Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
561 results about "Feed forward" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
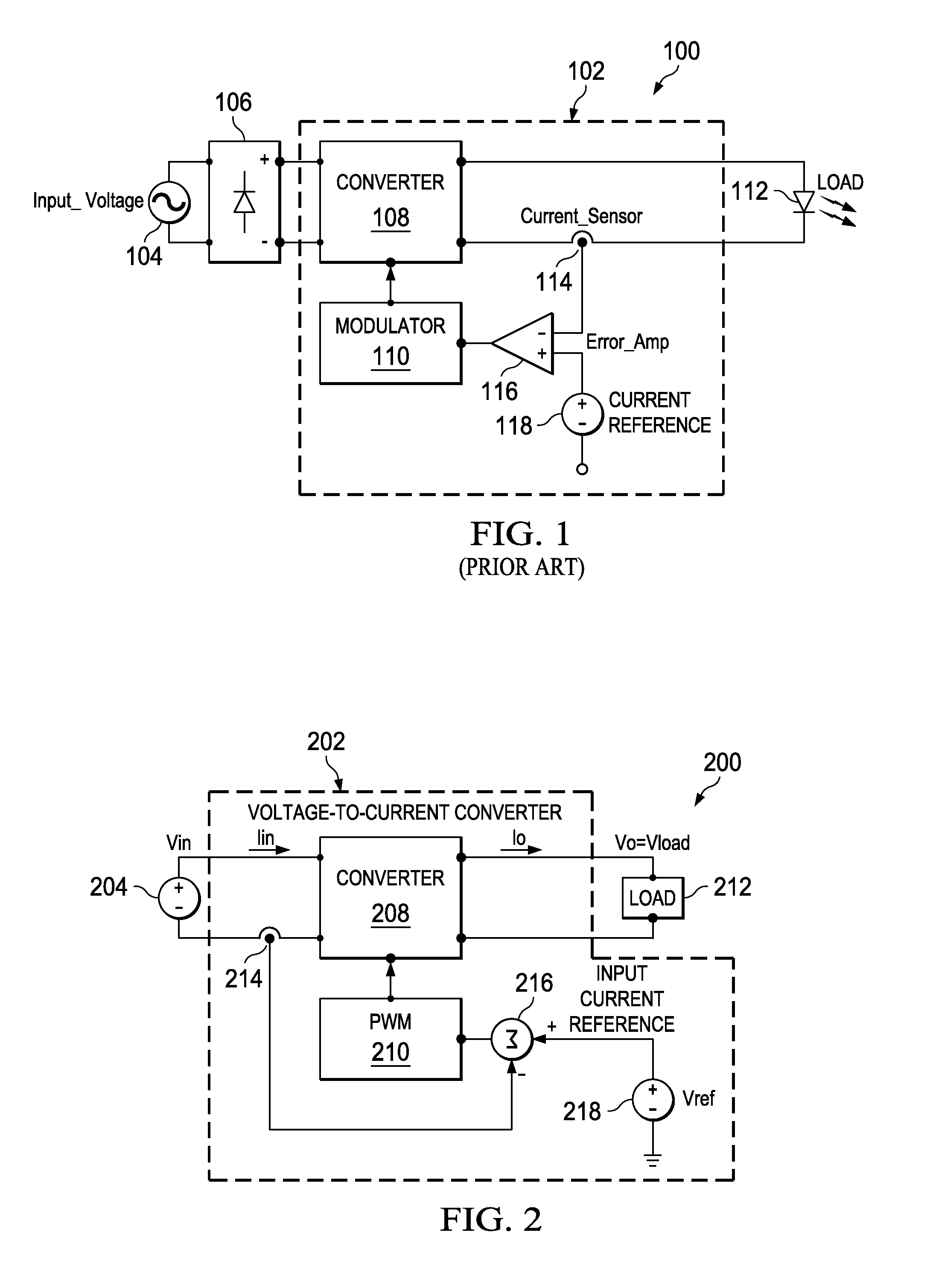
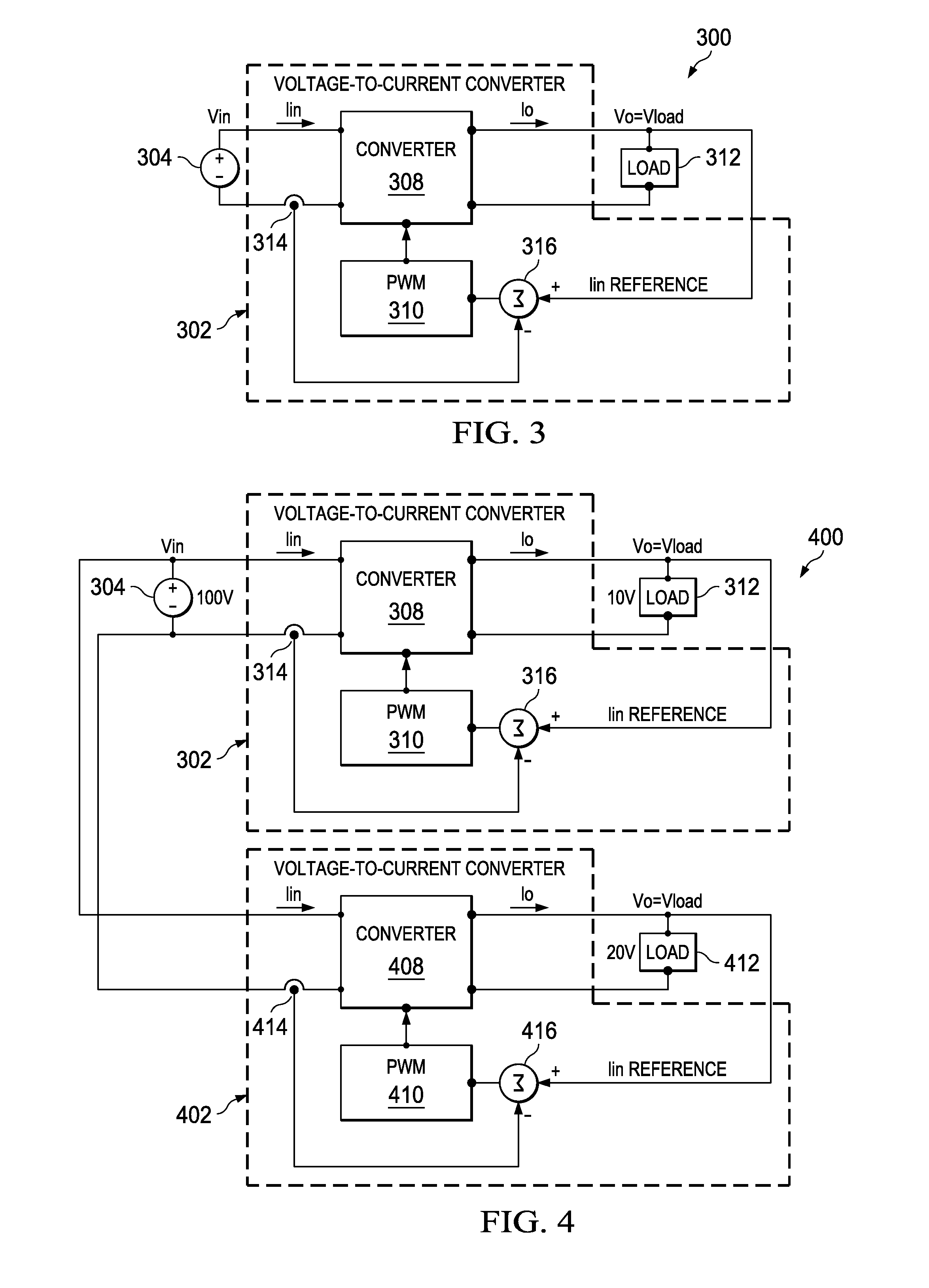
Feed forward, sometimes written feedforward, is a term describing an element or pathway within a control system that passes a controlling signal from a source in its external environment to a load elsewhere in its external environment. This is often a command signal from an external operator.
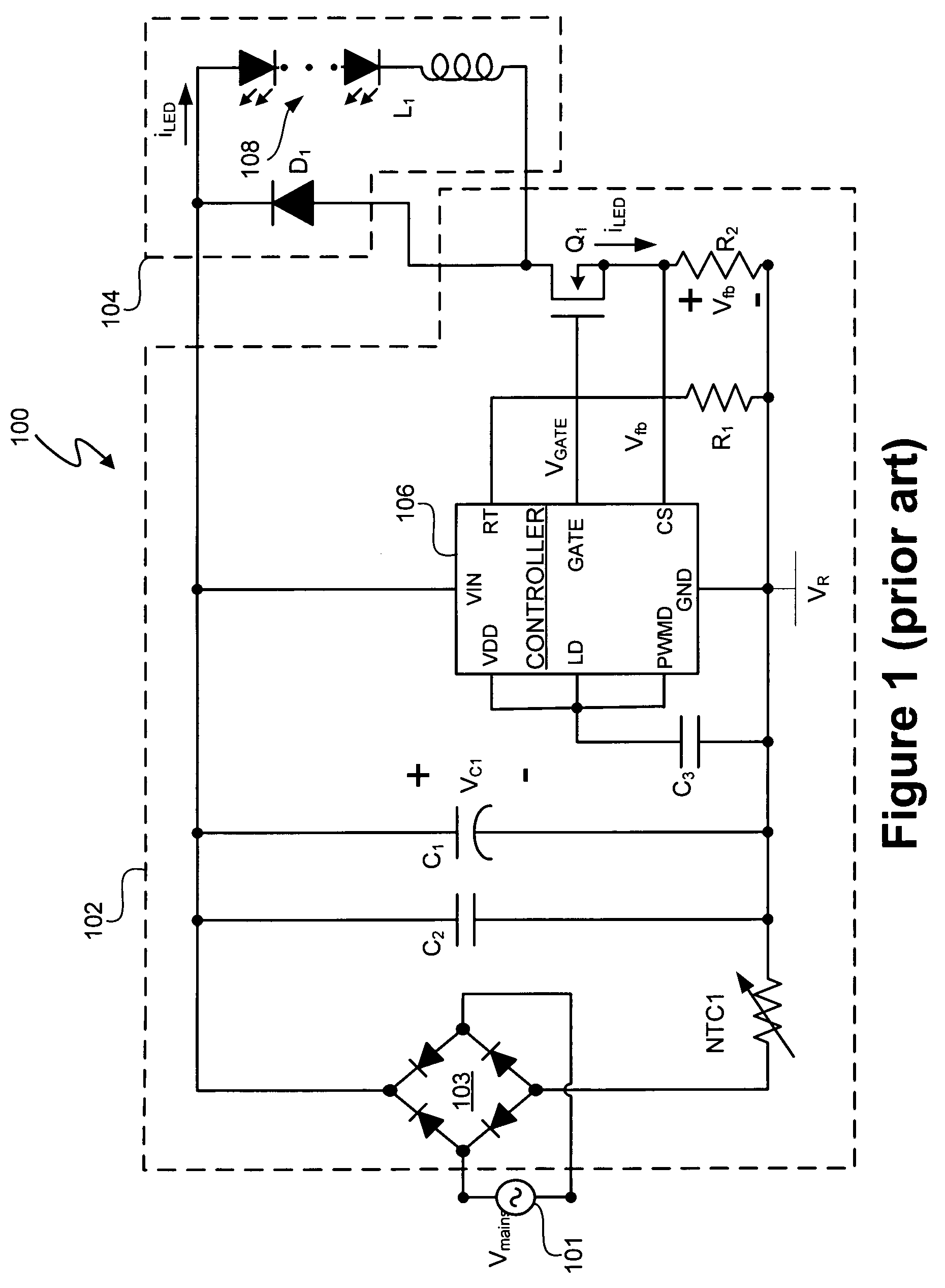
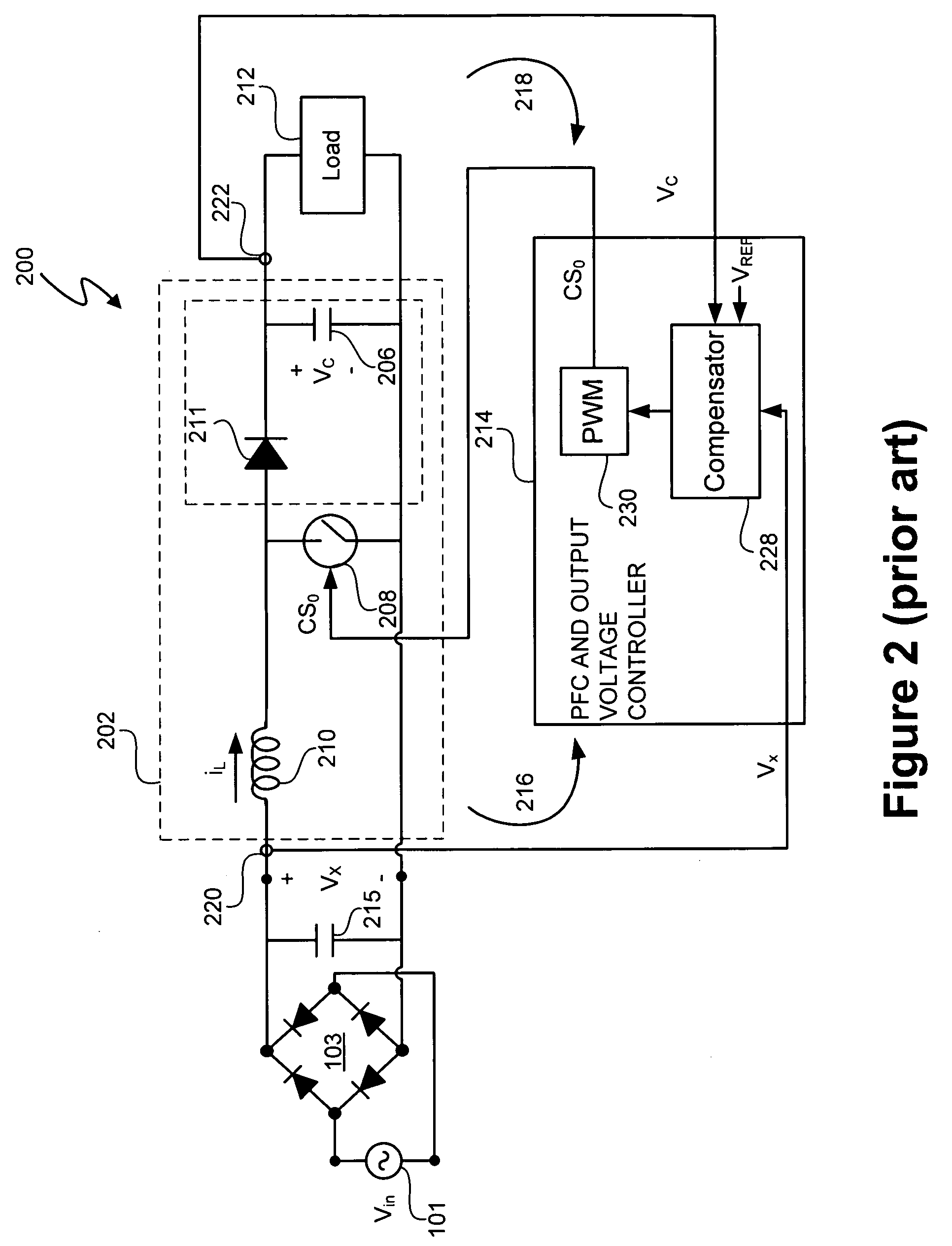
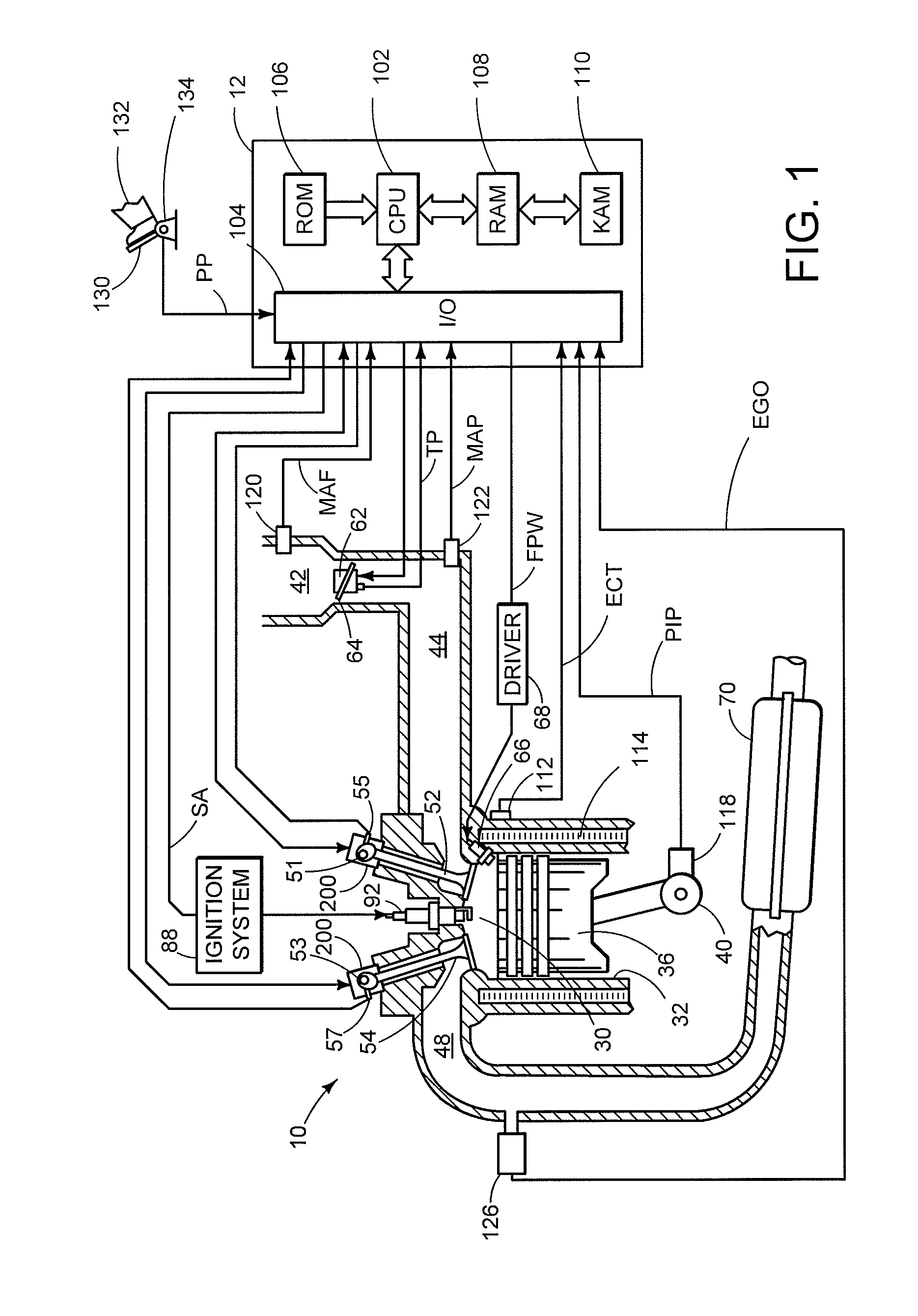
Power control system for current regulated light sources
ActiveUS20080224636A1Electroluminescent light sourcesDc-dc conversionPower control systemEffect light
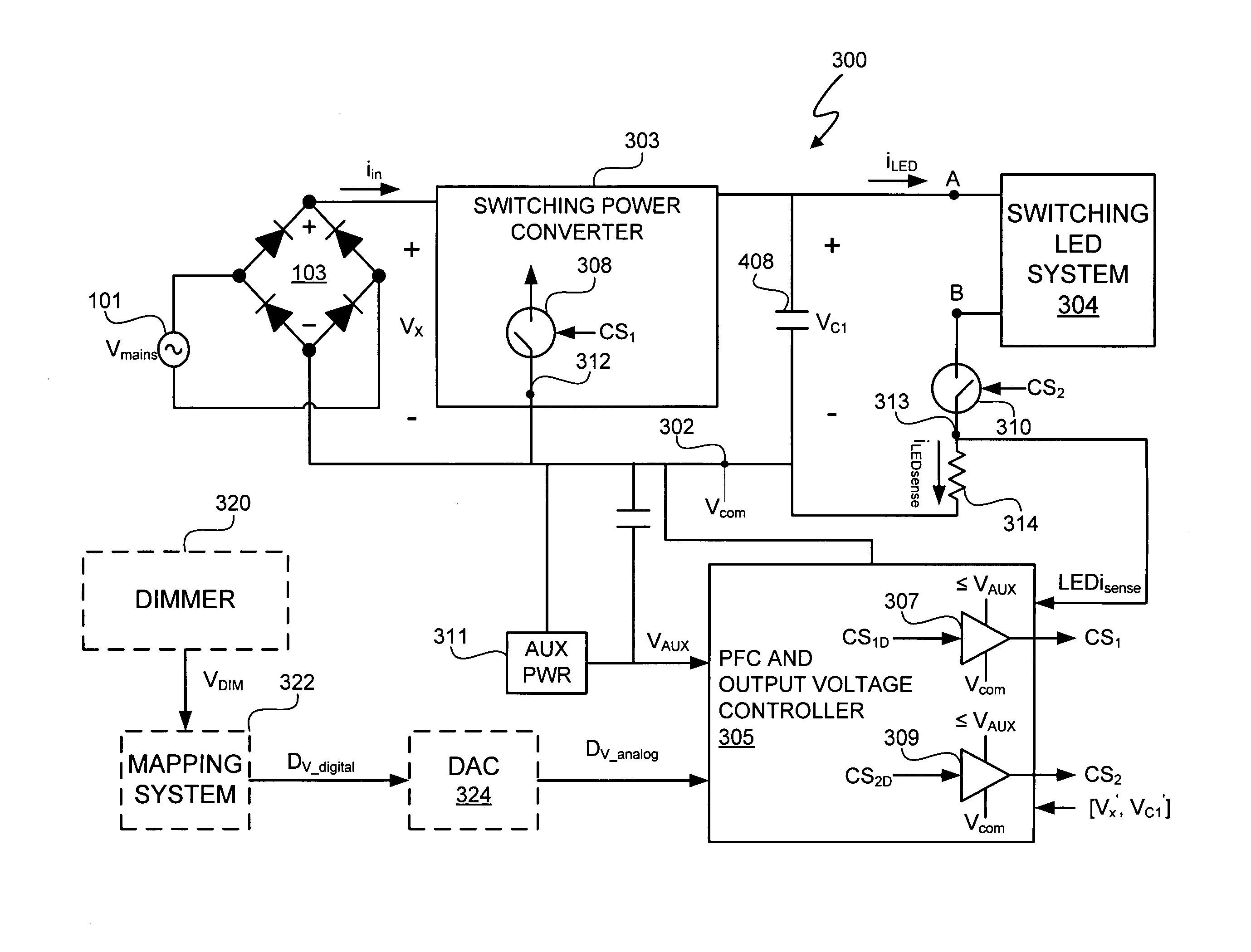
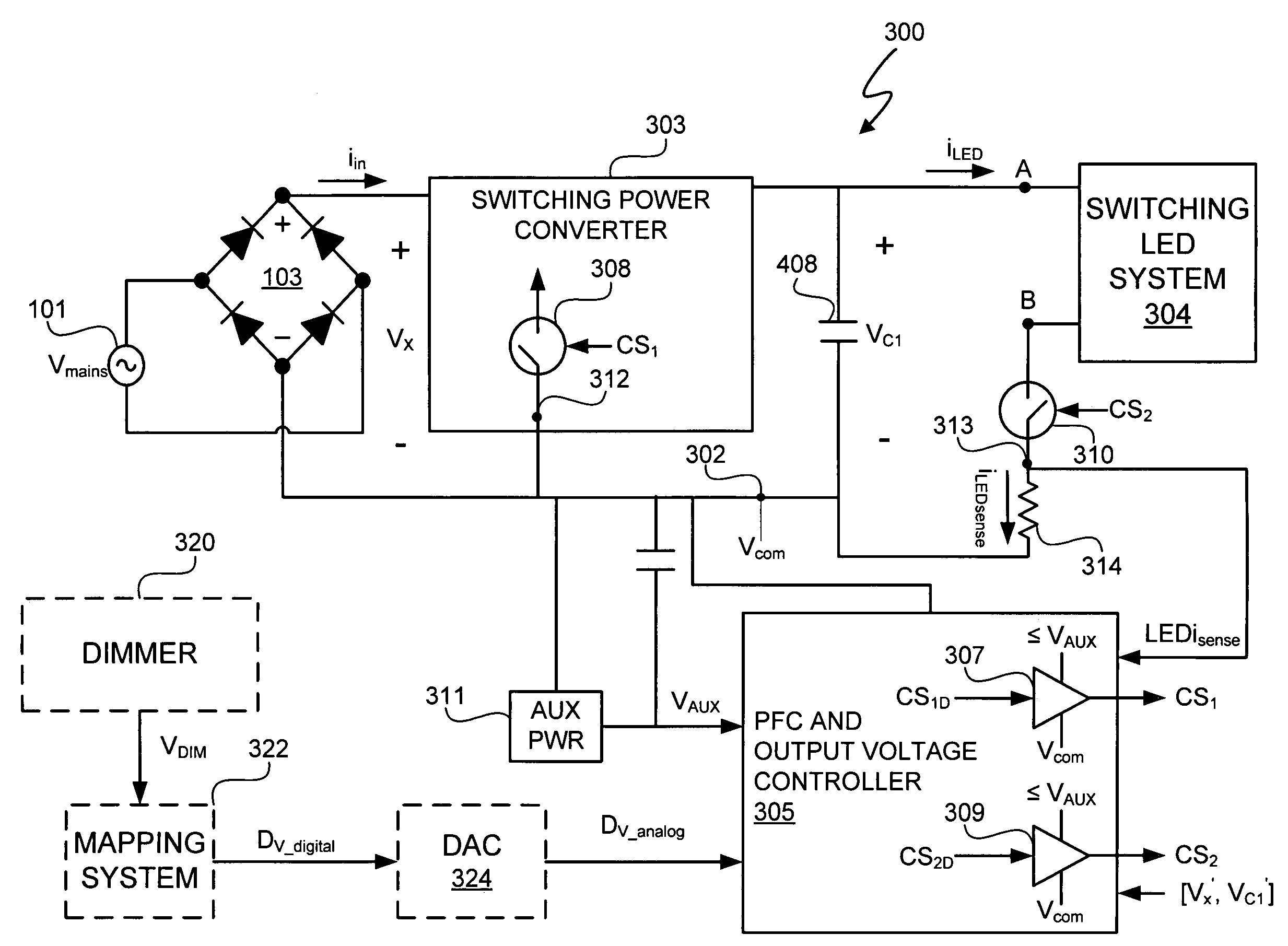
A light emitting diode (LED) lighting system includes a PFC and output voltage controller and a LED lighting power system. The controller advantageously operates from an auxiliary voltage less than a link voltage generated by the LED lighting power system. The common reference voltage allows all the components of lighting system to work together. A power factor correction switch and an LED drive current switch are coupled to the common reference node and have control node-to-common node, absolute voltage that allows the controller to control the conductivity of the switches. The LED lighting system can utilize feed forward control to concurrently modify power demand by the LED lighting power system and power demand of one or more LEDs. The LED lighting system can utilize a common current sense device to provide a common feedback signal to the controller representing current in at least two of the LEDs.
Owner:SIGNIFY HLDG BV
Power control system for current regulated light sources
A light emitting diode (LED) lighting system includes a PFC and output voltage controller and a LED lighting power system. The controller advantageously operates from an auxiliary voltage less than a link voltage generated by the LED lighting power system. The common reference voltage allows all the components of lighting system to work together. A power factor correction switch and an LED drive current switch are coupled to the common reference node and have control node-to-common node, absolute voltage that allows the controller to control the conductivity of the switches. The LED lighting system can utilize feed forward control to concurrently modify power demand by the LED lighting power system and power demand of one or more LEDs. The LED lighting system can utilize a common current sense device to provide a common feedback signal to the controller representing current in at least two of the LEDs.
