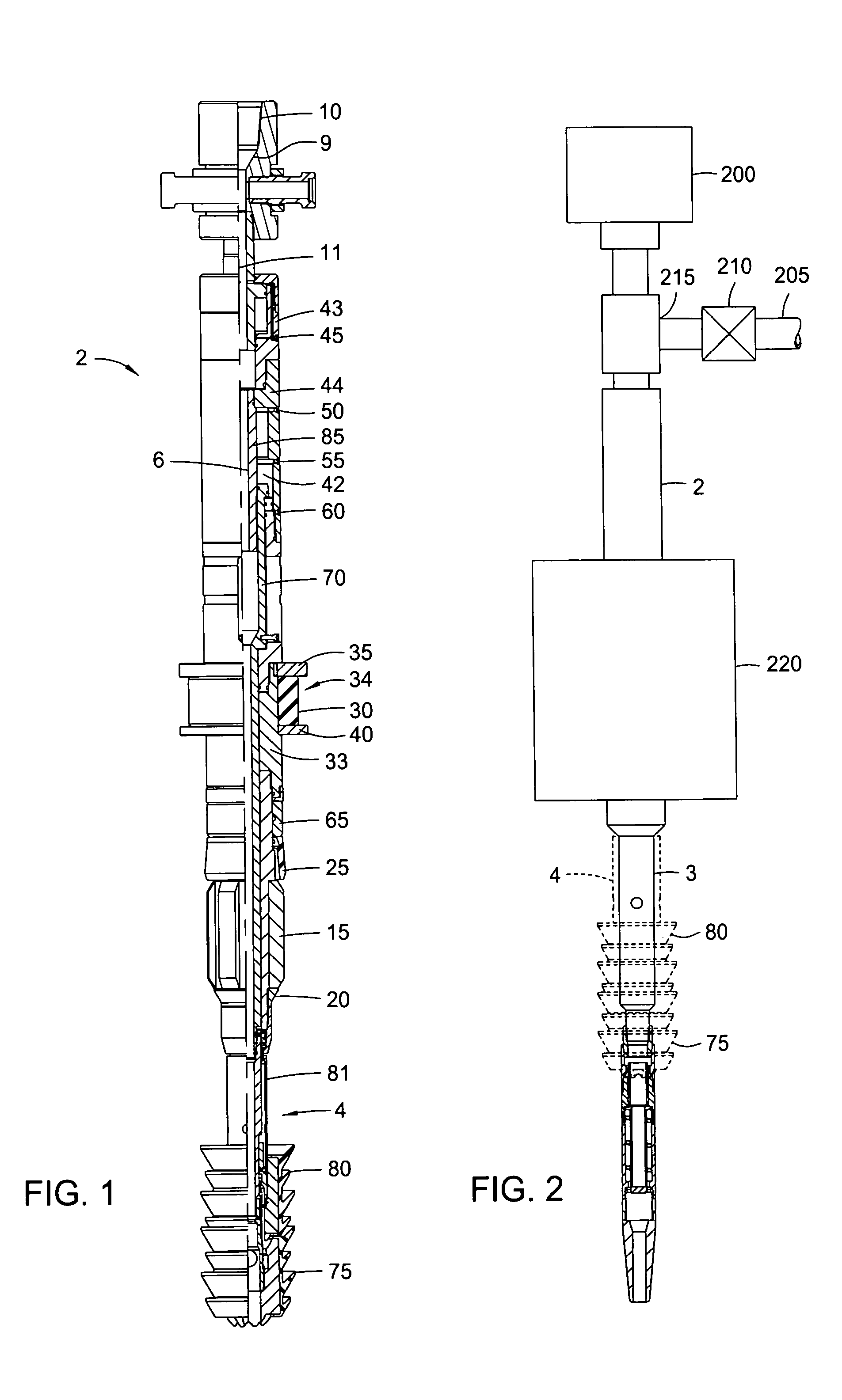
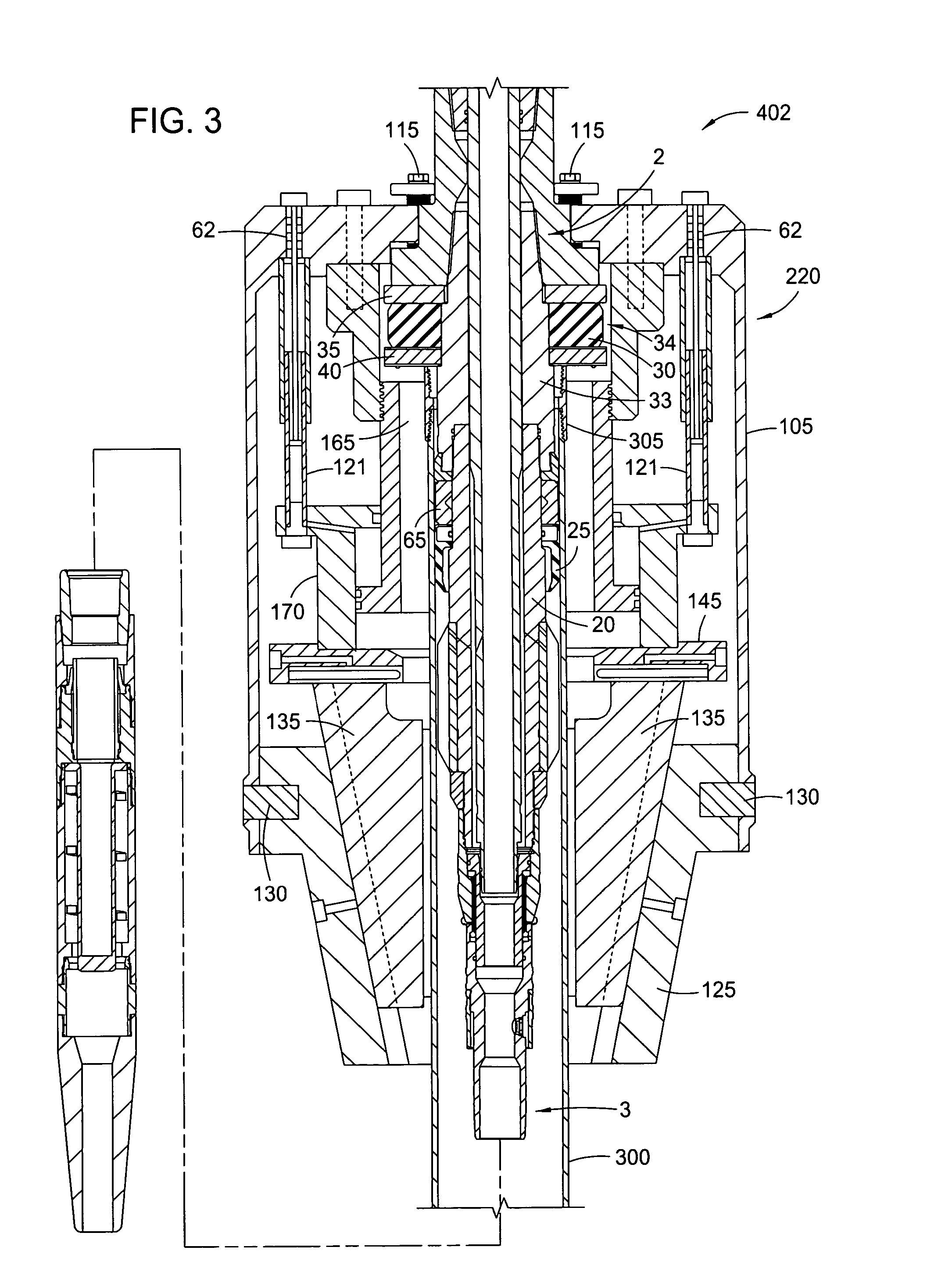
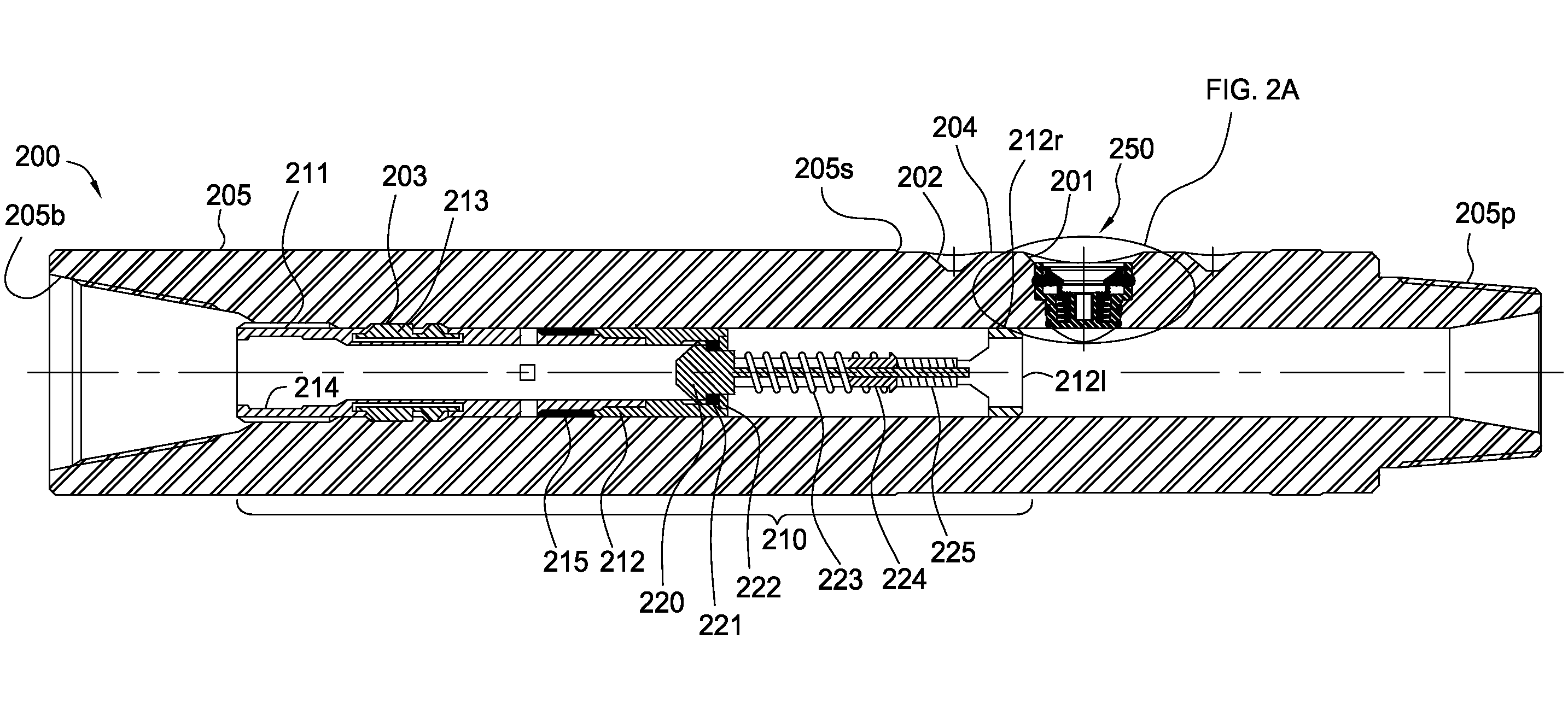
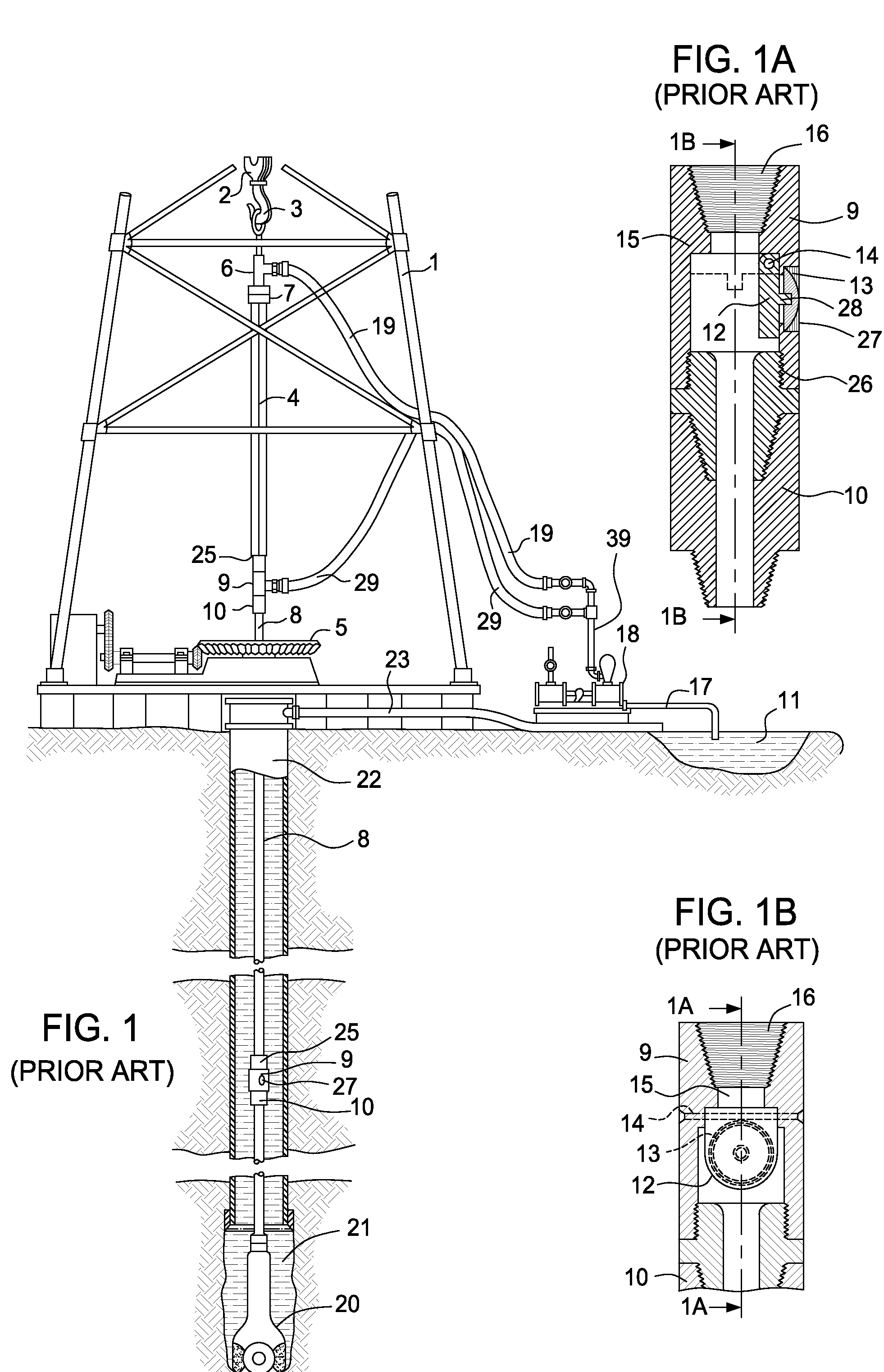
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
13921 results about "Well drilling" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
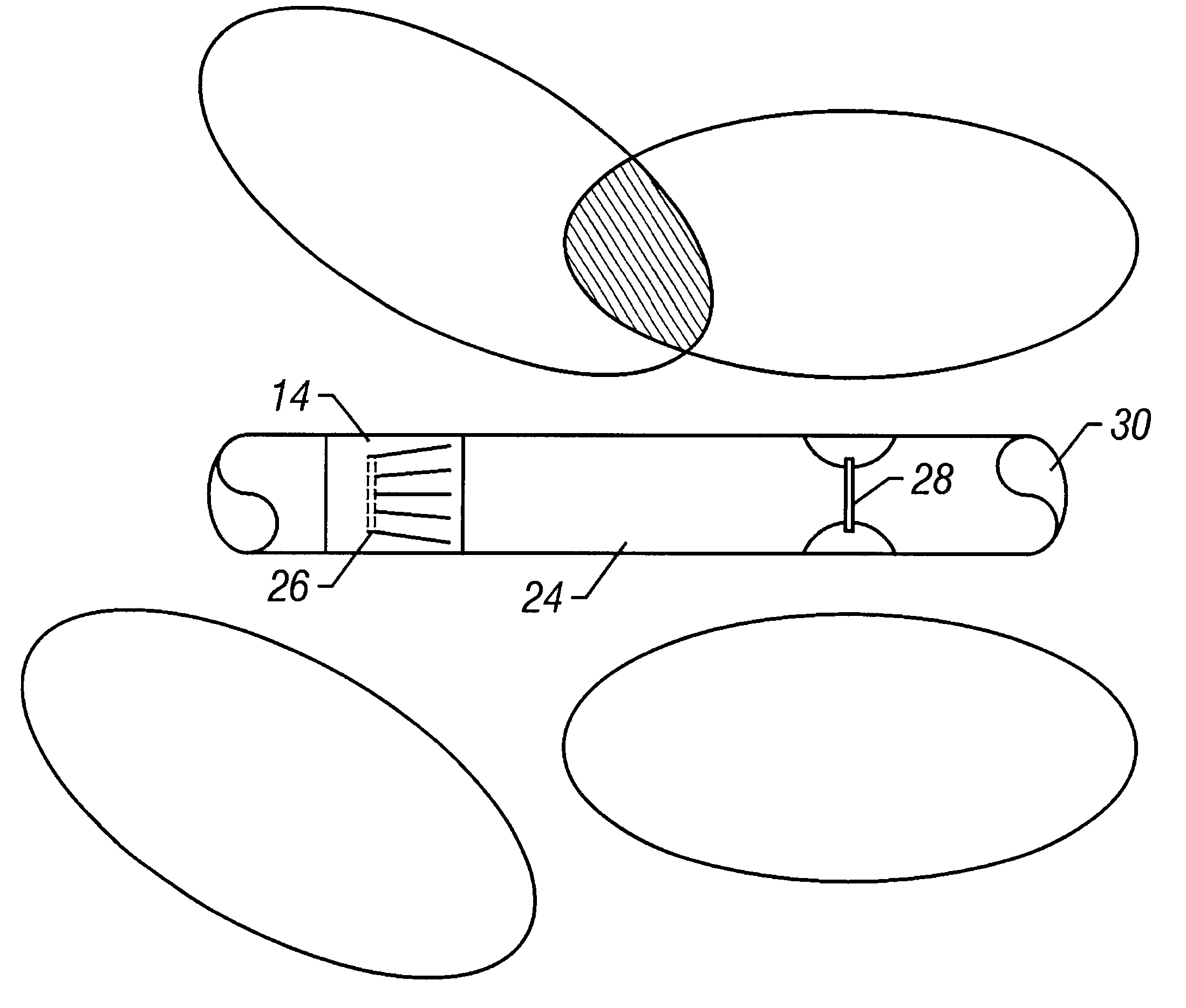
Application Year
Inventor
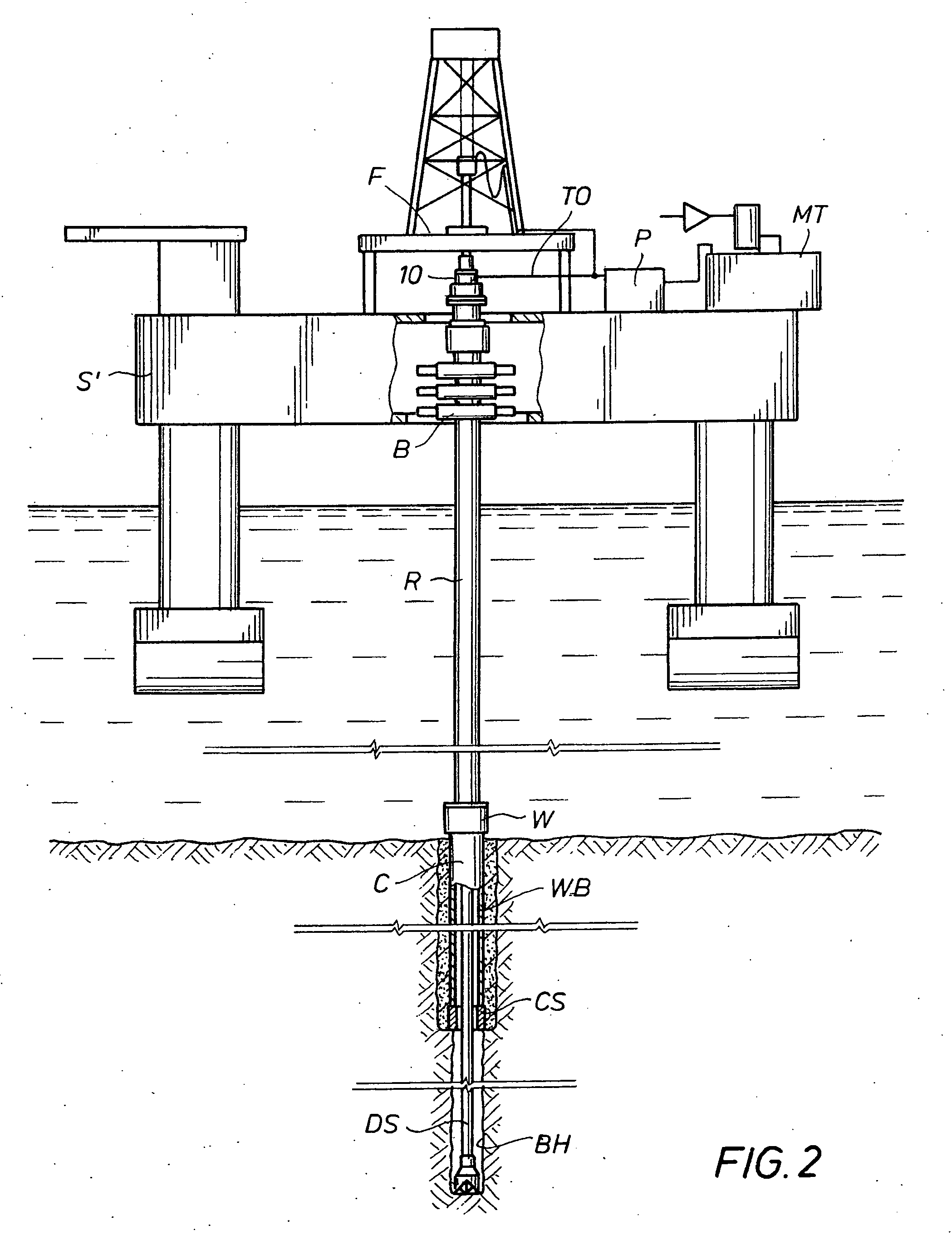
Well drilling is the process of drilling a hole in the ground for the extraction of a natural resource such as ground water, brine, natural gas, or petroleum, for the injection of a fluid from surface to a subsurface reservoir or for subsurface formations evaluation or monitoring. Drilling for the exploration of the nature of the material underground (for instance in search of metallic ore) is best described as borehole drilling.
