Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
5136 results about "PID controller" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
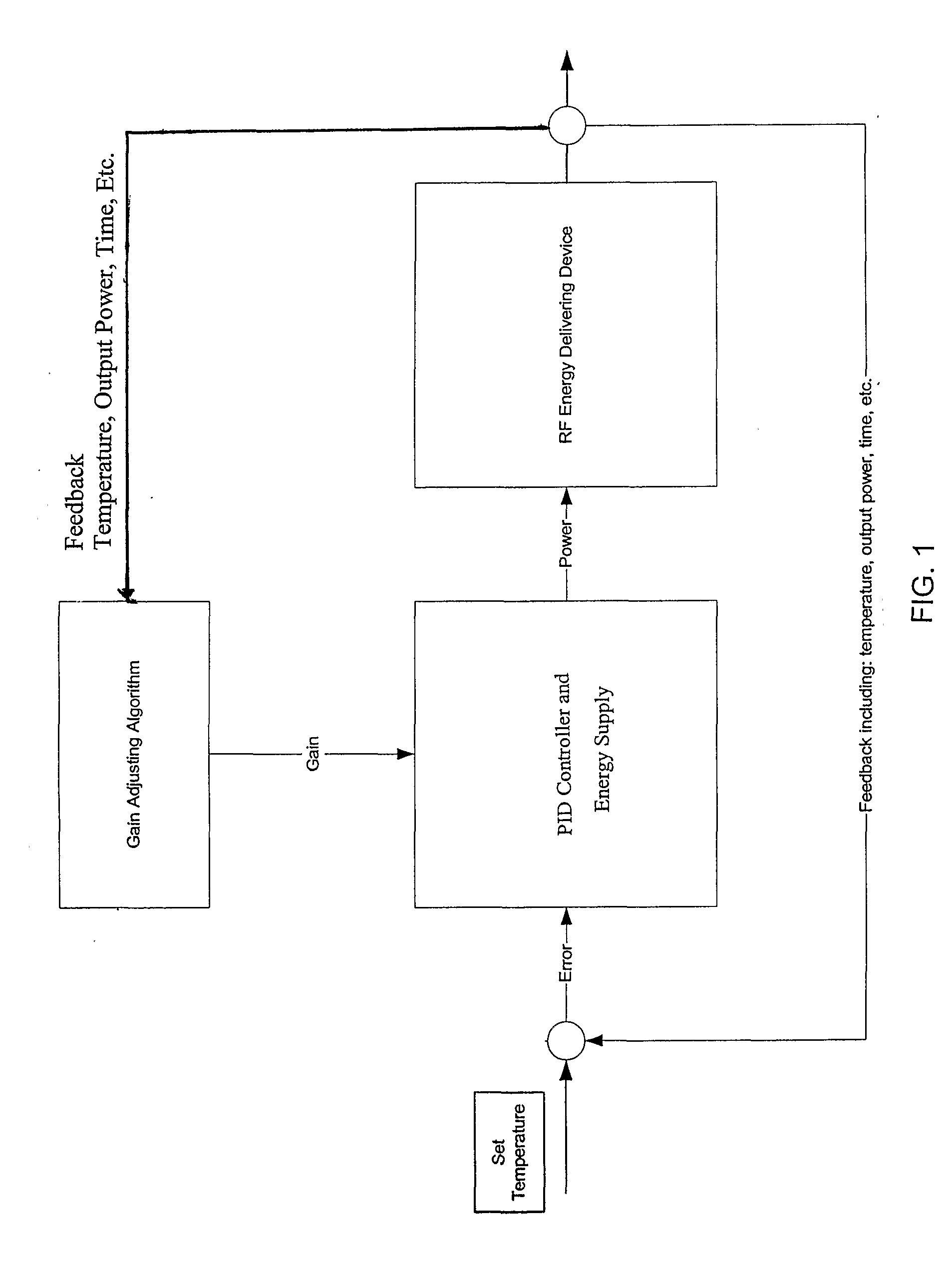
A proportional–integral–derivative controller (PID controller. or three-term controller) is a control loop mechanism employing feedback that is widely used in industrial control systems and a variety of other applications requiring continuously modulated control. A PID controller continuously calculates an error value e(t) as the difference between a desired setpoint (SP) and a measured process variable (PV) and applies a correction based on proportional, integral, and derivative terms (denoted P, I, and D respectively), hence the name.
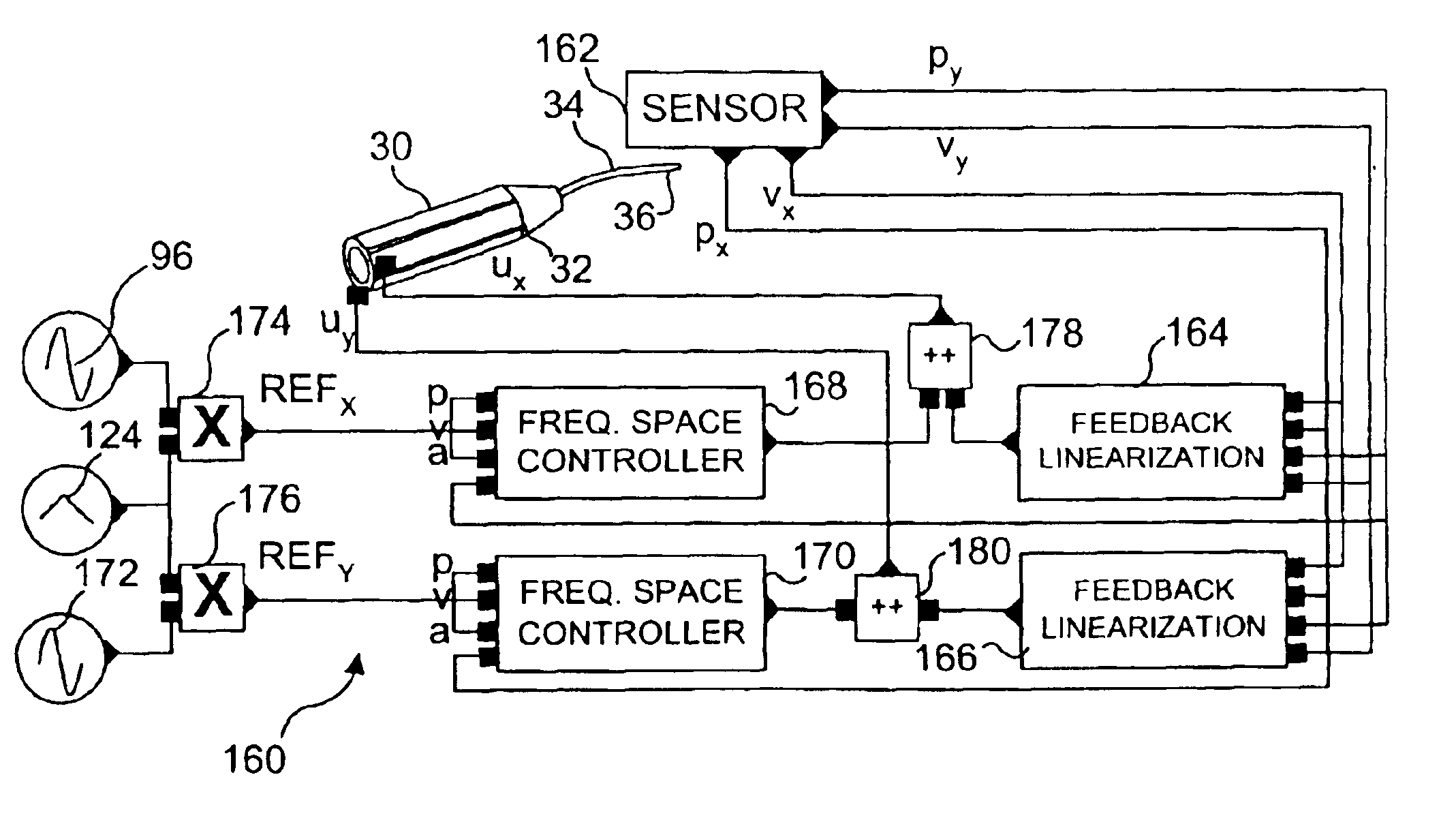
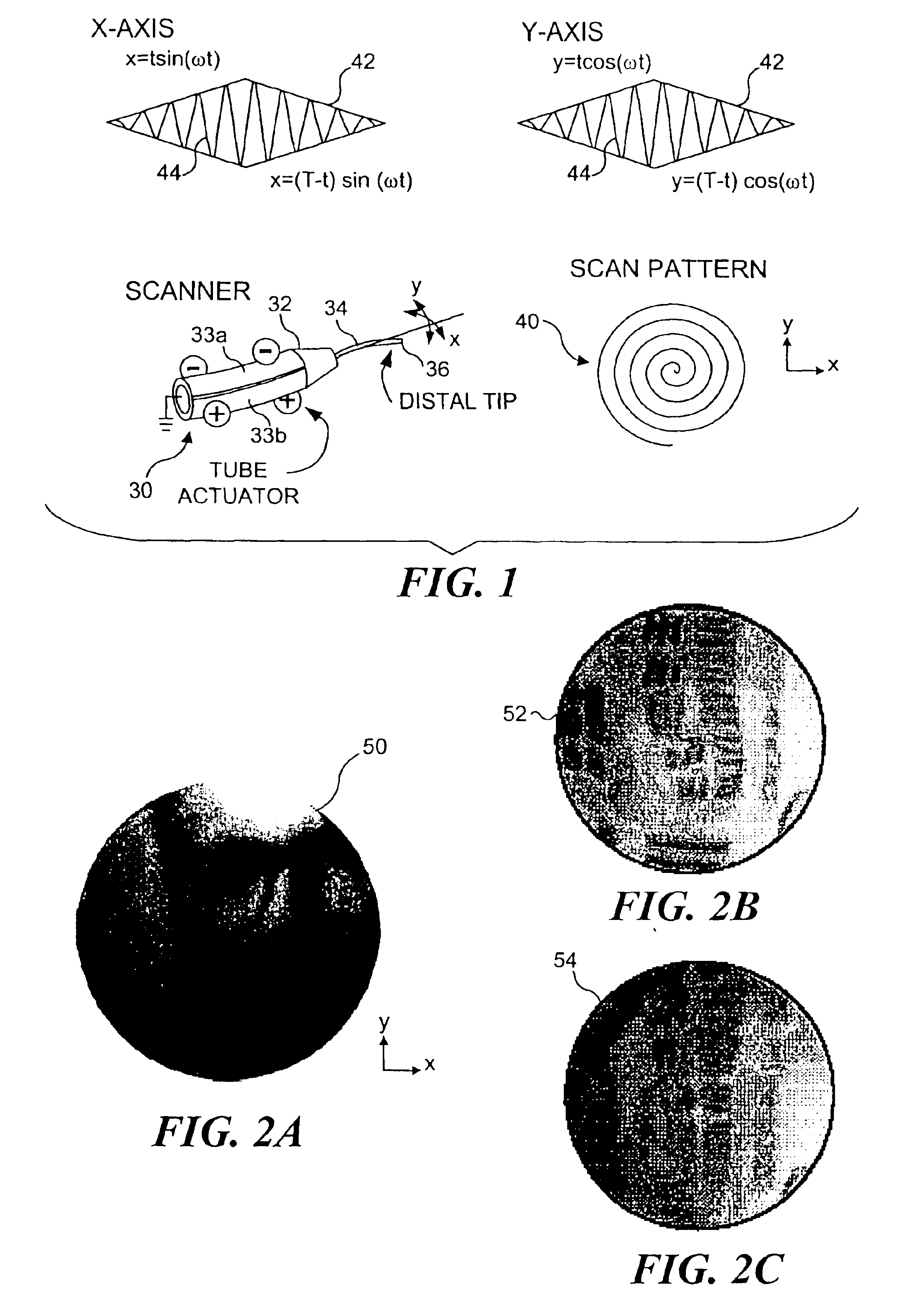
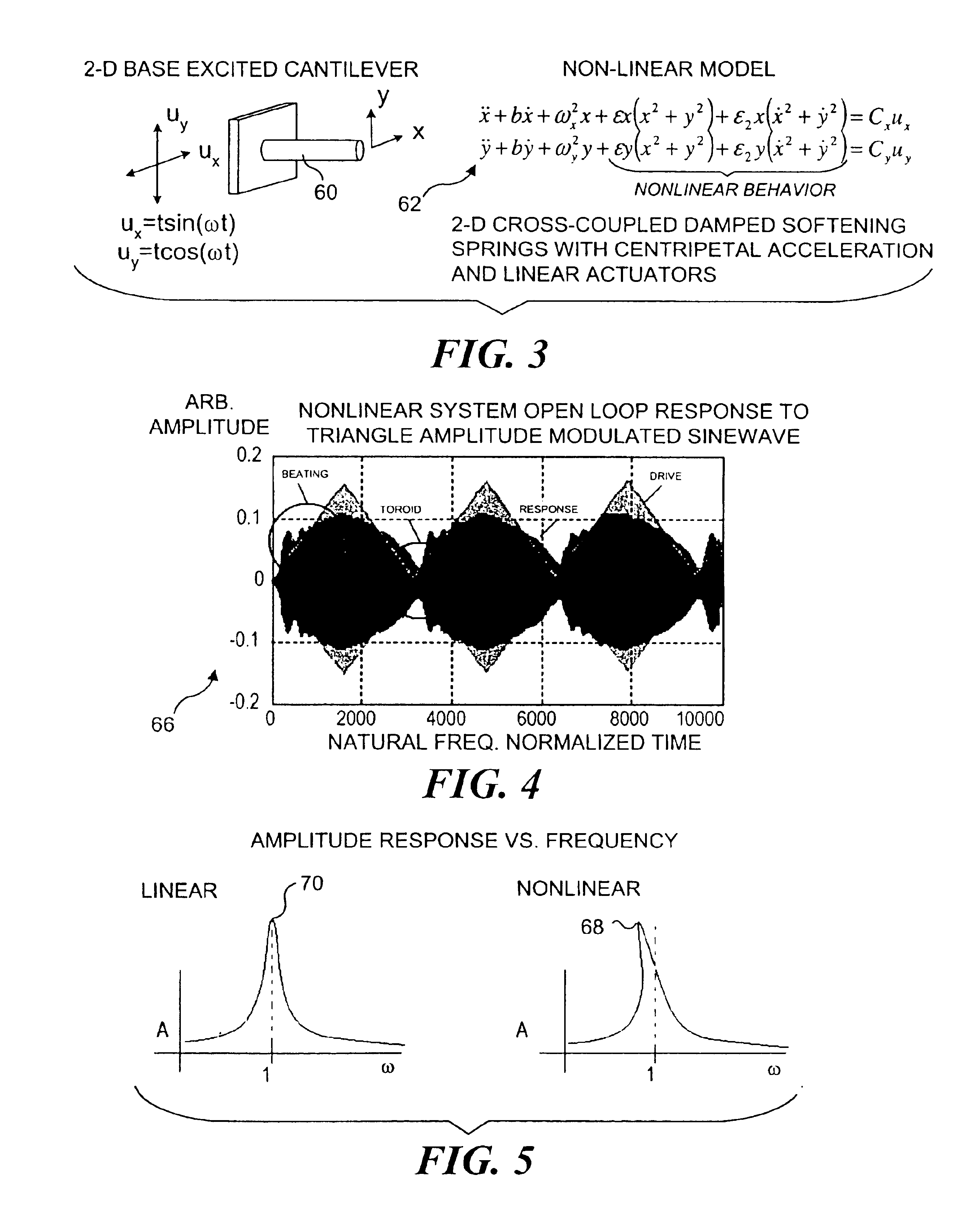
Control of an optical fiber scanner
InactiveUS6845190B1Remove nonlinear behaviorRobust cancellationSurgeryEndoscopesOptical scannersPhotodetector
Controls for an optical scanner, such as a single fiber scanning endoscope (SFSE) that includes a resonating optical fiber and a single photodetector to produce large field of view, high-resolution images. A nonlinear control scheme with feedback linearization is employed in one type of control to accurately produce a desired scan. Open loop and closed loops controllers are applied to the nonlinear optical scanner of the SFSE. A closed loop control (no model) uses either phase locked loop and PID controllers, or a dual-phase lock-in amplifier and two PIDs for each axis controlled. Other forms of the control that employ a model use a frequency space tracking control, an error space tracking control, feedback linearizing controls, an adaptive control, and a sliding mode control.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
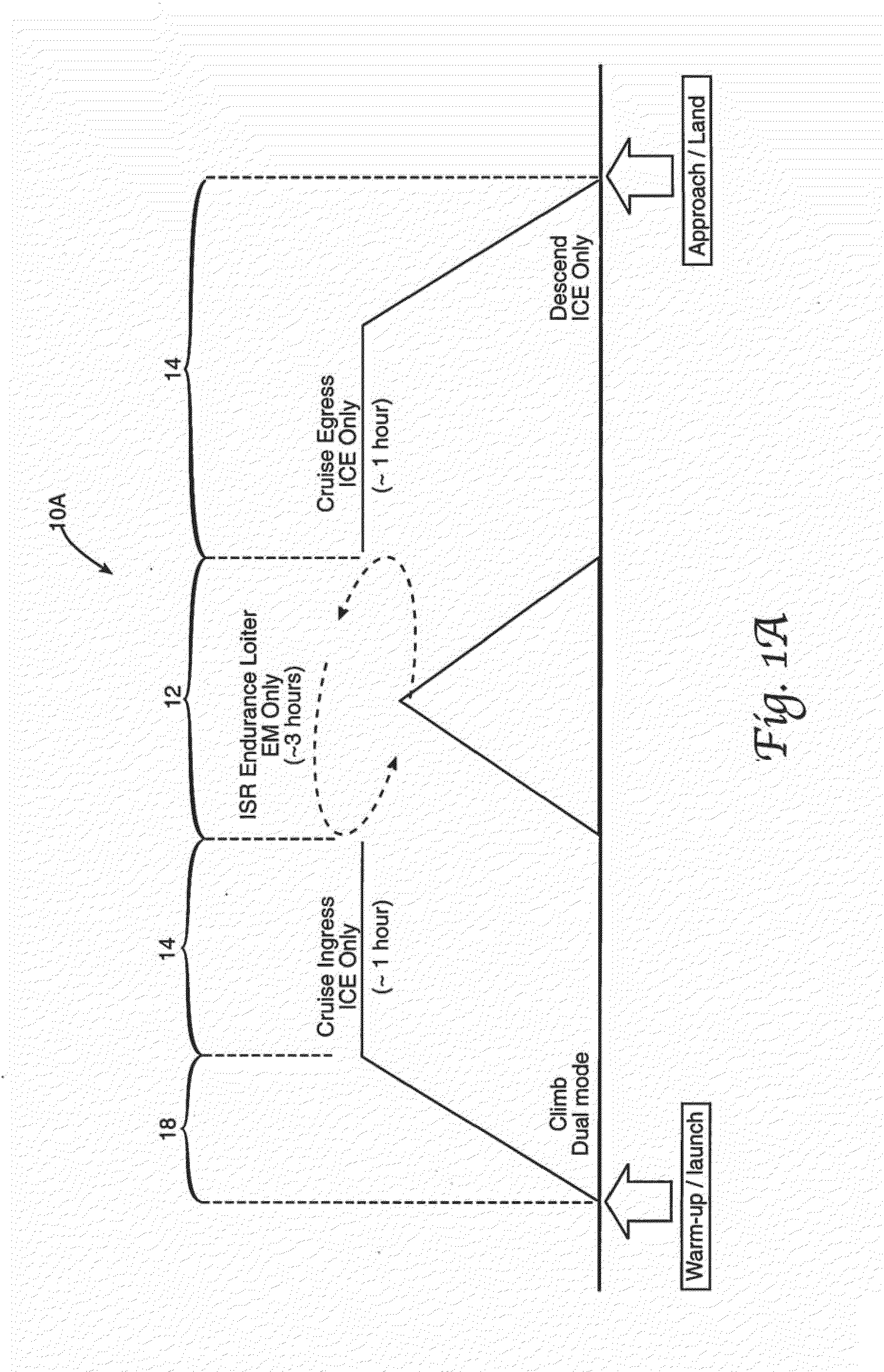
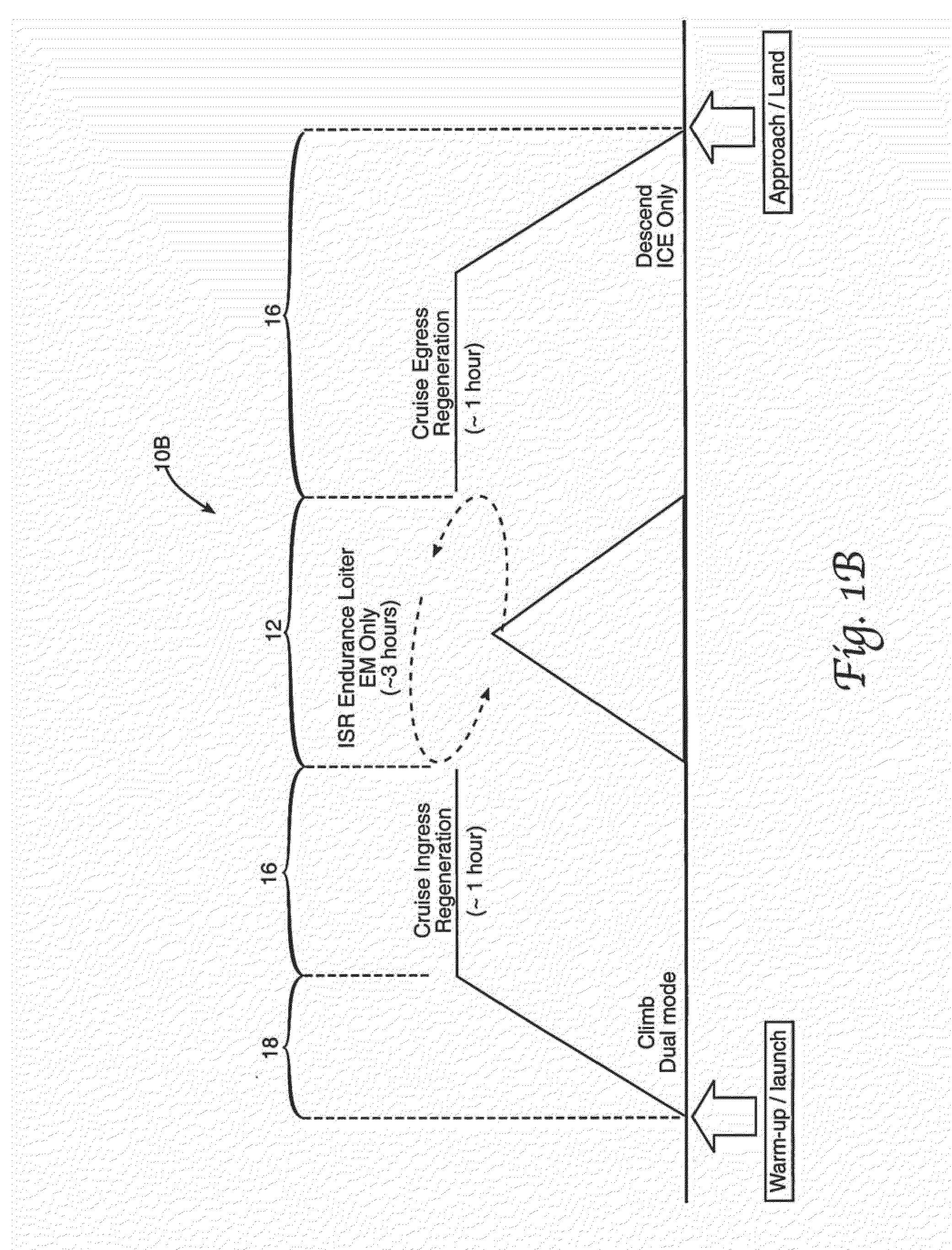
Parallel Hybrid-Electric Propulsion Systems for Unmanned Aircraft
An unmanned air vehicle is provided, which includes an airframe and a parallel hybrid-electric propulsion system mounted on the airframe. The parallel hybrid-electric propulsion system includes an internal combustion engine and an electric motor. A hybrid controller is configured to control both the internal combustion engine and the electric motor. A propeller is connected to a mechanical link. The mechanical link couples the internal combustion engine and the electric motor to the propeller to drive the propeller. An alternate unmanned air vehicle includes a second propeller driven by the electric motor. In this alternate unmanned air vehicle, the internal combustion engine is decoupled from the electric motor.
