Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
493 results about "Guidance control" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
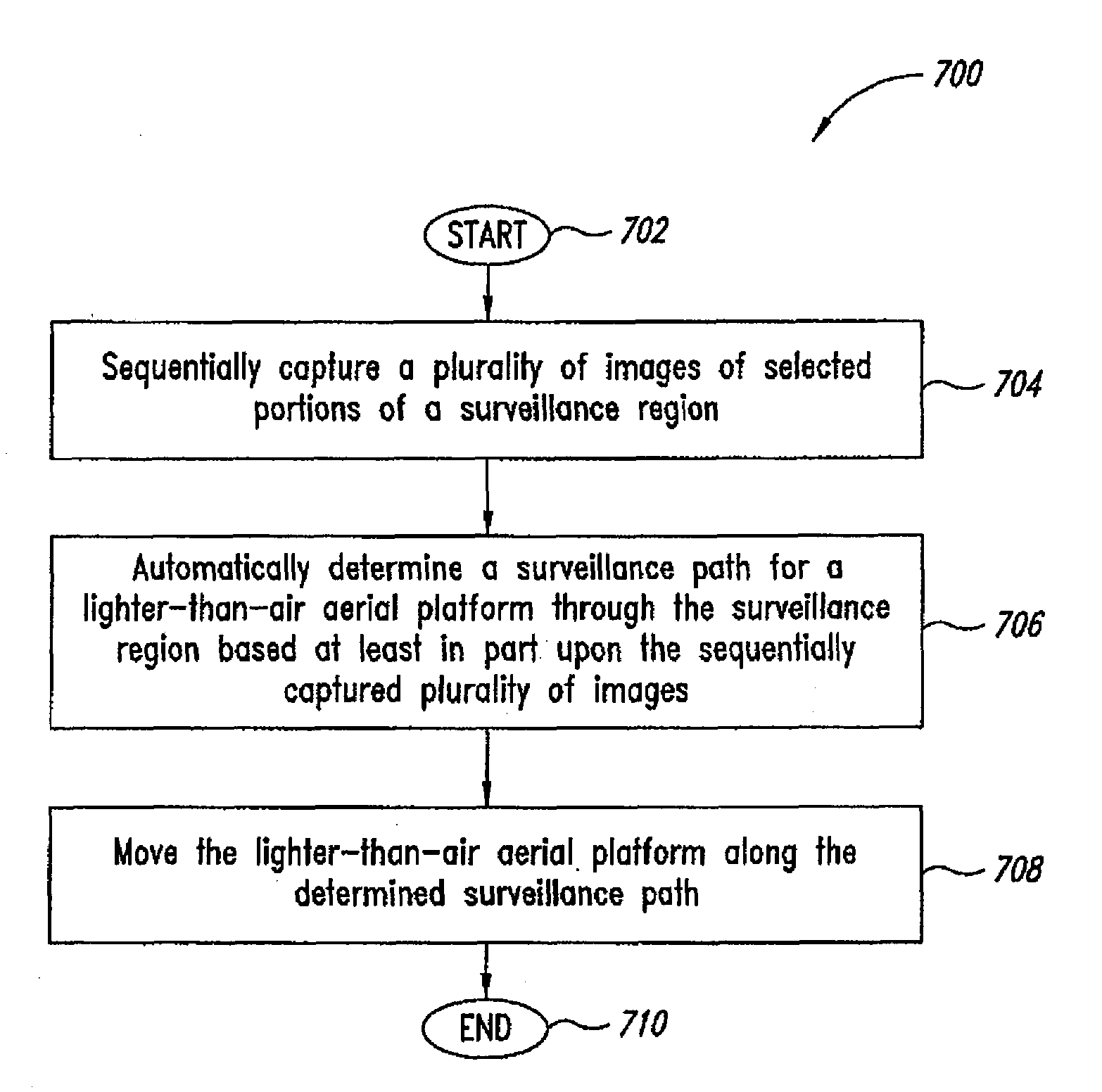
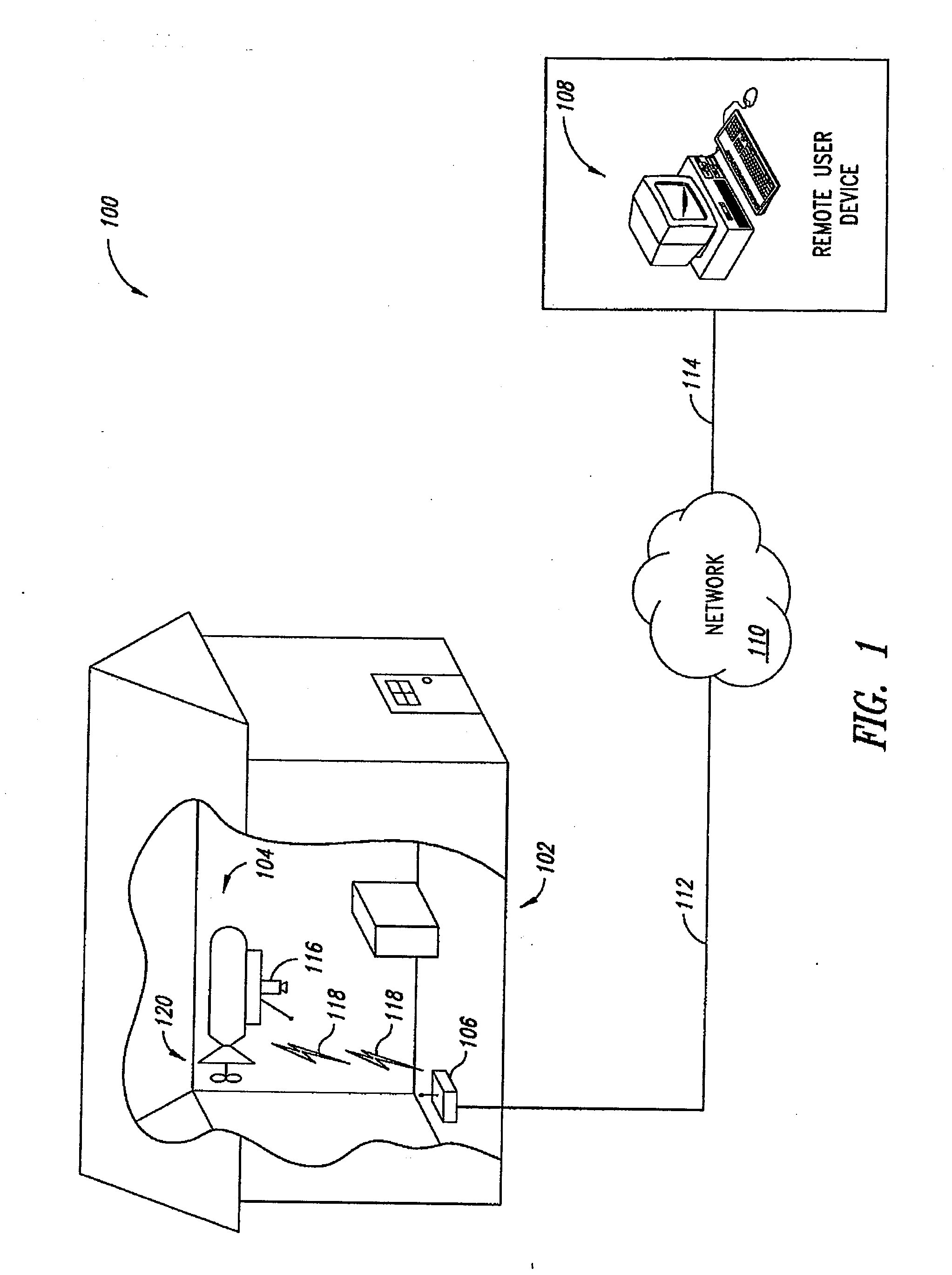
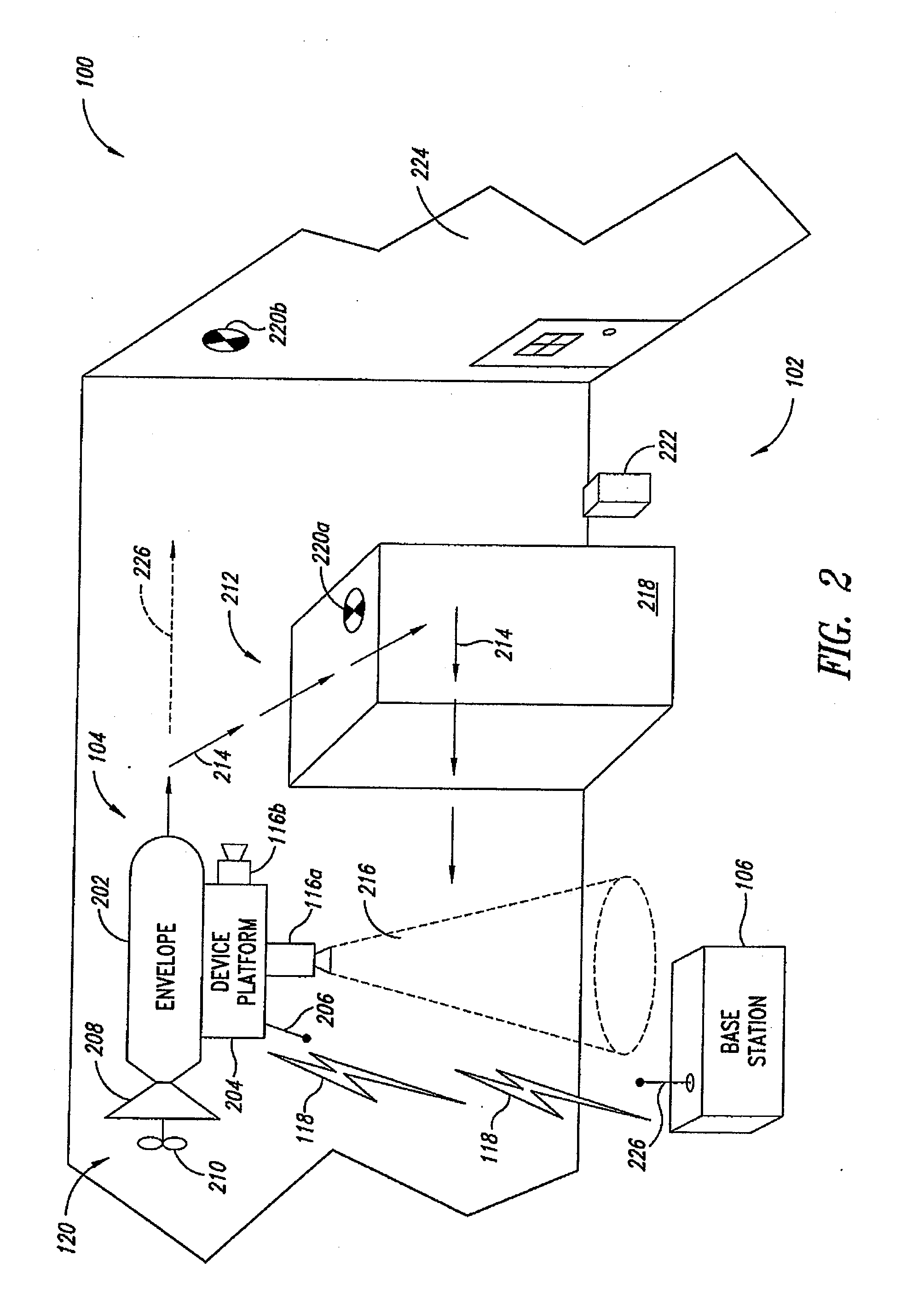
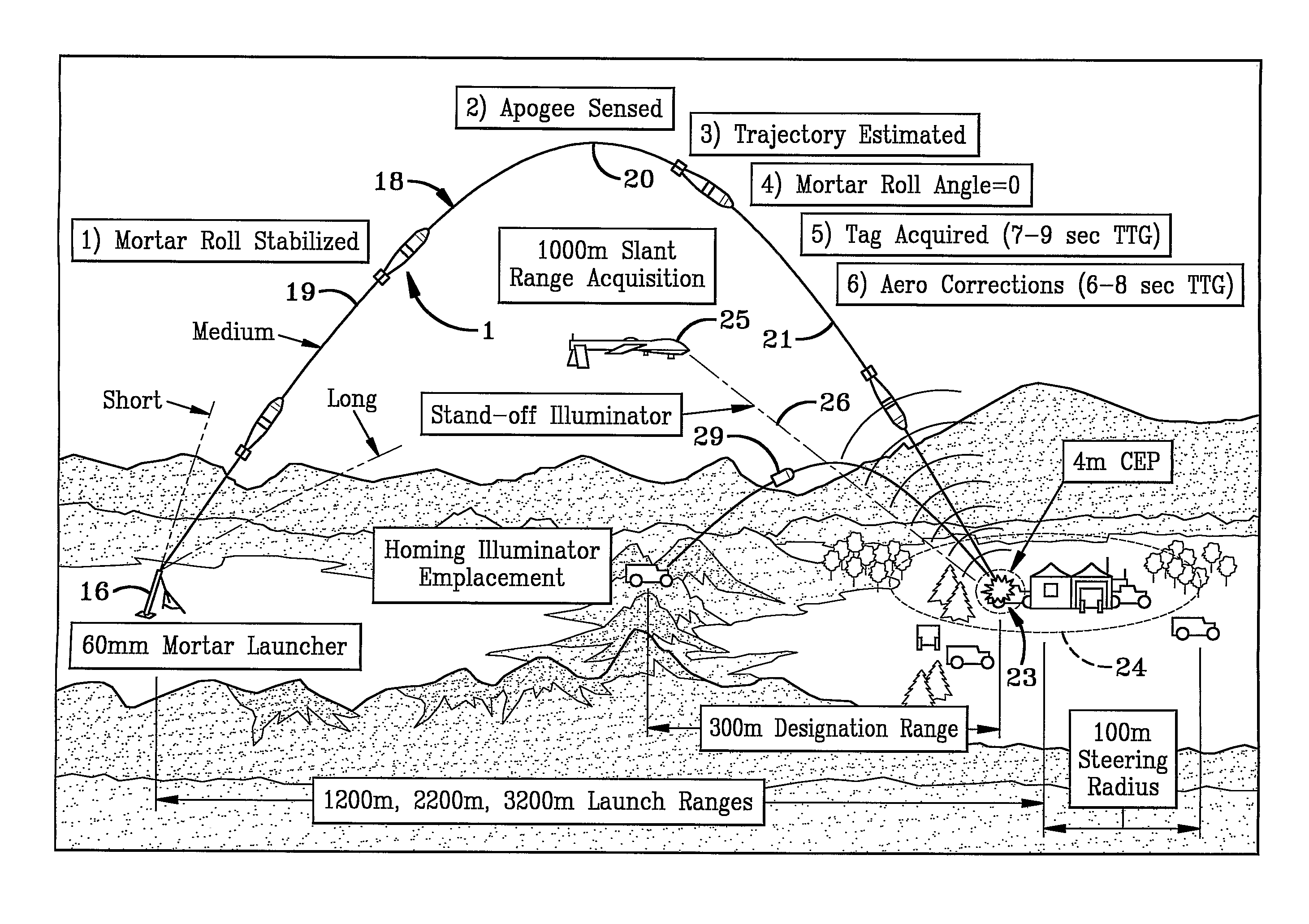
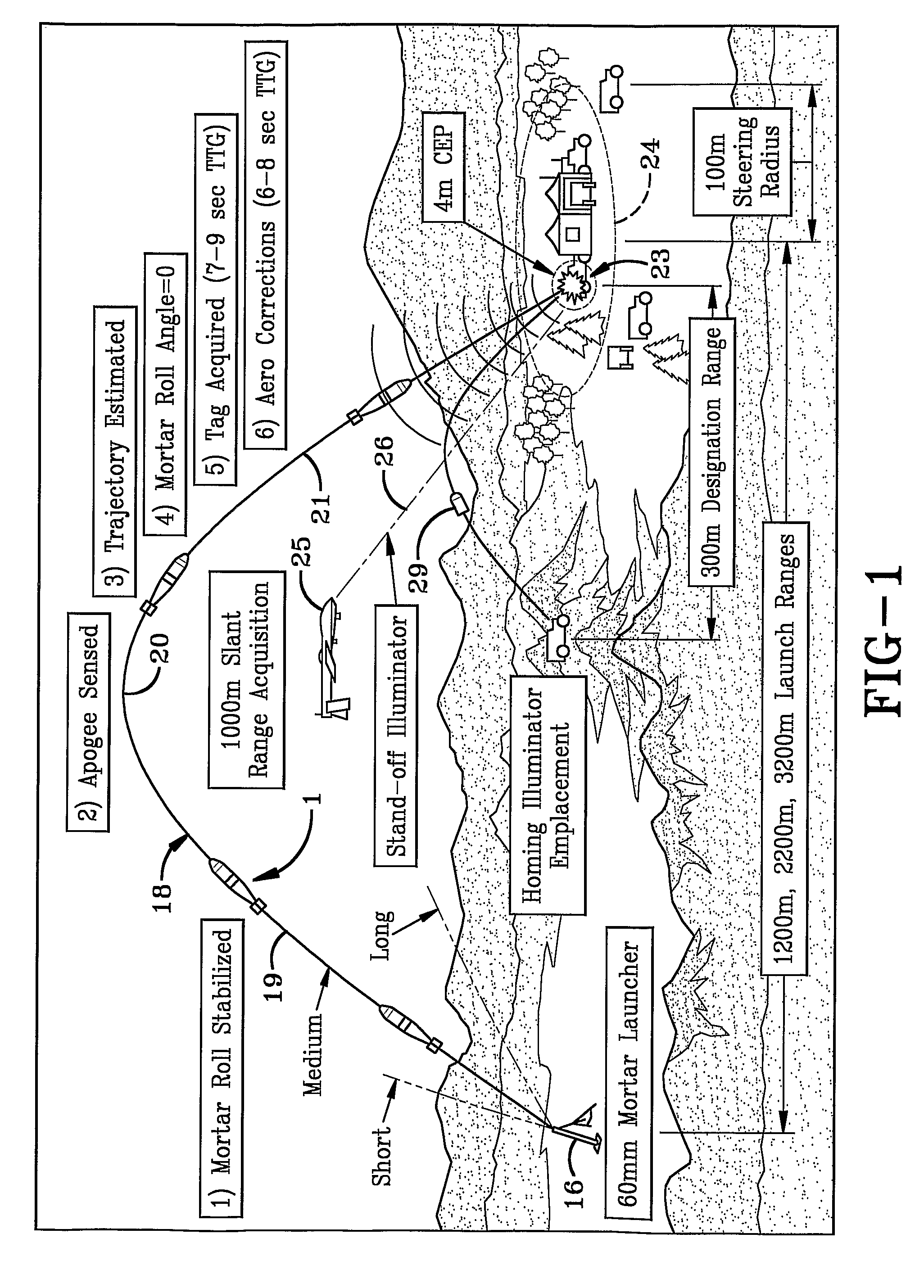
System and method of aerial surveillance
InactiveUS20080144884A1Improve drawing legibilityUnmanned aerial vehiclesPicture taking arrangementsGuidance controlEngineering
A system and method for an aerial surveillance system are disclosed. Briefly described, one embodiment comprises a lighter-than-air aerial platform, at least one image capture device carried by the lighter-than-air aerial platform and operable to sequentially capture a plurality of images, and at least one control surface physically coupled to the lighter-than-air aerial platform and operable to control direction of movement of the lighter-than-air aerial platform along a surveillance path in response to a guidance control signal determined in part upon the sequentially captured plurality of images.
Owner:ROBOTICVISIONTECH
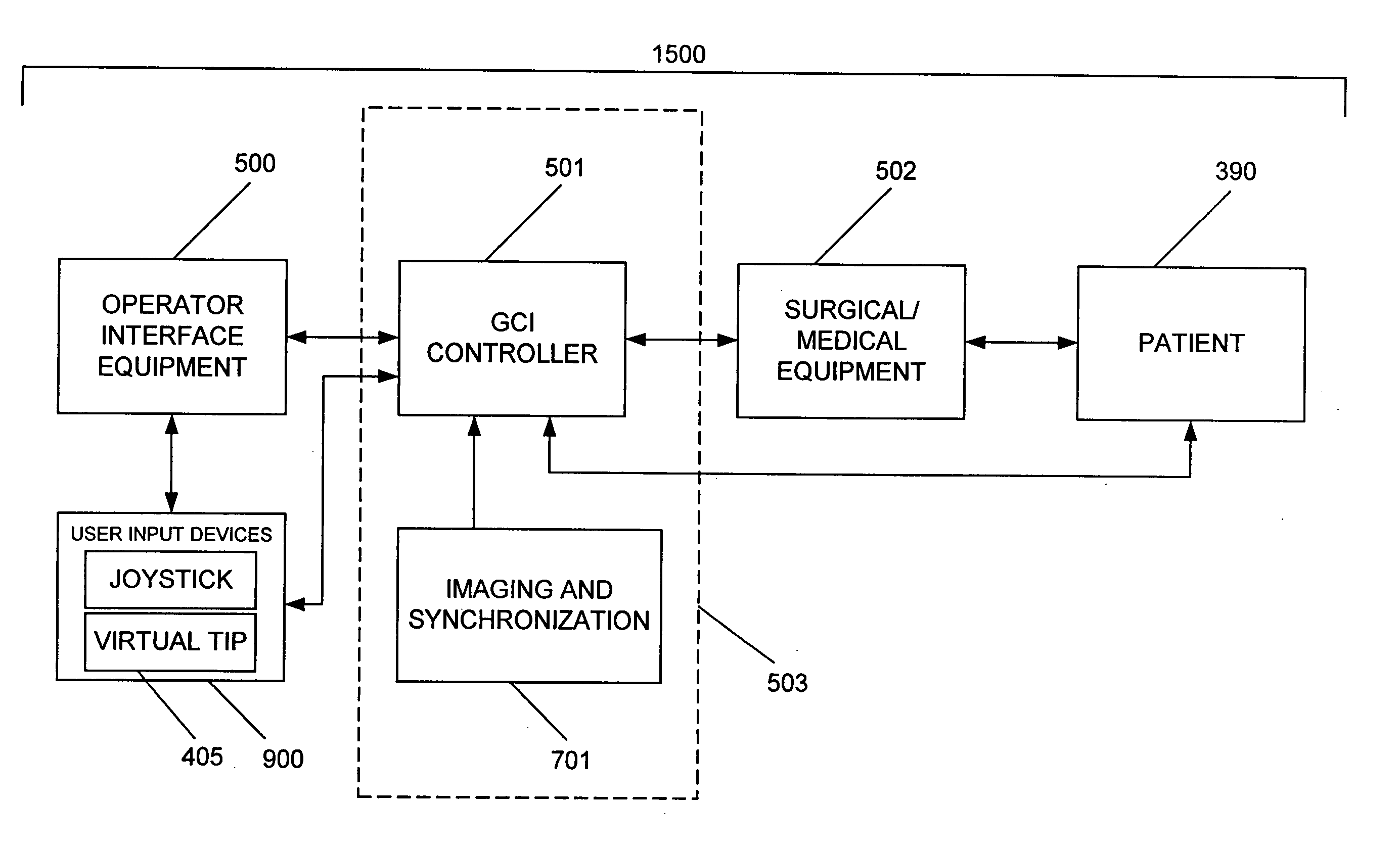
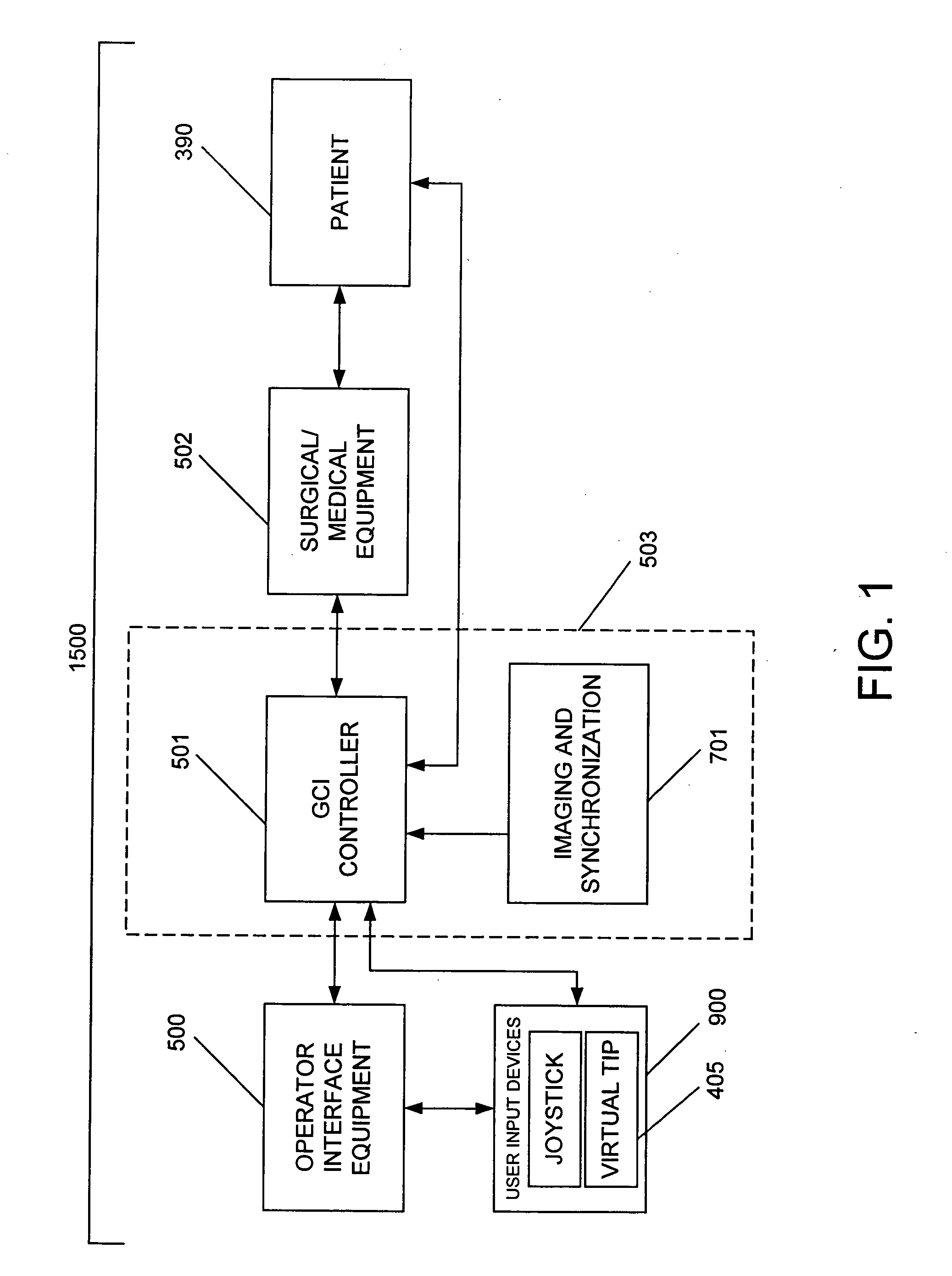
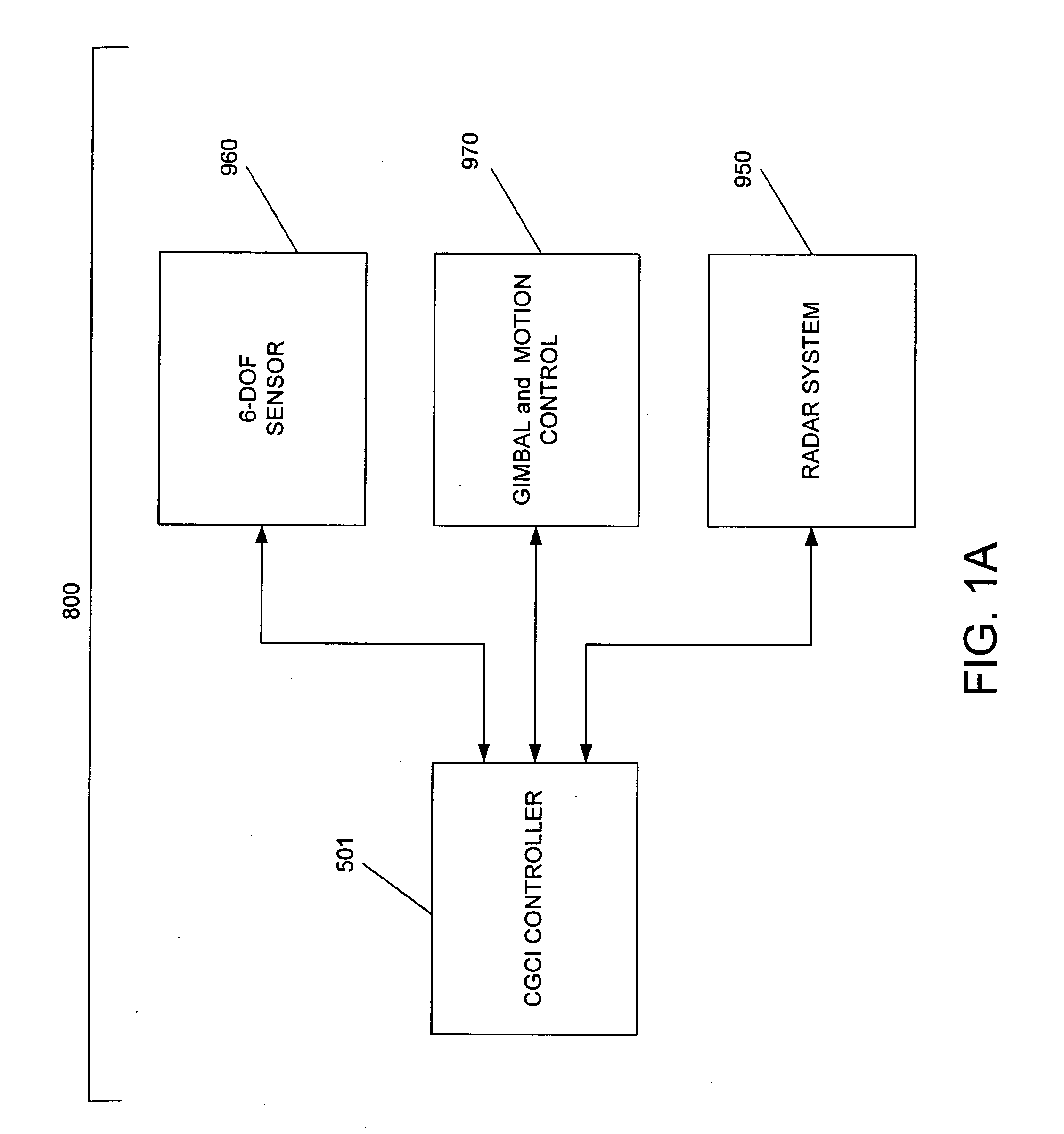
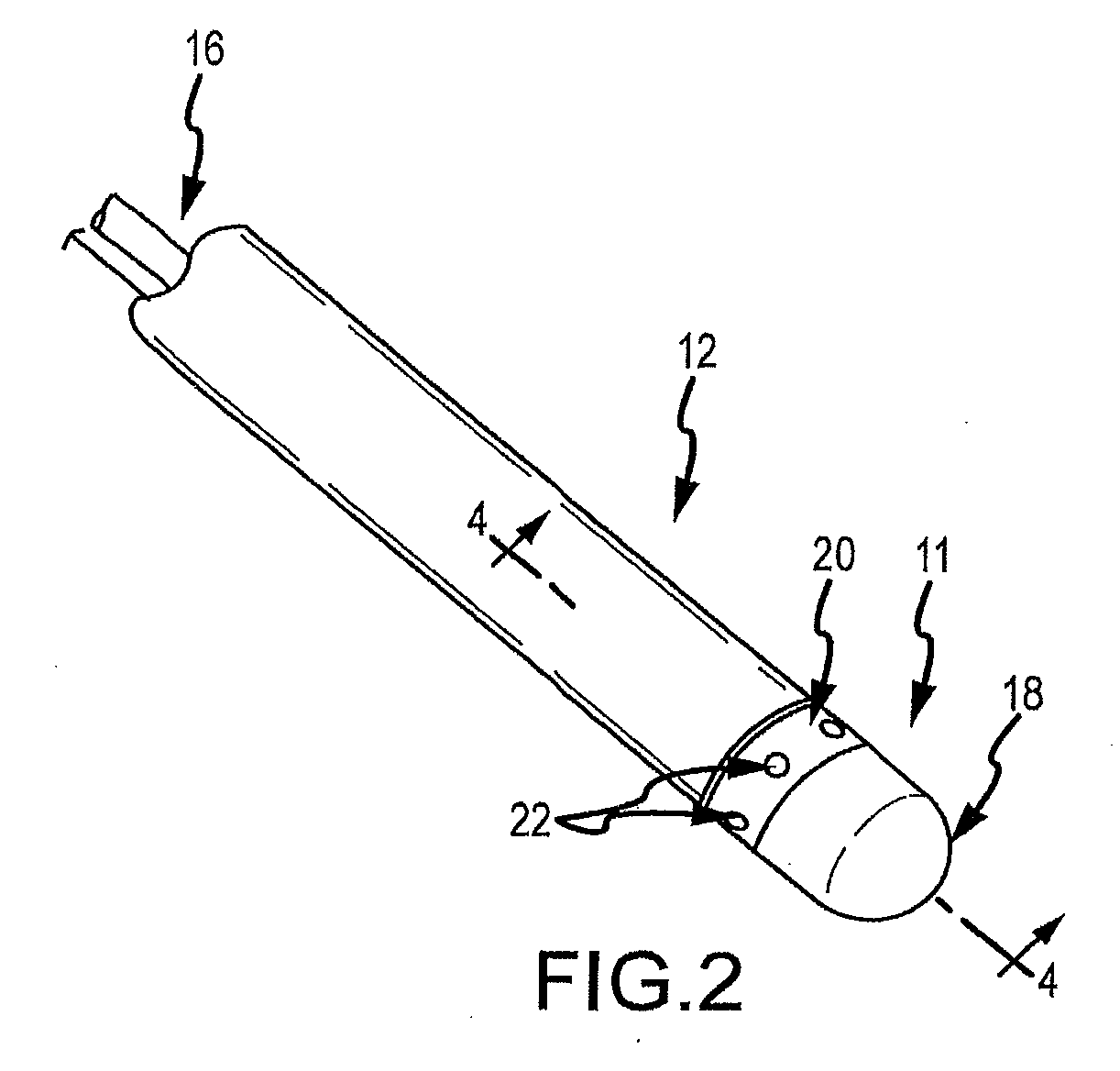
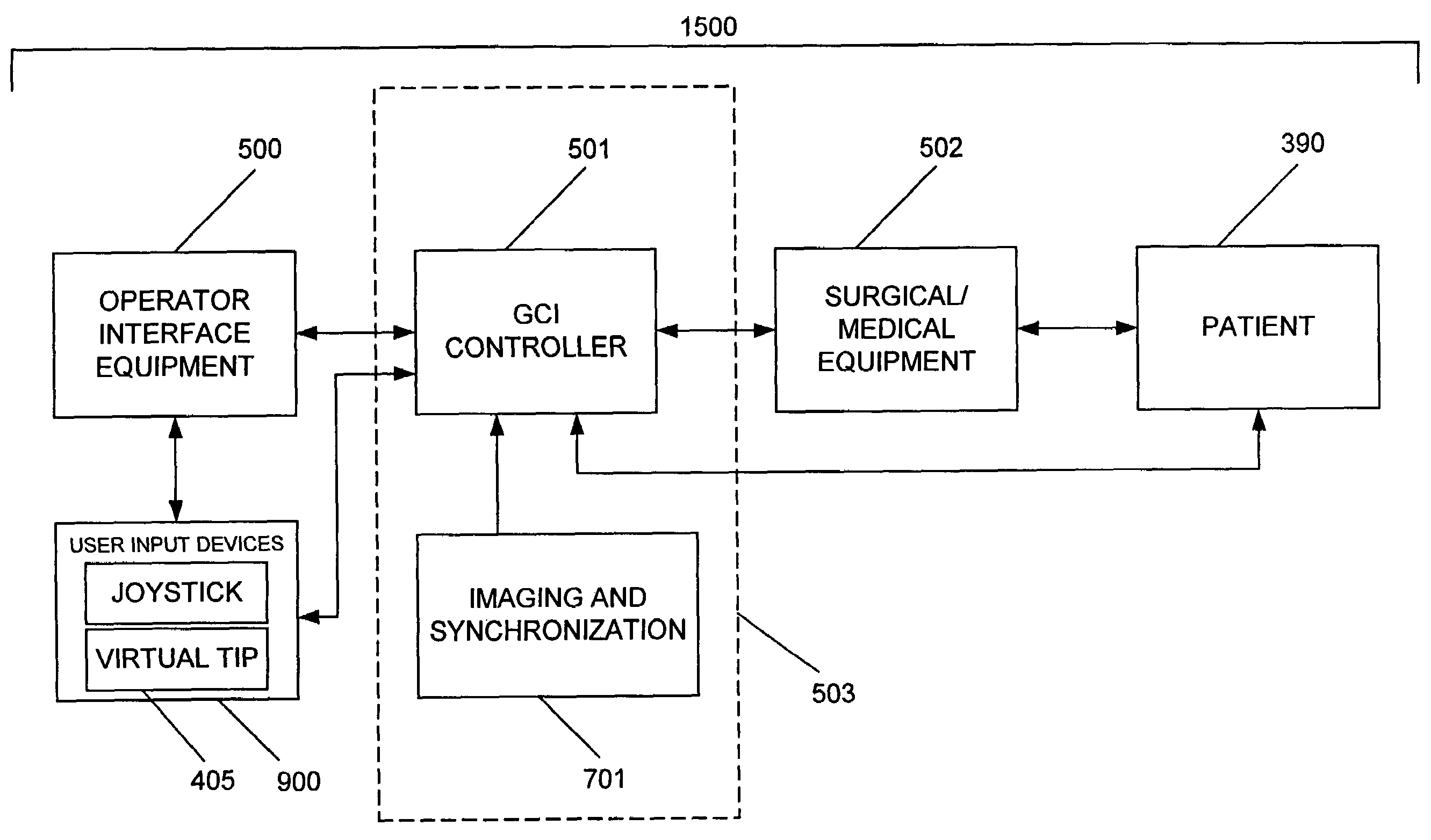
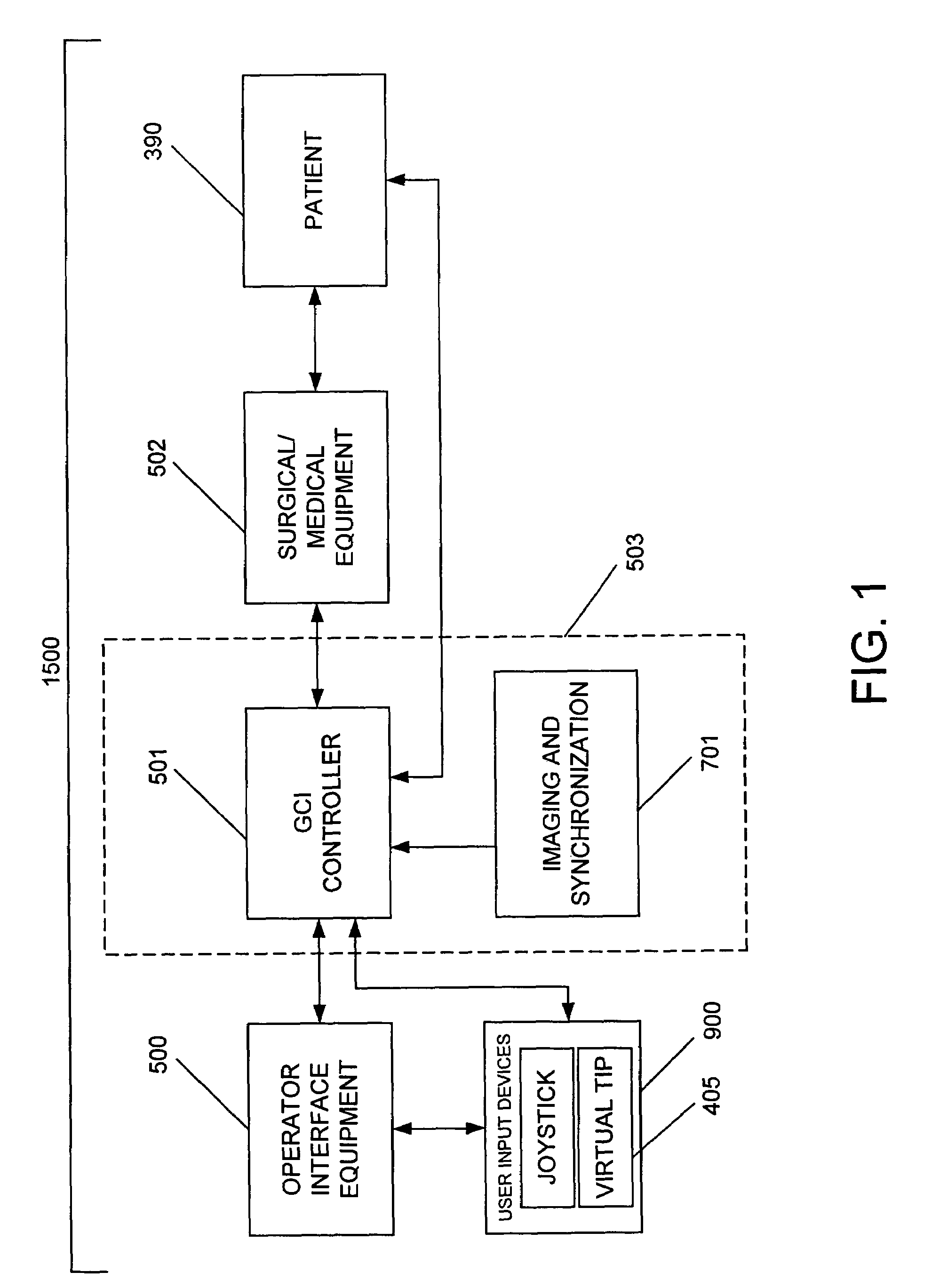
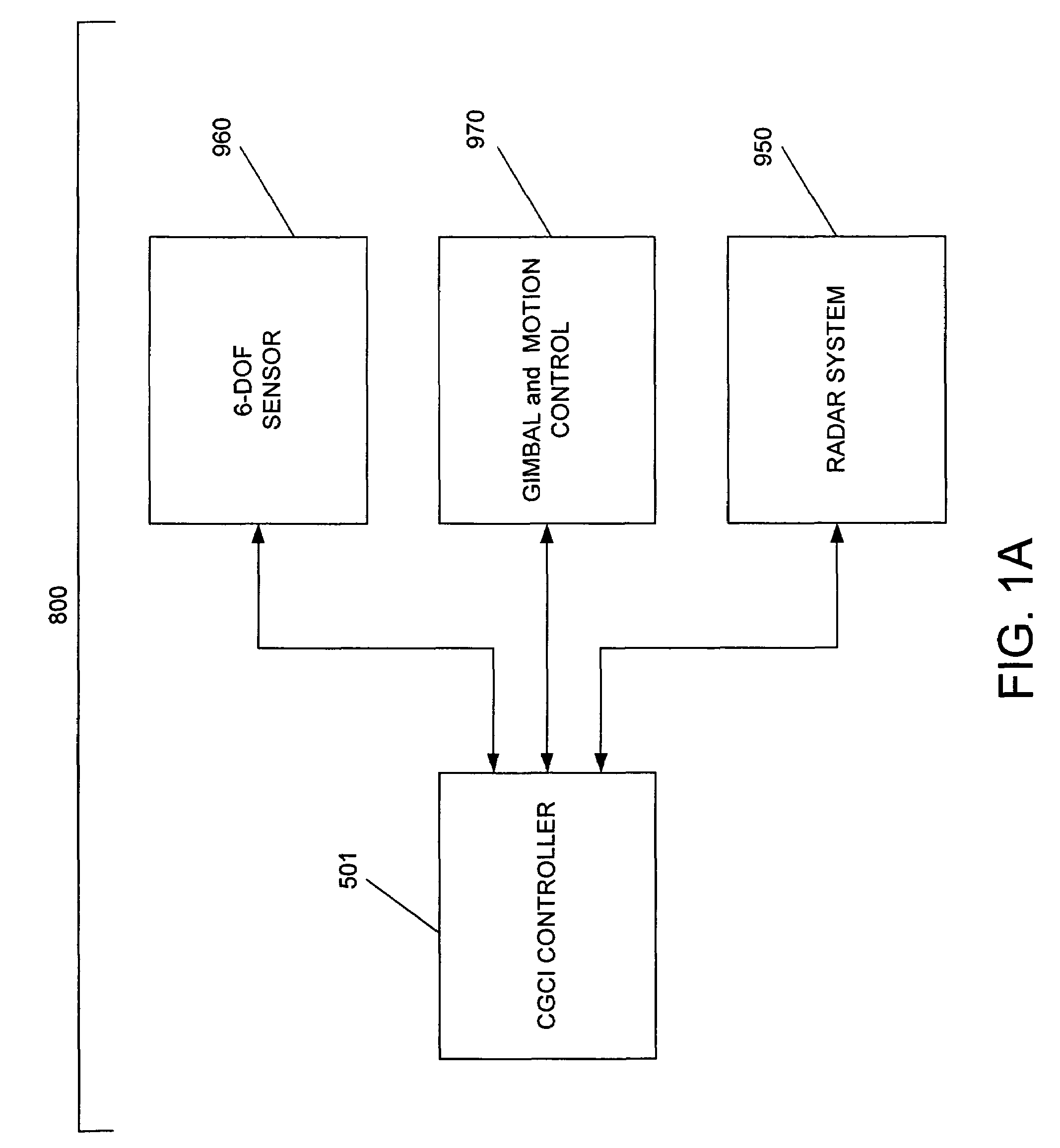
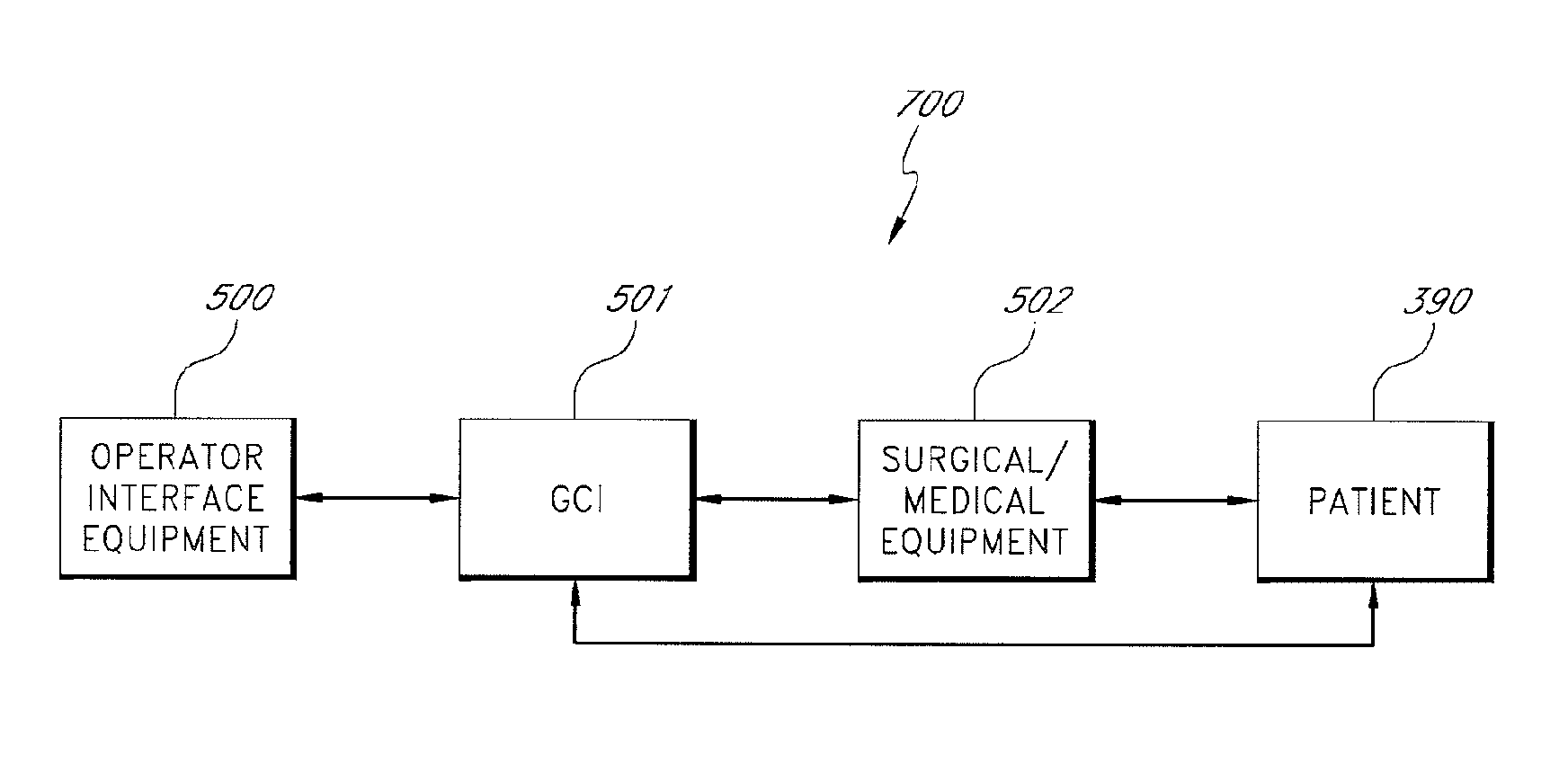
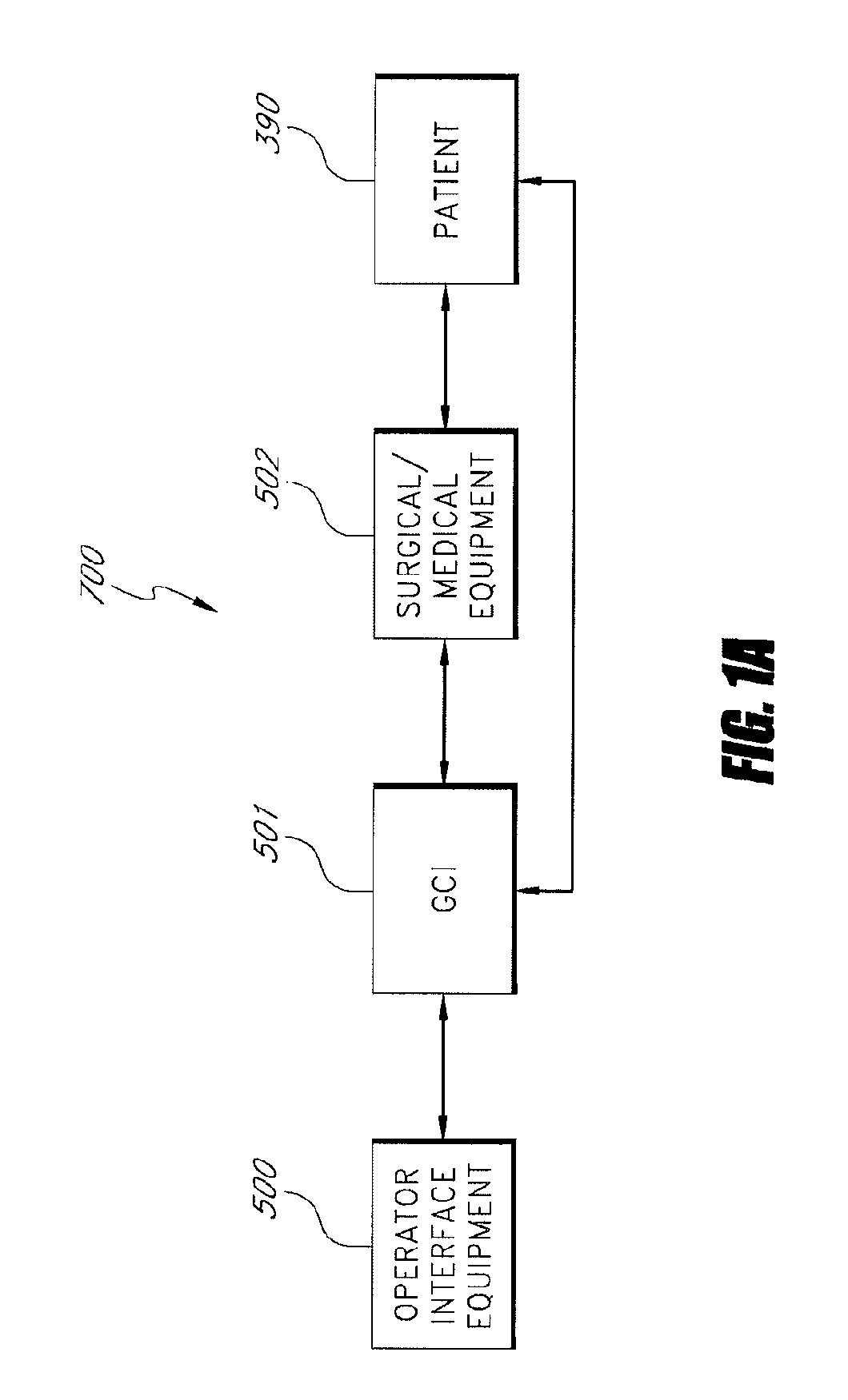
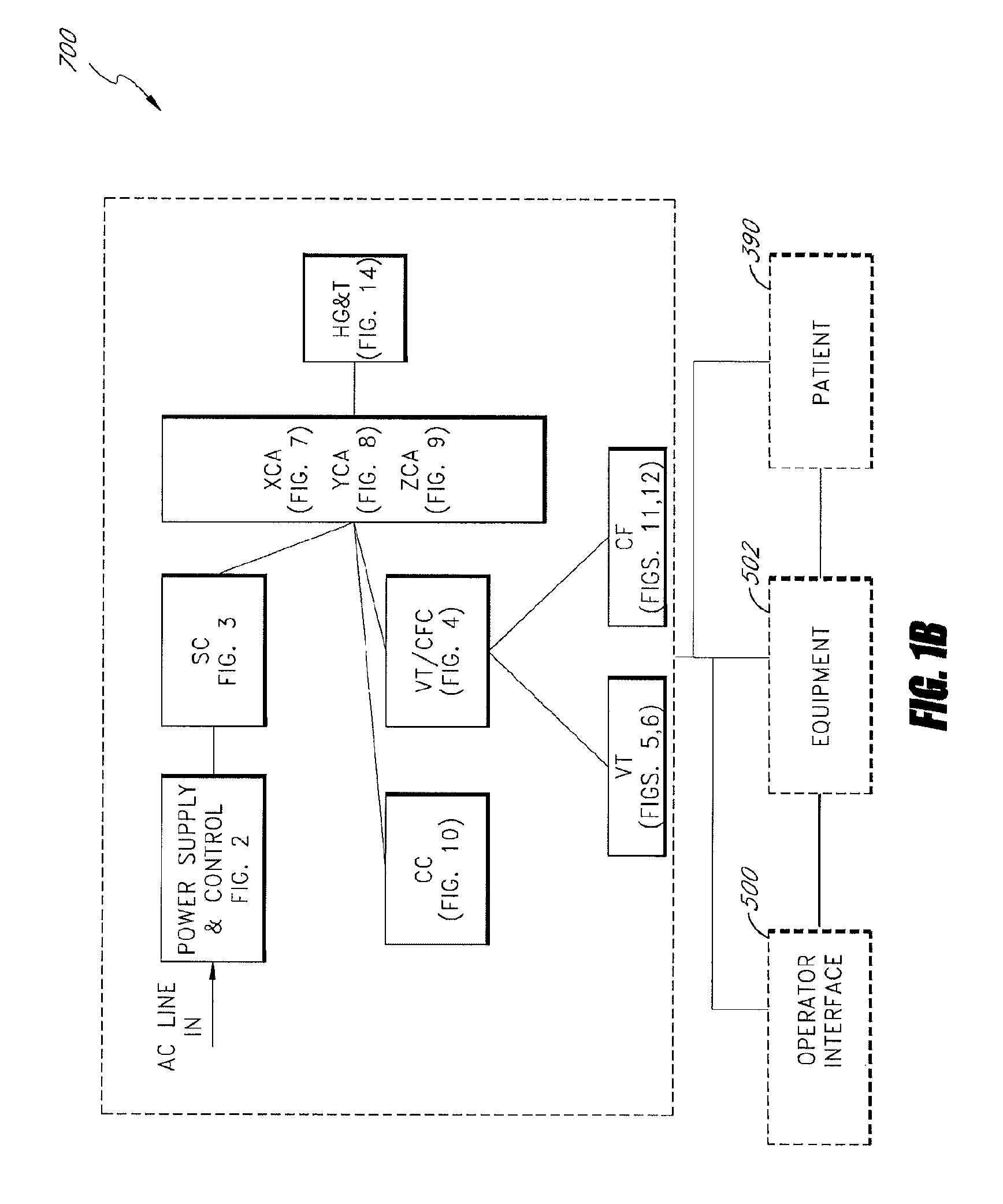
System and method for radar-assisted catheter guidance and control
InactiveUS20050096589A1Less trainingMinimizing and eliminating useEndoscopesMedical devicesRadar systemsGuidance control
A Catheter Guidance Control and Imaging (CGCI) system whereby a magnetic tip attached to a surgical tool is detected, displayed and influenced positionally so as to allow diagnostic and therapeutic procedures to be performed is described. The tools that can be so equipped include catheters, guidewires, and secondary tools such as lasers and balloons. The magnetic tip performs two functions. First, it allows the position and orientation of the tip to be determined by using a radar system such as, for example, a radar range finder or radar imaging system. Incorporating the radar system allows the CGCI apparatus to detect accurately the position, orientation and rotation of the surgical tool embedded in a patient during surgery. In one embodiment, the image generated by the radar is displayed with the operating room imagery equipment such as, for example, X-ray, Fluoroscopy, Ultrasound, MRI, CAT-Scan, PET-Scan, etc. In one embodiment, the image is synchronized with the aid of fiduciary markers located by a 6-Degrees of Freedom (6-DOF) sensor. The CGCI apparatus combined with the radar and the 6-DOF sensor allows the tool tip to be pulled, pushed, turned, and forcefully held in the desired position by applying an appropriate magnetic field external to the patient's body. A virtual representation of the magnetic tip serves as an operator control. This control possesses a one-to-one positional relationship with the magnetic tip inside the patient's body. Additionally, this control provides tactile feedback to the operator's hands in the appropriate axis or axes if the magnetic tip encounters an obstacle. The output of this control combined with the magnetic tip position and orientation feedback allows a servo system to control the external magnetic field.