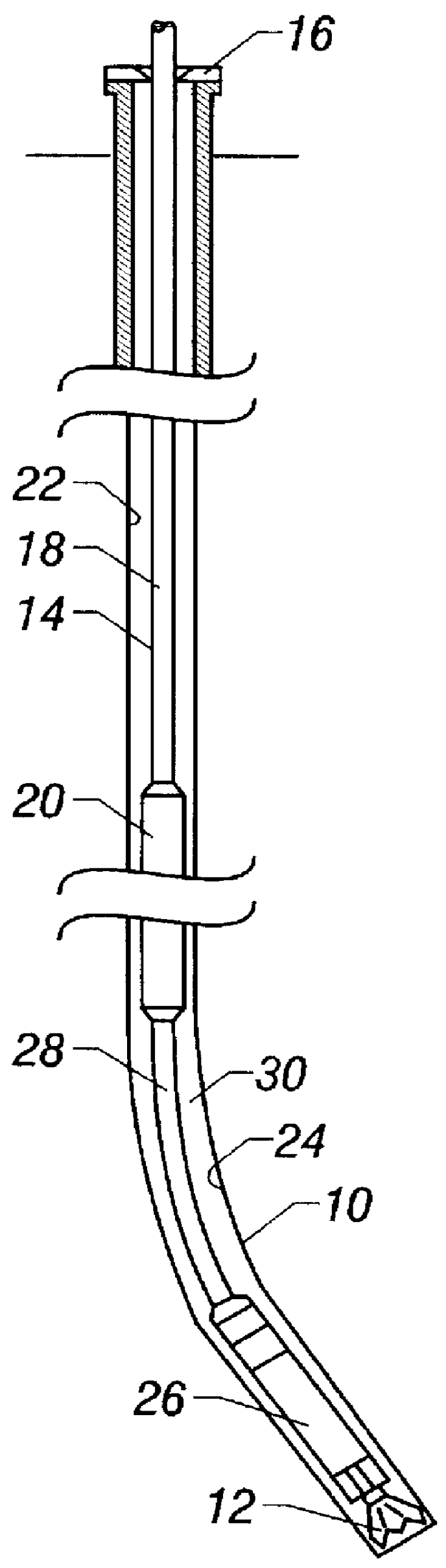
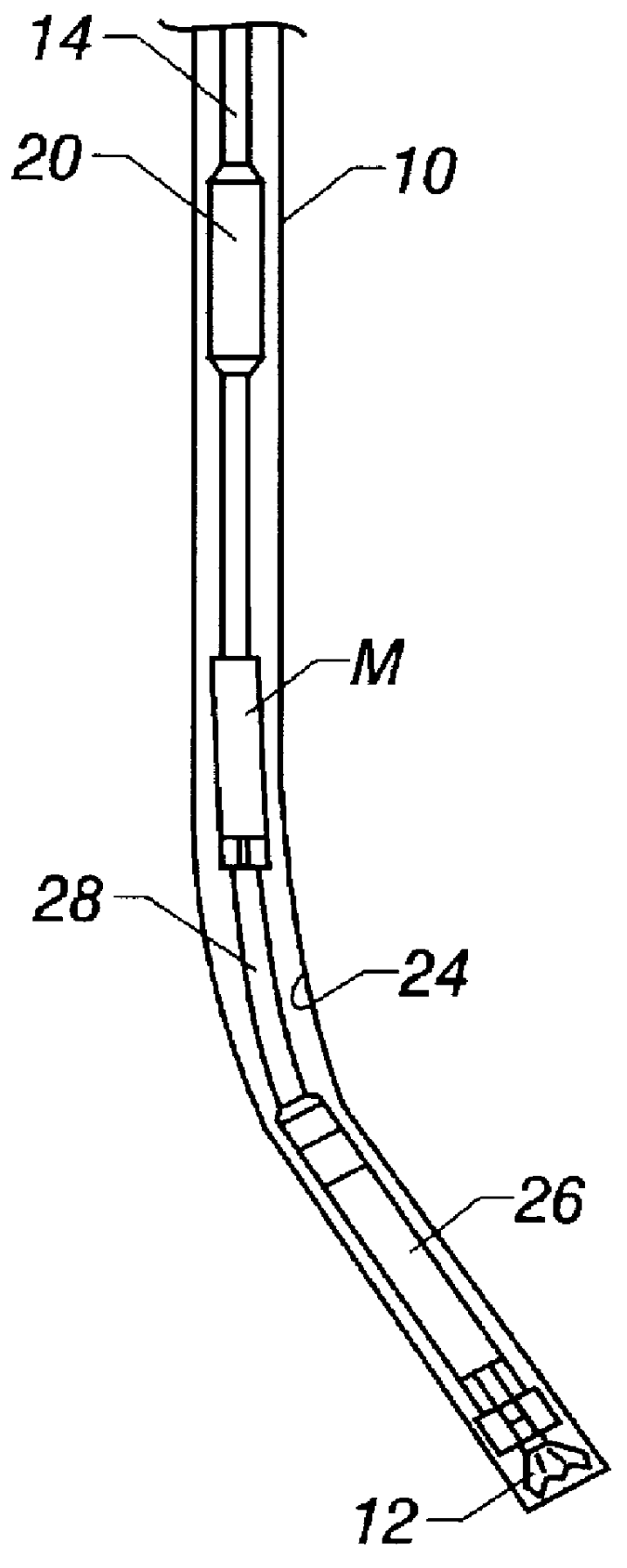
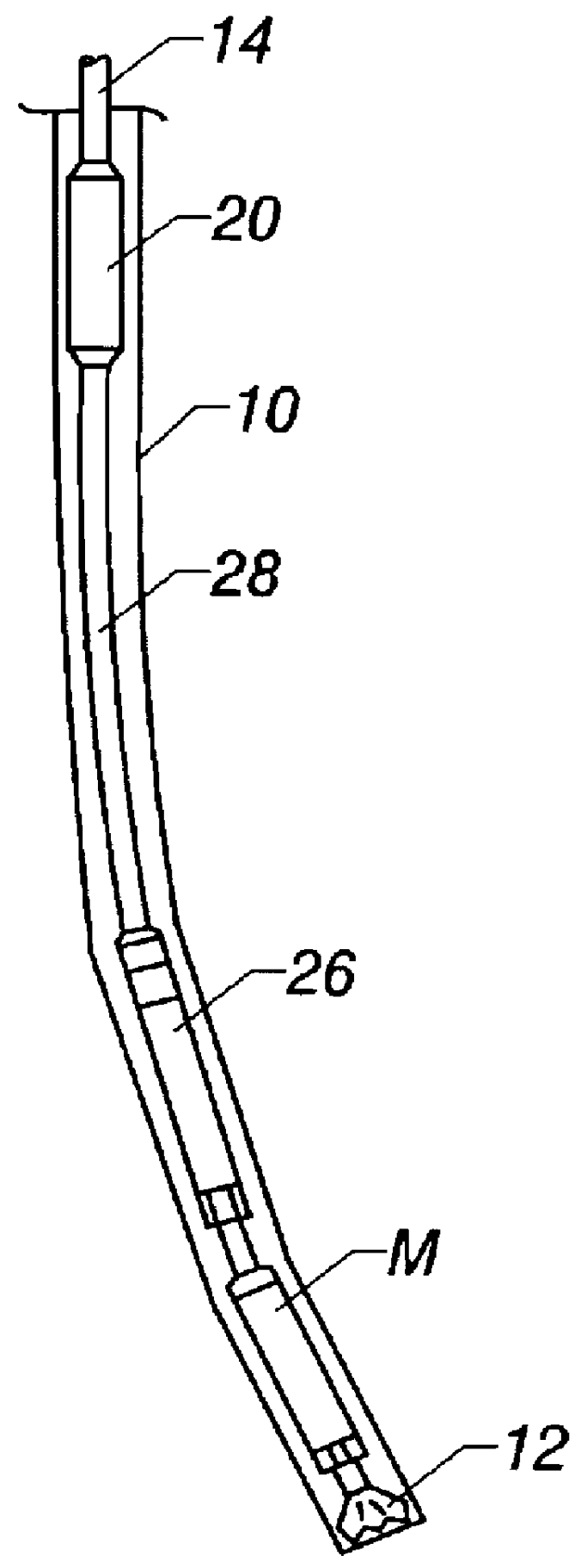
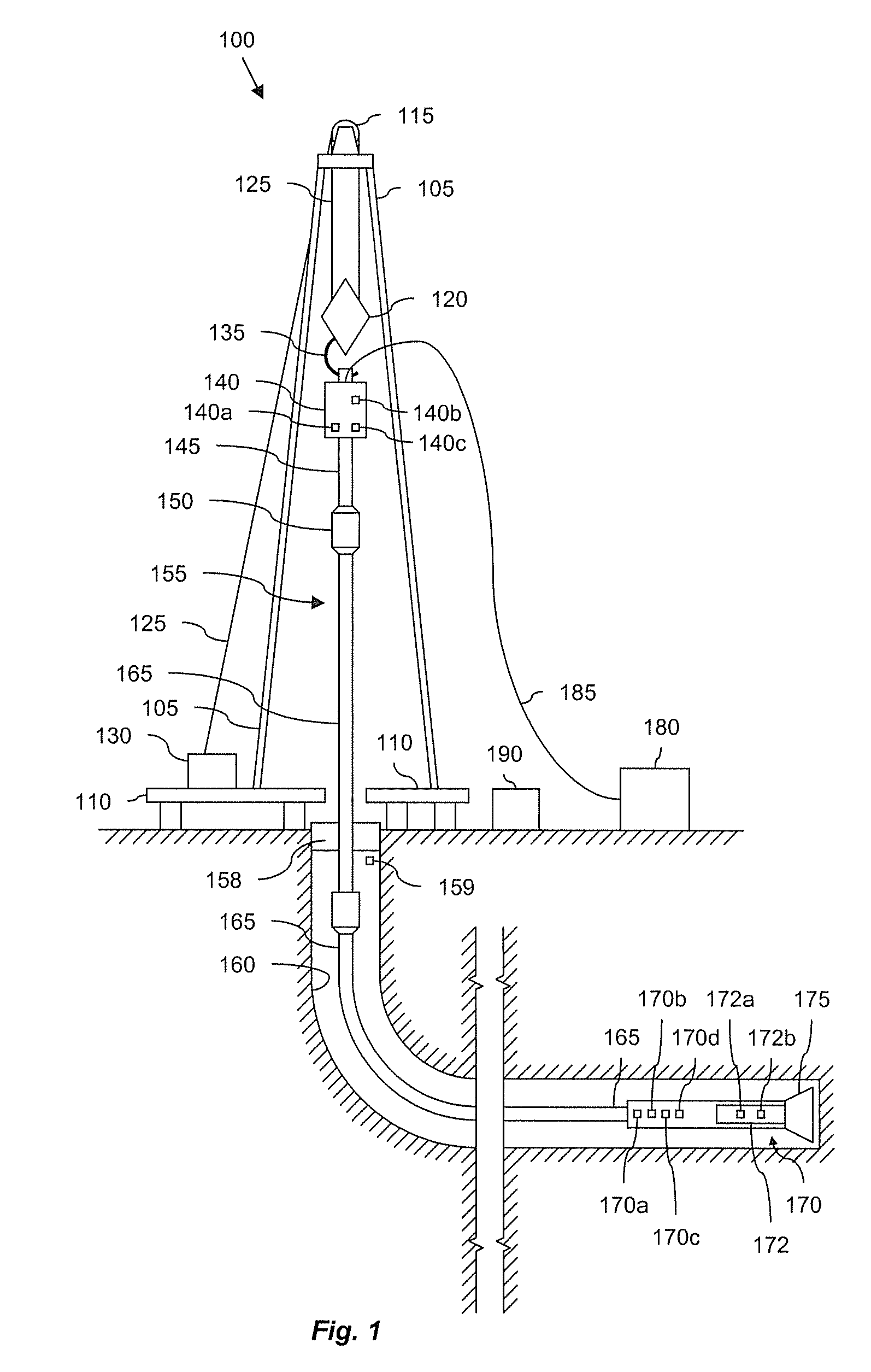
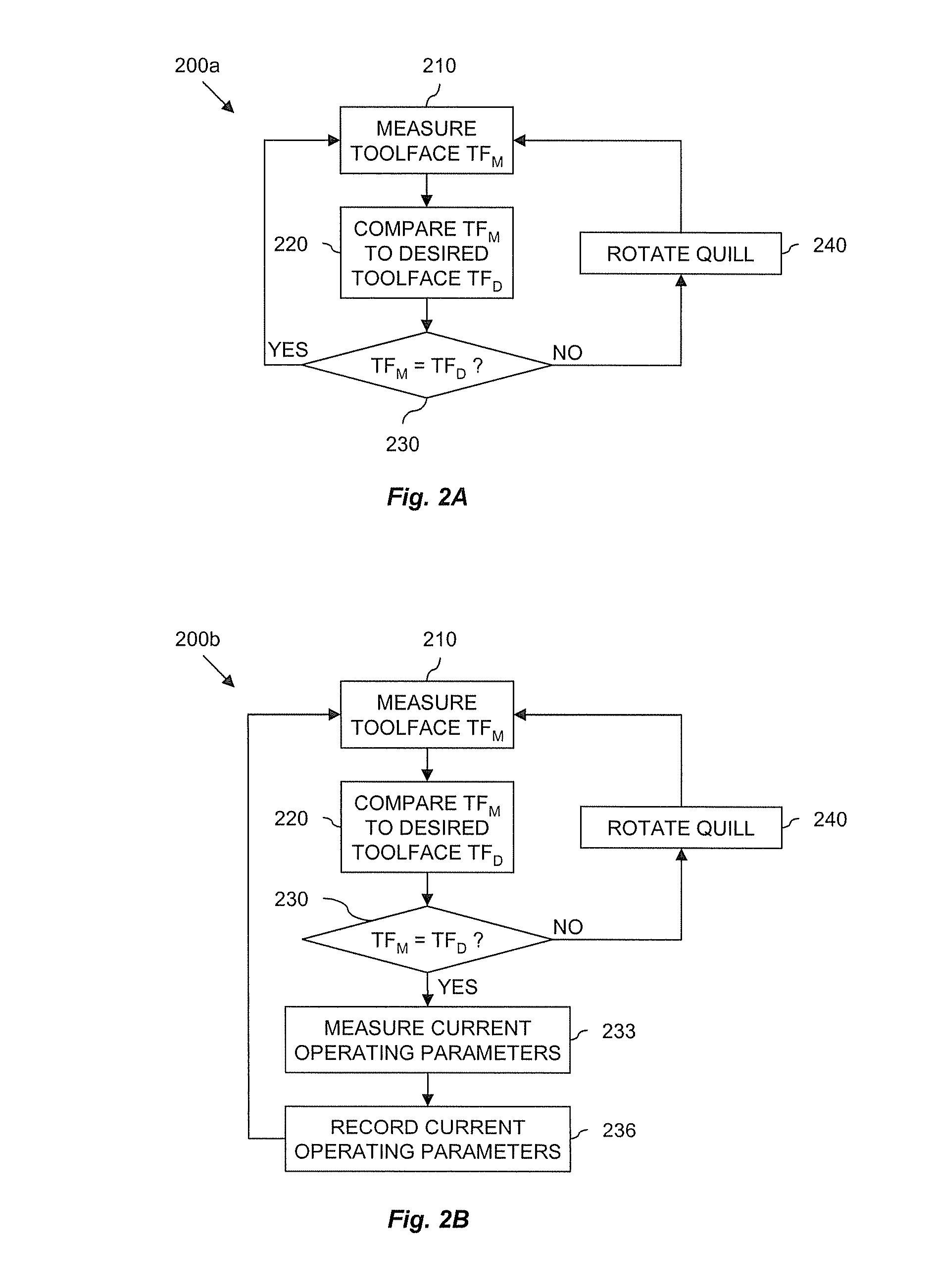
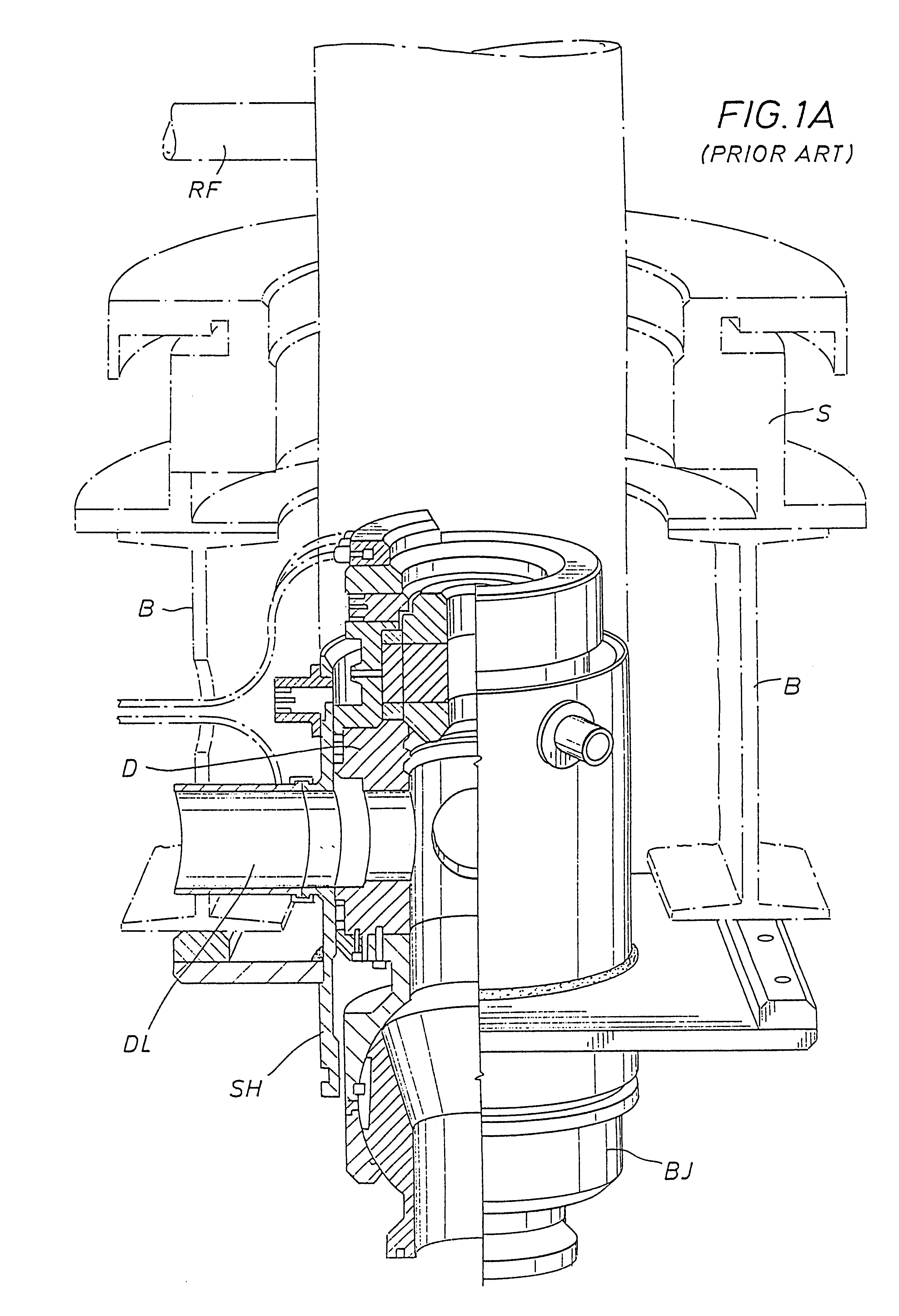
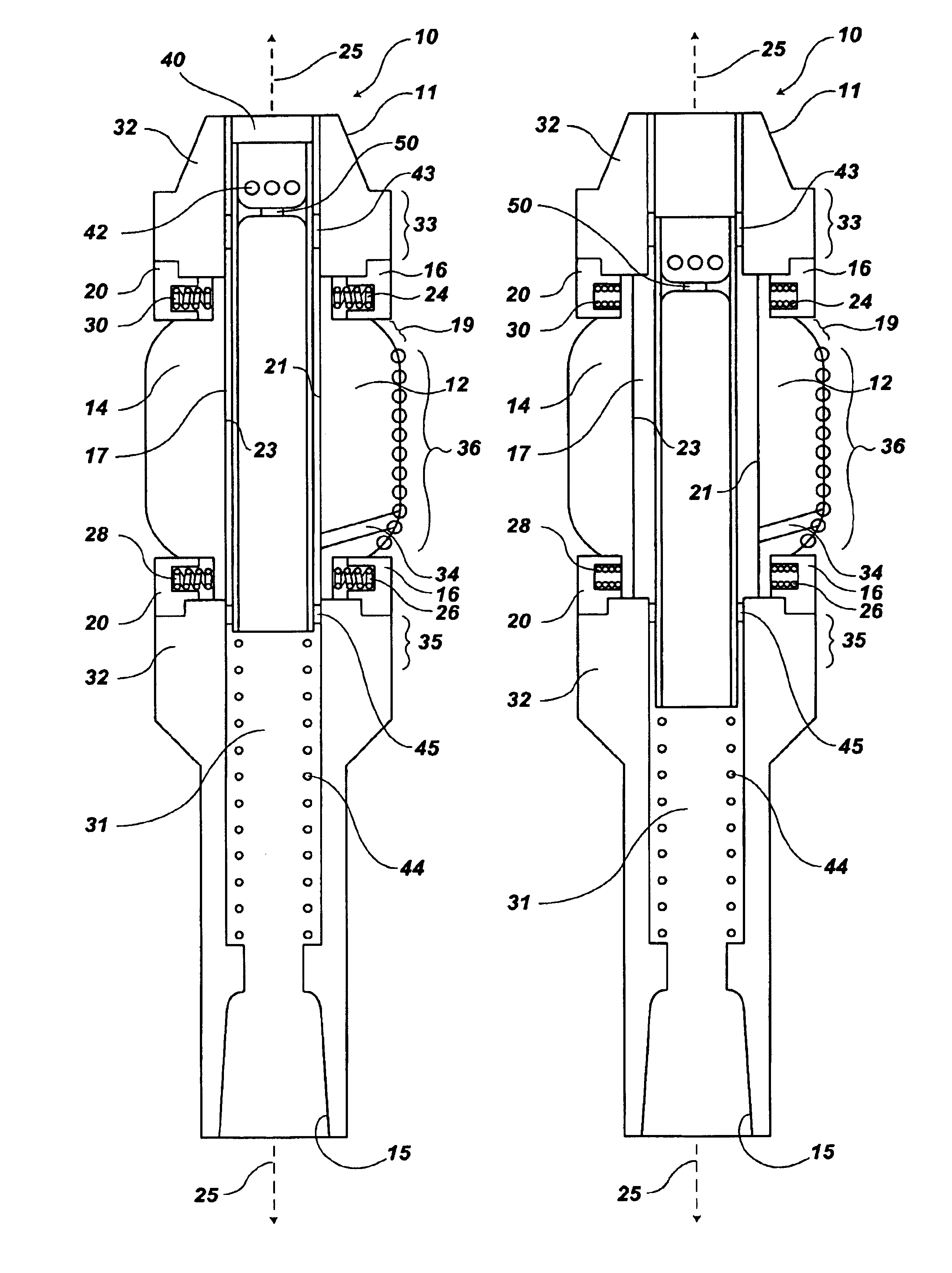
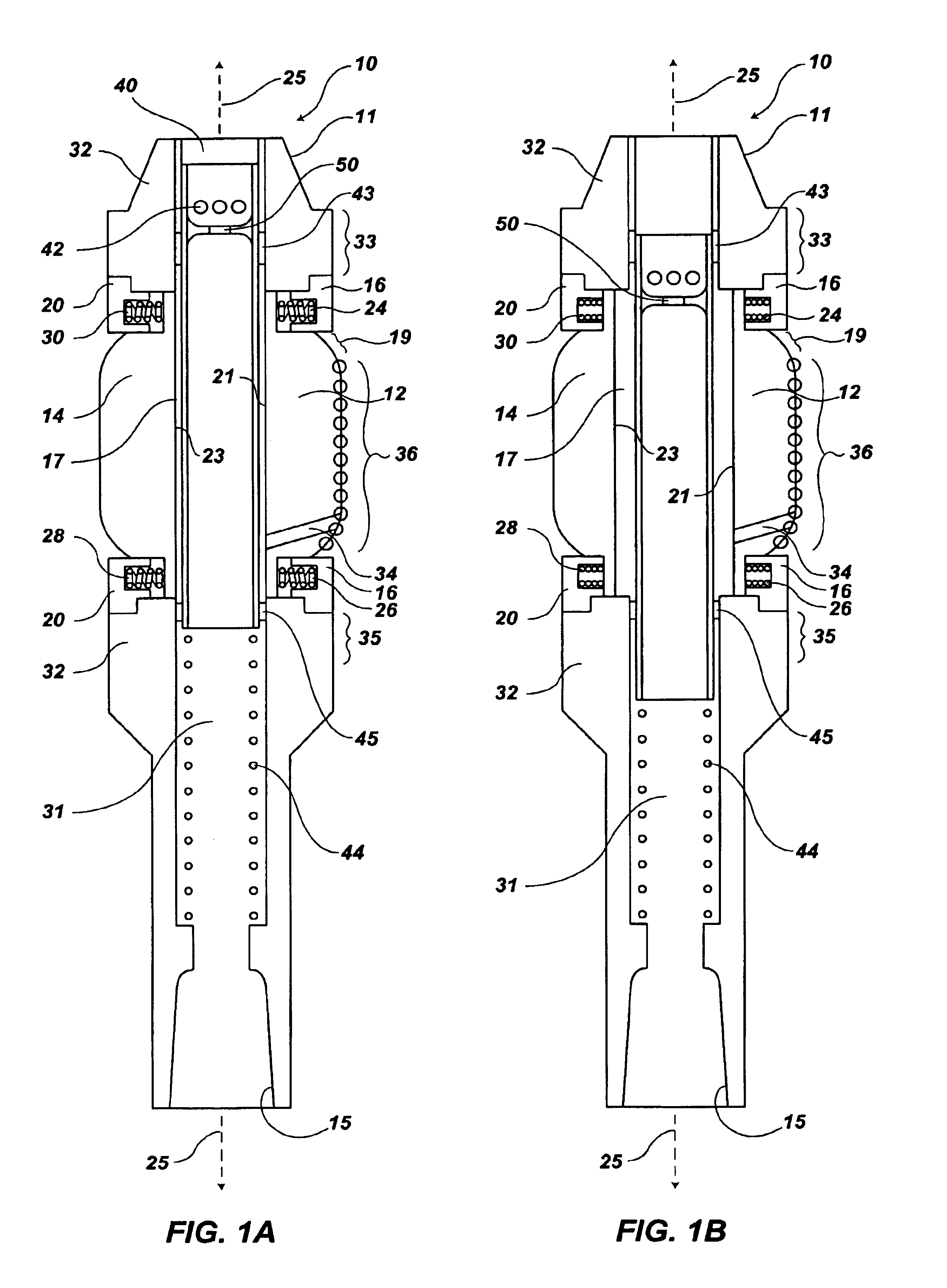
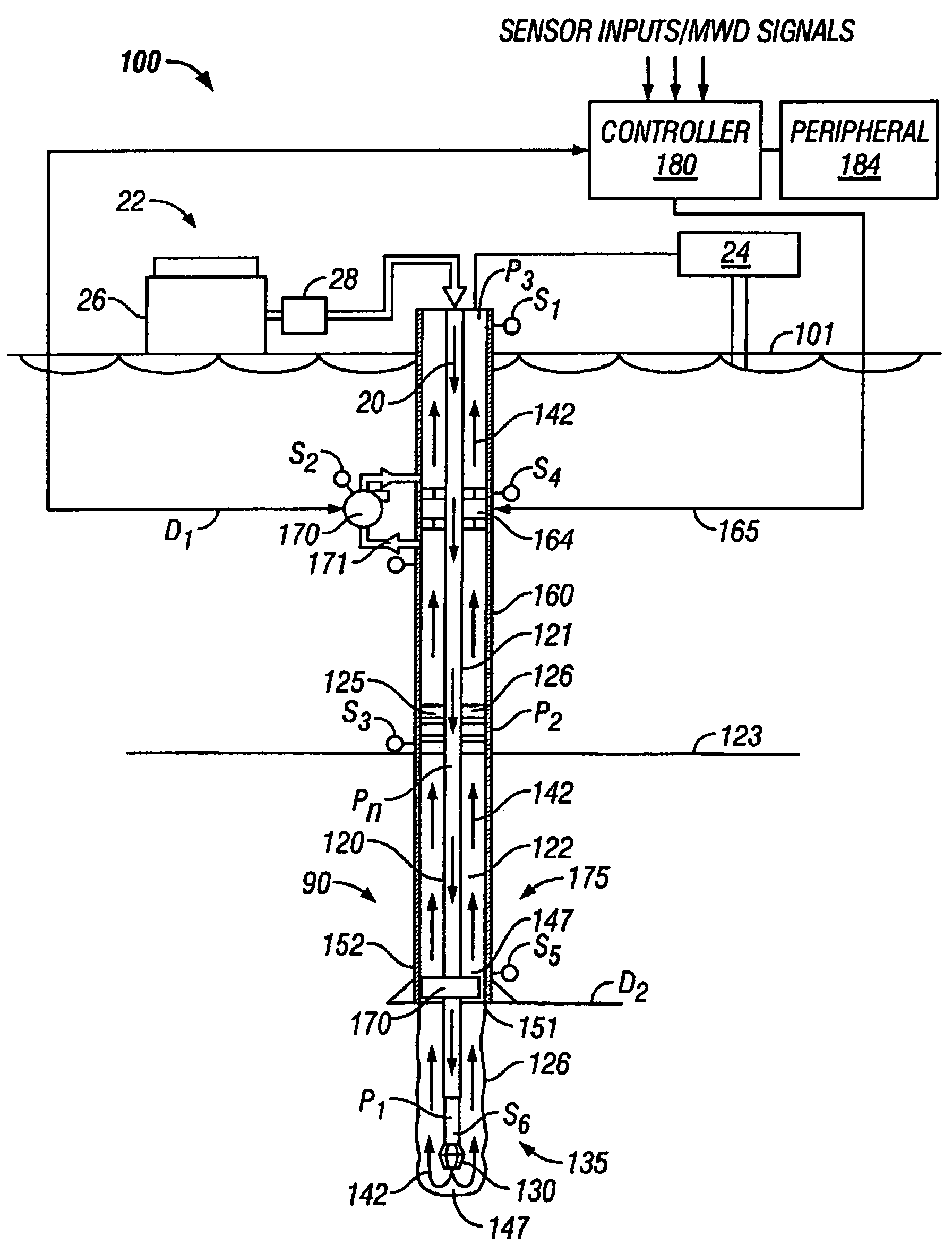
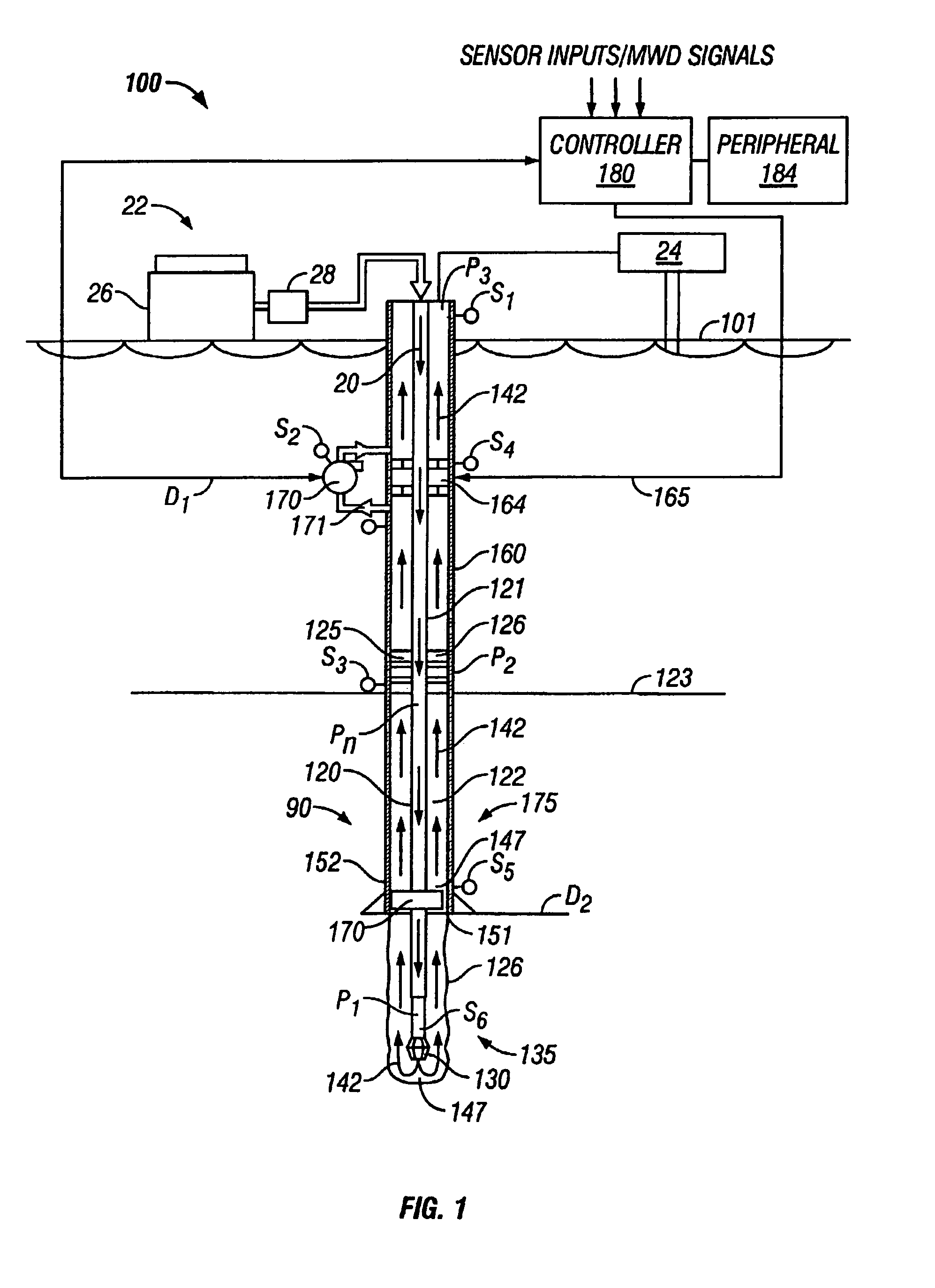
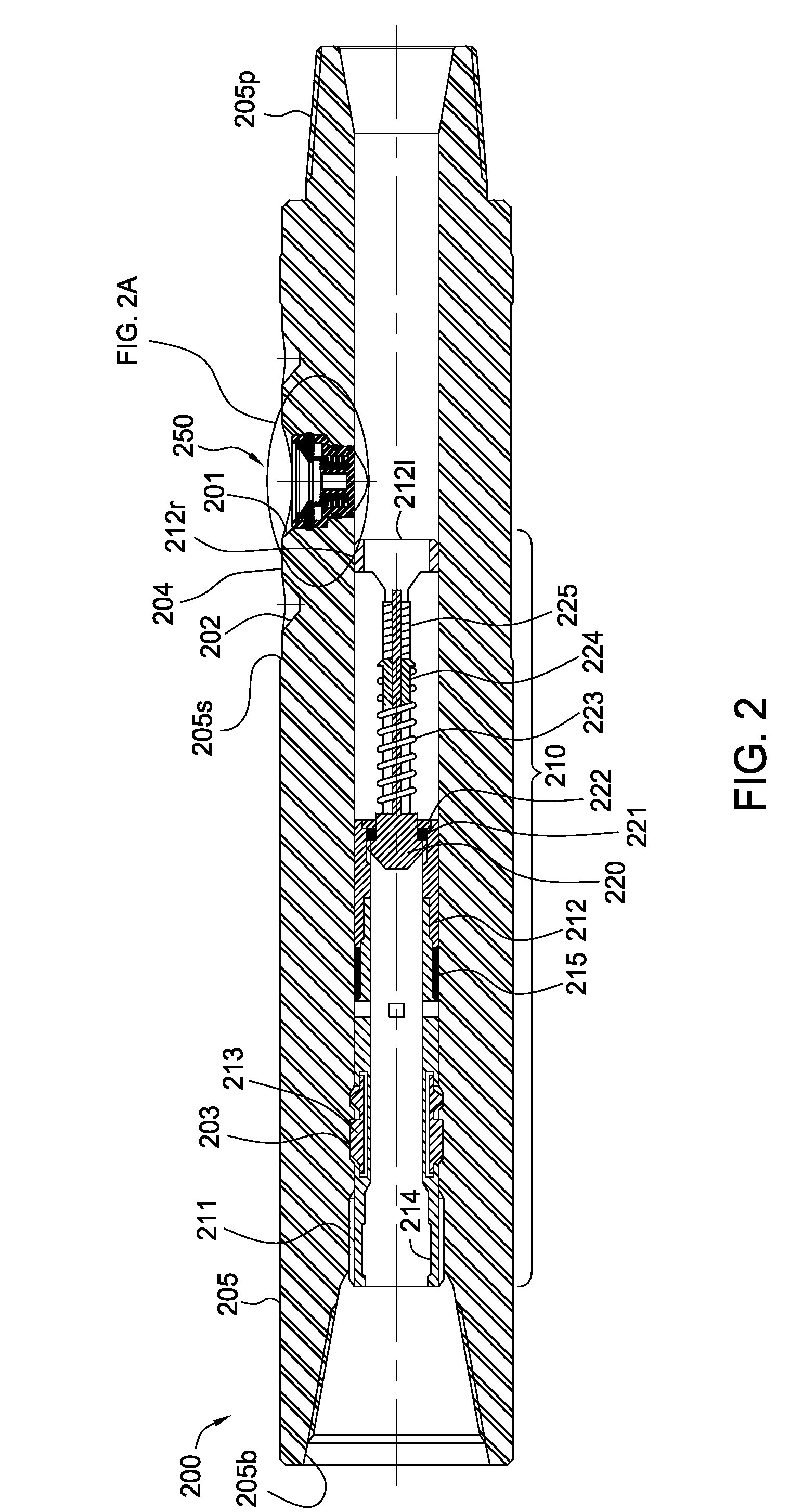
Actively controlled rotary steerable system and method for drilling wells
InactiveUS6092610AEfficient rotary speedPromote productionDrilling rodsConstructionsAccelerometerDirectional drilling
An actively controlled rotary steerable drilling system for directional drilling of wells having a tool collar rotated by a drill string during well drilling. A bit shaft has an upper portion within the tool collar and a lower end extending from the collar and supporting a drill bit. The bit shaft is omni-directionally pivotally supported intermediate its upper and lower ends by a universal joint within the collar and is rotatably driven by the collar. To achieve controlled steering of the rotating drill bit, orientation of the bit shaft relative to the tool collar is sensed and the bit shaft is maintained geostationary and selectively axially inclined relative to the tool collar during drill string rotation by rotating it about the universal joint by an offsetting mandrel that is rotated counter to collar rotation and at the same frequency of rotation. An electric motor provides rotation to the offsetting mandrel with respect to the tool collar and is servo-controlled by signal input from position sensing elements such as magnetometers, gyroscopic sensors, and accelerometers which provide real time position signals to the motor control. In addition, when necessary, a brake is used to maintain the offsetting mandrel and the bit shaft axis geostationary. Alternatively, a turbine is connected to the offsetting mandrel to provide rotation to the offsetting mandrel with respect to the tool collar and a brake is used to servo-control the turbine by signal input from position sensors.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
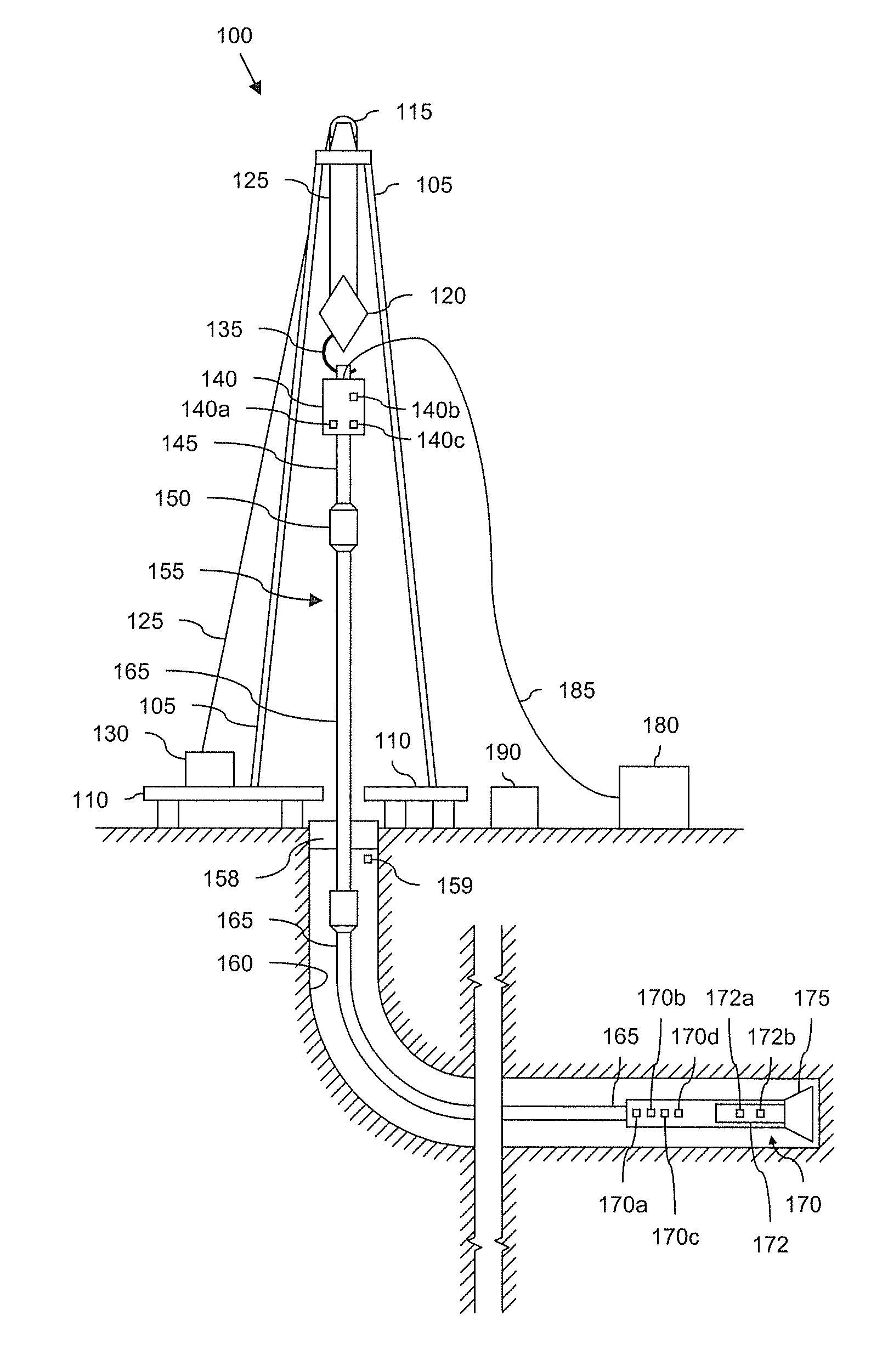
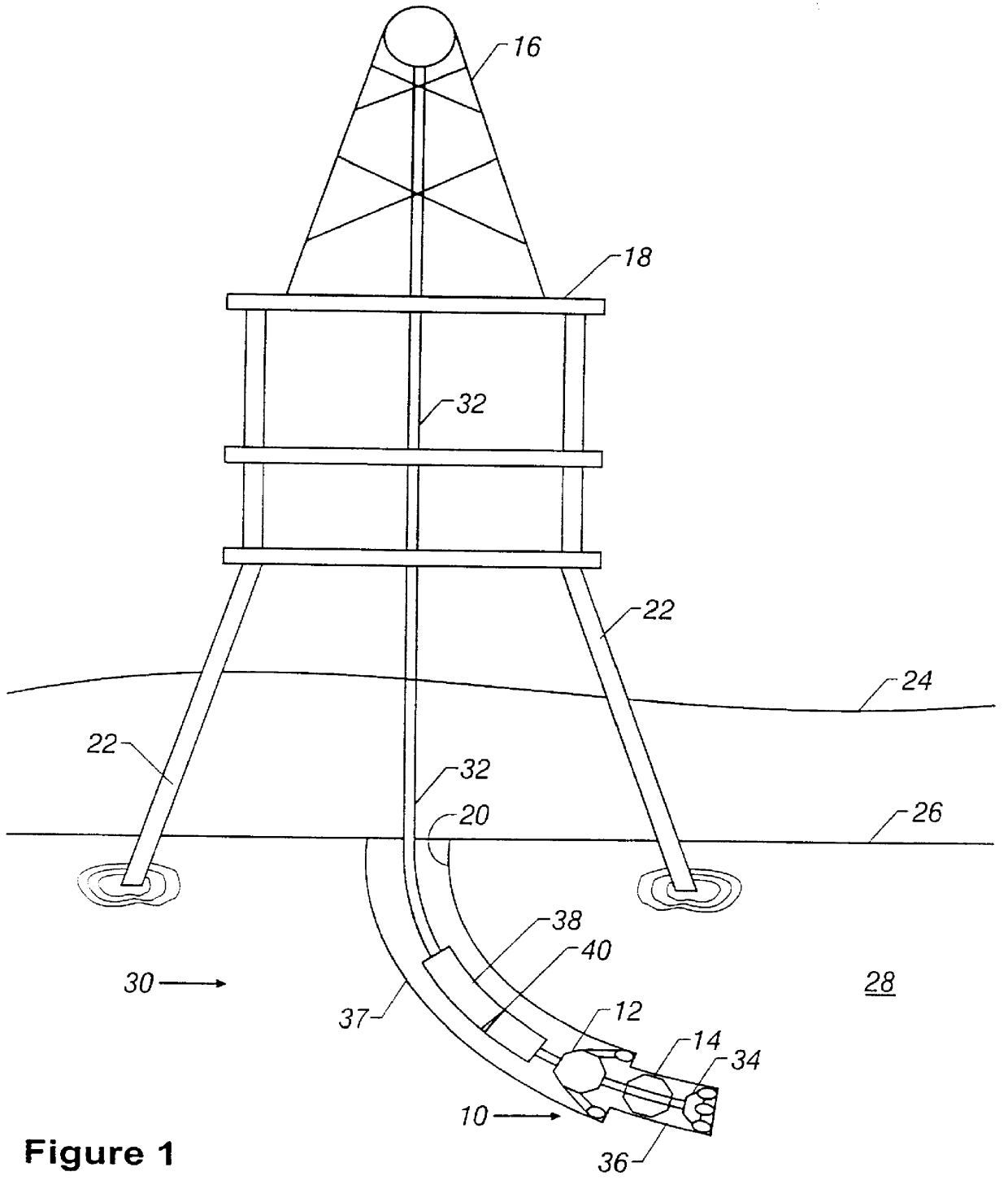
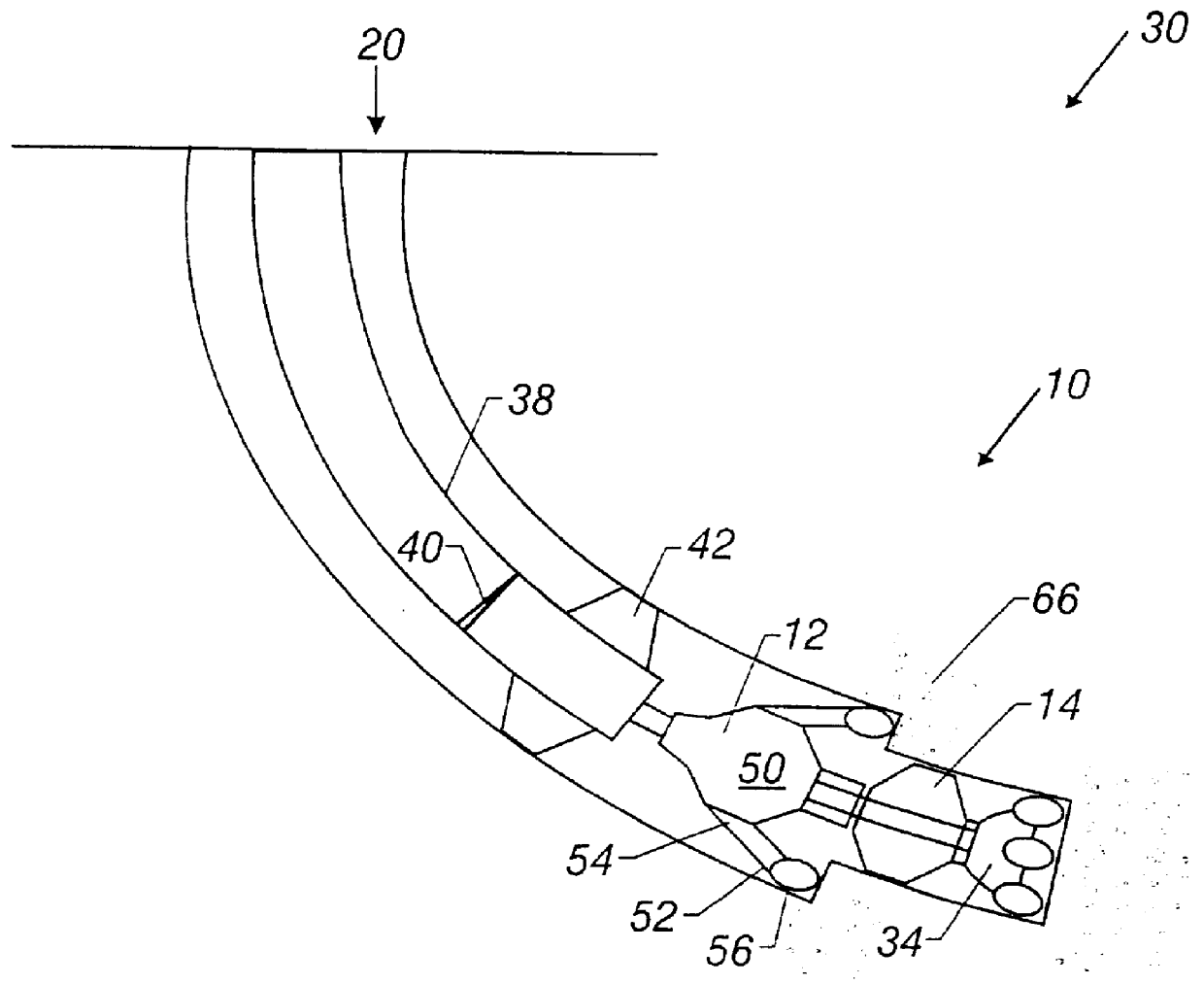
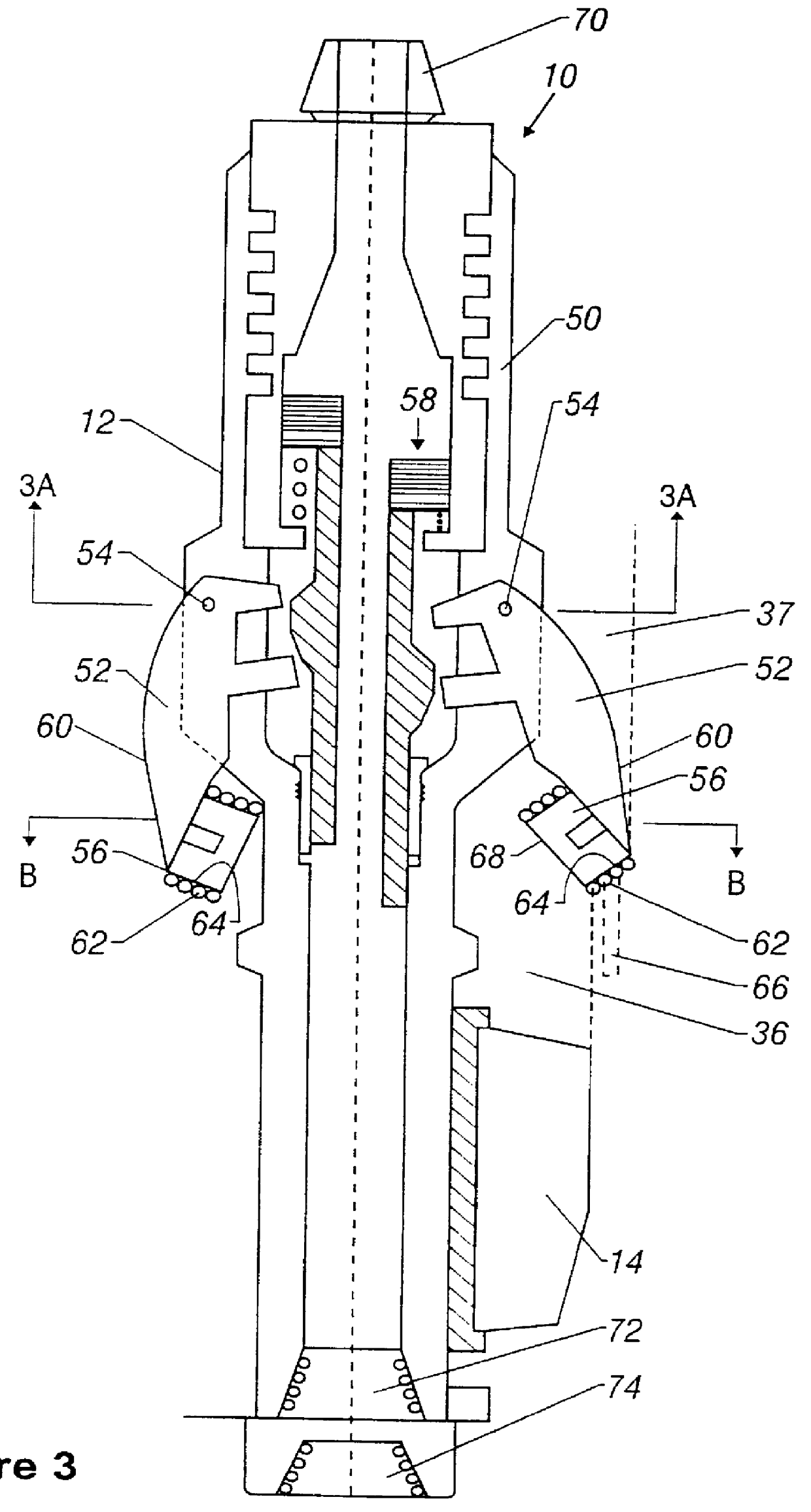
Automated directional drilling apparatus and methods
Methods and systems for drilling to a target location include a control system that receives an input comprising a planned drilling path to a target location and determines a projected location of a bottom hole assembly of a drilling system. The projected location of the bottom hole assembly is compared to the planned drilling path to determine a deviation amount. A modified drilling path is created to the target location as selected based on the amount of deviation from the planned drilling path, and drilling rig control signals that steer the bottom hole assembly of the drilling system to the target location along the modified drilling path are generated.
Owner:NABORS DRILLING TECH USA INC
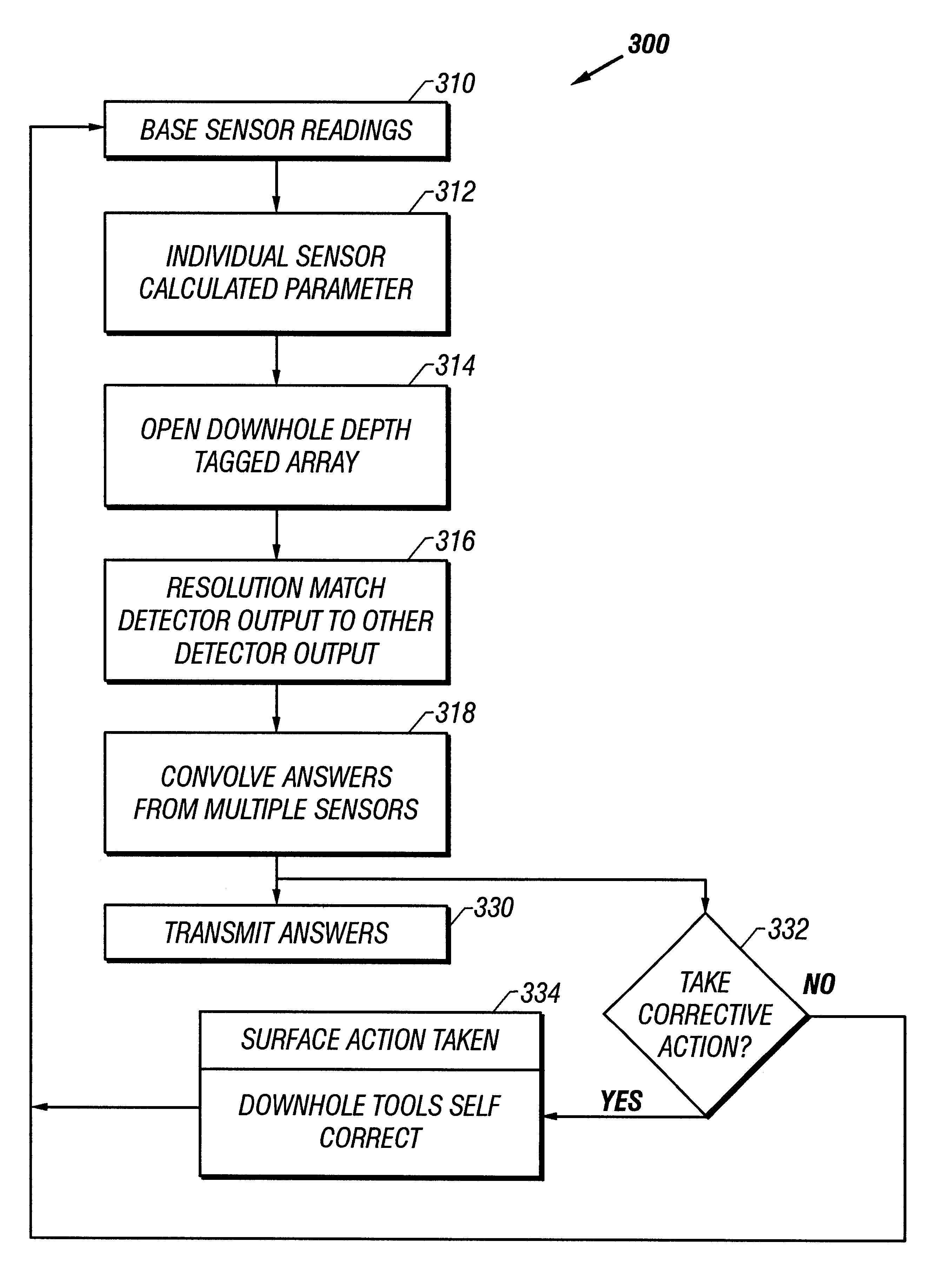
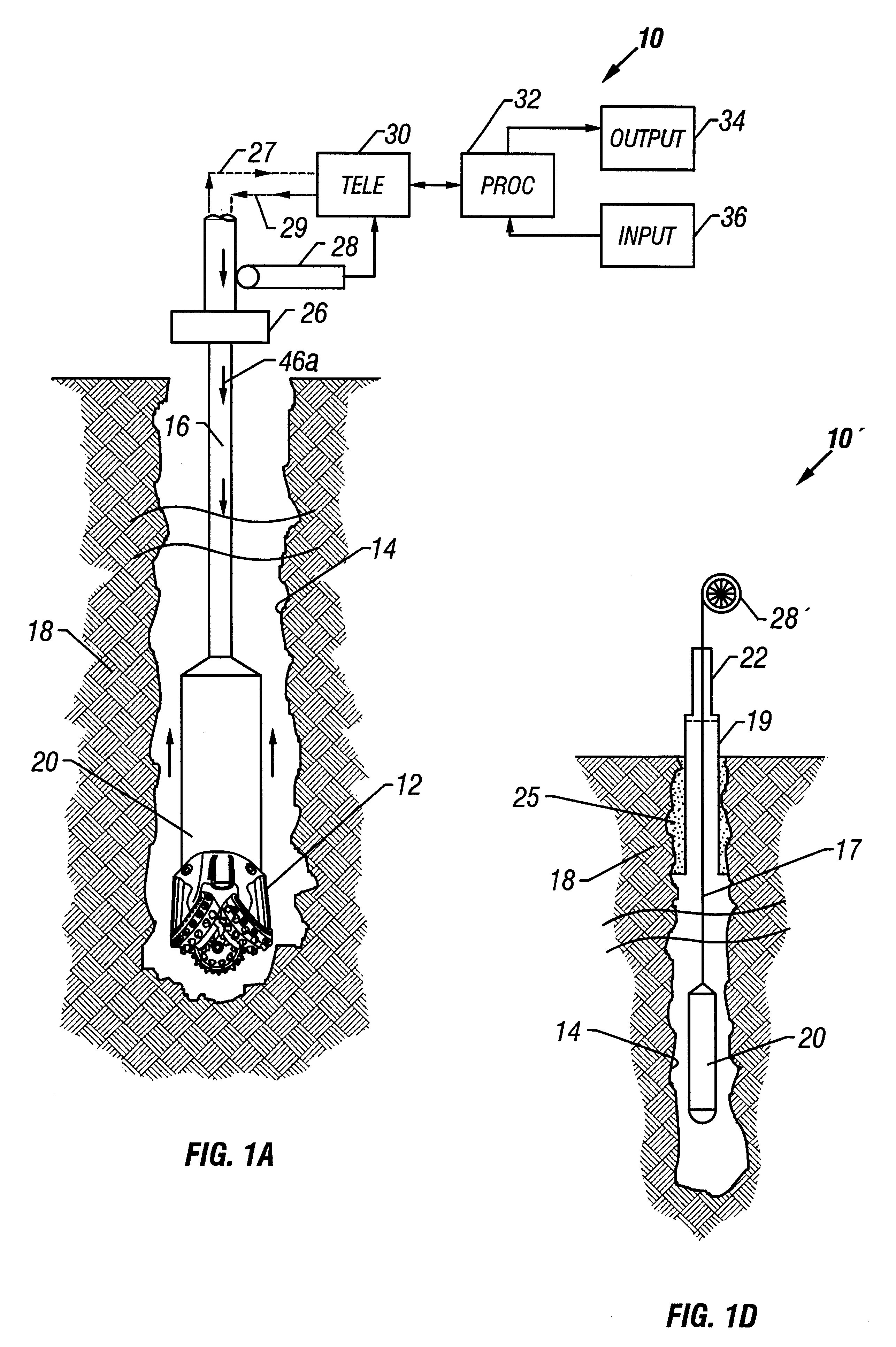
Drilling system with downhole apparatus for determining parameters of interest and for adjusting drilling direction in response thereto
