Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
9691 results about "Sound sources" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
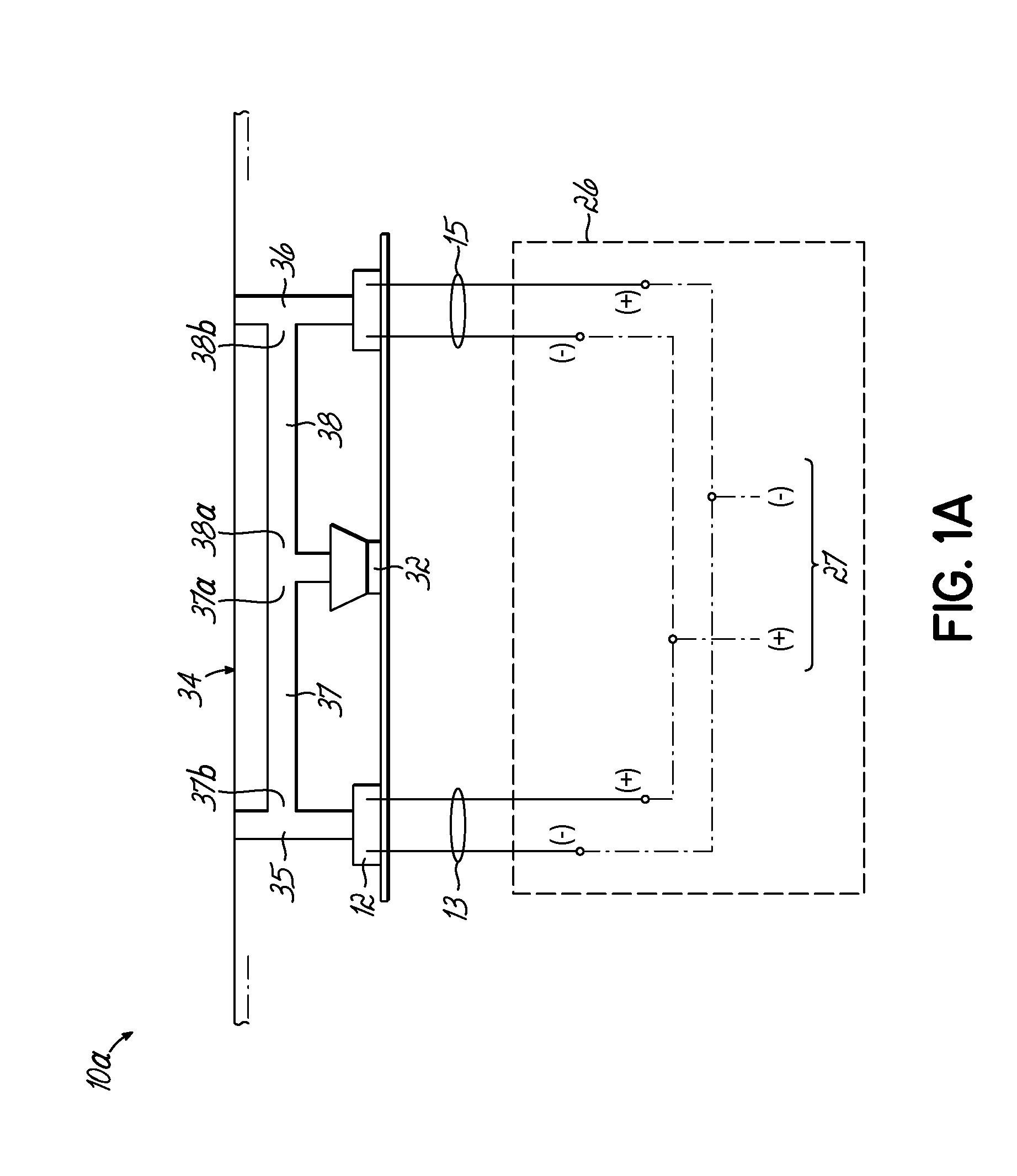
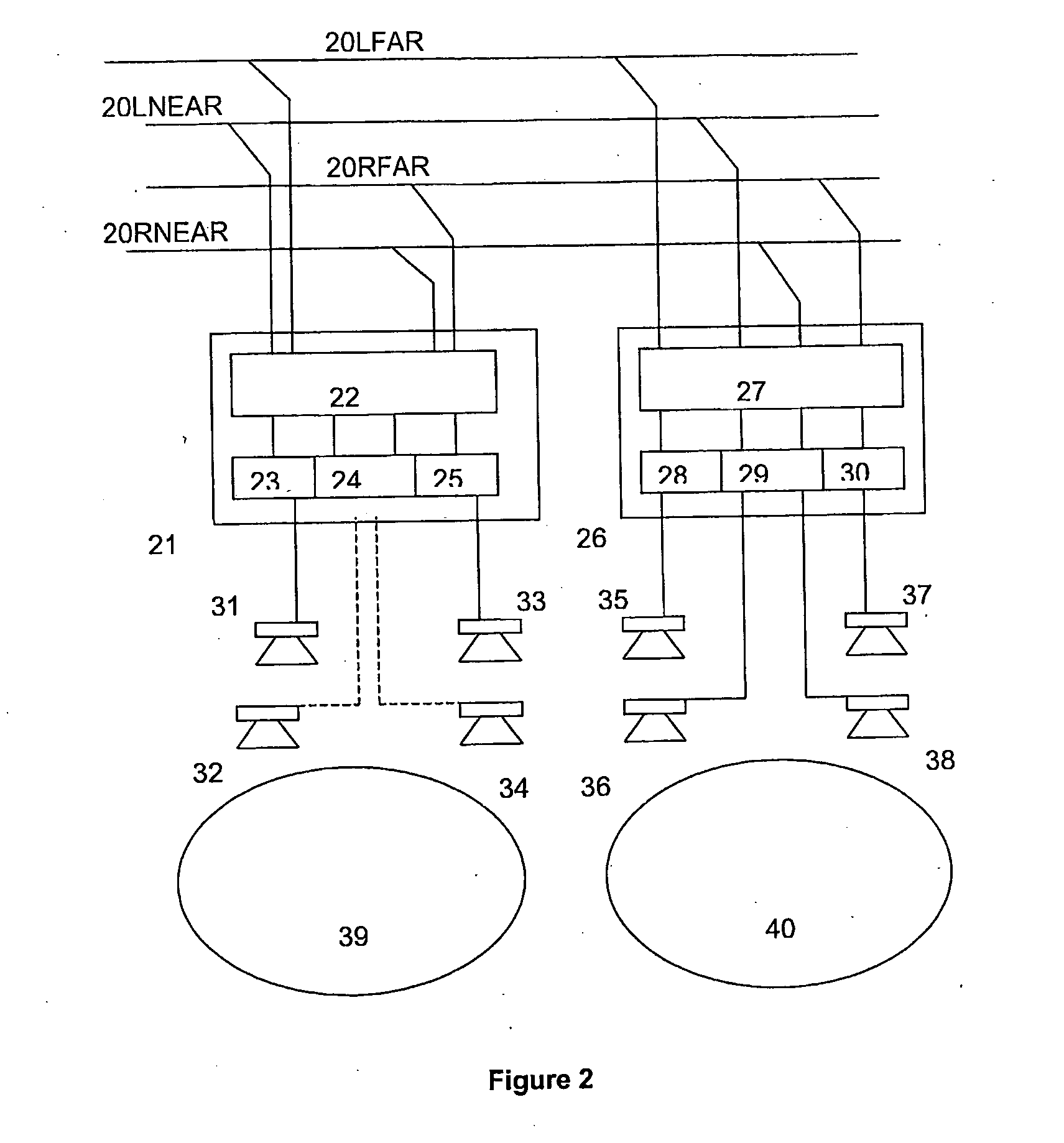
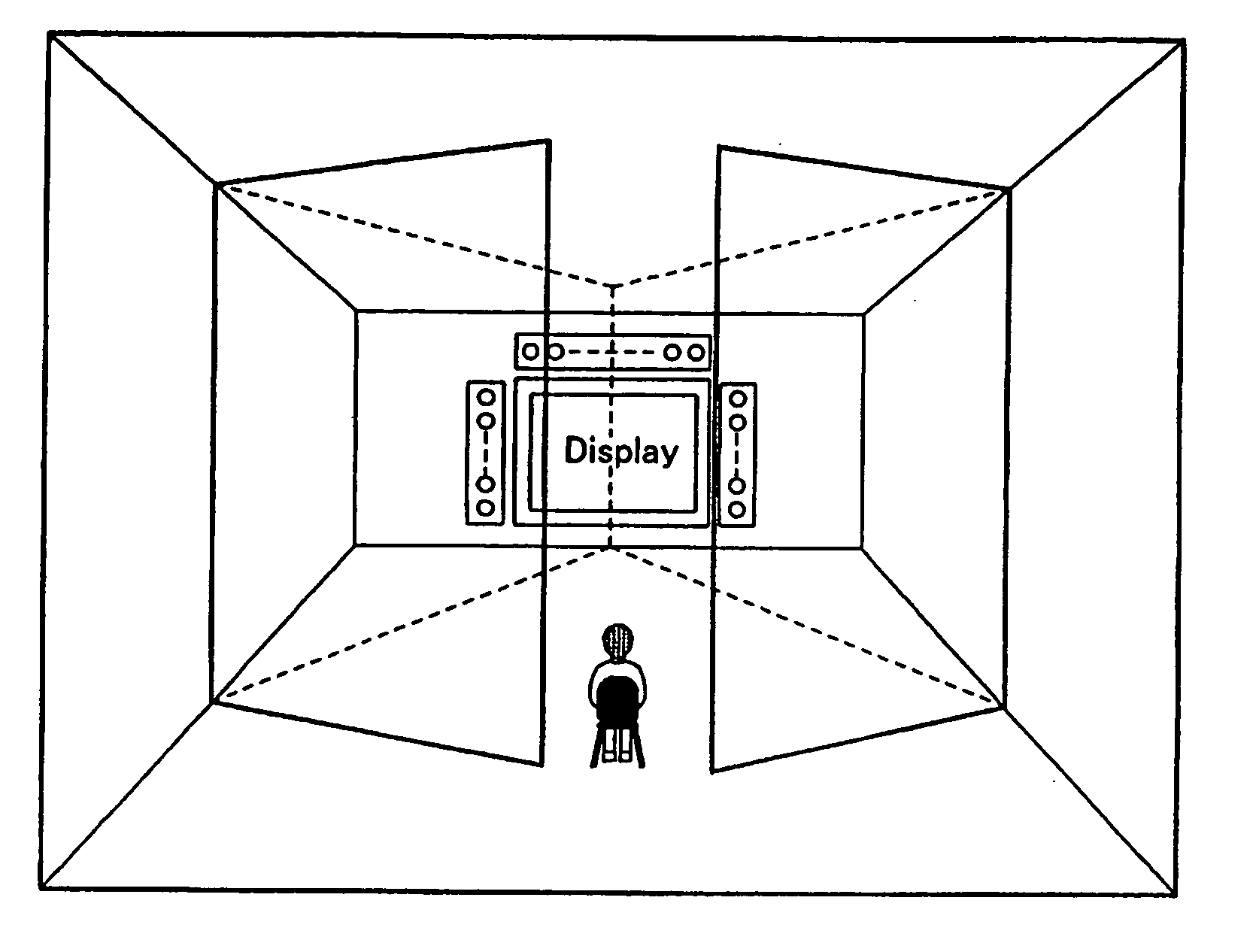
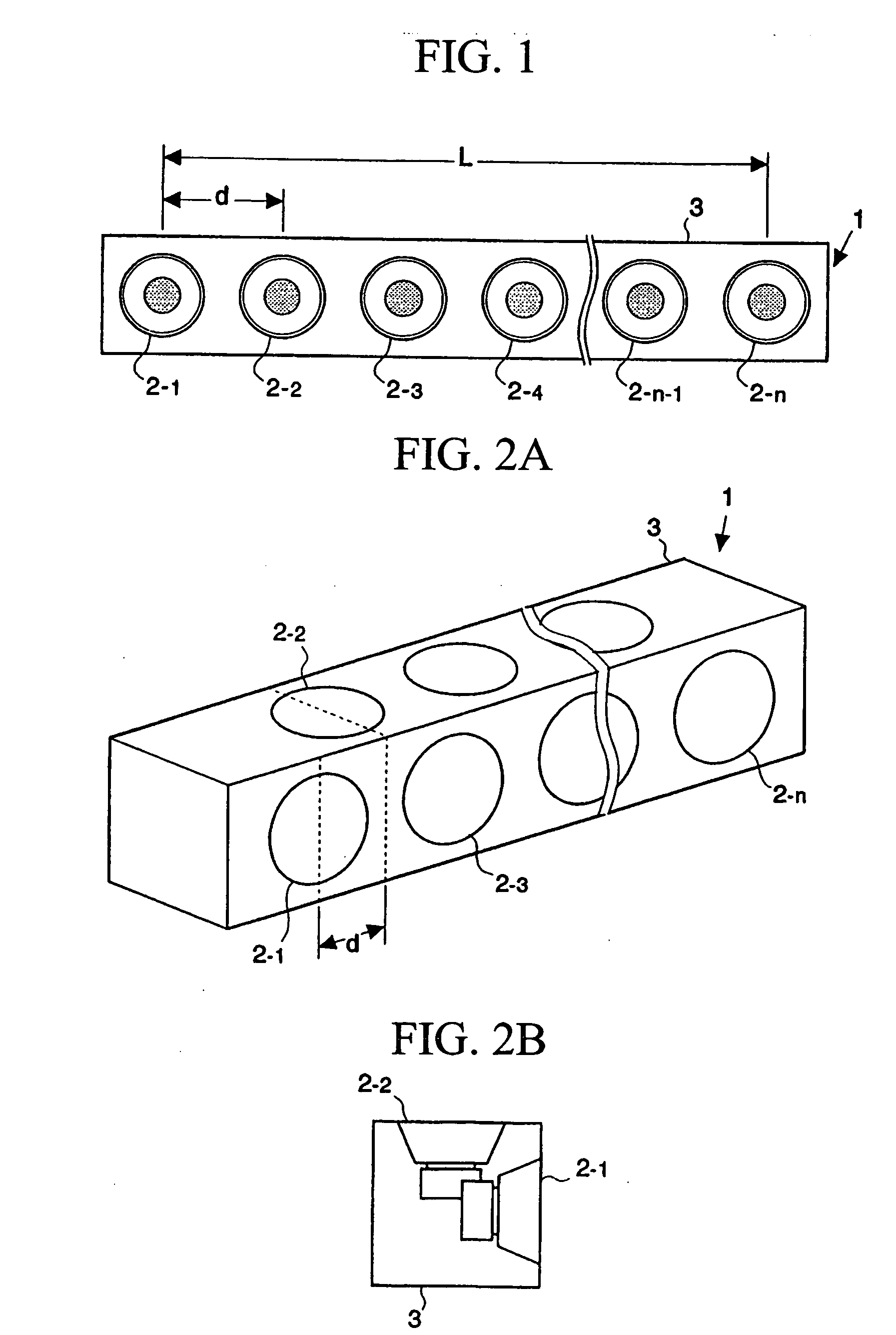
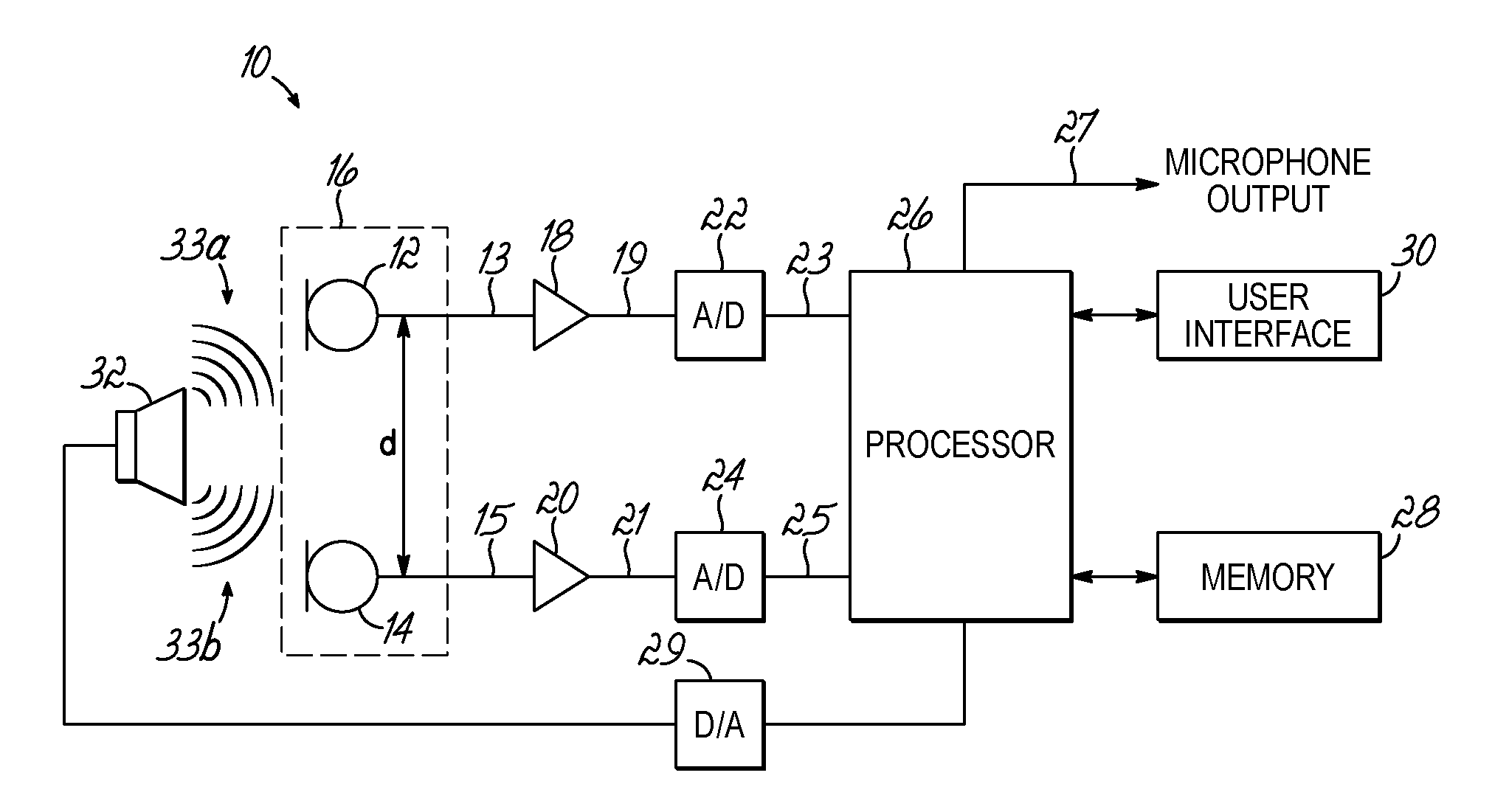
Self calibrating multi-element dipole microphone
ActiveUS8824692B2Maintain performancePiezoelectric/electrostrictive microphonesElectrostatic transducer microphonesSound sourcesDigital filter
Owner:VOCOLLECT
Methods and apparatus for targeted sound detection and characterization
ActiveUS20060239471A1Enhanced interactionRespondMicrophonesSignal processingSound detectionSound sources
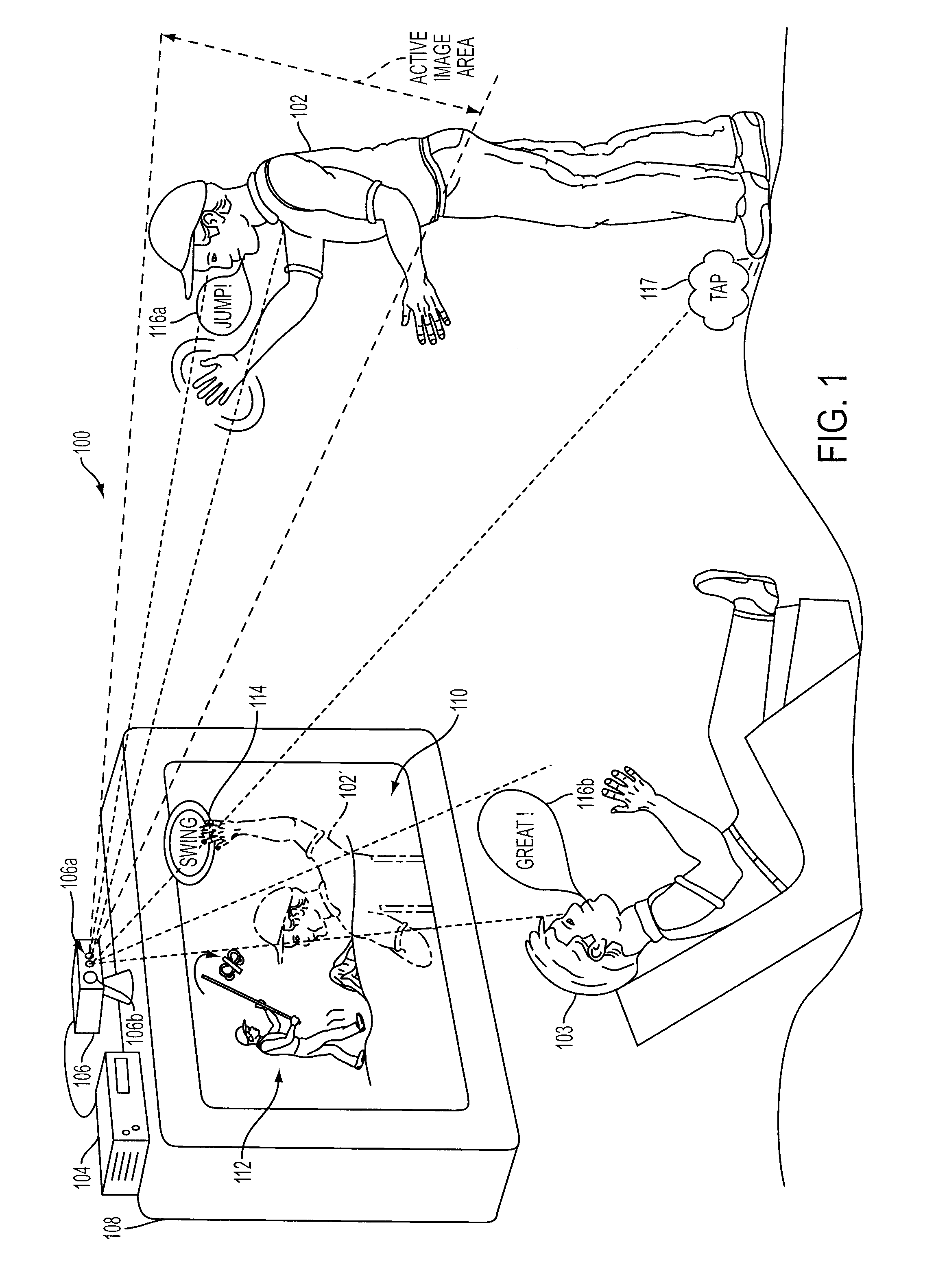
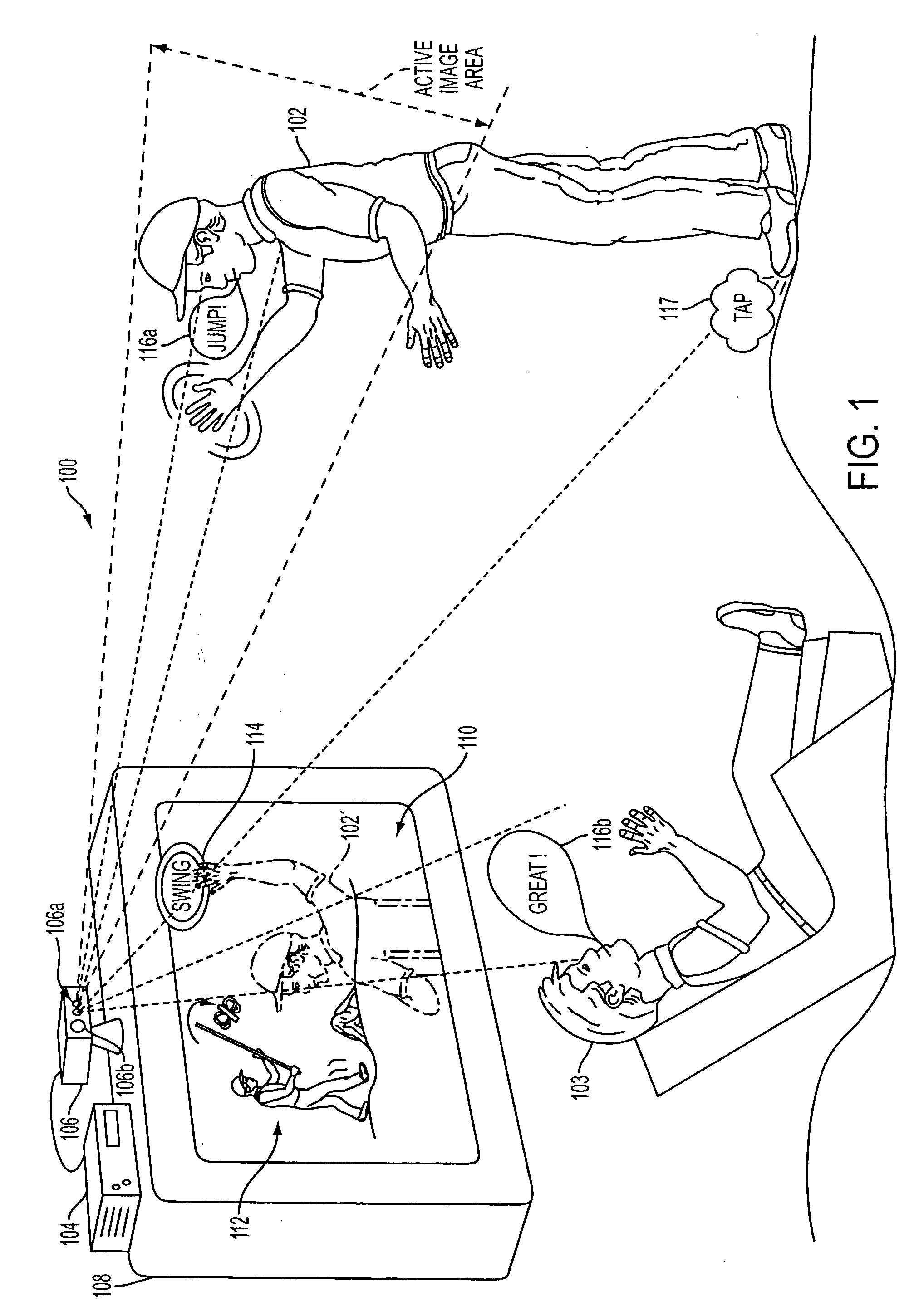
Sound processing methods and apparatus are provided. A sound capture unit is configured to identify one or more sound sources. The sound capture unit generates data capable of being analyzed to determine a listening zone at which to process sound to the substantial exclusion of sounds outside the listening zone. Sound captured and processed for the listening zone may be used for interactivity with the computer program. The listening zone may be adjusted based on the location of a sound source. One or more listening zones may be pre-calibrated. The apparatus may optionally include an image capture unit configured to capture one or more image frames. The listening zone may be adjusted based on the image. A video game unit may be controlled by generating inertial, optical and / or acoustic signals with a controller and tracking a position and / or orientation of the controller using the inertial, acoustic and / or optical signal.
Owner:SONY COMPUTER ENTERTAINMENT INC
Audio Apparatus And Method
InactiveUS20080144864A1Suitable sealMicrophones signal combinationFrequency/directions obtaining arrangementsSound sourcesHeightened perception
The invention enables the capture of sound fields with coding and efficient distribution of electrical signals representing the sound fields for subsequent reproduction in a listening environment utilising pairs of non-equidistant apparatus in various defined configurations such that the acoustic distance as well as direction of sound sources is consistently presented with regard to in front of, behind, beside or below from a listening point anywhere in the listening environment and for any listener orientation, thus making the whole listening area a sweet spot and enabling true shared audio experiences, without the need for worn apparatus. New apparatus and methods for capture, distribution and reproduction or render are also disclosed that enable enhanced perception of captured and reproduced sound for shared experiences with both common and individual capture and reproduction apparatus and new communications and control methods and apparatus for multiple users including heightened perception capability and also improved security aspects are also disclosed.