Owner:GOVERNMENT OF THE UNITED STATES AS REPRESENTD BY THE SEC OF THE AIR FORCE
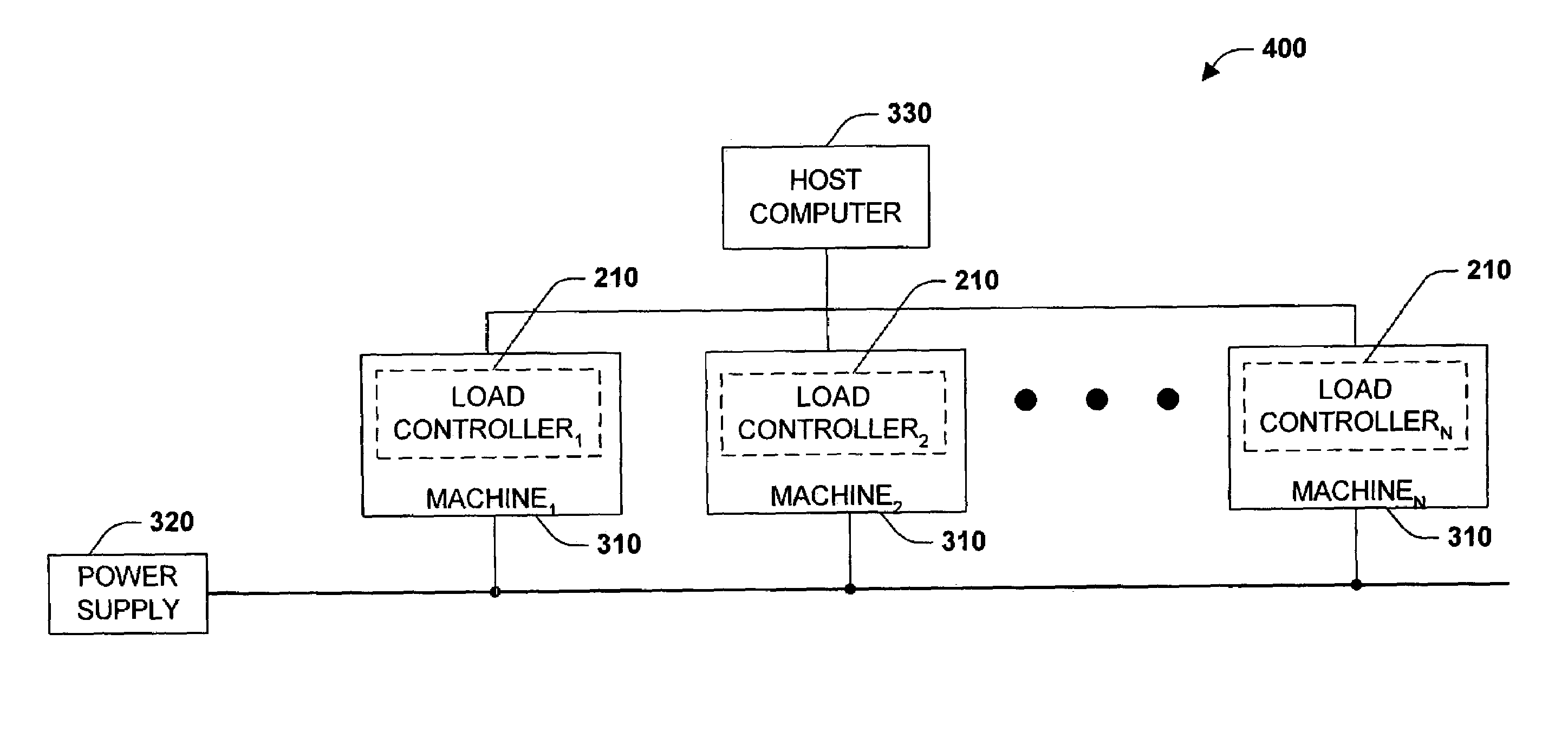
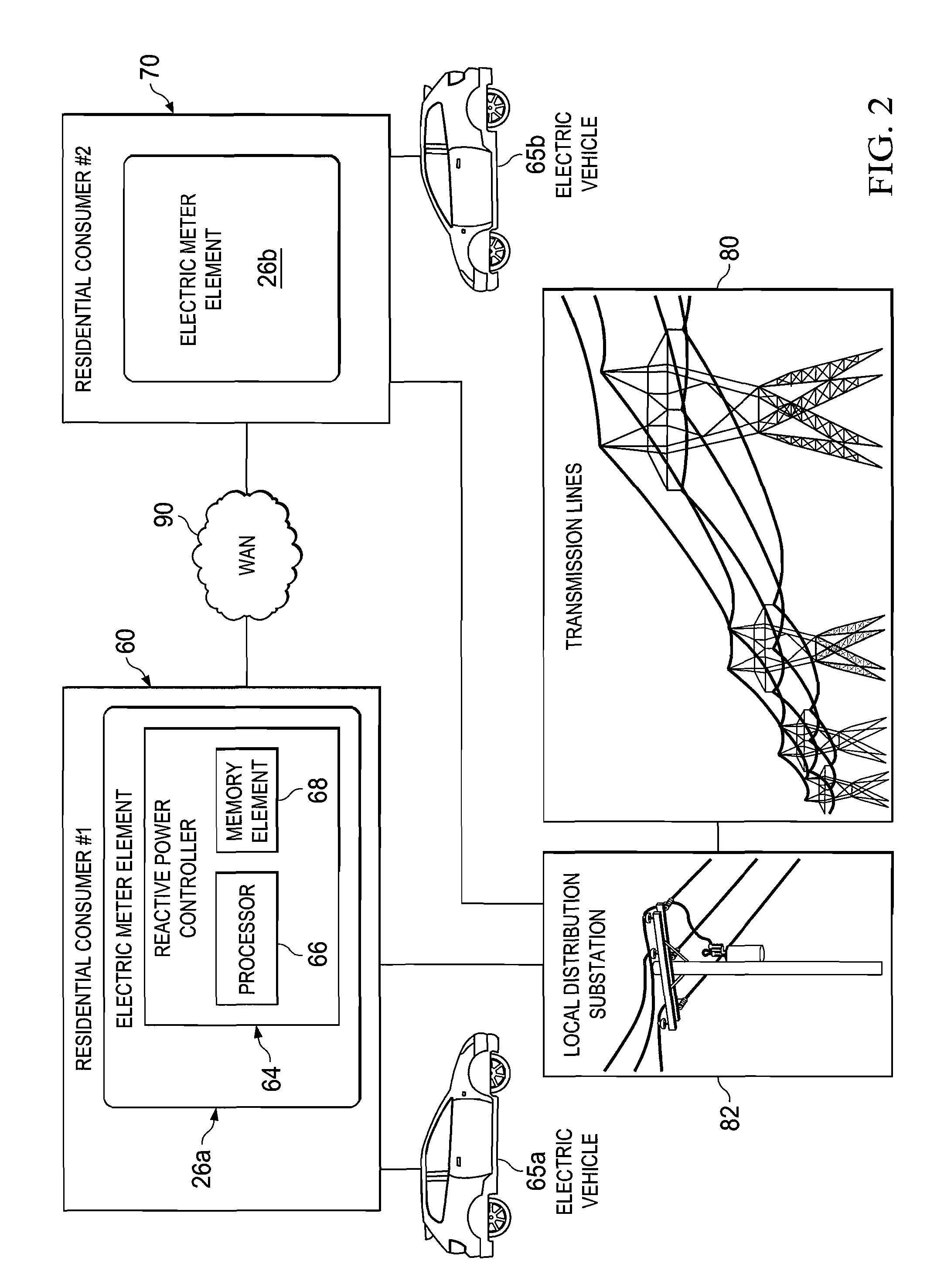
Decentralized energy demand management
A decentralized load management and control system and method are provided herein. A plurality of loads in a system are associated with a multitude of respective networked load controllers. If energy demand exceeds optimum limits in operation then the networked load controllers collaborate to determine which load(s) will be shed based on an optimization algorithm that considers, inter alia, variable load priority and business objectives. Additionally and / or alternatively, if the metered energy demand is less than optimum, the load controllers can determine which loads to reconnect again based at least upon load priority and business objectives.
Owner:ROCKWELL AUTOMATION TECH
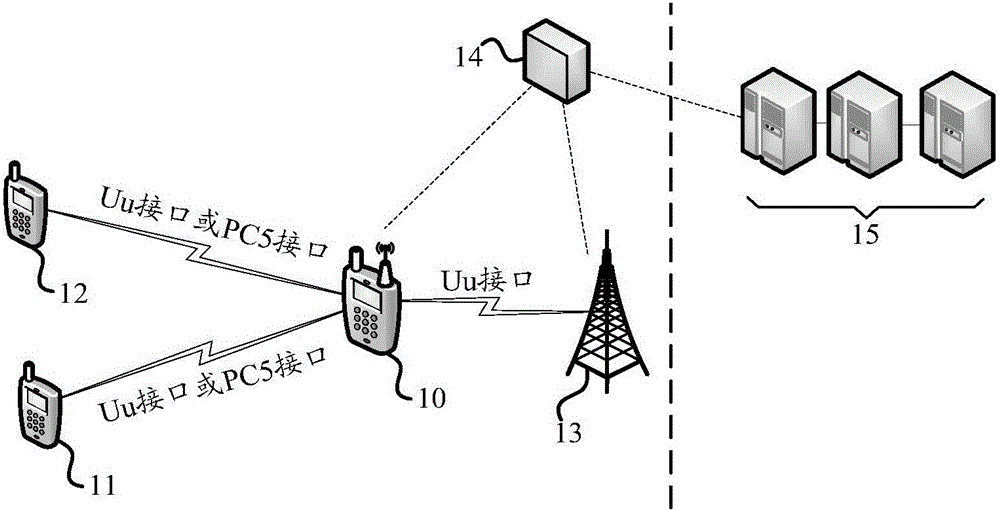
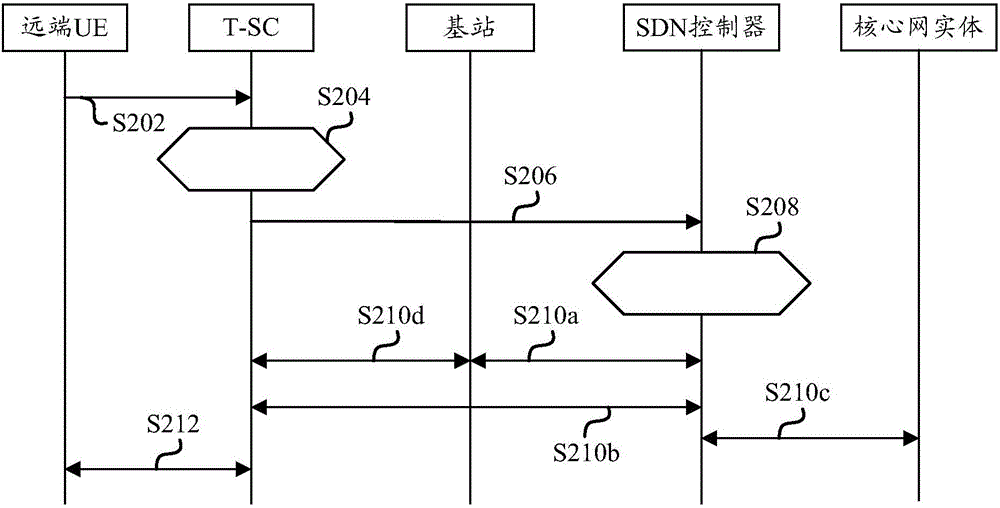
Method and apparatus for controlling access to network slicing, terminal small cell and SDN controller
ActiveCN106060900AImplementation supportAssess restrictionConnection managementUser needsTelecommunications
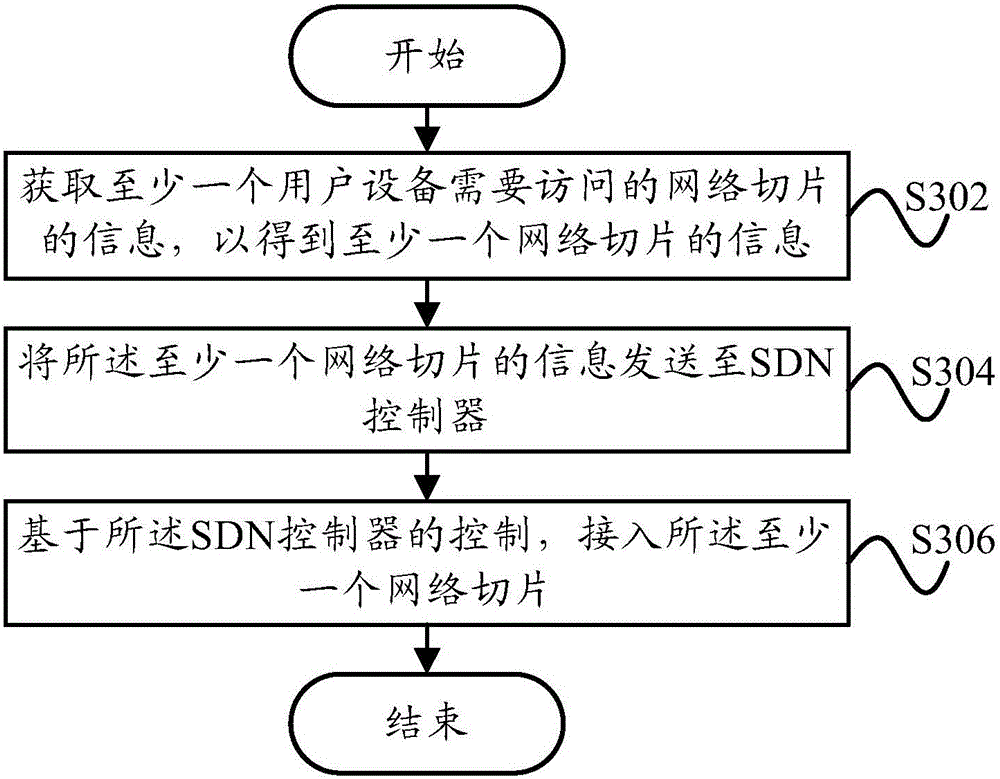
The invention provides a method and apparatus for controlling access to network slicing, a terminal small cell and a SDN controller. The control method which is suitable to the terminal small cell includes the following steps: acquiring information of at least one network slicing a user needs to access so as to obtain information of at least one network slicing; transmitting the information of at least one network slicing to the SDN controller; based on the control of the SDN controller, and accessing to the at least one network slicing. The technical solution of the invention enables the terminal small cell to access to a corresponding network slicing in advance so as to provide corresponding network service to a user device which is accessed to the terminal small cell, and realizes support of the terminal small cell to the network slicing.
Owner:YULONG COMPUTER TELECOMM SCI (SHENZHEN) CO LTD
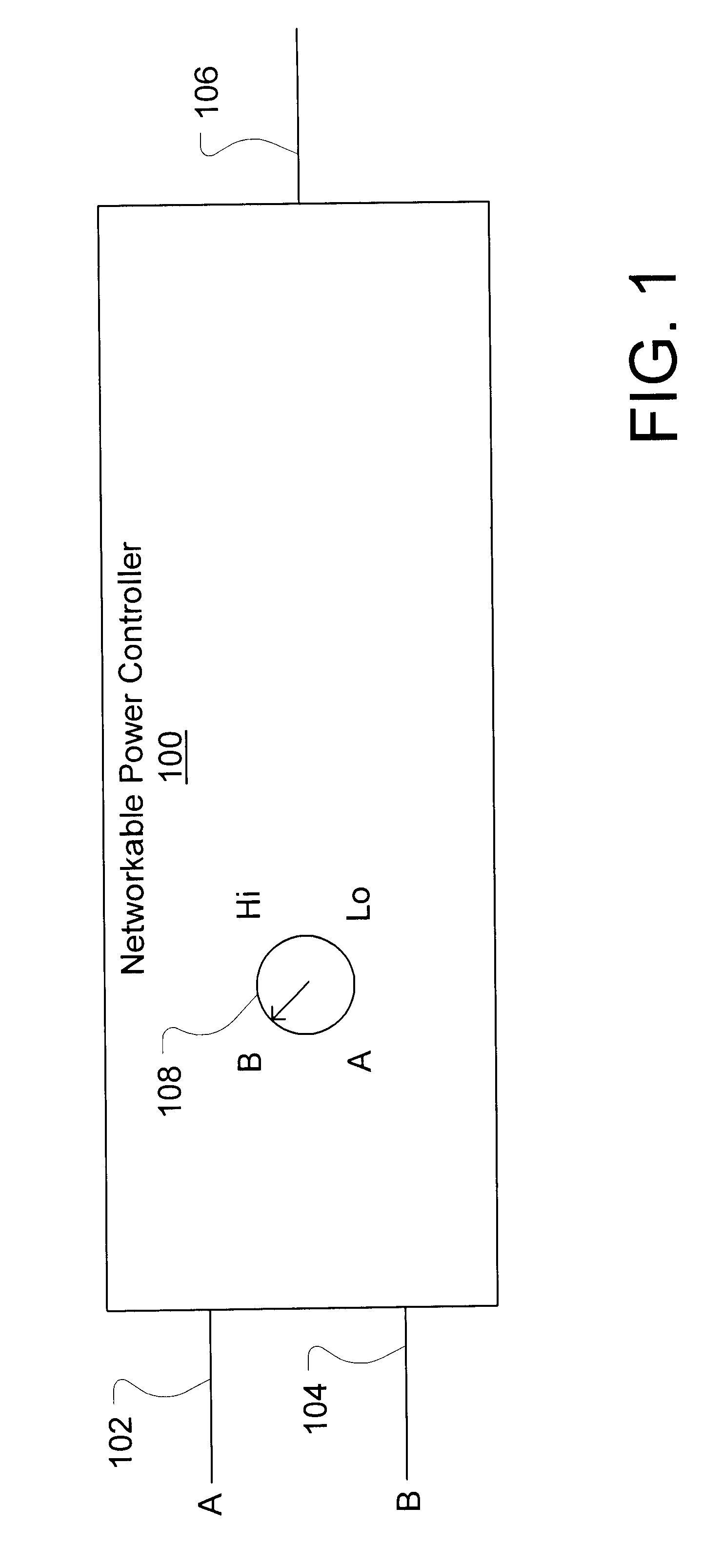
Networkable power controller
InactiveUS6400103B1Telemetry/telecontrol selection arrangementsSpace heating and ventilation safety systemsDigital controlBuilding automation
A networkable power controller includes a mode selector for selectively conducting of a plurality of input signals to an output of the networkable power controller, where the input signals and the output signals satisfy the same signaling protocol. The networkable power controller may be networked with other networkable power controllers, lighting ballasts and other building automation control devices, and user-controlled voltage selectors to provide a lighting control network. A power controller may include a mode selector that may be used in combination with other control devices or components, including a rotary dimmer control, a digital slide dimmer control, a demand load shedder component, a photometer component, and a communications interface. The communications interface allows digital control of the networkable power controller.
Owner:POWER CIRCUIT INNOVATIONS
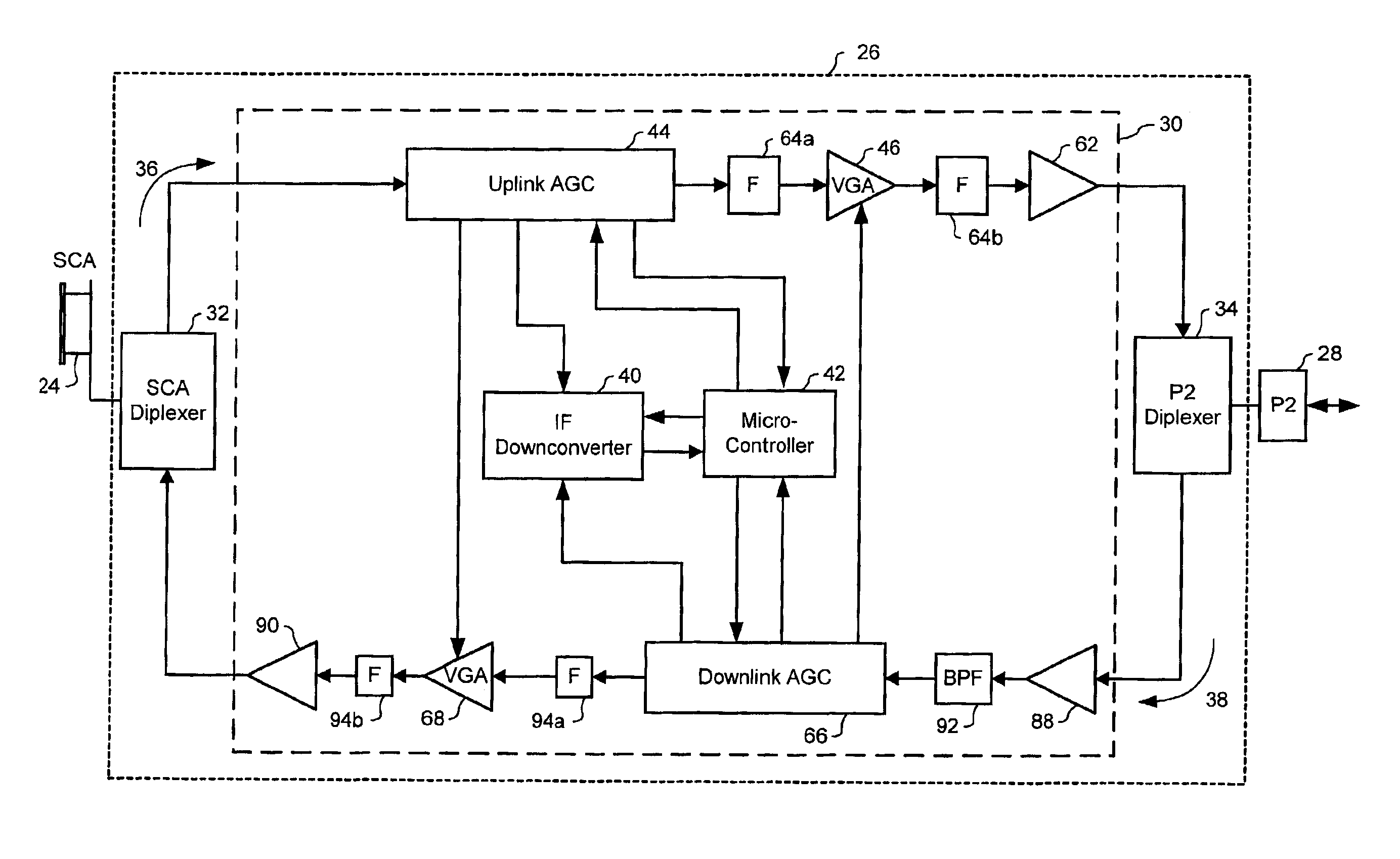
Intelligent gain control in an on-frequency repeater
An intelligent gain controller operates to control the gain in each one of wideband uplink and downlink signal paths. Weak desired signals, within each wideband signal path, are detected using a narrowband down converter and detector, and these desired signals monitored by the micro controller. Based on the monitored signals, the micro controller operates, under control of suitable software implementing an Adaptive Control Algorithm, to adjust the gain in each of the uplink and downlink paths in order to dynamically optimize performance.
