Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
2086results about "Target-seeking control" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Dynamic target tracking and positioning method of unmanned plane based on vision
The invention discloses a dynamic target tracking and positioning method of an unmanned plane based on vision, and belongs to the navigation field of the unmanned planes. The dynamic target tracking and positioning method comprises the following steps of: carrying out video processing, dynamic target detecting and image tracking; carrying out cloud deck servo control; establishing a corresponding relationship between a target in the image and a target in the real environment, and further measuring the distance between a camera and a dynamic target to complete precise positioning of the dynamic target; and enabling an unmanned plane control system to fly by automatically tracking the dynamic target on the ground. The dynamic target tracking and positioning method of the unmanned plane based on the vision can automatically realize the movement target detecting, image tracking and optical axis automatic deflecting without the full participation of the people, so that the dynamic target is always displayed at the center of an image-forming plane; and the distance between the unmanned plane and the dynamic target is measured in real time according to an established model on the basis of obtaining the height information of the unmanned plane. Therefore, the positioning of the dynamic target is realized; closed-loop control is formed by using the positioned dynamic target as a feedback signal, so that the tracking flight of the unmanned plane is guided.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
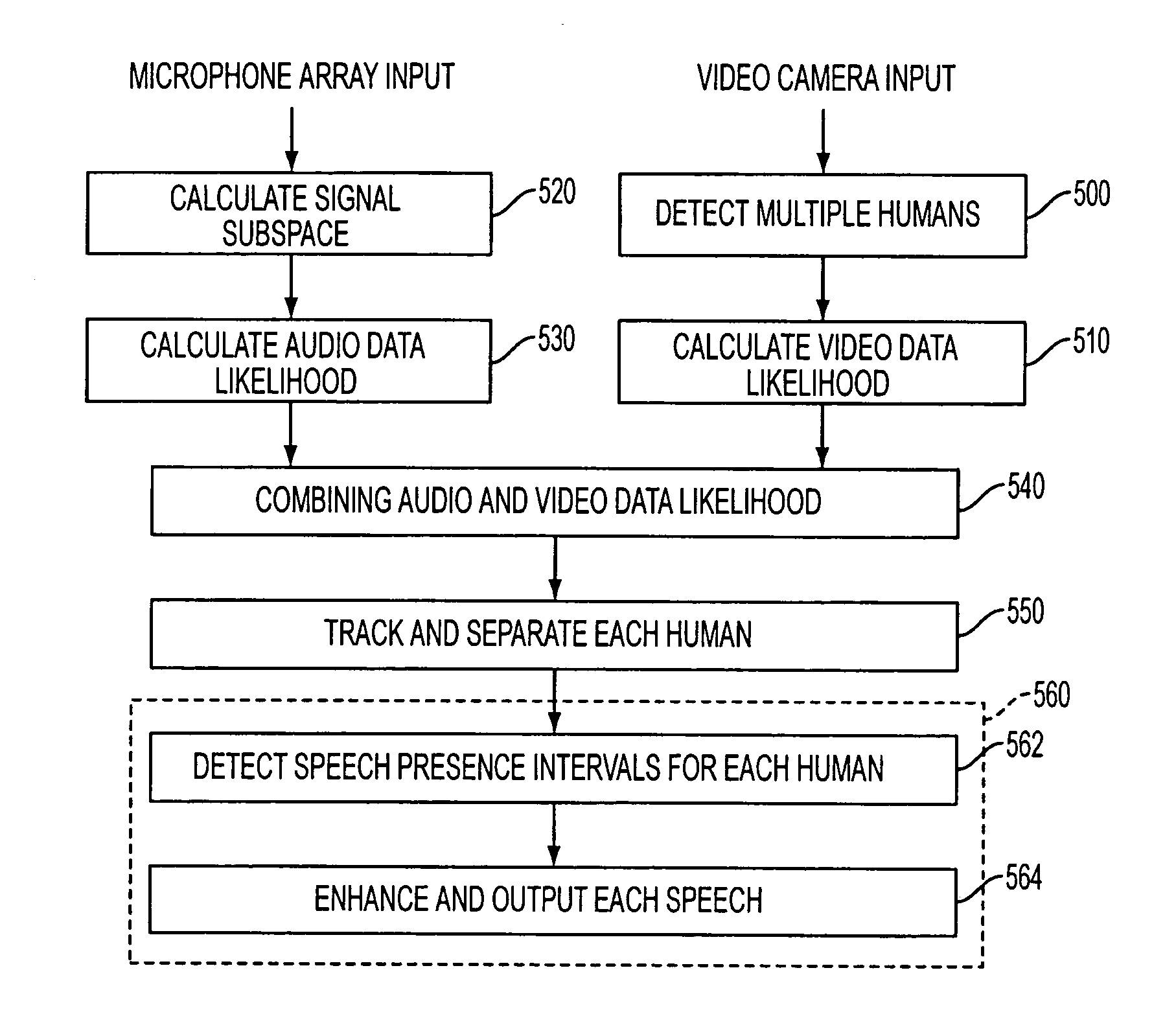
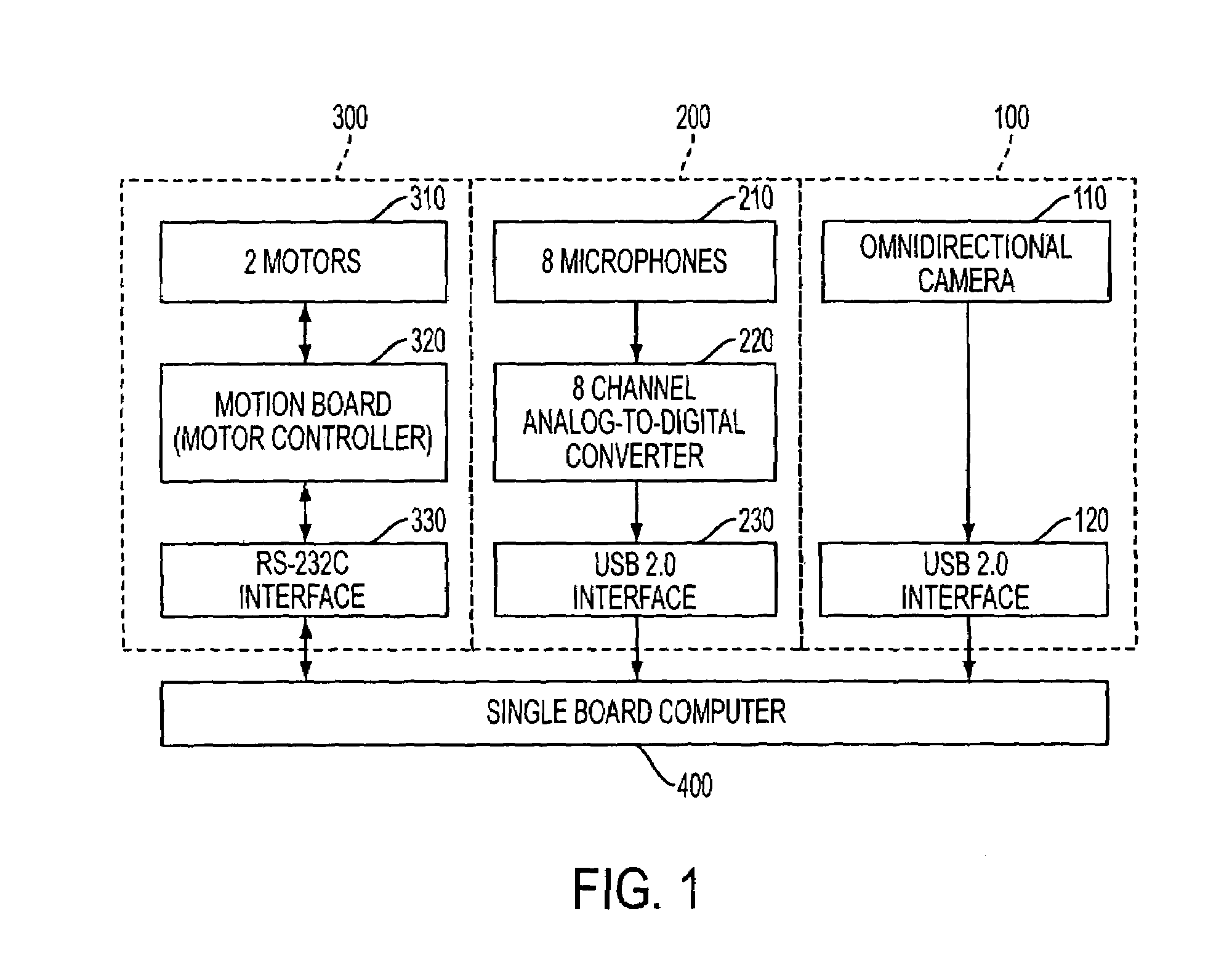
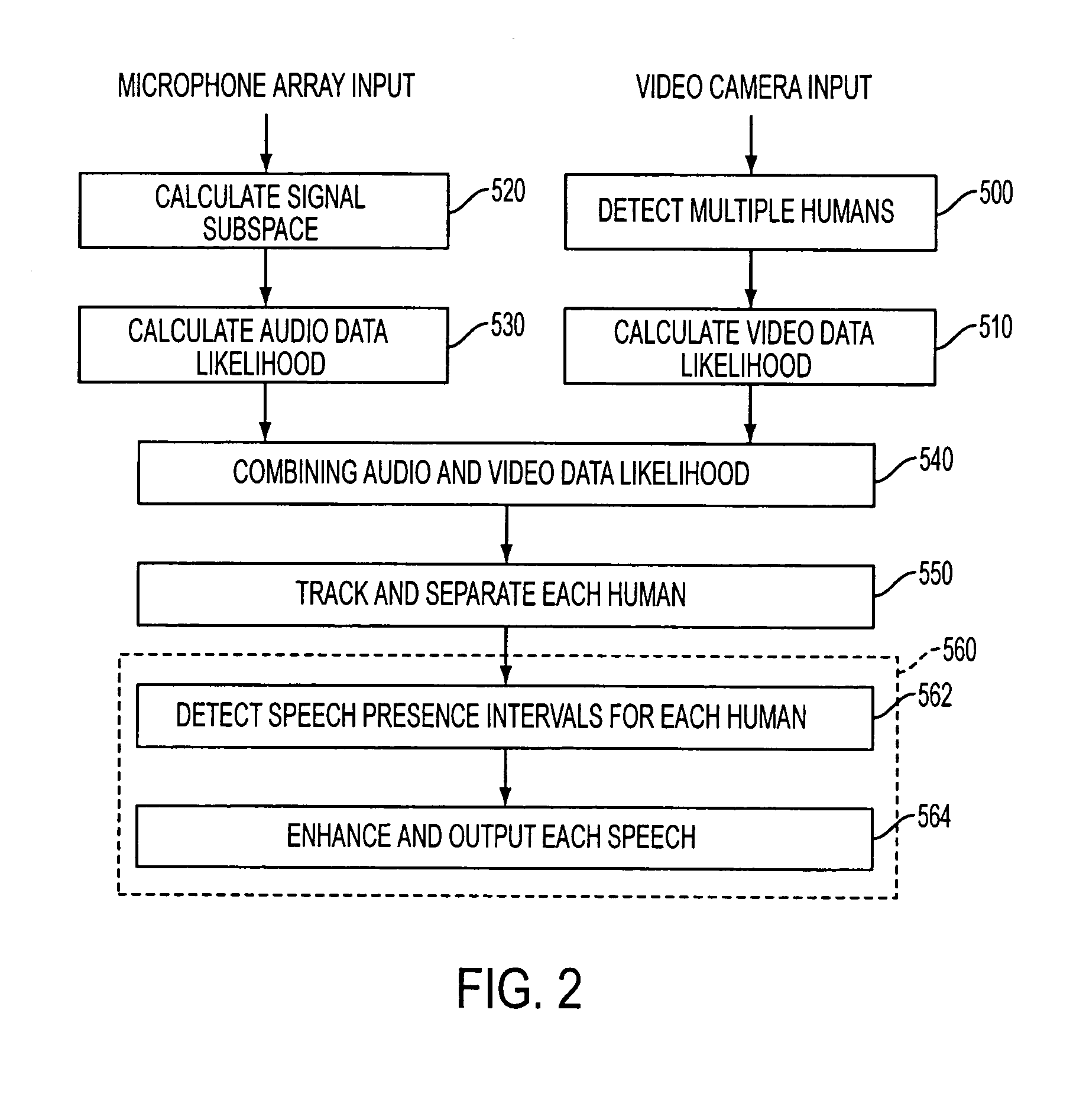
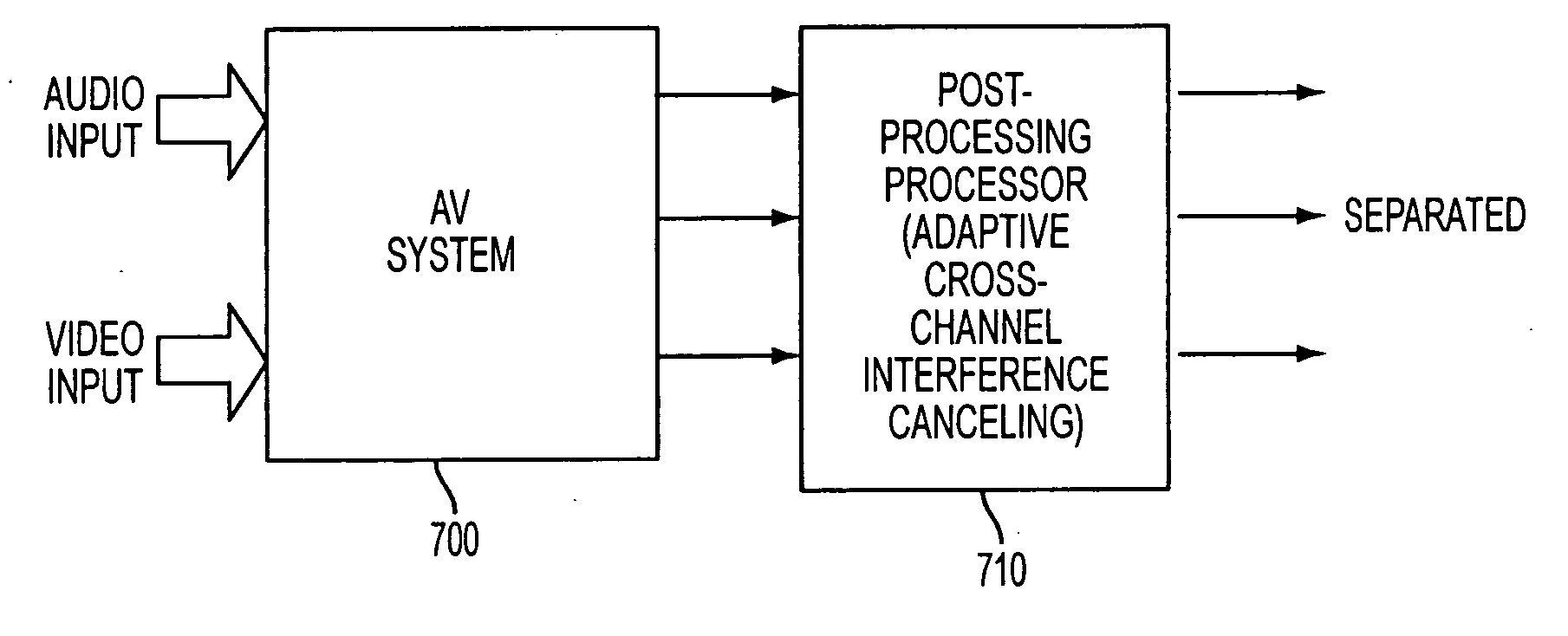
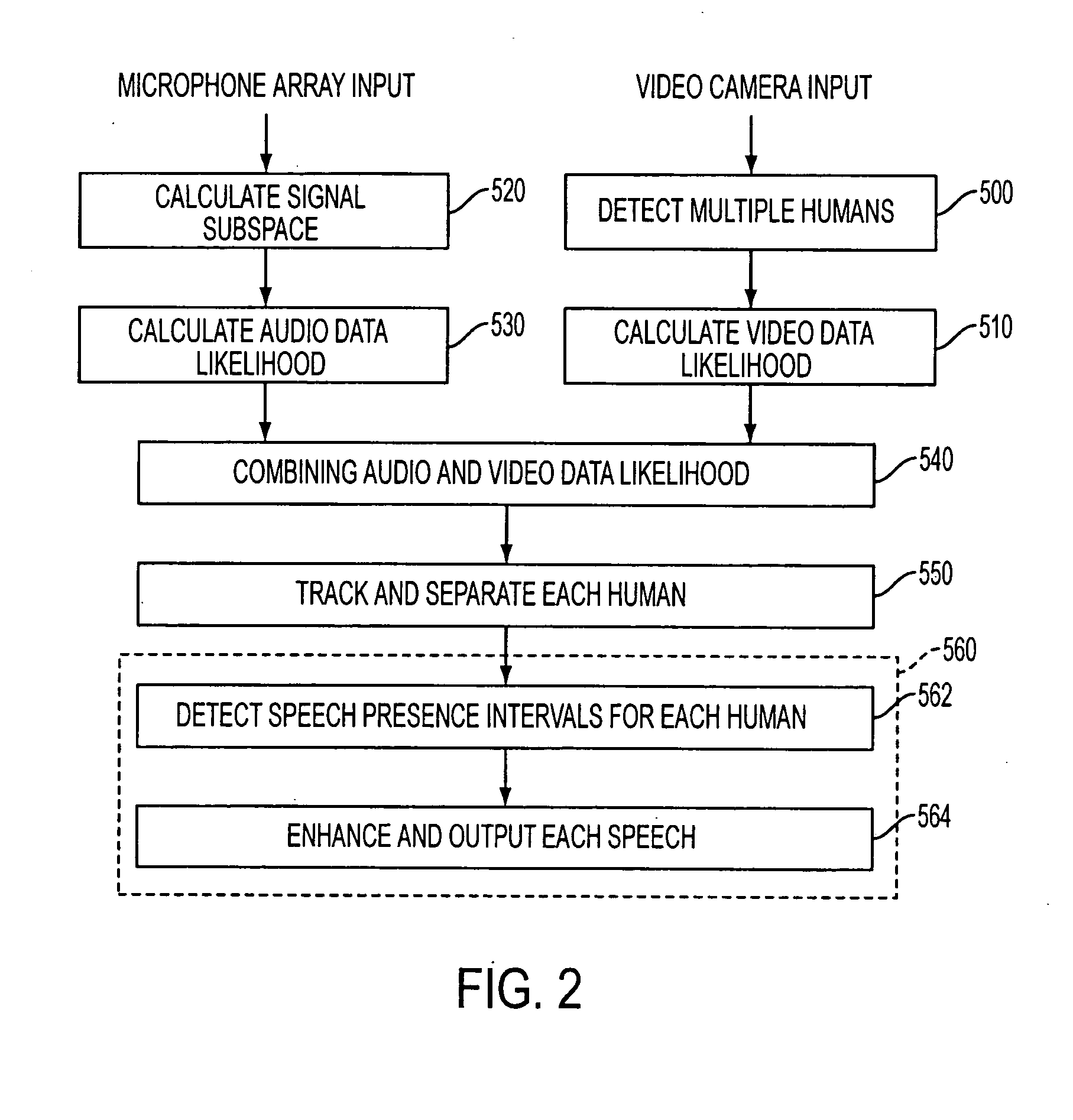
Apparatus and method performing audio-video sensor fusion for object localization, tracking, and separation
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
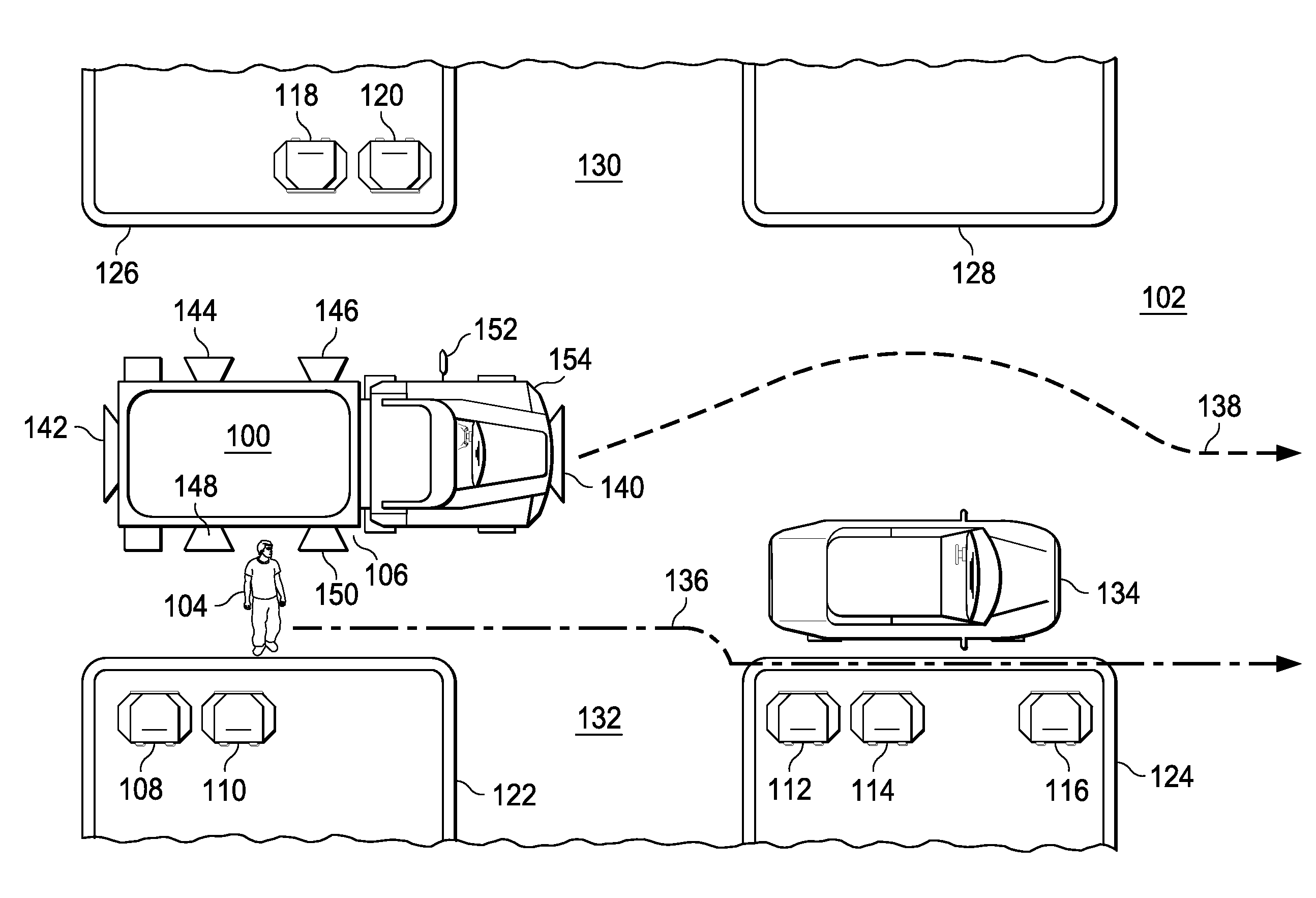
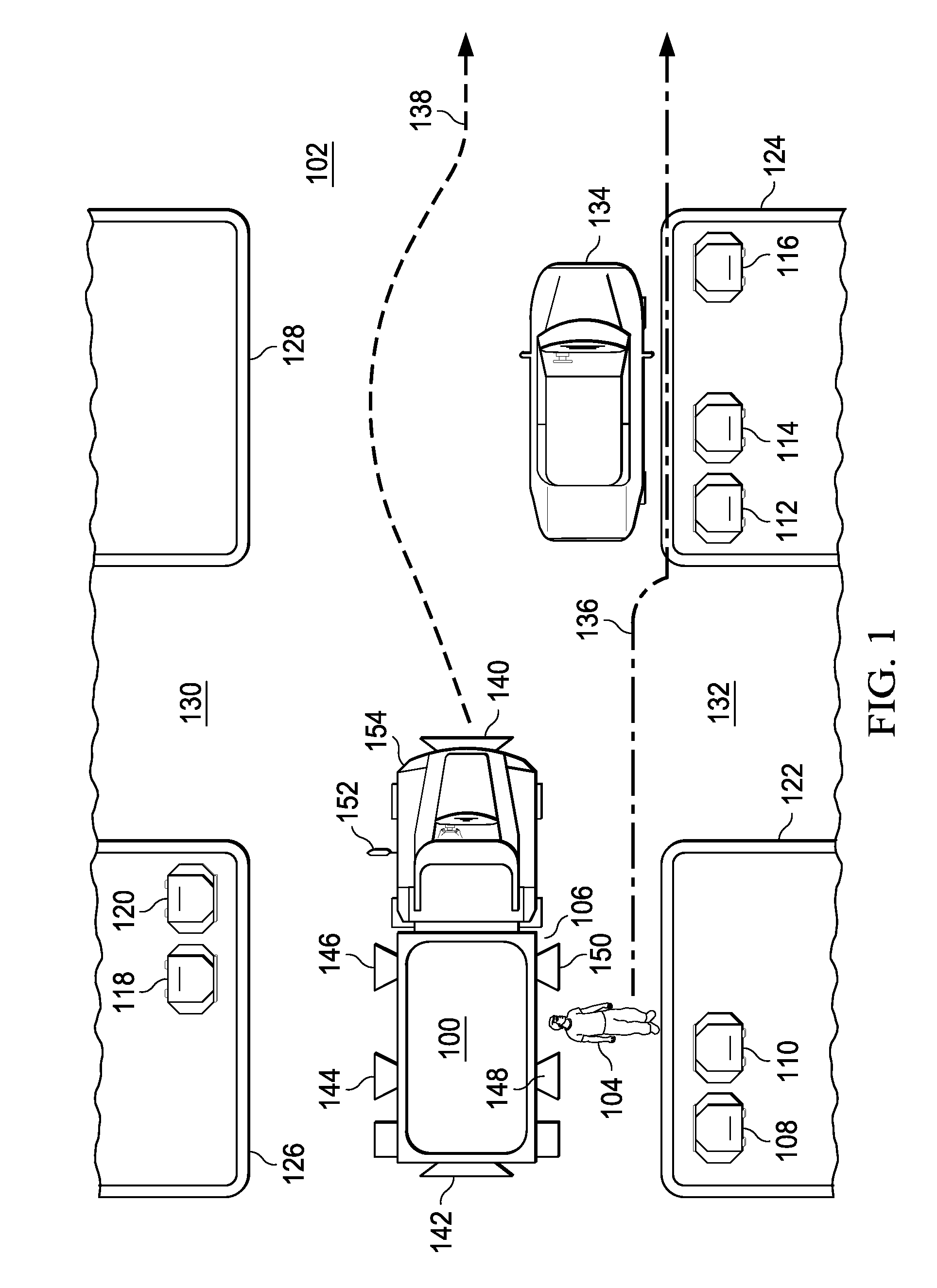
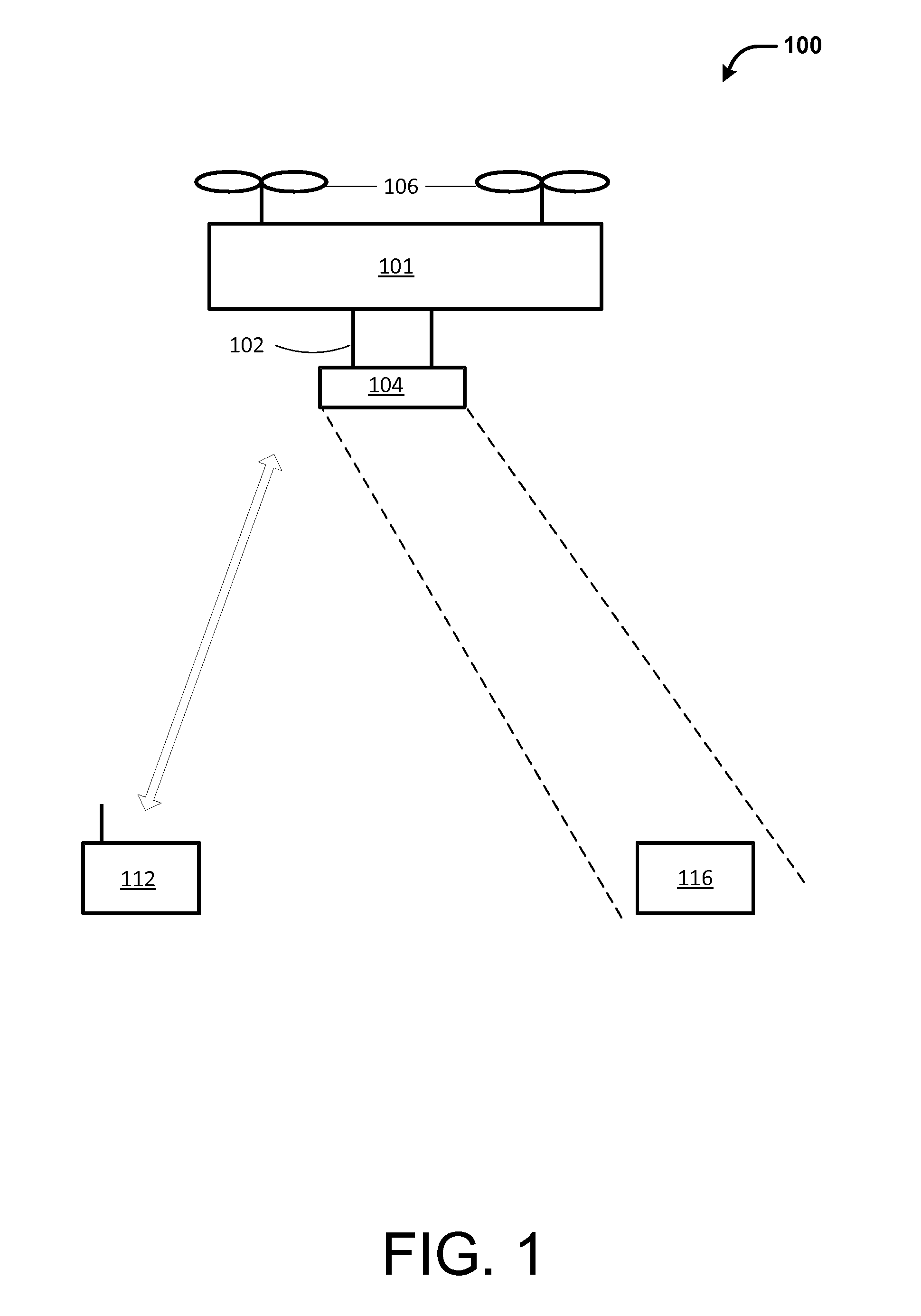
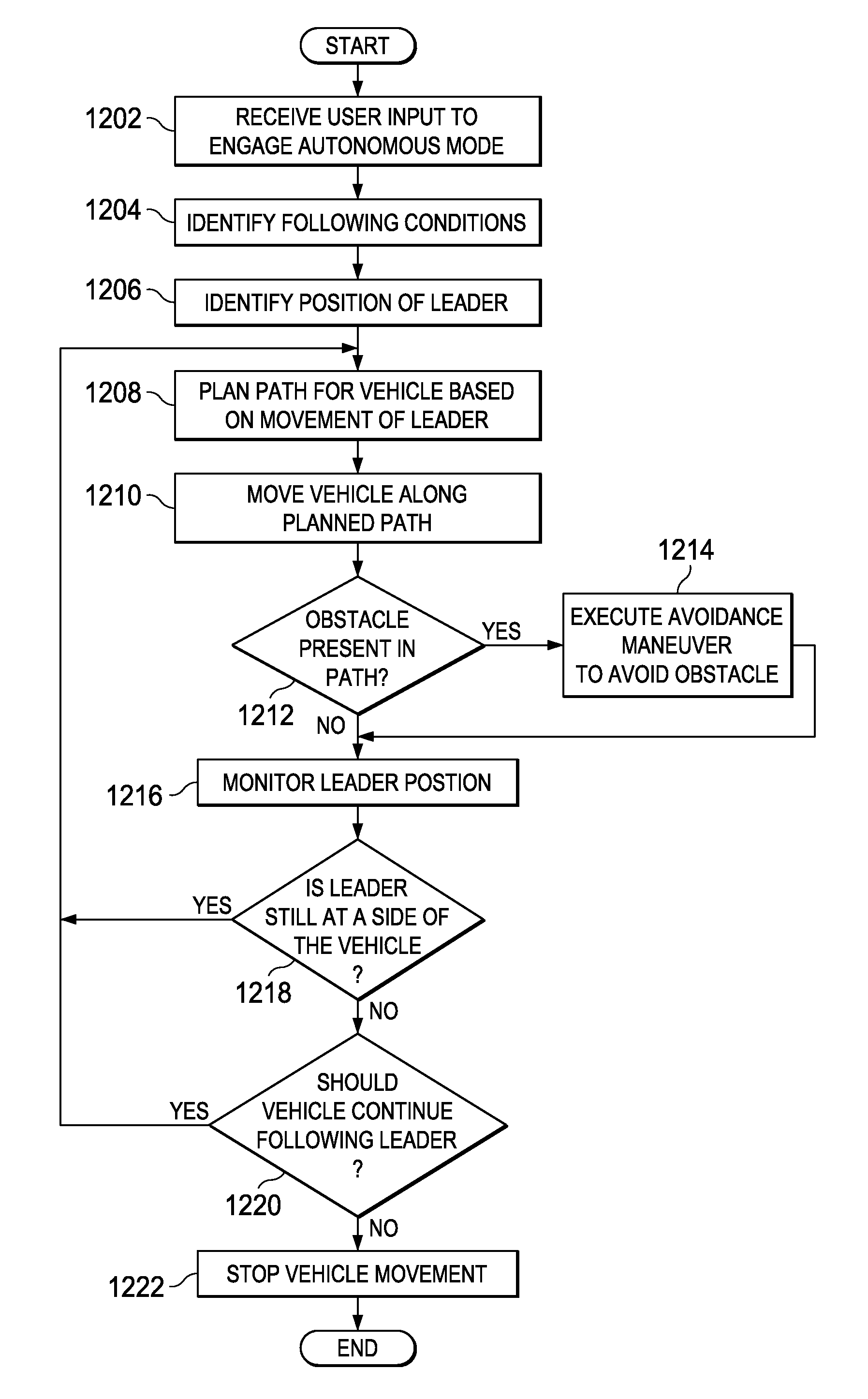
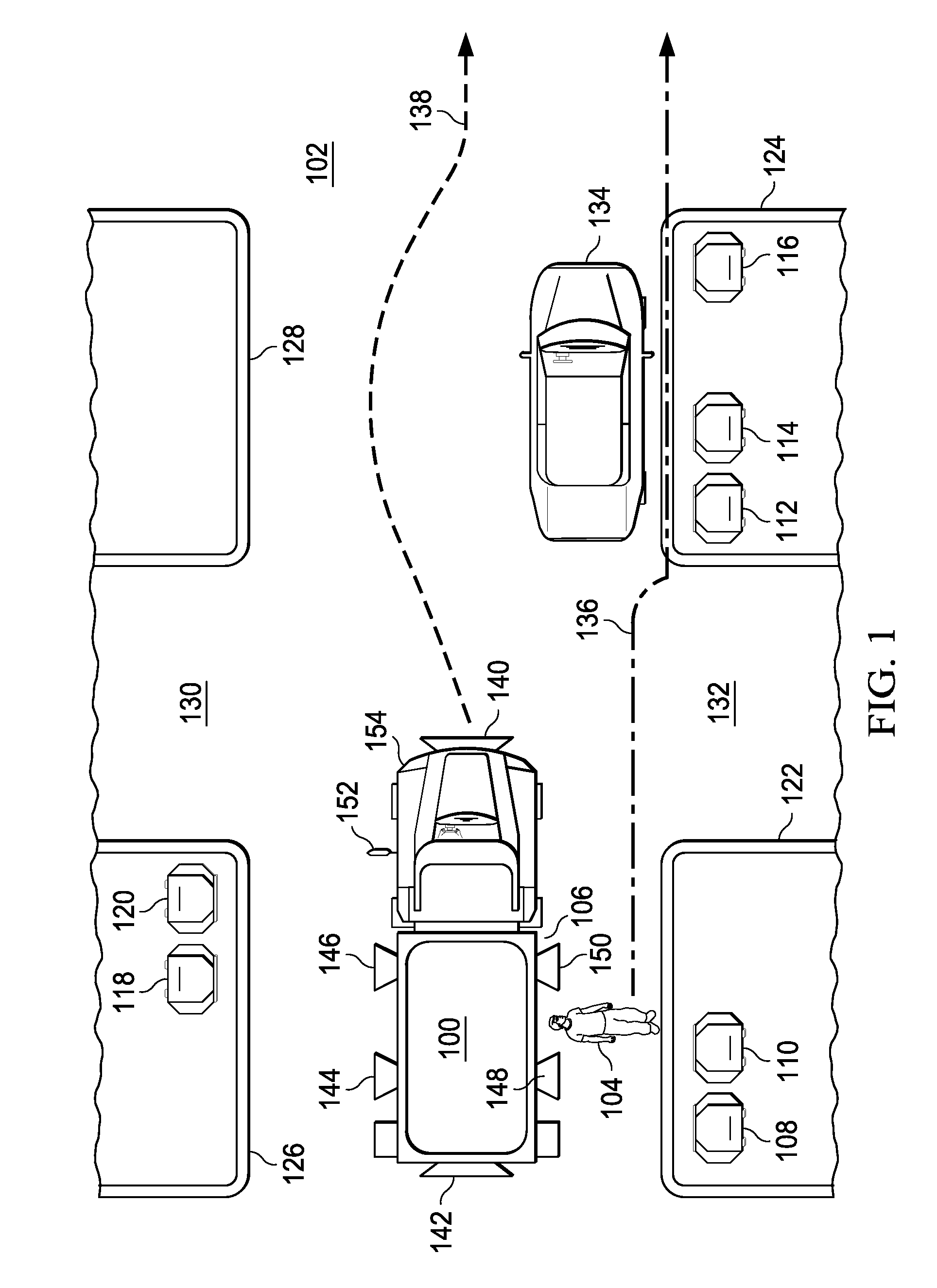
Leader-follower semi-autonomous vehicle with operator on side