Owner:SIGNIFY HLDG BV
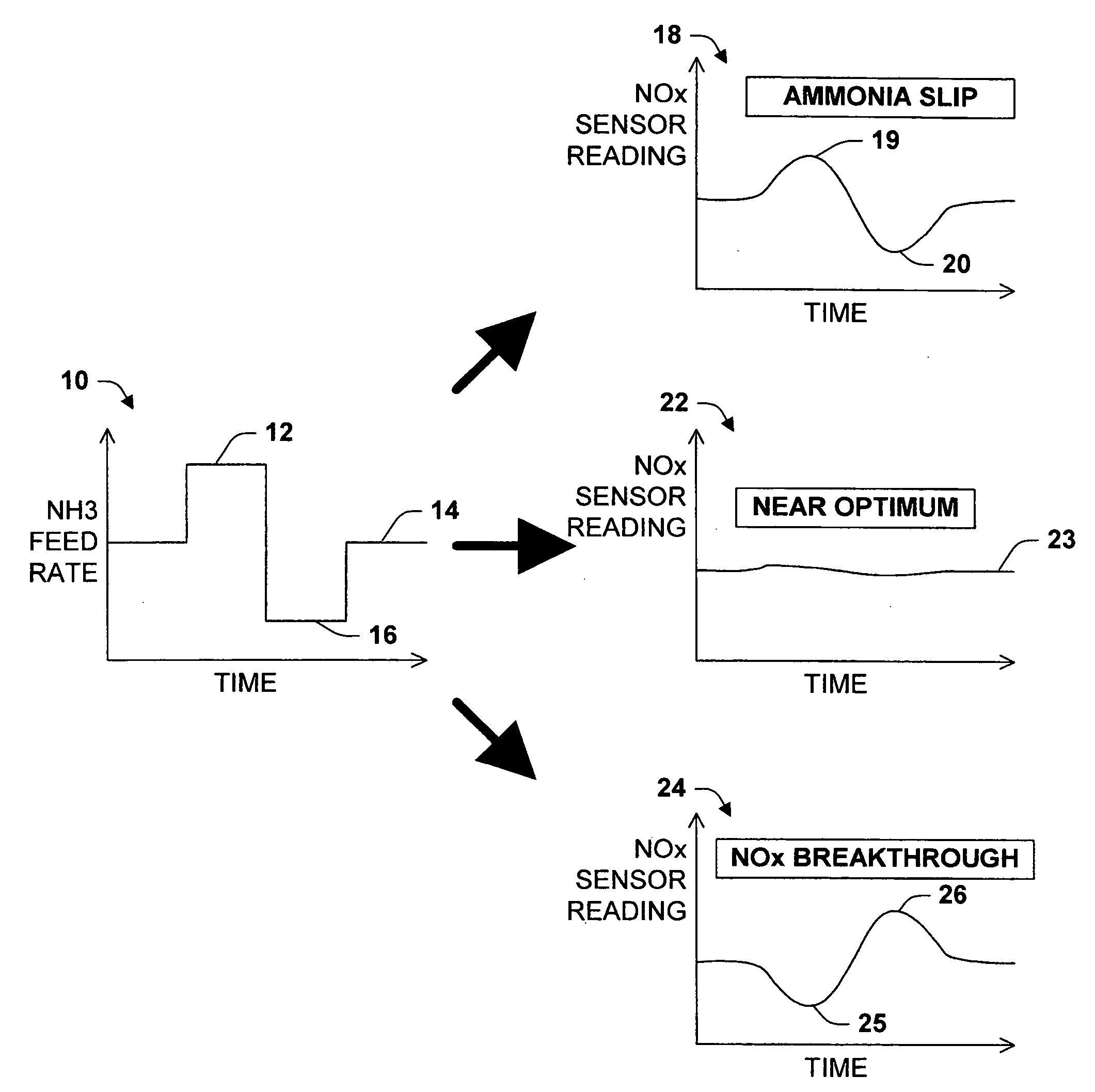
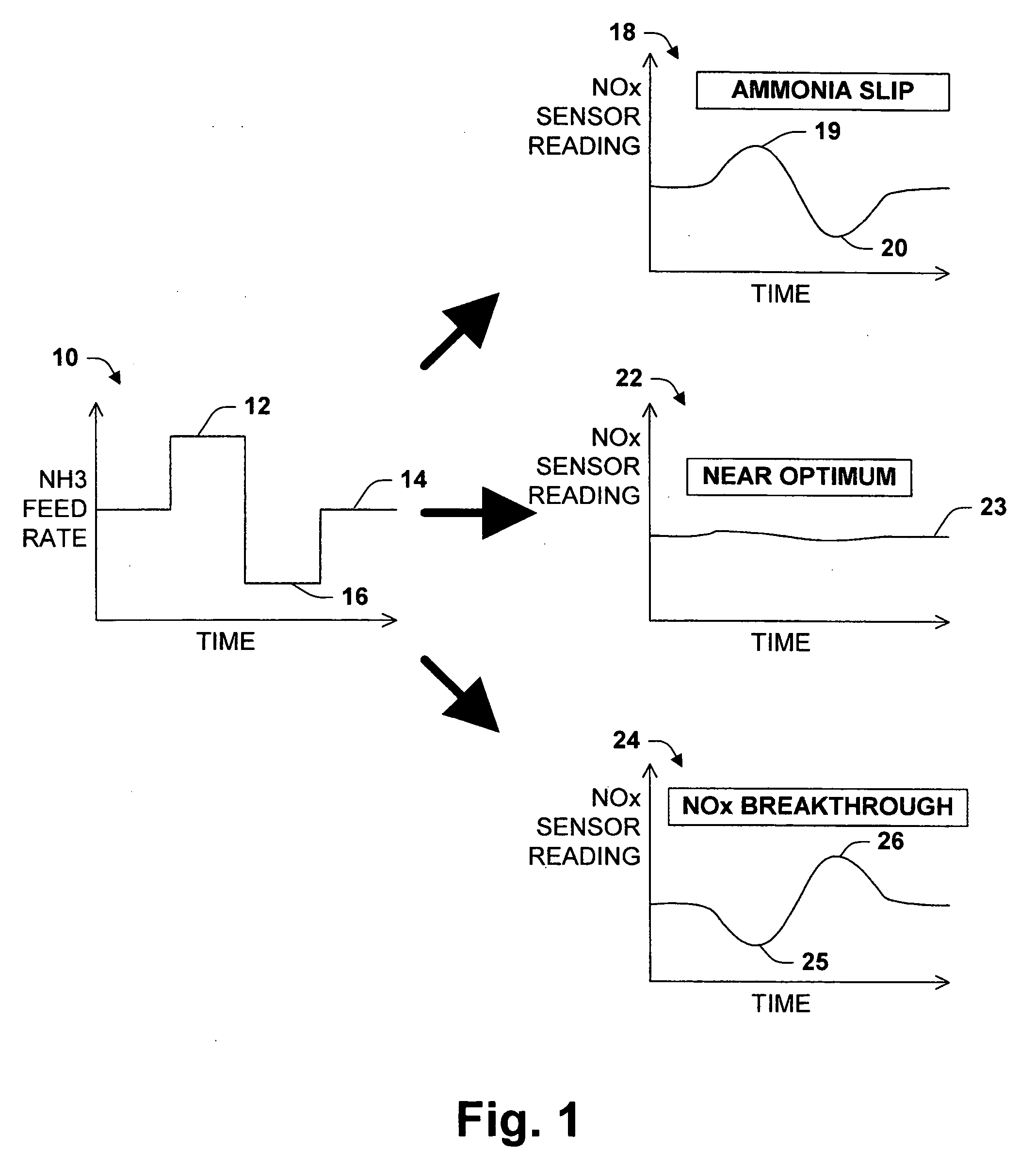
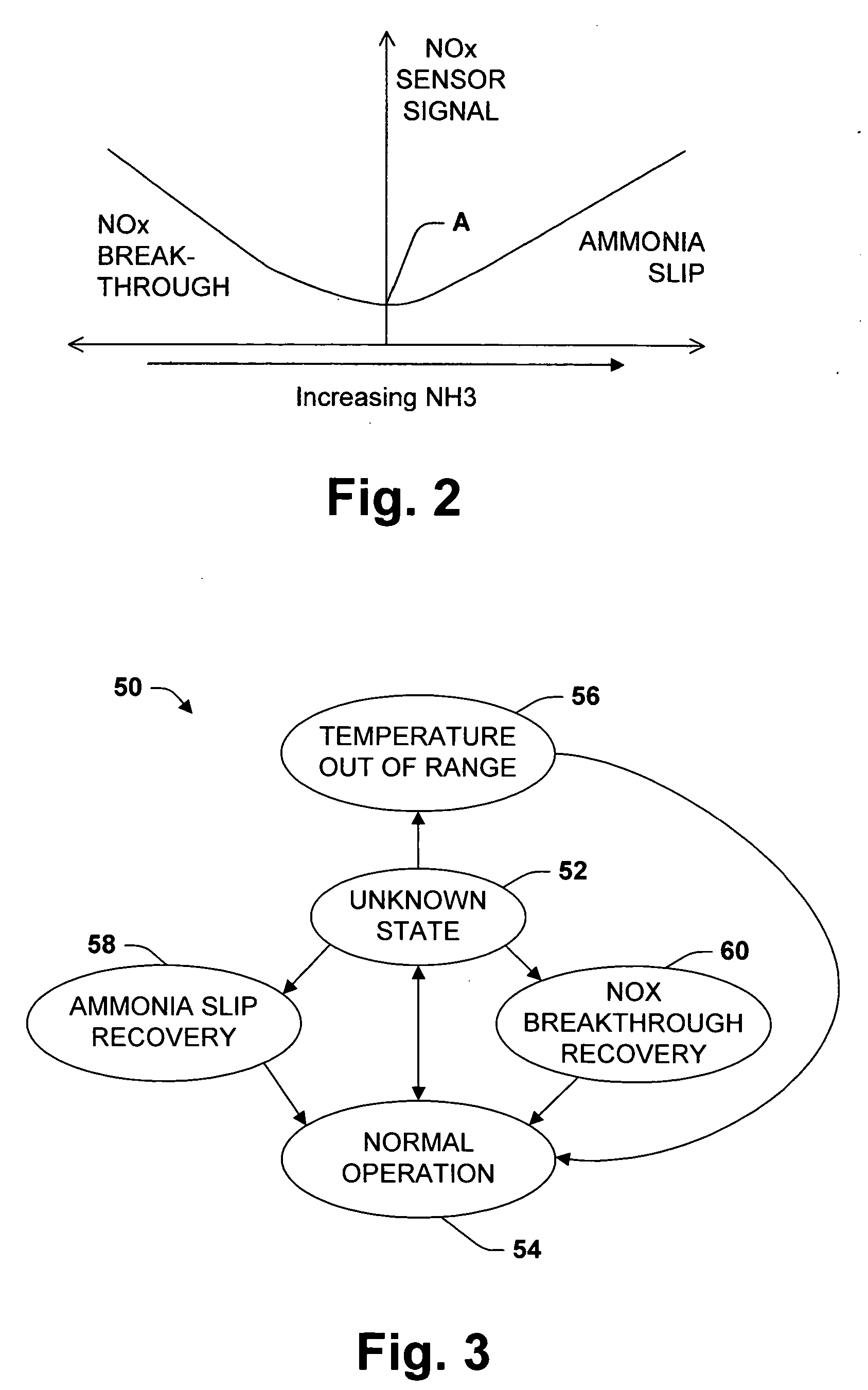
Strategy for controlling NOx emissions and ammonia slip in an SCR system using a nonselective NOx/NH3
InactiveUS20050282285A1Internal combustion piston enginesExhaust apparatusControl objectivePositive response
One aspect of the invention relates to controlling the ammonia feed rate to an SCR reactor using a NOx sensor cross-sensitive to ammonia. The sensor, positioned downstream of the reactor, is interrogated by introducing a pulse in the ammonia feed rate. A positive response to a positive pulse indicates ammonia slip. A negative response to a positive pulse indicates NOx breakthrough. Another aspect of the invention related to a combination of feed-back and feed-forward control. Upon detecting ammonia slip, the controller enters into an ammonia slip recovery mode in which the ammonia feed rate is reduced for a period to restore the reactor's ammonia or NOx buffering capacity. After the recovery period, feed-forward control is restored, optionally with an updated control objective. A further aspect of the invention relates to a learning probabilistic model for feed-forward control trained according to the occurrence or non-occurrence of NOx breakthrough and ammonia slip.
Owner:EATON CORP
Active noise control system
InactiveUS7062049B1Noise can be canceled outEasy to getEar treatmentNoise generationTrunk compartmentNoise control
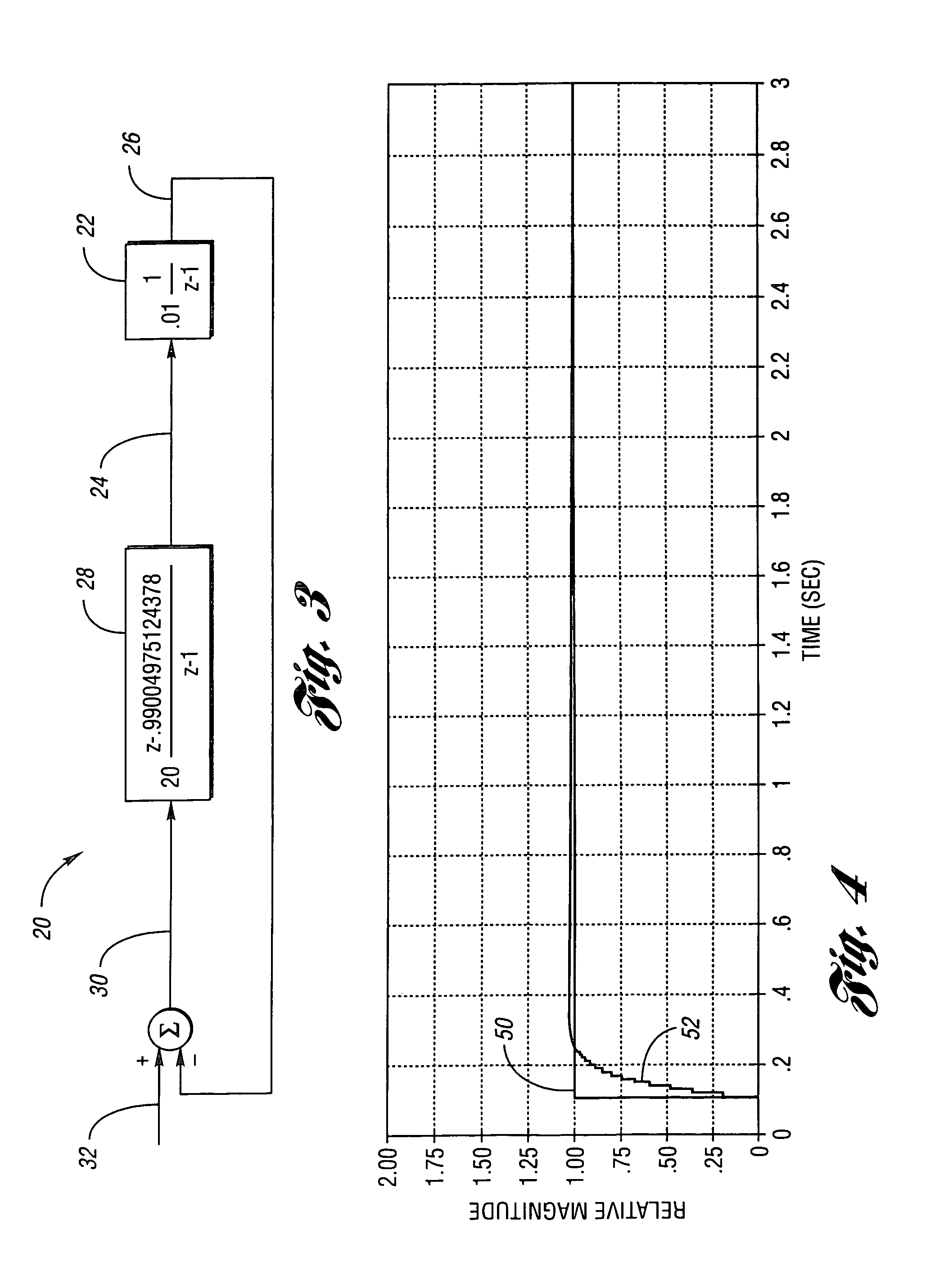
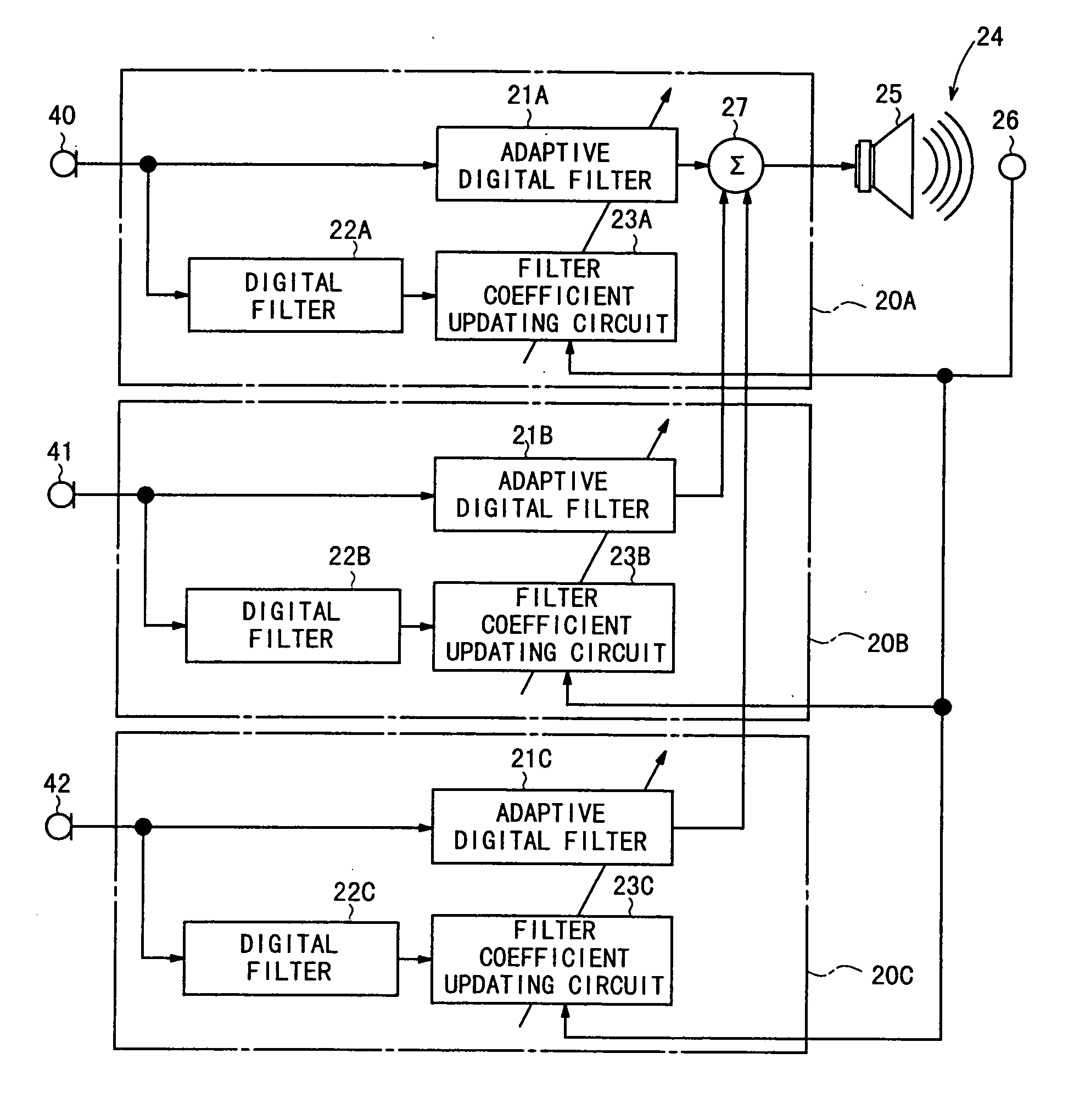
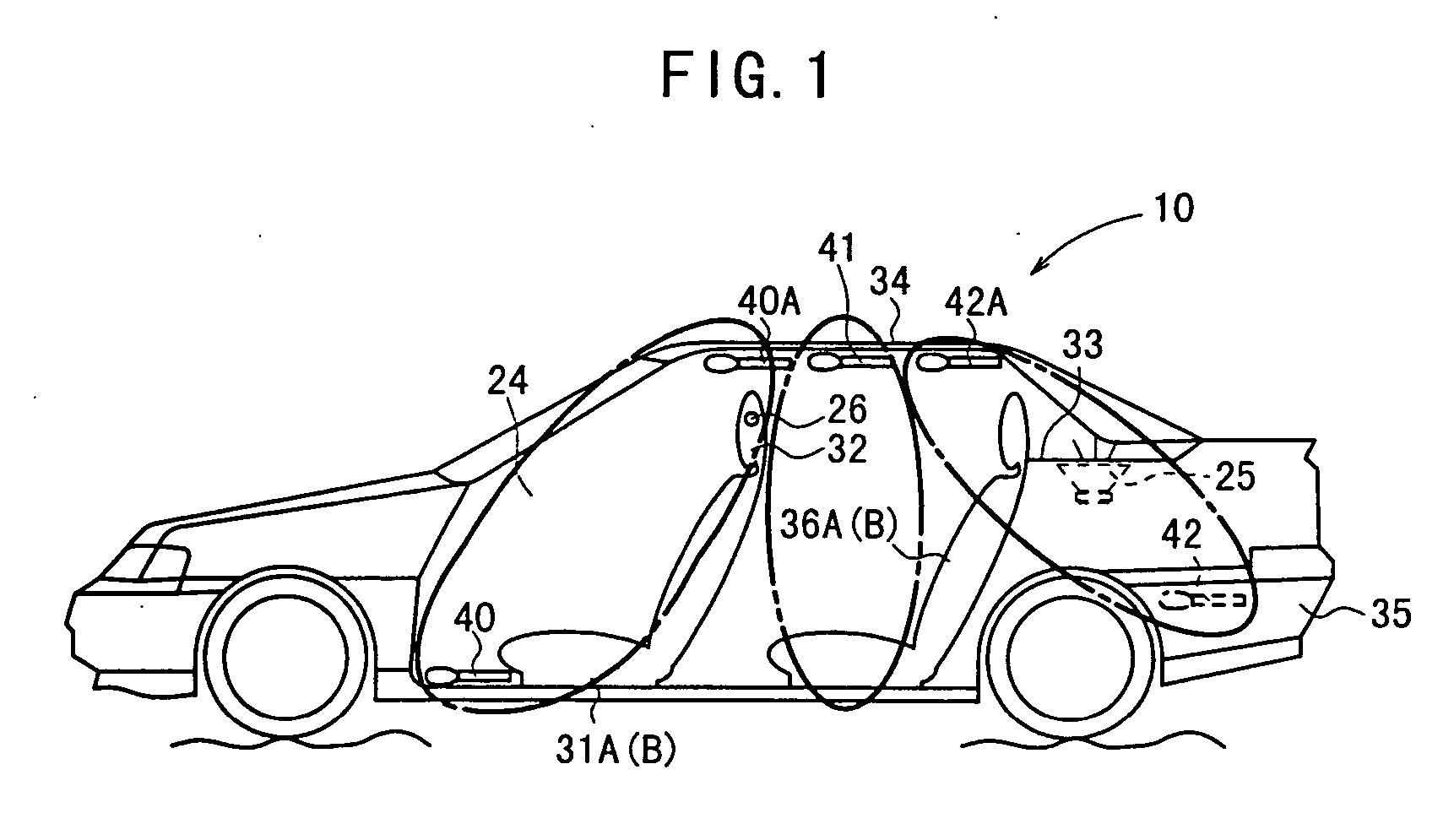
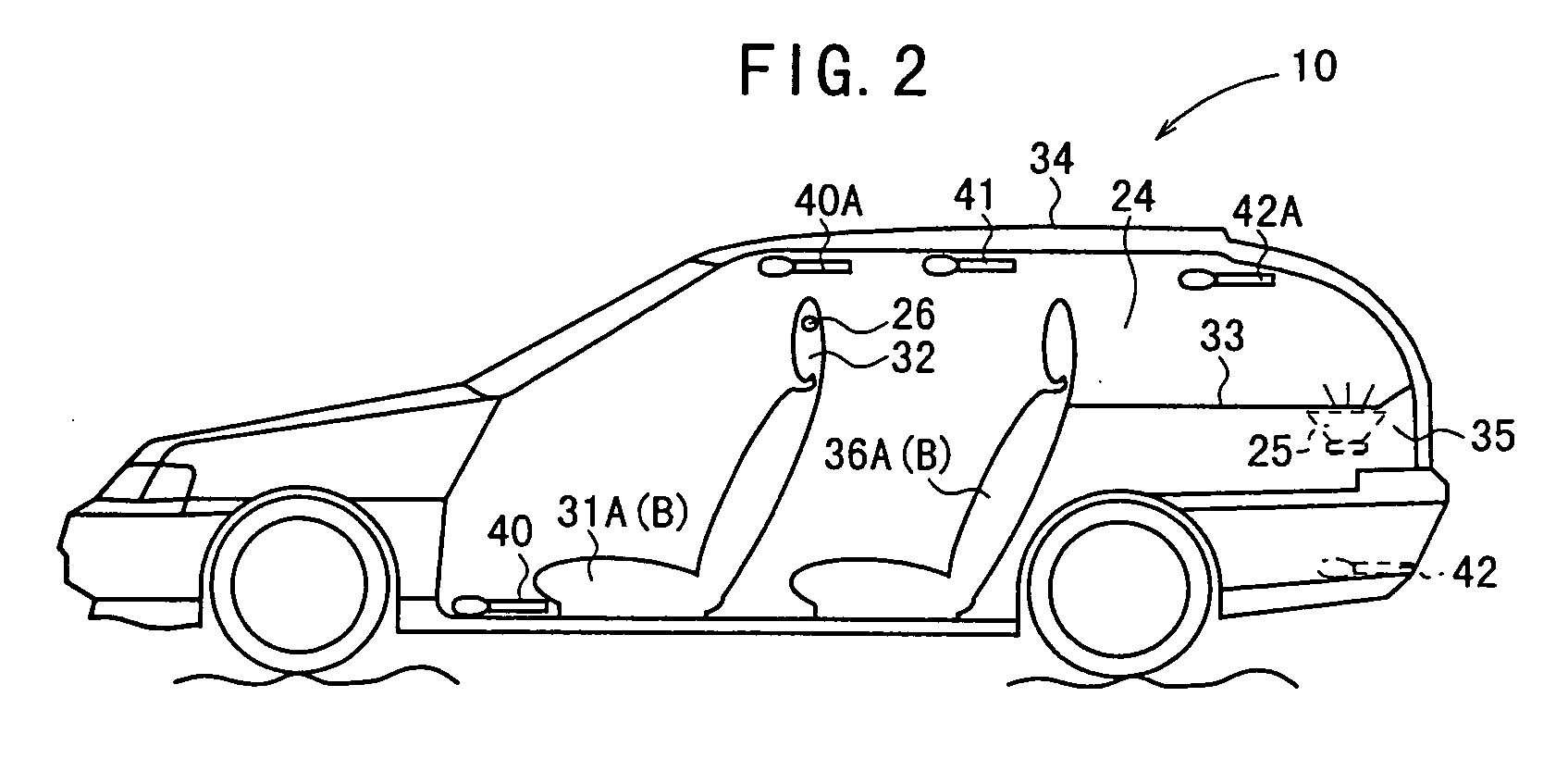
An active noise control system is capable of canceling out noise in the passenger compartment of a vehicle based on low-frequency road noise. The active noise control system has a feed-forward control unit for being supplied with reference signals highly correlated to noise from a noise source and generating a noise cancellation signal which is out of phase to noise in the passenger compartment of the vehicle, and a canceling sound generating unit disposed in the passenger compartment for generating a noise canceling sound in response to the noise cancellation signal from said feed-forward control unit. The active noise control system also has microphones for generating reference signals which are positioned respectively near the base of the front seat, near the center of a roof, and within a trunk compartment, i.e., respectively at vibrational antinodes of a primary or secondary acoustic normal mode of the passenger compartment in the longitudinal direction thereof. Output signals from the microphones are supplied as the reference signals.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD +1
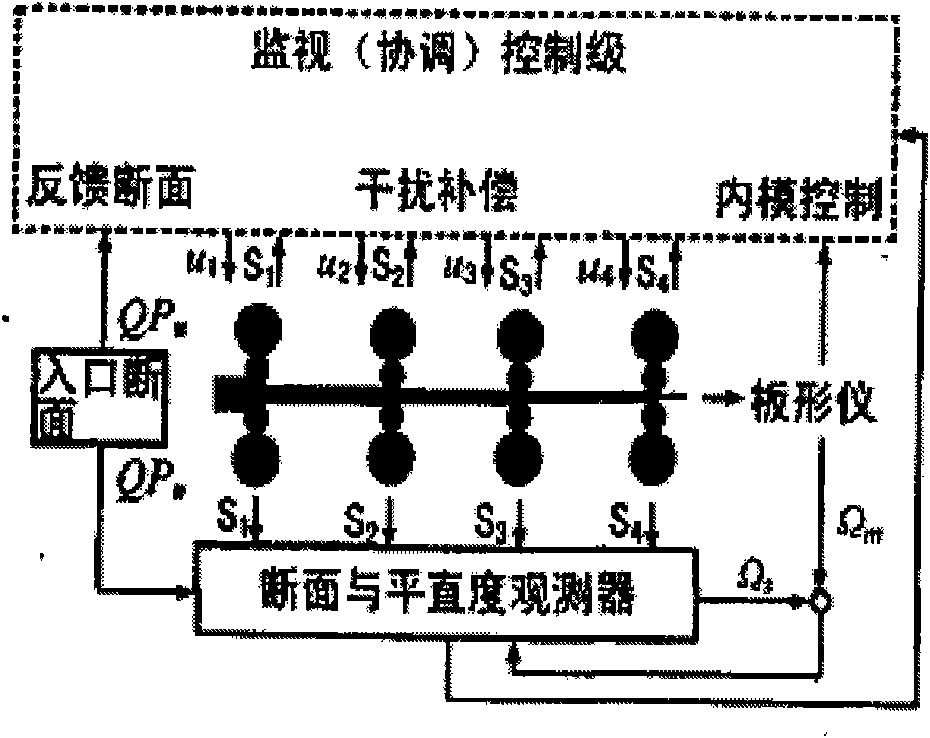
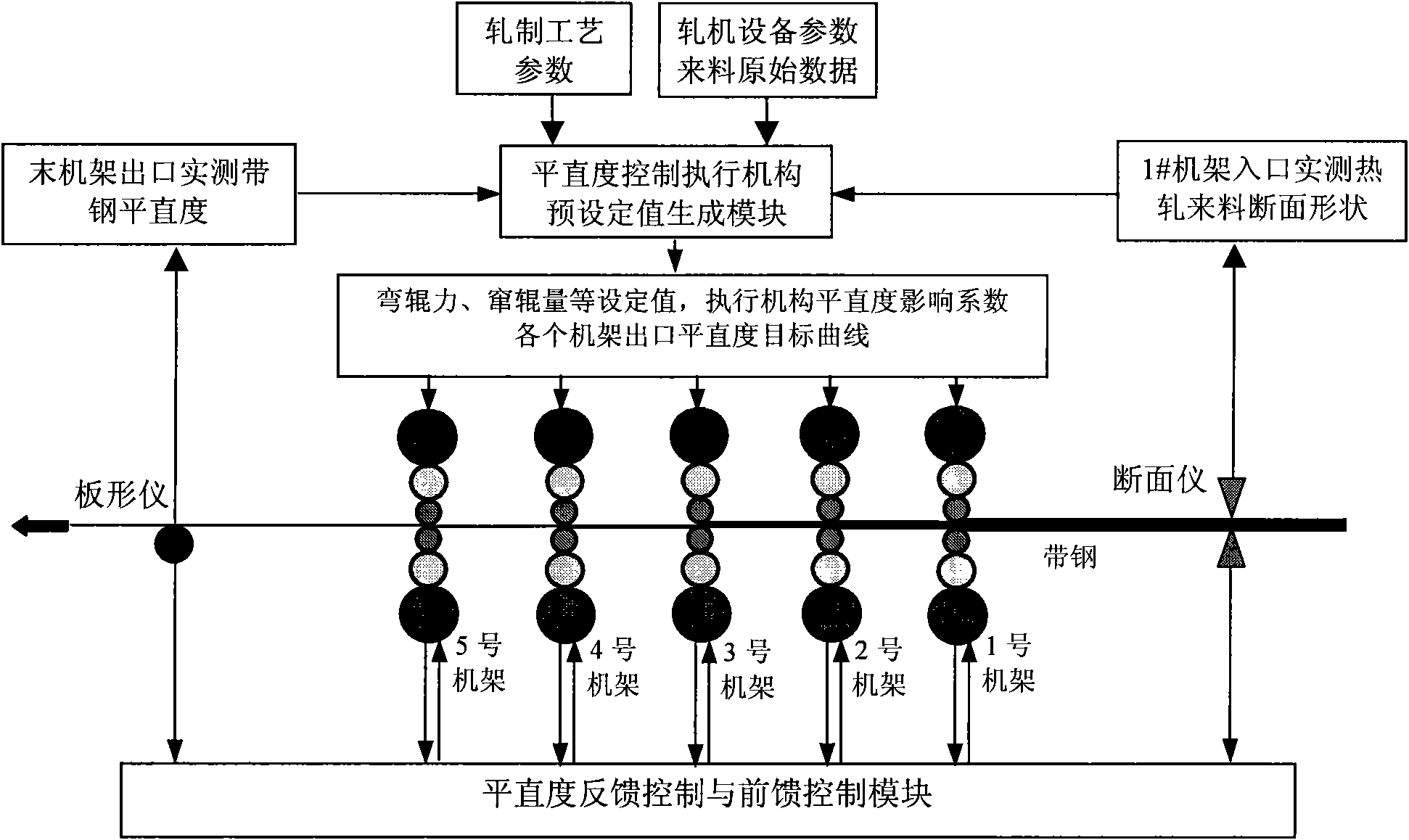
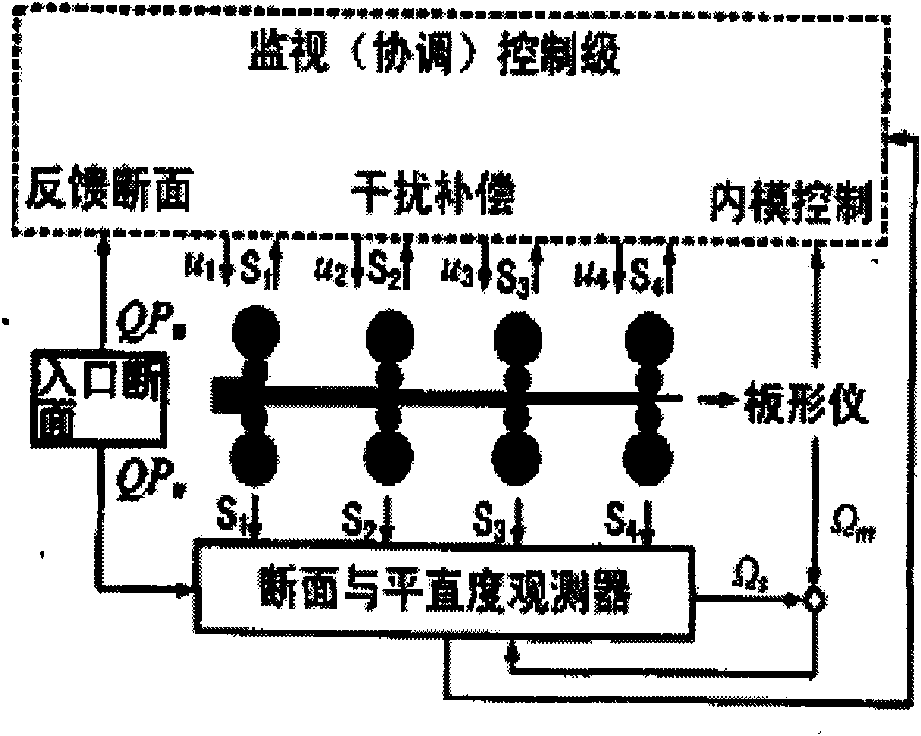
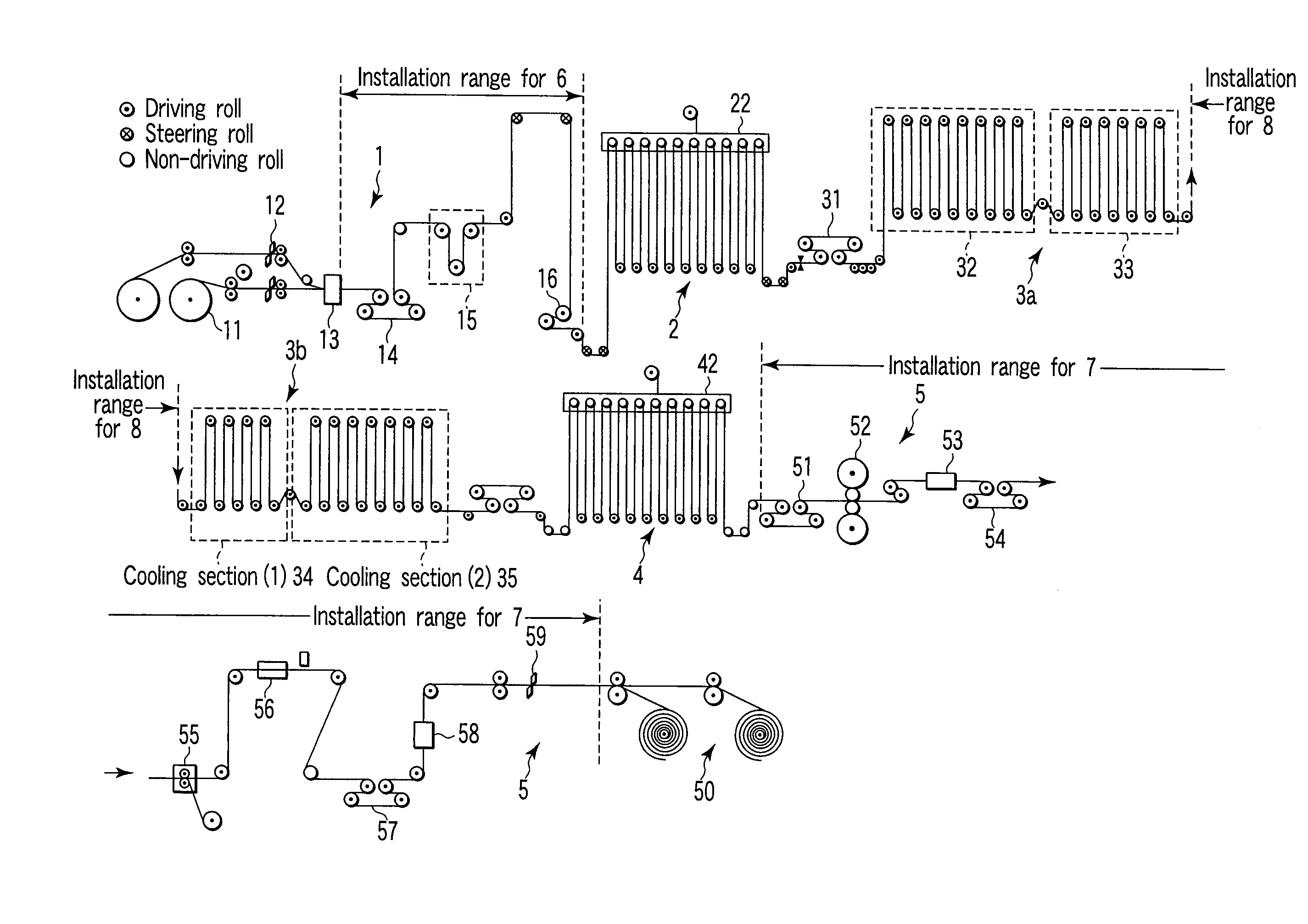
Method for controlling planeness of cold-rolling strip steel
ActiveCN101618402ARealize coordinated controlAccurate detectionRare end control deviceTemperature control deviceAutomatic controlEngineering
The invention discloses a method for controlling the planeness of cold-rolling strip steel, which comprises the following steps of: carrying out planeness feed-forward control, planeness feedback control and coordination control between both; detecting the cross-section shape and the planeness of a hot rolling incoming material, and actually-measured rolling technological parameters of each frame in real time based on a profiler configured on a No. 1 frame inlet, wherein the parameters comprise rolling force actually-measured values and plate shape adjusting mechanism actually-measured values, and carrying out the feed-forward control on the planeness of each frame outlet; and actually measuring the planeness of the cold-rolling strip steel based on a plate shape roller configured on an outlet of a cold rolling mill, and intensively carrying out the feedback control on the planeness of a final frame outlet. The method can eliminate the influences of the cross-section shape and the planeness of the hot rolling incoming material and fluctuations of the rolling technological parameters on the planeness of the final frame outlet to improve the planeness quality of the cold-rolling strip steel on the one hand, and can automatically control the planeness of each frame outlet, reduce incidence of abnormal conditions, such as fracture surfaces, deviation and the like, and improve the stability in the production process of tandem cold strip rolling on the other hand.