Owner:SPOTWAVE WIRELESS INC
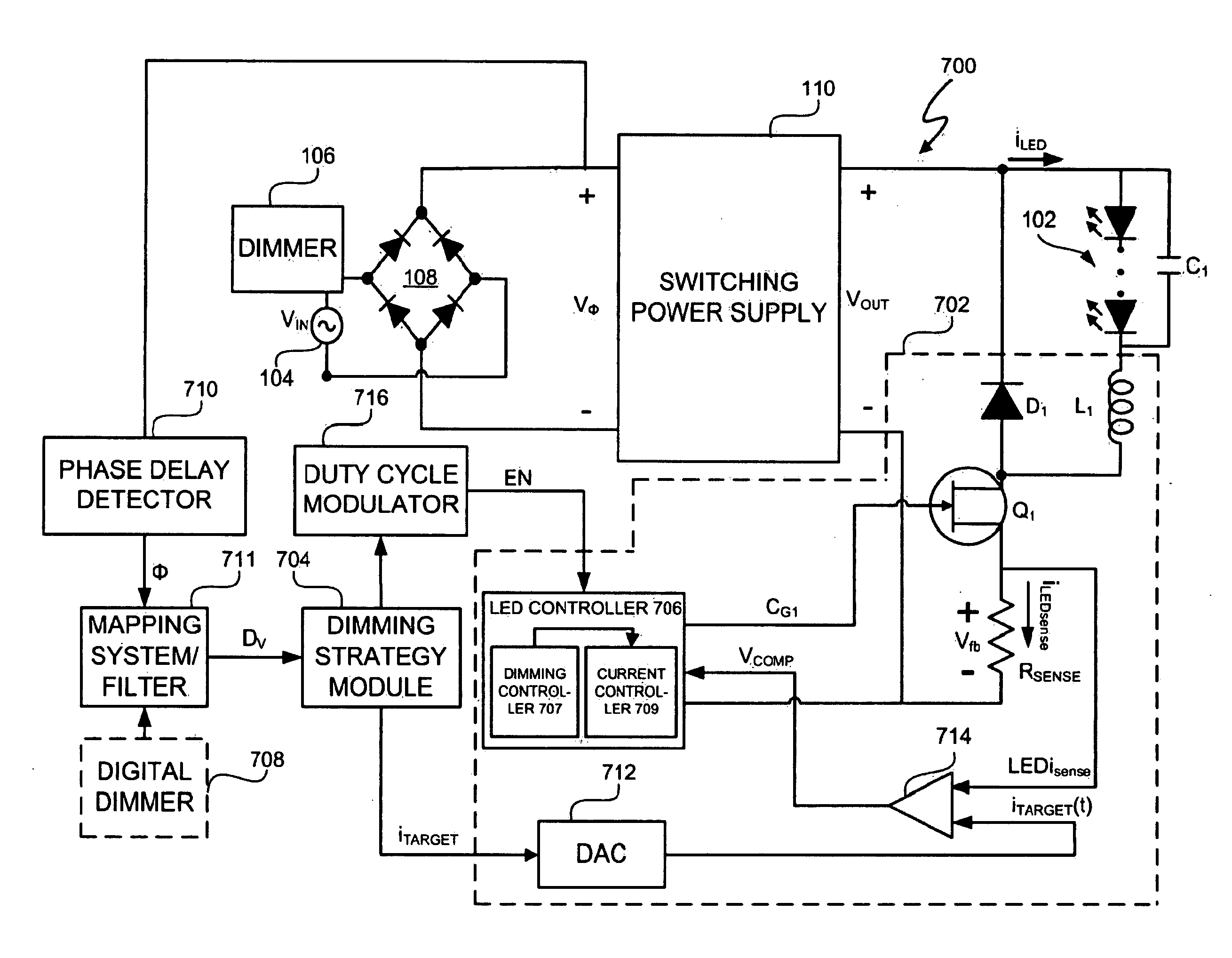
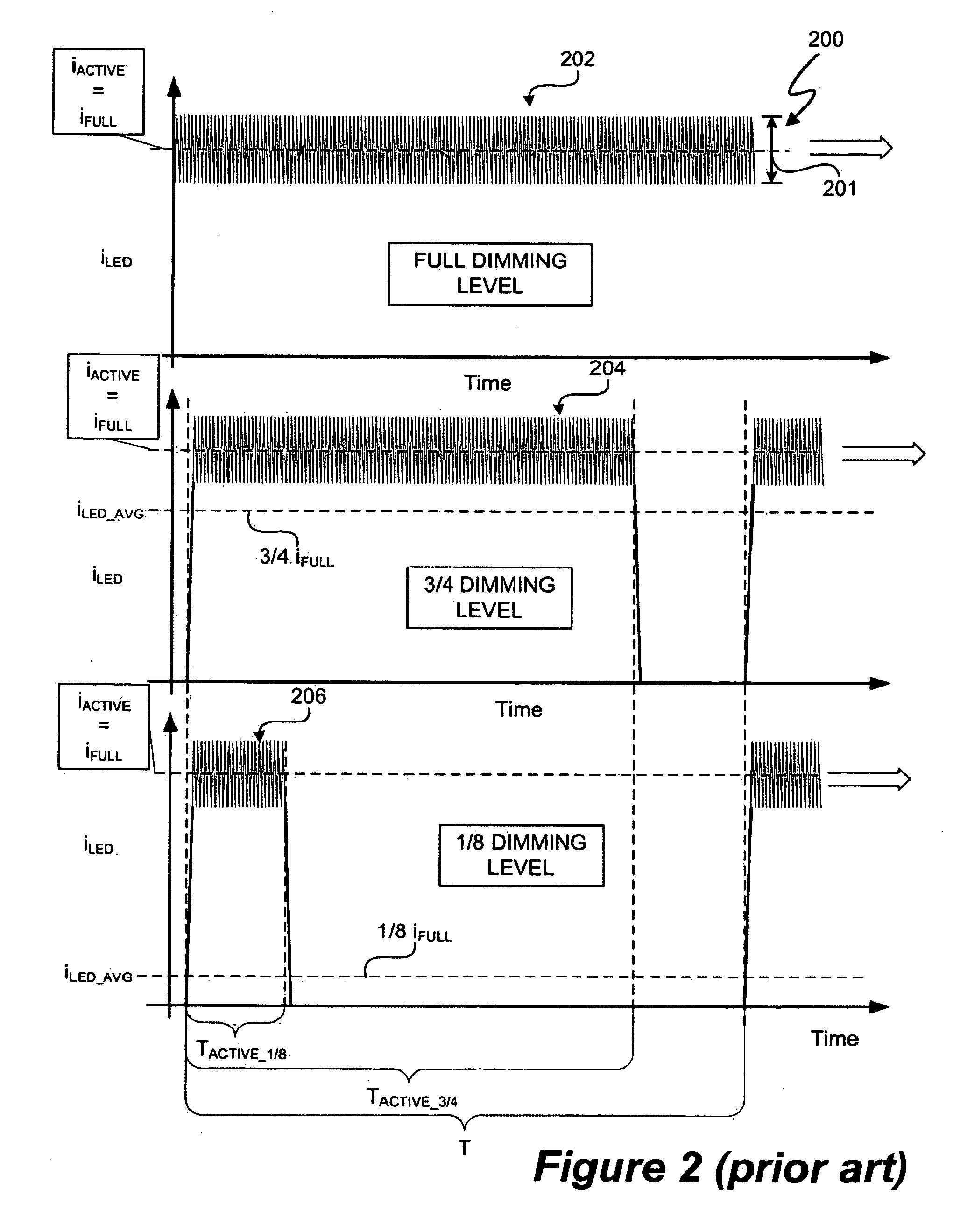
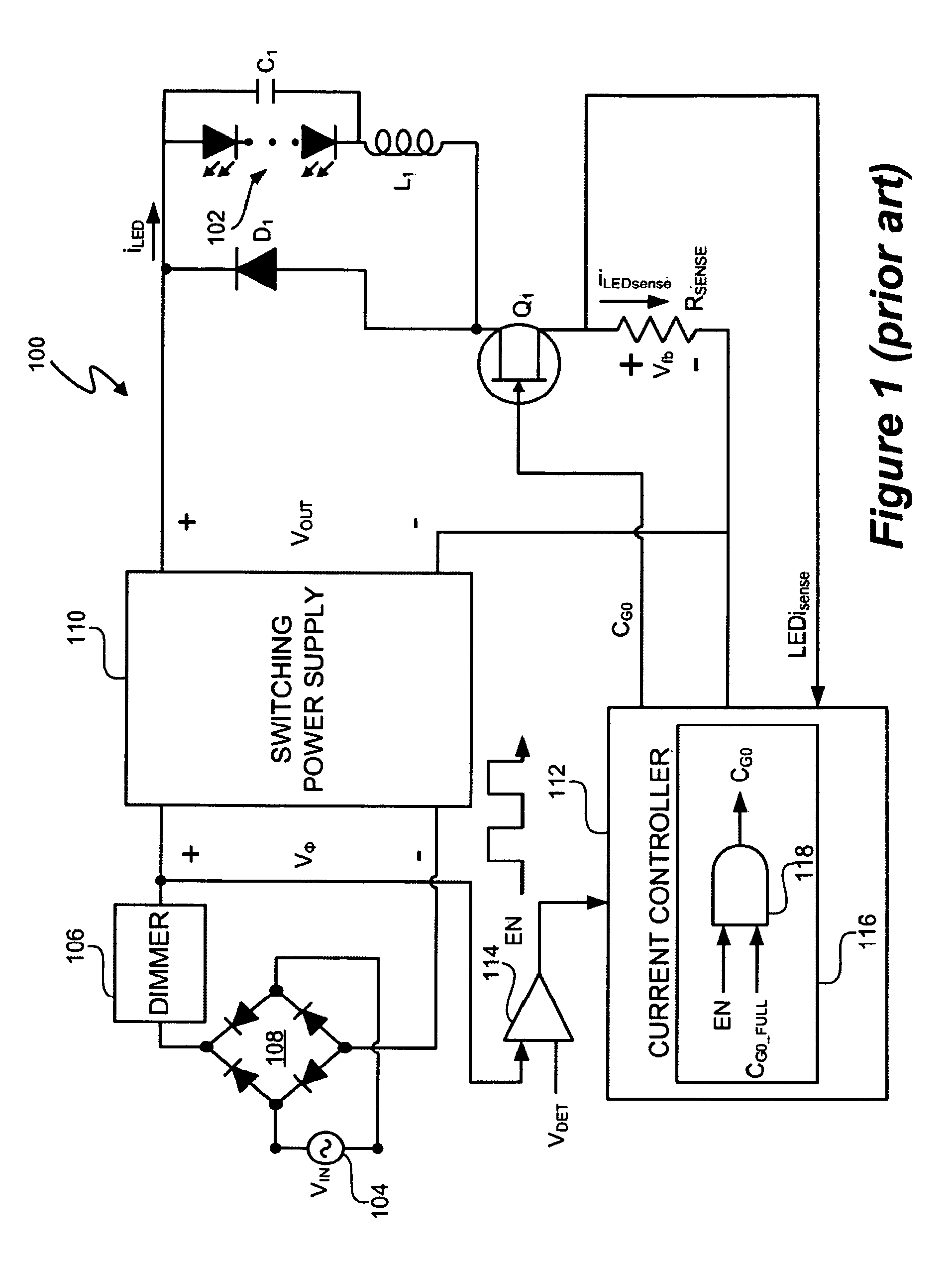
LED Lighting System with Accurate Current Control
A light emitting diode (LED) lighting system and method are disclosed. The LED lighting system and method include an LED controller to accurately control a current in an LED system. The LED controller includes components to calculate, based on the current and an active time period of an LED current time period, an actual charge amount delivered to the LED system wherein the LED current time period is duty cycle, modulated at a rate of greater than fifty (50) Hz and to utilize the actual charge amount to modify and provide a desired target charge amount to be delivered during a future active time period of the LED current time period. The LED system and method further involve components to compare the actual charge amount to a desired charge amount for the active time period and compensate for a difference between the actual charge amount and the desired charge amount during the future active time period.
Owner:SIGNIFY HLDG BV
System and method for providing collaborating power controllers
InactiveUS20110204717A1Batteries circuit arrangementsDc source parallel operationPower controllerEngineering
A method is provided in one example embodiment and includes receiving a message associated with a detection of reactive power in an energy system and inducing a first quantity of reactive power at a power level specified in the message. The first quantity of reactive power is induced in order to mitigate a second quantity of reactive power that is detected on a specific segment of the energy system. The first quantity of reactive power is induced at a local level on which a source associated with the second quantity of reactive power operates. In more specific embodiments, the message is sent in response to a sensor detecting the second quantity of reactive power, where the first quantity and the second quantity of reactive power are the same. In other embodiments, the method can include receiving a second message to stop mitigating the first quantity of reactive power.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
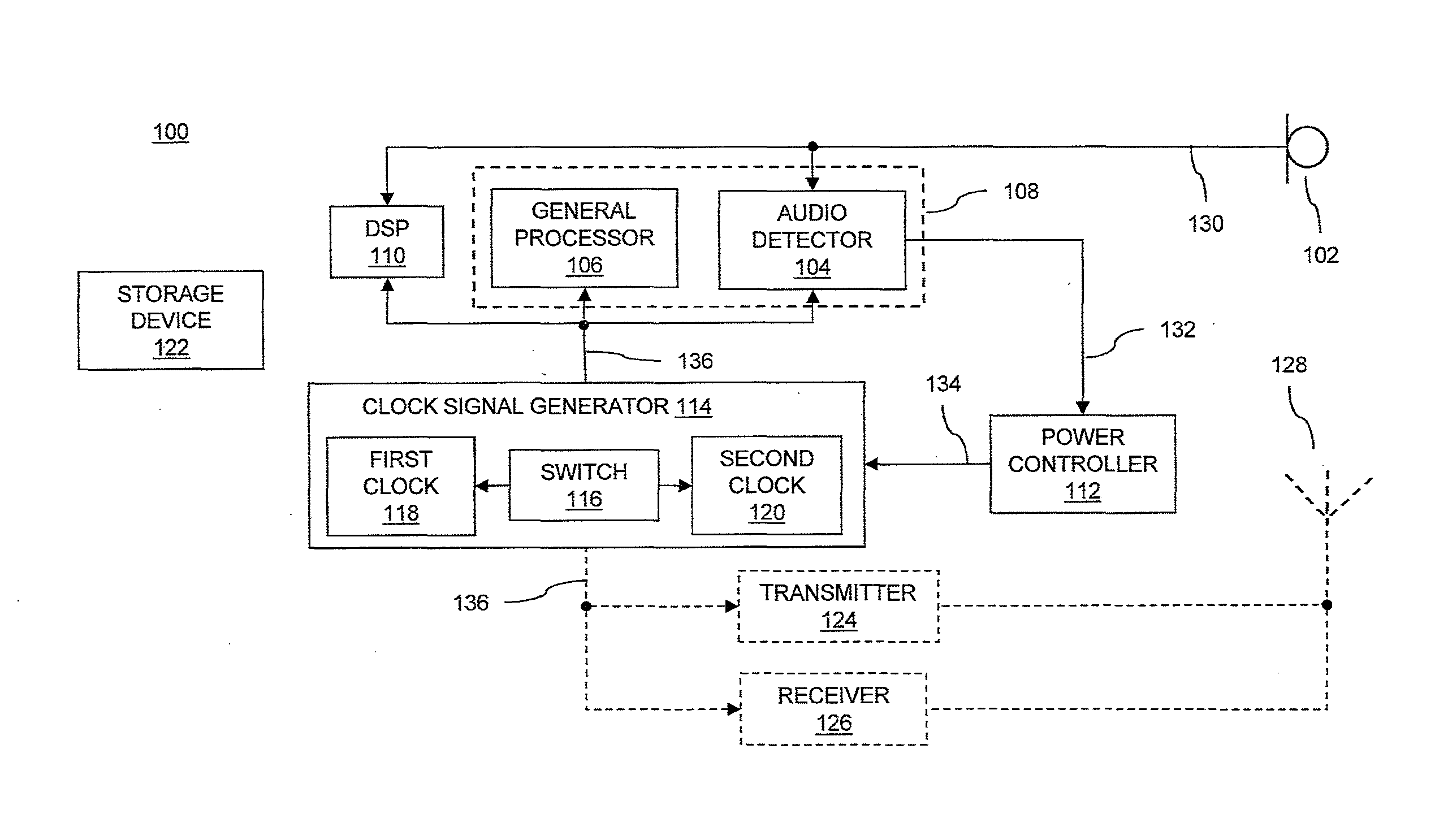
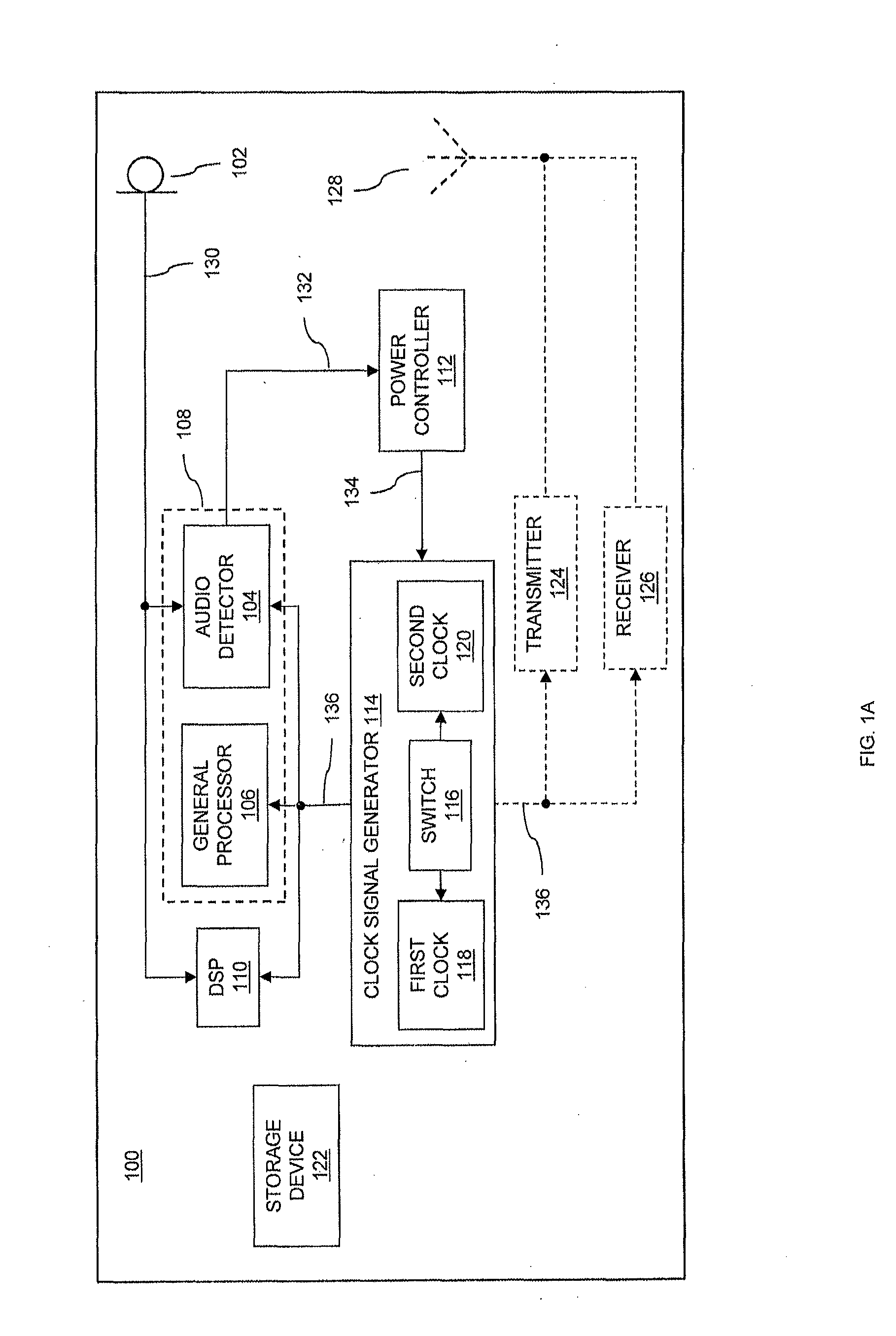
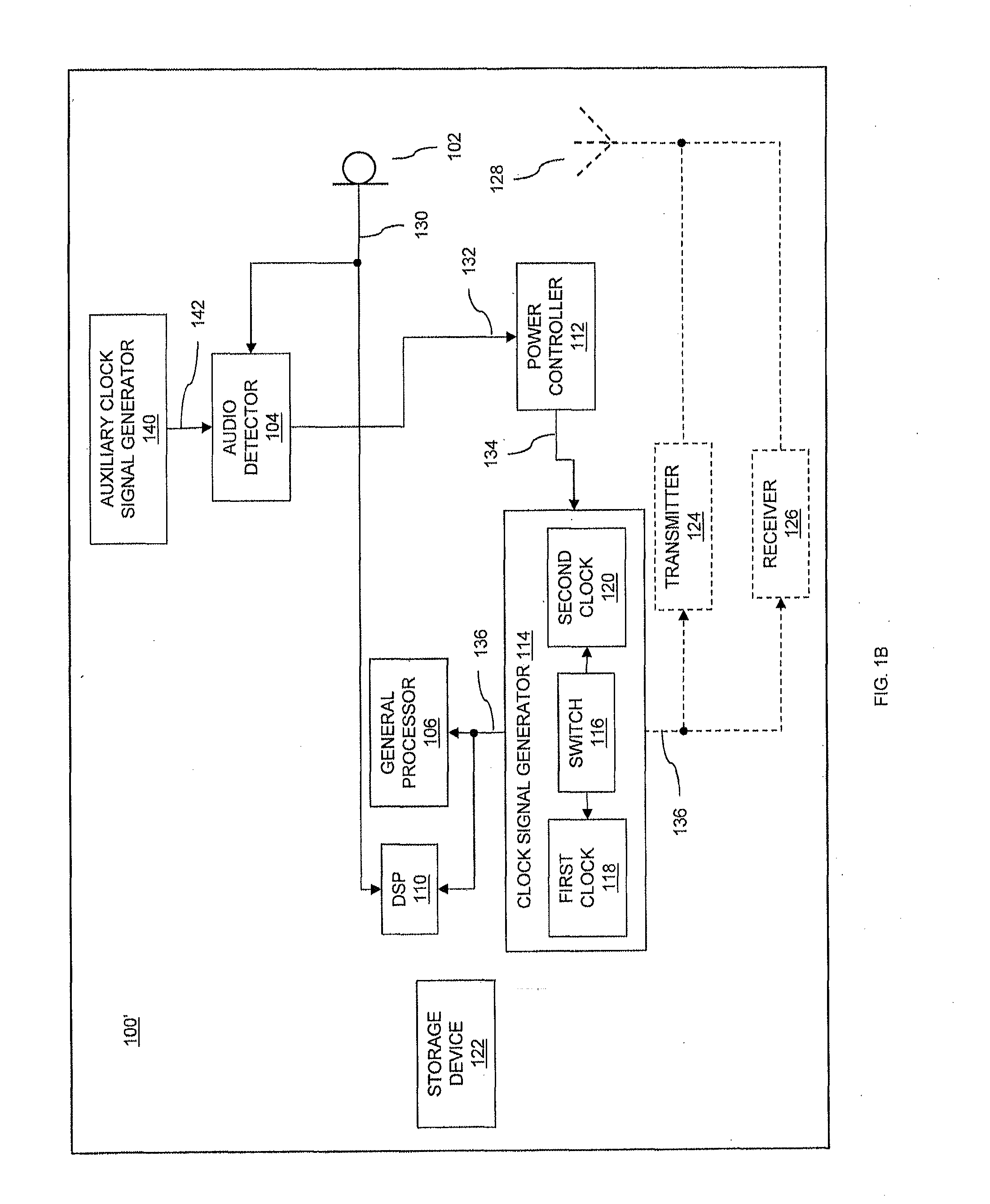
Low power audio detection
InactiveUS20130223635A1Reduce power consumptionIncrease power consumptionPower managementHearing device energy consumption reductionAudio signal flowLow power dissipation
Devices and methods of detecting a predetermined audio signal in audio signals are provided. A device includes a processor coupled to a clock signal generator, a power controller and an audio detector. The power controller controls a clock rate provided to the processor by the clock signal generator, to control the device to operate in a low power mode having a relatively low power consumption or in a normal power mode having a relatively high power consumption. The audio detector receives audio signals and detects, in the low power mode, probable presence of a predetermined audio signal in the audio signals. The power controller controls the device to switch from the low power mode to the normal power mode responsive to the detected presence of the predetermined audio signal by the audio detector.
Owner:QUALCOMM TECH INT
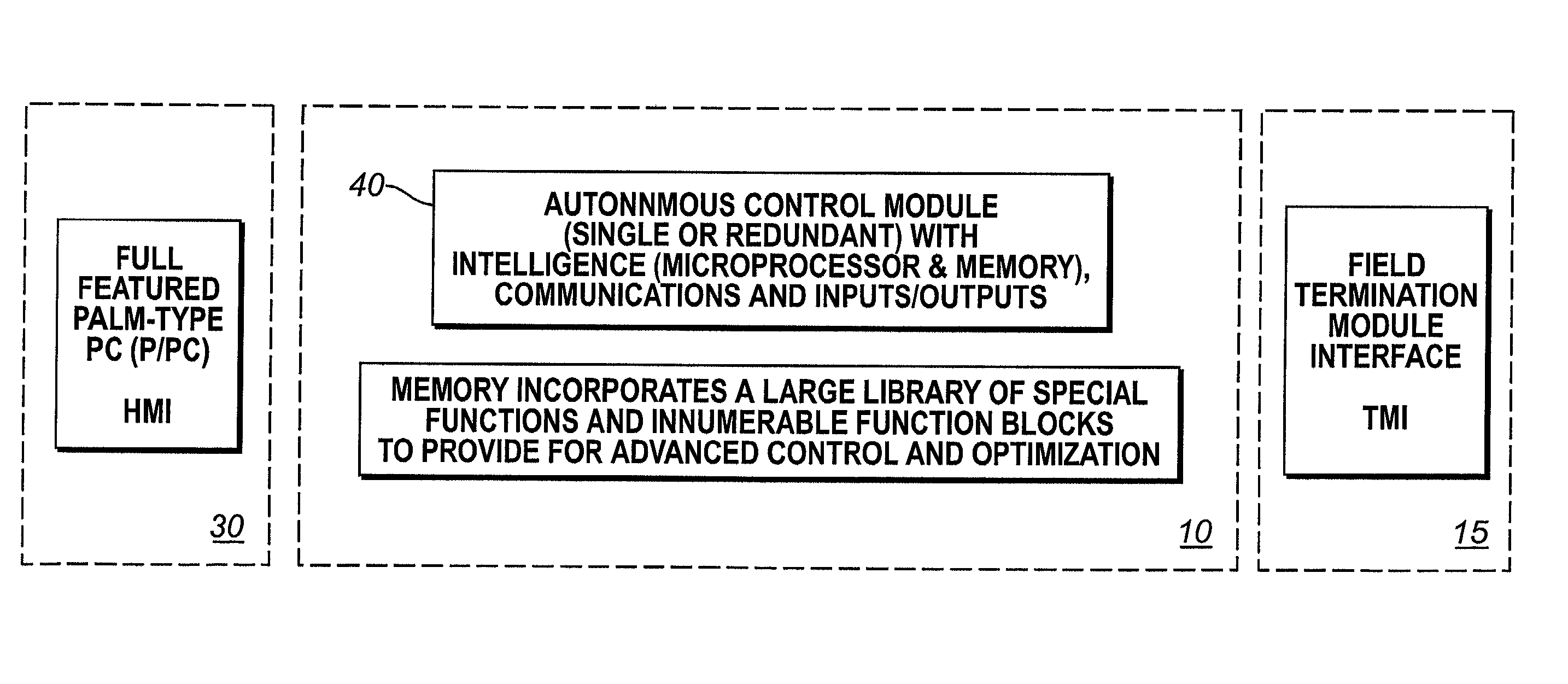
Unit controller with integral full-featured human-machine interface
An integrated unit controller / human-machine interface is disclosed which incorporates high-speed redundant control, sequence of events, supervisory control and data acquisition, alarm handling, trending & historian, process graphics and "open" communications in a compact form factor enclosure (the front panel less than 5x6 inches). The unit controller is composed of two primary hardware elements: the controller module (single or redundant) and the palm type computers (P / PC)-based human-machine interface (HMI) with touch screen. The controller covers a wide span of applications, from single process unit control to networked multi-unit management.