The illustrative embodiments provide a method and apparatus for controlling movement of a vehicle. User input selecting a path for the vehicle is received from an operator. The vehicle responds to the user input by moving along the selected path in a manner that maintains the operator on a side of the vehicle. The illustrative embodiments further provide a method and apparatus for improved machine control. The vehicle receives a power-up command, instructions to execute a planned path, and information identifying a leader. The leader is an operator. The vehicle then executes the planned path using the information identifying the leader in order to follow a path of the leader. The vehicle moves along the path in a manner that maintains the leader in a position proximate to a side of the vehicle.
Owner:DEERE & CO
Systems and methods for target tracking
The present invention provides systems, methods, and devices related to target tracking by UAVs. The UAV may be configured to receive target information from a control terminal related to a target to be tracked by an imaging device coupled to the UAV. The target information may be used by the UAV to automatically track the target so as to maintain predetermined position and / or size of the target within one or more images captured by the imaging device. The control terminal may be configured to display images from the imaging device as well as allowing user input related to the target information.
Owner:SZ DJI TECH CO LTD
Leader-follower semi-autonomous vehicle with operator on side
ActiveUS20100063680A1Analogue computers for trafficSteering initiationsDriver/operatorMachine control
The illustrative embodiments provide a method and apparatus for controlling movement of a vehicle. User input selecting a path for the vehicle is received from an operator. The vehicle responds to the user input by moving along the selected path in a manner that maintains the operator on a side of the vehicle. The illustrative embodiments further provide a method and apparatus for improved machine control. The vehicle receives a power-up command, instructions to execute a planned path, and information identifying a leader. The leader is an operator. The vehicle then executes the planned path using the information identifying the leader in order to follow a path of the leader. The vehicle moves along the path in a manner that maintains the leader in a position proximate to a side of the vehicle.
