Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
653 results about "Source separation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
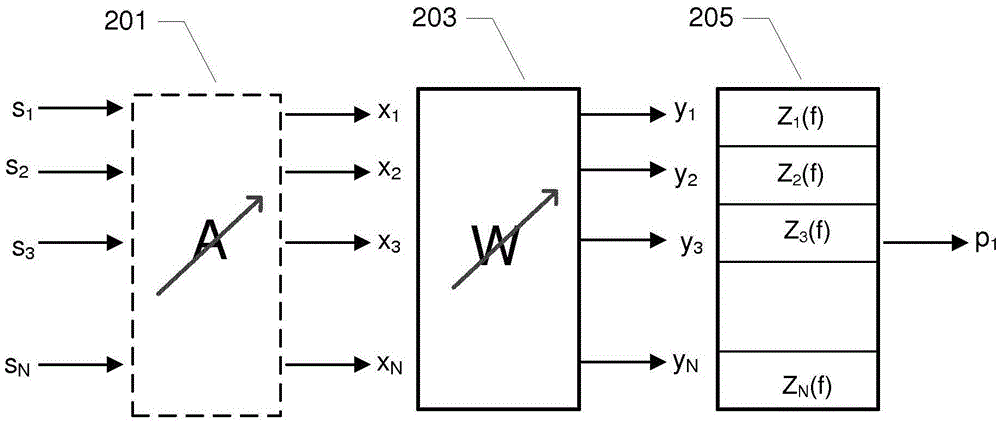
Source separation problems in digital signal processing are those in which several signals have been mixed together into a combined signal and the objective is to recover the original component signals from the combined signal. The classical example of a source separation problem is the cocktail party problem, where a number of people are talking simultaneously in a room, and a listener is trying to follow one of the discussions. The human brain can handle this sort of auditory source separation problem, but it is a difficult problem in digital signal processing. This was first analyzed by Colin Cherry. Several approaches have been proposed for the solution of this problem but development is currently still very much in progress. Some of the more successful approaches are principal components analysis and independent components analysis, which work well when there are no delays or echoes present; that is, the problem is simplified a great deal. The field of computational auditory scene analysis attempts to achieve auditory source separation using an approach that is based on human hearing. The human brain must also solve this problem in real time.
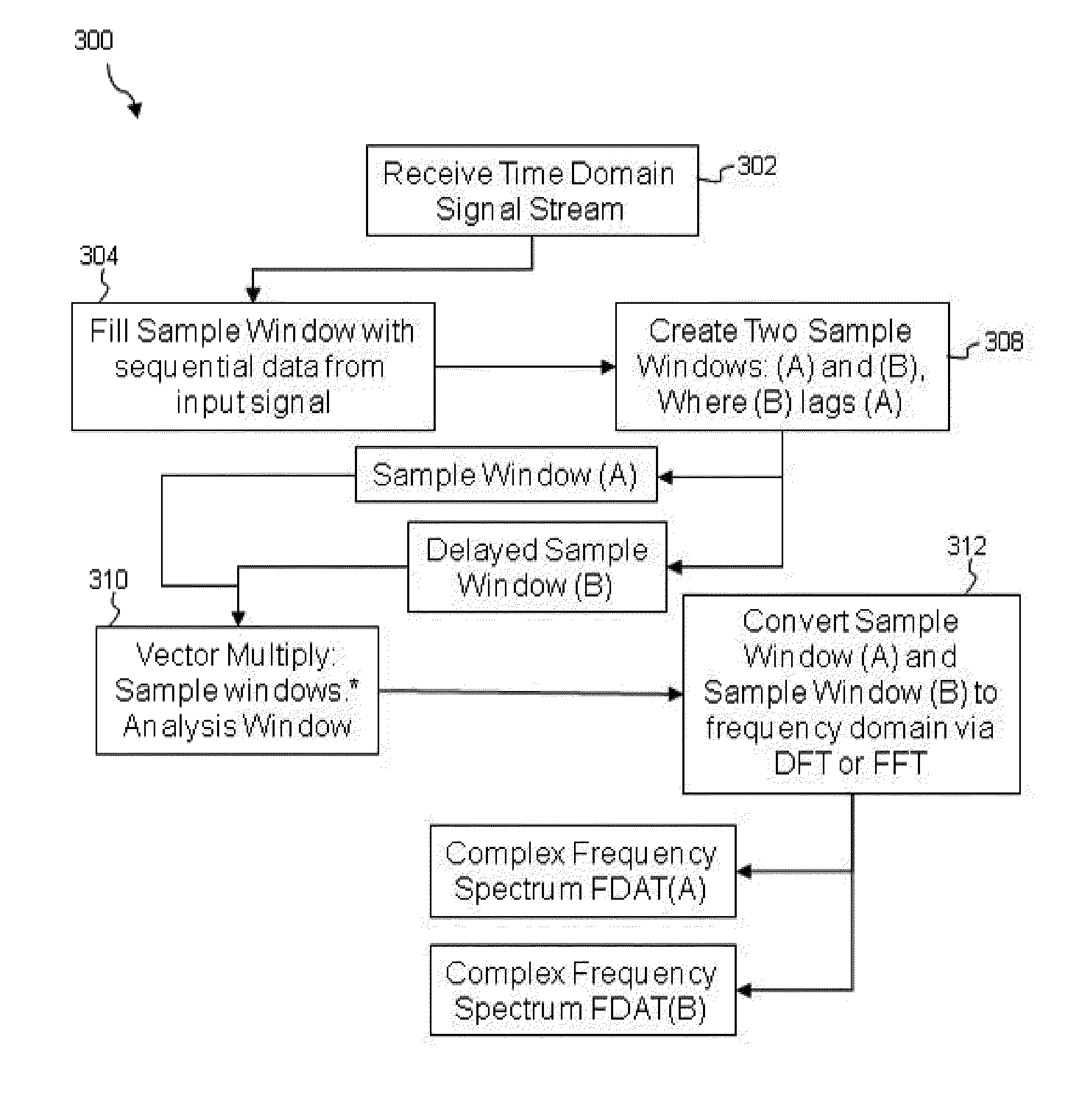
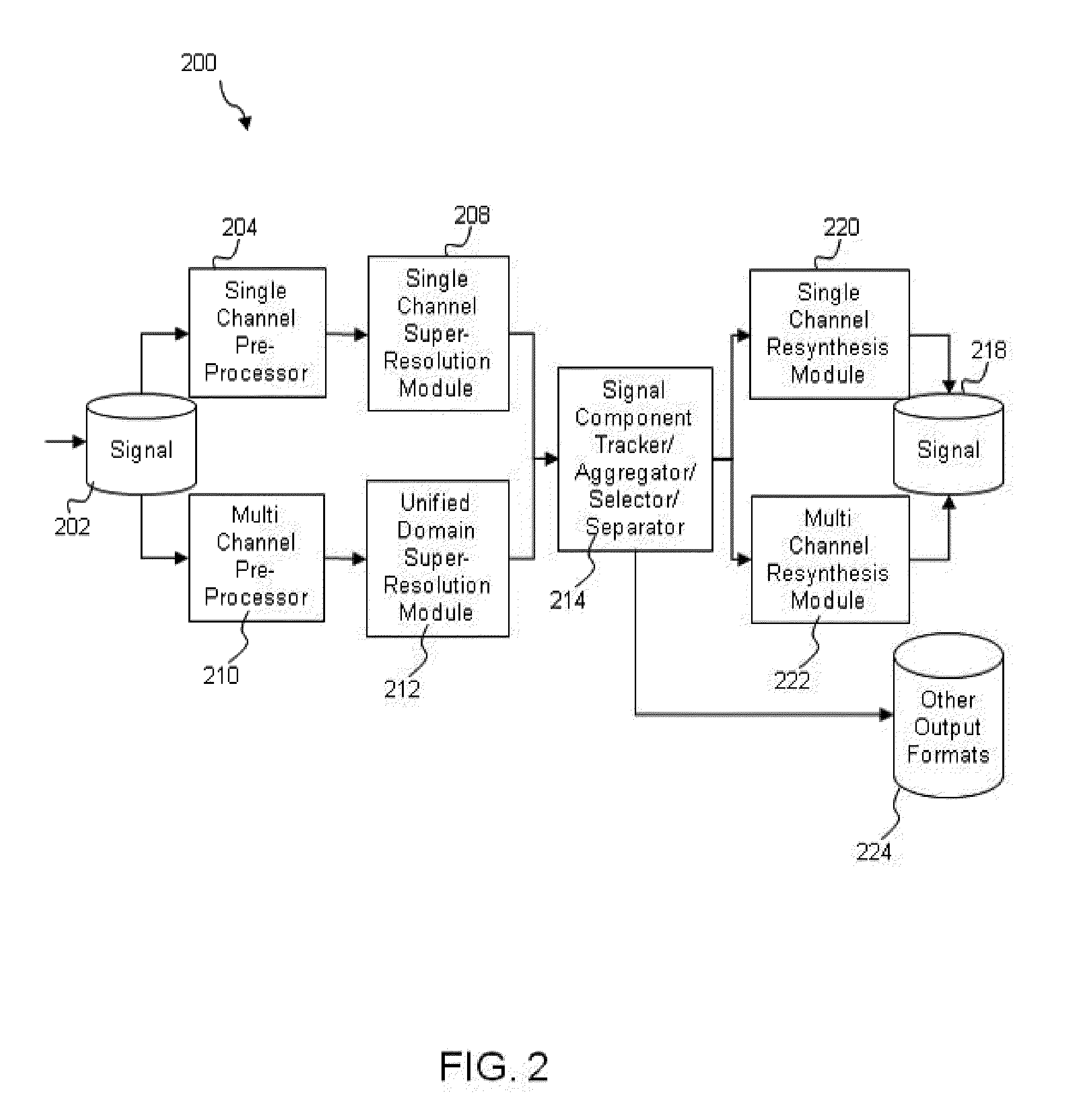
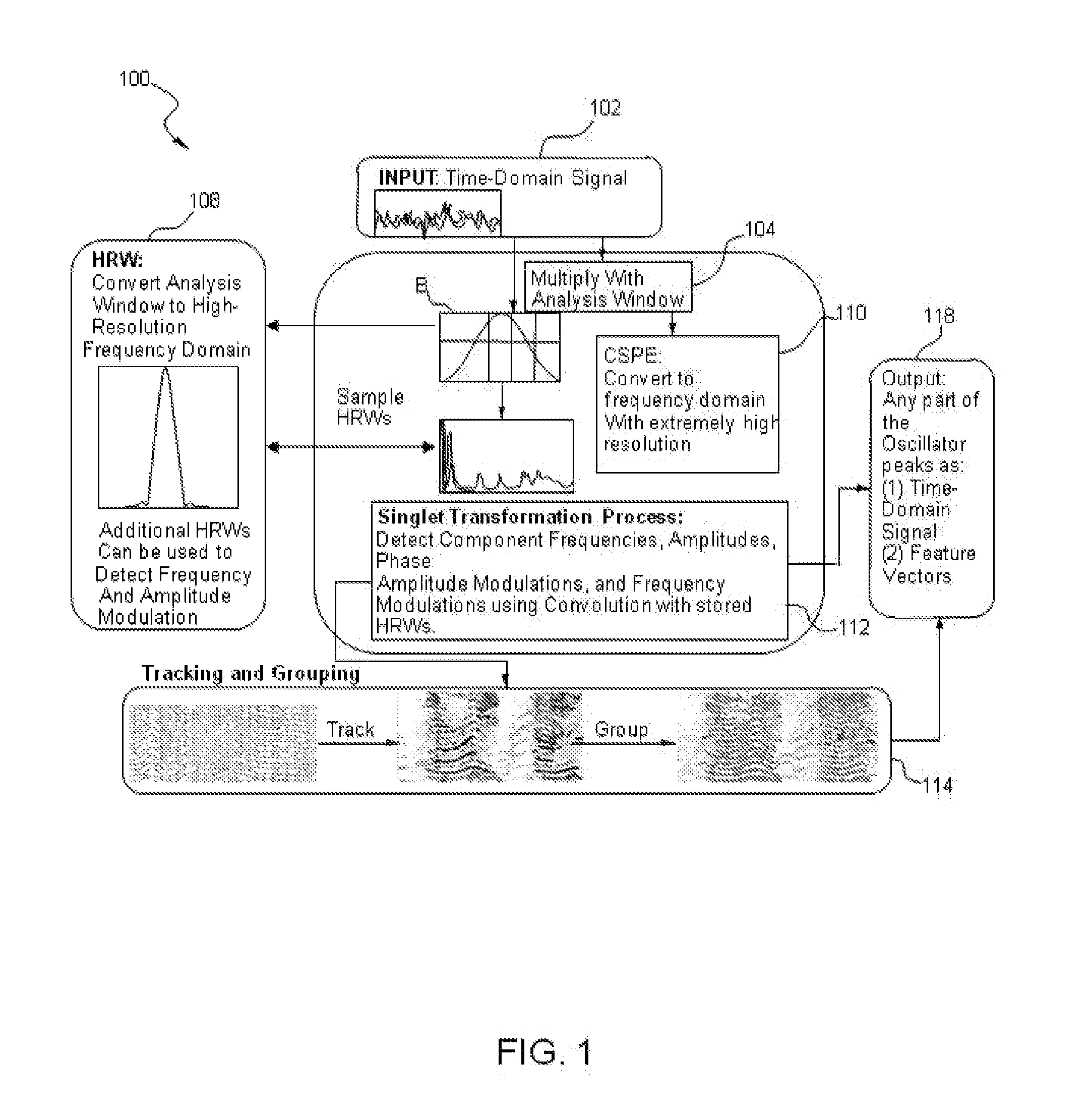
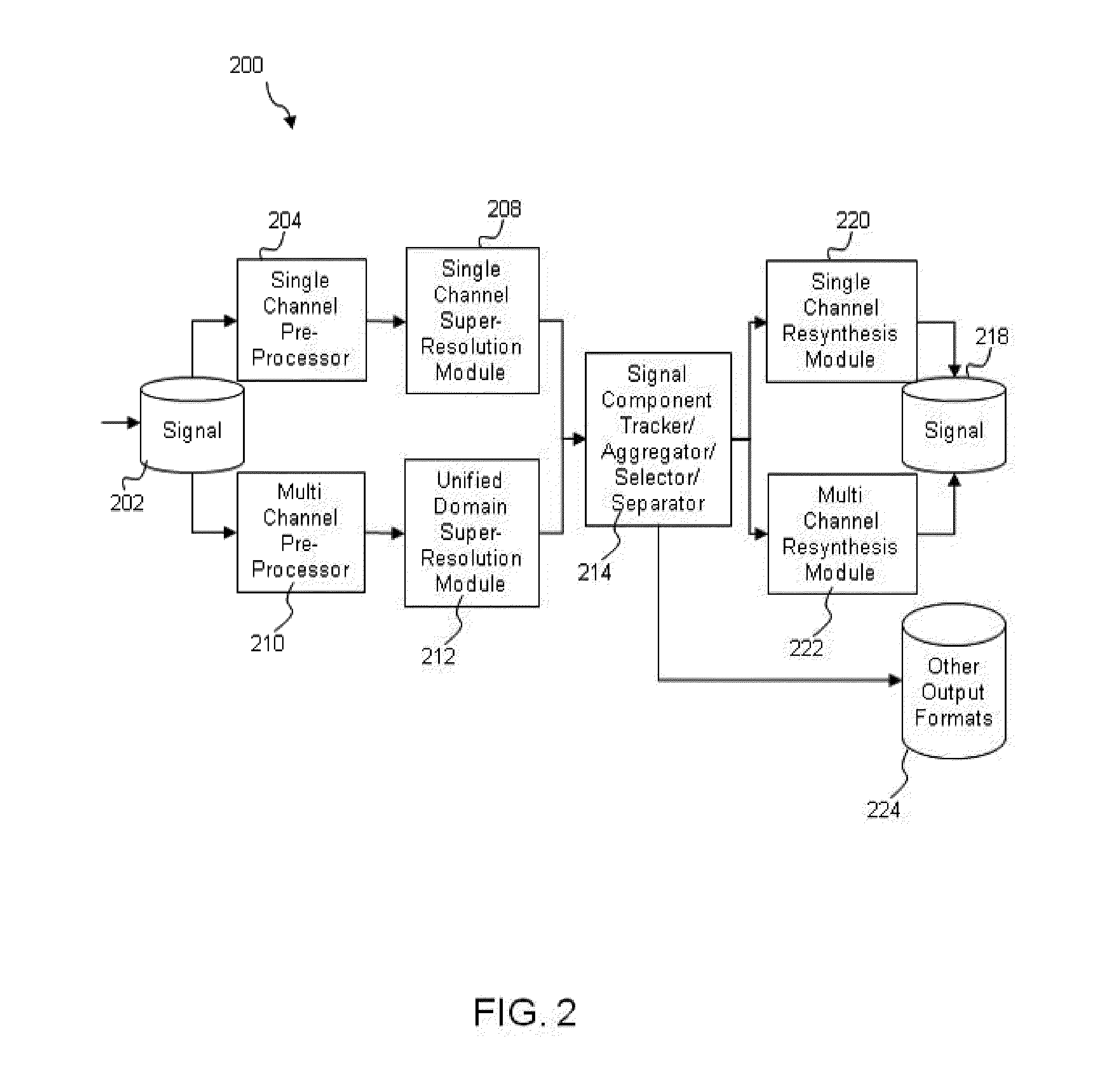
Systems and Methods for Source Signal Separation
ActiveUS20140079248A1Accurate reconstructionMulti-channel direction-finding systems using radio wavesMulti-channel direction findingTheoretical computer scienceSource separation
A method of processing a signal, including taking a signal formed from a plurality of source signal emitters and expressed in an original domain, decomposing the signal into a mathematical representation of a plurality of constituent elements in an alternate domain, analyzing the plurality of constituent elements to associate at least a subset of the constituent elements with at least one of the plurality of source signal emitters, separating at least a subset of the constituent elements based on the association and reconstituting at least a subset of constituent elements to produce an output signal in at least one of the original domain, the alternate domain and another domain.
Owner:XMOS INC
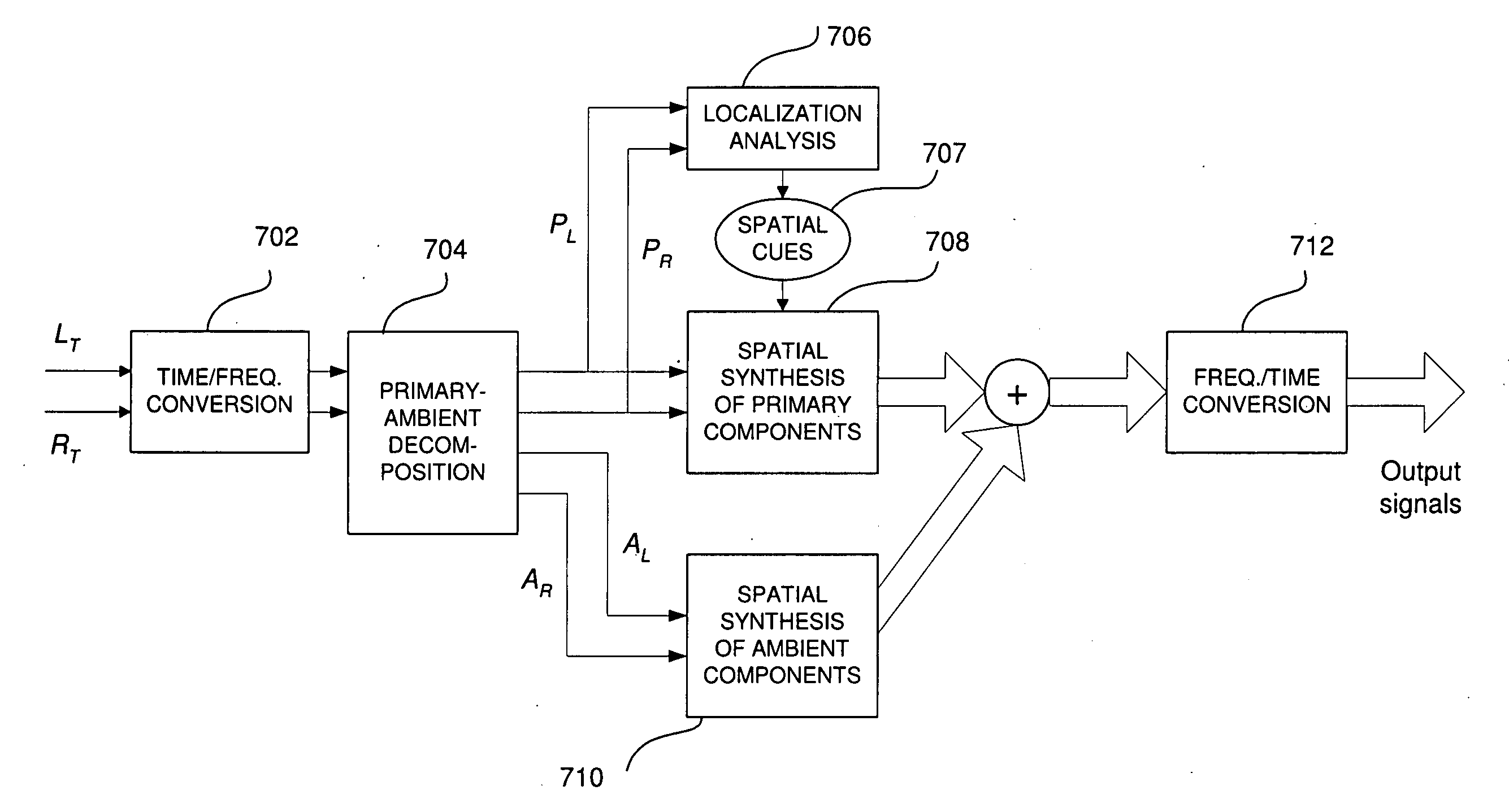
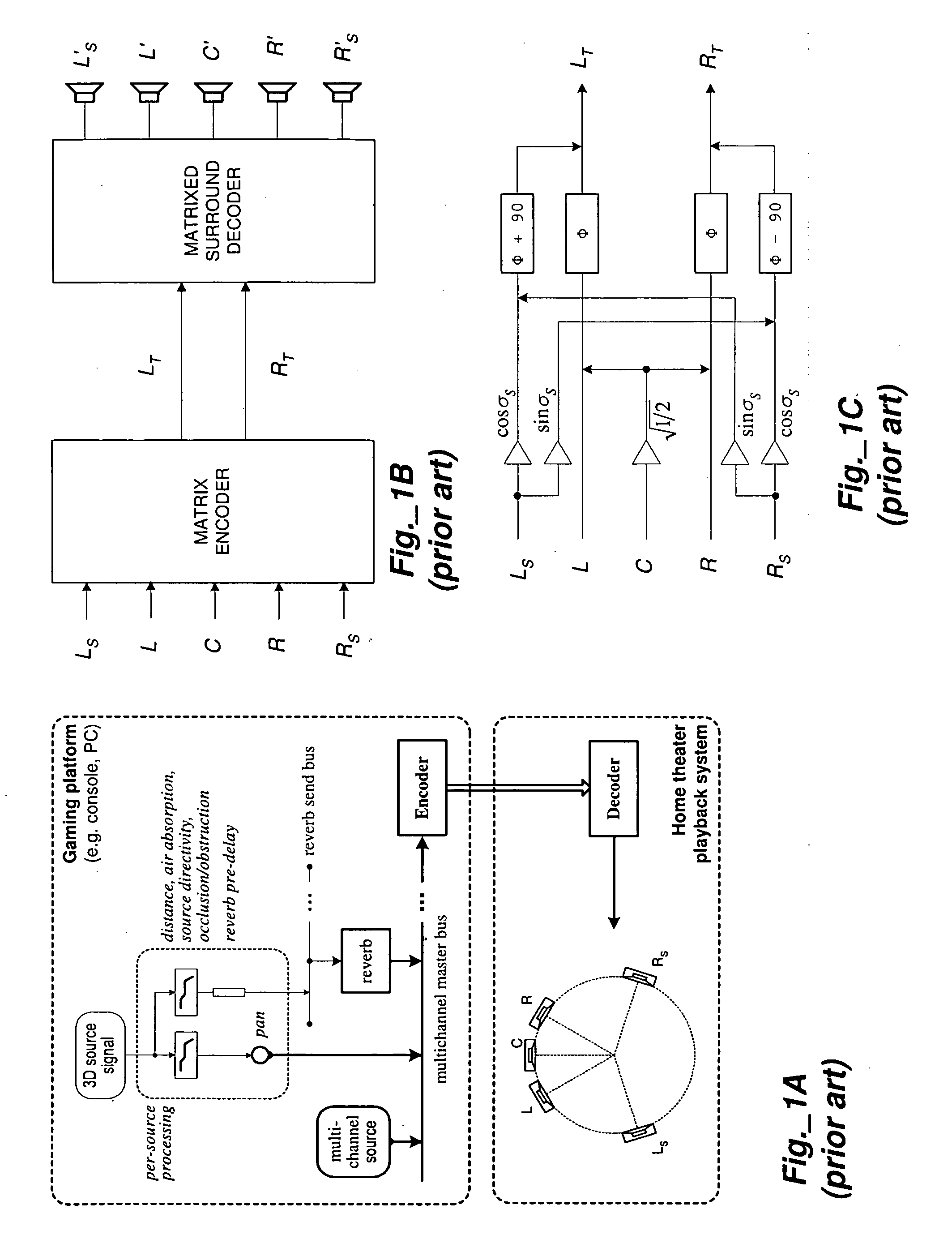
Phase-Amplitude 3-D Stereo Encoder and Decoder
ActiveUS20090092259A1Preserving source separationSpeech analysisStereophonic systemsSound sourcesSpatial analysis
Owner:CREATIVE TECH CORP
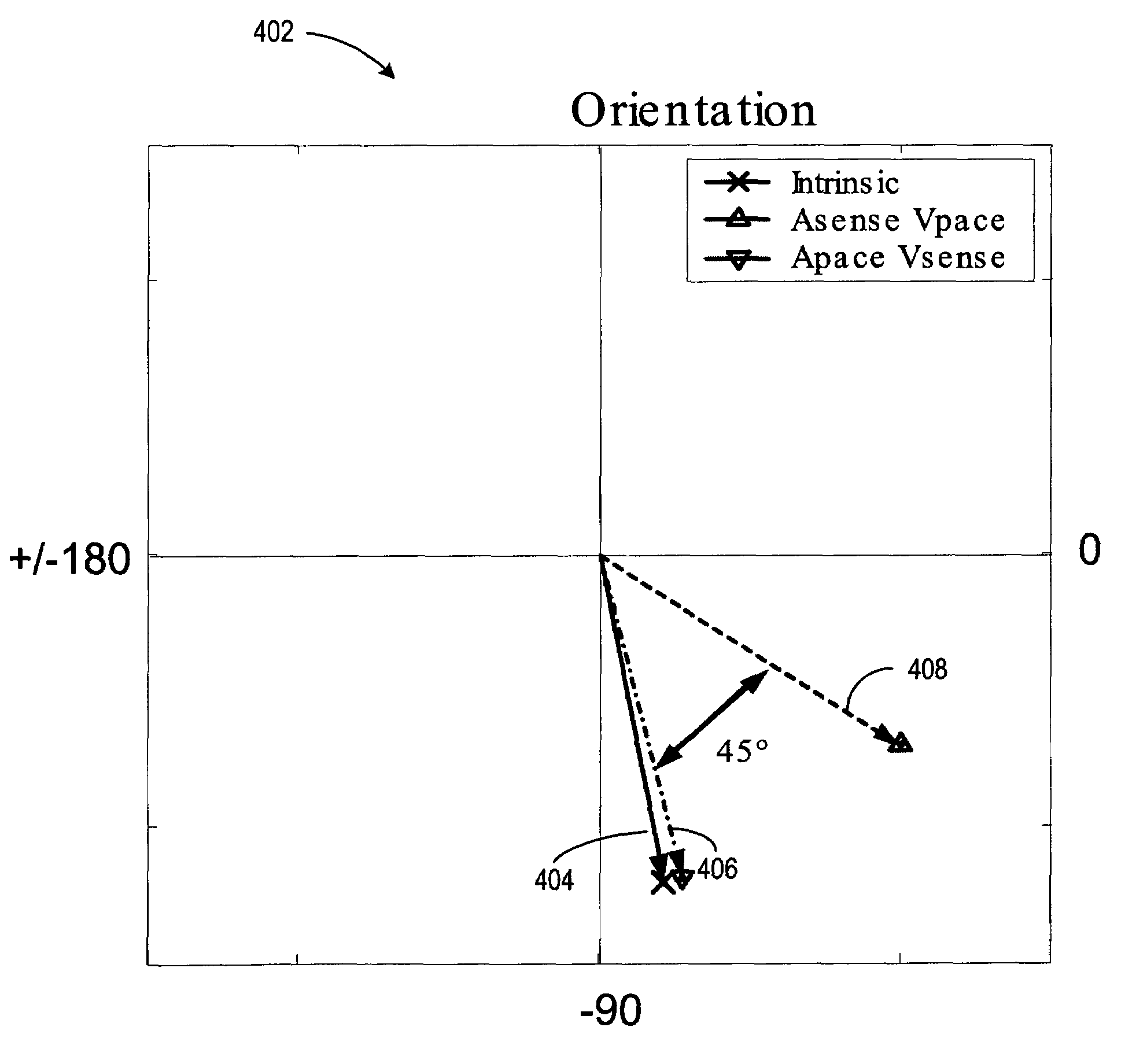
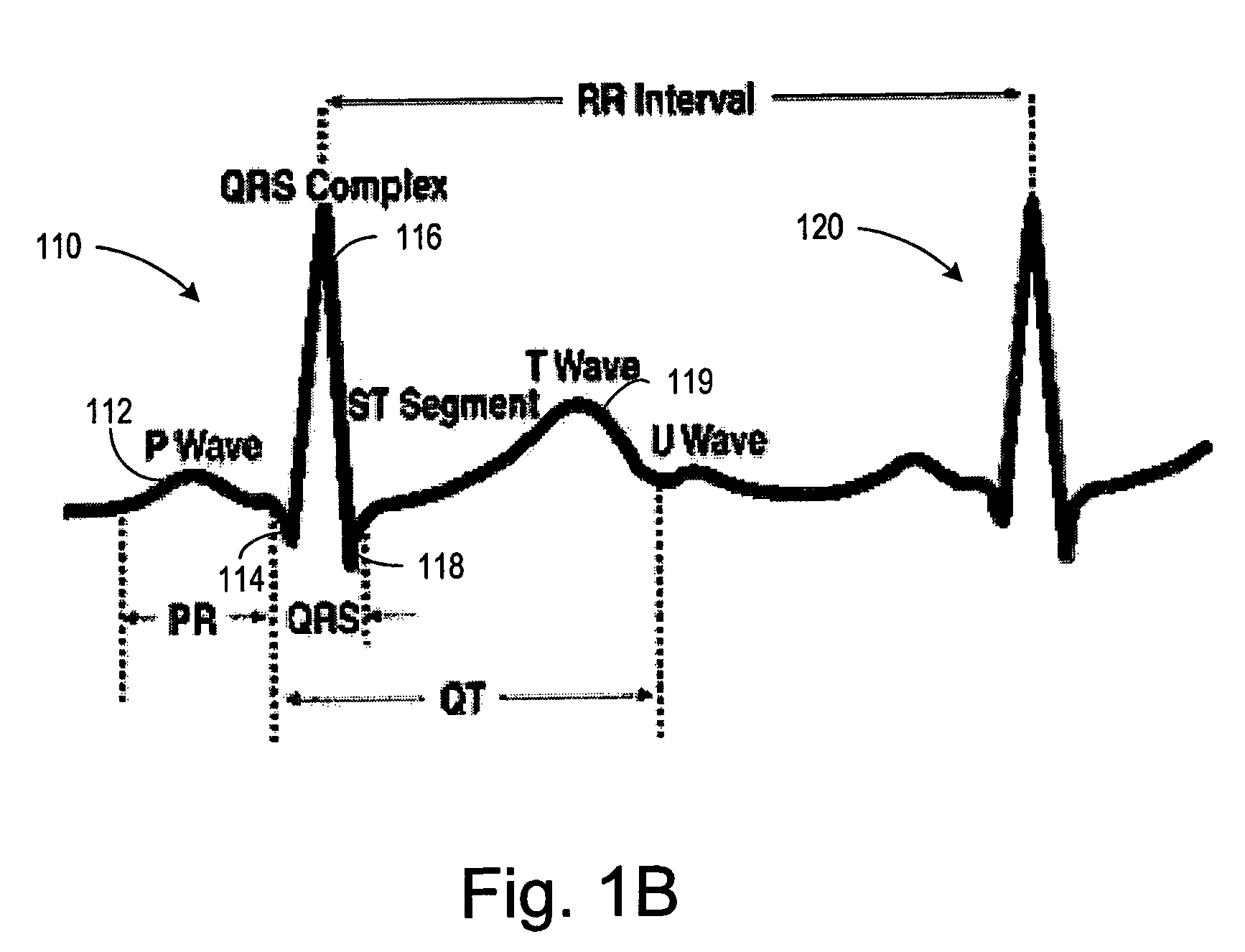
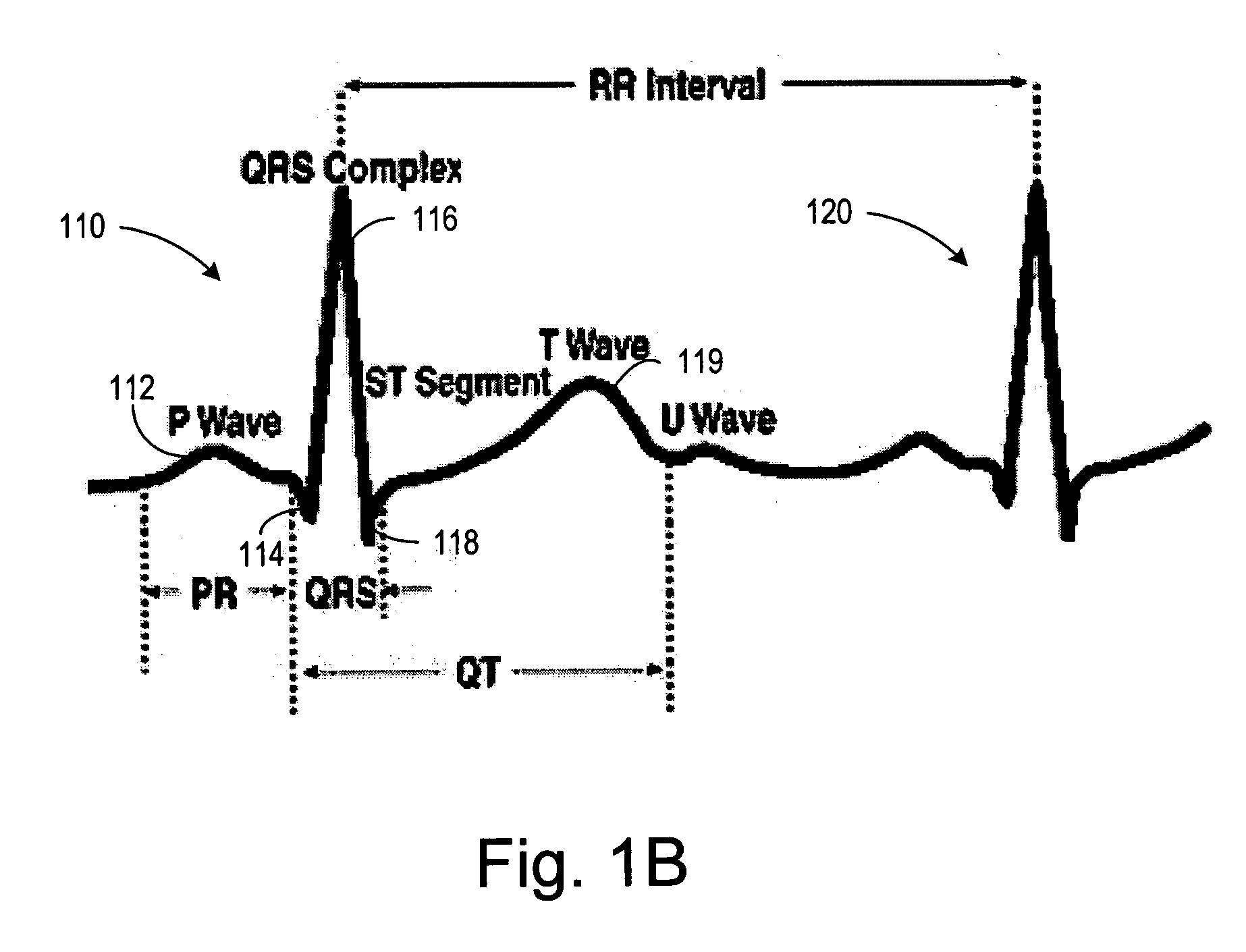
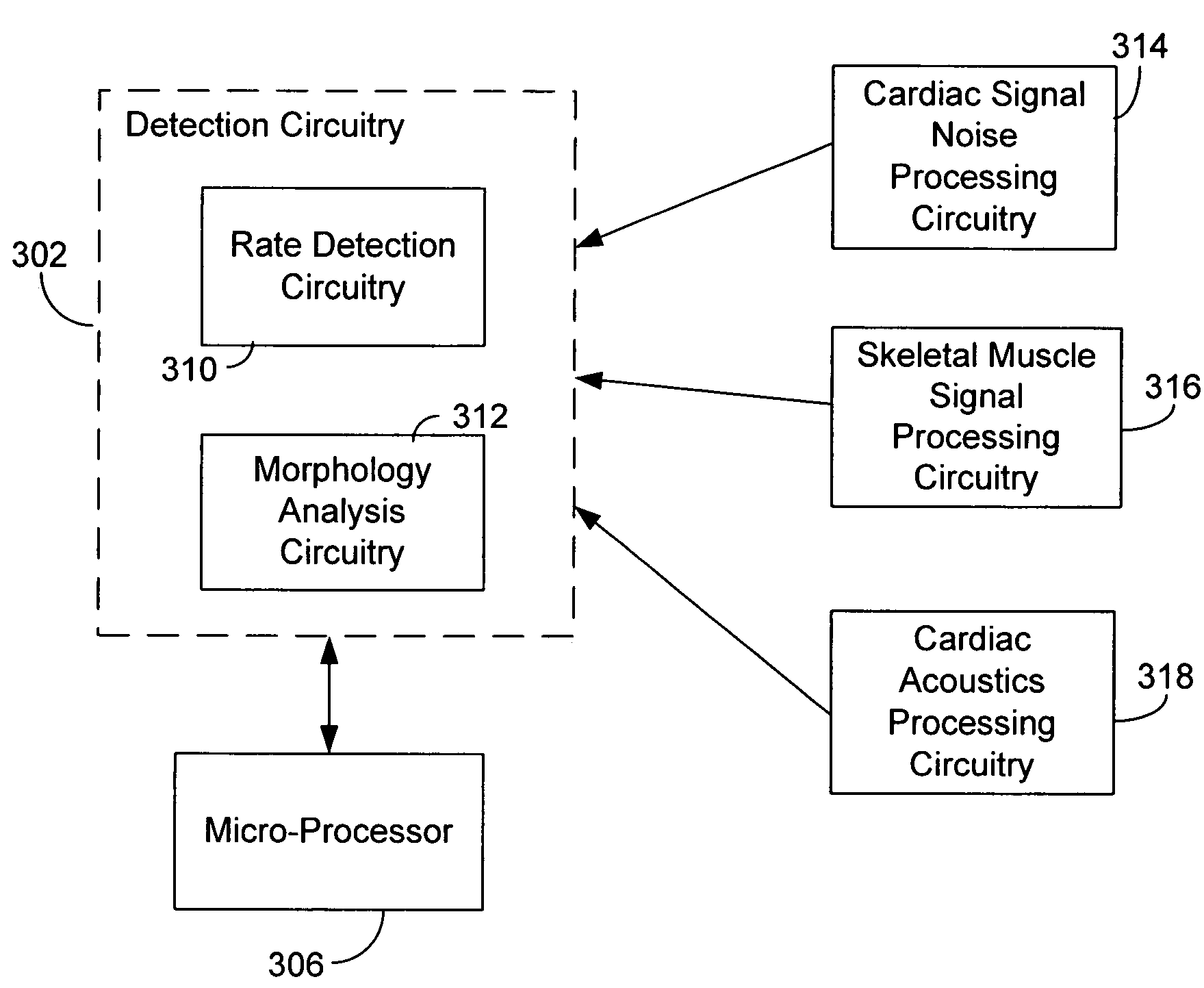
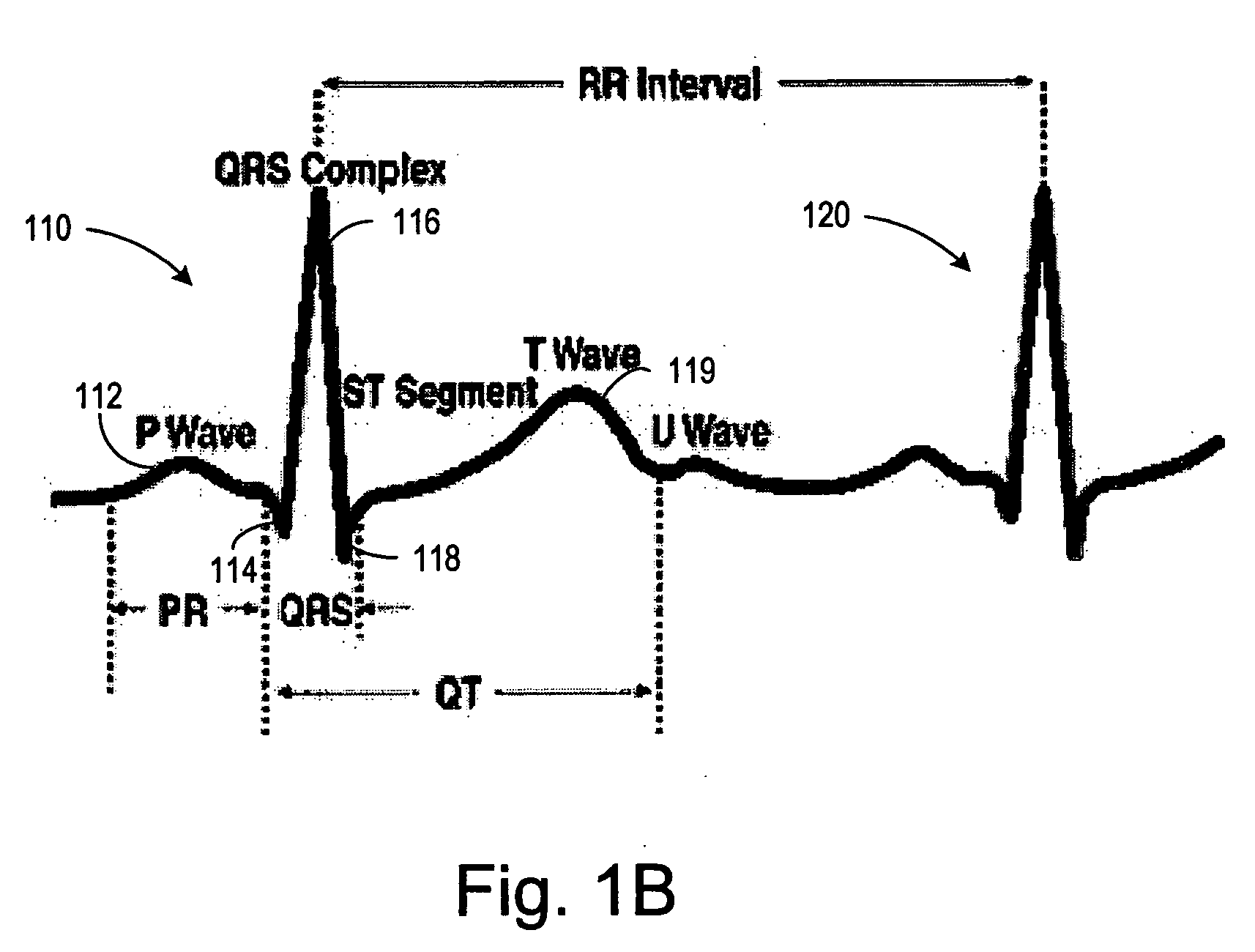
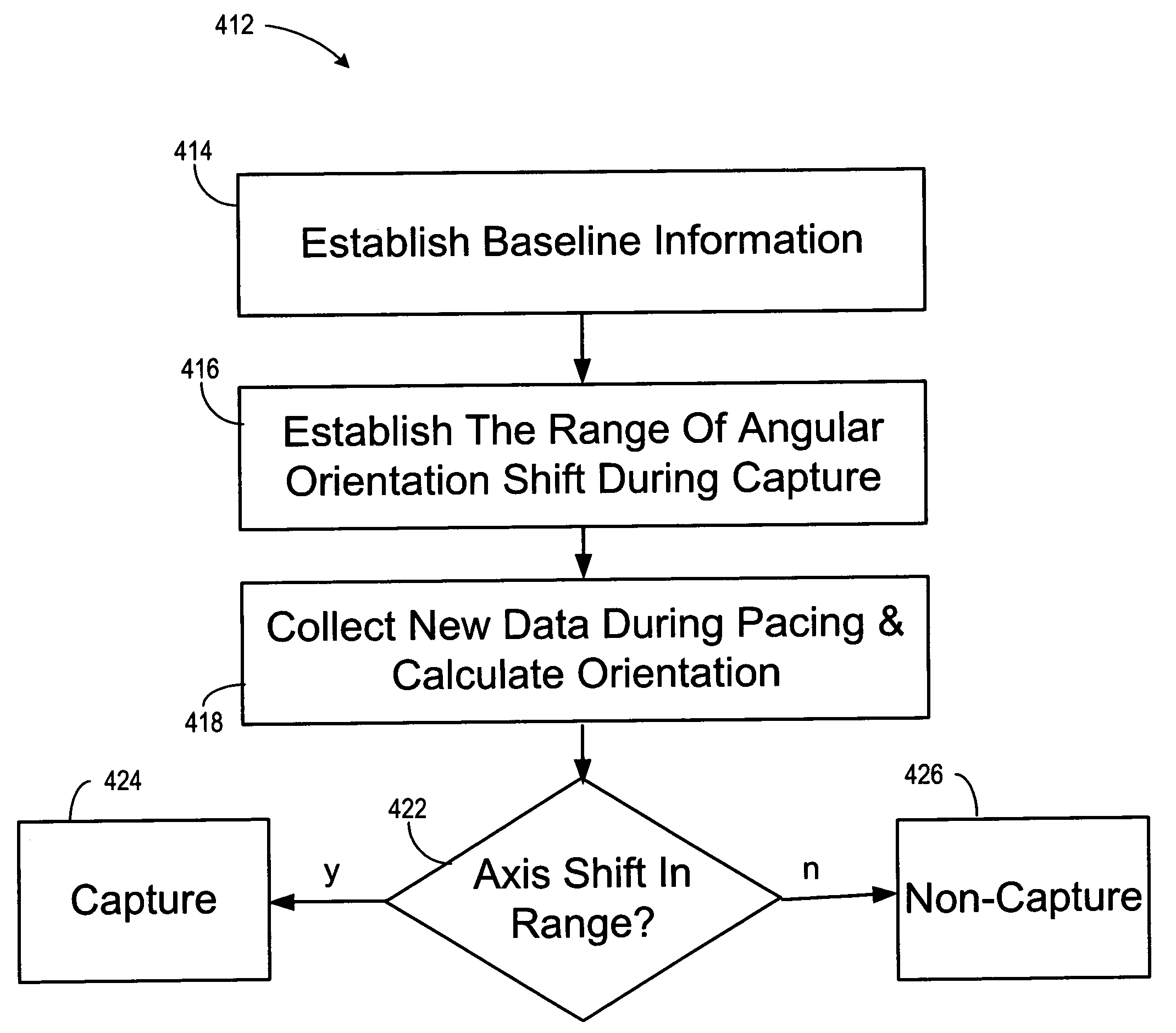
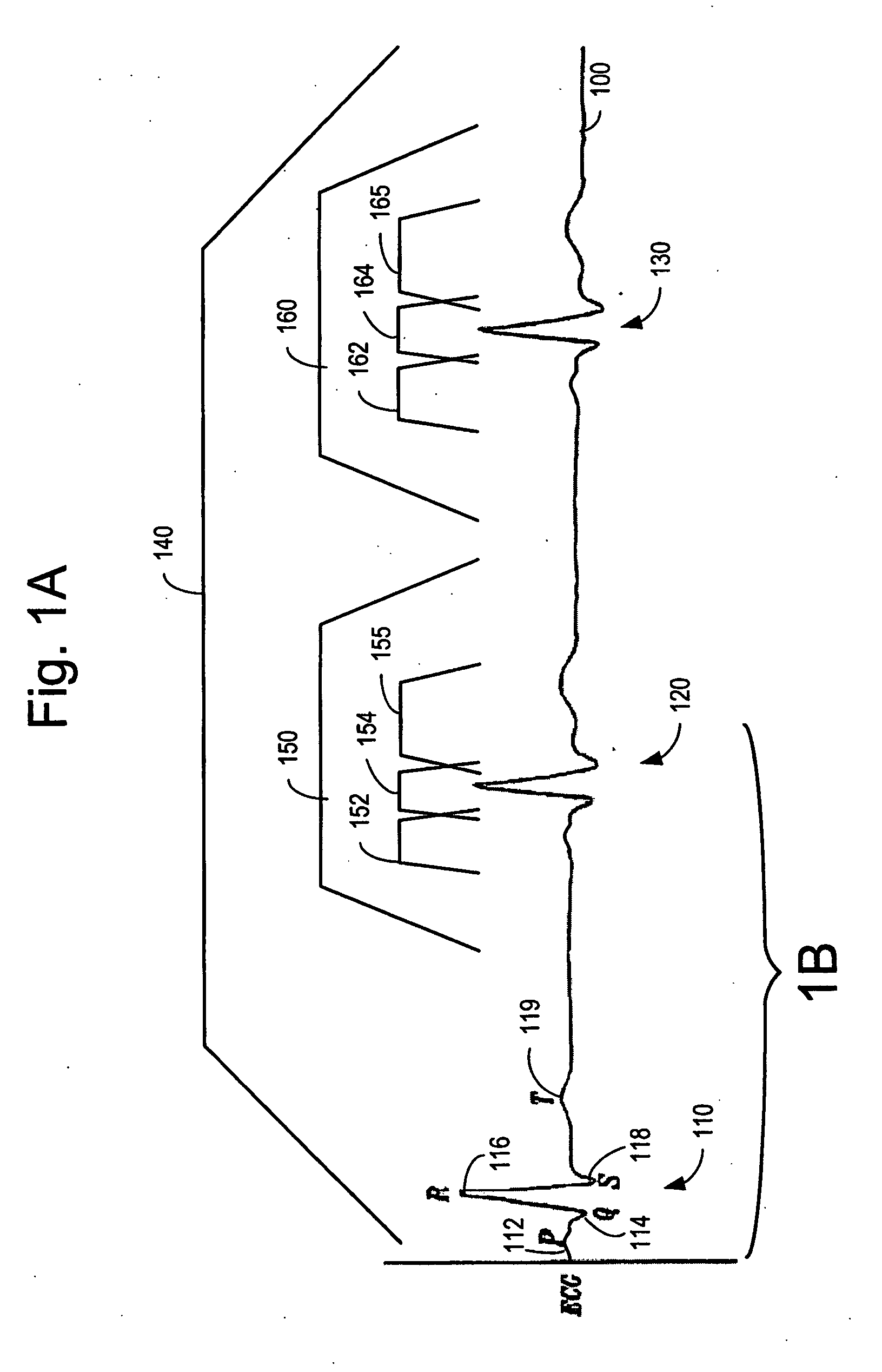
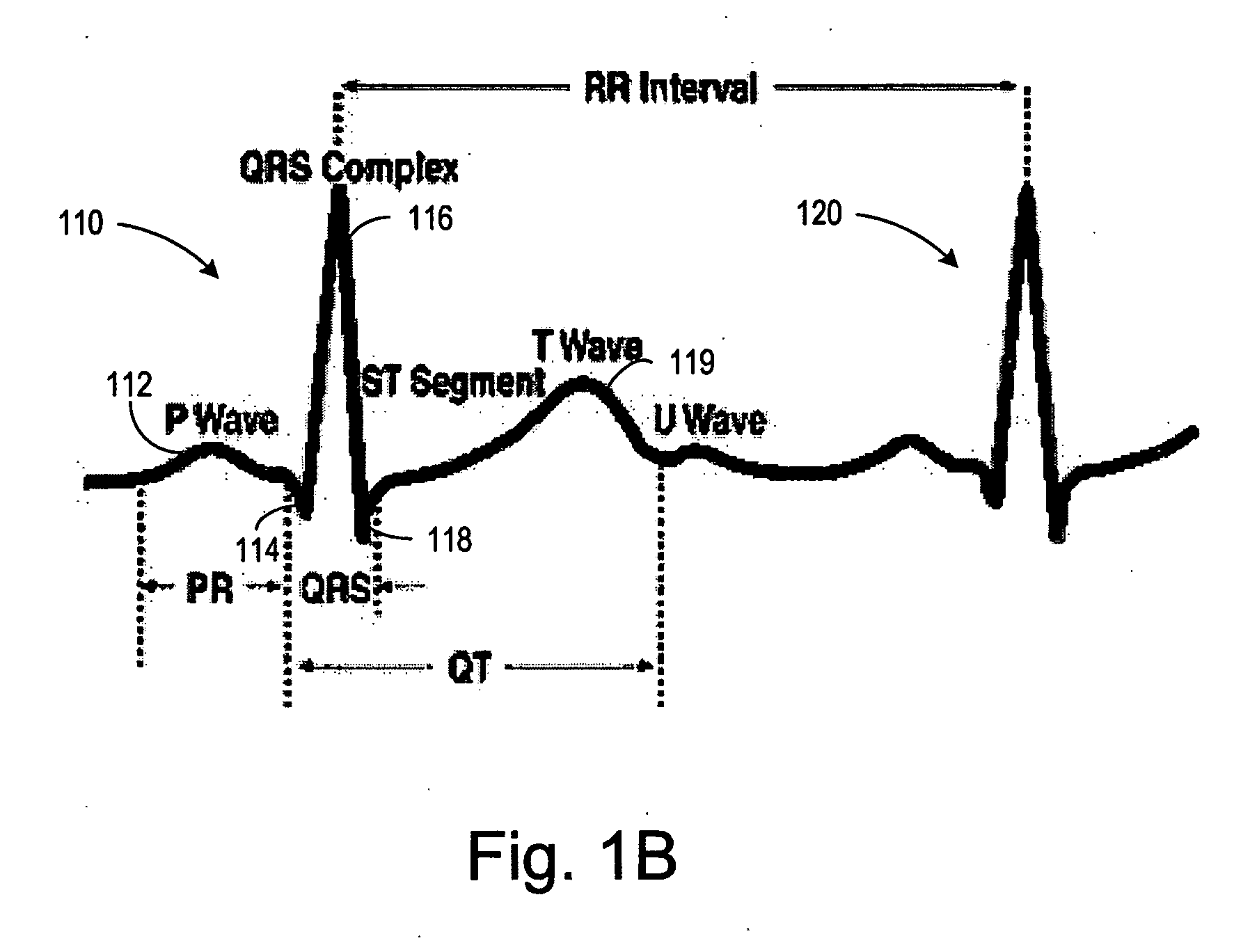
Automatic capture verification using electrocardiograms sensed from multiple implanted electrodes
InactiveUS7509170B2Heart stimulatorsDiagnostic recording/measuringImplantable ElectrodesCardiac monitoring
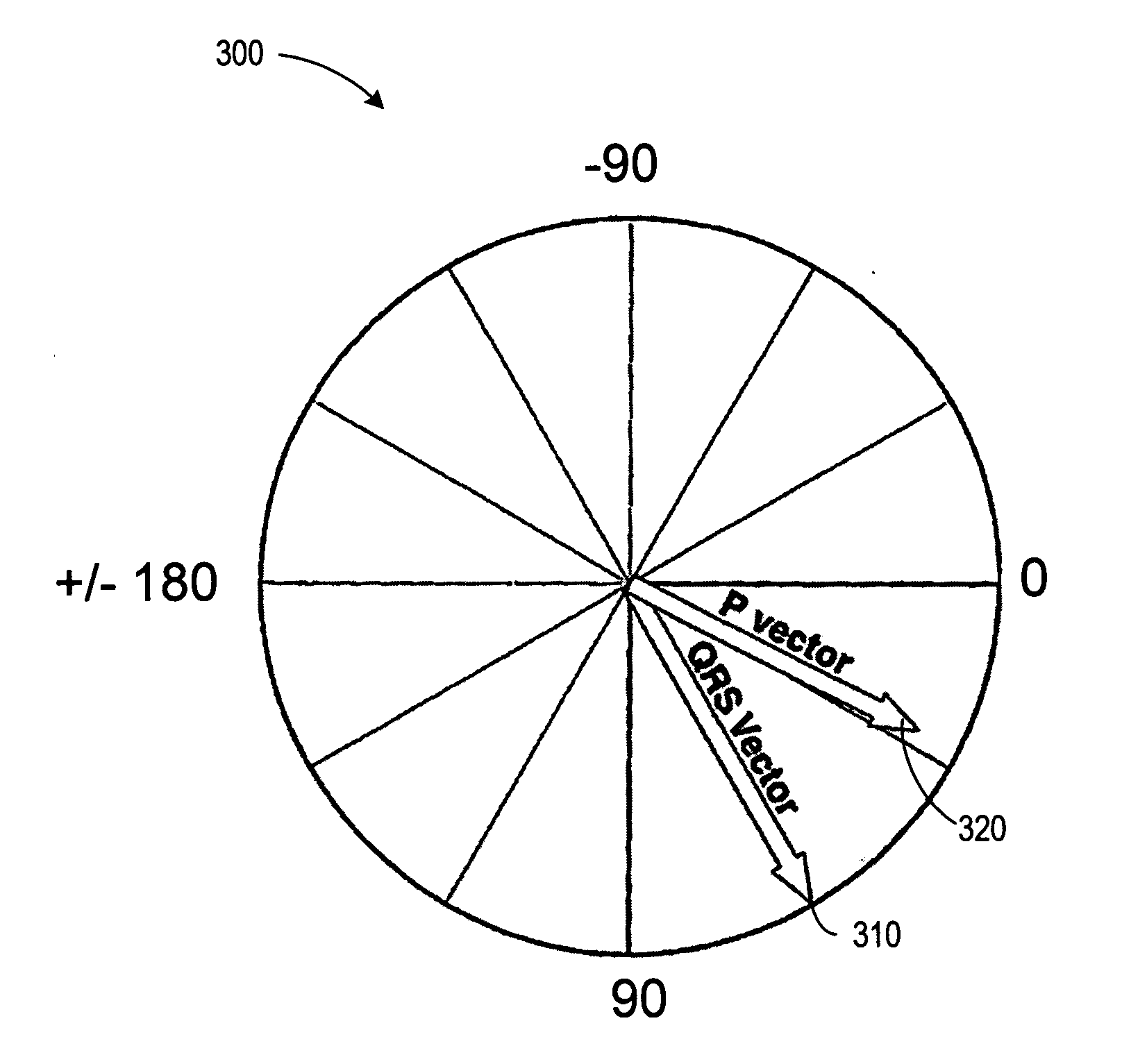
