Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
582 results about "Bottom hole assembly" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
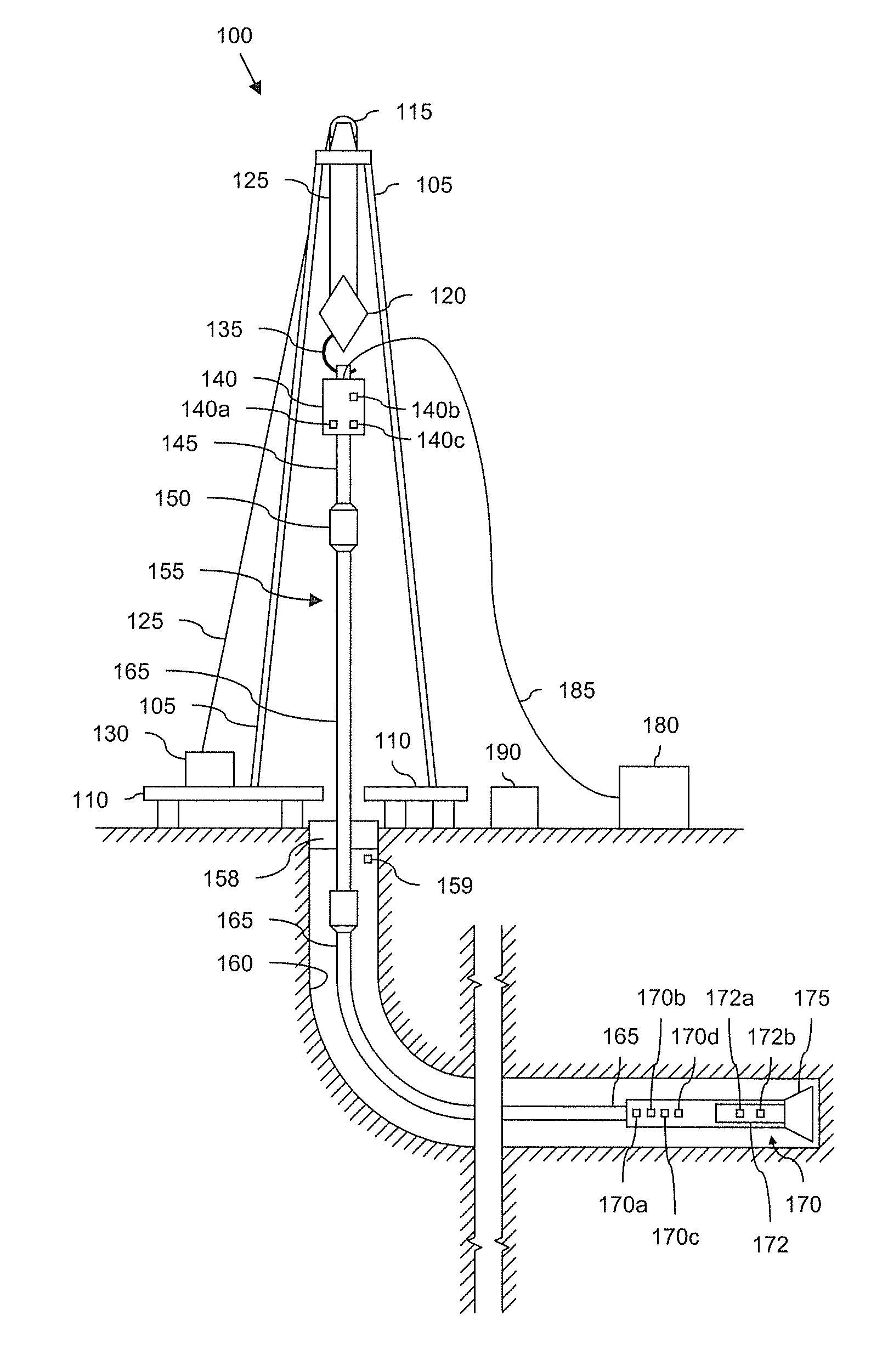
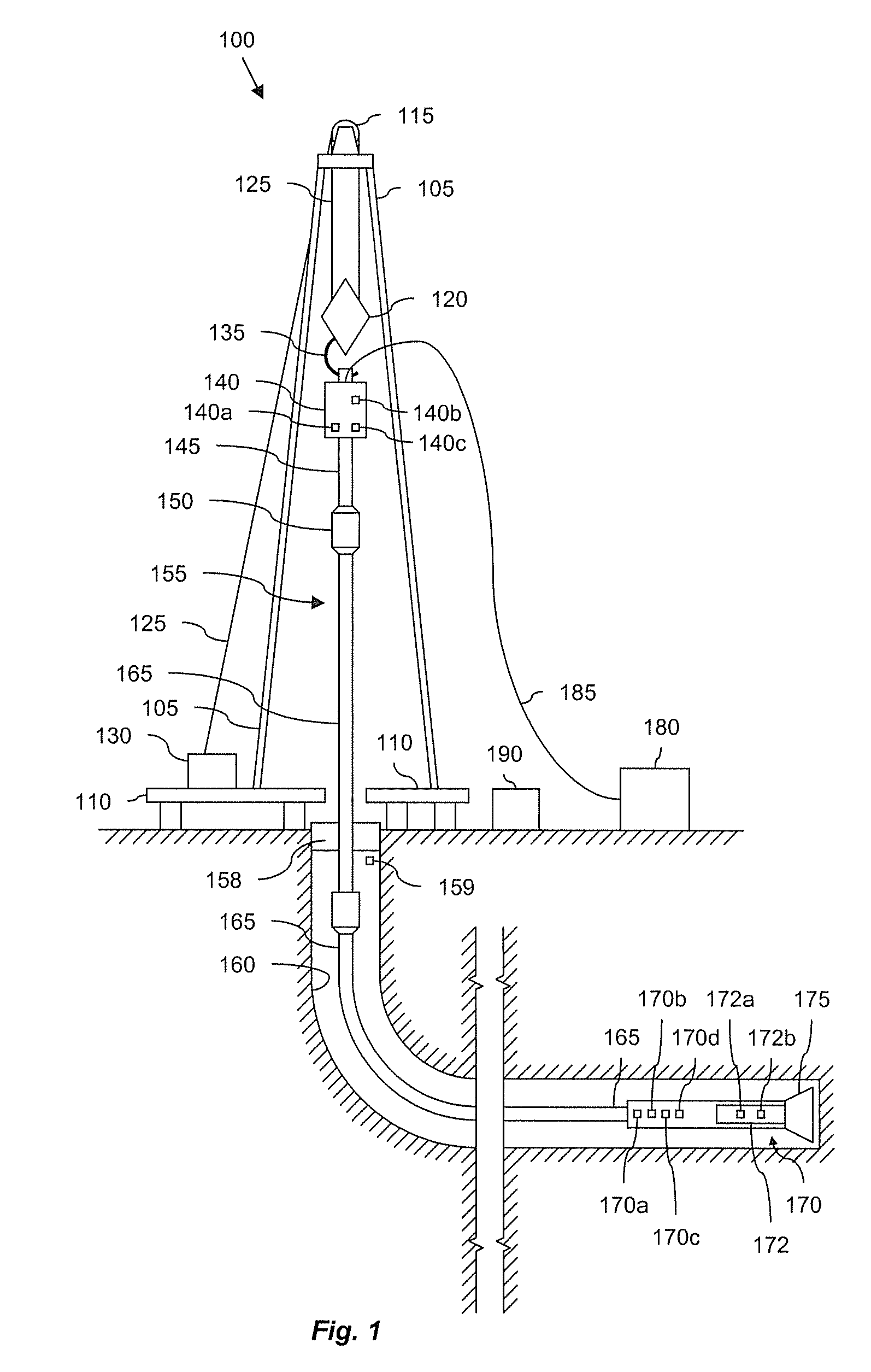
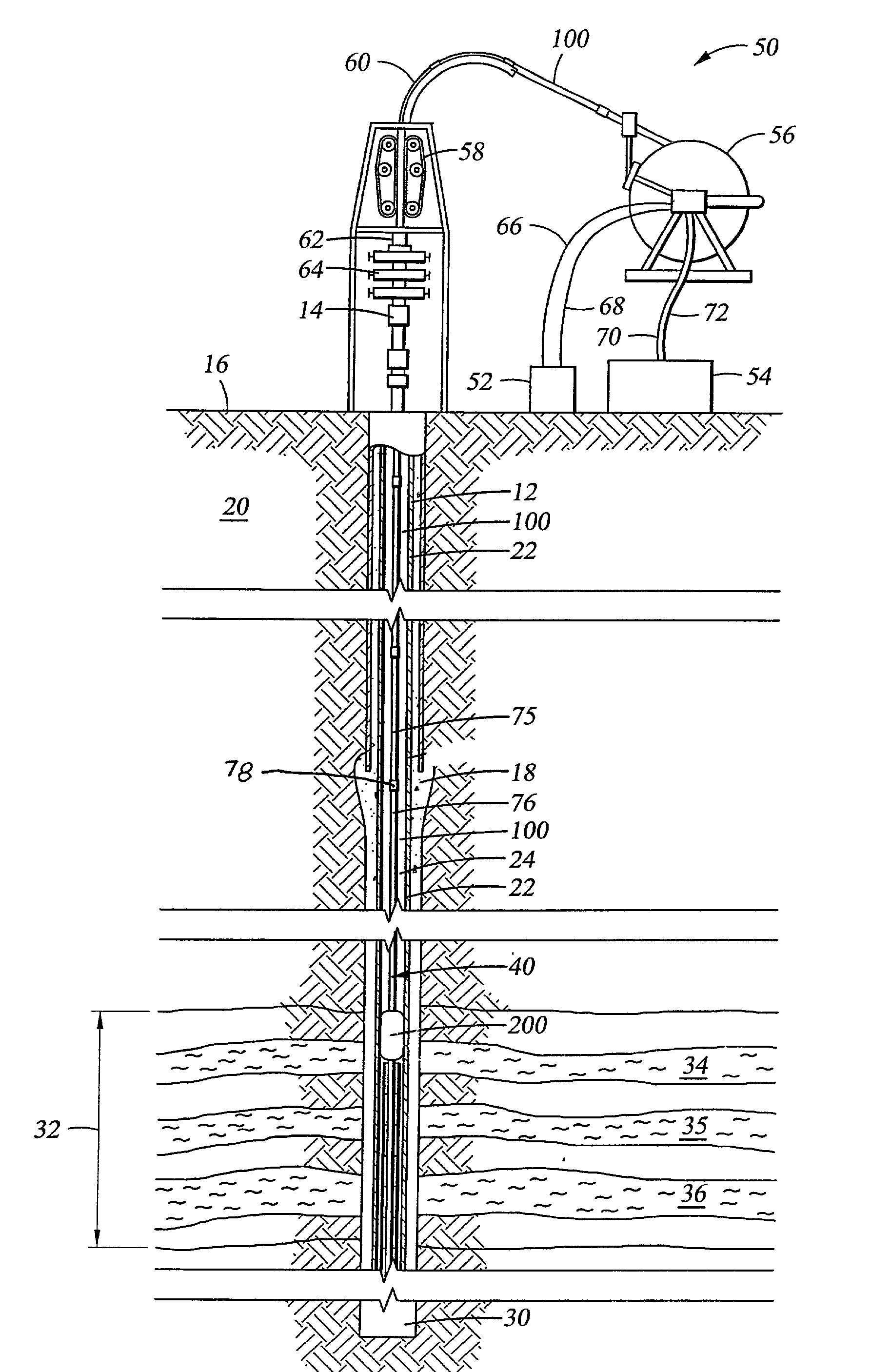
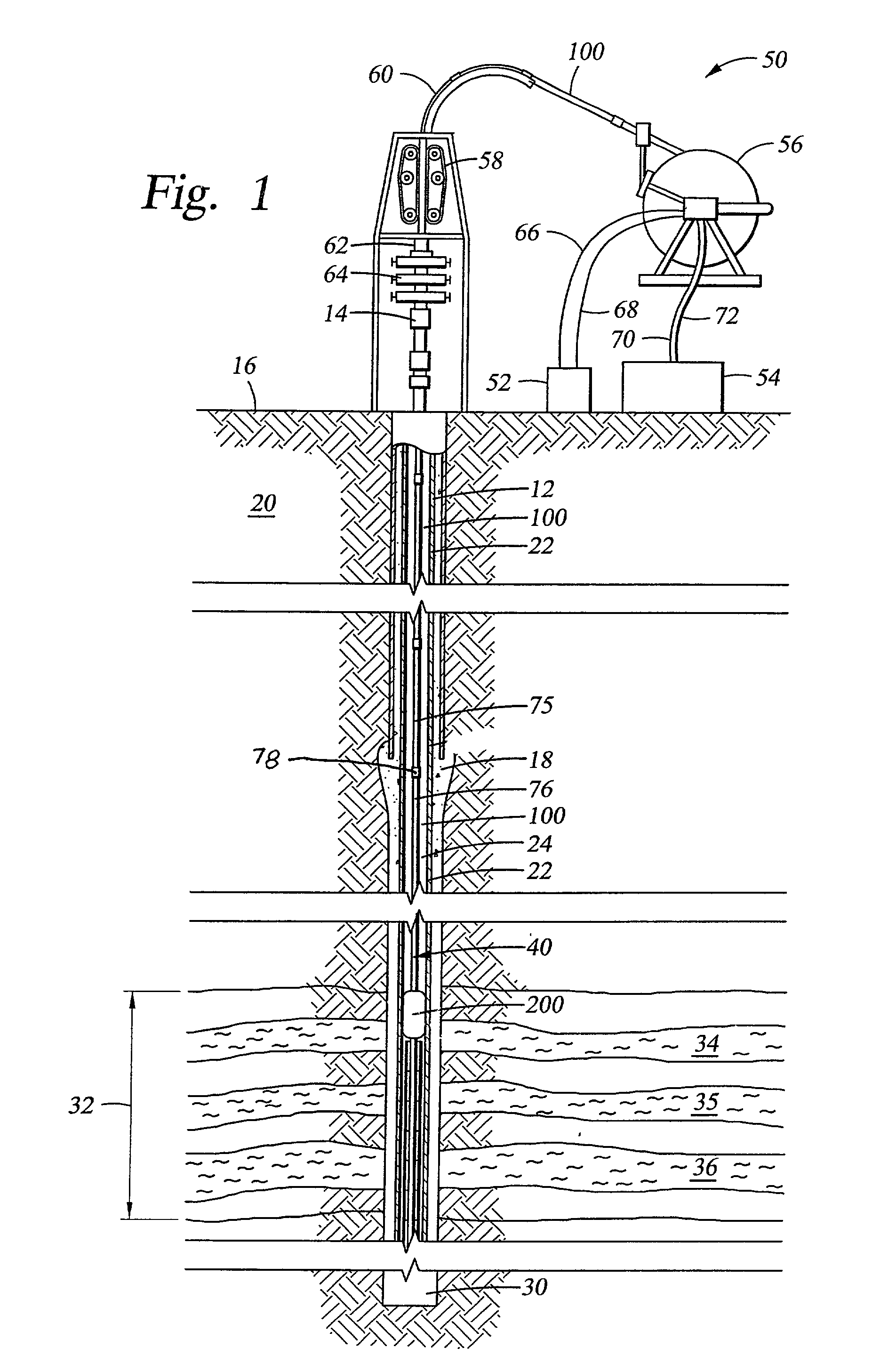
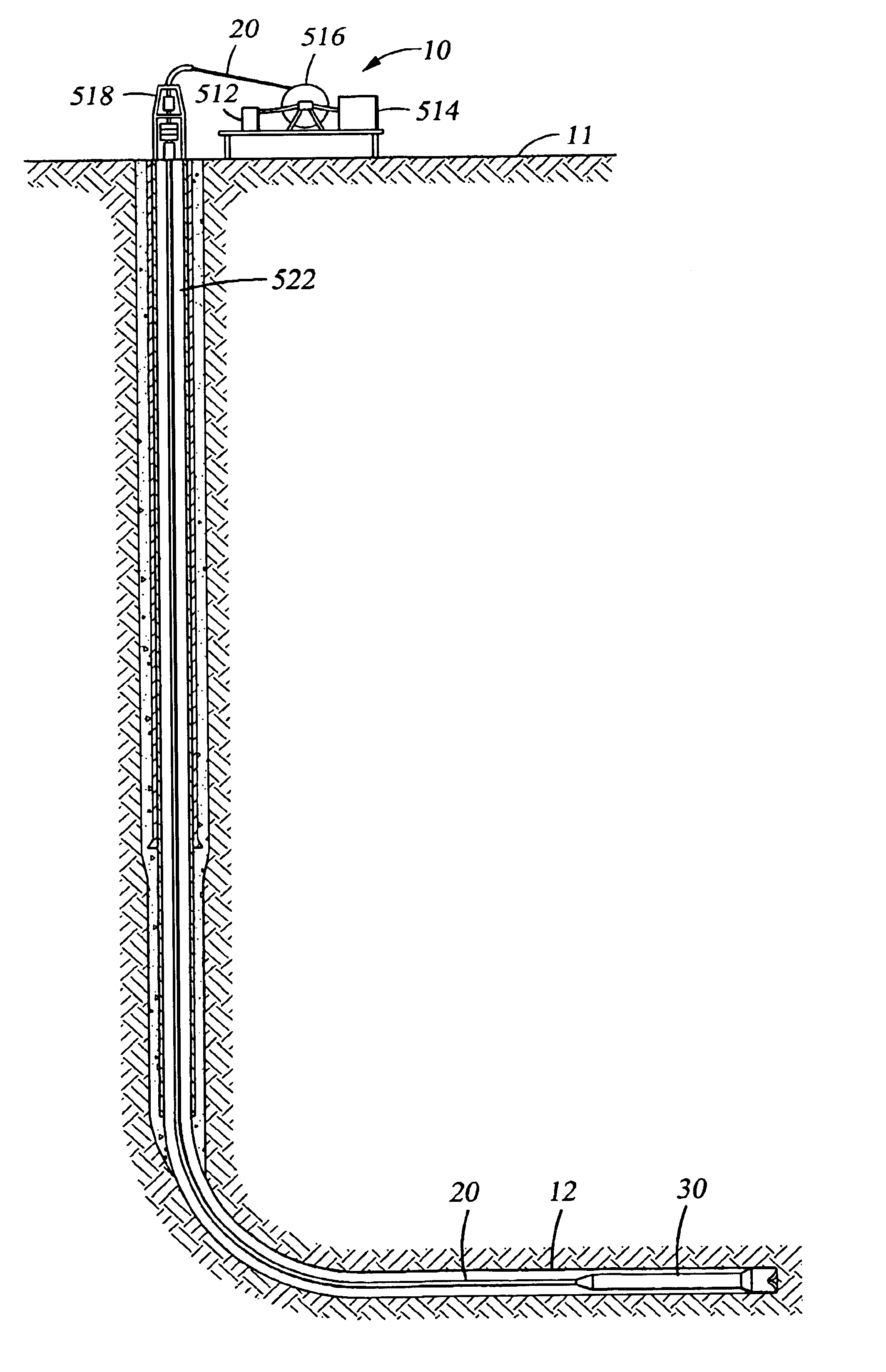
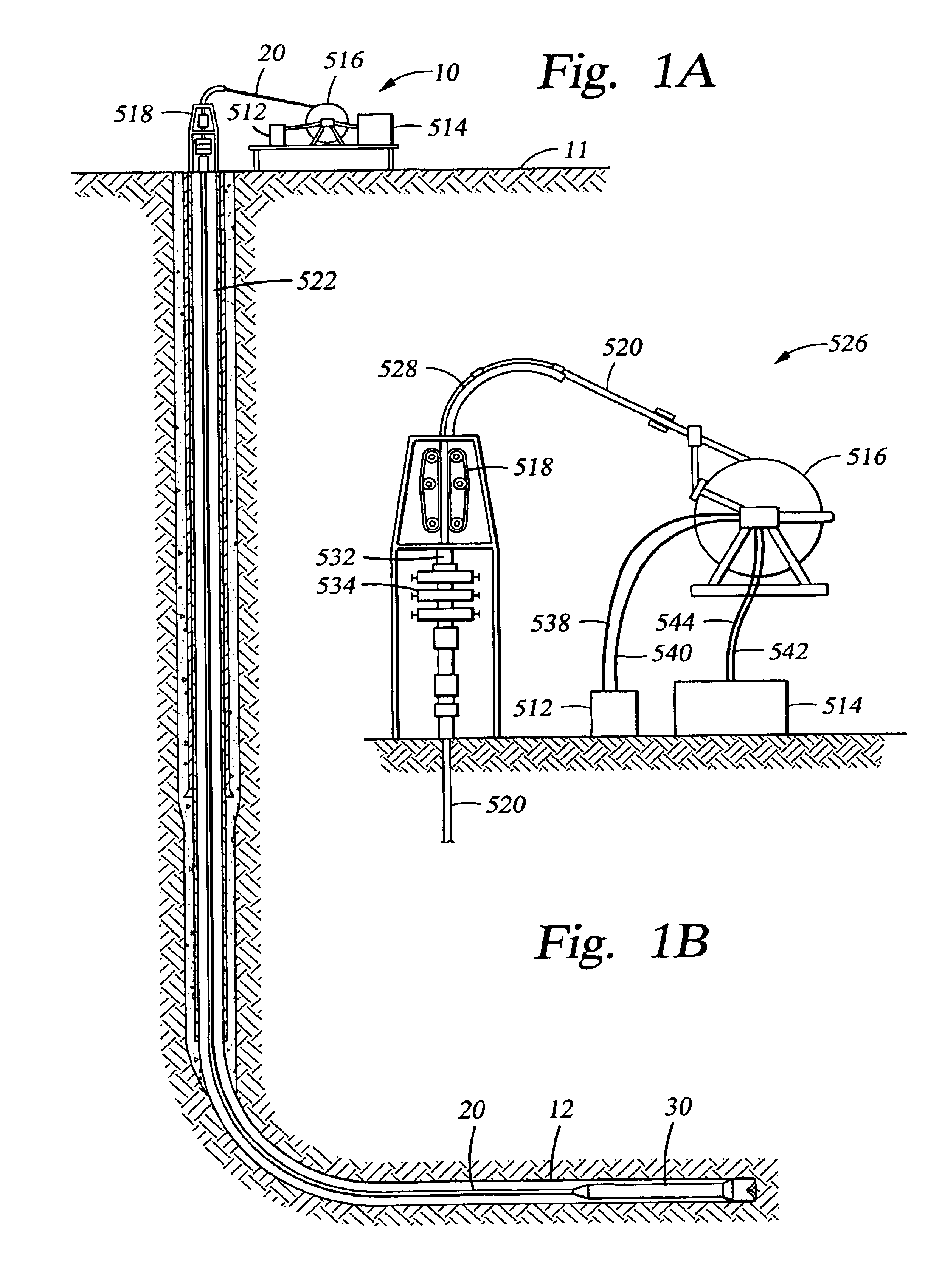
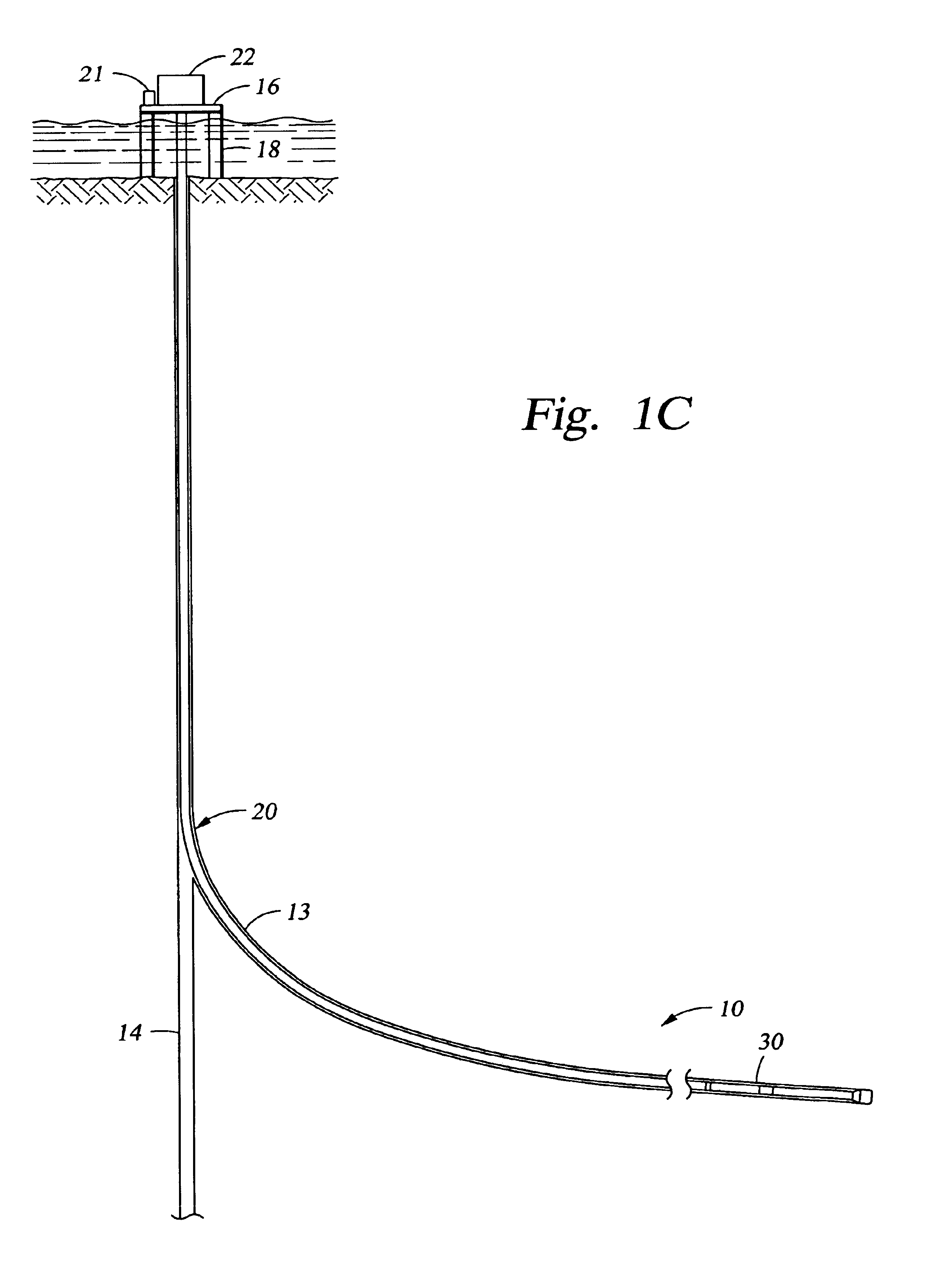
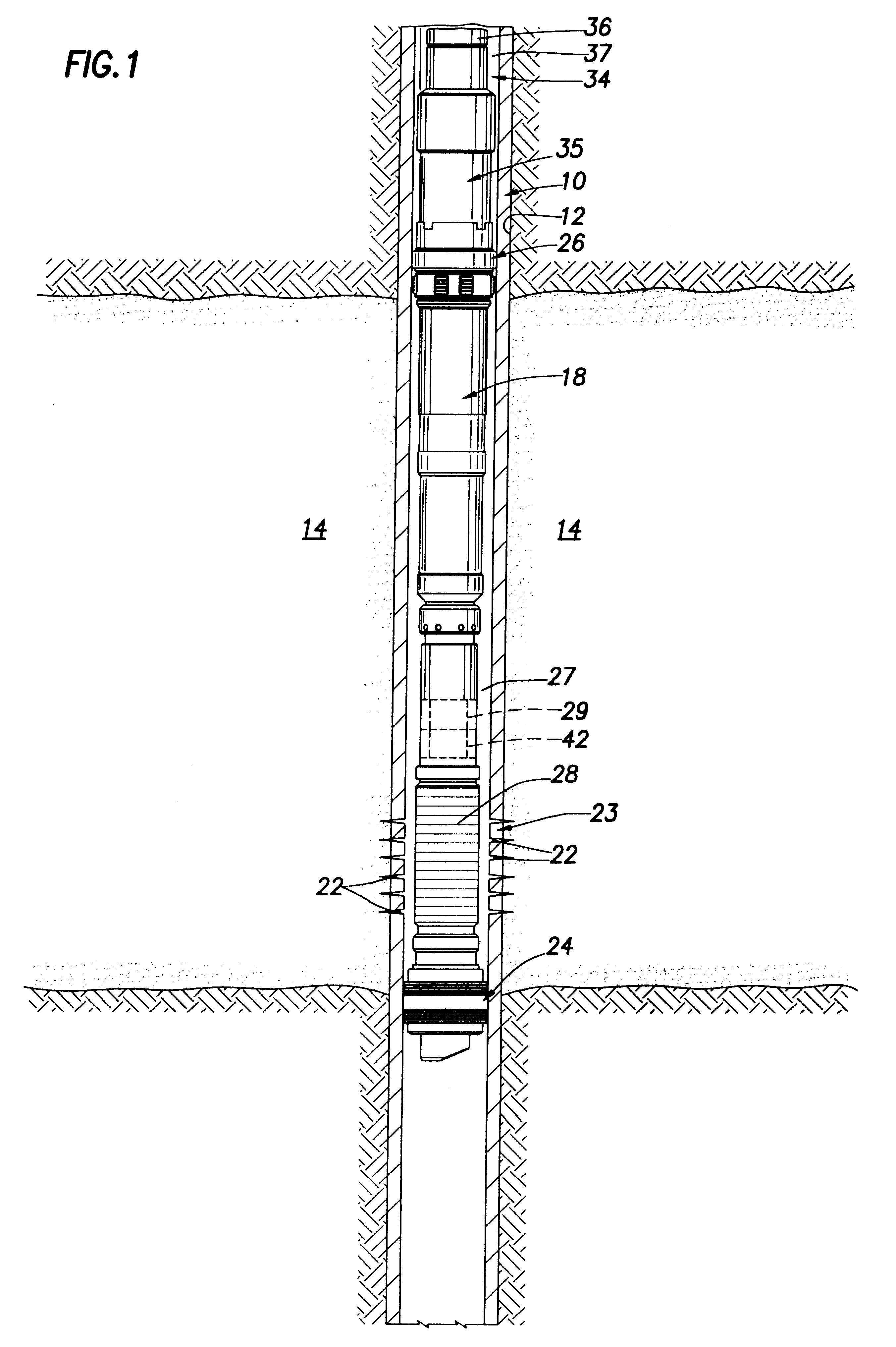
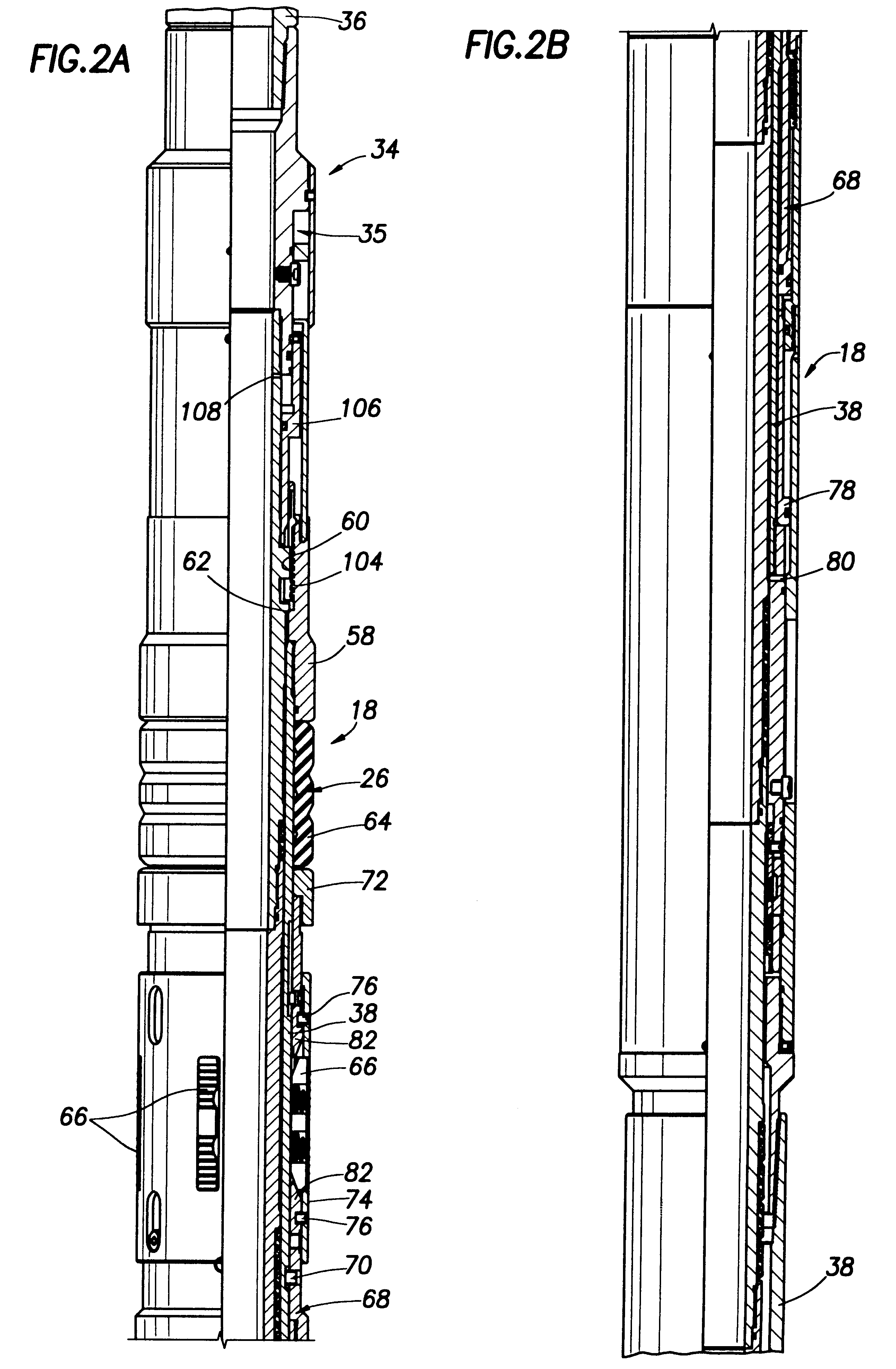
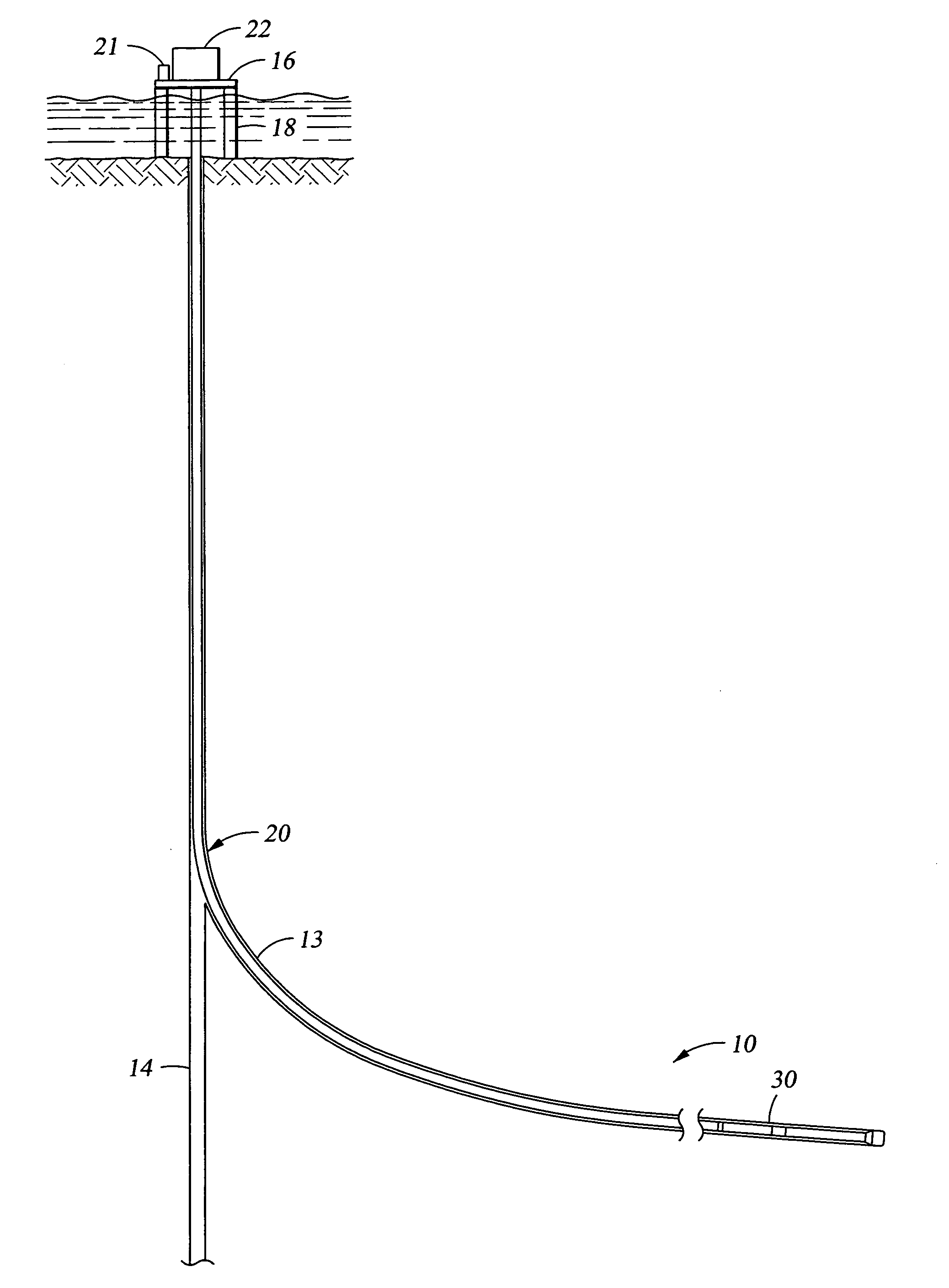
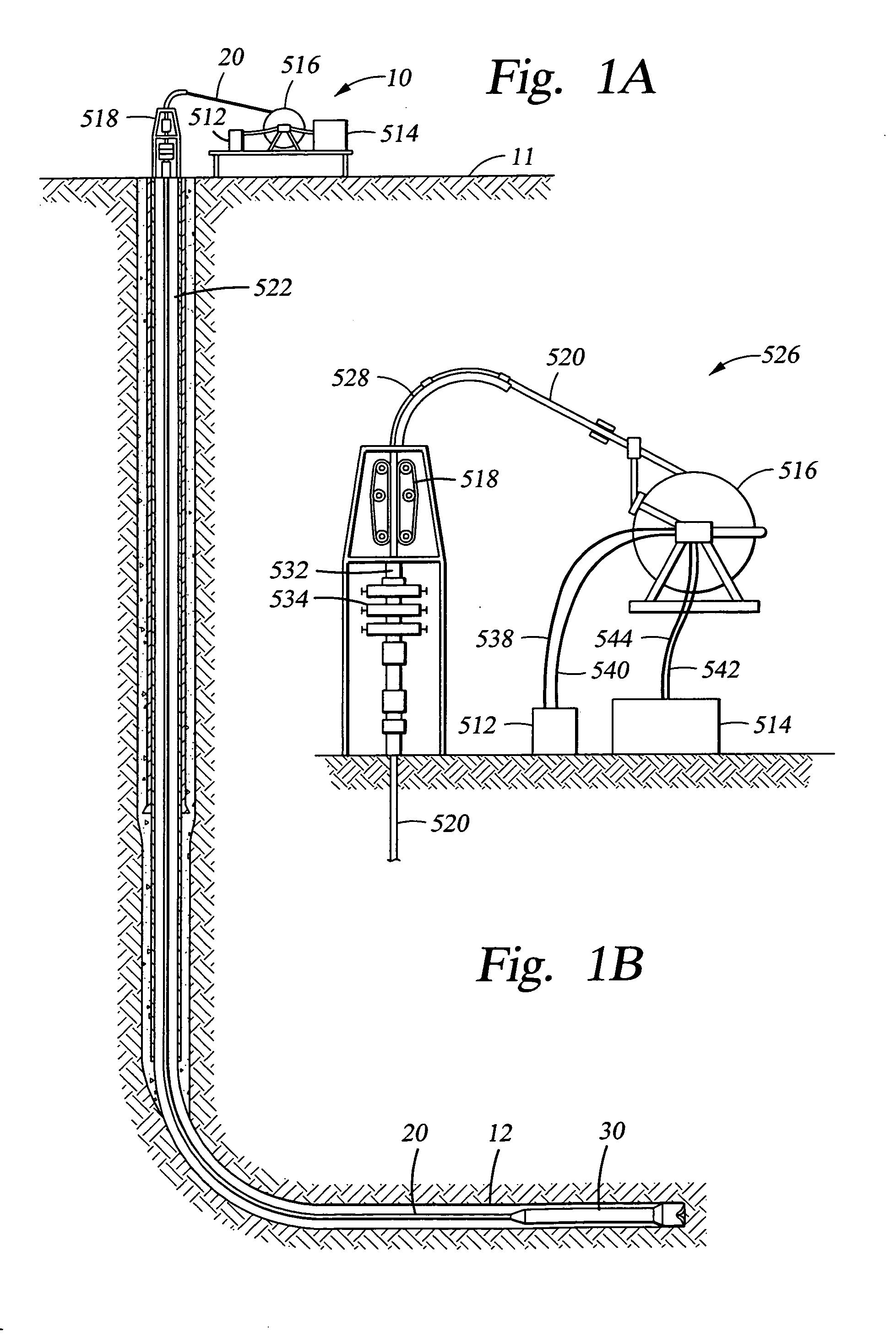
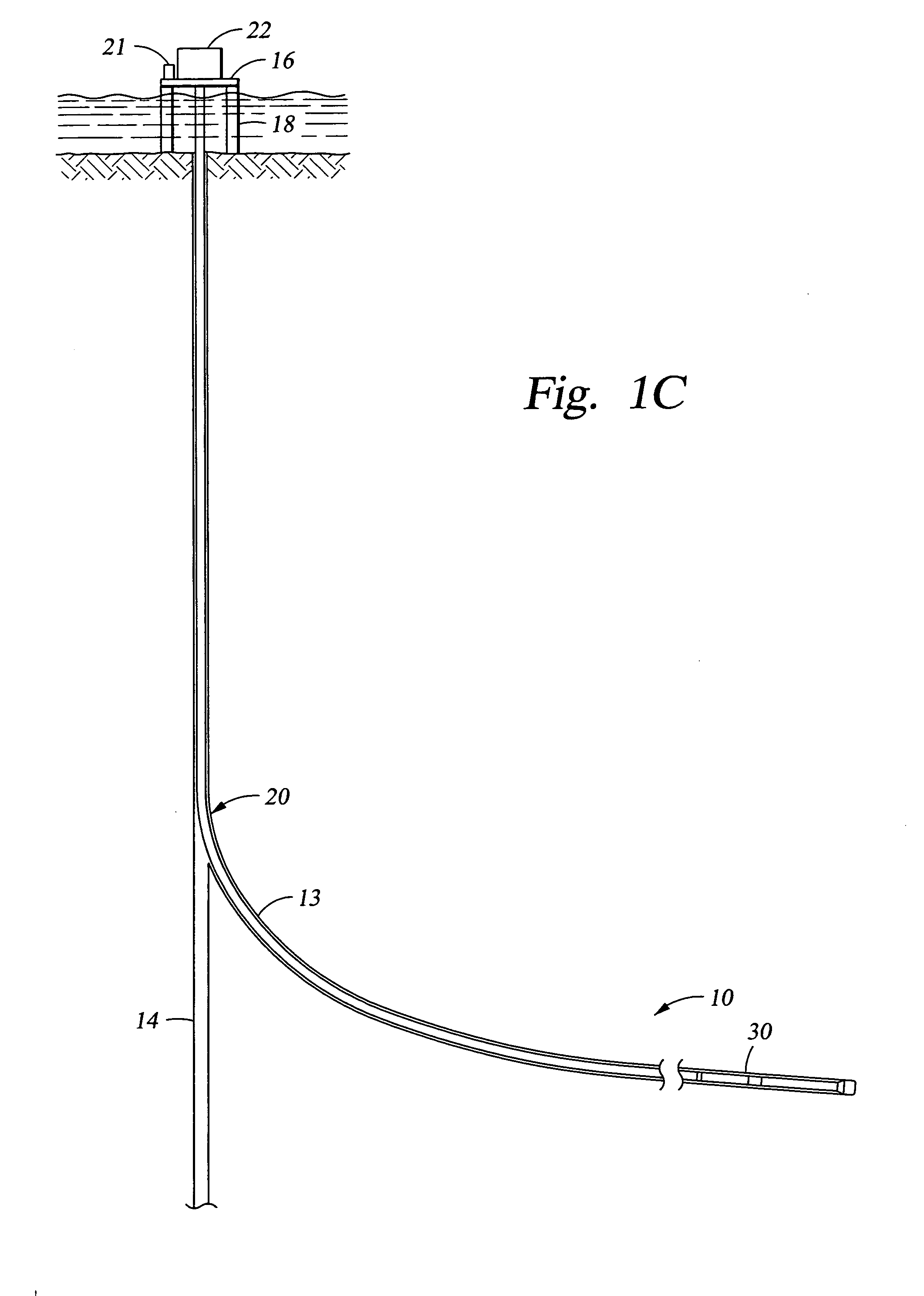
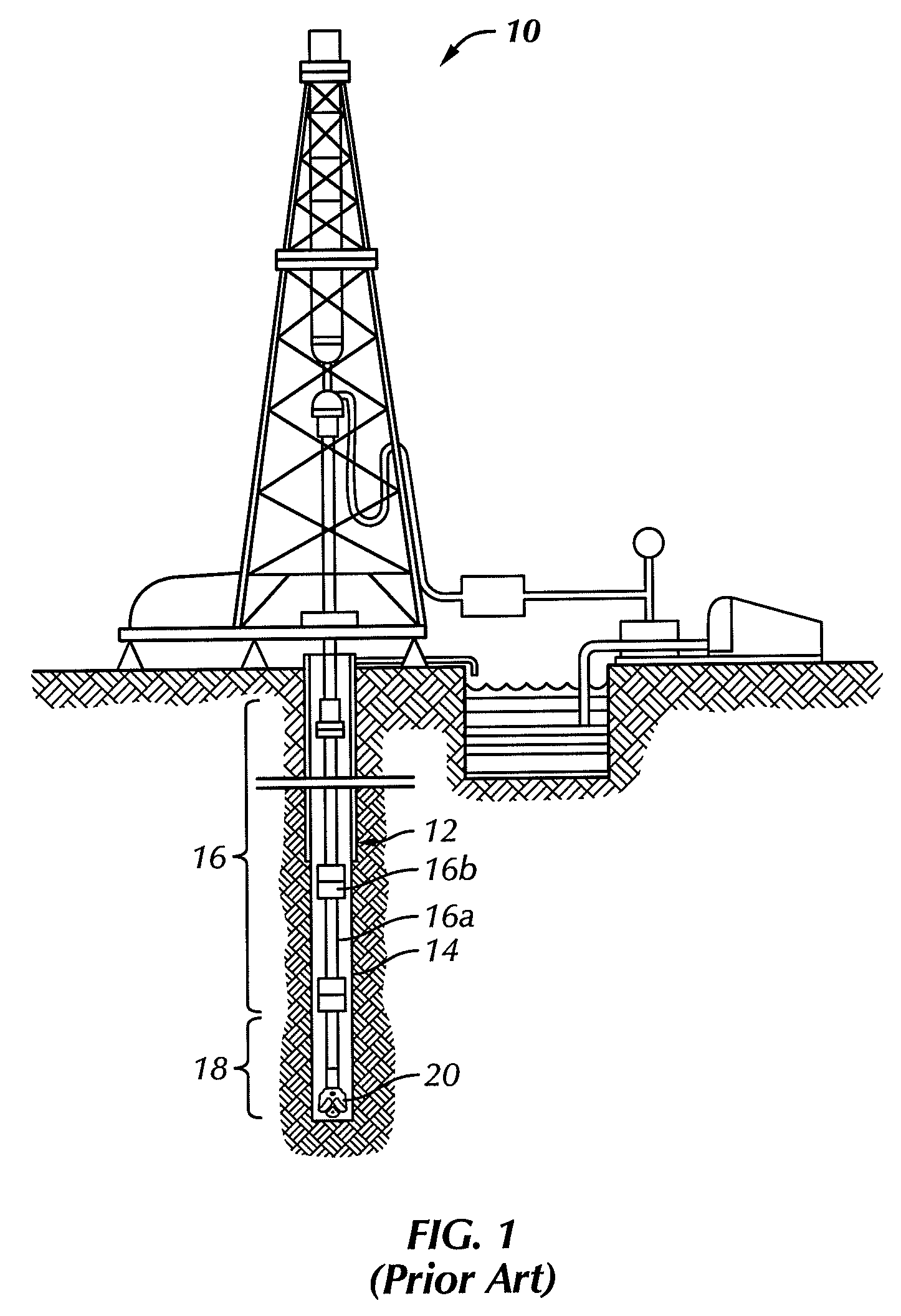
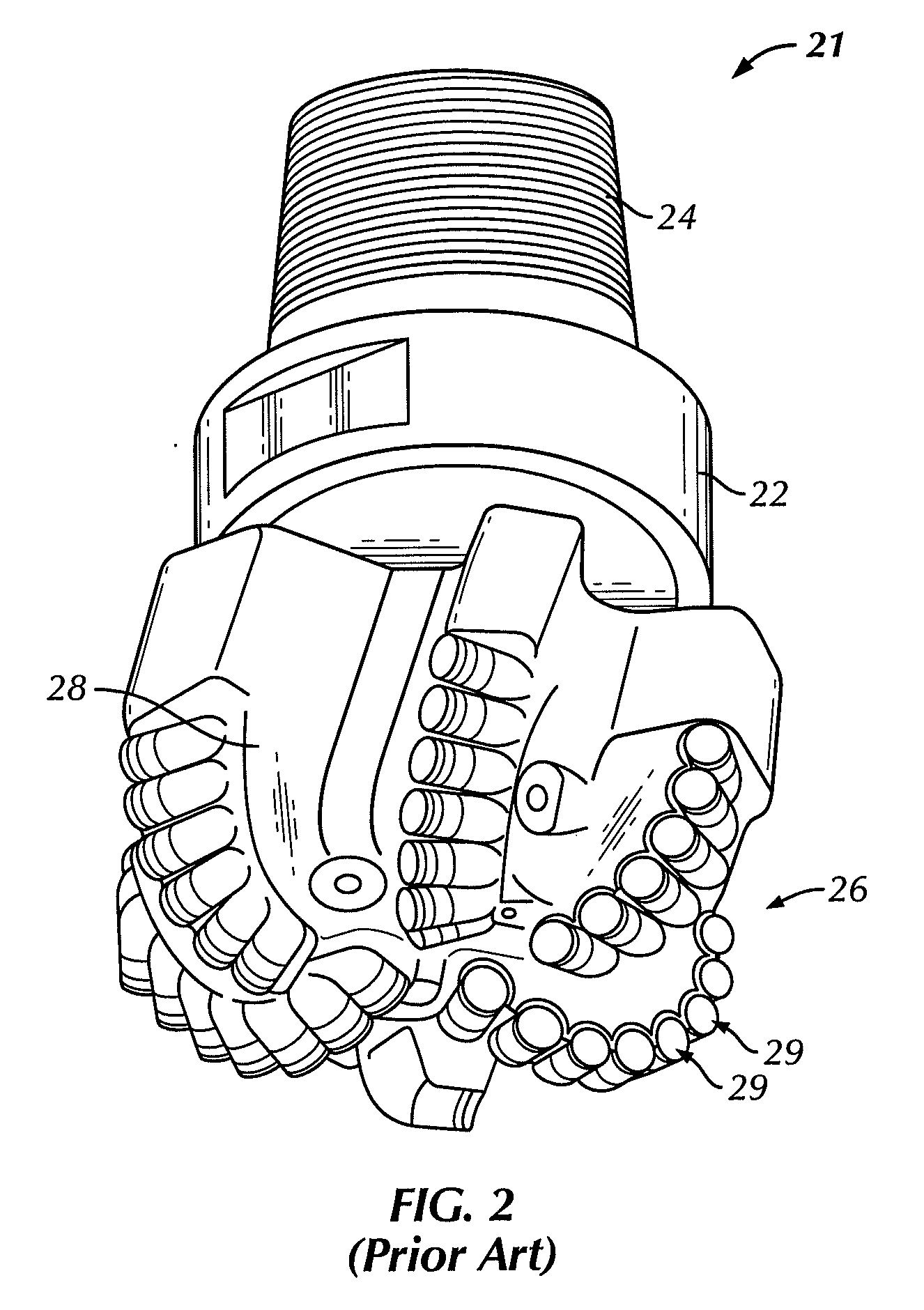
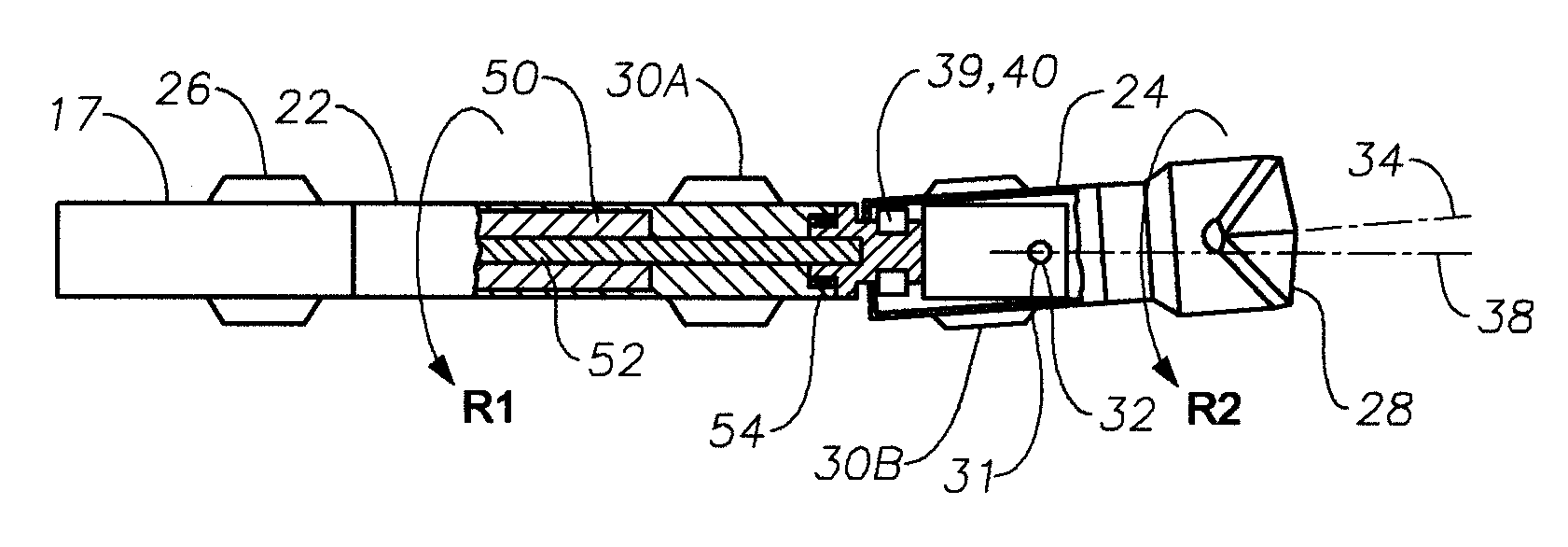
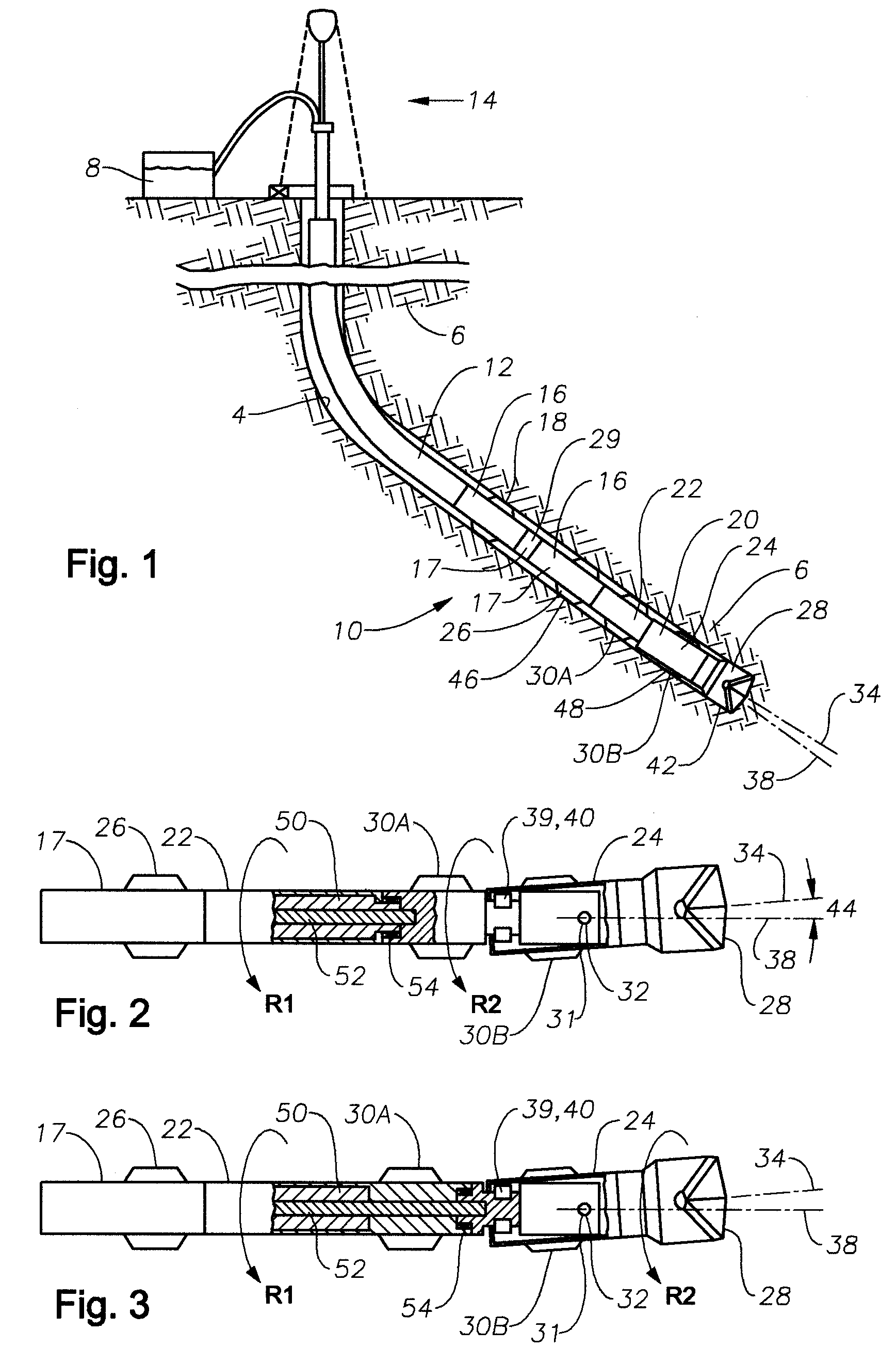
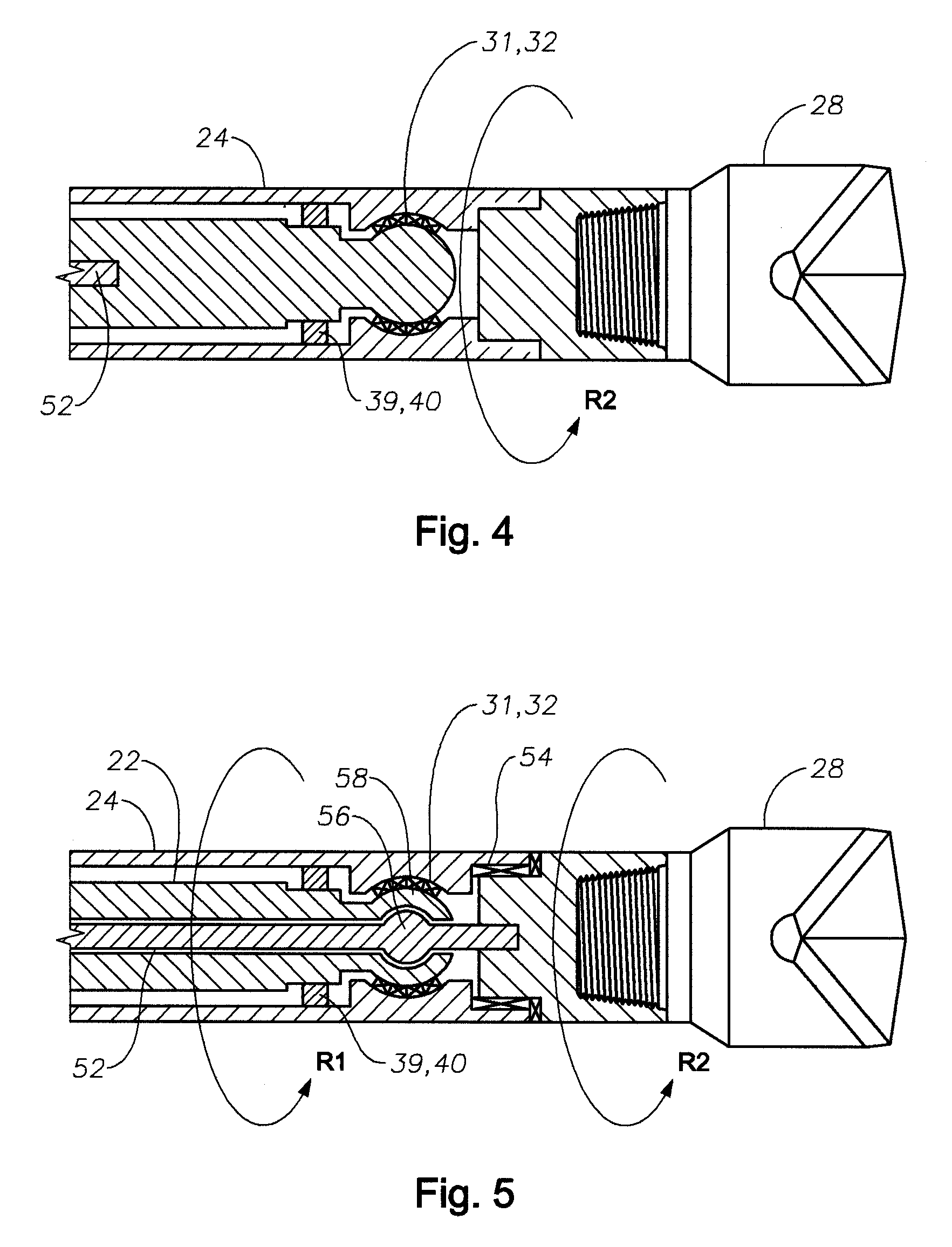
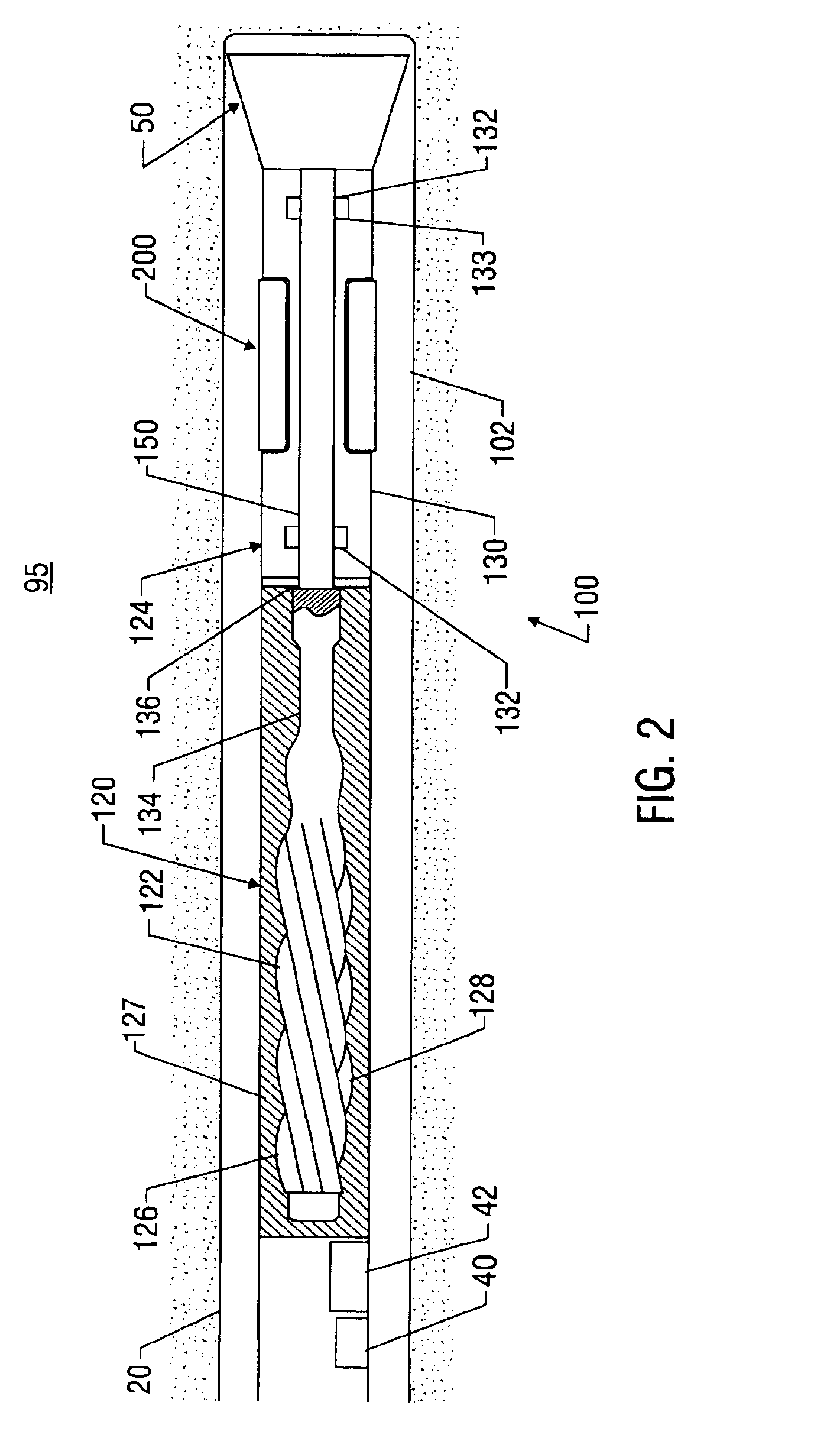
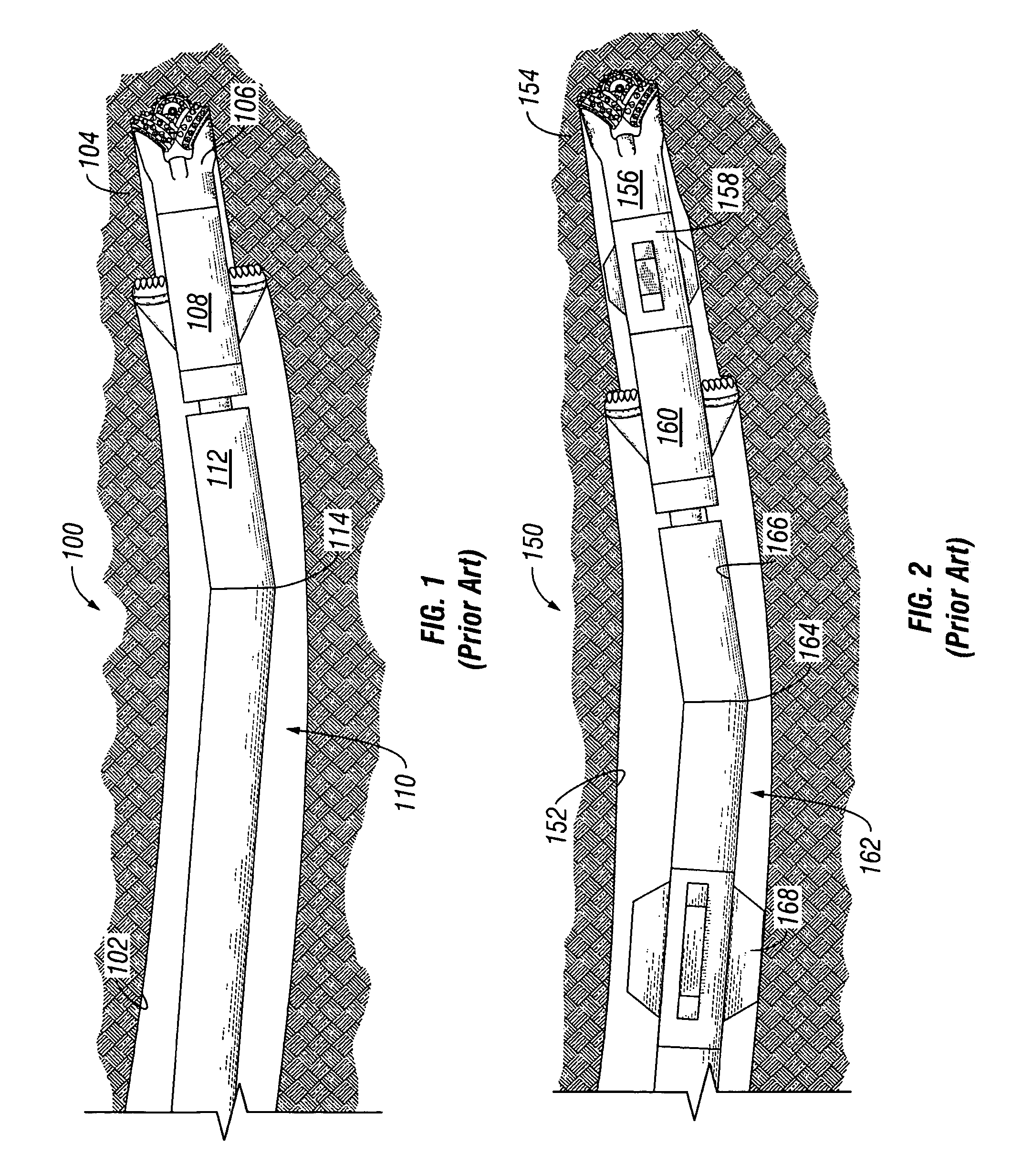
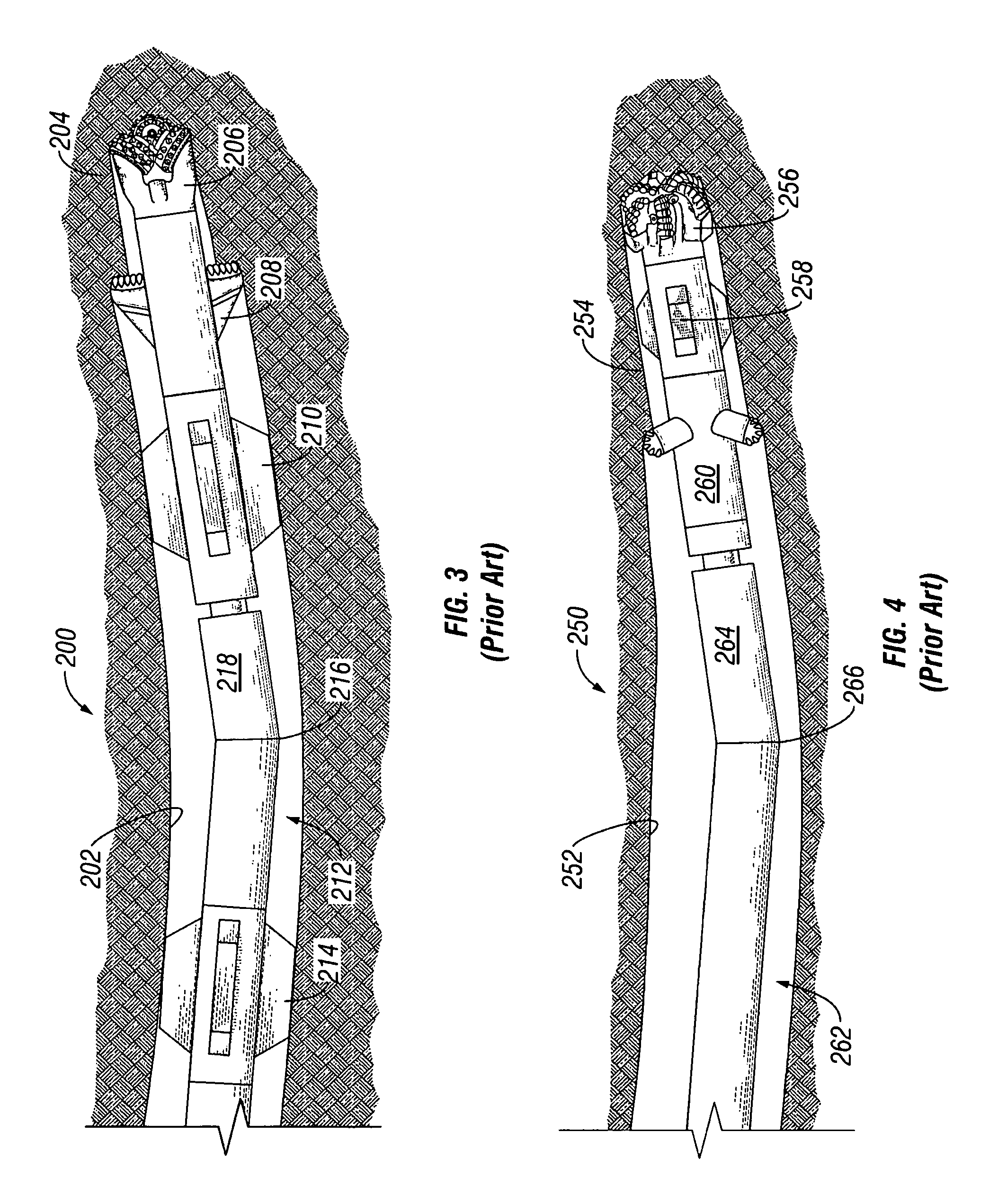
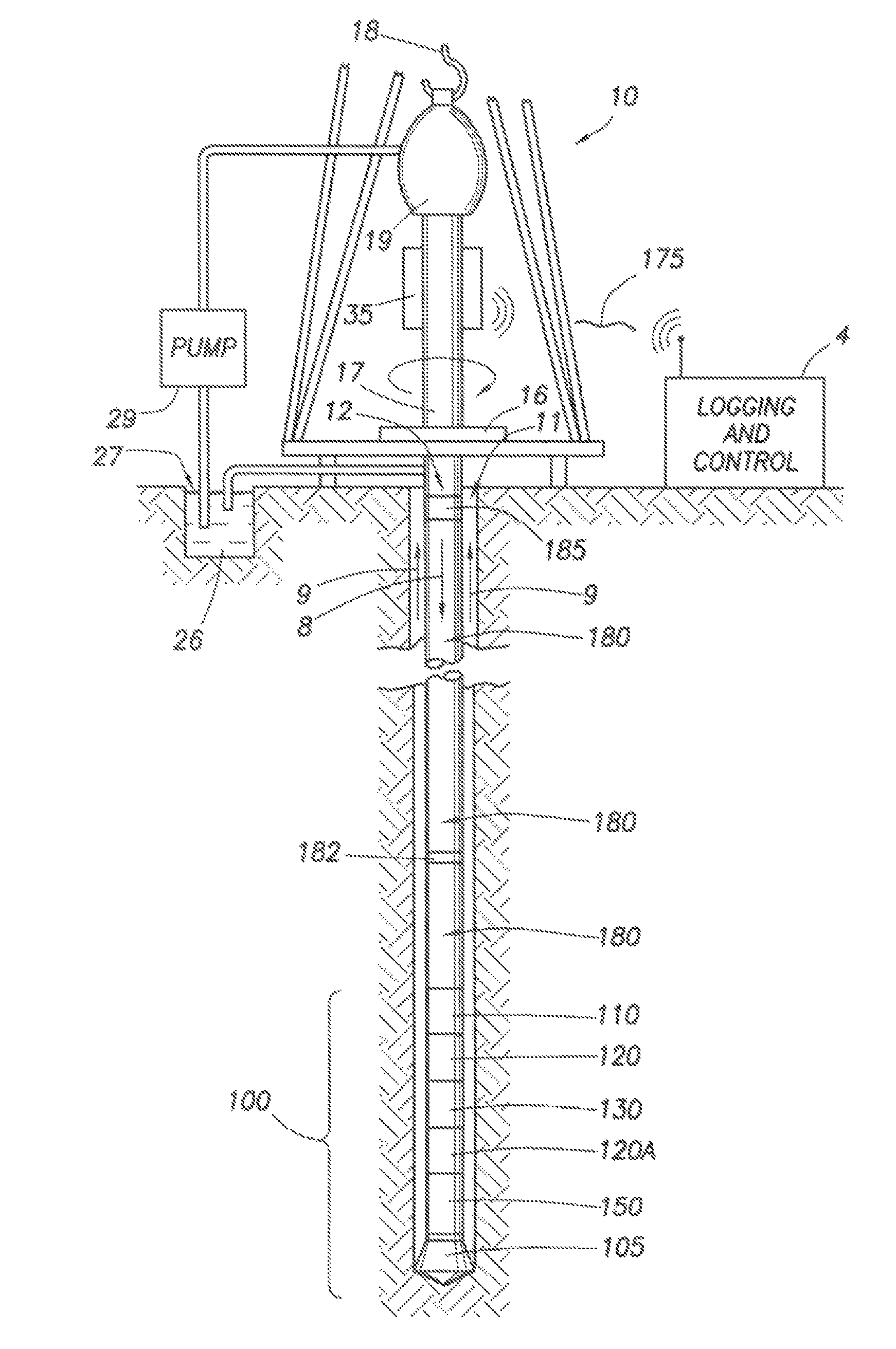
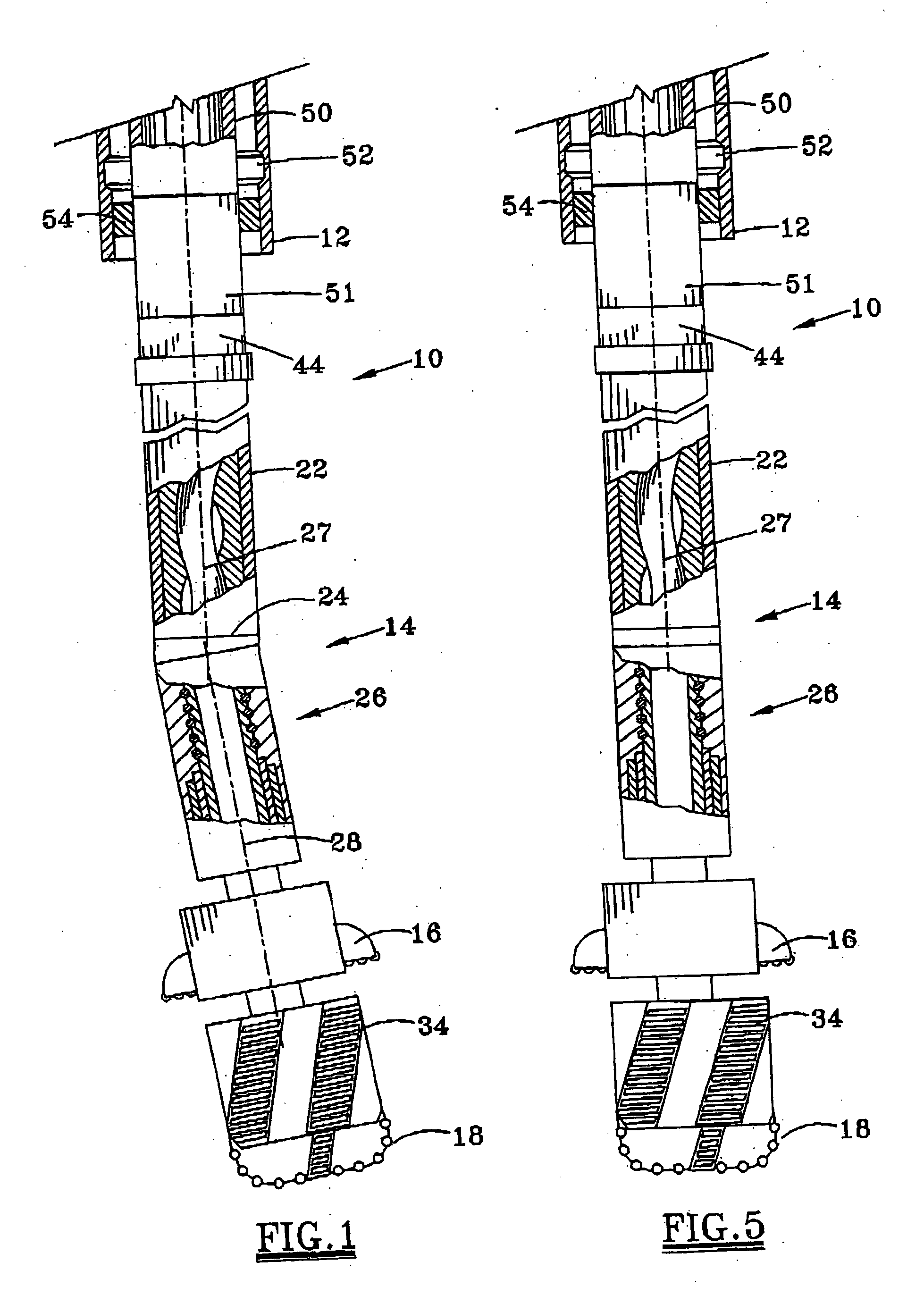
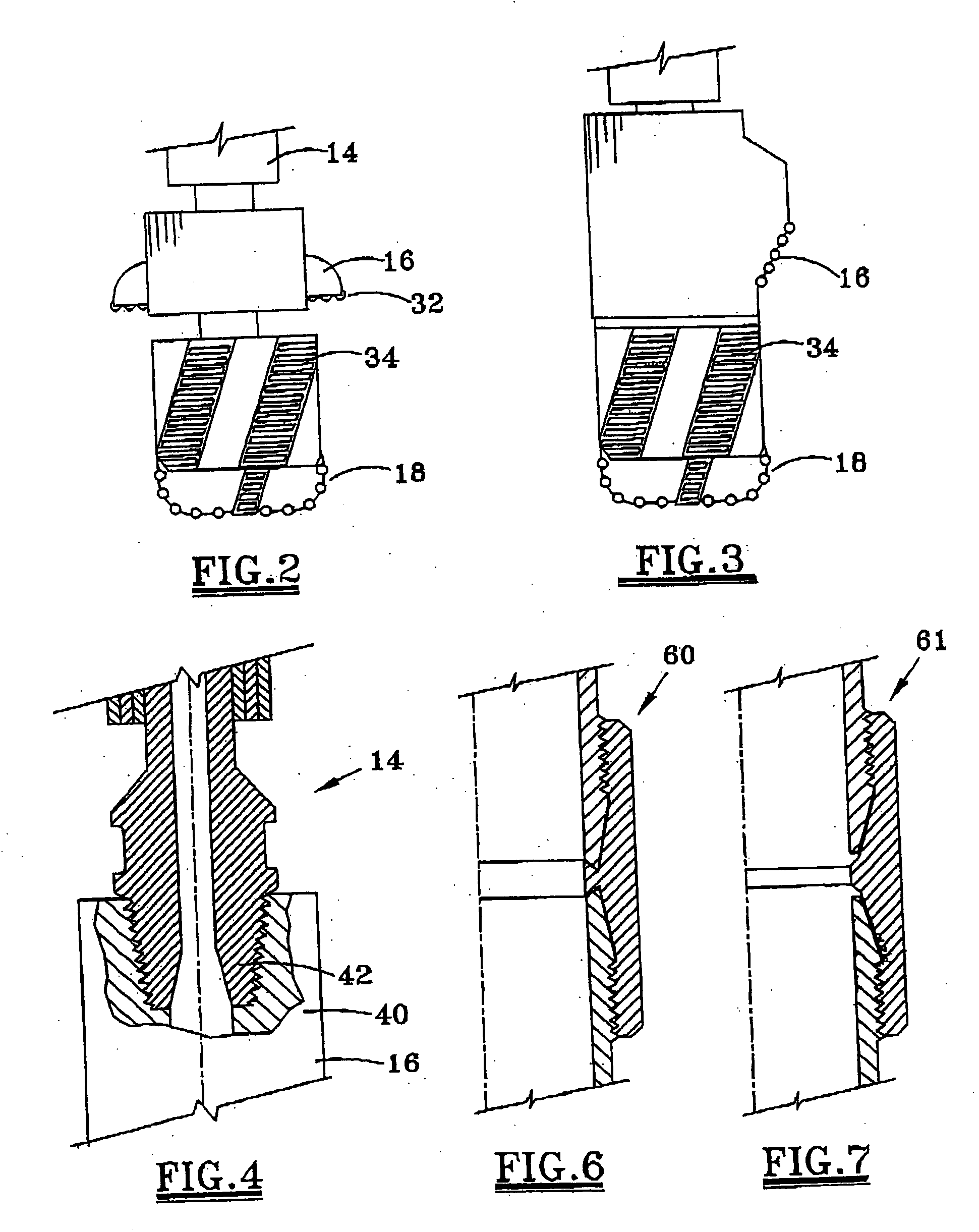
A bottom hole assembly (BHA) is a component of a drilling rig. It is the lowest part of the drill string, extending from the bit to the drill pipe. The assembly can consist of drill collars, subs such as stabilizers, reamers, shocks, hole-openers, and the bit sub and bit.
Automated directional drilling apparatus and methods
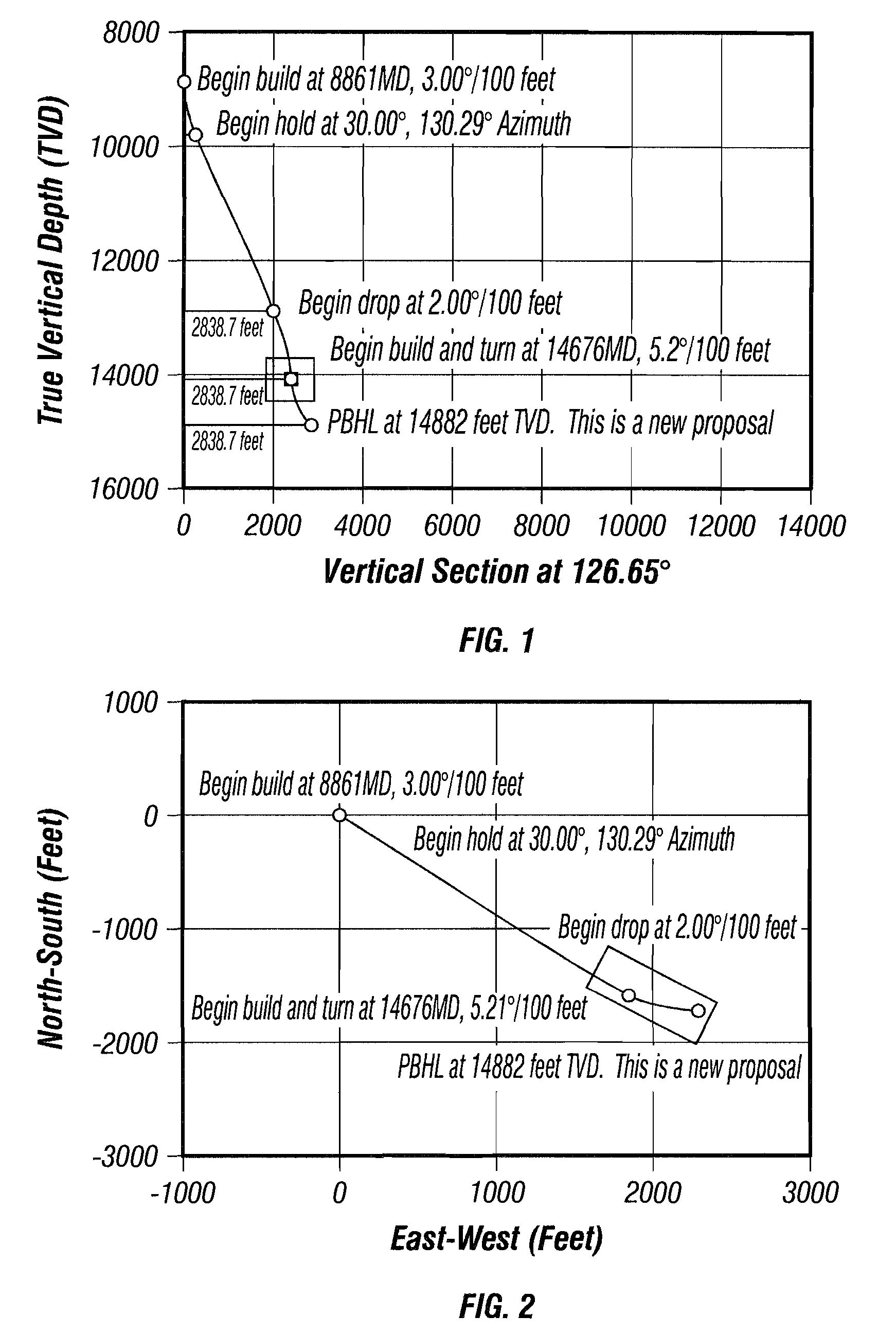
Methods and systems for drilling to a target location include a control system that receives an input comprising a planned drilling path to a target location and determines a projected location of a bottom hole assembly of a drilling system. The projected location of the bottom hole assembly is compared to the planned drilling path to determine a deviation amount. A modified drilling path is created to the target location as selected based on the amount of deviation from the planned drilling path, and drilling rig control signals that steer the bottom hole assembly of the drilling system to the target location along the modified drilling path are generated.
Owner:NABORS DRILLING TECH USA INC
Method of providing hydraulic/fiber conduits adjacent bottom hole assemblies for multi-step completions
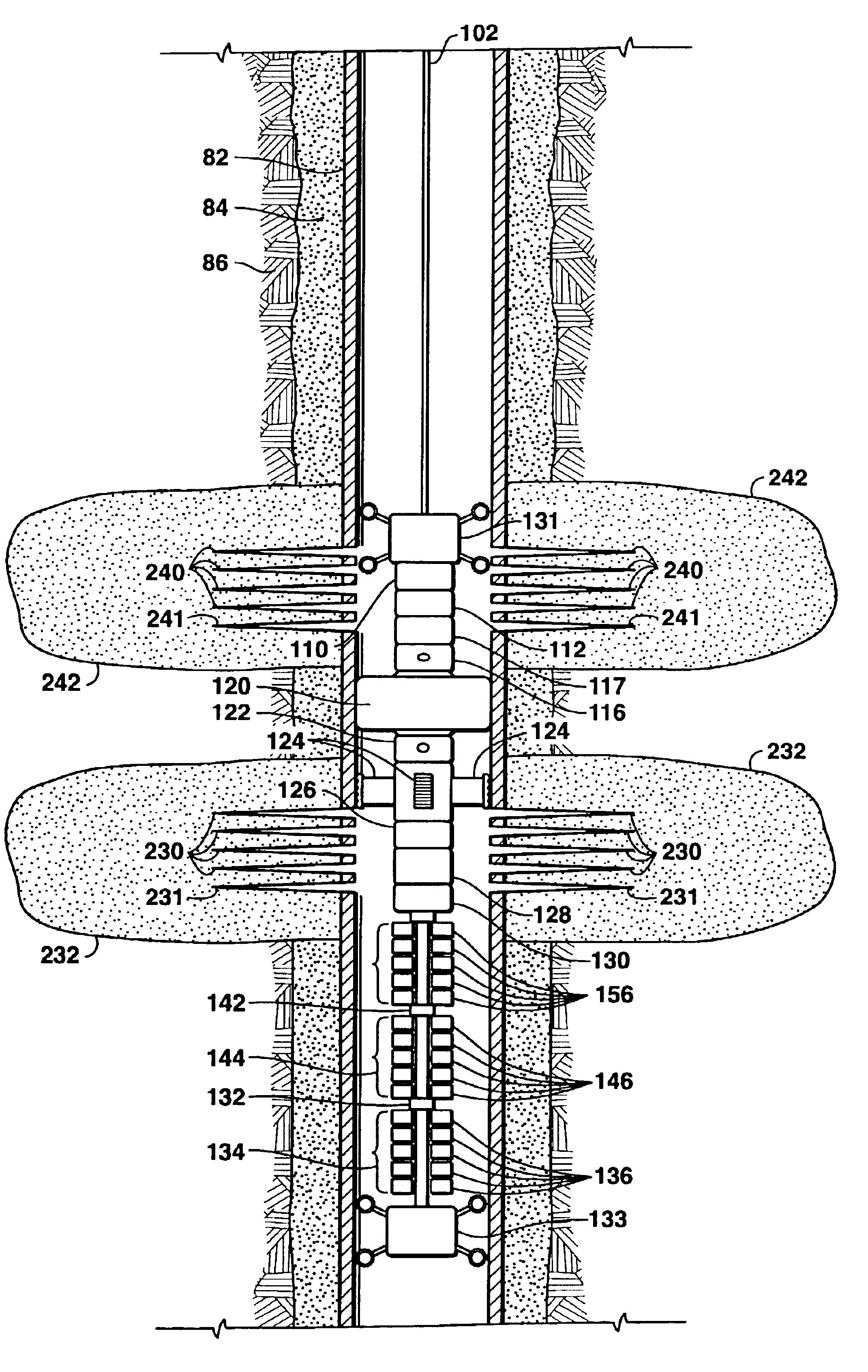
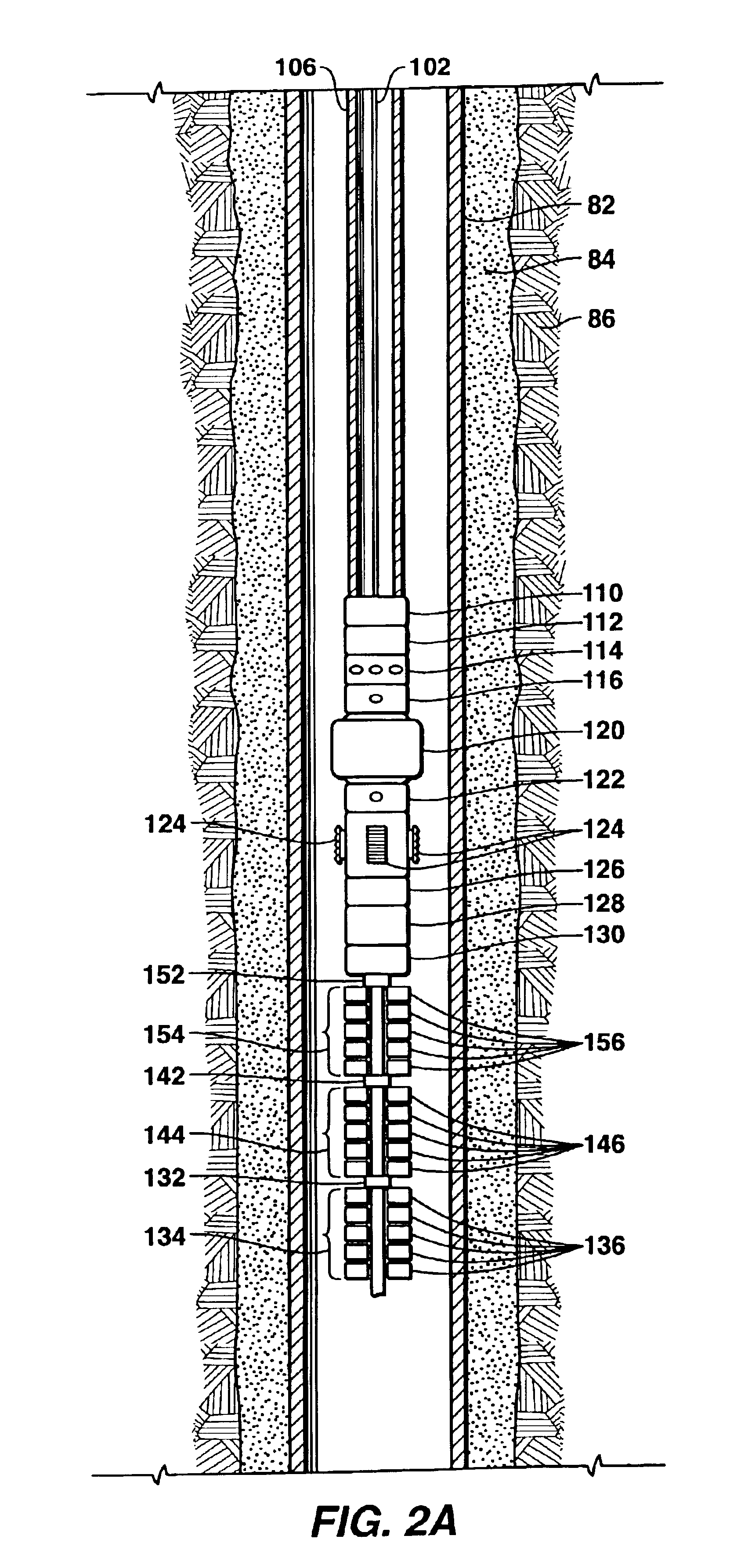
A technique for providing auxiliary conduits in multi-trip completions is disclosed. The technique has particular applicability to liner mounted screens which are to be gravel packed. In the preferred embodiment, a protective shroud is run with the gravel pack screens with the auxiliary conduits disposed in between. The auxiliary conduits terminate in a quick connection at a liner top packer. The gravel packing equipment can optionally be secured in a flow relationship to the auxiliary conduits so as to control the gravel packing operation. Subsequent to the removal of the specialized equipment, the production tubing can be run with an auxiliary conduit or conduits for connection down hole to the auxiliary conduits coming from the liner top packer for a sealing connection. Thereafter, during production various data on the well can be obtained in real time despite the multiple trips necessary to accomplish completion. The various completion and / or production activities can also be accomplished using the auxiliary conduits such as actuation of down hole flow control devices, chemical injection, pressure measurement, distributed temperature sensing through fiber optics, as well as other down hole parameters.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Well treatment apparatus and method