The present invention provides a measurement-while-drilling (MWD) system having a downhole computer and multiple downhole sensors. Relatively large amounts of basic or "raw" data are measured by downhole sensors, and these data are processed within a downhole computer to be reduced to parameters of interest, which may be utilized to control the drilling operation by downhole devices, stored downhole, telemetered to the surface, or both. The measurements may be correlated downhole with stored reference data thereby providing additional information pertaining to the drilling operation. Downhole depth correlation between downhole measured parameters may be made by utilizing surface determined or downhole determined borehole depth.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
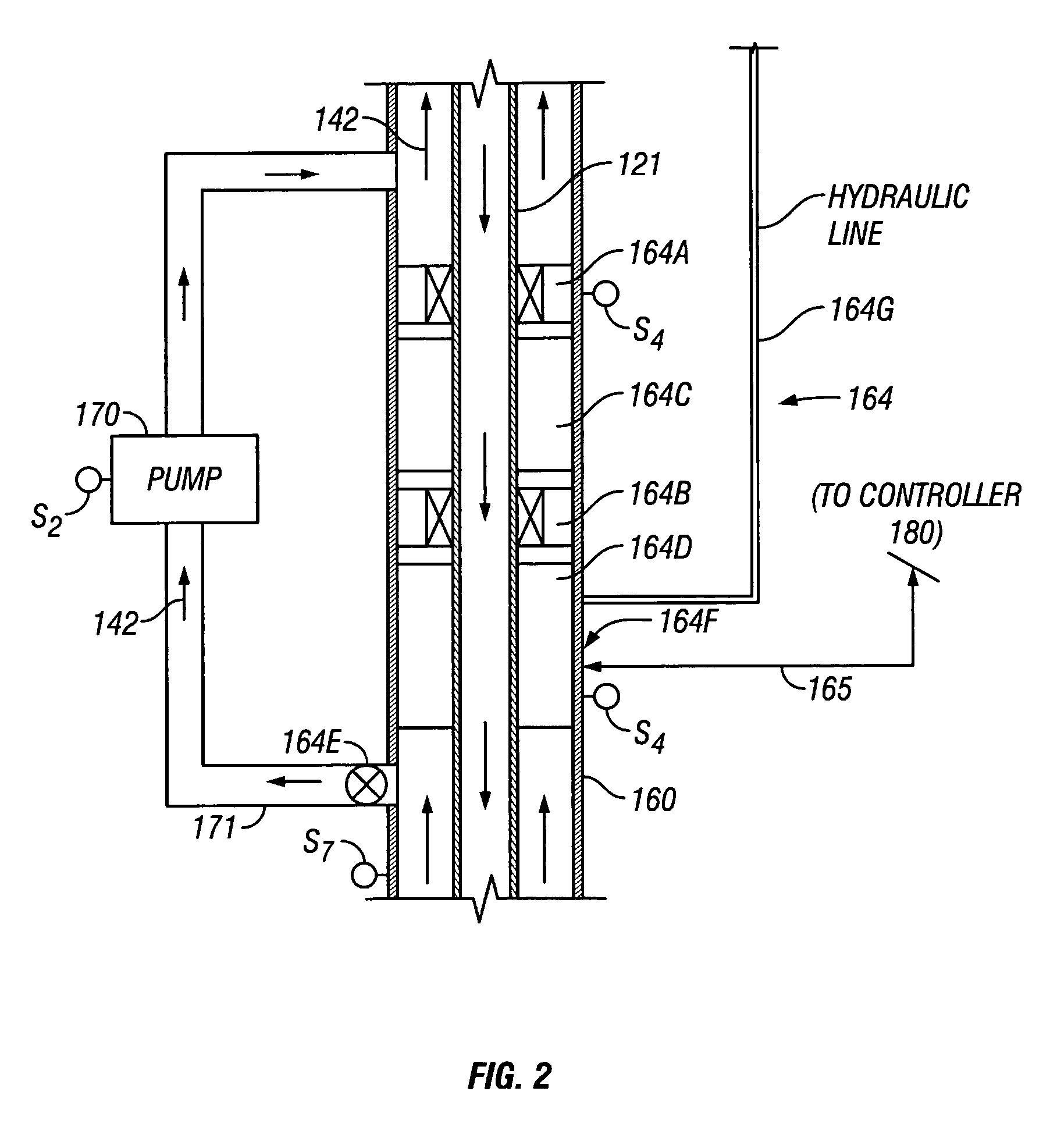
Annulus pressure control drilling systems and methods
In one embodiment, a method for drilling a wellbore includes an act of drilling the wellbore by injecting drilling fluid through a tubular string disposed in the wellbore, the tubular string comprising a drill bit disposed on a bottom thereof. The drilling fluid exits the drill bit and carries cuttings from the drill bit. The drilling fluid and cuttings (returns) flow to a surface of the wellbore via an annulus defined by an outer surface of the tubular string and an inner surface of the wellbore. The method further includes an act performed while drilling the wellbore of measuring a first annulus pressure (FAP) using a pressure sensor attached to a casing string hung from a wellhead of the wellbore. The method further includes an act performed while drilling the wellbore of controlling a second annulus pressure (SAP) exerted on a formation exposed to the annulus.
Owner:WEATHERFORD TECH HLDG LLC
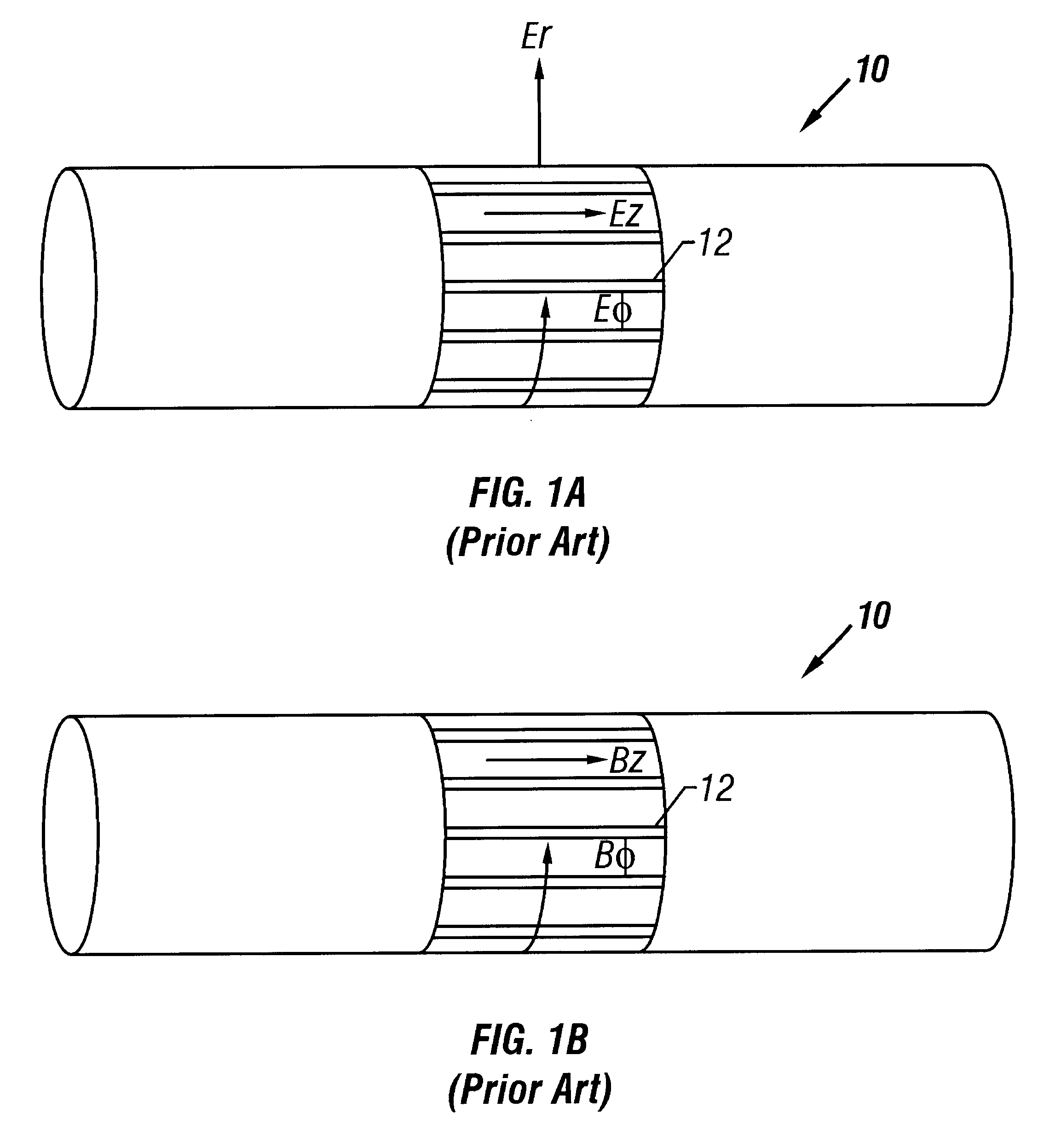
Method and apparatus for directional well logging with a shield having sloped slots
InactiveUS6297639B1Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingDetection using electromagnetic wavesUltrasound attenuationDirectional well
Methods and apparatus for making directional measurements of earth formations surrounding a borehole. New antenna coil shield designs are utilized to provide selective attenuation of at least one electromagnetic energy field component as the component interacts with the shield. The new shields are implemented in several downhole tool configurations to provide azimuthally focused formation measurements. In effect, the new shield filters interacting electromagnetic energy field components to pass those components corresponding to a magnetic dipole oriented at an angle from the tool axis. The shields thereby alter a coil's envelope of influence to electromagnetic energy. The new shields also form part of a system for making directional measurements while drilling.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
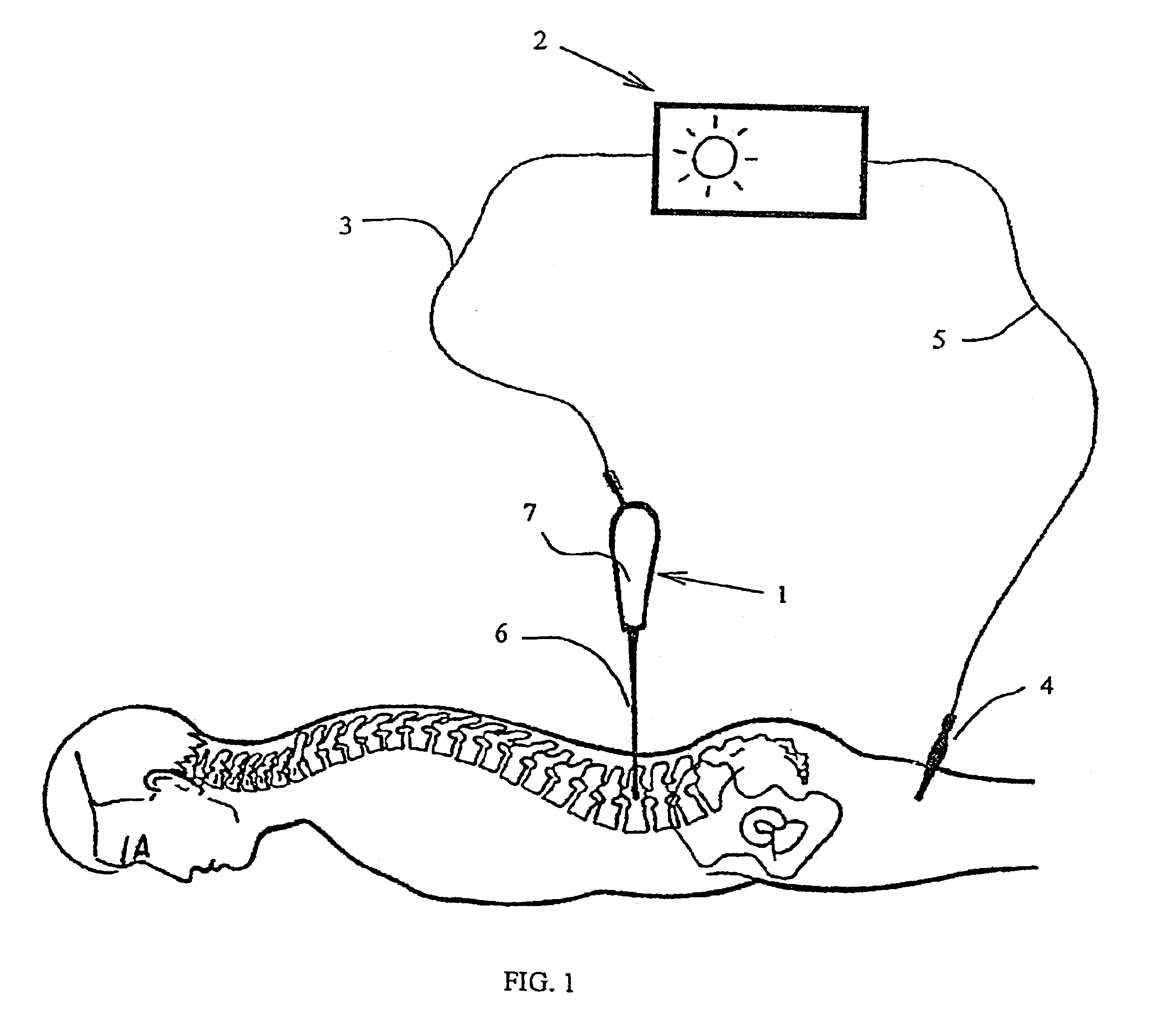
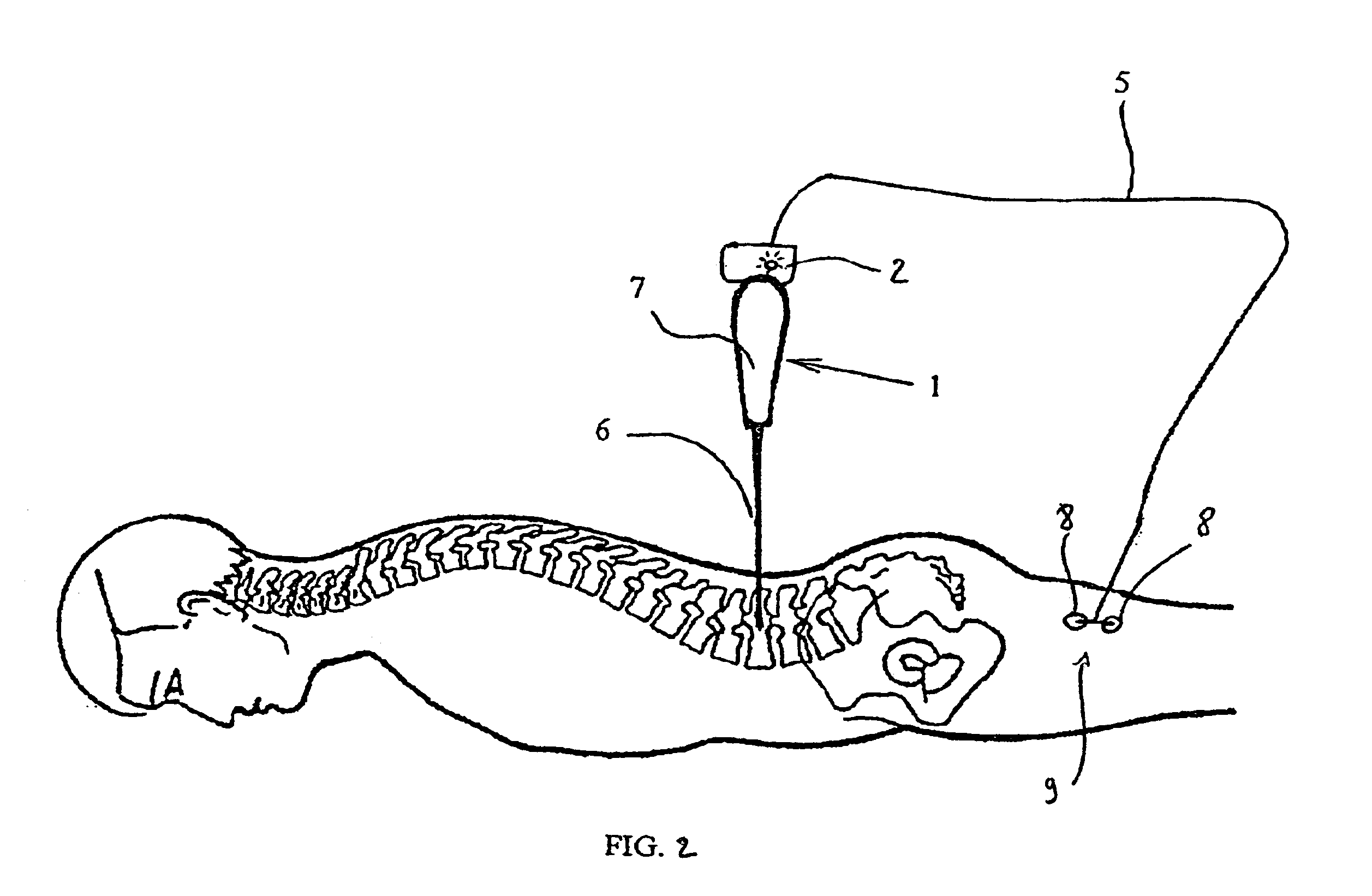
Method for drilling bone, in particular for setting a pedicle screw, equipment, instrument and control device for implementing said method
The present invention concerns a method and equipment for drilling bone, in particular for setting a pedicle screw using a manual or motorized drilling tool. The equipment includes a drilling instrument, a source of electric impulses and a connector for connecting the electric impulse source to the drilling instrument. The equipment includes at least one sensor for detecting a muscle signal either implanted in a muscle or placed on the skin in the vicinity of a muscle before and during drilling. An alert is produced in the event of detection by at least one sensor of a muscle signal correlated with the source of electric impulses connected to the drilling instrument.
