Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
2524results about "Optical surface grinding machines" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
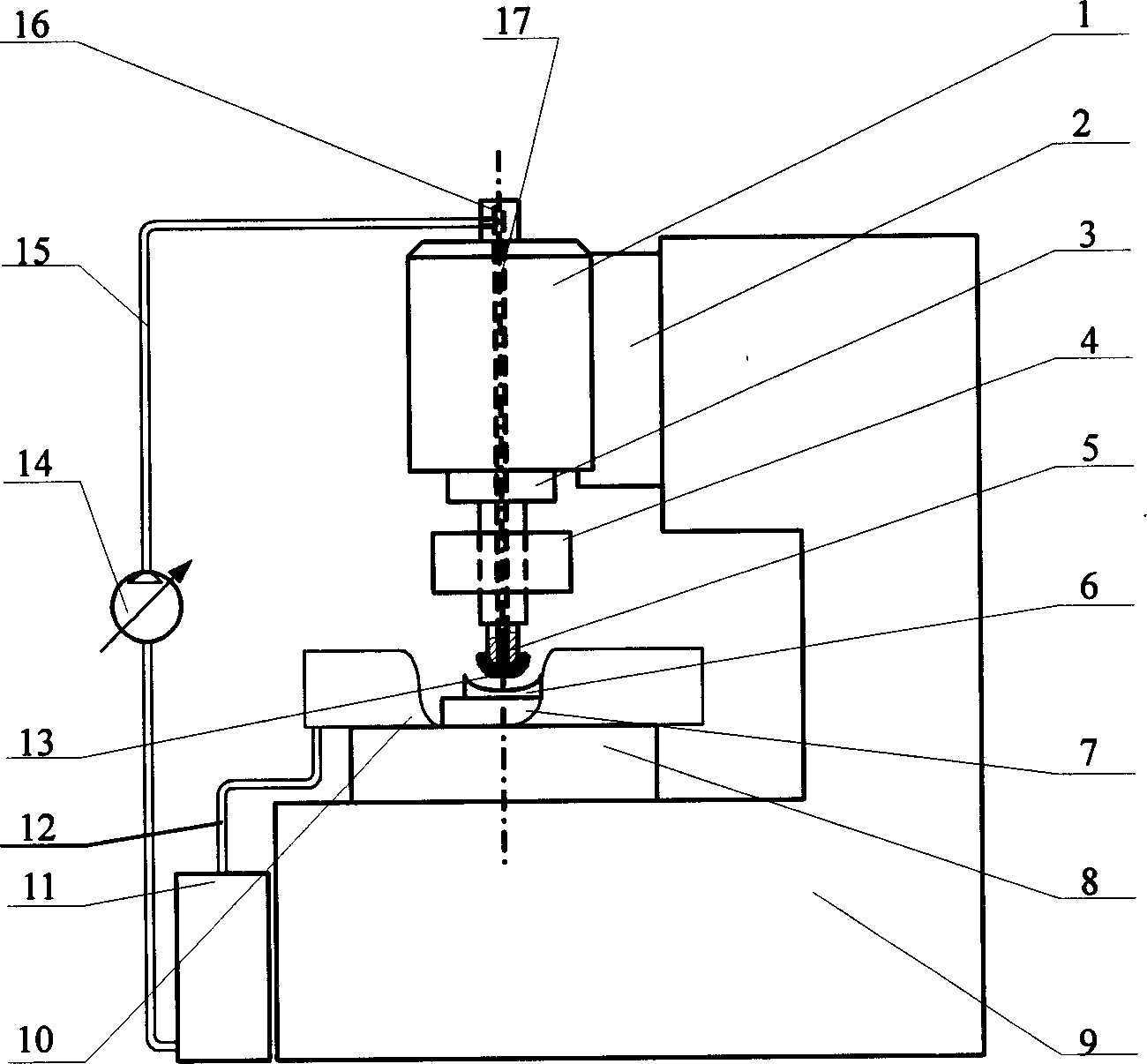
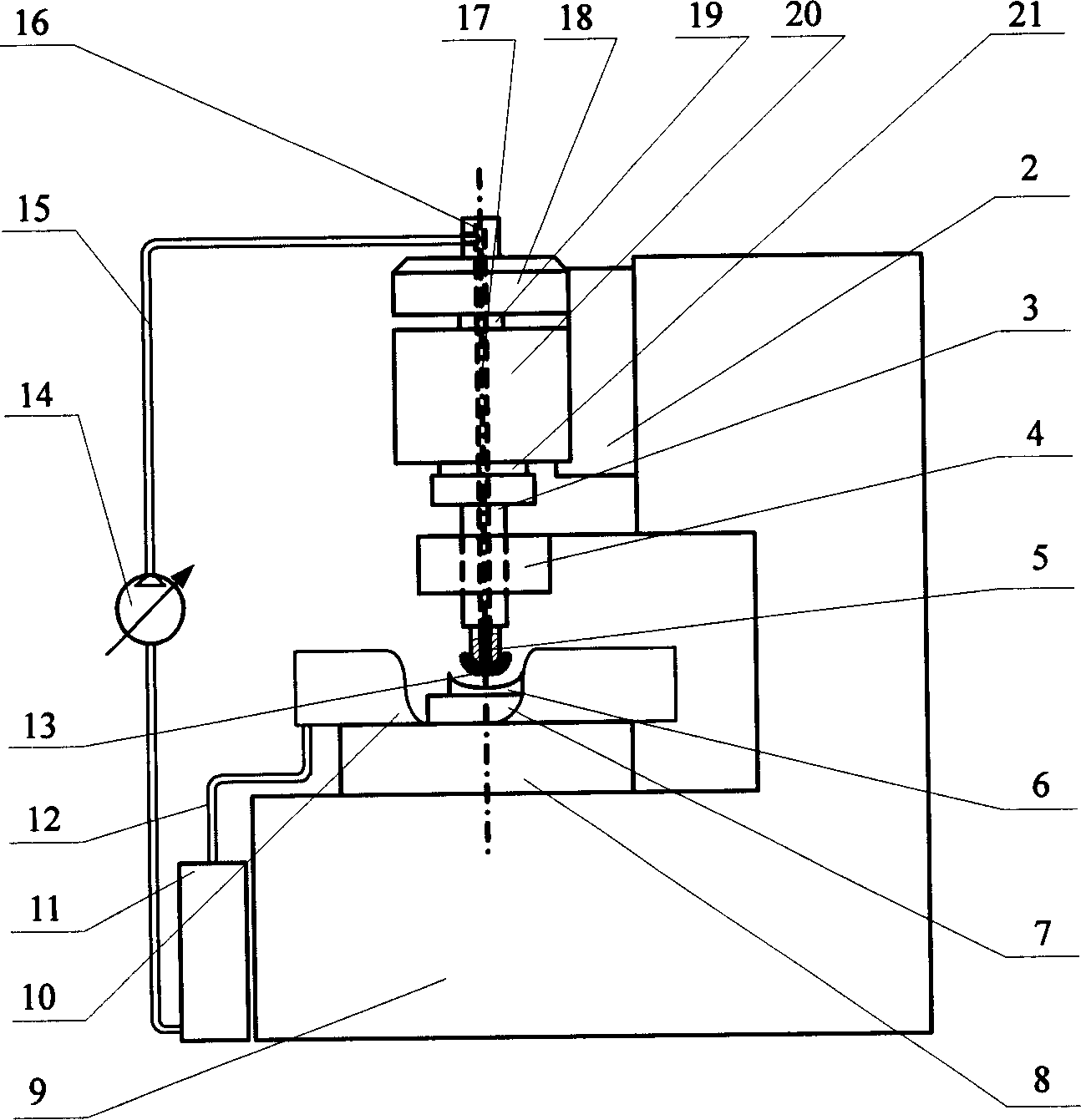
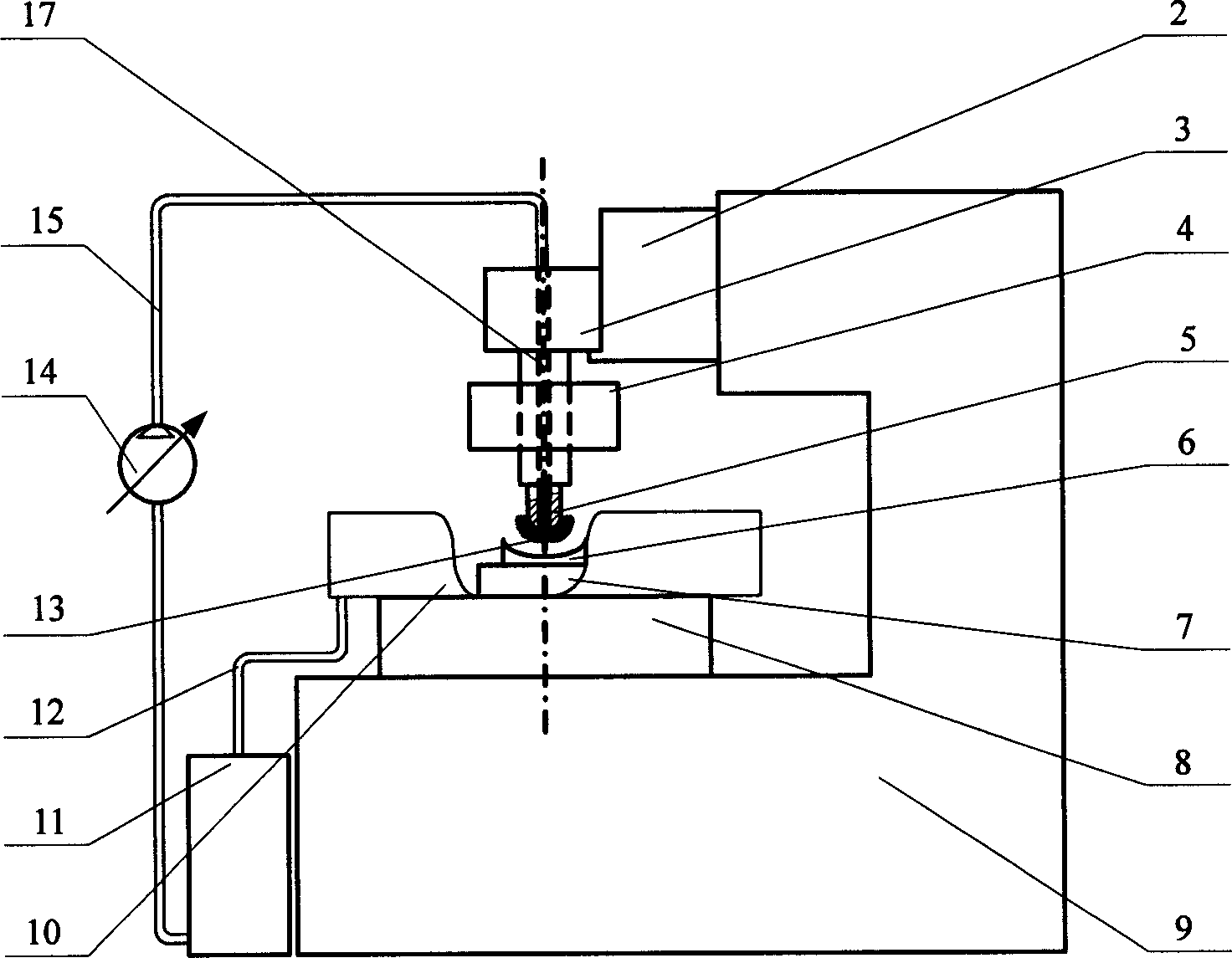
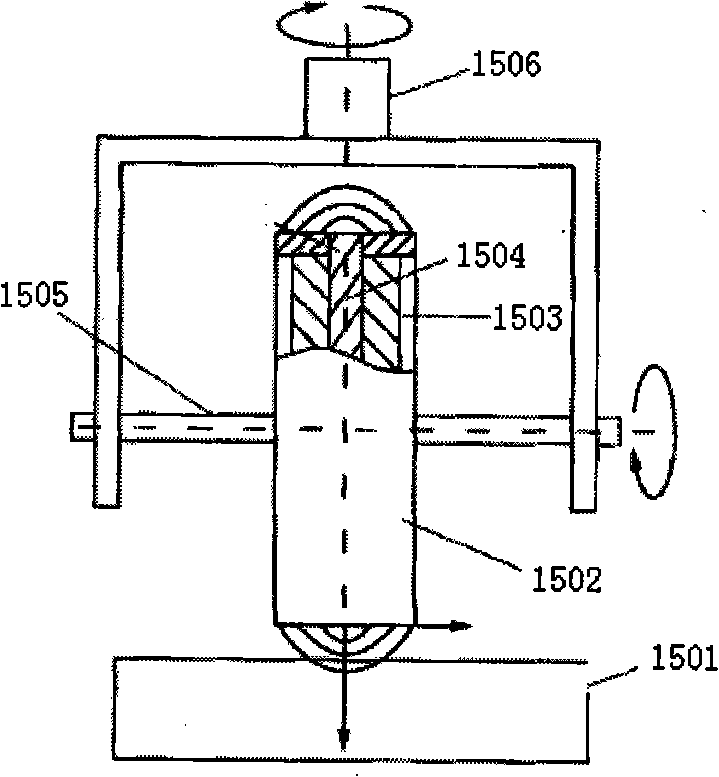
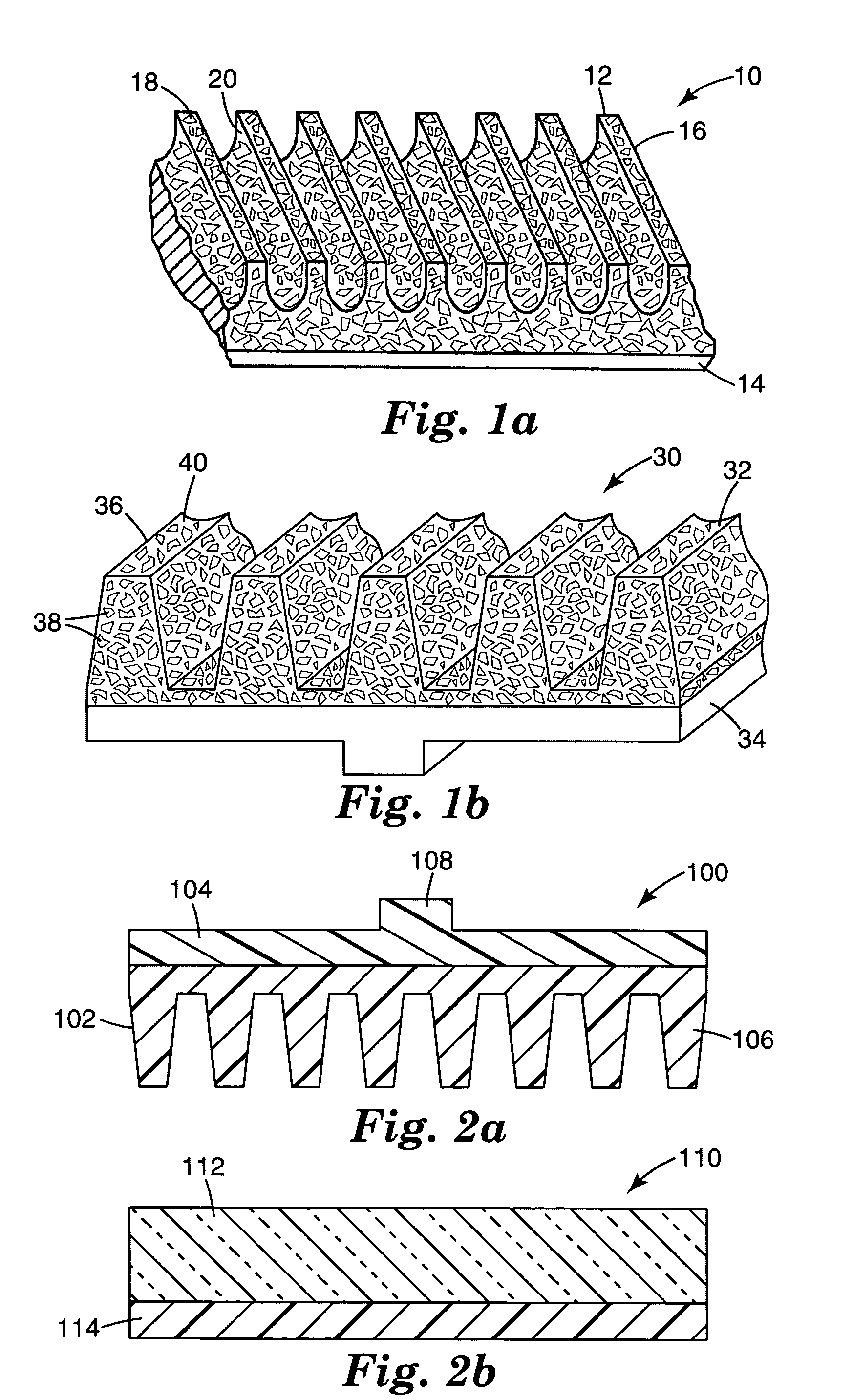
Ultrasonic magnetic rheological composite polishing method and polisher thereof
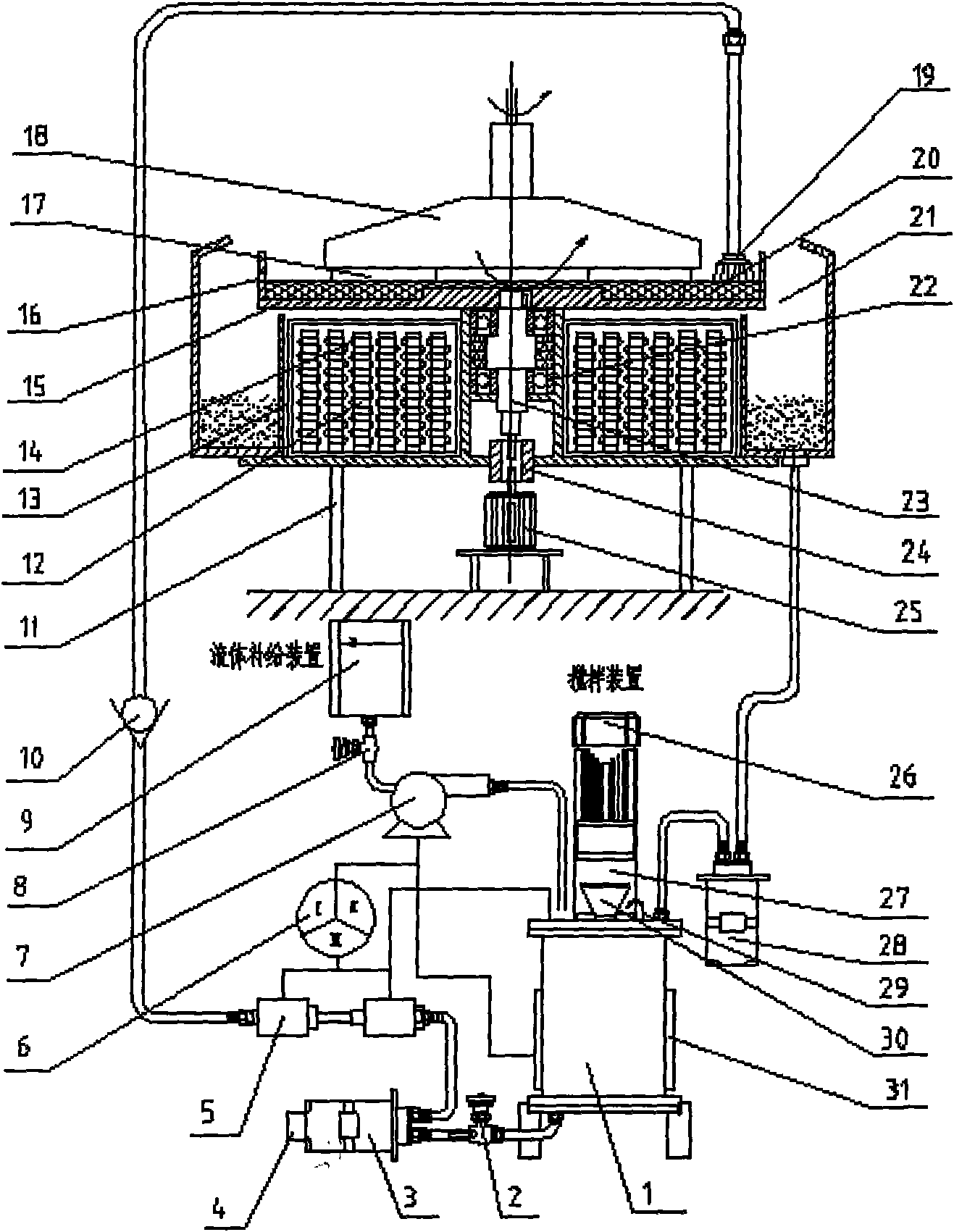
InactiveCN1613605AAchieve recyclingStable Polishing PropertiesOptical surface grinding machinesUltrasonic vibrationEngineering
An ultrasonic-magnetorheologic polishing method features that the mixture of abrasive material and magnetorheologic liquid is filled in a small-diameter rotary hollow polishing head and a magnetic field is applied to it to make the magnetorheologic liquid become flexible polishing liquid on the polishing head while the ultrasonic vibration is applied to it for higher polishing effect. Its apparatus is composed of polishing head, ultrasonic generator, and electromagnet.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
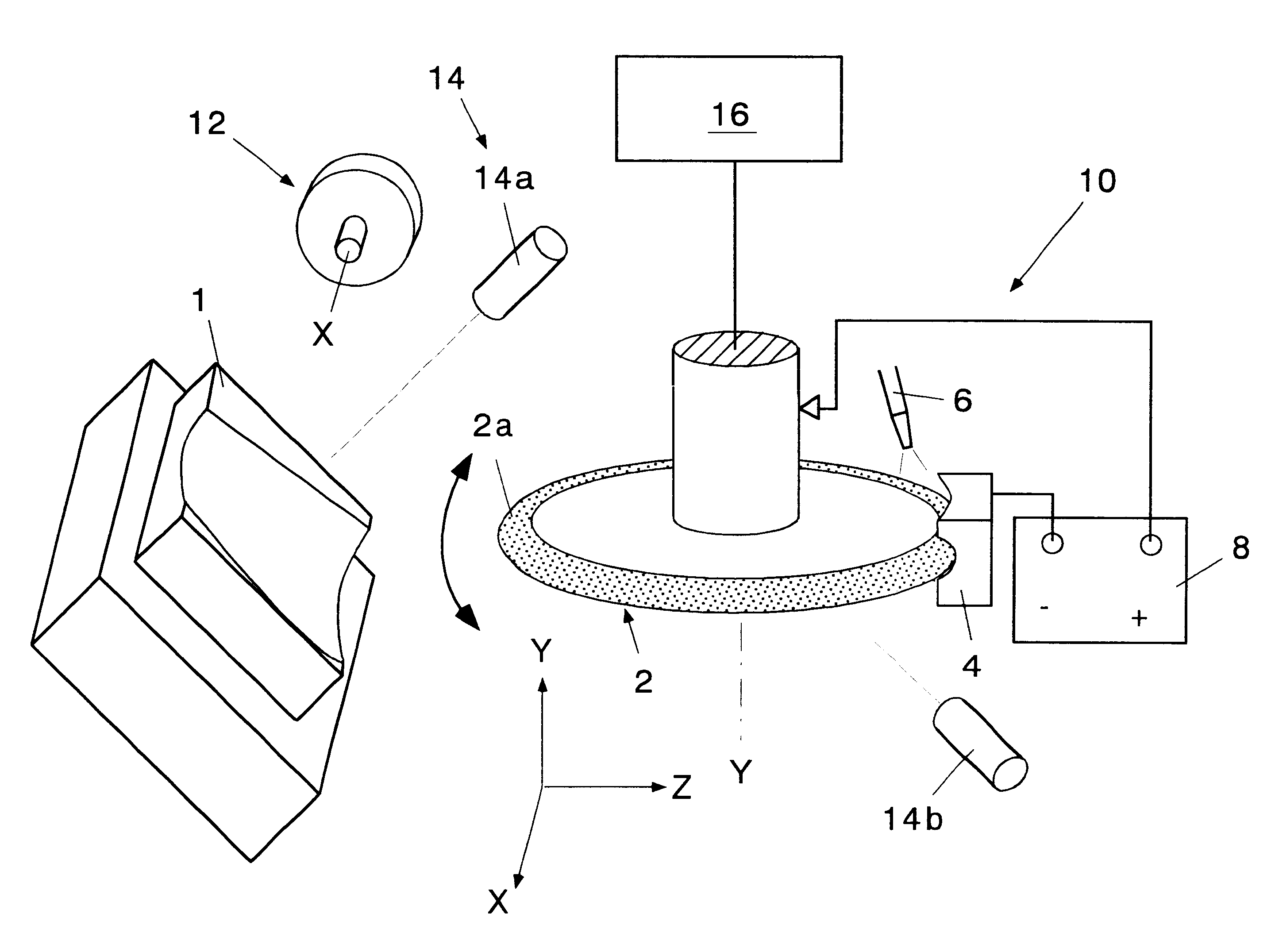
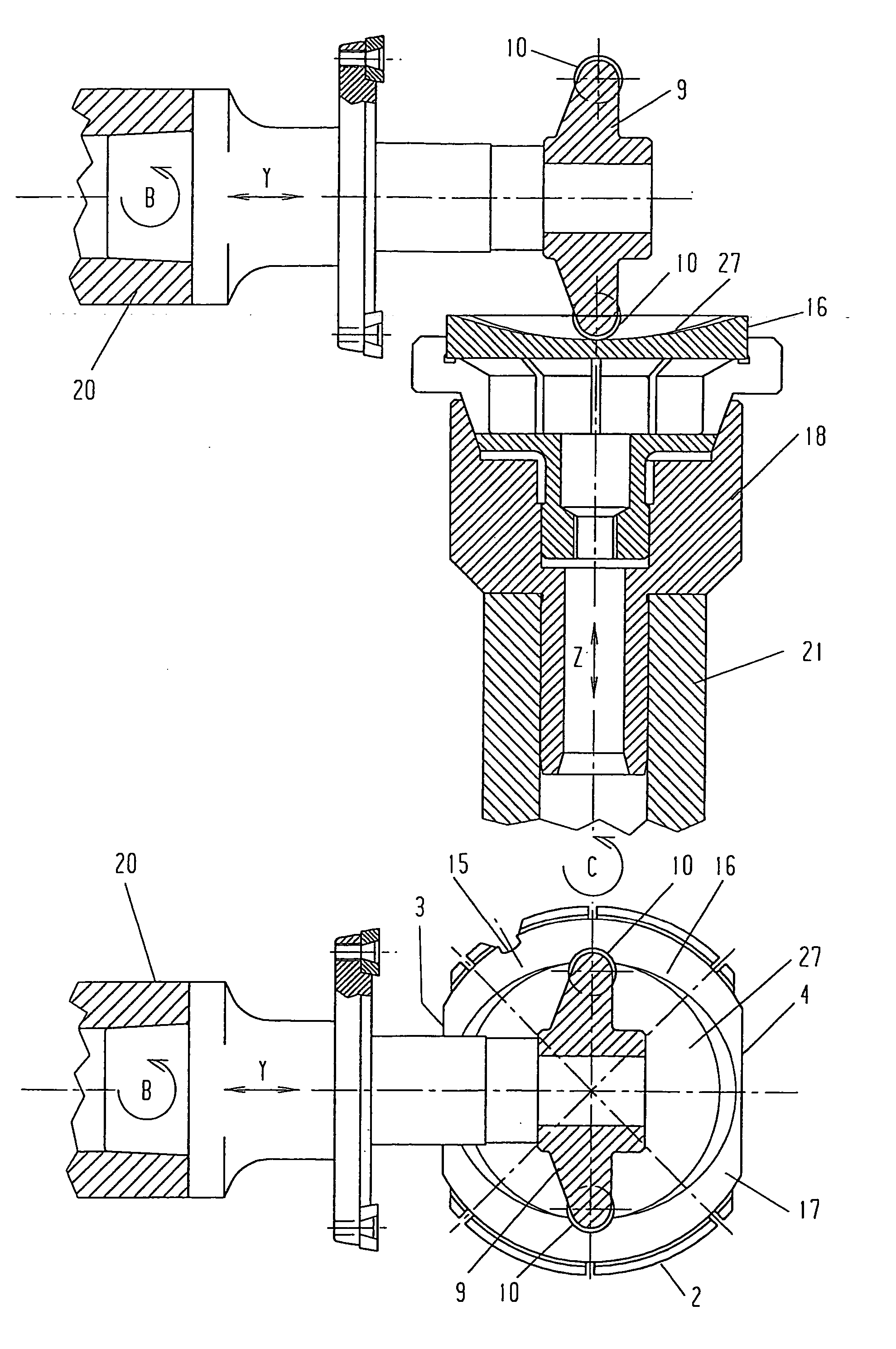
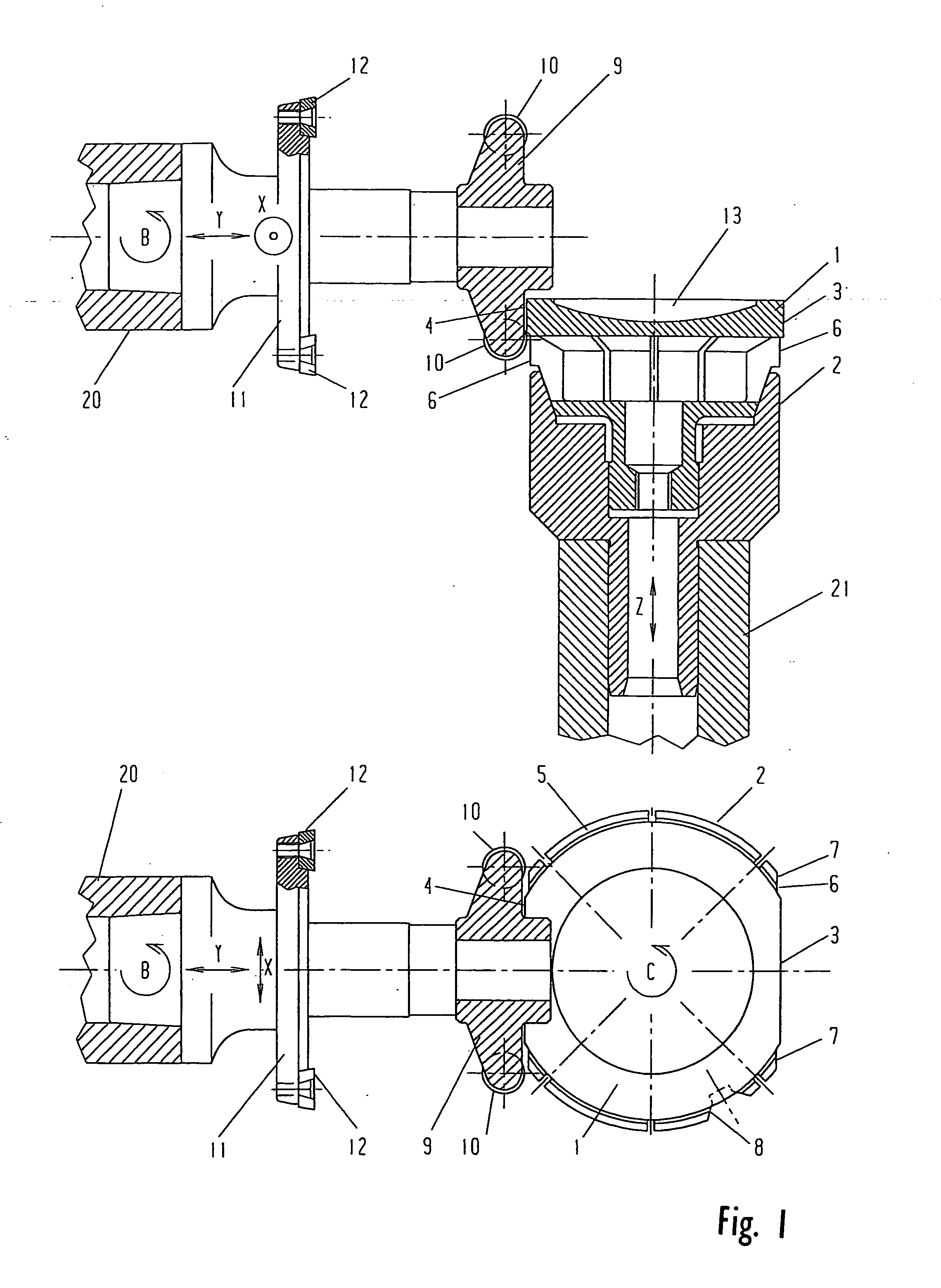
Method of grinding an axially asymmetric aspherical mirror
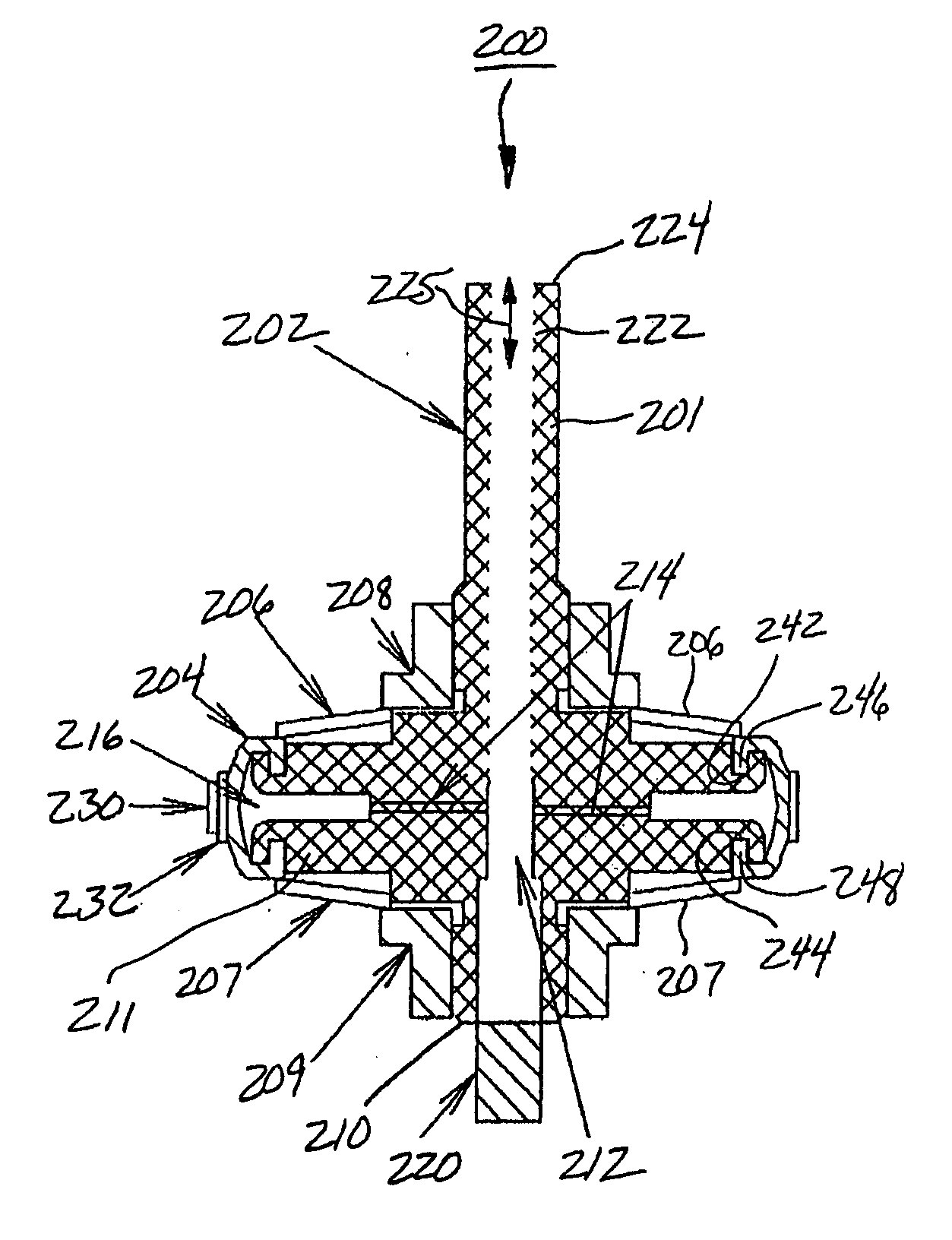
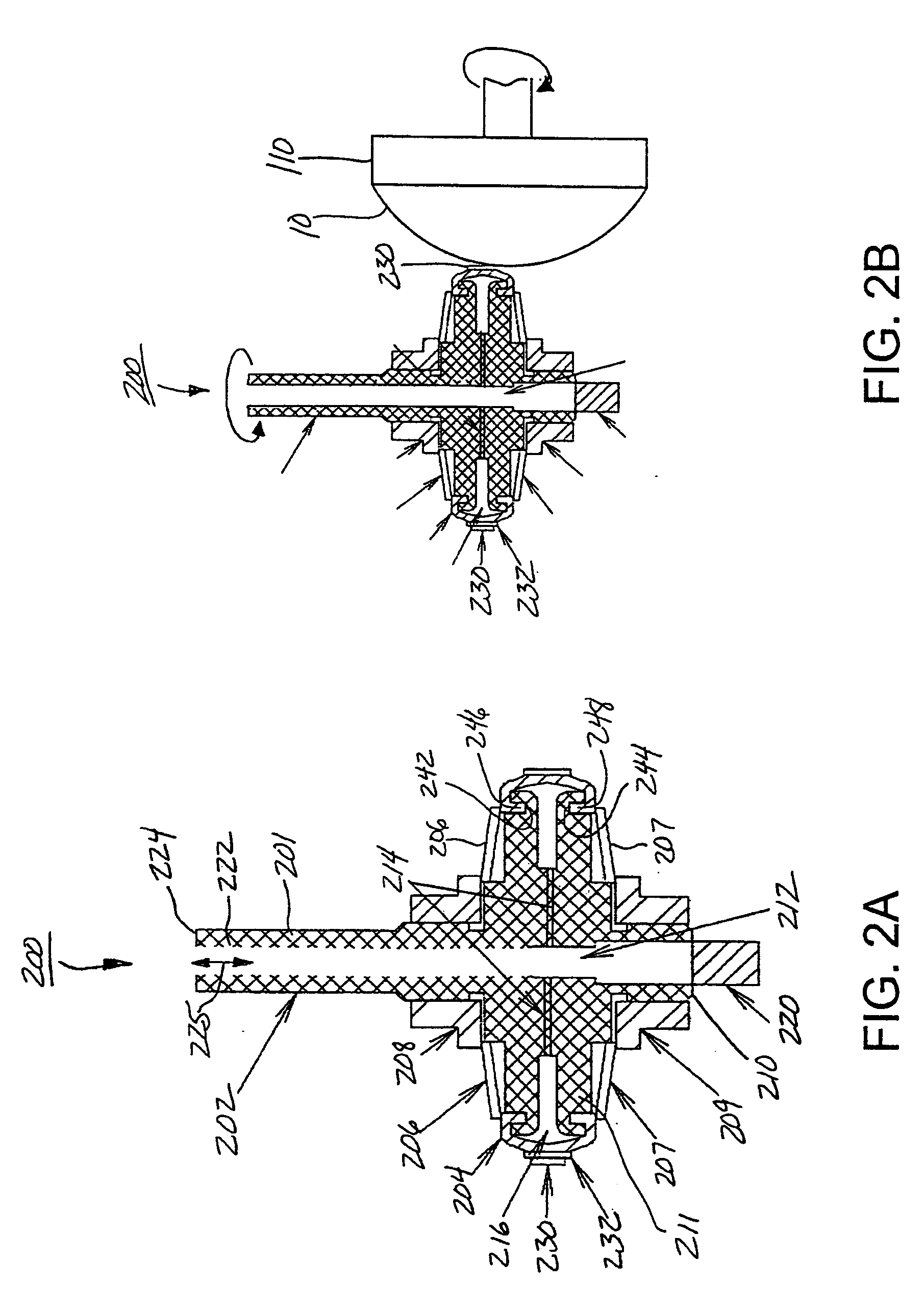
InactiveUS6537138B2Improve accuracyReliably madeEdge grinding machinesOptical surface grinding machinesNumerical controlSurface roughness
An electrolytic in-process dressing device 10 is provided with a disk-shaped metal-bonded grindstone 2 with a surface 2a with a circular arc shape with a radius R at its outer periphery and a numerical control device 16. The disk-shaped metal-bonded grindstone 2 rotates around an axis Y, and the grindstone is dressed electrolytically while the device 10 grinds the workpiece 1. The numerical control device 16 is provided with a rotary truing device 12 that rotates around the X axis that orthogonally crosses the axis of rotation Y and trues the circular arc surface 2a, a shape measuring device 14 for