Owner:HUONLABS
Method and apparatus for acoustically controlling liquid solutions in microfluidic devices
InactiveUS6948843B2Improve reaction speedAccelerating molecular interactionSequential/parallel process reactionsShaking/oscillating/vibrating mixersSound sourcesAcoustic energy
Acoustic energy is used to control motion in a fluid. According to one embodiment, the invention directs acoustic energy at selected naturally occurring nucleation features to control motion in the fluid. In another embodiment, the invention provides focussed or unfocussed acoustic energy to selectively placed nucleation features to control fluid motion. According to one embodiment, the invention includes an acoustic source, a controller for controlling operation of the acoustic source, and one or more nucleation features located proximate to or in the fluid to be controlled.
Owner:COVARIS INC
Personalized headphone virtualization
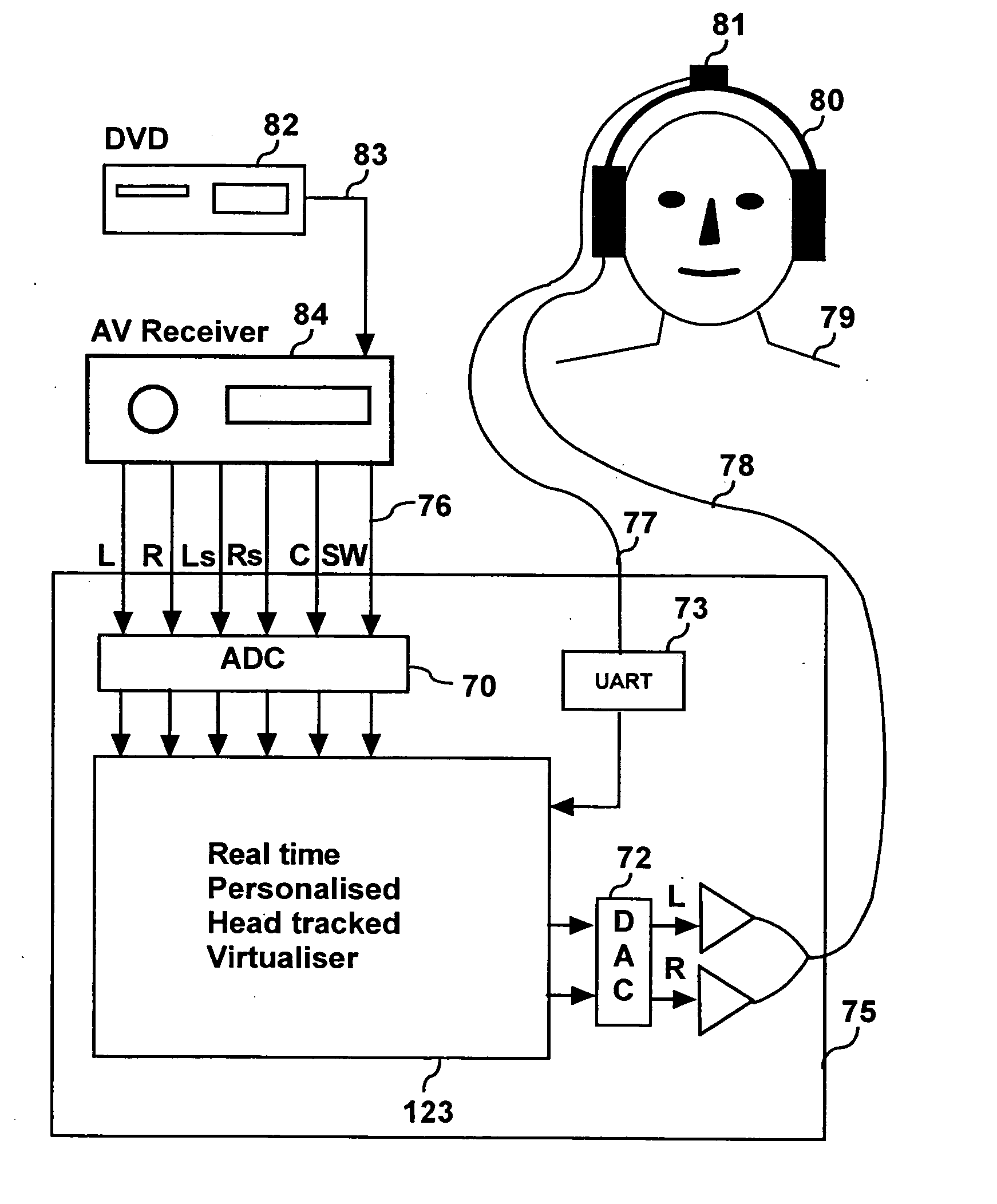
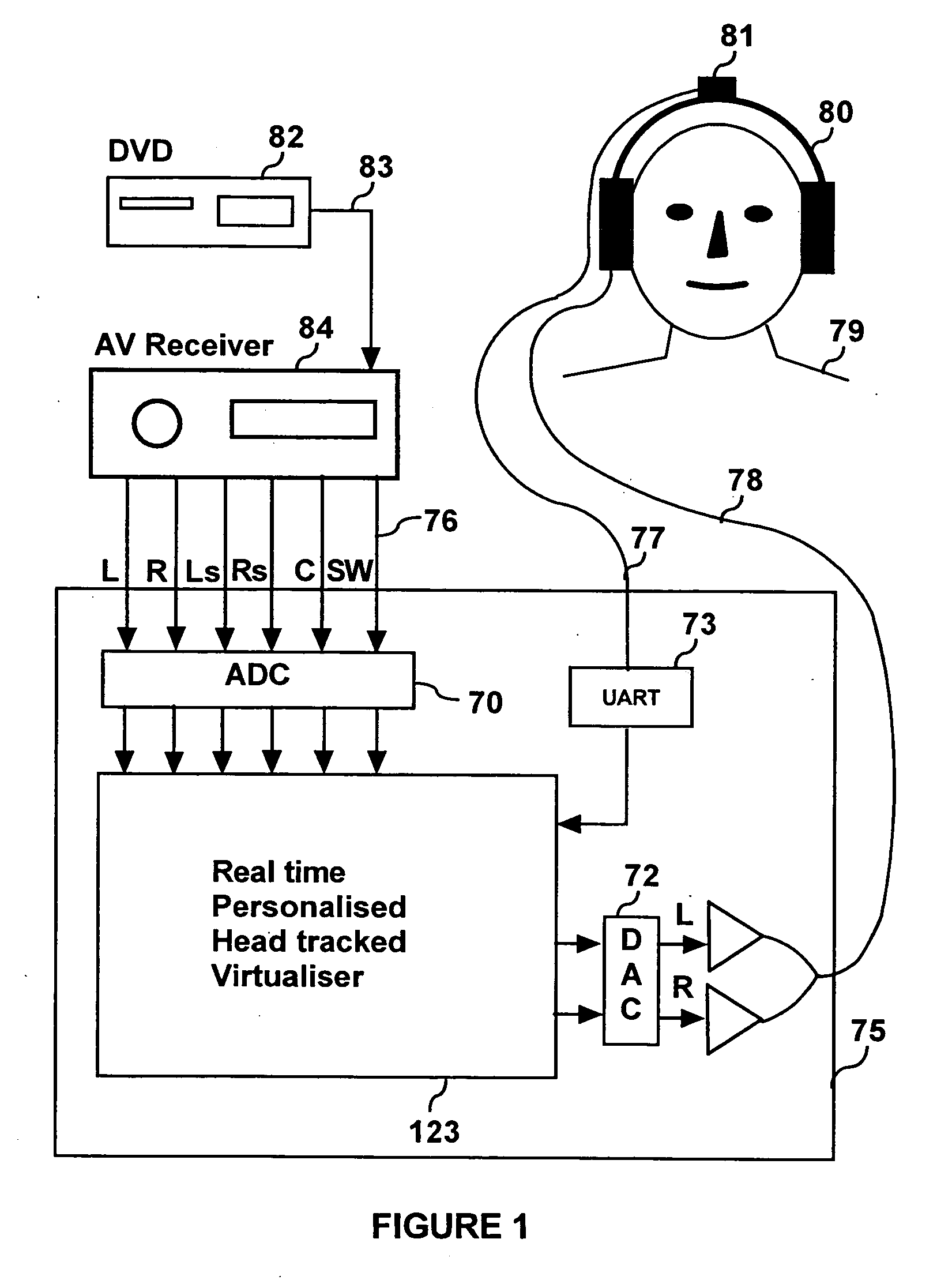
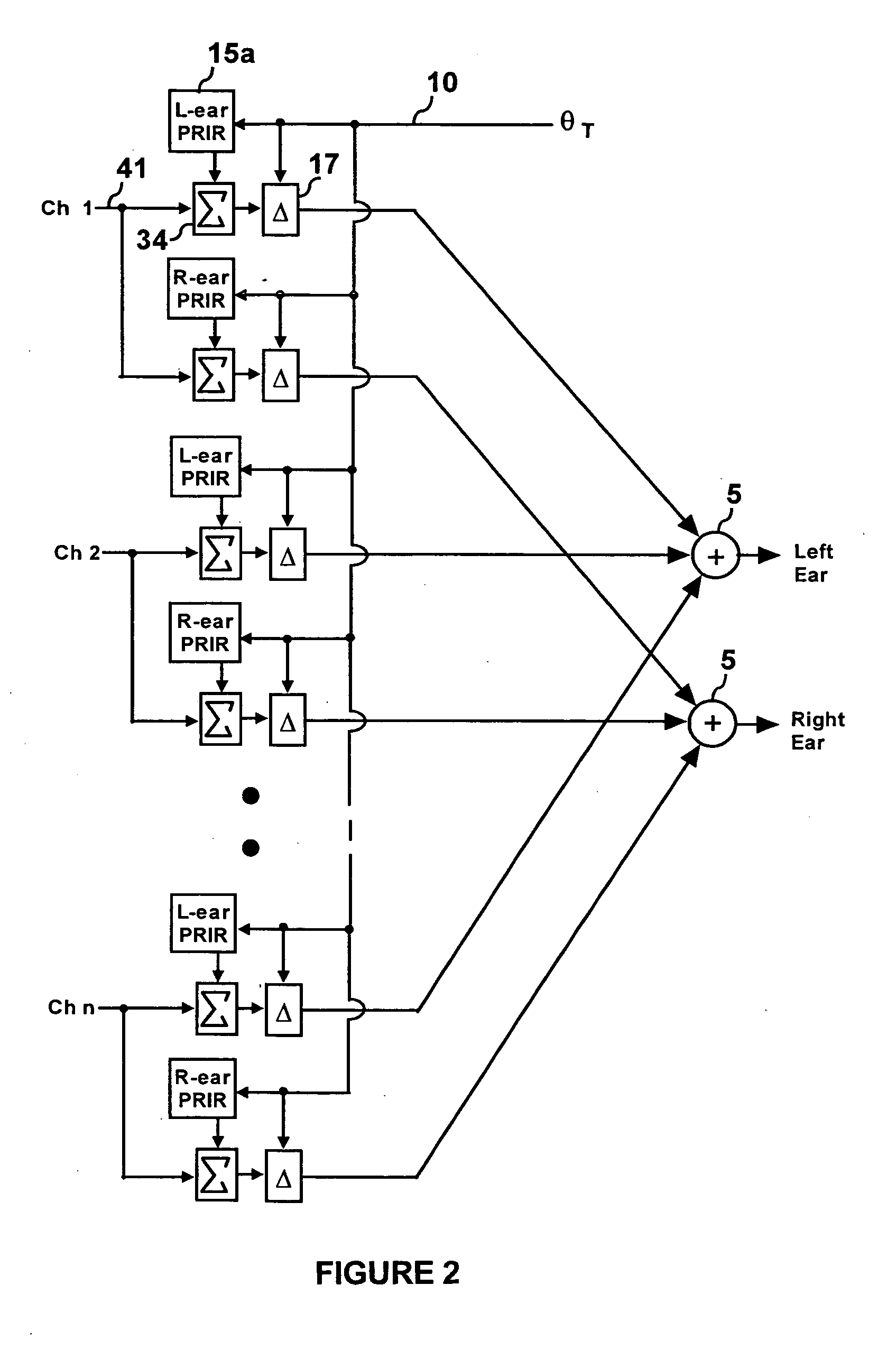
ActiveUS20060045294A1Improve accuracySound qualityHeadphones for stereophonic communicationEarpiece/earphone attachmentsVirtualizationPersonalization
A listener can experience the sound of virtual loudspeakers over headphones with a level of realism that is difficult to distinguish from the real loudspeaker experience. Sets of personalized room impulse responses (PRIRs) are acquired for the loudspeaker sound sources over a limited number of listener head positions. The PRIRs are then used to transform an audio signal for the loudspeakers into a virtualized output for the headphones. Basing the transformation on the listener's head position, the system can adjust the transformation so that the virtual loudspeakers appear not to move as the listener moves the head.
Owner:SMYTH RES
System and method for beamforming using a microphone array
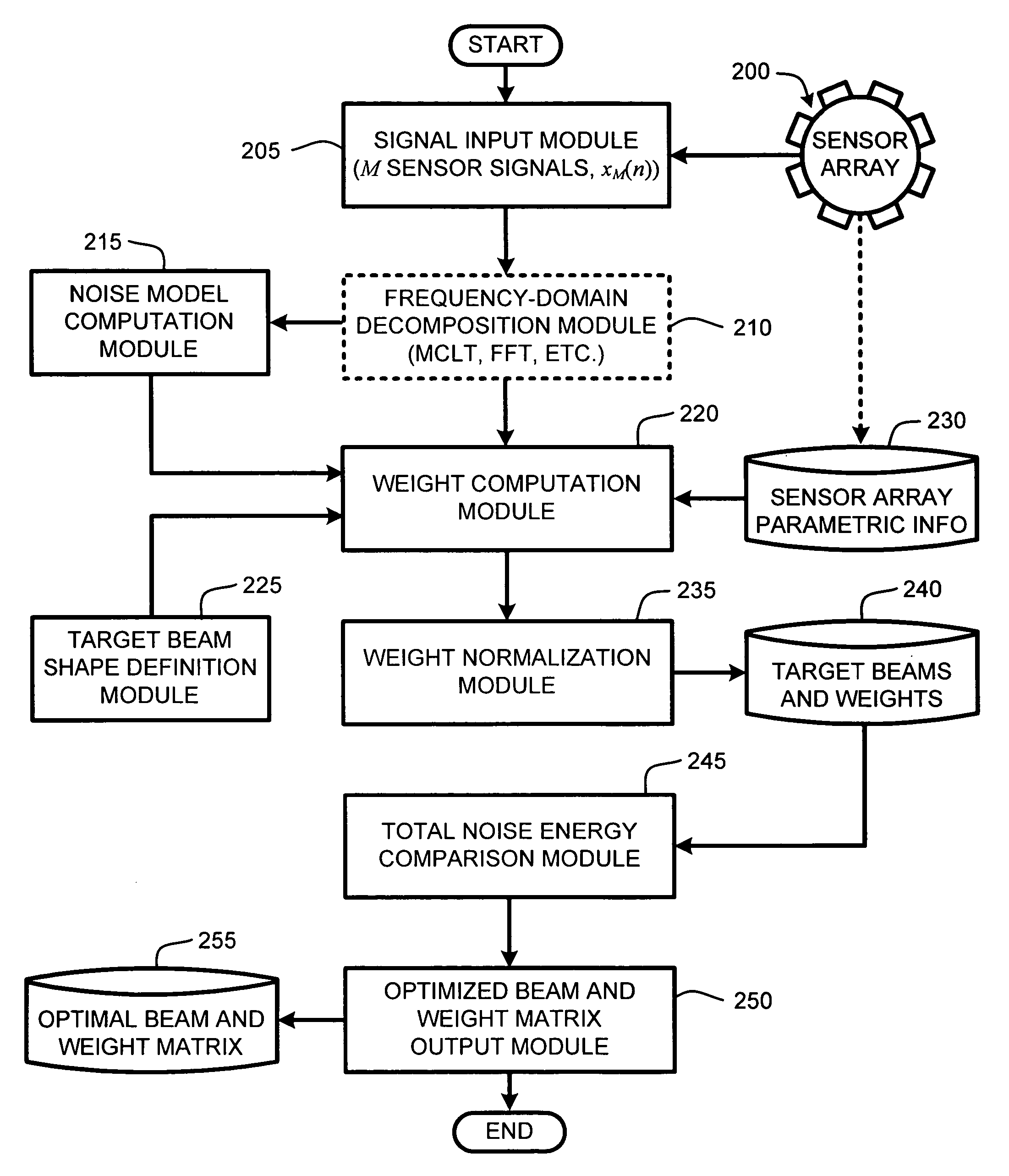
InactiveUS20050195988A1Maximal noise suppressionIncrease widthPosition fixationMicrophones signal combinationEnvironmental noiseSound sources
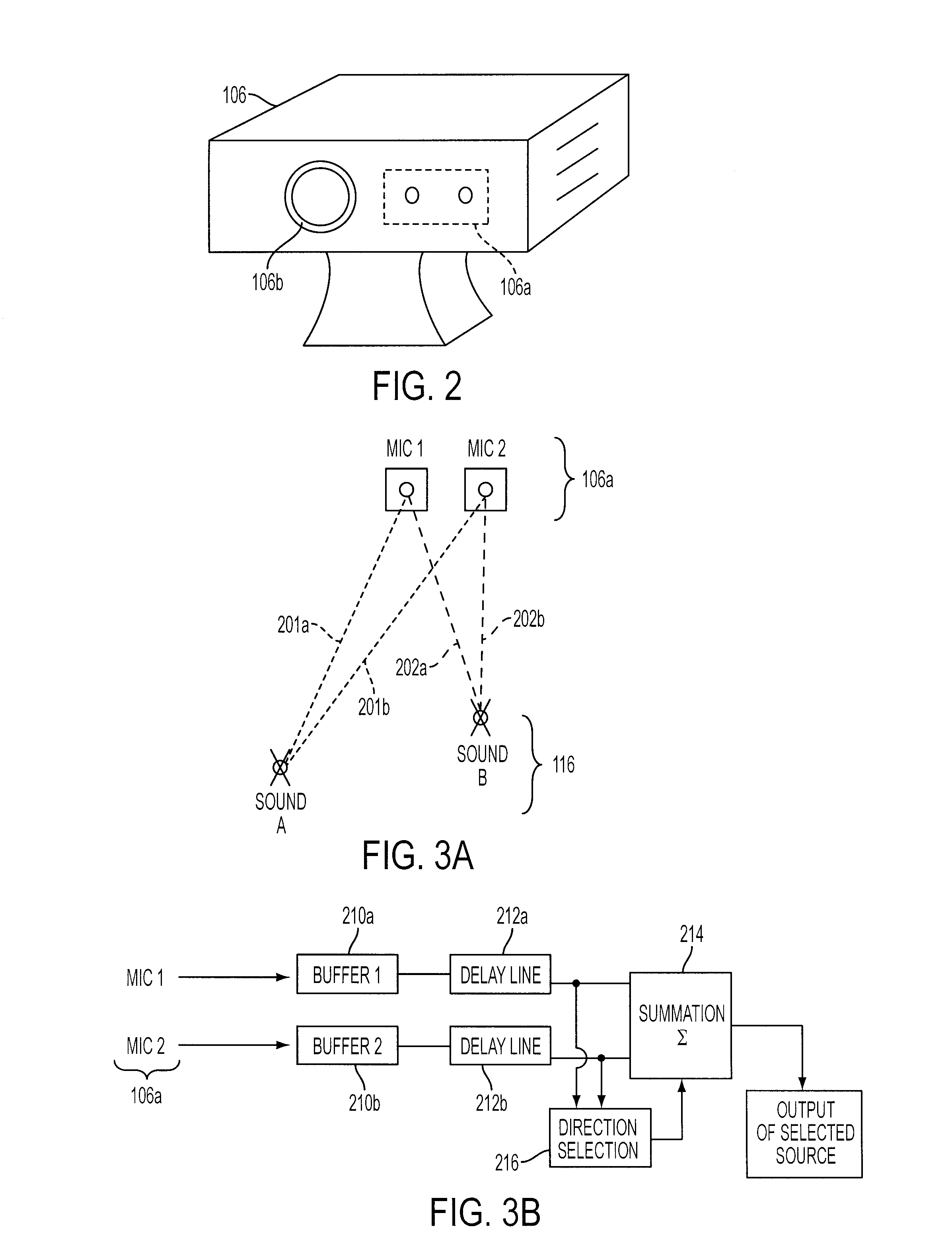
The ability to combine multiple audio signals captured from the microphones in a microphone array is frequently used in beamforming systems. Typically, beamforming involves processing the output audio signals of the microphone array in such a way as to make the microphone array act as a highly directional microphone. In other words, beamforming provides a “listening beam” which points to a particular sound source while often filtering out other sounds. A “generic beamformer,” as described herein automatically designs a set of beams (i.e., beamforming) that cover a desired angular space range within a prescribed search area. Beam design is a function of microphone geometry and operational characteristics, and also of noise models of the environment around the microphone array. One advantage of the generic beamformer is that it is applicable to any microphone array geometry and microphone type.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Method of enhancing sound for hearing impaired individuals
InactiveUS20090076825A1Improve functionalityImprove usabilitySpeech recognitionDeaf-aid setsDigital signal processingSound sources
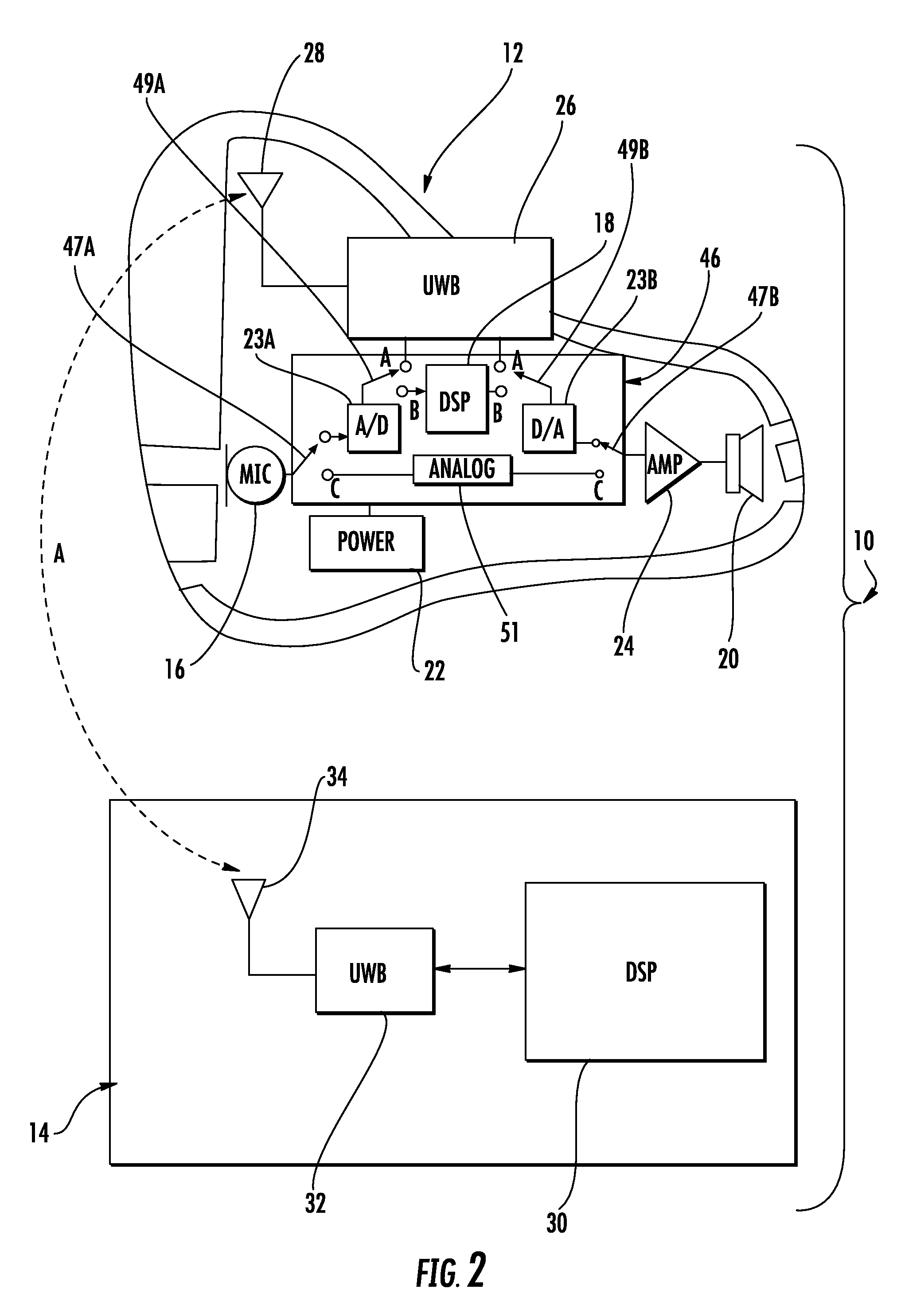
A portable assistive listening system for enhancing sound for hearing impaired individuals includes a fully functional hearing aid and a separate handheld digital signal processing (DSP) device. The focus of the present invention is directed to the handheld DSP device and a unique method of processing incoming audio signals. The DSP device includes a programmable digital signal processor, a UWB transceiver for communicating with the hearing aid and / or other wireless audio sources, an LCD display, and a user input device (keypad). The handheld device is user programmable to apply different sound enhancement algorithms for enhancing sound signals received from the hearing aid and / or other audio source. The handheld device is capable of receiving audio signals from multiple sources, and gives the user control over selection of incoming sound sources and selective enhancement of sound. In the context of being user programmable, the digital signal processing device includes a software platform that provides for the ability of the user to select, or plug-in, desired enhancement algorithms for application to selected incoming audio signals. Specifically, the invention focuses on a method of buffering an incoming audio signal, and selectively replaying the buffered audio. The method further includes converting the replayed audio signal to text for display on the handheld DSP device.
