Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
75 results about "Unmanned ground vehicle" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
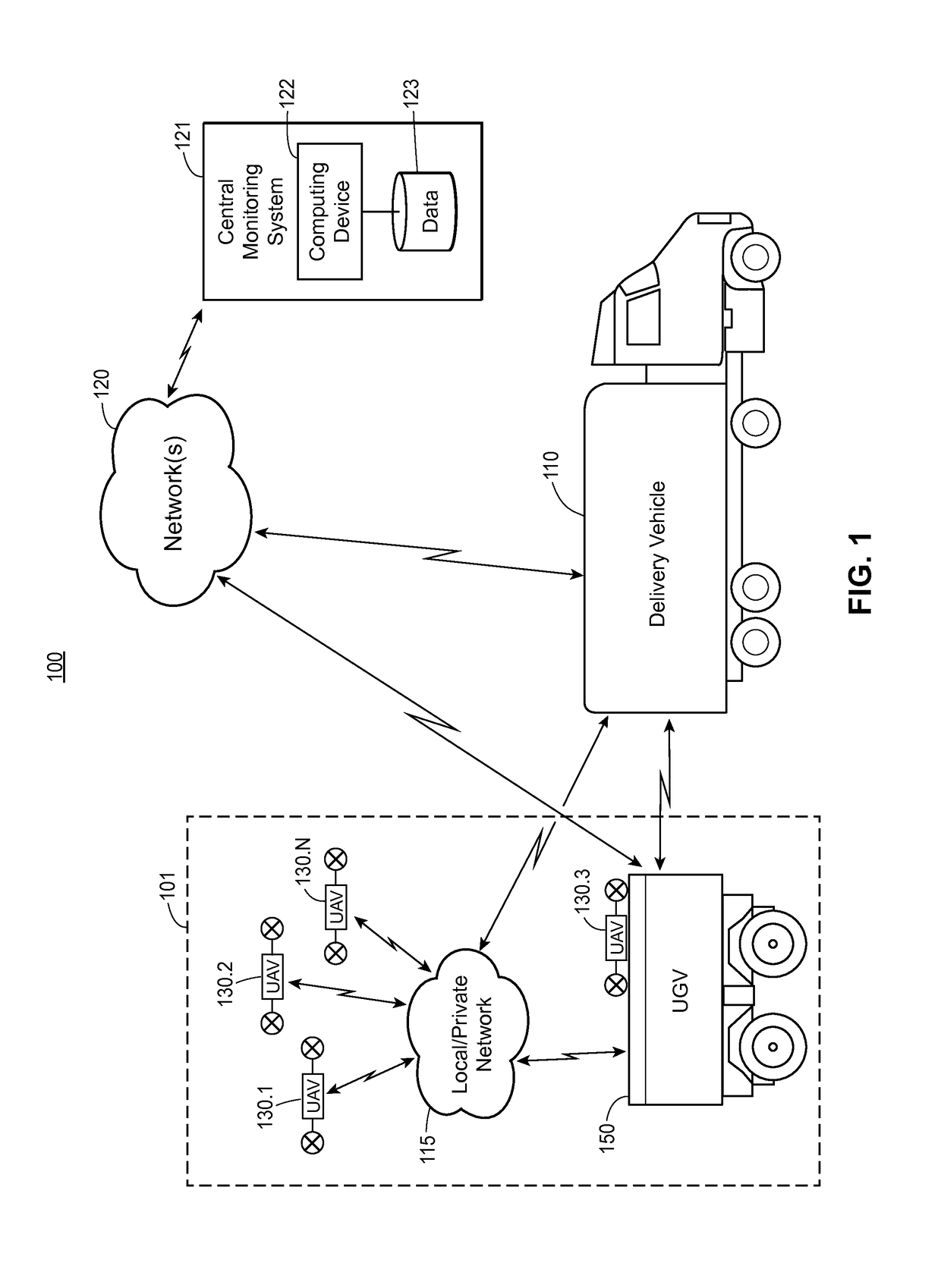
An unmanned ground vehicle (UGV) is a vehicle that operates while in contact with the ground and without an onboard human presence. UGVs can be used for many applications where it may be inconvenient, dangerous, or impossible to have a human operator present. Generally, the vehicle will have a set of sensors to observe the environment, and will either autonomously make decisions about its behavior or pass the information to a human operator at a different location who will control the vehicle through teleoperation.
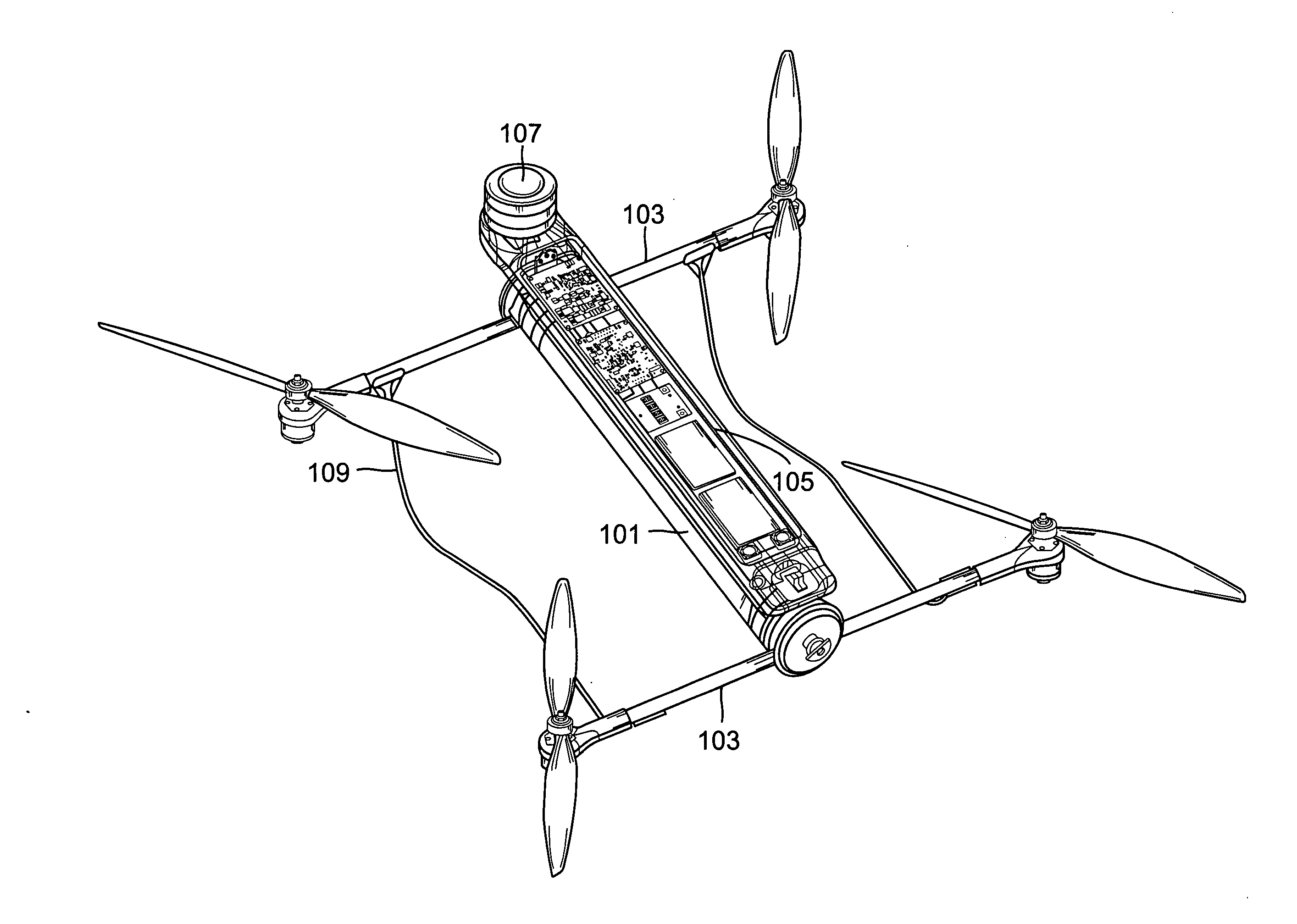
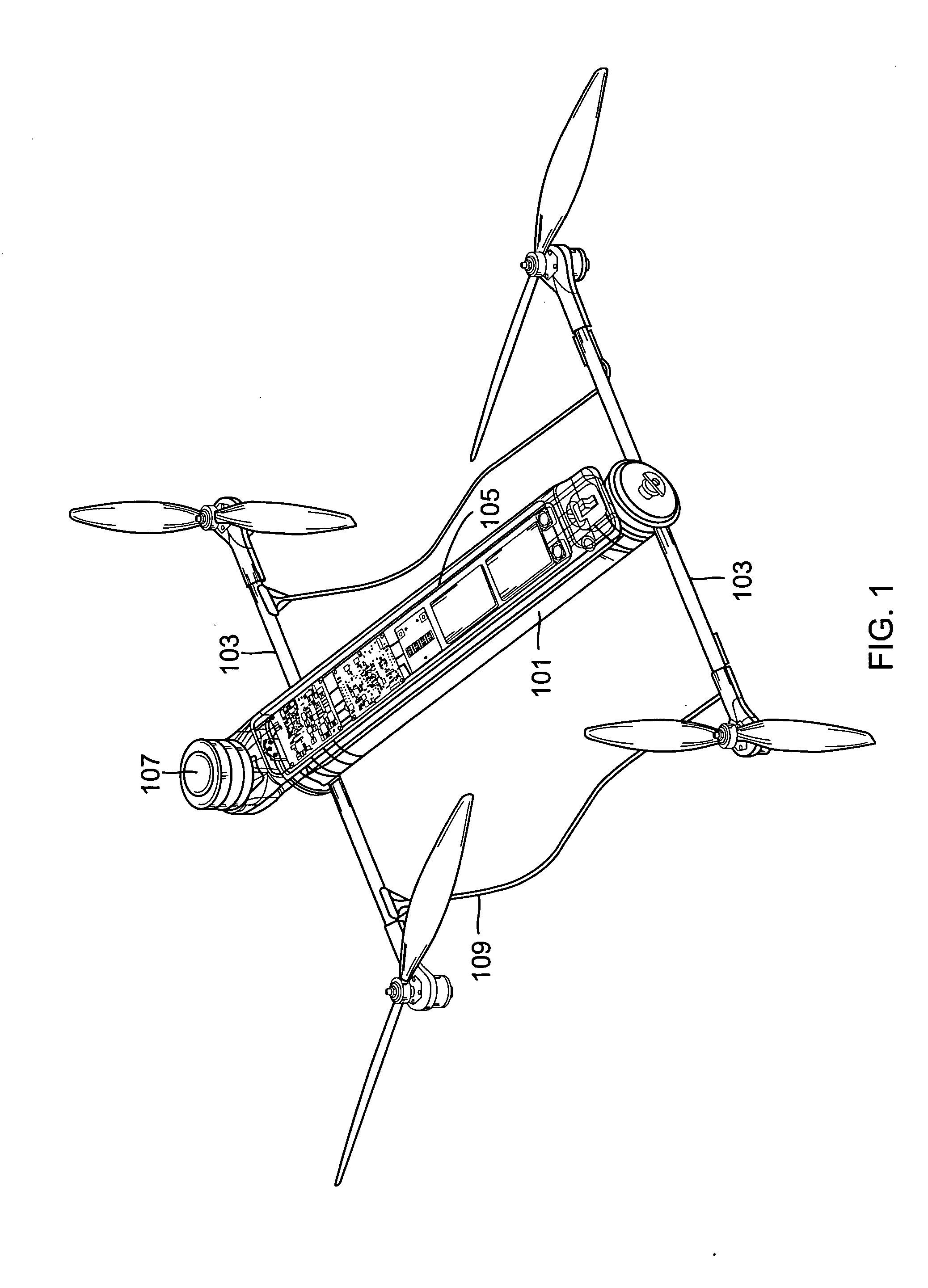
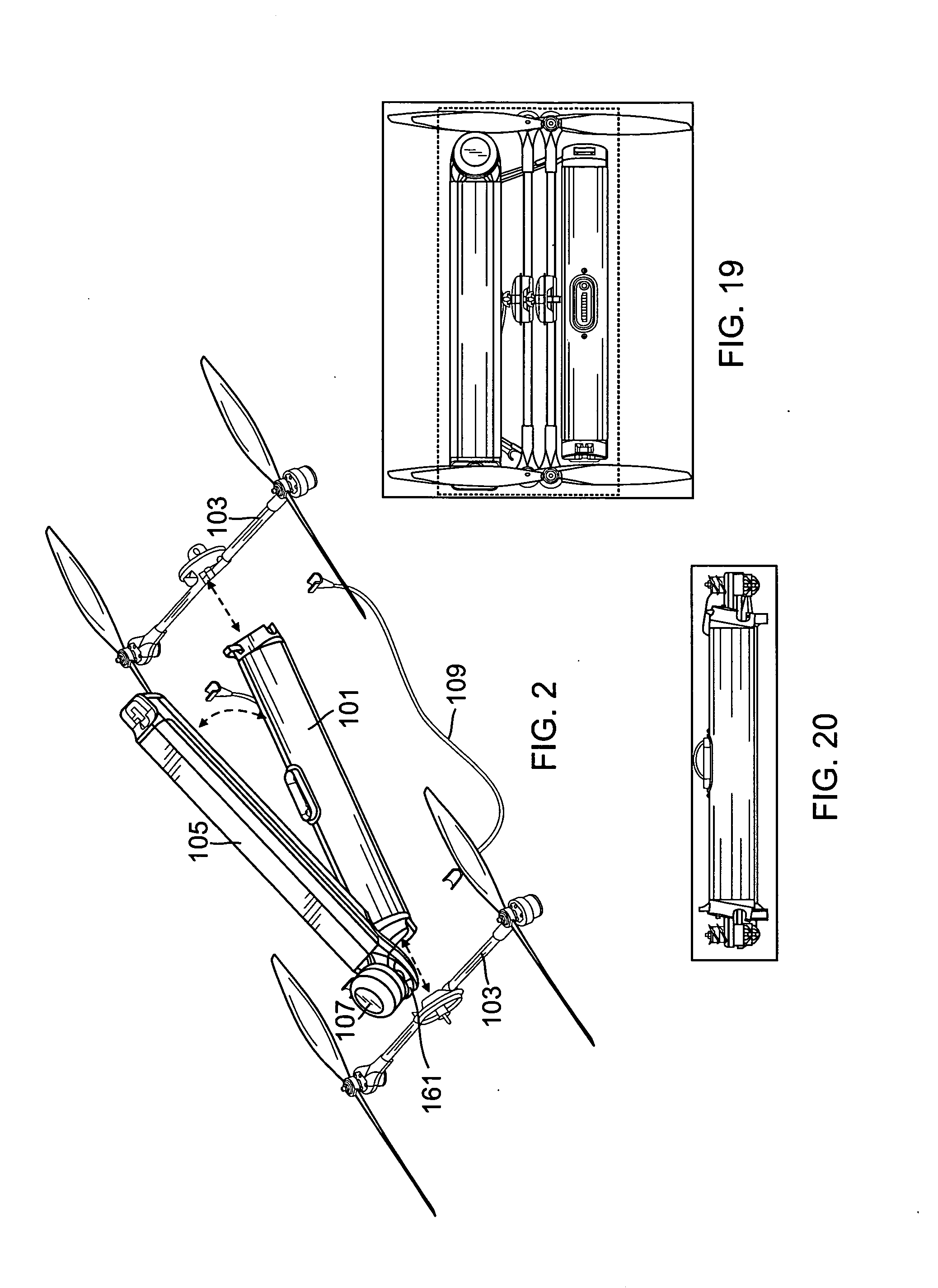
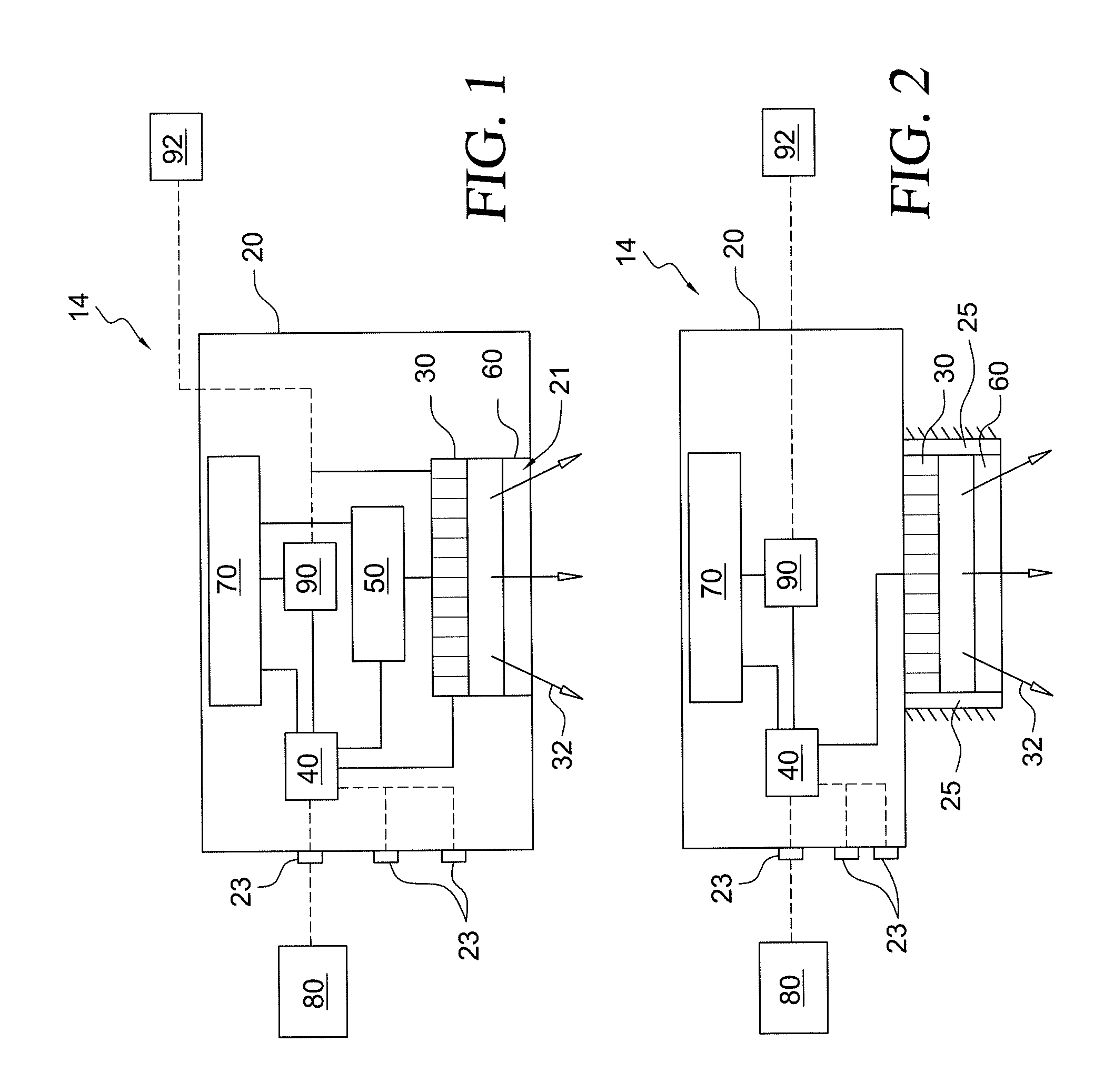
Reconfigurable battery-operated vehicle system
InactiveUS20140061376A1Reduce weightStable structureUnmanned surface vesselsRemote controlled aircraftReconfigurable antennaComputer module
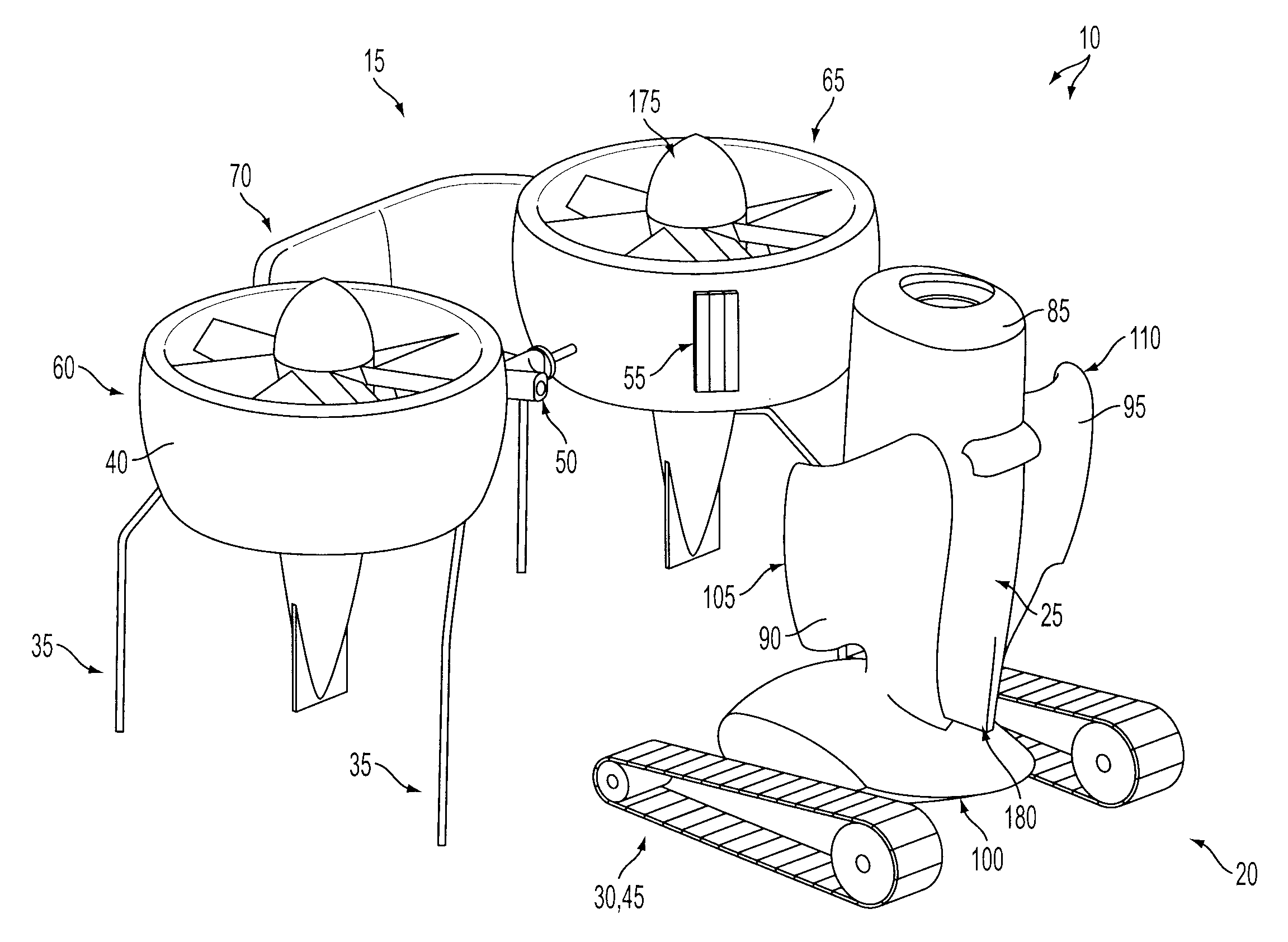
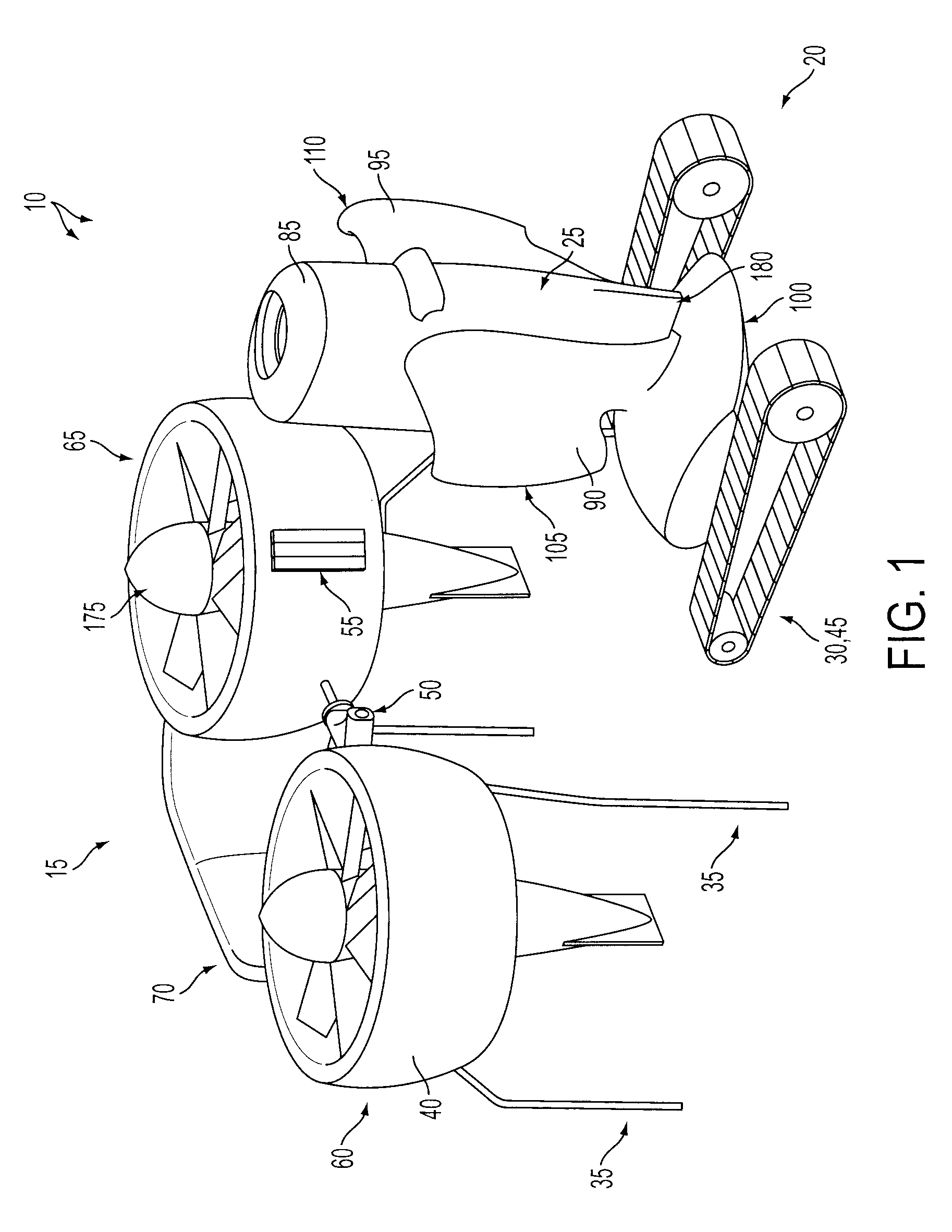
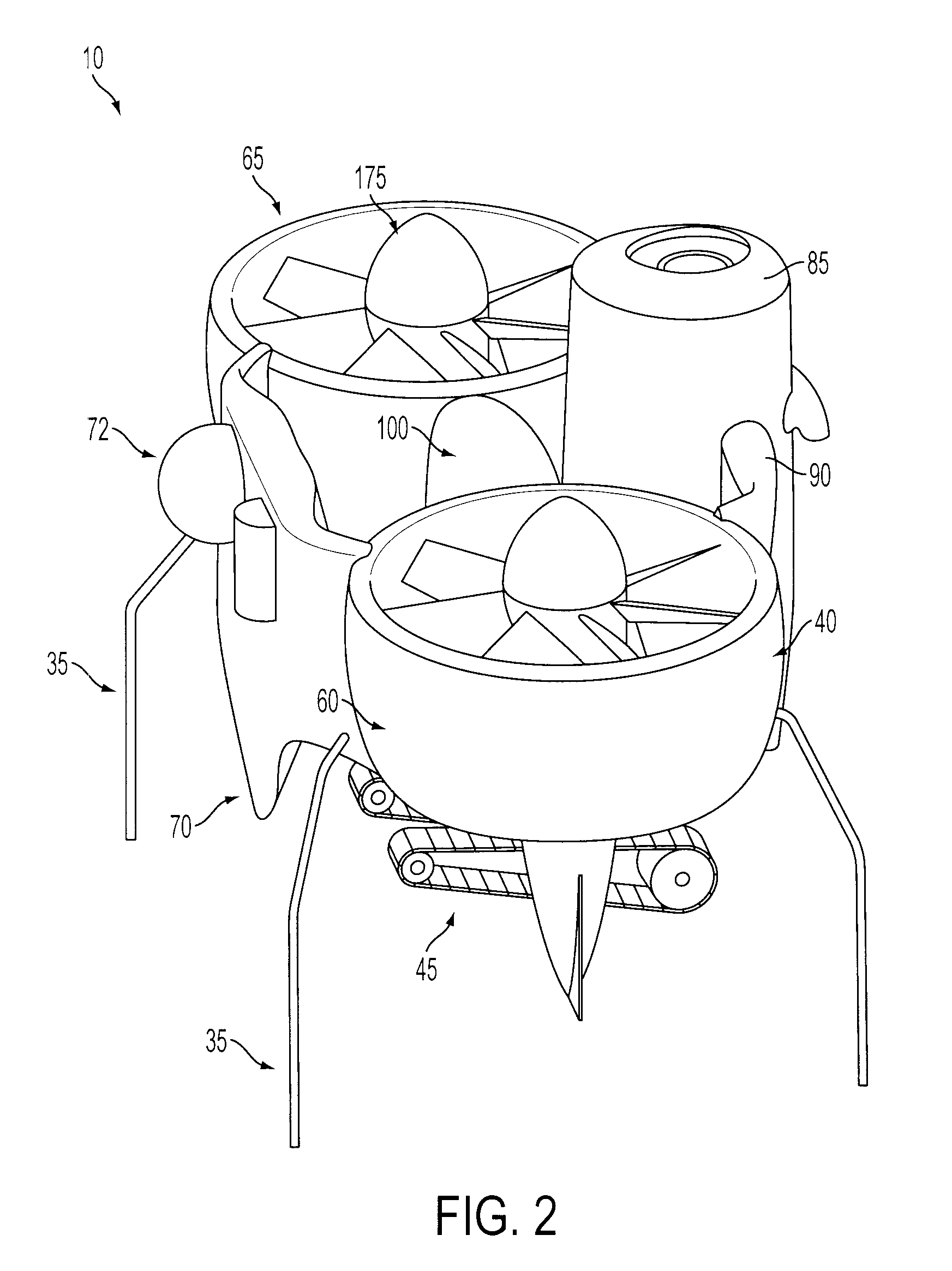
A quadrotor UAV including ruggedized, integral-battery, load-bearing body, two arms on the load-bearing body, each arm having two rotors, a control module mounted on the load-bearing body, a payload module mounted on the control module, and skids configured as landing gear. The two arms are replaceable with arms having wheels for ground vehicle use, with arms having floats and props for water-surface use, and with arms having pitch-controlled props for underwater use. The control module is configured to operate as an unmanned aerial vehicle, an unmanned ground vehicle, an unmanned (water) surface vehicle, and an unmanned underwater vehicle, depending on the type of arms that are attached.