Owner:SPINEGUARD
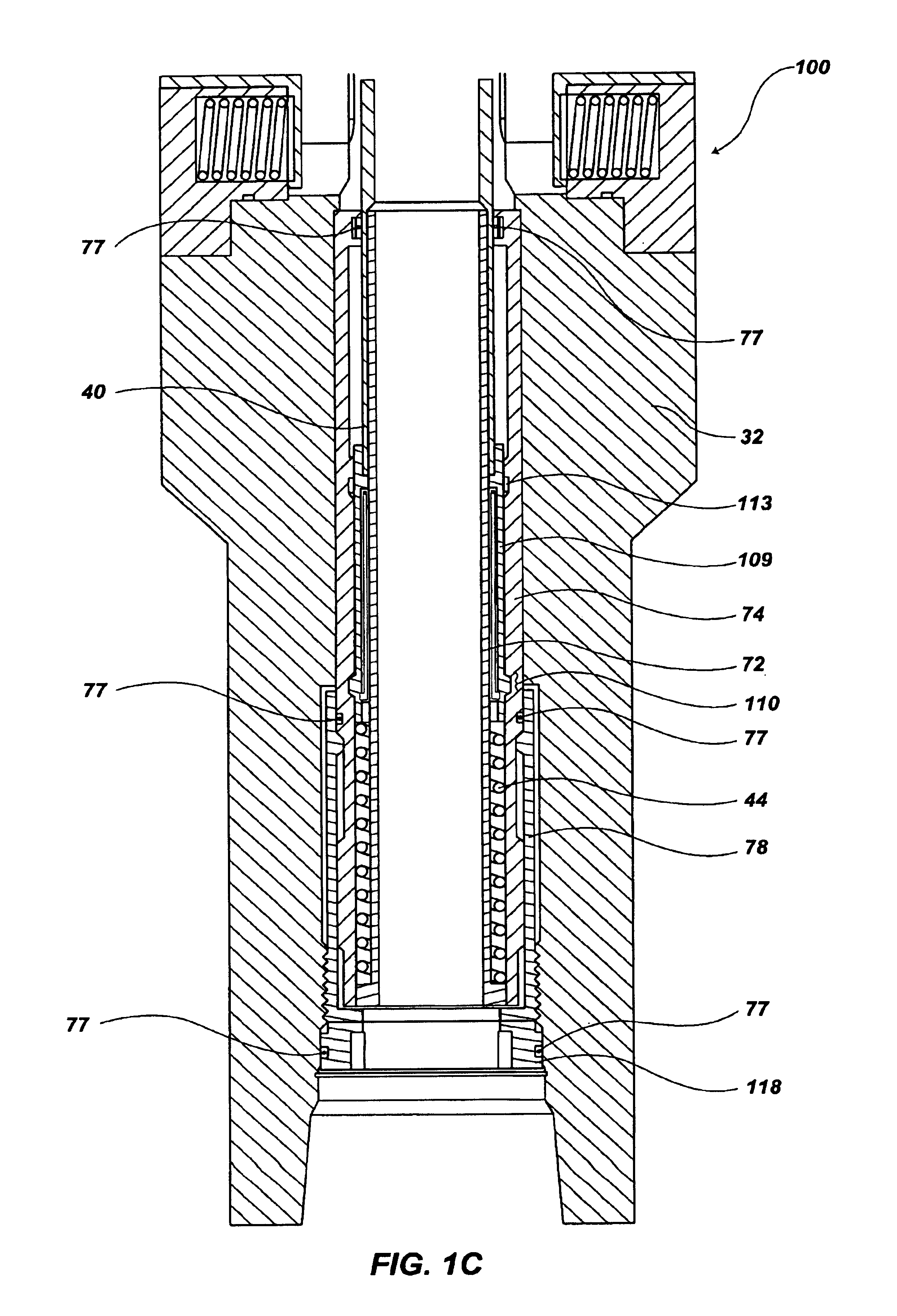
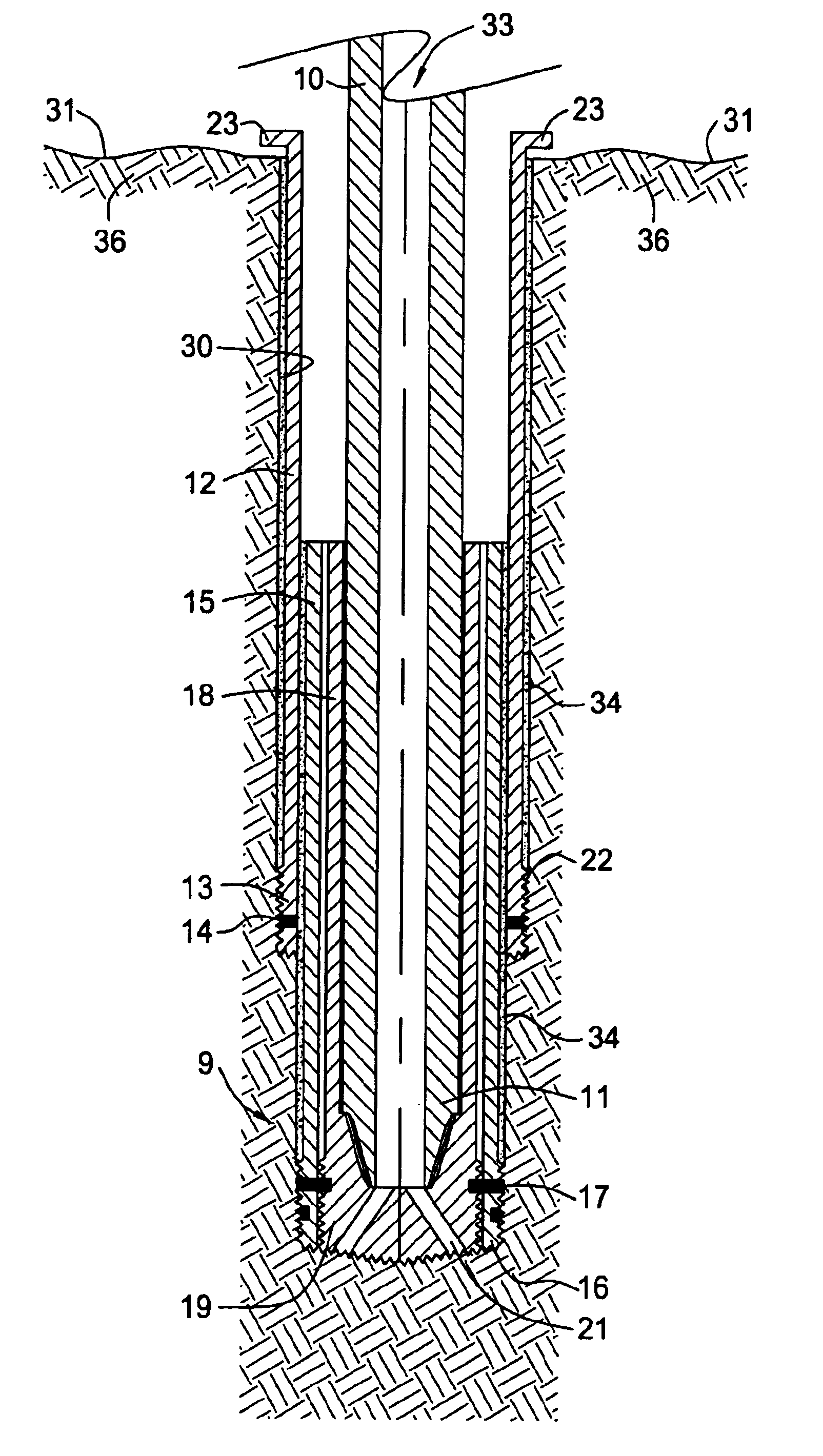
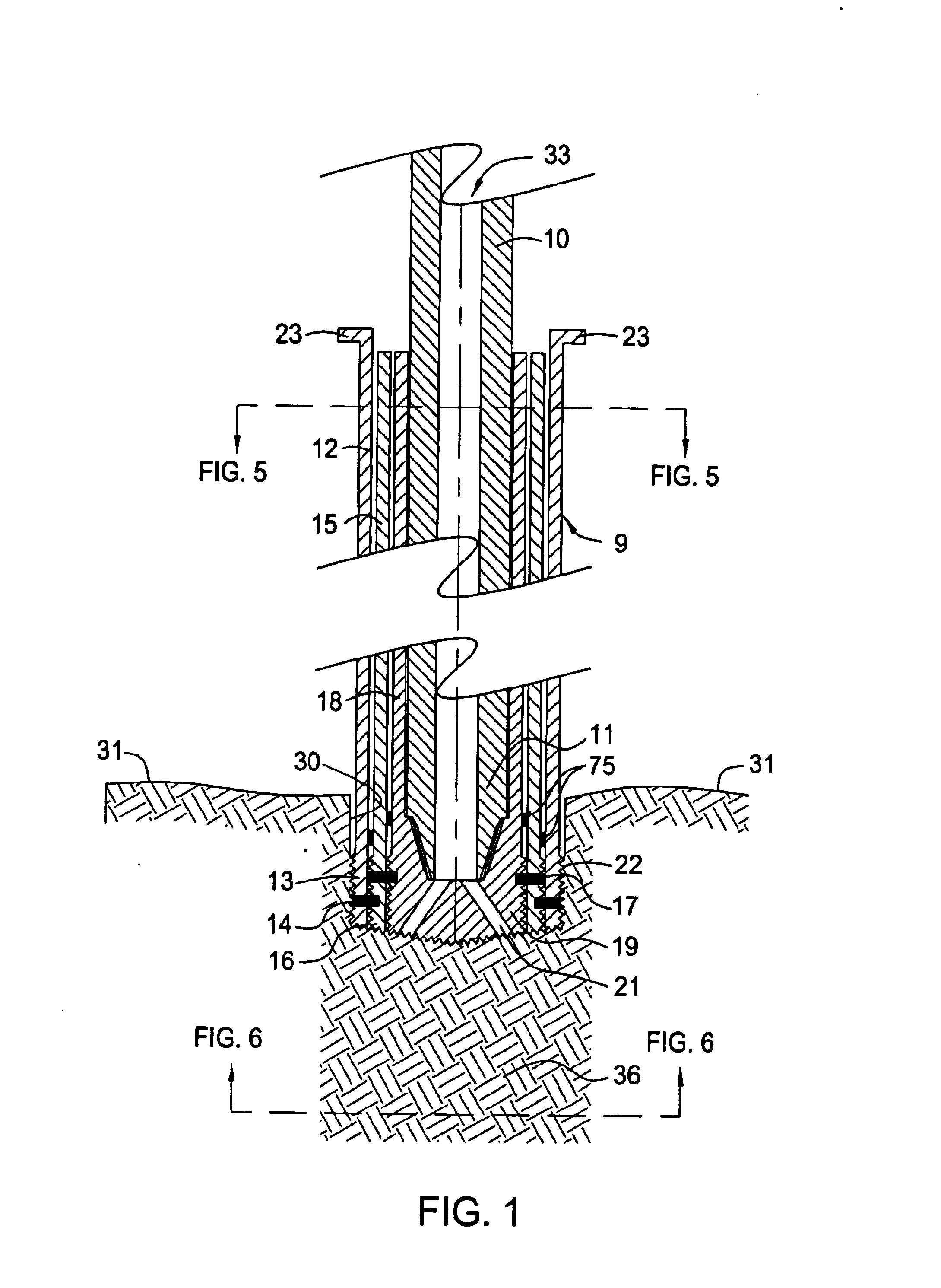
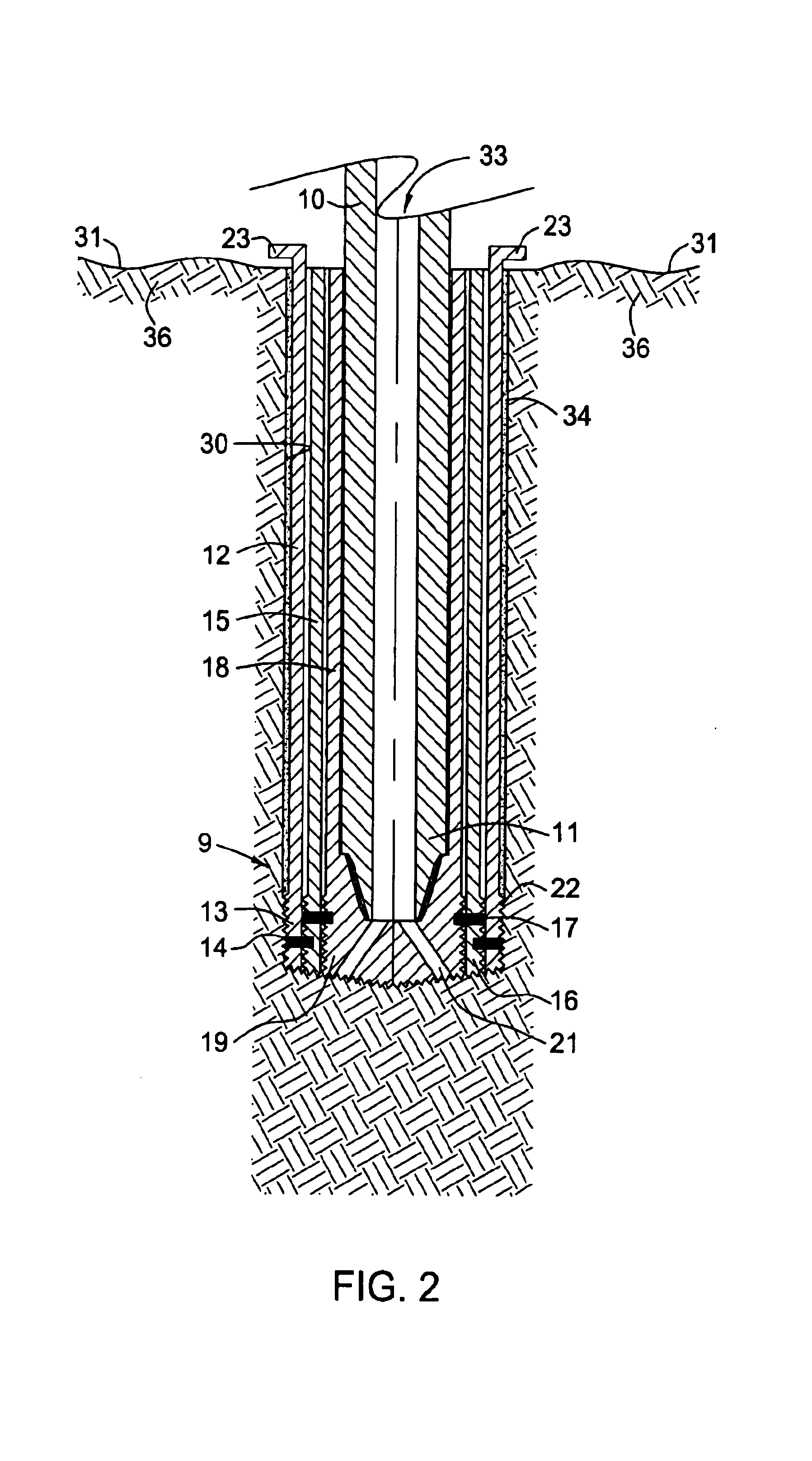
Underbalanced drill string deployment valve method and apparatus
Apparatus and methods for a deployment valve used with an underbalanced drilling system to enhance the advantages of underbalanced drilling. The underbalanced drilling system may typically comprise elements such as a rotating blow out preventer and drilling recovery system. The deployment valve is positioned in a tubular string, such as casing, at a well bore depth at or preferably substantially below the string light point of the drilling string. When the drilling string is above the string light point then the upwardly acting forces on the drilling string become greater than downwardly acting forces such that the drilling string begins to accelerate upwardly. The deployment valve has a bore sufficiently large to allow passage of the drill bit therethrough in the open position. The deployment valve may be closed when the drill string is pulled within the casing as may be necessary to service the drill string after drilling into a reservoir having a reservoir pressure. To allow the drill string to be removed from the casing, the pressure produced by the formation can be bled off and the drill string removed for servicing. The drill string can then be reinserted, the pressure in the casing above the deployment valve applied to preferably equalize pressure above and below the valve and the drill string run into the hole for further drilling.
Owner:WEATHERFORD TECH HLDG LLC
Methods and apparatus for handling and drilling with tubulars or casing
InactiveUS20050000691A1Shorten the timeReduce laborMechanical apparatusDrilling rodsTop driveWell drilling
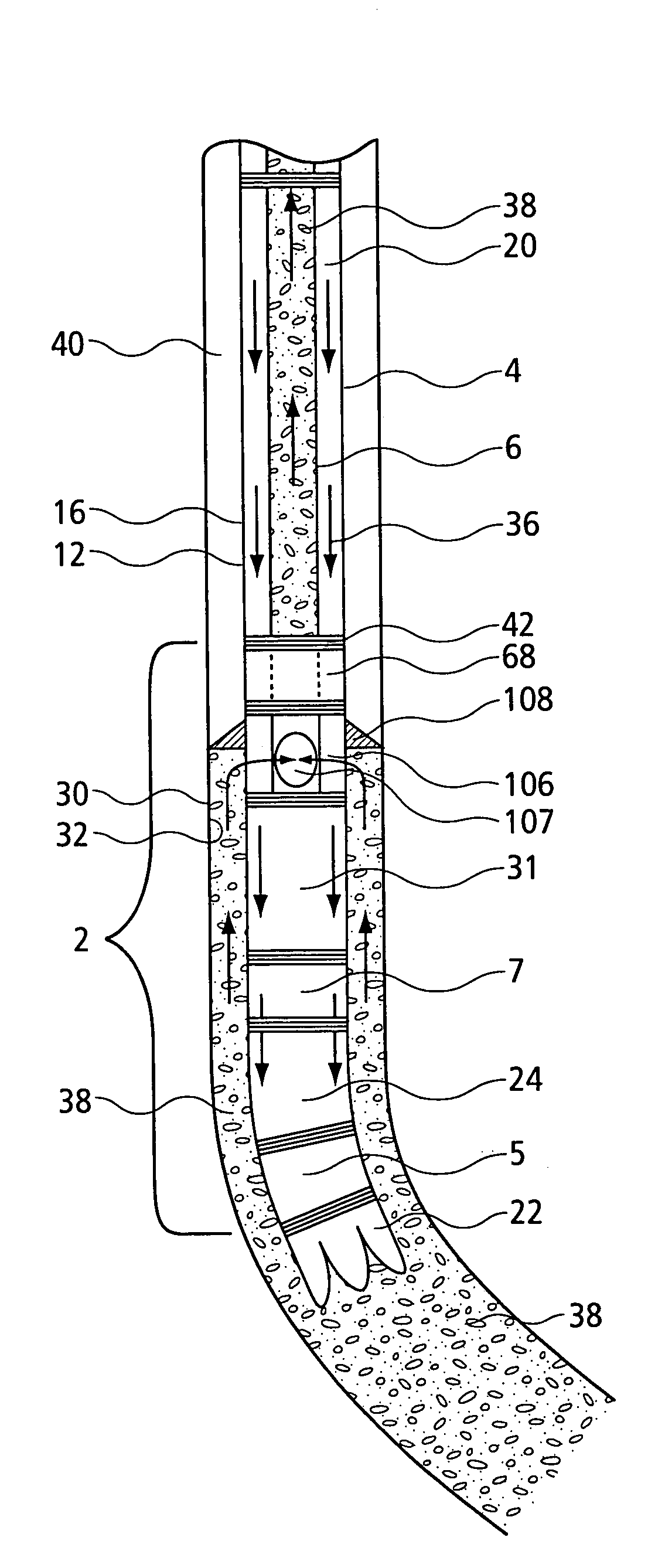
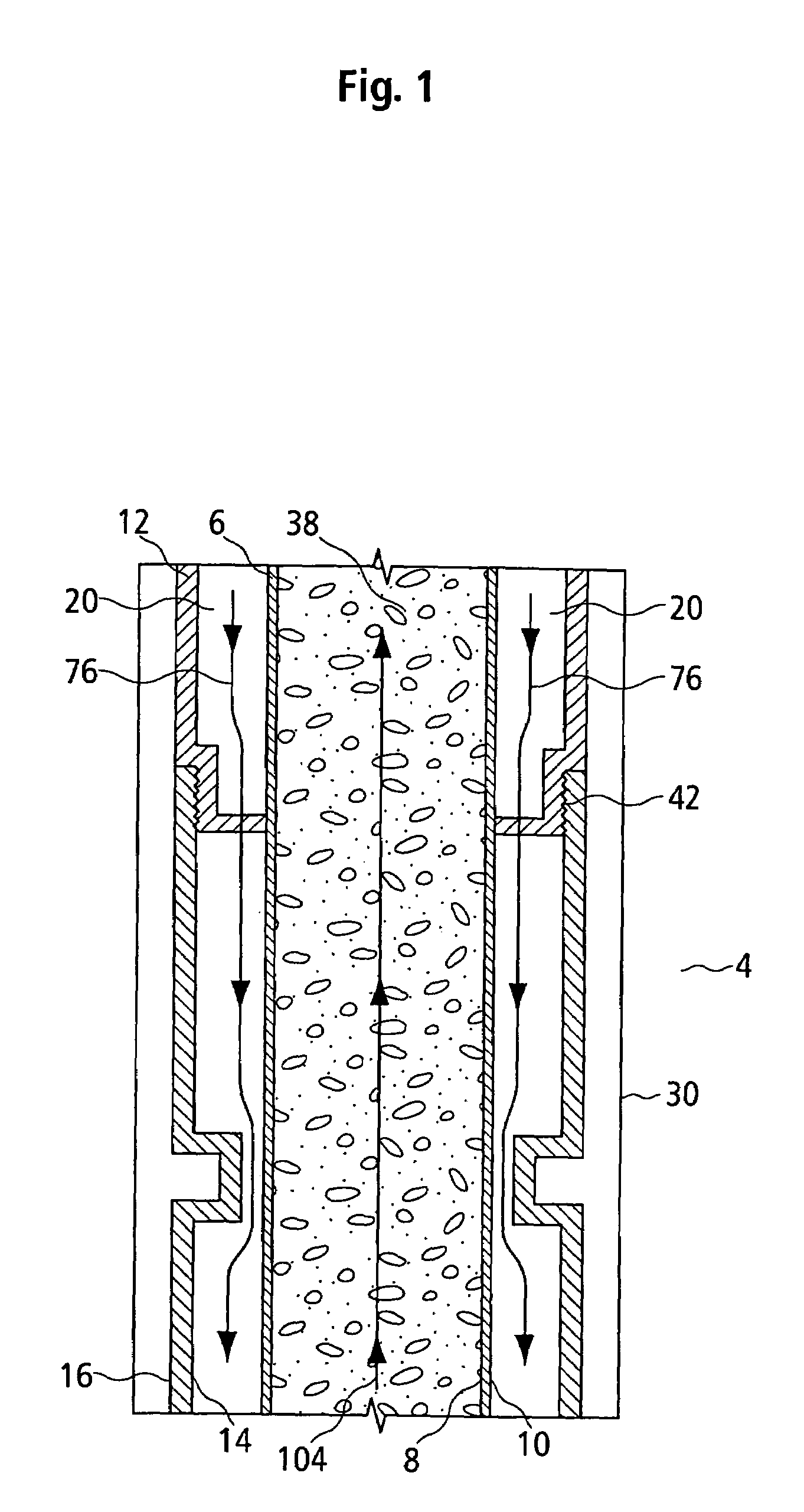
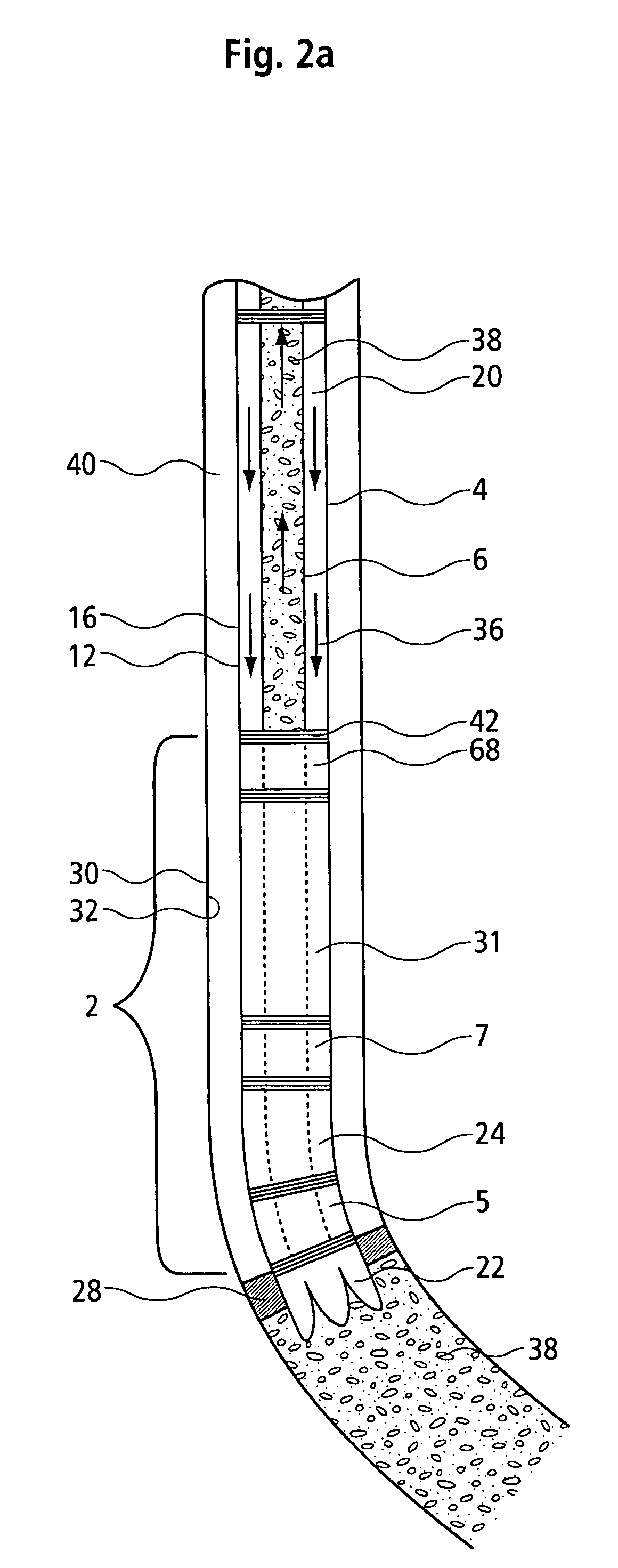
The present invention provides a method and apparatus for handling tubulars and drilling with tubulars such as casing into a formation. In one aspect of the invention, the apparatus comprises a circulating head and a cementing head operatively connectible to a gripping member. The circulating head is used to circulate drilling fluid while drilling with casing, and the cementing head is used to cement the casing string within the formation at a desired depth. The present invention also relates to methods and apparatus for isolating a tensile load from a drilling apparatus rotated by a top drive. In one aspect, the present invention provides a load isolator apparatus having an isolator body operatively connected to the top drive and a torque body at least partially disposed in the isolator body. In operation, the bearing assembly transfers the tensile load from the torque body to the isolator body.