Owner:BAOSHAN IRON & STEEL CO LTD
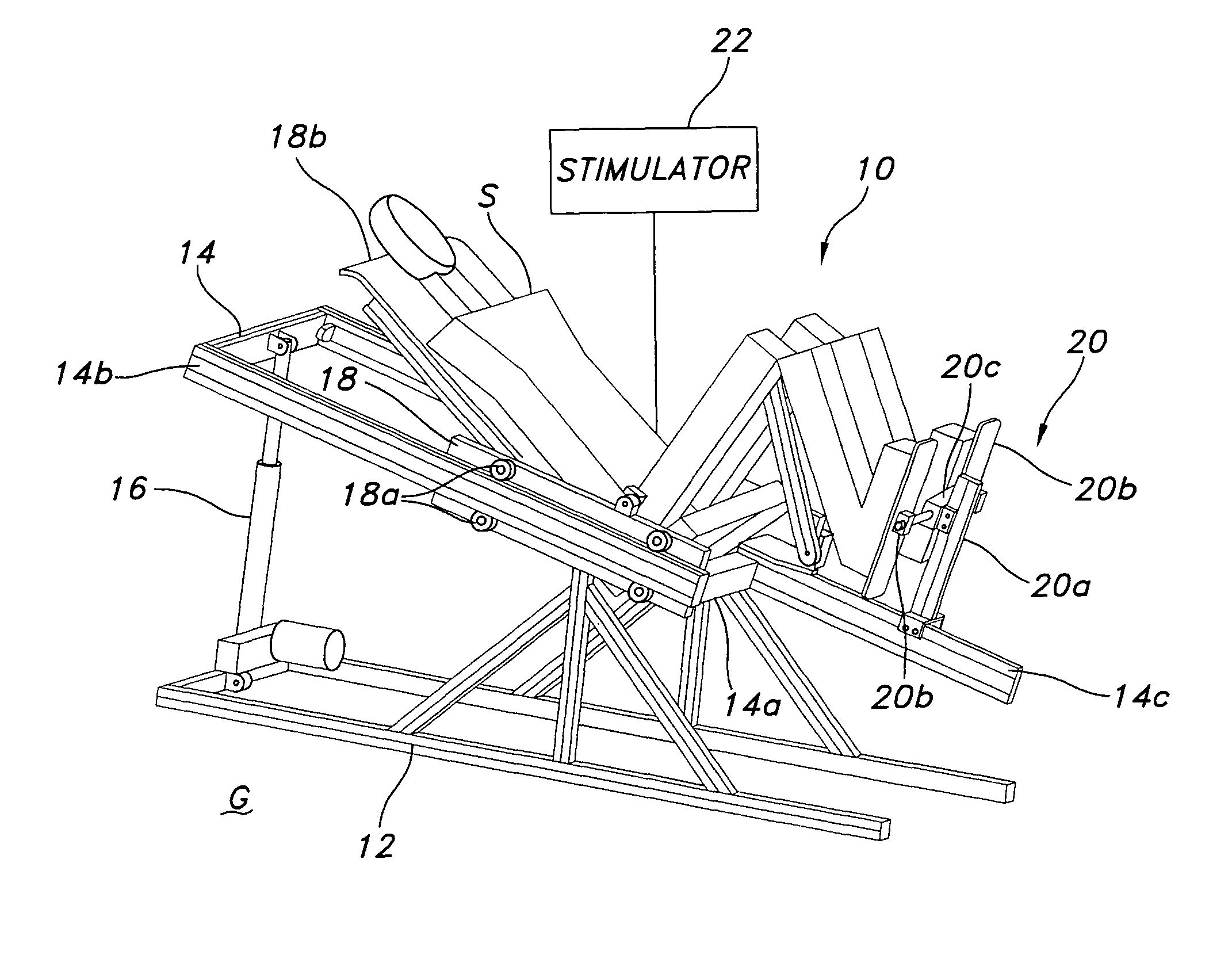
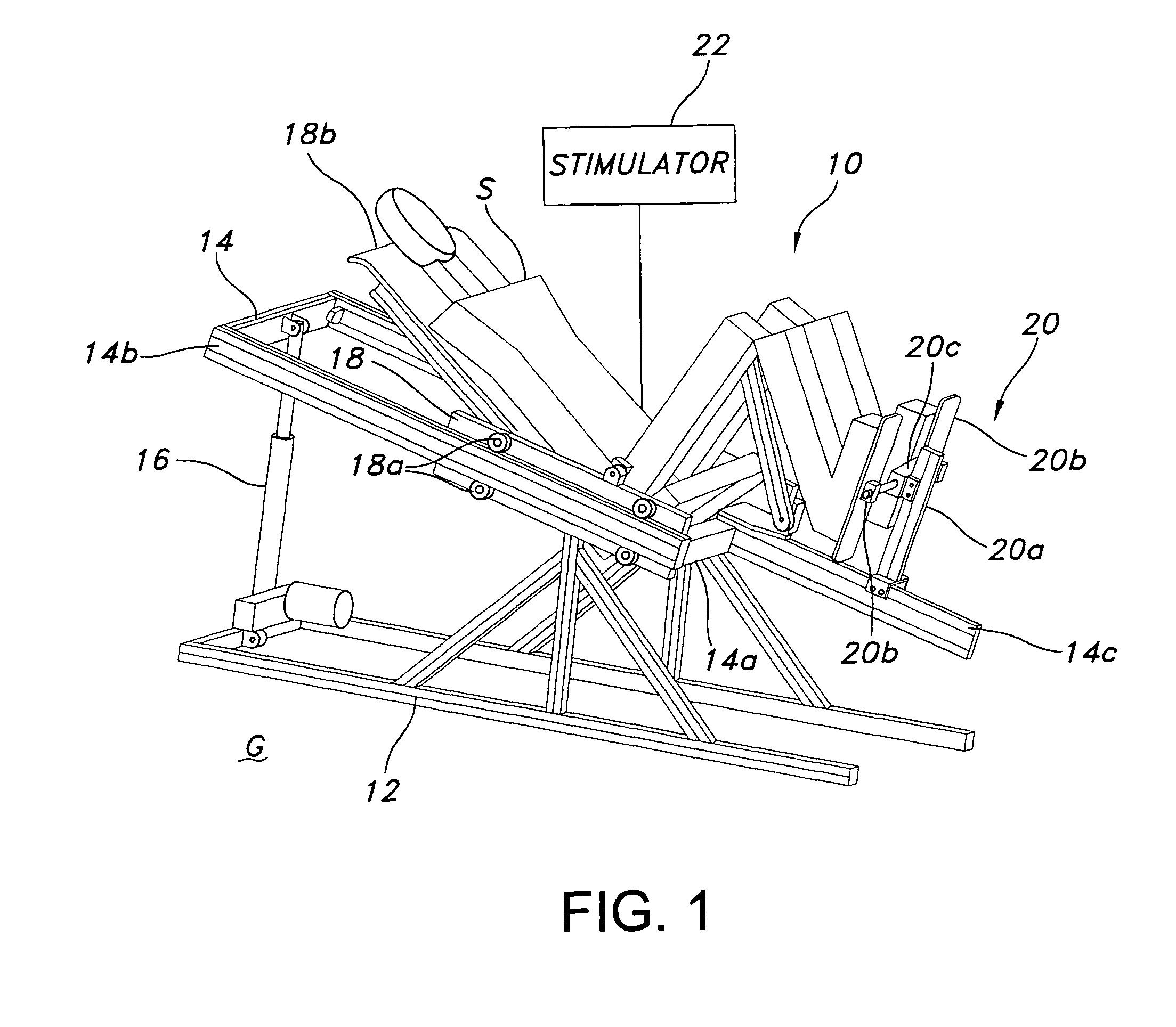
Lower extremity exercise device with stimulation and related methods
Owner:CUSTOMKYNETICS
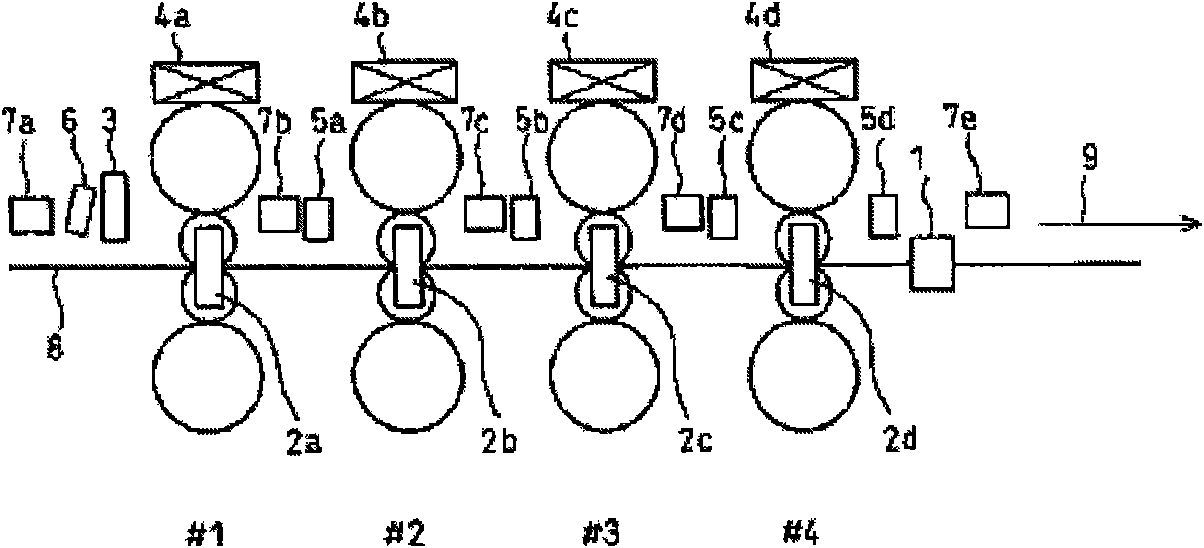
Integrated control method of cold-rolling strip steel flatness and lateral thickness difference
ActiveCN101683659AImprove stabilityGuaranteed stabilityMetal rolling arrangementsProfile control deviceStrip steelFeedback control
The invention discloses an integrated control method of cold-rolling strip steel flatness and lateral thickness difference, comprising: moderately and mainly controlling the shape of the strip steel section on the upstream rack of a cold-rolling mill, and mainly controlling strip steel flatness on the downstream rack; based on a profiler configured on a No.1 rack inlet of the cold-rolling mill, actually measuring and hot rolling incoming material section shape and flatness and rolling technological parameter measured values of each rack, wherein the rolling technological parameter measured values comprise rolling force and a plate shape regulating mechanism measured value; actually measuring the cold-rolling strip steel flatness on the basis of a shape meter configured on the cold-rollingmill outlet; performing feed-forward control to the shape of the strip steel section by taking the upstream rack, in particular the No. 1 rack as a key point; and performing feedback control to the strip steel flatness by taking the downstream rack, in particular an end rack as a key point to realize integrated control to the cold-rolling strip steel flatness and lateral thickness difference. Theinvention performs integrated coordination control by the strip steel flatness and section shape and reduces cold-rolling strip steel lateral thickness difference on the basis of further improving cold-rolling strip steel flatness quality.
Owner:BAOSHAN IRON & STEEL CO LTD
Anaerobic digester system
InactiveUS6296766B1Easy to monitorEasy to controlData processing applicationsBiological treatment regulationGrowth plantEnvironmental engineering
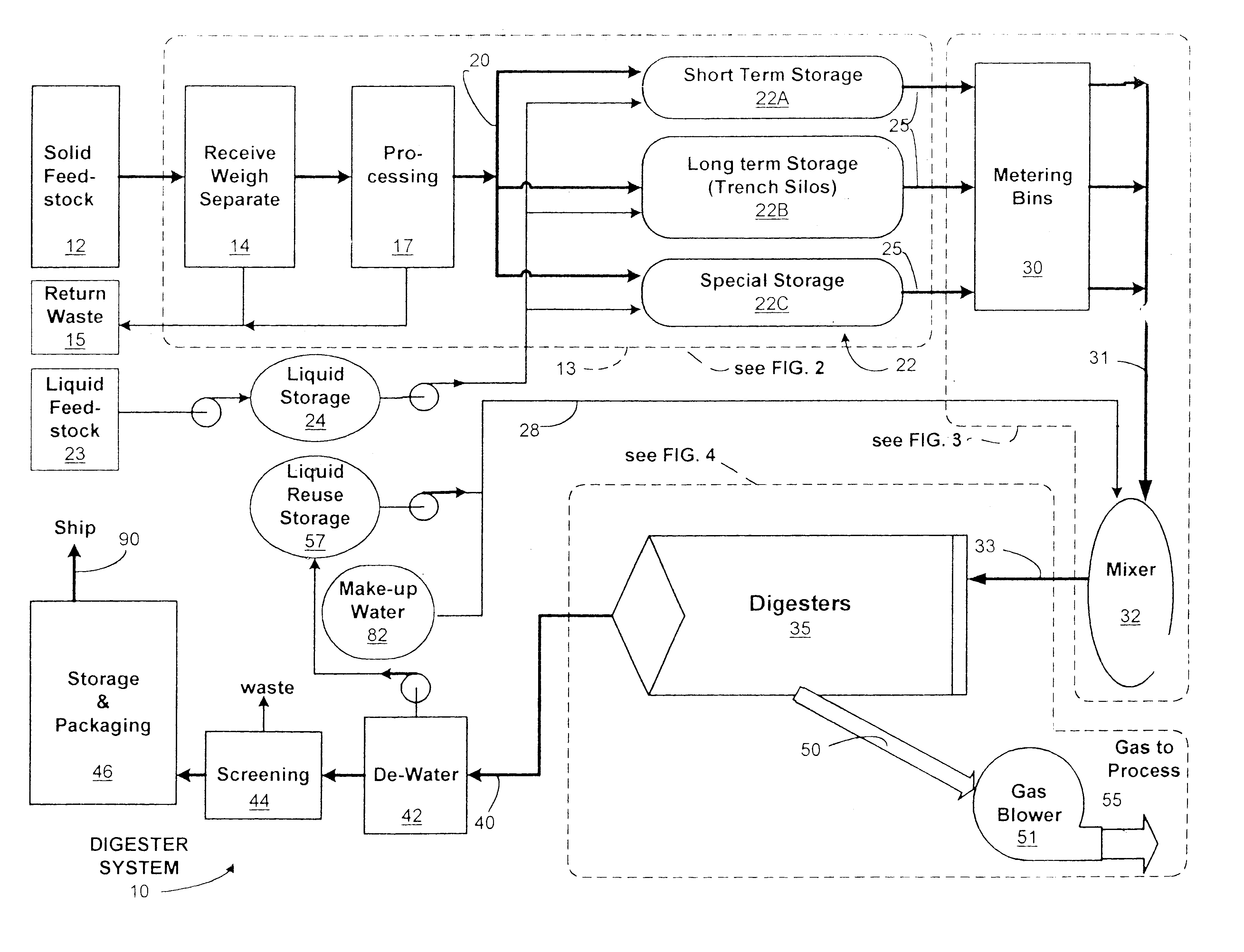
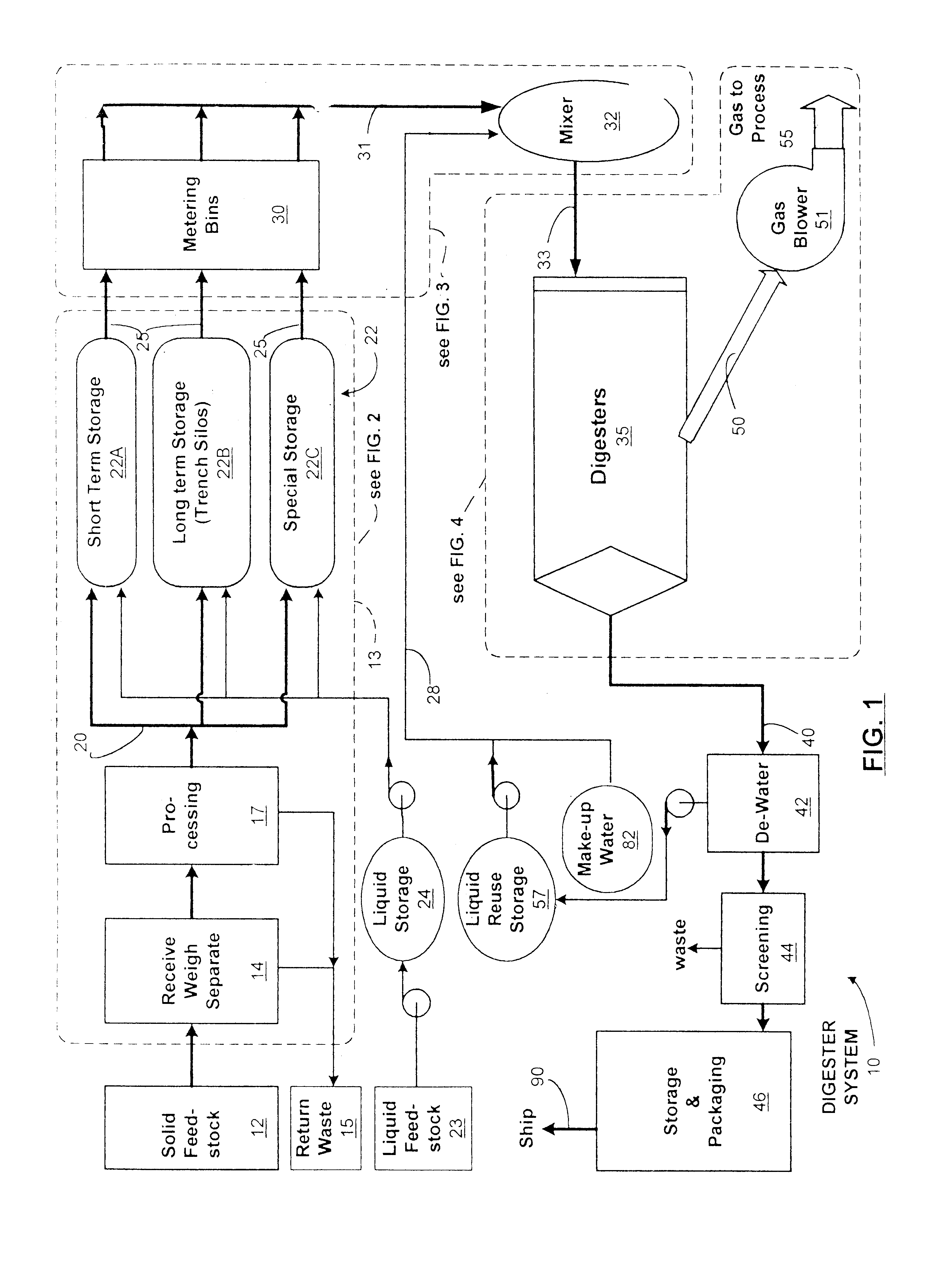
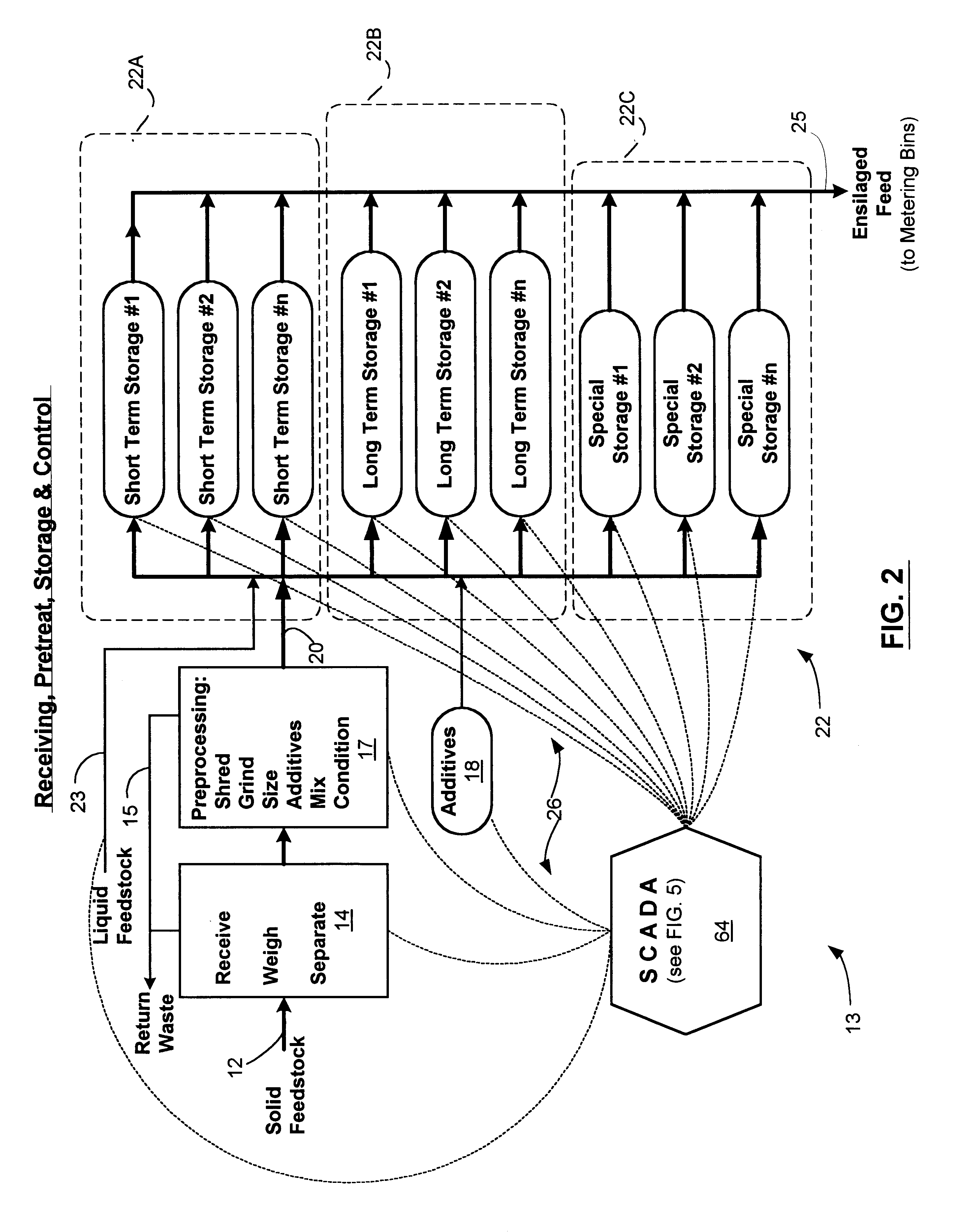
A method for an anaerobic digester system is provided that employs a cumulative data base to better monitor and control the anaerobic process, as compared with conventional anaerobic digester systems. The method includes the storing and ensiling of a feedstock, preferably a biomass, to form a digester feed material, which then processed by a digester. The process evolves a biogas and forms a digested material. The process is monitored, to collect a plurality of digester data from all stages of the process. These individual points or elements of the data are telemetered to a cumulative data base for storage and eventual retrieval and the cumulative data base is mined to compile predictive, feed forward controls and construct feedstock correlations between the metabolic activity within the digesters and an analysis of the feedstocks into the digesters. The method further includes the production of a high quality plant growth media from the digested mash, and recovery of the biogas generated within the digester. The biogas is collected with the aid of a biogas recovery system. The biogas is predominantly methane, and the anaerobic digester system is preferably operated to maximize the quantity and quality of methane generated.