Cardiac monitoring and / or stimulation methods and systems that provide one or more of monitoring, diagnosing, defibrillation, and pacing. Cardiac signal separation is employed for automatic capture verification using cardiac activation sequence information. Devices and methods sense composite cardiac signals using implantable electrodes. A source separation is performed using the composite signals. One or more signal vectors are produced that are associated with all or a portion of one or more cardiac activation sequences based on the source separation. A cardiac response to the pacing pulses is classified using characteristics associated with cardiac signal vectors and the signals associated with the vectors. Further embodiments may involve classifying the cardiac response as capture or non-capture, fusion or intrinsic cardiac activity. The characteristics may include an angle or an angle change of the cardiac signal vectors, such as a predetermined range of angles of the one or more cardiac signal vectors.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Arrhythmia discrimination using electrocardiograms sensed from multiple implanted electrodes
Cardiac monitoring and / or stimulation methods and systems provide for monitoring, diagnosing, defibrillation and pacing therapies, or a combination of these capabilities, including cardiac systems incorporating or cooperating with neuro-stimulating devices, drug pumps, or other therapies. Embodiments of the present invention relate generally to implantable medical devices employing automated cardiac activation sequence monitoring and / or tracking for arrhythmia discrimination. Embodiments of the invention are directed to devices and methods involving sensing a plurality of composite cardiac signals using a plurality of implantable electrodes. A source separation is performed using the sensed plurality of composite cardiac signals and the separation produces one or more cardiac signal vectors associated with one or more cardiac activation sequences that is indicative of ischemia. A change of the one or more cardiac signal vectors is detected using the one or more cardiac signal vectors. Cardiac arrhythmias are discriminated using the one or more cardiac signal vectors.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
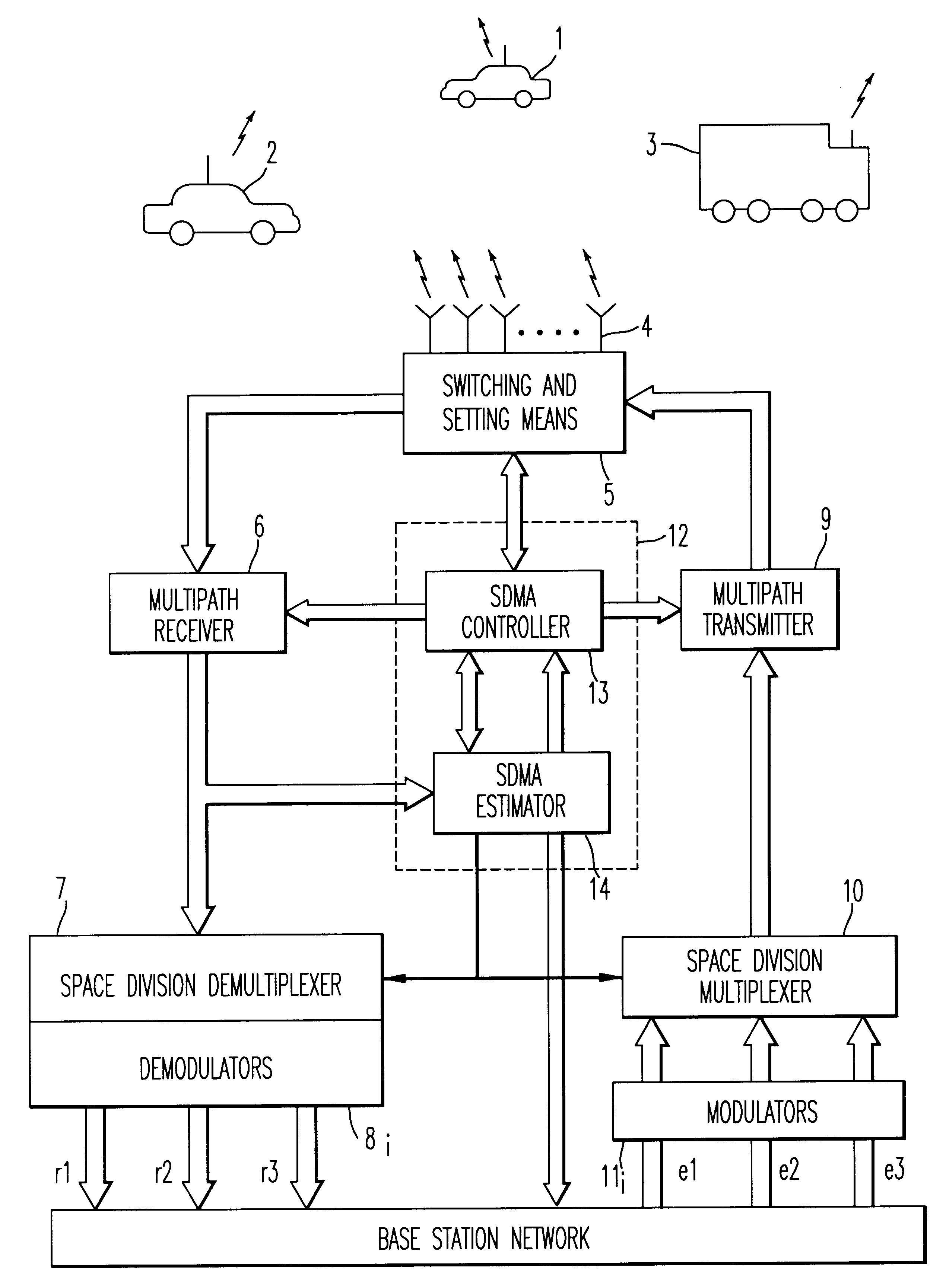
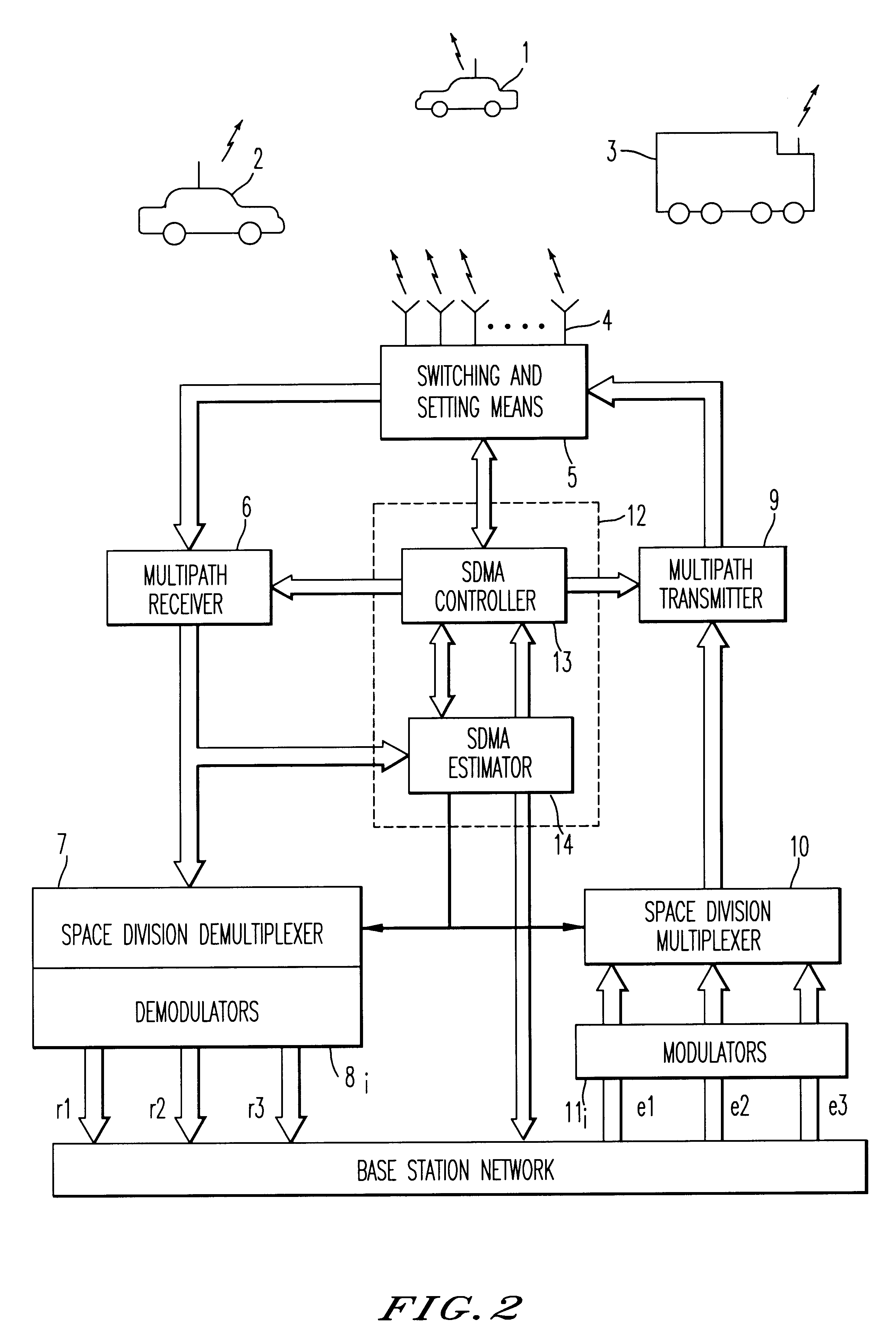
Method and device for space division multiplexing of radio signals transmitted in cellular radio communications
InactiveUS6240098B1Space can be allowedImprove performanceRadio wave direction/deviation determination systemsSpatial transmit diversityEngineeringTime-division multiplexing
A method and apparatus for spatial multiplexing and demultiplexing of radio signals. A multichannel transmitter and receiver is integrated in a base station and coupled to an antenna array. Using digital radio signals containing previously known or non-Gaussian sequences and arranged in frames, the spatial information about each mobile unit is estimated on the basis of the signal received by the receiver for the reception and transmission frequencies. This is done by known sequences or by blind source separation methods. The respective paths of each mobile unit with the power above a predetermined threshold is isolated by spatial filtering in the presence of multiple channel paths in order to provide spatial demultiplexing. Simultaneously, the intended signal is transmitted in the direction of the main path of each mobile unit while protecting each mobile unit from signals transmitted in the direction of other mobile units by spatial filtering with cancelling constraints in order to provide spatial multiplexing.