measuring the shape of the circular arc surface of the grindstone and the shape of the processed surface of workpiece 1 on the machine, and controls the grindstone numerically in the three directions along the axes X, Y and Z. The numerical control device 16 moves the grindstone in three axial directions and repeats the operations of truing, grinding and measurements on-line. Thus, an axially asymmetrical aspheric mirror with a highly accurate shape and extremely low surface roughness, that can precisely reflect or converge light can be manufactured within a short time with a high accuracy.
Owner:RIKEN +1
Efficient numerically controlled polishing process and apparatus for great aperture aspherical optical elements
InactiveCN101088705AReduce dependenceImprove efficiencyOptical surface grinding machinesOptical surfaceMachining process
The efficient numerically controlled polishing process and apparatus for great aperture aspherical optical elements belongs to the field of precise optical machine technology. The polishing process includes: constituting polishing process model based on the profile data obtained through measurement with interferometer or other instrument, determining the machining path, speed, pressure and other parameters of the element under the control of computer to perform simulating machining, verifying the technological parameters based on the simulating machining results and determining the ultimate technological parameters, creating NC program and machining. The present invention has high machining efficiency and high machining precision.
Owner:CHANGCHUN EQUIP TECH RES INST
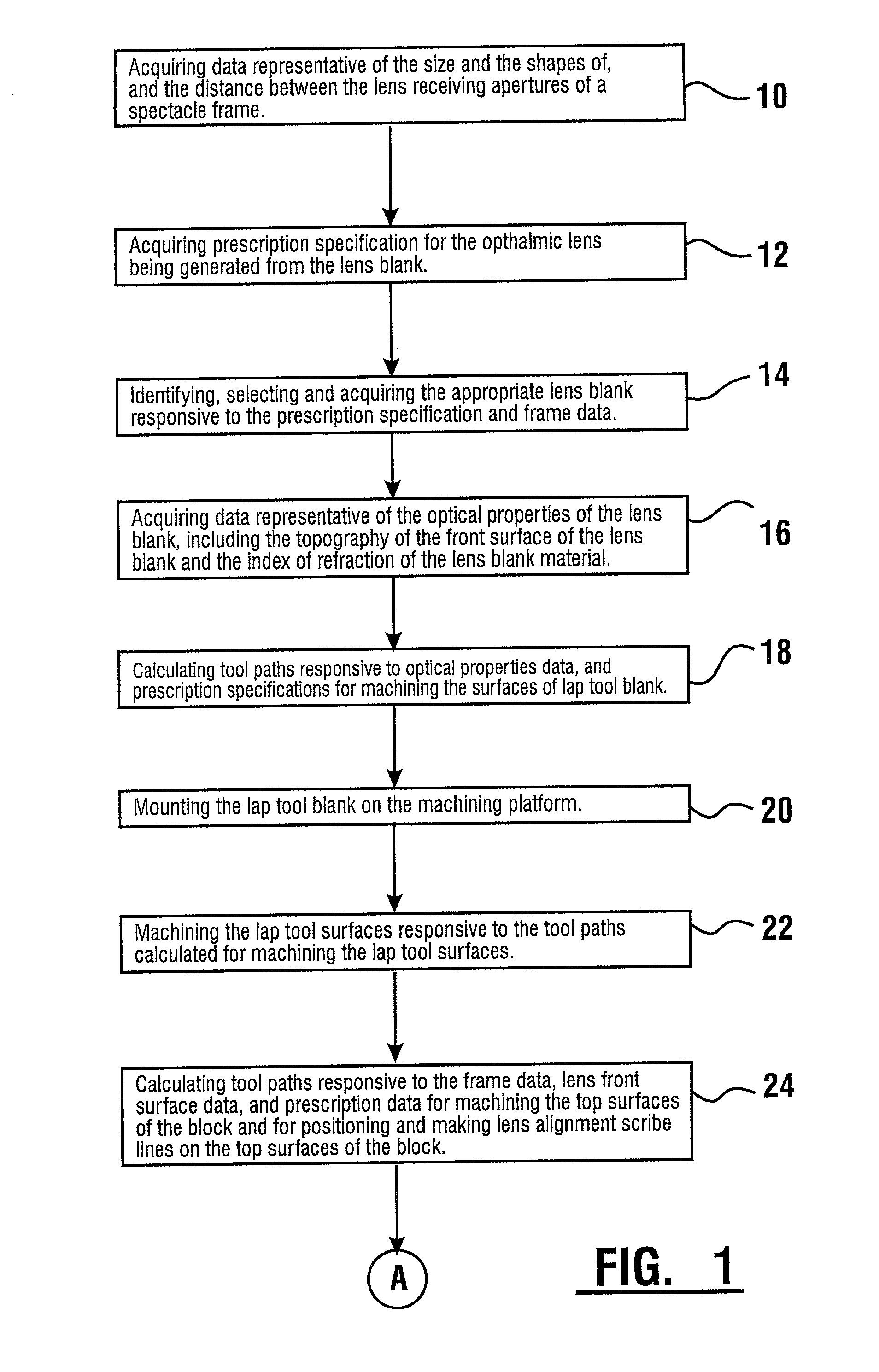
System for manufacturing an optical lens
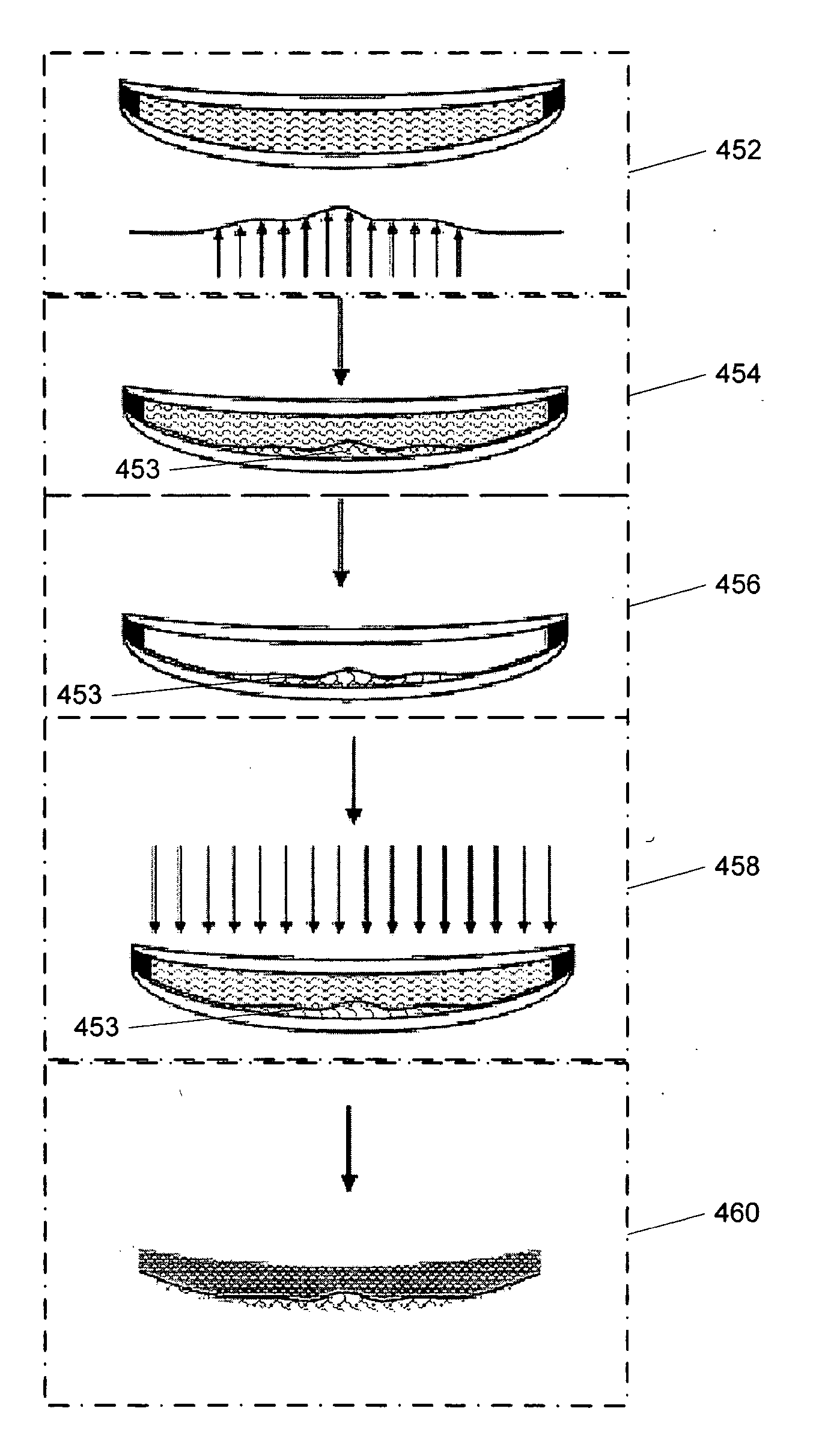
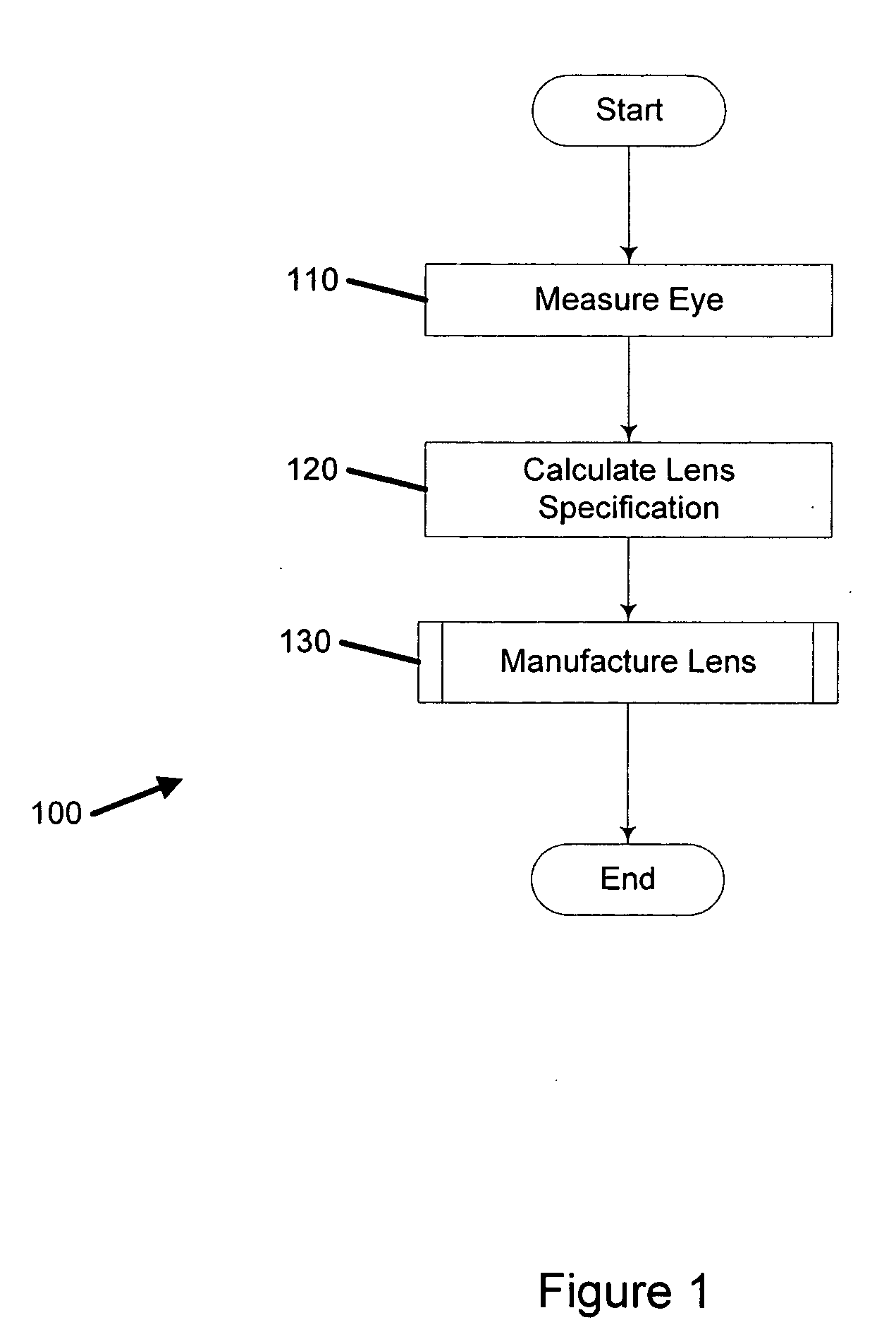
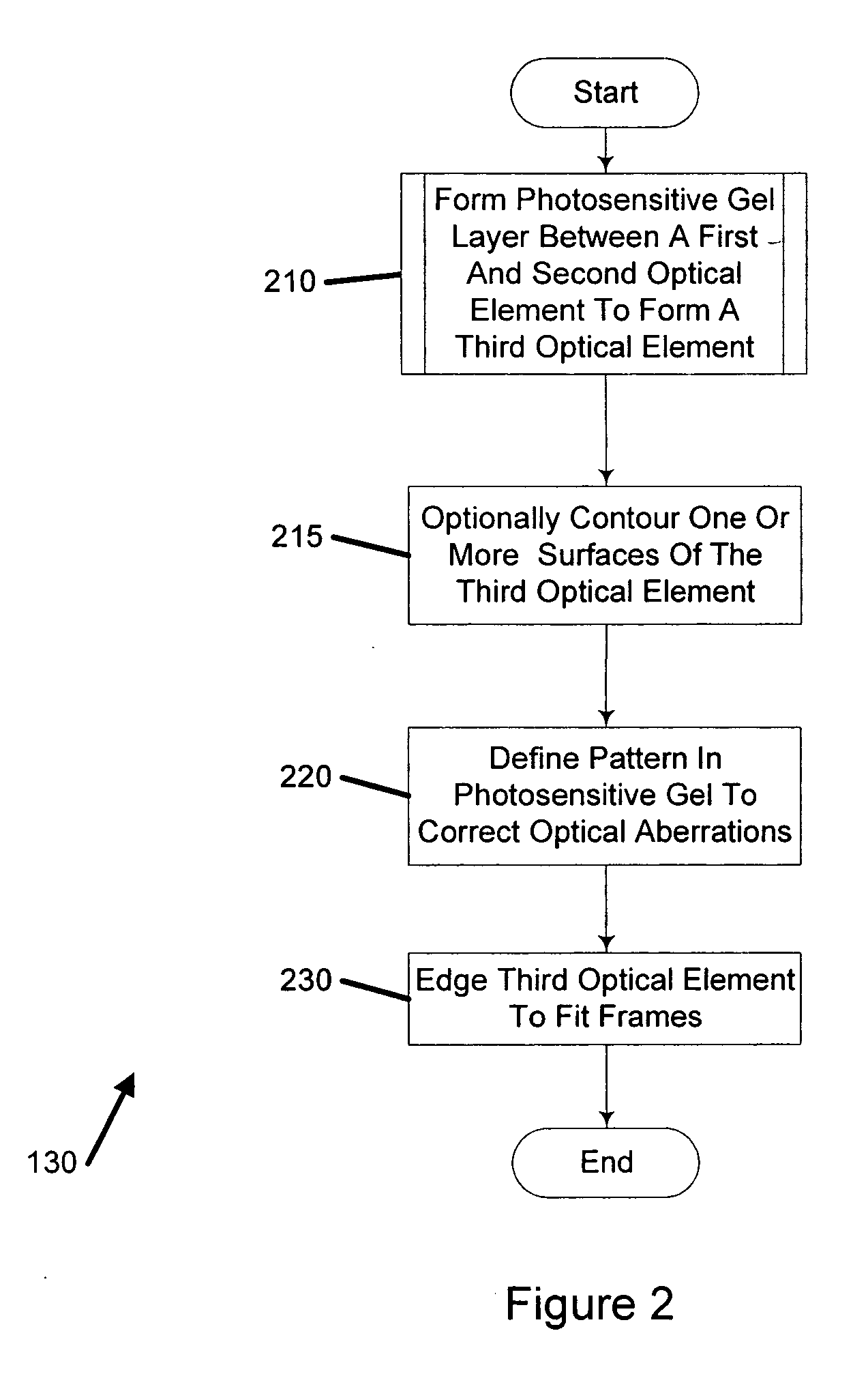
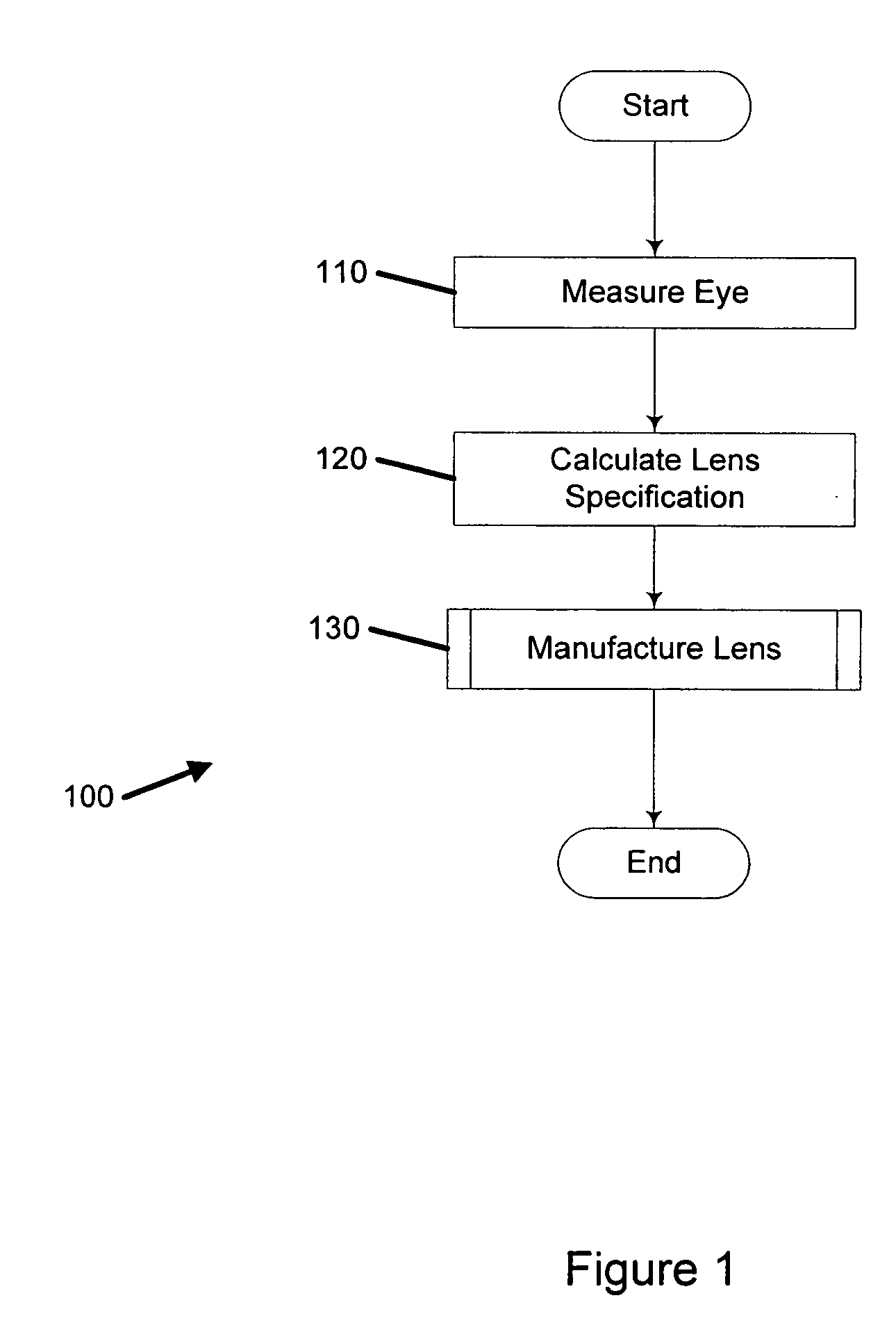
ActiveUS20050105048A1Convenient and economical methodSpectales/gogglesOptical surface grinding machinesOptical aberrationManufacturing systems
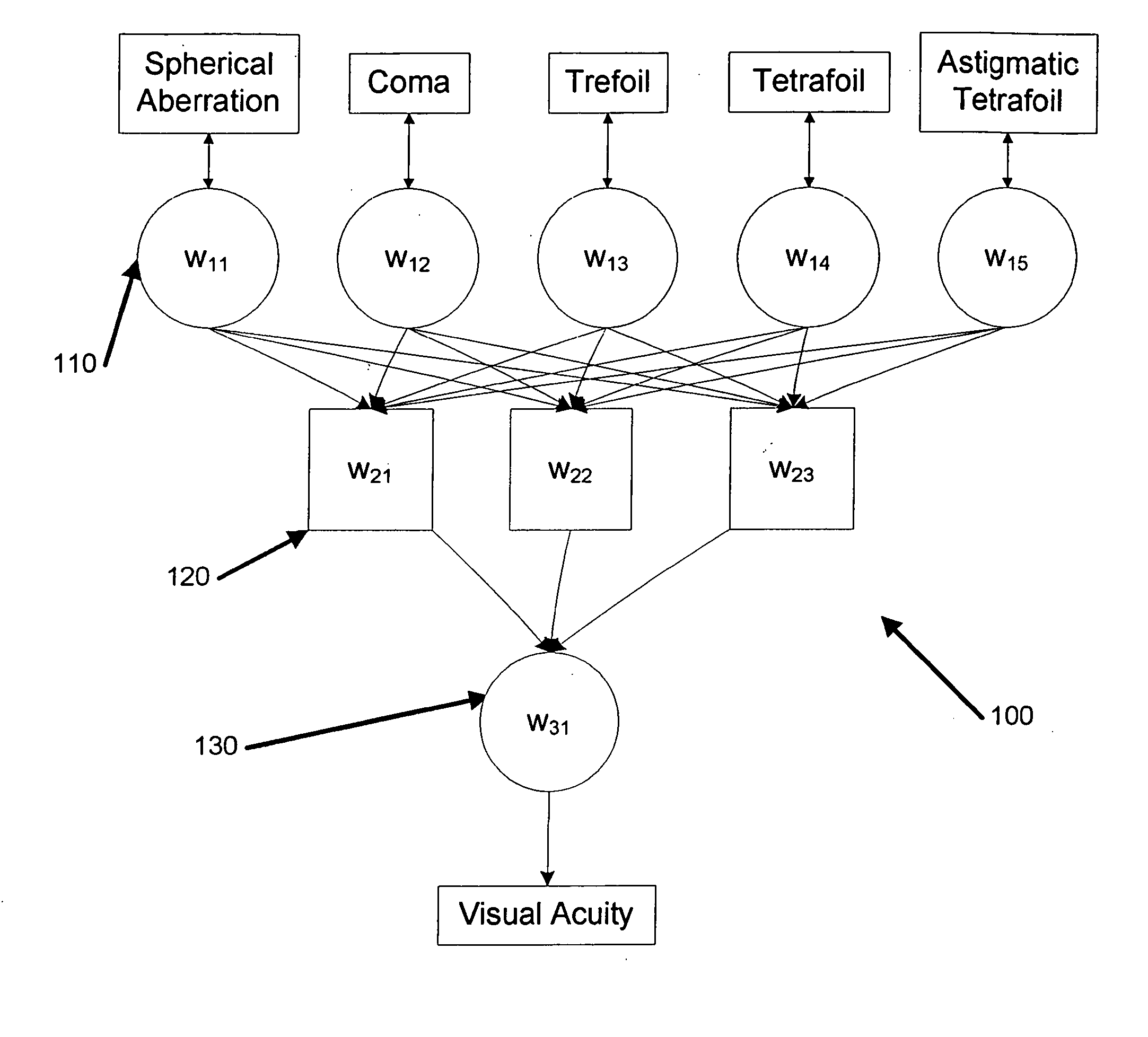
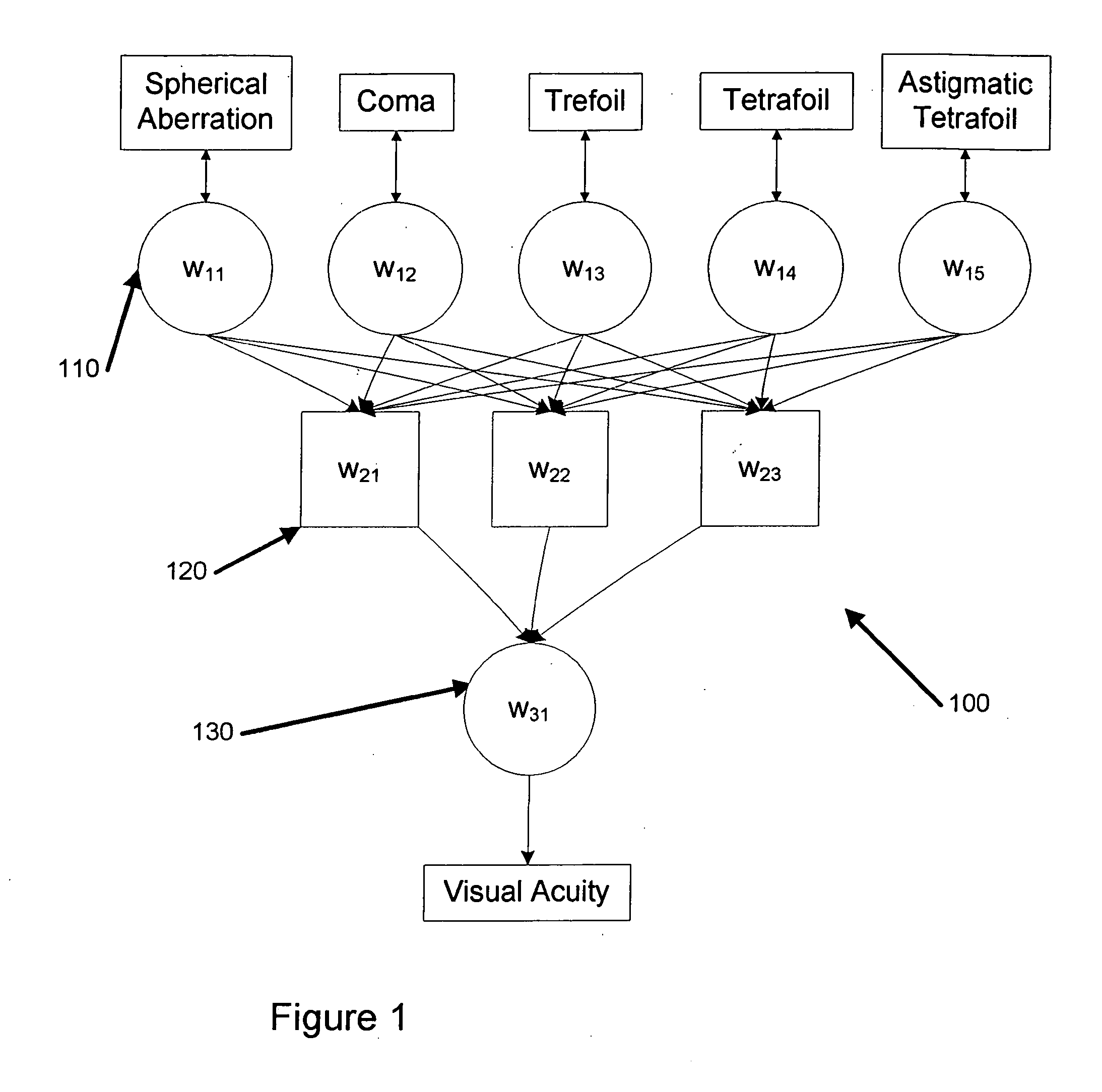
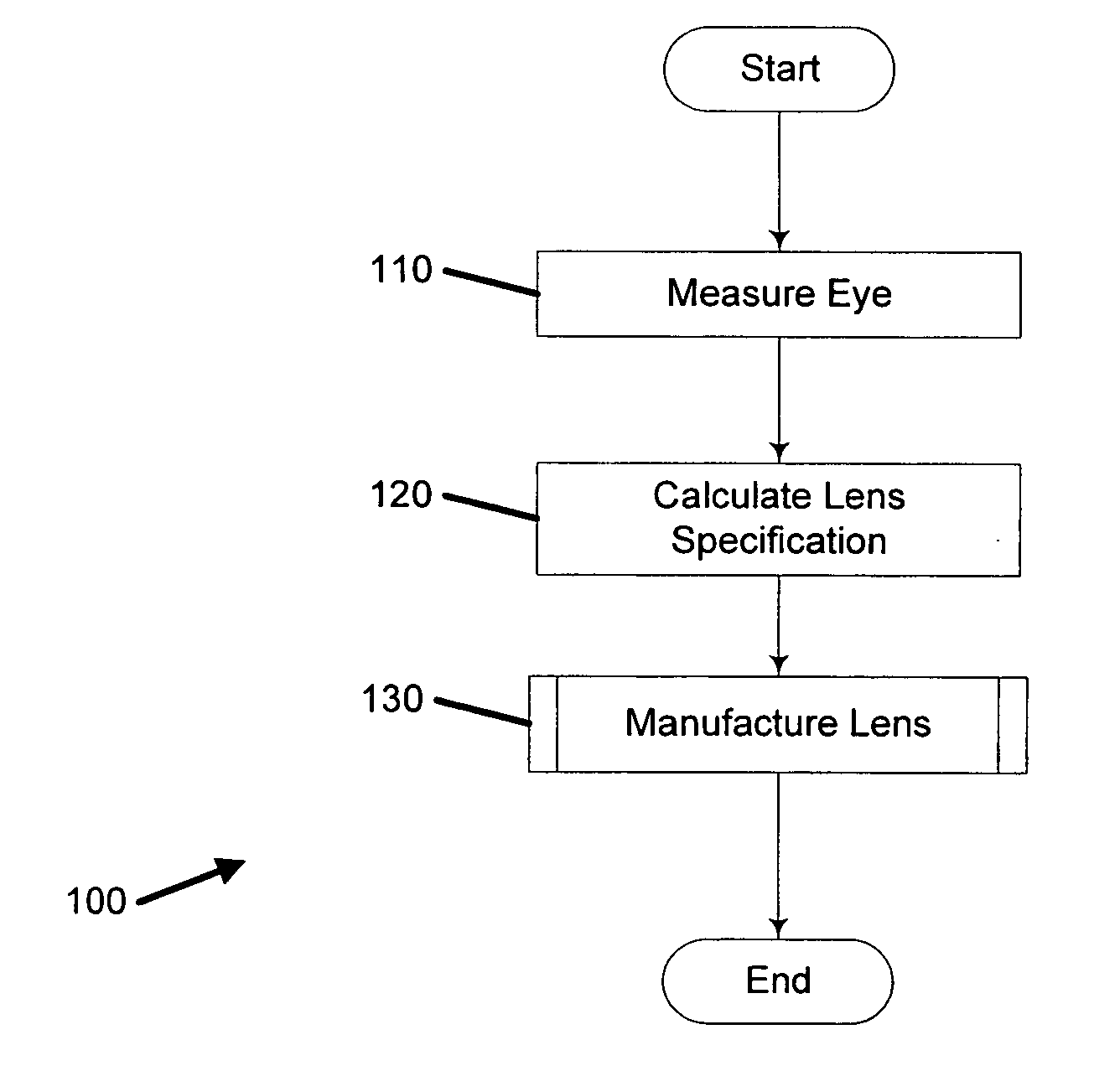