Owner:NEURO KINESIS CORP
Irrigated ablation catheter having magnetic tip for magnetic field control and guidance
InactiveUS20080091193A1Electrode surface coolingPrecise processDiagnosticsSurgical instruments for heatingGuidance controlIrrigation fluids
Embodiments of the present invention provide an irrigated ablation electrode assembly for use with an irrigated catheter device comprises at least one passageway for a fluid with an outlet disposed at an external surface of the electrode assembly; a permanent magnet; a shield separating the permanent magnet from the at least one passageway and from an exterior, the shield being substantially less oxidizable than the permanent magnet; and an electrode having an external electrode surface. A catheter guidance control and imaging system drives the permanent magnet to guide and control the catheter tip. In specific embodiments, the irrigation fluid flow paths through the electrode assembly are thermally insulated from the electrode and temperature sensor. The irrigation fluid is directed at target areas where coagulation is more likely to occur. One or more monitoring electrodes are provided for mapping or other monitoring functions.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
System and method for radar-assisted catheter guidance and control
InactiveUS7280863B2Less trainingMinimizing and eliminating useMedical devicesEndoscopesRadar systemsTip position
A Catheter Guidance Control and Imaging (CGCI) system whereby a magnetic tip attached to a surgical tool is detected, displayed and influenced positionally so as to allow diagnostic and therapeutic procedures to be performed is described. The tools that can be so equipped include catheters, guidewires, and secondary tools such as lasers and balloons. The magnetic tip performs two functions. First, it allows the position and orientation of the tip to be determined by using a radar system such as, for example, a radar range finder or radar imaging system. Incorporating the radar system allows the CGCI apparatus to detect accurately the position, orientation and rotation of the surgical tool embedded in a patient during surgery. In one embodiment, the image generated by the radar is displayed with the operating room imagery equipment such as, for example, X-ray, Fluoroscopy, Ultrasound, MRI, CAT-Scan, PET-Scan, etc. In one embodiment, the image is synchronized with the aid of fiduciary markers located by a 6-Degrees of Freedom (6-DOF) sensor. The CGCI apparatus combined with the radar and the 6-DOF sensor allows the tool tip to be pulled, pushed, turned, and forcefully held in the desired position by applying an appropriate magnetic field external to the patient's body. A virtual representation of the magnetic tip serves as an operator control. This control possesses a one-to-one positional relationship with the magnetic tip inside the patient's body. Additionally, this control provides tactile feedback to the operator's hands in the appropriate axis or axes if the magnetic tip encounters an obstacle. The output of this control combined with the magnetic tip position and orientation feedback allows a servo system to control the external magnetic field.