Owner:WEATHERFORD TECH HLDG LLC
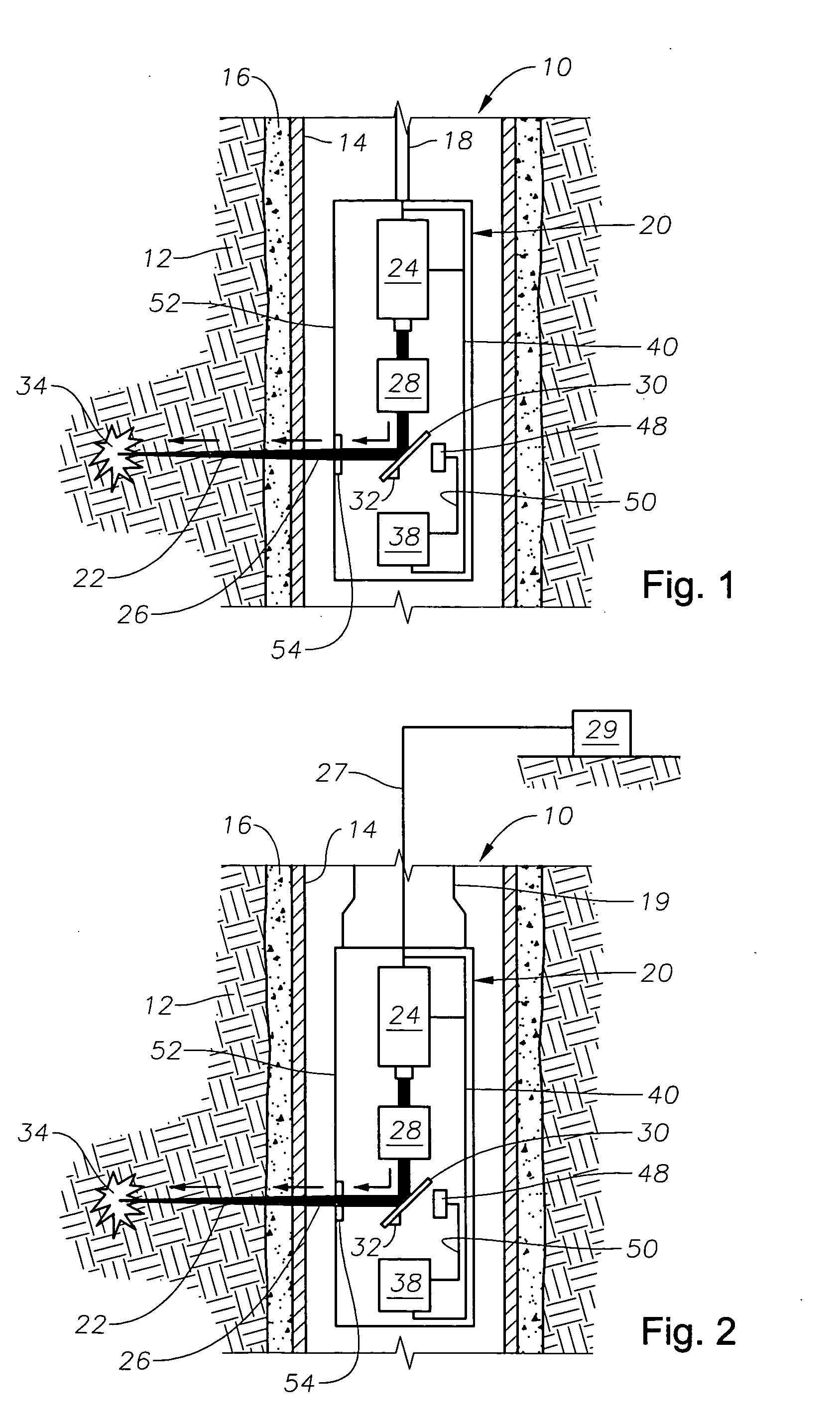
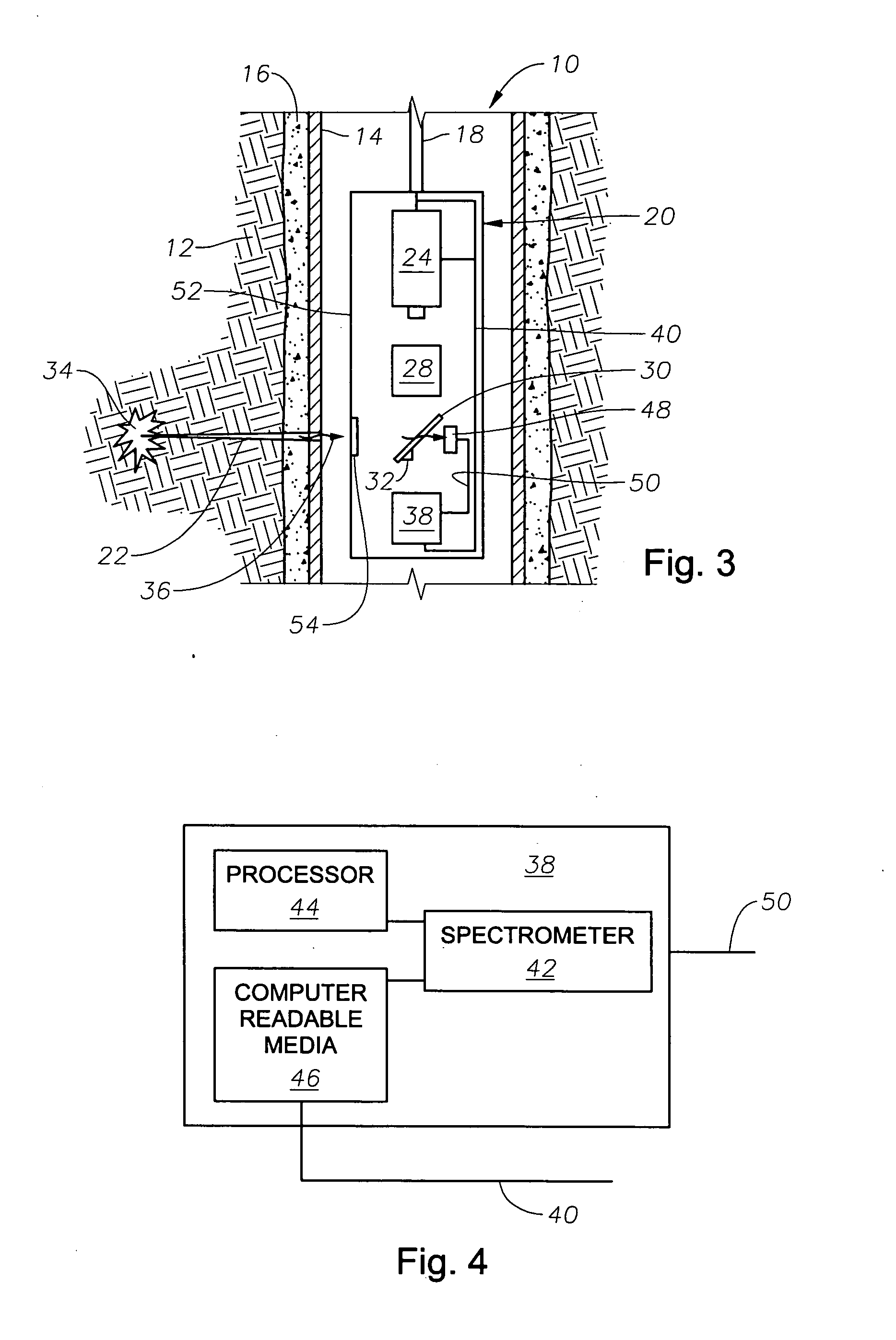
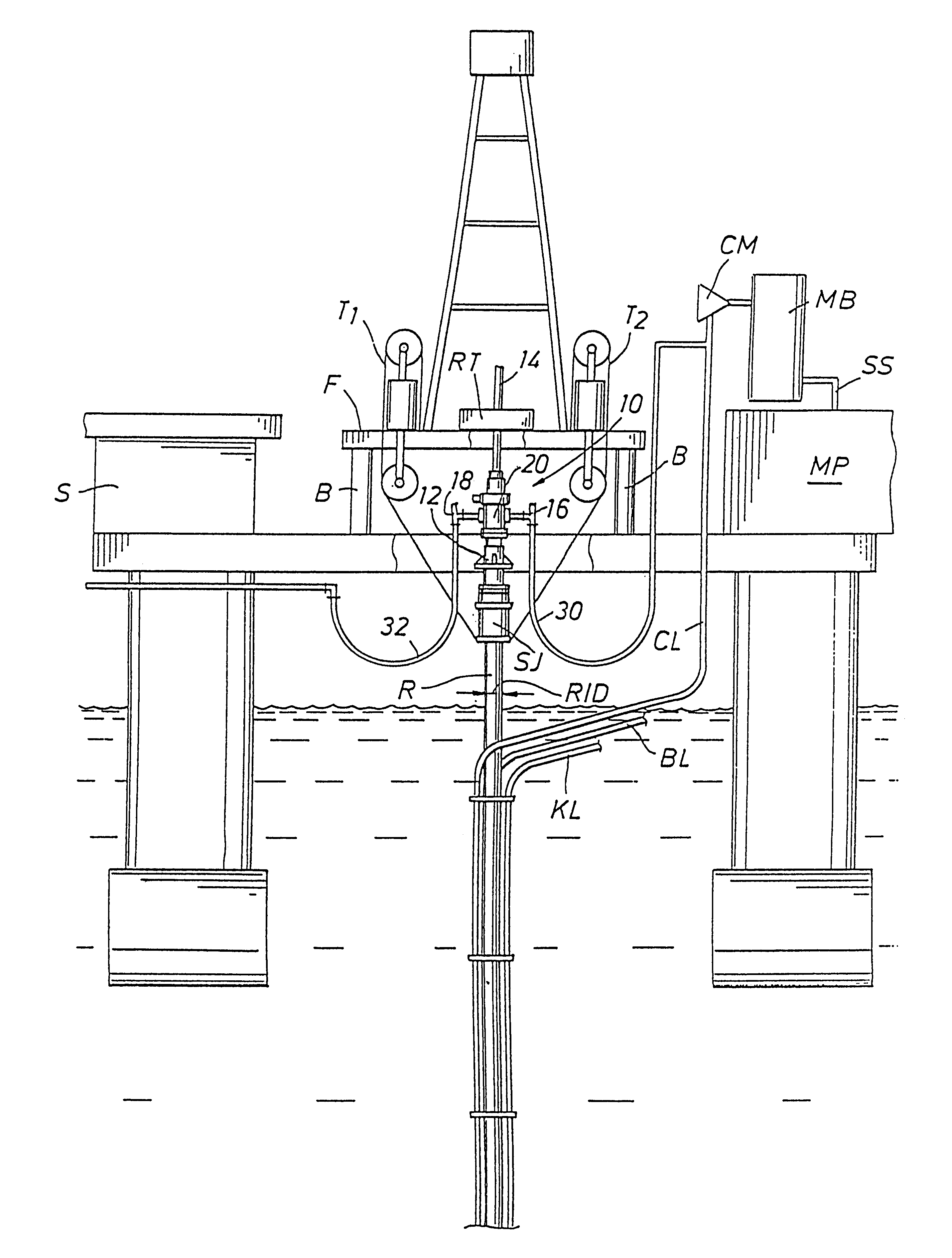
Drilling, perforating and formation analysis
ActiveUS20060102343A1Easy to useImprove breathabilitySpectrum investigationConstructionsMaterial removalWell drilling
A system and method of drilling and / or perforating uses a laser beam to remove material, such as to perforate the casing, cement and formation or drill a well bore. The system and method can further or alternately encompass material analysis that can be performed without removing the material from the well bore. The analysis can be performed apart from or in connection with drilling operations and / or perforating the casing, cement and formation. The analysis can be used in a feed back loop to adjust material removal, adjust material analysis, determine the location of future material removal, and for other uses.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
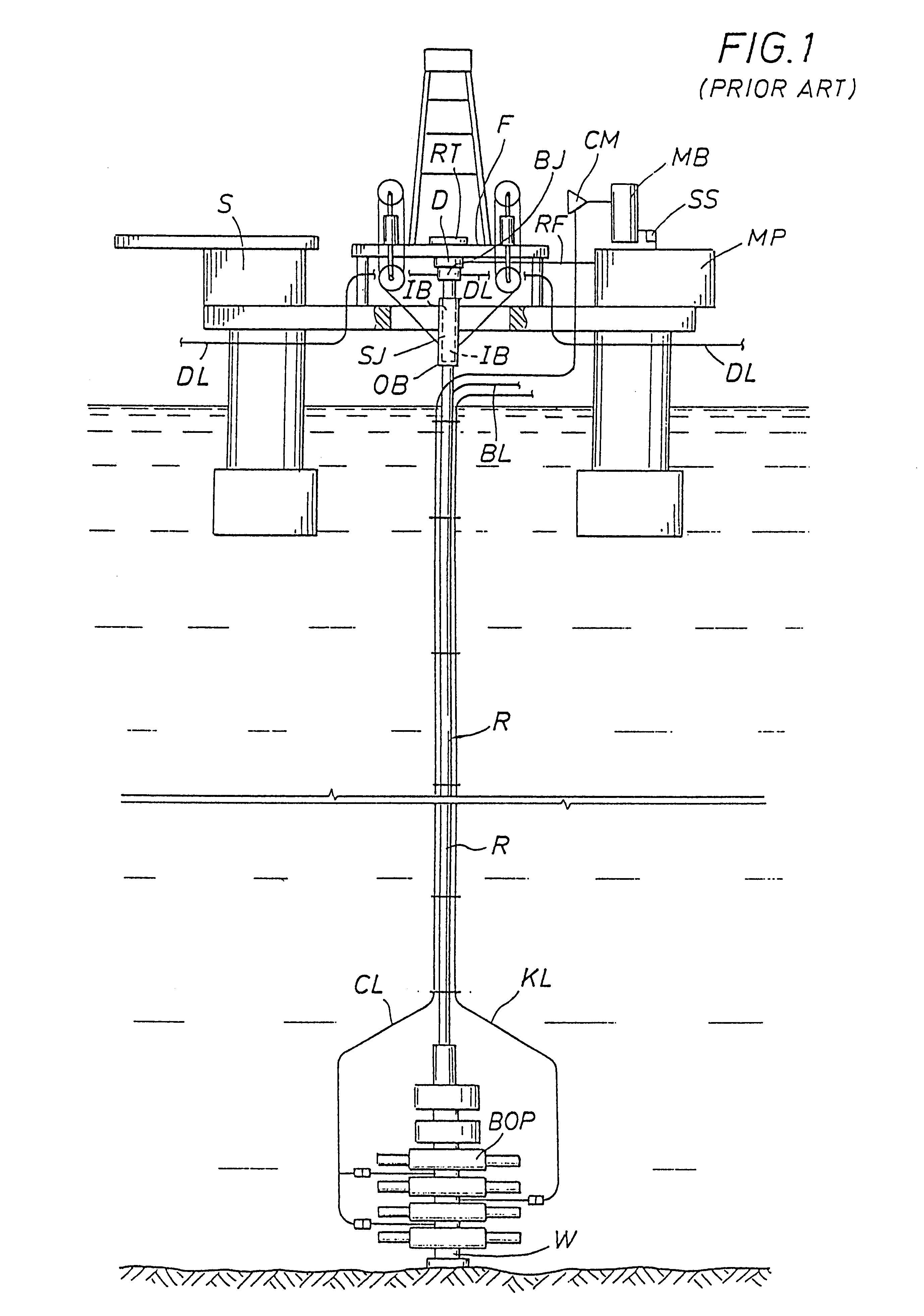
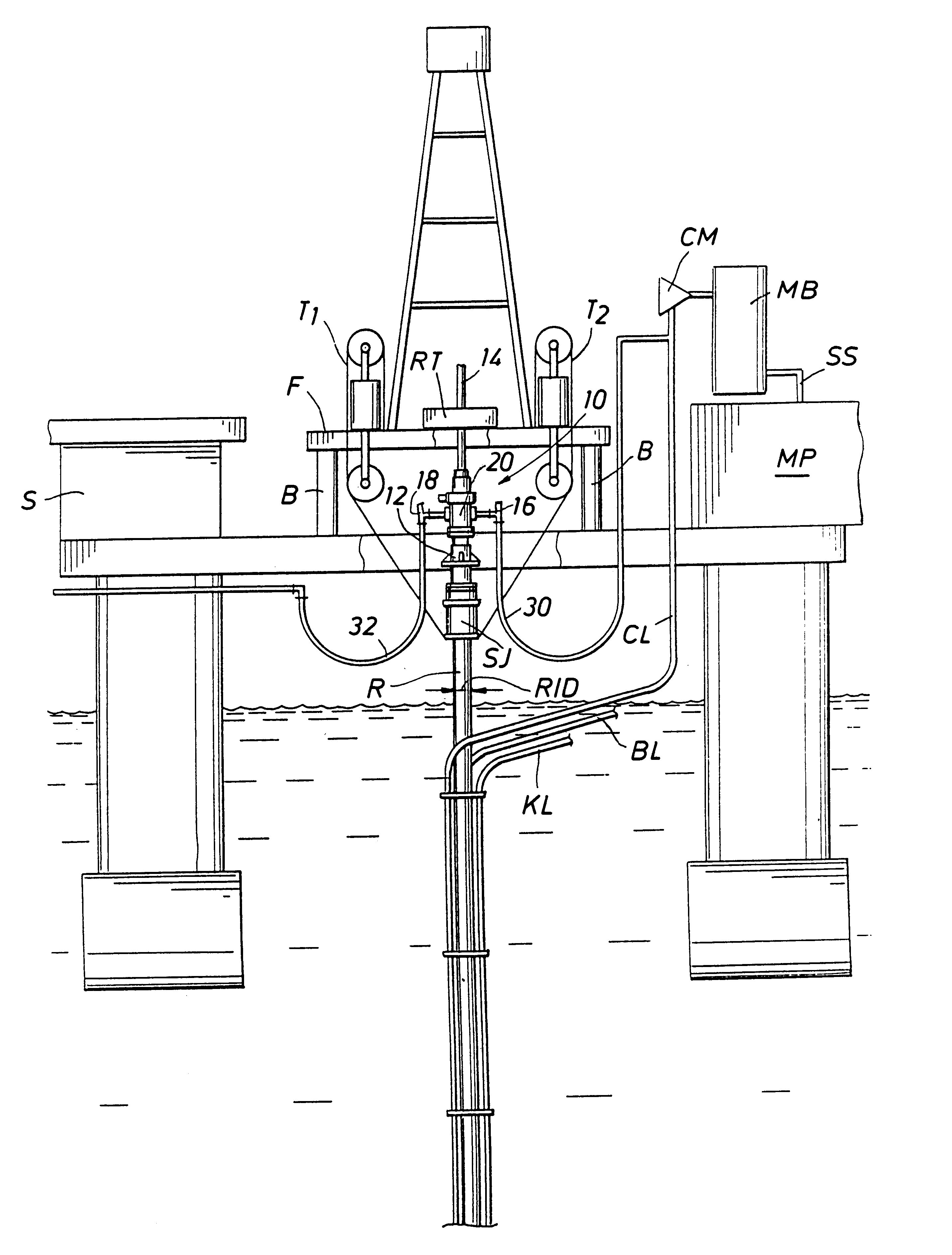
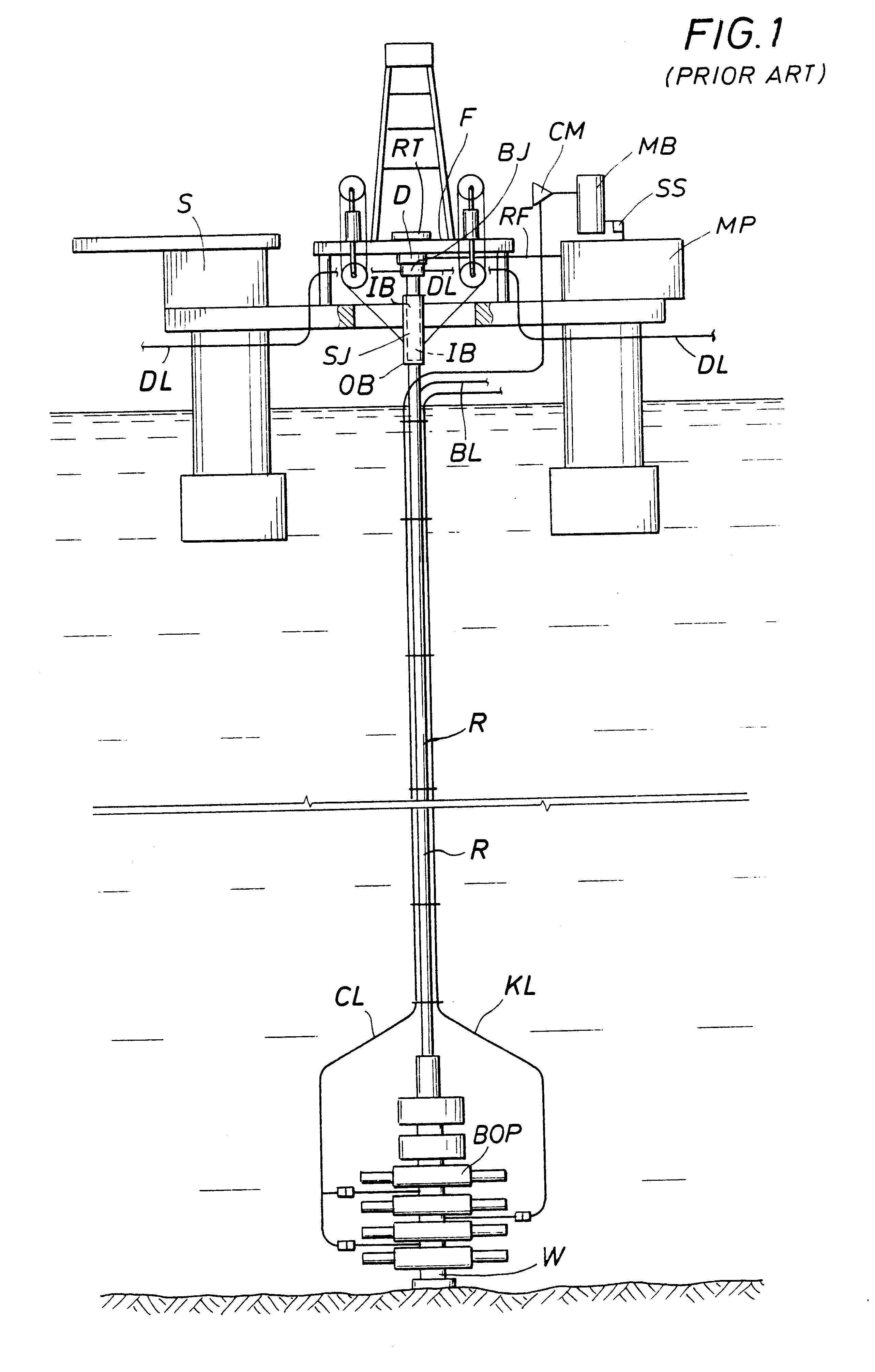
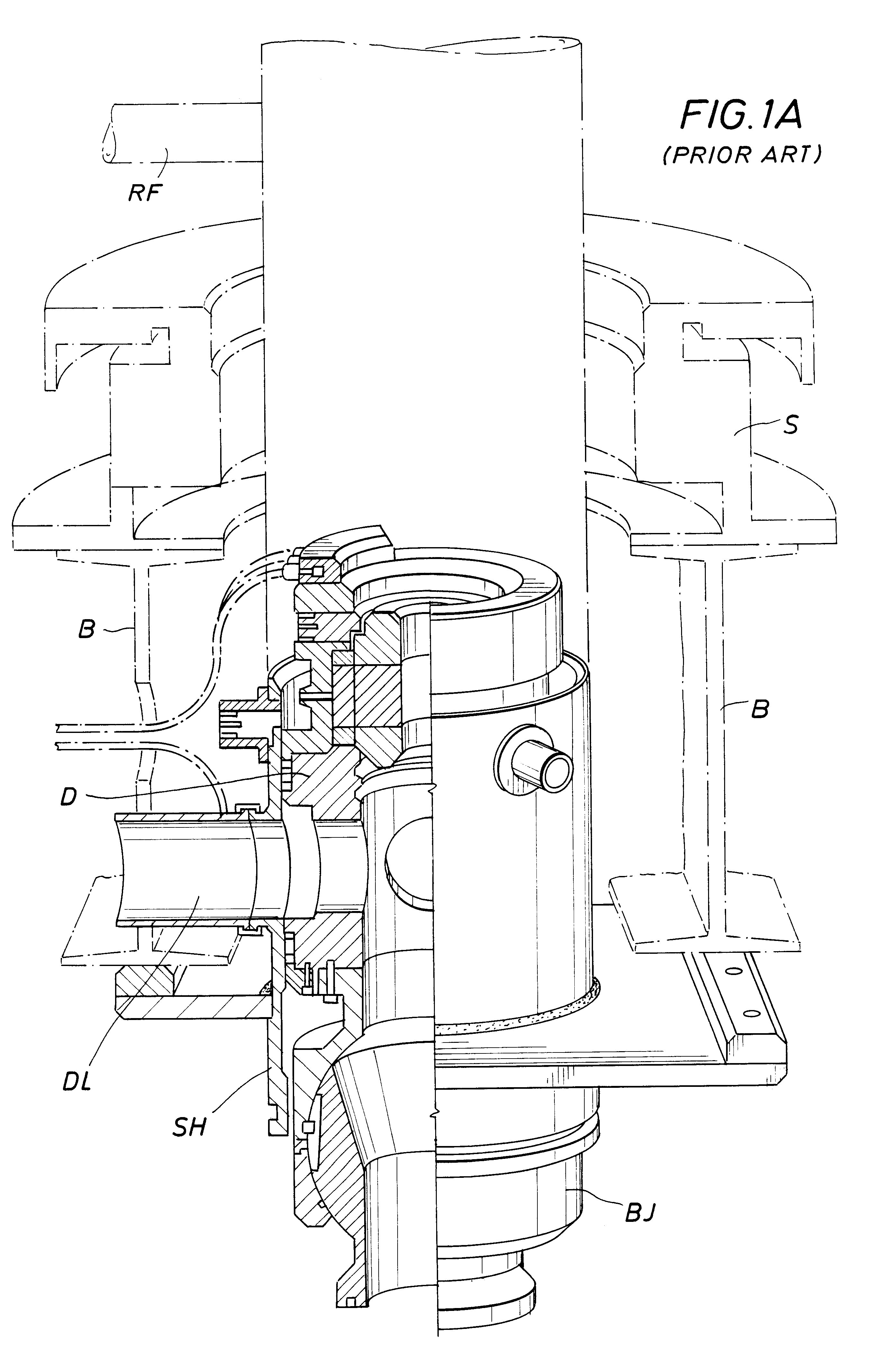
Method and system for return of drilling fluid from a sealed marine riser to a floating drilling rig while drilling
A floating rig or structure for drilling in the floor of an ocean using a rotatable tubular includes a seal housing having a rotatable seal connected above a marine riser fixed to the floor of the ocean. The seal rotating with the rotating tubular allows the riser and seal housing to maintain a predetermined pressure in the system that is desirable in underbalanced drilling, gas-liquid mud systems and pressurized mud handling systems. A flexible conduit or hose is used to compensate for the relative movement of the seal housing and the floating structure since the floating structure moves independent of the seal housing. A method for use of the system is also disclosed.