A system for manufacturing an optical lens that is configured to correct optical aberrations, including, e.g., high order aberrations such as described by Zernike polynomials. The system can include a measurement system configured to measure optical aberrations in a patient's eye and to create measured optical aberration data. A calculation system is configured to receive the measured optical aberration data and to determine a lens definition based on the measured optical aberration data. A fabrication system is configured to produce a correcting lens based on the lens definition.
Owner:ESSILOR INT CIE GEN DOPTIQUE +1
System and method for analyzing wavefront aberrations
InactiveUS20050200809A1Spectales/gogglesOptical surface grinding machinesWavefront aberrationStatistical model
A system and method for specifying a vision correction prescription for a patient's eye, wherein in one embodiment, the method includes obtaining a wavefront aberration measurement of the patient's eye, applying at least one value from the wavefront aberration measurement to a statistical model trained using a plurality of objectively measured aberration values and a plurality subjectively measured visual acuity values as training data; and predicting a vision correction prescription for the patient's eye based on the at least one value and the statistical model.
Owner:OPHTHONIX
Method of manufacturing an optical lens
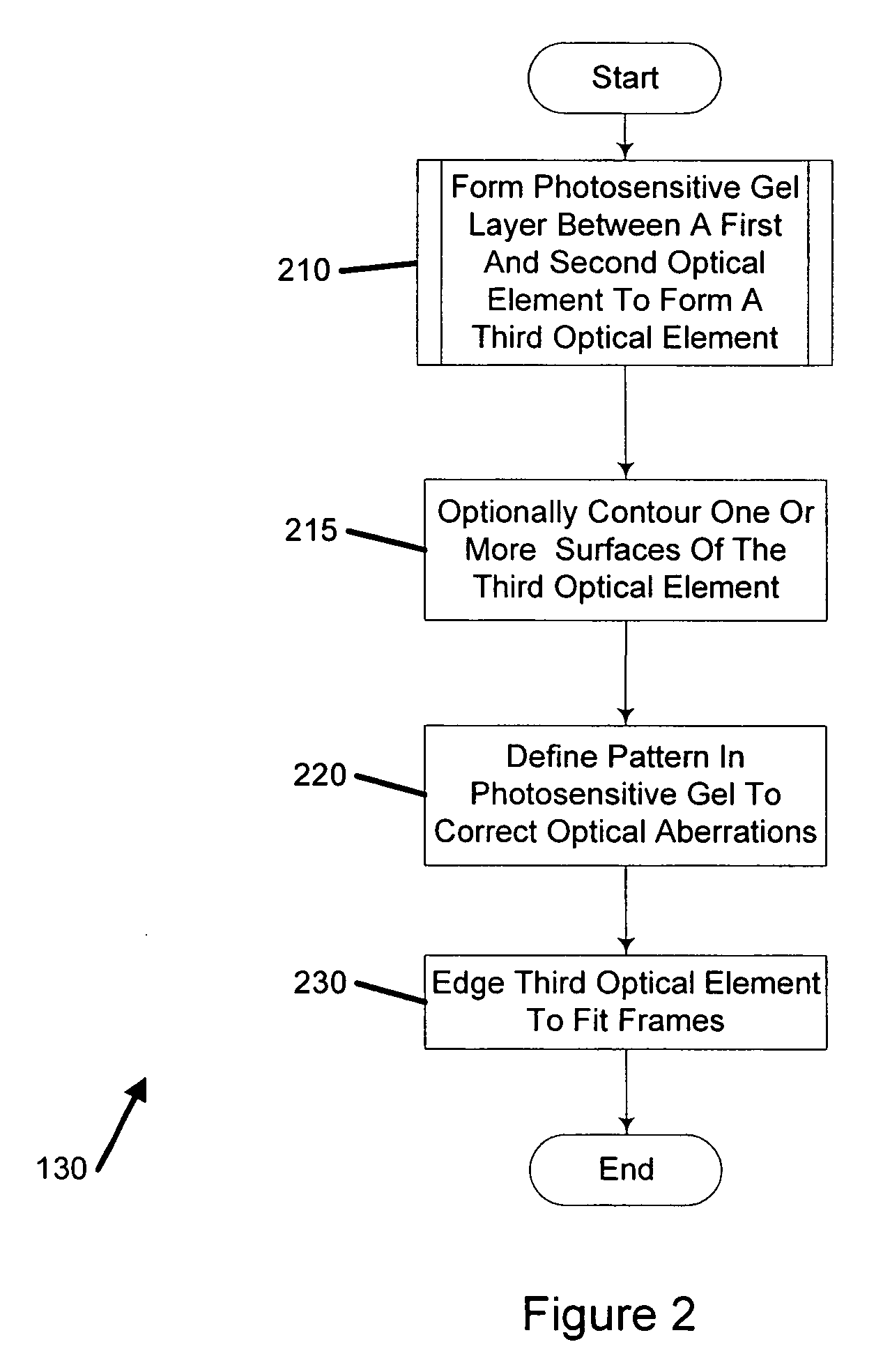
InactiveUS20050104240A1Convenient and economical methodHigh order aberrationSpectales/gogglesOptical surface grinding machinesCamera lensOptical correction
A method of manufacturing an optical lens that is configured to correct high order aberrations. One embodiment is a method of customizing optical correction in an optical system. The method includes measuring optical aberration data of the optical system. The method further includes calculating a lens definition based on the optical aberration data. Calculating the lens definition may include calculating a correction of at least one high order optical aberration. The method further includes fabricating a correcting lens based on the lens definition.