Owner:AEROVIRONMENT INC
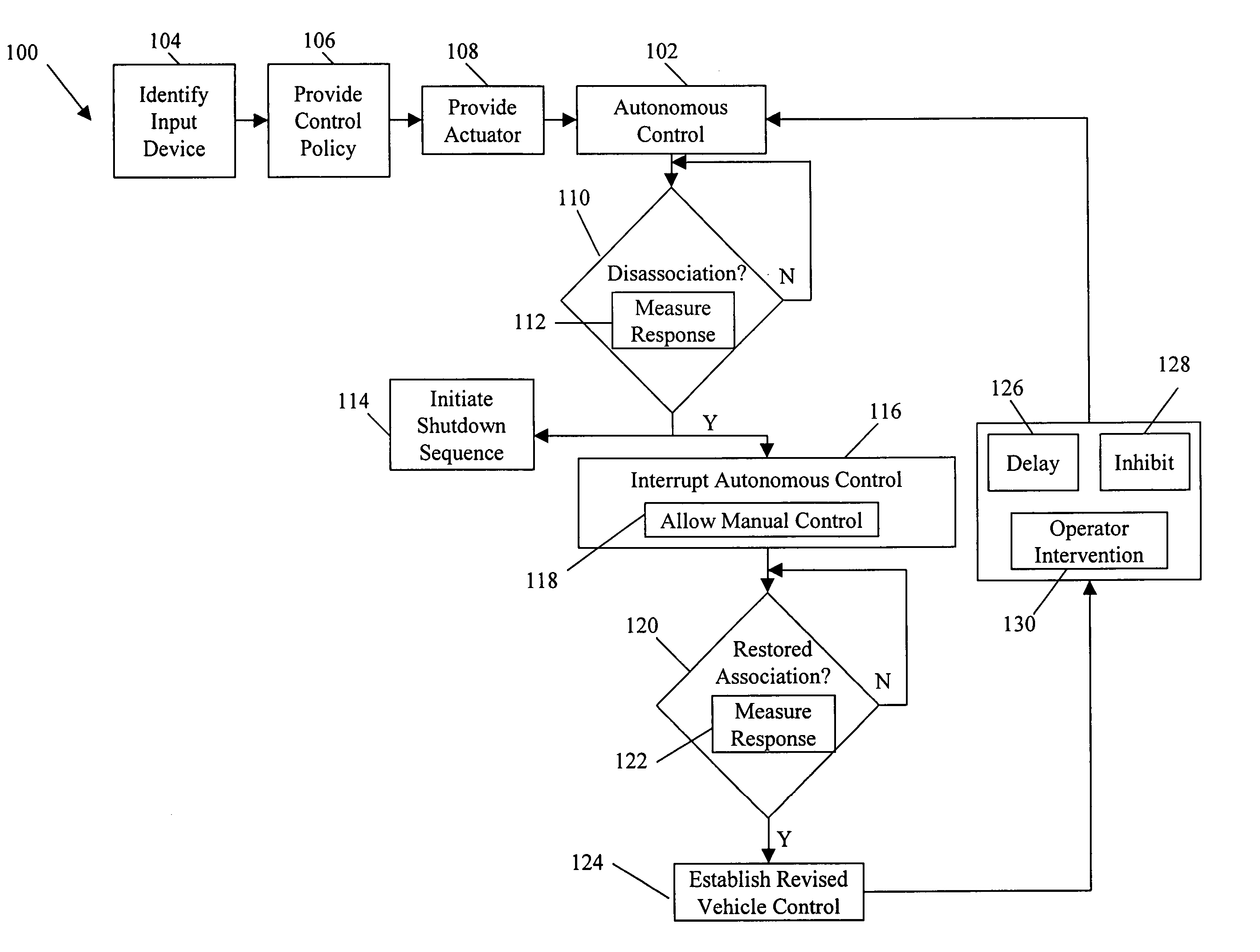
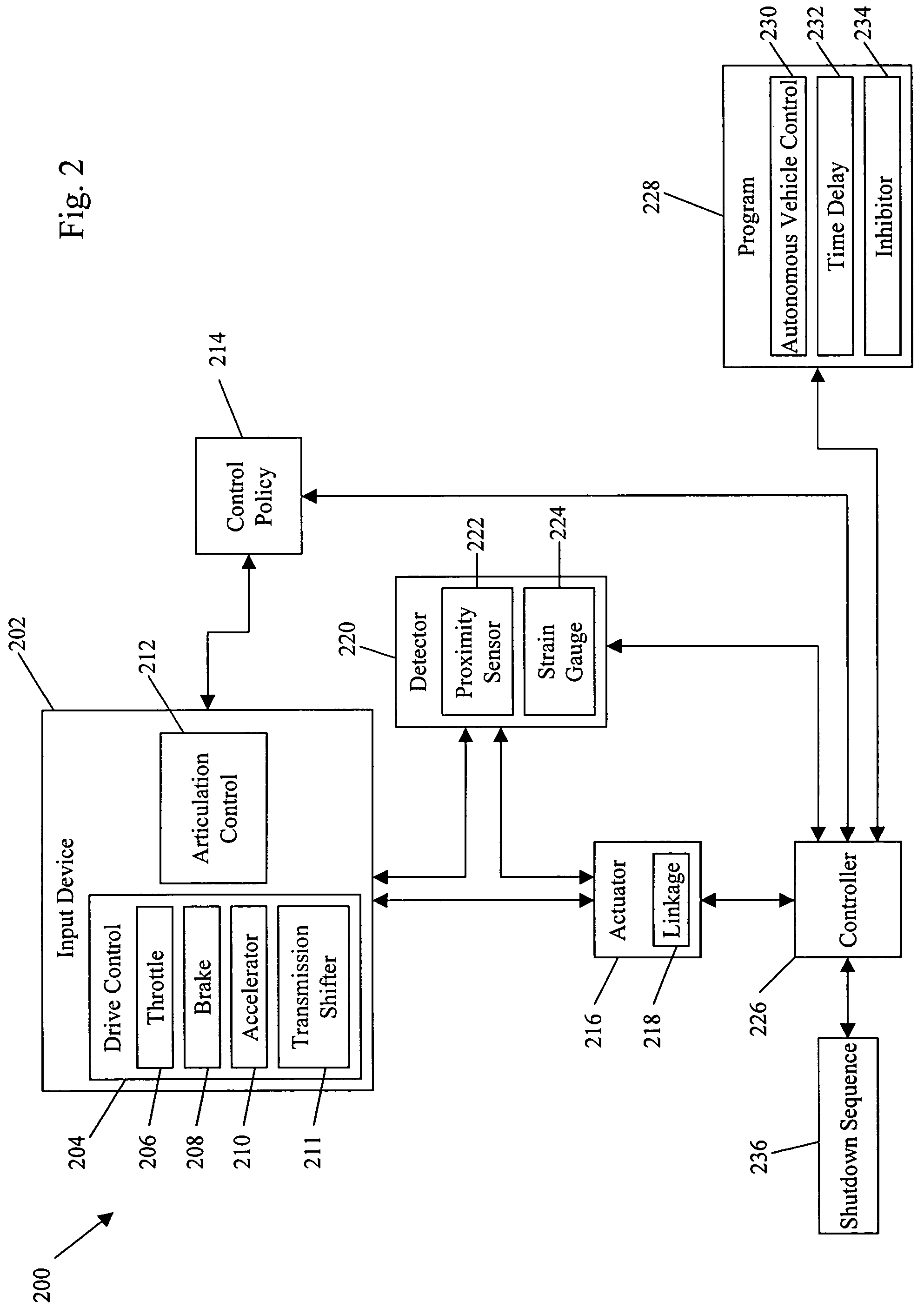
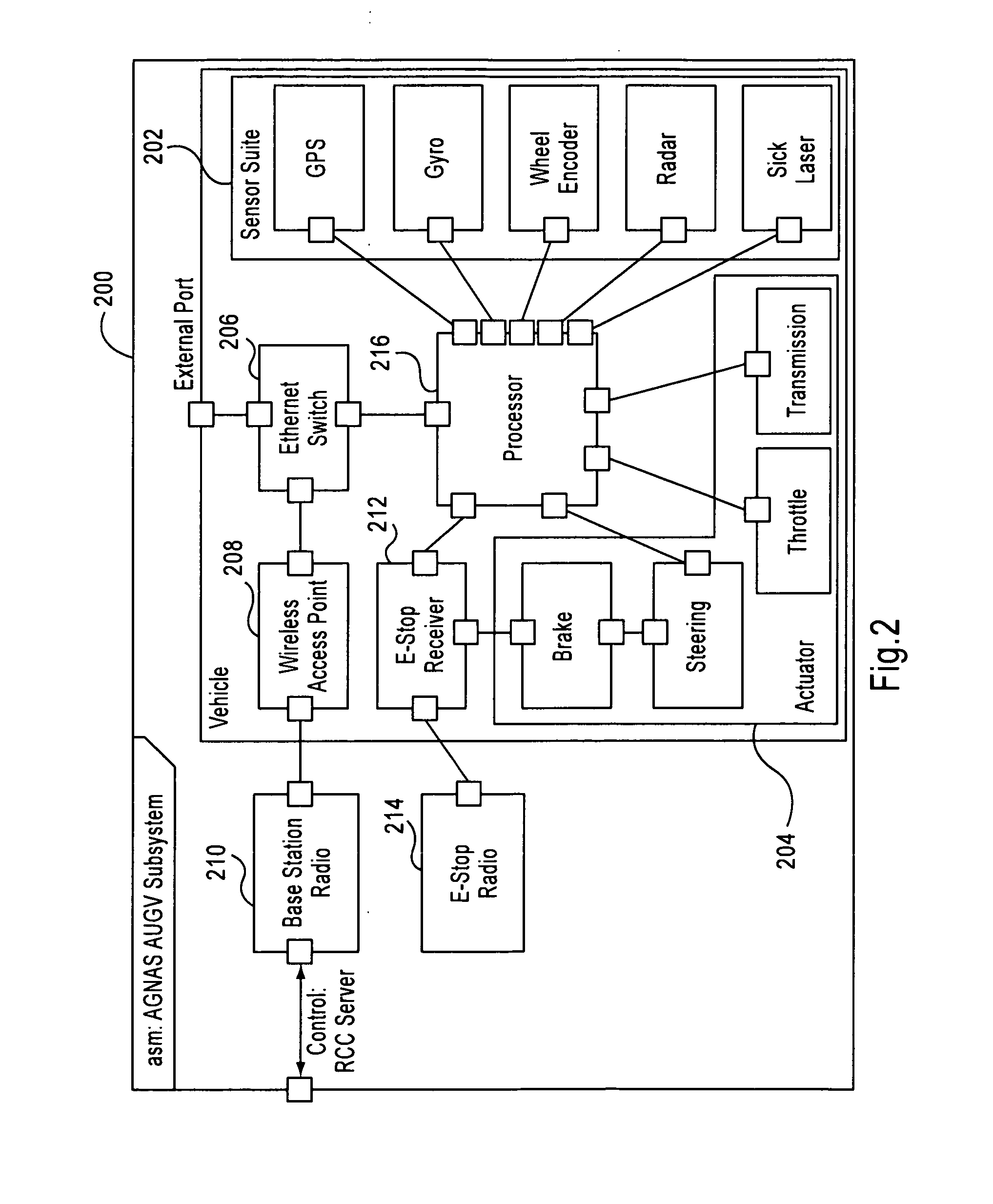
Systems and methods for control of an unmanned ground vehicle
InactiveUS20060089766A1Improve securityDecrease and eliminates need for manual interventionDigital data processing detailsVehicle position/course/altitude controlEngineeringGround vehicles
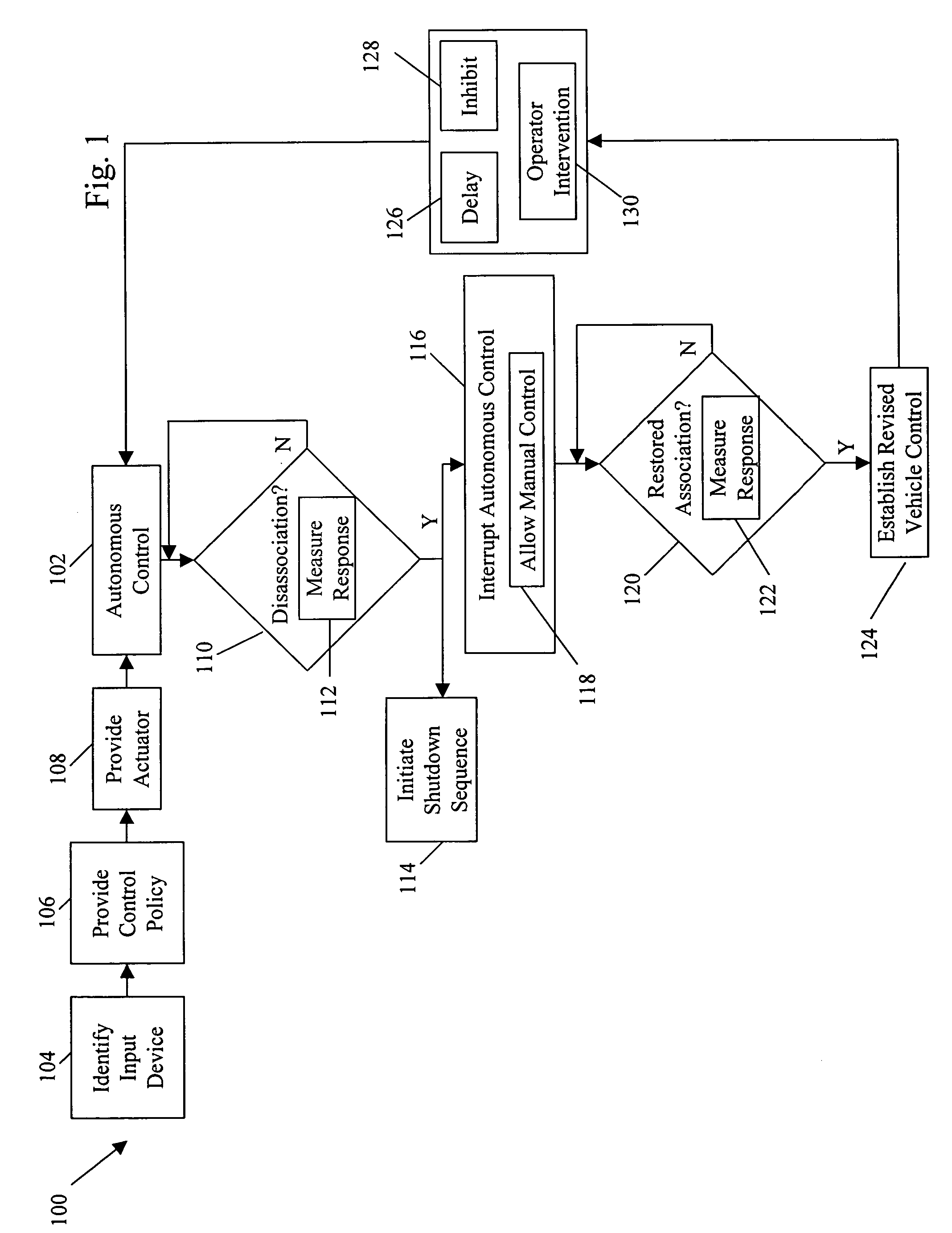
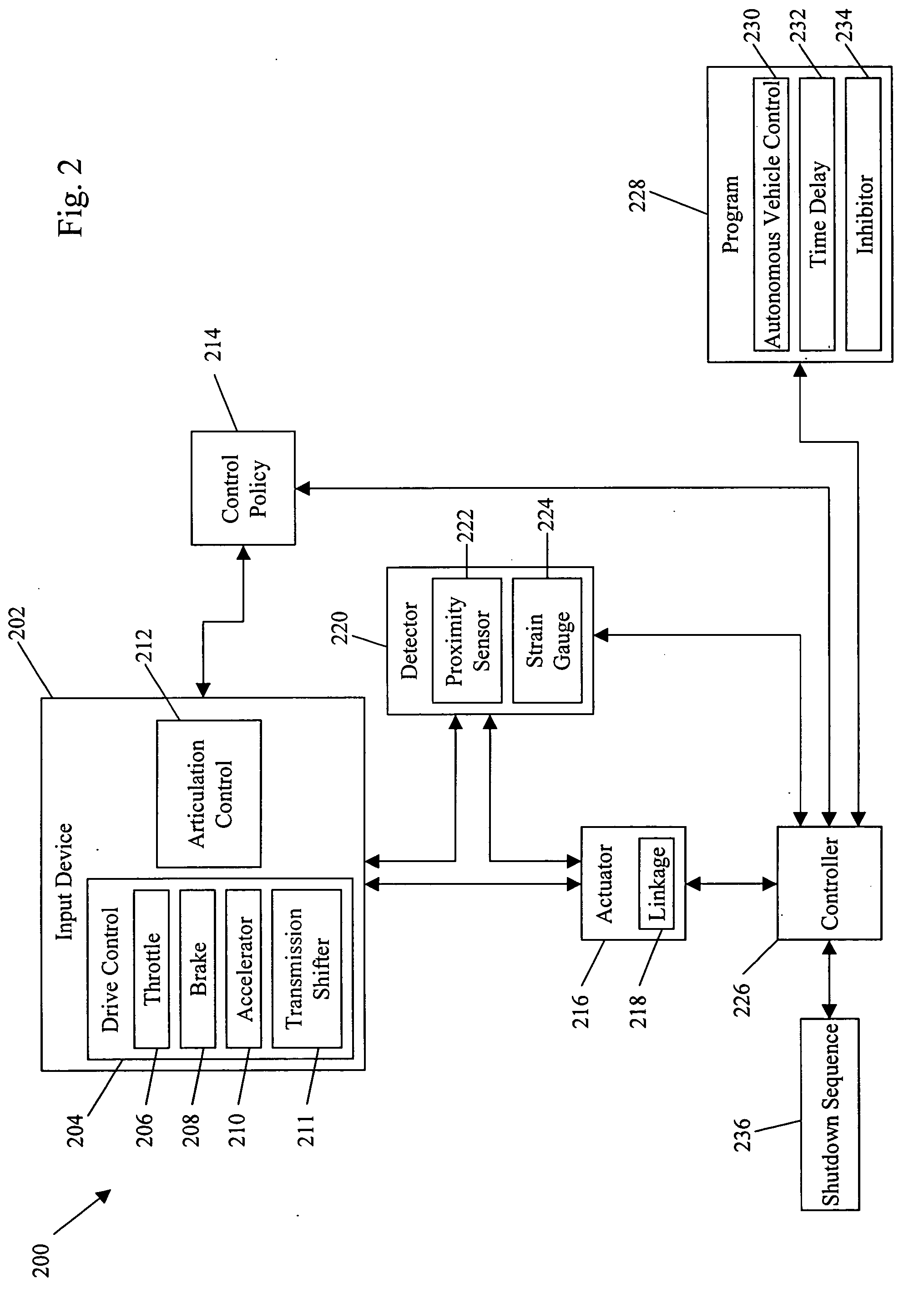
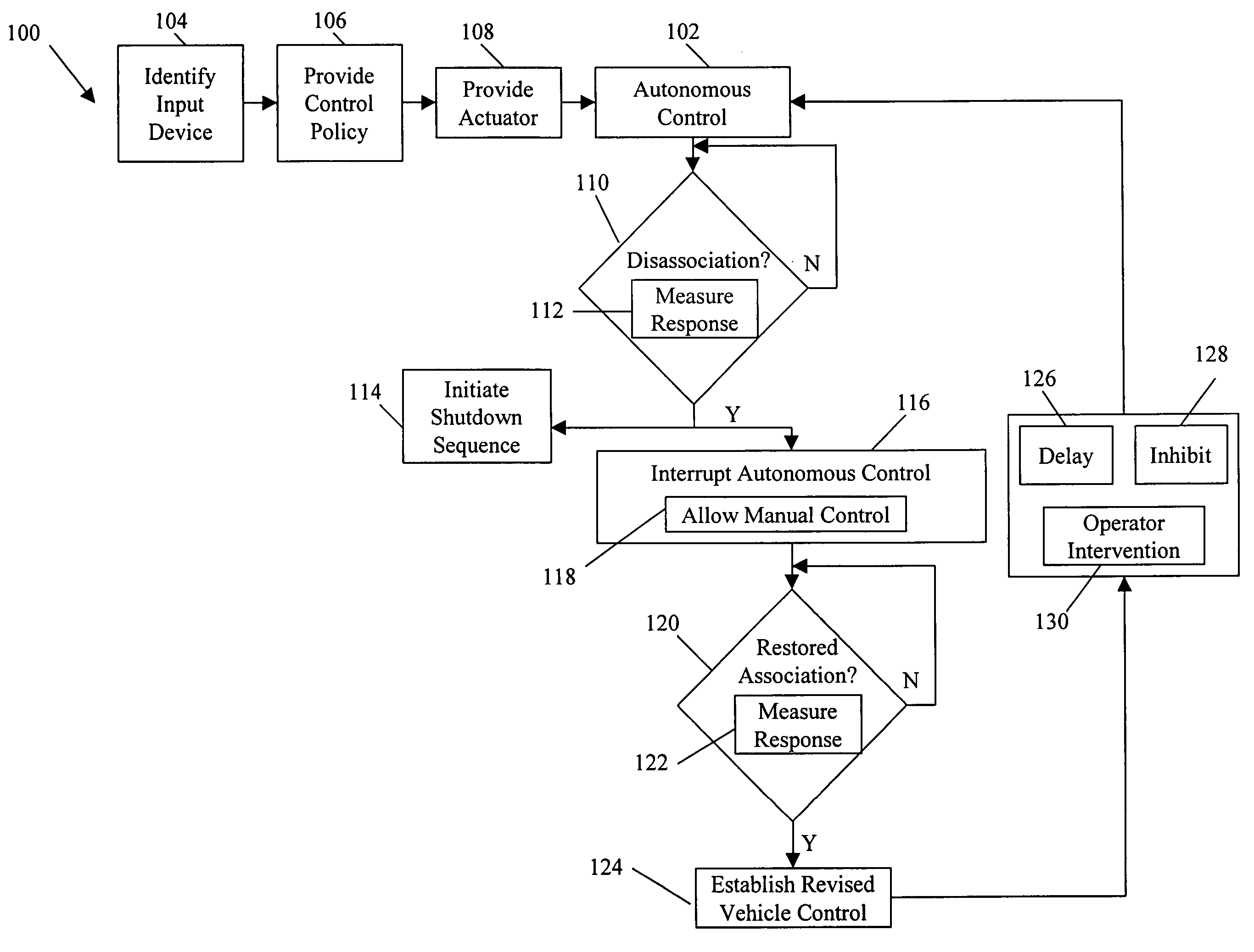
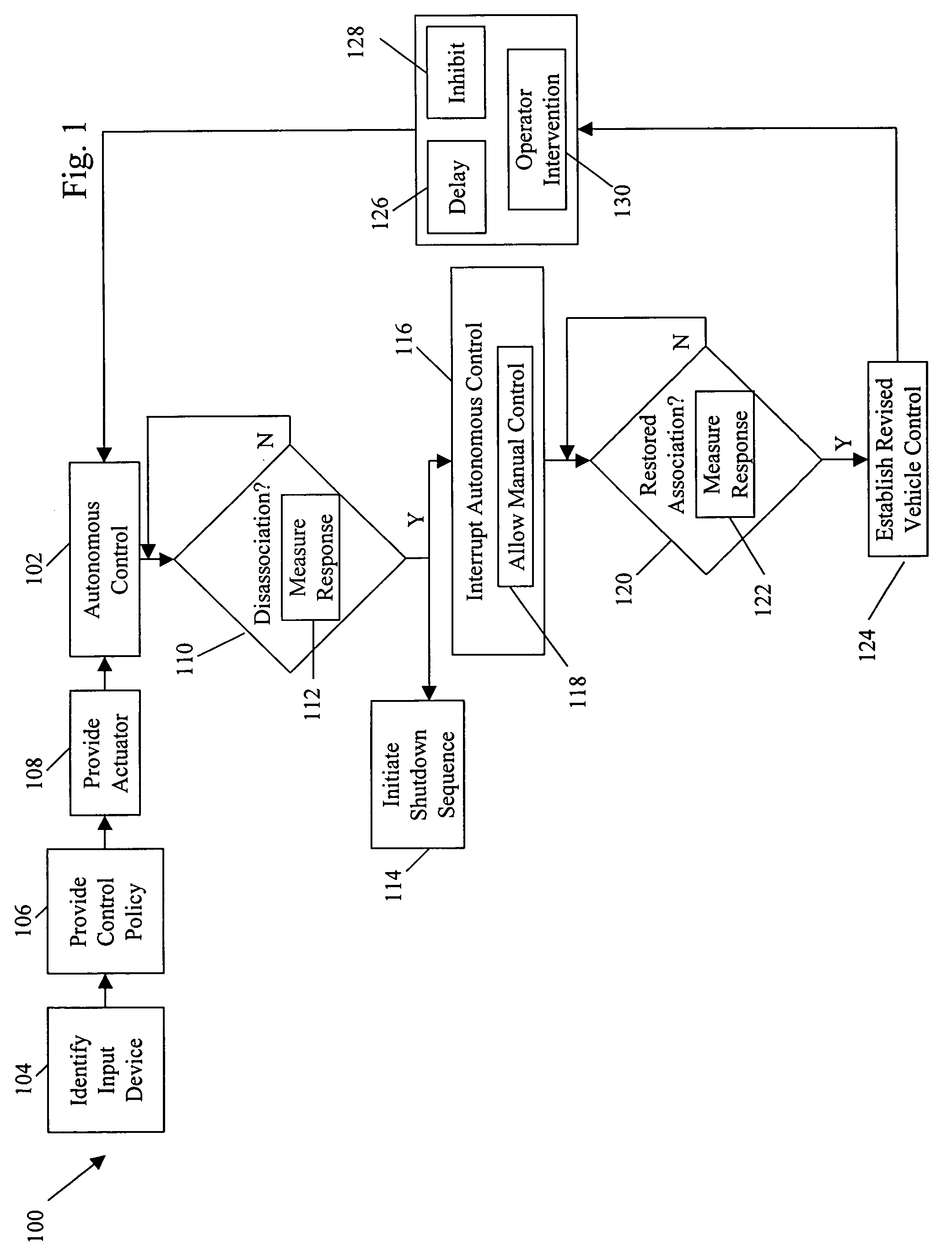
Systems and methods for interruptible autonomous control of a vehicle. Autonomous control is achieved by using actuators that interact with input devices in the vehicle. The actuators (e.g., linkages) manipulate the input devices (e.g., articulation controls and drive controls, such as a throttle, brake, tie rods, steering gear, throttle lever, or accelerator) to direct the operation of the vehicle. Although operating autonomously, manual operation of the vehicle is possible following the detection of events that suggest manual control is desired. Subsequent autonomous control may be permitted, permitted after a prescribed delay, or prevented.
