Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
634 results about "Magnetic source" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Tool for accurate quantification in molecular MRI
ActiveUS20110044524A1Minimize cost functionAccurate imagingCharacter and pattern recognitionMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsMagnetic sourceMagnetic susceptibility
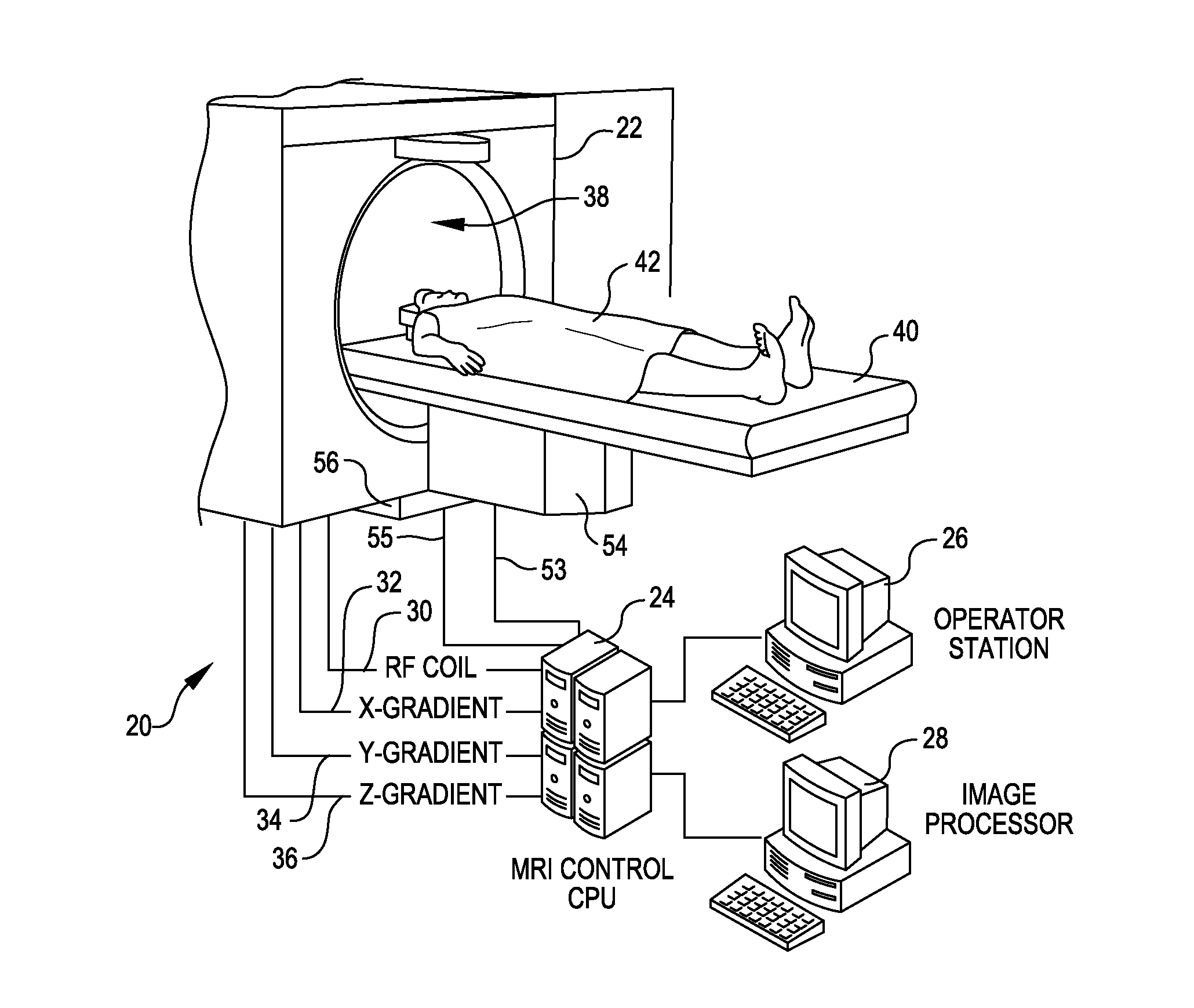
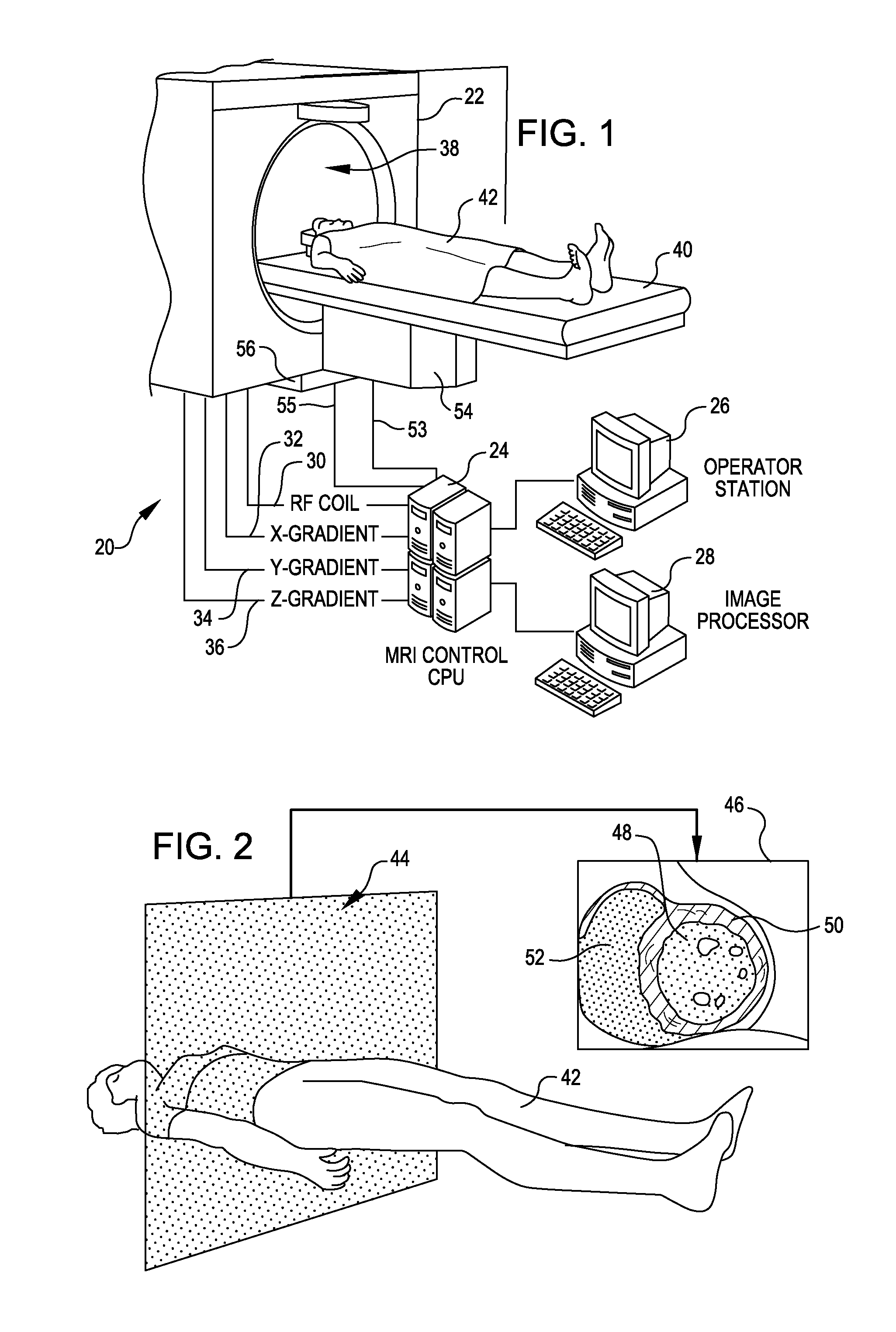
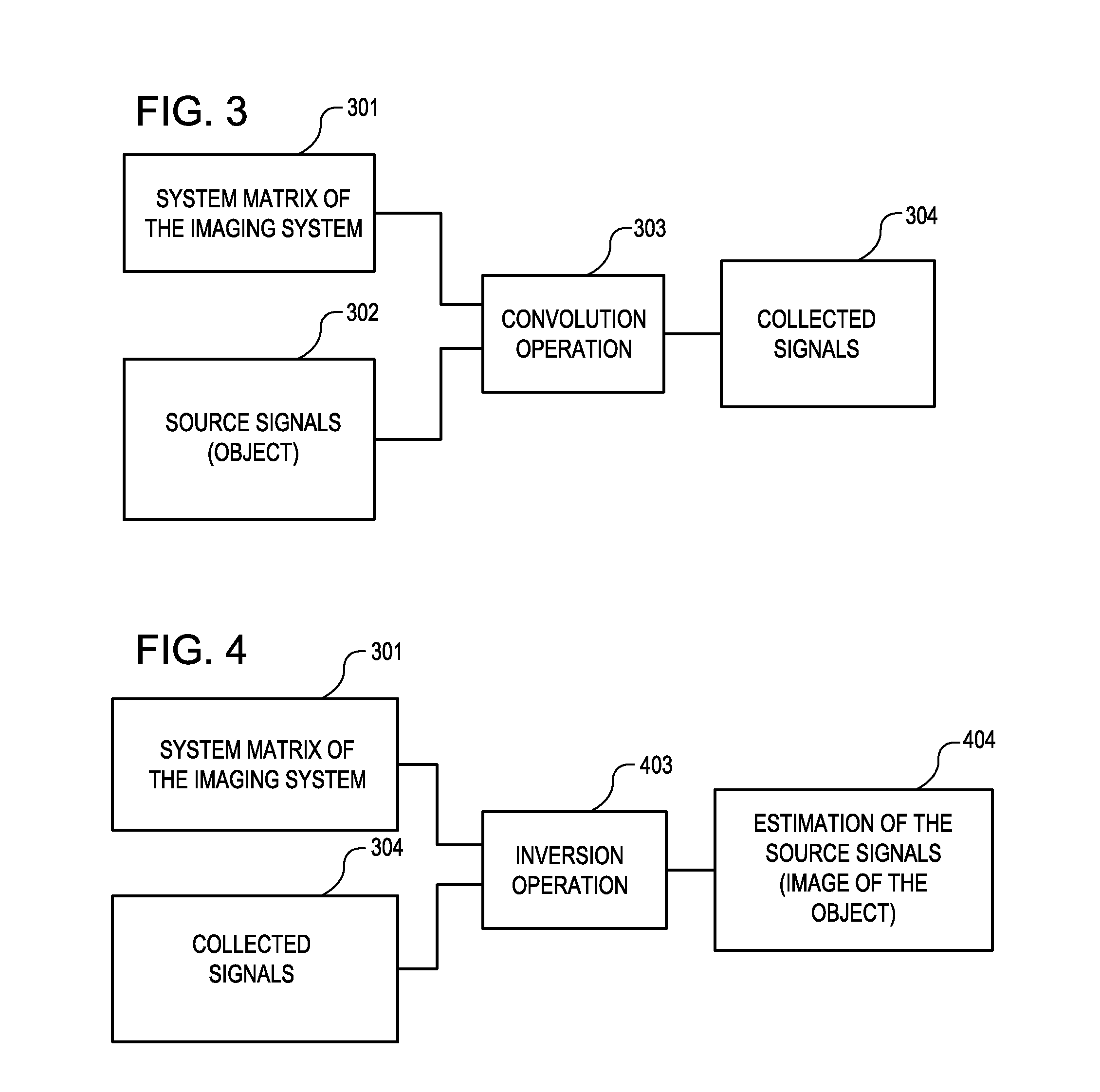
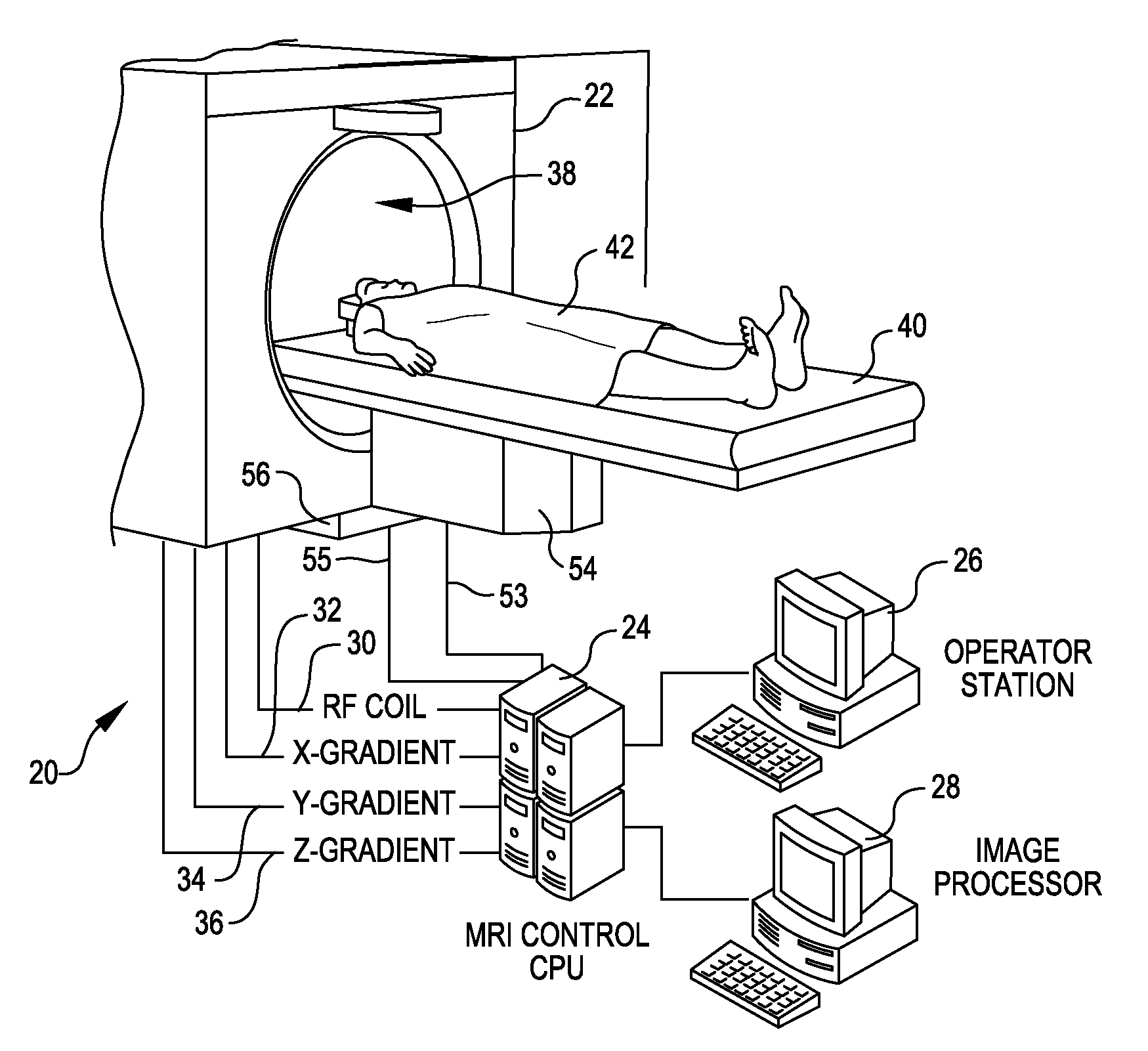
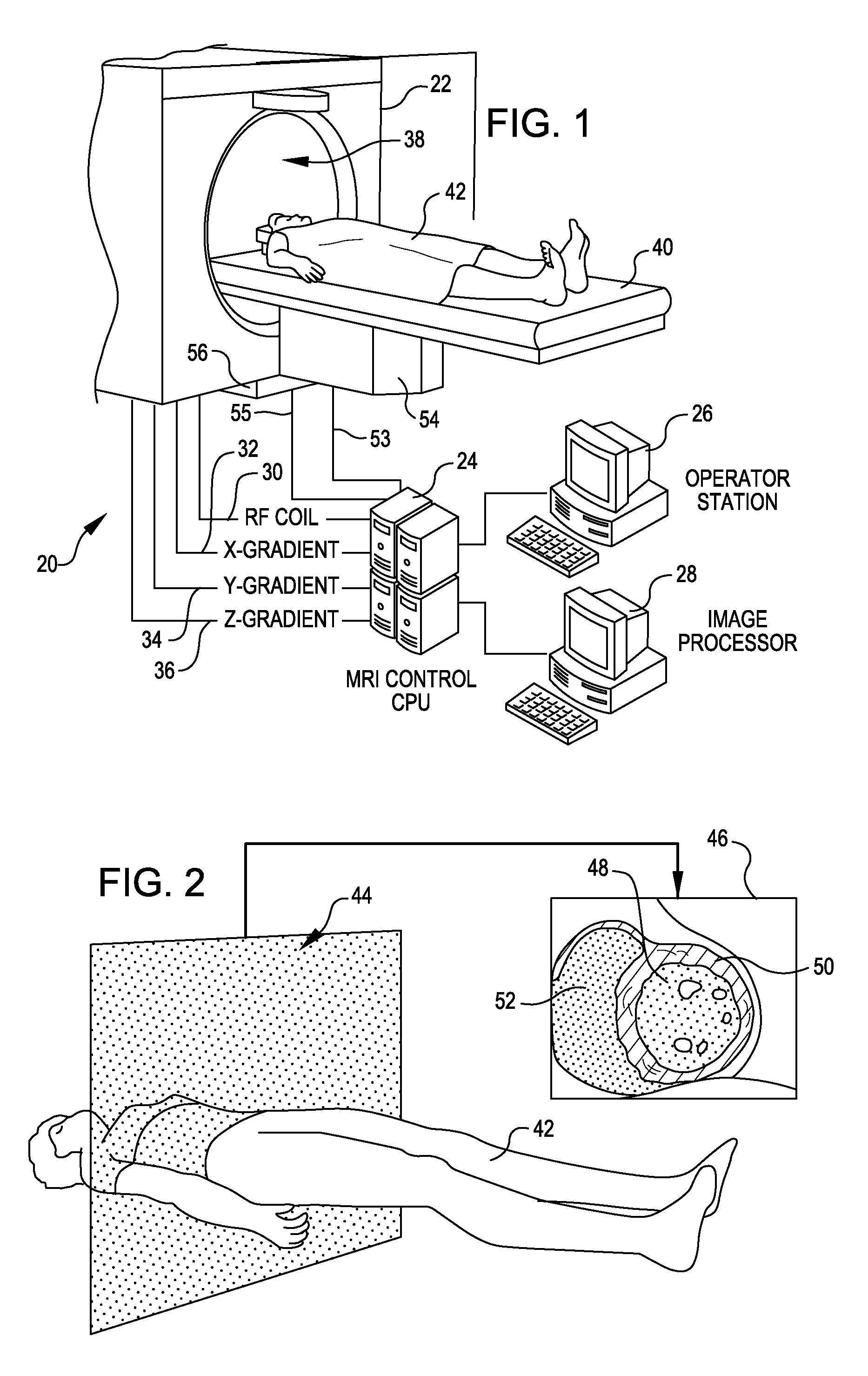
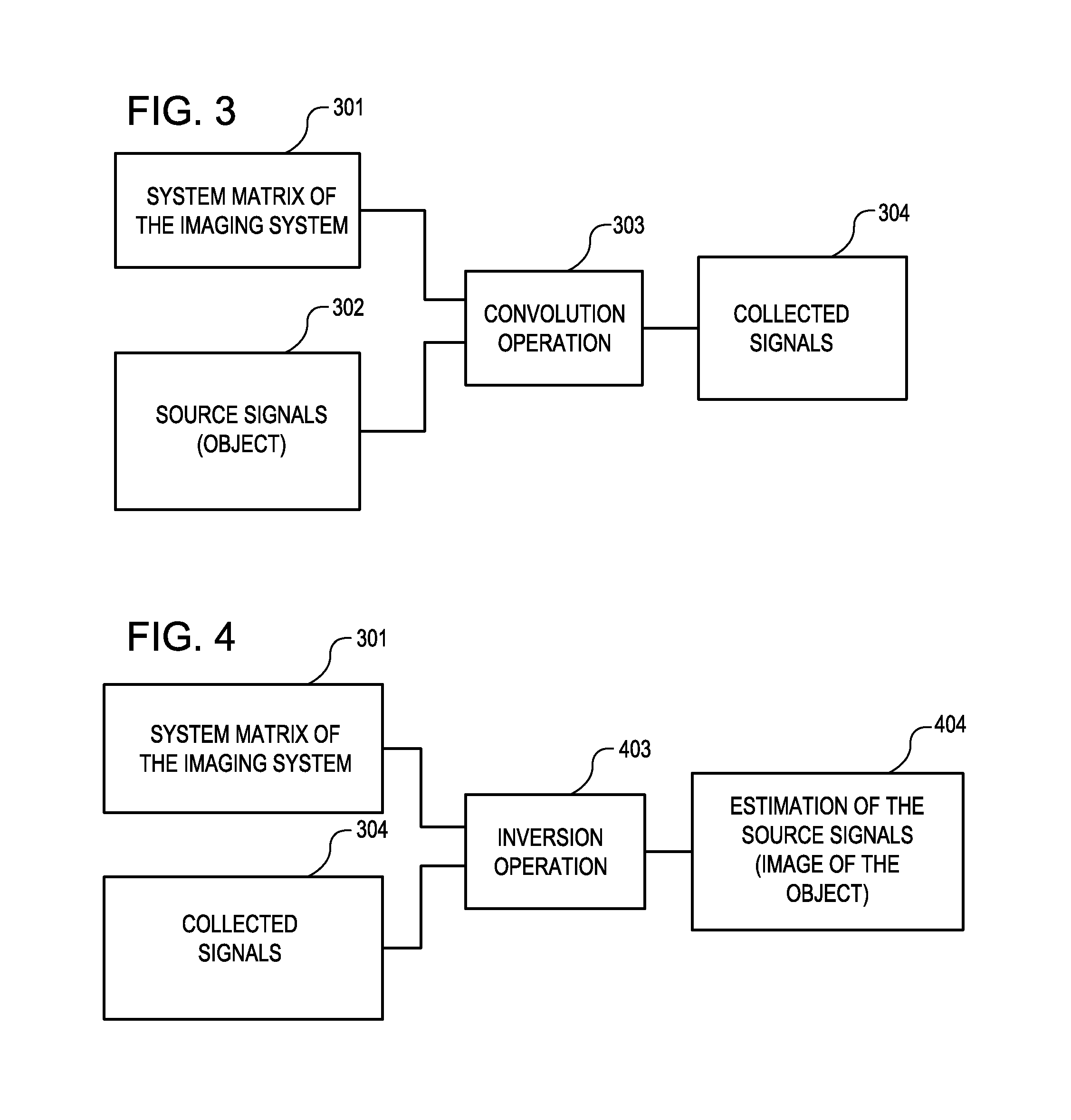
A method and apparatus is provided for magnetic source magnetic resonance imaging. The method includes collecting energy signals from an object, providing additional information of characteristics of the object, and generating the image of the object from the energy signals and from the additional information such that the image includes a representation of a quantitative estimation of the characteristics, e.g a quantitative estimation of magnetic susceptibility. The additional information may comprise predetermined characteristics of the object, a magnitude image generated from the object, or magnetic signals collected from different relative orientations between the object and the imaging system. The image is generated by an inversion operation based on the collected signals and the additional information. The inversion operation minimizes a cost function obtained by combining the data extracted from the collected signals and the additional information of the object. Additionally, the image is used to detect a number of diagnostic features including microbleeds, contract agents and the like.