Owner:WEATHERFORD TECH HLDG LLC
Integrated directional under-reamer and stabilizer
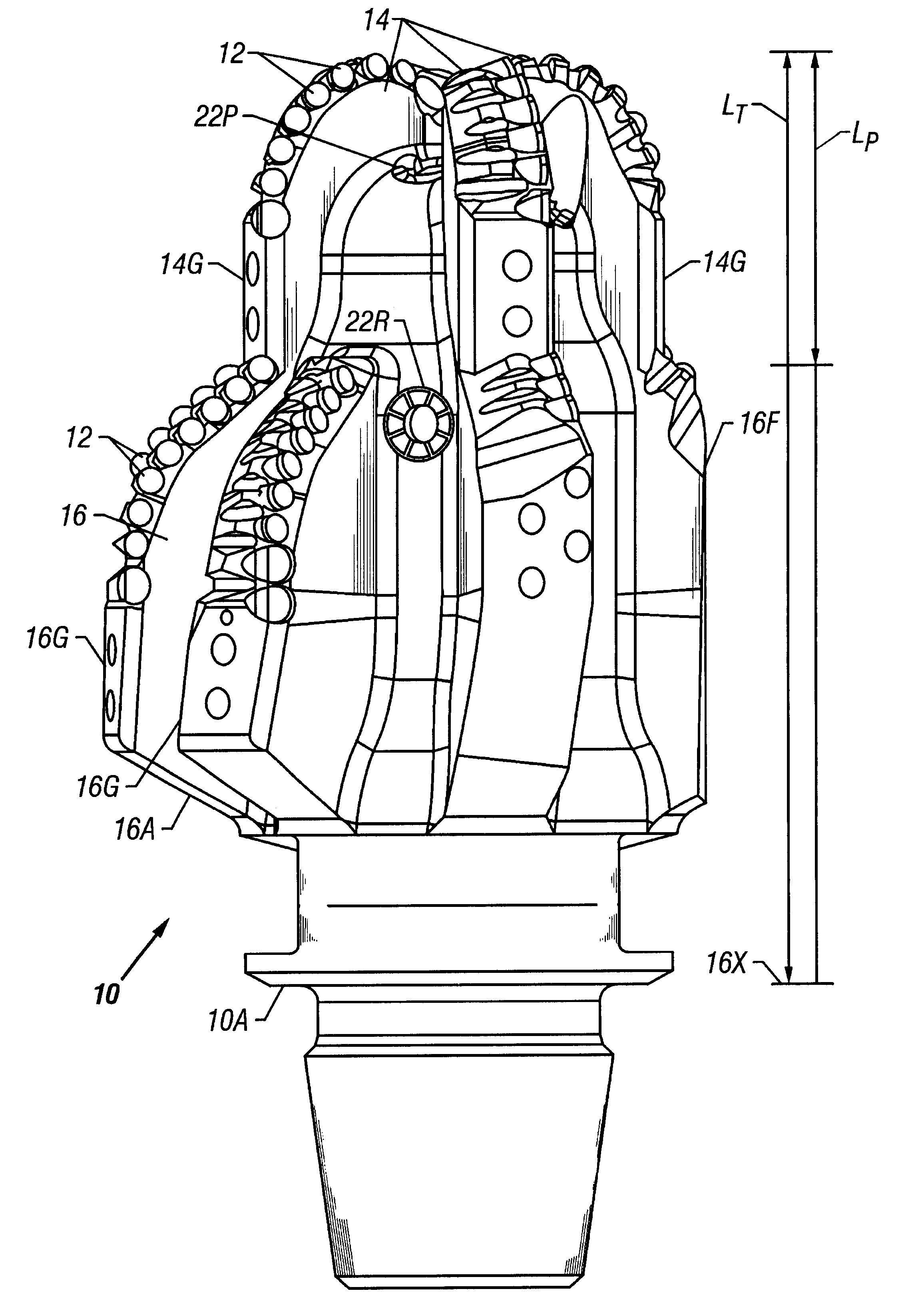
The present invention is an apparatus for use in drilling operations. It uses an under-reamer having a plurality of elongated arms with cutting elements at the ends of the arms for enlarging a previously drilled borehole drilled by a drill bit. One or more stabilizers in close proximity to the under-reamer provide stability to the under-reamer and the drill bit. The stabilizer could be rotating or non-rotating; and could be positioned between the under-reamer and the drill bit, or above the under reamer or above a directional device on the drillstring. The cutting arms are selectively operable to perform the enlargement. The stabilizer may be provided with members that closely fit the size of the borehole.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
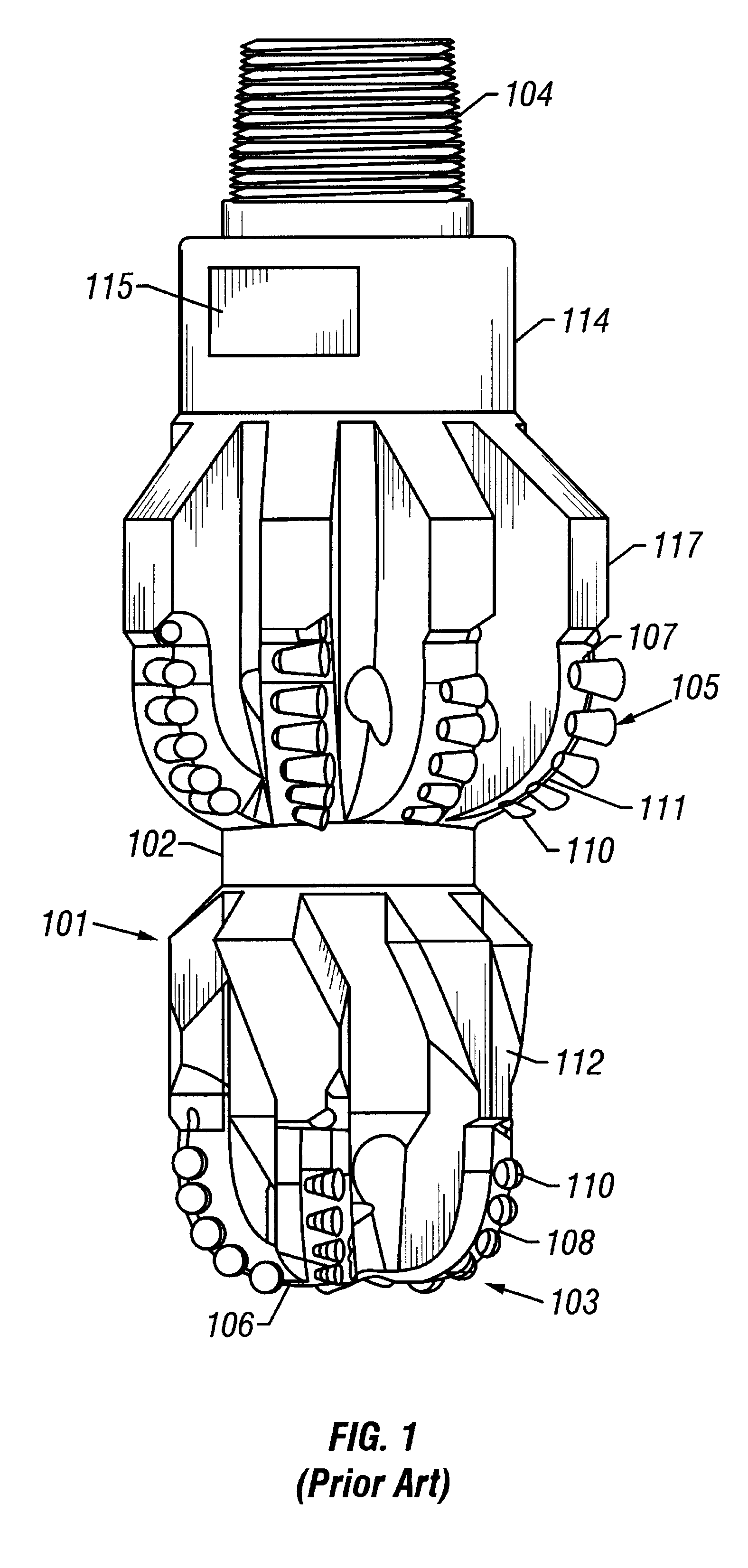
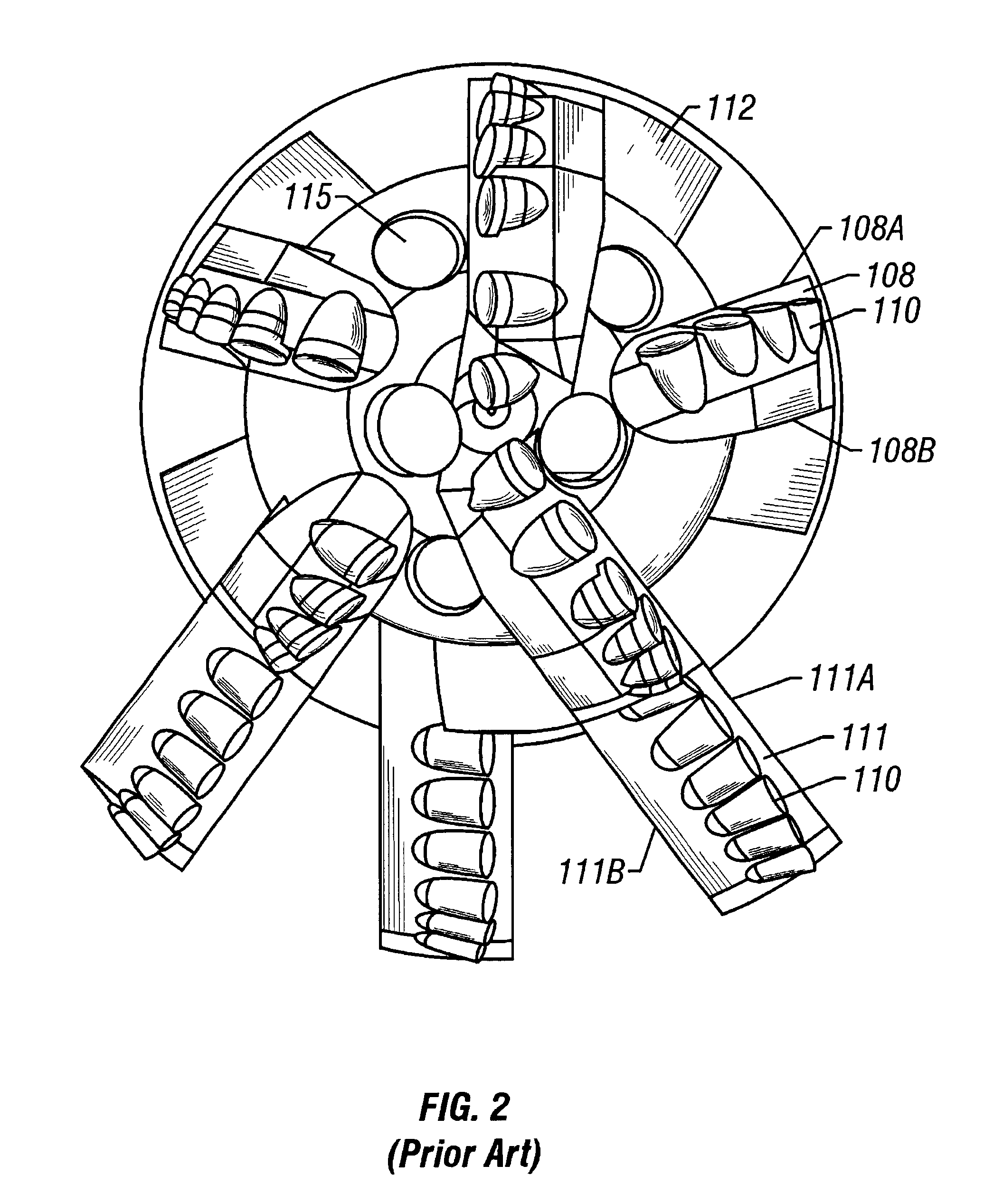
Bi-centered drill bit having improved drilling stability mud hydraulics and resistance to cutter damage
A bi-center drill bit includes pilot and reaming blades affixed to a body at azimuthally spaced locations. The blades have PDC cutters attached at selected positions. In one aspect, the pilot blades form a section having length along the bit axis less than about 80 percent of a diameter of the section. In another aspect, selected pilot blades and corresponding reaming blades are formed into single spiral structures. In another aspect, shapes and positions of the blades and inserts are selected so that lateral forces exerted by the reaming and the pilot sections are balanced as a single structure. Lateral forces are preferably balanced to within 10 percent of the total axial force on the bit. In another aspect, the center of mass of the bit is located less than about 2.5 percent of the diameter of the bit from the axis of rotation. In another aspect, jets are disposed in the reaming section oriented so that their axes are within about 30 degrees of normal to the axis of the bit. In another aspect, the reaming blades are shaped to conform to the radially least extensive, from the longitudinal axis, of a pass-through circle or a drill circle, so the cutters on the reaming blades drill at the drill diameter, without contact to the cutters on the reaming blades when the bit passes through an opening having about the pass-through diameter.
Owner:SMITH INT INC
Expandable reamer apparatus for enlarging boreholes while drilling and methods of use
ActiveUS7036611B2Reduce capacityReduce the cross-sectional areaSurveyDrill bitsFixed bearingWell drilling
An expandable reamer apparatus and methods for reaming a borehole, wherein a laterally movable blade carried by a tubular body may be selectively positioned at an inward position and an expanded position. The laterally movable blade, held inwardly by blade-biasing elements, may be forced outwardly by drilling fluid selectively allowed to communicate therewith by way of an actuation sleeve disposed within the tubular body. Alternatively, a separation element may transmit force or pressure from the drilling fluid to the movable blade. Further, a chamber in communication with the movable blade may be pressurized by way of a downhole turbine or pump. A ridged seal wiper, compensator, movable bearing pad, fixed bearing pad preceding the movable blade, or an adjustable spacer element to alter expanded blade position may be included within the expandable reamer. In addition, a drilling fluid pressure response indicating an operational characteristic of the expandable reamer may be generated.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES OILFIELD OPERATIONS LLC
Drilling with a high pressure rotating control device
ActiveUS20110024195A1Operational securityHigh safety factorSurveyDrilling rodsWell drillingControl system
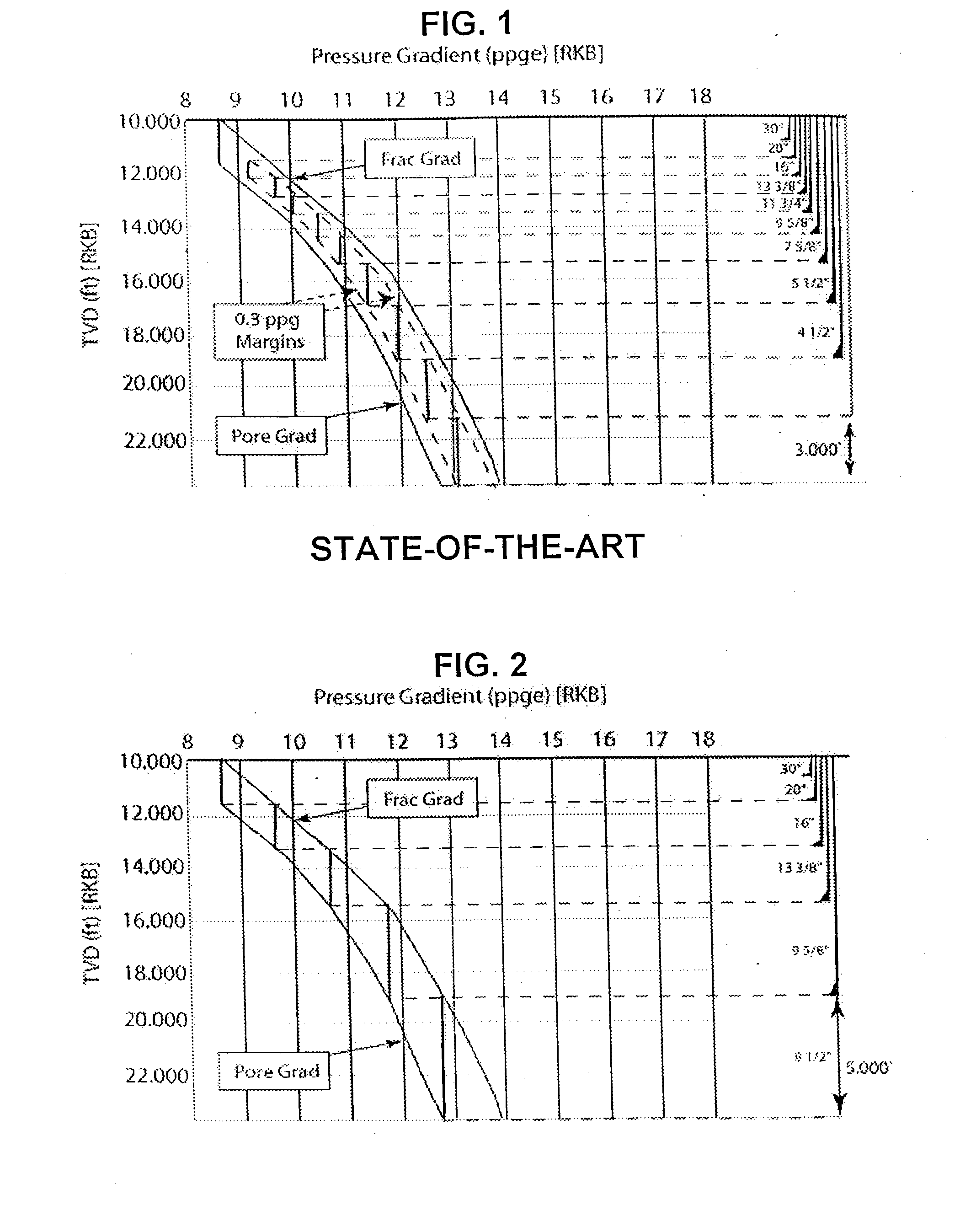
A Drill-To-The-Limit (DTTL) drilling method variant to Managed Pressure Drilling (MPD) applies constant surface backpressure, whether the mud is circulating (choke valve open) or not (choke valve closed). Because of the constant application of surface backpressure, the DTTL method can use lighter mud weight that still has the cutting carrying ability to keep the borehole clean. The DTTL method identifies the weakest component of the pressure containment system, such as the fracture pressure of the formation or the casing shoe leak off test (LOT). With a higher pressure rated RCD, such as 5,000 psi (34,474 kPa) dynamic or working pressure and 10,000 psi (68,948 kPa) static pressure, the limitation will generally be the fracture pressure of the formation or the LOT. In the DTTL method, since surface backpressure is constantly applied, the pore pressure limitation of the conventional drilling window can be disregarded in developing the fluid and drilling programs. Using the DTTL method a deeper wellbore can be drilled with larger resulting end tubulars, such as casings and production liners, than had been capable with conventional MPD applications.
Owner:WEATHERFORD TECH HLDG LLC
Reverse circulation directional and horizontal drilling using concentric drill string
InactiveUS7204327B2Avoid damageSafe and economical mannerDrilling rodsDirectional drillingWell drillingDirectional drilling
Method and apparatus for drilling a directional or horizontal wellbore in a hydrocarbon formation using concentric drill string having an inner pipe and an outer pipe defining an annulus there between. A bottomhole assembly comprising a directional drilling means such as an air hammer or a rotary drill bit and driving system is provide at the lower end of the concentric drill string and drilling medium is delivered through the annulus or inner pipe for operating the directional drilling means to form a borehole. Exhaust drilling medium, drilling cutting and hydrocarbon are removed from the wellbore by extracting the exhaust drilling medium, drilling cutting and hydrocarbon through the other of the annulus or inner pipe.
Owner:PRESSSOL
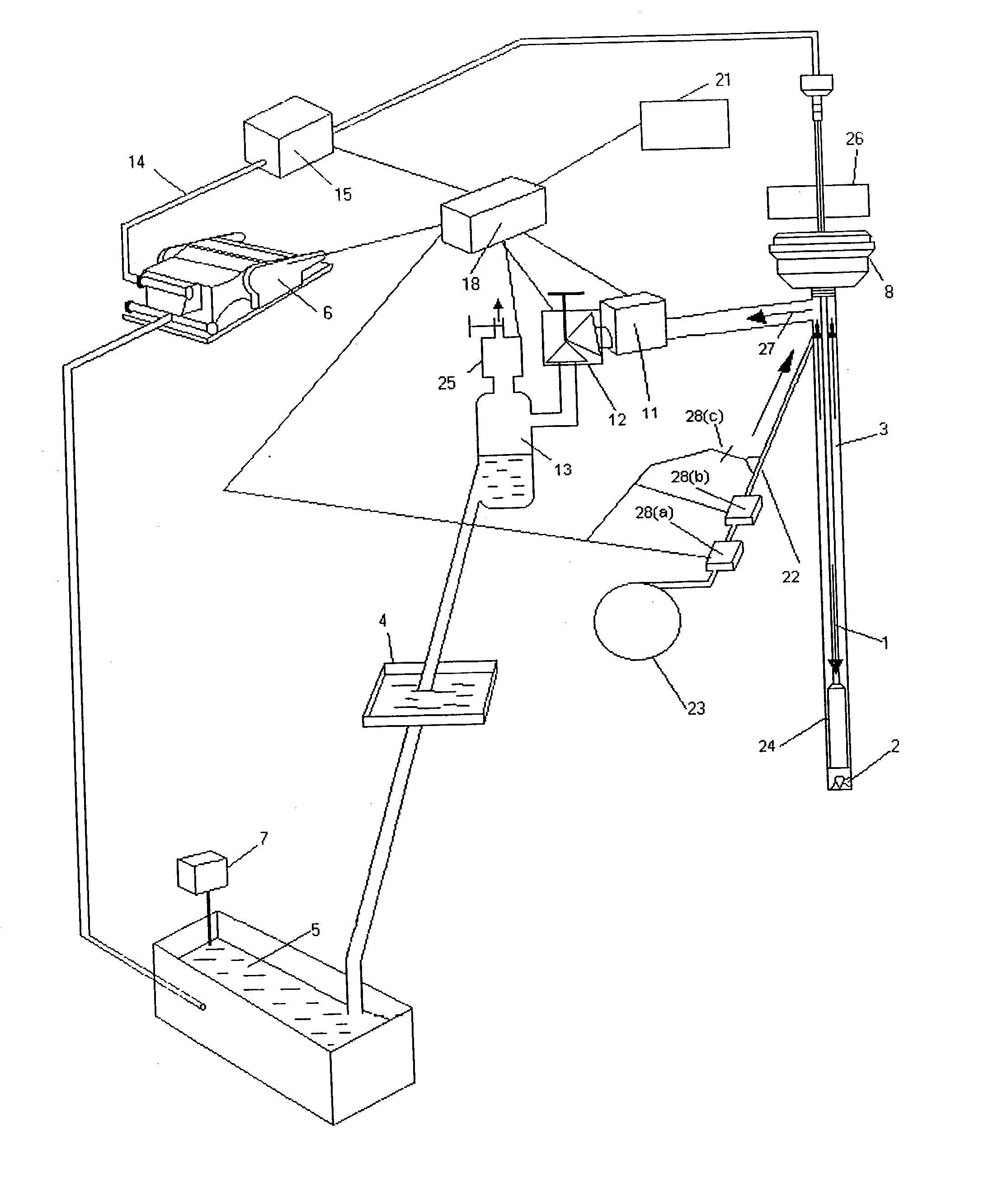
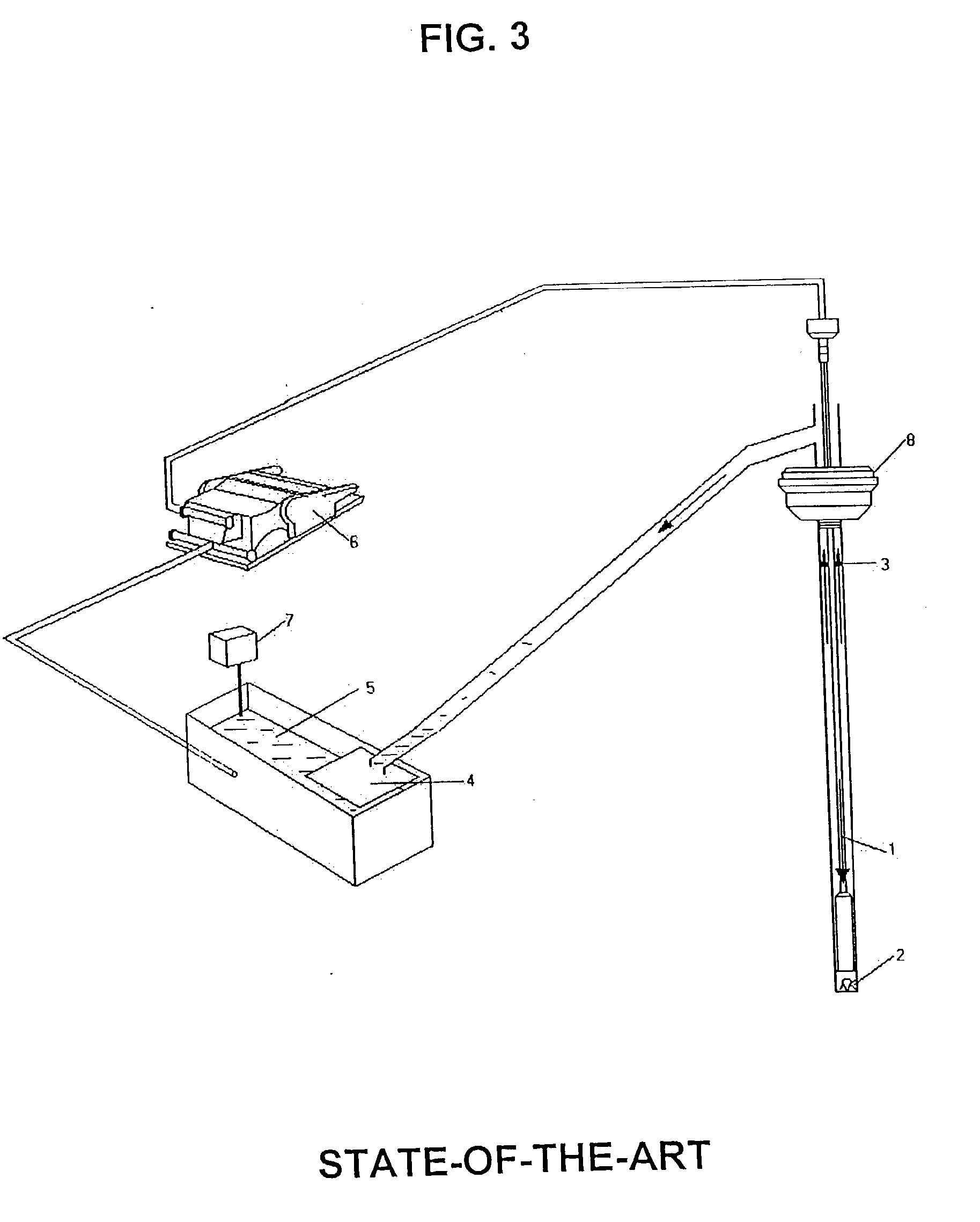
Drilling system and method for controlling equivalent circulating density during drilling of wellbores
A drilling system for drilling subsea wellbores includes a tubing-conveyed drill bit that passes through a subsea wellhead. Surface supplied drilling fluid flows through the tubing, discharges at the drill bit, returns to the wellhead through a wellbore annulus, and flows to the surface via a riser extending from the wellhead. A flow restriction device positioned in the riser restricts the flow of the returning fluid while an active fluid device controllably discharges fluid from a location below to just above the flow restriction device in the riser, thereby controlling bottomhole pressure and equivalent circulating density (“ECD”). Alternatively, the fluid is discharged into a separate return line thereby providing dual gradient drilling while controlling bottomhole pressure and ECD. A controller controls the energy and thus the speed of the pump in response to downhole measurement(s) to maintain the ECD at a predetermined value or within a predetermined range.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Drilling with concentric strings of casing
InactiveUS6857487B2Cost for assemblyReduce equipment costsEarth drilling toolsDrilling rodsWell drillingEngineering
The present invention provides a method and apparatus for setting concentric casing strings within a wellbore in one run-in of a casing working string. In one aspect of the invention, the apparatus comprises a drilling system comprising concentric casing strings, with each casing string having a drill bit piece disposed at the lower end thereof. The drill bit pieces of adjacent casing strings are releasably connected to one another. In another aspect of the invention, a method is provided for setting concentric casing strings within a wellbore with the drilling system. In another aspect of the invention, the releasably connected drill bit pieces comprise a drill bit assembly.