Owner:IROBOT CORP
Systems and methods for control of an unmanned ground vehicle
InactiveUS7499776B2Decrease and eliminates need for manual interventionImprove task efficiencyVehicle testingAnalogue computers for trafficEngineeringGround vehicles
Systems and methods for interruptible autonomous control of a vehicle. Autonomous control is achieved by using actuators that interact with input devices in the vehicle. The actuators (e.g., linkages) manipulate the input devices (e.g., articulation controls and drive controls, such as a throttle, brake, tie rods, steering gear, throttle lever, or accelerator) to direct the operation of the vehicle. Although operating autonomously, manual operation of the vehicle is possible following the detection of events that suggest manual control is desired. Subsequent autonomous control may be permitted, permitted after a prescribed delay, or prevented.
Owner:IROBOT CORP
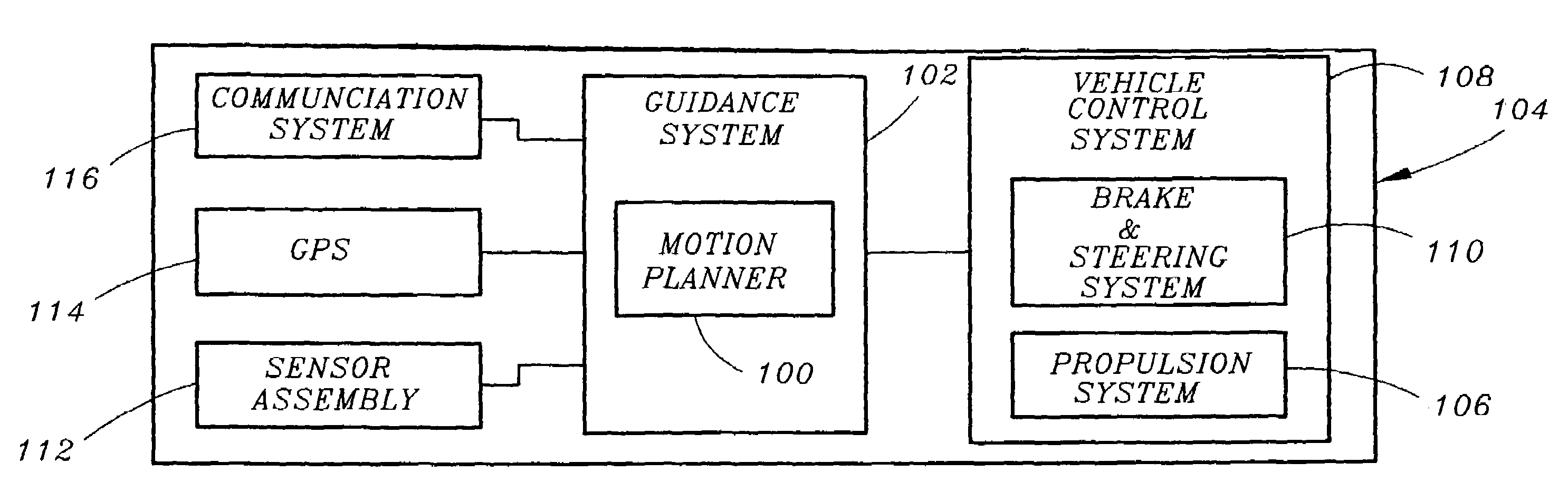
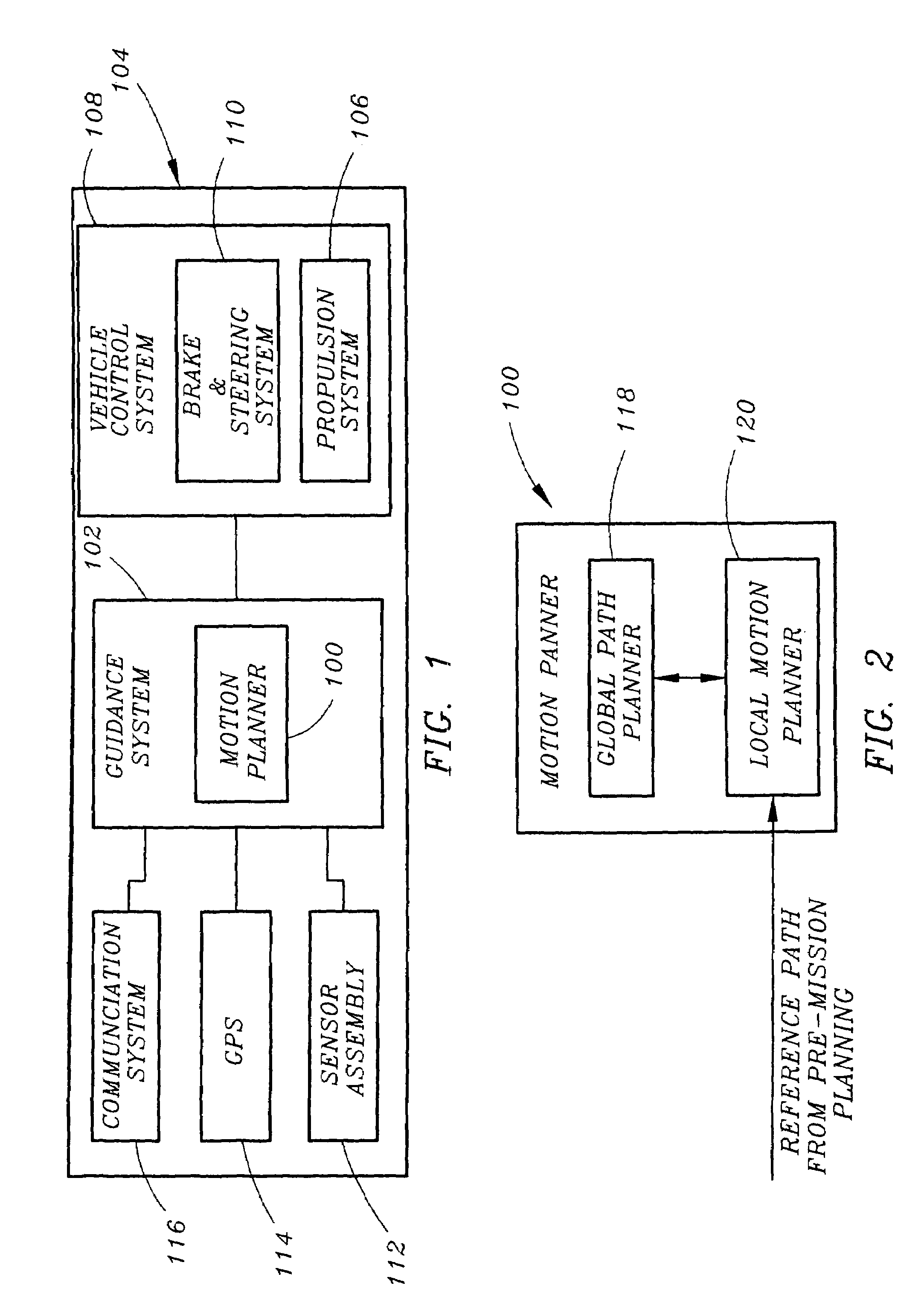
Motion planner for unmanned ground vehicles traversing at high speeds in partially known environments
InactiveUS7734387B1Low costIncrease speedInstruments for road network navigationAnti-collision systemsGround vehiclesMotion planning
A motion planner for unmanned ground vehicles capable of traversing at high speeds to reach remote locations in partially known environments. The motion planner comprises a global path planner and a local path planner in communication with the global path planner. The global path planner determines a path to reach a goal location. The local motion planner revises the path determined by the global path planner to generate a motion profile accounting for constraints on the maneuverability of the unmanned ground vehicle. The motion profile provides a revised path for being traversed by the unmanned ground vehicle to reach the goal location.
Owner:ROCKWELL COLLINS INC
Urban environment composition method for unmanned vehicles
ActiveCN104764457AImprove efficiencyReduce precisionInstruments for road network navigationPoint cloudRadar
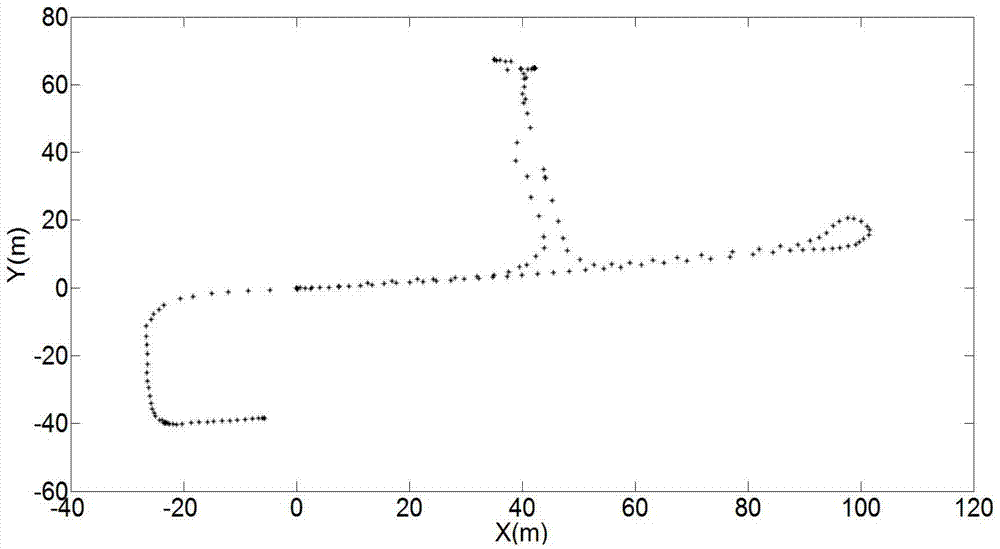
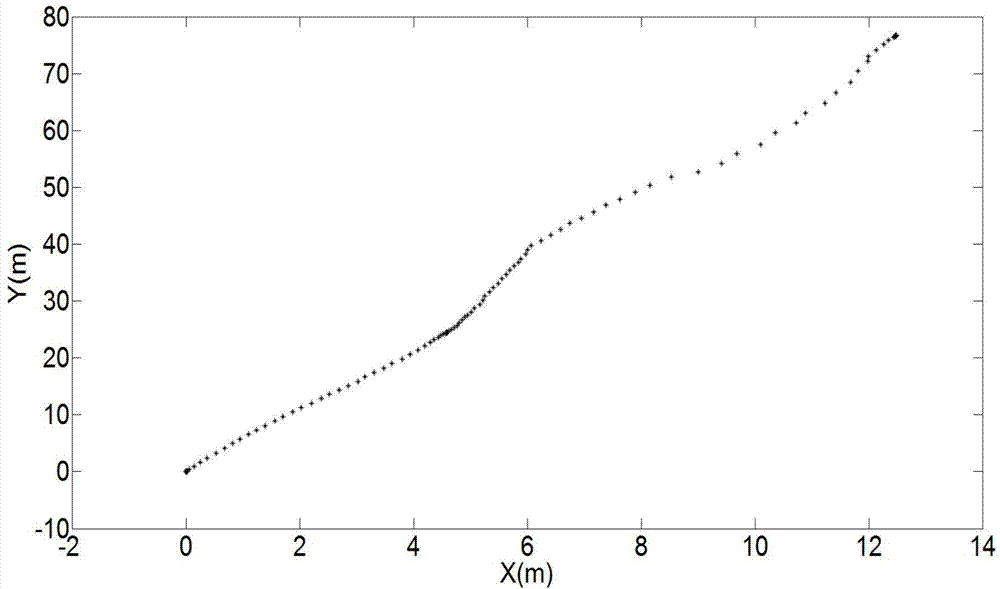
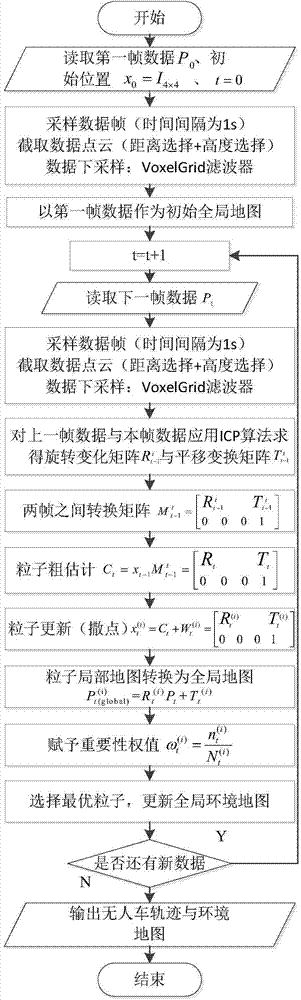
The invention discloses an urban environment composition method for unmanned vehicles. Under the condition of being independent of external positioning sensors such as speedometers, GPS and inertial navigators, the trajectory tracking and environment map building of an unmanned vehicle are completed by just using few particles for 3D laser-point cloud data returned by a vehicle-mounted laser radar, thereby providing basis for the autonomous running of the unmanned ground vehicle in an unknown environment; and according to the invention, an ICP algorithm is applied to adjacent two frames of data so as to obtain a coarse estimation on the real position and posture of a vehicle, and then redundance is performed near the coarse estimation based on gaussian distribution. Although the coarse estimation is not the real position and posture of the vehicle, the coarse estimation is a high-probability area of the real position and posture of the vehicle, so that an effect of relatively accurate positioning and composition is achieved by using a small amount of particles in the process of subsequent redundance, thereby avoiding the fitting of a vehicle trajectory by using a large amount of particles in a traditional method, improving the efficiency of the algorithm, and effectively restraining a phenomenon of particle degeneracy caused by bad particle estimation.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