Owner:ICS TRIPLEX TECH
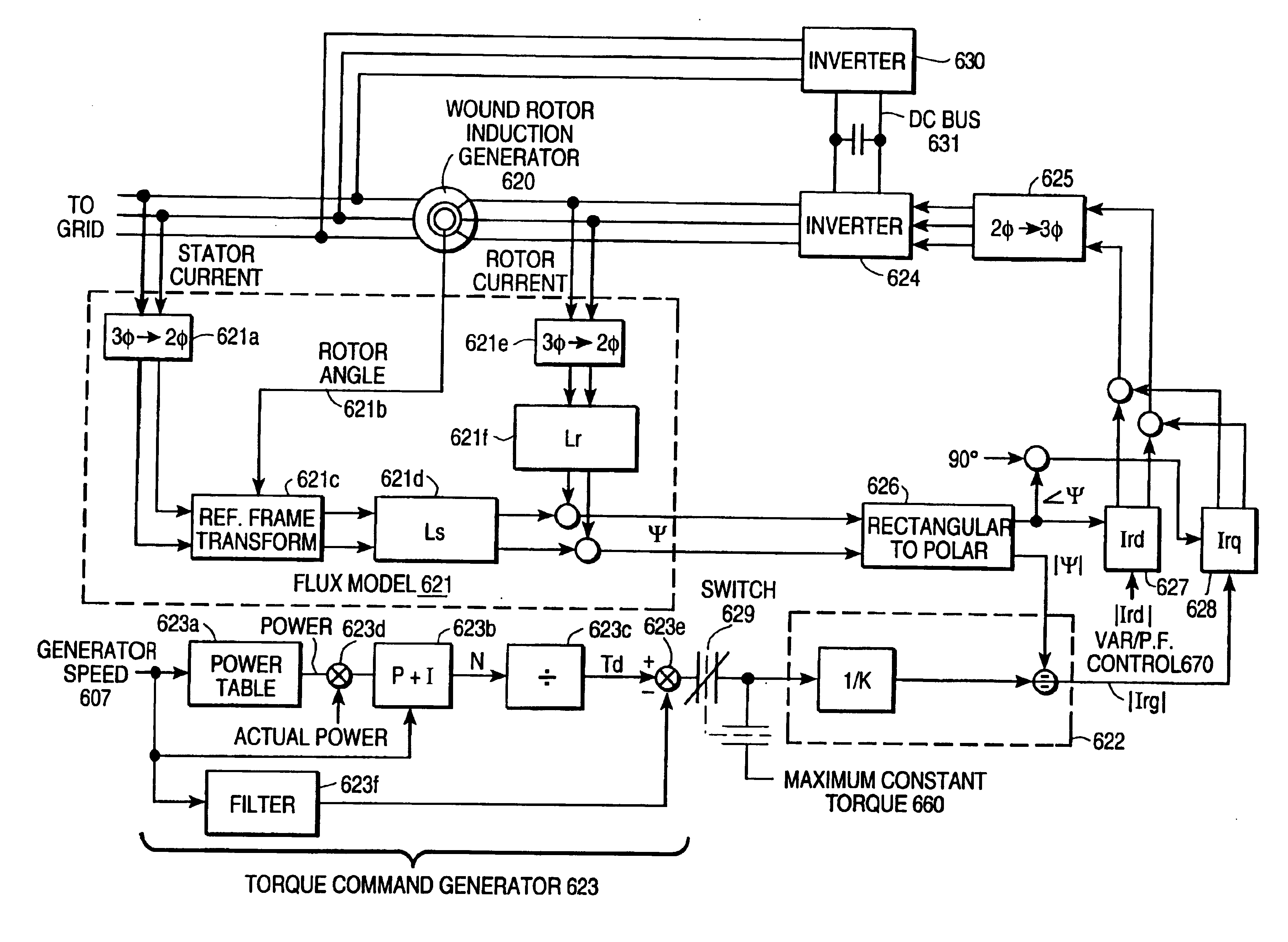
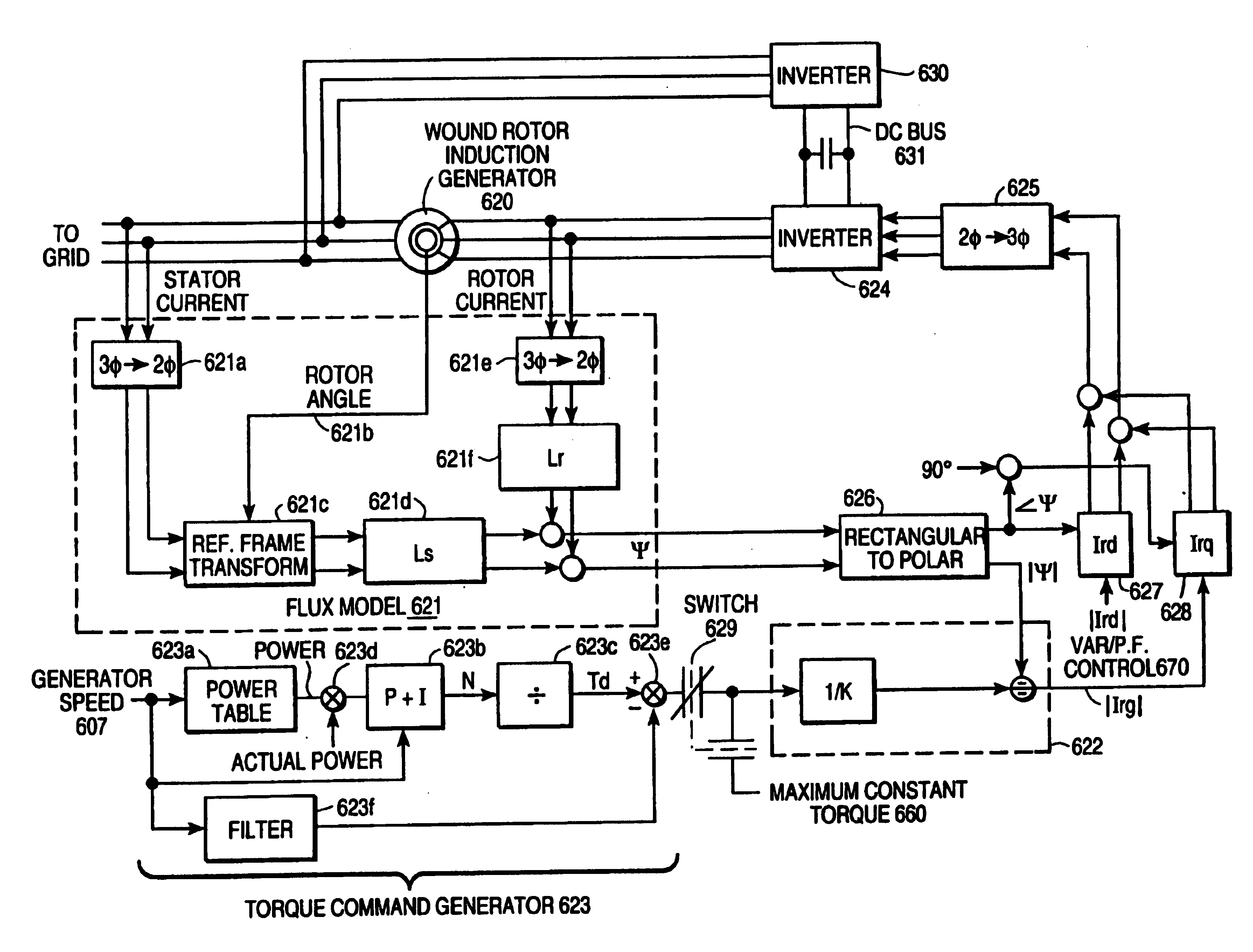
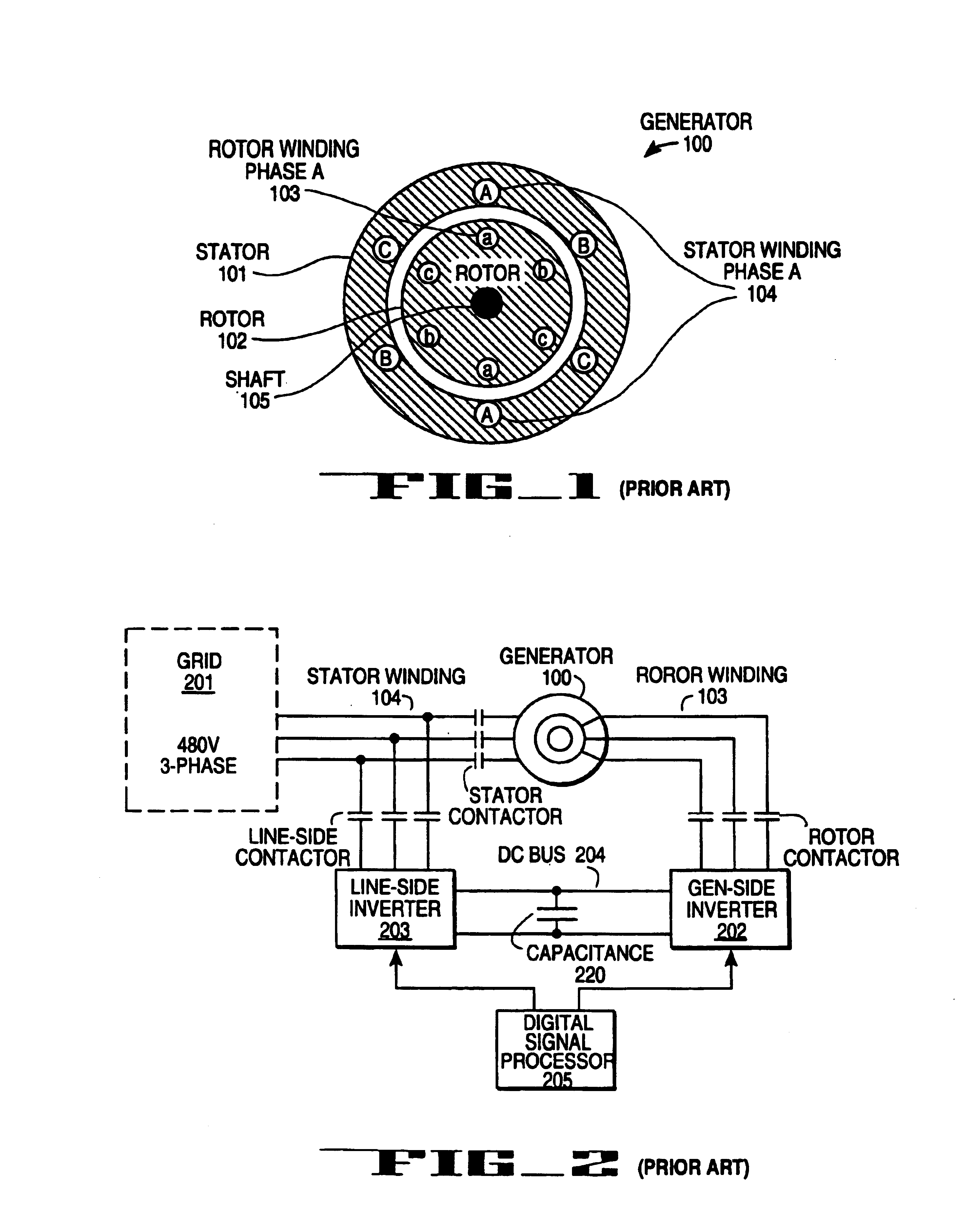
Variable speed wind turbine generator
InactiveUS6856039B2Generator control circuitsWind motor controlVariable speed wind turbineControl theory
A variable speed system for use in systems, such as, for example, wind turbines, is described. The system comprises a wound rotor induction generator, a torque controller and a proportional, integral derivative (PID) pitch controller. The torque controller controls generator torque using field oriented control, and the PID controller performs pitch regulation based on generator rotor speed.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
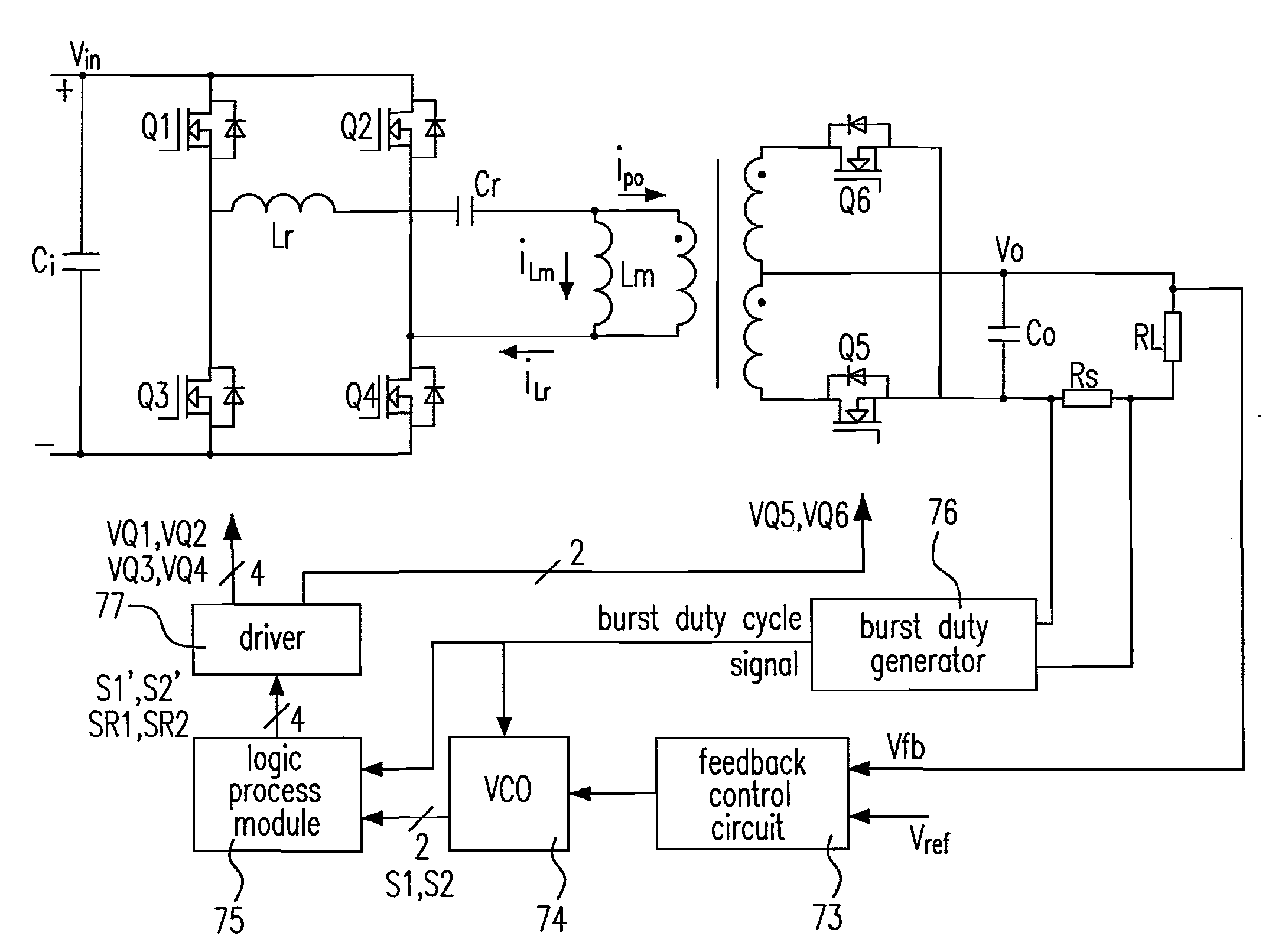
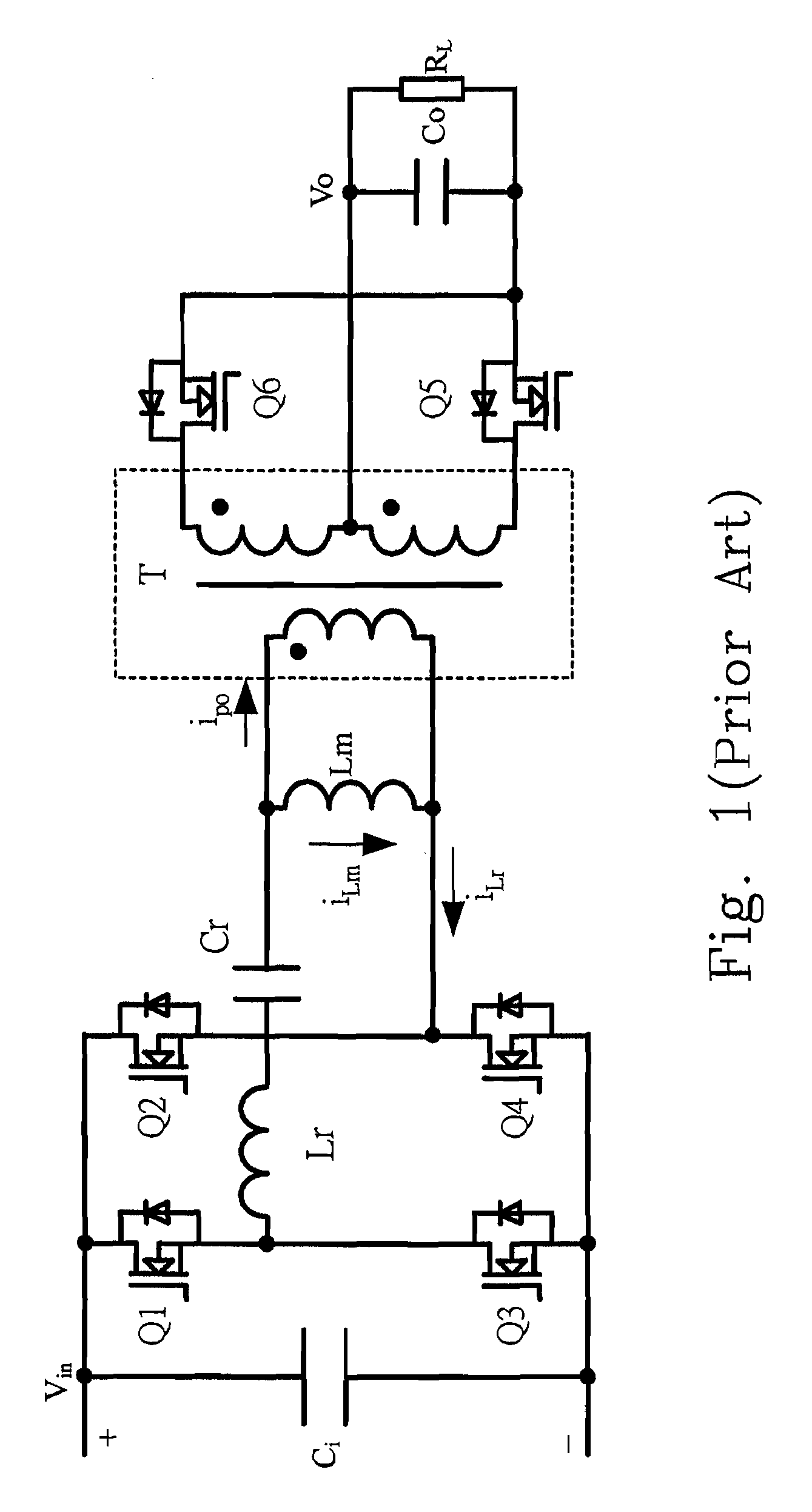
Synchronous rectification circuit having burst mode controller and controlling method thereof
ActiveUS20090244934A1Improve light load efficiencyReduce lossesEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionProcess moduleMode control
The configuration of a synchronous rectification circuit and a controlling method thereof are provided. The proposed circuit includes a converter including a first switch and a first synchronous rectifier, and a burst mode controller including a logic process module performing one of functions of delaying one of a non-integer and at least one operating periods to generate a synchronous rectification driving signal of the first synchronous rectifier counting from a beginning of a first pulse of a driving signal of the first switch during a working time of a burst period, and turning off the synchronous rectification driving signal of the first synchronous rectifier by one of the non-integer operating period and the at least one operating period ahead of an ending of a last operating period of the driving signal of the first switch during the working time of the burst period.