Owner:BIONICA CORP
Audio signal receiving apparatus, audio signal receiving method and audio signal transmission system
InactiveUS8116476B2Filamentary/web record carriersPublic address systemsSound sourcesAudio frequency
Owner:SONY CORP
Phase-Amplitude 3-D Stereo Encoder and Decoder
ActiveUS20090092259A1Preserving source separationSpeech analysisStereophonic systemsSound sourcesSpatial analysis
Owner:CREATIVE TECH CORP
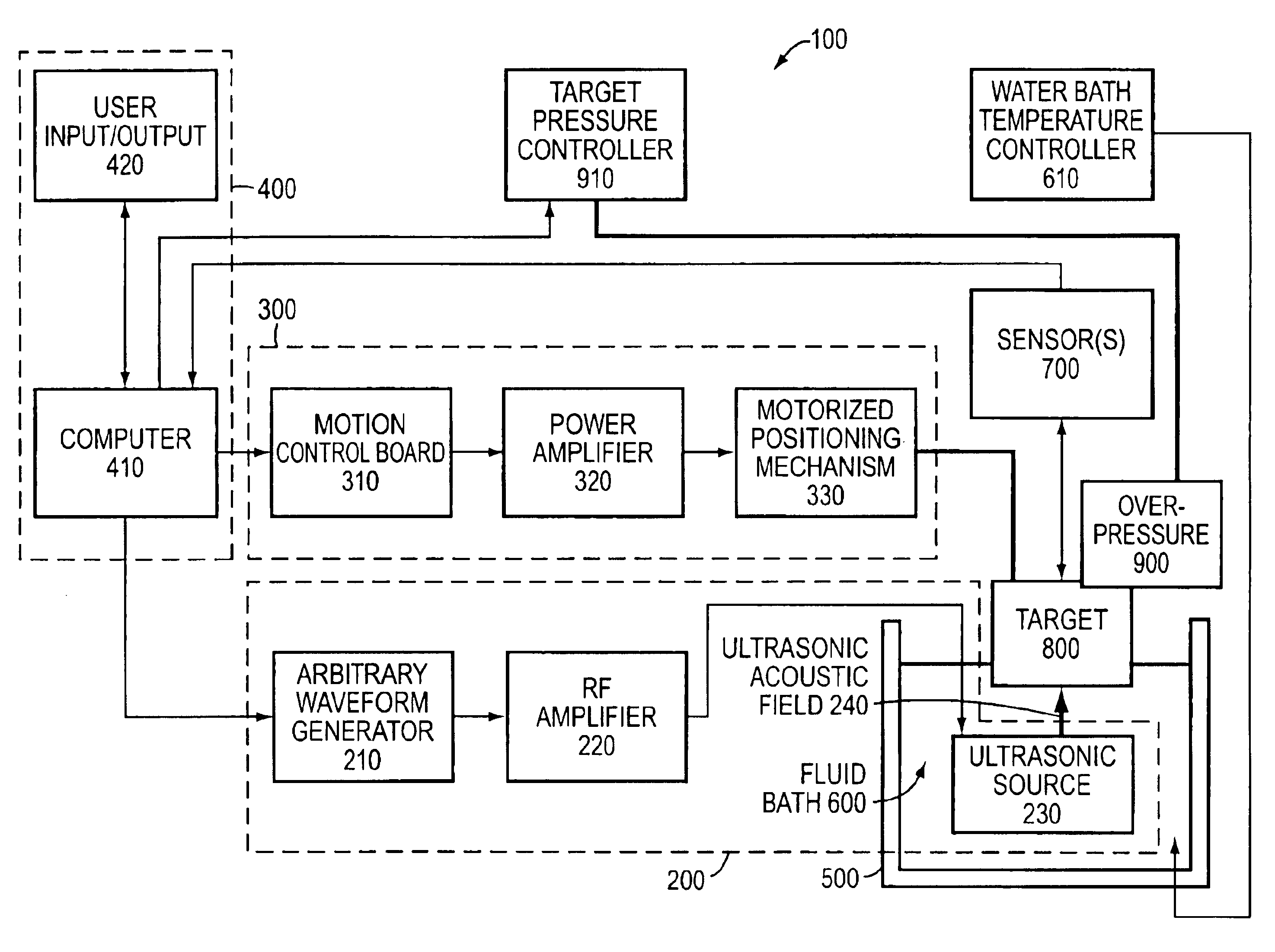
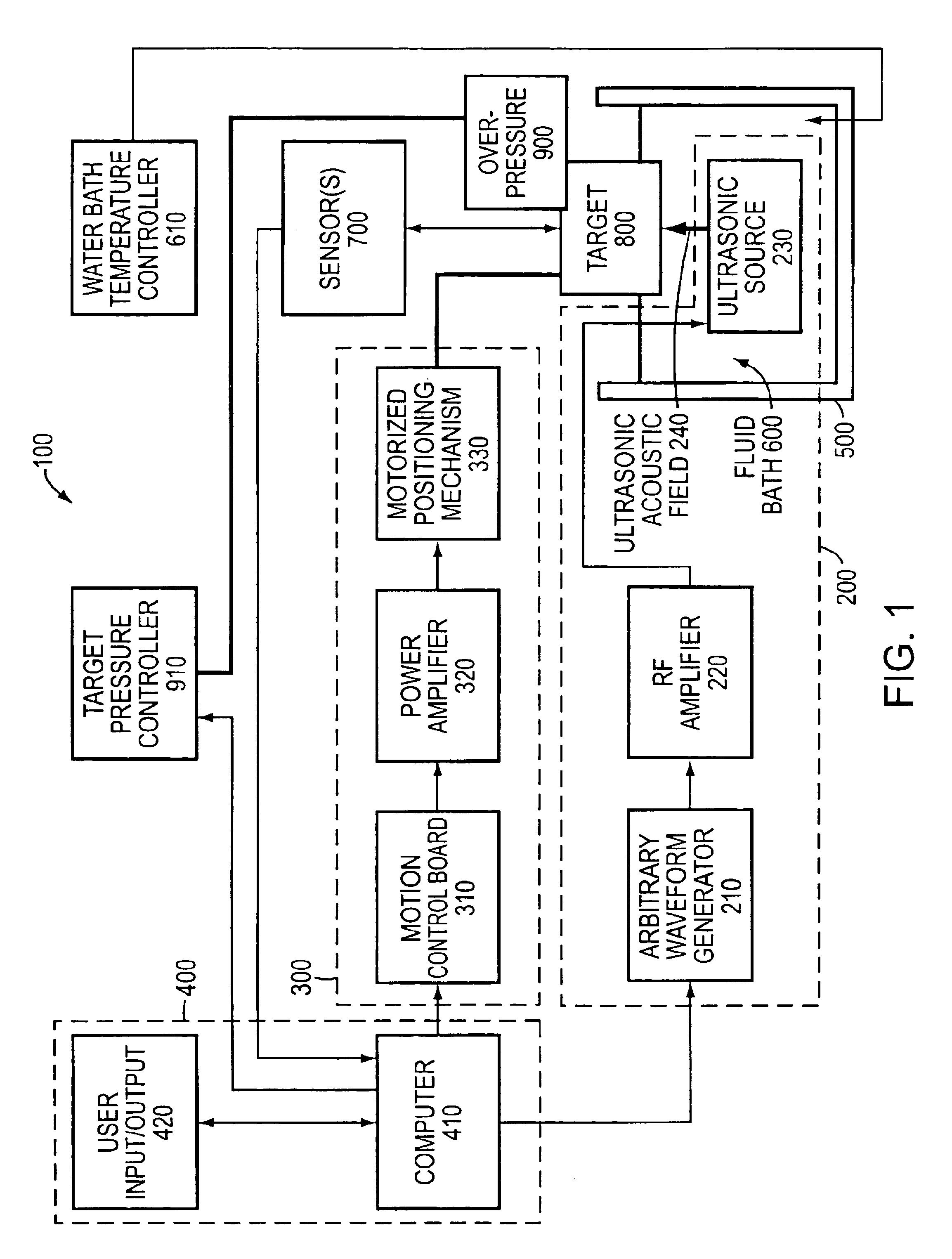
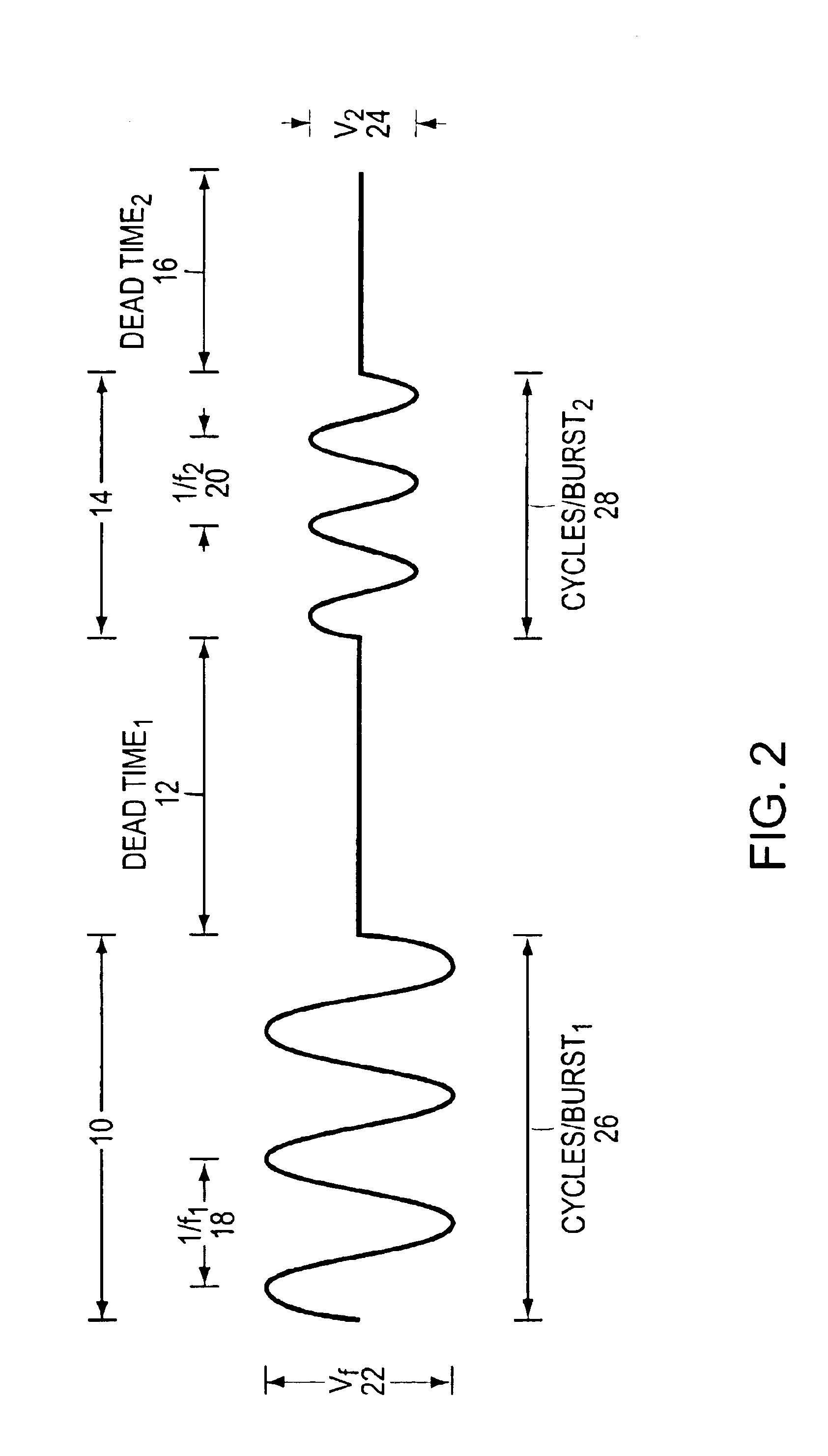
Systems and methods for determining intracranial pressure non-invasively and acoustic transducer assemblies for use in such systems
InactiveUS20050015009A1Accurate assessmentAccurate monitoringMedical data miningDiagnostics using vibrationsSound sourcesCentral sulcus artery
Systems and methods for determining ICP based on parameters that can be measured using non-invasive or minimally invasive techniques are provided, wherein a non-linear relationship is used to determine ICP based on one or more variable inputs. The first variable input relates to one or more properties of a cranial blood vessel and / or blood flow, such as acoustic backscatter from an acoustic transducer having a focus trained on a cranial blood vessel, flow velocity in a cranial blood vessel, and the like. Additional variables, such as arterial blood pressure (ABP), may be used in combination with a first variable input relating to one or more properties of a cranial blood vessel, such as flow velocity of the middle cerebral artery (MCA) to derive ICP using a non-linear relationship. Methods and systems for locating target areas based on their acoustic properties and for acoustic scanning of an area, identification of a target area of interest based on acoustic properties, and automated focusing of an acoustic source and / or detector on a desired target area are also provided. Acoustic transducer assemblies are described.
Owner:PHYSIOSONICS +1
Binaural synthesis, head-related transfer functions, and uses thereof
InactiveUS6118875AReduce the differenceFunction increaseTwo-channel systemsLoudspeaker spatial/constructional arrangementsTime domainSound sources
PCT No. PCT / DK95 / 00089 Sec. 371 Date Dec. 27, 1996 Sec. 102(e) Date Dec. 27, 1996 PCT Filed Feb. 27, 1995 PCT Pub. No. WO95 / 23493 PCT Pub. Date Aug. 31, 1995A method and apparatus for simulating the transmission of sound from sound sources to the ear canals of a listener encompasses novel head-related transfer functions (HTFs), novel methods of measuring and processing HTFs, and novel methods of changing or maintaining the directions of the sound sources as perceived by the listener. The measurement methods enable the measurement and construction of HTFs for which the time domain descriptions are surprisingly short, and for which the differences between listeners are surprisingly small. The novel HTFs can be exploited in any application concerning the simulation of sound transmission, measurement, simulation, or reproduction. The invention is particularly advantageous in the field of binaural synthesis, specifically, the creation, by means of two sound sources, of the perception in the listener of listening to sound generated by a multichannel sound system. It is also particularly useful in the designing of electronic filters used, for example, in virtual reality systems, and in the designing of an "artificial head" having HTFs that approximate the HTFs of the invention as closely as possible in order to make the best possible representation of humans by the artificial head, thereby making artificial head recordings of optimal quality.
Owner:M O SLASHED LLER HENRIK +3
Audio spatialization and environment simulation
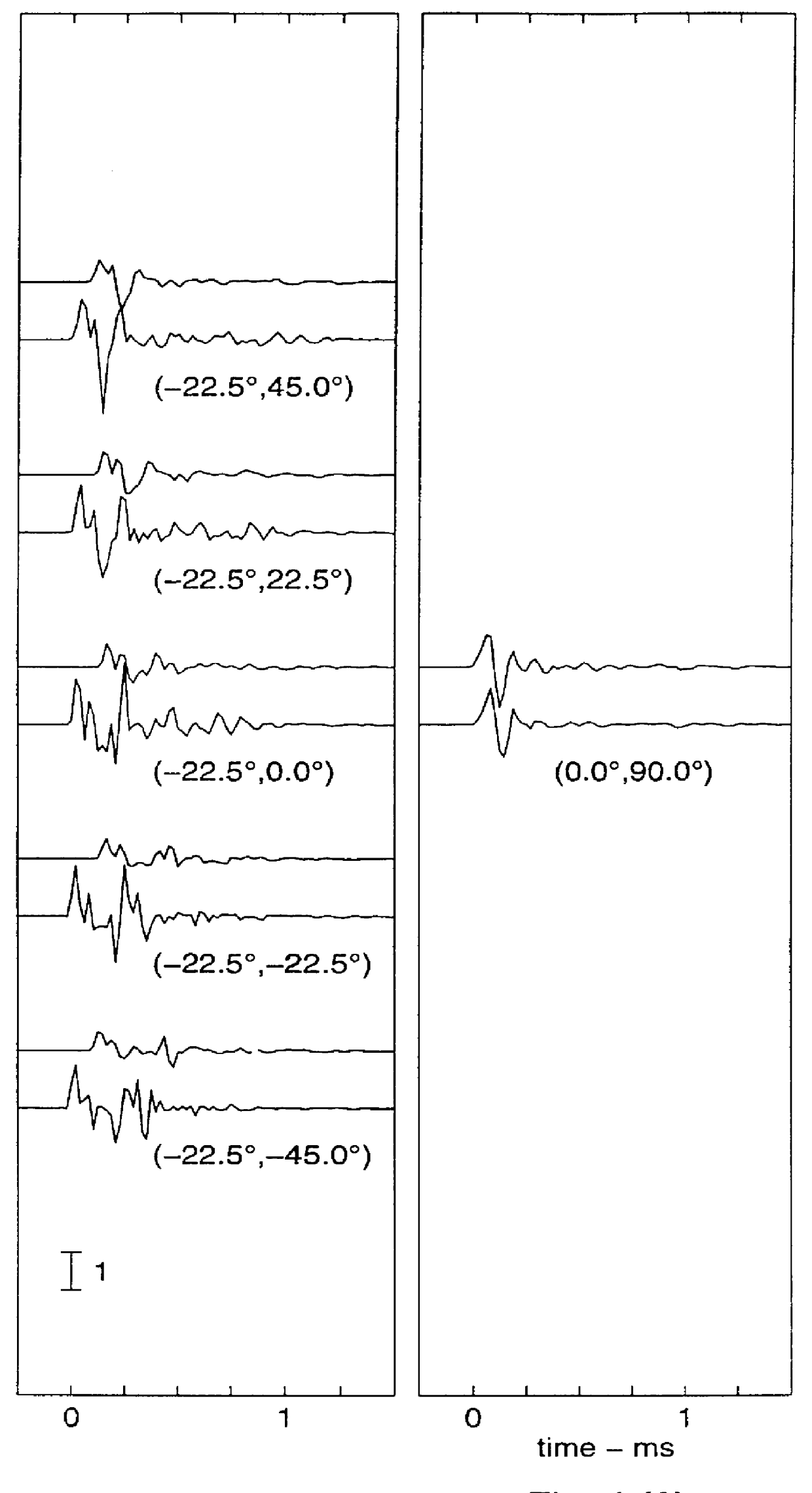
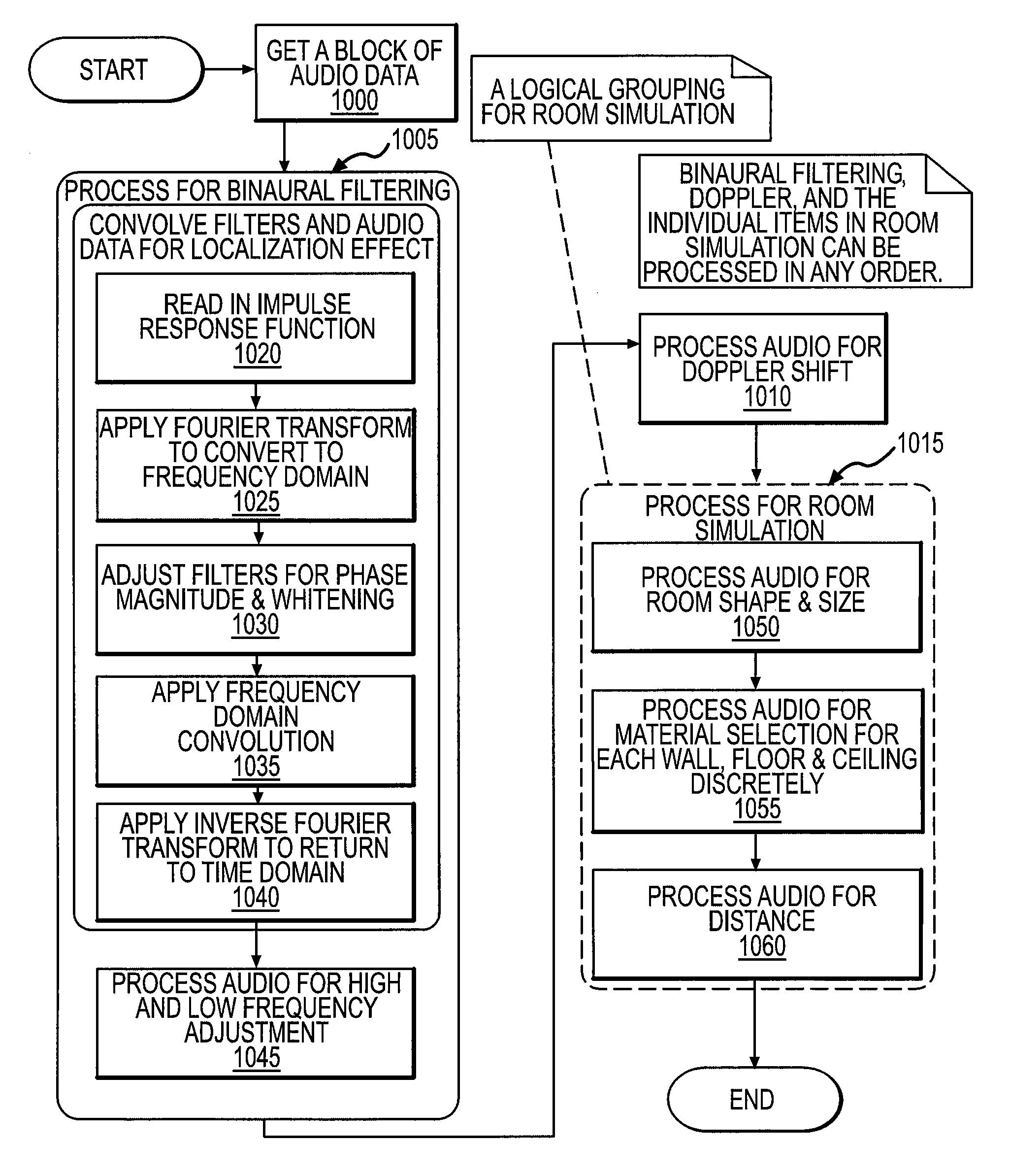
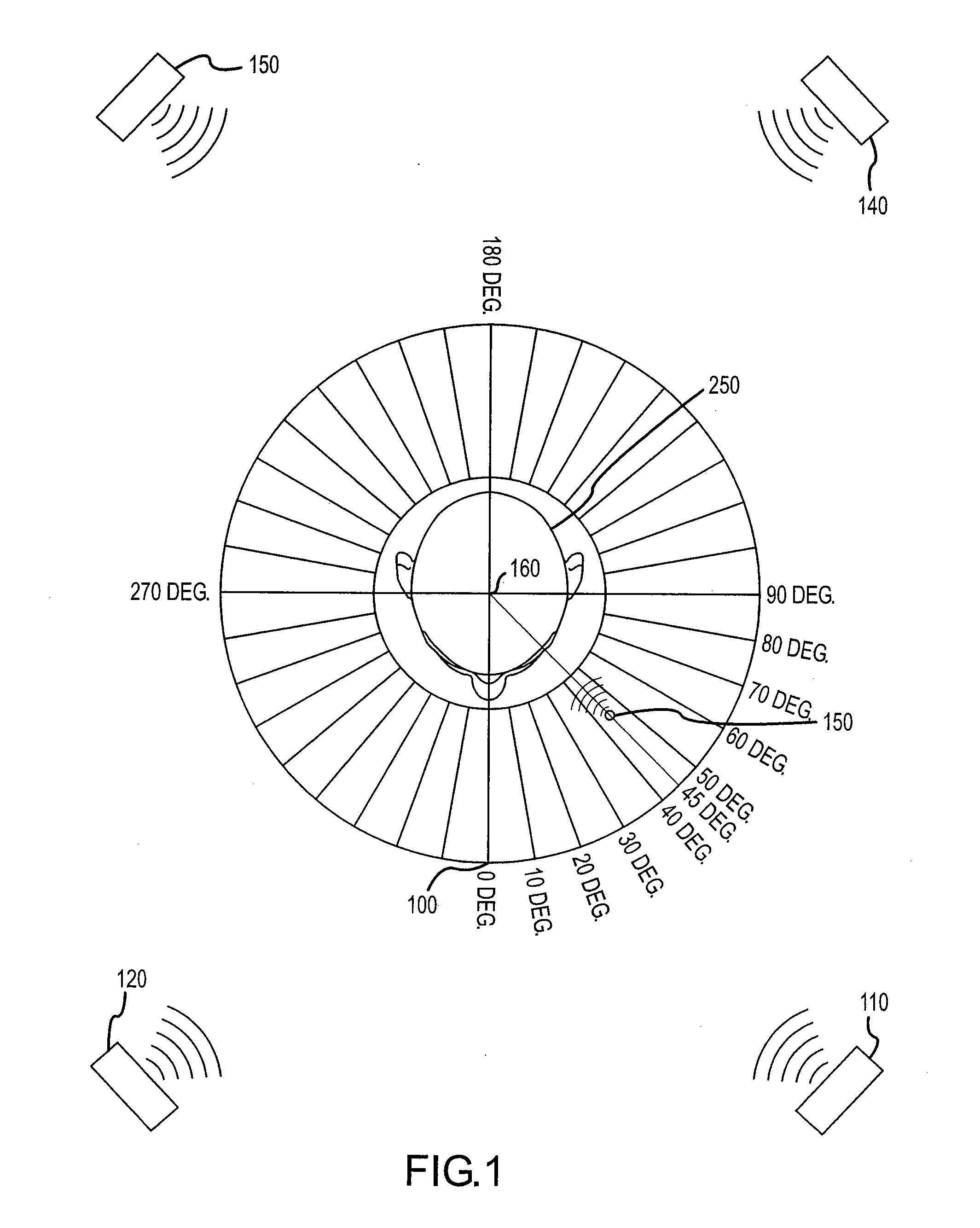
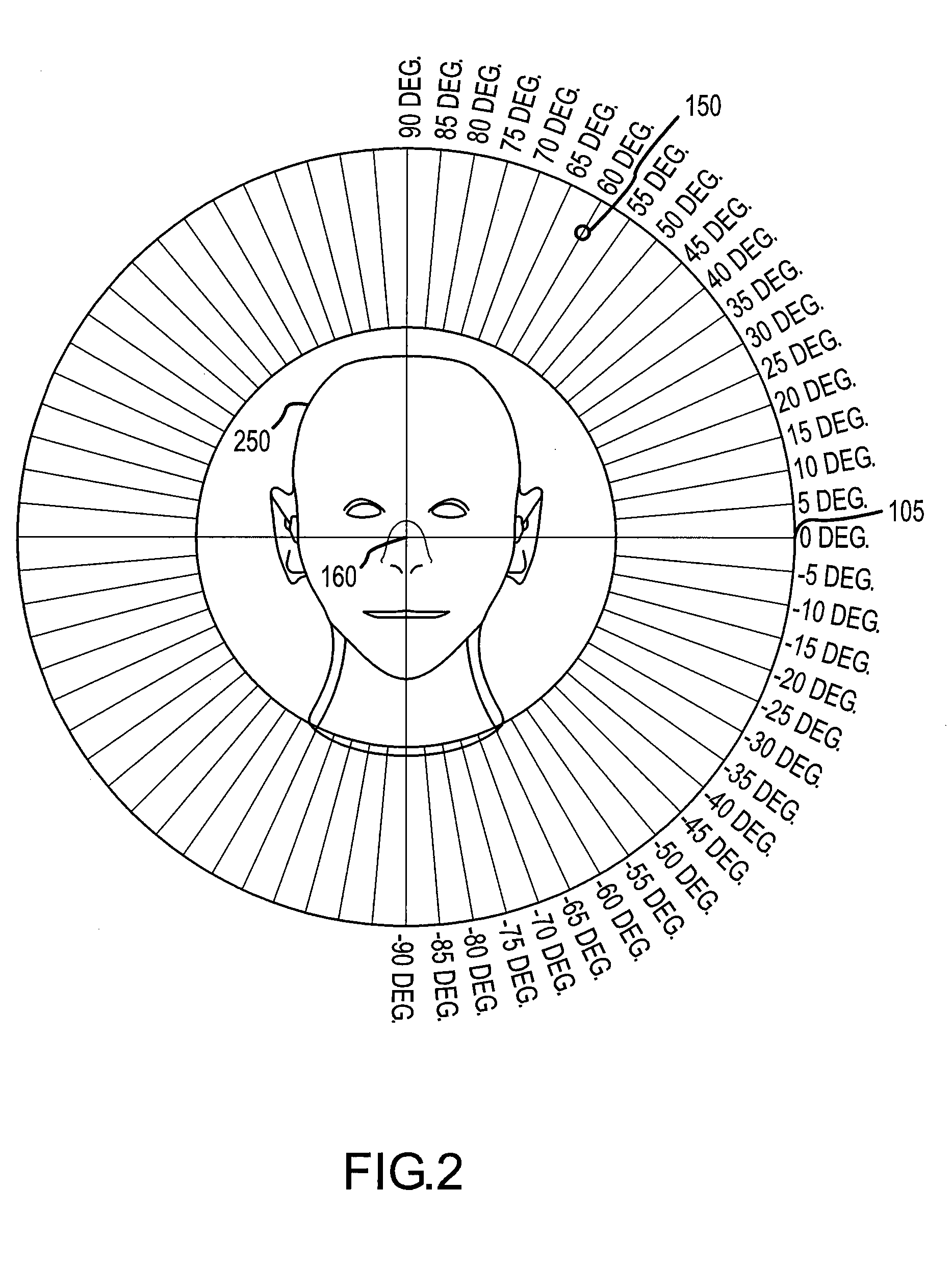
InactiveUS20090046864A1Accurate audio spatializationAccurate transfer functionHeadphones for stereophonic communicationStereophonic circuit arrangementsSound sourcesTime segment
A method and apparatus for processing an audio sound source to create four-dimensional spatialized sound. A virtual sound source may be moved along a path in three-dimensional space over a specified time period to achieve four-dimensional sound localization. A binaural filter for a desired spatial point is applied to the audio waveform to yield a spatialized waveform that, when the spatialized waveform is played from a pair of speakers, the sound appears to emanate from the chosen spatial point instead of the speakers. A binaural filter for a spatial point is simulated by interpolating nearest neighbor binaural filters chosen from a plurality of pre-defined binaural filters. The audio waveform may be processed digitally in overlapping blocks of data using a Short-Time Fourier transform. The localized sound may be further processed for Doppler shift and room simulation.