Owner:THOMSON CSF SA
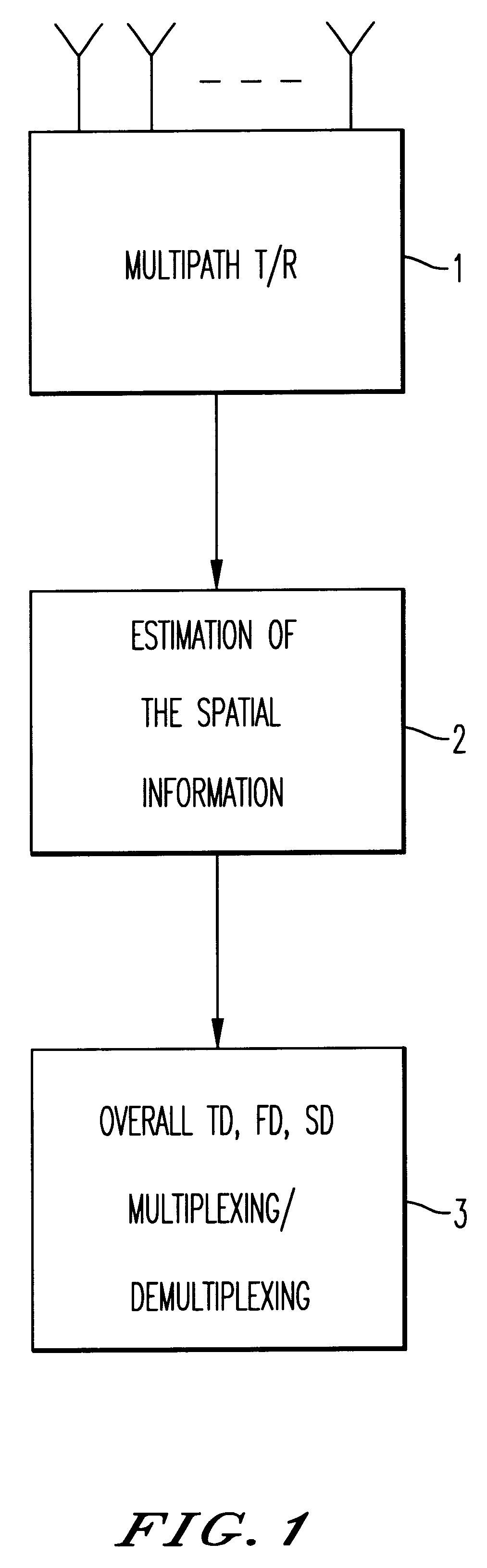
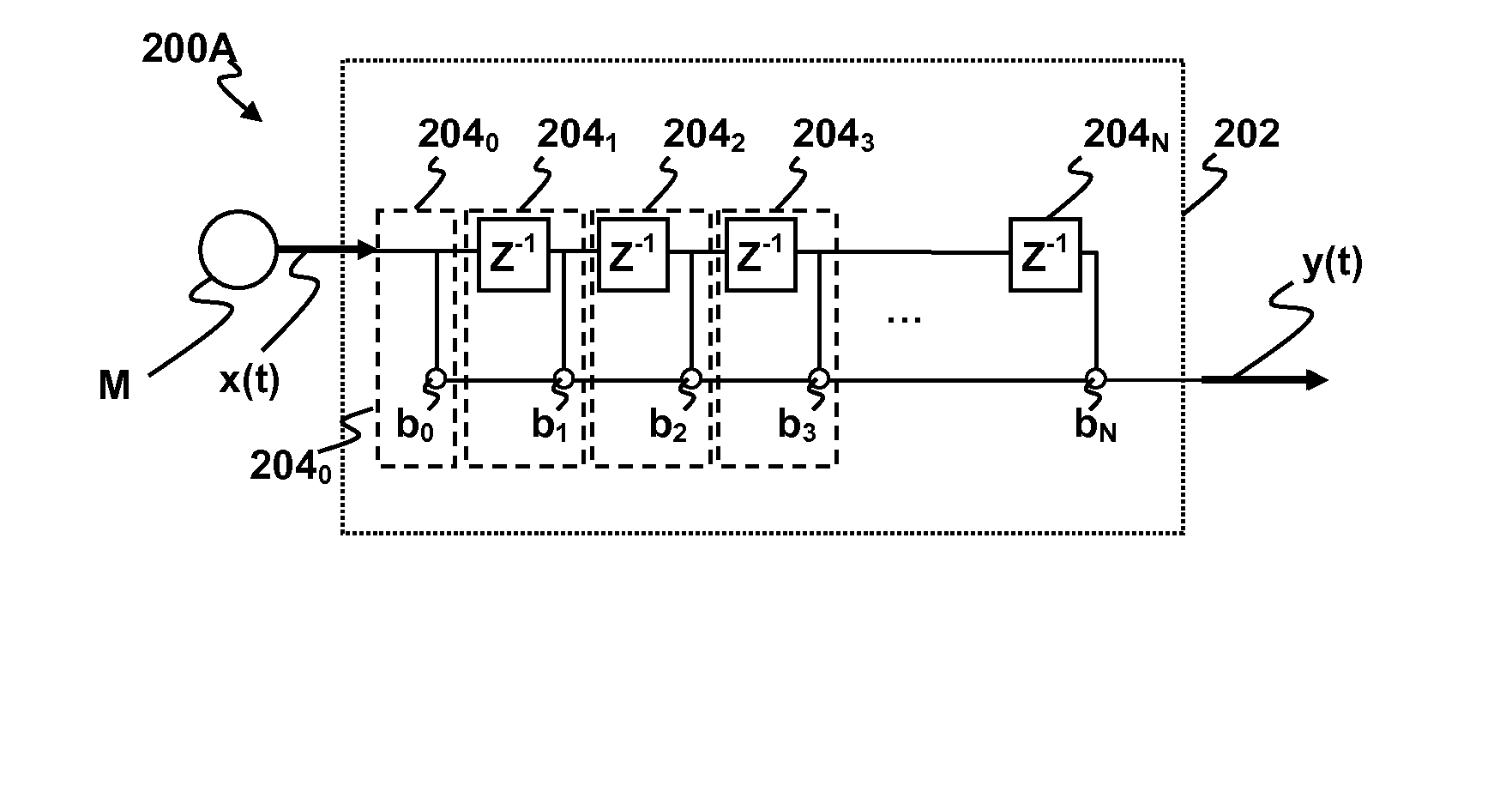
Ultra small microphone array
ActiveUS20070260340A1MicrophonesAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceFinite impulse responseTime domain
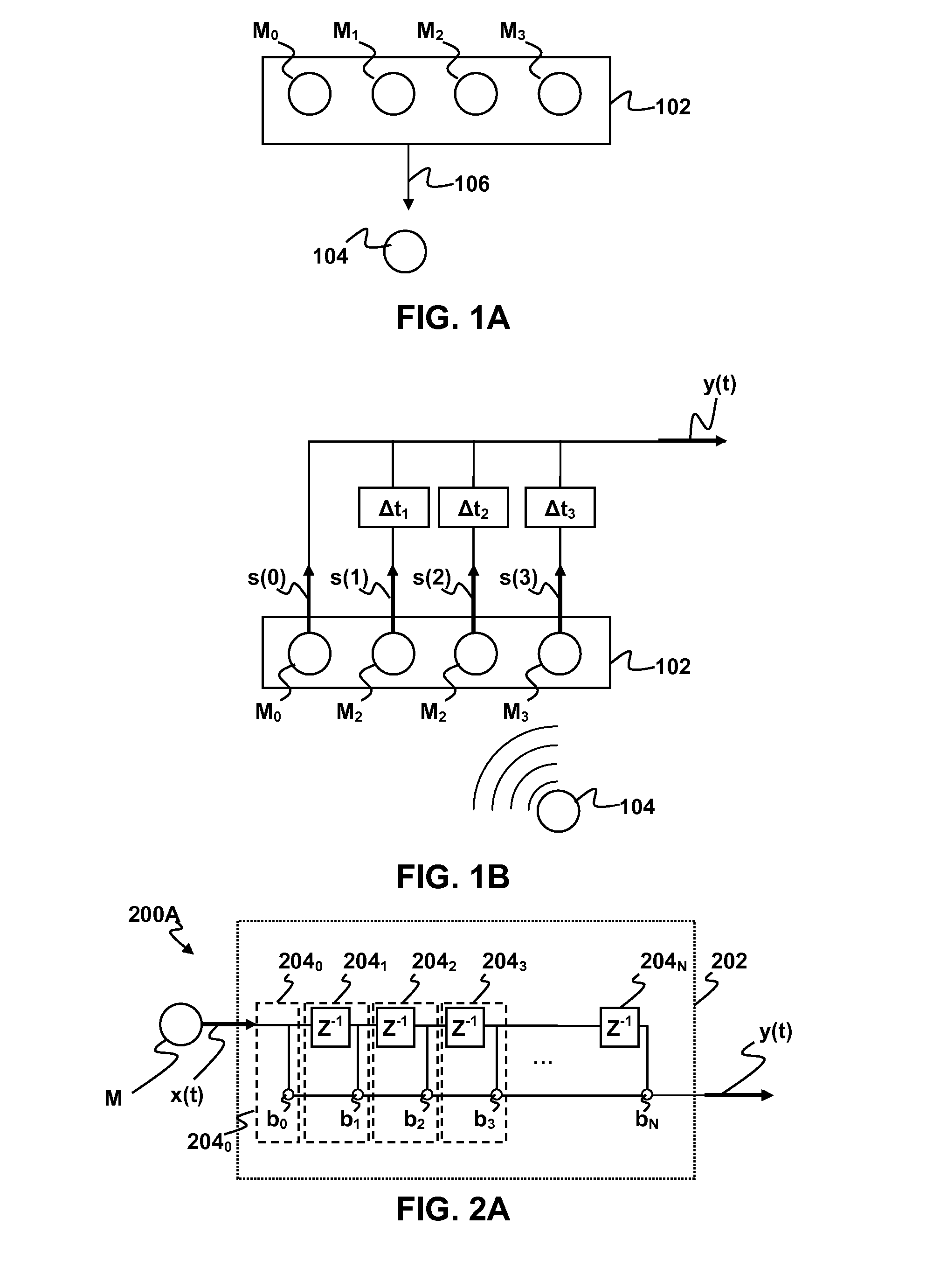
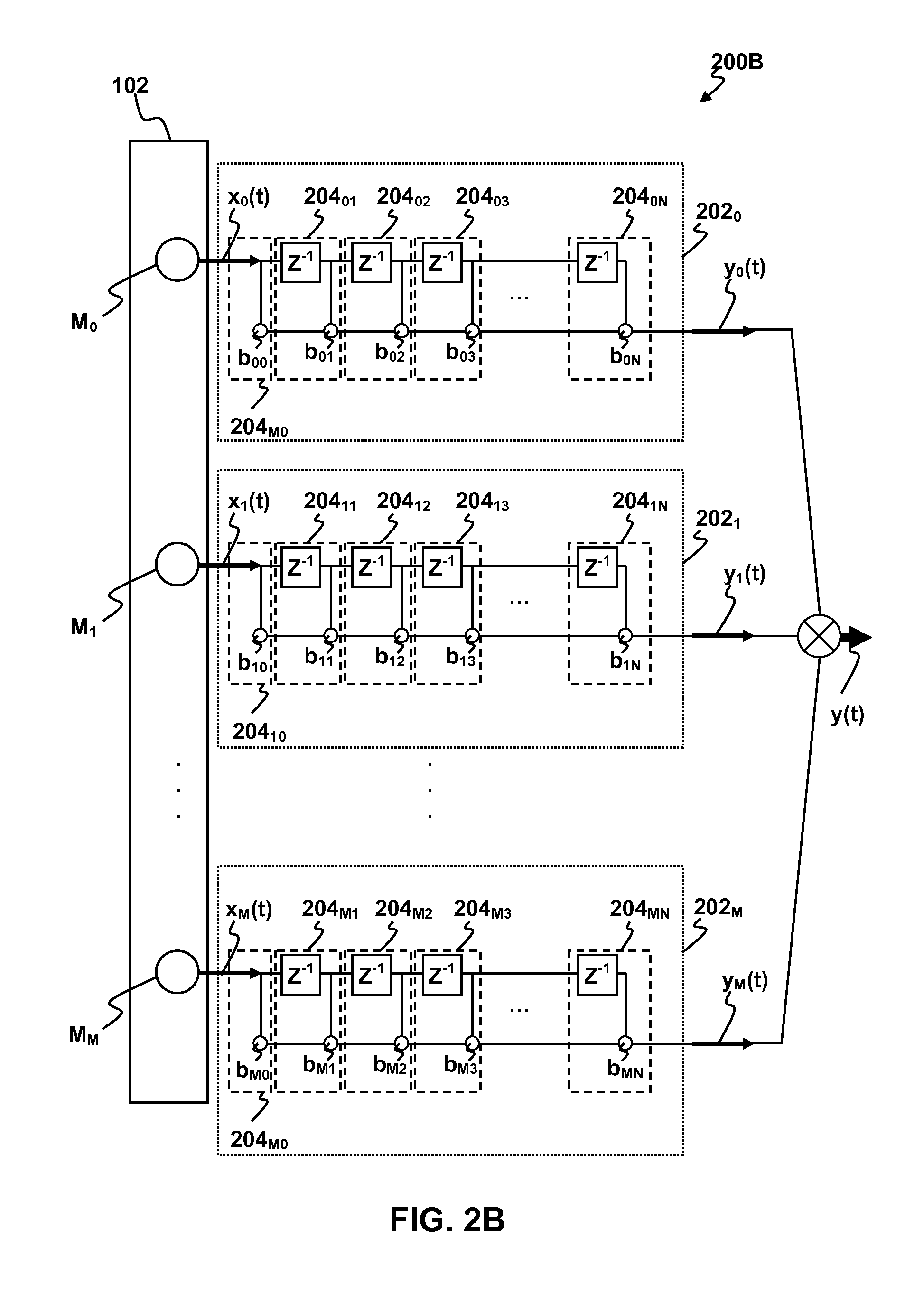
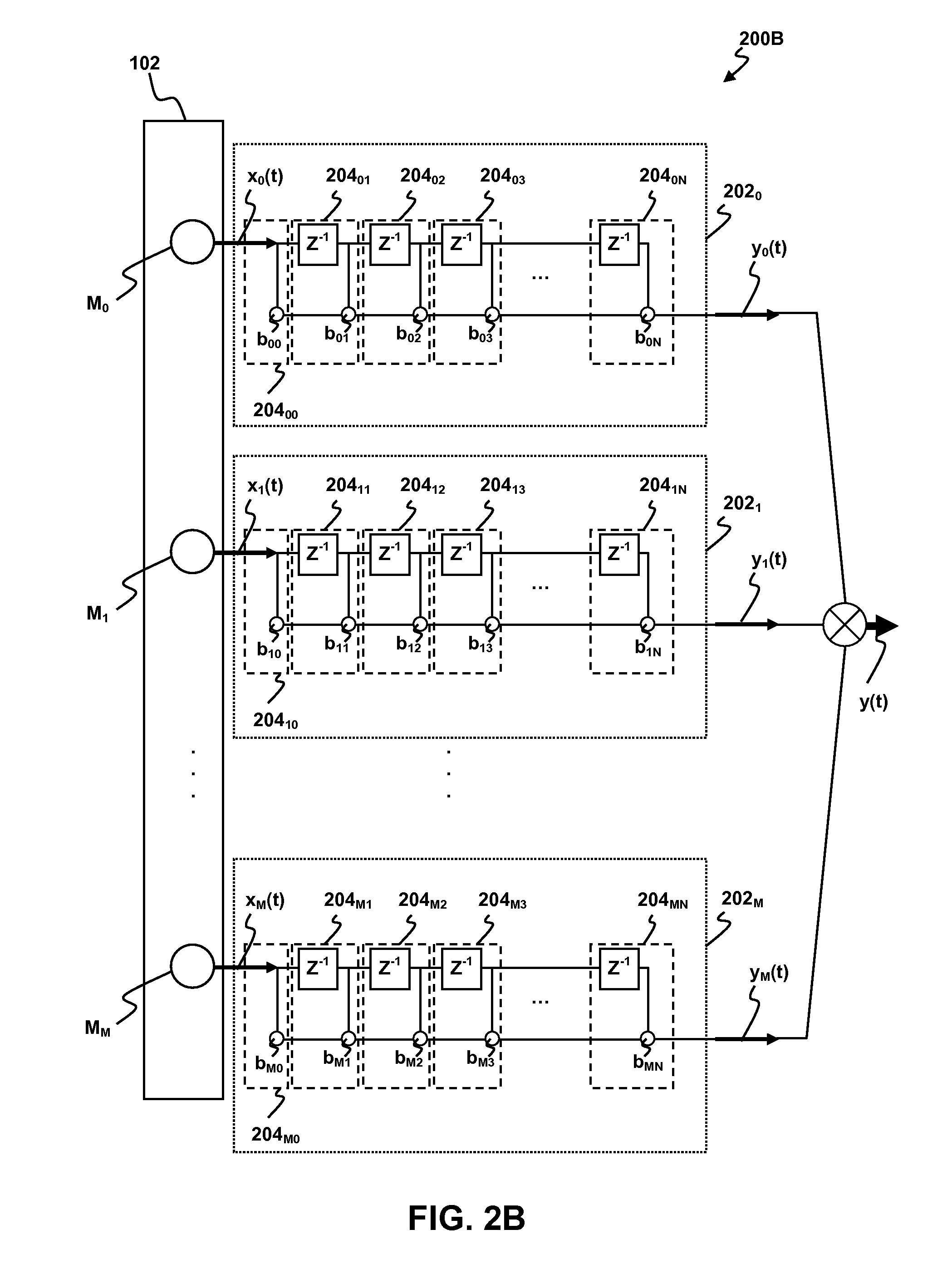
Methods and apparatus for signal processing are disclosed. A discrete time domain input signal xm(t) may be produced from an array of microphones M0 . . . MM. A listening direction may be determined for the microphone array. The listening direction is used in a semi-blind source separation to select the finite impulse response filter coefficients b0, b1 . . . , bN to separate out different sound sources from input signal xm(t). One or more fractional delays may optionally be applied to selected input signals xm(t) other than an input signal x0(t) from a reference microphone M0. Each fractional delay may be selected to optimize a signal to noise ratio of a discrete time domain output signal y(t) from the microphone array. The fractional delays may be selected to such that a signal from the reference microphone M0 is first in time relative to signals from the other microphone(s) of the array. A fractional time delay Δ may optionally be introduced into an output signal y(t) so that: y(t+Δ)=x(t+Δ)*b0+x(t−1+Δ)*b1+x(t−2+Δ)*b2+ . . . +x(t−N+Δ)bN, where Δ is between zero and ±1.
Owner:SONY COMPUTER ENTERTAINMENT INC +1
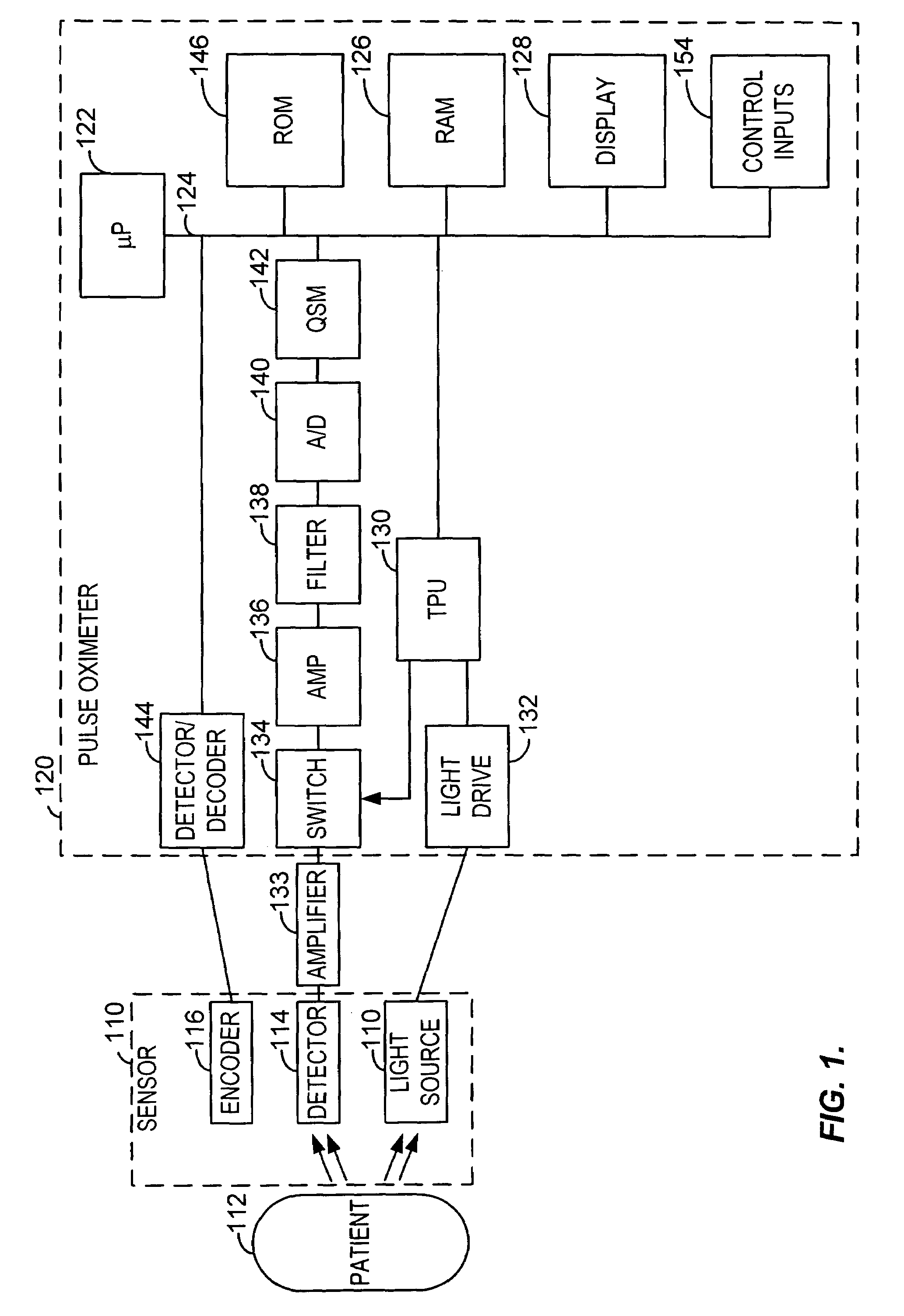
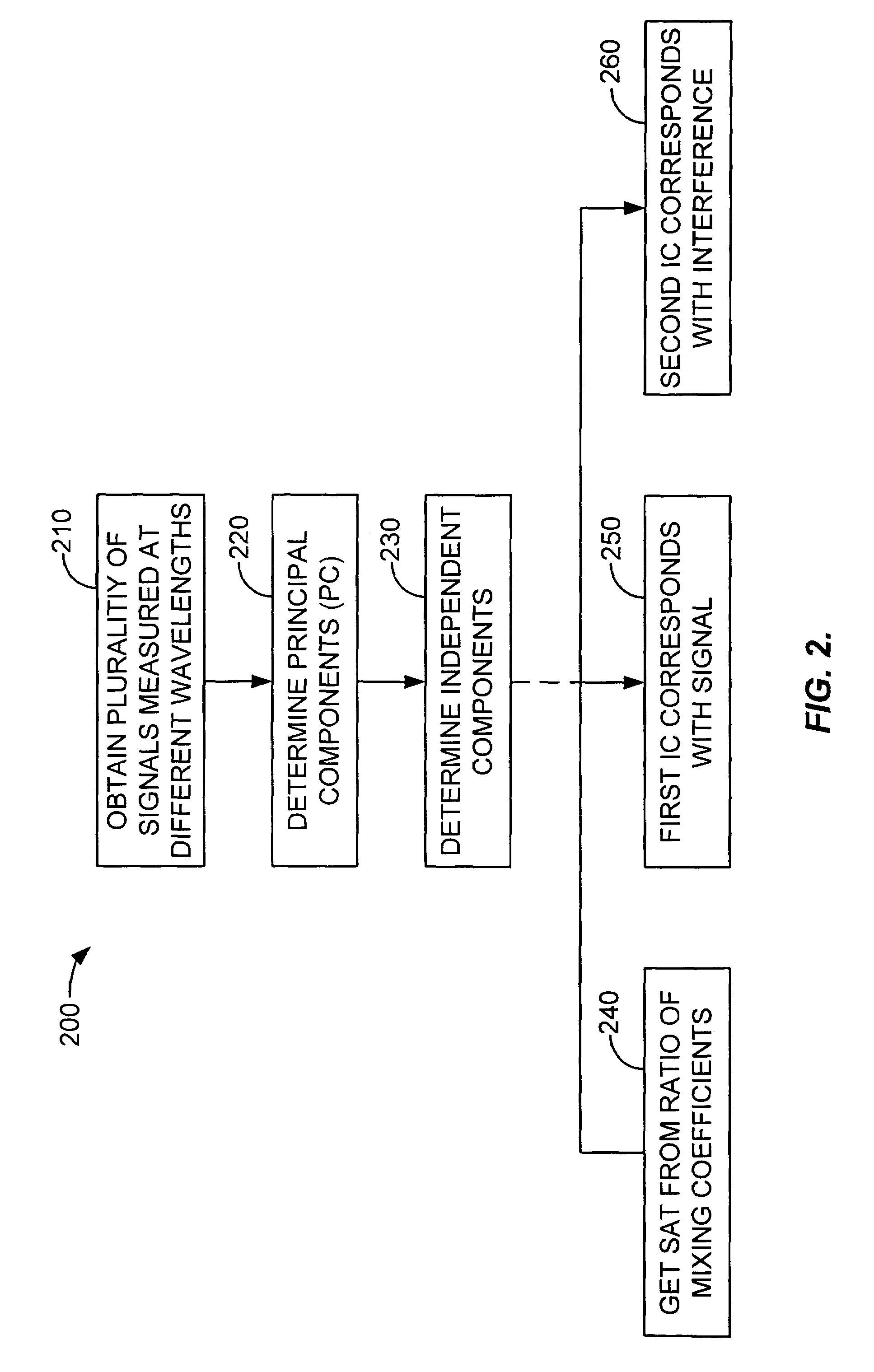
Blind source separation of pulse oximetry signals
InactiveUS7079880B2Minimize cross-correlationImprove performanceSensorsMeasuring/recording heart/pulse ratePrincipal component analysisPulse oximetry
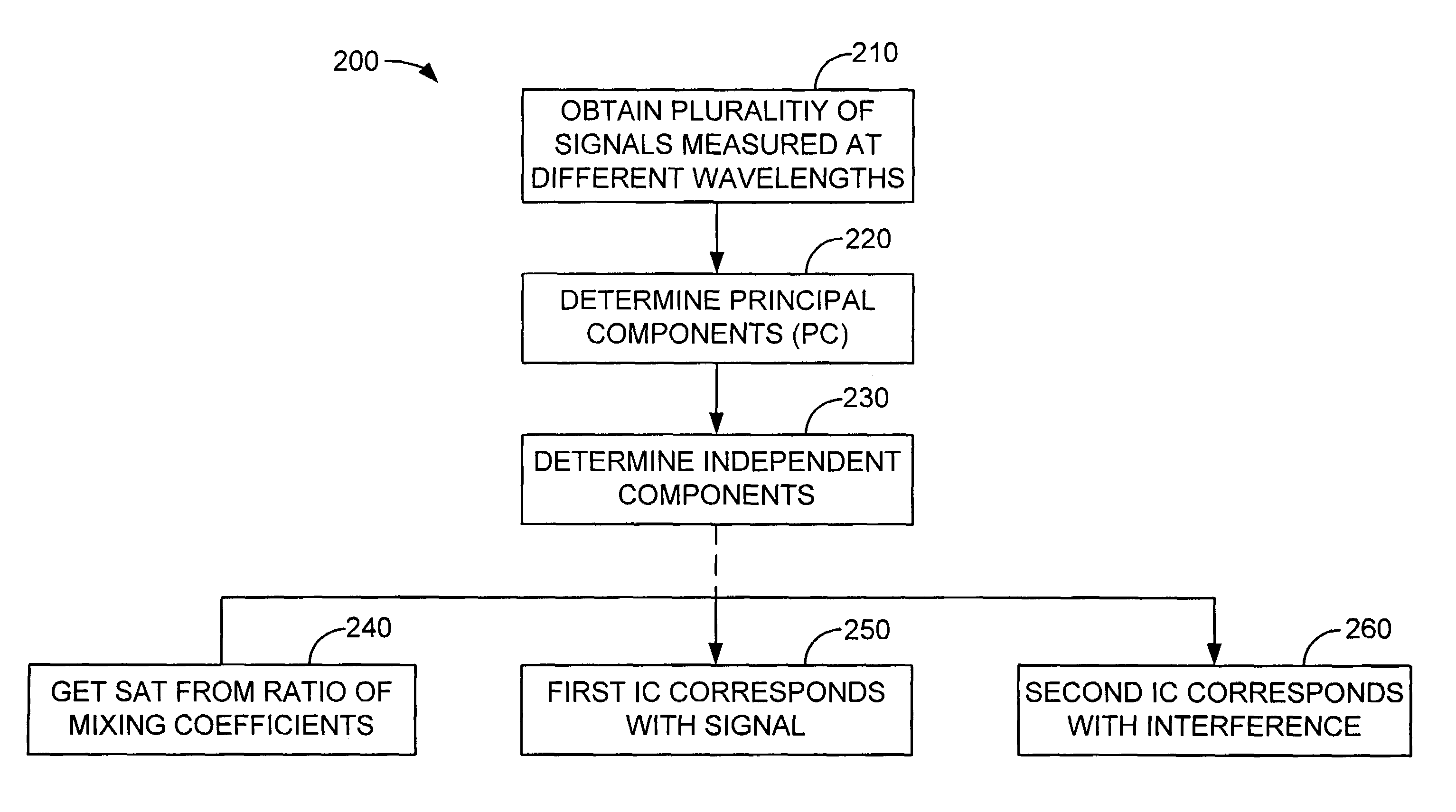
A method and apparatus for the application of Blind Source Separation (BSS), specifically independent Component Analysis (ICA) to mixture signals obtained by a pulse oximeter sensor. In pulse oximetry, the signals measured at different wavelengths represent the mixture signals, while the plethysmographic signal, motion artifact, respiratory artifact and instrumental noise represent the source components. The BSS is carried out by a two-step method including an ICA. In the first step, the method uses Principal Component Analysis (PCA) as a preprocessing step, and the Principal Components are then used to derive sat and the Independent Components, where the Independent Components are determined in a second step. In one embodiment, the independent components are obtained by high-order decorrelation of the principal components, achieved by maximizing the sum of the squares of the higher-order cumulants of the plurality of mixture signals.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
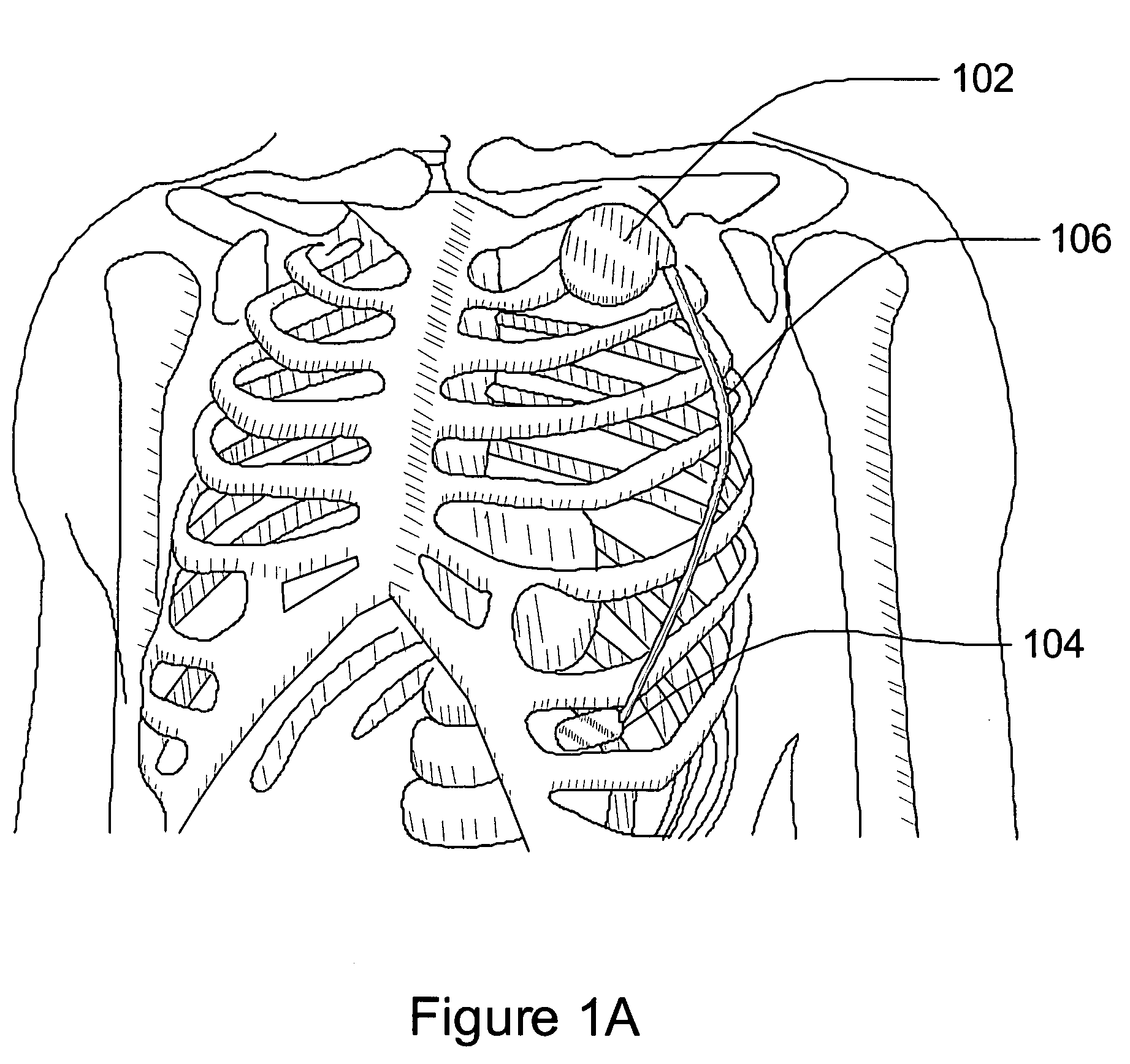
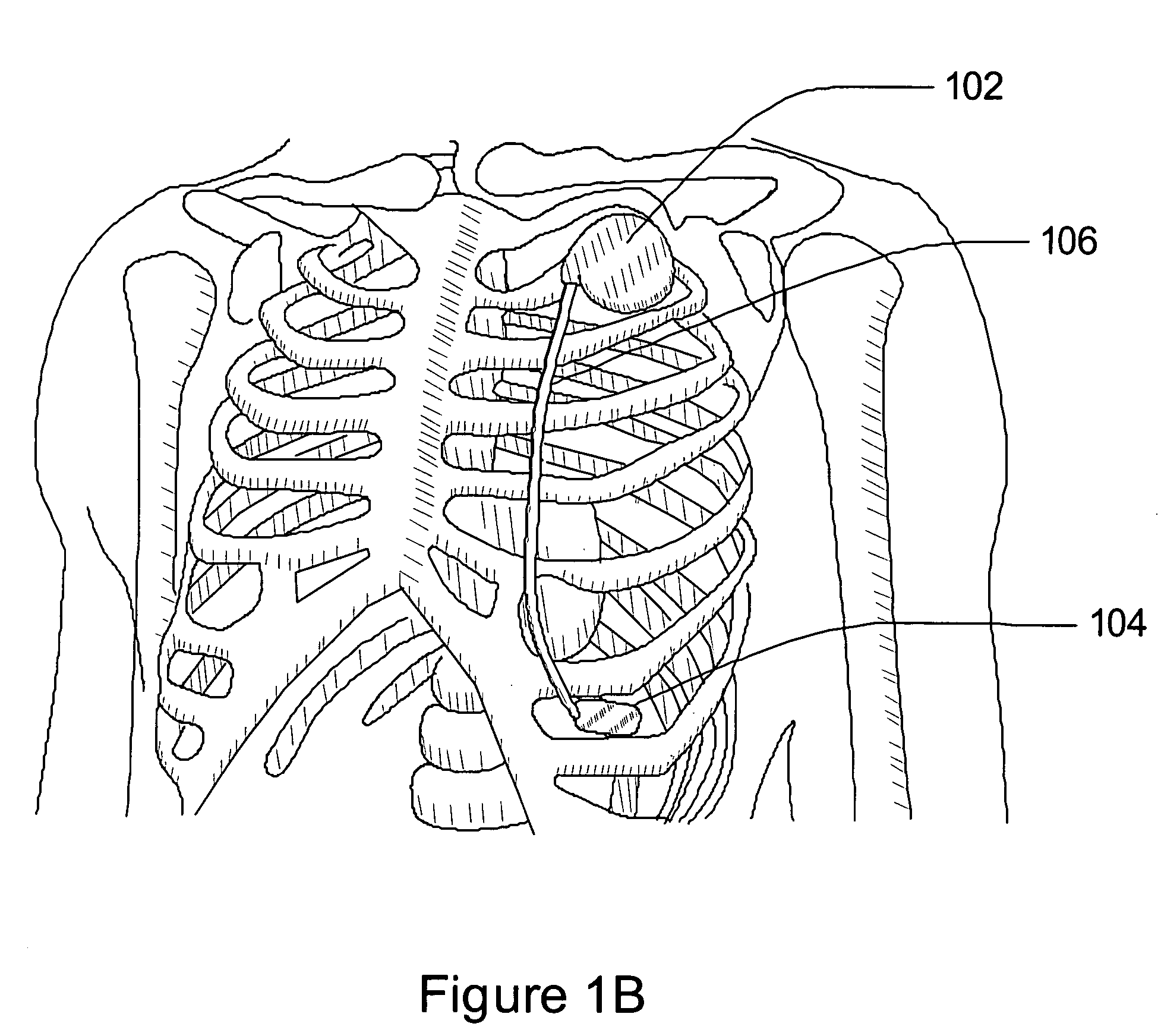
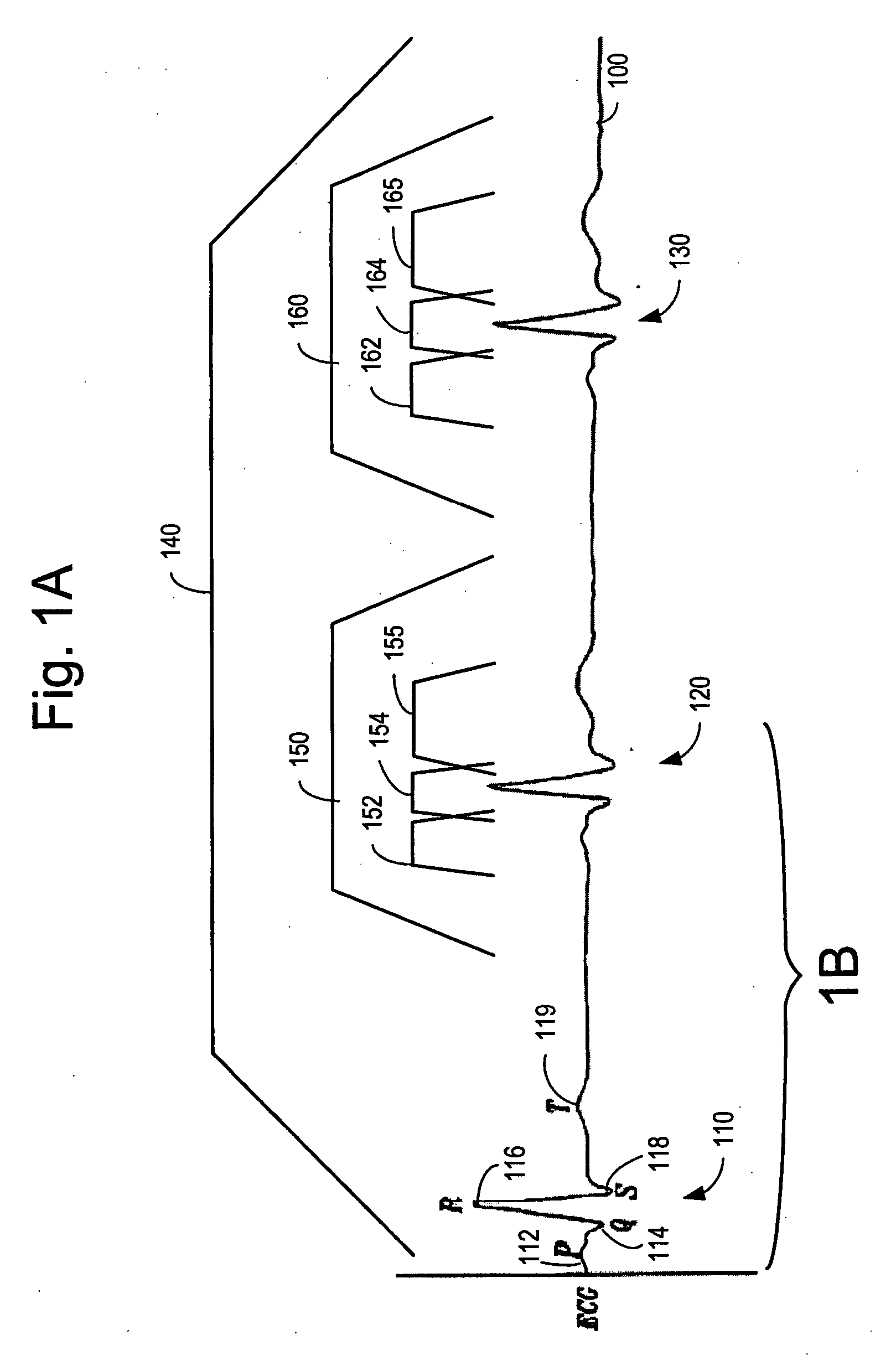
Separation of a subcutaneous cardiac signal from a plurality of composite signals