Owner:DELTA ELECTRONICS INC
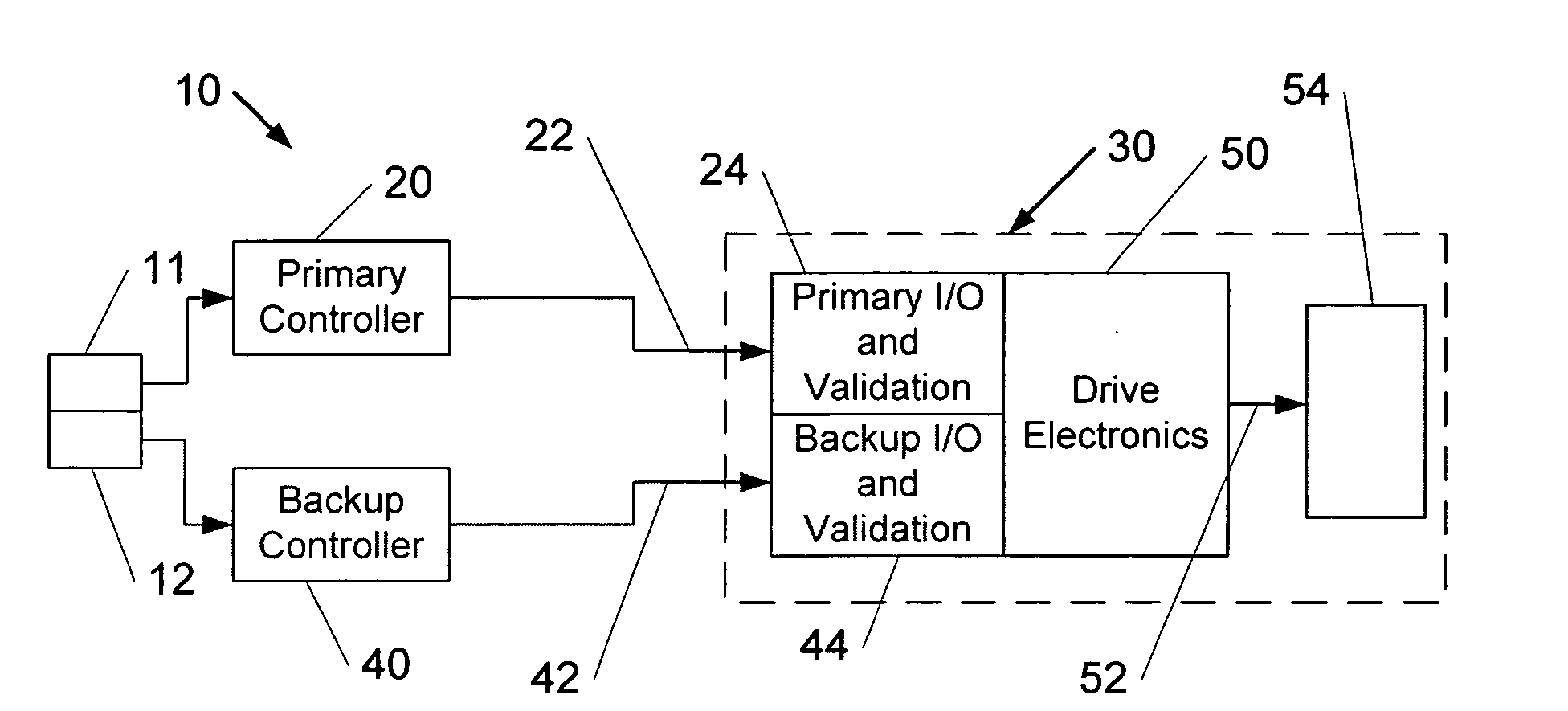
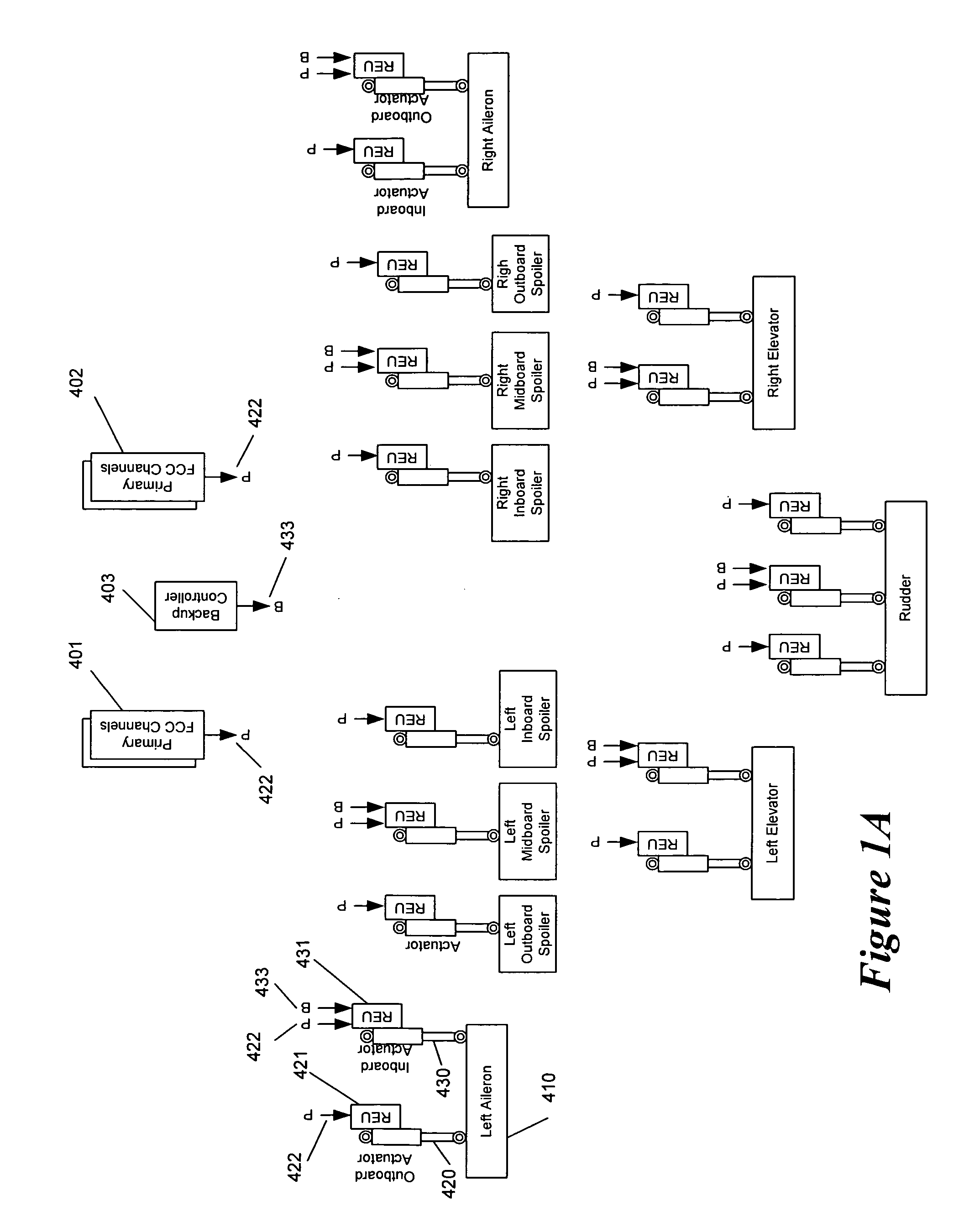
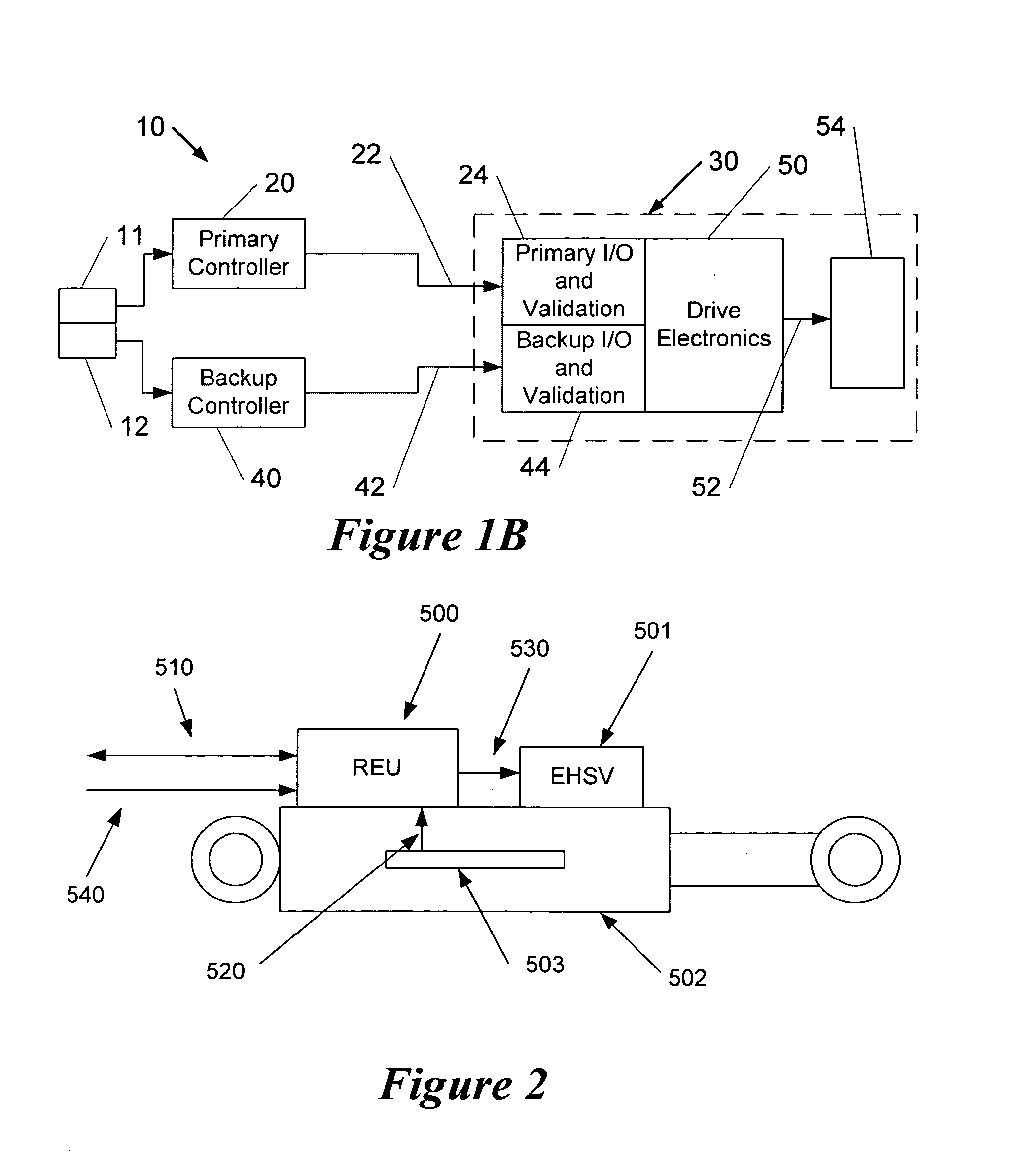
Apparatus and method for backup control in a distributed flight control system
ActiveUS20070164166A1Without compromisingWith power amplificationActuated automaticallyControl signalMaster controller
Embodiments of the invention relate to a flight control system for controlling an aircraft during flight. The flight control system may include a primary controller configured to receive an input from a pilot and to output a primary control signal and a primary transmission path connected to the primary controller and configured to relay the primary control signal. The flight control system may also include a backup controller configured to receive the input from the pilot and to output a backup control signal and a backup transmission path connected to the backup controller and configured to relay the backup control signal. Additionally, the flight control system may include an actuator having a remote electronics unit configured to receive the primary control signal and the backup control signal and to determine if the primary control signal is available and valid. The remote electronics unit may be configured to output an actuator command based on the primary control signal if the primary control signal is available and valid and to output the actuator command based on the backup control signal if the primary control signal is unavailable or invalid.
Owner:GULFSTREAM AEROSPACE CORP
Variable speed wind turbine generator
InactiveUS6847128B2Generator control circuitsWind motor controlVariable speed wind turbineControl theory
A variable speed system for use in systems, such as, for example, wind turbines, is described. The system comprises a wound rotor induction generator, a torque controller and a proportional integral derivative (PID) pitch controller. The torque controller controls generator torque using field oriented control, and the PID controller performs pitch regulation based on generator rotor speed.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
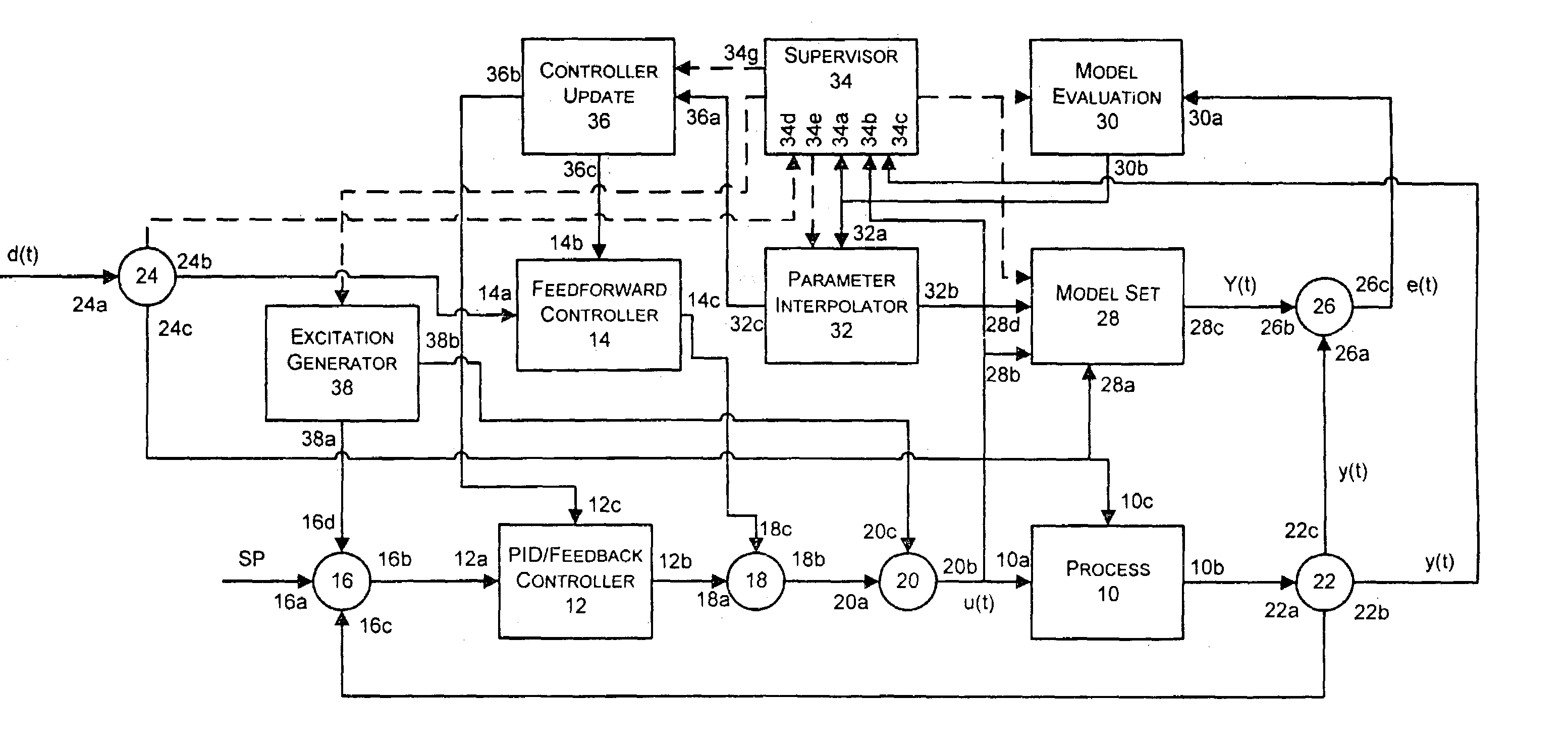
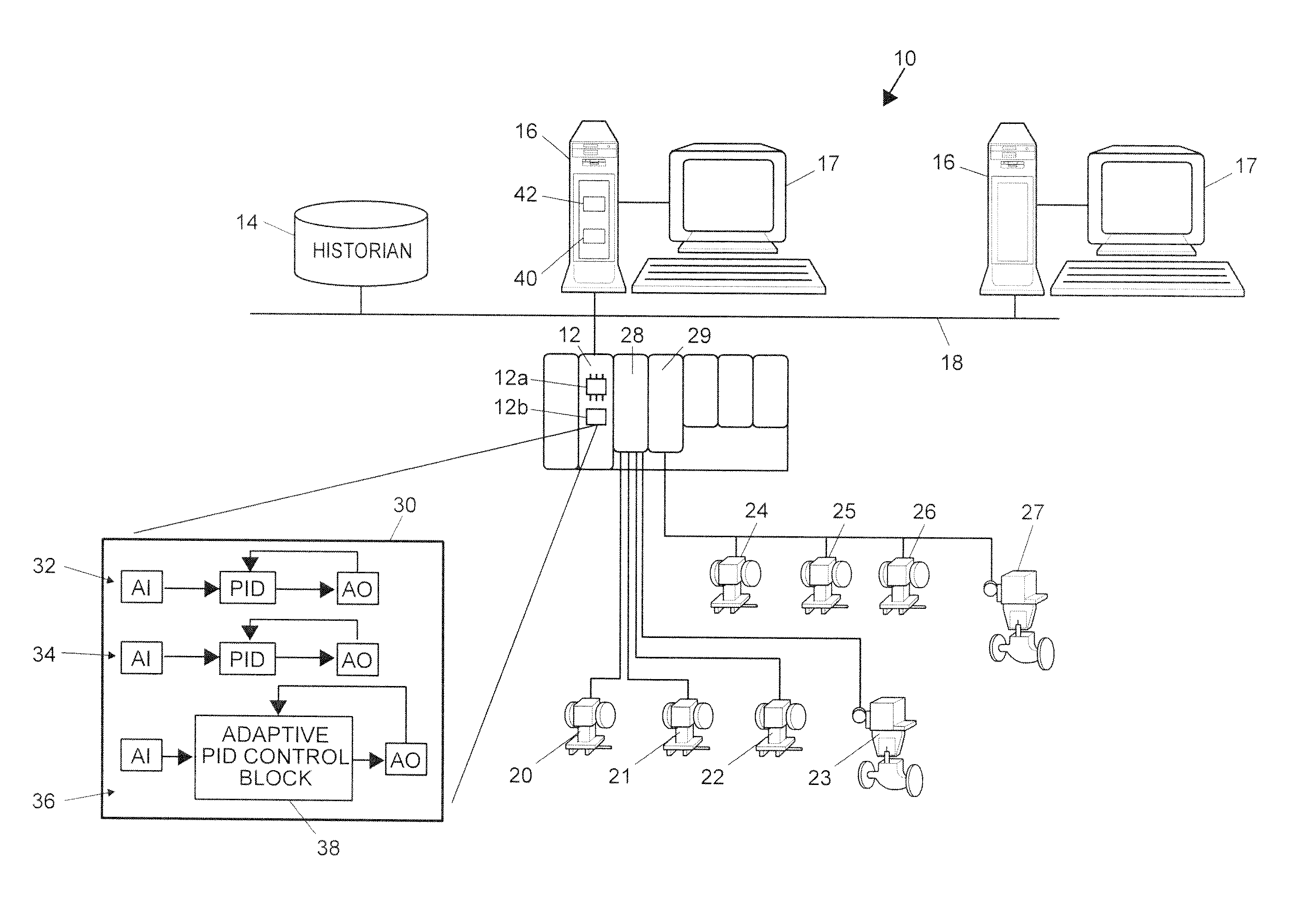
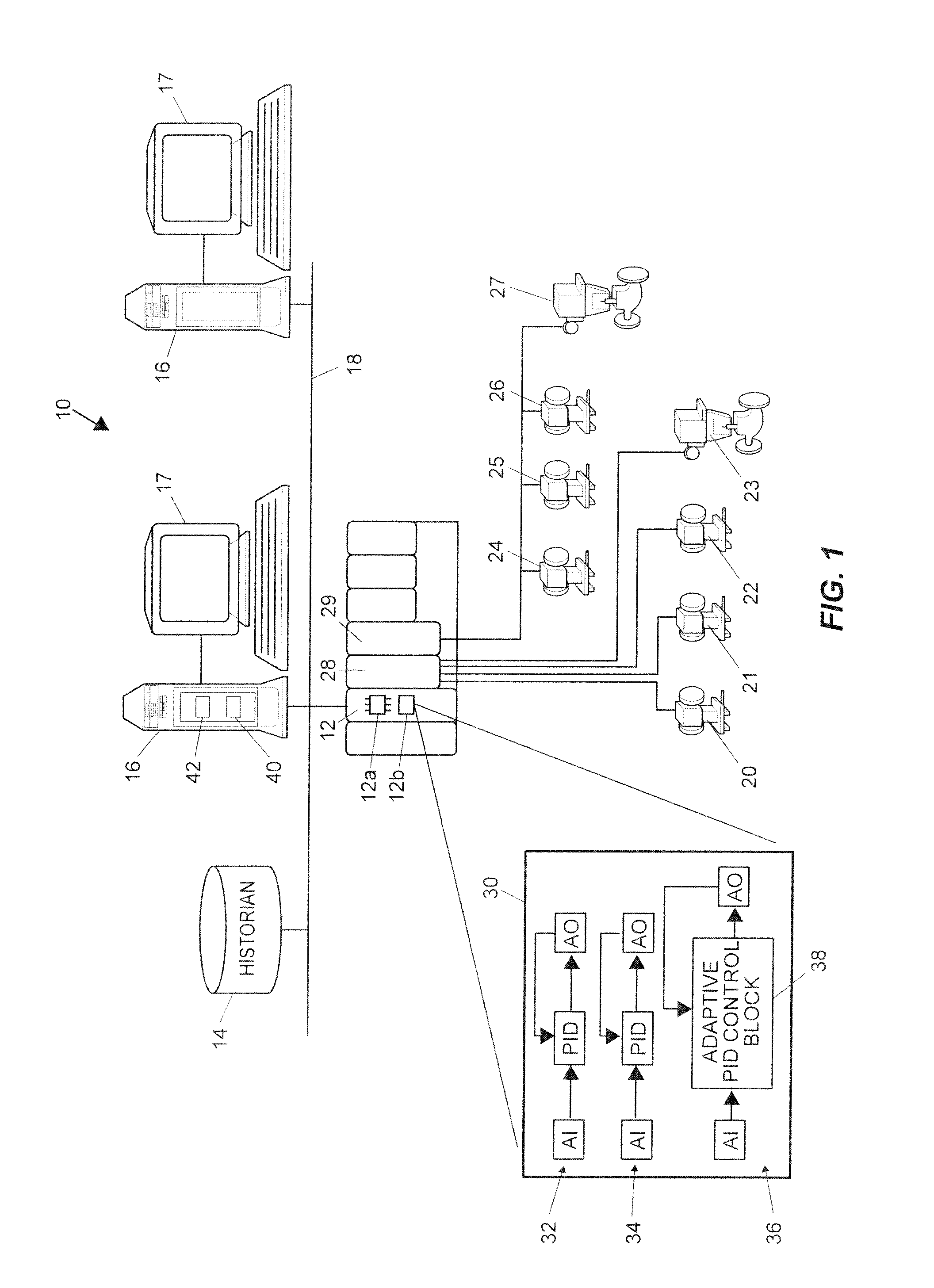
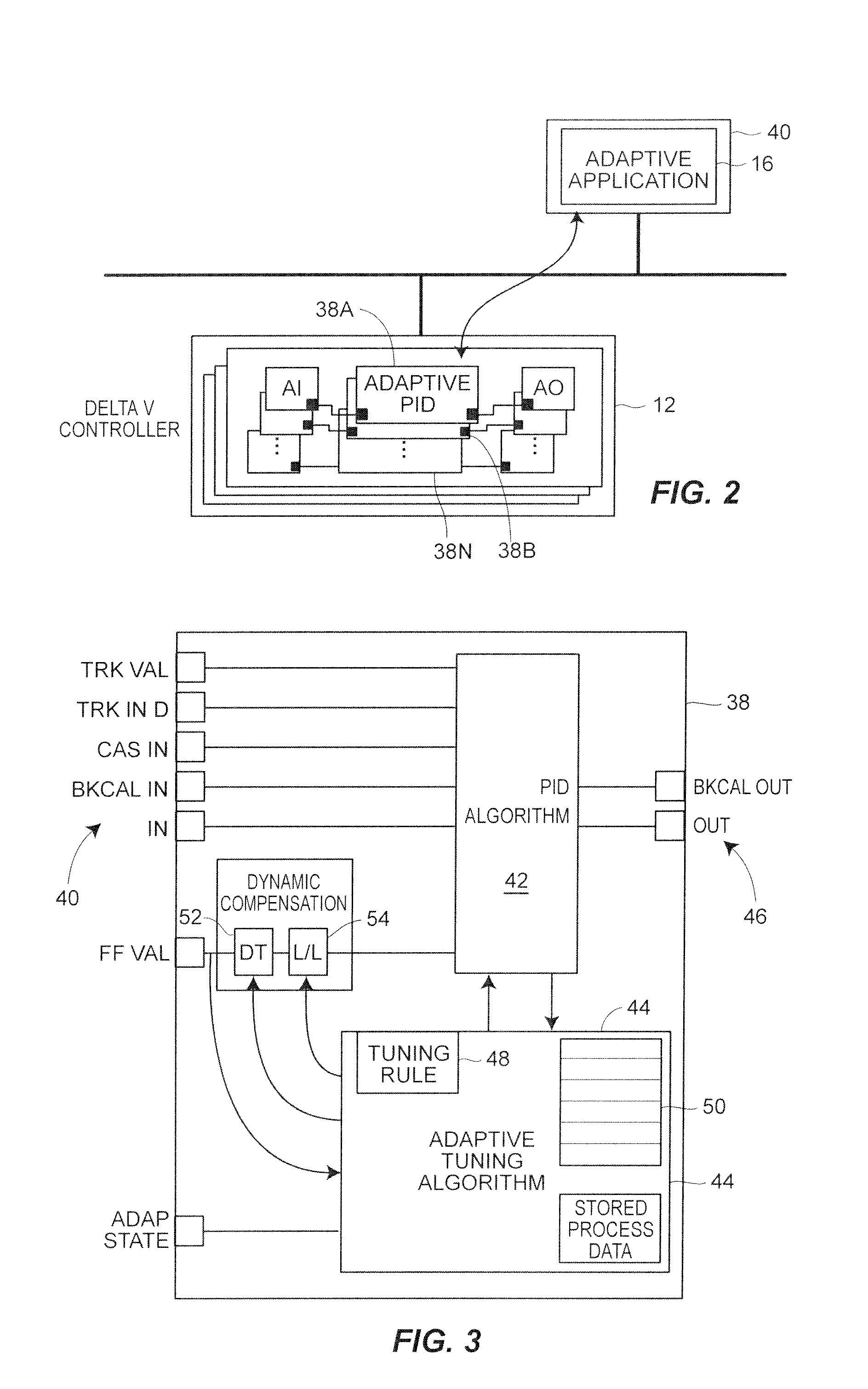
State based adaptive feedback feedforward PID controller
InactiveUS7113834B2Simulator controlControllers with particular characteristicsSelf adaptiveComputer science
A state based adaptive PID controller includes a model set component including a plurality of process models, each process model including a plurality of parameters. An error generator generates a model error signal representative of a difference between a model output signal and a process output signal. A model evaluation component computes a model squared error based on the model error signal. A parameter interpolator calculates an adaptive parameter value based on the model squared error. A controller update component updates adaptive controller parameter values based on adaptive parameter values.