InactiveUS20040040707A1Improve reliabilityImprove securitySurveyDrilling rodsElectric power transmissionElectrical conductor
Apparatus and methods are disclosed for sequentially treating multiple zones in underground formation in a single trip of the well treatment work string. In the one embodiment, the work string includes composite tubing having electrical conductors embedded within the walls, the conductors enabling power transmission and two way communication between the surface and the sensor or detectors downhole so that real time data can be sensed and communicated. Isolation packers are actuated via electrical signals from the surface communicated to the bottom hole assembly via the conductors. A detector located in the bottom hole assembly may be provided to detect perforations or other anomalies in the casing, such as joints, enabling the surface controller to position packers properly in blank segments of casing so that well intervals can be properly isolated and the adjacent formation effectively treated.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
Well system
InactiveUS6923273B2Excessive vibrationLess expensiveElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingDrilling rodsElectrical conductorEngineering
The drilling system includes a work string supporting a bottom hole assembly. The work string including lengths of pipe having a non-metallic portion. The work string preferably includes a composite coiled tubing having a fluid impermeable liner, multiple load carrying layers, and a wear layer. Multiple electrical conductors and data transmission conductors may be embedded in the load carrying layers for carrying current or transmitting data between the bottom hole assembly and the surface. The bottom hole assembly includes a bit, a gamma ray and inclinometer instrument package, a steerable assembly, an electronics section, a transmission, and a power section for rotating the bit. It may or may not include a propulsion system. The drilling system may be a gravity based drilling system that does include a propulsion system. Various motive means may be provided such as gravity, to apply weight on the bit.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
Ball drop circulation valve
A downhole tool can perform a series of operations with balls of the same size where movement caused by pressuring up on the first ball positions the next seat to accept another ball just like it. In a preferred embodiment a circulation sub is run in with a port closed and a first seat comprising of collets pushed together and preferably lined with a sleeve are in position to accept a first ball to perform a downhole operation and thereafter pass the ball and open the port. The act of opening the port gives support, by reducing their dimension, to the next assembly of collets also preferably lined with a sleeve so that they are energized to accept the same size ball. Pressuring up on the second ball can shift another sleeve to close the circulation port. The tool is modular and more than one module can be deployed in a given bottom hole assembly.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES OILFIELD OPERATIONS LLC