Owner:DEERE & CO
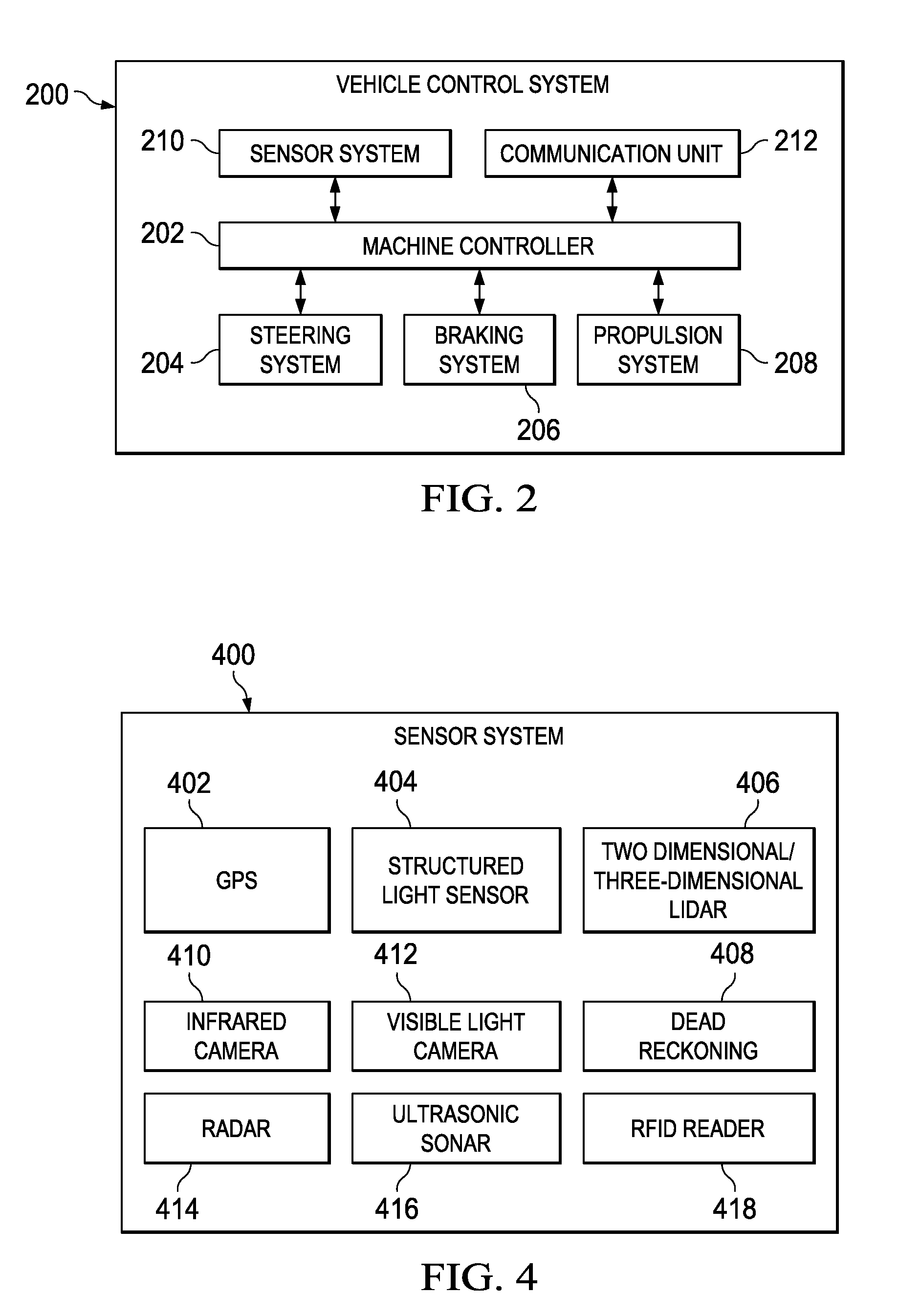
System and method for controlling movement of vehicles
ActiveUS20120277940A1Improve performanceSave fuelDigital data processing detailsTraffic regulationRemedial actionTransport network
A method includes determining an operational parameter of a first vehicle traveling with a plurality of vehicles in a transportation network and / or a route in the transportation network, identifying a failure condition of the first vehicle and / or the route based on the operational parameter, obtaining plural different sets of remedial actions that dictate operations to be taken based on the operational parameter, simulating travel of the plurality of vehicles in the transportation network based on implementation of the different sets of remedial actions, determining potential consequences on travel of the plurality of vehicles in the transportation network when the different sets of remedial actions are implemented in the travel that is simulated, and based on the potential consequences, receiving a selection of at least one of the different sets of remedial actions to be implemented in actual travel of the plurality of vehicles in the transportation network.
Owner:GE GLOBAL SOURCING LLC
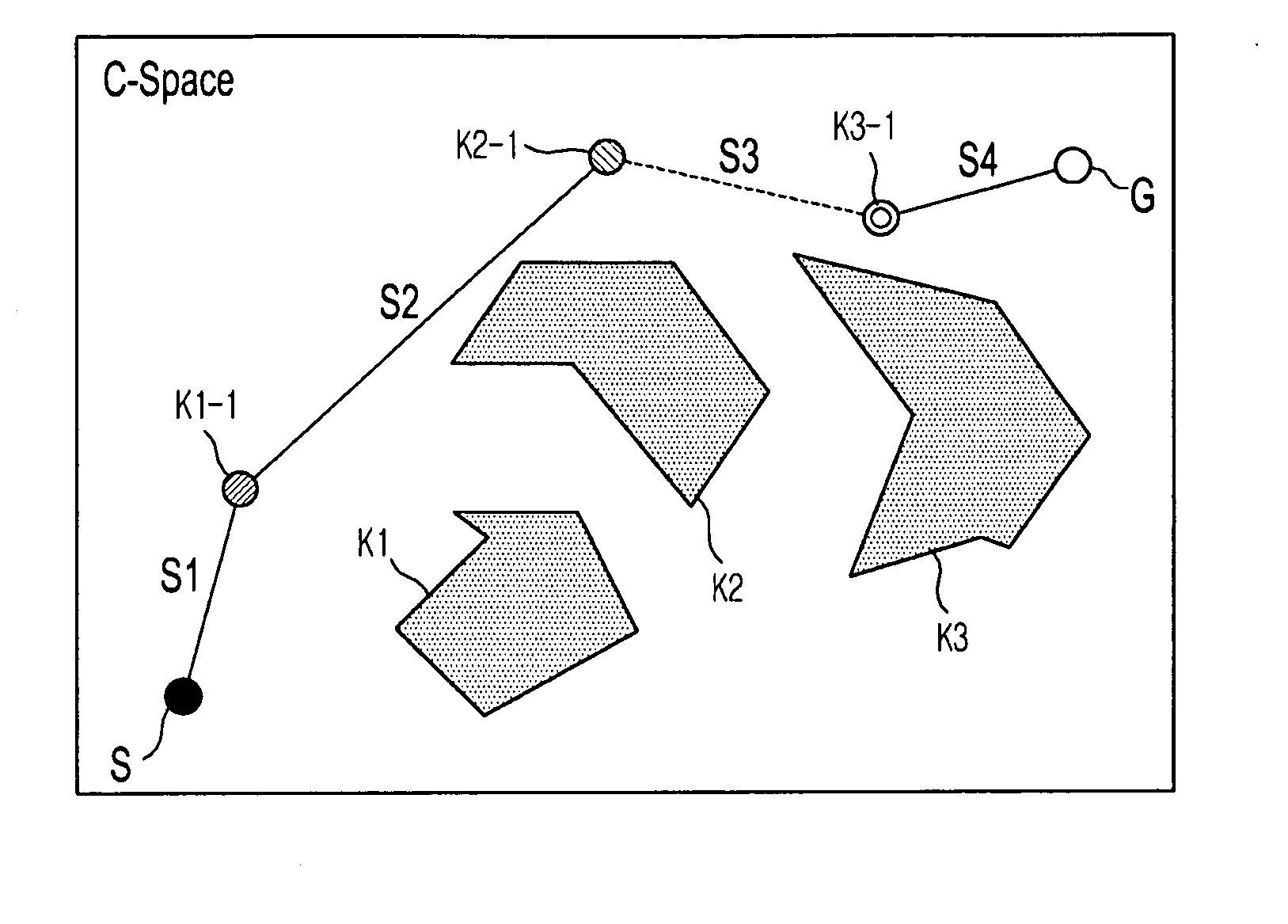
Method and apparatus to plan motion path of robot
ActiveUS20110035087A1Reduce probabilitySolution can be rapidly obtainedProgramme-controlled manipulatorInstruments for road network navigationAlgorithmRandom tree
A suitable waypoint is selected using a goal score, a section from a start point to a goal point through the waypoint is divided into a plurality of sections based on the waypoint with a solution of inverse kinematics, and trees are simultaneously expanded in the sections using a Best First Search & Rapidly Random Tree (BF-RRT) algorithm so as to generate a path. By this configuration, a probability of local minima occurring is decreased compared with the case where the waypoint is randomly selected. In addition, since the trees are simultaneously expanded in the sections each having the waypoint with a solution of inverse kinematics, the solution may be rapidly obtained. A time consumed to search for an optimal motion path may be shortened and path plan performance may be improved.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
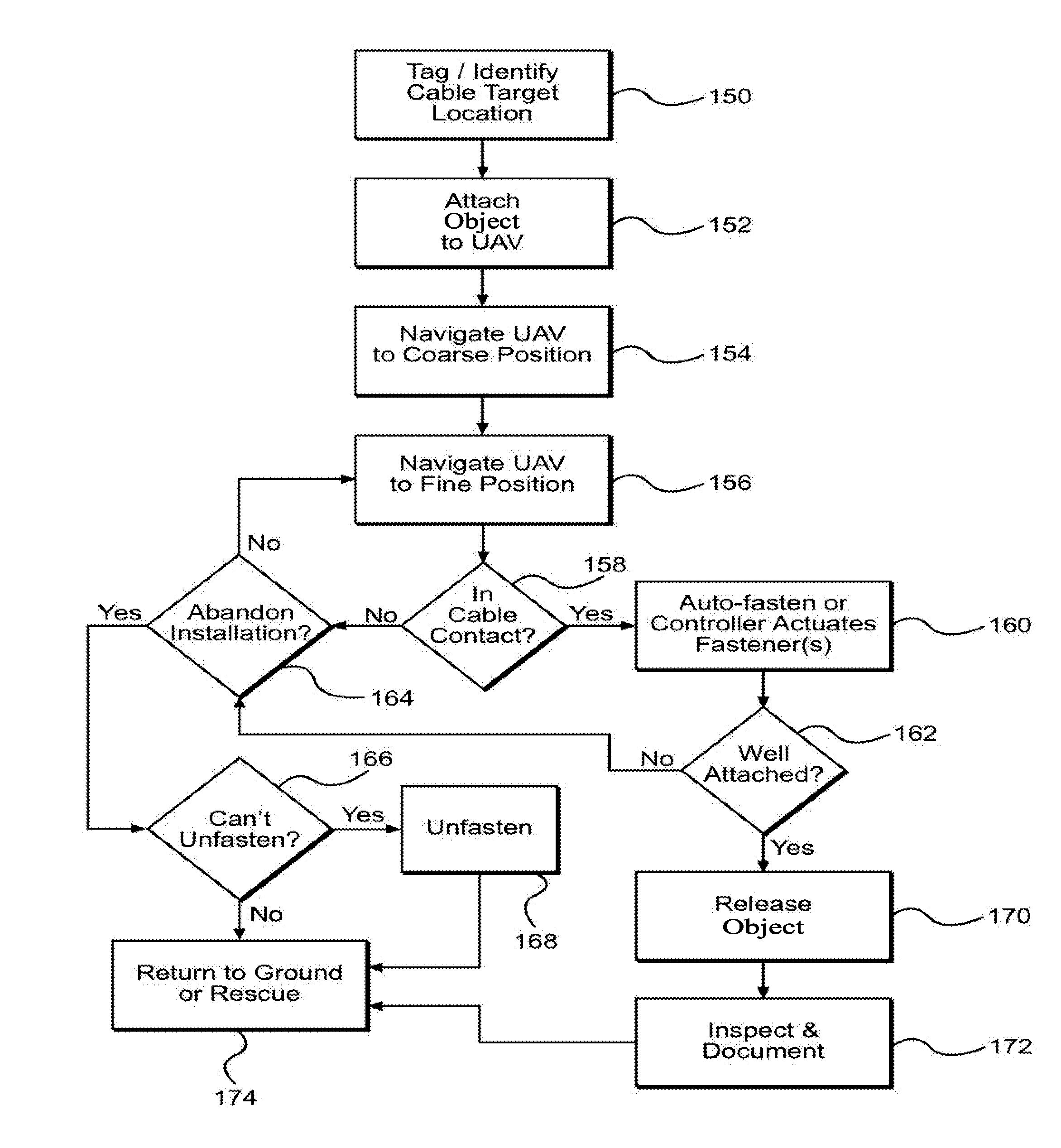
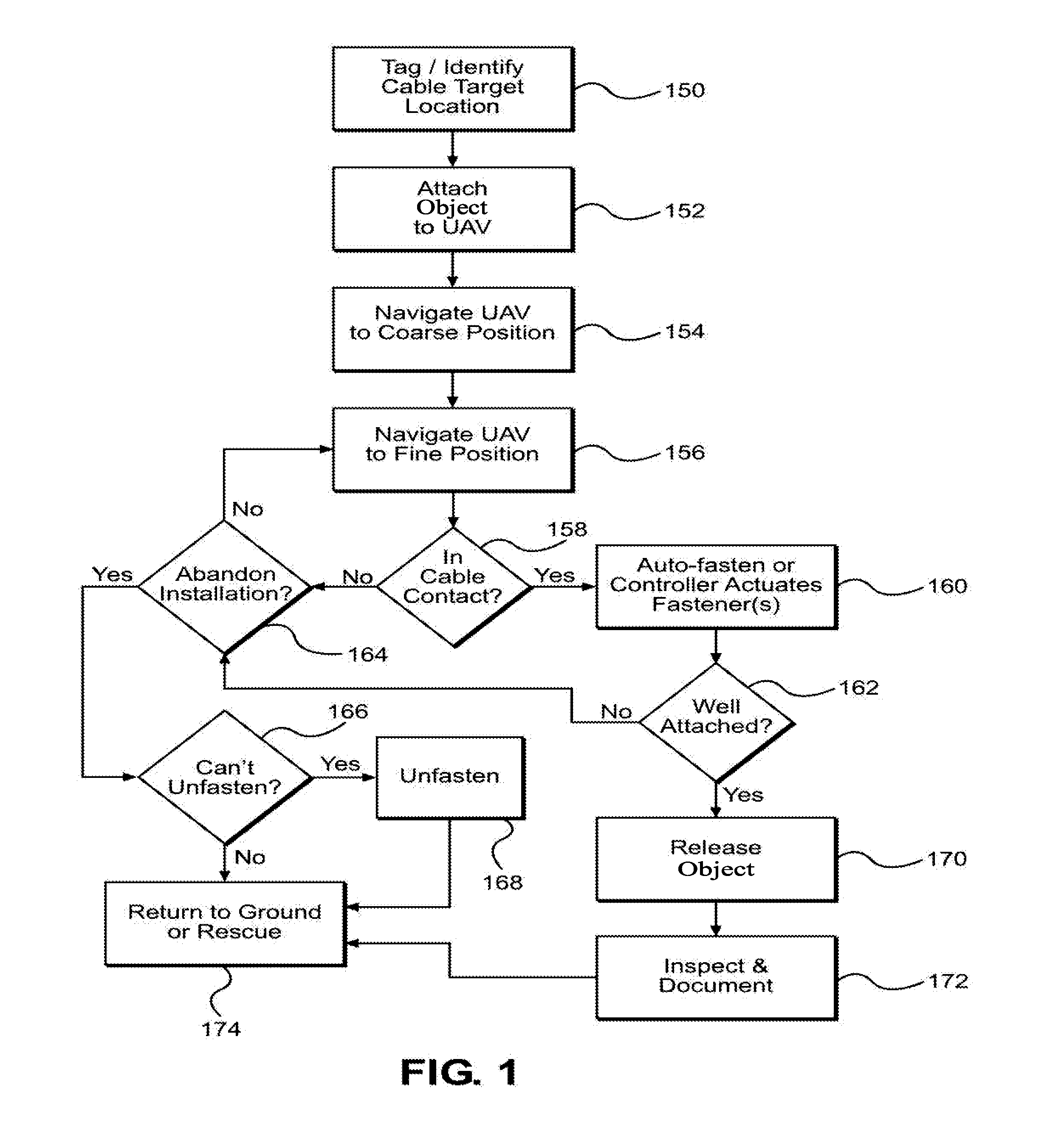
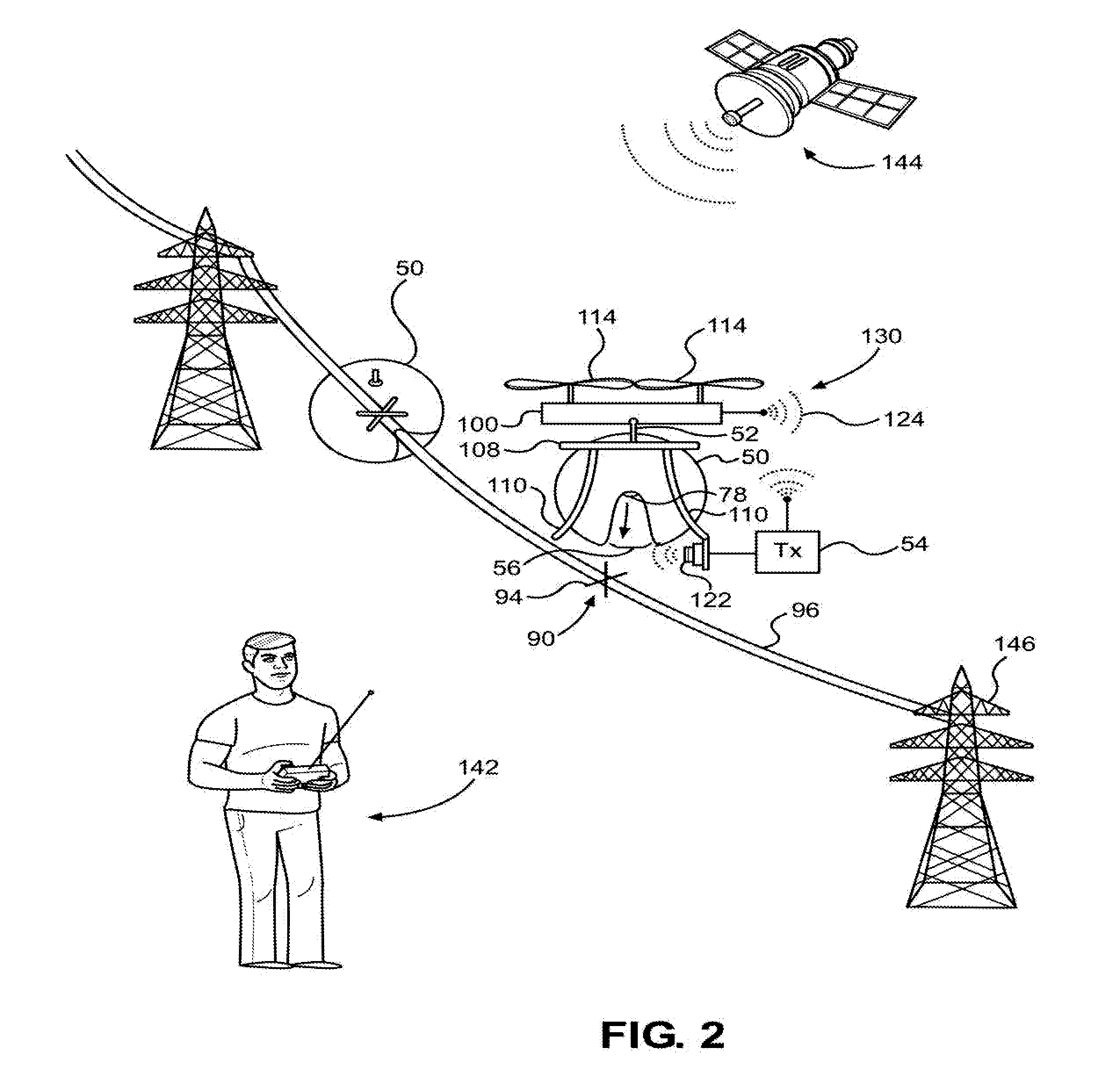
Method for installing an object using an unmanned aerial vehicle
ActiveUS20160023761A1Overhead installationUnmanned aerial vehiclesAircraft flight control systemMechanical devices
A method for using an unmanned aerial vehicle to install objects on wire and catenary structures is described. The method includes tagging the location, attaching the object to the UAV, navigating the UAV to the position, attaching the object, testing the attachment, releasing the object, inspecting the attachment, and returning the UAV to the ground. Sensors, flight control systems, means for attachment, and variations of embodiments of the methods, systems, and mechanical devices are described.
