Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
175 results about "Underbalanced drilling" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
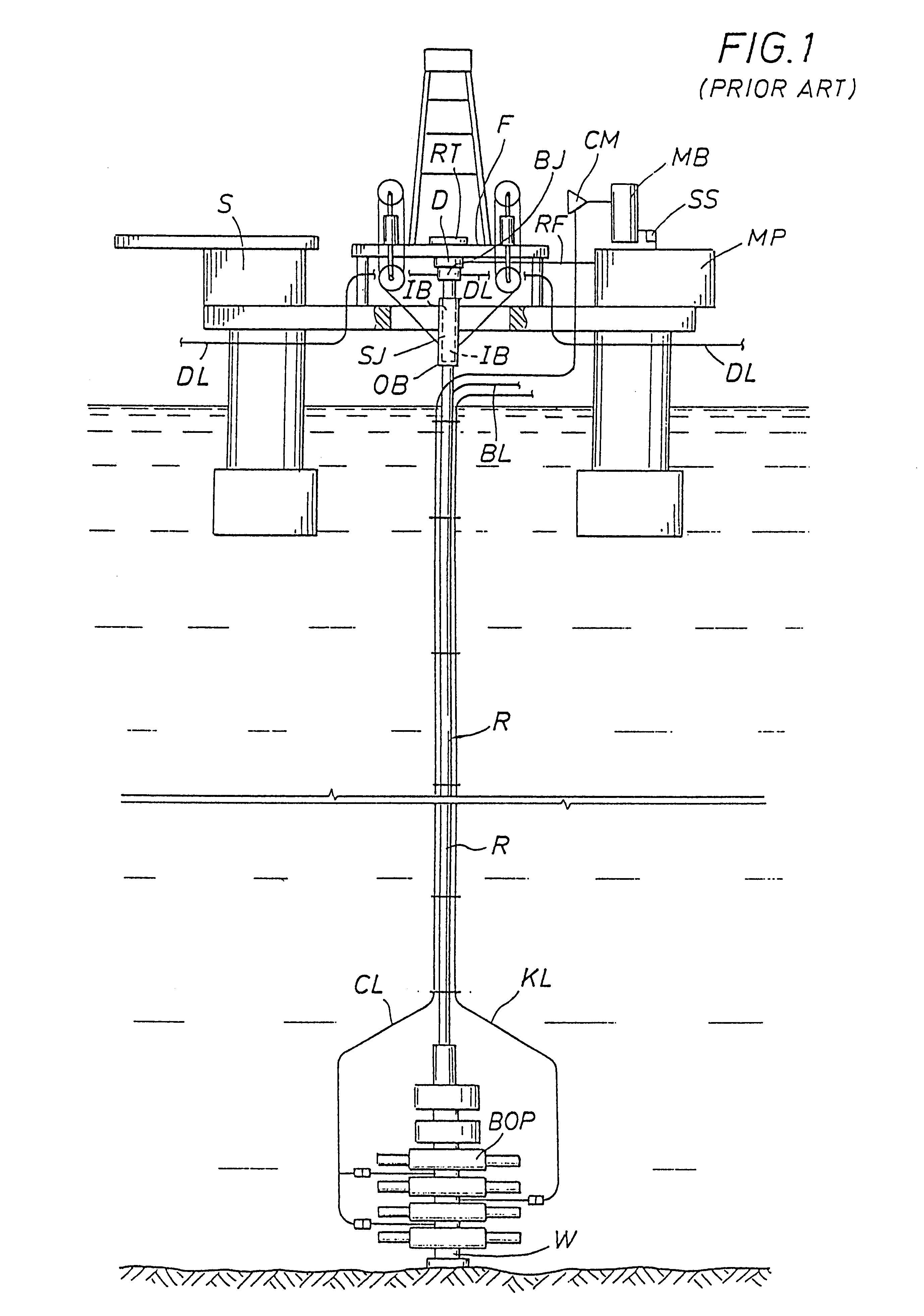
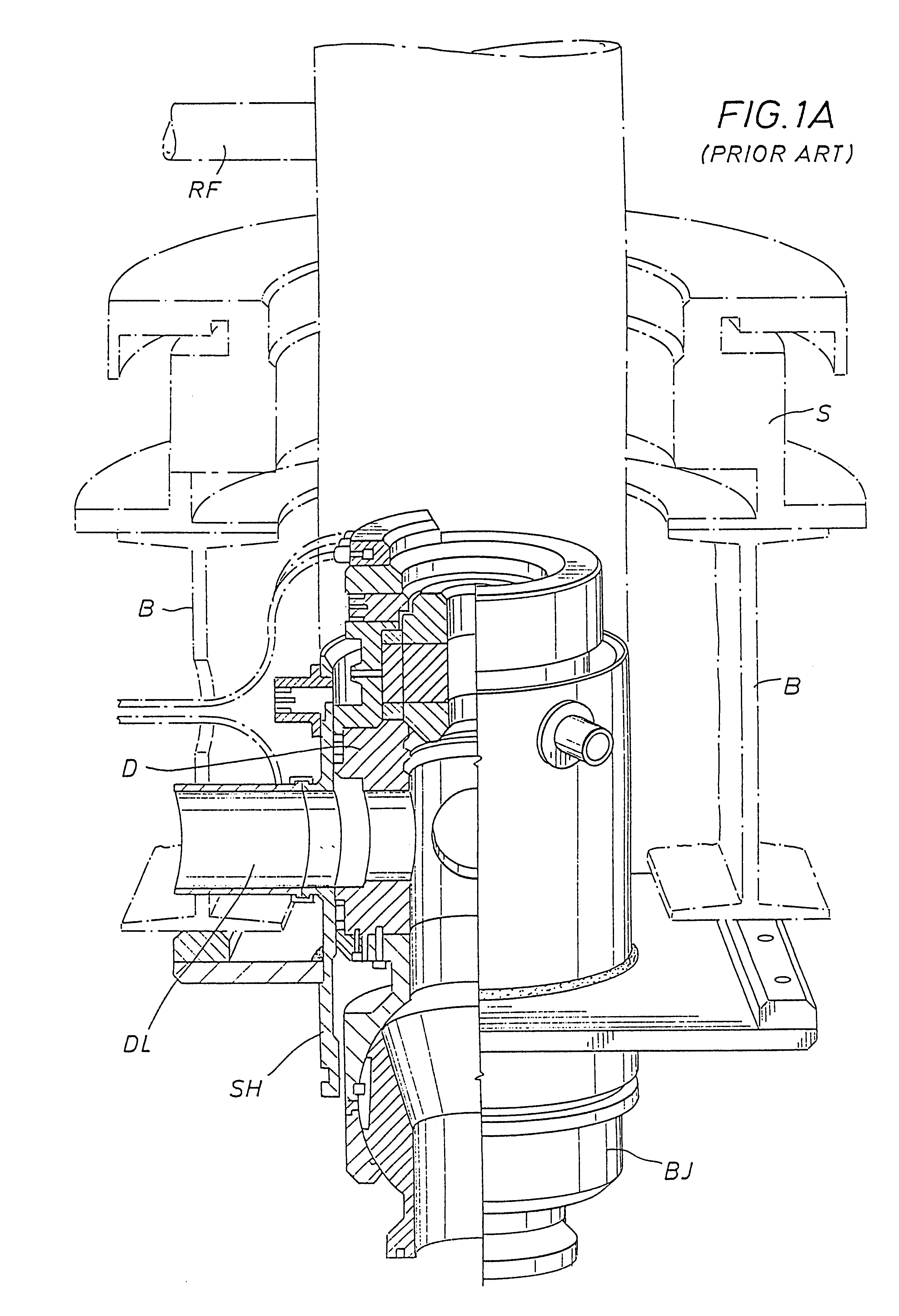
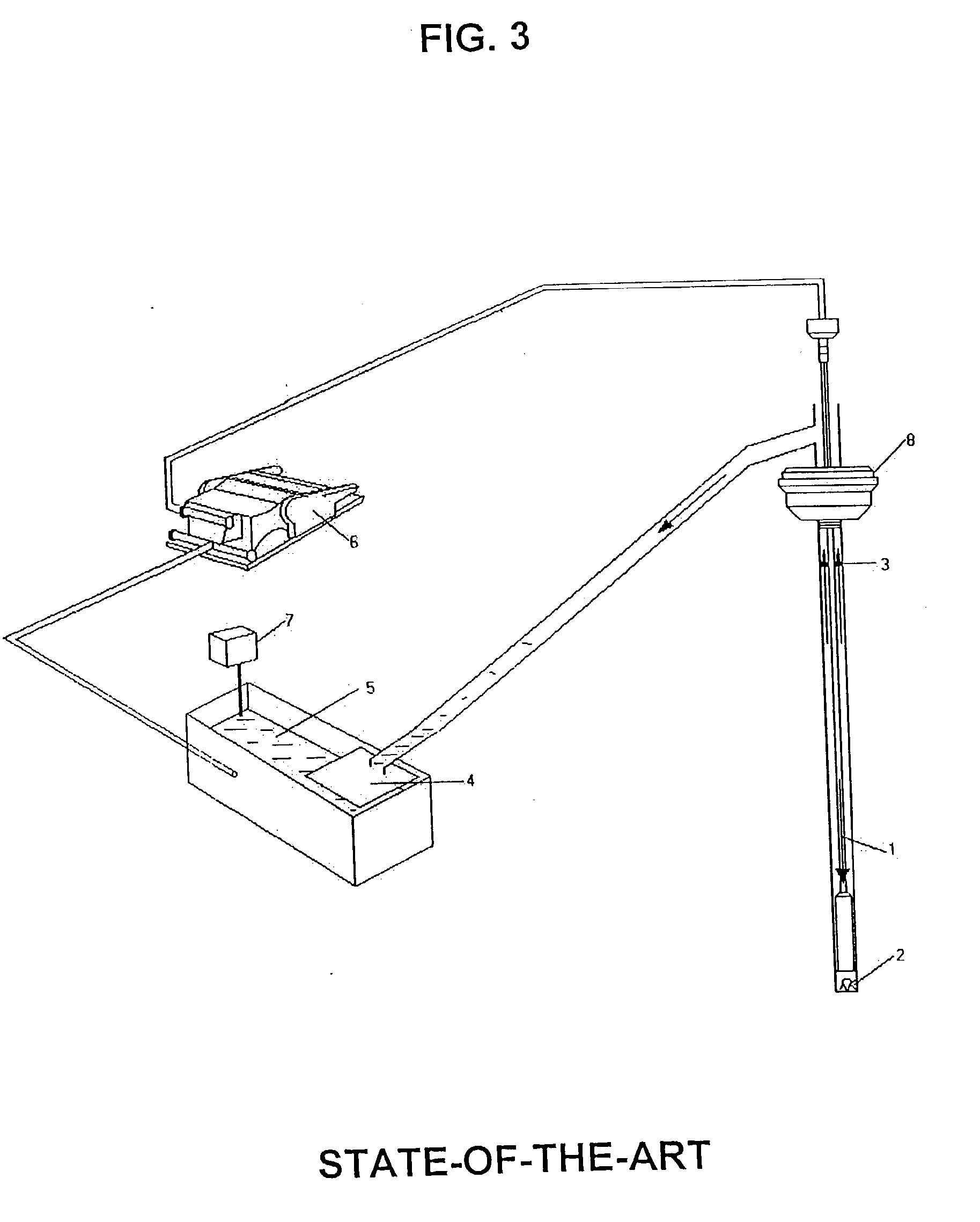
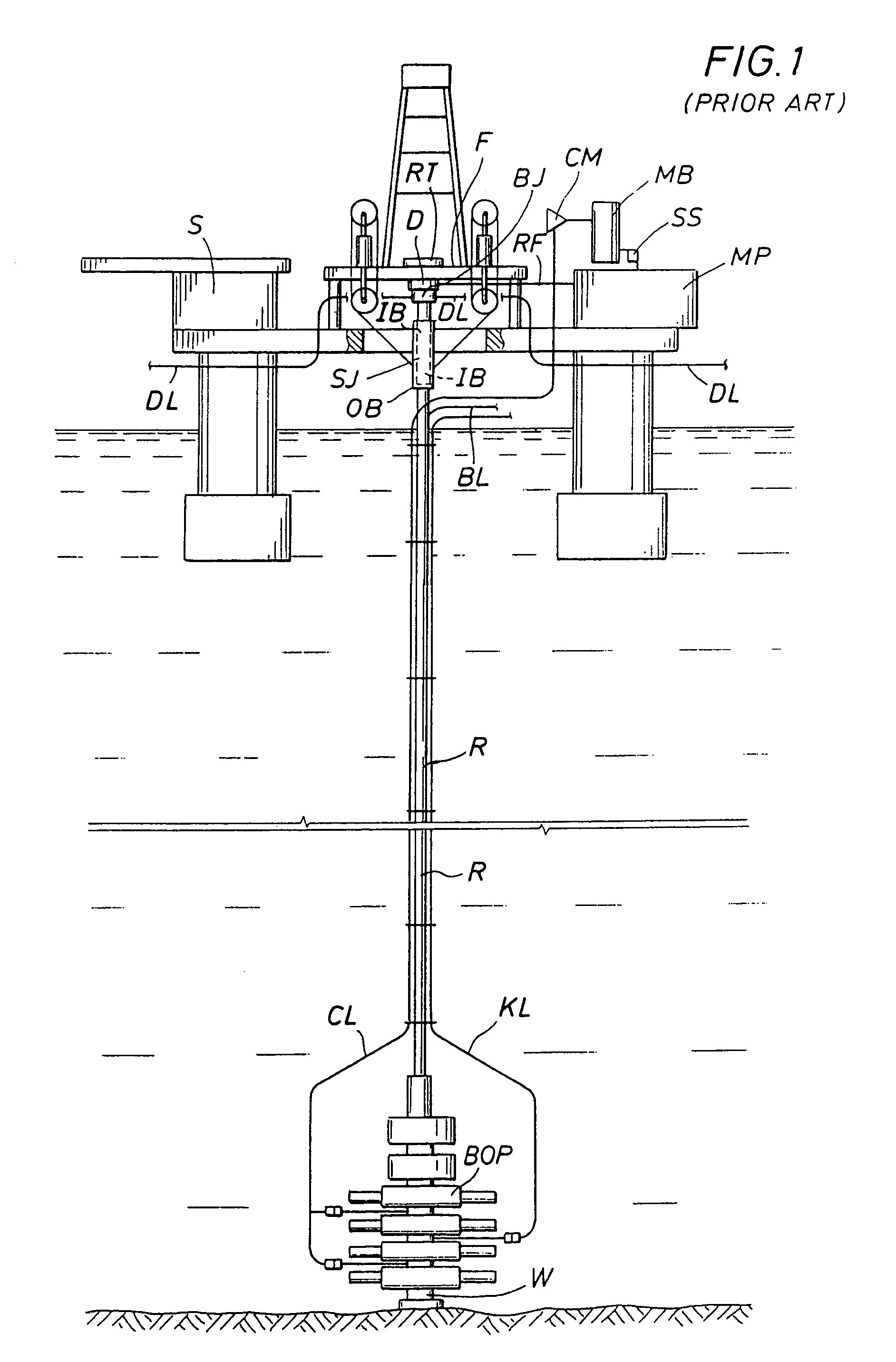
Underbalanced drilling, or UBD, is a procedure used to drill oil and gas wells where the pressure in the wellbore is kept lower than the static pressure then the formation being drilled. As the well is being drilled, formation fluid flows into the wellbore and up to the surface. This is the opposite of the usual situation, where the wellbore is kept at a pressure above the formation to prevent formation fluid entering the well. In such a conventional "overbalanced" well, the invasion of fluid is considered a kick, and if the well is not shut-in it can lead to a blowout, a dangerous situation. In underbalanced drilling, however, there is a "rotating head" at the surface - essentially a seal that diverts produced fluids to a separator while allowing the drill string to continue rotating.
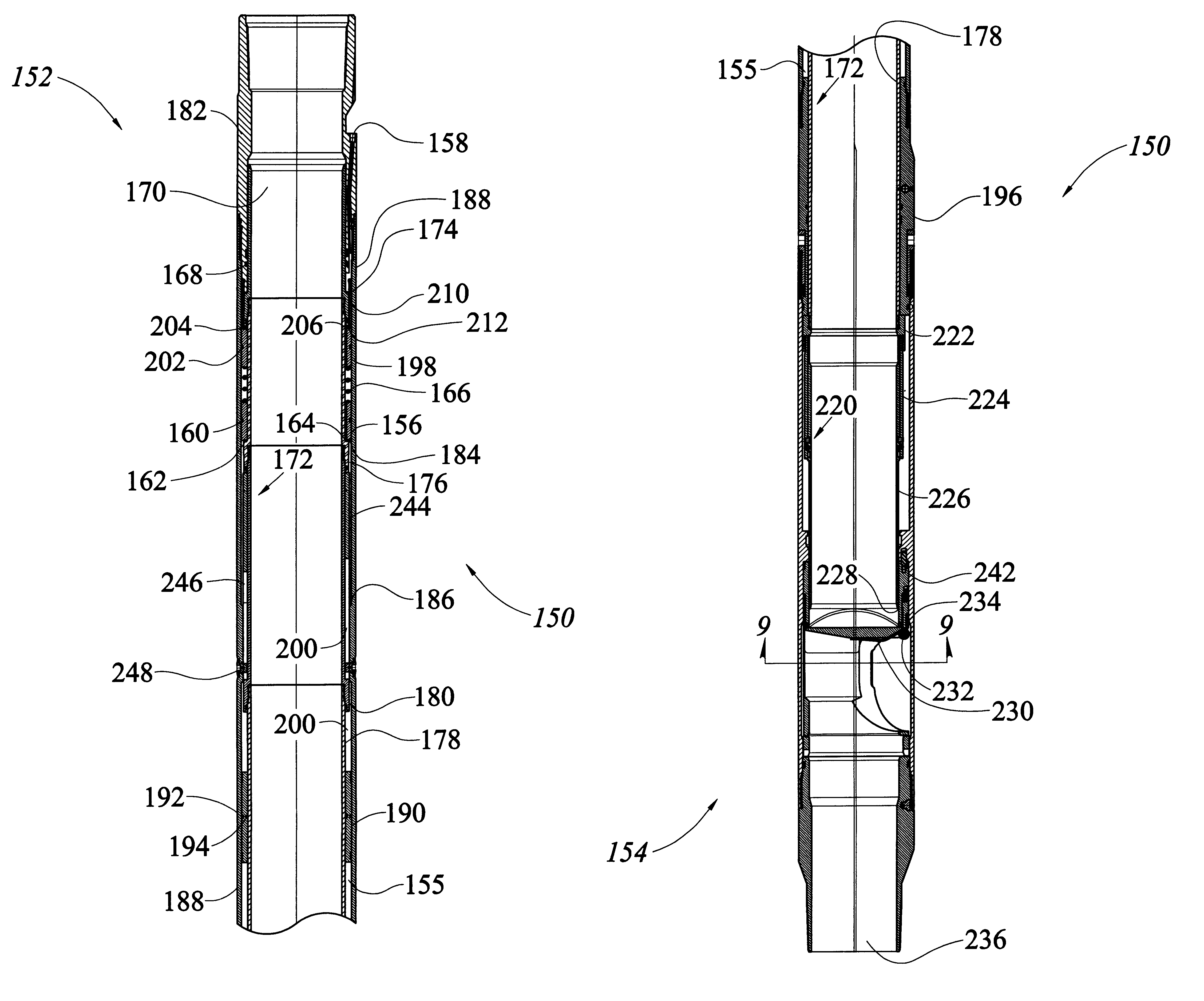
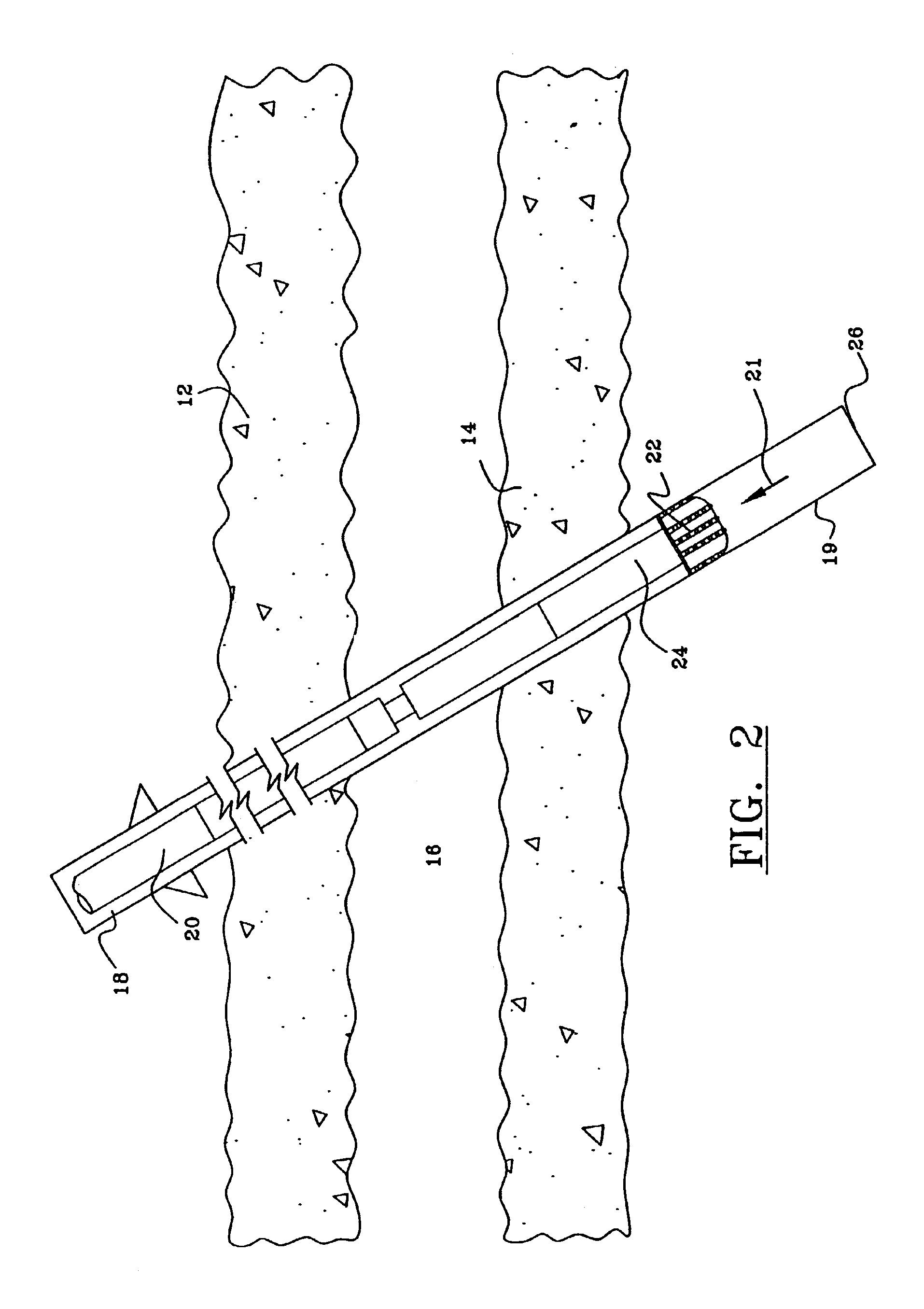
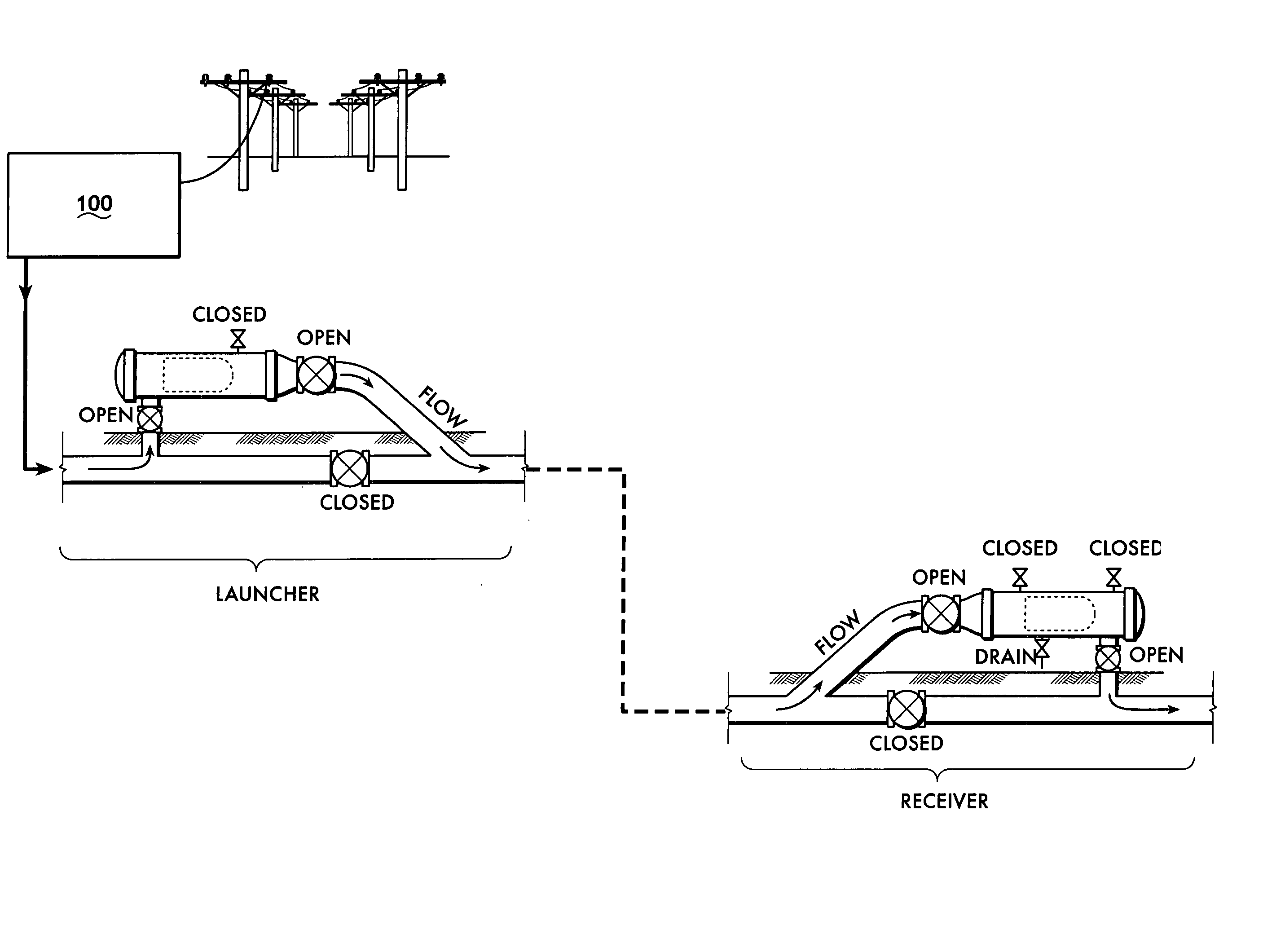
Underbalanced drill string deployment valve method and apparatus
Apparatus and methods for a deployment valve used with an underbalanced drilling system to enhance the advantages of underbalanced drilling. The underbalanced drilling system may typically comprise elements such as a rotating blow out preventer and drilling recovery system. The deployment valve is positioned in a tubular string, such as casing, at a well bore depth at or preferably substantially below the string light point of the drilling string. When the drilling string is above the string light point then the upwardly acting forces on the drilling string become greater than downwardly acting forces such that the drilling string begins to accelerate upwardly. The deployment valve has a bore sufficiently large to allow passage of the drill bit therethrough in the open position. The deployment valve may be closed when the drill string is pulled within the casing as may be necessary to service the drill string after drilling into a reservoir having a reservoir pressure. To allow the drill string to be removed from the casing, the pressure produced by the formation can be bled off and the drill string removed for servicing. The drill string can then be reinserted, the pressure in the casing above the deployment valve applied to preferably equalize pressure above and below the valve and the drill string run into the hole for further drilling.