Bidirectional drill string telemetry for measuring and drilling control
The disclosure has application for use in conjunction with an operation of drilling an earth borehole using: a drilling rig, a drill string having its generally upper end mechanically coupleable with and suspendable from the drilling rig, and a bottom hole assembly adjacent the lower end the drill string, the bottom hole assembly including a drill bit at its lower end. A method is set forth for obtaining information about at least one parameter sensed at the bottom hole assembly, including the following steps: providing at least one measuring device in the bottom hole assembly, the at least one measuring device producing measurement data representative of a measured condition at the bottom hole assembly; providing an uphole processor system at the earth's surface; providing a drill string telemetry system coupled with the at least one measuring device and coupled with the uphole processor system; and transmitting the data from the measuring device to the uphole processor system via the drill string telemetry system.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
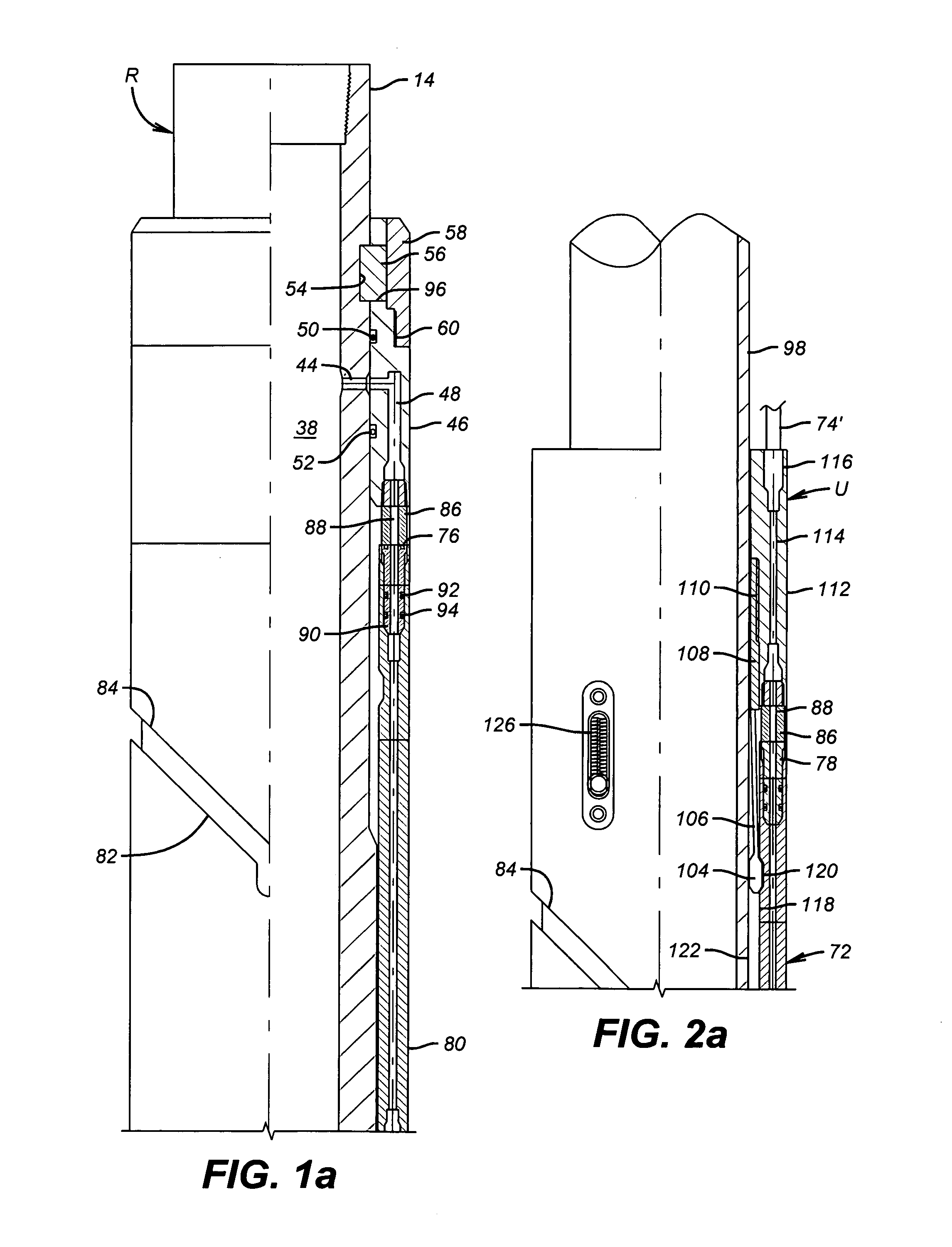
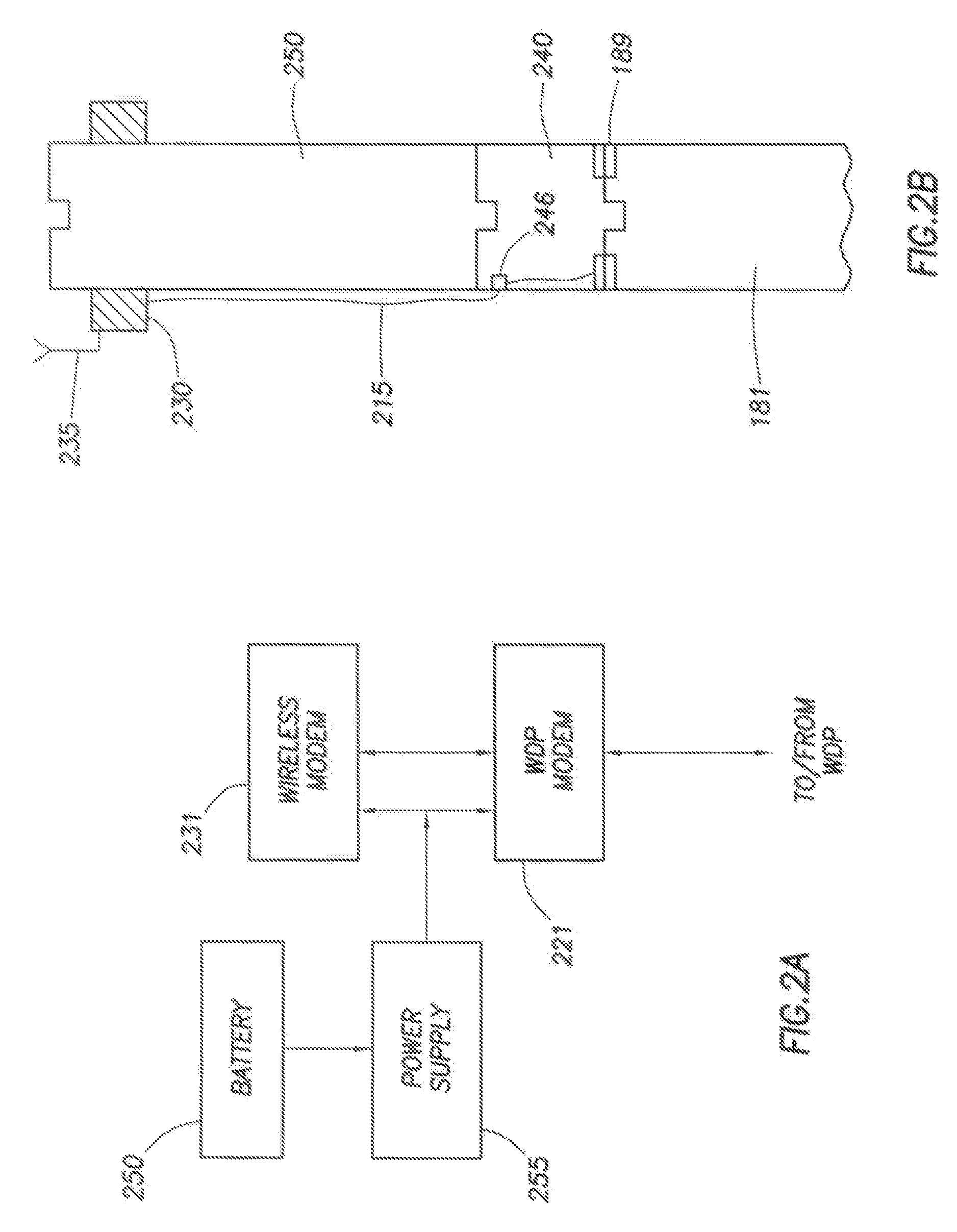
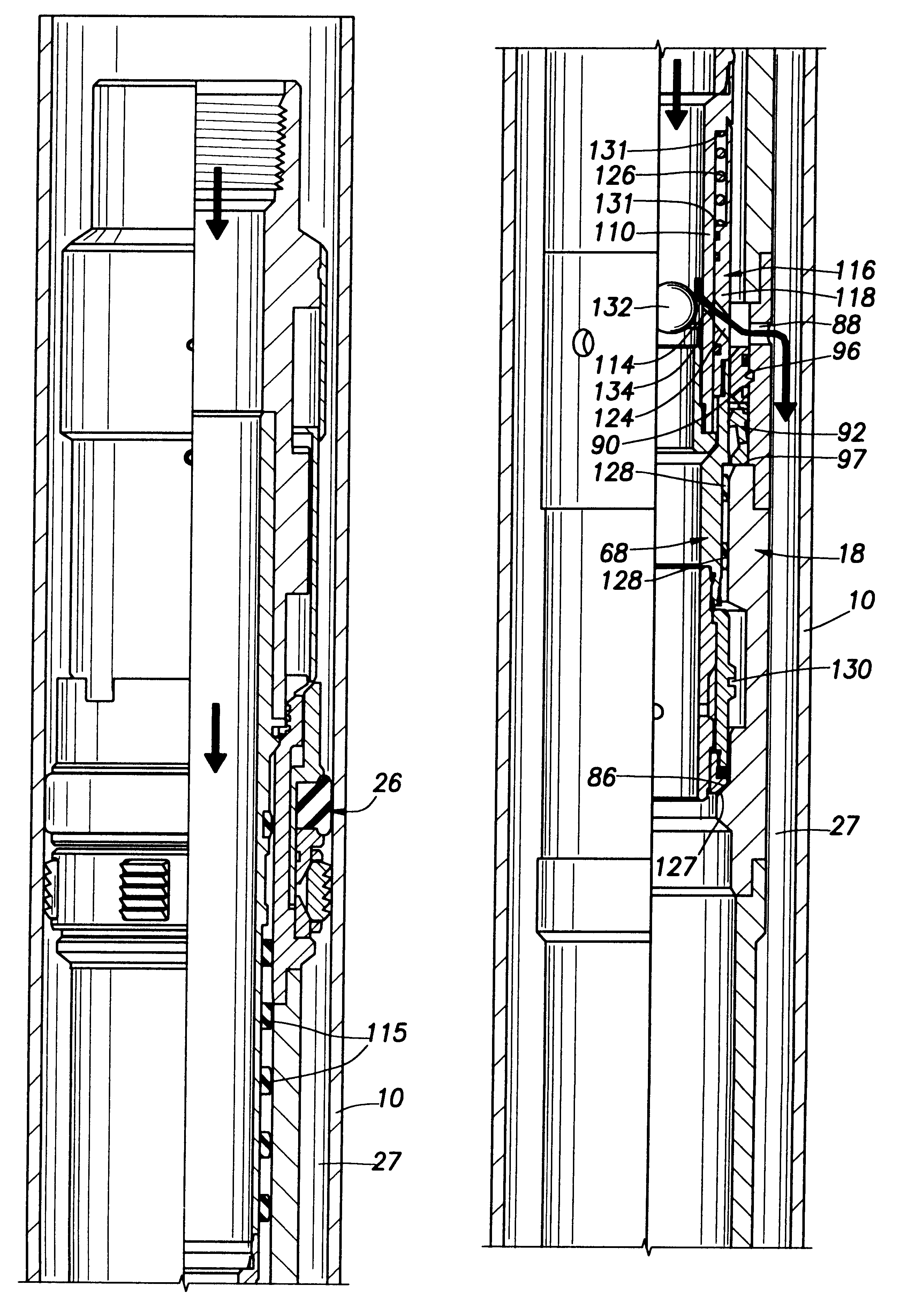
System for installation of well stimulating apparatus downhole utilizing a service tool string
A service tool string (34) is releasably attached to a bottom hole assembly (18) and forms a production string as well as a work string. The tool (35) has a mandrel (102) and a slide valve assembly (68) mounted on the mandrel for relative sliding movement. Crossover ports (114, 124) are provided in the mandrel (102) and the slide valve assembly (68). Slide valve assembly (68) moves by gravity and spring action when not contacted by the bottom hole assembly (18) to a position in which ports (114, 124) are blocked as shown in FIG. 7B. Upon contact of slidable valve assembly (68) with the bottom hole assembly (18), slide valve assembly is moved upwardly for alignment of ports (114, 124) as shown in FIGS. 5B and 6B. An equalizing valve (29) as shown in FIGS. 10-12 is effective to equalize the fluid pressure within the bottom hole assembly (18) with the fluid pressure outside the perforated casing section (23) so that in a reverse position as shown in FIG. 7B, the service tool (35) can be lifted to a position above the upper packer assembly (26) and above the bottom hole assembly (18). A diverter ball (132) seated on a ball catcher (134) is effective to divert the fracturing fluid outwardly through crossover ports (114, 124) as shown in FIG. 6B for downward flow through the annulus (27) into the formation adjacent the perforated casing section (23).