Owner:CORNELL UNIVERSITY
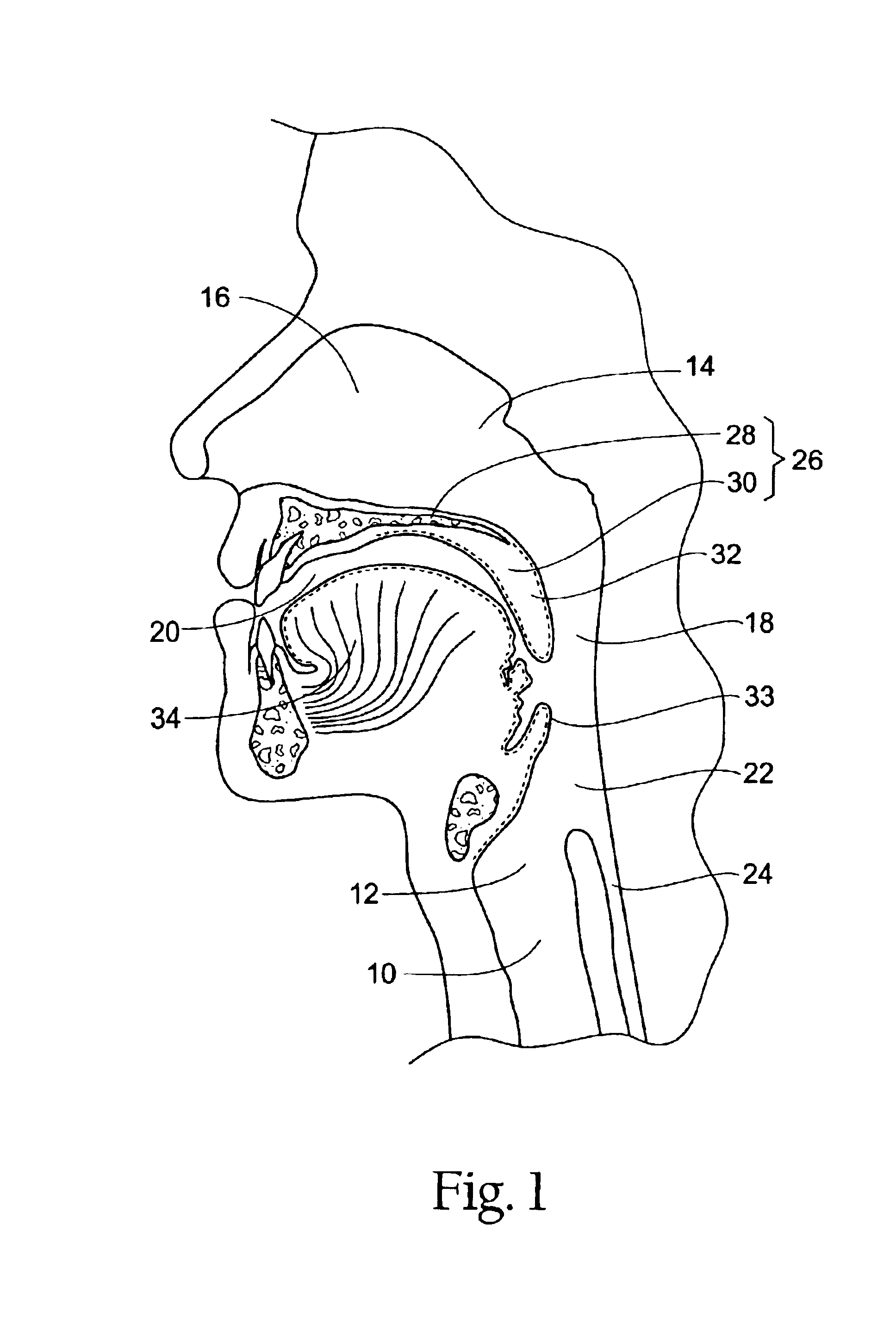
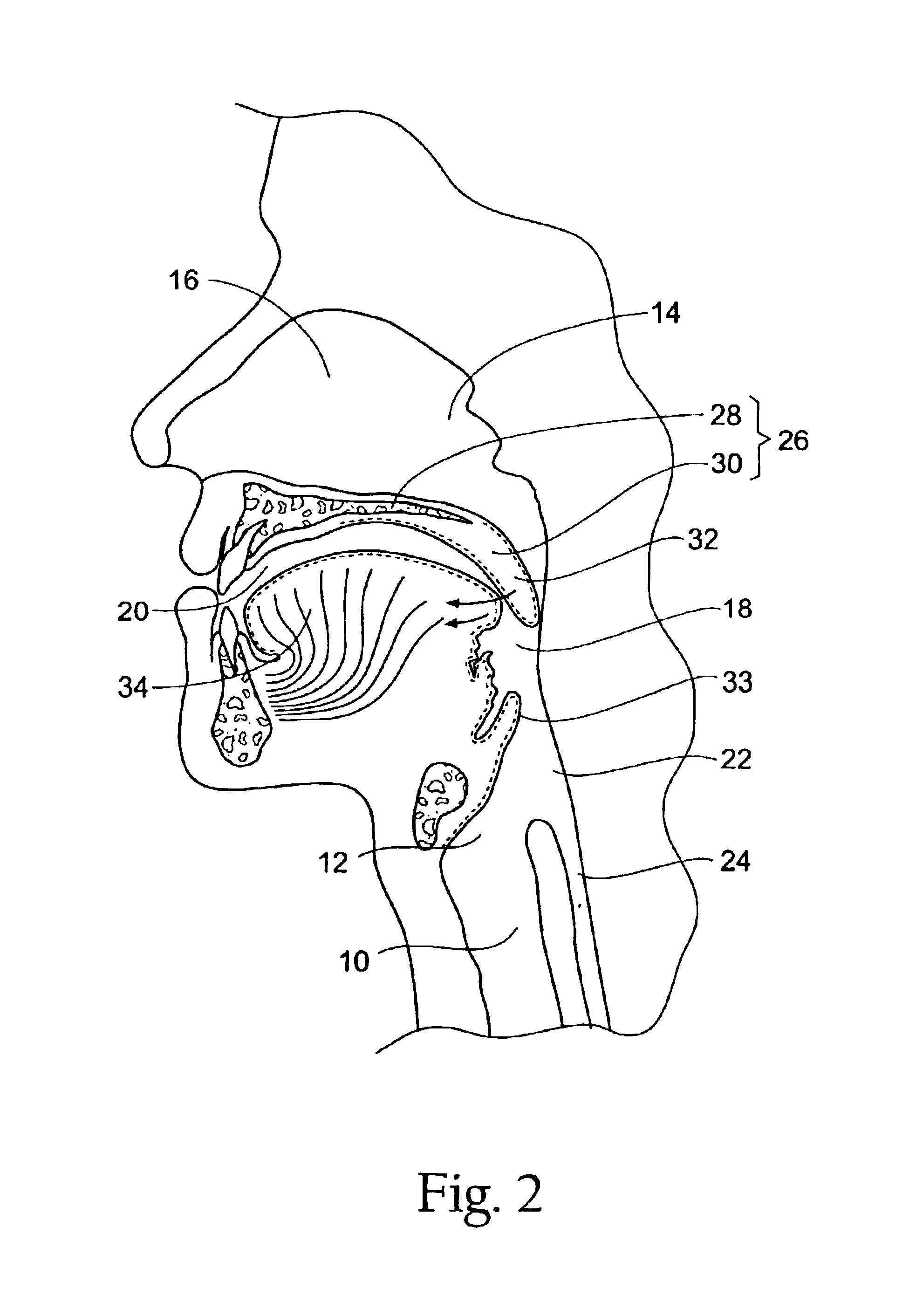
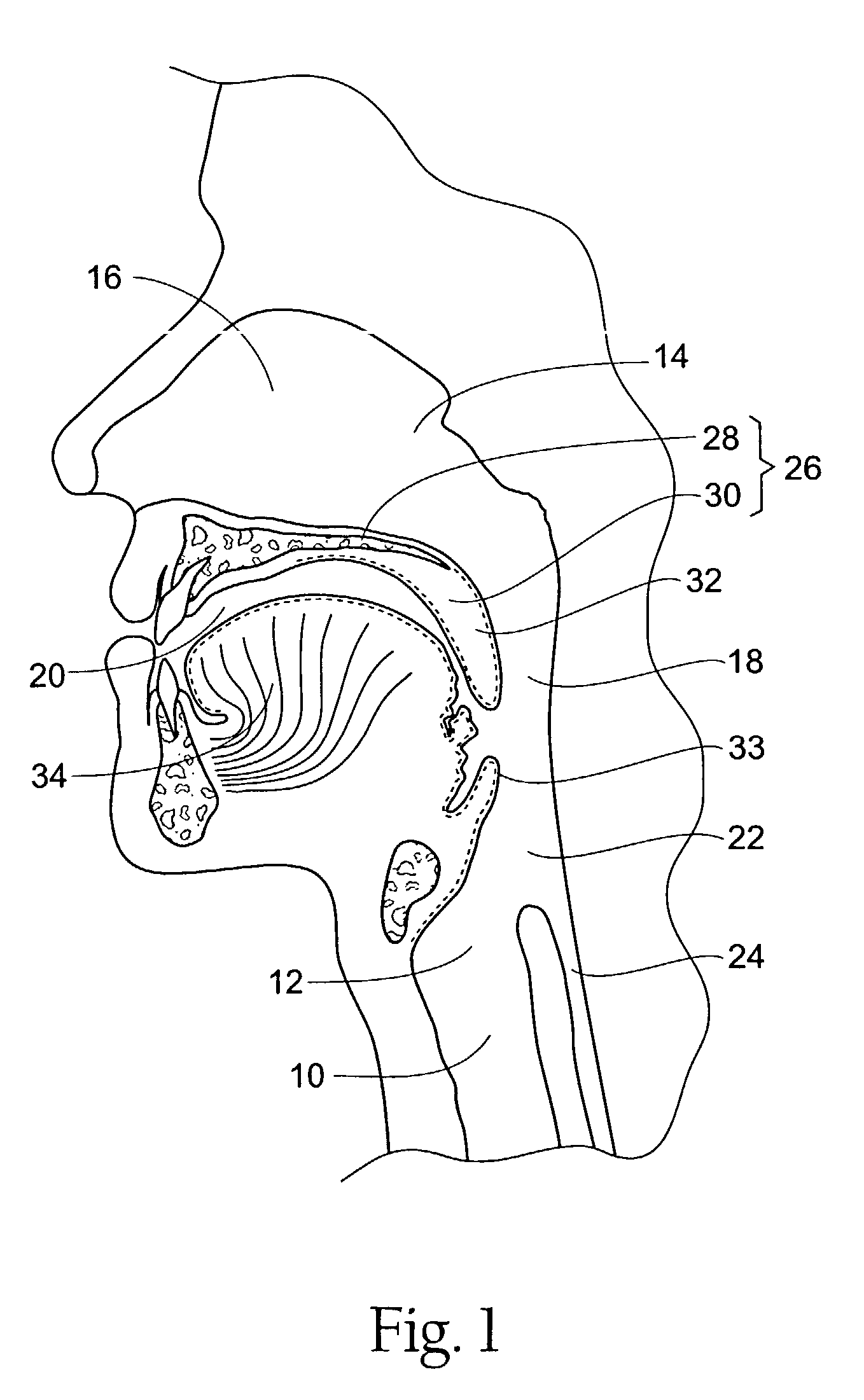
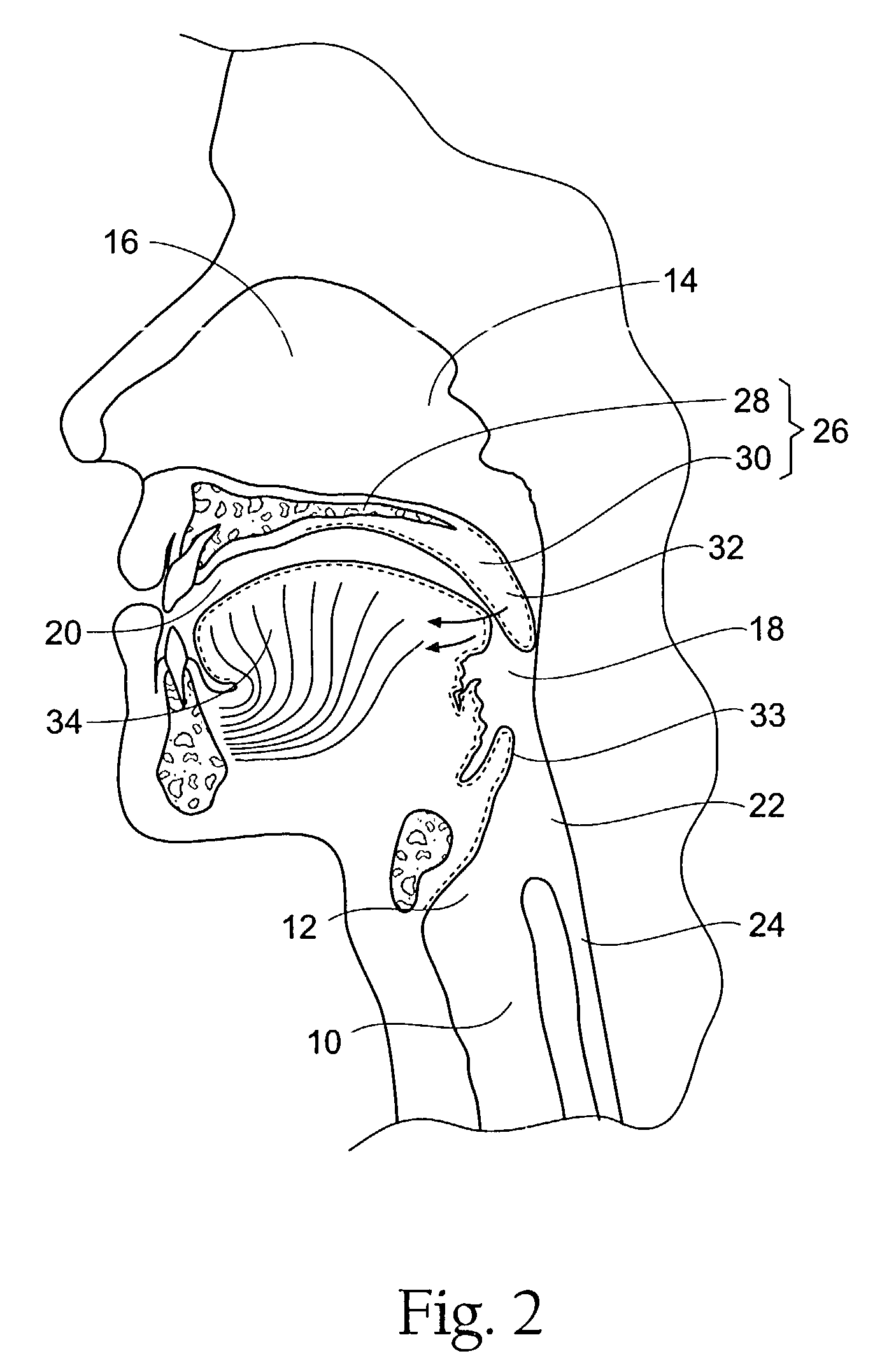
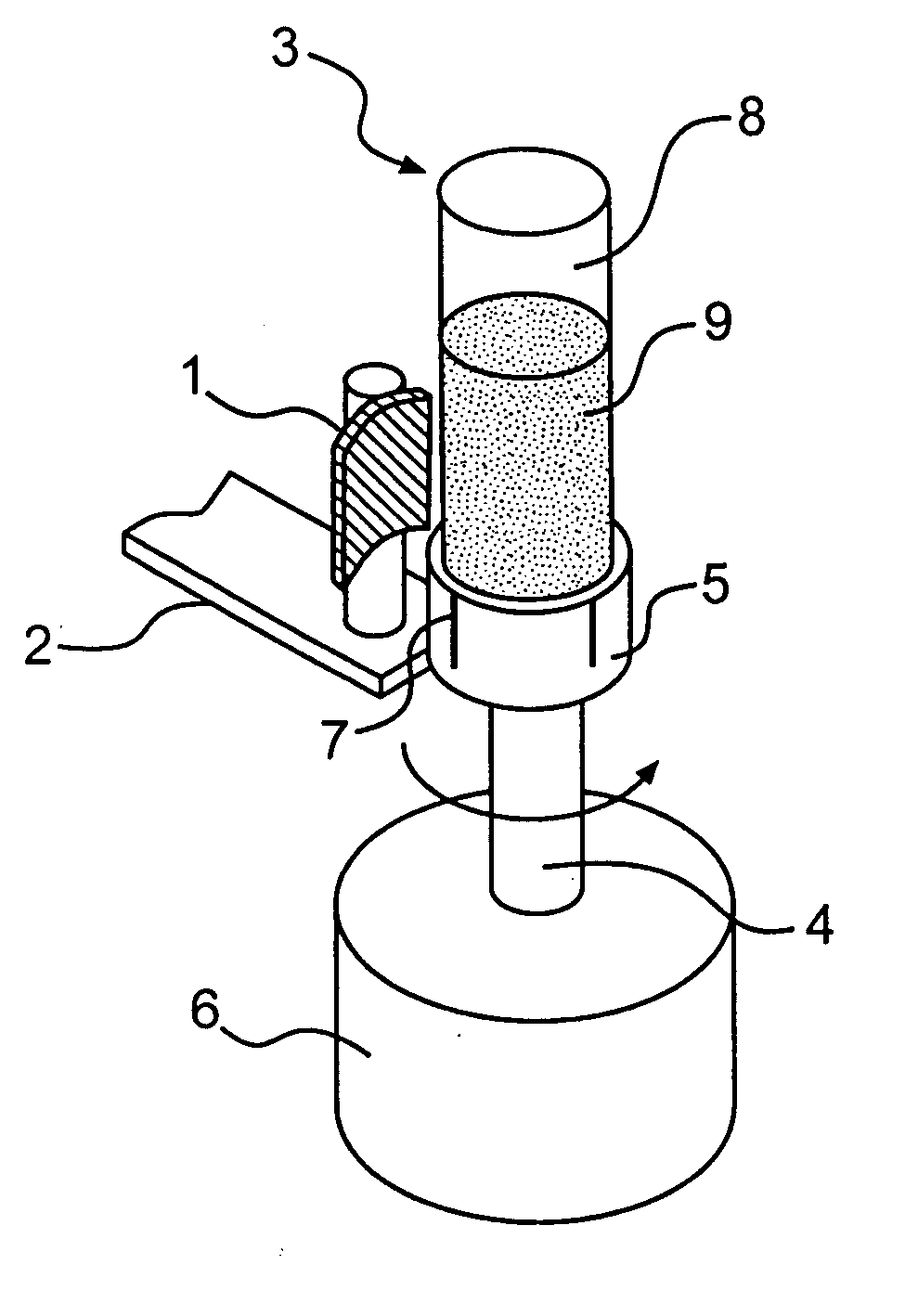
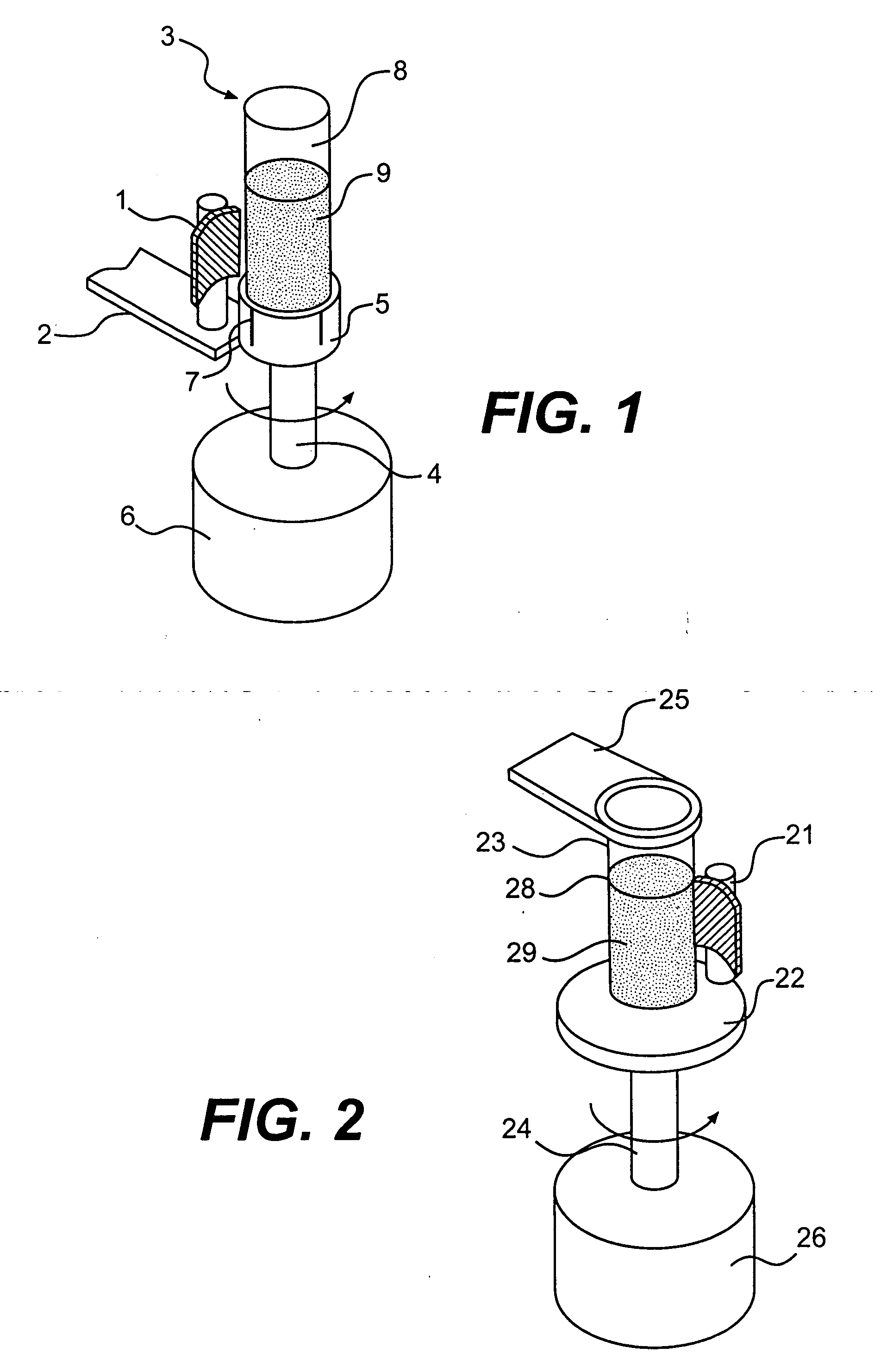
Systems and methods for moving and/or restraining the tongue in the oral cavity
InactiveUS6955172B2Simple and cost-effective deviceElectrotherapyTeeth fillingMagnetic sourceMobile tongue
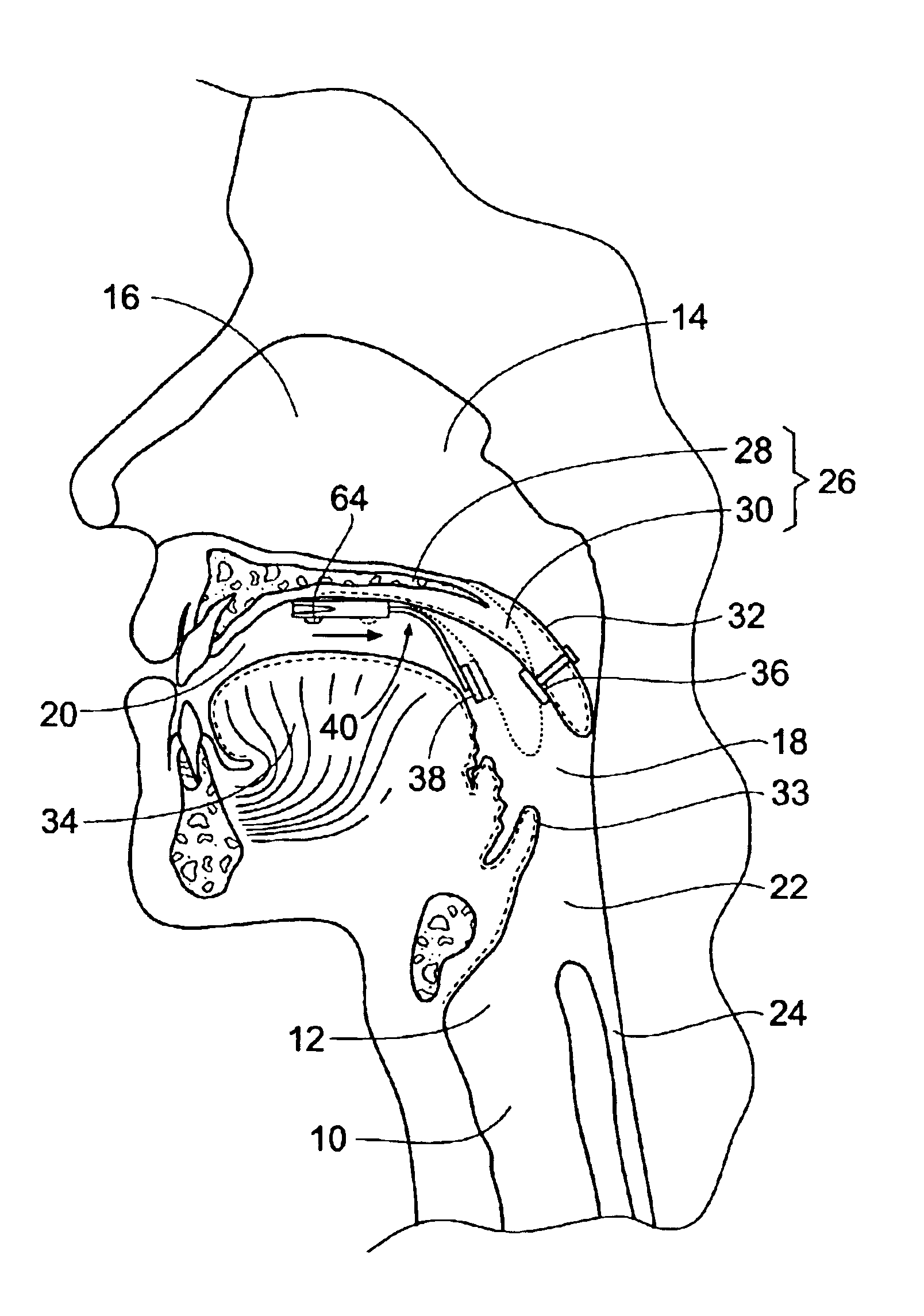
Systems and related methods treat snoring and other sleep related disorders by stabilizing the position of a tongue in an oral cavity. The systems and methods employ an operative element sized and configured to be fitted to less mobile tissue in the oral cavity. The operative element is further constructed and arranged to interact with a tongue in the airway to stabilize a preferred tissue orientation. The operative element can comprise a suction source sized and configured to draw more mobile tongue tissue toward the suction source. The operative element can comprise a magnetic source sized and configured to magnetically attract material fitted to more mobile tongue tissue in the airway.
Owner:SWAN MEDICAL +1
Magnetically enhanced convection heat sink
InactiveUS7031160B2Increased convection coolingHigh trafficElectromagnets without armaturesSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsMagnetic sourceConvection heat
A magnetically enhanced convection heat sink comprises a heat sink member for dissipating heat from a heat source. A magnetic source creates a magnetic field concentrated at a first location, the intensity of the magnetic field decreasing from the first location to a second location. The heat sink member is positioned within the magnetic field and in a gas flow path between the first and second locations. Gas, having paramagnetic properties, entering the heat sink at the first location is heated by the heat sink member, and as the gas becomes warmer is displaced by cooler gas causing the warmer gas to move toward the second location as it is further heated by the heat sink.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
LED multiplex source and method of use of for sterilization, bioactivation and therapy
InactiveUS20050256554A1Promotes directional and focused electromagnetic radiationReduce usageElectrotherapyDiagnosticsMulti bandMagnetic source
This invention discloses an LED multiplex source and a method of using multi-band-type energies from the source for sterilization, bioactivation, and therapy of a targeted body. The LED multiplex source is a pulsed / modulated LED source with at least one different member of the group of pulsed / modulated radiation sources consisting of: an electromagnetic, acoustic, electroluminescent, thermal, and / or magnetic source. The invention also teaches how to convert heat generated by the LED multiplex source into electromagnetic radiation and uses this radiation for sterilization, bioactivation, and therapy. The LED multiplex source is an energy-efficient radiation source, is compact, and also provides sensory feedback to optimize, in real-time, sterilization, bioactivation, and therapy processes. The invented source will replace some of the existing radiation sources and, as well, will open new areas of applications.
Owner:UNITED LAB & MFG
Tool for accurate quantification in molecular MRI
ActiveUS8781197B2Minimize cost functionAccurate imagingCharacter and pattern recognitionMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsMagnetic sourceMagnetic susceptibility
A method and apparatus is provided for magnetic source magnetic resonance imaging. The method includes collecting energy signals from an object, providing additional information of characteristics of the object, and generating the image of the object from the energy signals and from the additional information such that the image includes a representation of a quantitative estimation of the characteristics, e.g a quantitative estimation of magnetic susceptibility. The additional information may comprise predetermined characteristics of the object, a magnitude image generated from the object, or magnetic signals collected from different relative orientations between the object and the imaging system. The image is generated by an inversion operation based on the collected signals and the additional information. The inversion operation minimizes a cost function obtained by combining the data extracted from the collected signals and the additional information of the object. Additionally, the image is used to detect a number of diagnostic features including microbleeds, contract agents and the like.
Owner:CORNELL UNIVERSITY
GMR sensor with flux concentrators
ActiveUS20050280411A1Improve dynamic rangeMinimize impactMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsSolid-state devicesMagnetic sourceProximity sensor
A proximity sensor that is capable of producing a relatively larger output signal than past proximity sensors, and in some cases, an output signal that is relatively independent of the speed at which a target passes the sensor. In one illustrative embodiment, the proximity sensor includes a first magnetoresistive resistor and a second magnetoresistive resistor connected in a bridge configuration. The first magnetoresistive resistor is spaced from the second magnetoresistive resistor along the path of a moving ferrous target. A bias magnet source is positioned behind the proximity sensor, and the ferrous target passes in front of the proximity sensor. The ferrous target alters the direction of the bias magnetic field in the vicinity of the first and second magnetoresistive resistors as the ferrous target passes by the proximity sensor. Flux concentrators are positioned proximate to each of the first and second magnetoresistive resistors. The flux concentrators may help redirect or shunt the magnetic field component produced by the bias magnet source that is perpendicular to the direction of motion of the target through the first and second magnetoresistive resistors in a direction that is parallel to the direction of motion of the target.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Tool for accurate quantification in molecular mri
ActiveCN102077108AImprove sparsityMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsMagnetic variable regulationMagnetic sourceComputer science
A method and an apparatus are provided for magnetic source magnetic resonance imaging. The method includes collecting energy signals from an object, providing additional information of characteristics of the object, and generating the image of the object from the energy signals and from the additional information such that the image includes a representation of a quantitative estimation of the characteristics. The additional information may comprise predetermined characteristics of the object, a magnitude image generated from the object, or magnetic signals collected from different relative orientations between the object and the imaging system. The image is generated by an inversion operation based on the collected signals and the additional information. The inversion operation minimizes a cost function obtained by combining the data extracted from the collected signals and the additional information of the object. Additionally, the image is used to detect a number of diagnostic features including microbleeds, contract agents and the like.
