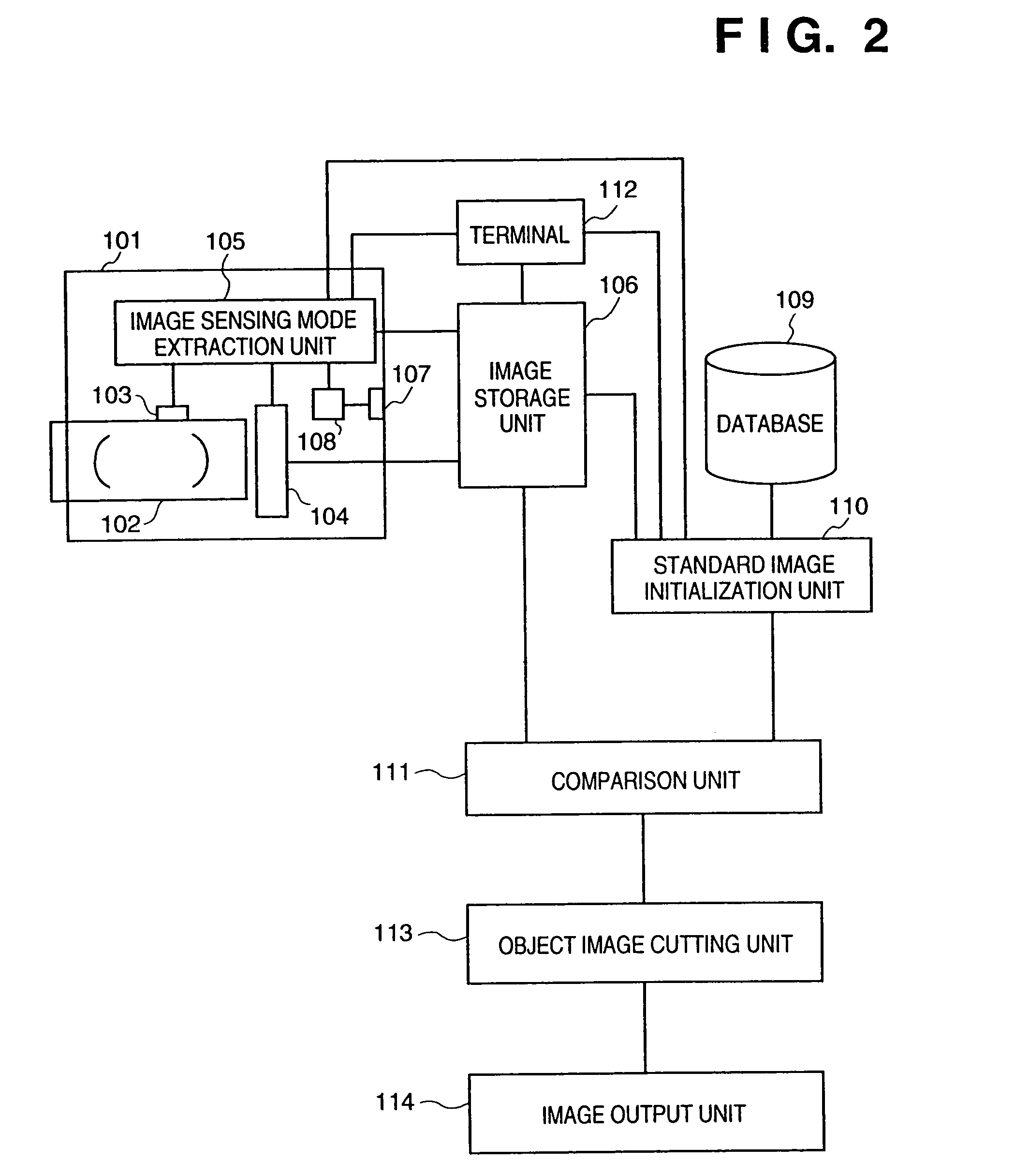
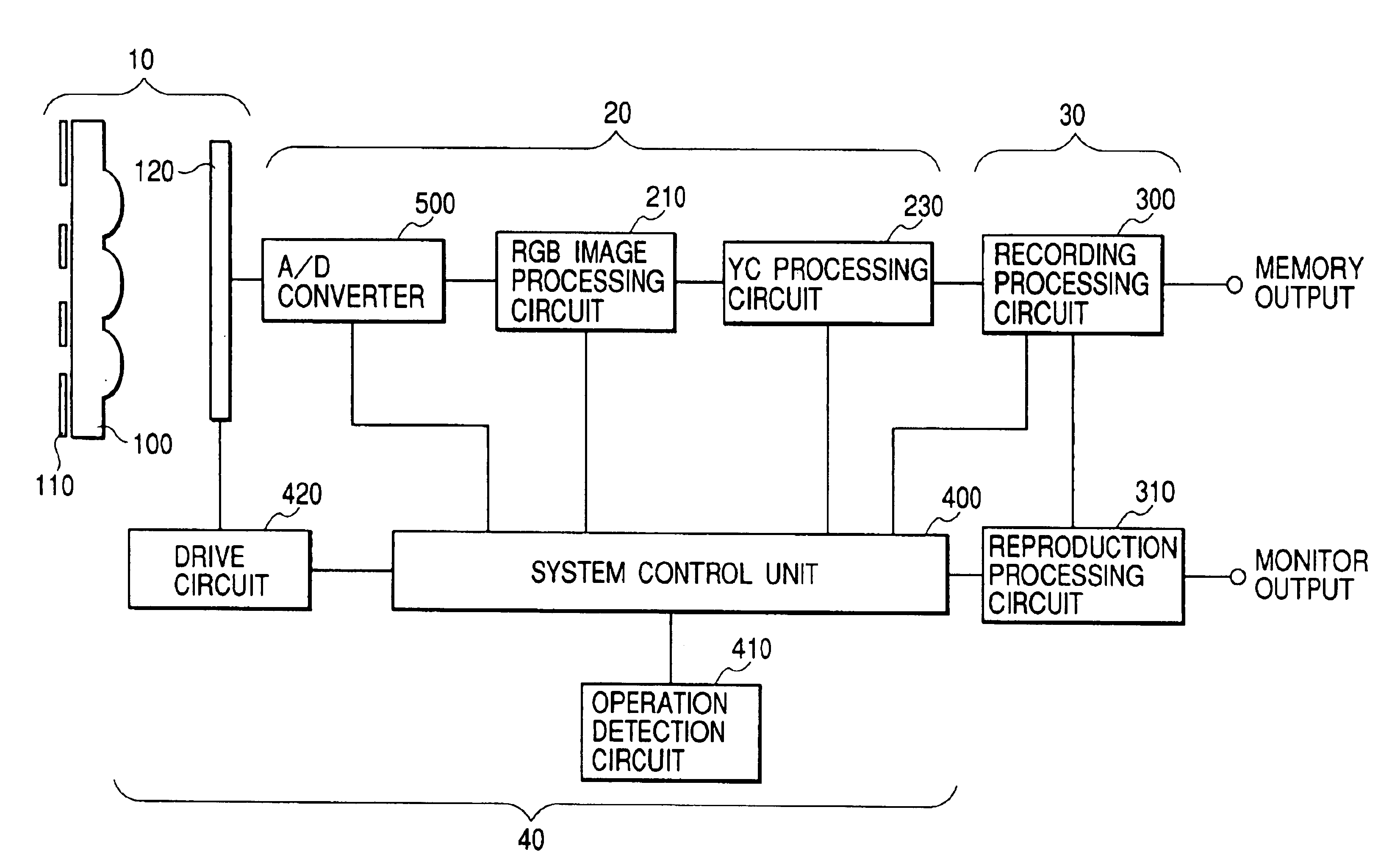
Object extraction method, and image sensing apparatus using the method
This invention provides an object extraction method for performing processing for extracting and cutting out a specific object from a sensed image at high speed, and an image sensing apparatus using the method. In this invention, in a method of extracting an object by comparing a sensed image and a standard image, a focusing signal, focal length data, visual axis direction data, and illumination conditions are detected, and the initial size, initial position, or initial color of the standard image is changed on the basis of the detection results, and extraction is started under optimal conditions. In a method of extracting a specific object from the background image, the background image is converted into an image having the same conditions as those of the object image. From a plurality of images obtained under different image sensing conditions, the contour of the object is accurately obtained at high speed. In an object extraction method using a template, the size of the template is determined on the basis of the object distance, object size, or the like.
Owner:CANON KK
Image pickup apparatus
InactiveUS6882368B1Improve image qualitySmall-sizedTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsOptical axisLength wave
An image pickup apparatus is provided having first and second image pickup portions for receiving at least first and second distinct wavelength components of object light, respectively, and first and second optical systems for guiding the first and second wavelength components to the first and second image pickup portions, respectively, via different optical paths. The first and second optical systems are formed to have respective shapes so that the focal length of the first optical system with regard to the first wavelength component is equal to the focal length of the second optical system with regard to the second wavelength component. When a virtual object distance, as defined as set forth herein, an interval between optical axes of the first and second optical systems is set such that a change in an interval between object images of the first and second wavelength components received by the first and second image pickup portions, respectively, between when an object exists at the virtual object distance and when it exists at infinity is smaller than a pixel pitch of the image pickup portions multiplied by two.
Owner:CANON KK
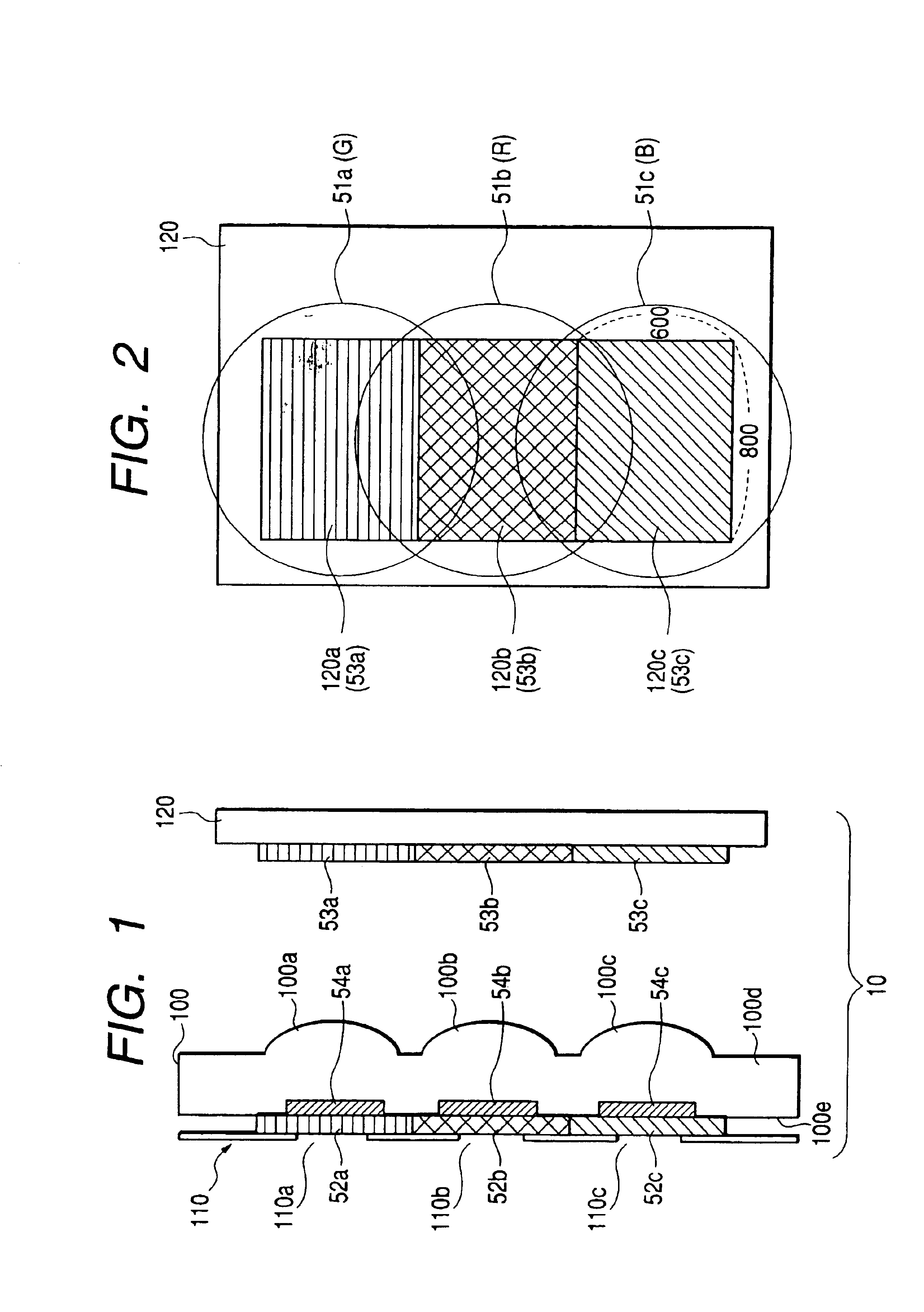
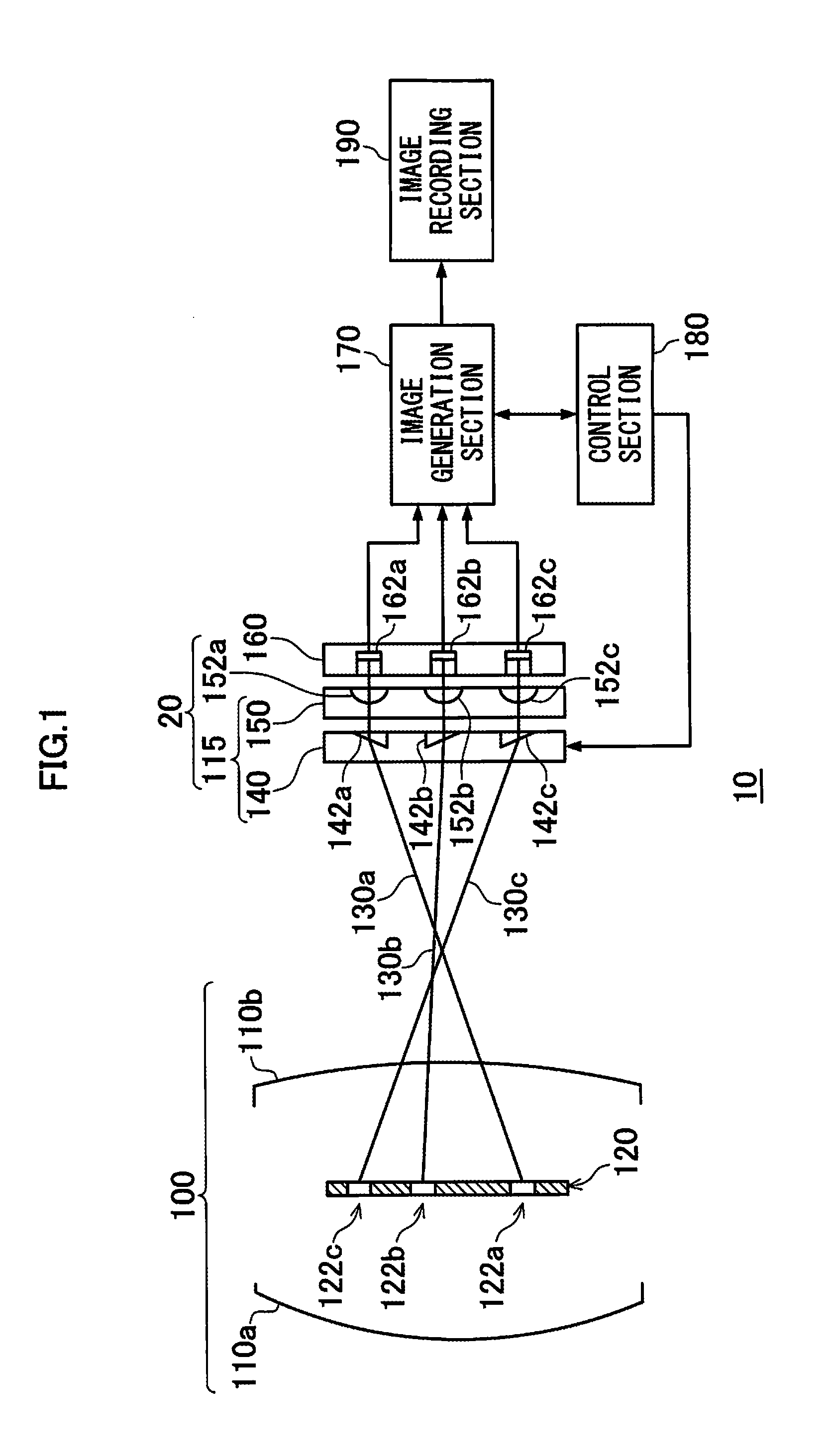
Imaging apparatus
An imaging apparatus, including: an image formation lens having focal lengths different in every region; a light receiving section having light receiving elements; optical elements corresponding to a plurality of the light receiving elements to make the corresponding light receiving elements receive an object light beam that passed through predetermined pupil regions in an exit pupil of the image formation lens; and an image generation section, wherein in the case of selecting, for generation of the image of the object, any one of the pupil regions in the exit pupil through which an object light beam passes, the image generation section selects, based on an object distance and focal lengths each corresponding to a plurality of the pupil regions of the exit pupil, at least one of the pupil regions through which an object light beam that forms an image at a position of the light receiving section passes.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Scale-invariant, resolution-invariant iris imaging using reflection from the eye
ActiveUS8243133B1Reduce sensitivityAcquiring/recognising eyesColor television detailsImage resolutionImage scale
An optical system includes an active focus element that maintains an image in focus over a range of object distances. The active focus element and aperture stop are positioned such that the image scale and the image spatial resolution are also invariant (or at least have a reduced sensitivity) with respect to object distance.