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Method and apparatus for stimulation of multiple formation intervals
Owner:EXXONMOBIL UPSTREAM RES CO
Drilling components and systems to dynamically control drilling dysfunctions and methods of drilling a well with same
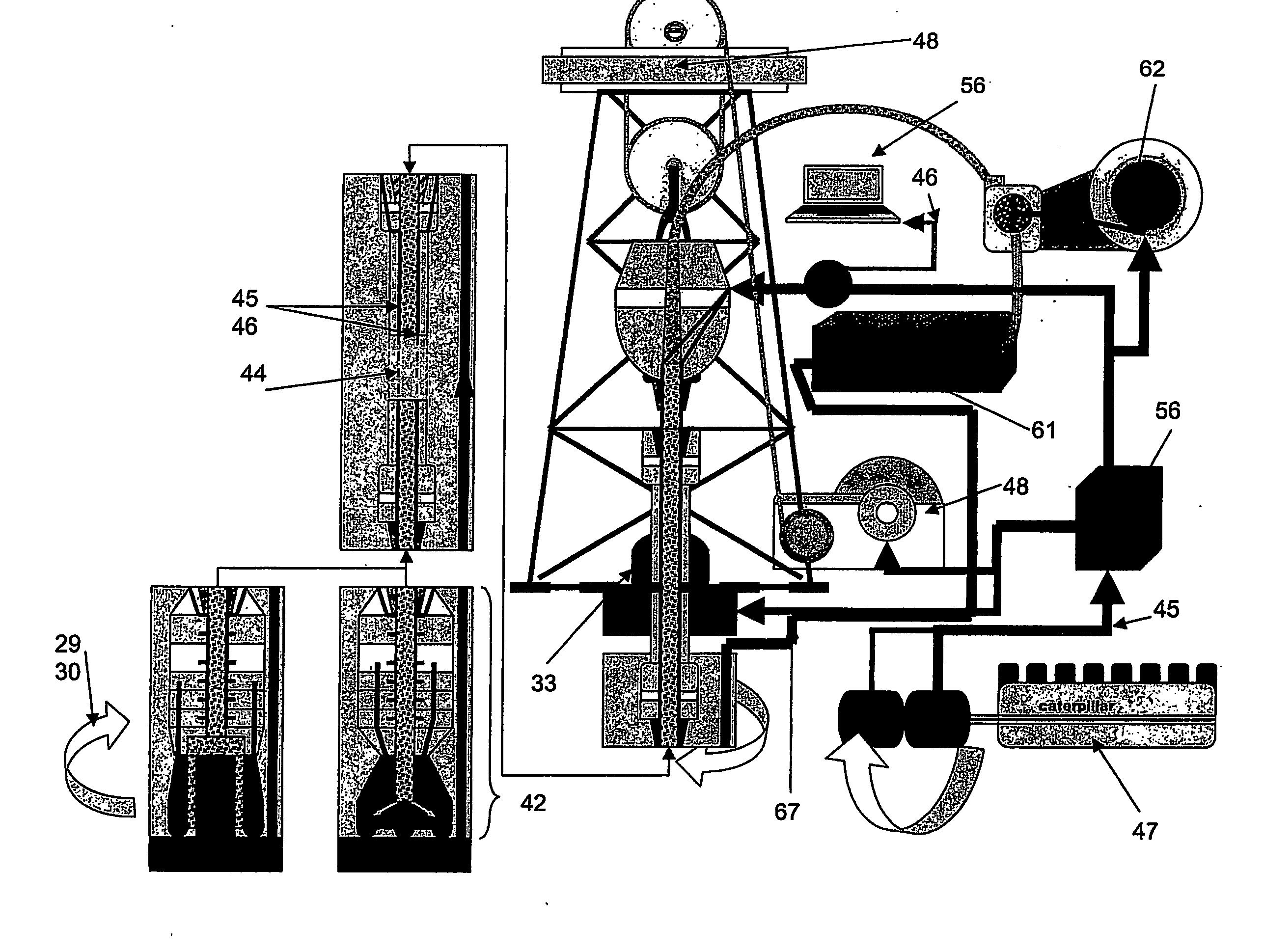
Drilling tools that may detect and dynamically adjust drilling parameters to enhance the drilling performance of a drilling system used to drill a well. The tools may include sensors, such as RPM, axial force for measuring the weight on a drill bit, torque, vibration, and other sensors known in the art. A processor may compare the data measured by the sensors against various drilling models to determine whether a drilling dysfunction is occurring and what remedial actions, if any, ought to be taken. The processor may command various tools within the bottom hole assembly (BHA), including a bypass valve assembly and / or a hydraulic thruster to take actions that may eliminate drilling dysfunctions or improve overall drilling performance. The processor may communicate with a measurement while drilling (MWD) assembly, which may transmit the data measured by the sensors, the present status of the tools, and any remedial actions taken to the surface.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Method and apparatus for locating well casings from an adjacent wellbore
ActiveUS20070126426A1Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingConstructionsEngineeringConductive materials
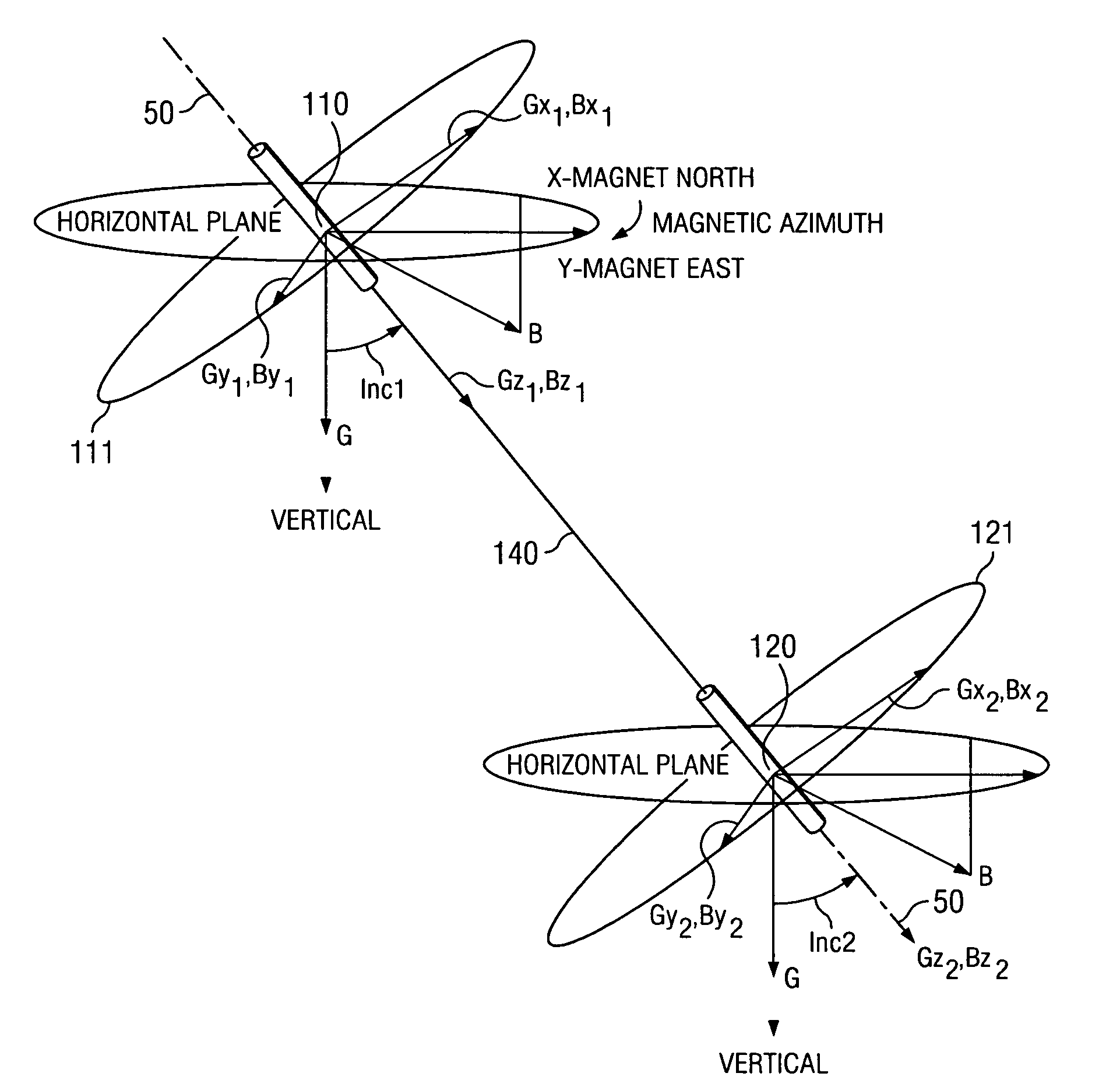
A wellbore tool for locating a target wellbore containing a conductive member from a second wellbore and directing the trajectory of the second wellbore relative to the target wellbore includes an electric current driver having an insulated gap; a three-axis magnetometer positioned within a non-magnetic housing that is disposed within a non-magnetic tubular, the three-axis magnetometer positioned below the electric current driver; a drill bit positioned below the three-axis magnetometer; a hollow tubular connected between the electric current driver and the three-axis magnetometer; and a measurement-while-drilling tool. The current driver generates an electric current across the gap to the portion of the tool below the insulated gap. In a method a current is generated across the insulated gap to the portion of the tool below the insulated gap to the conductive material in the target wellbore returning to a portion of the bottom hole assembly above the insulated gap thereby producing a target magnetic field. Measuring the target magnetic field at the bottom hole assembly and the earth's magnetic field; and determining the position of the second wellbore relative to the target wellbore. Then steering the bottom hole assembly to drill the second wellbore along a trajectory relative to the target wellbore.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Well system
InactiveUS20050115741A1Excessive vibrationLow costElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingDrilling rodsElectrical conductorCoiled tubing
The drilling system includes a work string supporting a bottom hole assembly. The work string including lengths of pipe having a non-metallic portion. The work string preferably includes a composite coiled tubing having a fluid impermeable liner, multiple load carrying layers, and a wear layer. Multiple electrical conductors and data transmission conductors may be embedded in the load carrying layers for carrying current or transmitting data between the bottom hole assembly and the surface. The bottom hole assembly includes a bit, a gamma ray and inclinometer instrument package, a steerable assembly, an electronics section, a transmission, and a power section for rotating the bit. It may or may not include a propulsion system. The drilling system may be a gravity based drilling system that does include a propulsion system. Various motive means may be provided, such as gravity, to apply weight on the bit.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
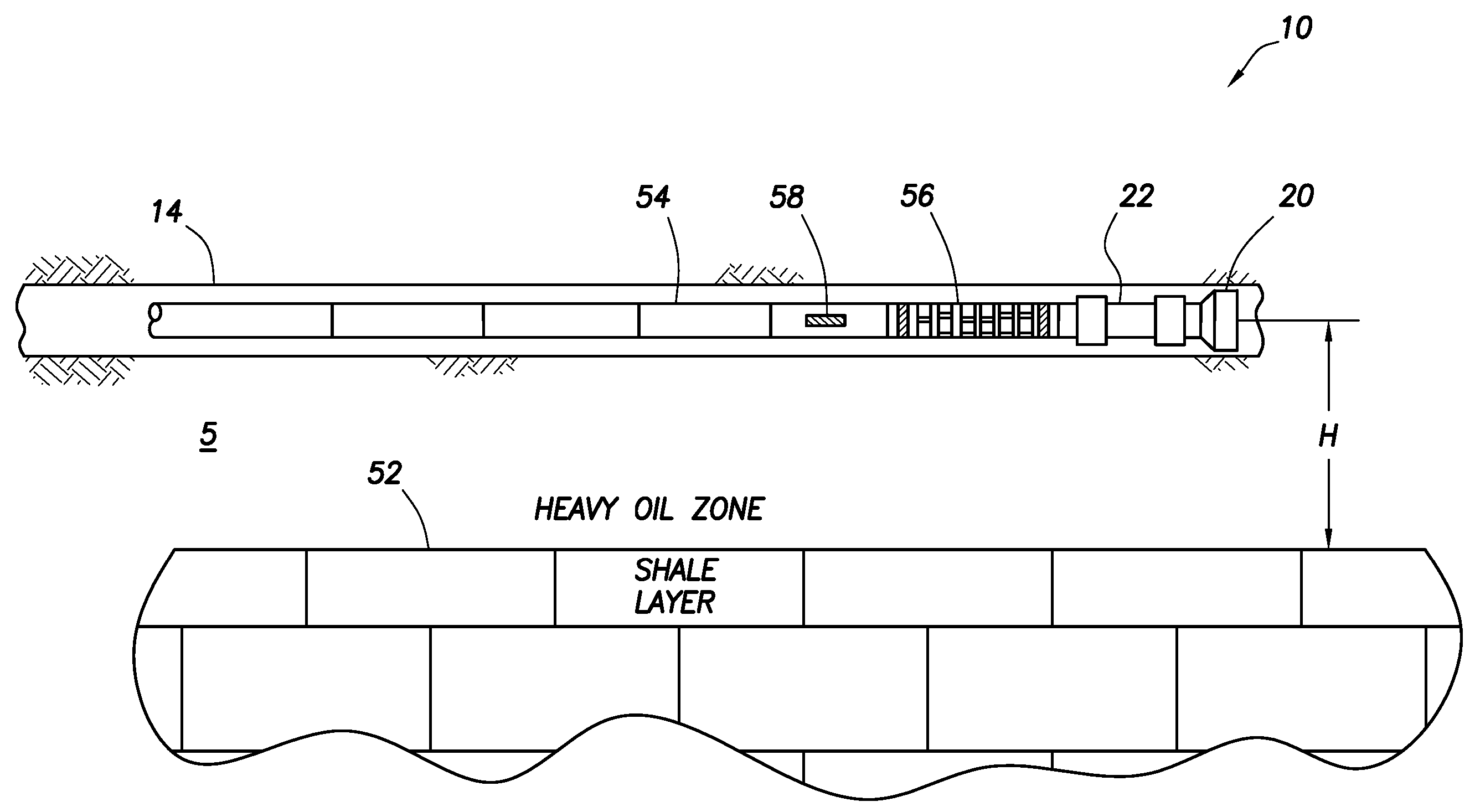
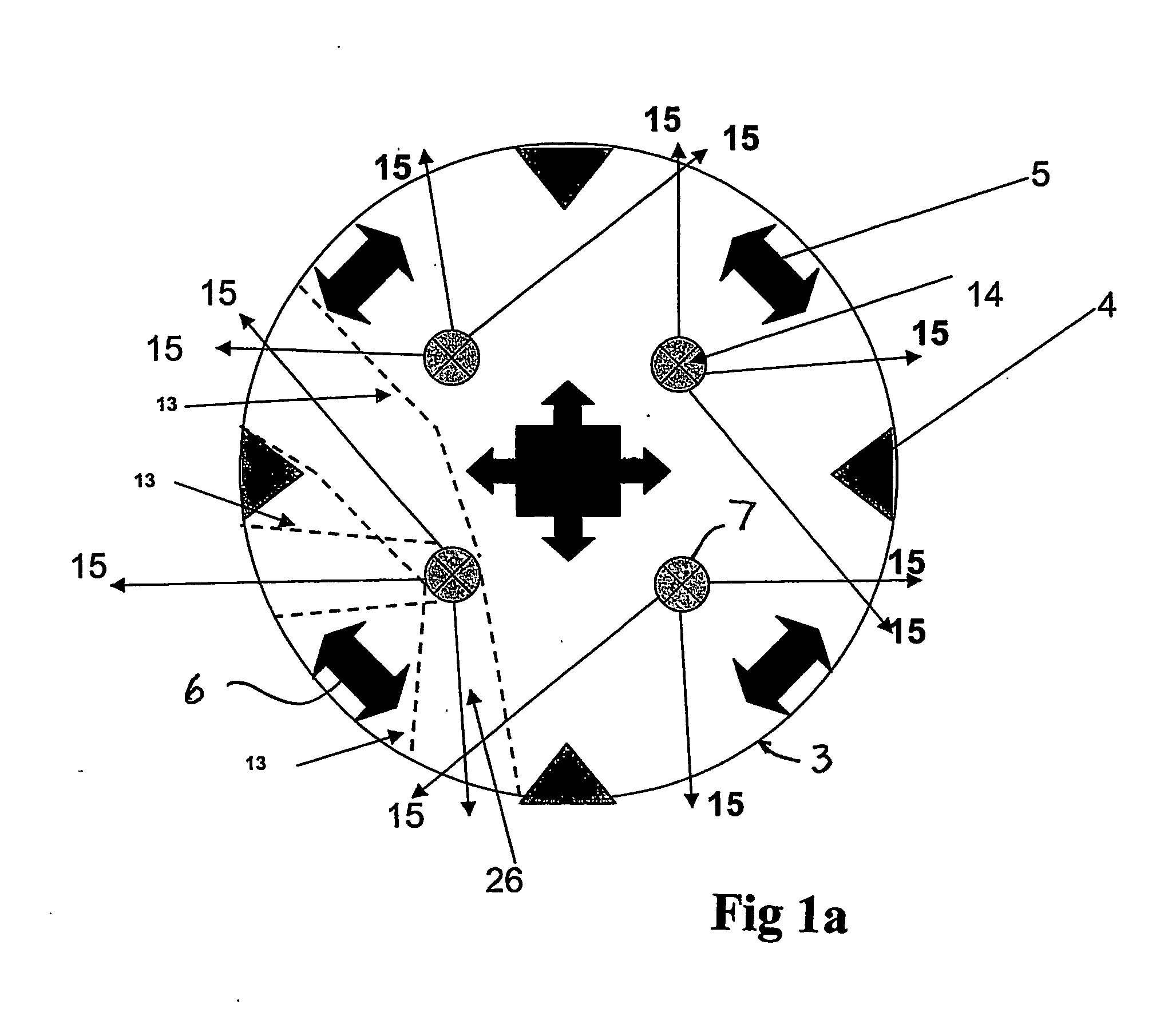
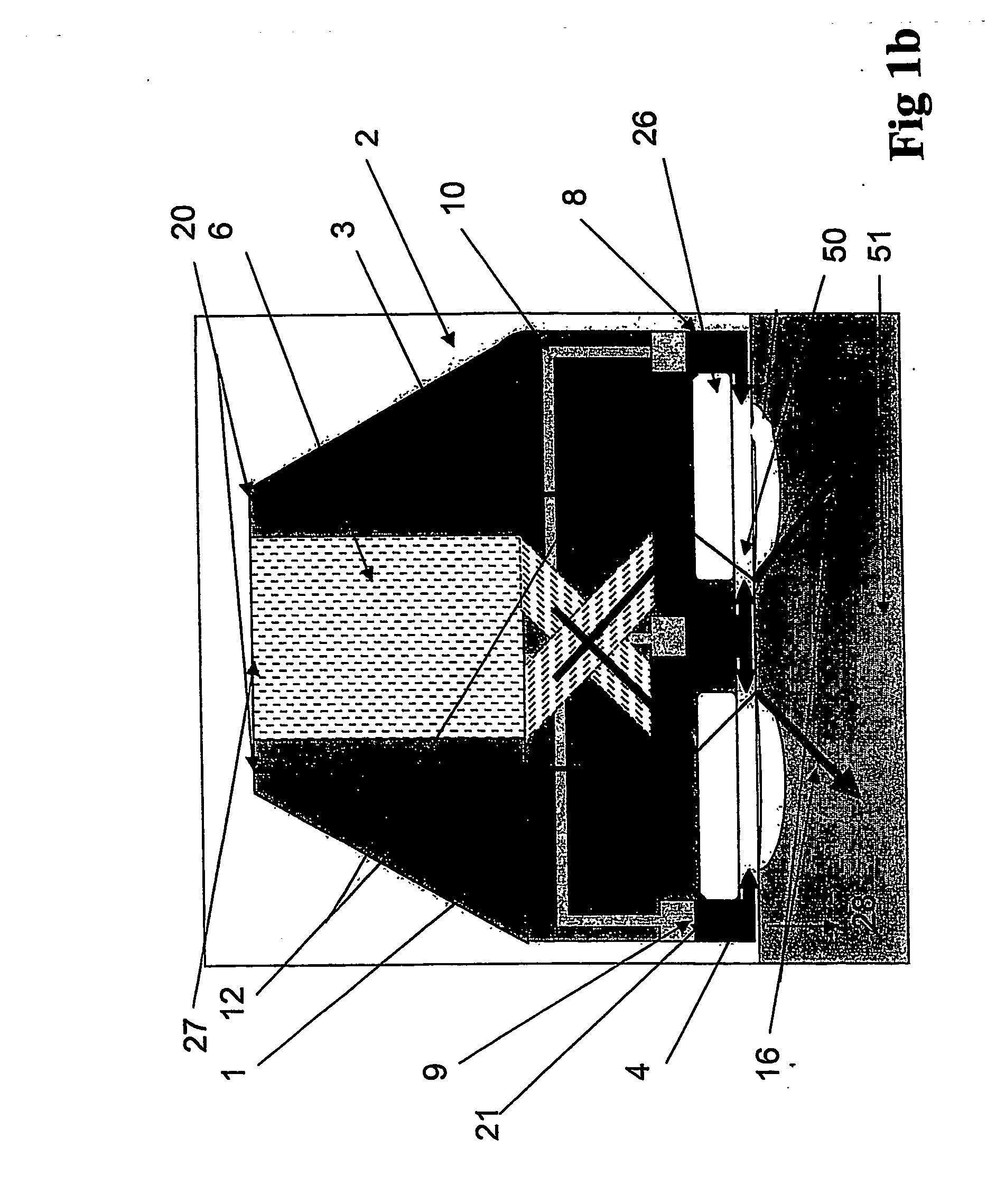
Method, Drilling Machine, Drill bit and Bottom Hole Assembly for Drilling by Electrical Discharge by Electrical Discharge Pulses
ActiveUS20090133929A1Efficiently provideIncrease drilling speedDrill bitsDisloding machinesElectric dischargeClosed loop
Machine for ground drilling, with a circulating fluid, by the utilization of electric discharge generated by high-voltage pulses between electrodes. It may comprise: —A drill-bit 1 with electrodes movable relative to each other, so that bottom-hole physical contact be secured for all the electrodes 4 on all bottom-hole topographies. —Pointed hydraulic nozzles for jetting the fluid, to remove primary cuttings and with pressure expansion across the nozzles 7 at no less than 4 MPa. —A high-voltage pulse generator deployed down-hole at a minimum distance from the drill-bit 1. —A rotating or oscillating bit causing the borehole cross-sectional excavation to occur, and electric discharge between a plurality of electrodes situated on the bit face along one or a few radii and tangents. —A bottom hole assembly for annular hole-making with core storage, transportation, down-hole closed loop discharge fluid circulation. A discharge fluid storage may be incorporated. A drilling method is also described.
Owner:UNODRILL
Flexible directional drilling apparatus and method
A bottom hole assembly to directionally drill a subterranean formation includes a drill bit, a stabilizer assembly located proximate to and behind the drill bit, a drilling assembly comprising a drive mechanism and a directional mechanism, and a flex member. Optionally, the flex member may be located between the drilling assembly and the stabilizer assembly or an integral to a housing of the drilling assembly. A method to drill a formation includes positioning a stabilizer assembly behind a drill bit and positioning a flex member between an output shaft of a drilling assembly and the stabilizer assembly. The method preferably includes rotating the drill bit, stabilizer assembly, and flex member with a drilling assembly and directing the trajectory of the drill bit and stabilizer assembly with a directional mechanism of the drilling assembly.
Owner:SMITH INT INC
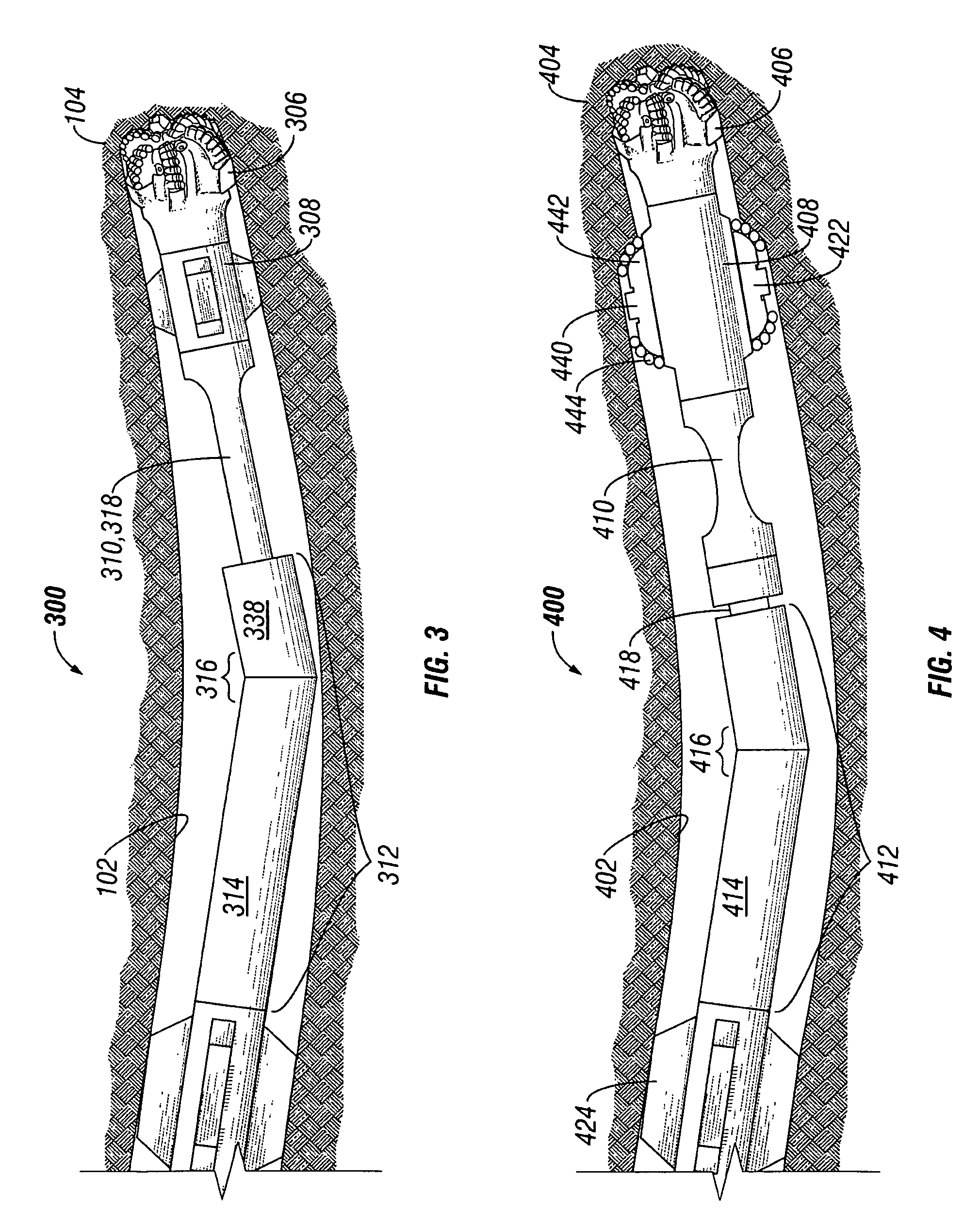
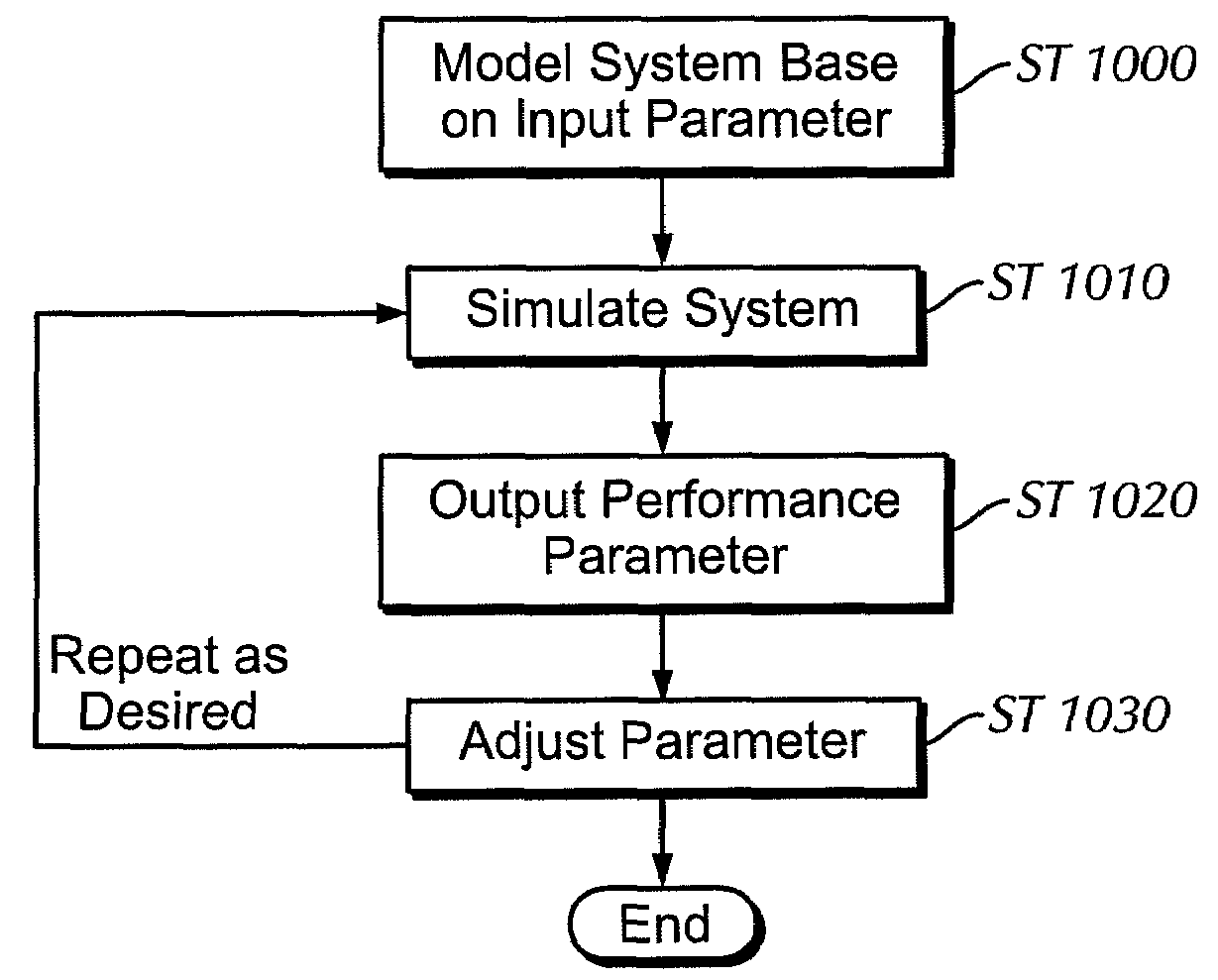
Methods for designing secondary cutting structures for a bottom hole assembly
InactiveUS20090055135A1Improve the situationImprove cutting performanceGeometric CADSurveyStructure basedBottom hole assembly
A method for designing a secondary cutting structure for use in a bottom hole assembly, the method including defining initial design parameters for the secondary cutting structure and analyzing forces acting on the secondary cutting structure. Additionally, the method includes modifying at least one design element of the secondary cutting structure and simulating an effect of the modifying on both the secondary cutting structure and a primary cutting structure to determine if an improved condition is met. Also, a method for designing a drilling tool assembly, the method including defining initial drilling tool assembly design parameters including a primary cutting structure and a secondary cutting structure, and simulating a dynamic response of the drilling tool assembly. Additionally, the method includes adjusting at least one design element of the secondary cutting structure based on the dynamic response of the drilling tool assembly, determining if the adjusted design element improved a condition of the drilling, and repeating the simulating and adjusting until the condition is optimized.