Owner:GENAUDIO
Audio playback apparatus, audio playback method, and program
InactiveUS7689304B2Electrophonic musical instrumentsRecord information storageSound sourcesSpeech recognition
Owner:SONY CORP
Forming beams with nulls directed at noise sources
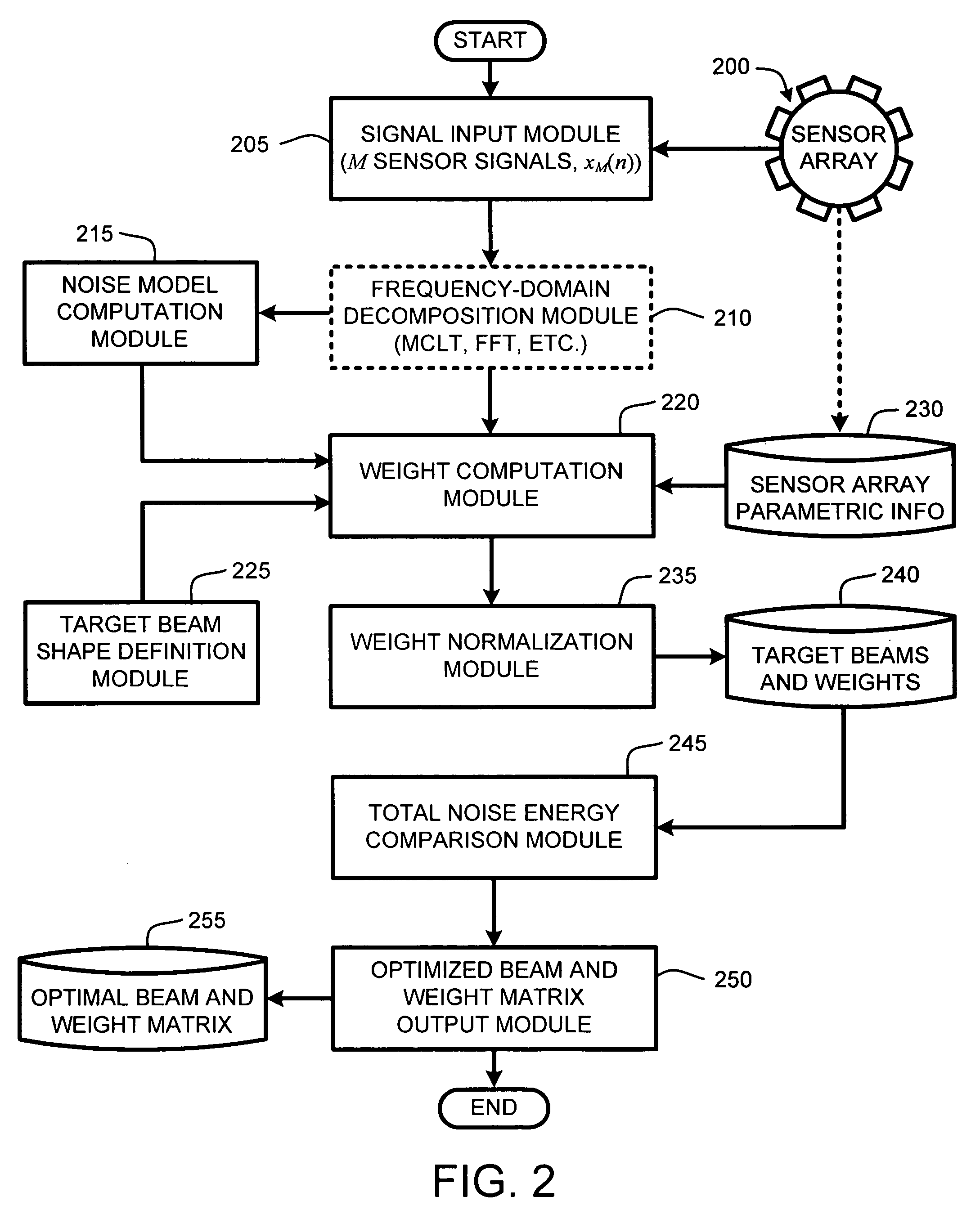
ActiveUS20060262943A1Signal processingMicrophones signal combinationCommunications systemSound sources
A communication system (e.g., a speakerphone) includes an array of microphones, a speaker, memory and a processor. The processor may perform a virtual broadside scan on the microphone array and analyze the resulting amplitude envelope to identify acoustic source angles. Each of the source angles may be further investigated with a directed beam (e.g., a hybrid superdirective / delay-and-sum beam) to obtain a corresponding beam signal. Each source may be classified as either intelligence or noise based on an analysis of the corresponding beam signal. The processor may design a virtual beam pointed at an intelligence source and having nulls directed at one or more of the noise sources. Thus, the virtual beam may be highly sensitive to the intelligence source and insensitive to the noise sources.
Owner:LIFESIZE INC
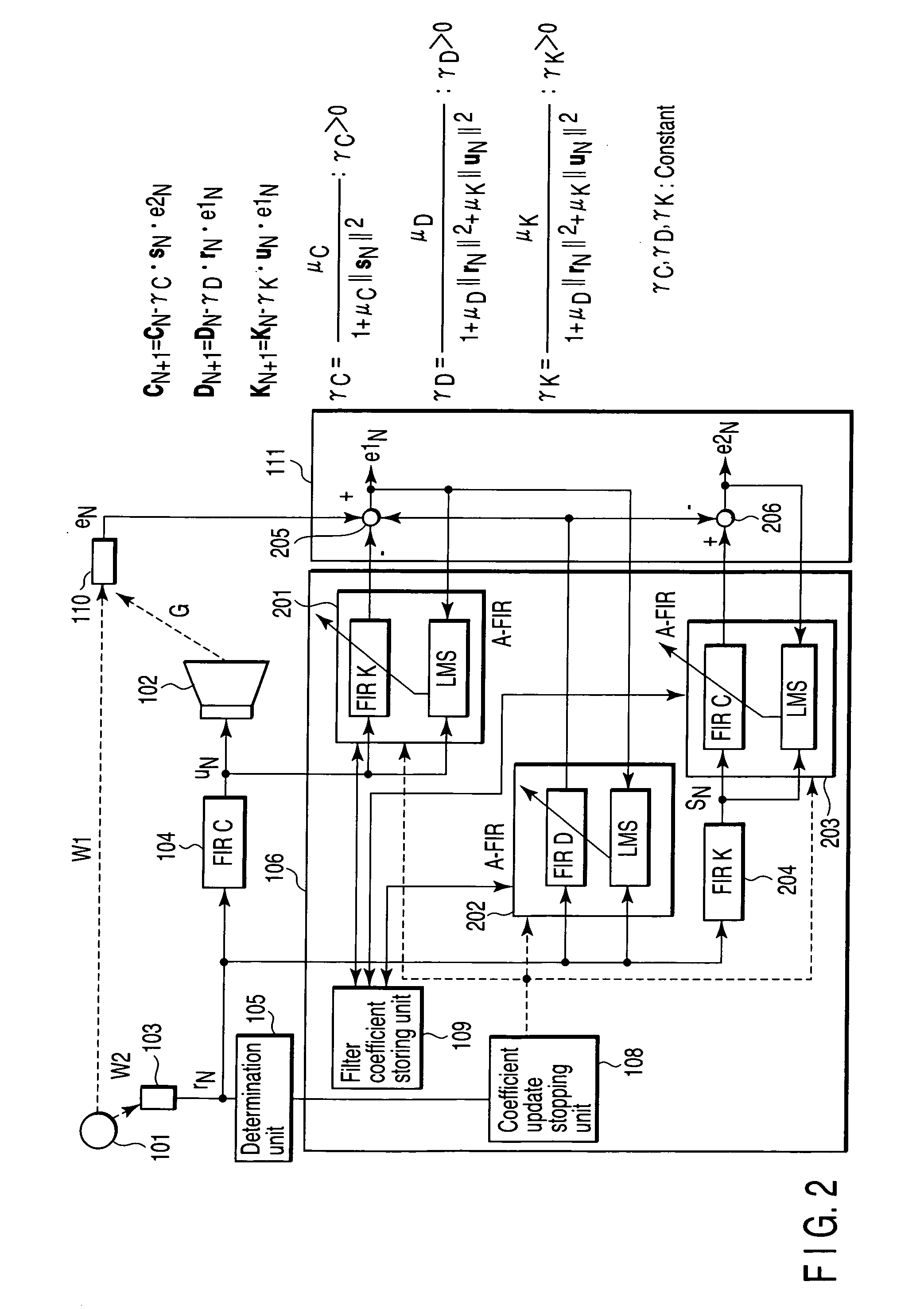
Active noise-reduction control apparatus and method
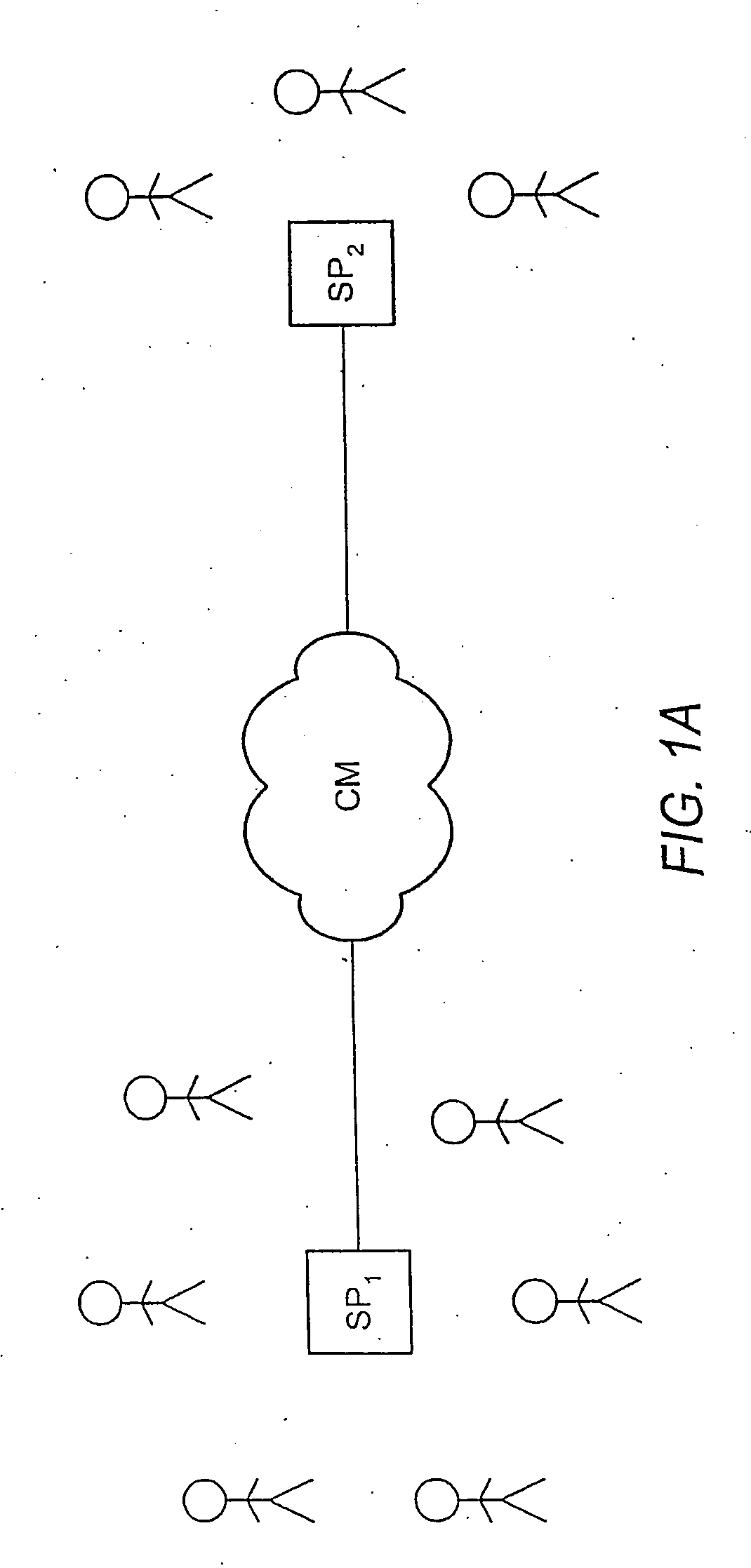
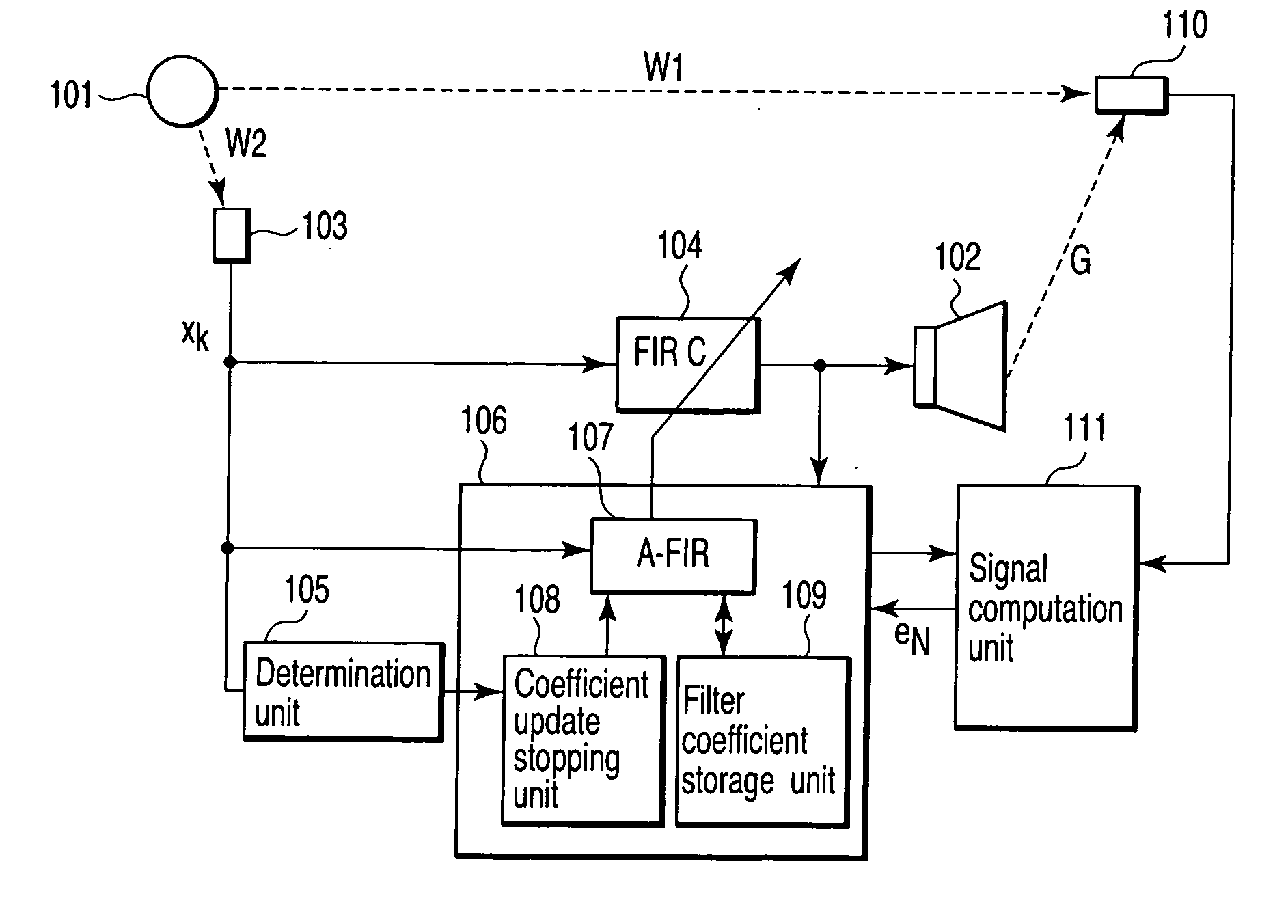
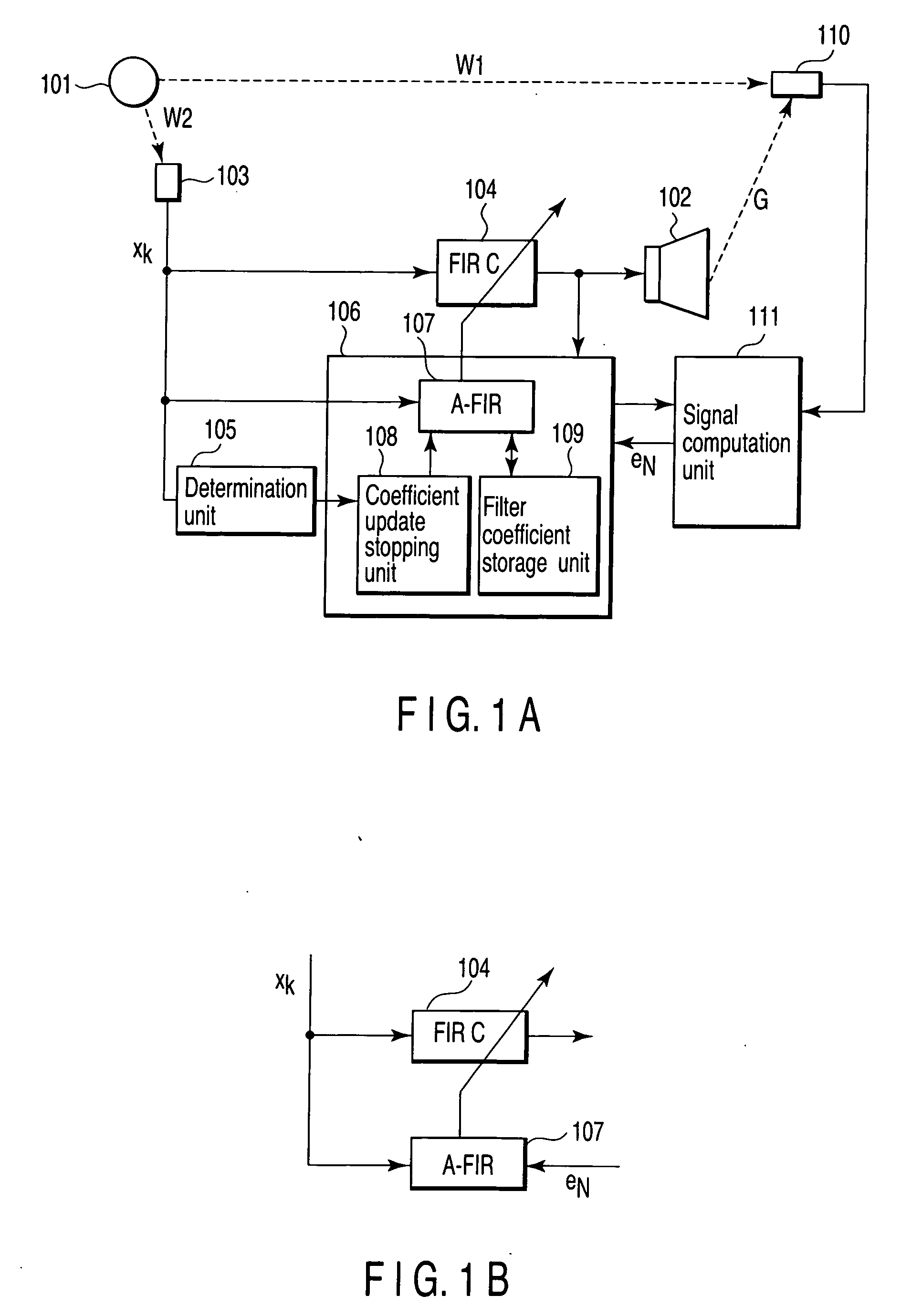
InactiveUS20070076896A1Reduce white noiseReduce noiseEar treatmentNoise generationAdaptive filterSound sources
Apparatus includes generator generating reference signal based on noise emitted from sound source, detector detecting level of reference signal and change in level, unit comparing change with threshold-value range and produce compared result, filter filtering reference signal, adaptive filter having variable filter coefficient, unit updating filter coefficient according to change of level of reference signal for obtaining an updated filter coefficient, unit stopping updating of filter coefficient in response to compared result when change falls outside threshold-value range, unit storing updated filter coefficient each time filter coefficient is updated, generator generating control signal using stored filter coefficient, unit generating control sound based on control signal, microphone detecting synthesis sound pressure of control sound and noise to produce an error signal, and unit setting stored filter coefficient to more accurate coefficient than stored filter coefficient based on error signal, and signal acquired by filtering control signal through filter.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