Owner:FISHER-ROSEMOUNT SYST INC
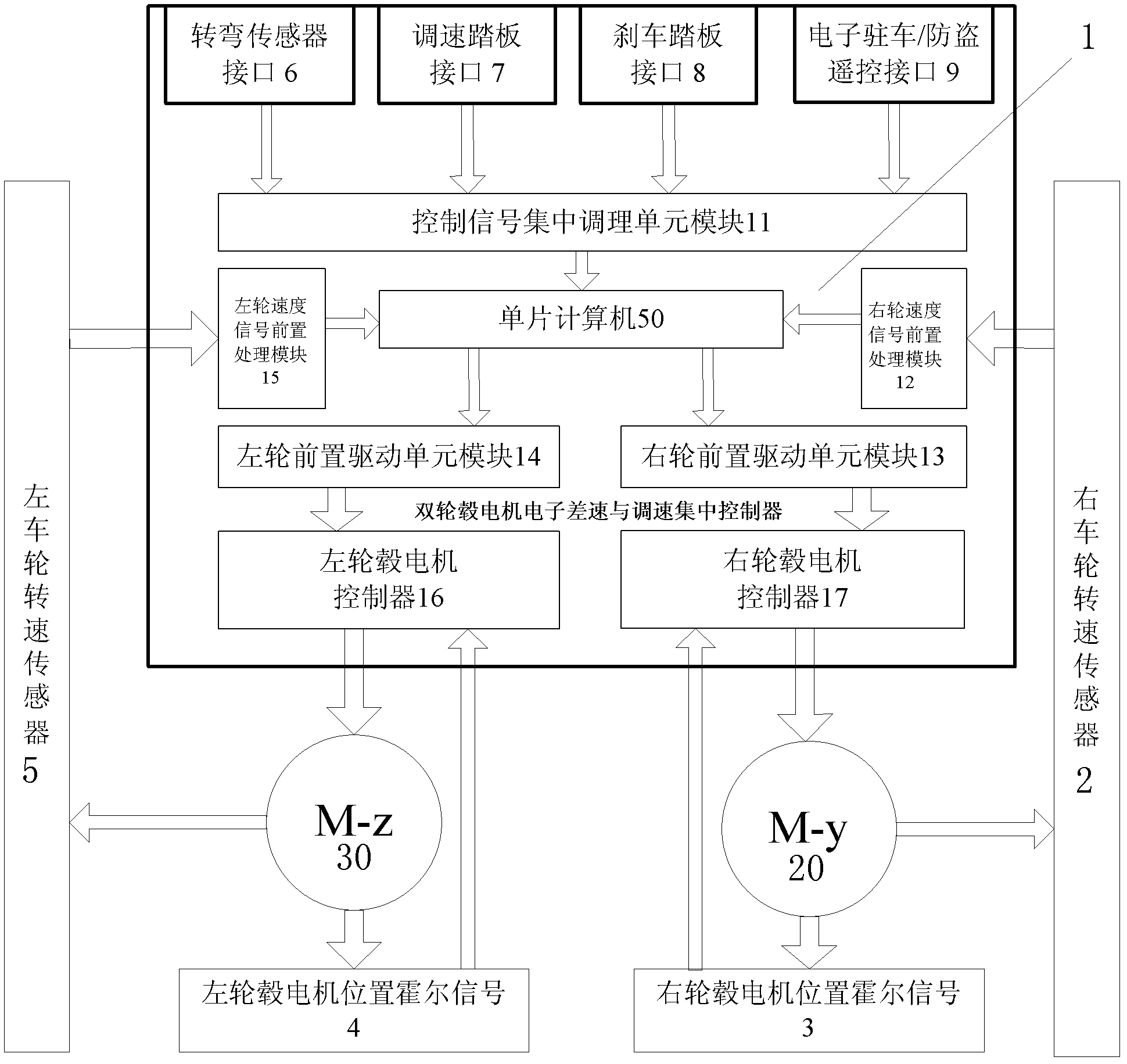
Double-hub electrical motor electronic differential and speed regulation integrated controller
ActiveCN103101451ARealize the advantages of electronic controlEasy wiringSpeed controllerControl devicesControl signalElectric vehicle
The invention provides a double-hub electronic motor electrical differential and speed regulation integrated controller. A control signal integrated adjusting unit module, a right wheel speed signal preprocessing module, a right wheel pre-driving unit module, a left wheel pre-driving unit module, a left wheel speed signal preprocessing module, a left hub electrical motor controller, a right hub electrical motor controller, a driving module unit and a monolithic computer are arranged inside the double-hub electrical motor electronic differential and speed regulation integrated controller. The double-hub electrical motor electronic differential and speed regulation integrated controller is characterized in that an electronic differential mechanism, the left hub electrical motor controller and the right hub electrical motor controller are combined into a whole inside the double-hub electrical motor electronic differential and speed regulation integrated controller simultaneously, and all components inside the double-hub electrical motor electronic differential and speed regulation integrated controller are of module structures. Meanwhile, a control signal and speed feedback signal processing module needed by an electric vehicle is arranged inside the controller, pre-control circuits and terminal driving circuits of a left electrical motor and a right electrical motor are inserted in the controller, and thus the fact that a control assembly of the electric motor driven by a double-hub electrical motor has differential control in turning, speed control in driving, stop control in temporary stop and anti-theft control in parking is guaranteed.
Owner:徐州科悦电子科技有限公司
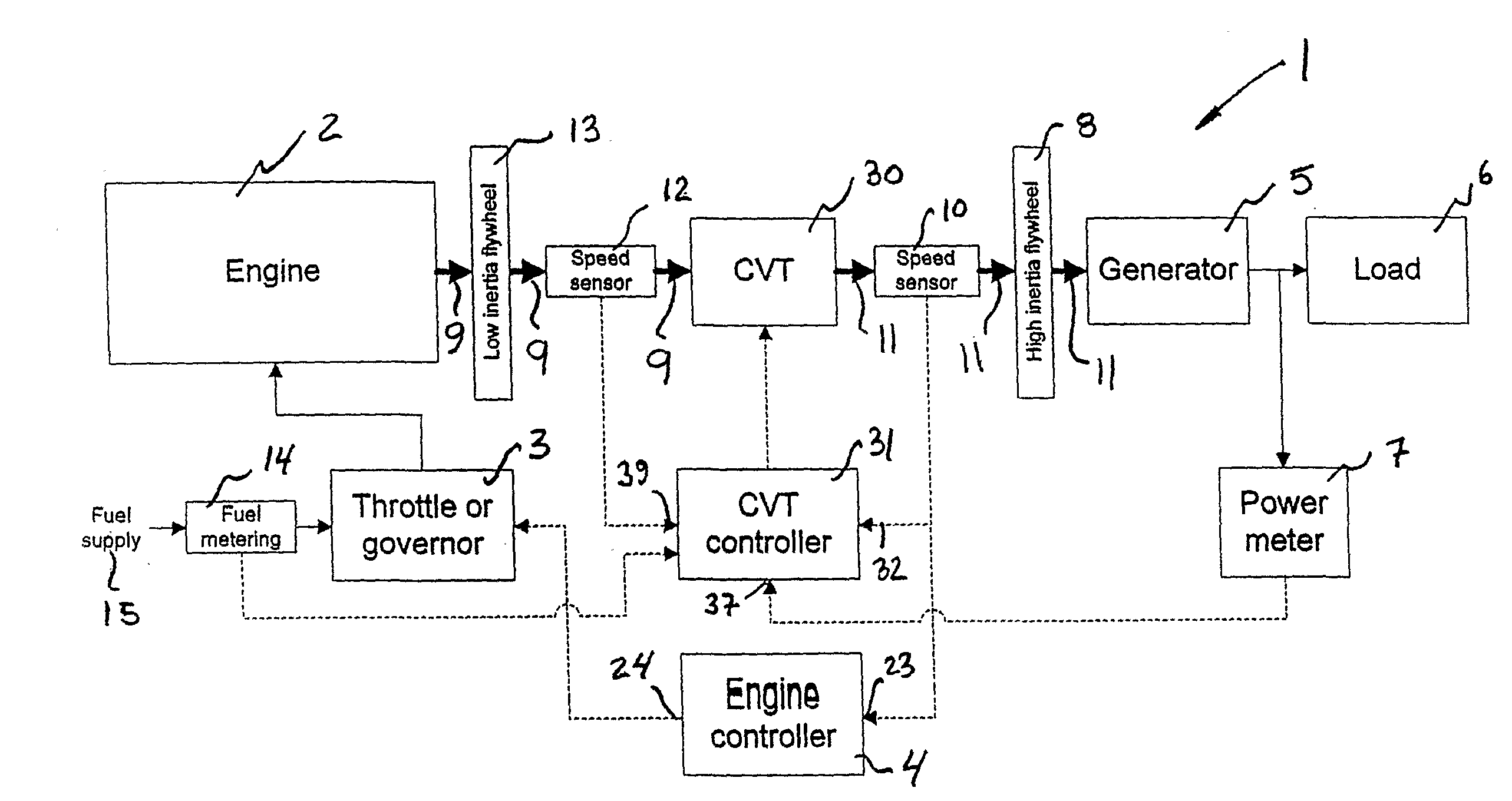
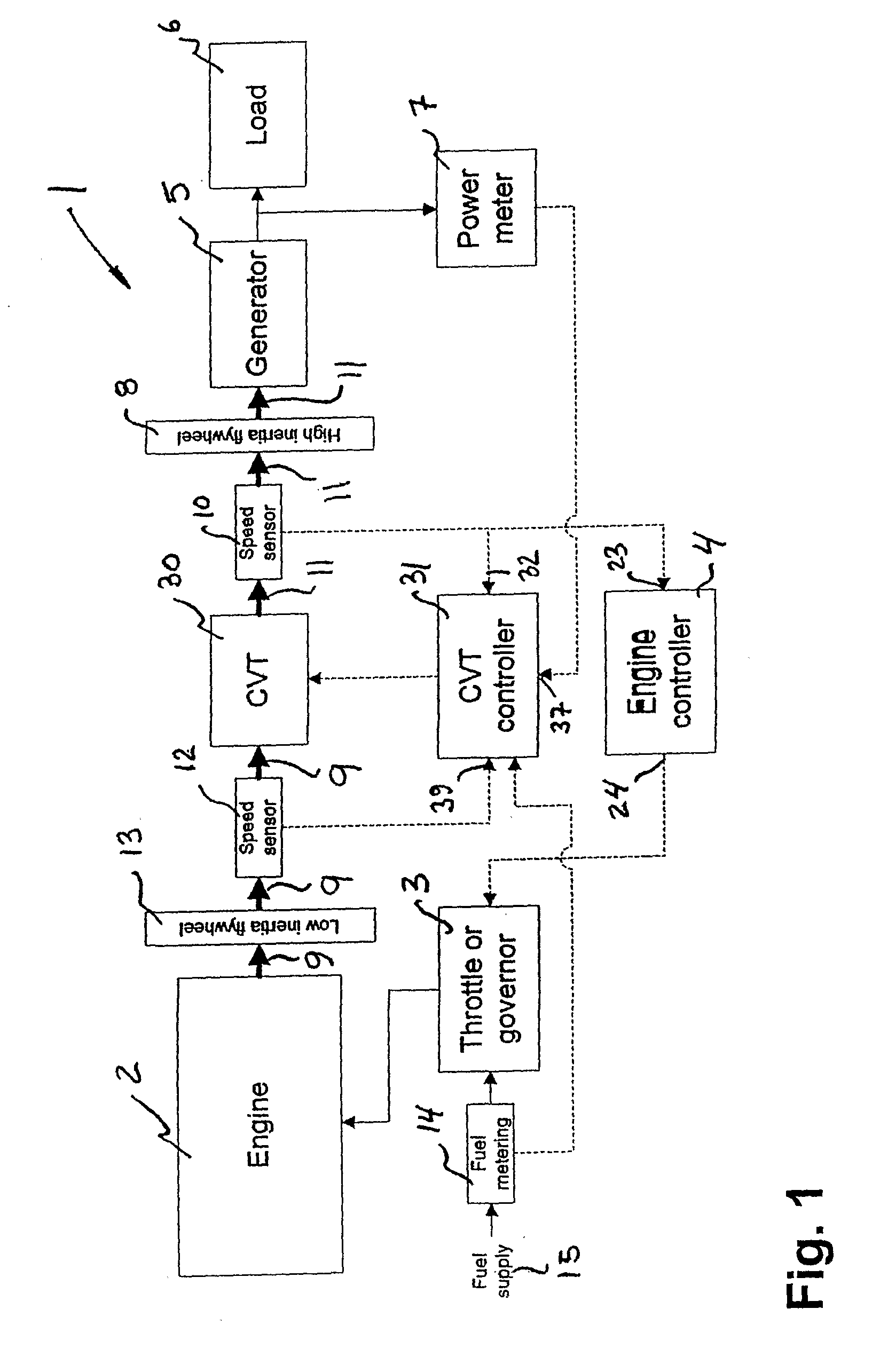
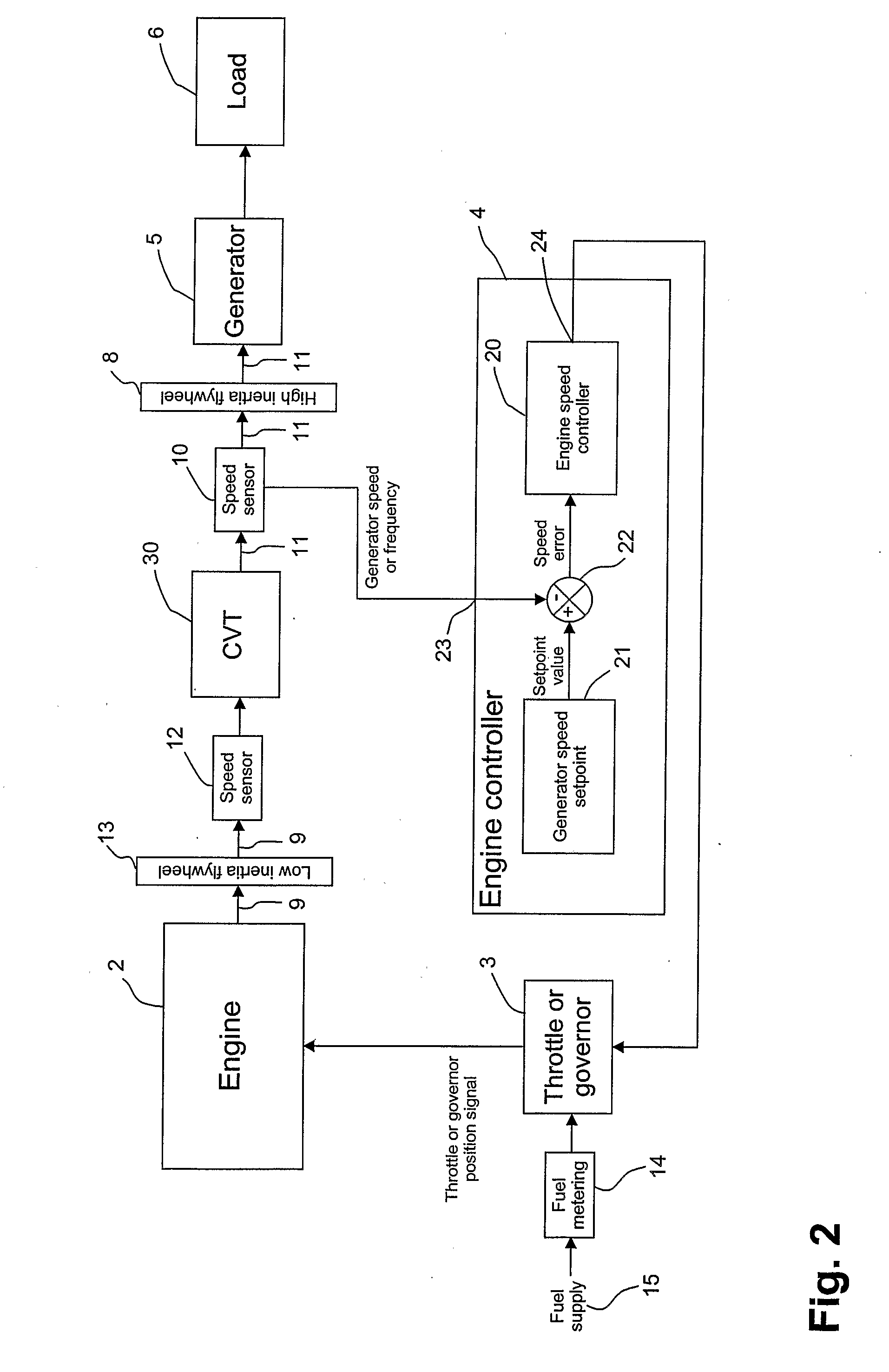
Steady-state and transitory control for transmission between engine and electrical power generator
InactiveUS20090023545A1Improve efficiencyDigital data processing detailsGearing controlSet pointElectric generator
A system (1) for transforming a variable output into an input having a desired speed value, including a transmission (30) receiving the output having a first speed (Ve) and producing the input having a second speed (Vgen), first, second and third sensors (12,10,7) producing data (39,32,37) corresponding to the first speed (Ve), second speed (Vgen) and a power demand (Pdem) for the input, a ratio set point controller (34), a ratio controller (36) and a speed controller (4). The ratio set point controller (34) receives the data (39,32,37) and calculates an available power (Pav), a stability level of the system (S,U1,U2), a desired value for the first speed (Ve), and a desired value and rate of change for the transmission ratio. The ratio controller (36) interfaces the ratio set point controller (34) and actuates the transmission (30) to change the transmission ratio to the desired value following the desired rate of change. The speed controller (4) changes the first speed (Ve) until the second speed (Vgen) corresponds to the desired speed value.
Owner:S O E TECH
LED lighting system with accurate current control
A light emitting diode (LED) lighting system and method are disclosed. The LED lighting system and method include an LED controller to accurately control a current in an LED system. The LED controller includes components to calculate, based on the current and an active time period of an LED current time period, an actual charge amount delivered to the LED system wherein the LED current time period is duty cycle, modulated at a rate of greater than fifty (50) Hz and to utilize the actual charge amount to modify and provide a desired target charge amount to be delivered during a future active time period of the LED current time period. The LED system and method further involve components to compare the actual charge amount to a desired charge amount for the active time period and compensate for a difference between the actual charge amount and the desired charge amount during the future active time period.
Owner:SIGNIFY HLDG BV
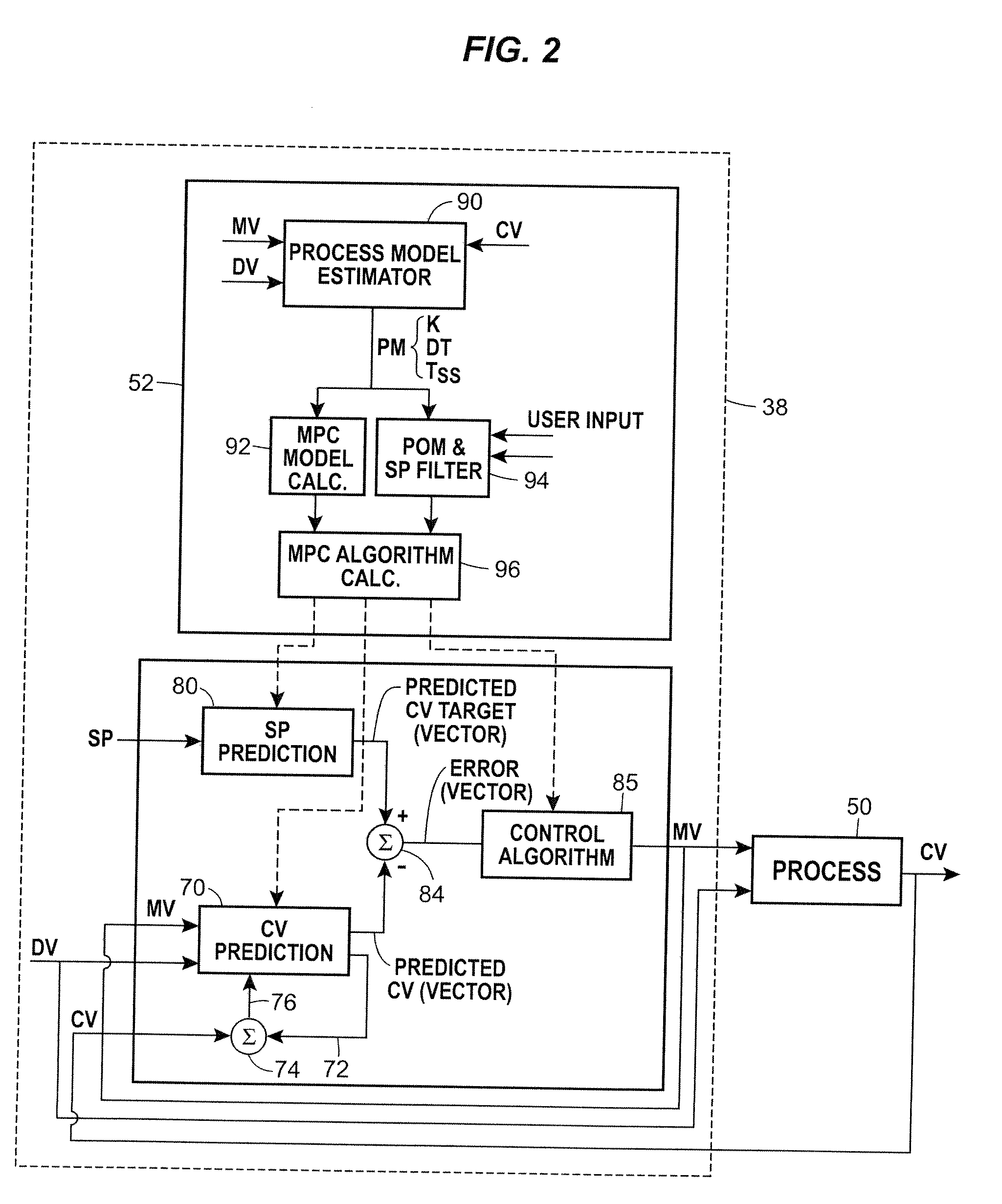
On-line adaptive model predictive control in a process control system
A method of creating and using an adaptive DMC type or other MPC controller includes using a model switching technique to periodically determine a process model, such as a parameterized process model, for a process loop on-line during operation of the process. The method then uses the process model to generate an MPC control model and creates and downloads an MPC controller algorithm to an MPC controller based on the new control model while the MPC controller is operating on-line. This technique, which is generally applicable to single-loop MPC controllers and is particularly useful in MPC controllers with a control horizon of one or two, enables an MPC controller to be adapted during the normal operation of the process, so as to change the process model on which the MPC controller is based to thereby account for process changes. The adaptive MPC controller is not computationally expensive and can therefore be easily implemented within a distributed controller of a process control system, while providing the same or in some cases better control than a PID controller, especially in dead time dominant process loops, and in process loops that are subject to process model mismatch within the process time to steady state.
Owner:FISHER-ROSEMOUNT SYST INC
Controllers, observers, and applications thereof
Controller scaling and parameterization are. described. Techniques that can be improved by employing the scaling and parameterization include, but are not limited to, controller design, tuning and optimization. The scaling and parameterization methods described here apply to transfer function based controllers, including PID controllers. The parameterization methods also apply to state feedback and state observer based controllers, as well as linear active disturbance rejection (ADRC) controllers. Parameterization simplifies the use of ADRC. A discrete extended state observer (DESO) and a generalized extended state observer (GESO) are described. They improve the performance of the ESO and therefore ADRC. A tracking control algorithm is also described that improves the performance of the ADRC controller. A general algorithm is described for applying ADRC to multi-input multi-output systems. Several specific applications of the control systems and processes are disclosed.