Owner:CORNELL UNIVERSITY
Subsurface conductivity imaging systems and methods
InactiveUS7023213B2Detection using electromagnetic wavesAcoustic wave reradiationMagnetic sourceElectricity
A subsurface imaging cable includes a plurality of sensor modules, wherein the plurality of the sensor modules are flexible and each of the plurality of the sensor modules is spaced apart on the subsurface imaging cable at a selected distance; and a flexible medium connecting the plurality of the sensor modules, wherein the subsurface imaging cable is flexible and adapted to be wound on a reel. A method for subsurface images includes acquiring direct-current measurements at a plurality of sites in a survey area; acquiring a first set of electric and magnetic measurements from natural electromagnetic fields at the plurality of sites; acquiring a second set of electric and magnetic measurements using controlled electric and magnetic sources at the plurality of sites; and determining a subsurface conductivity distribution from the direct-current measurements and the first set and the second set of electric and magnetic measurements.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
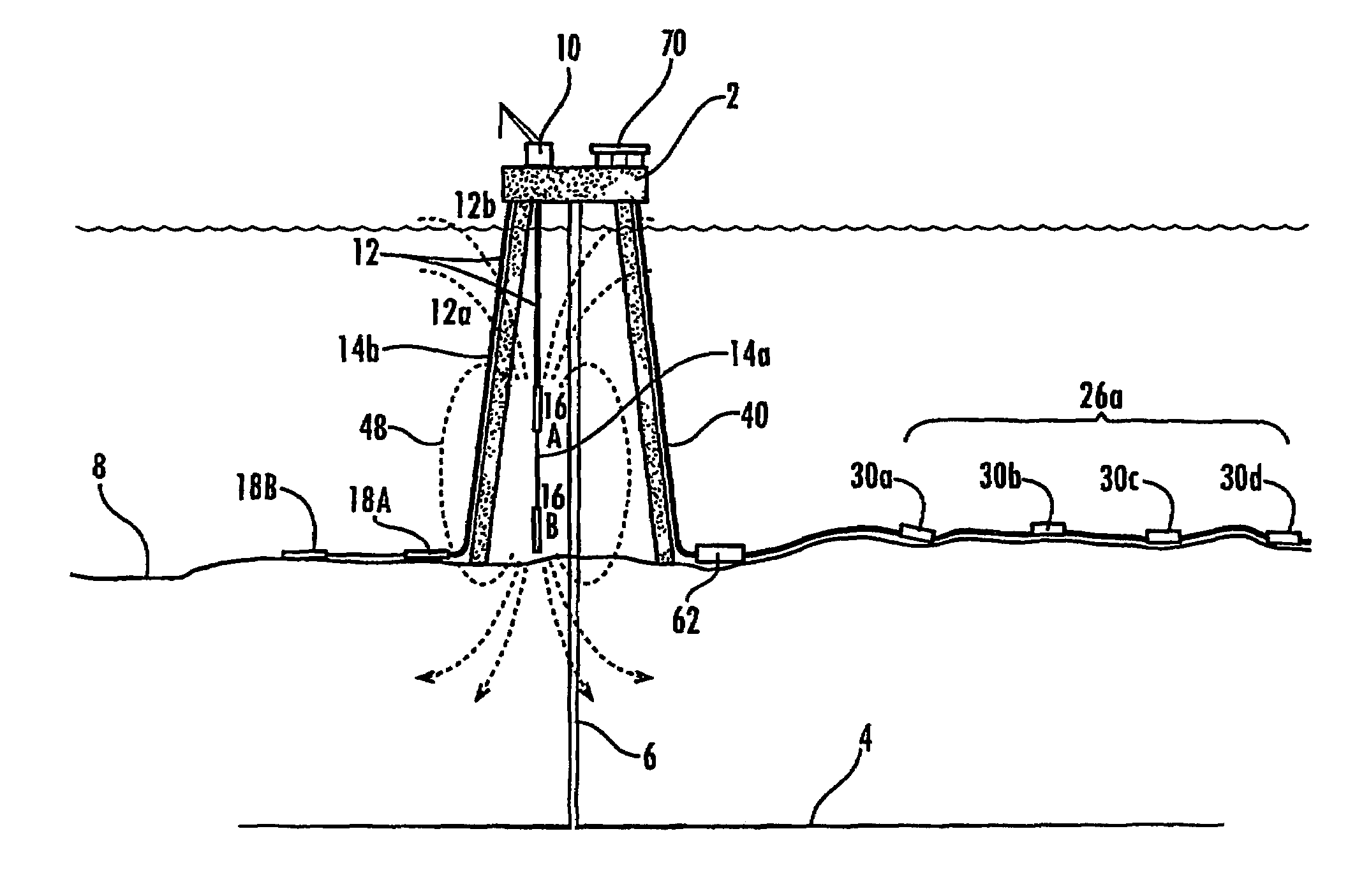
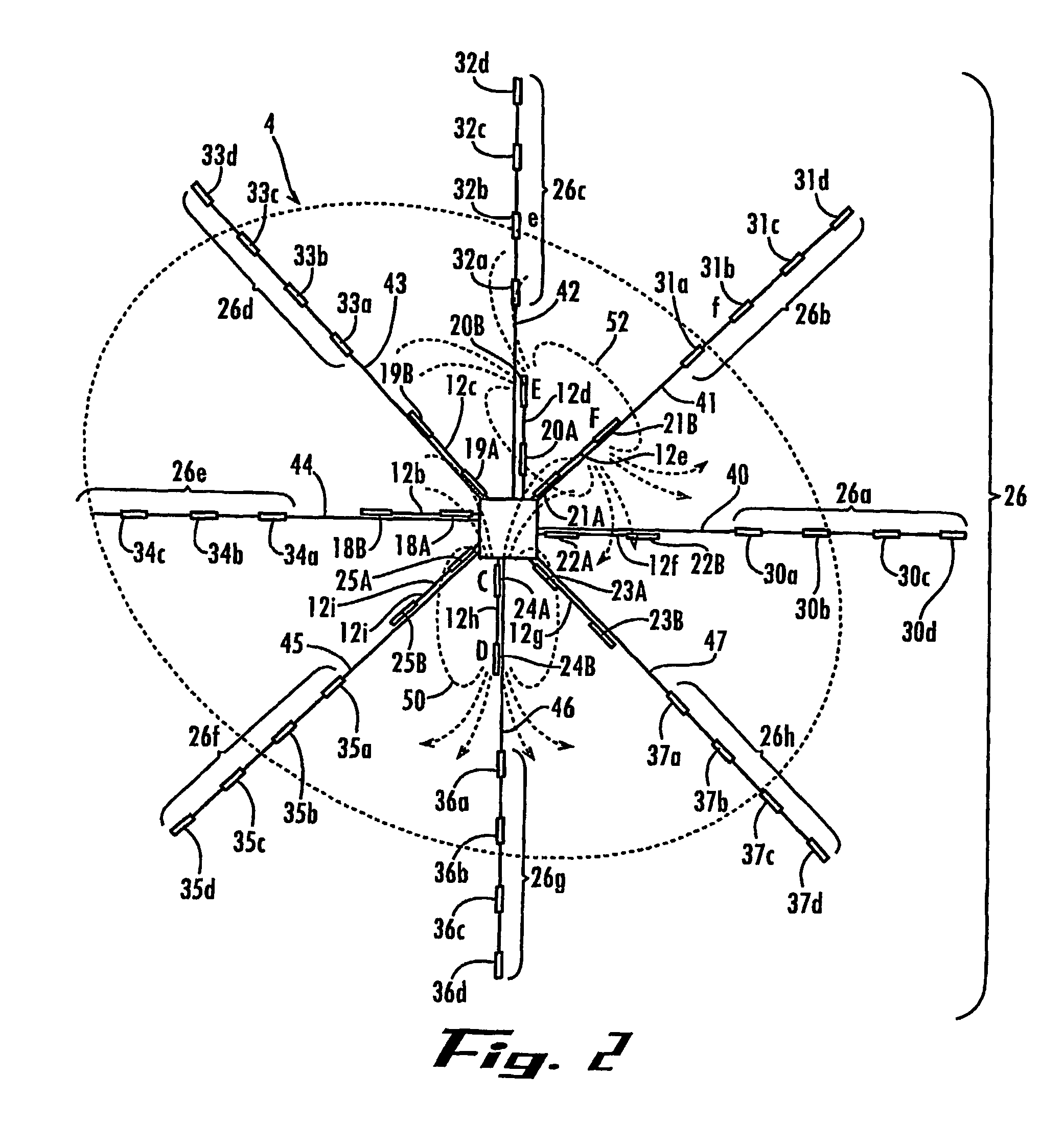
System and method for hydrocarbon reservoir monitoring using controlled-source electromagnetic fields
InactiveUS7109717B2Comprehensive imageWater resource assessmentDetection using electromagnetic wavesMagnetic sourceControlled source electro-magnetic
The system and method for real-time monitoring of a hydrocarbon reservoir (4) during extraction include an electro-magnetic source assembly (16) for transmitting a first plurality of electromagnetic fields. A plurality of seafloor antennae (30a–30d) is distributed over an area of the seafloor (8) corresponding to the reservoir (4), where each antenna (30a–30d) comprises recieves electrode array (30a–30d) adapted for receiving a second plurality of electromagnetic fields and generating signals corresponding to the detected fields. A data logging processor receives the signals over time and stores data corresponding to the signals. Different combinations of the receiver electrode are used in combination with transmitter antennae for measuring vertical, radial and / or azimuthal fields. Transmission and detection of the fields can be performed continuously or at timed intervals during hydrocarbon extraction to estimate the rate and efficiency of extraction.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
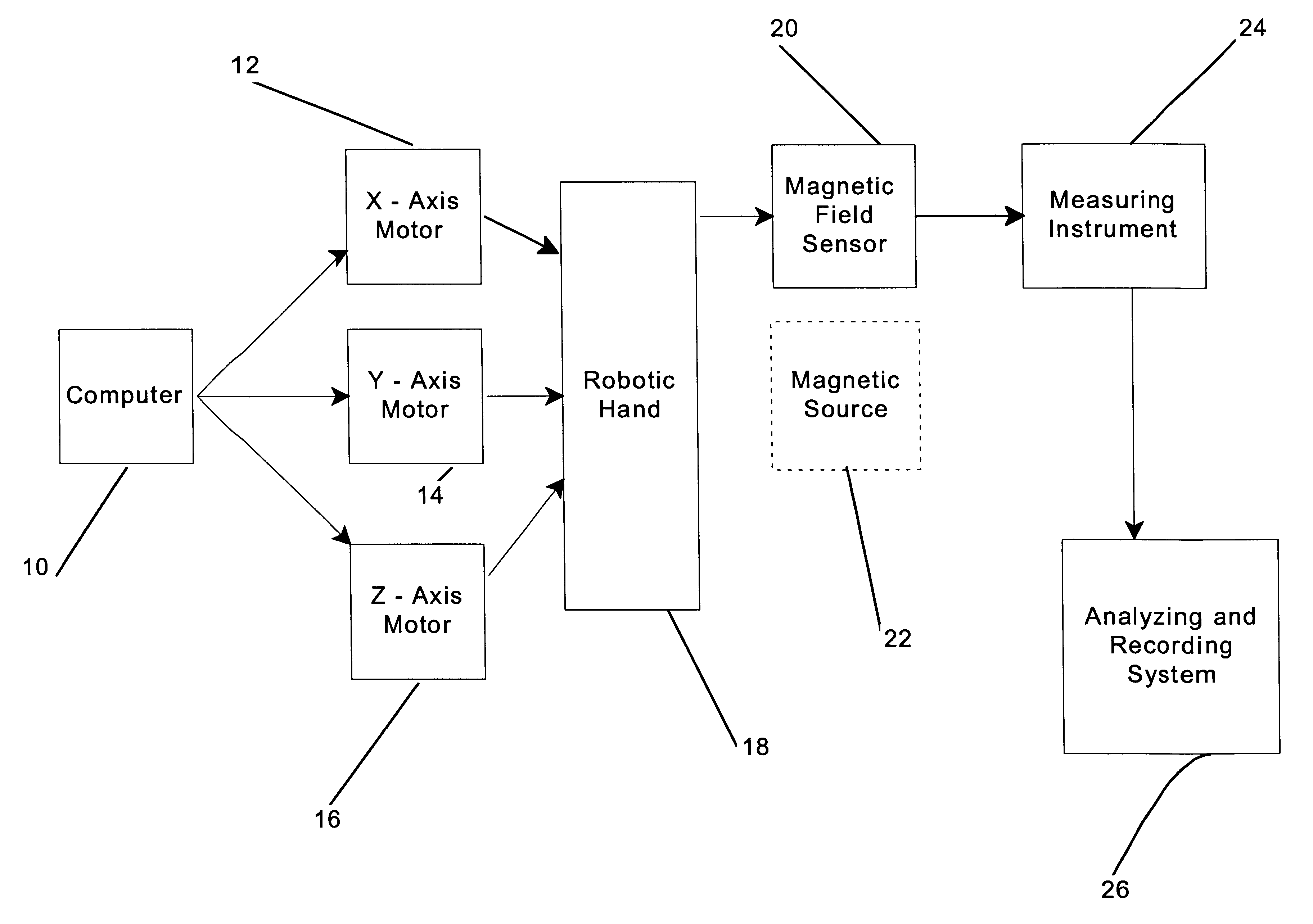
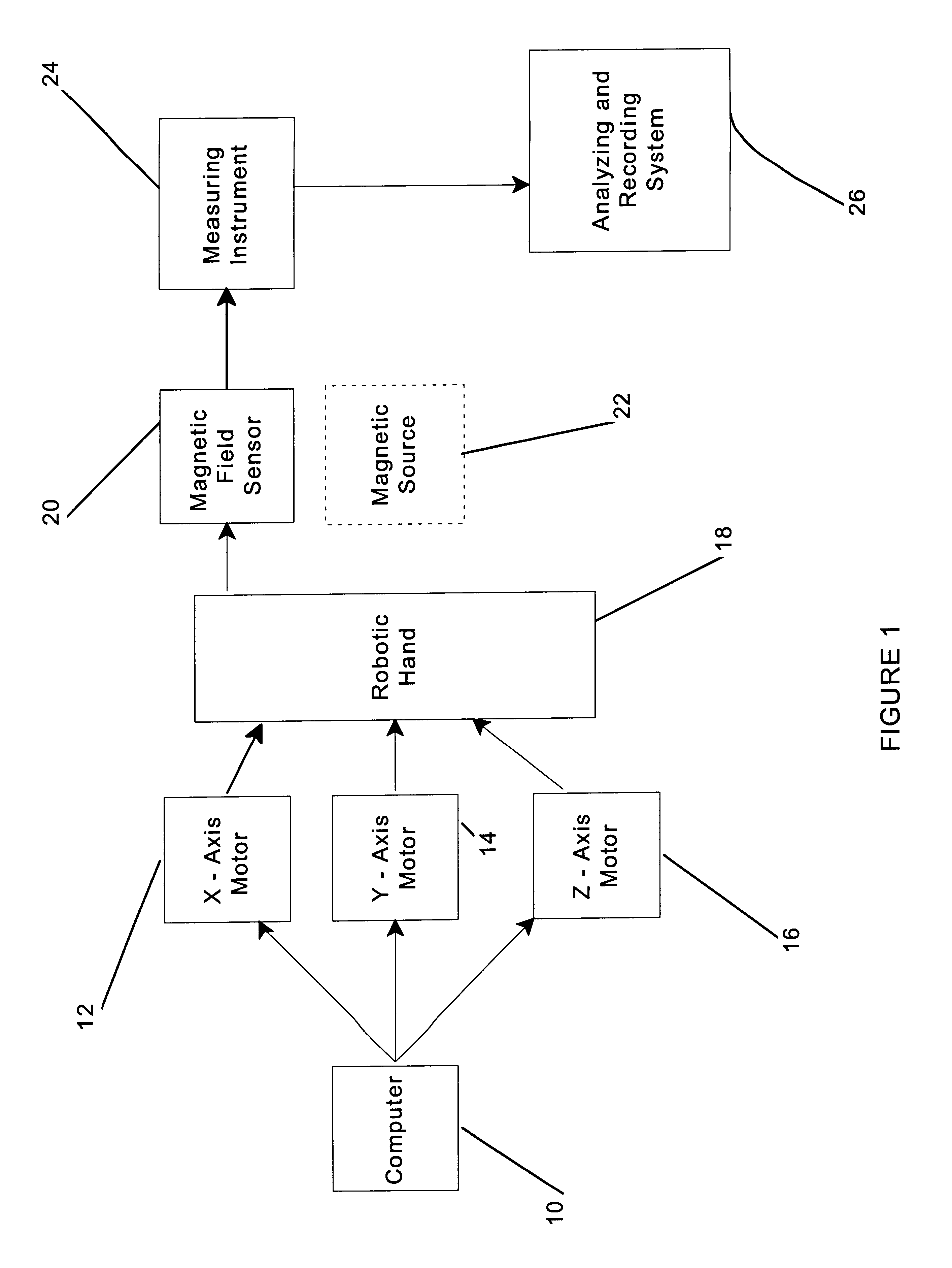
Magnetic field strength mapping system
The instant invention is directed toward a method and an apparatus for mapping the magnetic field strength or flux density of a magnetic source. The invention provides a robotically controlled sensor which is moved in a controlled manner throughout an area of flux density and the variations in the flux density are recorded. The position and recorded magnetic field strength at numerous points throughout the test area are recorded and the data is assembled into a graphical representation the end result of which is a multi-dimensional mapping of the magnetic field strength as a function of distance from the source. The testing method and apparatus provide a convenient methodology for accurately determining dosimetry and tissue penetration of therapeutic magnetic devices.
Owner:MAGNETHERAPY
Systems and methods for moving and/or restraining tissue in the upper respiratory system
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV +1
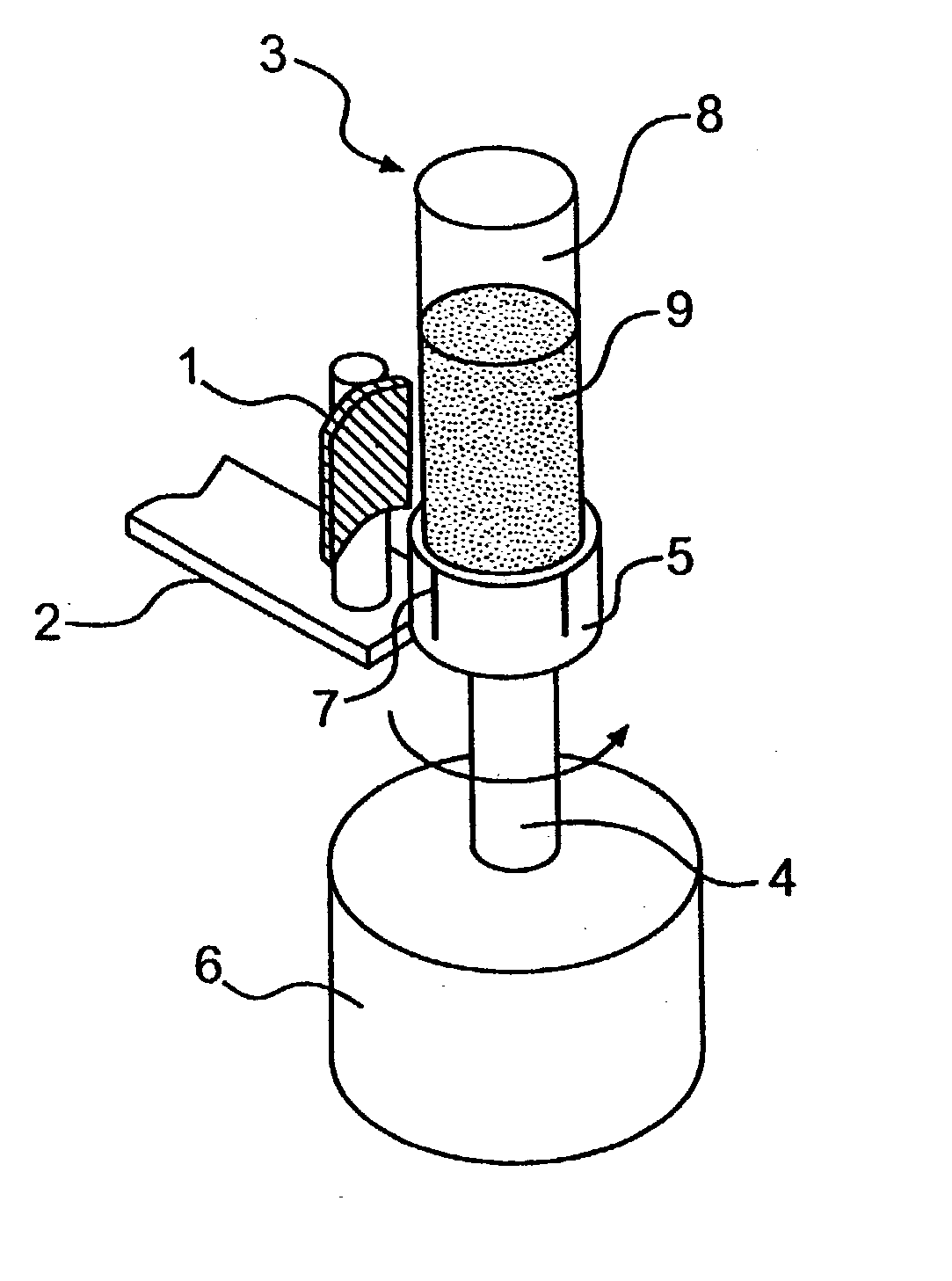
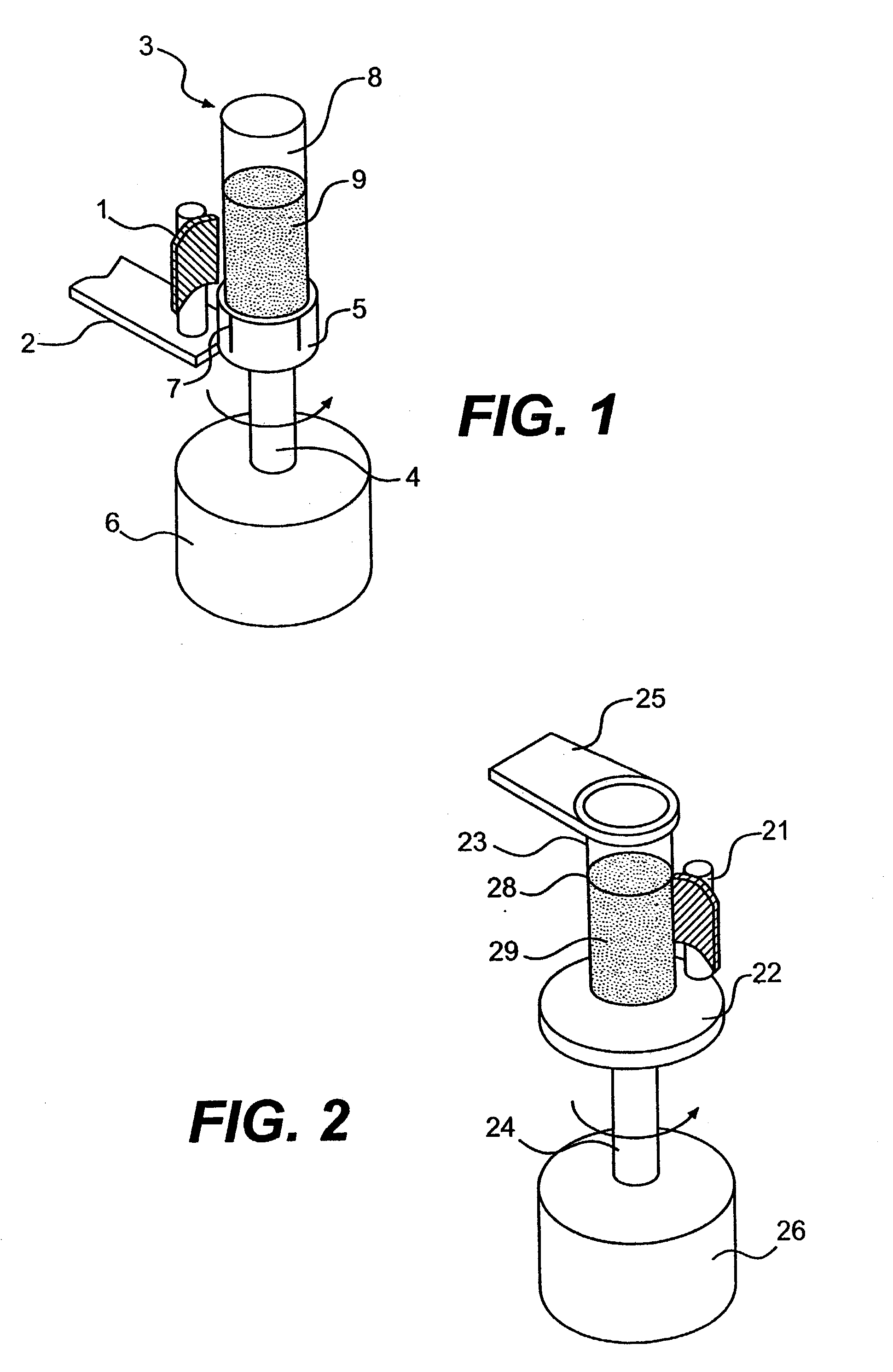
Apparatus and method for processing magnetic particles
InactiveUS20030127396A1Simple construction operationMaximizes mixing efficiencyElectrostatic separationWater/sewage treatment by magnetic/electric fieldsMagnetic gradientMagnetic source
An apparatus and method for carrying out the affinity separation of a target substance from a liquid test medium by mixing magnetic particles having surface immobilized ligand or receptor within the test medium to promote an affinity binding reaction between the ligand and the target substance. The test medium with the magnetic particles in a suitable container is removably mounted in an apparatus that creates a magnetic field gradient in the test medium. This magnetic gradient is used to induce the magnetic particles to move, thereby effecting mixing. The mixing is achieved either by movement of a magnet relative to a stationary container or movement of the container relative to a stationary magnet. In either case, the magnetic particles experience a continuous angular position change with the magnet. Concurrently with the relative angular movement between the magnet and the magnetic particles, the magnet is also moved along the length of the container causing the magnetic field gradient to sweep the entire length of the container. After the desired time, sufficient for the affinity reaction to occur, movement of the magnetic gradient is ended, whereby the magnetic particles are immobilized on the inside wall of the container nearest to the magnetic source. The remaining test medium is removed while the magnetic particles are retained on the wall of the container. The test medium or the particles may then be subjected to further processing.
Owner:SIGRIS RES
LED multiplex source and method of use of for sterilization, bioactivation and therapy
InactiveUS7328708B2Promotes directional and focused electromagnetic radiationReduce usageElectrotherapyDiagnosticsSensory FeedbacksMulti band
This invention discloses an LED multiplex source and a method of using multi-band-type energies from the source for sterilization, bioactivation, and therapy of a targeted body. The LED multiplex source is a pulsed / modulated LED source with at least one different member of the group of pulsed / modulated radiation sources consisting of: an electromagnetic, acoustic, electroluminescent, thermal, and / or magnetic source. The invention also teaches how to convert heat generated by the LED multiplex source into electromagnetic radiation and uses this radiation for sterilization, bioactivation, and therapy. The LED multiplex source is an energy-efficient radiation source, is compact, and also provides sensory feedback to optimize, in real-time, sterilization, bioactivation, and therapy processes. The invented source will replace some of the existing radiation sources and, as well, will open new areas of applications.