Owner:TASCENT INC
Method and apparatus for controlling a vehicle using an object detection system and brake-steer
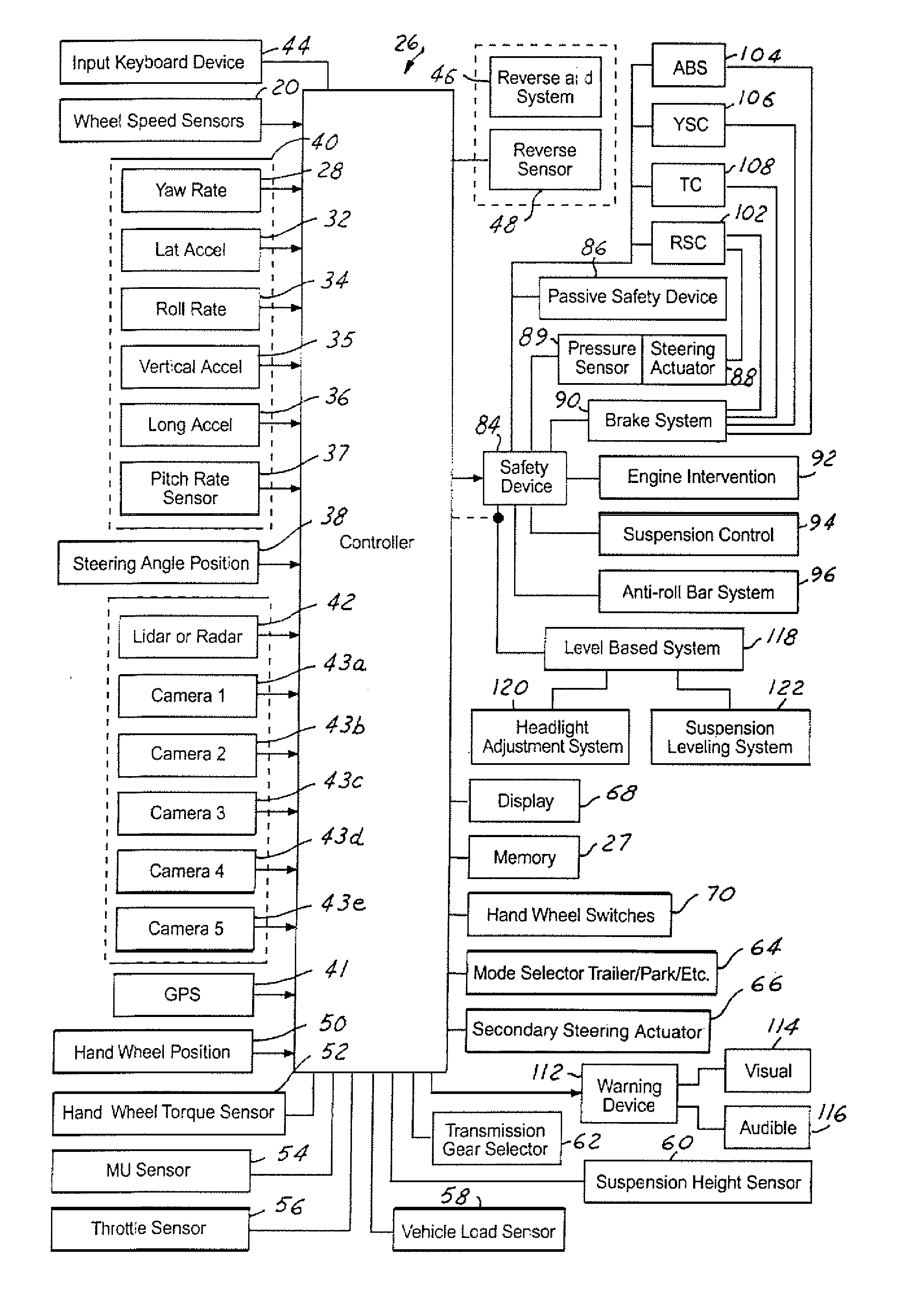
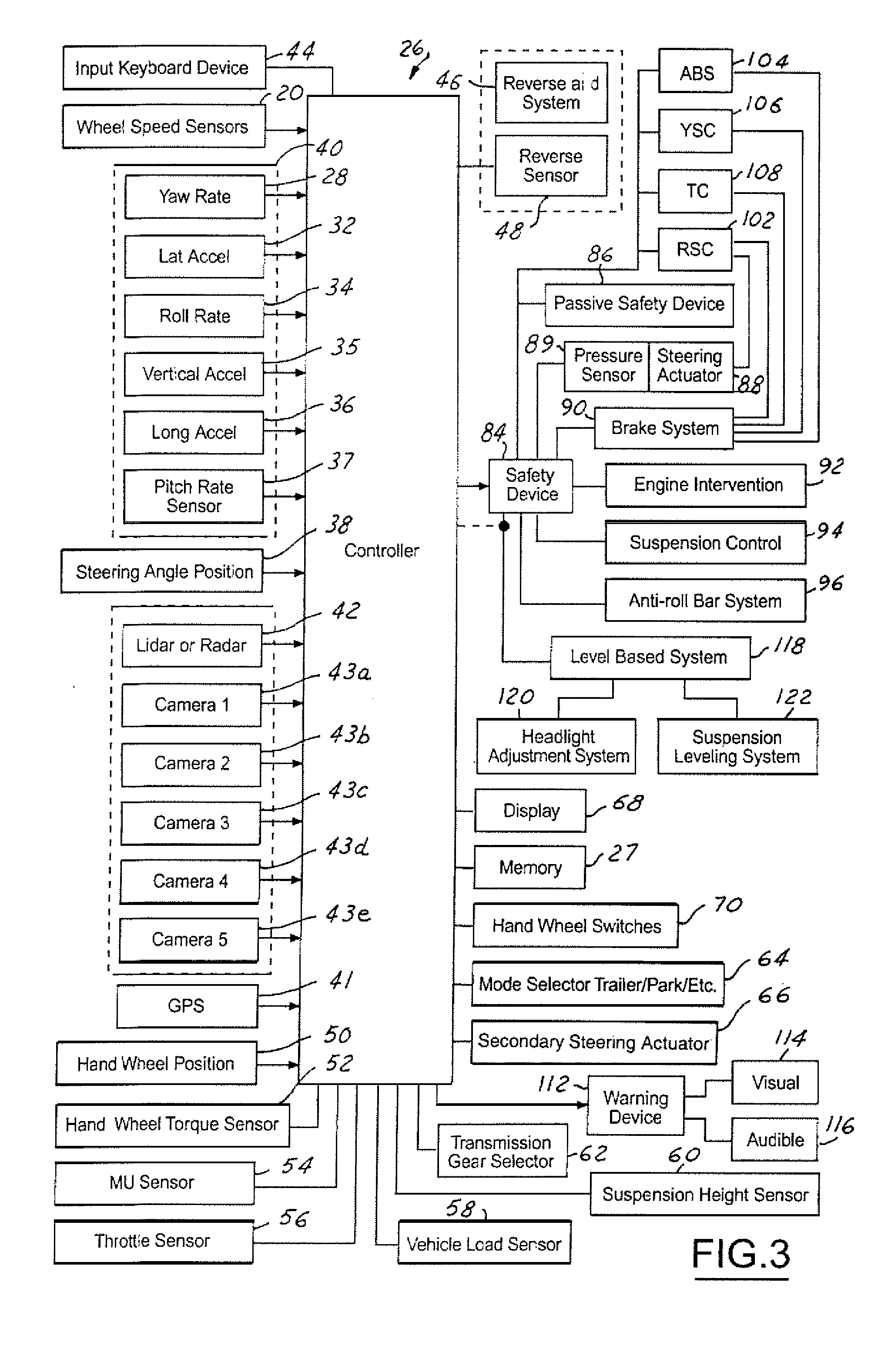
InactiveUS20050209762A1Analogue computers for trafficAutomatic initiationsControl systemControl signal
A control system for an automotive vehicle that has a brake system includes an object detection system that generates an object detection signal and an object distance signal. A controller is coupled to the object detection system. The controller generates a brake control signal proportional to the object distance signal in response to the object detection signal and the object distance signal. The controller controls the brake system in response to the brake control signal.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
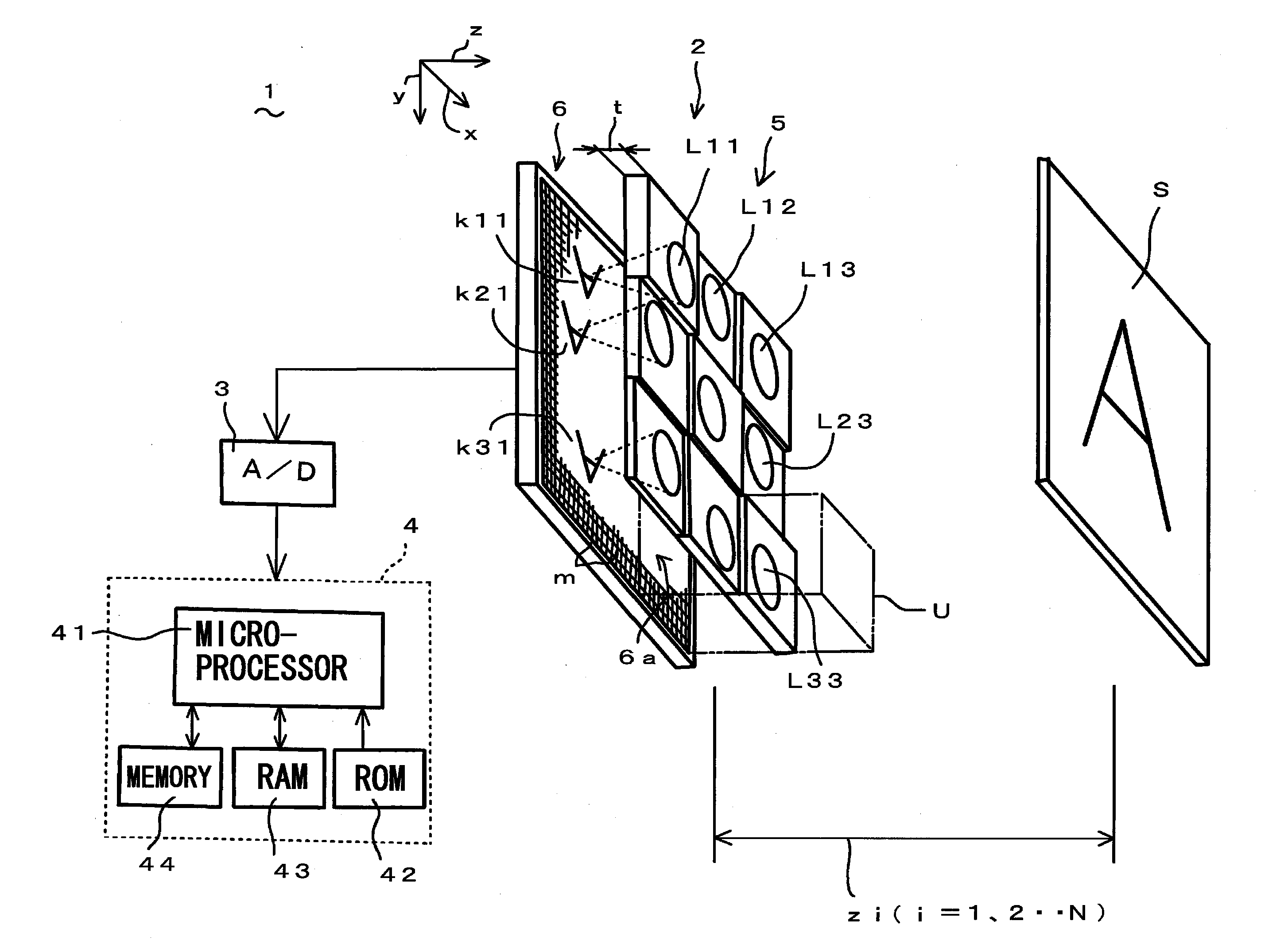
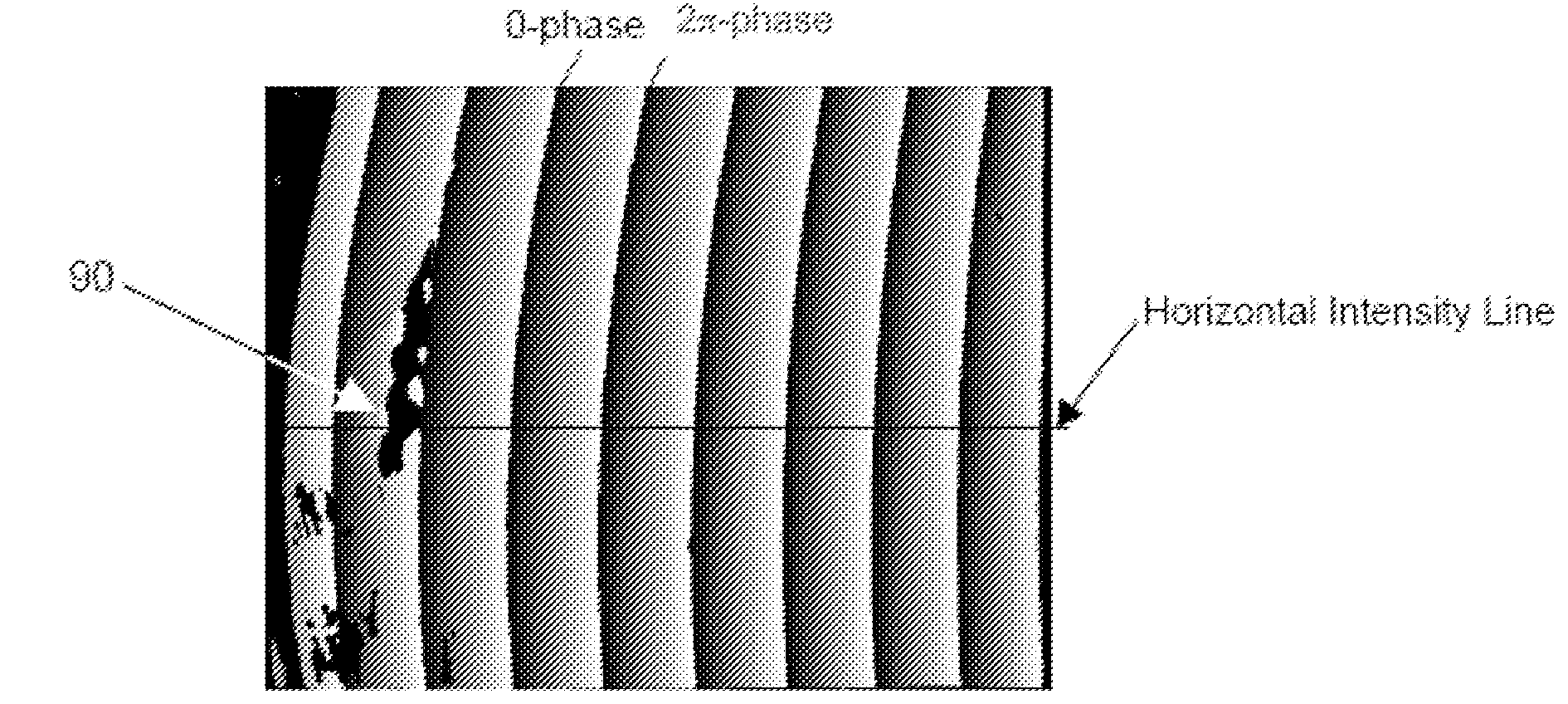
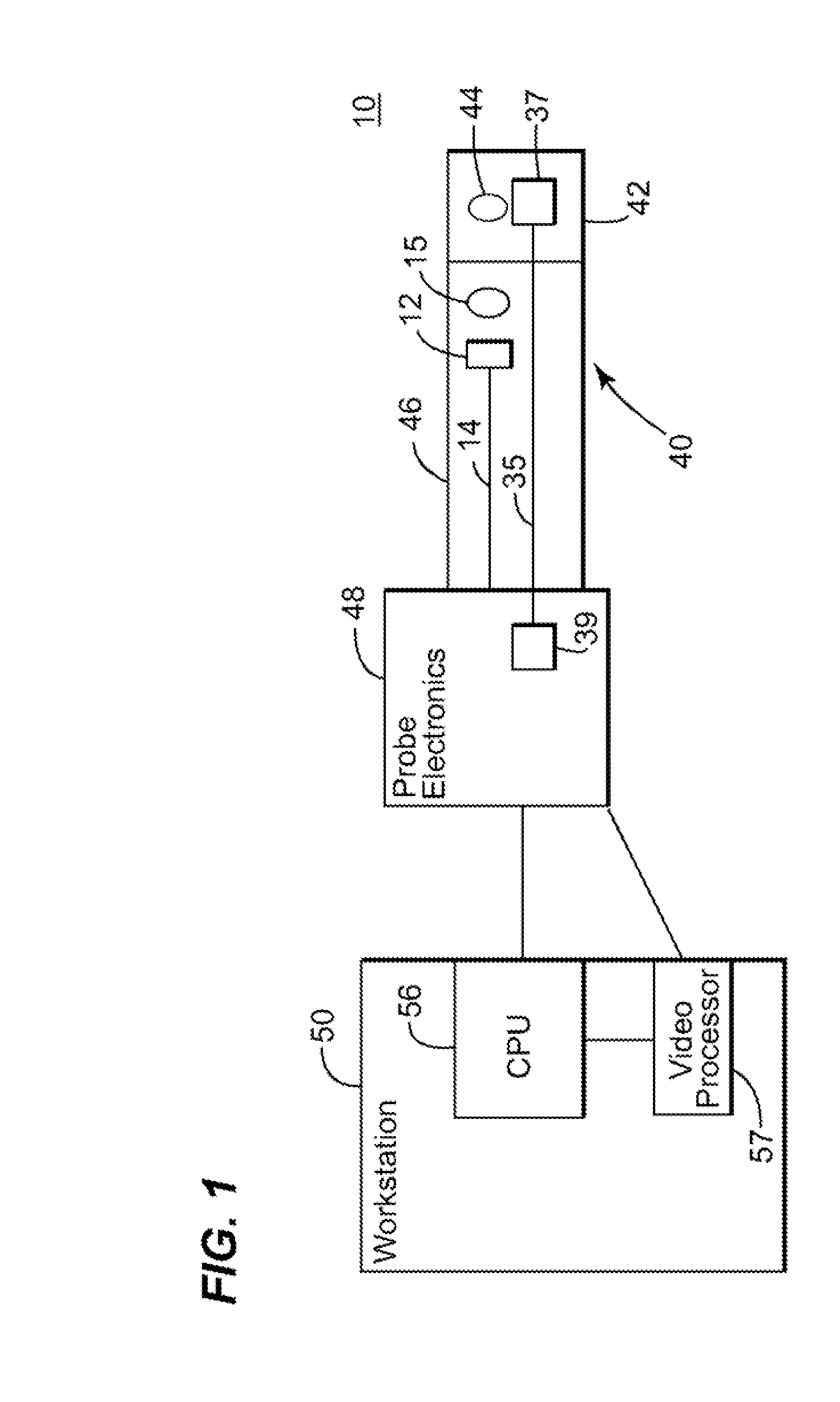
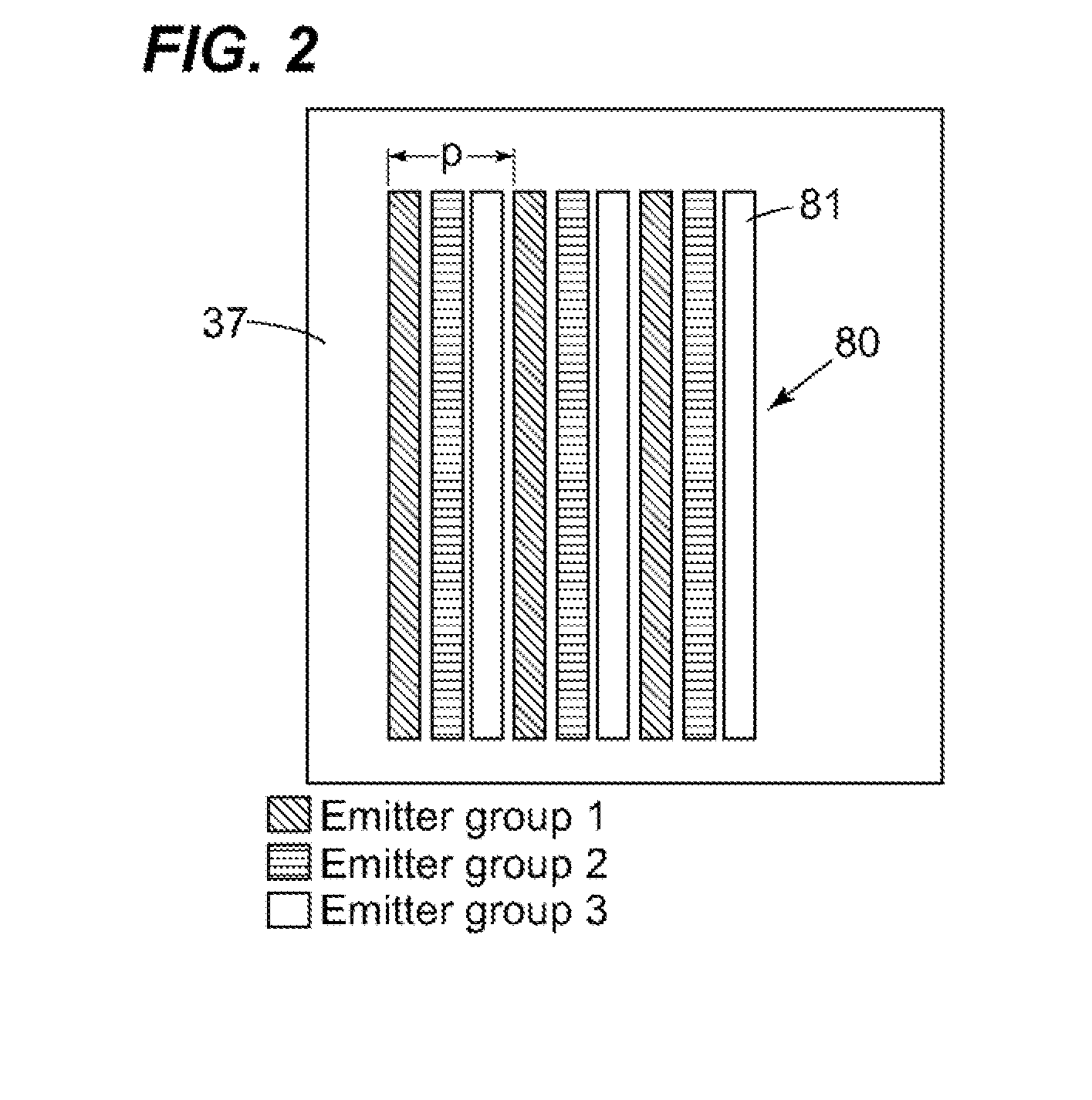
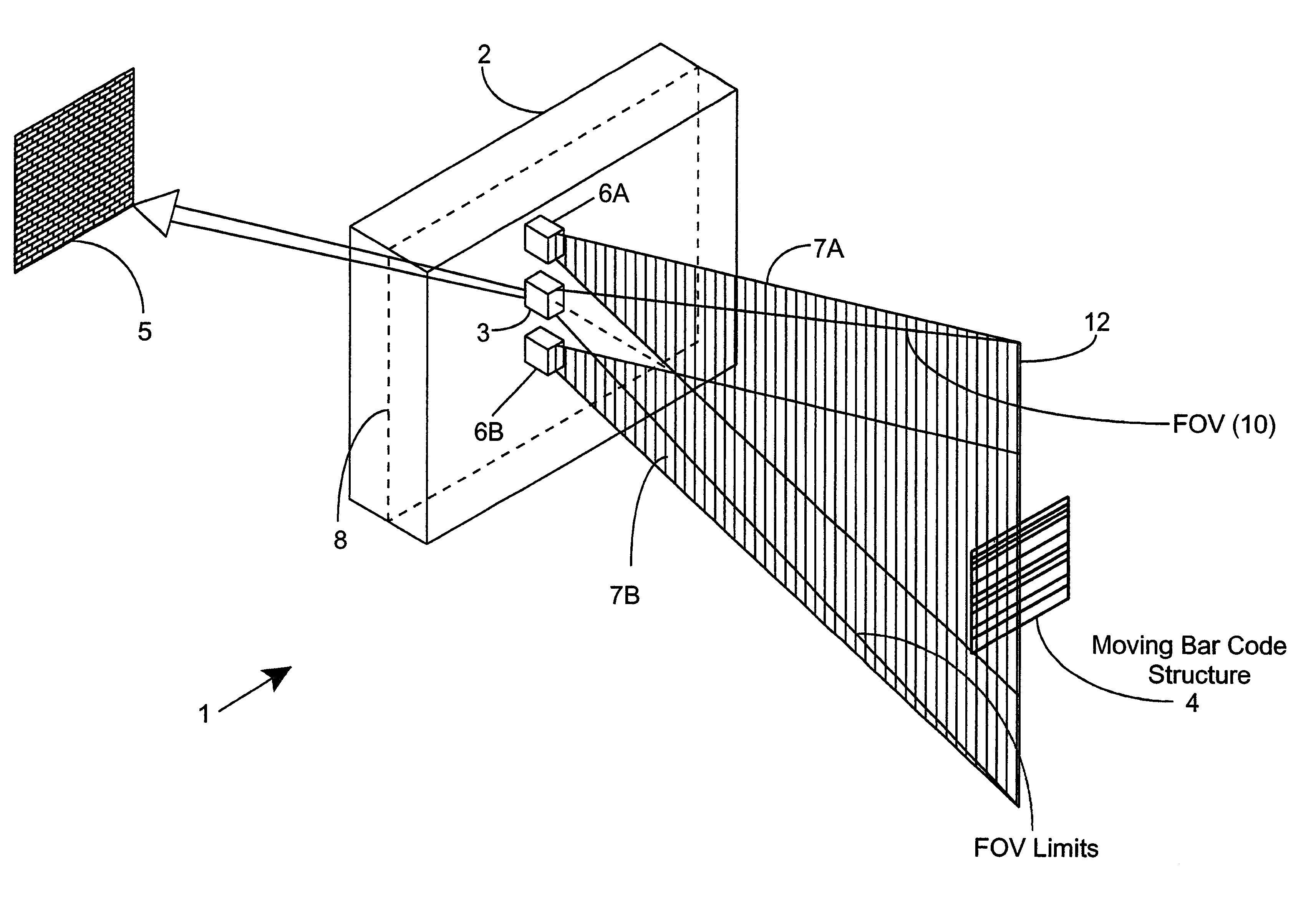
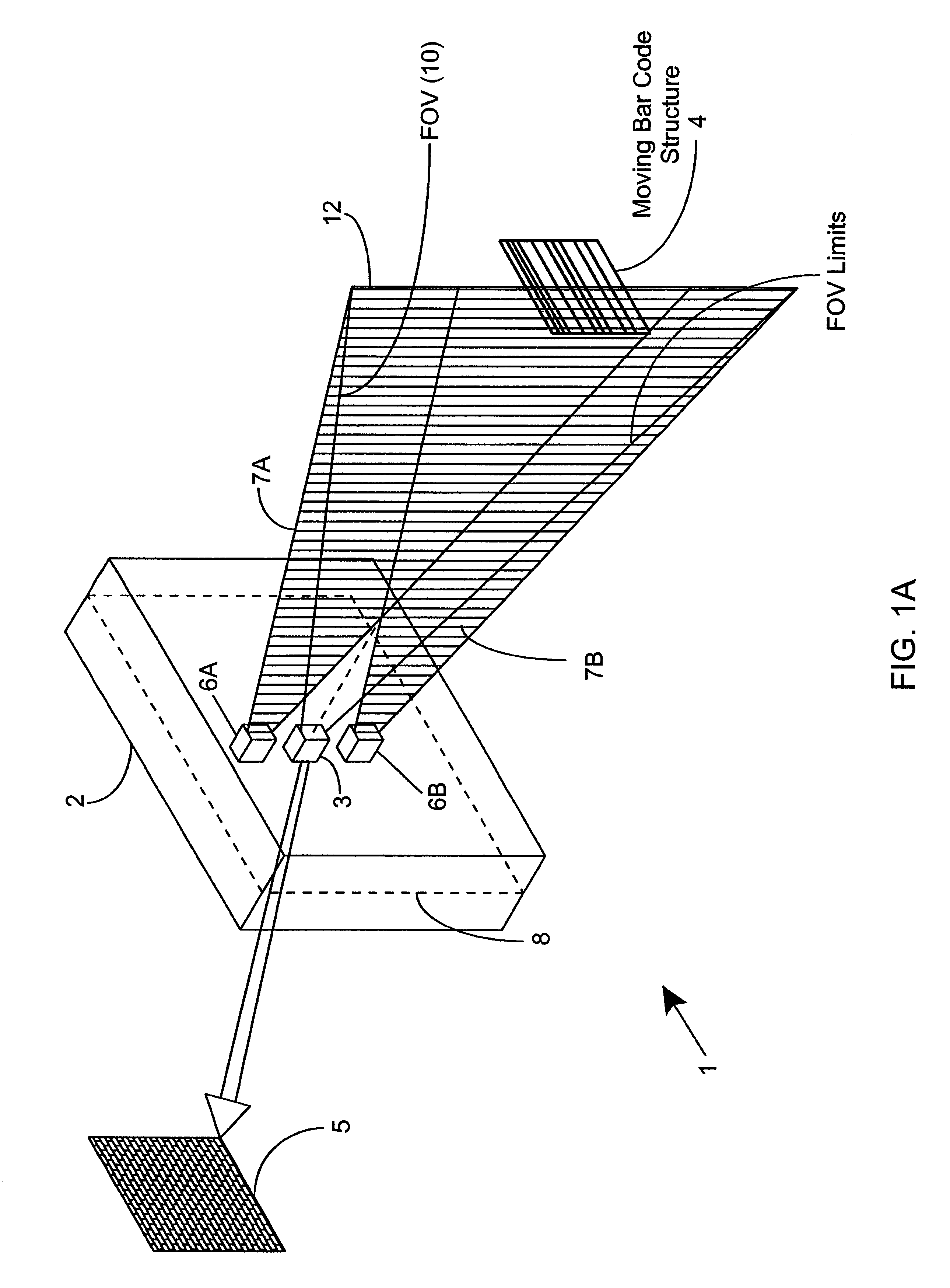
Phase-Shift Analysis System and Method
A system for determining an object distance z includes a plurality of light emitters. A group of at least one of the plurality of light emitters includes an emitter group, and the pattern projected when one emitter group is emitting includes a fringe set. The light pattern of one fringe set exhibits a phase-shift relative to the light patterns of the other fringe sets, and the phase-shift varies as the distance from the origin of the plurality of fringe sets varies. The system further includes a processing unit that is configured to compute a ripple metric value associated with each of a plurality of possible z values. The processing unit is further configured to determine an approximated z value using the computed ripple metric values. A probe system is also provided. The probe system is configured to project a plurality of fringe sets from the probe onto an object. The light pattern of one fringe set exhibits a phase-shift relative to the light patterns of the other fringe sets, and the phase-shift varies as the distance from the origin of the plurality of fringe sets varies. The probe system is further configured to compute a ripple metric value associated with each of a plurality of possible z values, where z is an object distance. The probe system is also configured to determine an approximated z value using the computed ripple metric values. A method for determining an object distance z is also provided.