Owner:TECHN INFORMATION
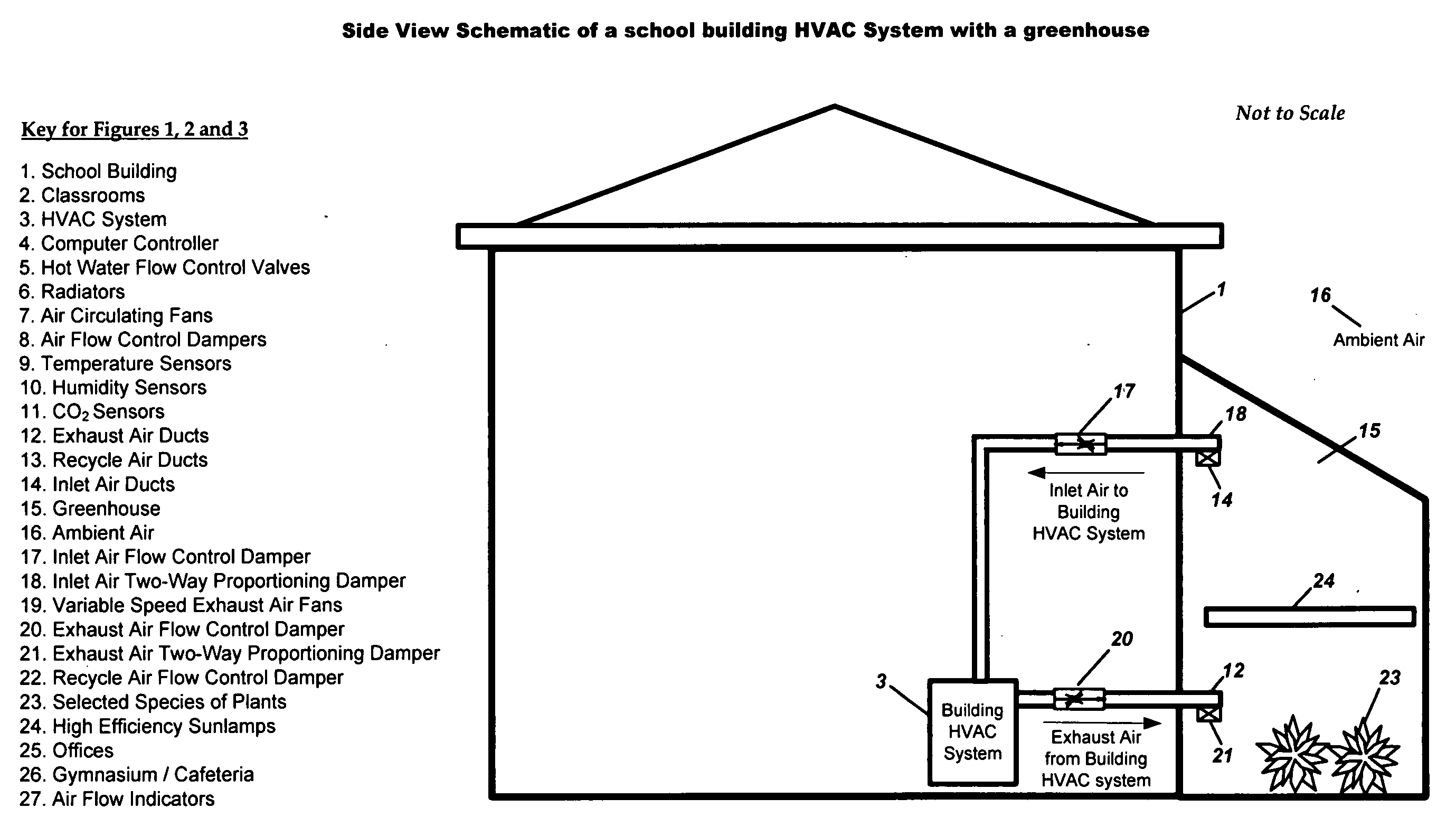
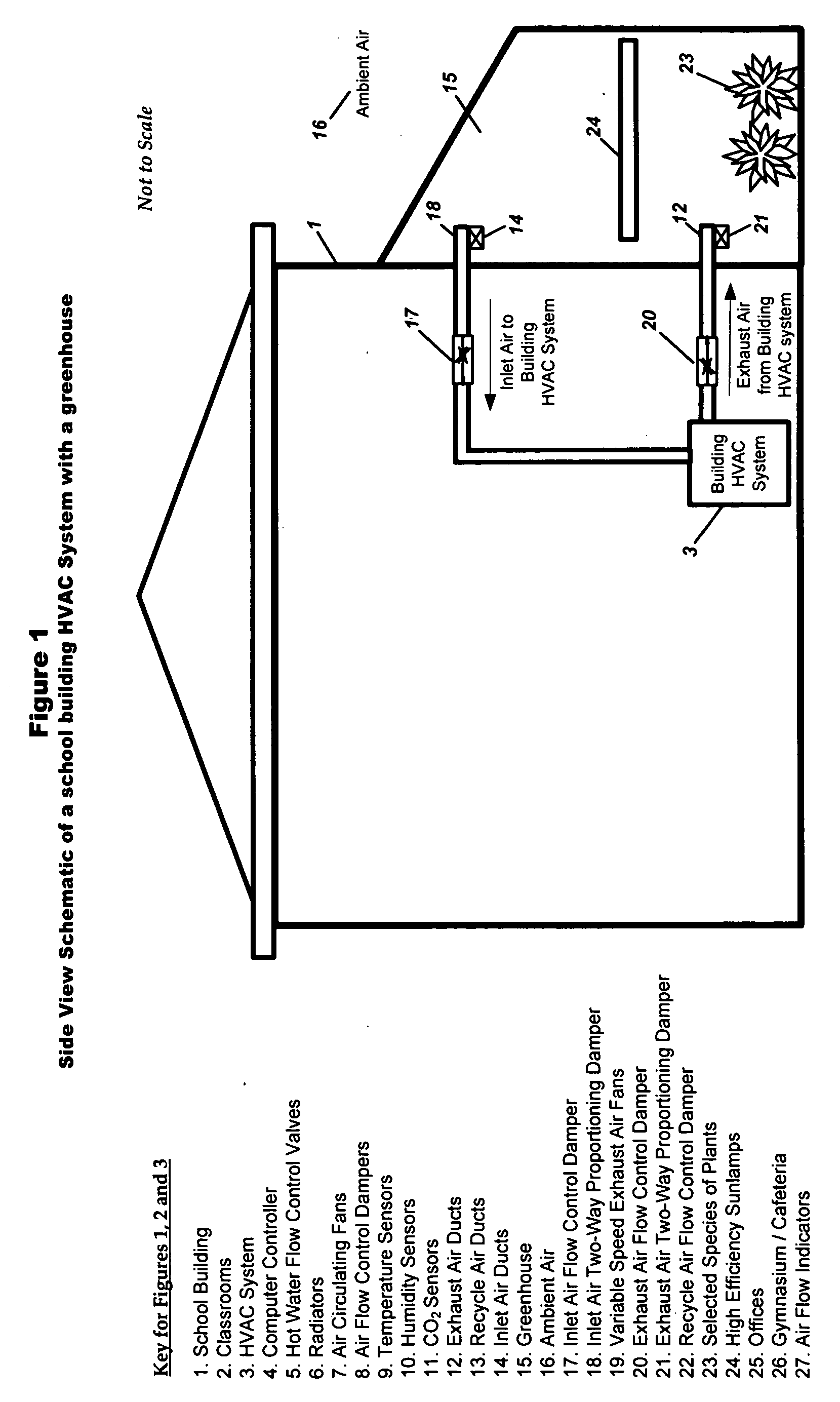
System for improving both energy efficiency and indoor air quality in buildings
InactiveUS20080014857A1Recover heat and humidityImprove indoor air qualityMechanical apparatusSpace heating and ventilation safety systemsIndoor air qualityGreenhouse
A building's Heating Ventilating and Air Conditioning (HVAC) system is made more energy efficient and the indoor air quality (IAQ) of the building's circulating air is improved by incorporating a greenhouse as an integral part of the HVAC system and by utilizing a novel feed forward control strategy that maintains the proper levels of temperature, humidity and CO2 concentration in the building under varying conditions of day, time, use and occupancy.A portion or all of the exhaust air from the building is discharged into a greenhouse where the heat and humidity are recovered in the winter by heating the greenhouse and the air conditioning is recovered in the summer by cooling the greenhouse. Selected plants are used in the greenhouse to remove CO2 and pollutants from the building's exhaust air while enriching the air with oxygen and beneficial negatively charged ions. The oxygenated, improved quality air from the greenhouse is then used to supply all or a portion of the intake air to the building's HVAC system.
Owner:SPADAFORA PAUL F +2
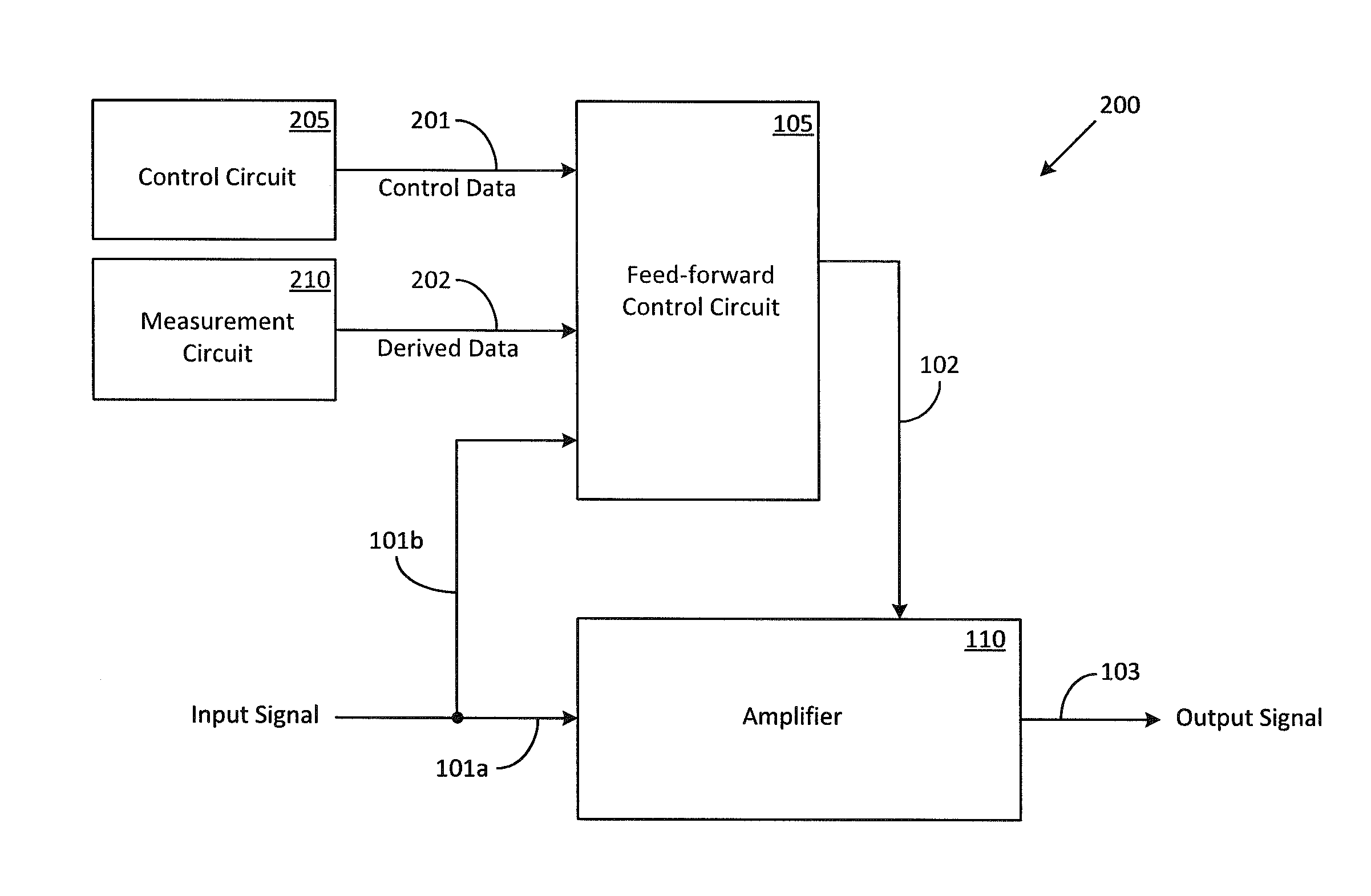
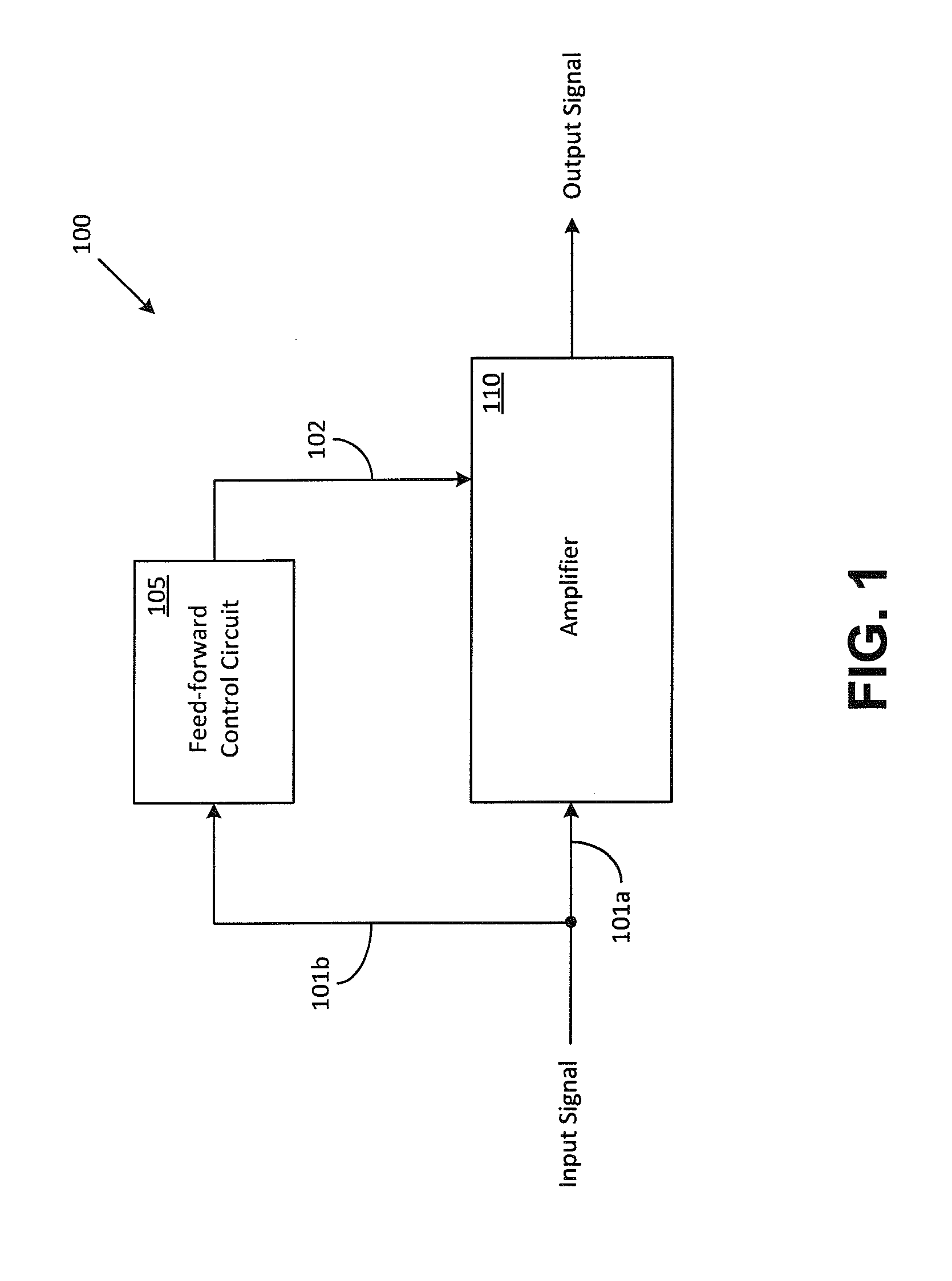
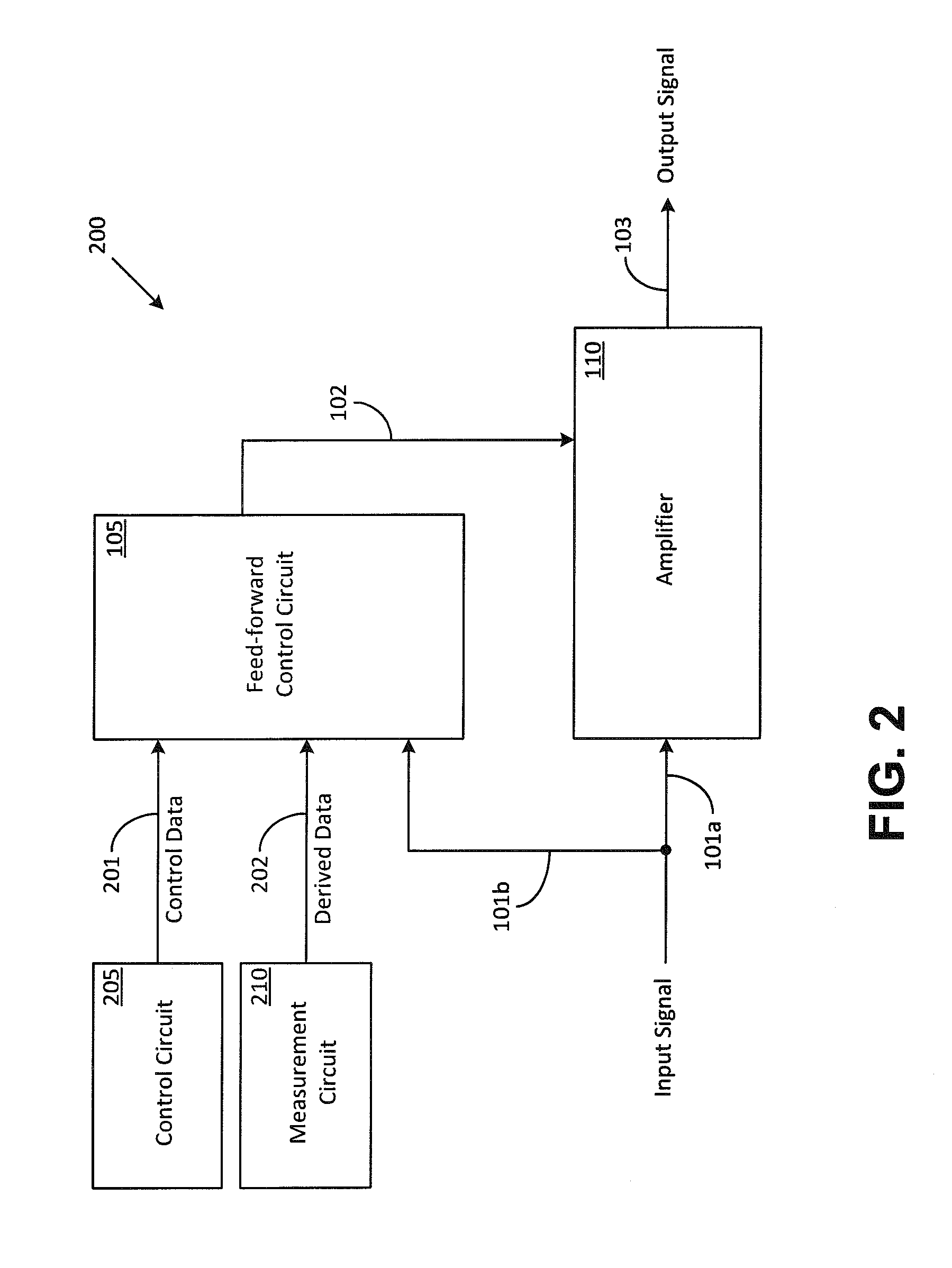
Systems and Methods for Optimizing Amplifier Operations
ActiveUS20140266433A1Easy to operateAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionGain controlAudio power amplifierControl signal
Methods and systems for optimizing amplifier operations are described. The described methods and systems particularly describe a feed-forward control circuit that may also be used as a feed-back control circuit in certain applications. The feed-forward control circuit provides a control signal that may be used to configure an amplifier in a variety of ways.
Owner:PSEMI CORP
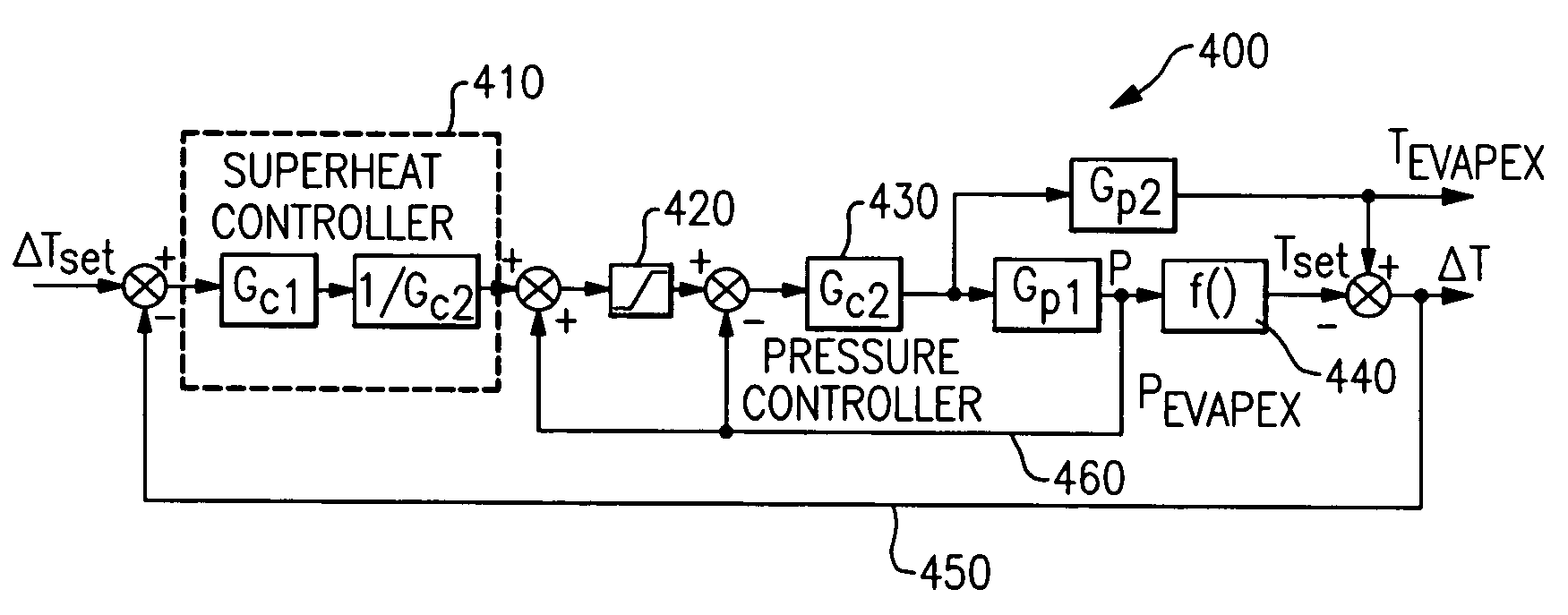
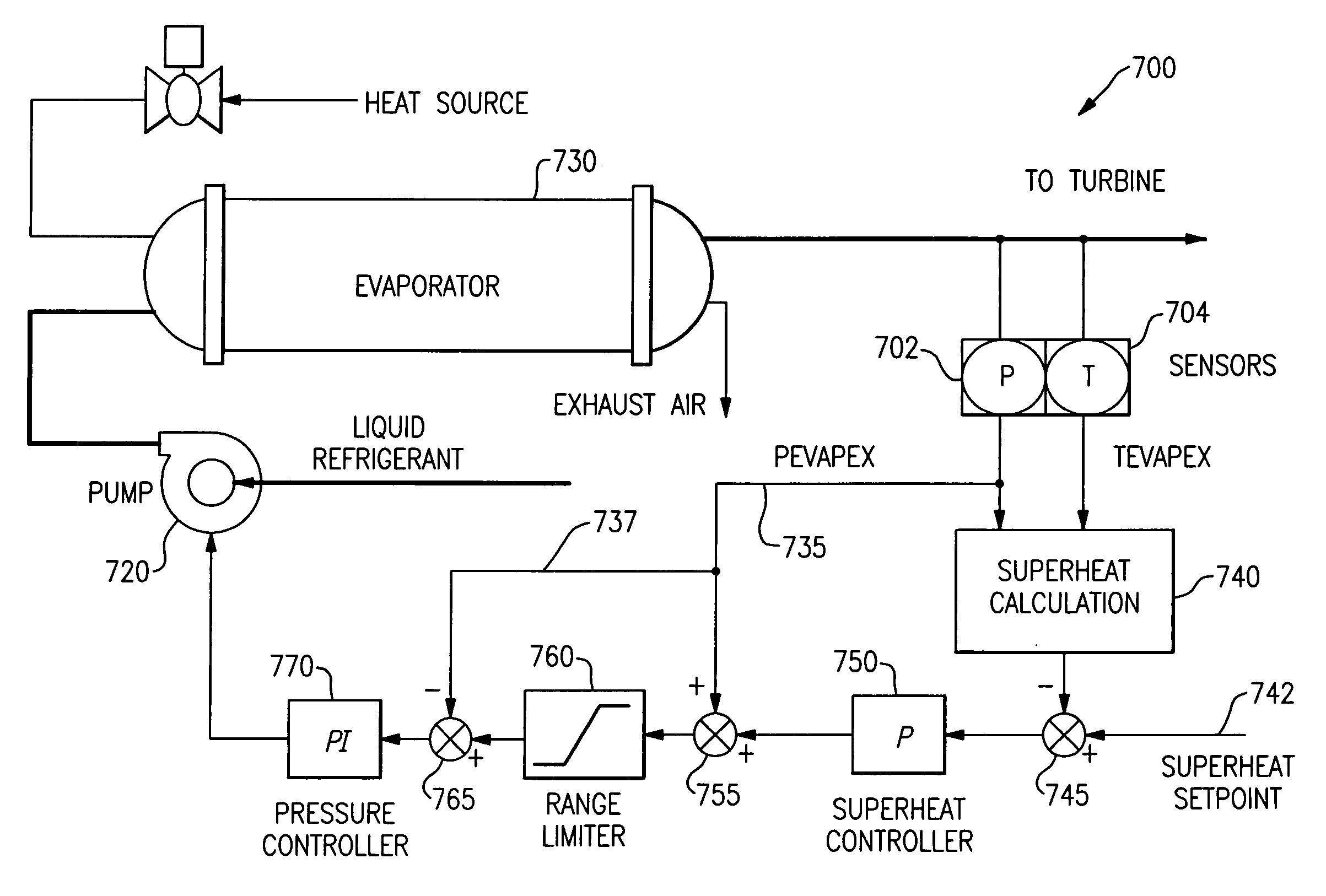
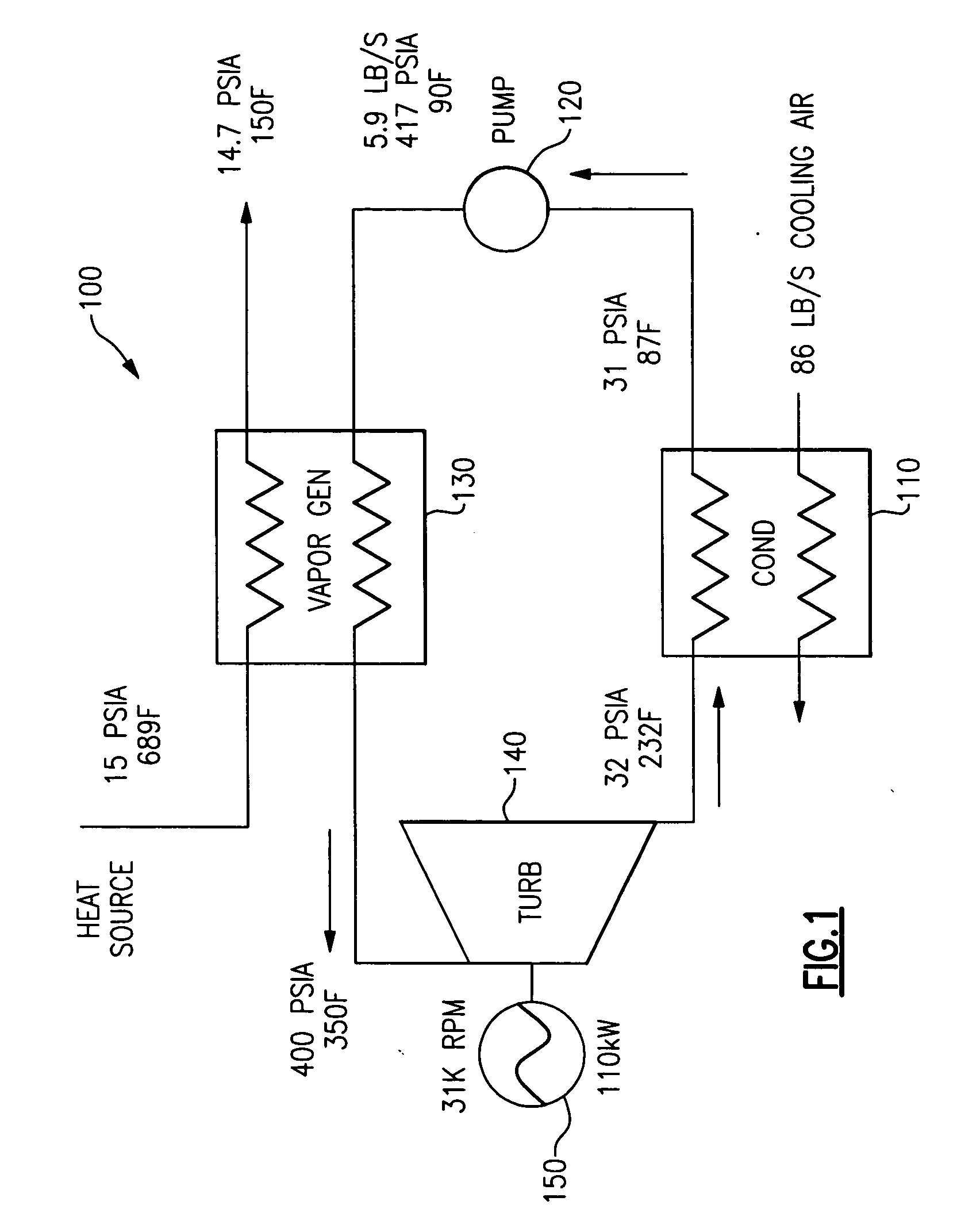
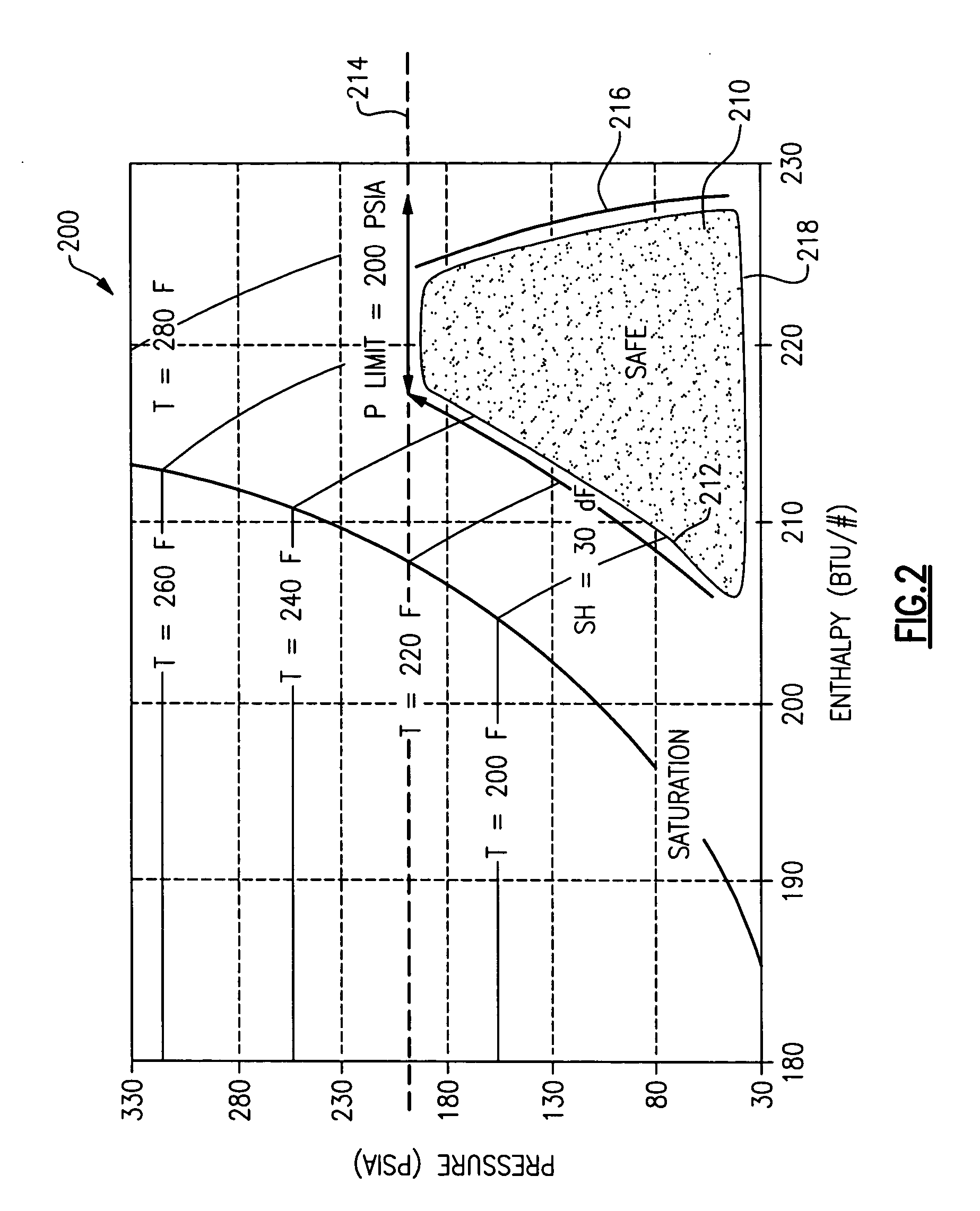
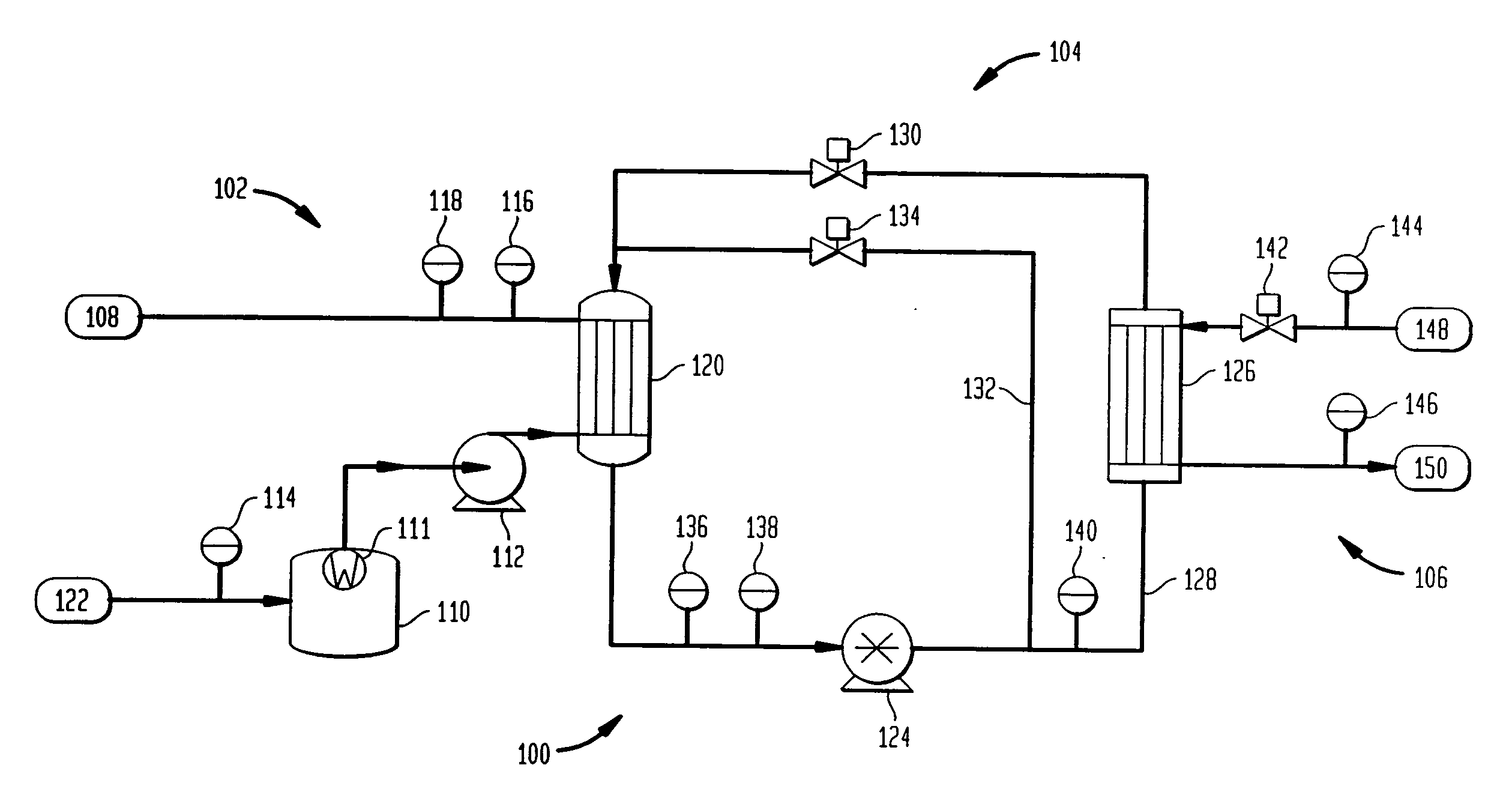
Startup and control methods for an ORC bottoming plant
The invention is a system and method for smoothly starting and controlling an ORC power plant. The system comprises a cascaded closed loop control that accounts for the lack of relationship between pump speed and pressure at startup so as to control pump speed and pressure, and that smoothly transitions into a steady state regime as a stable operating condition of the system is attained. The cascaded loop receives signals corresponding to a superheat setpoint, a pressure at an evaporator exit, and a temperature at an evaporator exit, and controls the pump speed and pressure upon startup to provide smooth operation. The system and method can further comprise a feed-forward control loop to deal with conditions at start-up and when external disturbances are applied to the ORC power plant.