Owner:NEURO KINESIS CORP
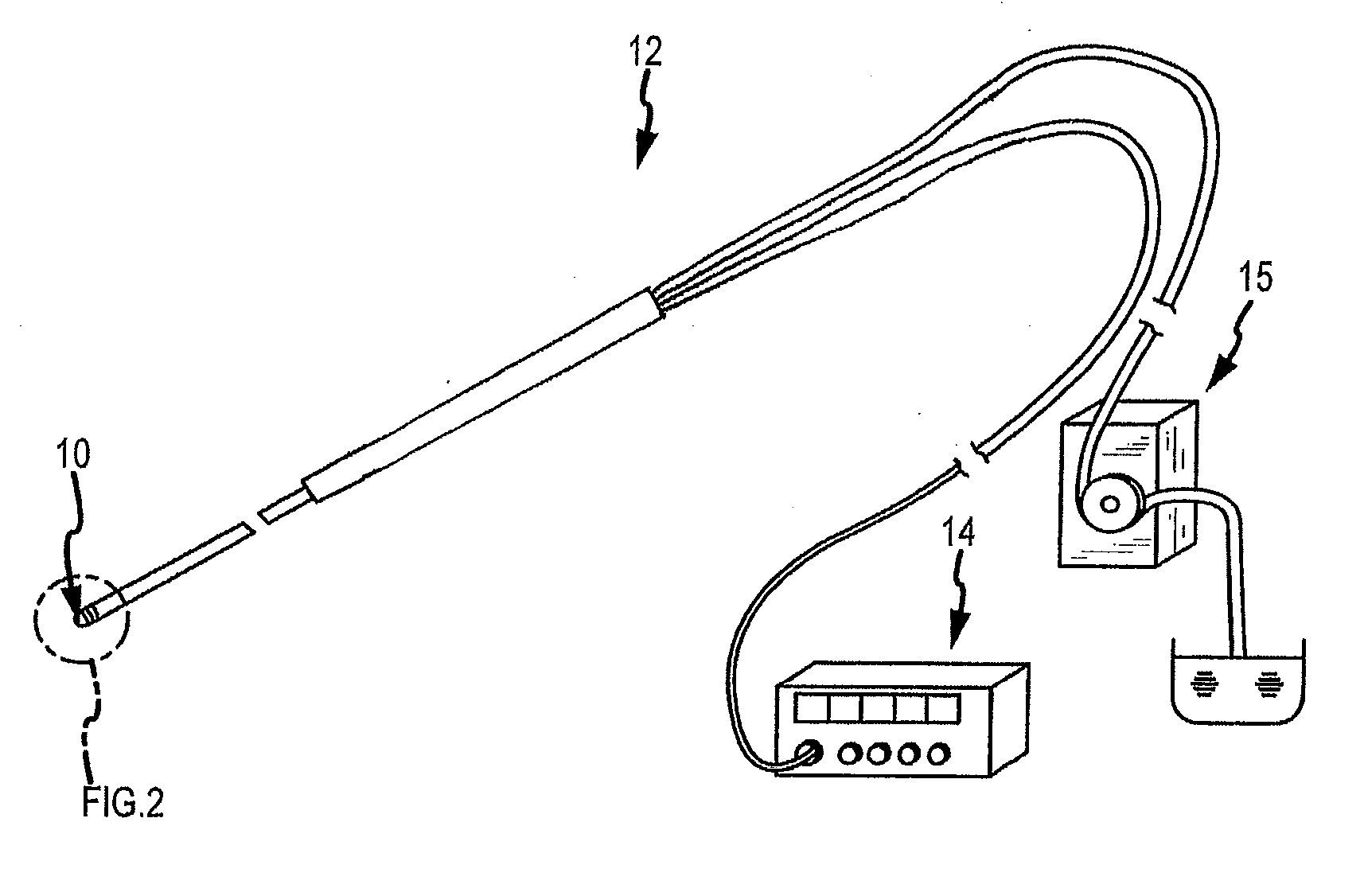
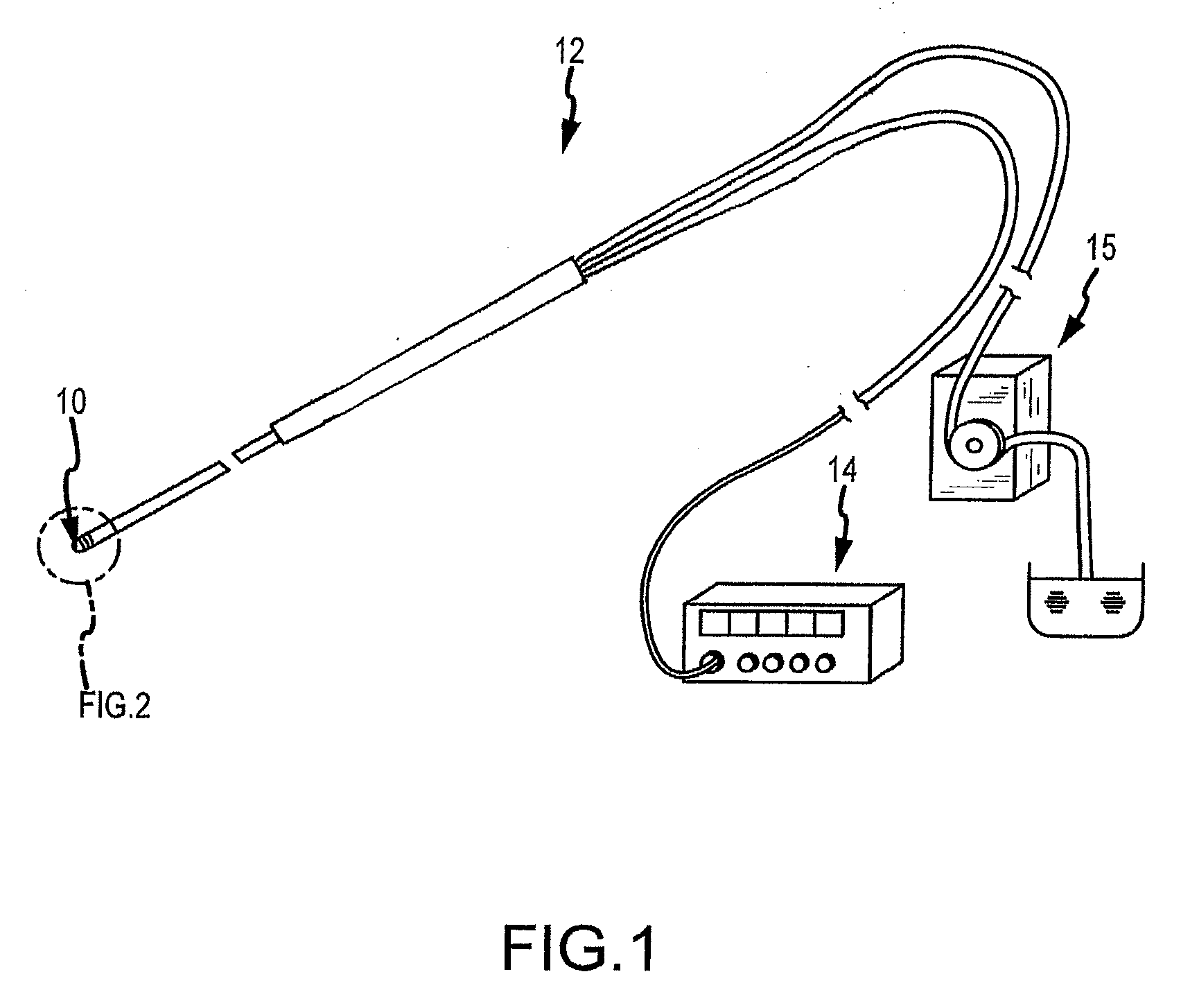
Apparatus and method for catheter guidance control and imaging
InactiveUS7769427B2Less trainingLess skillSurgical navigation systemsCatheterTip positionGuidance control
A system whereby a magnetic tip attached to a surgical tool is detected, displayed and positioned. A Virtual Tip serves as an operator control. Movement of the operator control produces corresponding movement of the magnetic tip inside the patient's body. Additionally, the control provides tactile feedback to the operator's hand in the appropriate axis or axes if the magnetic tip encounters an obstacle. The output of the control combined with the magnetic tip position and orientation feedback allows a servo system to control the external magnetic field by pulse width modulating the positioning electromagnet. Data concerning the dynamic position of a moving body part such as a beating heart offsets the servo systems response in such a way that the magnetic tip, and hence the secondary tool is caused to move in unison with the moving body part.
Owner:NEURO KINESIS CORP
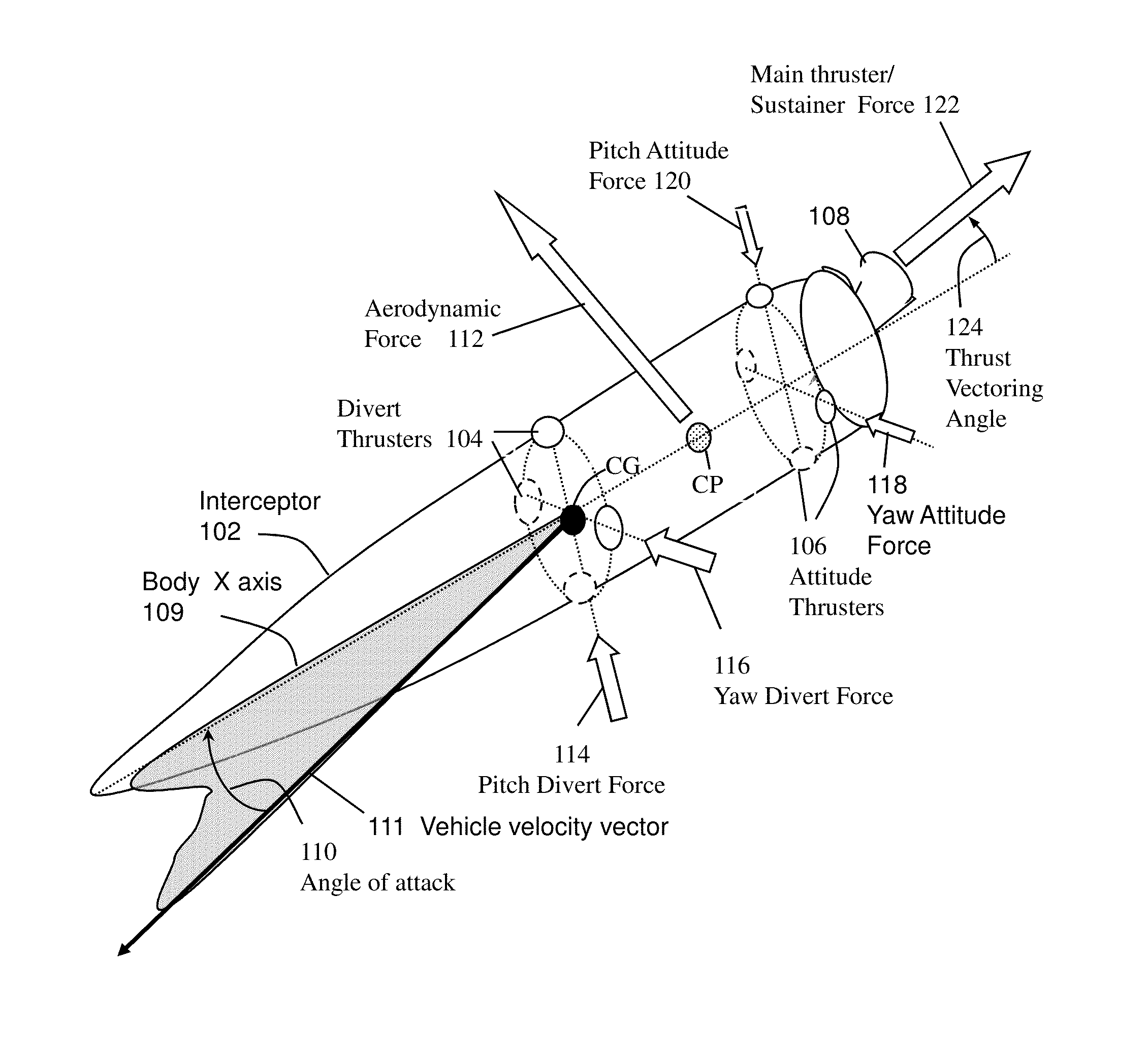
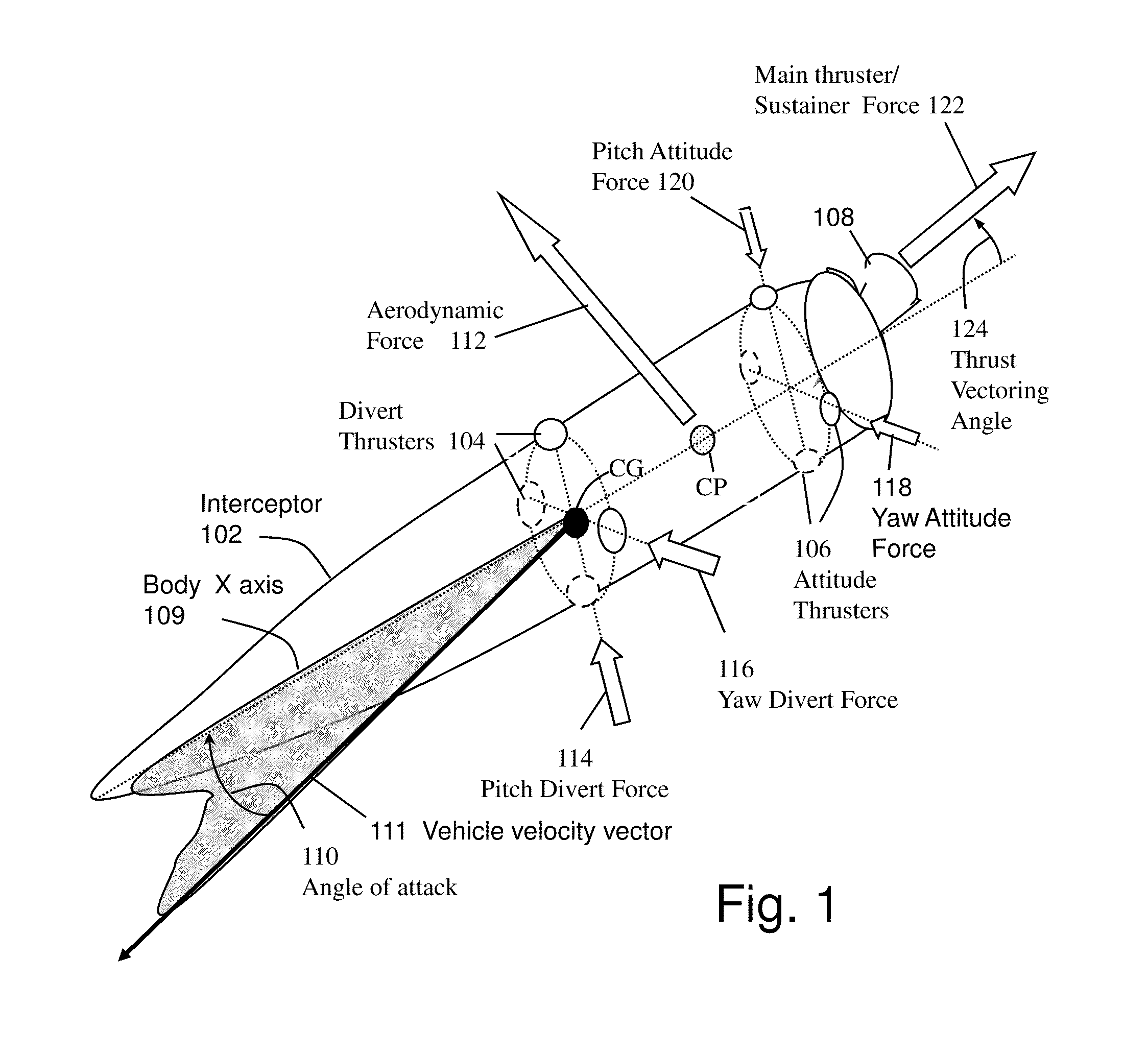
System and method for guiding and controlling a missile using high order sliding mode control
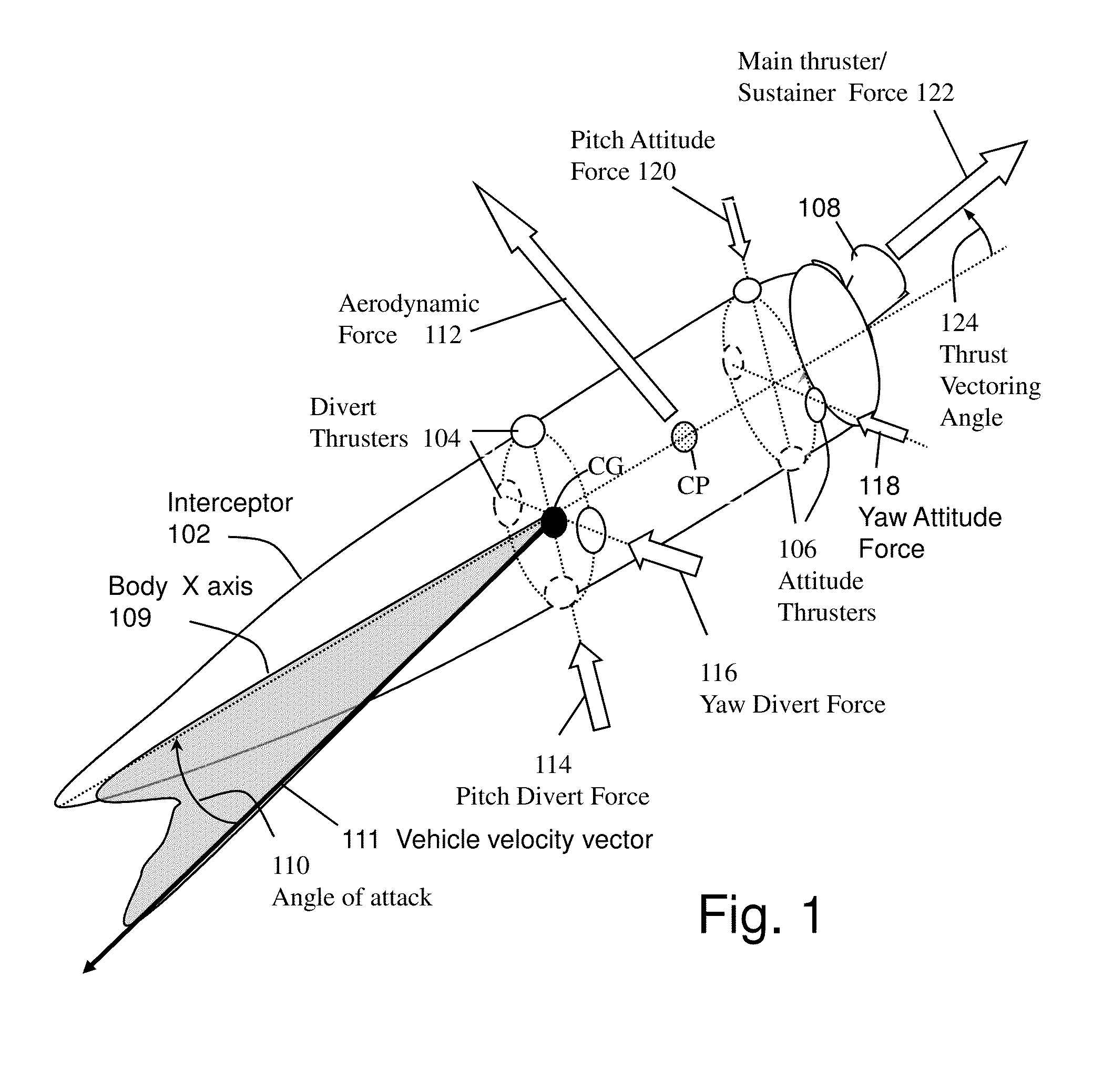
ActiveUS20130092785A1Reduce needPromote resultsDirection controllersTarget-seeking controlCouplingQuaternion
Higher Order Sliding Mode (HOSM) control techniques are applied to the Guidance Control (G&C) of interceptor missile in which velocity may be steered by combination of main thrust, aerodynamic lift and lateral on-off divert thrusters, and attitude may be steered by continuous or on-off actuators. Methods include the pointing of the seeker, its associated estimation processes, a guidance law that uses concurrent divert mechanisms, and an attitude autopilot. The insensitivity of the controller to matched disturbances allows the concurrent usage of the divert mechanisms without adverse effect on the accuracy. The controller also allows the de-coupling of the control of roll, pitch and yaw channels, and usage quaternions to represent body attitude and it provides control perfect robustness. While it conceivable to design separately the components of the G&C method, it is widely accepted that designing them in an integrated fashion usually produces a better result.
Owner:DAVIDSON TECH
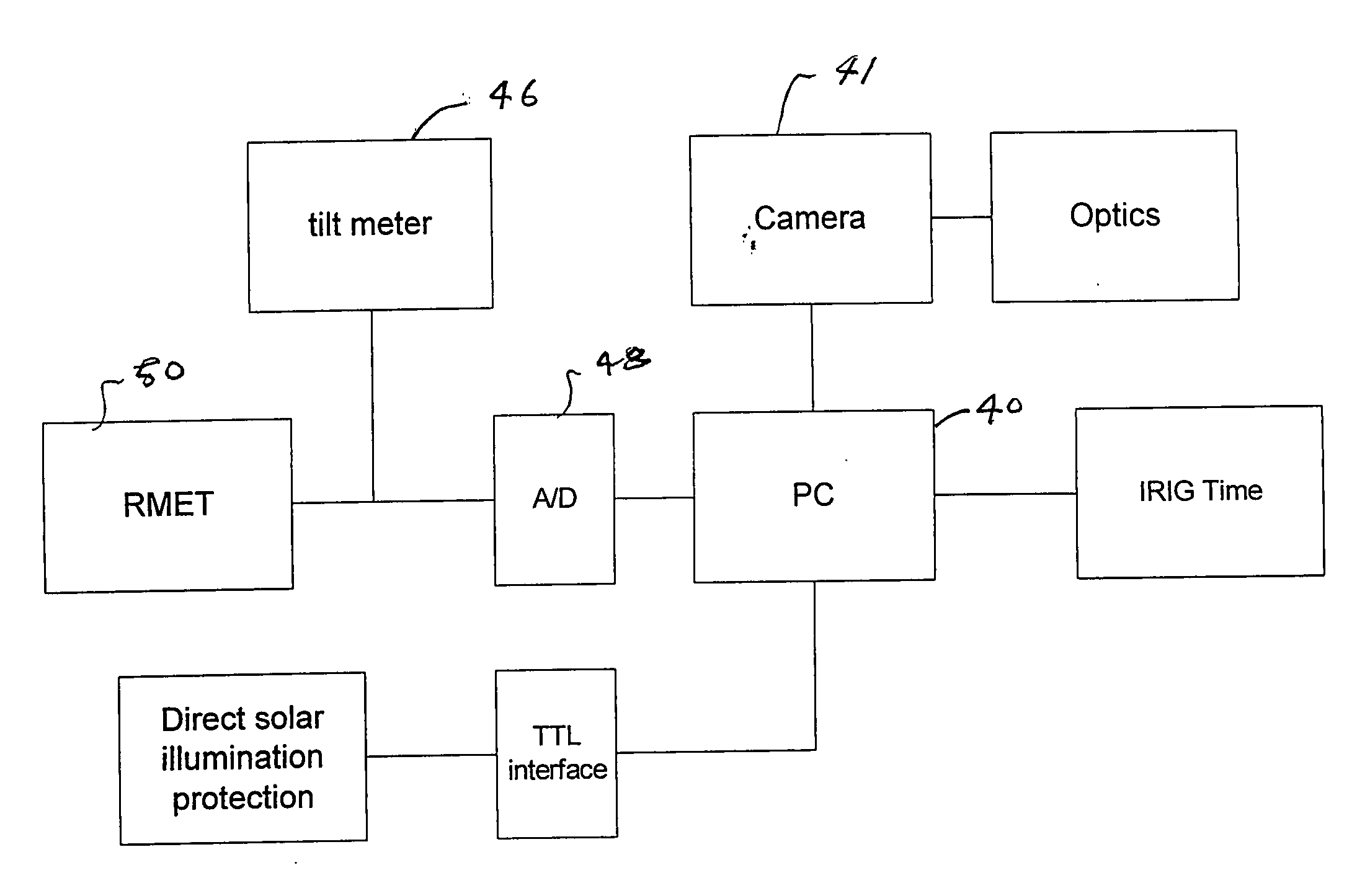
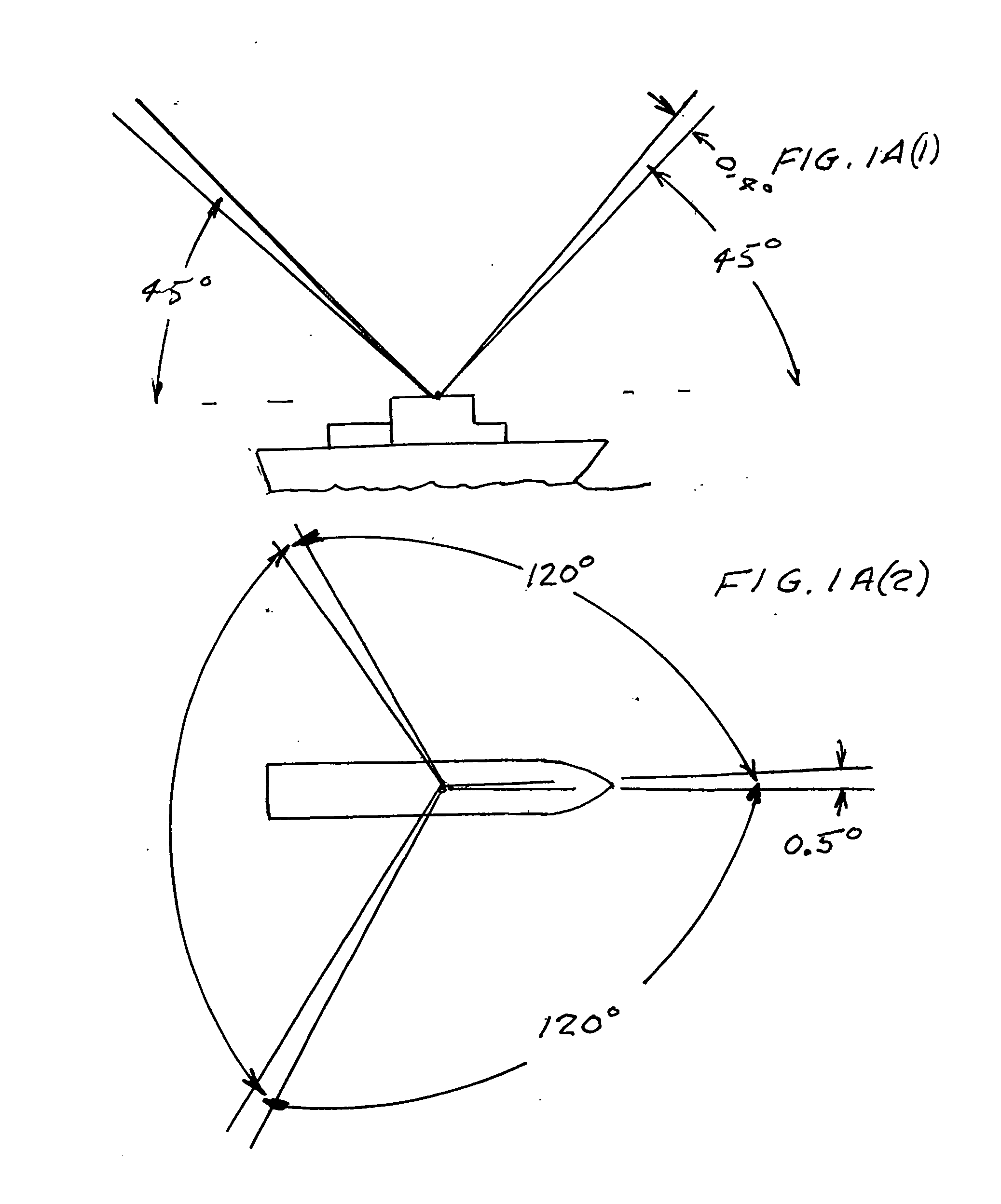
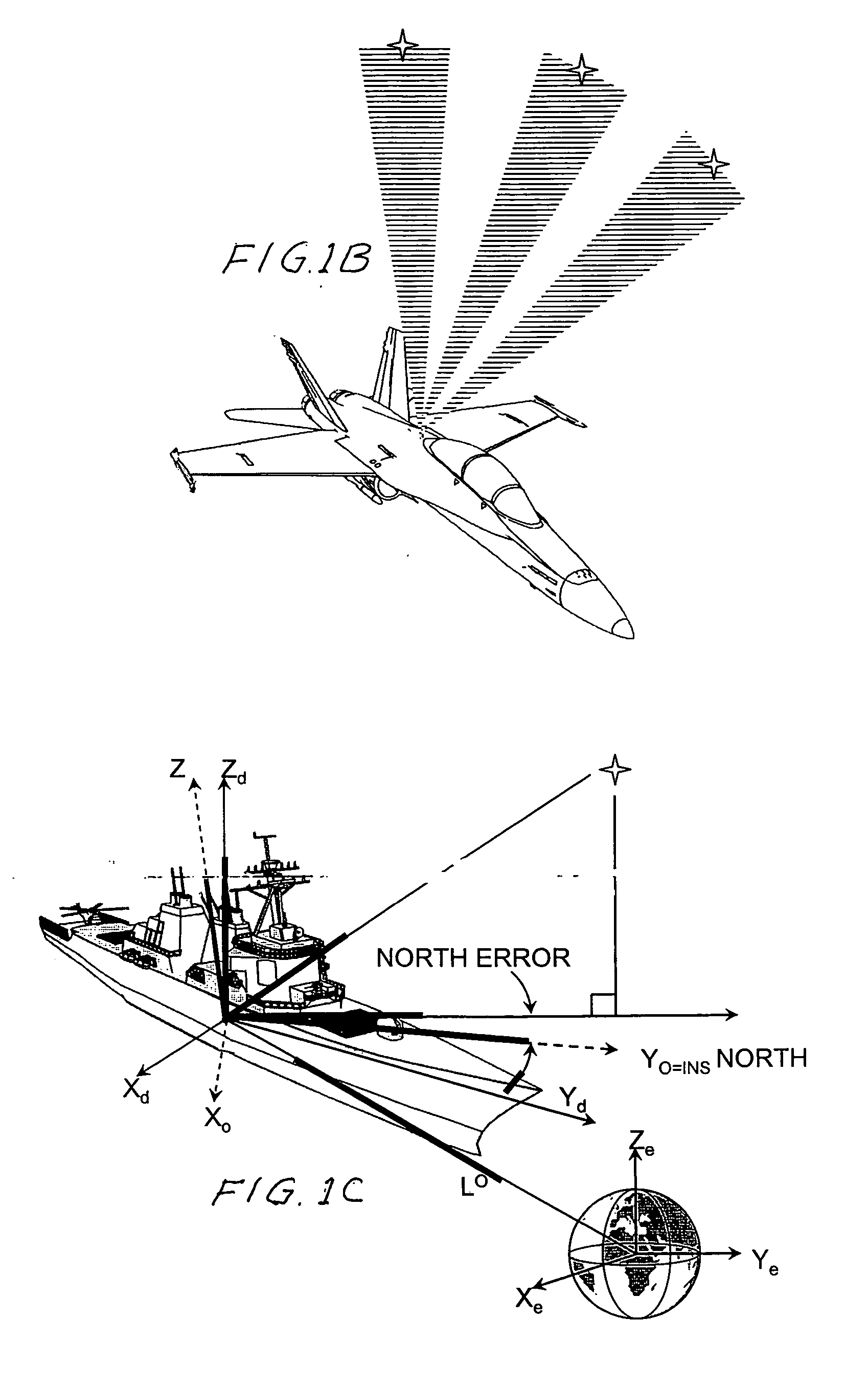
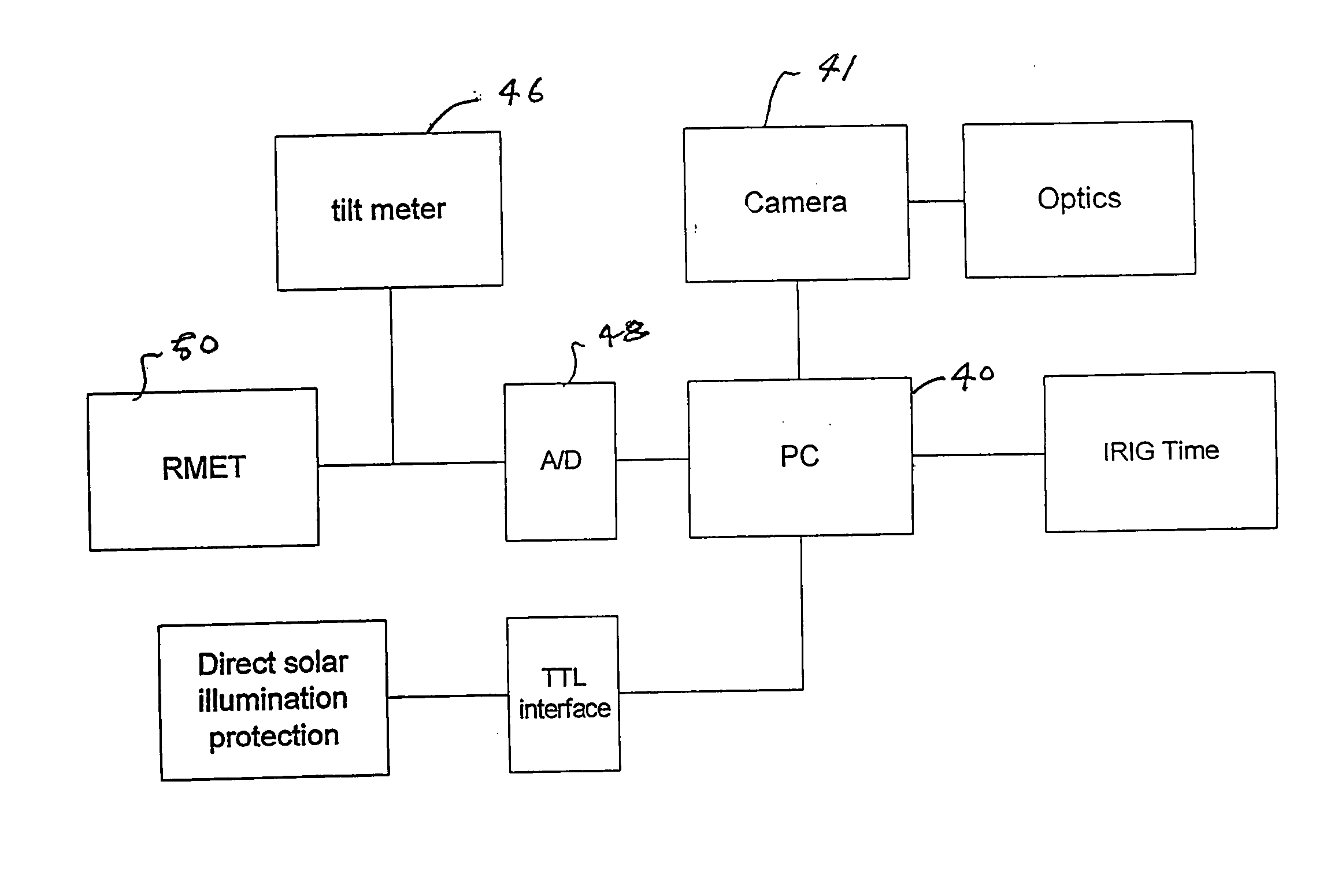
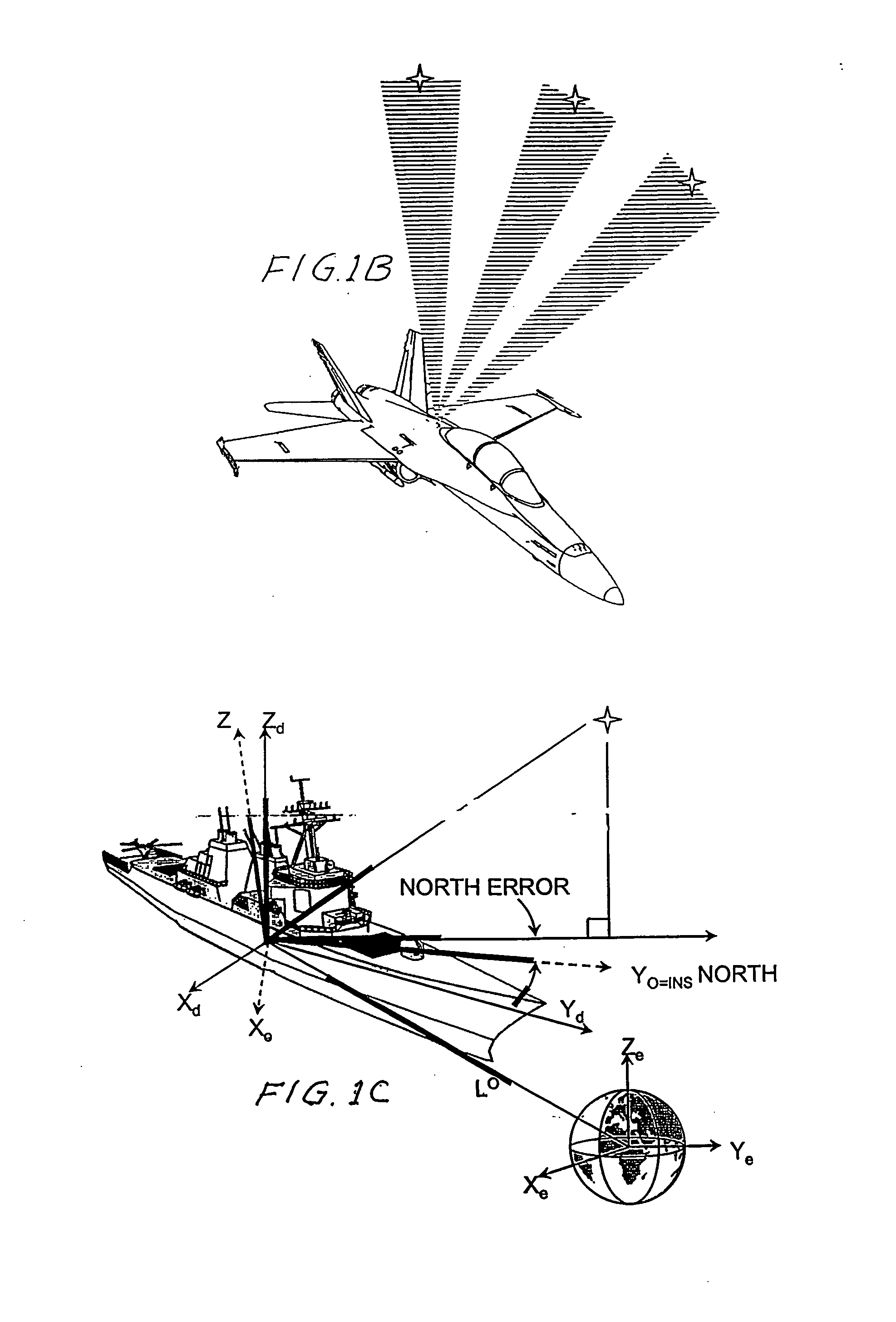
Daytime stellar imager
InactiveUS7349804B2Increase probabilityHighly preventive effectReactors manufactureNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsDisplay deviceLongitude
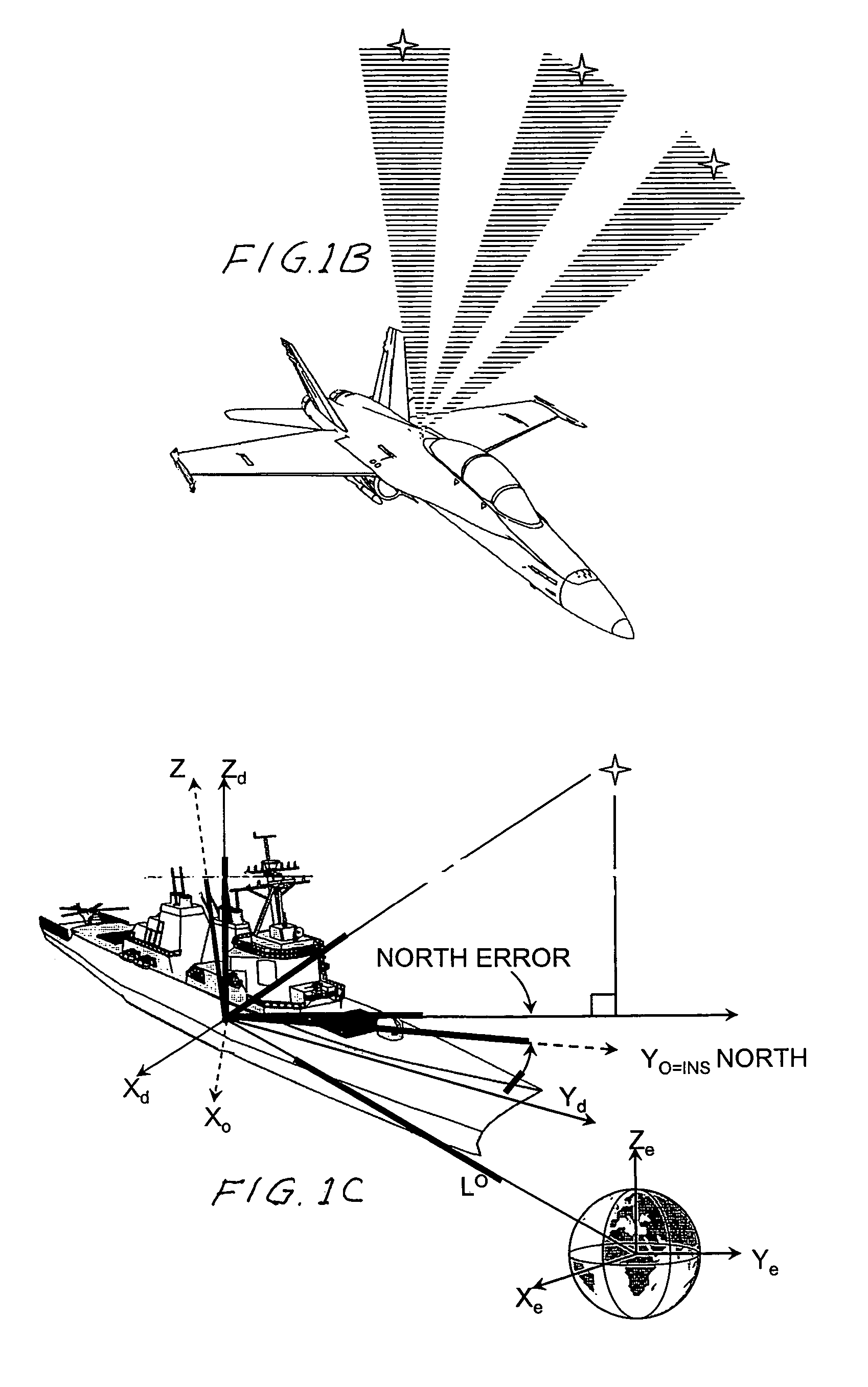
An automatic celestial navigation system for navigating both night and day by observation of K-band or H-band infrared light from multiple stars. In a first set of preferred embodiments three relatively large aperture telescopes are rigidly mounted on a movable platform such as a ship or airplane with each telescope being directed at a substantially different portion of sky. Embodiments in this first set tend to be relatively large and heavy, such as about one cubic meter and about 60 pounds. In a second set of preferred embodiments one or more smaller aperture telescopes are pivotably mounted on a movable platform such as a ship, airplane or missile so that the telescope or telescopes can be pivoted to point toward specific regions of the sky. Embodiments of this second set are mechanically more complicated than those of the first set, but are much smaller and lighter and are especially useful for guidance of aircraft and missiles. Telescope optics focus (on to a pixel array of a sensor) H-band or K-band light from one or more stars in the field of view of each telescope. Each system also includes an inclinometer, an accurate timing device and a computer processor having access to catalogued infrared star charts. The processor for each system is programmed with special algorithms to use image data from the infrared sensors, inclination information from the inclinometer, time information from the timing device and the catalogued star charts information to determine positions of the platform. Direction information from two stars is needed for locating the platform with respect to the celestial sphere. The computer is also preferably programmed to use this celestial position information to calculate latitude and longitude which may be displayed on a display device such as a monitor or used by a guidance control system. These embodiments are jam proof and insensitive to radio frequency interference. These systems provide efficient alternatives to GPS when GPS is unavailable and can be used for periodic augmentation of inertial navigation systems.
