Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1171 results about "Microphone signal" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
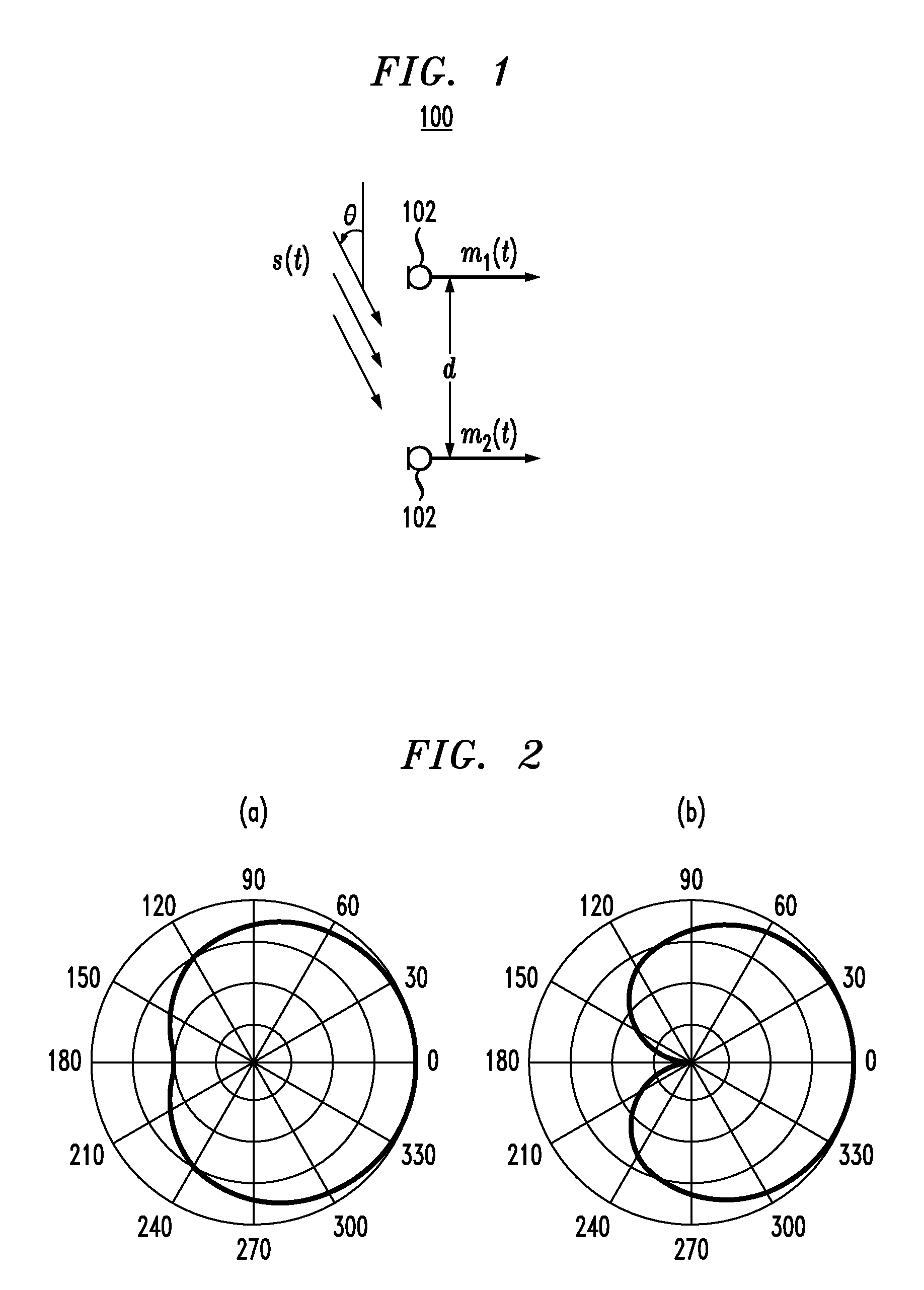
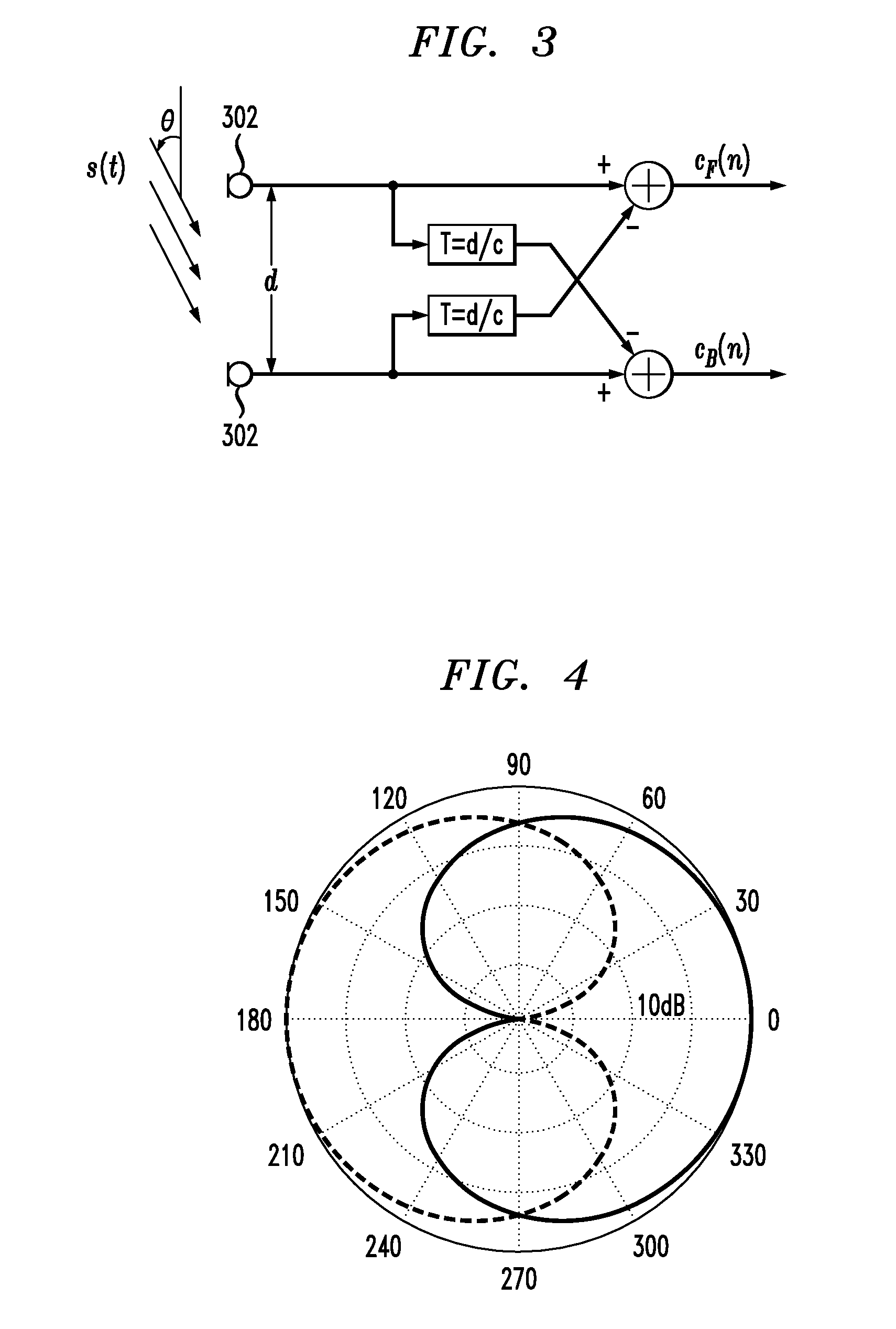
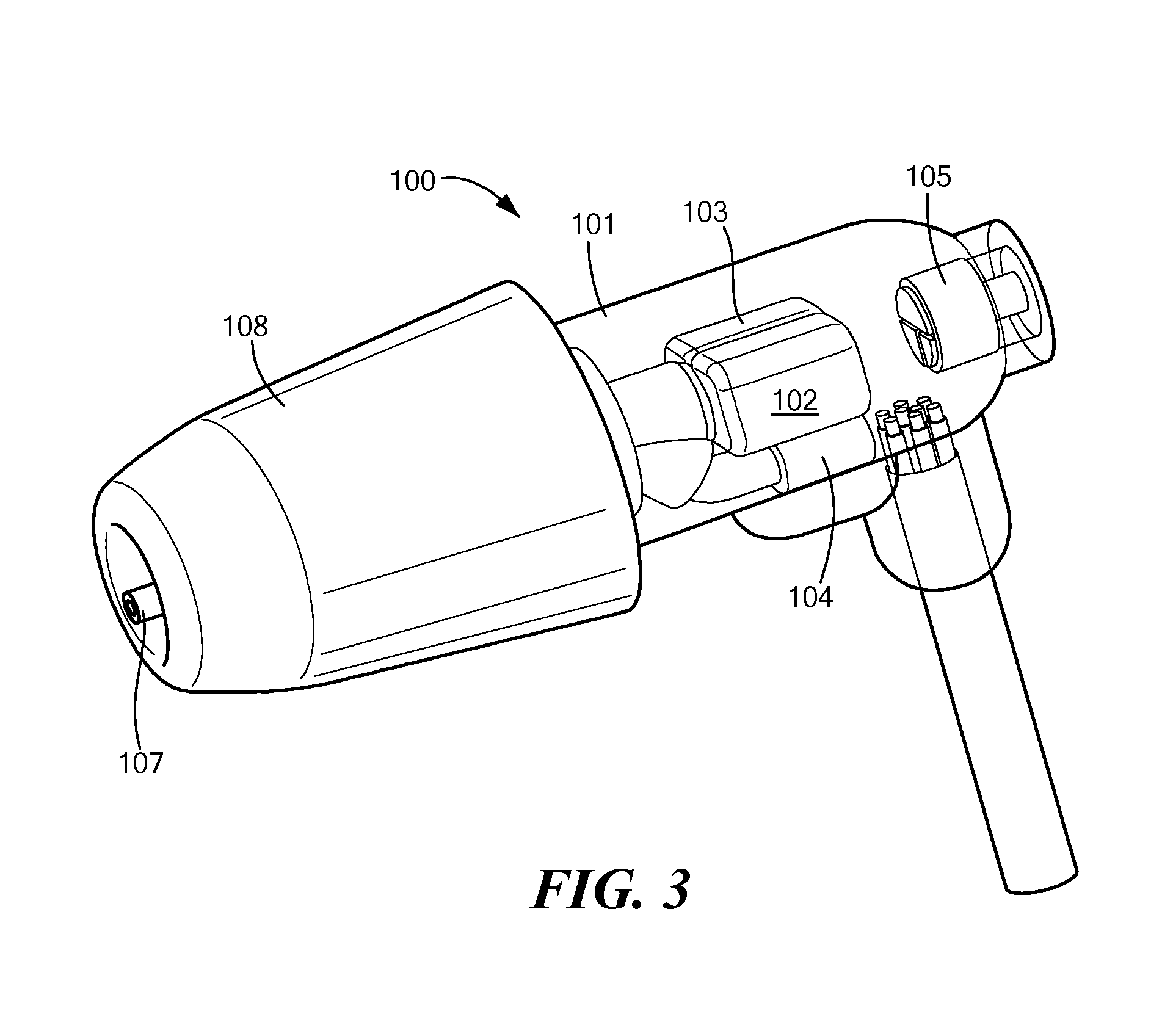
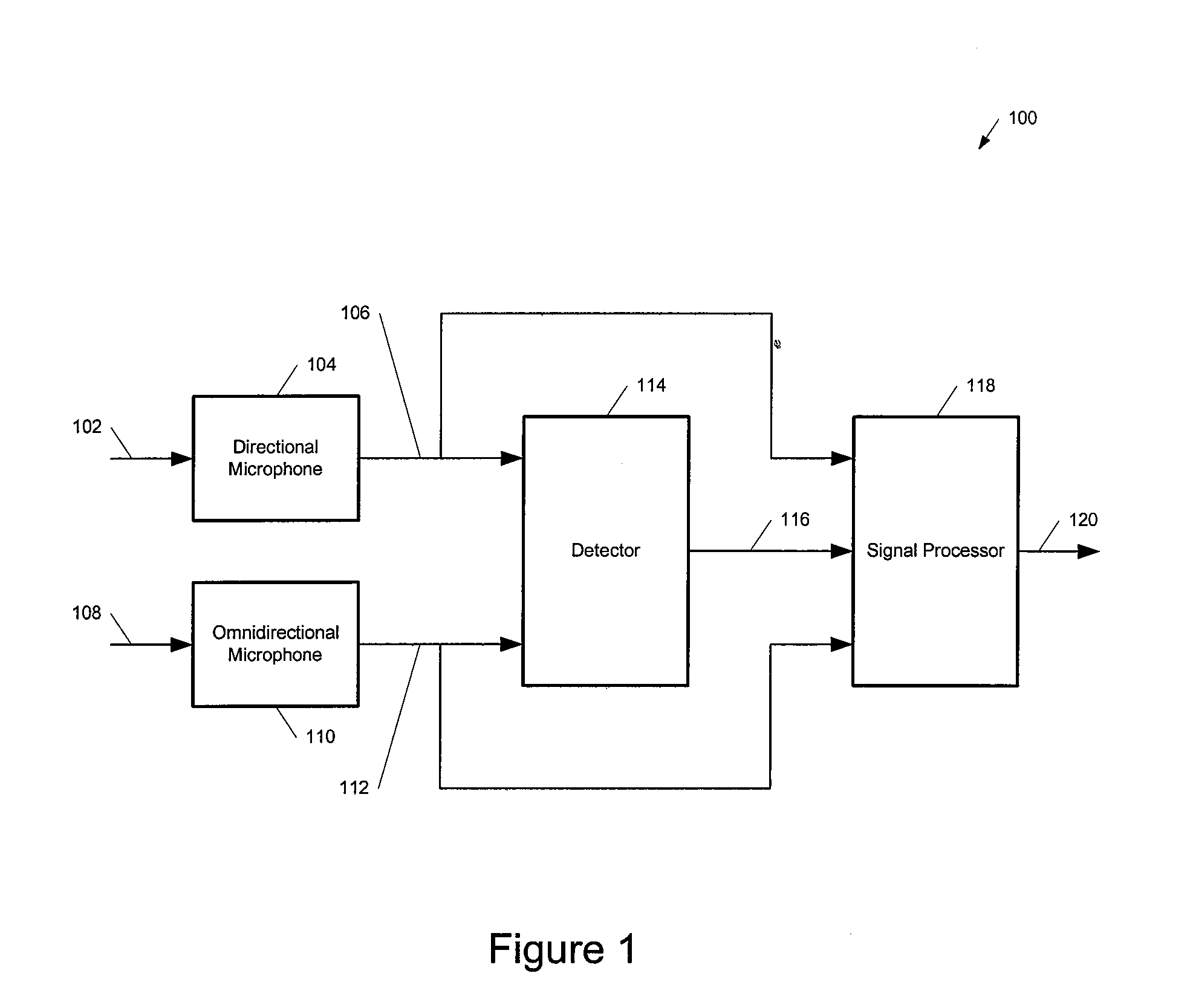
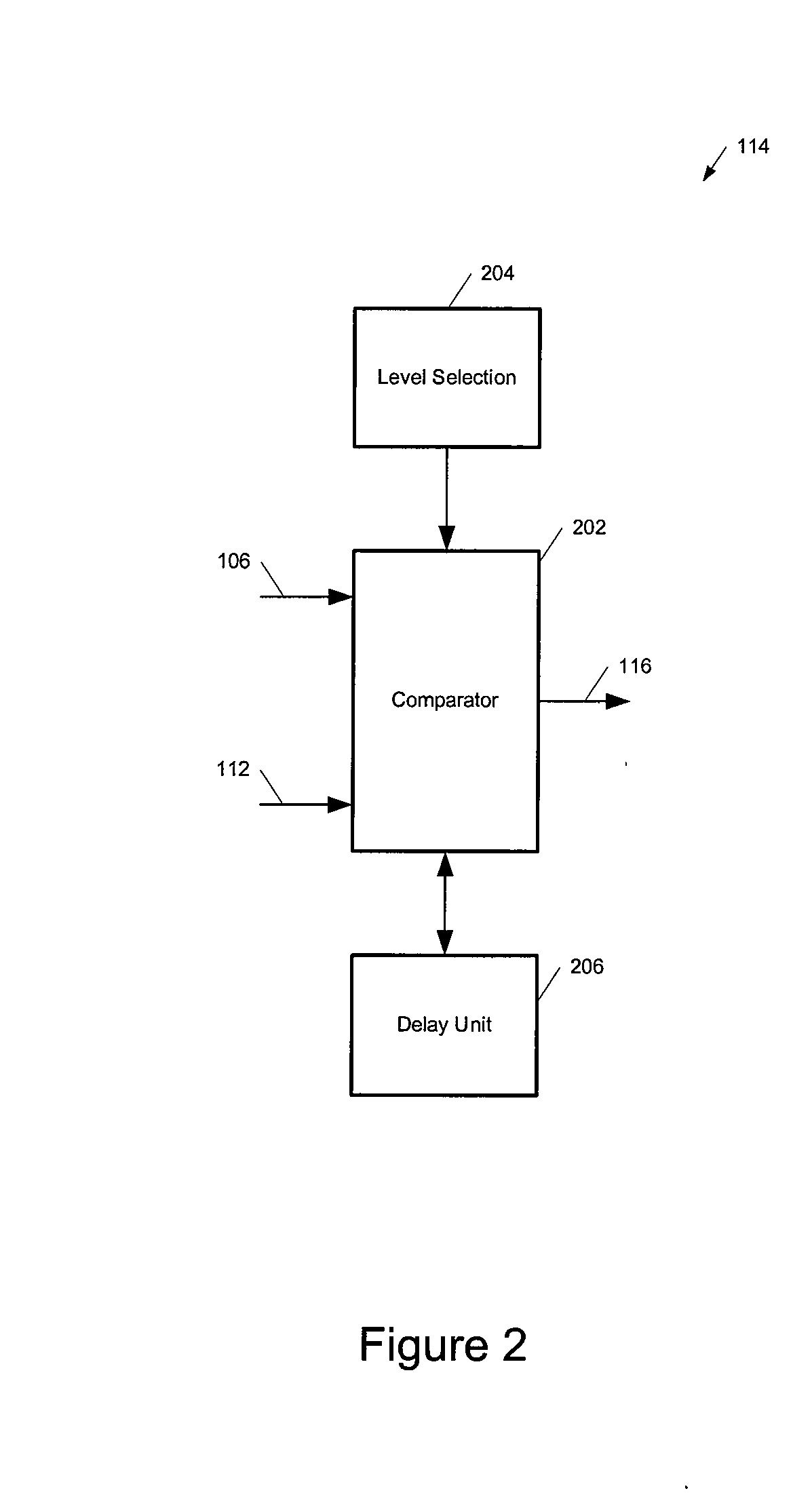
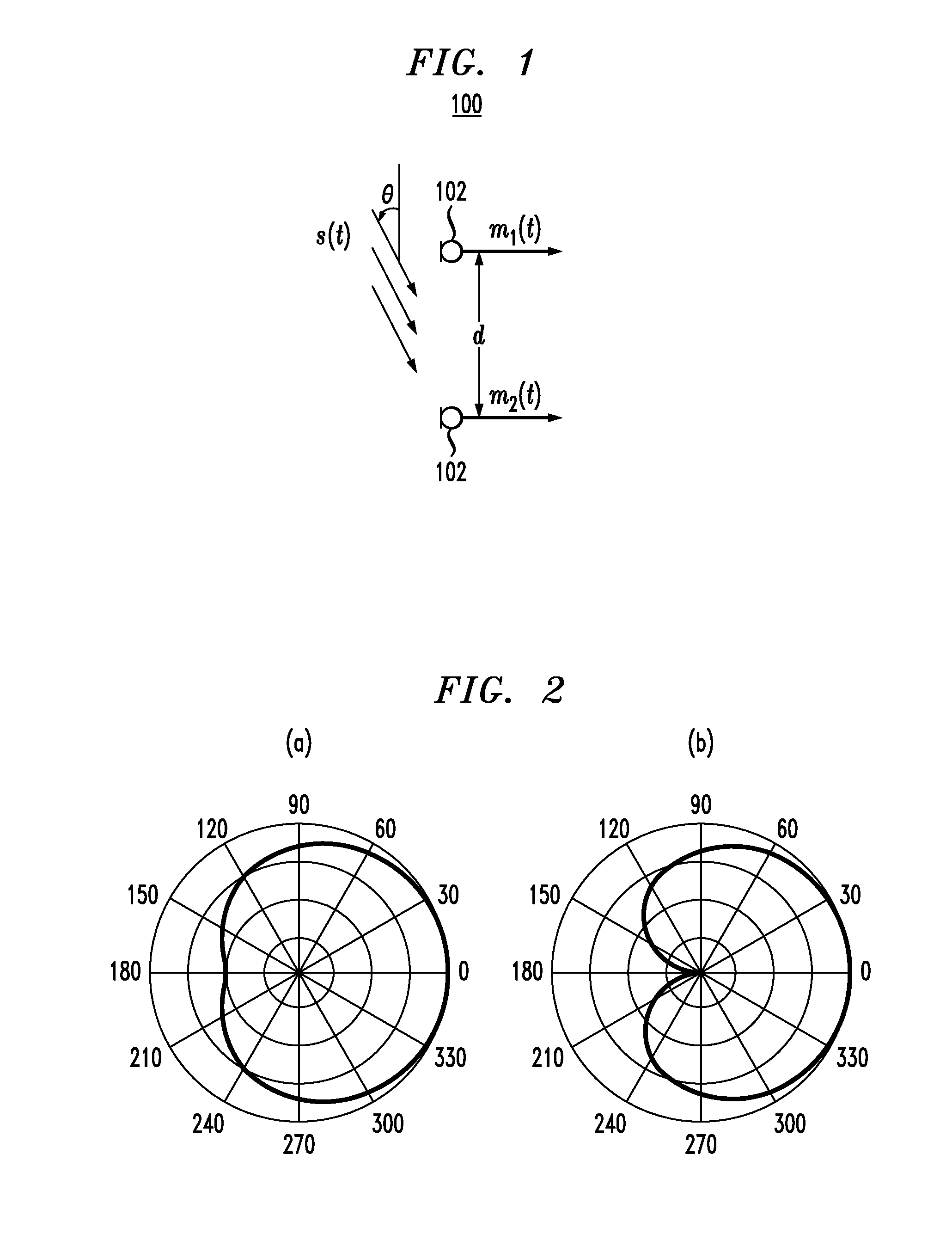
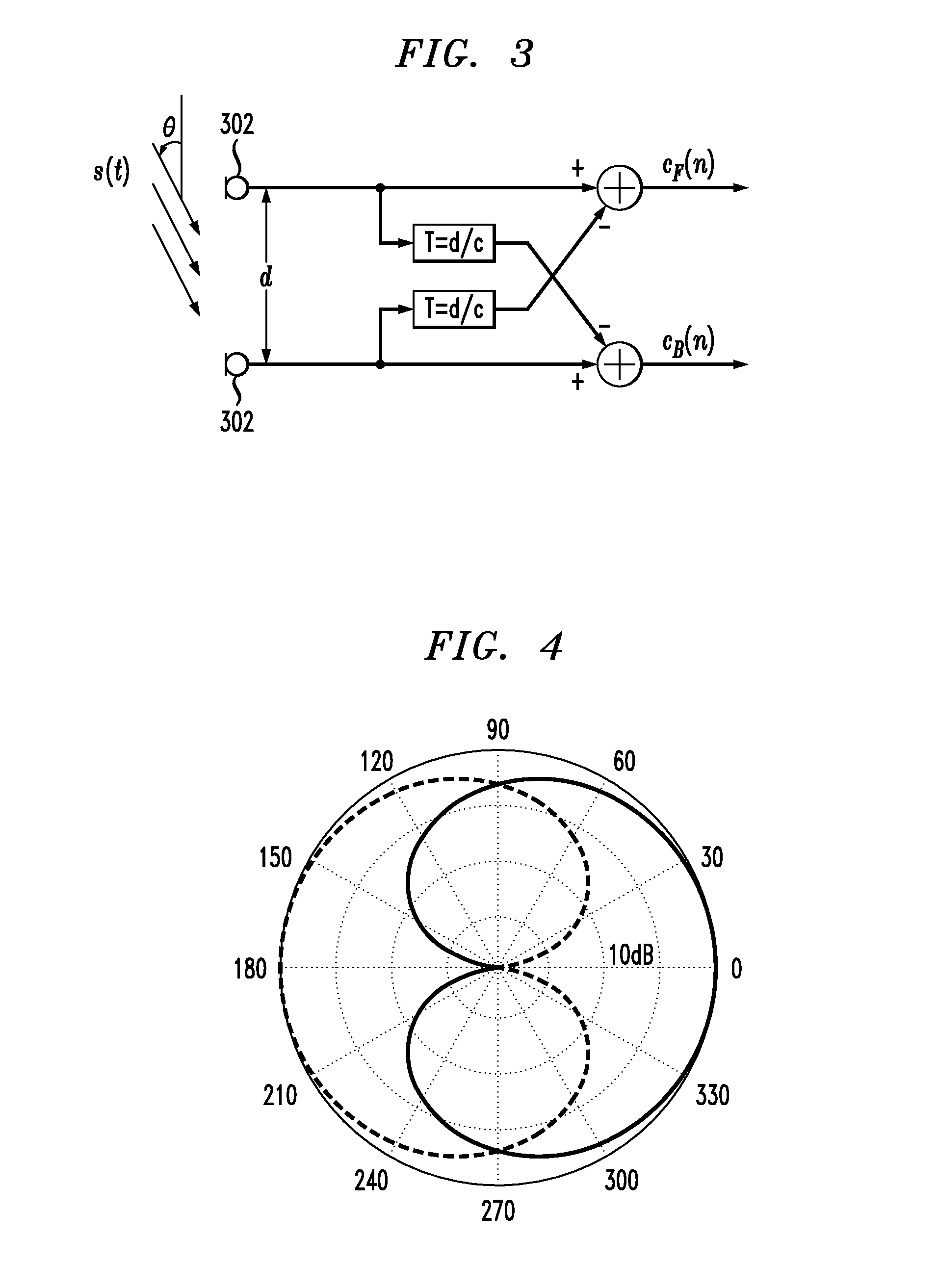
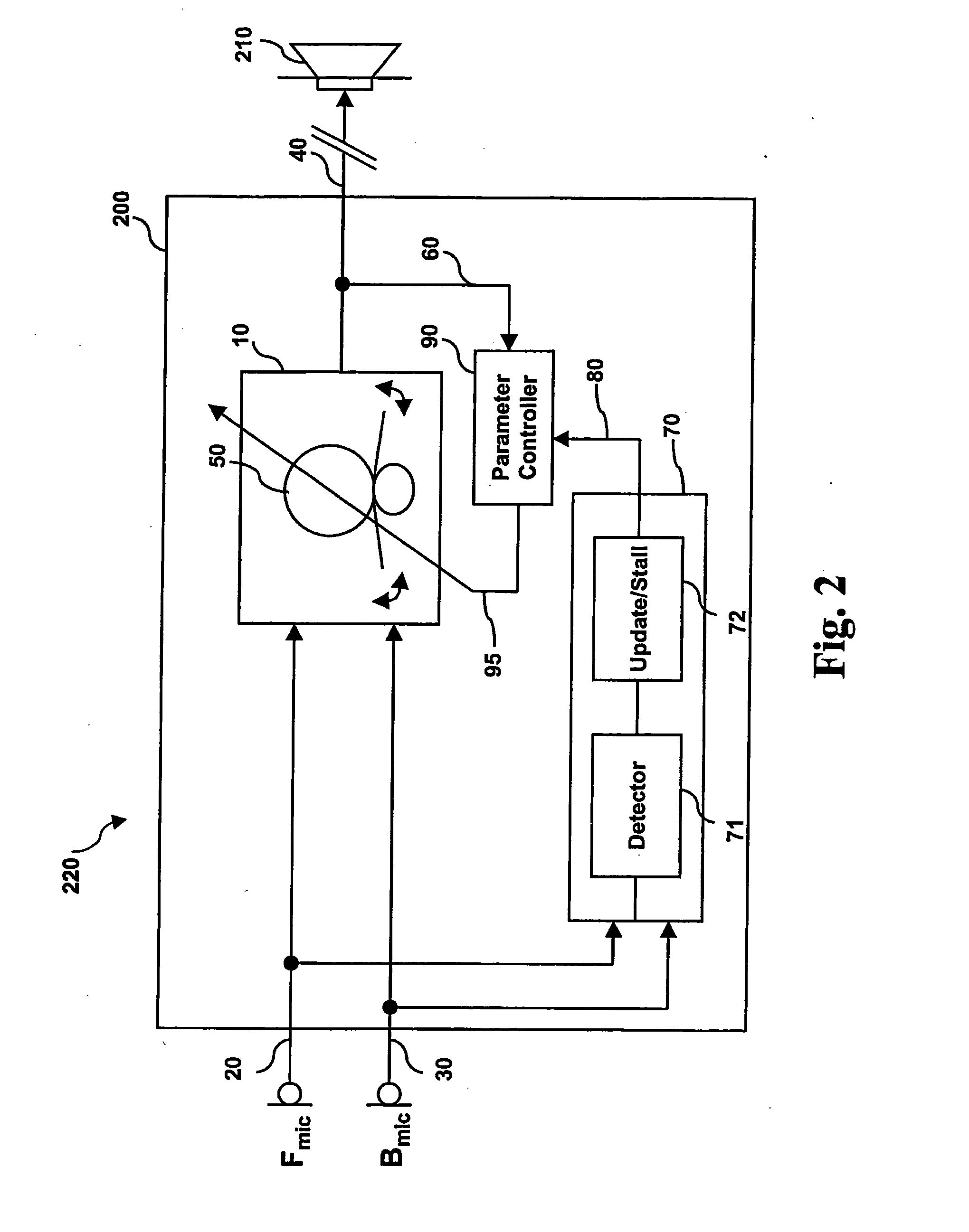
Noise-reducing directional microphone array
ActiveUS20090175466A1Efficient solutionNoise minimizationMicrophonesSignal processingSpatial noiseMicrophone signal
In one embodiment, a directional microphone array having (at least) two microphones generates forward and backward cardioid signals from two (e.g., omnidirectional) microphone signals. An adaptation factor is applied to the backward cardioid signal, and the resulting adjusted backward cardioid signal is subtracted from the forward cardioid signal to generate a (first-order) output audio signal corresponding to a beampattern having no nulls for negative values of the adaptation factor. After low-pass filtering, spatial noise suppression can be applied to the output audio signal. Microphone arrays having one (or more) additional microphones can be designed to generate second- (or higher-) order output audio signals.