Owner:WEATHERFORD TECH HLDG LLC
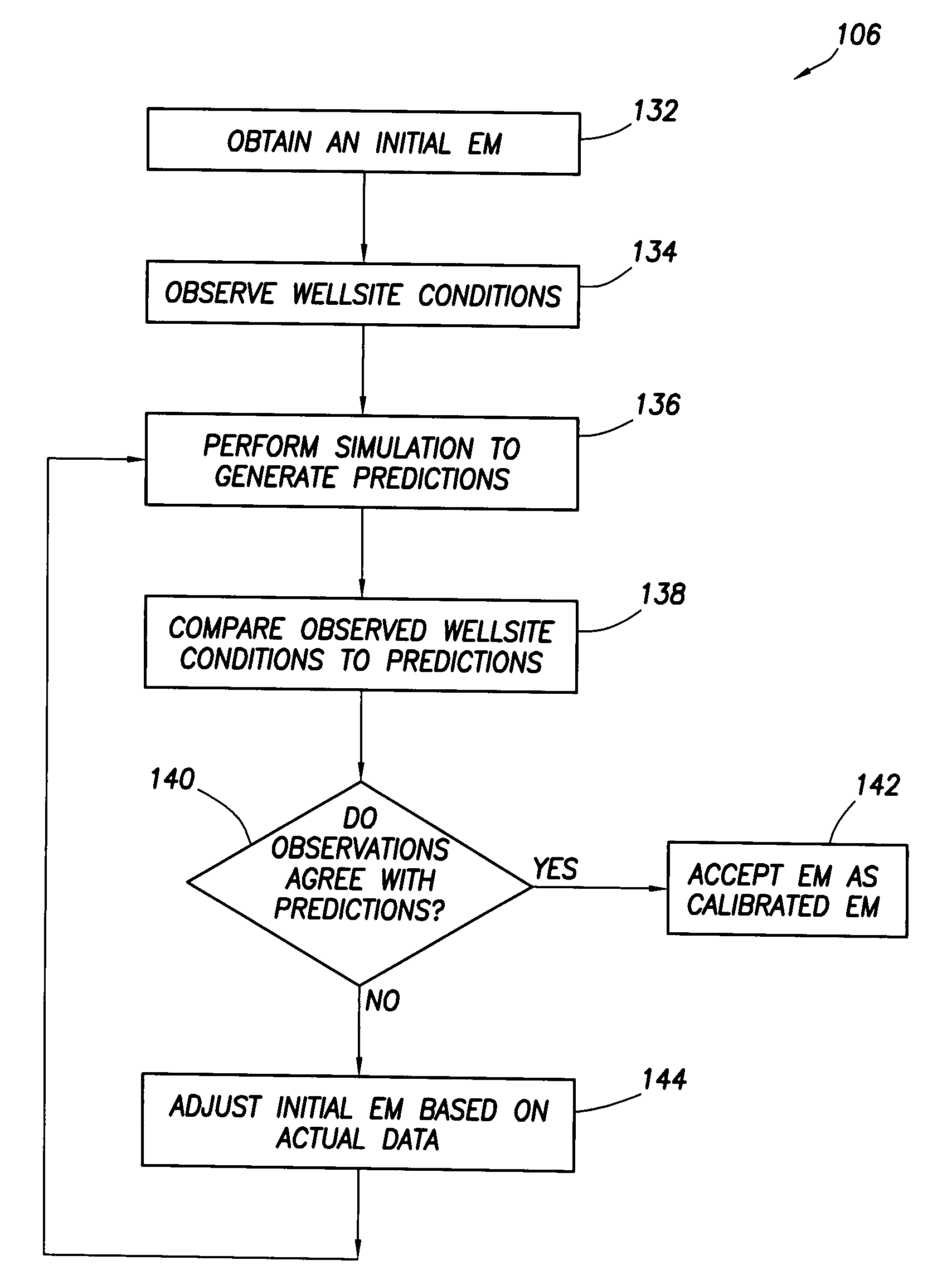
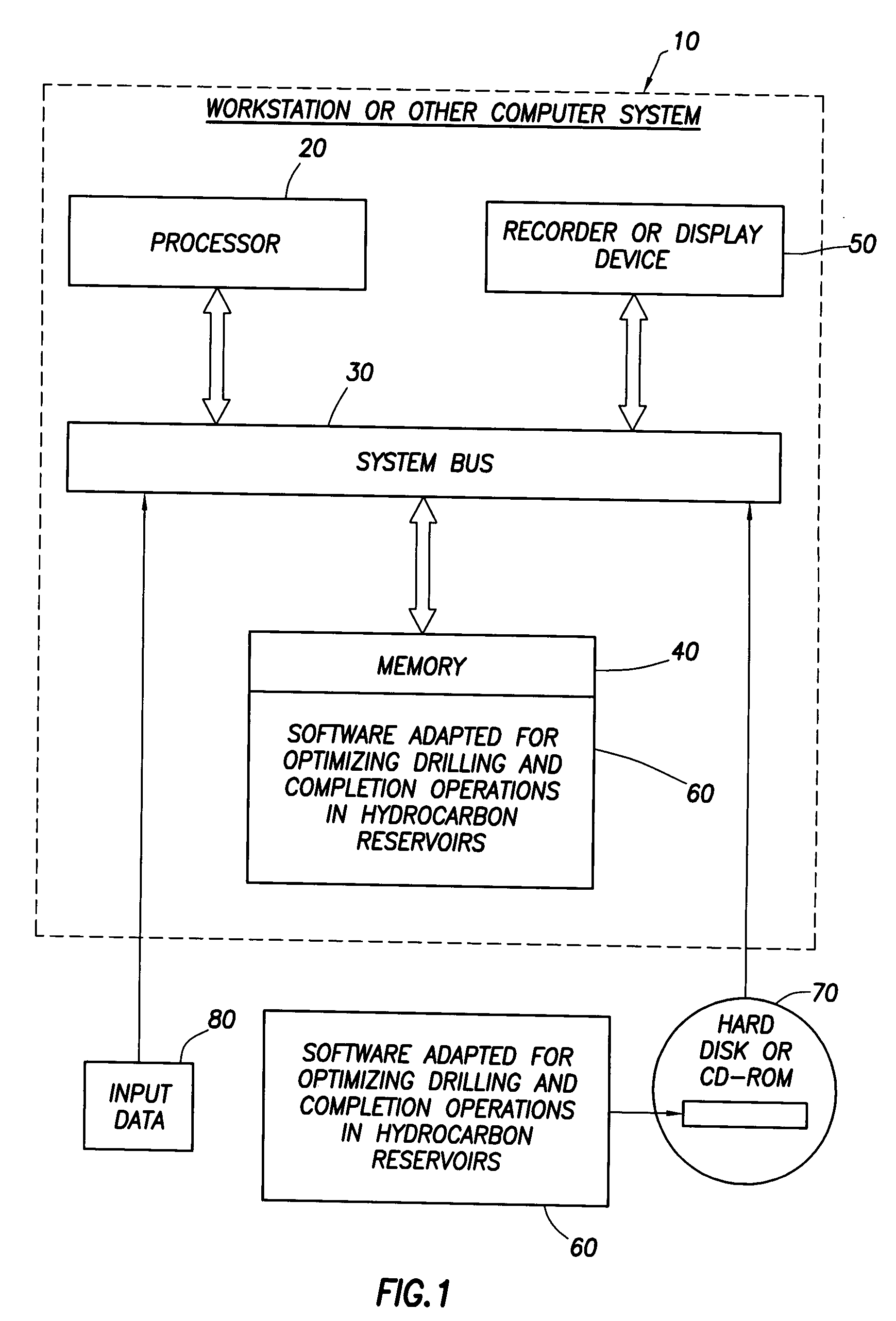
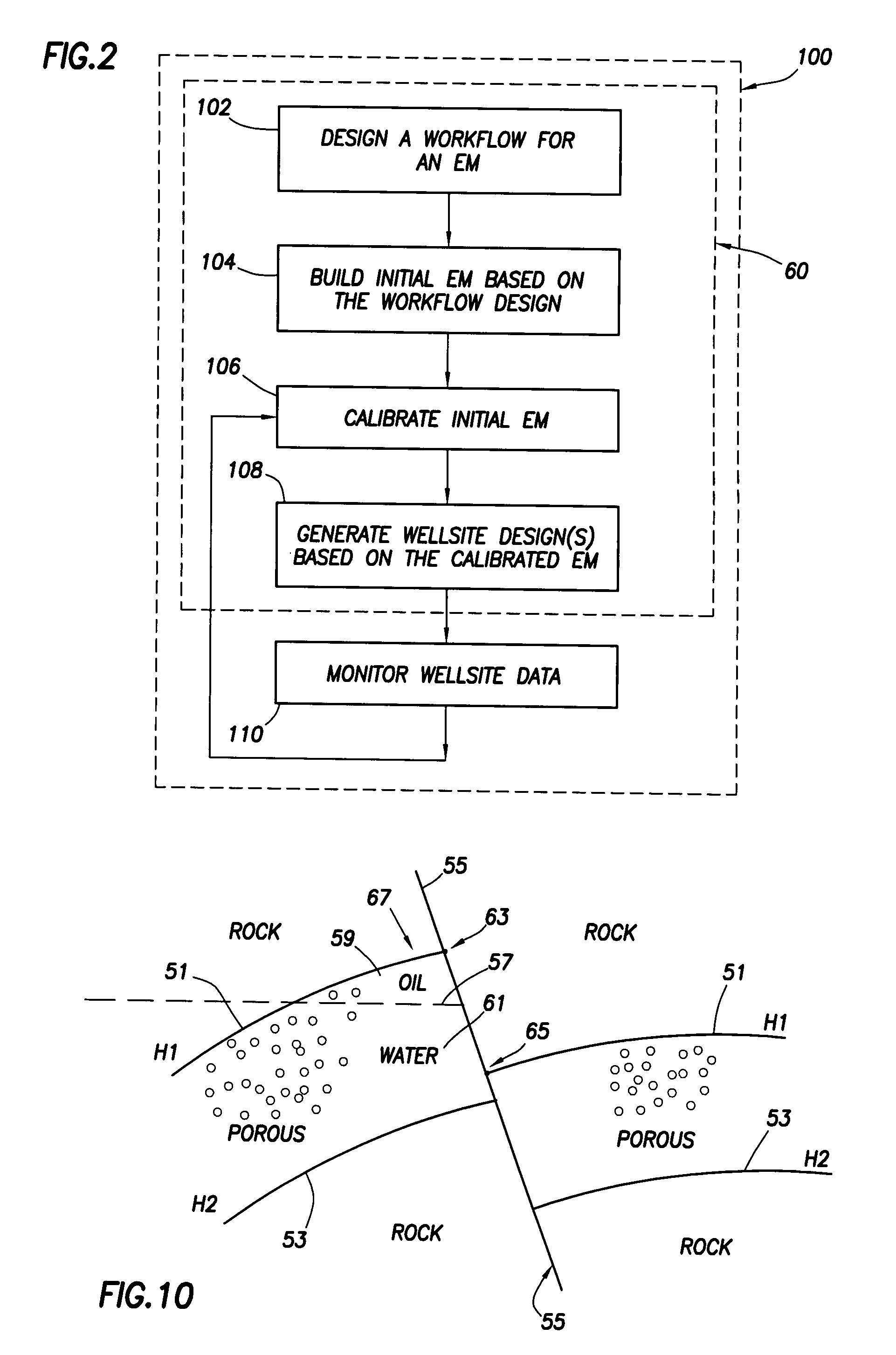
Method for designing and optimizing drilling and completion operations in hydrocarbon reservoirs
ActiveUS20070294034A1Speed maximizationMinimize damageGeometric CADElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingWell drillingEarth model
A method is disclosed for generating a wellsite design, comprising: designing a workflow for an Earth Model; building an initial Earth Model based on the workflow adapted for modeling drilling and completions operations in a hydrocarbon reservoir; calibrating the initial Earth Model thereby generating a calibrated Earth Model; and generating the wellsite design using the calibrated Earth Model.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Method and apparatus for evaluating the resistivity of formations with high dip angles or high-contrast thin layers
InactiveUS6304086B1Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSeismology for water-loggingWell loggingThin layer
A method and apparatus for evaluating the resistivity of earth formations surrounding a borehole, particularly high-contrast thin-layer formations or at high dip angles. The method involves positioning a pair of transmitters and a pair of receivers within the borehole, the receivers or transmitters adhering to specific spacing limitations, alternately transmitting electromagnetic energy of a particular frequency and receiving voltage data associated with the transmitted energy. Multiple voltage data are acquired and a representation of a resistivity or conductivity profile is created from a formulated difference of the data from a particular depth and / or neighboring depths. The apparatus forms part of a well logging system including a well tool adapted to be moveable through a borehole. The apparatus being coupled to the well tool and adapted with means to input voltage data developed by the receivers disposed on the well tool. The apparatus further adapted with means for performing calculations to determine a conductivity profile and for recording the profile on an output record medium.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
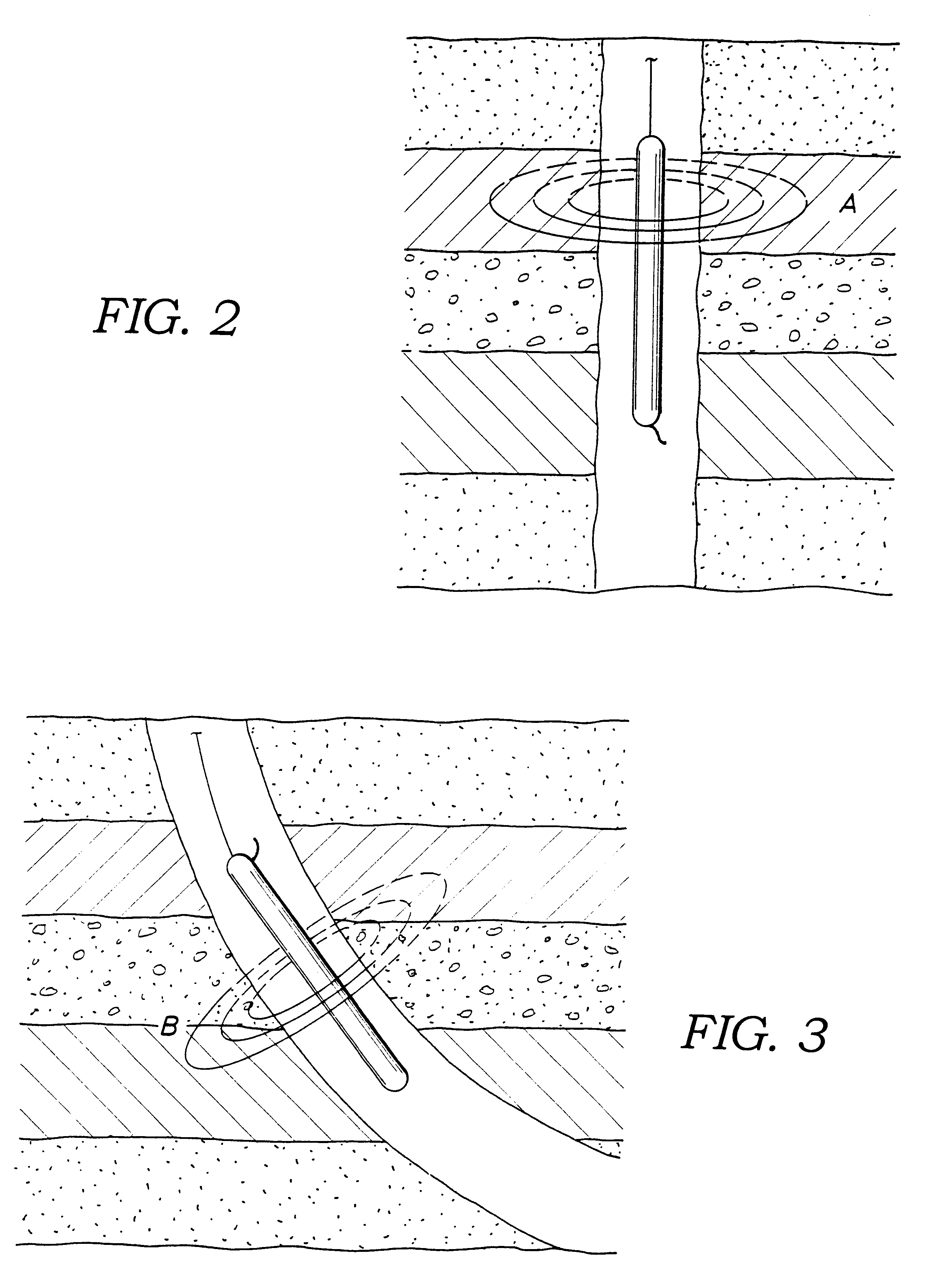
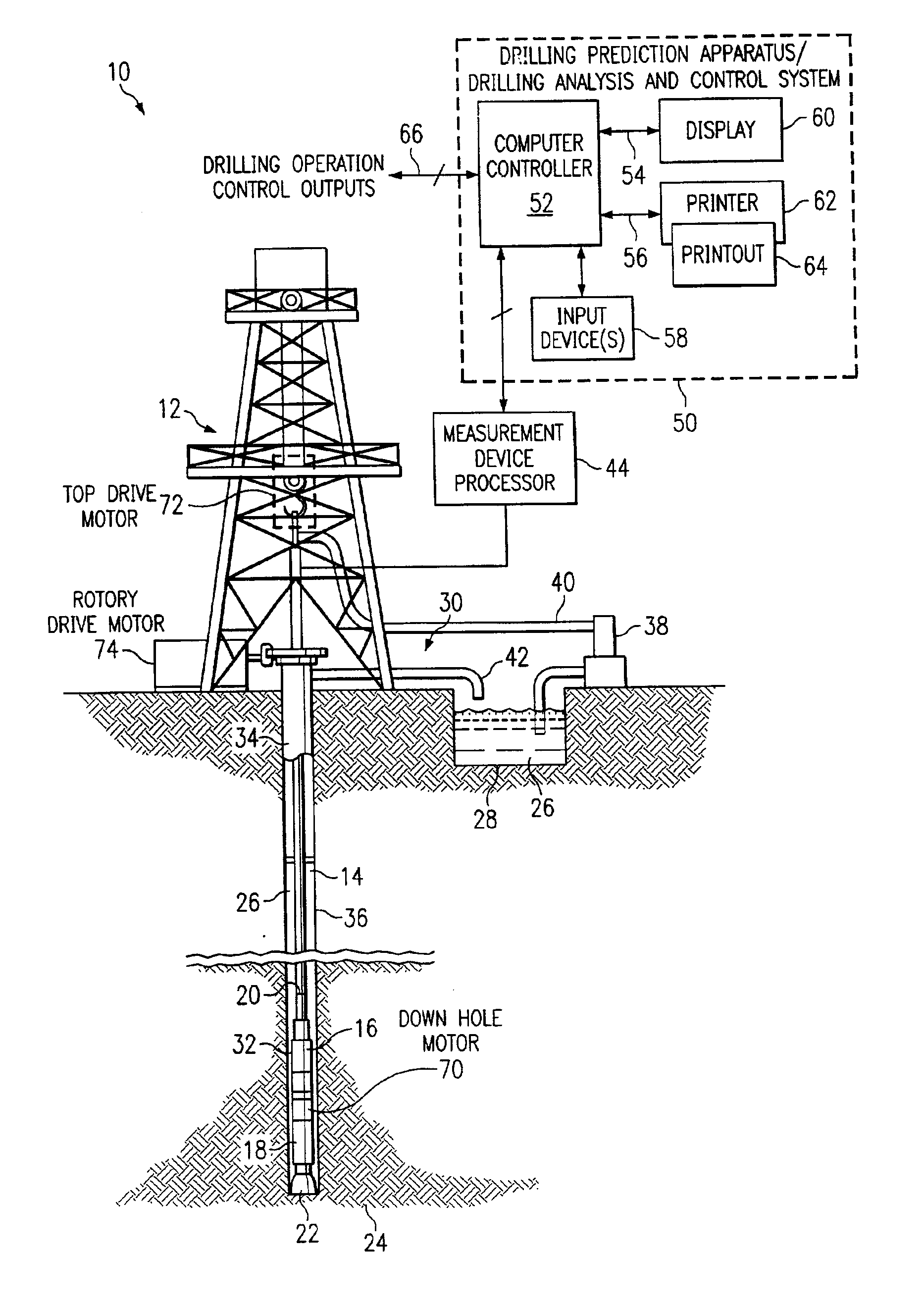
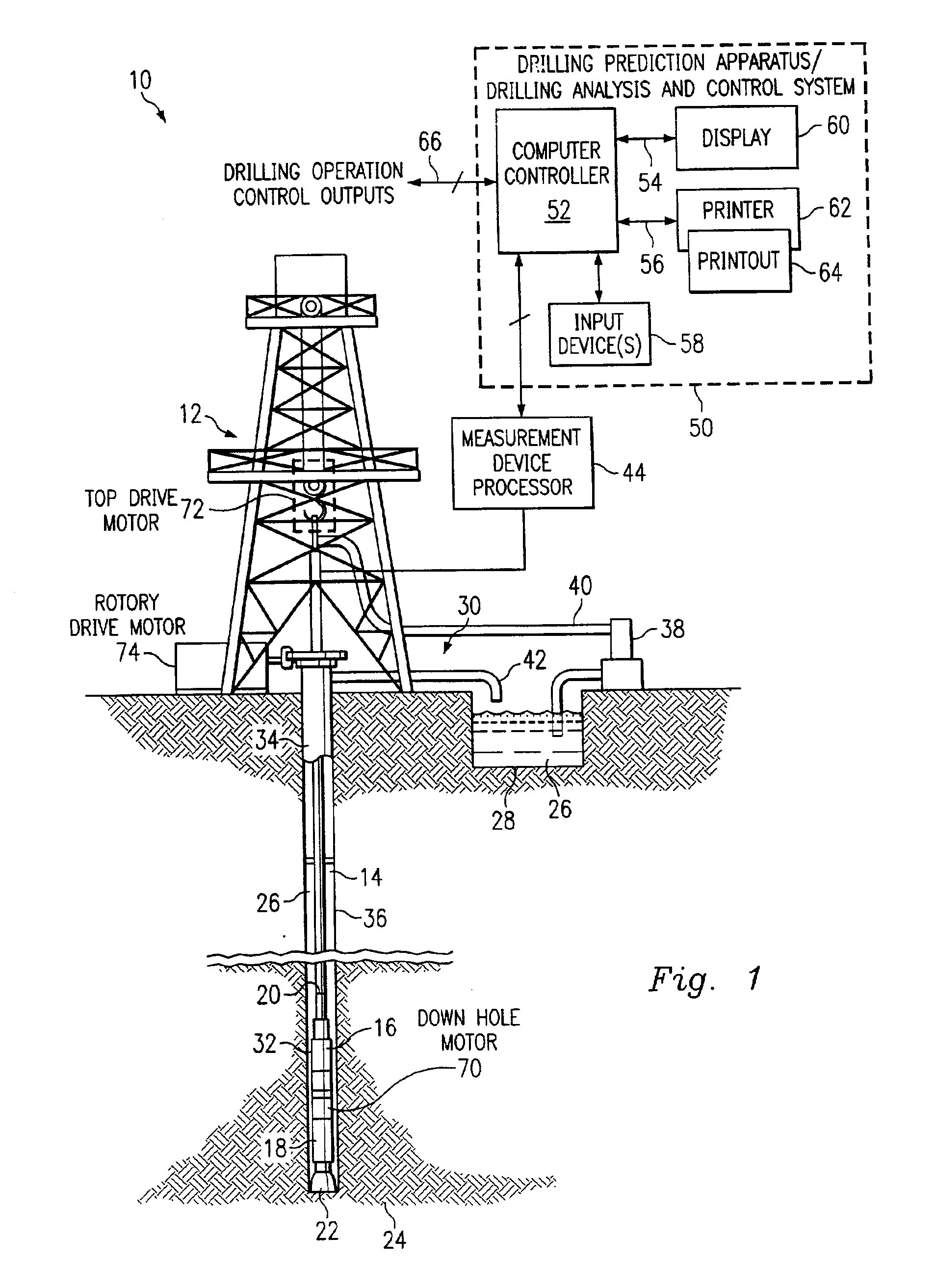
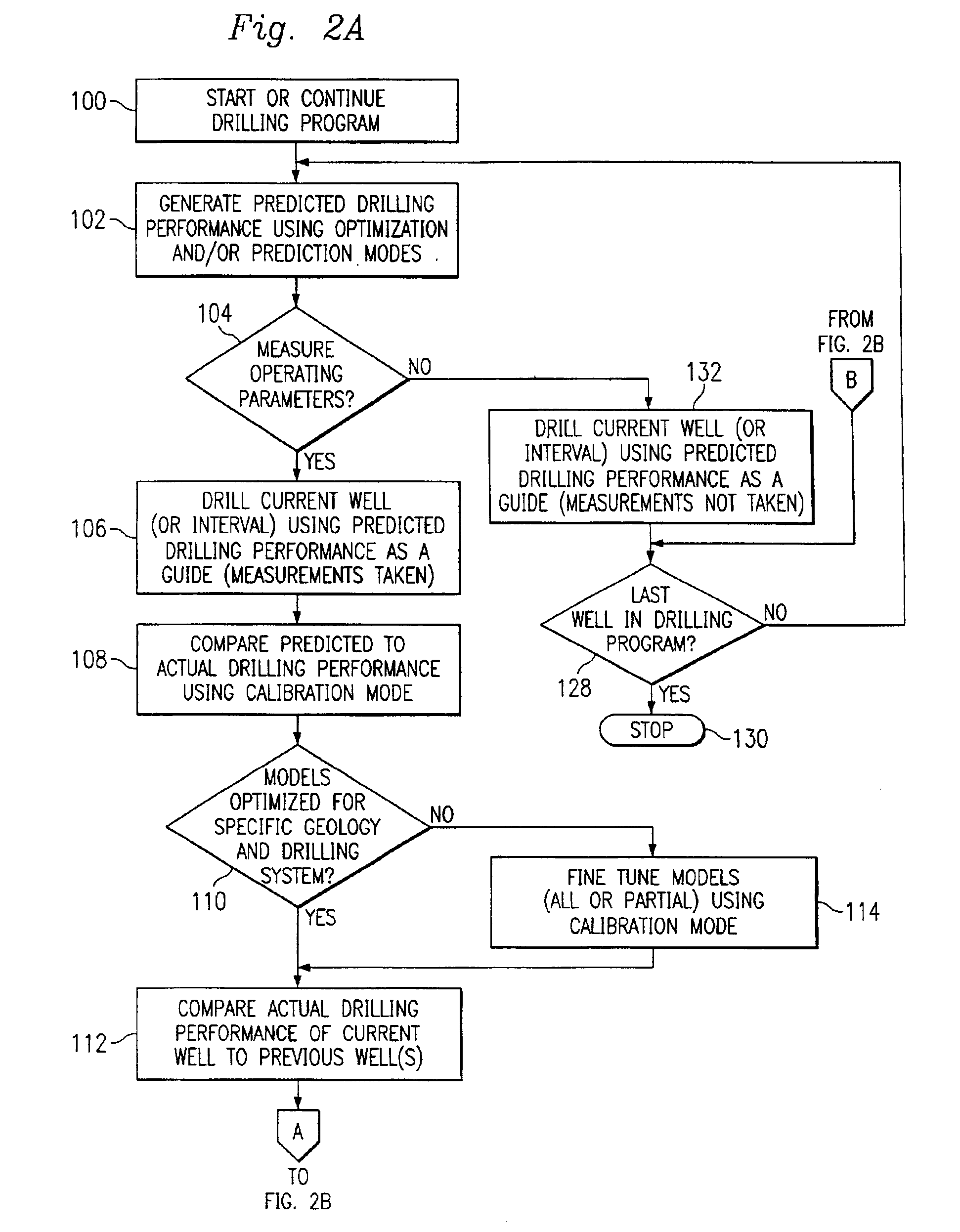
Method and system for predicting performance of a drilling system of a given formation
InactiveUS7032689B2Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingEarth drilling toolsComputer printingDisplay device
A method and apparatus for predicting the performance of a drilling system for the drilling of a well bore in a given formation includes generating a geology characteristic of the formation per unit depth according to a prescribed geology model, obtaining specifications of proposed drilling equipment for use in the drilling of the well bore, and predicting a drilling mechanics in response to the specifications as a function of the geology characteristic per unit depth according to a prescribed drilling mechanics model. Responsive to a predicted-drilling mechanics, a controller controls a parameter in the drilling of the well bore. The geology characteristic includes at least rock strength. The specifications include at least a bit specification of a recommended drill bit. Lastly, the predicted drilling mechanics include at least one of bit wear, mechanical efficiency, power, and operating parameters. A display is provided for generating a display of the geology characteristic and predicted drilling mechanics per unit depth, including either a display monitor or a printer.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
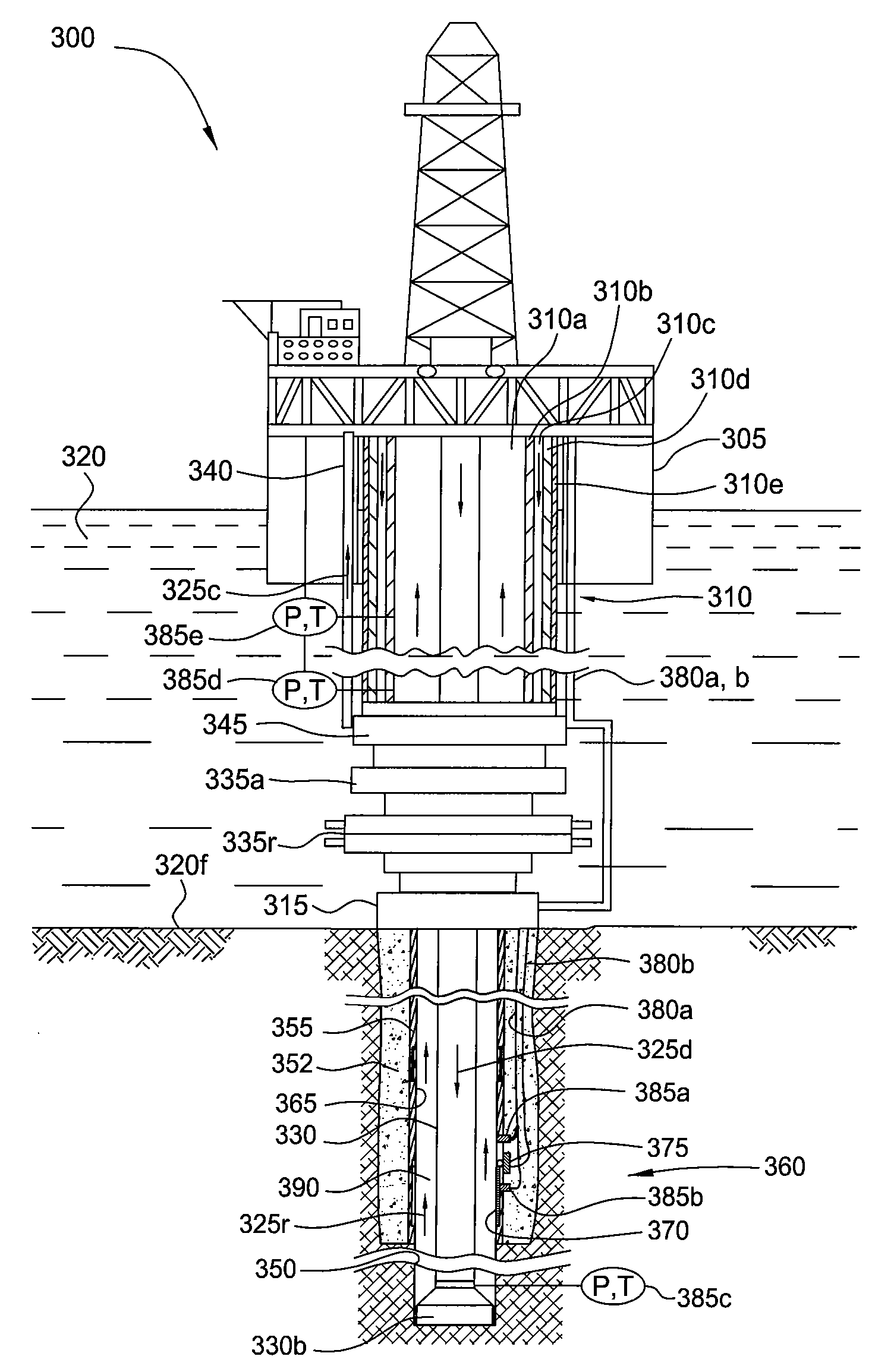
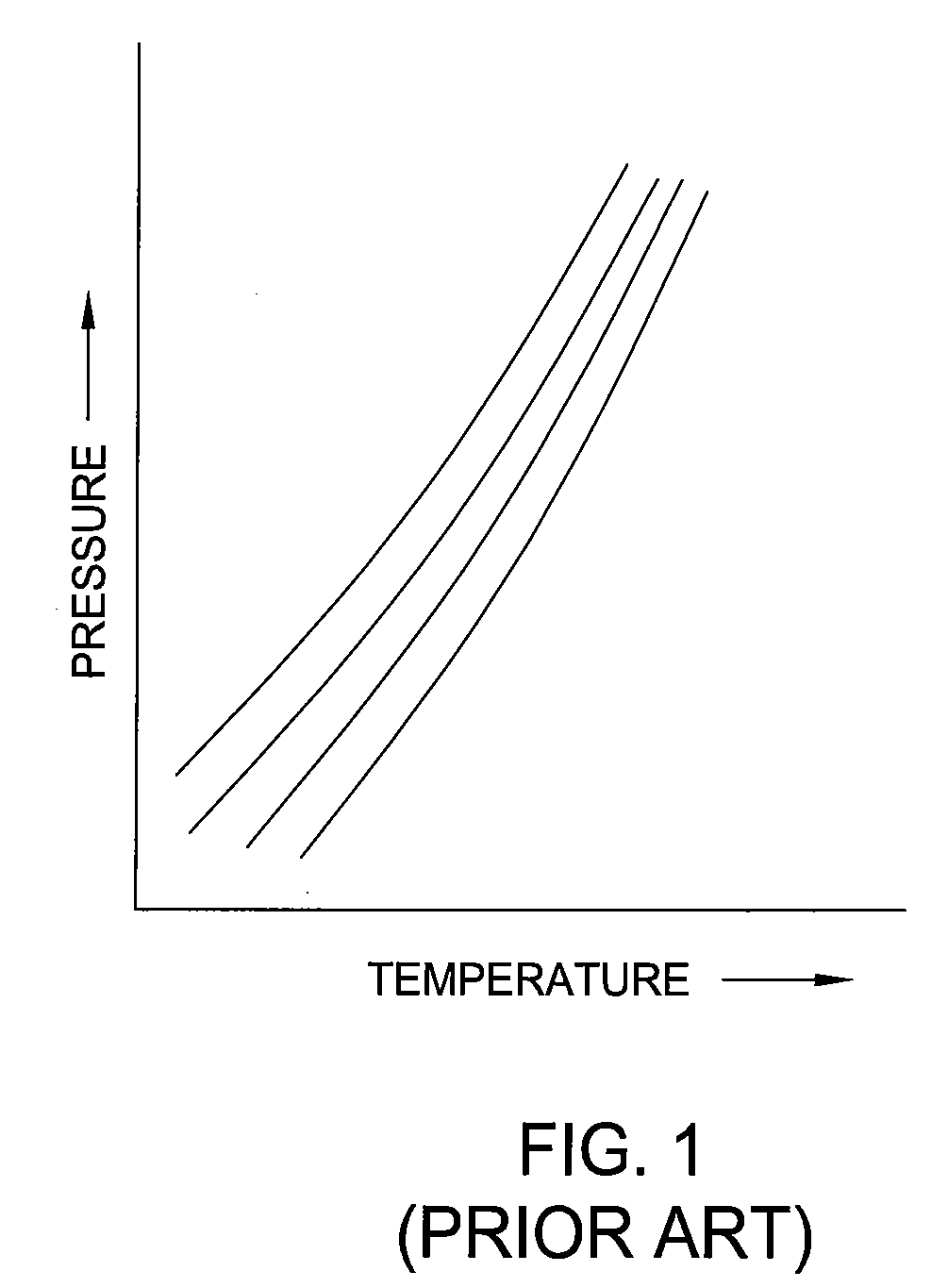
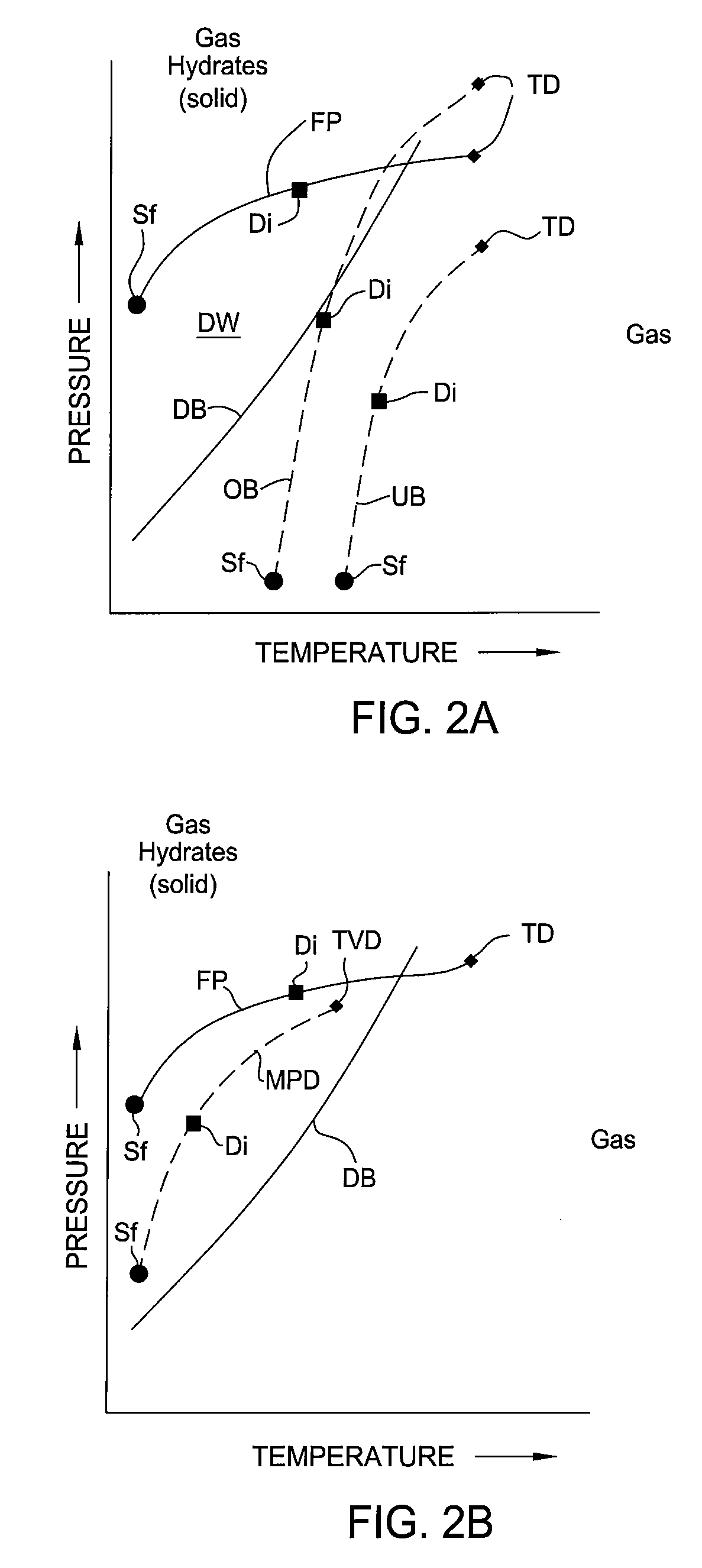
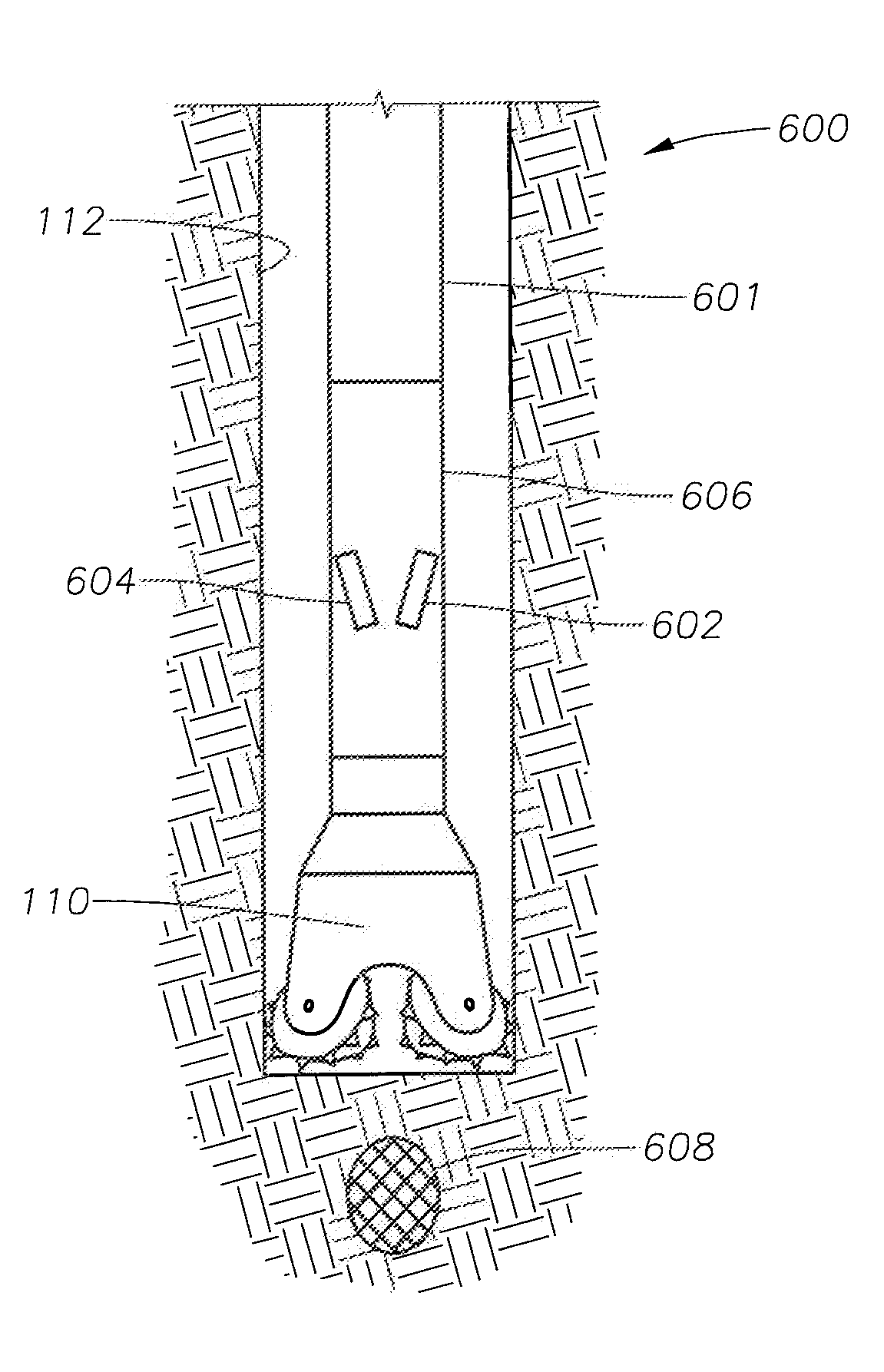
Managed pressure and/or temperature drilling system and method
The present invention relates to a managed pressure and / or temperature drilling system (300) and method. In one embodiment, a method for drilling a wellbore into a gas hydrates formation is disclosed. The method includes drilling the wellbore into the gas hydrates formation; returning gas hydrates cuttings to a surface of the wellbore and / or a drilling rig while controlling a temperature and / or a pressure of the cuttings to prevent or control disassociation of the hydrates cuttings.