Owner:UNITED LAB & MFG
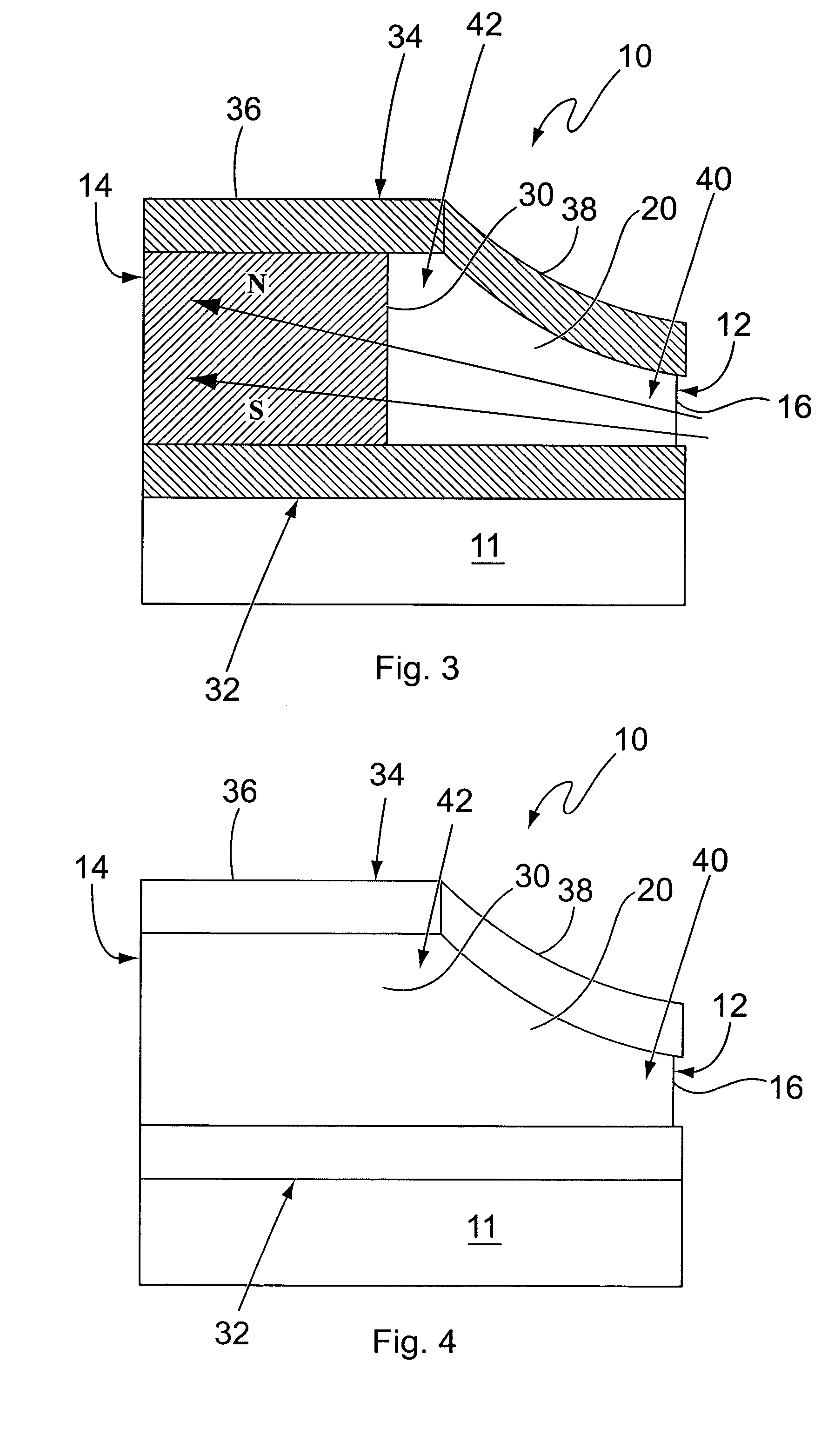
Optical, magnetic, electric composite navigational surgery positioning device and method
InactiveCN101049248AAchieve consistencyImprove calibration accuracySurgeryDiagnostic recording/measuringMagnetic sourceMachine vision
An electric, magnetic and optical navigations combined locating system for medical operation features that the magnetic source and marking point are arranged on operation tool, at least three magnetic receivers and a group of two CCD cameras, which are electrically connected to a computer, are respectively fixed to and above the operation table for taking the information about the position of operation tool in optical, magnetic and electric coordinate systems and its posture.
Owner:XIAN TECHNOLOGICAL UNIV
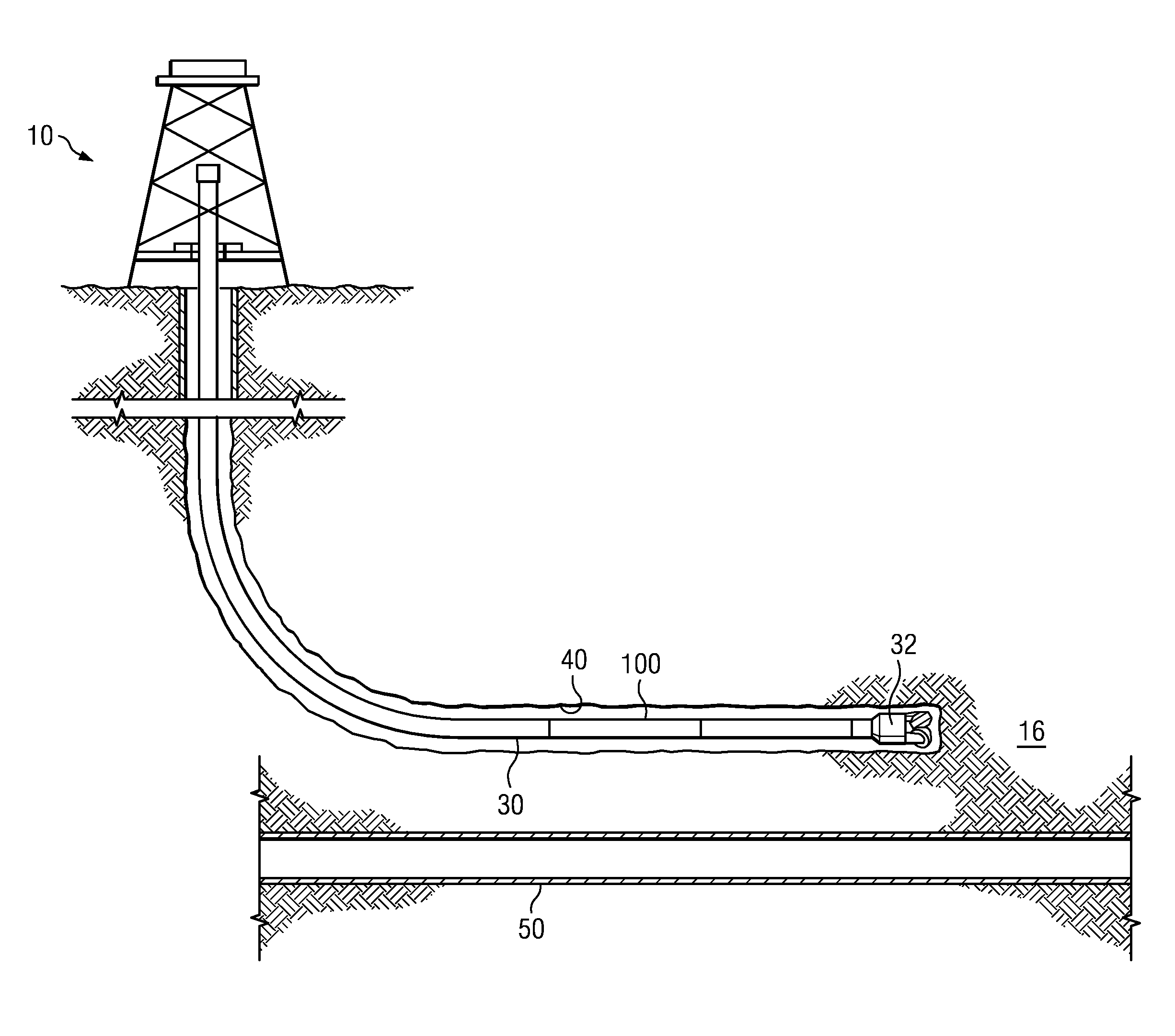
Magnetic ranging tool and method
ActiveUS20130173164A1Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingConstructionsMagnetic sourceEngineering
A downhole magnetic ranging tool includes first and second axially spaced magnetic sources deployed in a downhole tool body. The first and second magnetic sources have magnetic moments that axially opposed one another. A magnetic field sensor is deployed axially between the first and second magnetic sources. The tool may be utilized, for example, in subterranean well twinning, well intercept, and well avoidance operations to obtain a separation distance and dip angle between a drilling well and a target well.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
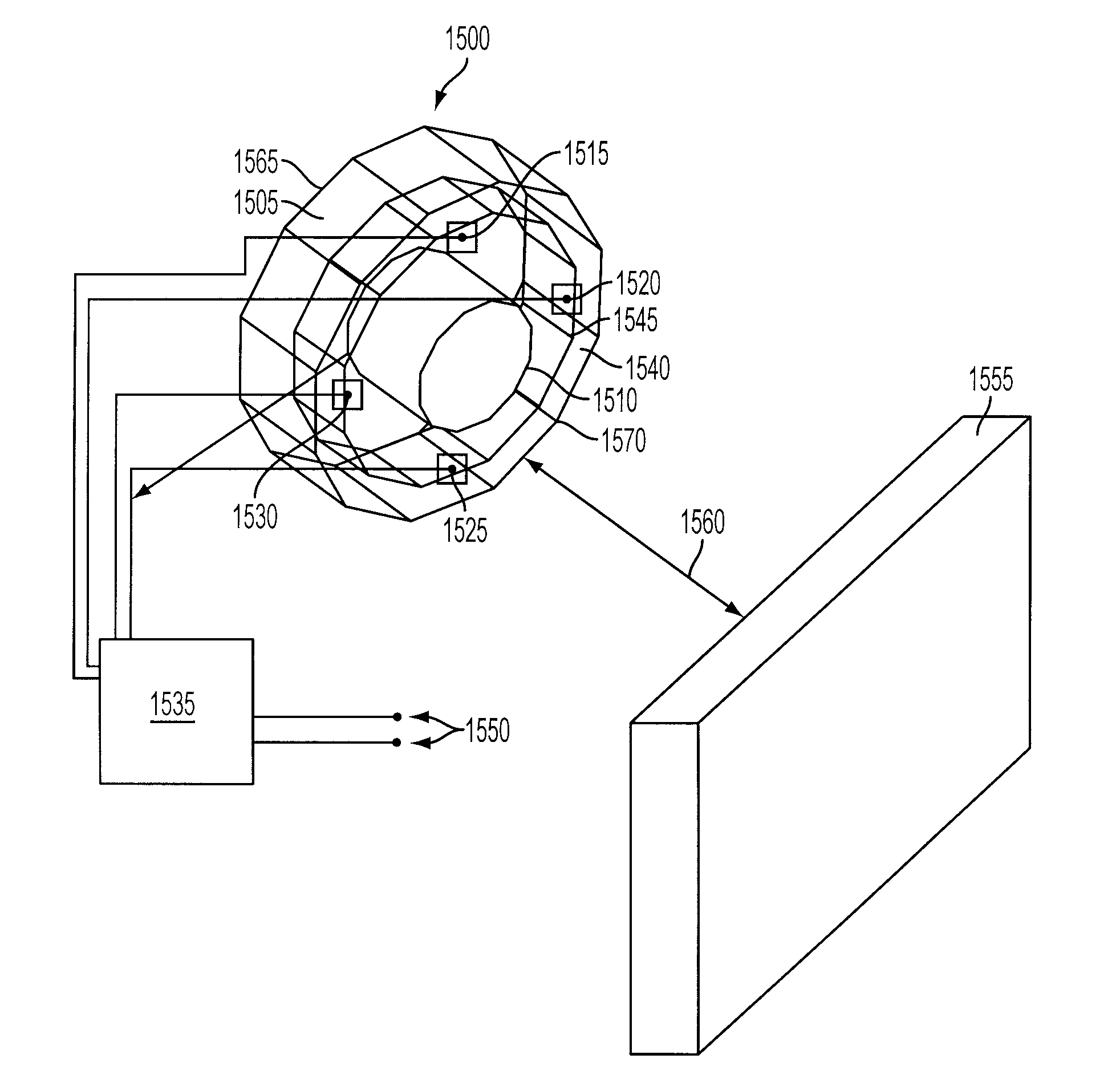
Mutually calibrated magnetic imaging array
ActiveUS9791536B1More transportableLess cumbersomeDiagnostic recording/measuringElectrical measurementsMagnetic tension forceMagnetic source
A mutually calibrated magnetic imaging array system is described. The system includes a non-target magnetic source rigidly attached to a magnetometer, and an attached control unit to measure and adjust several parameters of a magnetic imaging array. A non-target magnetic field source is used to generate a well-defined and distinguishable spatial magnetic field distribution. The source is rigidly attached directly to a magnetometer, while the relative positions of the magnetometers are unknown. The magnetic imaging array is used to measure the strength of the non-target source magnetic fields and the information is used to calibrate several parameters of the array, such as, but not limited to, effective magnetometer positions and orientations with respect to each other and cross-talk between the magnetometers. The system, and method described herein eliminates the need for a separate calibration phantom.
Owner:QUSPIN
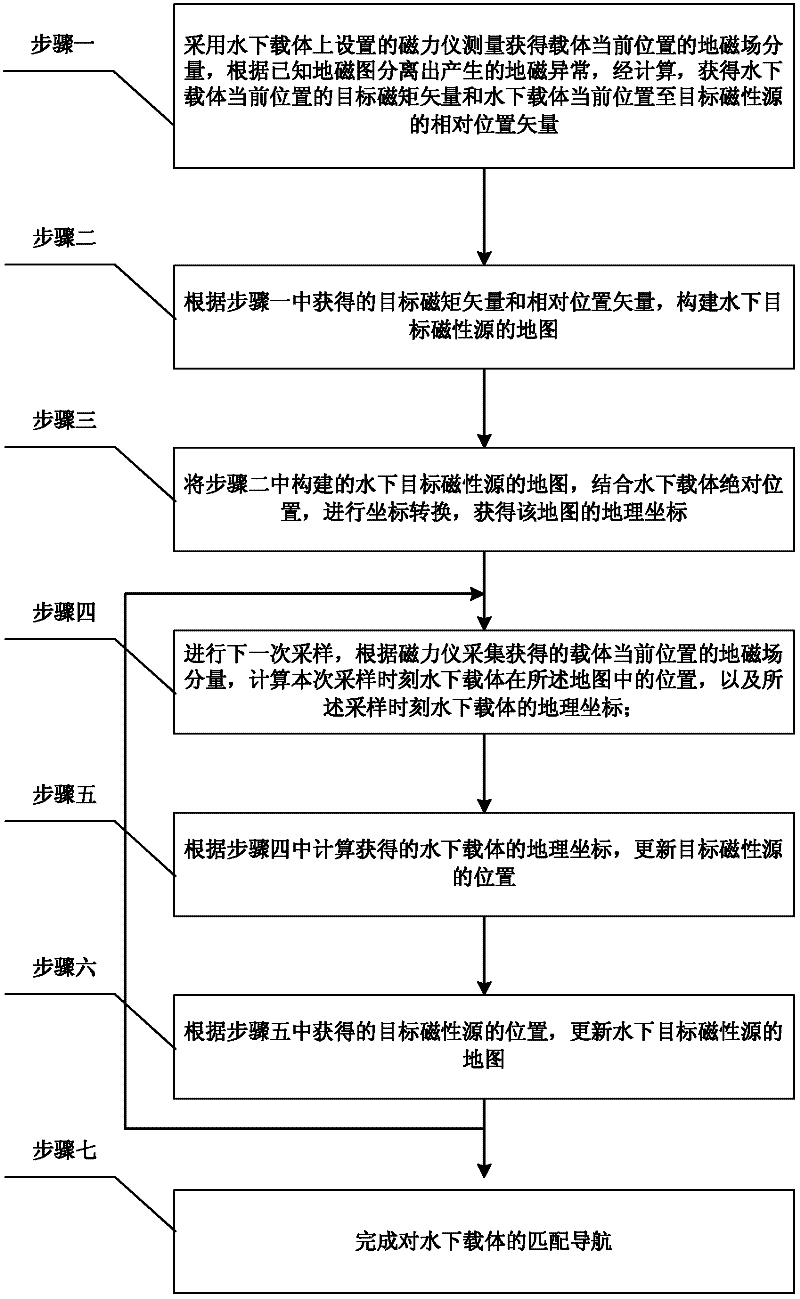
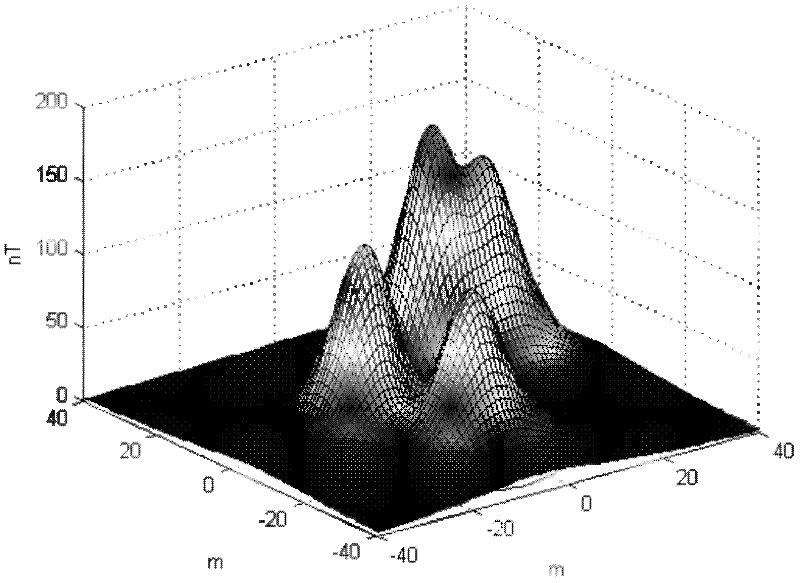
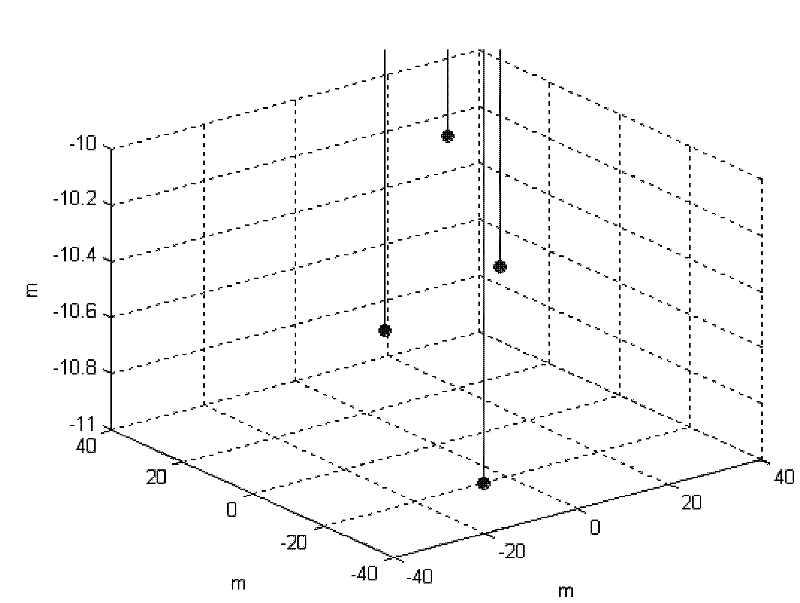
Underwater carrier geomagnetic anomaly feature points matching navigation method
InactiveCN102445201ARealize full navigationGuaranteed trappingNavigation by terrestrial meansNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsMagnetic sourceUnderwater navigation
An underwater carrier geomagnetic anomaly feature points matching navigation method belongs to the technical field of underwater navigation and solves the problem in the prior art that the location of an underwater carrier can not be determined according to geomagnetic field information. The method provided by the invention comprises the following steps of: acquiring a target magnetic moment vector of present position of the underwater carrier and a relative position vector from the present position of the underwater carrier to a target magnetic source; constructing a map of the underwater target magnetic source; carrying out coordinate transformation based on the absolute position of the underwater carrier so as to obtain geographic coordinates of the map; calculating the position of the underwater carrier in the map at sampling time and the geographic coordinates of the underwater carrier at the sampling time; updating the position of the target magnetic source; updating the map of the underwater target magnetic source; and repeating the above relative processes to complete the matching navigation of the underwater carrier. The invention is suitable for underwater carrier navigation.