Owner:WEATHERFORD TECH HLDG LLC
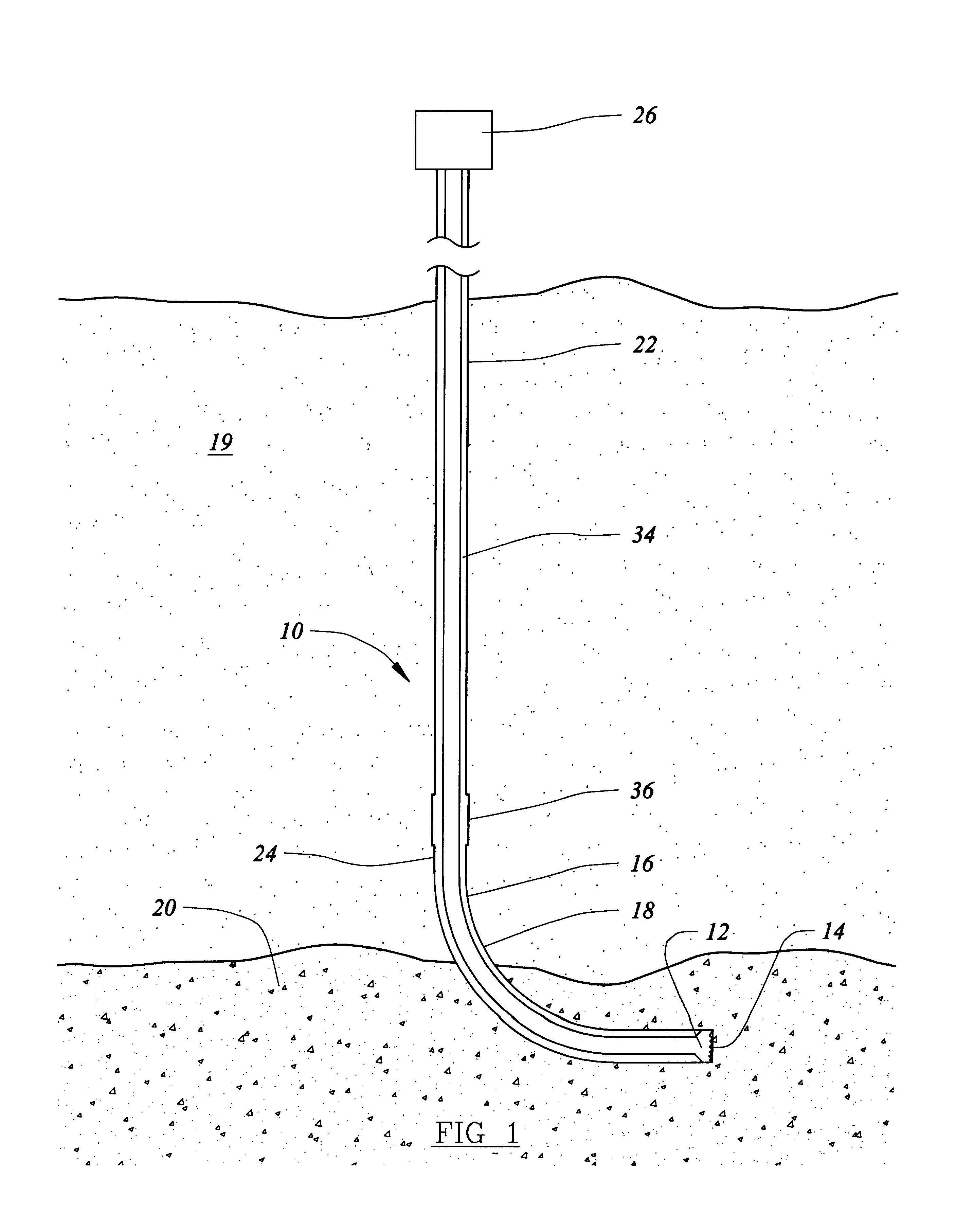
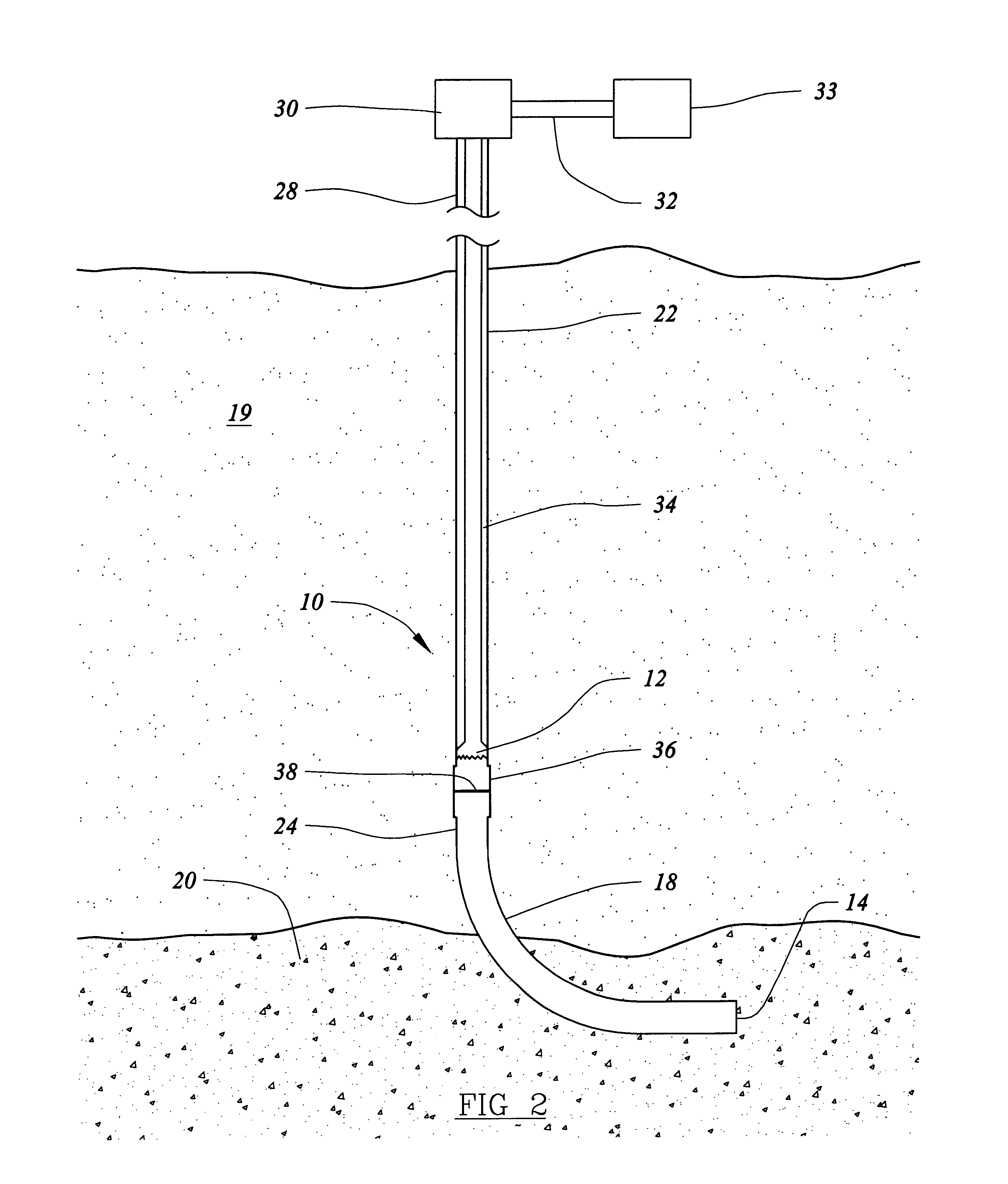
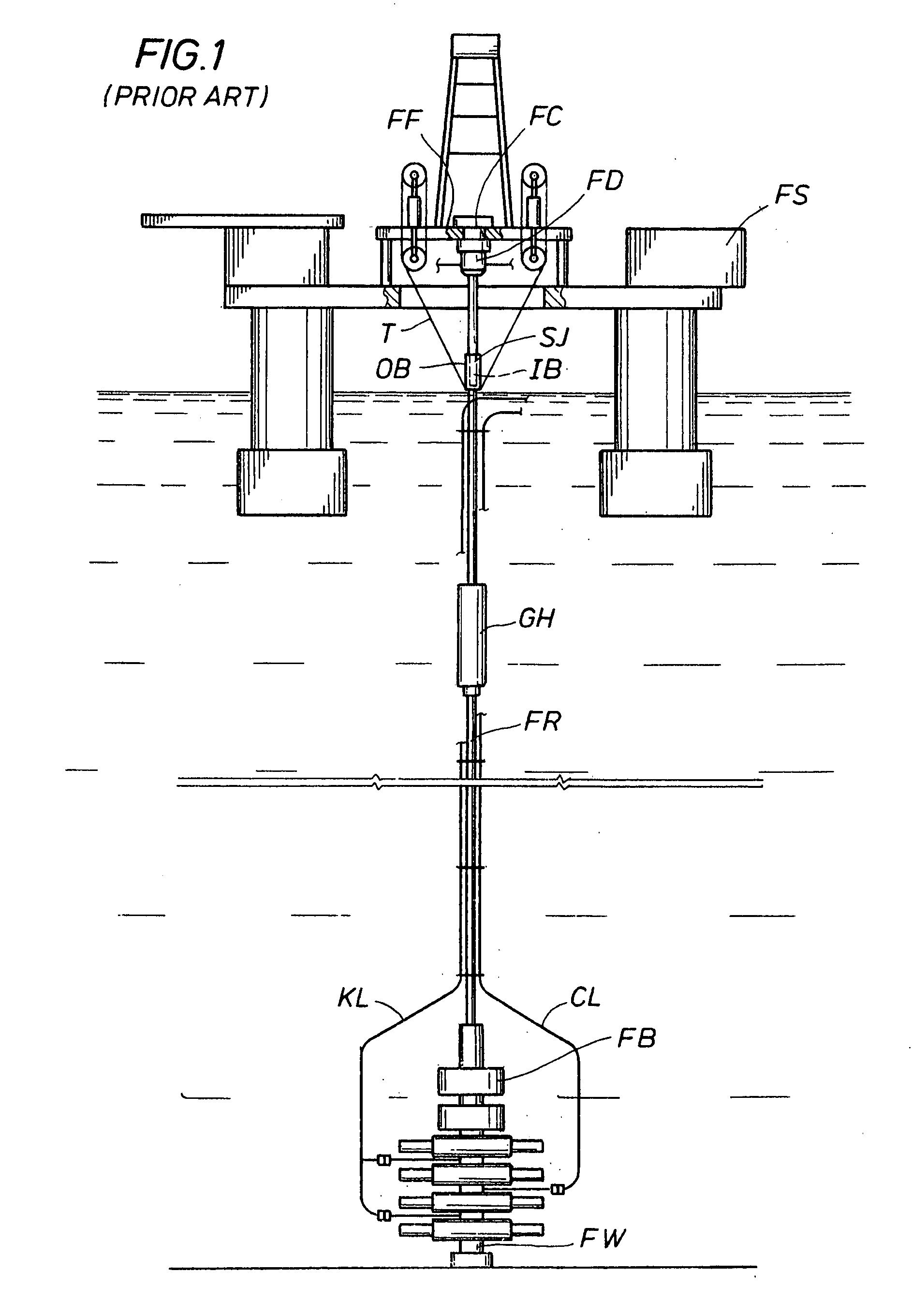
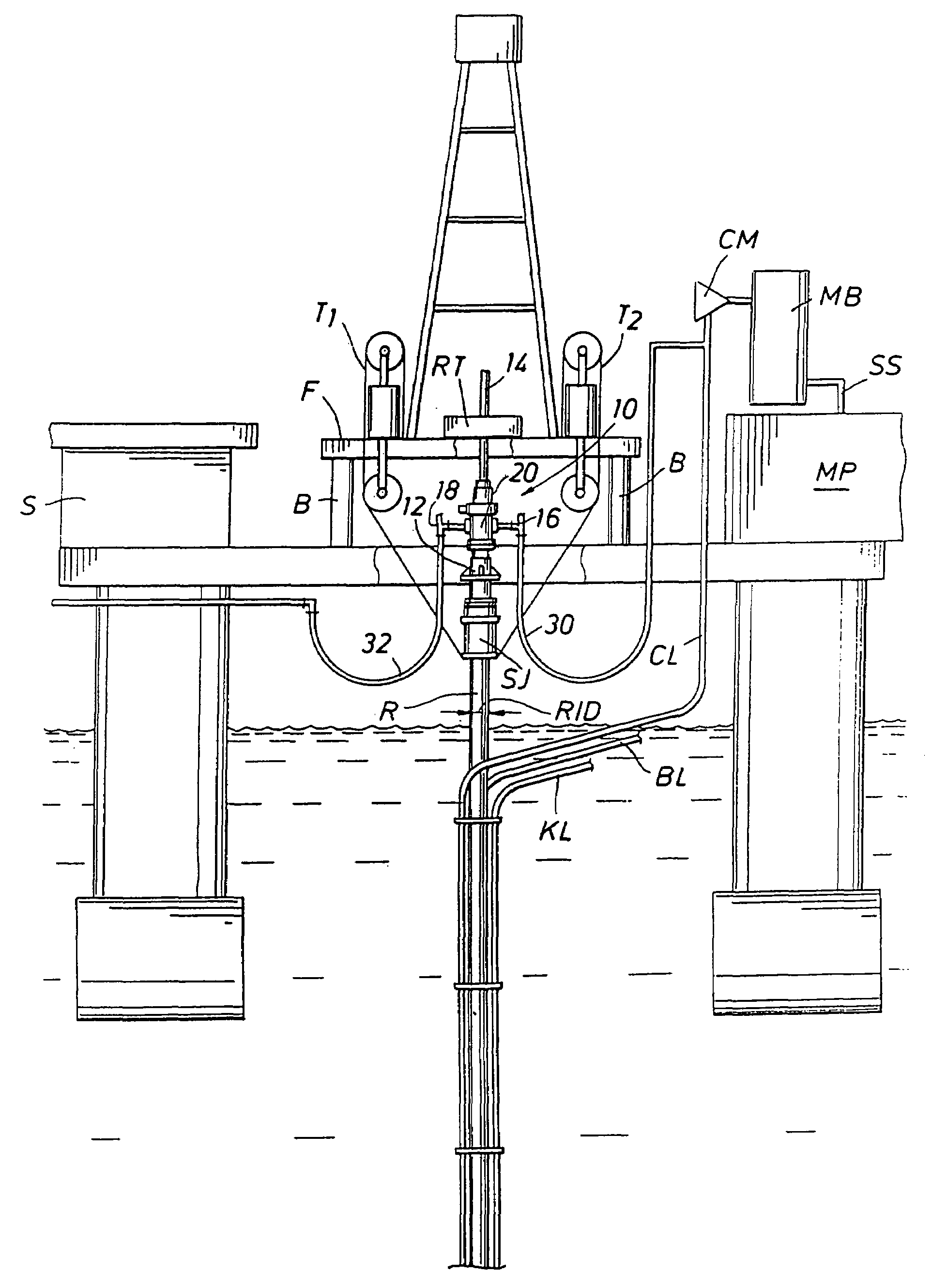
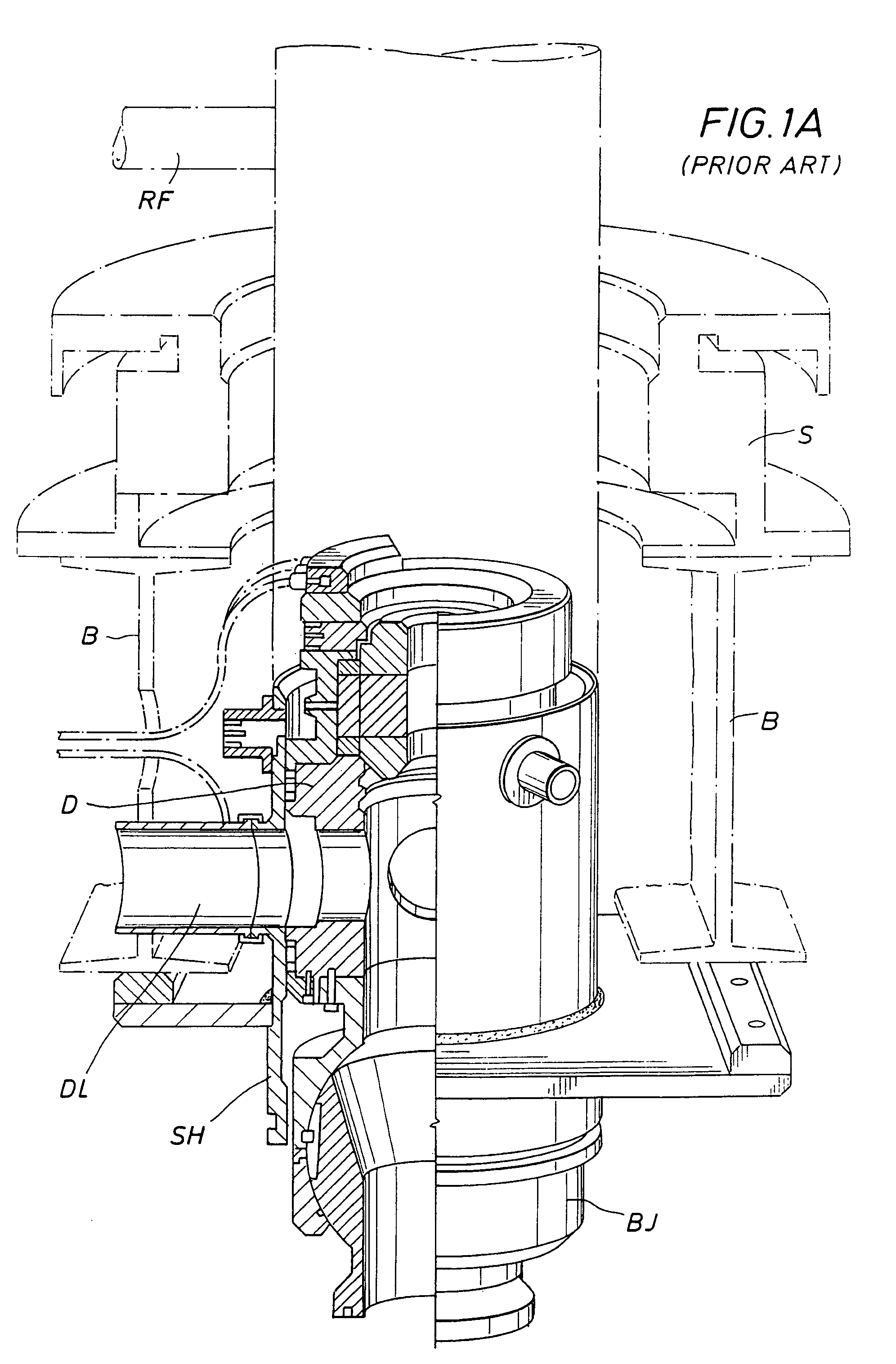
Method and system for return of drilling fluid from a sealed marine riser to a floating drilling rig while drilling
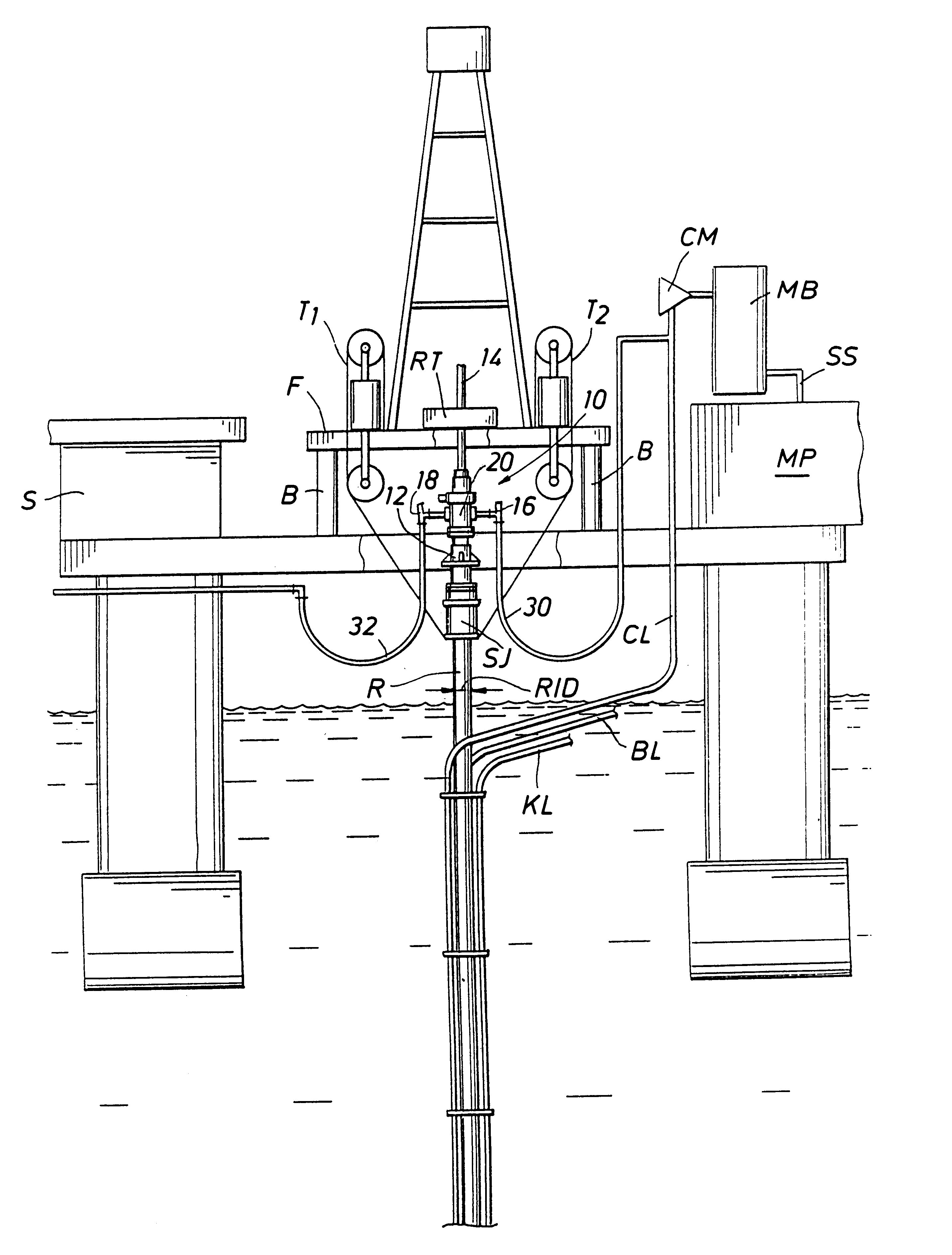
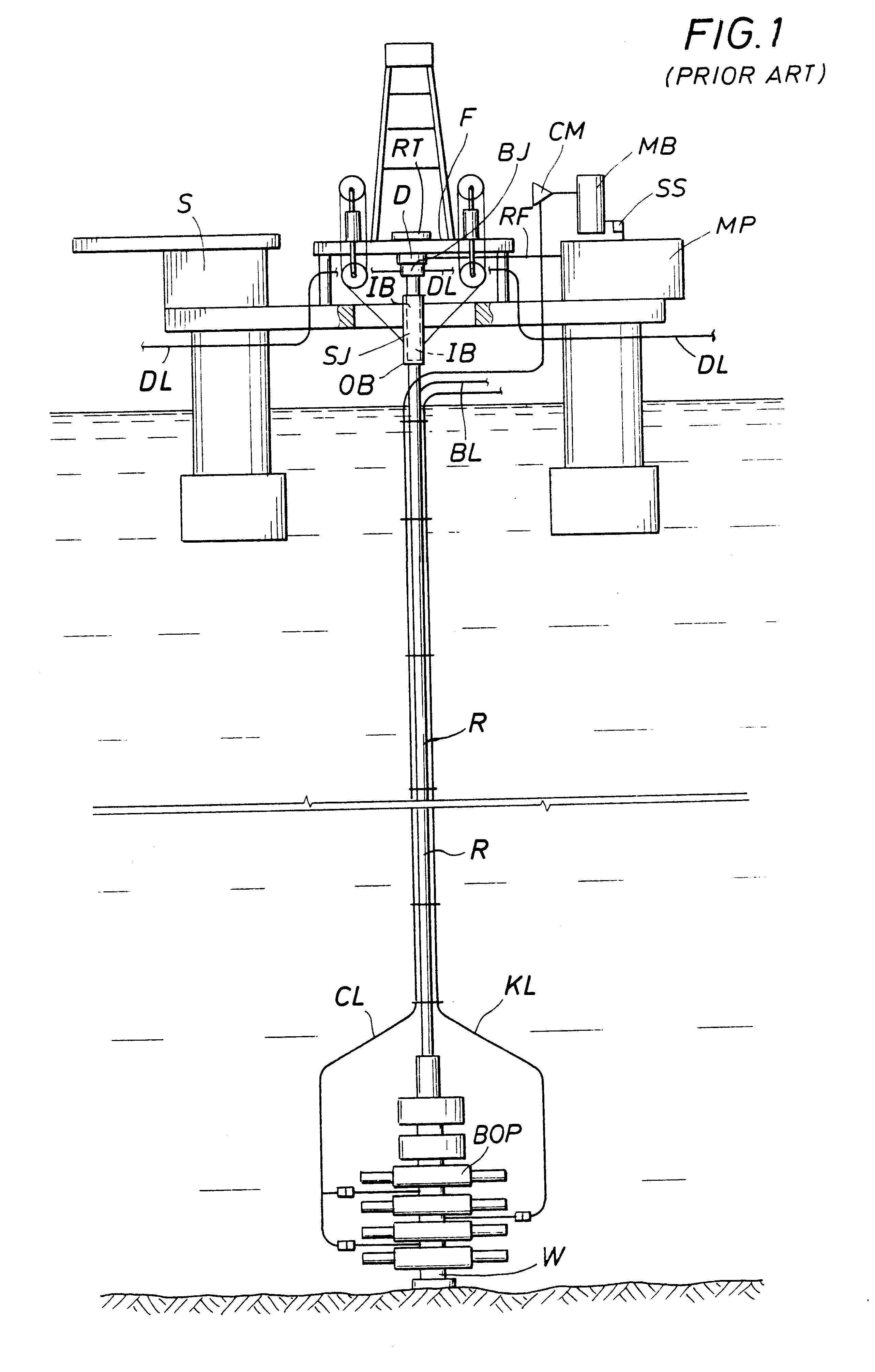
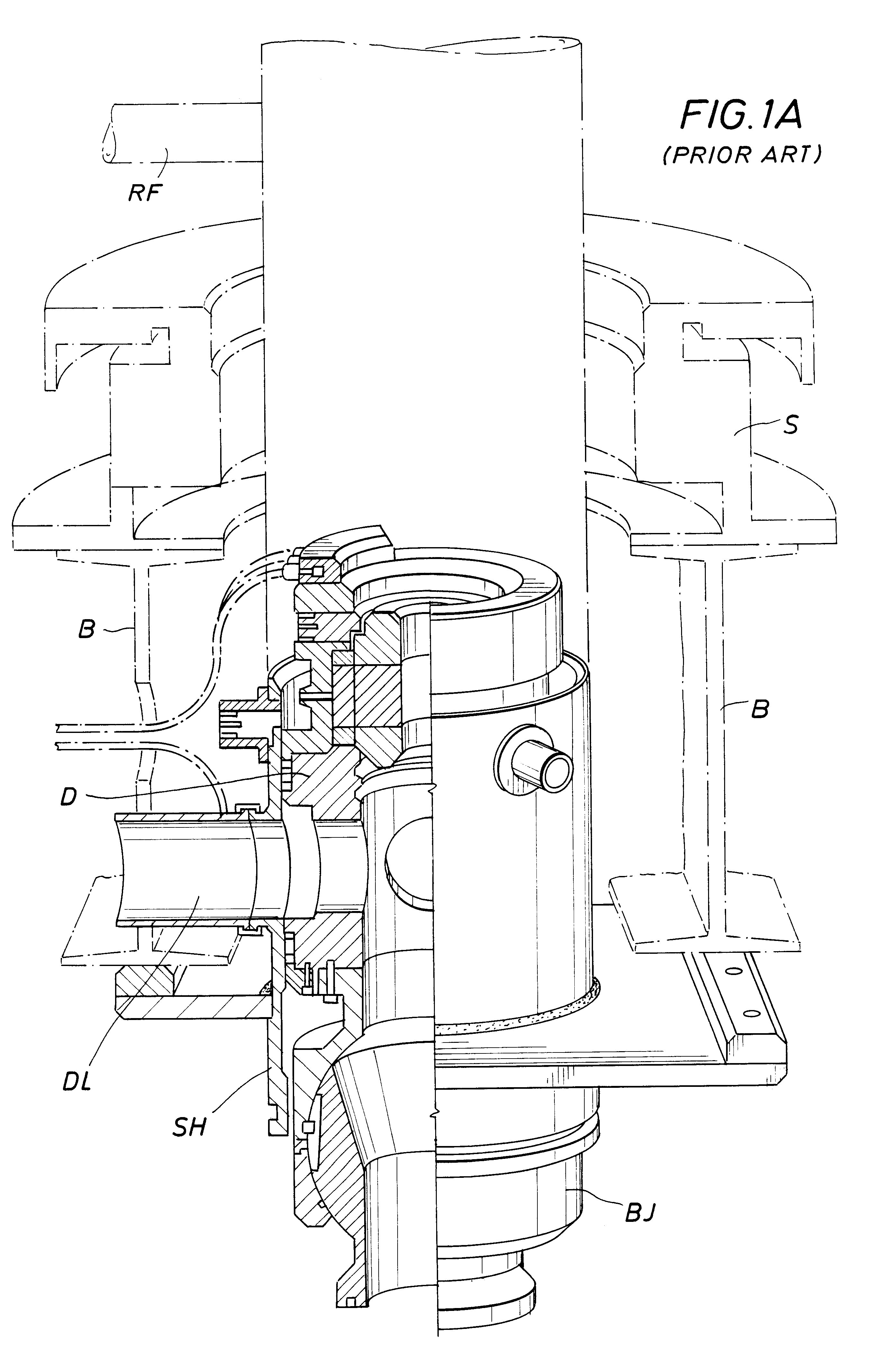
A floating rig or structure for drilling in the floor of an ocean using a rotatable tubular includes a seal housing having a rotatable seal connected above a marine riser fixed to the floor of the ocean. The seal rotating with the rotating tubular allows the riser and seal housing to maintain a predetermined pressure in the system that is desirable in underbalanced drilling, gas-liquid mud systems and pressurized mud handling systems. A flexible conduit or hose is used to compensate for the relative movement of the seal housing and the floating structure since the floating structure moves independent of the seal housing. A method for use of the system is also disclosed.
Owner:WEATHERFORD TECH HLDG LLC
Drilling system and method
InactiveUS20030079912A1Accurate calculationImprove securityConstructionsFlushingWell drillingEngineering
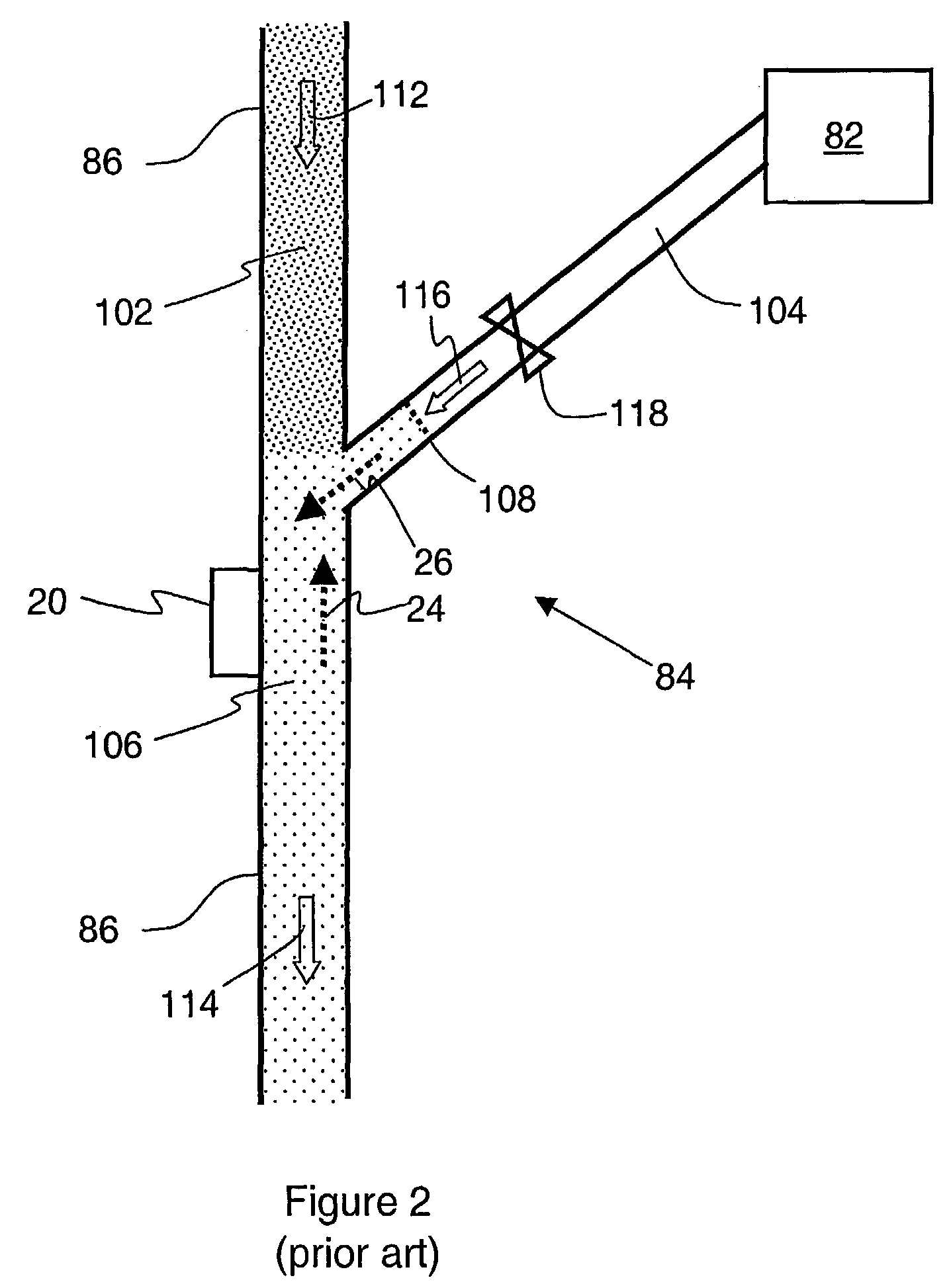
A closed-loop circulating system for drilling wells has control of the flow rates in and out of the wellbore. Kicks and fluid losses are quickly controlled by adjusting the backpressure. Kick tolerance and tripping margins are eliminated by real-time determination of pore and fracture pressure. The system can incorporate a rotating BOP and can be used with underbalanced drilling.
Owner:SECURE DRILLING INT
Method and system for return of drilling fluid from a sealed marine riser to a floating drilling rig while drilling
A floating rig or structure for drilling in the floor of an ocean using a rotatable tubular includes a seal housing having a rotatable seal connected above a portion of a marine riser fixed to the floor of the ocean. The seal rotating with the rotating tubular allows the riser and seal housing to maintain a predetermined pressure in the system that is desirable in underbalanced drilling, gas-liquid mud systems and pressurized mud handling systems. The seal is contemplated to be either an active seal or a passive seal. A flexible conduit or hose is used to compensate for relative movement of the seal housing and the floating structure because the floating structure moves independent of the seal housing. A method for use of the system is also disclosed.
Owner:WEATHERFORD TECH HLDG LLC
Rotating control device docking station
A system and method is provided for converting a drilling rig between conventional hydrostatic pressure drilling and managed pressure drilling or underbalanced drilling using a docking station housing mounted on a marine riser or bell nipple. This docking station housing may be positioned above the surface of the water. When a removable rotating control device is remotely hydraulically latched with the docking station housing, the system and method allows for interactive lubrication and cooling of the rotating control device, as needed, along with a supply of fluid for use with active seals.