Owner:ENTERPRISE PARTNERS VI
System and method for ophthalmic lens manufacture
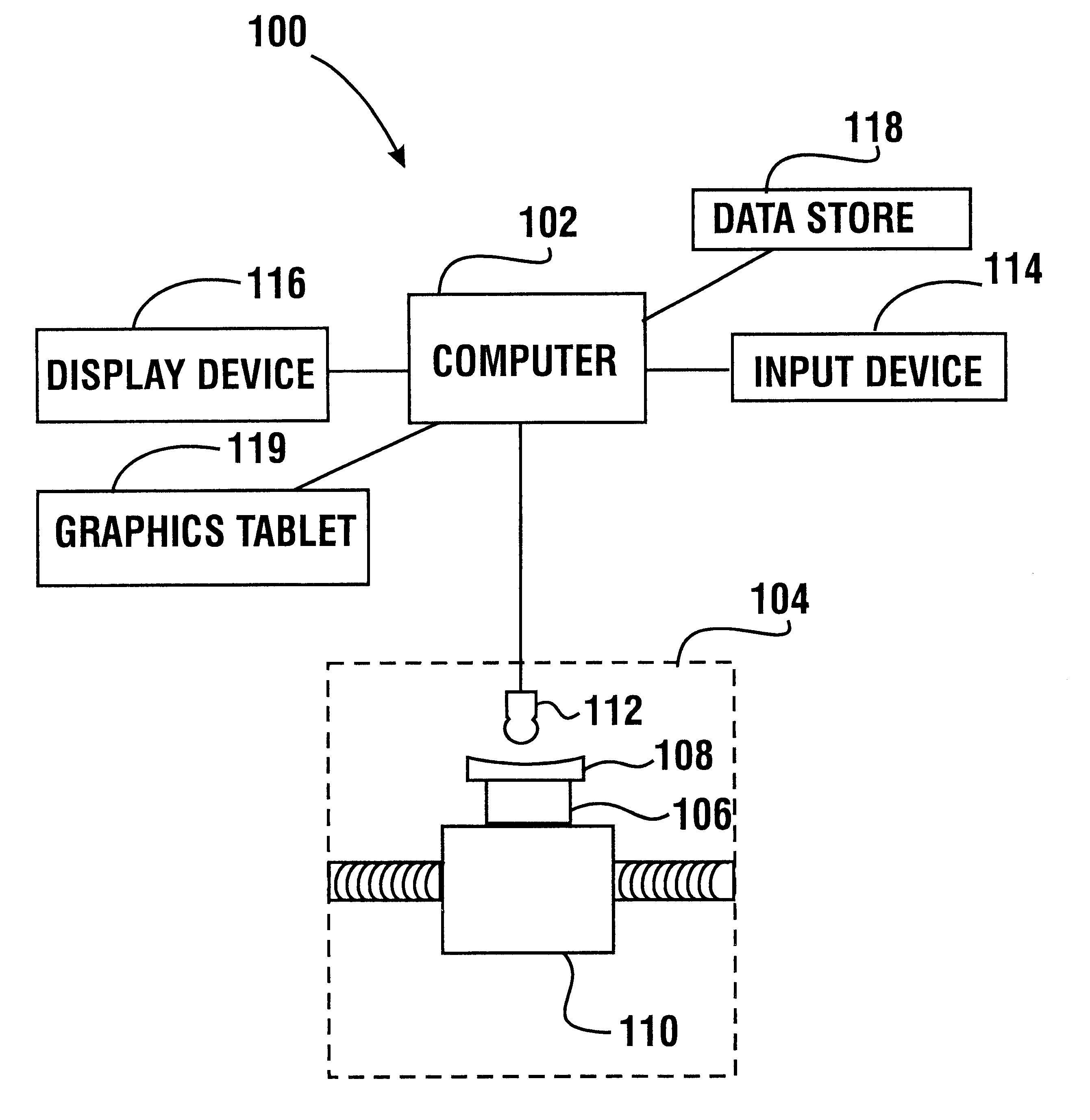
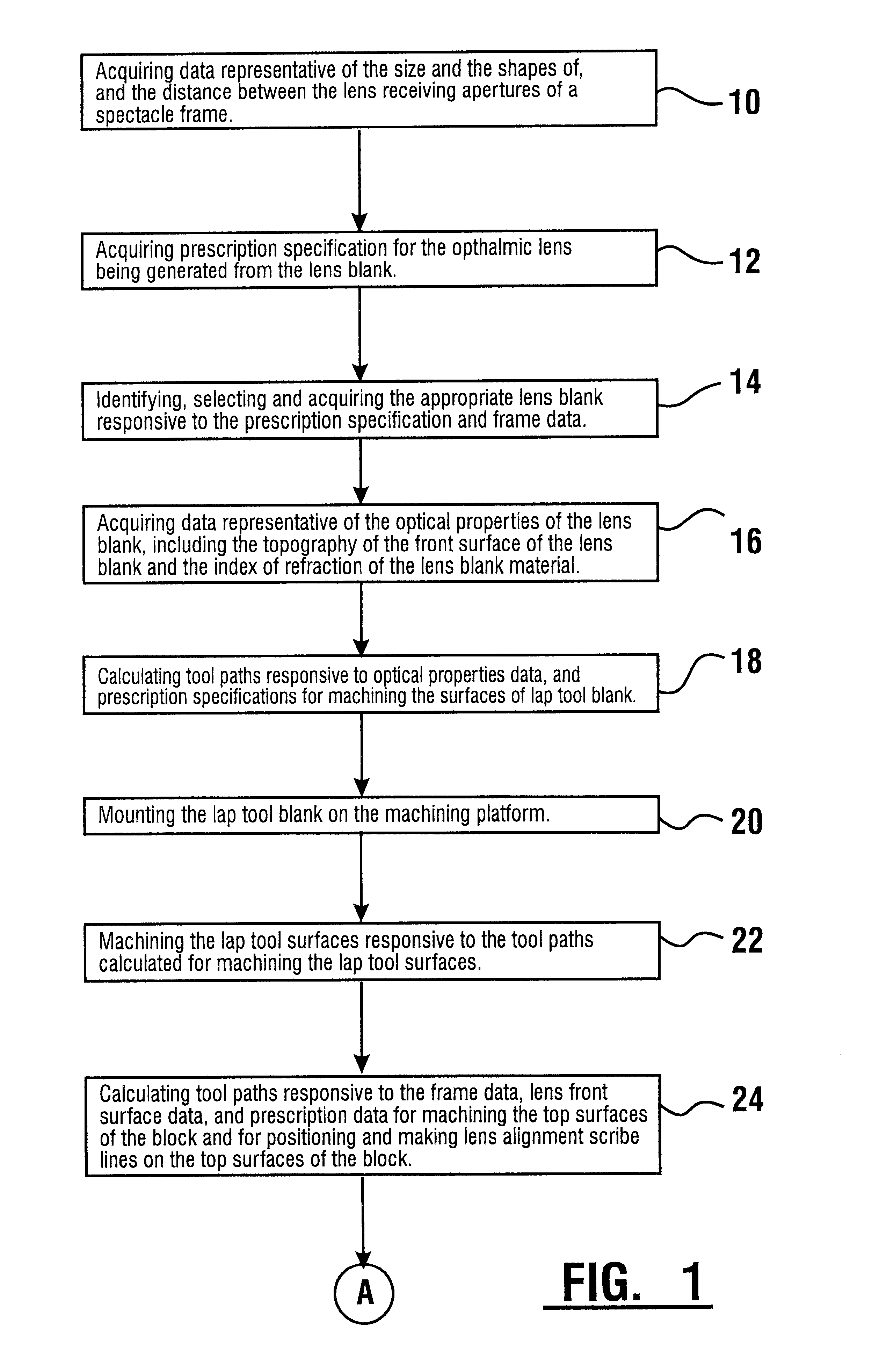
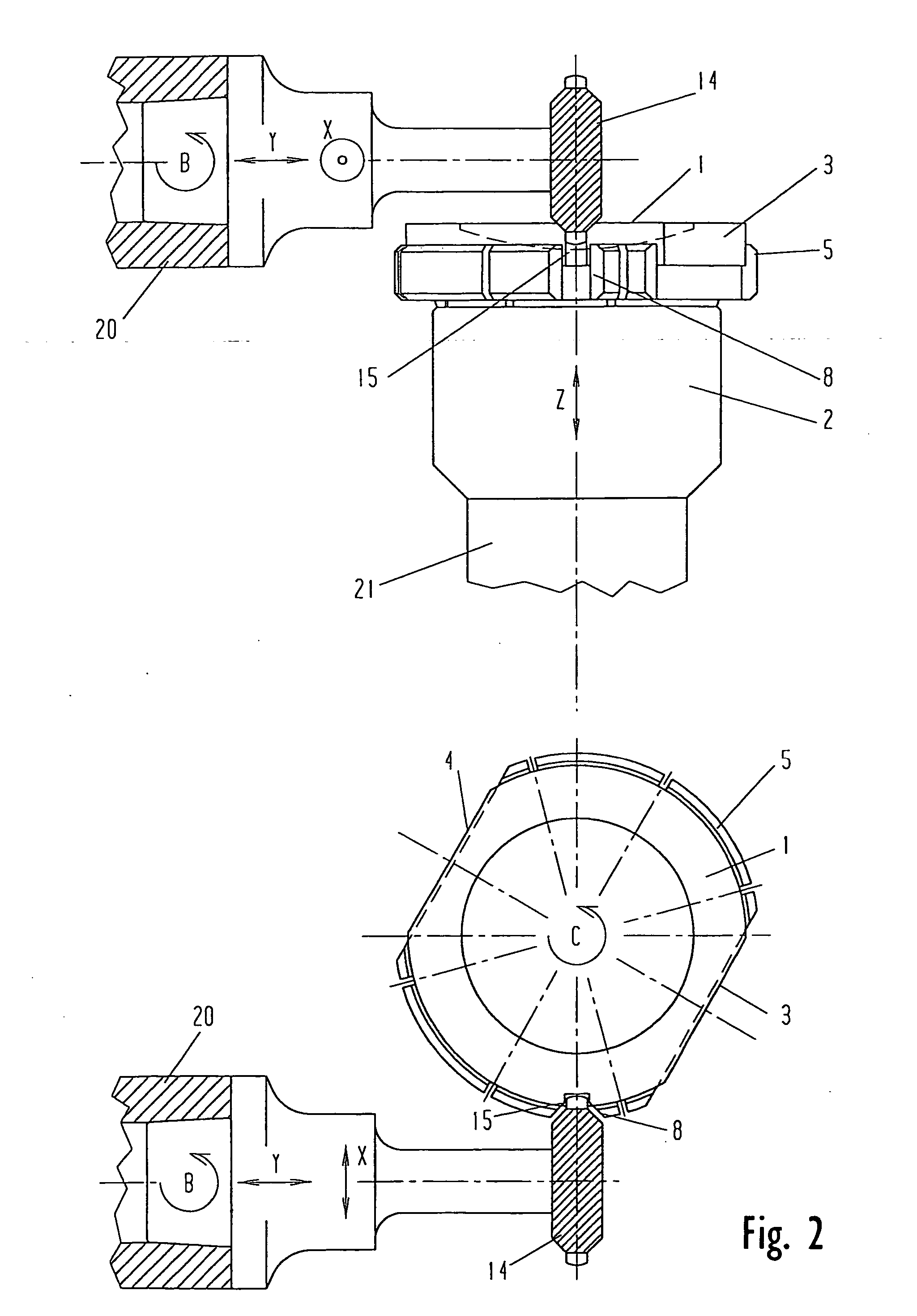
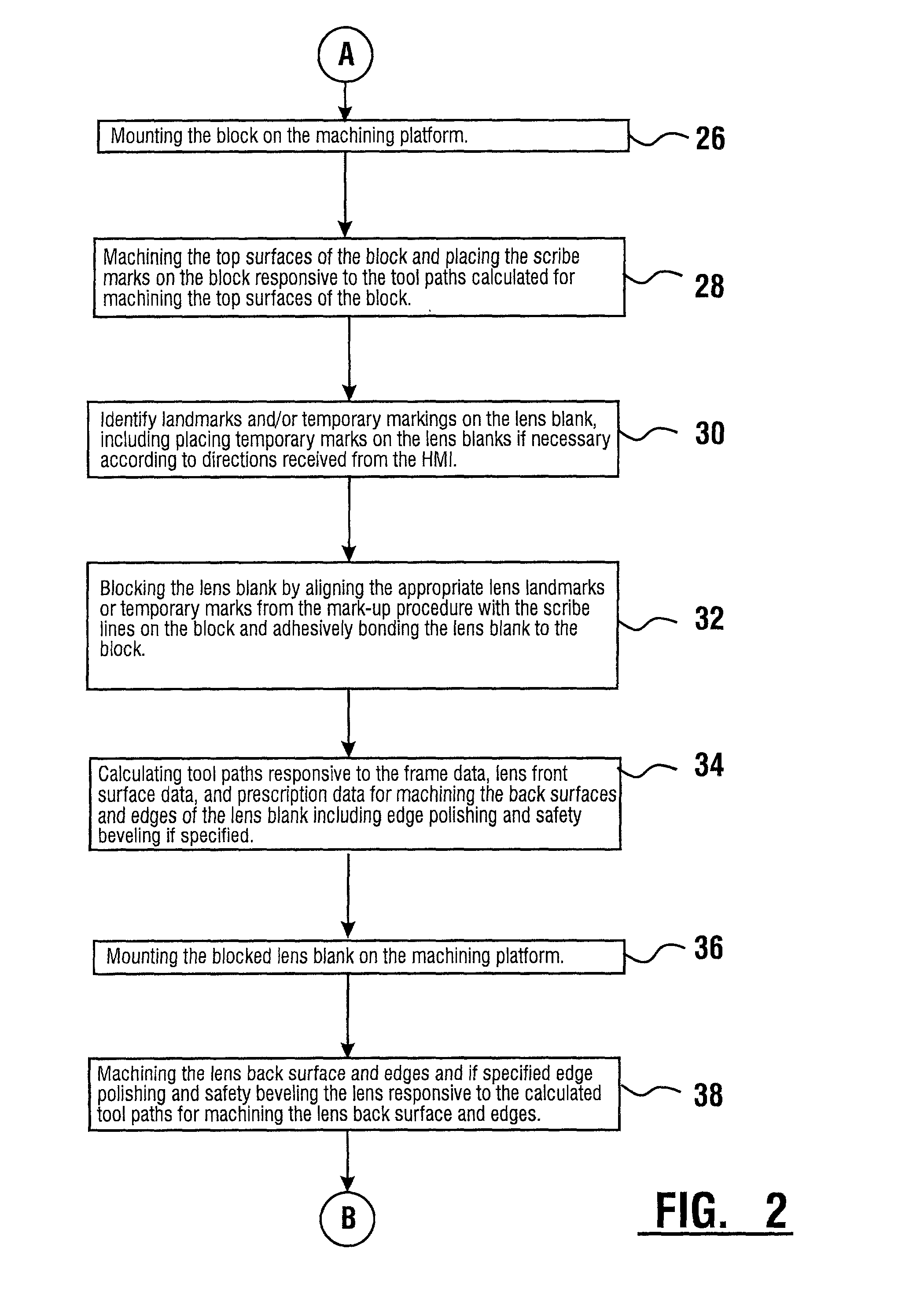
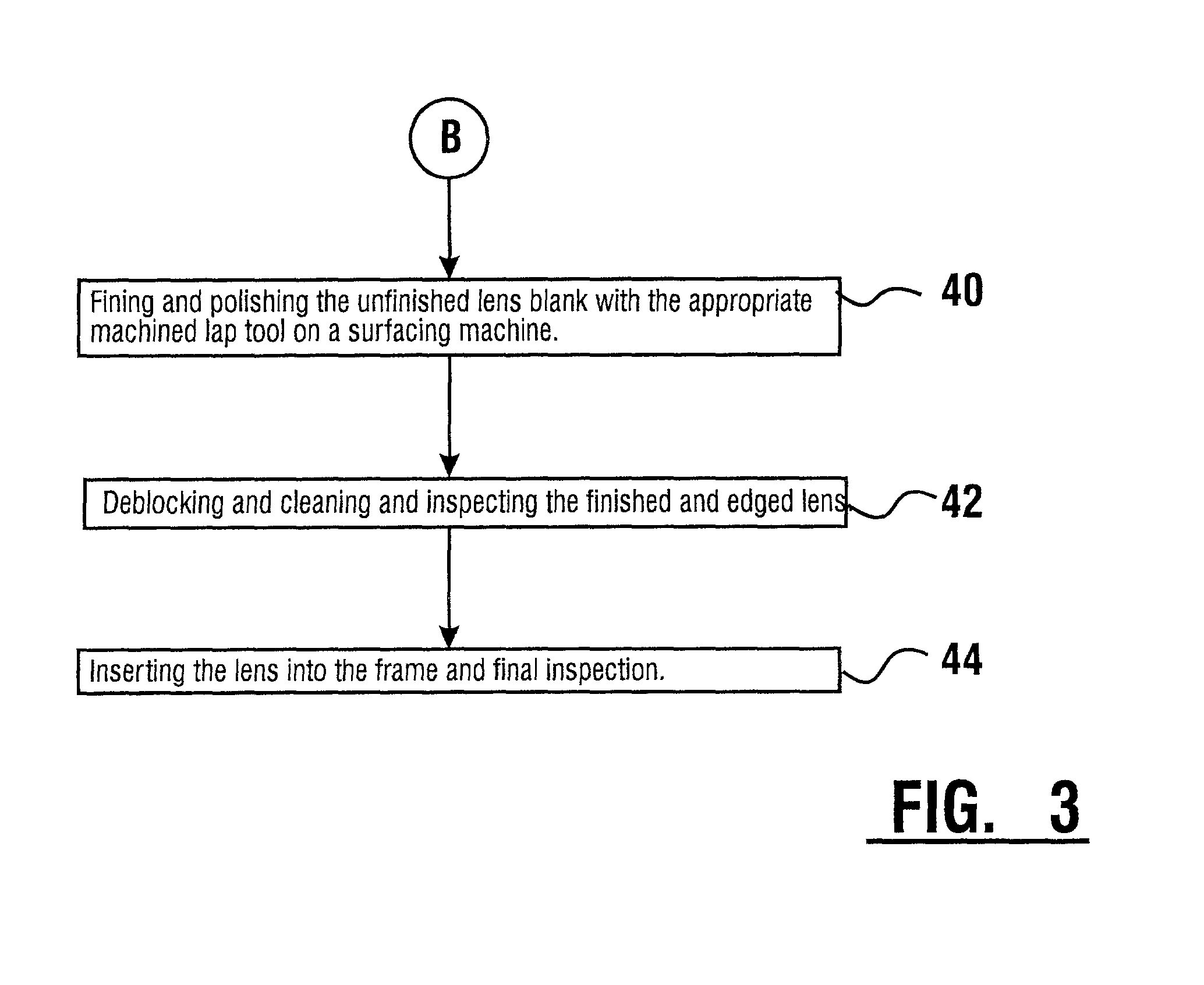
InactiveUS6568990B2Low costAccurately derivedEdge grinding machinesOptical surface grinding machinesEngineeringLens plate
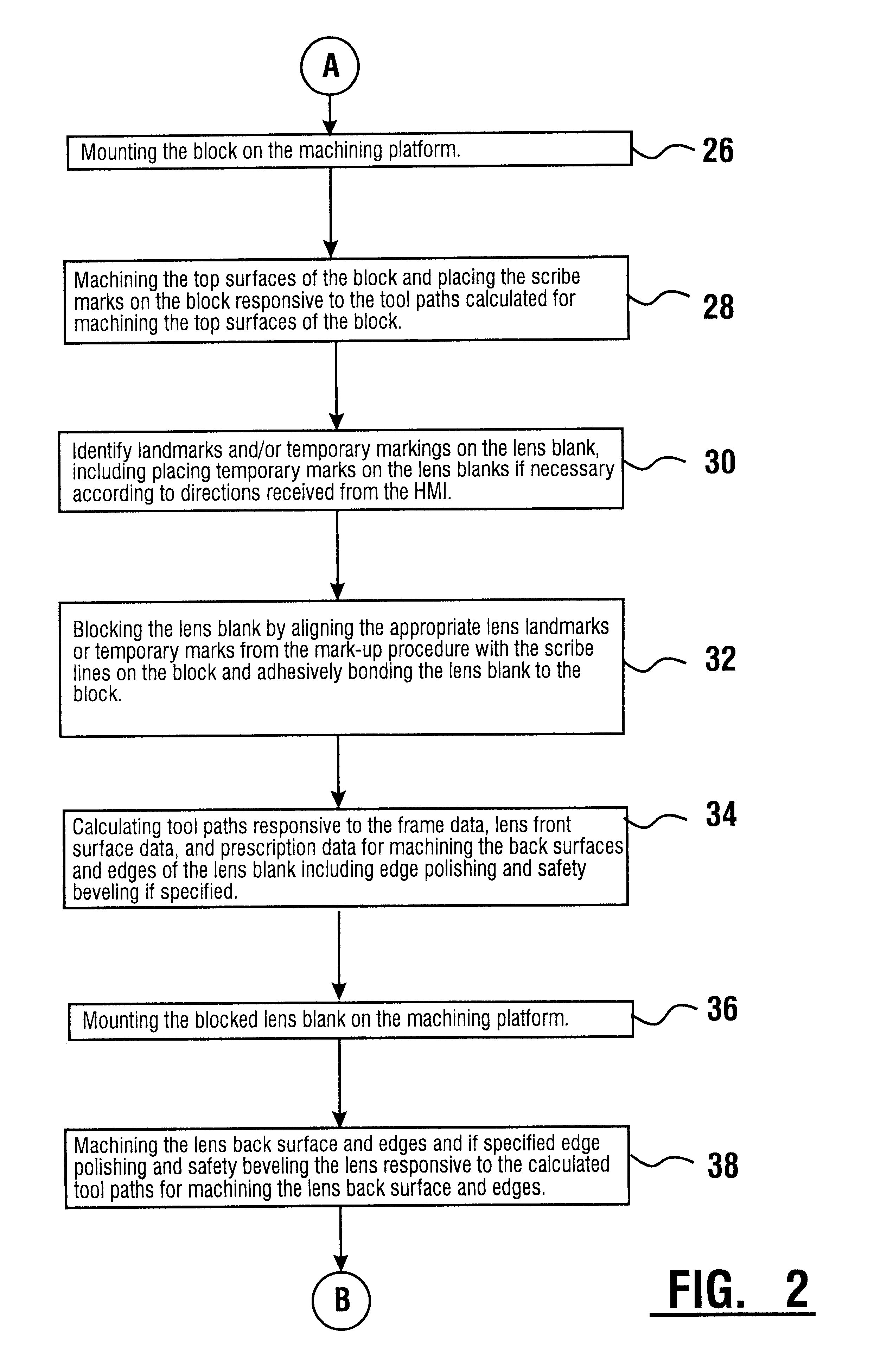
A method and system for the manufacture of ophthalmic lenses comprising a computer (102) and a CNC machining platform (104) in operative connection with the computer. The CNC machining platform includes a mounting stage (110), a block (106) in releasable connection with the mounting stage, and a machining tool (112). When an unfinished lens blank (108) is properly mounted on the block, the computer is operative to direct the CNC machining platform to perform both back surface generation and patternless edging of the lens blank in one machining cycle. The computer is further operative to direct the CNC machining platform to machine a lap tool for each lens and machine a block for receiving each lens. The block is machined by the platform to include scribe lines for facilitating proper alignment of lens blank.
Owner:NCRX OPTICAL SOLUTIONS
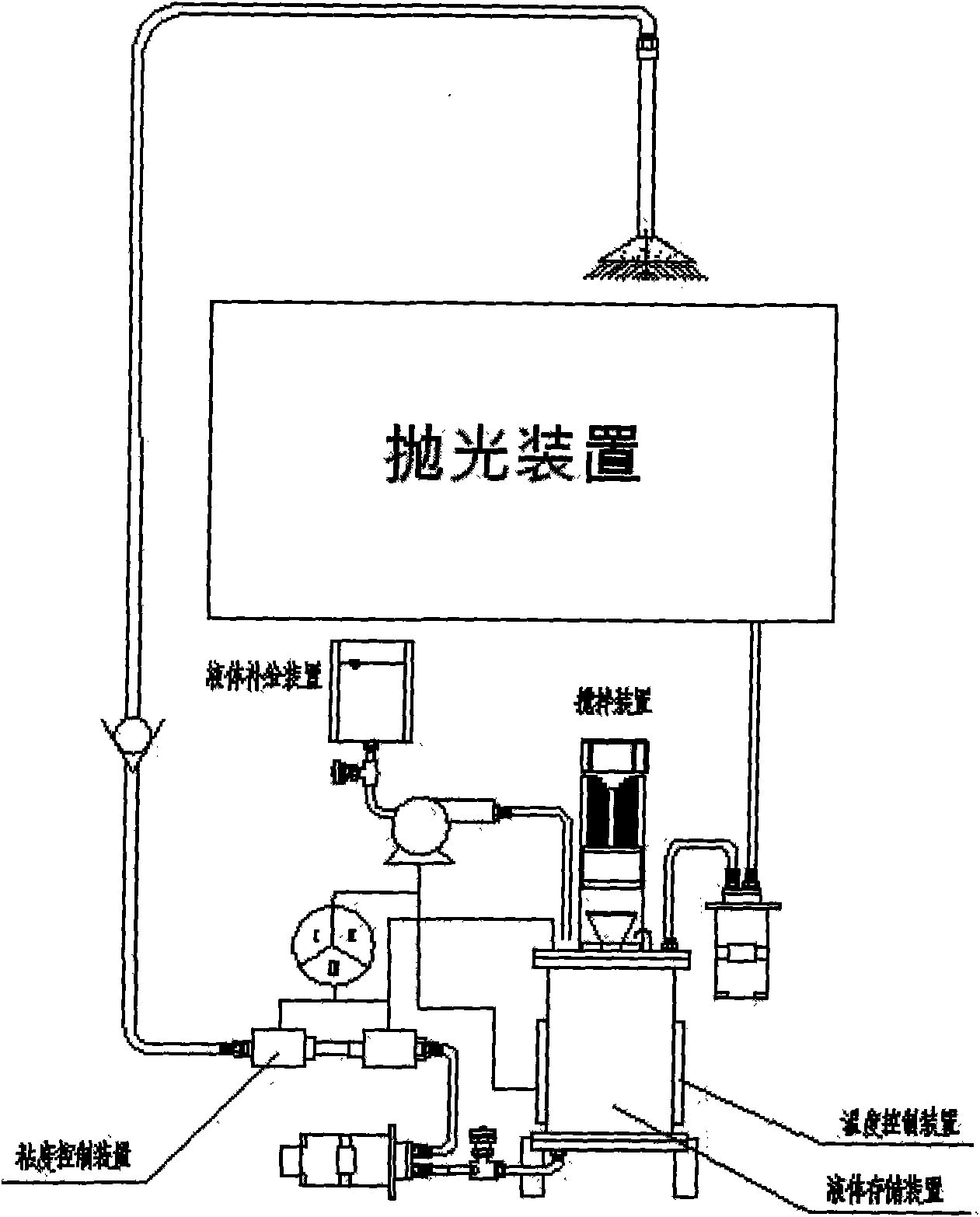
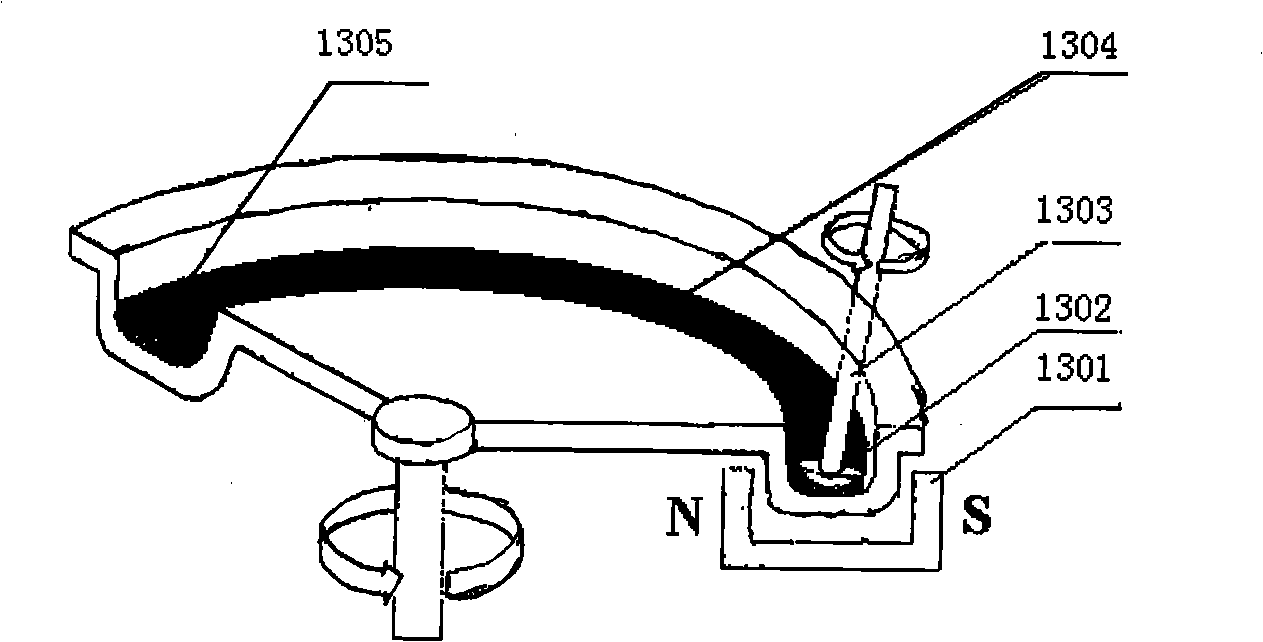
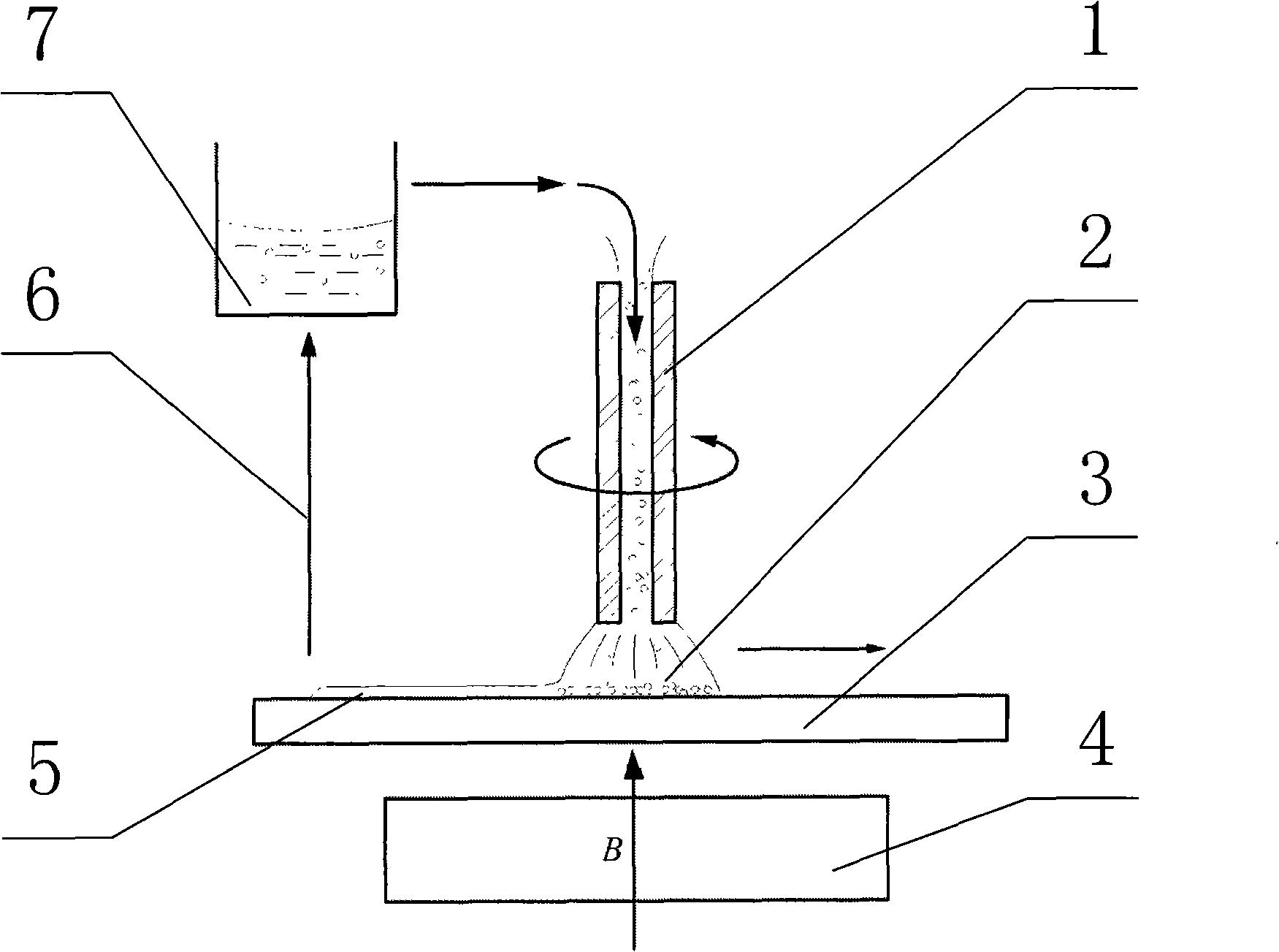
Precise magnetic flowage polishing system for optics parts and method thereof
InactiveCN101224556AImprove processing efficiencyEasy clampingOptical surface grinding machinesPeristaltic pumpTemperature control
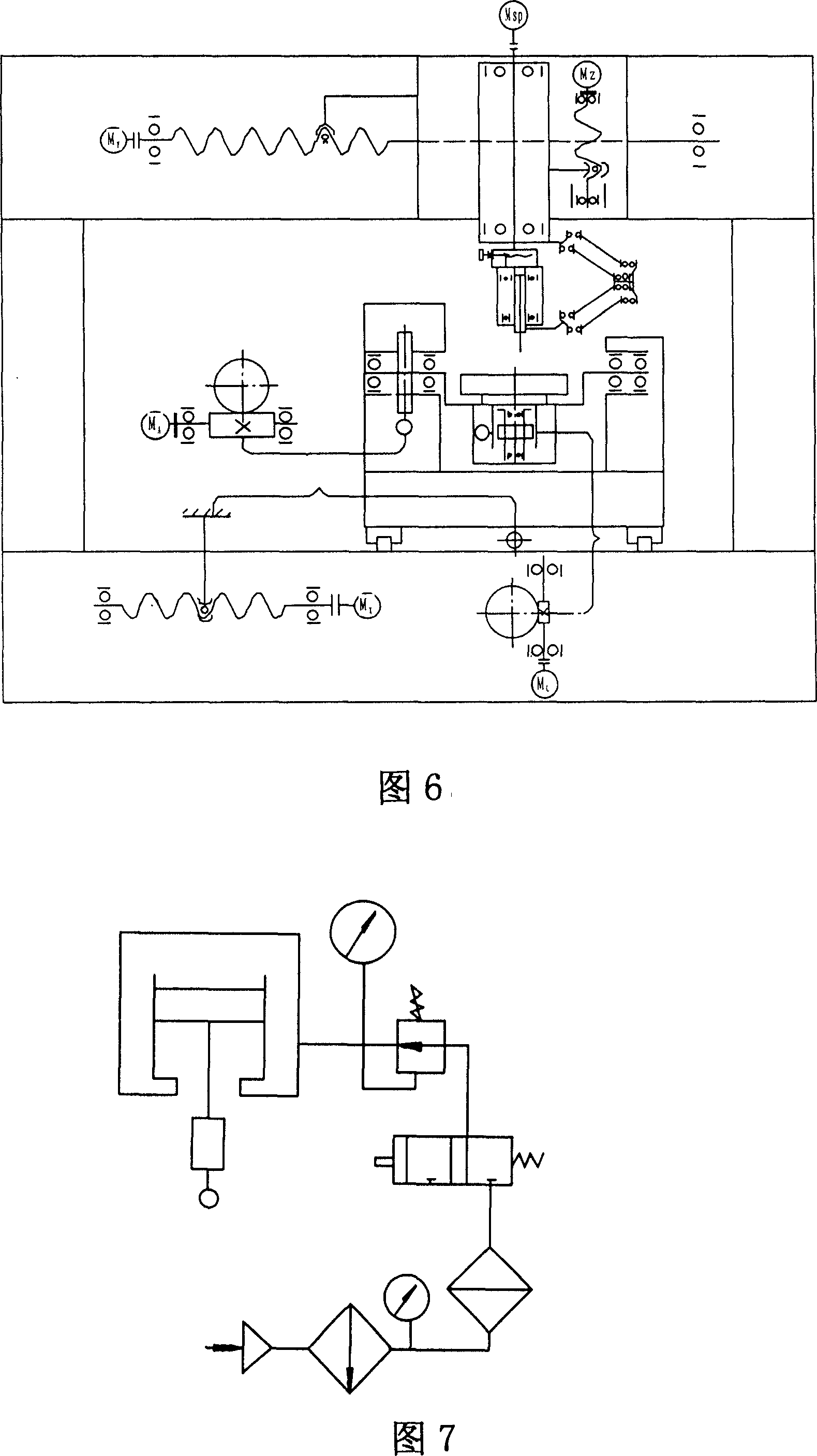
The invention relates to an optical part magnetic rheologic precise polishing system and a method; magnetic rheologic liquid which flows out of a liquid storage cylinder is pressurized by a peristaltic pump and then enters a polishing head through a rotating connector and a guide pipe; the clearance between a workpiece and the polishing head is fully filled by the magnetic rheologic liquid; under the action of electromagnetic field, the magnetic rheologic liquid is transformed from the liquid state to the half-solid state so as to form a flexible grinding head used for polishing. The polishing head of the invention is not directly contacted with the workpiece; the polishing heads with different shapes and specifications can be replaced according to the processed workpiece; a computer automatic control device can realize the viscousity control and the temperature control of the magnetic rheologic liquid, and different polishing efficiency and precisions can be obtained by changing the factors such as magnetic field and rotation speed, etc.; the method of the invention can process the curved workpieces and plane workpieces with different shapes, more particularly the ultra-precise polishing of the large plane optical parts; the system has the advantages of high processing efficiency, wide applicable range, high processing precision and convenient operation.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
High efficiency controllable multiple wheel head magnetic rheology buffing device
InactiveCN101579833ASolving 3D MotionFully contactedOptical surface grinding machinesEngineeringDigital control
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
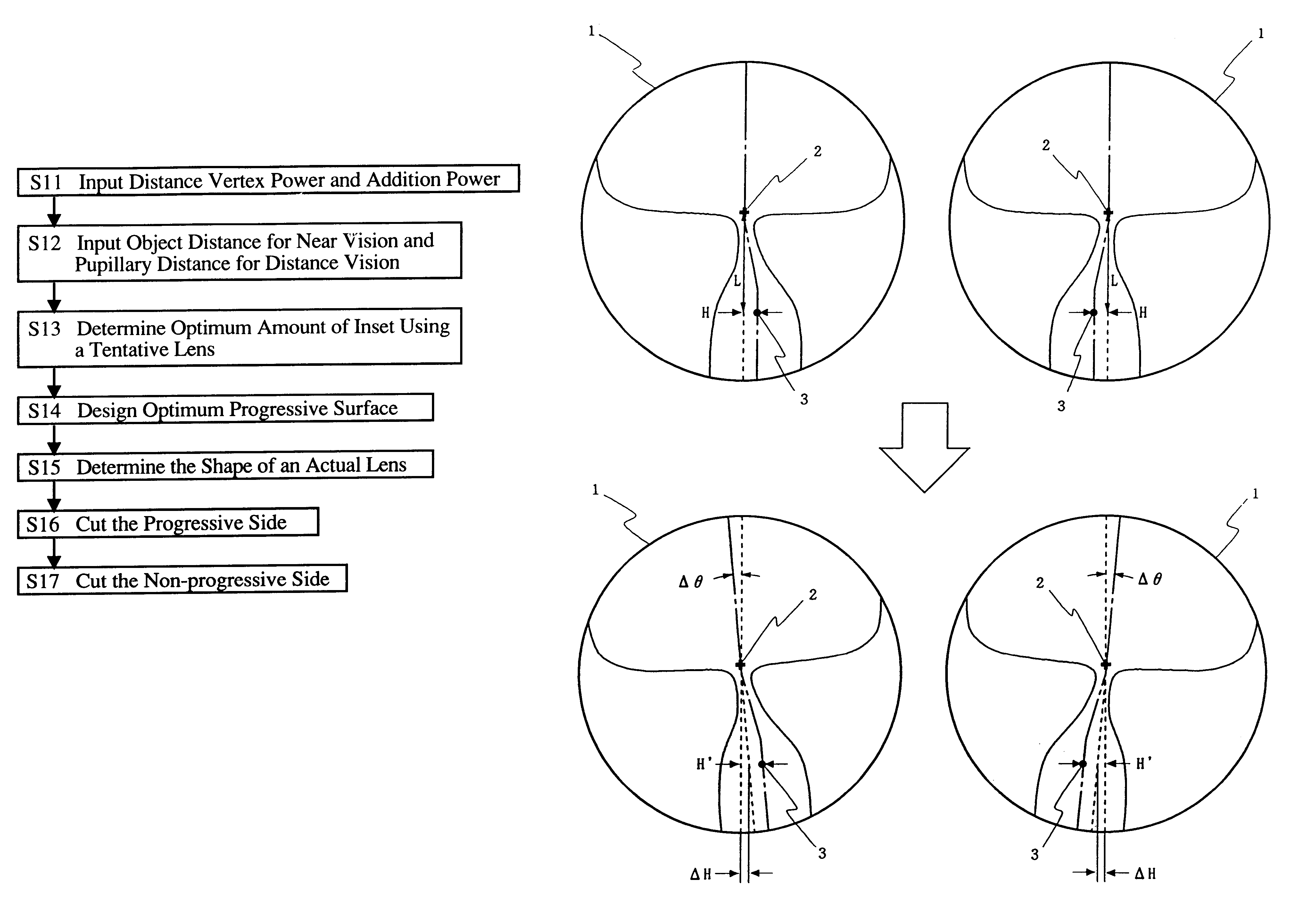
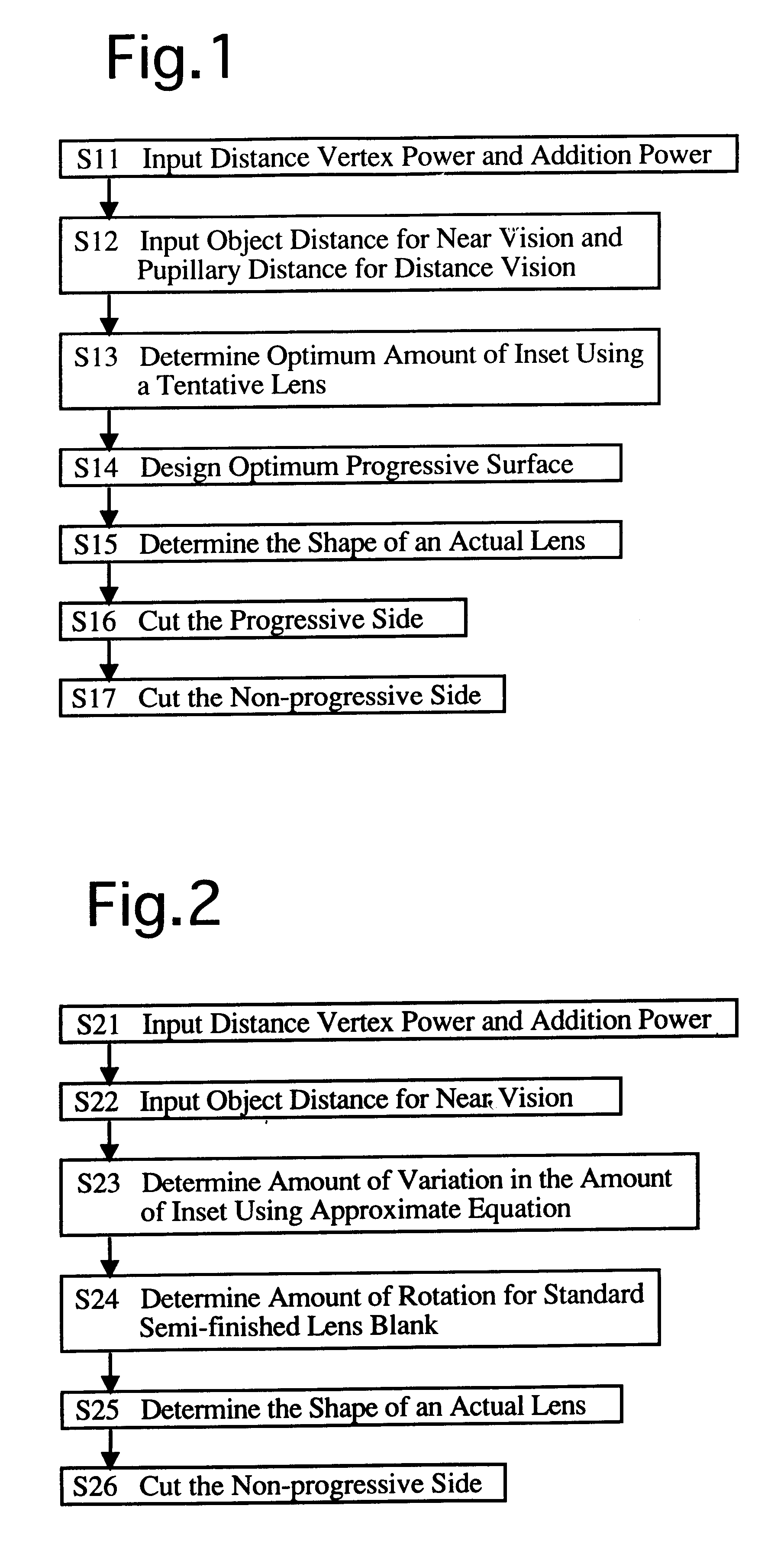
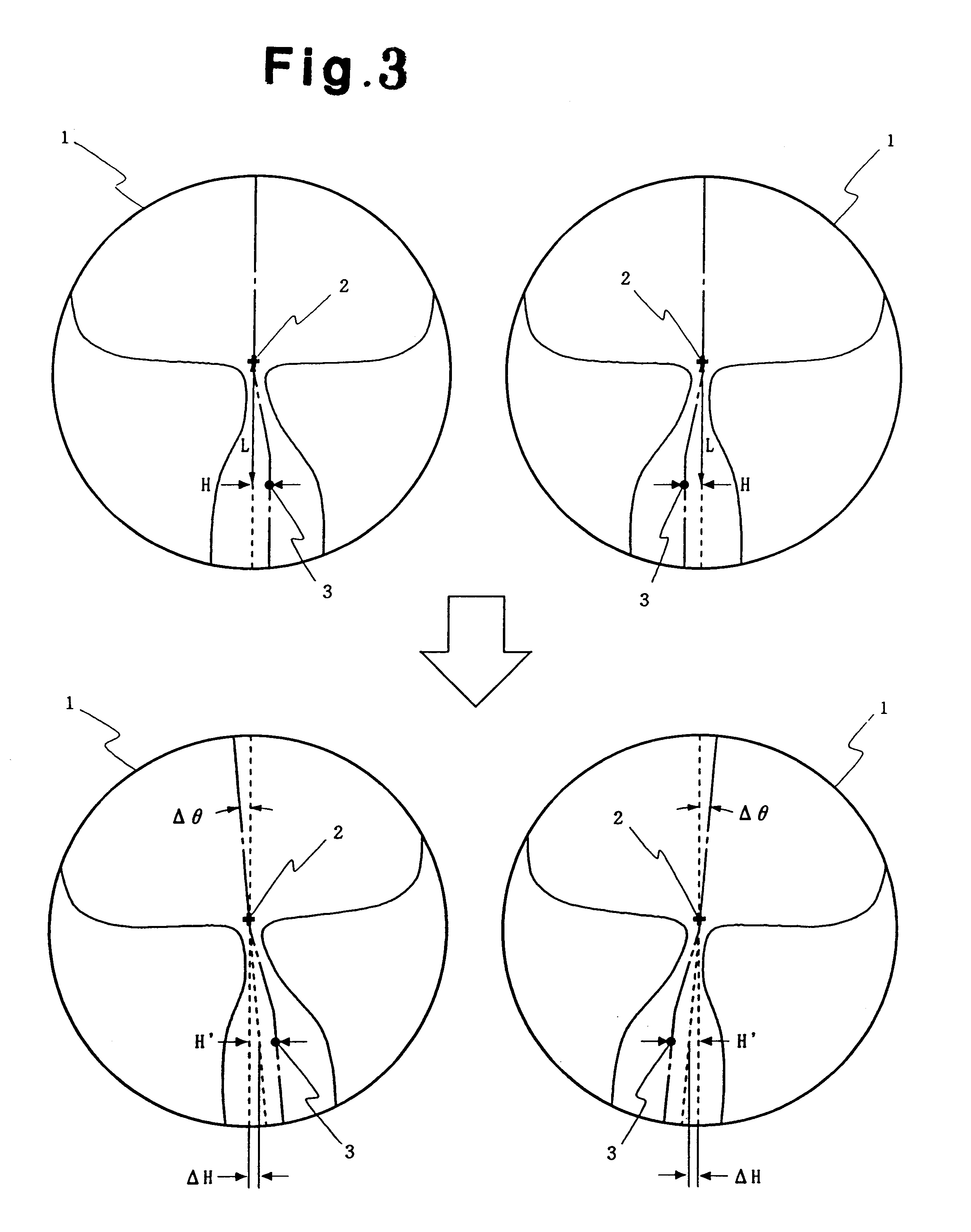
Method of manufacturing progressive power spectacle lenses
A method of manufacturing progressive power spectacle lenses includes preparing individual fitting condition data for a lens-wearer such as object distances for near and distance vision, the distance from the point-of-rotation of each eyeball of a lens-wearer to each spectacle lens, the pantoscopic angle of the spectacle lenses when fitted onto said lens-wearer, and determining an amount of inset in accordance with said individual fitting condition data.
Owner:SEIKO OPTICAL PROD TRADING AS SEIKO OPTICAL PROD +1
Magnetorheological finishing device for super large caliber aspheric surface optical part
InactiveCN101323097AImprove dynamic characteristicsMeet the needs of magnetorheological polishingOptical surface grinding machinesLinear motionControl system