Owner:NORTHEAST FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
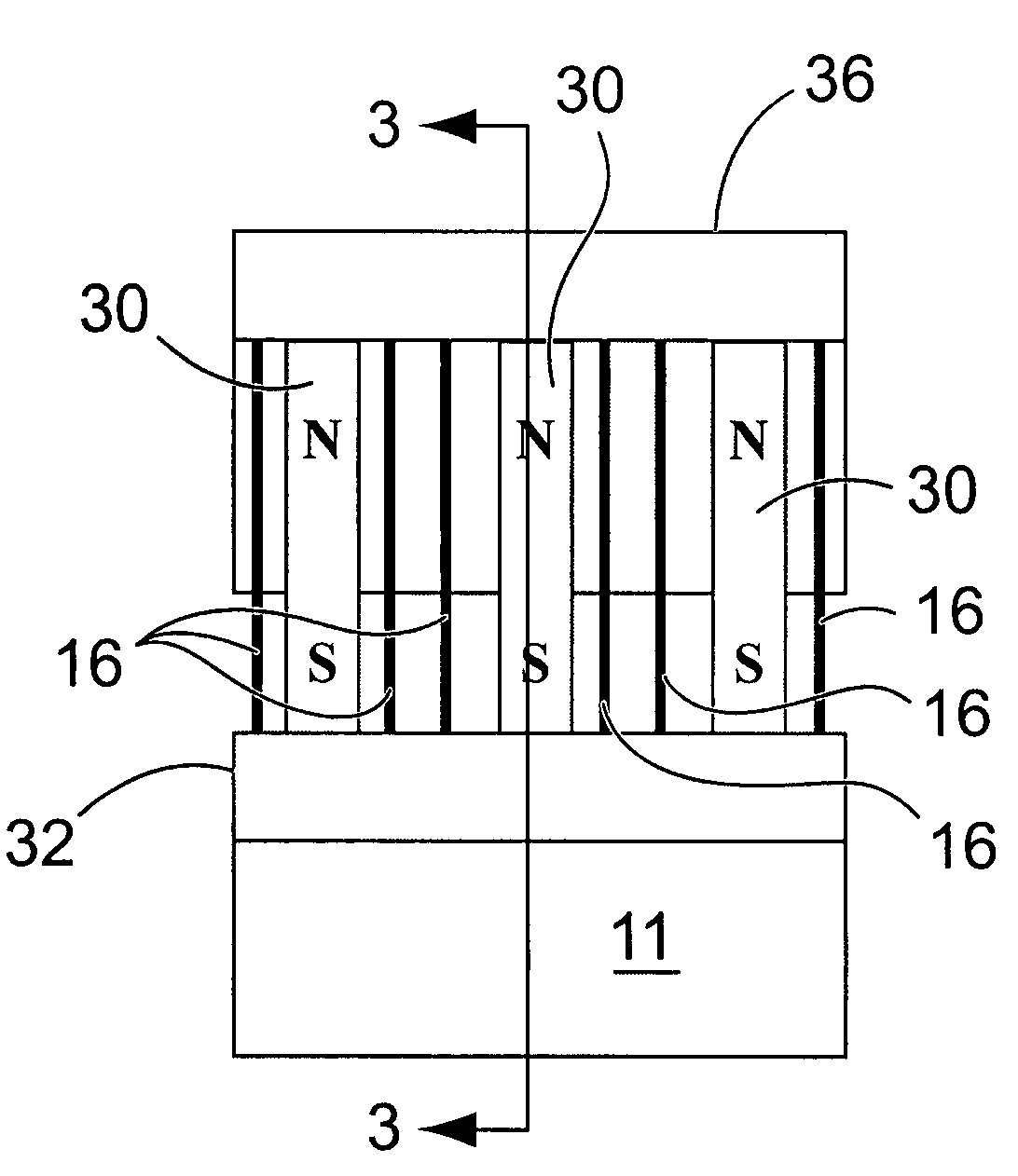
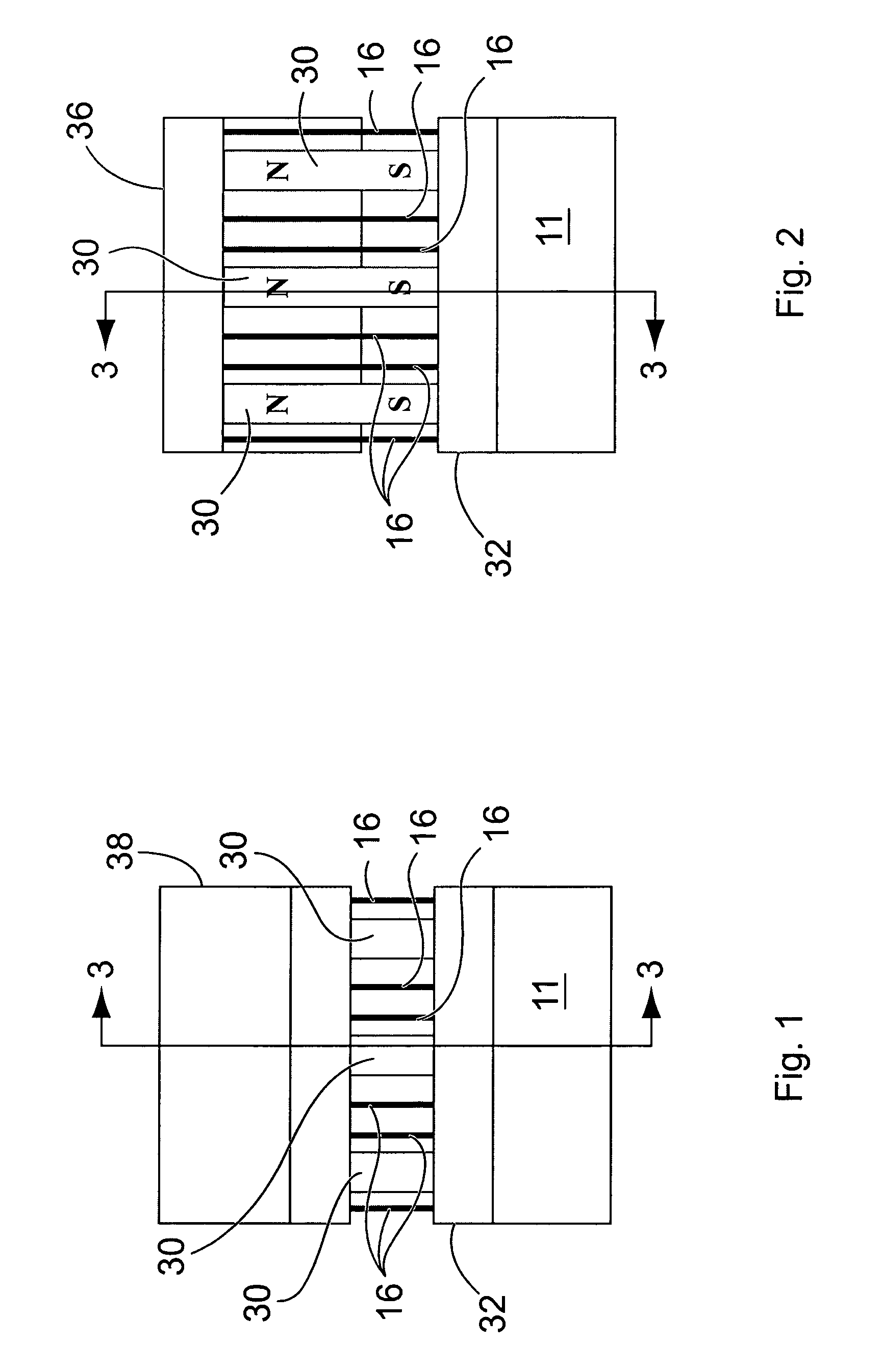
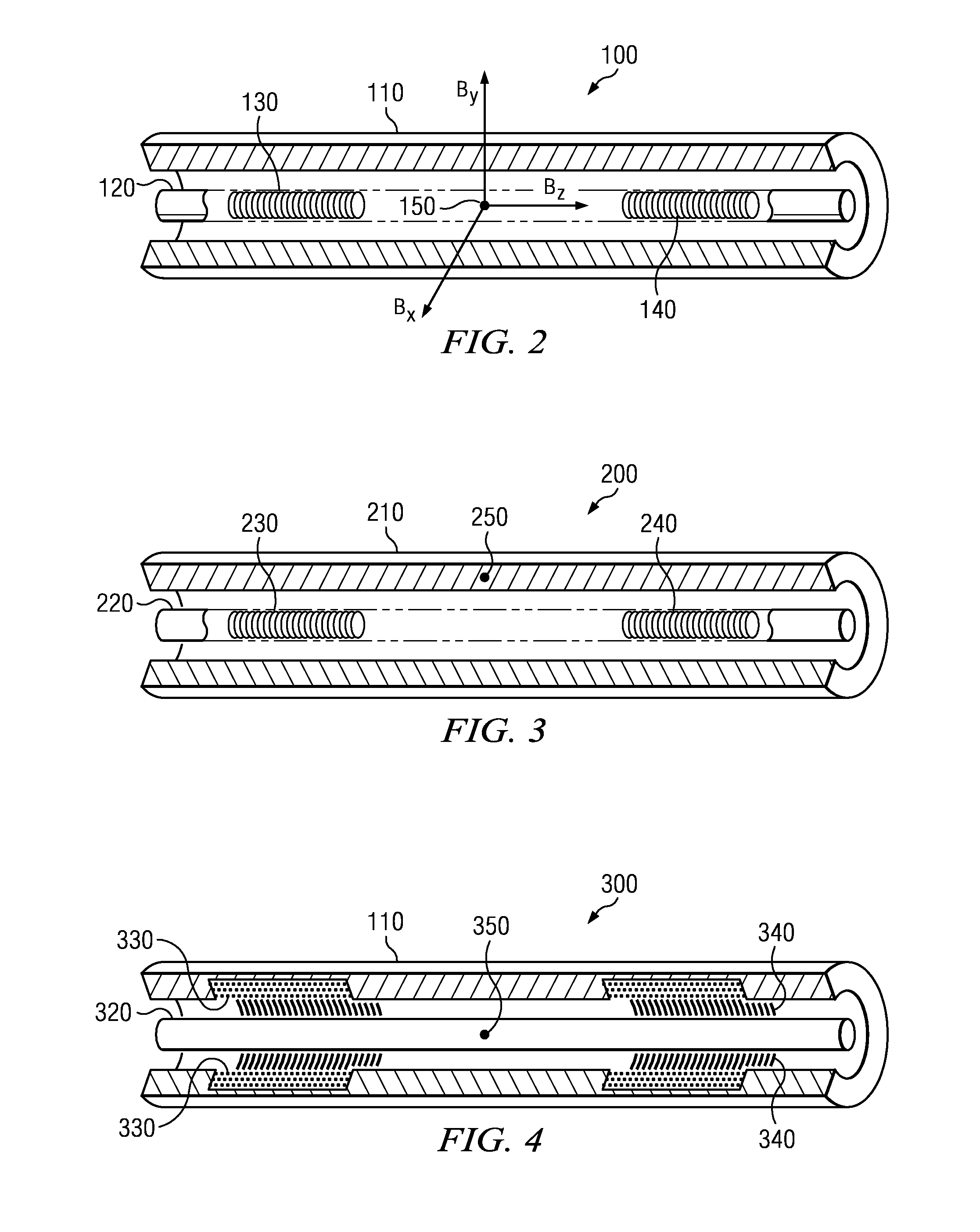
Position sensor system
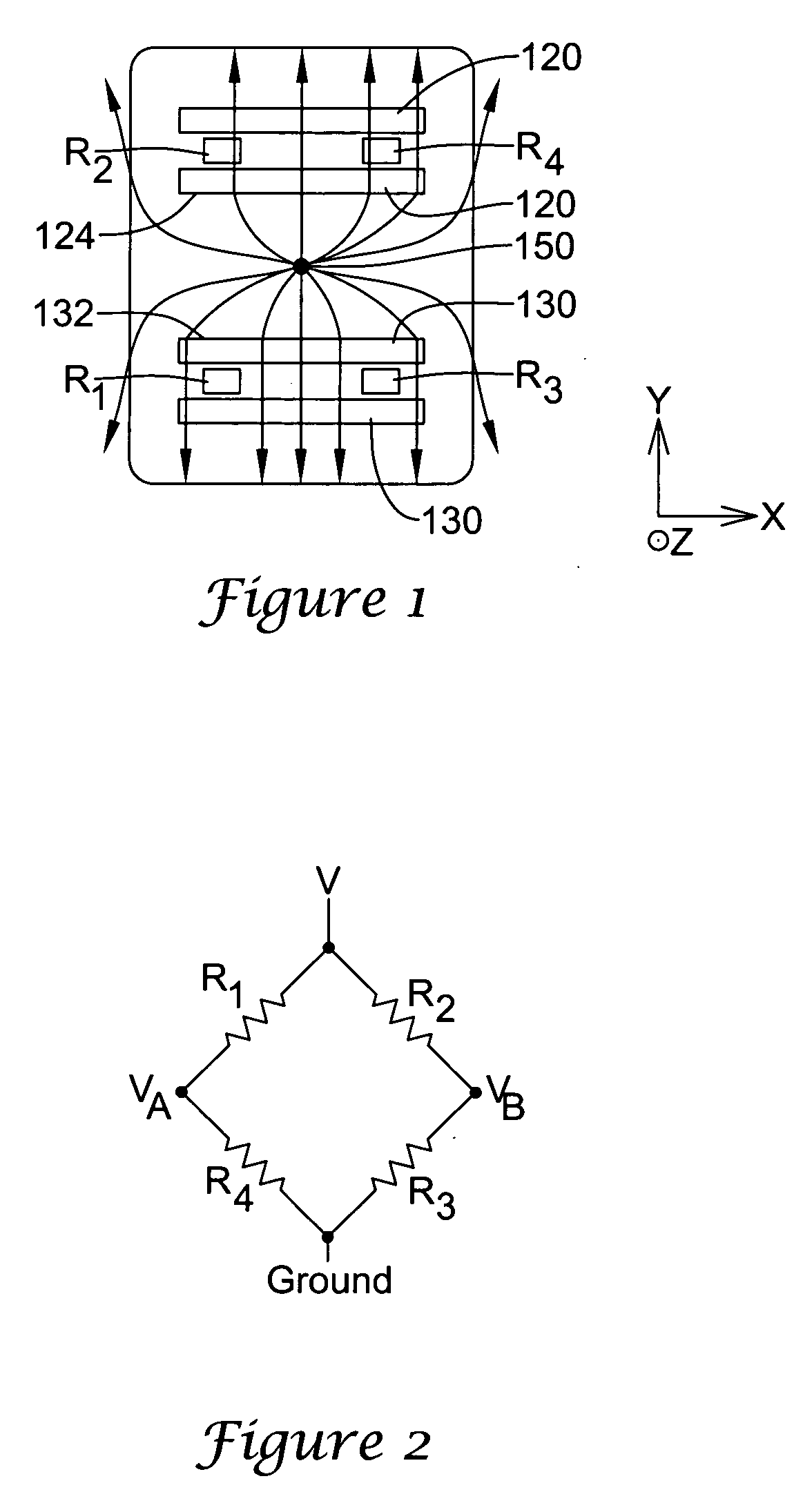
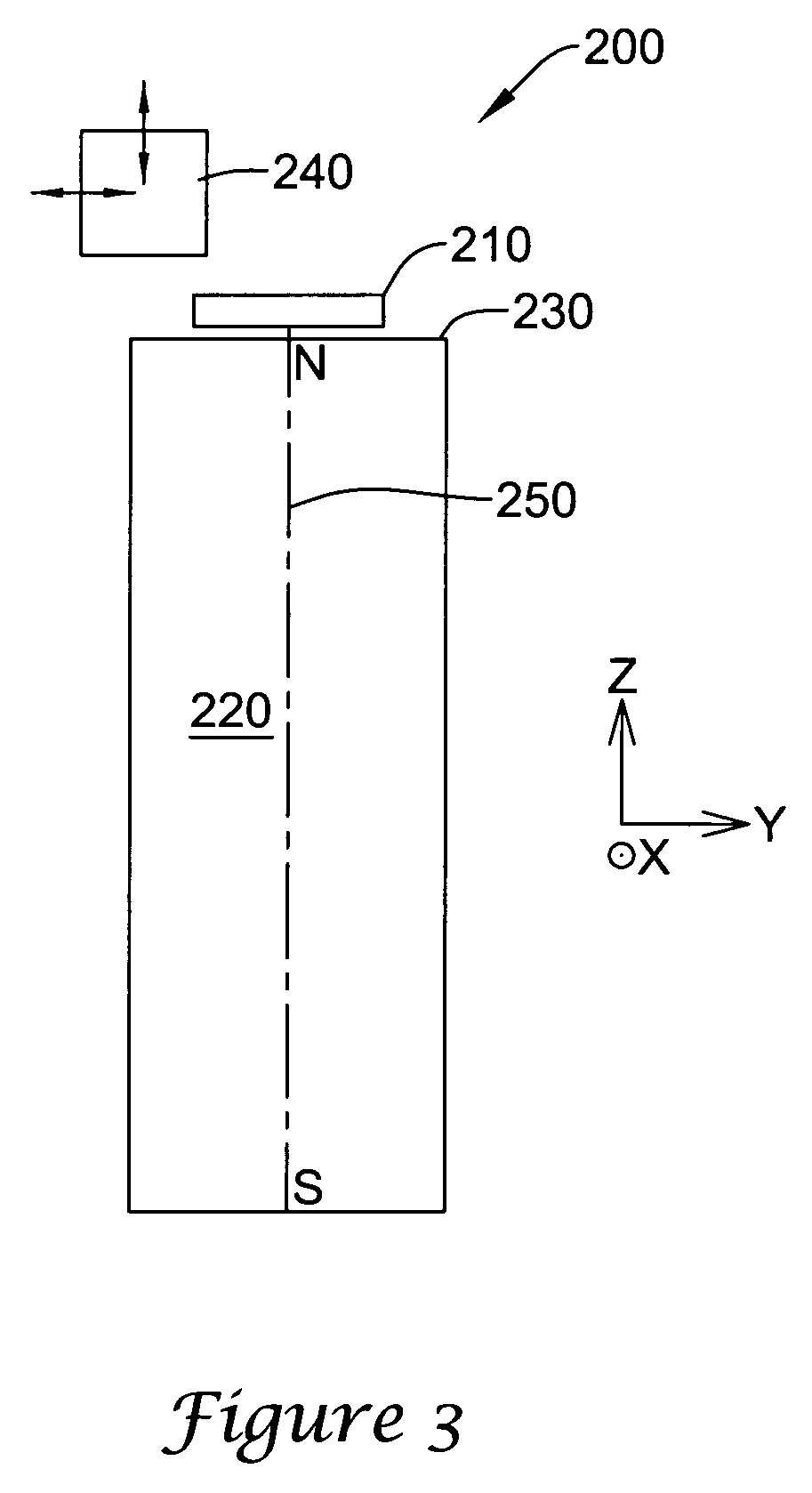
ActiveUS7834618B2Accurate eccentricityPrecise positioningUsing electrical meansConverting sensor outputMagnetic sourceMagnetic flux
A sensing mechanism includes a magnetic source, a magnetic flux sensor, a sensor backing on which the magnetic source and flux sensor are mounted, and a ferromagnetic target, where the magnetic source, magnetic flux sensor, and ferromagnetic target are positioned to form a magnetic circuit from the magnetic source to the target, from the target to the sensor, and returning to the magnetic source through the sensor backing.
Owner:BOOKS AUTOMATION US LLC
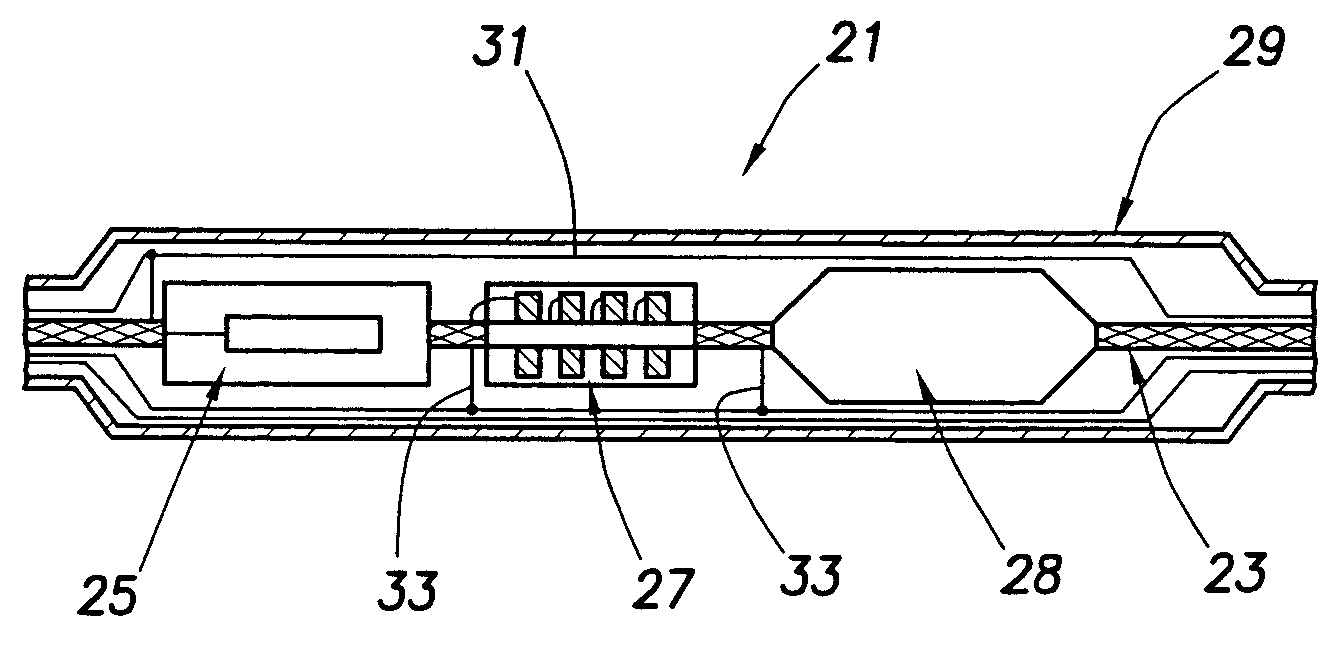
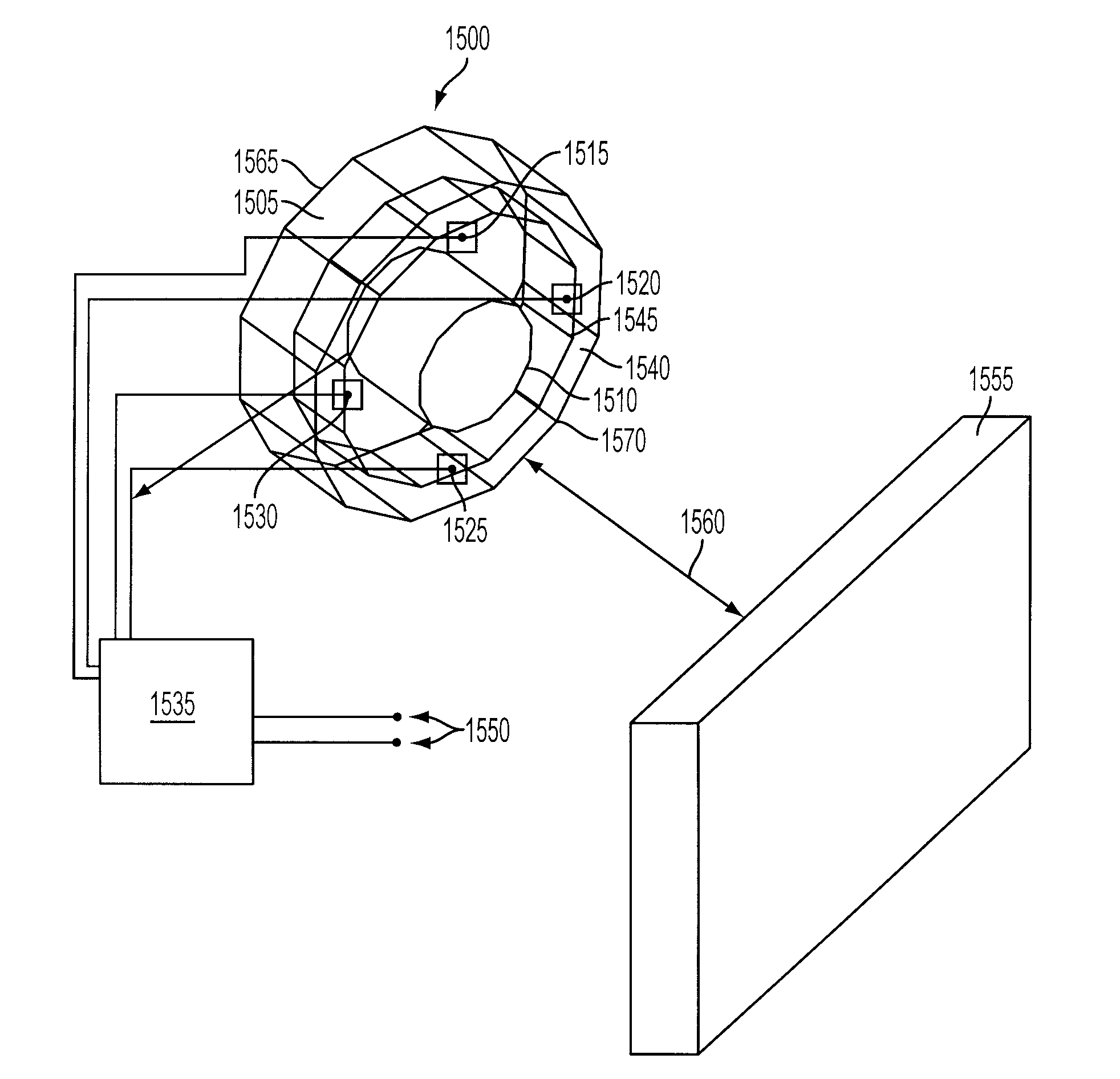
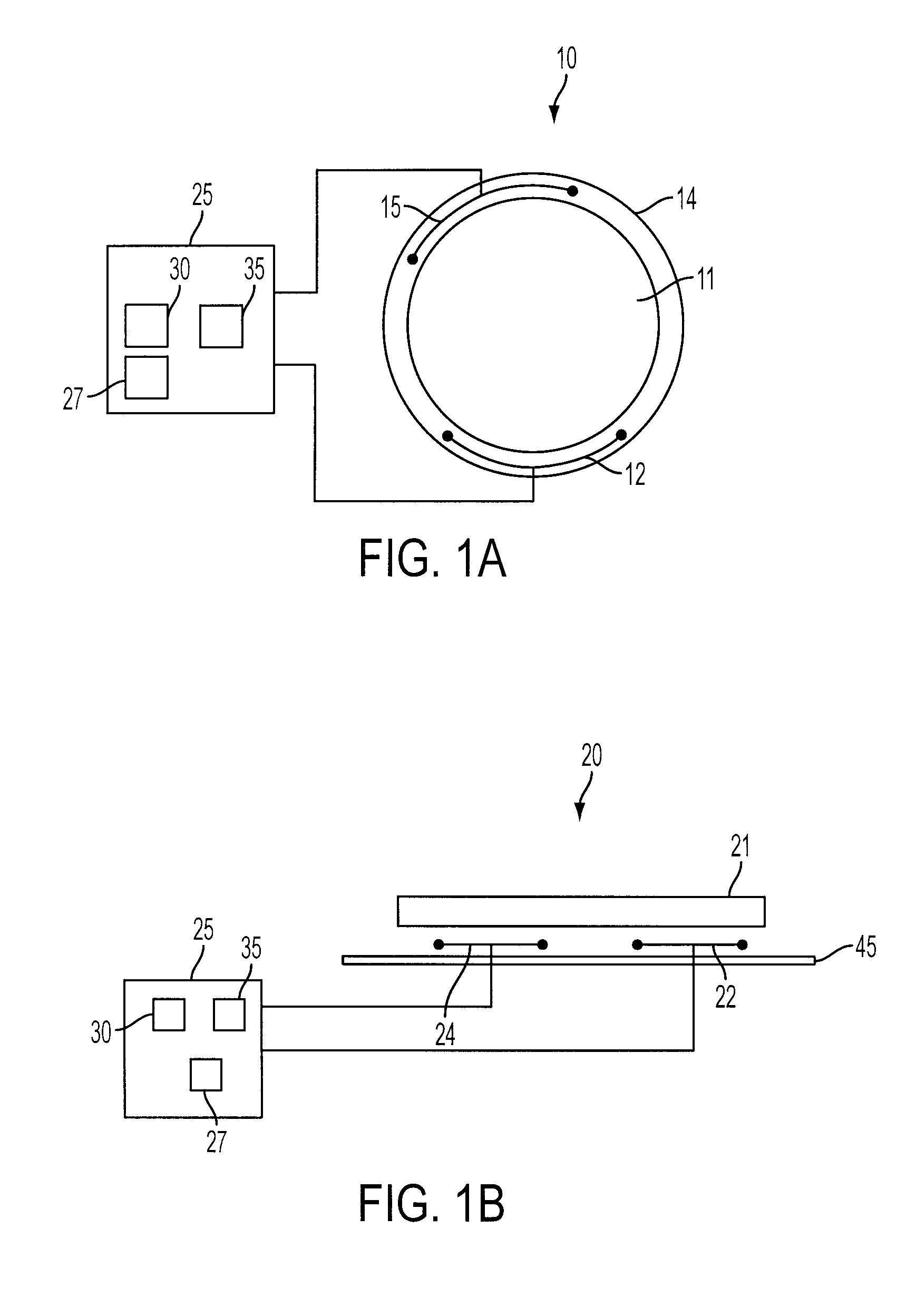
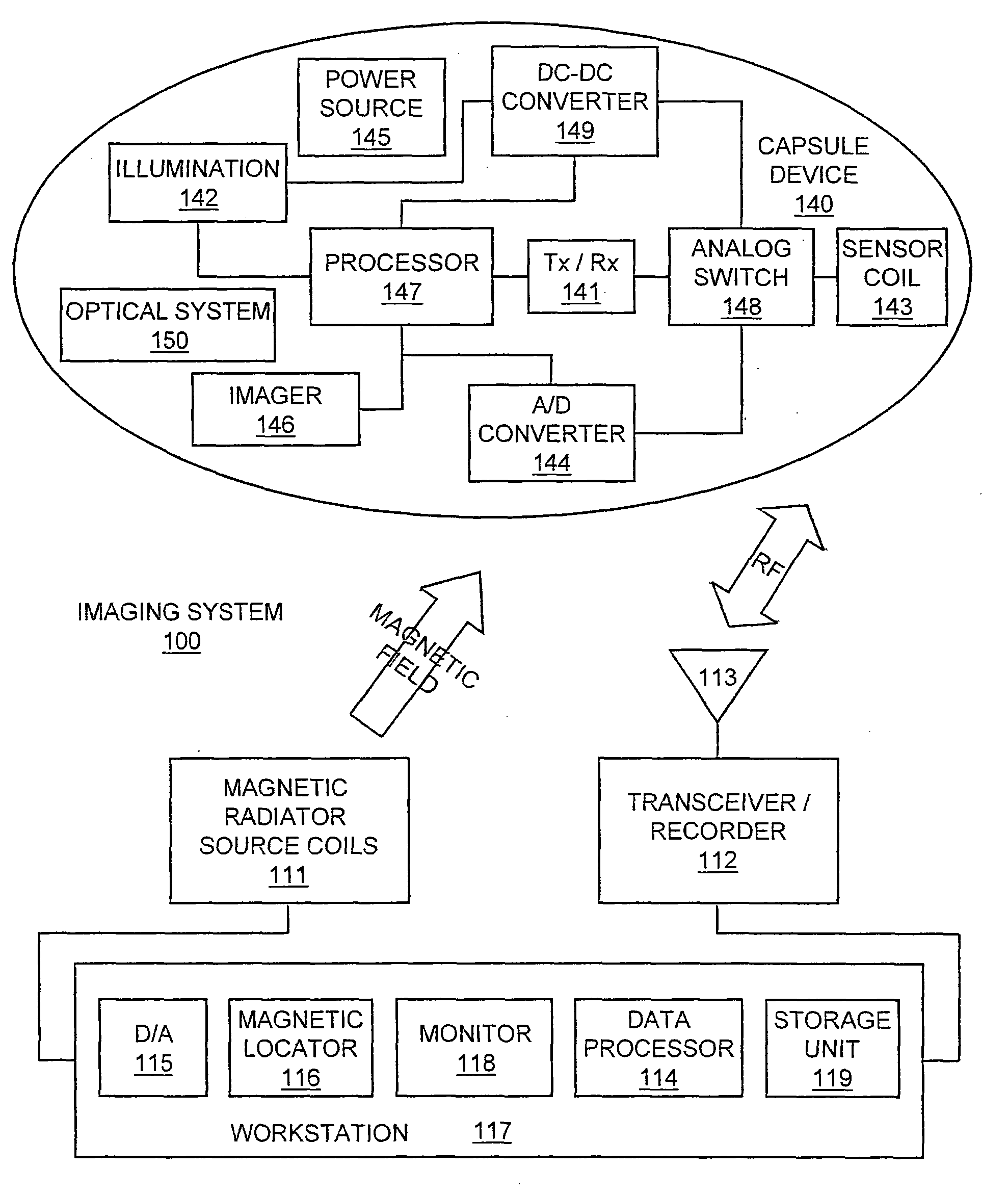
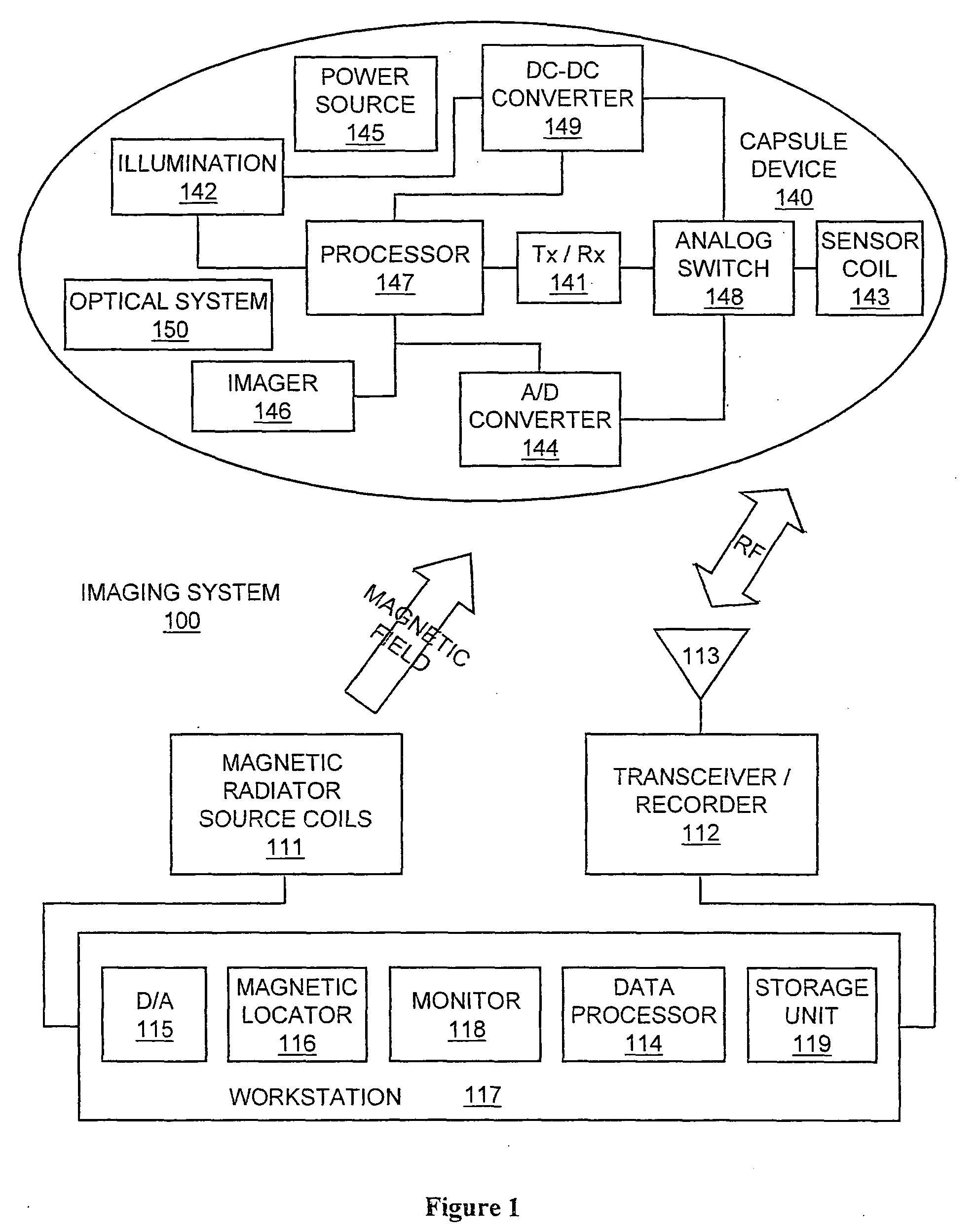
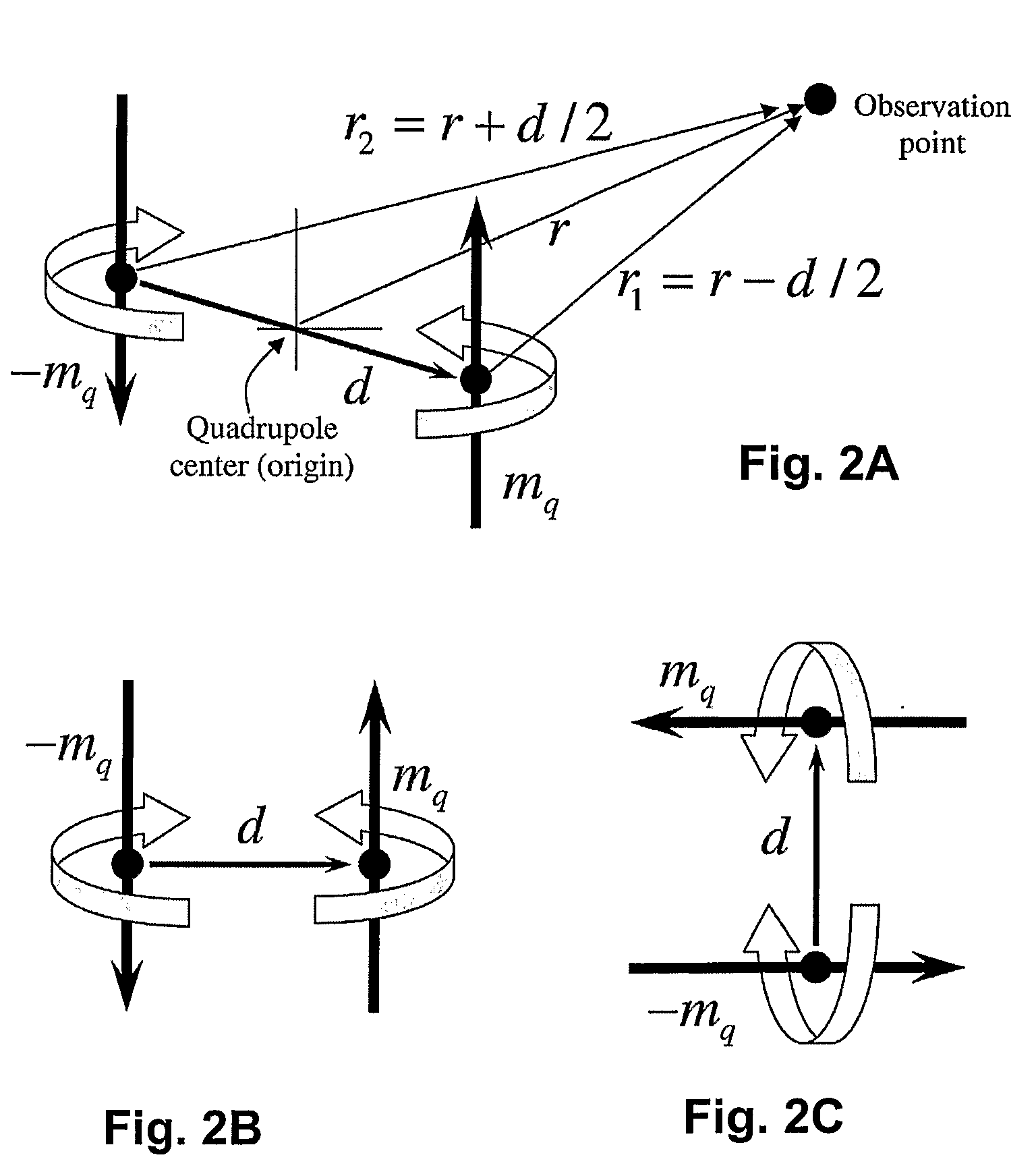
Localization of capsule with a synthetic source of quadrupoles and dipoles
This invention relates to methods and apparatus for localizing an in vivo imaging device by means of a single magnetic source coil assembly and a single magnetic detector coil assembly. This invention also relates to methods and apparatus to enable the use of a single magnetic source coil assembly to also transmit and receive information, images, and controls signals, as well as for the coil assembly to be used in DC-DC voltage conversion. A user interface with a display provides the user with the option of viewing selected images captured by the in vivo imaging device.