Owner:WEATHERFORD TECH HLDG LLC
Shale inhibition additive for oil/gas down hole fluids and methods for making and using same
ActiveUS7268100B2Reduction tendencyConstructionsFluid removalUnderbalanced drillingPetroleum engineering
Owner:WEATHERFORD TECH HLDG LLC
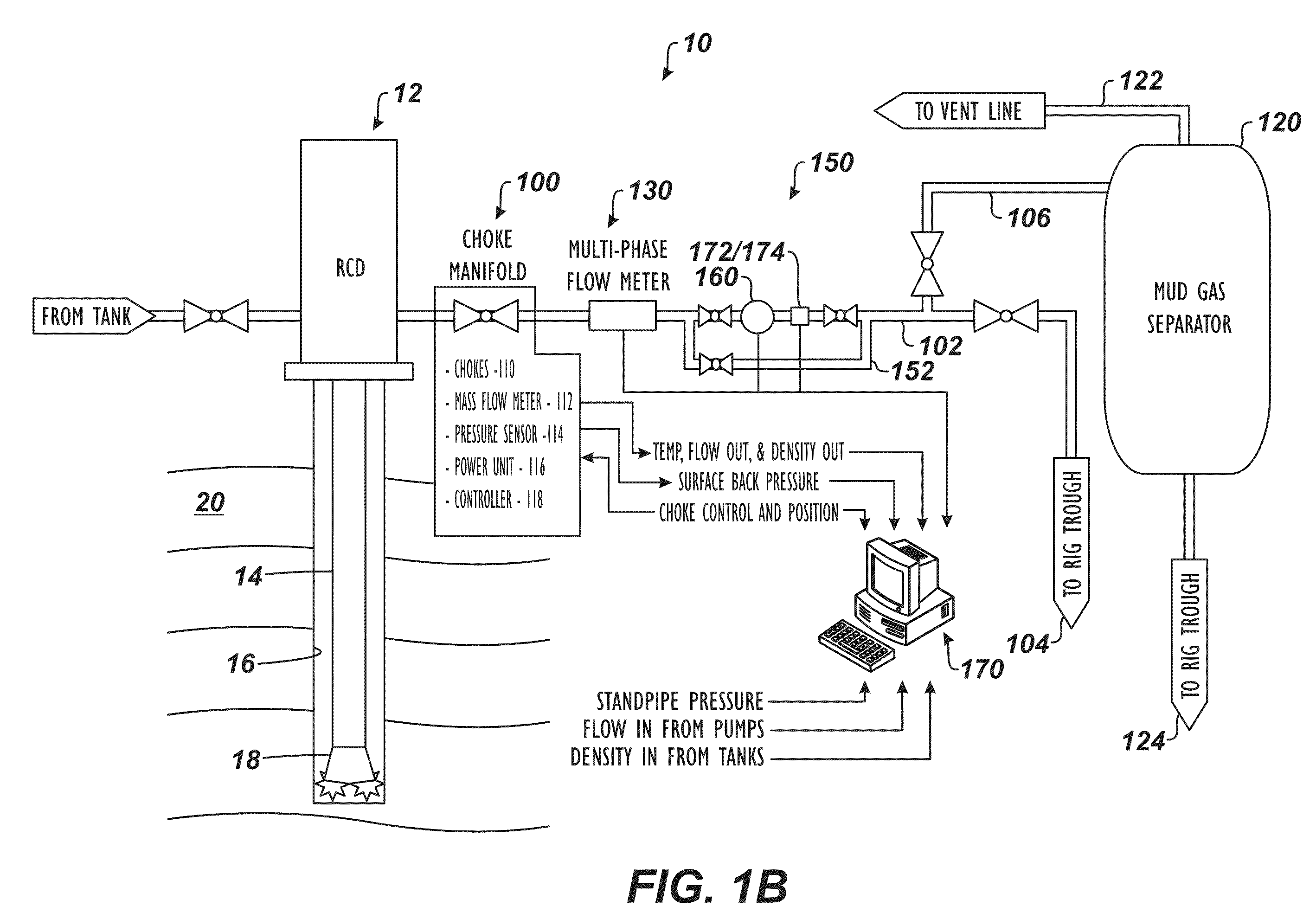
Surface Gas Evaluation During Controlled Pressure Drilling
A system and method have a choke in fluid communication with a rotating control device. The choke controls flow of drilling mud from the rotating control device to a gas separator during a controlled pressure drilling operation, such as managed pressure drilling (MPD) or underbalanced drilling (UBD). A probe is in fluid communication with the drilling mud between the choke and the gas separator. During operations, the probe evaluates gas in the drilling mud from the well passing from the choke to the gas separator.
Owner:WEATHERFORD TECH HLDG LLC
Rotating control device docking station
A system and method is provided for converting a drilling rig between conventional hydrostatic pressure drilling and managed pressure drilling or underbalanced drilling using a docking station housing mounted on a marine riser or bell nipple. This docking station housing may be positioned above the surface of the water. When a removable rotating control device is remotely hydraulically latched with the docking station housing, the system and method allows for interactive lubrication and cooling of the rotating control device, as needed, along with a supply of fluid for use with active seals.
Owner:WEATHERFORD TECH HLDG LLC
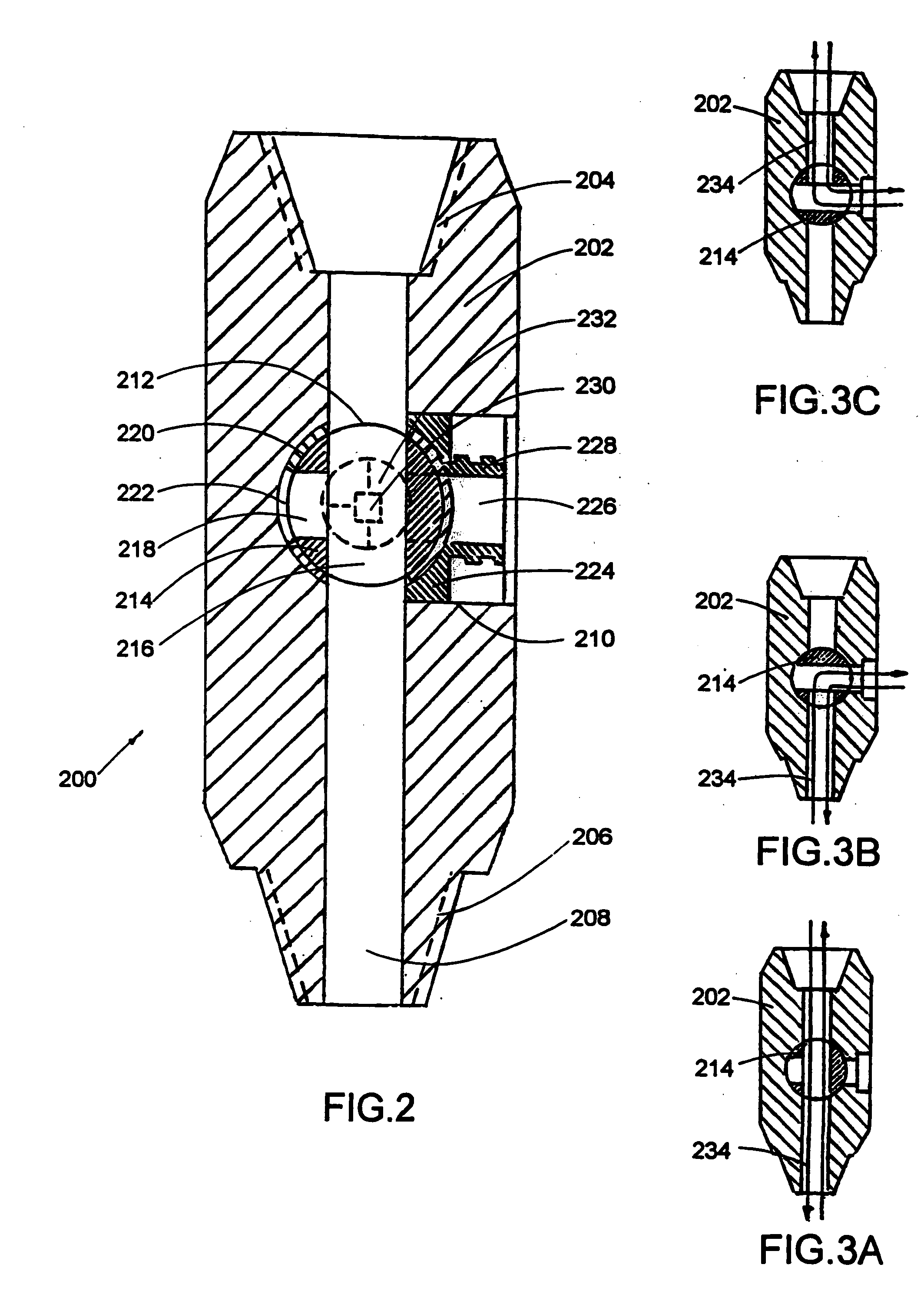
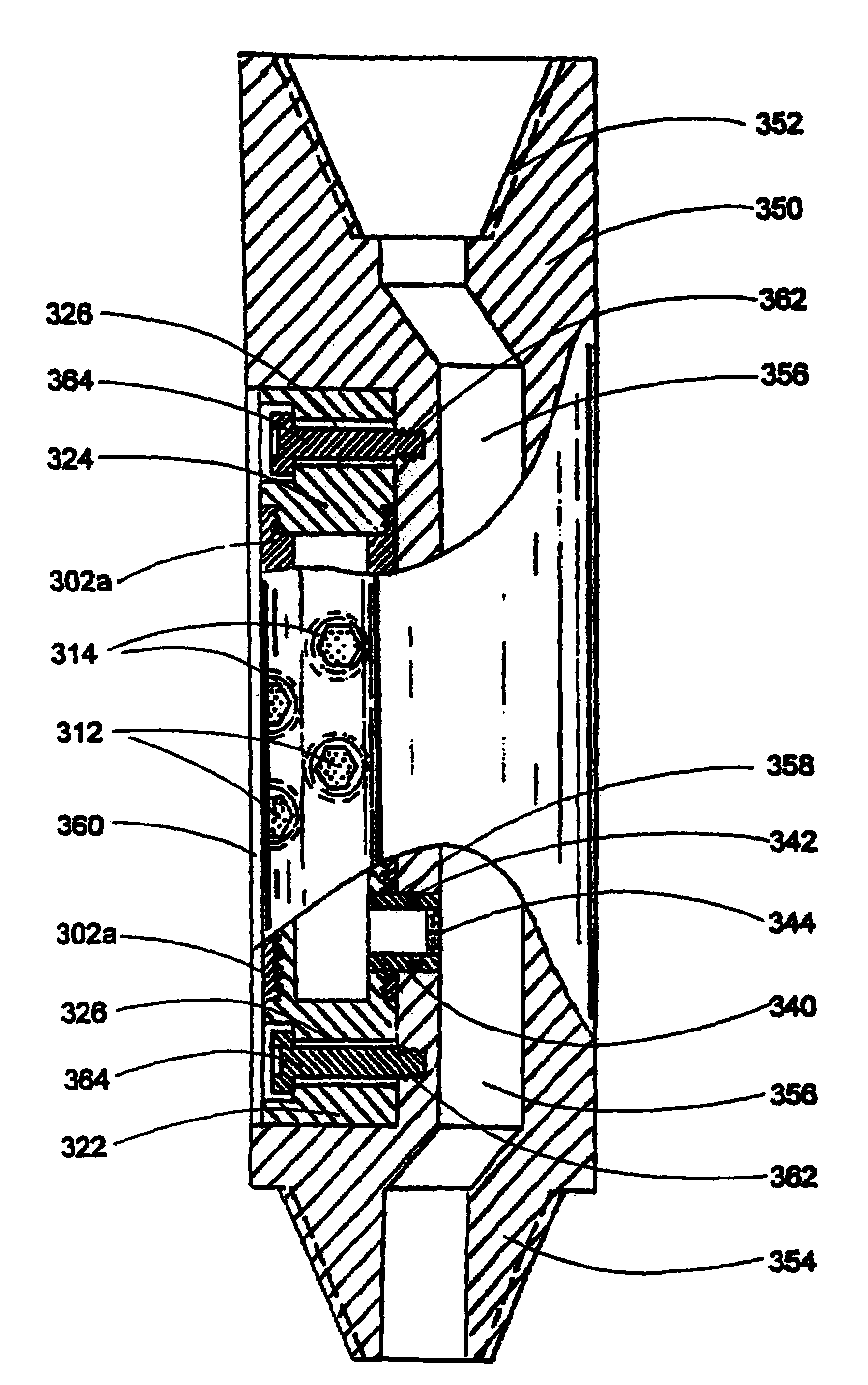
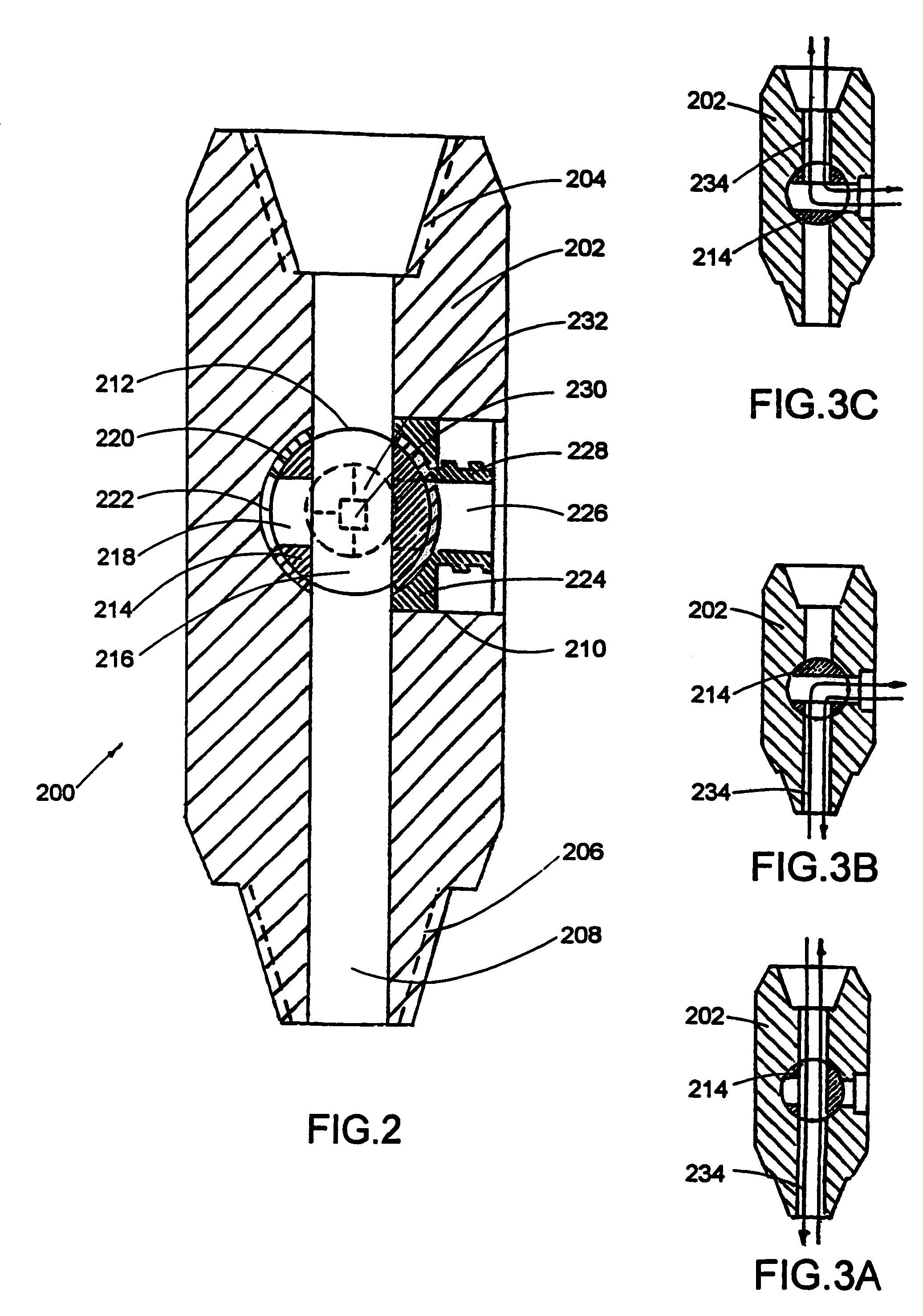
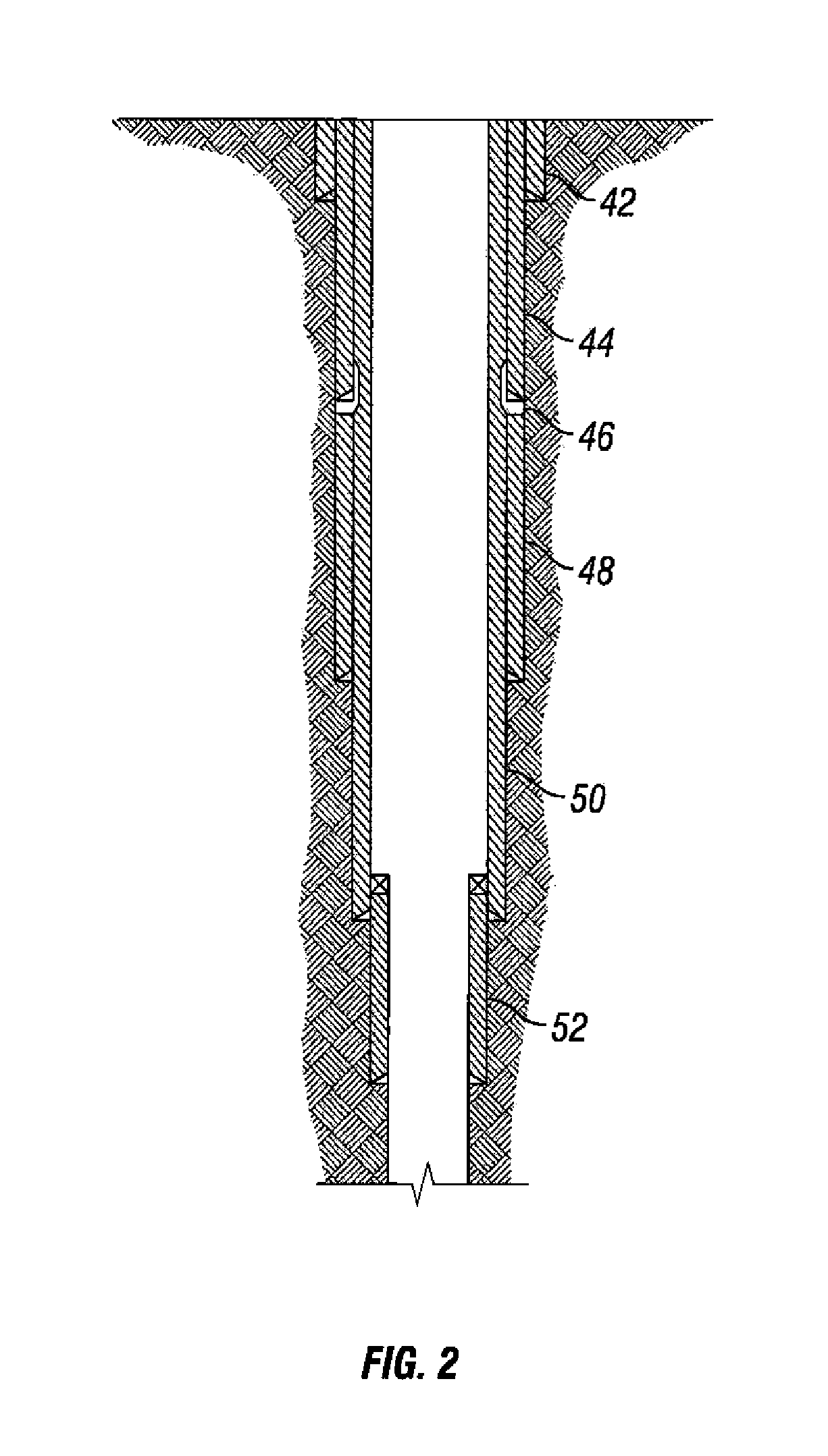
Wellbore isolation apparatus, and method for tripping pipe during underbalanced drilling
The present invention relates to an apparatus and method for isolating a wellbore condition such as formation pressure during a wellbore operation. The invention has particular application in connection with underbalanced drilling. In one arrangement, a formation isolation apparatus is provided that serves as a selectively actuatable plug. The plug in one aspect is selectively set and released by a setting / releasing tool. The setting / releasing tool includes a system for setting the plug in the wellbore, and a system for releasing the plug from the wellbore. The setting / releasing tool is releasably connected to the plug. Thus, after the plug has been set, the setting / releasing tool may be removed from the wellbore. The plug includes a flapper valve that is restrained in its open position by the setting / releasing tool. Removal of the setting / releasing tool from the wellbore allows the flapper valve to close, thereby isolating pressures in the wellbore below the flapper valve. The plug is wireline retrievable. In another aspect, a formation isolation apparatus is provided for use during sidetrack drilling operations. The sealing element is movable from a first released position below the lateral wellbore, to a set position above the lateral wellbore.
Owner:WEATHERFORD TECH HLDG LLC
Universal marine diverter converter
A universal marine diverter converter (UMDC) housing is clamped or latched to a rotating control device. The UMDC housing assembled with the RCD is inserted into a marine diverter above the water surface to allow conversion between conventional open and non-pressurized mud-return system drilling, and a closed and pressurized mud-return system used in managed pressure or underbalanced drilling.