Owner:SMITH INT INC
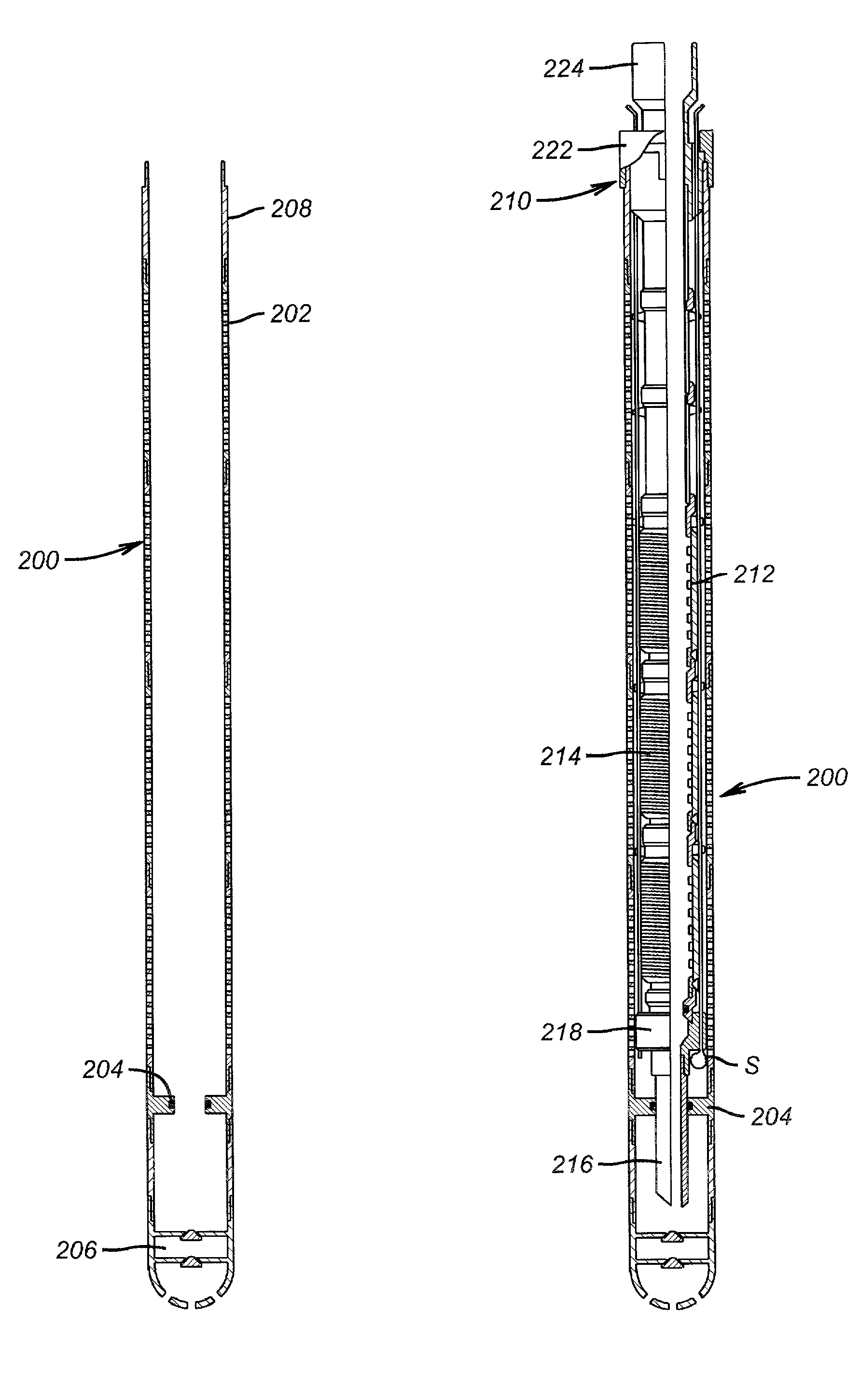
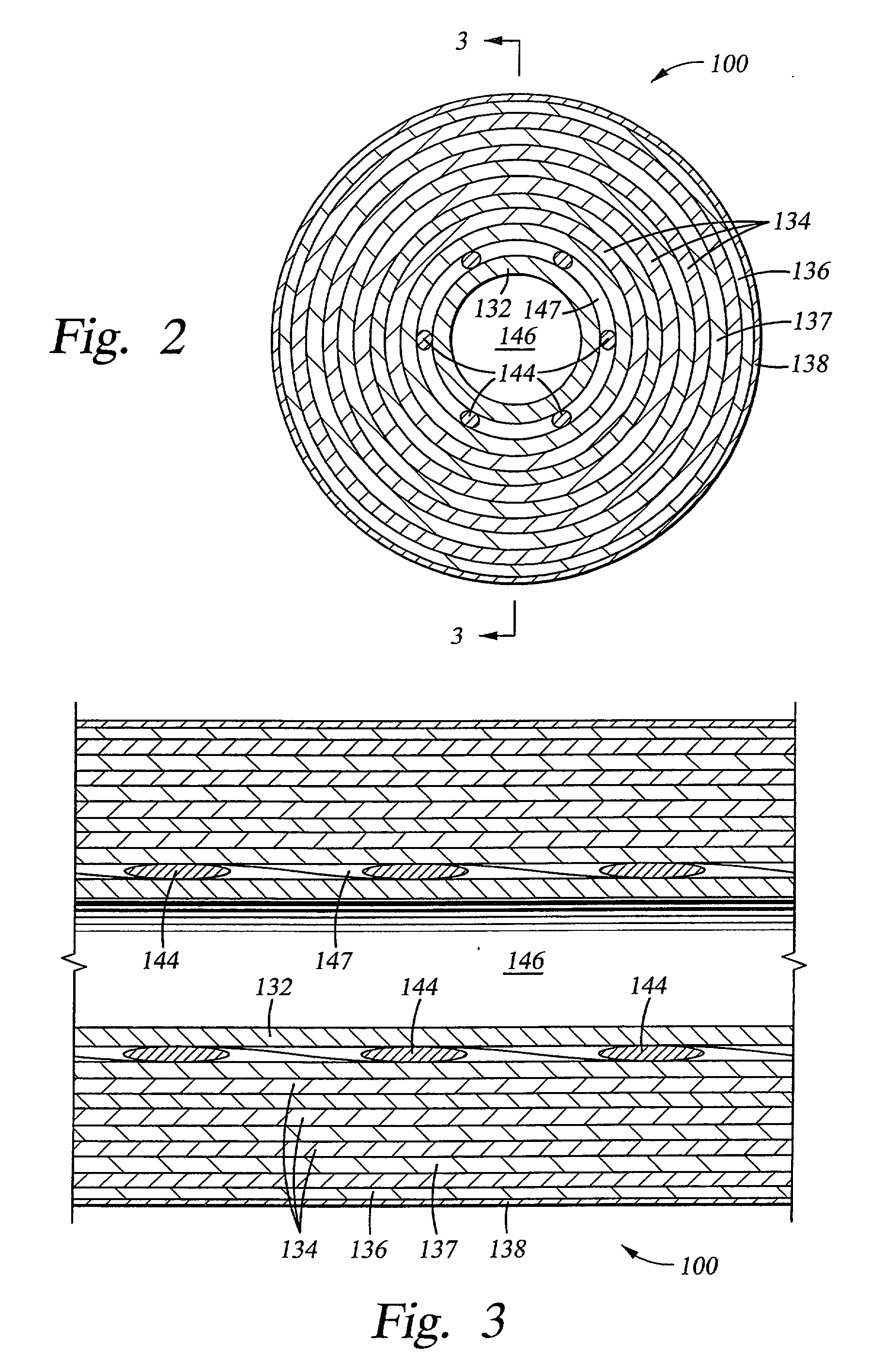
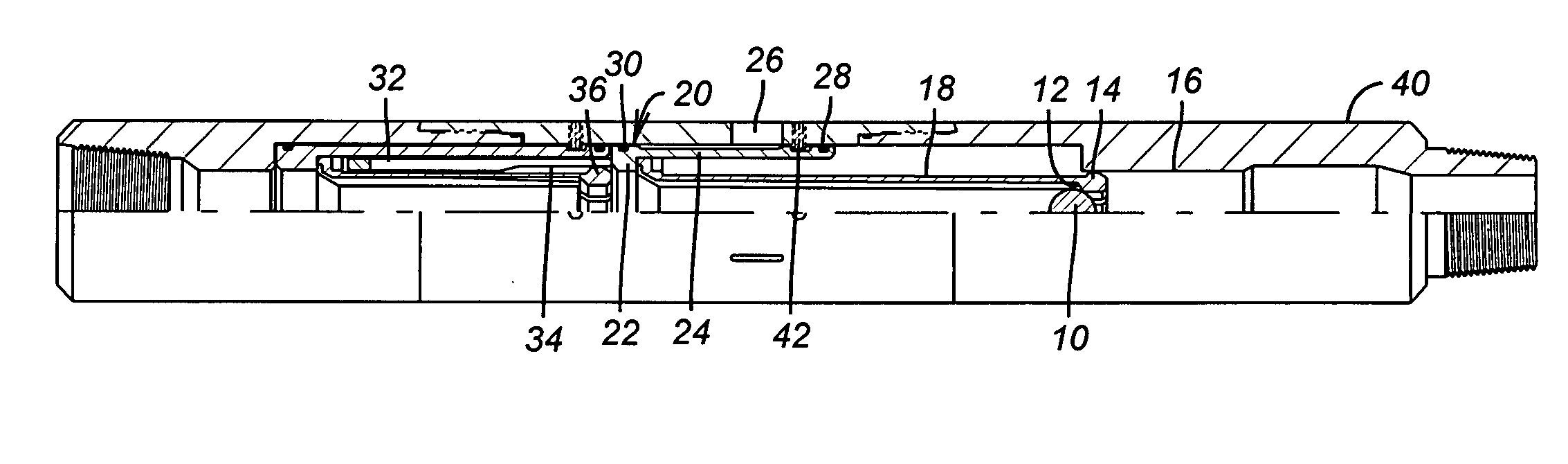
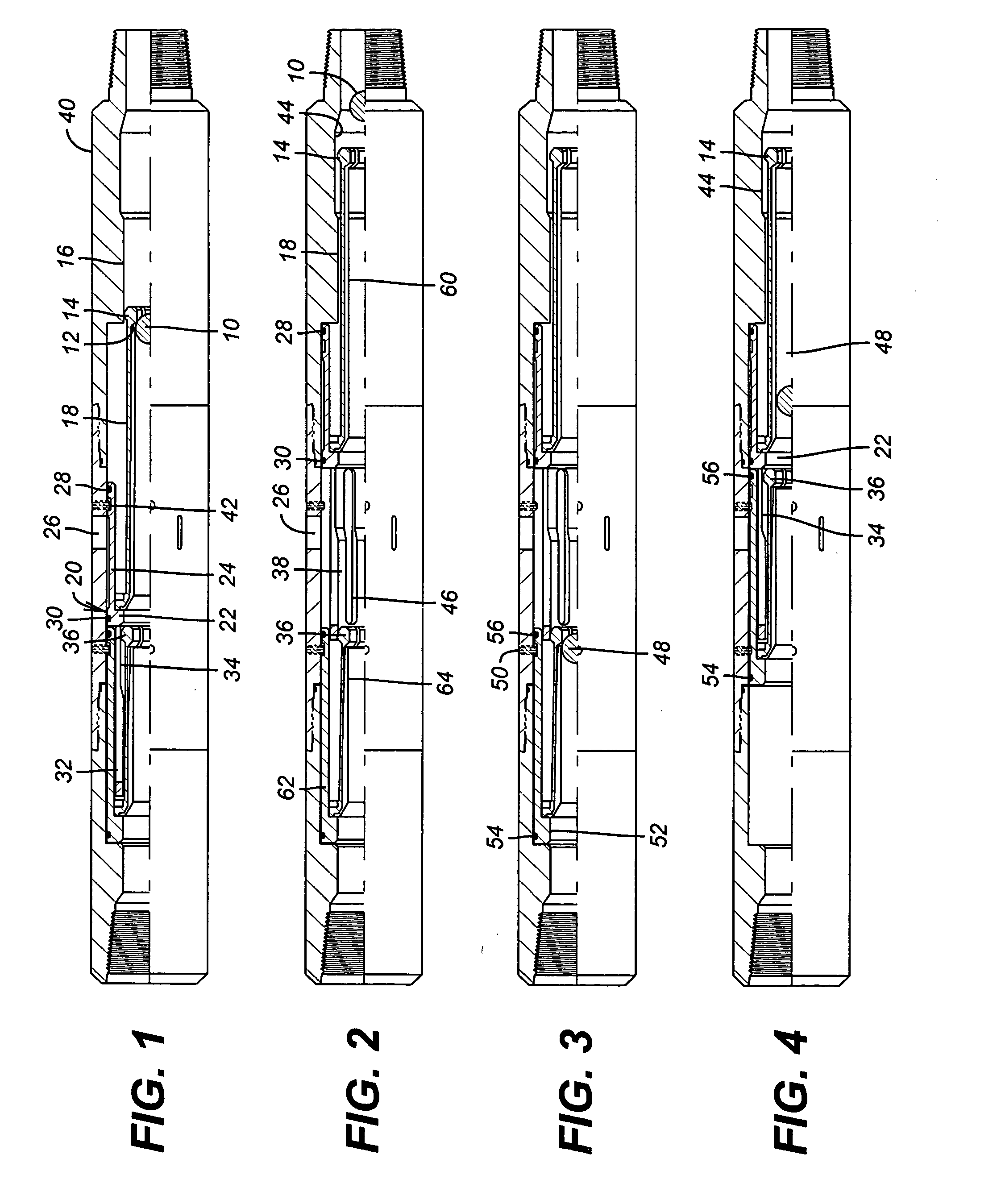
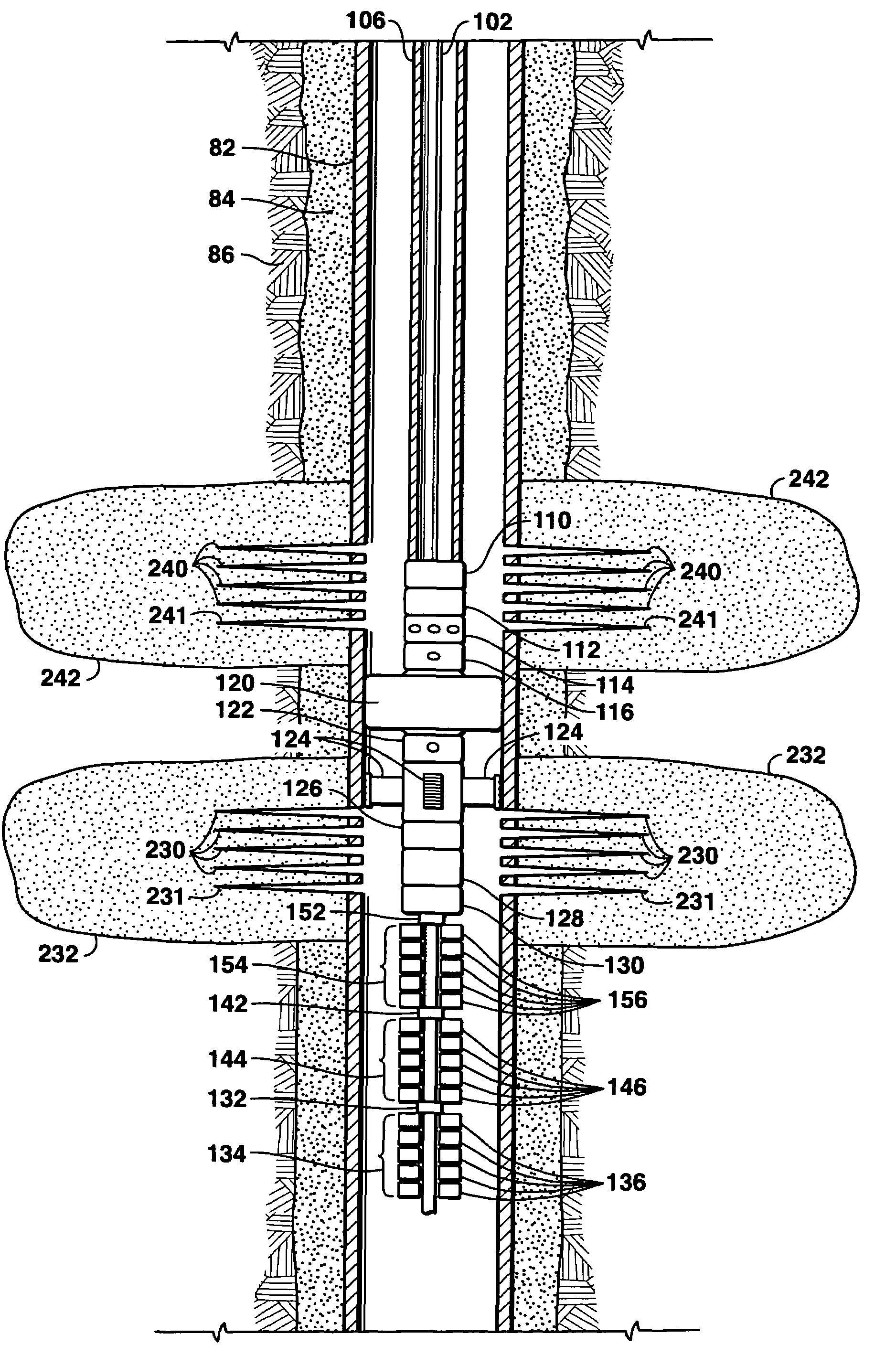
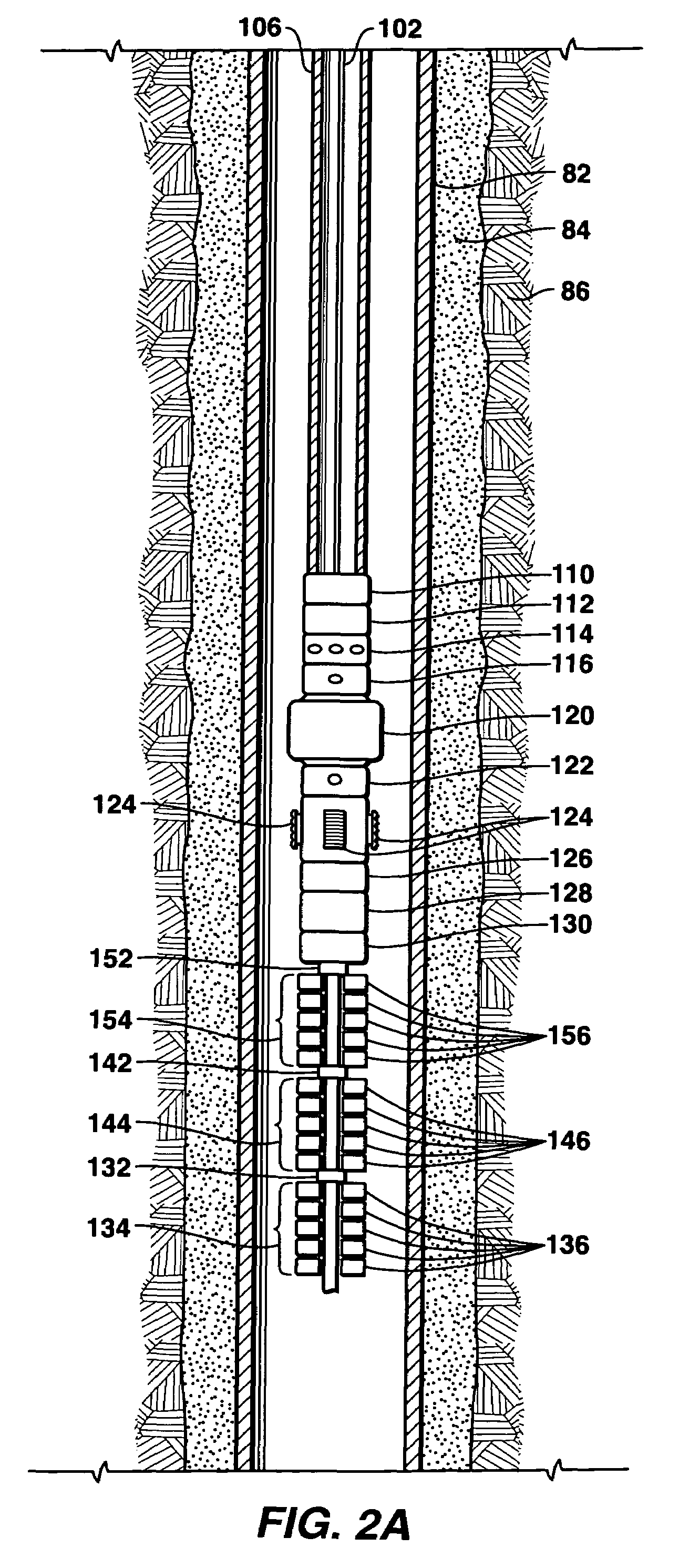
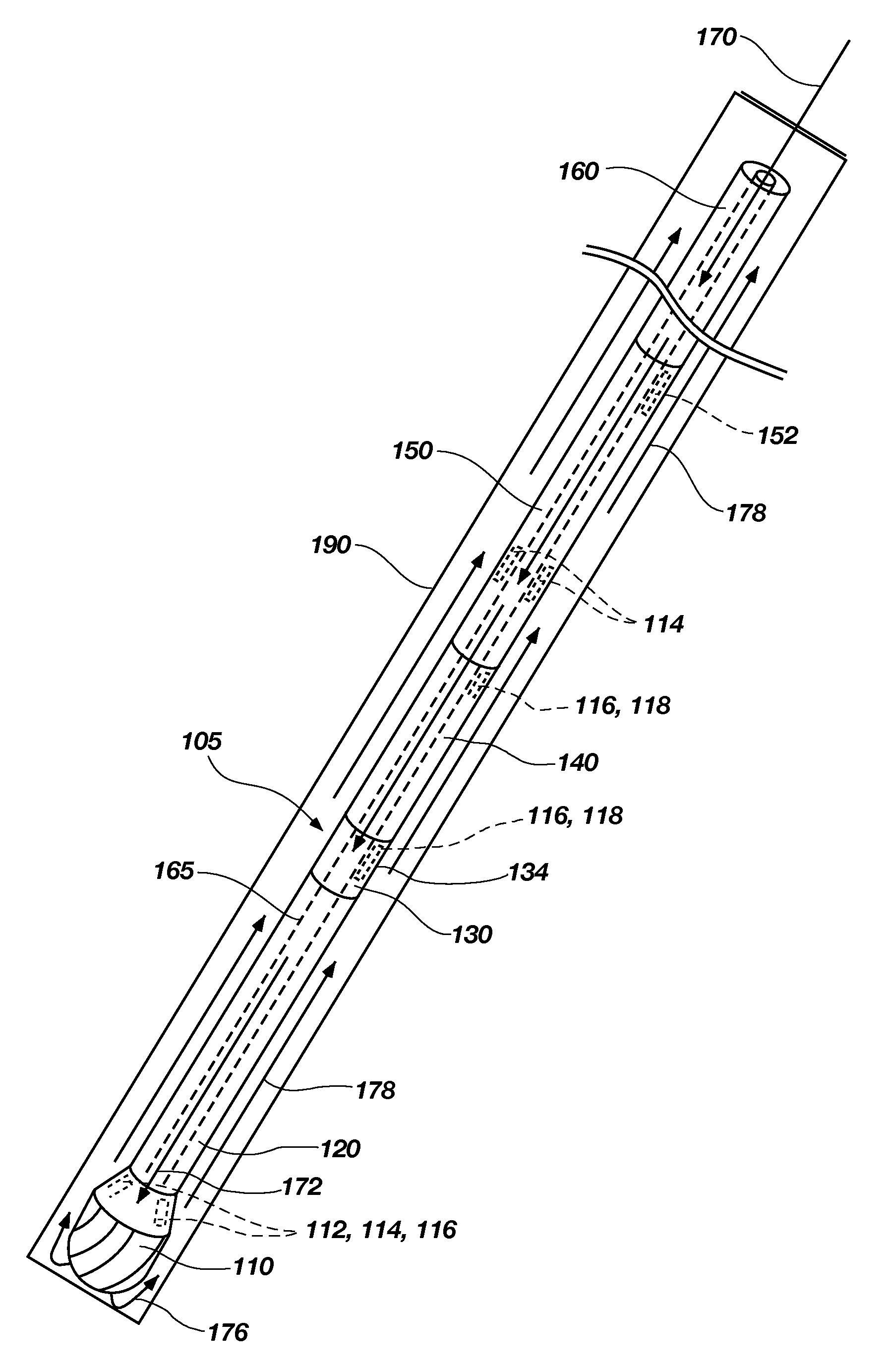
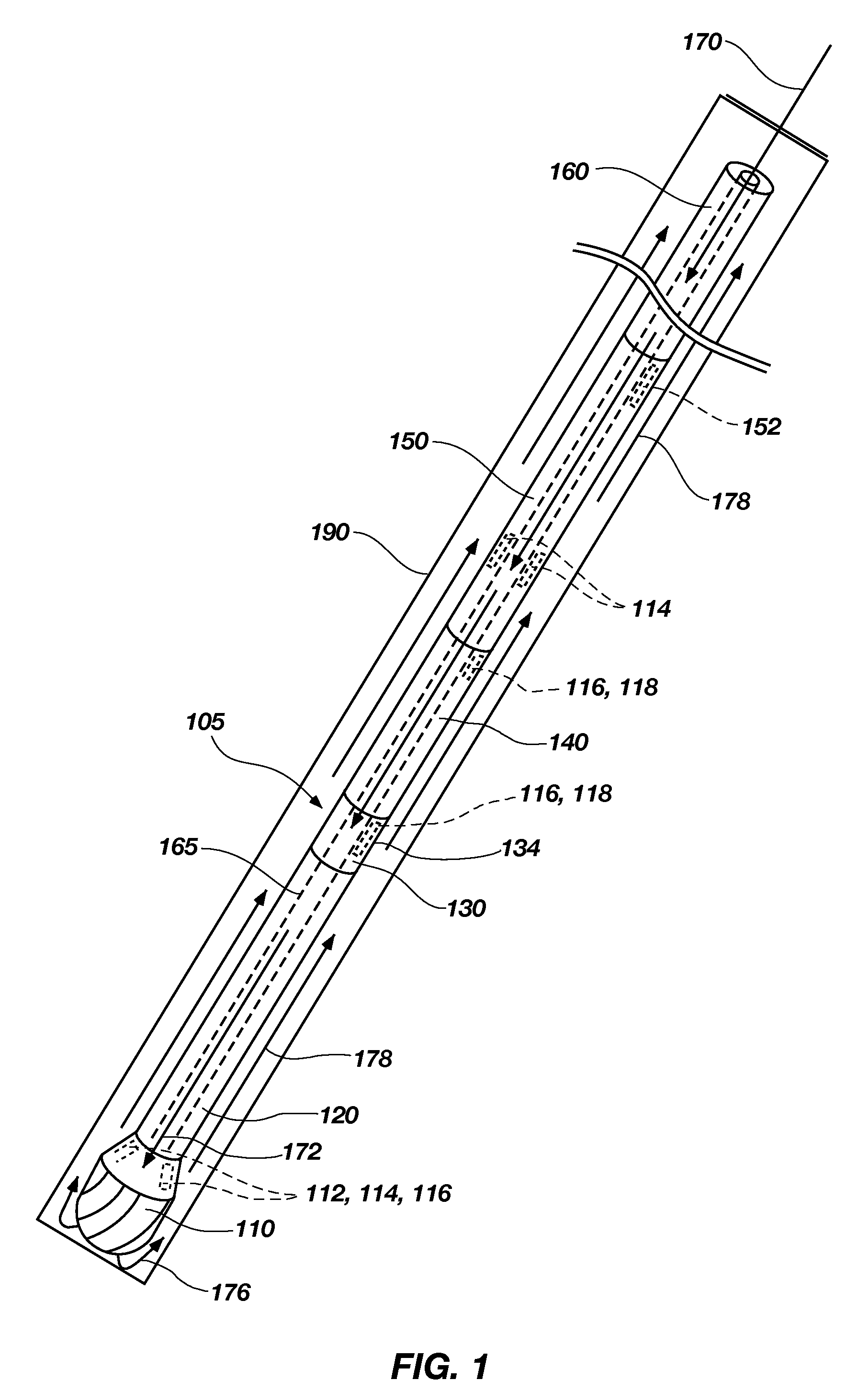
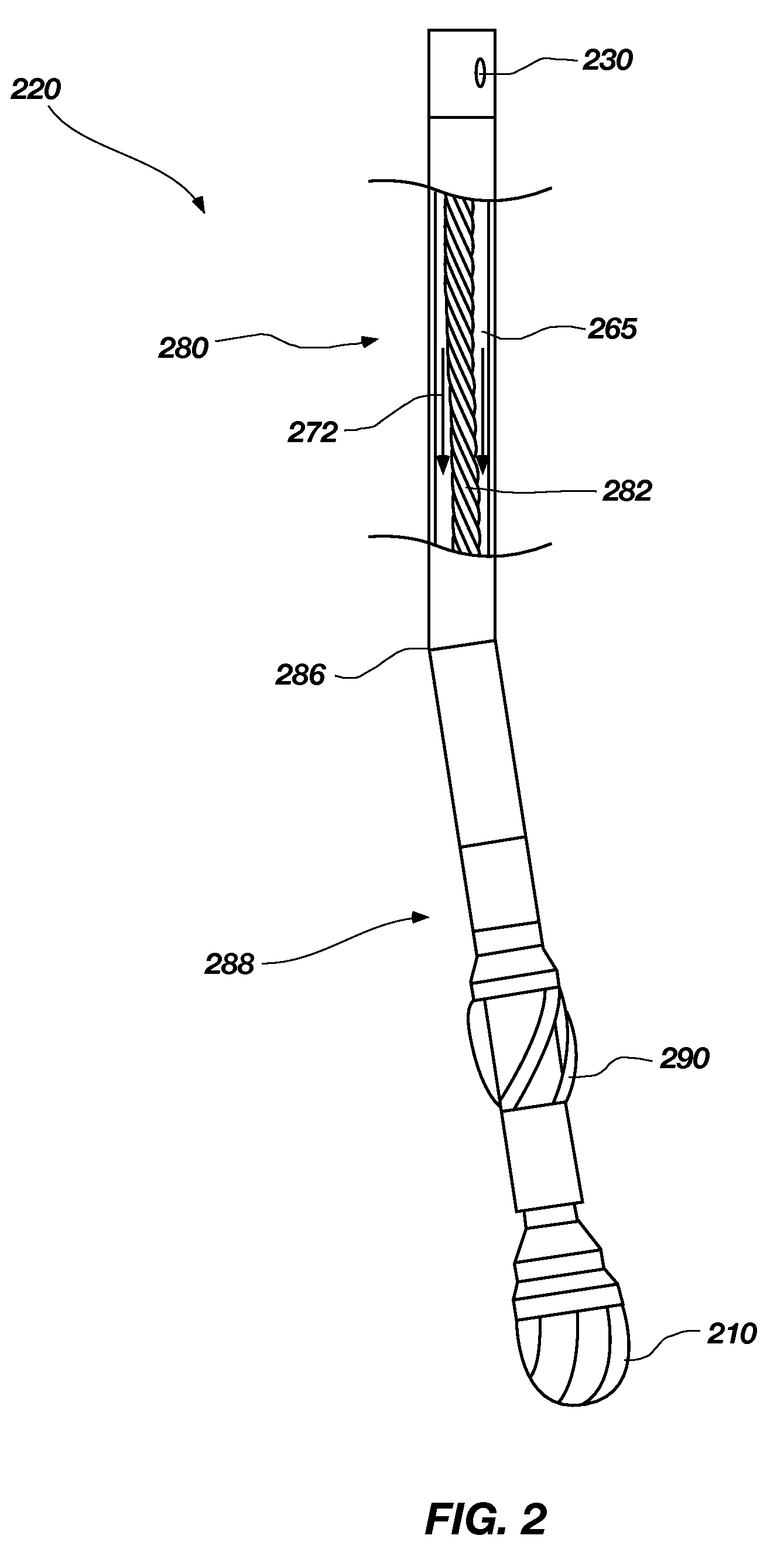
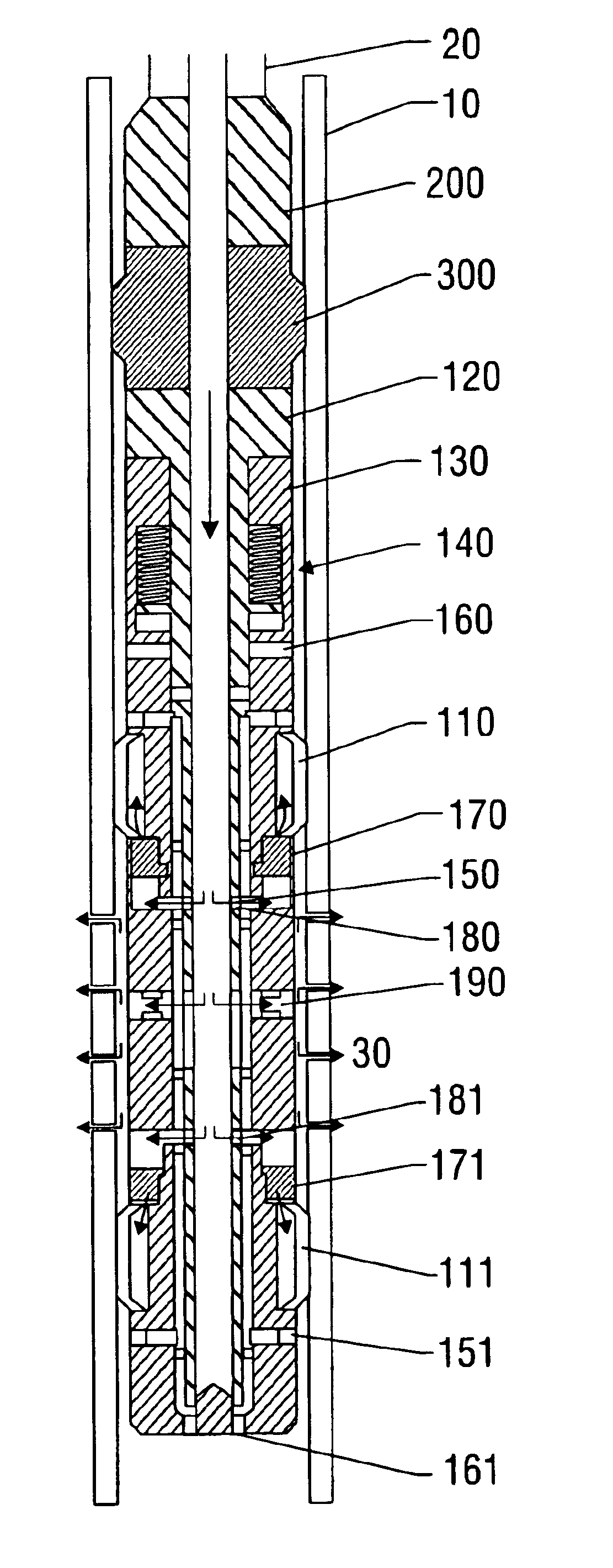
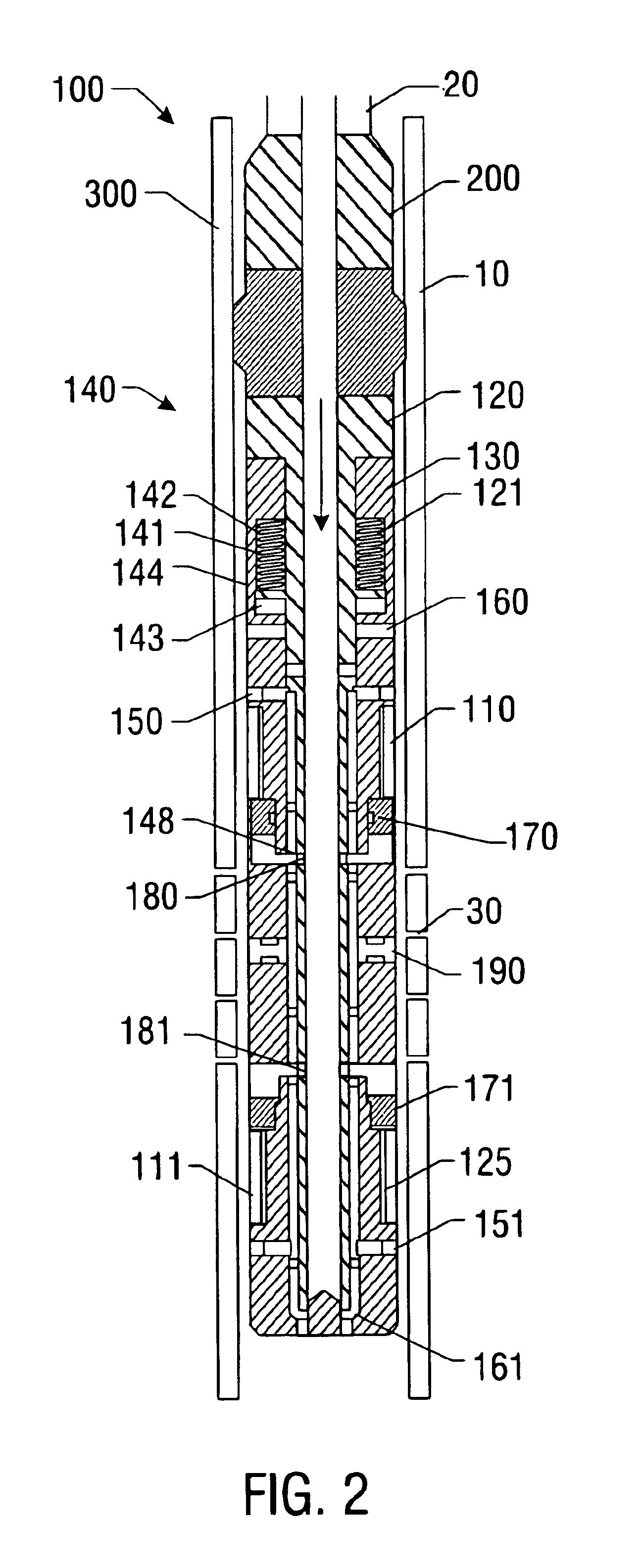
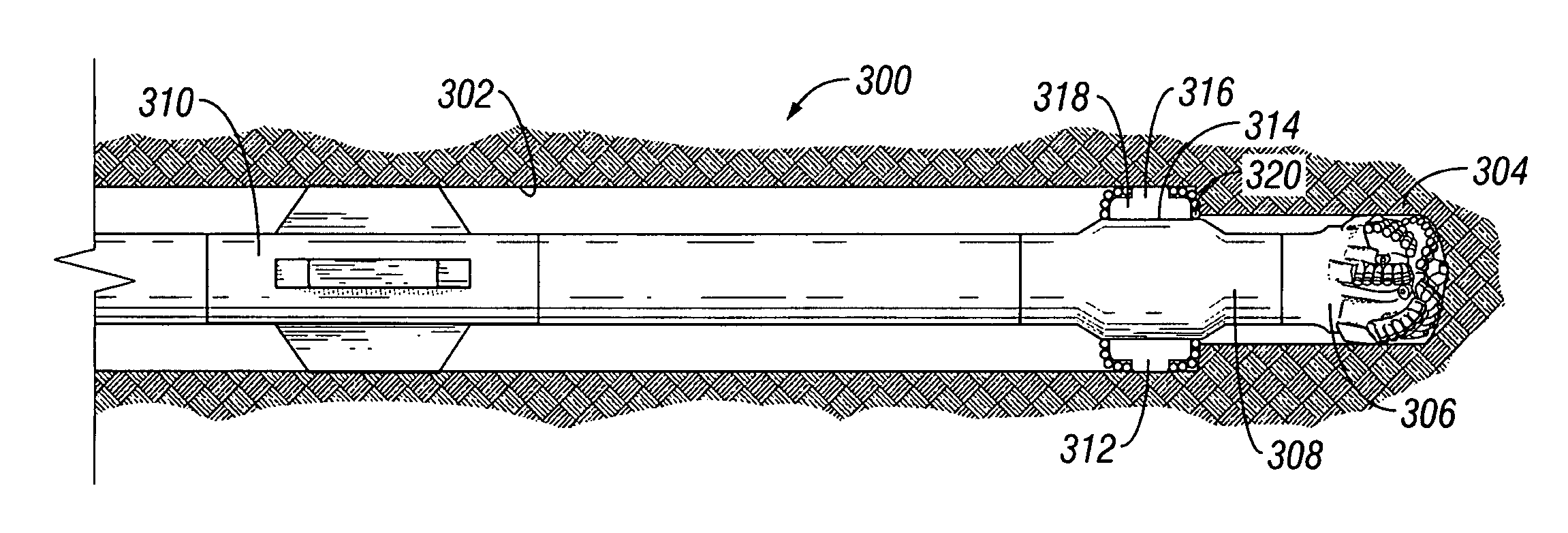
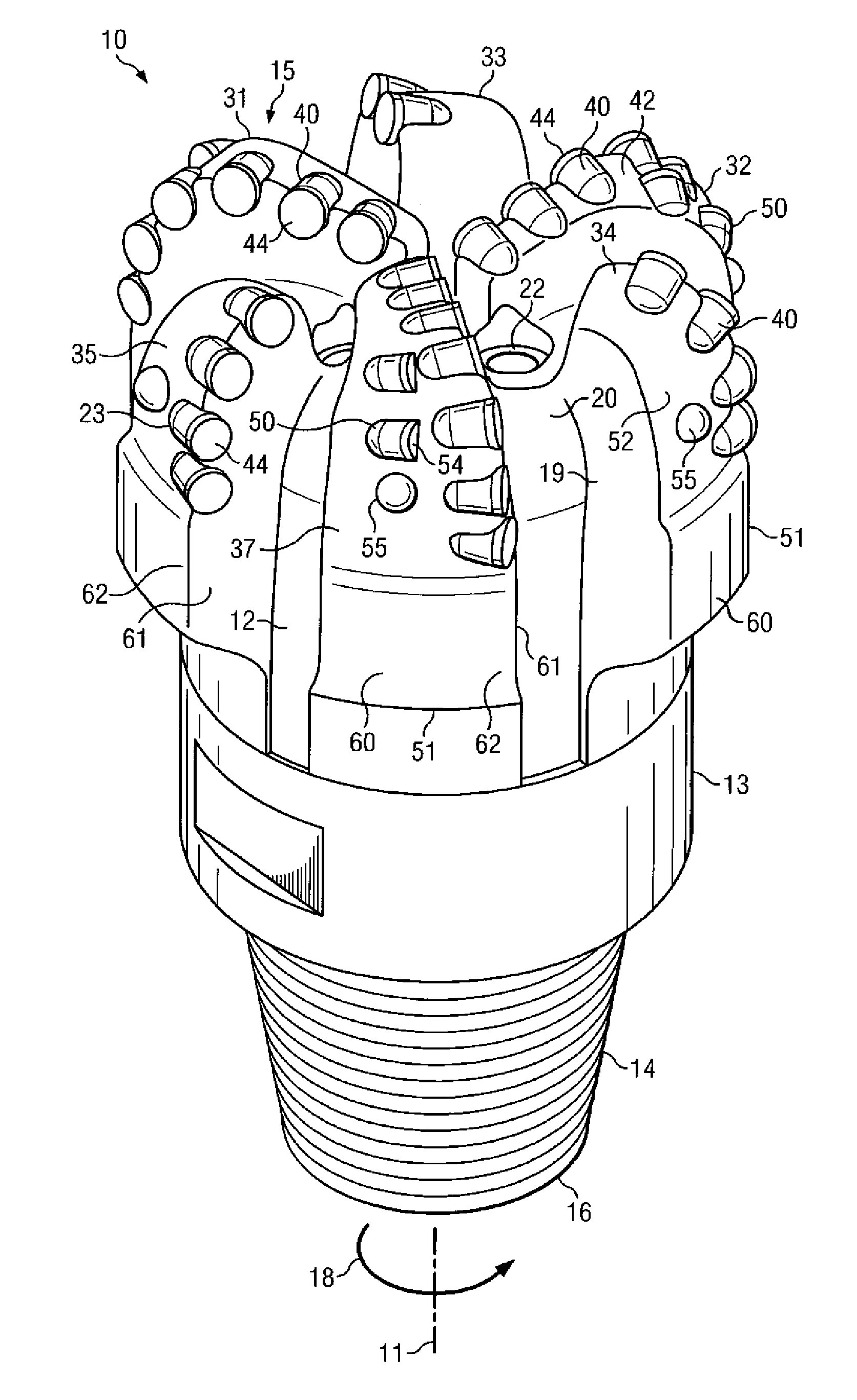
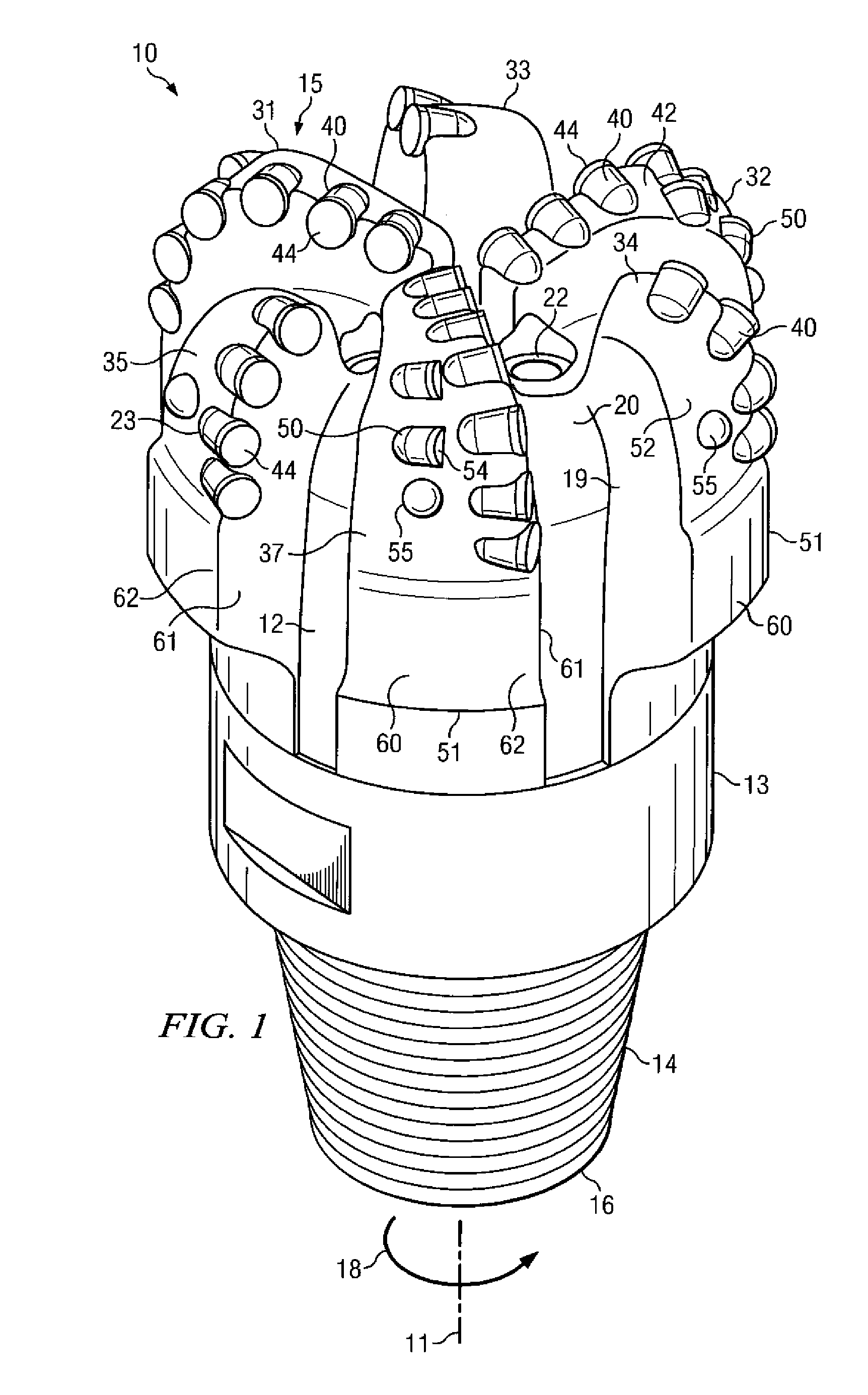
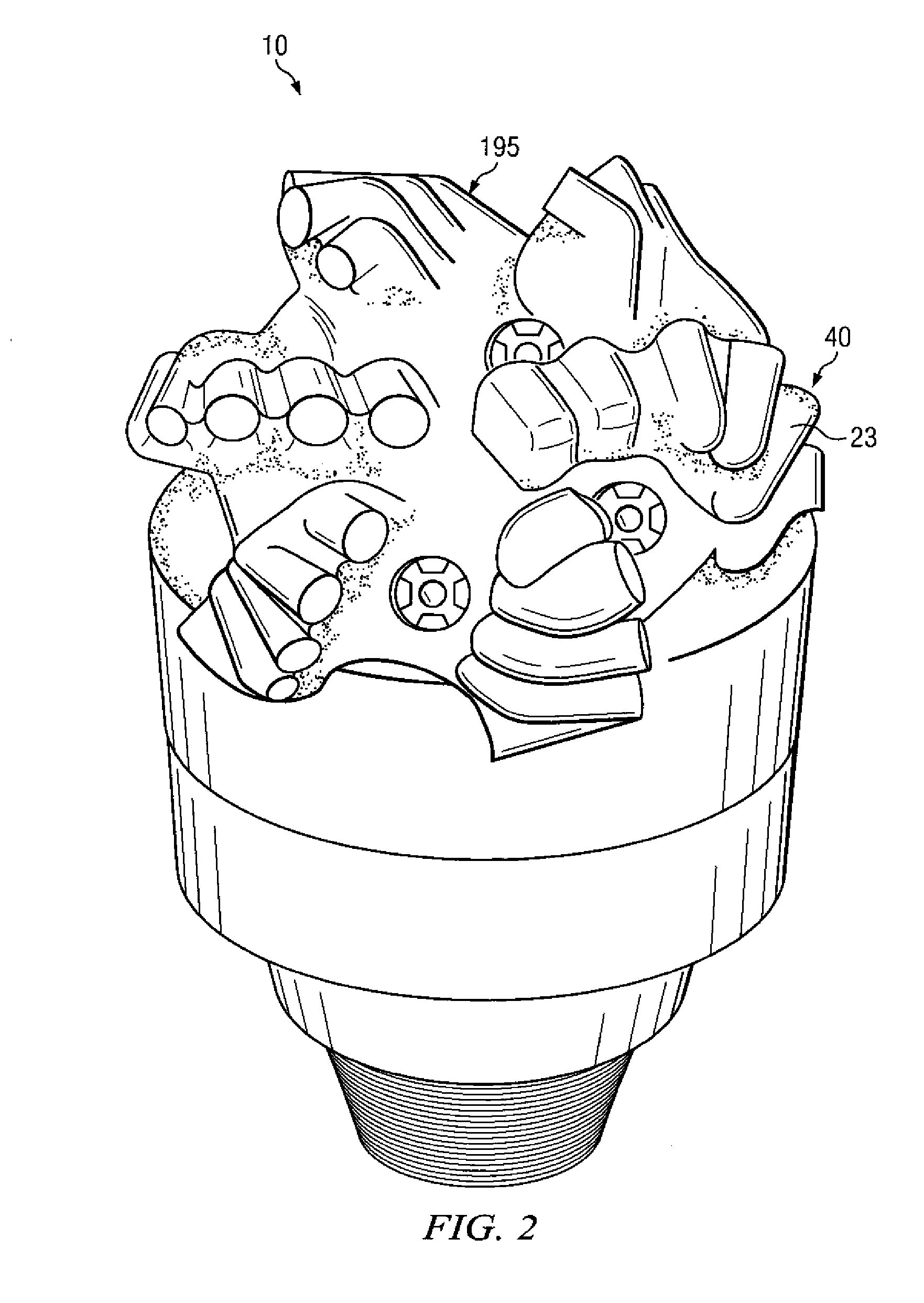
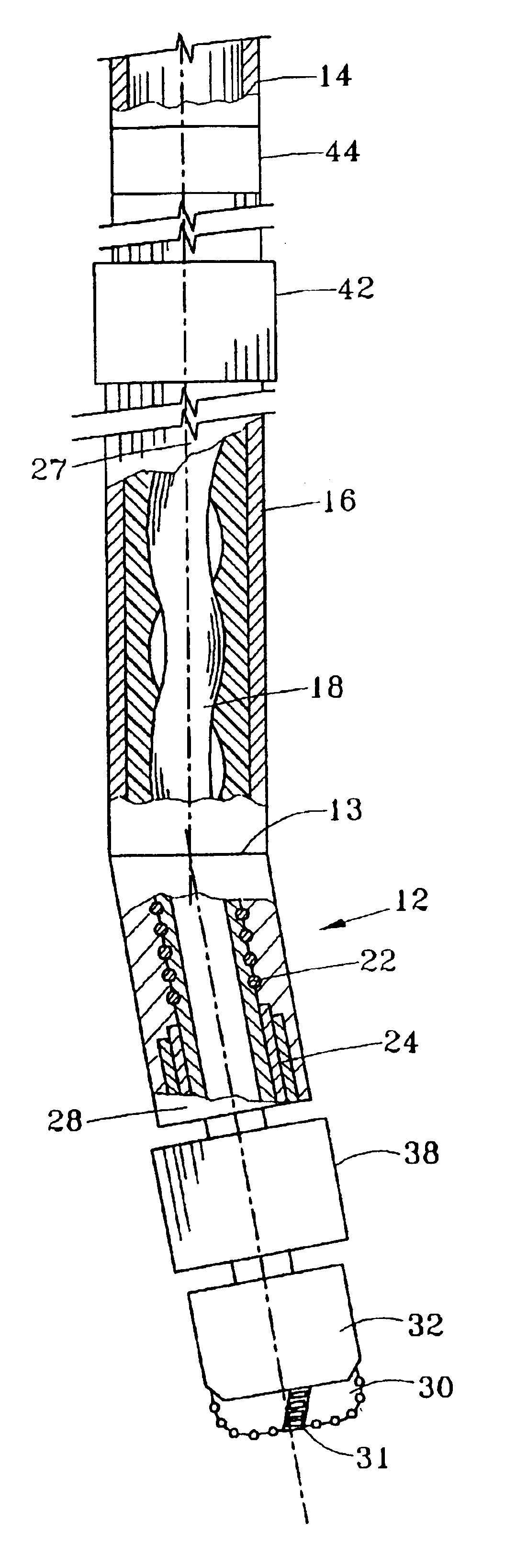
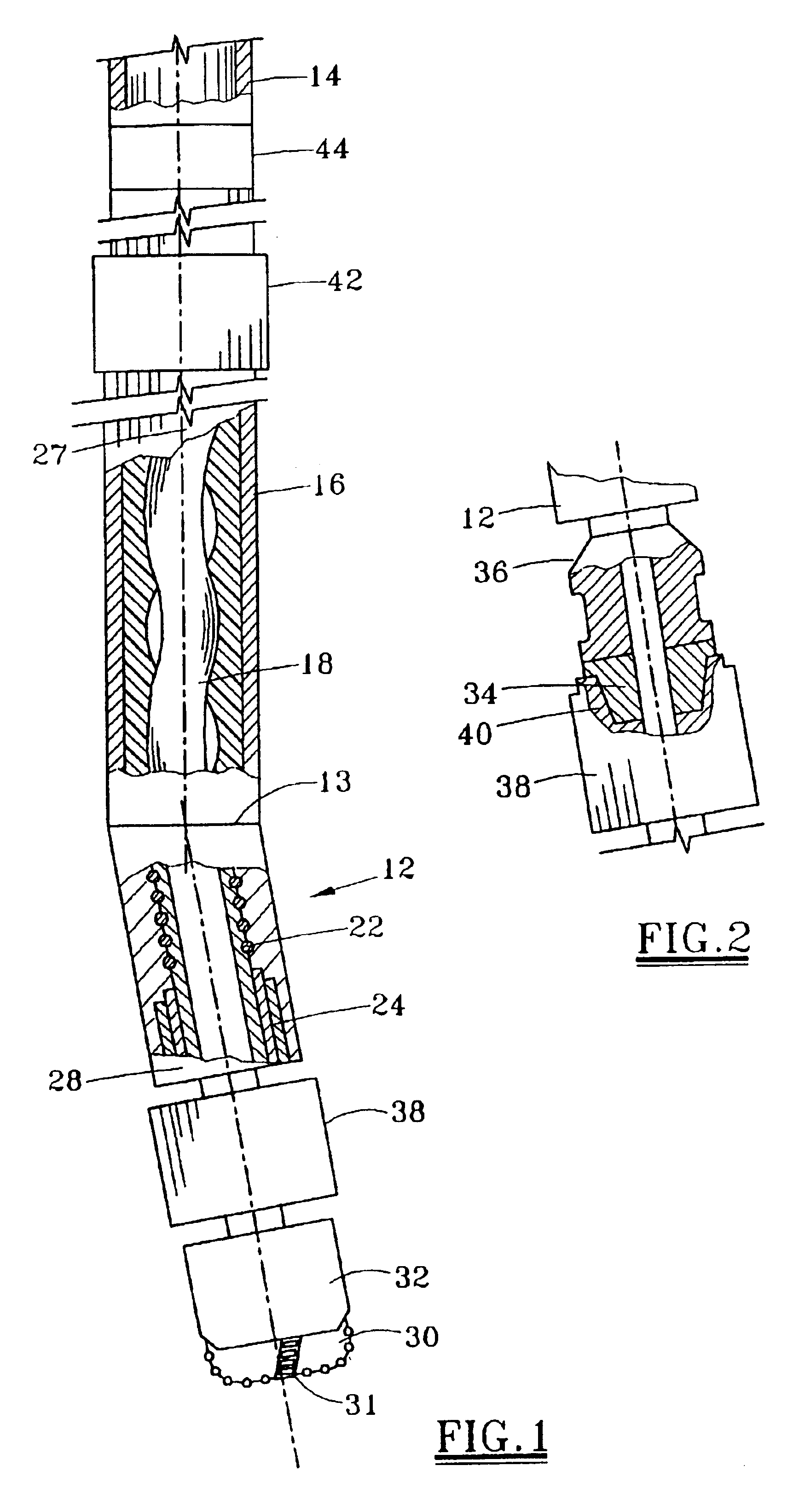
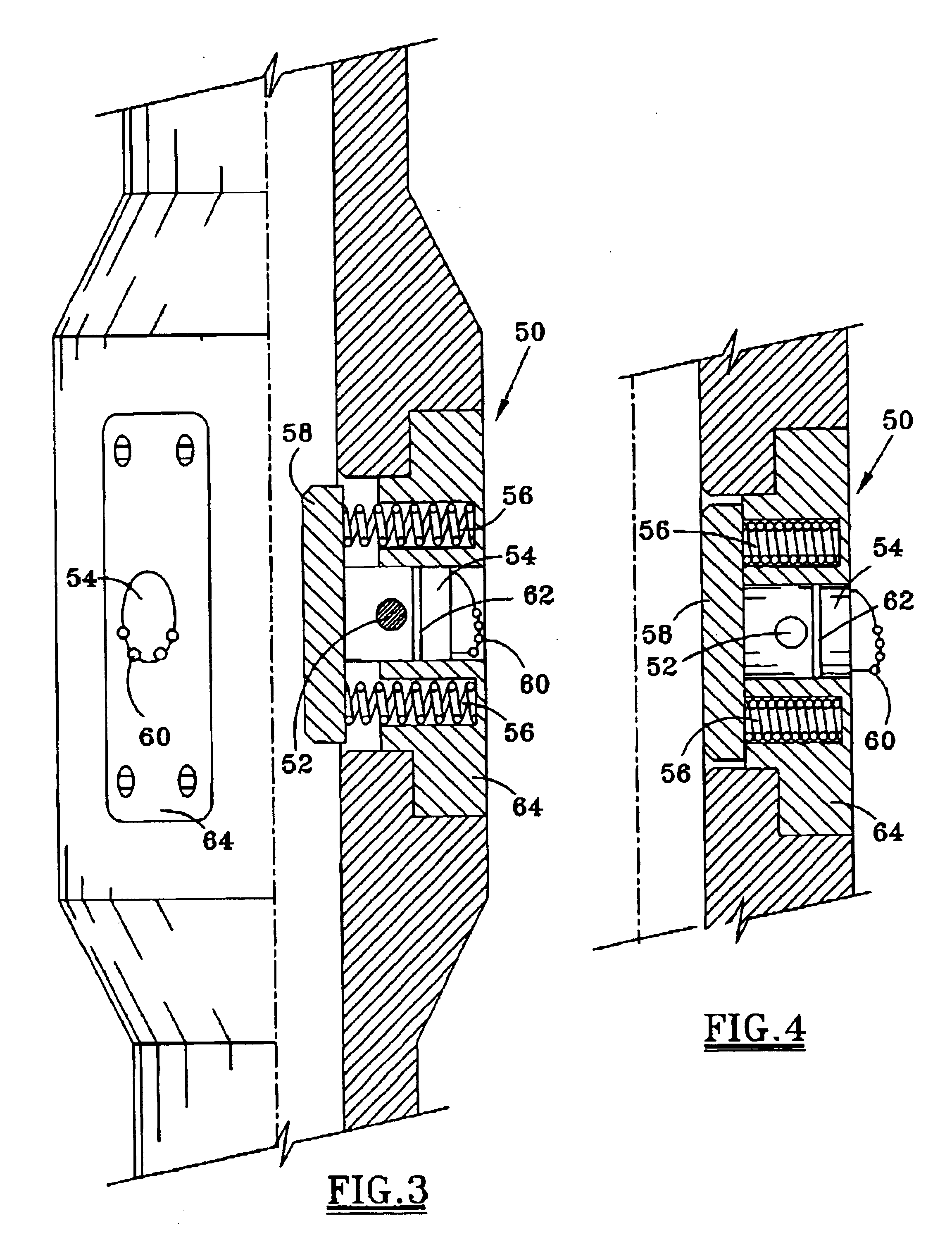
Bottom hole assembly
A bottom hole assembly for use with fracturing or fracing a wellbore using coiled tubing is described having a first packing element and a second packing on a mandrel. The bottom hole assembly may be run into the wellbore such that the packing elements straddle the zone to be fraced. Also described is a timing mechanism to prevent the closing of dump ports before the bottom hole assembly may be flushed of the sand. A release tool is described that allows an operator to apply force to the coiled tubing to dislodge a bottom hole