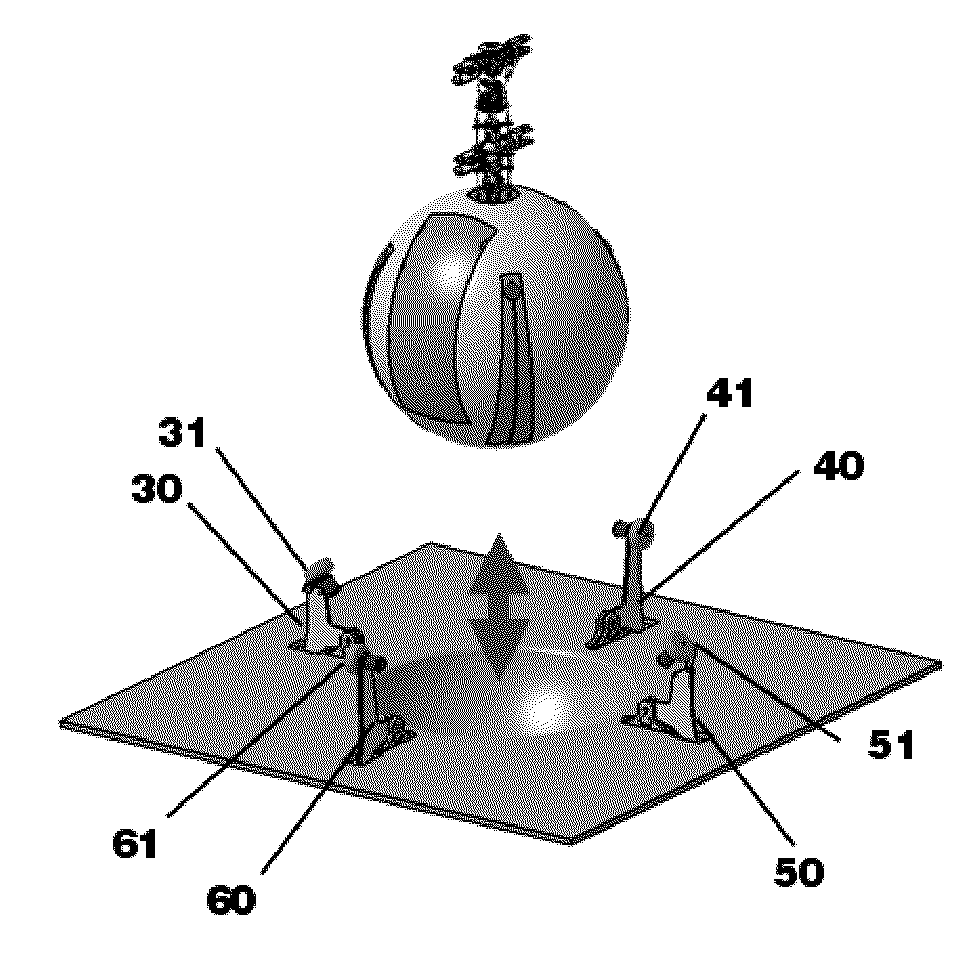
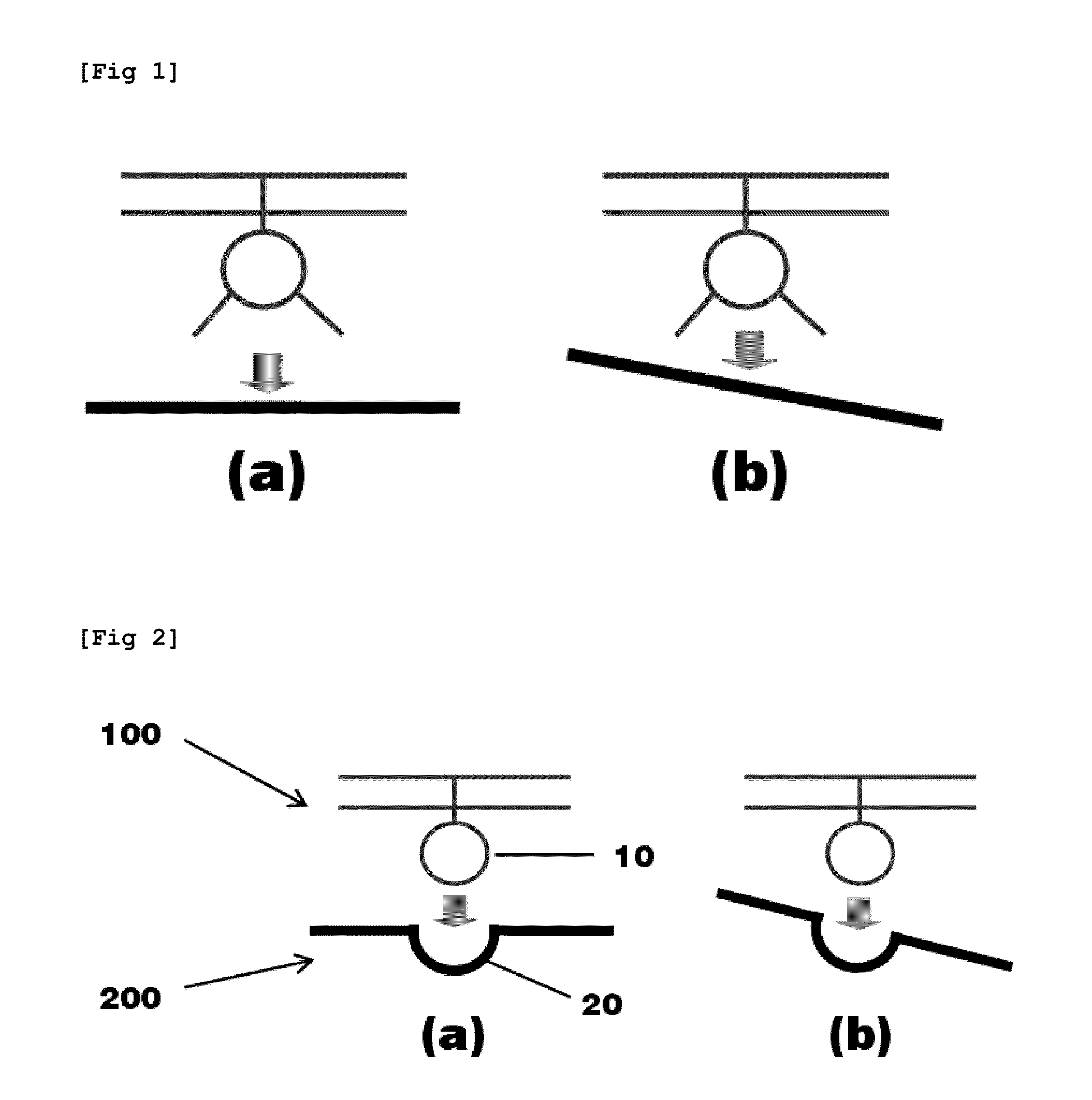
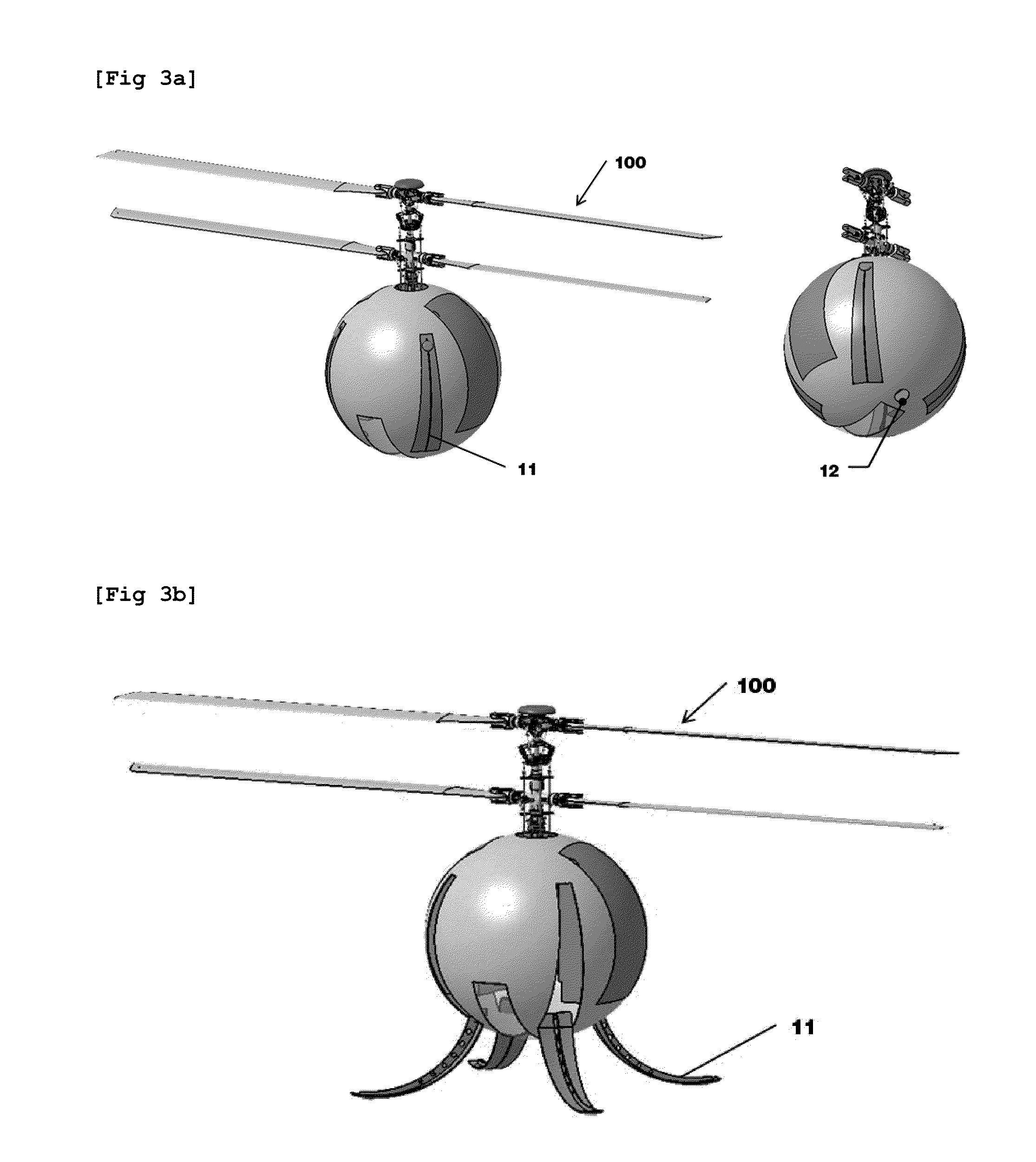
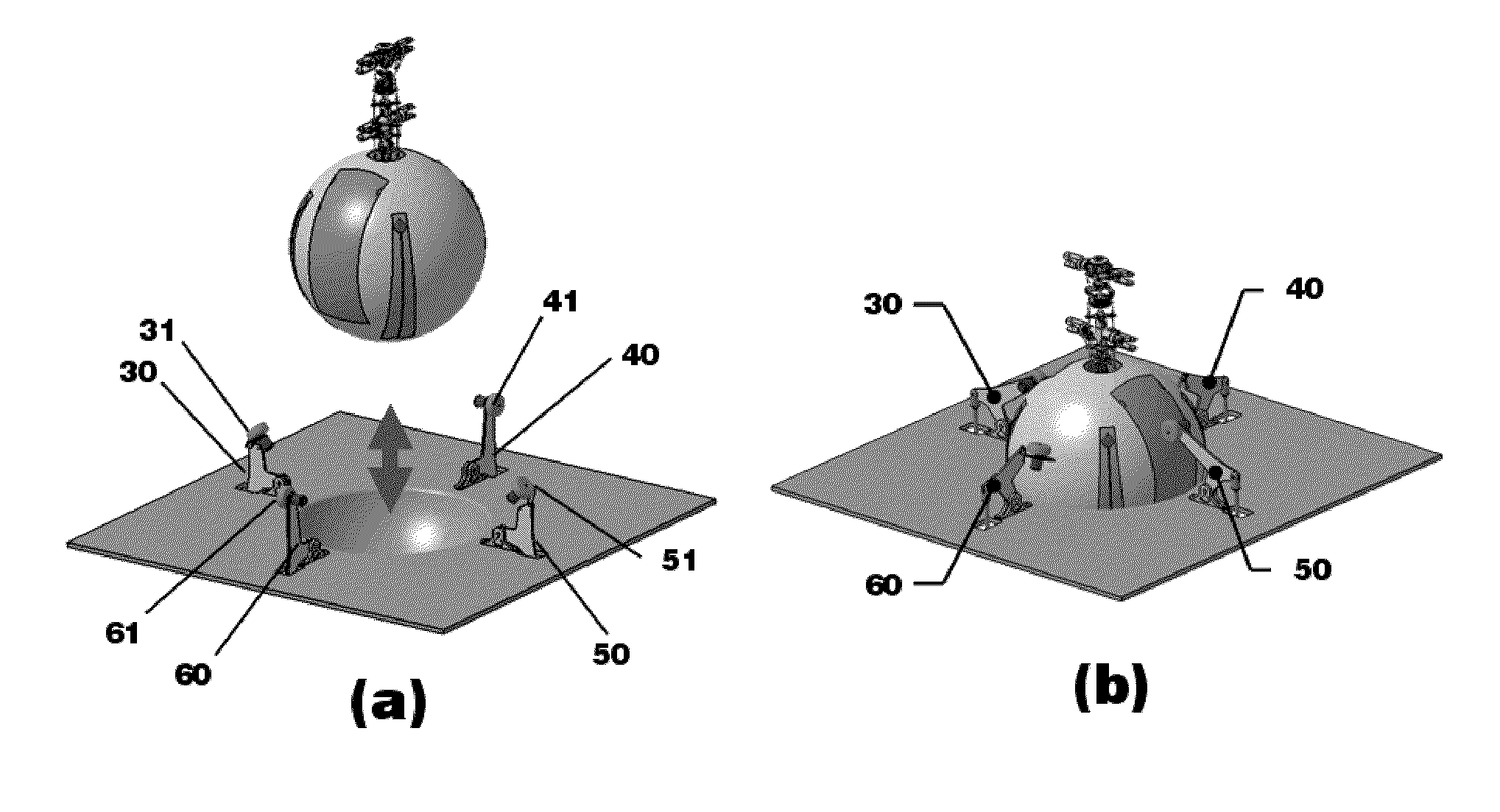
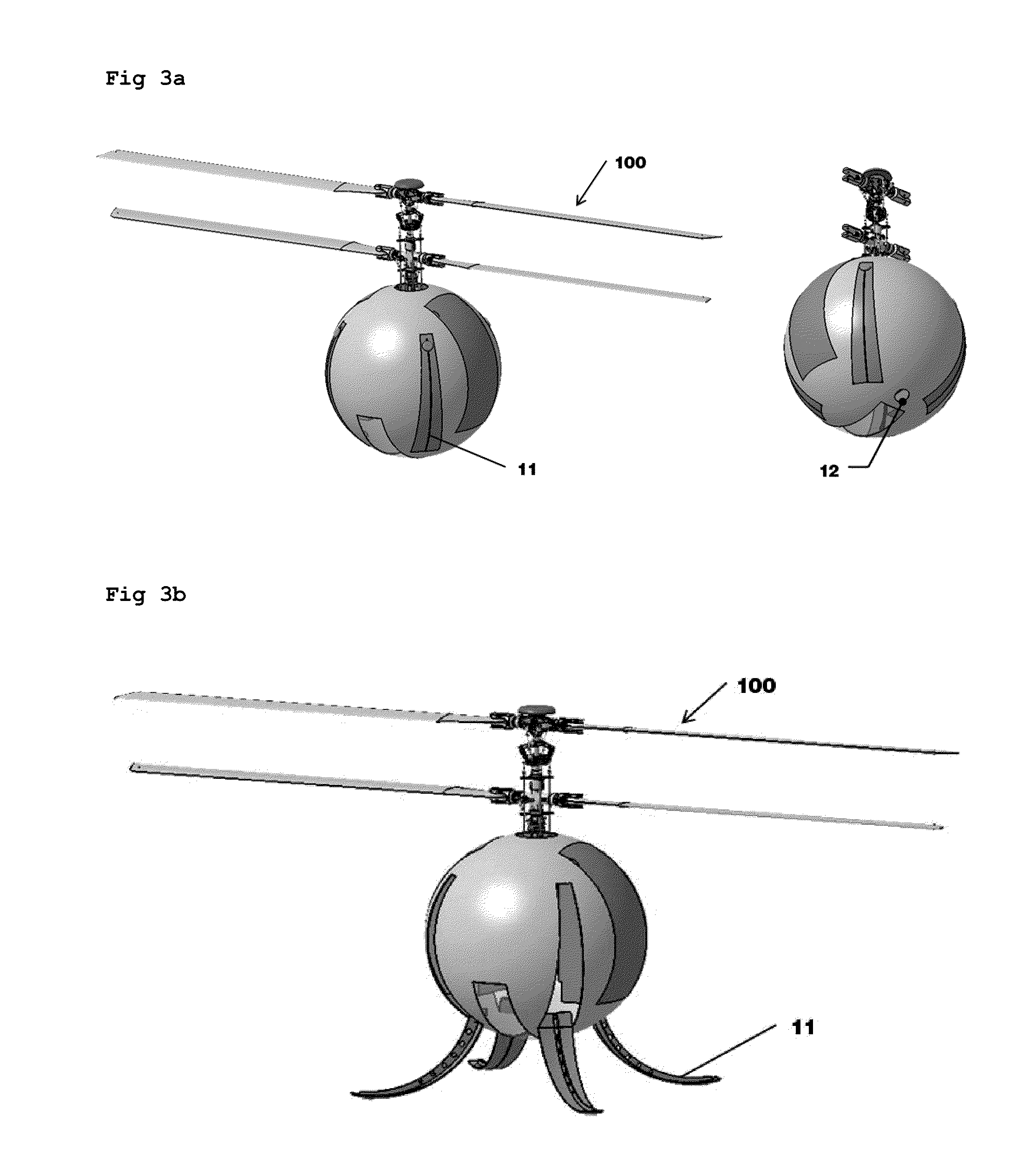
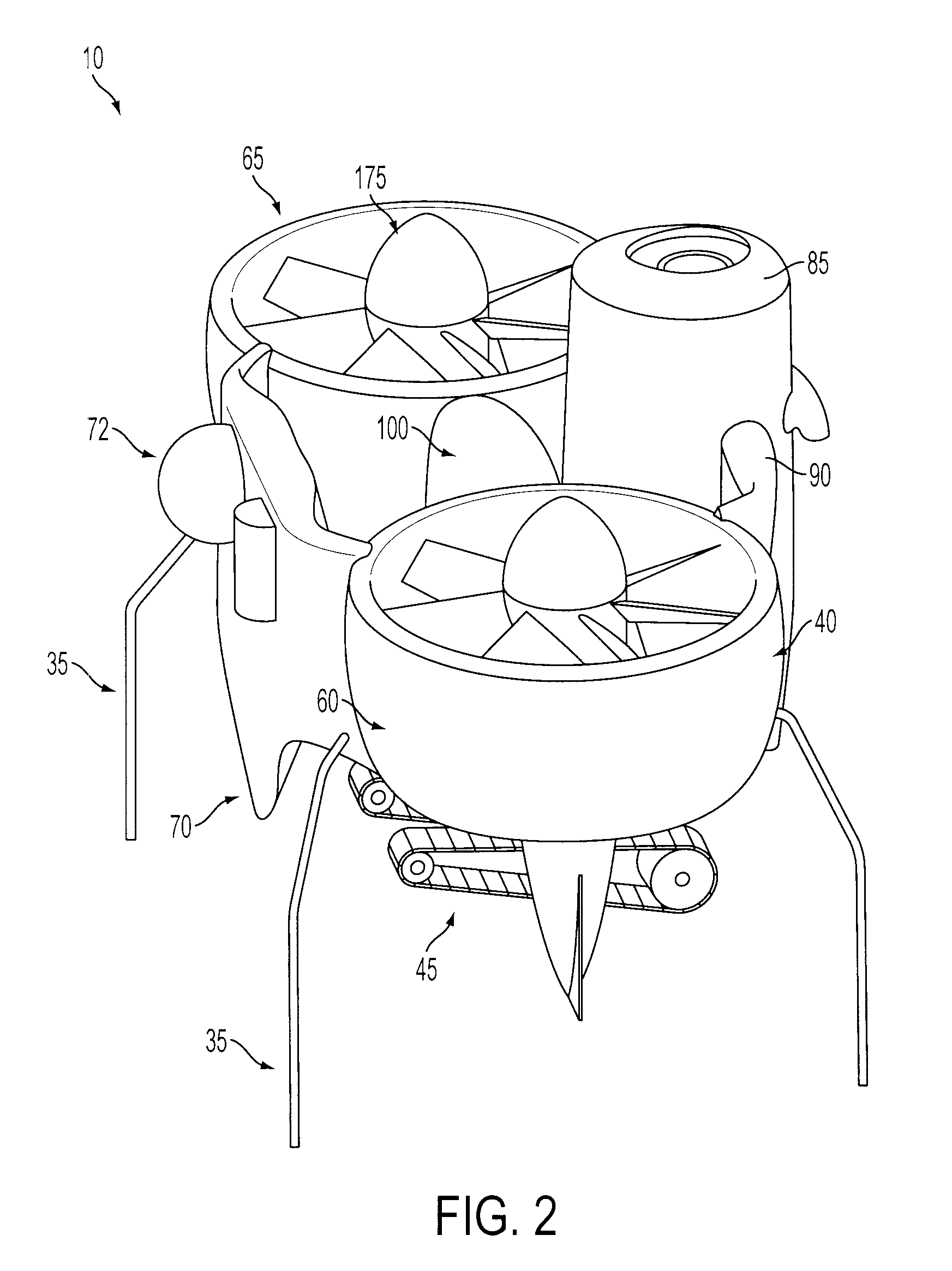
Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Having Spherical Loading Portion and Unmanned Ground Vehicle Therefor
InactiveUS20110068224A1Reduce weightThe location is limitedArresting gearUnmanned aerial vehiclesAerospace engineeringUnmanned ground vehicle
An unmanned aerial vehicle equipped with a spherical locking portion for landing on an unmanned ground vehicle is disclosed. The spherical locking portion can be the body of the unmanned aerial vehicle. Further, an unmanned ground vehicle for landing of an unmanned aerial vehicle, comprising a landing portion configured to have some of a spherical locking portion of the unmanned aerial vehicle inserted therein is disclosed.
Owner:PUSAN NAT UNIV IND UNIV COOPERATION FOUND
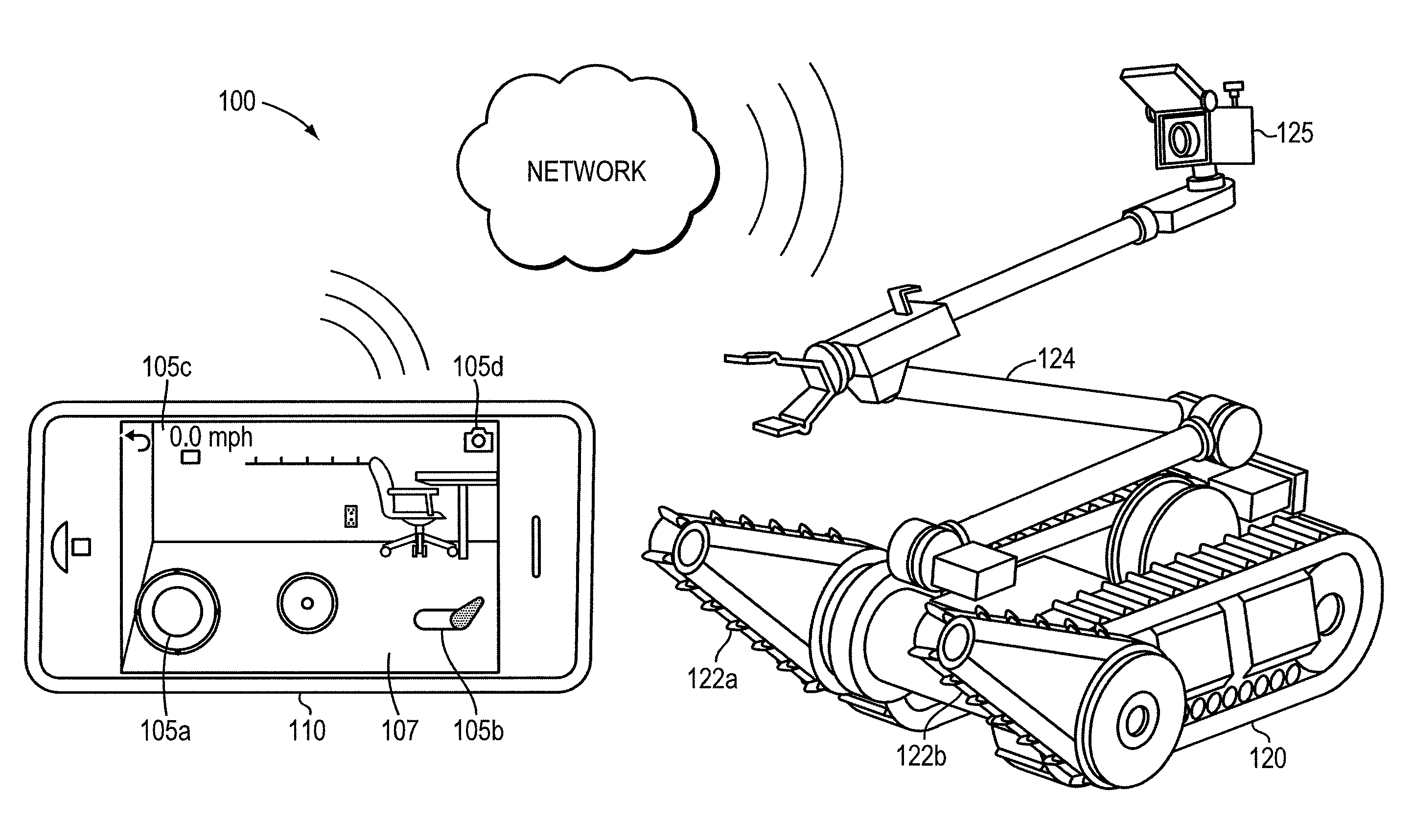
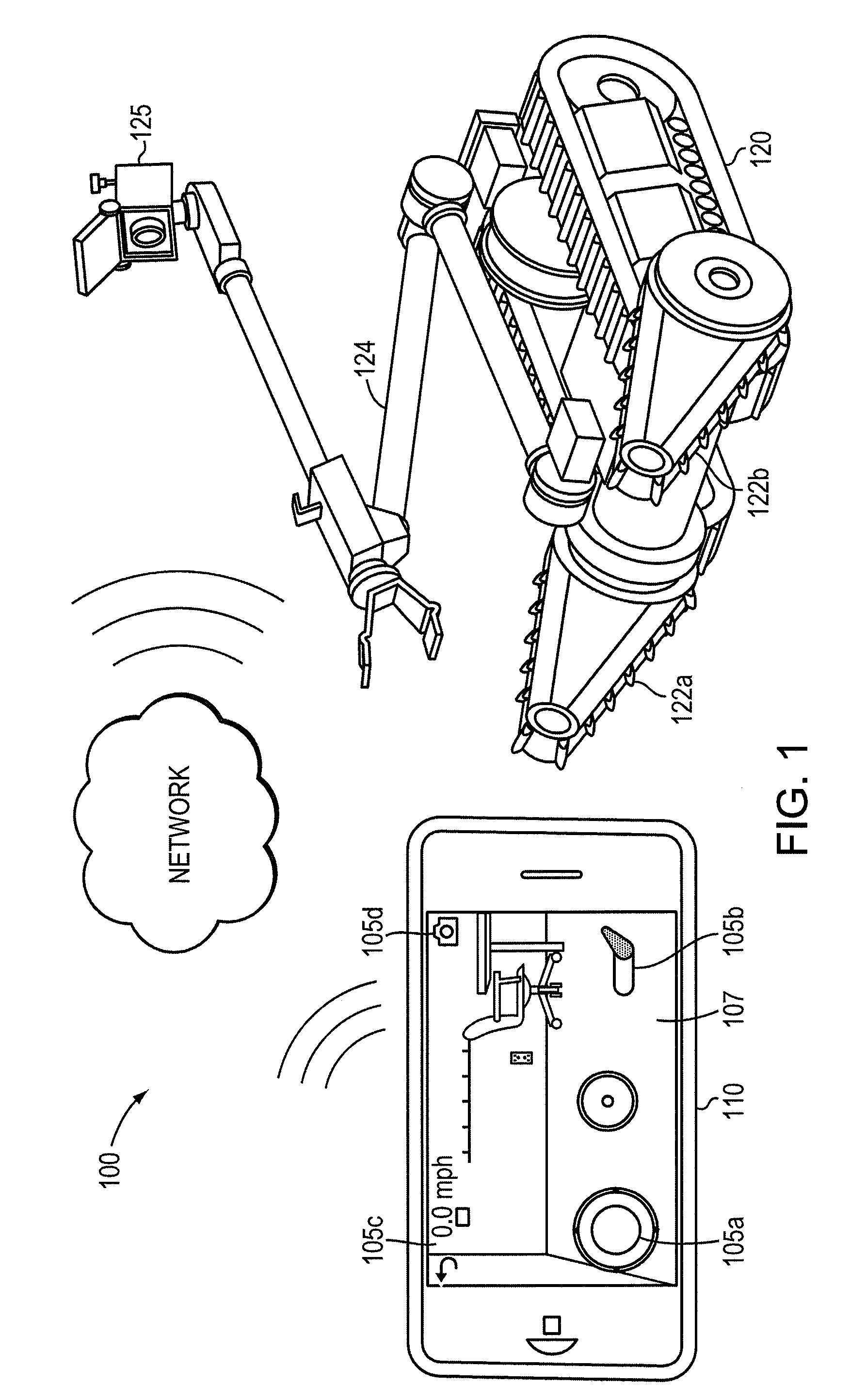
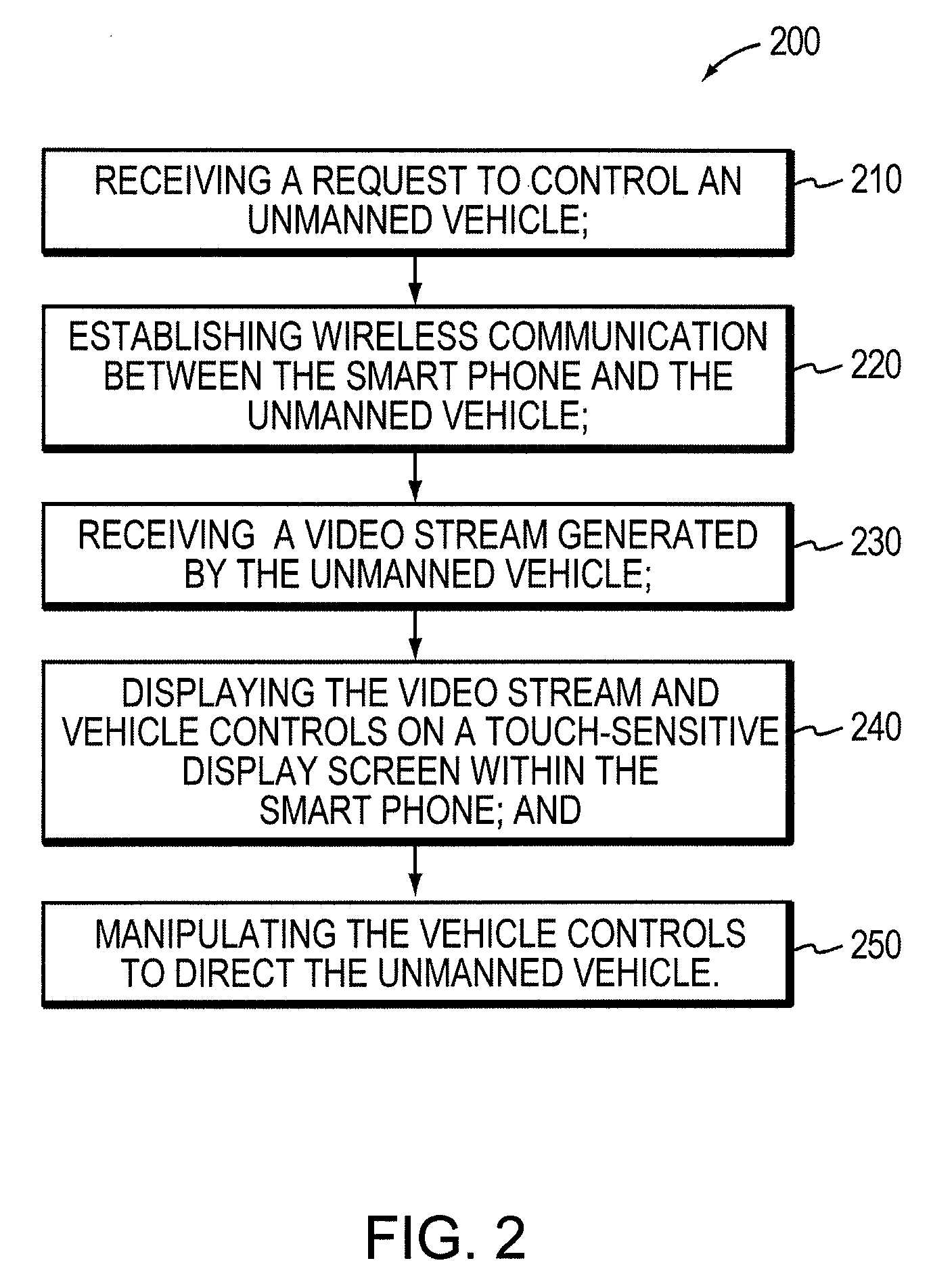
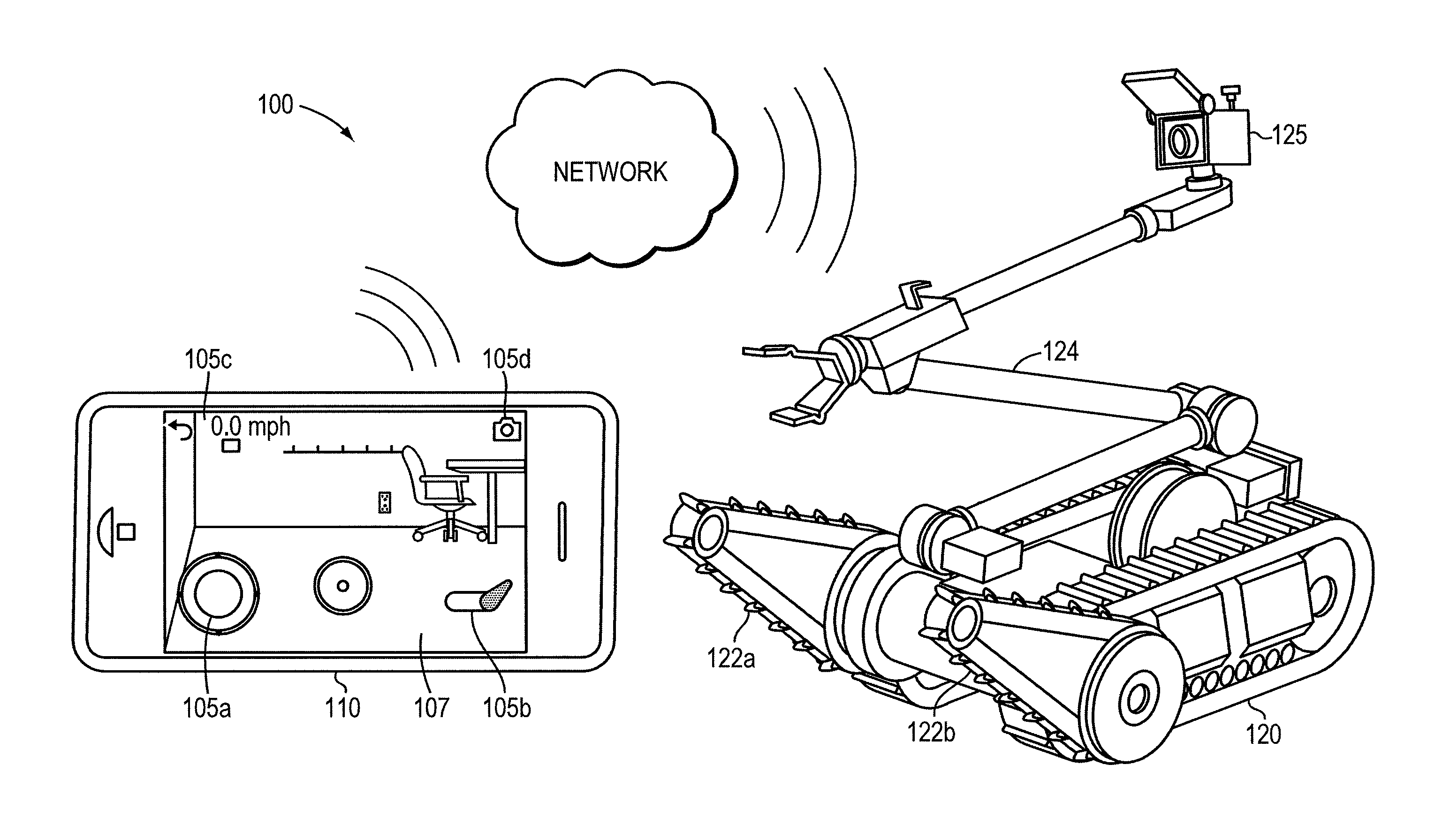
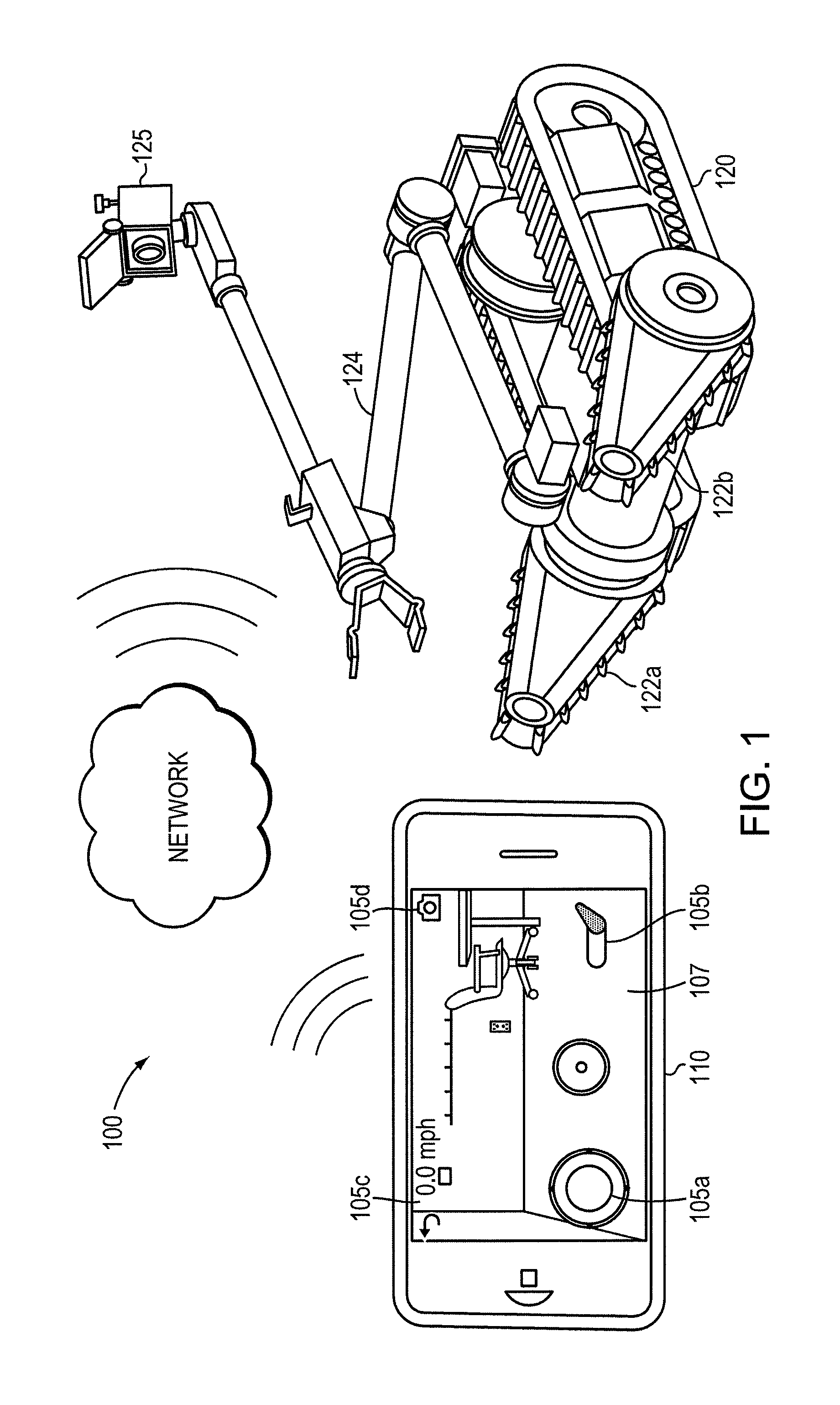
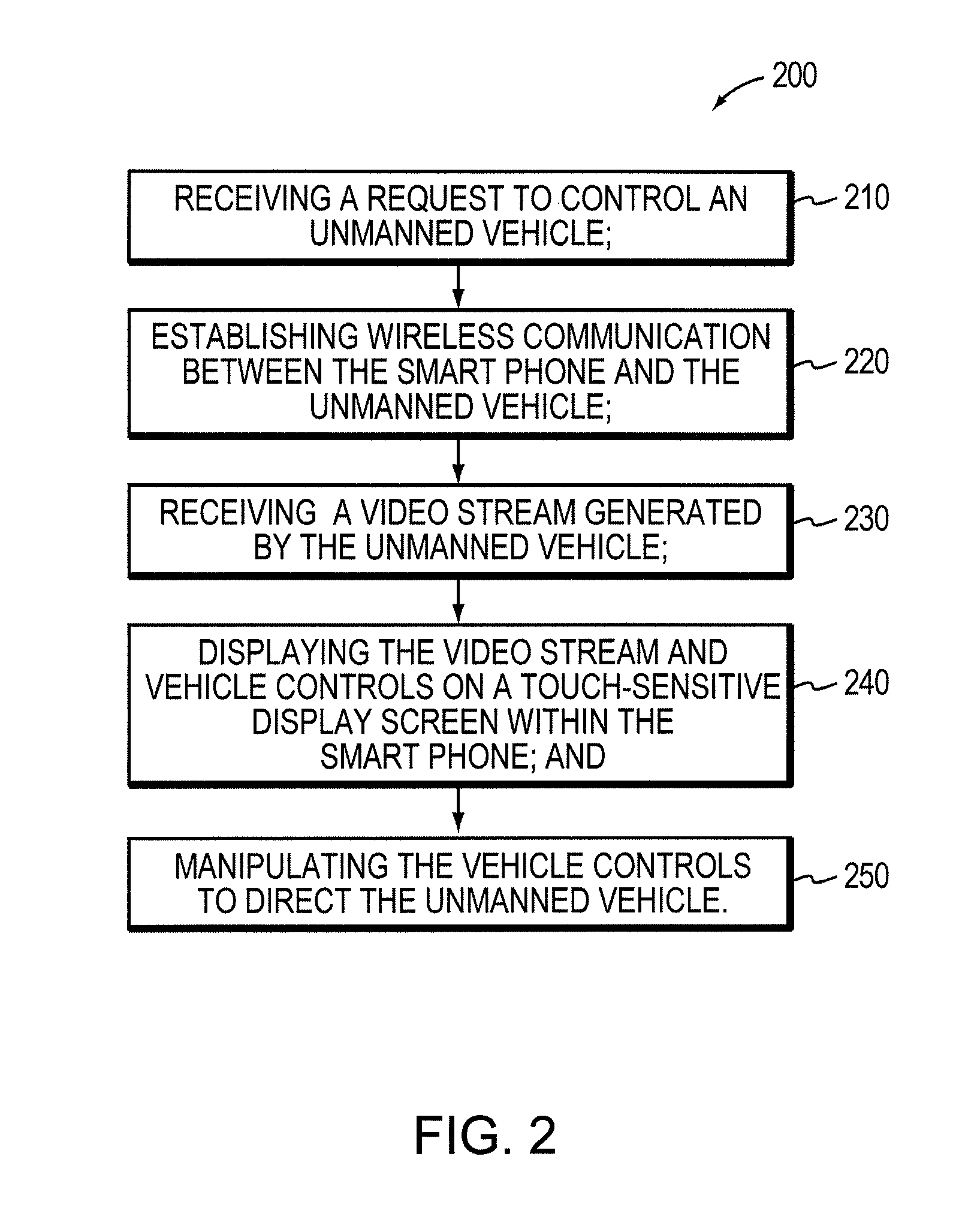
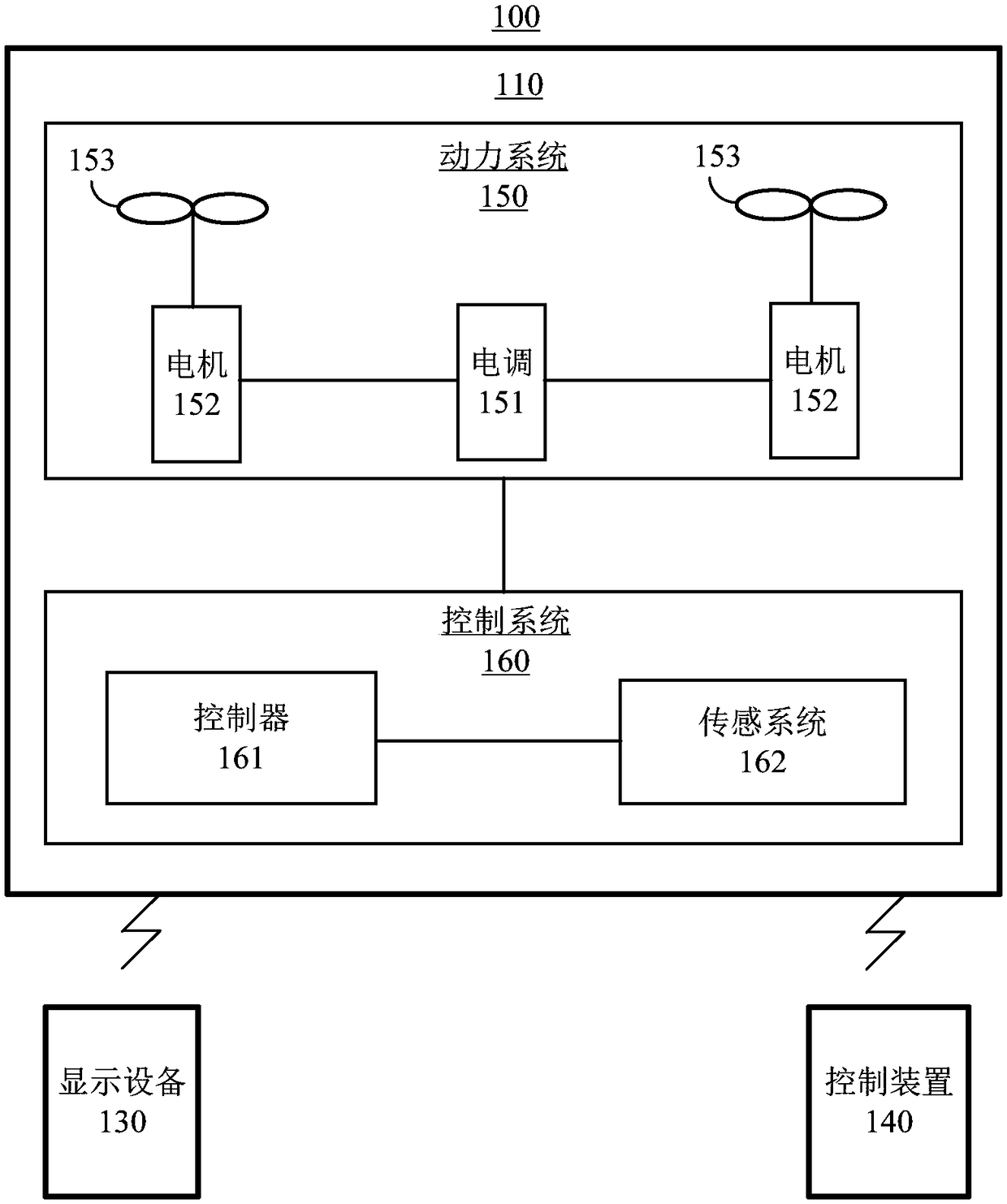
Teleoperation of Unmanned Ground Vehicle
ActiveUS20120191269A1Reduce operating errorsReduce errorsDigital data processing detailsRobotComputer scienceTeleoperation
Described are systems and methods, including computer program products for controlling an unmanned vehicle. A user controls one or more unmanned vehicles with a smart phone. The smart phone receives video stream from the unmanned vehicles, and the smart phone displays the controls from the unmanned vehicle over the video. The smart phone and the unmanned vehicle communicate wirelessly.
Owner:REMOTE IMAGING SOLUTIONS LLC
Collaborative engagement for target identification and tracking
ActiveUS8244469B2Facilitates control of and communication and exchangePromote collaborationProgramme-controlled manipulatorAnalogue computers for vehiclesGoal recognitionData exchange
A collaborative engagement system comprises: at least two unmanned vehicles comprising an unmanned air vehicle including sensors configured to locate a target and an unmanned ground vehicle including sensors configured to locate and track a target; and a controller facilitating control of, and communication and exchange of data to and among the unmanned vehicles, the controller facilitating data exchange via a common protocol. The collaborative engagement system controls the unmanned vehicles to maintain line-of-sight between a predetermined target and at least one of the unmanned vehicles.
Owner:AEROVIRONMENT INC +2
Transforming unmanned aerial-to-ground vehicle
