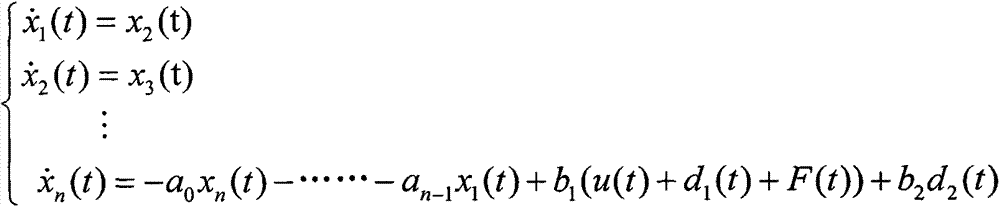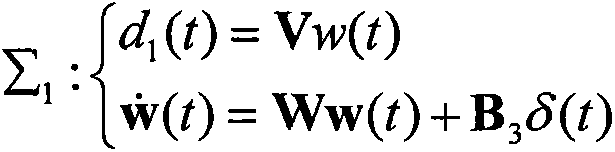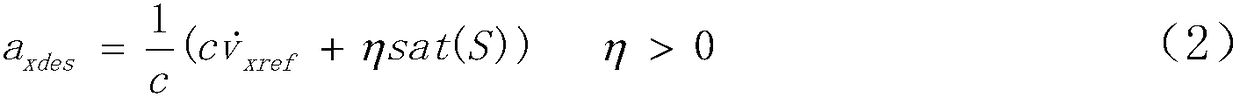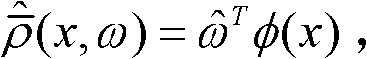Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1532 results about "Sliding mode control" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In control systems, sliding mode control (SMC) is a nonlinear control method that alters the dynamics of a nonlinear system by application of a discontinuous control signal (or more rigorously, a set-valued control signal) that forces the system to "slide" along a cross-section of the system's normal behavior. The state-feedback control law is not a continuous function of time. Instead, it can switch from one continuous structure to another based on the current position in the state space. Hence, sliding mode control is a variable structure control method. The multiple control structures are designed so that trajectories always move toward an adjacent region with a different control structure, and so the ultimate trajectory will not exist entirely within one control structure. Instead, it will slide along the boundaries of the control structures. The motion of the system as it slides along these boundaries is called a sliding mode and the geometrical locus consisting of the boundaries is called the sliding (hyper)surface. In the context of modern control theory, any variable structure system, like a system under SMC, may be viewed as a special case of a hybrid dynamical system as the system both flows through a continuous state space but also moves through different discrete control modes.
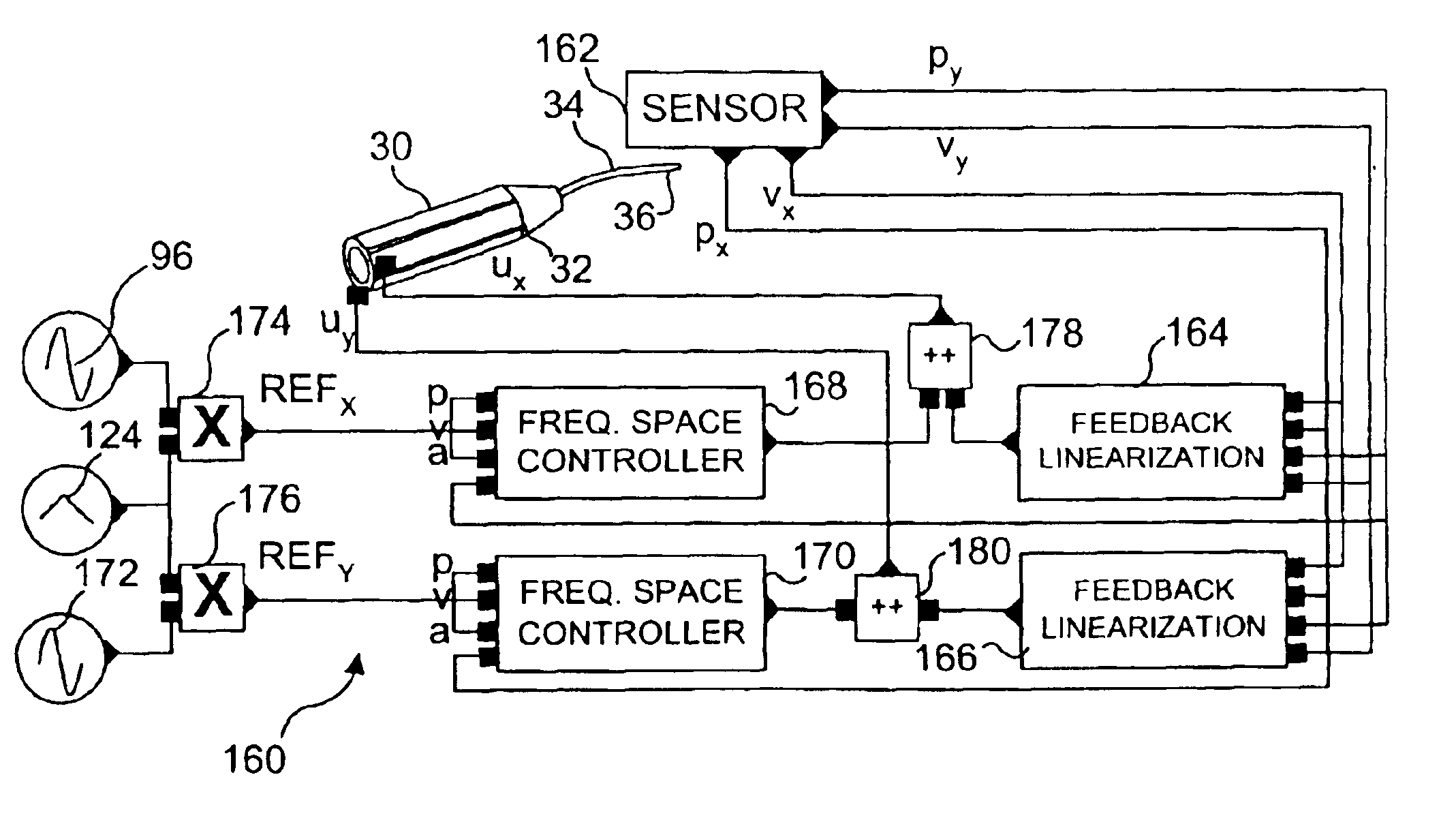
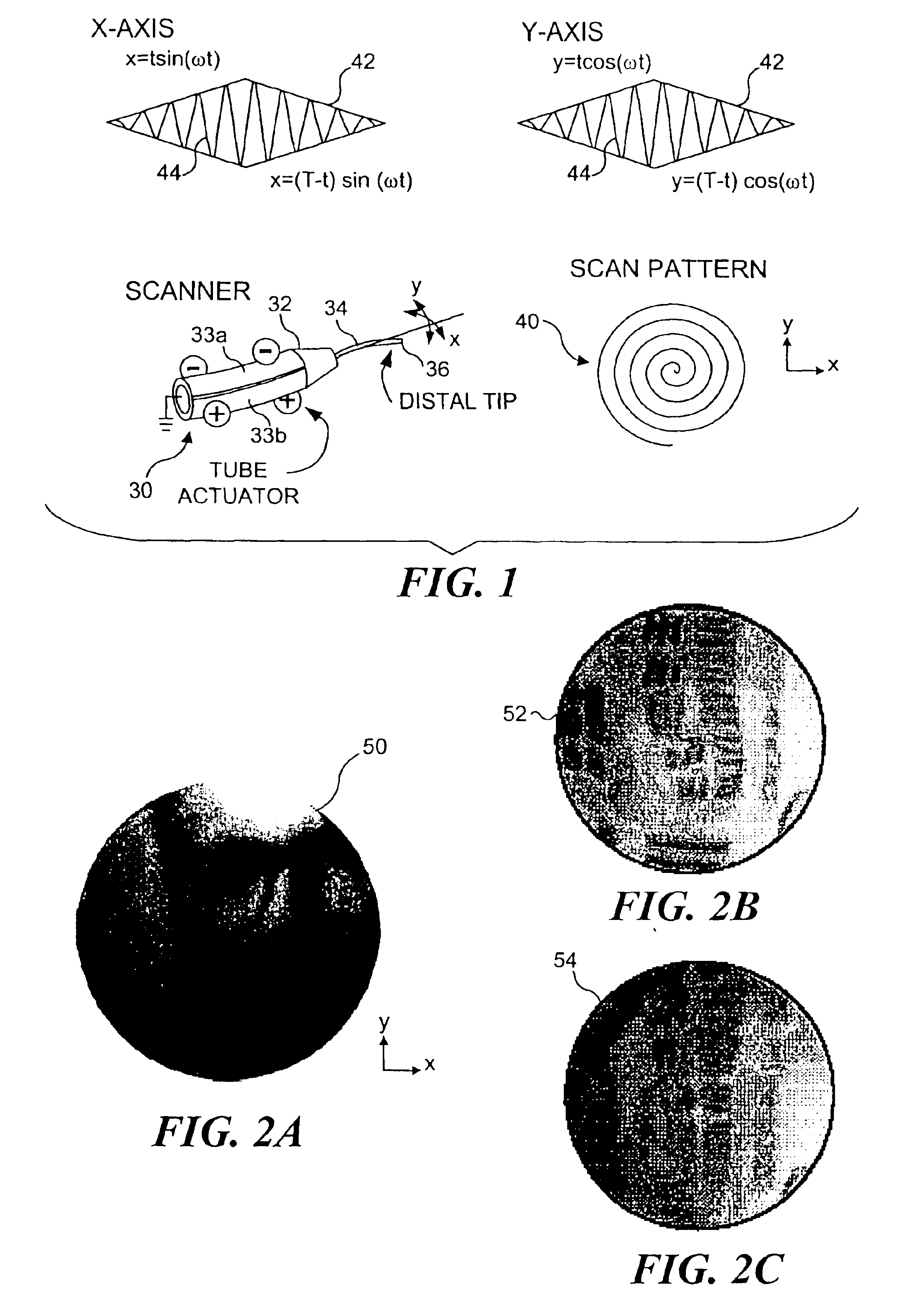
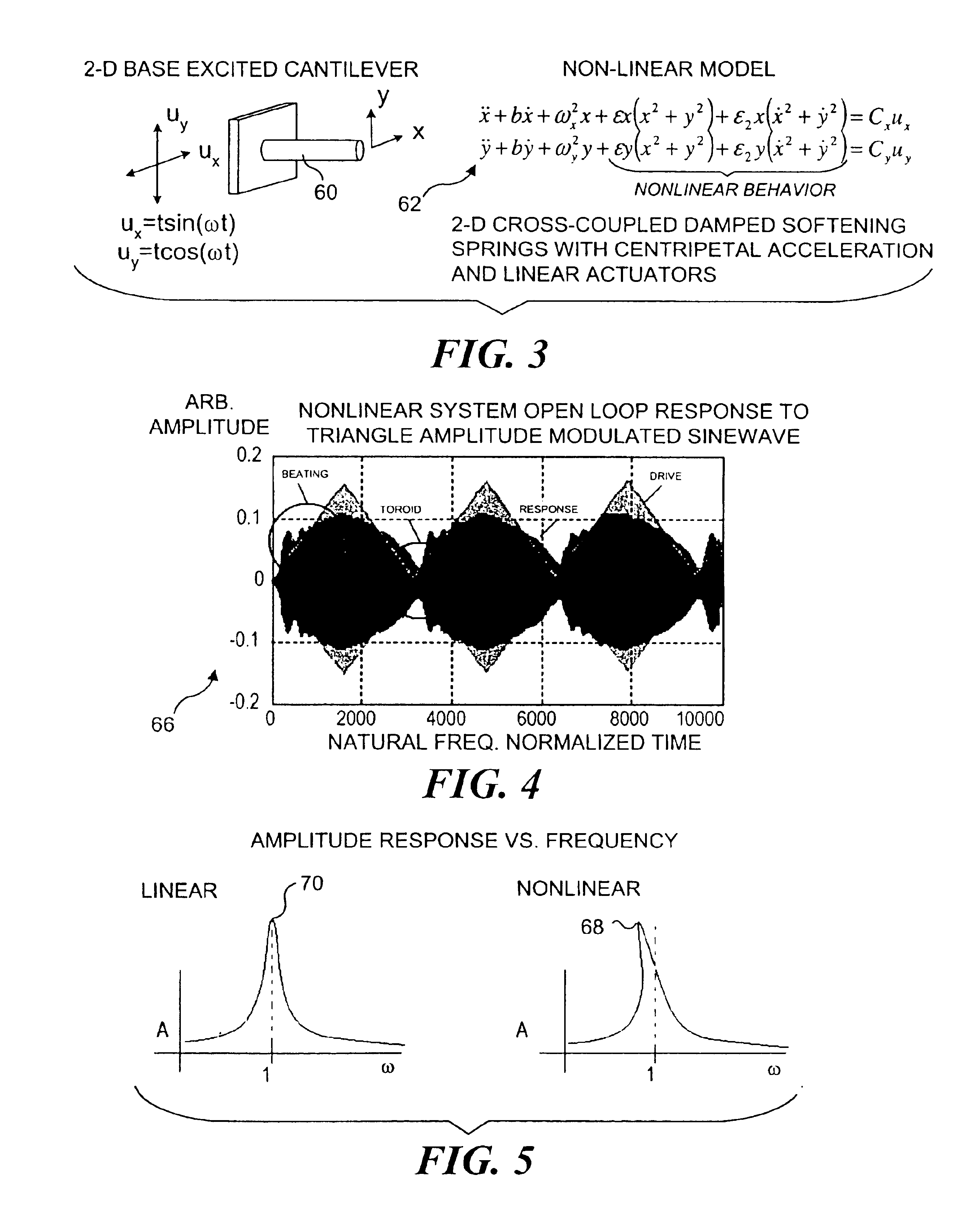
Control of an optical fiber scanner
InactiveUS6845190B1Remove nonlinear behaviorRobust cancellationSurgeryEndoscopesOptical scannersPhotodetector
Controls for an optical scanner, such as a single fiber scanning endoscope (SFSE) that includes a resonating optical fiber and a single photodetector to produce large field of view, high-resolution images. A nonlinear control scheme with feedback linearization is employed in one type of control to accurately produce a desired scan. Open loop and closed loops controllers are applied to the nonlinear optical scanner of the SFSE. A closed loop control (no model) uses either phase locked loop and PID controllers, or a dual-phase lock-in amplifier and two PIDs for each axis controlled. Other forms of the control that employ a model use a frequency space tracking control, an error space tracking control, feedback linearizing controls, an adaptive control, and a sliding mode control.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
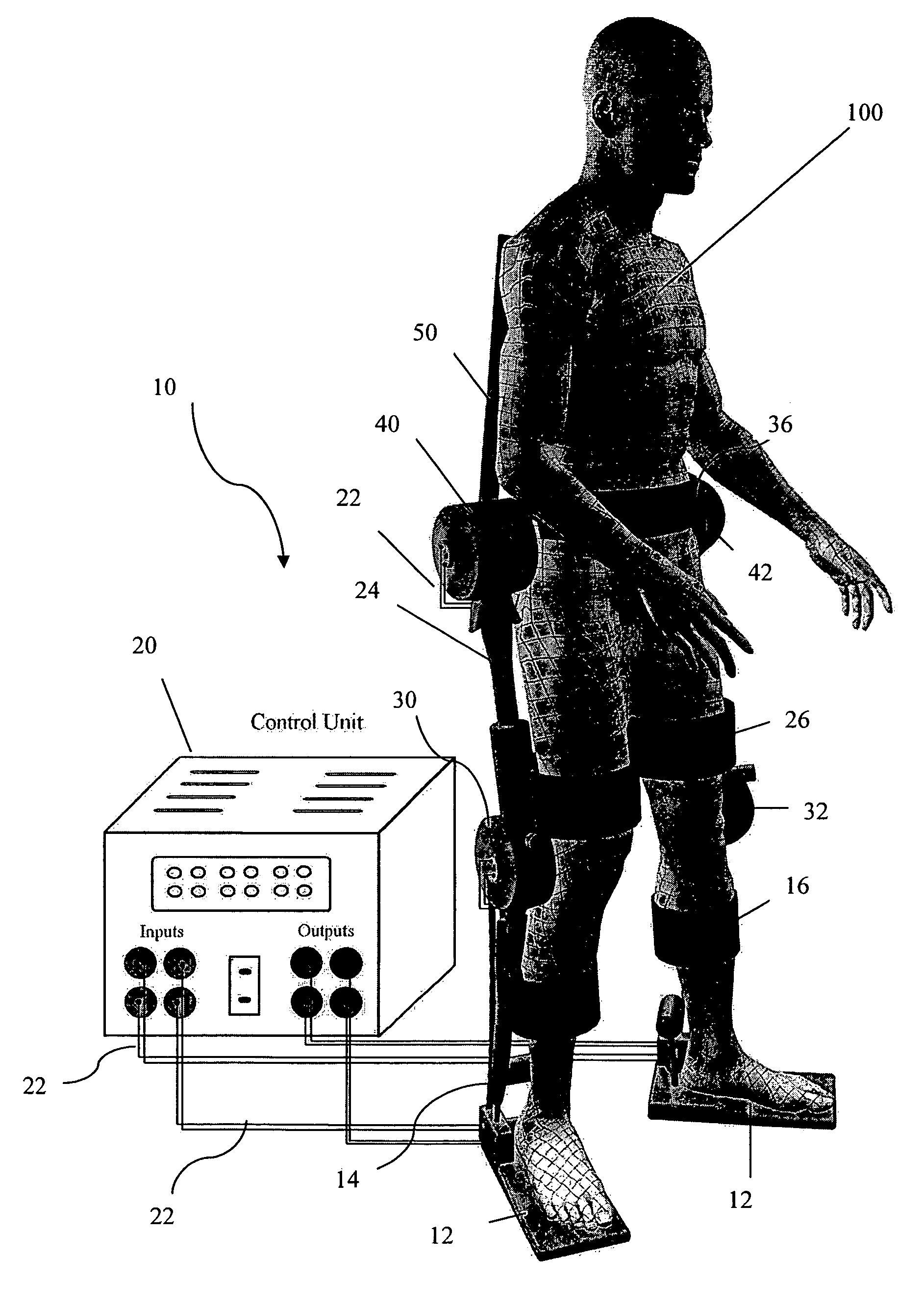
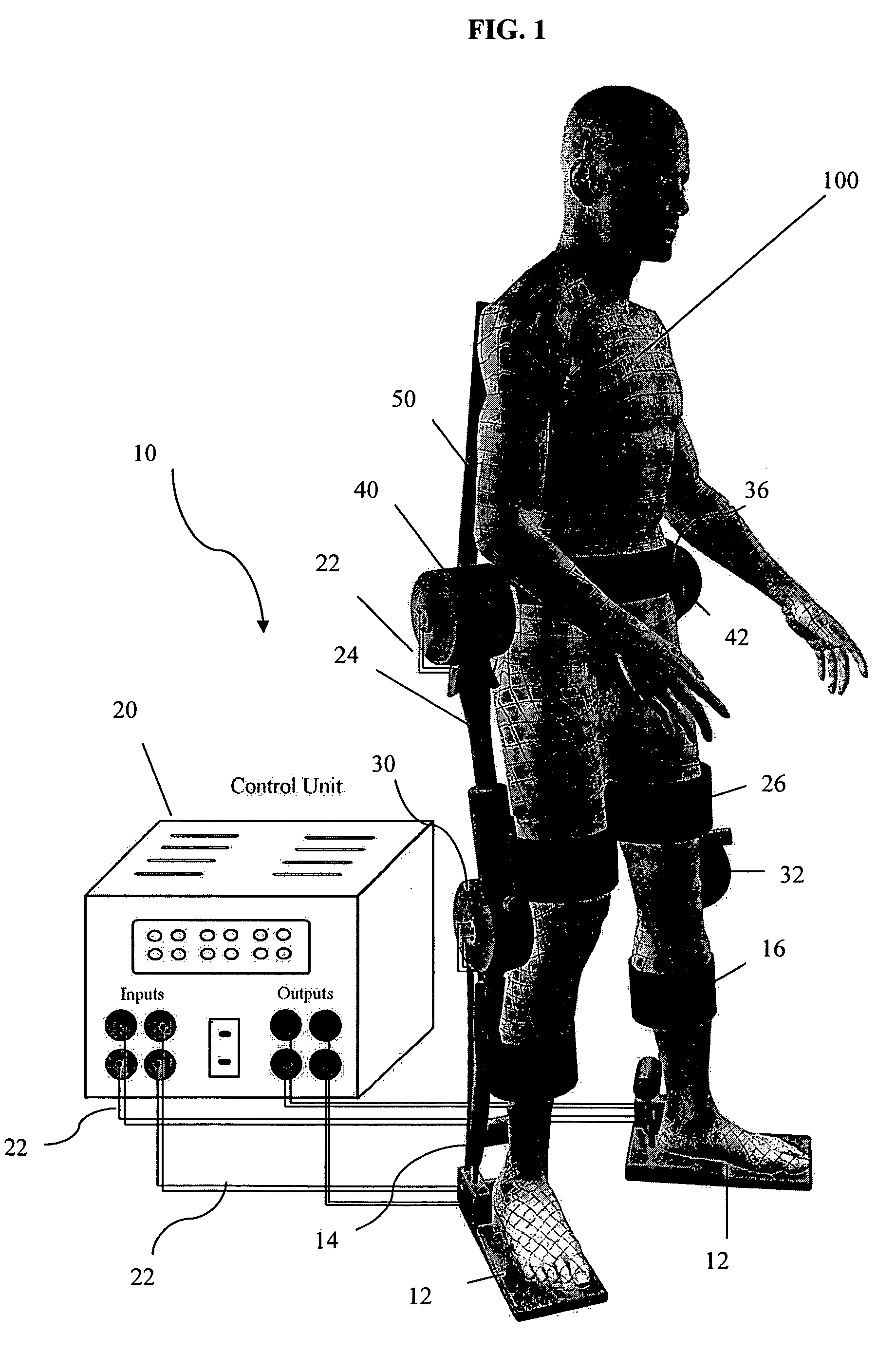
Exoskeletal device for rehabilitation
A modular exoskeletal device adapted to fit the lower extremities of a patient during rehabilitation. The device has only two actuators during the standing stage of rehabilitation. Two additional actuators can be added, as modules, during the walking stage of rehabilitation. The actuators are affixed to the patient and provide controlled motion to at least one of the joints of the patient. A stationary control unit is separated from the patient. The control unit communicates with and directs the actuators, and has a hybrid control algorithm, such that the actuator forces are adjusted as the patient regains control of some joint motions, which is based upon the sliding-mode control theory. A back brace is affixed to the patient and helps to keep the torso of the patient in a stable, substantially vertical position.