Owner:MH ACOUSTICS
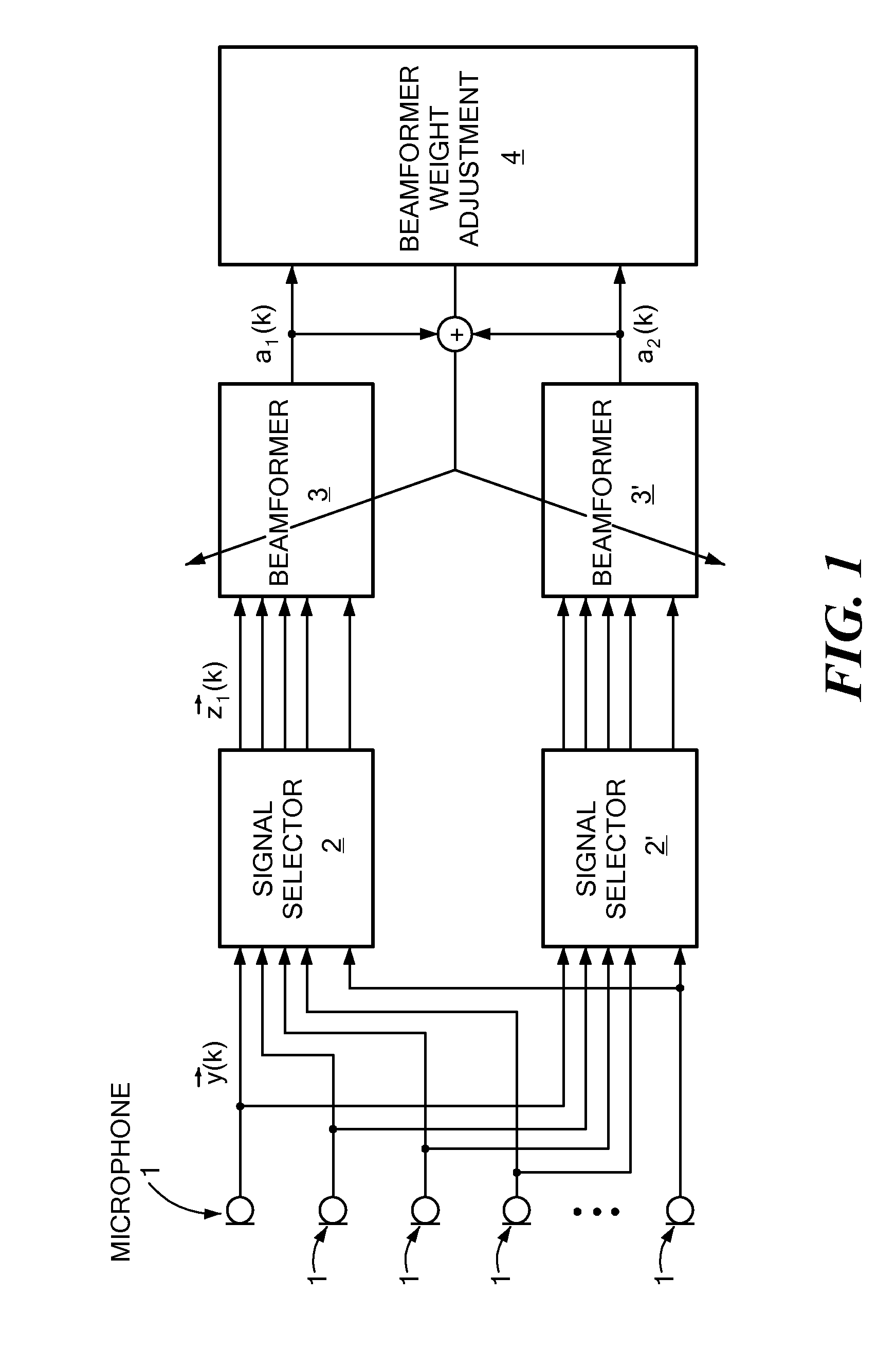
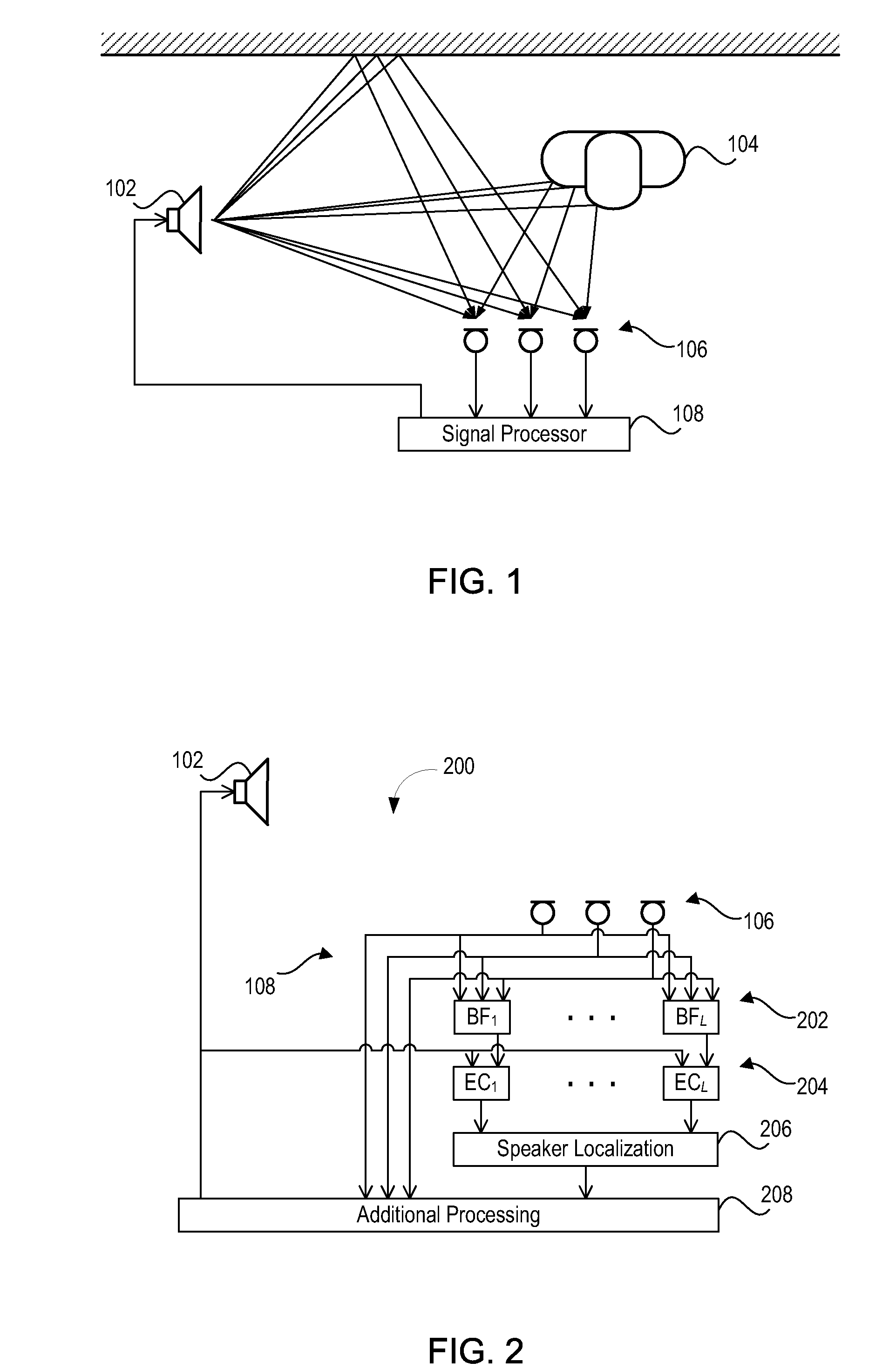
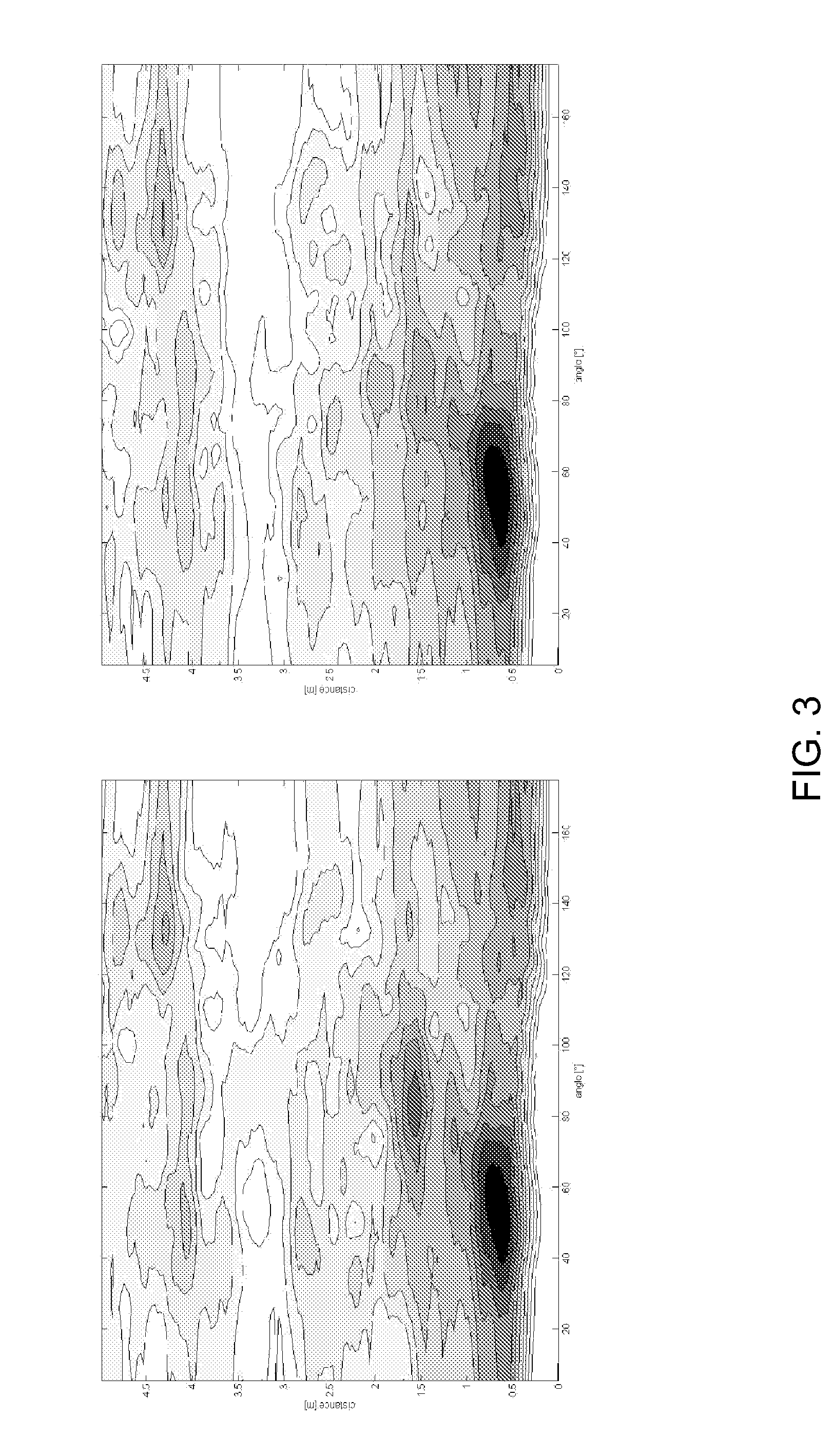
Beamforming Pre-Processing for Speaker Localization
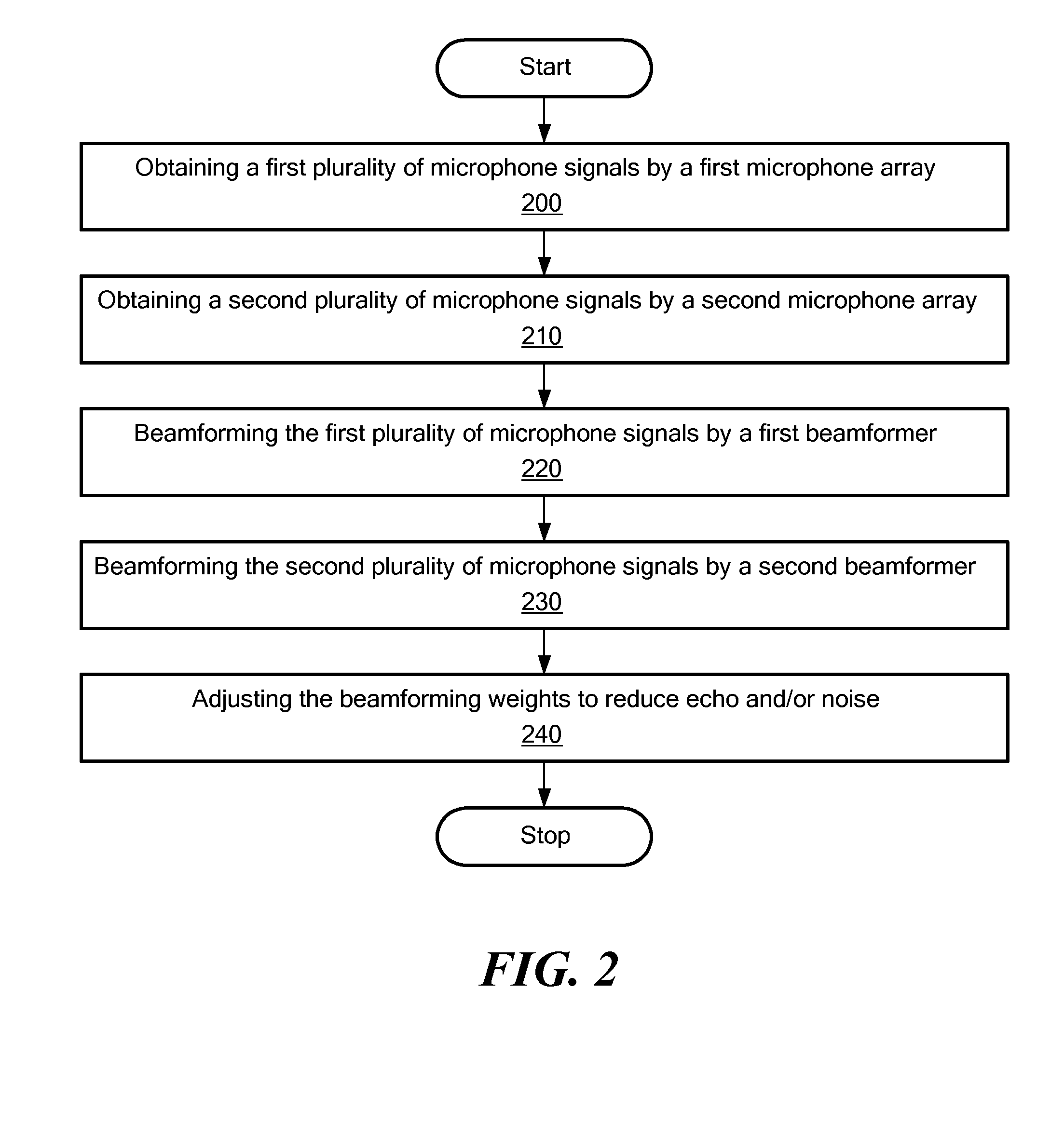
Embodiments of the present invention relate to methods, systems, and computer program products for signal processing. A first plurality of microphone signals is obtained by a first microphone array. A second plurality of microphone signals is obtained by a second microphone array different from the first microphone array. The first plurality of microphone signals is beamformed by a first beamformer comprising beamforming weights to obtain a first beamformed signal. The second plurality of microphone signals is beamformed by a second beamformer comprising the same beamforming weights as the first beamformer to obtain a second beamformed signal. The beamforming weights are adjusted such that the power density of echo components and / or noise components present in the first and second plurality of microphone signals is substantially reduced.
Owner:NUANCE COMM INC
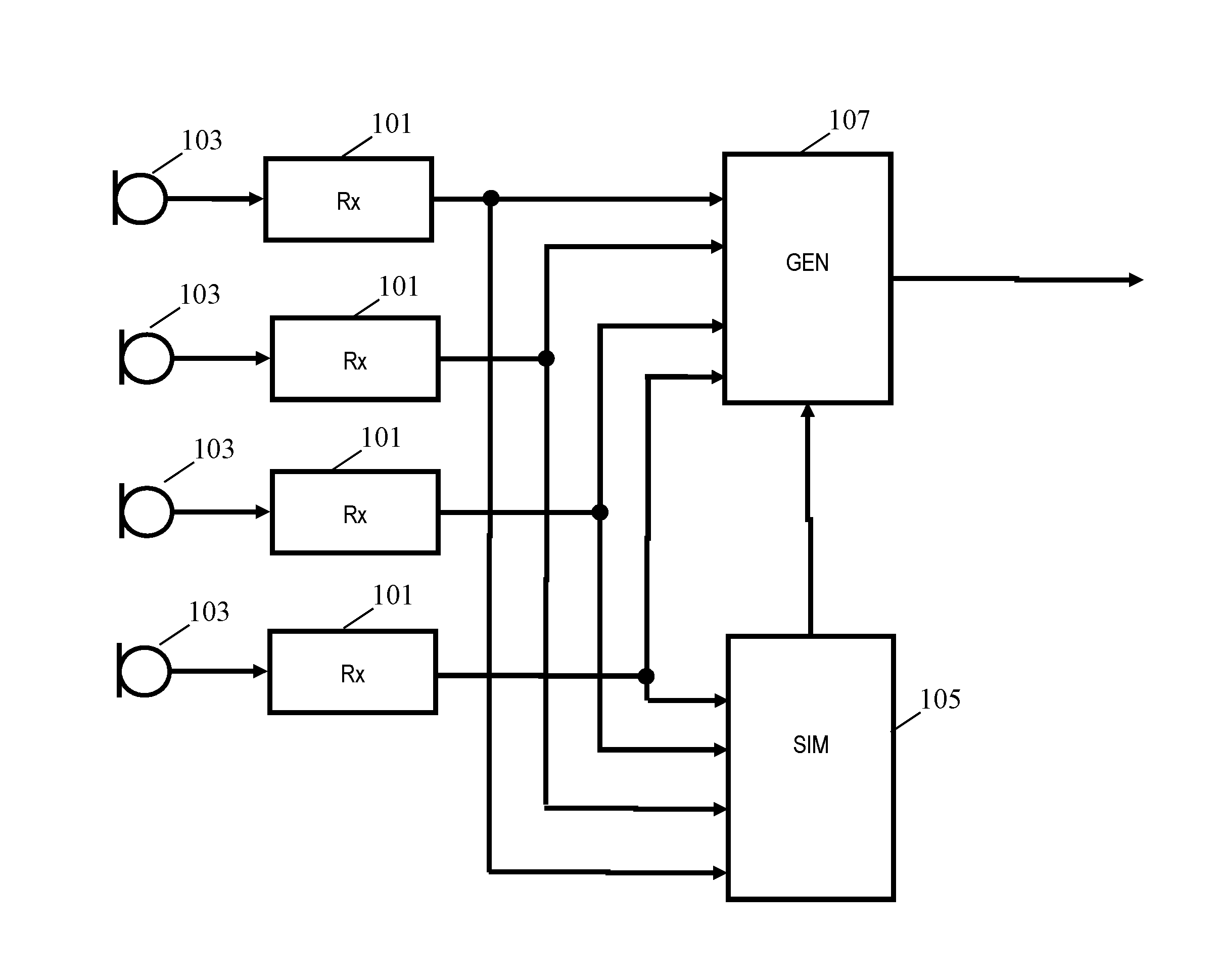
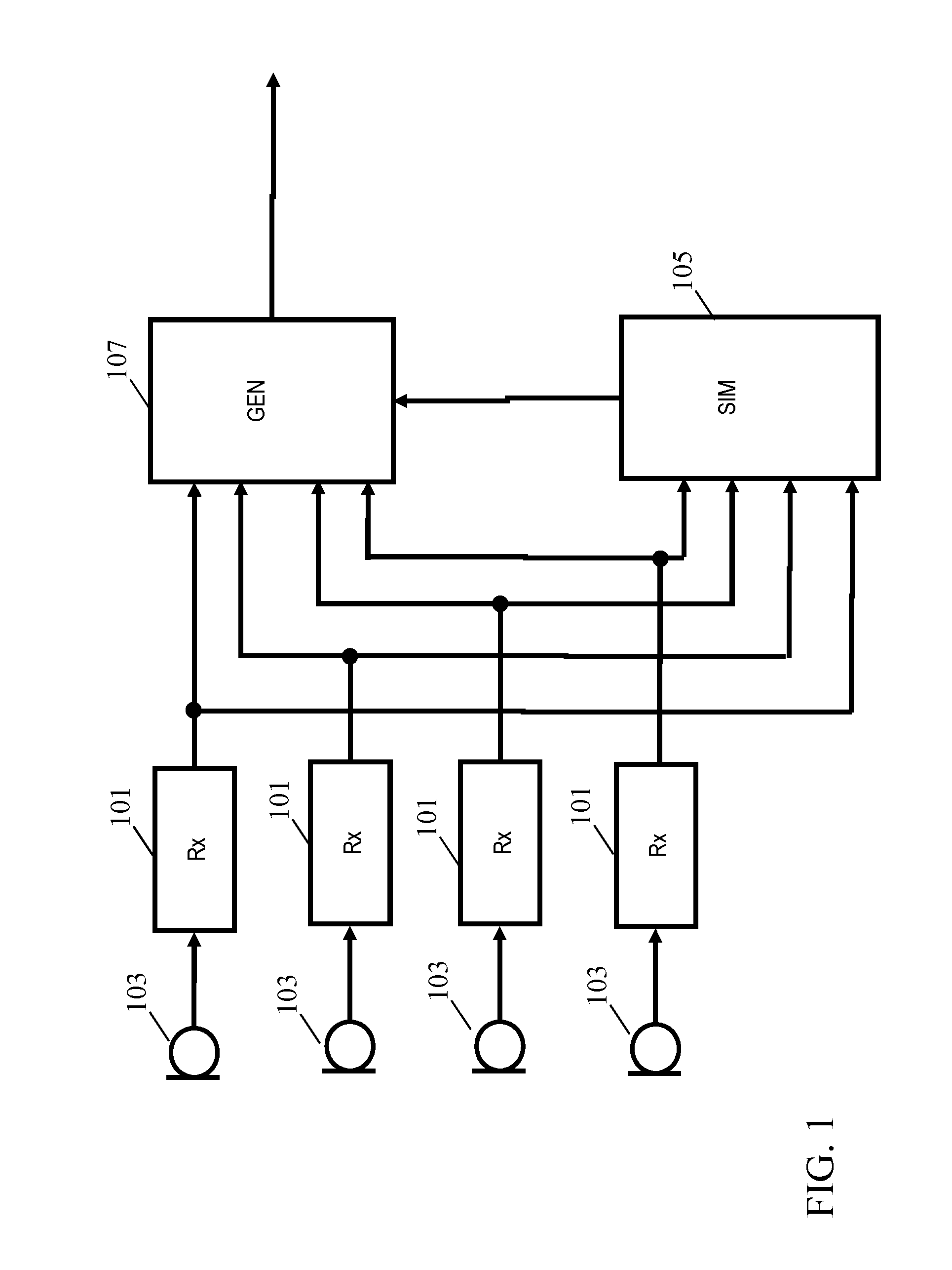
Method and apparatus for generating a speech signal
ActiveUS20150380010A1Enhanced signalLess reverberationMicrophonesLoudspeaker transducer fixingMicrophone signalSpeech sound
An apparatus comprises microphone receivers (101) which receive microphone signals from a plurality of microphones (103). A comparator (105) determines a speech similarity indication indicative of a similarity between the microphone signal and non-reverberant speech for each microphone signal. The determination is in response to a comparison of a property derived from the microphone signal to a reference property for non-reverberant speech. In some embodiments, the comparator (105) determines the similarity indication by comparing to reference properties for speech samples of a set of non-reverberant speech samples. A generator (107) generates a speech signal by combining the microphone signals in response to the similarity indications. In many embodiments, the apparatus may be distributed over a plurality of devices each containing a microphone, and the approach may determine the most suited microphone for generating the speech signal.
Owner:MEDIATEK INC
Non-linear echo cancellation
ActiveUS20130216056A1Two-way loud-speaking telephone systemsLine-transmissionMicrophone signalForm solution
A two-stage structure for performing non-linear echo cancellation is described in which a first echo canceller is used to attenuate linear echo components of a microphone signal and a second echo canceller is used to attenuate non-linear echo components of the output signal generated by the first echo canceller. One or both of the echo cancellers may be implemented using closed-form solutions, including a closed form solution for a hybrid method in the frequency domain.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
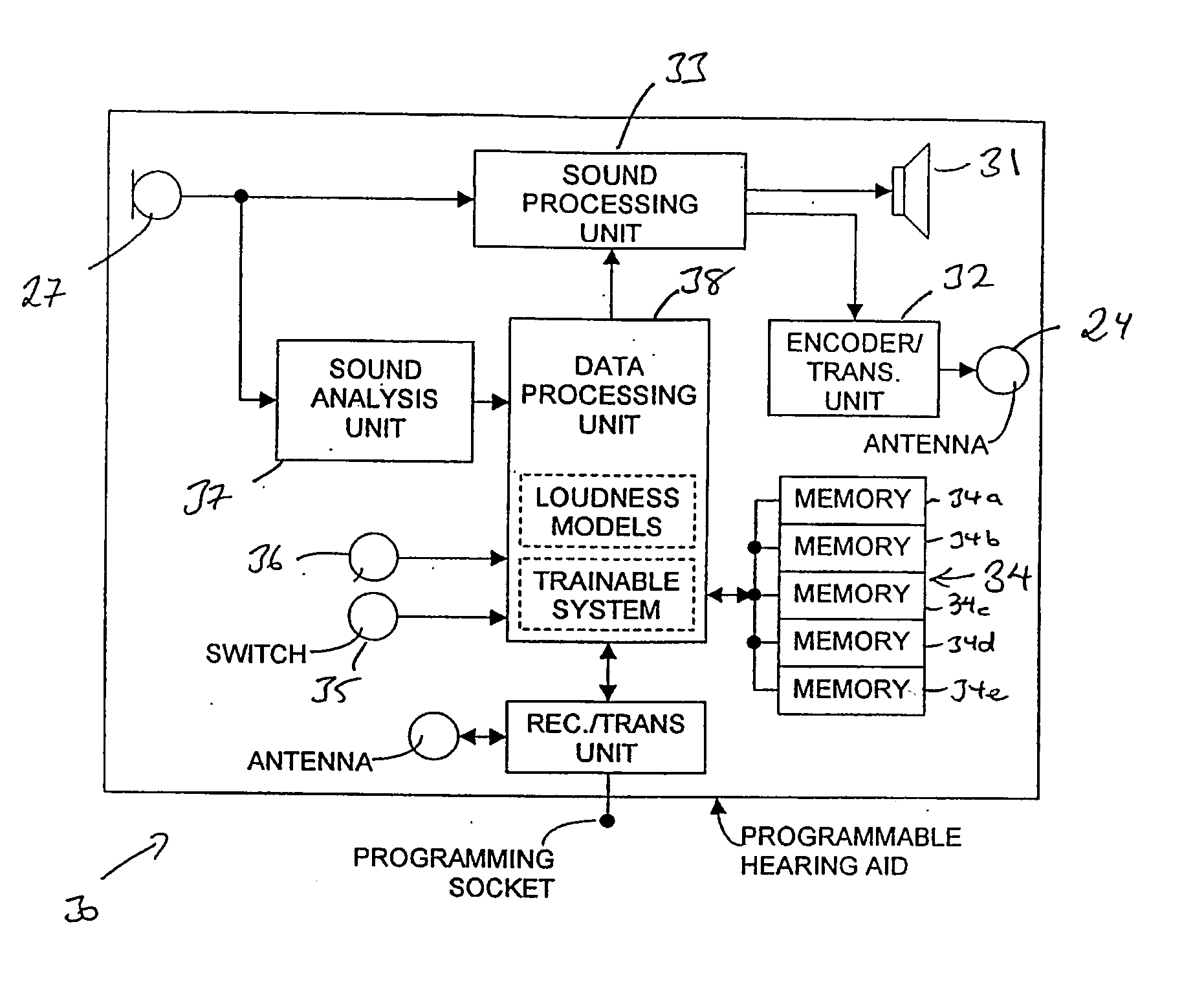
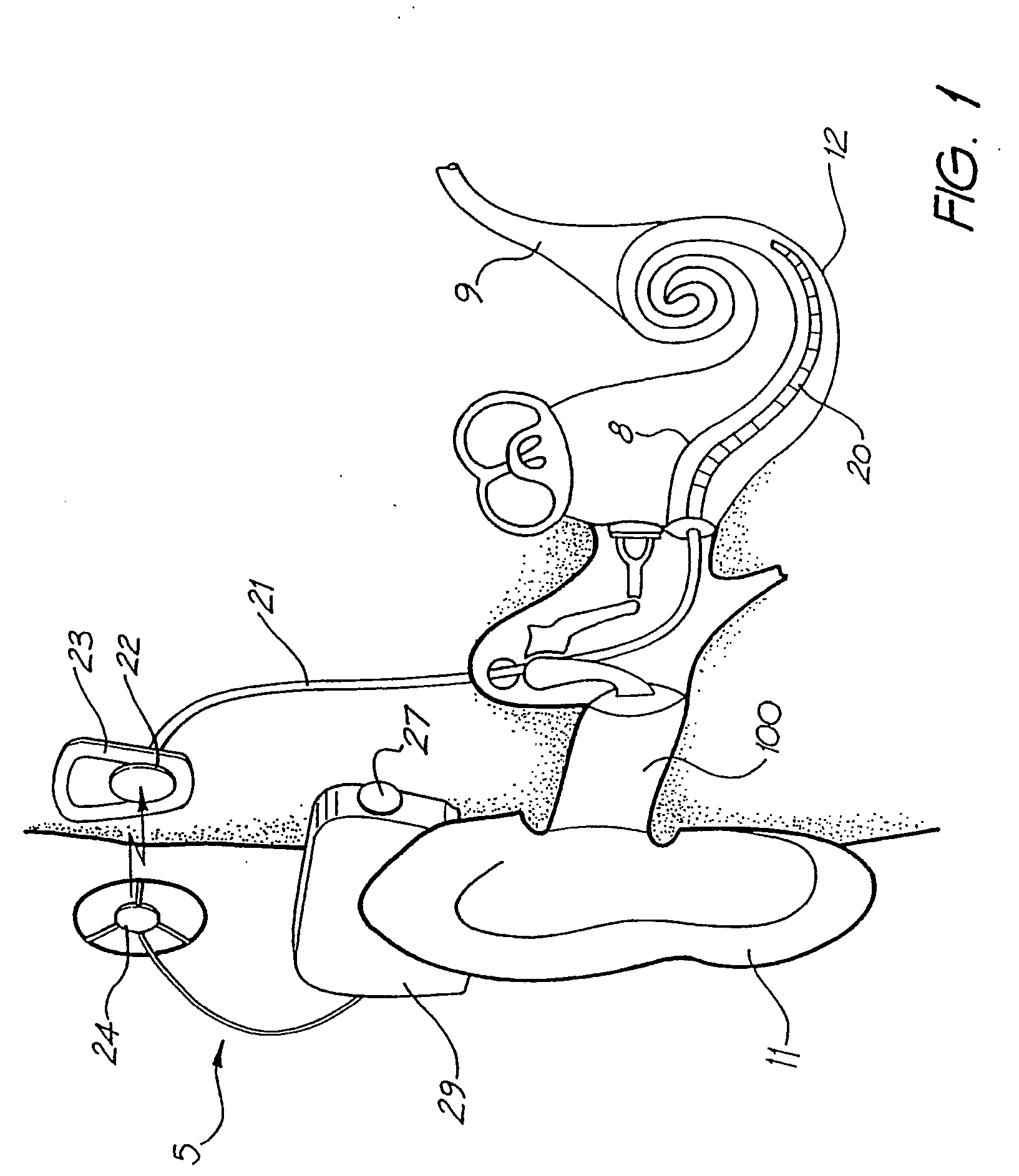
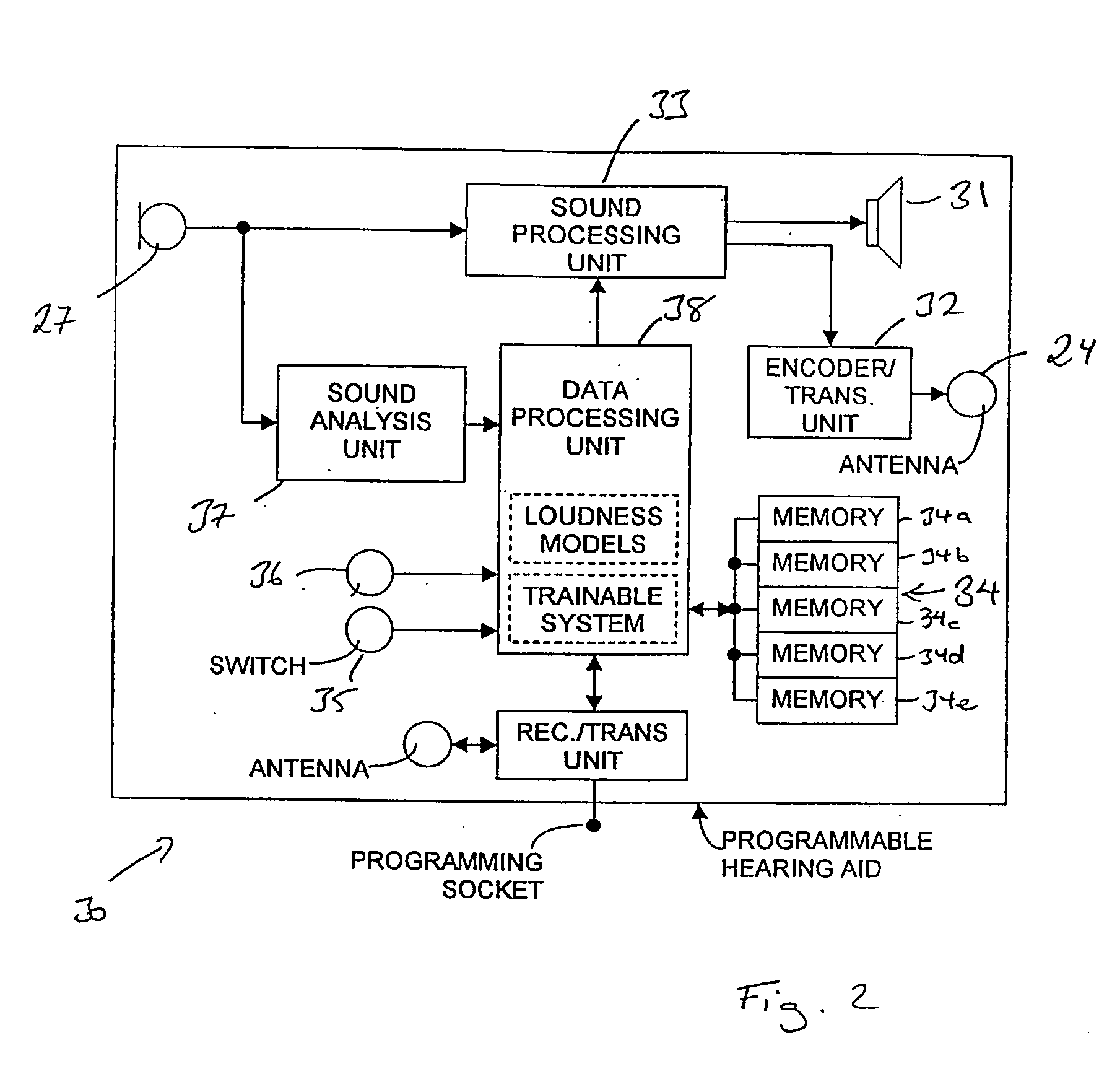
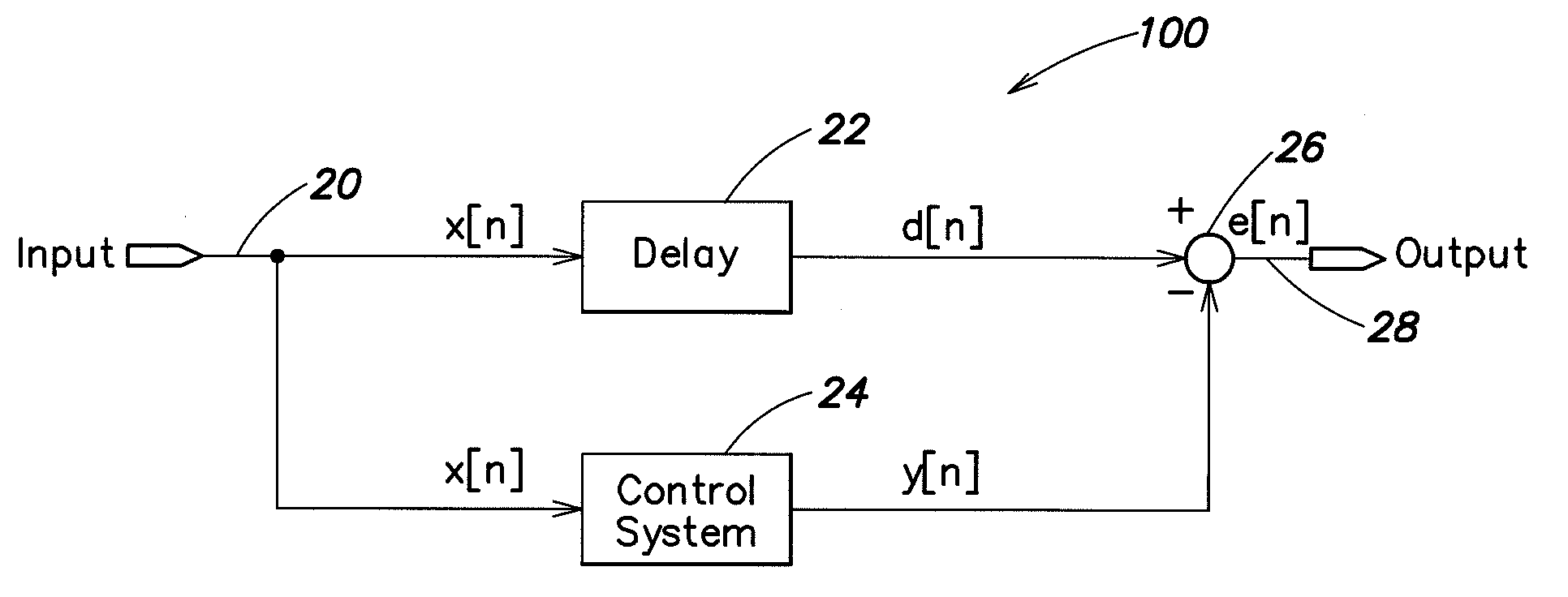
Programmable auditory prosthesis with trainable automatic adaptation to acoustic conditions
An auditory prosthesis (30) comprising a microphone (27) for receiving the sound and producing a microphone signal responding to the received sound, an output device for providing audio signals in a form receivable by a user of the prosthesis (30), a sound processing unit (33) operable to receive the microphone signal and carry out a processing operation on the microphone signal to produce an output signal in a form suitable to operate the output device, wherein the sound processing unit (33) is operable in a first mode in which the processing operation comprises at least one variable processing factor which is adjustable by a user to a setting which causes the output signal of the sound processing unit (33) to be adjusted according to the preference of the user for the characteristics of the current acoustic environment.