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Method of and system for producing images of objects using planar laser illumination beams and image detection arrays
InactiveUS6629641B2Avoid disadvantagesLower Level RequirementsSemiconductor laser arrangementsCharacter and pattern recognitionImage detectionHand held
Methods of and systems for illuminating objects using planar laser illumination beams having substantially-planar spatial distribution characteristics that extend through the field of view (FOV) of image formation and detection modules employed in such systems. Each planar laser illumination beam is produced from a planar laser illumination beam array (PLIA) comprising an plurality of planar laser illumination modules (PLIMs). Each PLIM comprises a visible laser diode (VLD, a focusing lens, and a cylindrical optical element arranged therewith. The individual planar laser illumination beam components produced from each PLIM are optically combined to produce a composite substantially planar laser illumination beam having substantially uniform power density characteristics over the entire spatial extend thereof and thus the working range of the system. Preferably, each planar laser illumination beam component is focused so that the minimum beam width thereof occurs at a point or plane which is the farthest or maximum object distance at which the system is designed to acquire images, thereby compensating for decreases in the power density of the incident planar laser illumination beam due to the fact that the width of the planar laser illumination beam increases in length for increasing object distances away from the imaging optics. By virtue of the present invention, it is now possible to use both VLDs and high-speed CCD-type image detectors in conveyor, hand-held and hold-under type scanning applications alike, enjoying the advantages and benefits that each such technology has to offer, while avoiding the shortcomings and drawbacks hitherto associated therewith.