Owner:VILLANOVA UNIVERSITY
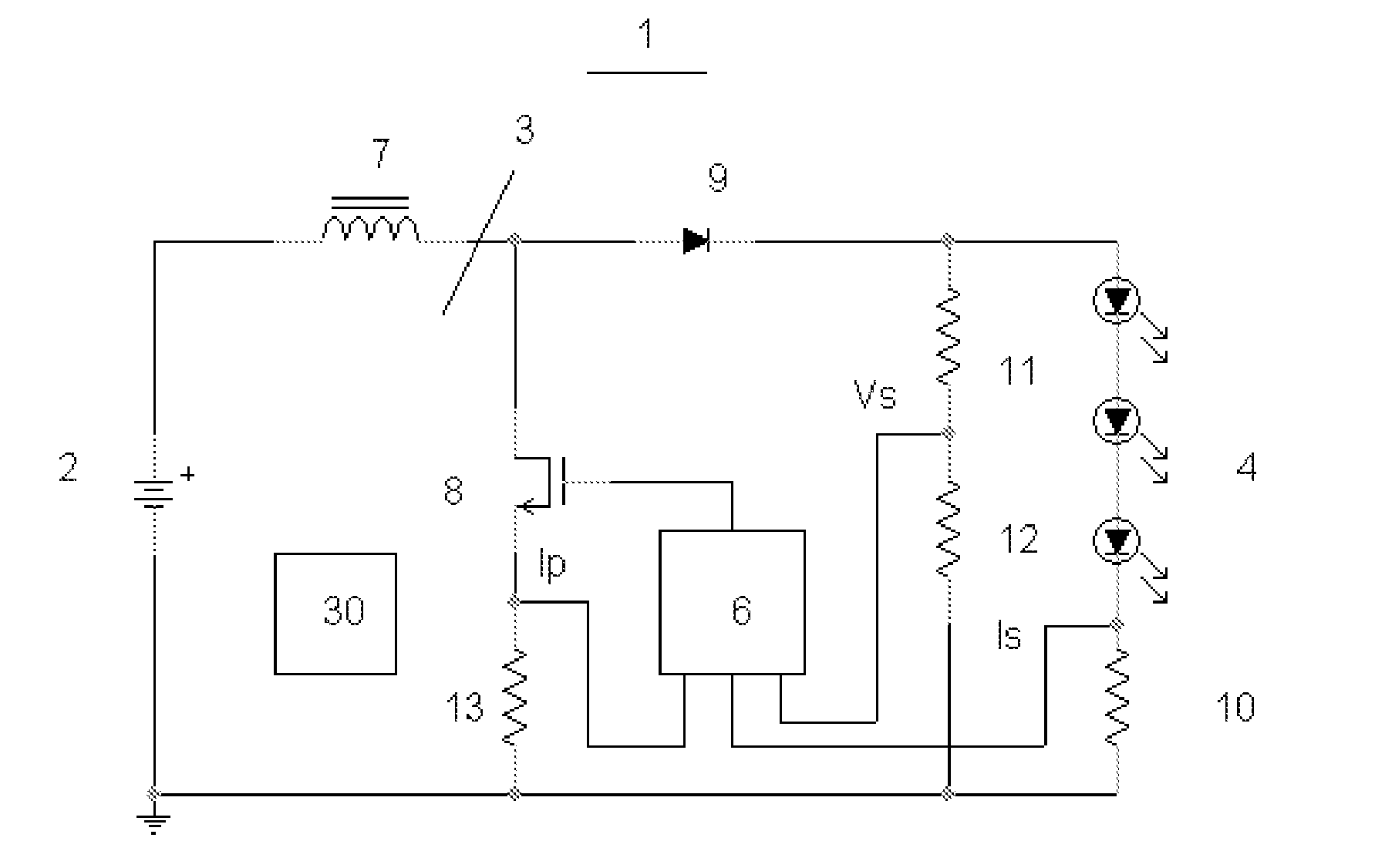
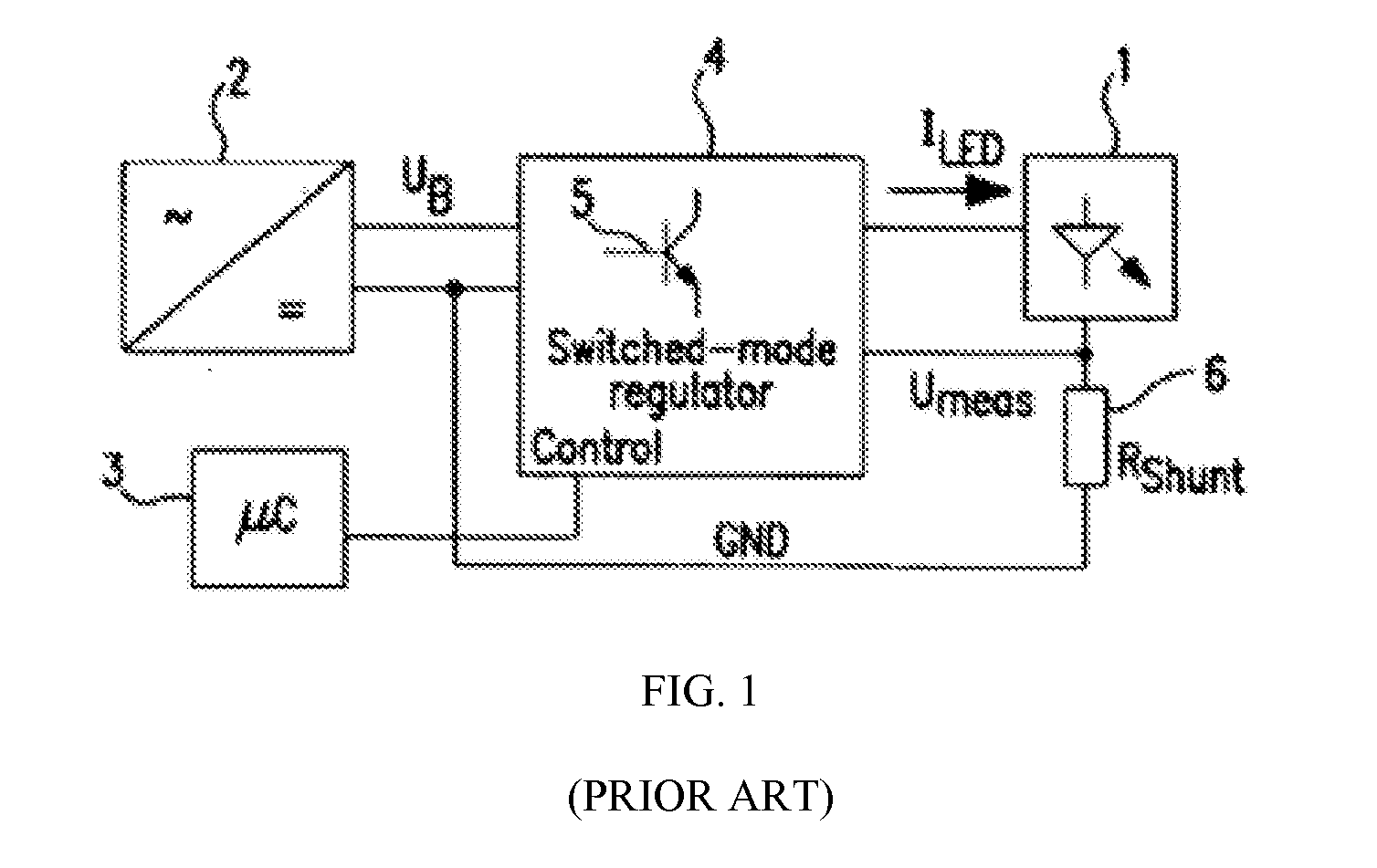
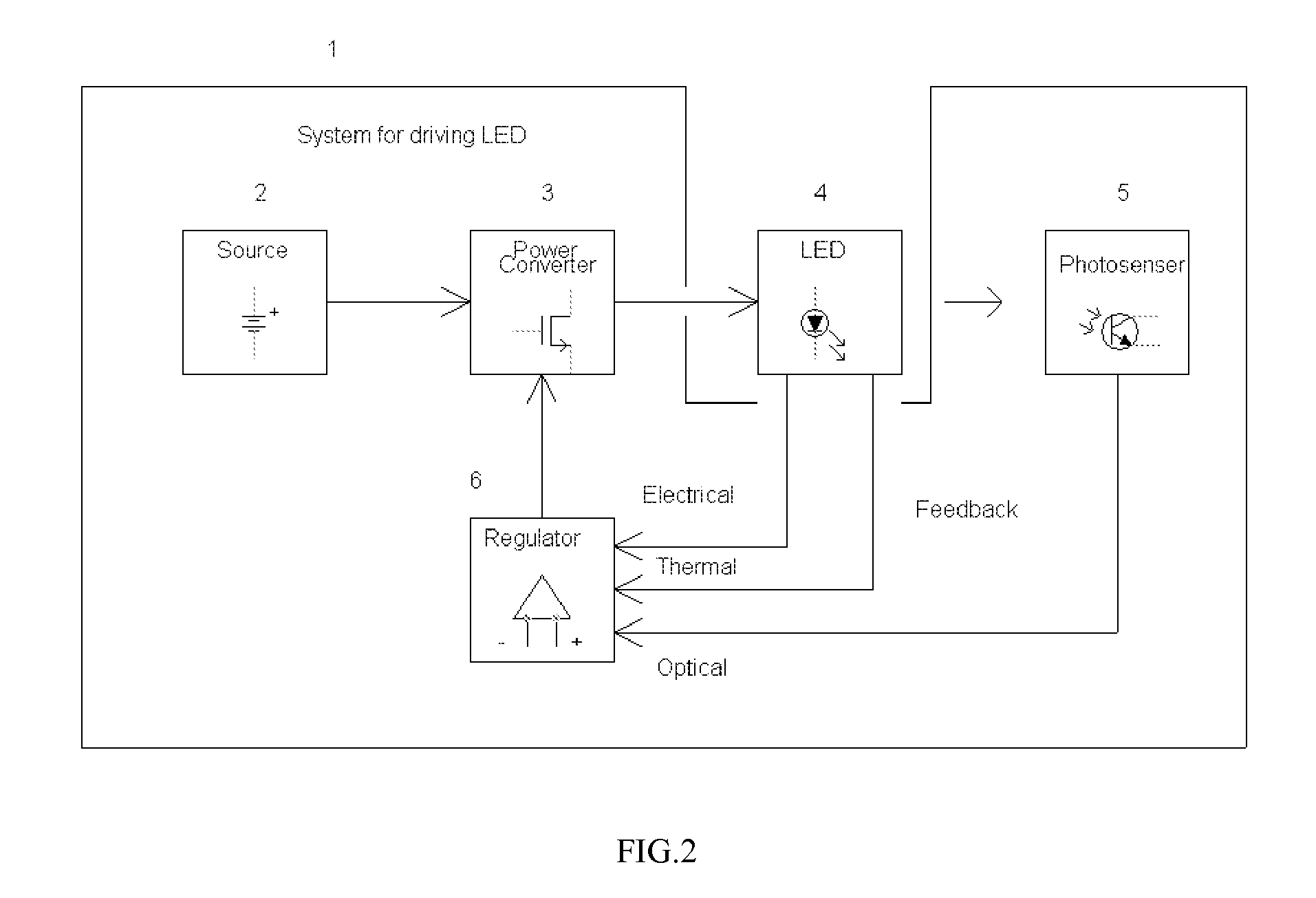
System and Method for Driving LED
ActiveUS20070285031A1Accurate estimateLow costElectroluminescent light sourcesDc-dc conversionAverage currentPeak value
Owner:CHEMTRON RES
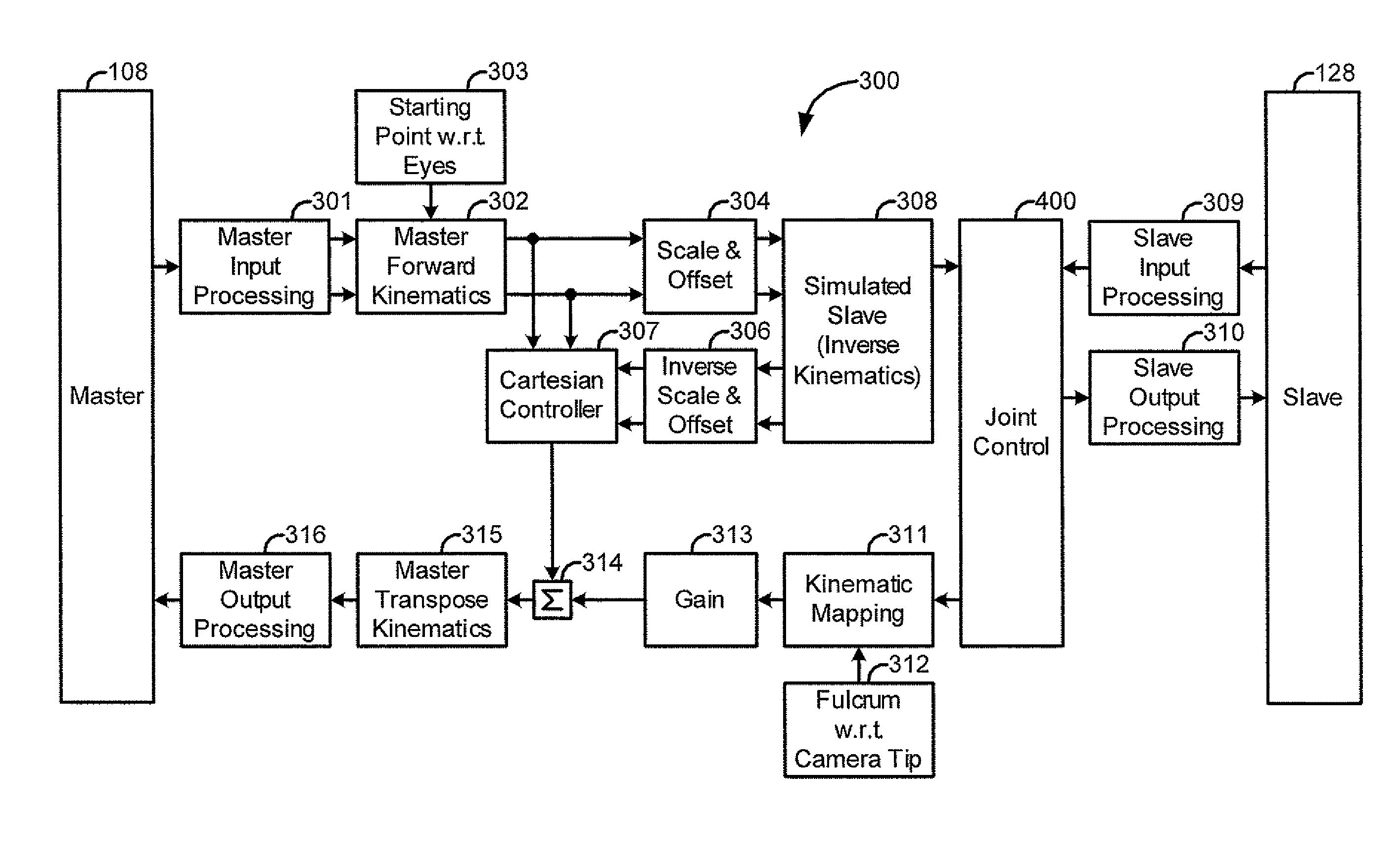
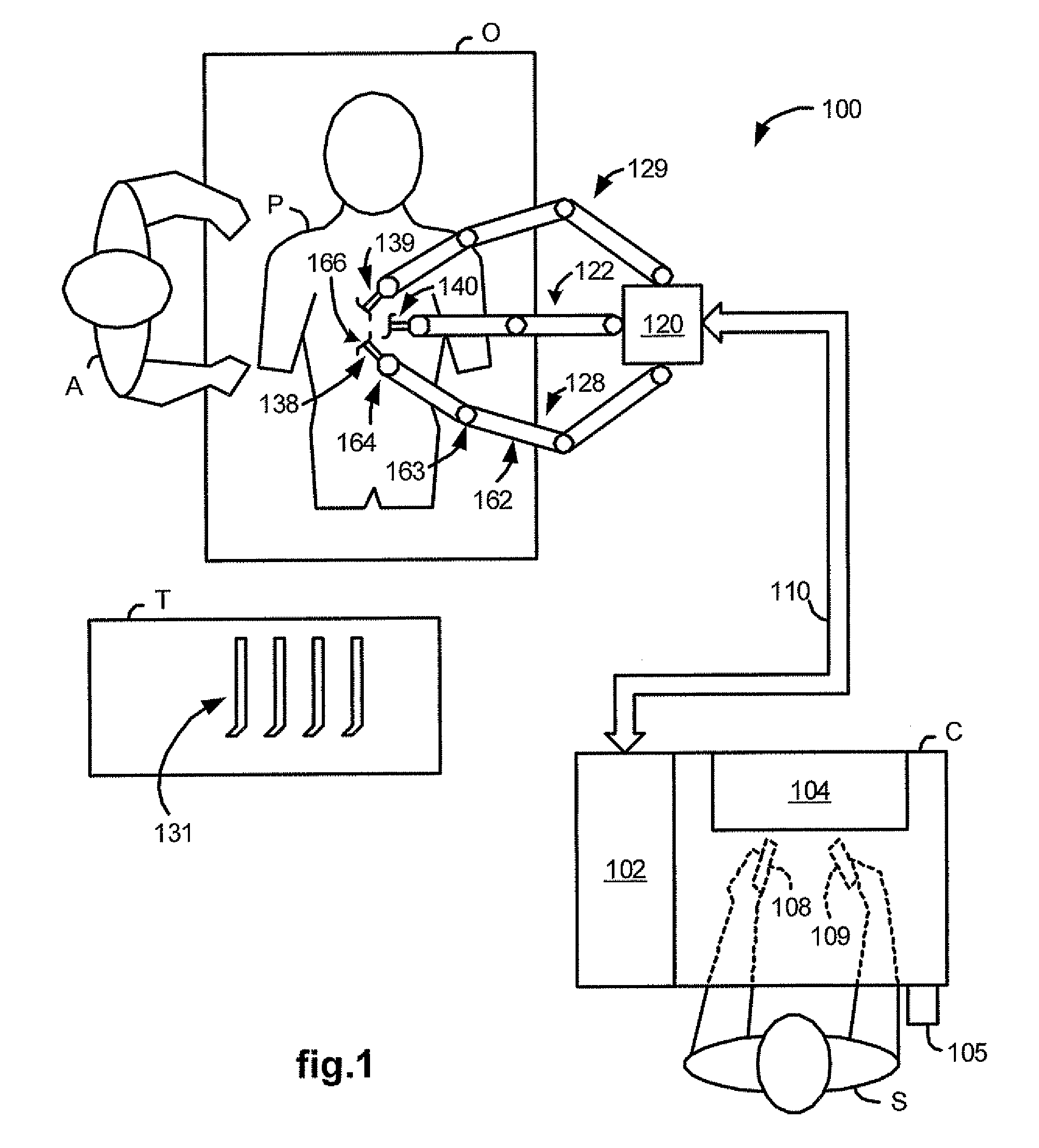
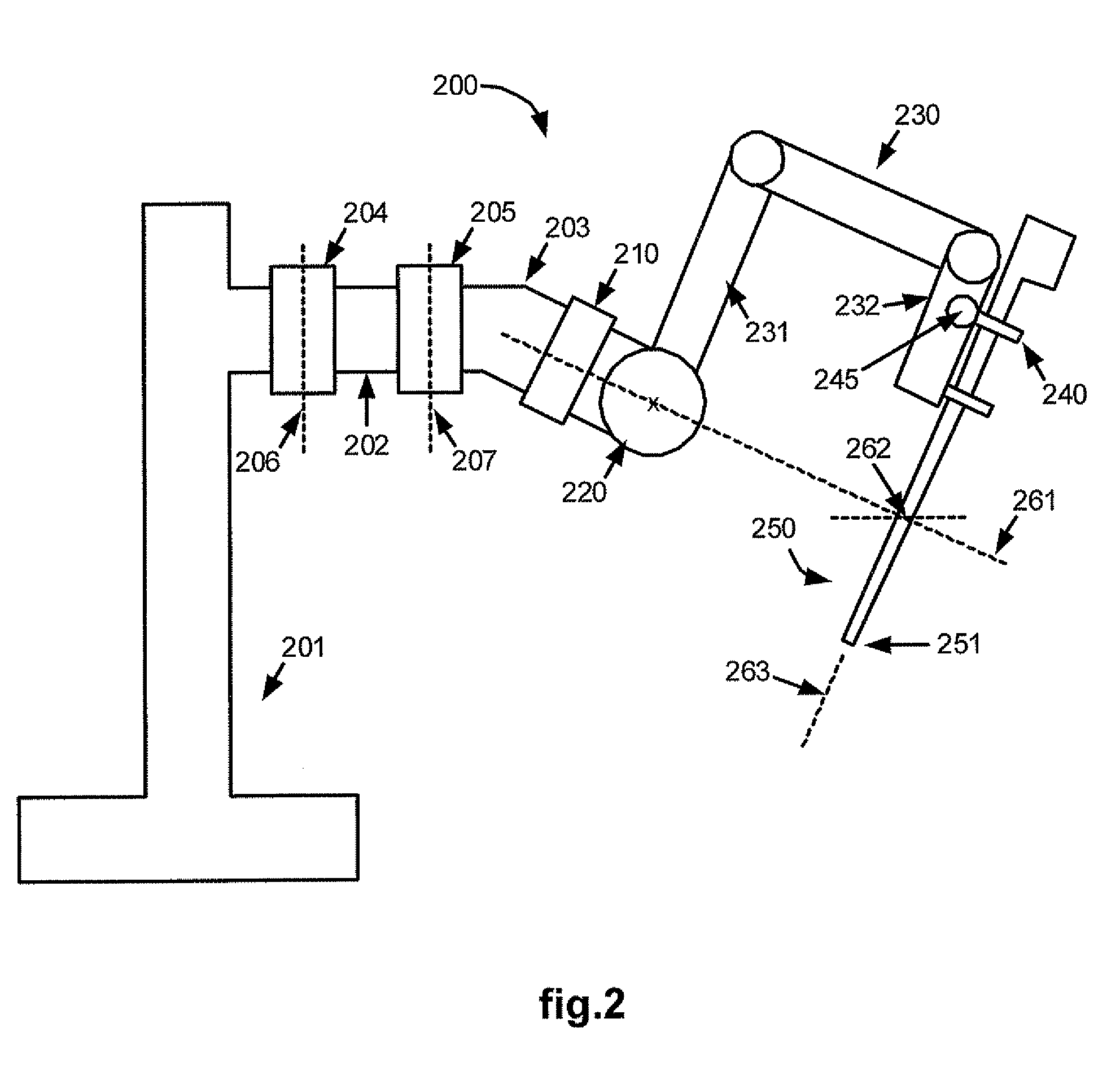
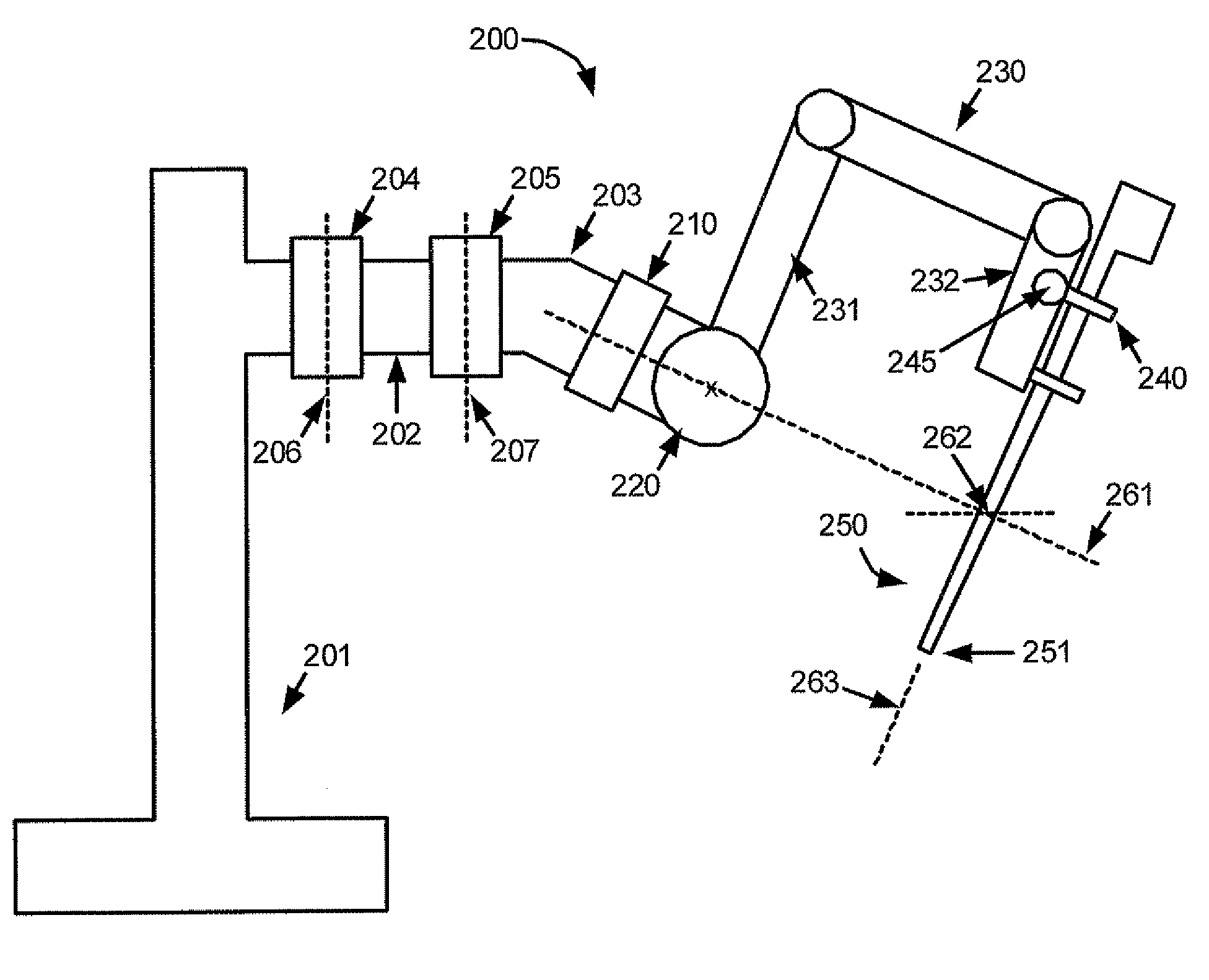
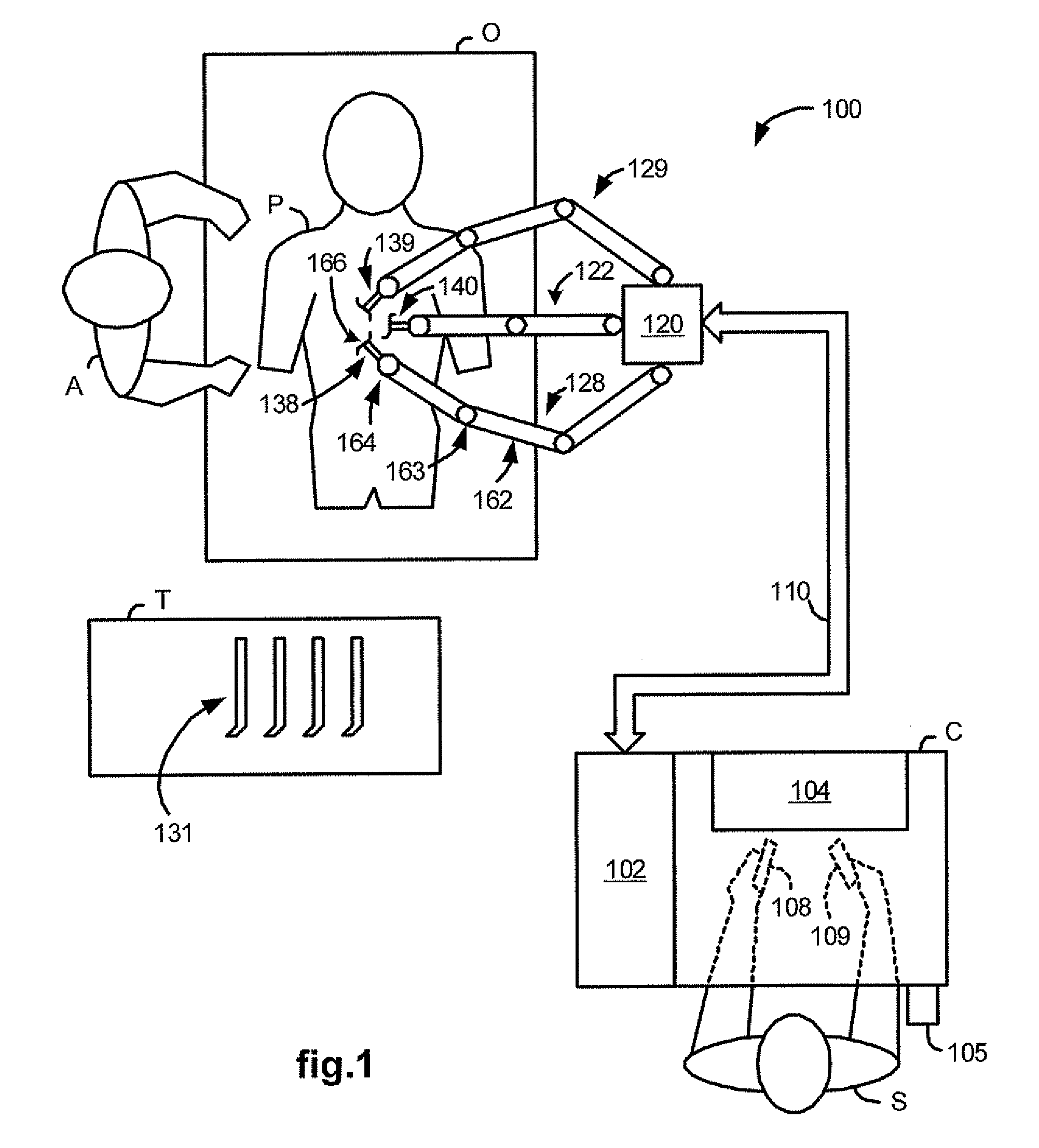
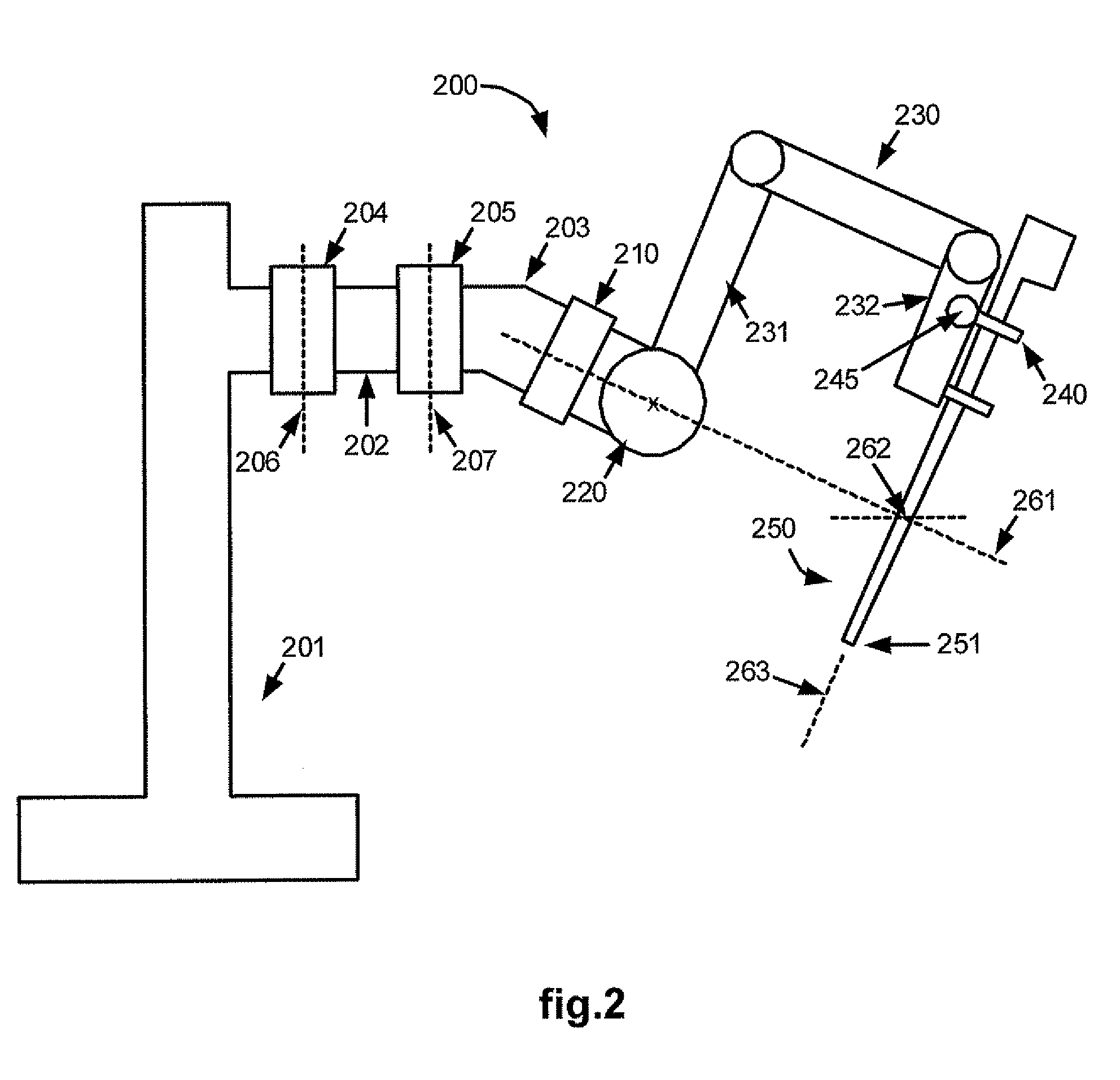
Medical robotic system with sliding mode control
ActiveUS7453227B2Reduces stick-slip behaviorProgramme-controlled manipulatorComputer controlRobotic armControl system
A medical robotic system has a joint coupled to medical device or a slave manipulator or robotic arm adapted to hold and / or move the medical device for performing a medical procedure, and a control system for controlling movement of the joint according to user manipulation of a master manipulator. The control system includes at least one joint controller having a sliding mode control for reducing stick-slip behavior on its controlled joint during fine motions of the joint. The sliding mode control computes a distance to a sliding surface, computes a reaching law gain, and processes the distance and reaching law gain to generate a sliding mode control action that is in absolute value less that a maximum desired feedback control action. The sliding mode control action is then further processed to generate a feedback torque command for the joint motor.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
Medical robotic system with sliding mode control
ActiveUS20070138992A1Reduces stick-slip behaviorProgramme-controlled manipulatorComputer controlRobotic systemsRobotic arm
A medical robotic system has a joint coupled to medical device or a slave manipulator or robotic arm adapted to hold and / or move the medical device for performing a medical procedure, and a control system for controlling movement of the joint according to user manipulation of a master manipulator. The control system includes at least one joint controller having a sliding mode control for reducing stick-slip behavior on its controlled joint during fine motions of the joint. The sliding mode control computes a distance to a sliding surface, computes a reaching law gain, and processes the distance and reaching law gain to generate a sliding mode control action that is in absolute value less that a maximum desired feedback control action. The sliding mode control action is then further processed to generate a feedback torque command for the joint motor.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
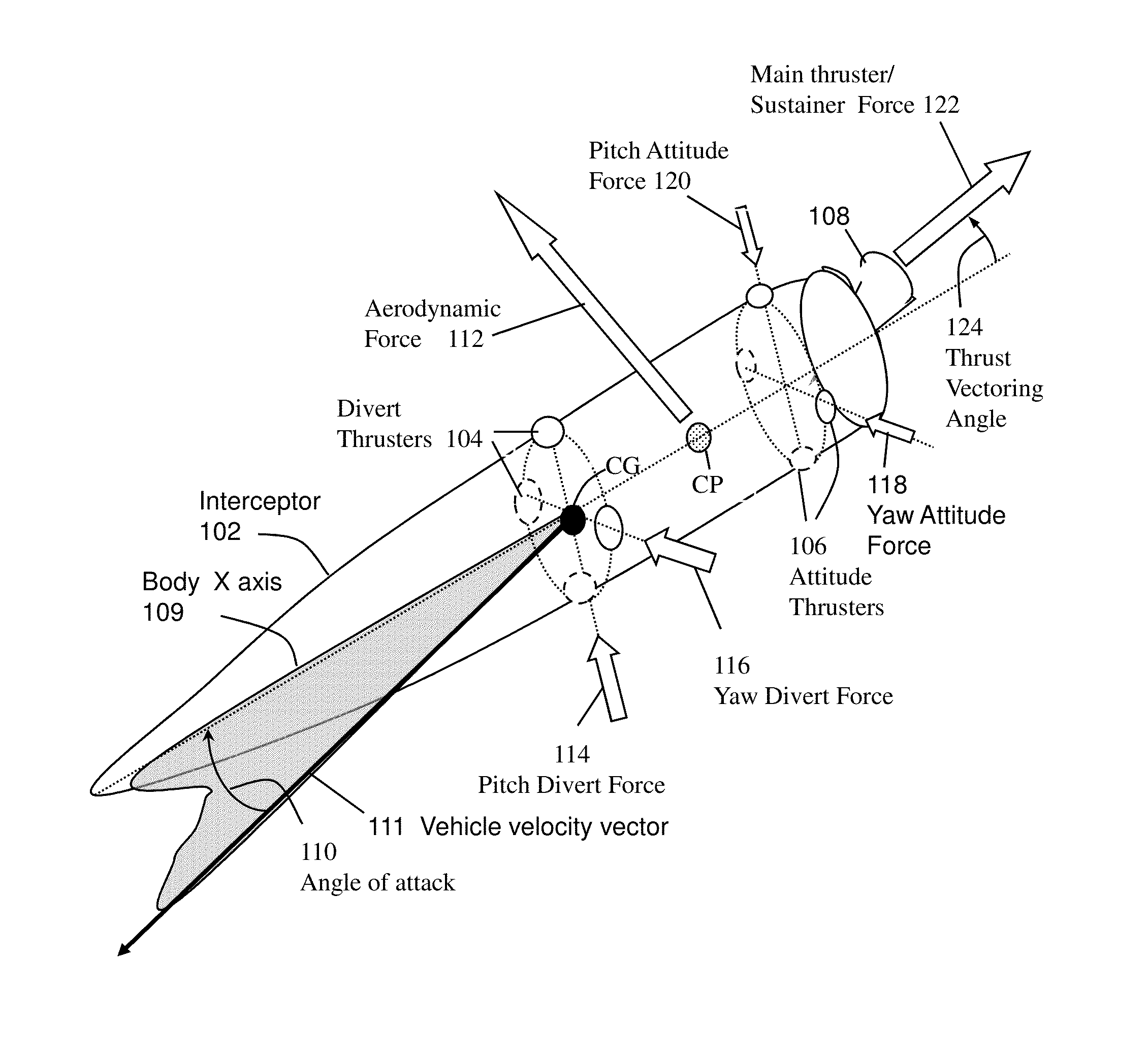
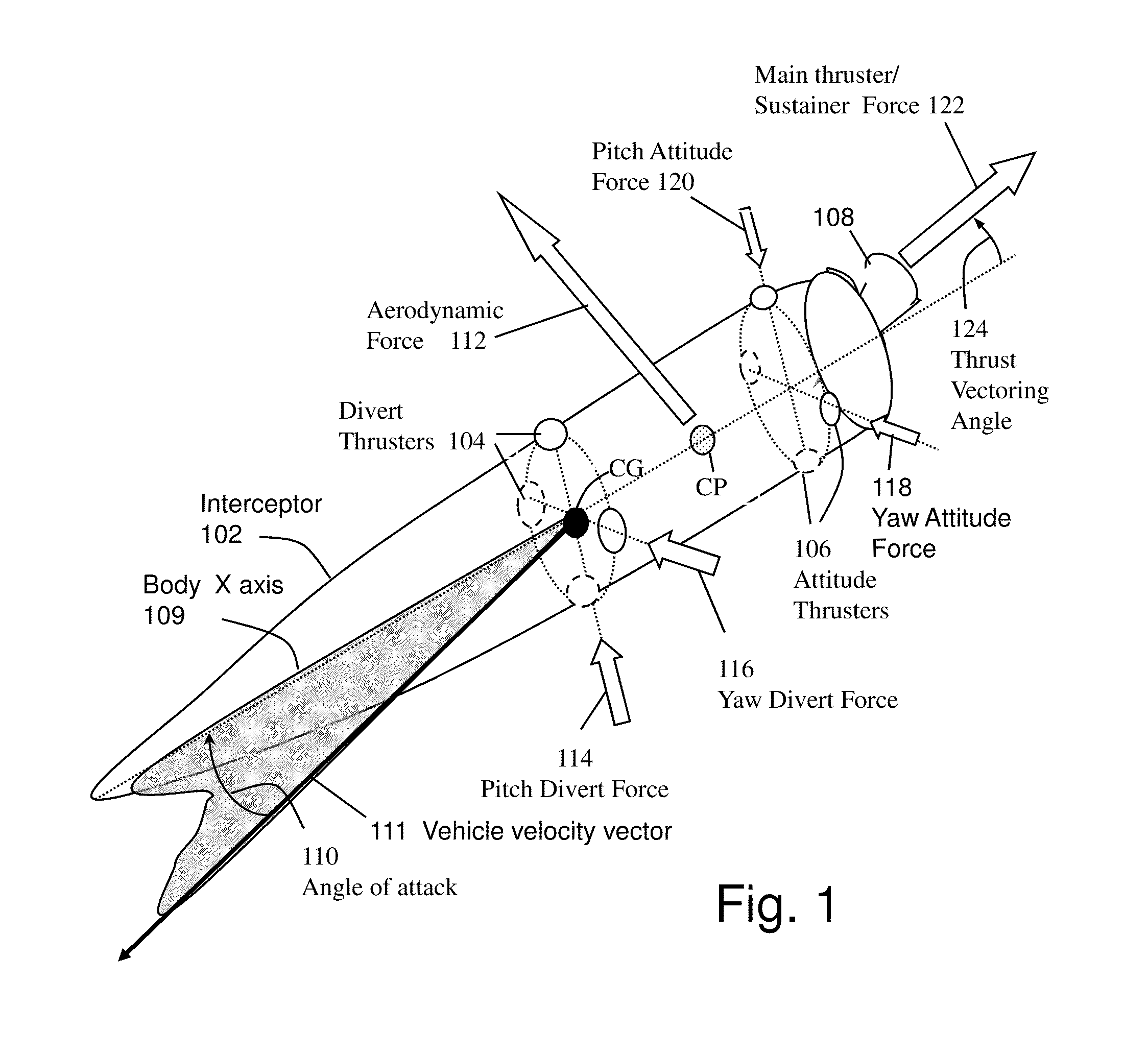
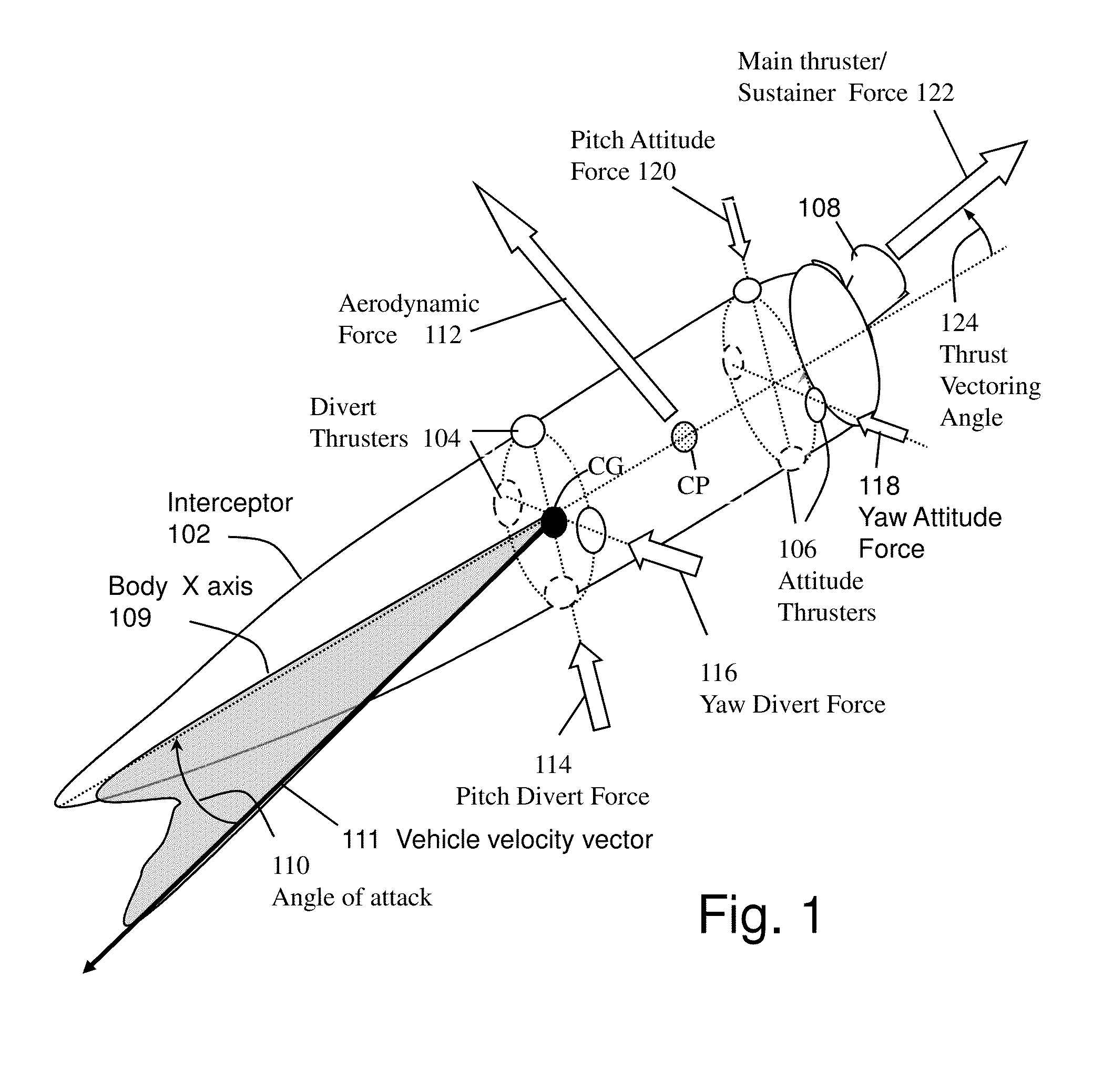
System and method for guiding and controlling a missile using high order sliding mode control
ActiveUS20130092785A1Reduce needPromote resultsDirection controllersTarget-seeking controlCouplingQuaternion