Owner:GIVEN IMAGING LTD
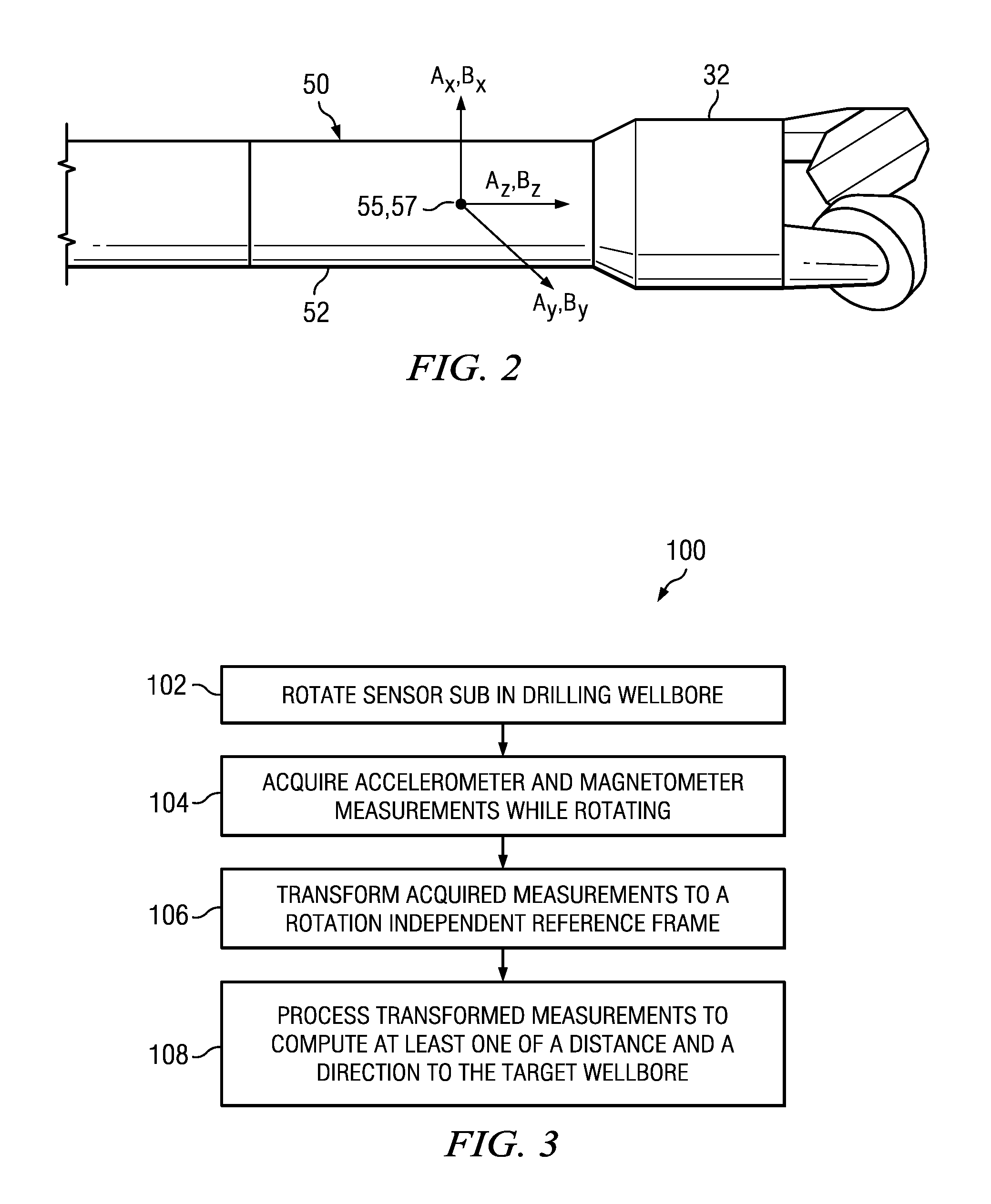
Magnetic Ranging To An AC Source While Rotating
A method for magnetic ranging includes rotating a downhole tool in a drilling well in sensory range of magnetic flux emanating from a target well having an AC magnetic source deployed therein. The downhole tool includes a magnetic field sensor deployed therein. The magnetic field sensor measures a magnetic field vector while rotating. The measured magnetic field vector is processed to compute at least one of a distance and a direction from a drilling well to a target well.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
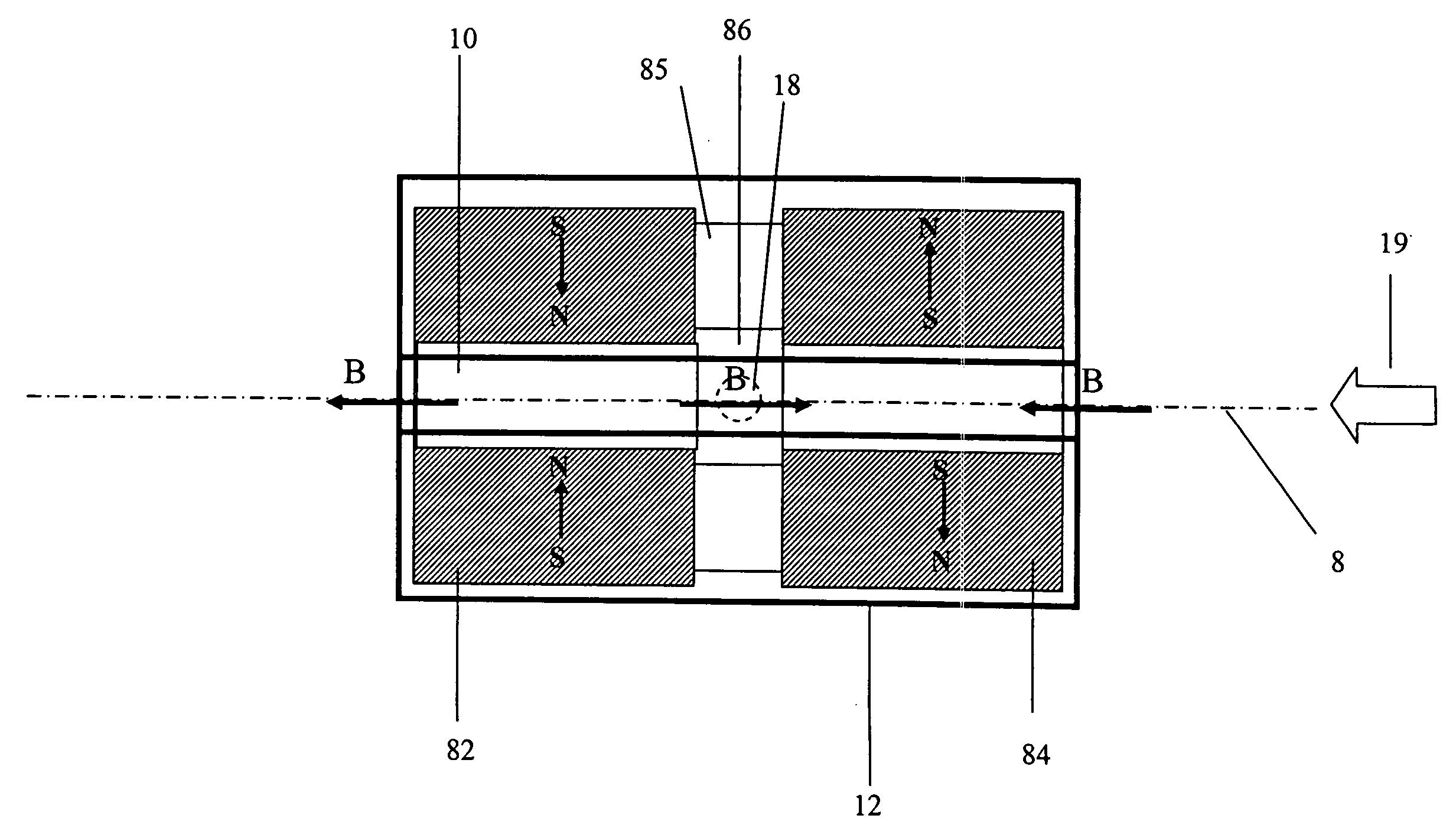
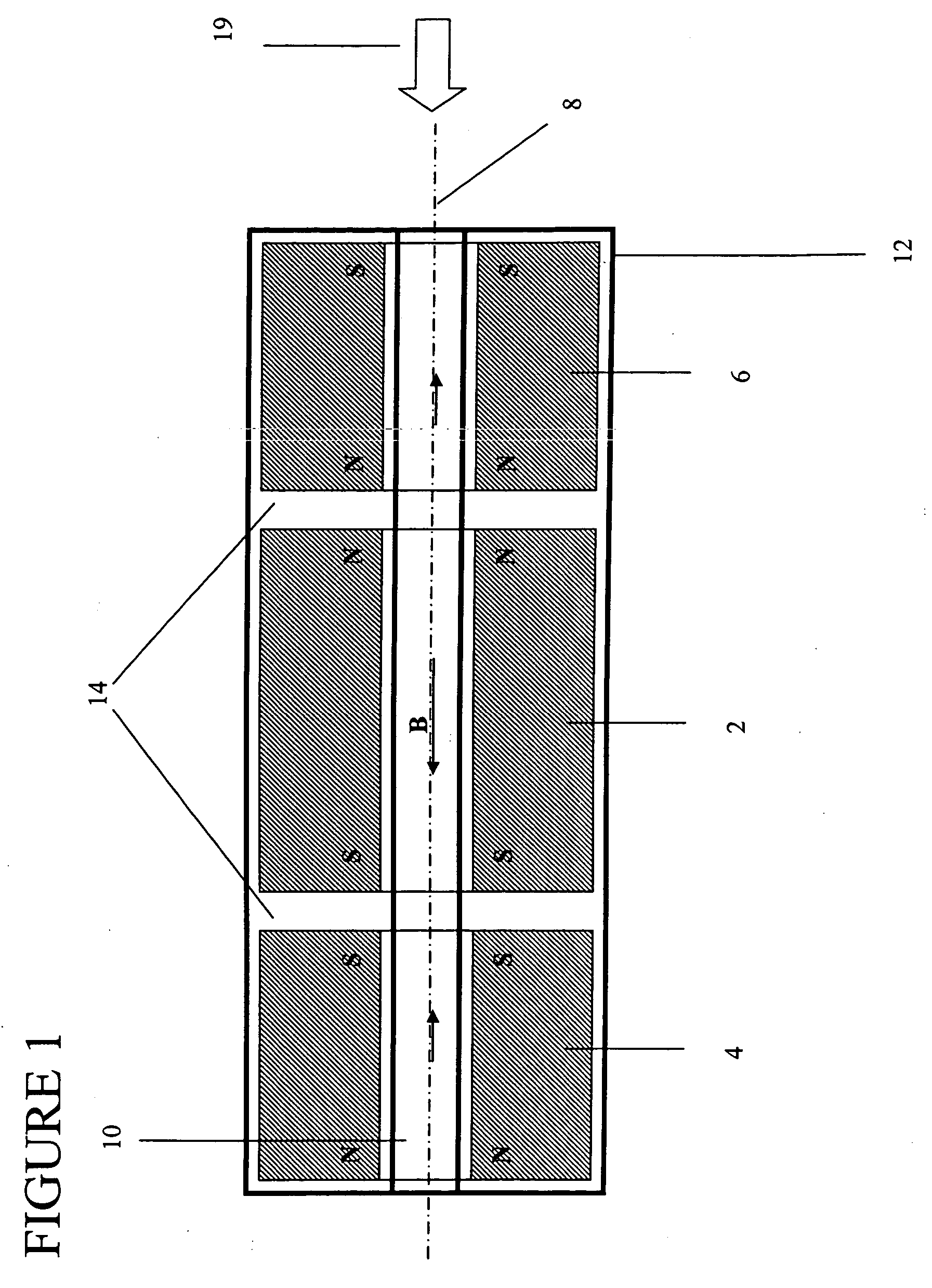
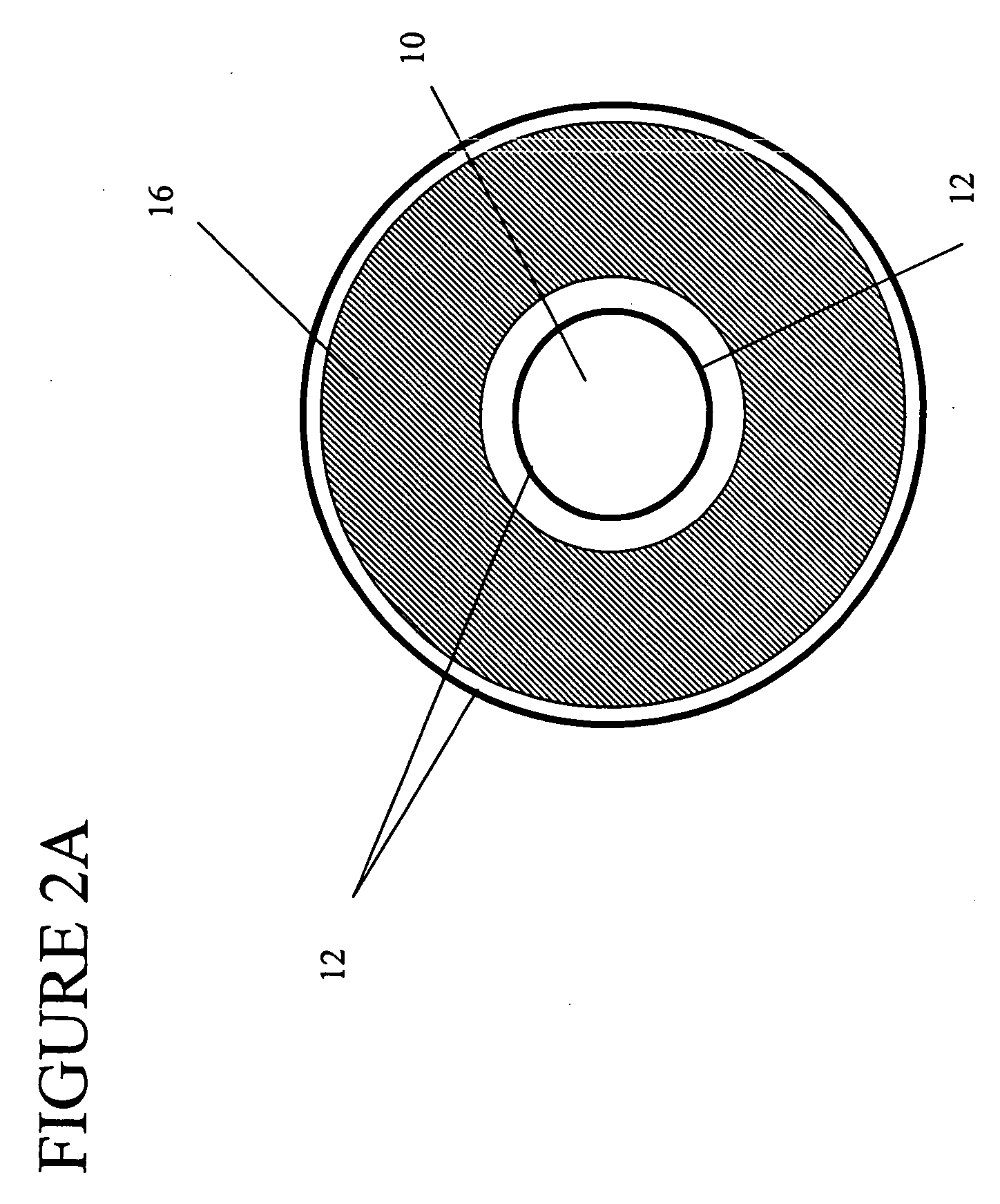
Permanent magnet structure with axial access for spectroscopy applications
InactiveUS20060232369A1Eliminate and overcomeMaximize the flux density generated per weight of magnetic materialPermanent magnetsOmegatronsMagnetic sourceMagnetic flux
A mass spectrometer with a magnet structure including a plurality of magnetic flux sources disposed along a common axis. The plurality of magnetic flux sources includes at least one permanent magnet flux source having at least one through-hole body along the common axis. The plurality of magnetic sources generates a resultant magnetic field. A direction of a magnetic field component of the resultant magnetic field along the common axis is at least once reversed along the common axis within the magnet structure.
Owner:MAKROCHEM
Apparatus for processing magnetic particles
InactiveUS20050155921A1Promote specific affinity binding reactionLength and efficiencyElectrostatic separationTransportation and packagingMagnetic field gradientMagnetic gradient
An apparatus and method for carrying out the affinity separation of a target substance from a liquid test medium by mixing magnetic particles having surface immobilized ligand or receptor within the test medium to promote an affinity binding reaction between the ligand and the target substance. The test medium with the magnetic particles in a suitable container is removably mounted in an apparatus that creates a magnetic field gradient in the test medium. This magnetic gradient is used to induce the magnetic particles to move, thereby effecting mixing. The mixing is achieved either by movement of a magnet relative to a stationary container or movement of the container relative to a stationary magnet. In either case, the magnetic particles experience a continuous angular position change with the magnet. Concurrently with the relative angular movement between the magnet and the magnetic particles, the magnet is also moved along the length of the container causing the magnetic field gradient to sweep the entire length of the container. After the desired time, sufficient for the affinity reaction to occur, movement of the magnetic gradient is ended, whereby the magnetic particles are immobilized on the inside wall of the container nearest to the magnetic source. The remaining test medium is removed while the magnetic particles are retained on the wall of the container. The test medium or the particles may then be subjected to further processing.
Owner:SIGRIS RES
Position feedback for self bearing motor
ActiveUS20090015248A1Accurate eccentricityPrecise positioningUsing electrical meansConverting sensor outputMagnetic sourceMagnetic flux
A sensing mechanism includes a magnetic source, a magnetic flux sensor, a sensor backing on which the magnetic source and flux sensor are mounted, and a ferromagnetic target, where the magnetic source, magnetic flux sensor, and ferromagnetic target are positioned to form a magnetic circuit from the magnetic source to the target, from the target to the sensor, and returning to the magnetic source through the sensor backing.