Owner:TREX ENTERPRISES CORP
Living body guidance control method for a biometrics authentication device, and biometrics authentication device
ActiveUS20080226136A1Improve reliabilityShorten the timePerson identificationImage data processing detailsComputer hardwareBiological body
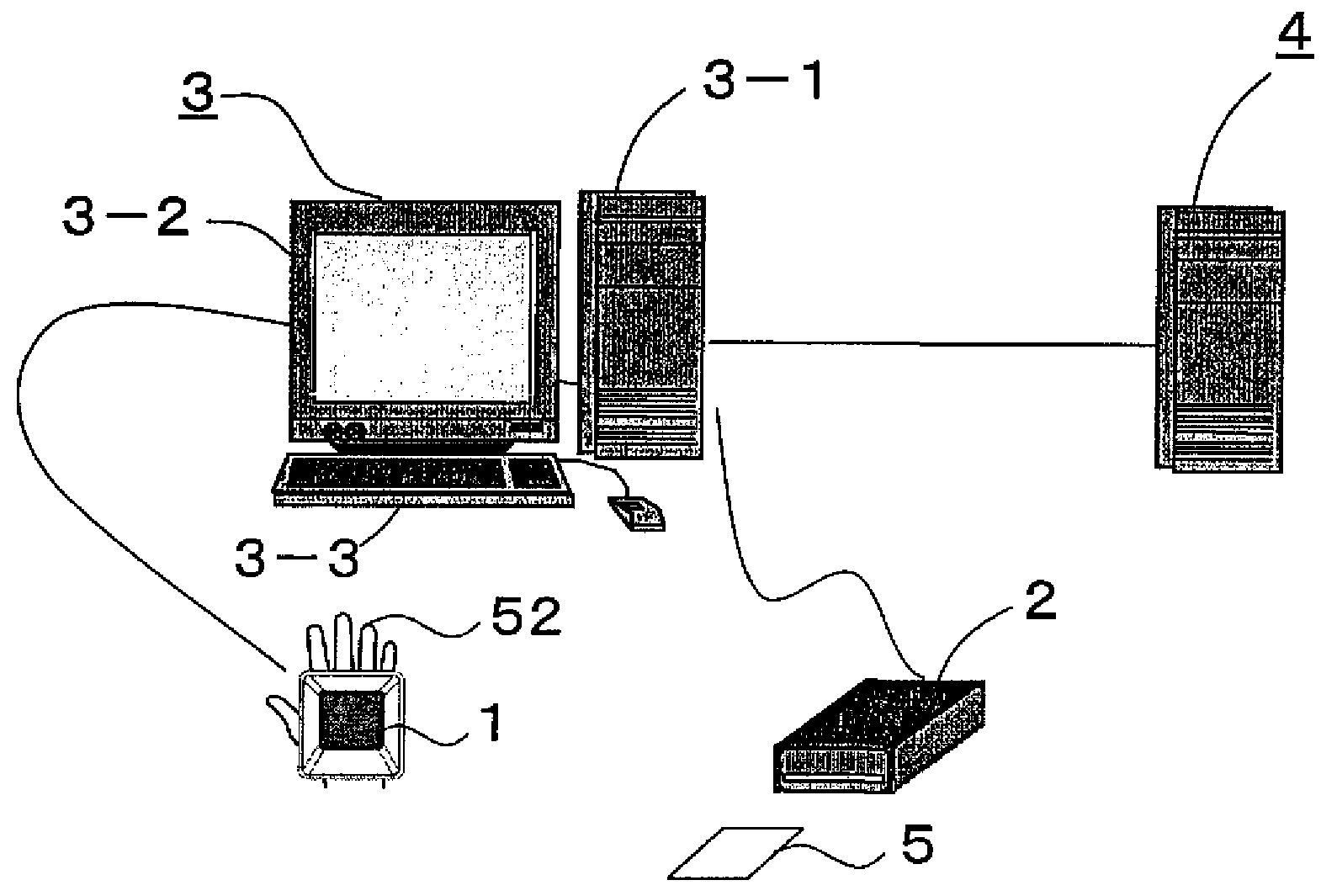
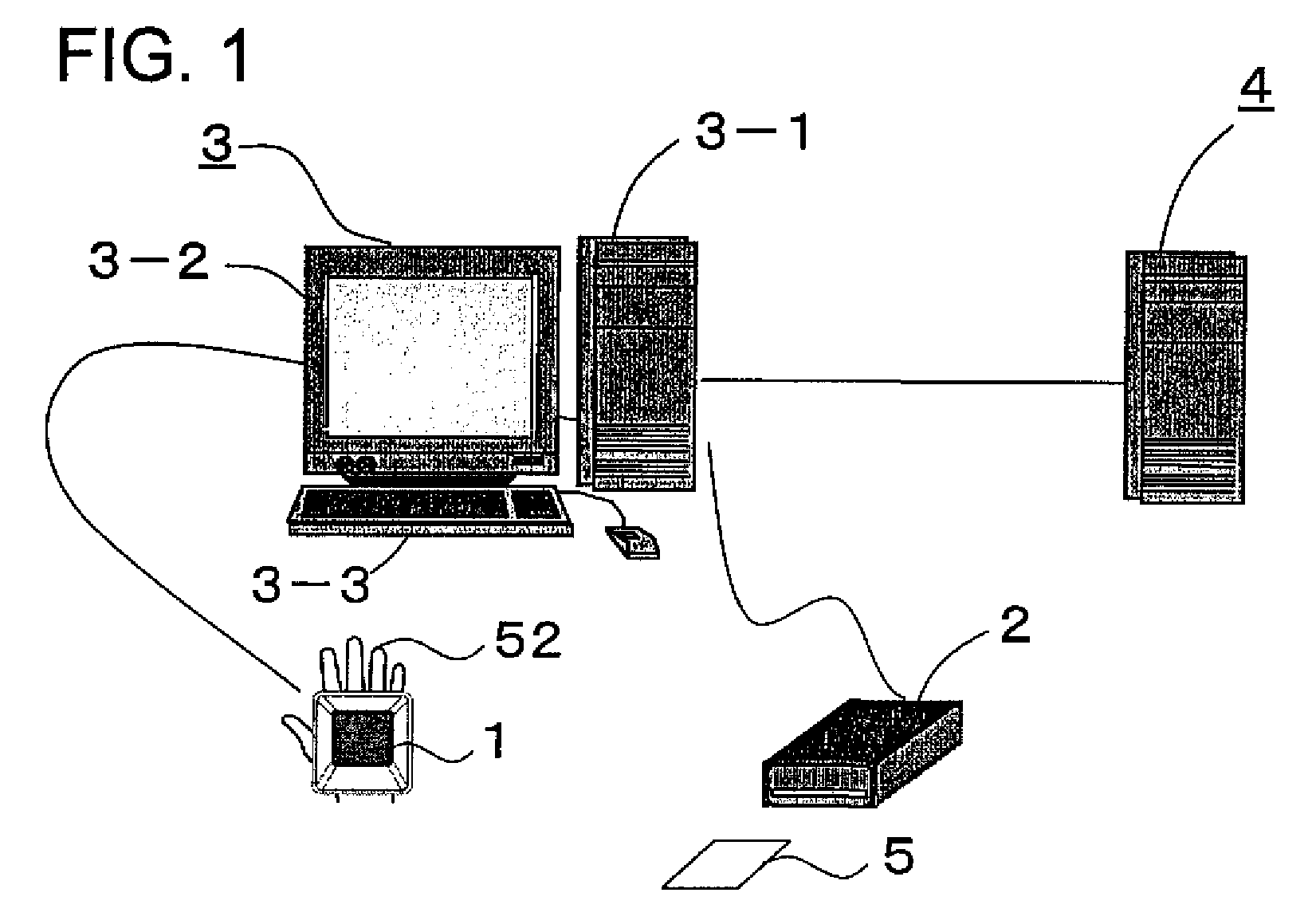
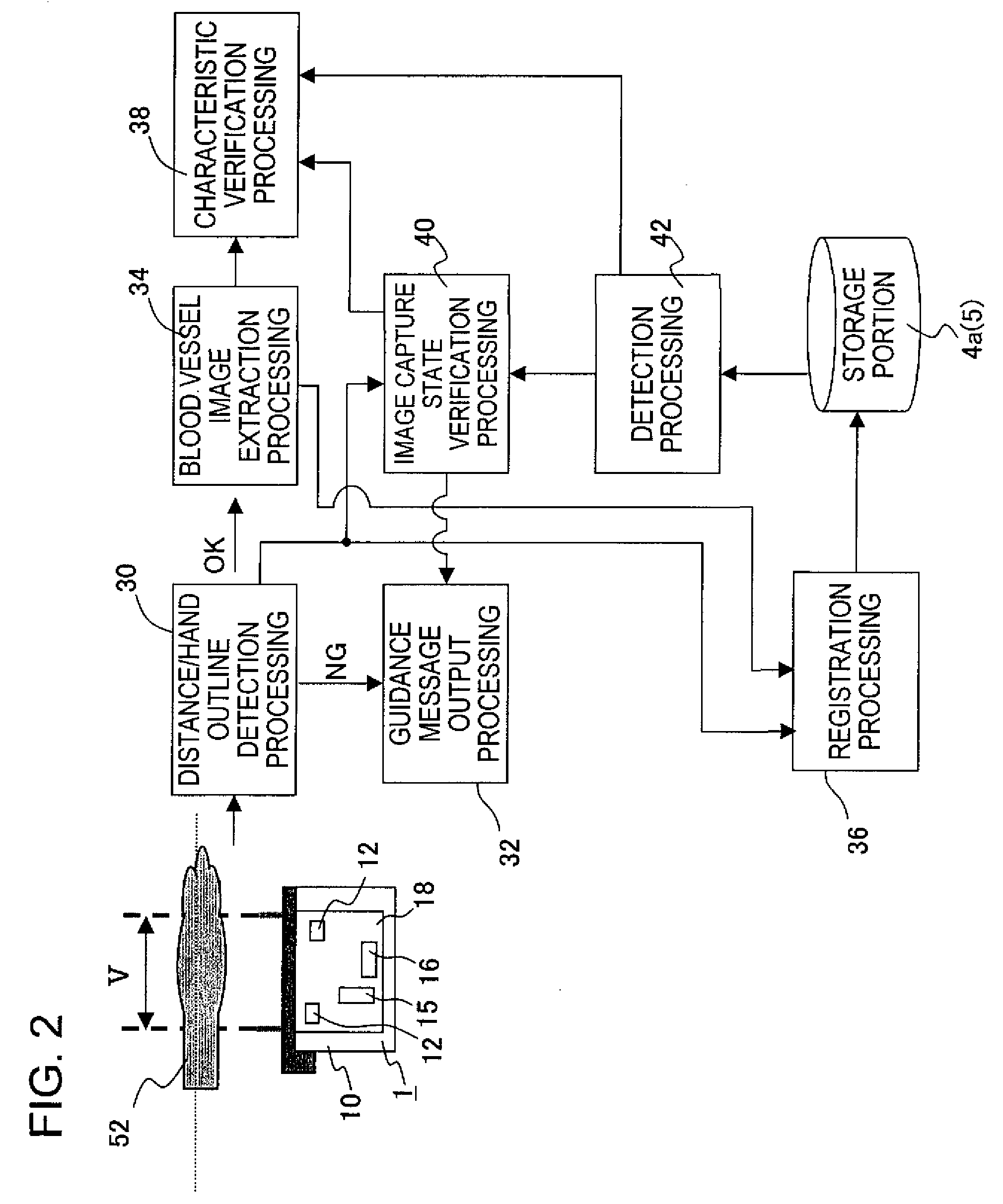
A biometrics authentication device identifies characteristics of the body from captured images of the body and performs individual authentication. The device guides a user, at the time of verification, to the image capture state at the time of registration of biometrics characteristic data. At the time of registration of biometrics characteristic data, body image capture state data is extracted from an image captured by an image capture unit and is registered in a storage unit, and at the time of verification the registered image capture state data is read from the storage unit and is compared with image capture state data extracted at the time of verification, and guidance of the body is provided. Alternatively, an outline of the body at the time of registration, taken from image capture state data at the time of registration, is displayed.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD +1
Daytime stellar imager
InactiveUS20070038374A1Small and light systemAvoid star image blurCosmonautic vehiclesDigital data processing detailsDisplay deviceLongitude
An automatic celestial navigation system for navigating both night and day by observation of K-band or H-band infrared light from multiple stars. In a first set of preferred embodiments three relatively large aperture telescopes are rigidly mounted on a movable platform such as a ship or airplane with each telescope being directed at a substantially different portion of sky. Embodiments in this first set tend to be relatively large and heavy, such as about one cubic meter and about 60 pounds. In a second set of preferred embodiments one or more smaller aperture telescopes are pivotably mounted on a movable platform such as a ship, airplane or missile so that the telescope or telescopes can be pivoted to point toward specific regions of the sky. Embodiments of this second set are mechanically more complicated than those of the first set, but are much smaller and lighter and are especially useful for guidance of aircraft and missiles. Telescope optics focus (on to a pixel array of a sensor) H-band or K-band light from one or more stars in the field of view of each telescope. Each system also includes an inclinometer, an accurate timing device and a computer processor having access to catalogued infrared star charts. The processor for each system is programmed with special algorithms to use image data from the infrared sensors, inclination information from the inclinometer, time information from the timing device and the catalogued star charts information to determine positions of the platform. Direction information from two stars is needed for locating the platform with respect to the celestial sphere. The computer is also preferably programmed to use this celestial position information to calculate latitude and longitude which may be displayed on a display device such as a monitor or used by a guidance control system. These embodiments are jam proof and insensitive to radio frequency interference. These systems provide efficient alternatives to GPS when GPS is unavailable and can be used for periodic augmentation of inertial navigation systems.
Owner:TREX ENTERPRISES CORP
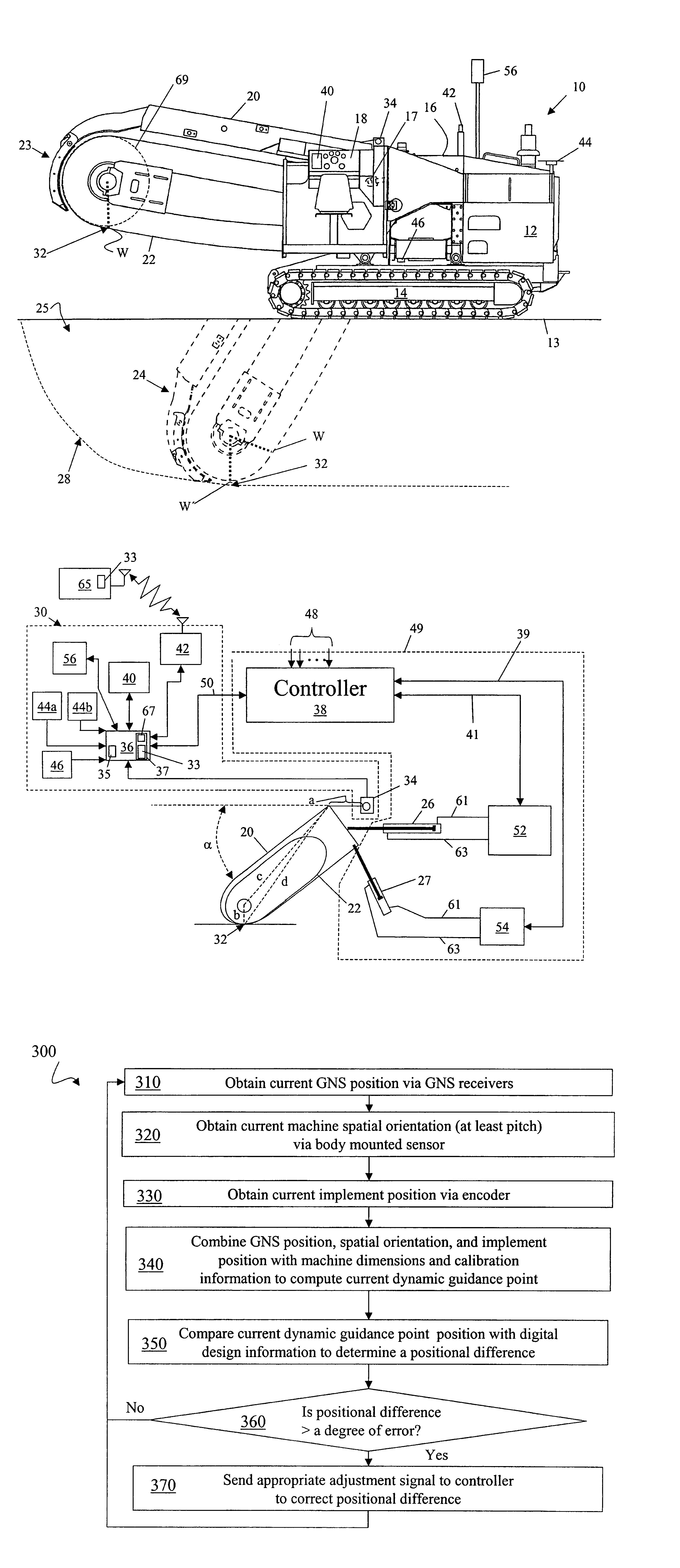
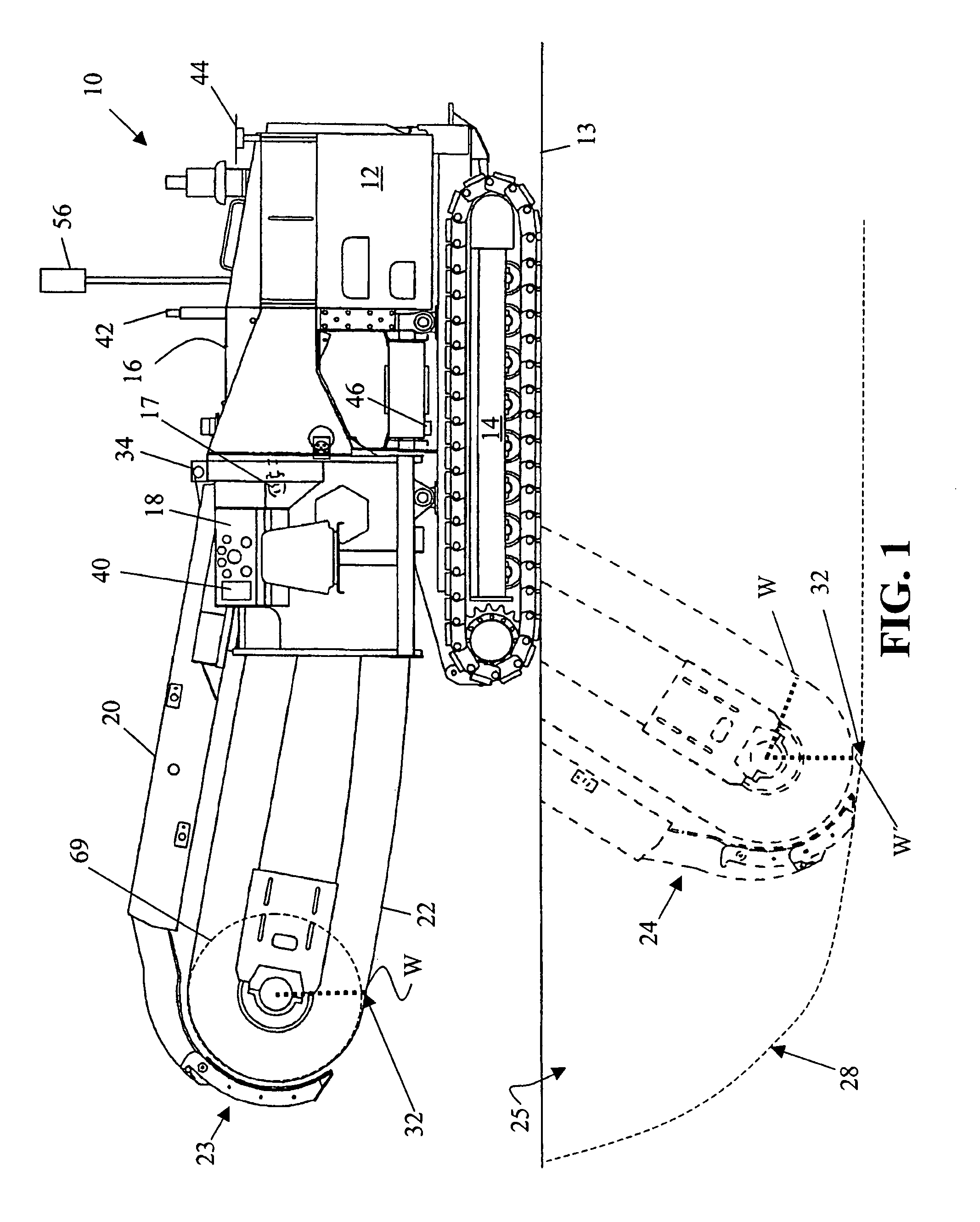
Trencher guidance via GPS
ActiveUS6954999B1Analogue computers for trafficSoil-shifting machines/dredgersSpatial OrientationsControl system
A guidance control system is configured to control the positioning and spatial orientation of a digging implement mounted on a frame of an trenching machine for working a subsurface of earth to a desired trench profile. The position of a dynamic cutting edge of the digging implement is monitored and then controlled so that the sensed dynamic cutting edge position is equal substantially to the calculated dynamic cutting edge position. The guidance control system includes sensors, a processor, and accessible memory providing digital design information regarding the desired trench profile.