Higher Order Sliding Mode (HOSM) control techniques are applied to the Guidance Control (G&C) of interceptor missile in which velocity may be steered by combination of main thrust, aerodynamic lift and lateral on-off divert thrusters, and attitude may be steered by continuous or on-off actuators. Methods include the pointing of the seeker, its associated estimation processes, a guidance law that uses concurrent divert mechanisms, and an attitude autopilot. The insensitivity of the controller to matched disturbances allows the concurrent usage of the divert mechanisms without adverse effect on the accuracy. The controller also allows the de-coupling of the control of roll, pitch and yaw channels, and usage quaternions to represent body attitude and it provides control perfect robustness. While it conceivable to design separately the components of the G&C method, it is widely accepted that designing them in an integrated fashion usually produces a better result.
Owner:DAVIDSON TECH
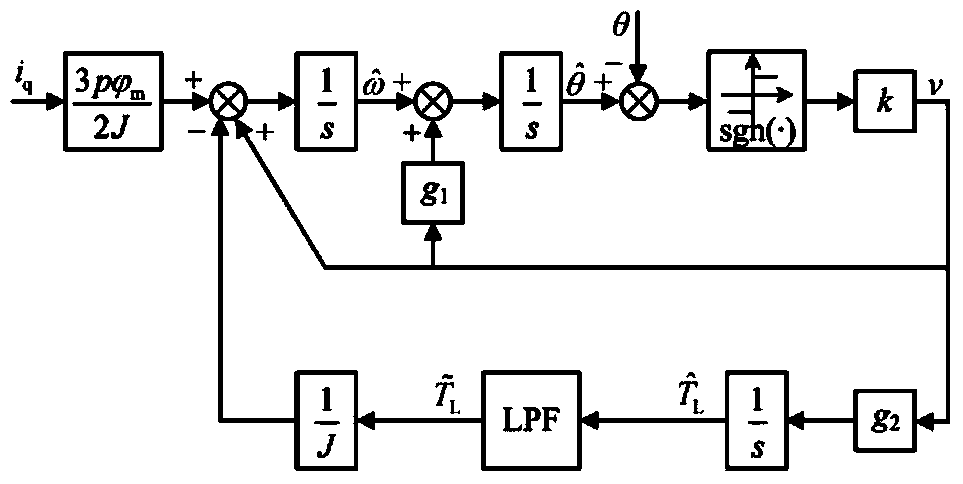
Permanent magnet motor sliding mode control strategy
ActiveCN103647490AReduce the valueSolve chattering problemsElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsControl vectorLoop control
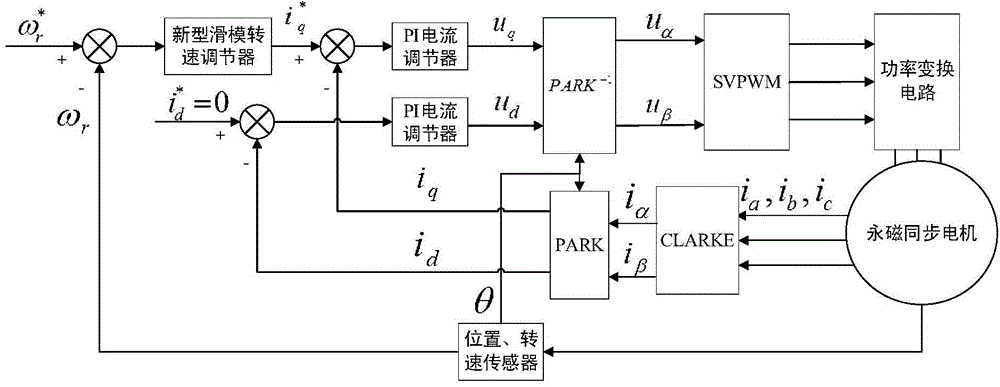
The invention pertains to the technical field permanent magnet motors, and relates to a permanent magnet motor sliding mode control strategy. The permanent magnet motor is controlled by adopting double-closed speed current. The permanent magnet motor sliding mode control strategy is characterized in that a sliding mode speed controller and an extended sliding mode observer are adopted in the control strategy, the sliding mode speed controller adopts an exponential approach law containing the speed error and the sliding mode surface information, the deviation between a given rotating speed and a feedback rotating speed is taken as the input quantity, and a q-axis current given value is outputted through the sliding mode control quantity; the extended sliding mode observer is used to estimate the rotor position, the rotating speed and the load torque on a real-time basis, the rotating speed and the rotor position are used to provide the information of speed closed-loop control and coordinate transformation, and the load torque is compensated to the sliding mode speed controller, so that the high-accuracy vector control of the permanent magnet motor can be realized. The control strategy of the invention can be used to make the system fast track a given speed in the dynamic state, reduce the speed overshoot and the current fluctuation, and improve the disturbance resistance performance of the system.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
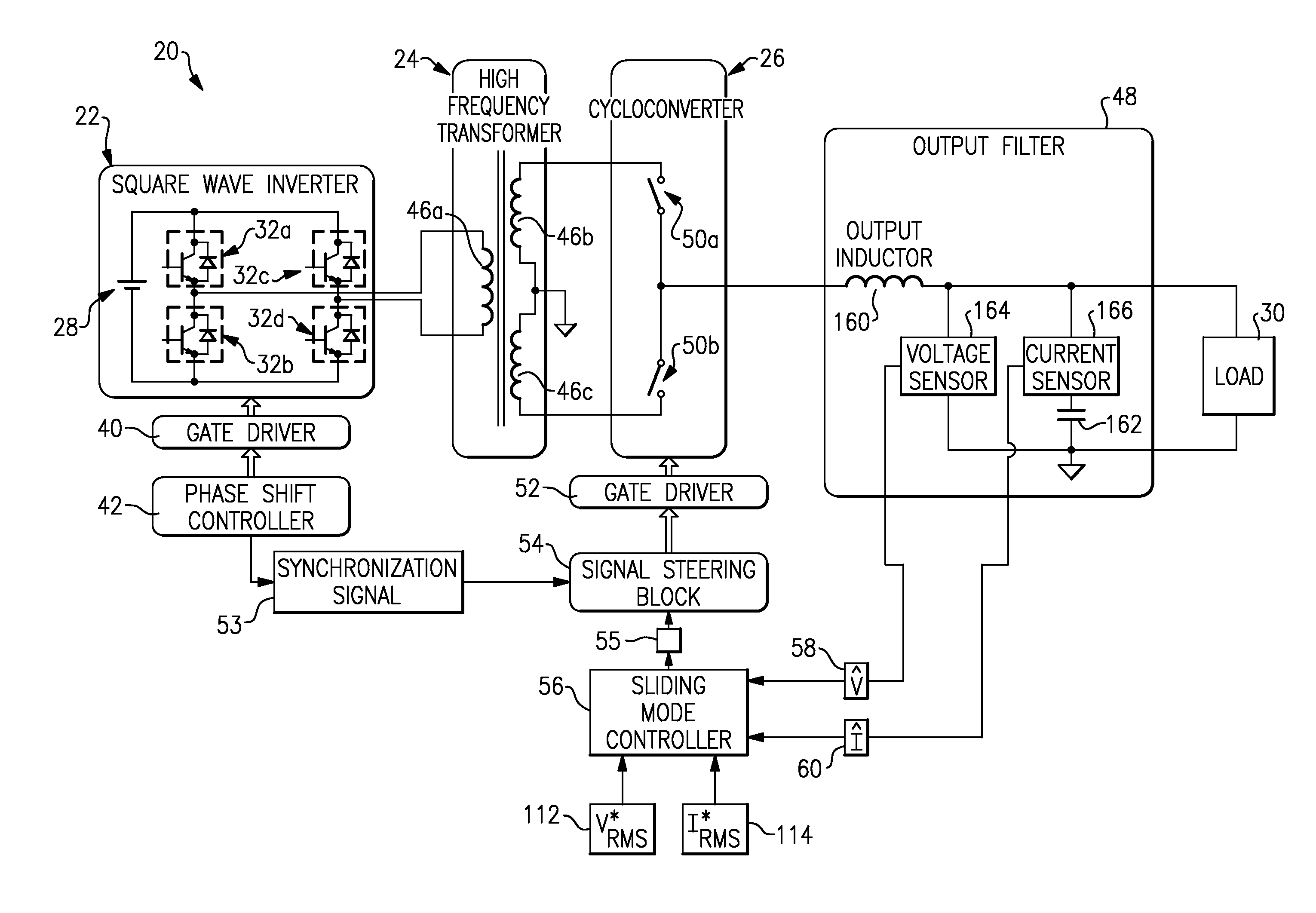
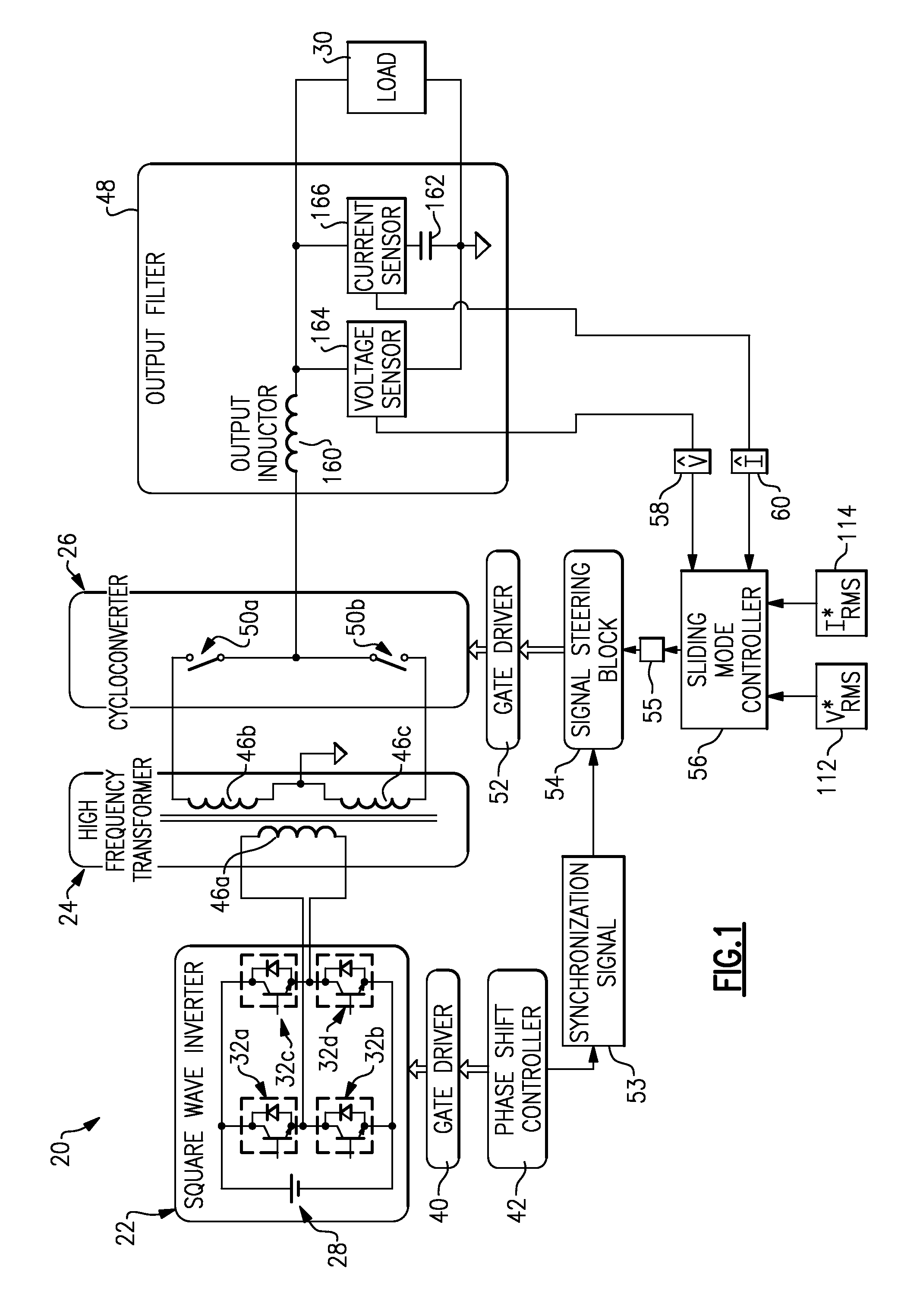
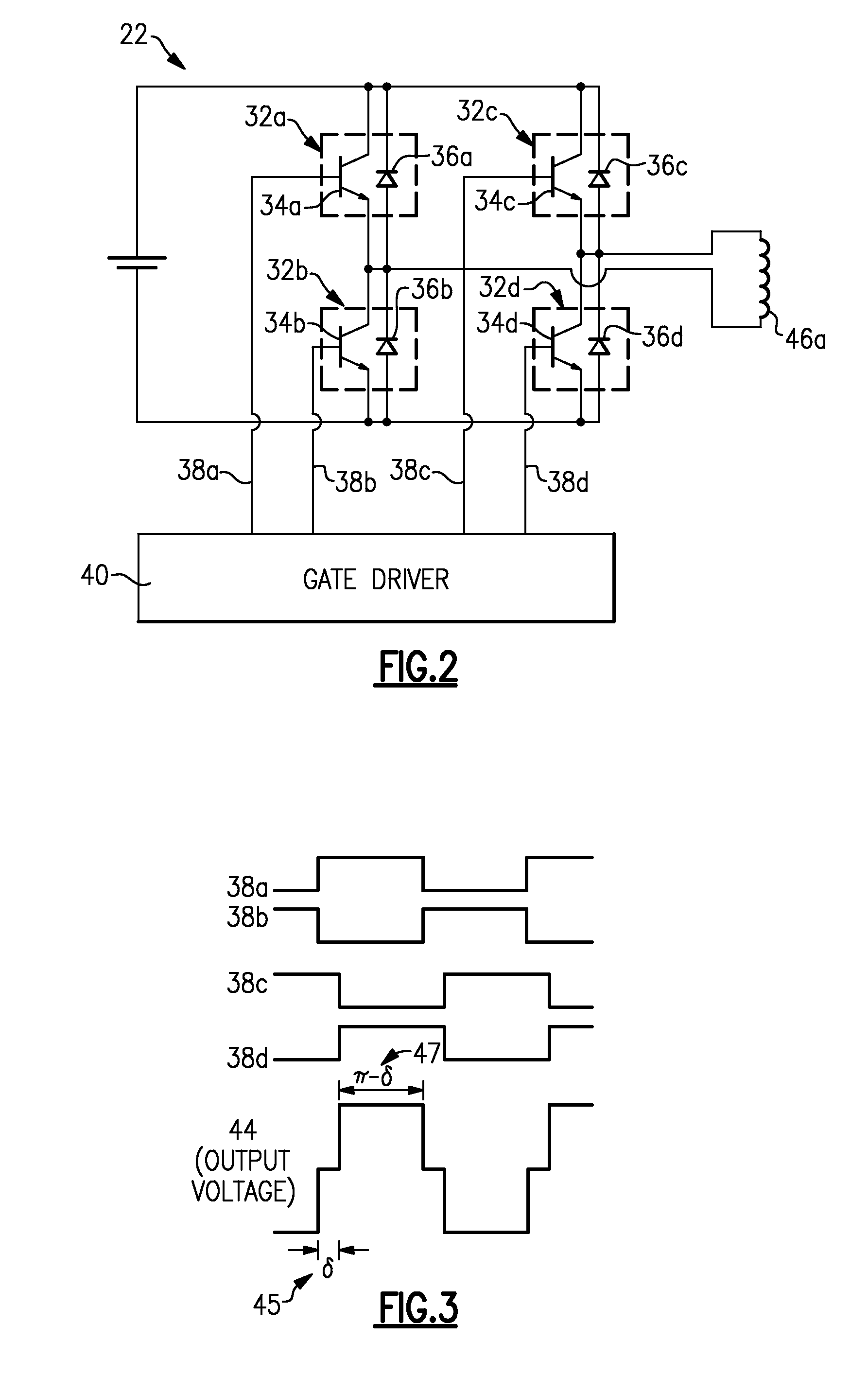
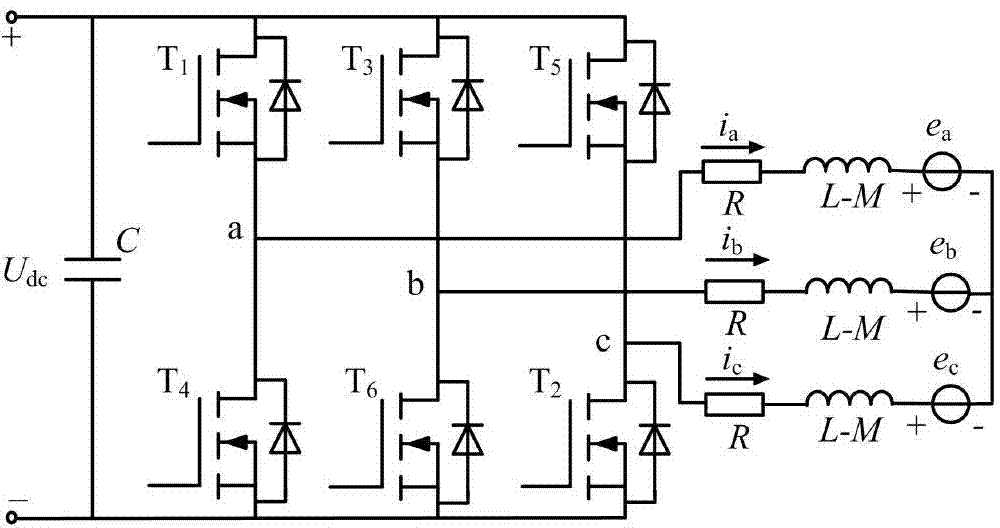
Power-conversion control system including sliding mode controller and cycloconverter
ActiveUS20100284208A1Minimize the differenceElectric devicesConversion without intermediate conversion to dcControl systemControl signal
A power-conversion control system includes an inverter, a cycloconverter, and a sliding mode controller. The inverter is operable to receive a DC voltage input and produce a first AC voltage output having a first frequency. The cycloconverter has a plurality of bidirectional switches, and is operable to receive the first AC voltage and to synthesize a second AC voltage having a second frequency that is lower than the first frequency. The sliding mode controller is operable to provide a control signal to command the plurality of bidirectional switches to turn OFF and ON when the first AC voltage is at a zero crossing condition. The sliding mode controller is also operable to selectively adjust the frequency and amplitude of the second AC voltage.