Owner:MCNALLY JONATHAN
Apparatus and method performing audio-video sensor fusion for object localization, tracking, and separation
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
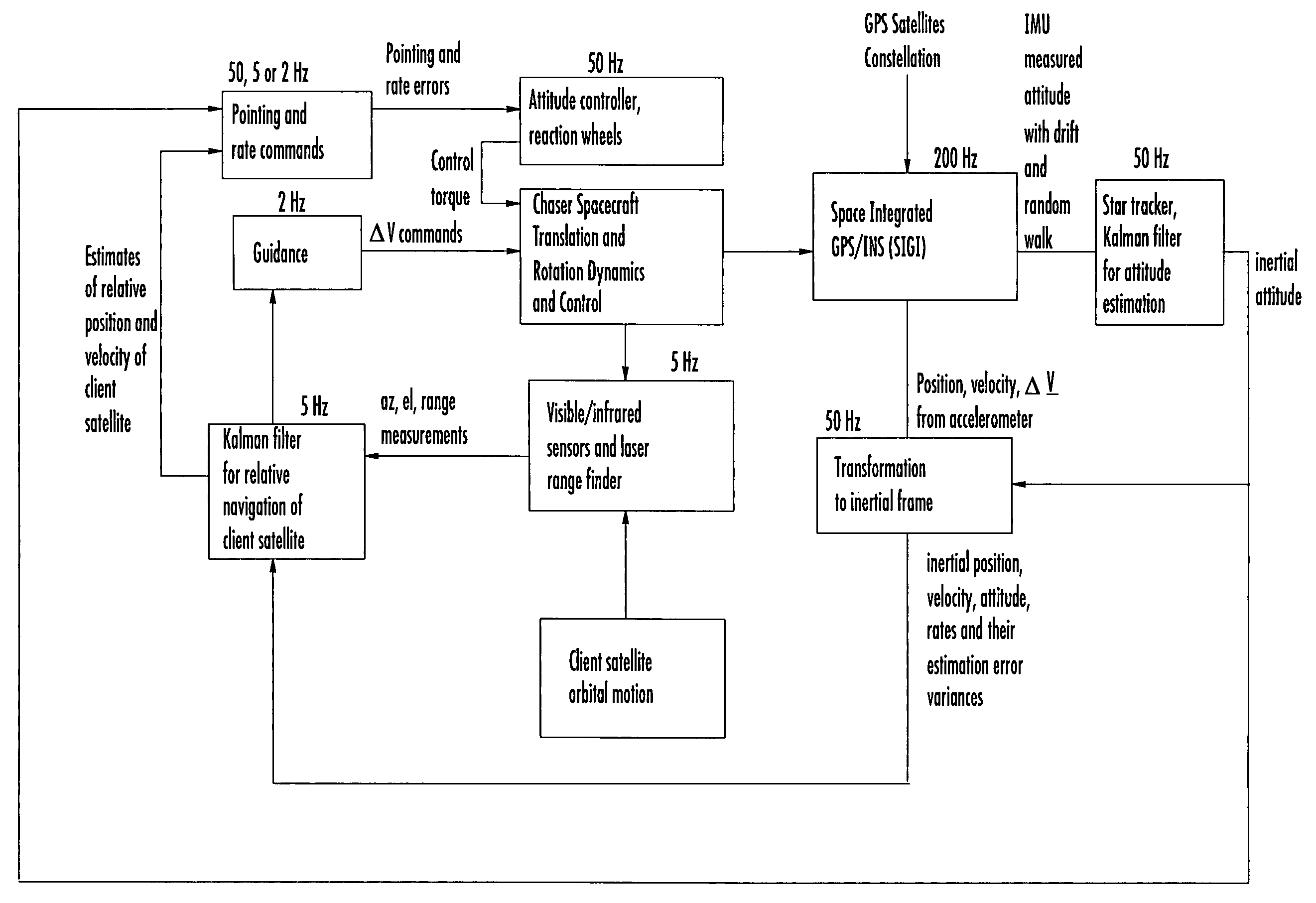
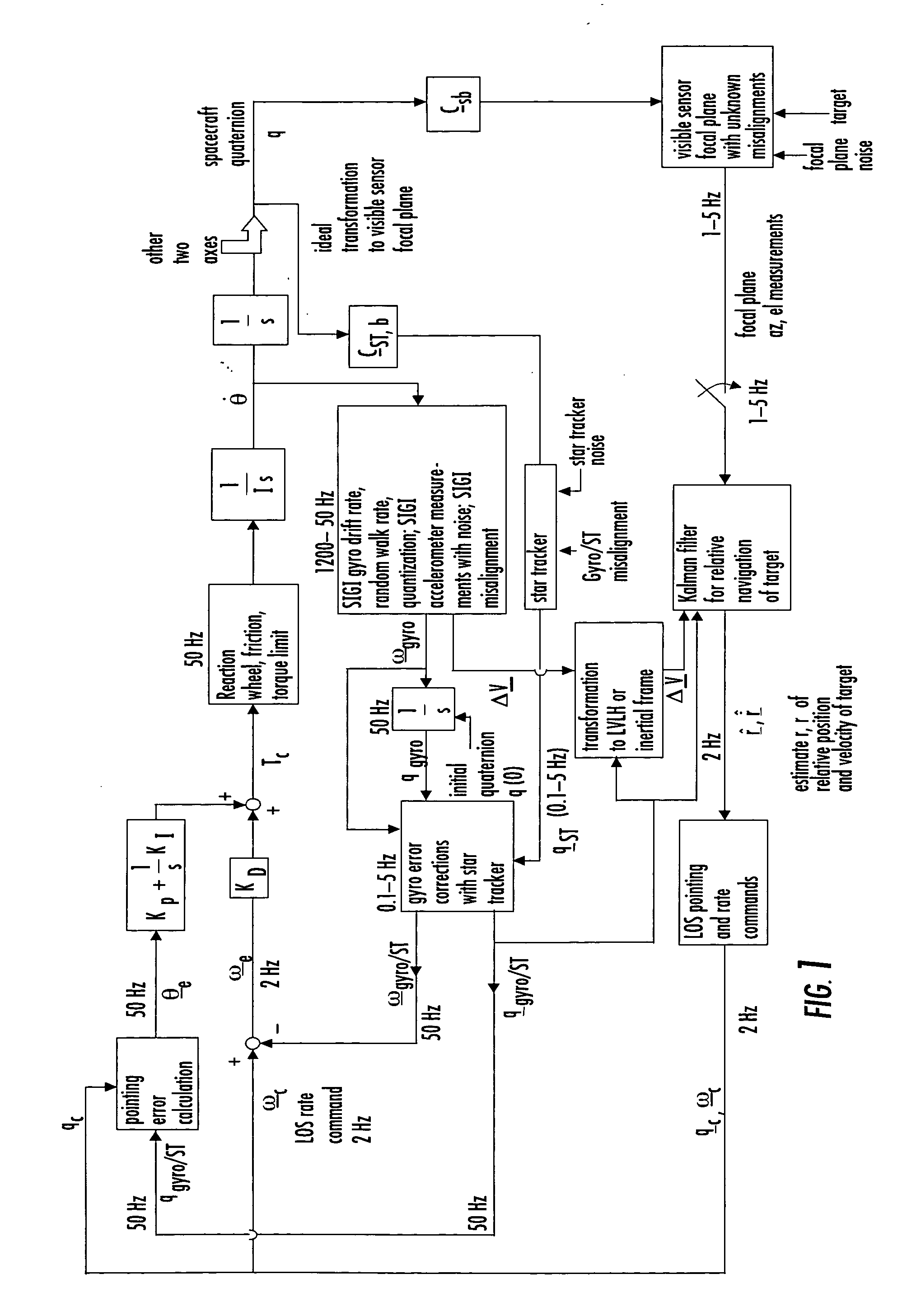
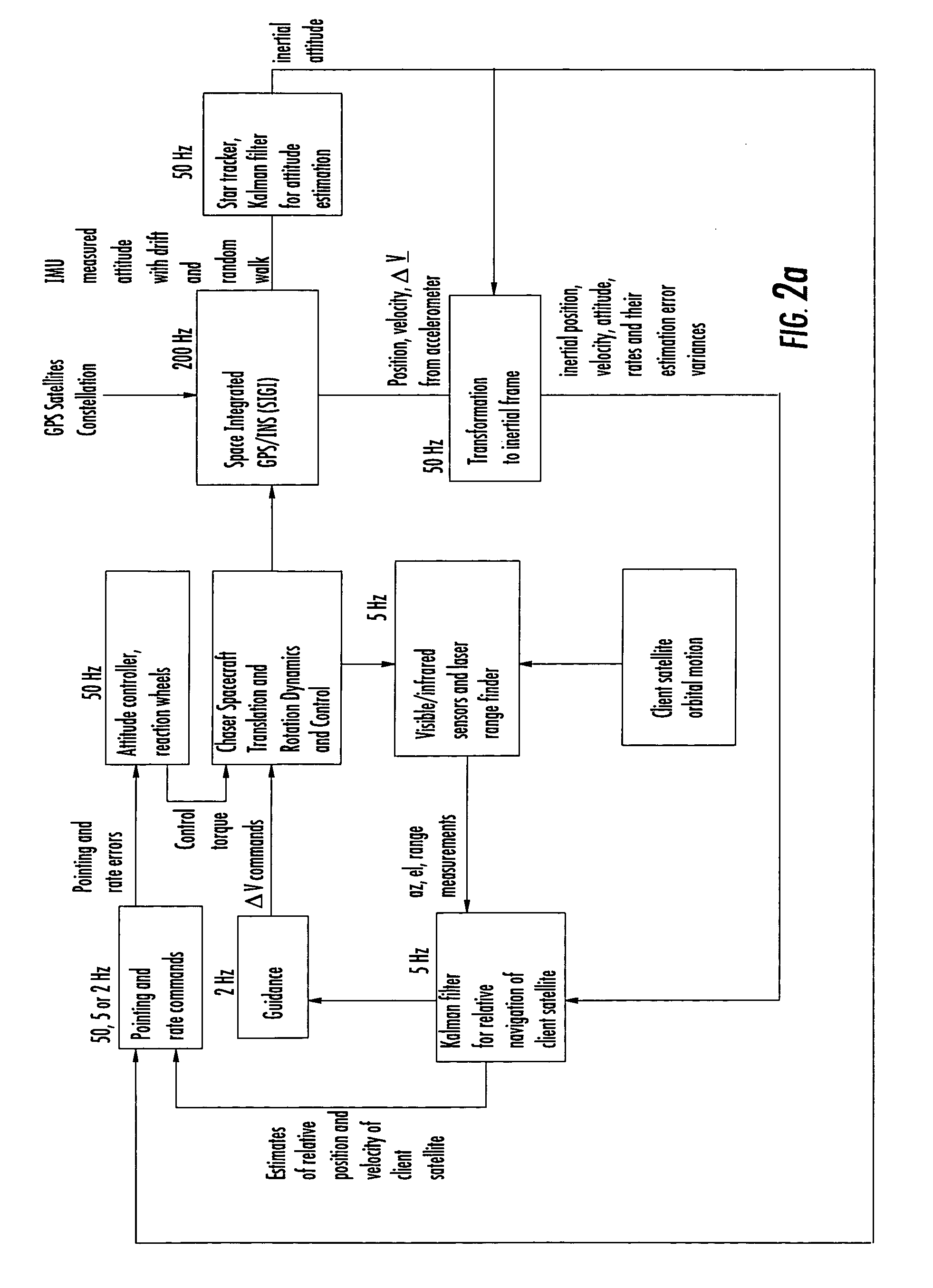
Laser range finder closed-loop pointing technology of relative navigation, attitude determination, pointing and tracking for spacecraft rendezvous
InactiveUS20050060092A1Improved functionality and precisionImprove ObservabilityInstruments for road network navigationCosmonautic vehiclesGyroscopeClosed loop
A closed-loop LRF pointing technology to measure the range of a target satellite from a chaser satellite for rendezvous is provided that includes several component technologies: LOS angle measurements of the target satellite on a visible sensor focal plane and the angles' relationships with the relative position of the target in inertial or LVLH frame, a relative navigation Kalman filter, attitude determination of the visible sensor with gyros, star trackers and a Kalman filter, pointing and rate commands for tracking the target, and an attitude controller. An analytical, steady-state, three-axis, six-state Kalman filter is provided for attitude determination. The system and its component technologies provide improved functionality and precision for relative navigation, attitude determination, pointing, and tracking for rendezvous. Kalman filters are designed specifically for the architecture of the closed-loop system to allow for pointing the laser rangefinder to a target even if a visible sensor, a laser rangefinder, gyros and a star tracker are misaligned and the LOS angle measurements from the visible sensor are interrupted.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Self-driving vehicle systems and methods
ActiveUS9429947B1Unlimited attention spanAbility of self-driving vehicles to save lives is so impressiveAutonomous decision making processSimultaneous control of electric and non-electric variablesHuman interactionHybrid approach
Although self-driving vehicles excel under “normal” driving conditions, they sometimes struggle with new situations that often would not be overly difficult for a person. Several embodiments described herein enable a hybrid approach that leverages the exceptional abilities of self-driving vehicles while soliciting human interaction in select situations. The resulting combination of machine intelligence and human intelligence significantly enlarges the potential of self-driving vehicles in a manner that will enable self-driving vehicles to become widespread much faster than would otherwise be the case.
Owner:DRIVENT LLC
Systems and methods for target tracking
The present invention provides systems, methods, and devices related to target tracking by UAVs. The UAV may be configured to receive target information from a control terminal related to a target to be tracked by an imaging device coupled to the UAV. The target information may be used by the UAV to automatically track the target so as to maintain predetermined position and / or size of the target within one or more images captured by the imaging device. The control terminal may be configured to display images from the imaging device as well as allowing user input related to the target information.