Owner:TRIMBLE NAVIGATION LTD
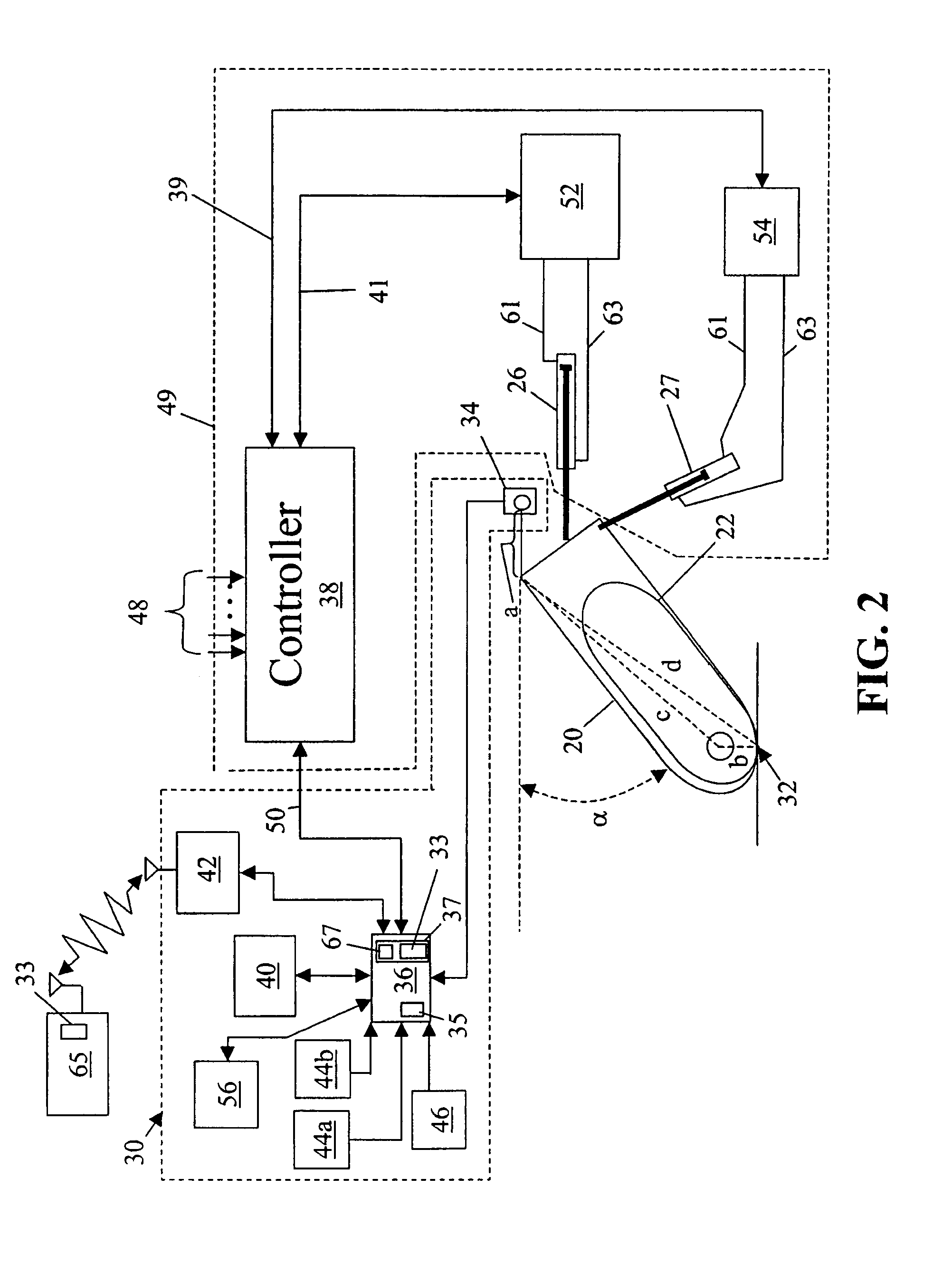
System and Method for Configuring a Guidance Controller
ActiveUS20100023229A1Analogue computers for trafficGuiding agricultural machinesGuidance controlEngineering
System and method for configuring guidance controllers. In one embodiment, a method includes detecting an implement, by a guidance controller, coupled to a machine. The method may further include determining a characteristic of the implement which affects a calibration parameter of the guidance controller and configuring the calibration parameter of the guidance controller based, at least in part, on the characteristic of the implement. An operational path of the machine may be controlled based on the calibration parameter.
Owner:TRIMBLE NAVIGATION LTD
Daytime stellar imager for attitude determination
InactiveUS20060085130A1Small and light systemAvoid star image blurInstruments for road network navigationPosition fixationJet aeroplaneGuidance control
An automatic celestial navigation system for navigating both night and day by observation of K-band or H-band infrared light from multiple stars. In a first set of preferred embodiments three relatively large aperture telescopes are rigidly mounted on a movable platform such as a ship or airplane with each telescope being directed at a substantially different portion of sky. Embodiments in this first set tend to be relatively large and heavy, such as about one cubic meter and about 60 pounds. In a second set of preferred embodiments one or more smaller aperture telescopes are pivotably mounted on a movable platform such as a ship, airplane or missile so that the telescope or telescopes can be pivoted to point toward specific regions of the sky. Embodiments of this second set are mechanically more complicated than those of the first set, but are much smaller and lighter and are especially useful for guidance of aircraft and missiles. Telescope optics focus (on to a pixel array of a sensor) H-band or K-band light from one or more stars in the field of view of each telescope. Each system also includes a GPS sensor and a computer processor having access to catalogued infrared star charts. The processor for each system is programmed with special algorithms to use image data from the infrared sensors, position and timing information from the GPS sensor, and the catalogued star charts information to determine orientation (attitude) of the platform. Direction information from two stars is needed for locating the platform with respect to the celestial sphere. The computer is also preferably programmed to calculate further information which may be used by a guidance control system. These systems provide efficient alternatives to inertial navigation systems when such systems are too expensive and can be used for periodic augmentation and calibration of inertial navigation systems.
Owner:TREX ENTERPRISES CORP
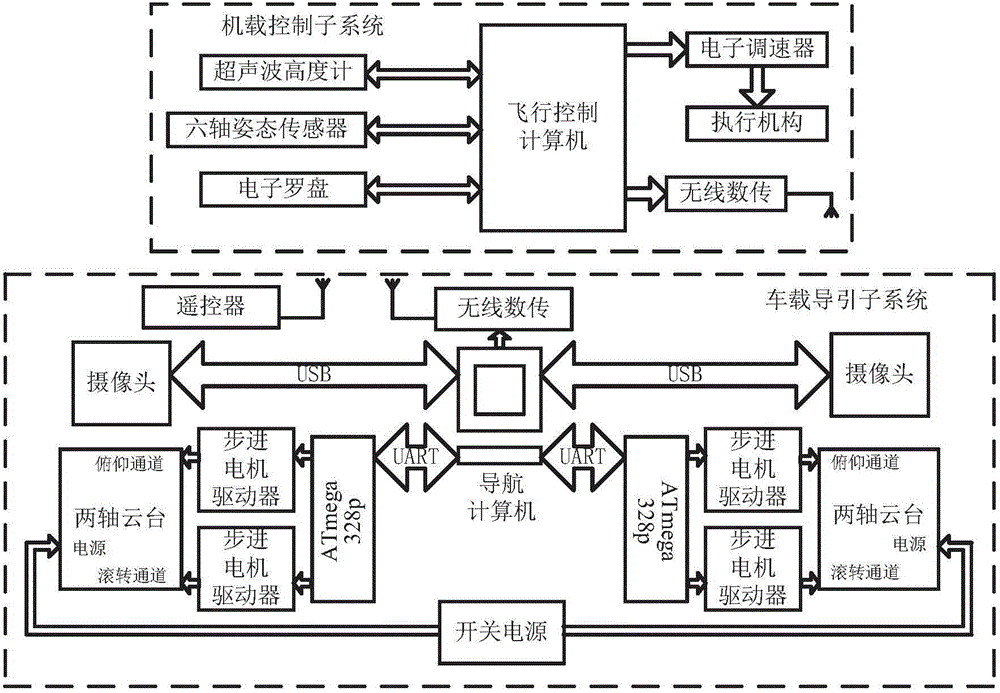
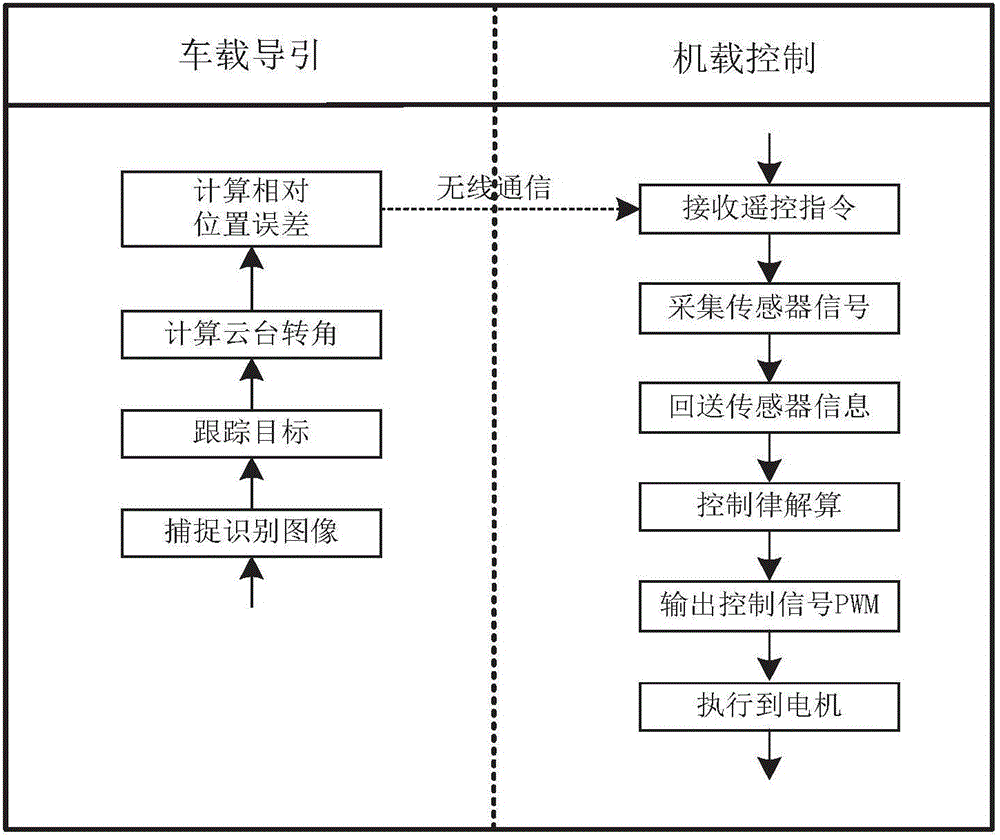
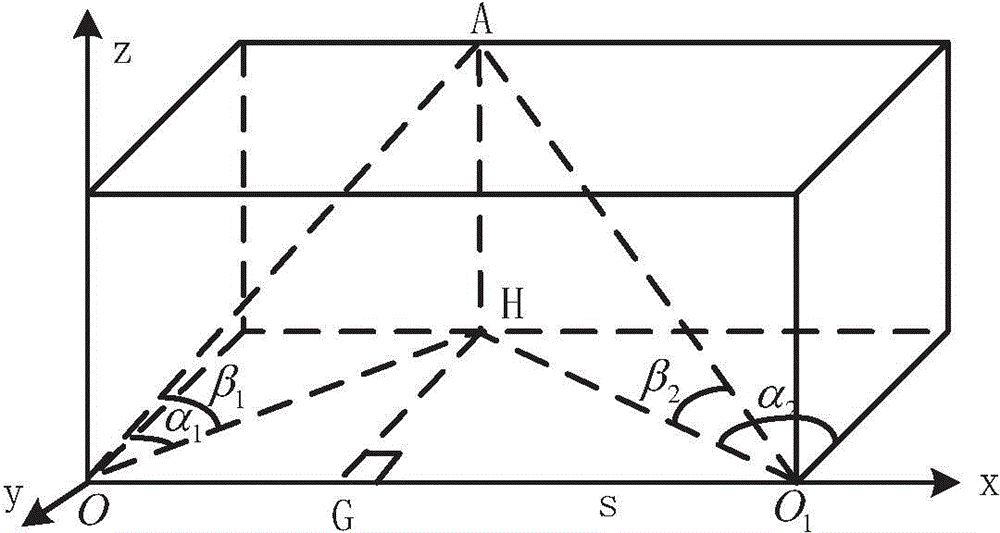
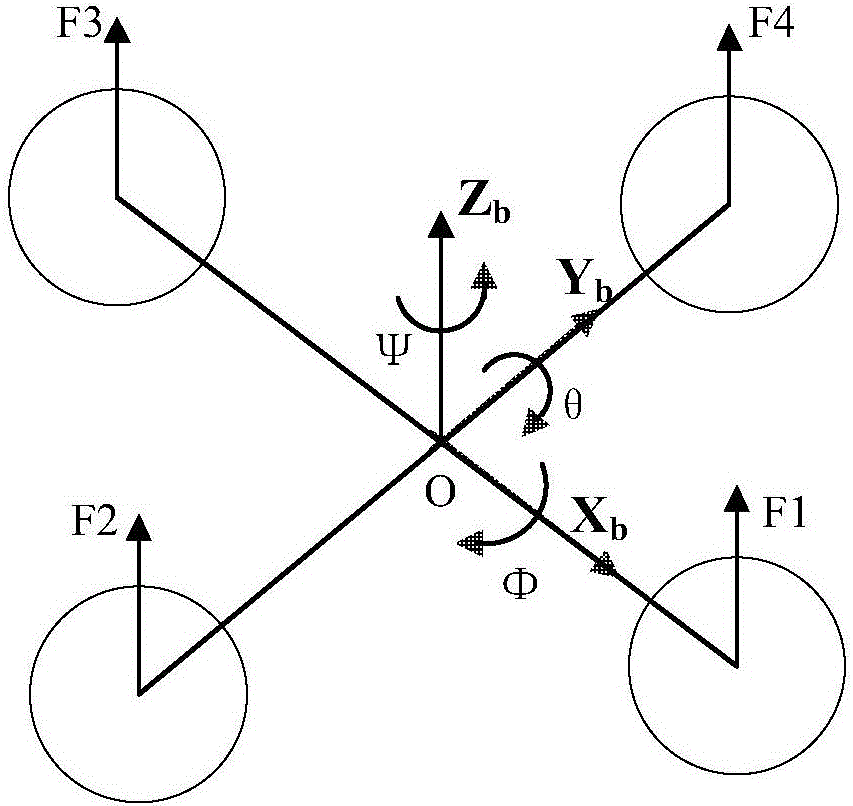
Vehicle-mounted multi-rotor unmanned helicopter landing guidance control system and guidance control method
InactiveCN104656664APrecise positioningImprove practicalityPosition/course control in three dimensionsControl systemGuidance control
The invention discloses a vehicle-mounted multi-rotor unmanned helicopter landing guidance control system and a guidance control method. The control system comprises a vehicle-mounted guidance subsystem and an airborne control subsystem, wherein the vehicle-mounted guidance subsystem mainly comprises two visual processing systems and a navigational computer. On the basis of the guidance control system and with the adoption of a binocular vision guidance method, a multi-rotor unmanned helicopter is accurately positioned according to data resolving of the two visual processing systems, a flying control computer controls the multi-rotor unmanned helicopter to land in the target position of a vehicle, the practicability of the multi-rotor unmanned helicopter is improved, and the application range of the multi-rotor unmanned helicopter is increased.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Low-altitude autonomous navigation system for rotary-wing unmanned plane
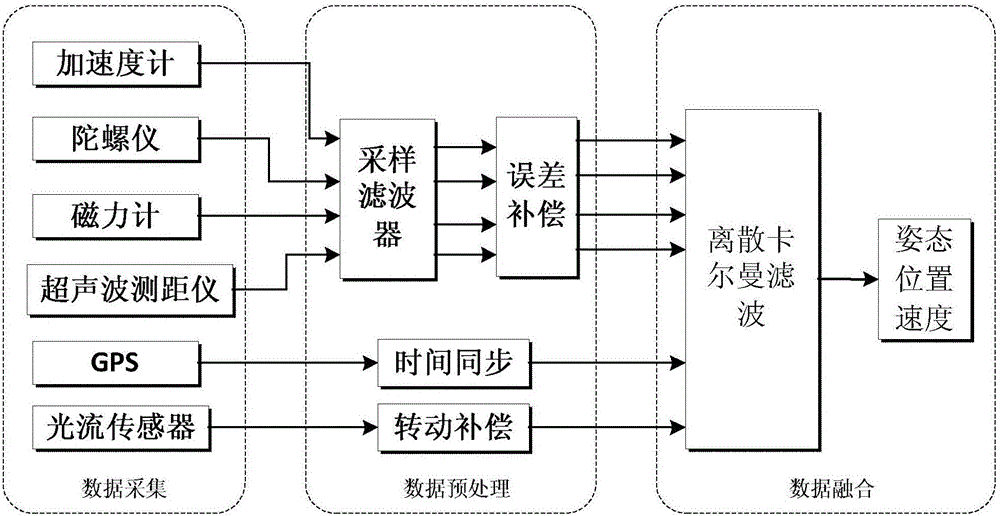
InactiveCN105094138AOvercome occlusionOvercoming distractionsAircraft power plantsAttitude controlAutonomous Navigation SystemGuidance control
The invention discloses a low-altitude autonomous navigation system for a rotary-wing unmanned plane. The low-altitude autonomous navigation system is composed of a data acquisition device, a data preprocessing module, a data fusion module, a guidance control loop module and an attitude control loop module. The data preprocessing module is used for carrying out sampling filtering and error compensation on current location data information collected by the data acquisition device; the data fusion module is used for carrying out fusion and updating and obtaining a current position and speed of the rotary-wing unmanned plane; the guidance control loop module is used for calculating an expected attitude angle and an expected height value; and the attitude control loop module is used for generating a controlled quantity. According to the technical scheme, a problem of poor attitude estimation precision of the conventional navigation system can be solved; and requirements of high-precision heading attitude calculation and position and speed fusion of the rotary-wing unmanned plane can be met. High-precision filtering of the system is realized. On the basis of the analysis and calculation of the autonomous navigation system, the flight route and height can be corrected and the flight attitude can be adjusted autonomously; and the autonomous flight of the unmanned plane can be realized.
Owner:NORTHEAST AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
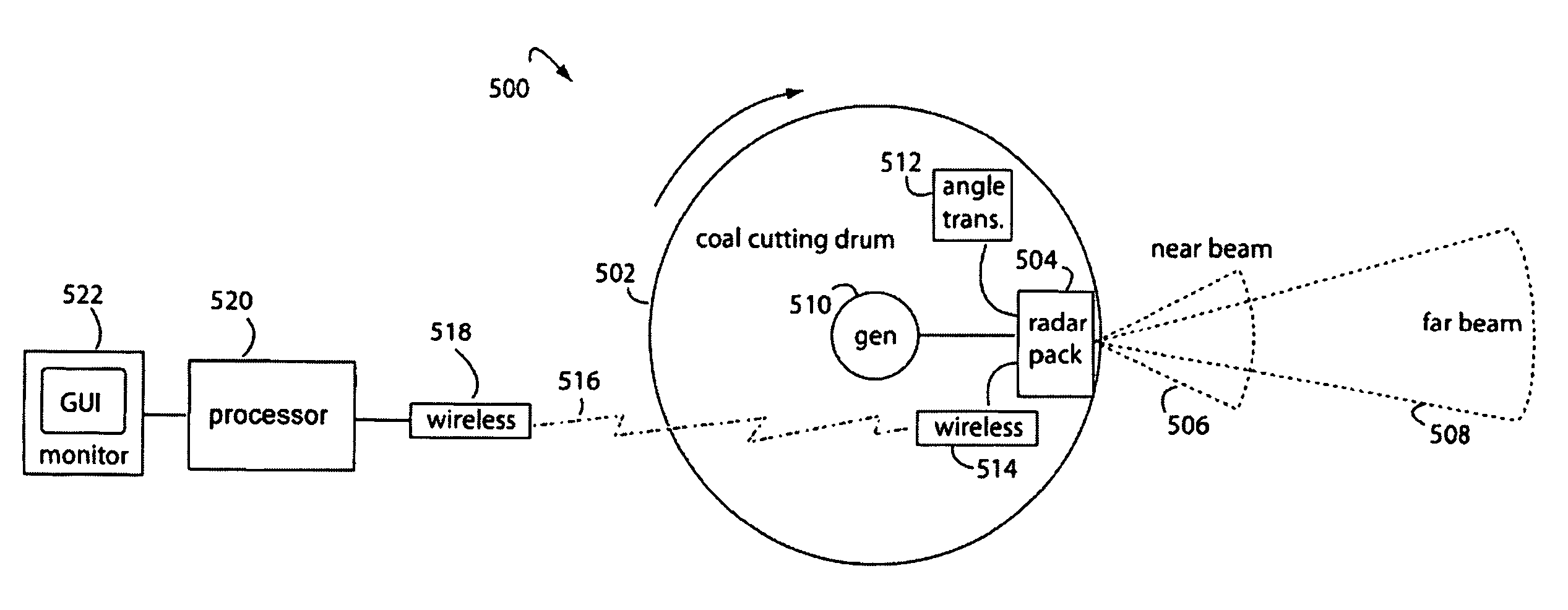
Radar mining guidance control system
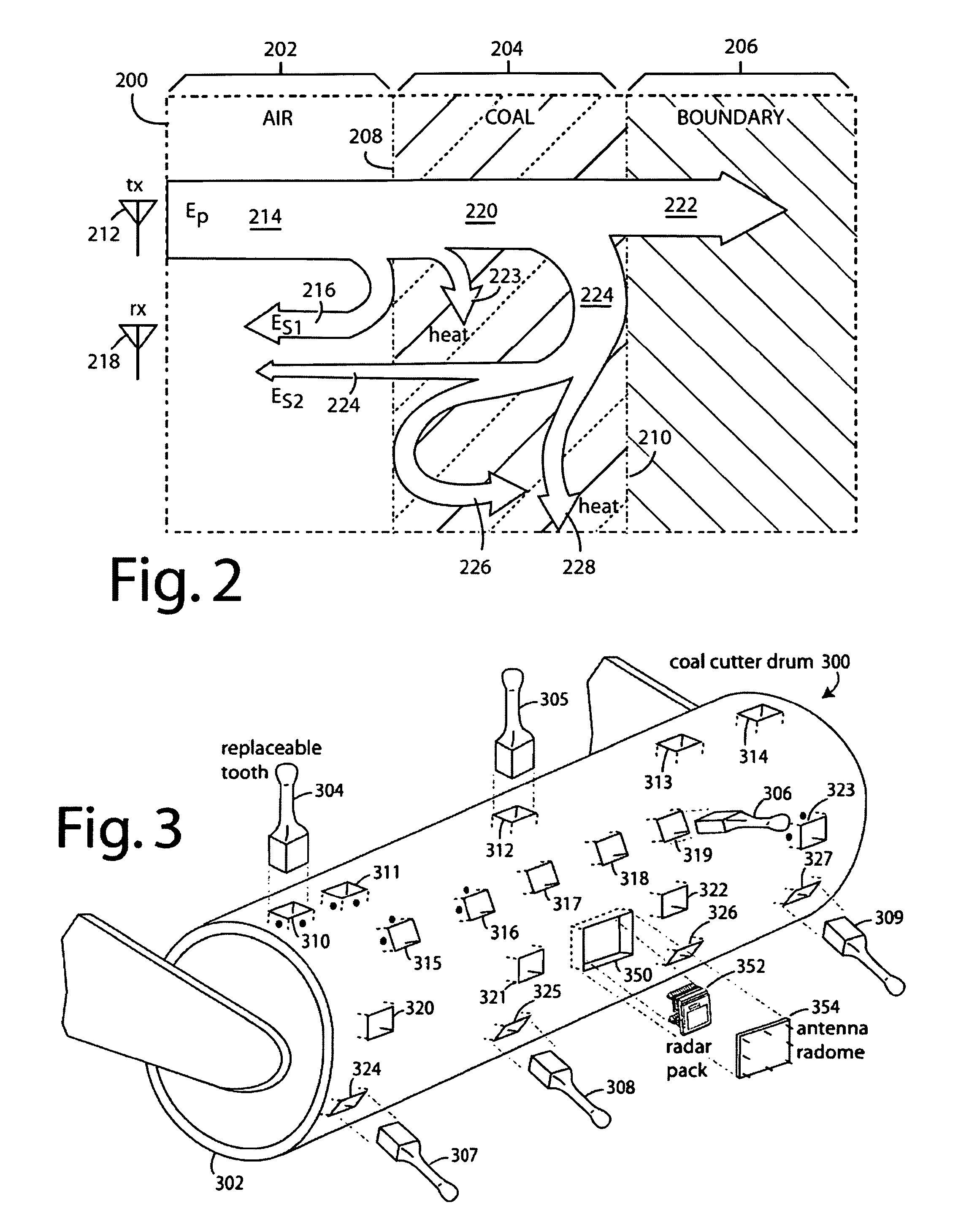
InactiveUS7659847B2Increase reflectionSlitting machinesDetection using electromagnetic wavesGuidance controlCarrier signal
A coal-mining machine uses a ground-penetrating radar based on a software-definable transmitter for launching pairs of widely separated and coherent continuous waves. Each pair is separated by a constant or variable different amount double-sideband suppressed carrier modulation such as 10 MHz, 20 MHz, and 30 MHz. Processing suppresses the larger first interface reflection and emphasizes the smaller second, third, etc. reflections. Processing determines the electrical parameter of the natural medium adjacent to the antenna. Deep reflections at 90-degrees and 270-degrees create maximum reflection and will be illuminated with modulation signal peaks. Quadrature detection, mixing, and down-conversion result in 0-degree and 180-degree reflections effectively dropping out in demodulation.