Owner:HAMILTON SUNDSTRAND CORP
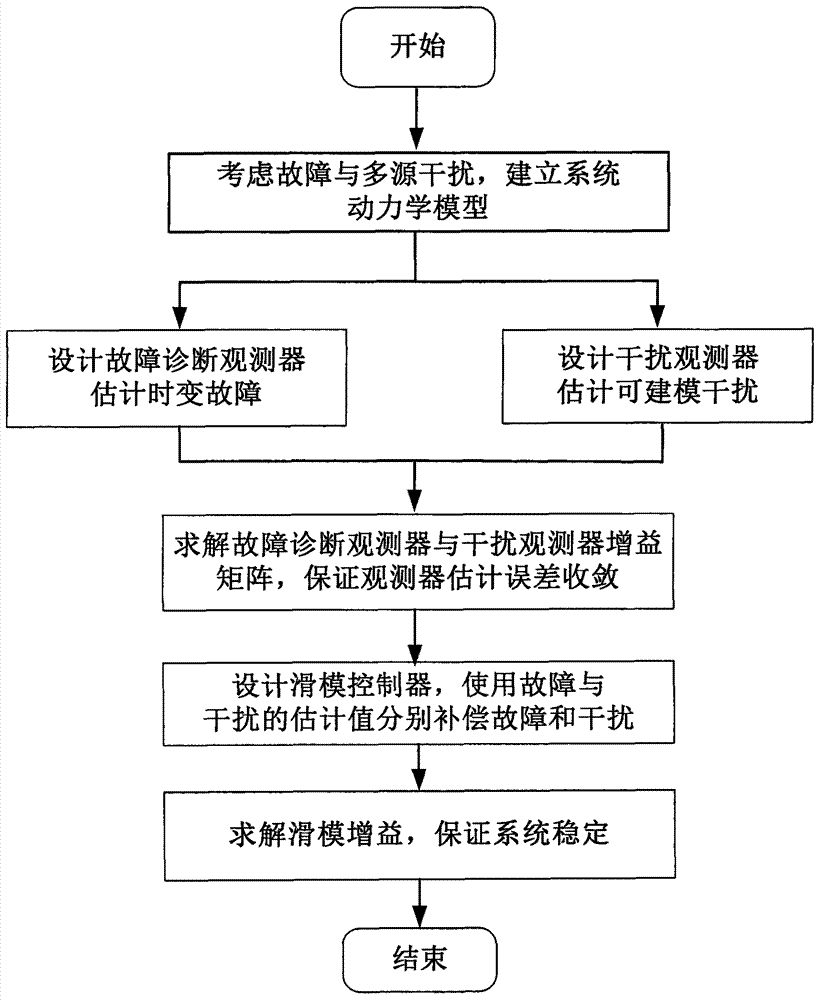
Sliding-mode control method with anti-interference fault-tolerance performance
Provided is a sliding-mode control method with anti-interference fault-tolerance performance. A sliding-mode controller with anti-interference fault-tolerance performance is designed and is specific to a system containing faults and interferences. Firstly, faults and multi-source interferences in the system are considered, so that a dynamical model of the system is established. Secondly, a fault diagnosis observer and a disturbance observer are designed to estimate the faults and interferences capable of being modeled. Thirdly, the gain matrix of the disturbance observer and the fault diagnosis observer is solved. Then, the sliding-mode controller is designed to offset faults and interferences respectively by using the estimated value of faults and interferences. Finally, stability of the controller is analyzed and the sliding-mode yield value is determined on the premise that the system input is saturated. According to the sliding-mode control method with anti-interference fault-tolerance performance, the anti-interference and fault-tolerance performance of the system are guaranteed, the buffeting of the sliding-mode control is improved, and the sliding-mode control method can be applied to the attitude control system of the fields of aviation, aerospace and deep space exploration.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
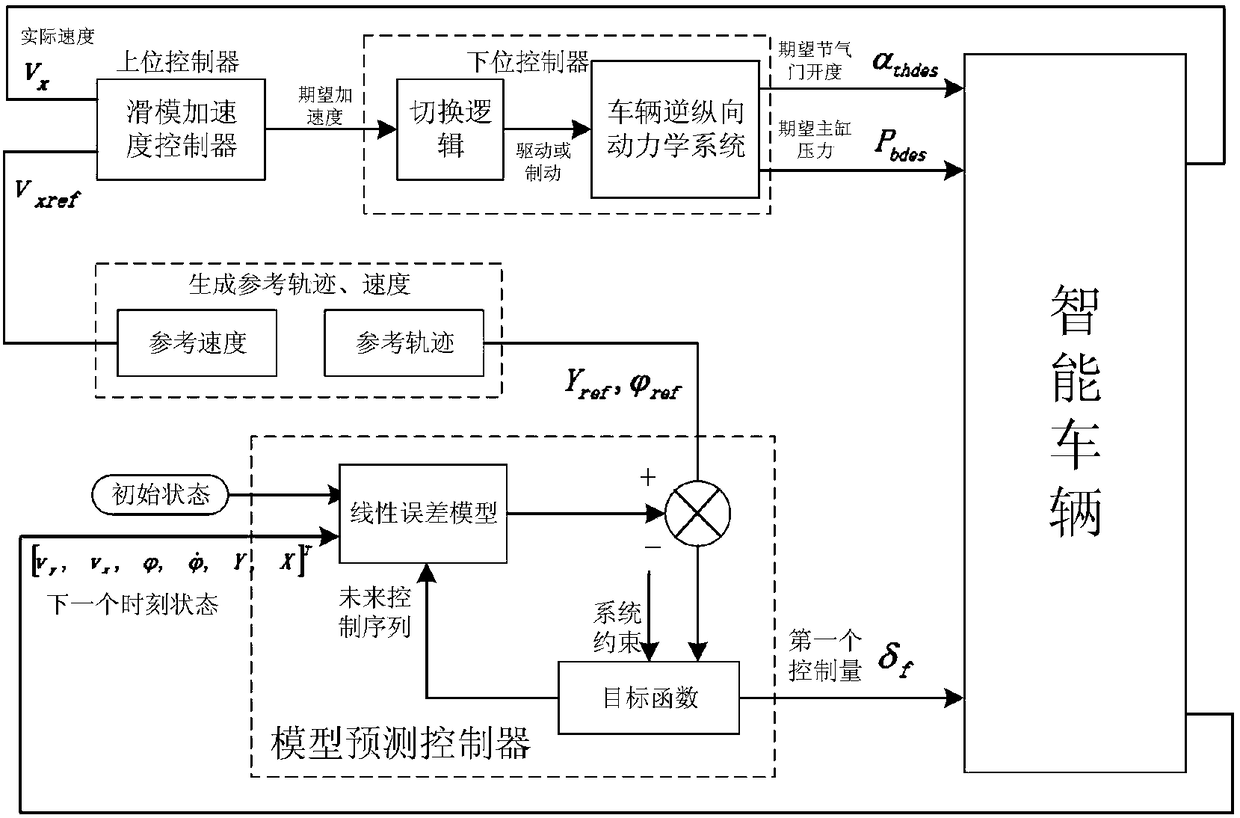
Horizontal and vertical coordination control method for trajectory tracking of intelligent vehicle
InactiveCN108248605AImprove lateral stabilityRealize longitudinal speed tracking controlControl devicesControl systemModel predictive control
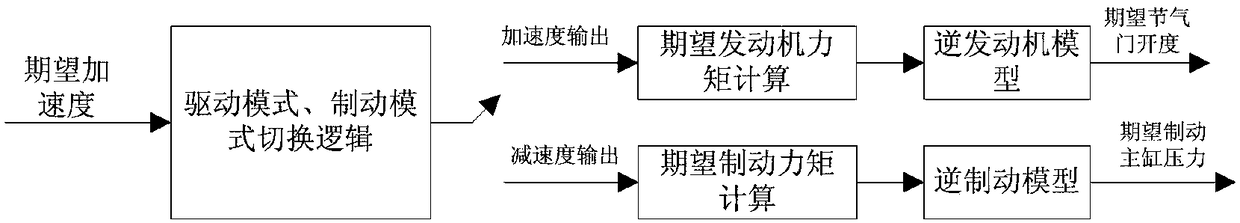
The invention relates to a horizontal and vertical coordination control method for trajectory tracking of an intelligent vehicle. For association and coupling characteristics of horizontal and vertical dynamics of the intelligent vehicle, a horizontal and vertical coordination controller for trajectory tracking of the intelligent vehicle is designed. By applying a model prediction control and sliding mode control algorithm, the opening degree of a throttle valve of an engine, the pressure of a main braking cylinder and the deflection angle of a front wheel are cooperatively controlled. In thedesign of a horizontal MPC, the state amount of the vehicle is selected at the formula which is shown in the description, and the state amount (vertical speed vx) is real-time changable vehicle speedoutput by the vehicle after vertical control; vy is a horizontal speed at the mass center of the vehicle; the formulas which are shown in the description are the heading angle and heading angle speedat the mass center of the vehicle; Y and X are a horizontal position and a vertical position under world coordinates. According to a horizontal and vertical coordination control system, the intelligent vehicle efficiently and stably tracks an expectation trajectory at the expected speed. Large-steering operation can be remarkably improved, and the horizontal stability of the intelligent vehicle inthe trajectory tracking process is improved.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Non-cooperative spacecraft attitude estimation method based on virtual sliding mode control
InactiveCN104406598AAccurate timingSmall amount of calculationInstruments for comonautical navigationMode controlVirtual slide
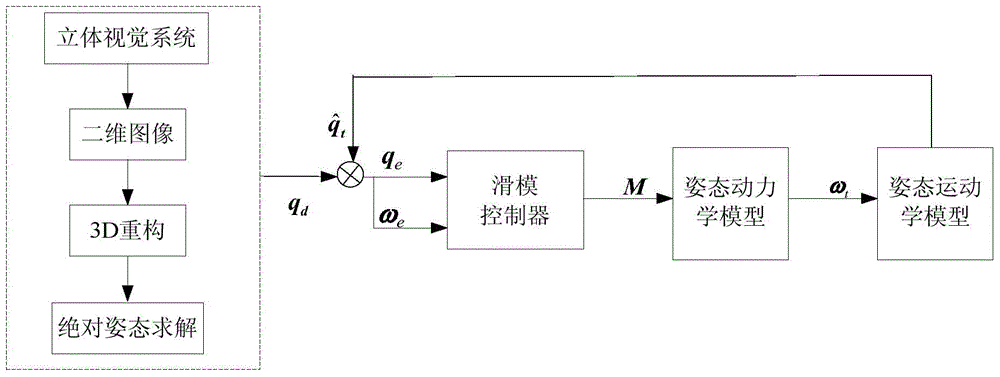
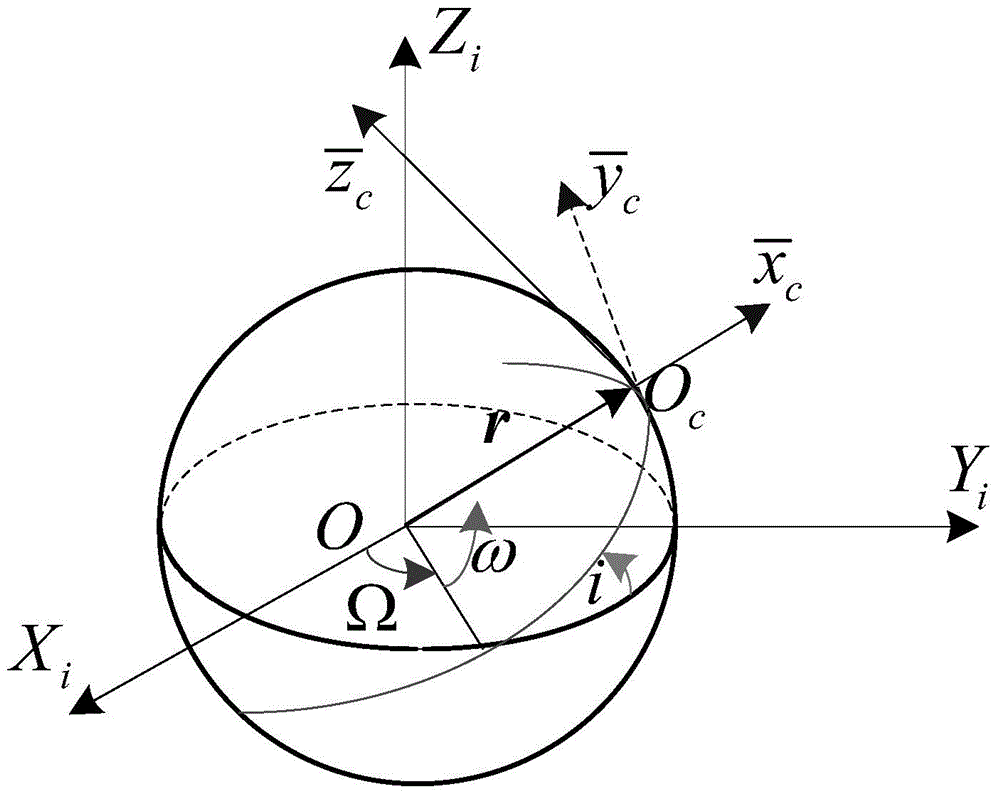
The invention discloses a non-cooperative spacecraft attitude estimation method based on virtual sliding mode control, and belongs to the technical field of non-cooperative spacecraft navigation. The non-cooperative spacecraft attitude estimation method comprises the following steps: utilizing a virtual control sliding mode controller based on the Lyapunov principle; using target satellite absolute attitude obtained by a stereoscopic vision system as a control objective; according to motion characteristics of the target satellite, establishing a virtual satellite motion model of the target satellite; using a kinetic model of the virtual satellite as a controlled member to obtain attitude parameters of the virtual satellite; using attitude parameters estimated by the virtual satellite and the target satellite absolute attitude obtained by the stereoscopic vision system as controlled input, and calculating the virtual revolving moment on the motion model of the virtual satellite through the virtual sliding mode controller, so as to realize the estimation of the target satellite attitude parameters by the virtual control sliding mode controller. The non-cooperative spacecraft attitude estimation method disclosed by the invention is low in calculated amount, and can still achieve higher convergence rate and higher precision when the initial error of the state variables is high or the system error emerges, so as to meet the requirements of the high performance navigation system.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
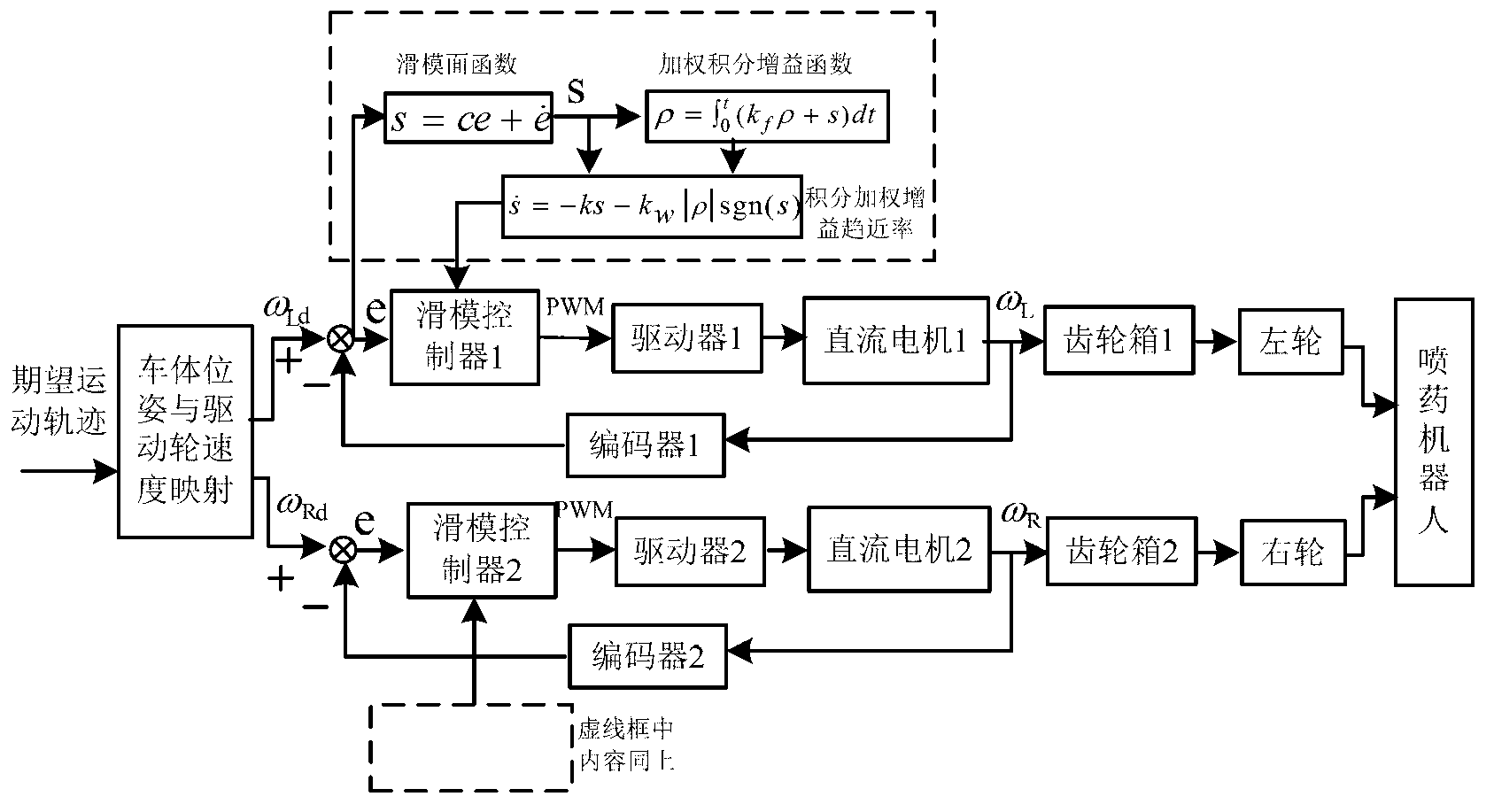
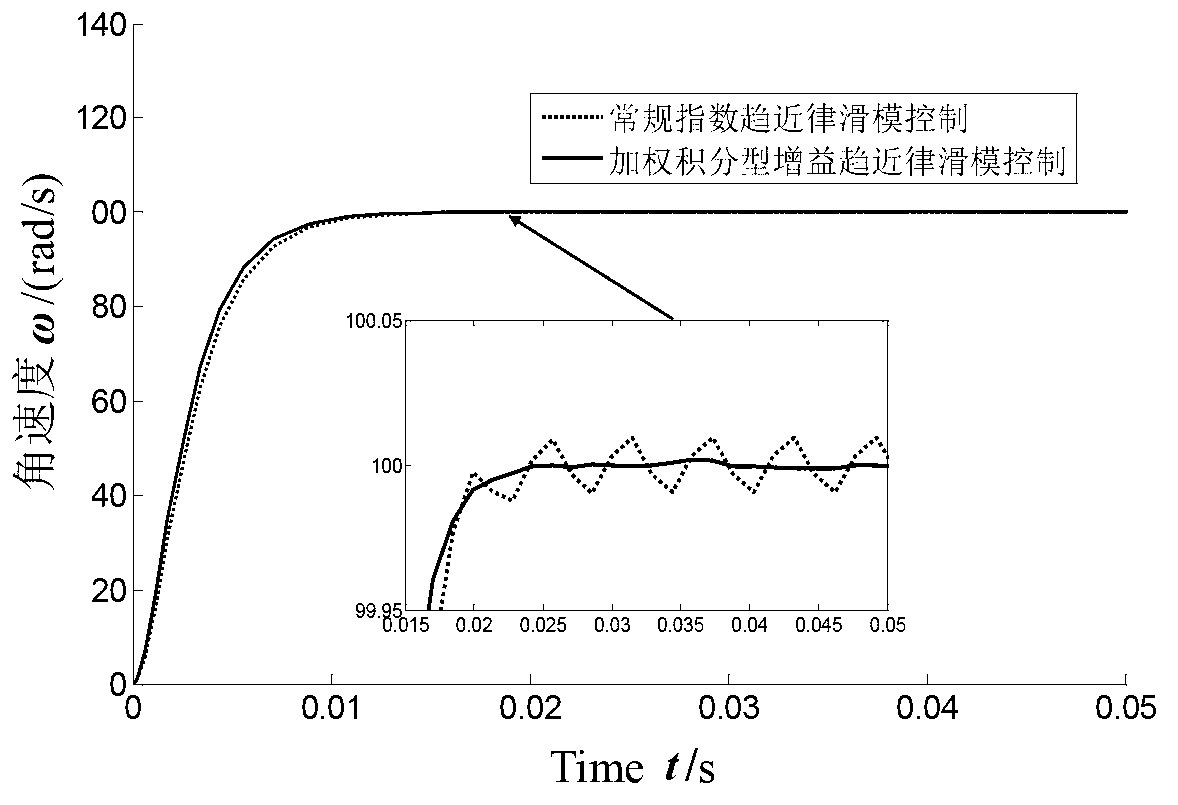
Trajectory tracking sliding mode control system and control method for spraying mobile robot
InactiveCN103019239ANon-linearWith couplingPosition/course control in two dimensionsDrive motorAngular acceleration
The invention discloses a trajectory tracking sliding mode control method for a spraying mobile robot. The method comprises the following steps of: performing mechanism analysis on a mobile robot, and establishing a mobile robot kinematic model with non-integrity constraint; establishing a controlled object mathematical model of each branch controller of a wheeled mobile robot provided with a motor driving shaft disturbance term; identifying a traveling path by utilizing a computer vision system, and determining an expected motion track of each branch driving motor according to the kinematic model deduced in the previous step; detecting the rotating speed of the motor, calculating the actual motion angular velocity and actual motion angular acceleration of left and right driving motors of the mobile robot, and calculating the deviation and deviation derivative between the expected angular velocity and the actual angular velocity of each driving motor; establishing a sliding mode switching function which meets the speed control requirement of the driving motor; determining the sliding mode controller control quantity of the left and right driving motors of the mobile robot on the basis of the sliding mode surface function s; and respectively transmitting the control quantity of the motor of the mobile robot to the left and right driving motors.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Mixed control method based on trace tracking of wheeled mobile robot