Owner:METROLOGIC INSTR
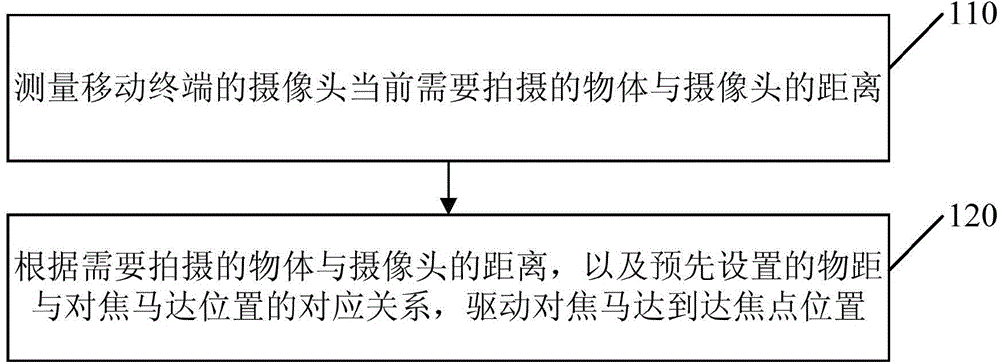
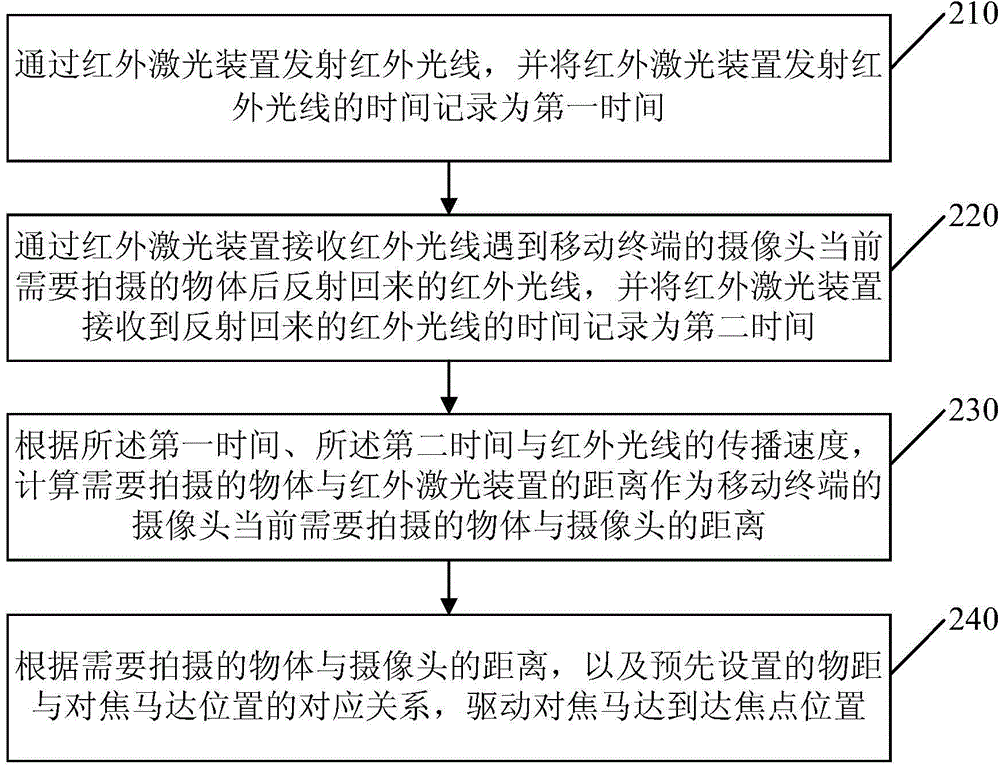
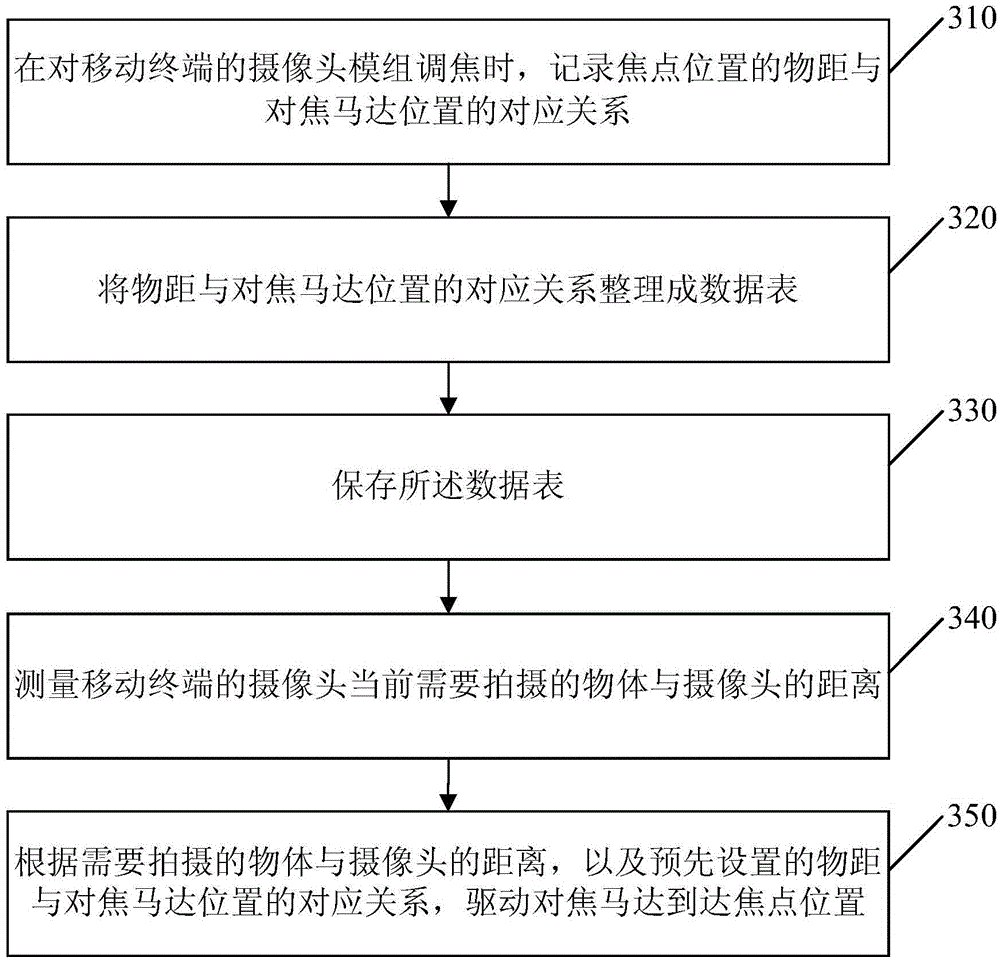
Focusing method and apparatus for mobile terminal
InactiveCN104883502AIncrease focus speedImprove accuracyTelevision system detailsColor television detailsComputer terminalObject distance
The invention discloses a focusing method and an apparatus for a mobile terminal. The method includes: measuring the distance between an object which is currently needed to be shot by a camera of the mobile terminal and the camera; and driving a focusing motor to the position of a focus according to the distance between the object in need of being shot and the camera and a preset corresponding relation between an object distance and the position of the focusing motor. According to the focusing method and the apparatus for the mobile terminal, the focusing motor can be directly driven to the position of the focus according to the preset corresponding relation between the object distance and the position of the focusing motor, and the focusing speed and the accuracy of the mobile terminal are improved.
Owner:GUANGDONG OPPO MOBILE TELECOMM CORP LTD
Method of and system for determining the lower limit of decoding resolution in an imaging-based bar code symbol reader
InactiveUS20050103863A1Visual representatino by photographic printingCharacter and pattern recognitionLower limitGraphics
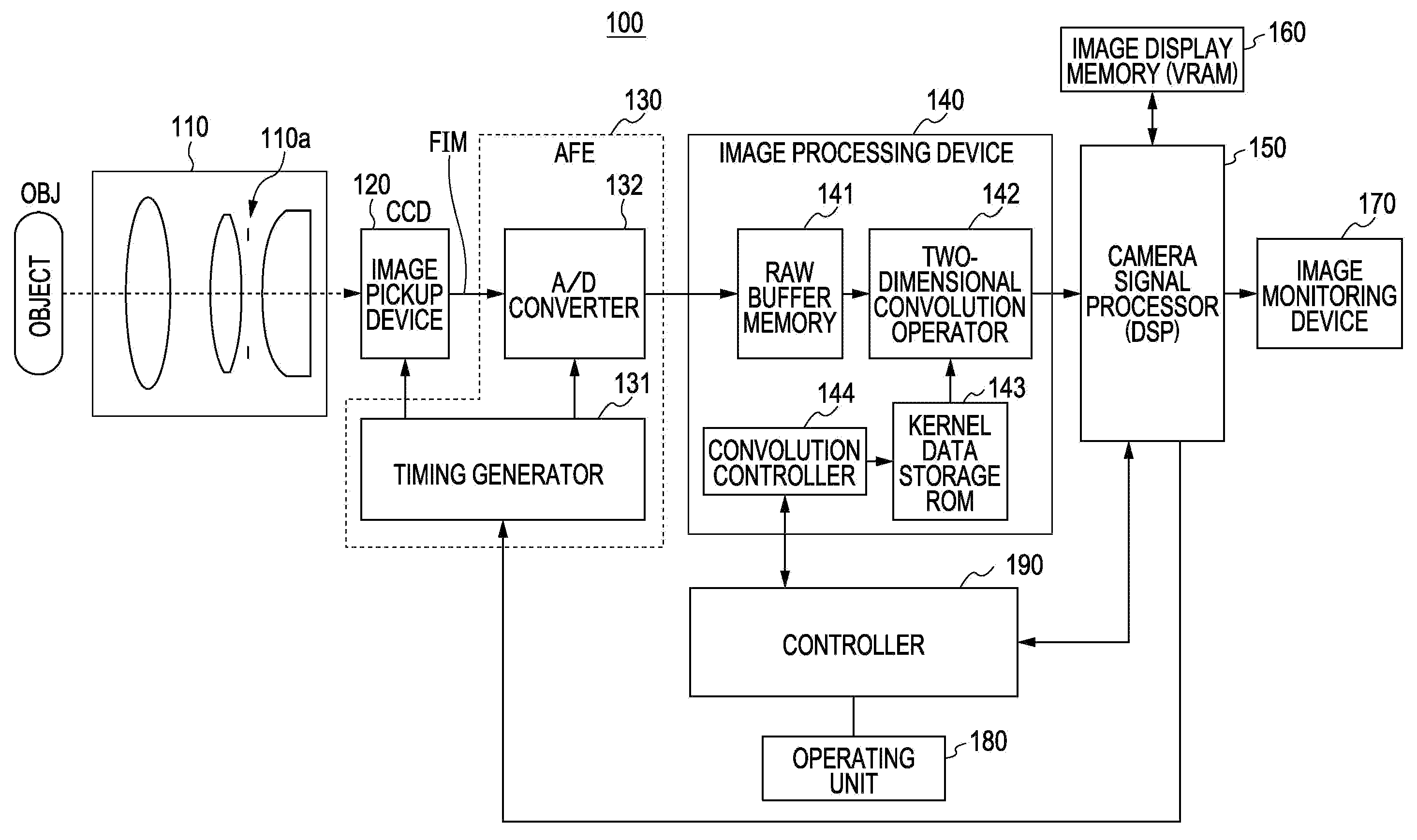
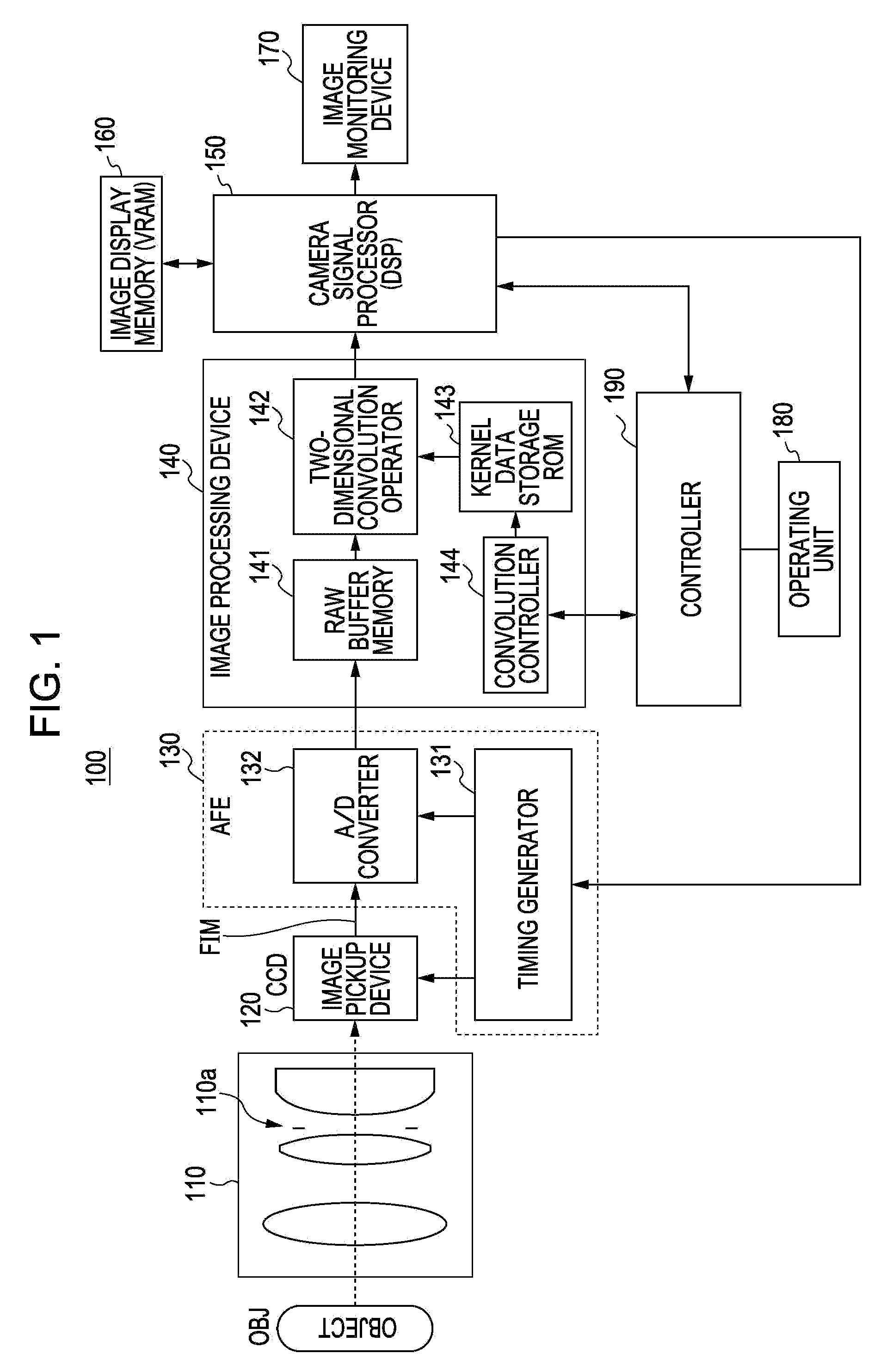
A method of determining the lower limit of decoding resolution in a digital imaging-based bar code symbol reader. A software-based optical design program is used to generate the composite DOF chart of image formation optics employed in the digital imaging-based bar code symbol reader. The modulation transfer function (MTF) of the object image is used to determine the smallest mil size code that can be decoded, at a given object distance, to produce an optical performance curve. The program calculates the size of the field of view (FOV) of a single sensor pixel, when projected through the image formation optics and out into object space. For both the 1.4 and 1.6 sampling limit pixel rules, the calculated FOV values are plotted on the same axes as the optical performance curve. Using graphical solution techniques, the sampling limit line of choice determines the lower limit of the decoding resolution in the imaging-based bar code symbol reader.