Owner:SIVANTOS PTE LTD
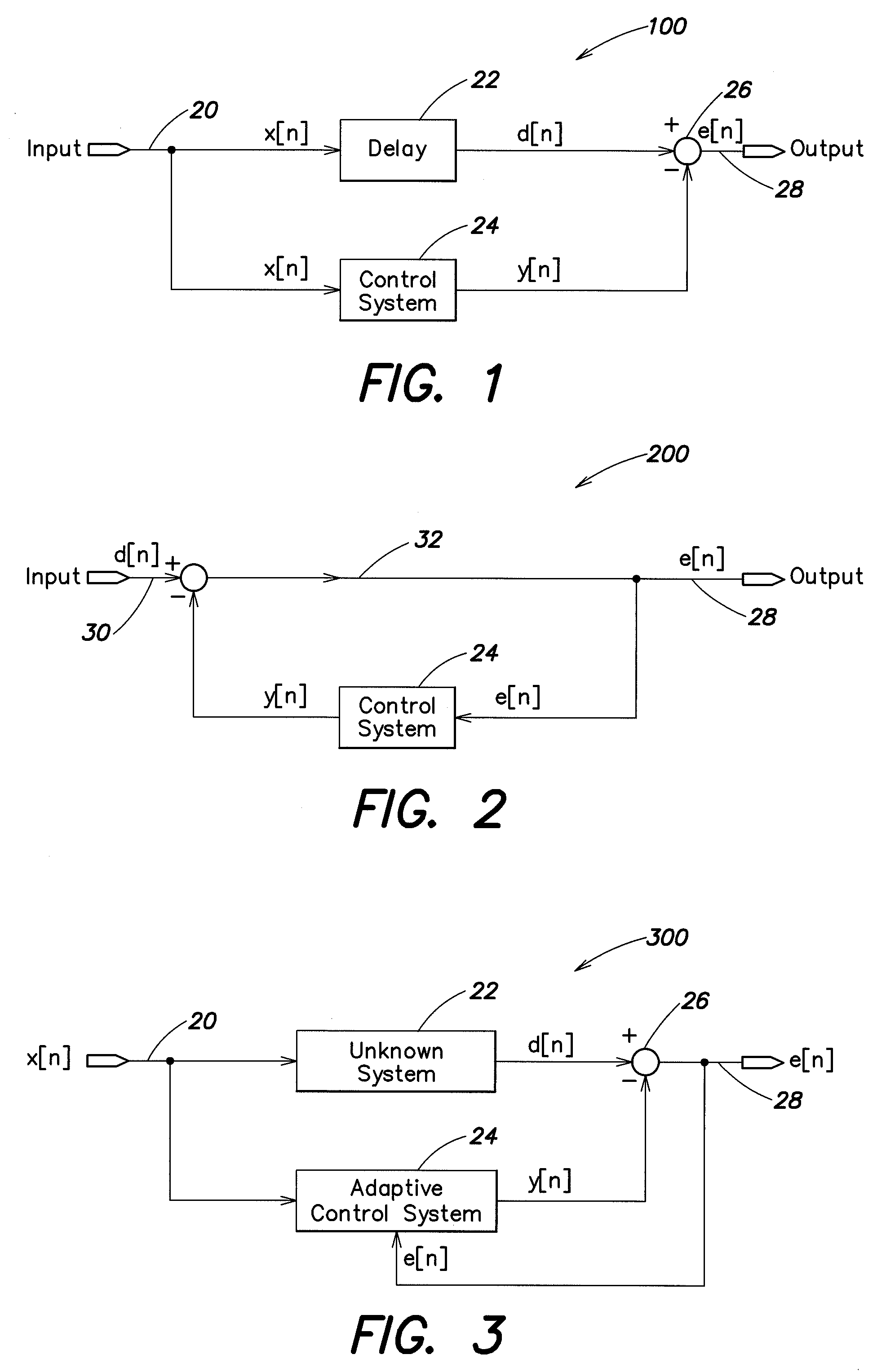
Adaptive noise control system
An active noise cancellation system includes an adaptive filter, a signal source, an acoustic actuator, a microphone, a secondary path and an estimation unit. The adaptive filter receives a reference signal representing noise, and provides a compensation signal in response to the received reference signal. The signal source provides a measurement signal. The acoustic actuator radiates the compensation signal and the measurement signal to the listening position. The microphone receives a first signal that is a superposition of the radiated compensation signal, the radiated measurement signal, and the noise signal at the listening position, and provides a microphone signal in response to the received first signal. The secondary path includes a secondary path system that represents a signal transmission path between an output of the adaptive filter and an output of the microphone. The estimation unit estimates a transfer characteristic of the secondary path system in response to the measurement signal and the microphone signal.
Owner:HARMAN BECKER AUTOMOTIVE SYST
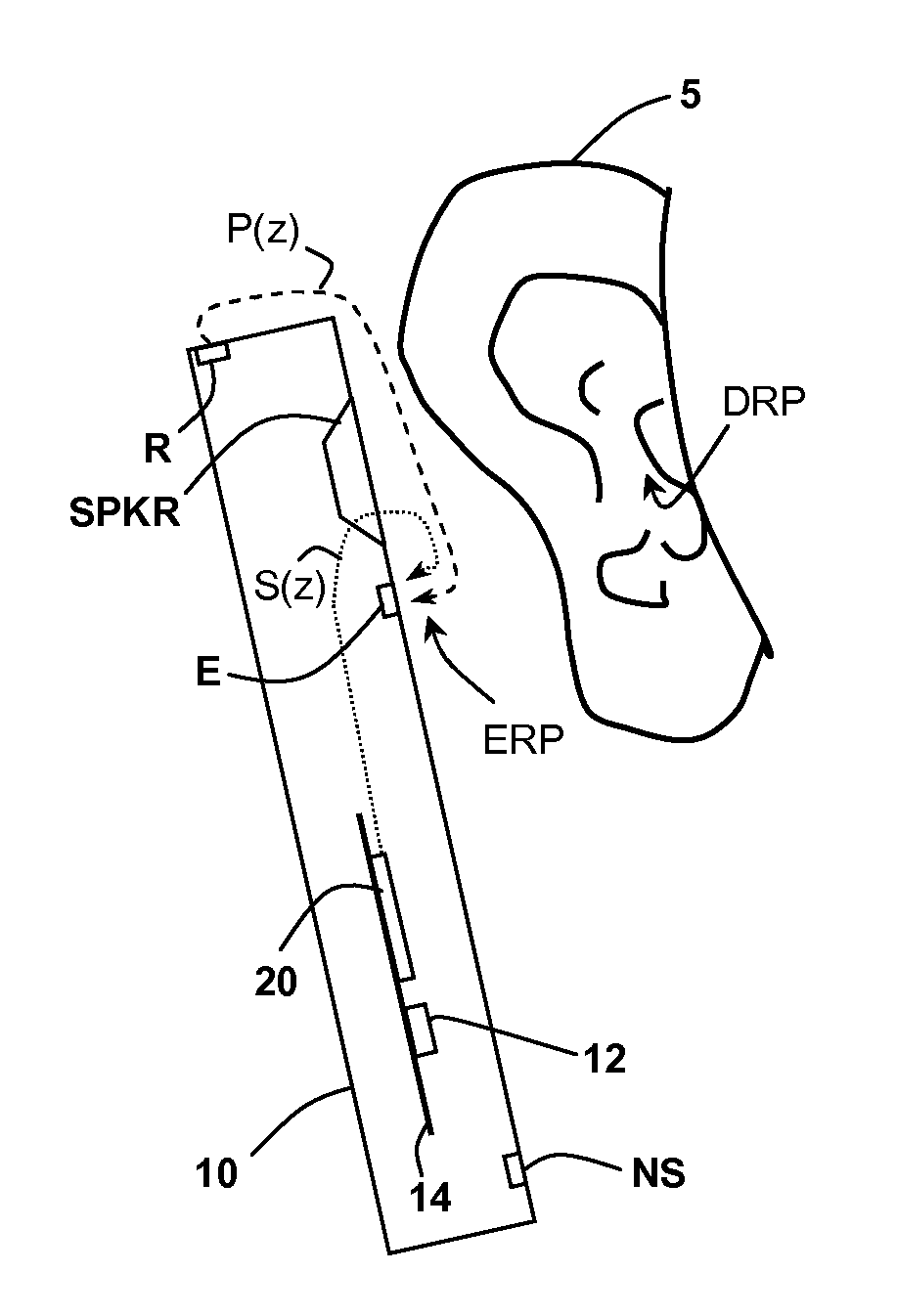
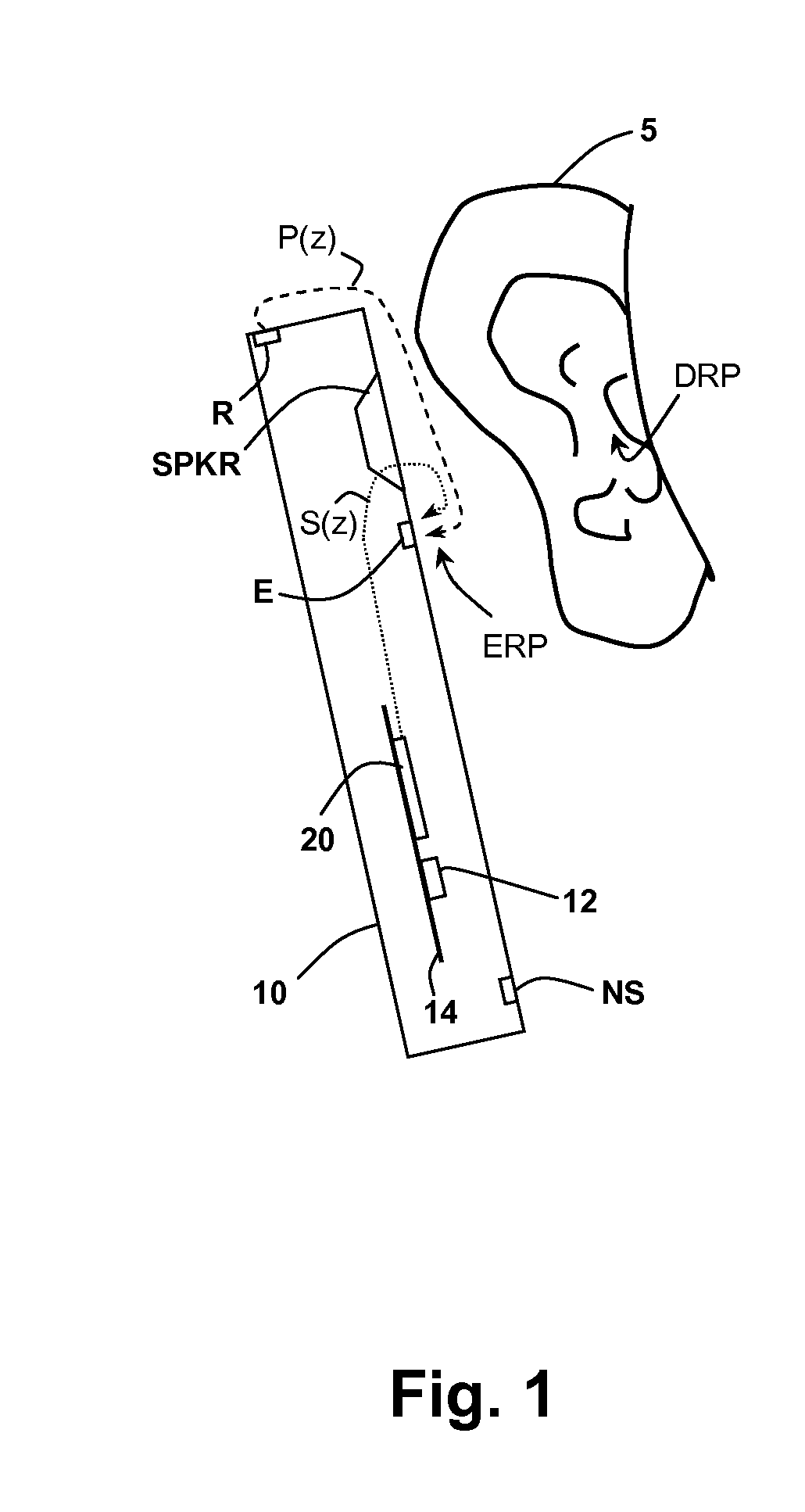
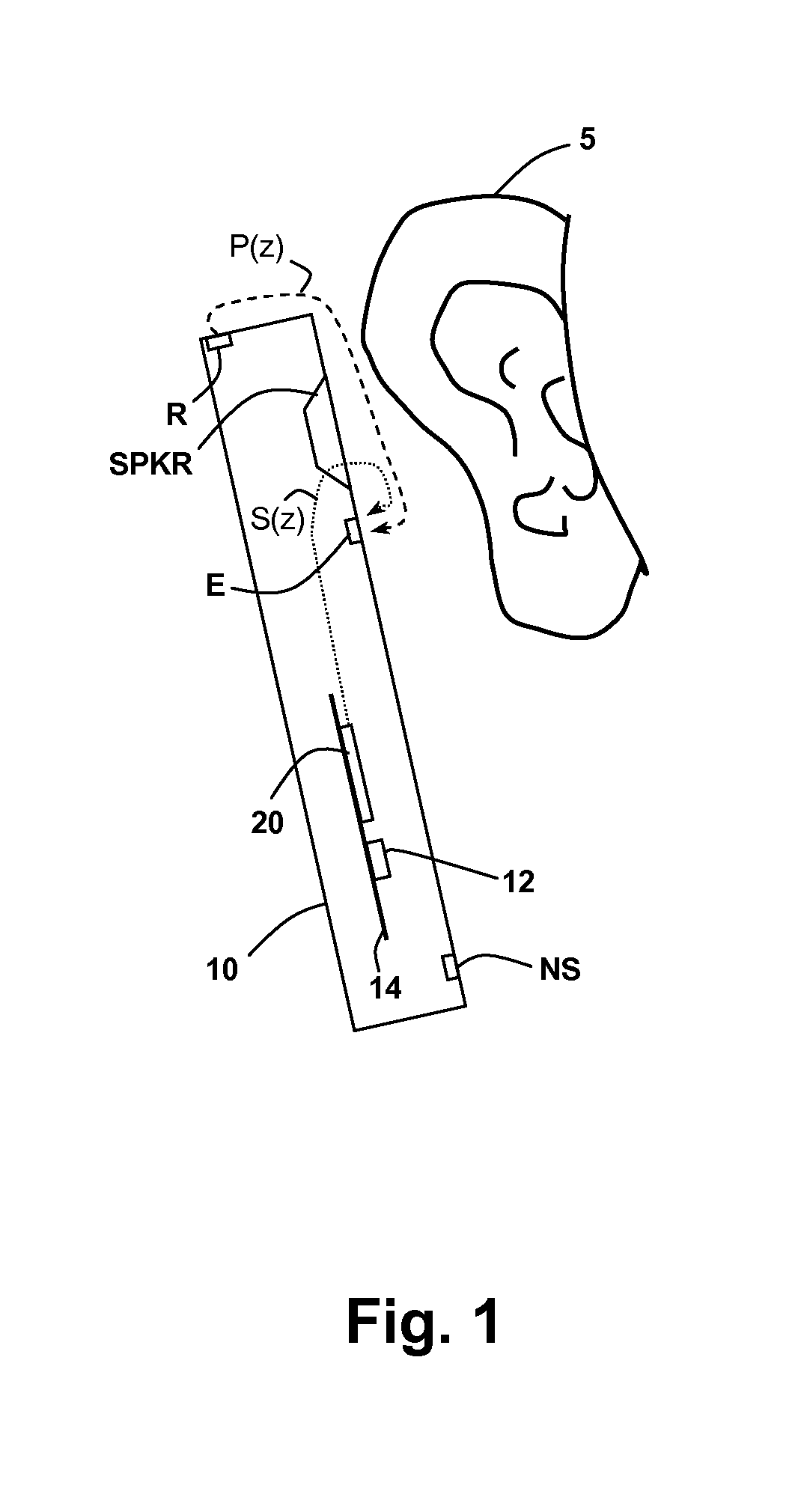
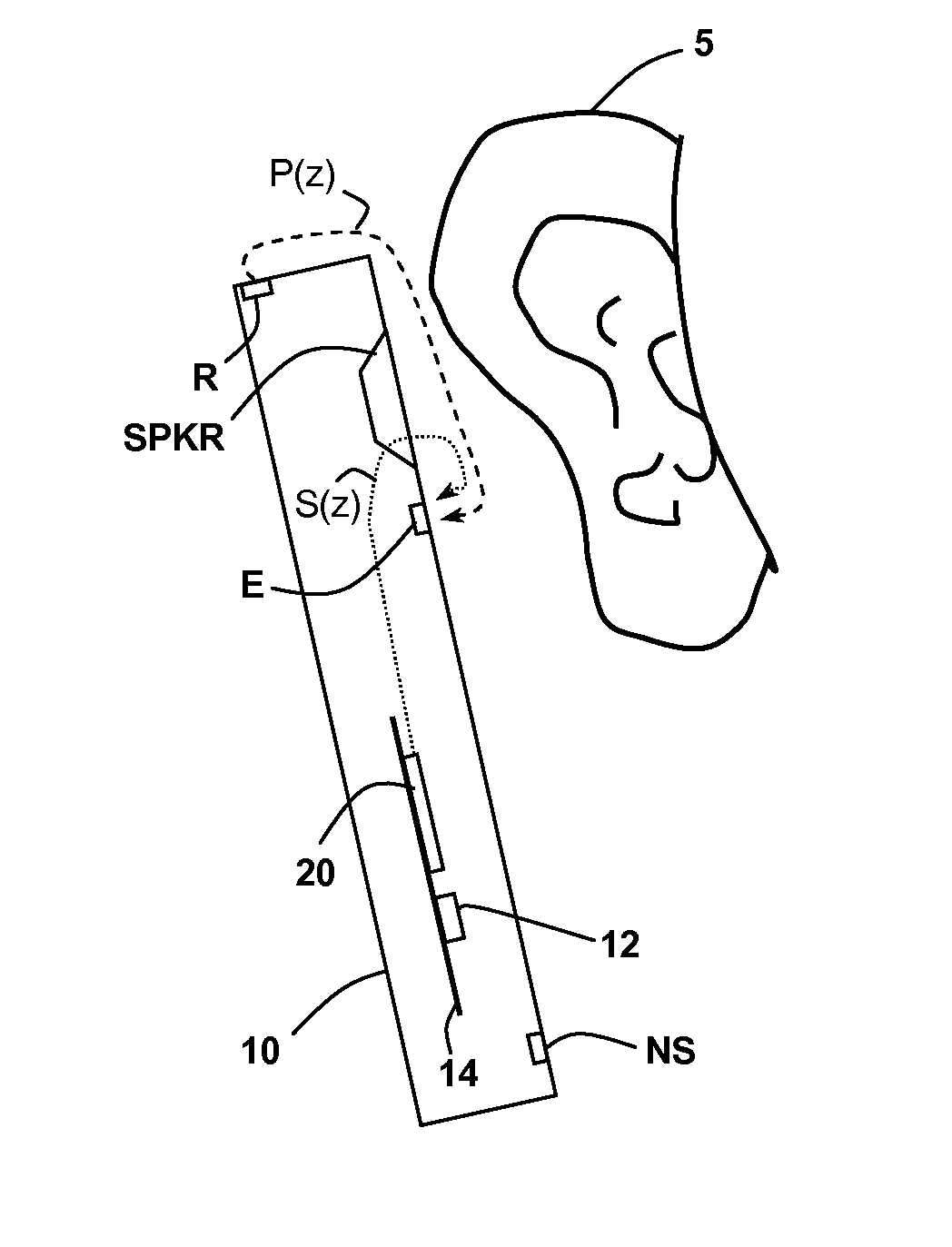
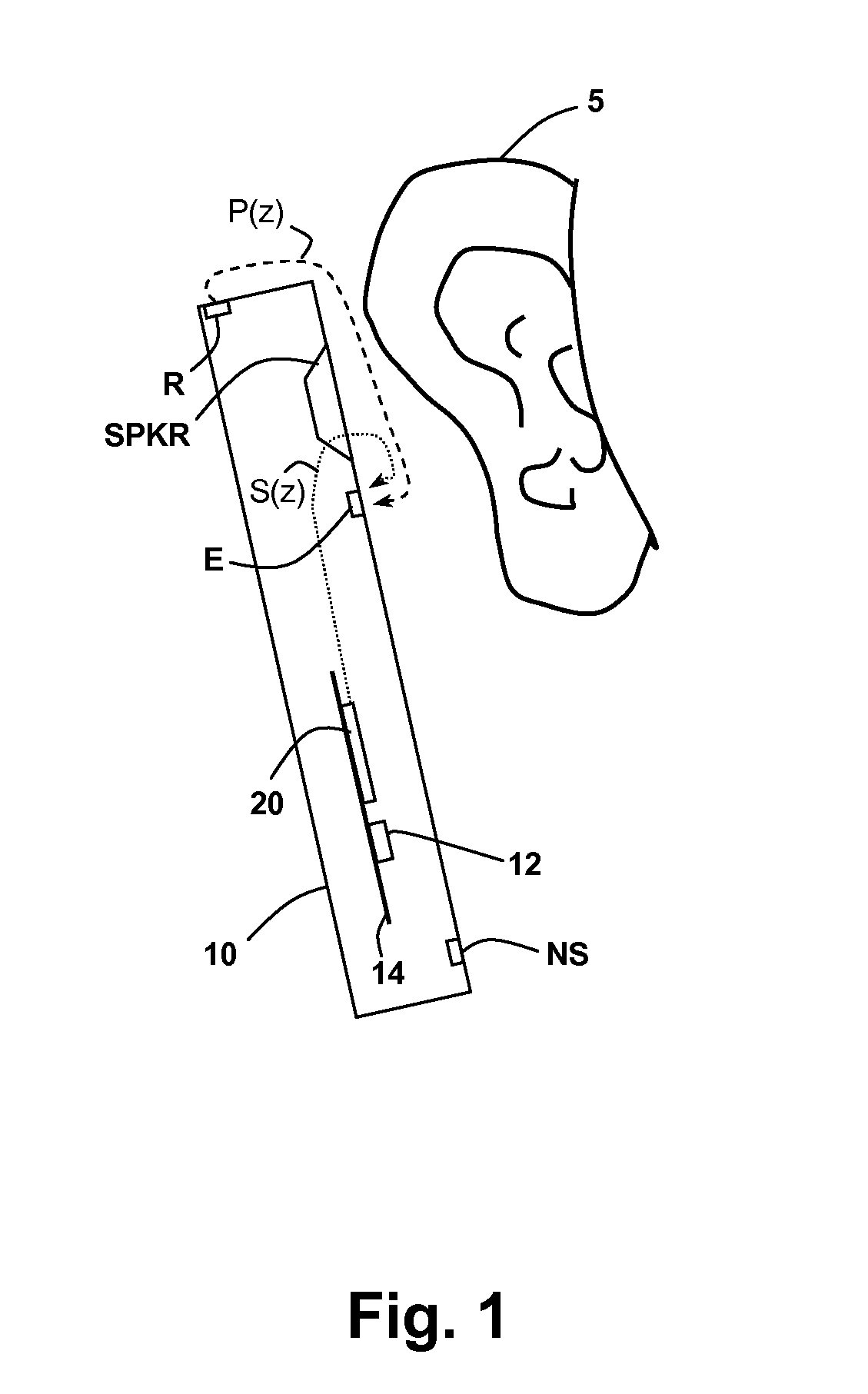
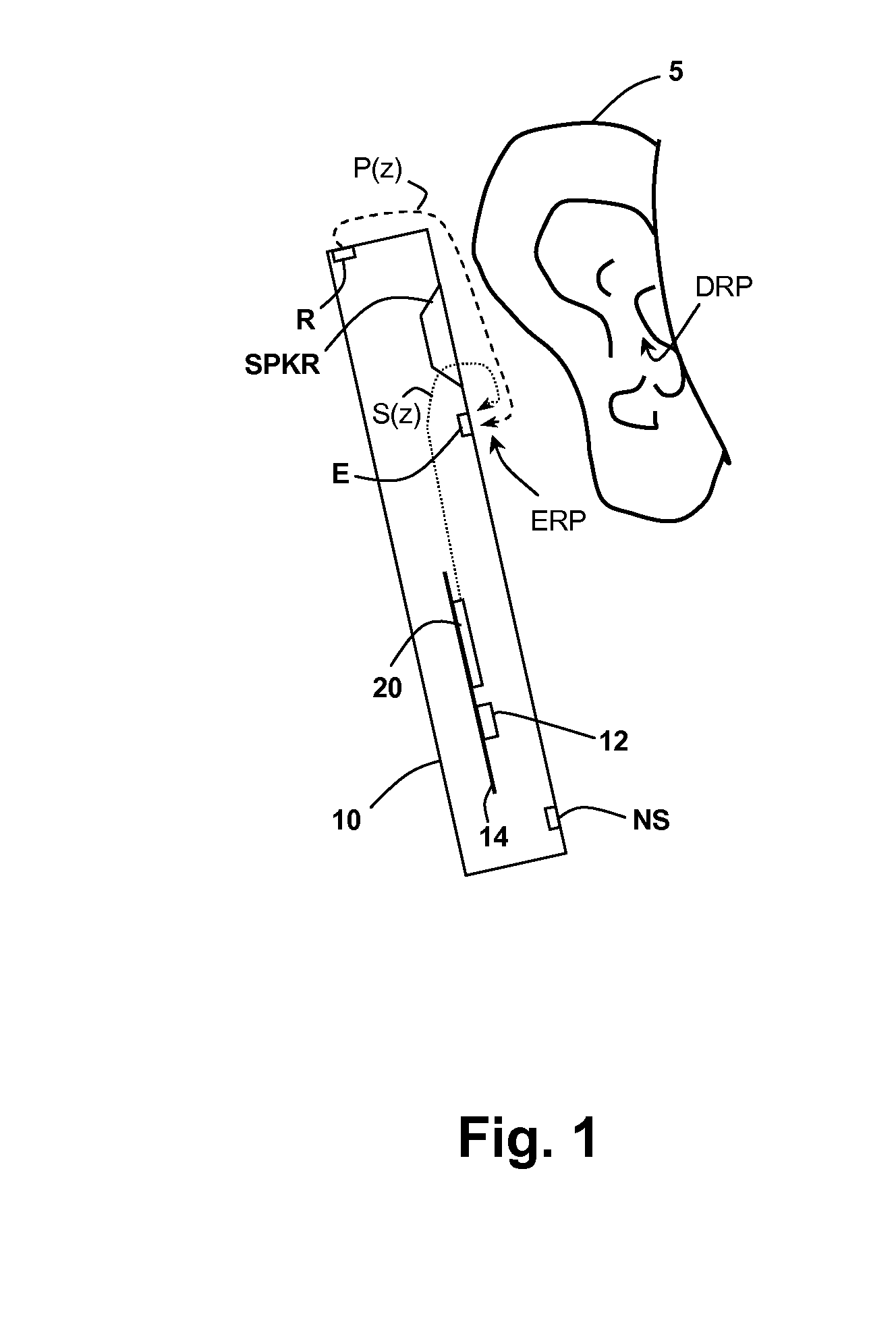
In-Ear Digital Electronic Noise Cancelling and Communication Device
ActiveUS20090080670A1Reduce external noiseEar treatmentHearing device active noise cancellationNoise reduction algorithmEngineering
A noise canceling and communication system is described. An in-ear device is adapted to fit in the ear canal of a device user. A passive noise reduction element reduces external noise entering the ear canal. An external microphone senses an external acoustic signal outside the ear canal to produce a representative external microphone signal. An internal microphone senses an internal acoustic signal proximal to the tympanic membrane to produce a representative internal microphone signal. One or more internal sound generators produce a noise cancellation signal and an acoustic communication signal, both directed towards the tympanic membrane. A probe tube shapes an acoustic response between the internal sound generator and the internal microphone to be relatively constant over a wide audio frequency band. An electronics module is located externally of the ear canal and in communication with the in-ear device for processing the microphone signals using a hybrid feed forward and feedback active noise reduction algorithm to produce the noise cancellation signal. The noise reduction algorithm includes a modeling component based on a transfer function associated with the internal sound generator and at least one of the microphones to automatically adjust the noise cancellation signal for fit and geometry of the ear canal of the user. The communication component also includes a modeling component based on a transfer function associated with the internal sound generator and at least one of the microphones to automatically adjust the communication signal for fit and geometry of the ear canal of the user and to assure that the communication signal does not interfere with the noise reduction algorithm and that the noise cancellation signal does not interfere with passing of the communication signal.