assembly without completely releasing the bottom hole assembly. Also disclosed is a collar locator capable of being utilized in a fracing process. Methods of using the above described components are also disclosed.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
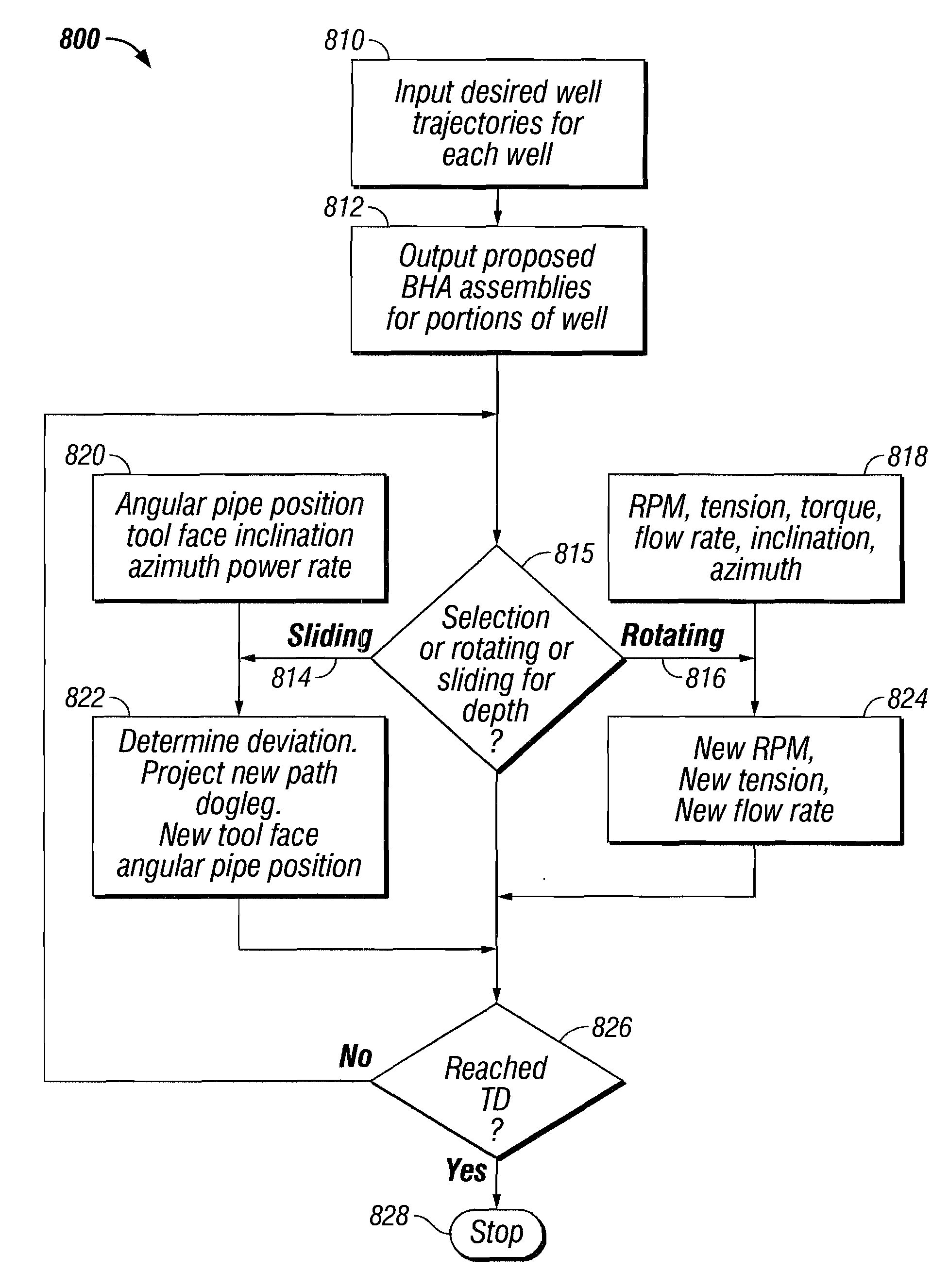
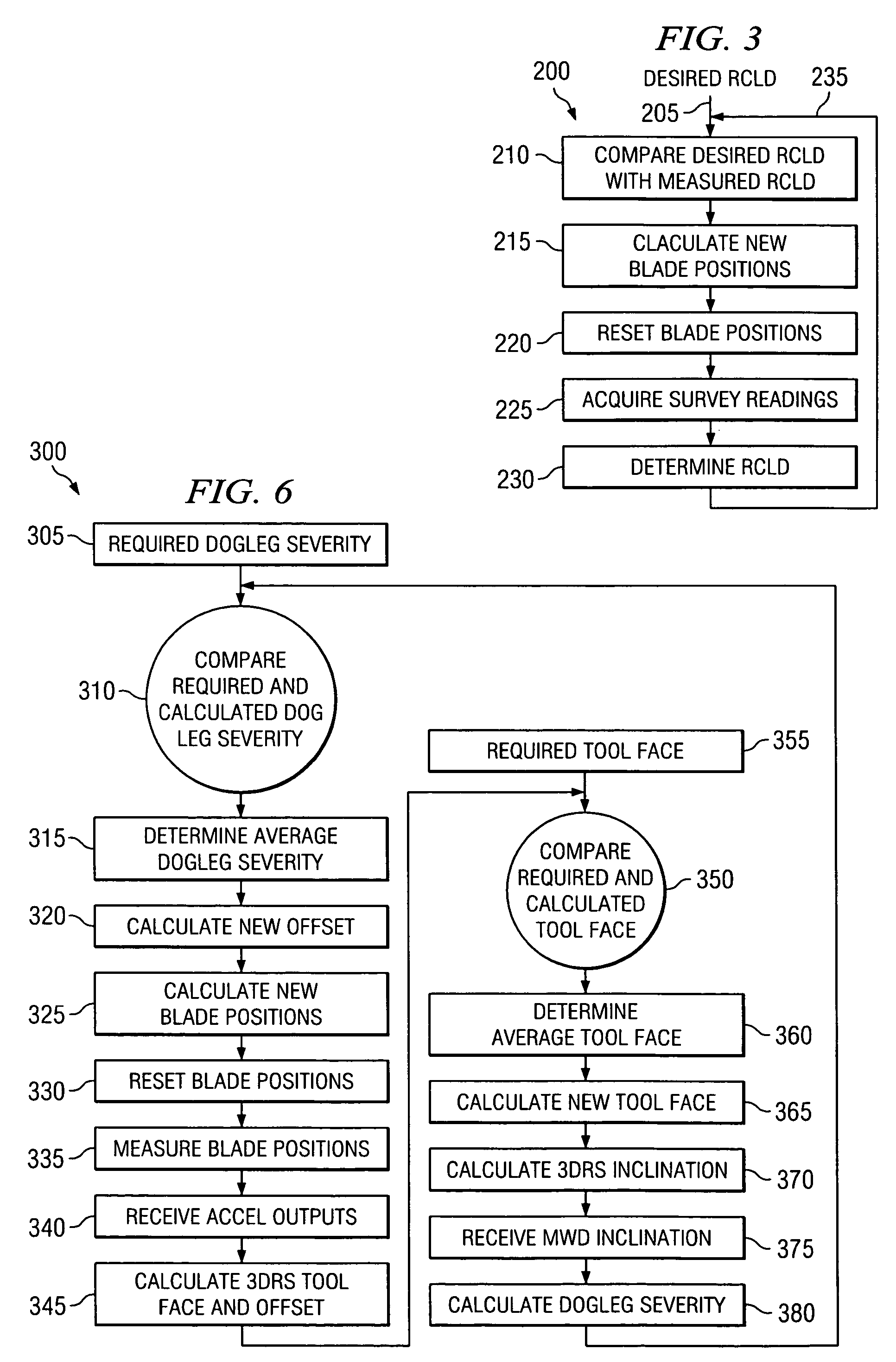
Directional Drilling System and Software Method
InactiveUS20080314641A1Eliminate needSurveyDirectional drillingBottom hole assemblyDirectional drilling
A software method for directionally drilling a plurality of wells capable of providing directional drilling services to hundreds of wells. The software method may comprise steps from determining a BHA for a portion of a well, determining a deviation between the desired trajectory of the well bore and an actual trajectory of the well bore as measured at the nonmagnetic measurement portion of the bottom hole assembly, determining a dogleg of the actual trajectory, and determining a correction trajectory to reduce the deviation between the desired trajectory and the actual trajectory which produces a dogleg less than a predetermined value. The trajectory may be projected to the bit even though the nonmagnetic measurement portion of the bottom hole assembly is often separated therefrom by significant distances.