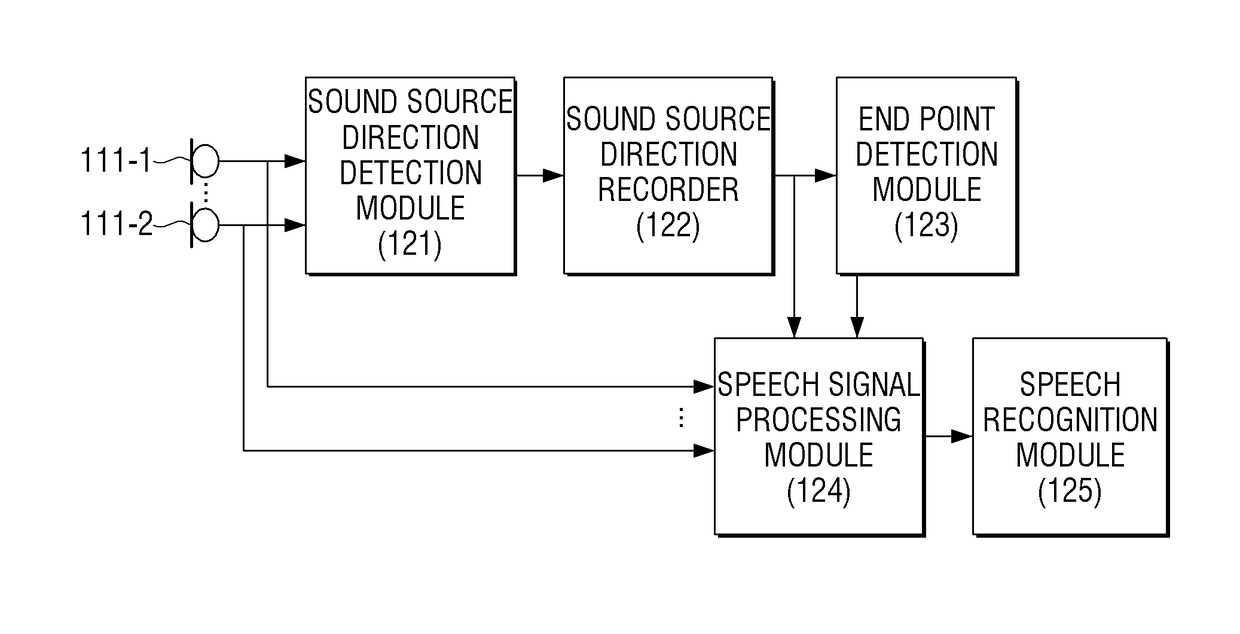
Electronic device and method for recognizing speech
An electronic device and a method for recognizing a speech are provided. The method for recognizing a speech by an electronic device includes: receiving sounds generated from a sound source through a plurality of microphones; calculating power values from a plurality of audio signals generated by performing signal processing on each sound input through the plurality of microphones and calculating direction information on the sound source based on the calculated power values and storing the calculated direction information; and performing the speech recognition on a speech section included in the audio signal based on the direction information on the sound source. As a result, the electronic device may correctly detect only a speech section from an audio signal while improving a speech section detection related processing speed.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Microphone Array System
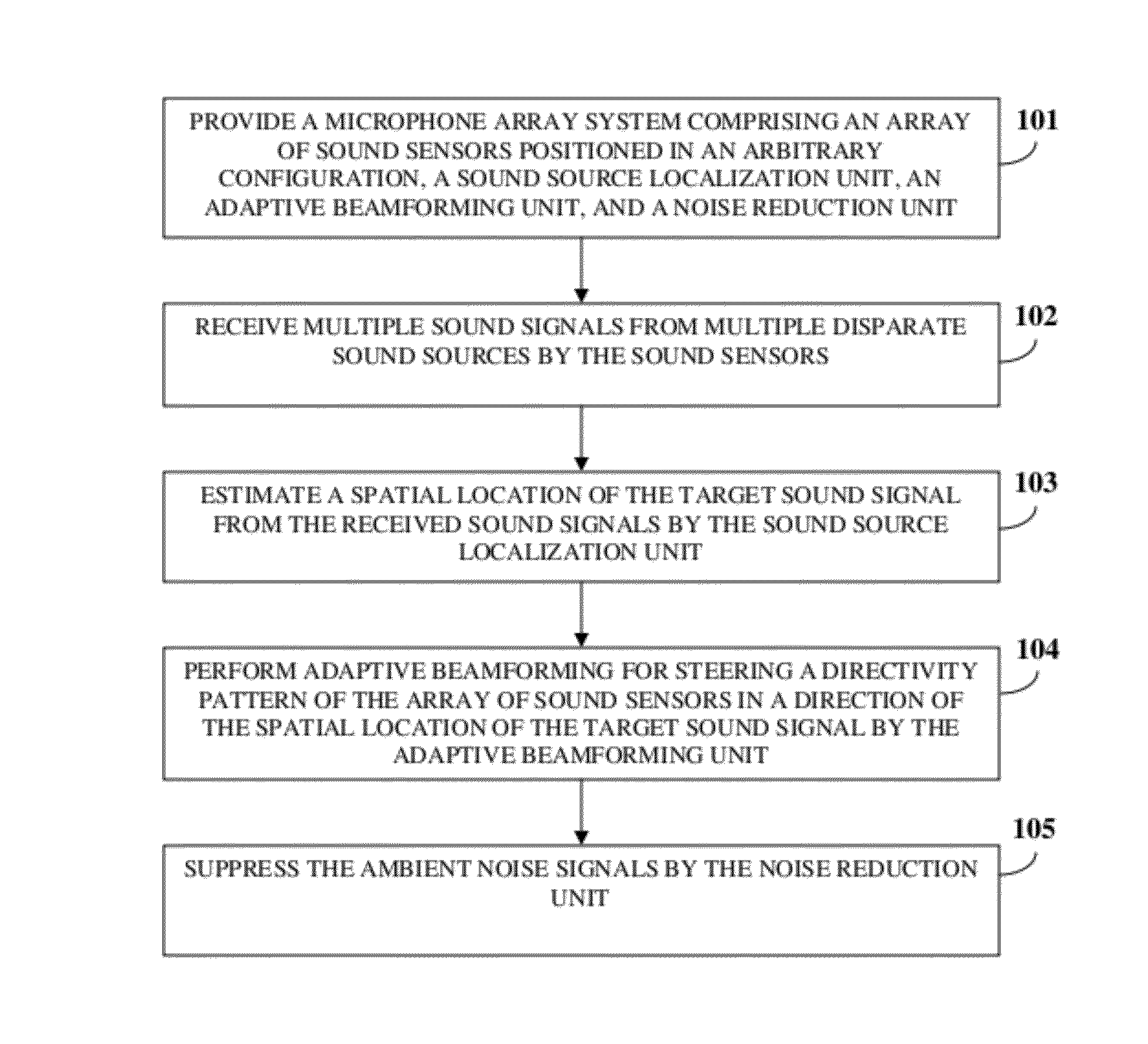
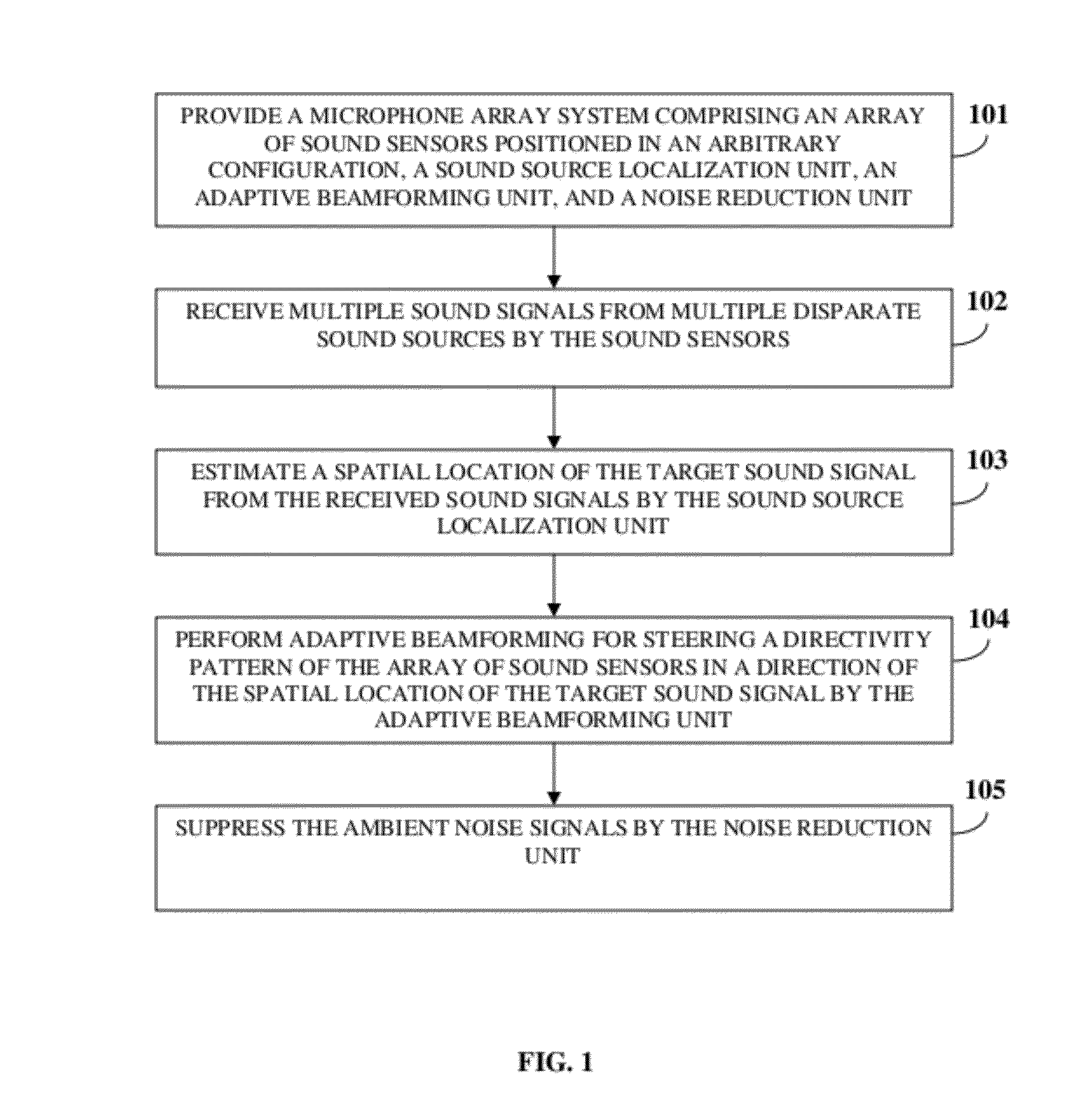
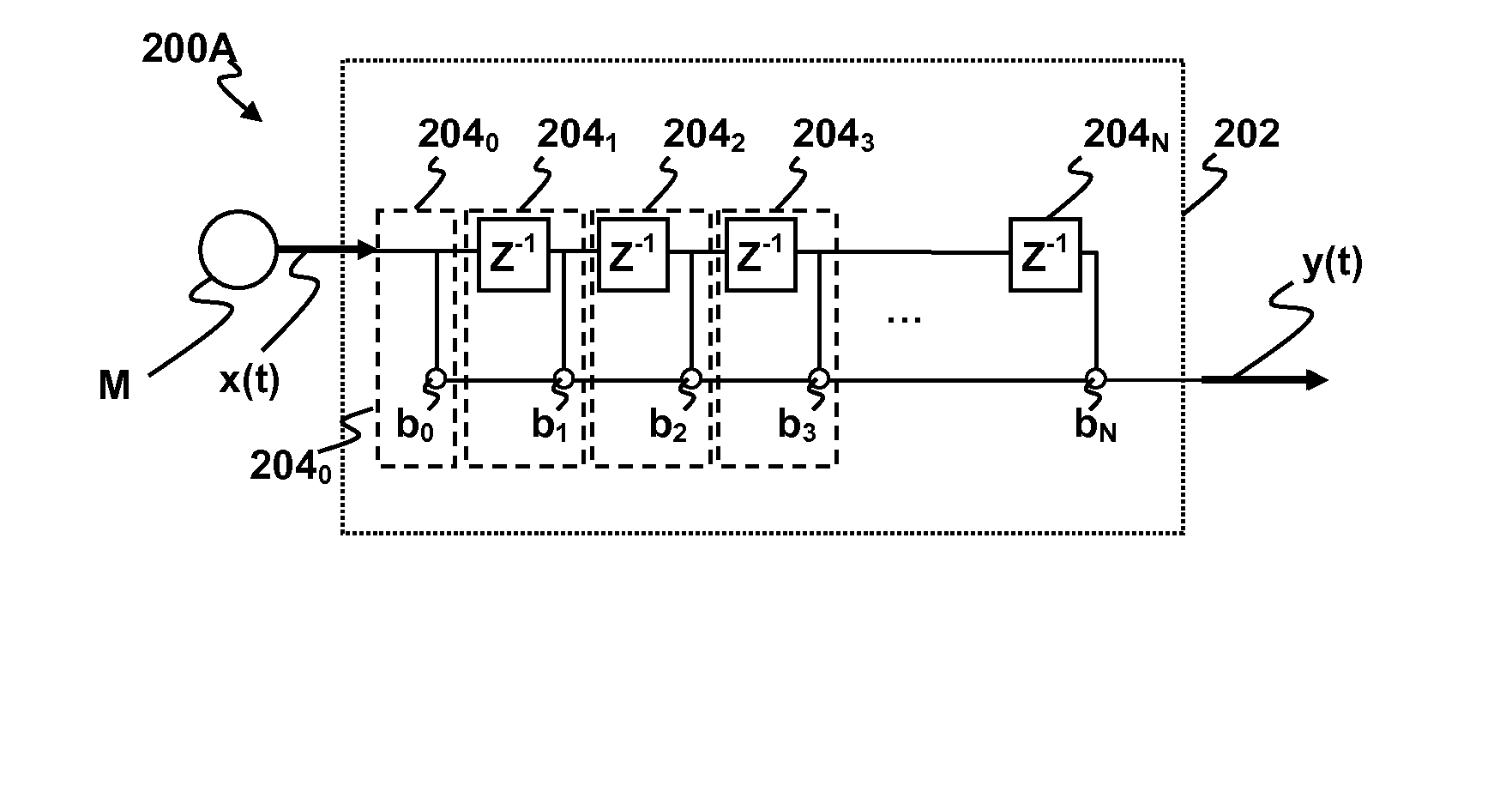
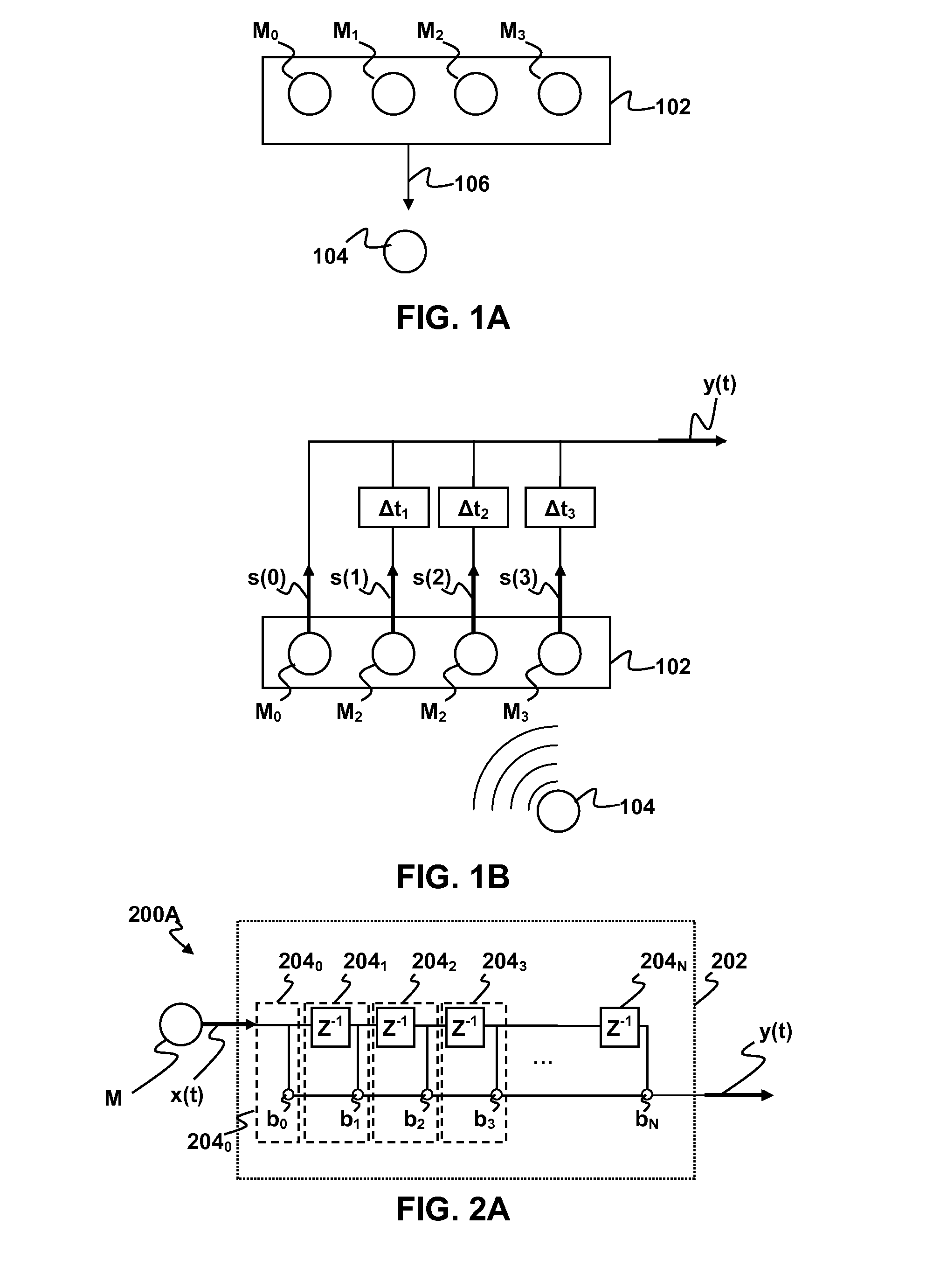
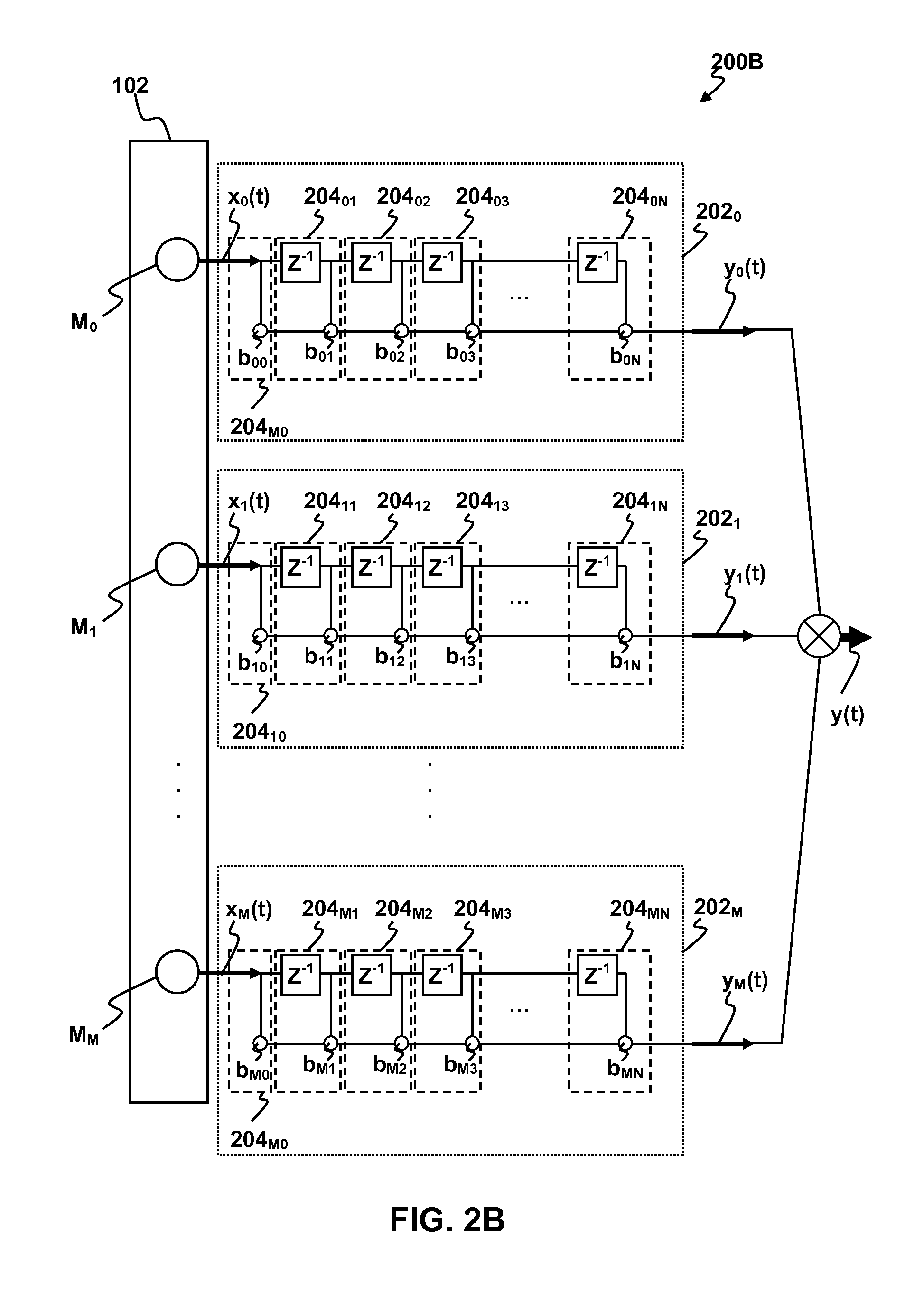
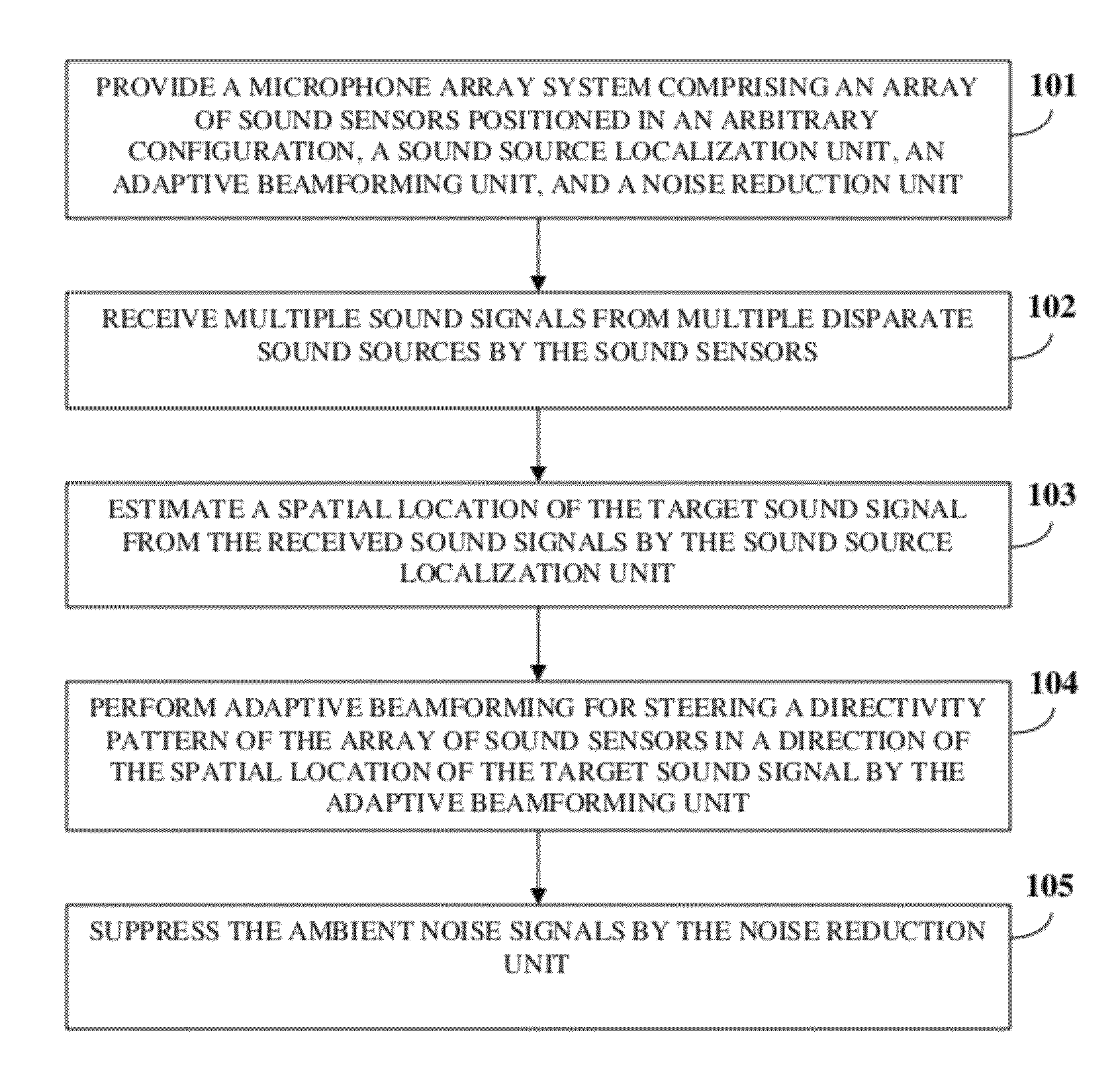
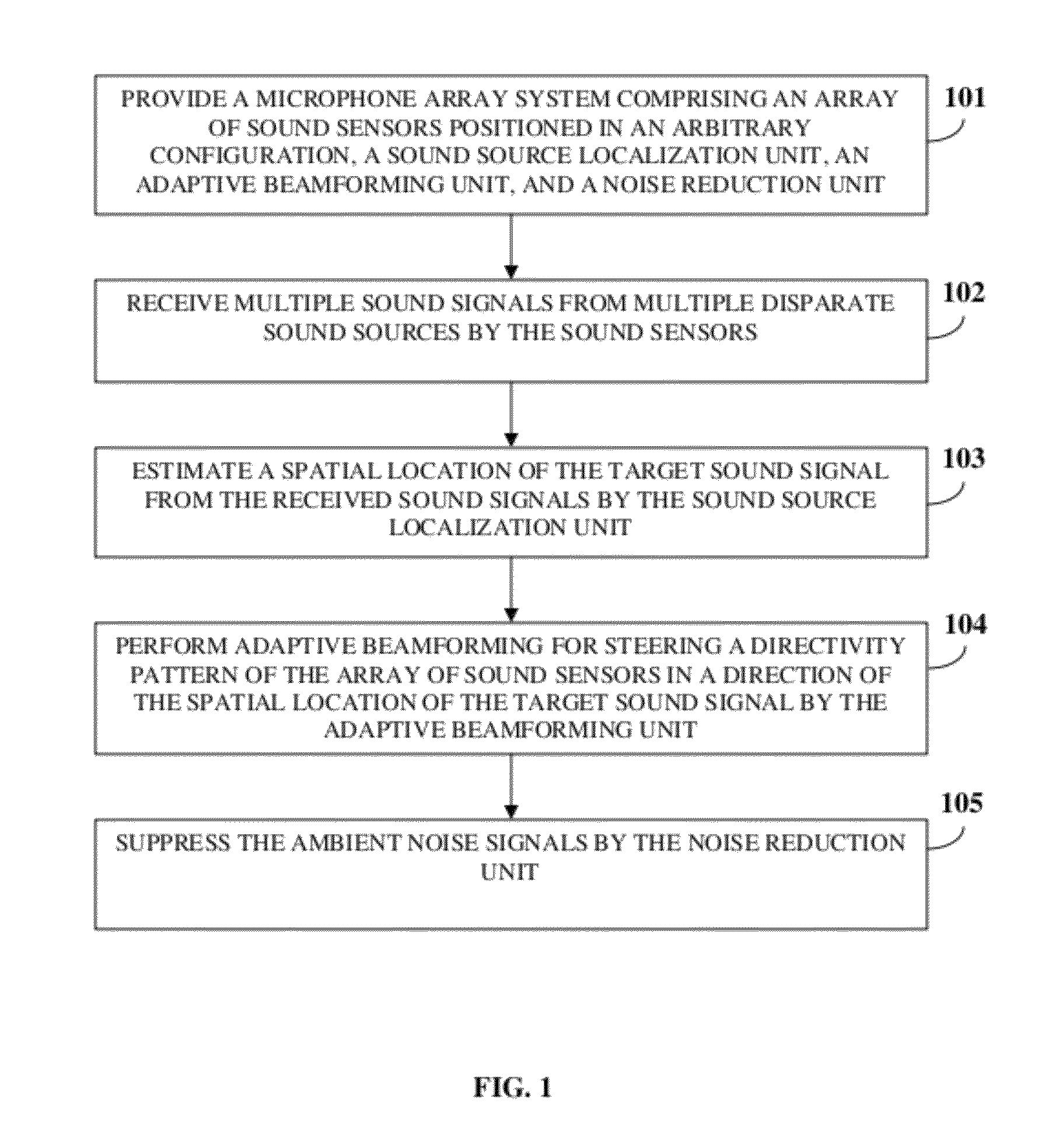
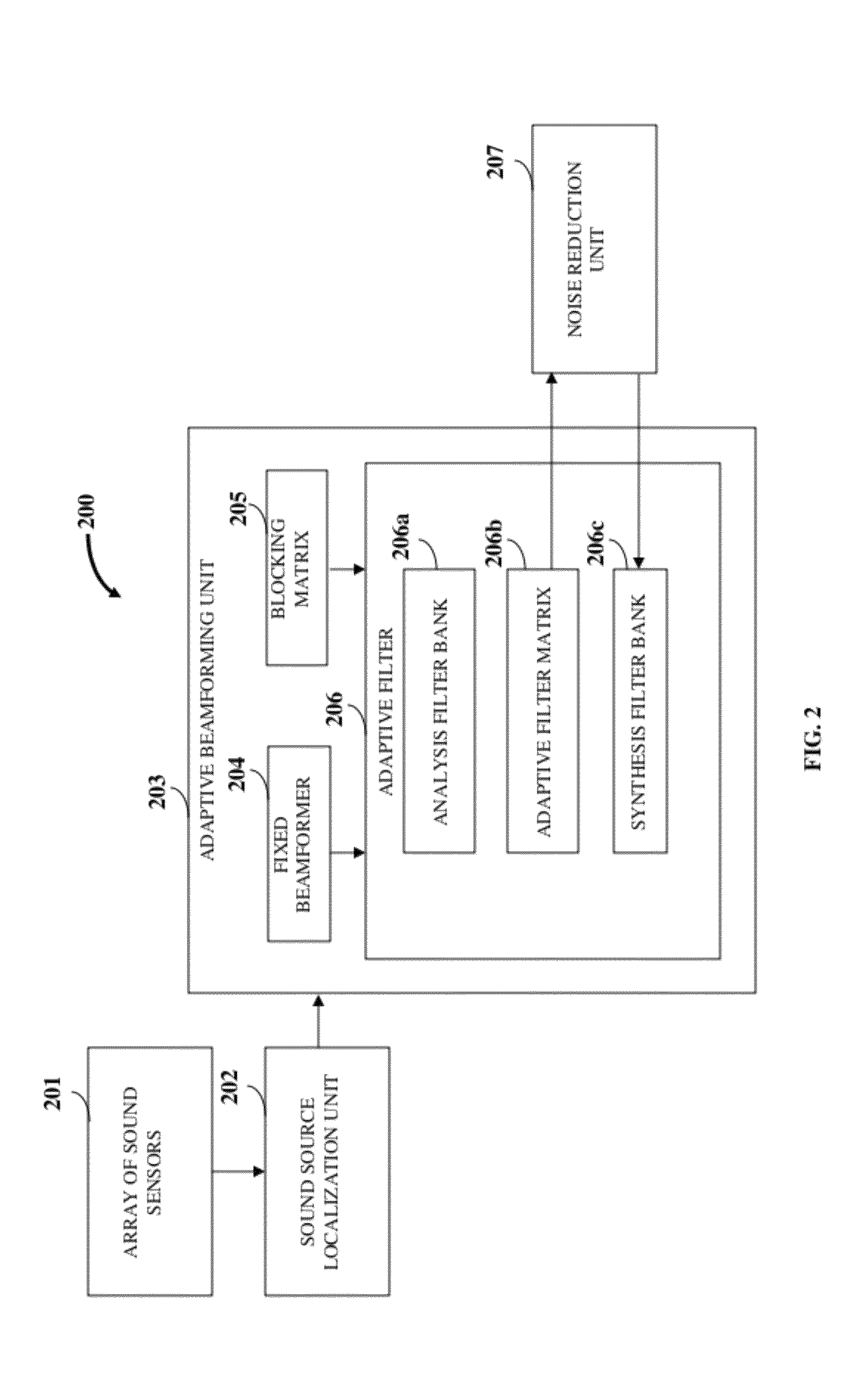
ActiveUS20120076316A1Increase heightPartially suppresses ambient noise signalMicrophonesEar treatmentSensor arrayEnvironmental noise
A method and system for enhancing a target sound signal from multiple sound signals is provided. An array of an arbitrary number of sound sensors positioned in an arbitrary configuration receives the sound signals from multiple disparate sources. The sound signals comprise the target sound signal from a target sound source, and ambient noise signals. A sound source localization unit, an adaptive beamforming unit, and a noise reduction unit are in operative communication with the array of sound sensors. The sound source localization unit estimates a spatial location of the target sound signal from the received sound signals. The adaptive beamforming unit performs adaptive beamforming by steering a directivity pattern of the array of sound sensors in a direction of the spatial location of the target sound signal, thereby enhancing the target sound signal and partially suppressing the ambient noise signals, which are further suppressed by the noise reduction unit.