Owner:SOUND INNOVATIONS
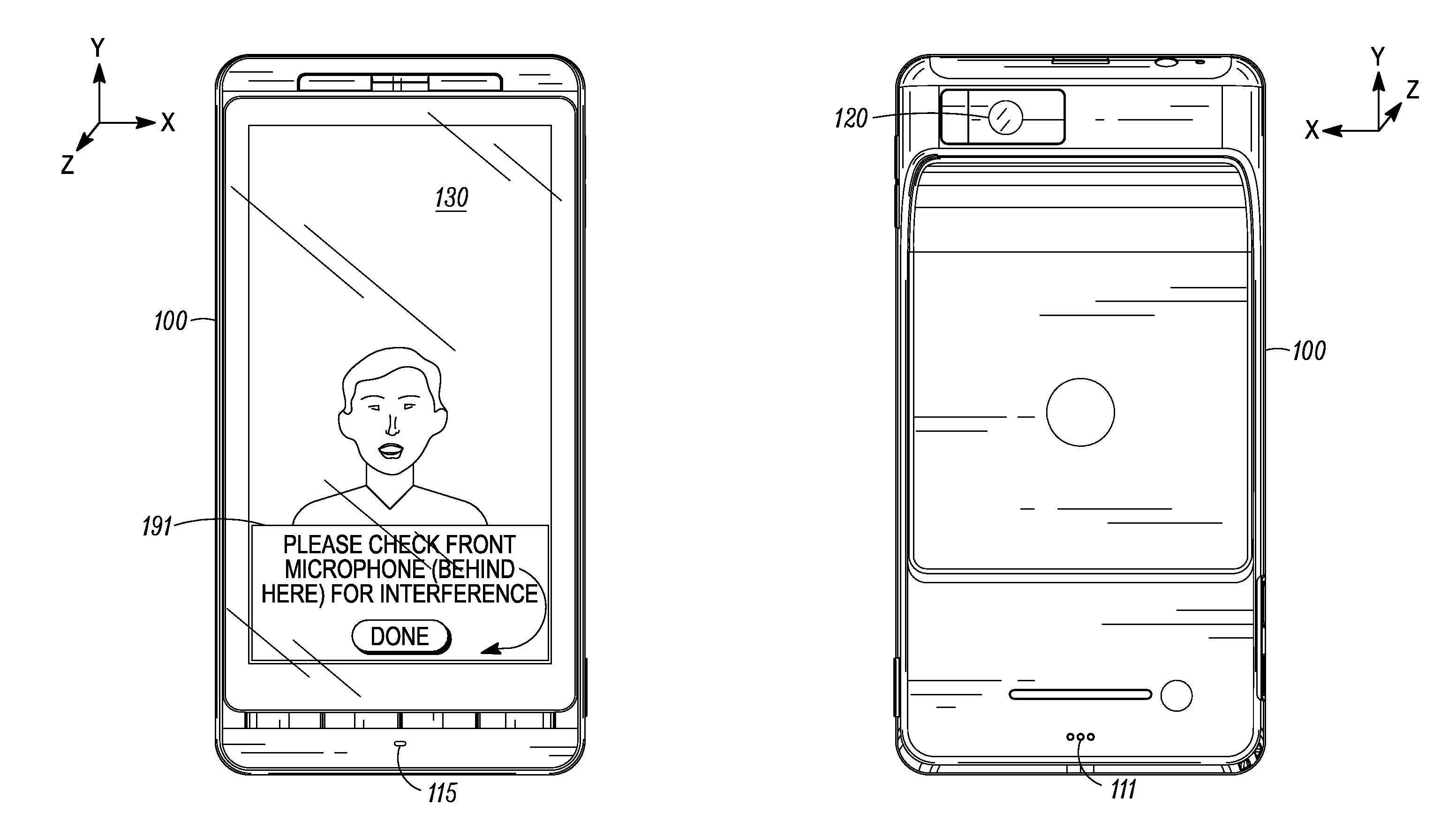
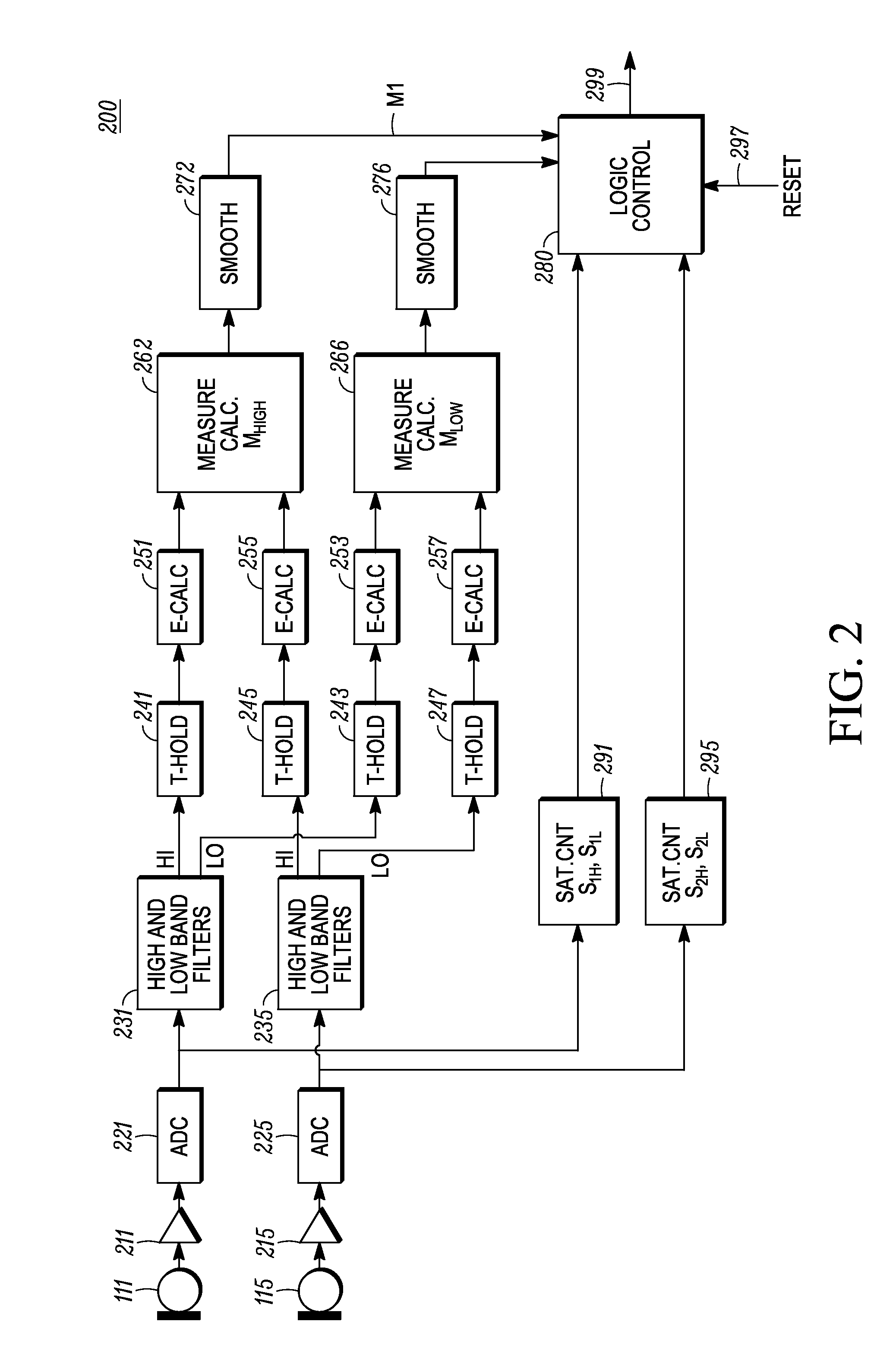
Microphone Interference Detection Method and Apparatus
A method and apparatus for detecting microphone interference includes first and second built-in microphones producing first and second microphone signals. A first filter bank creates first high-frequency-band and first low-frequency-band signals from the first microphone signal. A second filter bank creates second high-frequency-band and second low-frequency-band signals from the second microphone signal. A first measurement calculator determines a high-frequency-band energy value from the first high-frequency-band signal and the second high-frequency-band signal when the first and second high-frequency-band signals' magnitudes exceeds predetermined thresholds. A second measurement calculator calculates a low-frequency-band energy value from the first low-frequency-band signal and the second low-frequency-band signal when the first and second low-frequency-band signals' magnitudes exceed predetermined thresholds. A logic control block, coupled to the first measurement calculator and the second measurement calculator, detects microphone interference and produces an output signal indicating microphone occlusion or wind noise.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
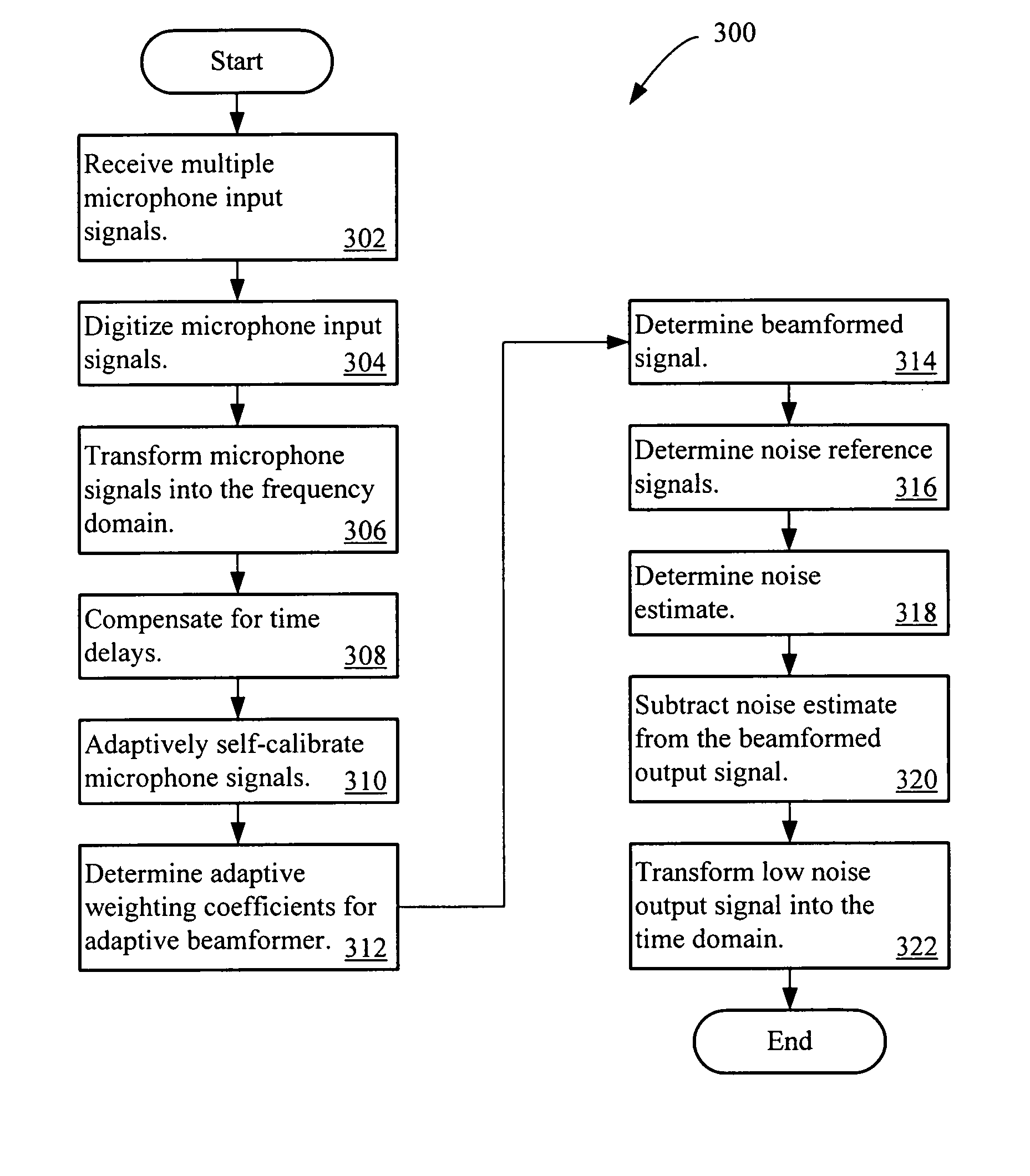
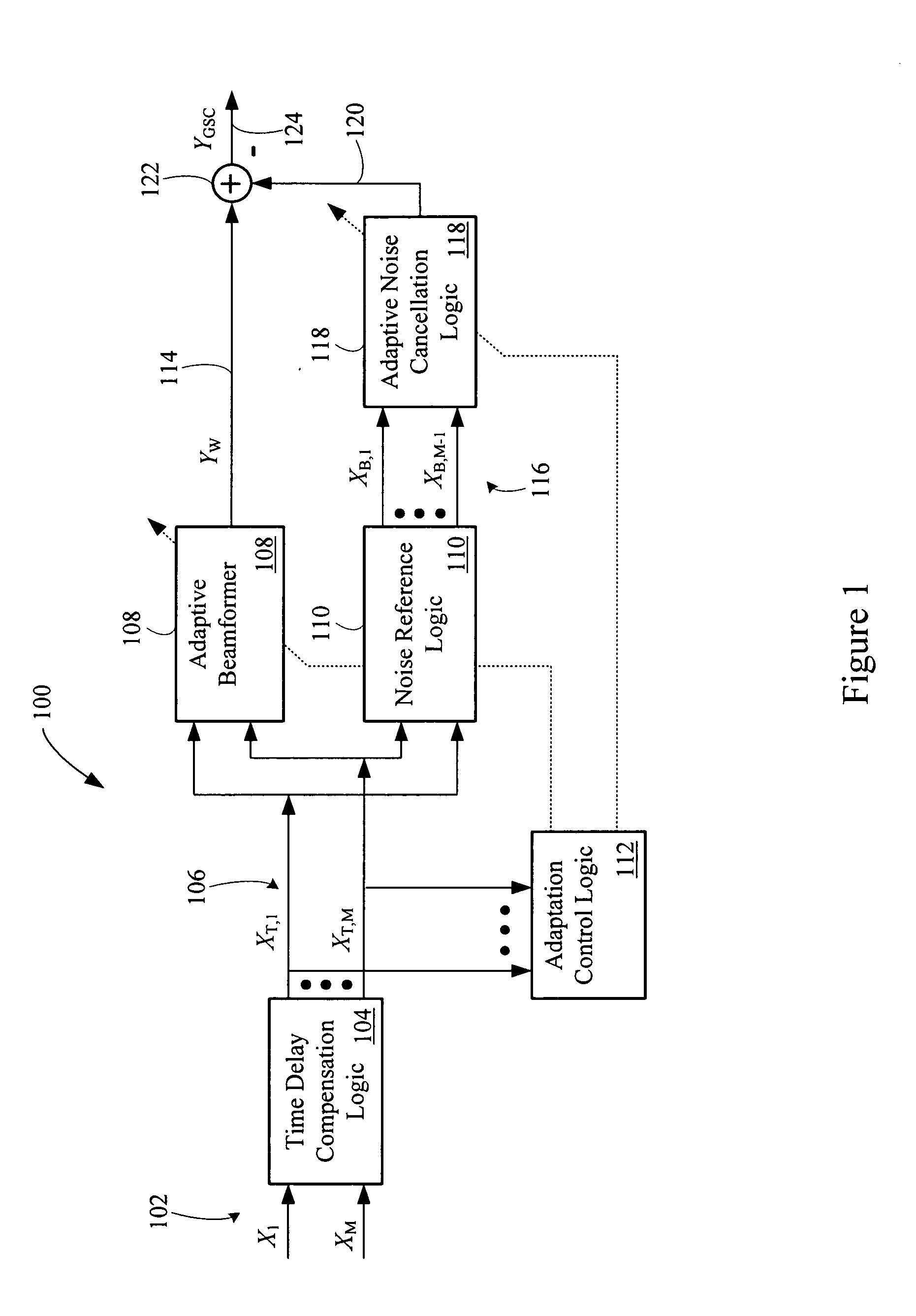
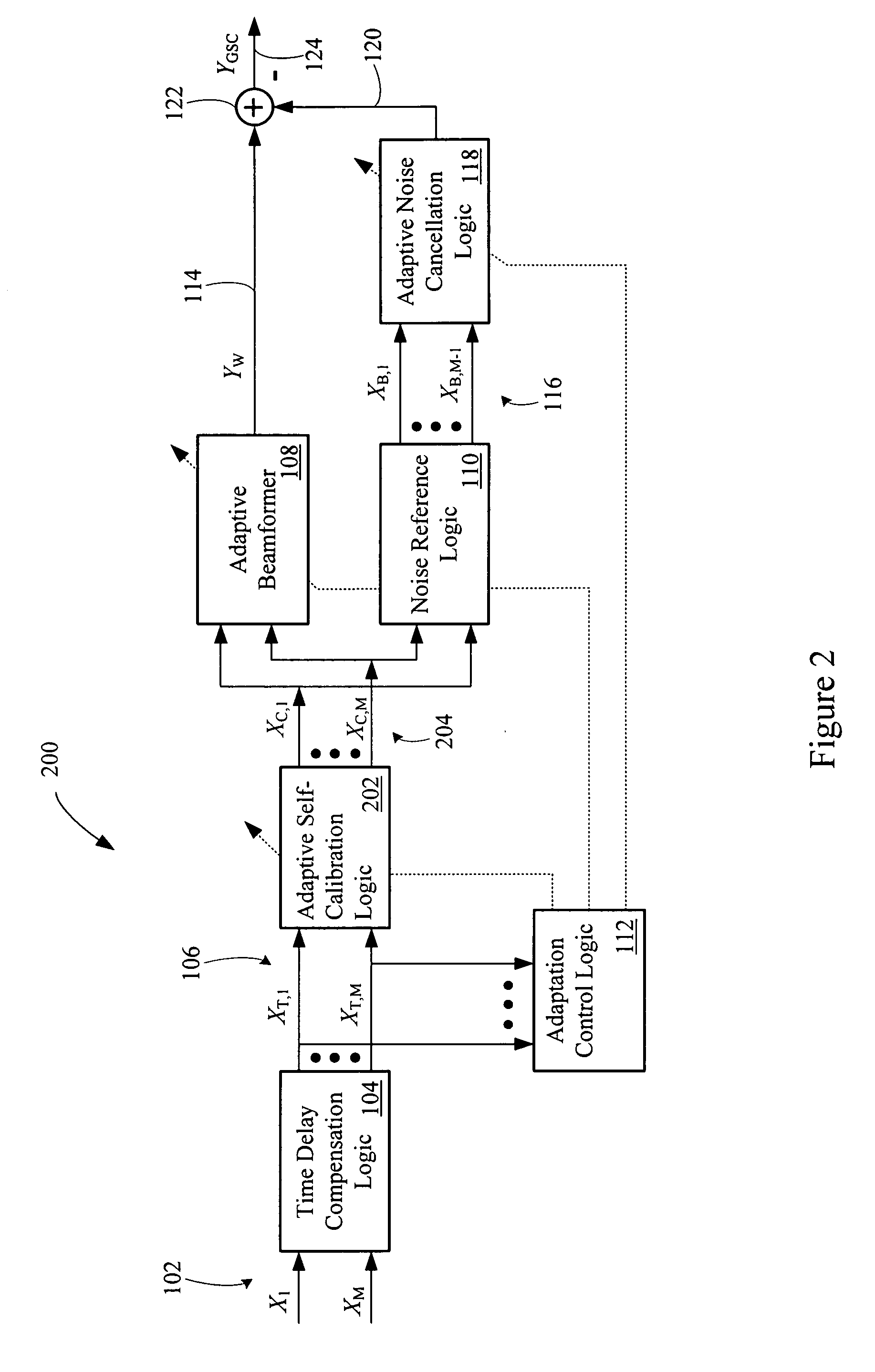
Multi-channel adaptive speech signal processing system with noise reduction
ActiveUS20060222184A1Improved speech signal clarityImprove intelligibilitySignal processingEar treatmentLow noiseHigh energy
An adaptive signal processing system eliminates noise from input signals while retaining desired signal content, such as speech. The resulting low noise output signal delivers improved clarity and intelligibility. The low noise output signal also improves the performance of subsequent signal processing systems, including speech recognition systems. An adaptive beamformer in the signal processing system consistently updates beamforming signal weights in response to changing microphone signal conditions. The adaptive weights emphasize the contribution of high energy microphone signals to the beamformed output signal. In addition, adaptive noise cancellation logic removes residual noise from the beamformed output signal based on a noise estimate derived from the microphone input signals.
Owner:HARMAN BECKER AUTOMOTIVE SYST WAVEMAKERS
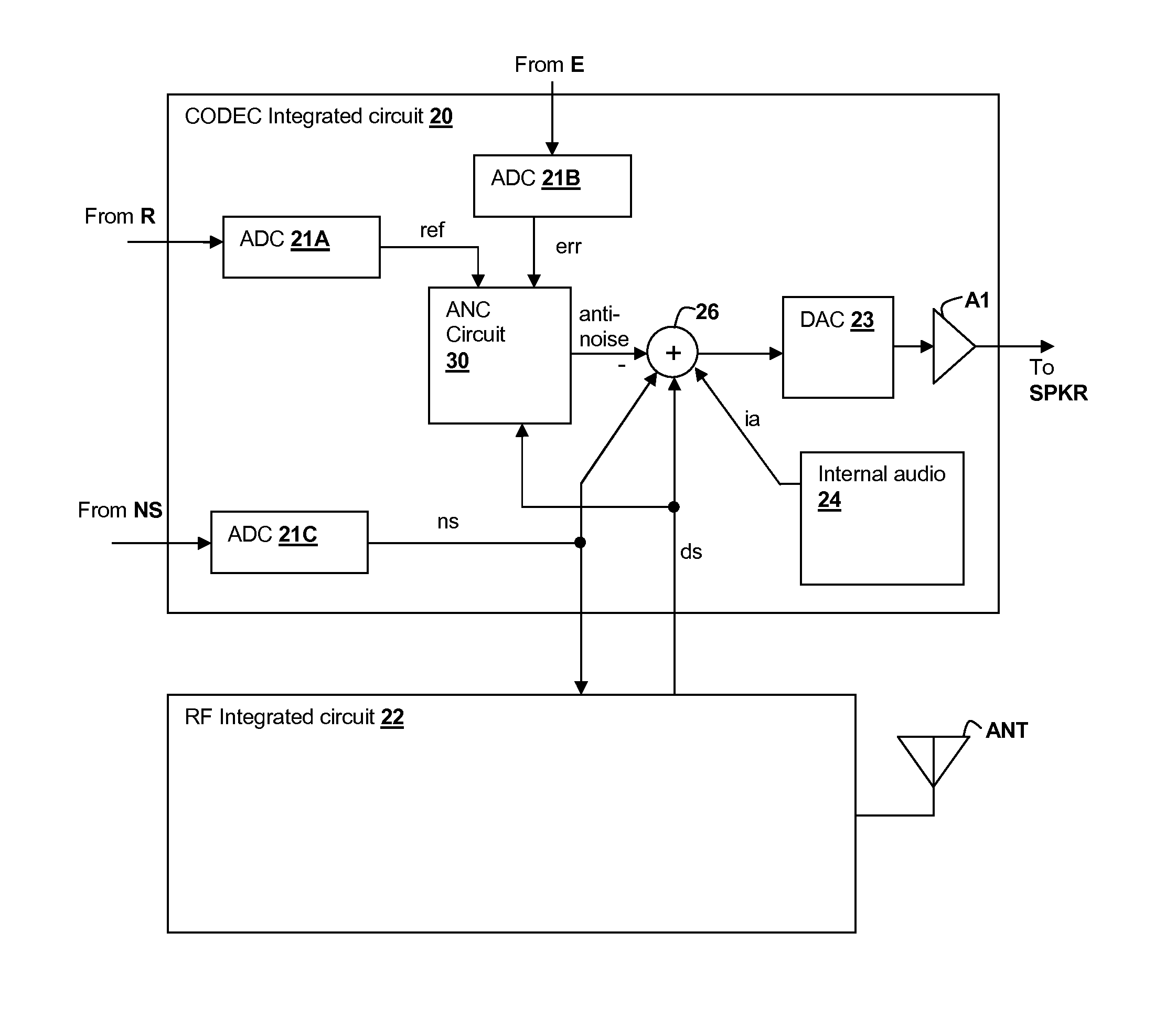
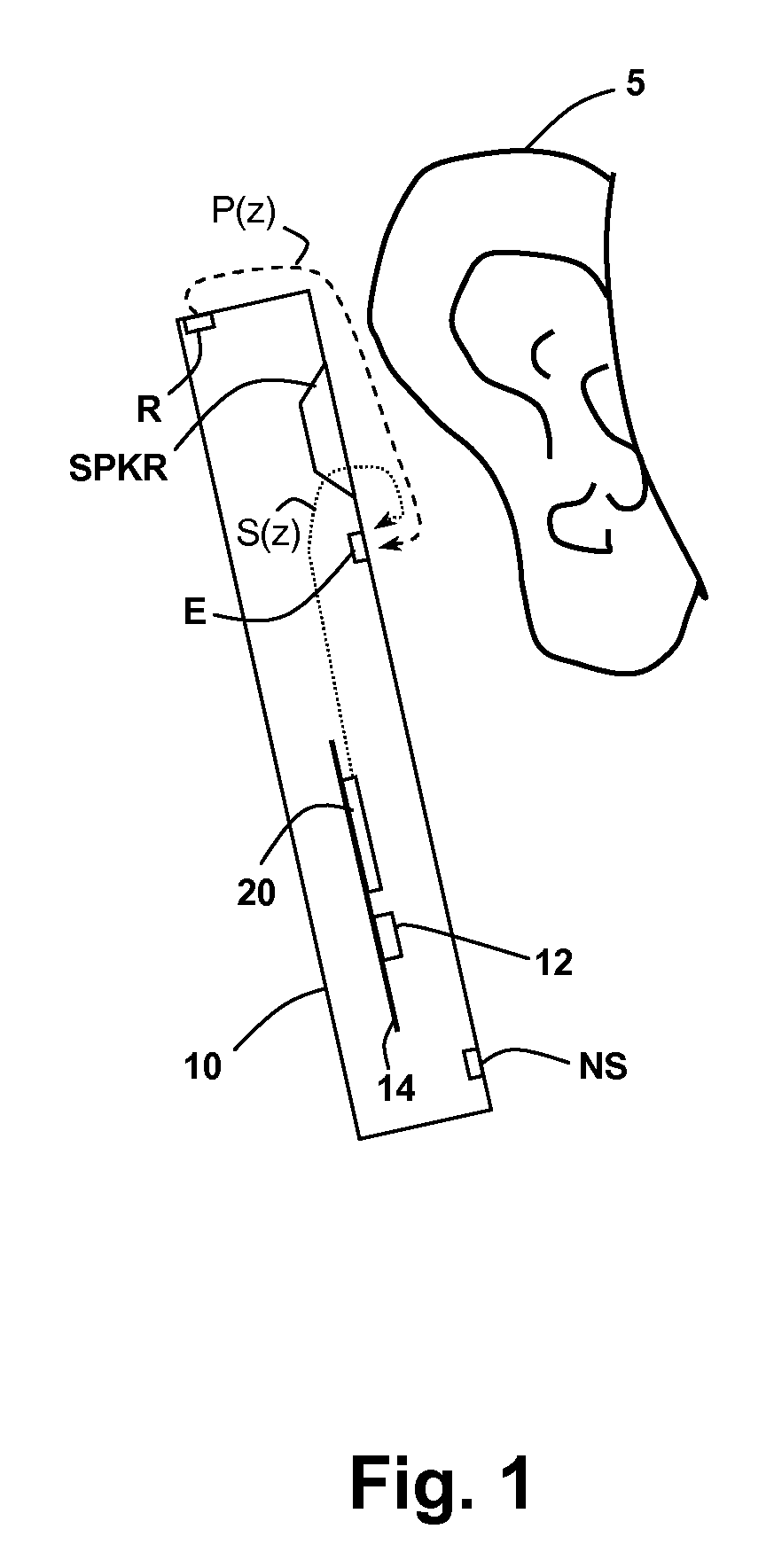
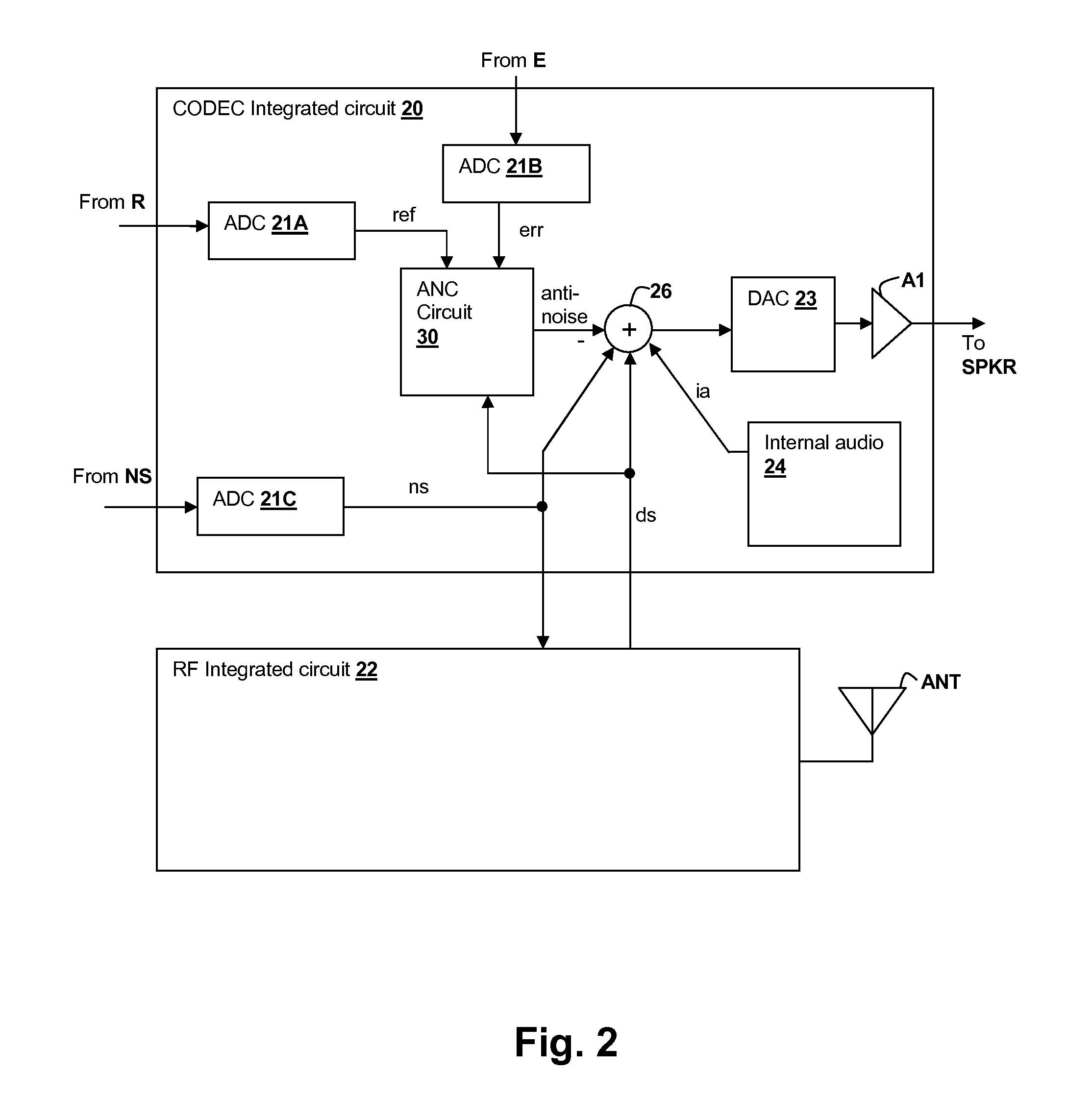
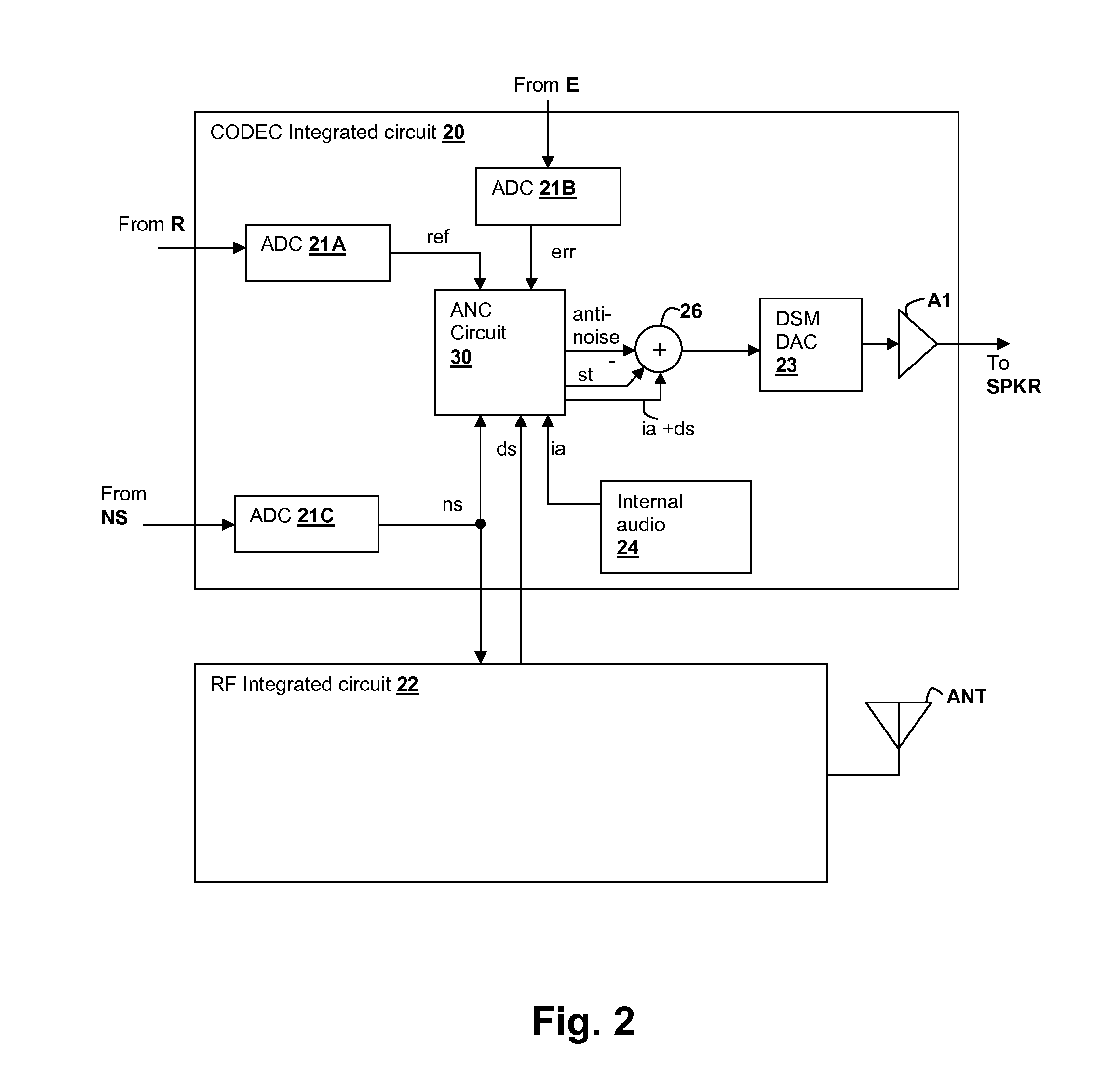
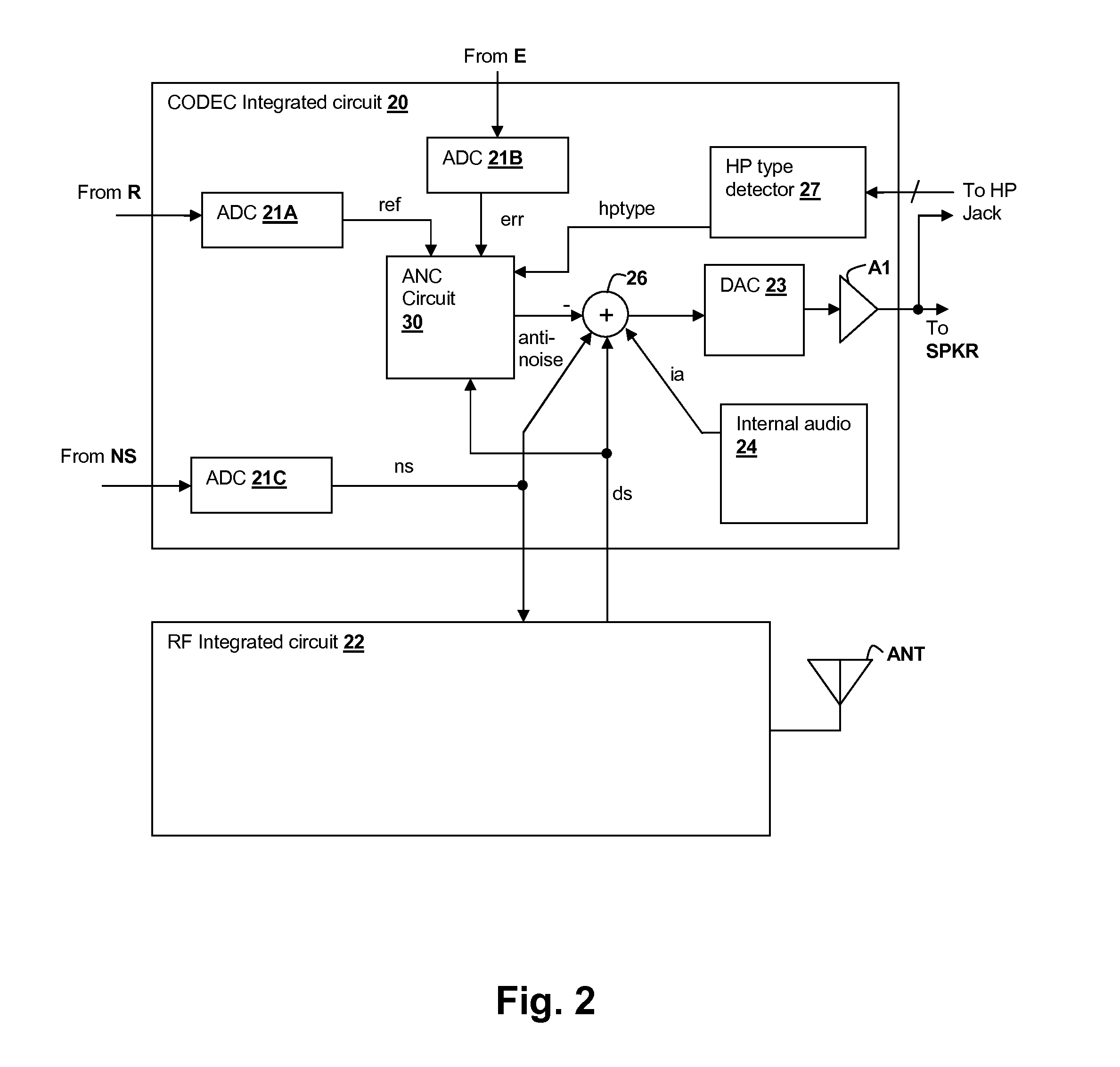
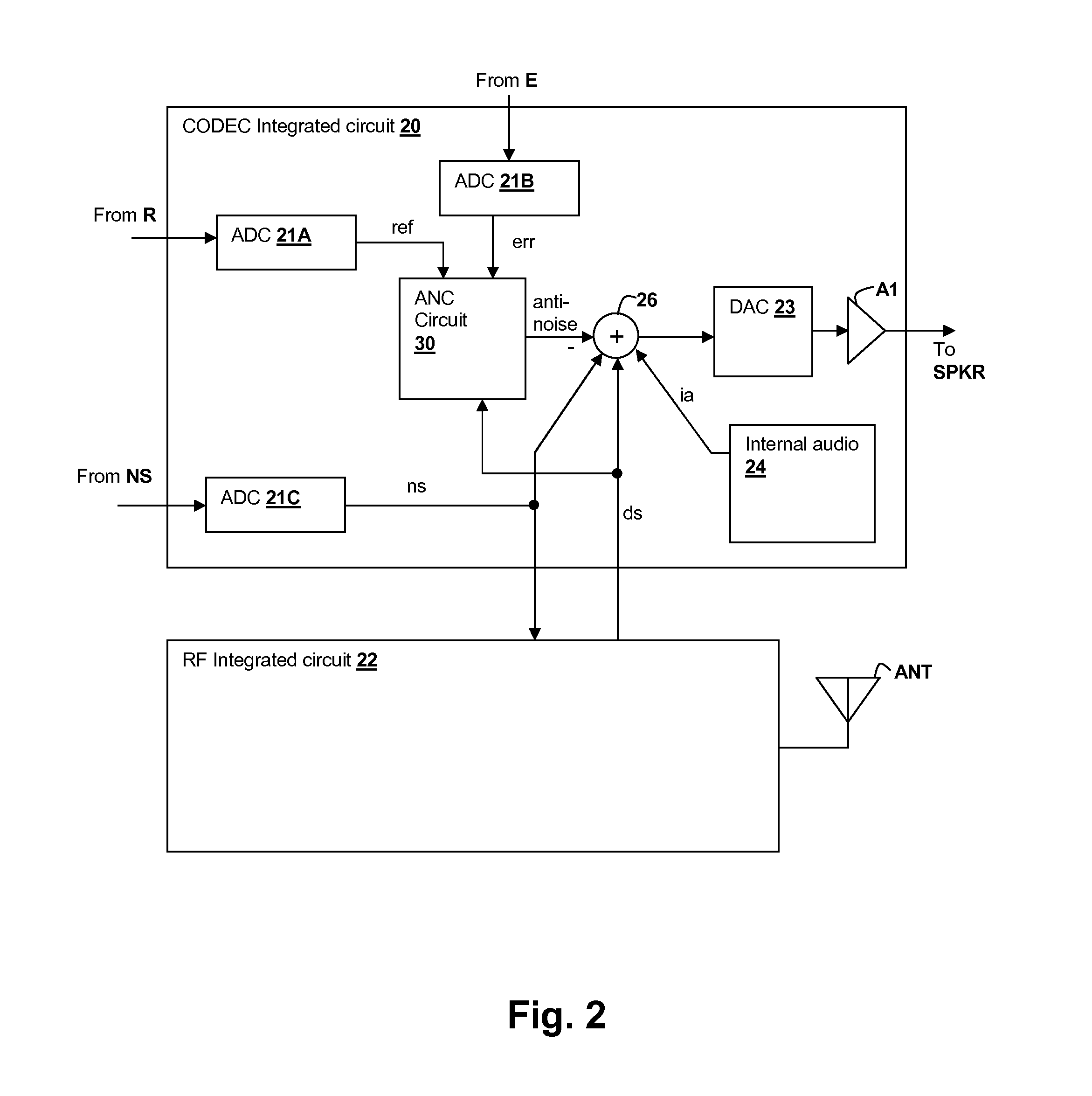
Oversight control of an adaptive noise canceler in a personal audio device
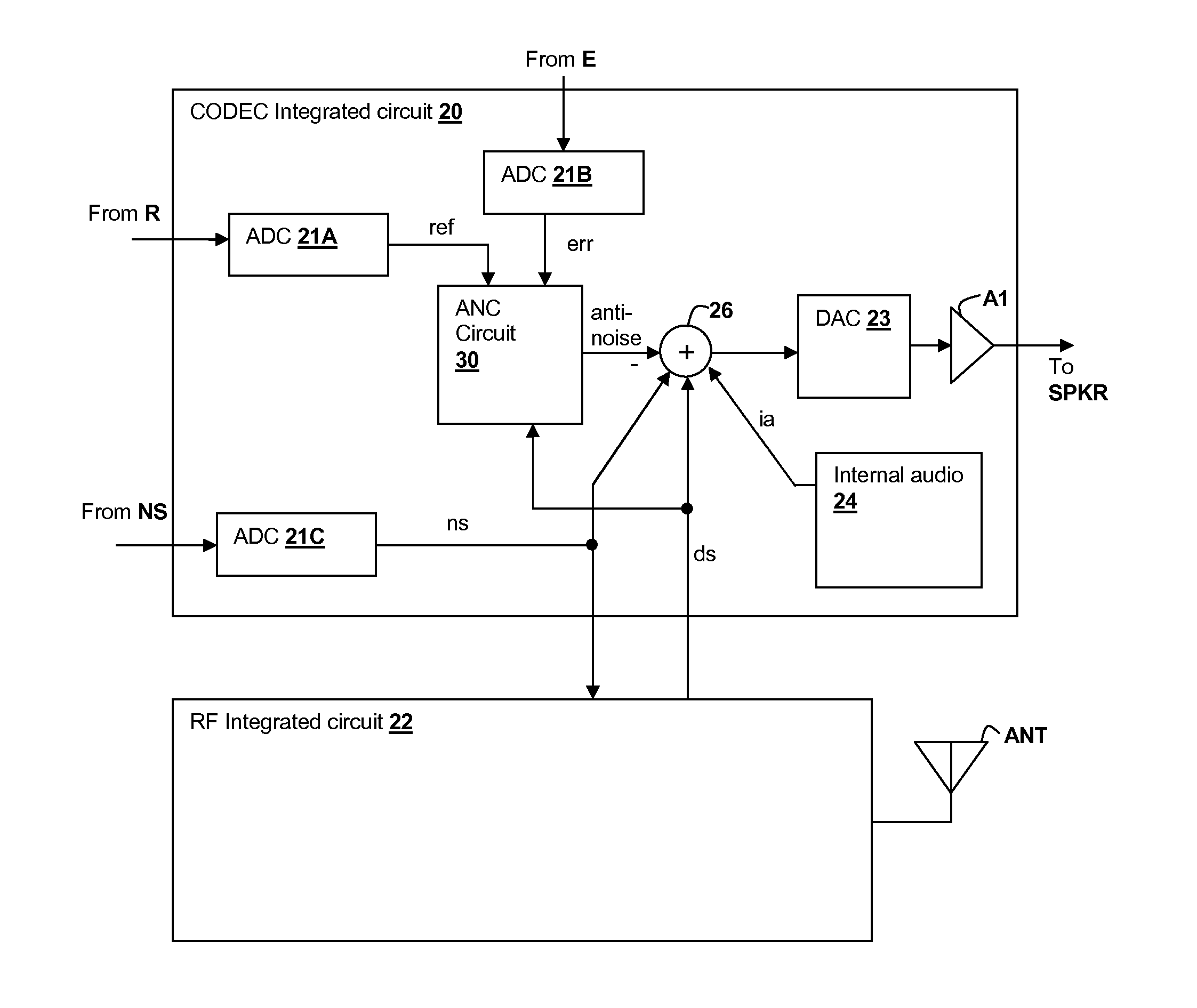
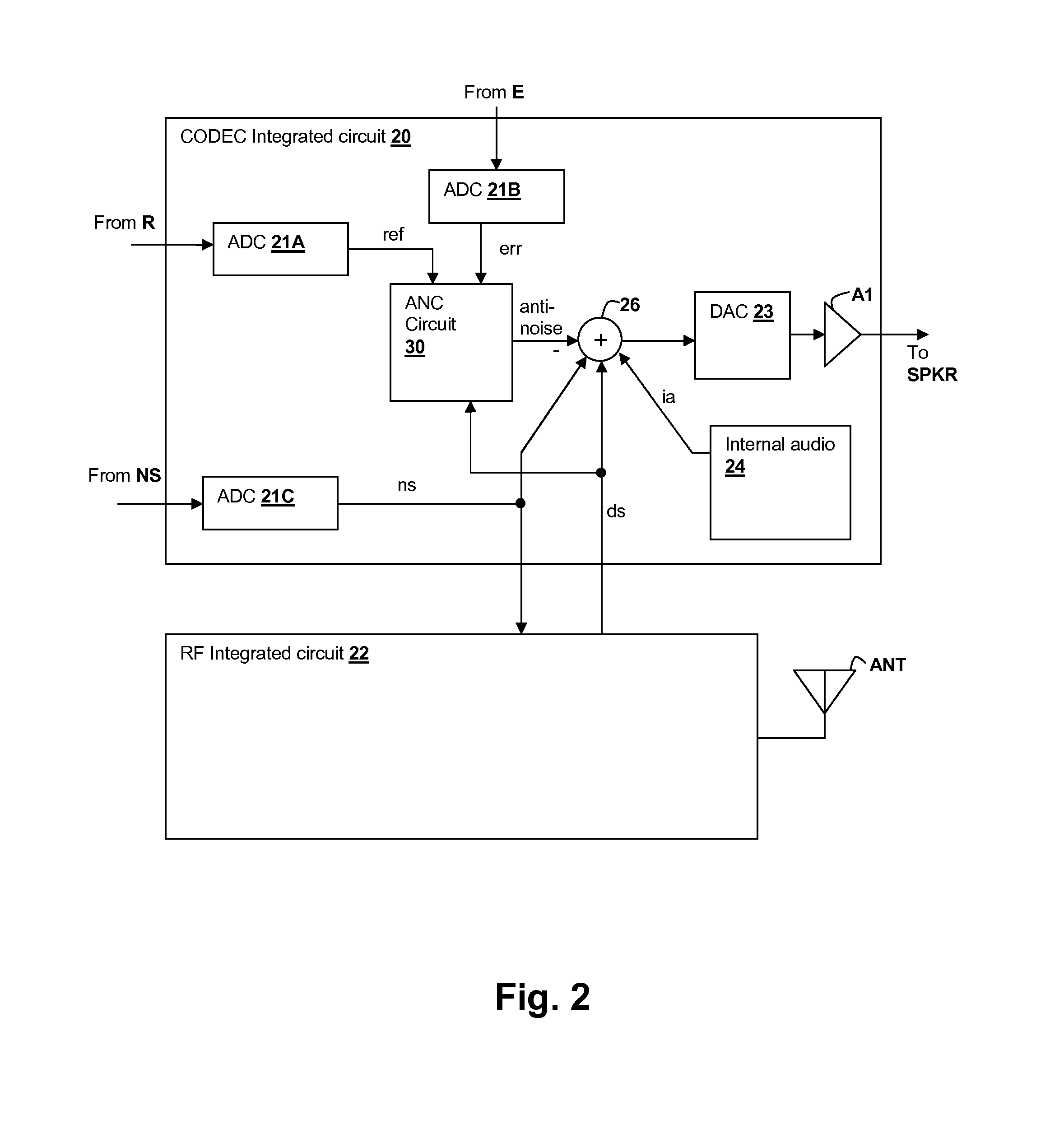
ActiveUS20120140943A1Reduce impactAvoid signalingEar treatmentHearing device active noise cancellationTransducerMicrophone signal
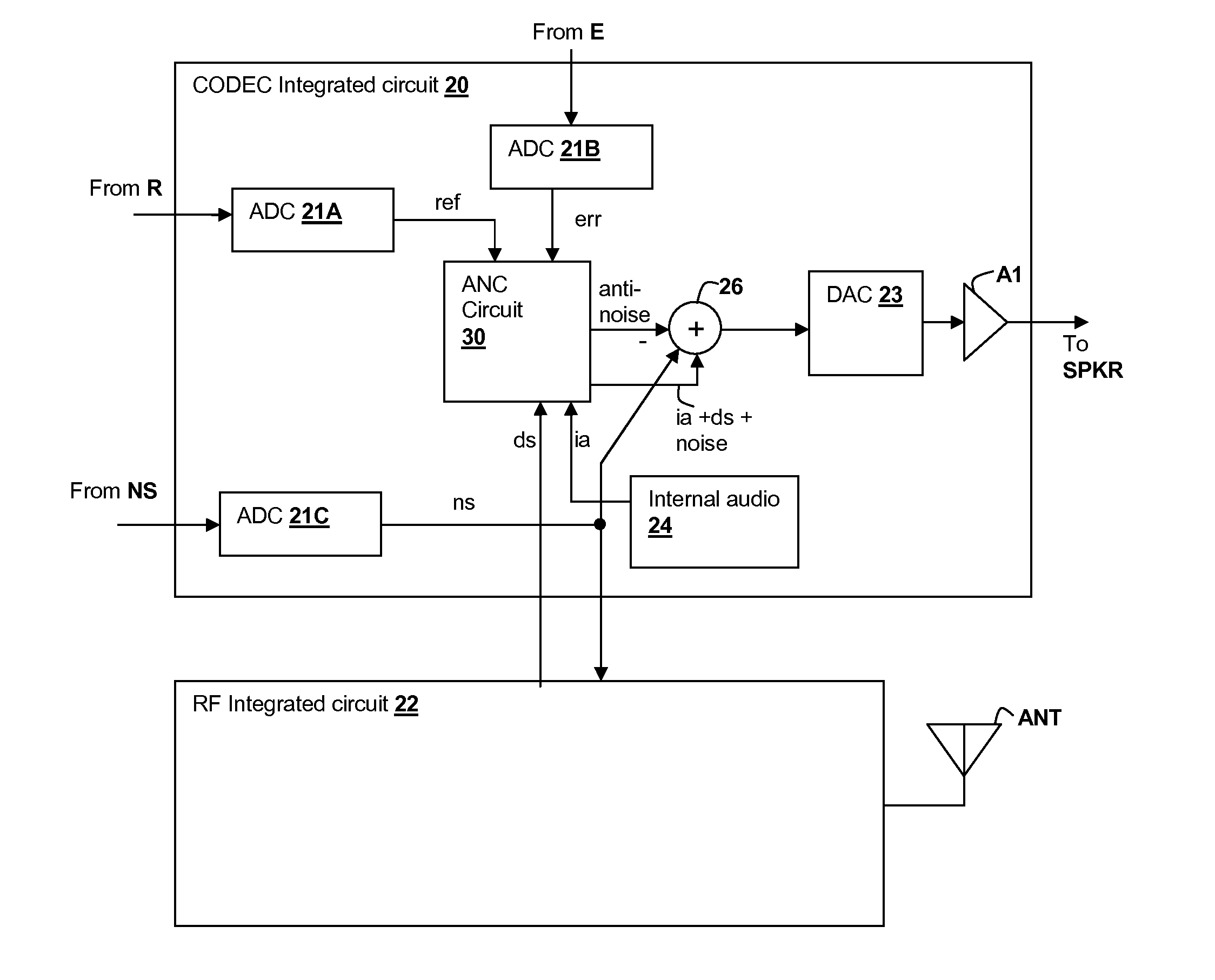
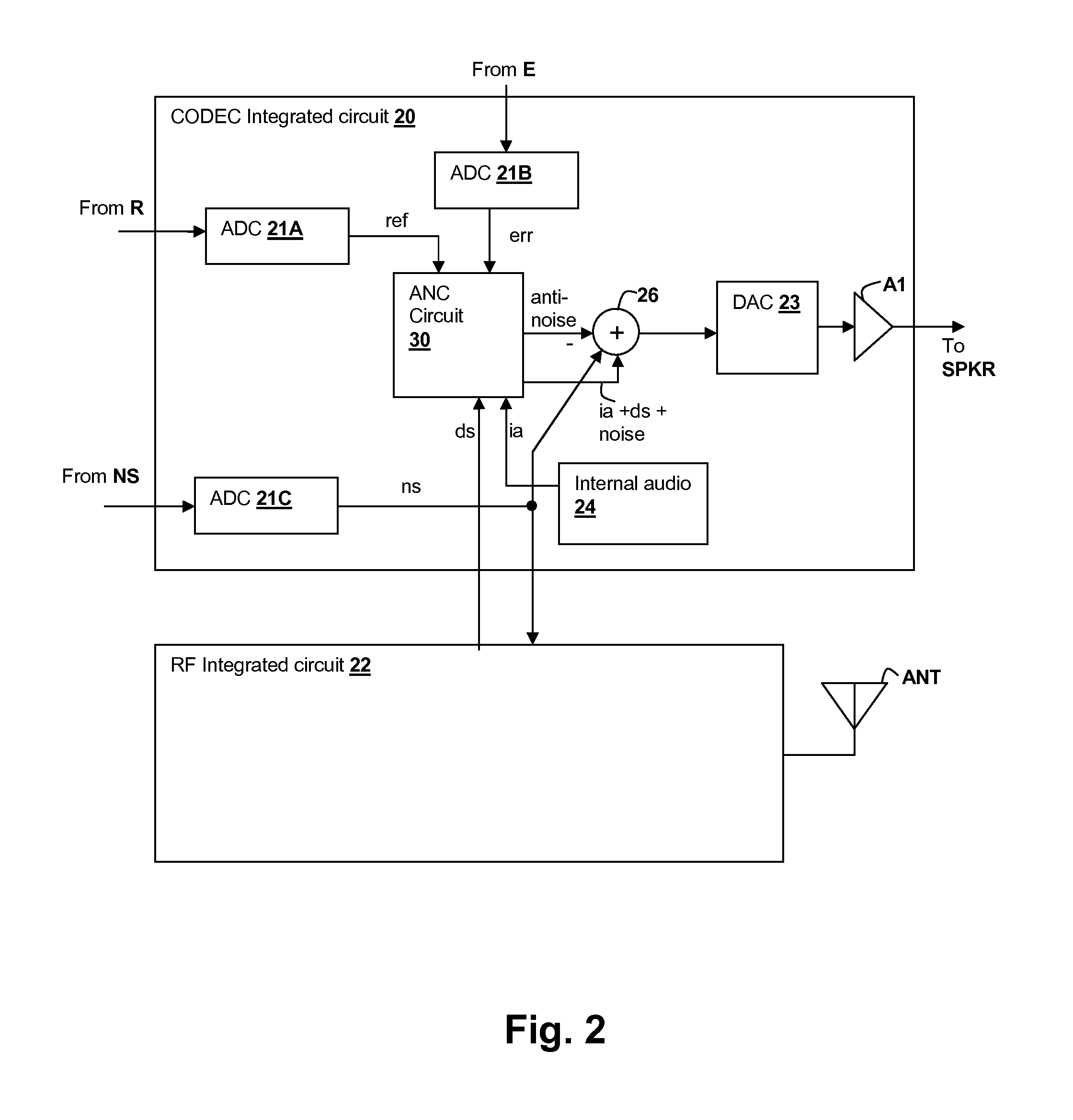