InactiveUS20100193626A1Rapid deploymentConvertible aircraftsLaunching/towing gearUncrewed vehicleEngineering
A transforming unmanned aerial-to-ground vehicle assembly comprising: an aerodynamic flying assembly comprising an unmanned aerial vehicle integrated with an unmanned ground vehicle, a power unit shared by the unmanned aerial vehicle and the unmanned ground vehicle, vehicle controls shared by the unmanned aerial vehicle and the unmanned ground vehicle, a disengagement mechanism to separate the unmanned ground vehicle from the unmanned aerial vehicle, one or more manipulator arms located on either the unmanned aerial vehicle or the unmanned ground vehicle, and landing gear.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Teleoperation of unmanned ground vehicle
ActiveUS8918230B2Reduce errorsAnalogue computers for trafficComputer controlTeleoperationUser control
Owner:REMOTE IMAGING SOLUTIONS LLC
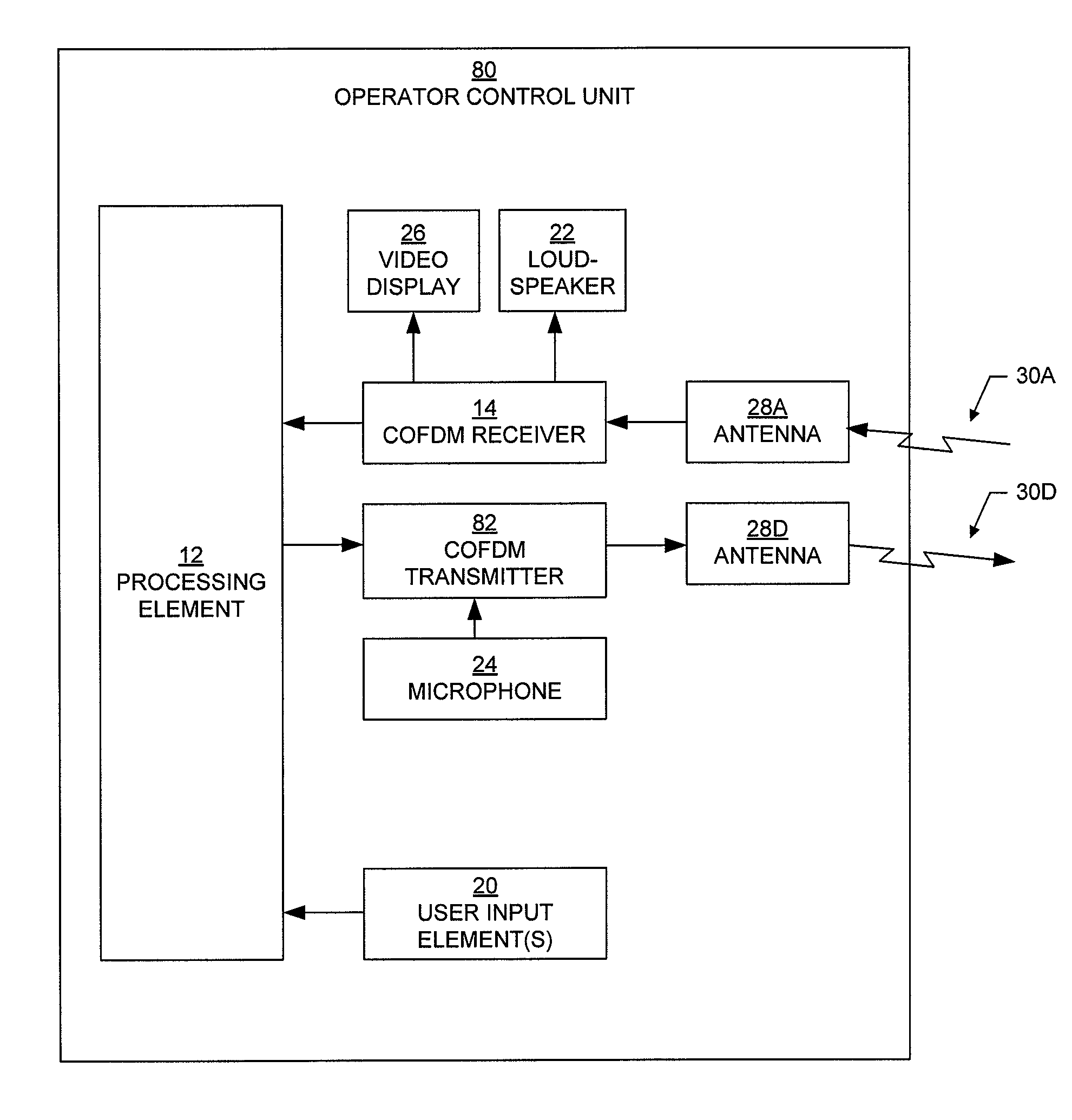
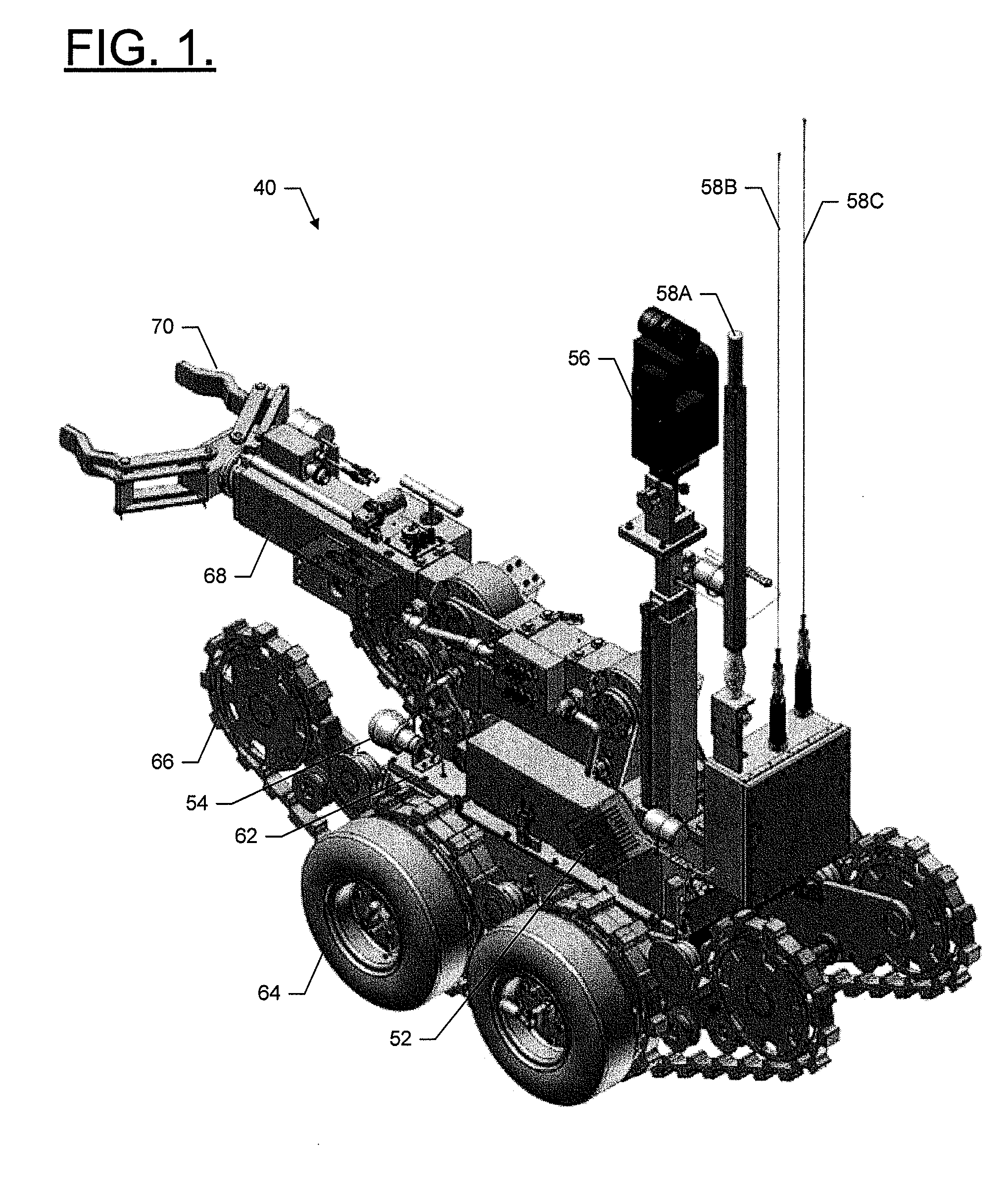
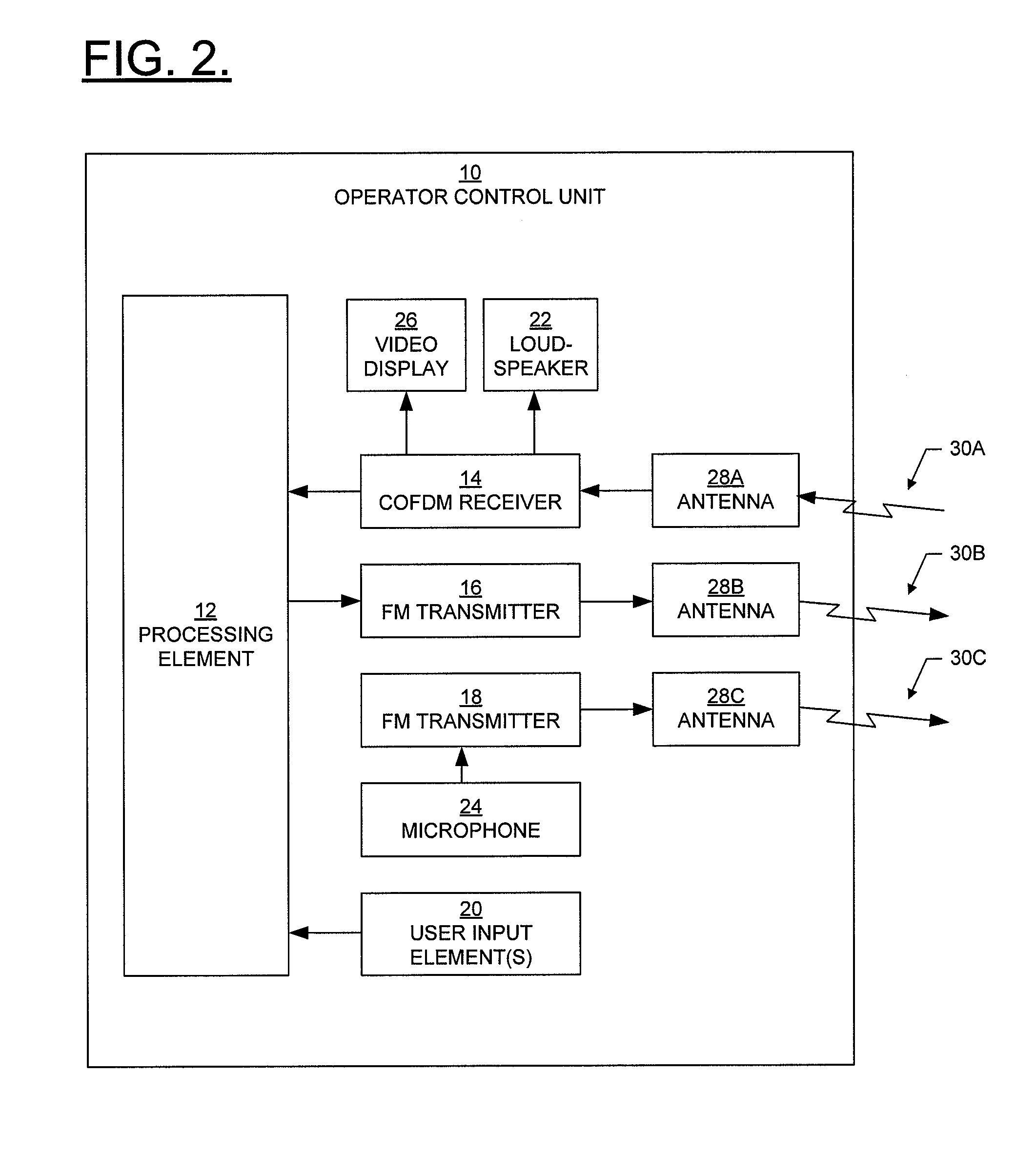
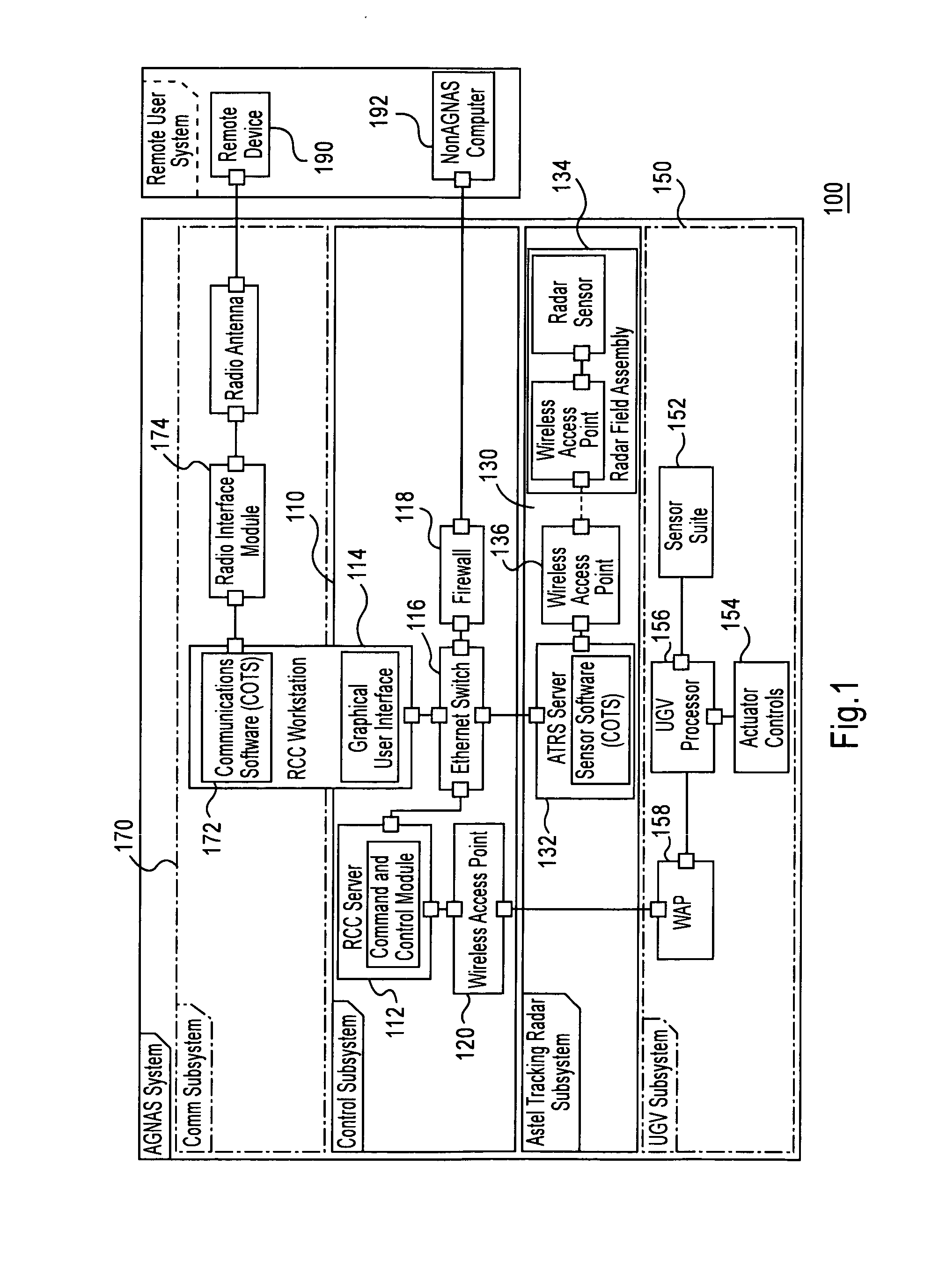
Wireless control system for ground-mobile robotic vehicles
A wireless control system for ground-mobile robotic systems in which communication between the operator control unit and the unmanned ground vehicle is transmitted via a plurality of spectrally efficient simplex communication links.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
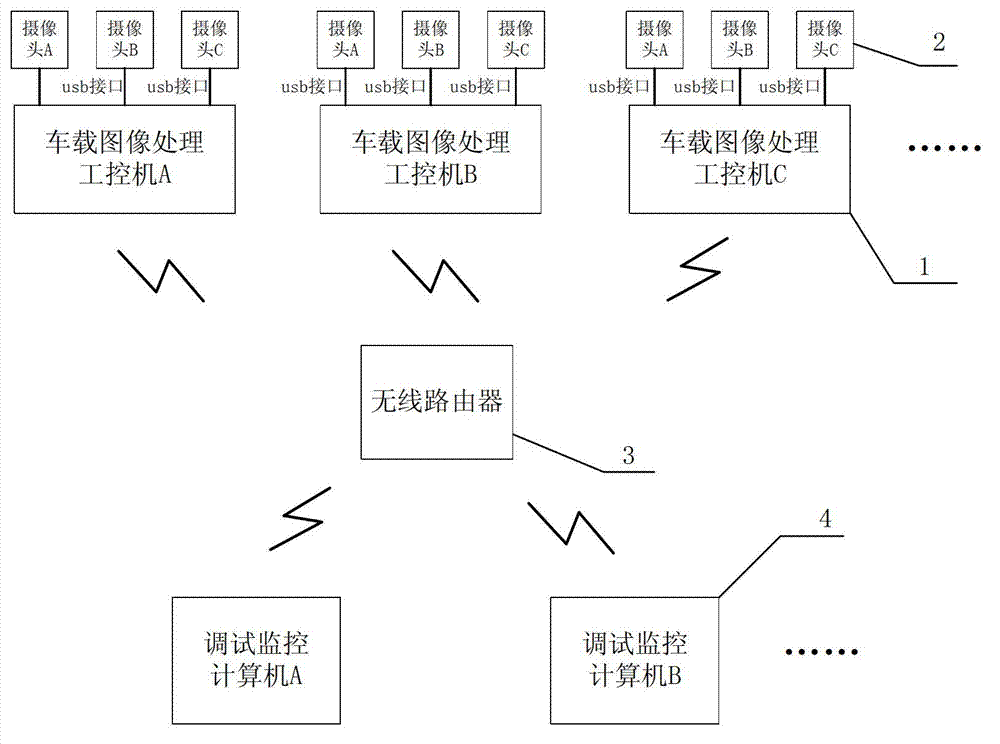
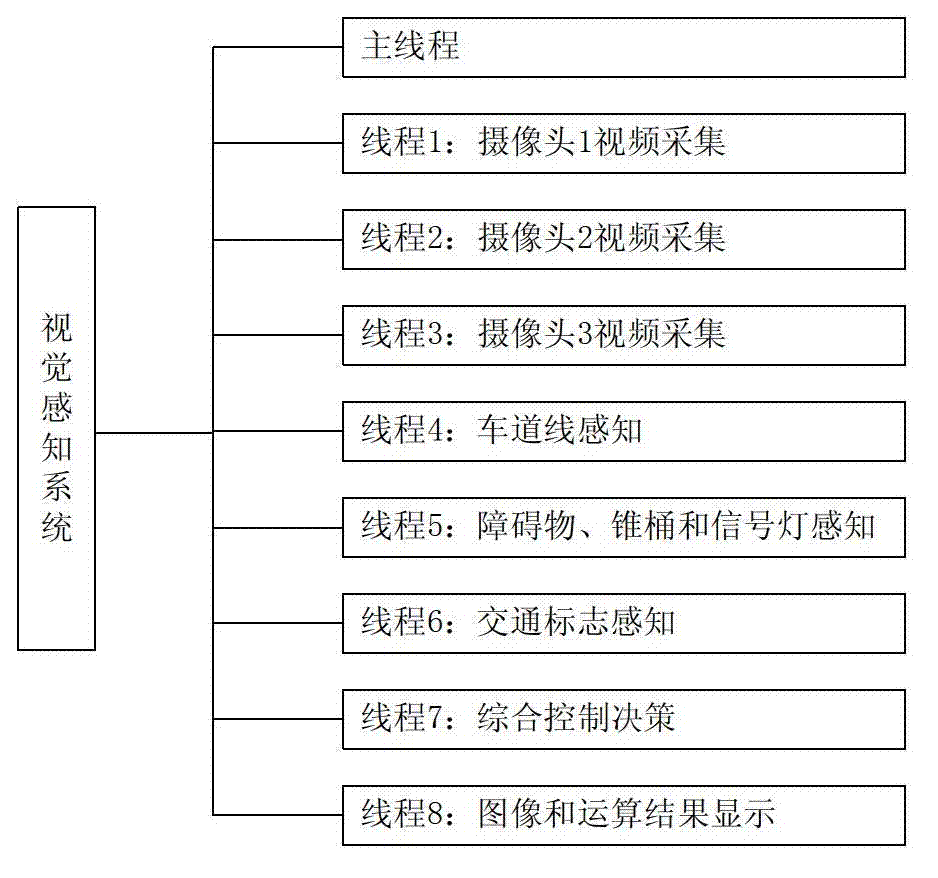
Multi-camera visual perception system for UGV (Unmanned Ground Vehicle)
ActiveCN102819263AImprove real-time performanceImprove stabilityPosition/course control in two dimensionsExtensibilityMulti camera
The invention belongs to the technical field of autonomous running and visual perception, particularly relates to a multi-camera visual perception system for a UGV (Unmanned Ground Vehicle) and aims to solve the problems of single perception algorithm, poor real-time performance, poor system expandability, inconvenience in debugging, limitation to the view field control and the like of an image processing system of the existing UGV and autonomous mobile robot. The system comprises a plurality of vehicle-mounted image processing industrial personal computers and one or a plurality of debugging monitoring computers, wherein each vehicle-mounted image processing industrial personal computer is connected with three cameras; one or a plurality of debugging monitoring computers are used for controlling the vehicle-mounted image processing industrial personal computers by a wireless router; and a control mode can be a redundancy control mode and also can be a respective control mode. In the system, an optimized visual perception method on the basis of multiple threads is adopted; and threads comprise a multi-camera video acquisition thread, a lane line perception thread, a barrier, cone bucket and signal lamp perception thread and the like. Compared with a conventional single-thread visual perception method, the optimized visual perception method on the basis of the multiple threads has higher real-time performance, stability and expandability.