ActiveCN104317299AReduce the amount of controlGuaranteed stabilityPosition/course control in two dimensionsKinematicsAngular velocity
The invention discloses a mixed control method based on trace tracking of a wheeled mobile robot. A kinematic virtual velocity controller, a sliding mode torque controller and a disturbance observer are involved in the mixed control method, wherein the sliding mode torque controller and the disturbance observer are based on dynamics. The virtual velocity controller is used for designing the linear velocity and the angular velocity of the robot; the sliding mode torque controller is used for designing a sliding mode face and a sliding mode control law, and the disturbance observer is used for observation of the external disturbance of a system to reduce the control quantity of the sliding mode controller and is introduced as a feedforward term. By means of the mixed control method, control over the trace tracking of the robot is achieved by the system under the condition that external change and external disturbance happen to a parameter. It is shown upon simulation experiments that by means of the mixed control method, chatter output by sliding mode control and output of the control quantity can be effectively reduced, and good robustness is achieved.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Reentry aircraft finite time control method based on disturbance observer
The invention discloses a reentry aircraft finite time control method based on a disturbance observer and relates to the reentry aircraft finite time control method. The reentry aircraft finite time control method belongs to the field of aircraft control technology. The reentry aircraft finite time control method comprises the following steps: a first step, establishing a reentry aircraft dynamic model, presenting a finite time gesture tracking task; a second step, performing feedback linear processing on a model which is established in the first step; a third step, providing a finite time control law; a fourth step, providing a finite time disturbance observer for estimating system uncertainty and outer disturbance; and a fifth step, providing a finite time global sliding mode control method based on the disturbance observer, and effectively improving tracking precision of a gesture control system through substituting an estimated disturbance value into the control law. The reentry aircraft finite time control method has functions of improving system error convergence speed, preventing a singular problem and improving uncertainty of the controlled system to the parameter, global robustness of outer disturbance and tracking precision.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
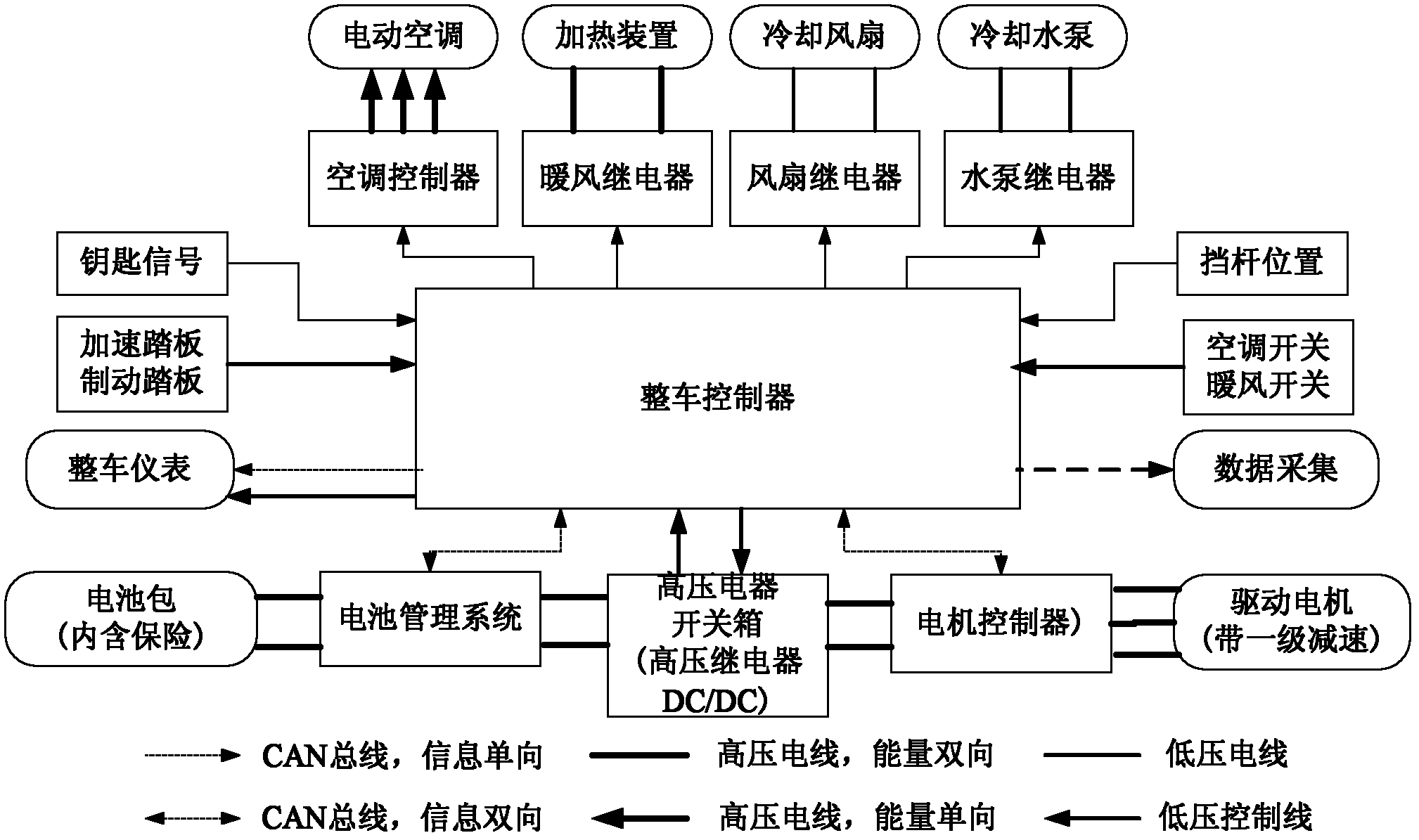
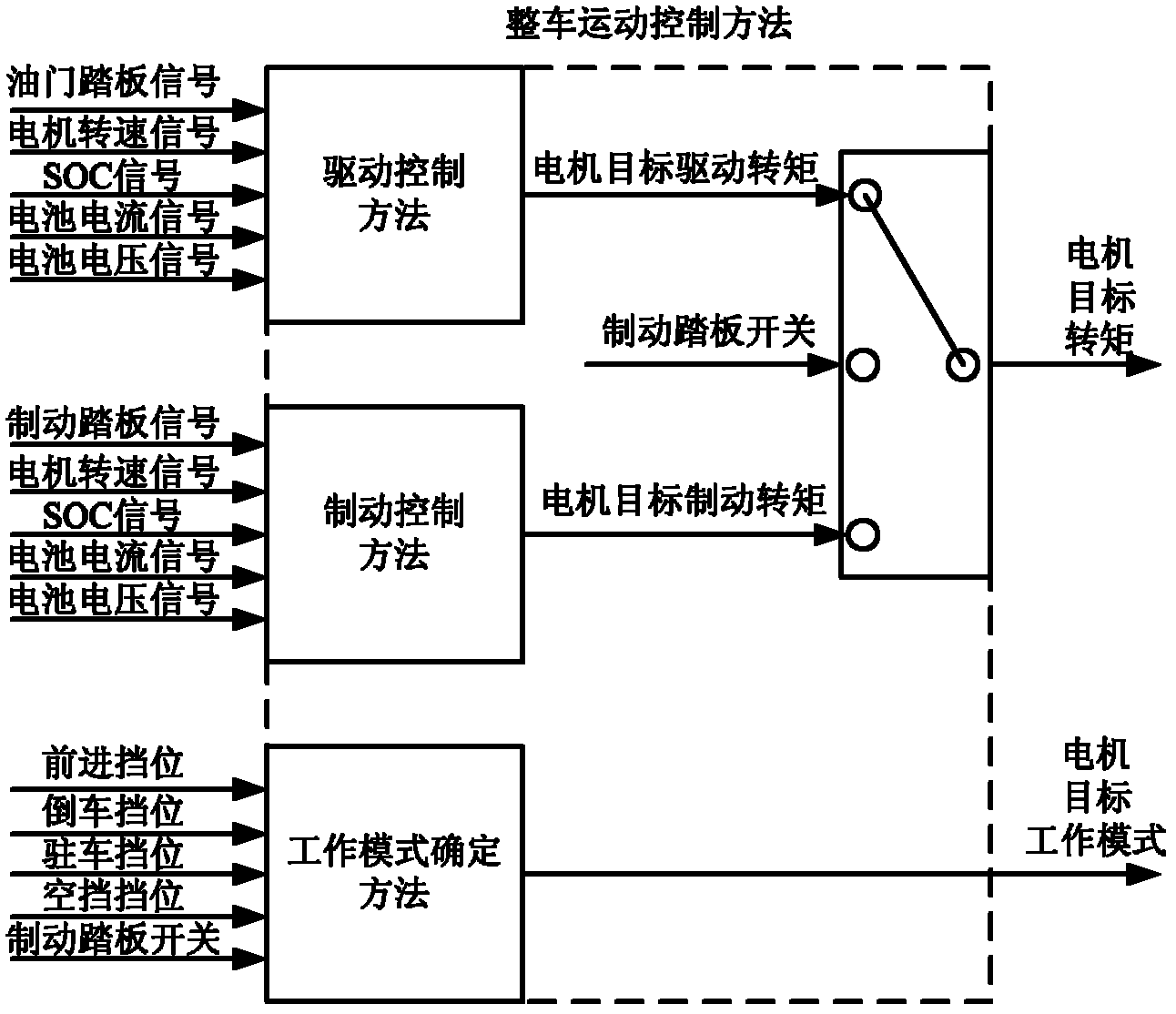
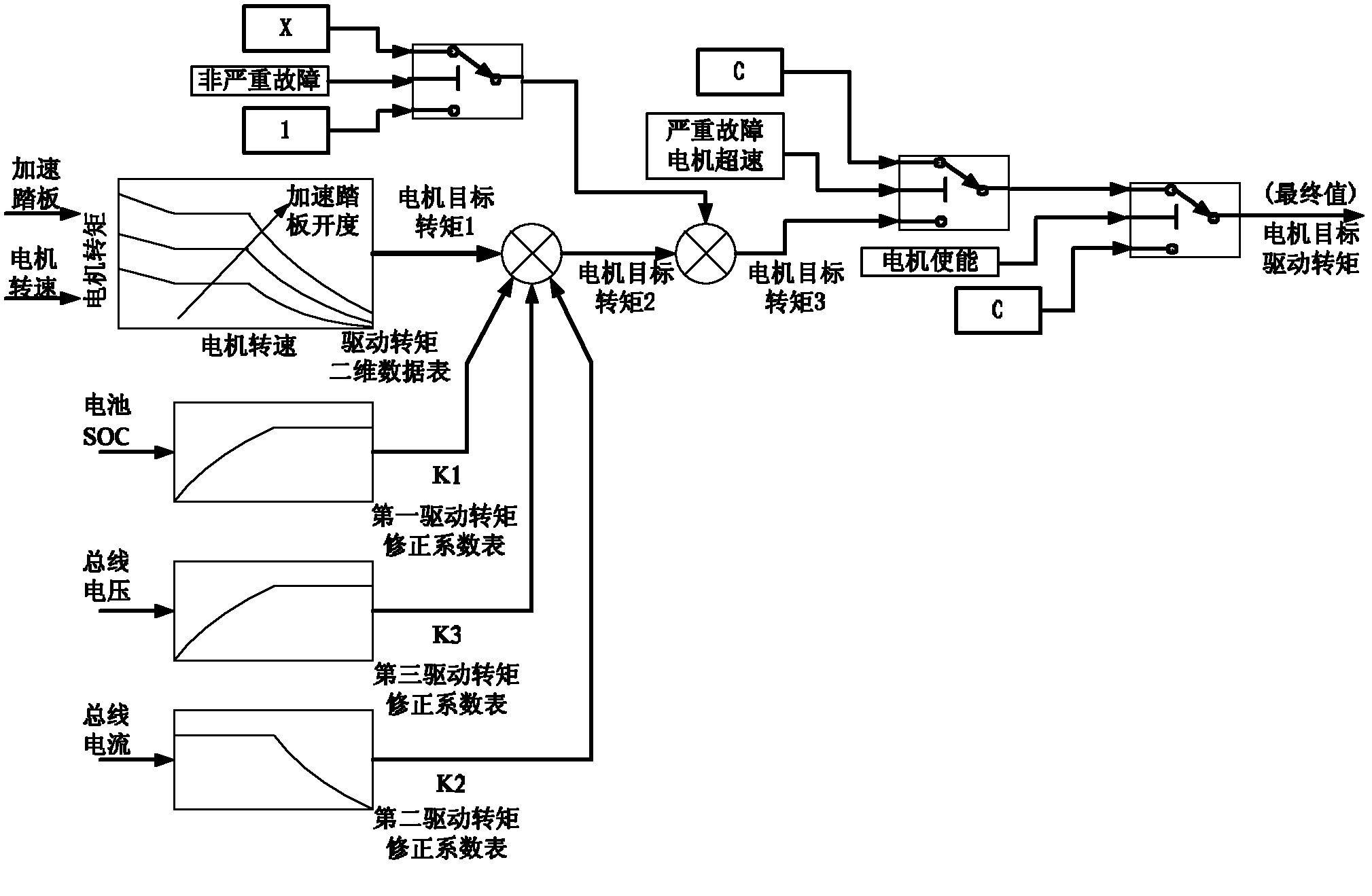
Pure electric automobile movement control method
ActiveCN102431466AConsistent operationEasy shifting logicSpeed controllerElectric energy managementElectrical batteryMode control
A pure electric automobile movement control method is characterized by comprising driving control, braking control and working mode control. The driving control method comprises the steps of: obtaining a target driving torque of a motor by regarding an aperture signal of an accelerator pedal and a motor rotating speed signal as an input; and then correcting the target driving torque of the motor according to a battery charge state, a battery current and a bus voltage fed back by a control area network (CAN) bus. The braking control method comprises the steps of: obtaining a target braking torque according to the braking pedal signal and the motor rotating speed signal; and then correcting the target braking torque of the motor according to the battery charge state, a battery current signal and a battery voltage signal fed back by the CAN bus. The working mode control method comprises the steps of: determining by combining current state of the motor according to a gear signal acquired by a whole automobile controller; and sending the motor target torque and the motor target working mode to the CAN bus by the whole automobile controller to control the movement of the automobile.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRICAL ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
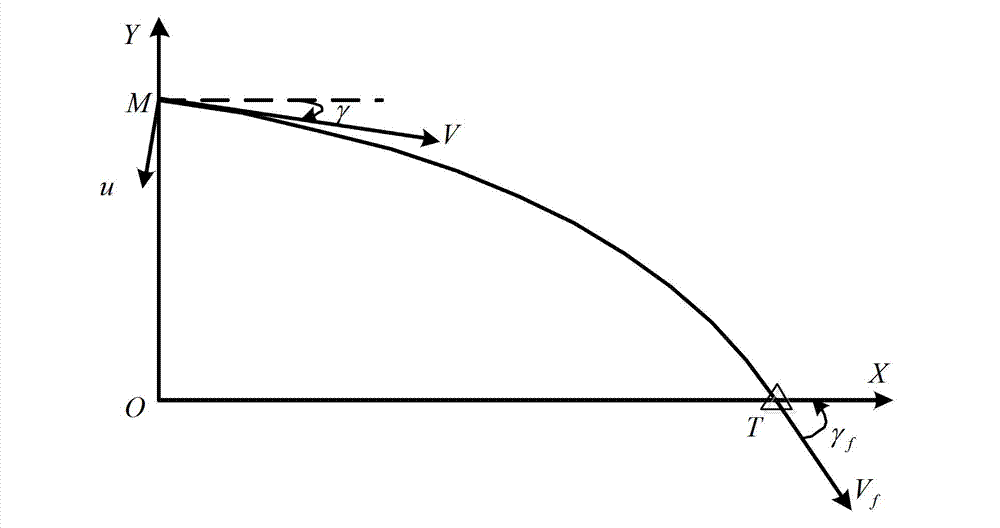
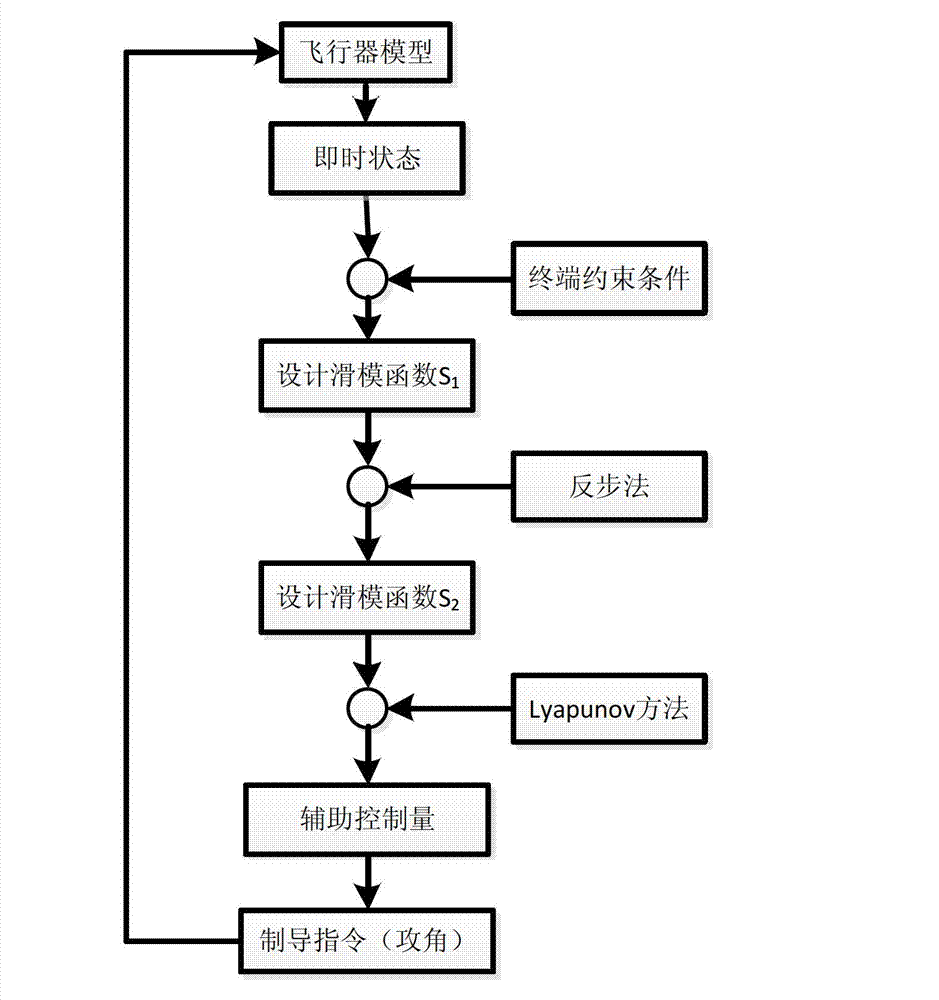
Tail angle restraining guidance method based on sliding mode control
InactiveCN103090728AEasy to trackLess information requiredAiming meansDifferential coefficientKinematics
The invention relates to a tail angle restraining guidance method based on sliding mode control, and belongs to the technical field of guidance. Firstly, a novel aircraft kinematics and dynamics model is built, then tail time is guided, distance between aircraft position coordinates and target position coordinates (xf, yf) is minimum, an expected tail end trajectory dip angle gamma f is a designed target, according to a back stepping method, a virtual control volume is designed to enable a sliding mode function and a differential coefficient to be simultaneously up to 0 in the tail time of flying, and according to Lyapunov method, trajectory dip angle change rate gamma' of an auxiliary control volume is obtained in a solving mode. The trajectory dip angle change rate is converted into an attack angle alpha, an aircraft novel model which is initially built is inputted, a track of the aircraft is adjusted in a real-time mode so as to meet an expected terminal condition, and therefore tail guidance is achieved. The method considers effect of aerodynamic characteristics of the aircraft on a guidance process, is more close to an actual condition, needs little information volume, and is wide in obtained trajectory dip angle tail value range, and smooth in obtained control volume change, and an attitude control system is easy to track.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
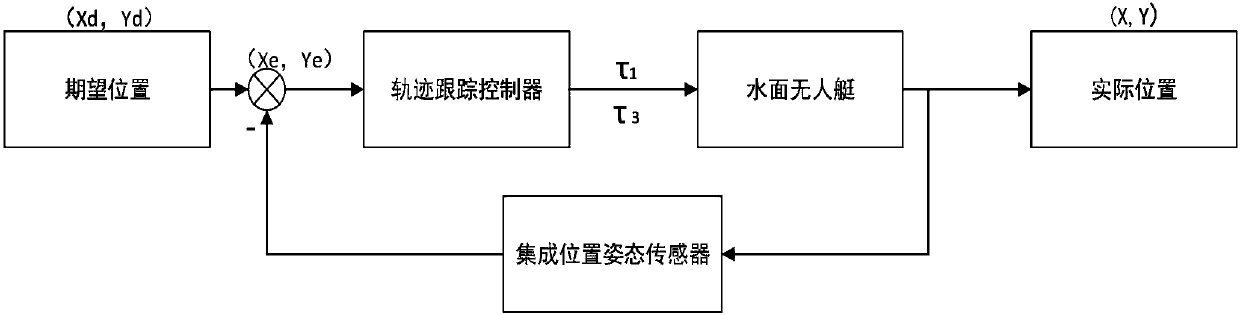
Sliding mode-reverse step double loop trace tracking control method of underactuated unmanned surface vehicle
InactiveCN108319138AMeet the requirements of straight line track tracking controlSave volume and spaceAdaptive controlPosition/course control in two dimensionsBacksteppingThree degrees of freedom