Owner:MCCLARD KEVIN
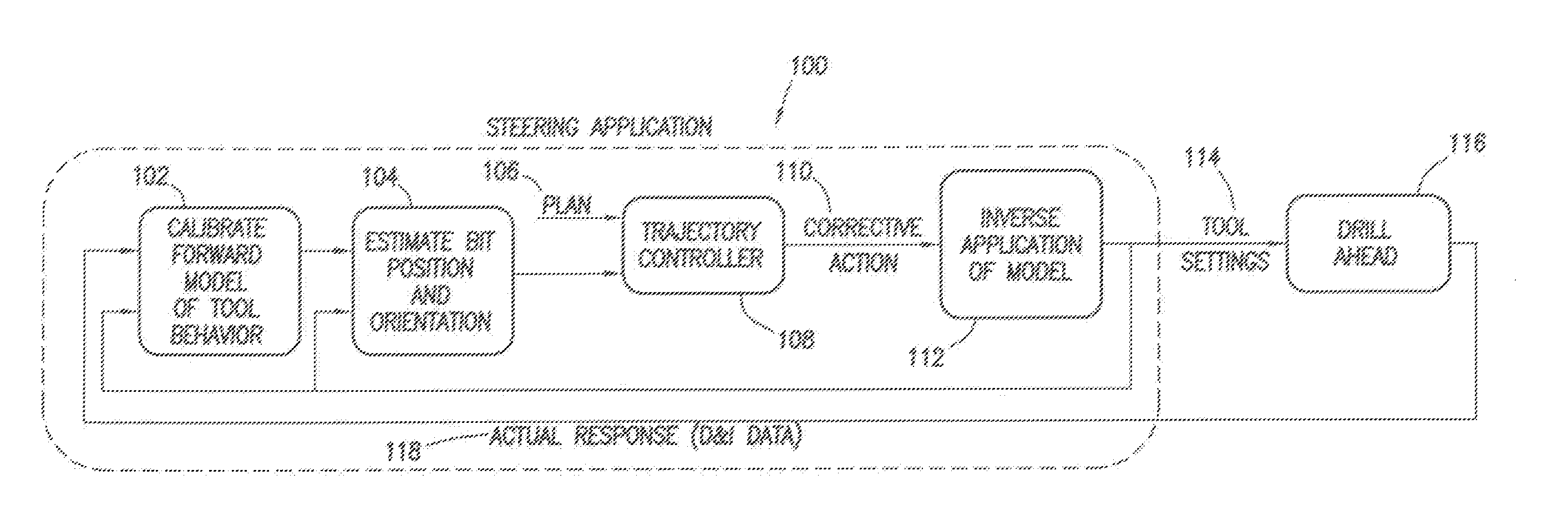
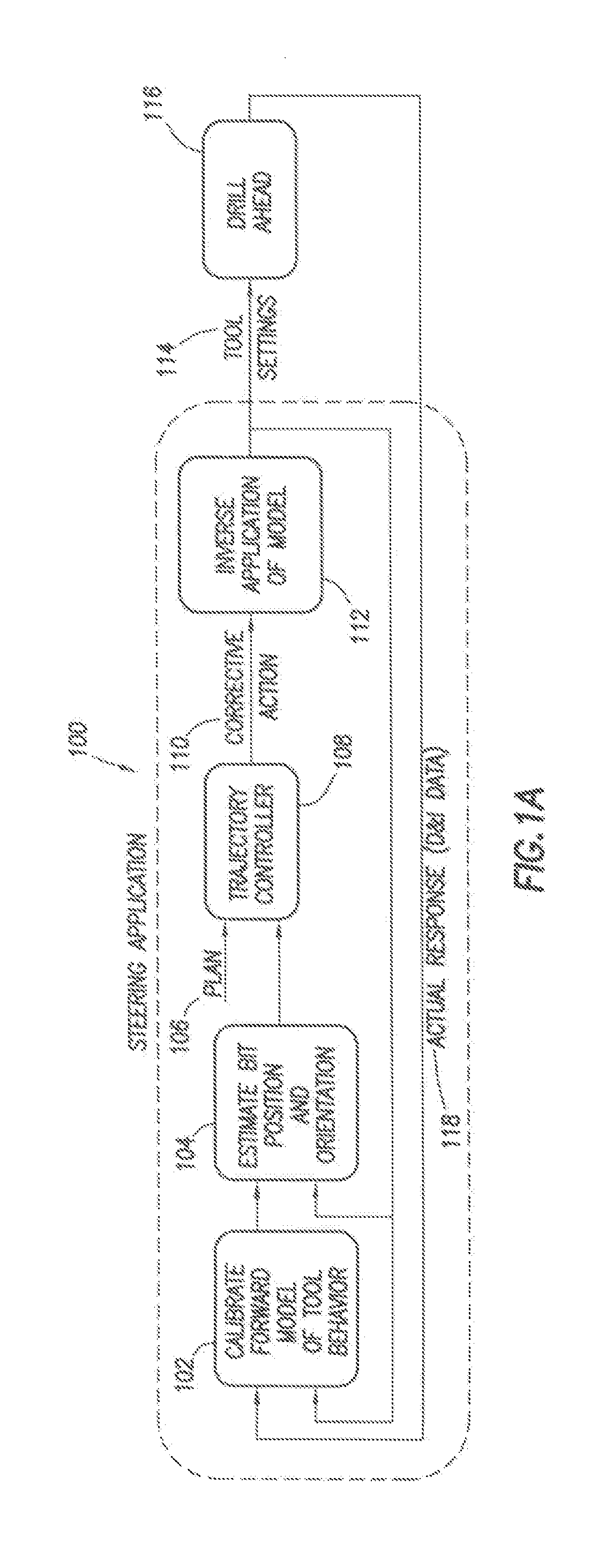
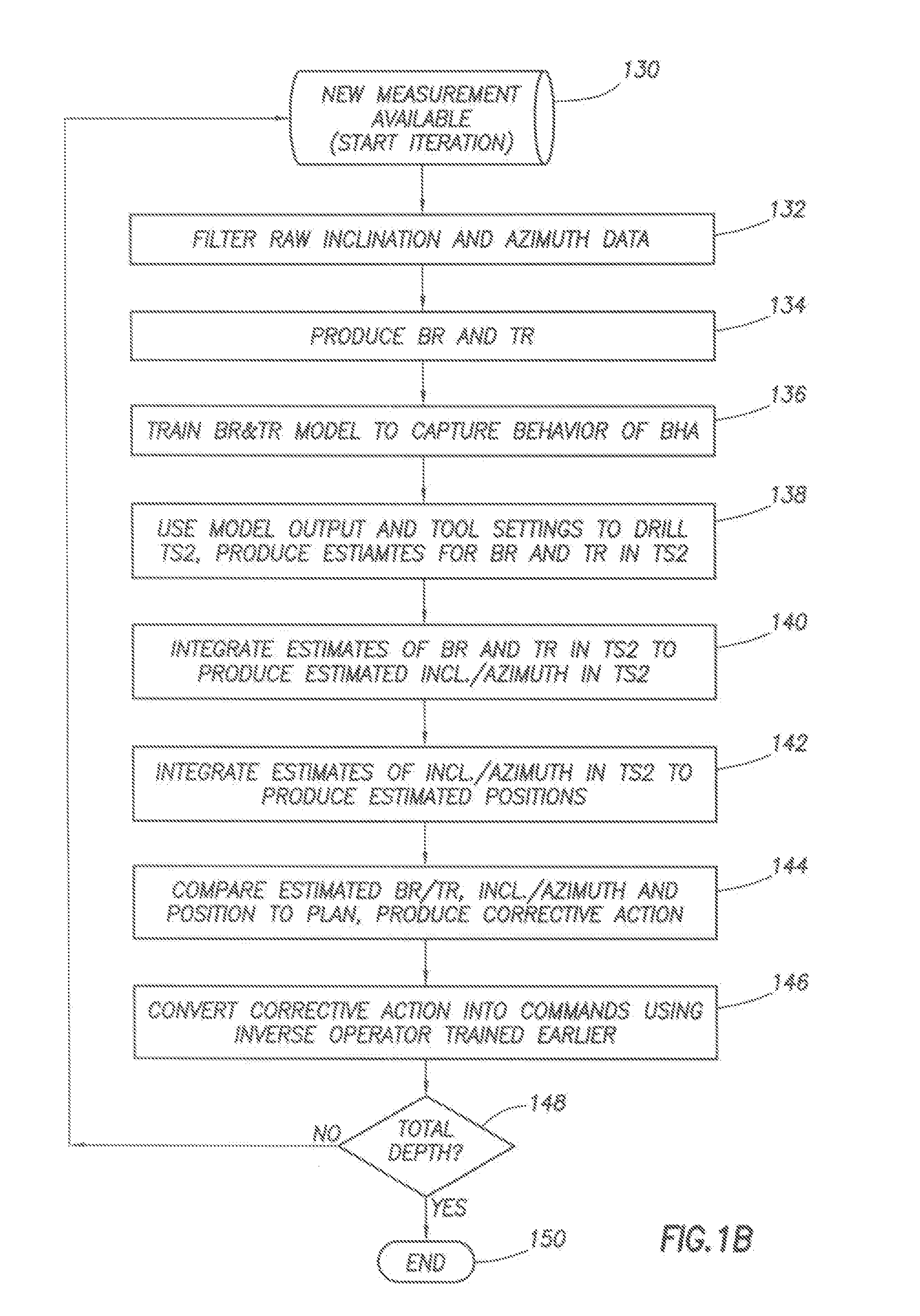
Method of Automatically controlling the Trajectory of a Drilled Well
ActiveUS20090000823A1Minimizing varianceElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingDirectional drillingRate equationAutomatic control
Steering behavior model can include build rate and / or turn rate equations to modal bottom-hole assembly behavior. Build and / or turn rate equations can be calibrated by adjusting model parameters thereof to minimize any variance between actual response 118 and estimated response produced for an interval of the well. Estimated position and orientation 104 of a bottom-hole assembly along a subsequent interval can be generated by inputting subsequent tool settings into the calibrated steering behavior model. Estimated position and orientation 104 can be compared to a well plan 106 with a controller 108 which determines a corrective action 110. Corrective action 110 can be converted from a build and / or turn rate to a set of recommended tool settings 114 by using an inverse application 112 of the steering behavior model. As additional data 118 becomes available, steering behavior model can be further calibrated 102 through iteration.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Motor Driven Hybrid Rotary Steerable System
InactiveUS20030127252A1Minimizes amount of electrical powerGood flexibilityDrilling rodsDerricks/mastsMotor driveShaft collar
Abstract of Disclosure A bottom hole assembly is rotatably adapted for drilling directional boreholes into an earthen formation. It has an upper stabilizer mounted to a collar, and a rotary steerable system. The rotary steerable system has integral drilling motor, an upper section connected to the collar, a steering section, and a drill bit arranged for drilling the borehole attached to the steering section. The steering section is joined at a swivel with the upper section. The steering section is actively tilted about the swivel. A lower stabilizer is mounted upon one of the upper section or the steering section such that the swivel is intermediate the drill bit and the lower stabilizer.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER WCP
Closed loop drilling assembly with electronics outside a non-rotating sleeve
InactiveUS6913095B2Increase drilling speedExtended drilling assembly lifeDrilling rodsDerricks/mastsClosed loopEngineering
A closed-loop drilling system utilizes a bottom hole assembly (“BHA”) having a steering assembly having a rotating member and a non-rotating sleeve disposed thereon. The sleeve has a plurality of expandable force application members that engage a borehole wall. A power source and associated electronics for energizing the force application members are located outside of the non-rotating sleeve. A preferred drilling system includes a surface control unit and a BHA processor cooperate to guide the drill bit along a selected well trajectory in response to parameters detected by one or more sensors. In a preferred closed-loop mode of operation, the BHA processor automatically adjusts the force application members in response to data provided by one or more sensors. In a preferred embodiment, the non-rotating sleeve and rotating member include a sensor that determines the orientation of the sleeve relative to the rotating member.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Steerable underreamer/stabilizer assembly and method
A bottom hole assembly includes a drill bit, a stabilized underreamer assembly located behind the drill bit, and a drilling assembly. A method to drill a formation includes positioning a stabilized underreamer assembly behind a drill bit, positioning a drilling assembly behind the stabilized underreamer assembly, and rotating the drill bit and stabilized underreamer assembly with the drilling assembly. A stabilized underreamer located between a directional drilling assembly and a drill bit includes at least one arm assembly extending from the stabilized underreamer assembly, wherein the arm assembly includes a stabilizer portion and an underreamer cutting structure.
Owner:SMITH INT INC
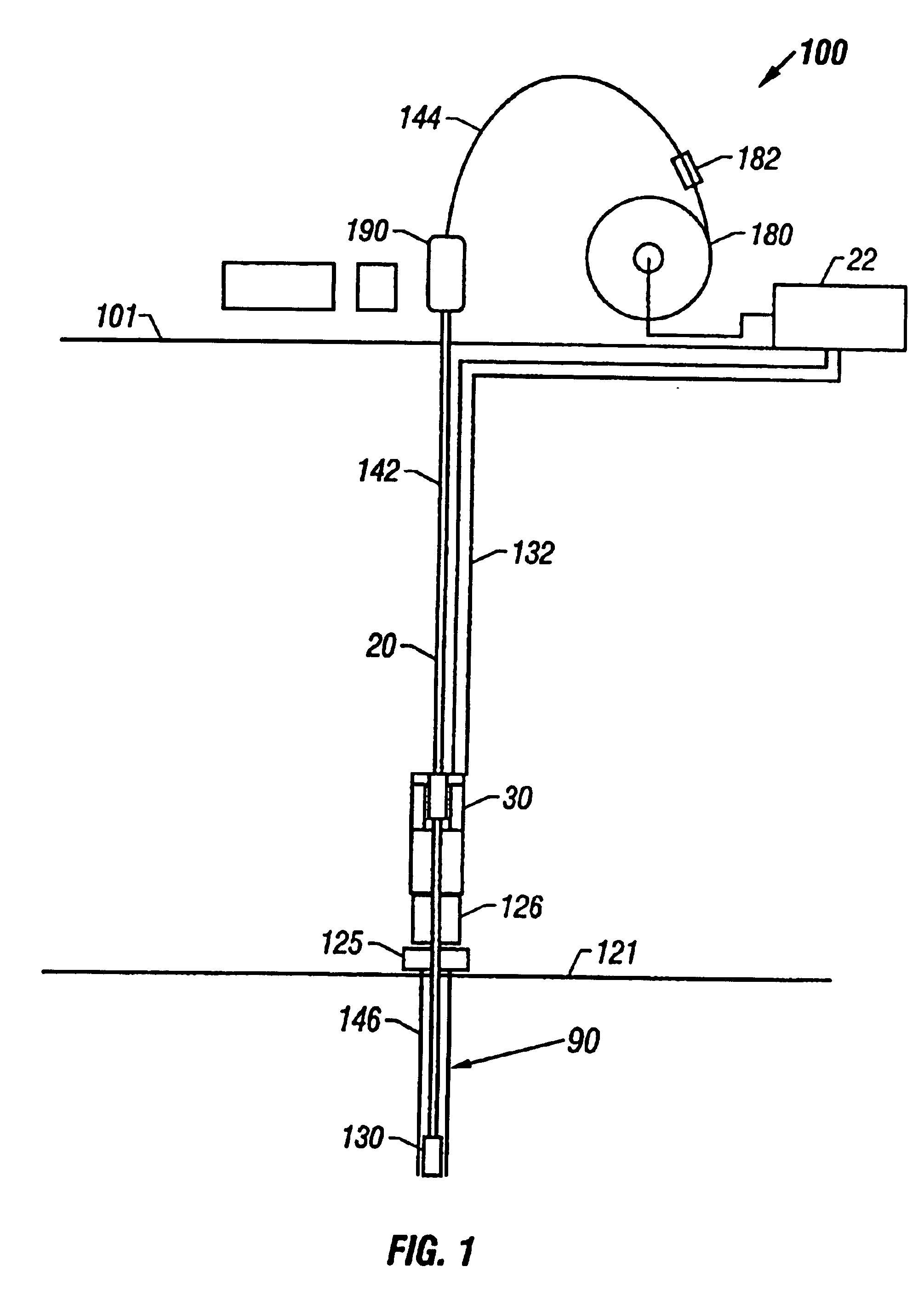
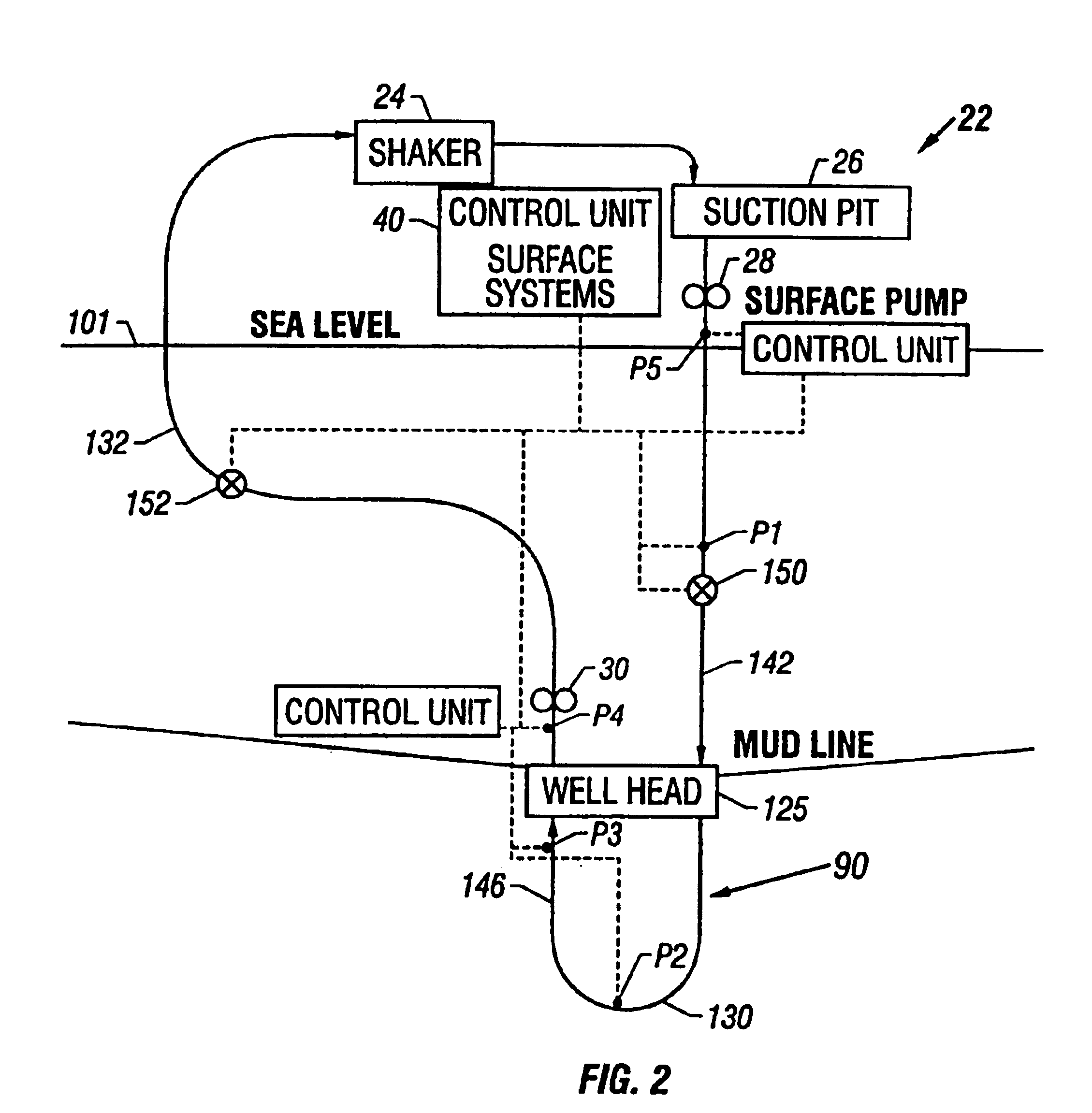
Subsea wellbore drilling system for reducing bottom hole pressure
InactiveUS6854532B2Easy to deployFaster and effective subsea downhole operationDrilling rodsConstructionsDelivery systemBottom hole assembly
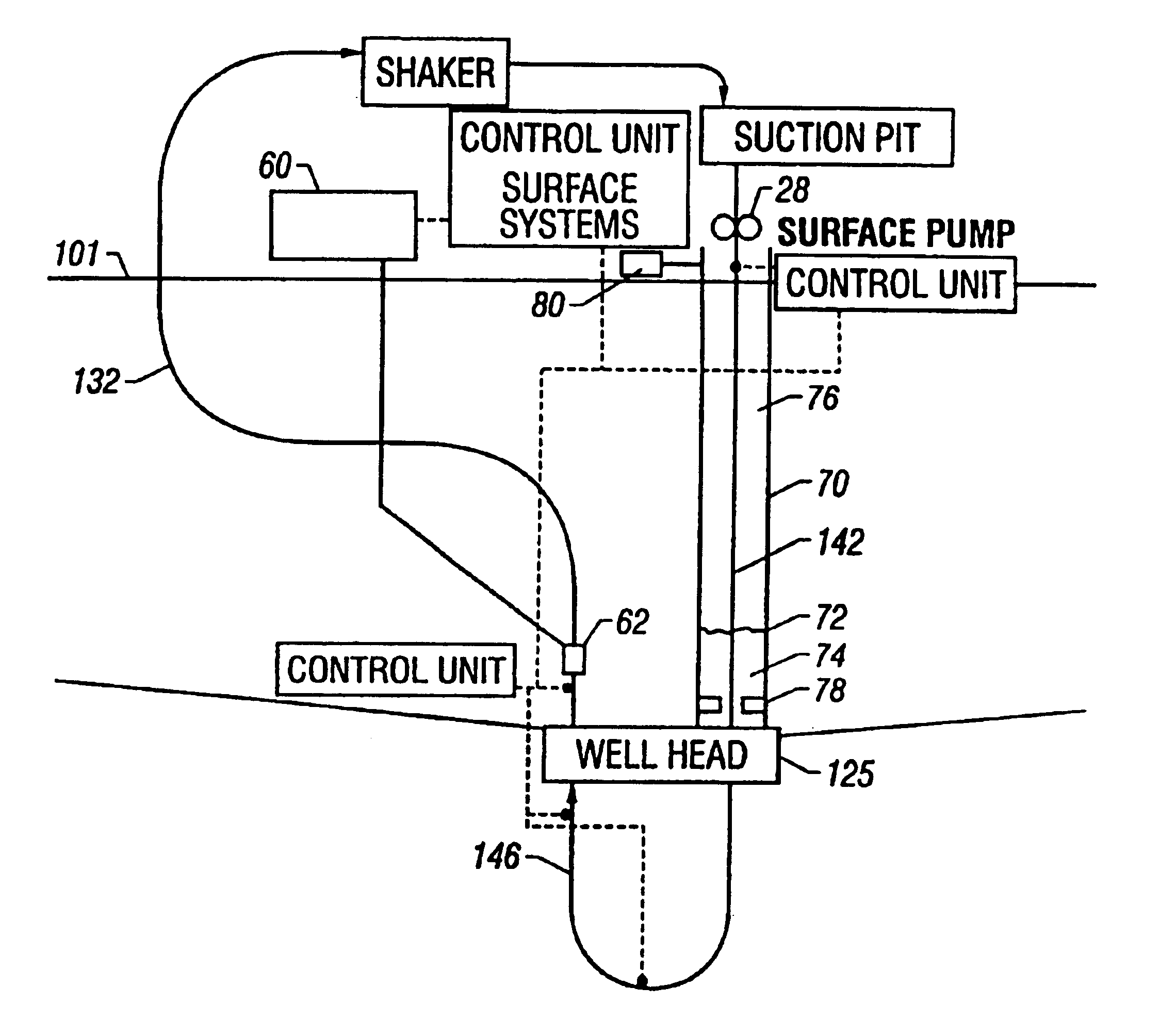
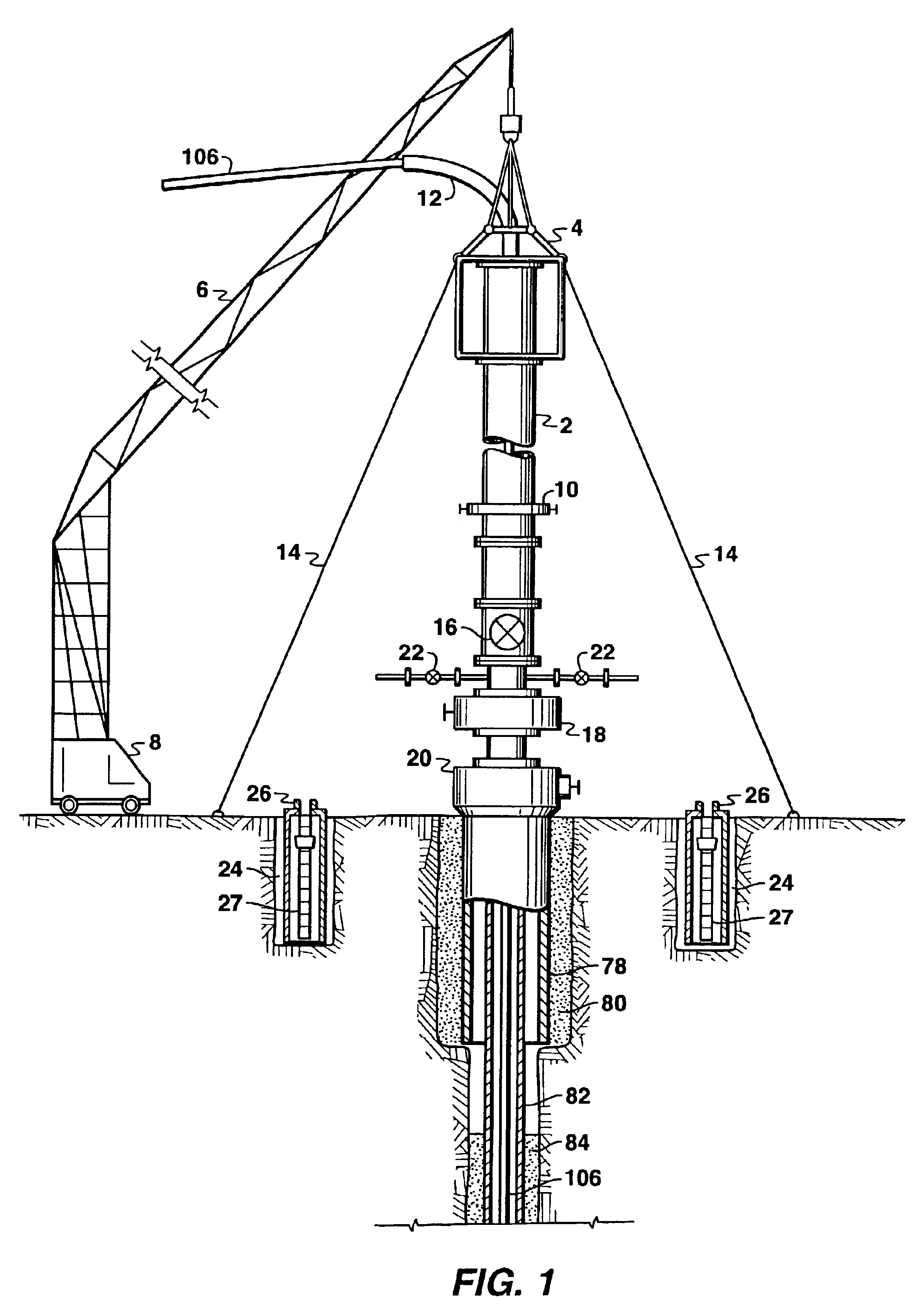
The present invention provides drilling systems for drilling subsea wellbores. The drilling system includes a tubing that passes through a sea bottom wellhead and carries a drill bit. A drilling fluid system continuously supplies drilling fluid into the tubing, which discharges at the drill bit bottom and returns to the wellhead through an annulus between the tubing and the wellbore carrying the drill cuttings. A fluid return line extending from the wellhead equipment to the drilling vessel transports the returning fluid to the surface. In a riserless arrangement, the return fluid line is separate and spaced apart from the tubing. In a system using a riser, the return fluid line may be the riser or a separate line carried by the riser. The tubing may be coiled tubing with a drilling motor in the bottom hole assembly driving the drill bit. A suction pump coupled to the annulus is used to control the bottom hole pressure during drilling operations, making it possible to use heavier drilling muds and drill to greater depths than would be possible without the suction pump. An optional delivery system continuously injects a flowable material, whose fluid density is less than the density of the drilling fluid, into the returning fluid at one or more suitable locations the rate of such lighter material can be controlled to provide supplementary regulation of the pressure. Various pressure, temperature, flow rate and kick sensors included in the drilling system provide signals to a controller that controls the suction pump, the surface mud pump, a number of flow control devices, and the optional delivery system.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
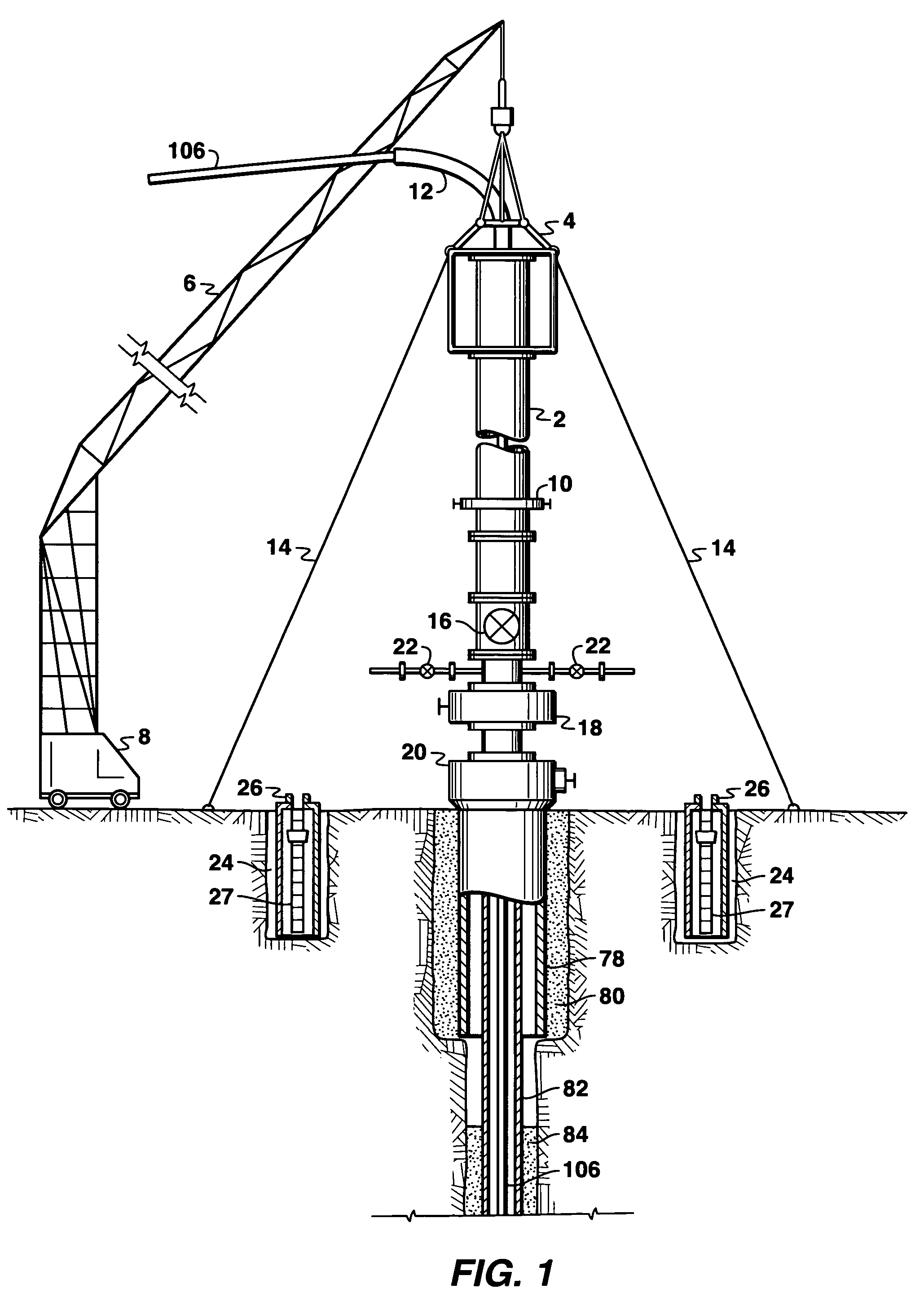
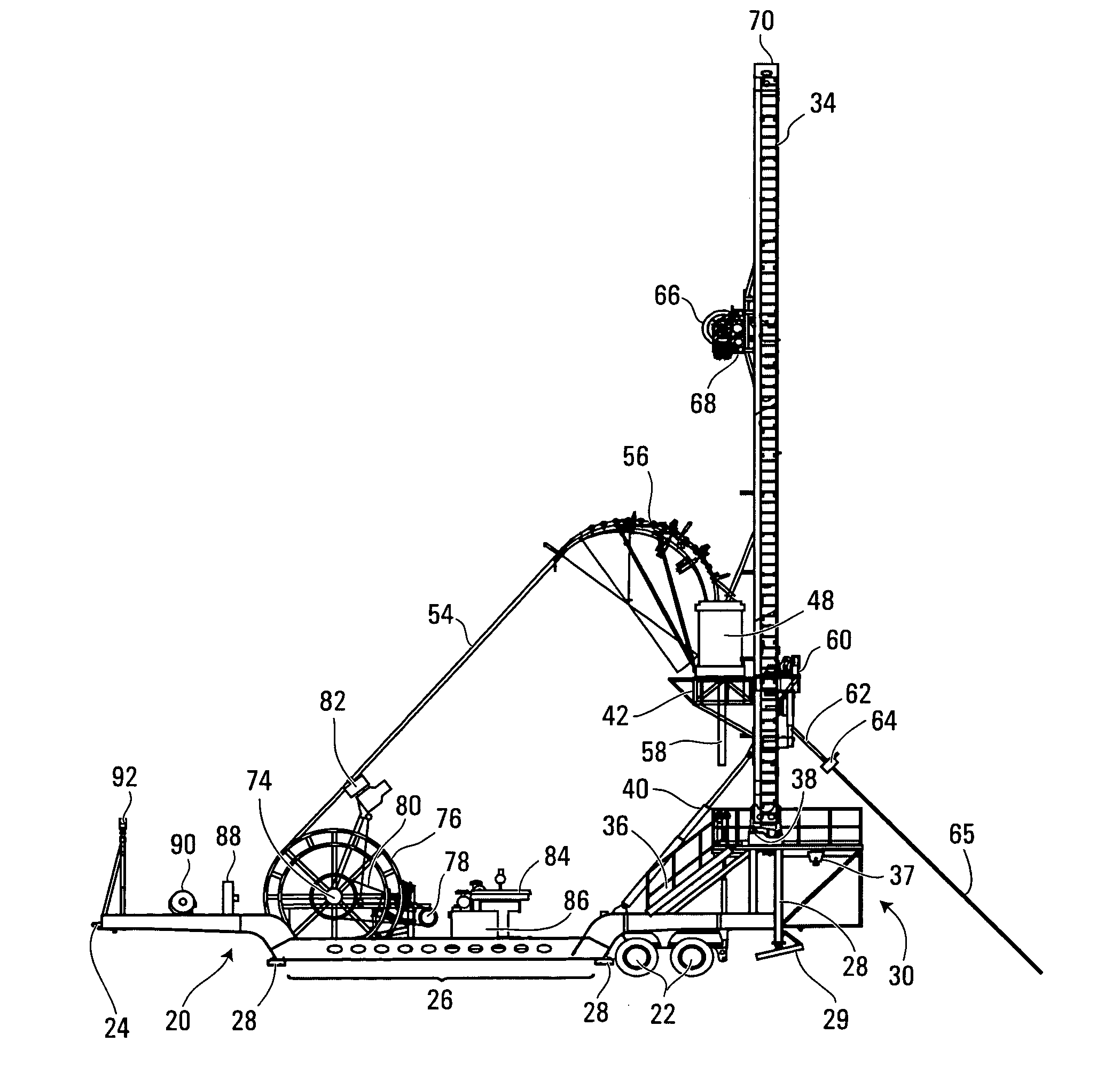
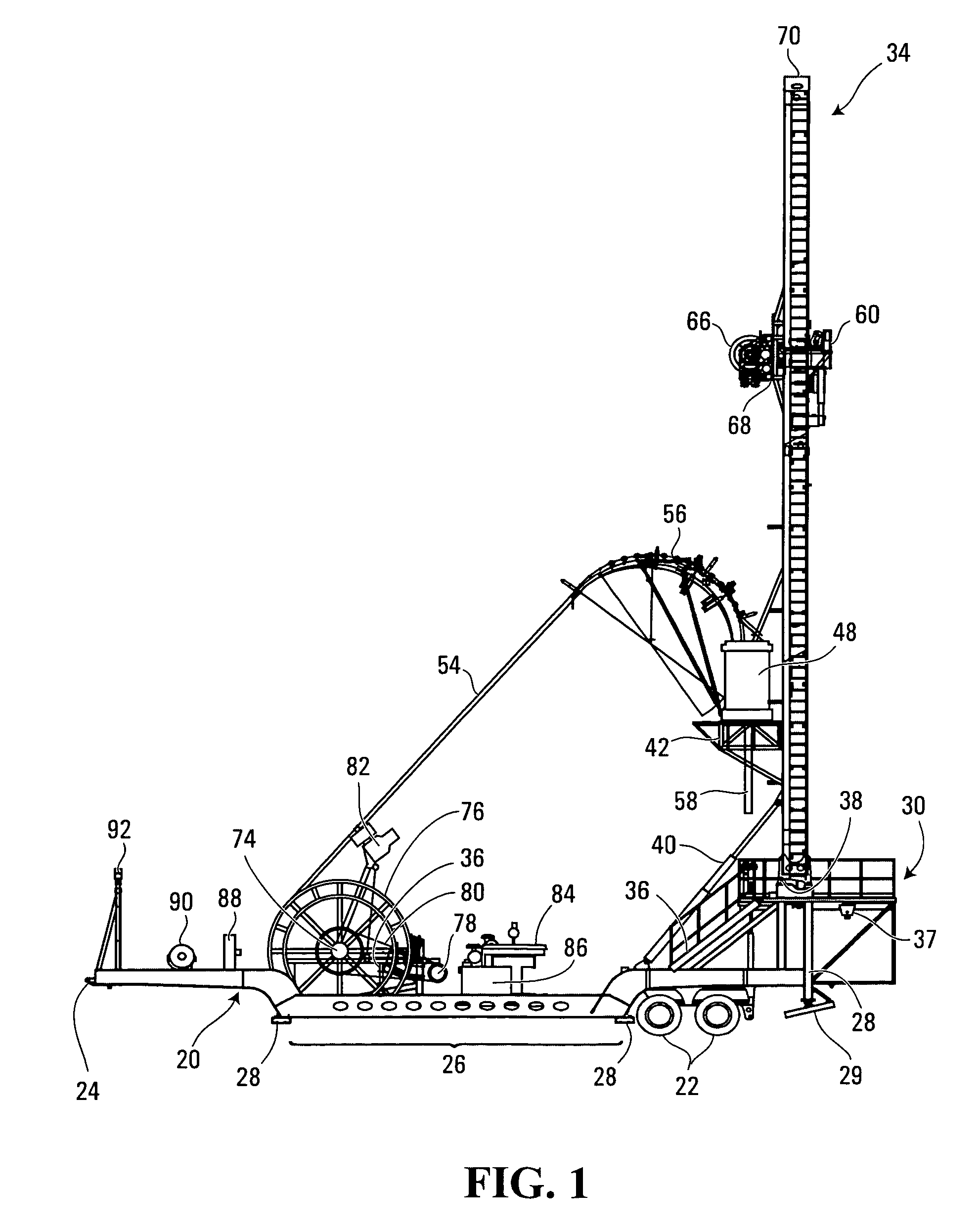
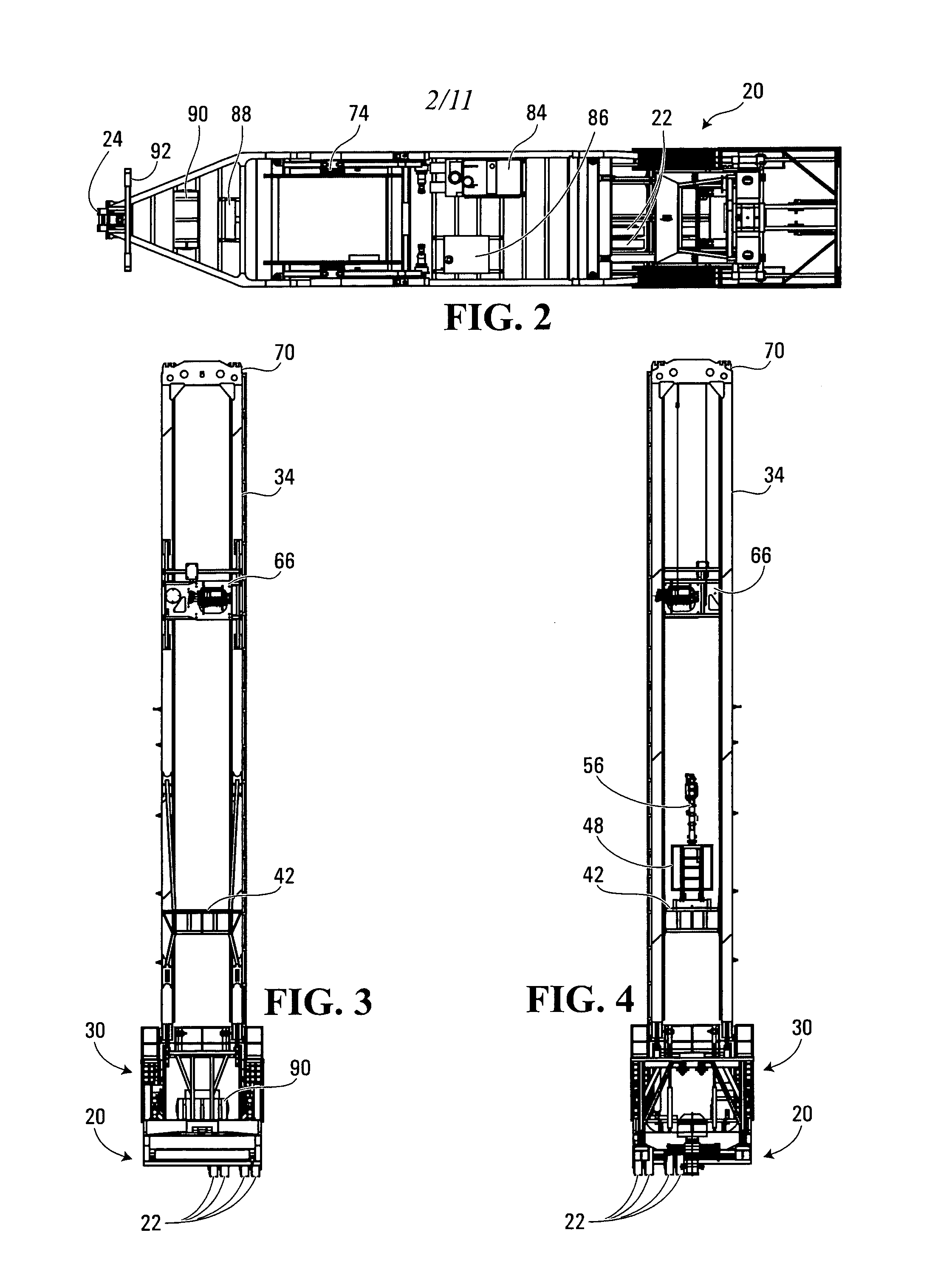
Drilling rig apparatus and downhole tool assembly system and method
A drilling rig is provided which is adapted to selectively drill using coiled tubing and jointed-pipe. The rig includes a base, a mast, a top drive slidably mounted to said mast for performing jointed-pipe operations, and a tubing injector for performing coiled tubing operations, mounted on said mast for selective movement from a first position in which the injector is in line with the mast and a second position in which the injector is out of line with the mast to permit jointed-pipe operations by the top drive. The rig is uniquely suited to easily and quickly assemble bottom hole assemblies (BHA's), and to connect such BHA's to coiled tubing.