Owner:SZ DJI TECH CO LTD
Mobile robot and a mobile robot control method
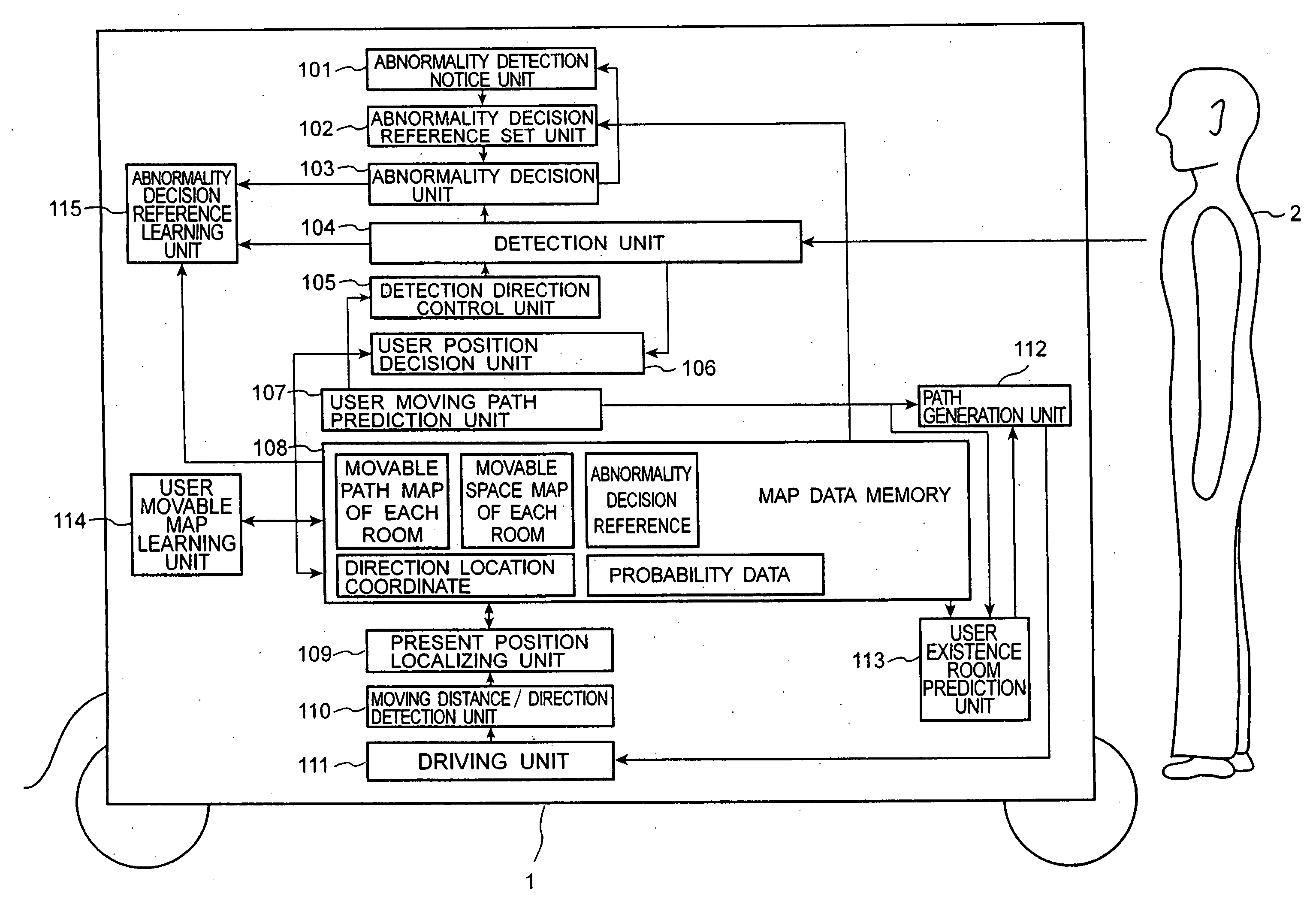
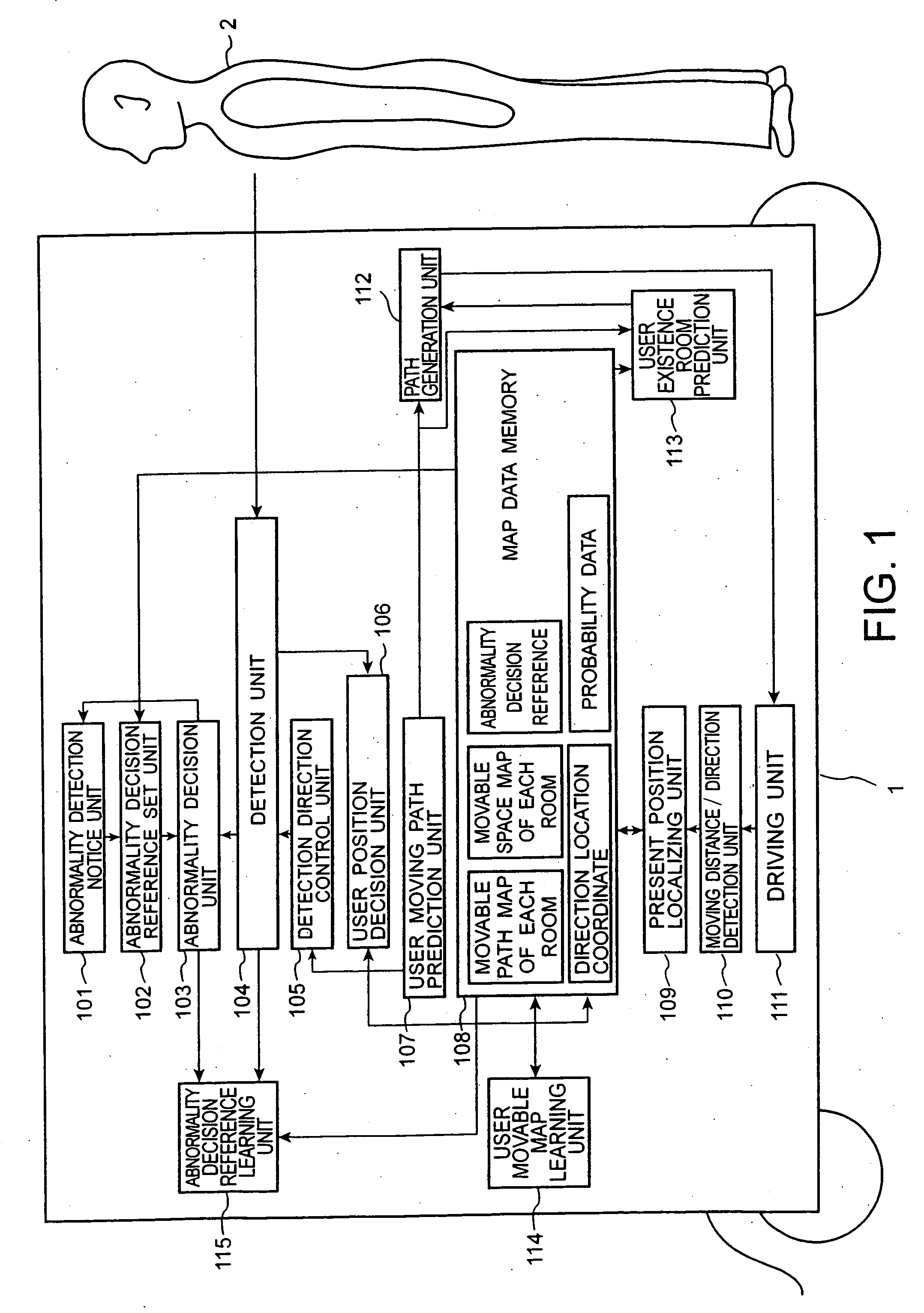
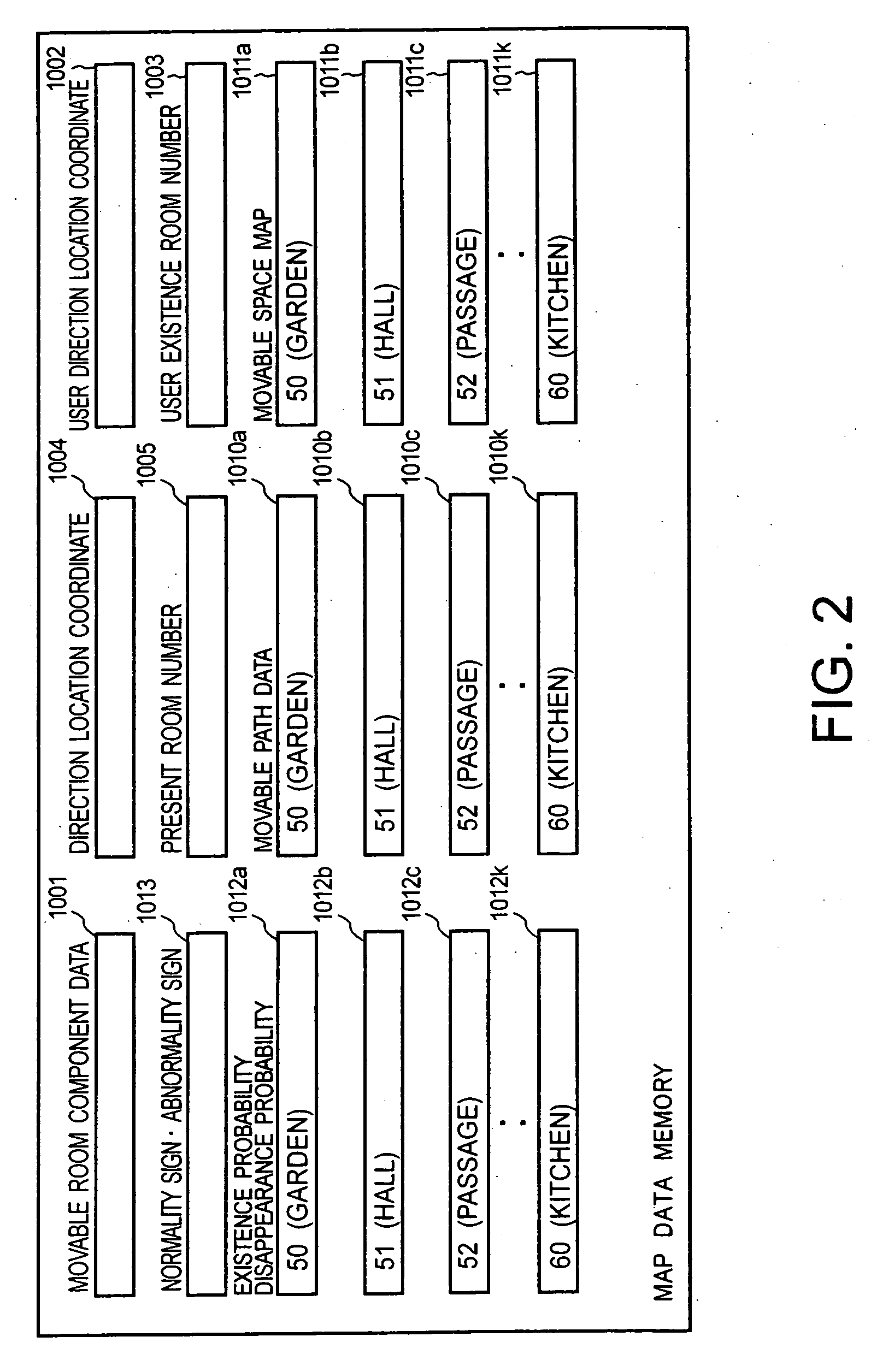
InactiveUS20070027579A1Improve abilitiesTelemedicineTarget-seeking controlMobile robot controlHuman–computer interaction
In a mobile robot, a user position data acquisition unit acquires user position data representing a user's location. A user movable space generation unit generates user movable space data representing a space in which the user moves based on the user position data. A position relationship control unit controls a position relationship between the user and the mobile robot based on the user movable space data.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Real-time target tracking of an unpredictable target amid unknown obstacles
ActiveUS6917855B2Reduce capacityProgramme-controlled manipulatorAnti-collision systemsVisibilityTree (data structure)
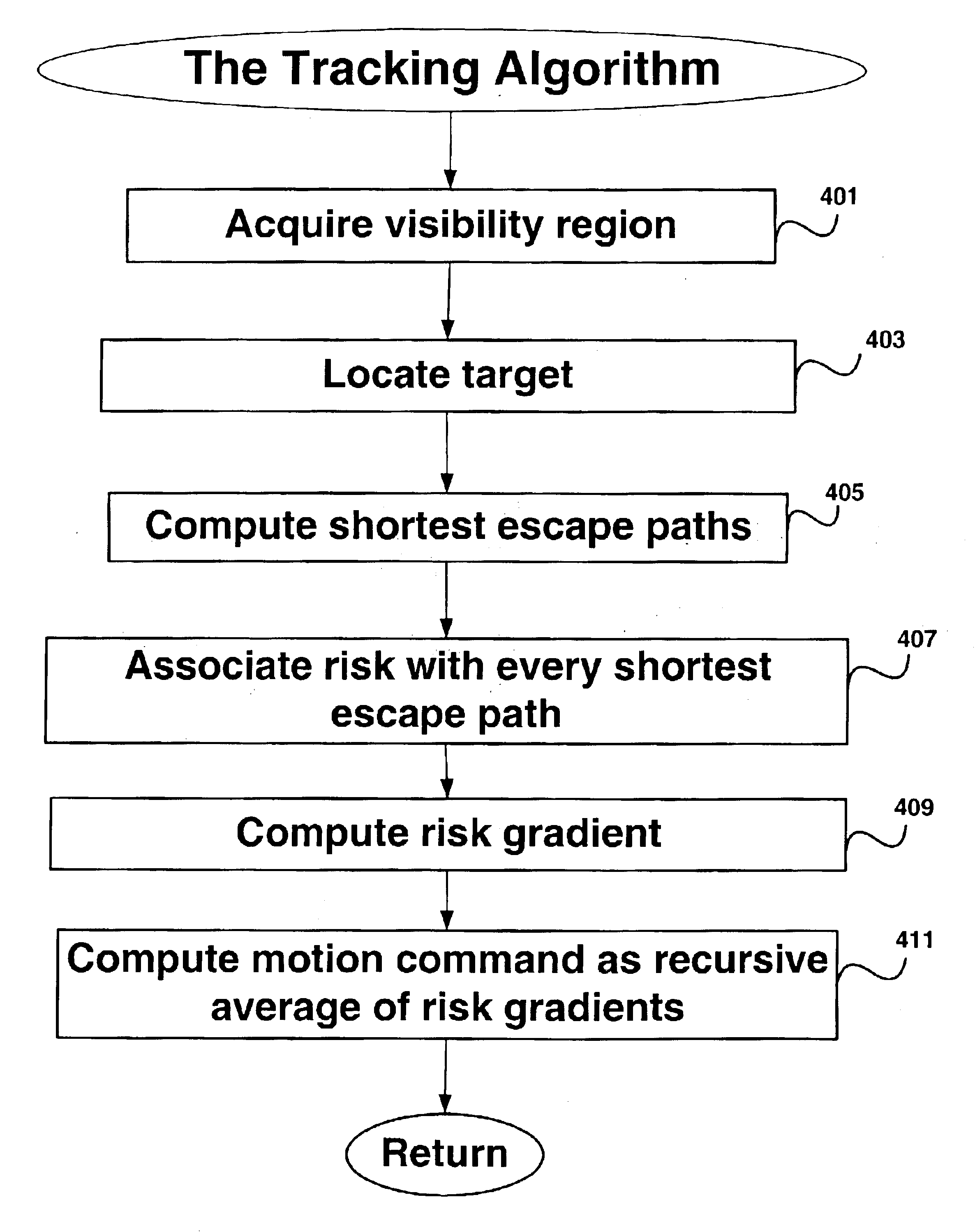
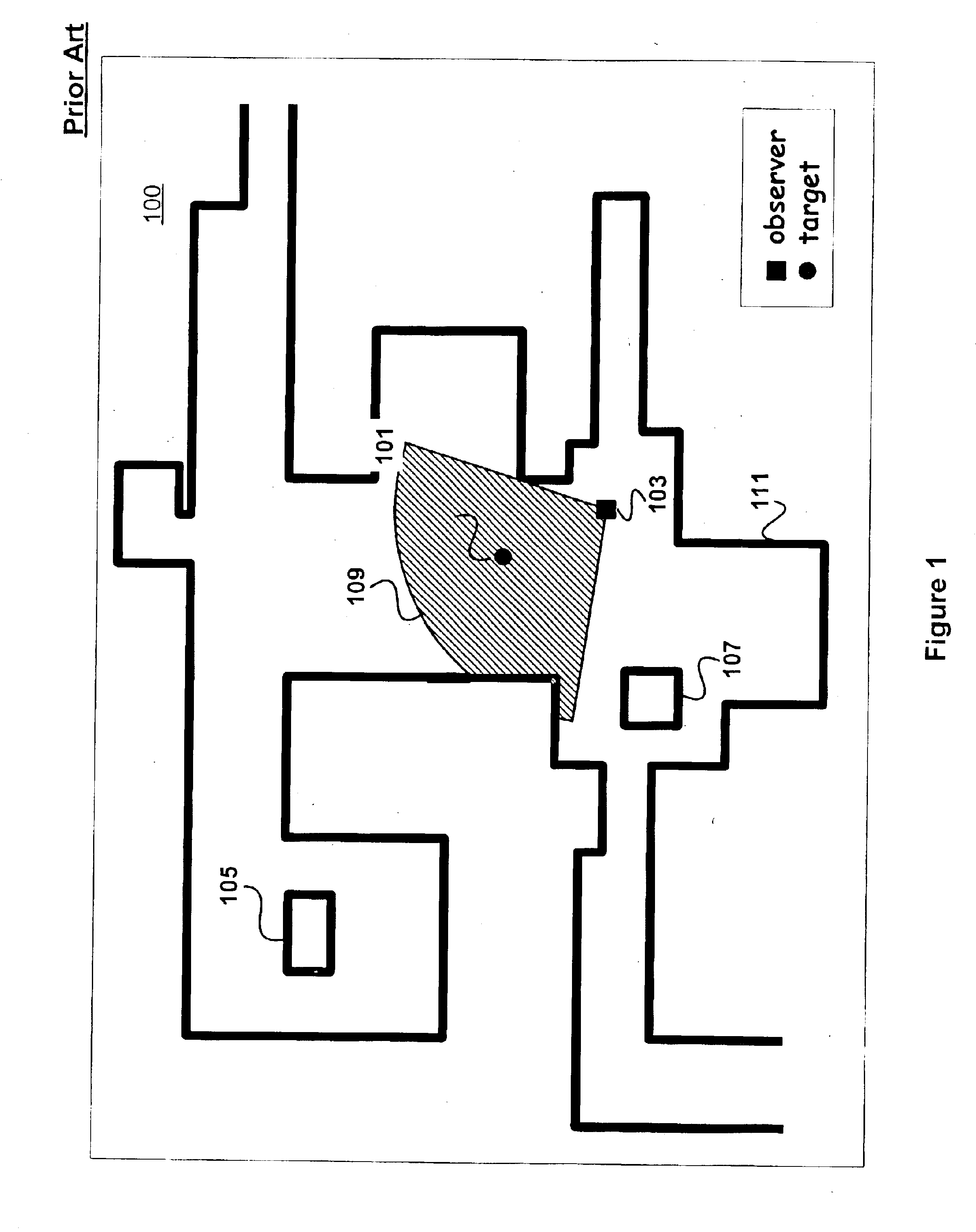
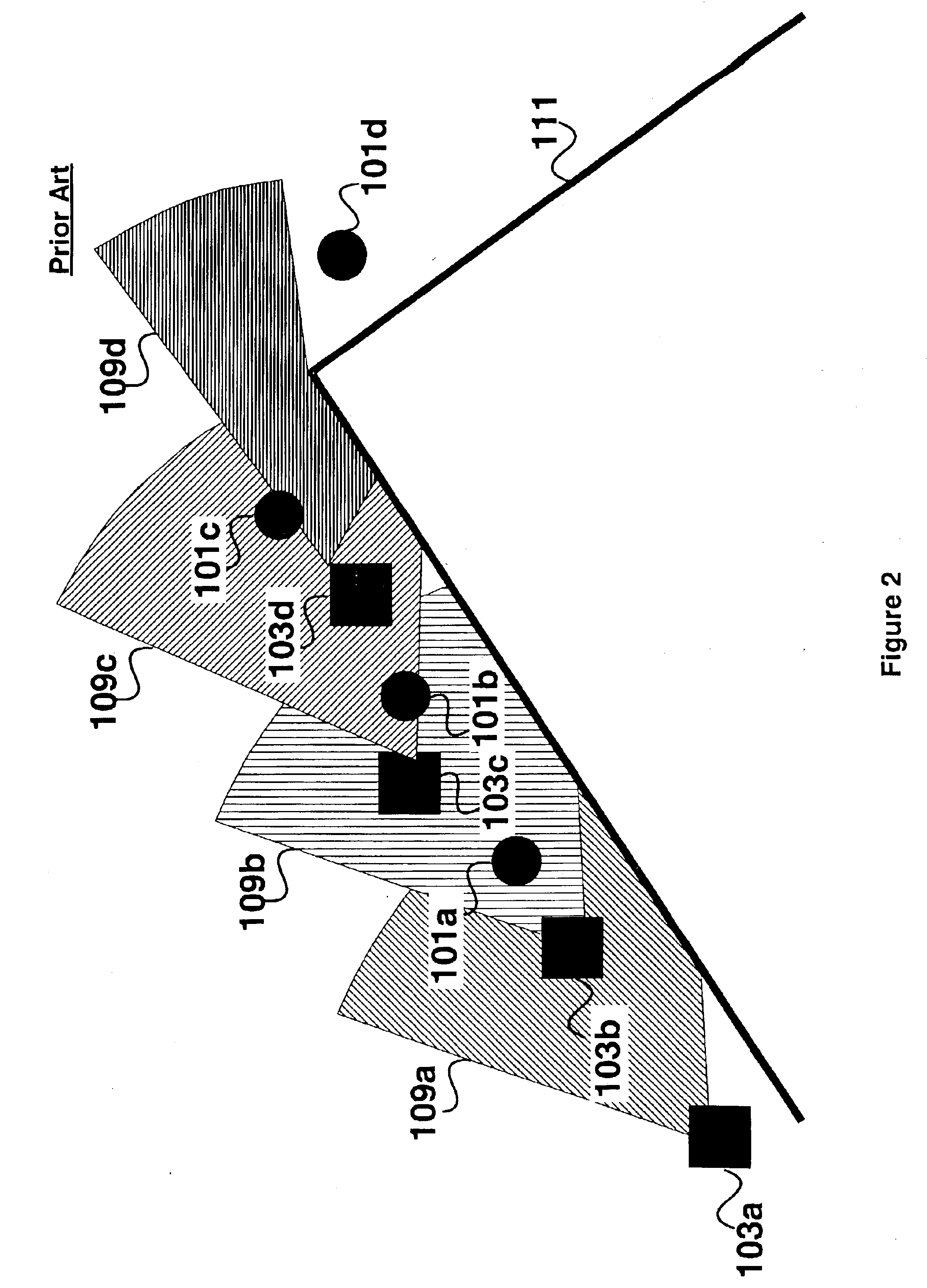
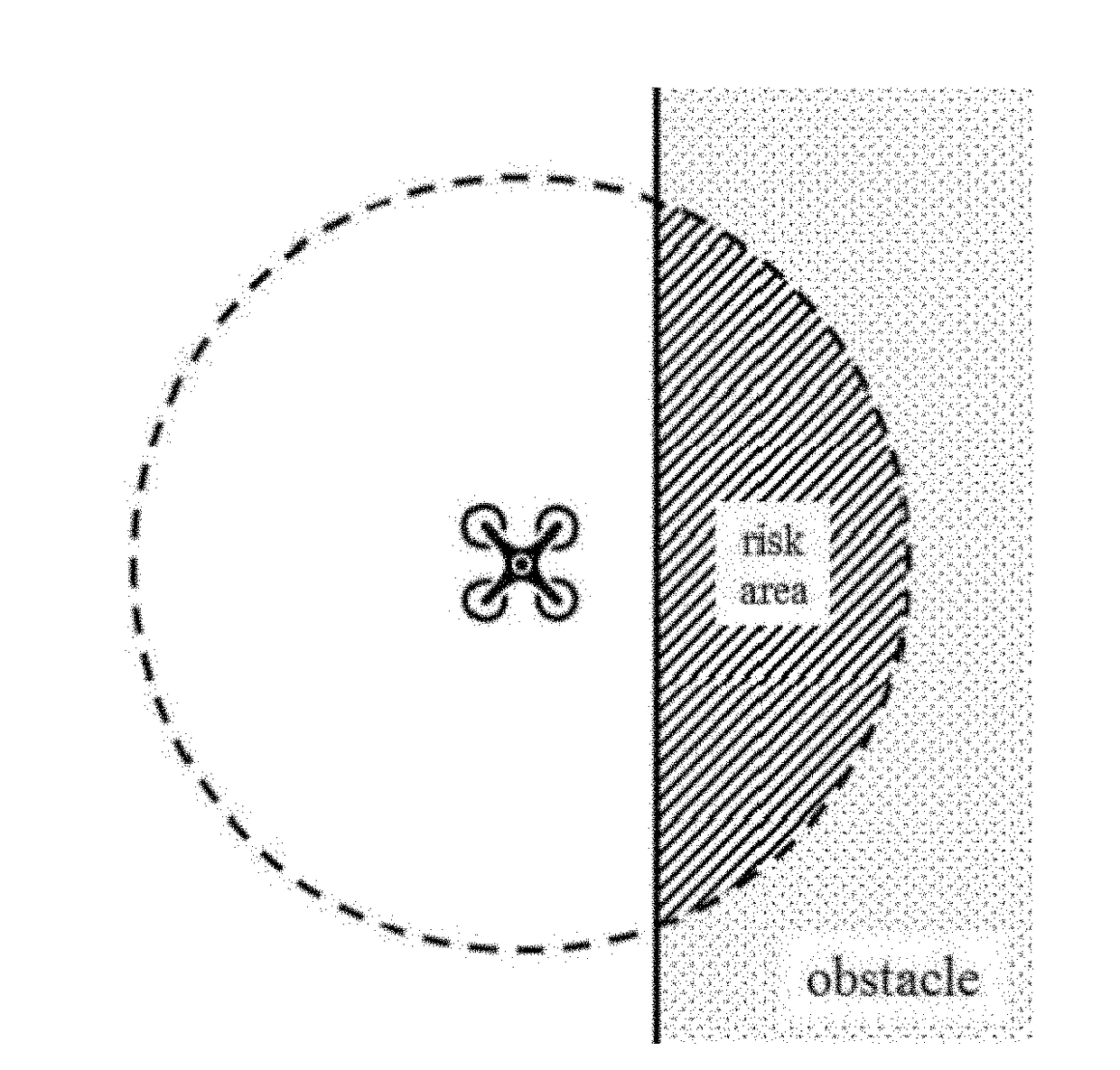
Embodiments provide a strategy for computing the motions of a mobile robot operating in an obstacle-laden environment without requiring prior knowledge of the distribution of obstacles in the environment or knowing the trajectory of a target tracked by the robot. Embodiments provide an algorithm that governs the motion of the observer robot based on measurements of the target's position and the location of obstacles in the environment. The algorithm computes a description of the geometric arrangement between the target and the observer's visibility region produced by the obstacles and computes a continuous control rule using this description. Embodiments employ an escape-path tree data structure to categorize the target's possible modes of escaping from the observer robot's sensors and use the escape-path tree to determine the target's shortest escape path.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD +1
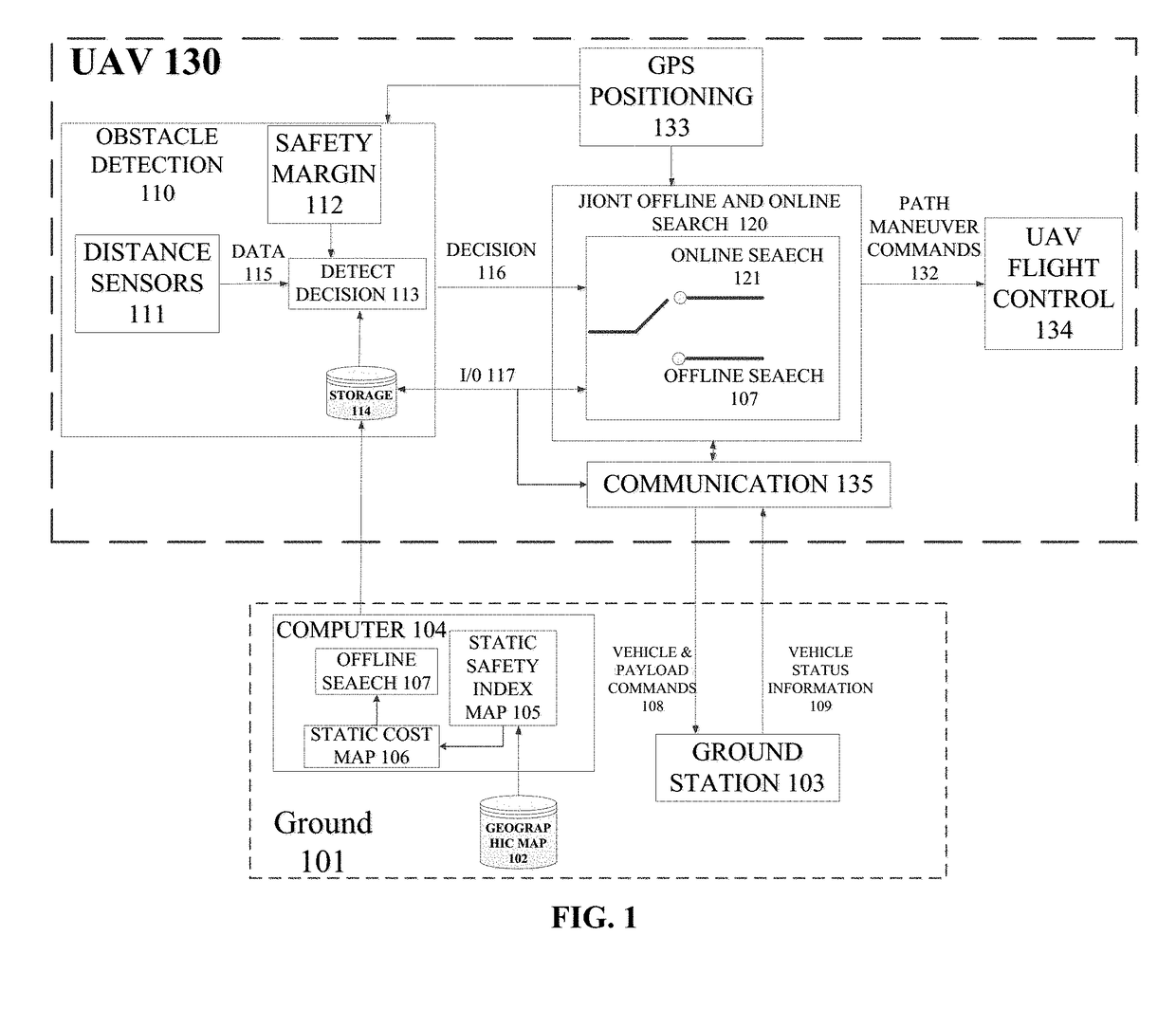
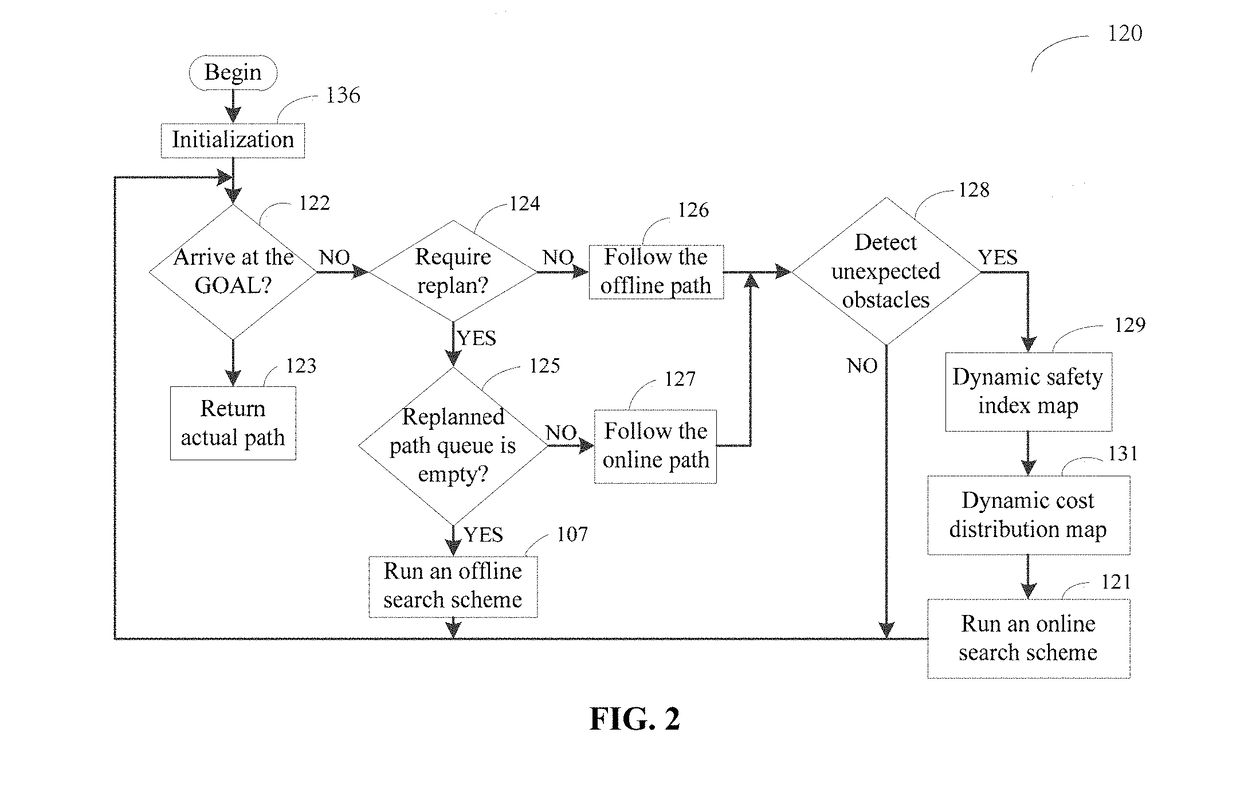
Joint search method for UAV multiobjective path planning in urban low altitude environment
ActiveUS20180308371A1Lower requirementReduce computational complexityRemote controlled aircraftTarget-seeking controlSafety indexPath plan
A joint search method for UAV multiobjective path planning in an urban low altitude environment first constructs a static safety index map based on static known obstacles. Meanwhile, based on proactively detected obstacles that are not marked on a geographic map by a UAV, the method constructs online a dynamic safety index map. Second, a multiobjective path planning problem is solved using a joint offline and online search method. Moreover, this method first plans offline the least cost path from a starting point to an end point and then invokes the online search scheme to replan online a changed path when the UAV detects unknown obstacles. Thus, the UAV can avoid dynamic obstacles effectively. The online search scheme has a small search space and can quickly replan a safe path for the UAV, thus satisfying the requirement of UAV on the real-time path planning.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
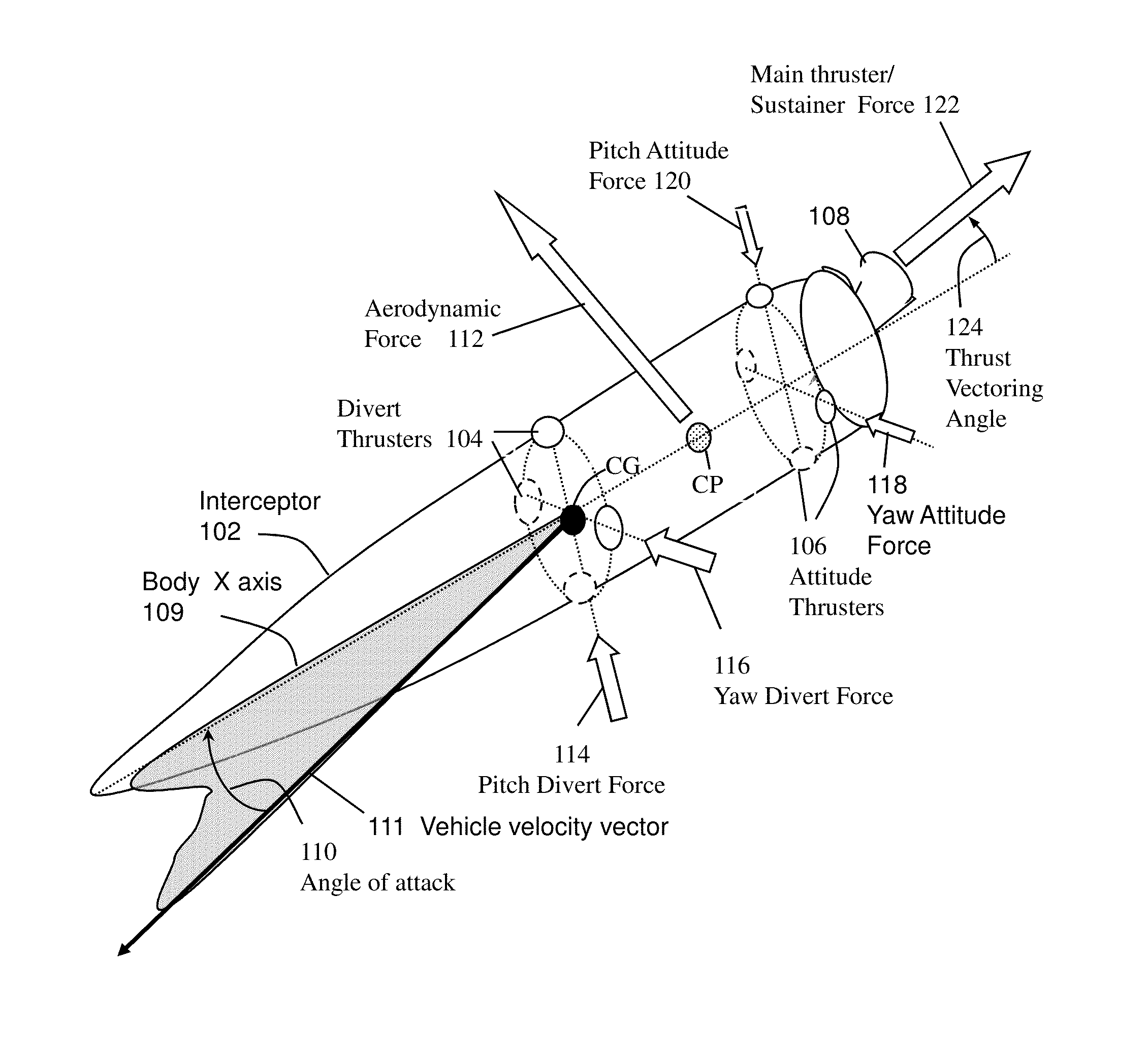
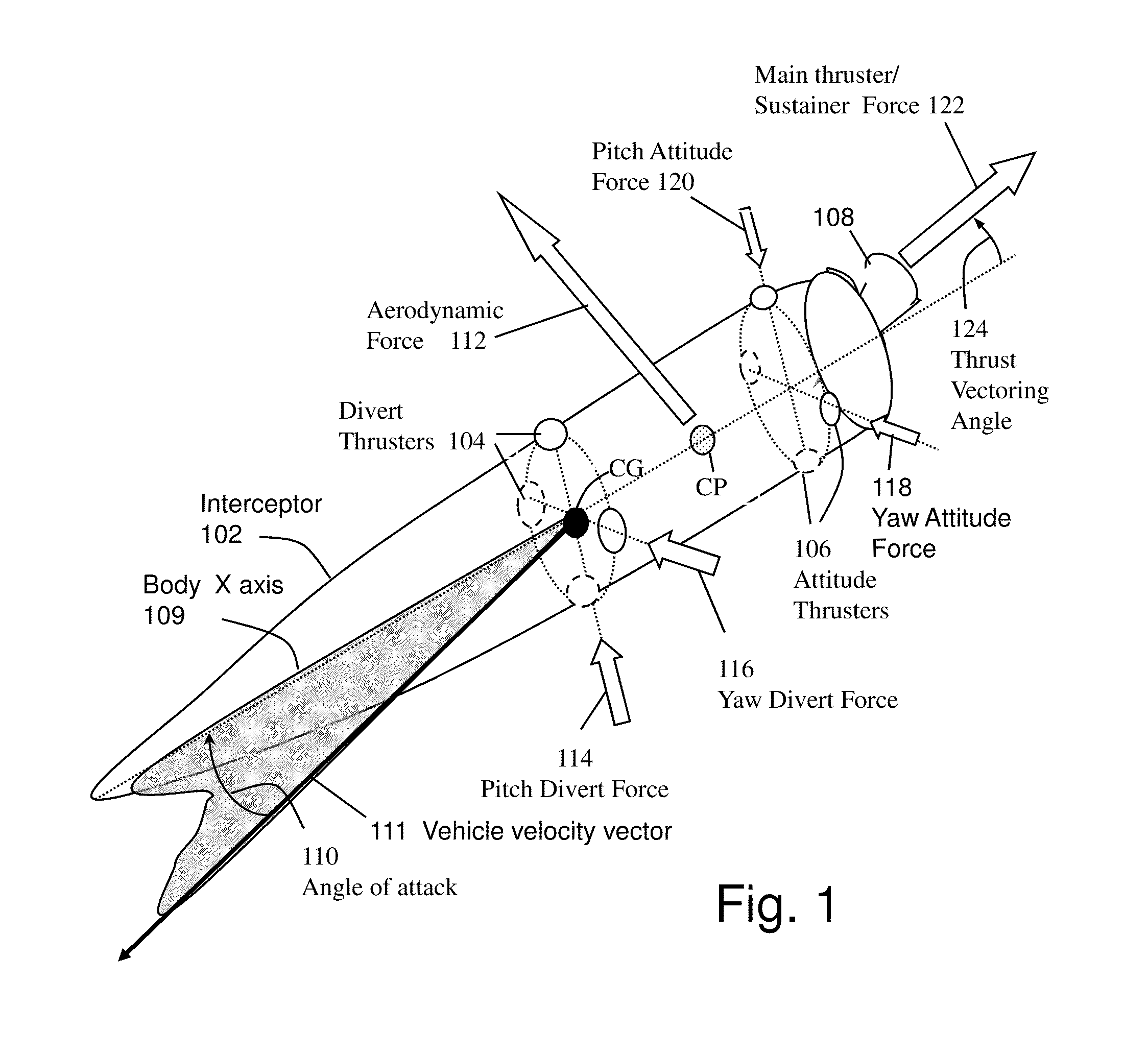
System and method for guiding and controlling a missile using high order sliding mode control