Owner:NANJING TICA AIR CONDITIONING CO LTD
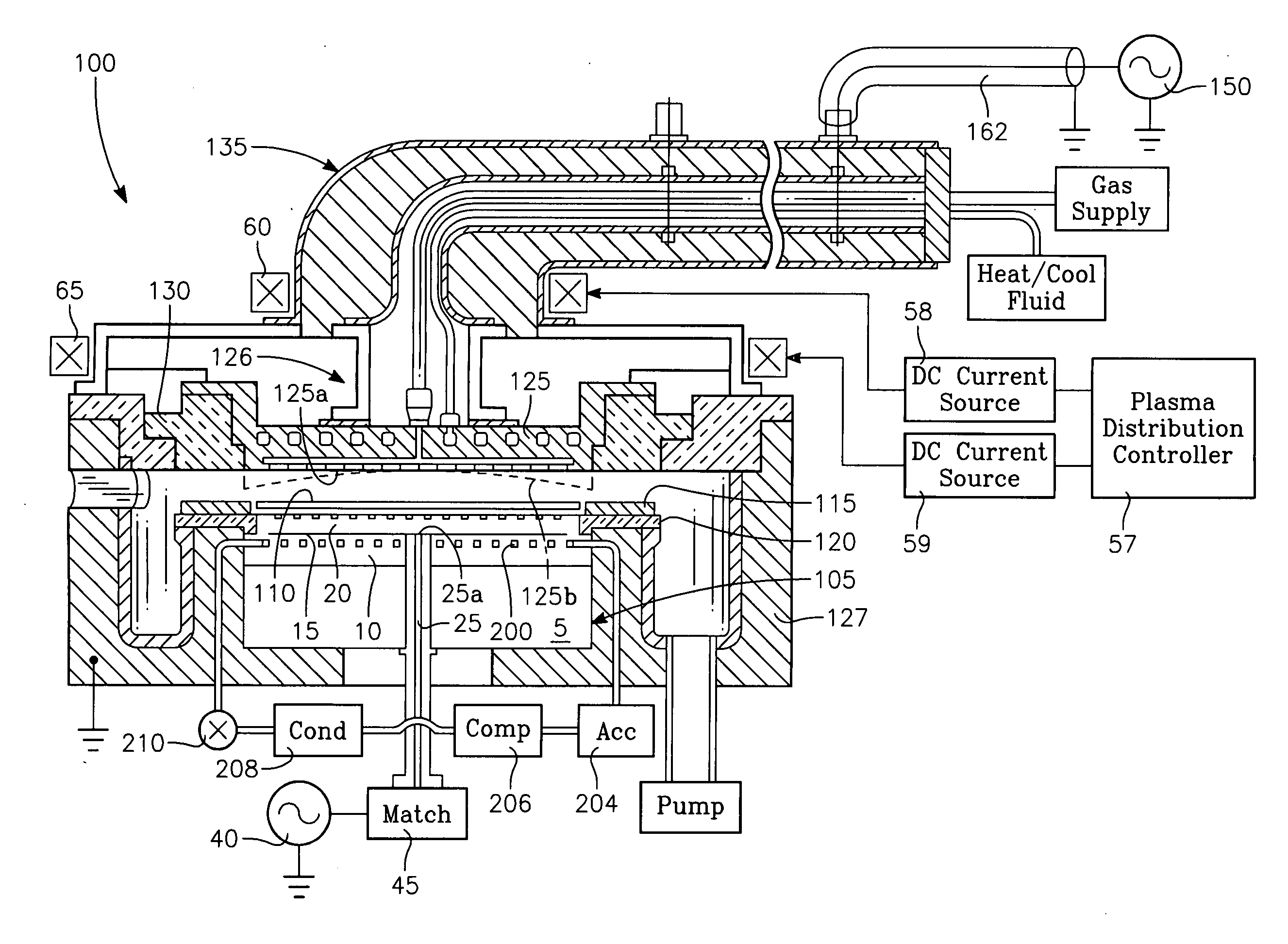
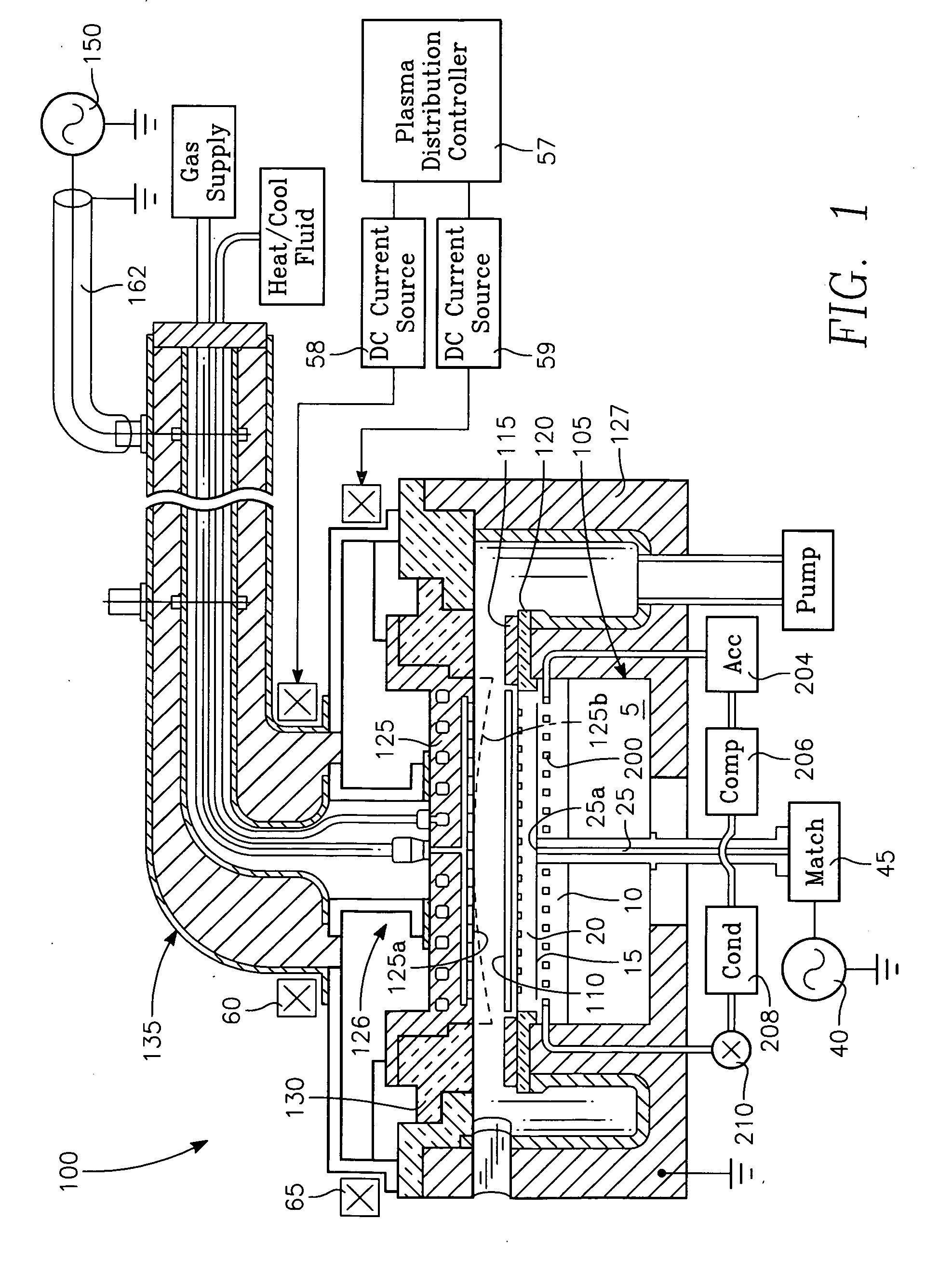
Plasma reactor with a multiple zone thermal control feed forward control apparatus
ActiveUS20070089834A1Electric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringPlasma reactor
A plasma reactor having a reactor chamber and an electrostatic chuck having a surface for holding a workpiece inside the chamber includes inner and outer zone backside gas pressure sources coupled to the electrostatic chuck for applying a thermally conductive gas under respective pressures to respective inner and outer zones of a workpiece-surface interface formed whenever a workpiece is held on the surface, and inner and outer evaporators inside respective inner and outer zones of the electrostatic chuck and a refrigeration loop having respective inner and outer expansion valves for controlling flow of coolant through the inner and outer evaporators respectively. The reactor further includes inner and outer zone temperature sensors in inner and outer zones of the electrostatic chuck and a thermal model capable of simulating heat transfer through the inner and outer zones, respectively, between the evaporator and the surface based upon measurements from the inner and outer temperature sensors, respectively. Inner and outer zone agile control processors coupled to the thermal model govern the inner and outer zone backside gas pressure sources, respectively, in response to predictions from the model of changes in the respective pressures that would bring the temperatures measured by the inner and outer zone sensors, respectively, closer to a desired temperature.
Owner:ADVANCED THERMAL SCI
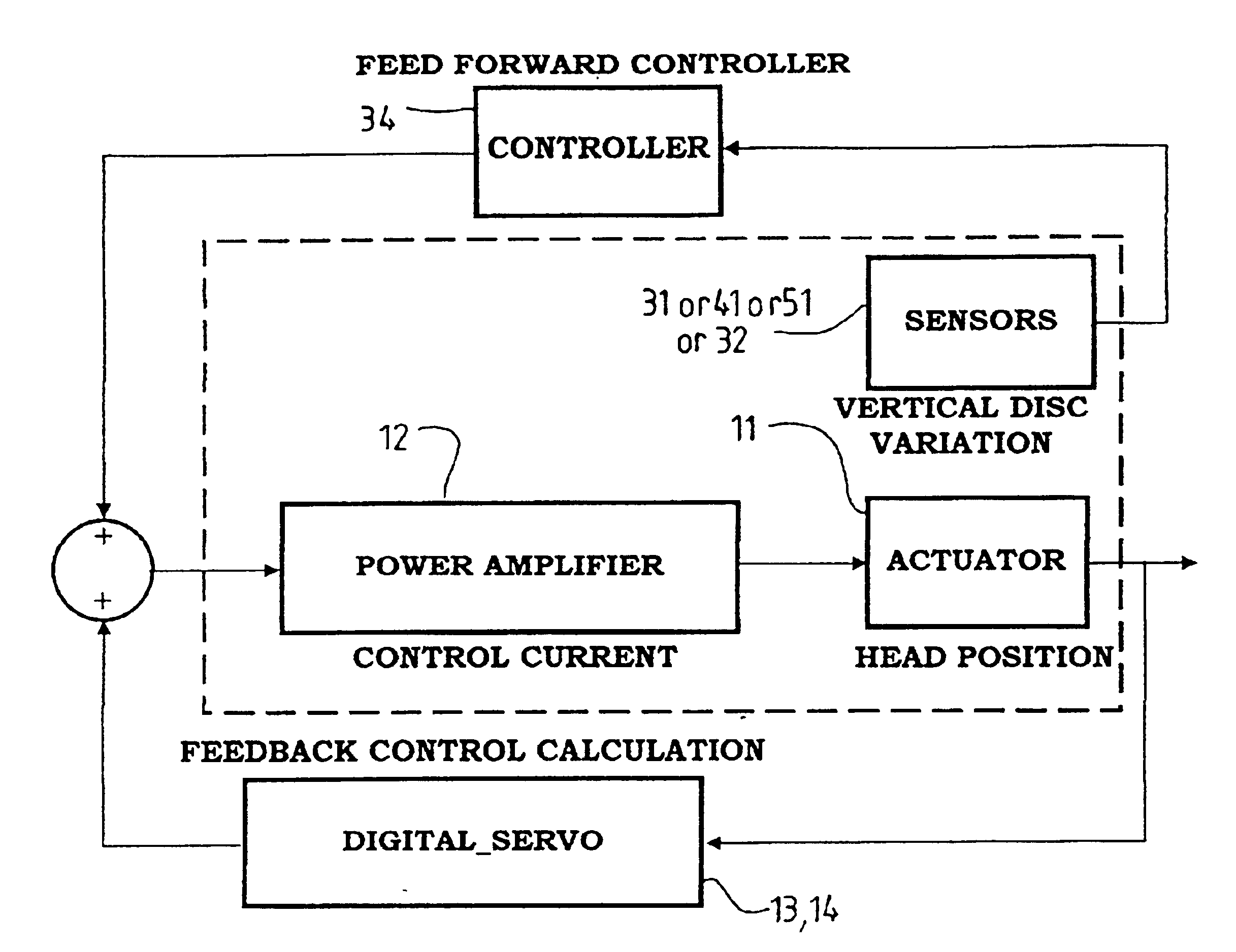
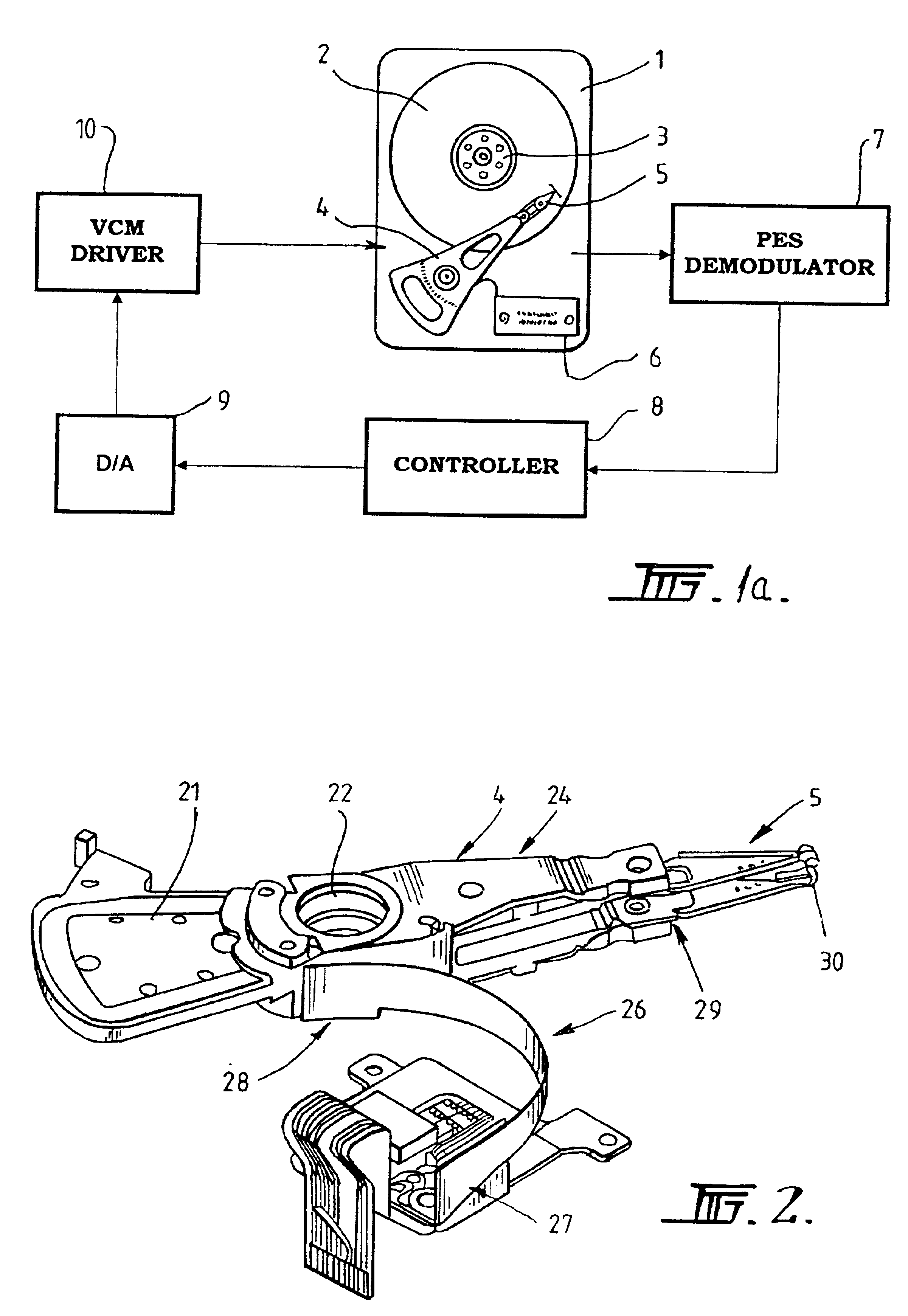
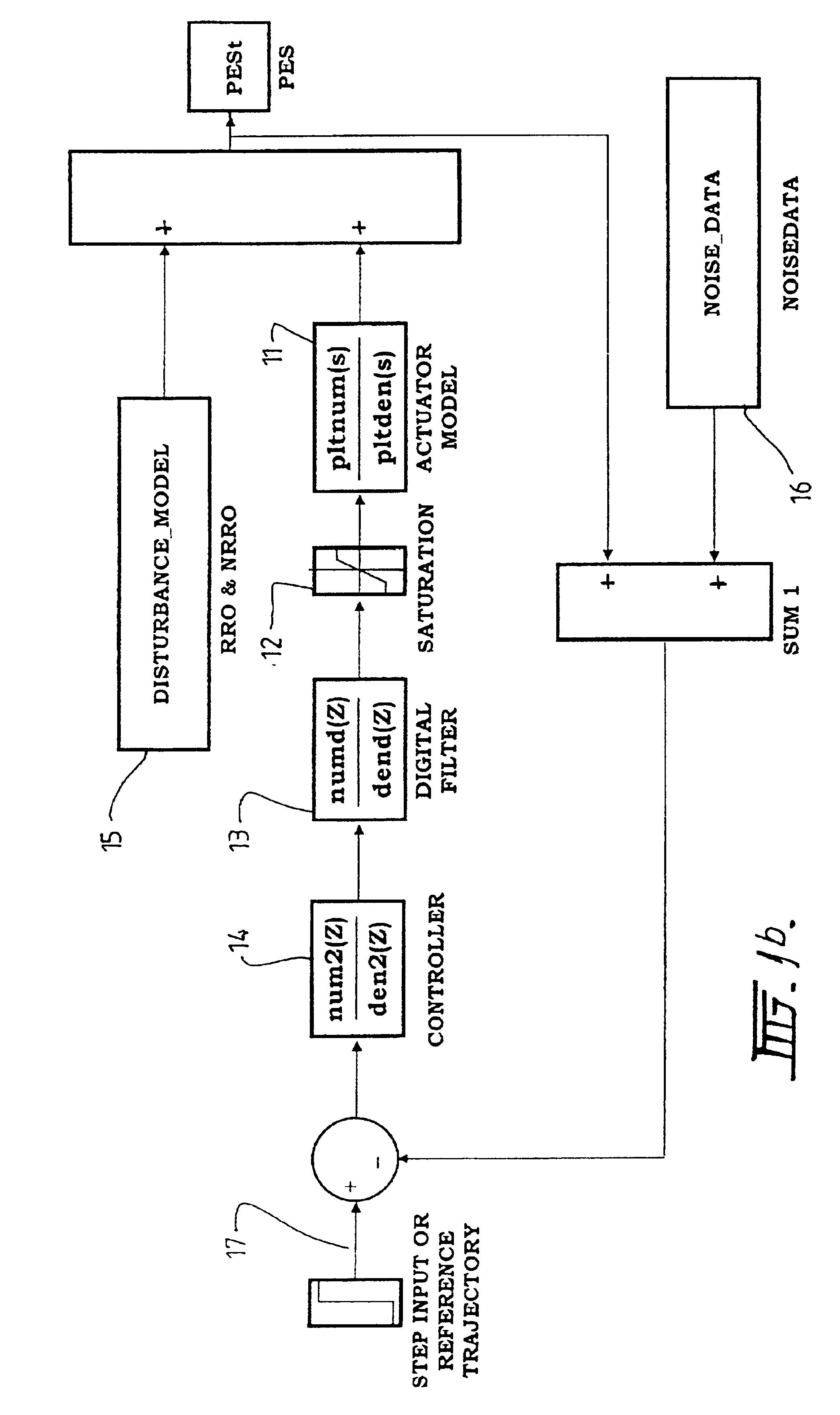
Active control system and method for reducing disk fluttering induced track misregistrations
InactiveUS6888694B2Easy to mergeNot affect stability of systemTrack finding/aligningRecord information storageVibration amplitudeVertical vibration
The present invention relates to controlling an actuator for positioning a read / write head in storage devices such as disk drives. More specifically, the invention relates to using a sensor to detect the disk vibration amplitude perpendicular to the disk surface, and using feed forward control to cancel or counteract the tendency of the read / write head to deviate off-track due to disk vibration. Various approaches are proposed to detect the disk vertical vibration.
Owner:AGENCY FOR SCI TECH & RES
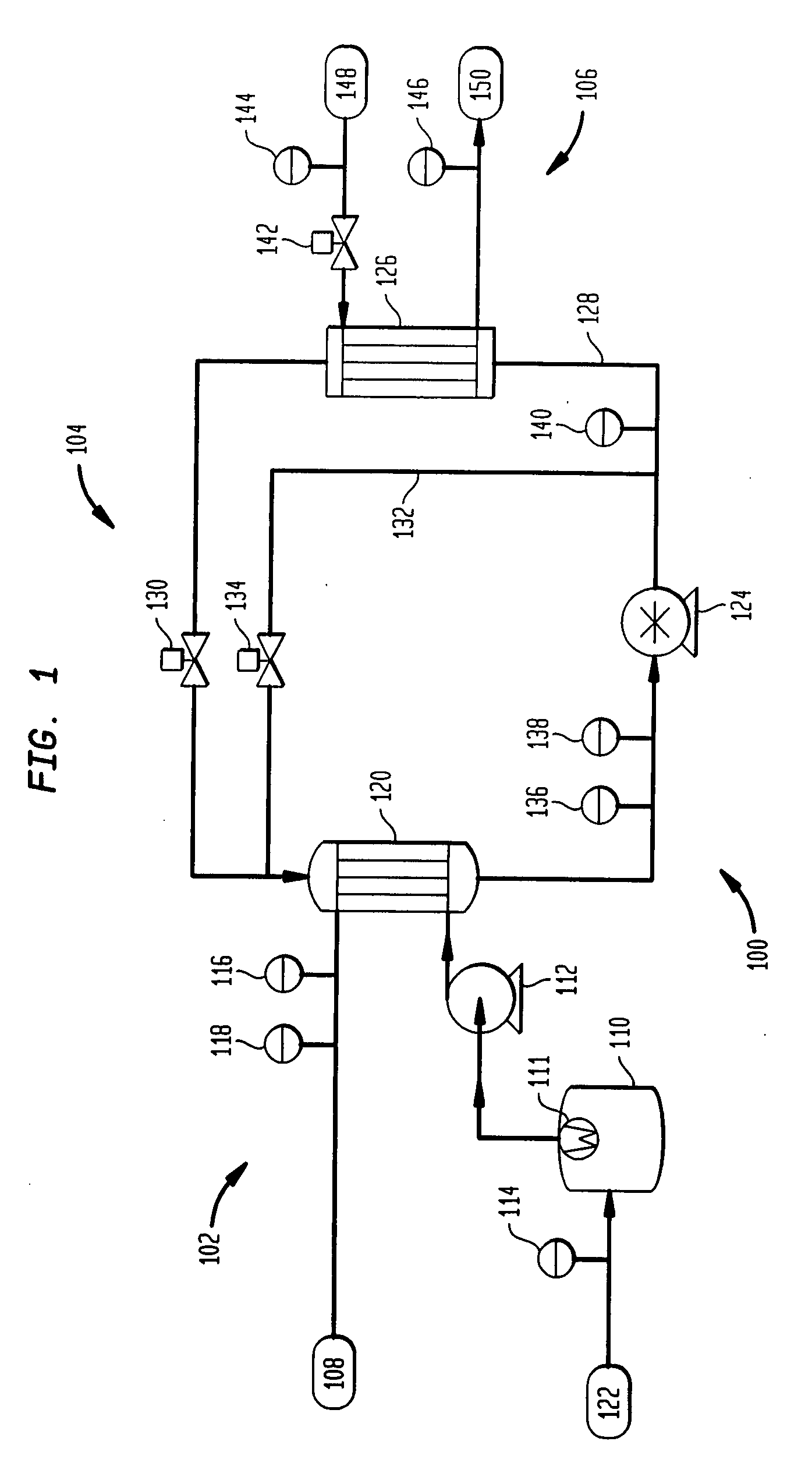
Startup and control methods for an orc bottoming plant
ActiveUS20050247056A1Reduce pumping speedControl pressureAir coolingCompression machines with non-reversible cyclePower stationClosed loop
The invention is a system and method for smoothly starting and controlling an ORC power plant. The system comprises a cascaded closed loop control that accounts for the lack of relationship between pump speed and pressure at startup so as to control pump speed and pressure, and that smoothly transitions into a steady state regime as a stable operating condition of the system is attained. The cascaded loop receives signals corresponding to a superheat setpoint, a pressure at an evaporator exit, and a temperature at an evaporator exit, and controls the pump speed and pressure upon startup to provide smooth operation. The system and method can further comprise a feed-forward control loop to deal with conditions at start-up and when external disturbances are applied to the ORC power plant.