The invention relates to a magnetic rheological polishing device used in an aspheric optical part with a super large caliber, comprising a machine tool, a magnetic rheological polishing device and a control system which is connected with the above components. The machine tool comprises a lathe bed on which the work piece to be processed is placed, an X axial linear motion mechanism is arranged on the two sides of the lathe bed, a movable portal is fixed on a slider of the X axial linear motion mechanism, a Y axial linear motion mechanism is arranged on a cross beam of the movable portal, a Z axial linear motion mechanism is fixed on a slider of the Y axial linear motion mechanism, an A axial rotary table used for arranging the magnetic rheological polishing device is fixed on a slider of the Z axial linear motion mechanism, the magnetic rheological polishing device is fixed on the cross beam by a fourth linear motion mechanism, the two have opposite directions of motion, and the magnetic rheological polishing device is arranged right above the work piece to be processed. The device of the invention has the advantages of simple and compact structure, low cost, easy control and strong processing capacity, and can process the aspheric optical part with the super large caliber.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Method and device for polishing magnetic field auxiliary flexible rotary brush for optical element
InactiveCN101559571ACompact structureImprove removal efficiencyOptical surface grinding machinesPolishing compositions with abrasivesFree formMagnetorheological fluid
The invention belongs to the technical field of precise optical polishing processing, and in particular relates to a method and a device for polishing a magnetic field auxiliary flexible rotary brush for an optical element. The method comprises that a ferromagnetic main shaft capable of rotating at a high speed drives a magnetorheological fluid which can be updated circularly to be adsorbed on a finished surface under certain pressure and the action of a magnetic field to form a flexible rotary polishing grinding head which finishes the polishing processing of a whole concave surface in a composite motion mode of self rotation and workpiece rotation. The device is applicable to polishing the concave surface of a conformal optical element; and the method has the characteristic of flexible fine machining and stable polishing removal, can adopt a computer to control the polishing removal distribution, is capable of controlling a polished surface shape, has the advantages of high precision and high surface quality, and is applicable to polishing aspheric surface and free-form surface elements with thin-walls and high gradients.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Method and an Apparatus for Manufacturing an Optical Lens
ActiveUS20110257930A1Improve optical qualityReduce dispersionGrinding drivesOptical articlesOptical propertyEngineering
Owner:ESSILOR INT CIE GEN DOPTIQUE
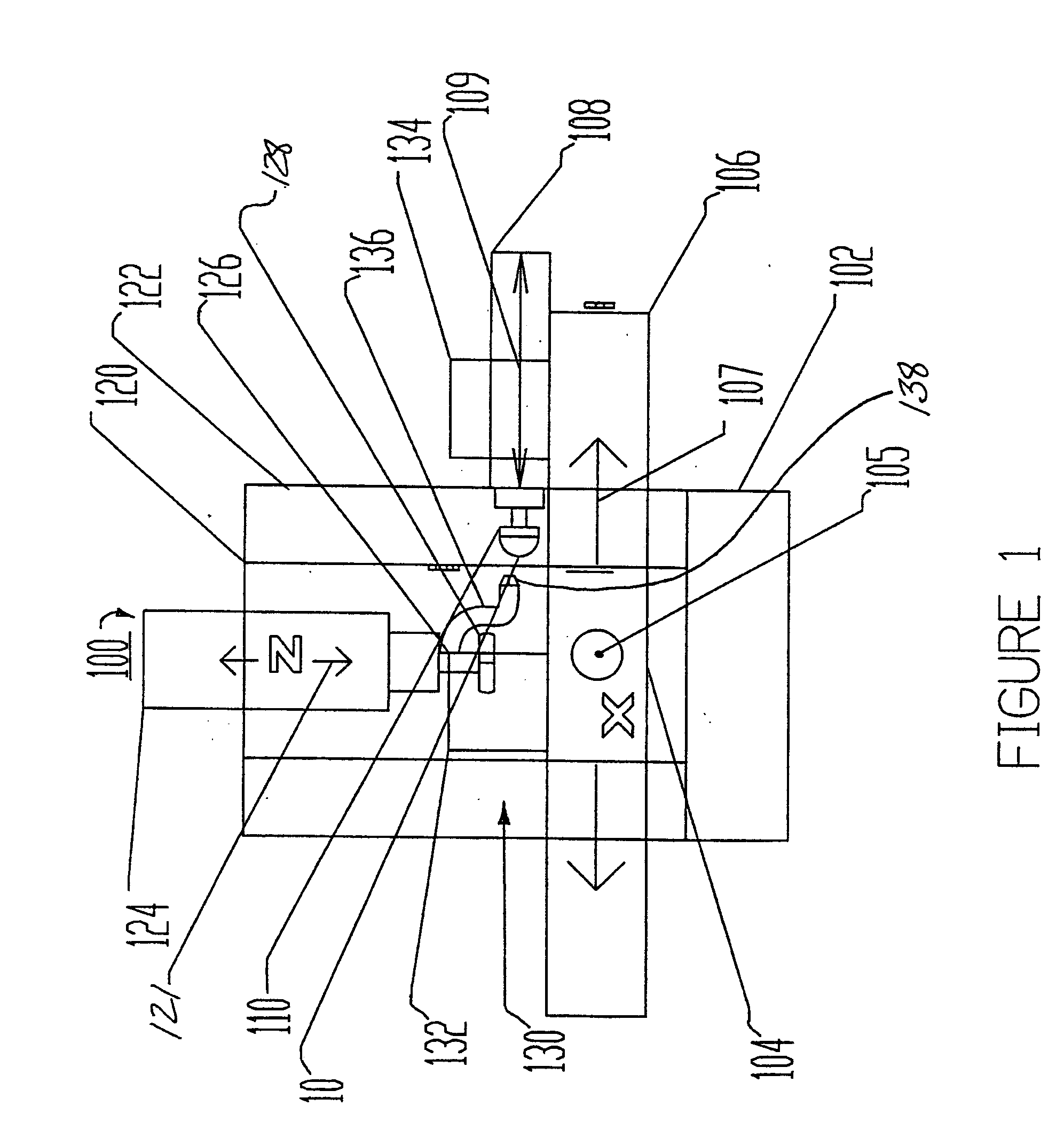
Process for manufacturing a light emitting array
InactiveUS20060094322A1Optical surface grinding machinesSolid-state devicesLight sourceOptical materials
A method for fabricating a light emitting array utilizes a precisely shaped patterned abrasive to abrade optical material. One or more patterned abrasives contact and abrade along one or more intersecting axes of the optical material. The resulting precisely shaped and located optical elements are aligned with and bonded to an array of light sources.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
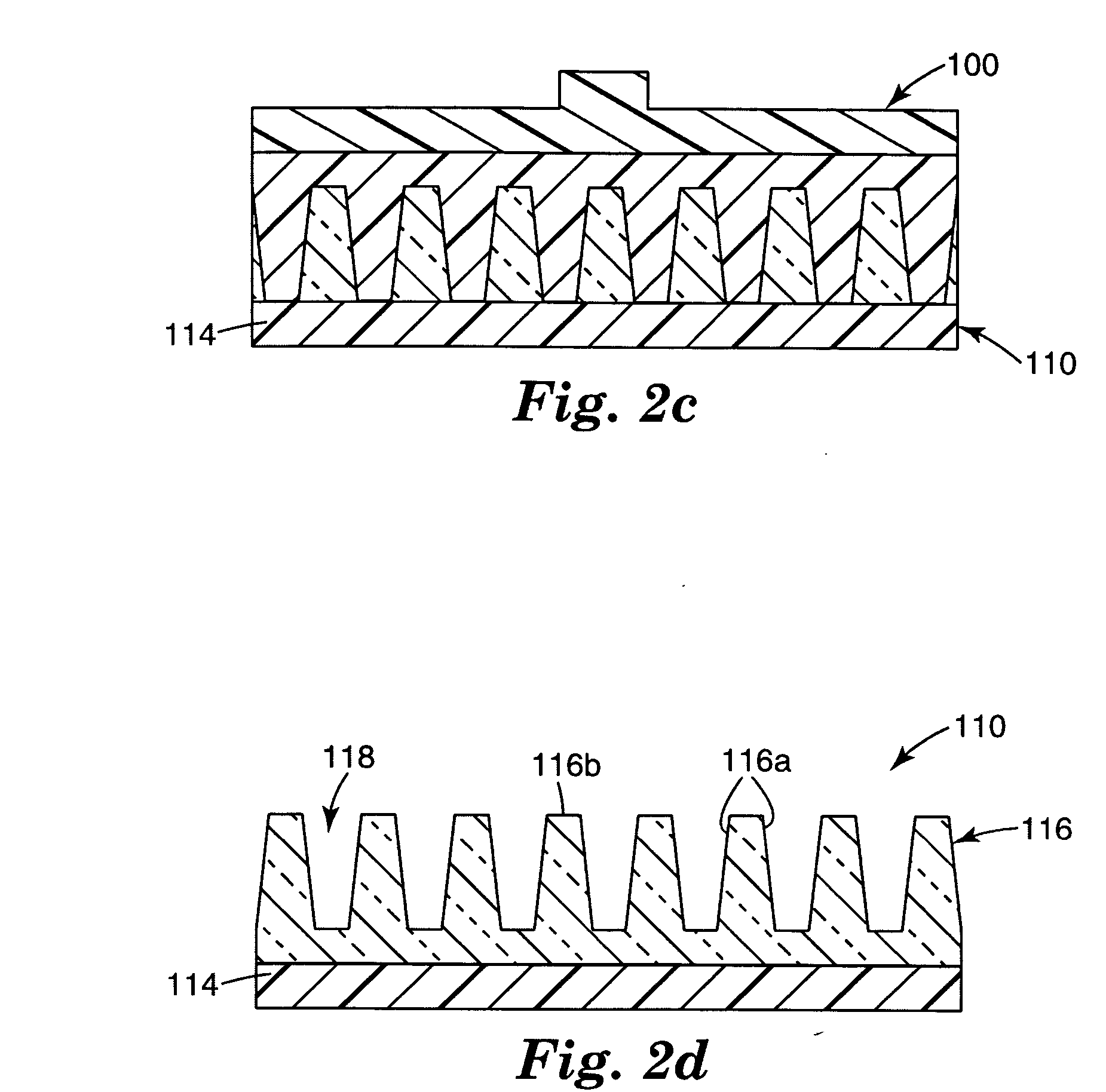
Method for producing spectacle lens and lens processing system
InactiveUS6743486B1Reduce variationImprove production yieldElectric discharge heatingRadiation applicationsOphthalmologyEyewear
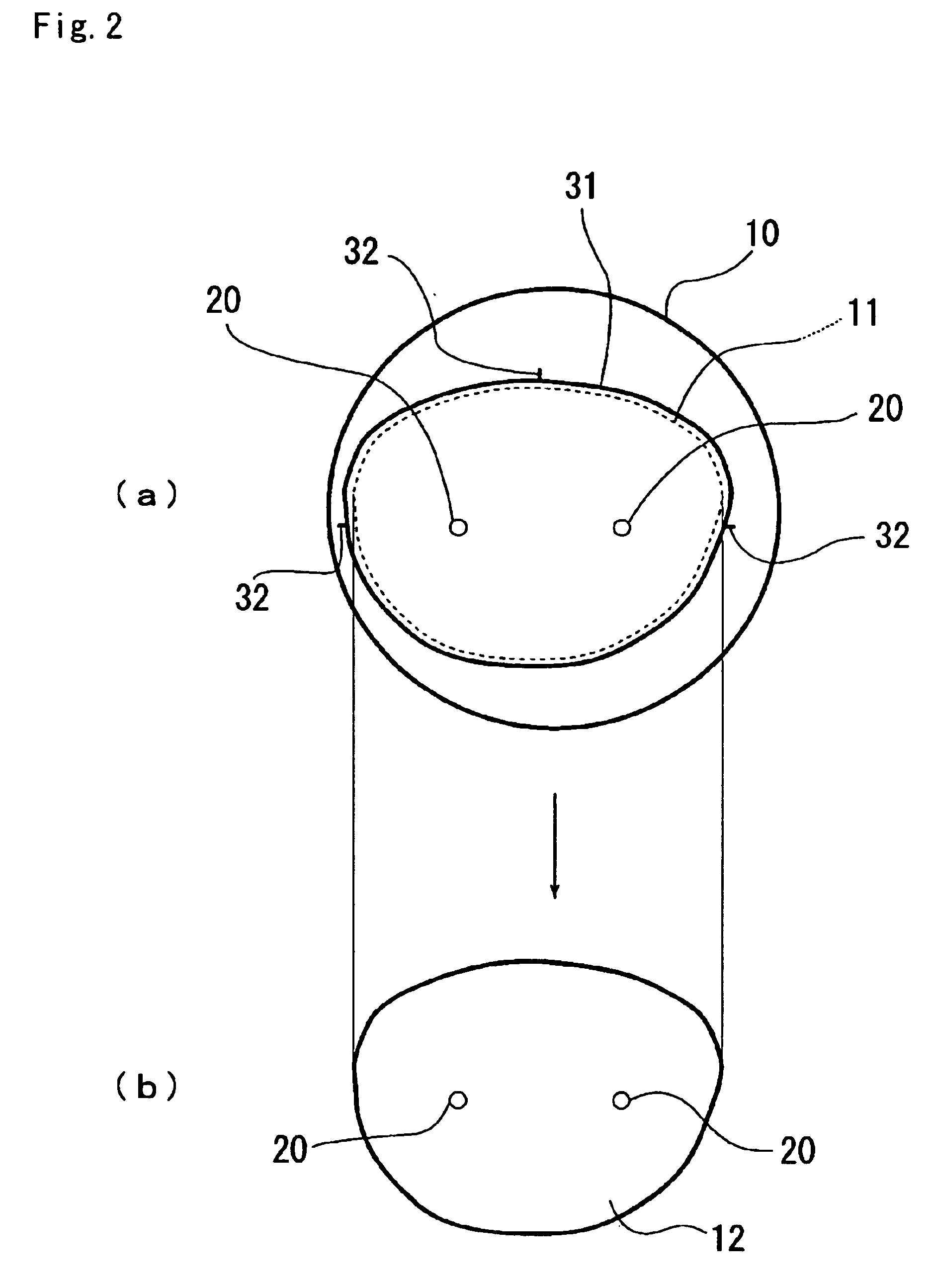
Production information such as an edging mark 31 indicating a region of a lens remaining after edging and reference position marks 32 are depicted in a region, to be cut off by the edging, of a surface of a lens 10 for spectacles. Any production information does not remain on the finished lens 10 after the edging. A lens processing system 100 includes a reference position detecting apparatus (120 and 130) for detecting a reference position of a spectacle lens, and a marking apparatus (170, 160, 150 and 110) for depicting production information of the lens on a specific surface of the spectacle lens on the basis of the reference position information obtained by the reference position detecting apparatus (120 and 130).