ActiveUS20130092785A1Reduce needPromote resultsDirection controllersTarget-seeking controlCouplingQuaternion
Higher Order Sliding Mode (HOSM) control techniques are applied to the Guidance Control (G&C) of interceptor missile in which velocity may be steered by combination of main thrust, aerodynamic lift and lateral on-off divert thrusters, and attitude may be steered by continuous or on-off actuators. Methods include the pointing of the seeker, its associated estimation processes, a guidance law that uses concurrent divert mechanisms, and an attitude autopilot. The insensitivity of the controller to matched disturbances allows the concurrent usage of the divert mechanisms without adverse effect on the accuracy. The controller also allows the de-coupling of the control of roll, pitch and yaw channels, and usage quaternions to represent body attitude and it provides control perfect robustness. While it conceivable to design separately the components of the G&C method, it is widely accepted that designing them in an integrated fashion usually produces a better result.
Owner:DAVIDSON TECH
Method and System For Aviation Navigation
InactiveUS20070138345A1Minimizes flight timeFuel consumption is minimizedAircraft controlTarget-seeking controlAviationMarine navigation
A system operates to guide an aircraft to or along a route designed to maintain the aircraft within a safe glide distance of an acceptable emergency landing area. The system uses a database of emergency landing areas with glide characteristics of an aircraft to determine a route that minimizes travel time or other specified parameter, while keeping the aircraft within a safe glide distance of a landing area in the database meeting the landing requirements for the aircraft.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL VENTURES I LLC
Intelligent multi-mode flying shooting equipment and flying control method thereof
ActiveCN104828256AHas a sense of lensHas a shocking effectAircraft componentsTarget-seeking controlFly controlAviation
The invention discloses intelligent multi-mode flying shooting equipment and a flying control method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of aviation. The flying shooting equipment comprises a rack, a flying mechanism, a shooting device and a control mechanism; the control mechanism also comprises an automatic tracking module, a shooting action setting module and a shooting strategy setting module, wherein the automatic tracking module is used for recognizing a target object, and realizing track tracing and follow shooting in allusion to the target object; the shooting action setting module is used for predefining at least one shooting action of the flying shooting equipment; the shooting strategy setting module is used for setting a corresponding shooting strategy according to the preset condition of the target object, and executing a corresponding shooting action when the preset condition is met. According to the intelligent multi-mode flying shooting equipment and the flying control method thereof disclosed by the invention, on the technological base of the traditional automatic follow shooting on the target object, intelligent situational shooting is completed with a rich shooting mode; under the condition that artificial control is not needed completely, a shooting effect with a lens sense and a shocking effect can be generated.