Owner:STOLAR
System and method for guiding and controlling a missile using high order sliding mode control
ActiveUS8436283B1Promote resultsDirection controllersDigital data processing detailsMode controlGuidance control
Owner:DAVIDSON TECH
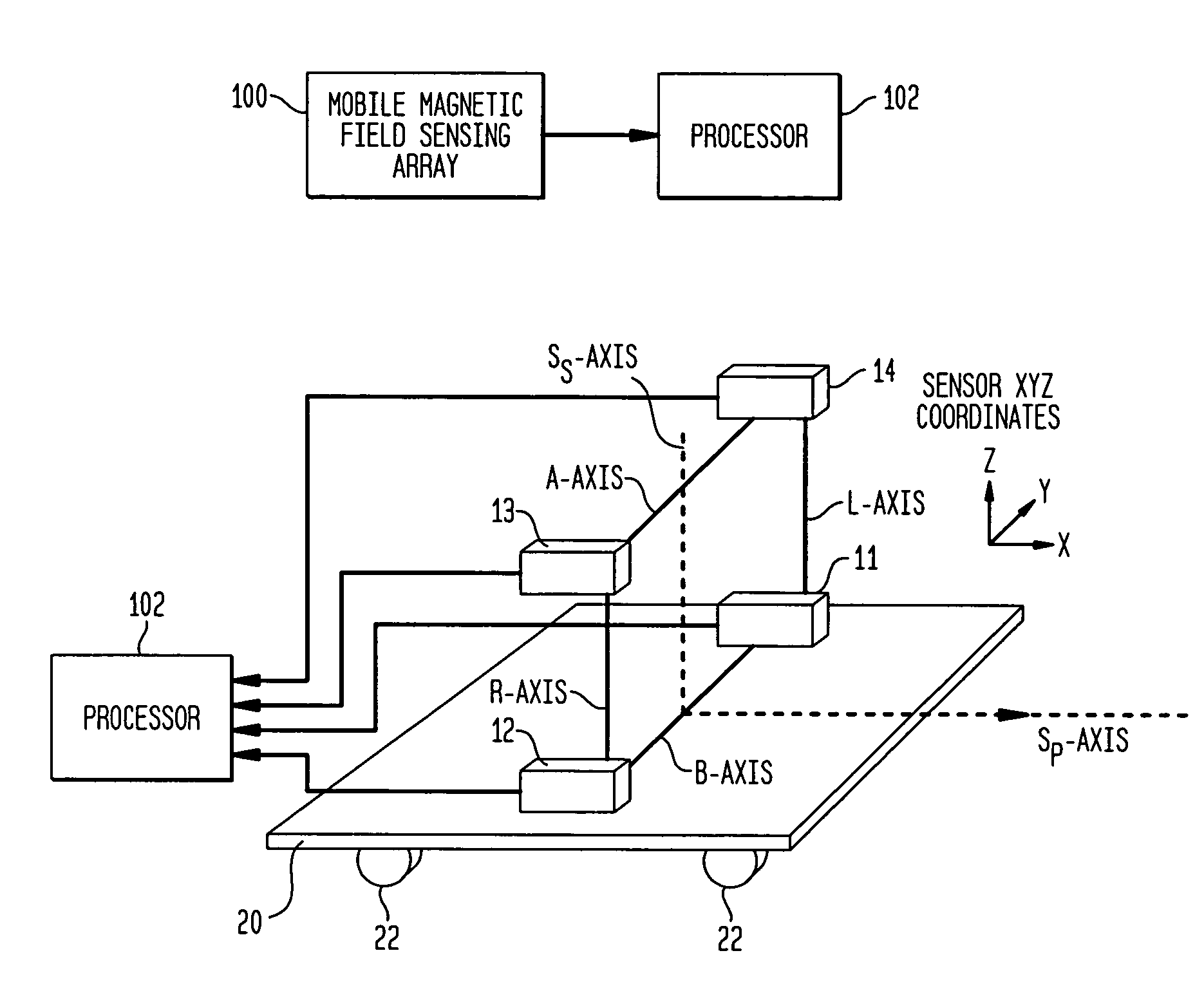
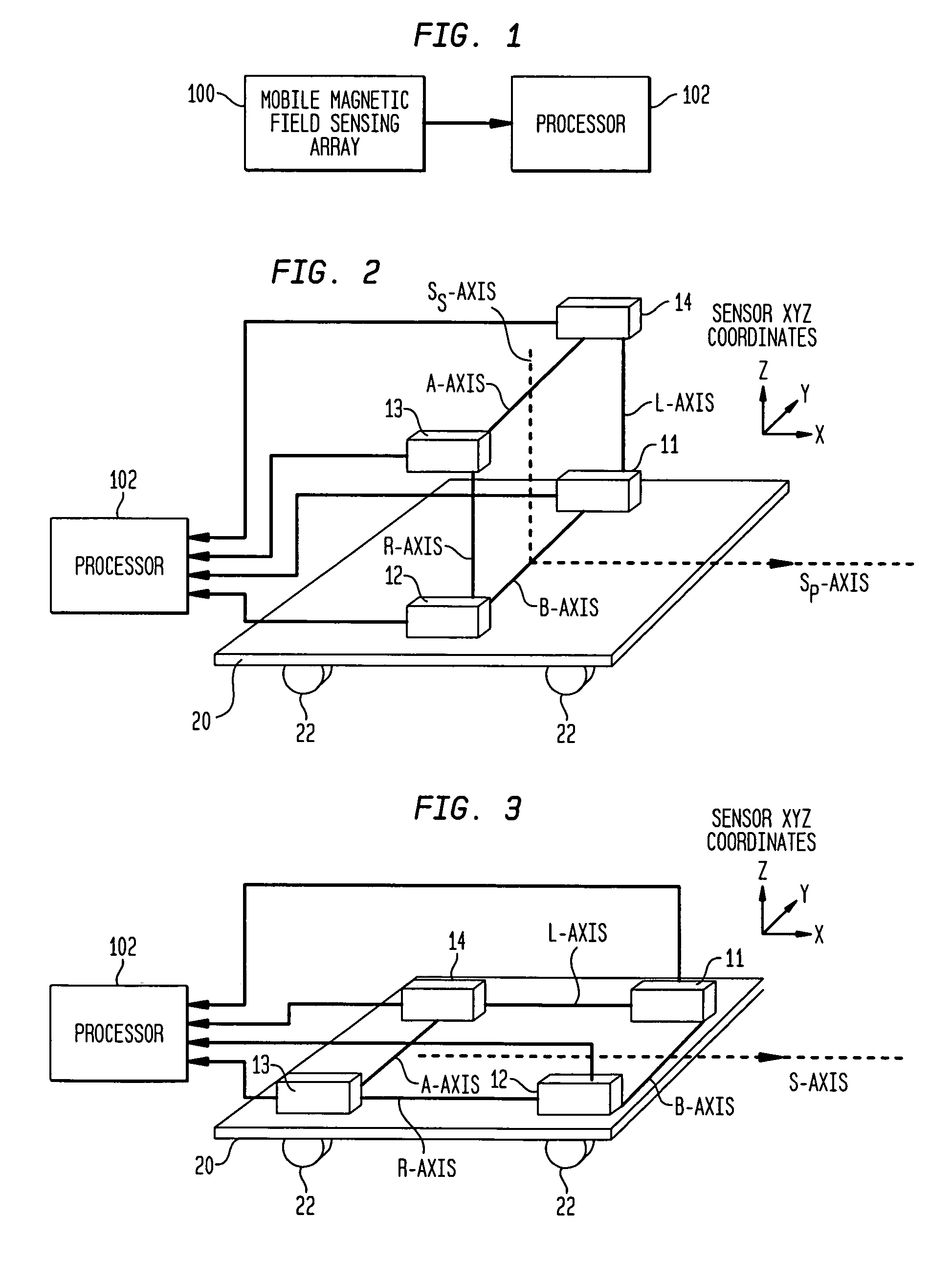
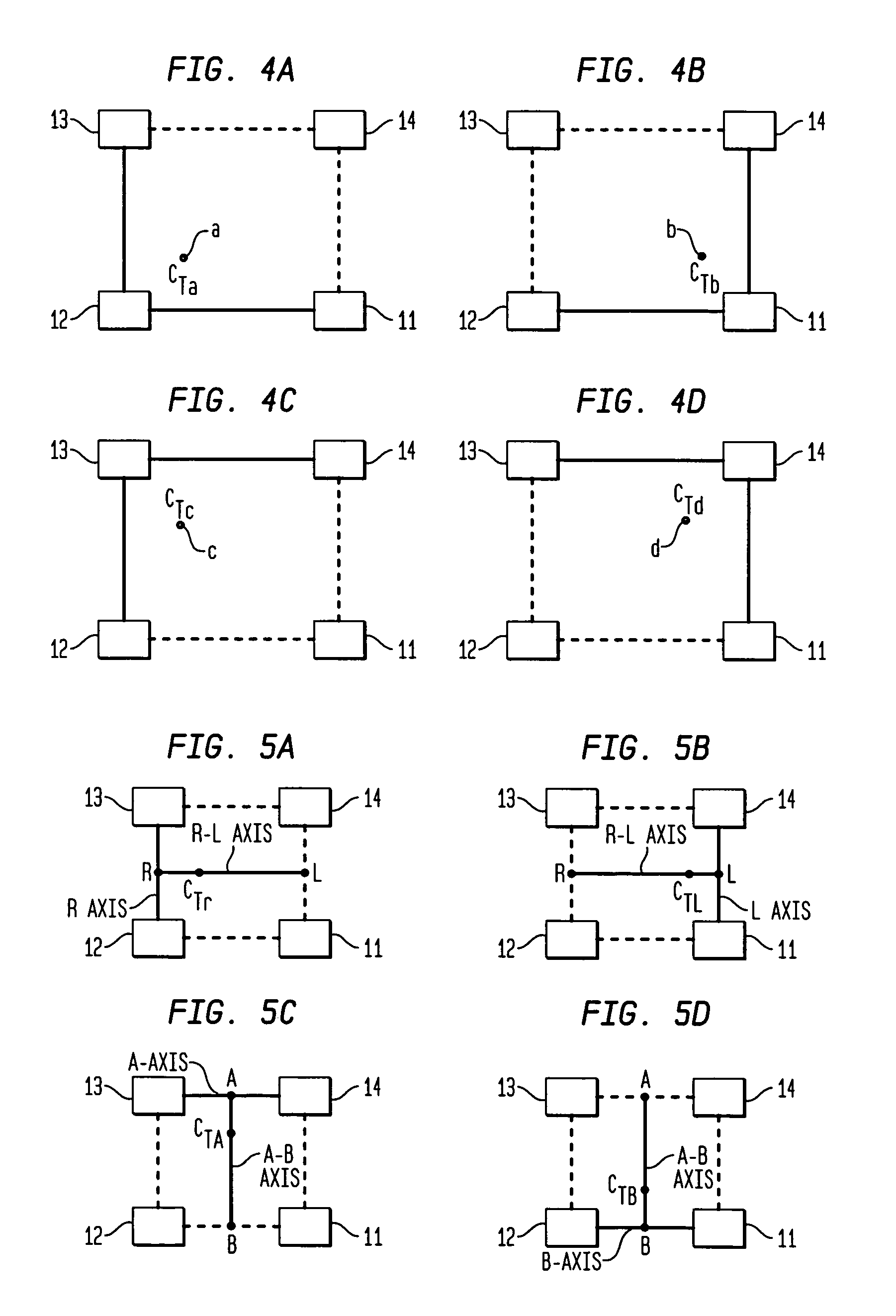
Magnetic anomaly homing system and method using rotationally invariant scalar contractions of magnetic gradient tensors
InactiveUS7038458B1Electric/magnetic detectionMagnitude/direction of magnetic fieldsMagnetic gradientGuidance control
A magnetic anomaly homing system and method utilize an array of four triaxial magnetometer (TM) sensors coupled to a non-magnetic platform. The four TM sensors are positioned at the vertices of a rectangular parallelogram. The magnetic field sensed at the four TM sensors is processed to generate complete gradient tensors and corresponding scalar gradient contractions thereof for four two-axis gradiometers formed by the array. The scalar gradient contractions define guidance control parameters used to steer the platform toward the magnetic anomaly.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
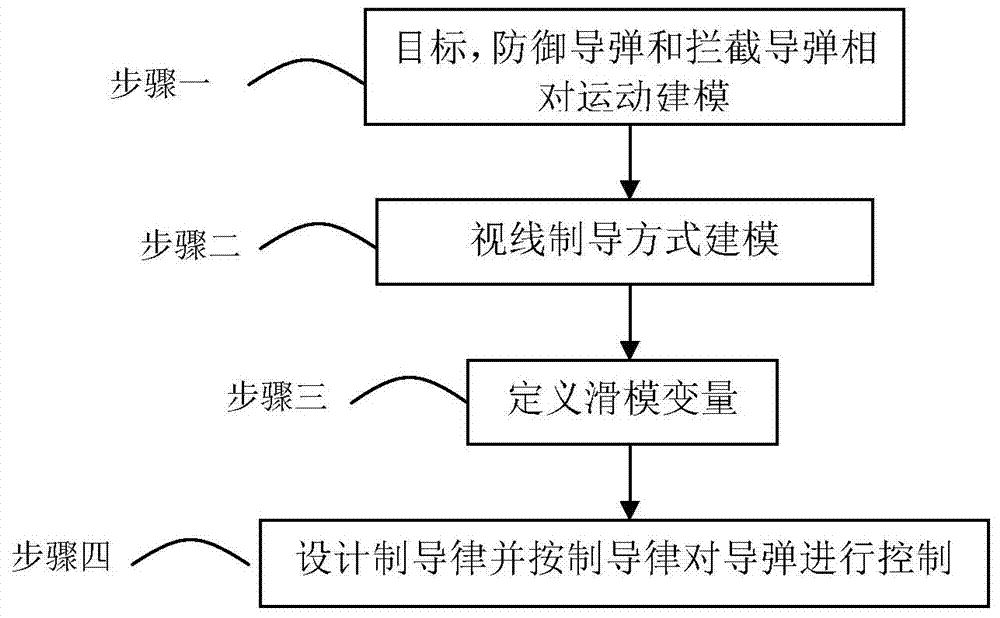
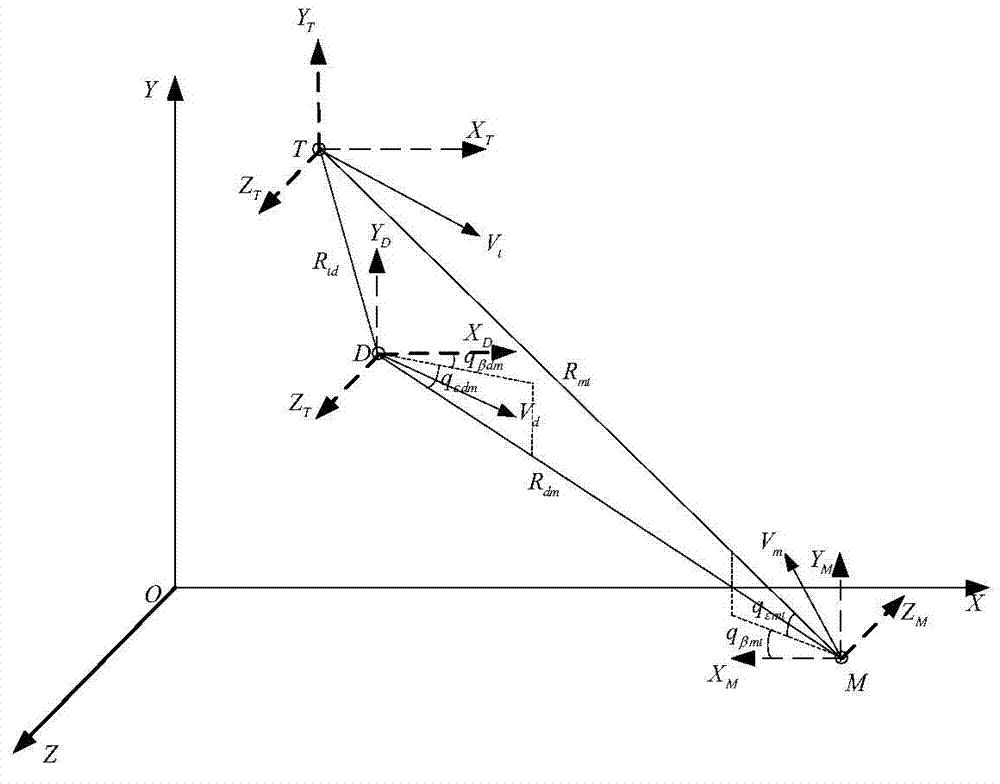
Sight line based finite time convergence active defense guidance control method
ActiveCN104266546AReduce demand overloadDirection controllersSpecial data processing applicationsLongitudinal planeGuidance control
The invention provides a sight line based finite time convergence active defense guidance control method, relates to a guidance control method, in particular to an active defense guidance control method, and aims at solving the problem that a defensive missile is limited in overload capacity. The sight line based finite time convergence active defense guidance control method comprises the steps of firstly modeling relative motions of a target, the defensive missile and an intercept missile, adopting a sight line guidance mode to design a guidance rule for the defensive missile, then adopting a nonsingular terminal sliding mode to control the designed guidance rule, respectively defining sliding mode variables (shown in the description) of a longitudinal plane and a lateral plane, performing derivation on the sliding mode variables, substituting relative motion equations of the target, the defensive missile and the intercept missile into the variables and obtaining the guidance rule (shown in the description) of the longitudinal plane and the guidance rule (shown in the description) of the lateral plane through compilation, and controlling the missiles according to the guidance rules. By means of the sight line based finite time convergence active defense guidance control method, overload needed by the defensive missile can be effectively reduced. The sight line based finite time convergence active defense guidance control method is suitable for active defense guidance control.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Vehicle for aerial delivery of fire retardant
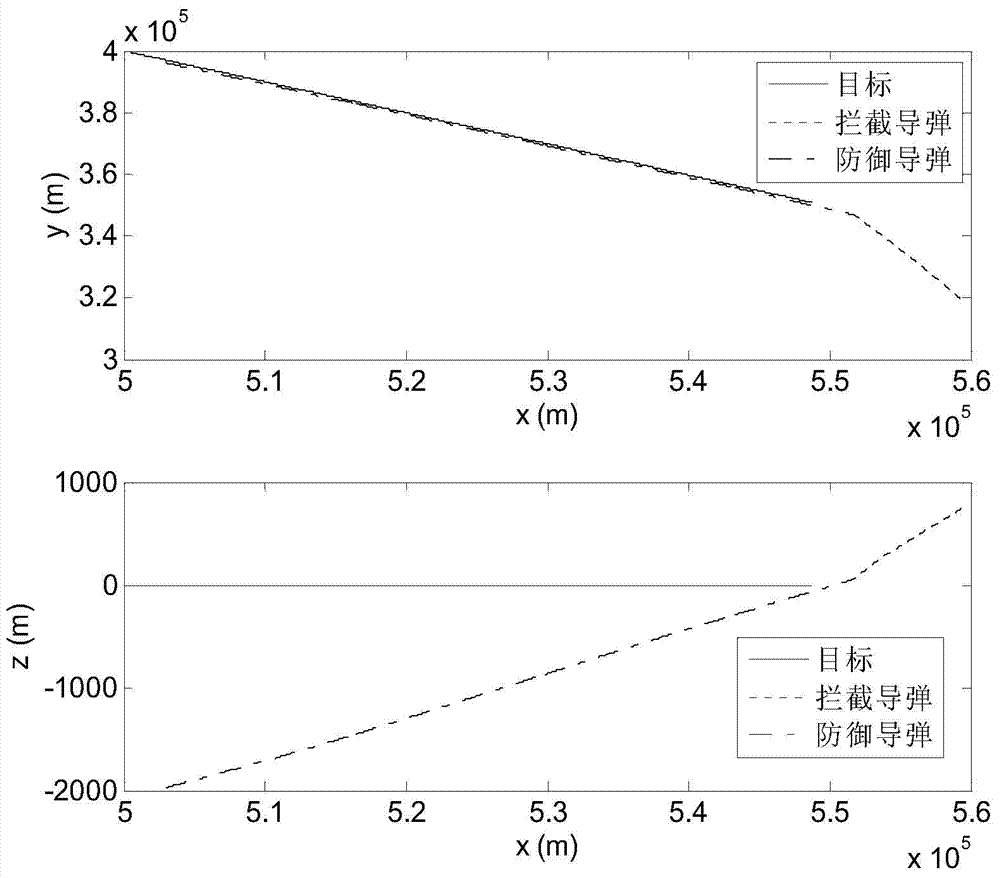
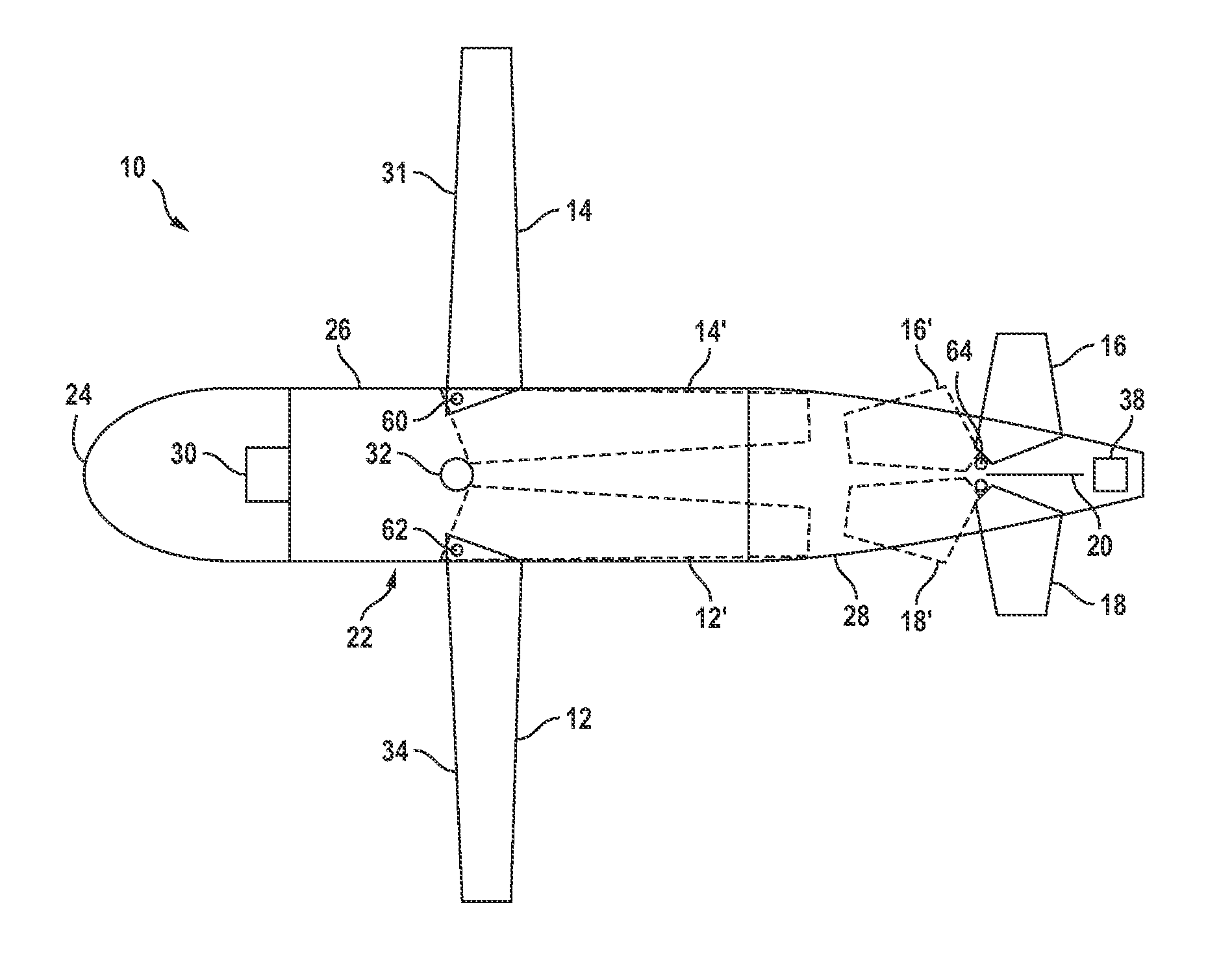
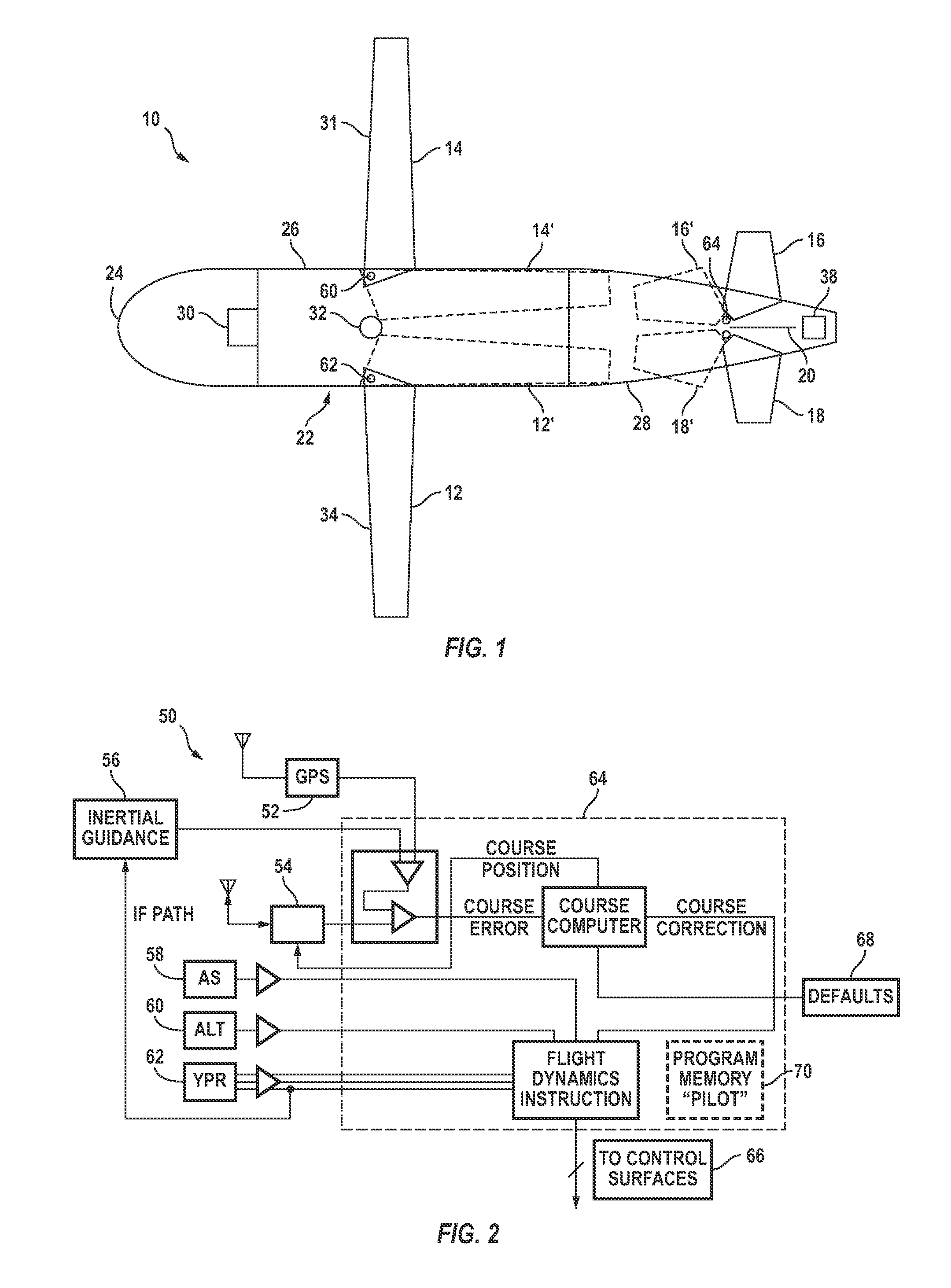
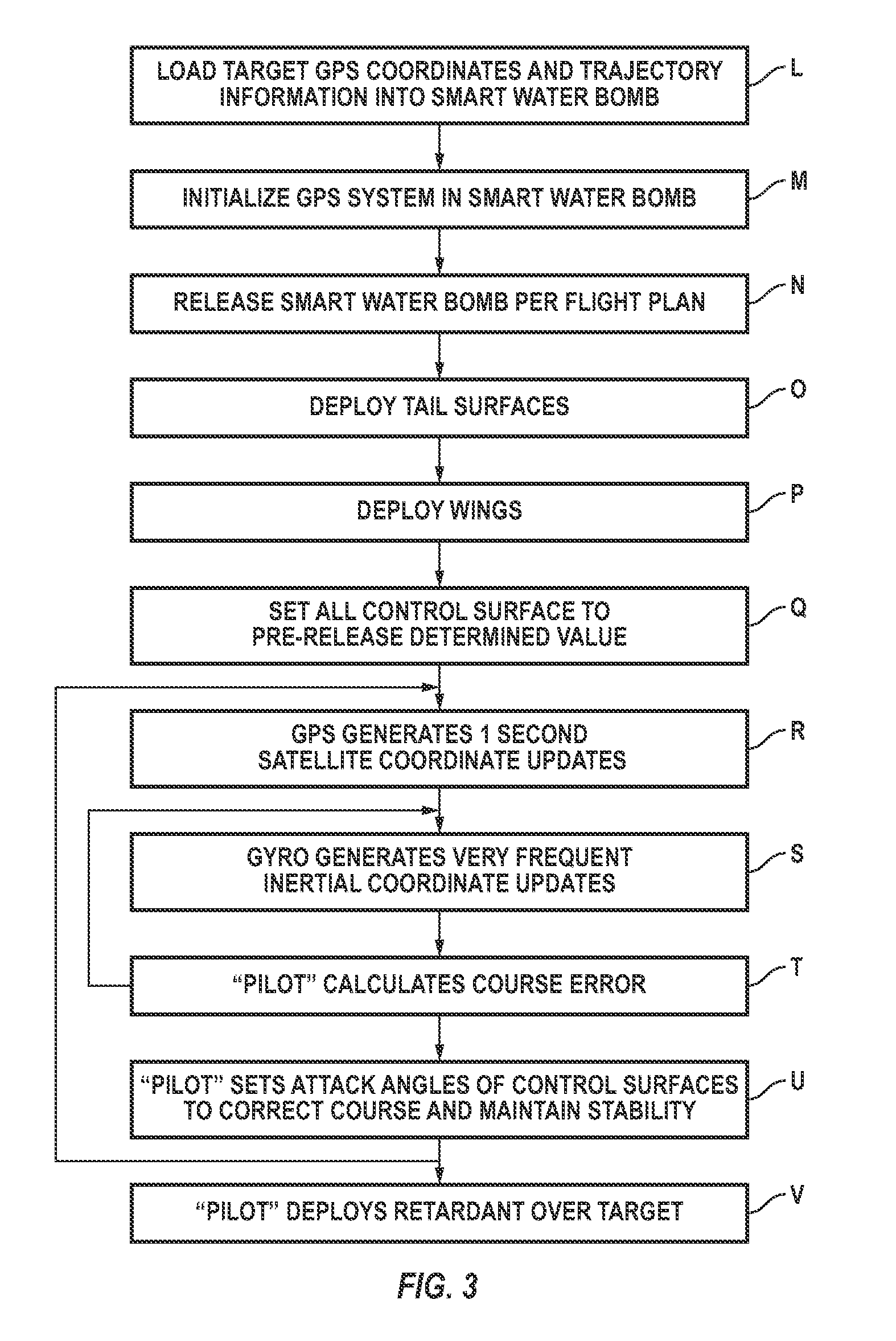
InactiveUS7975774B2Low costLift restrictionsAmmunition projectilesAircraft componentsGuidance controlFire retardant
A guided fire-retardant-containing bomb comprises a container with retractable wings, tail and elevators having the form factor of a conventional release vehicle, where the control surfaces are coupled via a controller to a GPS with inertial guidance control and an ability to receive external instructions, and a charge core to disintegrate and disperse the fire retardant or water.