Owner:VOCALIFE LLC +1
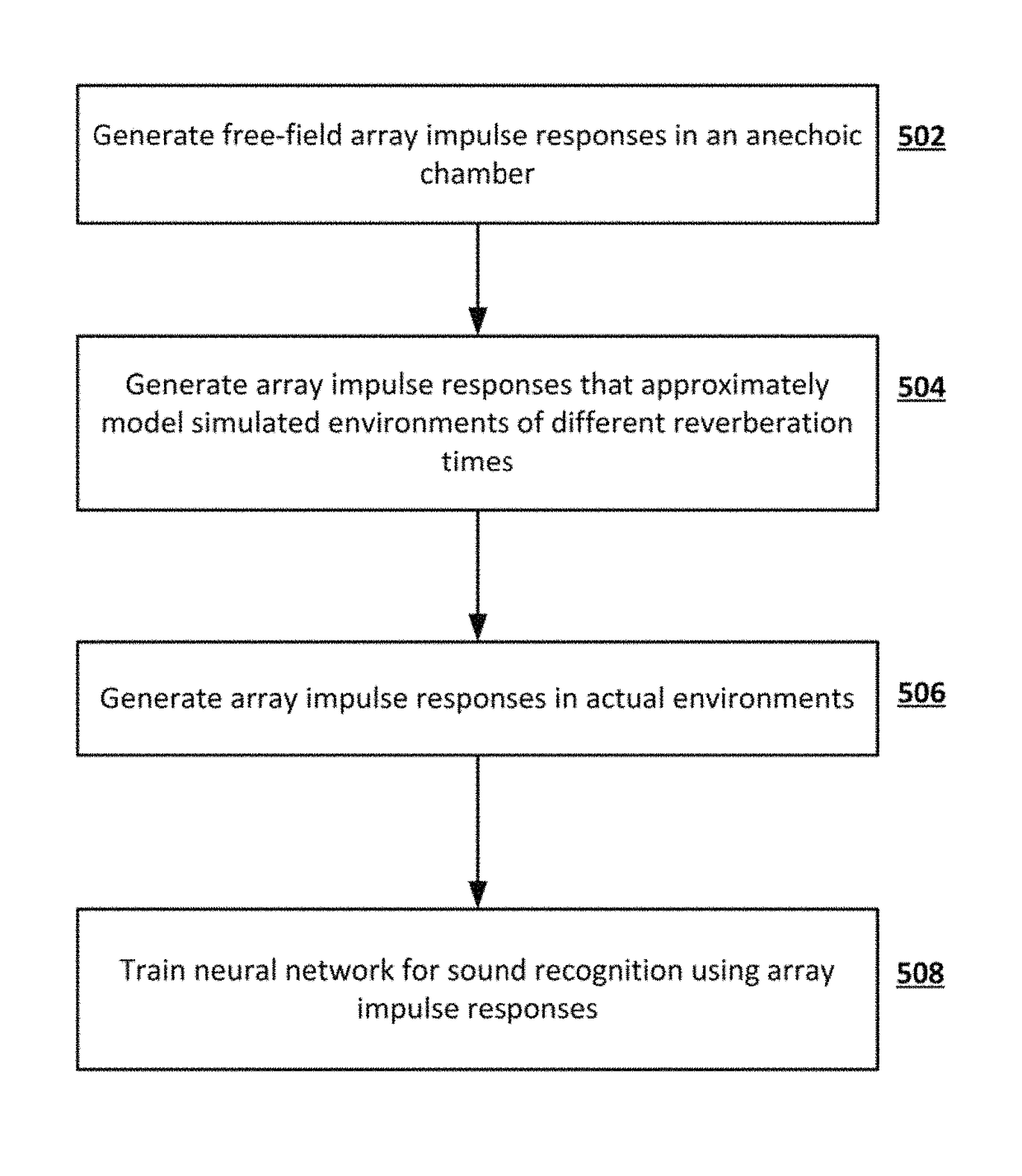
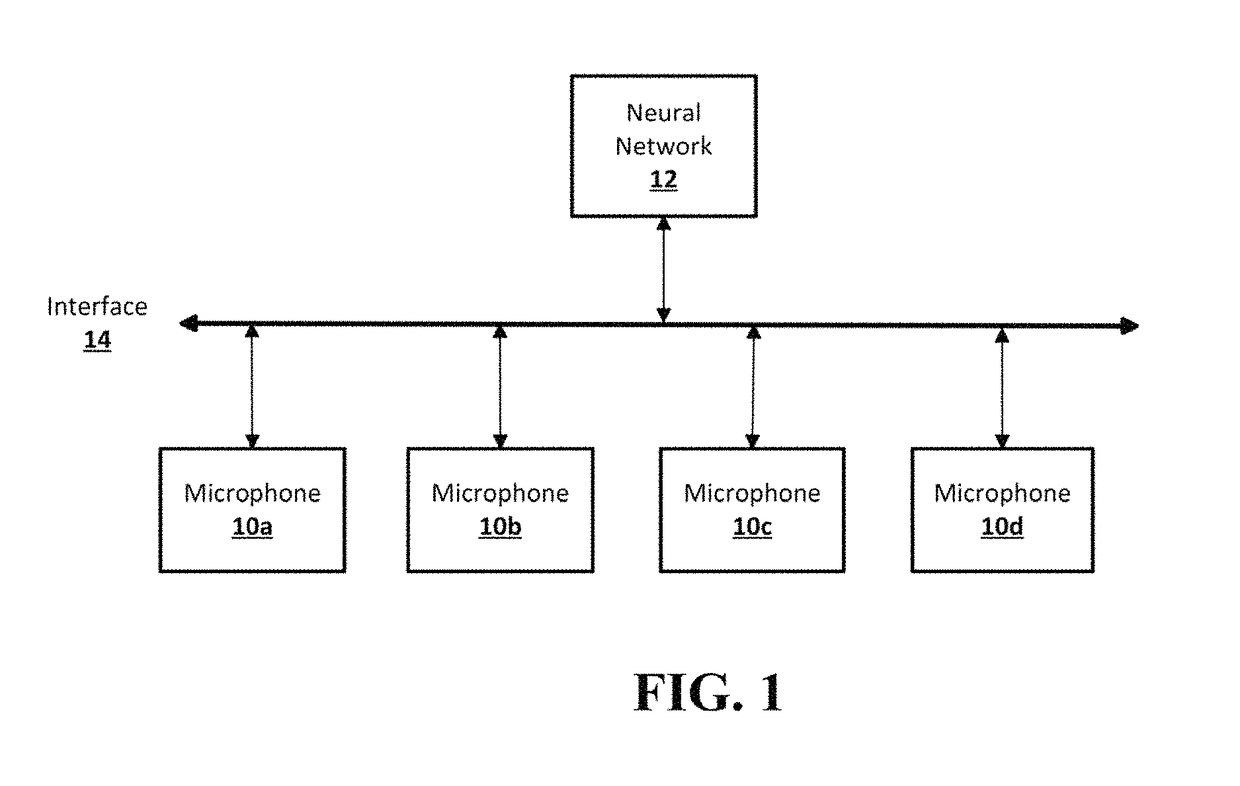
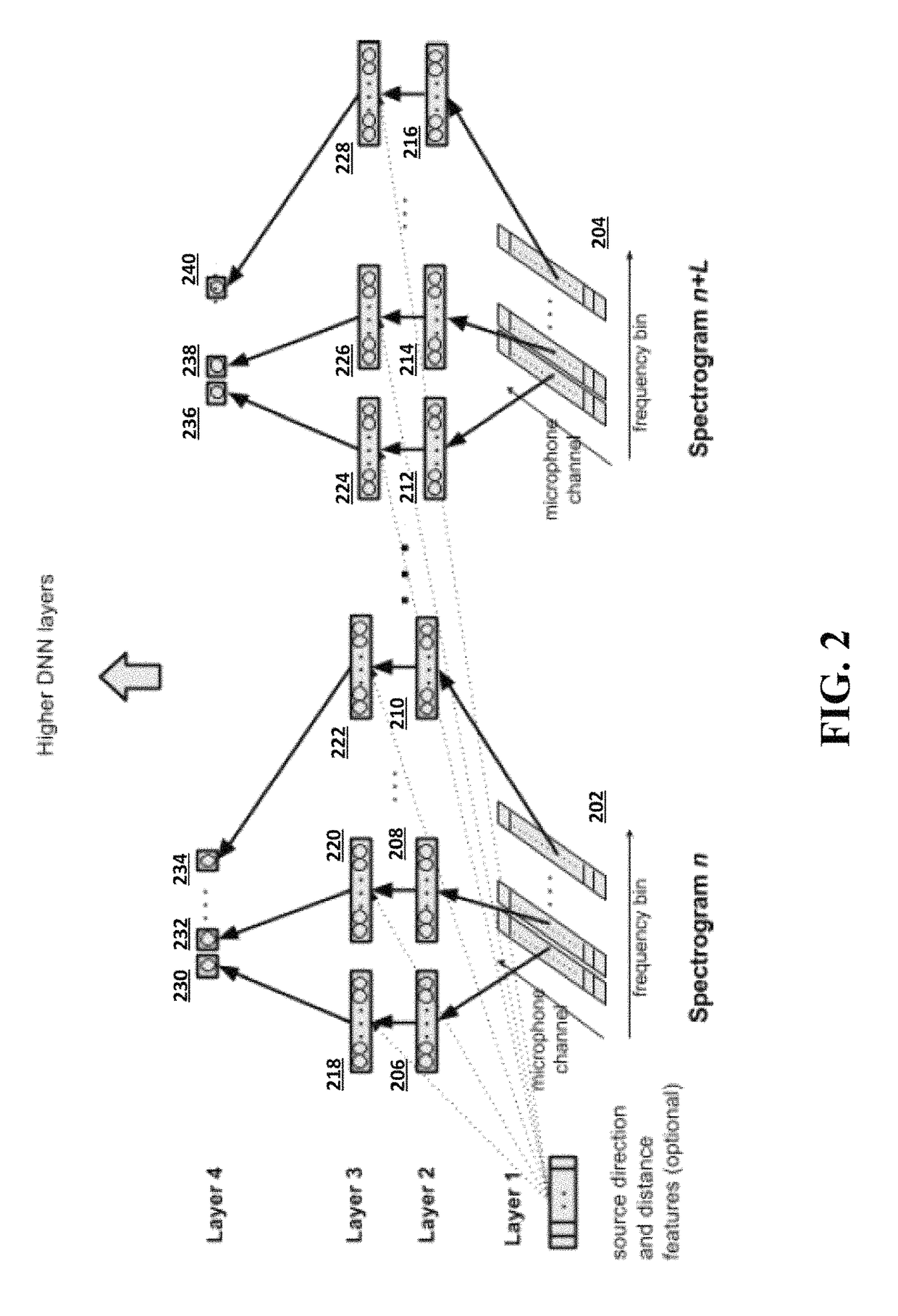
Multi-microphone neural network for sound recognition
A neural network is provided for recognition and enhancement of multi-channel sound signals received by multiple microphones, which need not be aligned in a linear array in a given environment. Directions and distances of sound sources may also be detected by the neural network without the need for a beamformer connected to the microphones. The neural network may be trained by knowledge gained from free-field array impulse responses obtained in an anechoic chamber, array impulse responses that model simulated environments of different reverberation times, and array impulse responses obtained in actual environments.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
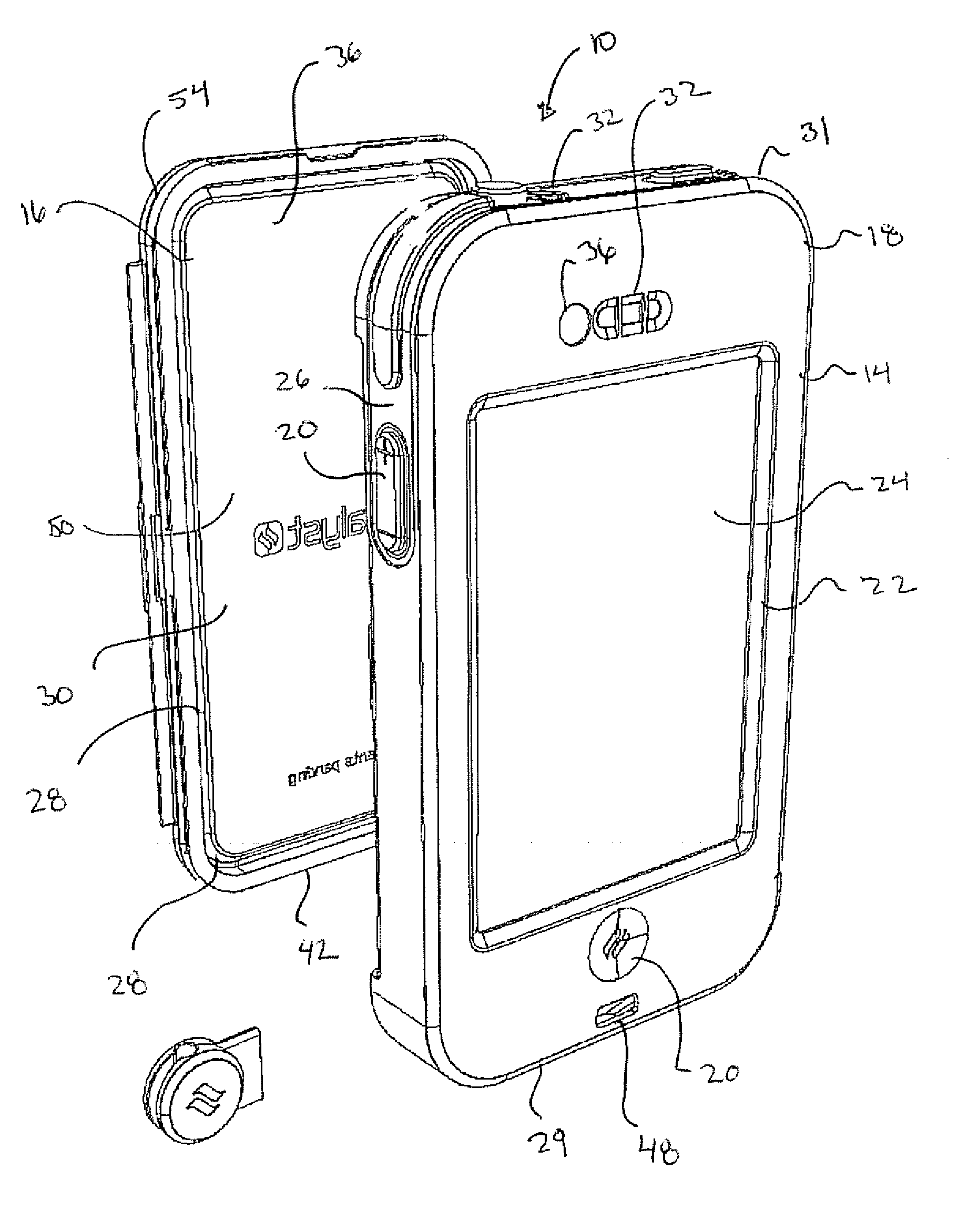
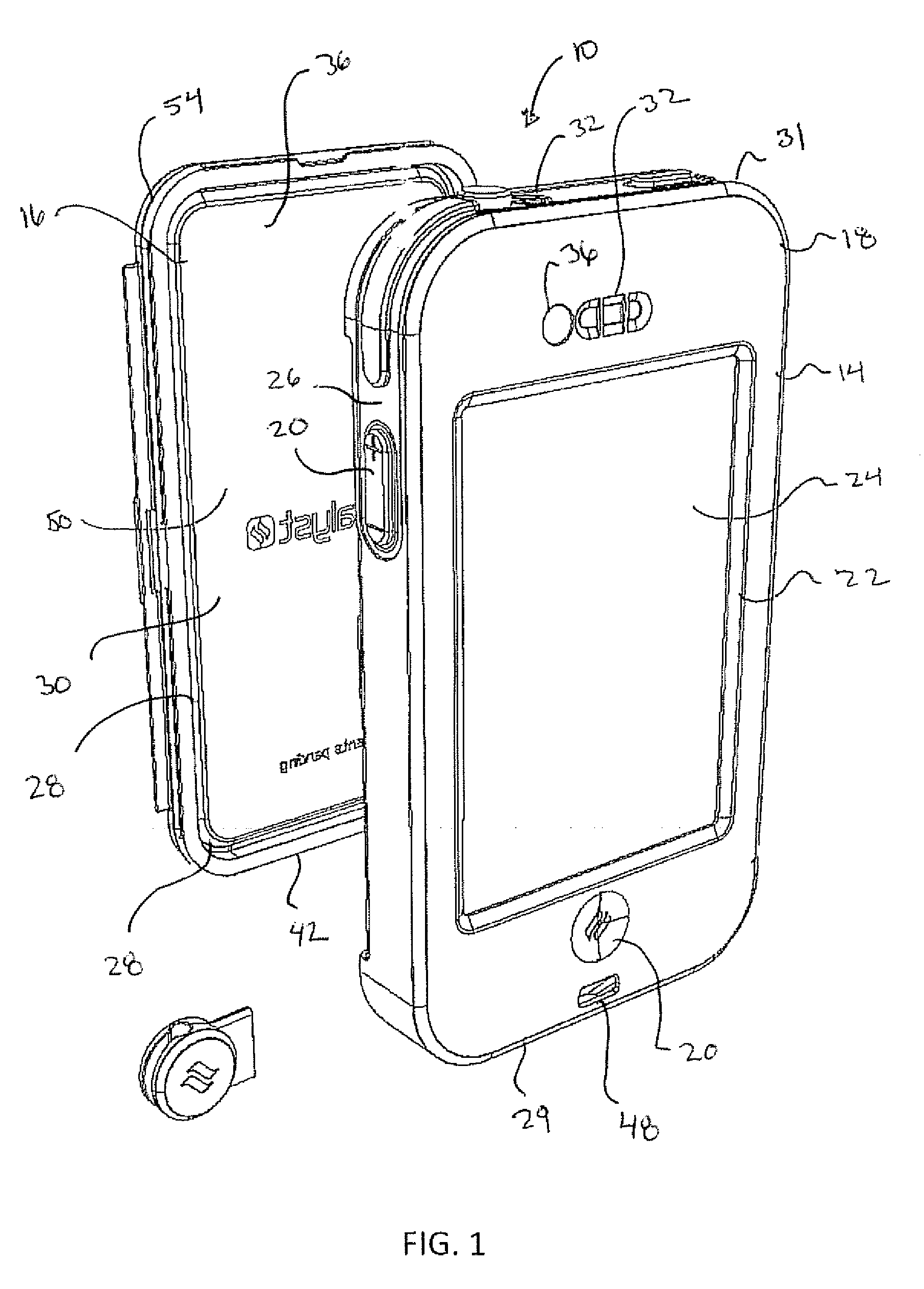
Waterproof case
A protective case for an electronic device includes a main housing and a lid. The main housing and lid are removably joined to define a water tight volume receiving an electronic device. Air trapped within the protective case transfers acoustic energy from a sound source within the case to at least one membrane wherein the membrane vibrates in response to an air pressure differential transmitting sound to an exterior of the case.
Owner:CATALYST LIFESTYLE
Selective sound source listening in conjunction with computer interactive processing
InactiveUS20060204012A1Enhanced interactionRespondVideo gamesStereophonic systemsSound sourcesComputer science
A method and apparatus for capturing image and sound during interactivity with a computer program is provided. The apparatus includes an image capture unit that is configured to capture one or more image frames. Also provided is a sound capture unit. The sound capture unit is configured to identify one or more sound sources. The sound capture unit generates data capable of being analyzed to determine a zone of focus, at which to process sound to the substantial exclusion of sounds outside of the zone of focus. In this manner, sound that is captured and processed for the zone of focus is used for interactivity with the computer program.
Owner:SONY COMPUTER ENTERTAINMENT INC
Audio playback method and apparatus using line array speaker unit
A multi-channel audio system is constituted using at least one line array speaker unit, in which plural speakers are arrayed in line, wherein the same audio signal is supplied with a prescribed delay time to each of the speakers, thus forming plural sound beams. The plural sound beams are reflected on a wall surface and a ceiling of a room so as to form plural virtual sound sources surrounding a listening position, and emission directions and intensities of the sound beams are controlled so as to localize a phantom at a prescribed position based on the plural virtual sound sources. By appropriately arranging plural line array speaker units horizontally, vertically, and slantingly in such a way that each line array speaker unit forms sound beams distributed and spread in a sectorial form, it is possible to realize a surround audio system having a high degree of freedom with regard to setup positions for forming virtual sound sources.