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
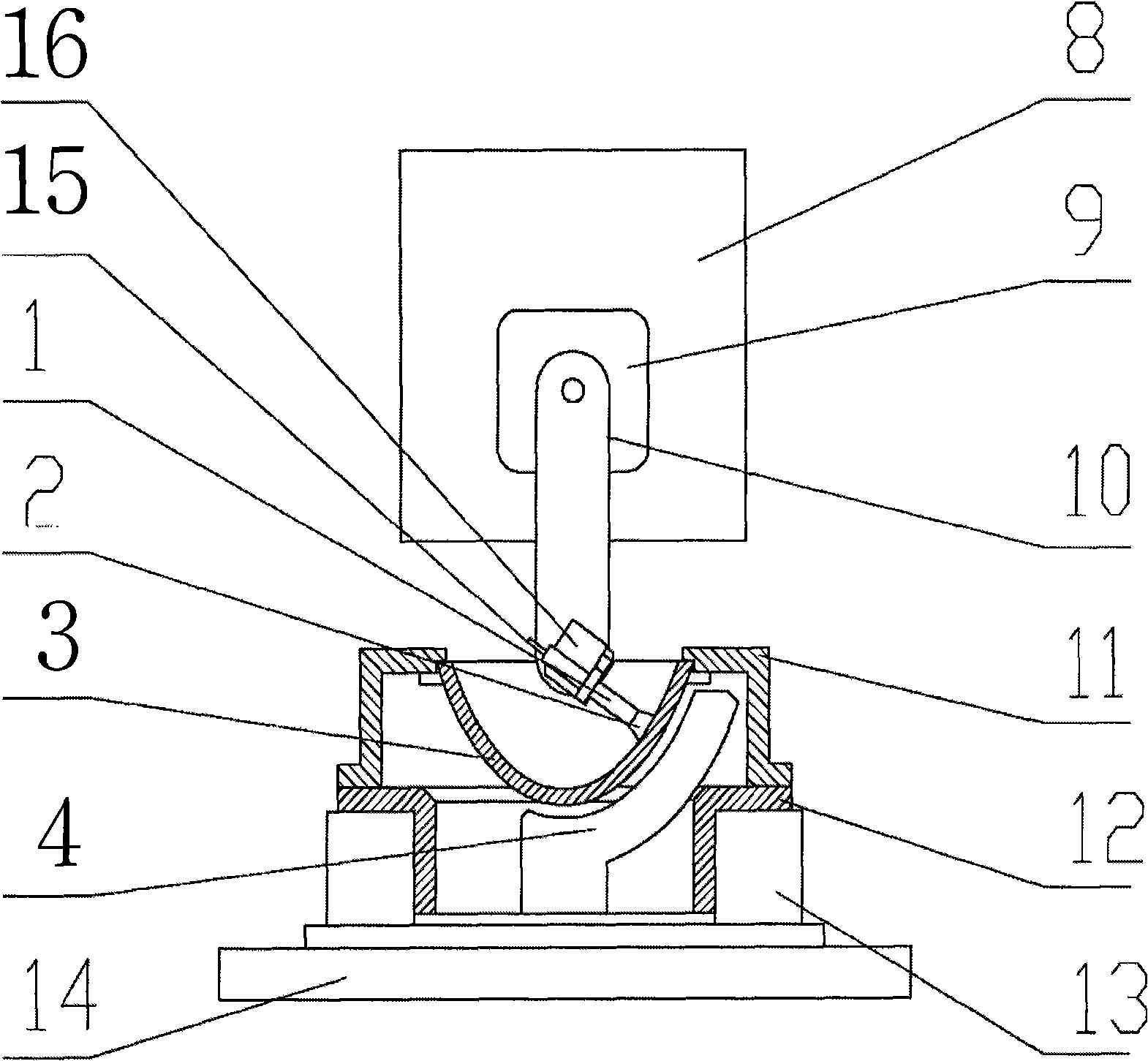
Method for polishing inner concave surface of optical elements as well as device
InactiveCN101352826AImprove controllabilityHigh utility valueOptical surface grinding machinesPolishing compositions with abrasivesMagnetic polesHigh surface
The invention belongs to the technical field of precision optical polish finish, in particular to a polishing method of the inner concave surface of optical elements and a polishing device. A core mould with a tank circuit and inosculating with the shape of the inner concave surface to be processed is fixed below the inner concave surface of a work piece to be processed, and the work piece rotates around the own rotary shaft, keeps a micro clearance from the core mould and applies magnetic fields to processing regions by an external magnetic pole tool head and an internal magnetic pole exciting coil. When magneto-rheological fluids with polishing abrasives flow through the processing region along the tank circuit, a flexible polishing head is formed under the action of magnetic field and absorbed on the inner concave surface and polishing effects are generated. The polishing method and the device can realize the inner concave surface polishing of conformal optical elements with small curvature radiuses or deep cavity structure and other cyclically symmetric high gradient aspheric surfaces, and can remove distribution by utilizing computer-controlled polishing, and besides the polishing method and the device have the polishing surface shape control ability and both the advantages of high precision and high surface quality.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Combination machining method for removing high-frequency errors in optical elements
ActiveCN102848287AImprove high frequency errorOptical surface grinding machinesEngineeringSpectral density
The invention discloses a combination machining method for removing high-frequency errors in optical elements. The combination machining method includes measuring surface shape errors of an optical element to be machined by an interferometer, carrying out PSD (power spectral density) analysis, and determining distribution characteristics of the medium and high-frequency errors on the basis of a DSD curve; acquiring an optimized removal function model according to predetermined machining time and machining precision, and acquiring an amplitude spectral line of a removal function; acquiring cut-off frequency of the removal function according to the amplitude spectral line; machining by a magneto-rheological finishing process if correctable medium and high-frequency errors with the frequency lower than the cut-off frequency exist according to the frequency distribution of the medium and high-frequency errors; and machining by a computer controlled optical surfacing process if uncorrectable medium and high-frequency errors with the frequency higher than the cut-off frequency exist according to the frequency distribution of the medium and high-frequency errors. By the combination machining method, technical advantages of MRF (magneto-rheological finishing) and technical advantages of CCOS (computer controlled optical surfacing) can be sufficiently combined, efficient uniform convergence of all-band errors of the optical element can be realized, and performance of the optical element is effectively improved.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Method for polishing ion beam with high-gradient mirror surface
InactiveCN101898324ASolve the problems in polishingAchieving Deterministic PolishingOptical surface grinding machinesElectric discharge tubesNumerical controlOptical axis
The invention discloses a method for polishing an ion beam with a high-gradient mirror surface. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) measuring incidence angles theta of all points on the mirror surface; (2) confirming a compensation factor K of each point according to a model; (3) measuring an initial surface error E of a workpiece by utilizing interferometry; (4) compensating the E according to the K to acquire a compensation surface error E'; (5) acquiring a removal function R of an ion beam in the vertical incidence of the mirror surface through removal function experiment; (6) confirming residence time distribution T and generating a numerical control code according to E' and R; (7) processing by utilizing a generating device of the removal function and the generated numerical control code, enabling the ion beam to enter the mirror surface along a direction parallel to the optical axis direction of the workpiece in processing and trimming the mirror surface through a triaxiality linkage system; and (8) repeating the steps until the trimming result satisfies the requirement of surface convergence accuracy. The method of the invention has the advantages of simple operation, good stability, high processing accuracy, strong controllability, low requirement for equipment, and the like in processing the high-gradient mirror surface.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Method, apparatus and adhesive composition for ophthalmic lens blocking
InactiveUS20050139309A1Optical surface grinding machinesPolyureas/polyurethane adhesivesOphthalmologyEye lens
A method is provided for blocking a lens according to which a lens block is obtained which transmits UV and visible light. An adhesive curable by light within the UV and visible spectrum is applied between the lens blank and a lens mounting face of the lens block. The lens blank is placed adjacent the lens block with the adhesive extending therebetween. UV light is applied to cure the adhesive. The adhesive is selected to have a suitable low dimensional change on setting so as not to impart any undue stresses on the lens blank which being capable of total adhesive failure without lens damage or leaving a residue upon application of a suitable stripping force.
Owner:MICRO OPTICS DESIGN
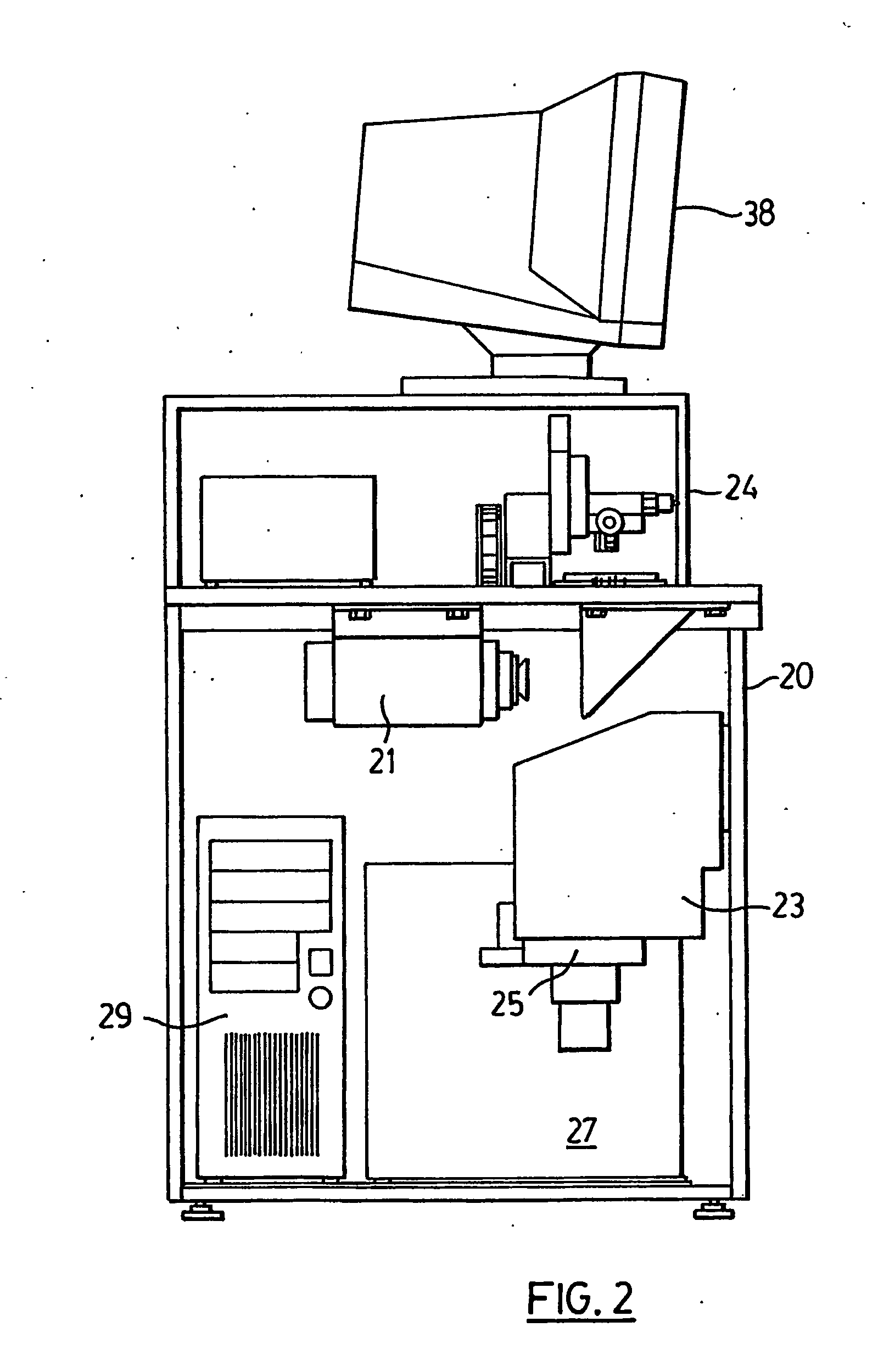
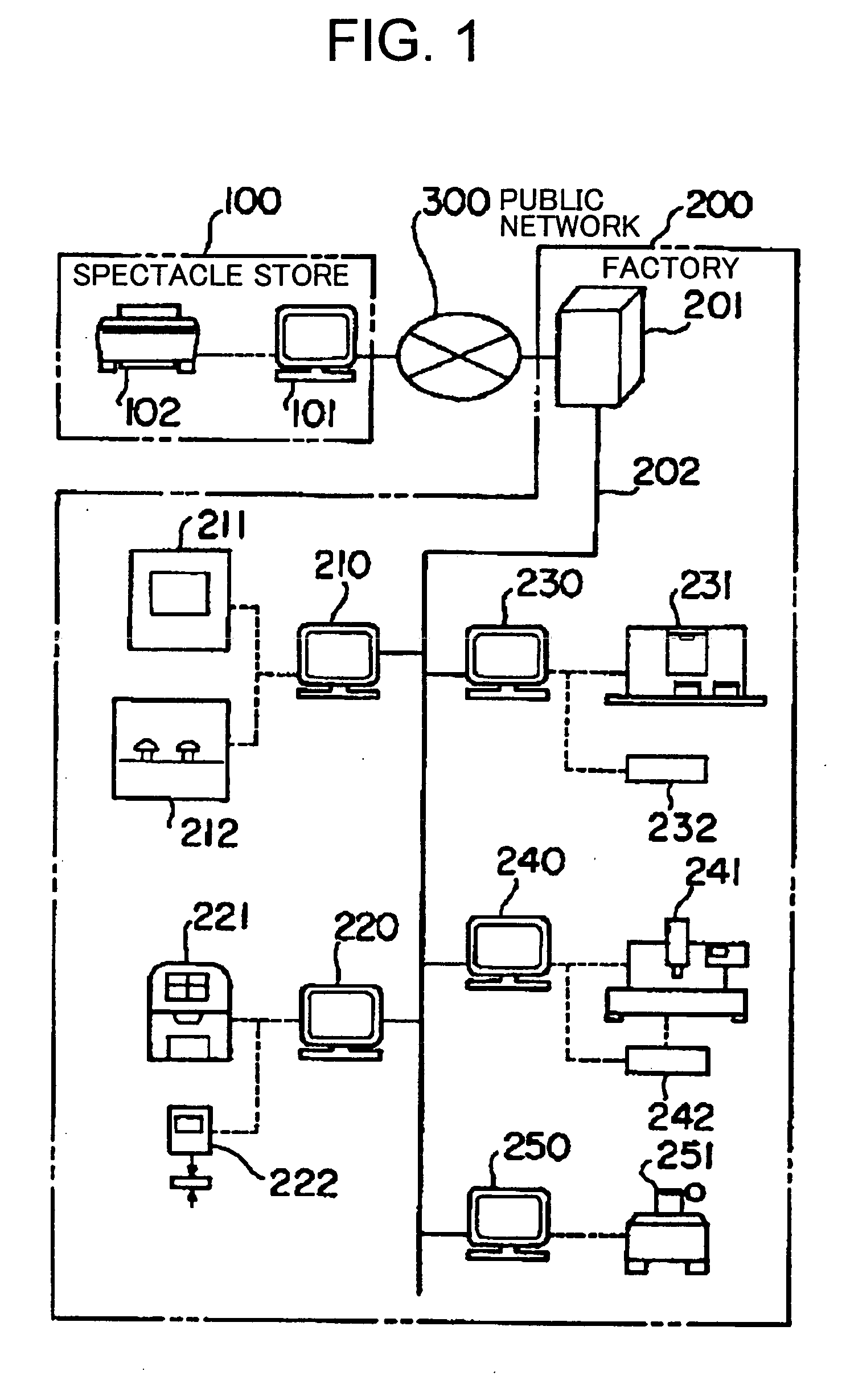
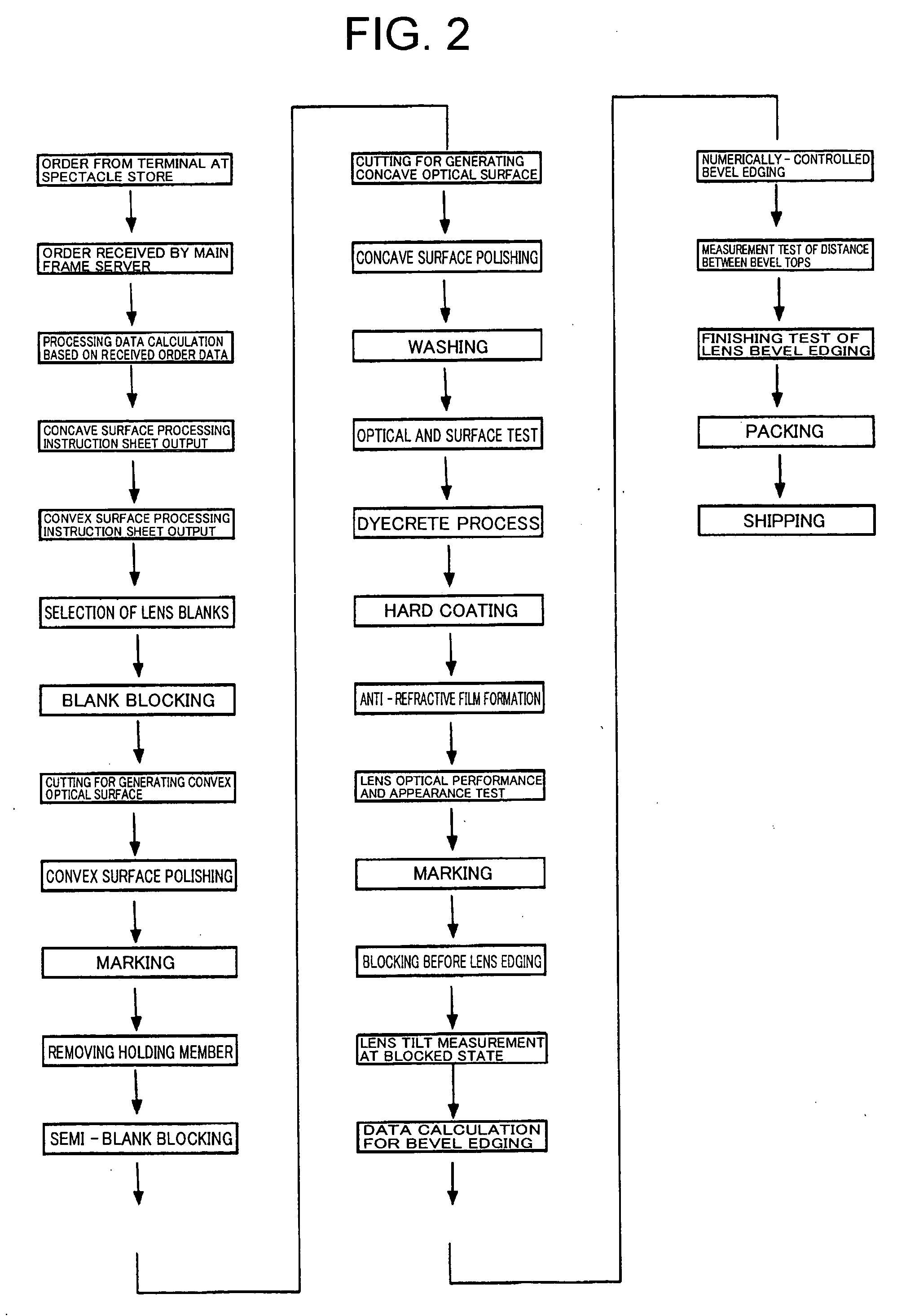
Spectacle lens manufacturing method and spectacle lens manufacturing system
InactiveUS20060189255A1Reduce wasteFast preparationEdge grinding machinesPolishing machinesNumerical controlPlastic materials
Aims to reduce the types of blanks such as a semi-finished lens blank, materials, and processing time. A spectacle lens design device 201 disposed at a factory 200 on a manufacturing side and a lens processing device connected thereto block an applicable semi-finished lens blank or lens blank so that a reference surface thereof tilts at a predetermined angle using a numerical-control curve generator based on order information sent from an order terminal 101 disposed at an spectacle store 100 on a order-placement side, and form both surfaces of a plastic material so that a geometric center of an edge shape positions at a center of a circle of a circular lens to thereby satisfy an optical specification of the spectacle lens-related to the order, and next, the circular lens is processed to have the edge shape of the spectacle lens-related to the order to thereby obtain the spectacle lens-related to the order.