Owner:LONESTAR INVENTIONS LP
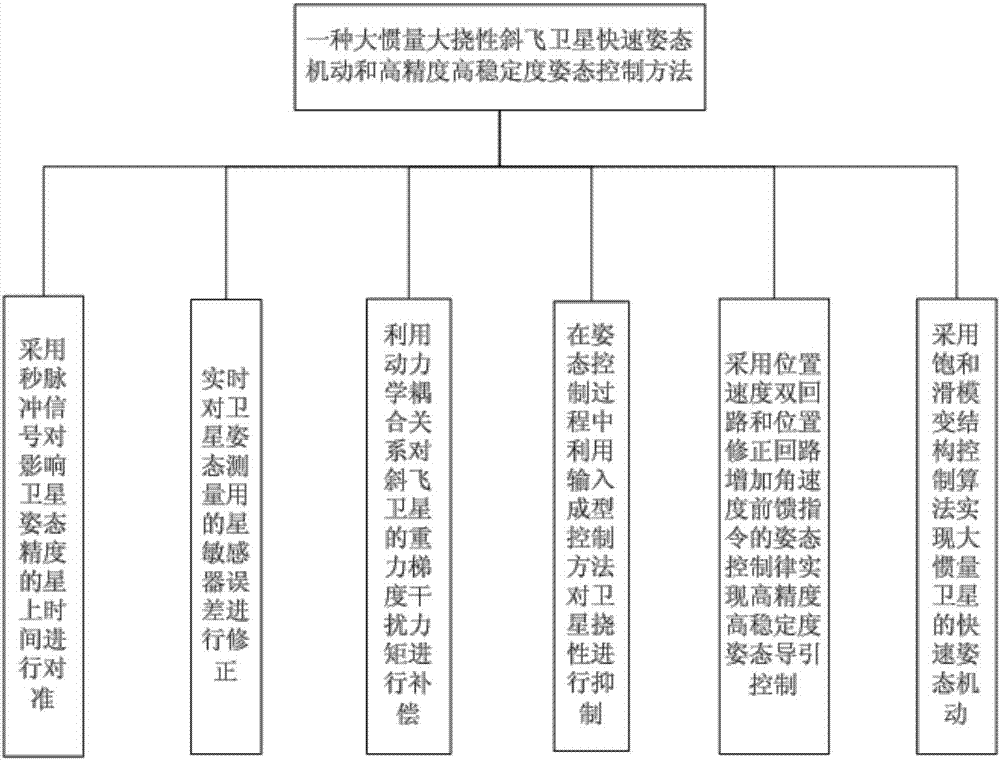
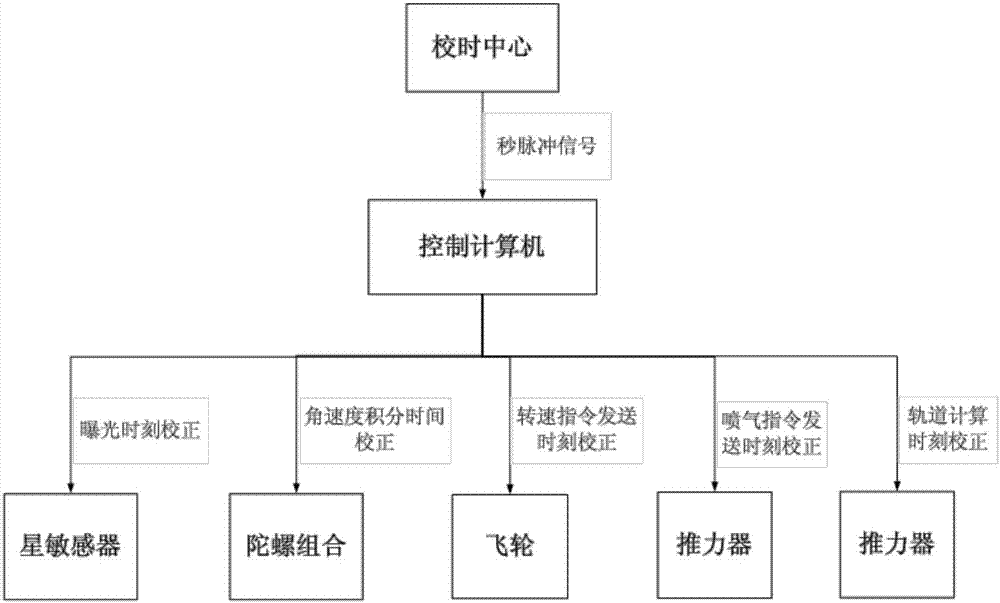
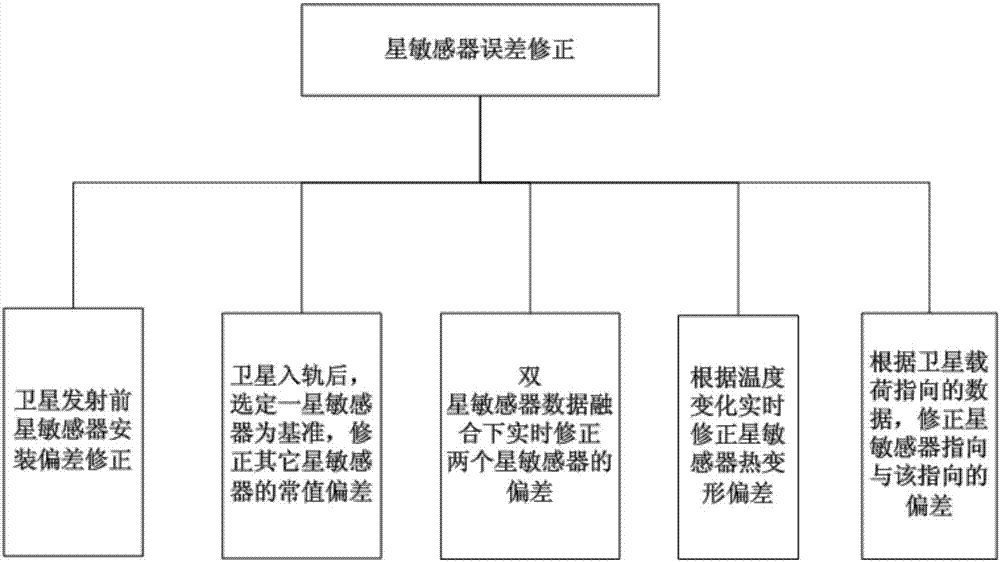
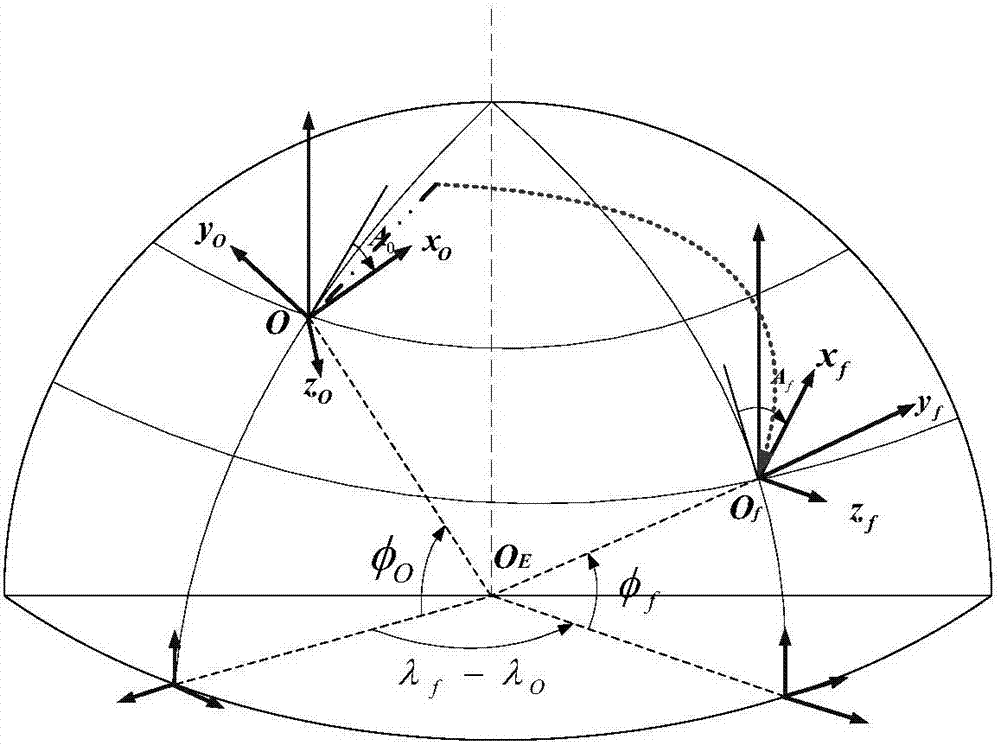
Attitude control method
ActiveCN106915477AImprove performanceReduce development costsCosmonautic vehiclesAttitude controlAttitude controlGuidance control
The invention discloses an attitude control method. The attitude control method comprises the following procedures that the on-satellite time influencing the satellite attitude precision is aligned through a second pulse signal; a satellite sensor error used for satellite attitude measurement is corrected in real time; the gravity gradient disturbance torque of an oblique flying satellite is compensated through a dynamics coupling relationship; the satellite flexibility is restrained through an input forming control method in the attitude controlling process; the attitude control law of an angular velocity feedforward instruction is increased through position and speed double loops and a position correcting loop to achieve high-precision and high-stability attitude guidance control; and quick attitude maneuver of the large-inertia satellite is achieved through a saturated sliding mold structural control algorithm. The attitude control method has the advantages that the computing method is simple, control is flexible, the attitude control method can be applied to attitude control of the large-inertia large-flexible oblique flying satellite, the property of the satellite is greatly improved, and researching and manufacturing cost of satellite hardware is reduced.
Owner:SHANGHAI AEROSPACE CONTROL TECH INST
Designing method for guidance law applicable to vertical recovery phase of rocket
ActiveCN107966156ASolving Guidance and Control ProblemsImprove adaptabilityInstruments for comonautical navigationPosition/course control in three dimensionsCarrying capacityGuidance control
The invention relates to a designing method for a guidance law applicable to the vertical recovery phase of a rocket. The designing method comprises the following steps: acquiring the full-distance standard trajectory of the rocket; according to the full-distance standard trajectory, acquiring the latitude and longitude of a target point, the motion parameters of the rocket at the starting point of an aerodynamic deceleration phase, and the latitude and longitude of a point below the rocket, and constructing an auxiliary coordinate system; based on the auxiliary coordinate system, additionallysetting terminal angular constraints on the basis of a proportional guidance process so as to obtain a biased proportional guidance law; and applying the biased proportional guidance law in the aerodynamic deceleration phase and applying the biased proportional guidance law with an additional main power deceleration algorithm in a vertical descending phase. The improved biased proportional guidance method in the invention can effectively solve problems in guidance control under the condition of multiple constraints by location, velocity and attitude during rocket recovery; the guidance law for a vertical landing phase employs aerodynamic deceleration and tail-phase short-time main-power deceleration, so no impact is exerted on the carrying capacity of the rocket in an in-orbit flying phase; and at the same time, proportional guidance has better adaptability to various non-guidance deviations.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF ASTRONAUTICAL SYST ENG +1
Missile weapon system design method aiming at efficiency on basis of performance indexes
ActiveCN105910495AImprove performance indicatorsExcellent actual combat abilityAiming meansDesign optimisation/simulationGuidance controlPerformance index
The invention discloses a missile weapon system design method aiming at efficiency on the basis of performance indexes, relates to the field of missile weapon system overall design and aims to solve the problem that the relation of the performance indexes and efficiency indexes is not accurately described in the existing missile weapon system design process. The missile weapon system design method aiming at the efficiency on the basis of the performance indexes definitely comprises the performance indexes of a fragment killing combating part, a propulsion system, a missile body shape, aerodynamic layout, the trajectory guidance control capacity and definitely comprises the efficiency indexes of the defense penetration capacity, the damage capacity, the hit probability, the survivability, the maneuvering capacity, the anti-interference capacity, the maintainability and the reliability; and finally the relation of components of the performance indexes and components of the efficiency indexes is built, and missile overall design is carried out. By means of the missile weapon system design method, the efficiency indexes of a missile are improved overall, so that the actual combat capacity of the missile achieves the best.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
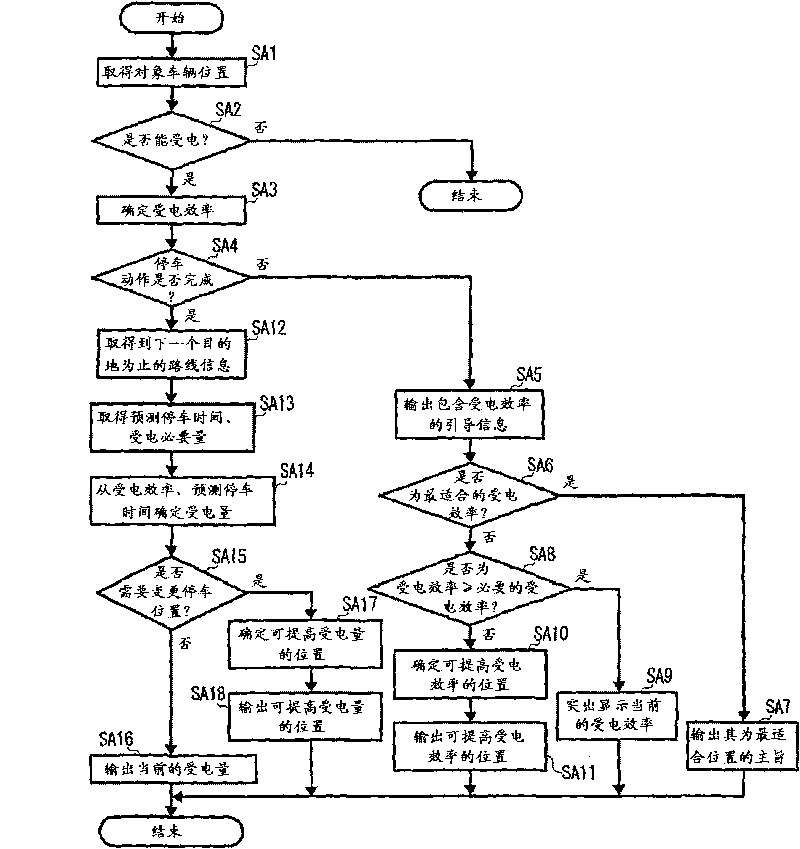
Devices, methods, and programs that provide vehicle guidance for power reception
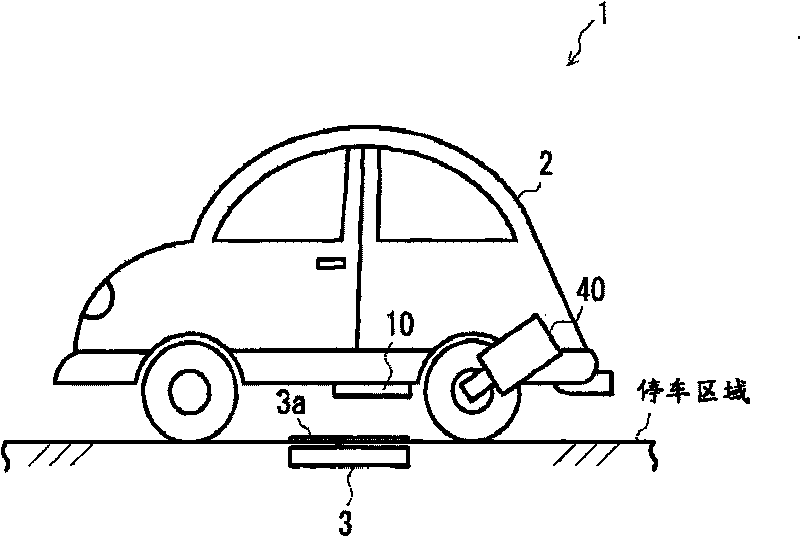
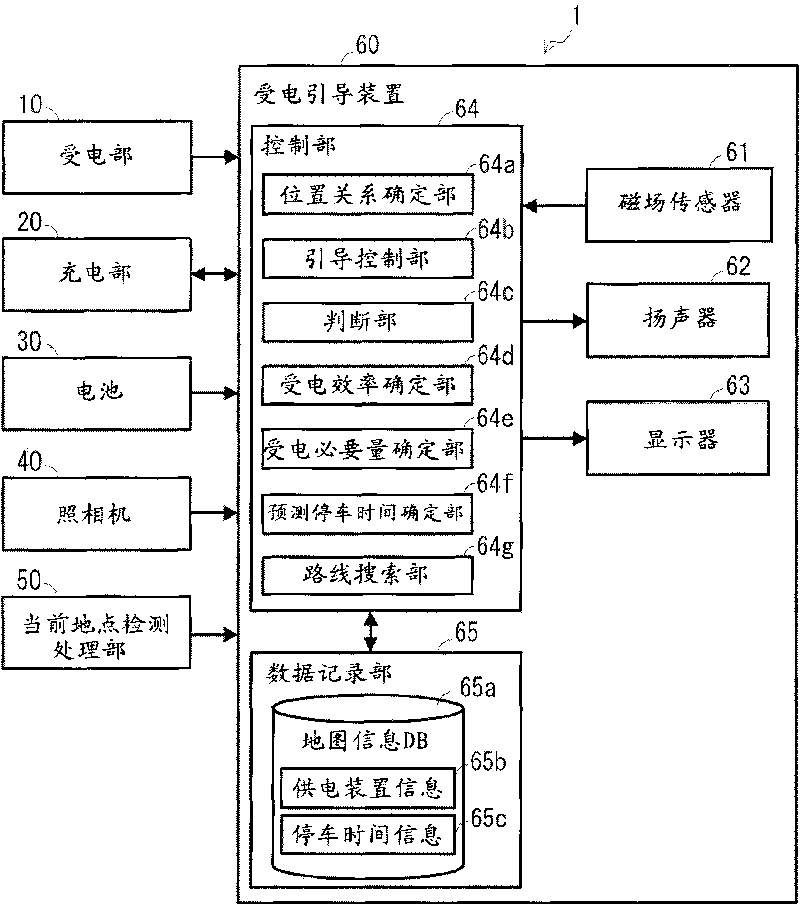
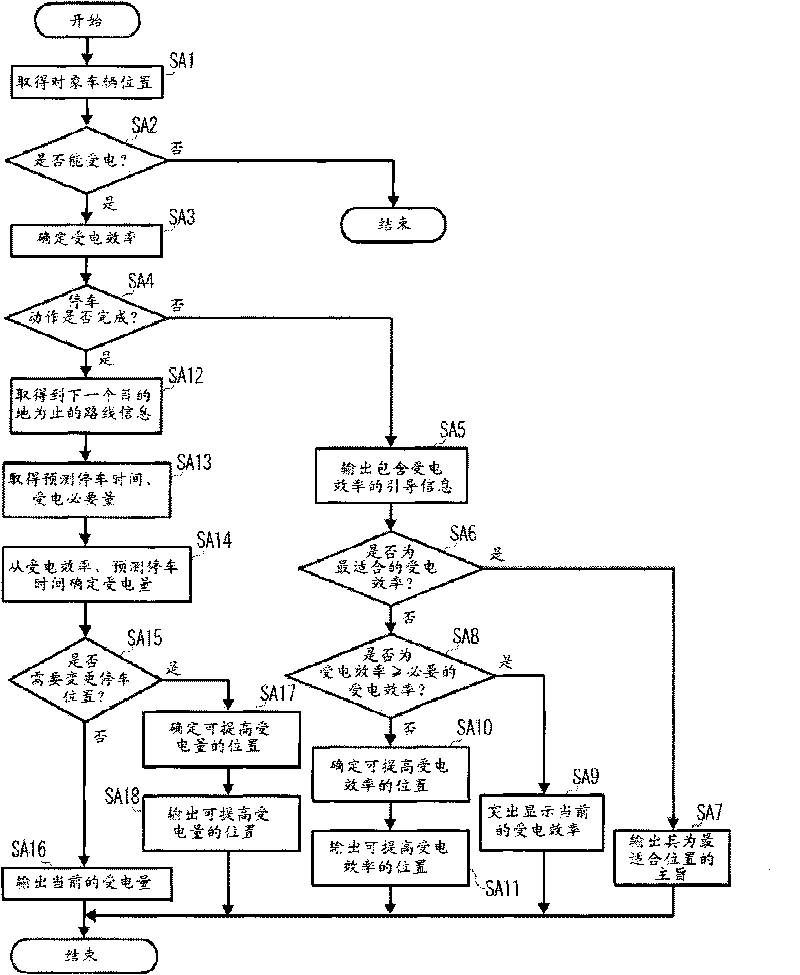
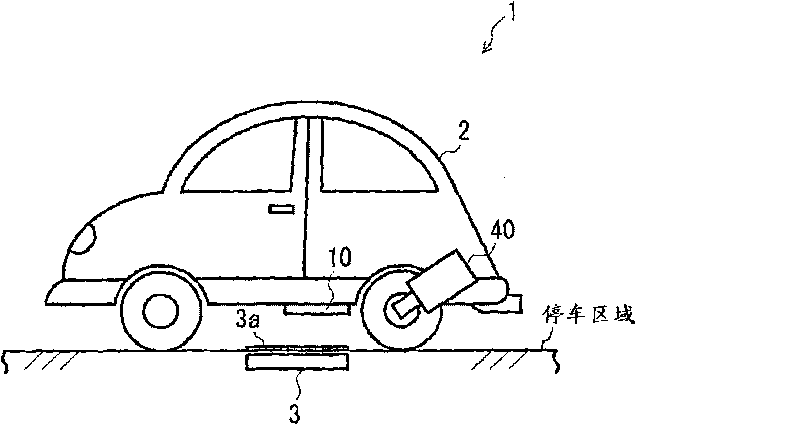
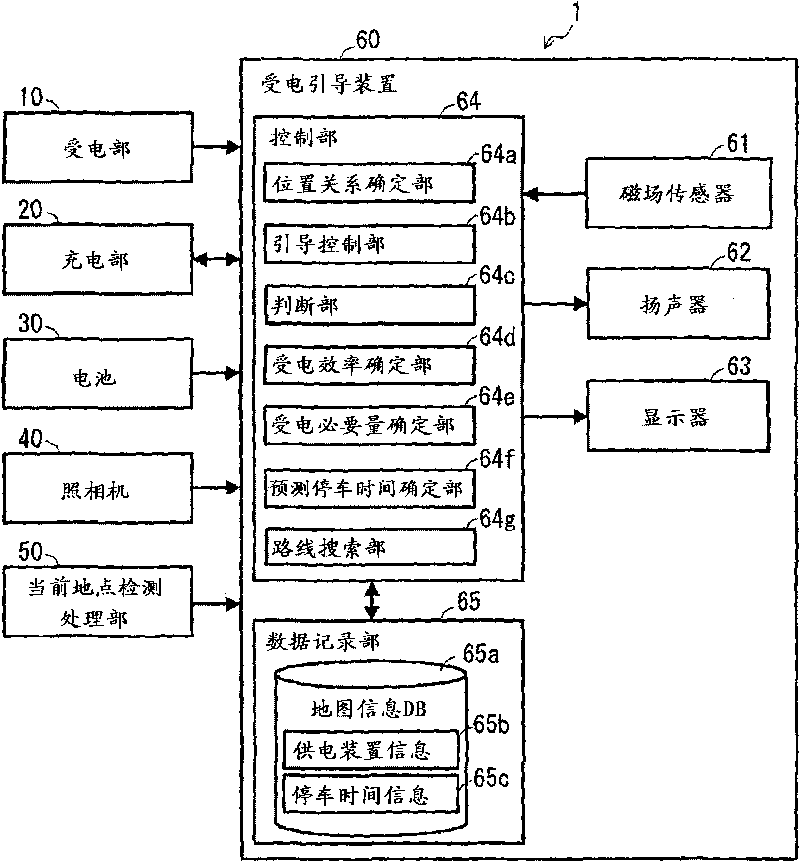
InactiveCN101764435ADetermination of receiving efficiencyBatteries circuit arrangementsElectromagnetic wave systemParking areaGuidance control
A power reception guidance device that provides guidance pertaining to a non-contact power supply from a power supply unit (3) installed in a parking area to a power receiving unit (10) installed in a vehicle (2), comprising: a power receiving efficiency specifying unit (64d) that specifies a power receiving efficiency of the power receiving unit (10) at a current position of the vehicle (2) when a parking operation is started; and a guidance control unit (64b) that outputs through an output unit (62, 63) information pertaining to the power receiving efficiency specified by the power receiving efficiency specifying unit (64d).
Owner:AISIN AW CO LTD
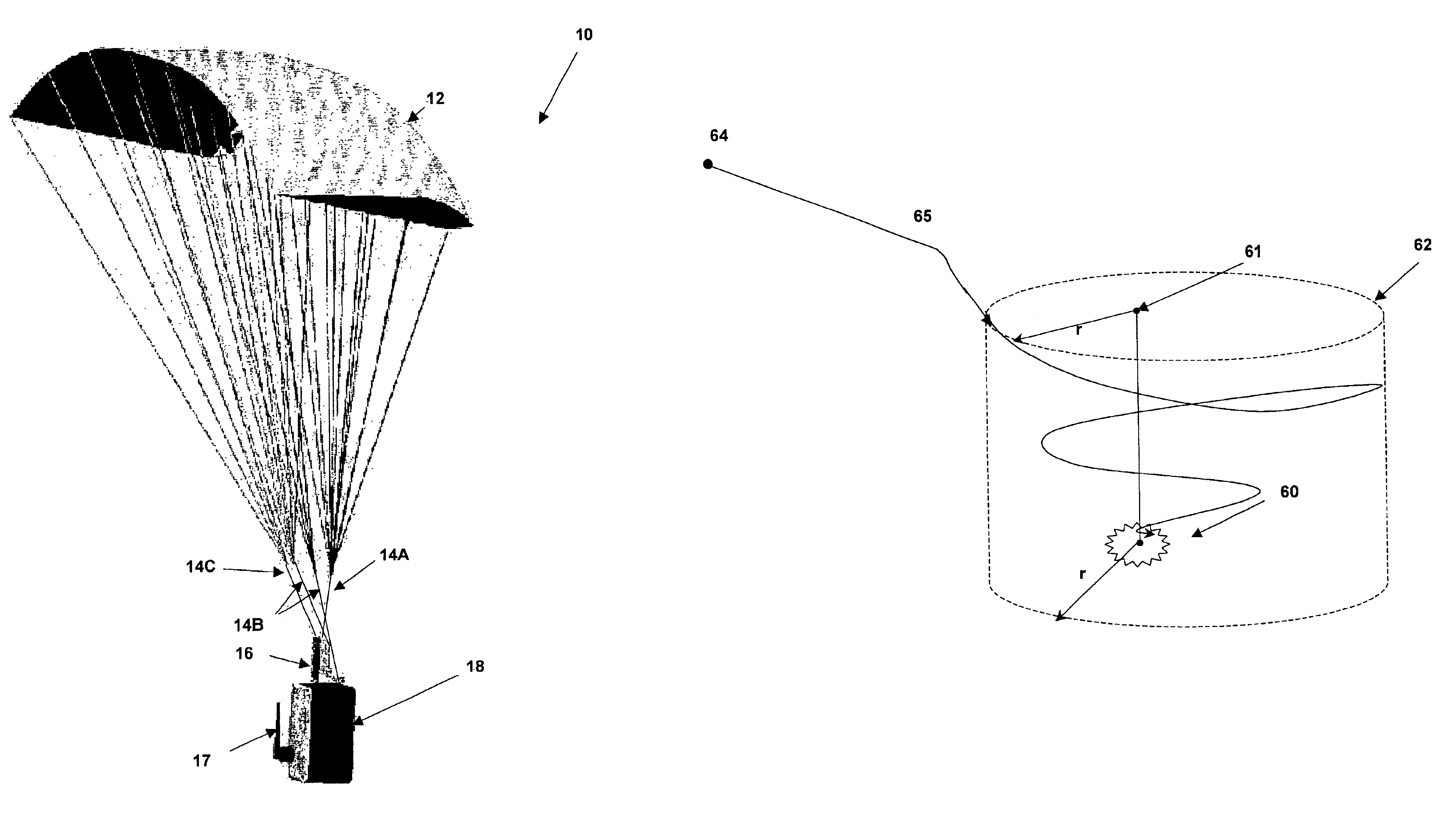
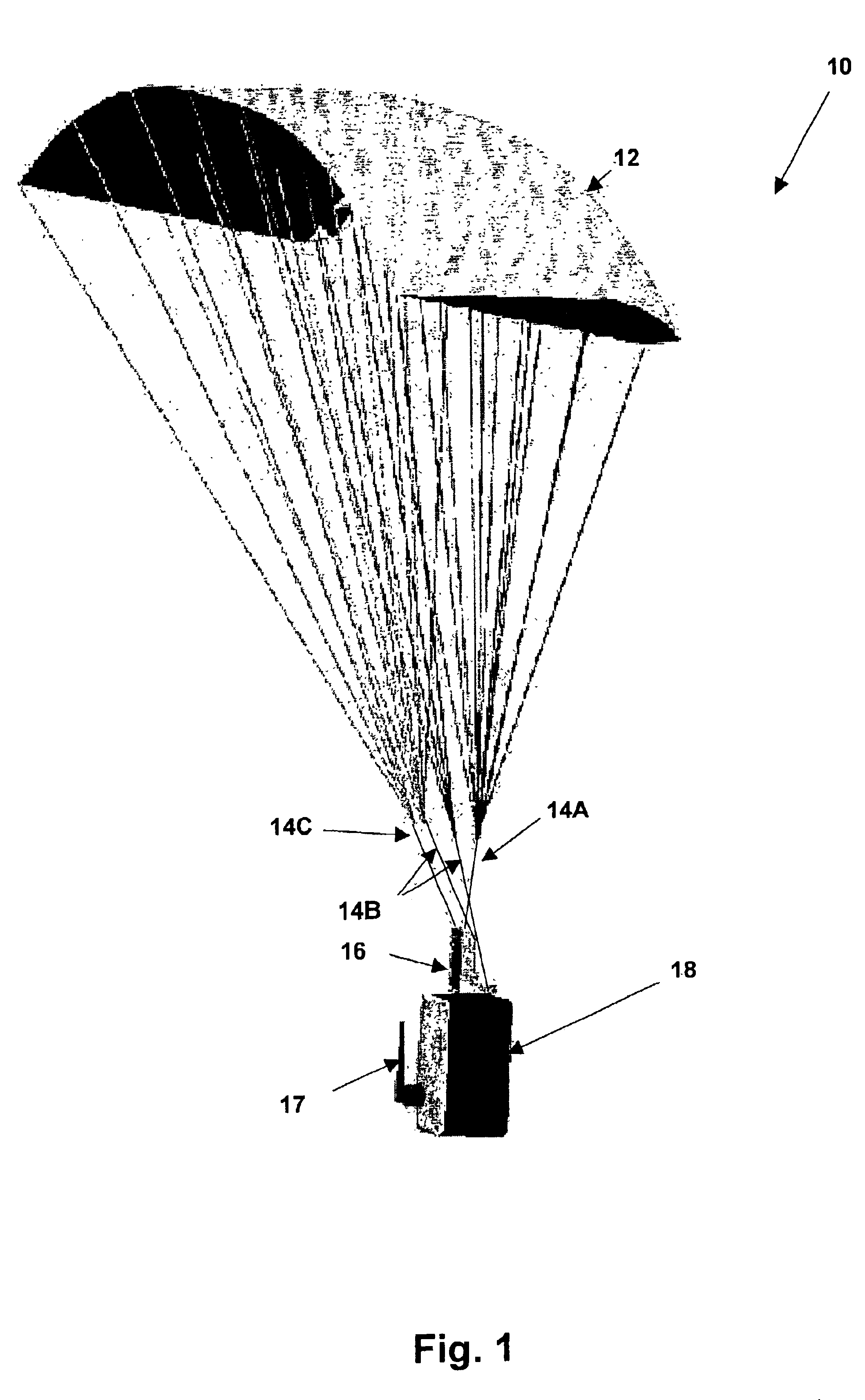
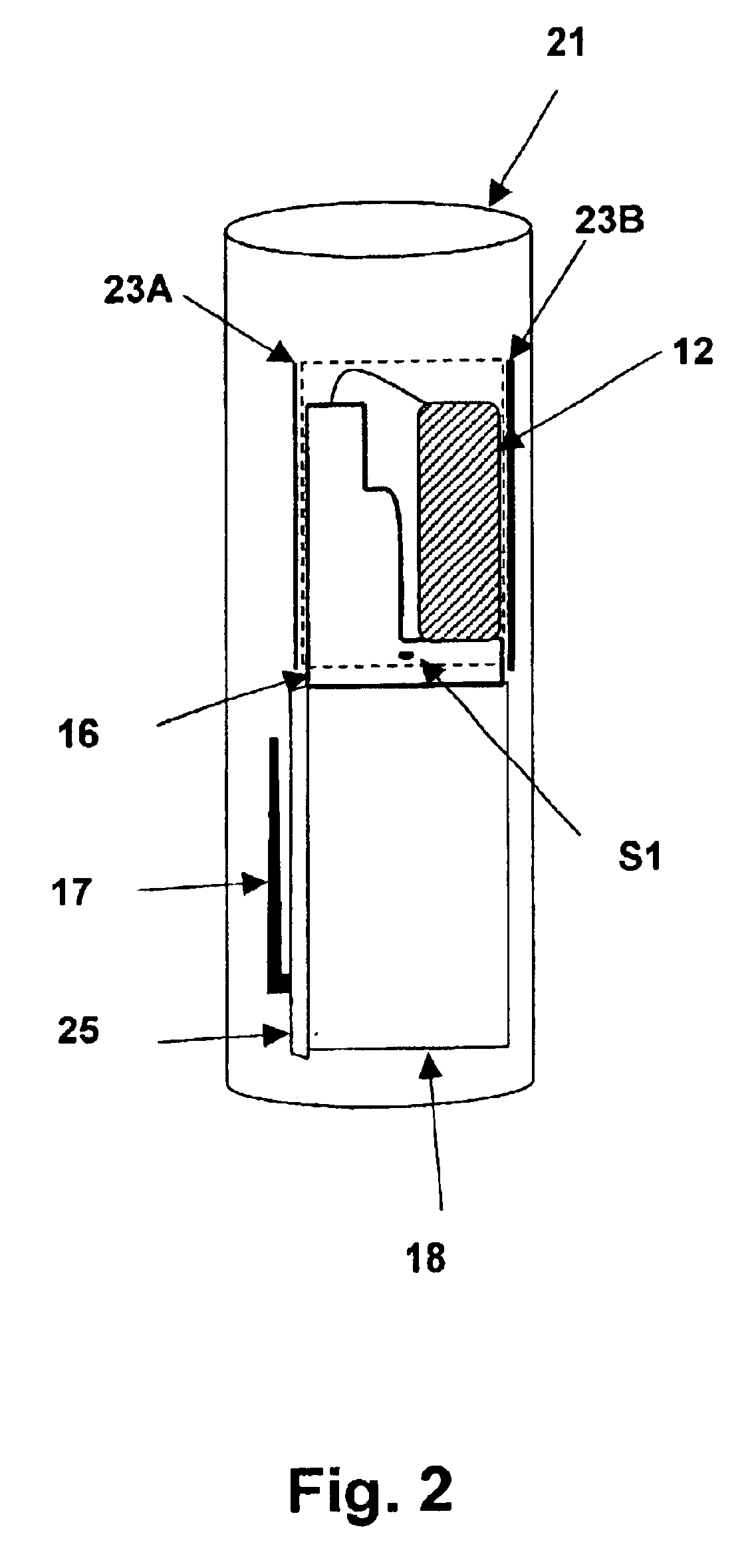
Guided parafoil system for delivering lightweight payloads
InactiveUS6758442B2Parachutes testing apparatusNon-canopied parachutesControl systemGuidance control
A guided parafoil system for delivering lightweight payloads provides an accurate, small and low-cost delivery system for small payloads such as chemical sensor packages. The delivery system is adapted to fit along with the payload within a standardized canister. The delivery system includes a parafoil and a guidance control system that includes a global positioning system (GPS) receiver and an electronic compass to detect a deviation and bearing from a desired target. The parafoil is guided by a single motor that turns the parafoil in a horizontal direction perpendicular to the current direction of travel in response to deviations detected from a desired course. The desired course is initially linear until the system reaches a predetermined horizontal radius from the target and then the course becomes a circular path around and above the target.