The invention discloses a method in a boat control field and especially relates to the sliding mode-reverse step double loop trace tracking control method of an underactuated unmanned surface vehicle.The method comprises the following steps of firstly, establishing a three-degree-of-freedom motion mathematical model of the heading, the surging and the swaying of the unmanned surface vehicle; then, through an integrated pose sensor, measuring the current position information of the unmanned surface vehicle, combining the real-time position and the reference trace of the unmanned surface vehicle, calculating an error under a boat body coordinate system; and then, designing a kinematic loop trace tracking controller based on a backstepping method, and designing a dynamic loop trace trackingcontroller based on a sliding mode control algorithm. Through a sliding mode-reverse step double loop trace tracking controller, the trace tracking control of the unmanned surface vehicle Is realized,the unmanned surface vehicle can track a linear trace, and the stability and accuracy of unmanned surface vehicle navigation can be increased.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
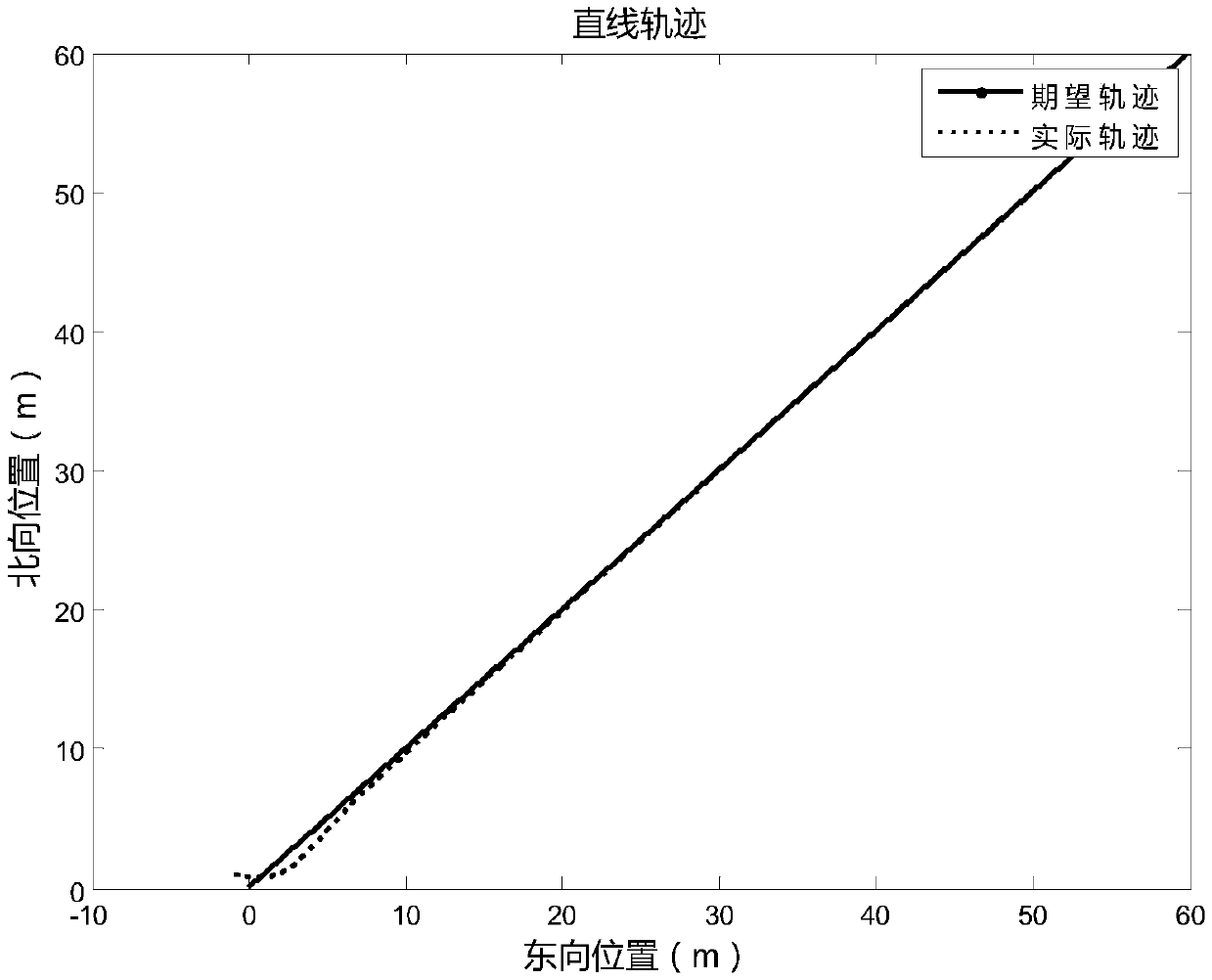
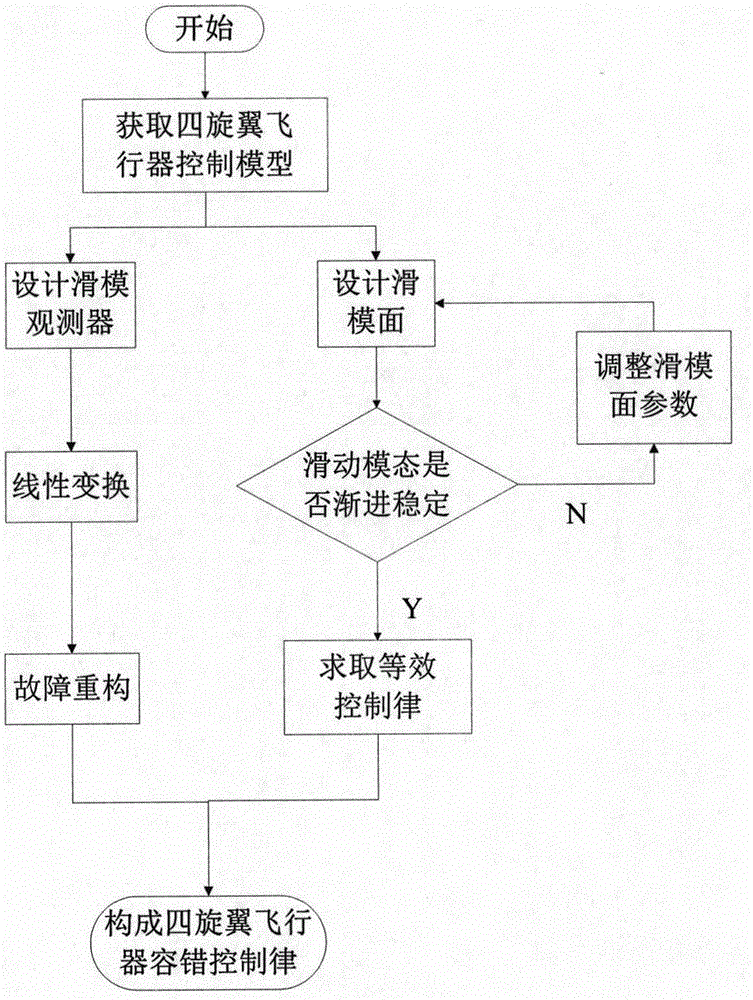
Active fault tolerance control method of four-rotor aircraft based on sliding-mode observer
InactiveCN105353615AImprove robustnessImprove practicalityAdaptive controlSliding mode controlActive fault
The invention discloses an active fault tolerance control method of a four-rotor aircraft based on a sliding-mode observer. The active fault tolerance control method is provided by considering that a performer may have faults when the four-rotor aircraft is in a state delay condition and combining the sliding-mode observer with sliding-mode control. The sliding-mode observer is designed, linear transformation is carried out on the system, faults of the performer are reconstructed on the basis of the ideal of equivalent error injection, compensation control is added into sliding-mode control by utilizing the reconstructed estimation value of the performer faults, and a complete active fault tolerance controller is formed. According to the invention, the sliding-mode observer is designed, the faults are reconstructed and estimated, online adjustment of the controller gain is realized, the provided control law is optimal, the control precision and response speed of flight of the four-rotor aircraft are effectively improved, and a design basis of the fault tolerance controller is provided for the complex four-rotor aircraft with performer faults. The method can be applied to active fault tolerance control for the four-rotor aircraft with time variation and time lag.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
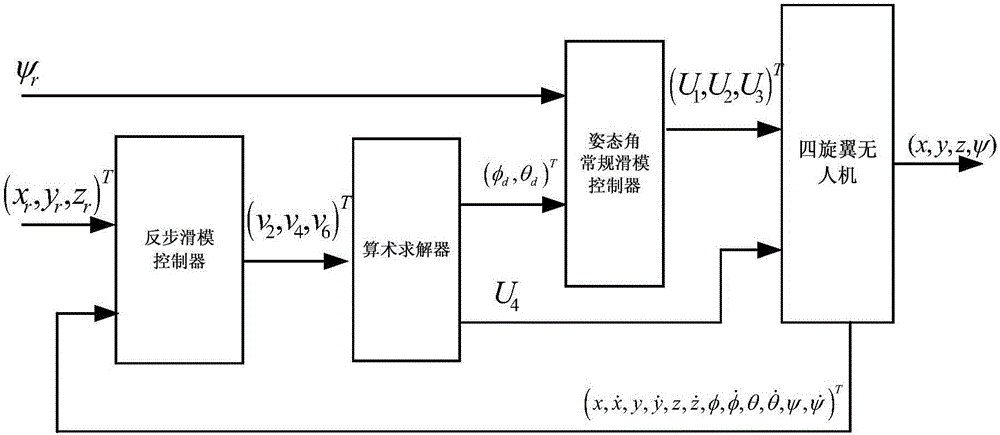
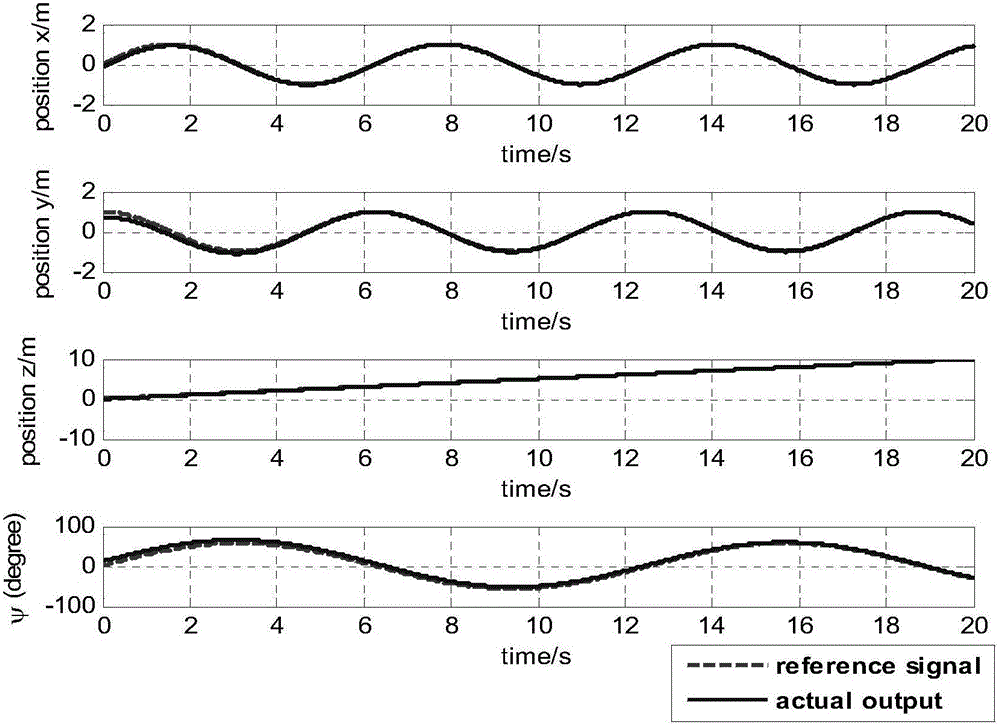
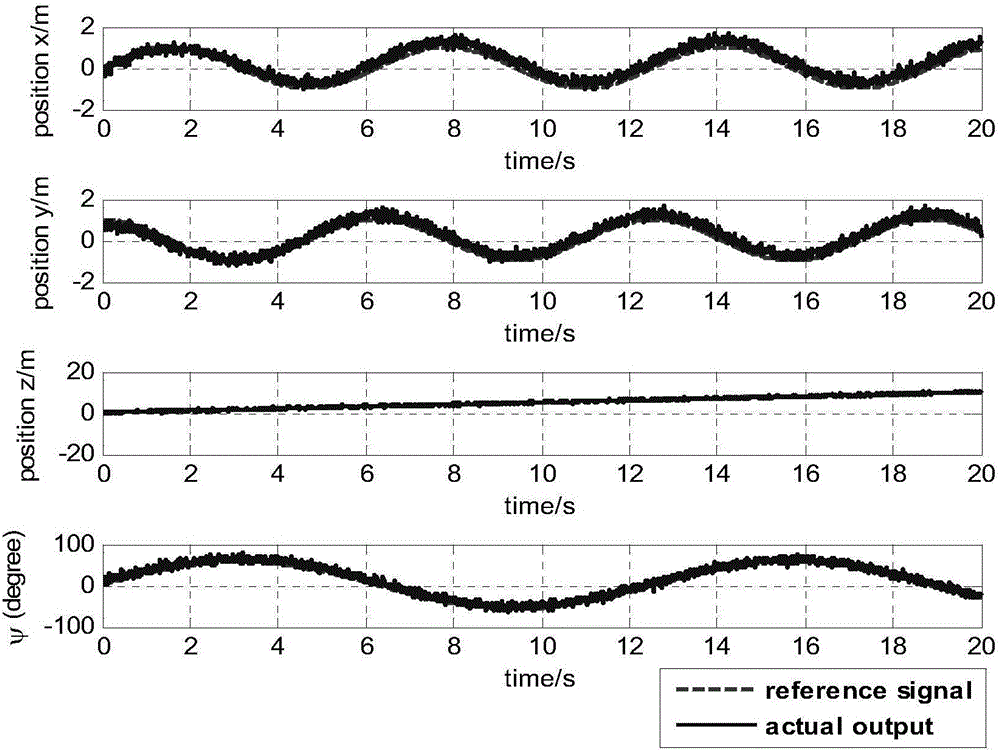
Nonlinear robust controller design method based on back-stepping and sliding mode control technologies and aimed at nonlinear model of quad-rotor unmanned plane
InactiveCN105676641AAvoid negative effectsAvoid restrictionsAttitude controlAdaptive controlSystems designNonlinear model
The invention discloses a nonlinear robust controller design method based on back-stepping and sliding mode control technologies and aimed at a nonlinear model of a quad-rotor unmanned plane. A sliding mode controller of a speed-constant reaching law is designed to an attitude angle system of the quad-rotor unmanned plane, and rapid tracking for the attitude angle is ensured. To realize track tracking for the spatial position of the quad-rotor unmanned plane, a sliding mode surface and a virtual control quantity are constructed according to a stepping back control idea to realize nonlinear control law design and system stability design from the kernel to the external layer of a system. After an equation of the related virtual control quantity is obtained, an expected track value of the attitude angle is obtained by solving the equation via arithmetic inverse operation, and a design method of the speed-constant reaching law is used to determine a final input control law of the quad-rotor unmanned plane system. According to the method of the invention, the characteristic that sliding mode control is uncertain for the model and insensitive to external interference is utilized, robust trace tracking for the nonlinear quad-rotor unmanned plane can be controlled under interference.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
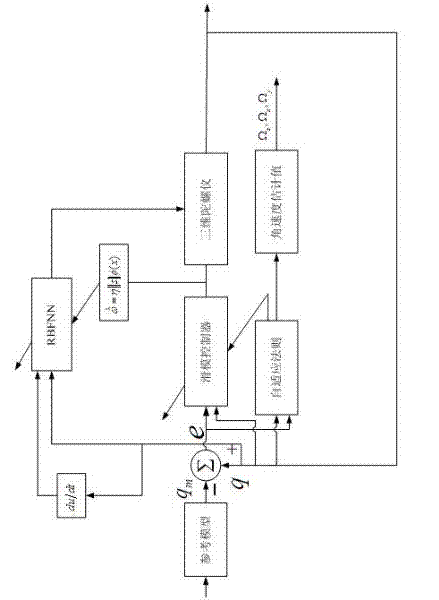
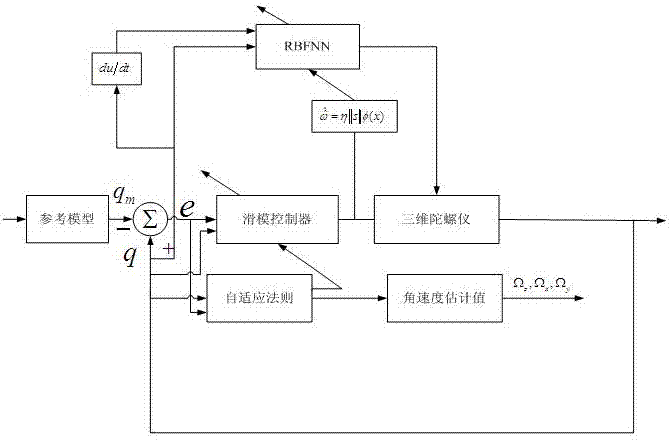
Adaptive control system based on radial basis function (RBF) neural network sliding mode control for micro-electromechanical system (MEMS) gyroscope
The invention discloses an adaptive control system based on a radial basis function (RBF) neural network sliding mode control for a micro-electromechanical system (MEMS) gyroscope, and the system comprises a gyroscope and a control circuit, wherein the control circuit comprises a sliding mode controller and an RBF neural network; the difference of displacement of the three-axis gyroscope in the directions of three coordinate axes x, y and z and displacement of a reference model is taken as the input of the sliding mode controller. In the adaptive control system, an adaptive sliding mode control method is applied in controlling the gyroscope, so as to improve the stability and reliability of the system; and the RBF neural network is adopted to carry out adaptive learning on upper boundary of uncertain interference, thus reducing the influence of measurement error and external interference, effectively lowering the occurrence of buffeting, and achieving a better control effect.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV CHANGZHOU
System and method for guiding and controlling a missile using high order sliding mode control
ActiveUS8436283B1Promote resultsDirection controllersDigital data processing detailsMode controlGuidance control
Owner:DAVIDSON TECH
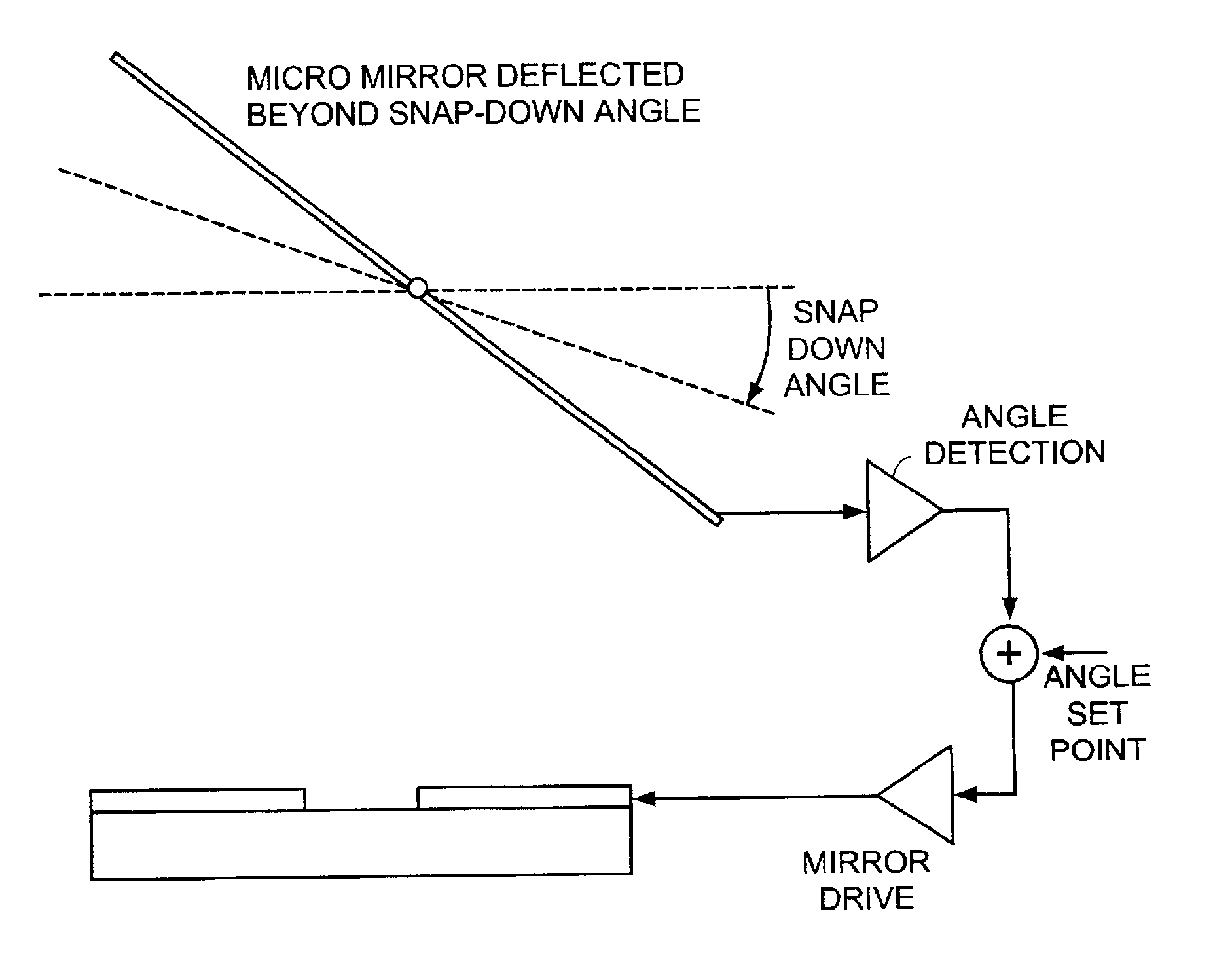
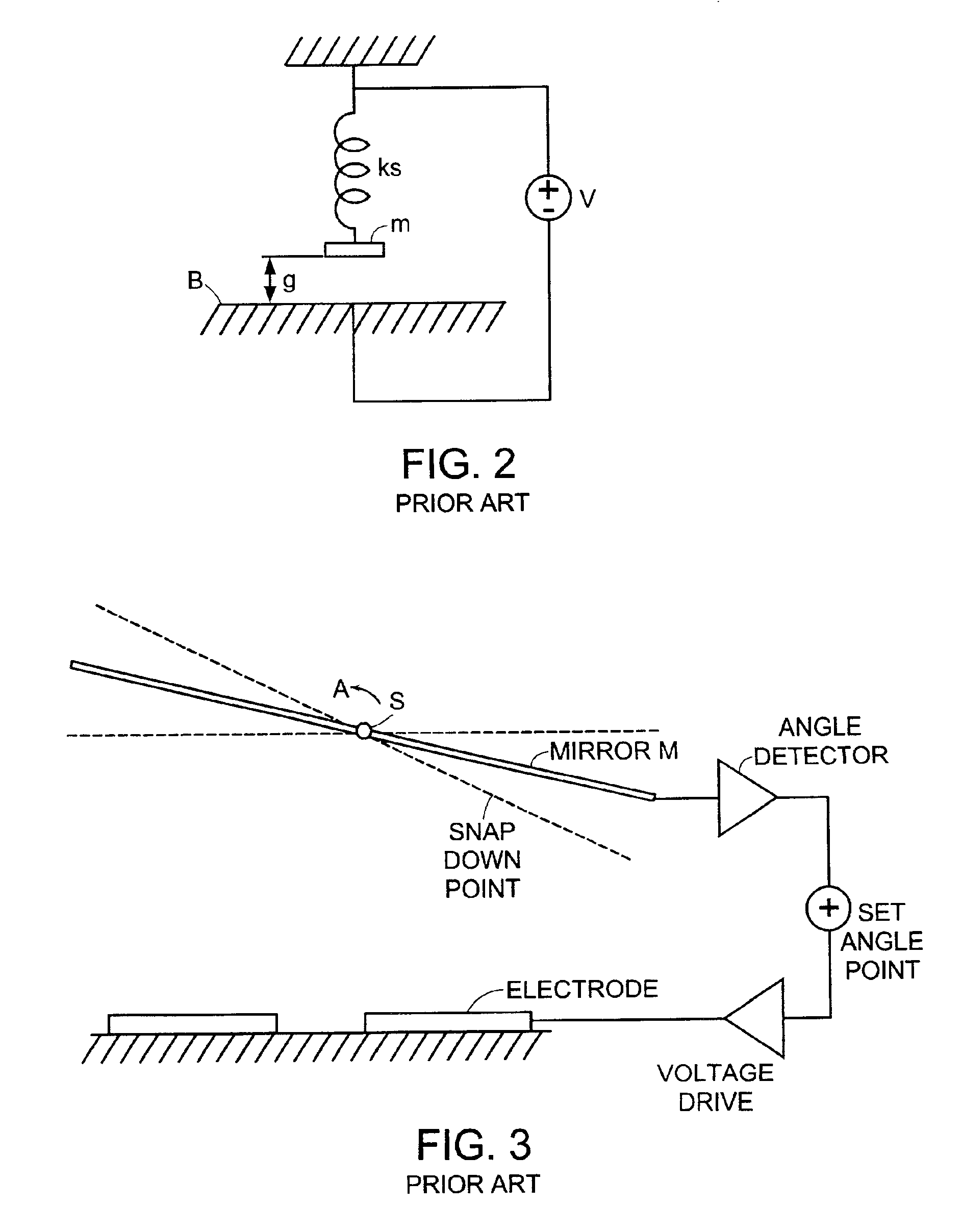
Pointing angle control of electrostatic micro mirrors
InactiveUS6985271B2InterferenceInterference minimizationNon-linear opticsOptical elementsCapacitanceControl system
The present invention is directed to a control system for a MEMS device, such as a MEMS mirror, that uses sliding mode analysis to accurately and predictably control the position of the mirrors in a MEMS device. The present invention also uses the capacitance of the mirror to detect the position of the mirror. In one embodiment, a MEMS mirror device mounted on a substrate is described that includes, a micro mirror that is pivotable about an axis, a first conductive layer on the mirror, a second conductive layer on the substrate, the first and second conductive layers form a first capacitor for determining the position of the mirror. The sliding mode control can be implemented using various drive mechanisms, including electrostatic drives. When used with electrostatic drives, conductive layers that create the capacitors can also be used to drive the mirror. The detection-drive system can be time multiplexed to simplify implementation and to avoid cross talk. An application Specific Integrated Circuit (ASIC) can be used to control the detection and drive of the mirrors.