Owner:NANJING TICA AIR CONDITIONING CO LTD
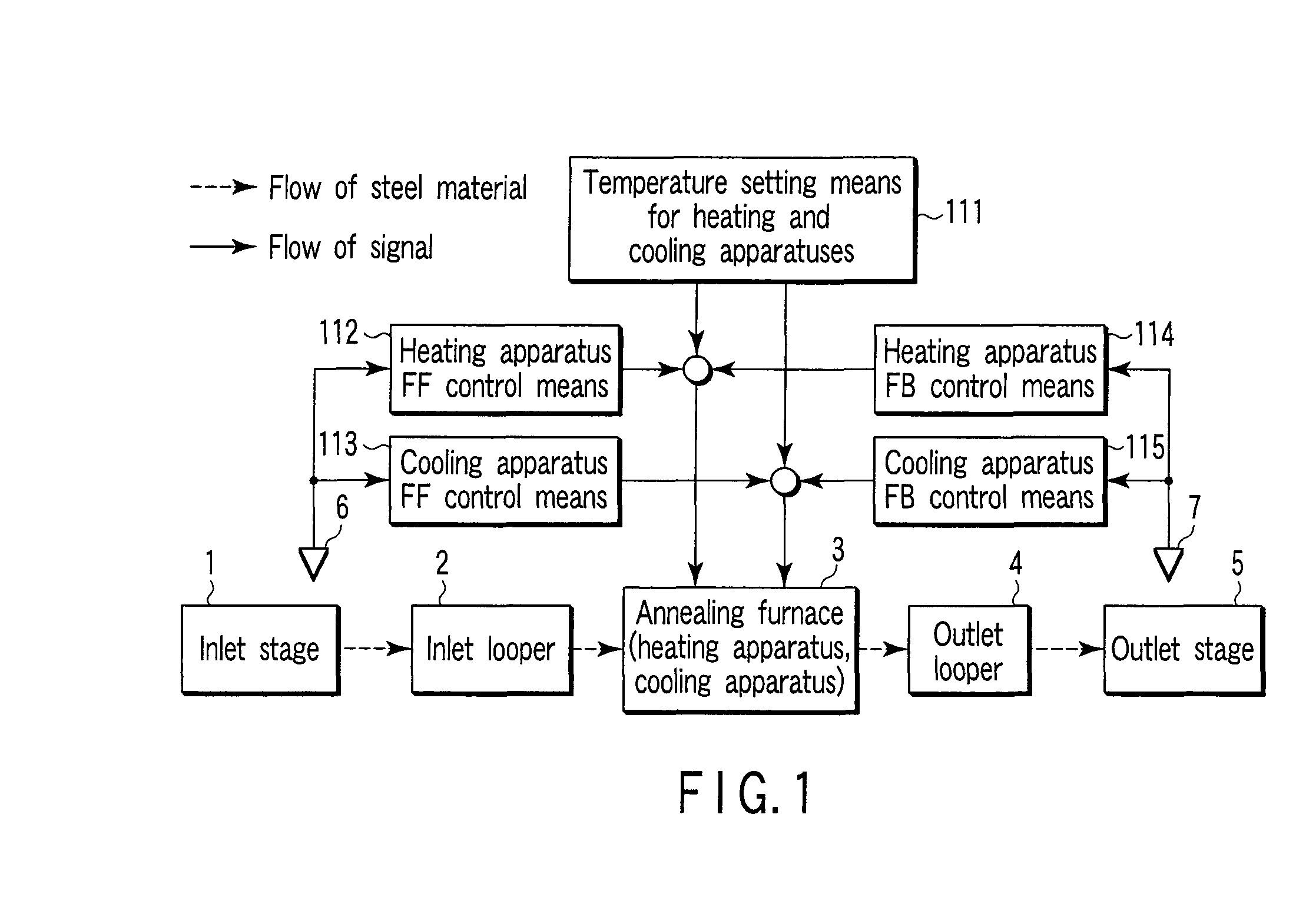
Process line control apparatus and method for controlling process line
InactiveUS20100219567A1Quality improvementHot-dipping/immersion processesFurnace typesProduction lineValue set
A process line control apparatus which controls a process line including an annealing furnace (3) including a heating process apparatus executing a heating process and a cooling process apparatus executing a cooling process, the heating and cooling processes being continuously executed on a steel material, the apparatus having feed forward control means (112, 113) for measuring quality of the steel material by a material quality measuring apparatus (6) installed in an inlet stage (1) preceding the heating process in the annealing furnace (3), and on the basis of measurement results, determining modifications for respective temperature set values set by temperature setting means (111) for the heating and cooling apparatuses in the annealing furnace (3), and feedback control means (114, 115) for measuring the quality of the steel material by a material quality measuring apparatus (7) installed in an outlet stage (5) succeeding the cooling process in the annealing furnace (3), and on the basis of measurement results, determining modifications for the respective temperature set values set by the temperature setting means (111) for the heating and cooling apparatuses in the annealing furnace (3).
Owner:TOSHIBA MITSUBISHI-ELECTRIC IND SYST CORP
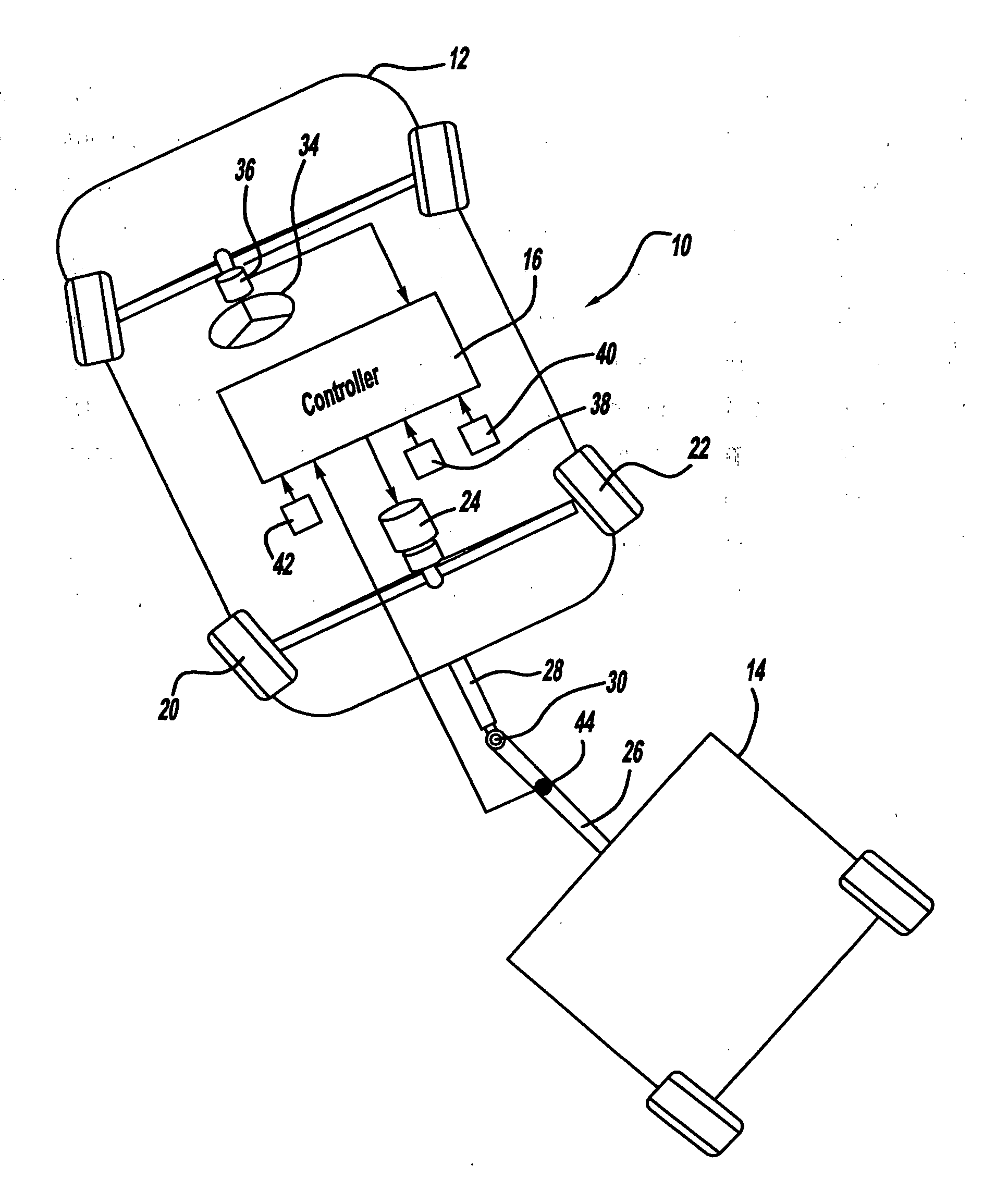
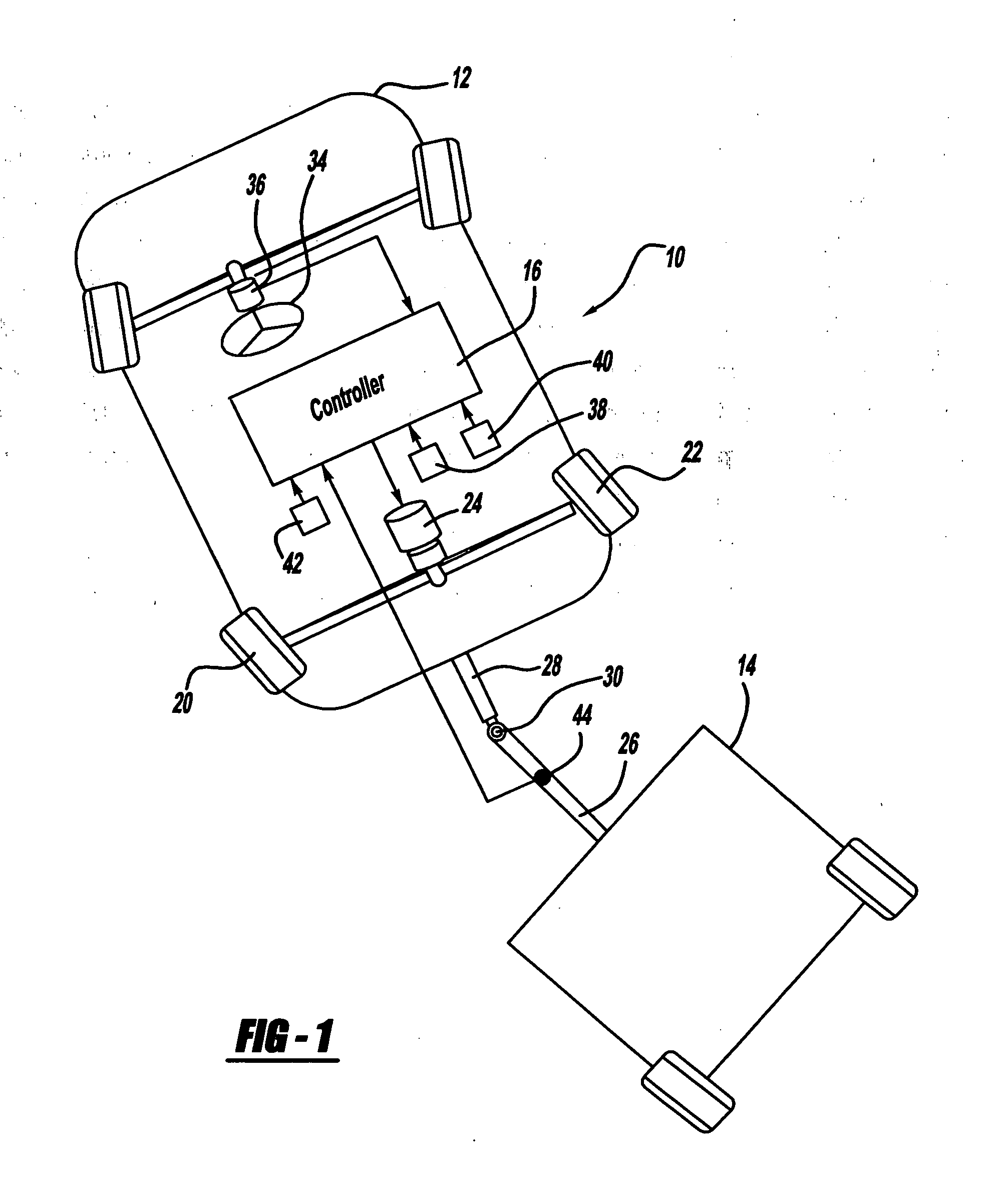
Vehicle-trailer stability and handling performance improvement using rear-wheel steering control
ActiveUS20060229782A1Improve vehicle/trailer combination stabilityImprove handling performanceDigital data processing detailsSteering initiationsSteering wheelControl system
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
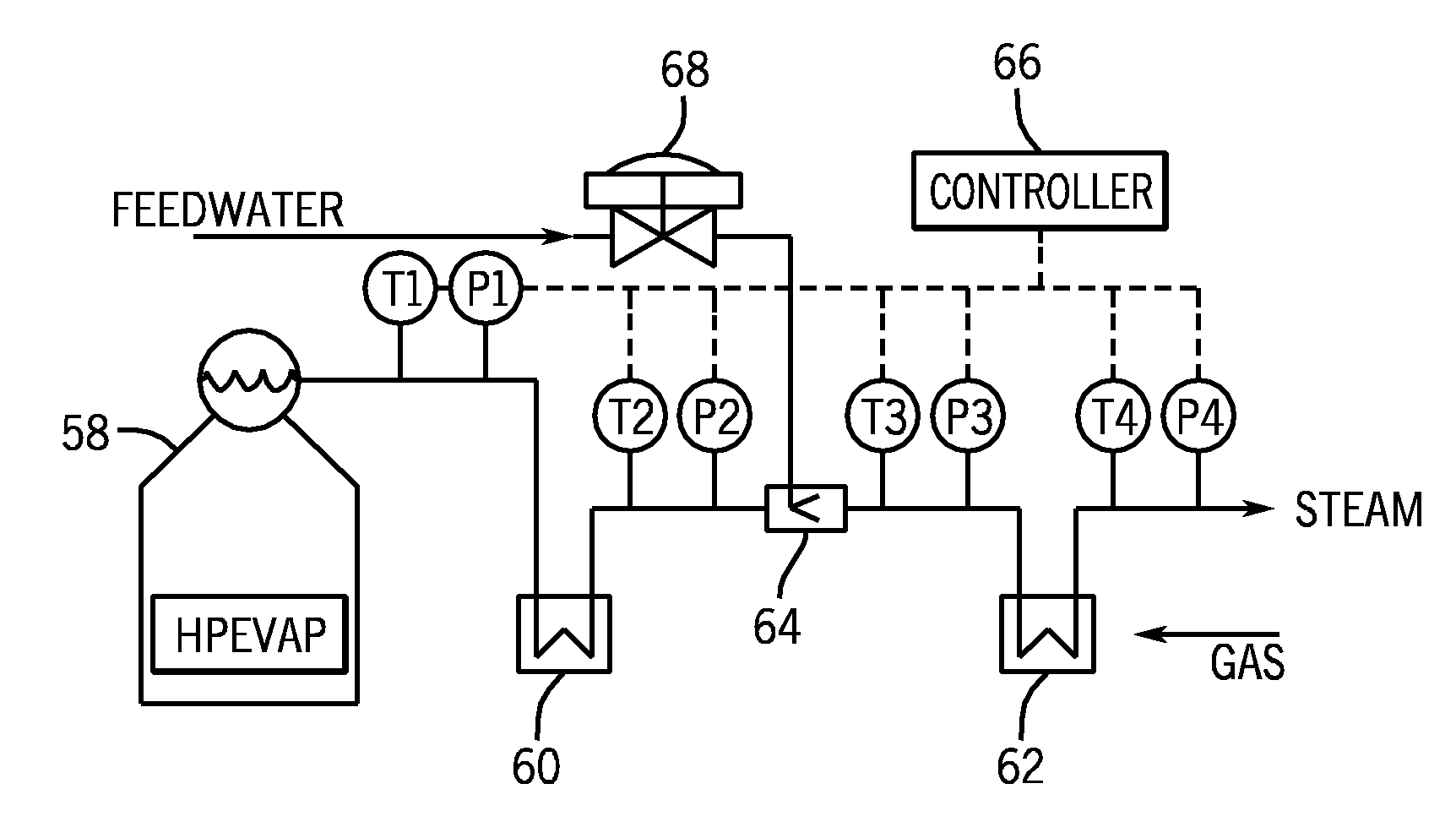
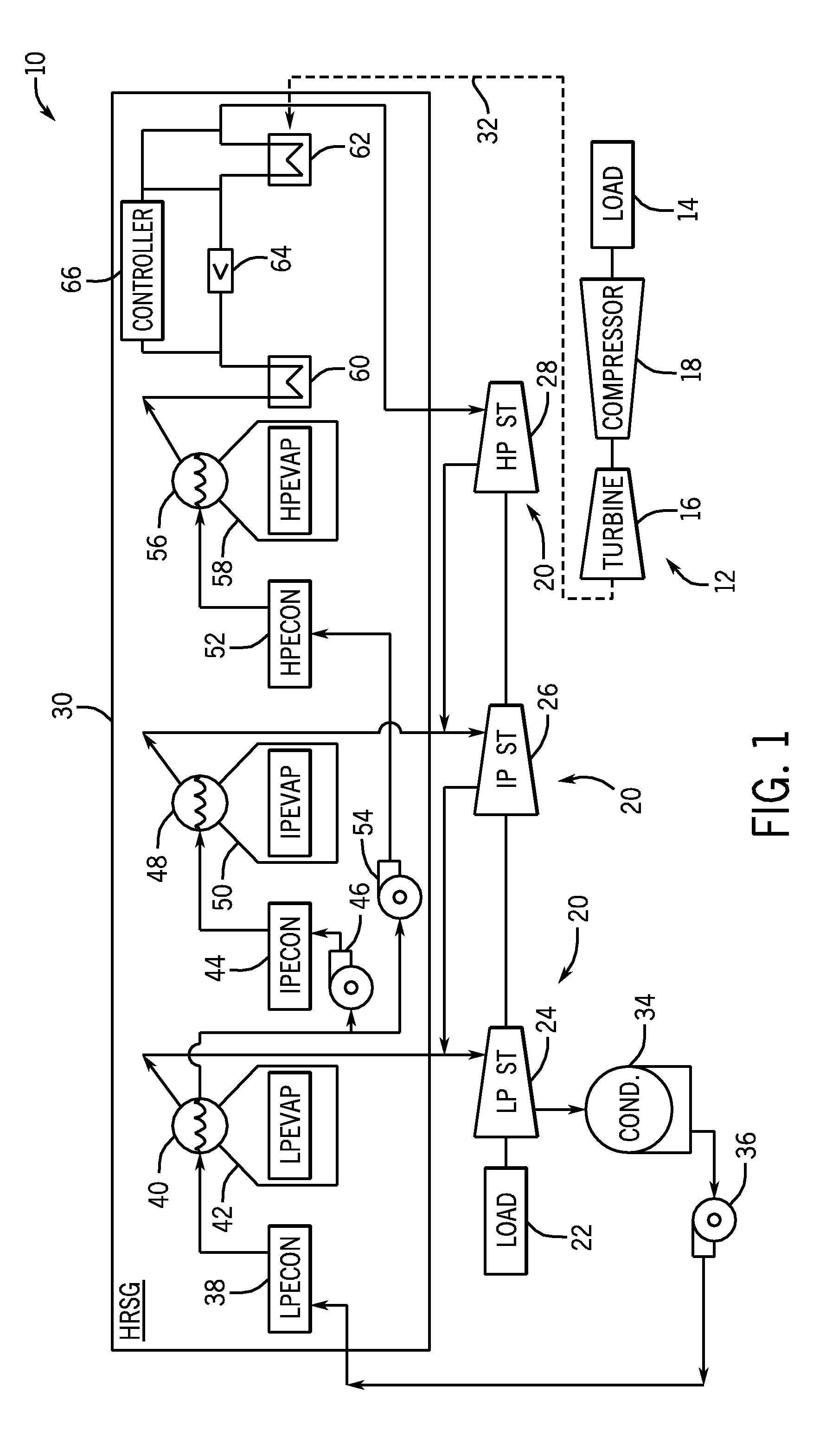
Inter-stage attemperation system and method
Systems and methods for controlling exhaust steam temperatures from a finishing superheater are provided. In certain embodiments, the system includes a controller which includes control logic for predicting an exhaust temperature of steam from the finishing superheater using model-based predictive techniques (e.g., based on empirical data or thermodynamic calculations). Based on the predicted exhaust temperature of steam, the control logic may use feed-forward control techniques to control the operation of an inter-stage attemperation system upstream of the finishing superheater. The control logic may determine if attemperation is required based on whether the predicted exhaust temperature of steam from the finishing superheater exceeds a set point temperature as well as whether the inlet temperature of steam into the finishing superheater drops below a set point temperature of steam. The attemperation system may include a characterizing function to linearize the valve operation controlled by the control logic to inject cooled, high-pressure feedwater into the steam upstream of the finishing superheater, which may, in turn, control the exhaust temperature of steam from the finishing superheater. The disclosed embodiments may also be applied to any systems where an outlet temperature of a fluid from a heat transfer device may be controlled.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
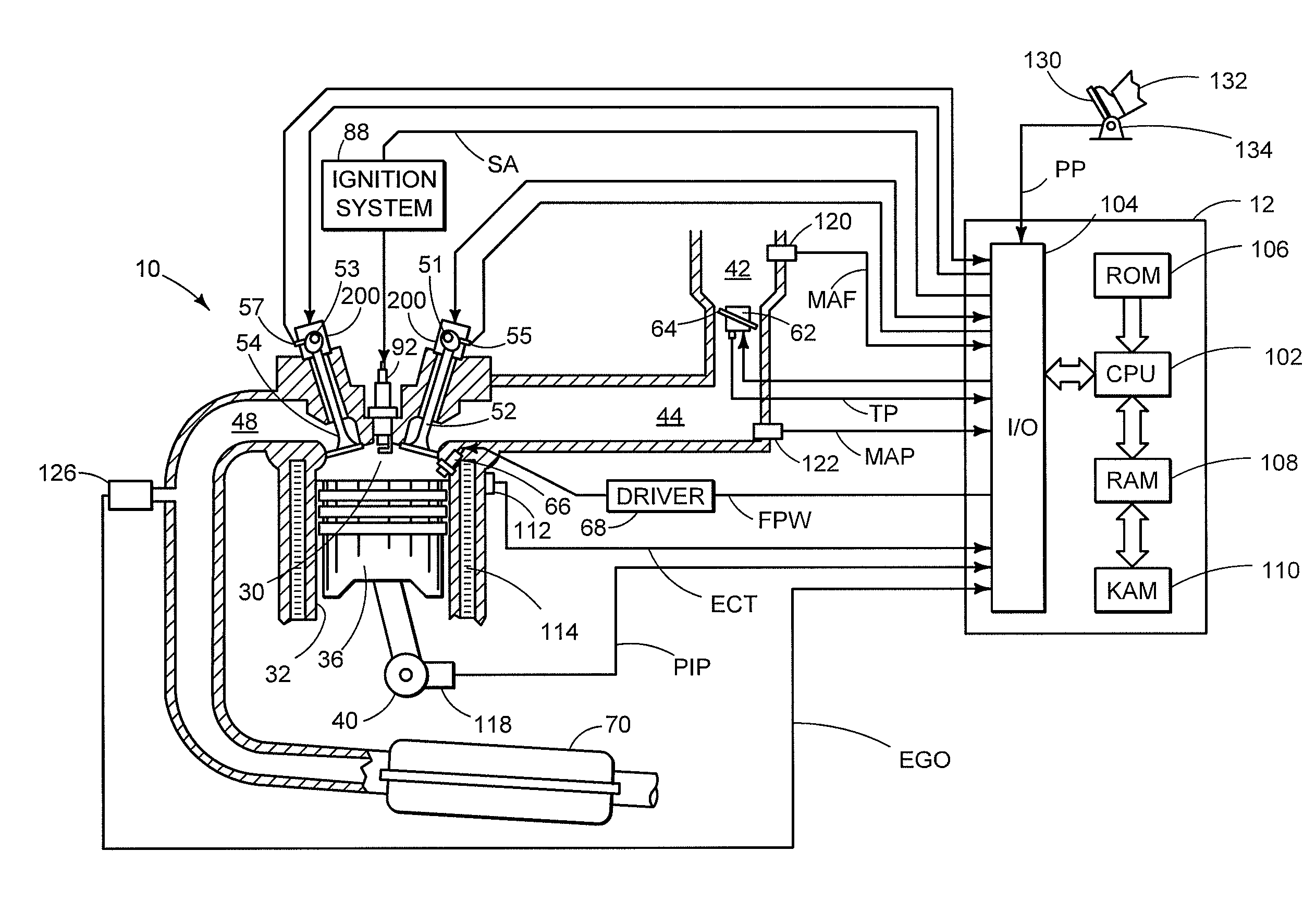
Method of manufacturing semiconductor devices
InactiveUS20030049876A1Reduce variationHigh precision machiningSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesResistEngineering
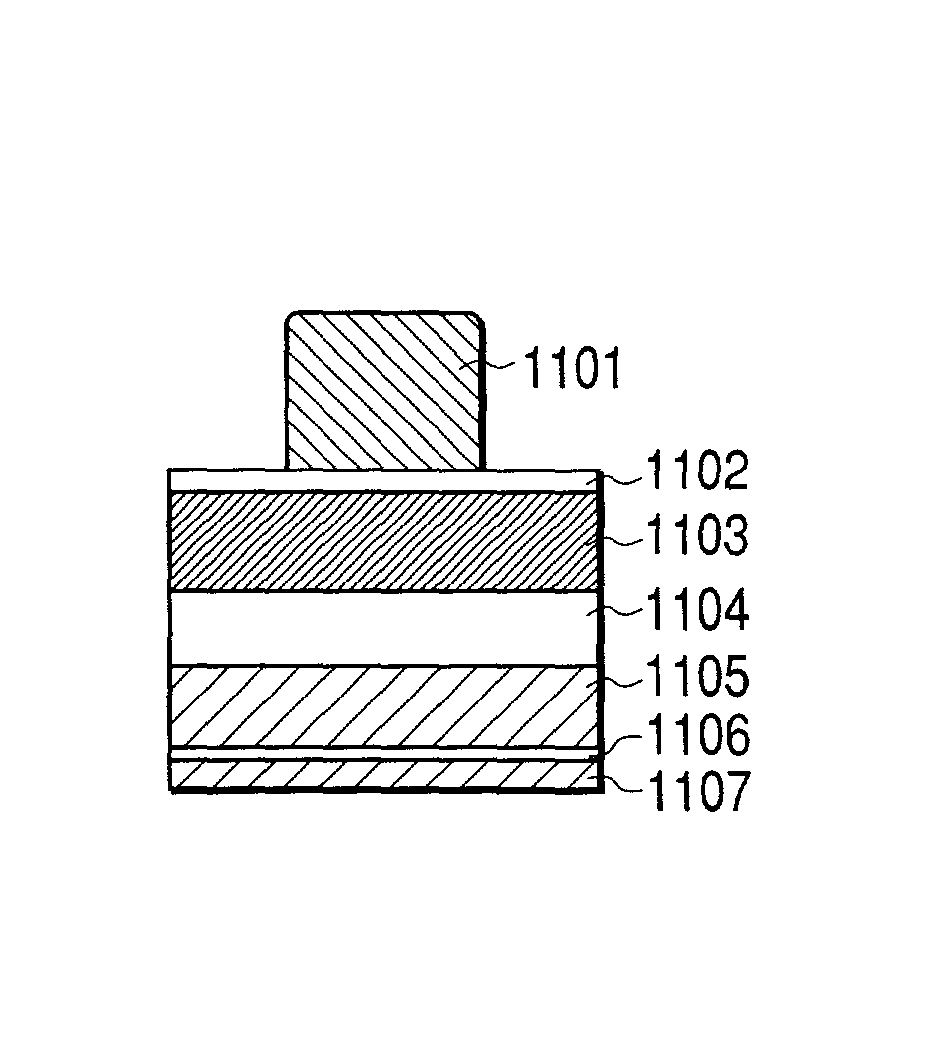
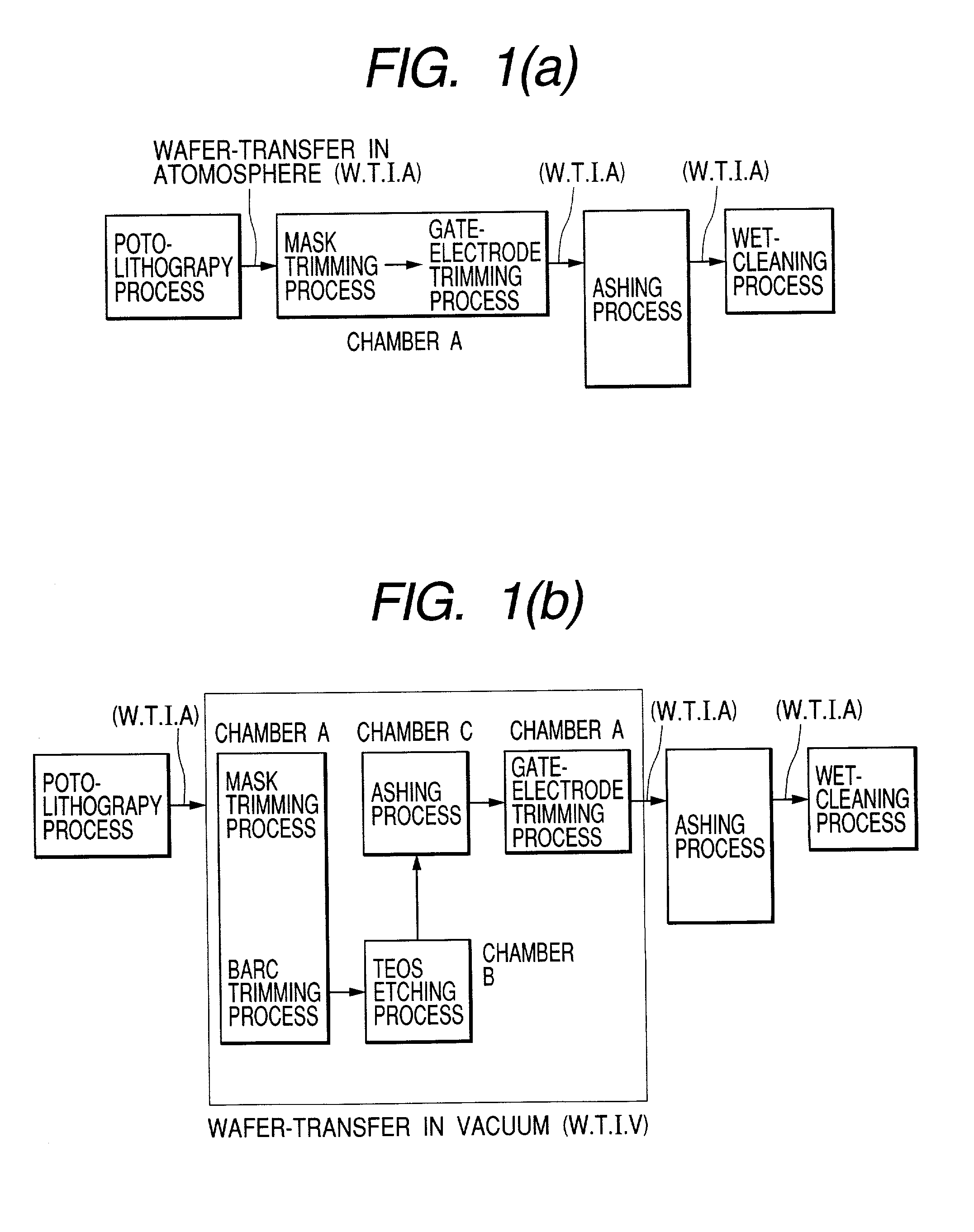
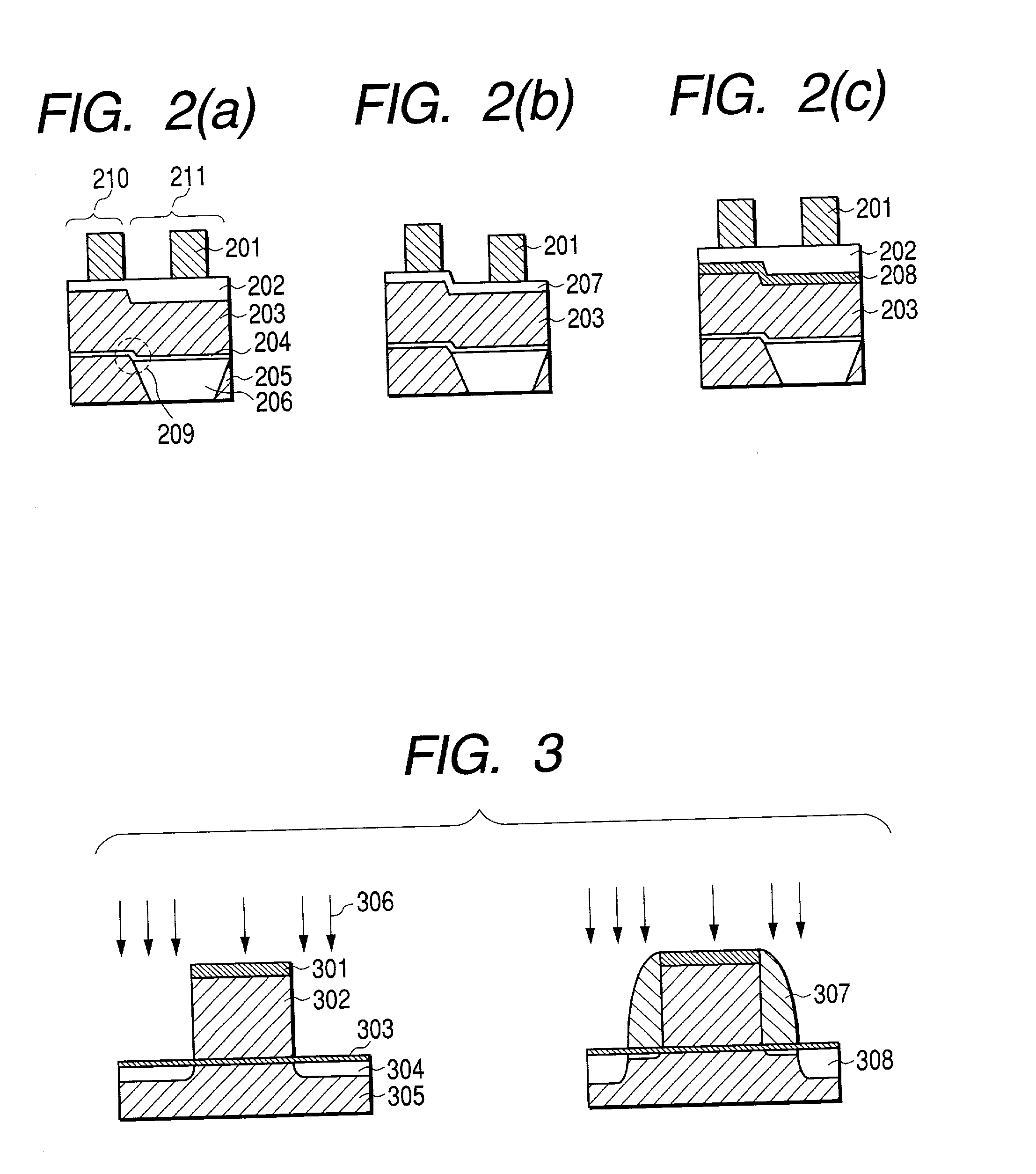
A process for economical and efficient fabrication of gate electrodes no larger than 50 nm, which is beyond the limit of exposure, is characterized by gate-electrode trimming and mask trimming with high resist selectivity which are performed in combination. The process is also preferably characterized by performing trimming and drying cleaning in a vacuum environment and may also include steps of inspecting dimensions and contamination in a vacuum environment. The process can be implemented to provide the effects of forming a gate no longer than 50 nm (beyond the limit of exposure) without restrictions on the resist thickness; reducing contamination resulting from transfer of wafers from one step to next, thereby improving yields; preventing resist from hydrolysis by ArF laser, thereby reducing roughening which adversely affects the gate width; and ensuring stable yields despite variation in dimensions and contamination owing to the additional dry cleaning step and feed-forward control based on CD inspection and contamination inspection.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Double-shaft photoelectric rotary table compound control system and control method based on fuzzy decision
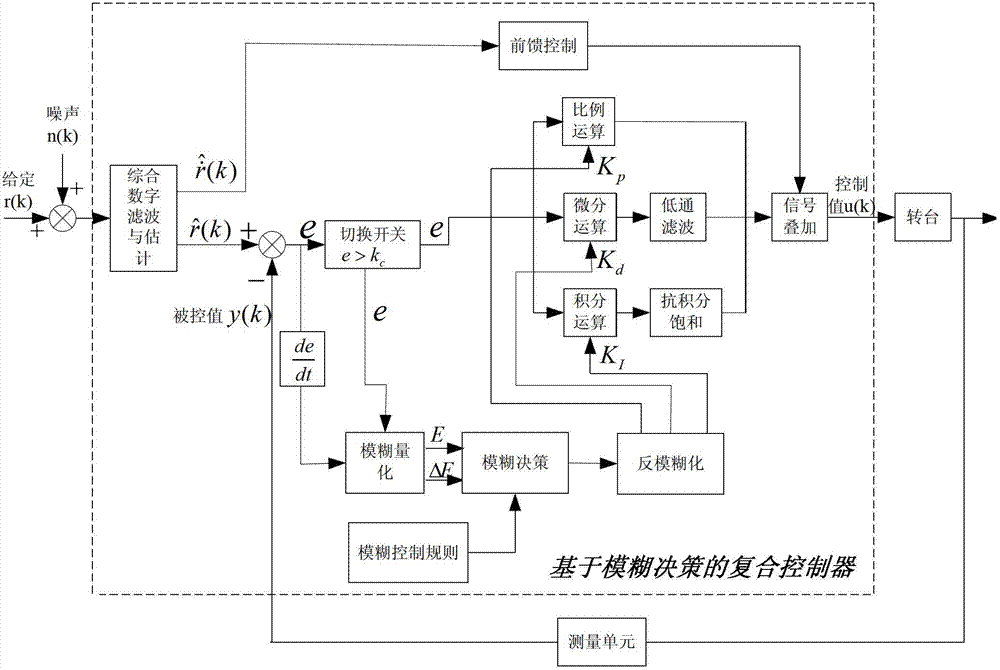
ActiveCN103034249AImprove tracking accuracyImprove stabilityControl using feedbackFuzzy decisionControl system
The invention discloses a double-shaft photoelectric rotary table compound control system and a control method based on fuzzy decision. The control system comprises an integrated digital filtering, an estimation unit, a feed-forward control unit, a measuring unit, a change-over switch, a fuzzy-decision unit, a piping and instrument diagram (PID) controller, and a signal superposition unit. The double-shaft photoelectric rotary table position error e is compared with an error threshold K c set in advance, when e is less than K c, the fussy regulation is entered and regulation output controlled quantities delta kp, delta k and delta kd are obtained. PID control and regulation parameters kp, ki and kd are further obtained, and PID calculation is conducted. Otherwise, PID calculation is conducted by the utilization of the fixed regulation parameter set in advance and control signals outputted by PID are obtained. The effects of nonlinearity, time-varying characteristics, and model uncertainty on accuracy of the double-shaft photoelectric rotary table are effectively reduced. The problems of integral saturation and high frequency disturbance in the PID controller are solved, stochastic noise in the given stochastic signals is overcome, and long-term continuous stable work of the double-shaft photoelectric rotary table compound control system is ensured.