Owner:WEATHERFORD TECH HLDG LLC
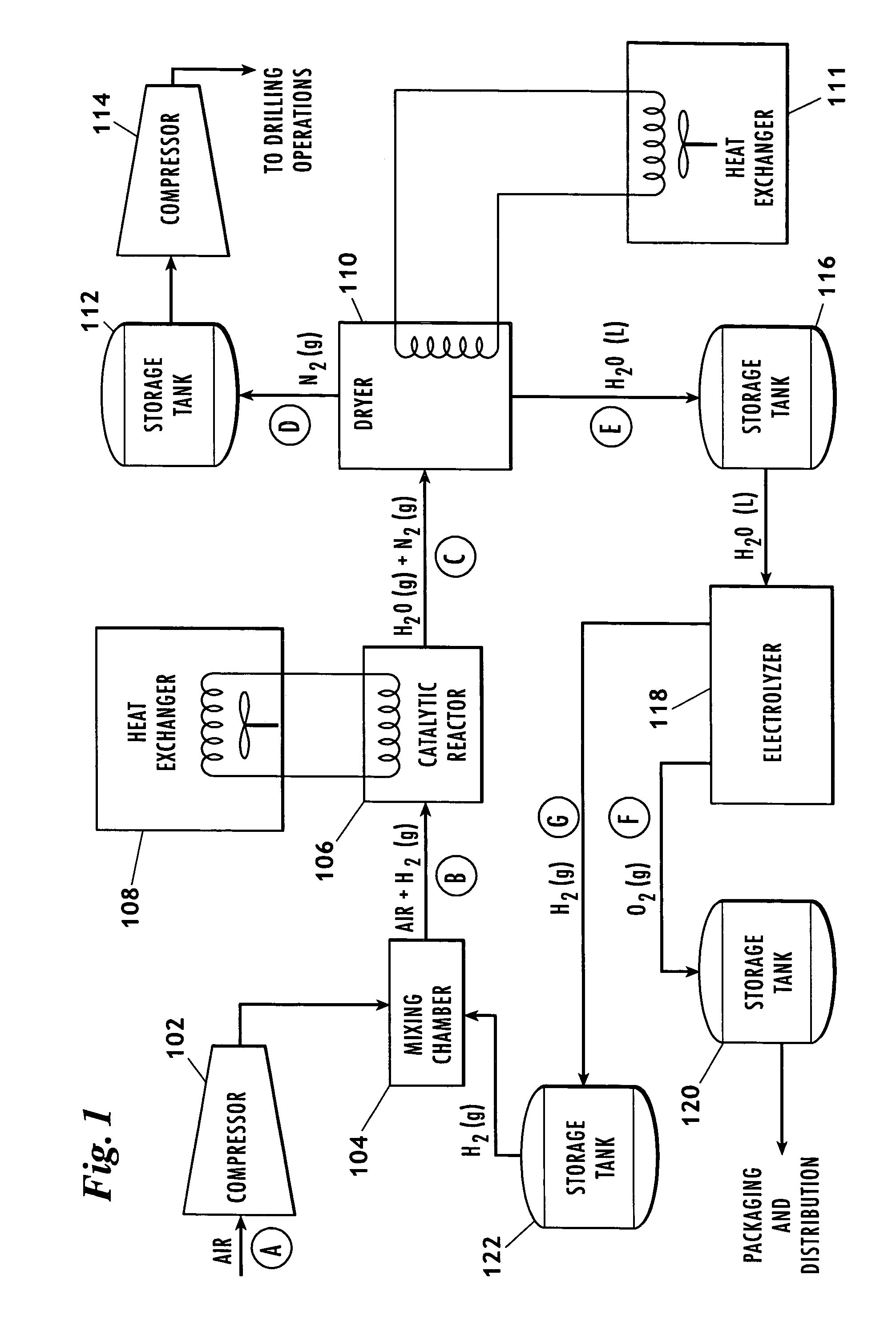
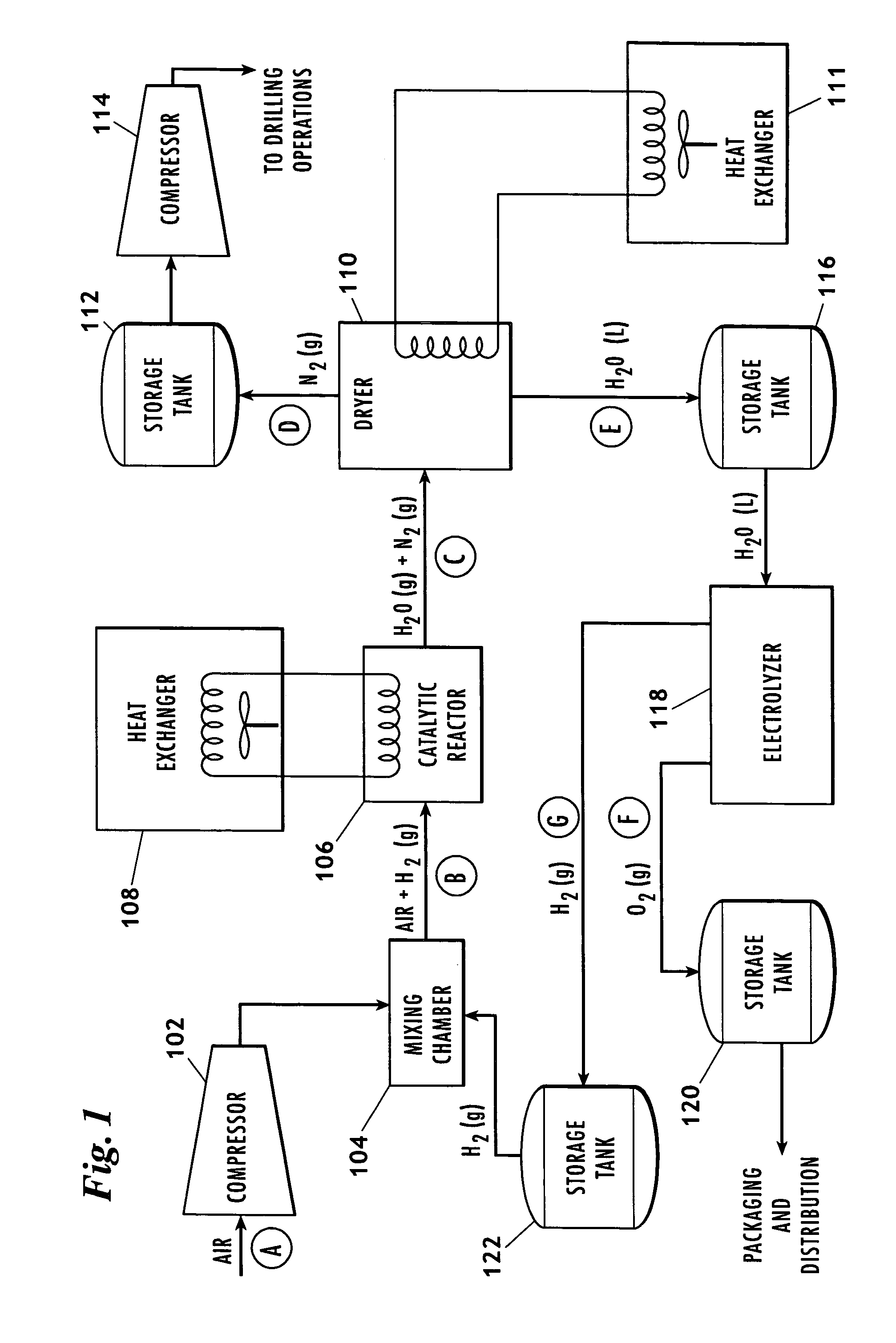
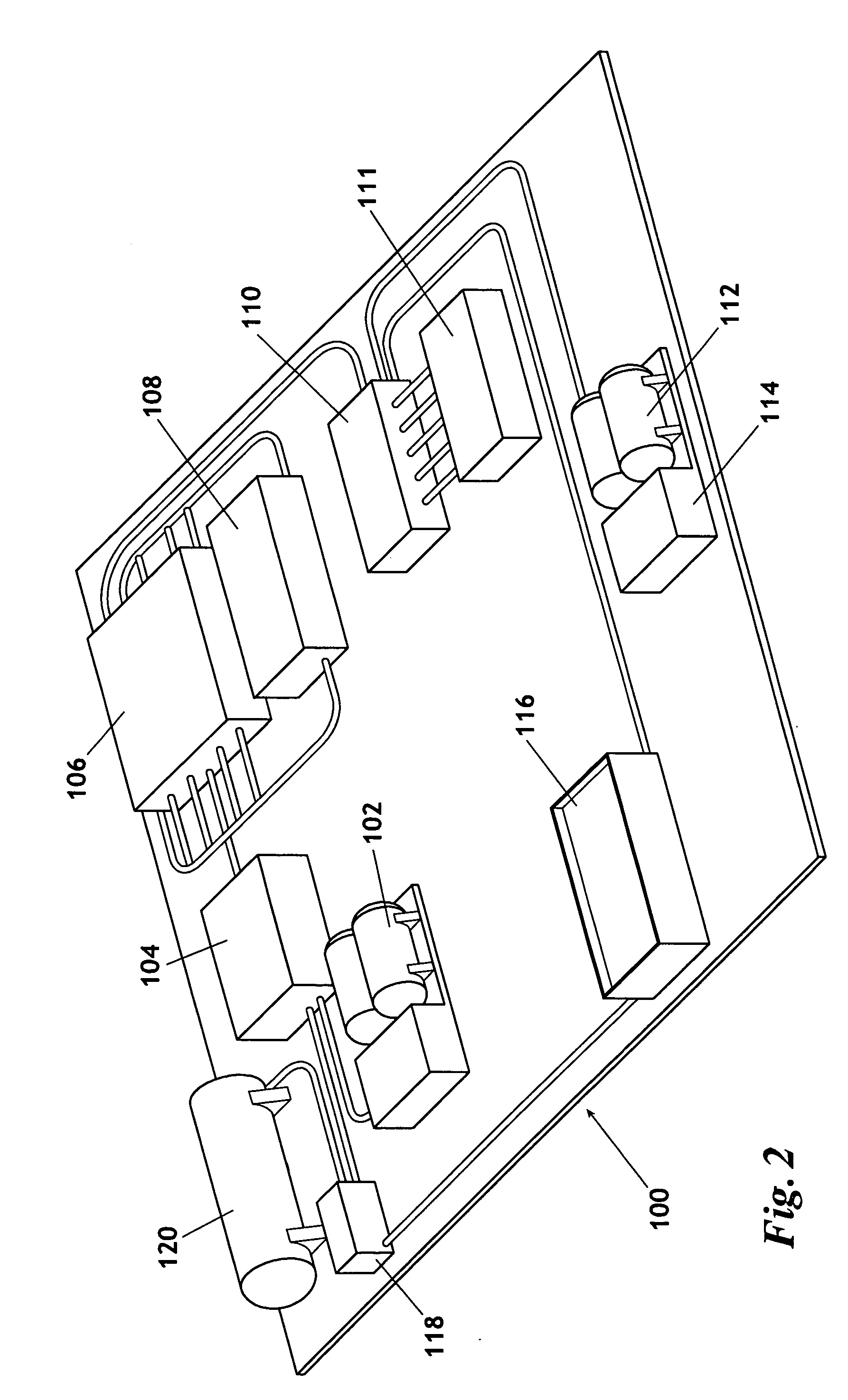
Method for producing nitrogen to use in under balanced drilling, secondary recovery production operations and pipeline maintenance
InactiveUS7468173B2Offsetting costsNitrogen purification/separationDispersed particle separationElectrolysisAtmospheric air
The invention uses a feed of atmospheric air and mixes the air with hydrogen. The hydrogen and air mixture is fed into a catalytic reactor where a deoxygenation reaction occurs. The deoxygenation reaction uses a platinum catalyst to produce water from oxygen and hydrogen. The nitrogen passes through the catalytic reactor without reacting with the hydrogen, the oxygen, or the water. The water is separated from the nitrogen in a dryer. The nitrogen may then be used in drilling and production operations. The water is fed into an electrolyzer where an electrolysis reaction occurs. The electrolyzer passes an electrical current through the water to produce gaseous oxygen and hydrogen. The hydrogen is recycled back to the catalytic reactor and the oxygen may be vented or sold.
Owner:SUNSTONE TECH
Universal marine diverter converter
A universal marine diverter converter (UMDC) housing is clamped or latched to a rotating control device. The UMDC housing assembled with the RCD is inserted into a marine diverter above the water surface to allow conversion between conventional open and non-pressurized mud-return system drilling, and a closed and pressurized mud-return system used in managed pressure or underbalanced drilling.
Owner:WEATHERFORD TECH HLDG LLC
Multi seam coal bed/methane dewatering and depressurizing production system
InactiveUS6923275B2Minimal environmental impactEliminate infrastructure long-term maintenance and environmental impactFluid removalDirectional drillingWell drillingProduct gas
A process for underbalanced drilling into multiple coal and shale formations, and dewatering the drilled formations, which includes drilling a first borehole through several coal seams to a certain depth, defined as a cased borehole; lowering an upstock on the end of a carrier string to the depth of the upper coal seam; lowering a drill string in the carrier string, and angling off of the upstock, to drill a lateral or horizontal borehole within the coal seam; repeating the process for the second coal seam; setting a packer in place above the first coal seam in the annulus between the cased borehole and the carrier string; forming perforations in the wall of the carrier string below the packer; retrieving the upstock from the carrier string; lowering an electrical submersible pump to the bottom of the principal borehole, defined as a sump portion of the borehole; collecting methane gas from the two coal seams through the annulus between the second drill string and the carrier string to the surface; pumping water from the sump portion to the surface within the annulus of the second drill string, while gas within the annulus between the carrier string and the outer casing enters the plurality of perforations in the carrier string to be carried up to the surface.
Owner:GARDES ROBERT
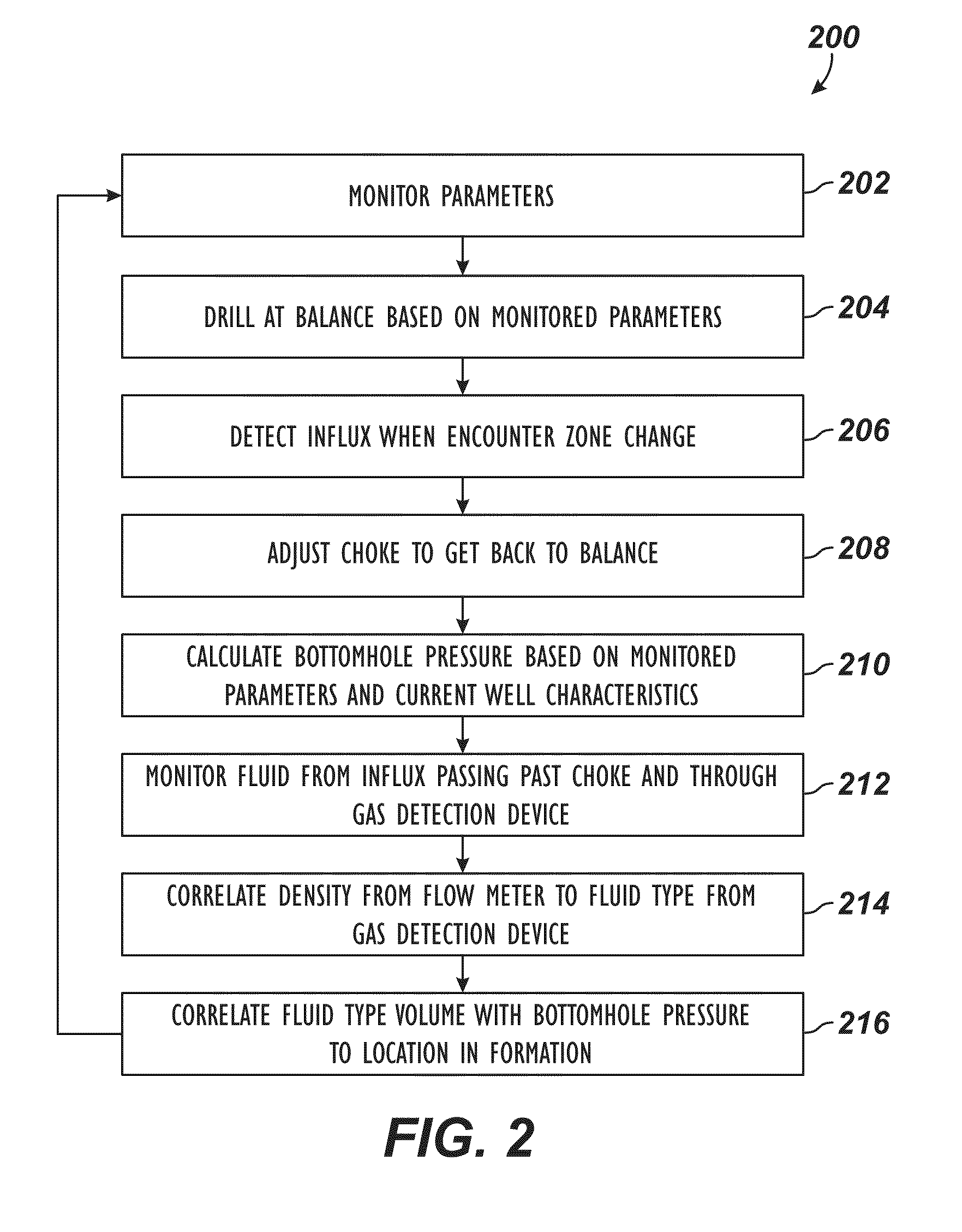
Automatic control system and method for bottom hole pressure in the underbalance drilling
ActiveUS20050096848A1Easy to controlHigh adjustment accuracyElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingConstructionsAutomatic controlEngineering
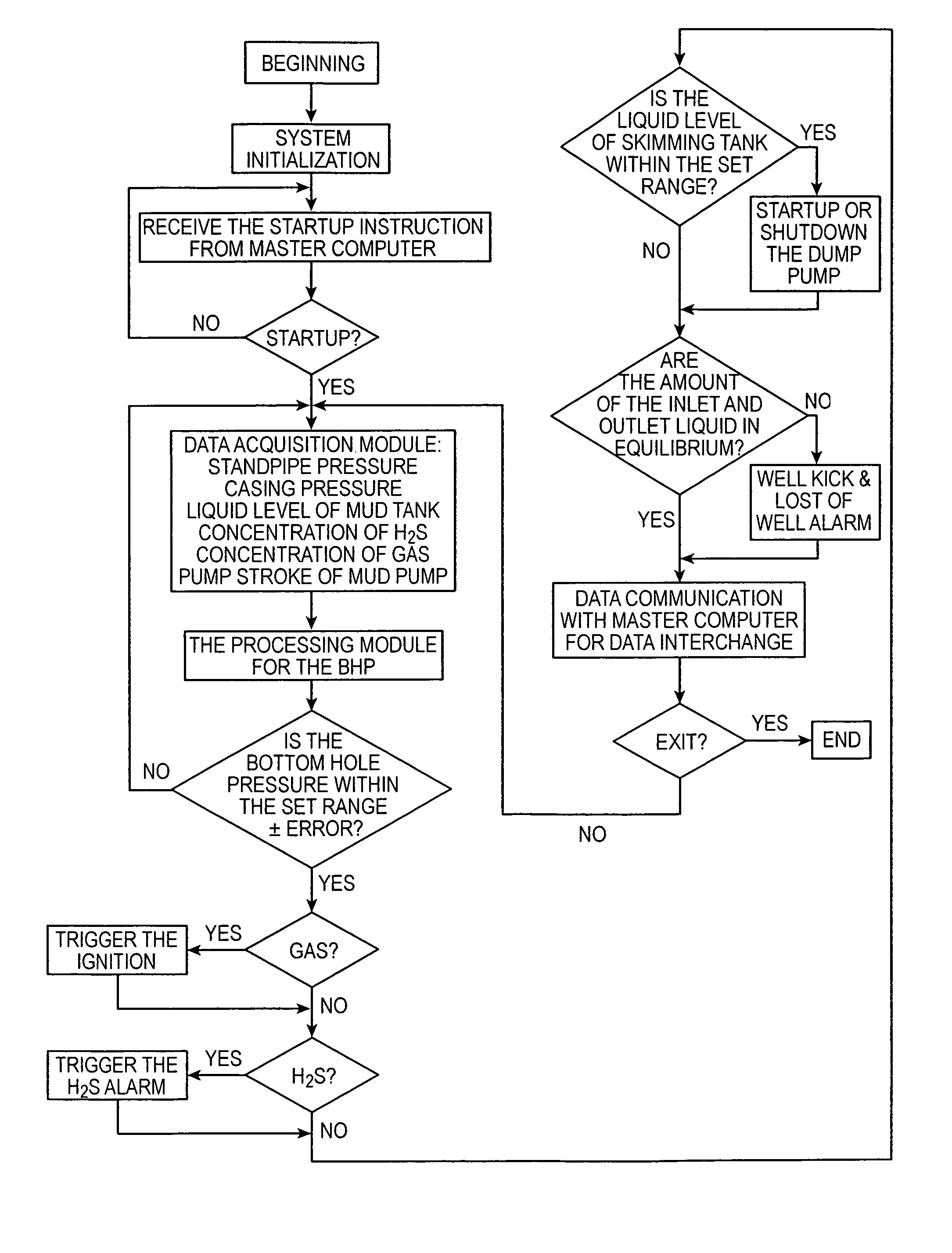
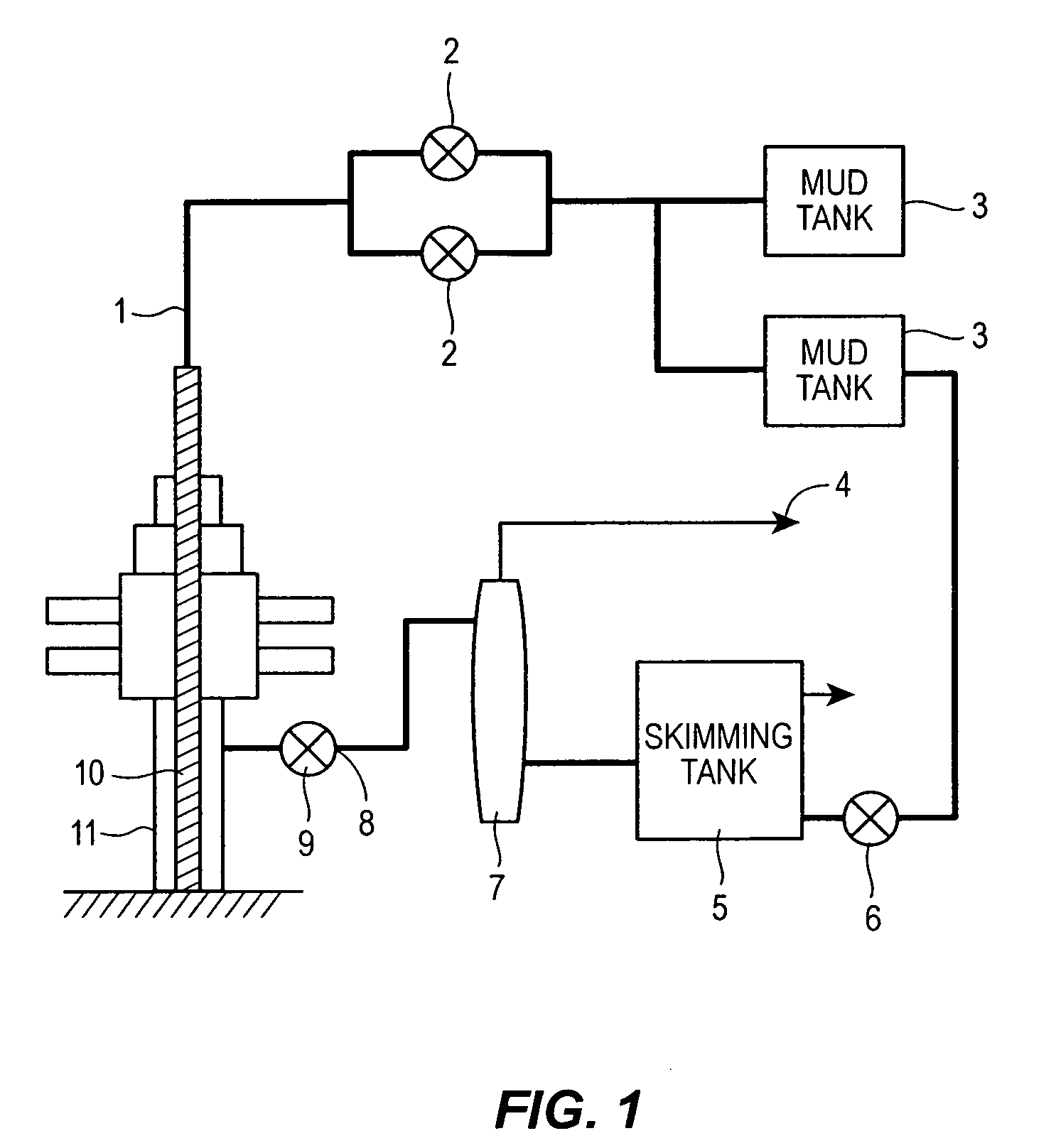
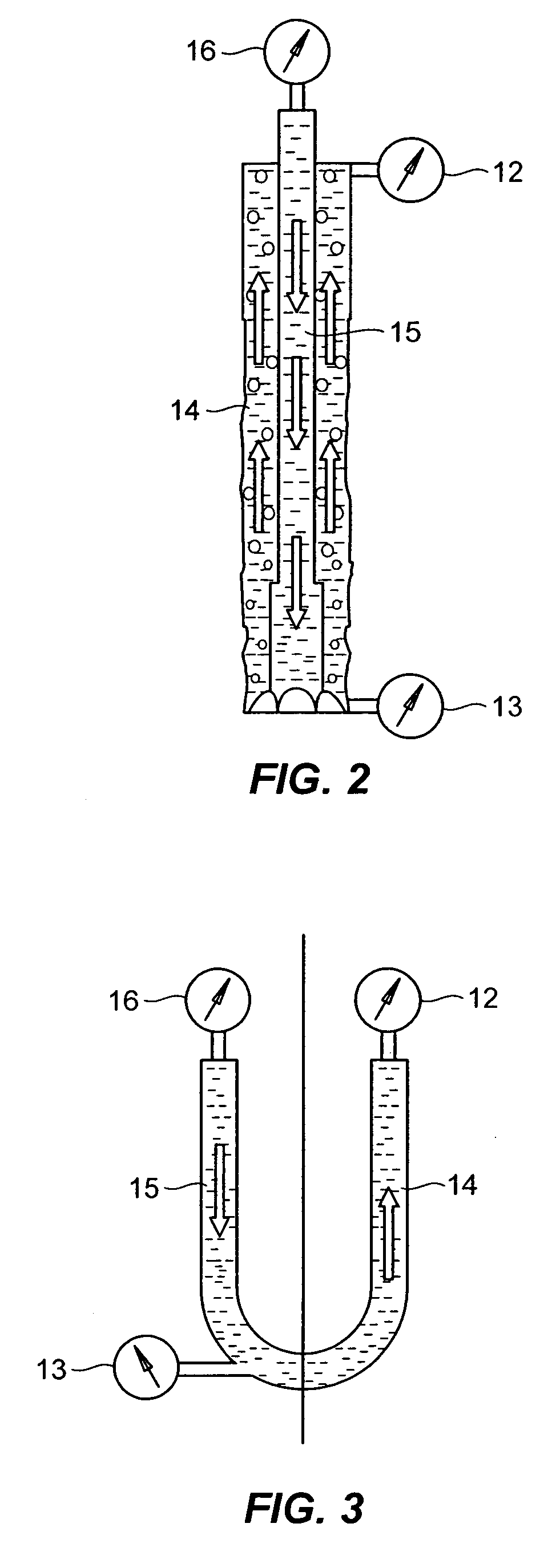
This invention provides an automatic control system and method for bottom hole pressure (BHP) in the underbalance drilling. It relates to a computer automatic control technology. The automatic control system according to the invention includes a processing module for the BHP based on the mechanisms of hydraulics. The BHP in the underbalance drilling is calculated from the acquired standpipe pressure (SPP), the calculated circulating pressure loss in the drilling tools, drill bit pressure drop and the fluid column pressure in the drill string. The resulting BHP is then compared with the set pressure value of the system. In case that the BHP is higher or lower than the set pressure, an instruction to regulate throttle valve opening will be issued in order to bring the BHP back to the set pressure range and complete BHP monitoring and control. The automatic control system and method according to the invention enable real-time tracking of the changes in BHP and achieve accurate and timely adjustment and control of BHP. The automatic control system and method improve the level of automation in the underbalance drilling process, and also enhance the reliability and safety in the underbalance drilling operation, which have wide foreground for application.