Owner:HOYA CORP
Method and device for polishing magneto-rheological inclined shaft
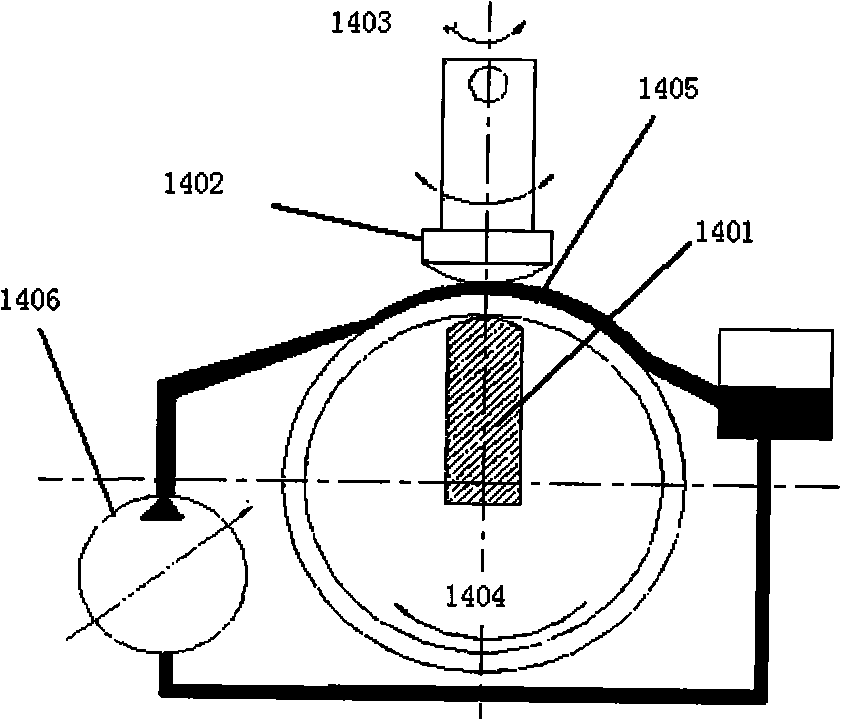
InactiveCN101564824AReduce size requirementsAvoid interferenceOptical surface grinding machinesEngineeringMagneto rheological
A method and a device for polishing a magneto-rheological inclined shaft relate to the technical field of precise finishing machining. A polishing tool head and the axial direction of a workpiece have an angle so that the normal of the working arc of the polishing tool head is coincident with the polishing surface normal of the workpiece; the shell of the polishing tool head rotates; furthermore, the rear end of the shaft in the shell passes through the hollow shaft of an adjustable speed motor and is fixedly connected with a machine body; the fixed shaft is provided with an excitation device; one part of the small front area of the shell of the polishing tool head is provided with a magnetic field and the other part thereof has no magnetic field or has weak magnetic field, thus facilitating updating the magneto-rheological liquid; the contact point of the workpiece and the magneto-rheological point is always the normal direction of the polishing area of the workpiece; the shell of the polishing tool head rotates and the magneto-rheological body generates a high shearing force at the clearance between the polishing tool head and the workpiece, thus removing trace of the material. By adopting the inclined shaft polishing, the interference is prevented from being generated; by planning path and controlling relevant parameters, the specific ultra-precise polishing process can be carried out to the surfaces of minitype non-spherical optical parts, dies and workpieces of general dimensions.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
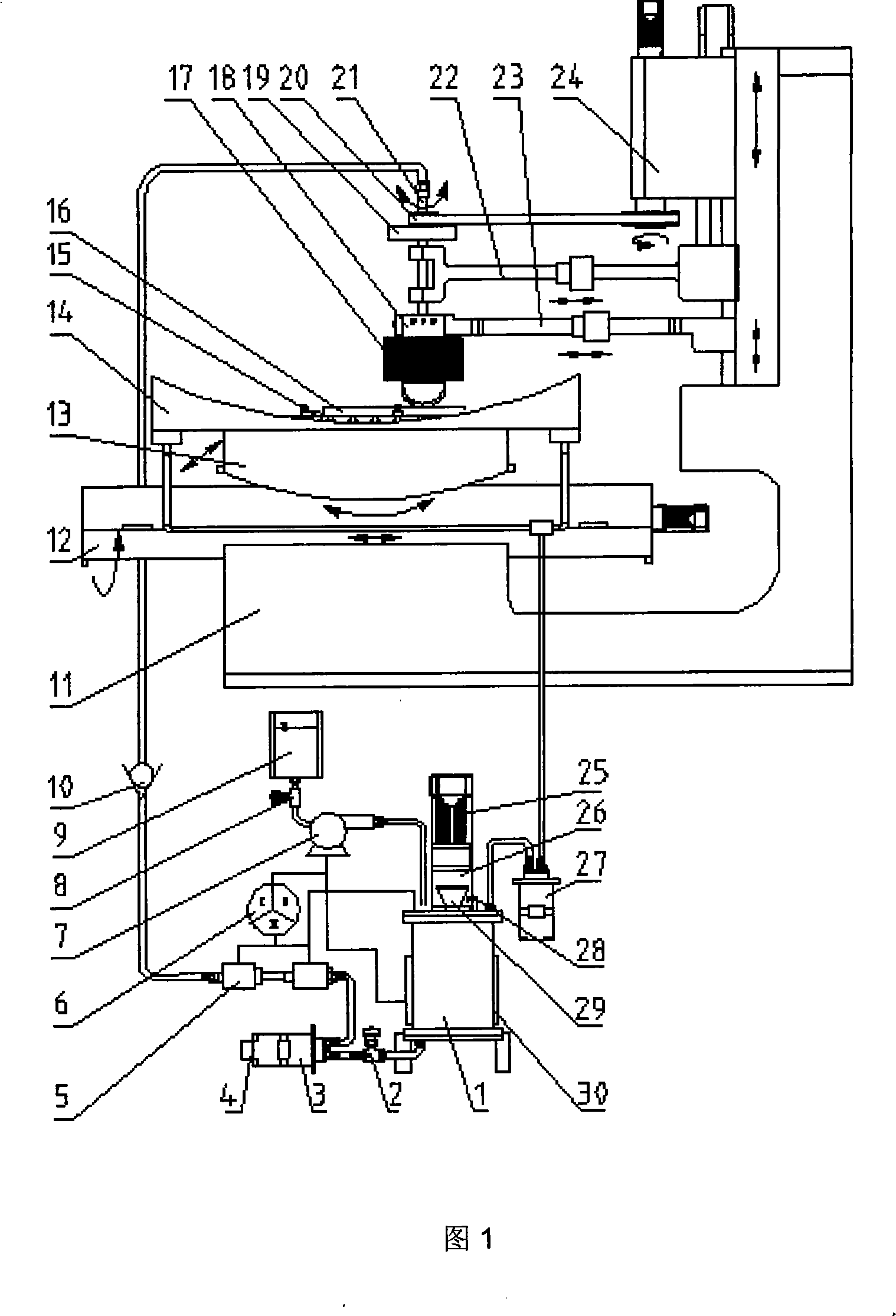
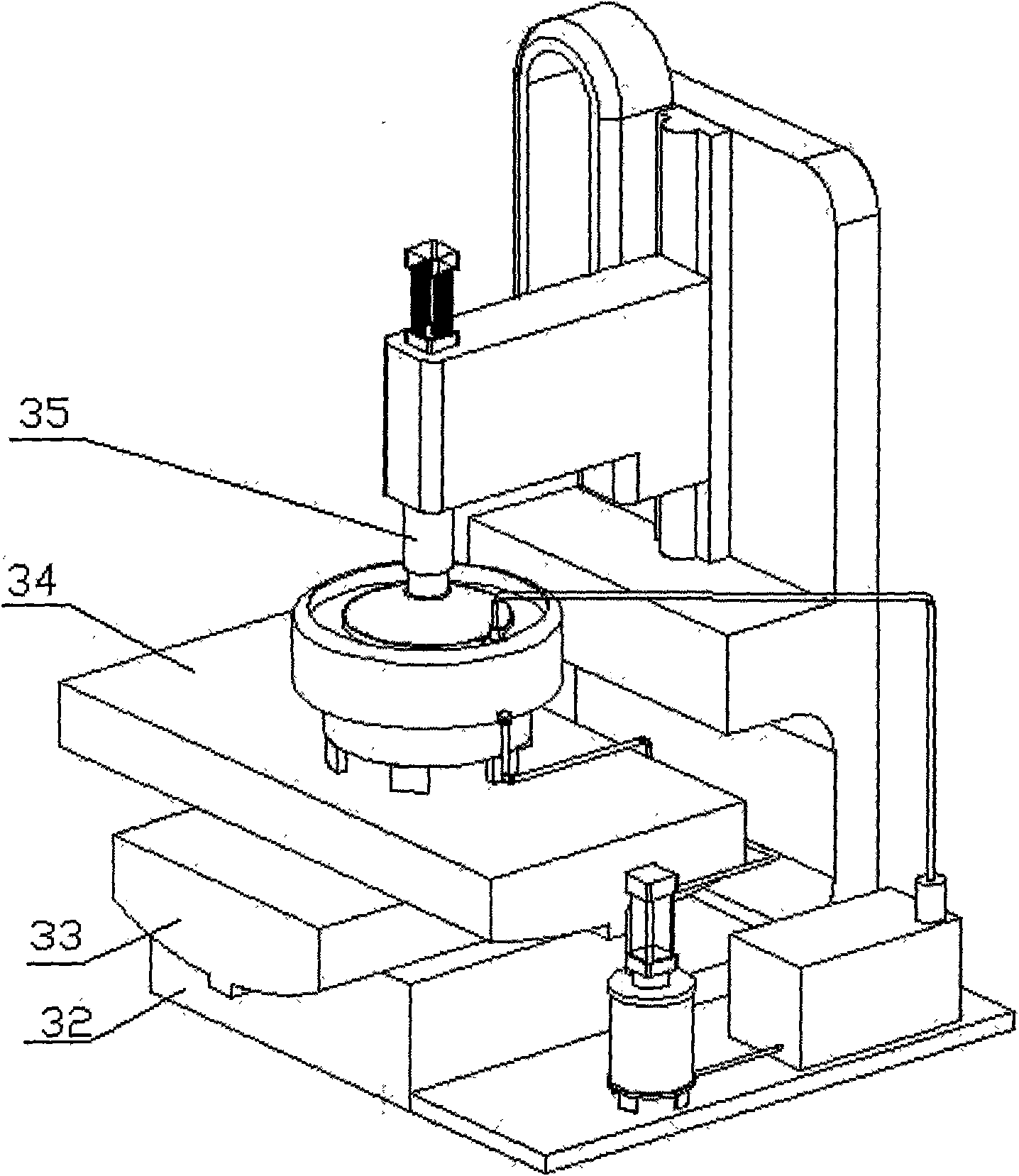
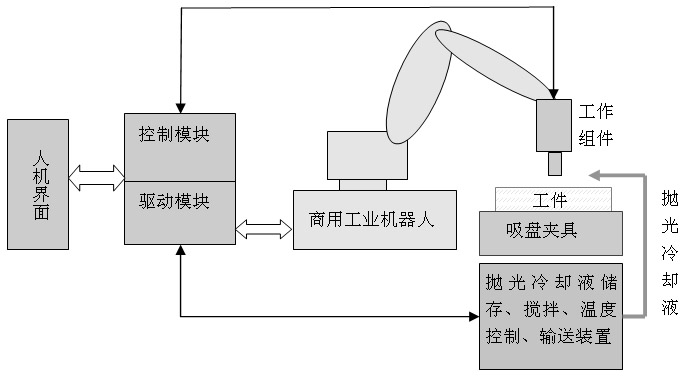
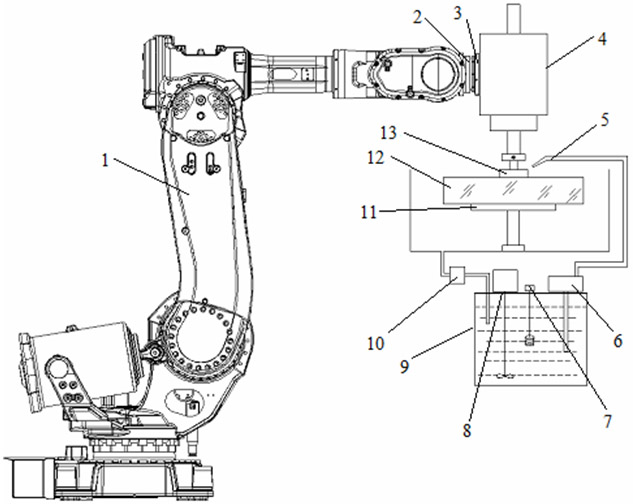
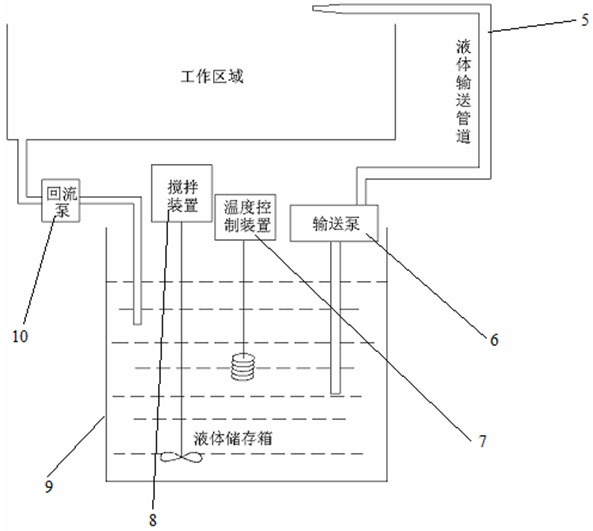
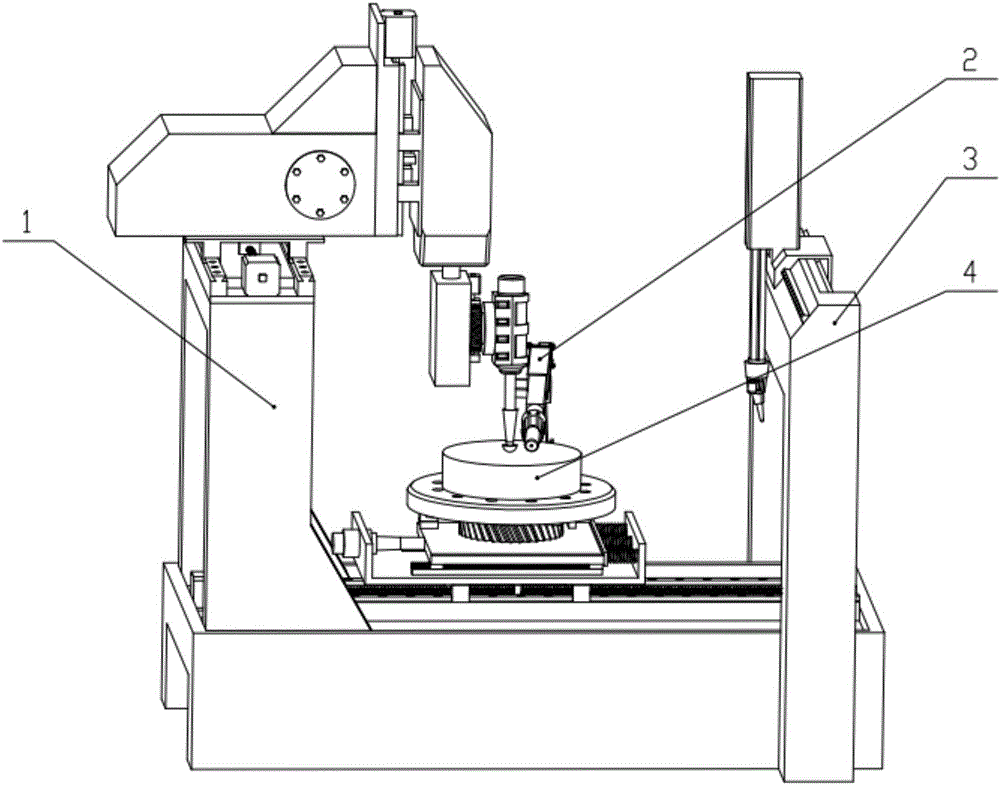
Milling, grinding and polishing device based on intelligent numerically-controlled platform
InactiveCN101983838AAchieve deterministic grindingRealize the processing effectOptical surface grinding machinesGrinding feed controlSurface typeSpatial movement
The invention relates to a milling, grinding and polishing device based on an intelligent numerically-controlled platform, belonging to the technical field of modern optical processing. The device comprises an industrial robot, a control module, a driving module, a human-computer interaction interface, a working component, a polishing and cooling liquid cyclic control system and a sucker clamp, wherein the control module and the driving module control and drive the spatial movement and spatial positioning of the industrial robot, thereby controlling the working state of the working component, namely a grinding / polishing module; the control module also controls the human-computer interaction interface and simultaneously controls a stirring device, a temperature control device and a conveying device of the polishing and cooling liquid cyclic control system; and the sucker clamp is used for clamping a workpiece to be processed. The device of the invention has low manufacturing cost, large processing caliber and wide processed surface types, and two functions of grinding and polishing can be realized by replacing grinding heads.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV +1
Method and device for producing ophthalmic lenses and other shaped bodies with optically active surfaces
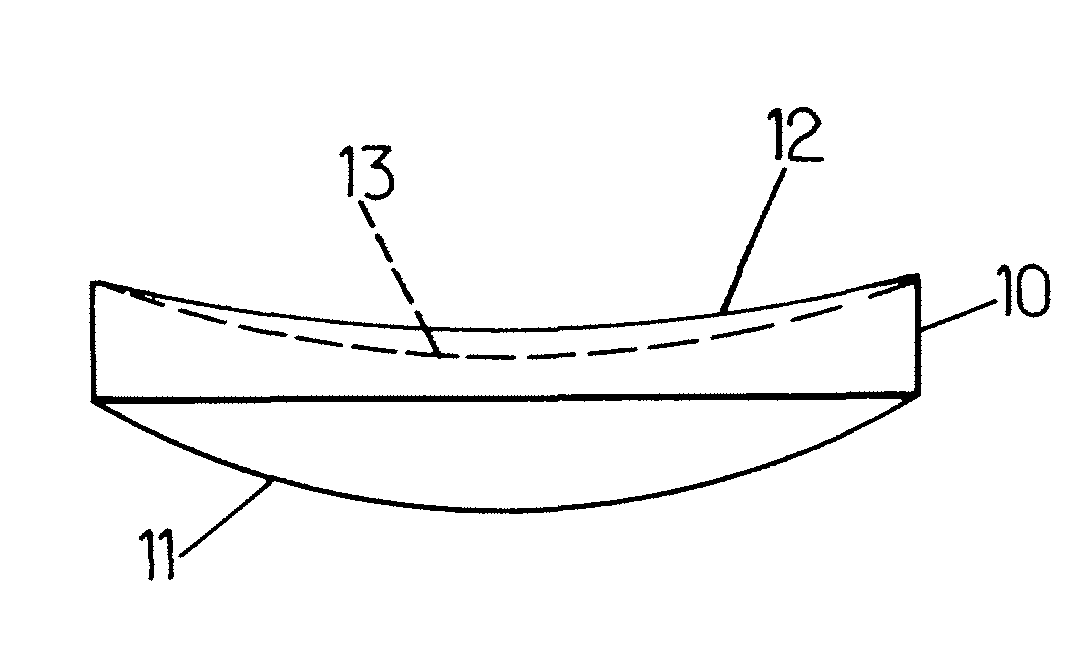
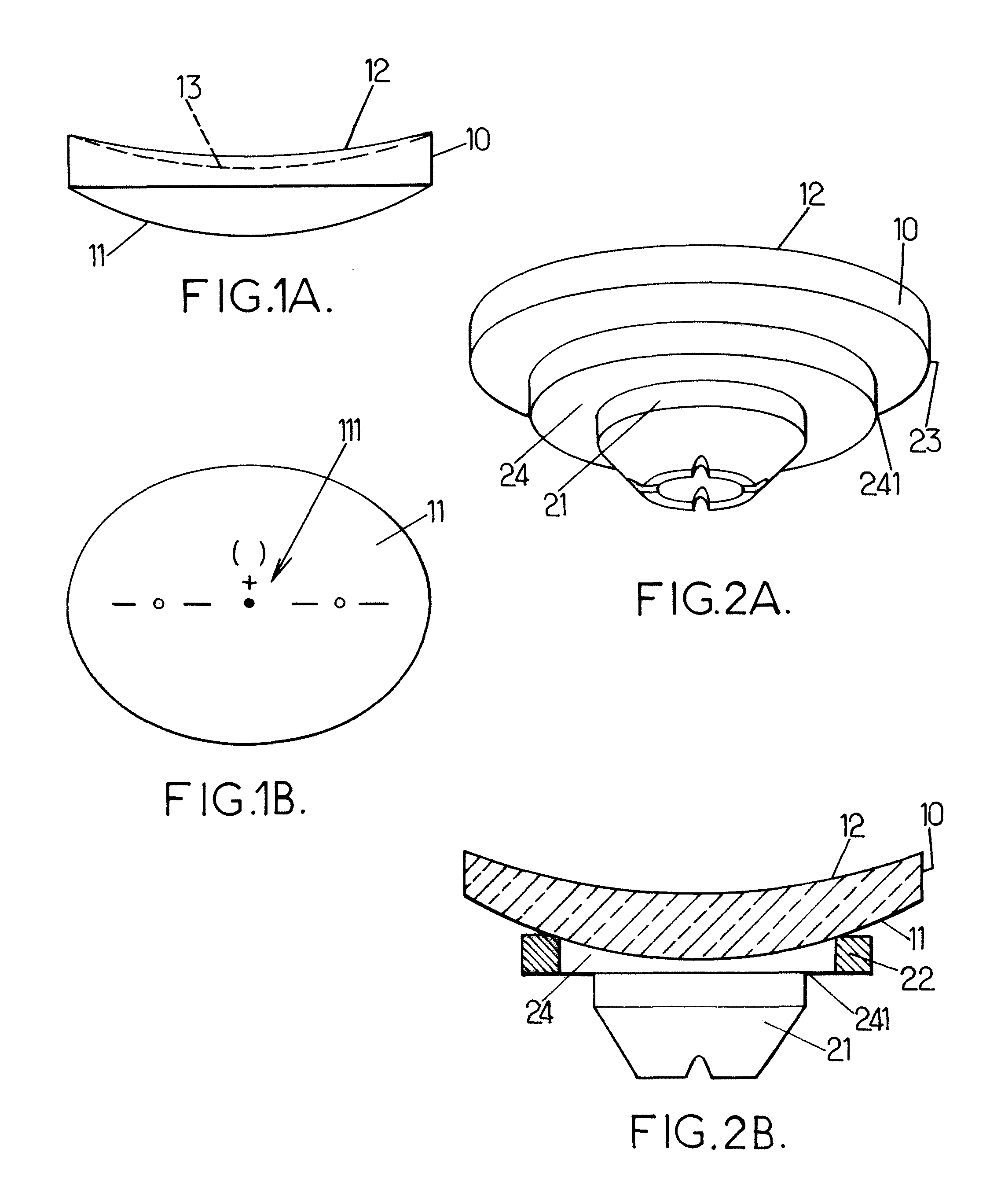
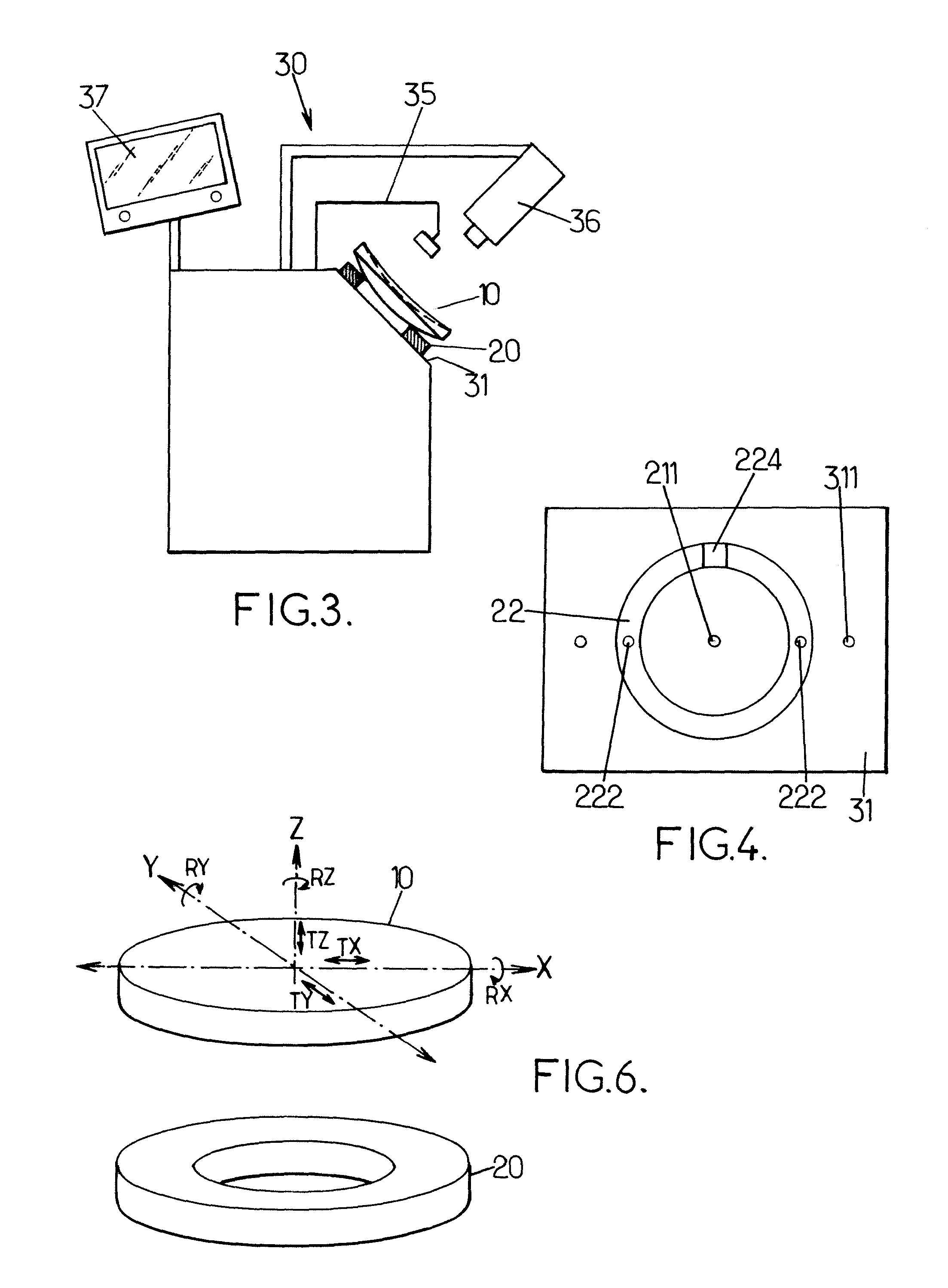
ActiveUS20060073771A1Inhibit thermal stressSmall possible weightRevolution surface grinding machinesOptical surface grinding machinesCircular discEngineering
The invention concerns a method for producing ophthalmic lenses that uses plastic blanks in the form of flat, round discs. The outer edge of said plastic blanks is clamped and the desired final surface geometry and surface quality of the front faces of the lens are subsequently produced by a machining process using grinders and / or lathes and by smoothing and polishing processes. During machining, a thicker annular region is retained on the outer circumference of the workpiece. The annular region clamps or arranges the workpiece during machining and transport operations and stabilizes the lens for additional machining. Shaped pieces for identifying the machining axes are attached to the annular region. The lens is provided with fine markings to characterize the lens that has been produced, with the lens then being separated from the region.
Owner:OPTOTECH OPTIKMASCHEN +1
System and method for ophthalmic lens manufacture
InactiveUS20010051490A1Low costEdge grinding machinesOptical surface grinding machinesEngineeringLens plate
A method and system for the manufacture of ophthalmic lenses comprising a computer (102) and a CNC machining platform (104) in operative connection with the computer. The CNC machining platform includes a mounting stage (110), a block (106) in releasable connection with the mounting stage, and a machining tool (112). When an unfinished lens blank (108) is properly mounted on the block, the computer is operative to direct the CNC machining platform to perform both back surface generation and patternless edging of the lens blank in one machining cycle. The computer is further operative to direct the CNC machining platform to machine a lap tool for each lens and machine a block for receiving each lens. The block is machined by the platform to include scribe lines for facilitating proper alignment of lens blank.
Owner:NCRX OPTICAL SOLUTIONS
Tool, apparatus, and method for precision polishing of lenses and lens molds
InactiveUS20050079812A1Low costImprove accuracyOptical surface grinding machinesSupport wheelsParallel plateEngineering
A tool for polishing objects having a wide variety of materials and shapes including precision optical surfaces, injection mold inserts, and thin film coating dies. The tool has an elastic solid bladder with a curved surface, upon which is disposed an abrasive band. The curved bladder surface is produced by compressing the bladder between two parallel plates. The apparatus comprises a multi-axis computer controlled machine to which the tool is attached.