A personal audio device, such as a wireless telephone, includes an adaptive noise canceling (ANC) circuit that adaptively generates an anti-noise signal from a reference microphone signal and injects the anti-noise signal into the speaker or other transducer output to cause cancellation of ambient audio sounds. An error microphone is also provided proximate the speaker to measure the ambient sounds and transducer output near the transducer, thus providing an indication of the effectiveness of the noise canceling. A processing circuit uses the reference and / or error microphone, optionally along with a microphone provided for capturing near-end speech, to determine whether the ANC circuit is incorrectly adapting or may incorrectly adapt to the instant acoustic environment and / or whether the anti-noise signal may be incorrect and / or disruptive and then take action in the processing circuit to prevent or remedy such conditions.
Owner:CIRRUS LOGIC INC
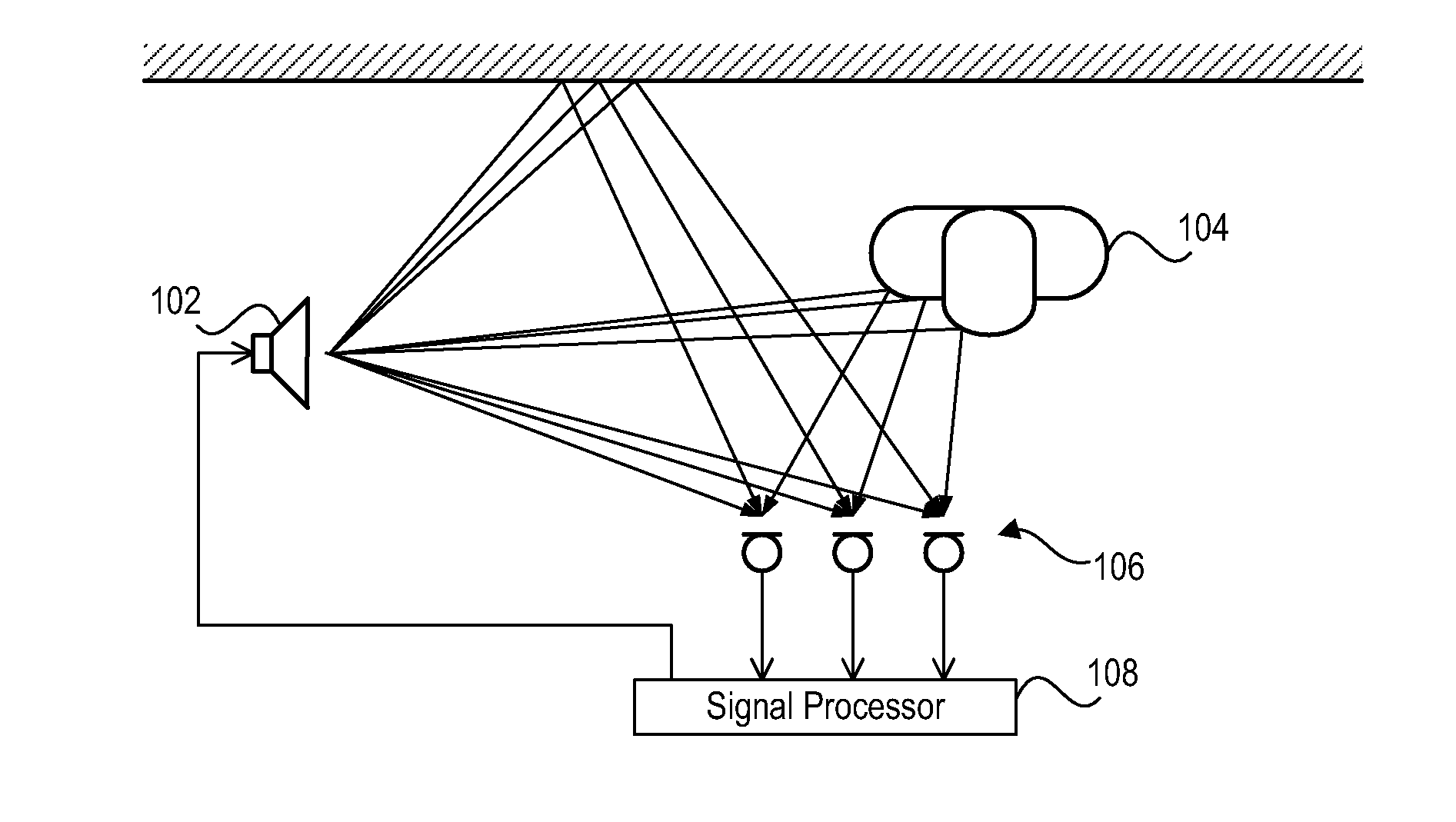
Acoustic localization of a speaker
A system locates a speaker in a room containing a loudspeaker and a microphone array. The loudspeaker transmits a sound that is partly reflected by a speaker. The microphone array detects the reflected sound and converts the sound into a microphone signal. A processor determines the speaker's direction relative to the microphone array, the speaker's distance from the microphone array, or both, based on the characteristics of the microphone signals.
Owner:NUANCE COMM INC
Beamforming method based on arrays of microphones and corresponding apparatus
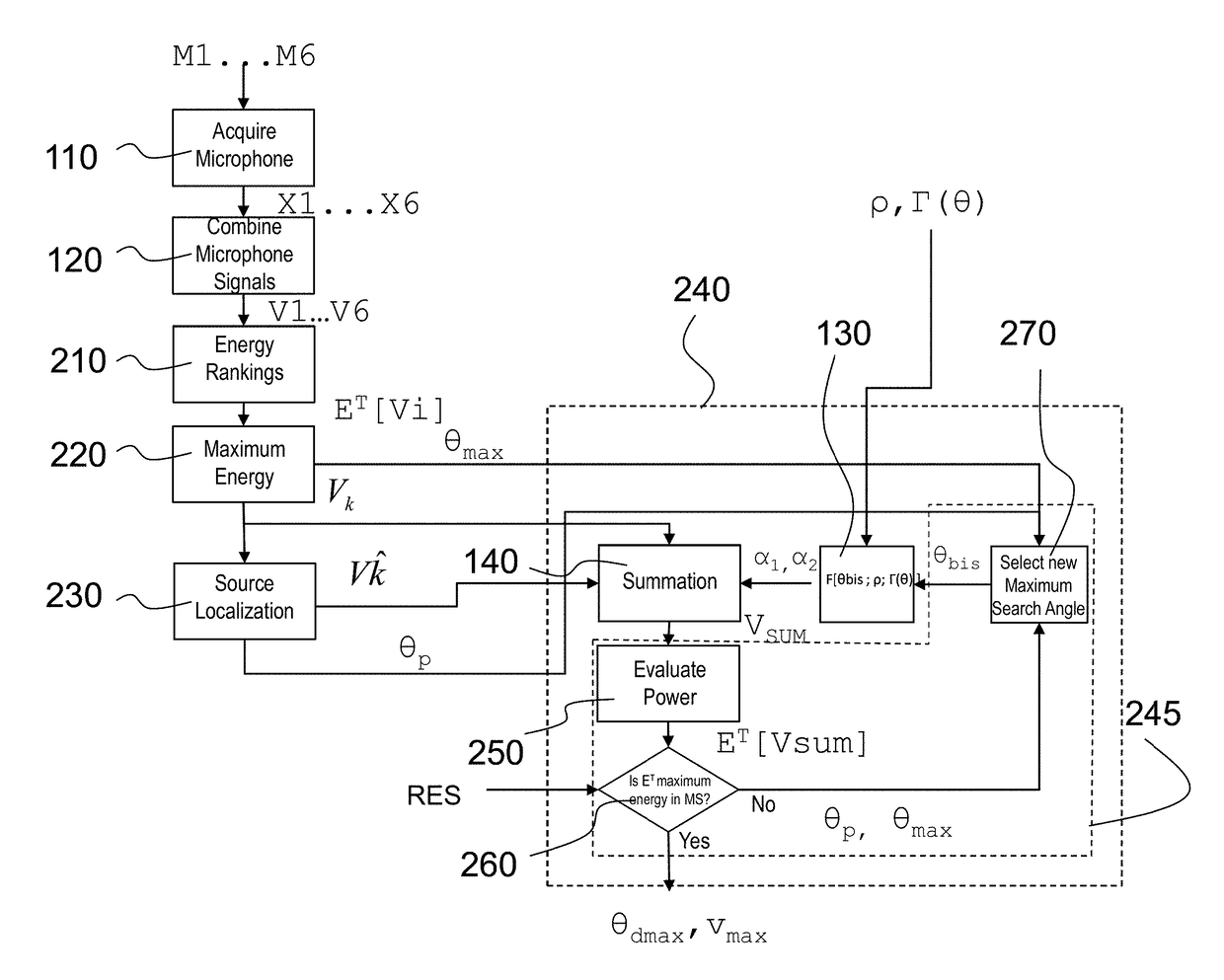
A beamforming method employs a plurality of microphones arranged in an array with respect to a reference point. The method includes acquiring microphone signals from the microphones and combining the microphone signals (x1 . . . xM) to obtain Virtual Microphones, combining the microphone signals to obtain a pair of directional Virtual Microphones having respective signals determining respective patterns of radiation with a same origin corresponding to the reference point and rotated at different pattern direction angles, defining a separation angle between them, obtaining a sum radiation signal of a sum Virtual Microphone with a sum radiation pattern, associating a respective weight to the signals of the pair of directional Virtual Microphones, obtaining respective weighted signals of radiation and summing the weighted signals, computing respective weights as a function of a determined pattern direction angle of the pattern of radiation of the pair of directional Virtual Microphones and of the separation angle.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
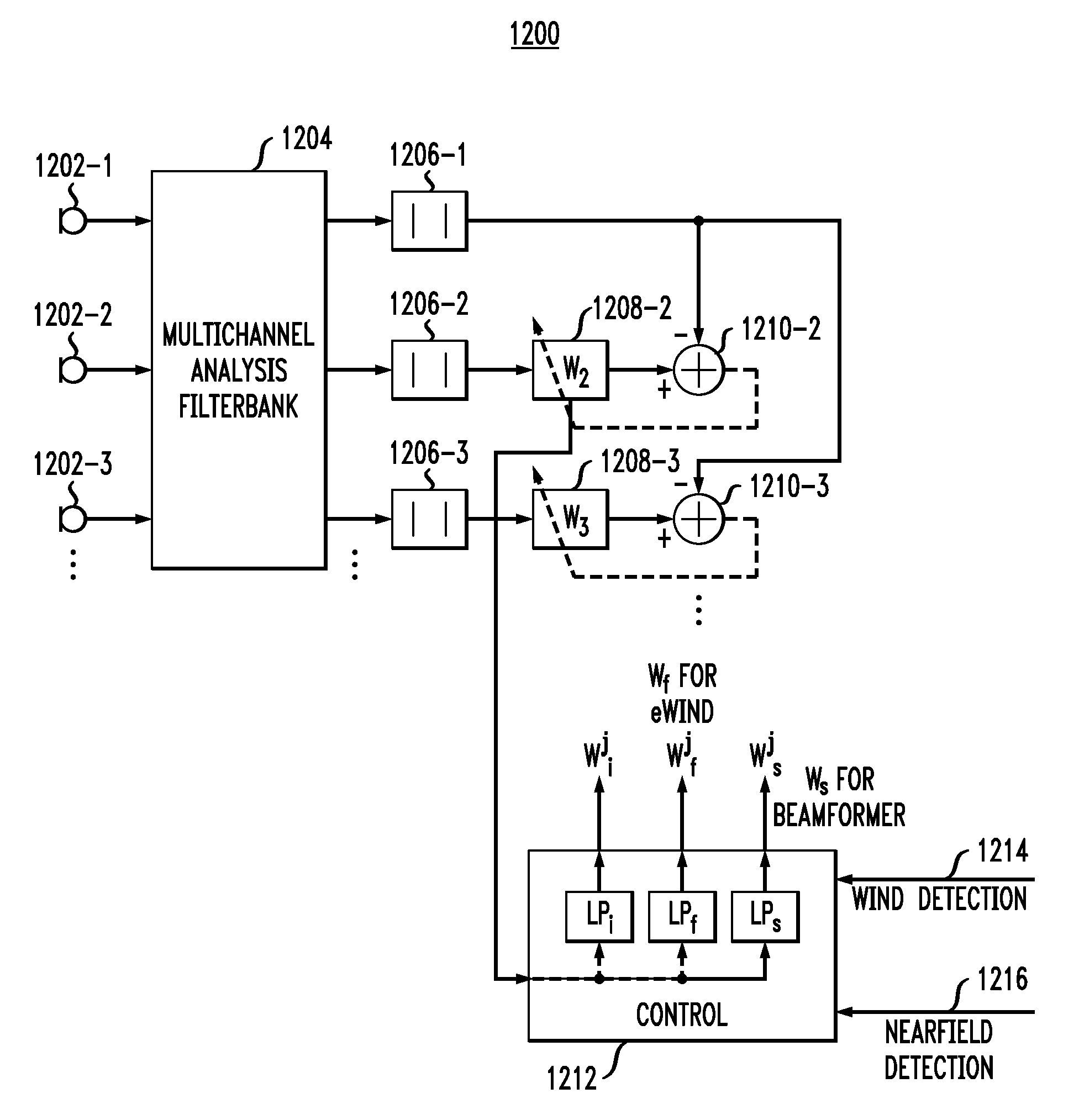
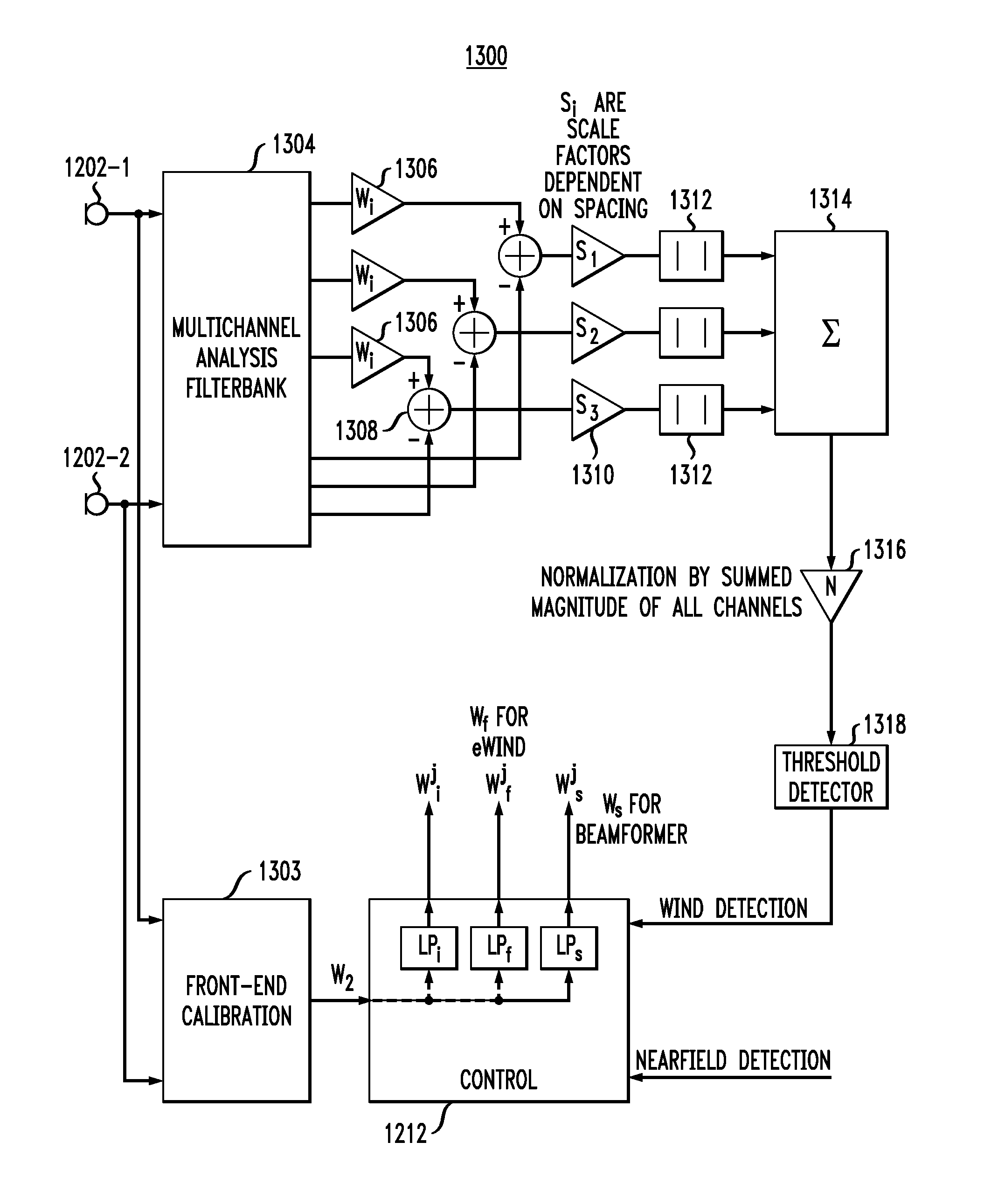
Detection and suppression of wind noise in microphone signals
To reliably and consistently detect desirable sounds, a system detects the presence of wind noise based on the power levels of audio signals. A first transducer detects sound originating from a first direction and a second transducer detects sound originating from a second direction. The power levels of the sound are compared. When the power level of the sound received from the second transducer is less than the power level of the sound received from the first transducer by a predetermined value, wind noise may be present. A signal processor may generate an output from one or a combination of the audio signals, based on a wind noise detection.