Owner:CHINA PETROCHEMICAL CORP +1
Method and system for return of drilling fluid from a sealed marine riser to a floating drilling rig while drilling
Owner:WEATHERFORD TECH HLDG LLC
Multi seam coal bed/methane dewatering and depressurizing production system
InactiveUS20050252689A1Eliminate infrastructure long-term maintenance and environmental impactLarge partFluid removalDirectional drillingUnderbalanced drillingDrill hole
A process for underbalanced drilling into multiple coal and shale formations, and dewatering the drilled formations, which includes drilling a first borehole through several coal seams to a certain depth, defined as a cased borehole; lowering an upstock on the end of a carrier string to the depth of the upper coal seam; lowering a drill string in the carrier string, and angling off of the upstock, to drill a lateral or horizontal borehole within the coal seam; repeating the process for the second coal seam; setting a packer in place above the first coal seam in the annulus between the cased borehole and the carrier string; forming perforations in the wall of the carrier string below the packer; retrieving the upstock from the carrier string; lowering an electrical submersible pump to the bottom of the principal borehole, defined as a sump portion of the borehole; collecting methane gas from the two coal seams through the annulus between the second drill string and the carrier string to the surface; pumping water from the sump portion to the surface within the annulus of the second drill string, while gas within the annulus between the carrier string and the outer casing enters the plurality of perforations in the carrier string to be carried up to the surface. Under a first option, water from the two coal seams is pumped by the ESP through perforations in the wall of the casing, to a first lower water injection zone below the coal seams. In a second option, the water can be first delivered to the surface, and then returned down the annulus between the outer casing and carrier string to be injected into a water injection zone above the coal seams. It is foreseen that multiple wells can be drilled, and when the water is returned to the surface, the water would be routed to one of the wells which would return the water to the water injection zone. The objective of underbalanced drilling of coal and shale is to have the hydrostatic pressure of the drilling process to be lower than the formation pressure, as to not invade the formation with fines that may plug the fractures or fluid that may interact with the formation causing the swelling of clay particles or phase trapping commonly referred to as formation damage.
Owner:GARDES ROBERT
Vibration-dampening drill collar
InactiveUS20050217898A1Reduce vibrationEffective dampeningDrilling rodsConstructionsUnderbalanced drillingEngineering
A drill collar primarily for use with measurement-while-drilling and logging-while-drilling sensors, the drill collar composed of a non-magnetic nickel alloy, and having three or four elongate nitral elastomer ribs parallel the longitudinal axis and mounted on the inner surface of the drill collar, defining a central aperture for receiving the down-hole sensor and inter-rib apertures for receiving drilling fluid. This novel drill collar is especially useful in rough or underbalanced drilling applications, protecting the sensor and enhancing measurement accuracy by dampening flow-based harmonic vibrations, absorbing vibration from lateral tool movement, and stabilizing / centralizing the sensor within the central aperture. Also, the novel drill collar allows the operator to run lower fluid rates while drilling, minimizing formation damage from fluid invasion.
Owner:PHOENIX TECH SERVICES
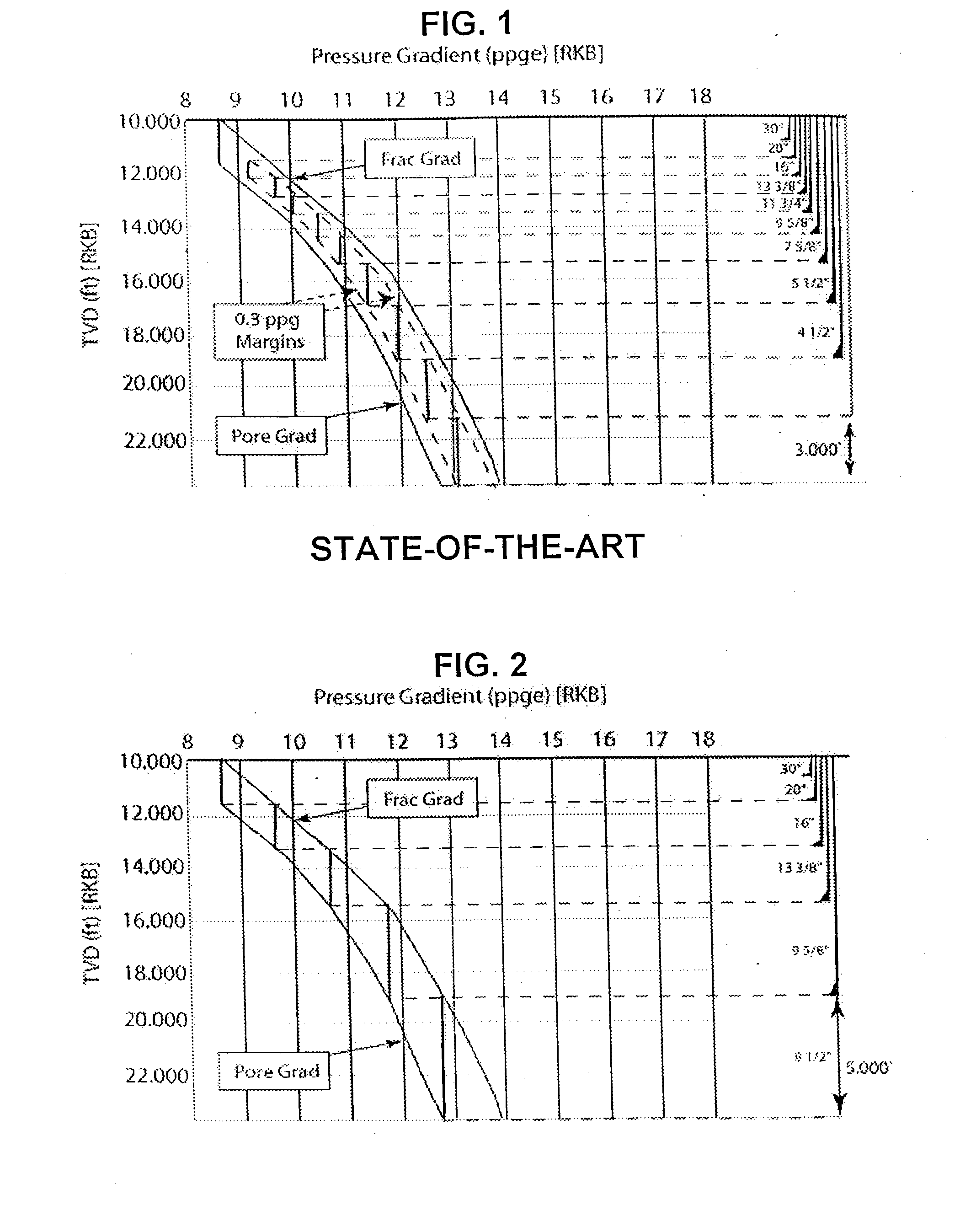
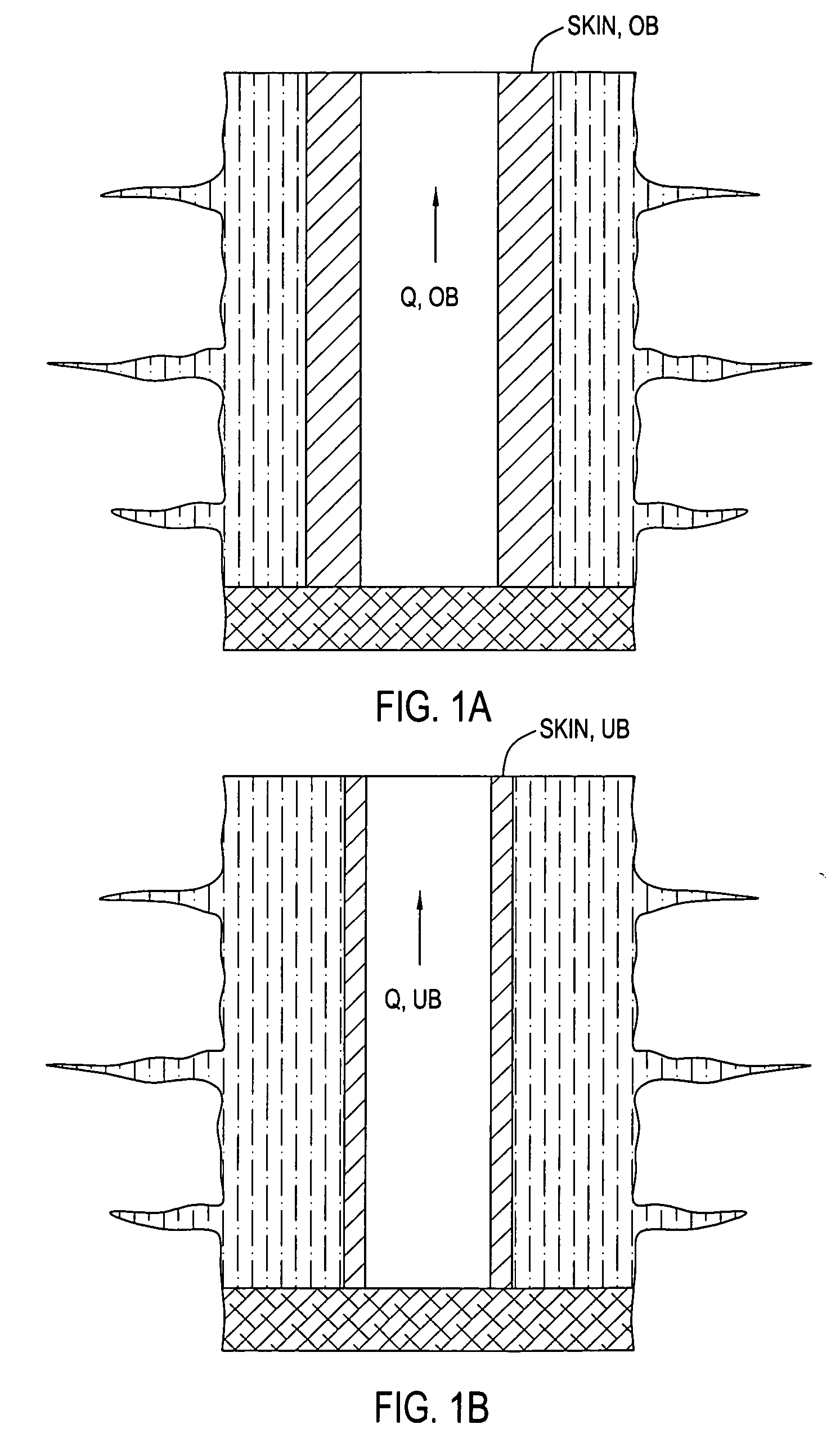
System for evaluating over and underbalanced drilling operations
InactiveUS20050192855A1Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingAdvertisingSkin factorStatistical analysis
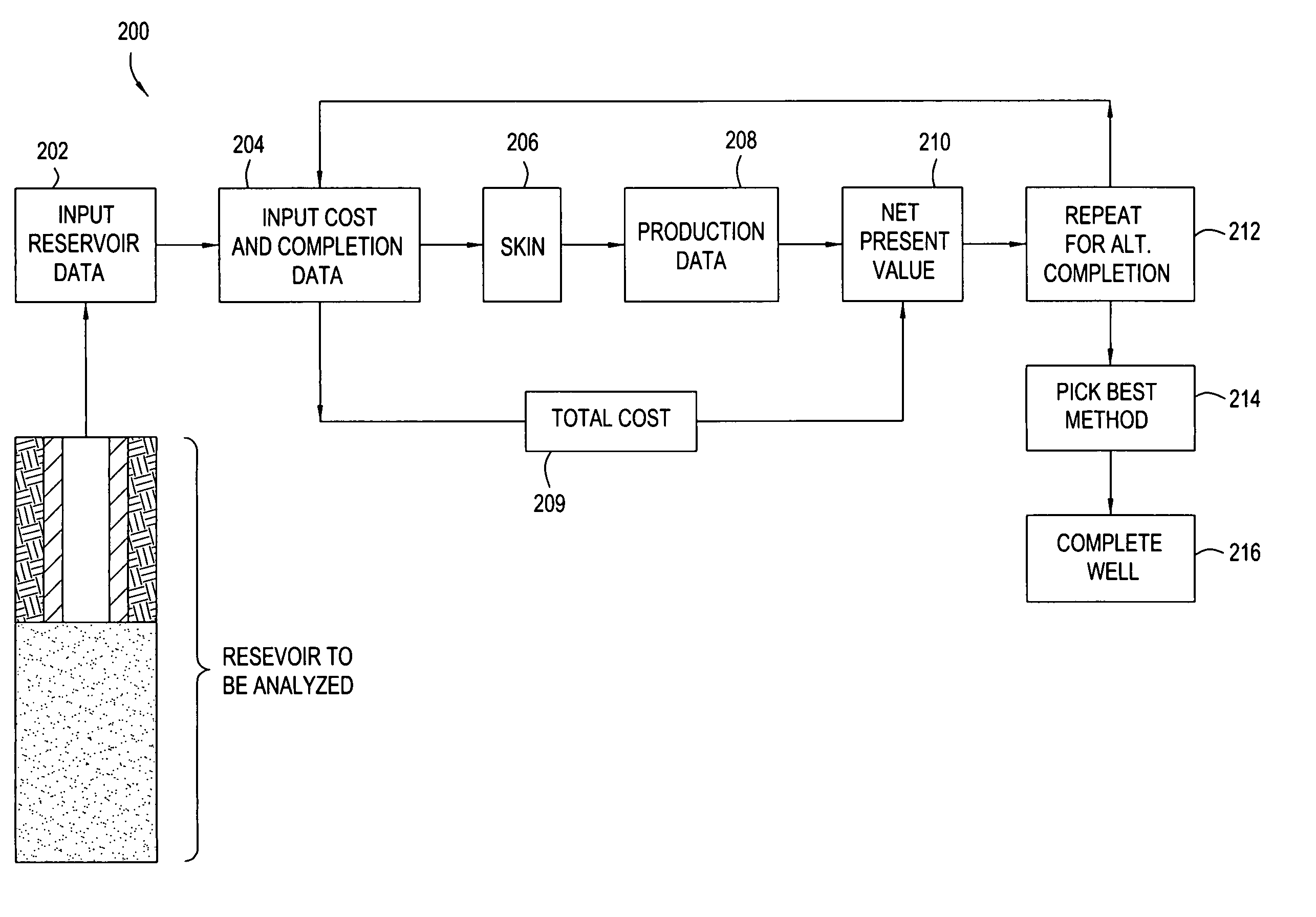
A method and a computer program for economic evaluation of completion methods for drilling a well. An extensive user interface is provided for inputting of reservoir data and parameters relating to a first completion method. A rigorous first skin factor is generated based on the reservoir data and first drilling parameters. An interface is preferably provided for entering cost data related to the first completion technique and a first total cost can be generated. Production data is optionally generated from the first skin factor. The production and cost data can then be combined to generate an economic analysis of the first completion technique. The process can be repeated for alternate completion techniques. Preferably, ranges can be entered for certain reservoir and / or cost variables. Multiple iterations can be performed on the ranges resulting in total cost and production ranges which can be combined to yield ranges of economic data for statistical analysis. This results in a user being able to choose the most advantageous completion method.