Owner:CHINA ELECTRONICS TECH GRP NO 26 RES INST
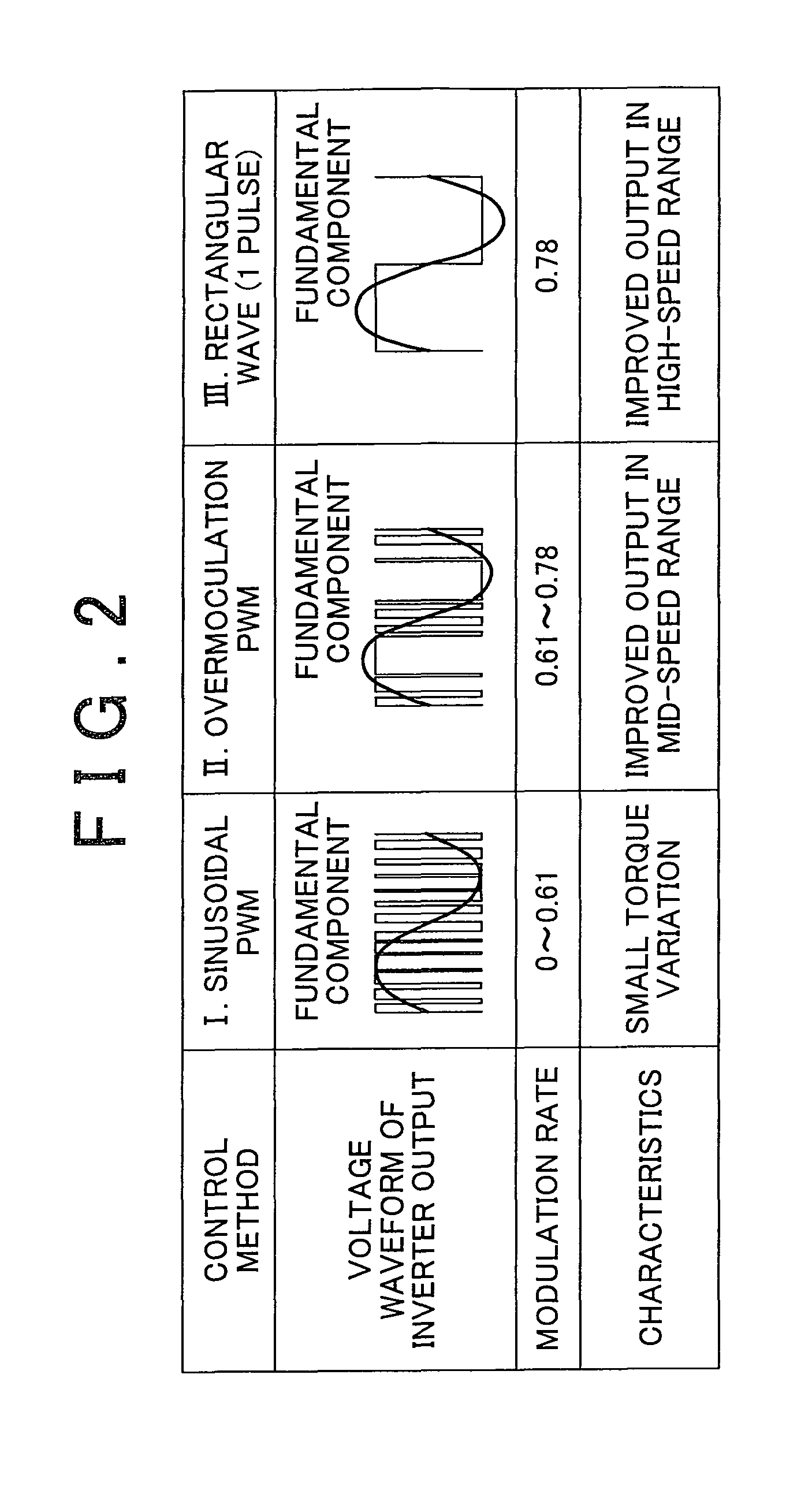
Control system for ac motor
InactiveUS20110248663A1Simple computationSimple calculationVector control systemsConversion with intermediate conversion to dcOperating pointControl system
A control system for an AC motor determines a slope Ktl of a tangent TL at an operating point Pa corresponding to the current motor operating state and voltage phase (θ0) on a torque characteristic curve that is plotted according to a torque equation representing an output torque characteristic with respect to the motor operating state and the voltage phase of the rectangular wave voltage. The control system further calculates a voltage phase change amount θff for use in feed-forward control, according to ΔTtl / Ktl obtained by dividing a torque compensation amount ΔTtl for feed-forward control by the slope Ktl.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Vehicle-mounted pick-up stable platform
ActiveCN101872198AImprove command response speedAvoid changeImage analysisUsing electrical meansEngineeringImage tracking
Owner:BEIJING INST OF AEROSPACE CONTROL DEVICES
Active heave compensation control system
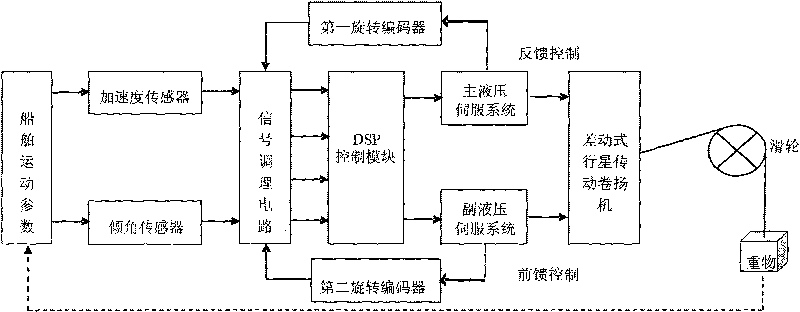
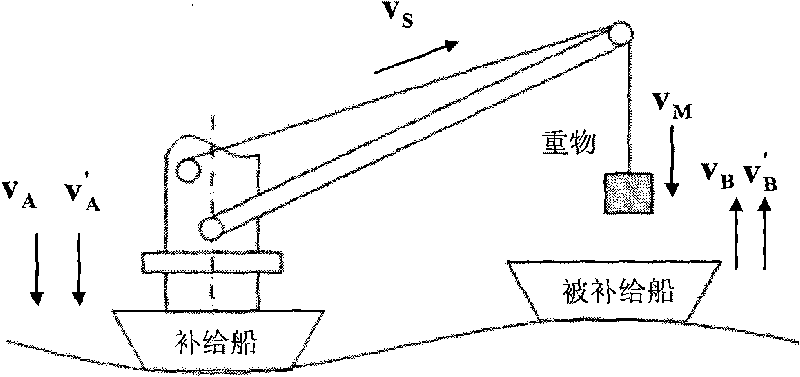
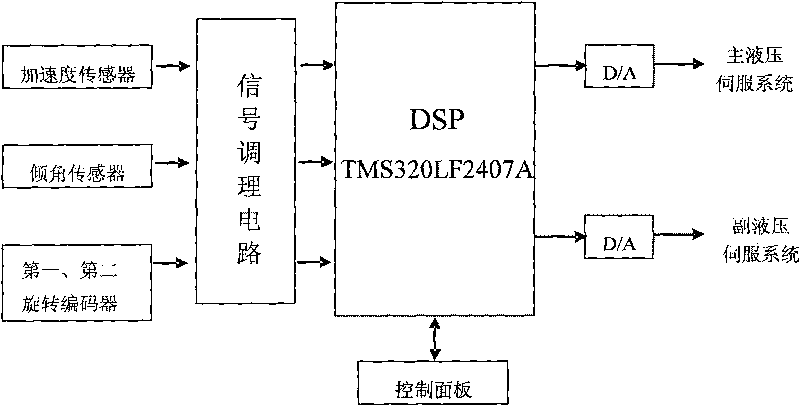
The invention discloses an active heave compensation control system comprising a ship kinematic parameter detection module, a DSP control module and an execution module, wherein the kinematic parameter detection module comprises an accelerated speed sensor, a dip angle sensor, a first rotary encoder, a second rotary encoder and a signal conditioning circuit; the execution module comprises a main hydrauservo system, a secondary hydrauservo system and a differential planetary drive windlass. The invention has the following characteristics: 1. a feedback control mode is combined with a feed-forward control mode; 2. the active compensation of weight lowering speed is realized by detecting and predicting the ship kinematic parameter; 3. the heeling movement and the trimming movement of the ship are converted into heaving movement by the dip angle sensor to realize the heave compensation in three degrees of freedom, namely, heeling, trimming and heaving; and 4. the differential planetary drive windlass is used to realize speed composition of the feedback control and the feed-forward control.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
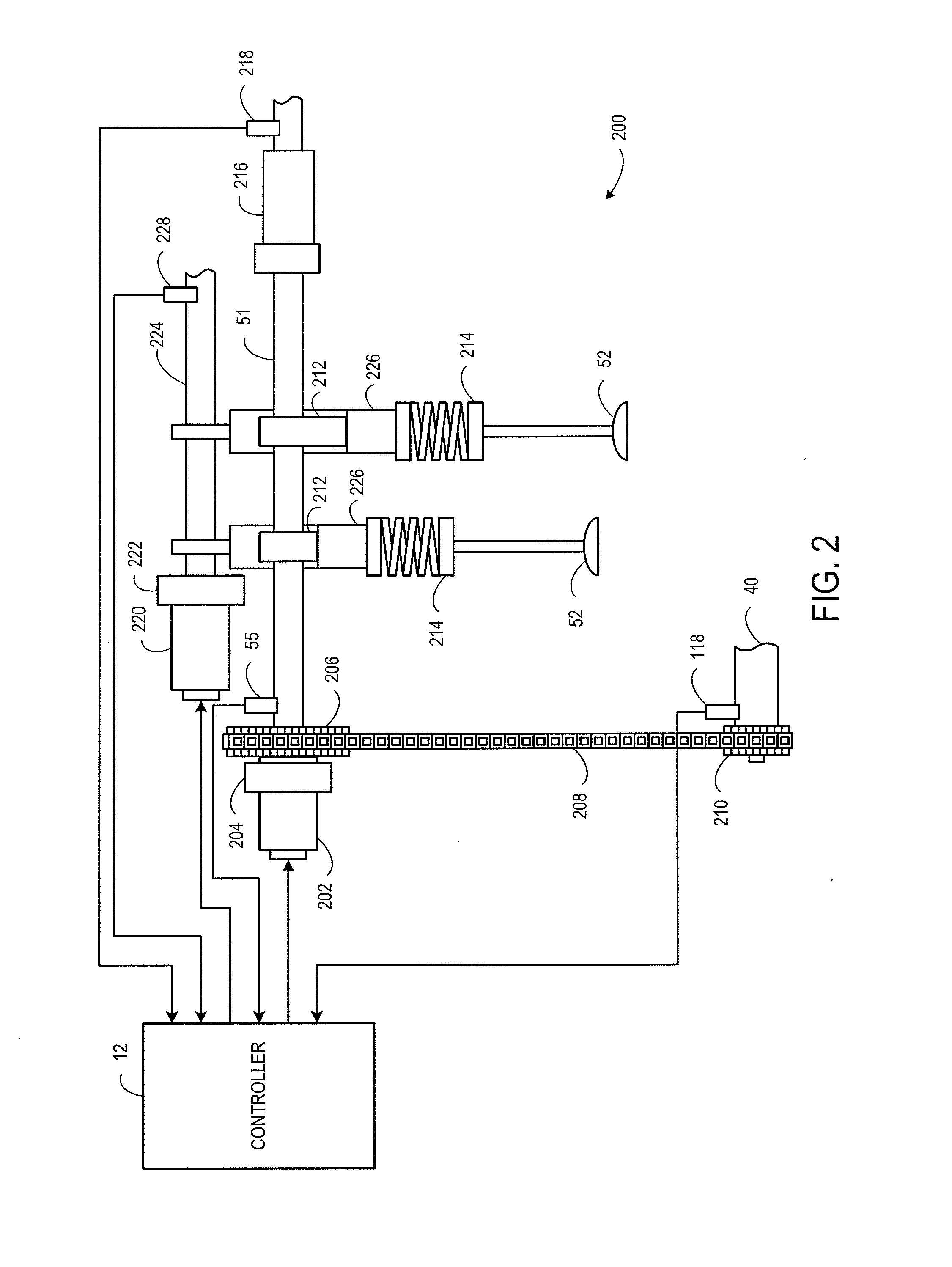
Feed Forward Control for Electric Variable Valve Operation
InactiveUS20120031357A1Easy to operateImprove fuel economyElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesCylinder ValveControl theory
Periodic torque disturbances that affect cylinder valve operation are anticipated, and an appropriate reaction torque is provided by an electric motor to counteract the periodic torque disturbances to position a cylinder valve at a desired position.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Method for controlling temperature
InactiveUS20080006044A1Mechanical apparatusEvaporators/condensersTemperature controlNuclear engineering
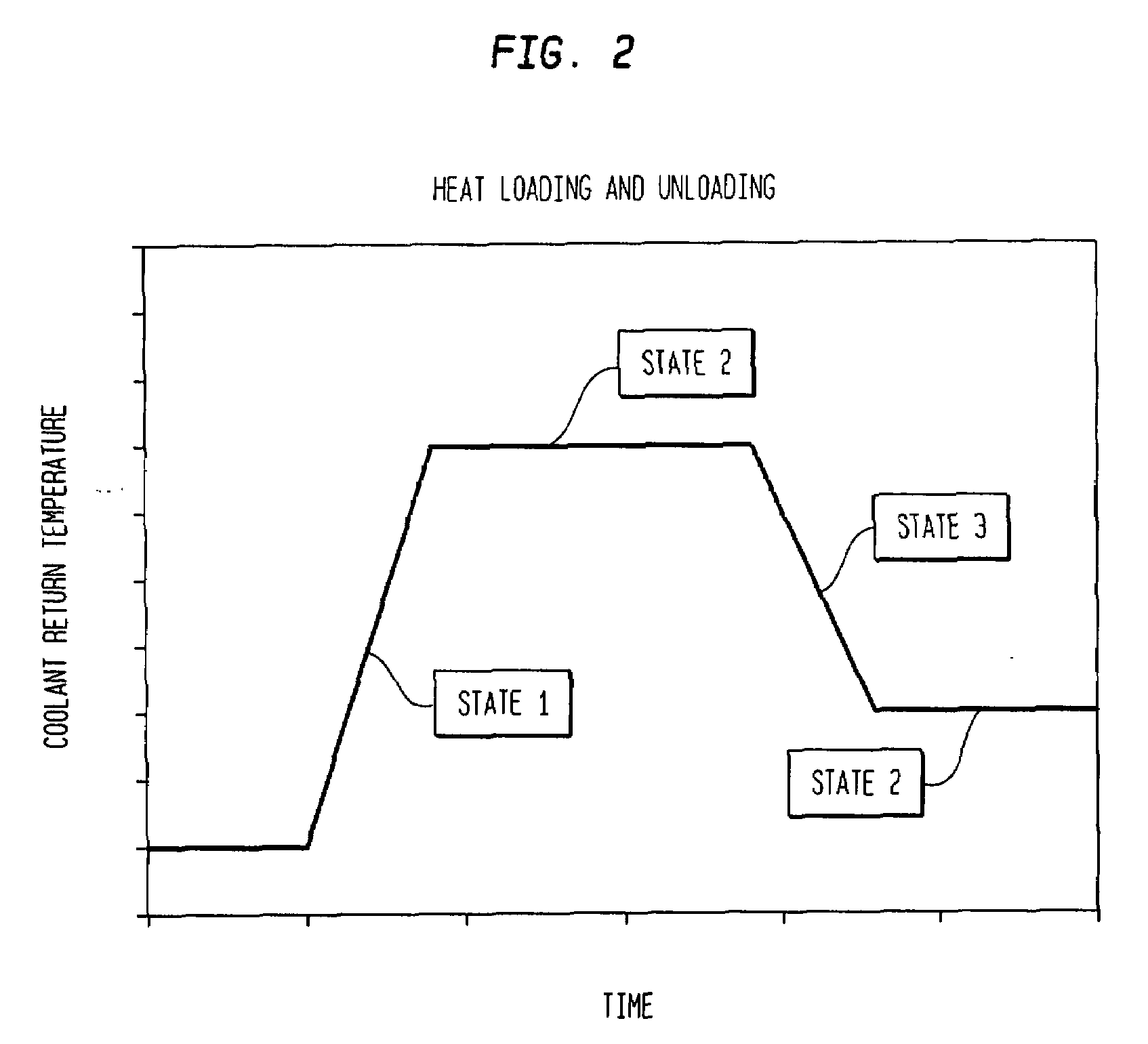
A method for controlling the temperature of a coolant supplied to a process, such as a semiconductor process. The method provides for chilling a coolant to a predetermined temperature, controlling the coolant at the predetermined temperature and delivering the coolant to the semiconductor process. The method includes feedback and feed-forward control algorithms to control the temperature to within about ±0.1° C. under steady state conditions and to within about ±0.75° C. under maximum heat loading and unloading conditions. The invention may be used in any fluid or component temperature control application (e.g. semiconductor, pharmaceutical, or food applications).
Owner:EDWARDS VACUUM INC
VVT (Variable Valve Timing) control method capable of combining self-learning feed-forward and active anti-interference feedback
ActiveCN102374038AHigh control precisionImprove response speedInternal combustion piston enginesOutput powerVariable valve timingControl signal
The invention discloses a VVT (Variable Valve Timing) control method capable of combining self-learning feed-forward and active anti-interference feedback, which can improve the response speed of a VVT phase control, reduce the energy consumption of a regulating process and increase the adaptability to the operating environment change and the state change of an engine. The control method disclosed by the invention comprises the following steps of: carrying out a feed-forward control, an active anti-interference feedback control and a self-learning correction; regulating a hydraulic oil demandvolume of a solenoid valve and a demand current I of a VVT solenoid valve through the feed-forward control; and obtaining a control signal It of a VVT system through the active anti-interference feedback control. The self-learning correction comprises the steps of concluding and calculating a characteristic parameter of the VVT system according to a VVT control quantity (a duty ratio of a PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) wave) and a response characteristic yr of the VVT system during the regulation of the VVT system so as to correct a calculating coefficient in a feed-forward controller model, thereby continuously increasing the calculation accuracy of the feed-forward control, improving the control capability of the feed-forward control, reducing the dependence on the feedback control and effectively improving the response speed and the accuracy of the control of the VVT system.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
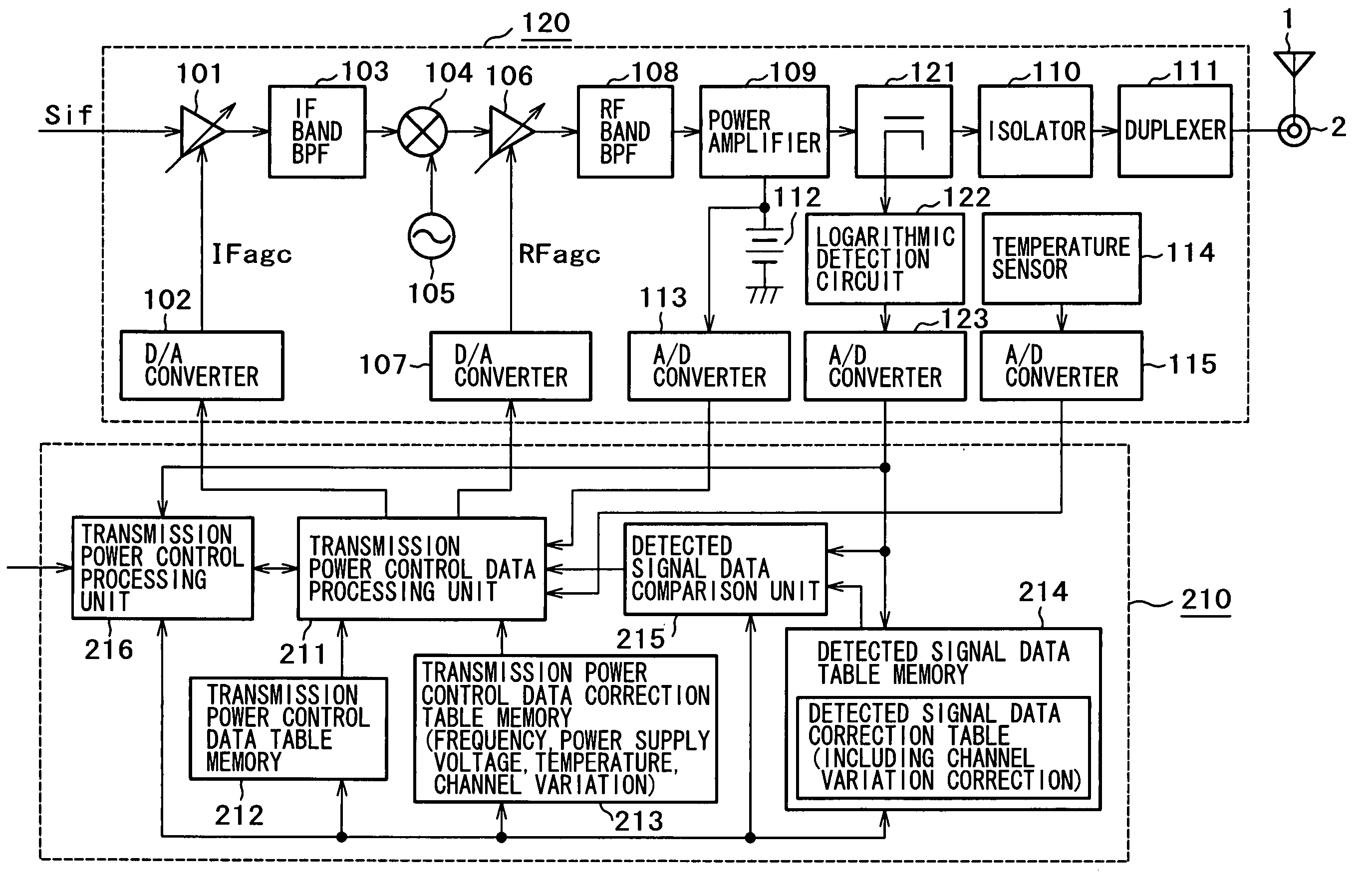
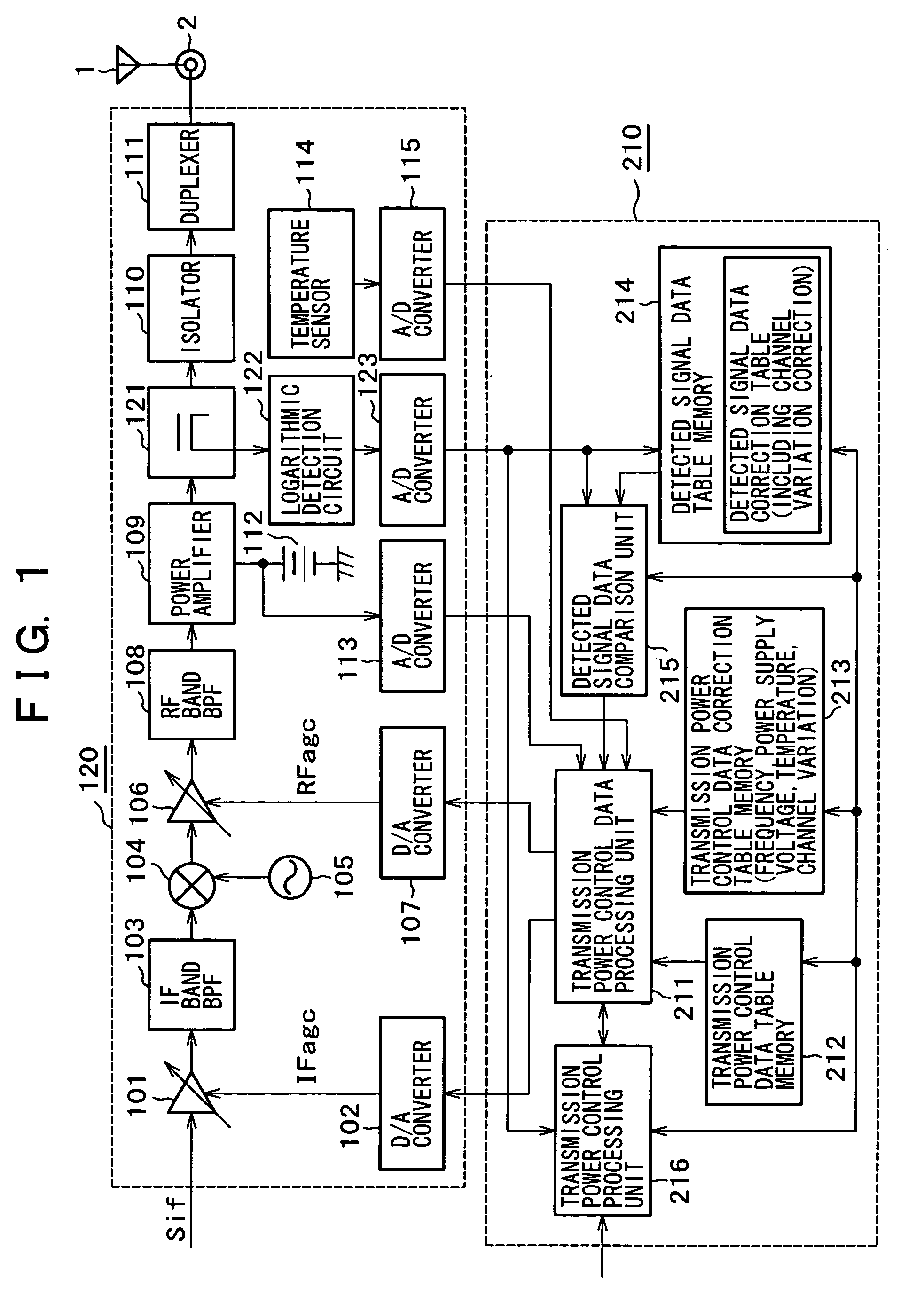
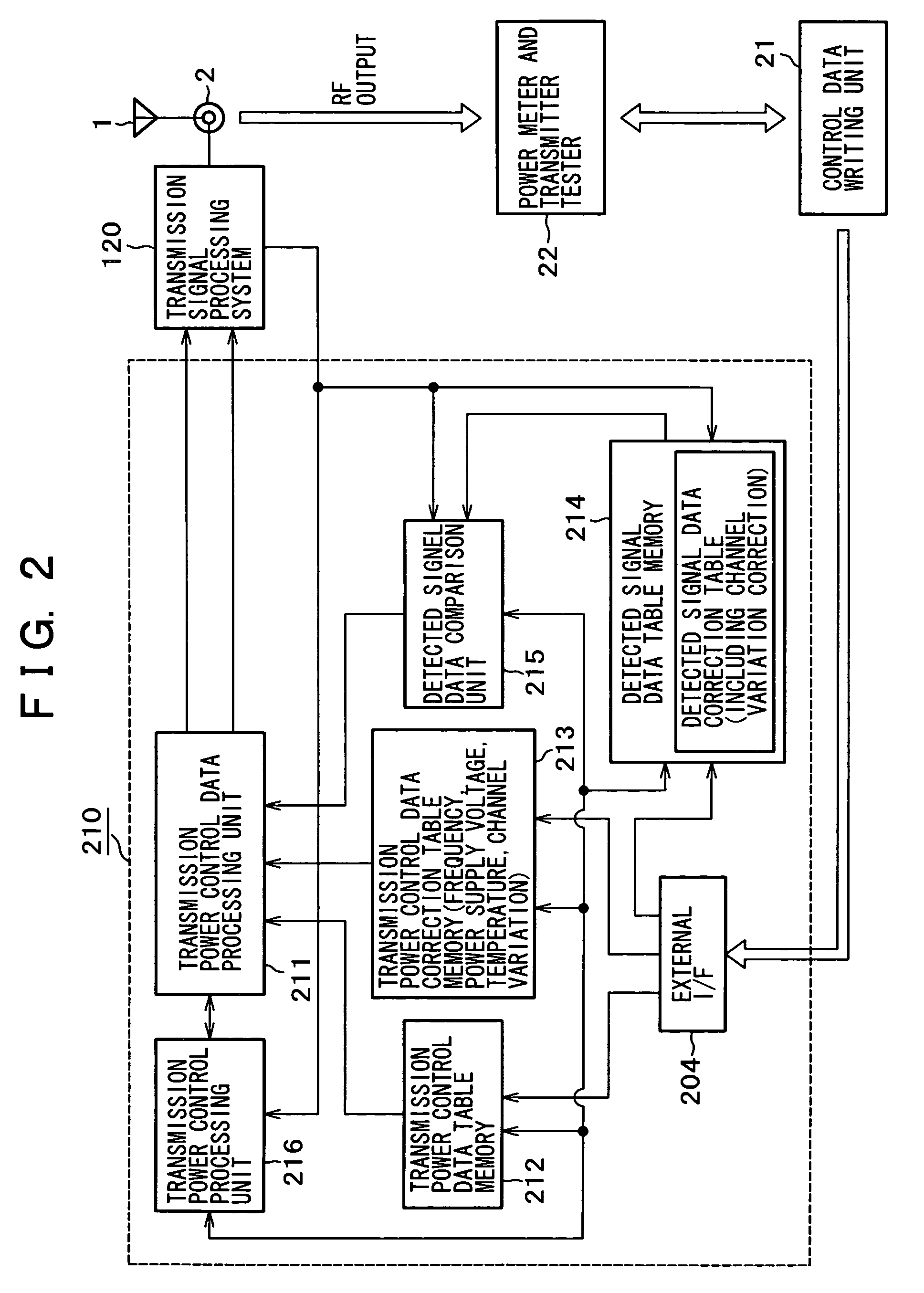
Transmission output circuit and mobile communication terminal
InactiveUS7139537B2Satisfactory characteristicAvoid defectsTransmitters monitoringPower managementControl signalControl data
A transmission output circuit can always perform correct transmission power control, and can detect the abnormality of transmission power, which interferes with other users, and part troubles, which cause erroneous transmission. The transmission output circuit includes transmission power control data generation means for generating a gain control signal for performing the feed forward control of gain control amplification means in order that the output signal level of the power amplification means may be a target transmission power output level, detection means for detecting the output signal of the power amplification means to obtain detected signal data, and judgment means for judging the existence of the occurrence of trouble in the transmission output system by using the detected signal data from the detection means.