Owner:HARMAN BECKER AUTOMOTIVE SYST WAVEMAKERS +1
Apparatus and method of noise and echo reduction in multiple microphone audio systems
ActiveUS20090089054A1Two-way loud-speaking telephone systemsAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceEngineeringMicrophone signal
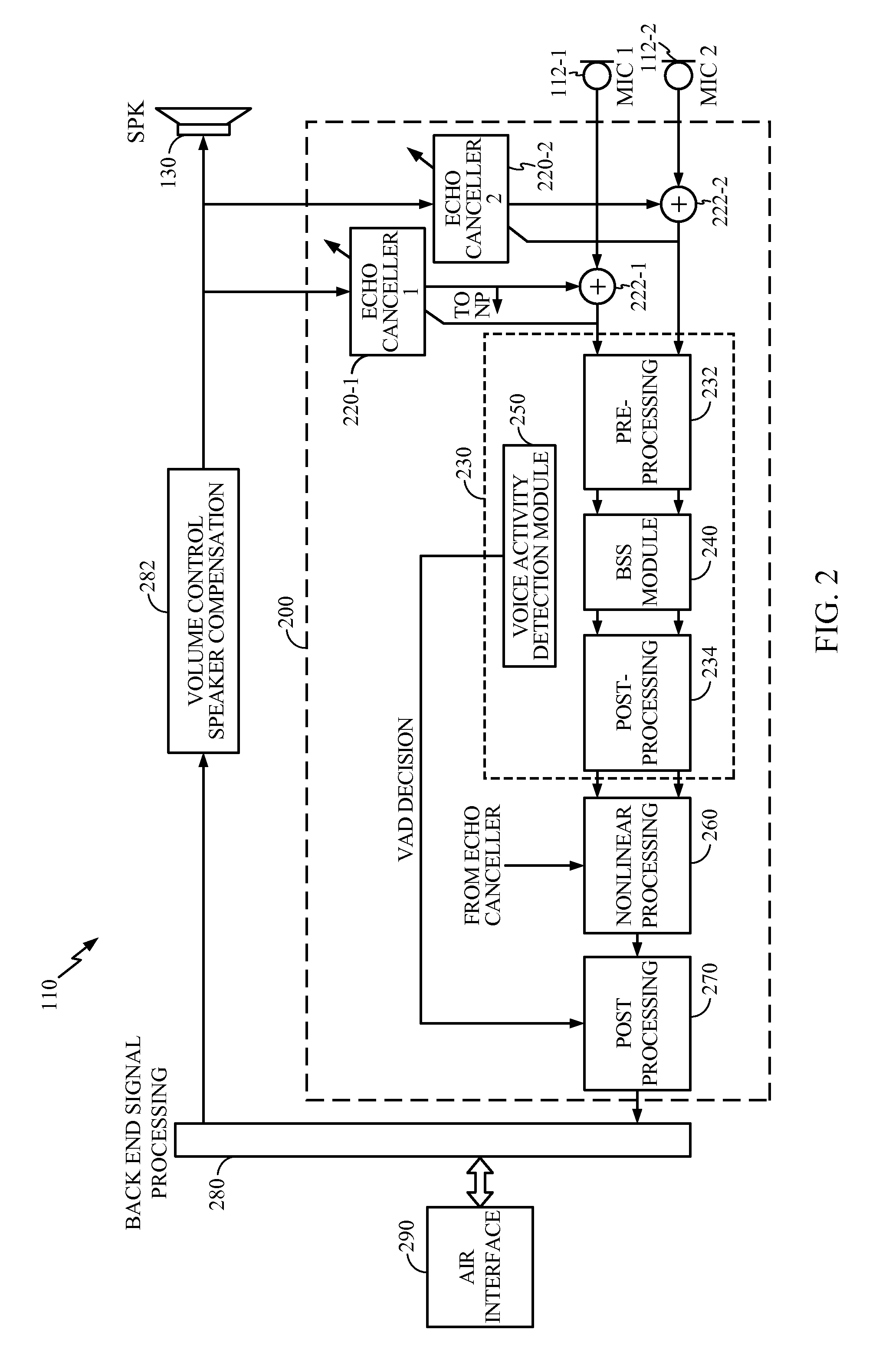
Multiple microphone noise suppression apparatus and methods are described herein. The apparatus and methods implement a variety of noise suppression techniques and apparatus that can be selectively applied to signals received using multiple microphones. The microphone signals received at each of the multiple microphones can be independently processed to cancel echo signal components that can be generated from a local audio source. The echo cancelled signals may be processed by some or all modules within a signal separator that operates to separate or otherwise isolate a speech signal from noise signals. The signal separator can include a pre-processing de-correlator followed by a blind source separator. The output of the blind source separator can be post filtered to provide post separation de-correlation. The separated speech and noise signals can be non-linearly processed for further noise reduction, and additional post processing can be implemented following the non-linear processing.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Method for dynamic suppression of surrounding acoustic noise when listening to electrical inputs
ActiveUS20110137649A1Improved listening comfortAccurate monitoringHearing device active noise cancellationHearing aids signal processingElectricityEngineering
A listening instrument includes a) a microphone unit for picking up an input sound from the current acoustic environment of the user and converting it to an electric microphone signal; b) a microphone gain unit for applying a specific microphone gain to the microphone signal and providing a modified microphone signal; c) a direct electric input signal representing an audio signal; d) a direct gain unit for applying a specific direct gain to the direct electric input signal and providing a modified direct electric input signal; e) a detector unit for classifying the current acoustic environment and providing one or more classification parameters; f) a control unit for controlling the specific microphone gain applied to the electric microphone signal and / or the specific direct gain applied to the direct electric input signal based on the one or more classification parameters.
Owner:OTICON
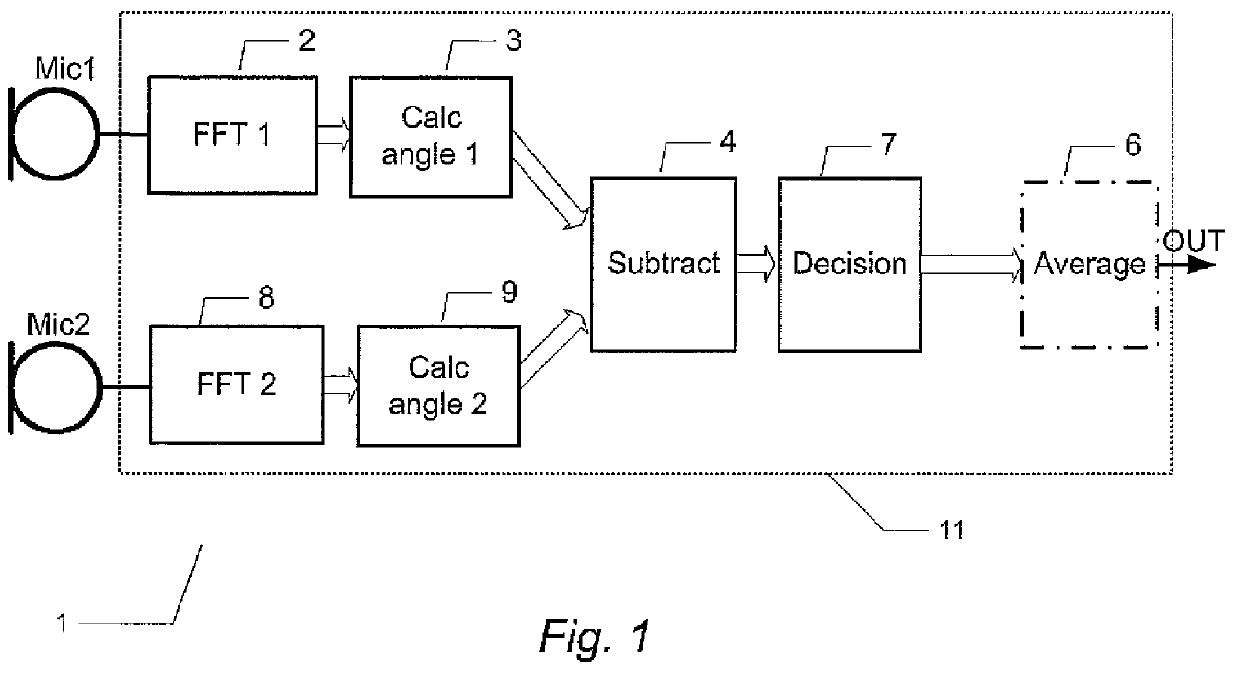
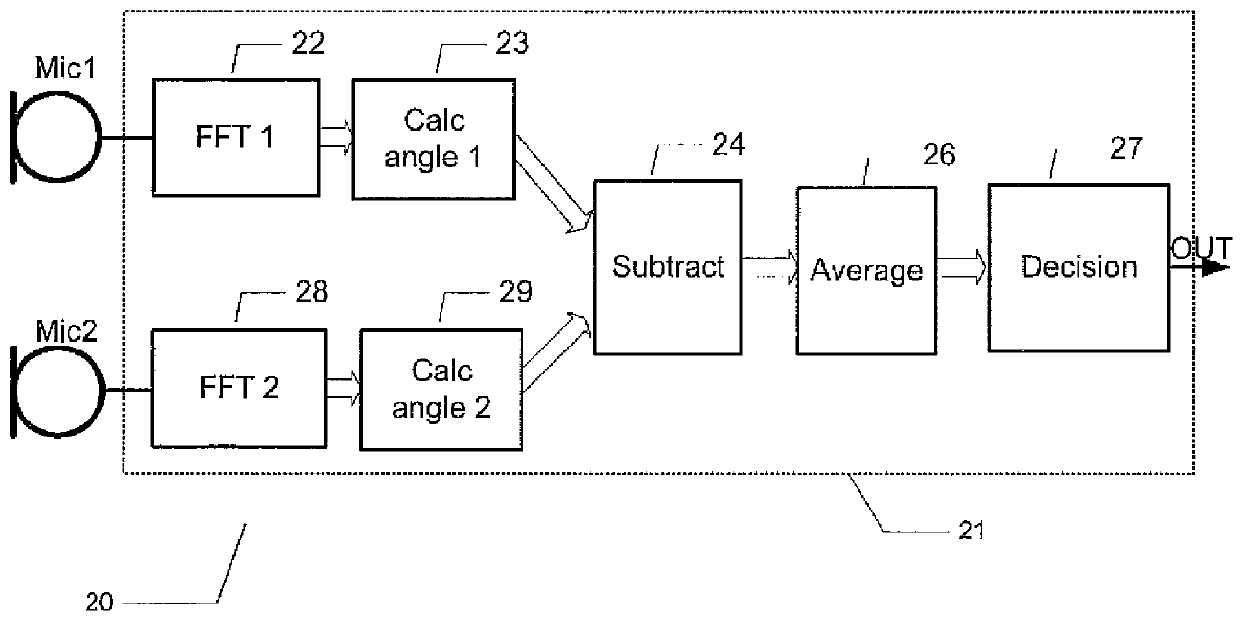
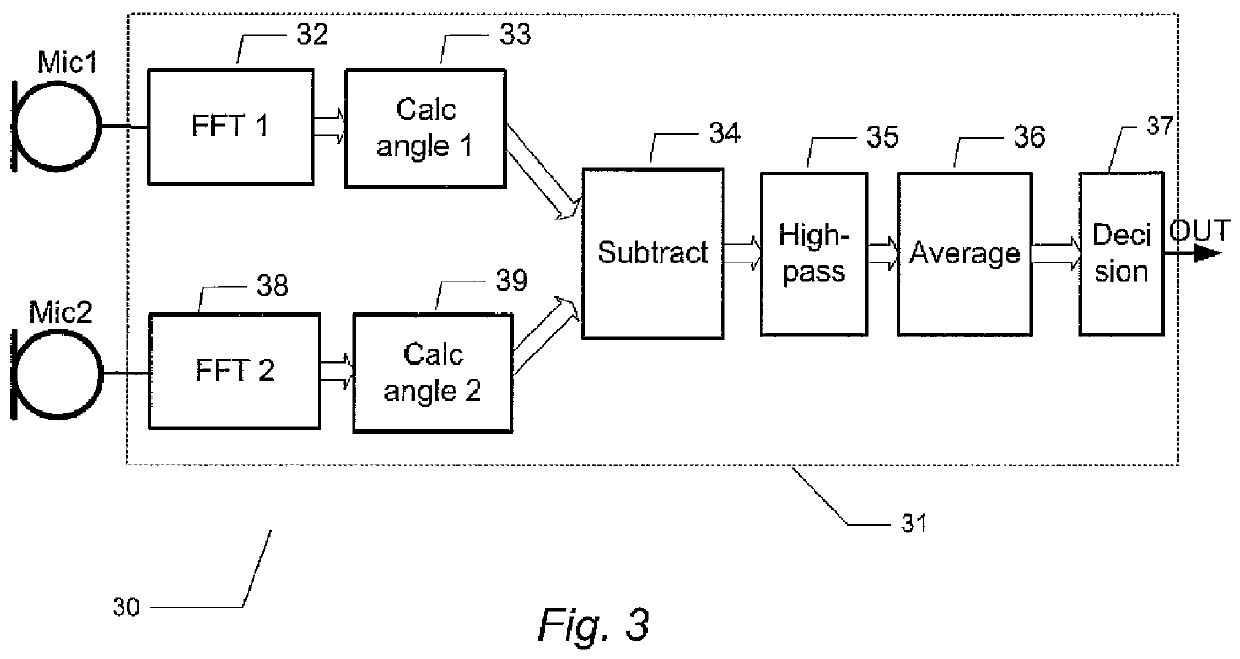
Microphone array structure able to reduce noise and improve speech quality and method thereof
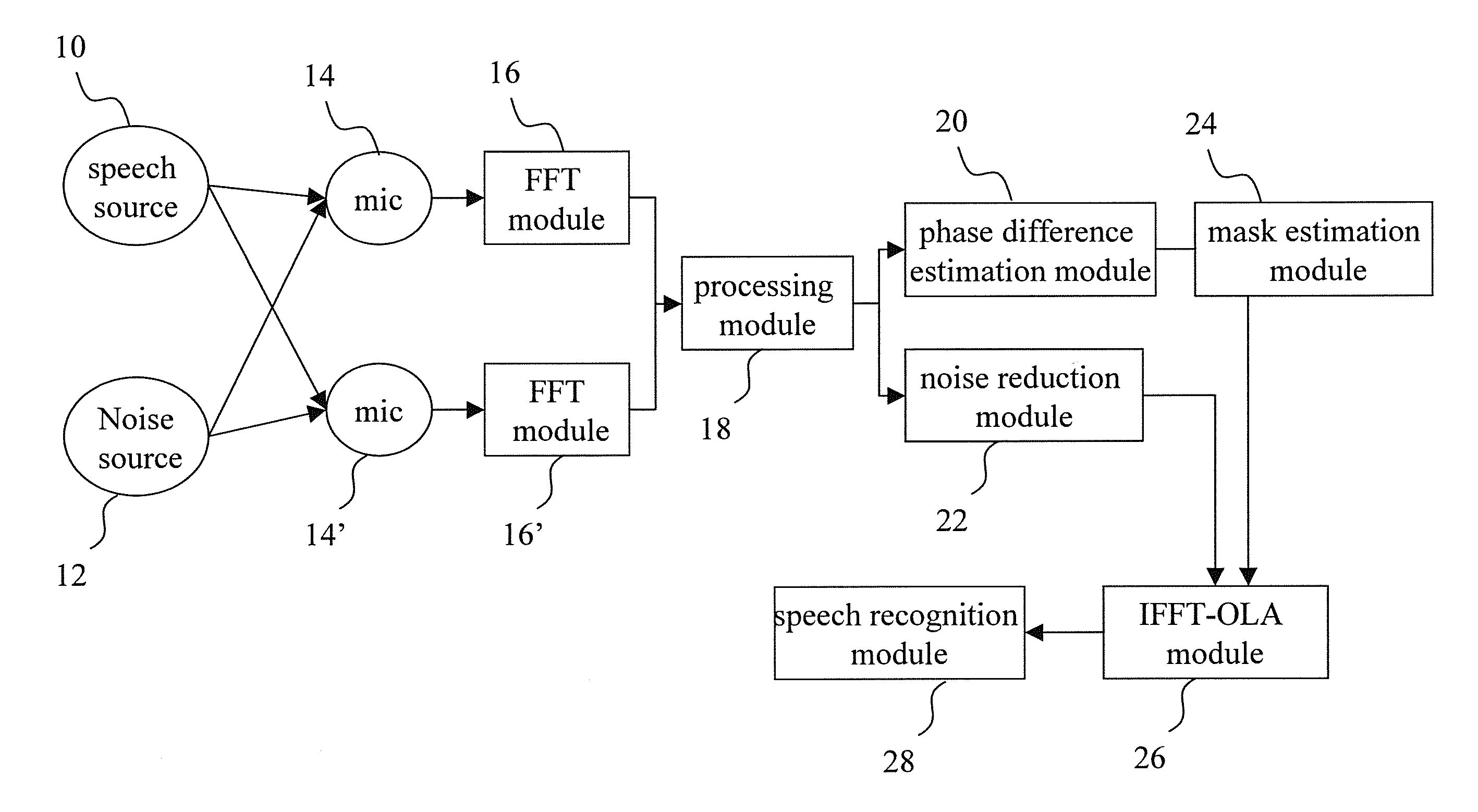
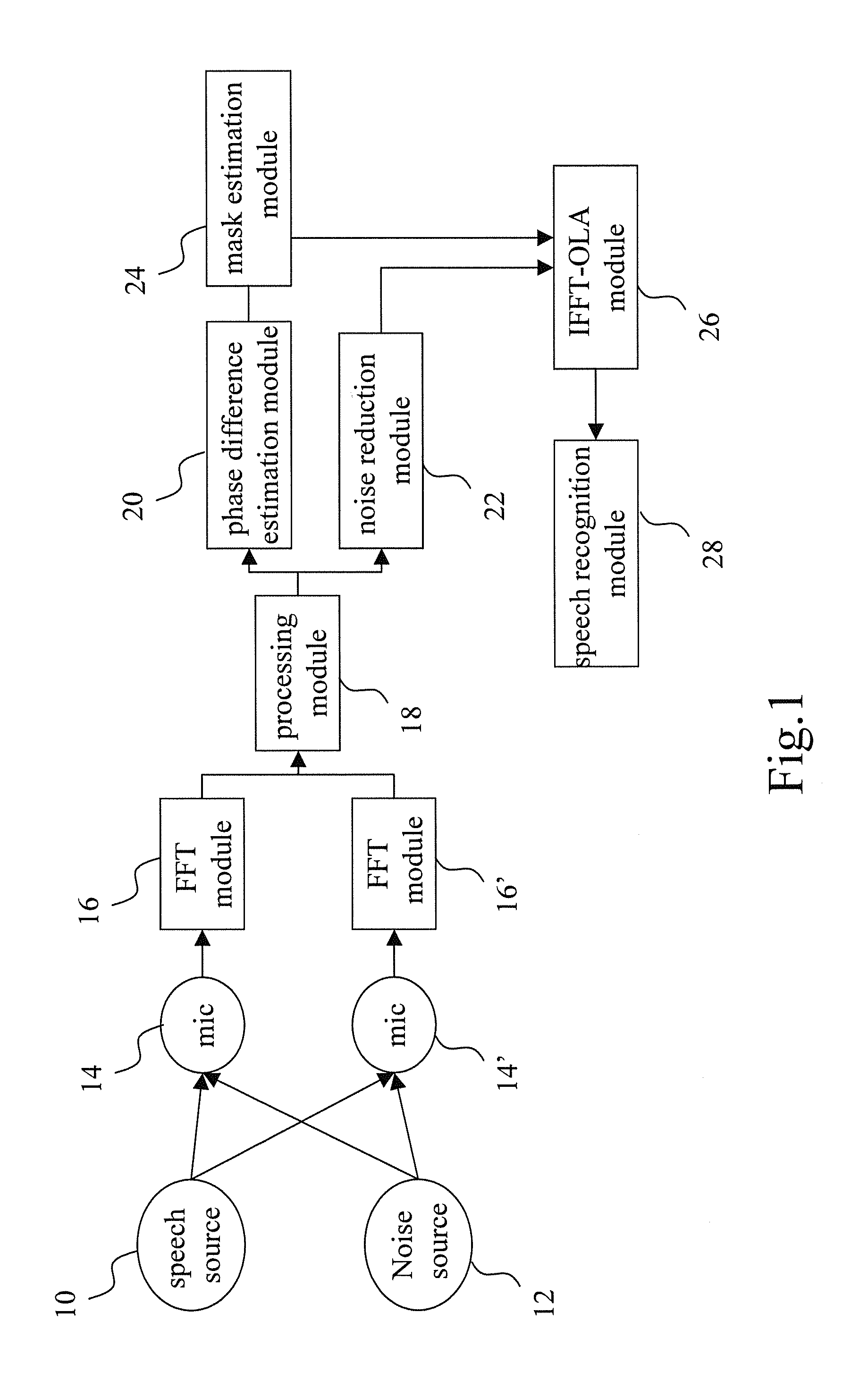
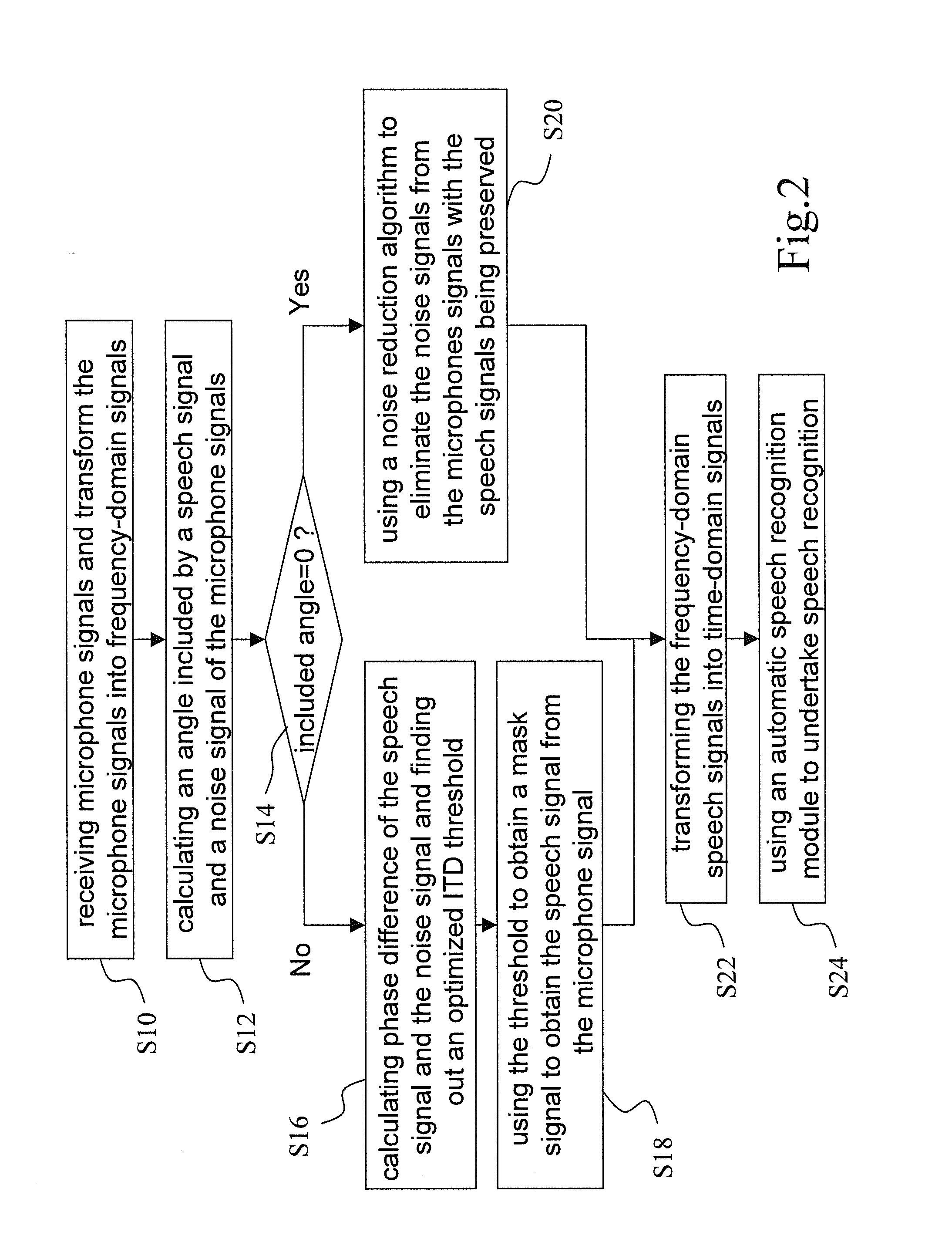
ActiveUS20120148069A1Reduce noiseImprove voice qualitySignal processingMicrophones signal combinationPhase differenceNoise reduction algorithm
The present invention discloses a microphone array structure able to reduce noise and improve speech quality and a method thereof. The method of the present invention comprises steps: using at least two microphone to receive at least two microphone signals each containing a noise signal and a speech signal; using FFT modules to transform the microphone signals into frequency-domain signals; calculating an included angle between a speech signal and a noise signal of the microphone signal, and selecting a phase difference estimation algorithm, a noise reduction algorithm or both to reduce noise according to the included angle; if the phase difference estimation algorithm is used, calculating phase difference of the microphone signals to obtain a time-space domain mask signal; and multiplying the mask signal and the average of the microphone signals to obtain the speech signals of the microphone signals. Thereby is eliminated noise and improve speech quality.
Owner:U MEDIA COMM
Speech-responsive portable speaker
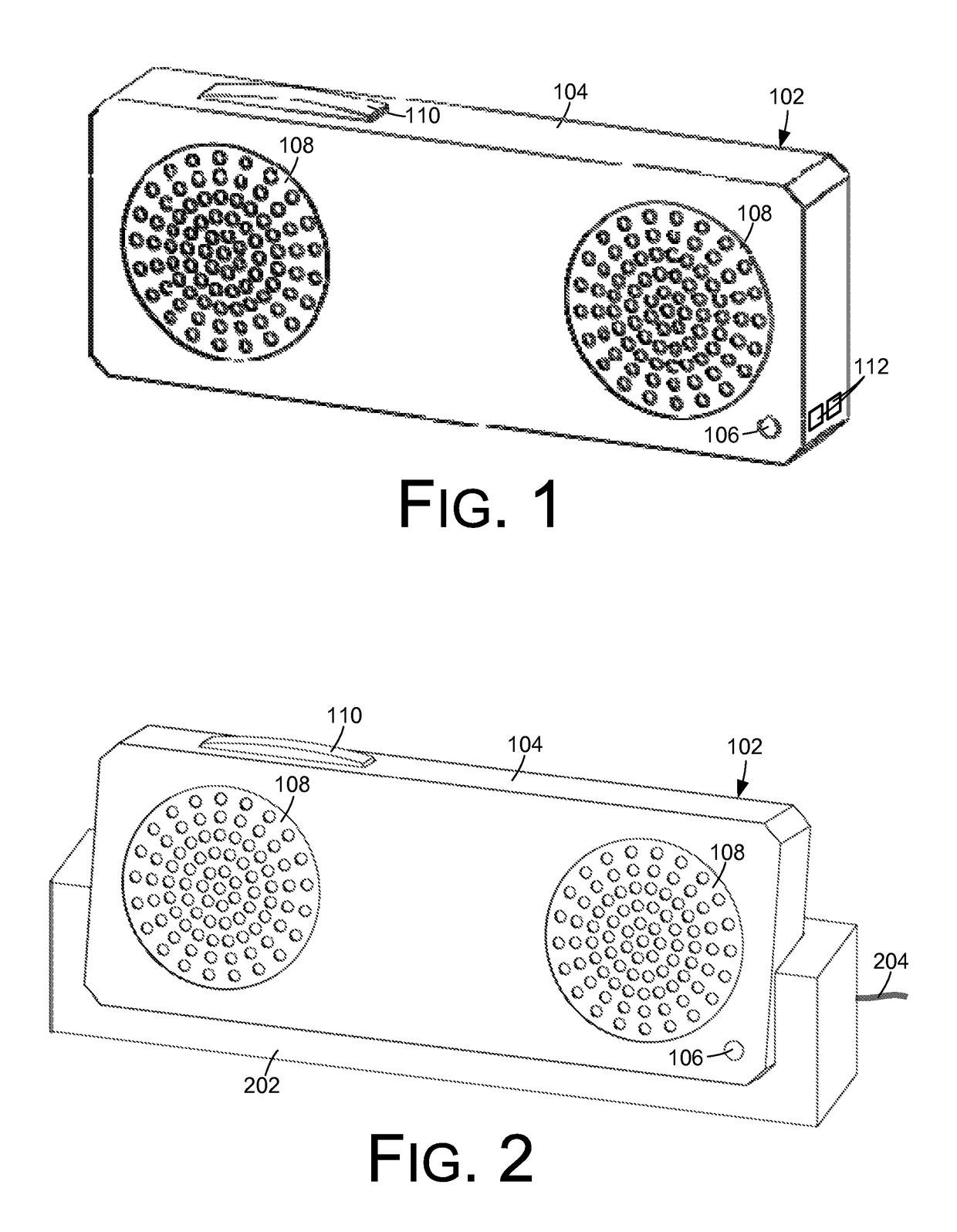
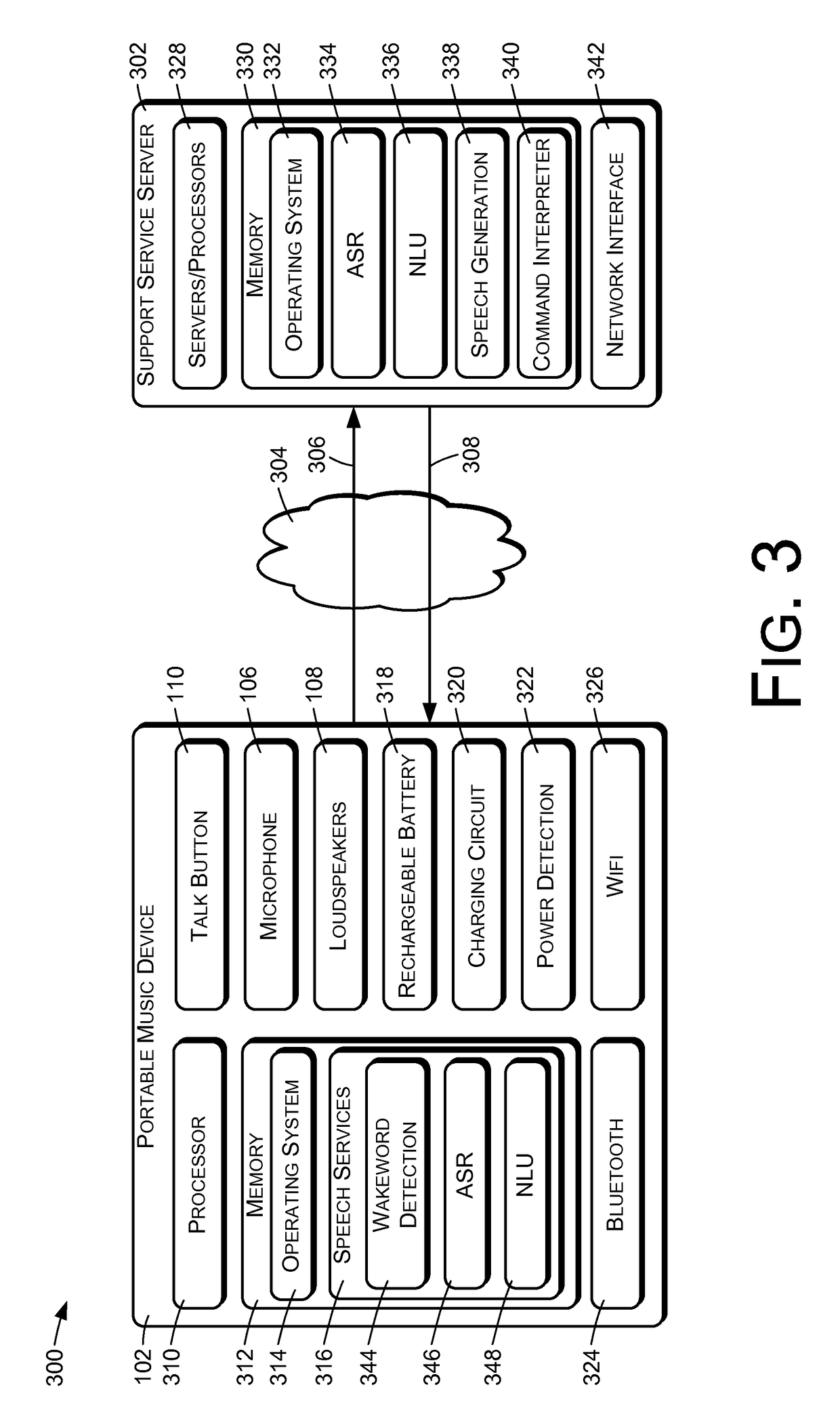
A portable music device may operate in response to user speech. In situations in which the music device is operating primarily from battery power, a push-to-talk (PTT) button may be used to indicate when the user is directing speech to the device. When the music device is receiving external power, the music device may continuously monitor a microphone signal to detect a user utterance of a wakeword, which may be used to indicate that subsequent speech is directed to the device. When operating from battery power, the device may send audio to a network-based support service for speech recognition and natural language understanding. When operating from external power, the speech recognition and / or natural language understanding may be performed by the music device itself.
Owner:AMAZON TECH INC
Noise-reducing directional microphone array
ActiveUS20130010982A1Efficient solutionNoise minimizationMicrophonesSignal processingNoiseSpatial noise
Owner:MH ACOUSTICS
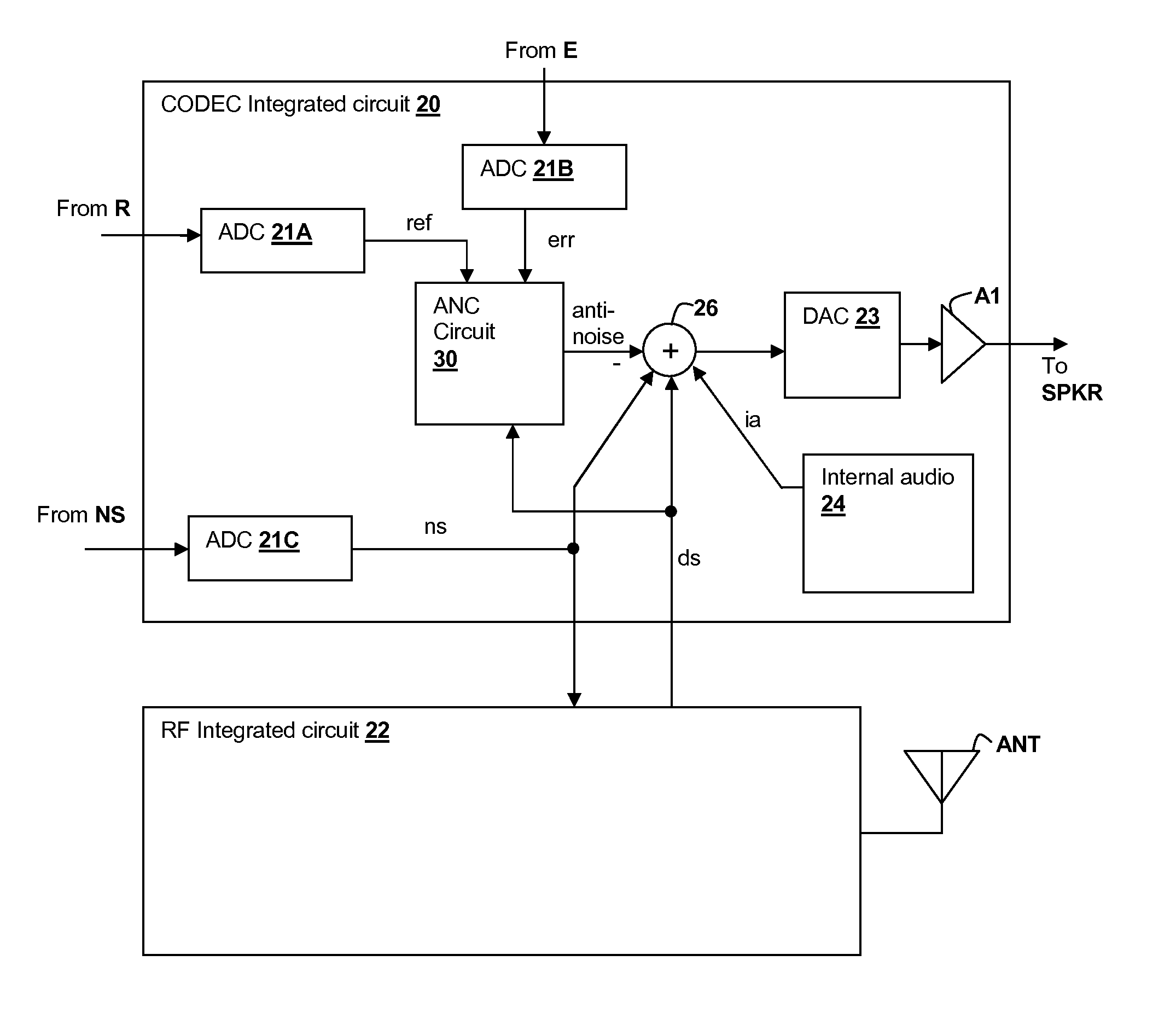
Adaptive-noise canceling (ANC) effectiveness estimation and correction in a personal audio device
ActiveUS20140270223A1Cancel improvementEar treatmentHearing device active noise cancellationAdaptive filterTransducer
Techniques for estimating adaptive noise canceling (ANC) performance in a personal audio device, such as a wireless telephone, provide robustness of operation by triggering corrective action when ANC performance is low, and / or by saving a state of the ANC system when ANC performance is high. An anti-noise signal is generated from a reference microphone signal and is provided to an output transducer along with program audio. A measure of ANC gain is determined by computing a ratio of a first indication of magnitude of an error microphone signal that provides a measure of the ambient sounds and program audio heard by the listener including the effects of the anti-noise, to a second indication of magnitude of the error microphone signal without the effects of the anti-noise. The ratio can be determined for different frequency bands in order to determine whether particular adaptive filters are trained properly.