Owner:METROLOGIC INSTR
Method and device for preventing shaking of video image
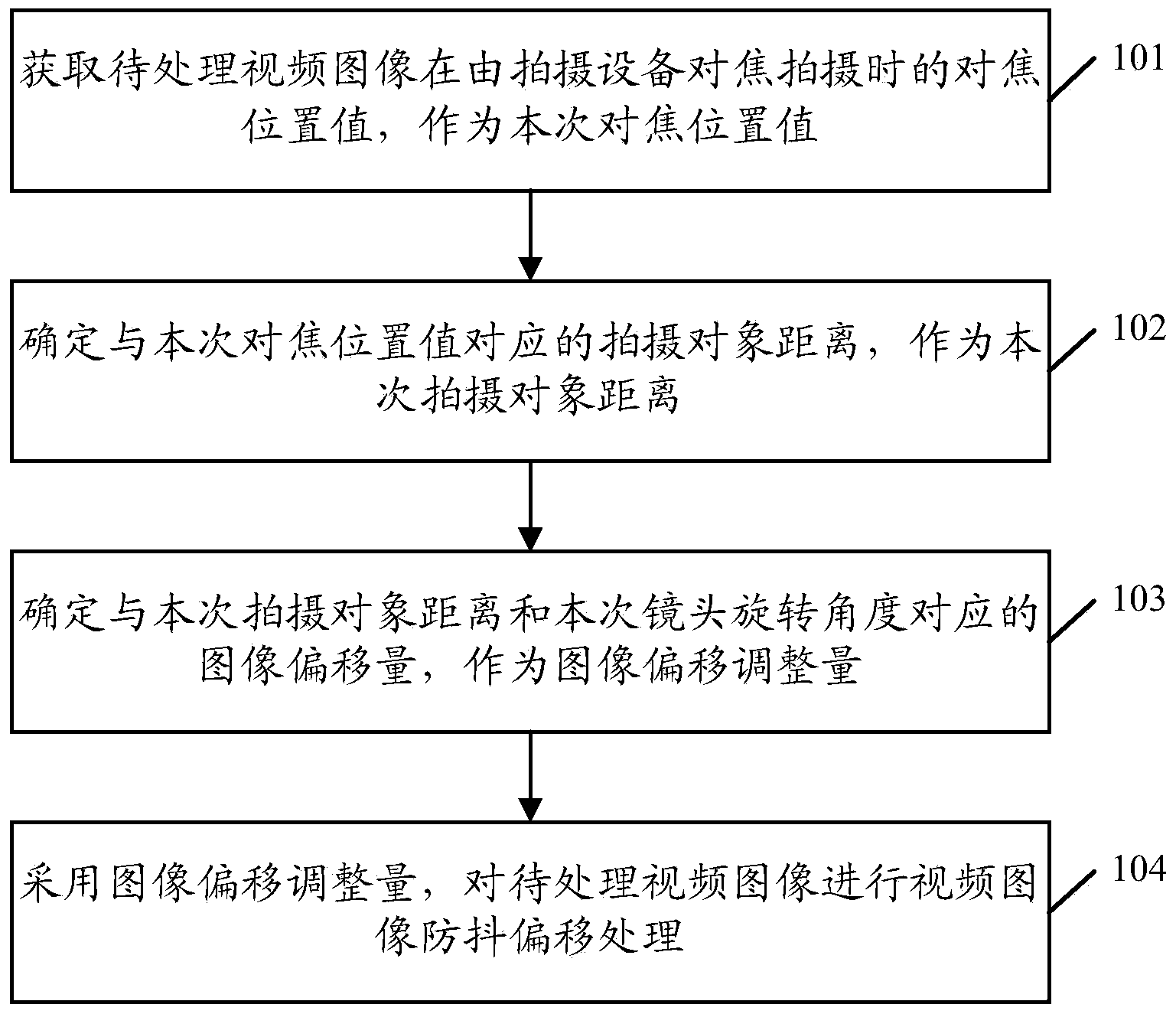
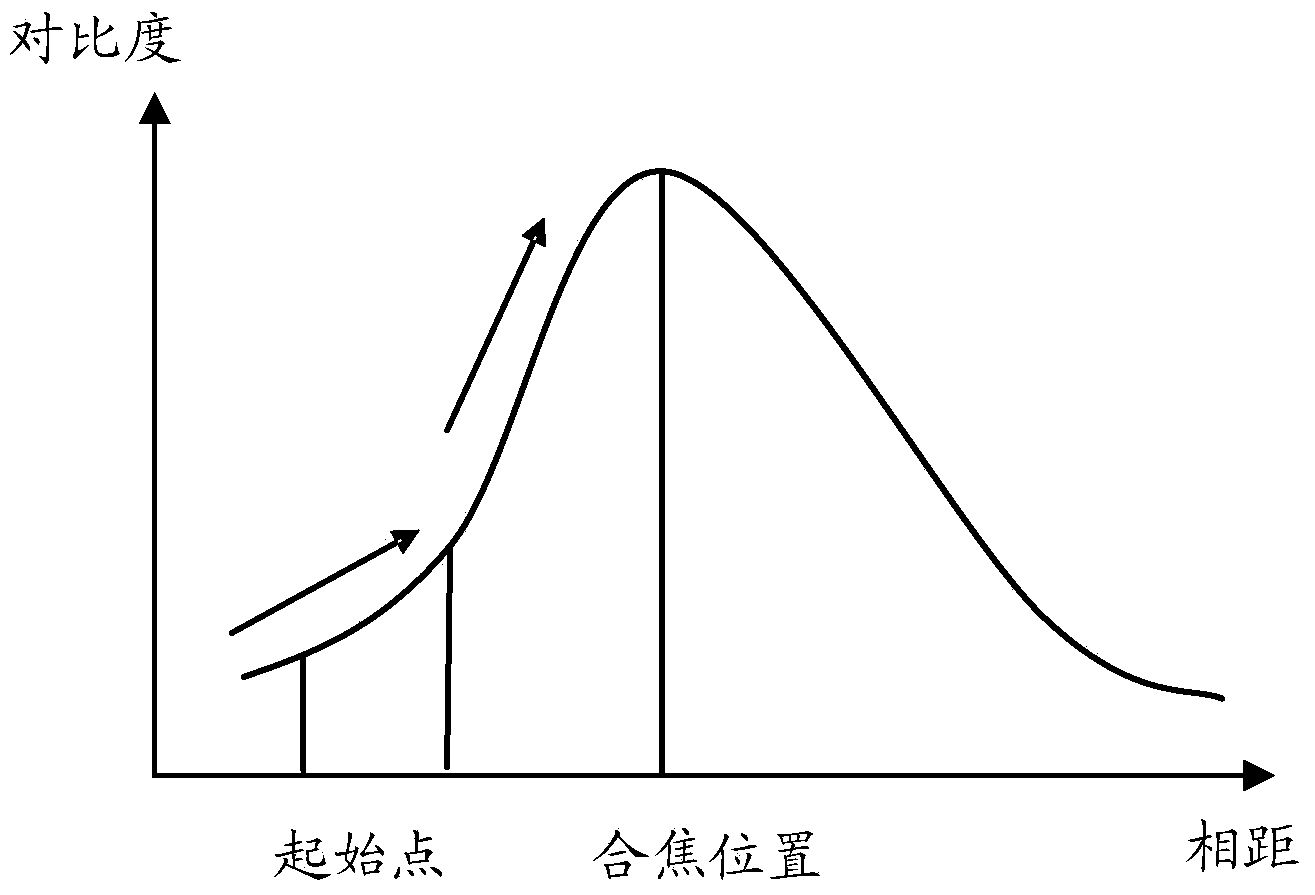
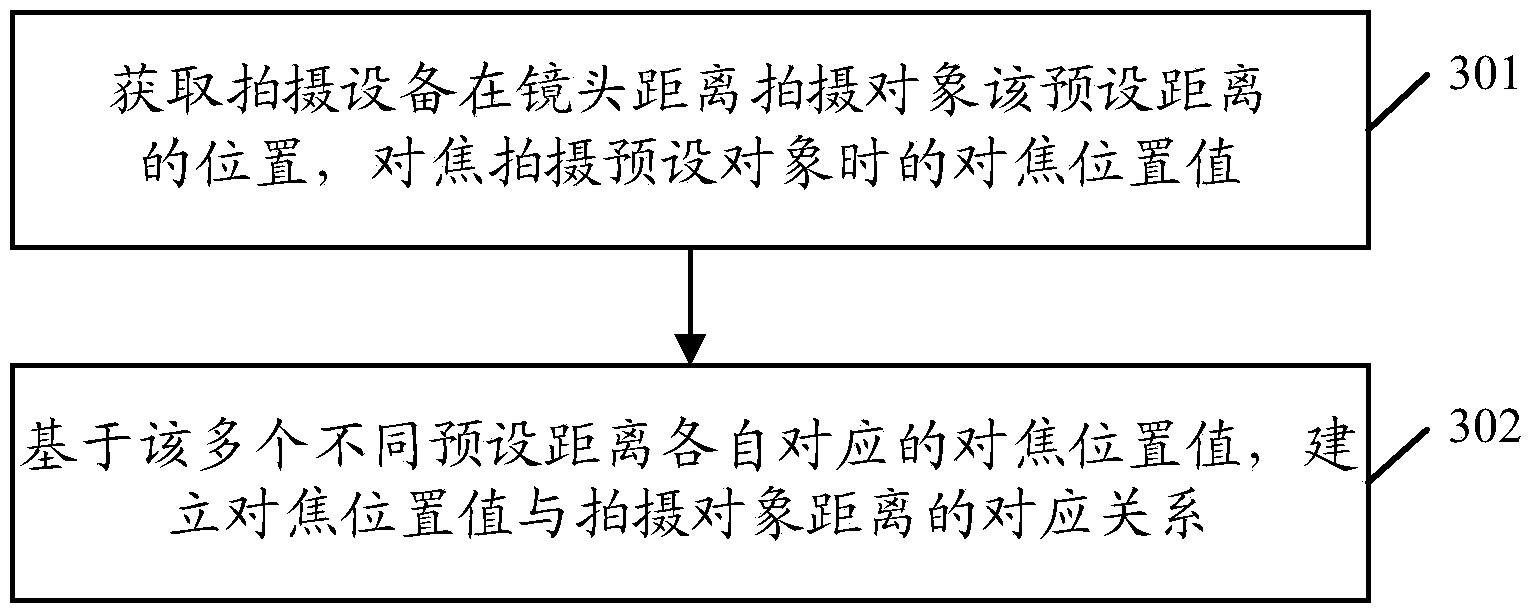
InactiveCN103685950AImprove the anti-shake effectTelevision system detailsColor television detailsCamera lensVideo image
The invention discloses a method and device for preventing shaking of a video image. The method for preventing shaking of the video image comprises the steps that the focusing positional value of a video image to be processed when focusing shooting is conducted by shooting equipment is obtained and serves as a current focusing positional value; a shooting object distance corresponding to the current focusing positional value is determined based on the corresponding relation between a focusing positional value and a shooting object distance which are established in advance, and the shooting object distance corresponding to the current focusing positional value serves as the current shooting object distance; the image offset corresponding to the current shooting object distance and a current camera lens rotating angle is determined based on the corresponding relation among the shooting object distance, a camera lens rotating angle and image offset which are established in advance, and the image offset corresponding to the current shooting object distance and the current camera lens rotating angle serves as the adjustment amount of image offset, wherein a camera rotating angle, of the video image to be processed, which is obtained when focusing shooting is conducted by the shooting equipment serves as the current camera lens rotating angle, and video image anti-shaking offset processing is conducted on the video image to be processed by means of the adjustment amount of image offset. By the adoption of the method for preventing shaking of the video image, the anti-shaking effect of the video image is improved.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Optical apparatus
InactiveUS6864910B1Small sizeLow costCharacter and pattern recognitionStereoscopic photographyParallaxComputer science
An optical apparatus is arranged to automatically control, on the basis of an object distance, a convergence distance of right and left optical systems arranged to cause right and left optical images having a predetermined amount of parallax to enter a photographing optical system, and has a plurality of modes in which a difference between the convergence distance and the object distance varies.