A cardiac monitoring and / or stimulation method and systems provide monitoring, defibrillation and / or pacing therapies, including systems detecting and / or treating cardiac arrhythmia. A system includes a housing coupled to a plurality of electrodes configured for subcutaneous non-intrathoracic sensing. A signal processor receives a plurality of composite signals associated with a plurality of sources, separates a signal from the plurality of composite signals using blind source separation, and identifies a cardiac signal. The signal processor may iteratively separate signals from the plurality of composite signals until the cardiac signal is identified. A method of signal separation includes detecting a plurality of composite signals at a plurality of locations, separating a signal using blind source separation, and identifying a cardiac signal. The separation may include a principal component analysis and / or an independent component analysis. The composite signals may be filtered before separation using band-pass filtering, adaptive, or other filters.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
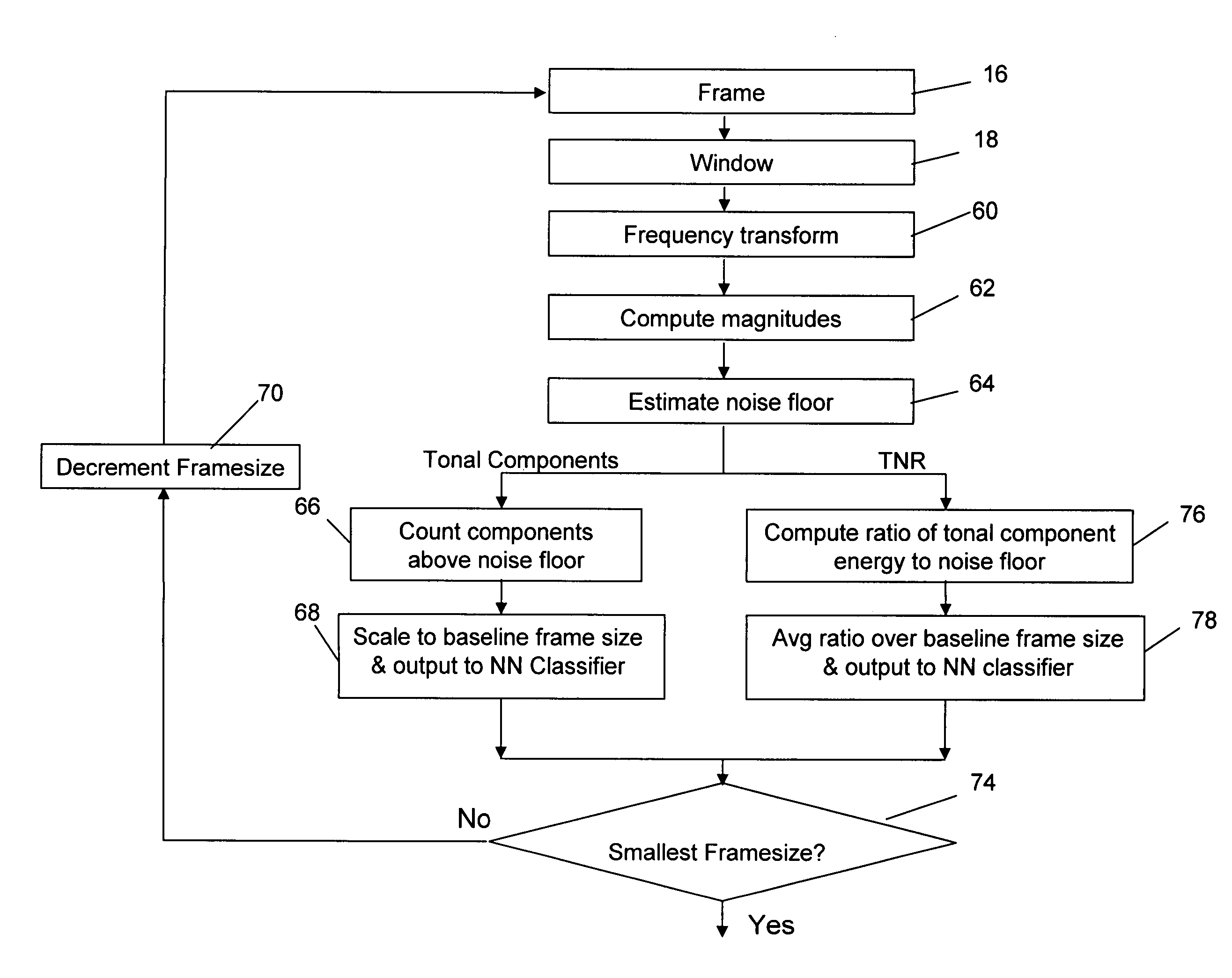
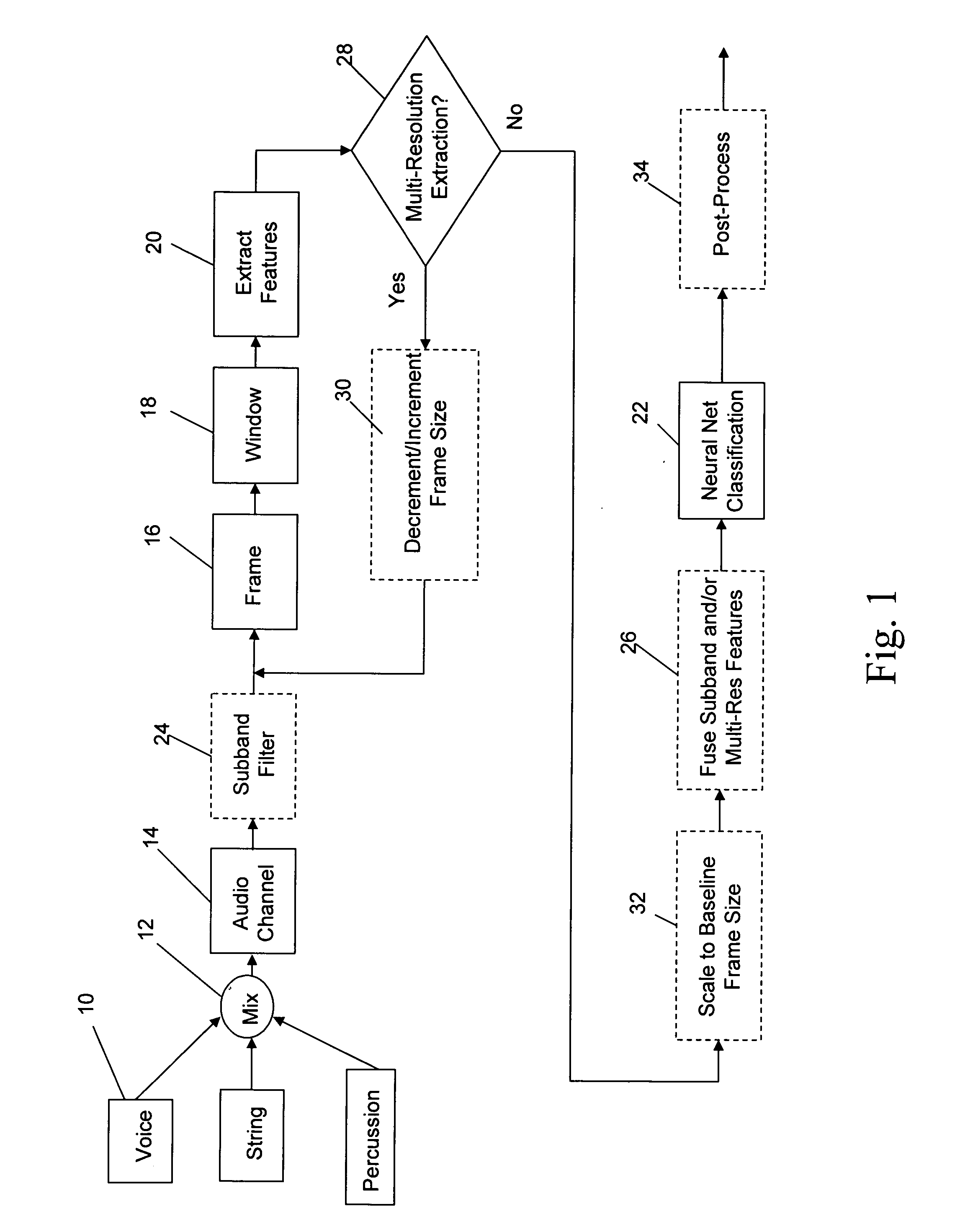
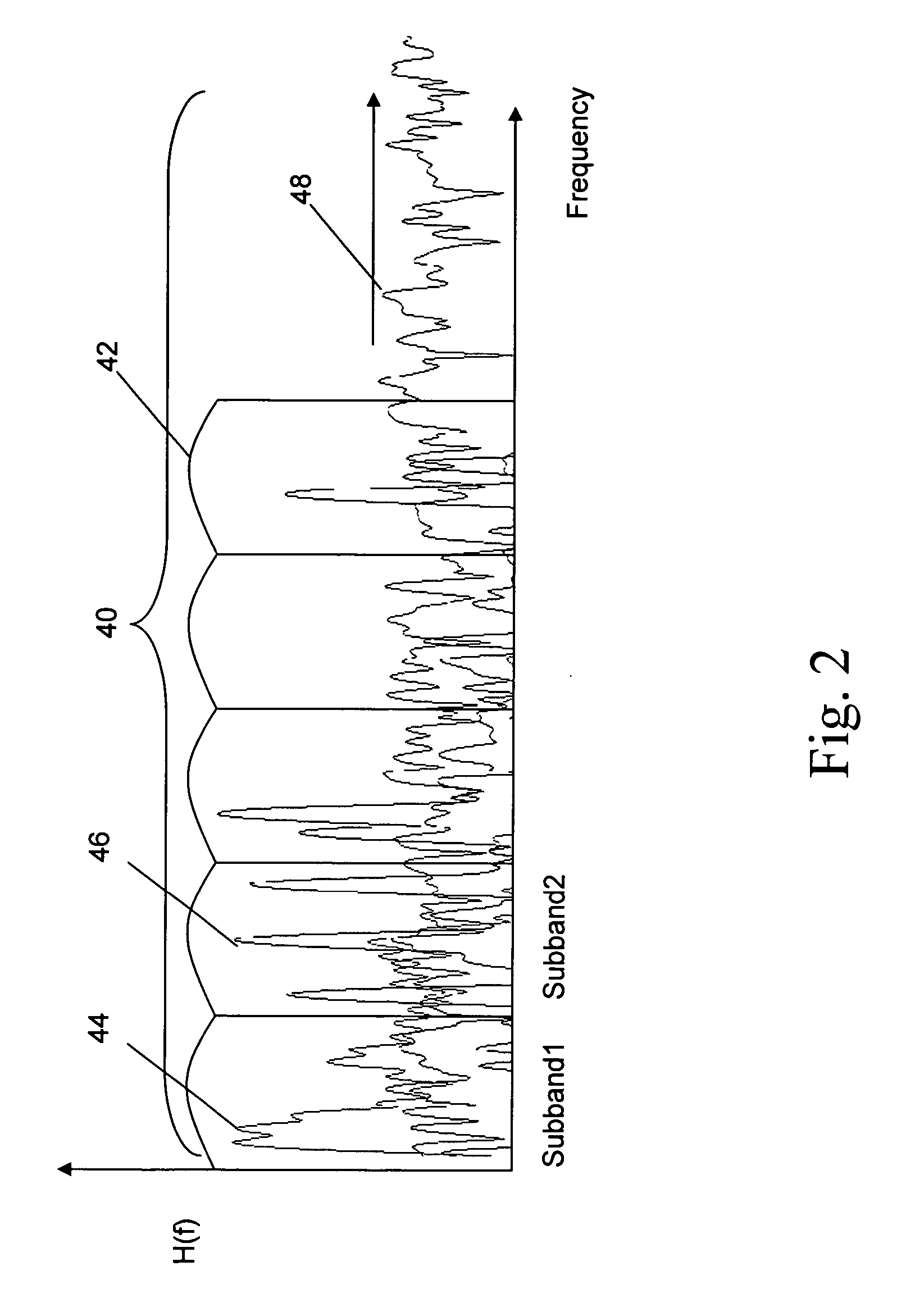
Neural network classifier for separating audio sources from a monophonic audio signal
InactiveUS20070083365A1Improve robustnessEasy to separateSpeech recognitionNetwork outputAudio signal
A neural network classifier provides the ability to separate and categorize multiple arbitrary and previously unknown audio sources down-mixed to a single monophonic audio signal. This is accomplished by breaking the monophonic audio signal into baseline frames (possibly overlapping), windowing the frames, extracting a number of descriptive features in each frame, and employing a pre-trained nonlinear neural network as a classifier. Each neural network output manifests the presence of a pre-determined type of audio source in each baseline frame of the monophonic audio signal. The neural network classifier is well suited to address widely changing parameters of the signal and sources, time and frequency domain overlapping of the sources, and reverberation and occlusions in real-life signals. The classifier outputs can be used as a front-end to create multiple audio channels for a source separation algorithm (e.g., ICA) or as parameters in a post-processing algorithm (e.g. categorize music, track sources, generate audio indexes for the purposes of navigation, re-mixing, security and surveillance, telephone and wireless communications, and teleconferencing).
Owner:DTS
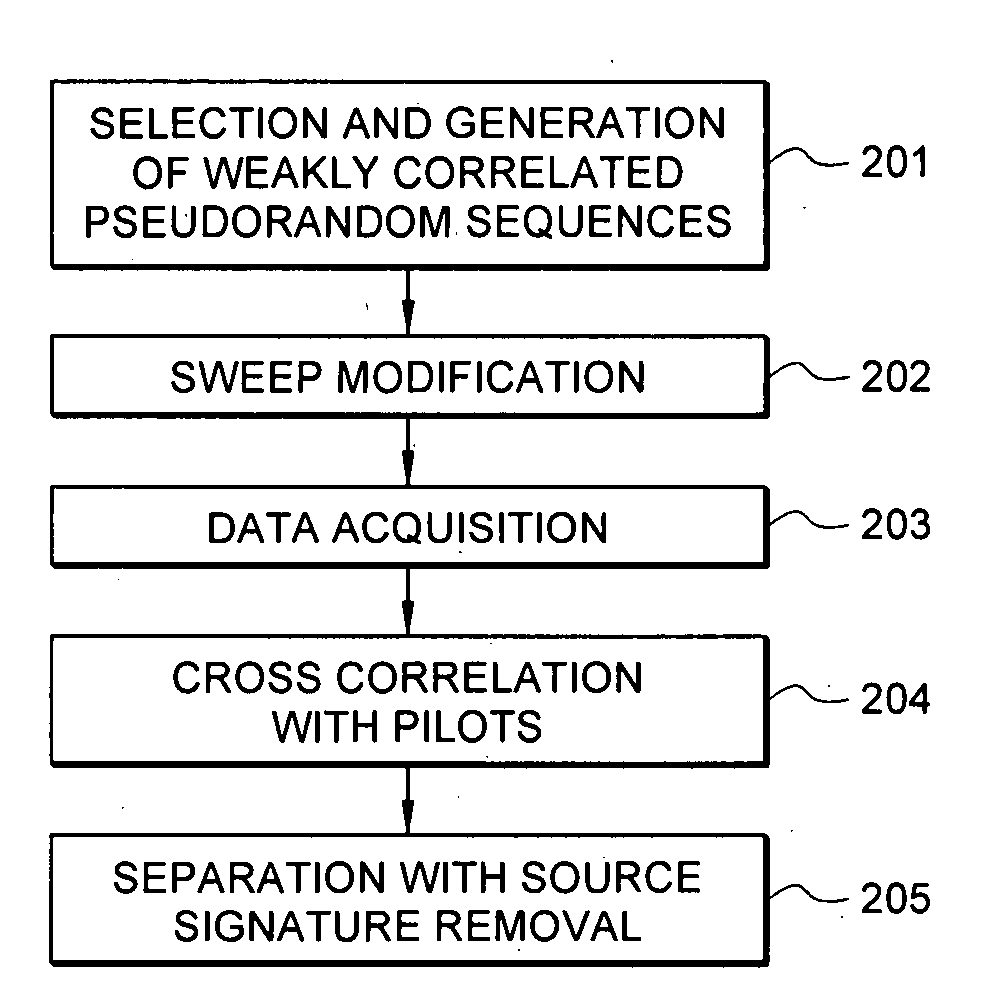
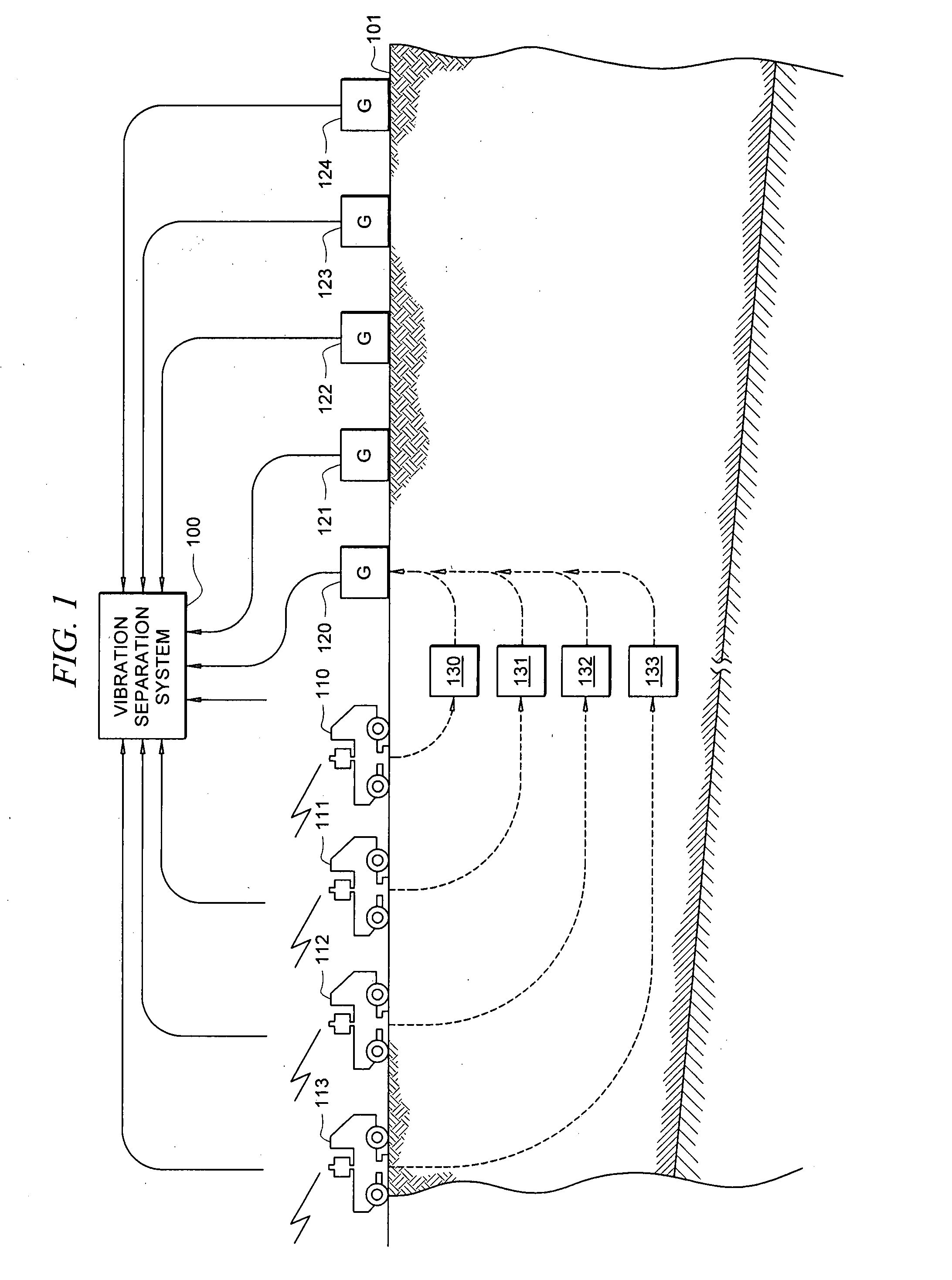
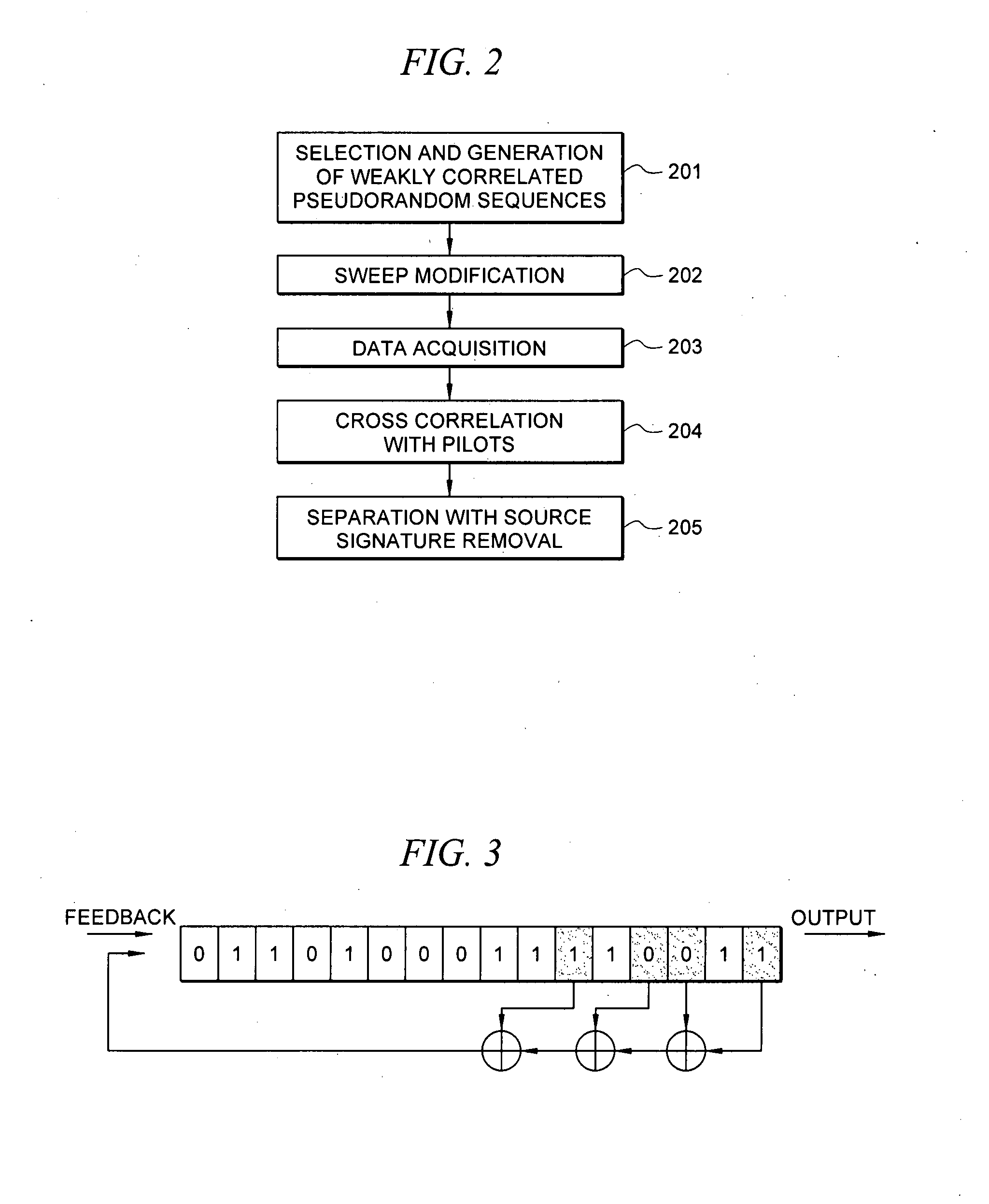
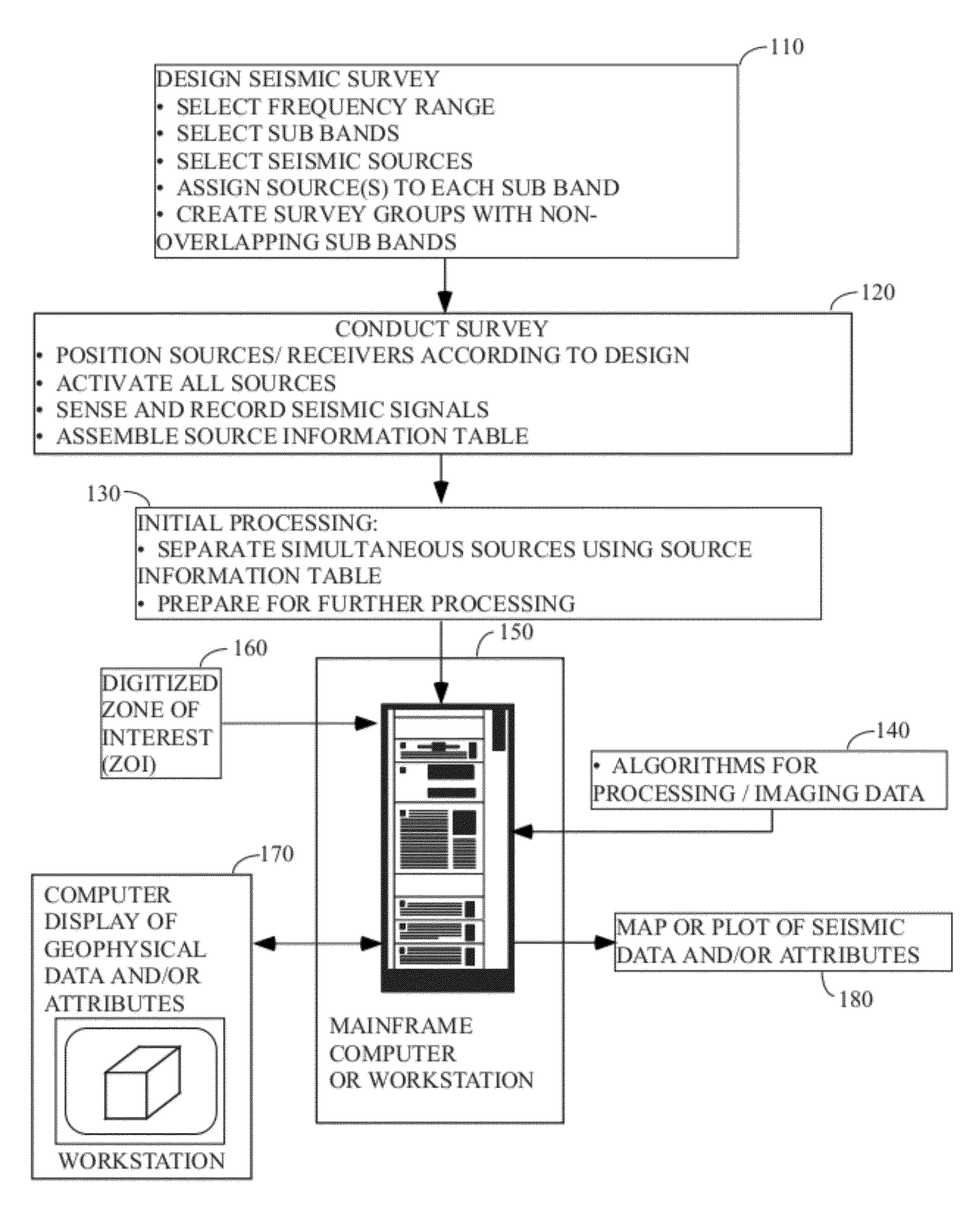
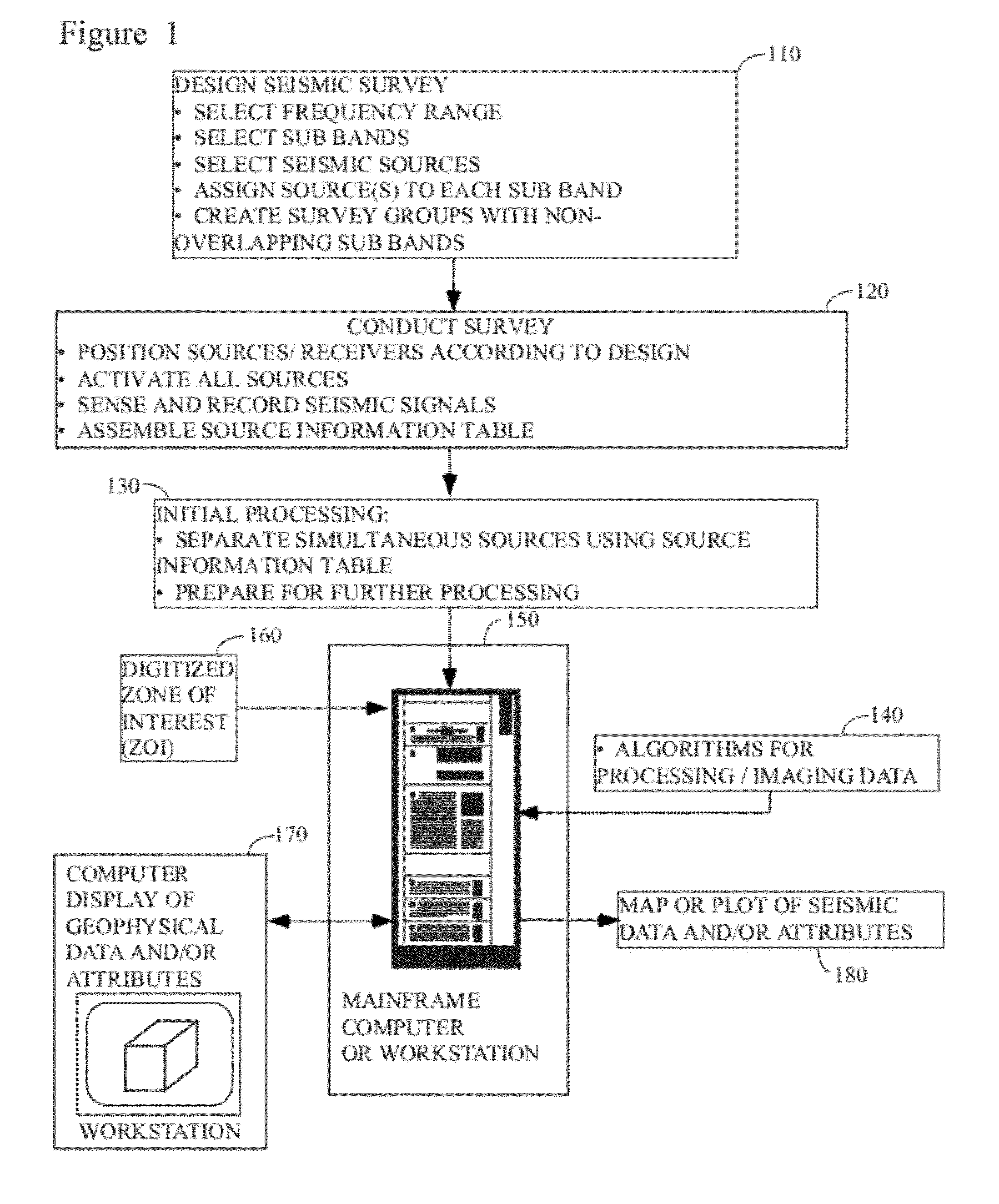
Efficient seismic data acquisition with source separation
ActiveUS20090010103A1Minimize crosstalkSeismic data acquisitionSeismic energy generationTime domainFrequency spectrum
A method for the simultaneous operation of multiple seismic vibrators using unique modified pseudorandom sweeps and recovery of the transmission path response from each vibrator is disclosed. The vibrator sweeps are derived from pseudorandom binary sequences modified to be weakly correlated over a time window of interest, spectrally shaped and amplitude level compressed. Cross-correlation with each pilot signal is used to perform an initial separation of the composite received signal data set. Recordings of the motion of each vibrator are also cross-correlated with each pilot, windowed, and transformed to form a source cross-spectral density matrix in the frequency domain useful for source signature removal and for additional crosstalk-suppression between the separated records. After source signature removal in the frequency domain an inverse transform is applied to produce an estimate of each source-to-receiver earth response in the time domain. The method has application to both land and marine geophysical exploration.