Owner:CIRRUS LOGIC INC
Adaptive noise canceling architecture for a personal audio device
ActiveUS20120308025A1Reduce widthEffective noise cancellationEar treatmentMicrophones signal combinationAdaptive filterTransducer
A personal audio device, such as a wireless telephone, includes an adaptive noise canceling (ANC) circuit that adaptively generates an anti-noise signal from a reference microphone signal that measures the ambient audio and an error microphone signal that measures the output of an output transducer plus any ambient audio at that location and injects the anti-noise signal at the transducer output to cause cancellation of ambient audio sounds. A processing circuit uses the reference and error microphone to generate the anti-noise signal, which can be generated by an adaptive filter operating at a multiple of the ANC coefficient update rate. Downlink audio can be combined with the high data rate anti-noise signal by interpolation. High-pass filters in the control paths reduce DC offset in the ANC circuits, and ANC coefficient adaptation can be halted when downlink audio is not detected.
Owner:CIRRUS LOGIC INC
Frequency and direction-dependent ambient sound handling in personal audio devices having adaptive noise cancellation (ANC)
ActiveUS20130301846A1Avoid generating anti-noiseEar treatmentTransducer circuit dampingTransducerEngineering
A personal audio device, such as a wireless telephone, includes noise canceling circuit that adaptively generates an anti-noise signal from a reference microphone signal and injects the anti-noise signal into the speaker or other transducer output to cause cancellation of ambient audio sounds. An error microphone may also be provided proximate the speaker to measure the output of the transducer in order to control the adaptation of the anti-noise signal and to estimate an electro-acoustical path from the noise canceling circuit through the transducer. A processing circuit that performs the adaptive noise canceling (ANC) function also detects frequency-dependent characteristics in and / or direction of the ambient sounds and alters adaptation of the noise canceling circuit in response to the detection.
Owner:CIRRUS LOGIC INC
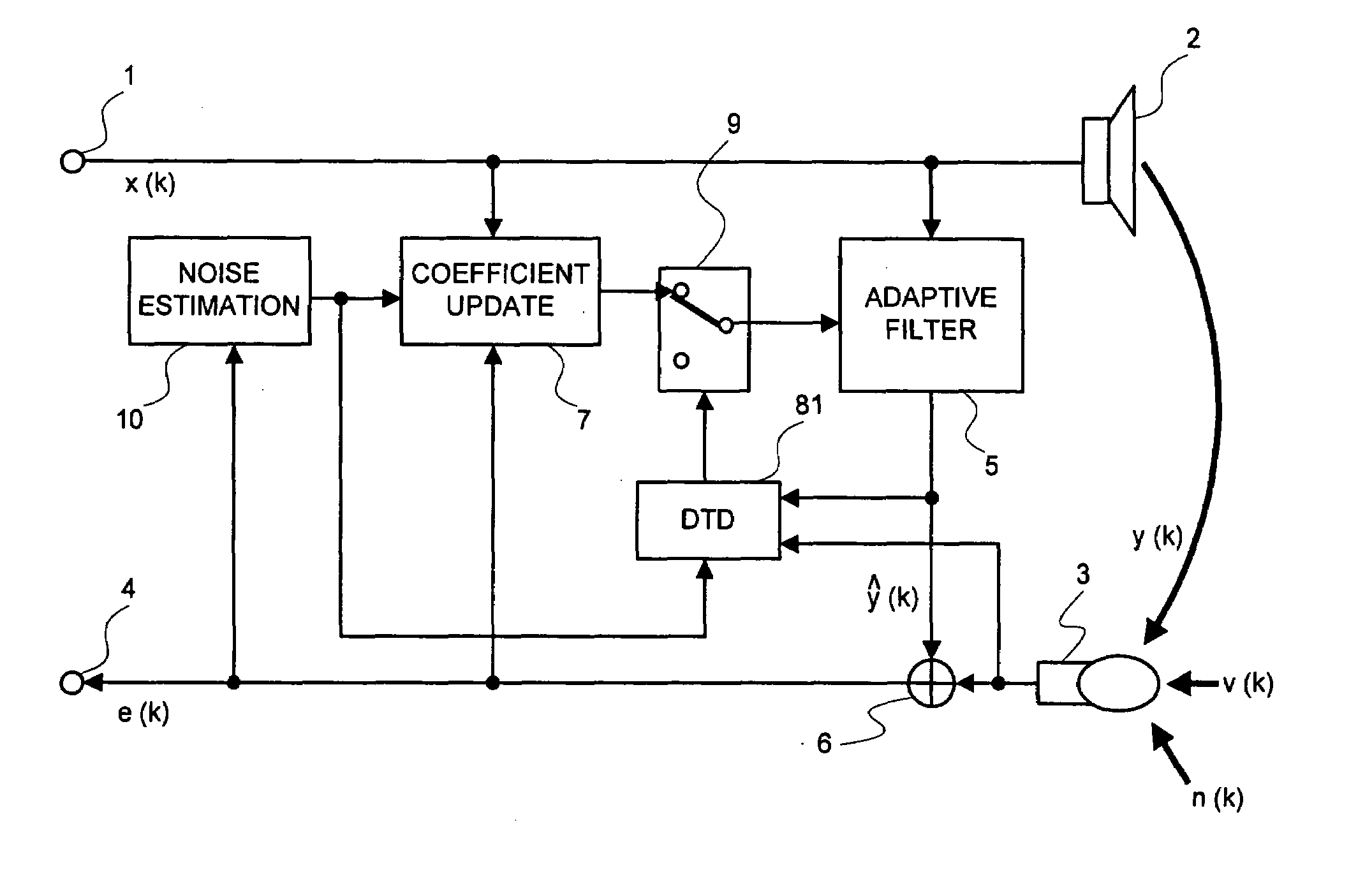
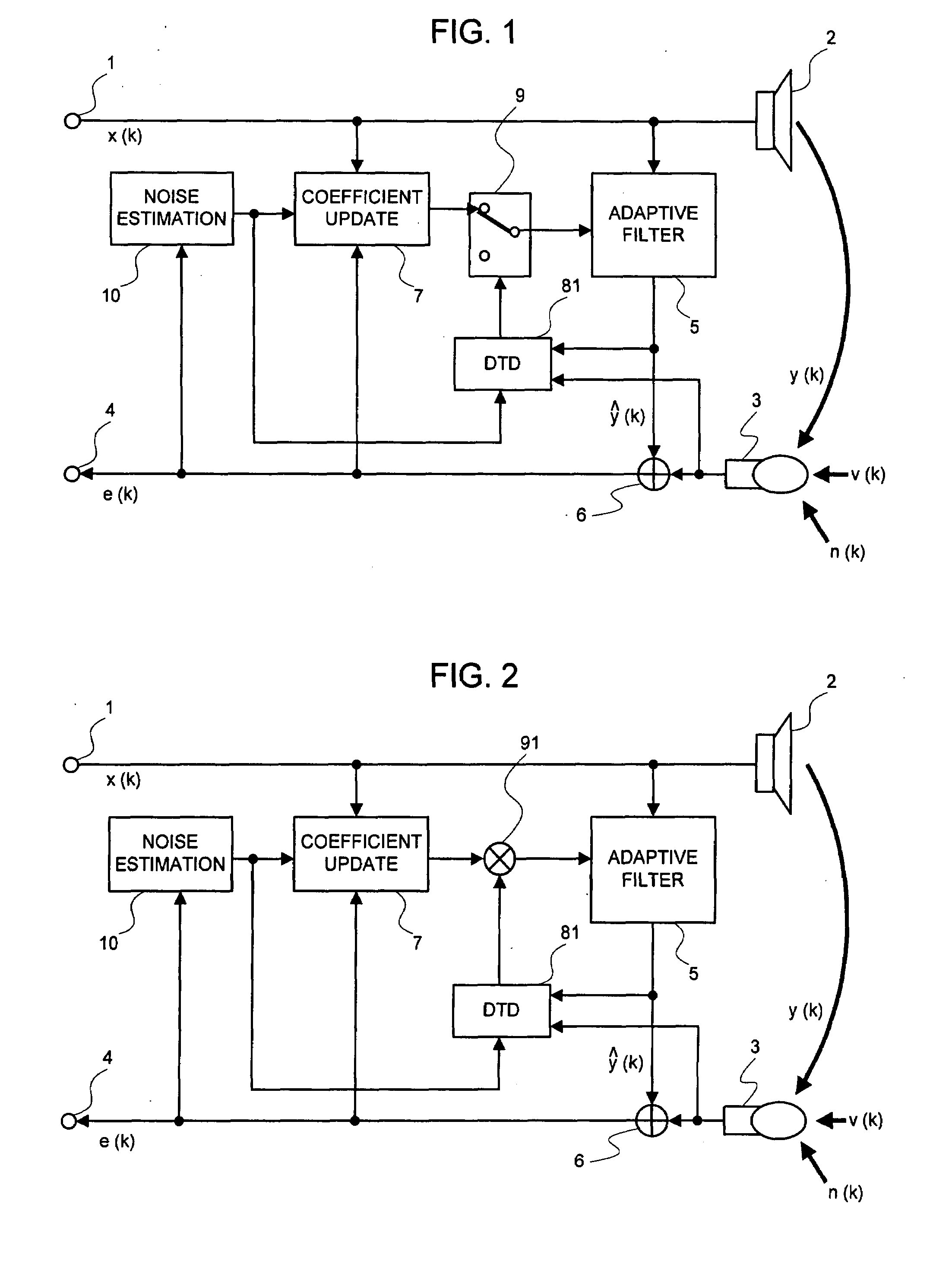
Signal Processing Method, Signal Processing Device, and Signal Processing Program
InactiveUS20080101622A1Improve performanceEasy to controlMicrophonesInterconnection arrangementsEngineeringMicrophone signal
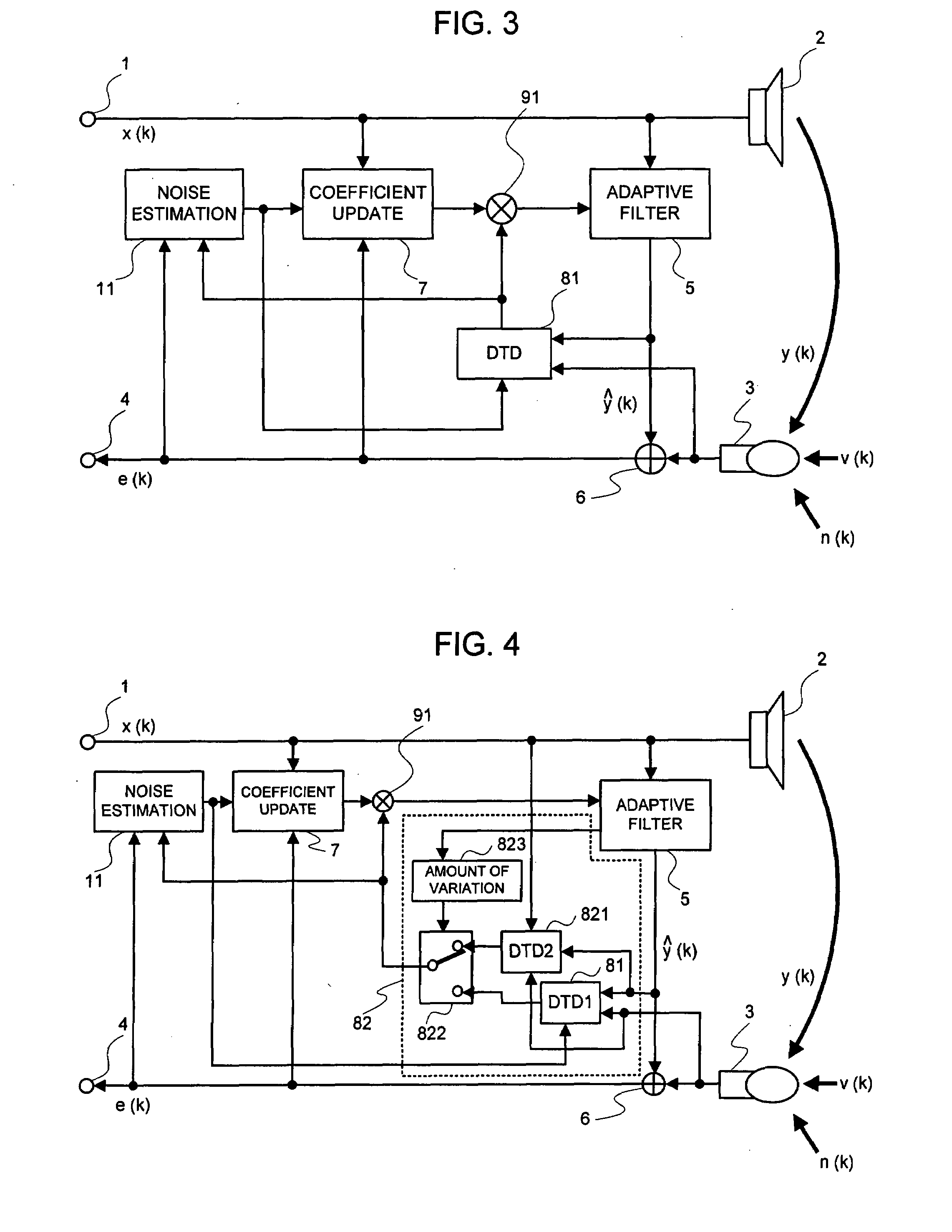
A signal processing device includes an adaptive filter (5), a noise estimation circuit (10), and a double talk detection circuit (81) and operates so that the double talk detection circuit (81) detects a double talk by using the estimated noise obtained by the noise estimation circuit (10). The signal processing device further includes noise estimation means and detects a double talk by using an estimated noise, a microphone signal, and pseudo-echo. An echo removal method and device detect a double talk by using a reliability coefficient expressed as continuous values between 0 and 1. By using continuous values instead of two values 0 and 1, it is possible to reduce the affect of a detection error.
Owner:NEC CORP
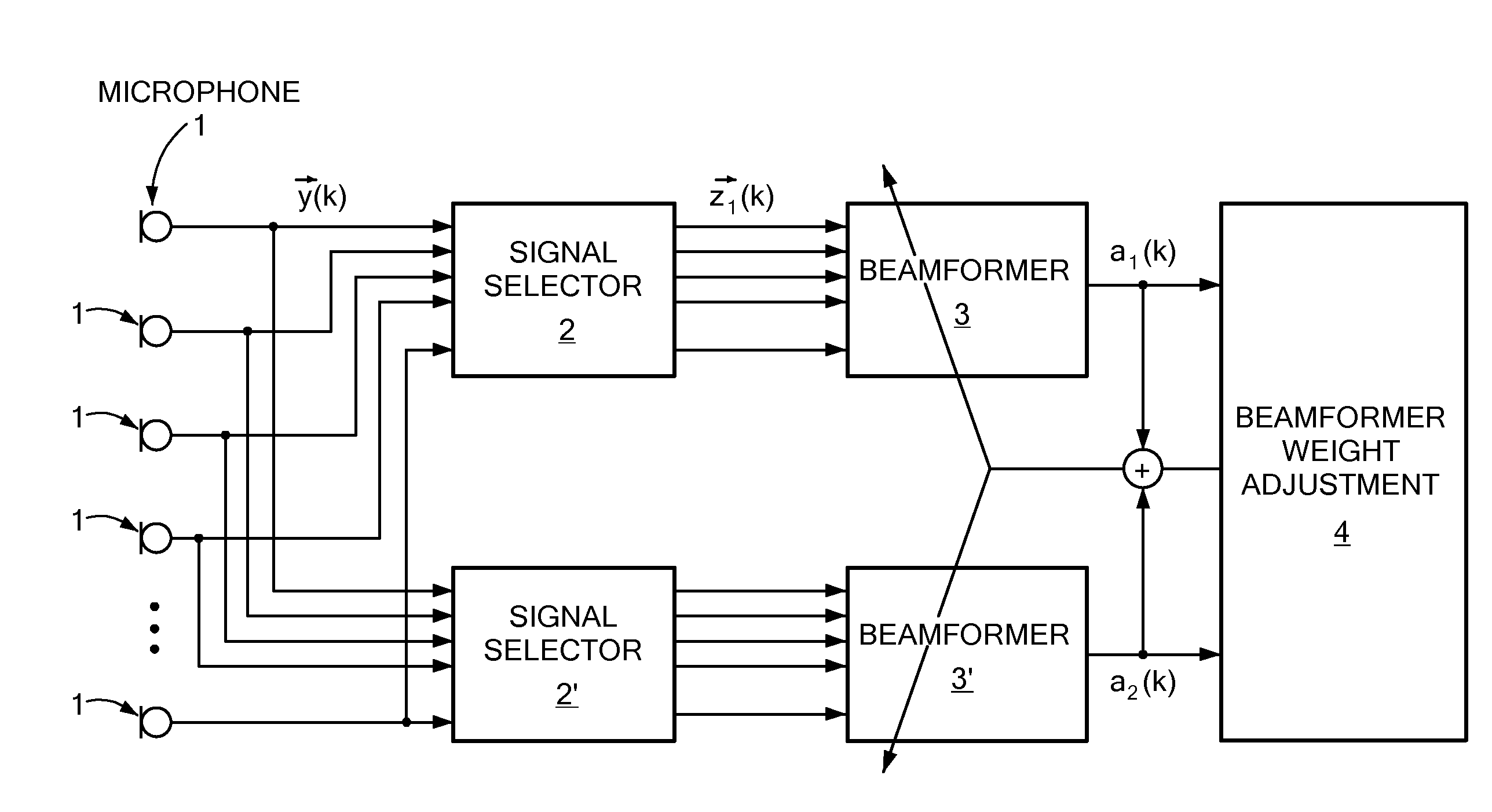
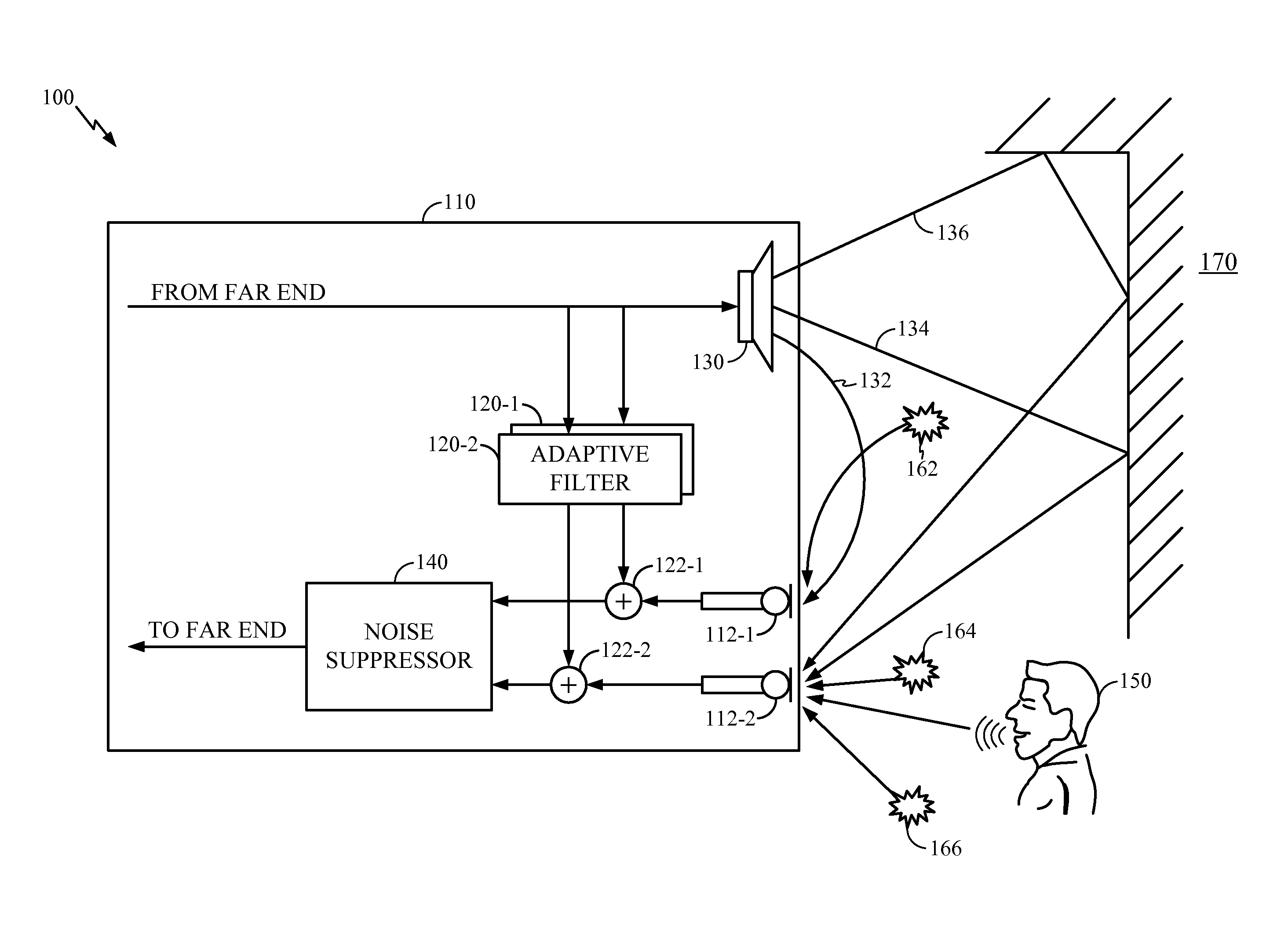
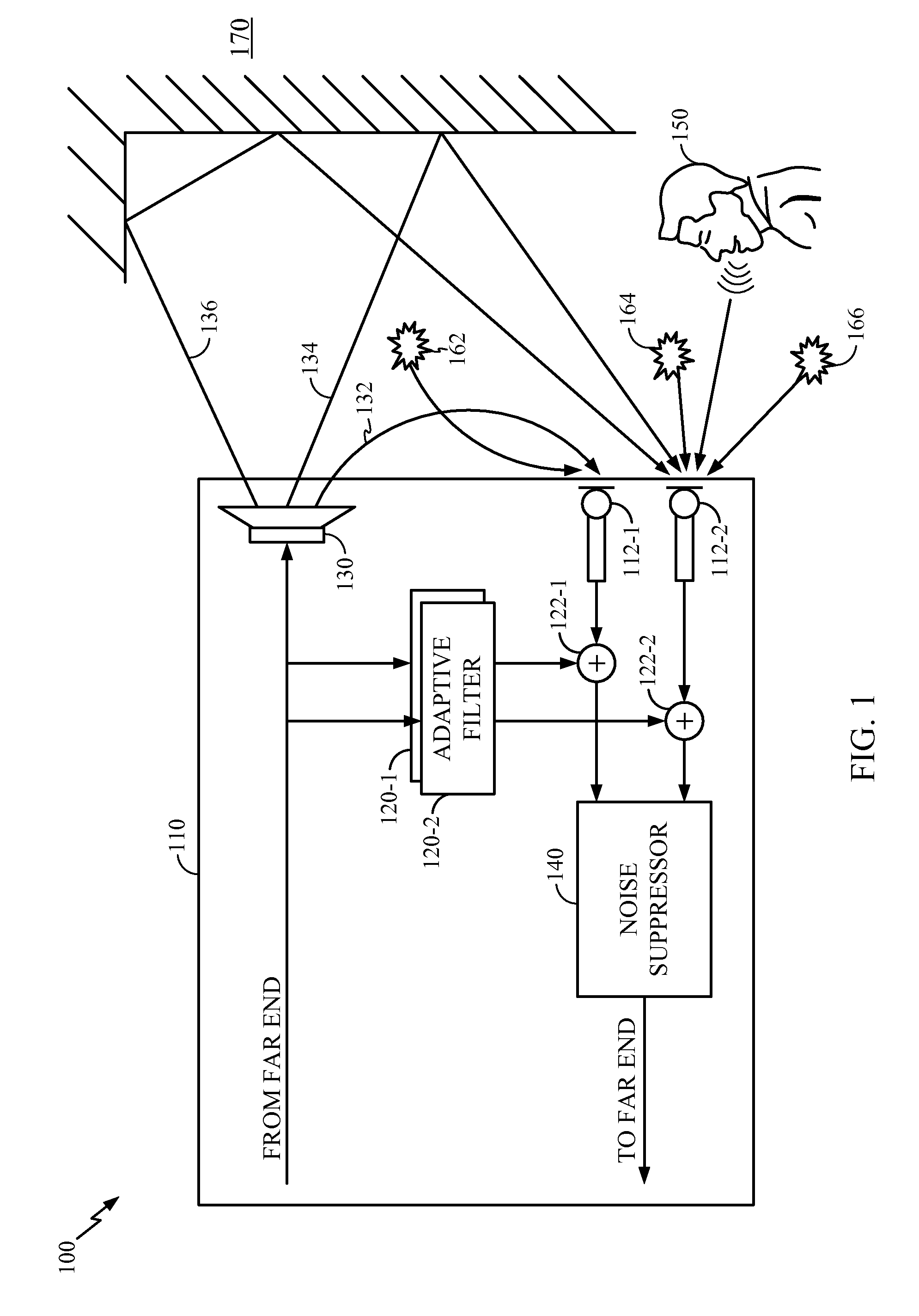
High quality audio conferencing with adaptive beamforming
ActiveUS20050094795A1Two-way loud-speaking telephone systemsSpecial service for subscribersMicrophone signalOmni directional
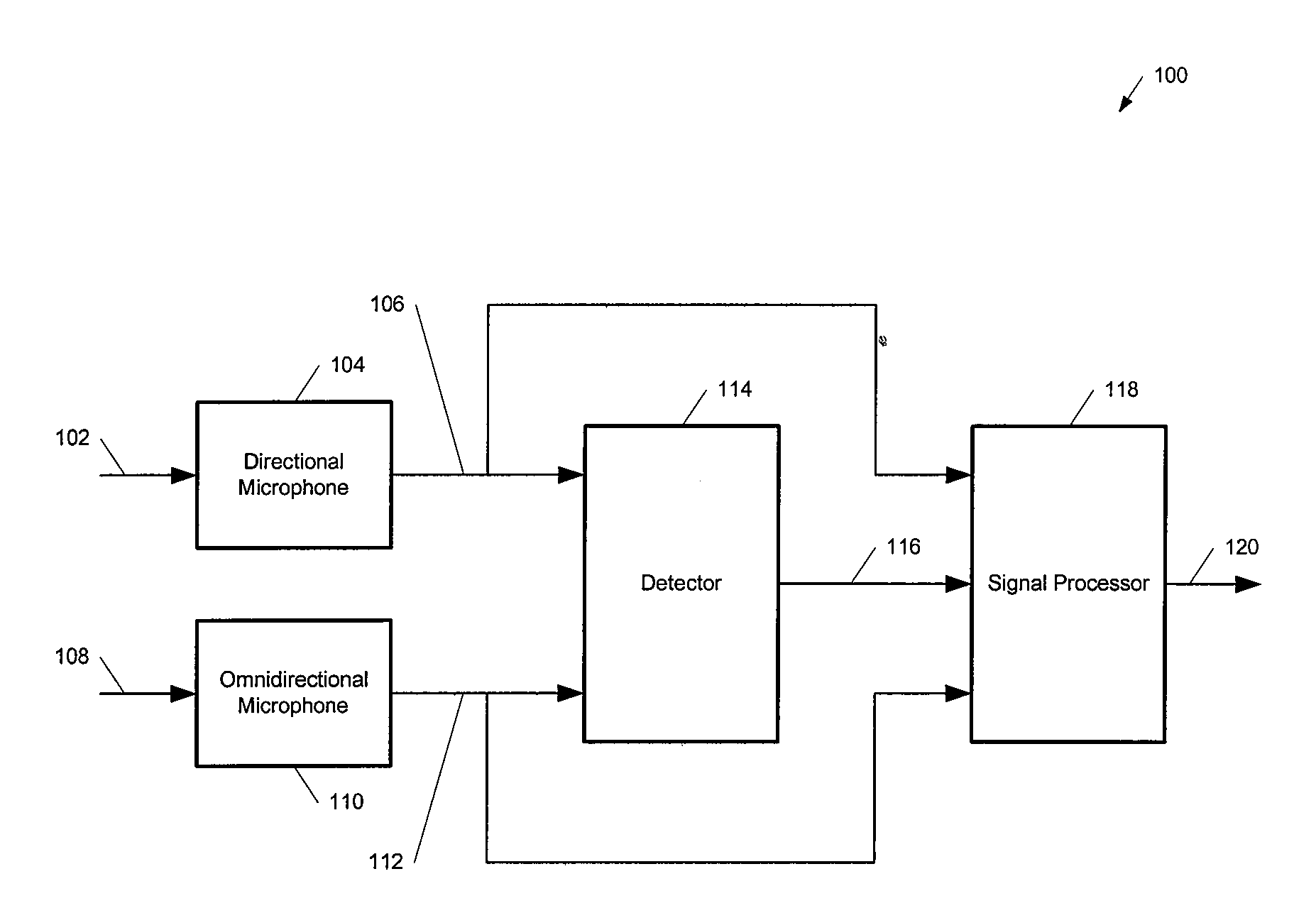
Systems and methods that enable high quality audio teleconferencing are disclosed. In one embodiment of the present invention, a signal processor receives signals from a spatially dispersed set of directional microphones, processing the microphone signals and the far-end received audio into a signal for transmission to a far-end party. The processing may comprise the use of one or more algorithms that reduce conference room noise and may selectively increase participant audio levels by processing the microphone signals using beamforming techniques. An embodiment of the present invention may also comprise one or more omni-directional microphones that may be used in cooperation with the directional microphones to adjust for background noise, acoustic echo, and the existence of side conversations.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
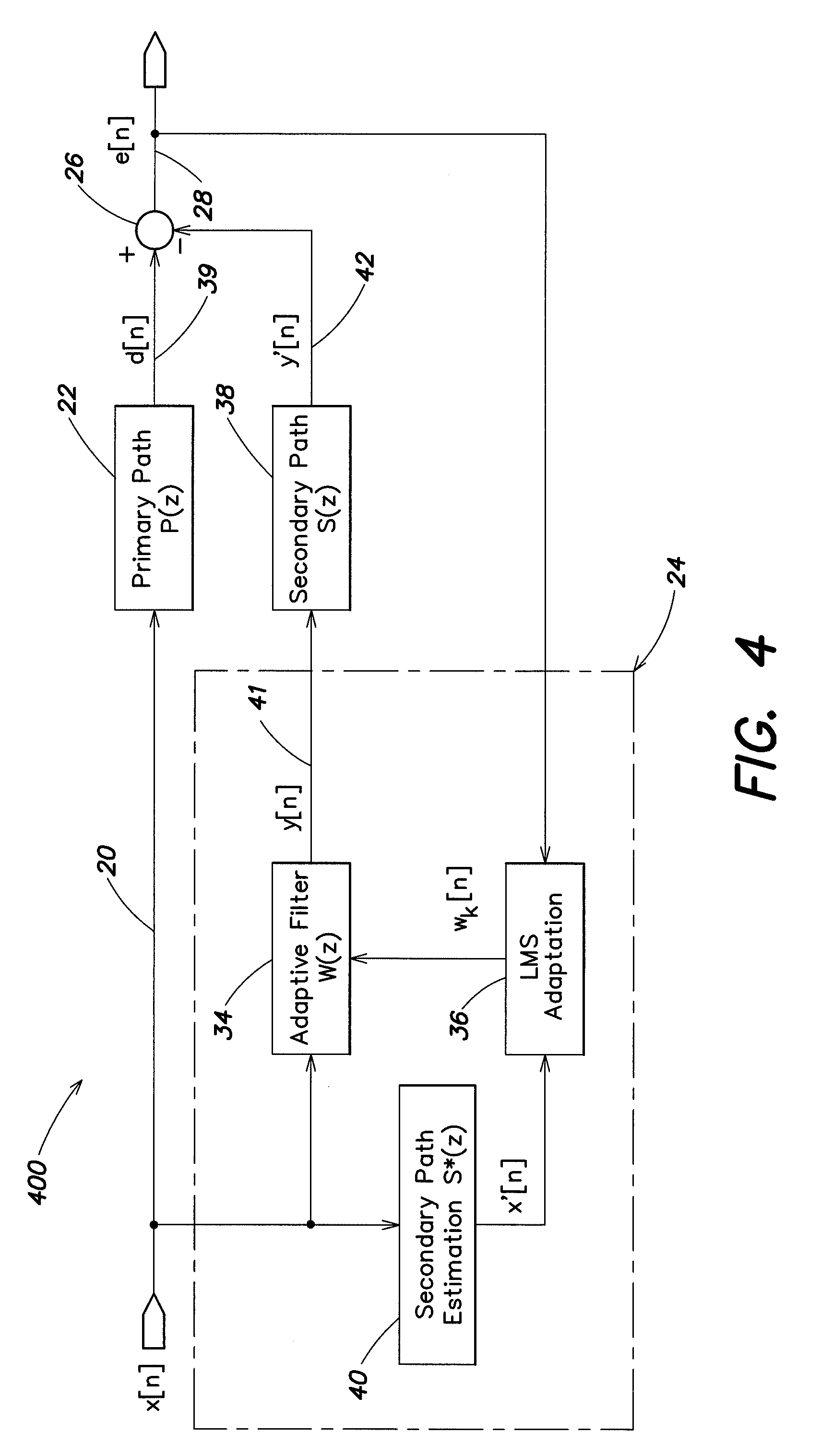
Continuous adaptation of secondary path adaptive response in noise-canceling personal audio devices
ActiveUS20120308027A1Maximal cancellationEar treatmentSound producing devicesAdaptive filterTransducer
A personal audio device, such as a wireless telephone, includes an adaptive noise canceling (ANC) circuit that adaptively generates an anti-noise signal from a reference microphone signal and injects the anti-noise signal into the speaker or other transducer output to cause cancellation of ambient audio sounds. An error microphone is also provided proximate the speaker to provide an error signal indicative of the effectiveness of the noise cancellation. A secondary path estimating adaptive filter is used to estimate the electro-acoustical path from the noise canceling circuit through the transducer so that source audio can be removed from the error signal. Noise is injected either continuously and inaudibly below the source audio, or in response to detection that the source audio is low in amplitude, so that the adaptation of the secondary path estimating adaptive filter can be maintained, irrespective of the presence and amplitude of the source audio.