Owner:CORNING INC
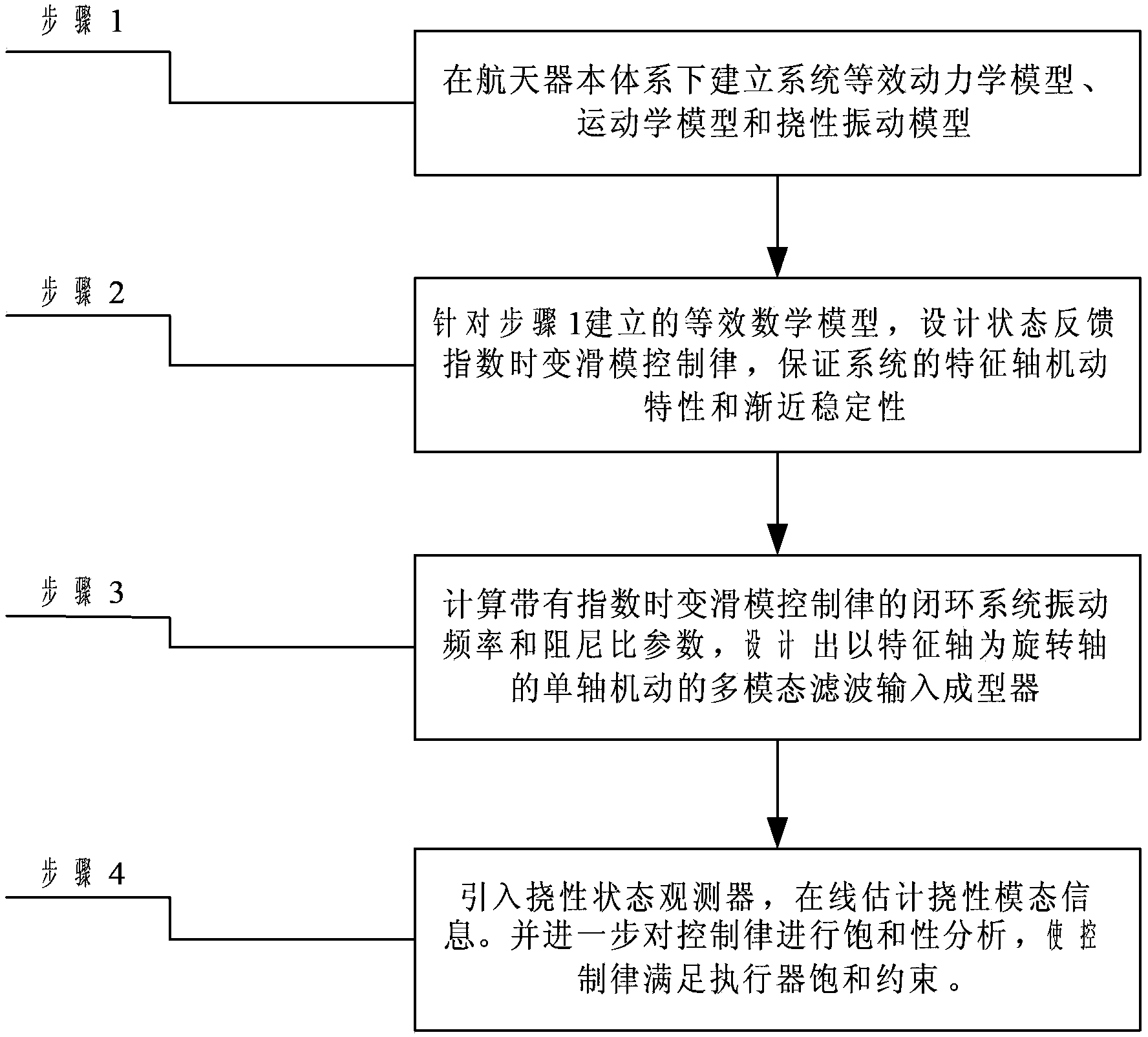
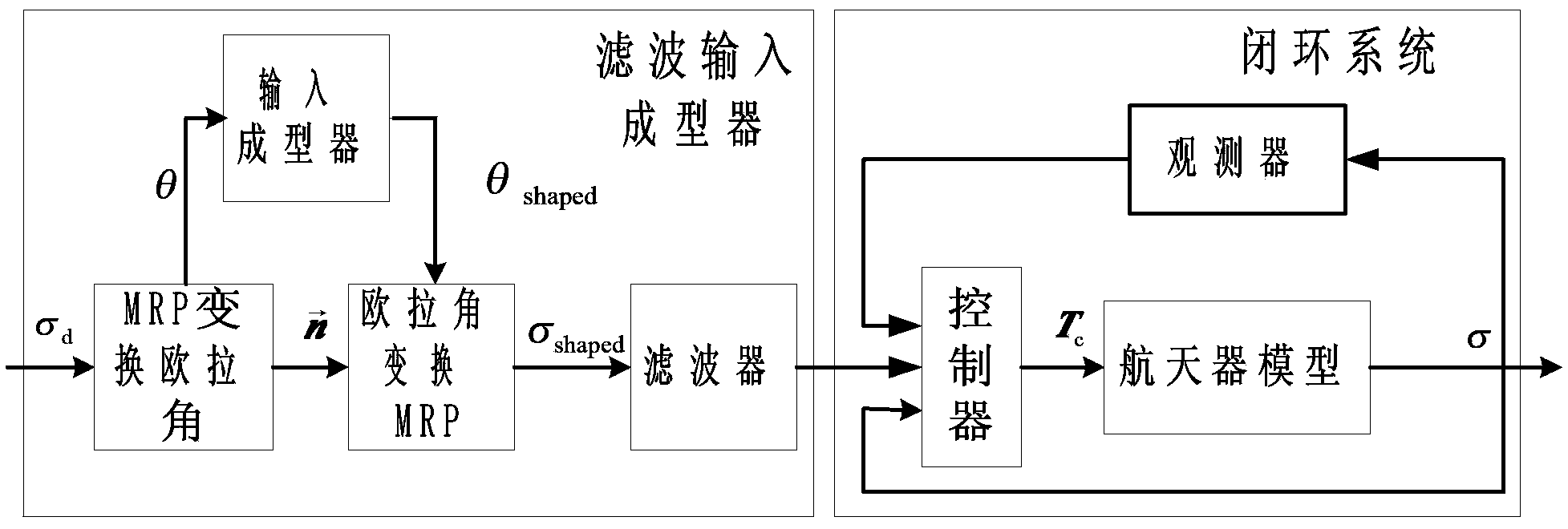
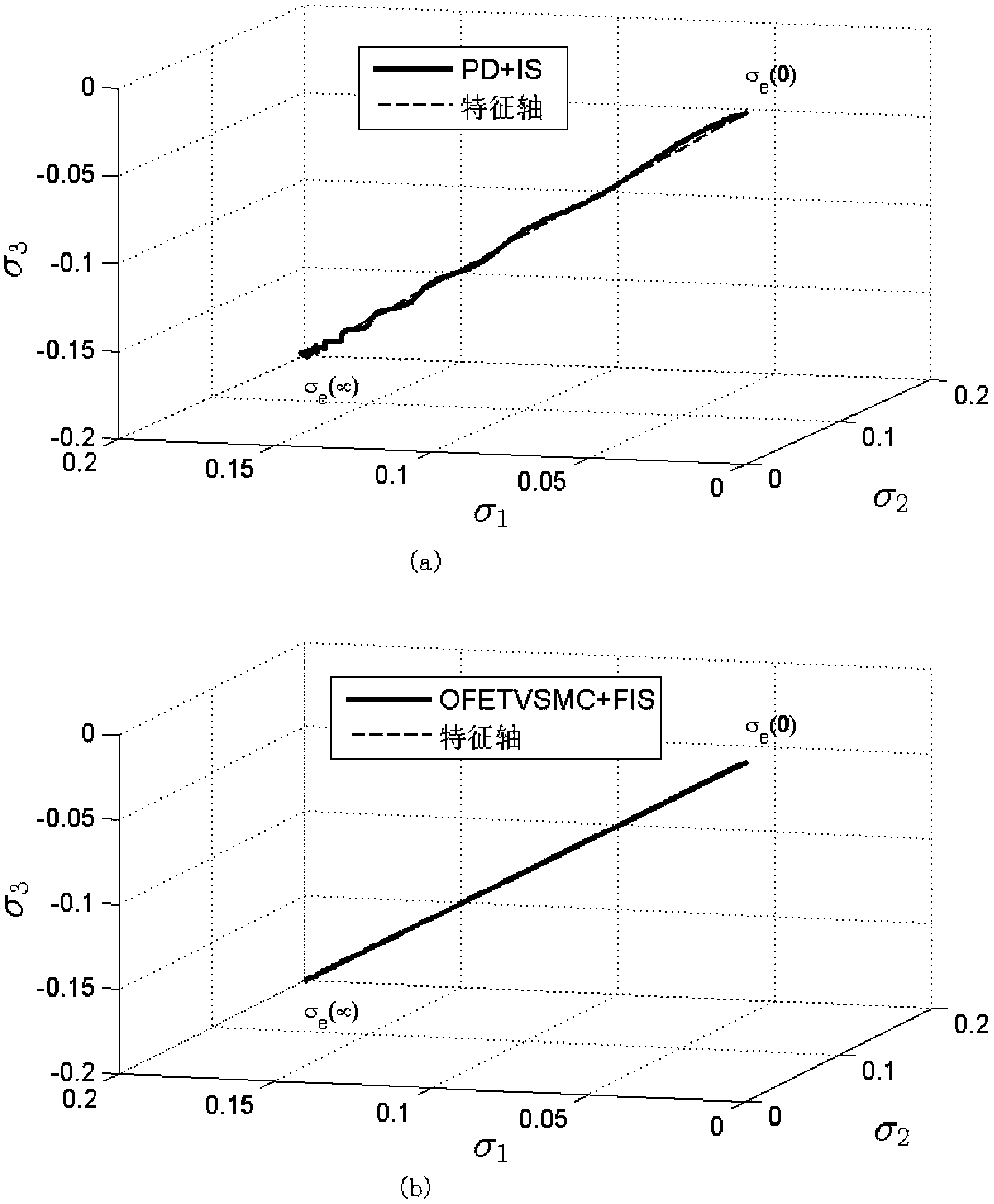
Method for controlling index time-varying slide mode of flexible spacecraft characteristic shaft attitude maneuver
ActiveCN103412491ASuppress residual vibrationAvoid complex coupling relationshipsAdaptive controlDynamic modelsSpace vehicle control
The invention relates to a method for controlling an index time-varying slide mode of flexible spacecraft characteristic shaft attitude maneuver, and belongs to the technical field of spacecraft control. The method comprises the steps that firstly, a system dynamically equivalent model, a dynamic model and a flexible vibration model are established under a spacecraft system, then, the vibration frequency and the damping ratio parameter of a closed loop system with the index time-varying slide mode control law are calculated, and a single-shaft multi-modality filtering input shaping device with a characteristic shaft as a rotary shaft is designed according to the designing method of the single-shaft input shaping device to restrain flexible vibration in three-shaft motion. Meanwhile, a state observer is designed to estimate flexible modal information in real time, and the method for controlling an output feedback index time-varying slide mode is formed. At last, saturability analysis is conducted on control torque so as to satisfy the physical saturation constraint of the control torque. By means of the method, the application range of existing input shaping is expanded, the input shaping technology is expanded from single-shaft maneuver to three-shaft maneuver, the self-robustness of filter input shaping is enhanced, and the purpose that the attitude maneuver path of the spacecraft is the shortest is achieved.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
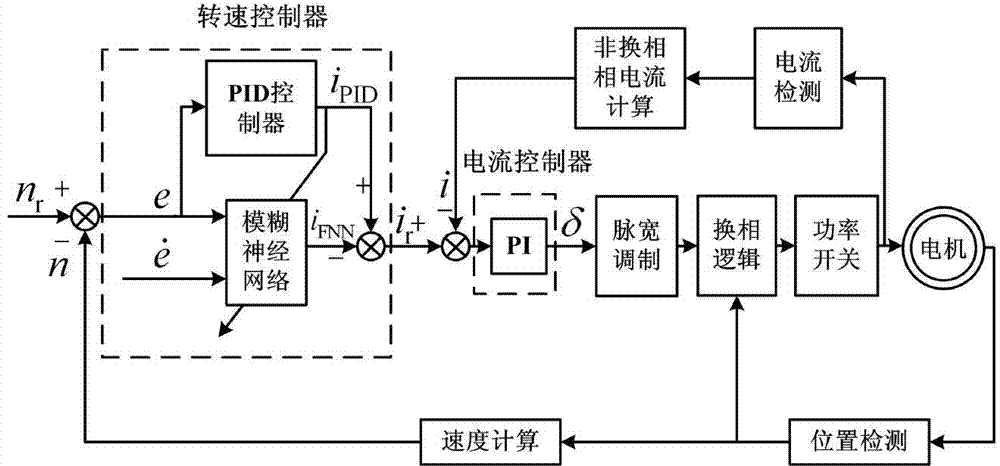
Motor rotating-speed tracking control method based on self-adaptive fuzzy neural network
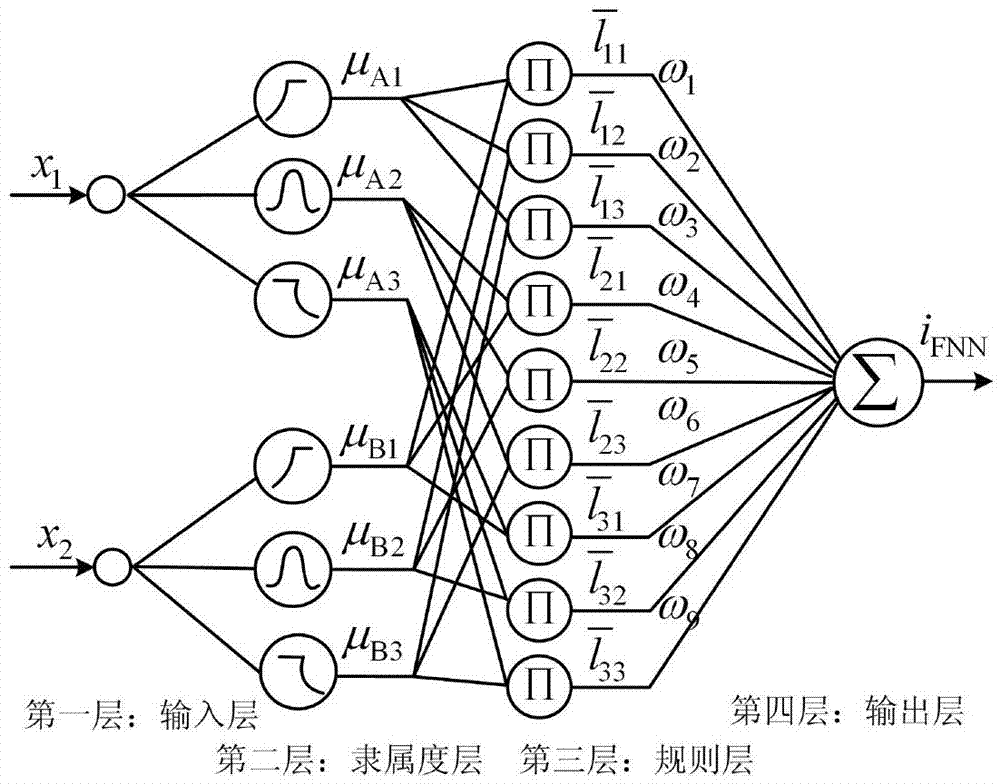
The invention relates to a motor rotating-speed tracking control method based on a self-adaptive fuzzy neural network, wherein rotating-speed and current double closed-loop control is adopted, an outer ring is a rotating-speed ring, a sliding-mode control theory-based fuzzy neural-network controller (SMFNN) is designed, an inner ring is a current ring, and a PI (Proportional-Integral) controller is adopted; a fuzzy neural-network rotating-speed controller comprises two parts, wherein one part is a PID (Proportional-Integral-Derivative) controller, and the other part is the fuzzy neural network, online real-time learning is carried out through the fuzzy neural network by utilizing a parameter correcting method designed on the basis of the sliding-mode control theory, and the two parts jointly act to obtain the output ir of the rotating-speed controller, i.e. a difference obtained by subtracting the output iFNN of the fuzzy neural network from the output iPID of the PID controller is used as the output ir of the rotating-speed controller. The control precision and the anti-interference performance of a motor speed-adjusting system can be improved through the control strategy of the motor rotating-speed tracking control method.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Permanent magnet synchronous motor sliding-mode control strategy based on novel reaching law
ActiveCN104953915ASuppress fluctuationsRealize high-precision vector controlElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsControl vectorHarmonic
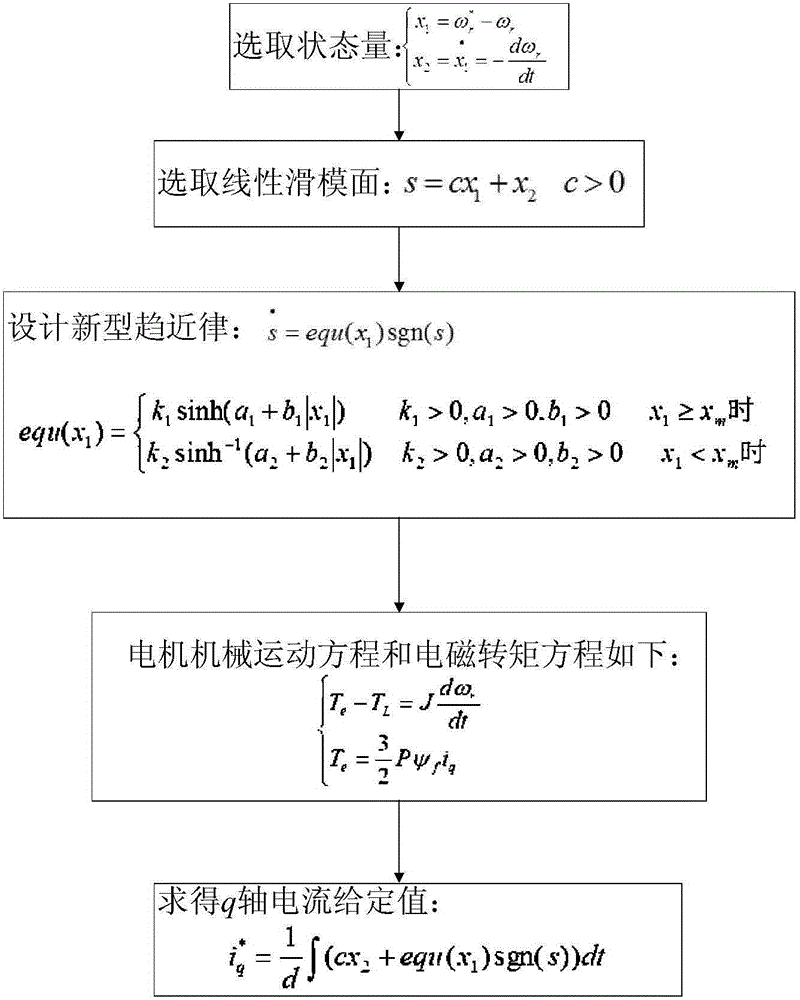
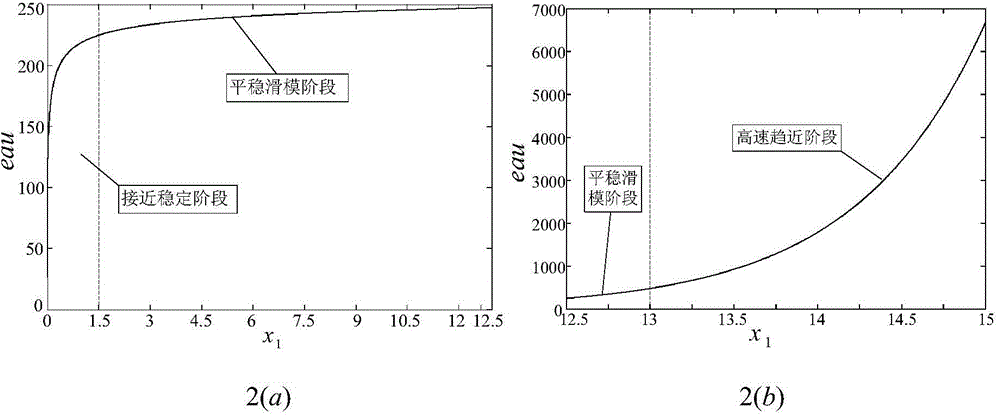
The invention discloses a permanent magnet synchronous motor sliding-mode control strategy based on a novel reaching law. The permanent magnet synchronous motor control strategy adopts speed and current double-closed-loop control, a current loop adopts a PI (proportional-integral) controller, and a rotating speed loop adopts sliding-mode control based on the novel reaching law; a speed regulator adopts a novel speed change reaching law containing speed errors and sliding-mode surface information, deviation of a set rotor angular speed and a feedback rotor angular speed is used as the input quantity, and a q-axis current set value iq<*> is output through the sliding-mode control quantity. With the adoption of the strategy, the problems that a traditional reaching law is slow and large in steady-state buffeting are solved, the set rotating speed can be tracked quickly in a dynamic state, speed overshoot and current fluctuation are reduced, the harmonic content, produced by high-frequency buffeting, of a system can be decreased in a steady state, the performance of the system is greatly improved, and high-precision vector control on the permanent magnet synchronous motor speed regulating system is realized.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
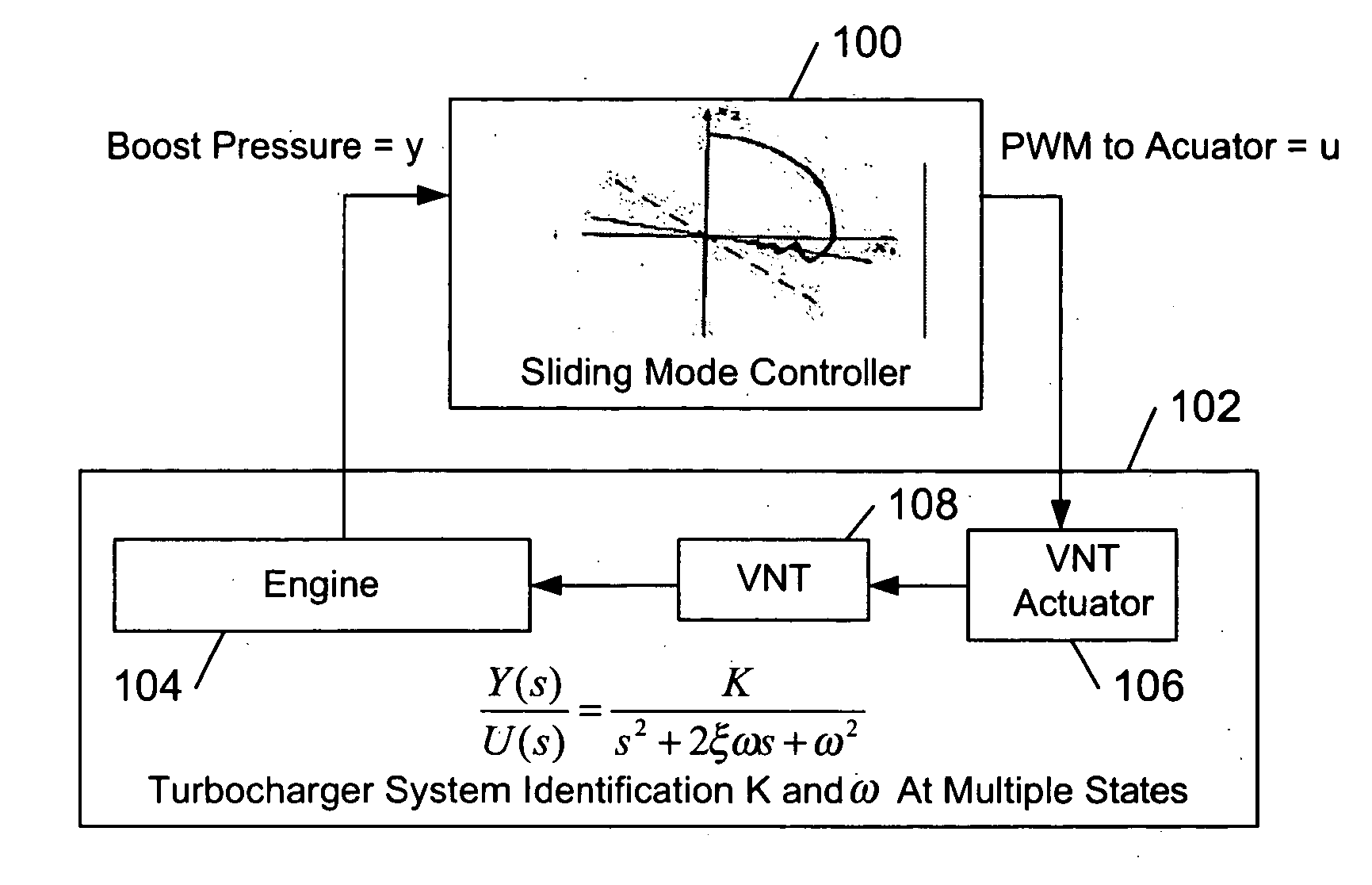
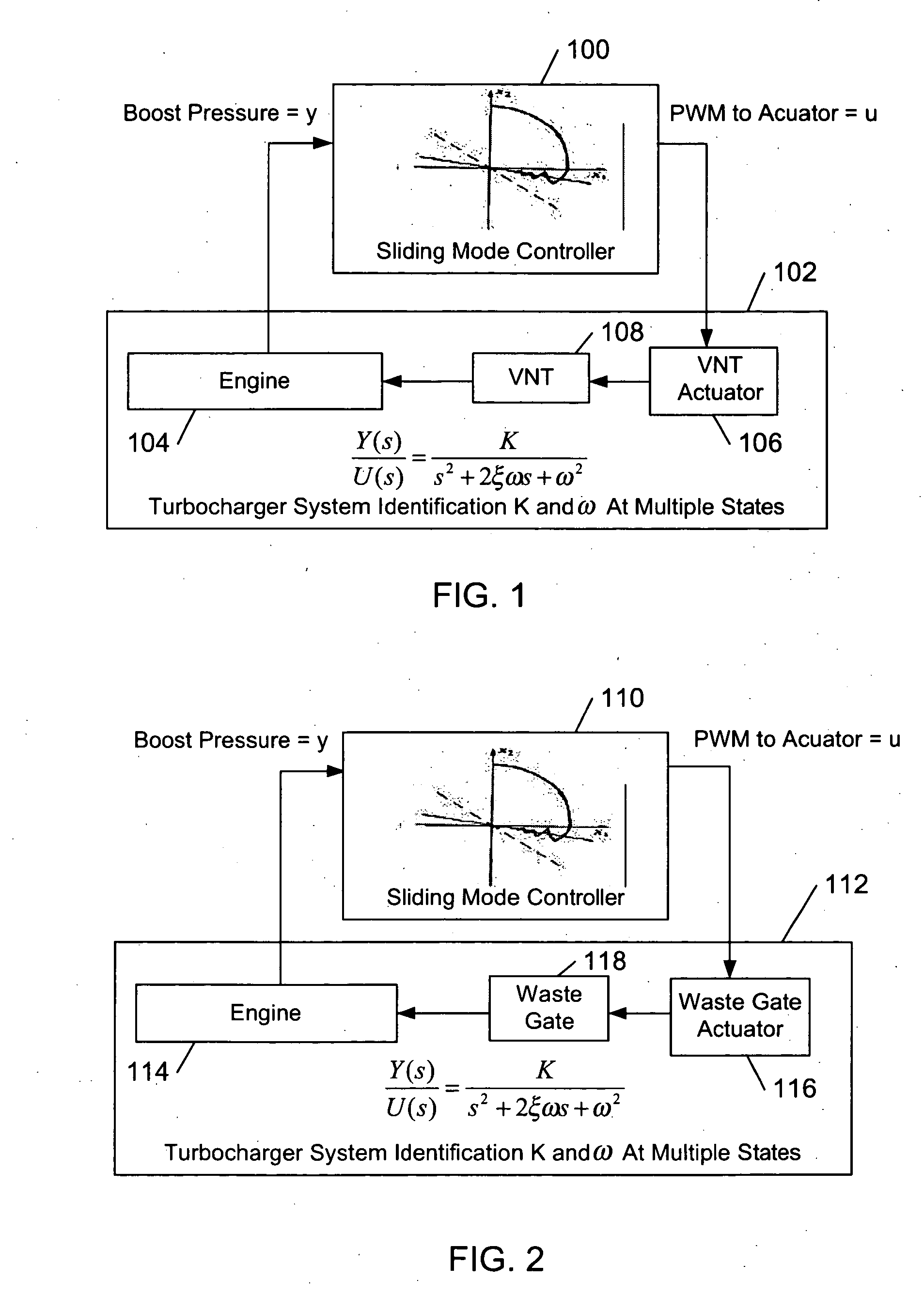
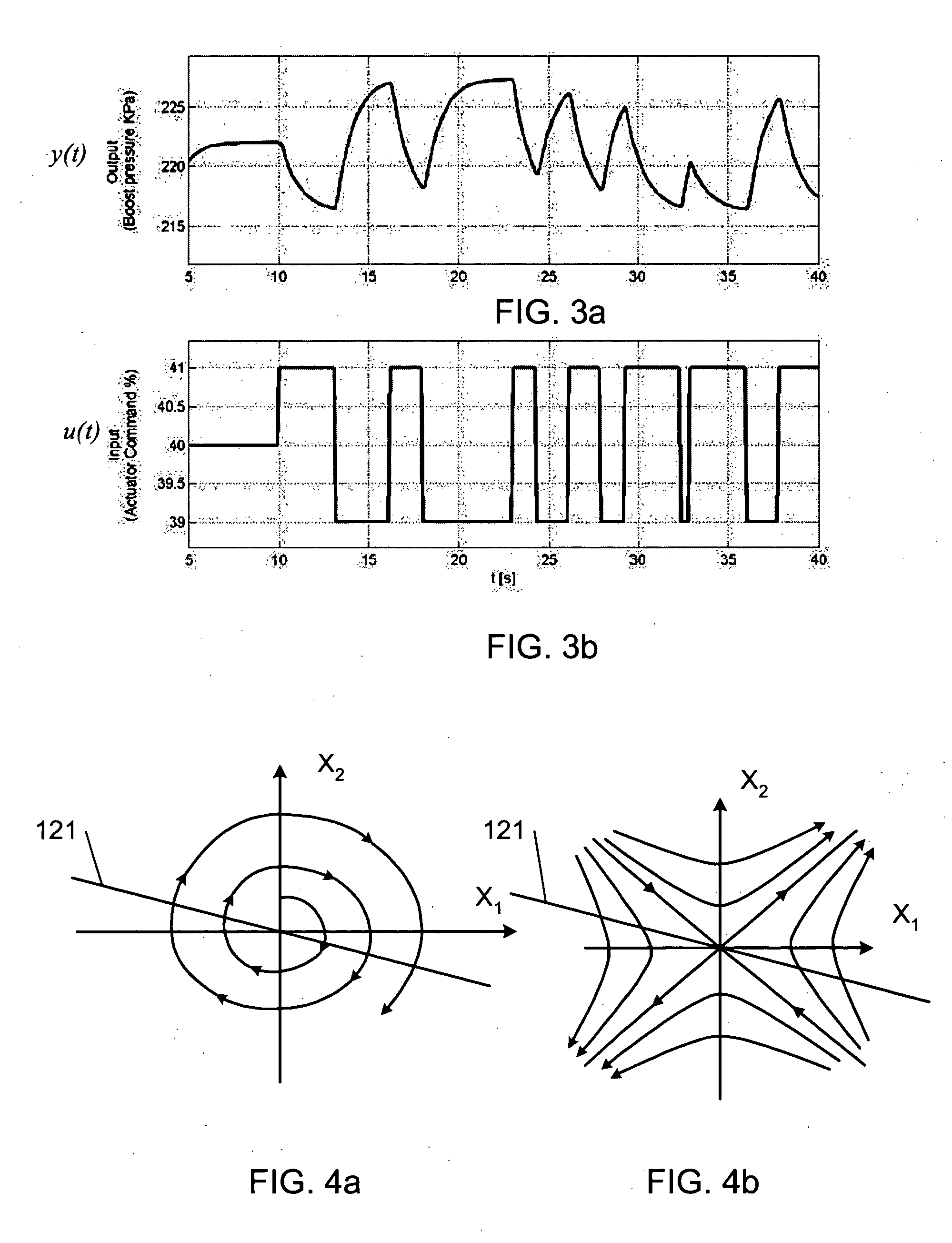
Method and system for sliding mode control of a turbocharger
ActiveUS20050137777A1Minimizes square errorAnalogue computers for vehiclesElectrical controlControl systemTurbocharger
A method for defining a sliding mode control system for a turbocharger system is provided. The method includes perturbing a turbocharger actuator and measuring turbocharger boost pressure output from the perturbation. The perturbation and measurements are repeated for a plurality of states of operation of the turbocharger. System parameters identified for each of the plurality of states from the plurality of perturbations and measurements. A sliding mode control law may be defined for each of the plurality of states from the system parameters. A sliding mode control system for controlling the boost pressure of a turbocharger is also provided. An actuator for controlling the boost pressure is electrically controlled by a sliding mode controller to stabilize the turbocharger system toward a setpoint on a sliding surface. The control law is determined from a plurality of linear models from a plurality of operating states of the turbocharger system.