Owner:BOOKS AUTOMATION US LLC
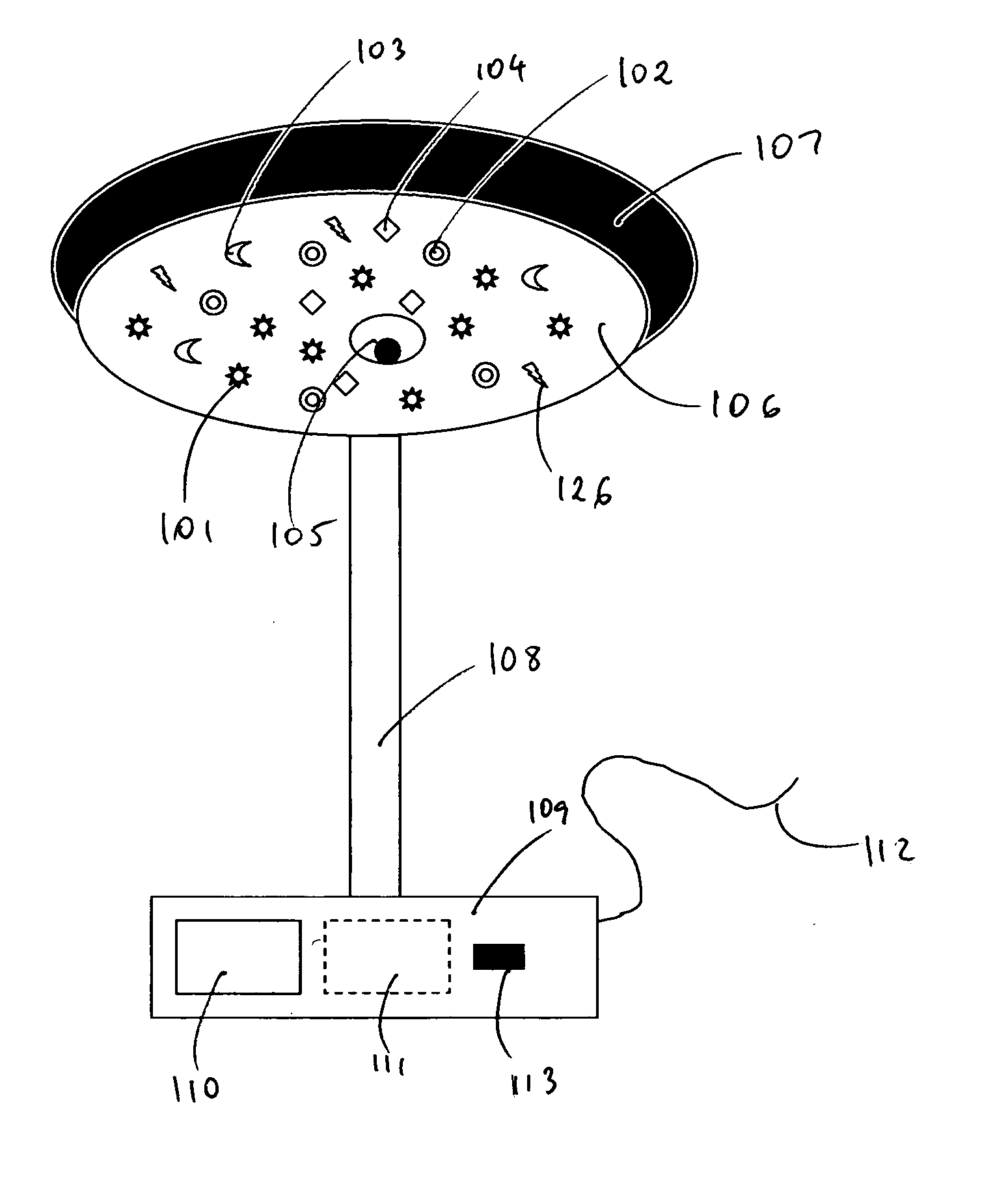
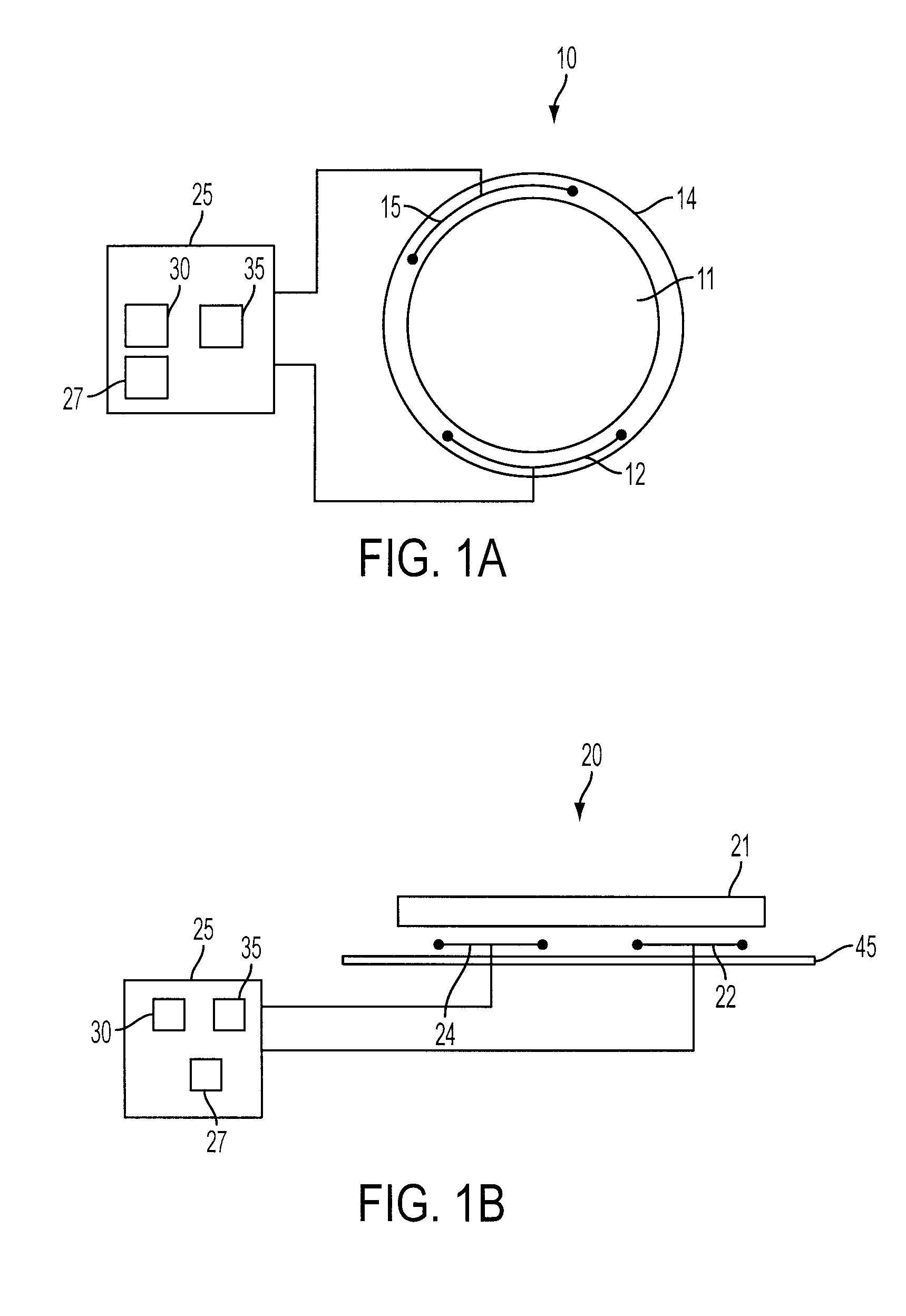
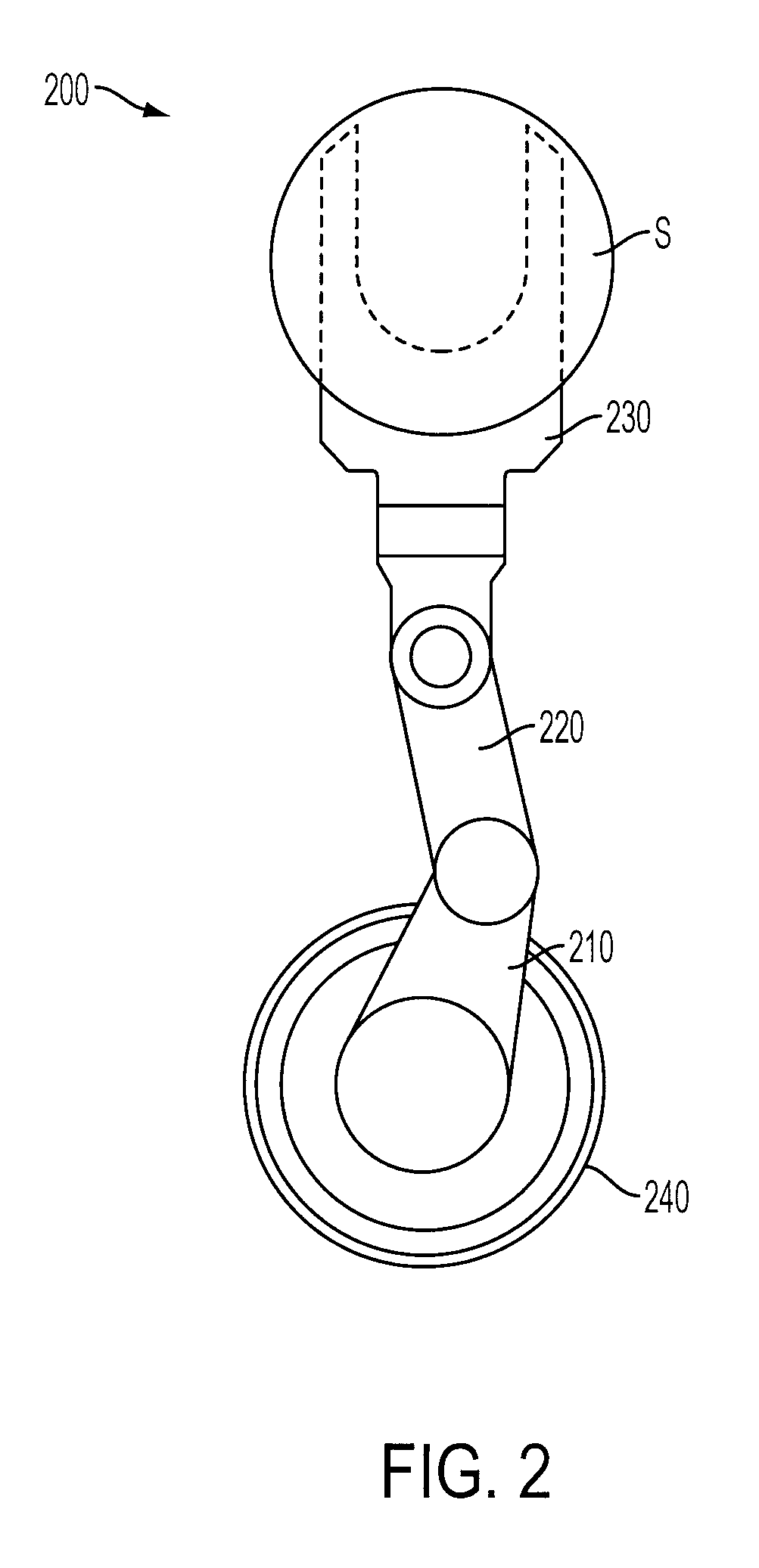
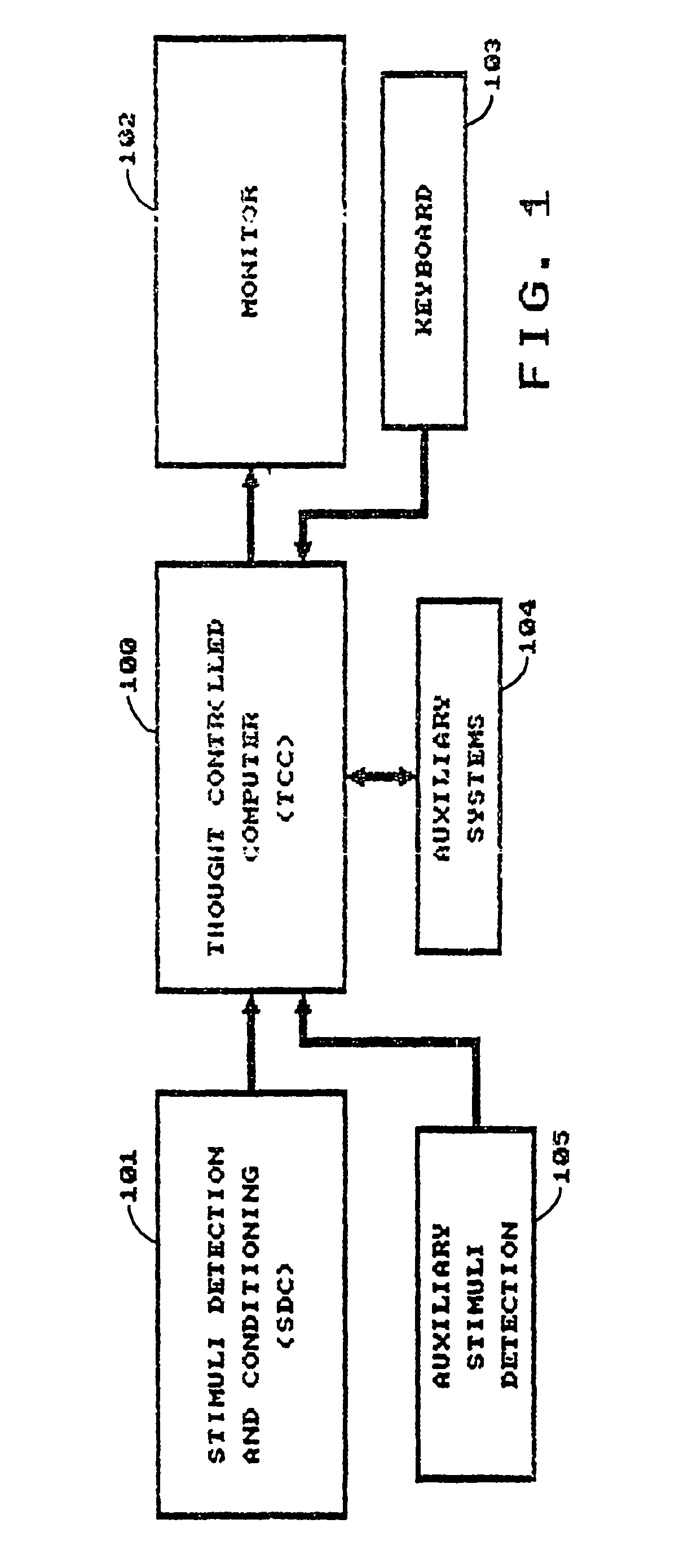
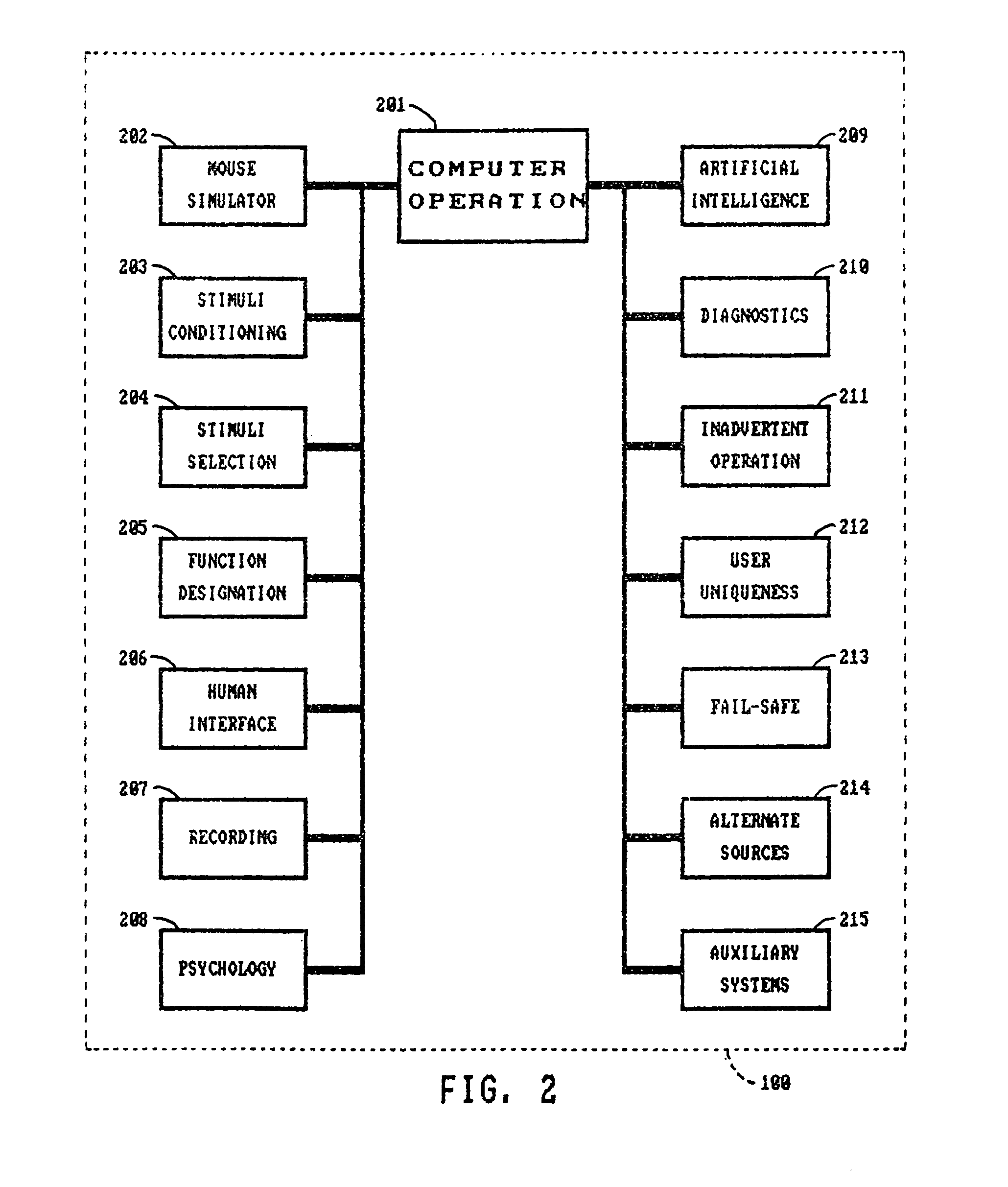
Thought controlled system
InactiveUS8350804B1Optimization mechanismImprove accuracyElectronic switchingCathode-ray tube indicatorsControl systemDependability
A system for controlling a computer by thoughts in the user's brain. The system applies stimuli of the brain via magnetic source imaging (MSI) for controlling the computer. Patterns of brain stimuli are recorded along with the particular thoughts that produced them and these thoughts are interpreted as functions for controlling the computer in much the same way as inputs from a keyboard or mouse. Criteria of acceptance of thought stimuli are generated by the system. Body stimuli, in addition to the brain stimuli, are monitored and used by the system. A user profile is maintained and displayed along with selected pictures for assisting with stimuli / thought pattern utilization. Artificial intelligence is used to enhance stimuli selection, human factors and reliability, as well as analyzing past errors, adverse occurrences and performance. Analyses and summaries are produced by the system for psychiatrists, psychologists, researchers and users to study system enhancement, biofeedback, psychological impact, brain activity, localization and identification of feelings and thought patterns. Stimuli are monitored at brain and body locations. Various functions are applied to animals.
Owner:MOLL EDWARD W
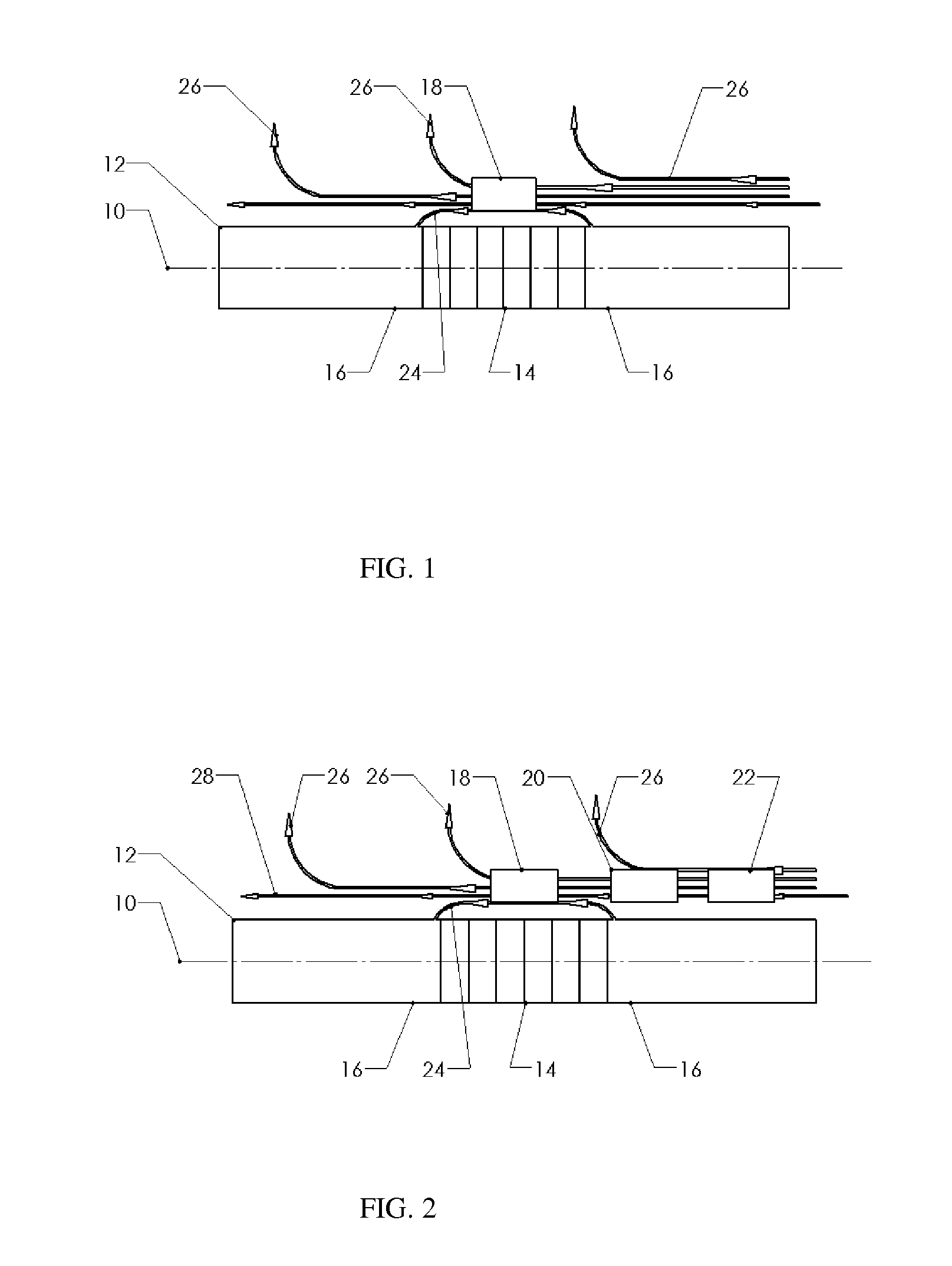
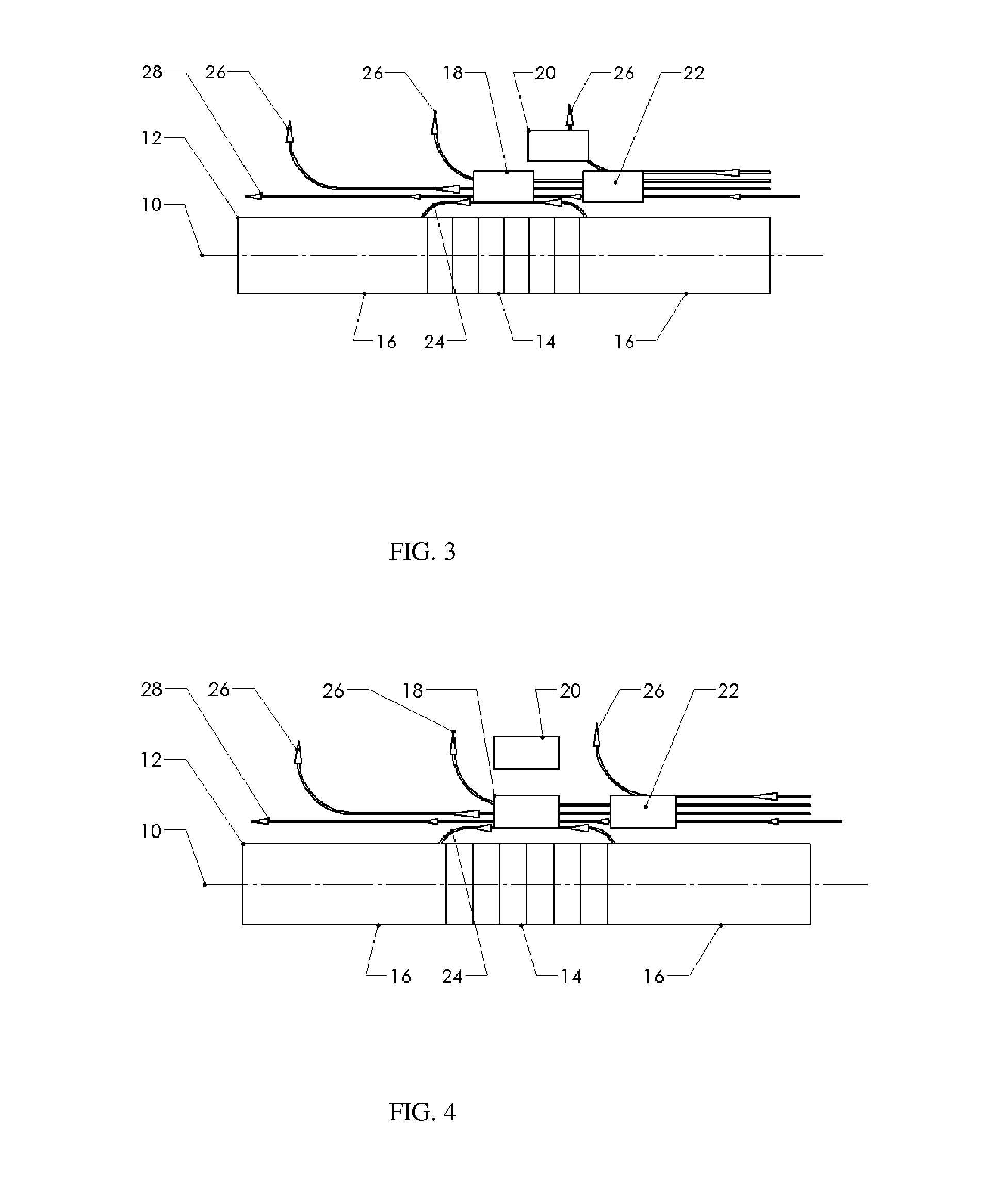
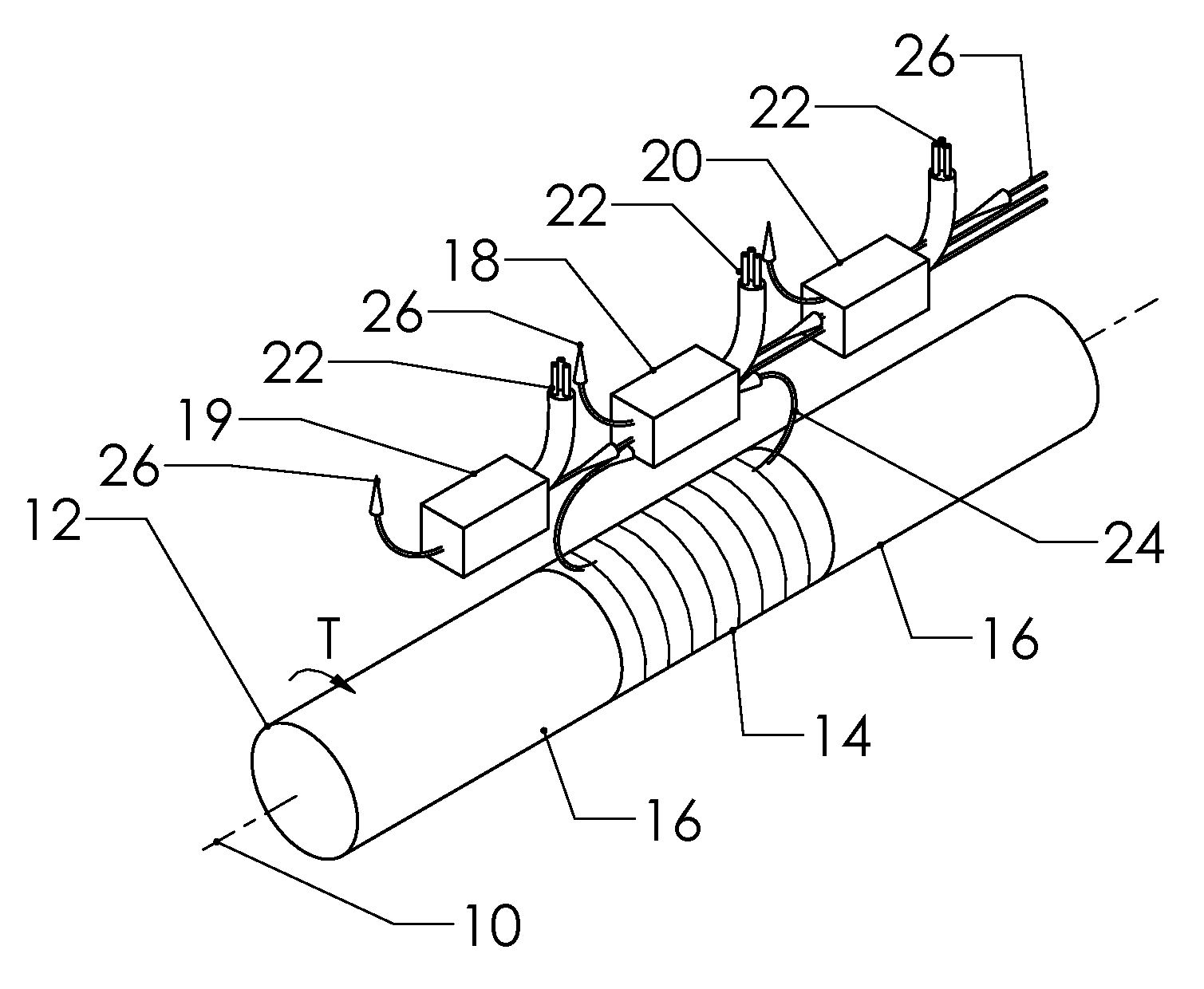
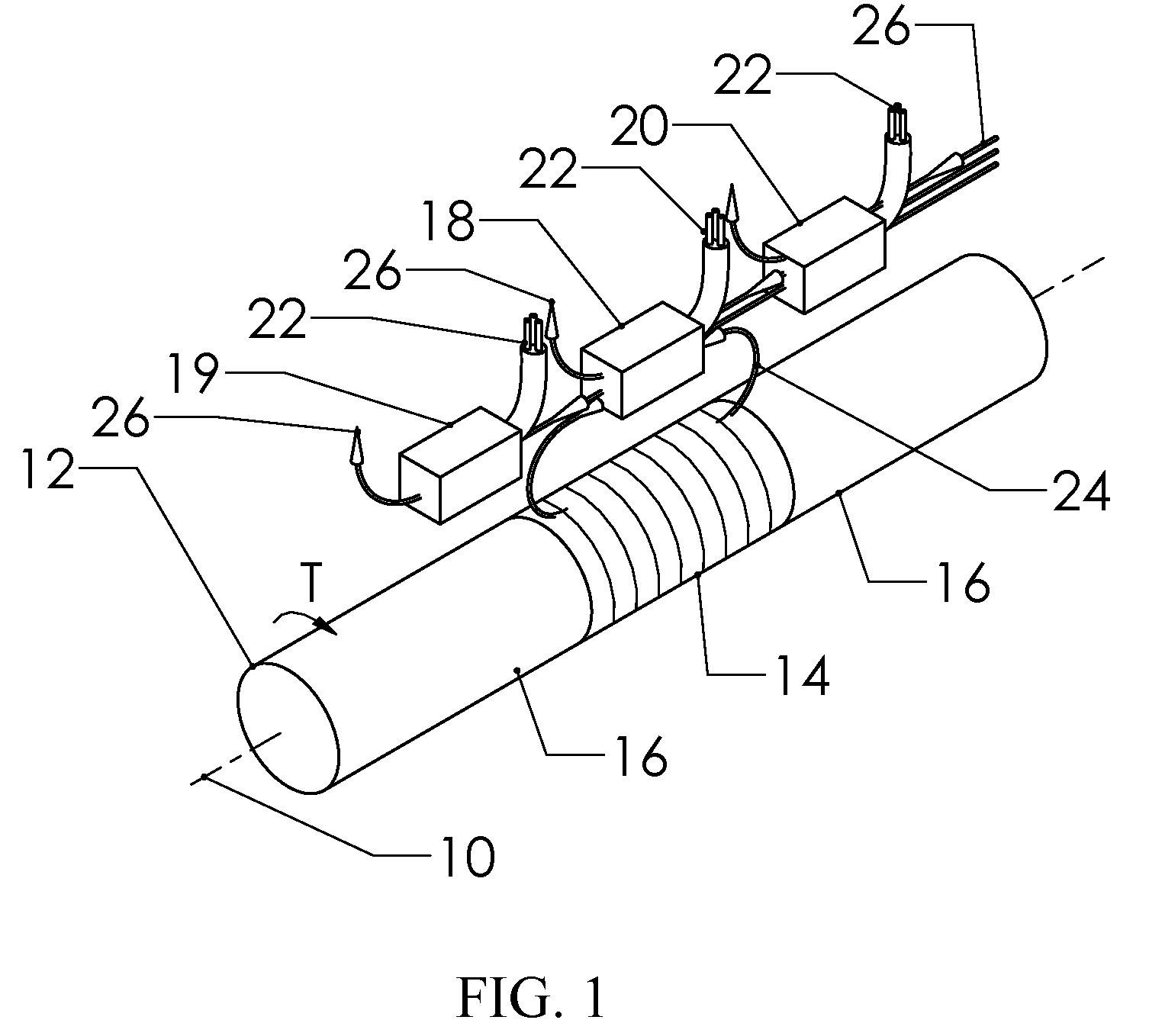
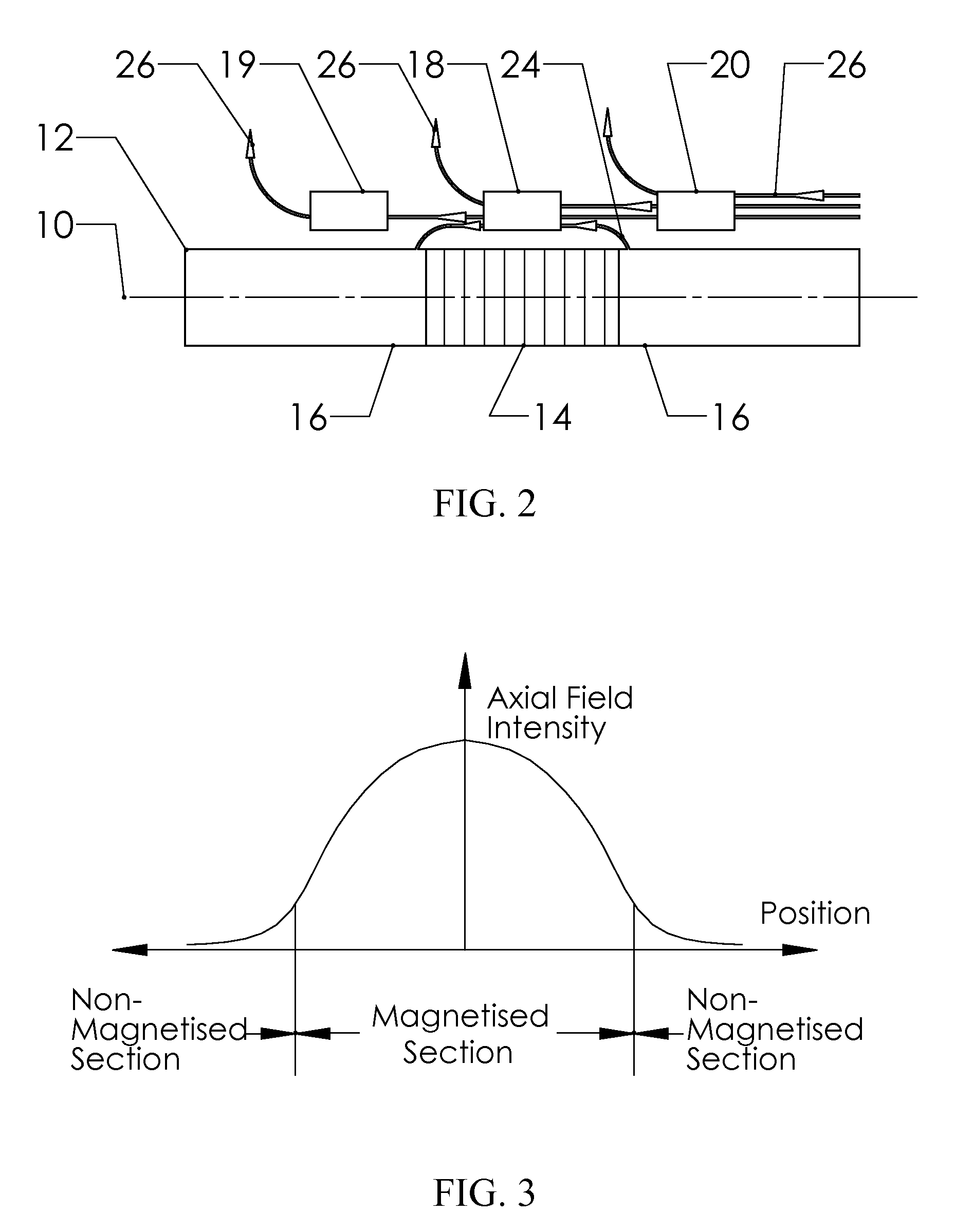
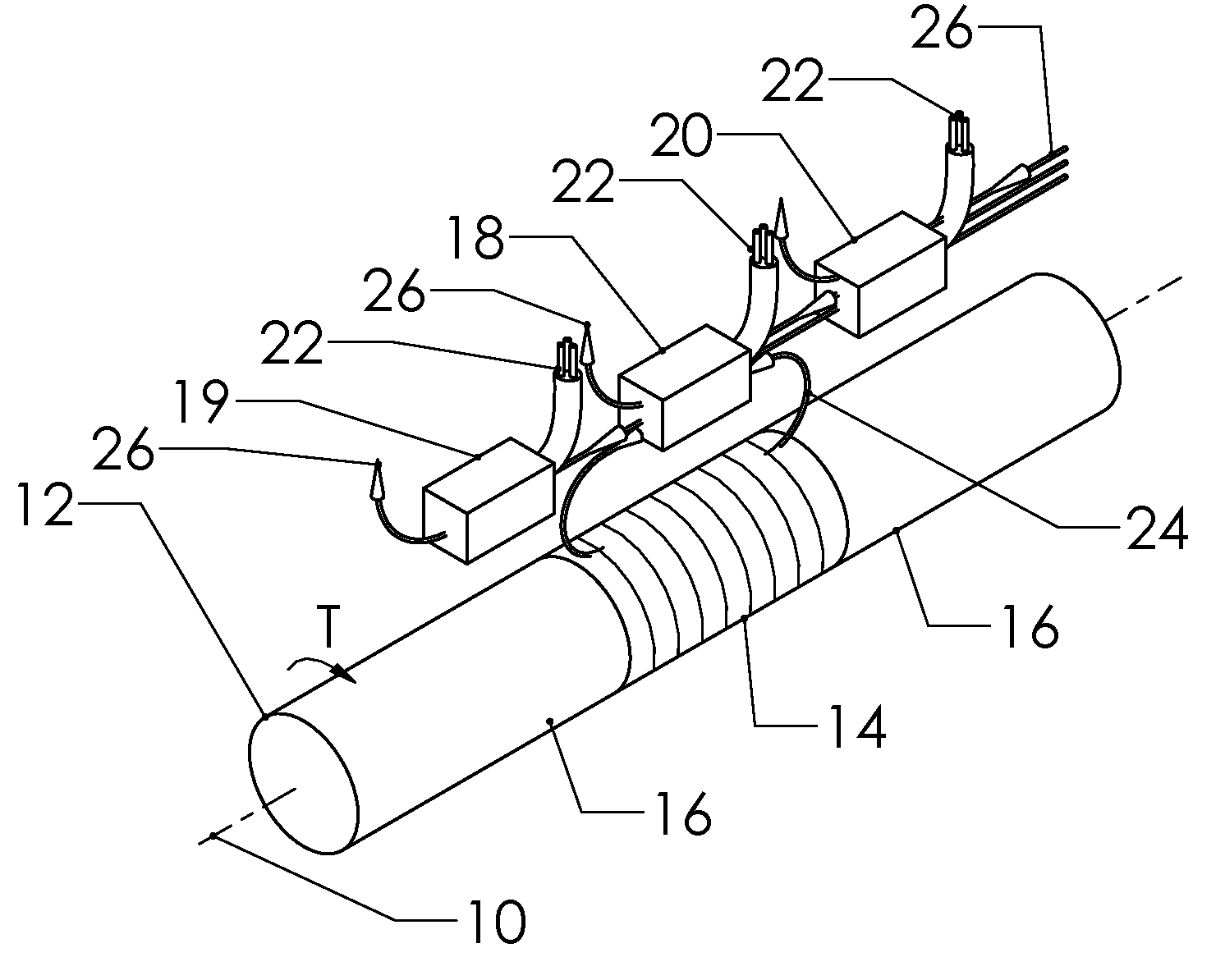
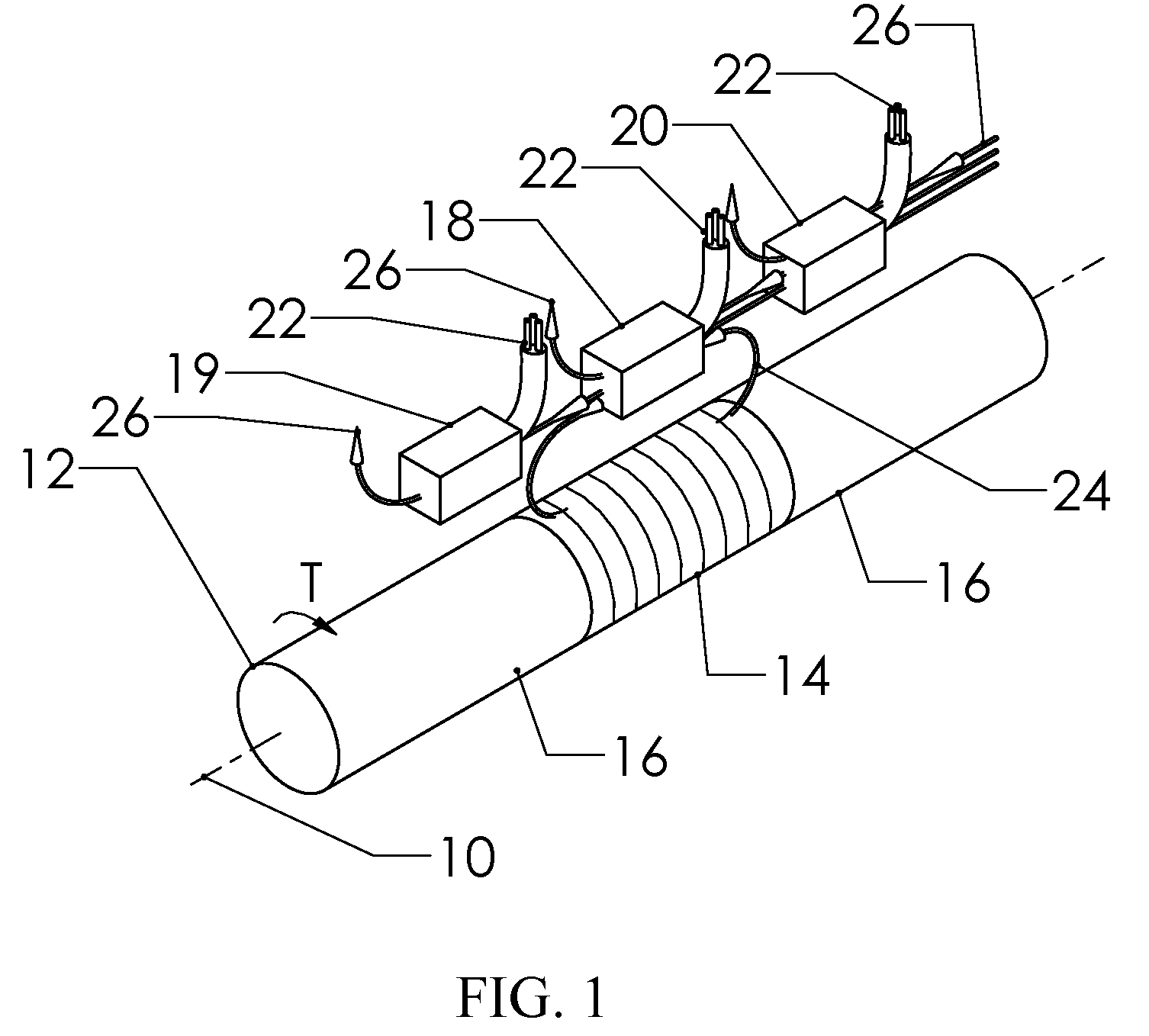
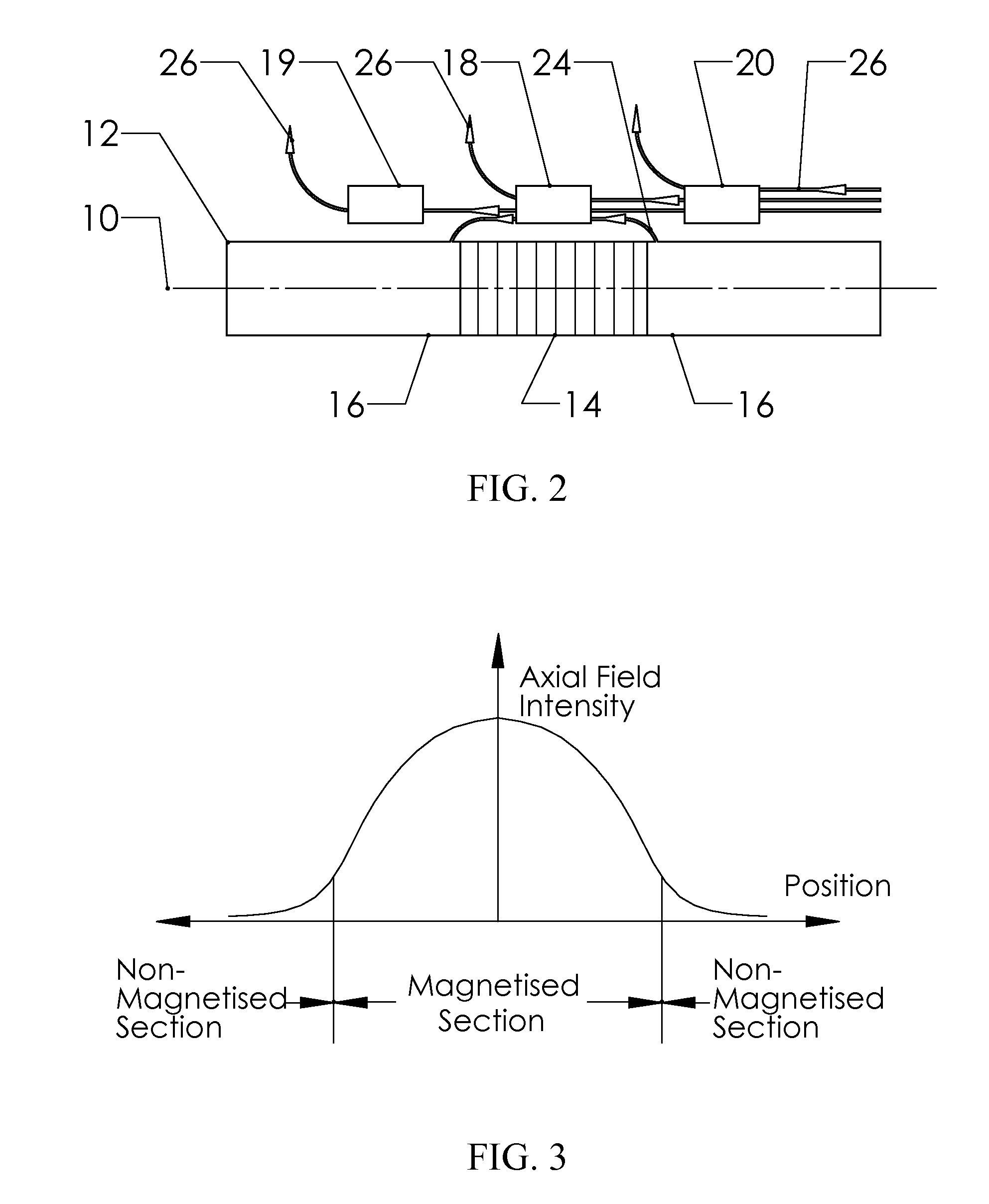
Reduced Ambient Fields Error In A Magnetoelastic Torque Sensor System
InactiveUS20110162464A1Minimize error amountWork measurementTorque measurementHigh magnetic field strengthMagnetic source
An improved magnetic torque transducer involves a method and apparatus for compensating effects of uniform and / or non-uniform magnetic sources by placing three sets of magnetic field sensors around a shaft with at least one magnetized zone. The set of primary magnetic field sensor or sensors is placed proximate to the magnetized zone, both the second and third sets of secondary magnetic field sensors being placed by pre-determined distances to the primary set of magnetic field sensor or sensors, so that primary field sensors always in a position with higher magnetic field strength arise from applied torque than that of secondary sensors. And a method is developed to use the second and third signals from secondary sensors to adjust the primary signal to compensating for the effects of the uniform and / or non-uniform ambient magnetic field sources.
Owner:SMTS
Self-compensating magnetoelastic torque sensor system
InactiveUS8001849B2Improve reliabilityWork measurementMagnetostrictive property measurementsHigh magnetic field strengthMagnetic source
A magnetic torque transducer arrangement for self-compensating effects of external magnetic sources and temperature offset includes a shaft with at least one magnetized zone, at least one active magnetic field sensor and at least one passive magnetic field sensor disposed in such a way that the active field sensor is always in a position with higher magnetic field strength arising from applied torque than that of the passive sensor. Passive field sensors may also be placed on both sides of the active field sensor, or on only one side of the active field sensor. The transducer output is obtained by subtracting the output of the passive field sensors from that of the active field sensor, thus canceling out the effect of the interfering magnetic field flux and temperature offset on the torque transducer, and partially filtering out the temperature sensitivity drift and rotational dependant signal.
Owner:WENG WENSHENG
Method for preparing sludge-based formed magnetic active carbon
ActiveCN103521180AUniform sizeHigh compressive strengthOther chemical processesAlkali metal oxides/hydroxidesMagnetic stabilitySludge