Owner:NO 8357 RES INST OF THE THIRD ACADEMY OF CHINA AEROSPACE SCI & IND
Unmanned aircraft and unmanned ground vehicle teaming for remote infrastructure inspection
InactiveUS20170073071A1Aircraft componentsRemote controlled aircraftUnmanned spacecraftUnmanned ground vehicle
Infrastructure is remotely inspected using a sensor pod such as an unmanned ground vehicle and sensors adapted to inspect a surface of the infrastructure and an unmanned aircraft adapted to interoperate with the sensor pod. The sensor pod drives along the surface of the infrastructure being inspected. A tether to the unmanned aircraft deploys and retrieves the sensor pod on the surface of the infrastructure. Electronic sensors of the sensor pod are deployable in a crevice of the surface of the infrastructure obstructed from view by the unmanned aircraft. The unmanned aircraft can comprise a radio repeater adapted to relay ground commands to the sensor pod.
Owner:GUIDED SYST TECH
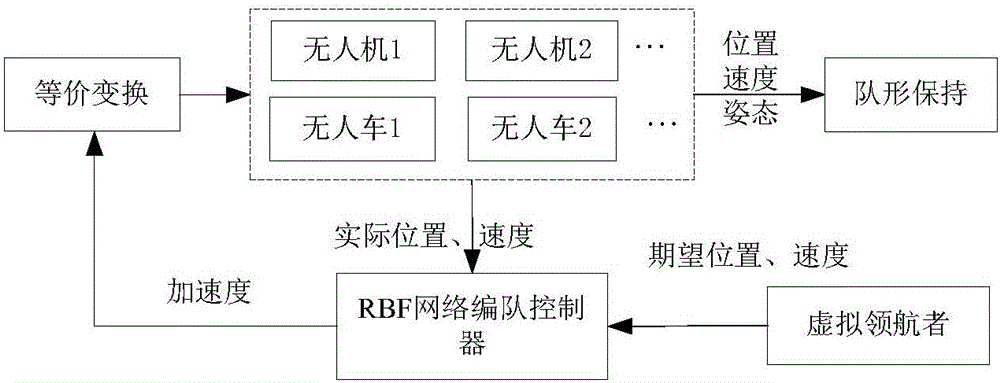
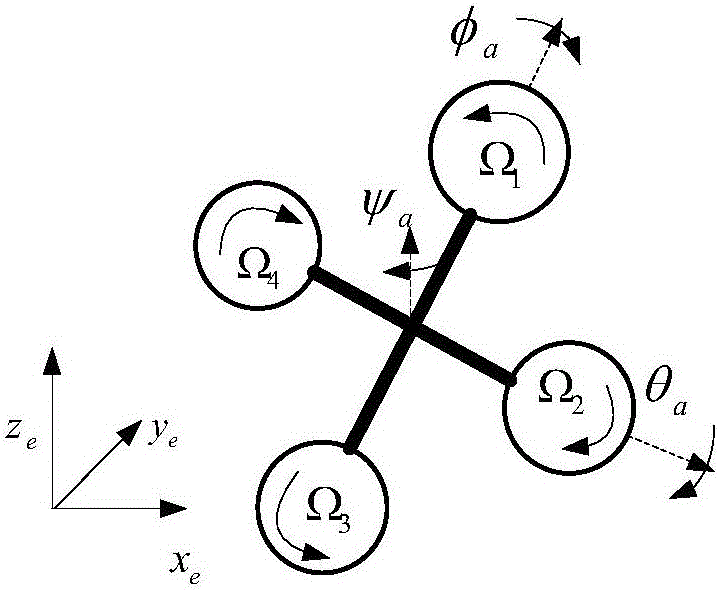
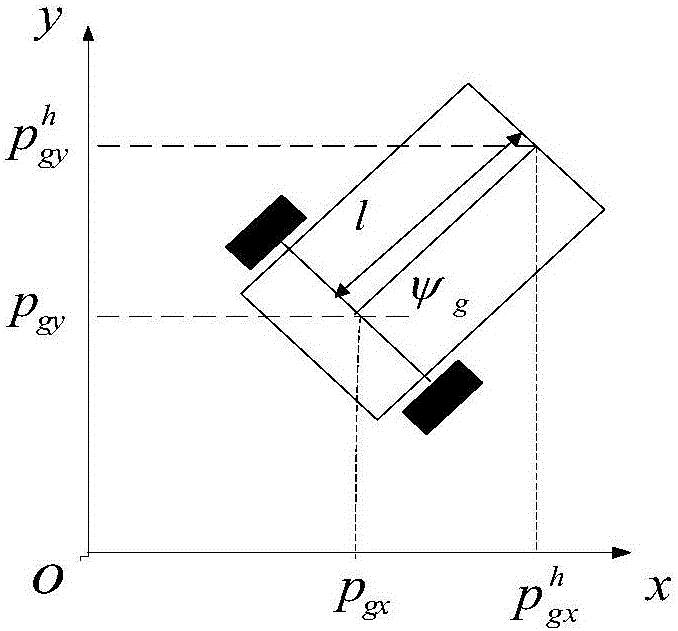
Unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV)-unmanned ground vehicle (UGV) combined formation cooperative control method
ActiveCN106054922ATracking error zeroStable and reliable formation structurePosition/course control in three dimensionsControl objectiveControl signal
The invention discloses an unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV)-unmanned ground vehicle (UGV) combined formation cooperative control method, comprising the following steps: step 1, establishing nonlinear dynamical models of unmanned vehicles in UAV-UGV combined formation; step 2, processing the nonlinear dynamical models of a UAV and a UGV via equivalent transformation, and taking acceleration as a common control target quantity, obtaining a unified control model taking acceleration as a control input in the combined formation; step 3, establishing a ground-air combined formation structure based on a virtual pilot to obtain a stable control signal for the UAV-UGV combined formation and obtain an error model of the combined formation, wherein the control signal is acceleration obtained in step 2 as a common control target quantity; and step 4, designing a UAV-UGV combined formation controller by adopting a RBF (Radial Basis Function) network algorithm according to the control model, the error model and the acceleration serving as a control signal and a control target quantity at the same time, so that the combined formation is stable and reliable.
Owner:汇佳网(天津)科技有限公司
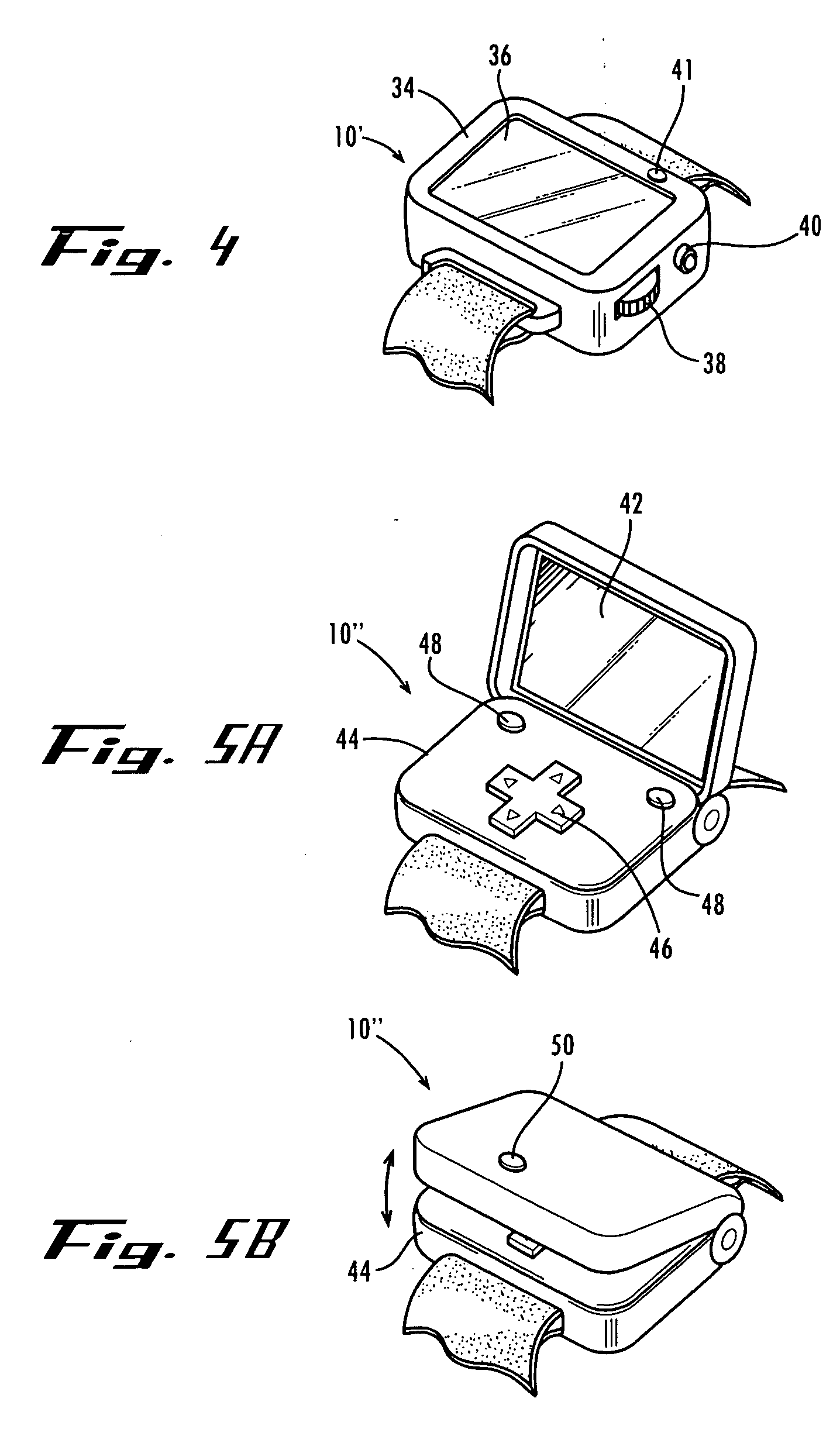
Wrist-attached display system for unmanned vehicle imagery and communication
InactiveUS20060197835A1Color television detailsClosed circuit television systemsDisplay deviceDigital imagery
A display system includes a wristwatch-sized device that a user, such as a soldier on a battlefield, can wear, a data receiver, and a small video display. The device can receive data, such as video or still digital imagery captured by an unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) in flight or unmanned ground vehicle, and display it in real-time for the user to view.
Owner:L 3 COMM CORP
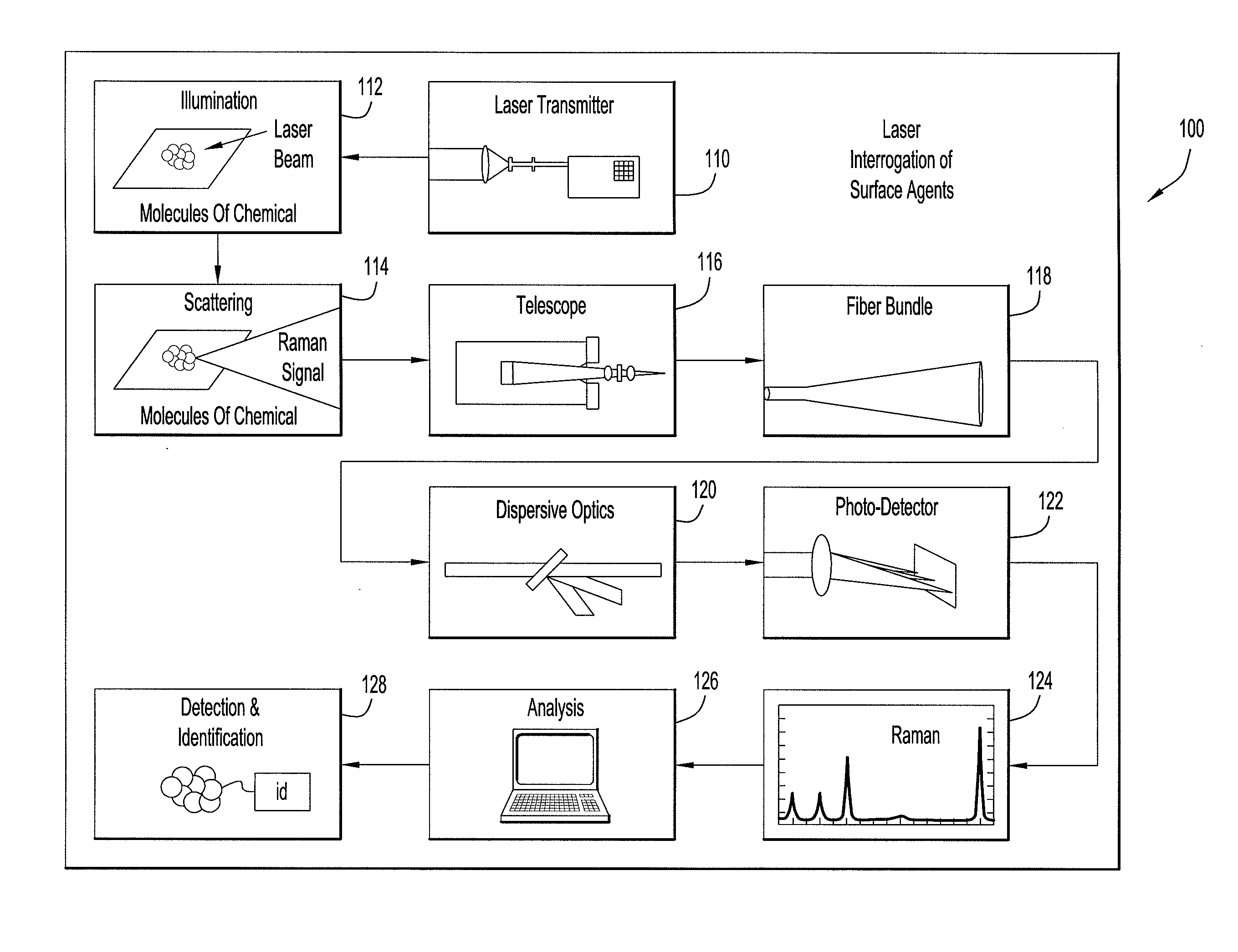
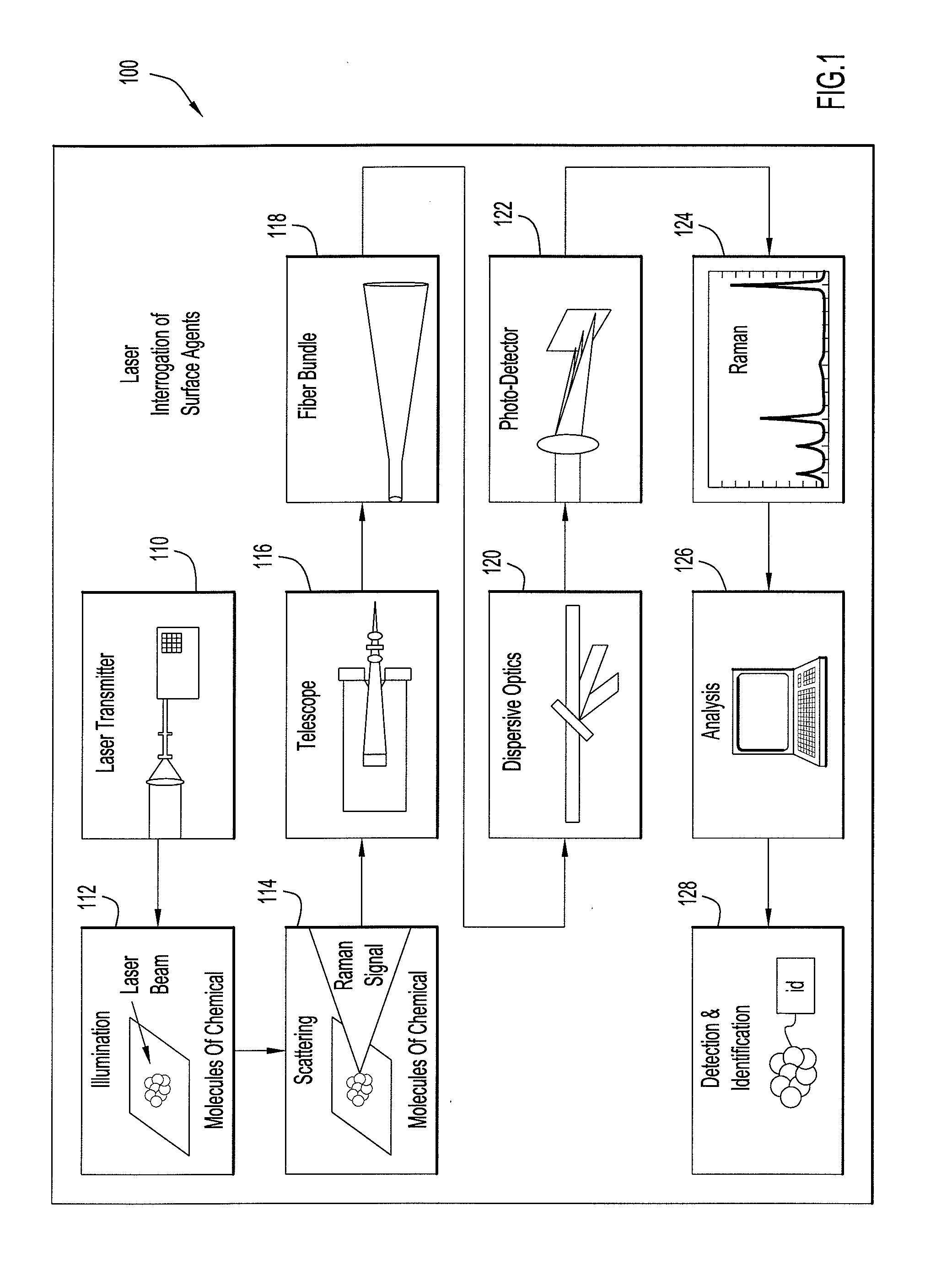
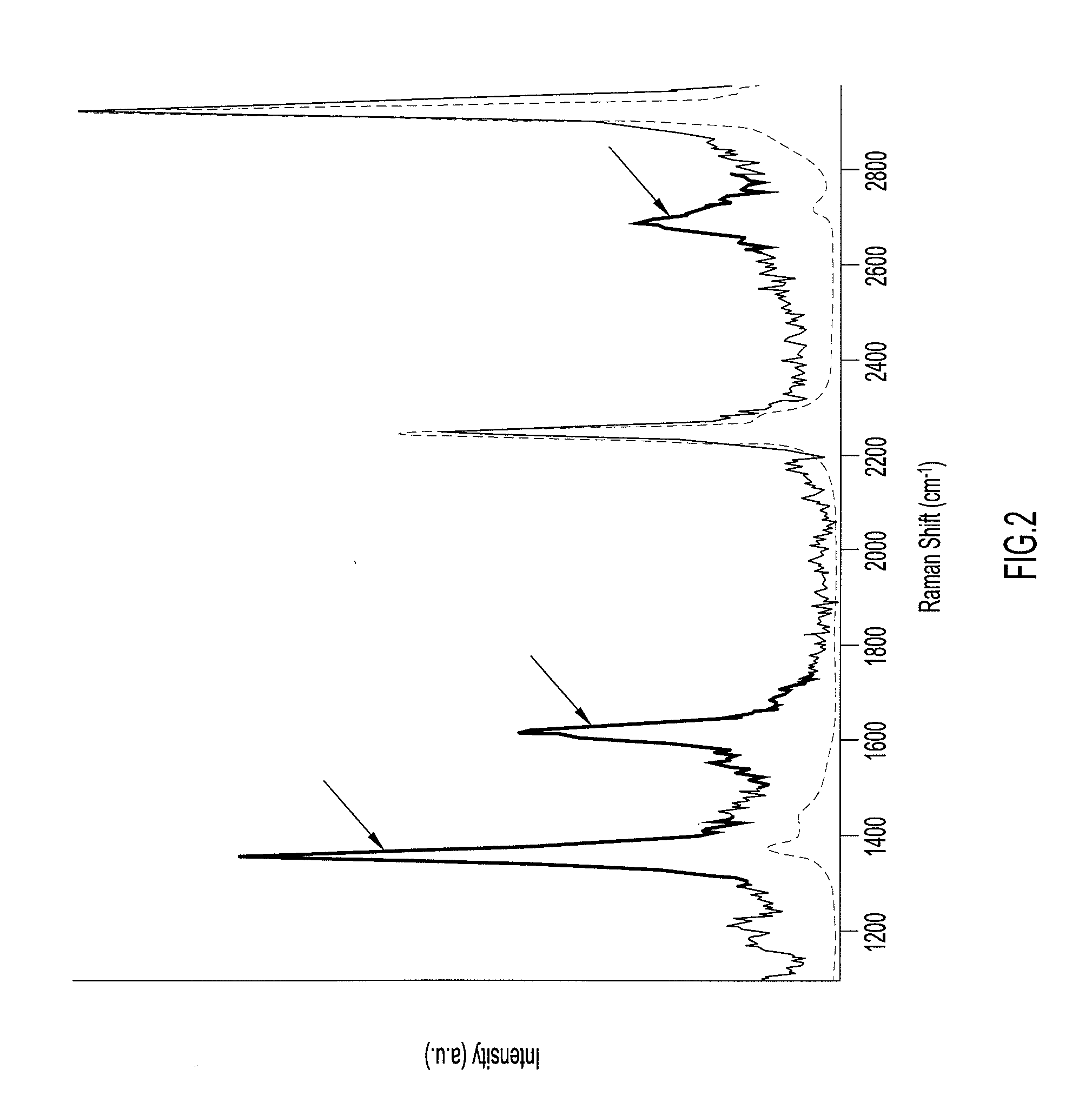
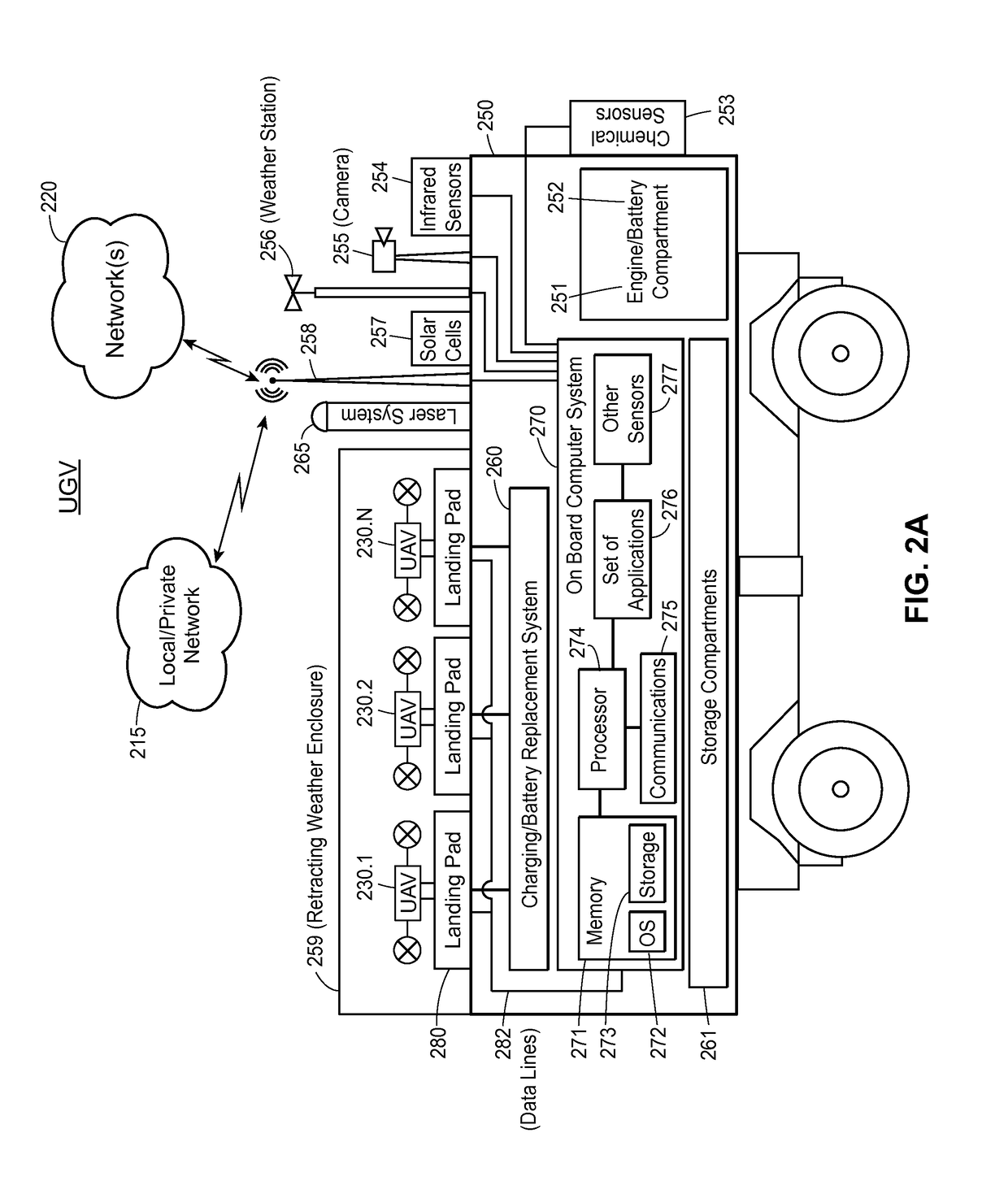
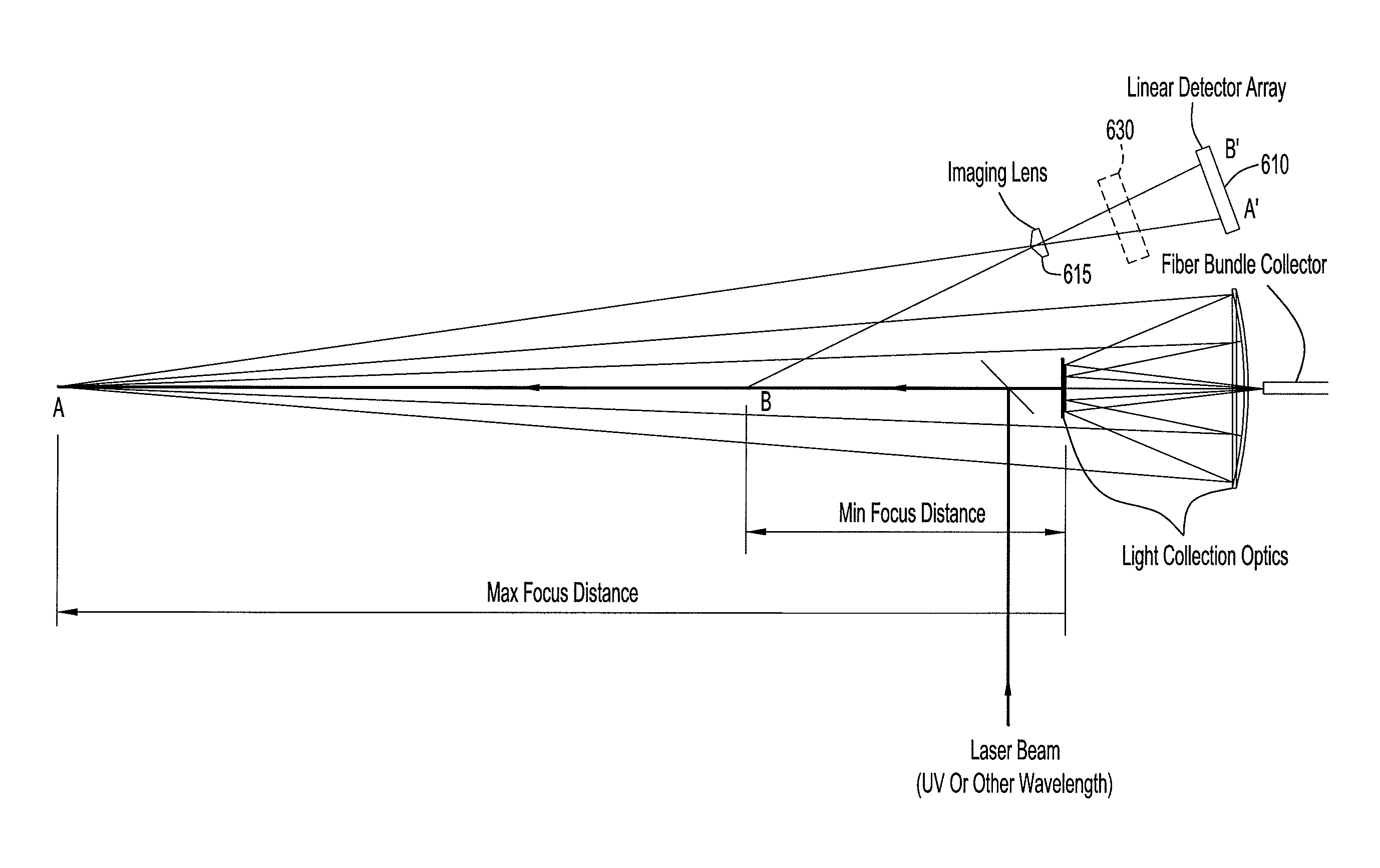
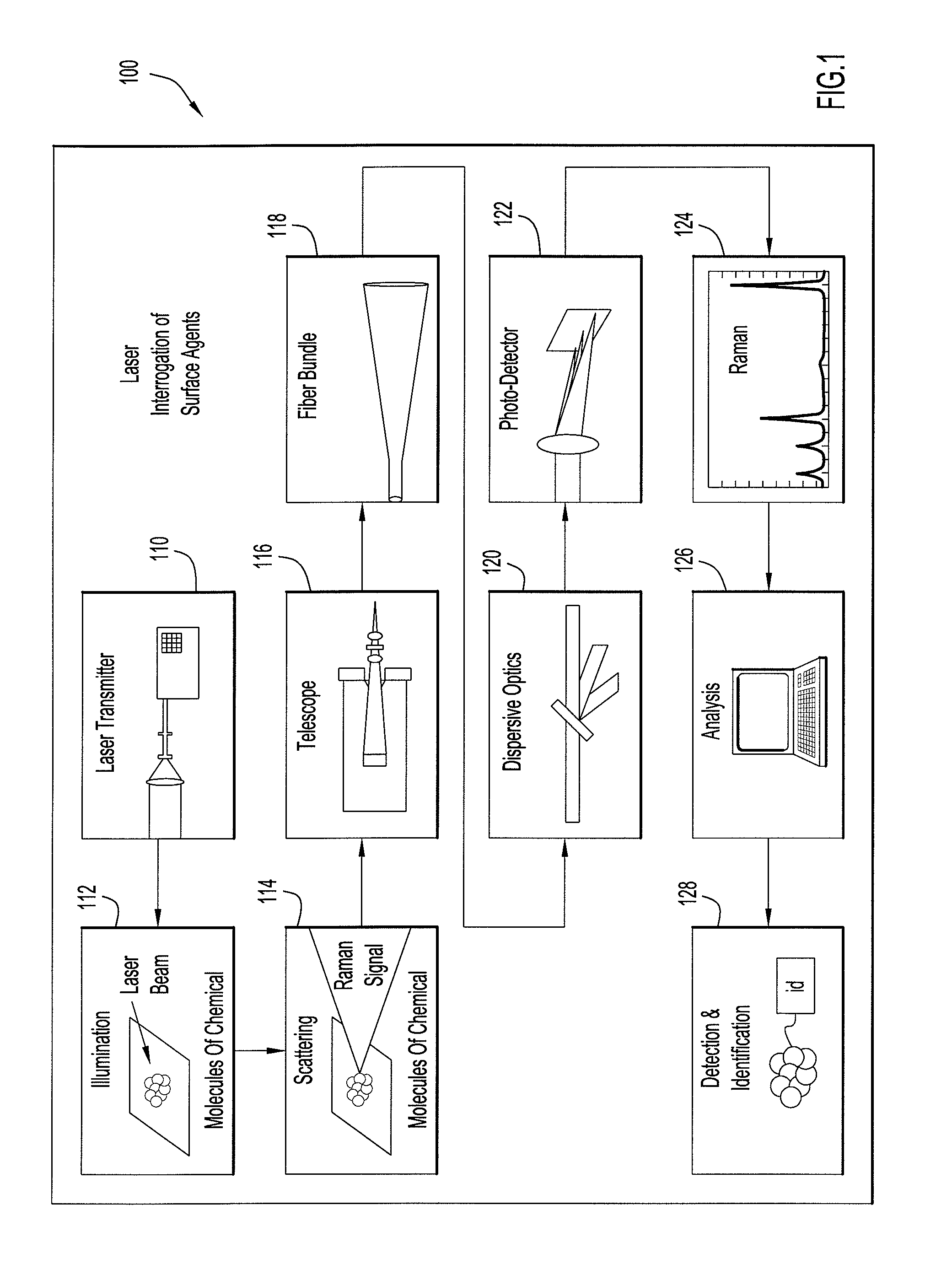
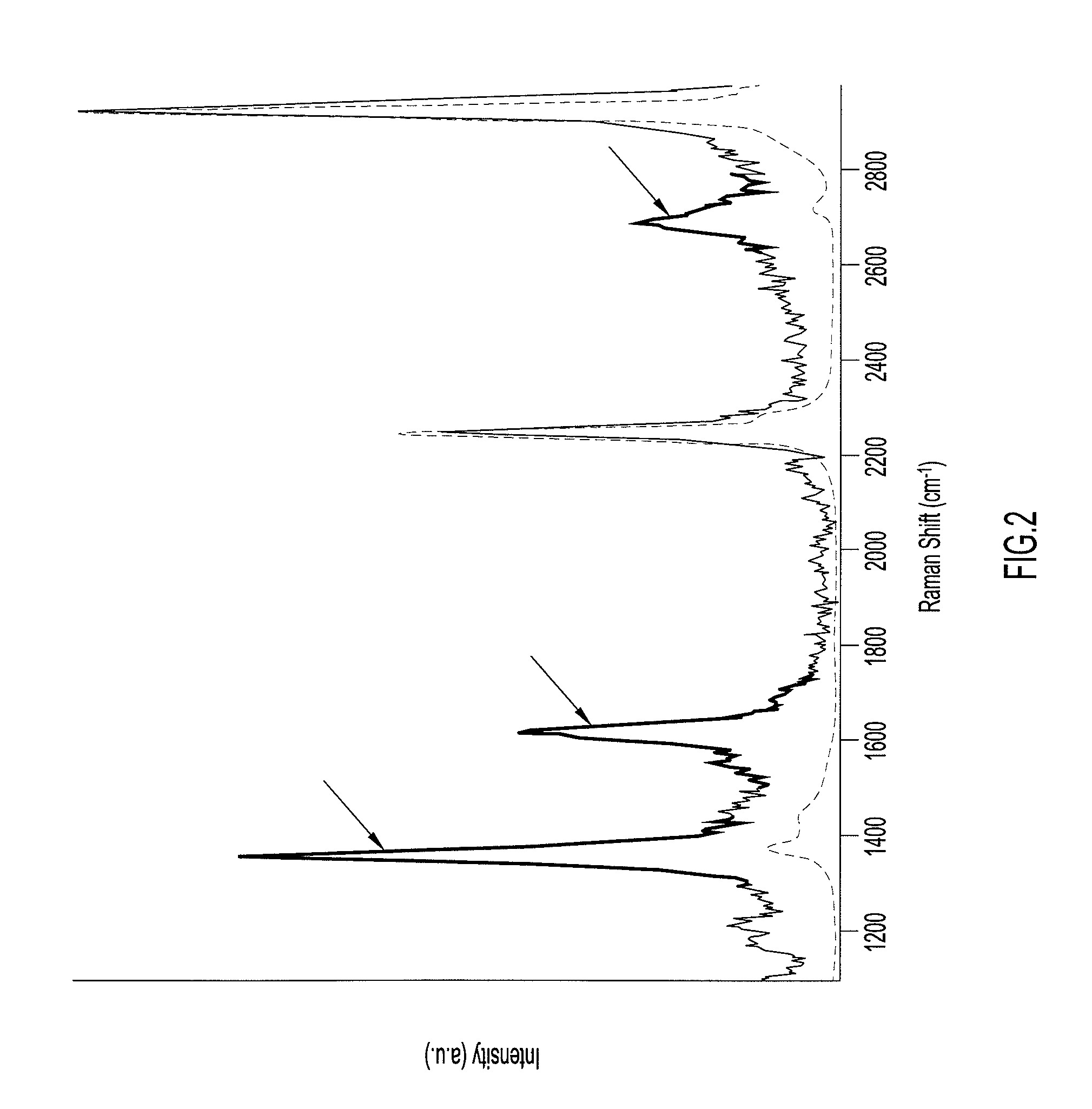
Systems and Methods For Remote Unmanned Raman Spectroscopy
ActiveUS20100277723A1Dangerous substanceEasy to operateRadiation pyrometryRaman scatteringAutomatic controlDisplay device