Owner:高域(北京)智能科技研究院有限公司
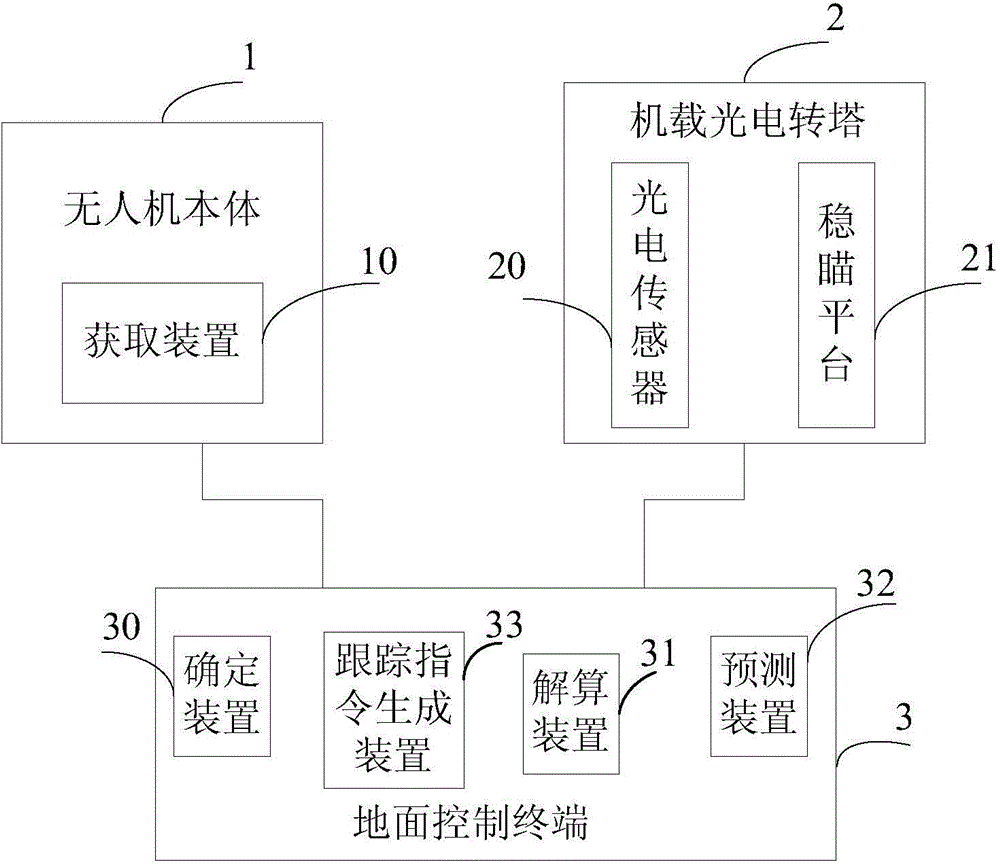
Unmanned aerial vehicle system and method for dynamically positioning ground moving target
ActiveCN103604427AMeet initial alignment requirementsHigh positioning accuracyNavigation instrumentsTarget-seeking controlLongitudeUncrewed vehicle
The invention discloses an unmanned aerial vehicle system and a method for dynamically positioning a ground moving target, belonging to the fields of unmanned aerial vehicle system application and the like. The unmanned aerial vehicle system comprises an unmanned aerial vehicle body, a vehicle-mounted photoelectric rotating tower and a ground control terminal, wherein the unmanned aerial vehicle body comprises an acquisition device, the vehicle-mounted photoelectric rotating tower comprises a photoelectric sensor and a sight-stabilizing platform, and the ground control terminal comprises a determining device, a trace command generating device, a resolving device and a predicting device. According to the technical scheme provided by the invention, geographical coordinate information including latitude, longitude and the like of a tracked ground moving target can be output in real time, the original geographical coordinate information can be accurately and quickly fitted, the moving trend of the ground moving target can be predicted and evaluated, and the original geographical coordinate information can be screened to realize display and prediction of the track of the moving target; the positioning accuracy acquired by the unmanned aerial vehicle system and the method approaches that of static positioning and can meet requirements for initial alignment of weapons including artilleries and the like, and the probability of fusion processing of an unmanned aerial vehicle intelligence system and an entire-army intelligence gathering network is provided.
Owner:CHINA ACAD OF AEROSPACE AERODYNAMICS
Autonomous obstacle avoidance and navigation method for unmanned aerial vehicle-based field search and rescue
InactiveCN107656545AGuaranteed accuracySatellite radio beaconingTarget-seeking controlUltrasonic sensorDetect and avoid
An autonomous obstacle avoidance and navigation method for unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV)-based field search and rescue provided by the invention includes global navigation based on GPS signals and anautonomous obstacle avoidance and navigation algorithm based on binocular vision and ultrasound. First, a UAV carries out search under the navigation of GPS signals according to a planned path. Aftera target is found, the autonomous obstacle avoidance and navigation algorithm based on binocular vision and ultrasound is adopted. A binocular camera acquires a disparity map containing depth information. The disparity map is re-projected to a 3D space to get a point cloud. A cost map is established according to the point cloud. The path is re-planned using the cost map to avoid obstacles. When there is no GPS signal, a visual inertial odometry (VIO) is used to ensure that the UAV flies according to the planned path, and an ultrasonic sensor is used to detect and avoid obstacles below the UAVto approach the rescued target. UAV autonomous obstacle avoidance and navigation in a field search and rescue scene is realized.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Automatic charging method of robot and its automatic charging device
InactiveCN100999078AEffective regressionImprove work efficiencyNon-electrical signal transmission systemsTarget-seeking controlButt jointSignal on
The present invention relates to a robot automatic charging method and its automatic charging device. The invented method includes the following steps: (1), when the robot has need of supplementing power supply, the infrared signal receiving device positioned in the front portion of said robot is switched on, said robot can be randomly walked to search infrared charging guide signal on the charging socket; (2), after the guide signal is found, the infrared receiving tube by which the guide signal is received can be defined, and the infrared receiving tube can be utilized to calculate the distance and angle from the charging socket to robot; (3), the position of said robot can be regulated to the right in robot's ahead; (4), the robot can be walked toward the right ahead, the butt electrode of said robot is contacted with charging electrode on the charging socket to implement butt-joint; and (5), the infrared signal receiving device can be switched off.
Owner:田角峰
Automatic Taking-Off And Landing System
ActiveUS20120078451A1Wide rangeAnalogue computers for vehiclesUnmanned aerial vehiclesObject basedComputer science
The invention provides an automatic taking-off and landing system, comprising a flying object and a taking-off and landing target, wherein the flying object has an image pickup device 21 for taking images found in downward direction, navigation means 4, 5, 6, 8, 9, 10 and 11, and a control unit for processing images acquired by the image pickup device and for controlling the navigation means, and wherein the control unit calculates a positional relation between the taking-off and landing target and the flying object based on the image of the taking-off and landing target as acquired by the image pickup device and controls taking-off and landing operations of the flying object based on a result of the calculation.
Owner:KK TOPCON
Semiautonomous flight director
InactiveUS20020030142A1Reduce a skilled pilots' workloadUnmanned aerial vehiclesActuated automaticallyWorkloadDigital control
A device for programming industry standard autopilots by unskilled pilots. The effect of the invention is such that when the invention is employed in a flying body comprising an industry standard autopilot with a digital flight control system, the invention provides for the safe operation of any aircraft by an unskilled pilot. The device additionally affords skilled pilots a more rapid and simplified means of programming autopilots while in flight thus reducing a skilled pilot's cockpit workload for all aircraft flight and directional steering, way points, and aircraft flight functions reducing the possibility of pilot error so as to effect safer flight operations of an aircraft by affording a skilled pilot to direct aircraft steering and function while under continuous autopilot control.
Owner:JAMES TERRY JACK
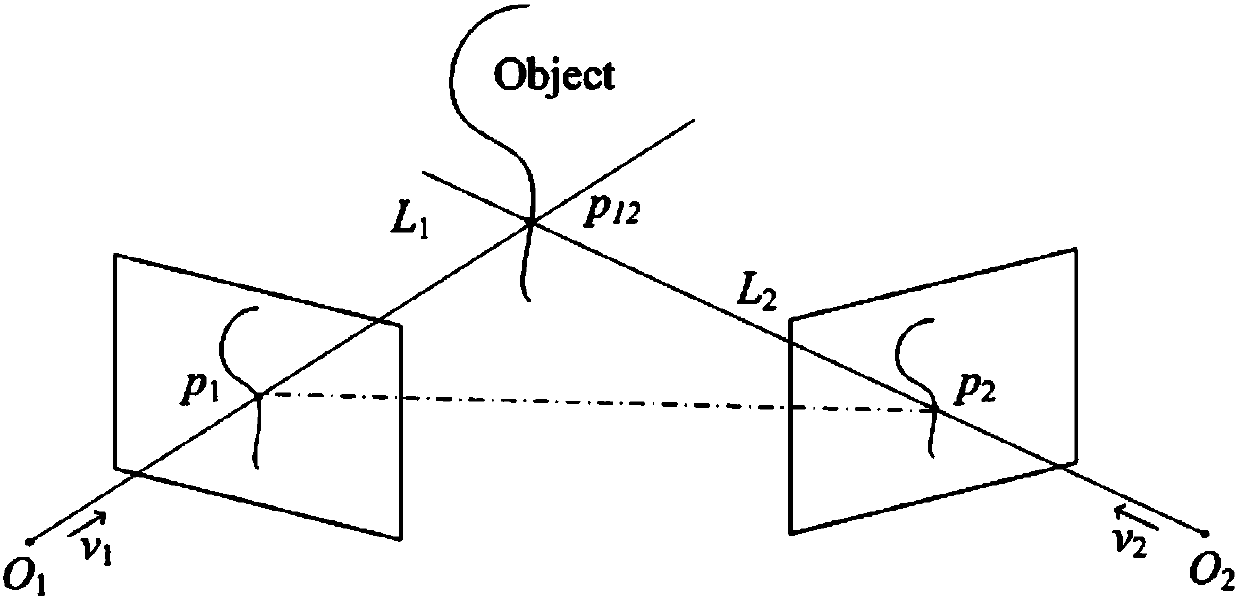
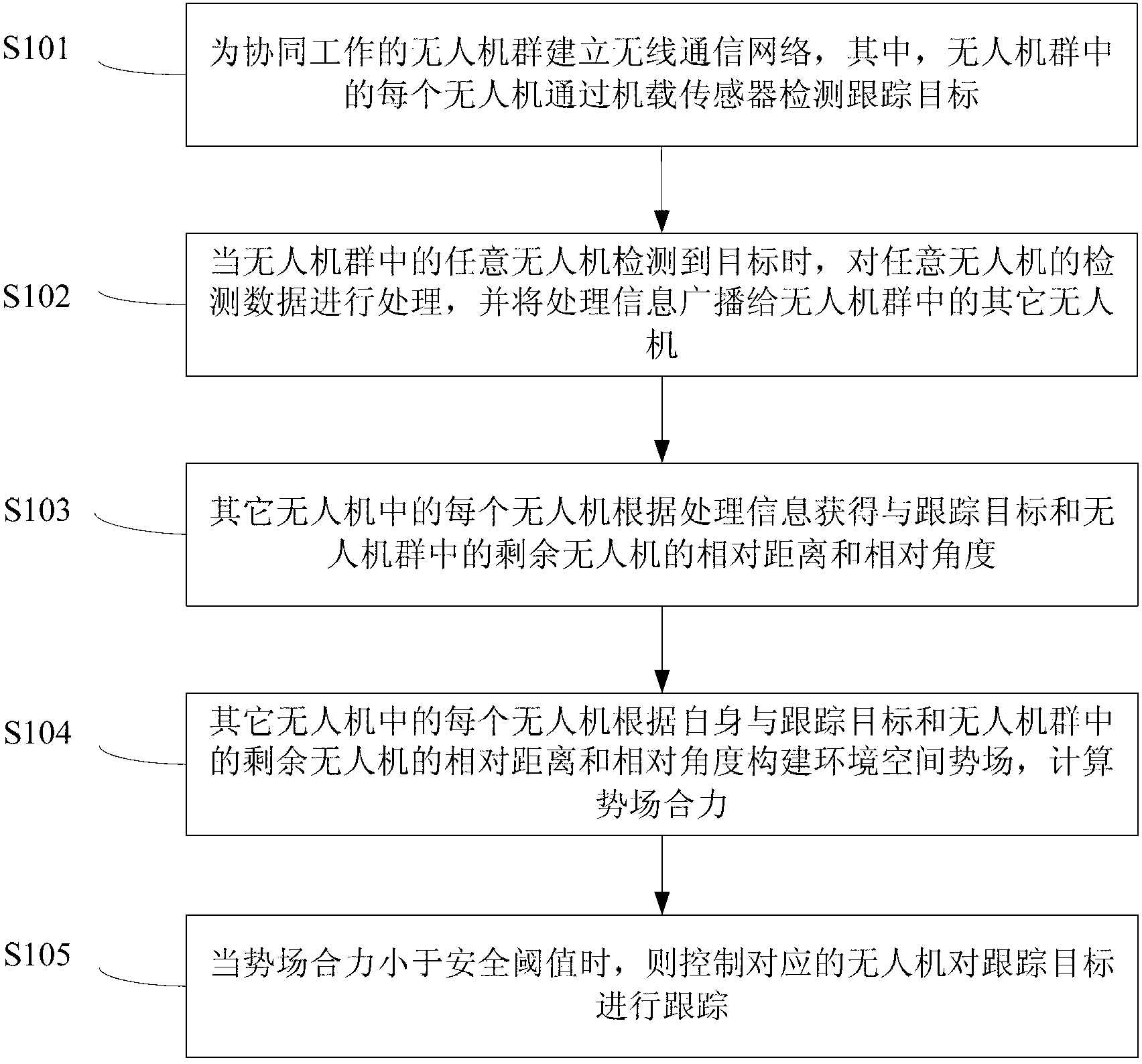
Method and system for cooperatively tracking target by unmanned aerial vehicle cluster
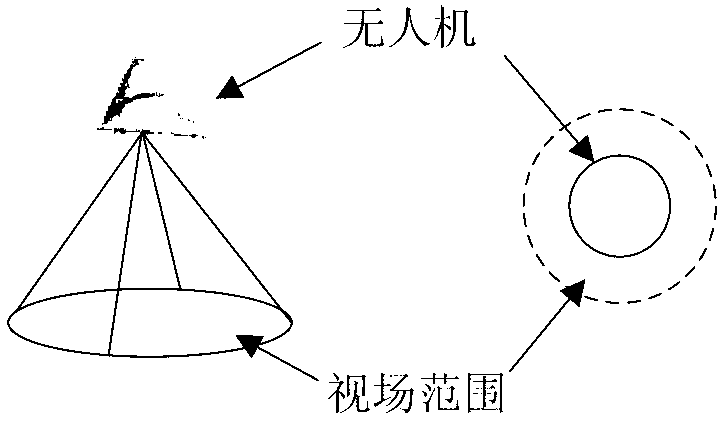
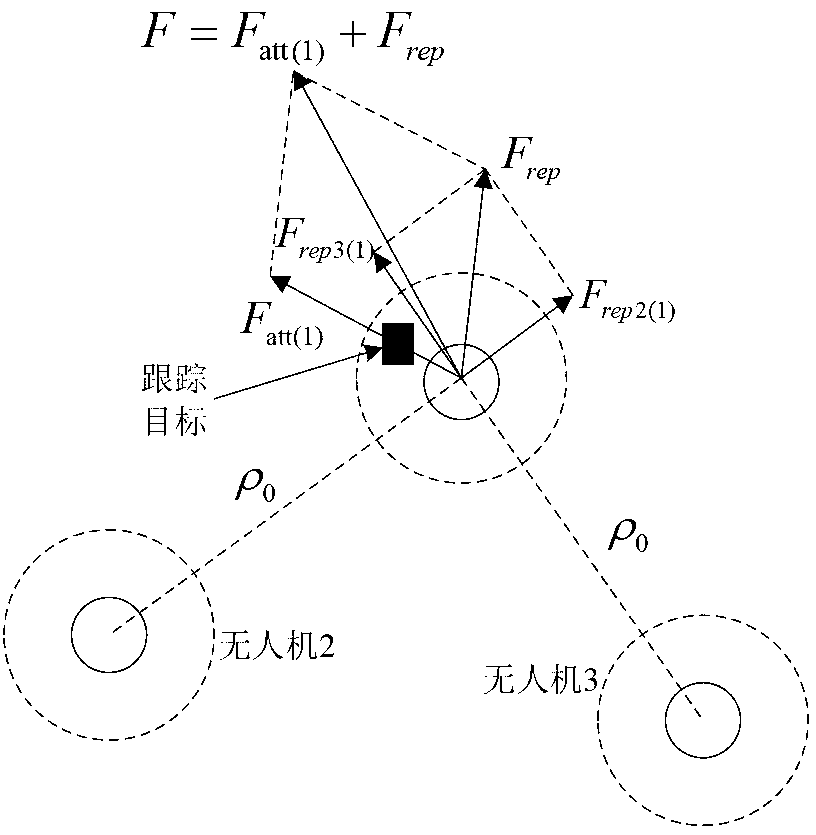
ActiveCN103197684AImprove efficiencyGuaranteed real-timeNavigational calculation instrumentsNetwork topologiesPotential fieldUncrewed vehicle
The invention provides a method and a system for cooperatively tracking a target by an unmanned aerial vehicle cluster. The method comprises the following steps of: establishing a wireless communication network for the cooperatively operated unmanned aerial vehicle cluster, and detecting a tracked target by utilizing an onboard sensor; when an optional unmanned aerial vehicle in the unmanned aerial vehicle cluster detects the target, processing detection data of the optional unmanned aerial vehicle, and broadcasting processing information to the other unmanned aerial vehicles; acquiring relative distances and relative angles among each unmanned aerial vehicle, the tracked target and the rest unmanned aerial vehicles in the unmanned aerial vehicle cluster according to the processing information by each unmanned aerial vehicle in the other unmanned aerial vehicles; constructing an environmental space potential field by each unmanned aerial vehicle in the other unmanned aerial vehicles according to the relative distances and the relative angles among each unmanned aerial vehicle, the tracked target and the rest unmanned aerial vehicles in the unmanned aerial vehicle cluster by each unmanned aerial vehicle in the other unmanned aerial vehicles, and calculating a resultant force of the potential field; and when the resultant force of the potential field is smaller than a safety threshold, controlling the corresponding unmanned aerial vehicle to track the tracked target. According to the method provided by the embodiment of the invention, sensor information is shared by utilizing the unmanned aerial vehicle cluster, and the high efficiency and the instantaneity of the cooperative target tracking are guaranteed.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