Owner:SAVANNA ENERGY SERVICES
Method and apparatus for stimulation of multiple formation intervals
The invention discloses methods of, as well as apparatus and systems for, perforating and treating multiple intervals of one or more subterranean formations intersected by a wellbore by deploying within said wellbore a bottom-hole assembly (“BHA”) having a perforating device and a sealing mechanisms, wherein pressure communication is established between the portions of the wellbore above and below the sealing mechanism. The BHA is positioned within the wellbore such that the sealing mechanism, when actuated, establishes a hydraulic seal in the wellbore to positively force fluid to enter the perforations corresponding to the interval to be treated. A treating fluid is pumped down the wellbore and into the perforations created in the perforated interval. The sealing mechanism is released, and the steps are repeated for as many intervals as desired, without having to remove the BHA from said wellbore.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL UPSTREAM RES CO
Bidirectional drill string telemetry for measuring and drilling control
The disclosure has application for use in conjunction with an operation of drilling an earth borehole using: a drilling rig, a drill string having its generally upper end mechanically coupleable with and suspendable from the drilling rig, and a bottom hole assembly adjacent the lower end the drill string, the bottom hole assembly including a drill bit at its lower end. A method is set forth for obtaining information about at least one parameter sensed at the bottom hole assembly, including the following steps: providing at least one measuring device in the bottom hole assembly, the at least one measuring device producing measurement data representative of a measured condition at the bottom hole assembly; providing an uphole processor system at the earth's surface; providing a drill string telemetry system coupled with the at least one measuring device and coupled with the uphole processor system; and transmitting the data from the measuring device to the uphole processor system via the drill string telemetry system.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
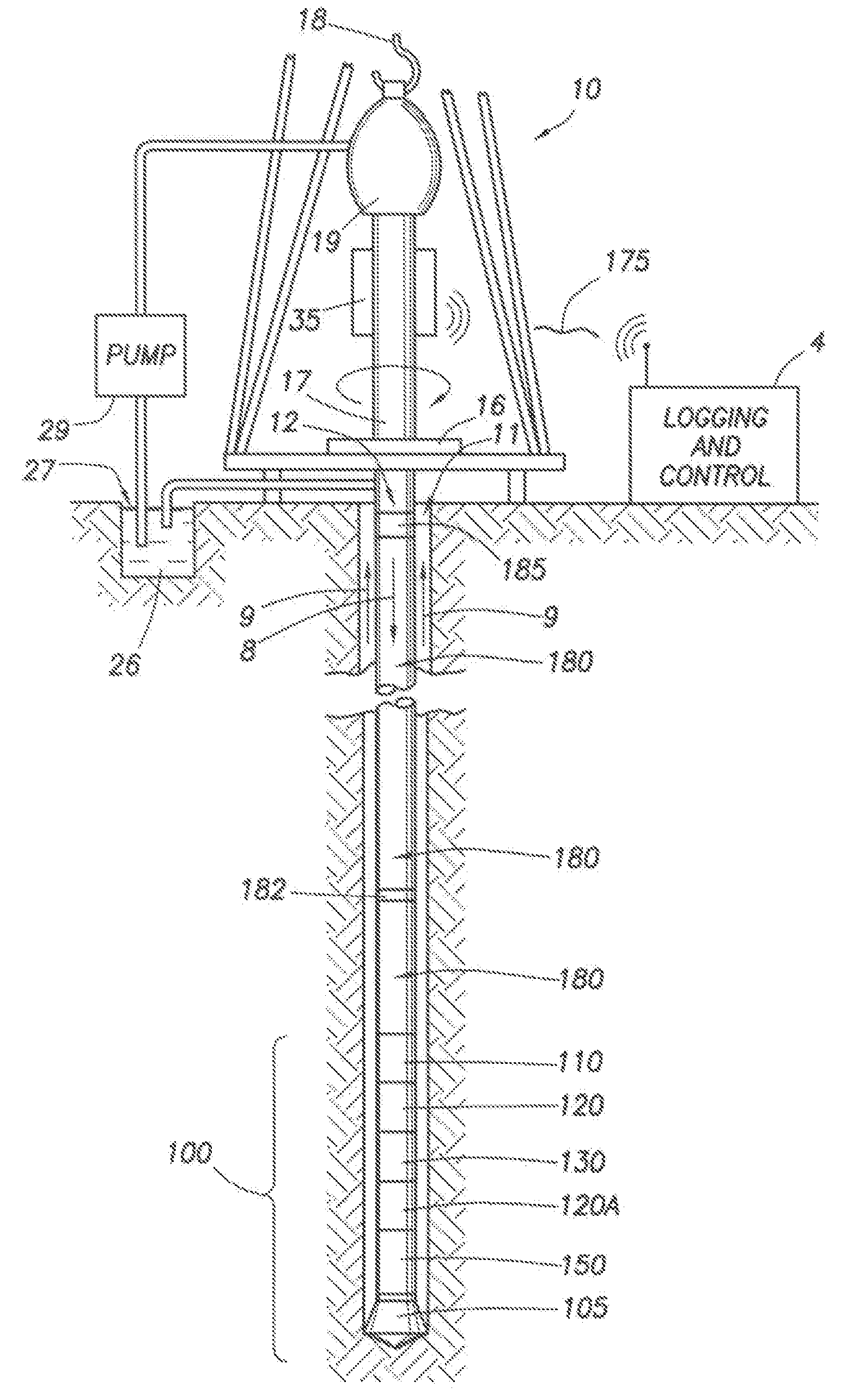
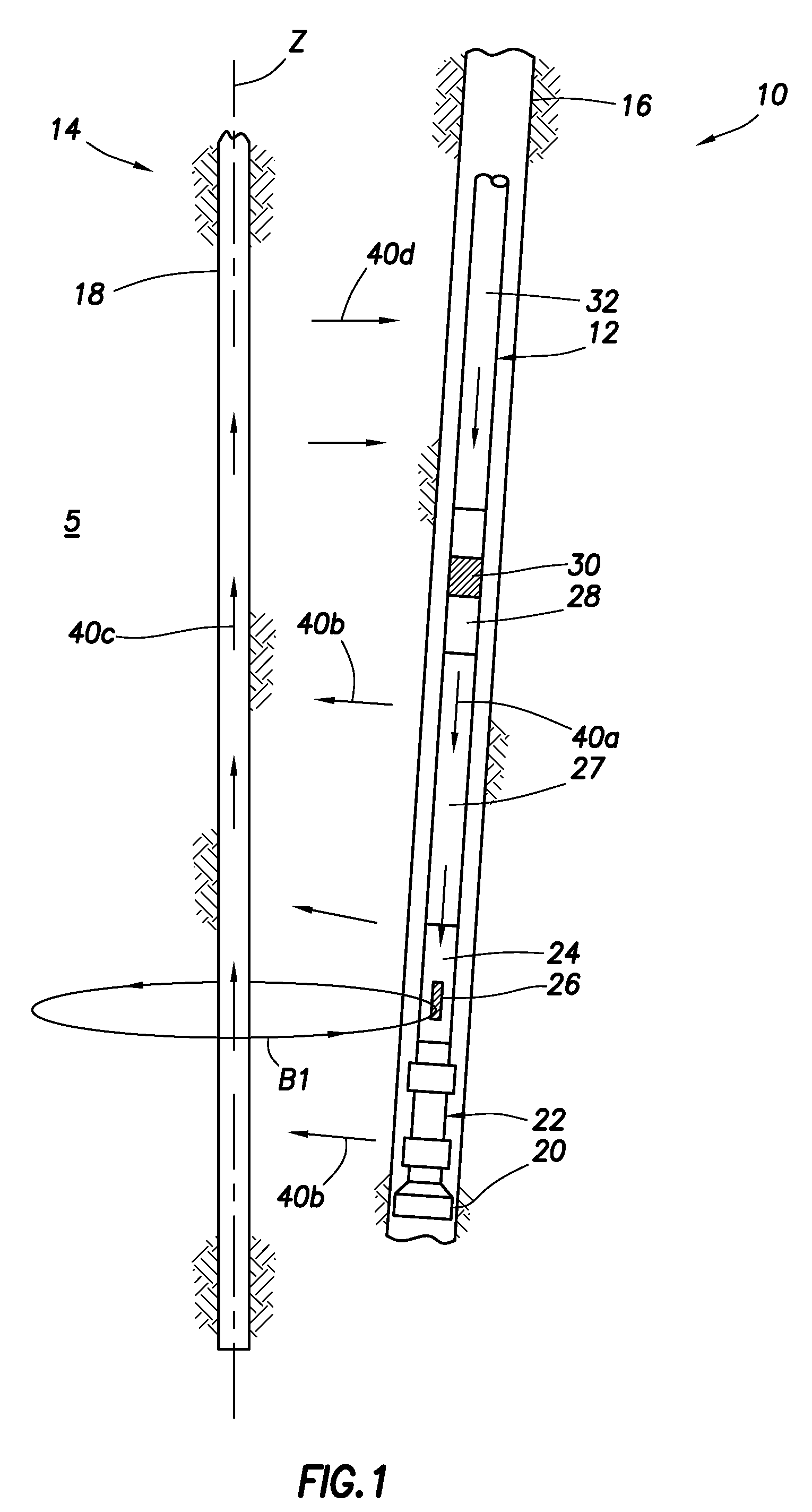
Drilling system and method
A drilling system for drilling a bore hole into an earth formation, the bore hole having an inside wall. A drill string reaches into the bore hole from a surface, leaving a drilling fluid return passage between the drill string and the bore hole inside wall. A bottom hole assembly is supported by the drill string, and a drilling fluid discharge conduit is provided in fluid communication with the drilling fluid return passage. A drilling fluid is pumped through the drill string into the bore hole and to the drilling fluid discharge conduit via the drilling fluid return passage. Means are provided for obtaining information on the existing down hole pressure of the drilling fluid in the vicinity of the bottom hole assembly and back pressure means for controlling the drilling fluid back pressure. Back pressure control means control the back pressure means, wherein the back pressure control means comprises a programmable pressure monitoring and control system arranged to receive the information on the existing down hole pressure, calculate a predicted down hole pressure using a model, compare the predicted down hole pressure to a desired down hole pressure, and to utilize the differential between the calculated and desired pressures to control said fluid back pressure means.
Owner:SHELL OIL CO
Method of Designing a Bottom Hole Assembly and a Bottom Hole Assembly
A bottom hole assembly containing a drill bit. The drill bit additionally has a plurality of primary cutter elements mounted thereto. The plurality of cutter elements comprise one or more first cutter elements and one or more second cutter elements. The second cutter element differs from the first cutter element in at least one cutter element property. The first cutter element has a diamond body containing a first region comprising an infiltrant material disposed within the interstitial regions. The first region is located remote from the working surface of the diamond body. The first cutter element also contains a second region comprising interstitial regions that are substantially free of the infiltrant material. The second region is located along at least the working surface of the diamond body. Also included are a cutter element, method of designing a bottom hole assembly as well as method of designing a drill bit.
Owner:SMITH INT INC
Drilling with casing
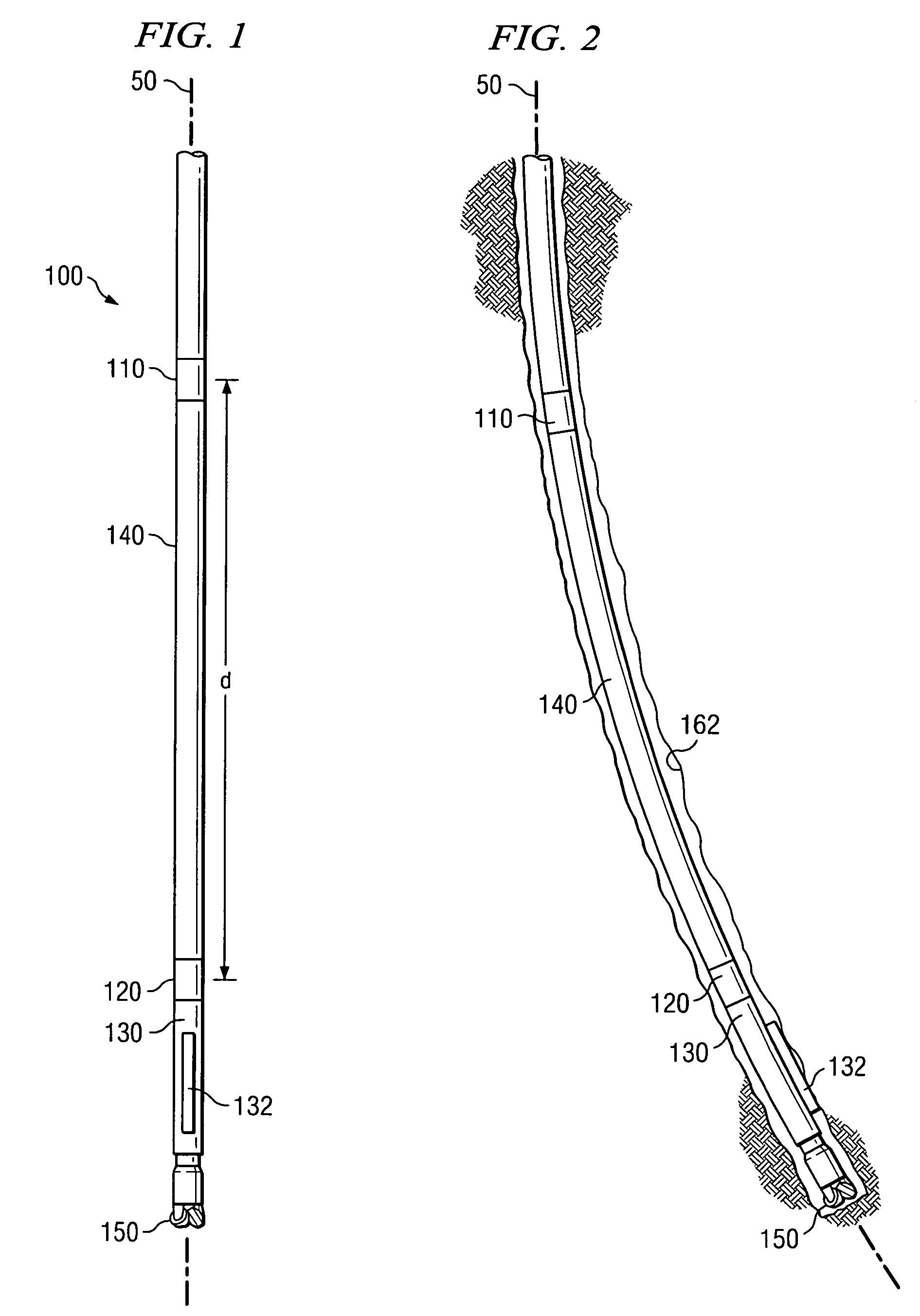
A borehole may be drilled utilizing the bottom hole assembly 10, 50 with a downhole motor 14, 110, which may offset at a selected bend angle. A bend for directional drilling may be provided by a PDM, or by a RSD. A gauge section 36 secured to the pilot bit 18 has a uniform diameter bearing surface along an axial length of at least 60% of the pilot bit diameter. The bit or reamer 16 has a bit face defining the cutting diameter of the drilled hole. The axial spacing between the bend and the bit face is controlled to less than fifteen times the bit diameter. The downhole motor, pilot bit and bit may be retrieved from the well while leaving the casing string in the well.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
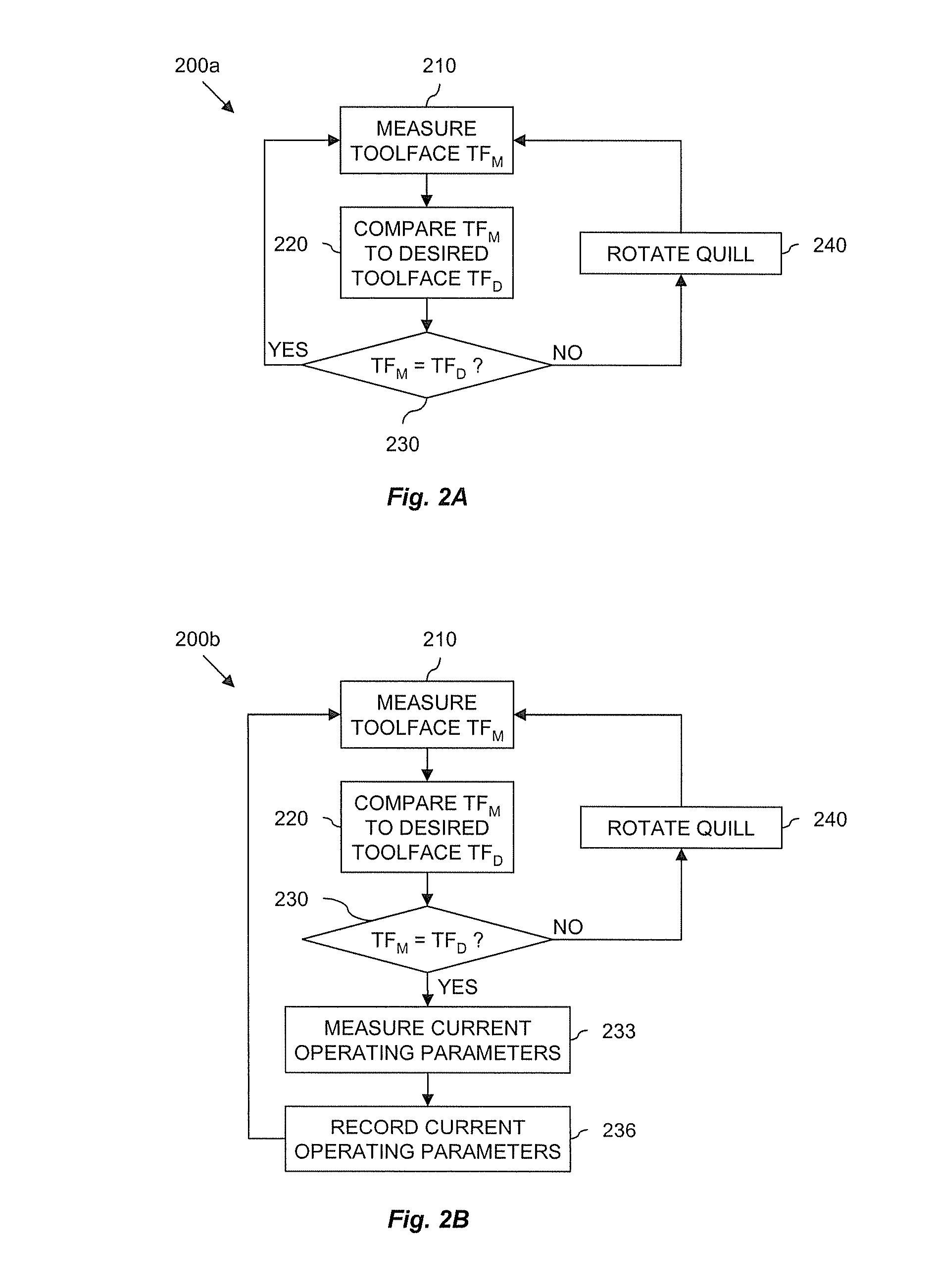
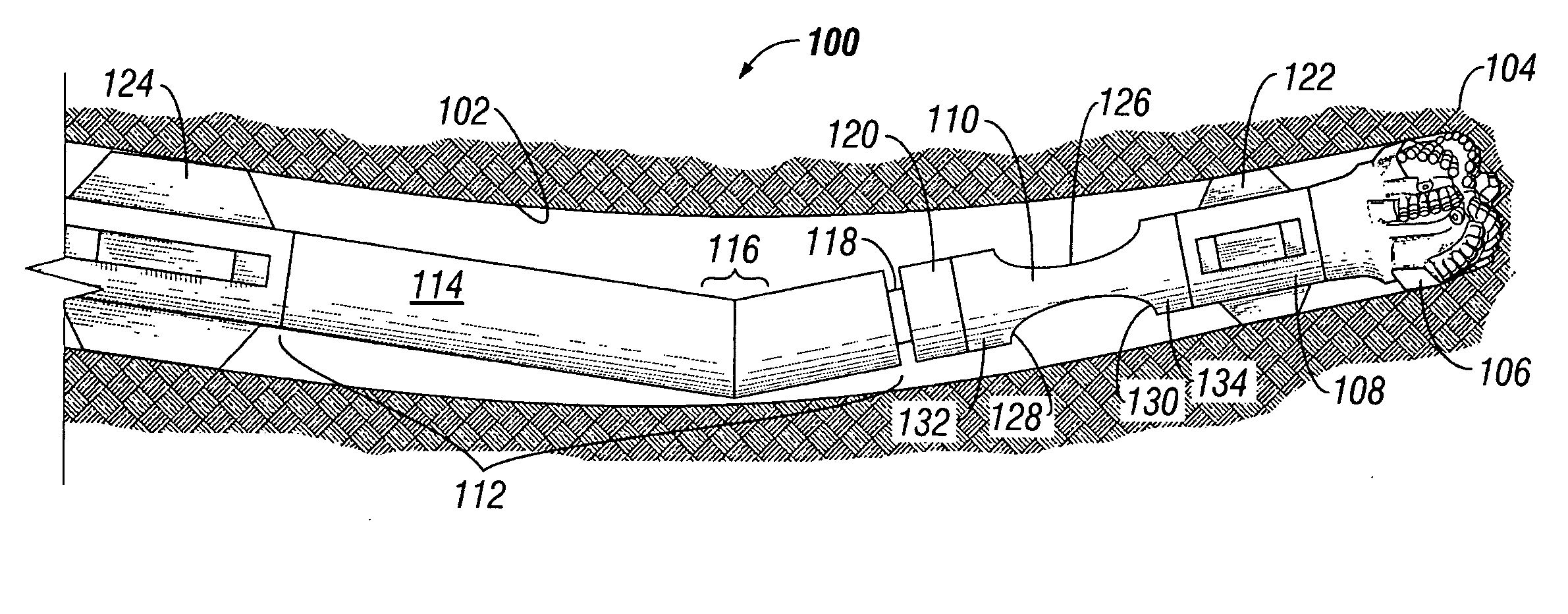
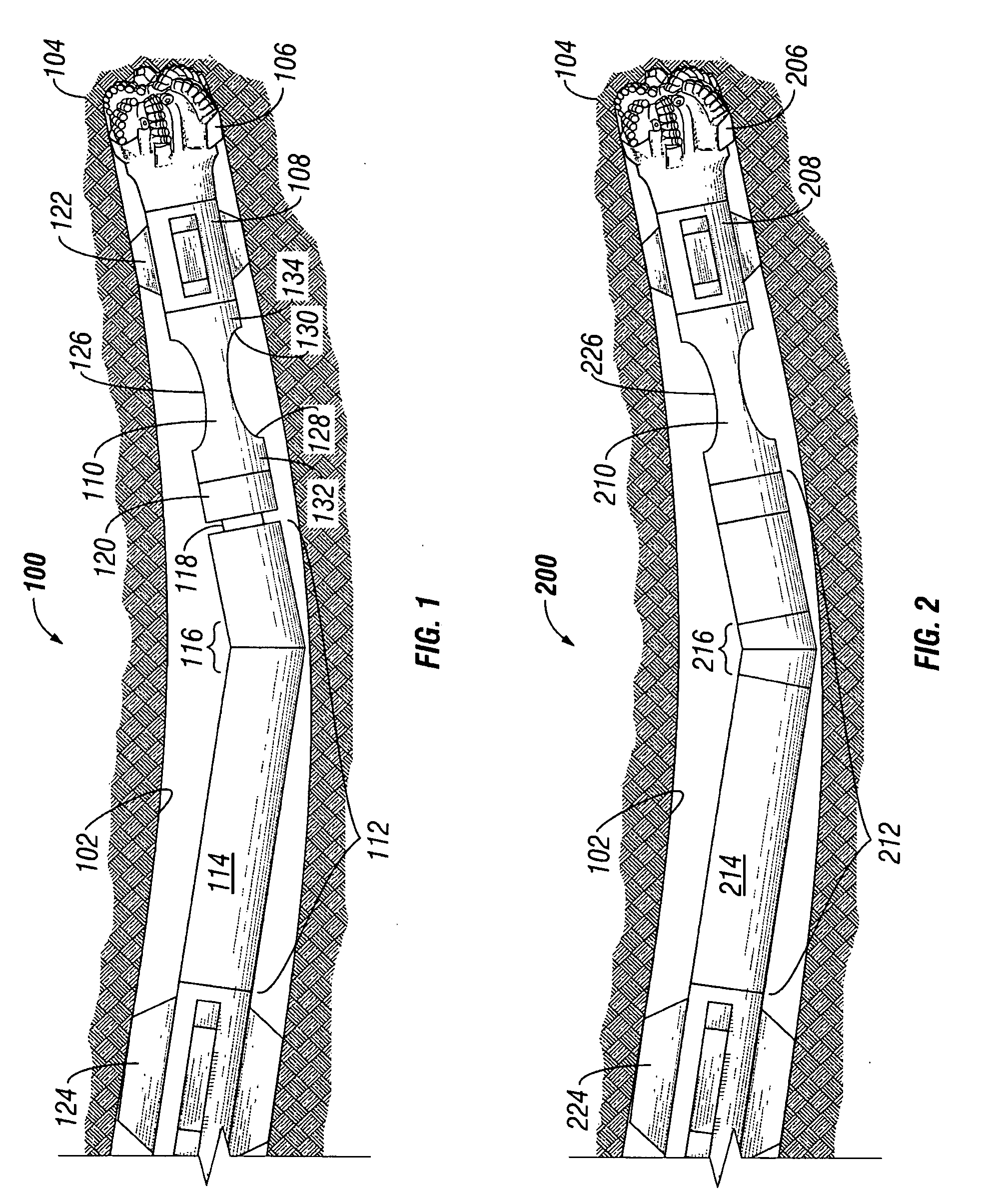
Control method for downhole steering tool
ActiveUS7243719B2Reduce twistMinimize (or even eliminate) needSurveyDirectional drillingWell drillingEngineering
A method for determining a rate of change of longitudinal direction of a subterranean borehole is provided. The method includes positioning a downhole tool in a borehole, the tool including first and second surveying devices disposed thereon. The method further includes causing the surveying devices to measure a longitudinal direction of the borehole at first and second longitudinal positions and processing the longitudinal directions of the borehole at the first and second positions to determine the rate of change of longitudinal direction of the borehole between the first and second positions. The method may further include processing the measured rate of change of longitudinal direction of the borehole and a predetermined rate of change of longitudinal direction to control the direction of drilling of the subterranean borehole. Exemplary embodiments of this invention tend to minimize the need for communication between a drilling operator and the bottom hole assembly, thereby advantageously preserving downhole communication bandwidth.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
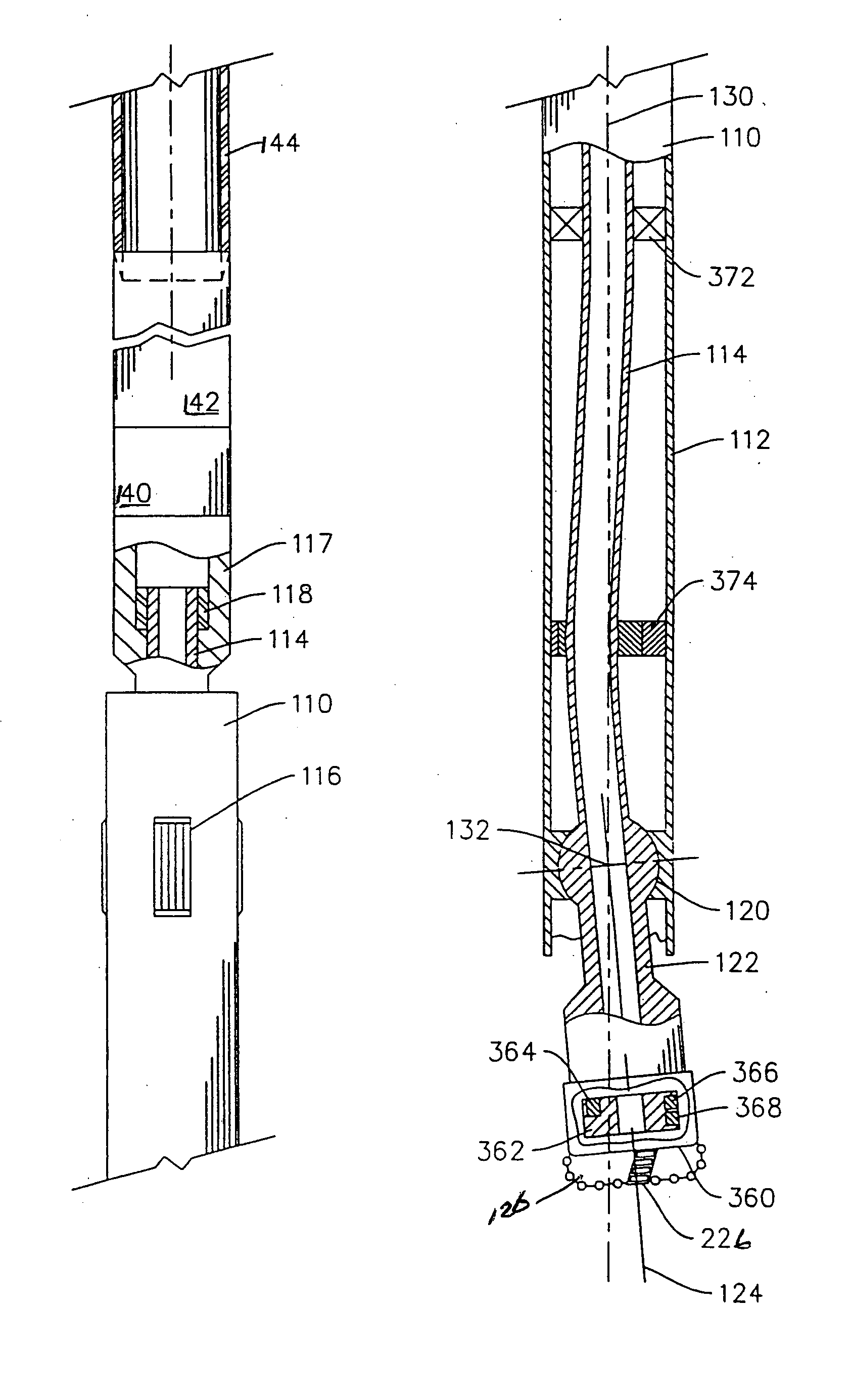
Release tool for coiled tubing
A bottom hole assembly for use with fracturing or fracing a wellbore using coiled tubing is described having a first packing element and a second packing element on a mandrel. The bottom hole assembly may be run into the wellbore such that the packing elements straddle the zone to be fraced. Also described is a timing mechanism to prevent the closing of dump ports before the bottom hole assembly may be flushed of the sand. A release tool is described that allows an operator to apply combination of force for a given amount of time to the coiled tubing to dislodge a bottom hole assembly without completely releasing the bottom hole assembly. Also disclosed is a collar locator capable of being utilized in a fracing process. Methods of using the above-described components are also disclosed.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Steerable underreaming bottom hole assembly and method
A steerable bottom hole assembly may be used for drilling both a curved section and straight section of the borehole, with the bottom hole assembly including a reamer beneath the downhole motor 12. The bottom hole assembly includes a bit 30 having a bit face defining a bit diameter, and a gauge section 32 having a substantially uniform diameter cylindrical surface approximating the bit diameter and having an axially length of at least 75% of the bit diameter. The motor is preferably run slick without stabilizers for engaging the wall of the borehole.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com