Owner:SONY CORP +1
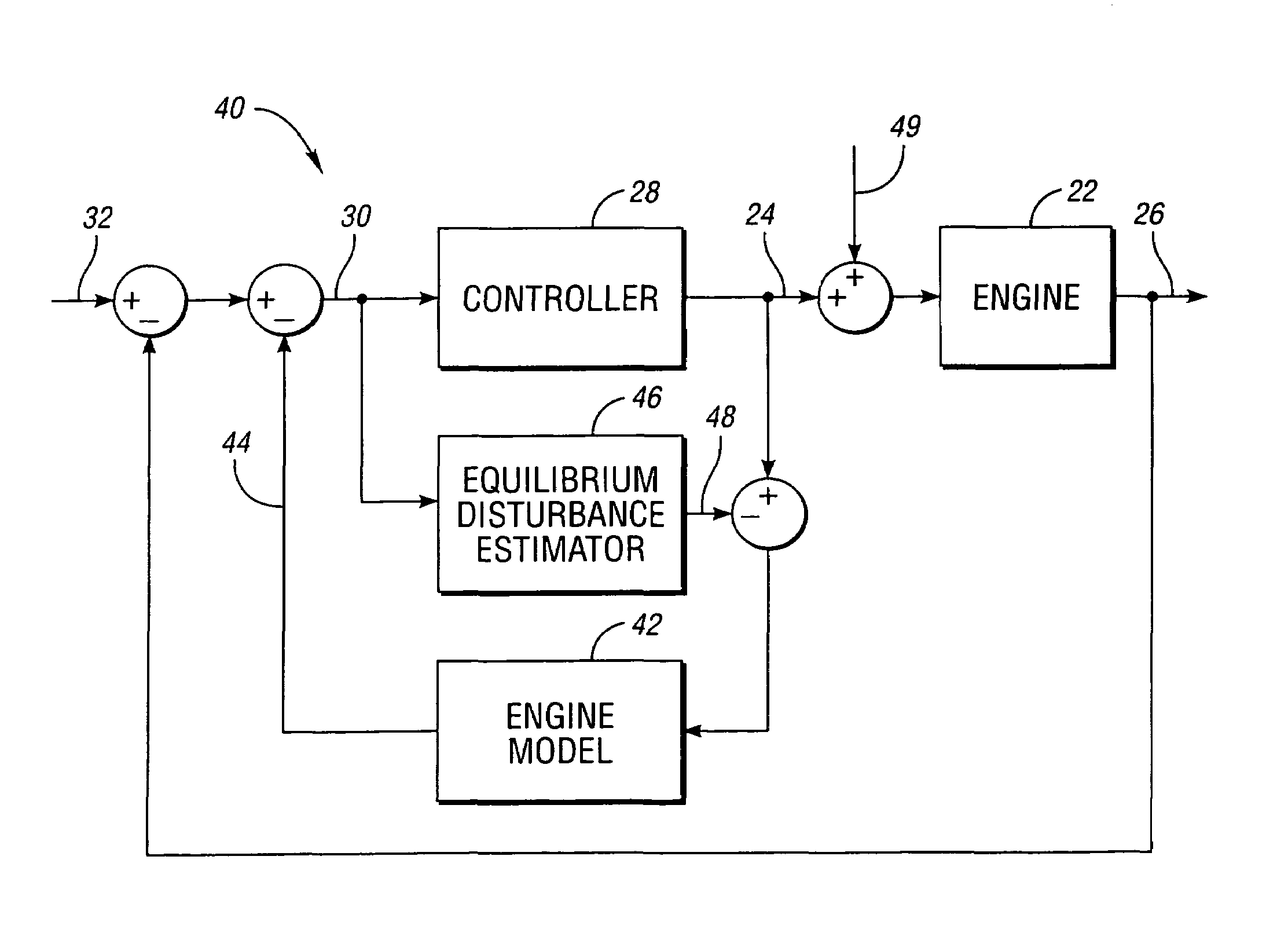
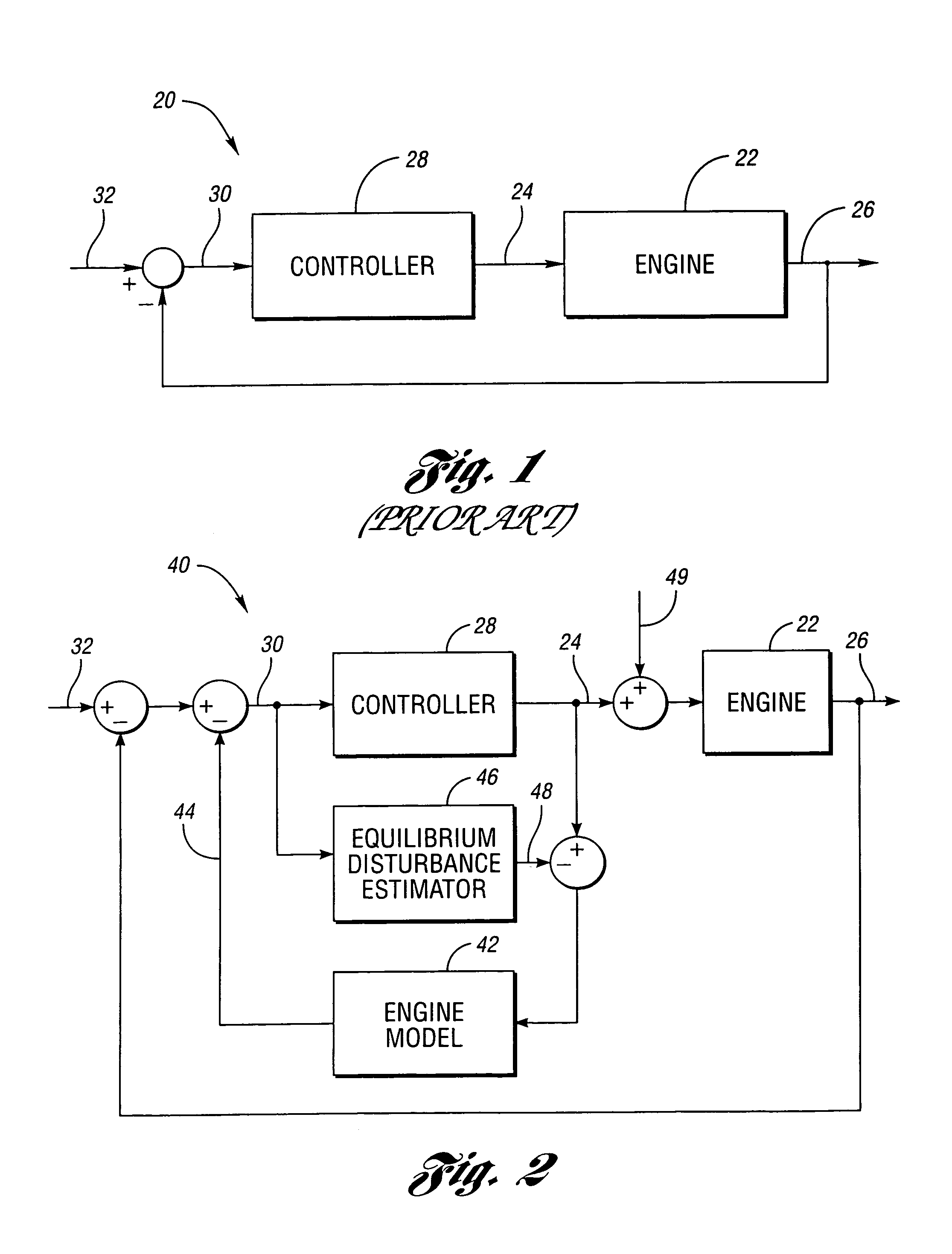
Engine delay compensation
An engine with inertial integration and delay is controlled through the use of a disturbance estimator. Control logic includes a feed-forward control path driving a control input with a control signal. The feed-forward control path is designed to provide closed-loop control of the controlled parameter without the presence of transport delay. The disturbance estimator generates an estimate of the engine disturbance. A Smith predictor generates a compensation signal for the feed-forward control path based on the control signal and the engine disturbance estimate.
Owner:DETROIT DIESEL CORP
Active noise control system
InactiveUS20060188107A1Noise can be canceled outEasy to getEar treatmentNoise generationTrunk compartmentControl system
An active noise control system is capable of canceling out noise in the passenger compartment of a vehicle based on low-frequency road noise. The active noise control system has a feed-forward control unit for being supplied with reference signals highly correlated to noise from a noise source and generating a noise cancellation signal which is out of phase to noise in the passenger compartment of the vehicle, and a canceling sound generating unit disposed in the passenger compartment for generating a noise canceling sound in response to the noise cancellation signal from said feed-forward control unit. The active noise control system also has microphones for generating reference signals which are positioned respectively near the base of the front seat, near the center of a roof, and within a trunk compartment, i.e., respectively at vibrational antinodes of a primary or secondary acoustic normal mode of the passenger compartment in the longitudinal direction thereof. Output signals from the microphones are supplied as the reference signals.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD +1
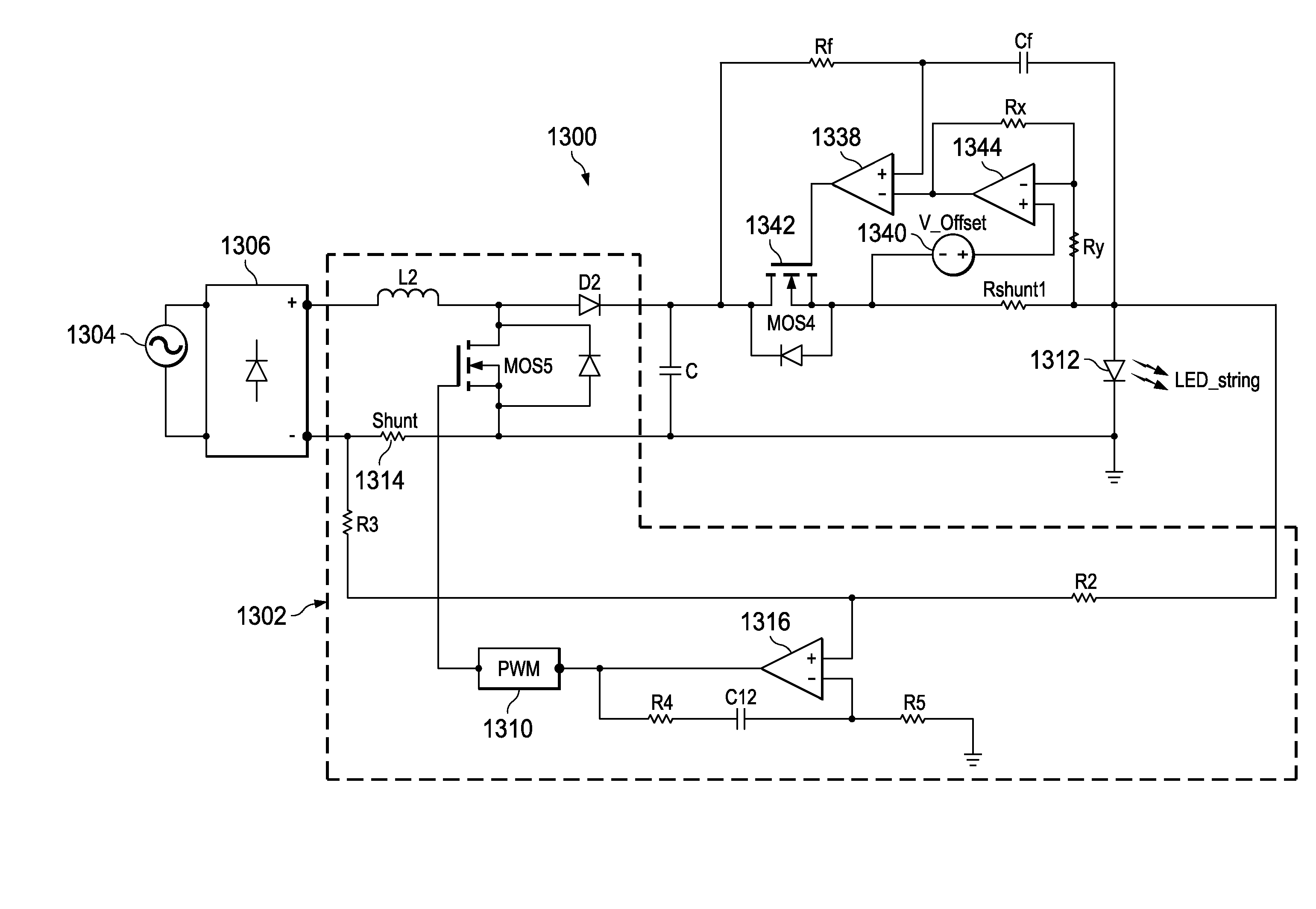
Feed forward controlled voltage to current source for LED driver
InactiveUS20130082611A1Efficient driveDelay problemEfficient power electronics conversionConversion with intermediate conversion to dcCurrent sensorControl circuit
A DC to DC converter receives a DC input voltage and generates an output DC voltage. A current sensor measures a DC input current. A control circuit is coupled to the current sensor for controlling the DC to DC converter to have a constant DC input current.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
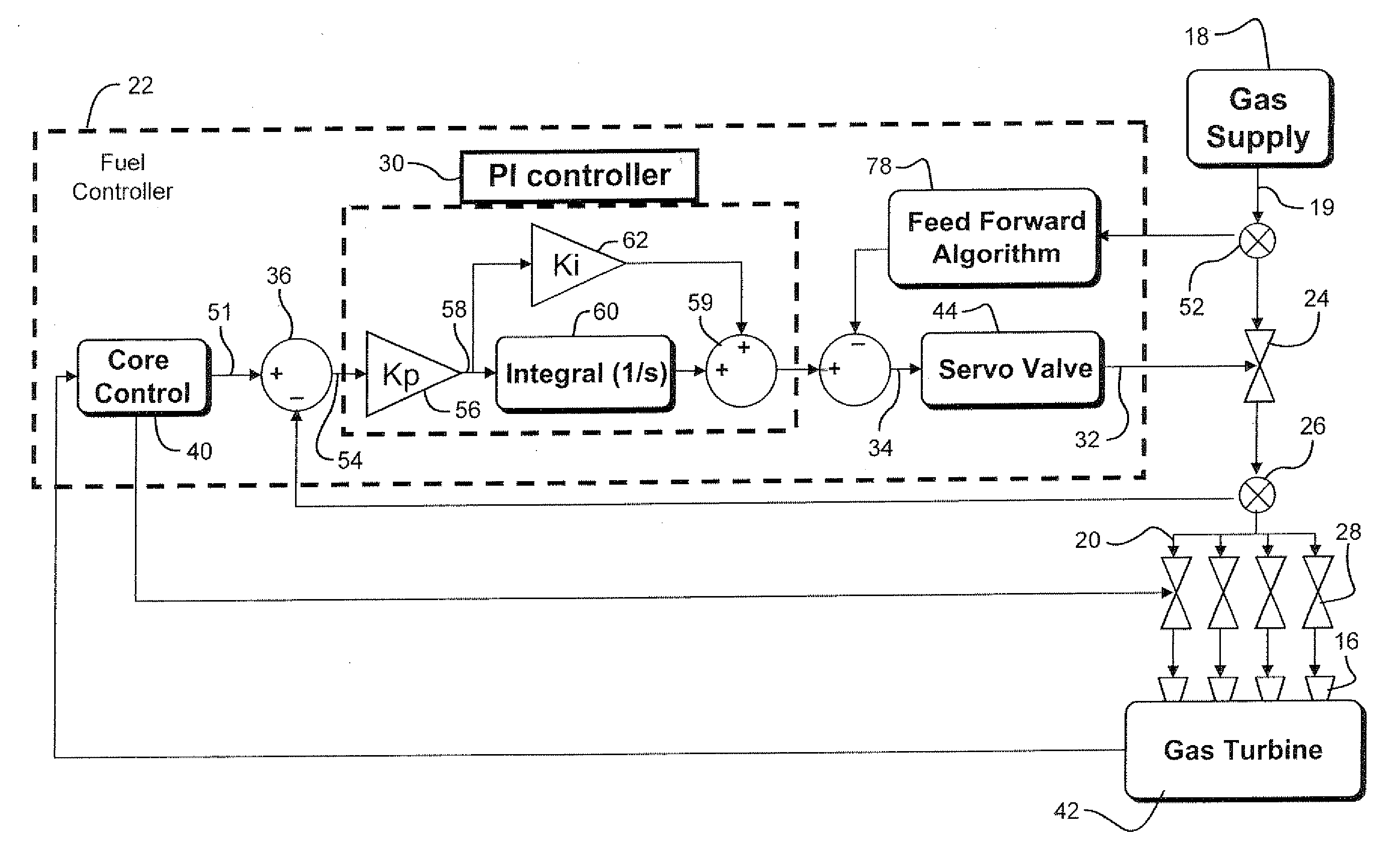
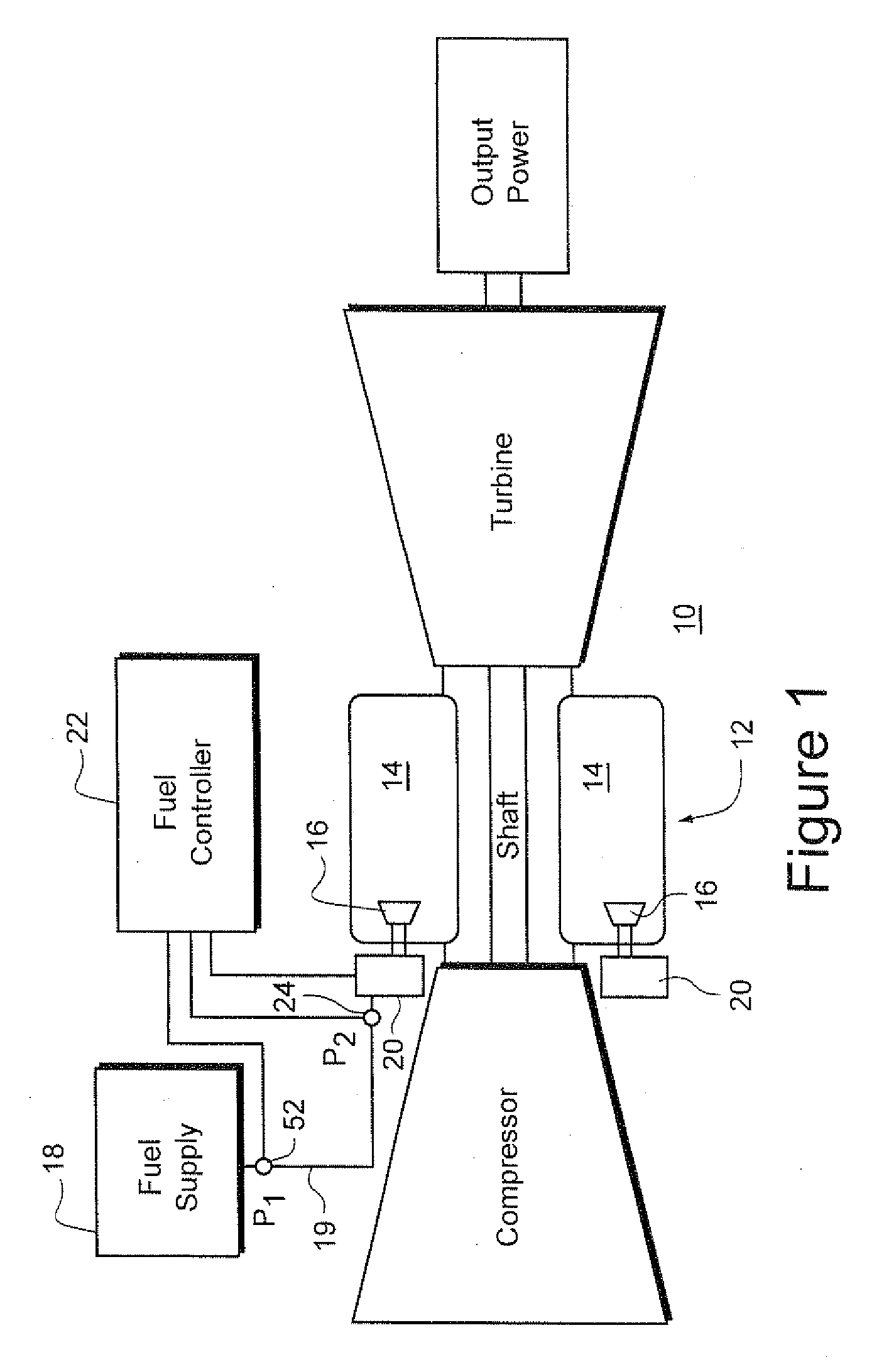
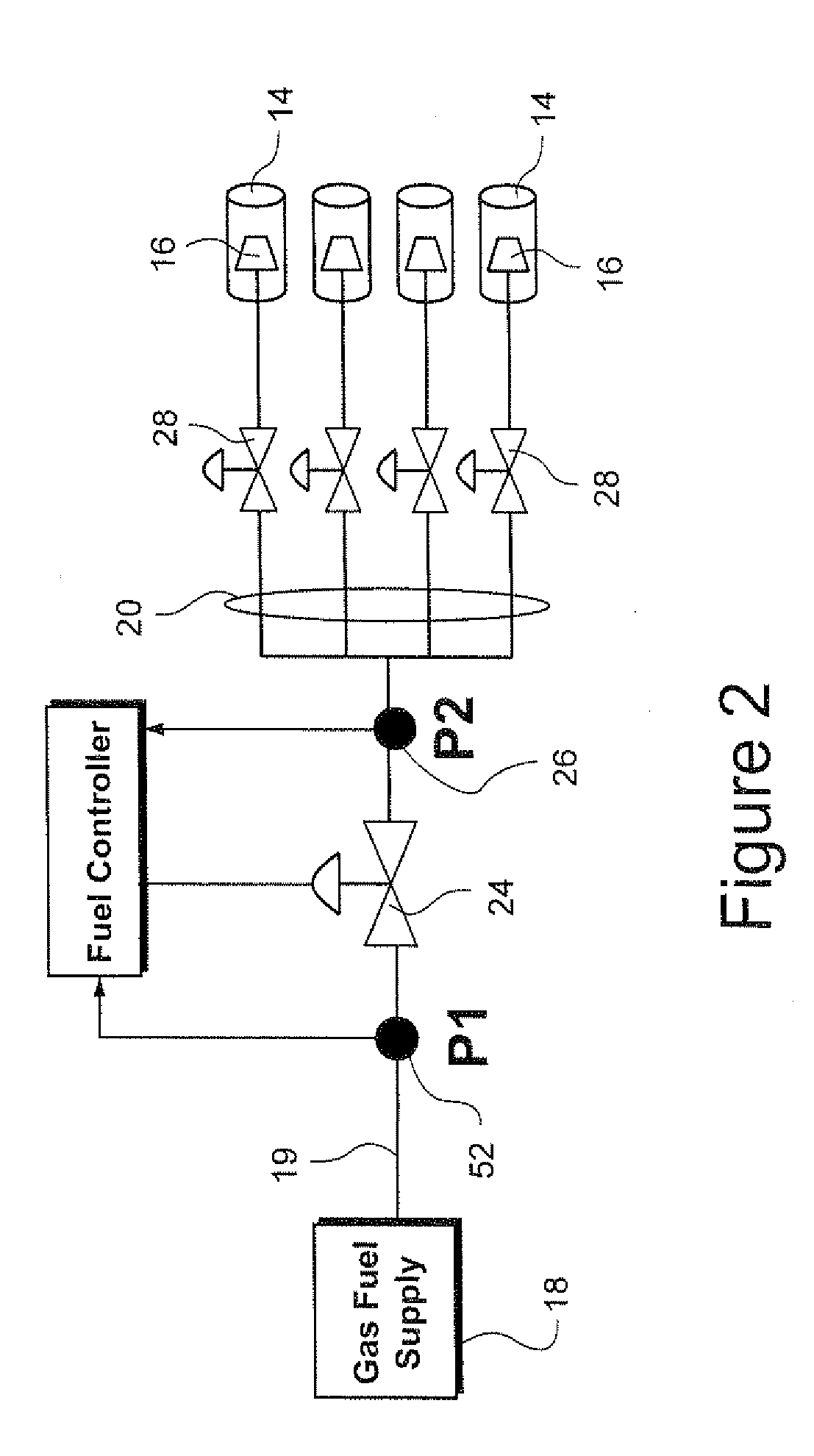
Fuel control system for gas turbine and feed forward control method
InactiveUS20100122535A1Analogue computers for vehiclesGas turbine plantsCombustion systemControl system
A fuel controller for a combustion system in a gas turbine having a combustion system, a fuel supply, a pressure control valve proximate the combustion system and a first pressure sensor proximate the pressure control valve, the fuel controller including: a proportional-integrated (PI) logic unit generating a control command for the pressure control valve and receiving input signals representing a desired fuel pressure at the pressure control valve and an input signal from the first pressure sensor representing an actual fuel pressure at the pressure control valve, and a plurality of control gains stored in electronic memory of the controller, wherein each control gain is applicable to a predefined operating condition of the gas turbine, and wherein the controller determines which set of control gains is to be applied by the PI logic unit based on an actual operating condition of the gas turbine.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com