Owner:CLEVELAND STATE UNIVERSITY
Control system and process for application of energy to airway walls and other mediums
InactiveUS20060247726A1Improve conductivityElectrotherapySurgical instruments for heatingControl systemEngineering
The present invention includes a system for delivering energy to an airway wall of a lung comprising an energy delivering apparatus and a PID controller having one or more variable gain factors which are rest after energy deliver has begun. The energy delivering apparatus may include a flexible elongated member and a distal expandable basket having at least one electrode for transferring energy to the airway wall and at least one temperature sensor for measuring temperature. The PID controller determines a new power set point base on an error between a preset temperature and the measured temperature. The algorithm can be Pii+1=Pi+G(αei+βei-1+γei-2) where α, β and γ are preset values and a is from 1 to 2; β is from −1 to −2; and 7 is from −0.5 to 0-5. In another variation, the controller is configured to shut down if various measured parameters are exceeded such as, for example, energy, impedance, temperature, temperature differences, activation time and combinations thereof. Methods for treating a target medium using a PID algorithm are also provided.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Method and apparatus for controlling a self-refreshing display device coupled to a graphics controller
InactiveUS20120206461A1Reduce generationDigital data processing detailsDigital computer detailsDisplay deviceData storing
A method and apparatus for controlling a self-refreshing display device coupled to a graphics controller are disclosed. A self-refreshing display device has a capability to drive the display based on video signals generated from a local frame buffer in the display device. A graphics controller coupled to the display device may optimally be placed in one or more power saving states when the display device is operating in a panel self-refresh mode. The graphics controller detects one or more progressive levels of idleness in the graphics controller and the pixel data stored in a frame buffer. Based on the detected idleness, the graphics controller signals the display device to enter or exit the panel self-refresh mode and enters a power saving state. When exiting the panel self-refresh mode, the display device and / or graphics controller ensure that the video signals generated by the local controller and the graphics controller are aligned.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
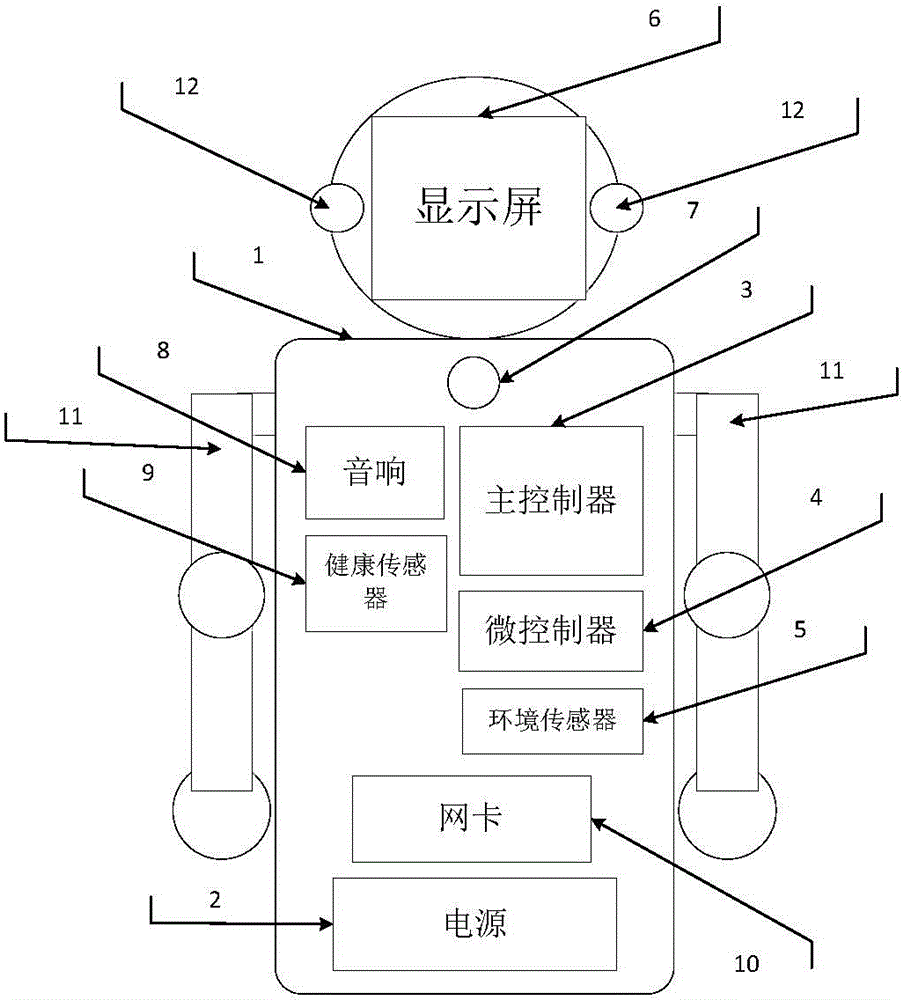
Household information acquisition and user emotion recognition equipment and working method thereof
InactiveCN104102346AVarious functionsImprove scalabilityProgramme controlInput/output for user-computer interactionMicrocontrollerAudio electronics
The invention discloses a household information acquisition and user emotion recognition equipment, which comprises a shell, a power supply, a main controller, a microcontroller, multiple environmental sensors, a screen, a microphone, an audio, multiple health sensors, a pair of robot arms and a pair of cameras, wherein the microphone is arranged on the shell; the power supply, the main controller, the microcontroller, the environmental sensors, the audio and the pair of cameras are arranged symmetrically relative to the screen respectively on the left and right sides; the robot arms are arranged on the two sides of the shell; the main controller is in communication connection with the microcontroller, and is used for controlling the microcontroller to control the movements of the robot arms through motors of the robot arms; the power supply is connected with the main controller and the microcontroller, and is mainly used for providing energy for the main controller and the microcontroller. According to the household information acquisition and user emotion recognition equipment, the intelligent speech recognition technology, the speech synthesis technology and the facial expression recognition technology are integrated, thus the use of the household information acquisition and user emotion recognition equipment is more convenient, and the feedback is more reasonable.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Continuously Scheduled Model Parameter Based Adaptive Controller
InactiveUS20090319060A1Short adaptation timeReduce processSimulator controlComputation using non-denominational number representationOperating pointModel parameters
An adaptive process controller performs continuously scheduled process model parameter interpolation to determine a particular set of process model parameters which are used to develop controller tuning parameters for controller tuning. More particularly, a state-based, adaptive PID controller described herein uses a new technique to determine an appropriate process model to be used to perform adaptive tuning over the various operating regions of the plant, and in particular, uses a process model parameter determination technique that enables continuously scheduled process model parameter update over the various plant operating regions or points. The use of this continuously scheduled process model parameter update method provides for smoother transitions between tuning parameters used in the PID controller during adaptive tuning procedures which are implemented based on changes in the operating region or the operating point of the process, thereby providing for better overall control.
Owner:FISHER-ROSEMOUNT SYST INC
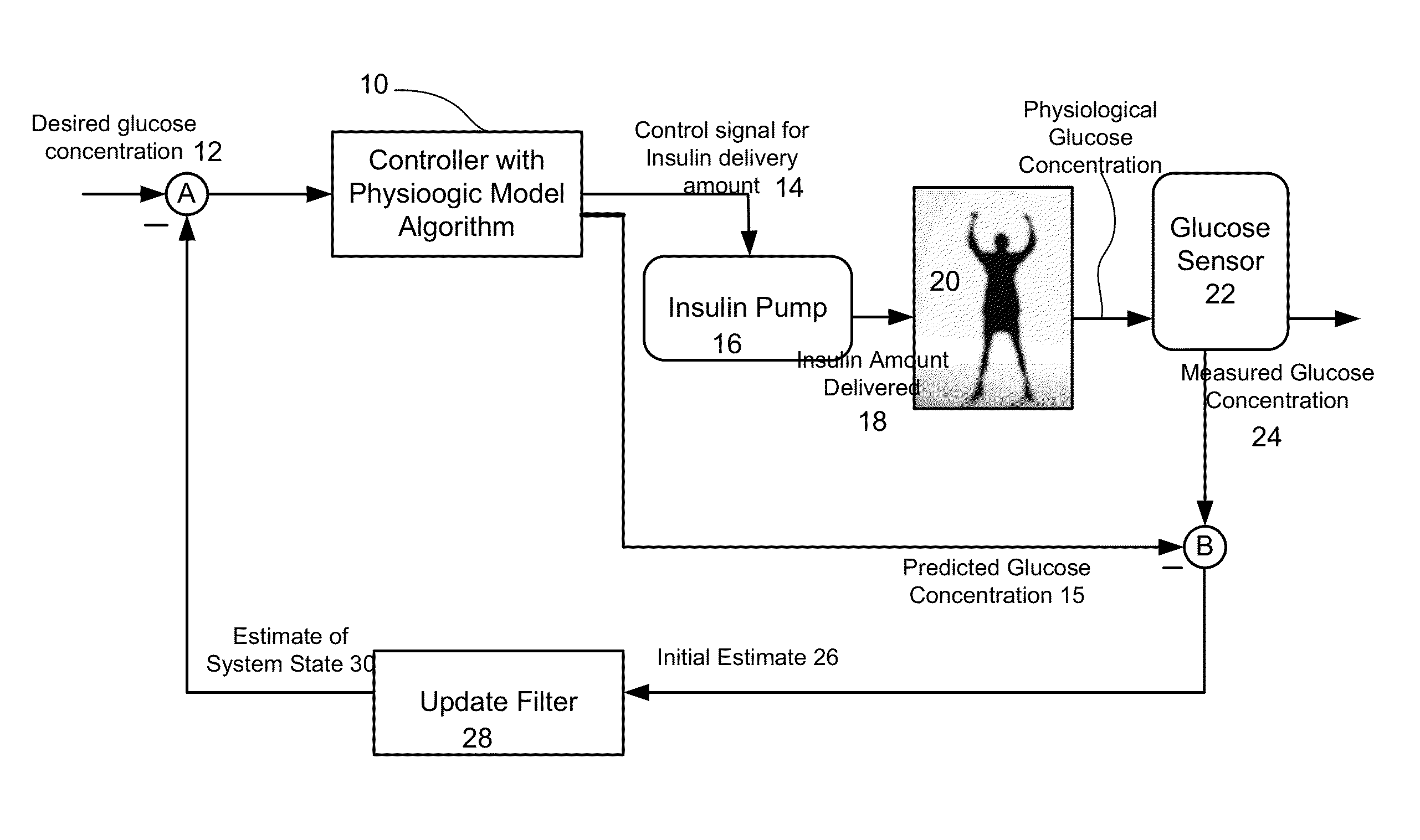
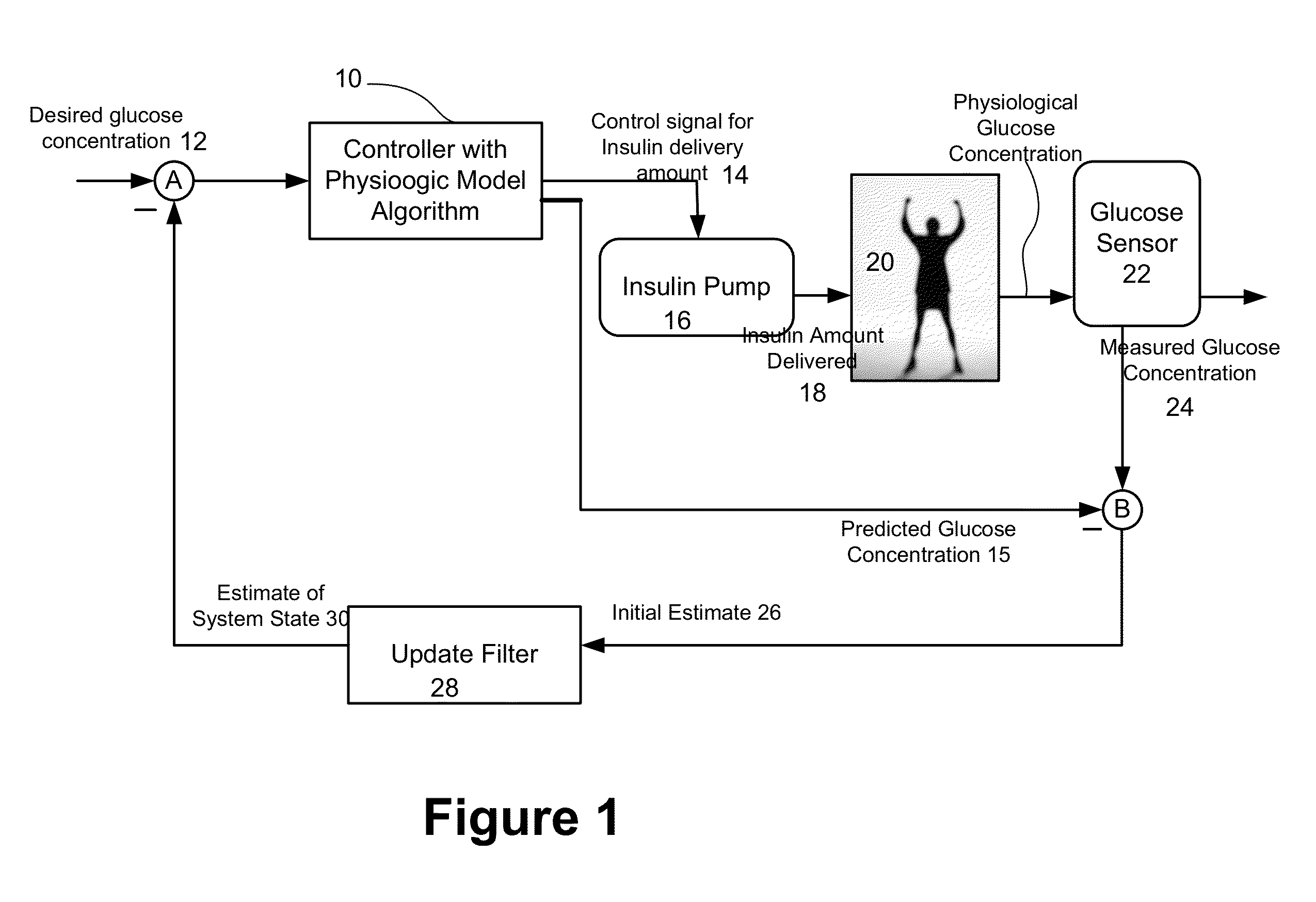
Method and system to handle manual boluses or meal events for closed-loop controllers
ActiveUS20140005633A1Negates portionReduce the impactDrug and medicationsMedical devicesGlucose sensorsDiabetes management
Described and illustrated is a diabetes management system that includes an infusion pump, glucose sensor and controller with a method programmed into the controller. The infusion pump is configured to deliver insulin to a subject. The glucose sensor is configured to sense glucose levels in the subject and provide output signals representative of the glucose levels in the subject. The controller is programmed to receive signals from at least one of the glucose sensor and the pump and configured to issue signals to the pump to deliver an amount of insulin determined by a feedback controller that utilizes a model predictive control and also configured to deliver at least the basal amount of insulin whenever the subject has initiated a manual bolus of insulin and a sensed or measured glucose level is at least a first threshold within a first duration of time.
Owner:JDRF INT +1
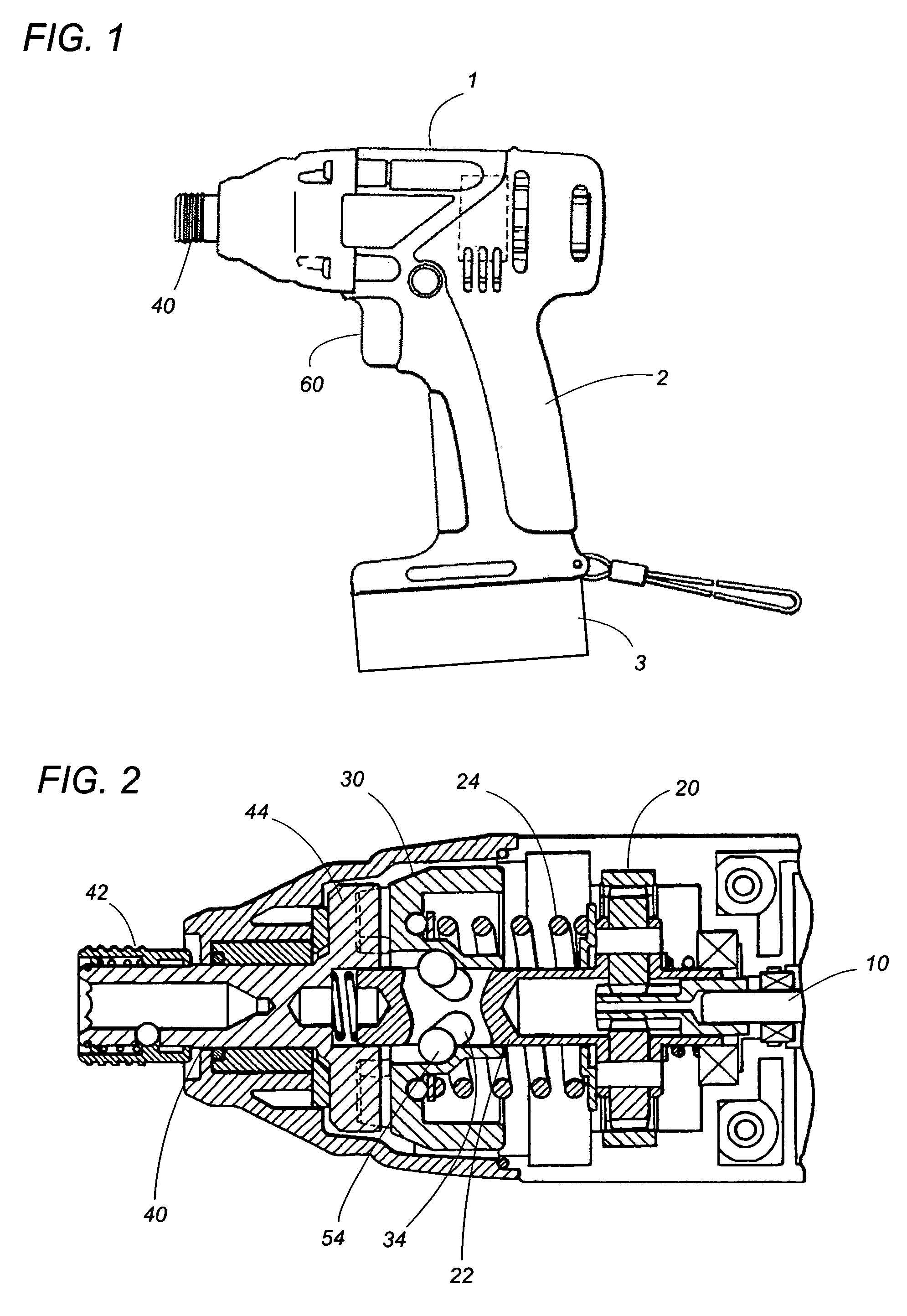
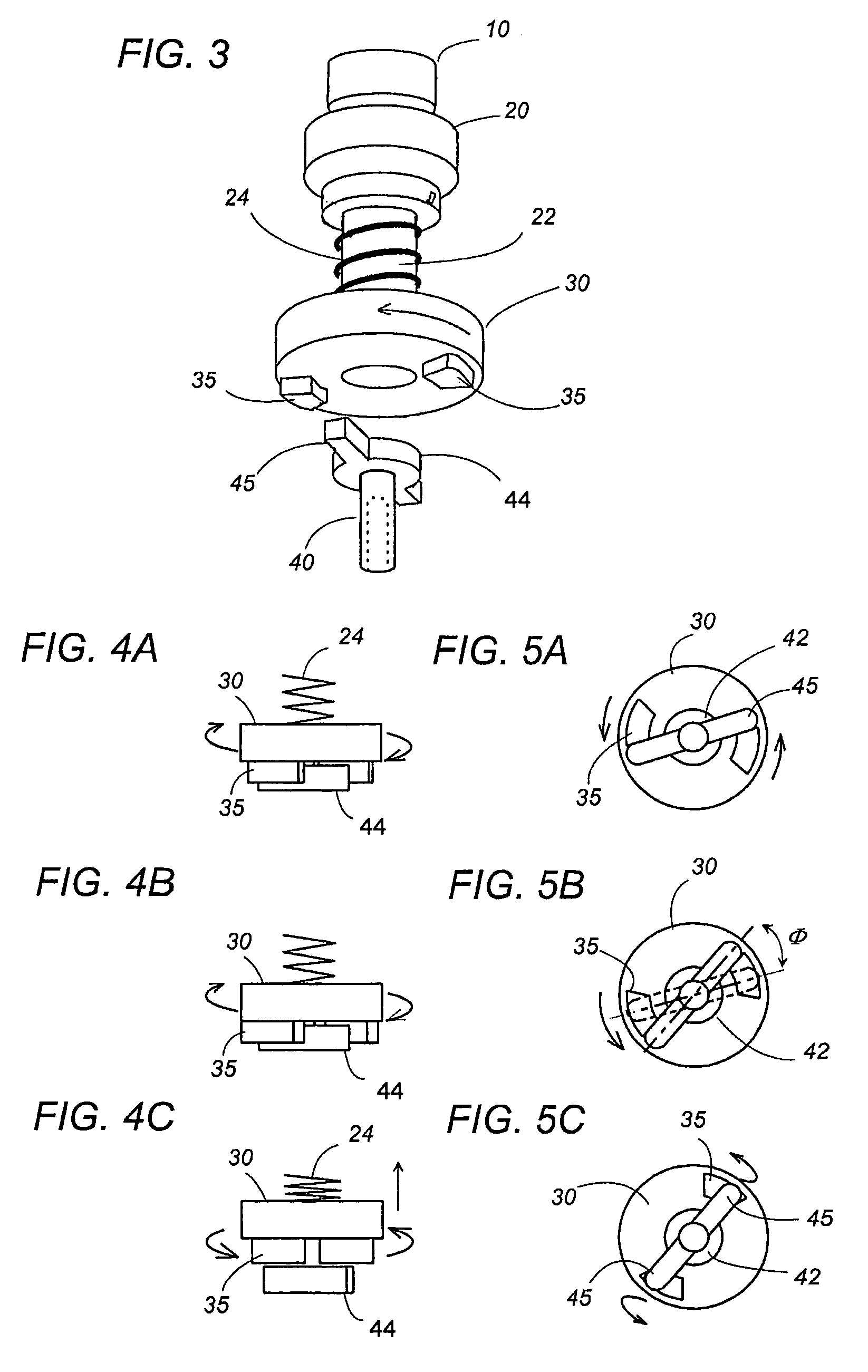
Rotary impact power tool
A impact power tool includes a motor rotating a drive shaft, an output shaft holding a tool bit, and a hammer coupled to the drive shaft. The hammer is rotatable together with the drive shaft and is engageable with an anvil fixed to the output shaft so as to give a rotary impact to the output shaft. The tool includes a speed commander generating a target speed intended by a user, and a speed detector for detection of a speed of the drive shaft. A speed controller generates a control signal for driving the motor by referring to the target speed and the detected speed. The speed controller provides a detection time frame, and to adopt a predefined pseudo-detection speed as a substitute for the detected speed when no speed detection is available within the detection time frame. Accordingly, even if no speed detection continues, i.e., the motor is stalled over the detection time frame, the speed controller can successfully generate the control signal by making the use of the pseudo-detection speed, thereby continuing to rotate the drive shaft for generating the impact regularly and consistently without causing a delay.