Owner:YAMAHA CORP
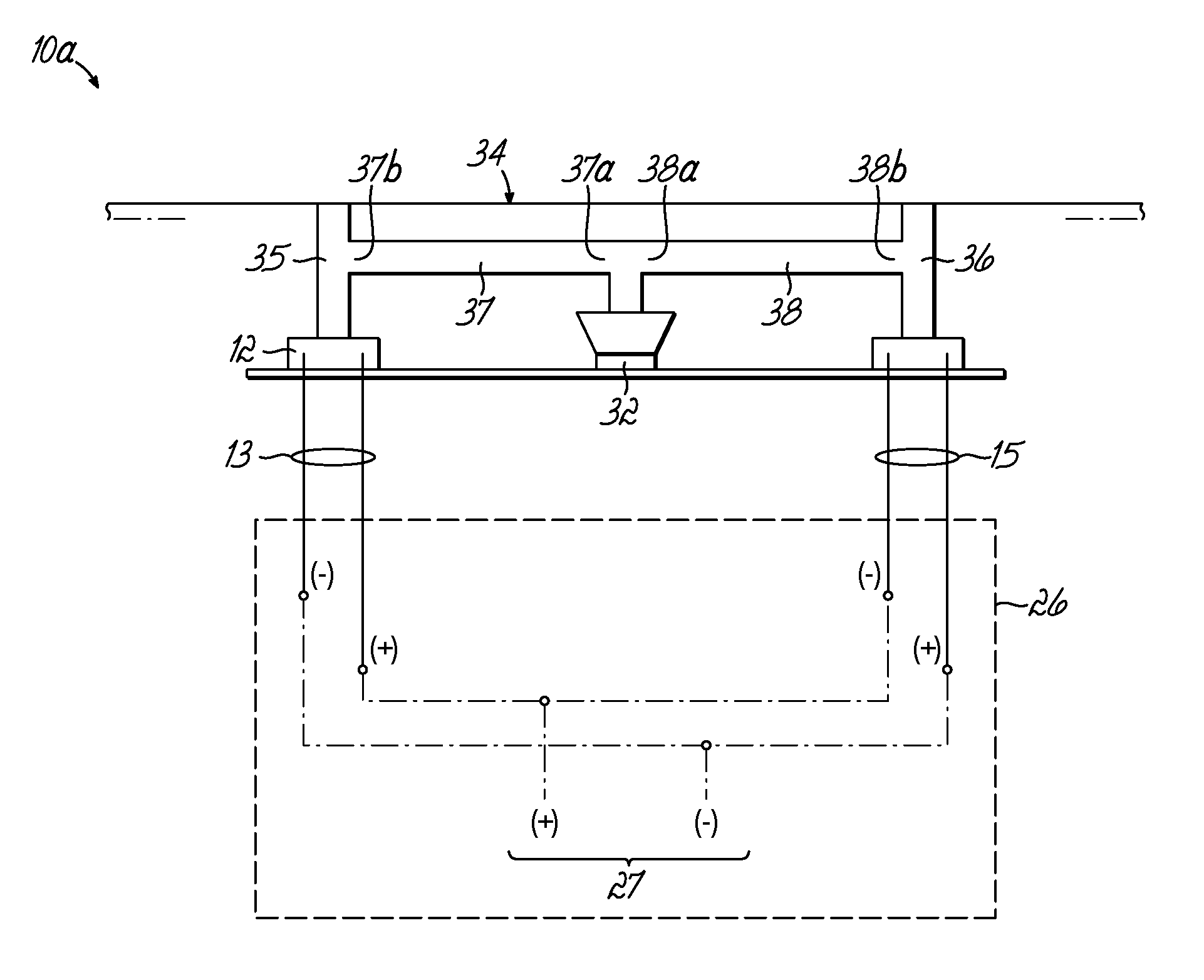
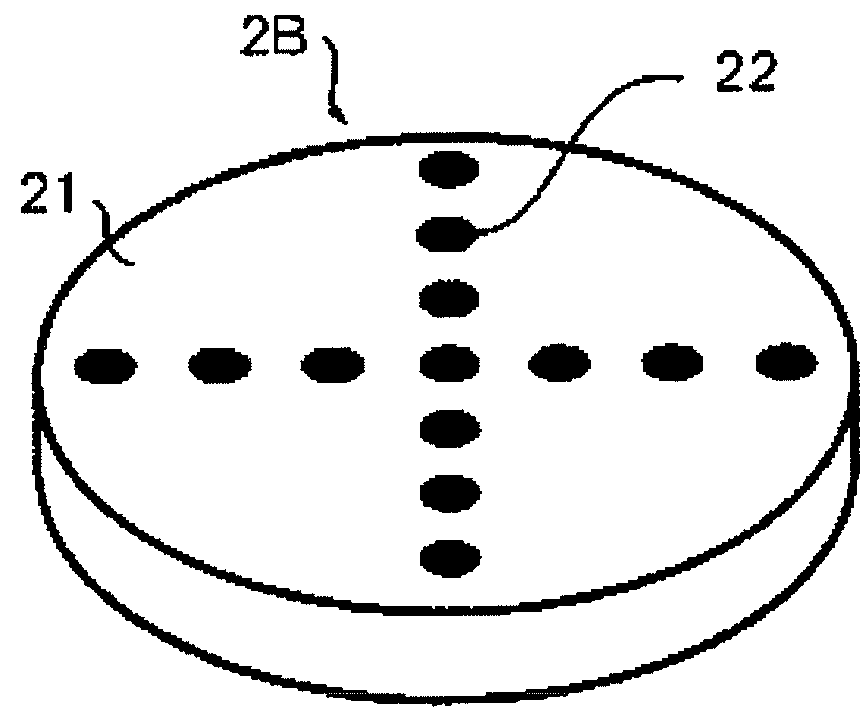
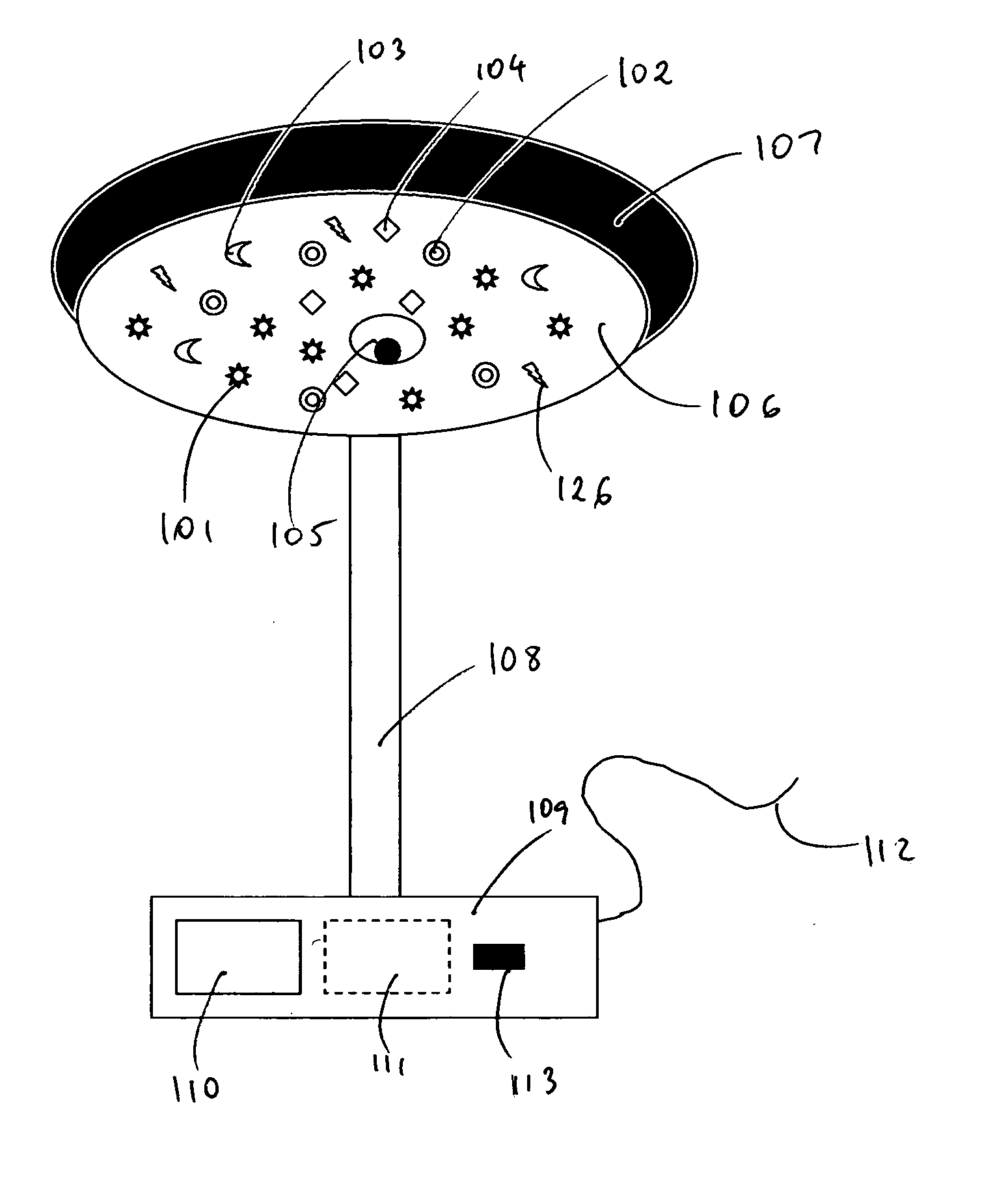
Self calibrating multi-element dipole microphone
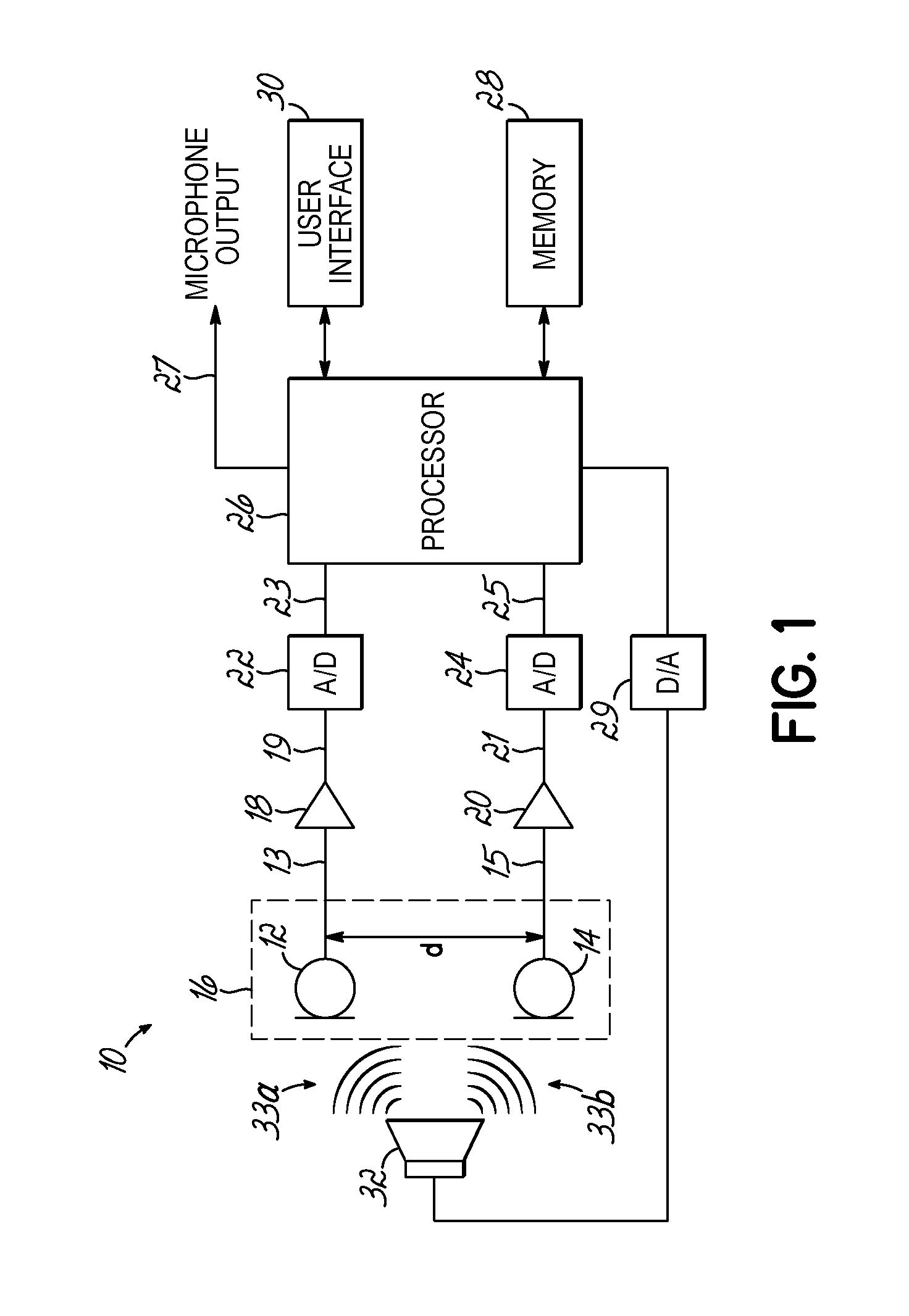
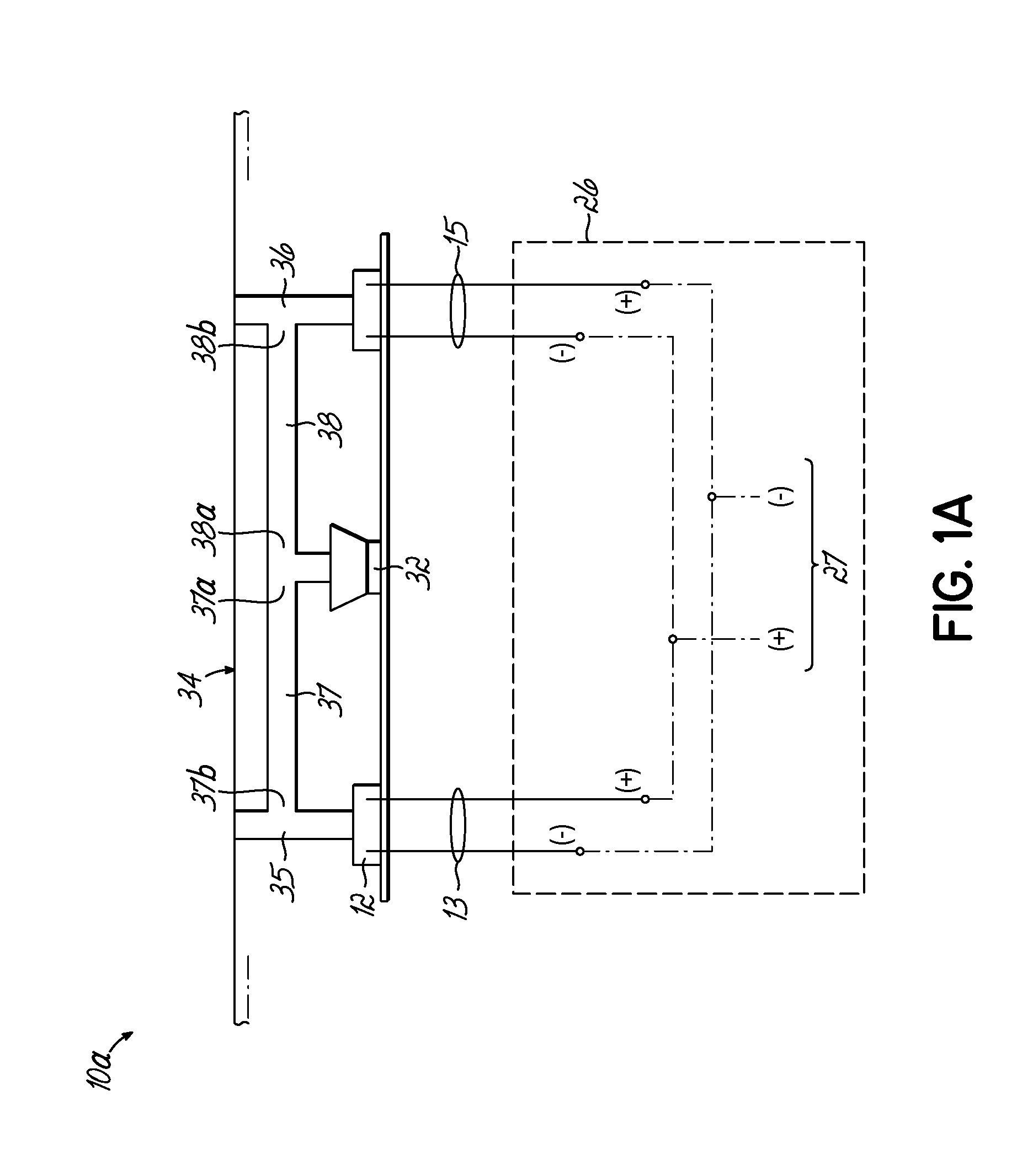
ActiveUS20120269356A1Maintain performancePiezoelectric/electrostrictive microphonesElectrostatic transducer microphonesSound sourcesDigital filter
A self calibrating dipole microphone formed from two omni-directional acoustic sensors. The microphone includes a sound source acoustically coupled to the acoustic sensors and a processor. The sound source is excited with a test signal, exposing the acoustic sensors to acoustic calibration signals. The responses of the acoustic sensors to the calibration signals are compared by the processor, and one or more correction factors determined. Digital filter coefficients are calculated based on the one or more correction factors, and applied to the output signals of the acoustic sensors to compensate for differences in the sensitivities of the acoustic sensors. The filtered signals provide acoustic sensor outputs having matching responses, which are subtractively combined to form the dipole microphone output.
Owner:VOCOLLECT
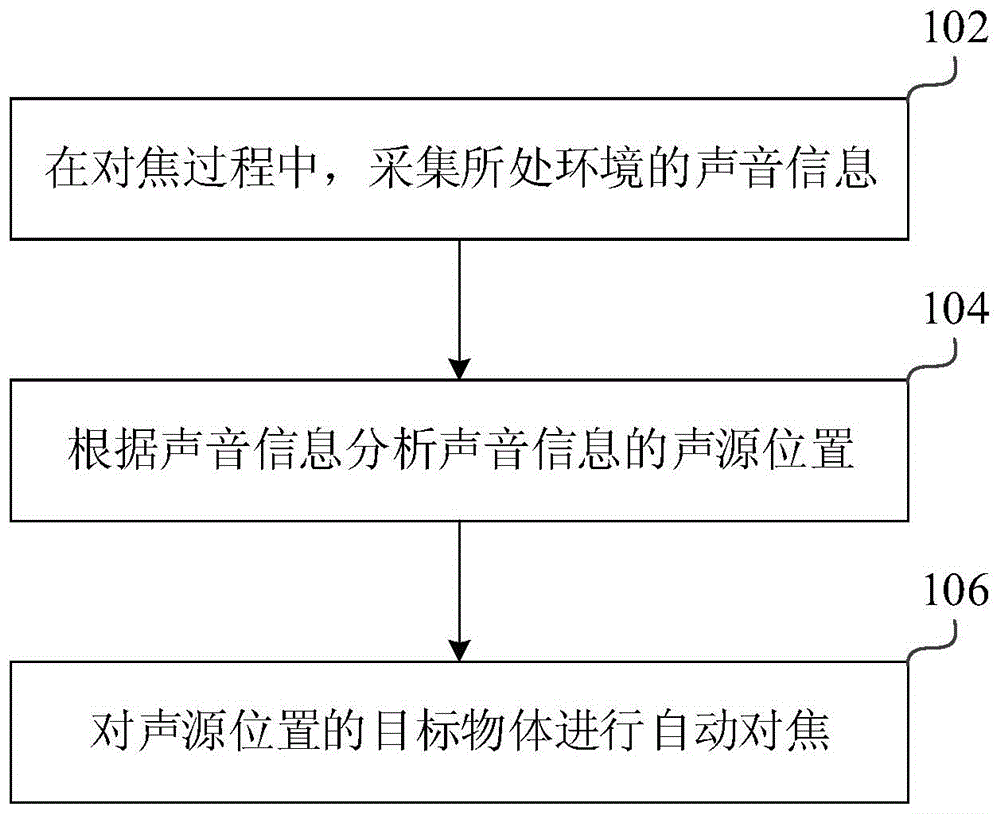
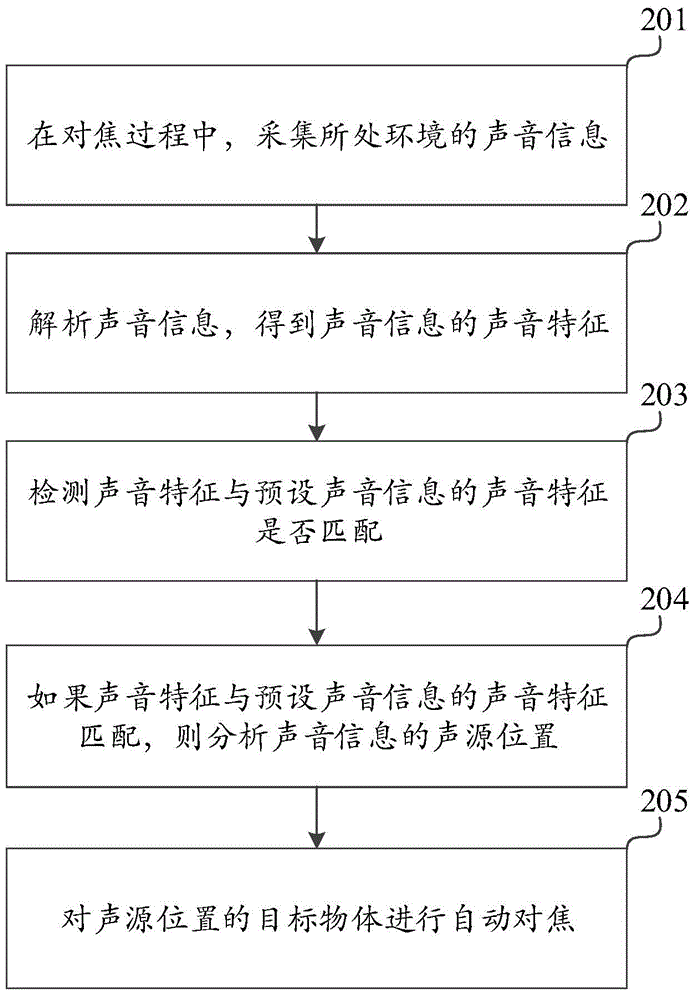
Automatic focusing method and apparatus
Owner:XIAOMI INC
Nonwoven containing acoustical insulation laminate
The present invention relates to an acoustical insulation material containing a first layer formed from a nonwoven web having a density of at least 50 kg / m3 wherein the nonwoven web is formed from thermoplastic [meltblown] fibers having an average fiber diameter of less than about 7 microns; and a second layer of a high loft material. The high loft material of the present invention provides bulk to the first layer and may or may not have sound attenuating properties. Examples of the high loft material include, for example, fiberglass and high loft nonwoven webs. Also disclosed in a method of attenuating sound waves passing from a sound source area to a second area. The method includes positioning an acoustical insulation material containing a first layer formed from a nonwoven web having a density of at least 50 kg / m3 wherein the nonwoven web is formed from thermoplastic [meltblown] fibers having an average fiber diameter of less than about 7 microns; and a second layer of a high loft material, between the sound source area and the second area.
Owner:KIMBERLY-CLARK WORLDWIDE INC
Ultra small microphone array
ActiveUS20070260340A1MicrophonesAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceFinite impulse responseTime domain
Methods and apparatus for signal processing are disclosed. A discrete time domain input signal xm(t) may be produced from an array of microphones M0 . . . MM. A listening direction may be determined for the microphone array. The listening direction is used in a semi-blind source separation to select the finite impulse response filter coefficients b0, b1 . . . , bN to separate out different sound sources from input signal xm(t). One or more fractional delays may optionally be applied to selected input signals xm(t) other than an input signal x0(t) from a reference microphone M0. Each fractional delay may be selected to optimize a signal to noise ratio of a discrete time domain output signal y(t) from the microphone array. The fractional delays may be selected to such that a signal from the reference microphone M0 is first in time relative to signals from the other microphone(s) of the array. A fractional time delay Δ may optionally be introduced into an output signal y(t) so that: y(t+Δ)=x(t+Δ)*b0+x(t−1+Δ)*b1+x(t−2+Δ)*b2+ . . . +x(t−N+Δ)bN, where Δ is between zero and ±1.
Owner:SONY COMPUTER ENTERTAINMENT INC +1
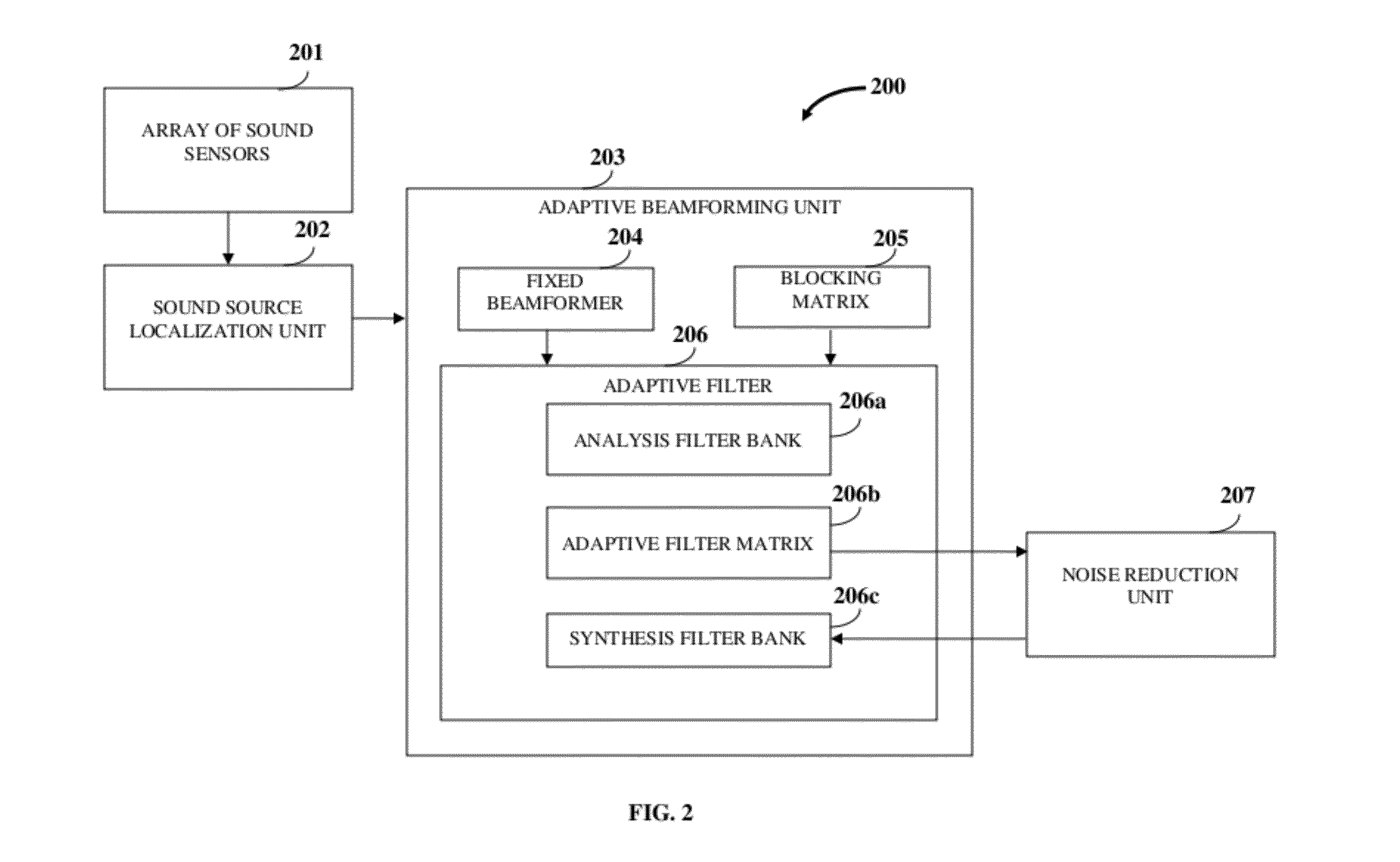
Microphone array system
ActiveUS8861756B2Partially suppresses ambient noise signalEnhanced signalEar treatmentGain controlSensor arraySound sources
Owner:VOCALIFE LLC +1
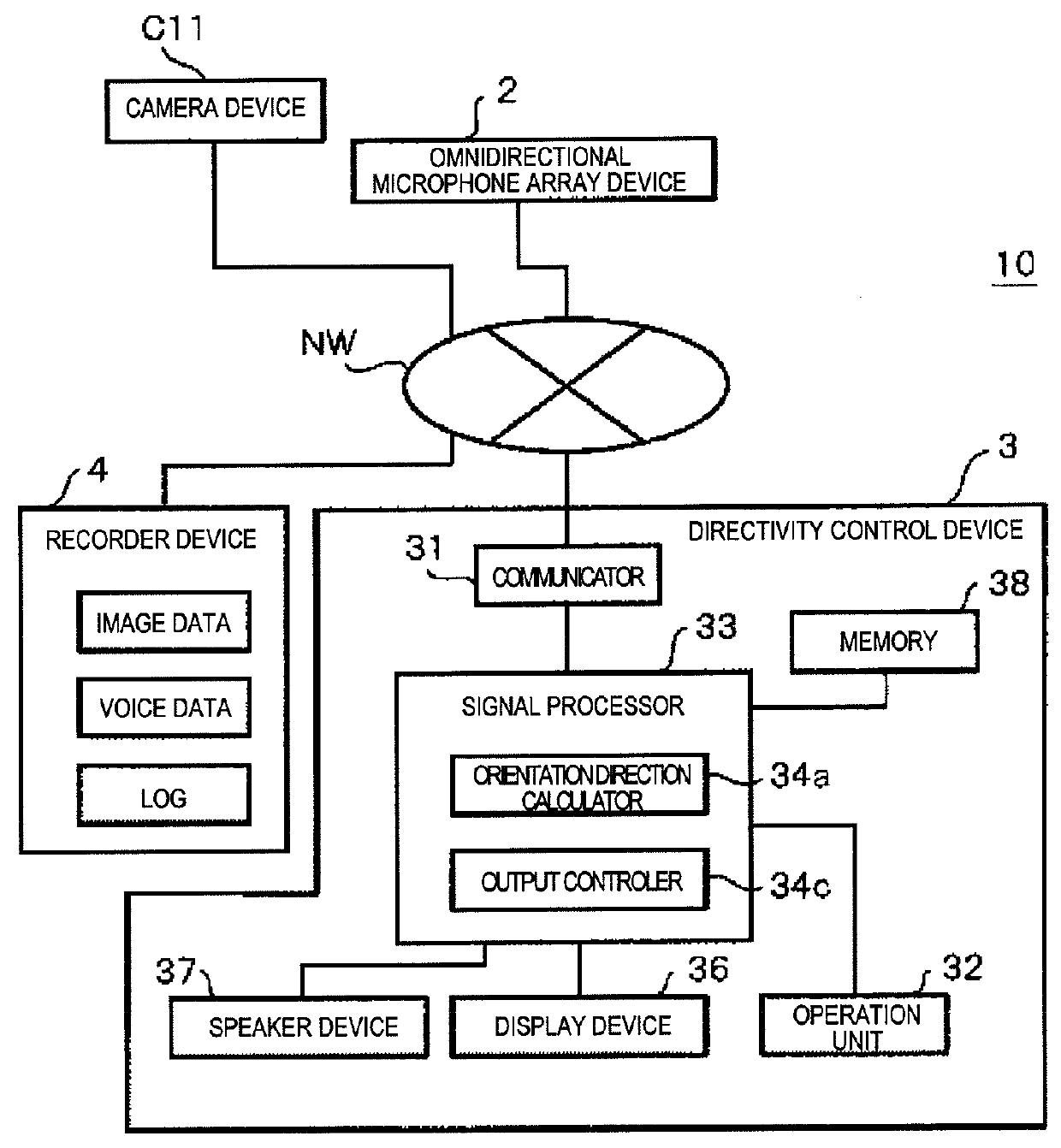
Failure detection system and failure detection method
A failure detection system includes an omnidirectional microphone array device having a plurality of microphone elements and a directivity control device that calculates a delay time of a voice propagated from a sound source to each microphone element and forms a directivity of the voice using the delay time and the voice collected by the omnidirectional microphone array device, and detects a failure of the microphone element. A smoothing unit calculates an average power of one microphone element. An average calculator calculates a total average power of a plurality of usable microphone elements included in the omnidirectional microphone array device. A comparison unit compares whether or not a difference between the average power and the total average power exceeds a range of ±6 dB, and determines whether the microphone element is in failure based on the comparison result.