Owner:CANON KK
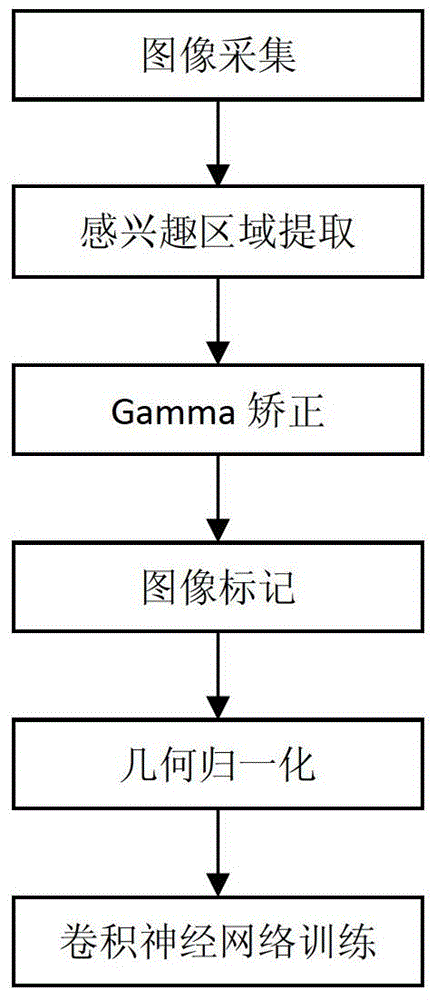
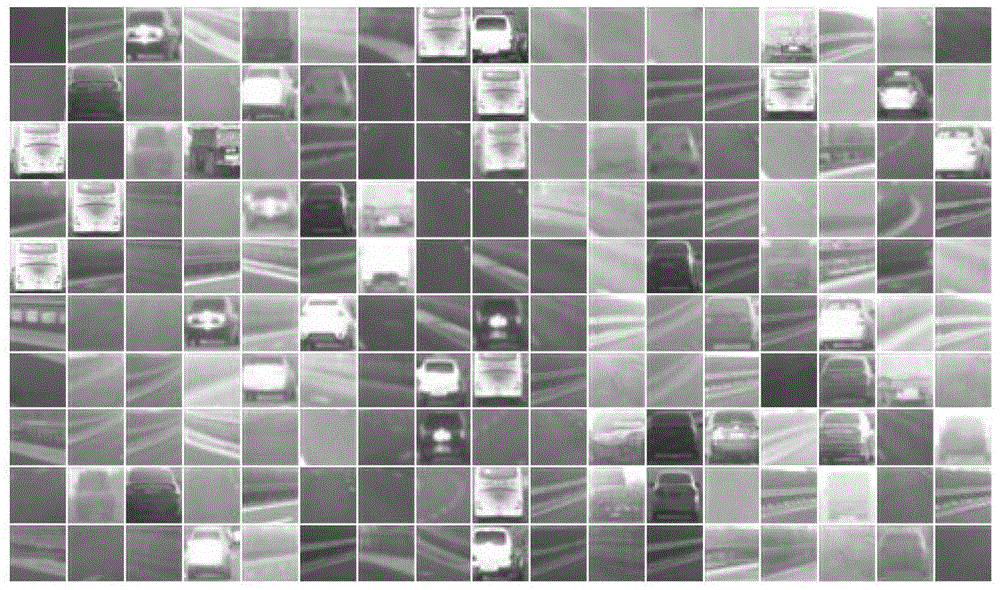
Vehicle front trafficability analyzing method based on convolution nerve network
InactiveCN103279759AHigh-resolutionAvoid the effects of target recognitionCharacter and pattern recognitionNerve networkImage resolution
The invention discloses a vehicle front trafficability analyzing method based on a convolution nerve network. The method comprises the following steps: first, a vidicon arranged in the front of a vehicle is used for collecting a large number of actual vehicle traveling environment images; a Gamma rectification function is used for pre-processing the images; training of the convolution nerve network is conducted. According to the method, a nonlinear function superimposed Gamma rectification method is used for pre-processing the images, so that influence of light illumination of strong changes on identification of objects is avoided, and the image resolution ratio is improved. According to the method, a geometry normalization method is used, so that the resolution ratio difference caused by identifying the distance of an object distance vidicon is reduced. The convolution nerve network LeNet-5 adopted in the method can extract implicit expression characteristics with class distinguishing capacity and is simple in extracting process. The LeNet-5 is combined with a local receptive field, weight share and secondary sampling to ensure robustness of simple geometry deformation, reduce training parameters of the network, and simplify the structure of the network.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
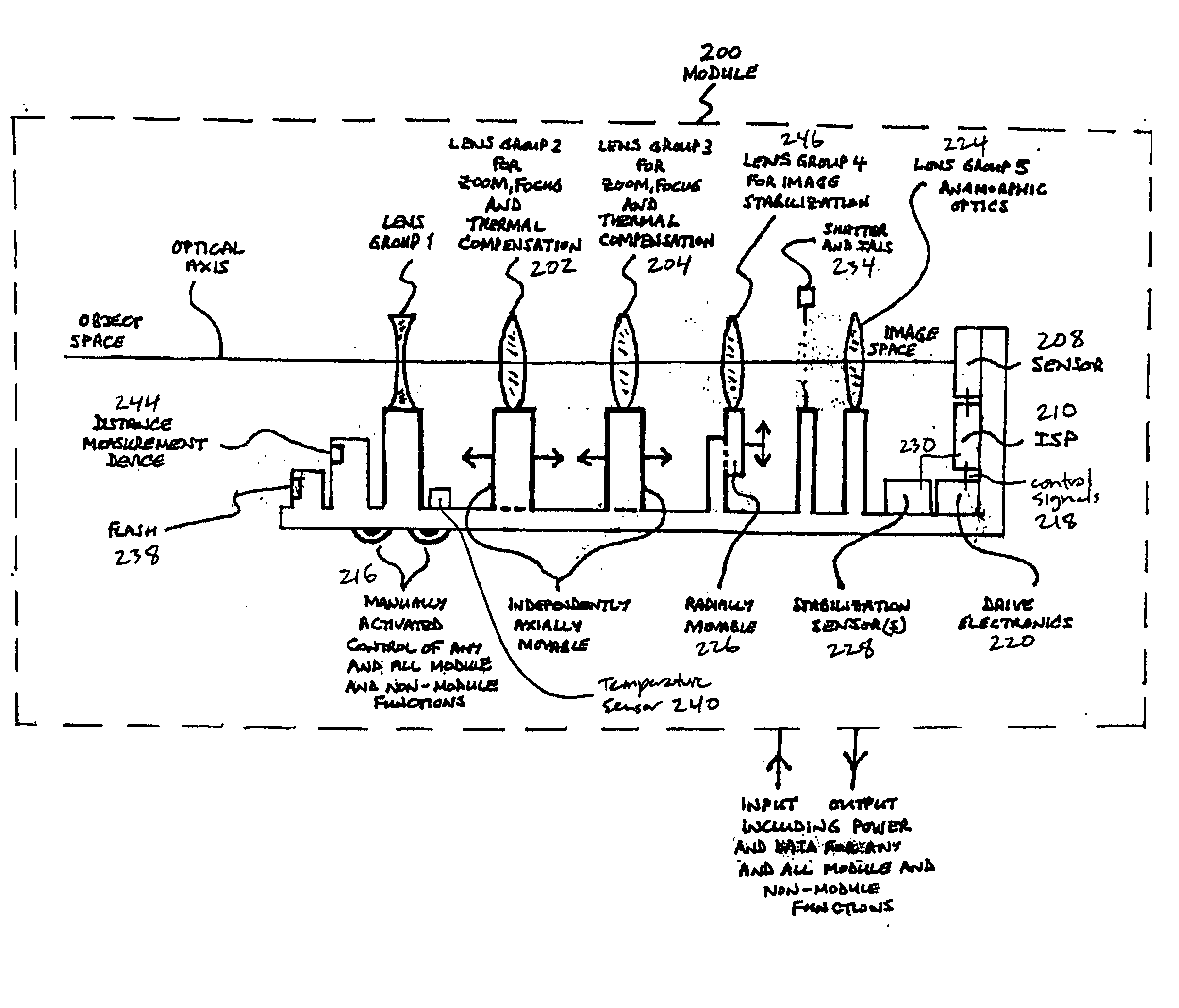
Method and apparatus for controlling a lens, and camera module incorporating same
InactiveUS20060045504A1Reduce the amount requiredShorten the timeTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsEngineeringFlash light
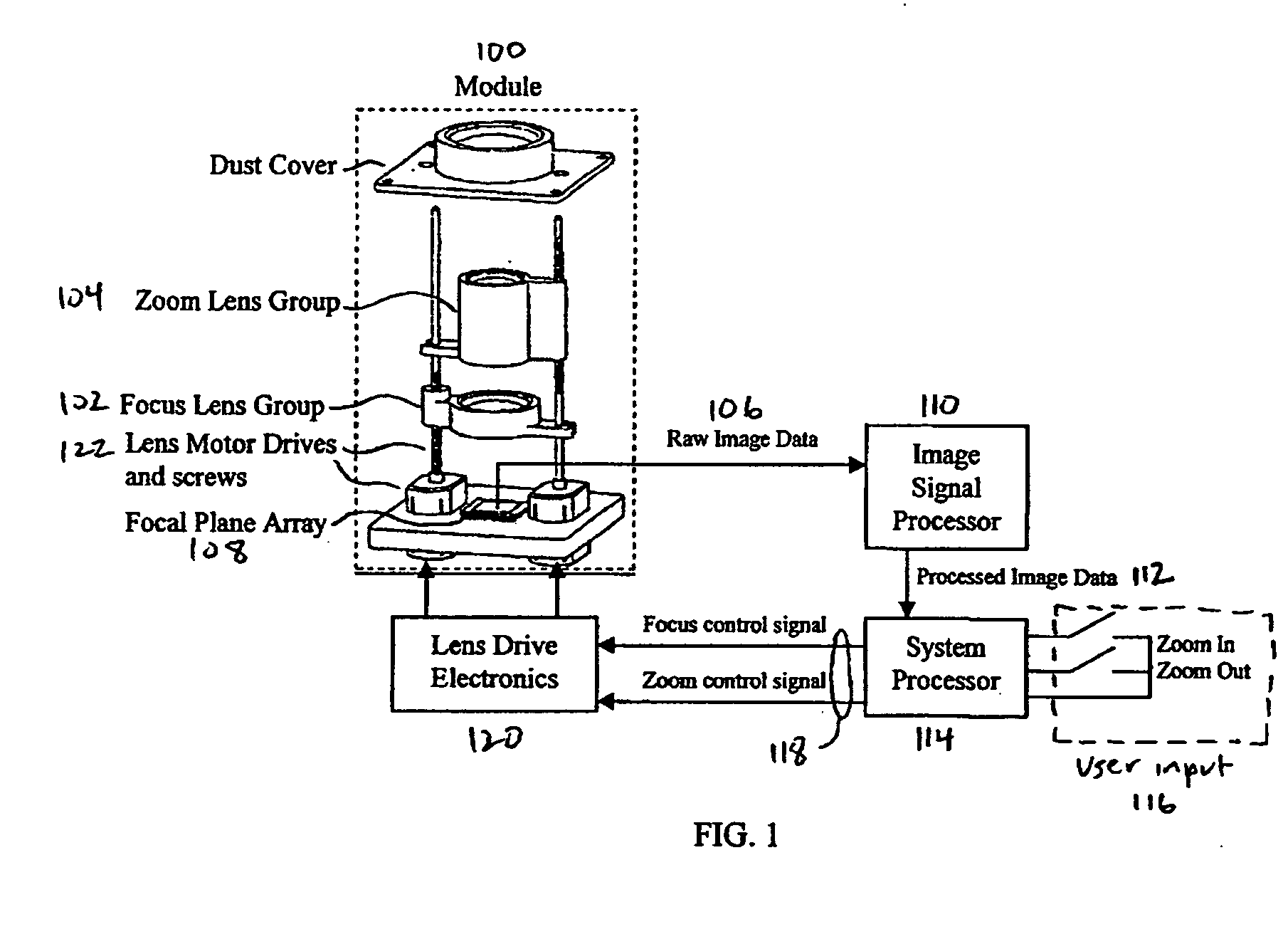
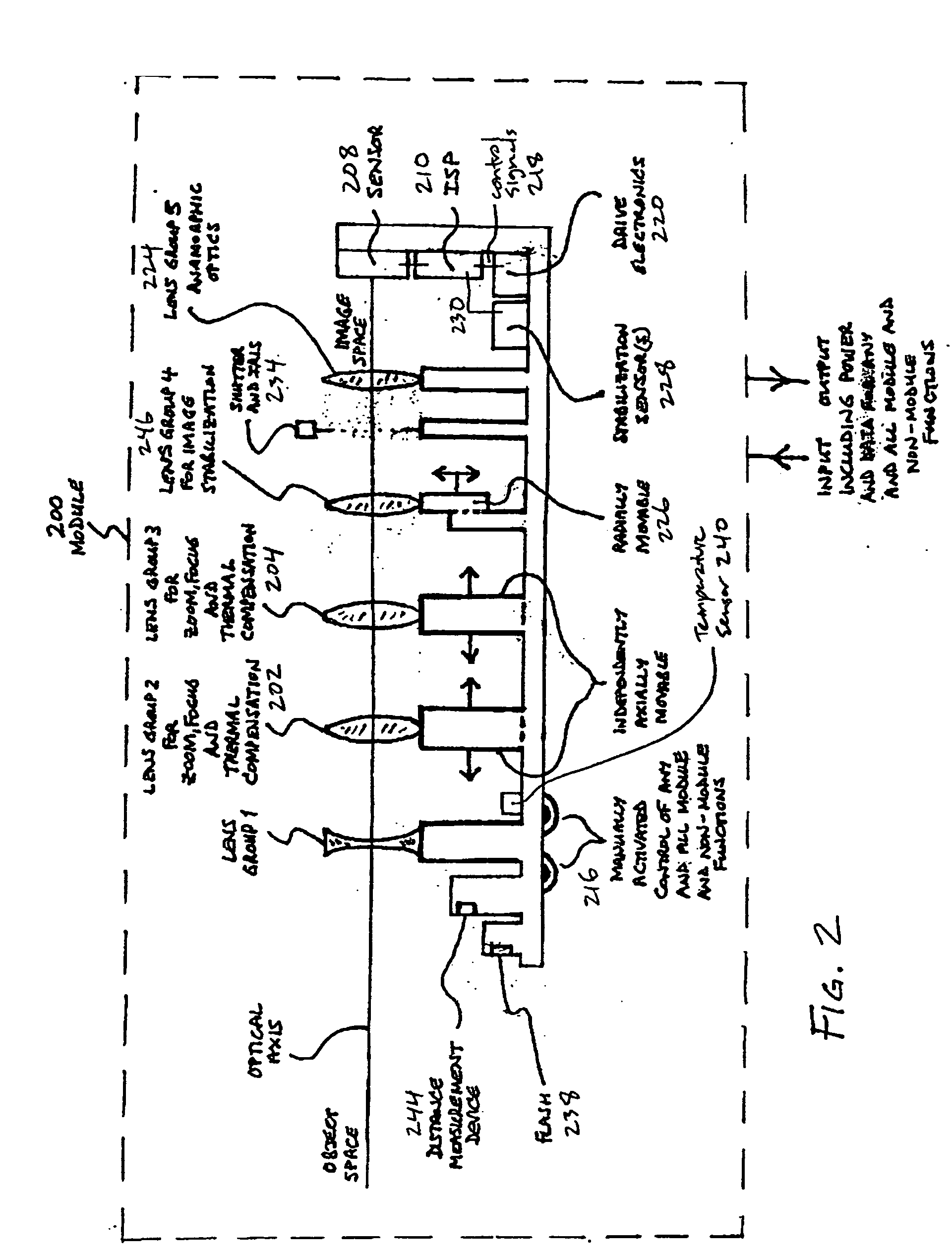
An efficient image capture system is disclosed that integrates functions to control a lens including one or more of focus or object distance, zoom, temperature compensation, and stabilization within an image signal processor (ISP) with appropriate algorithms. In particular, the integrated ISP circuitry may control the motion of the focus and zoom optics of an optical assembly, control stabilization, control the flash, provide enhanced functions and features for controlling the zoom and focus lenses to enable enhanced image capture sequences and / or tracking lens data, provide a set of algorithms within the ISP to alter the aspect ratio (both height and width of an image) of the image, for example to compensate for the addition of an anamorphic lens, and integrate an anamorphic lens into the module to alter an image's projected aspect ratio onto the focal plane array.
Owner:DYNAMAX IMAGING
Image pickup apparatus and method and apparatus for manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20080007797A1Increase contrastLittle blurTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsWavefrontObject based
An image pickup apparatus includes an element-including optical system, a detector, and a converter. The element-including optical system has an optical system and an optical wavefront modulation element which modulates an optical transfer function. The detector picks up an object image that passes through the optical system and the optical wavefront modulation element. The converter generates an image signal with a smaller blur than that of a signal of a blurred object image output from the detector by performing a filtering process of the optical transfer function to improve a contrast. A focal position of the element-including optical system is set by moving the element-including optical system to the focal position which is corresponding to a predetermined object distance using a contrast of the object based on the image signal.