Owner:MATSUSHITA ELECTRIC WORKS LTD
Duty-ratio controller
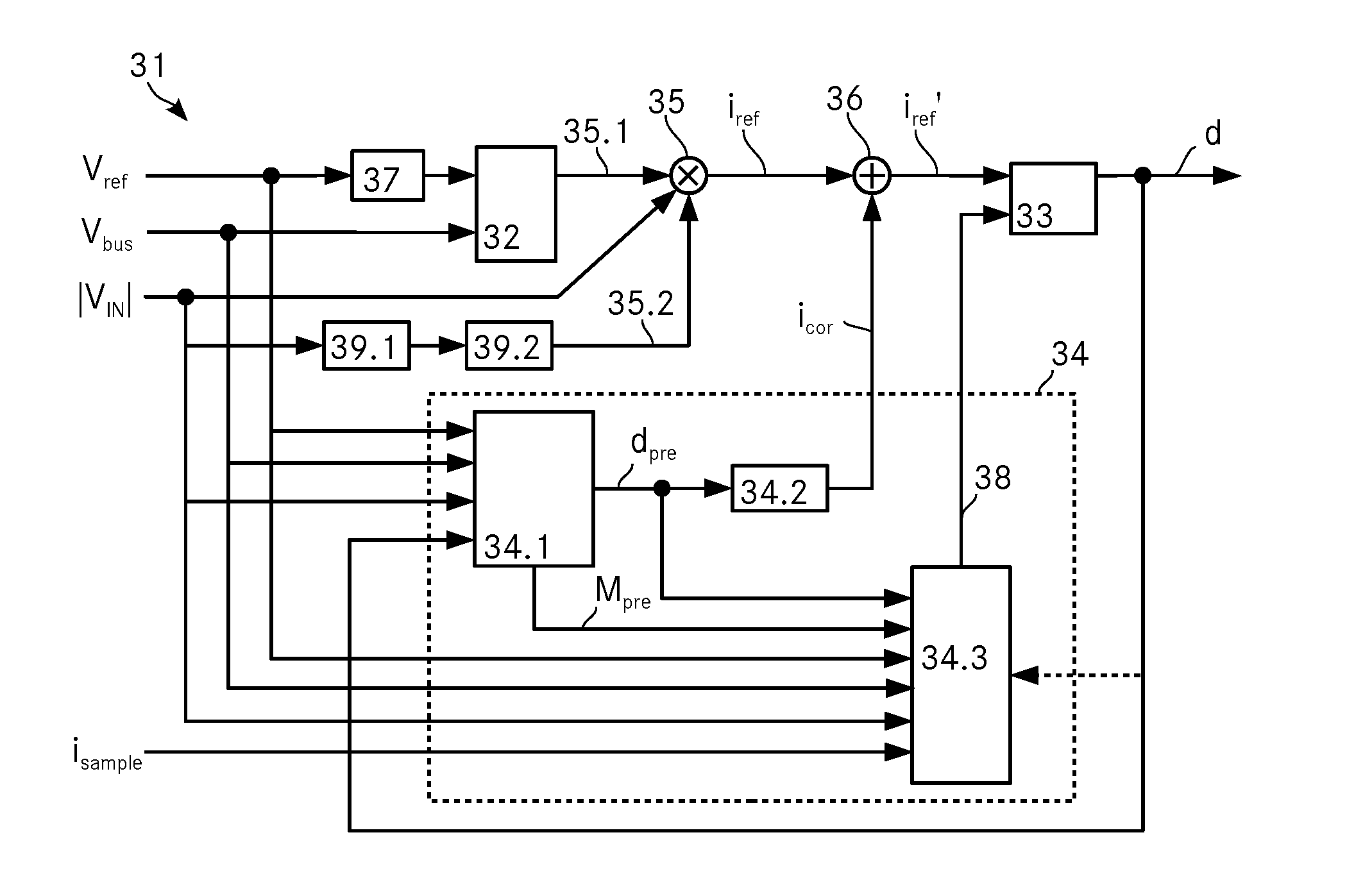
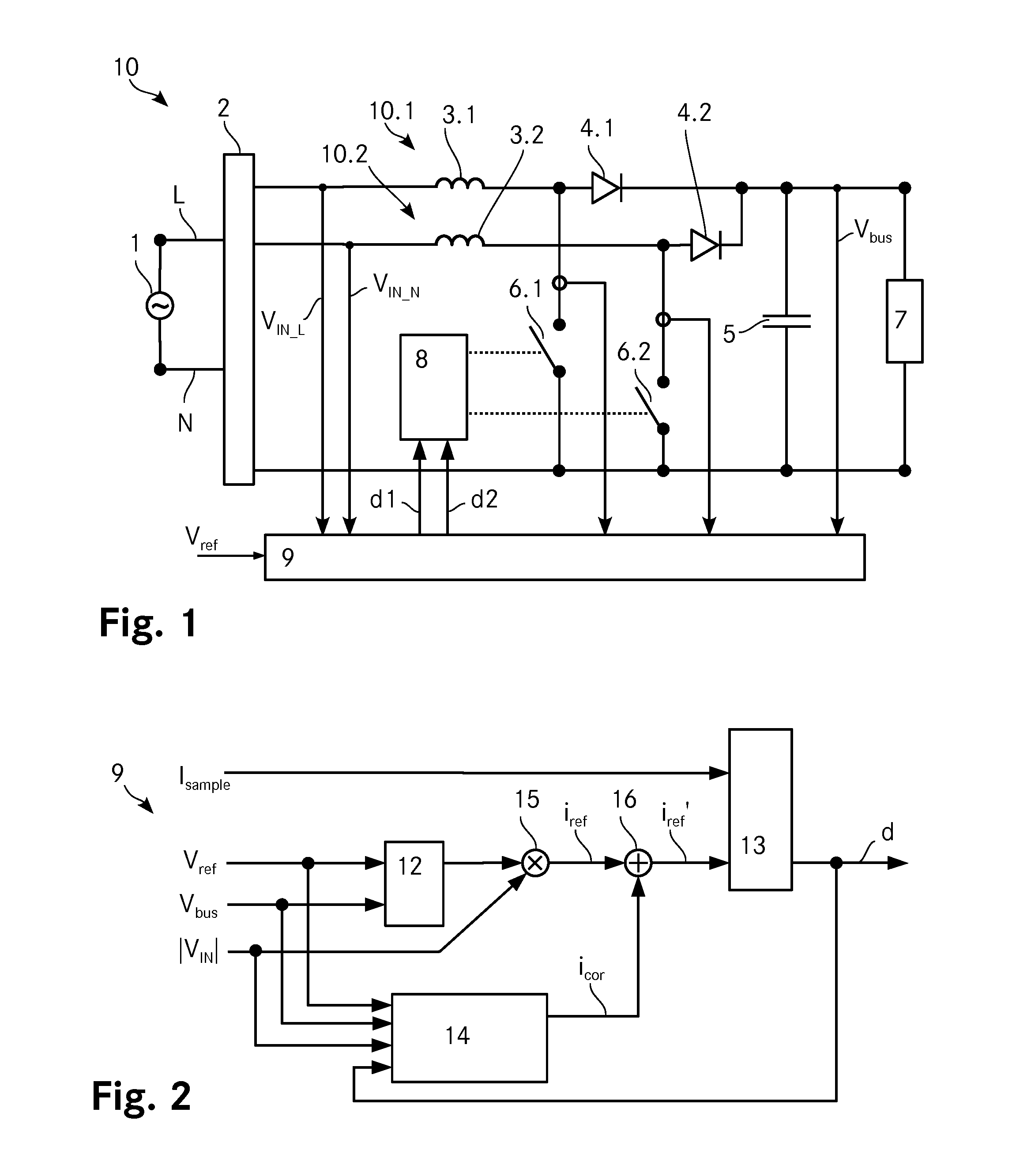
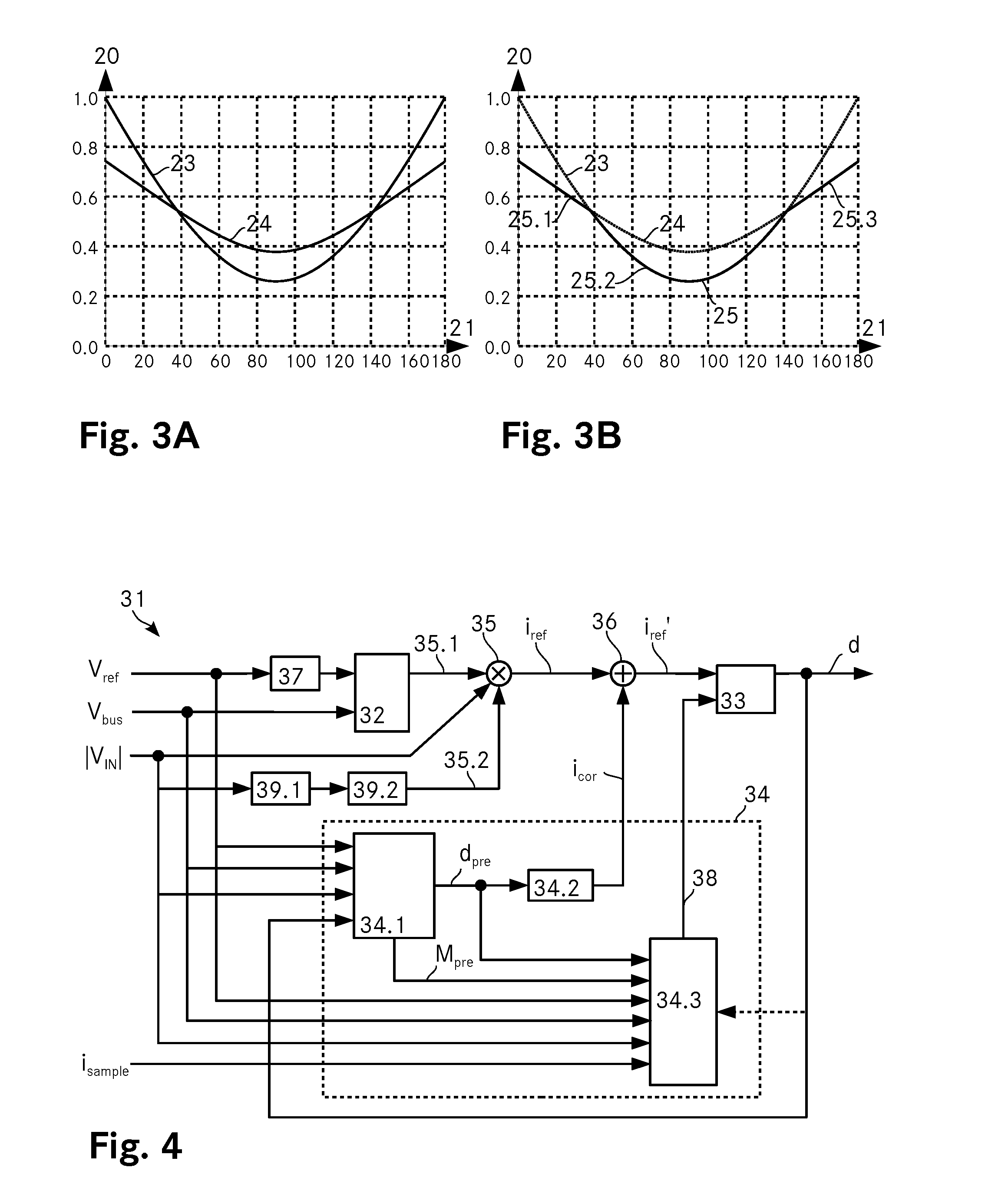
ActiveUS20150263609A1Simple designLow costEfficient power electronics conversionEnergy industryCurrent samplePower flow
A controller for determining the duty-ratio for a pulse width modulator of a converter includes an inner current loop, an outer voltage loop and a multiplier with an input voltage feed forward to connect both loops. A prediction unit determines a correction signal icor that is added to the reference current iref by means of an adder and it further determines a sample correction signal to correct the current samples in the current loop. This error-controlled duty-ratio prediction with sample correction results in an improved total harmonic distortion as well as in an improved power factor of the converter.
Owner:DELTA ELECTRONICS (THAILAND) PUBLIC CO LTD
Control system and process for application of energy to airway walls and other mediums
InactiveUS20060247727A1Improve conductivityElectrotherapySurgical instruments for heatingControl systemEngineering
The present invention includes a system for delivering energy to an airway wall of a lung comprising an energy delivering apparatus and a PID controller having one or more variable gain factors which are rest after energy deliver has begun. The energy delivering apparatus may include a flexible elongated member and a distal expandable basket having at least one electrode for transferring energy to the airway wall and at least one temperature sensor for measuring temperature. The PID controller determines a new power set point base on an error between a preset temperature and the measured temperature. The algorithm can be Pi+1=Pi+G(αei+βei−1+γei−2) where α, β and γ are preset values and α is from 1 to 2; β is from −1 to −2; and γ is from −0.5 to 0-5. In another variation, the controller is configured to shut down if various measured parameters are exceeded such as, for example, energy, impedance, temperature, temperature differences, activation time and combinations thereof. Methods for treating a target medium using a PID algorithm are also provided.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Continuous variable quantum key distribution system and synchronous realization method thereof
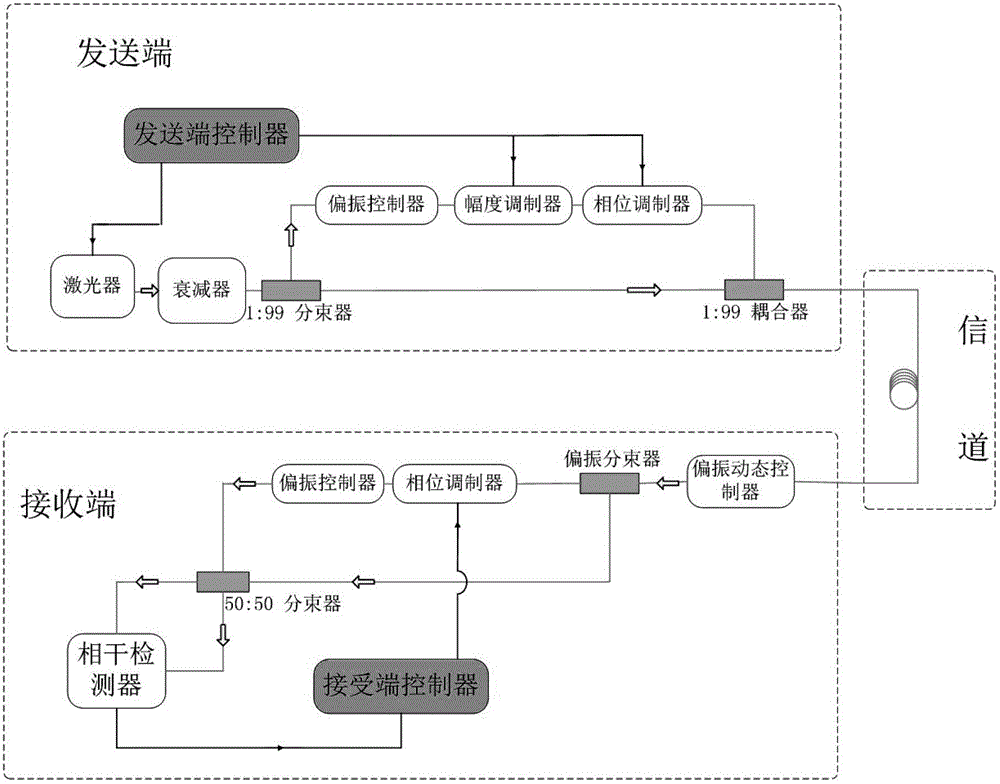
ActiveCN102724036AImprove bit error rateAvoid interferenceKey distribution for secure communicationMulti-frequency code systemsBeam splitterAmplitude control
The invention discloses a continuous variable quantum key distribution system and a synchronous realization method thereof. The continuous quantum key distribution system consists of a light path part and a circuit control part, wherein the light path part mainly consists of a laser, an attenuator, a beam splitter, a polarization controller, am amplitude controller, a phase controller and a coupler. A control part is a transmission end controller module and consists of a true random key generator, an analog voltage output and a trigger clock output. The synchronous method comprises a bit synchronizing step and a frame synchronizing step. The invention provides a completely novel synchronous realization scheme based on properties of continuous variable quantum in an optical fiber, the practical orientation of the continuous variable quantum key distribution system is promoted, and the interference that the continuous variable quantum on the synchronous realization in the optical communication process also can be effectively overcome.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAODA INTELLECTUAL PORPERTY MANAGEMENT CO LTD +1
Intelligent insomnia therapeutic instrument
InactiveCN101559252AGood treatment effectElectrotherapyDiagnostic recording/measuringMedicineAnalog signal
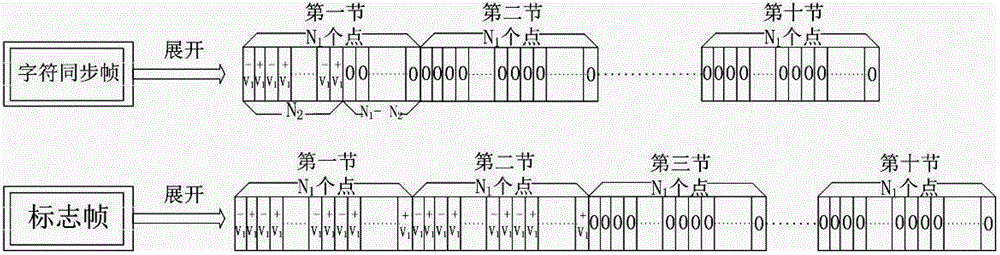
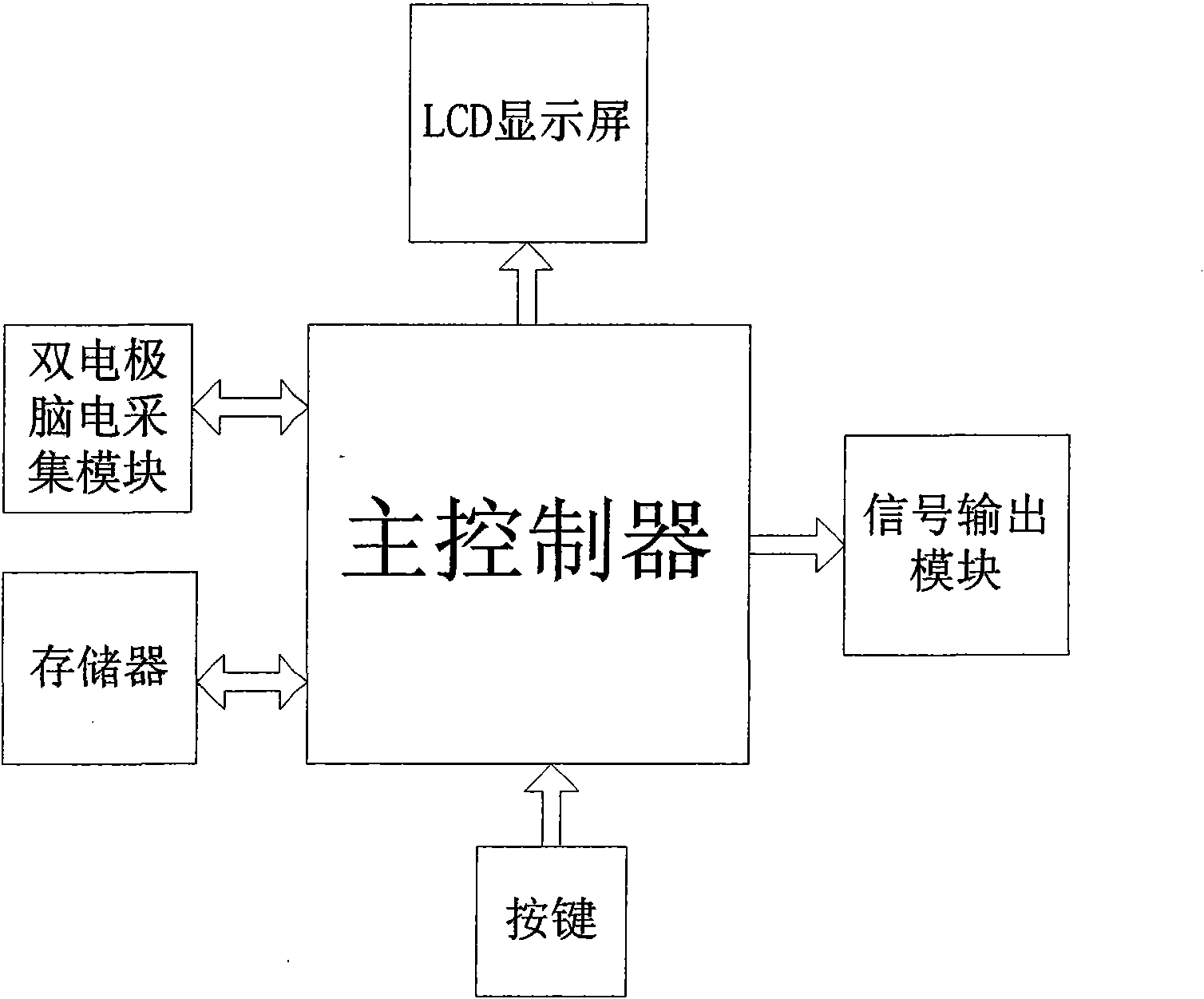
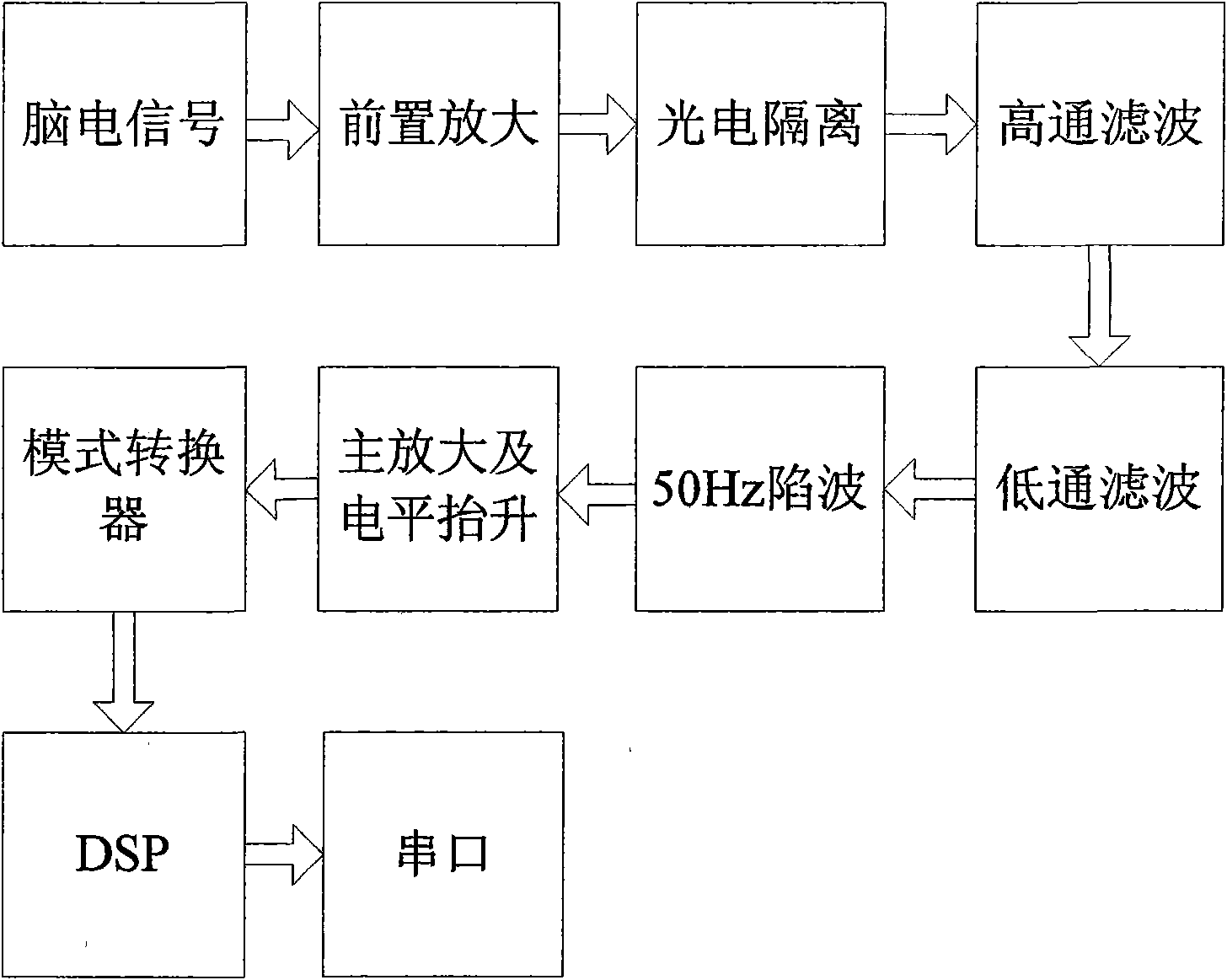
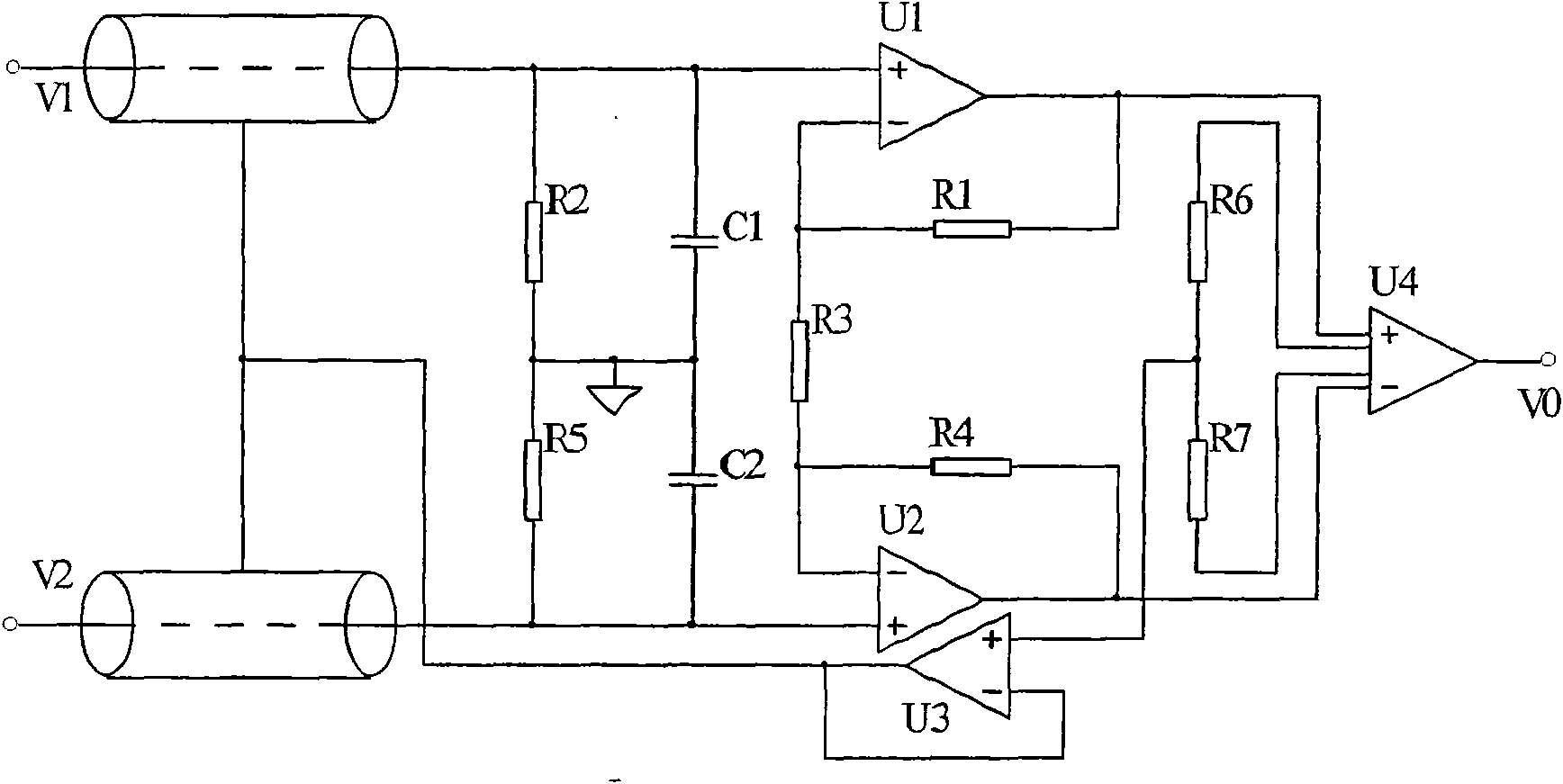
The invention relates to an intelligent insomnia therapeutic instrument, aiming at providing a therapeutic instrument which can induce and regulate potential action of the sleep center of a patient so as to accelerate the falling asleep speed of the patient and improve the sleep quality or realize a natural timing awaking function. The technical proposal is as follows: the instrument comprises a signal output module generating time varying magnetic fields, a bipolar electrode brain wave acquiring module acquiring real-time brain waves of the patient and a main controller obtaining the brain waves and carrying out down-conversion or up-conversion, wherein the signal output module converts digital brain signals output by the main controller into analogue signals which are amplified so as to drive a magnetic field generator to generate time varying magnetic fields used for treating.
Owner:JIANGXI SHIMEILE BIOTECH DEV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com