Owner:WEATHERFORD TECH HLDG LLC
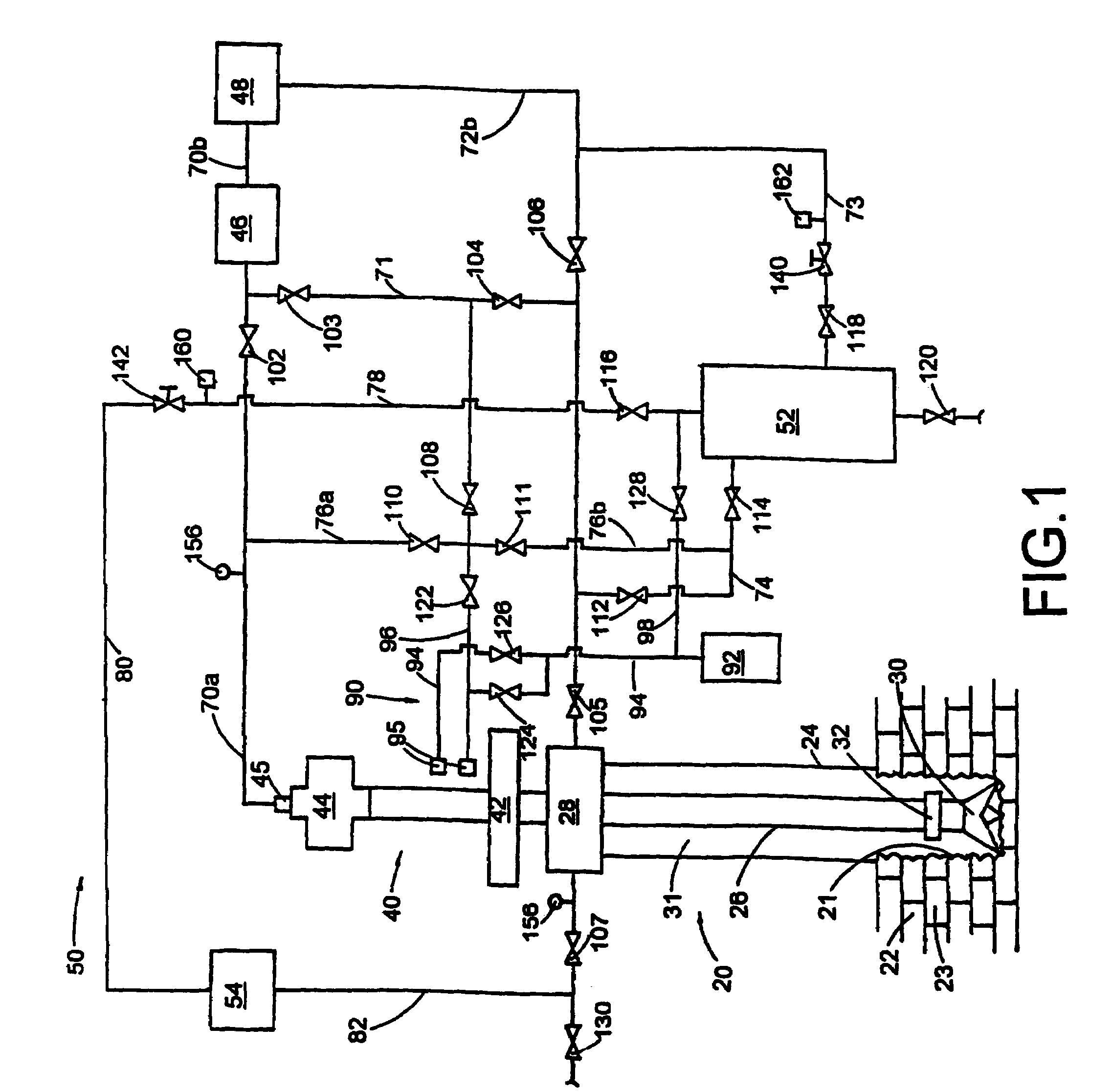
Underbalanced drilling method and apparatus
InactiveUS20050269134A1Loss is particularly problematicCost-effectiveDrilling rodsConstructionsGas liftMechanics
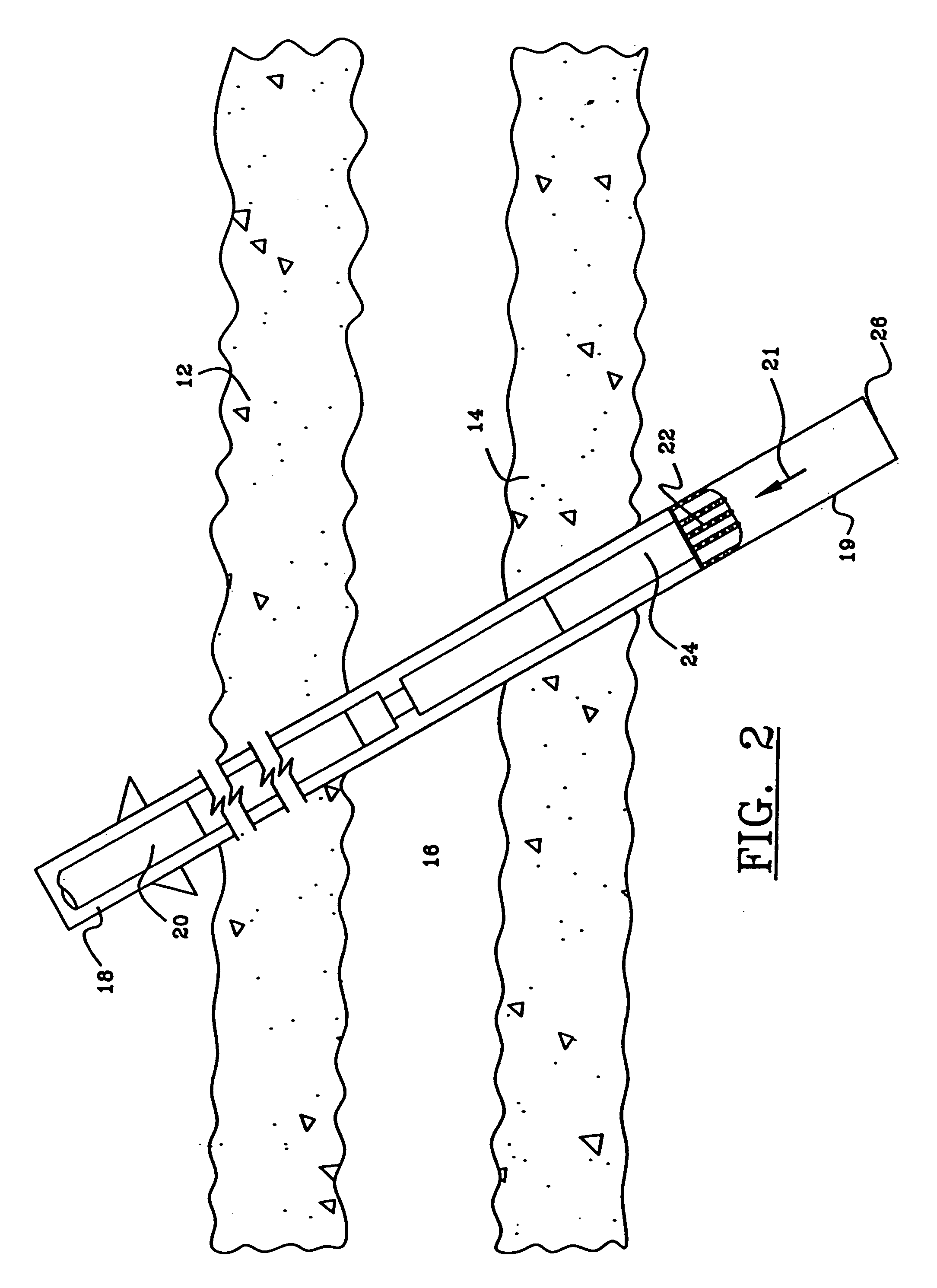
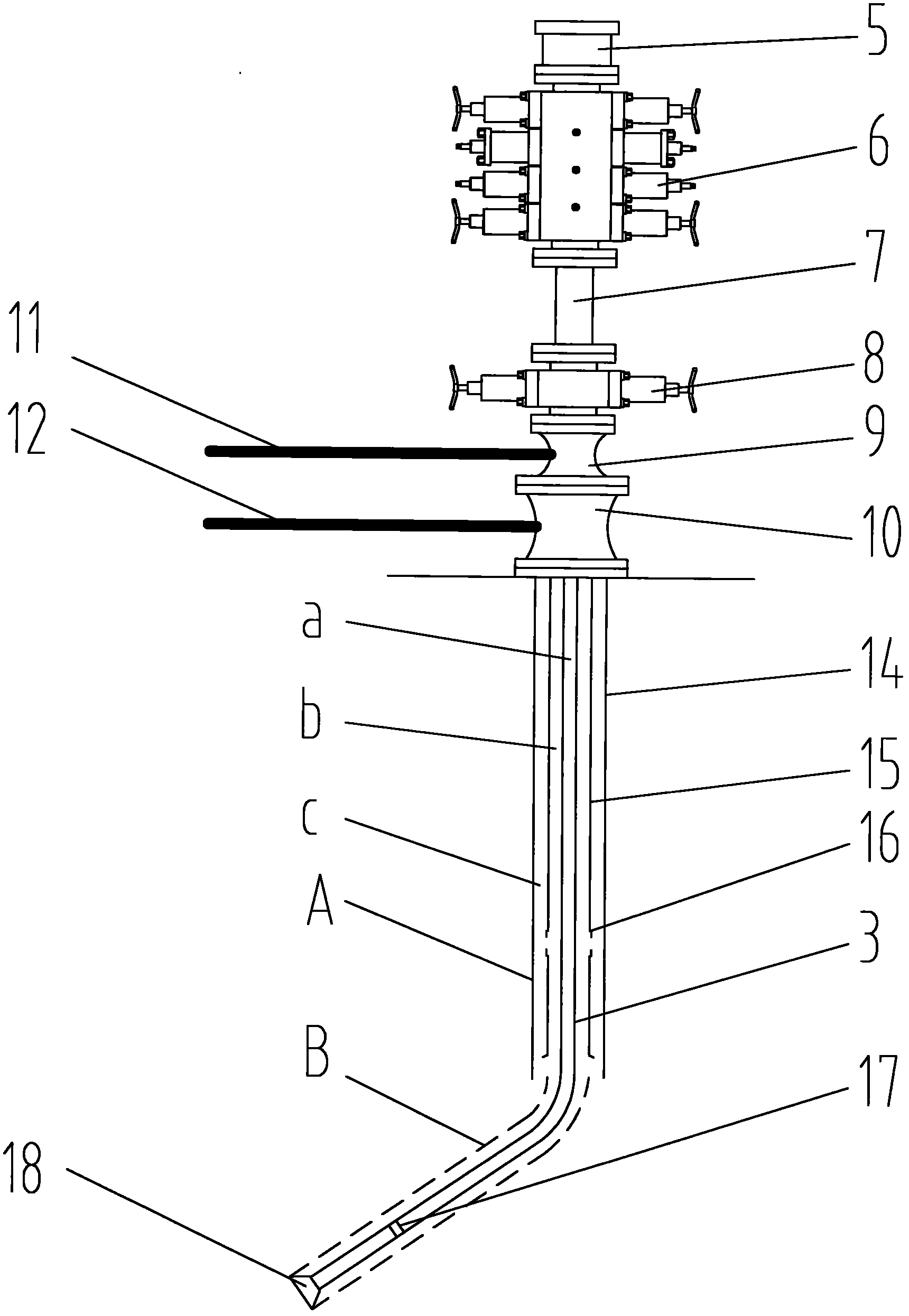
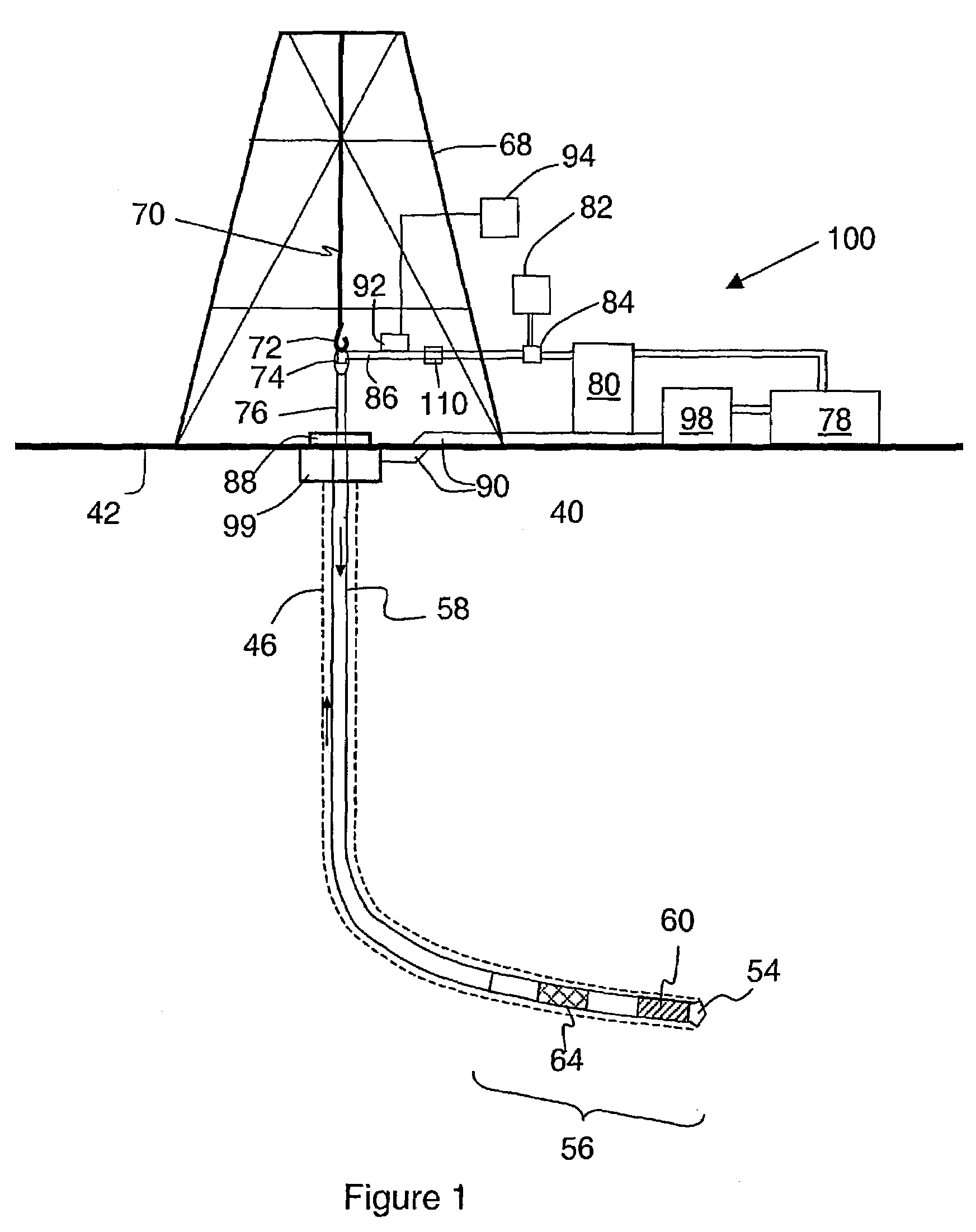
A method of drilling well bore (20) through and below permeable formation (22) bearing such fluids as gas, oil, water wherein drill cuttings may be evacuated by formation fluid (23) being produced through the drill string (26) either by decreasing well head back pressure or by gas lift. Production rate is kept substantially stable by operating choke valves (140) and (142) placed after separator (52). Formation fluid being produced while drilling may be pumped into well bore (20) through annulus (31) or utilized. The unique injector included in the drill string provides for possibility to pump simultaneously into annulus (31) lifting gas and produced liquid and may be operated from the surface. A method and system (90) comprising a plurality of special 3-way valves included in drill string (26), are provided for making connections without interrupting flushing the well bore.
Owner:STRAZHGORODSKIY SEMEN IOSIPHOVICH
Underbalanced drilling method and apparatus
InactiveUS7308952B2Eliminate the problemAvoid excessive volumeConstructionsFluid removalGas liftMechanics
A method of drilling well bore (20) through and below permeable formation (22) bearing such fluids as gas, oil, water wherein drill cuttings may be evacuated by formation fluid (23) being produced through the drill string (26) either by decreasing well head back pressure or by gas lift. Production rate is kept substantially stable by operating choke valves (140) and (142) placed after separator (52). Formation fluid being produced while drilling may be pumped into well bore (20) through annulus (31) or utilized. The unique injector included in the drill string provides for possibility to pump simultaneously into annulus (31) lifting gas and produced liquid and may be operated from the surface. A method and system (90) comprising a plurality of special 3-way valves included in drill string (26), are provided for making connections without interrupting flushing the well bore.
Owner:STRAZHGORODSKIY SEMEN IOSIPHOVICH
Automatic control system and method for bottom hole pressure in the underbalance drilling
ActiveUS7158886B2Accurate calculationRelatively small errorElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingConstructionsAutomatic controlAutomated control system
This invention provides an automatic control system and method for bottom hole pressure (BHP) in the underbalanced drilling. It relates to a computer automatic control technology. The automatic control system according to the invention includes a processing module for the BHP based on the mechanisms of hydraulics. The BHP in the underbalanced drilling is calculated from the acquired standpipe pressure (SPP), the calculated circulating pressure loss in the drilling tools, drill bit pressure drop and the fluid colunm pressure in the drill string. The resulting BHP is then compared with the set pressure value of the system. In case that the BHP is higher or lower than the set pressure, an instruction to regulate throttle valve opening will be issued in order to bring the BHP back to the set pressure range and complete BHP monitoring and control.
Owner:CHINA PETROCHEMICAL CORP +1
Well drilling method of through tubing of gas lift under-balanced coiled tubing
ActiveCN101942962AOvercoming the effect of jacking forcePromote maturityDirectional drillingFlushingDirectional wellSlurry
The invention relates to a well drilling method of a through tubing of a gas lift under-balanced coiled tubing, which is applied in the technical field of petroleum well drilling. The through tubing operation way of the coiled tubing is adopted for carrying out under-balanced well drilling or low-pressure well drilling on target well sections at the lower part in a shaft with a drilled upper borehole, wherein the target well sections are a vertical well, a directional well or a horizontal well. The method has the following effects: the adoption of the through tubing operation of the coiled tubing can form three circulation channels by utilizing the coiled tubing, an oil tube and a sleeve, and a matching pipe column has good universality, does not need a special drilling column or an inner tube and does not need to use a rotary blowout preventer and other special equipment; a gas injection channel and a slurry injection channel are independent mutually, thereby being capable of more conveniently controlling the well bottom pressure and the under-pressure value and using an underground power drilling tool and a slurry pulse measurement system which are applicable to slurry well drilling to carry out well drilling operation and trajectory control; and the method does not need to be connected with a single and can keep the continuous circulation during the tripping process and the drilling process, and realize the full-process controllable under-balanced well drilling operation and the full-process controllable low-pressure well drilling operation.
Owner:BC P INC CHINA NAT PETROLEUM CORP +2
Multi seam coal bed/methane dewatering and depressurizing production system
InactiveUS7243738B2Eliminate infrastructure long-term maintenance and environmental impactLarge partFluid removalDirectional drillingUnderbalanced drillingMaterial Perforation
A process for underbalanced drilling into multiple coal and shale formations, and dewatering the drilled formations, which includes drilling a first borehole through several coal seams to a certain depth; lowering an upstock on the end of a carrier string to the depth of the upper coal seam; lowering a drill string in the carrier string, and angling off of the upstock, to drill a lateral or horizontal borehole within the coal seam; repeating the process for the second coal seam; setting a packer in place above the first coal seam in the annulus between the cased borehole and the carrier string; forming perforations in the wall of the carrier string below the packer; retrieving the upstock from the carrier string; lowering an electrical submersible pump to the bottom of the principal borehole; pumping water from the sump portion to the surface within the annulus of the second drill string.
Owner:GARDES ROBERT
Method for producing nitrogen to use in under balanced drilling, secondary recovery production operations and pipeline maintenance
InactiveUS20050186130A1Offsetting cost of projectEconomically feasibleNitrogen purification/separationDispersed particle separationElectrolysisPtru catalyst
The invention uses a feed of atmospheric air and mixes the air with hydrogen. The hydrogen and air mixture is fed into a catalytic reactor where a deoxygenation reaction occurs. The deoxygenation reaction uses a platinum catalyst to produce water from oxygen and hydrogen. The nitrogen passes through the catalytic reactor without reacting with the hydrogen, the oxygen, or the water. The water is separated from the nitrogen in a dryer. The nitrogen may then be used in drilling and production operations. The water is fed into an electrolyzer where an electrolysis reaction occurs. The electrolyzer passes an electrical current through the water to produce gaseous oxygen and hydrogen. The hydrogen is recycled back to the catalytic reactor and the oxygen may be vented or sold.