Owner:SERCEL INC
Closed loop cardiac resynchronization therapy using cardiac activation sequence information
Cardiac monitoring and / or stimulation methods and systems that provide one or more of monitoring, diagnosing, defibrillation, and pacing. Cardiac signal separation is employed to detect, monitor, track and / or trend closed-loop cardiac resynchronization therapy using cardiac activation sequence information. Devices and methods involve sensing a plurality of composite cardiac signals using a plurality of electrodes, the electrodes configured for implantation in a patient. A source separation is performed using the sensed plurality of composite cardiac signals, producing one or more cardiac signal vectors associated with all or a portion of one or more cardiac activation sequences. A cardiac resynchronization therapy is adjusted using one or both of the one or more cardiac signal vectors and the signals associated with the one or more cardiac signal vectors. In further embodiments, the cardiac resynchronization therapy may be initiated, terminated, or one or more parameters of the resynchronization therapy may be altered.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
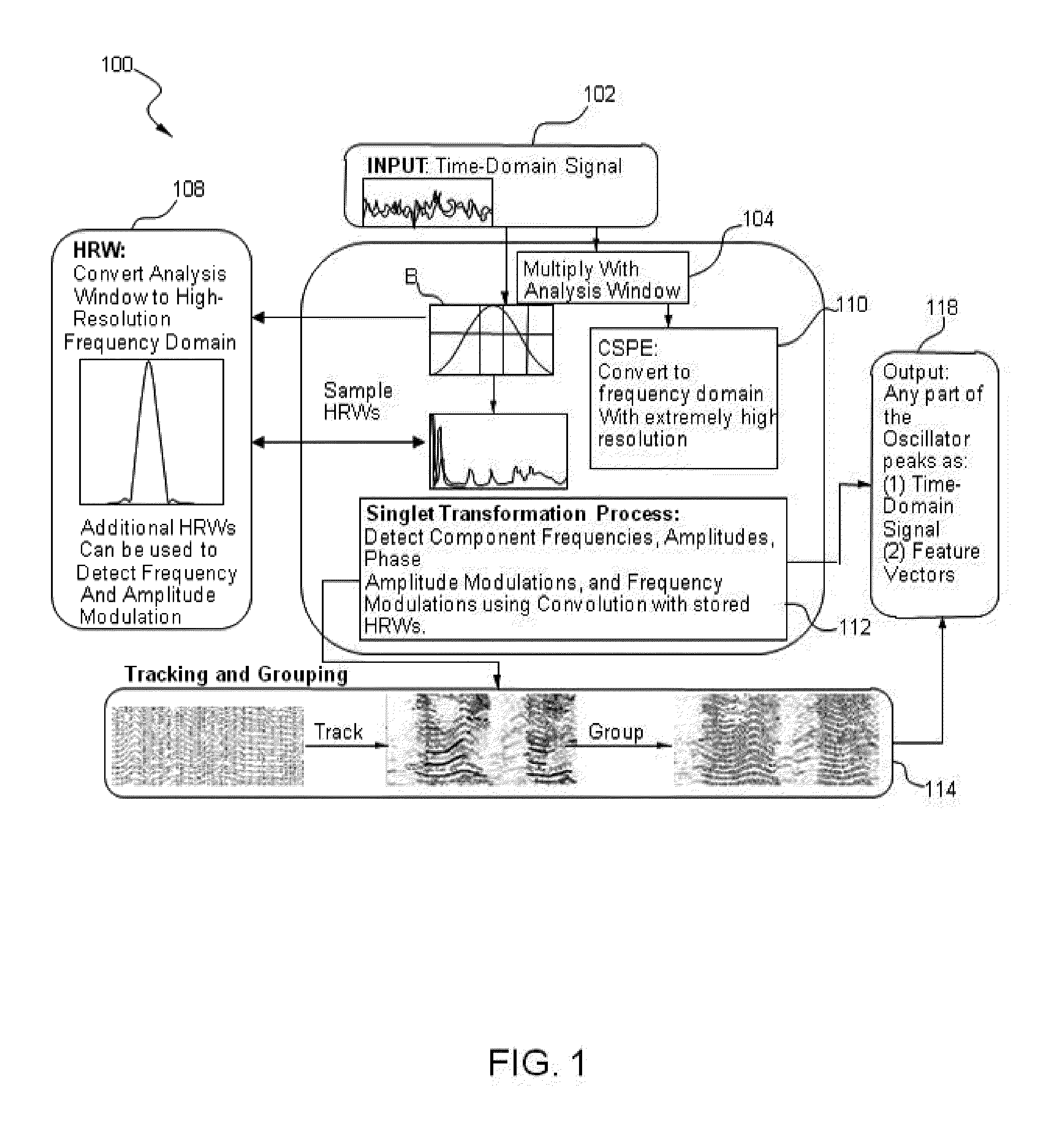
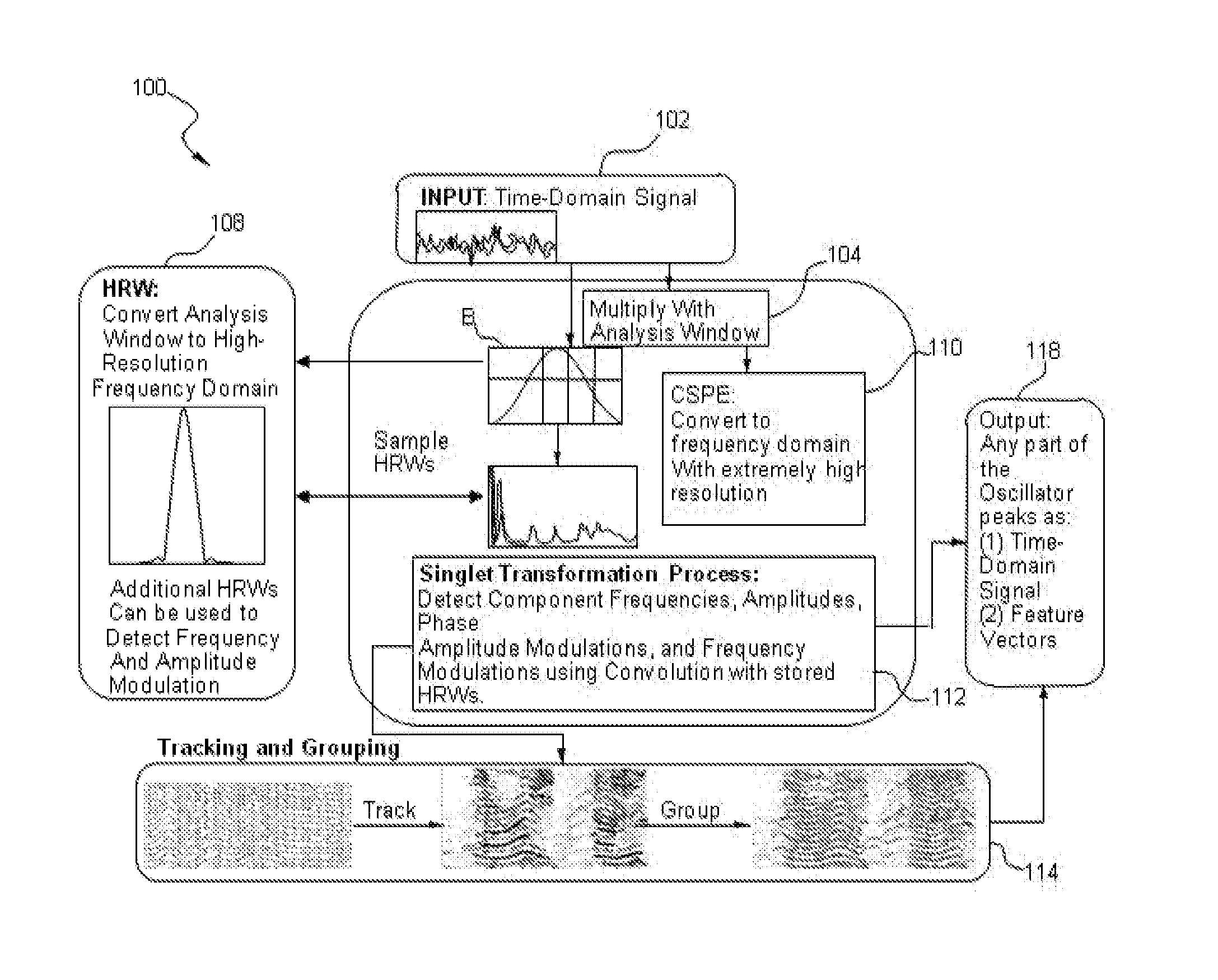
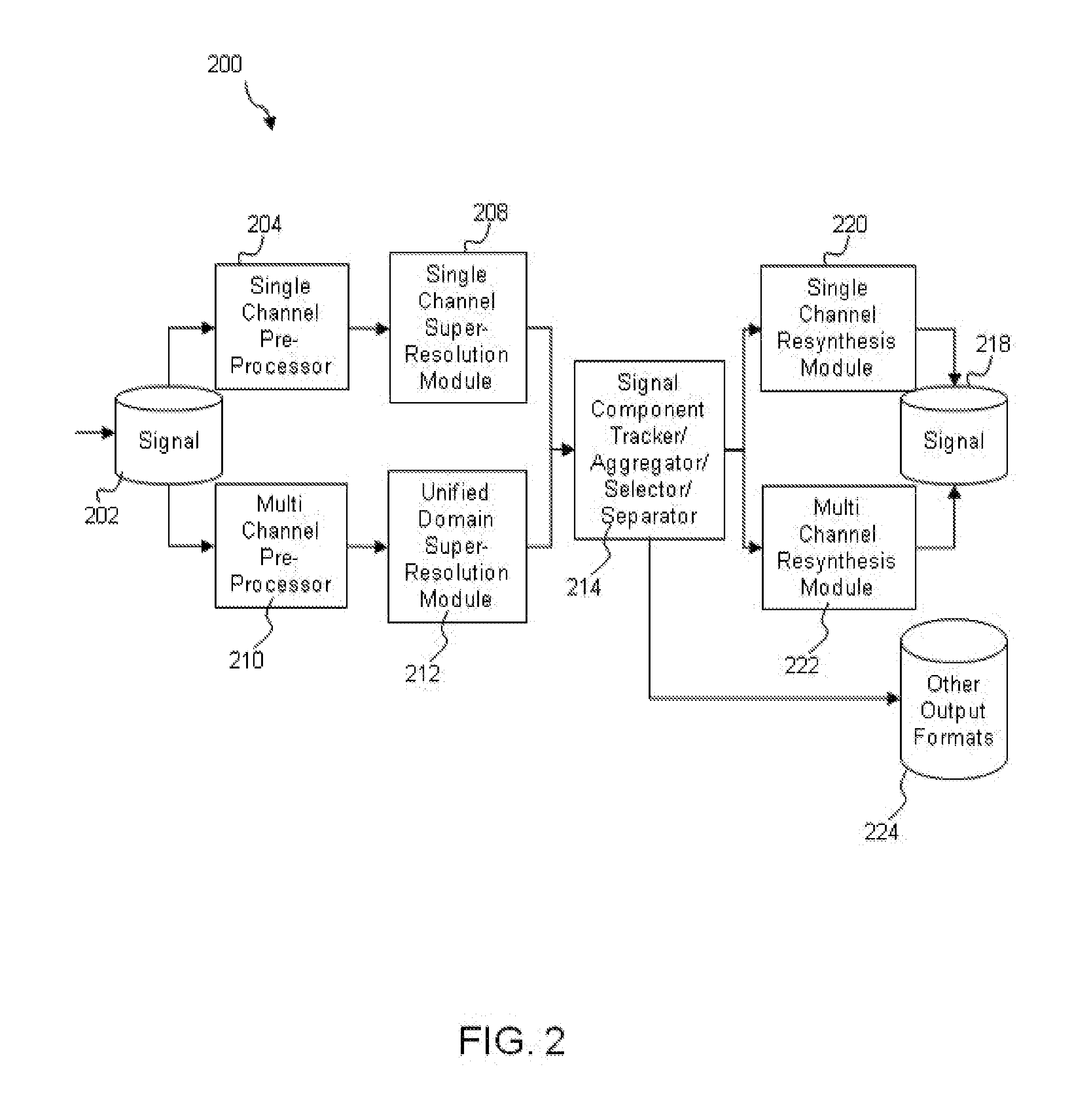
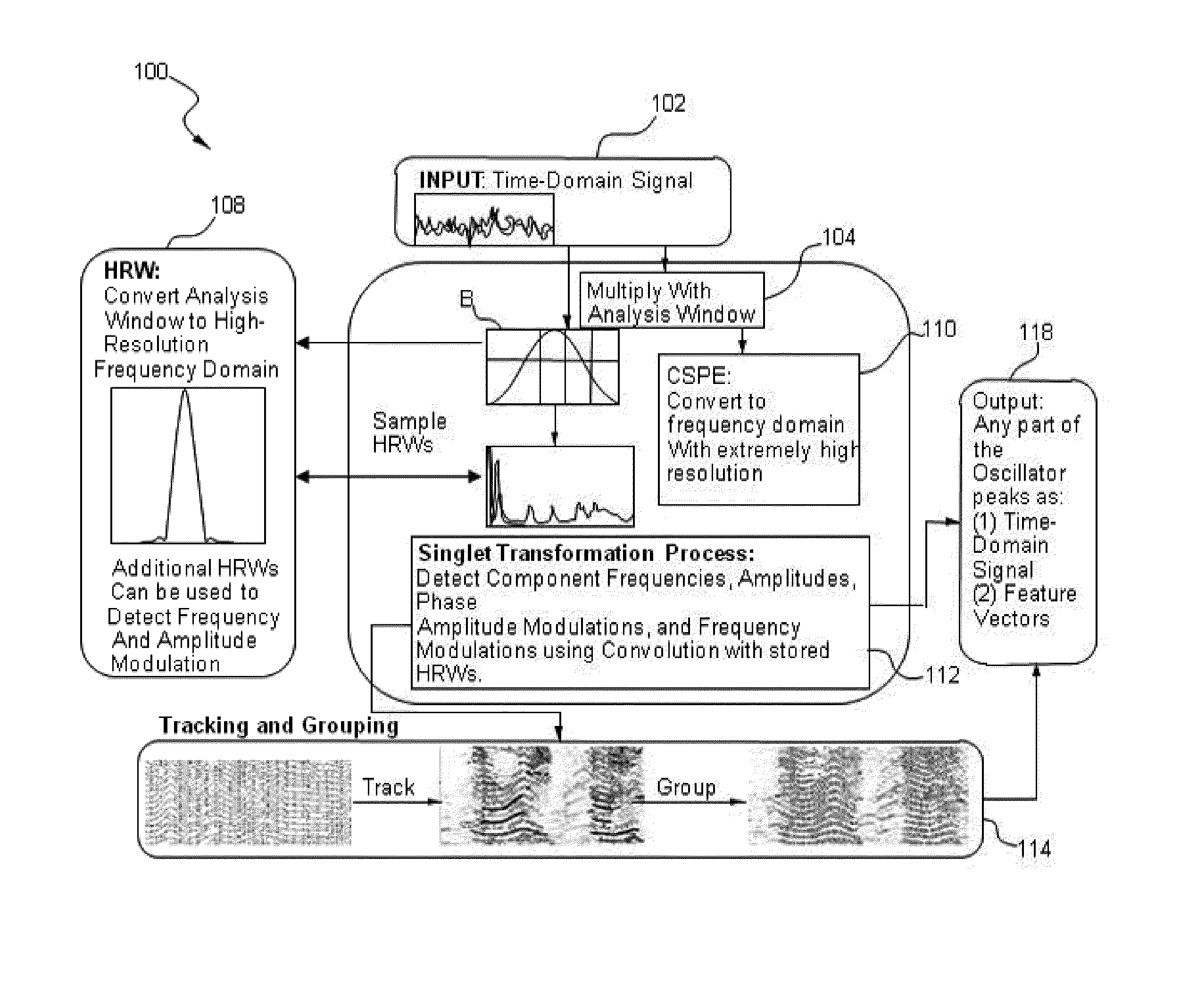
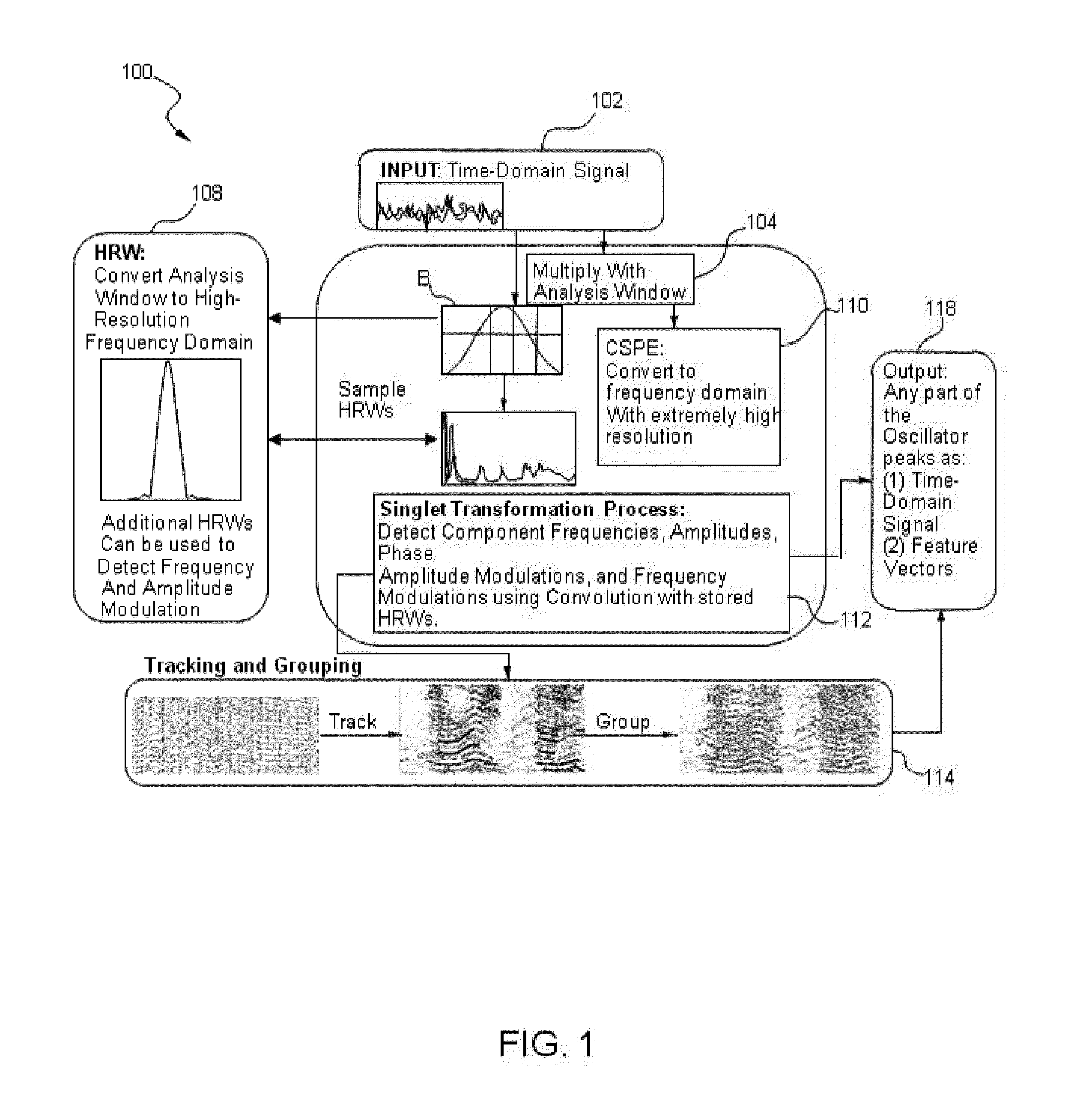
Methods and systems for improved measurement, entity and parameter estimation, and path propagation effect measurement and mitigation in source signal separation
ActiveUS20150287422A1Multi-channel direction-finding systems using radio wavesSpeech recognitionPeak valuePropagation effect
A method of processing a signal includes taking a signal recorded by a plurality of signal recorders, applying at least one super-resolution technique to the signal to produce an oscillator peak representation of the signal comprising a plurality of frequency components for a plurality of oscillator peaks, computing at least one Cross Channel Complex Spectral Phase Evolution (XCSPE) attribute for the signal to produce a measure of a spatial evolution of the plurality of oscillator peaks between the signal, identifying a known predicted XCSPE curve (PXC) trace corresponding to the frequency components and at least one XCSPE attribute of the plurality of oscillator peaks and utilizing the identified PXC trace to determine a spatial attribute corresponding to an origin of the signal.
Owner:XMOS INC
Automatic capture verification using electrocardiograms sensed from multiple implanted electrodes
InactiveUS20060253164A1Heart stimulatorsDiagnostic recording/measuringImplantable ElectrodesCardiac monitoring
Cardiac monitoring and / or stimulation methods and systems that provide one or more of monitoring, diagnosing, defibrillation, and pacing. Cardiac signal separation is employed for automatic capture verification using cardiac activation sequence information. Devices and methods sense composite cardiac signals using implantable electrodes. A source separation is performed using the composite signals. One or more signal vectors are produced that are associated with all or a portion of one or more cardiac activation sequences based on the source separation. A cardiac response to the pacing pulses is classified using characteristics associated with cardiac signal vectors and the signals associated with the vectors. Further embodiments may involve classifying the cardiac response as capture or non-capture, fusion or intrinsic cardiac activity. The characteristics may include an angle or an angle change of the cardiac signal vectors, such as a predetermined range of angles of the one or more cardiac signal vectors.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
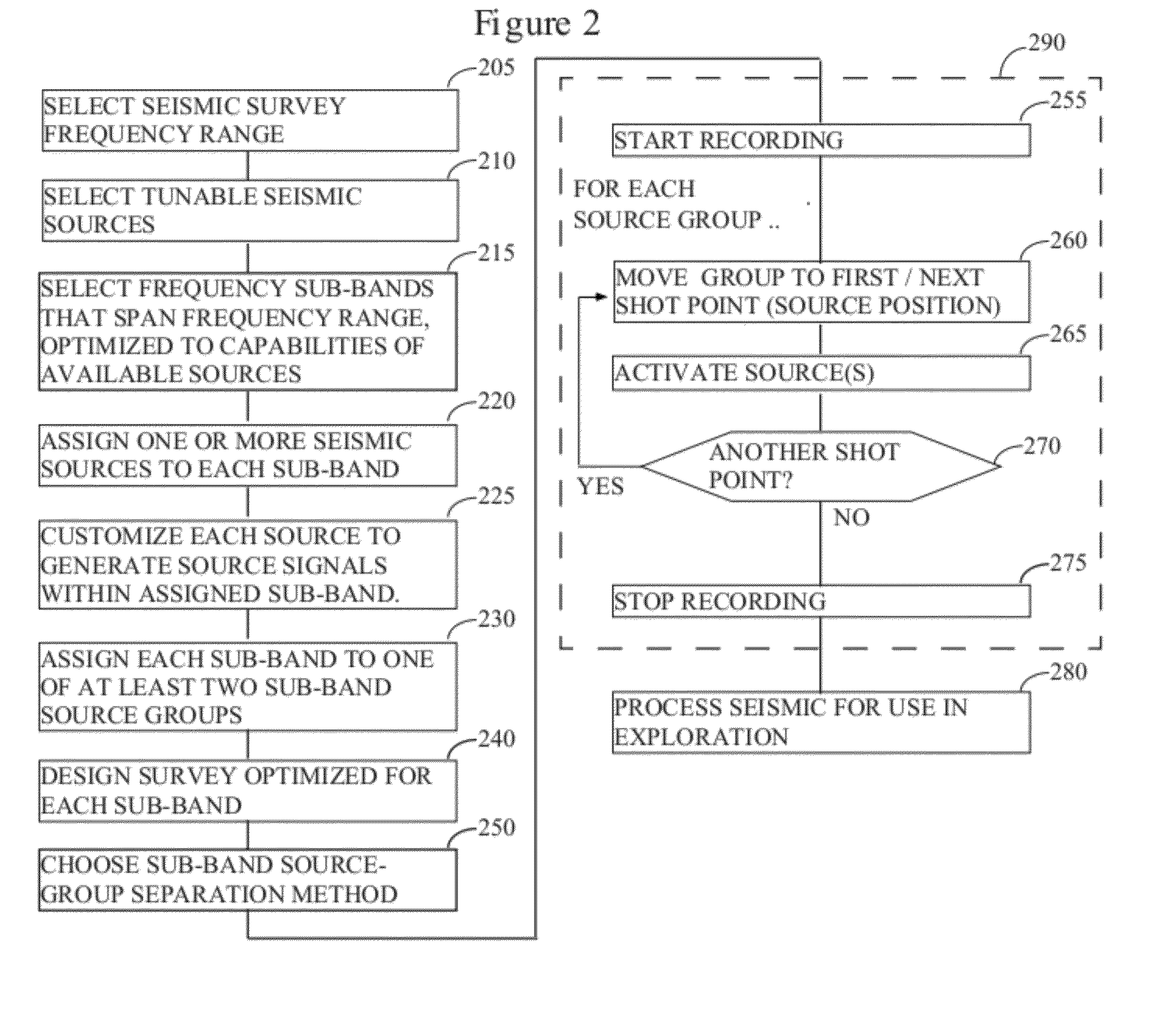
Distance- and frequency-separated swept-frequency seismic sources
InactiveUS20120147699A1Enhance simultaneous source separationEasy to separateSeismic data acquisitionSeismic signal recordingBandpass filteringFrequency separation
There is provided a method of seismic acquisition that utilizes a bank of restricted-bandwidth swept-frequency sub-band sources as a seismic source. Each seismic source will cover a restricted sub-band of frequencies, with all the sources taken together covering the full frequency range. Adjacent frequency bands may partially overlap, but non-adjacent frequency bands should not. The sources may be divided into two or more groups, with no sources covering adjacent frequency bands being placed in the same group. The sources within a group can then be separated by bandpass filtering or by conventional simultaneous source-separation techniques. The source groups may be operated simultaneously but separated in space, and the individual sources themselves may each operate independently, on a sweep schedule customized for that particular source.