Owner:OPTIPRO SYST
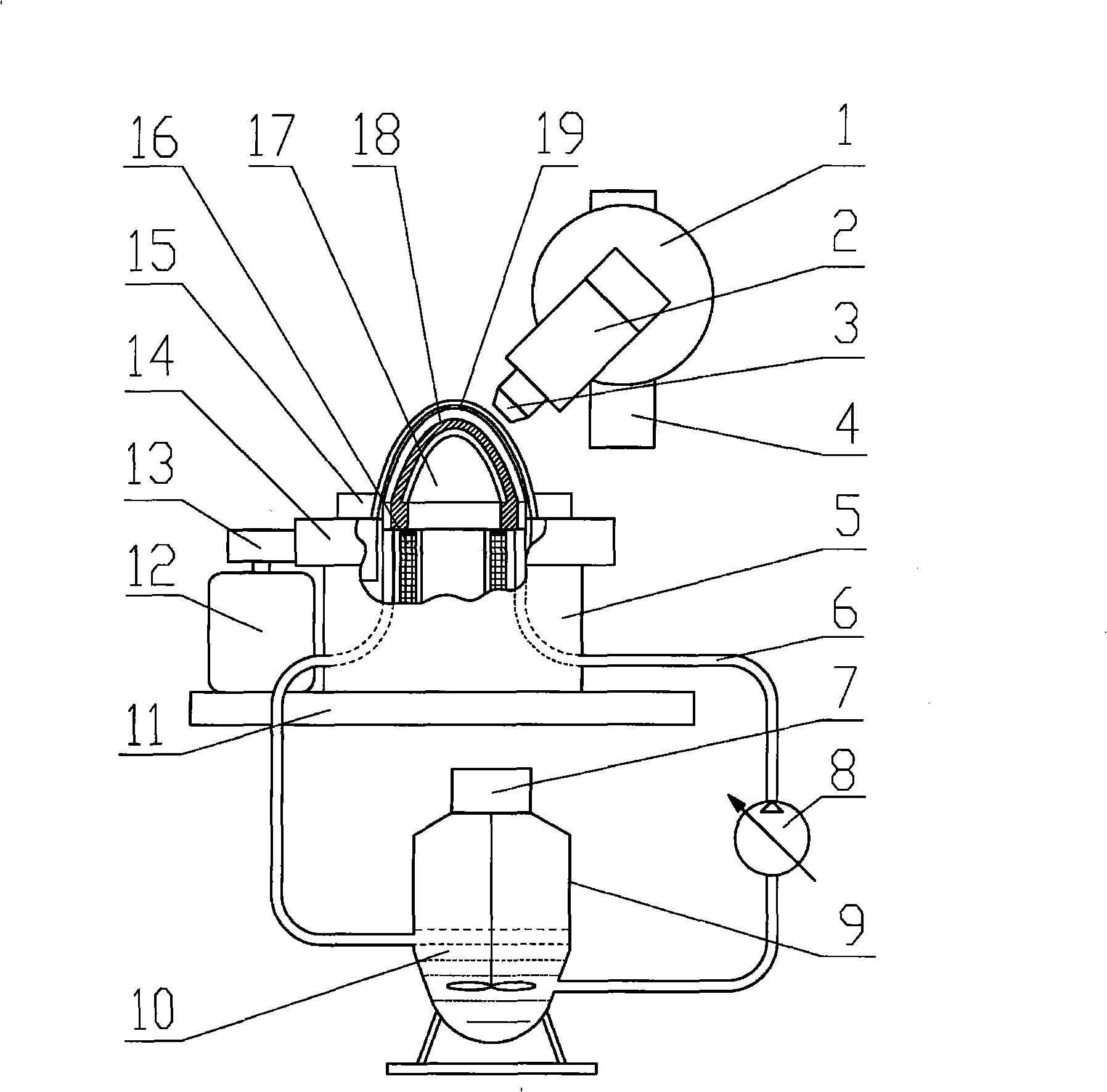
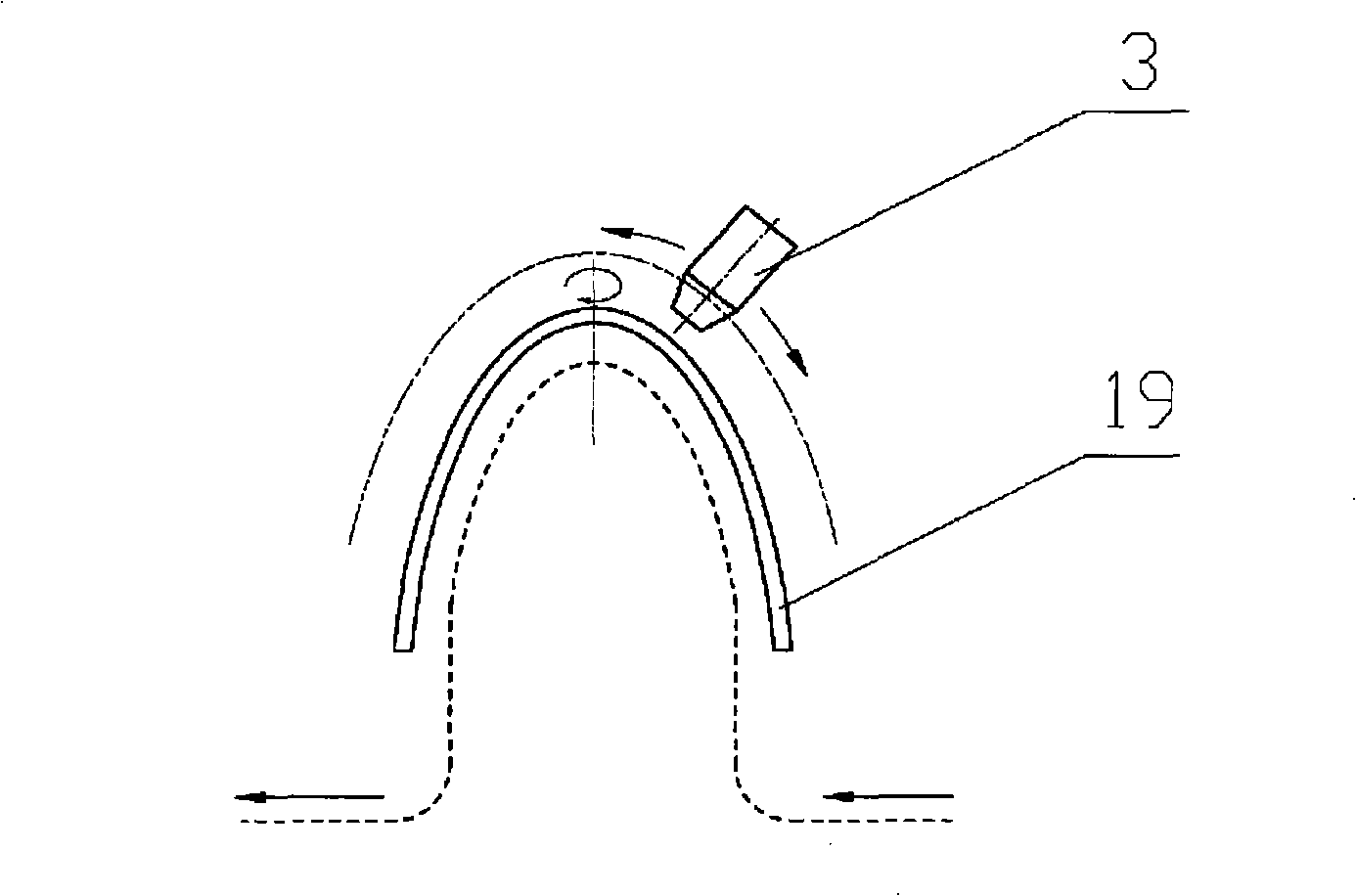
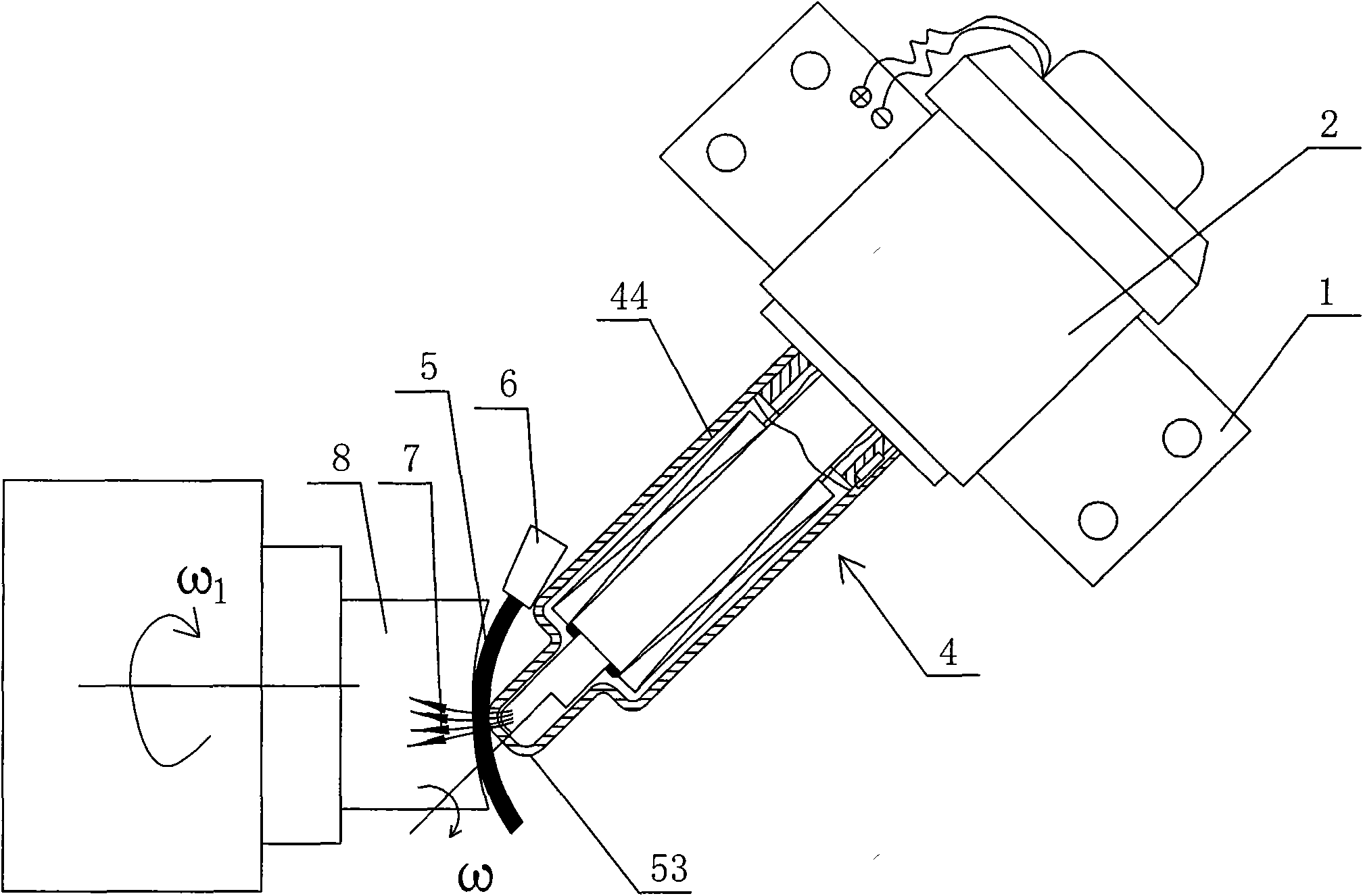
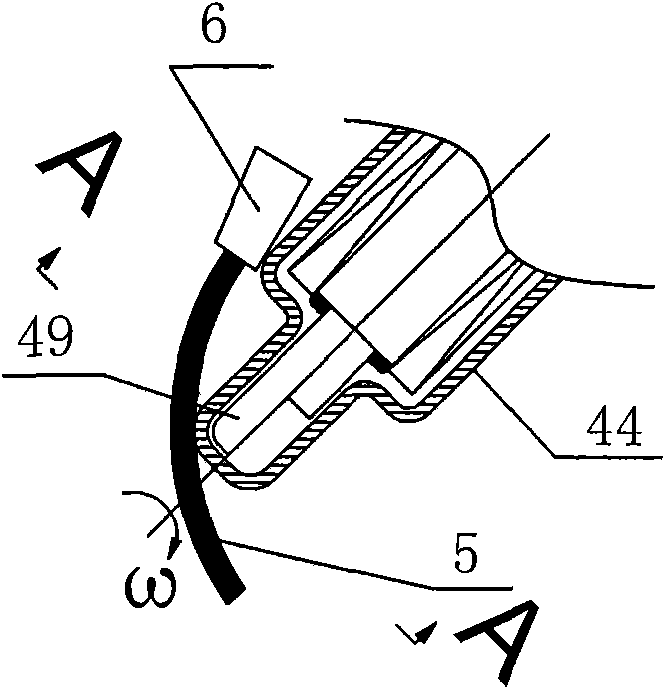
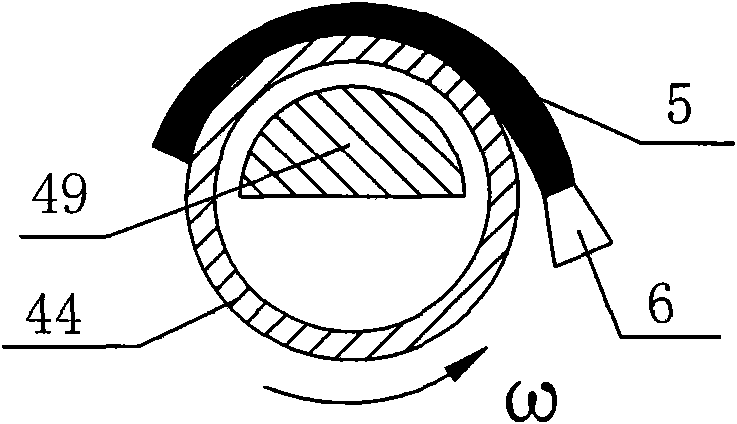
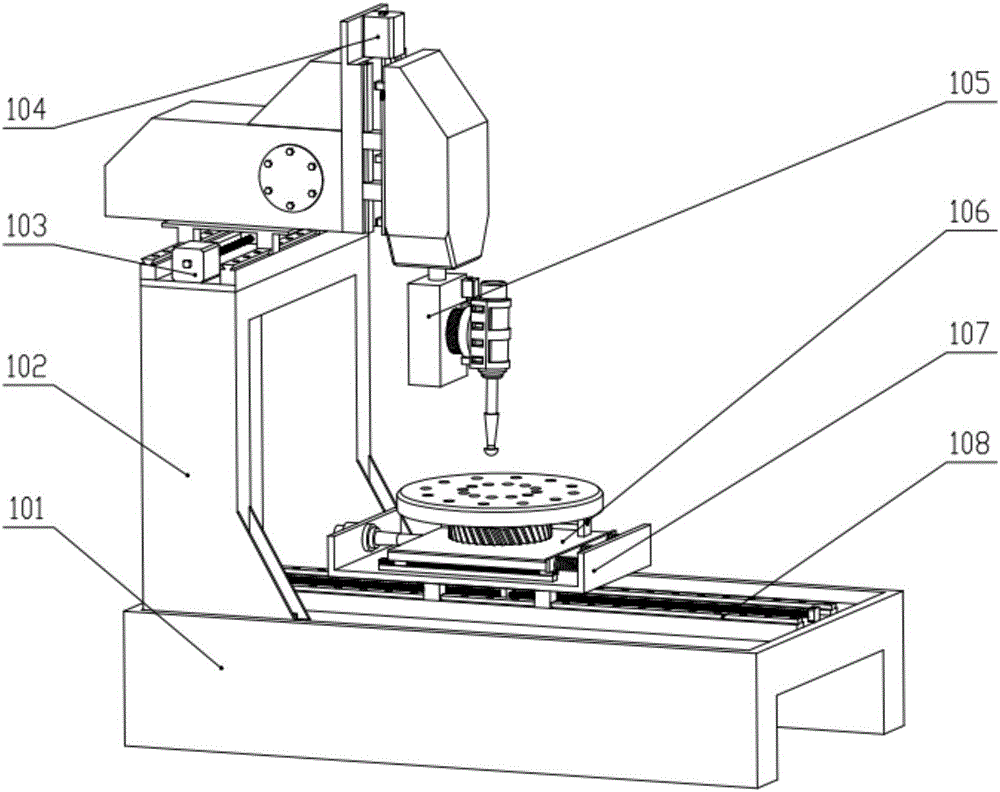
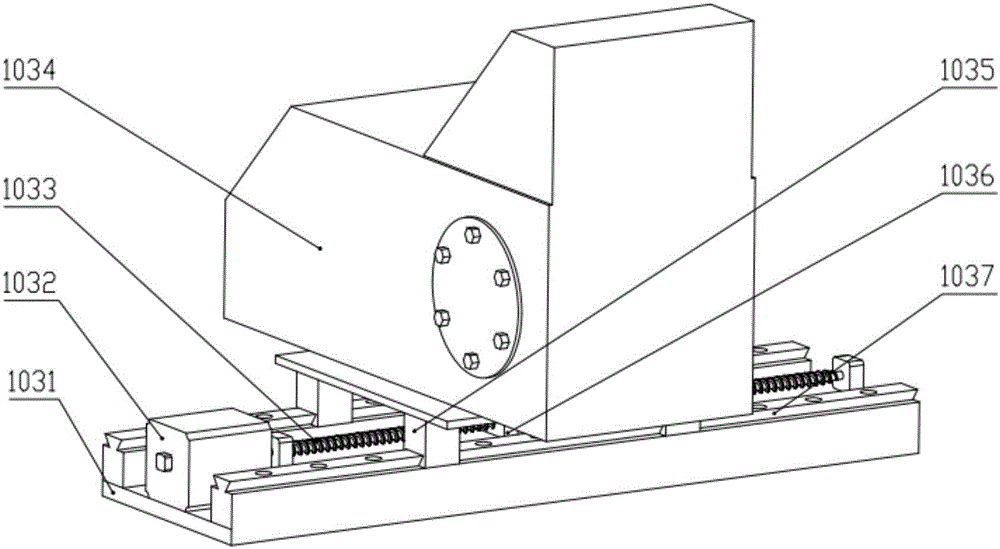
Five-axis three-dimensional ultrasonic polishing machine tool for optical curved surface machining and use method of five-axis three-dimensional ultrasonic polishing machine tool
ActiveCN106736992AGood removal effectImprove efficiencyGrinding carriagesOptical surface grinding machinesUltrasonic vibrationEngineering
The invention discloses a five-axis three-dimensional ultrasonic polishing machine tool for optical curved surface machining. The five-axis three-dimensional ultrasonic polishing machine tool comprises a machine tool, an ultrasonic atomization device for applying polishing liquid and a workpiece on-line detection device. An X-direction travel mechanism, a Z-direction travel mechanism and a Y-direction travel mechanism are arranged on the machine tool; a spindle ultrasonic vibration polishing device is arranged on the Z-direction travel mechanism; a Y-direction ultrasonic vibration device is arranged on the Y-direction travel mechanism; a C-direction rotating work table is arranged on the Y-direction ultrasonic vibration device; the machine tool can enable the axis line direction of a polishing head parallel to the normal line of a polishing point of a workpiece through five-axis linkage; when the polishing head rotates, the ultrasonic wave of the Y-direction ultrasonic vibration device and the ultrasonic wave of the ultrasonic vibration polishing device which swings around the Z direction are vertically coupled in a plane; when the amplitude A1 of the Y-direction ultrasonic vibration device is greater than the amplitude A2 of the ultrasonic vibration polishing device, the polishing head and the workpiece can form an elliptic machining track where a long axis is in the Y-direction and a short axis is in the normal line position of the polishing point of the workpiece, so that the contact area between the polishing head and the workpiece is increased, and the curved surface removal rate and the polishing machining efficiency can be greatly improved.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
Structure for a polishing machine of an optical disk
InactiveUS6846228B2Simple structureThe effect is accurateEdge grinding machinesPolishing machinesEngineeringTimer
A structure for a polishing machine of an optical disk, which comprises a motor, a turntable unit integrated with a housing, at least two polishing wheel positioned on a cover which can cover up the housing, and a timer. When the cover is closed, the polishing wheel can polish the optical disk. The primary objective of this invention is to provide a structure for a polishing machine with a precise polishing effect and higher automation to increase the quality of polishing. The secondary objective of the present invention is to provide a structure for a polishing machine which is simplified in structure, miniaturize in volume and is easily stored and used.
Owner:LIN MING SHENG
Optical glass
ActiveCN101613184AHigh refractive indexExcellent glass stabilityOptical surface grinding machinesOptical elementsRefractive indexOptical glass
The invention provides an optical glass having a very high refractive index in spite of its low-dispersion property, having excellent glass stability and having less susceptibility to coloring. An optical glass is an oxide glass and is characterized in that the optical glass comprises, by cationic %, 0 to 30% of Si<4>, 10 to 55% of B<3>, less than 5% of total of Li<>, Na<> and K<>, less than 5% of total of Mg<2>, Ca<2> and Sr<2>, 0 to 8% of Ba<2>, 0.1 to 15% of Zn<2>, 10 to 50% of La<3>, 0 to 20% of Gd<3>, 0 to 15% of Y<3>, 0 to 10% of Yb<3>, 0 to 20% of Zr<4>, 0.1 to 22% of Ti<4>, 0 to 20% of Nb<5>, 0 to 8% of Ta<5>, 0 to 5% of W<6>, 0 to 8% of Ge<4>, 0 to 10% of Bi<3>, and 0 to 10% of Ai<3>, the cationic ratio of the content of Si<4> to the content of B<3>, Si<4> / B<3>, being less than 1.0, the total content of Nb2O5 and Ta2O5 as oxides being less than 14 mass %, the optical glass having a refractive index nd of 1.92 to 2.2 and an Abbe's number nud of 25 to 45.
Owner:HOYA CORP
Processing method of aspherical optical element of optical glass and silicon monocrystal
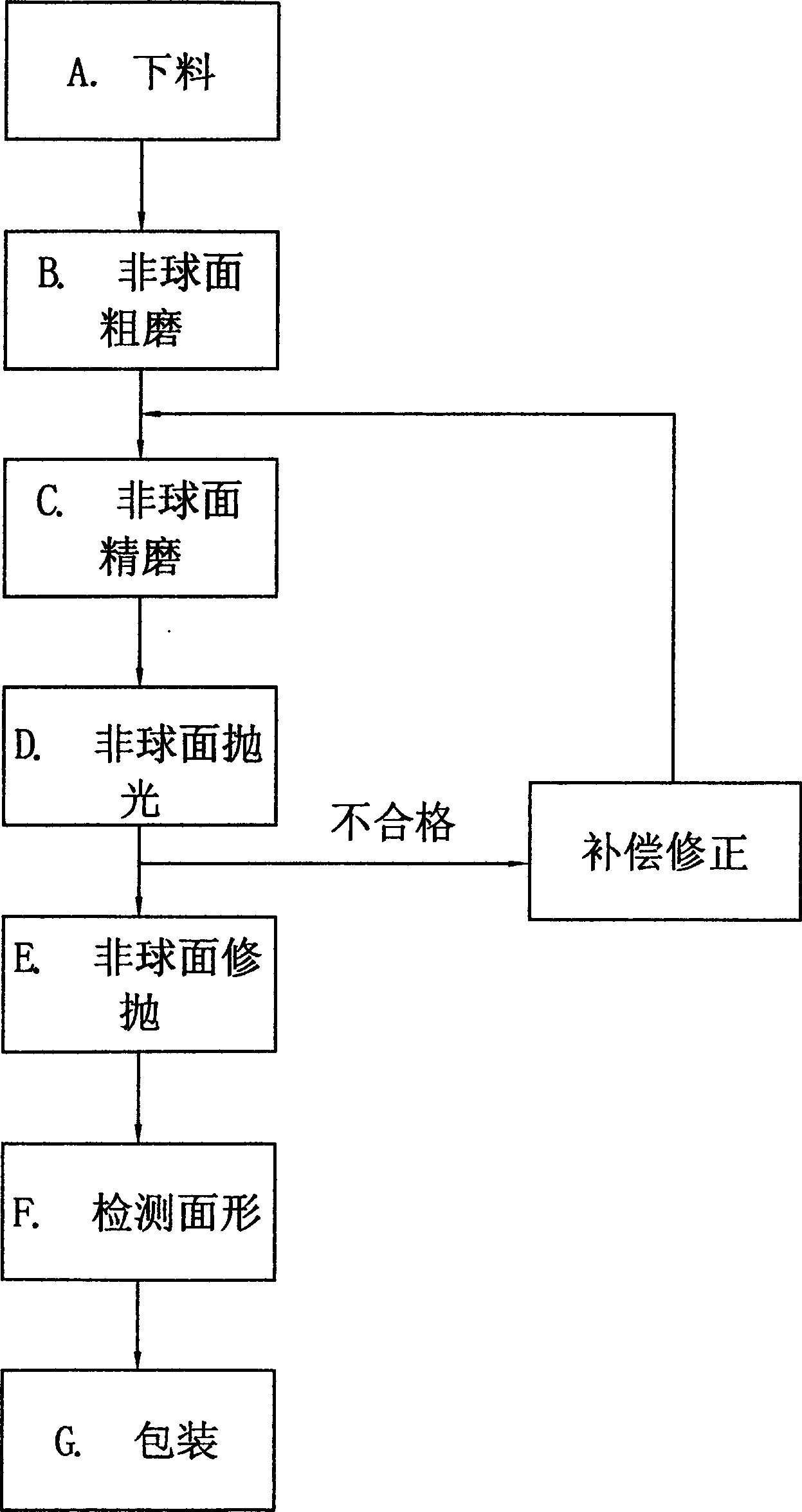
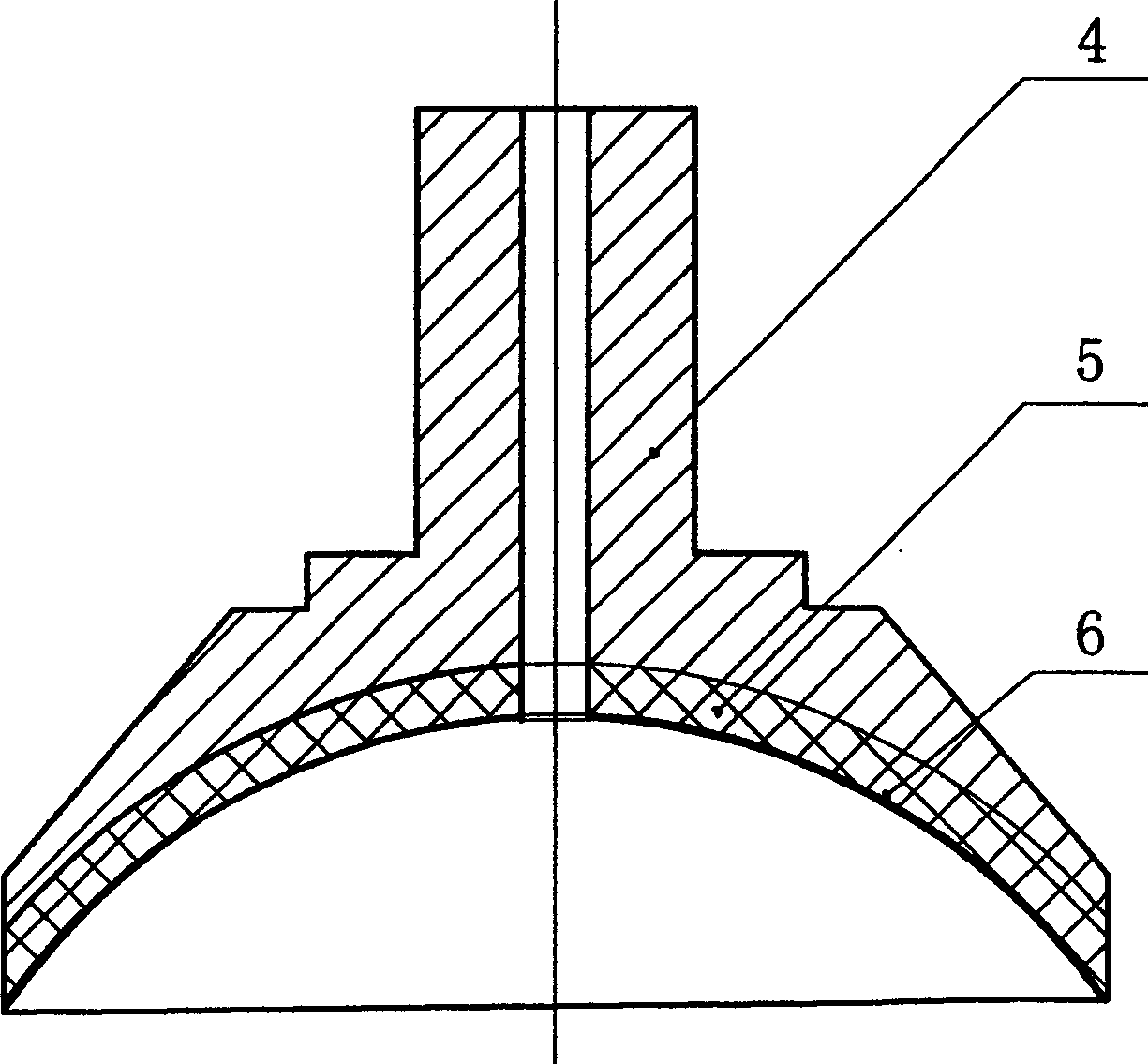
InactiveCN1846937AImprove surface qualityIncrease productivityOptical surface grinding machinesSingle crystalEngineering
The present invention discloses optical element processing technology, and is especially processing method of aspherical optical element of optical glass and silicon monocrystal. The present invention features that optical glass and silicon monocrystal is processed in computerized numerically controlled grinder and computerized numerically controlled polishing machine through a new technological process including the steps of fine grinding of aspherical, polishing of aspherical, trim polishing of aspherical, profile detection, etc. The present invention is superior to traditional method, and has low production cost, stable quality and high efficiency.
Owner:云南北方光学电子集团有限公司
Glass material for press molding, method of manufacturing glass material for press molding and method of manufacturing optical element
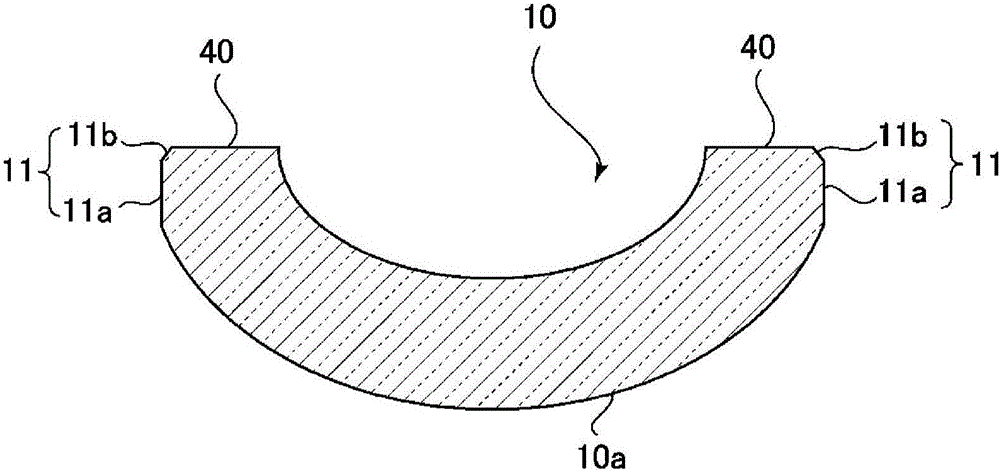
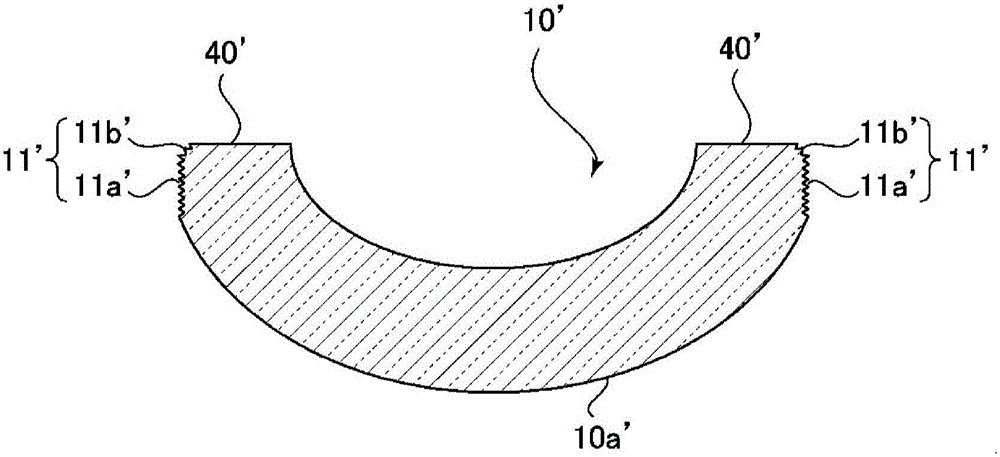
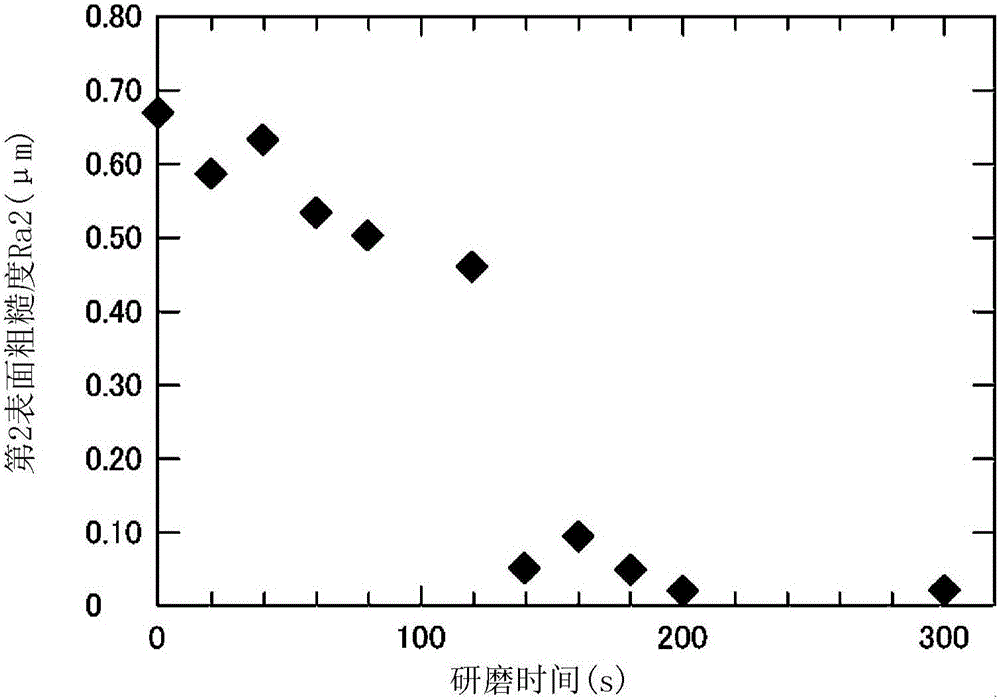
PendingCN106256794AGood optical performanceLow costGlass pressing apparatusGlass press-moulding apparatusSurface roughnessOptoelectronics
The invention provides a glass material for press molding, a method for manufacturing a glass material for press molding, and a method of manufacturing an optical element, which are capable of obtaining a desired optical performance without impairing the shape accuracy of the optical element obtained by press molding and providing such at low cost. According to the invention, a glass blank (10) for press molding is provided, wherein the glass material (10) for press molding comprises at least one convex surface (10a) having a surface roughness Ra being a first surface roughness Ra1 and a side end face (11) configured around the convex surface and having a surface roughness Ra being a second surface roughness Ra2, the second surface roughness Ra2 being less than 0.10 m, and the second surface roughness Ra2 being larger than the first surface roughness Ra1.
Owner:HOYA CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com