Owner:STARA TECH
Devices, methods, and programs that provide vehicle guidance for power reception
InactiveCN101764434AImprove accuracyHybrid vehiclesAnalogue computers for vehiclesElectricityParking area
A power reception guidance device that provides guidance pertaining to a non-contact power supply from a power supply unit (3) installed in a parking area to a power receiving unit (10) installed in a vehicle (2), comprising: a power receiving efficiency specifying unit (64d) that specifies a power receiving efficiency of the power receiving unit (10) at a parking position of the vehicle (2) in the parking area; a determination unit (64c) that determines whether the parking position must be changed based on the power receiving efficiency specified by the power receiving efficiency specifying unit (64d); and a guidance control unit that outputs through an output unit (62, 63) information based on the determination result of the determination unit (64c).
Owner:AISIN AW CO LTD
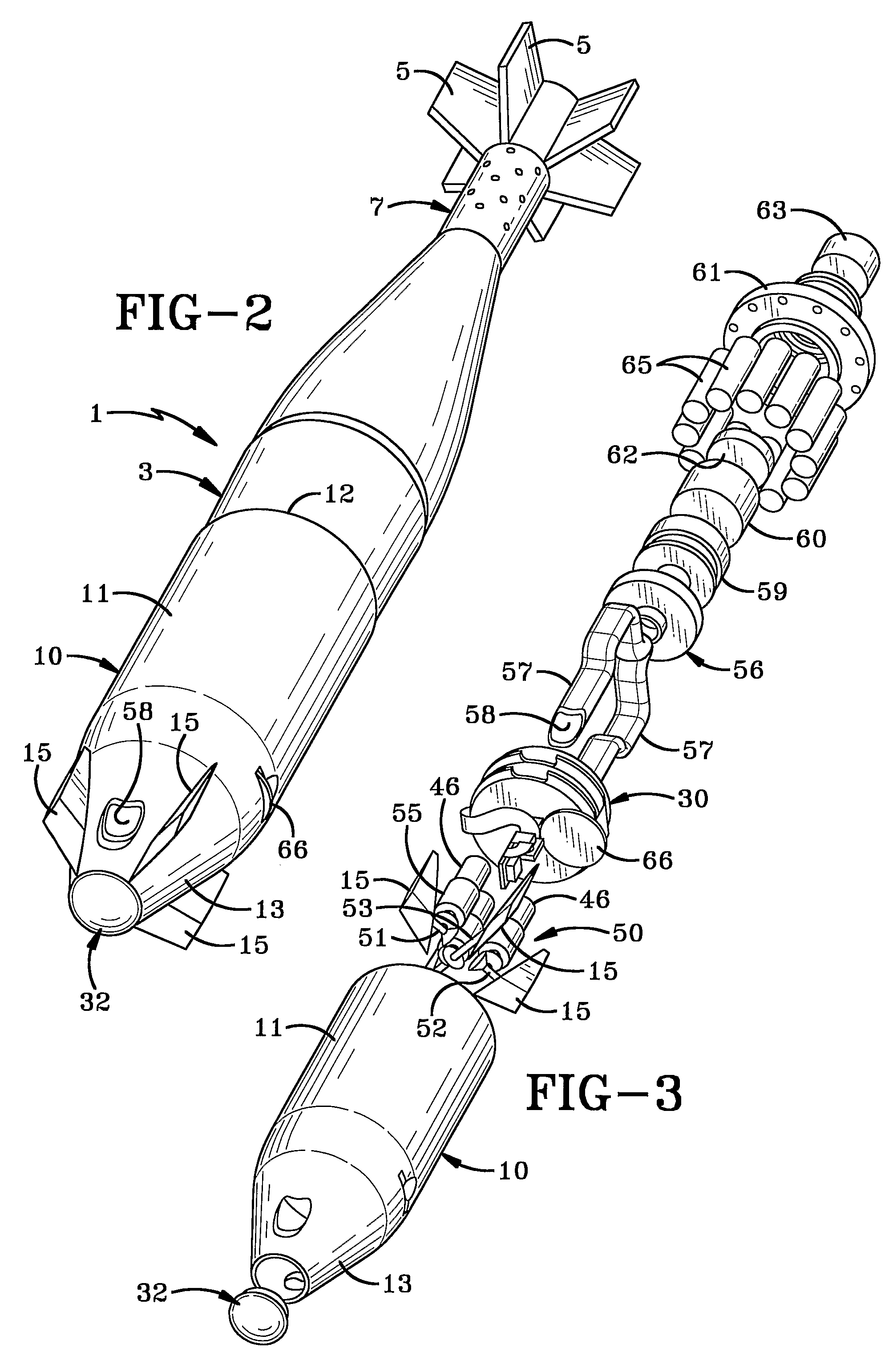
Small caliber guided projectile
A non-spinning projectile that is self-guided to a laser designated target and is configured to be fired from a small caliber smooth bore gun barrel has an optical sensor mounted in the nose of the projectile, a counterbalancing mass portion near the fore end of the projectile and a hollow tapered body mounted aft of the counterbalancing mass. Stabilizing strakes are mounted to and extend outward from the tapered body with control fins located at the aft end of the strakes. Guidance and control electronics and electromagnetic actuators for operating the control fins are located within the tapered body section. Output from the optical sensor is processed by the guidance and control electronics to produce command signals for the electromagnetic actuators. A guidance control algorithm incorporating non-proportional, “bang-bang” control is used to steer the projectile to the target.
Owner:NAT TECH & ENG SOLUTIONS OF SANDIA LLC
Ballistic Guidance Control for Munitions
ActiveUS20070241227A1Maneuver is maximizedAmmunition projectilesDirection controllersTrajectory of a projectileFlight control surfaces
A method and system for guiding and controlling an ordinance body having a trajectory and a bore sight angle including making corrections to the trajectory based on bore sight angle vs. time history. The system is incorporated with existing fuse components in a replacement kit for existing munitions. The method determines nominal time values of the ballistic trajectory of the munition in relation to launch time and determines deviation from the nominal time values by an algorithm by analyzing signals received from a source of radiation located at the target. A processor determines lateral (left / right) and range errors and provides steering commands to a plurality of flight control surfaces mounted on the munition.
Owner:BAE SYST INFORMATION & ELECTRONICS SYST INTERGRATION INC
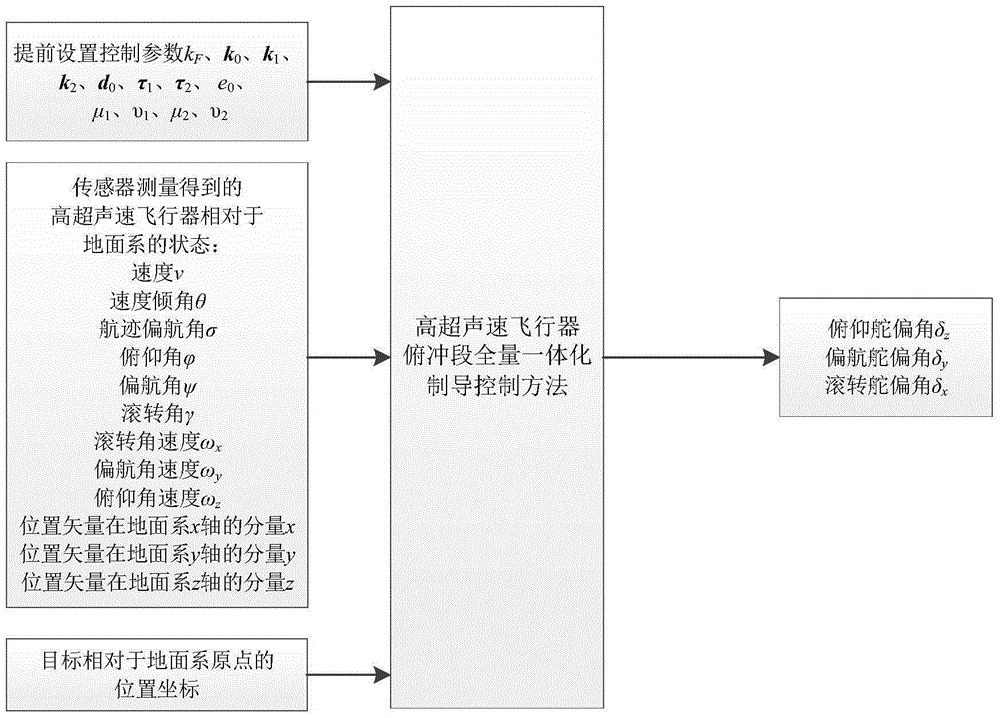
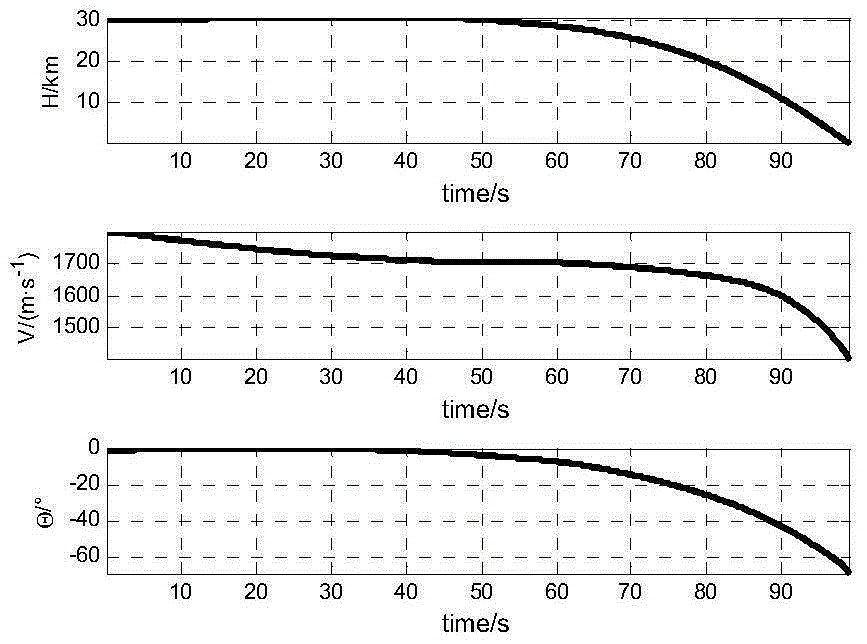
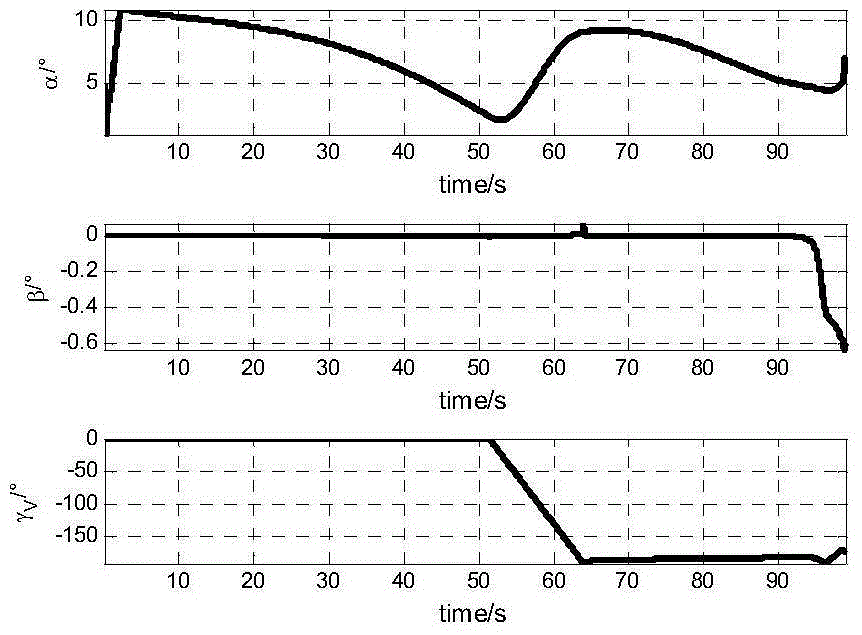
Hypersonic flight vehicle dive segment full amount integration guidance control method
InactiveCN105182985AImprove performanceImprove robustnessAttitude controlPosition/course control in three dimensionsSystems designGuidance control
The invention provides a hypersonic flight vehicle dive segment full amount integration guidance control method. A technical scheme is characterized in that firstly, a sensor measures states of a hypersonic flight vehicle relative to a ground system, wherein the states comprise a speed, a speed inclination angle, a track yaw angle, a rolling angular speed, a yaw angular speed, a pitching angular speed, a pitch angle, a yaw angle, a rolling angle and the like; then the above obtained quantities of states, positional information of an object relative to the ground system and a control parameter are substituted into a formula so as to calculate a rudder deflection angle vector, wherein the positional information is measured in advance; finally, the rudder deflection angle vector is used to control the hypersonic flight vehicle. In the invention, based on an aircraft full amount coupling integration guidance control model, an adaptive-block dynamic surface inversion method is used to realize integrated guidance control, and a problem of repeated design can be effectively avoided so that time and economic cost of a guidance control system design are reduced.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
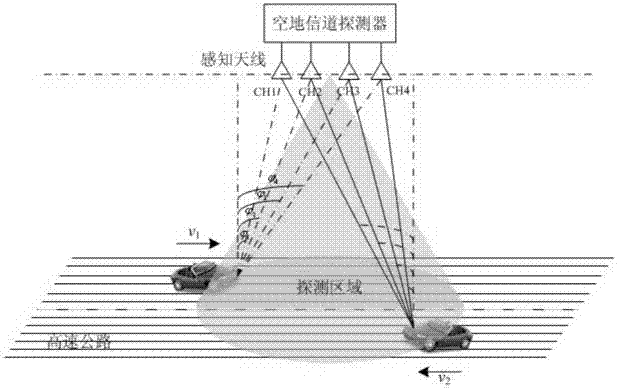
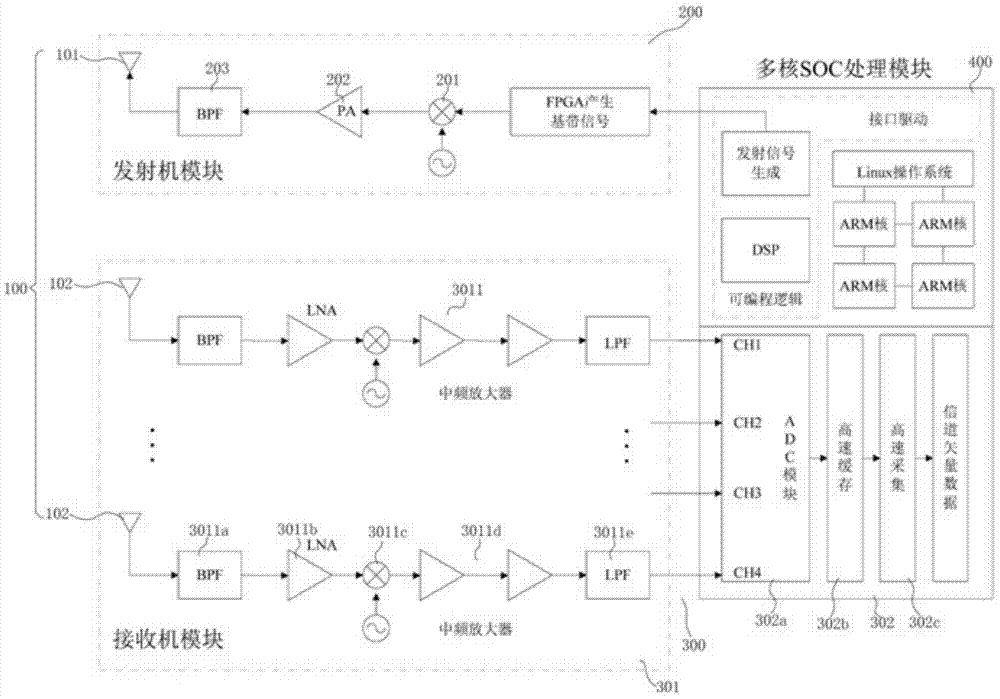
Expressway vehicle sensing system and method based on space channel detection
ActiveCN103905131AImprove perceptionAchieving Global Traffic AwarenessSpatial transmit diversityDetection of traffic movementAir monitoringGuidance control
The invention discloses an expressway vehicle sensing system and method based on space channel detection. An unmanned aerial vehicle space channel detection method is used, and expressway multilane and multi-vehicle real-time scanning detection is performed through a receiving and transmitting antenna array arranged at the bottom of an unmanned aerial vehicle detector. According to the analysis on the variation characteristics on a space moving channel, multi-dimensional parameters of the moving channel can be obtained in real time, and the position, the speed and the vehicle type of moving vehicles on an expressway are accurately estimated. The expressway vehicle sensing system and method based on space channel detection break through the limitation of vehicle sensing based on traditional sensors such as an infrared sensor and a video sensor, an advanced space moving channel detection and vehicle sensing technology is utilized, the all-weather vehicle sensing capacity in the intelligent transportation system application is improved, and the expressway rod vehicle sensing system and method based on space channel detection can be applied to the fields of intelligent transportation system air control, expressway traffic dispersion, after-calamity traffic guidance control, military exercise air monitoring and the like.
Owner:上海克里浠智能科技有限公司
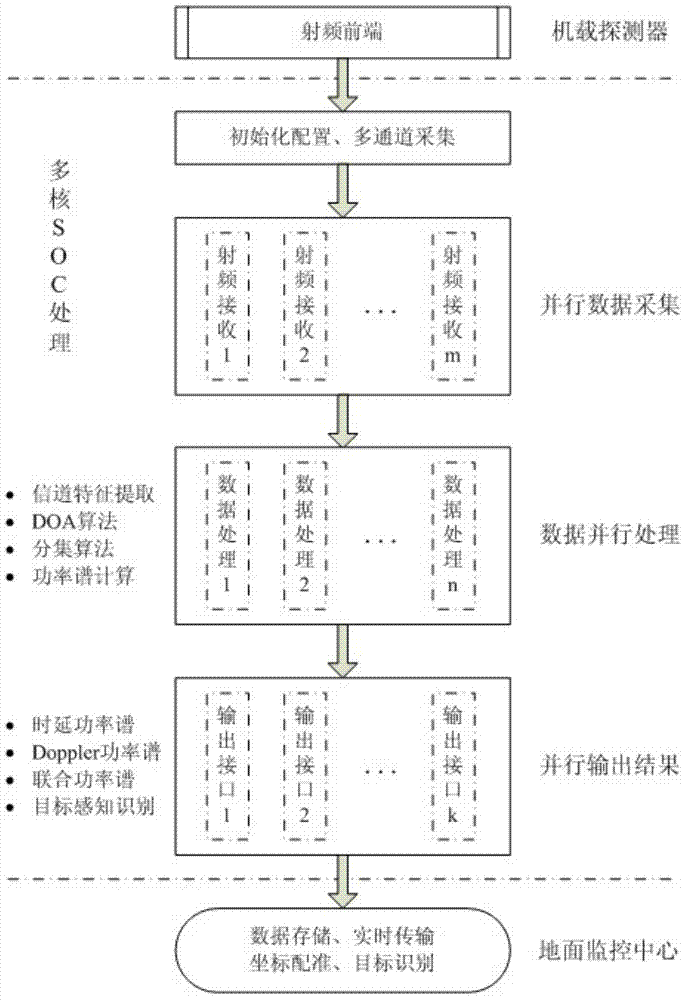
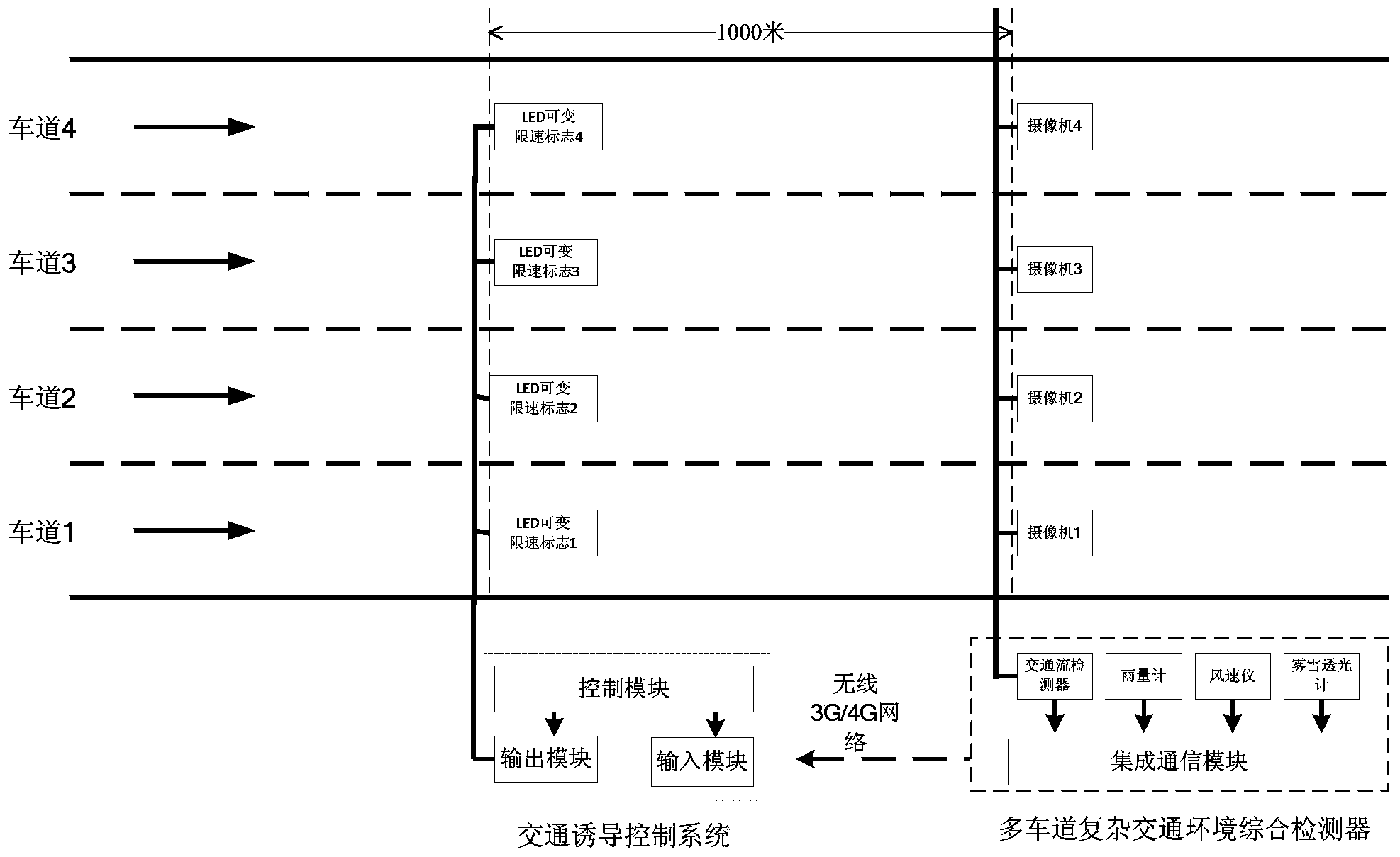
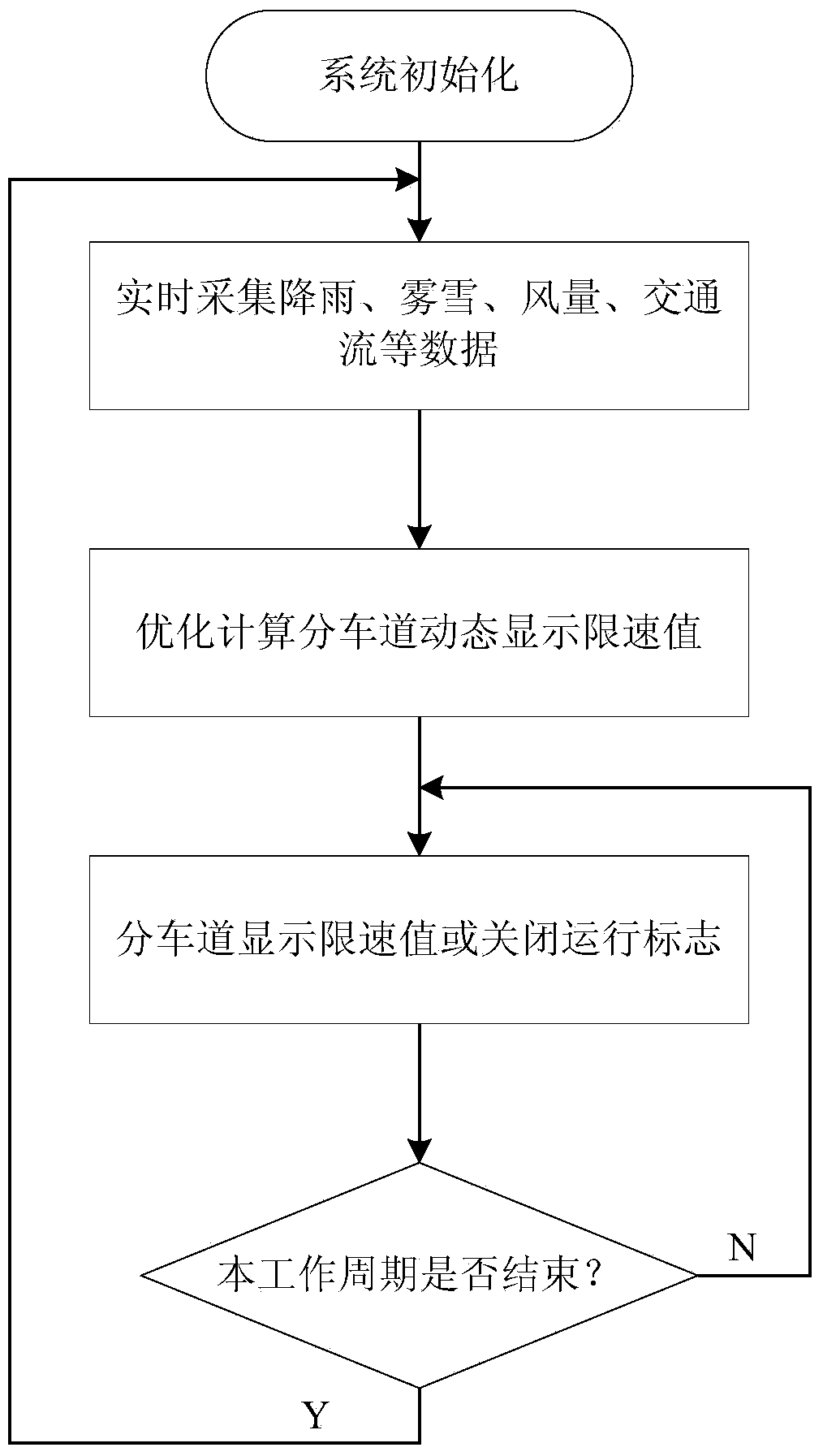
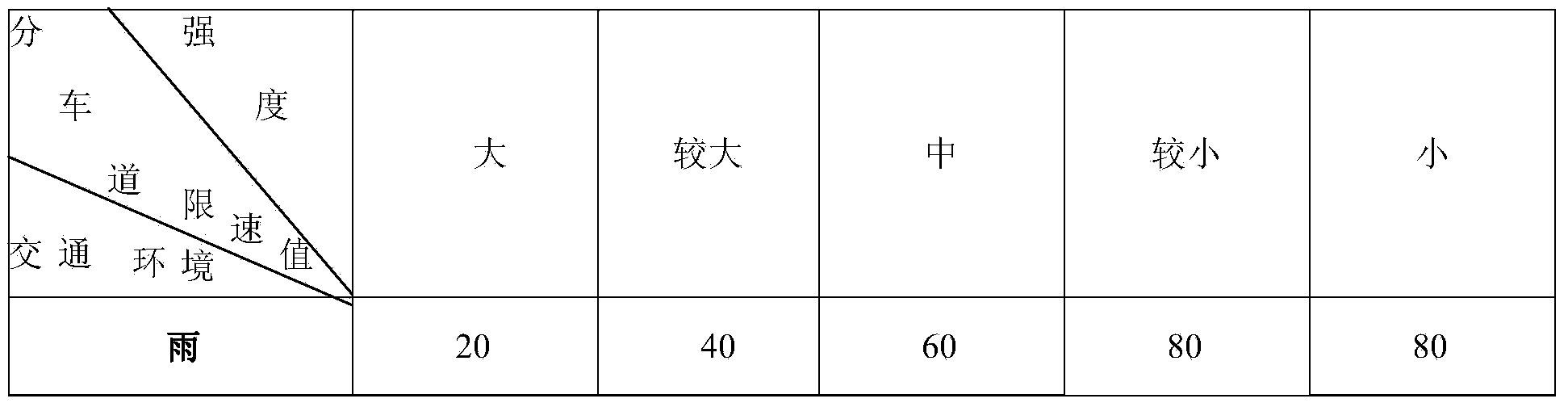
Vehicle speed control system for expressway main line
The invention provides a vehicle speed control system for an expressway main line. The system comprises a multichannel traffic environment comprehensive detector, divided lane LED variable speed-limit signs and a traffic guidance control system, wherein the multichannel traffic environment comprehensive detector, the divided lane LED variable speed-limit signs and the traffic guidance control system are arranged on the expressway main line road segment, the multichannel traffic environment comprehensive detector comprises an integrated communication module, a rain gauge, a fog and snow light-transmitting gauge, an anemoscope and a traffic flow detector, and the rain gauge, the fog and snow light-transmitting gauge, the anemoscope and the traffic flow detector are connected with the integrated communication module. The integrated communication module outputs data to the traffic guidance control system through a unified communication interface, and the traffic guidance control system is combined with speed limiting restraining conditions of divided lanes, optimally provides dynamic speed limiting values or lane-closing running instructions of the divided lanes, and outputs the values and instructions to the divided lane LED variable speed-limit signs. The vehicle speed control system has the advantages of optimally providing the dynamic speed limiting values or no-entry instructions of the divided lanes on basis of comprehensively considering the rain, snow, fog, wind and traffic congestion conditions, and ensuring the running safety on the expressway main line under the complex traffic condition.
Owner:TRAFFIC MANAGEMENT RES INST OF THE MIN OF PUBLIC SECURITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com