Owner:BP CORP NORTH AMERICA INC
Posture monitoring using cardiac activation sequences
Cardiac monitoring and / or stimulation methods and systems that provide one or more of monitoring, diagnosing, defibrillation, and pacing. Cardiac signal separation is employed to detect, monitor, track and / or trend a patient's posture using cardiac activation sequence information. Devices and methods in accordance with the present invention involve sensing a plurality of composite cardiac signals using a plurality of implantable electrodes. A source separation is performed using the composite cardiac signals, which produces one or more cardiac signal vectors associated with all or a portion of one or more cardiac activation sequences. A change in a patient's posture is detected using the cardiac signal vectors. Further embodiments involve sensing the plurality of composite cardiac signals during the patient's predominant cardiac rhythm before detecting the change in the patient's posture. Other embodiments involve discriminating between one of a postural related change and a cardiac rhythm related change using the cardiac signal vectors.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
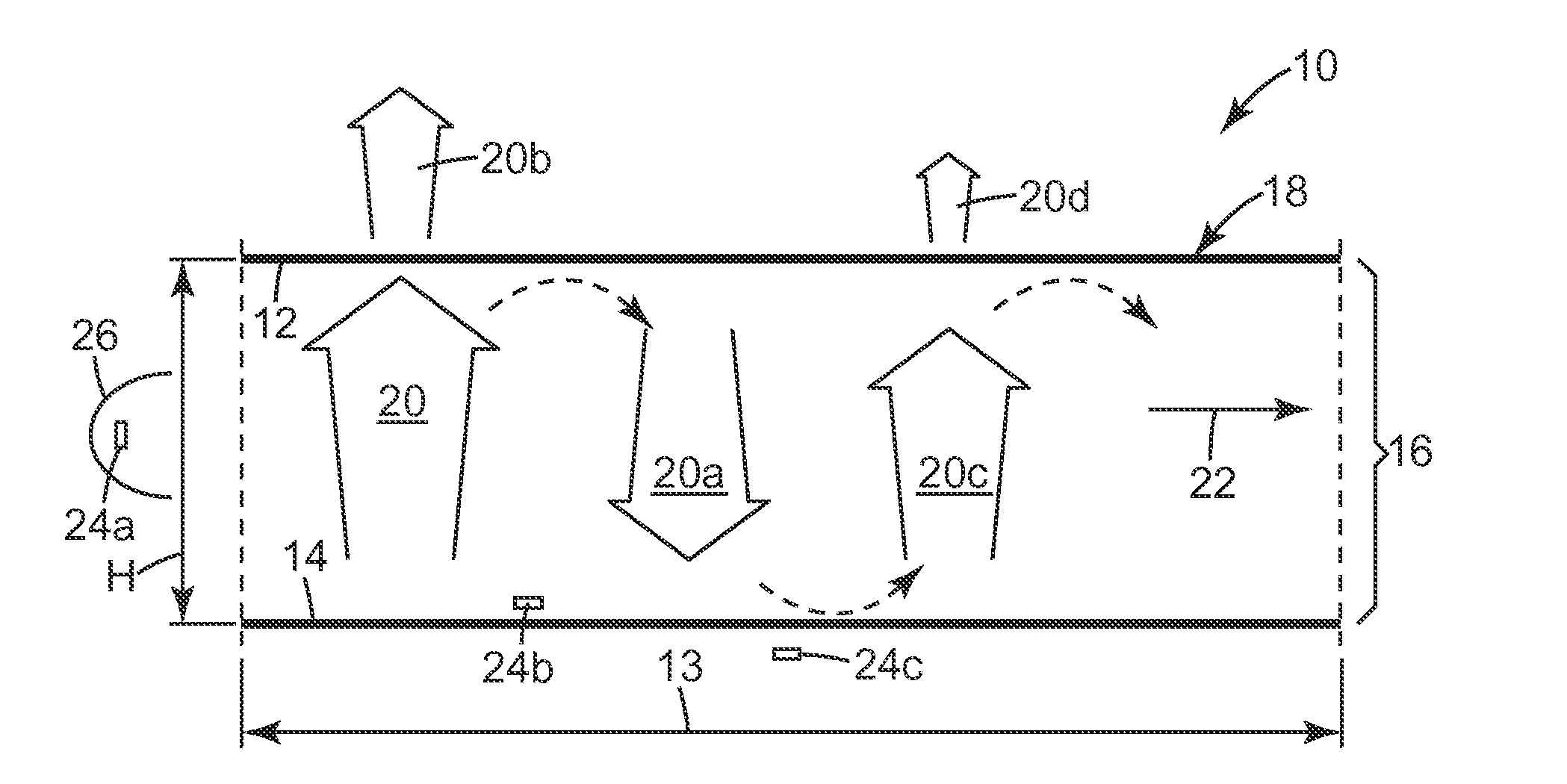
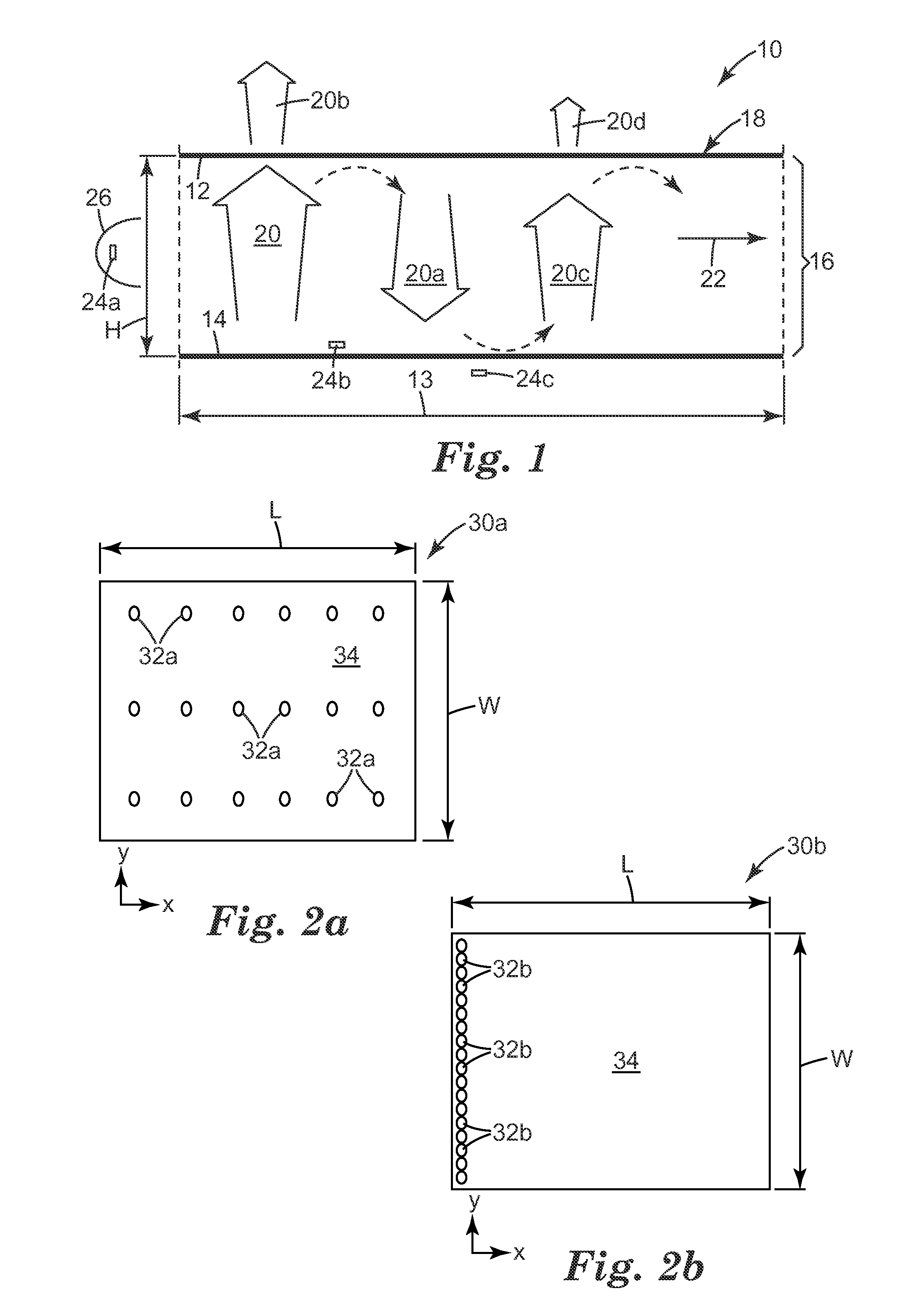
Thin hollow backlights with beneficial design characteristics
InactiveUS20100156953A1Reduce the total massLosses associated with the light sources are kept to minimal levelsCathode-ray tube indicatorsHollow light guidesBack reflectorLight guide
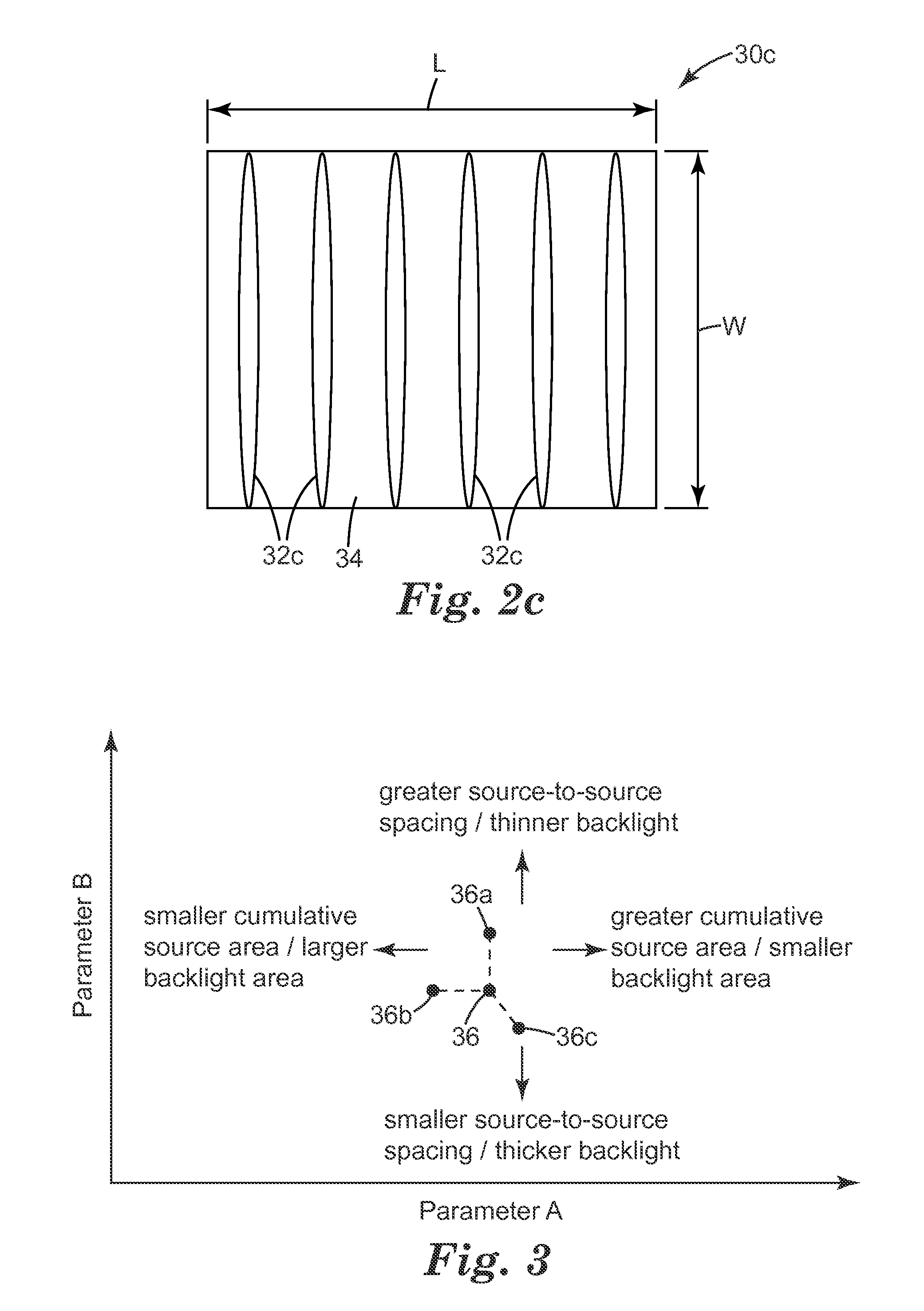
A backlight unit (10) has a hollow cavity (16) instead of employing a light guide. One or more light sources (24a-c), such as LEDs, are arranged to emit light into the cavity, which is formed by a front (12) and a back reflector (14). The backlight is typically of the edge-lit type. The backlight can have a large area, is thin and consists of fewer components than conventional devices. Its design permits light recycling. The unit emits light of a predefined polarisation and can be arranged to have desired horizontal / vertical viewing angle properties. Light is uniformly distributed within the guide and the light output (20b, 2Od) is substantially collimated. Such backlights occupy a specific region in a parameter space defined by two parameters: first, the ratio of the output emission area to the total source emission area should lie in the range 0.0001 to 0.1; and second, the ratio of the SEP to the height of the cavity (H) should be in the range 3 to 10, where the SEP is an average plan view source separation, a special measure of the average spacing of light sources in the plane of the unit. There is also a discussion on the required number of light sources N, their arrangement near the periphery of the cavity, as well as the shape and size of the output emission area. A required minimum brightness uniformity (VESA) value to be maintained, when a subset of Madjacent sources is switched off (where M is at least 0.1 N or M>2 or both), is also disclosed. The backlight can be used for a display or for general lighting purposes.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Systems and methods for source signal separation
ActiveUS8694306B1Accurate reconstructionMulti-channel direction-finding systems using radio wavesDigital computer detailsTheoretical computer scienceSource separation
A method of processing a signal, including taking a signal formed from a plurality of source signal emitters and expressed in an original domain, decomposing the signal into a mathematical representation of a plurality of constituent elements in an alternate domain, analyzing the plurality of constituent elements to associate at least a subset of the constituent elements with at least one of the plurality of source signal emitters, separating at least a subset of the constituent elements based on the association and reconstituting at least a subset of constituent elements to produce an output signal in at least one of the original domain, the alternate domain and another domain.
Owner:XMOS INC
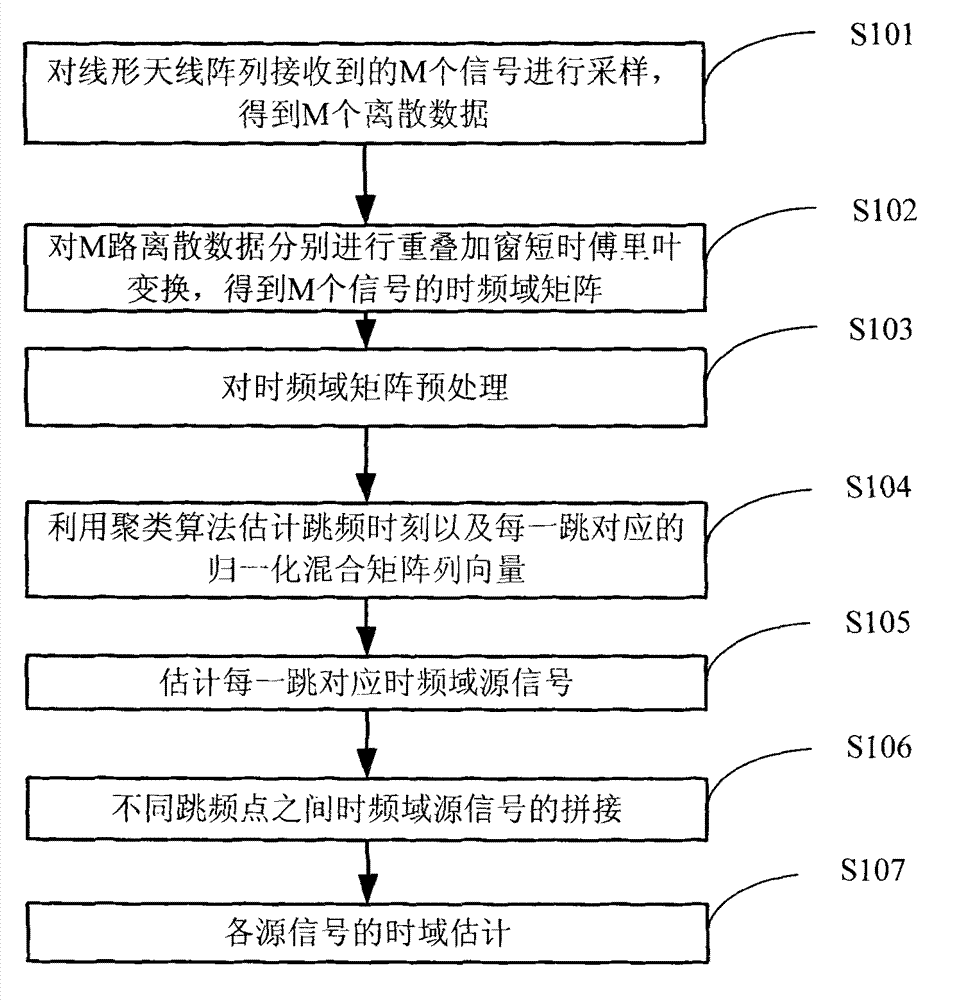
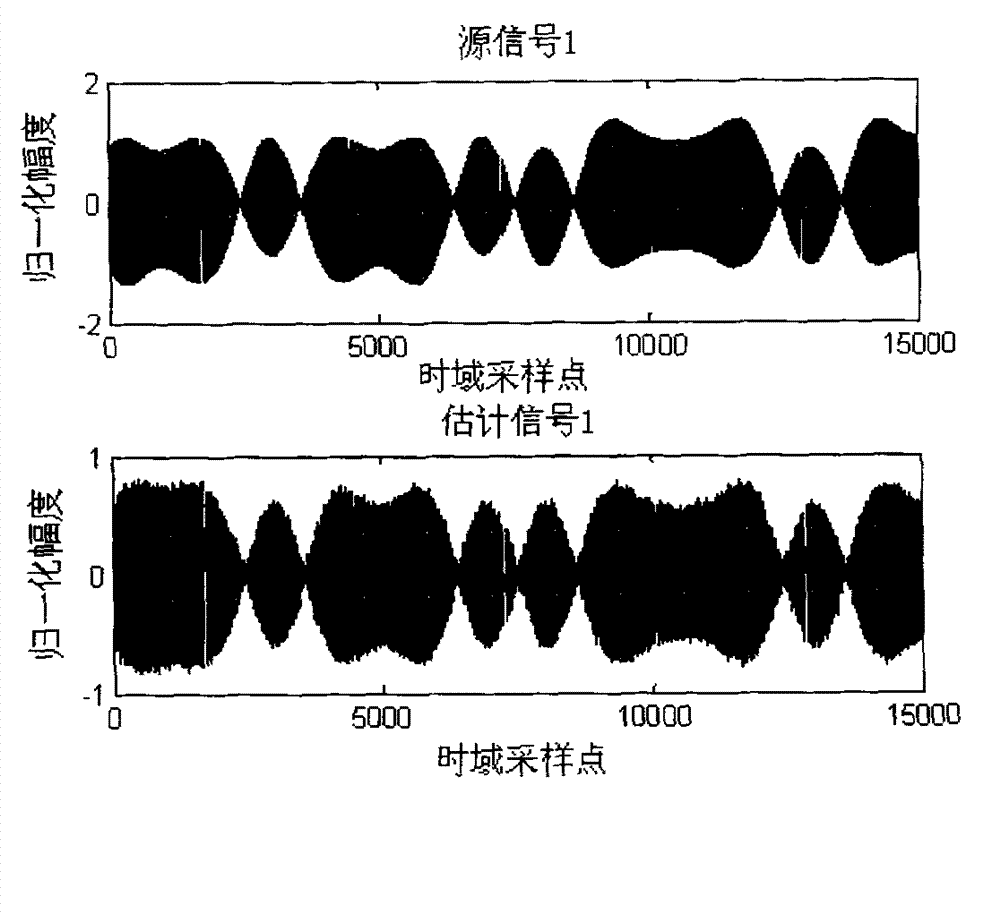
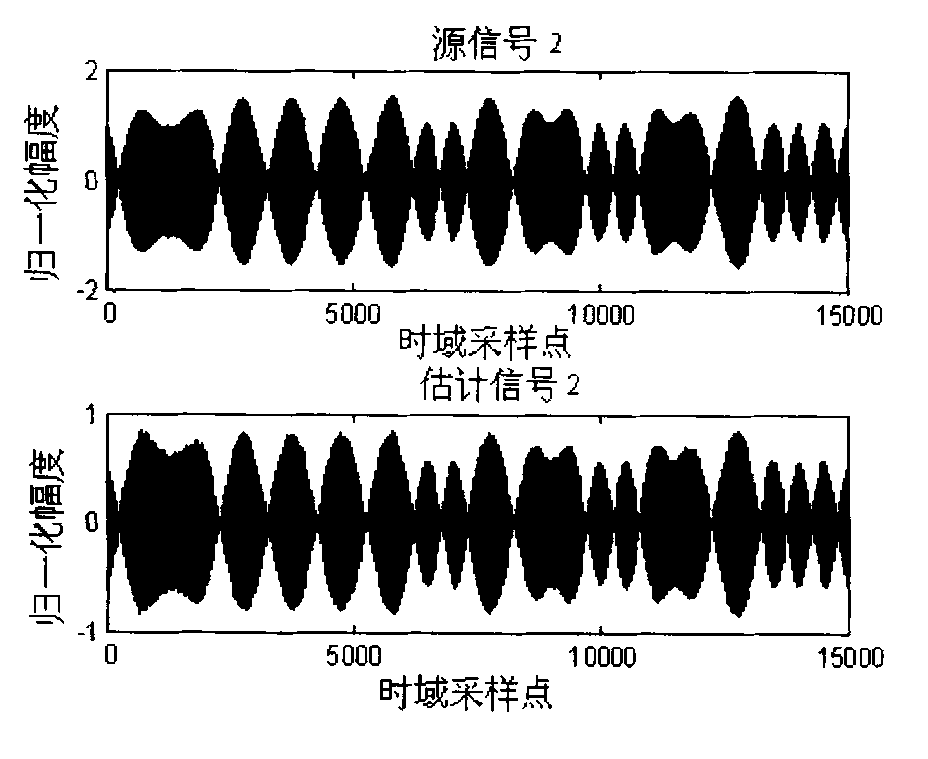
Clustering-based blind source separation method for synchronous orthogonal frequency hopping signals
InactiveCN103051367ASmall amount of calculationEasy to implementSpatial transmit diversityMulti-frequency code systemsTime domainDiscrete time domain
The invention discloses a clustering-based blind source separation method for synchronous orthogonal frequency hopping signals. The method comprises the following steps of: acquiring M sampled paths of discrete time-domain mixed signals; obtaining M time-frequency domain matrixes of the mixed signals; preprocessing the time-frequency domain matrixes of the frequency hopping mixed signals; estimating frequency hopping moments, normalized mixed matrix column vectors and frequency hopping frequency; estimating time-frequency domain frequency hopping source signals by utilizing the estimated normalized mixed matrix column vectors; splicing the time-frequency domain frequency hopping source signals between different frequency hopping points; and recovering time-domain source signals according to time-frequency domain estimate values of the source signals. According to the method, the frequency hopping source signals are estimated only according to the received mixed signals of a plurality of frequency hopping signals under the condition of unknown channel information, and the frequency hopping signals can be subjected to blind estimation under the condition that the number of receiving antennae is smaller than that of the source signals; short-time Fourier transform is utilized, so that the method is low in computation amount; and the frequency hopping signals are subjected to blind separation, and meanwhile, a part of parameters can also be estimated, so that the method is high in practicability.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Closed loop cardiac resynchronization therapy using cardiac activation sequence information
Cardiac monitoring and / or stimulation methods and systems that provide one or more of monitoring, diagnosing, defibrillation, and pacing. Cardiac signal separation is employed to detect, monitor, track, and / or trend closed-loop cardiac resynchronization therapy using cardiac activation sequence information. Devices and methods involve sensing a plurality of composite cardiac signals using a plurality of electrodes, the electrodes configured for implantation in a patient. A source separation is performed using the sensed plurality of composite cardiac signals, producing one or more cardiac signal vectors associated with all or a portion of one or more cardiac activation sequences. A cardiac resynchronization therapy is adjusted using one or both of the one or more cardiac signal vectors and the signals associated with the one or more cardiac signal vectors. In further embodiments, the cardiac resynchronization therapy may be initiated, terminated, or one or more parameters of the resynchronization therapy may be altered.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
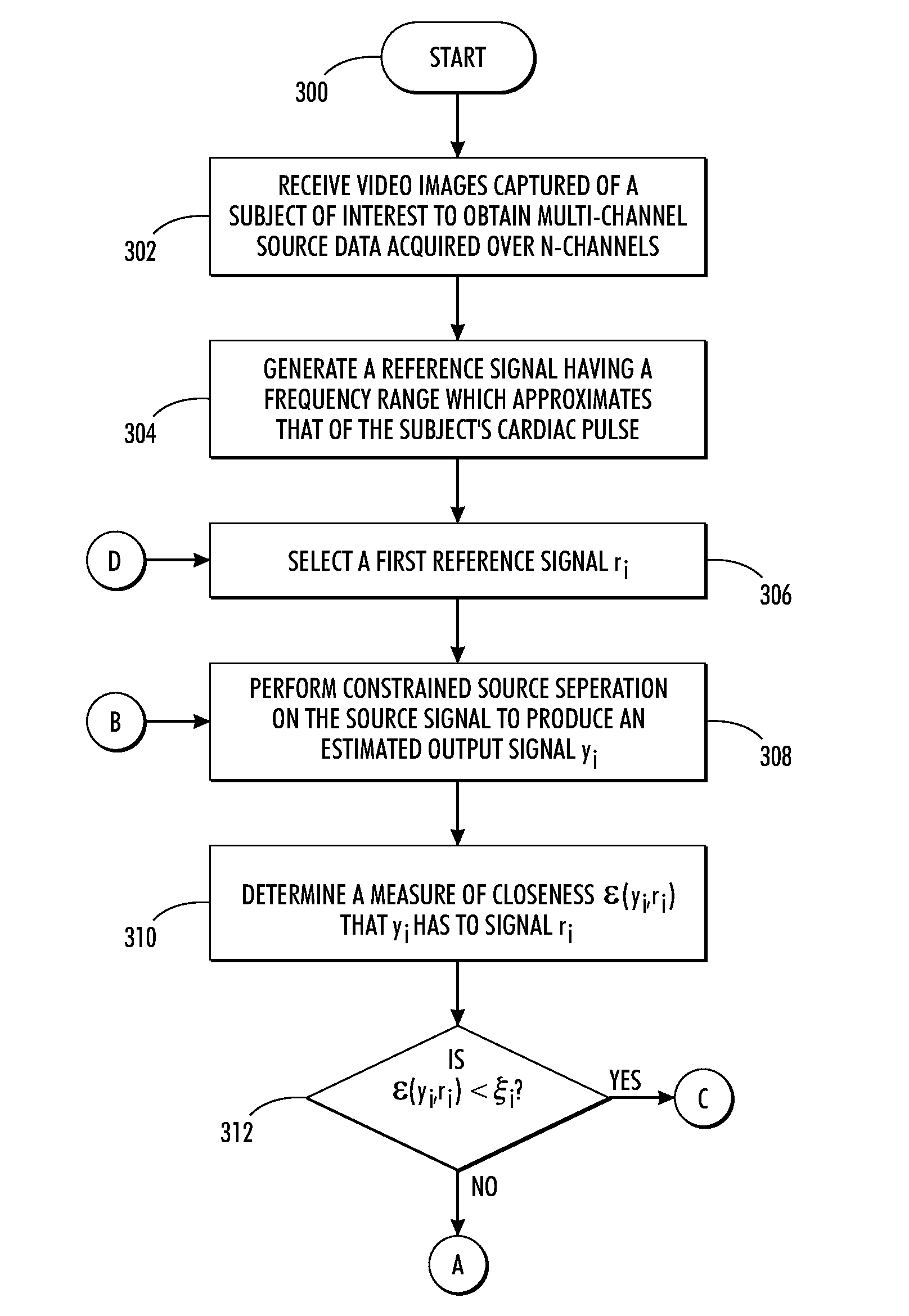
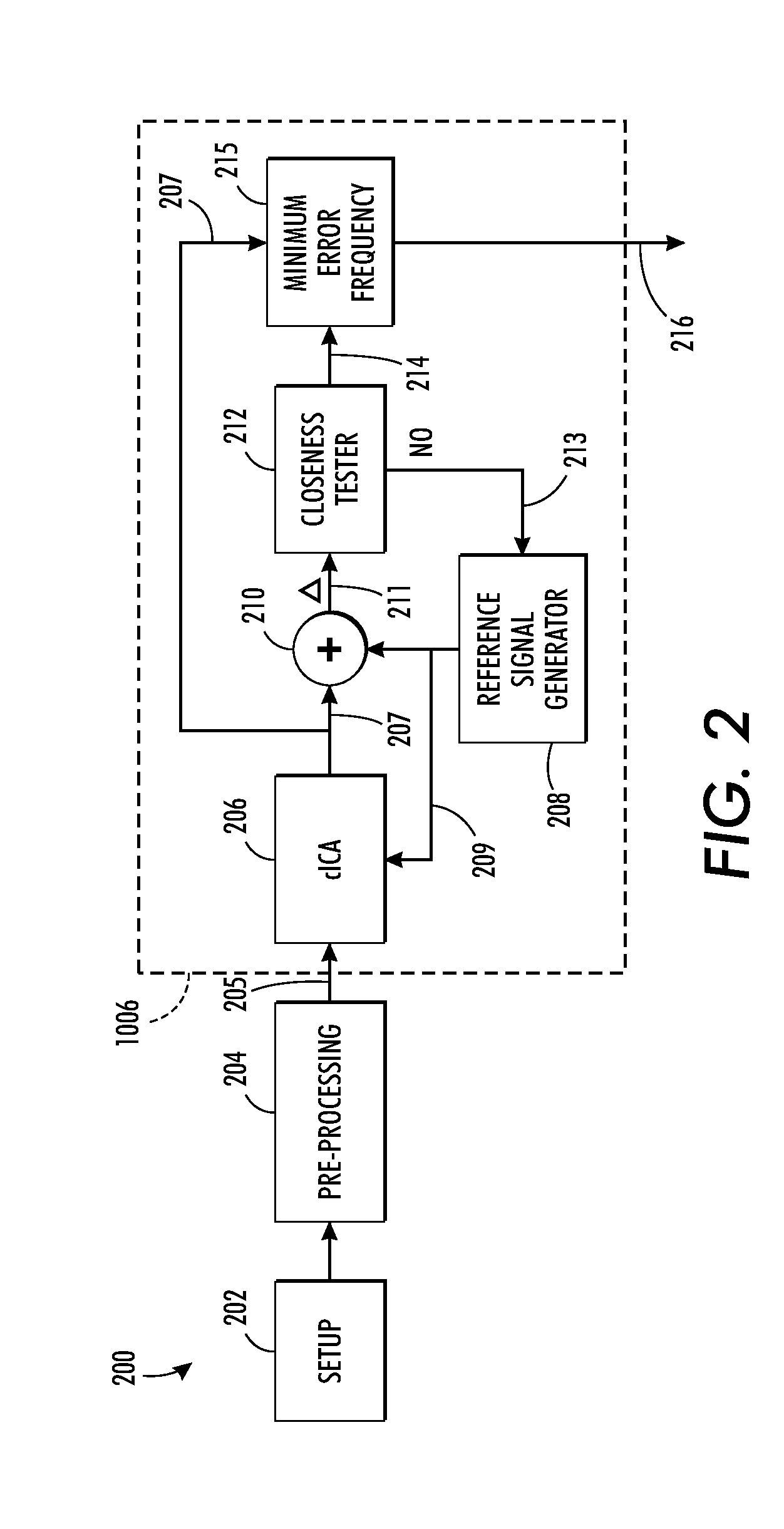
Estimating cardiac pulse recovery from multi-channel source data via constrained source separation
What is disclosed is a system and method for recovering a patient's cardiac pulse rate from a sequence of video images recording of that patient. In one embodiment, a reference signal of a particular frequency is generated at predetermined frequency intervals and a constrained source separation is performed on the source data to obtain an estimation of the source signal intended to be recovered. The reference signal is updated and constrained source separation is again performed. These operations are repeated for all frequencies of the reference signal. The frequency at which a minimum error is achieved is determined to be the subject's recovered cardiac pulse frequency. In such a manner, the source signal is extracted and recovered reliably from captured multi-channel RGB signals or multispectral signals. The teachings hereof find their uses in a variety of medical solutions including various military, security and telemedicine applications. Various embodiments are disclosed.
Owner:XEROX CORP
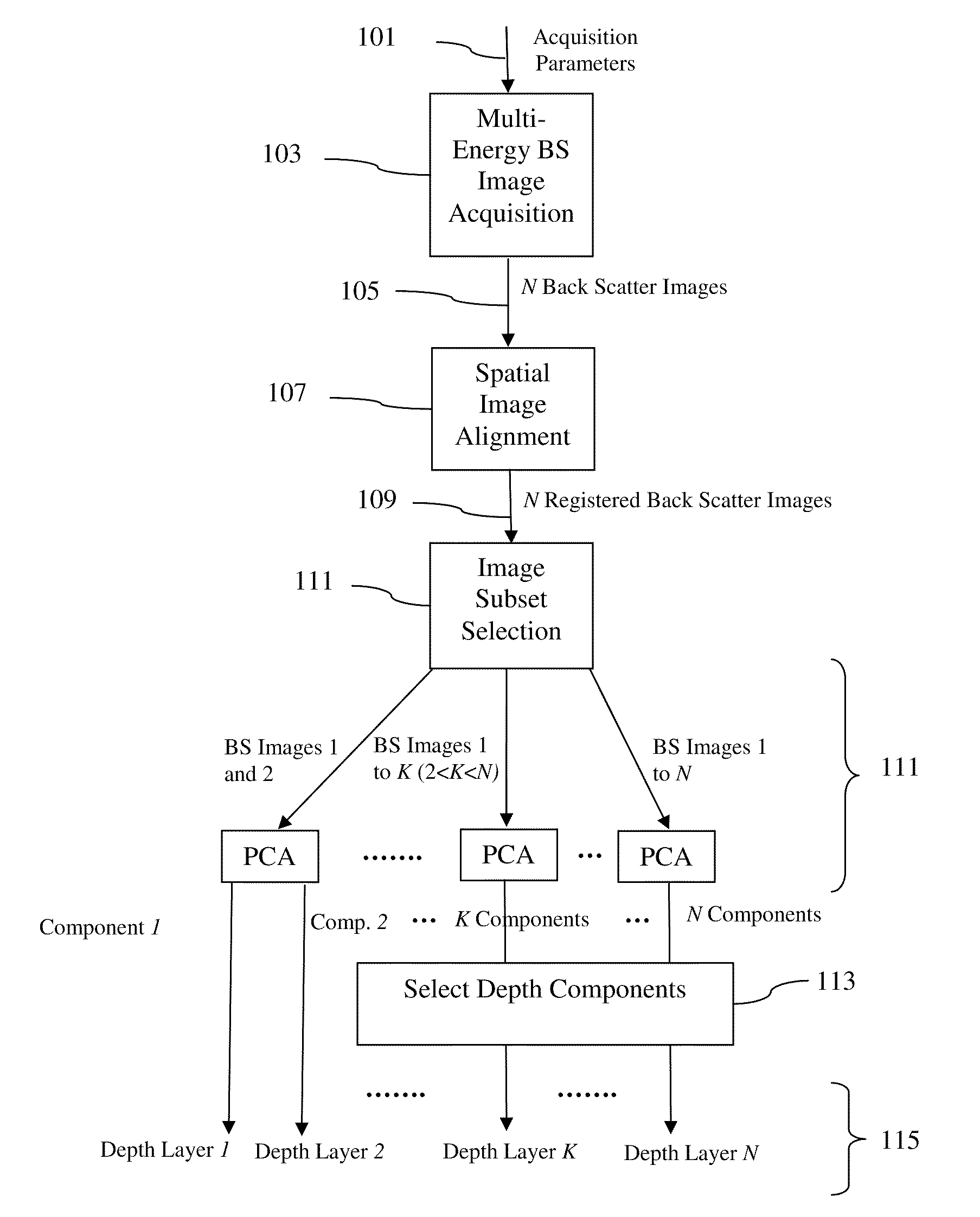
SEM imaging method
ActiveUS8232523B2Material analysis using wave/particle radiationElectric discharge tubesSpatially resolvedDepth level
Owner:FEI CO
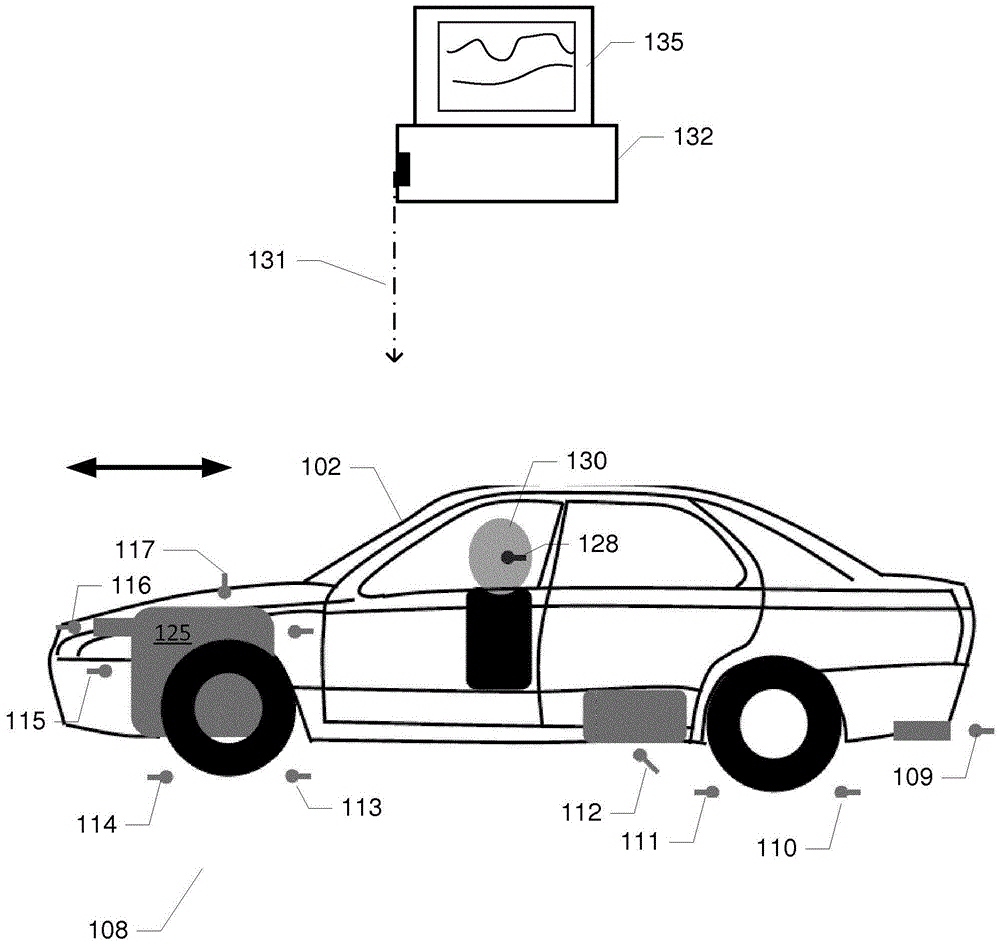
Method of determining noise sound contributions of noise sources of a motorized vehicle
The present invention relates to a method and an acoustic measurement system for determining individual noise sound contributions of a plurality of physical noise sources of a motorized vehicle at a target or reference location. The method comprises steps of placing a plurality of reference microphones at respective reference positions adjacent to respective ones of the physical noise sources, placing a measurement microphone at the target location, recording a plurality of noise sound signals and recording a target noise signal. The plurality of noise sound signals are adaptively separated using blind source separation to produce a plurality of mutually independent noise sound signals representing respective estimated noise sound signals of the plurality of physical noise sources. Each of the mutually independent noise sound signals is correlated with the recorded target noise signal to determine time domain or frequency domain characteristics of a plurality of linear transfer path filters representing respective transfer functions between the plurality of independent noise sound signals and the measurement microphone at the target location. At least one of the independent noise sound signals, representing one of the physical noise sources, may be applied to the corresponding linear transfer path filter to generate at least one target noise signal component representing the individual noise sound contribution of the physical noise source at the target location.