Owner:WEATHERFORD TECH HLDG LLC
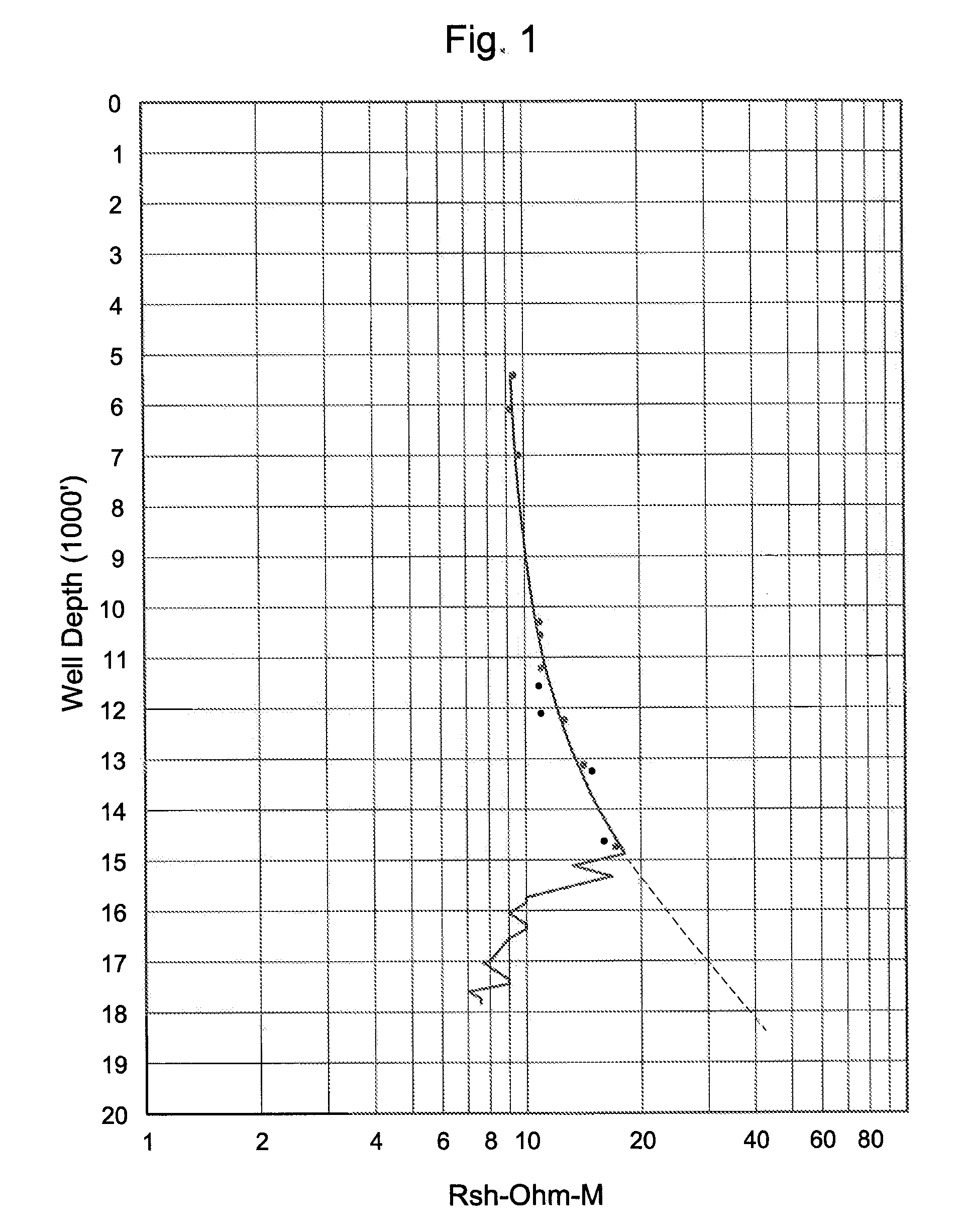
Method to detect formation pore pressure from resistivity measurements ahead of the bit during drilling of a well
ActiveUS20100000791A1Risk minimizationReduce riskElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSurveyWell drillingRegion of interest
Methods are described using resistivity ahead of a drill bit measurements obtained while drilling a subterranean well using a drilling mud. Resistivity data ahead of the bit is gathered during drilling and prior to penetrating a region of interest of a known subterranean formation using the drill bit and the drilling mud. The drill string progresses at known dip and azimuth angles toward the subterranean formation. The resistivity data is used to determine pore pressure ahead of the drill bit in the formation as a function of resistivity ahead of the drill bit in the formation while the drill bit advances toward but before the bit penetrates the formation while drilling. In certain embodiments, the methods include redirecting the drill bit while drilling toward locations in the formation where pore pressure is within an acceptable range. In other embodiments, a drilling mud parameter is adjusted based on the pore pressure in front of the bit.
Owner:BP CORP NORTH AMERICA INC
Methods of well stimulation during drilling operations
The present invention relates to subterranean well stimulation. More particularly, the present invention relates to improved methods of stimulating subterranean formations during drilling operations. In some embodiments, the present invention discloses methods of stimulating a section of a subterranean formation comprising (a) forming at least a portion of a well bore that at least penetrates a section of the subterranean formation using a drilling operation; (b) stimulation a section of the subterranean; and (c) continuing the drilling operation. In other embodiments, the present invention discloses methods of stimulation a section of a subterranean formation comprising (a) forming at least a portion of a well bore that at least penetrates a section of the subterranean formation using a drilling operation; (b) stimulating a section of the subterranean formation; and (c) continuing the drilling operation.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
Methods of consolidating formations
InactiveUS6837316B2High mechanical strengthSimple methodLiquid/gas jet drillingFluid removalCross-linkWater soluble
Methods of consolidating formations include drilling a well bore with a drilling fluid that comprises water, a polymeric cationic catalyst which is adsorbed on minerals and rocks in weak unconsolidated zones or formations and then further contacting the unconsolidated formation with a treating fluid comprising a water soluble or dispersible polymer which is cross-linked by a thermoset resin and causes the resin to be hard and tough when cured, and a water soluble or dispersible thermoset resin which cross-links the polymer, is catalyzed and cured by the catalyst and consolidates the weak zone or formation so that sloughing is prevented.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
Method of releasing stuck pipe or tools and spotting fluids therefor
Aphron-containing spotting fluids and their use in releasing pipe or tools stuck in the filter cake on the sides of a borehole are disclosed. The spotting fluids comprise a liquid, either aqueous, oleaginous, or mixtures thereof, a viscosifier which imparts a low shear rate viscosity to the fluids of at least 10,000 centipoise, an aphron-generating surfactant, and aphrons. The spotting fluids are used in a conventional method of releasing pipes or tools stuck in the filter cake on the sides of a borehole during conventional drilling or well servicing operations.
Owner:ENVENTIVES LLC
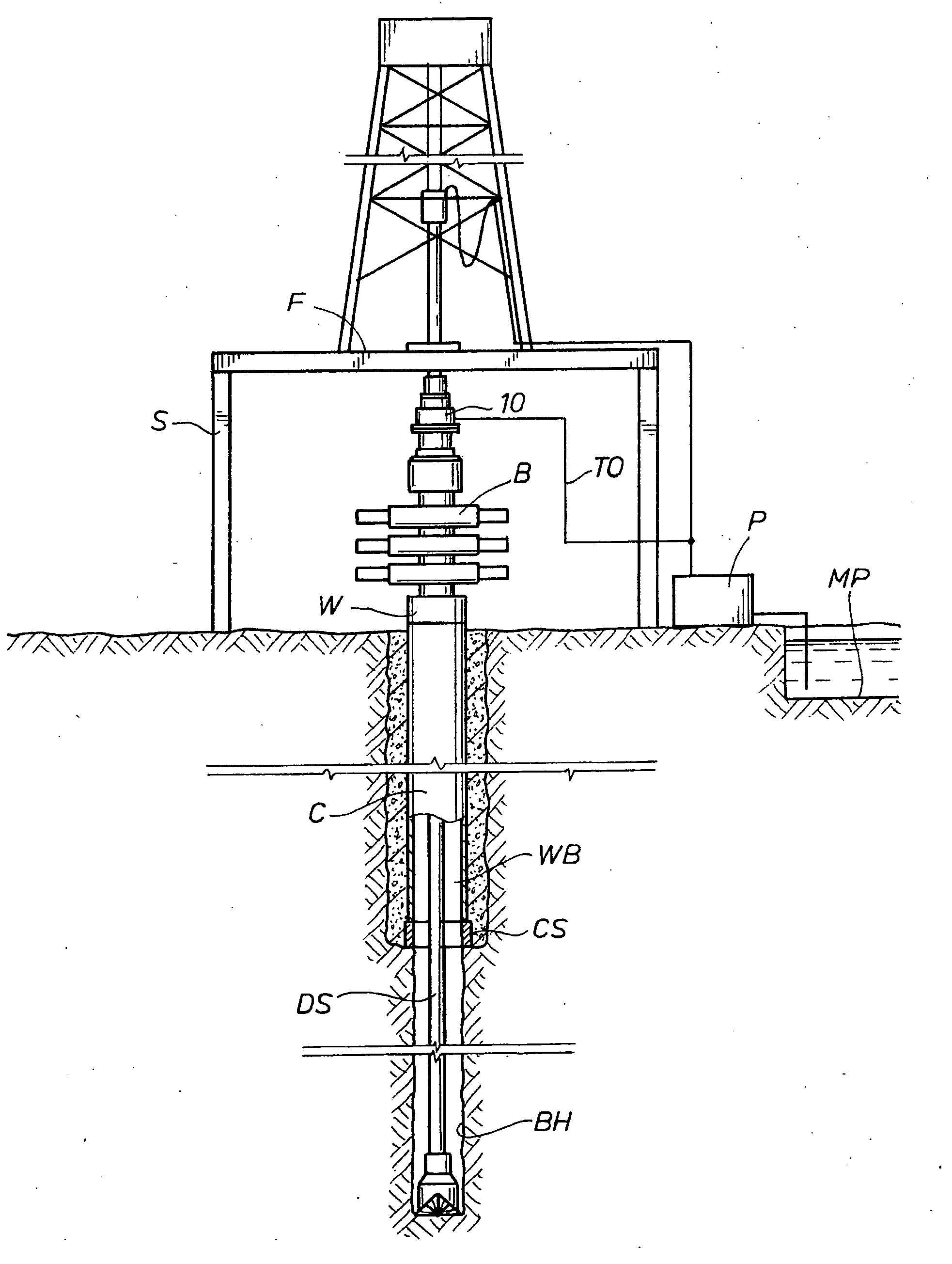
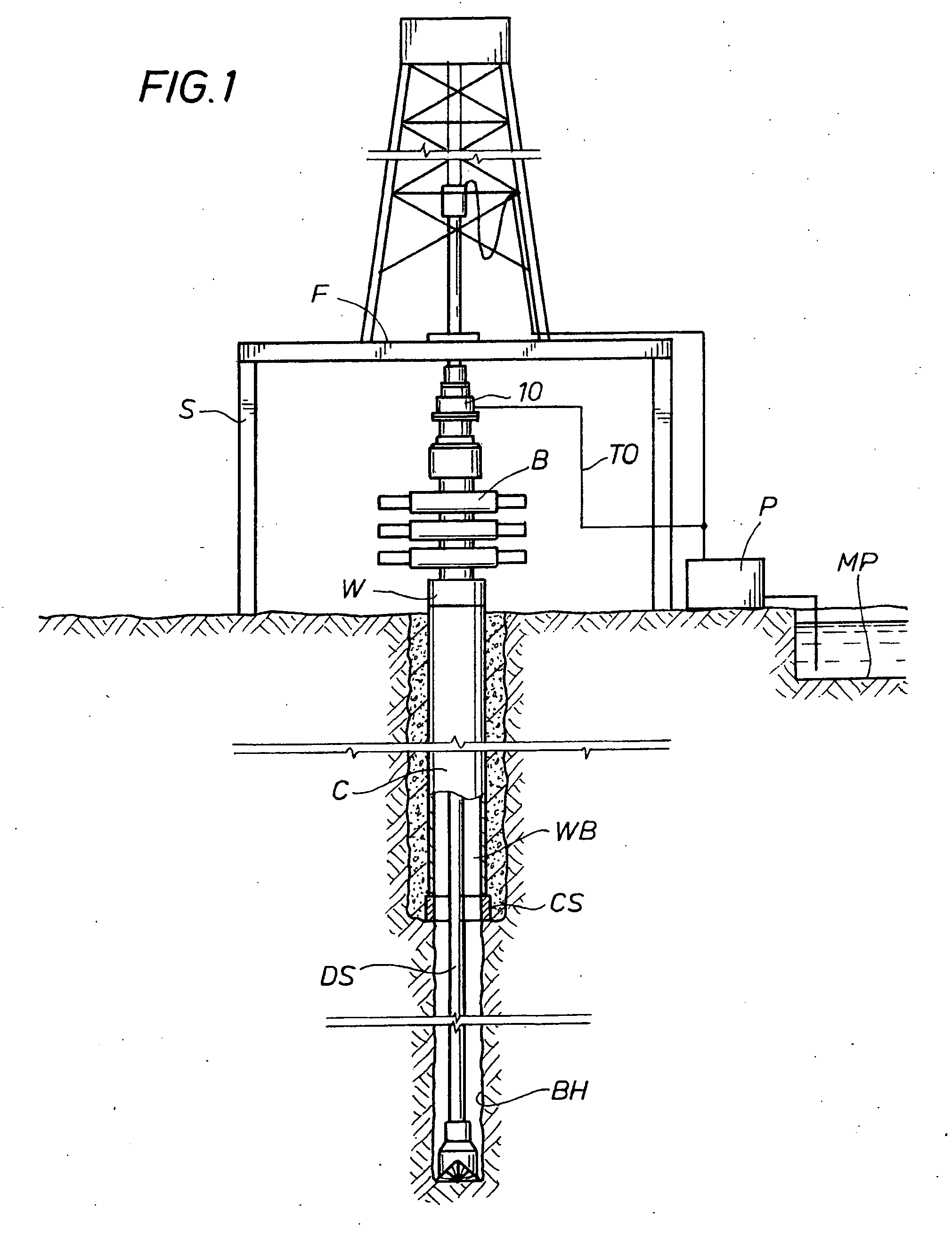
Drilling system and method
InactiveUS20030079912A1Accurate calculationImprove securityConstructionsFlushingWell drillingEngineering
A closed-loop circulating system for drilling wells has control of the flow rates in and out of the wellbore. Kicks and fluid losses are quickly controlled by adjusting the backpressure. Kick tolerance and tripping margins are eliminated by real-time determination of pore and fracture pressure. The system can incorporate a rotating BOP and can be used with underbalanced drilling.
Owner:SECURE DRILLING INT
Methods and apparatus for handling and drilling with tubulars or casing
InactiveUS7325610B2Reduce laborShorten the timeMechanical apparatusDrilling rodsTop driveWell drilling
The present invention provides a method and apparatus for handling tubulars and drilling with tubulars such as casing into a formation. In one aspect of the invention, the apparatus comprises a circulating head and a cementing head operatively connectible to a gripping member. The circulating head is used to circulate drilling fluid while drilling with casing, and the cementing head is used to cement the casing string within the formation at a desired depth. The present invention also relates to methods and apparatus for isolating a tensile load from a drilling apparatus rotated by a top drive. In one aspect, the present invention provides a load isolator apparatus having an isolator body operatively connected to the top drive and a torque body at least partially disposed in the isolator body. In operation, the bearing assembly transfers the tensile load from the torque body to the isolator body.
Owner:WEATHERFORD TECH HLDG LLC
Continuous flow drilling systems and methods
In one embodiment, a method for drilling a wellbore includes injecting drilling fluid into a top of a tubular string disposed in the wellbore at a first flow rate. The tubular string includes: a drill bit disposed on a bottom thereof, tubular joints connected together, a longitudinal bore therethrough, and a port through a wall thereof. The drilling fluid exits the drill bit and carries cuttings from the drill bit. The cuttings and drilling fluid (returns) flow to the surface via an annulus defined between the tubular string and the wellbore. The method further includes rotating the drill bit while injecting the drilling fluid; remotely removing a plug from the port, thereby opening the port; and injecting drilling fluid into the port at a second flow rate while adding a tubular joint or stand of joints to the tubular string. The injection of drilling fluid into the tubular string is continuously maintained between drilling and adding the joint or stand to the drill string. The method further includes remotely installing a plug into the port, thereby closing the port. The first and second flow rates may be substantially equal or different.
Owner:WEATHERFORD TECH HLDG LLC
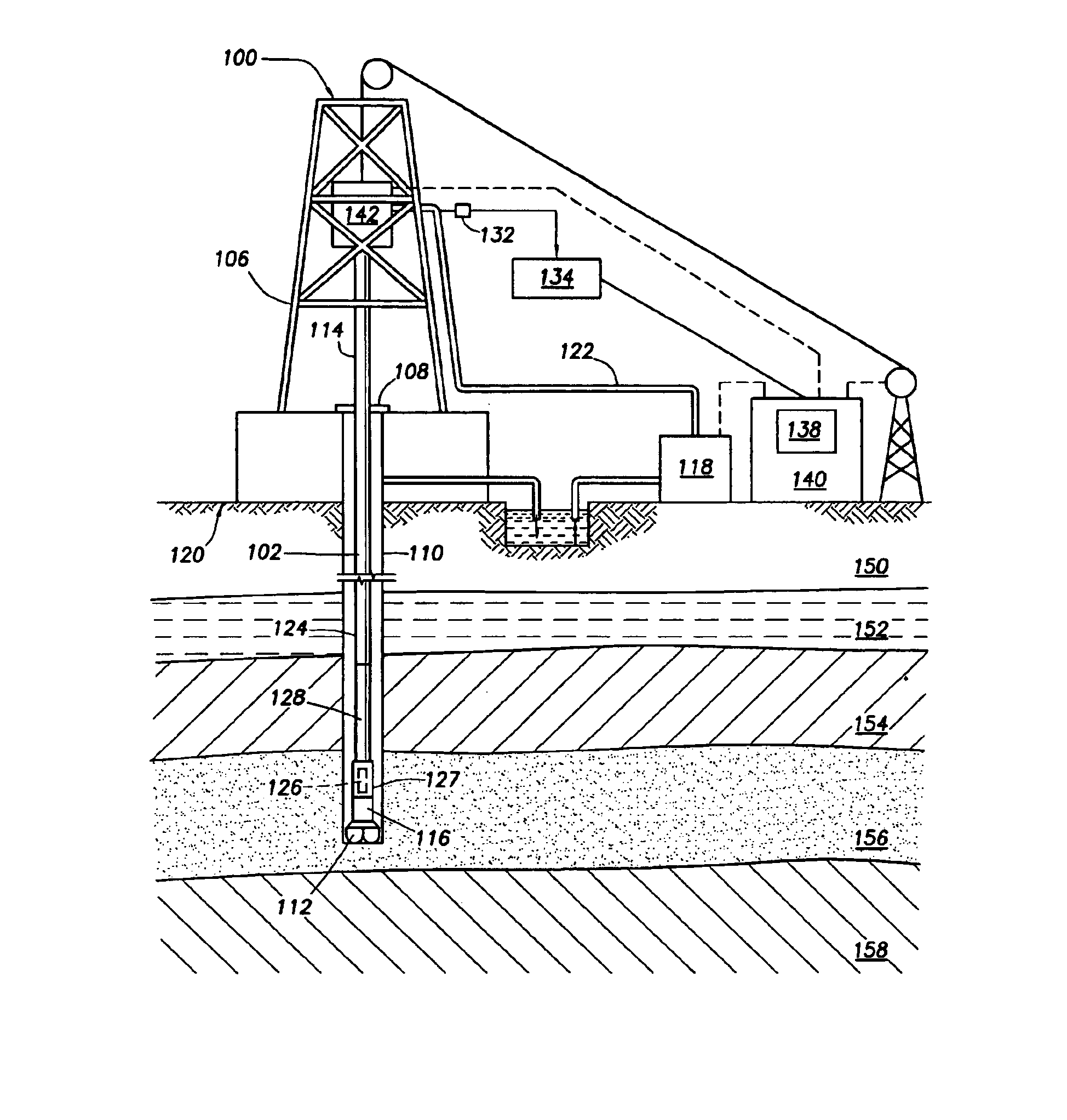
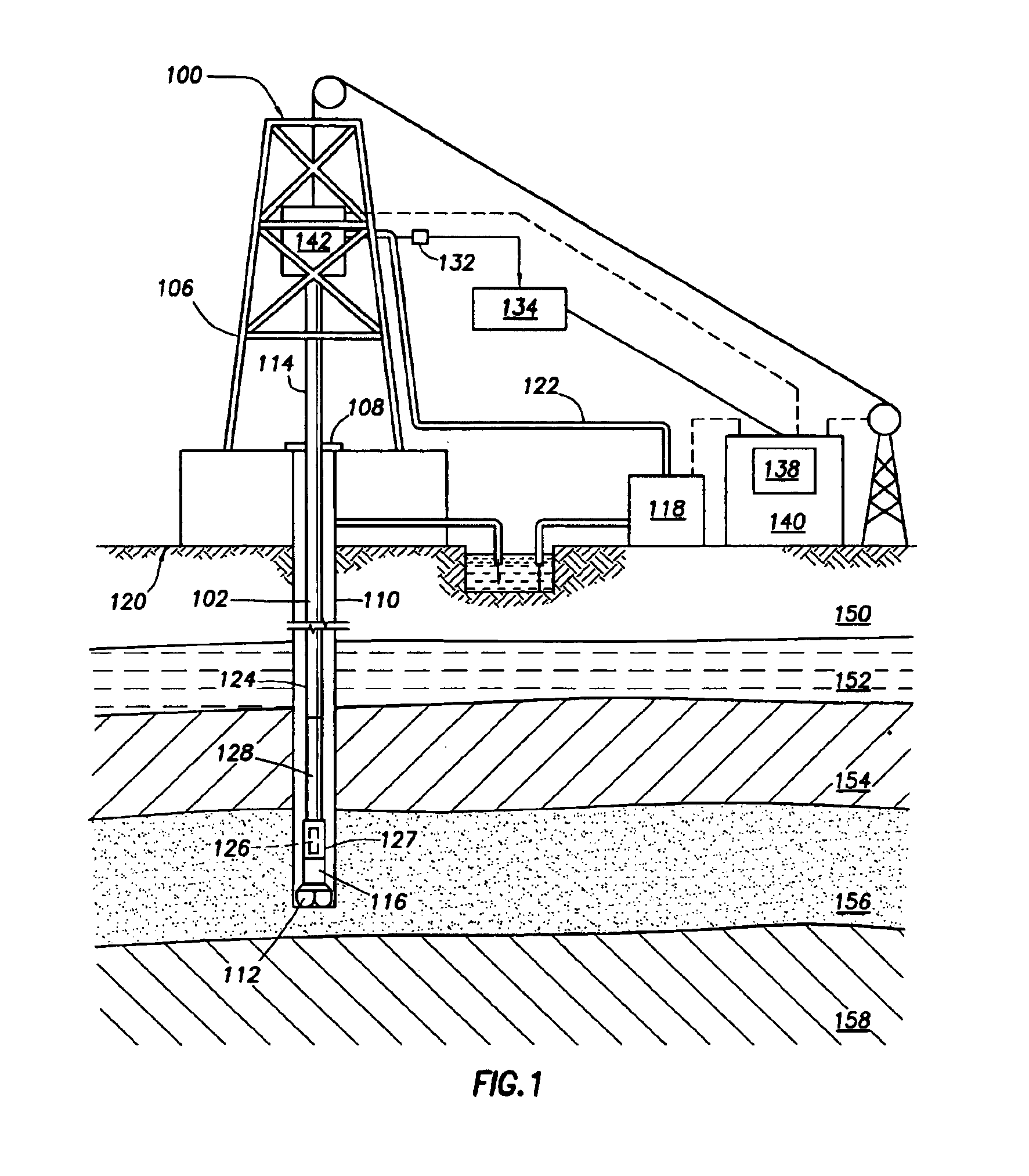
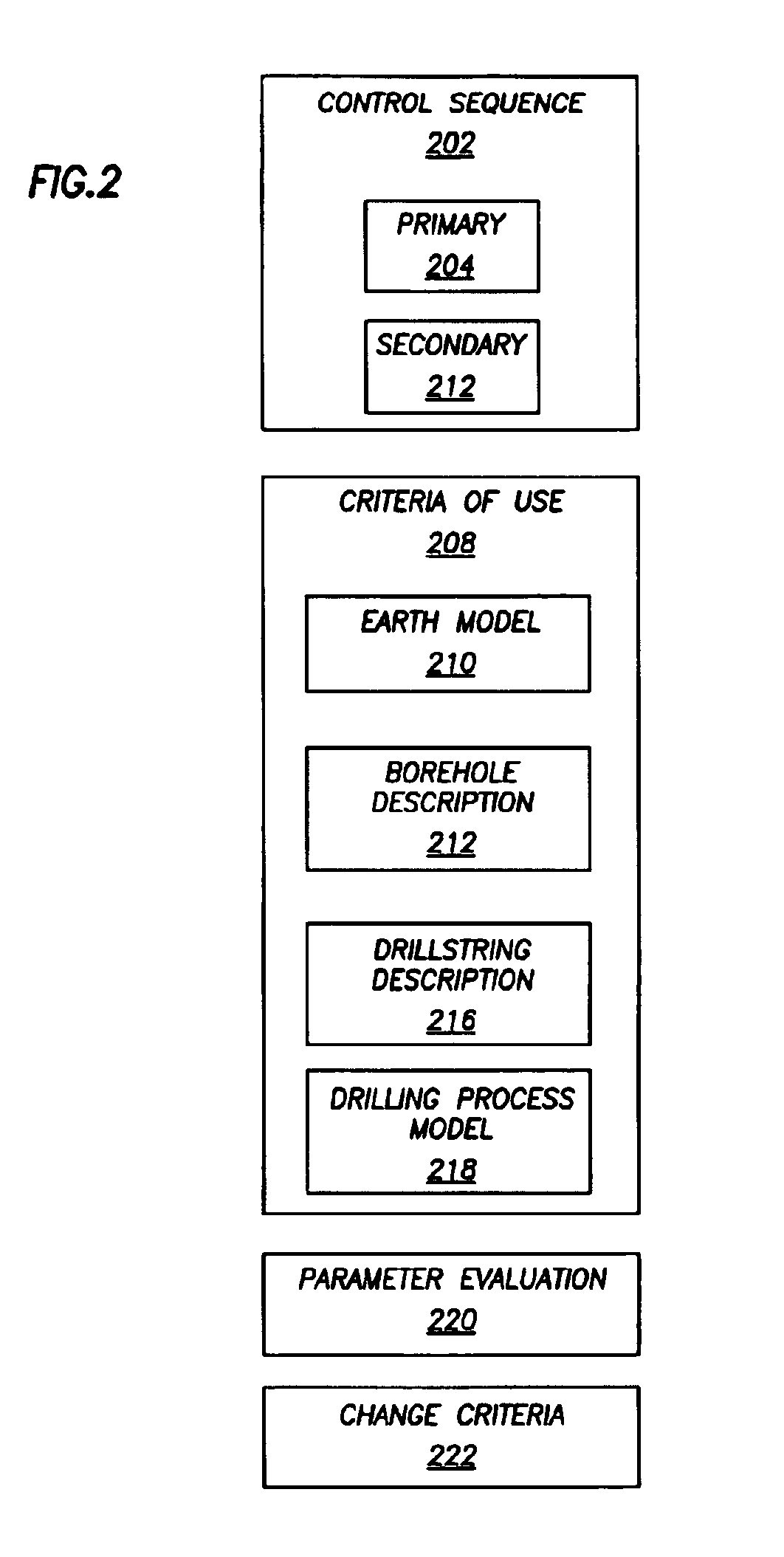
Realtime control of a drilling system using the output from combination of an earth model and a drilling process model
A system is for controlling borehole operations using a computational drilling process model representing the combined effect of downhole conditions and the operation of a drillstring. The drilling process model is continually updated with downhole measurements made during a drilling operation. From the updated drilling process model, a set of optimum drilling parameters is determined and communicated to a surface equipment control system. Further, the system allows the surface equipment control system to automatically adjust current surface equipment control settings based on the updated optimum drilling parameters. Various control scripts are generated and executed to inform the surface equipment control system based on a present drilling mode.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Method and system for return of drilling fluid from a sealed marine riser to a floating drilling rig while drilling
A floating rig or structure for drilling in the floor of an ocean using a rotatable tubular includes a seal housing having a rotatable seal connected above a portion of a marine riser fixed to the floor of the ocean. The seal rotating with the rotating tubular allows the riser and seal housing to maintain a predetermined pressure in the system that is desirable in underbalanced drilling, gas-liquid mud systems and pressurized mud handling systems. The seal is contemplated to be either an active seal or a passive seal. A flexible conduit or hose is used to compensate for relative movement of the seal housing and the floating structure because the floating structure moves independent of the seal housing. A method for use of the system is also disclosed.
Owner:WEATHERFORD TECH HLDG LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com