Owner:CIRRUS LOGIC INC
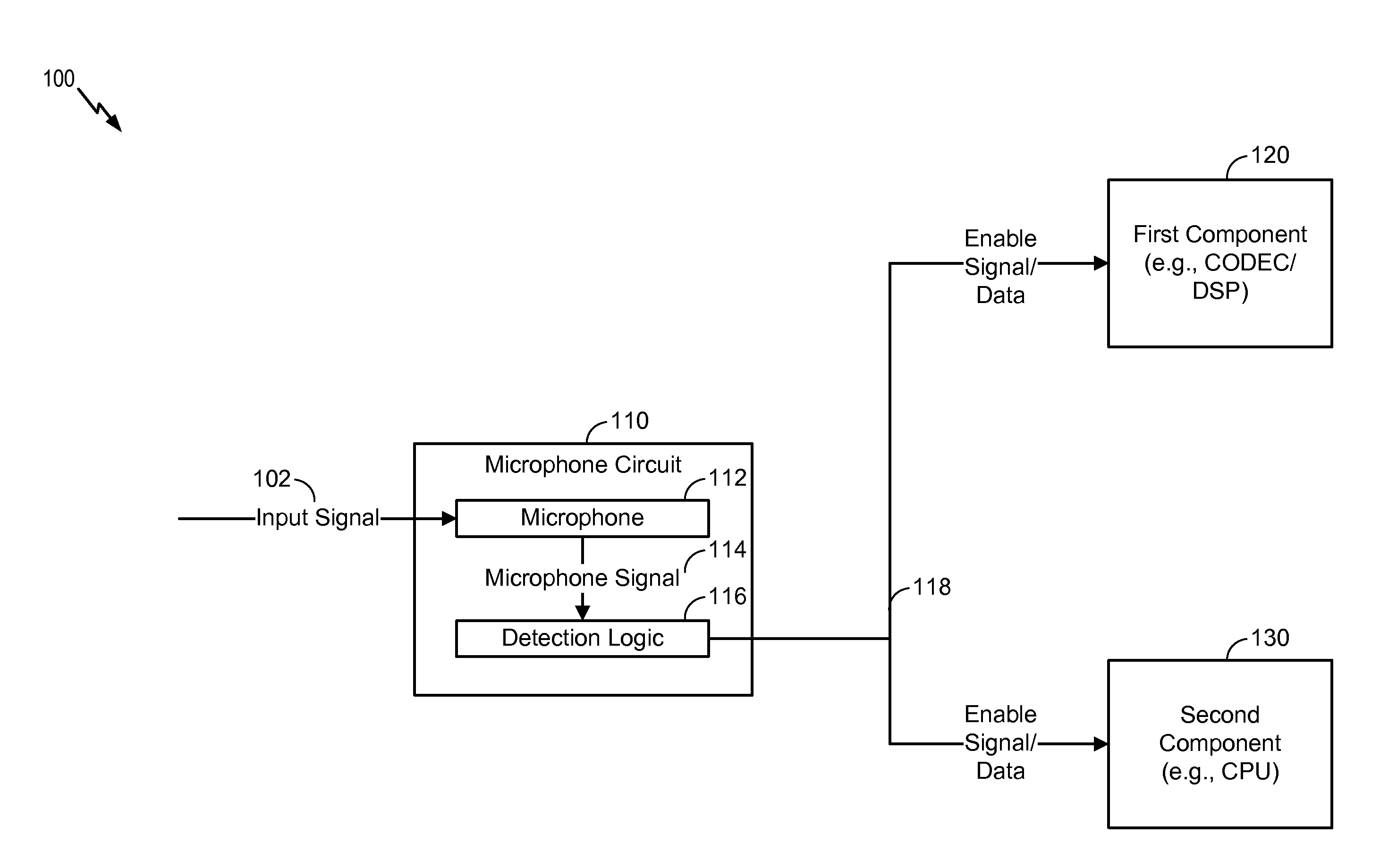
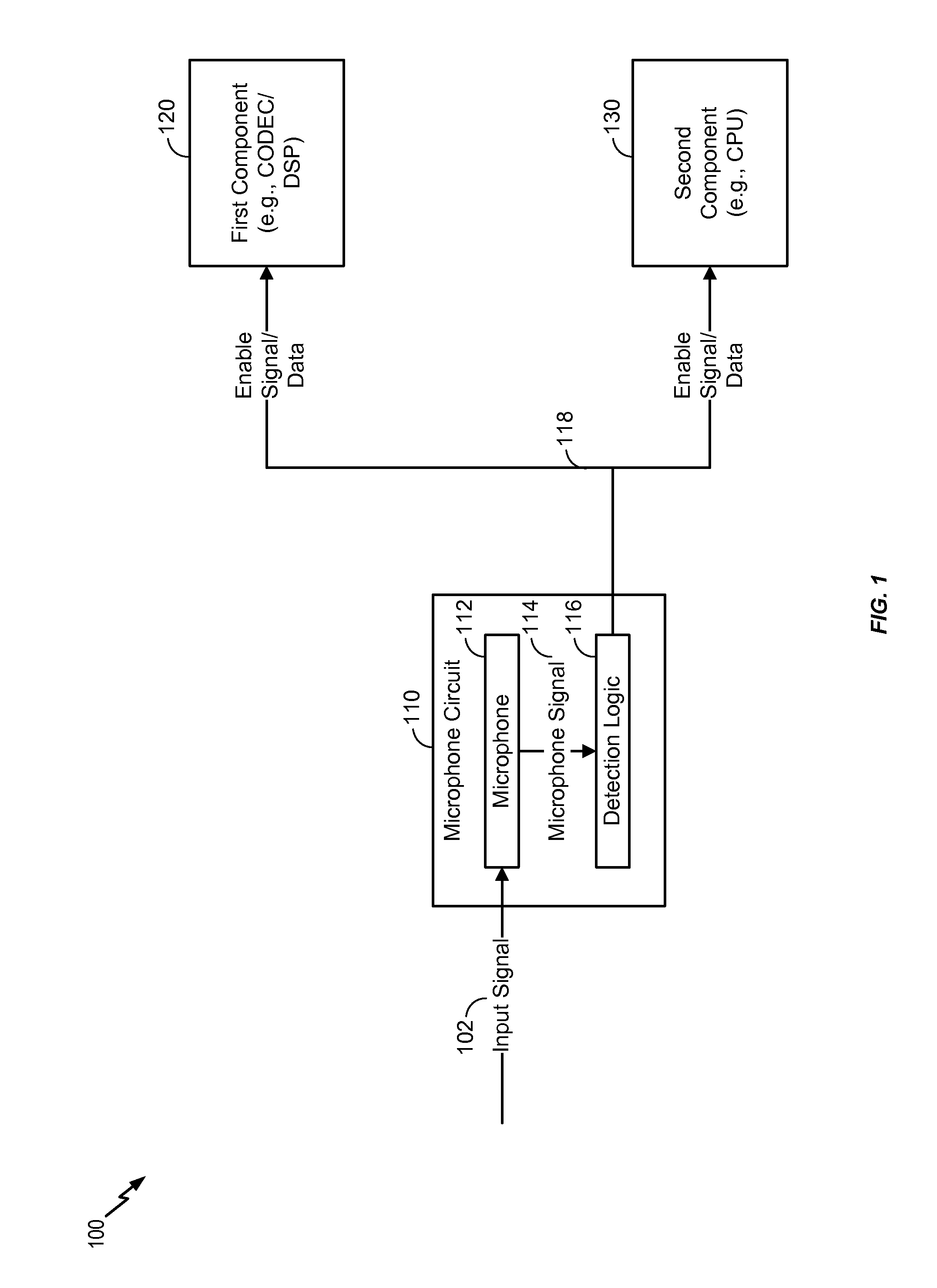
Selective enabling of a component by a microphone circuit
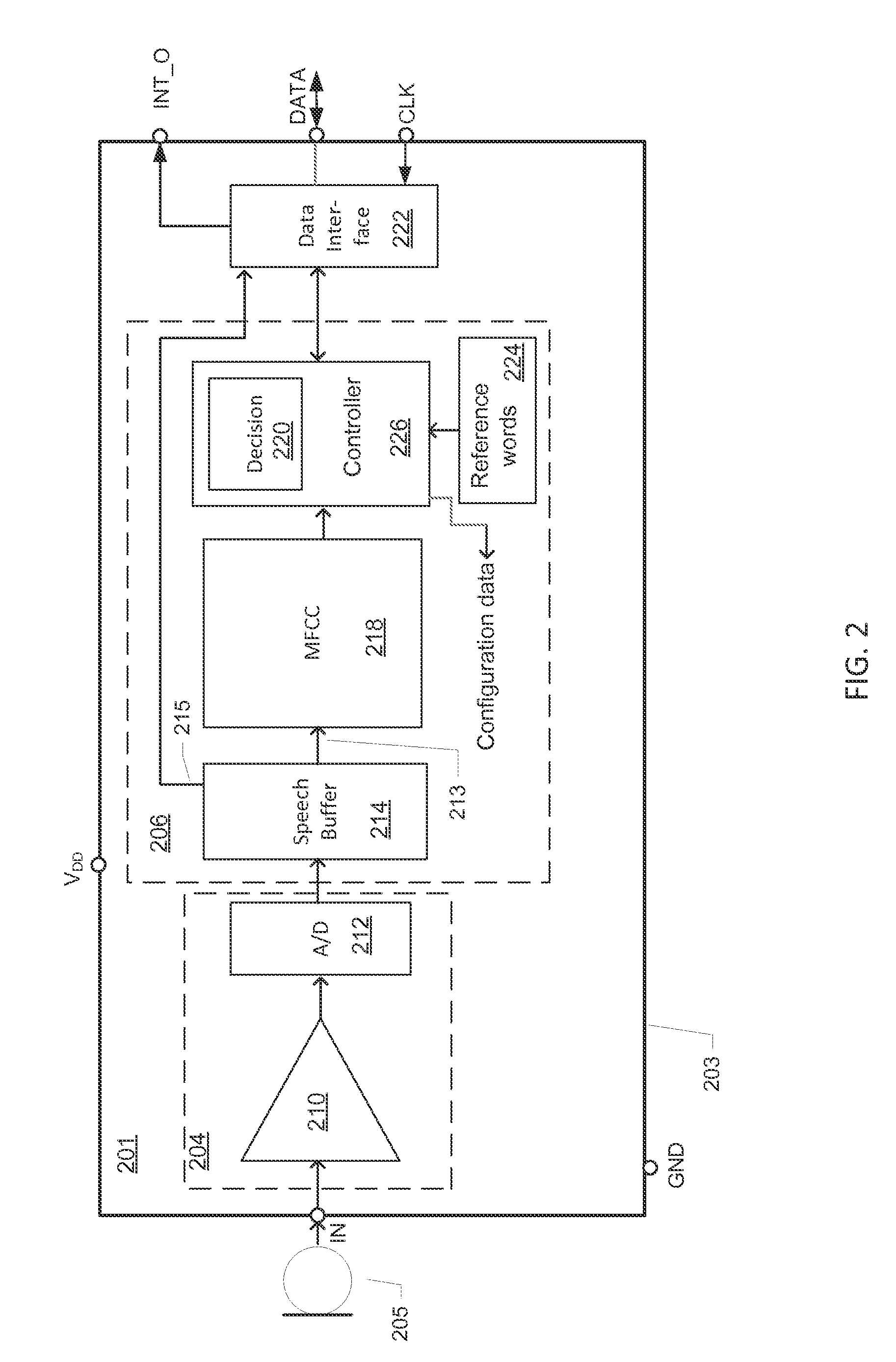
ActiveUS20160066113A1Reduce power consumptionDigital data processing detailsMouthpiece/microphone attachmentsSound detectionMicrophone signal
A microphone circuit includes a microphone configured to generate a microphone signal. The microphone circuit also includes a processor configured to perform sound detection based on the microphone signal and to determine whether to enable a component based on the sound detection. For example, the processor may be a digital signal processor (DSP) of the microphone circuit and the component may be external to the microphone circuit, such as a coder / decoder (CODEC), another DSP, and / or an application processor.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
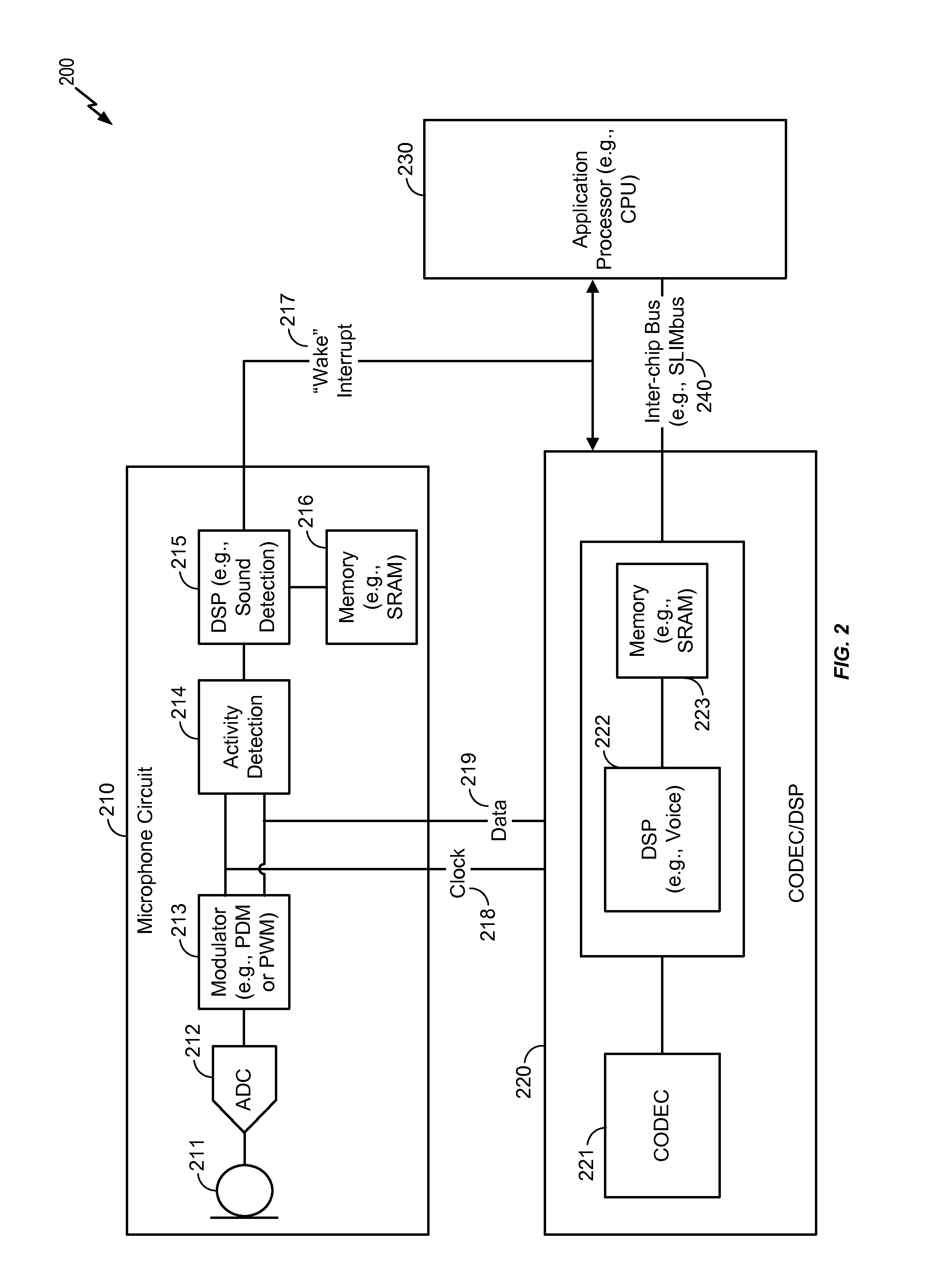
Microphone circuit assembly and system with speech recognition
ActiveUS20140257813A1Reduce consumptionReduce loadHearing aids signal processingSpeech recognitionAnalog-to-digital converterApplication processor
A microphone circuit assembly for an external application processor, such as a programmable Digital Signal Processor, may include a microphone preamplifier and analog-to-digital converter to generate microphone signal samples at a first predetermined sample rate. A speech feature extractor is configured for receipt and processing of predetermined blocks of the microphone signal samples to extract speech feature vectors representing speech features of the microphone signal samples. The microphone circuit assembly may include a speech vocabulary comprising a target word or target phrase of human speech encoded as a set of target feature vectors and a decision circuit is configured to compare the speech feature vectors generated by the speech feature extractor with the target feature vectors to detect the target speech word or phrase.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INT UNLTD
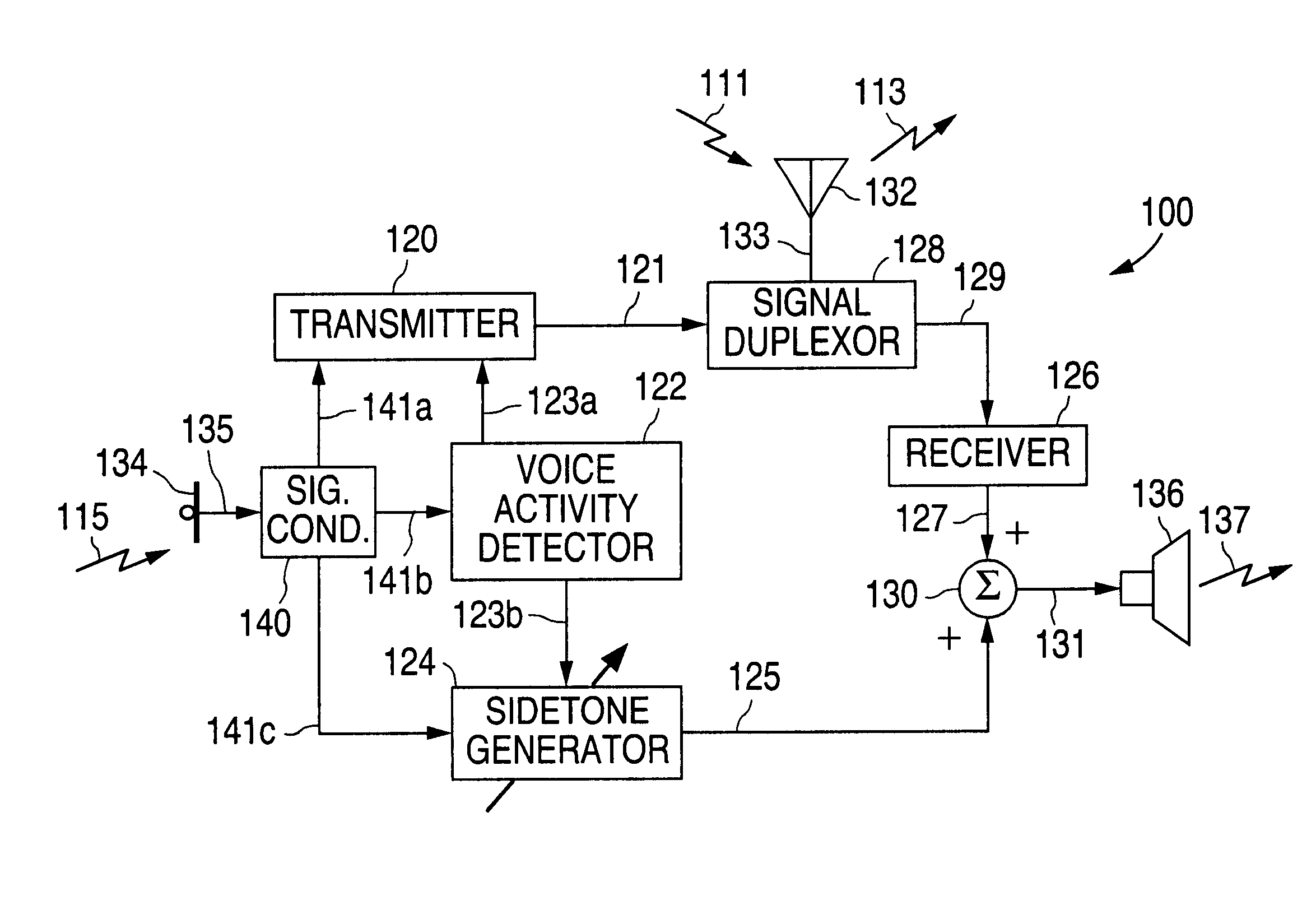
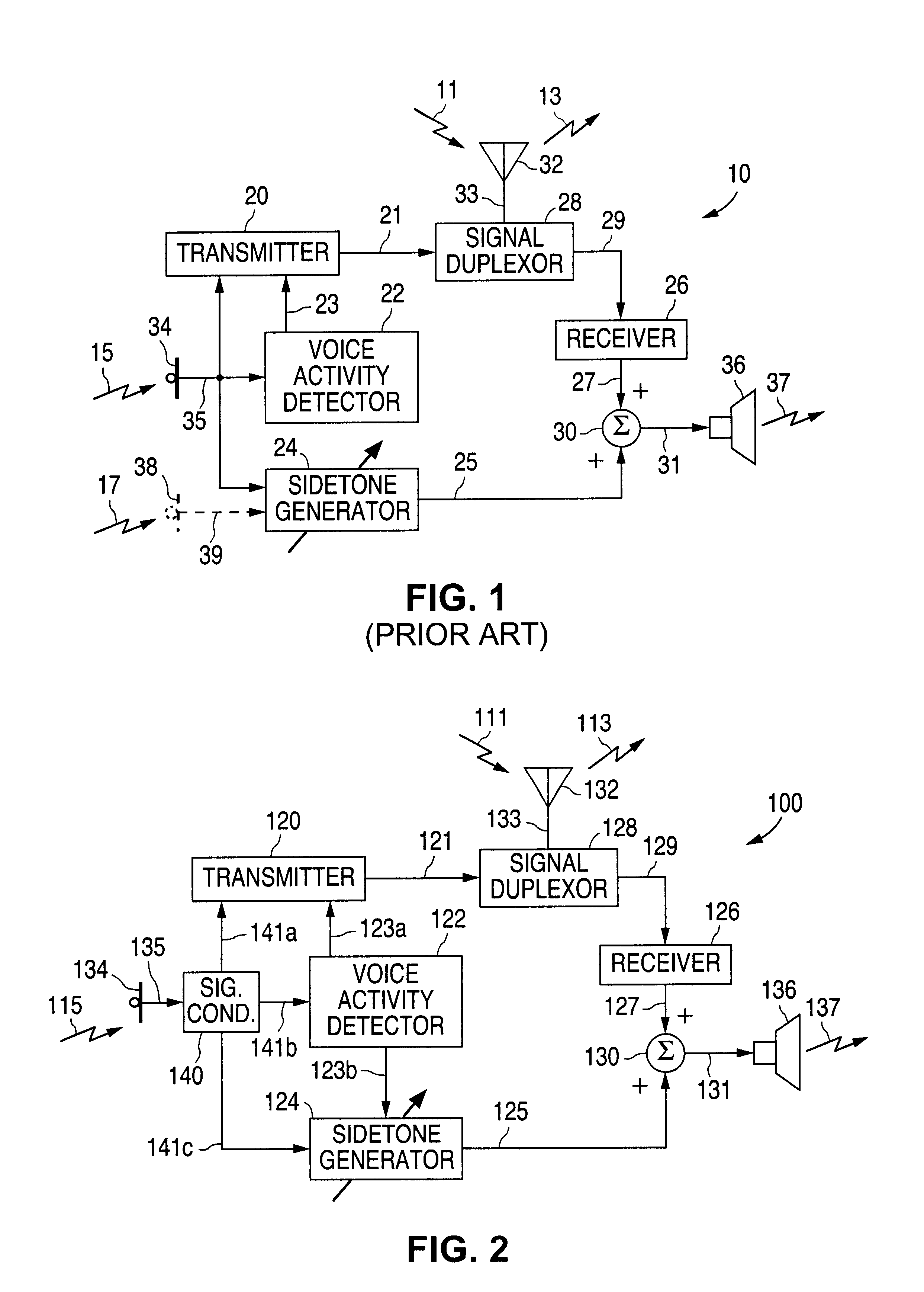
Telephone receiver circuit with dynamic sidetone signal generator controlled by voice activity detection
InactiveUS6850617B1Reduce signalingInterconnection arrangementsAnti-side-tone circuitsSidetoneMicrophone signal
A telephone receiver circuit with sidetone signal generation controlled by voice activity detection in accordance with the present invention uses the voice activity detector (VAD) to detect the presence of voice activity within the microphone signal and dynamically adjust the sidetone signal generation to compensate for noisy environments by eliminating or reducing the sidetone signal in the absence of voice activity. Hence, a sidetone signal is generated in the presence of voice activity, when feedback is required, while the sidetone signal is not generated in the absence of voice activity, since audio feedback for the user is not required then.
Owner:NAT SEMICON CORP
Bandlimiting Anti-noise in personal audio devices having adaptive noise cancellation (ANC)
ActiveUS20120308024A1Maximal cancellationAvoids generating anti-noiseEar treatmentSound producing devicesAdaptive filterTransducer
A personal audio device, such as a wireless telephone, includes noise canceling circuit that adaptively generates an anti-noise signal from a reference microphone signal and injects the anti-noise signal into the speaker or other transducer output to cause cancellation of ambient audio sounds. An error microphone may also be provided proximate the speaker to measure the output of the transducer in order to control the adaptation of the anti-noise signal and to estimate an electro-acoustical path from the noise canceling circuit through the transducer. A processing circuit that performs the adaptive noise canceling (ANC) function also either adjusts the frequency response of the anti-noise signal with respect to the reference microphone signal, and / or by adjusting the response of the adaptive filter independent of the adaptation provided by the reference microphone signal.
Owner:CIRRUS LOGIC INC
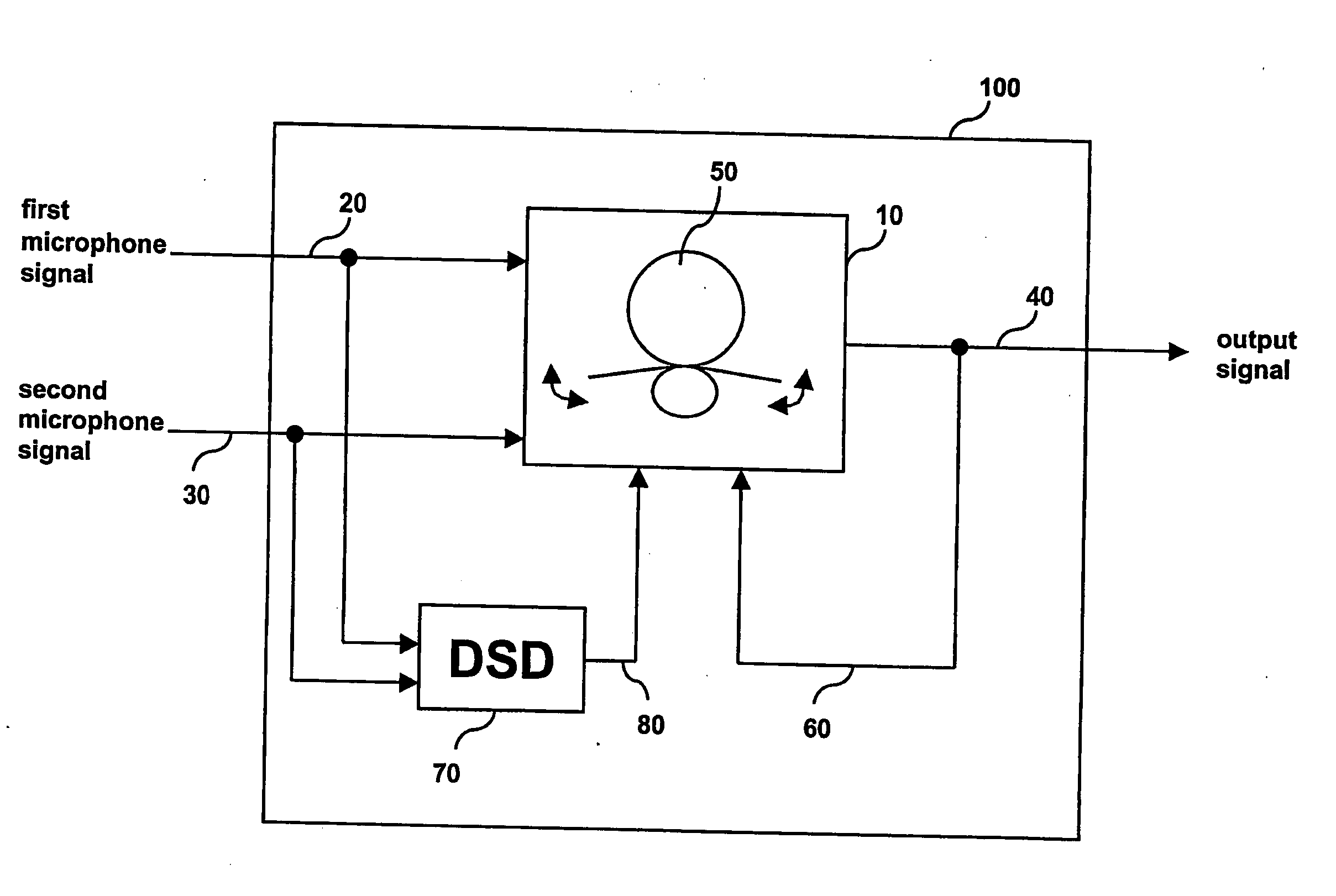
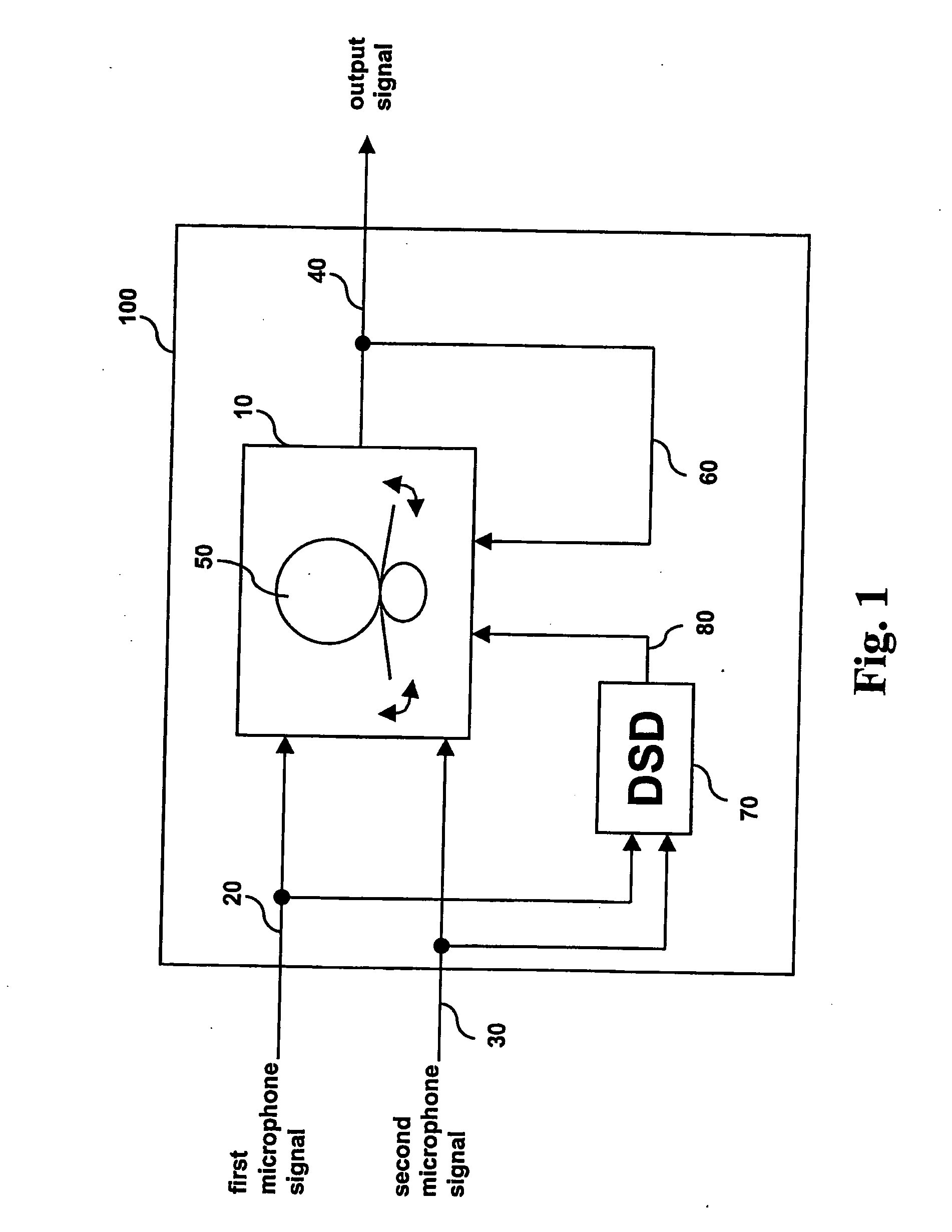
Method for controlling the directionality of the sound receiving characteristic of a hearing aid and a signal processing apparatus
ActiveUS20060177079A1Minimize output signalMinimize microphone noiseDoor/window protective devicesCurtain accessoriesSignal analyzerEngineering
A signal processing apparatus (100) for a hearing aid with a controllable directional characteristic is provided which comprises a directional controller (10) receiving first and second microphone signals (20, 30) and output an output signal (40), a signal analyzer (70) which detects whether at least one of said first and second microphone signals being undesired signals, and wherein said directional controller minimizes the output signal by adjusting the directional characteristic only if the signal analyzer has detected undesired signals.
Owner:WIDEX AS
Wind noise detection method and system
ActiveUS20120148067A1Save computing resourcesReduce power consumptionMicrophonesMicrophones signal combinationPhase differencePhase angle difference
The present invention relates to a multi-microphone system and method adapted to determine phase angle differences between a first microphone and a second microphone signal to detect presence of wind noise.
Owner:INVENSENSE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com