A Raman spectroscopy sensor integrated with an unmanned ground vehicle (UGV) includes a UGV having a robot arm and a camera mounted on the robot arm. A laser and telescope associated with a Raman sensor are mounted on the robot arm in such a way as to point in substantially the same direction in which the camera is pointed. A Raman spectral data acquisition and control module is mounted on the UGV and is configured to receive Raman spectral data from the telescope. A remote base station having a display and a data processing and analysis module is configured to receive data from the data acquisition and control module and to display for an operator images from the camera and information related to the Raman sensor. An autofocus system is preferably employed to automatically control telescope focus and thereby enable the Raman sensor to operate over a wide range, e.g., 0.5 m to 10 m.
Owner:PERATON INC
Unmanned ground vehicle real-time track planning method based on speed impediment
InactiveCN104933228AEfficient Trajectory PlanningHigh precisionSpecial data processing applicationsMobile searchSimulation
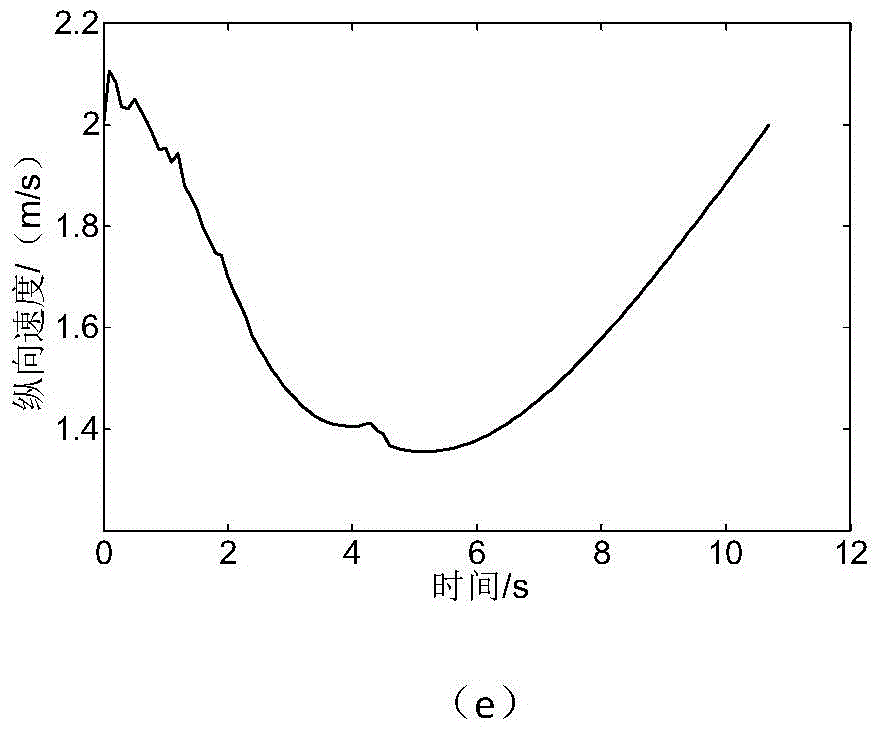
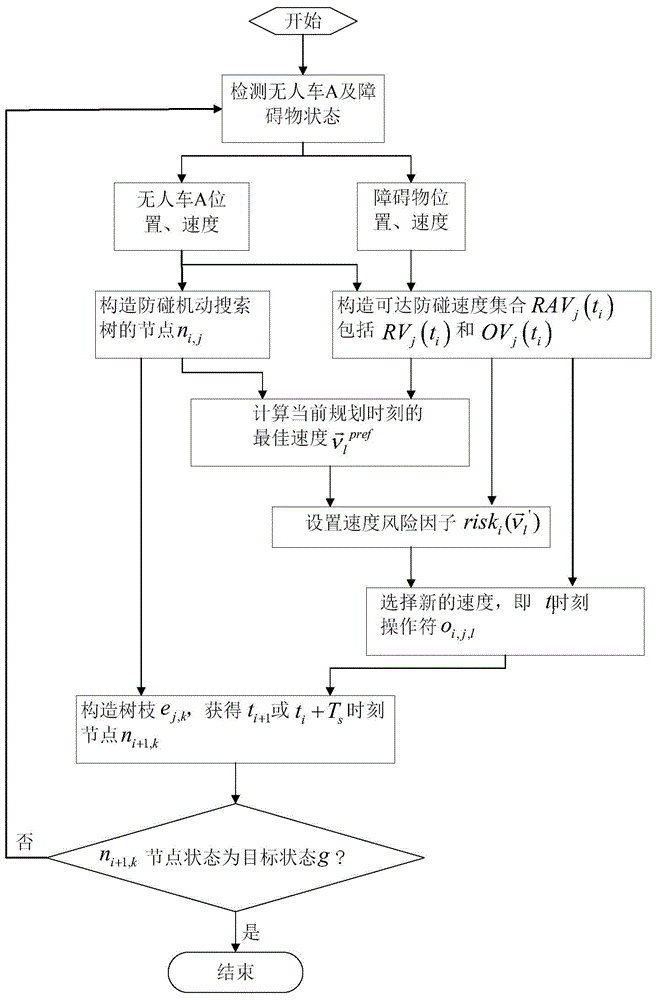
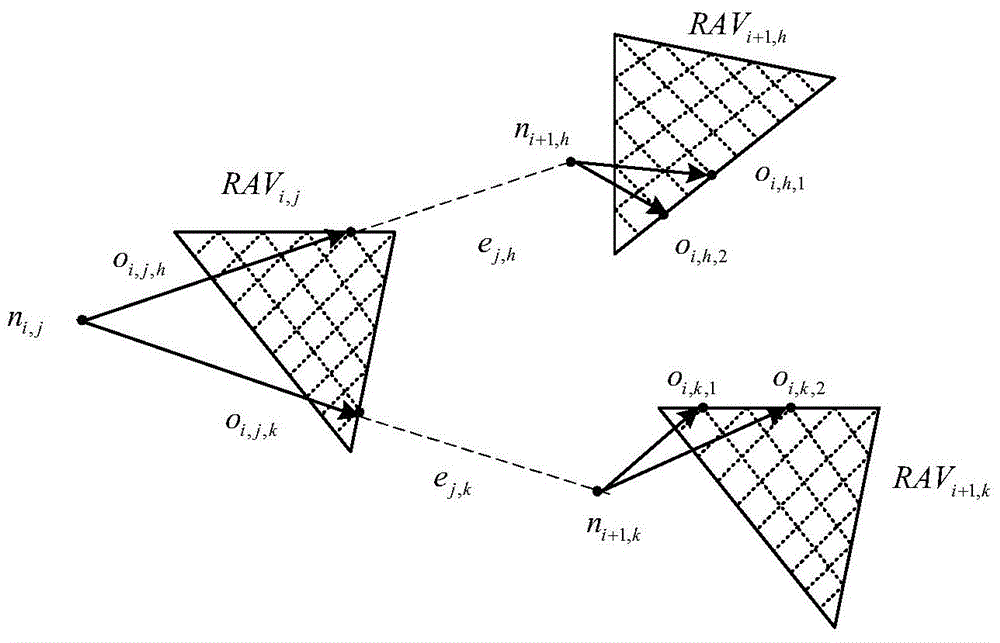
The invention discloses an unmanned ground vehicle real-time track planning method based on a speed impediment. The method comprises the following steps of: 1, constructing a node n<i, j> of an anti-collision mobile search tree on the basis of the current position of an unmanned ground vehicle A; 2, constructing a reachable anti-collision speed set RAV<j>(t) of the unmanned ground vehicle A on the basis of the speed of the unmanned ground vehicle A and the speed of an obstacle; 3, calculating the optimum speed (defined as in the description) of the current planning moment through a cubic polynomial smooth controllable unit; 4, setting a speed risk factor (defined as in the description); 5, selecting a new speed, i.e., an operational character o<i, j, l> at the moment t, on the basis of the reachable speed set RAV<j>(t) and the speed risk factor; 6, constructing a branch e<j, k> on the basis of the node n<i, j> and the operational character o<i, j, l>, and obtaining a node n<i+1, k> at the moment t<i+1> or the moment t+T<S>; and 7, if the n<1+i, k> node state is in a minimum neighborhood of the target state g, completing the algorithm, and otherwise, returning to the first step for cyclic calculation. The method provided by the invention is applicable to real-time track planning under various mobile conditions such as unmanned ground vehicle lane change, crossing turning and obstacle avoiding; the real-time performance and the high precision of the planning can be ensured under the condition of existence of a plurality of dynamic obstacles; and the requirements of the planning speed and the track smoothness can be met to the maximum degree.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Systems and methods for remote data collection using unmanned vehicles
ActiveUS9894327B1Television system detailsUnmanned aerial vehiclesUncrewed vehicleEnvironmental data
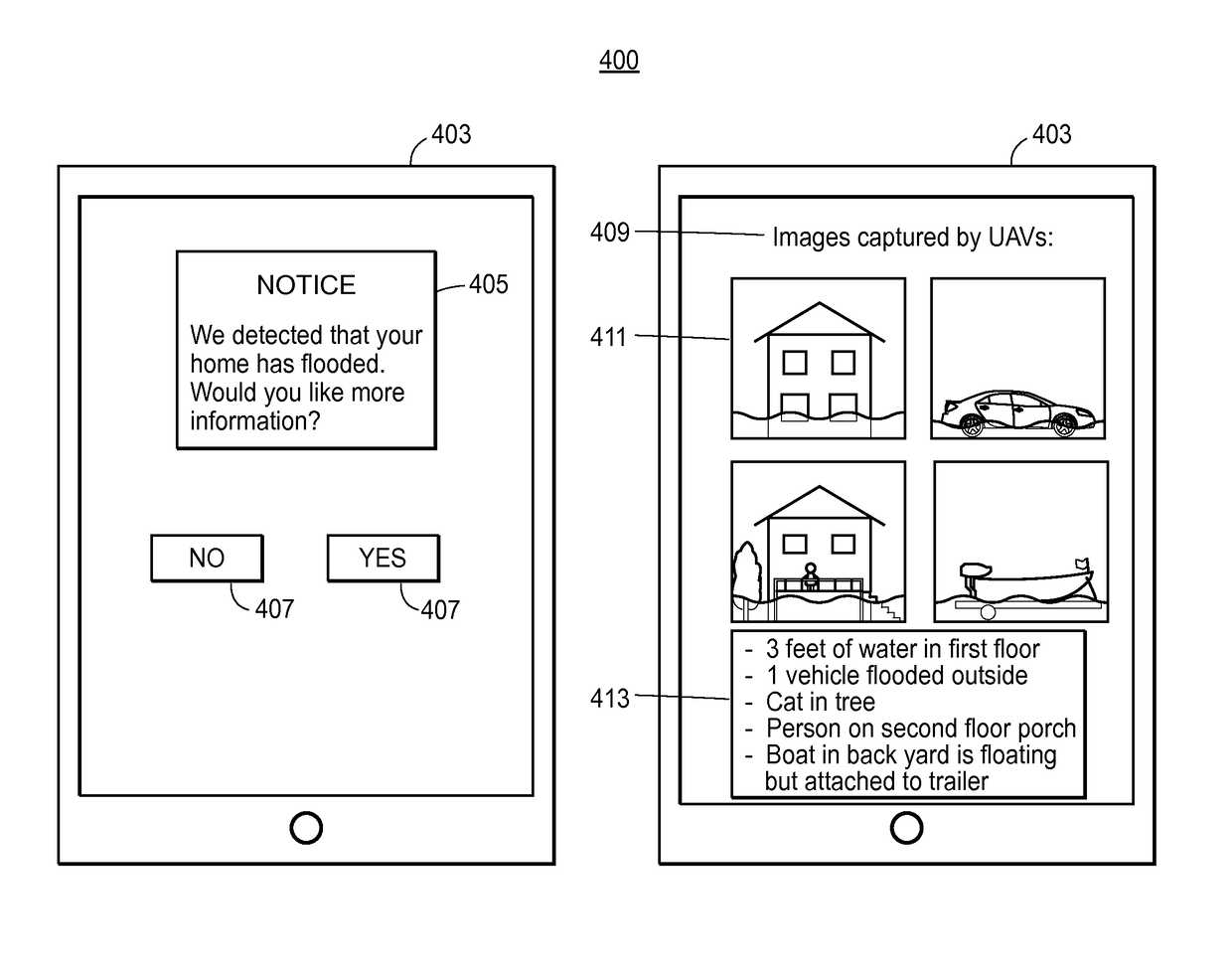
Systems and methods for using unassisted vehicles to assess damage in a particular location are described. According to certain aspects, the systems and methods may utilize an unmanned ground vehicle (UGV) and a plurality of unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs). The UGV and the UAVs may be configured with various sensors to capture various damage or environmental data. The UGV and / or the UAVs may also transmit captured data to a central facility for processing. The UGV may serve as a mobile docking and recharging platform for the UAVs and may therefore extend the range and endurance of the UAVs. The UGV may be configured for remote operation, thus eliminating the need to send personnel into a potentially dangerous environment.