Owner:BRUEL & KJAER SOUND & VIBRATION MEASUREMENT
Method and system for on-line blind source separation
InactiveUS6898612B1Efficient separationAdaptive networkSpeech analysisNO storageFinite impulse response
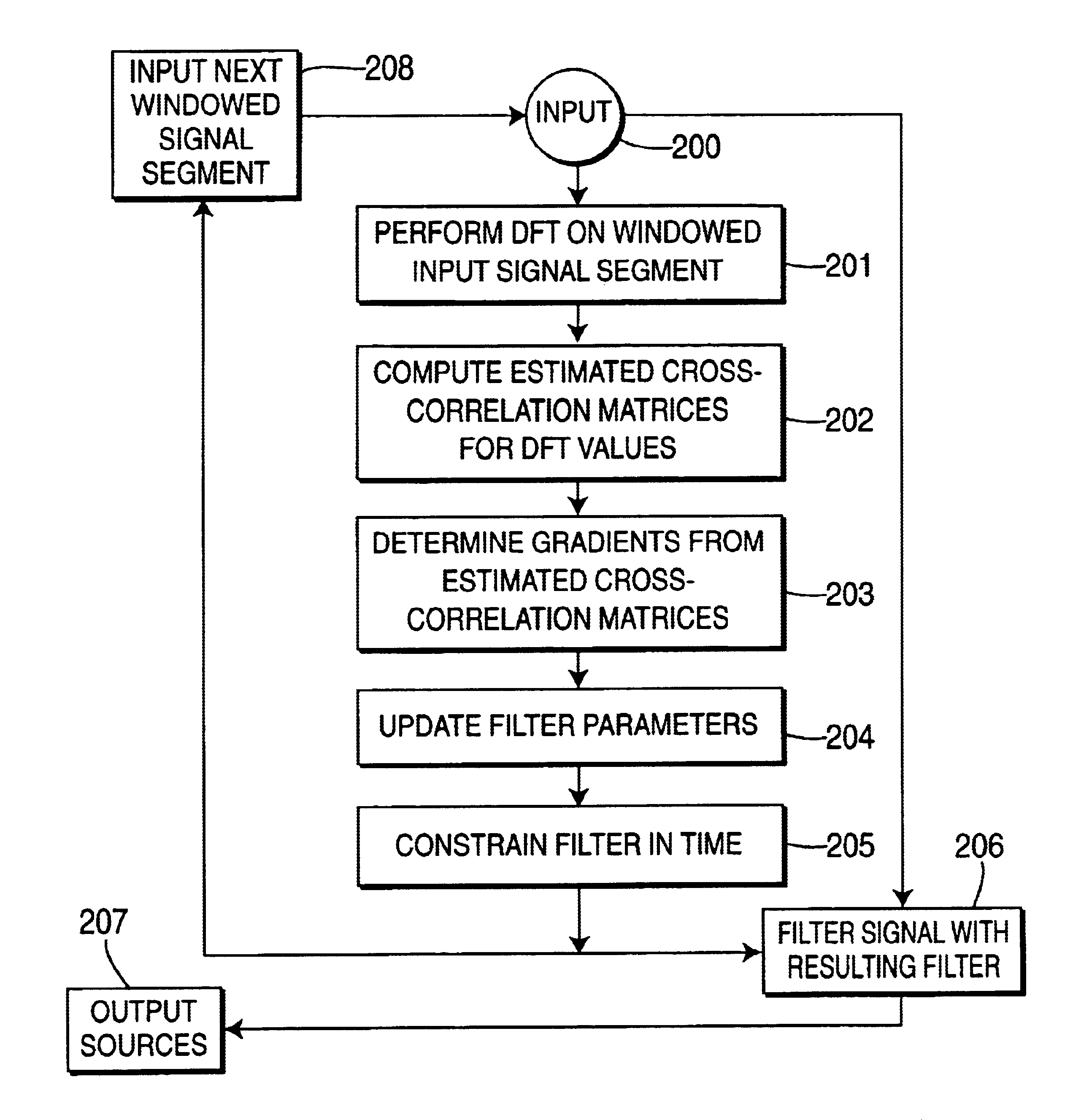
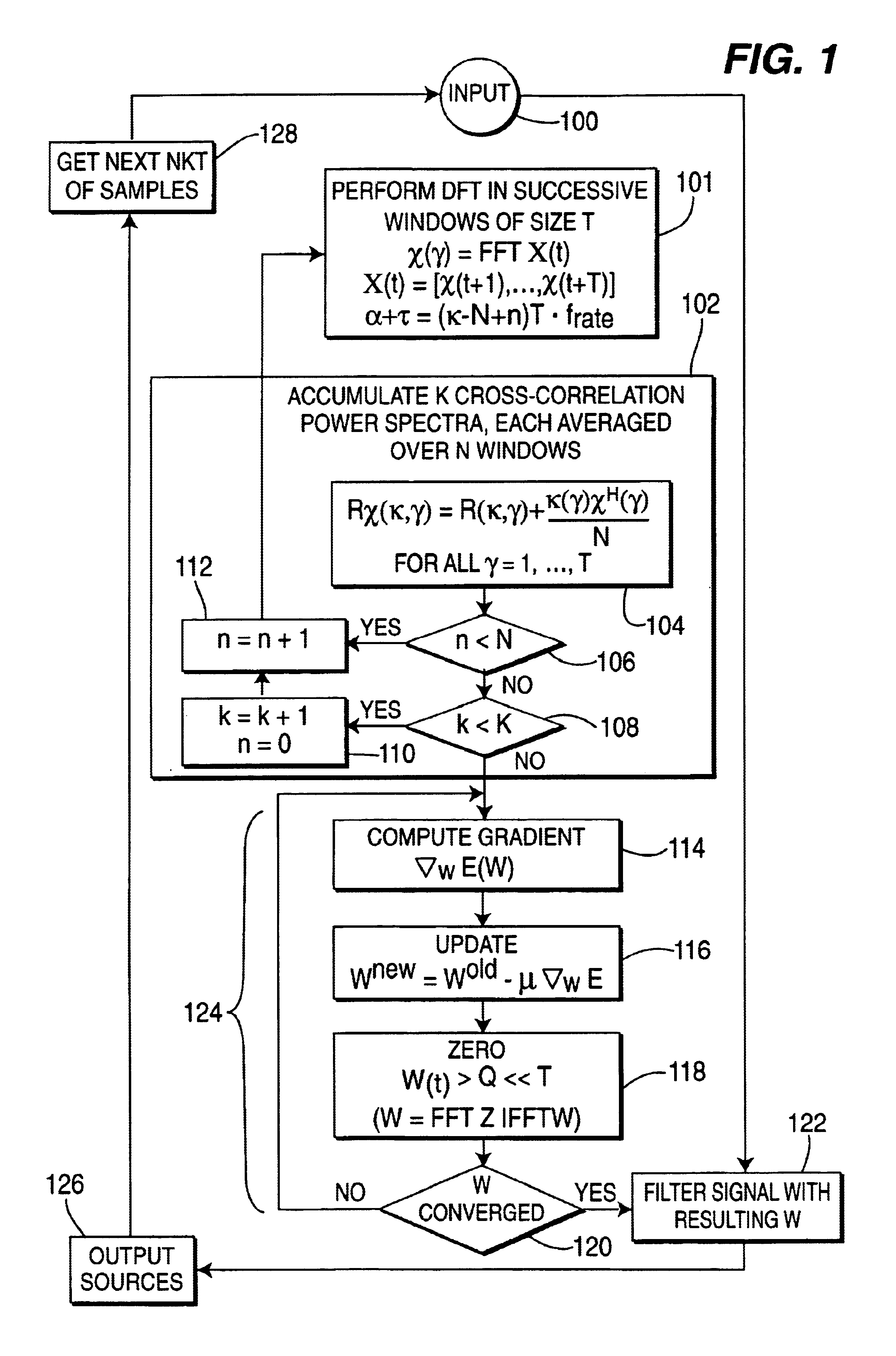
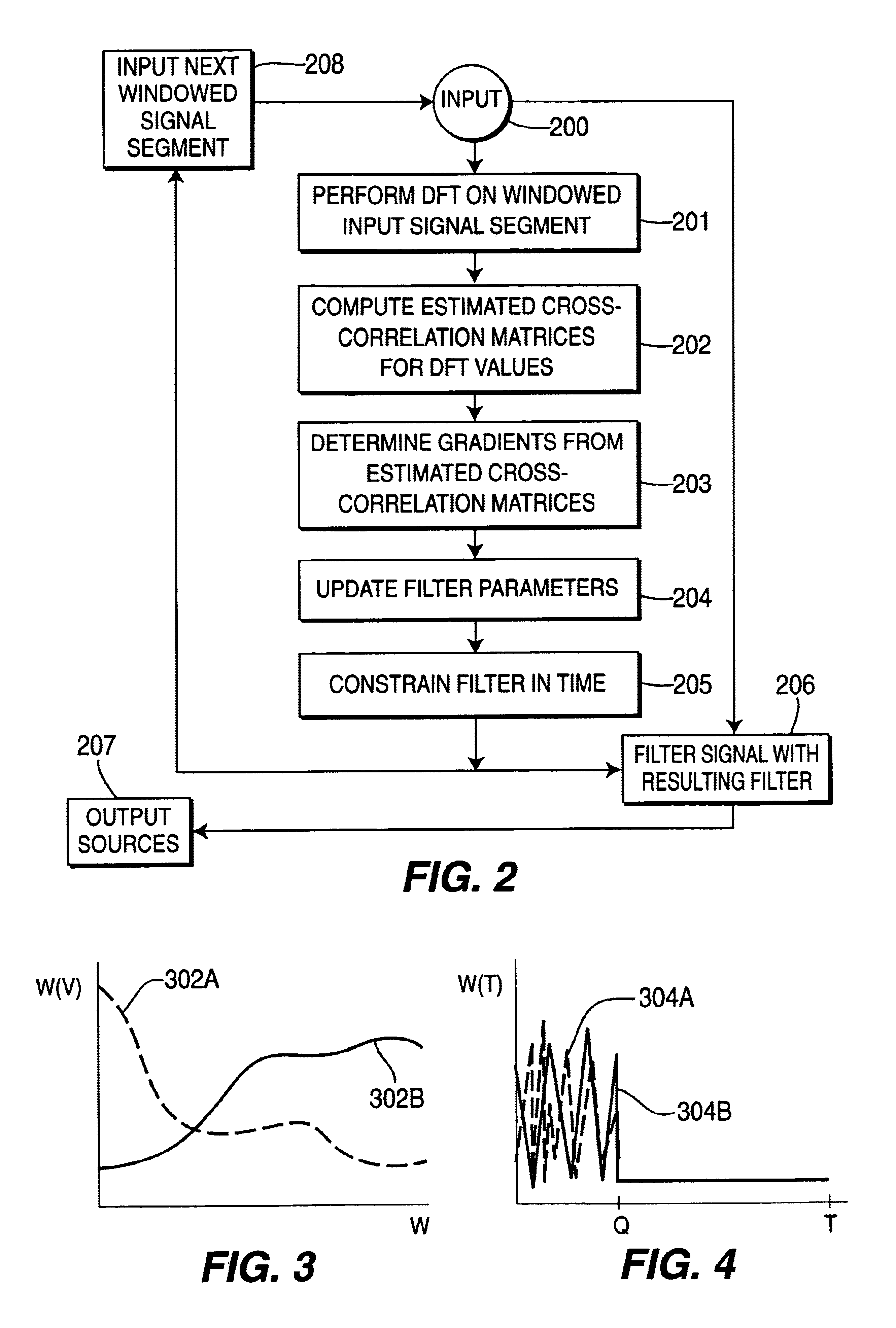
A method and apparatus is disclosed for performing blind source separation using convolutive signal decorrelation. For a first embodiment, the method accumulates a length of input signal (mixed signal) that includes a plurality of independent signals from independent signal sources. The invention then divides the length of input signal into a plurality of T-length periods (windows) and performs a discrete Fourier transform (DFT) on the, signal within each T-length period. Thereafter, estimated cross-correlation values are computed using a plurality of the averaged DFT values. A total number of K cross-correlation values are computed, where each of the K values is averaged over N of the T-length periods. Using the cross-correlation values, a gradient descent process computes the coefficients of a finite impulse response (FIR) filter that will effectively separate the source signals within the input signal. A second embodiment of the invention is directed to on-line processing of the input signal—i.e., processing the signal as soon as it arrives with no storage of the signal data. In particular, an on-line gradient algorithm is provided for application to non-stationary signals and having an adaptive step size in the frequency domain based on second derivatives of the cost function. The on-line separation methodology of this embodiment is characterized as multiple adaptive decorrelation.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Non-contact type automatic heart rate measurement system and measurement method
InactiveCN104138254AToleranceOvercoming the Effects of Motion ArtifactsDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsHeart rate measurementVideo record
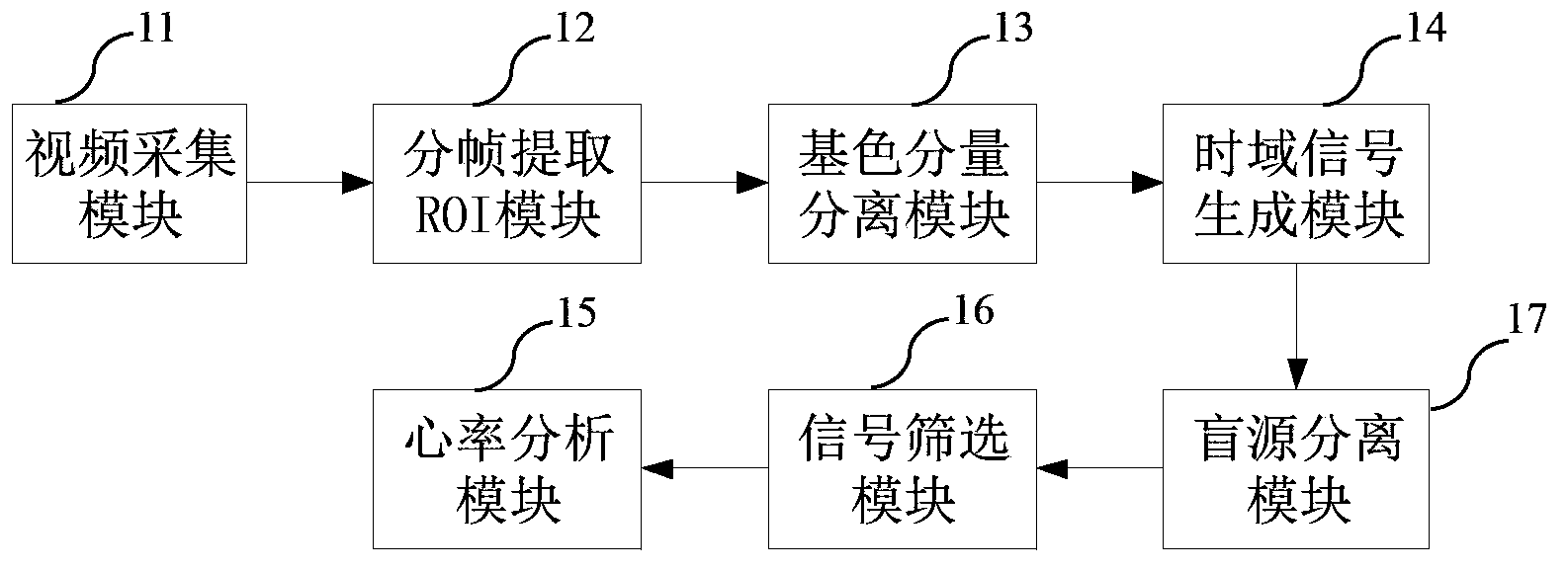
The invention relates to the field of electronic health detection, and discloses a non-contact type automatic heart rate measurement system and a measurement method. The non-contact type automatic heart rate measurement system adopts a non-contact mode to remotely collect video data of a measured person and performs data conversion to realize automatic heart rate measurement, and is characterized by comprising a video collection module, a framing extraction ROI (region of interest) module, a primary color component separation module, a time-domain signal generation module, a blind source separation module, a signal screening module and a heart rate analysis module. Compared with the prior art, the non-contact type automatic heart rate measurement system and the measurement method are based on an automatic face track and blind source separation technology, adopt a noninvasive and non-contact type remote physiological signal detection method, overcome influence of motion artifact in video record, has motion tolerance, is high in measurement accuracy, and can perform heart rate measurement automatically and simultaneously.
Owner:TIANJIN DIANKANG TECH
Ultra small microphone array
ActiveUS7809145B2MicrophonesAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceFinite impulse responseTime domain
Methods and apparatus for signal processing are disclosed. A discrete time domain input signal xm(t) may be produced from an array of microphones M0 . . . MM. A listening direction may be determined for the microphone array. The listening direction is used in a semi-blind source separation to select the finite impulse response filter coefficients b0, b1 . . . , bN to separate out different sound sources from input signal xm(t). One or more fractional delays may optionally be applied to selected input signals xm(t) other than an input signal x0(t) from a reference microphone M0. Each fractional delay may be selected to optimize a signal to noise ratio of a discrete time domain output signal y(t) from the microphone array. The fractional delays may be selected to such that a signal from the reference microphone M0 is first in time relative to signals from the other microphone(s) of the array. A fractional time delay Δ may optionally be introduced into an output signal y(t) so that: y(t+Δ)=x(t+Δ)*b0+x(t−1+Δ)*b1+x(t−2+Δ)*b2+ . . . +x(t−N+Δ)bN, where Δ is between zero and ±1.
Owner:SONY COMPUTER ENTERTAINMENT INC +1
SEM Imaging Method
ActiveUS20110266440A1Material analysis using wave/particle radiationElectric discharge tubesSpatially resolvedData set
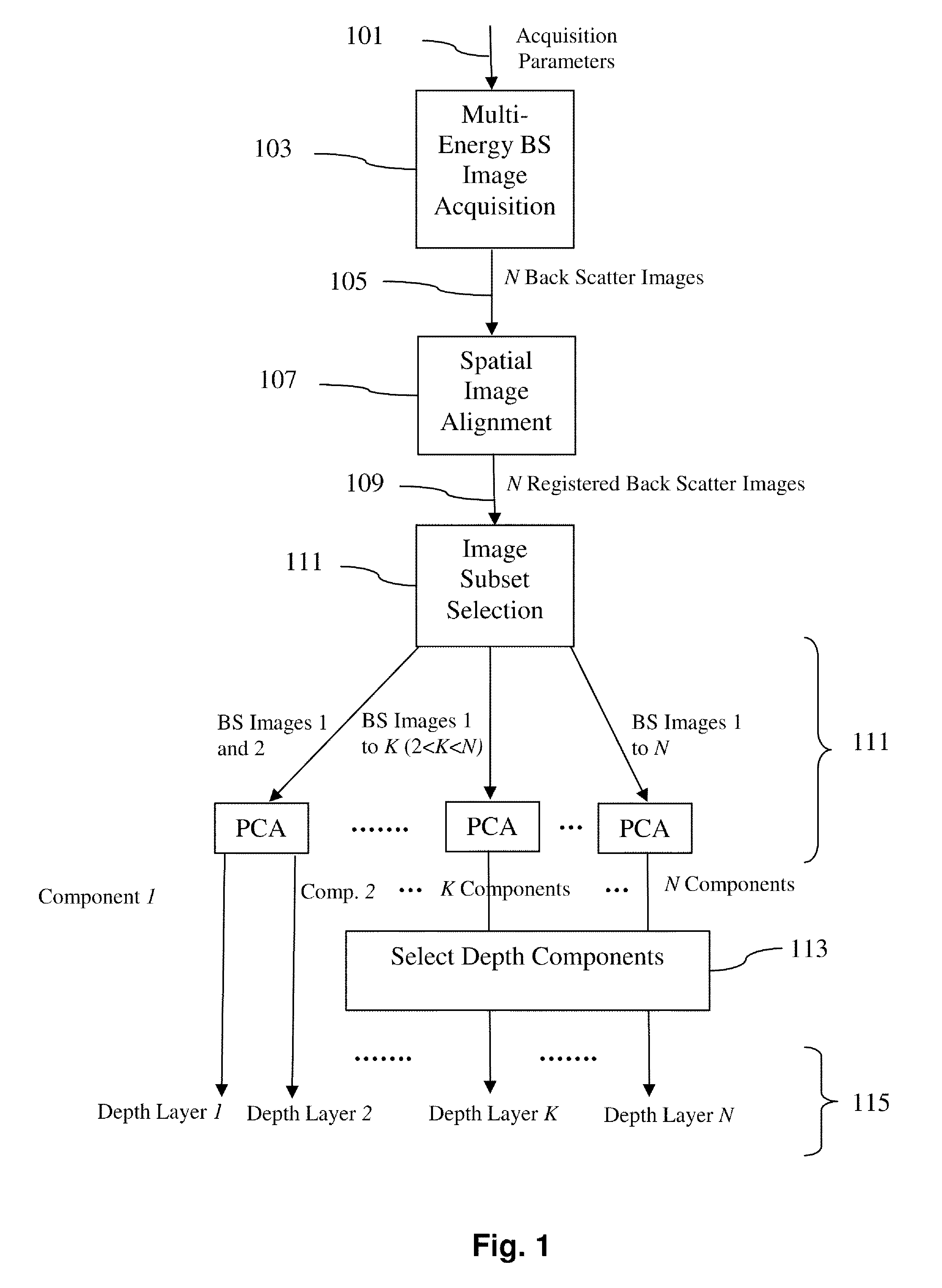
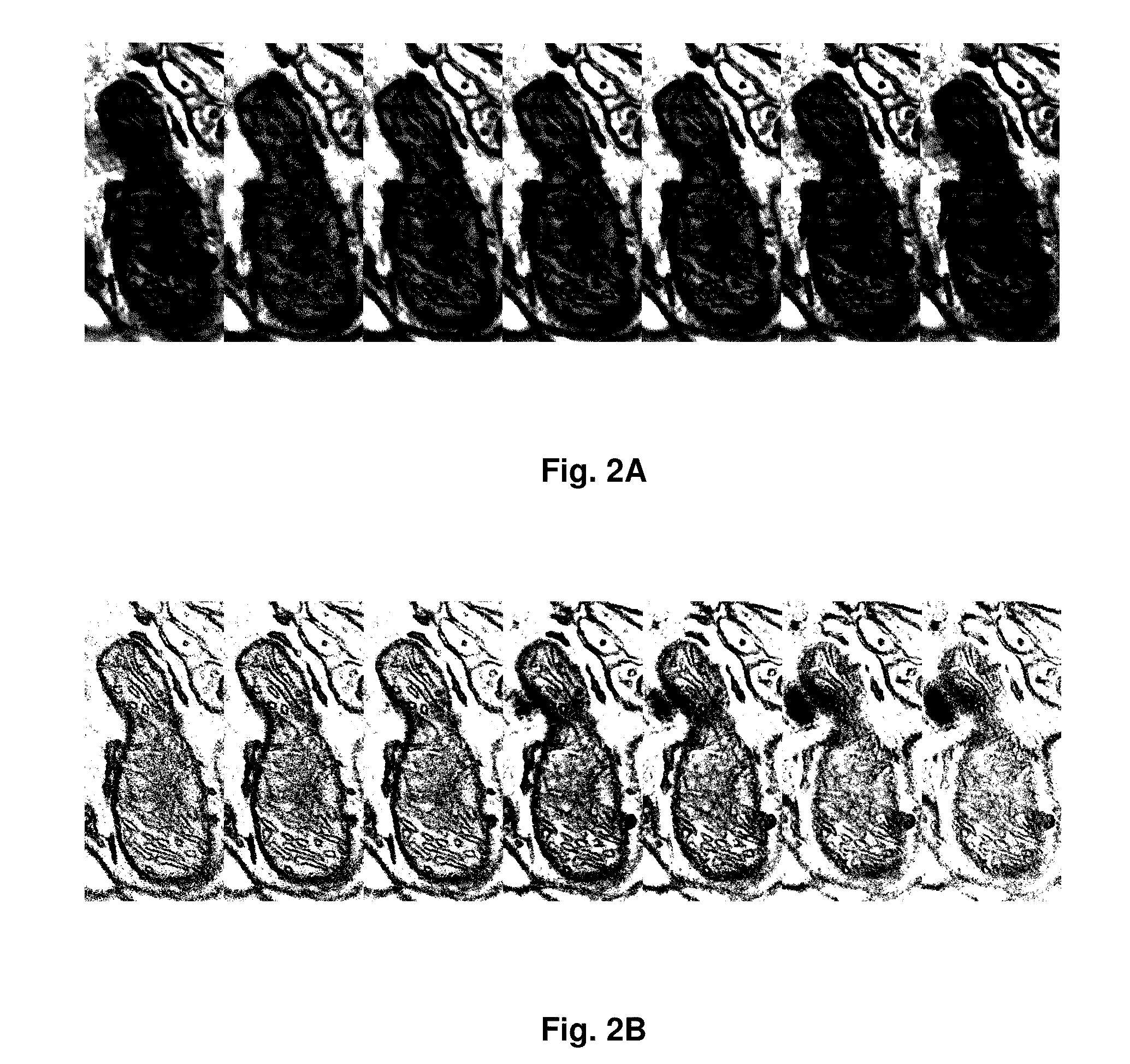
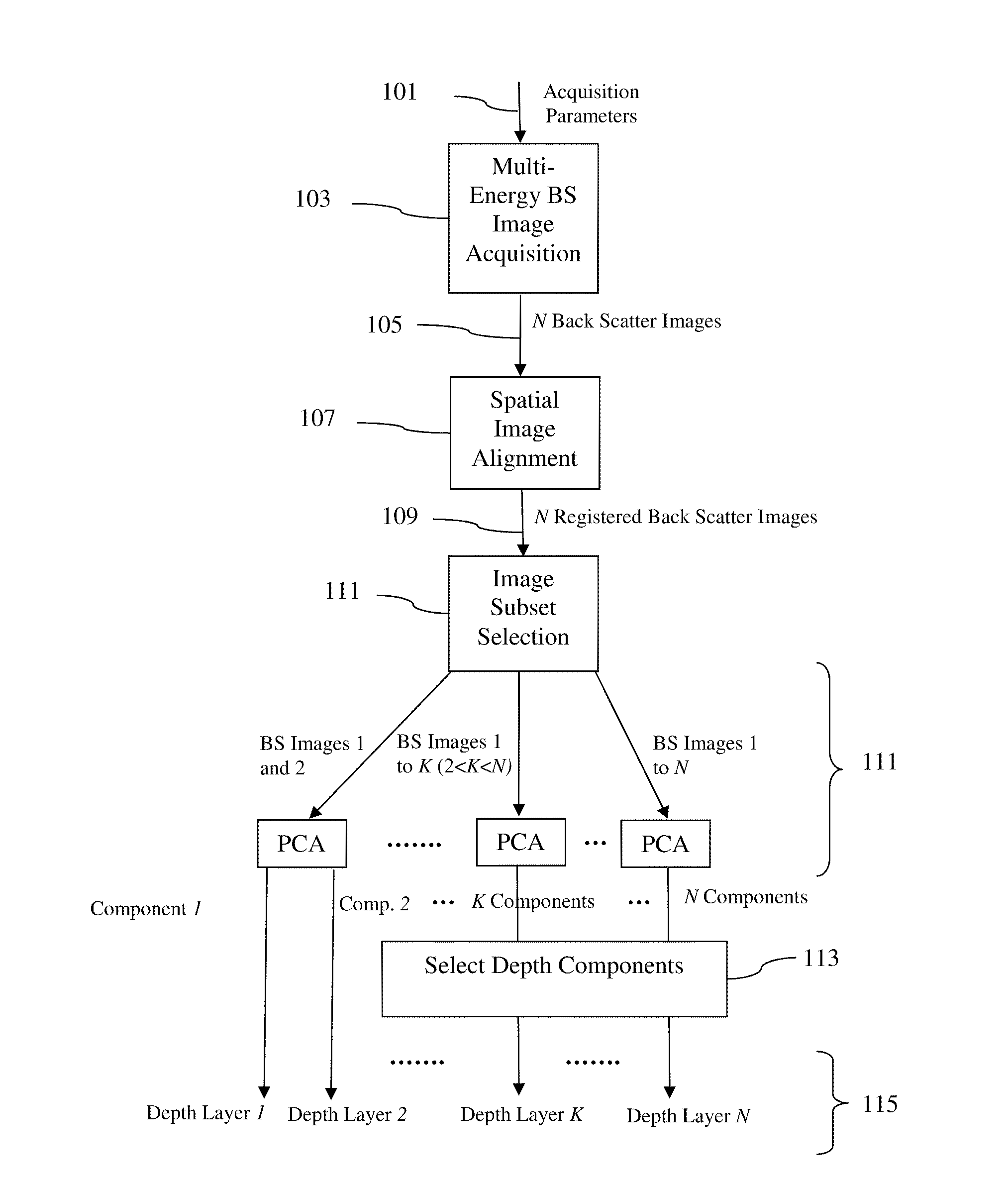
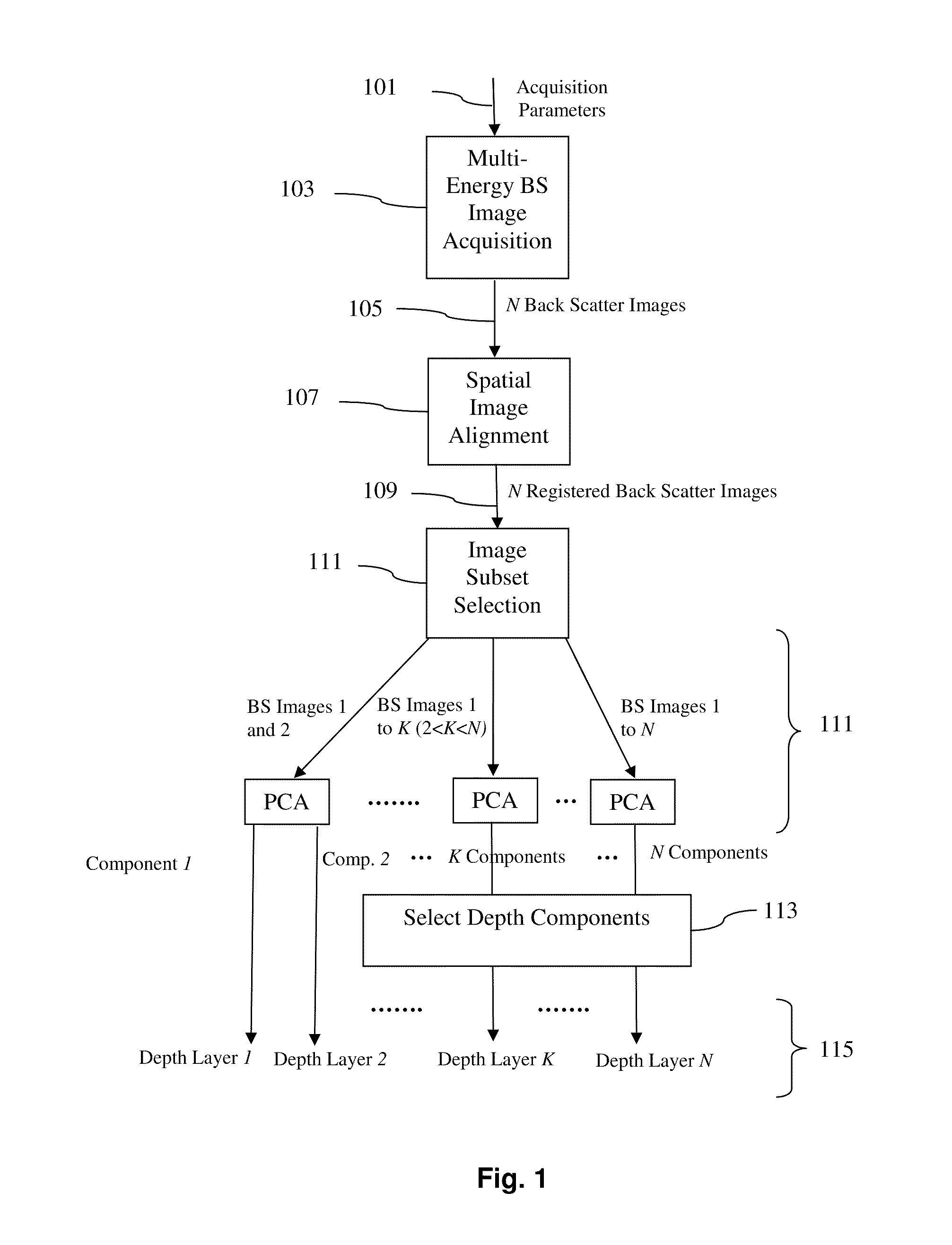
A method of investigating a sample using Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM), comprising the following steps:Irradiating a surface (S) of the sample using a probing electron beam in a plurality (N) of measurement sessions, each measurement session having an associated beam parameter (P) value that is chosen from a range of such values and that differs between measurement sessions;Detecting stimulated radiation emitted by the sample during each measurement session, associating a measurand (M) therewith and noting the value of this measurand for each measurement session, thus allowing compilation of a data set (D) of data pairs (Pi, Mi), where 1≦i≦N,wherein:A statistical Blind Source Separation (BSS) technique is employed to automatically process the data set (D) and spatially resolve it into a result set (R) of imaging pairs (Qk, Lk), in which an imaging quantity (Q) having value Qk is associated with a discrete depth level Lk referenced to the surface S.
