Tool, apparatus, and method for precision polishing of lenses and lens molds
a technology for polishing tools and lenses, applied in the field of polishing tools, can solve the problems of high cost, high cost, and high cost of prior art process, and achieve the effects of low cost, high throughput, and high precision
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
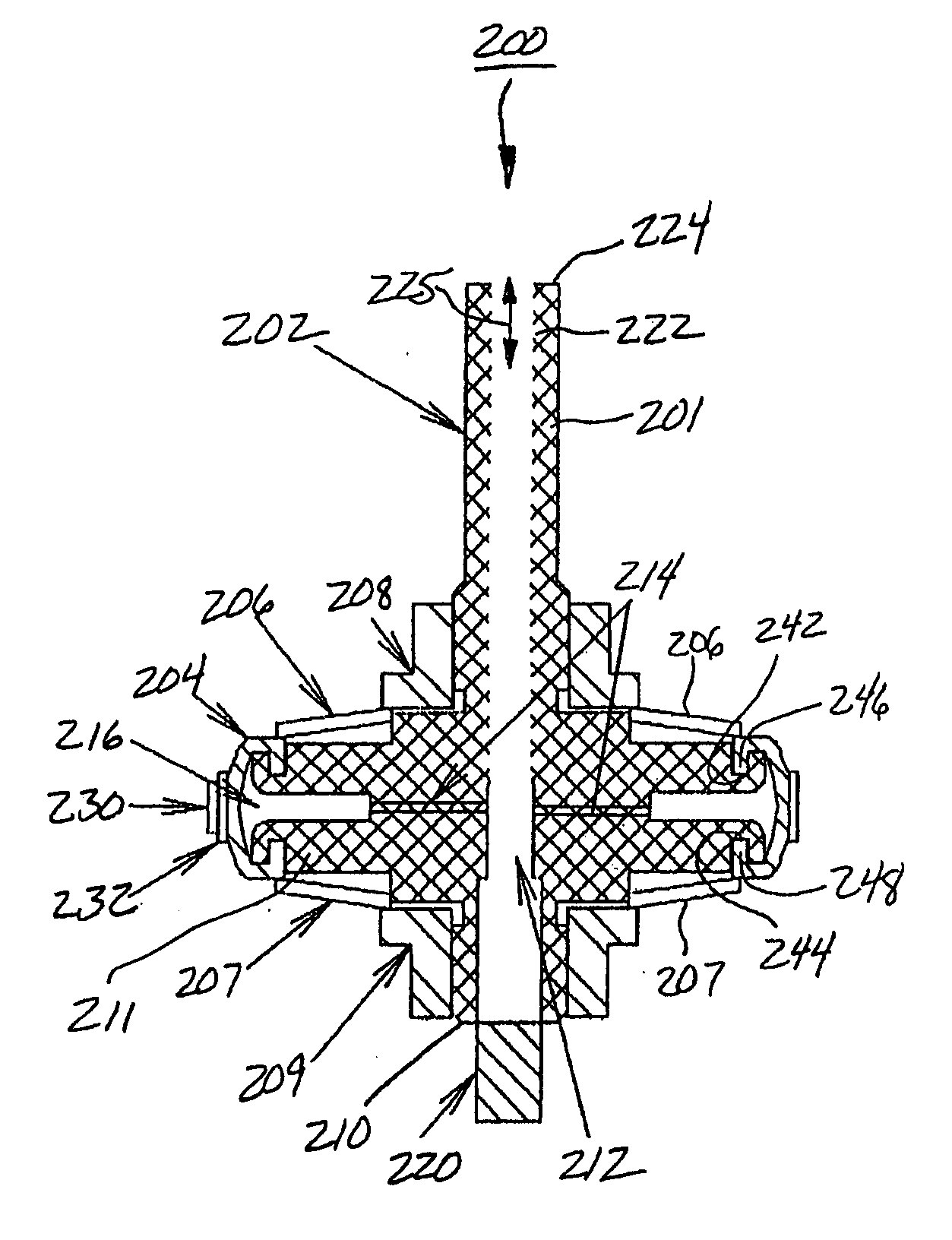
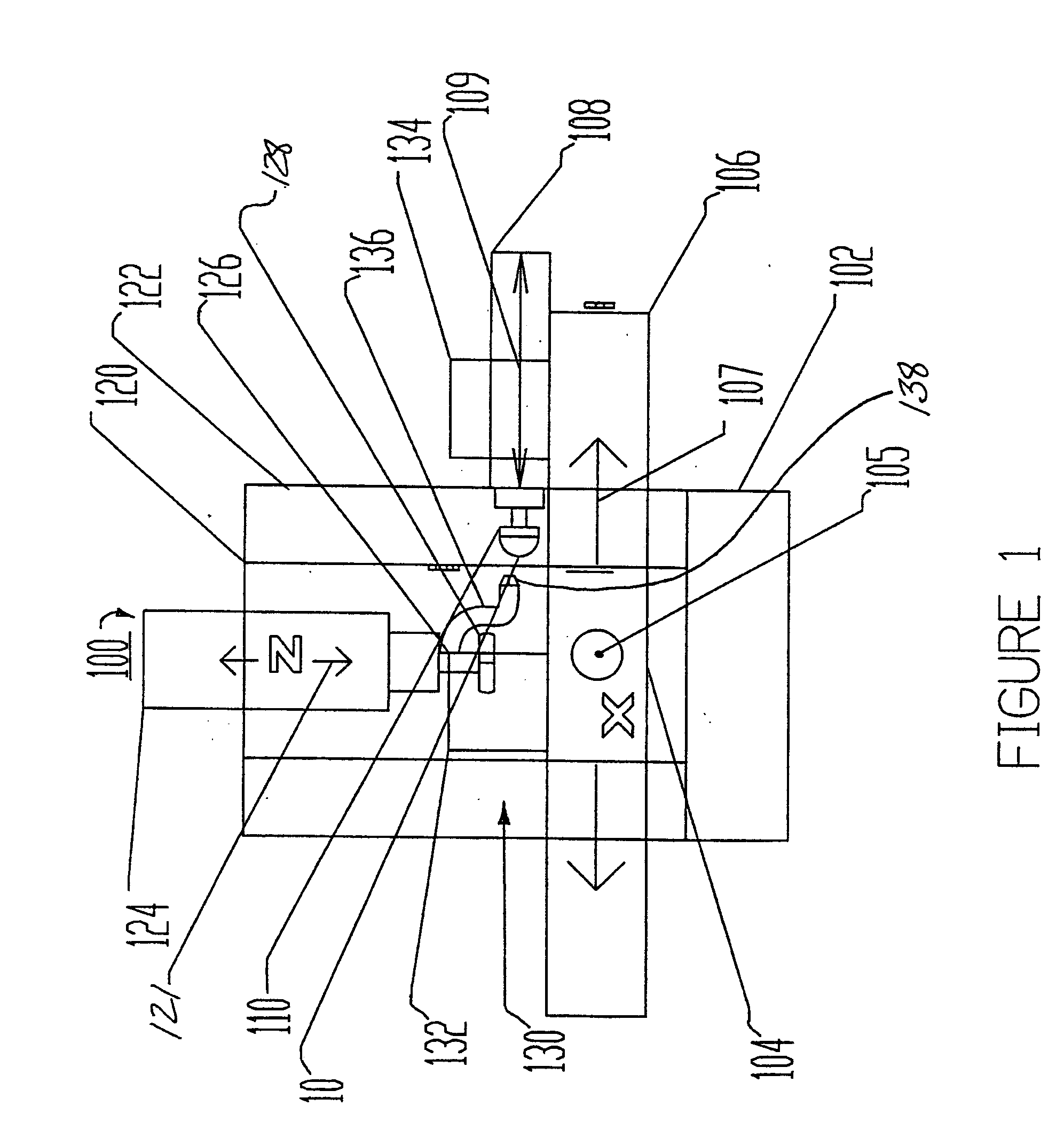
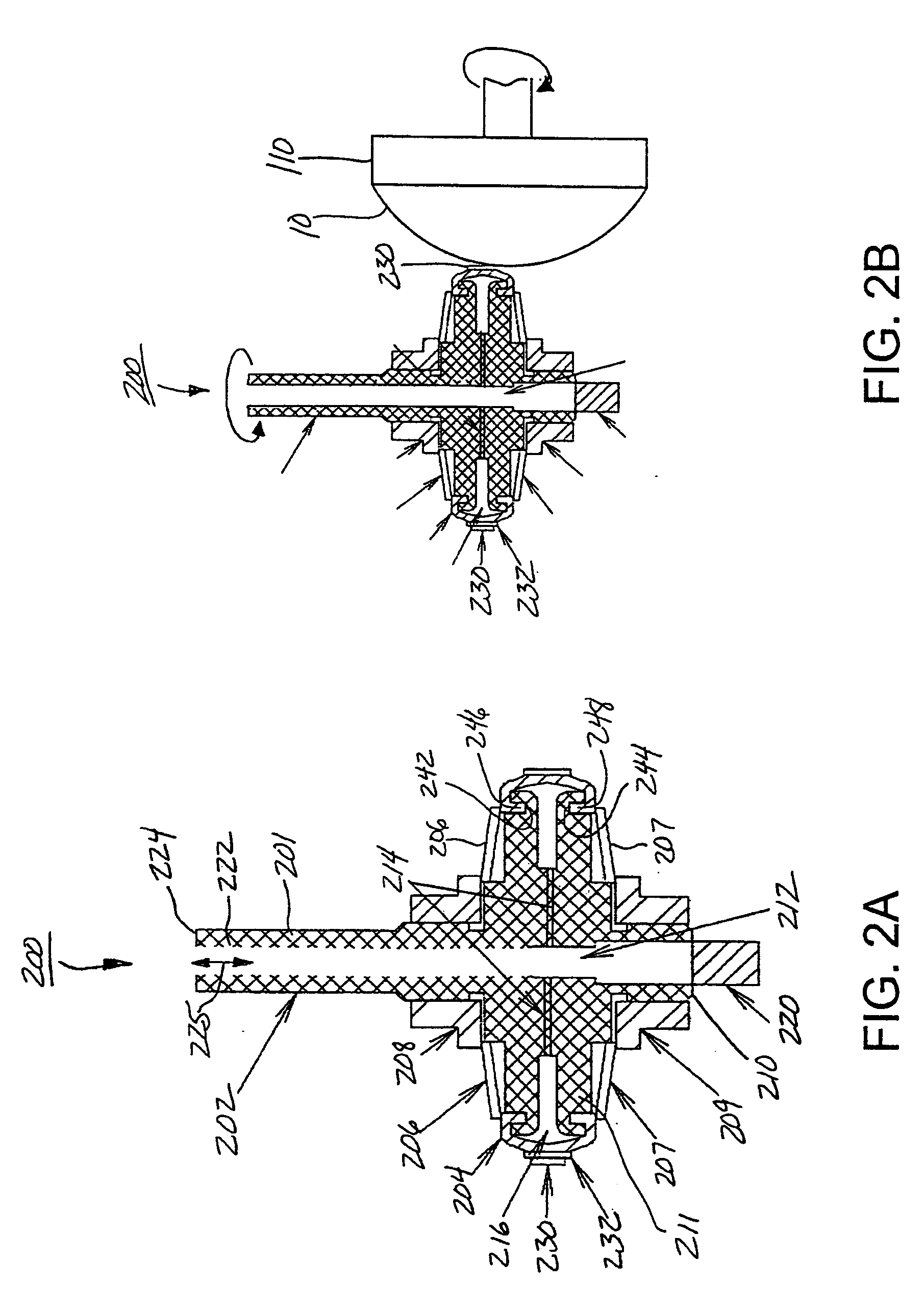
[0064] For a general understanding of the present invention, reference is made to the drawings. In the drawings, like reference numerals have been used throughout to designate identical elements. In describing the present invention, the following term(s) have been used in the description:
[0065] As used herein, the term figure error (or form error) is the measured global deviation from the desired surface shape e.g., a sphere, asphere or polynomial geometric shape.
[0066] As used herein, form error is a low frequency error. Traditionally in optics, irregularity and power are the two specifications that need to be considered. Irregularity is the deviation from a perfect surface. Power is the resulting average surface dimensions e.g., radius of curvature.
[0067] As used herein, the term zonal enhancement is meant to indicate a correction of the figure error, which is located symmetrically or asymmetrically at one specific location (zone) on the work piece. For example, if a cylindrica...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Shape | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com