Owner:SUNSTONE TECH
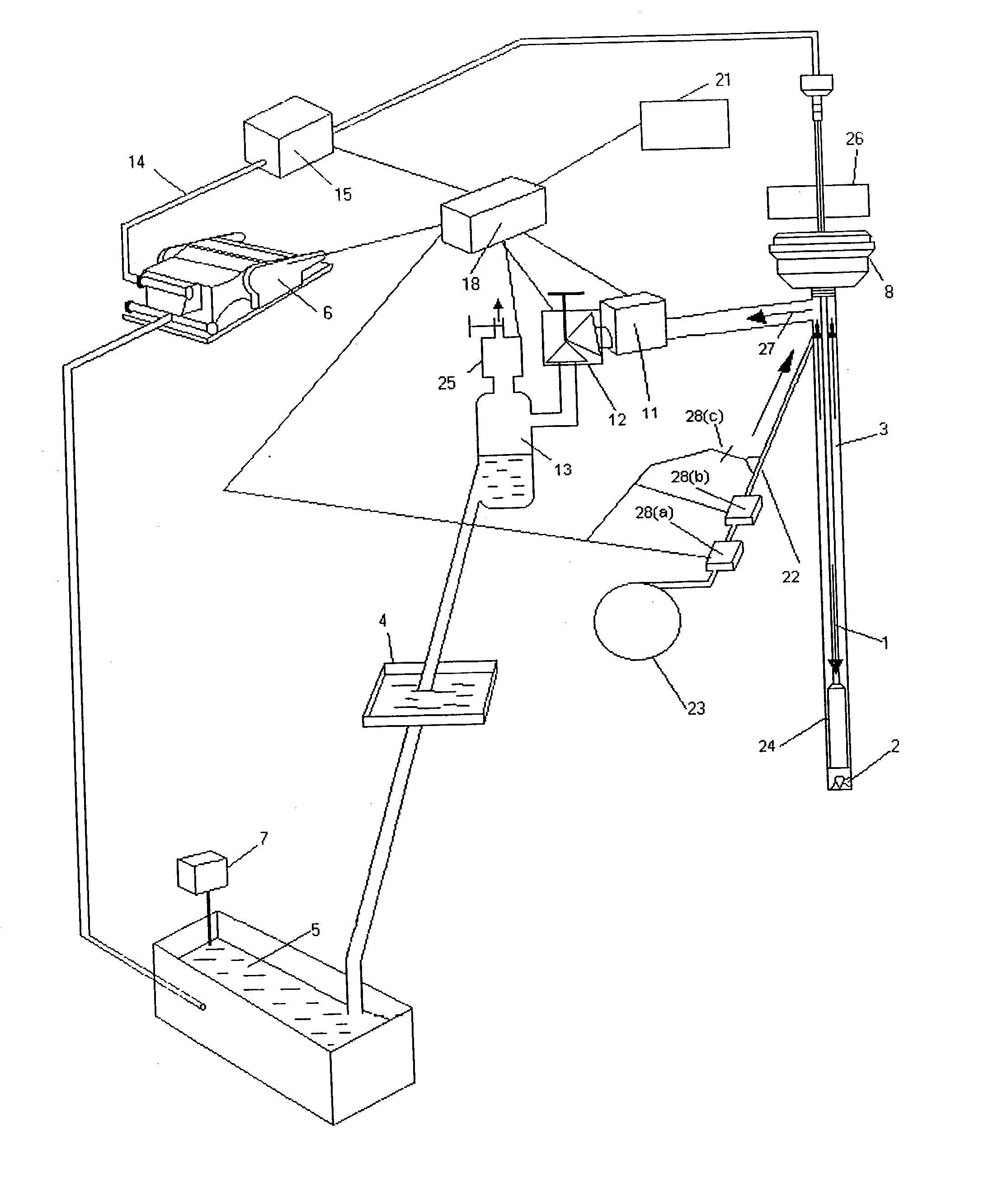
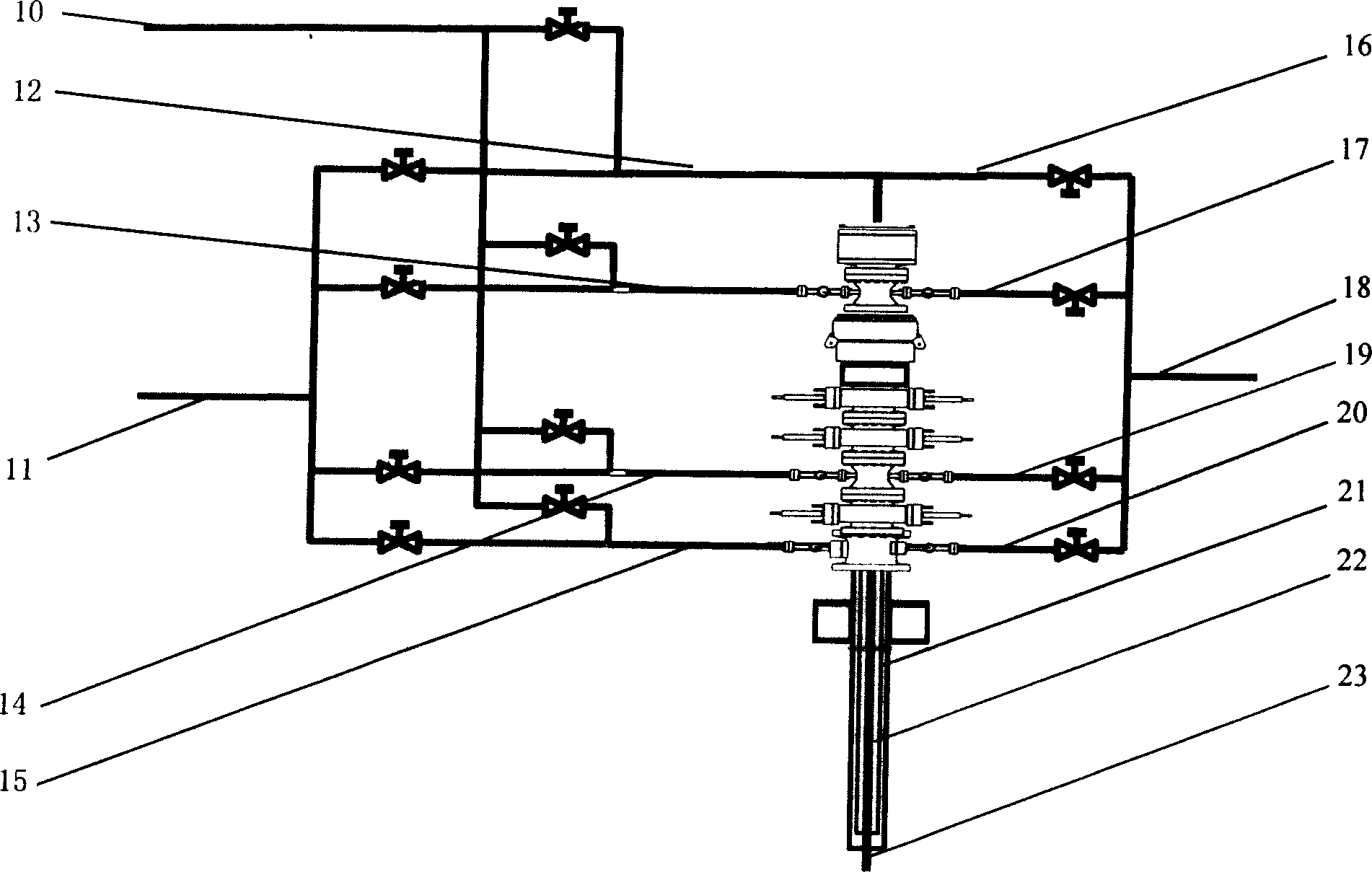
Continuous circulation system for oil and gas well and usage thereof
The invention relates to continuous circulation system that is constituted by multifunction injection system, in well circulation system and ground returning system. The injection system includes drilling fluid that has three densities, two or three mud pumps, and high pressure gas injection device. By the method of injecting two drilling fluids that have different density and fast mixing, or injecting high pressure gas, the in-well liquid column pressure would be adjusted fast and flexibly. The in-well circulation system includes double tube well structure and in-well drilling column, and supplies three flowing channels as the returning channel or injecting channel. The ground returning system includes well head control combination, casing head and gas-liquid-solid separating device. The continuous circulation system is constituted by eight purposes and improves the safety of the well.
Owner:SOUTHWEST PETROLEUM UNIV
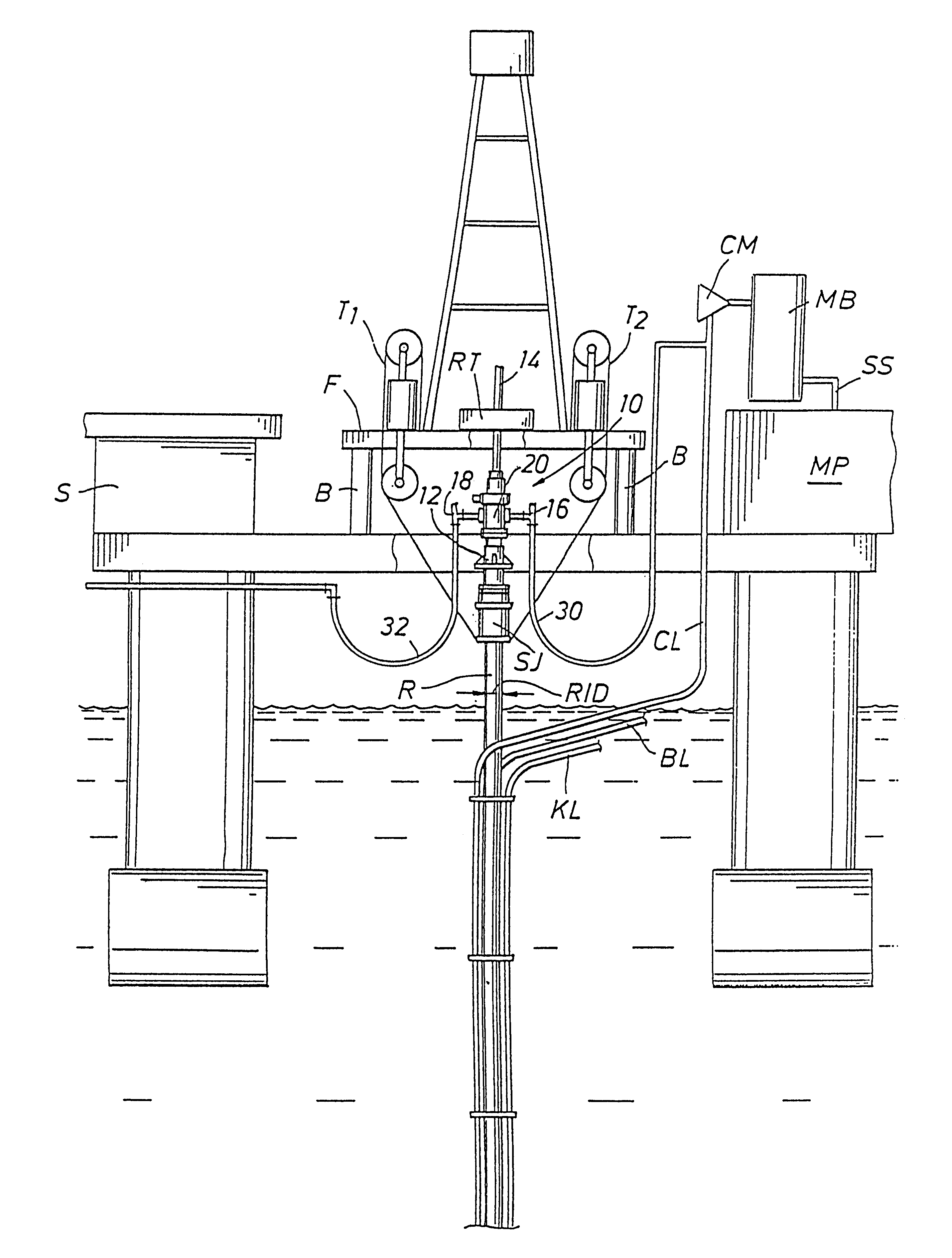
Assembly and method for subsea well drilling and intervention
InactiveUS20110127040A1Reduce in quantityHigh pressure environmentDrilling rodsFluid removalWell drillingUnderbalanced drilling
An assembly suitable for subsea drilling and intervention operations includes a dual blow out preventer system having an upper blow out preventer located between a drill floor and a riser string, and a lower blow out preventer located below the riser string and above a wellhead. The dual BOP system is adapted to enable advanced drilling and intervention operations such as Managed Pressure Drilling (“MPD”), Underbalanced Drilling (“UBD”), or Through Tubing Rotary Drilling (“TTRD”) in an offshore deepwater environment.
Owner:STENA DRILLING
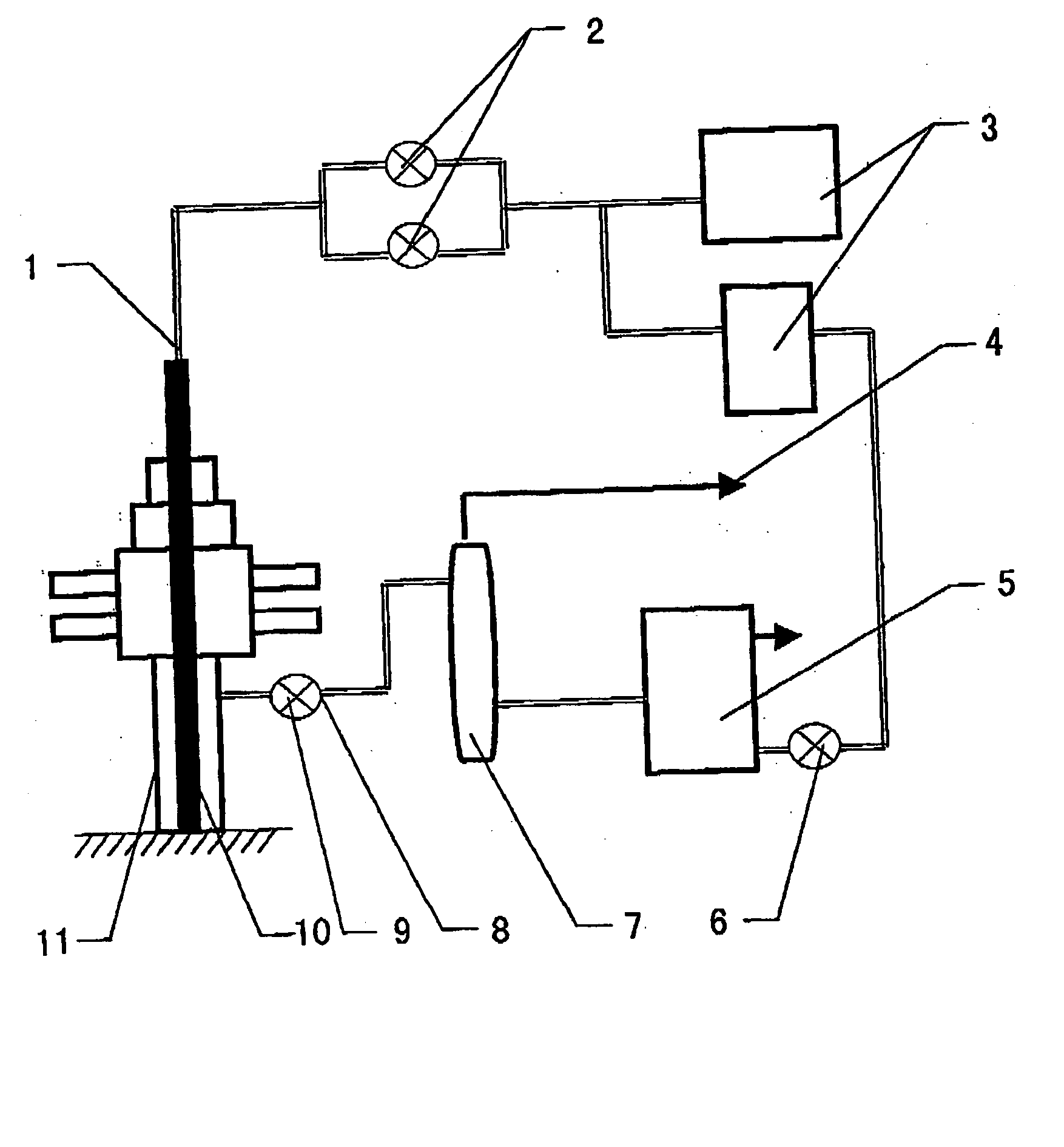
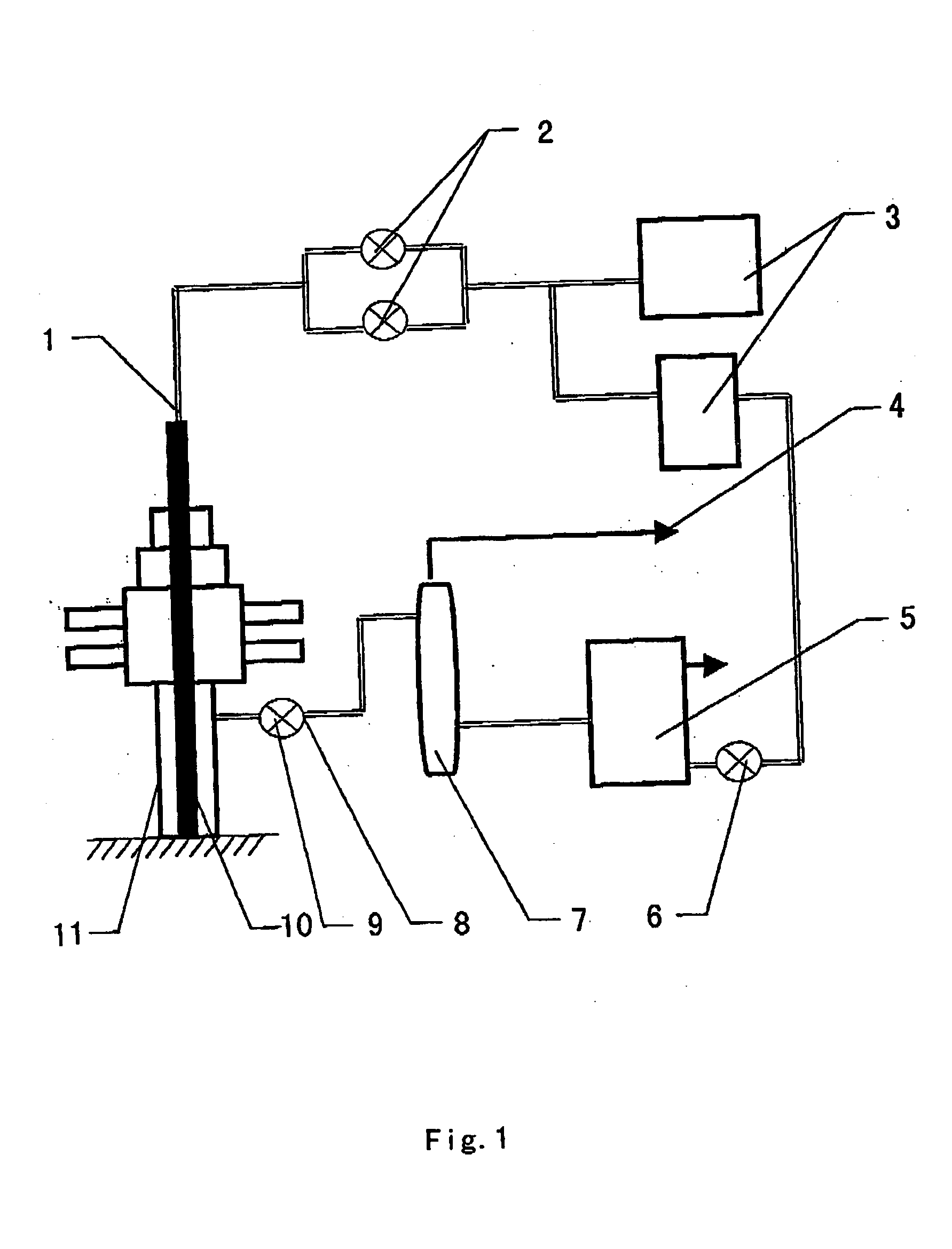
Overall process under-balance drilling pressure compensation system and method
InactiveCN101929331APressure balanceEnsure safe implementationFlushingSealing/packingHigh pressureBlowout preventer
The invention relates to an overall process under-balance drilling pressure compensation system and a method for oil and gas drilling, an underground casing valve (10) is connected on a superior casing string, a wellhead rotary blowout preventer (11) is arranged at an upper end of a wellhead blowout preventer group and is connected with an under-balance throttle manifold (8) through a high-pressure hose (9), a well control manifold (12) which is connected out of a normal wellhead control device by four-pass is connected with a drilling fluid continuous pouring system in parallel by two-pass; and drilling is pulled to the front of the underground casing valve (10), the drilling fluid continuous pouring system grouts, the under-balance throttle manifold (8) controls the pressure in a shaft, and the drilling fluid which is circulated out enters a normal drilling fluid circulating system. In the drilling pulling process, the drilling fluid can be continuously poured into the shaft by a ground pressure compensation system and the bottom-hole pressure can be dynamically controlled simultaneously, thus effectively preventing formation fluid from intruding into the shaft in the drilling pulling process and keeping the steady under-balance state of the shaft.
Owner:中国石油集团西部钻探工程有限公司克拉玛依钻井工艺研究院
Aerated underbalanced drilling method for coal-bed gas
The invention relates to an aerated underbalanced drilling method for coal-bed gas, which comprises the following steps of: drilling a vertical well; drilling a horizontal well with a vertical channel and a horizontal channel; drilling a drilling vertical shaft in the horizontal channel and injecting drilling fluid into the drilling vertical shaft simultaneously to wash away rock debris and the like until the horizontal channel is communicated with the lower end of the vertical well; injecting gas into the vertical well while drilling the drilling vertical shaft and making the gas mixed with the drilling fluid injected from the horizontal well to obtain first gas-fluid two-phase flow; stopping injecting the drilling fluid from the horizontal well during preparation work of drilling a next drilling vertical shaft and injecting the drilling fluid into the vertical well while keeping injecting the gas into the vertical well to form second gas-fluid two-phase flow; after finishing the preparation work, stopping injecting the drilling fluid into the vertical well and injecting the drilling fluid from the horizontal well in the process of drilling the next drilling vertical shaft; and repeating the steps after finishing drilling operation until the drilling process of the coal-bed gas horizontal well is finished. The method can effectively prevent the rock debris from sinking to bury a drilling tool when the pump of the horizontal well is stopped.
Owner:BEIJING ORION ENERGY TECH DEV
Method and apparatus for enhanced acoustic mud pulse telemetry during underbalanced drilling
InactiveUS7138929B2Enhanced acoustic mud pulse telemetryImprove the situationElectric signal transmission systemsSurveyVena contracta diameterCommunications system
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
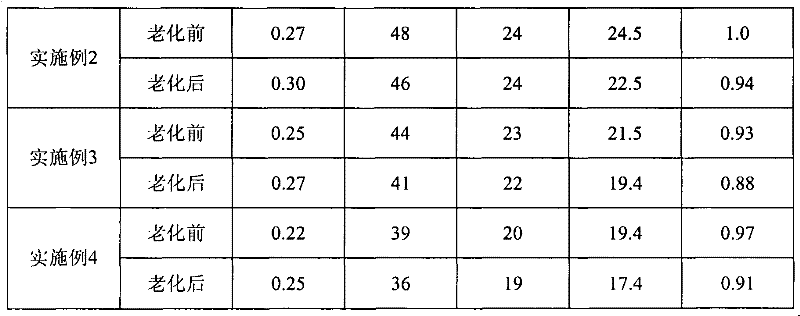
Environmentally-friendly high-temperature-resistant synthetic base foam drilling fluid and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses environmentally-friendly high-temperature-resistant synthetic base foam drilling fluid and a preparation method thereof. The drilling fluid comprises the following components in parts by weight: 1-3 parts of organic soil, 1-2 parts of high-temperature oil-based foaming agent, 1-3 parts of self-made high-temperature oil-based foam stabilizer and 92-97 parts of synthetic base liquid namely alpha-olefin. The dispersion medium of the synthetic base foam drilling fluid is foam liquid using alpha-olefin as the main component, the dispersed phase is air, and the drilling fluid is prepared through high-speed stirring. The drilling liquid system has stable performance, good heat resistance and antipollution capability and good compatibility to the reservoir; and the drilling fluid can be used in deep well underbalanced drilling and can be used to effectively inhibit the hydration and expansion of the shale, stabilize the well wall, prevent well leakage and protect the oil and gas formation. In addition, the synthetic base liquid namely alpha-olefin and the foaming agent are both non-toxic, are biodegradable and have no harmful effect on the environment.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA) +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com