The invention provides a method for preparing sludge-based formed magnetic active carbon. The method comprises the steps as follows: sludge is used as a raw material, an activating agent is added for carbonizing and activating the sludge; nano-sized Fe3O4 is used as a magnetic source for magnetizing the sludge active carbon; and sodium carboxymethylcellulose and aluminum salt are composited to an organic-inorganic binding agent, the binding agent and a p-toluenesulfonhydrazide foaming agent are used for uniformly binding powdery magnetic active carbon into a formed magnetic active carbon precursor with abundant pore structures, and finally, the formed magnetic active carbon precursor is heated to obtain the sludge-based formed magnetic active carbon. According to the method, the sludge is used as a main raw material, the resource utilization of the sludge is achieved, the recycling is convenient, and reutilization can be achieved; and further, the sludge-based formed magnetic active carbon has a stable structure and good magnetic stability, and can be widely used in the fields such as sewage treatment, soil pollution treatment and the like.
Owner:FUJIAN UNIV OF TECH
Self-compensating magnetoelastic torque sensor system
InactiveUS20100242626A1Improve reliabilityWork measurementMagnetostrictive property measurementsHigh magnetic field strengthMagnetic source
An improved magnetic torque transducer arrangement for self-compensating effects of external magnetic sources and temperature offset comprises a shaft with at least one magnetized zone, at least one active magnetic field sensor and at least one passive magnetic field sensor disposed in such a way that active field sensor always in a position with higher magnetic field strength arise from applied torque than that of passive sensor. Passive field sensors may also be placed in both sides of the active field sensor, or on one side of active field sensor only. The transducer output is obtained by subtract the output of passive field sensors from that of active field sensor thus cancel out the effect of interfering magnetic field flux and temperature offset on the torque transducer, and partially filter out temperature sensitivity drift and rotational dependant signal. The sensitivity of active and passive field sensors can also be electrically matched by calibrating them in a uniform magnetic field, thus a completely common mode rejection can be achieved. The sensor arrangements may also be utilized in other type of sensors that extract changes in magnetic fields to indirectly detect direction, speed, presence, force, linear position, or angle to cancel out interfering magnetic field and temperature offset effect.
Owner:WENG WENSHENG
Multivariable generator and method of using the same
InactiveUS20060087187A1Extended service lifeLow heat generationAcyclic motorsSynchronous machines with stationary armatures and rotating magnetsMagnetic sourceEngineering
Owner:MAGNETIC TORQUE INT
Method for obtaining radar cross section (RCS) of homogeneous bi-isotropic medium object
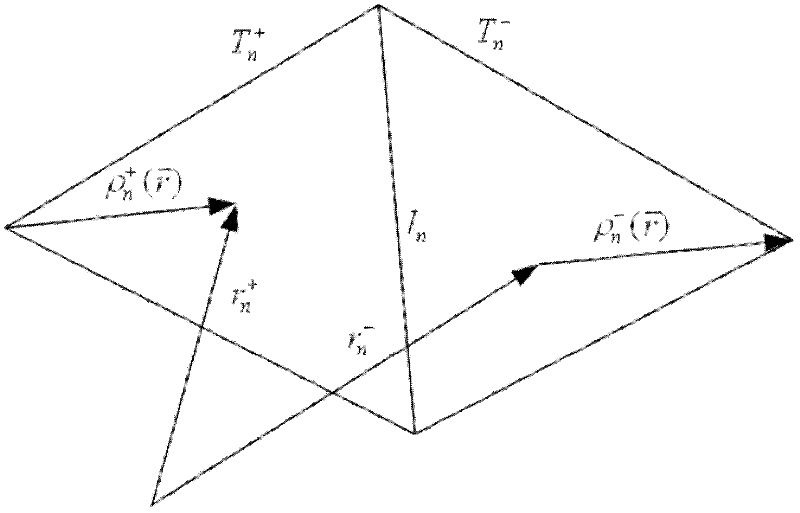
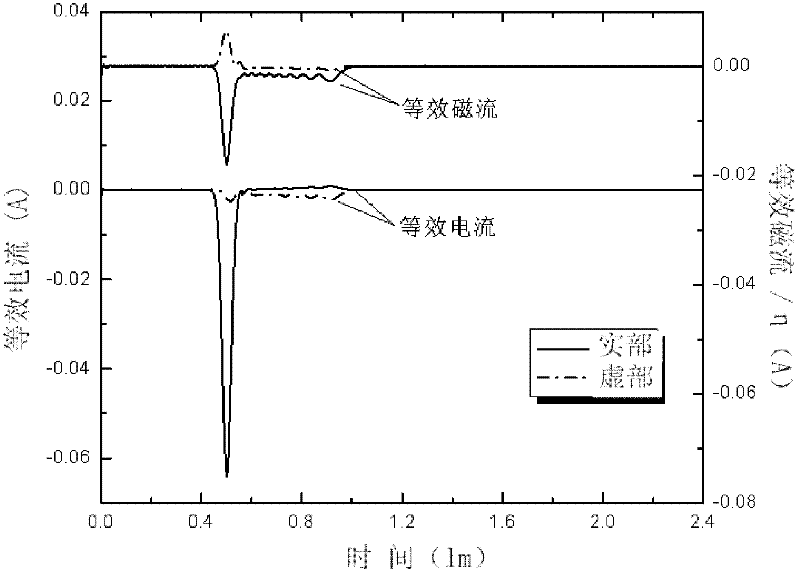
InactiveCN102508220AUniform Scattering Cross SectionScattered field stabilizationWave based measurement systemsMagnetic sourceRao wilton glisson
The invention relates to the field of electromagnetic wave and radar monitoring and provides a method for obtaining radar cross section (RCS) of a homogeneous bi-isotropic medium object. The method comprises the following steps of: building a geometrical model of the homogeneous bi-isotropic medium object and dividing the surface of the model into a plurality of triangular patches in seamless connection; introducing a planar power source vector function and a planar magnetic source vector function; applying a field decomposition method in the homogeneous bi-isotropic medium object; obtaining a boundary integral equation on the surface of a scatterer according to the boundary conditions; applying a moment method to carry out numerical solution on the boundary integral equation, including space test and time test; adopting RWG (Rao-Wilton-Glisson) basis functions as the spatial basis function and test function and adopting Laguerre functions with amplitude factors as the temporal basis function and test function; and obtaining electromagnetic scattering of an observation point according to the equivalence principle and then applying Fourier transform to obtain the RCS. The method has the following advantages that: the obtained scattered field of the homogeneous bi-isotropic medium object is stable; and the RCS with wide frequency range can be obtained.
Owner:郑州微纳科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com