Owner:GARRETT TRANSPORATION I INC
Trajectory tracking control method for mobile robot based on sliding mode variable structure
InactiveCN107168340AReduce chatteringHigh precisionPosition/course control in two dimensionsControl systemMATLAB
The invention discloses a trajectory tracking control method for a mobile robot based on a sliding mode variable structure. According to the trajectory tracking control method, advantages and disadvantages of different reaching laws are comprehensively analyzed, and a reaching law with better rapidity and stability is proposed and designed. The reaching law is composed of two items, wherein the first item is that the system state is controlled to rapidly approach to a sliding mode surface when being far away from the sliding mode surface, and the second item is that the system state is controlled to keep stable running in the sliding mode surface. The trajectory tracking control method comprises the steps of firstly building a kinematics model and a trajectory tracking error model of the mobile robot, and deducing a mobile robot trajectory tracking error differential equation; and then designing a switching function based on the sliding mode variable structure, and deducing a sliding mode control law according to the designed reaching law, wherein the control law can enable the mobile robot to rapidly converge to an expected trajectory and expected speed. It is indicated by MATLAB numerical simulation that the trajectory tracking control method can effectively weaken a chattering phenomenon in the tracking process and improve the trajectory running accuracy. In addition, the trajectory tracking control method has good stability and robustness.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
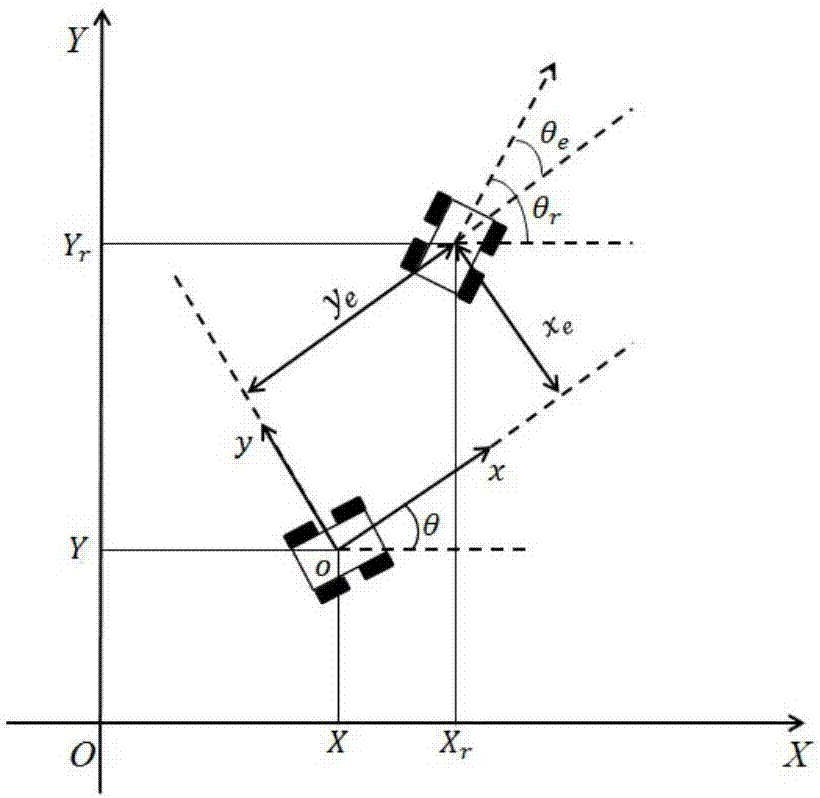
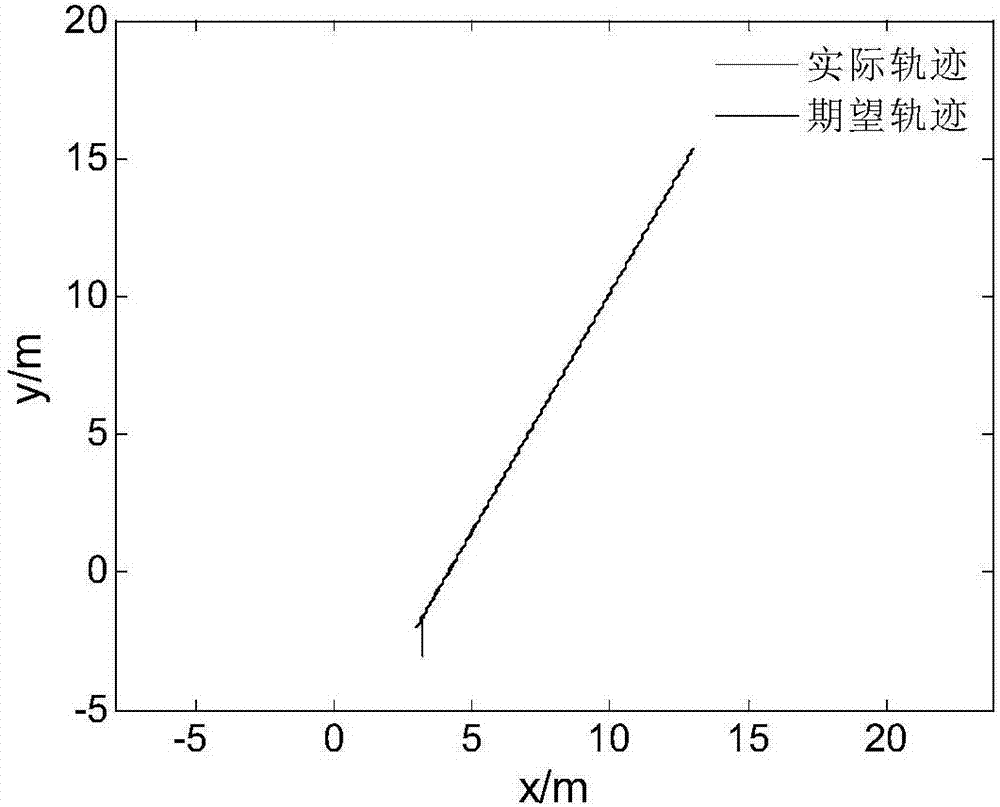
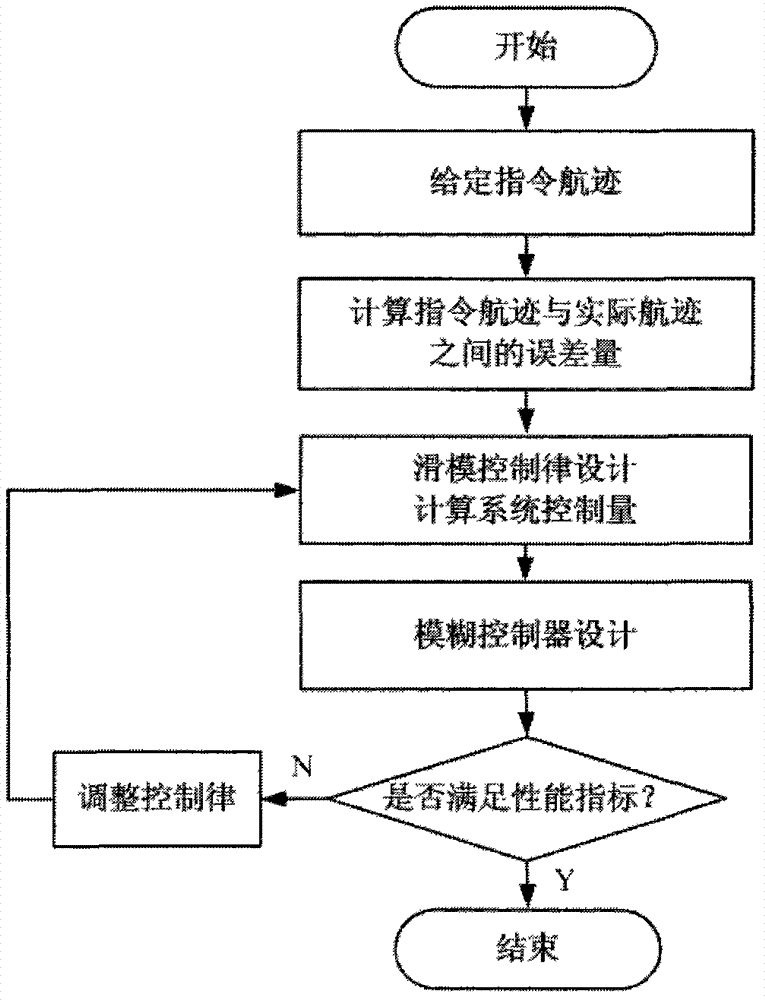
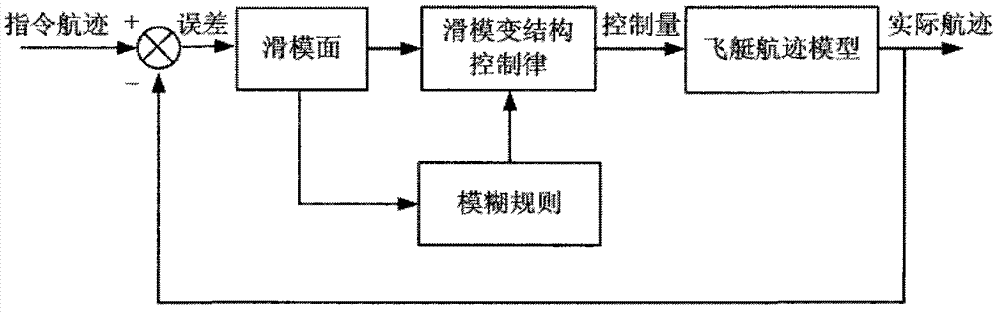
Control method for flight path of airship on stratosphere
ActiveCN102759928AOvercome limitationsBroaden the range of working pointsPosition/course control in three dimensionsFuzzy ruleControl system design
The invention discloses a control method for the flight path of an airship on the stratosphere. The control method comprises the following steps: firstly, giving out an instruction flight path of the airship; secondly, calculating an error margin e between the induction flight path of the airship and the actual flight path; thirdly, selecting a sliding mode surface s and a reaching law, designing a sliding mode control law and calculating the system control amount tau; and fourthly, designing a fuzzy controller with the sliding mode surface s as an input of the fuzzy controller and with a control parameter as an output of the fuzzy controller and adjusting the control parameter according to a fuzzy rule. According to the control method, the induction flight path can be stably tracked, the problem of buffeting caused by sliding mode control is solved, favorable robustness and dynamic performance are realized and an effective scheme is provided for designing a flight path control system of the airship on the stratosphere.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
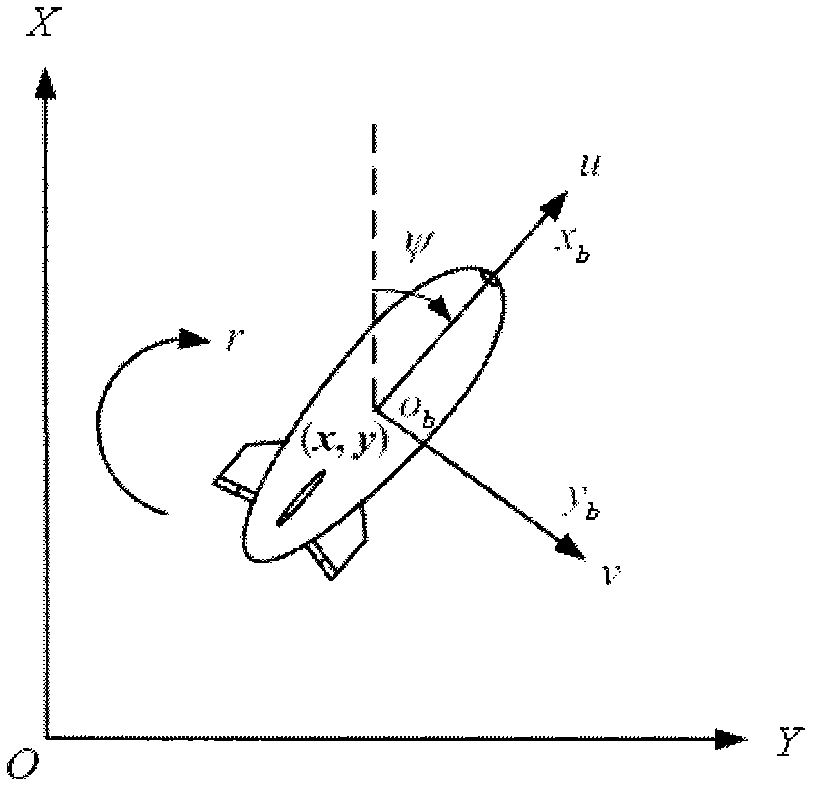
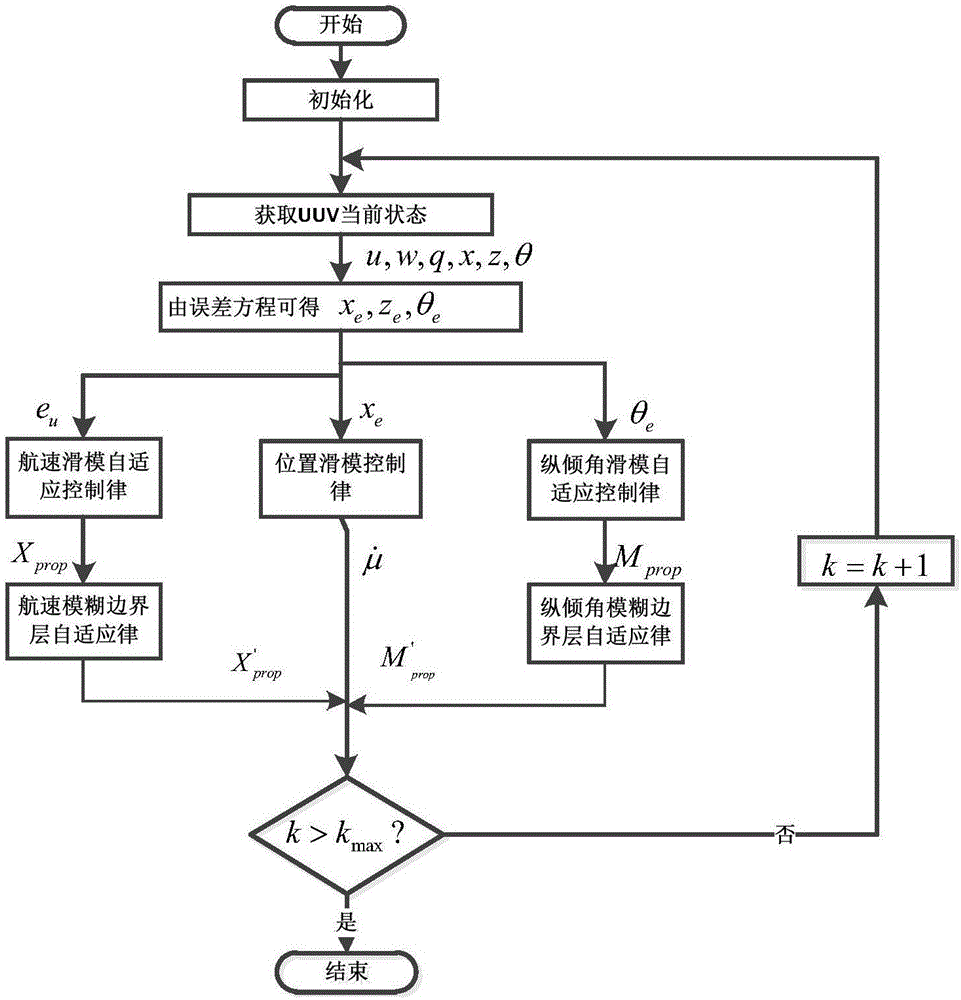
Sliding-mode control method for parameter-free driving-insufficient UUV (Unmanned Underwater Vehicle) vertical plane route tracking
ActiveCN106444794AGet rid of dependenceImprove speed tracking accuracyAltitude or depth controlVertical planeControl system
The invention provides a sliding-mode control method for parameter-free driving-insufficient UUV (Unmanned Underwater Vehicle) vertical plane route tracking. The sliding-mode control method comprises the following steps: I, performing initialization; II, acquiring a current state of a UUV; III, establishing an error equation of the horizontal plane of the driving-free UUV so as to obtain position deviation values xe and ze and course deviation value theta e; IV, according to a sliding-mode control method, respectively designing traveling speed sliding-mode self-adaptive control rules, position sliding-mode control rules and trimming angle sliding-mode self-adaptive control rules, controlling propelling force Xprop, an excepted traveling speed U and a torque Mprop, wherein eu is 0, xe is 0 and theta e is 0; V, designing fuzzy control rules for a boundary layer, setting k to be equal to k+1, turning to step II, and updating control rules and self-adaptive rules of a next time. By adopting the sliding-mode control method, a controller for stabilizing a system can be designed only according to a vertical surface kinetic model, self-adaptive rules can be designed for water kinetic parameters with uncertainties, furthermore a control system can be relieved from dependency on parameters, the system has robustness, and the influence of the uncertainties on the sliding-mode control approaching process can be reduced.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
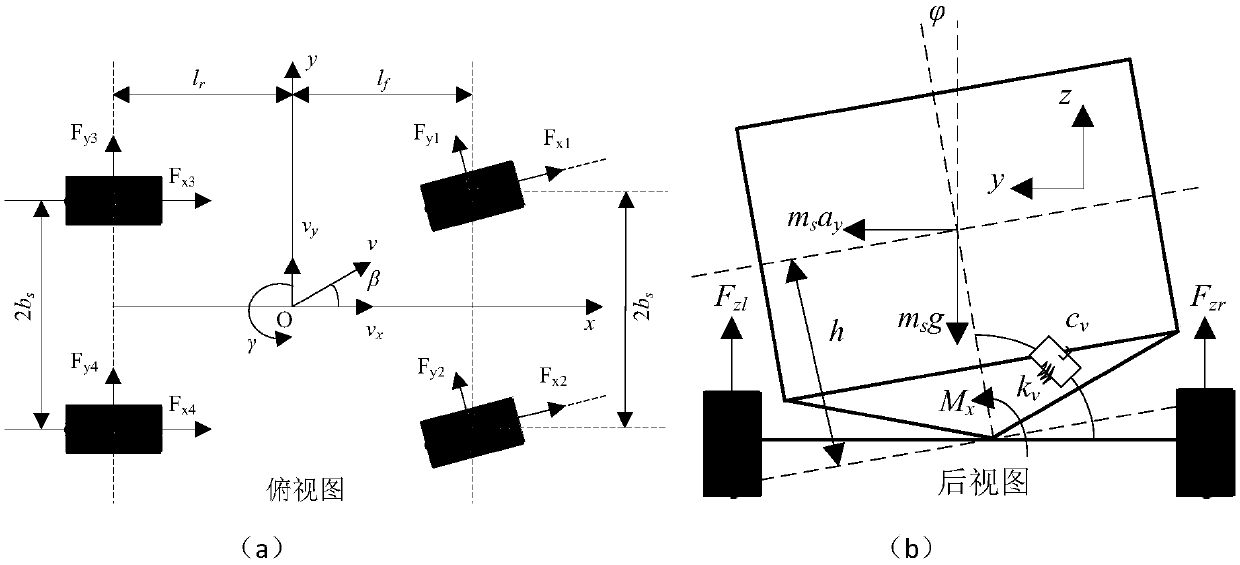
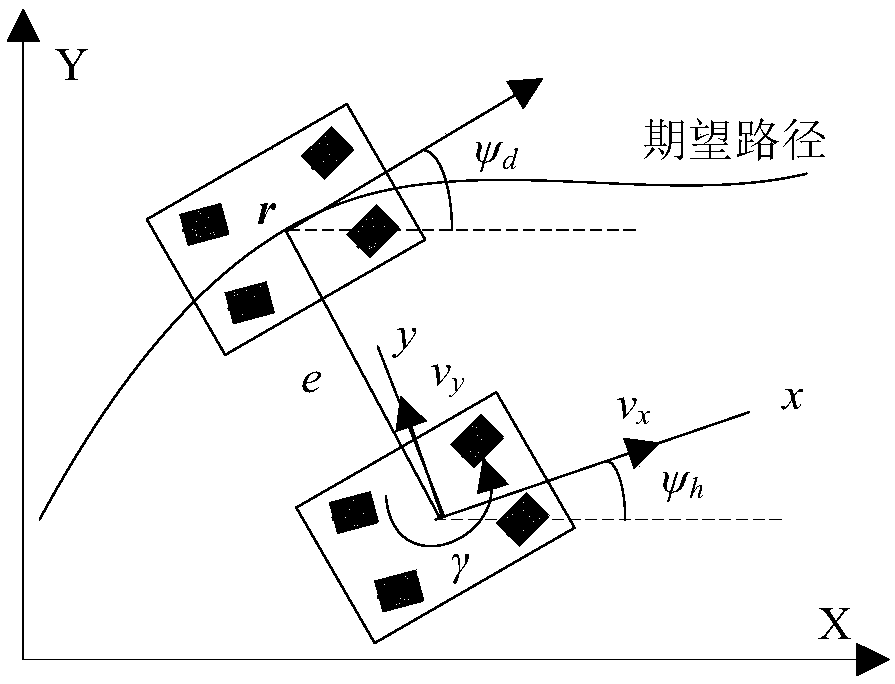
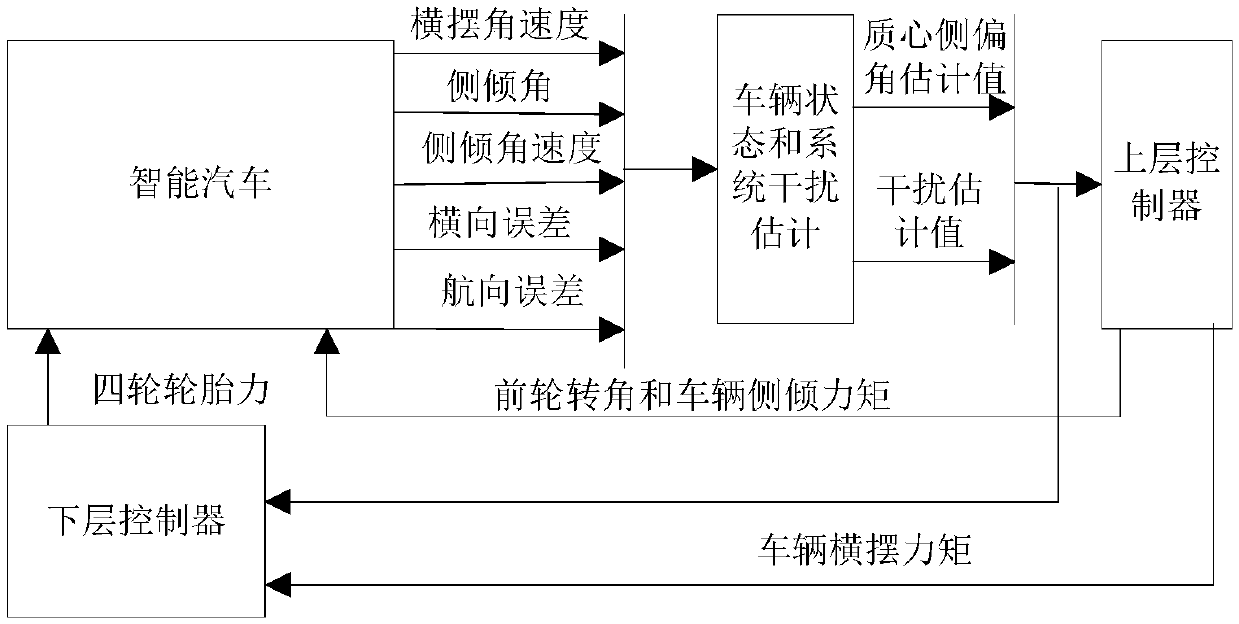
Coordination control method for vehicle path tracking and stability
ActiveCN109606352ASmall amount of calculationReduce time consumptionControl devicesVehicle dynamicsEstimation methods
The invention provides a coordination control method for vehicle path tracking and stability. The method includes the following steps: step S1. performing vehicle modeling; step S2. performing estimation on a vehicle state and system interference based on Kalman filtering; and step S3. performing integrated control on the vehicle path tracking and stability. The method establishes a vehicle dynamics model and a path tracking model, and designs an estimation method of the vehicle state and steering system interference. An upper-layer controller is designed by using a sliding mode control method, which aims to ensure the stability of a vehicle itself while reducing course deviation and lateral deviation during a path tracking process. In a lower-layer controller, a method for optimal distribution of a wheel tire force is designed, and according to requirements of the upper-layer controller and combining yaw and roll stability conditions of the vehicle, directional control distribution ofthe wheel tire force is achieved. The coordination control method can ensure that a wheel independently drives the smart automobile to achieve a path tracking effect, and also ensures lateral and roll stability of the smart automobile itself.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com