Owner:KYOCERA CORP
Method of manufacturing progressive power spectacle lenses
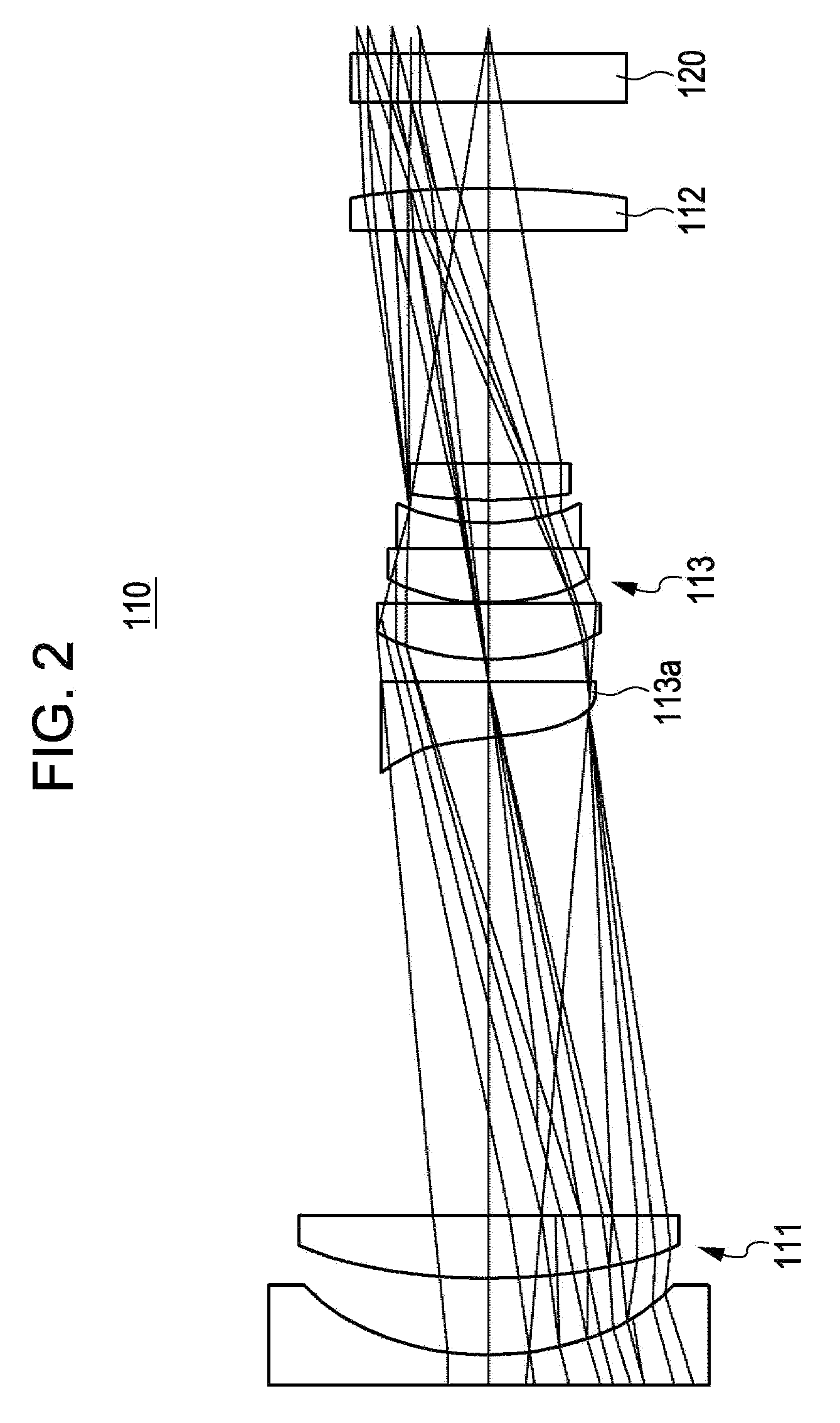
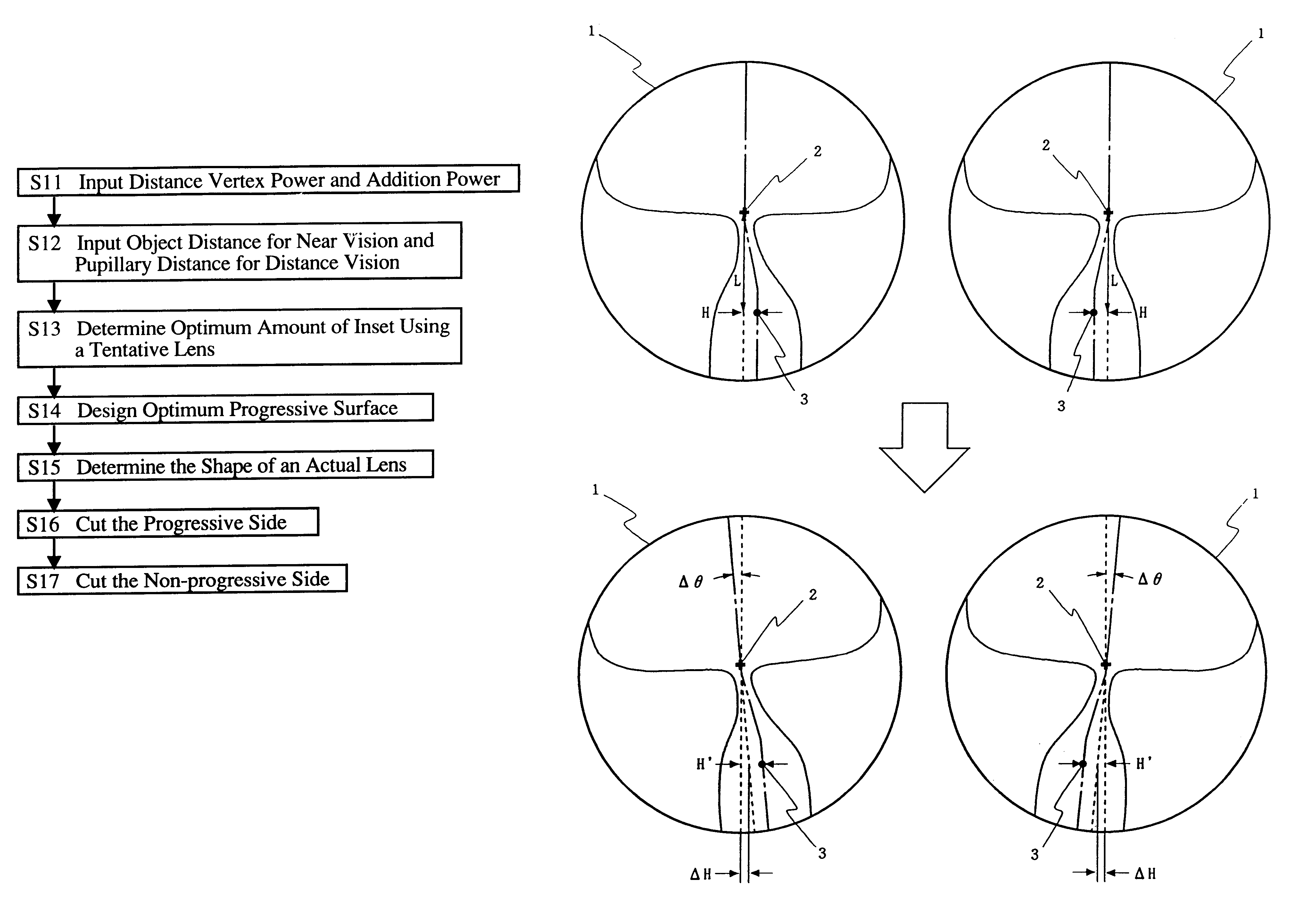
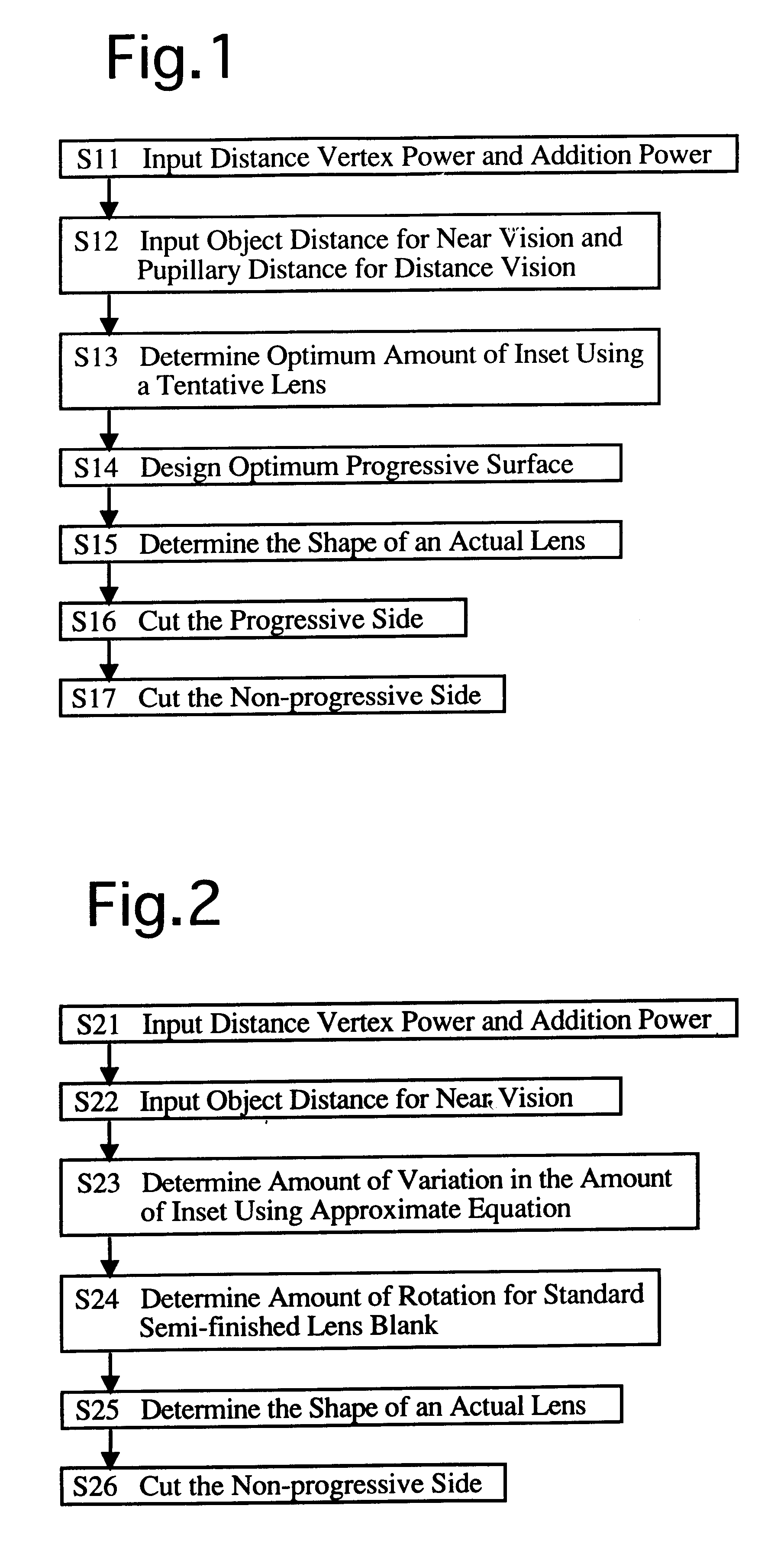
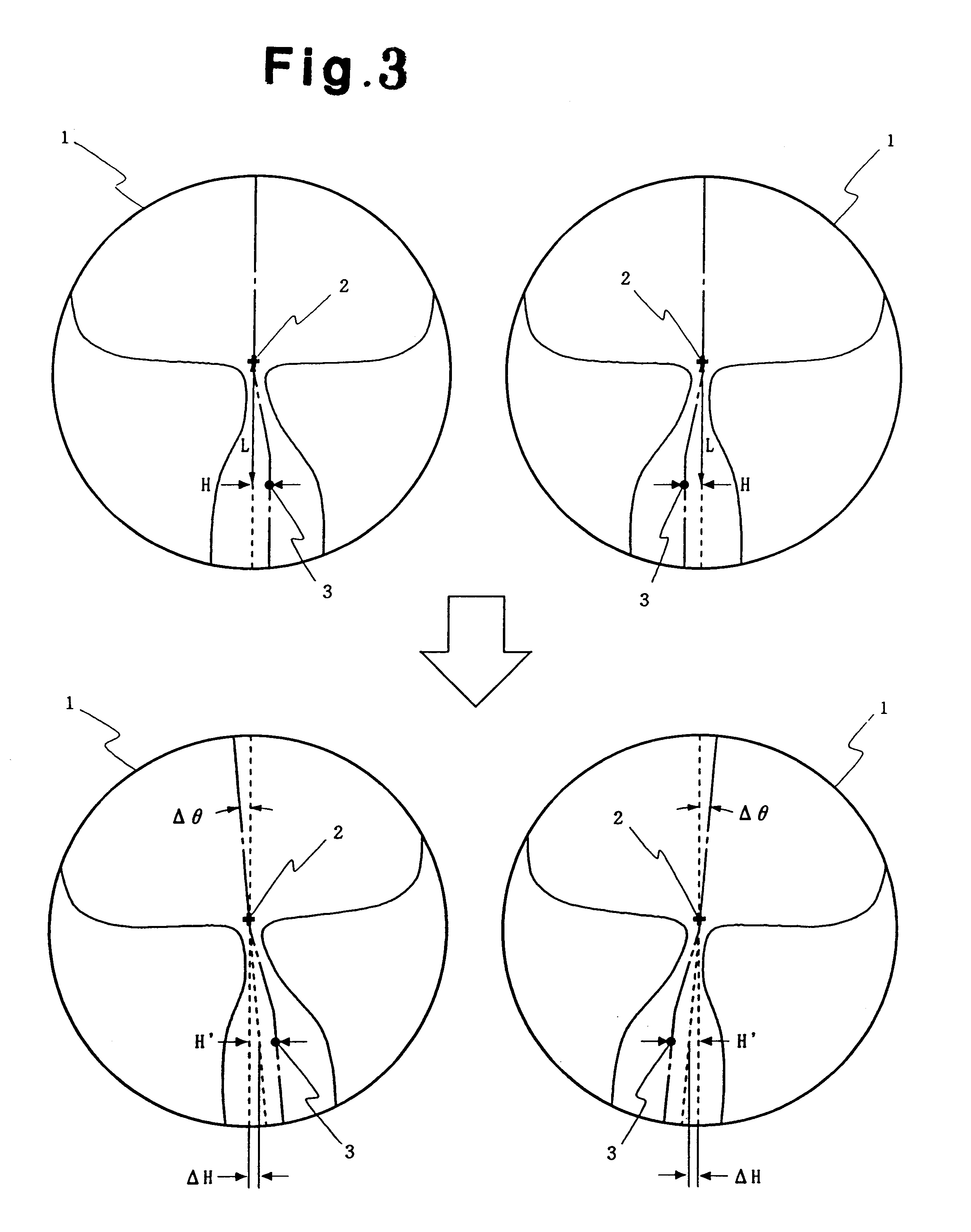
A method of manufacturing progressive power spectacle lenses includes preparing individual fitting condition data for a lens-wearer such as object distances for near and distance vision, the distance from the point-of-rotation of each eyeball of a lens-wearer to each spectacle lens, the pantoscopic angle of the spectacle lenses when fitted onto said lens-wearer, and determining an amount of inset in accordance with said individual fitting condition data.
Owner:SEIKO OPTICAL PROD TRADING AS SEIKO OPTICAL PROD +1
Process for automatic focusing
InactiveCN1464323AGuaranteed accuracyEasy to removeTelevision system detailsColor television detailsLarge distanceDigital image
The automatic focusing technology is used for finding out optimized focus position in the cases of insufficient background brightness, over large distance between the taken body and the background and varying background during focusing. The automatic focusing process includes the following steps: adjusting the focal length of the lens in the focusing range to obtain one frame of digital image in each relative position; separating the digital image into several regions and finding out the evaluation value for each region; weighting each region; finding out relative position evaluation value to the digital image found for each relative position based on the region evaluation value and region weight; recording the relative position with maximum evaluation value and focusing the lens to the position as optimal focusing position.