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY MANAGEMENT CO LTD
Binaural signal processing using multiple acoustic sensors and digital filtering
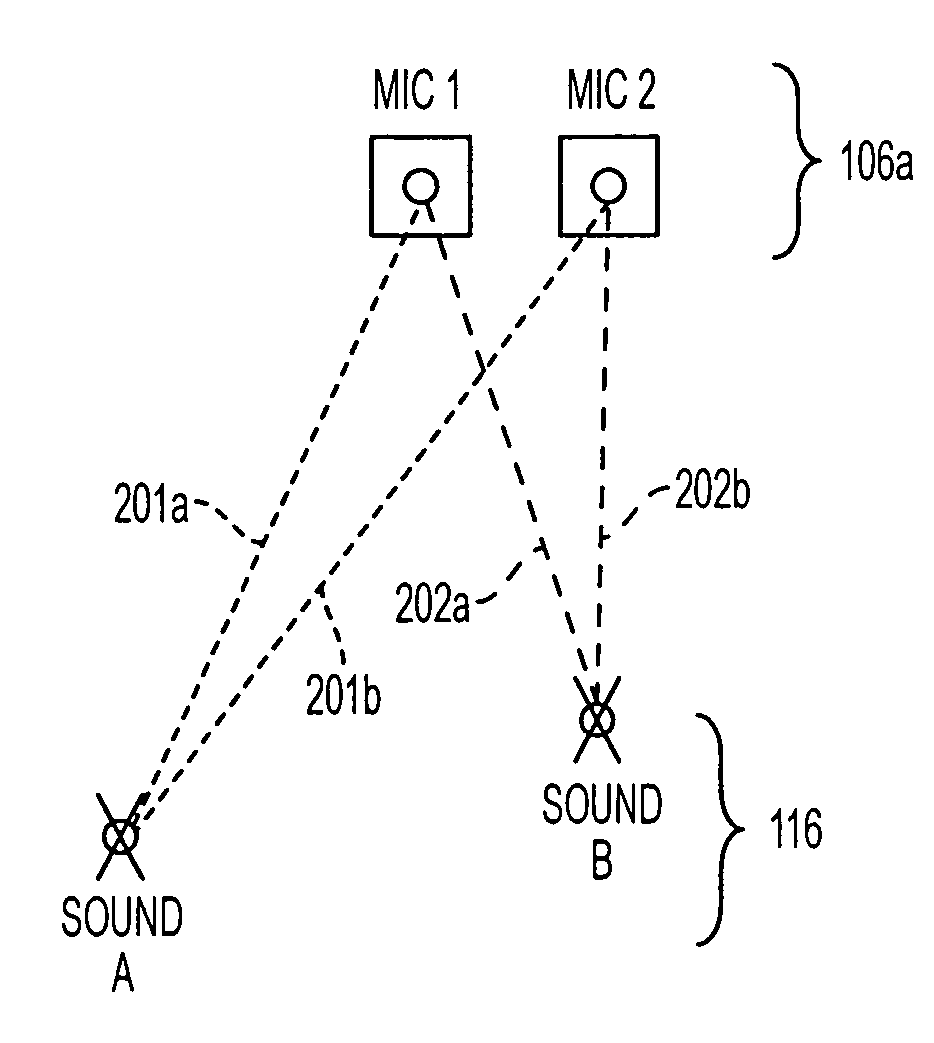
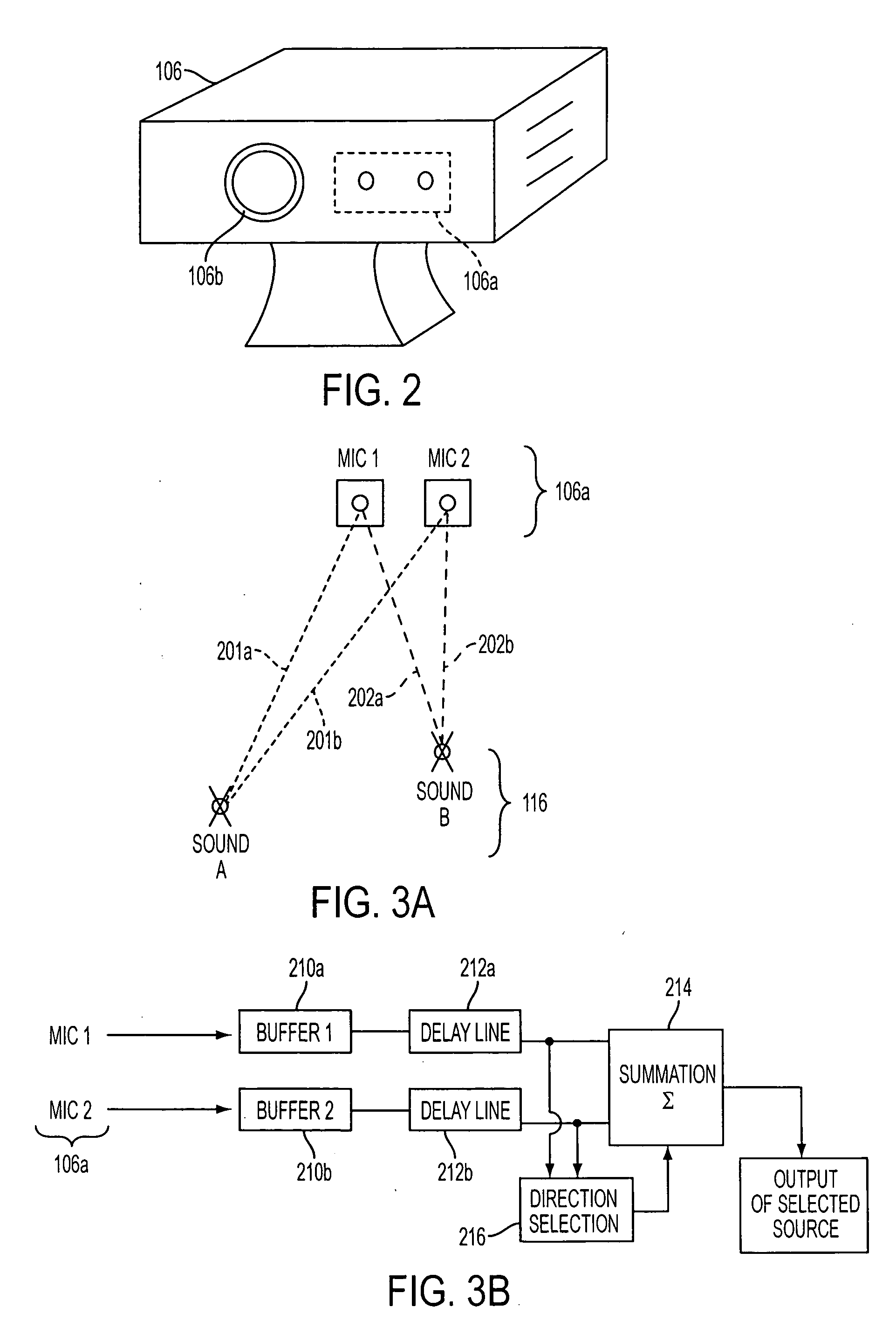
InactiveUS6978159B2Easy extractionExtensive computationTwo-way loud-speaking telephone systemsSubstation equipmentFrequency spectrumSound sources
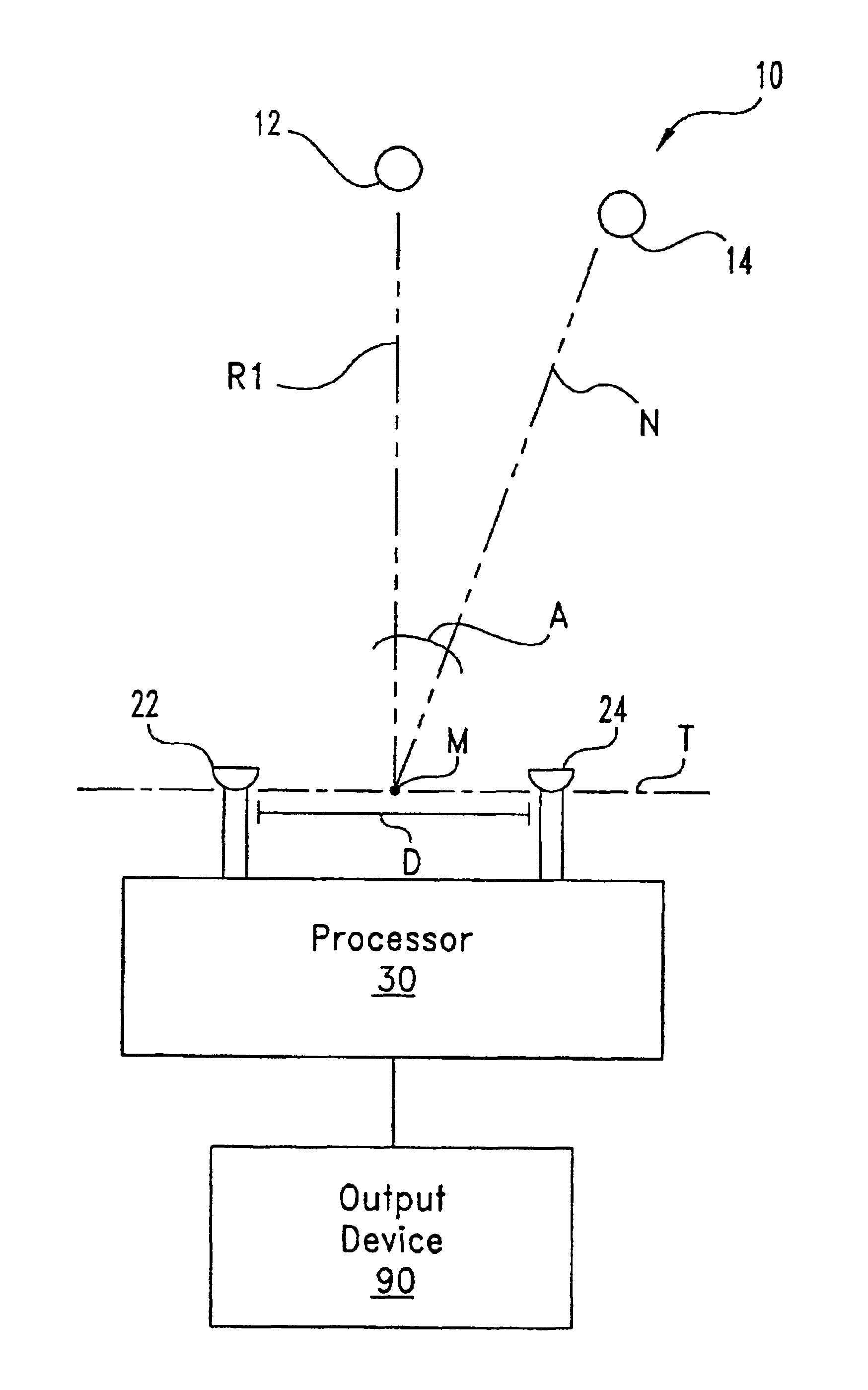
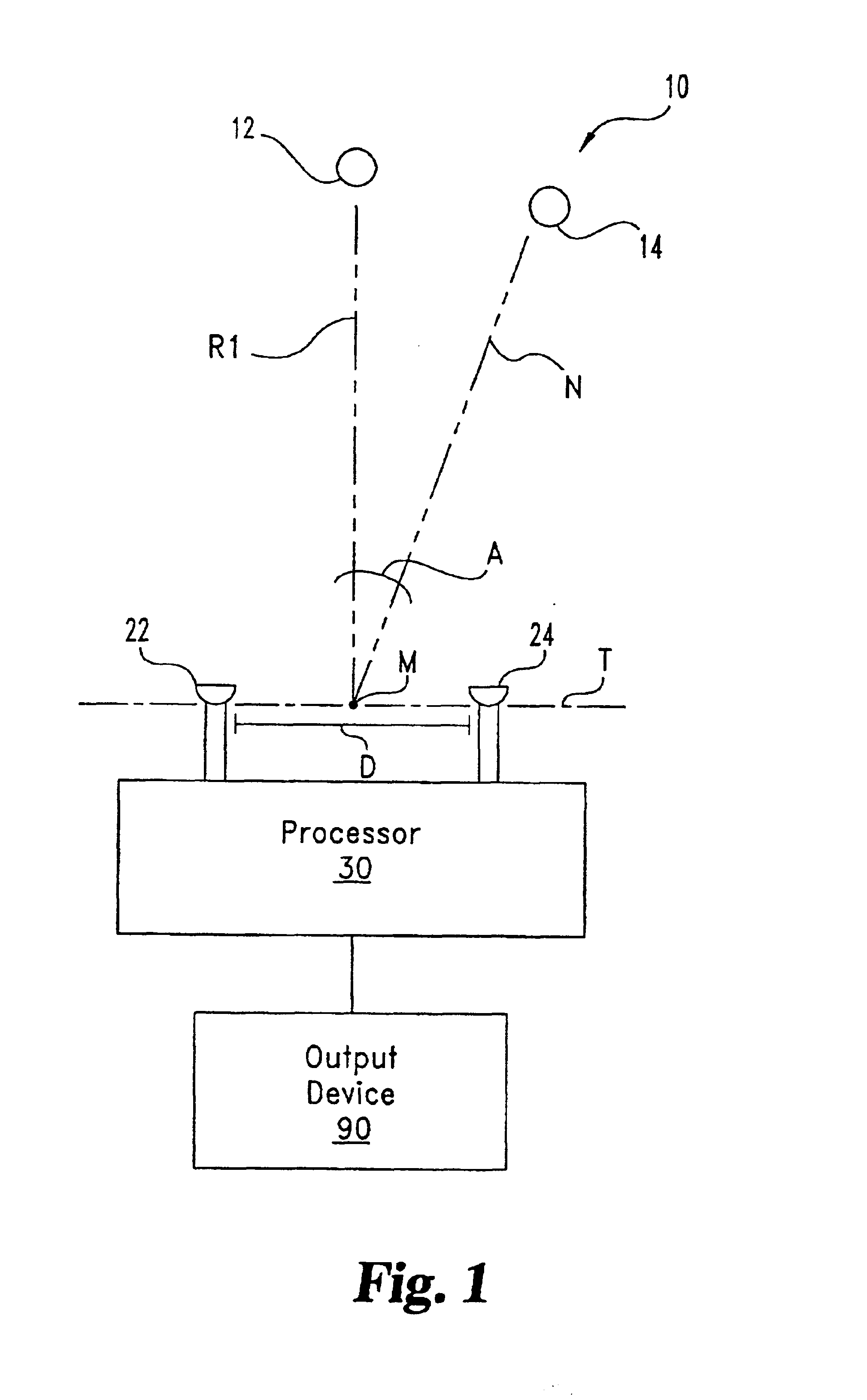
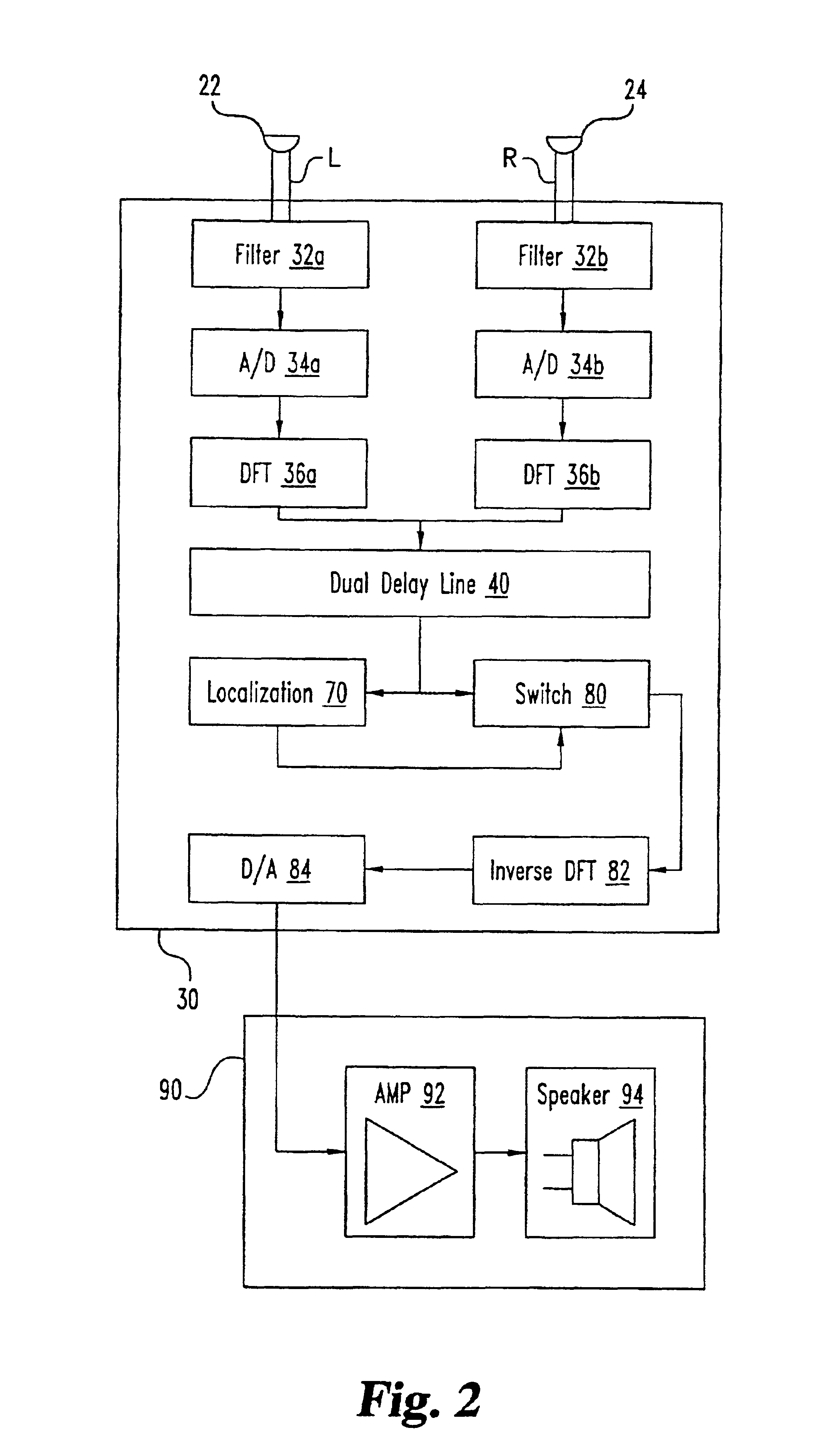
A desired acoustic signal is extracted from a noisy environment by generating a signal representative of the desired signal with processor (30). Processor (30) receives aural signals from two sensors (22, 24) each at a different location. The two inputs to processor (30) are converted from analog to digital format and then submitted to a discrete Fourier transform process to generate discrete spectral signal representations. The spectral signals are delayed to provide a number of intermediate signals, each corresponding to a different spatial location relative to the two sensors. Locations of the noise source and the desired source, and the spectral content of the desired signal are determined from the intermediate signal corresponding to the noise source locations. Inverse transformation of the selected intermediate signal followed by digital to analog conversion provides an output signal representative of the desired signal with output device (90). Techniques to localize multiple acoustic sources are also disclosed. Further, a technique to enhance noise reduction from multiple sources based on two-sensor reception is described.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
LED multiplex source and method of use of for sterilization, bioactivation and therapy
InactiveUS20050256554A1Promotes directional and focused electromagnetic radiationReduce usageElectrotherapyDiagnosticsMulti bandMagnetic source
This invention discloses an LED multiplex source and a method of using multi-band-type energies from the source for sterilization, bioactivation, and therapy of a targeted body. The LED multiplex source is a pulsed / modulated LED source with at least one different member of the group of pulsed / modulated radiation sources consisting of: an electromagnetic, acoustic, electroluminescent, thermal, and / or magnetic source. The invention also teaches how to convert heat generated by the LED multiplex source into electromagnetic radiation and uses this radiation for sterilization, bioactivation, and therapy. The LED multiplex source is an energy-efficient radiation source, is compact, and also provides sensory feedback to optimize, in real-time, sterilization, bioactivation, and therapy processes. The invented source will replace some of the existing radiation sources and, as well, will open new areas of applications.
Owner:UNITED LAB & MFG
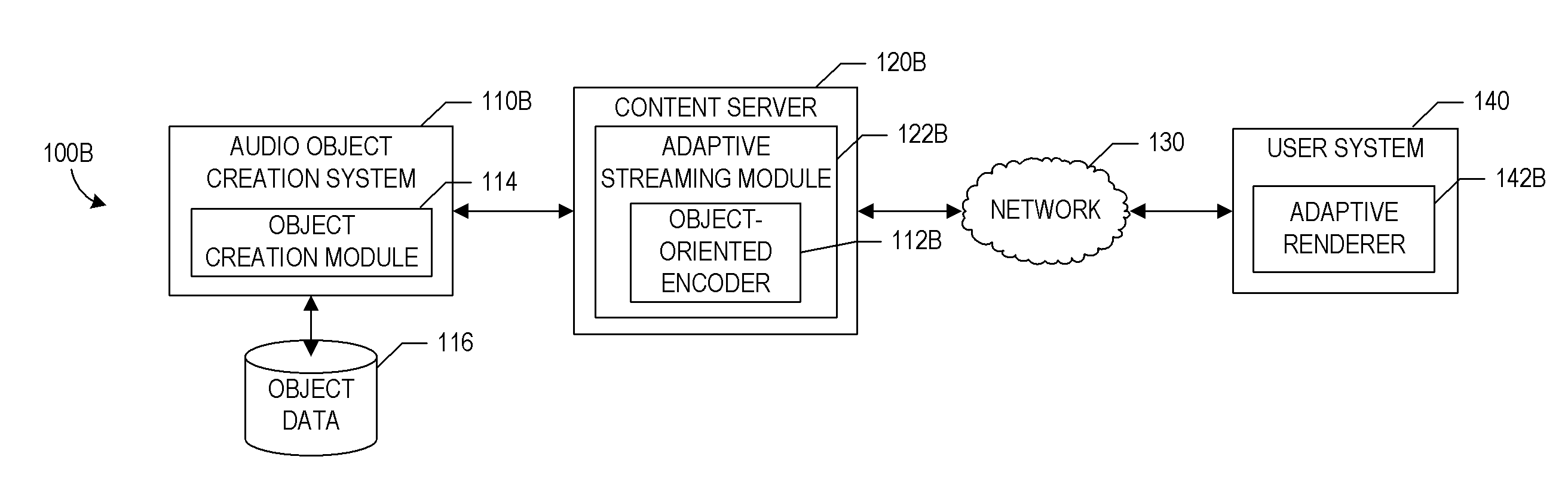
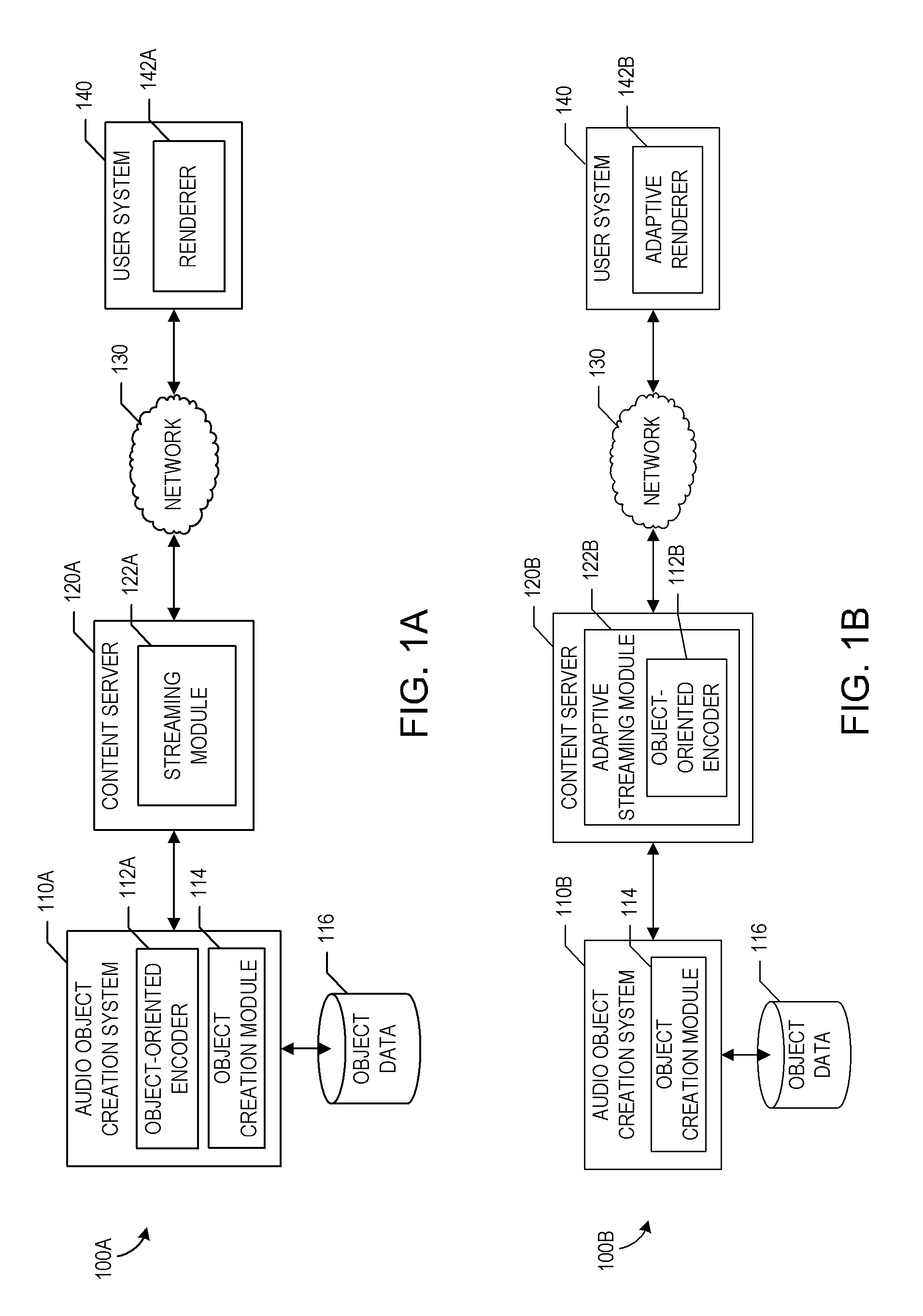
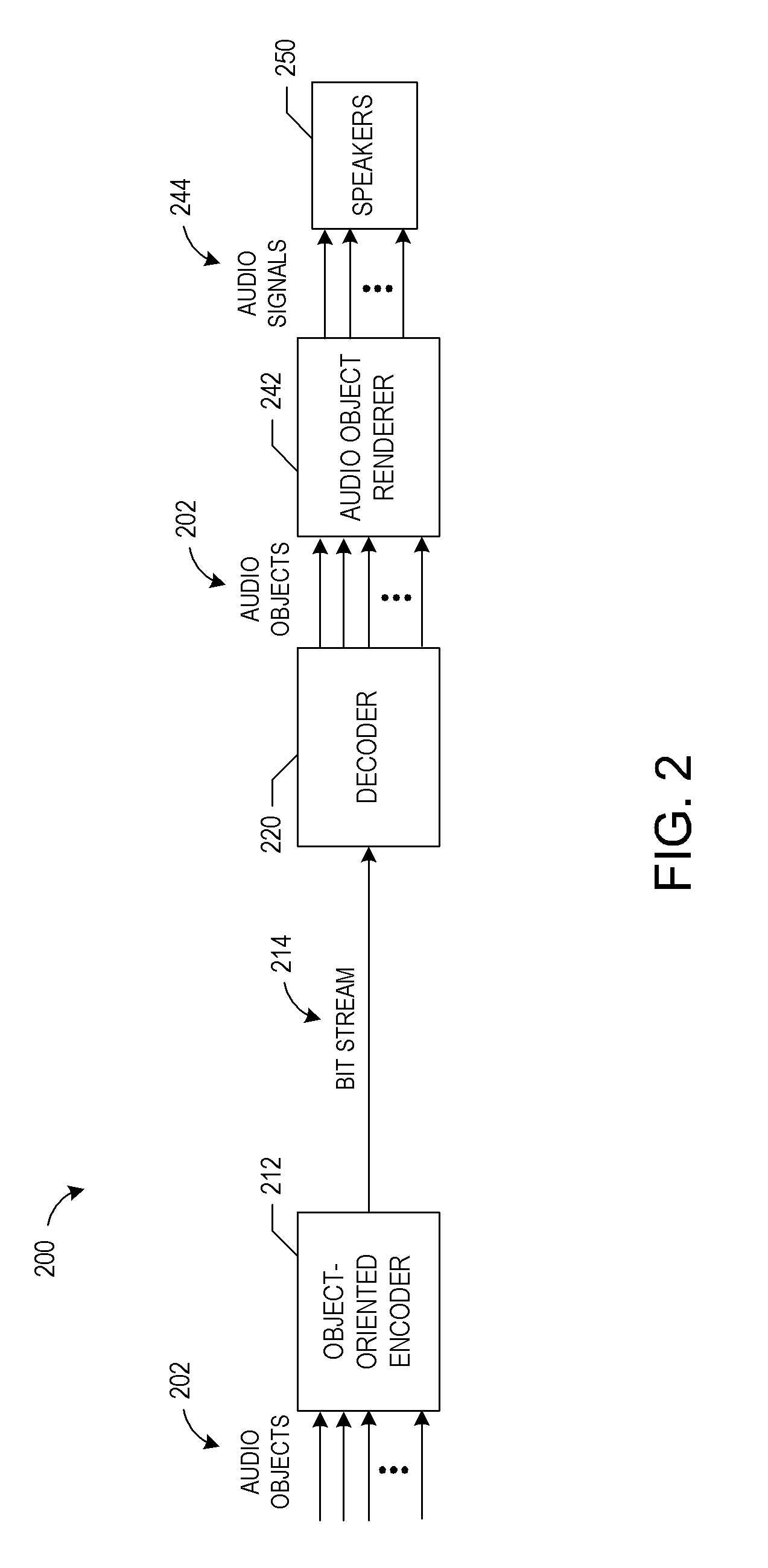
Object-oriented audio streaming system
Systems and methods for providing object-oriented audio are described. Audio objects can be created by associating sound sources with attributes of those sound sources, such as location, velocity, directivity, and the like. Audio objects can be used in place of or in addition to channels to distribute sound, for example, by streaming the audio objects over a network to a client device. The objects can define their locations in space with associated two or three dimensional coordinates. The objects can be adaptively streamed to the client device based on available network or client device resources. A renderer on the client device can use the attributes of the objects to determine how to render the objects. The renderer can further adapt the playback of the objects based on information about a rendering environment of the client device. Various examples of audio object creation techniques are also described.
Owner:DTS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com