Owner:STATE FARM MUTUAL AUTOMOBILE INSURANCE
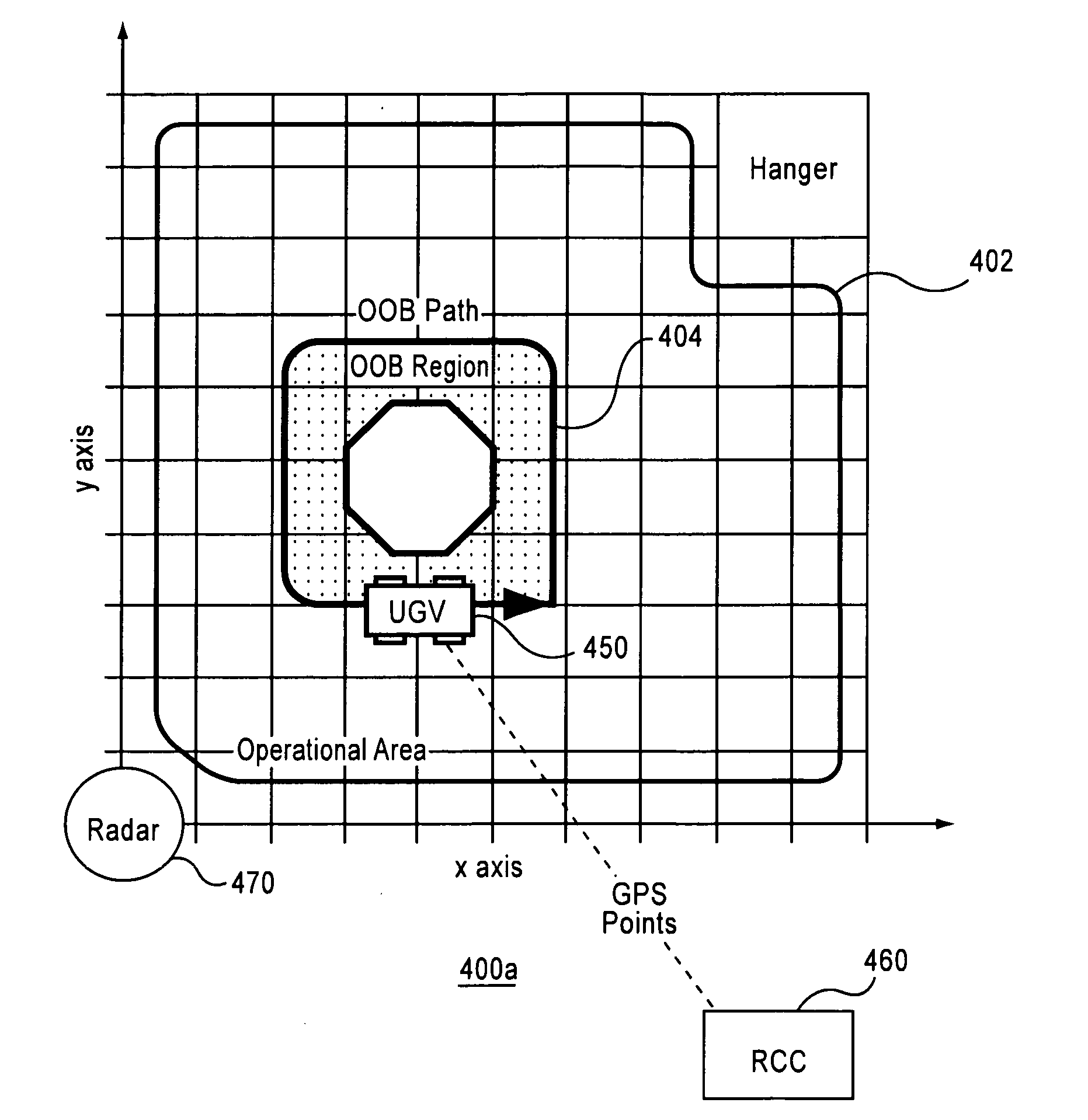
Aviation ground navigation system
InactiveUS20110015816A1Enhances aviation operationImprove efficiencyNavigational calculation instrumentsVehicle position/course/altitude controlAviationRadar
Transporting aircraft within an airport operational area. An airport operational area within which an unmanned ground vehicle is configured to selectively tow aircraft is defined. A ground tracking system provides position data signals to determine the position of the unmanned ground vehicle position relative to positions in at least one operational area path contained in the airport operational area. This positioning is supplemented by the position as determined from an electronic tracking system, such as a radar-based system. The unmanned ground vehicle is then selectively guided to engage and tow the aircraft to a selected position within the airport operational area.
Owner:MOUNTAINTOP TECH
Transfer station for transferring containers between unmanned aerial vehicles and unmanned ground vehicle
ActiveUS9975651B1Unmanned aerial vehiclesFreight handling installationsInterior spaceTransfer system
A transfer station includes a housing defining an inner space, and having a front passage for passage of a UGV and a top passage for passage of a container. One or more funnels are provided at the top passage for guiding the passage of containers therethrough, and an actuator system is provided for, selectively, engaging a container with a UAV suspension system and disengaging a container from a UAV suspension system. Also provided is a transfer system that is inclusive of the transfer station, a UAV, a UGV, and a reusable container; and methods of transferring reusable containers between UAVs and UGVs.
Owner:ECK BRANDON +1
Systems and methods for remote unmanned raman spectroscopy
ActiveUS8159662B2Dangerous substanceEasy to operateRadiation pyrometryRaman scatteringAutomatic controlDisplay device
A Raman spectroscopy sensor integrated with an unmanned ground vehicle (UGV) includes a UGV having a robot arm and a camera mounted on the robot arm. A laser and telescope associated with a Raman sensor are mounted on the robot arm in such a way as to point in substantially the same direction in which the camera is pointed. A Raman spectral data acquisition and control module is mounted on the UGV and is configured to receive Raman spectral data from the telescope. A remote base station having a display and a data processing and analysis module is configured to receive data from the data acquisition and control module and to display for an operator images from the camera and information related to the Raman sensor. An autofocus system is preferably employed to automatically control telescope focus and thereby enable the Raman sensor to operate over a wide range, e.g., 0.5 m to 10 m.
Owner:PERATON INC
Unmanned aerial vehicle having spherical loading portion and unmanned ground vehicle therefor
InactiveUS8418959B2Easily take off and landReduce weightHelicopter landing platformLaunching/towing gearEngineeringUnmanned spacecraft
Owner:PUSAN NAT UNIV IND UNIV COOPERATION FOUND
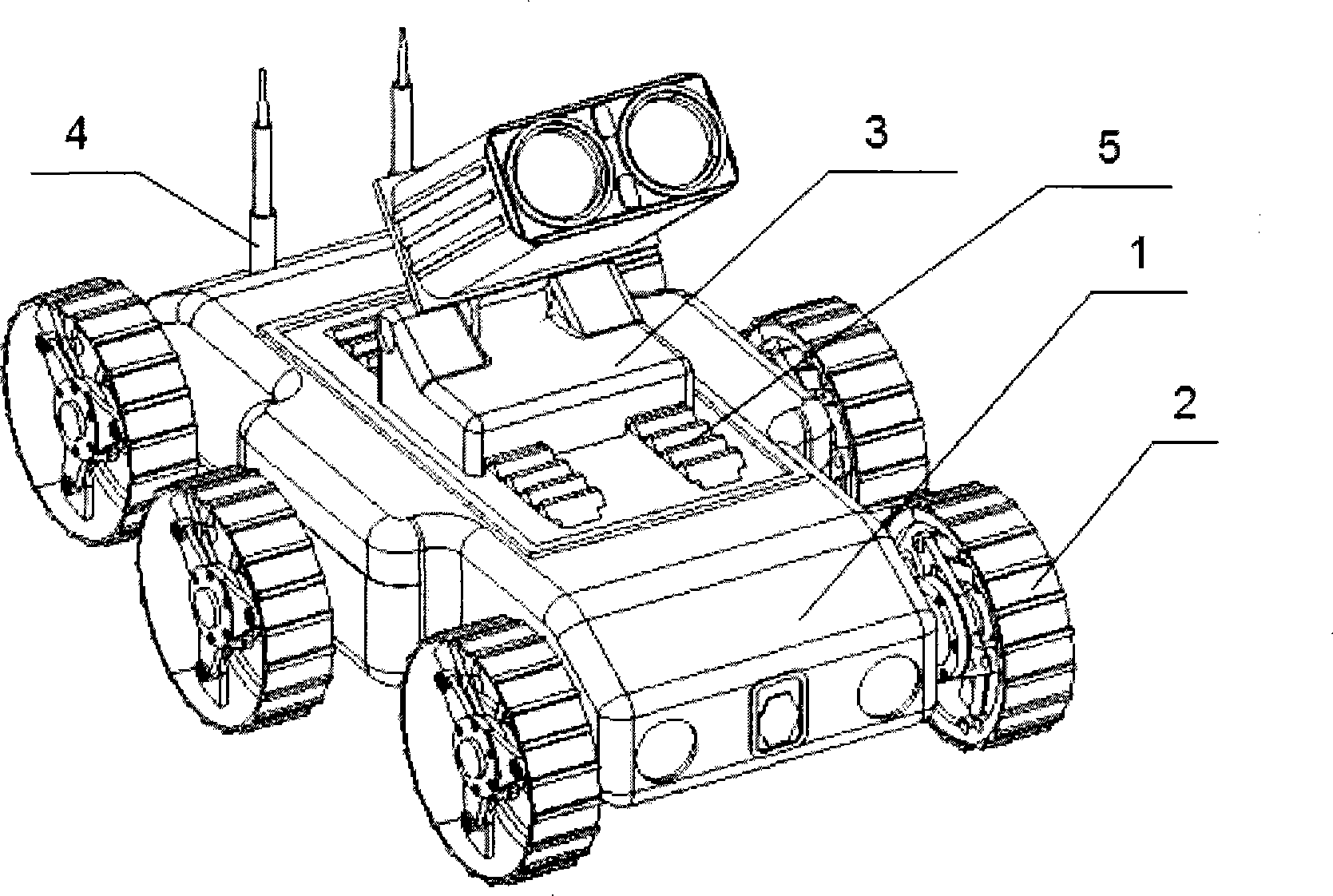
Portable moving device with wheel-leg hybrid advancing function
ActiveCN104249599AAdaptableRealize the compound propulsion function of wheel and footWheelsVehiclesLeg typeTerrain
The invention relates to a portable moving device with a wheel-leg hybrid advancing function and belongs to the technical field of the robot or unmanned ground vehicle. Using a special design of the vehicle wheel structure, the portable moving device of the invention enables the vehicle wheels to unfold to a leg type state and to fold to a wheel type state, so that the wheel-leg hybrid advancing function is realized, thereby giving the device adaptability to complex terrain.
Owner:CHINA NORTH VEHICLE RES INST
Transforming unmanned aerial-to-ground vehicle
InactiveUS8205820B2Rapid deploymentConvertible aircraftsLaunching/towing gearUncrewed vehicleEngineering
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
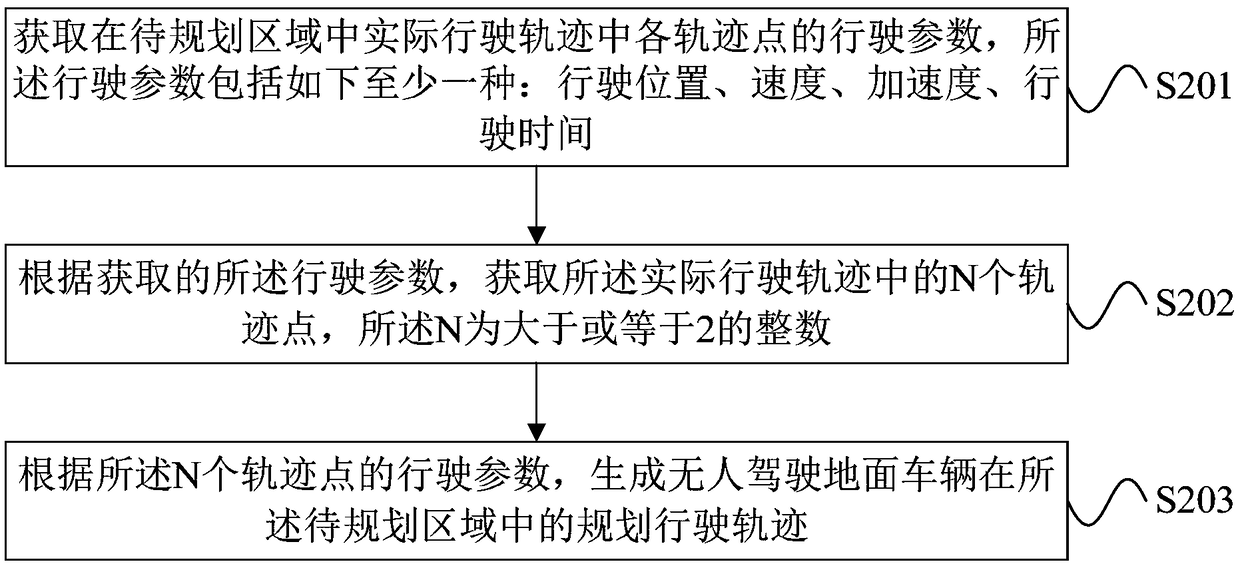
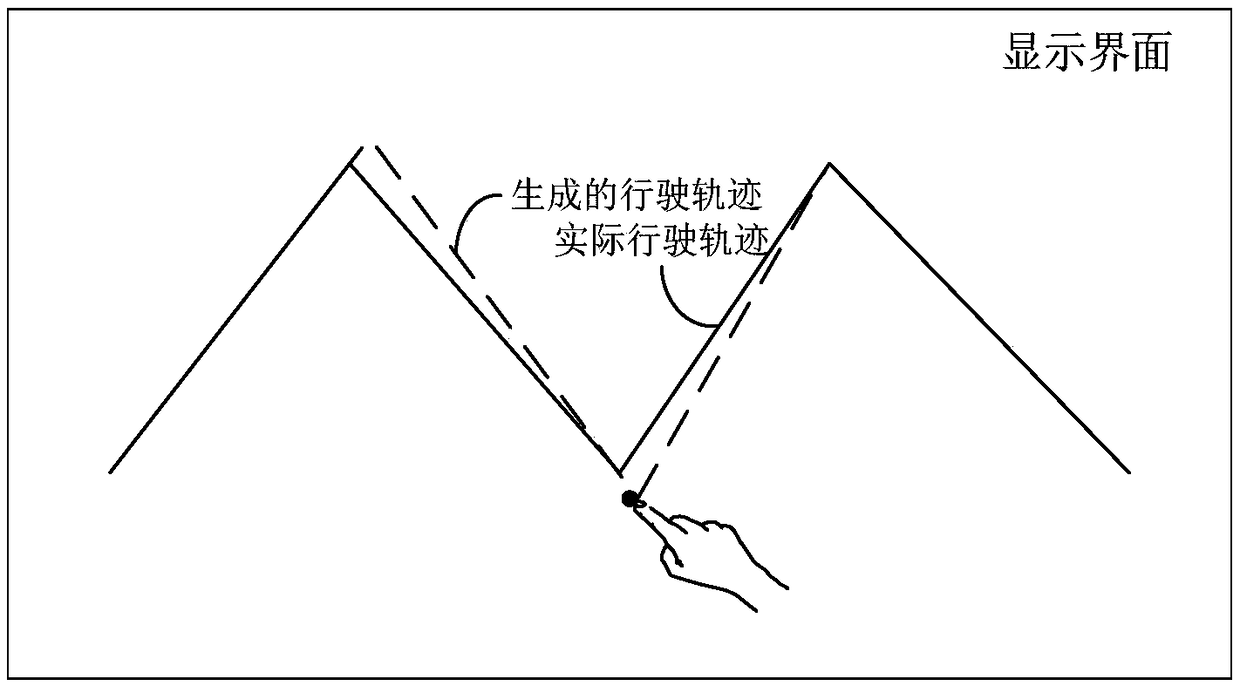
Trajectory generation method and device and unmanned ground vehicle
ActiveCN109154821AImprove accuracyImprove efficiencyNavigational calculation instrumentsPosition/course control in two dimensionsGround vehiclesTrajectory planning
An embodiment of the present invention provides trajectory generation method and device and an unmanned ground vehicle. The method includes: acquiring a driving parameter of each trajectory point in an actual driving trajectory in an area to be planned, where the driving parameter includes at least one of the following: a driving position, speed, acceleration and travel time; according to the obtained driving parameters, obtain N track points in the actual driving track, N is an integer greater than or equal to 2; according to the driving parameters of the N track points, generate an unmannedground vehicle The planned travel trajectory in the area to be planned. The planned driving track in this embodiment is generated according to the actual driving parameter of the track point in the actual driving track, so the planned driving track is very close to the actual driving track, and the user only needs to operate the machine to actually travel once, without artificially drawing high. In the accuracy area, it is not necessary to perform trajectory planning artificially. Therefore, the planned traveling trajectory generated by the embodiment has higher accuracy and higher efficiency.
Owner:SZ DJI TECH CO LTD
Generation method, device and system of lane line of map and storage medium
ActiveCN109470254AAvoid failure to collectDriving safetyInstruments for road network navigationCharacter and pattern recognitionComputer graphics (images)Unmanned ground vehicle
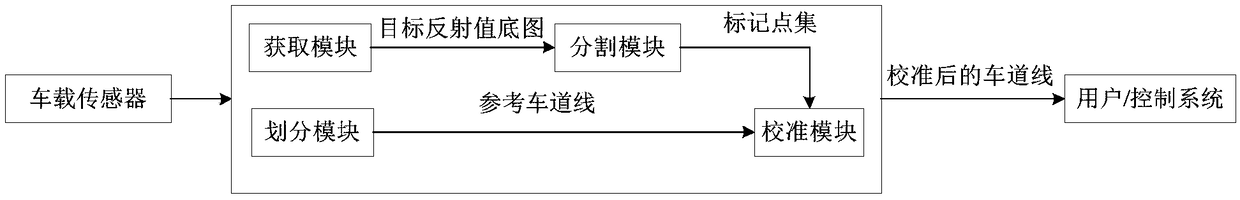
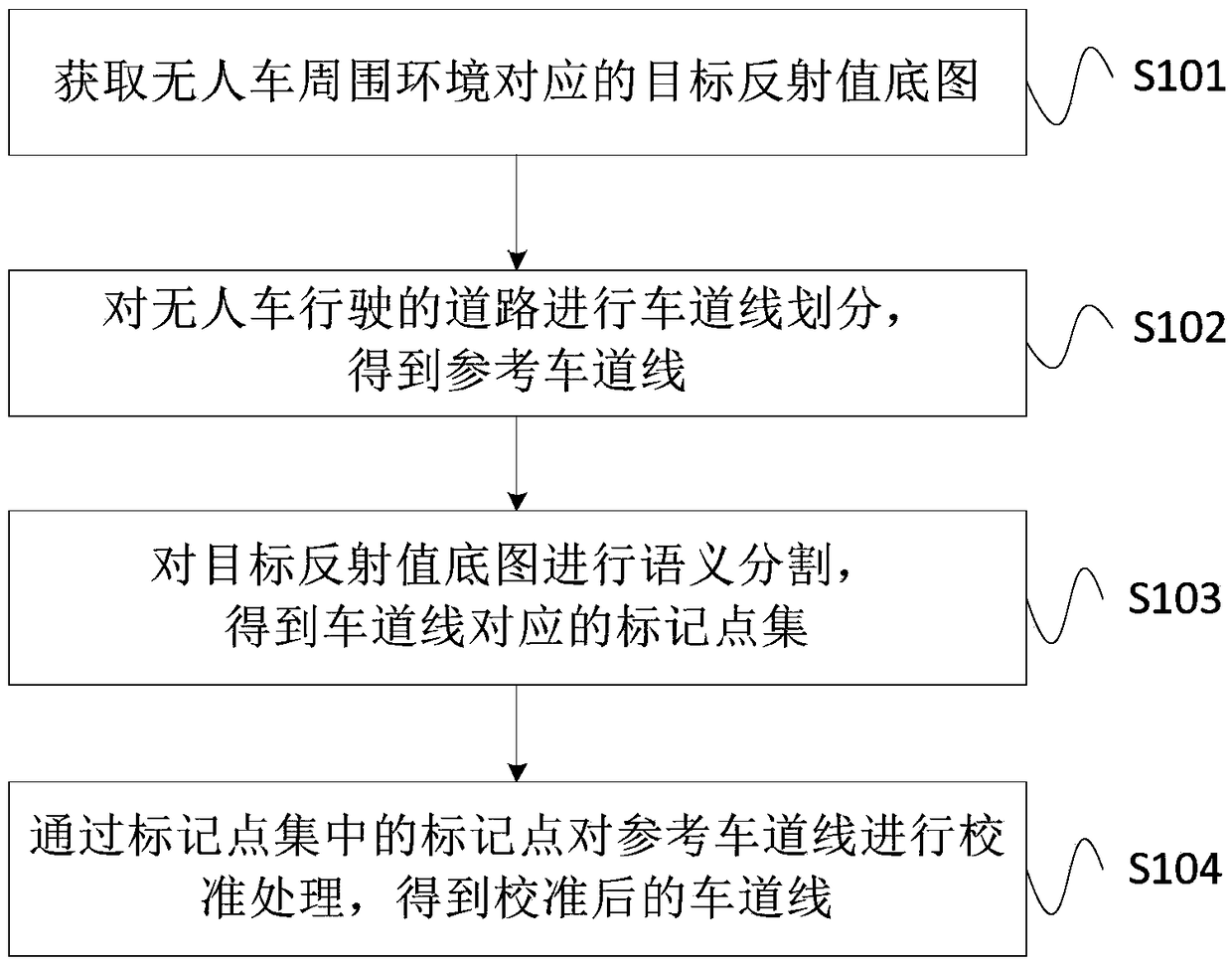
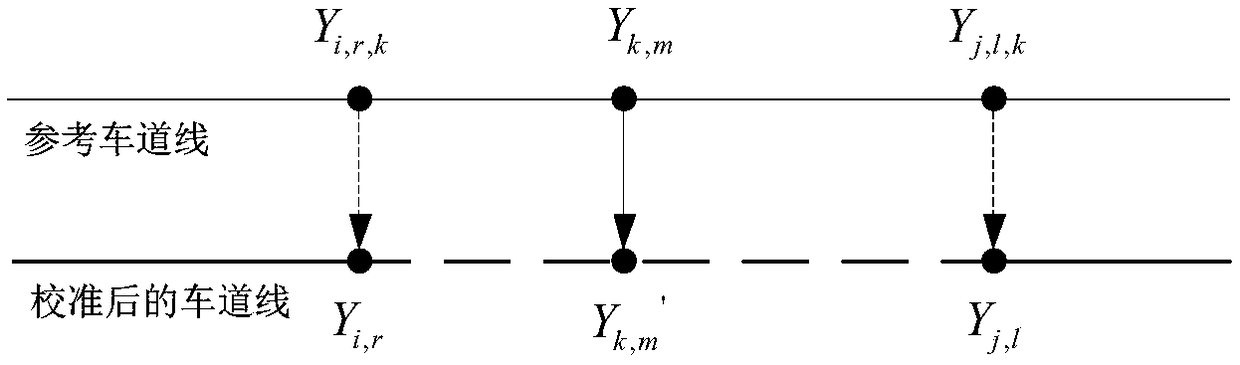
The invention provides a generation method, device and system of lane lines of a map and a storage medium. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring a target reflected value base map corresponding to a surrounding environment of a UGV (unmanned ground vehicle); dividing lane lines on a road, on which the UGV drives, so as to obtain reference lane lines; performing semantic segmentation on the target reflected value base map, so as to obtain a gauge point set corresponding to the lane lines; calibrating the reference lane lines according to gauge points in the gauge point set, so as to obtain calibrated lane lines. The clean and continuous lain lines can be automatically generated, so that the clear lane lines cannot be acquired by the UGV, which is caused by the problems that thelane lines on the road are covered, worn and the like, is avoided, and the problems of incompleteness and breaking of the lane lines generated according to the reflected value base map are also avoided. Therefore, the UGV can drive safely according to the lane lines.
Owner:BAIDU ONLINE NETWORK TECH (BEIJIBG) CO LTD
Accurate planting system and method
The invention discloses an accurate planting system and a method. The system comprises an autonomous navigation unmanned aerial vehicle, a ground planting system, and a ground computer for processinginformation, wherein the ground computer is used for analyzing vegetation information obtained by the unmanned aerial vehicle and generating replanting trajectory diagram to control the unmanned aerial vehicle to perform autonomous airline flying and an unmanned vehicle to perform autonomous traveling. The system can perform detection and checking in a large scope, obtains and analyzes vegetationcoverage information of forest land, performs positioning and accomplishes seeding through the unmanned aerial vehicle and planting through the unmanned ground vehicle; the seeding through the unmanned aerial vehicle can solve the planting problems arising from complicated terrains and saves manpower; the ground planting through the unmanned ground vehicle has a high survival rate; the planting efficiency is improved; and the accurate and efficient planting is achieved.
Owner:NANJING FORESTRY UNIV
Reconfigurable battery-operated vehicle system
InactiveUS20160221676A1Robust structureAvoid the needUnmanned aerial vehiclesPropulsion power plantsGround vehiclesSlide plate
A quadrotor UAV including ruggedized, integral-battery, load-bearing body, two arms on the load-bearing body, each arm having two rotors, a control module mounted on the load-bearing body, a payload module mounted on the control module, and skids configured as landing gear. The two arms are replaceable with arms having wheels for ground vehicle use, with arms having floats and props for water-surface use, and with arms having pitch-controlled props for underwater use. The control module is configured to operate as an unmanned aerial vehicle, an unmanned ground vehicle, an unmanned (water) surface vehicle, and an unmanned underwater vehicle, depending on the type of arms that are attached.
Owner:AEROVIRONMENT INC
System and method for friend or foe identification
ActiveUS20110231035A1Laser active region structureBeacon systems using electromagnetic wavesEngineeringQuantum cascade laser
A system for use in identifying one of an unmanned ground vehicle and an unmanned aerial vehicle includes a signal emitter associated with the unmanned vehicle. The signal emitter includes at least one quantum cascade laser. The signal emitter emits a signal having a wavelength between approximately 2 μm and approximately 30 μm, and the signal is detectable to identify the unmanned vehicle as friendly at a distance from the signal emitter greater than approximately 1 meter.
Owner:LMD APPL SCI LLC
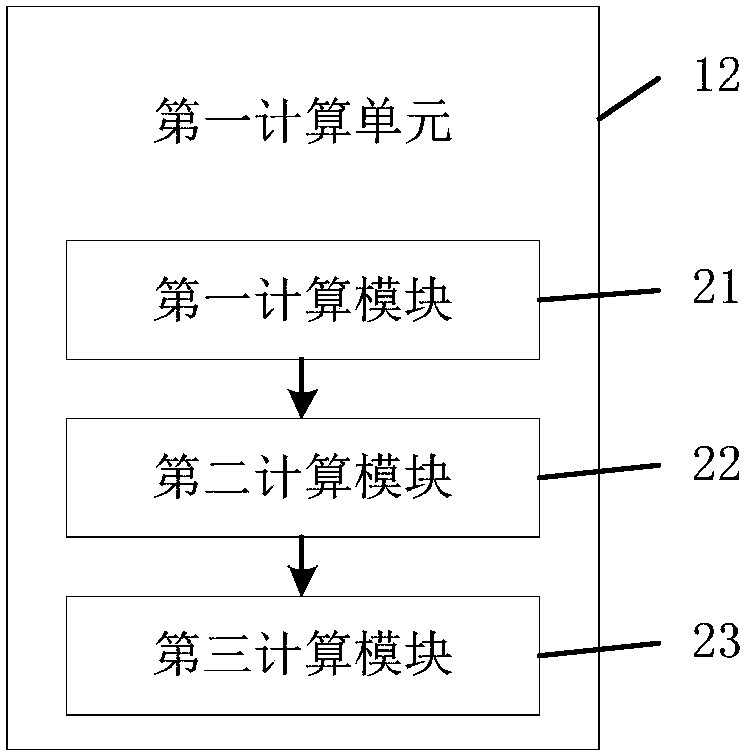
Road point cloud data processing system
ActiveCN108267141ASolve the large amount of data, difficult to transferSave solutionInstruments for road network navigationData processing systemSimultaneous localization and mapping
An embodiment of the invention provides a road point cloud data processing system and belongs to the technical field of point cloud data processing. The road point cloud data processing system comprises: an acquisition unit for acquiring road point cloud data and vehicle position data of a vehicle at a same moment corresponding to the road point cloud data; a first calculating unit for acquiring vehicle attitude through an SLAM (simultaneous localization and mapping) algorithm according to the road point cloud data and the vehicle position data; a second calculating unit for calculating three-dimensional point cloud map data according to the vehicle attitude; a third calculating unit for extracting, in the three-dimensional point cloud map data, repeated structural data corresponding eachof multiple preset shape parameters so as to obtain extracted three-dimensional point cloud map data; a processing unit for determining three-dimensional point cloud map data compressed. The road point cloud data processing system helps solve the problem of the prior art that three-dimensional point cloud map data high in quantity are difficult to transit and store; the compressed three-dimensional point cloud map data are transmitted to unmanned ground vehicles at high speed.
Owner:FAFA AUTOMOBILE (CHINA) CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com