Owner:GUANGDONG VIMICRO
Method and system achieving integrated camera automatic focusing
InactiveCN103546692AImplement mobile controlMeet real-time requirementsTelevision system detailsColor television detailsComputer scienceMobility control
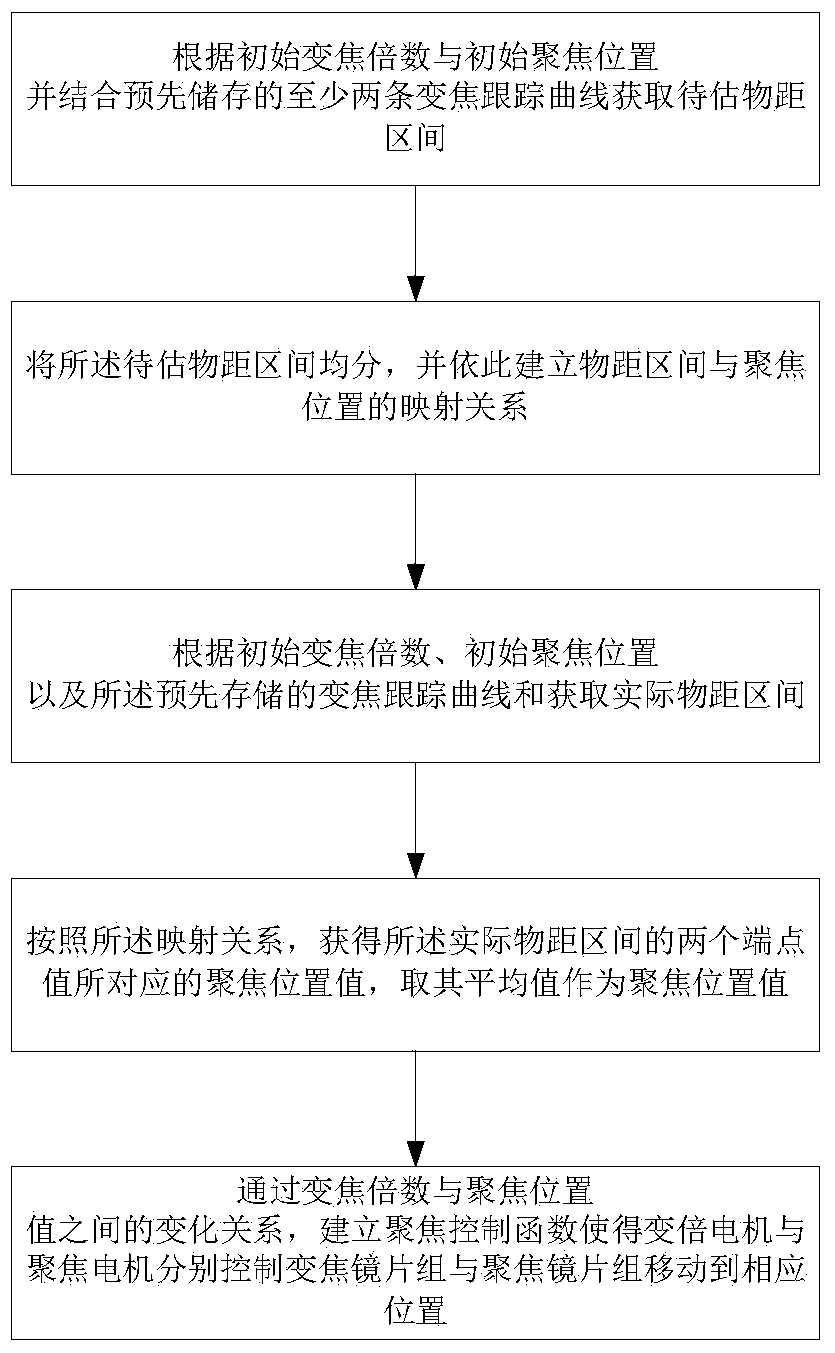
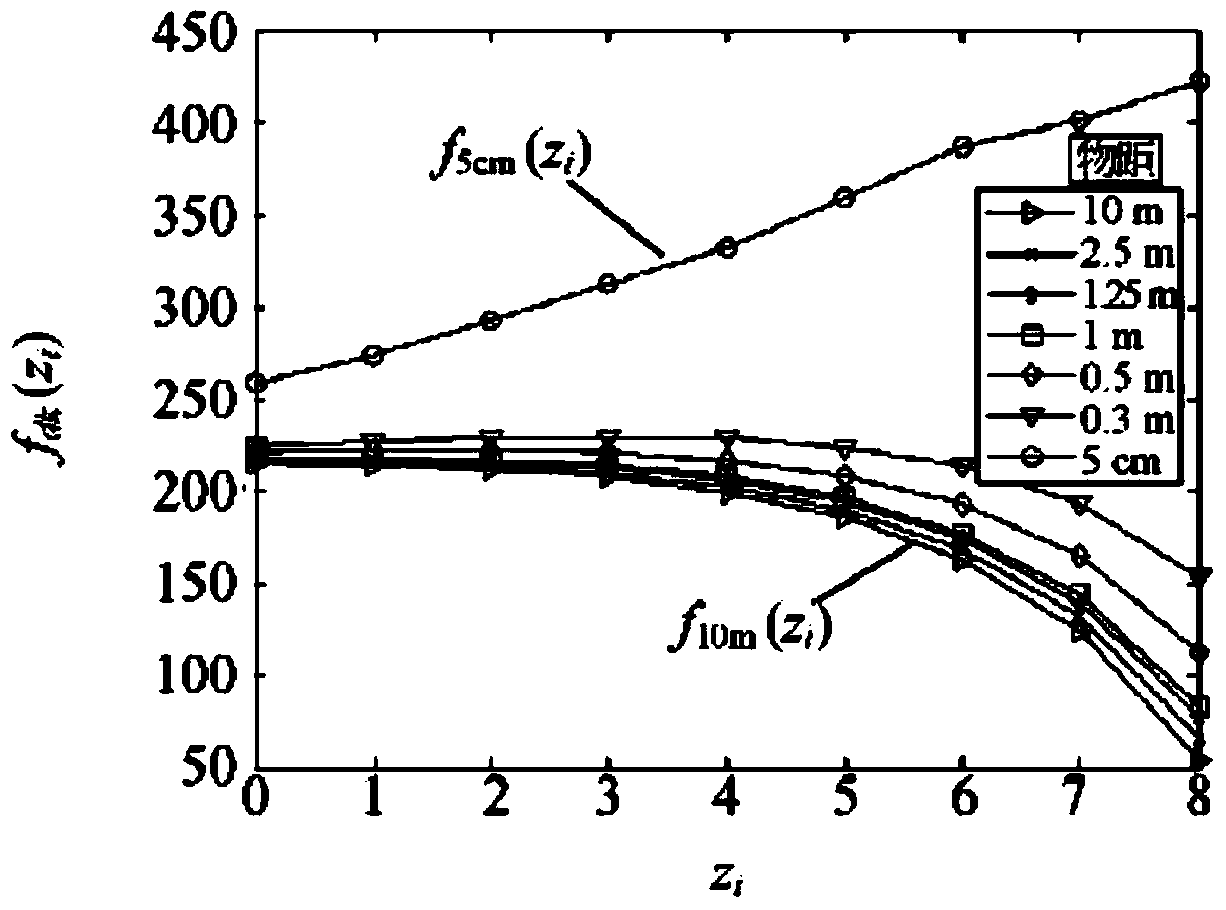
The invention provides a method and system for achieving integrated camera automatic focusing, and provides a zooming tracking method based on a relationship type, namely for a shot object at a fixed object distance, according to the initial zooming multiple, the value of an initial focusing position and a plurality of zooming tracking curves stored in advance, the mapping relation between the object distance interval and the focusing position is constructed, and the position to be focused is calculated in real time. Then, a gradient control function obtained by the combination of the statistical law of a lot of experimental data is utilized to achieve mobility control over a zooming motor and a focusing motor, the value of the position to be focused is improved and amended to a certain degree, the value of the position to be focused is closer to a real zooming tracking curve, and an automatic focusing effect is more accurate. Meanwhile, the zooming tracking curves are not needed to be stored in advance, all the zooming tracking curves corresponding to different object distances are not needed to be calculated point by point, an algorithm is simple, it is possible that the zooming speed meets a real-time property, and the focusing effect can meet the requirement for clearness in the whole process.
Owner:SUZHOU KEDA TECH
Method for obtaining three-dimensional information of space non-cooperative object
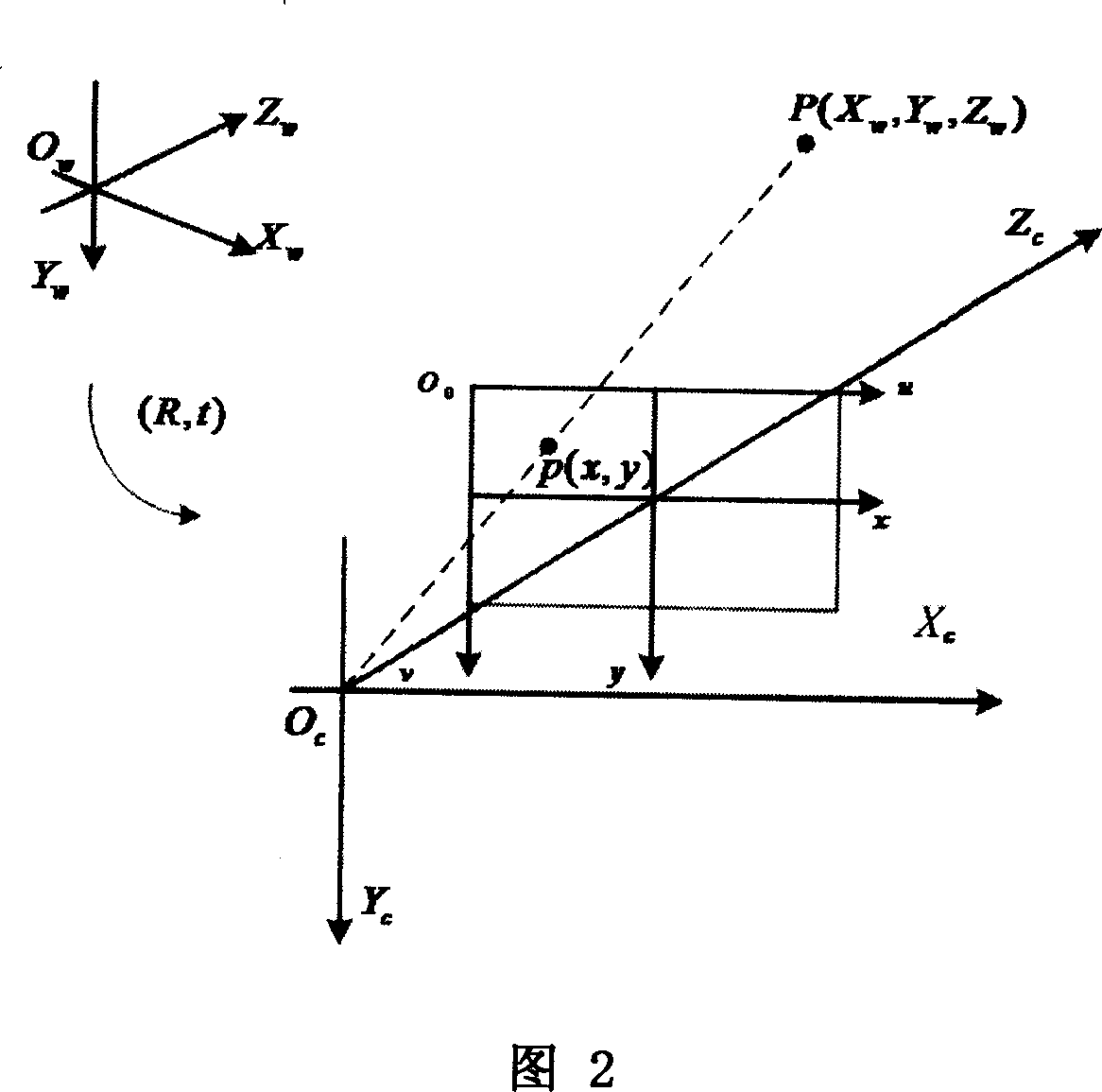
InactiveCN101033972AImprove estimation accuracyImprove reliabilityNavigation by astronomical meansElectromagnetic wave reradiationSpace objectDigital image processing
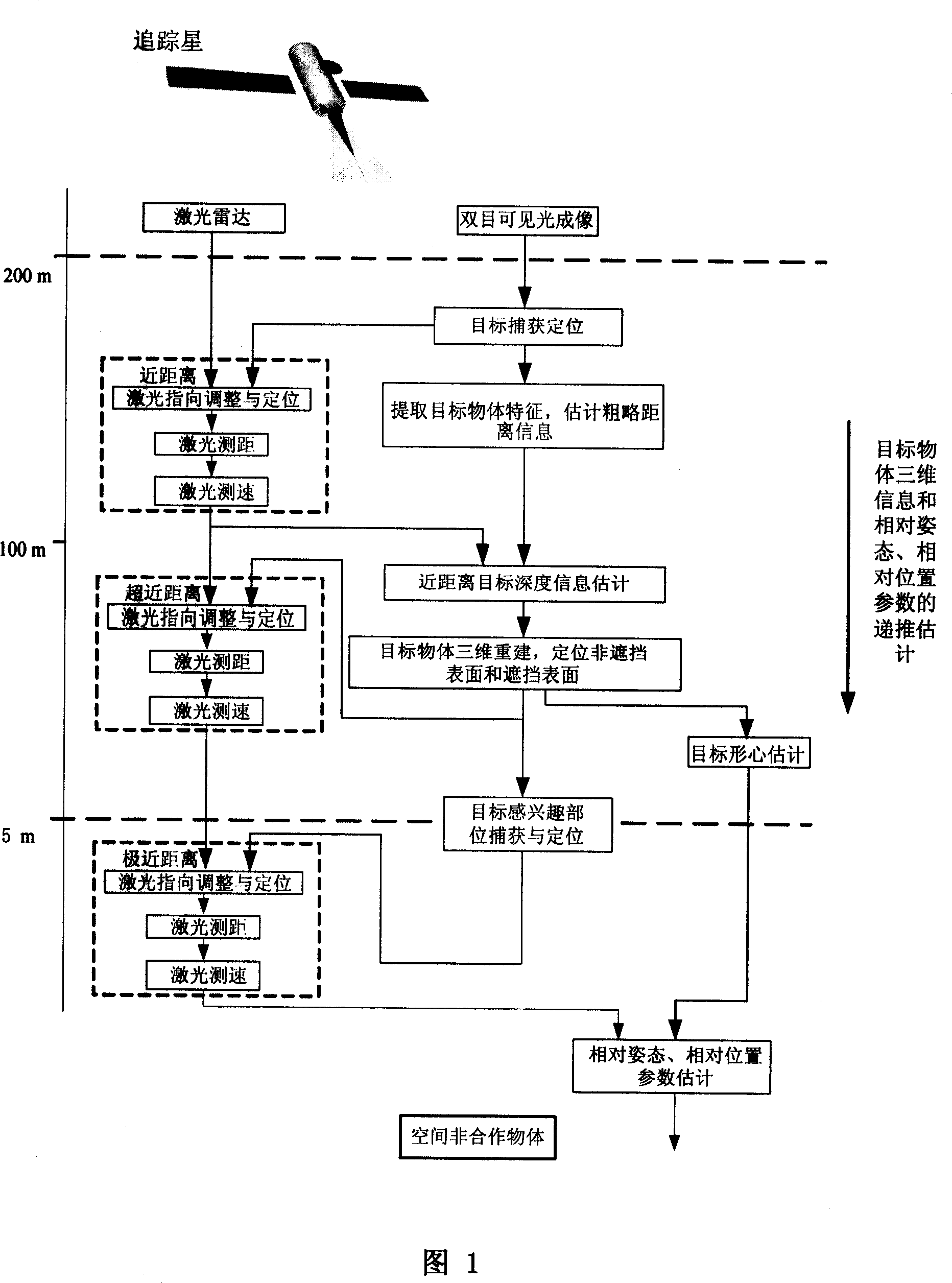
This invention relates to the obtaining method of a kind of space non-cooperation objects three dimensional information, belong to digital image processing. This invention is designed to observe the close-range approaching course of star and space non-cooperation objects, order include:(1) processing procedure of closer object estimate, from object distance 200m to 100m, (2) processing procedure of exceed closer object estimate, and object distance 100m to 5m;(3) Processing procedure of terrible closer object estimate, and object distance 5m to 0m. Along the successive approximation of star and space object, estimated accuracy of each handle parameter increasing, error drop off, reliability increasing, real-time character and accuracy all get guarantee; Can be use for independence image guide when slowly move to object that possess polyhedron character under unknown environment.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com