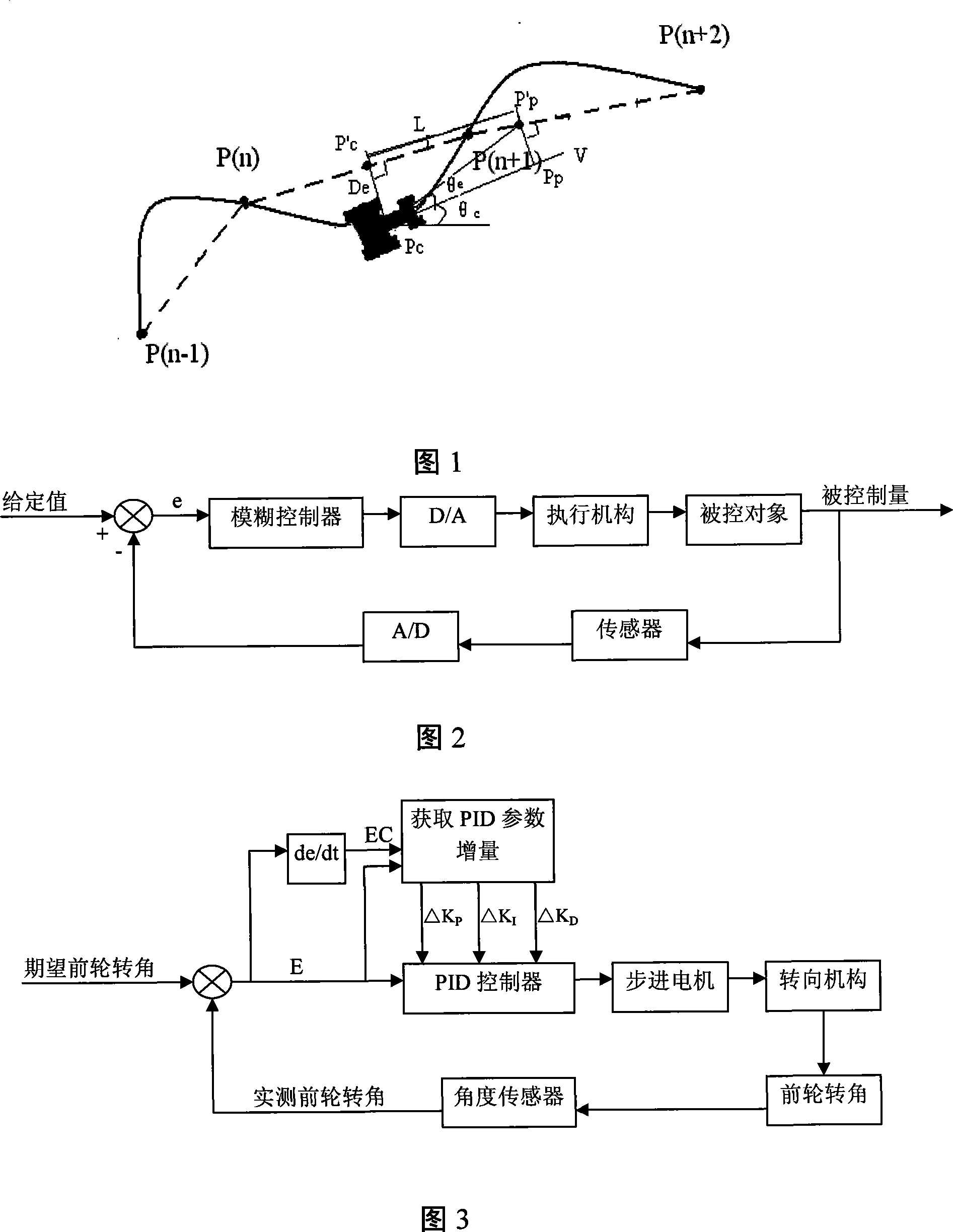
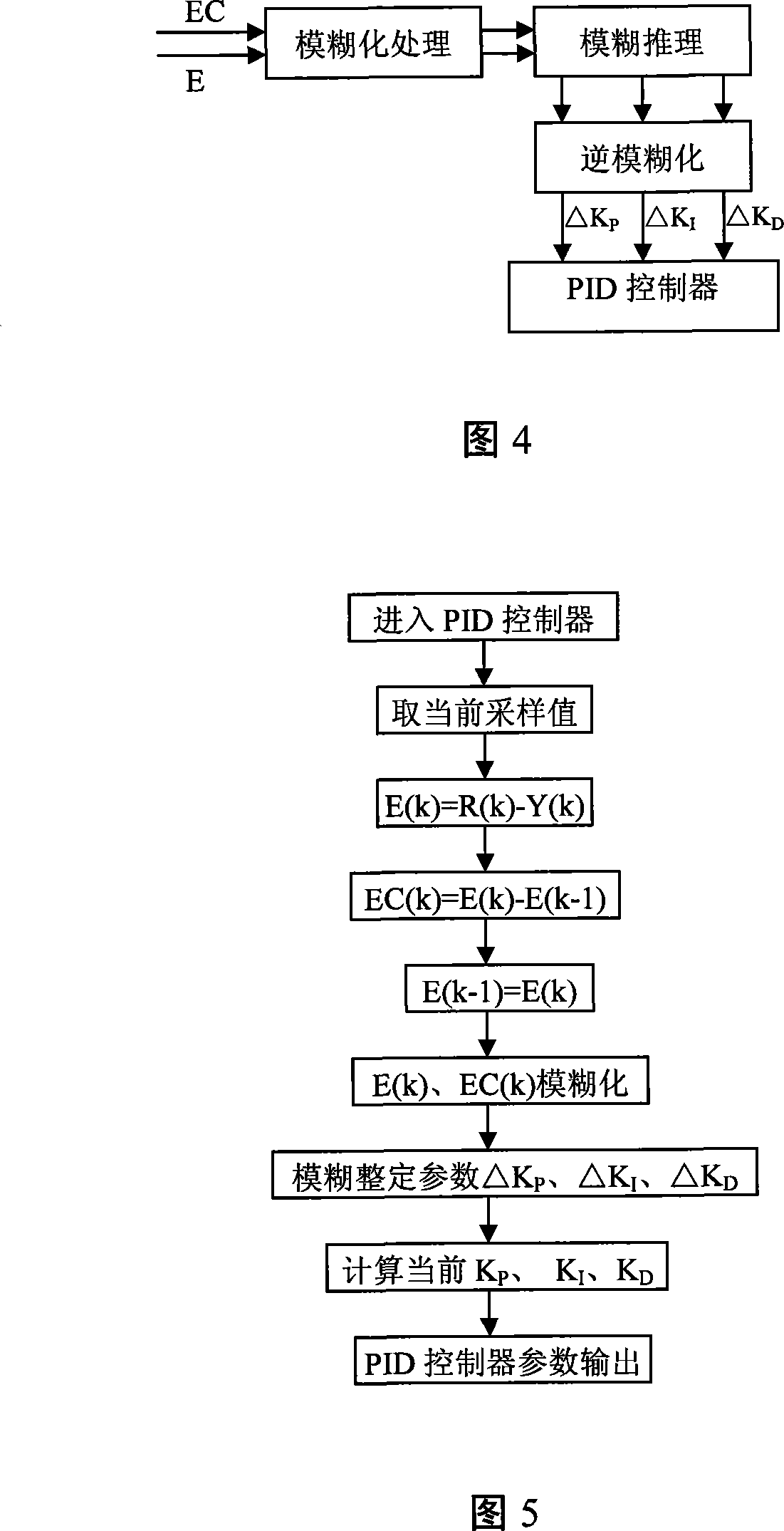
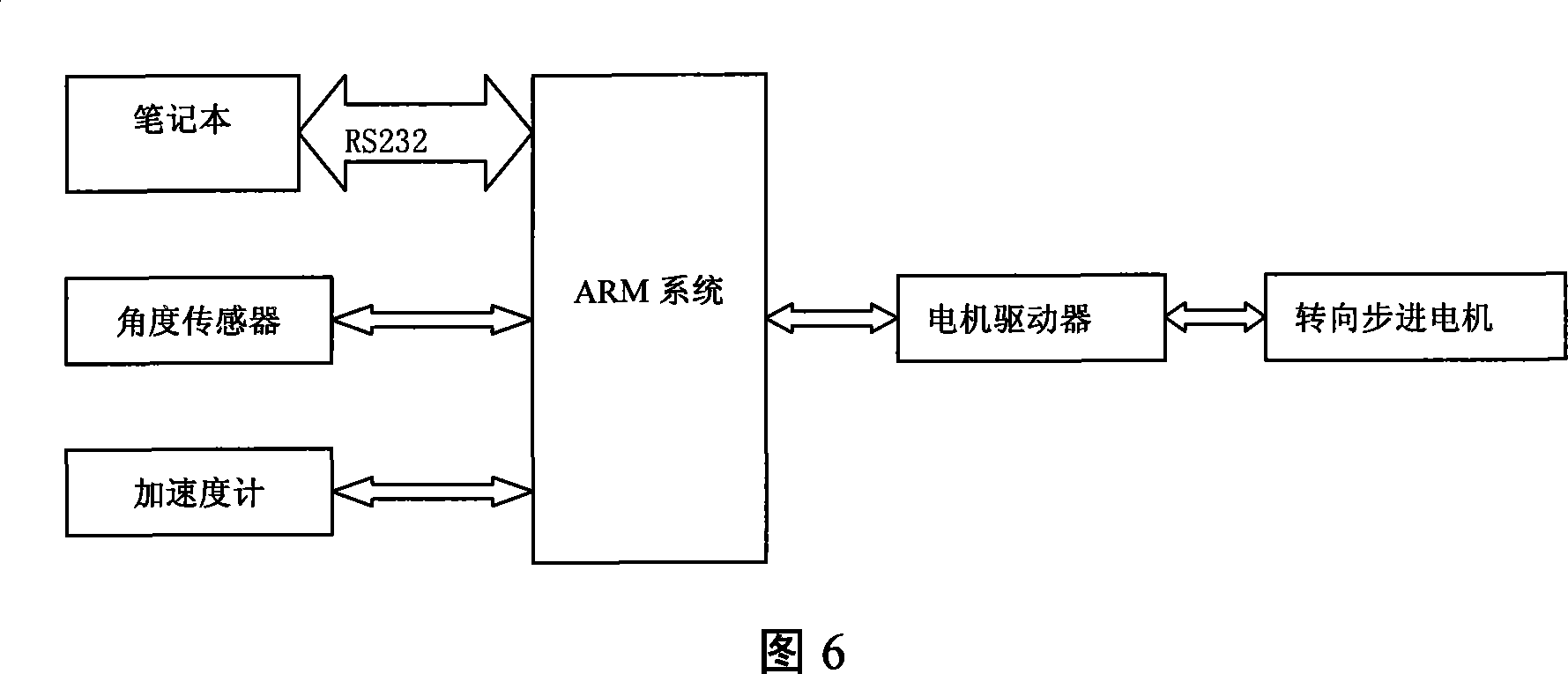
Mechanical automatic steering control method
InactiveCN101221447AHigh control precisionFlexibleGuiding agricultural machinesTarget-seeking controlAutomatic steeringPid control algorithm
The invention relates to a machinery automatic steering control method which comprises the following steps that: positional deviation and course deviation are determined; according to the variance in the practical front wheel rotating angle of an agricultural machine, online setting of PID parameter is completed by means of parameter self-setting PID control algorithm; moreover, the expected front wheel rotating angle of the next moment is calculated, thereby realizing automatic steering control of the agricultural machine. Based on conventional PID navigation control method, the invention makes full use of the fuzzy control method; according to the variance in the practical front wheel rotating angle of an agricultural machine, the invention meets the different requirements of the machine on PID control parameter under different errors and error change rate, thereby realizing online setting of PID parameter. The invention not only has the advantages of fuzzy control such as flexibility and adaptability, but also has the characteristics of higher precision of PID control; therefore, the invention can increase the stability and precision of agricultural machine automatic steering control and the robustness of a control system.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
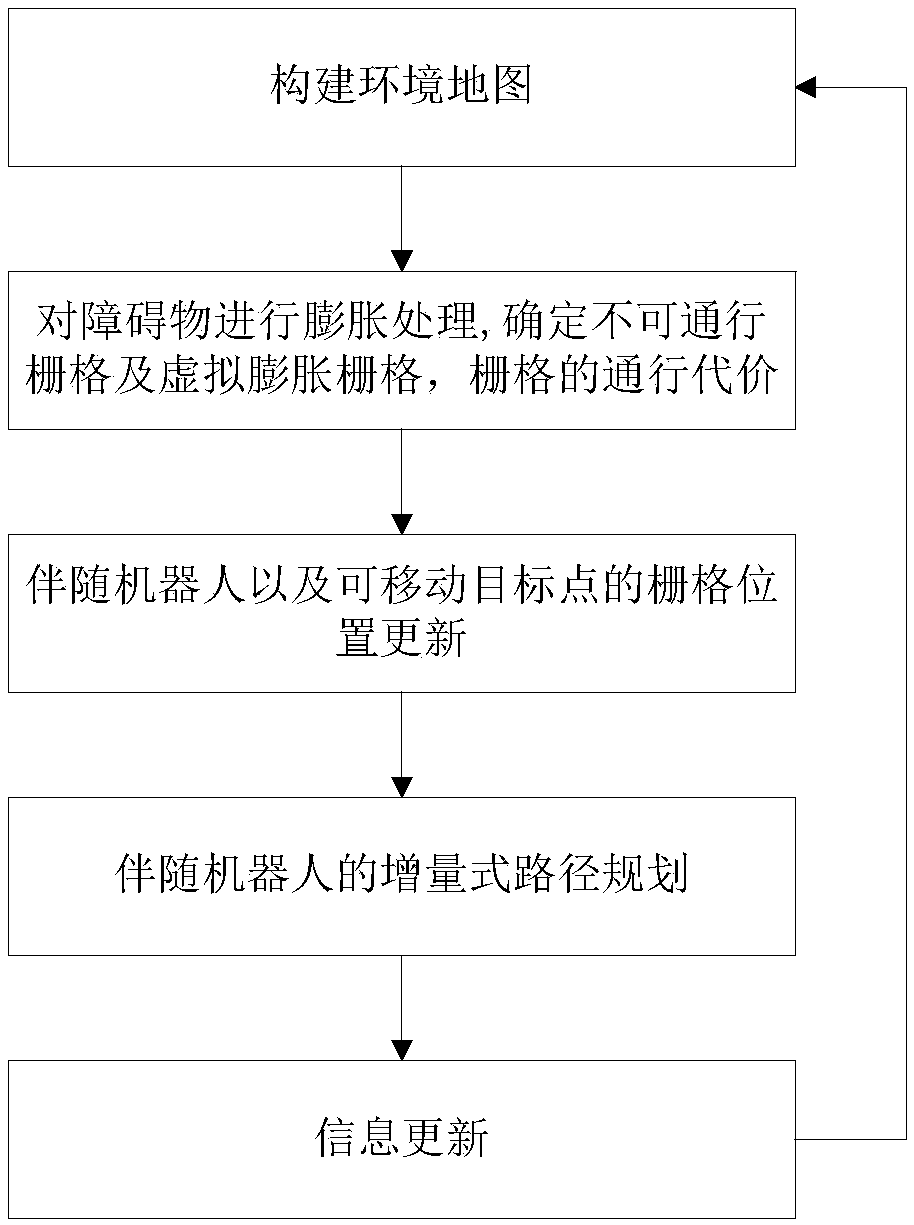
Accompanying robot path planning method and system based on obstacle virtual expansion
InactiveCN108775902AChange pass valueSolve the blockageNavigational calculation instrumentsTarget-seeking controlSlide windowShortest distance
The invention discloses an accompanying robot path planning method and system based on obstacle virtual expansion. The method includes a step of constructing an environment map, namely a step of constructing a two-dimensional occupancy grid map according to an actual scene, with each grid being labeled as an obstacle zone or a walkable zone; a step of setting initial coordinate positions of an accompanying robot and a movable target in the grid map; a step of constructing a sliding window for the robot; a step of subjecting the obstacle zones to expansion processing, namely a step of performing initial expansion on grids where an obstacle is according to a shortest distance between the center of the robot and a body edge, determining the number of grid layers expanded on the basis of the minimum impassable zone, adopting the grids in the expanded zones as obstacle virtual expansion grids, and labeling the grade of danger of obstacle influences on the obstacle virtual expansion grids; and a step of planning a path for the accompanying robot based on an A* algorithm and an incremental path planning process. Incremental path updating is performed by adopting a path of the last moment,thus saving path planning time and increasing the response speed of the accompanying robot.
Owner:QILU UNIV OF TECH
Unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) visual tracking method, apparatus, and UAV
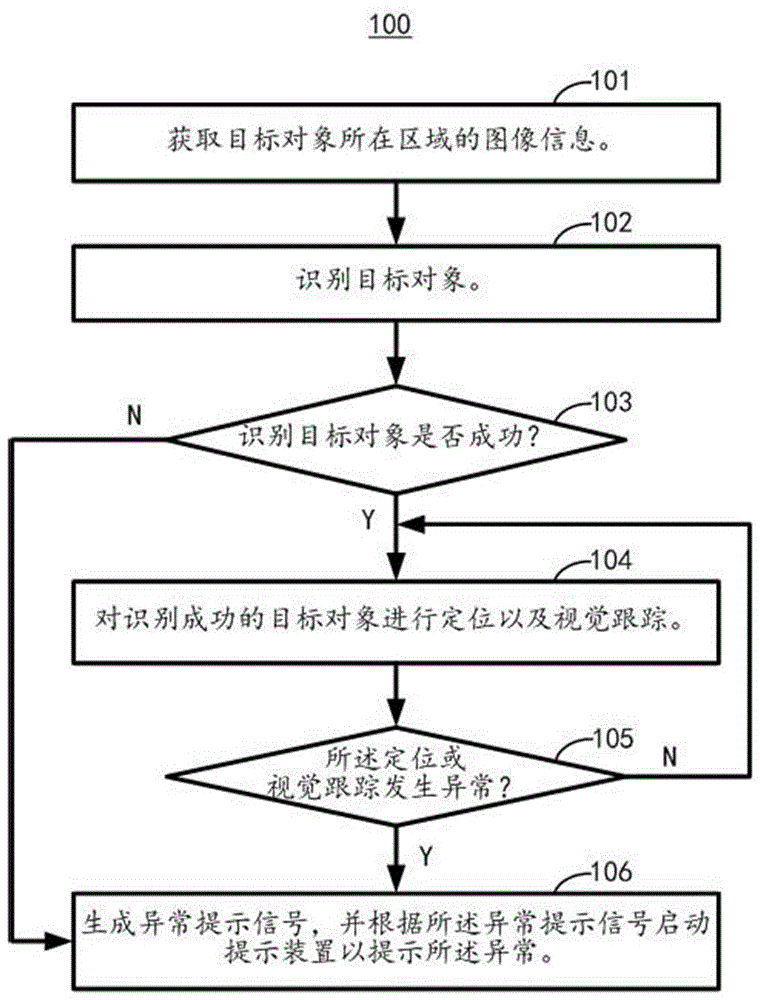
ActiveCN105759839AImprove experienceTimely feedbackImage enhancementImage analysisUncrewed vehicleComputer vision
A unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) visual tracking method comprises the steps of obtaining image information of a region where a target object is located; identifying the target object, including acquiring target object information in the image information and determining the target object according to the target object information; positioning and visual tracking the successfully identified target object; and generating an abnormal prompt signal when the target object is not successfully identified or the positioning or visual tracking is abnormal, and actuating a prompt device according to the abnormal prompt signal to prompt the abnormality. The invention further relates to a UAV visual tracking apparatus and a UAV. The UAV visual tracking method can feed back clear and concise results of a visual tracking algorithm and a flight control system in time, thereby improving the visual tracking effect and user experience.
Owner:SZ DJI TECH CO LTD
Collaborative engagement for target identification and tracking
ActiveUS8244469B2Facilitates control of and communication and exchangePromote collaborationProgramme-controlled manipulatorAnalogue computers for vehiclesGoal recognitionData exchange
A collaborative engagement system comprises: at least two unmanned vehicles comprising an unmanned air vehicle including sensors configured to locate a target and an unmanned ground vehicle including sensors configured to locate and track a target; and a controller facilitating control of, and communication and exchange of data to and among the unmanned vehicles, the controller facilitating data exchange via a common protocol. The collaborative engagement system controls the unmanned vehicles to maintain line-of-sight between a predetermined target and at least one of the unmanned vehicles.
Owner:AEROVIRONMENT INC +2
Flight control using computer vision
A flight control operation of a reference aerial vehicle is performed. For example, an image captured by an image sensor of the reference aerial vehicle is received. A target is detected in the image. A three-dimensional relative location of the target with respect to the reference aerial vehicle is determined based on the image. The flight control operation is performed based on the three-dimensional relative location of the target with respect to the reference aerial vehicle.
Owner:AIRSPACE SYST INC
Micro coaxial dual-rotor helicopter control device and method
InactiveCN101916115AIncrease profitRealize networking communicationClosed circuit television systemsTarget-seeking controlGyroscopeUltrasonic sensor
The invention relates to a micro coaxial dual-rotor helicopter control device and micro coaxial dual-rotor helicopter control method, which belong to the technical field of helicopter control. The device comprises a ground device and an air device, wherein the ground device comprises a video wireless receiver, a ground wireless transmission module, a ground processor, a displayer and an upper computer; and the air device comprises a three-axis magnetic direction sensor, a three-axis gyroscope, a three-axis acceleration sensor, a GPS, a air pressure gauge, an ultrasonic transducer, an ARM processor, a micro wireless camera, a video decoding module, a video wireless transmission module and an air wireless transmission module. The device and the method have the advantage of improving the utilization rate of resources. In the invention, the network communication of helicopter groups can be realized conveniently. The system can realize aerial photographing and task setting automatic flight and ground tracking automatic flight and realize convenient automatic and manual operation switching.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV LIAONING
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com