Owner:FEI CO
Method and apparatus for blind source separation using two sensors
ActiveUS20040230428A1Cancel noiseSpeech analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionUltrasound attenuationFrequency spectrum
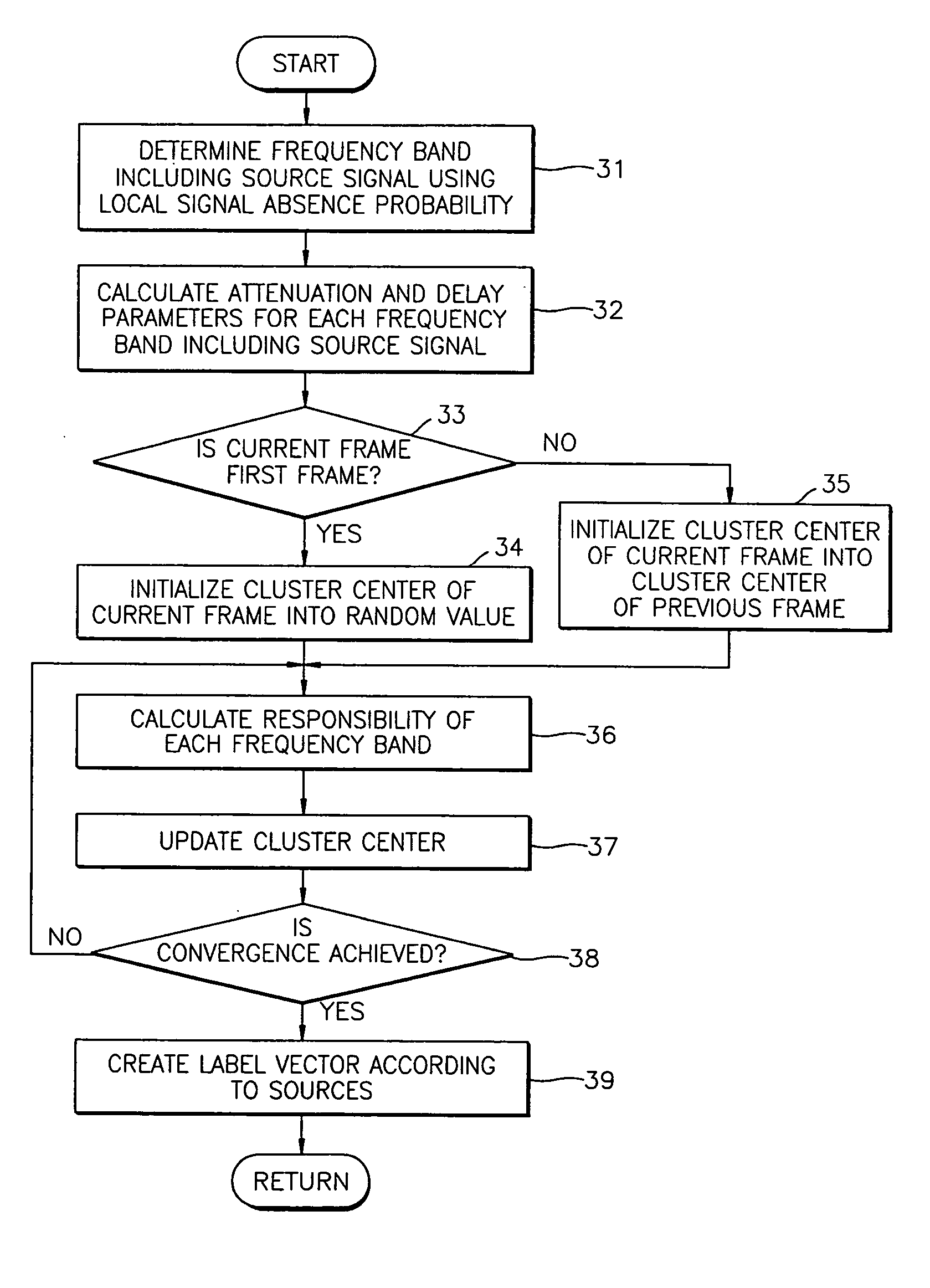
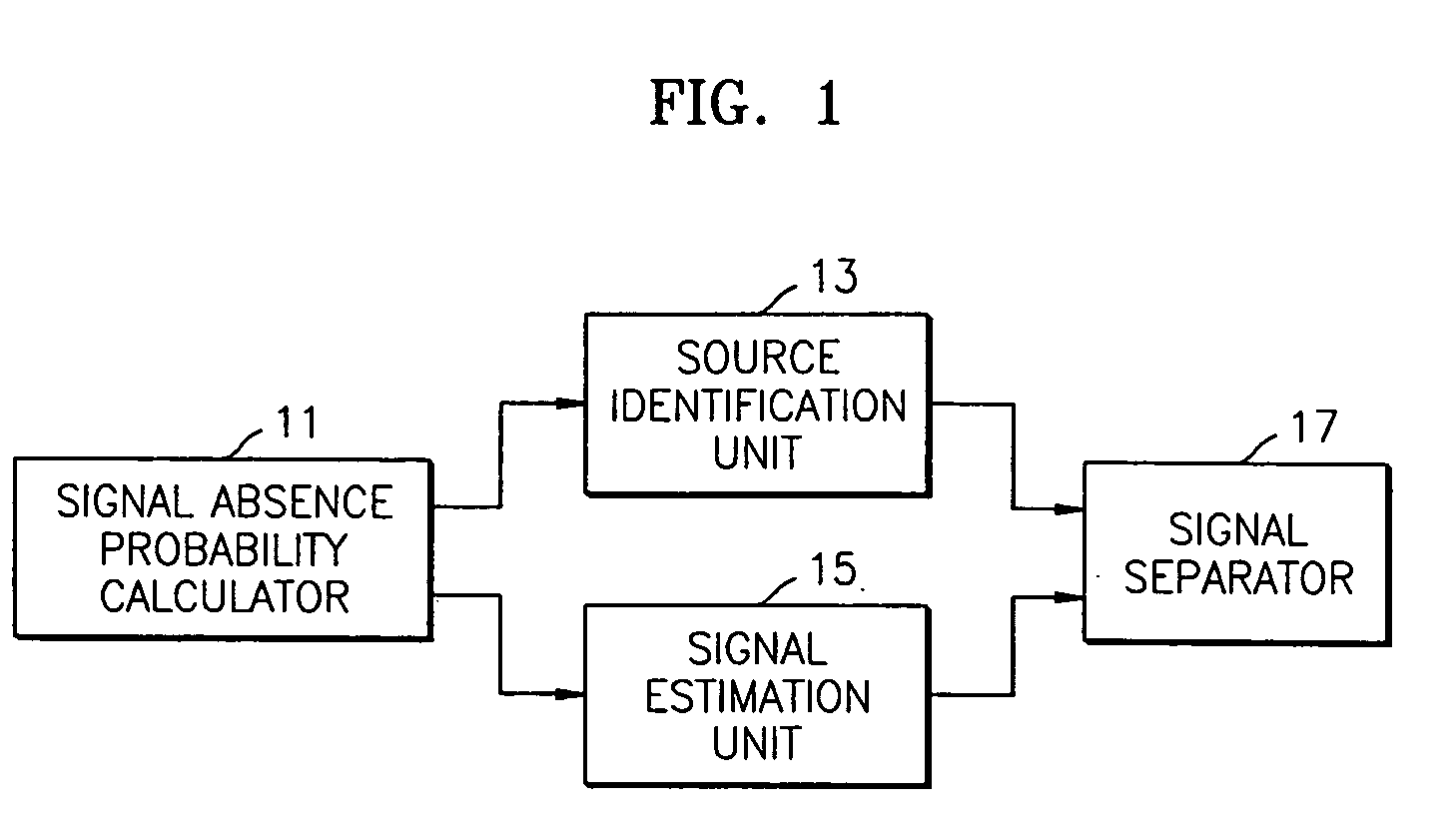
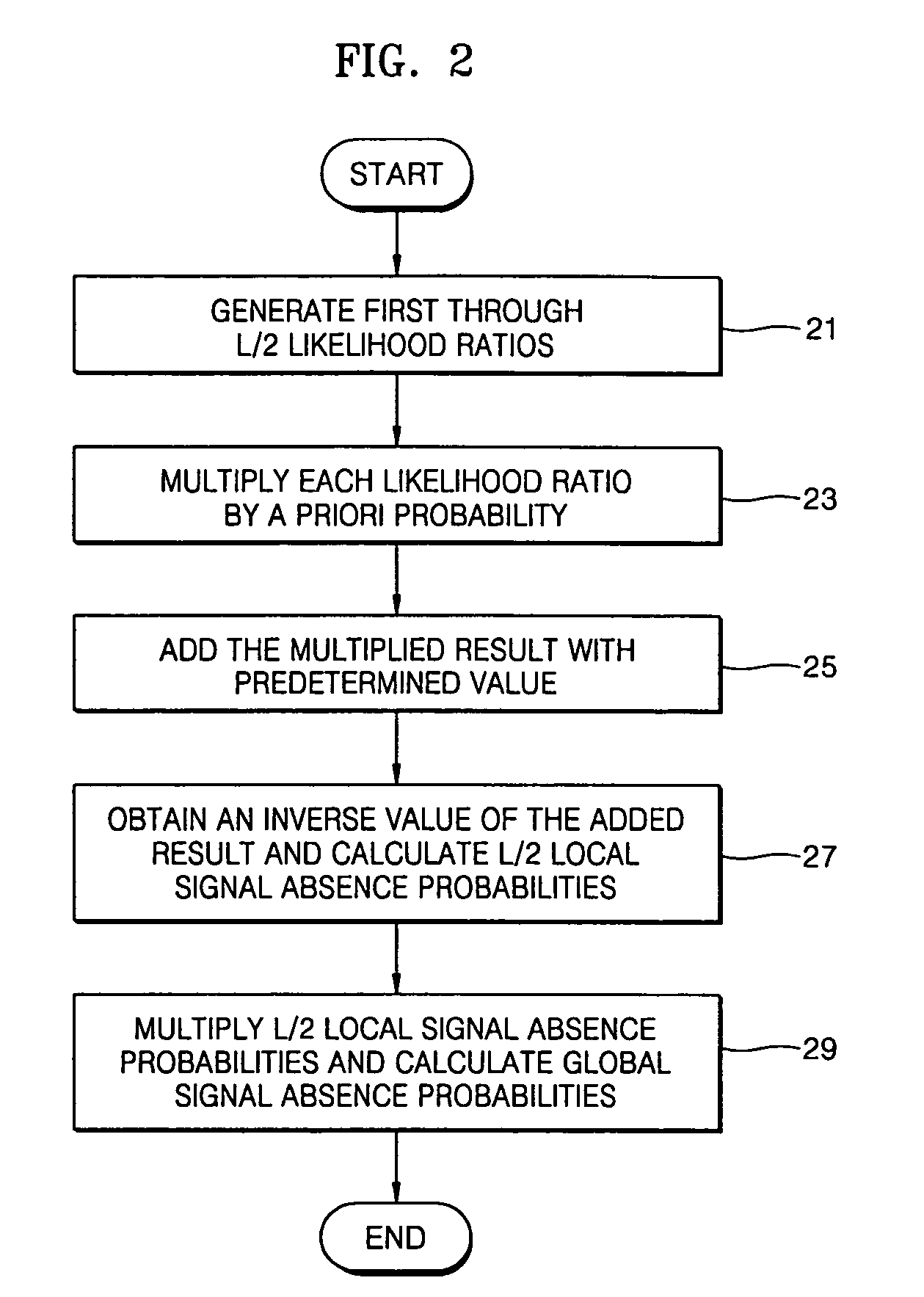
A method and apparatus to separate first and second mixture signals received from two sensors and transformed into the frequency domain in two or more source signals. The signal separation method includes: calculating a global signal absence probability for each frame and a local signal absence probability for each frequency band of a corresponding frame for at least one of the first and second mixture signals; estimating a spectrum vector for each frequency band in which a noise signal is eliminated using the global signal absence probability; determining a plurality of frequency bands including at least one of a noise signal and a source signal using the local signal absence probability, and generating a source label vector which consists of a plurality of frequency bands assigned to each source, using an attenuation parameter and a delay parameter generated for each of the determined frequency bands; and multiplying the spectrum vector estimated for each frequency band by the source label vector, and obtaining signals separated according to the source signals.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method for processing audio-signals
ActiveUS20070100605A1Enhance speech signalSpeech analysisHearing aids signal processingMicrophone signalComputer science
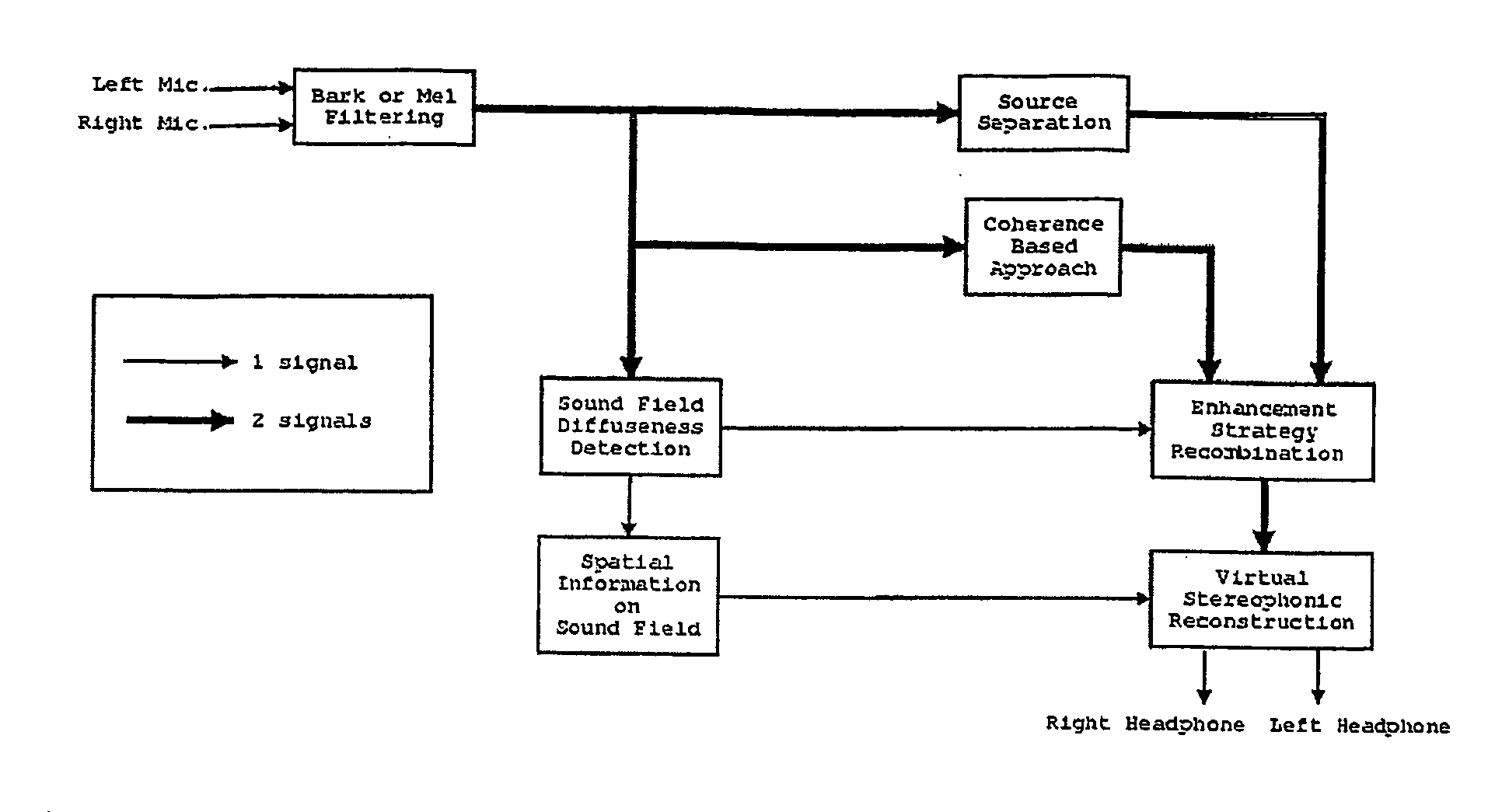
The invention regards a method for processing audio-signals whereby audio signals are captured at two spaced apart locations and subject to a transformation in the perceptual domain (Bar or Mel), whereupon: a) a (blind or supervised) source separation process is performed to give a first estimate of the wanted signal parts and the noise parts of the microphone signals and b) a coherence based separation process is performed to give a second estimate of the wanted signal parts and the noise parts of the microphone signals, and where further a sound field diffuseness detection is performed on the at least two signals, whereby further the sound field diffuseness detections is used to mix the output from the blind source separation and the coherence based separation process in order to achieve the best possible signal. The transfer functions calculated from the source separation are used to reconstruct a virtual stereophonic sound field in restore the spatial information about the source position in the enhanced signals.
Owner:OTICON
Method for carrying out blind source separation on convolutionary aliasing voice signals
InactiveCN101667425AImprove performanceImprove convergence efficiencySpeech recognitionPhonetic environmentComputation complexity
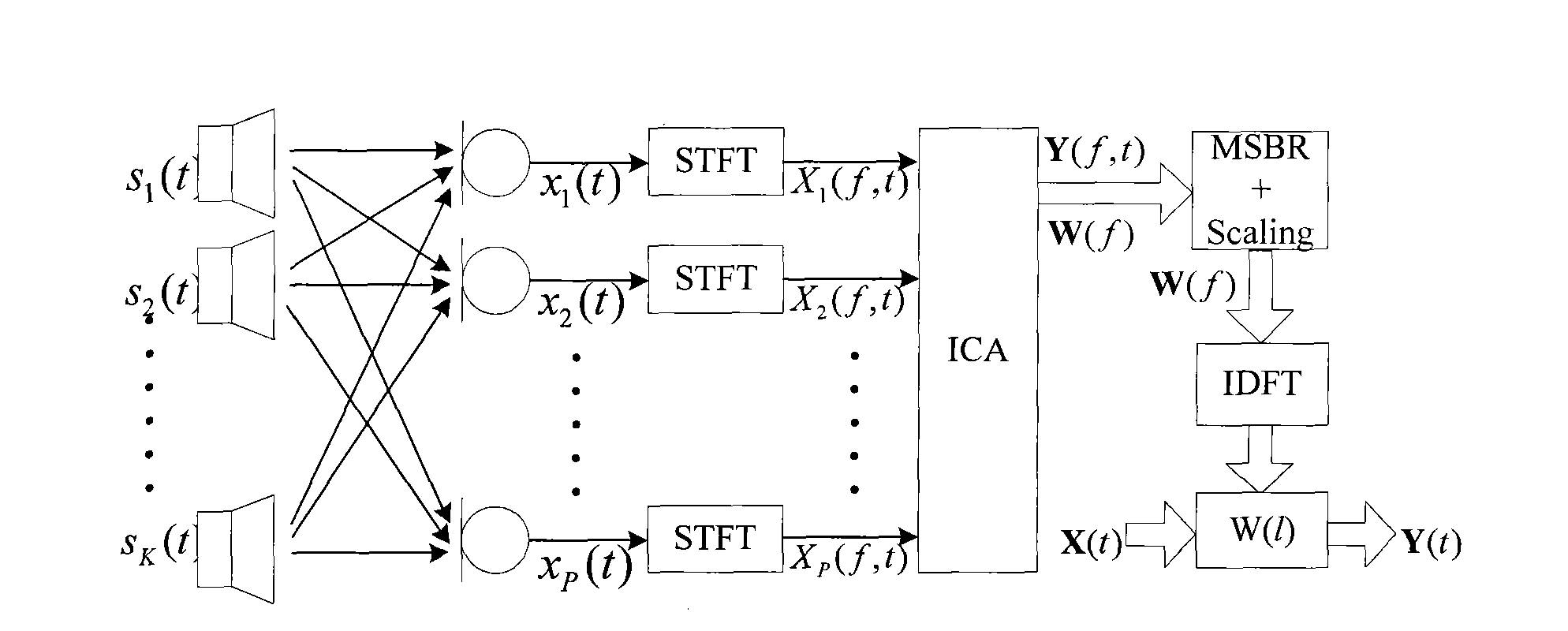
The invention provides a method for carrying out blind source separation on convolutionary aliasing voice signals. Firstly, a time domain convolutionary aliasing model is converted into a frequency domain multi-channel linear instantaneous convolutionary aliasing model, which can be realized by the following steps: firstly, converting convolutionary aliasing time domain signals into a frequency domain; then carrying out relatively independent ICA operations on each channel to obtain independent components. Next, the independent components are rearranged by an MSBR algorithm, which specificallycomprising the following steps: firstly, classifying signals of different frequency bands; then progressively obtaining transposed matrixes according to different object functions step by step, wherein the steps of rearrangement are mutually complementary. The MSBR algorithm utilizes the strong relevance of harmonic frequency to improve the iteration accuracy and solves the residual uncertainty of residual frequency bands according to the continuity of adjacent frequency bands and corresponding reference frequencies, and the computational complexity of the MSBR algorithm is approximately in direct proportion to the number of reference frequency bands. The invention improves the convergence efficiency and the accuracy, is more suitable for real-time processing, has good separation performance of convolutionary mixed voice signals and can also be applied to real phonetic environment.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
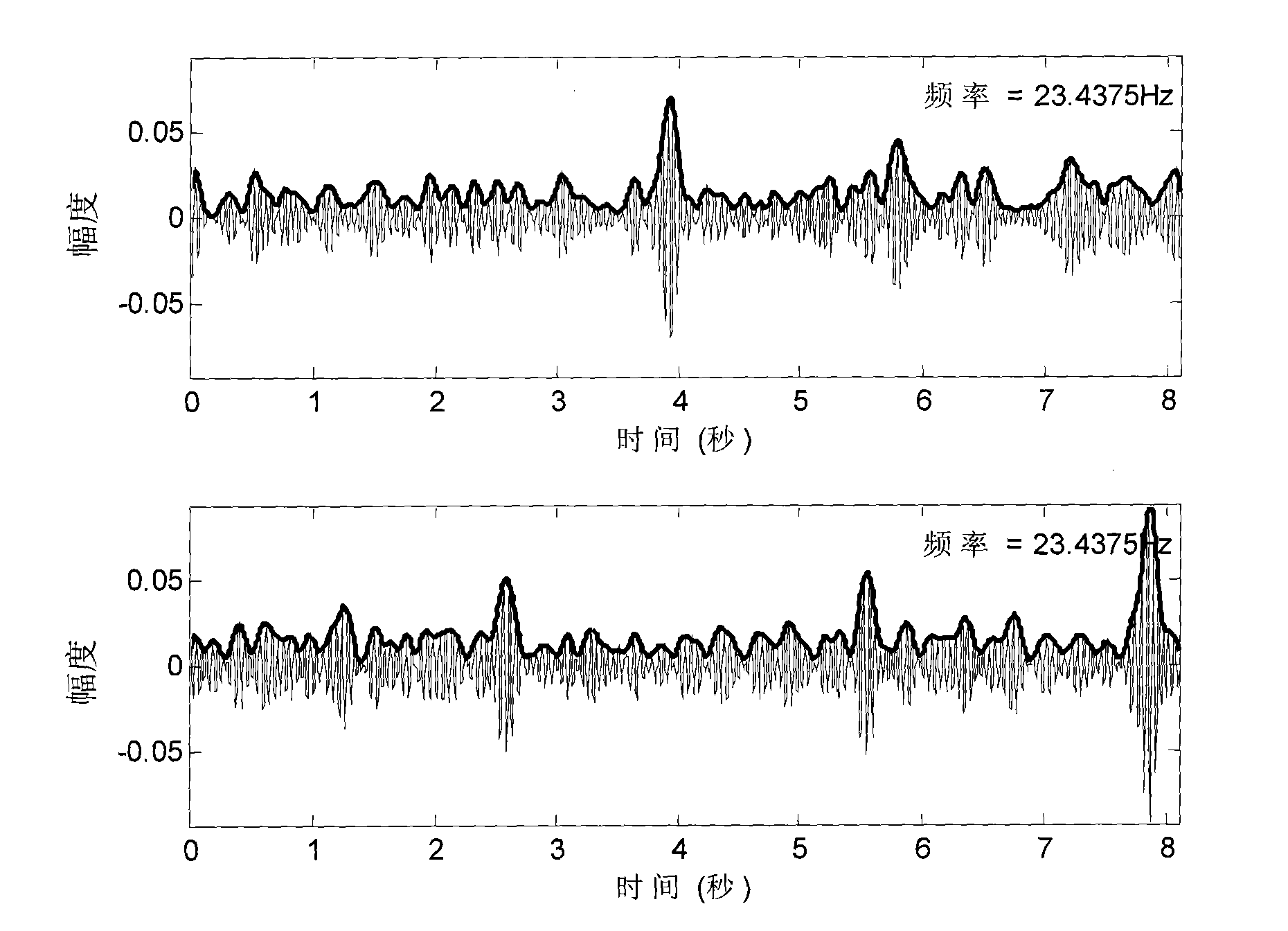
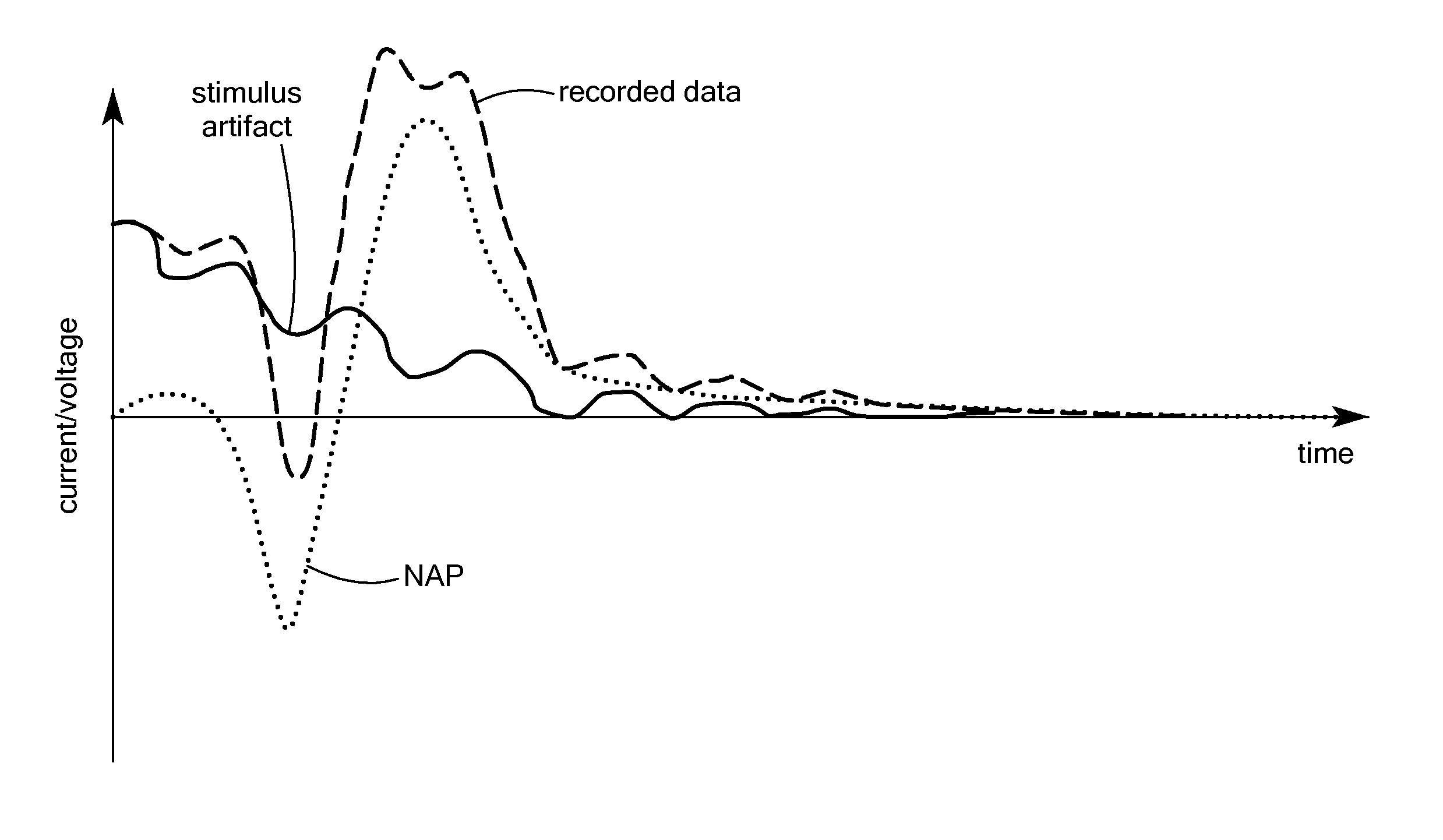
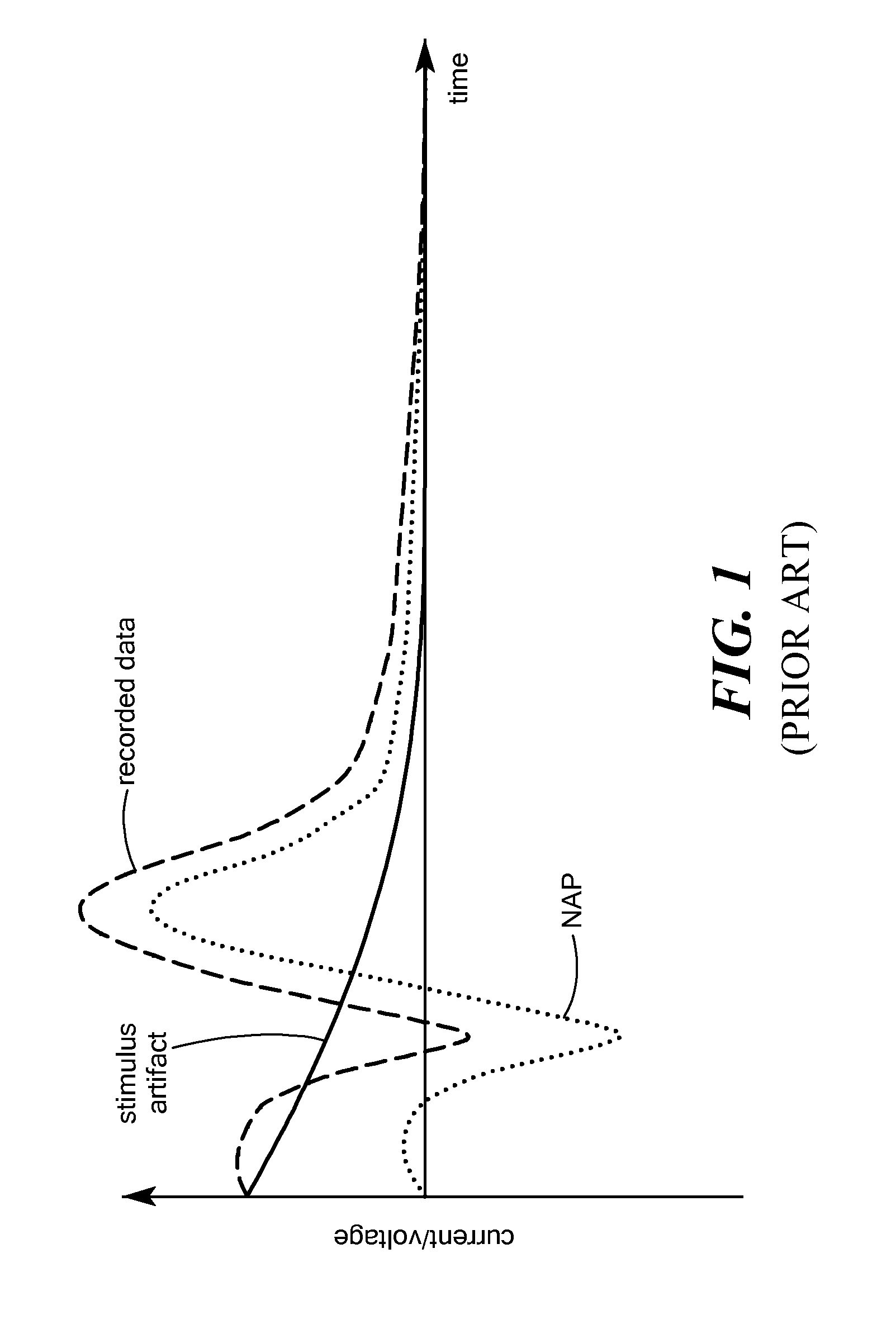
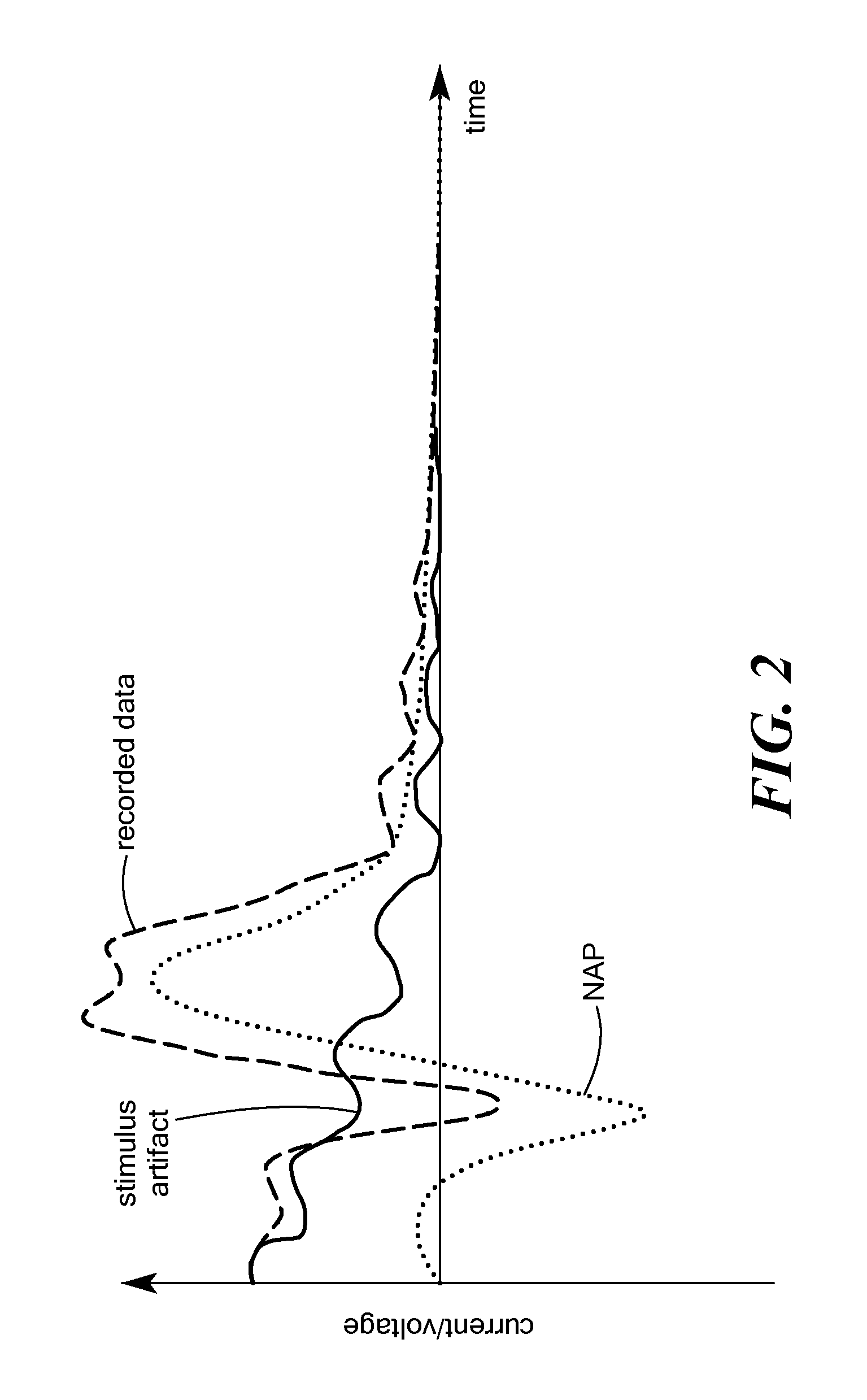
Stimulus artifact removal for neuronal recordings
A method is described for processing an electrical stimulation response measurement waveform signal measured in response to delivery of a selected electrical stimulation signal to neural tissue. The electrical stimulation response measurement waveform signal contains a stimulus artifact and one or more neuronal action potentials. The electrical stimulation signal is selected based on satisfying a cost function comparison between at least one stimulus artifact component and a plurality of known neuronal action potential waveforms. The electrical stimulation response waveform signal is then processed using a source separation algorithm to remove the stimulus artifact component.
Owner:MED EL ELEKTROMEDIZINISCHE GERAETE GMBH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com